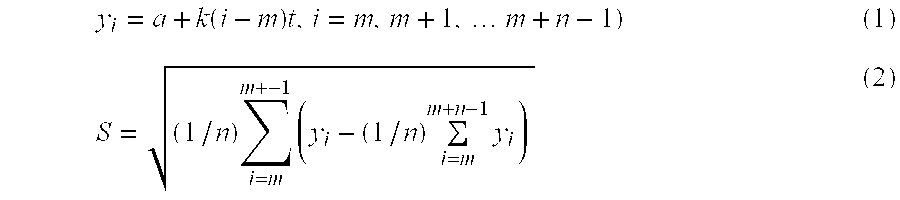Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
659 results about "Subcooling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
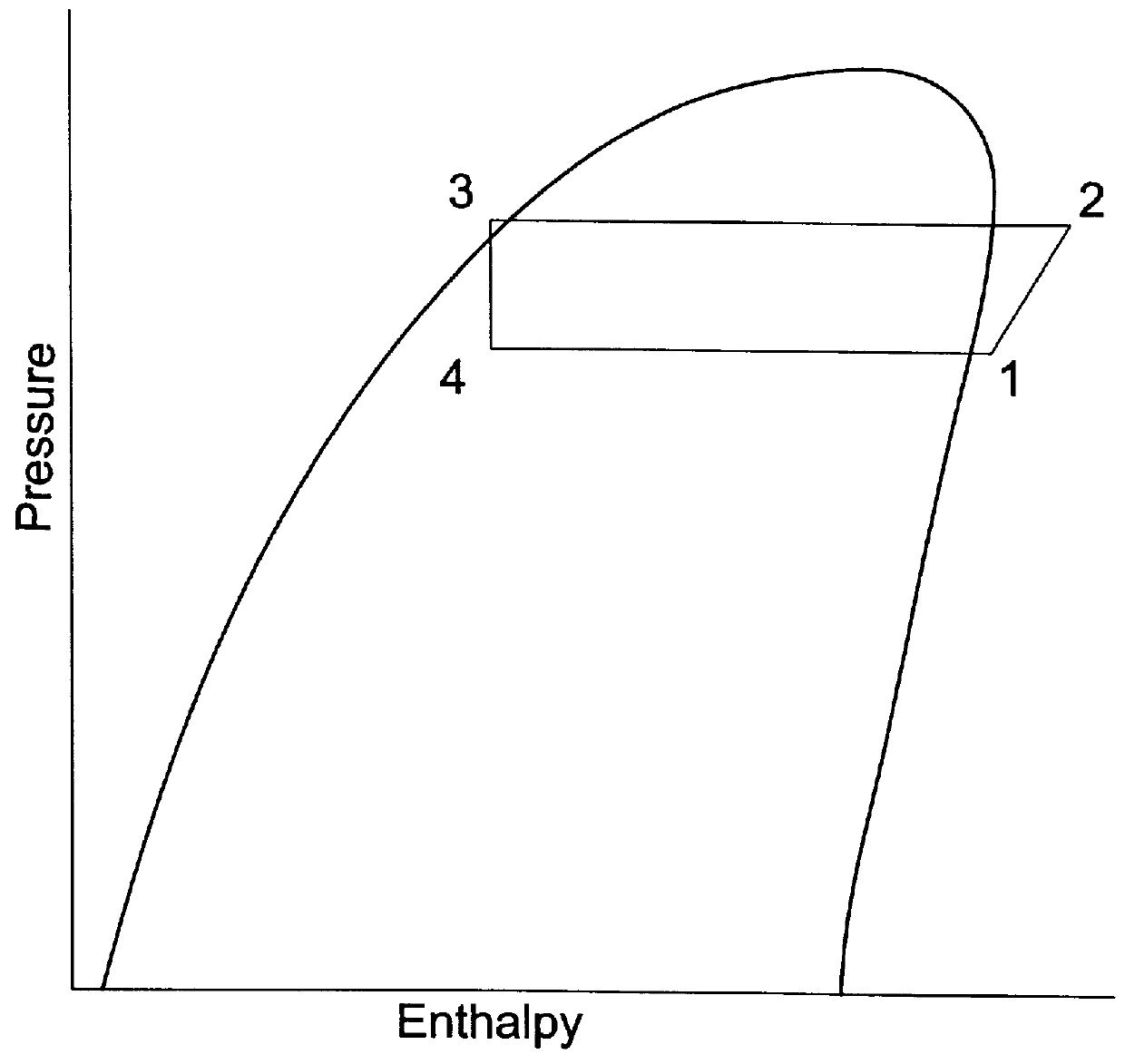
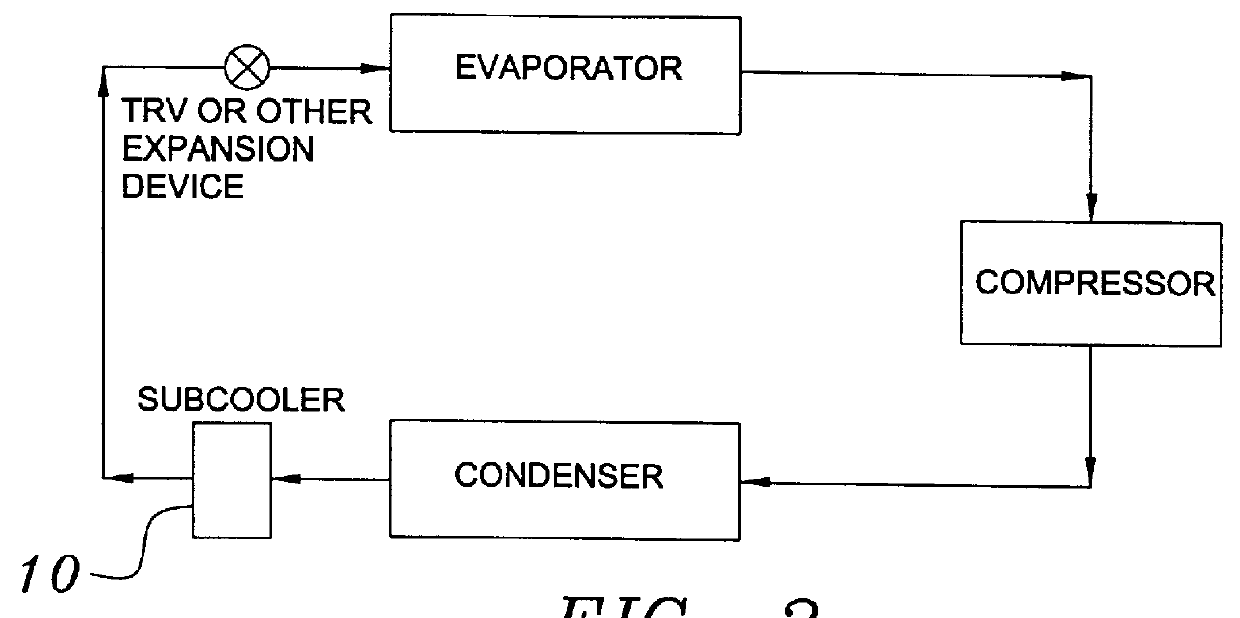
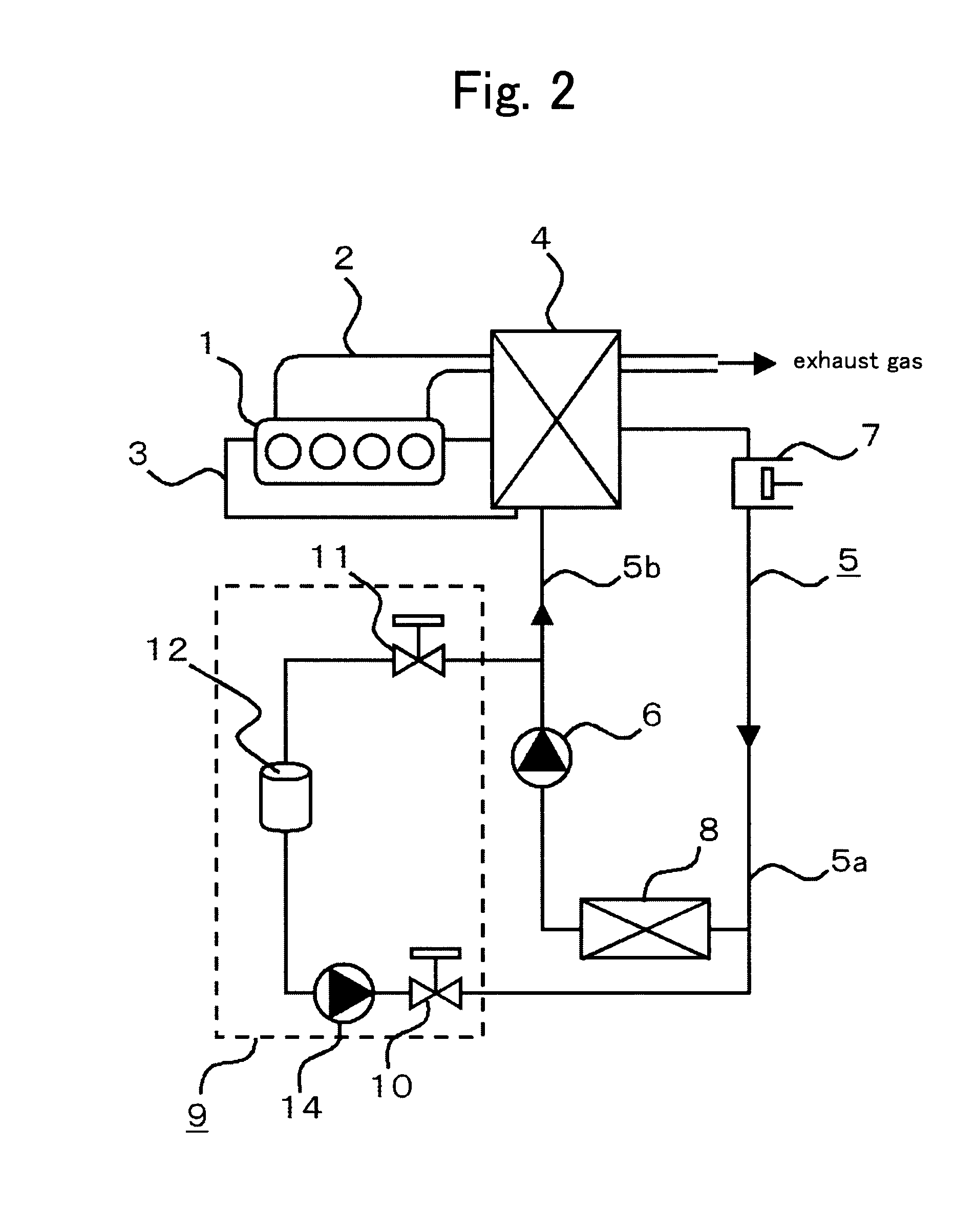
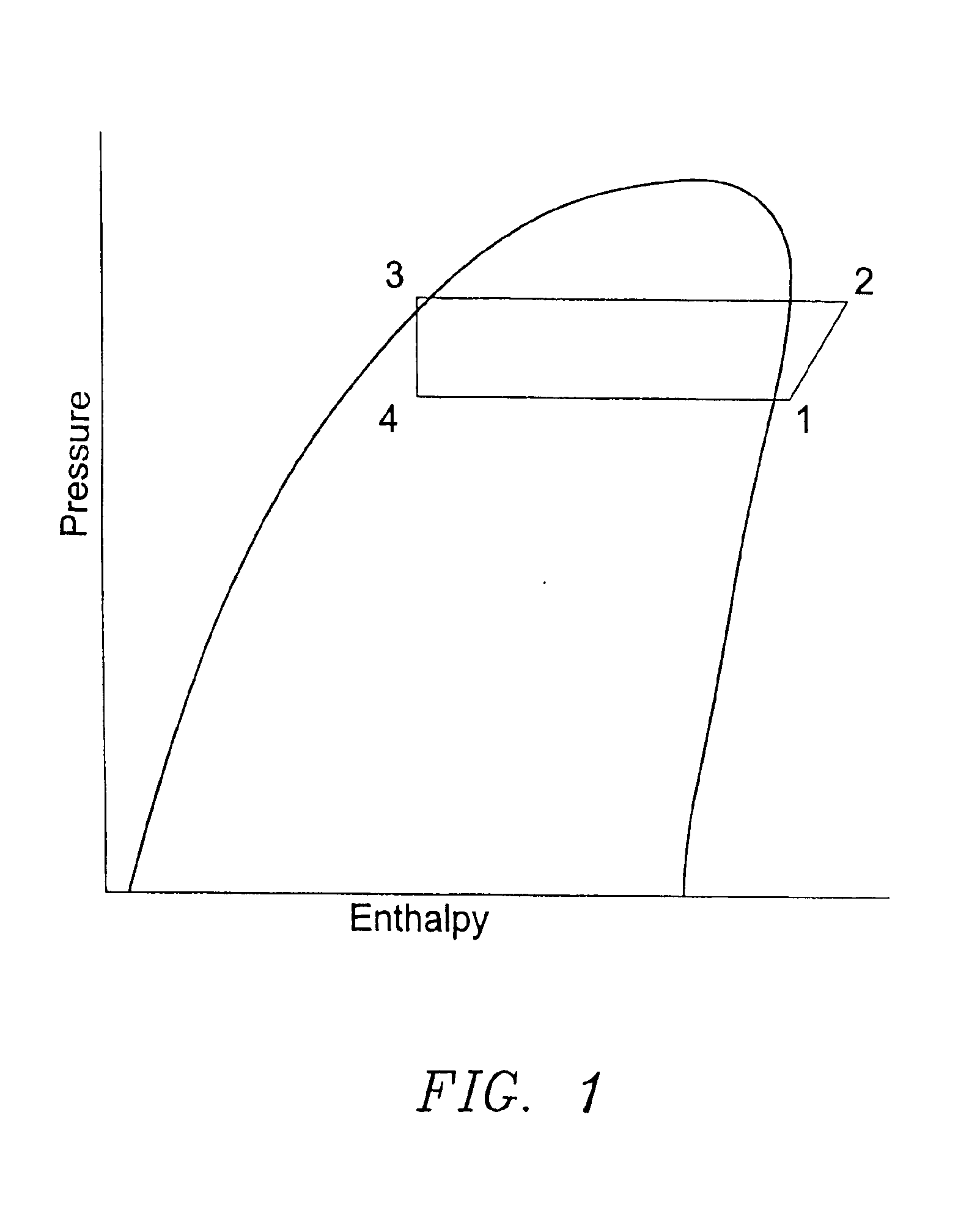
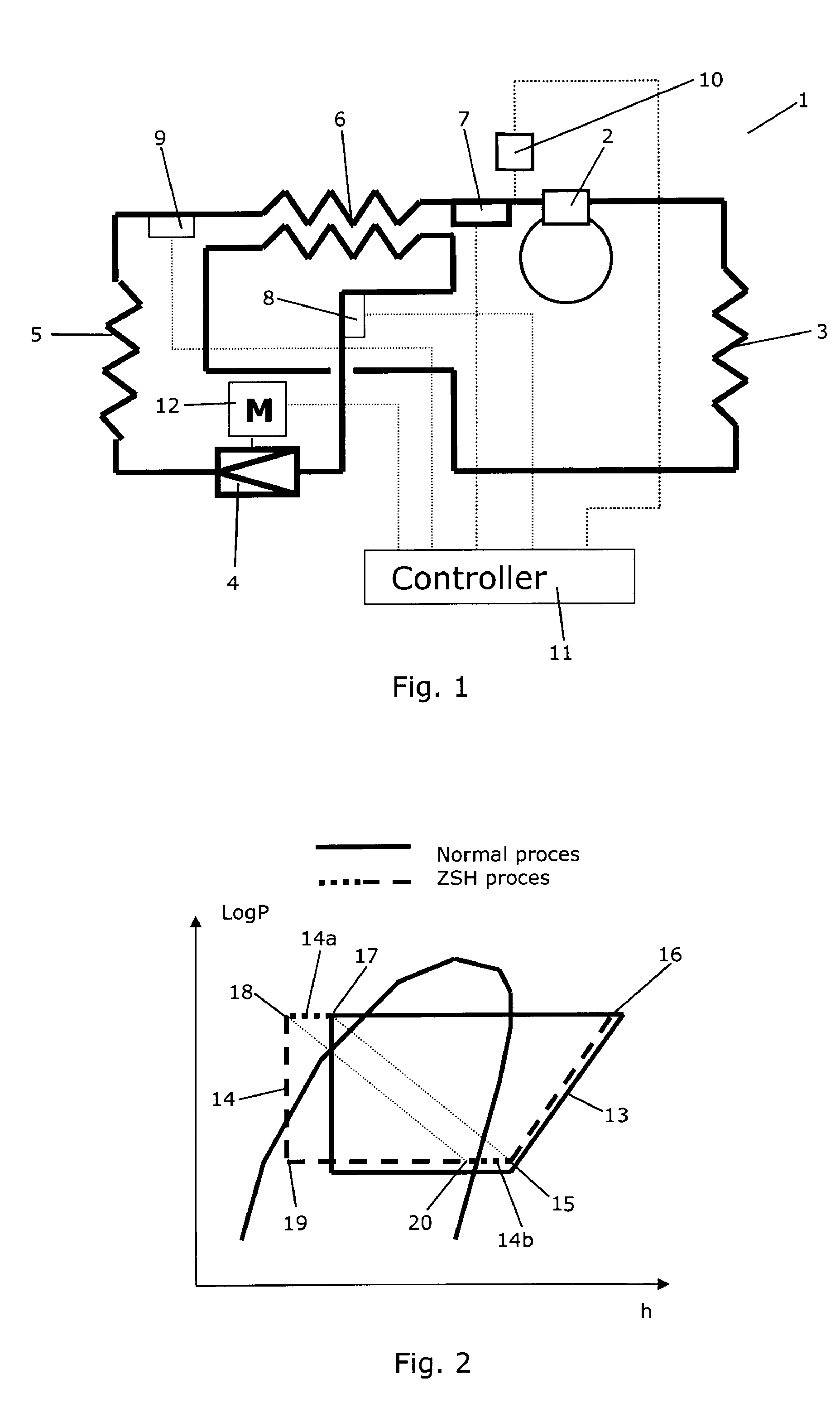
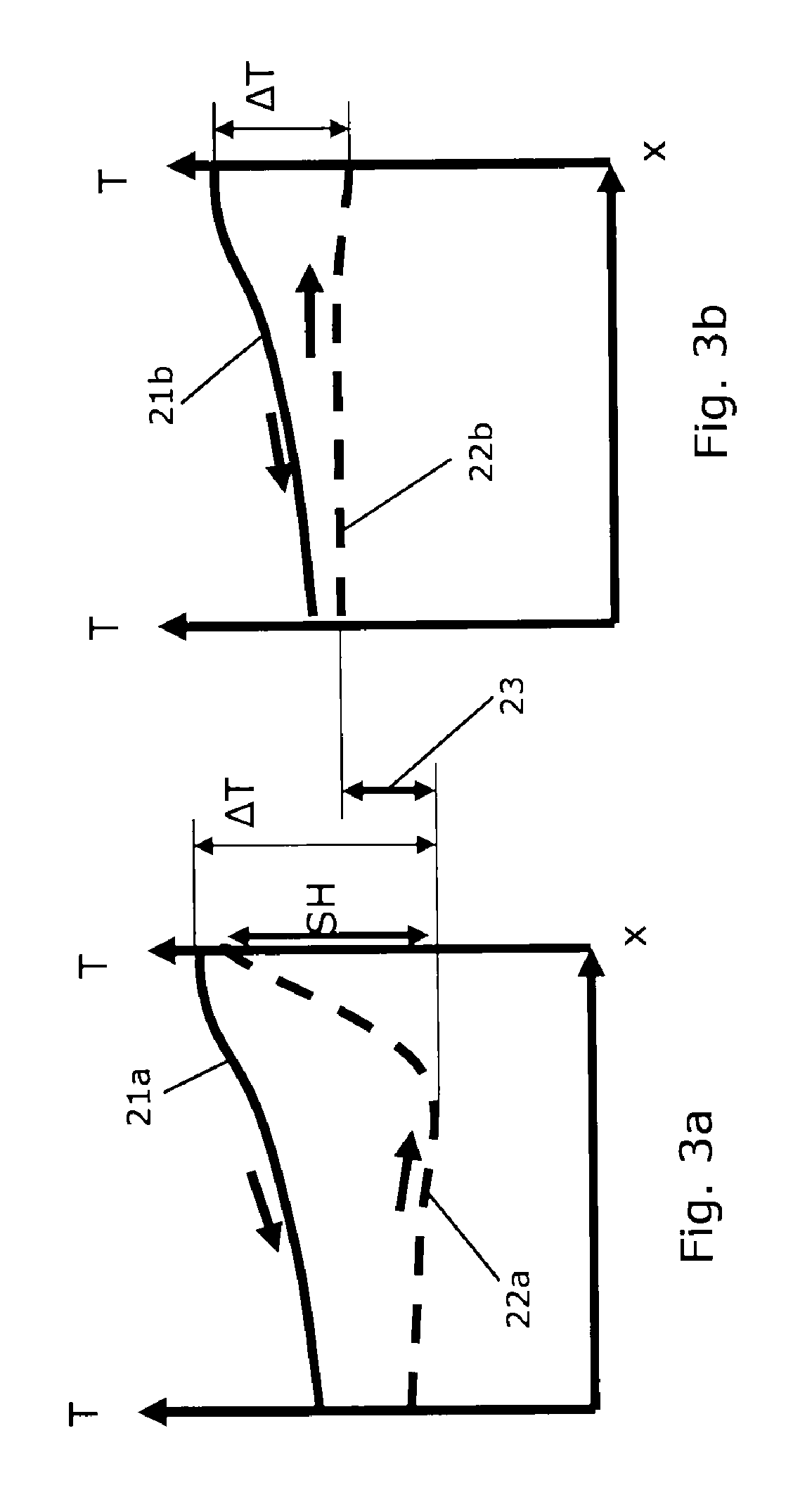
The term subcooling also called undercooling refers to a liquid existing at a temperature below its normal boiling point. For example, water boils at 373 K; at room temperature (300 K) the water is termed "subcooled". A subcooled liquid is the convenient state in which, say, refrigerants may undergo the remaining stages of a refrigeration cycle. Normally, a refrigeration system has a subcooling stage, allowing technicians to be certain that the quality, in which the refrigerant reaches the next step on the cycle, is the desired one. Subcooling may take place in heat exchangers and outside them. Being both similar and inverse processes, subcooling and superheating are important to determine stability and well-functioning of a refrigeration system.
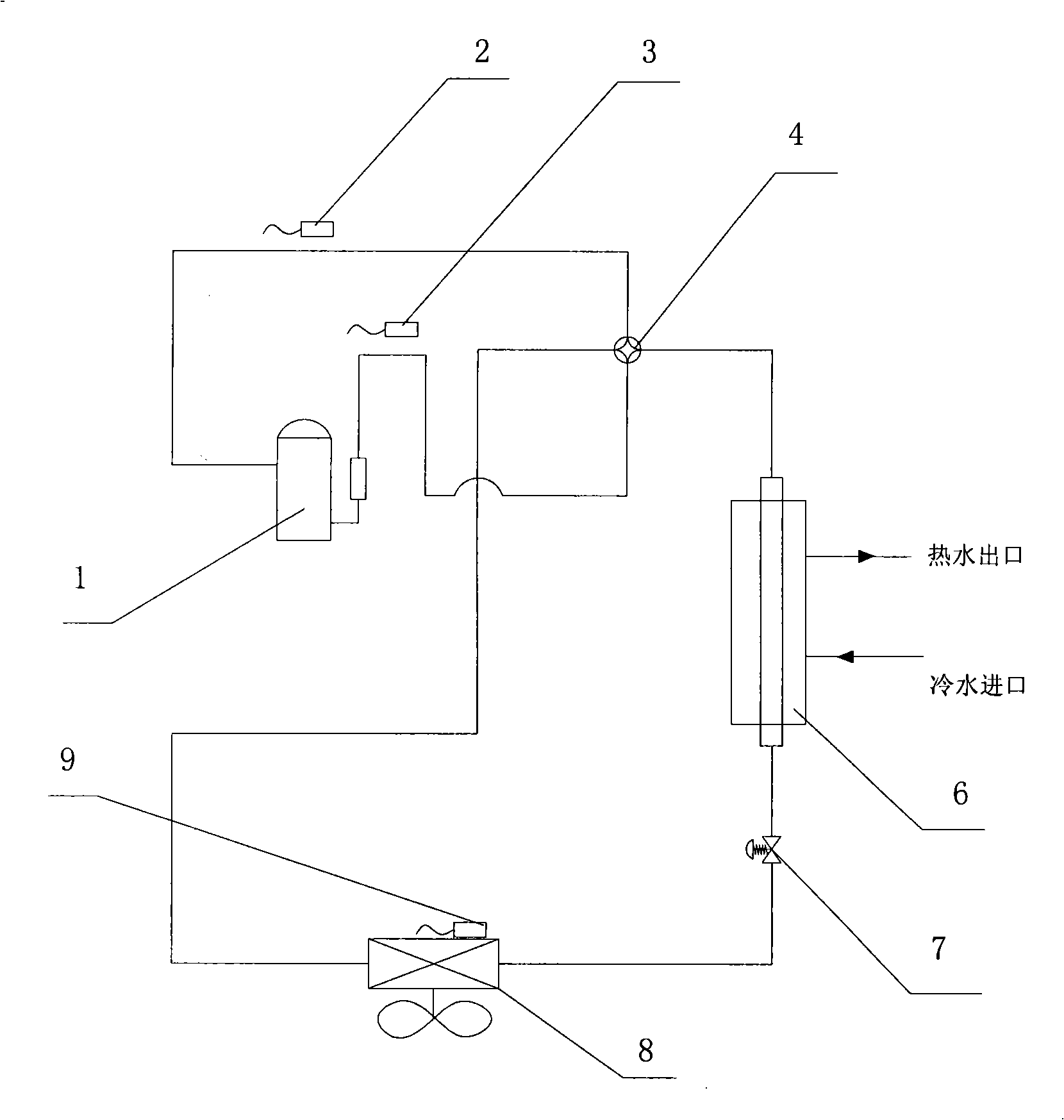
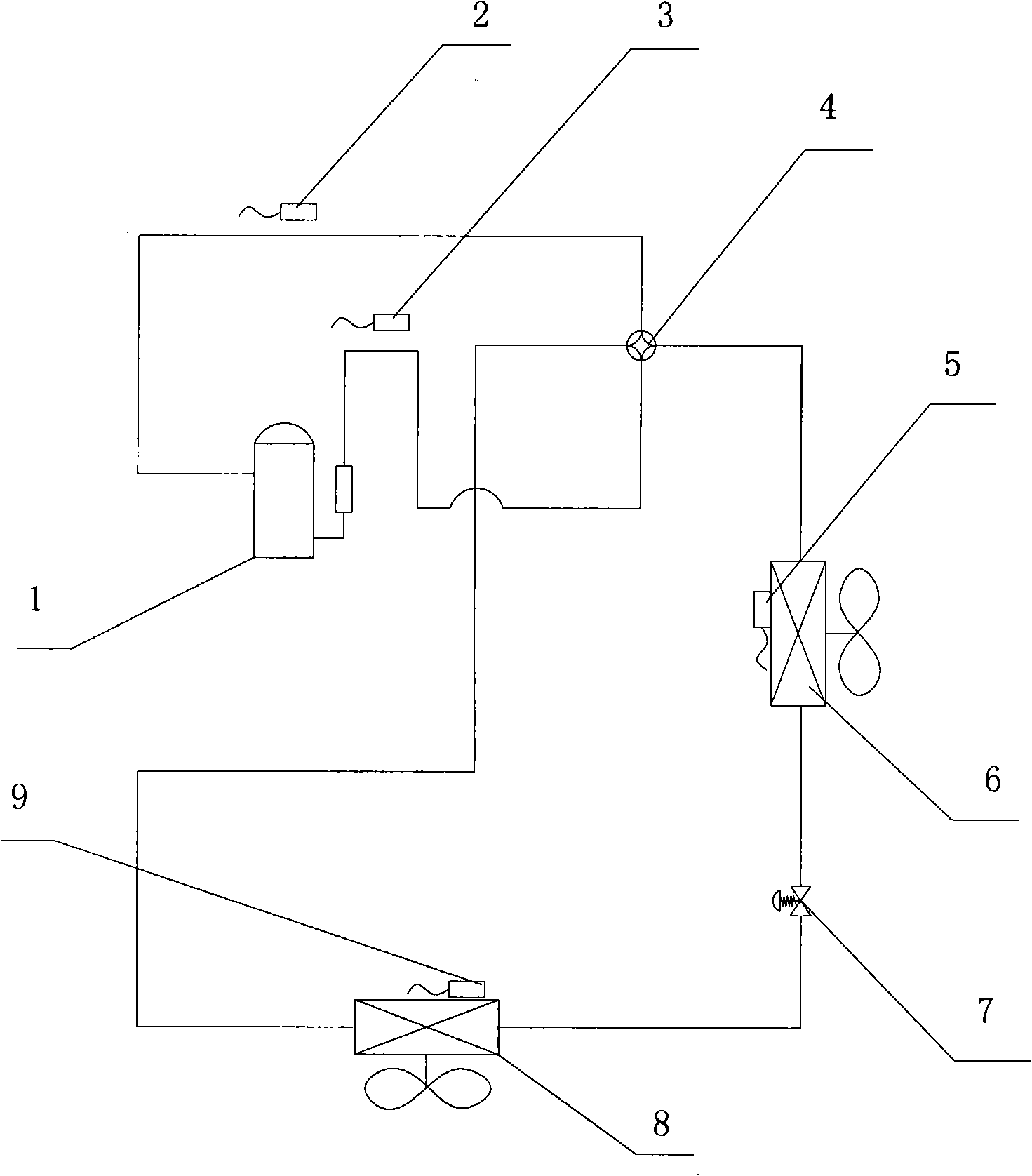
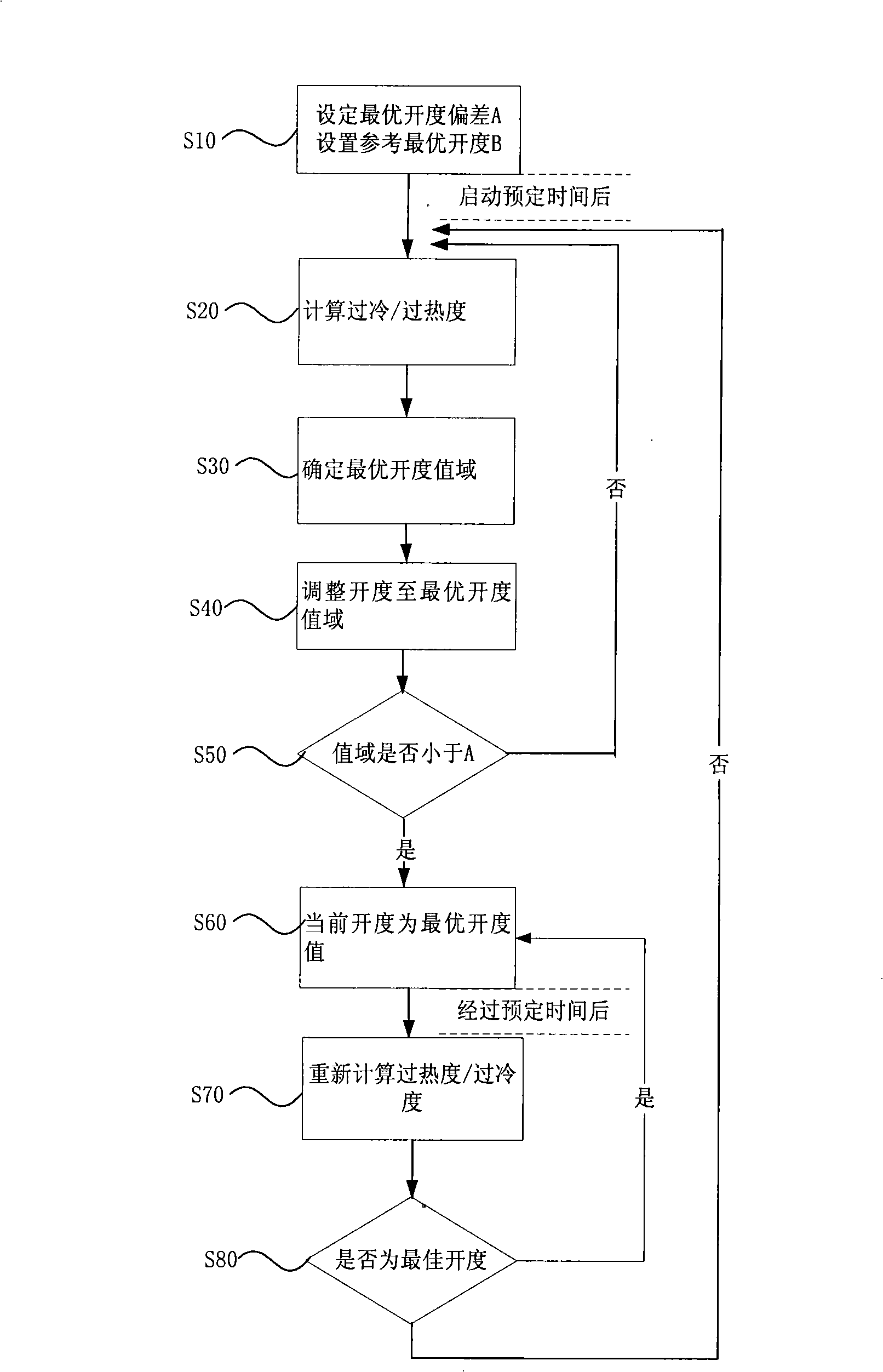
Control method of electronic expansion valve
ActiveCN101276226ARealize automatic controlGuaranteed uptimeEfficient regulation technologiesFluid circulation arrangementAutomatic controlEngineering
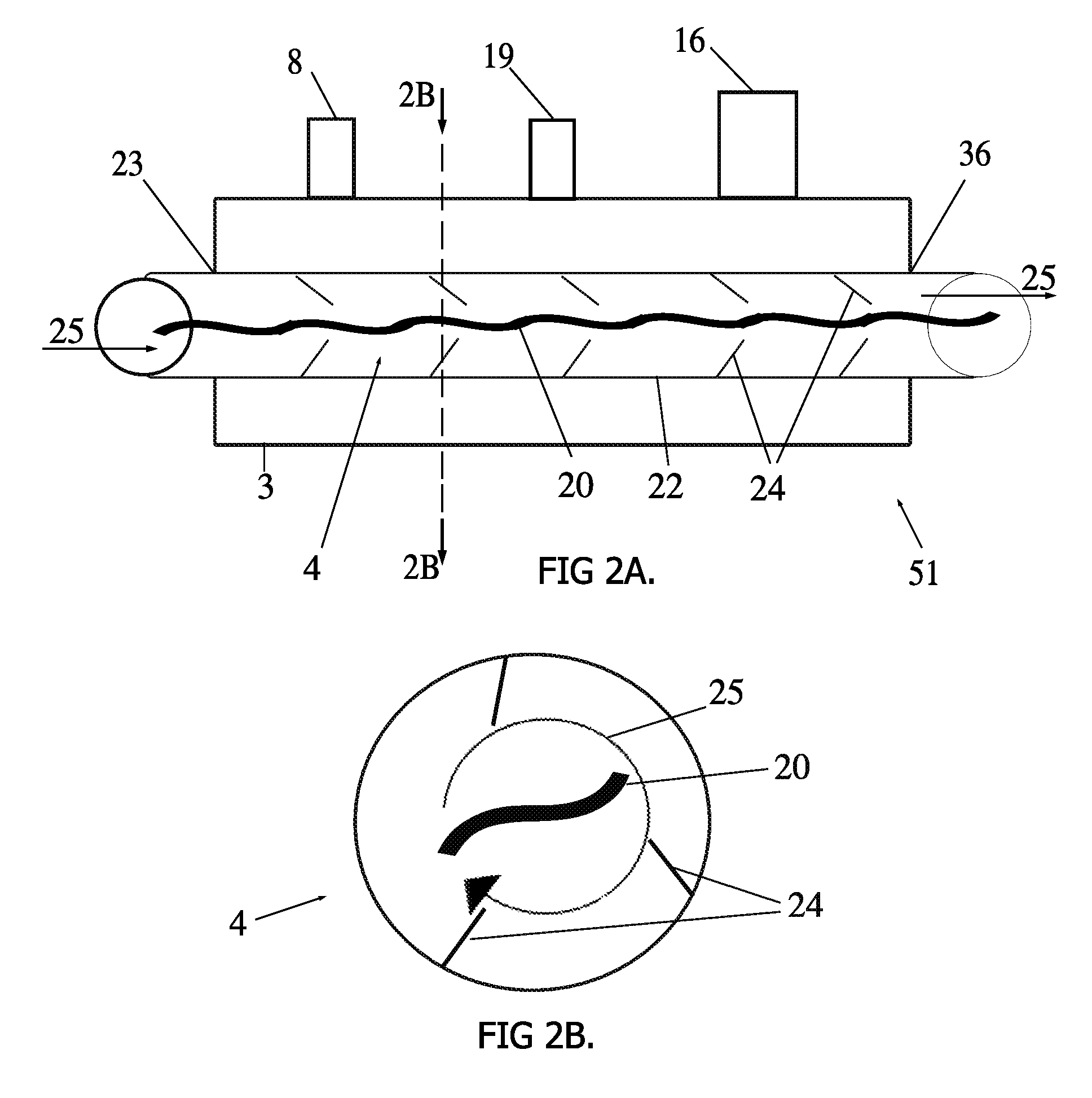
The present invention provides a control method of an electronic expansion valve, the electronic expansion valve is provided in a refrigerant circulation loop of equipment, the circulation loop is also provided with an evaporator, characterized in that the control method includes following steps: S10: starting the electronic expansion valve to process initialization, setting the opening of the electronic expansion valve in a predetermined initial value; S20: after starting the predetermined time, determining the real superheat / subcooling of the electronic expansion valve according to the difference between the outlet temperature and the inlet temperature of the evaporator; S30: comparing the object superheat / subcooling with the real superheat / subcooling, determining the optimal opening range of the electronic expansion valve; S40: adjusting the opening of the electronic expansion valve to the optimal opening range. The invention realizes the automatic control of refrigerant volume and throttle degree of equipment, and capable of adapting the working condition to control automatically, so as to protect the optimal state in the system operation ,ensuring credibility and safety operation.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
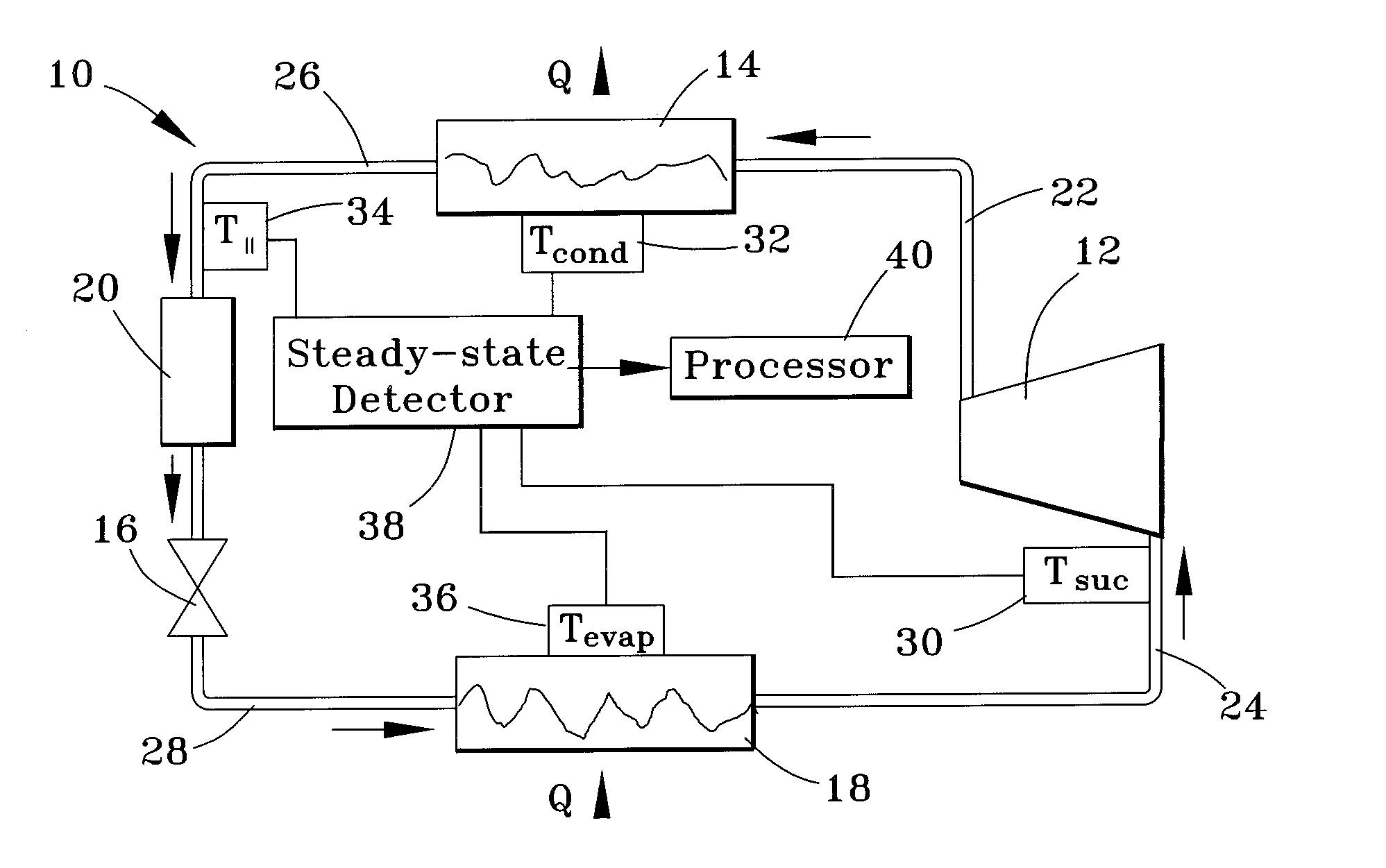
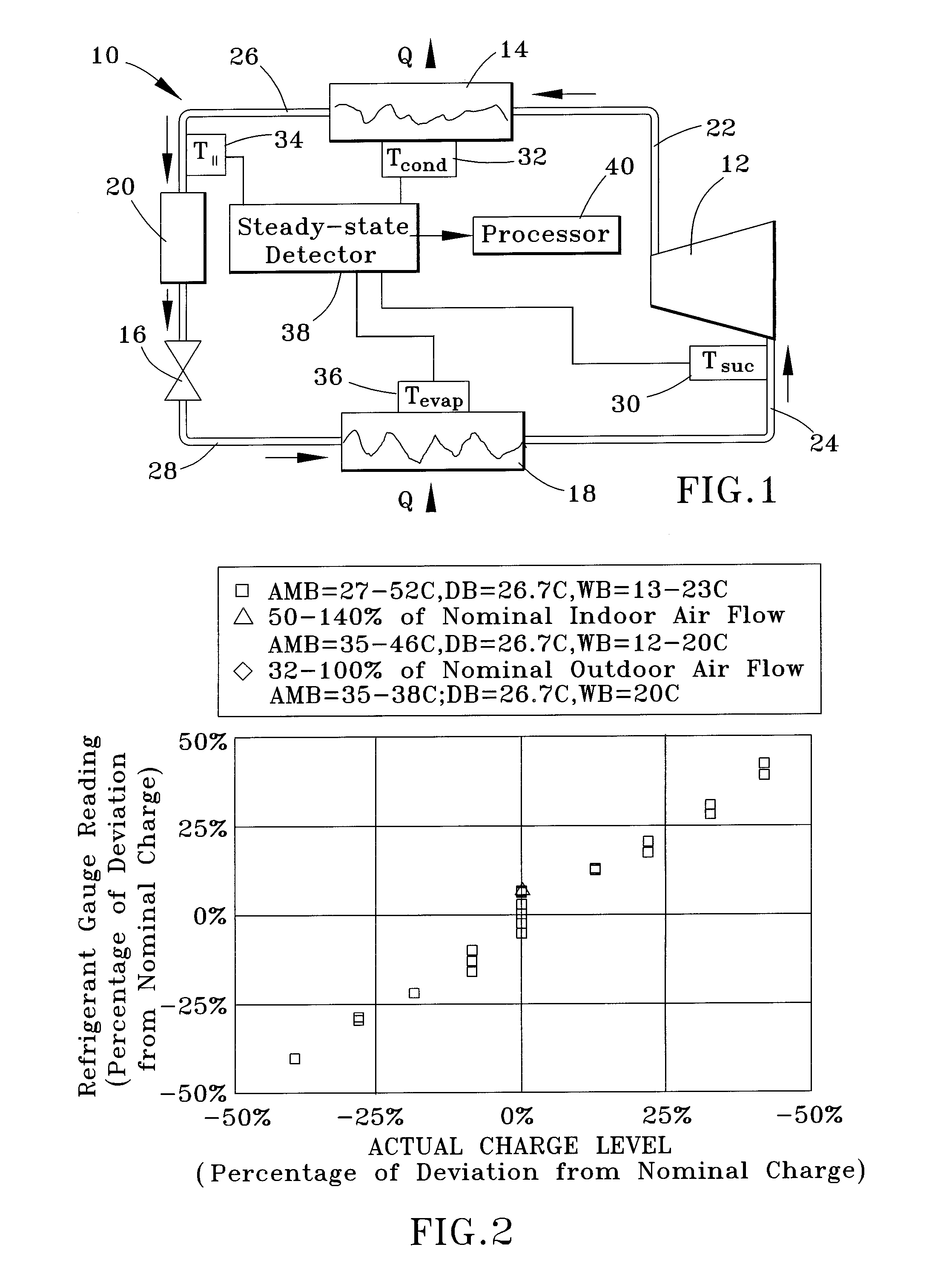
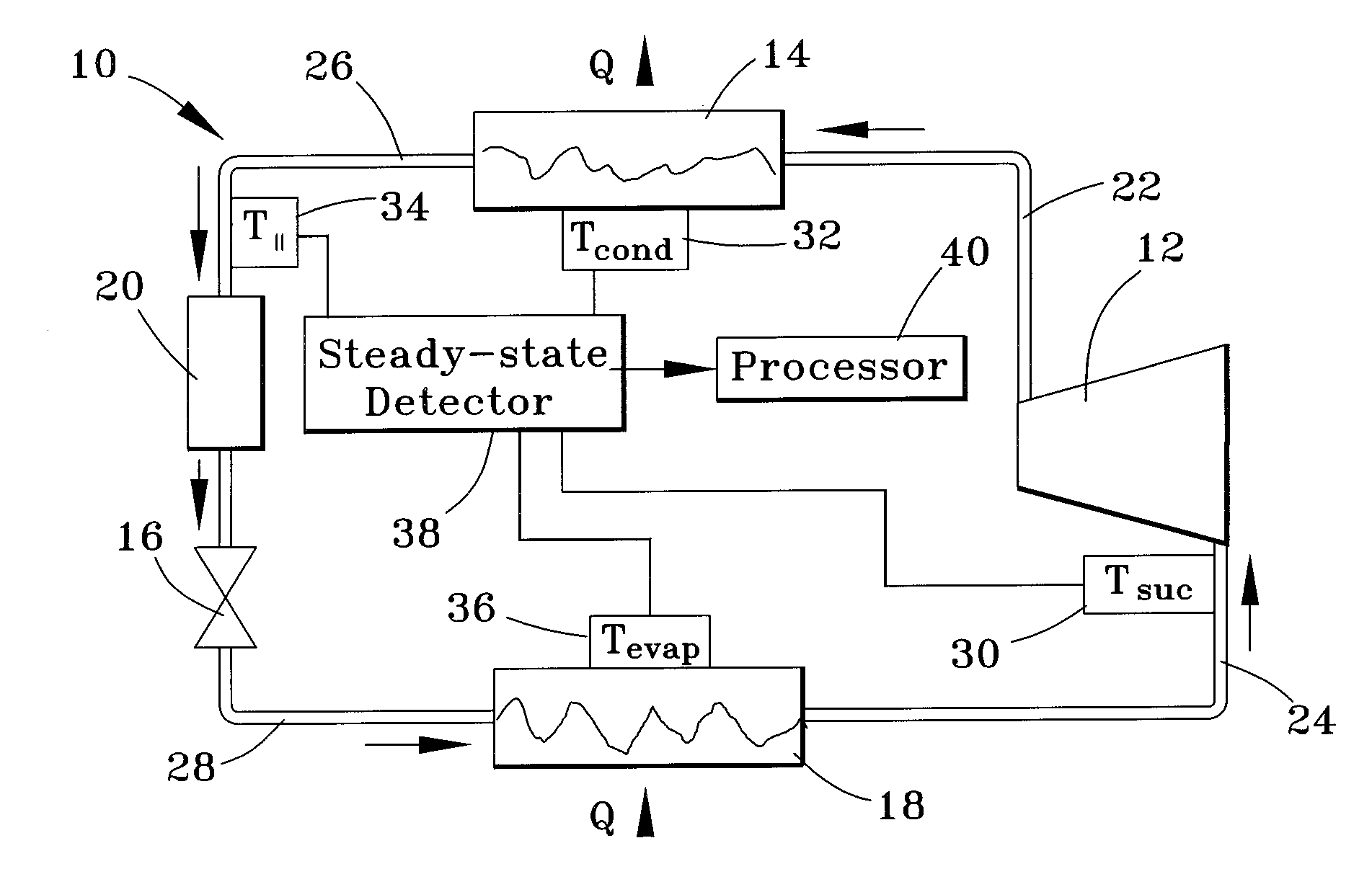
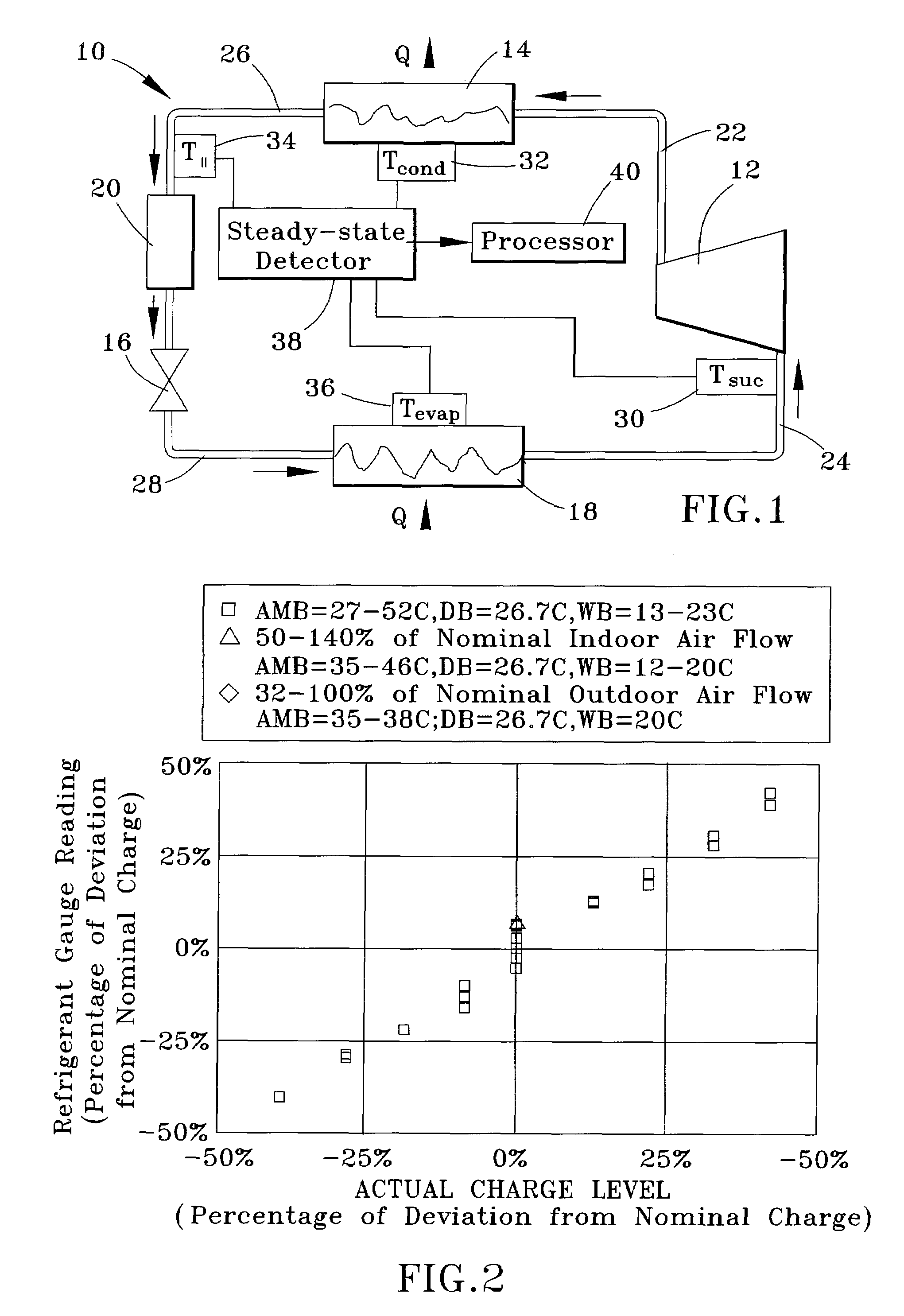
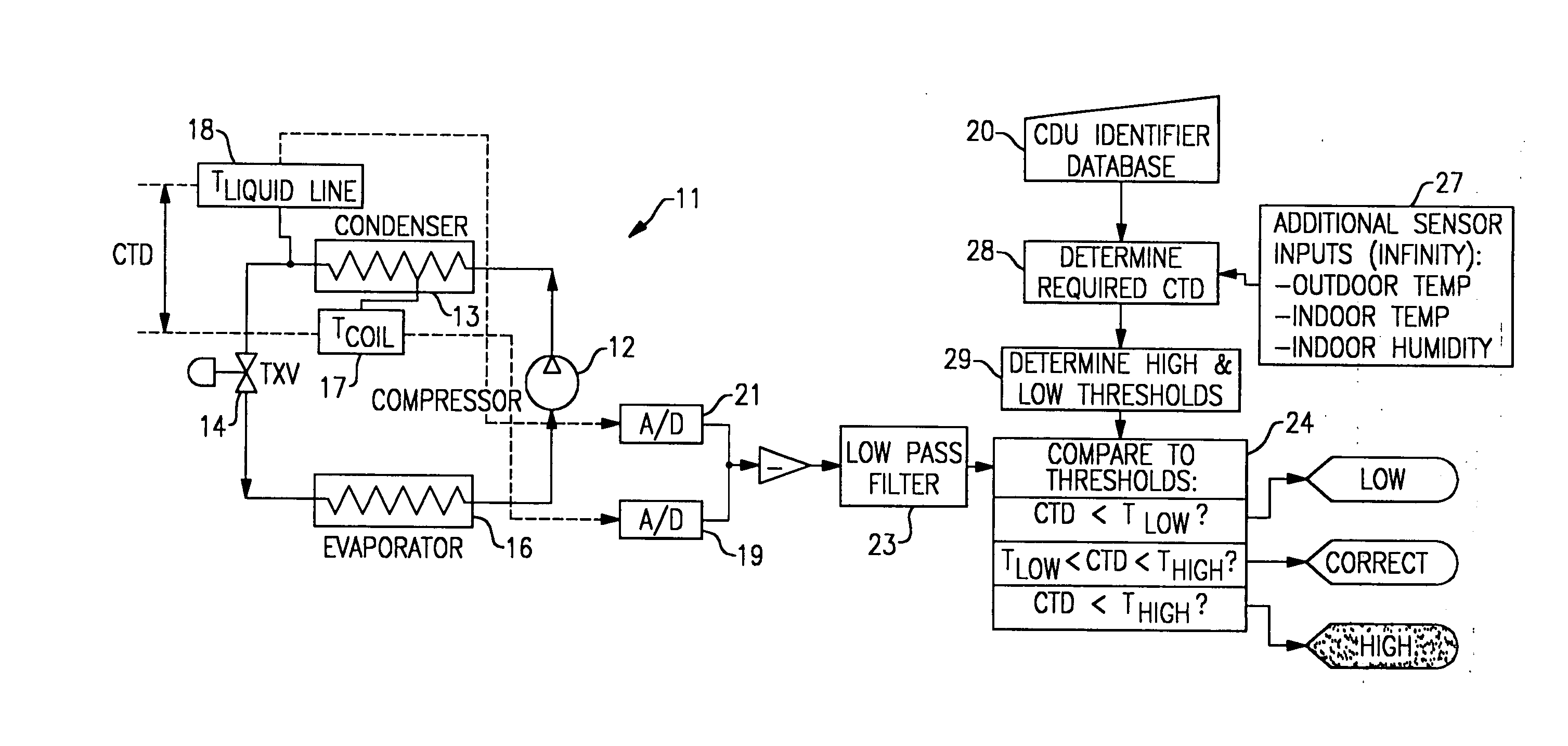
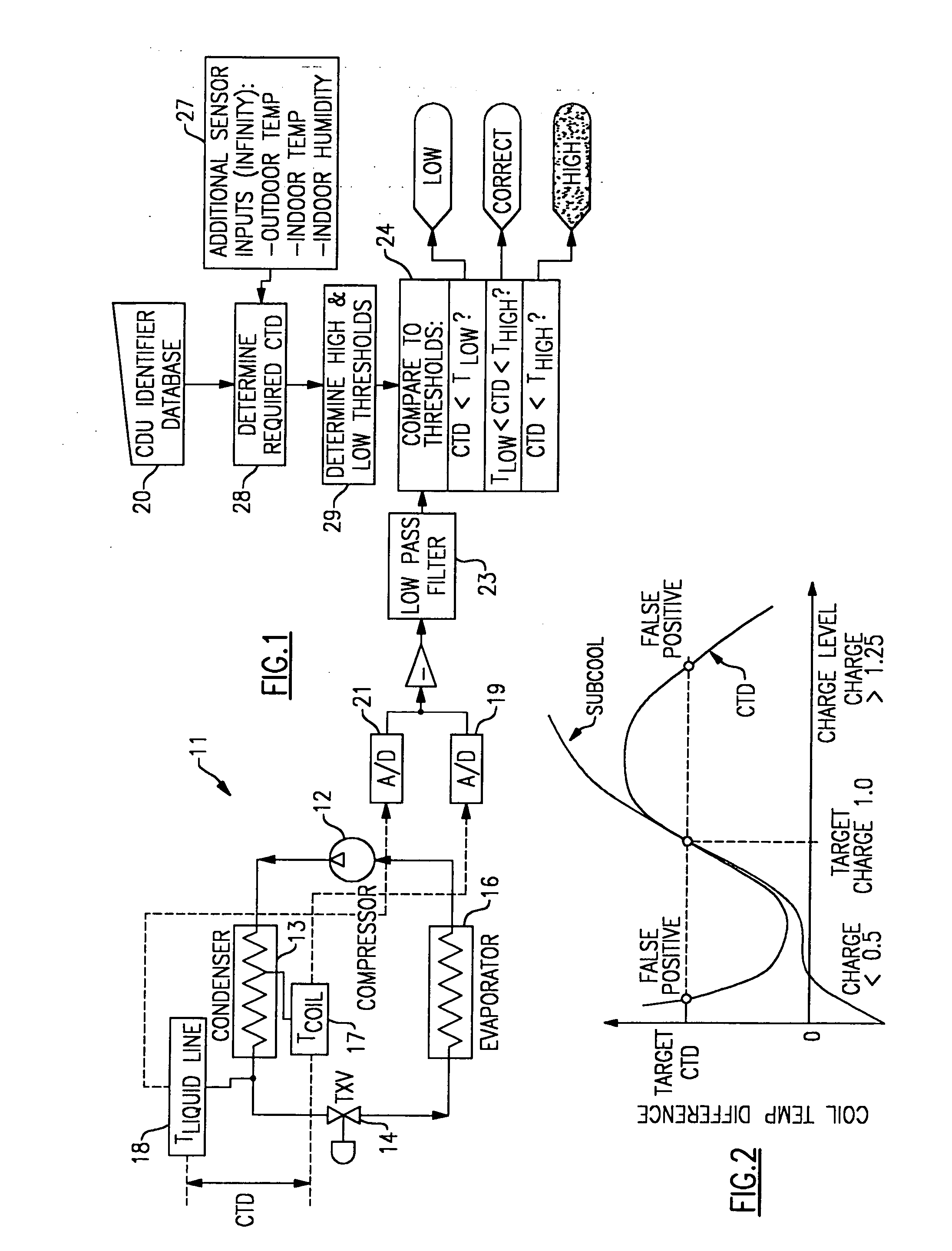
Apparatus and method for determining refrigerant charge level
ActiveUS20070163276A1Low-cost non-invasiveLow costThermometer applicationsRefrigeration safety arrangementLiquid lineStable state
A method and apparatus for non-invasively determining a charge level of a refrigerant in a vapor-compression cycle system. The method and apparatus monitor the system while the system is operated to ascertain that the system is operating at approximately steady-state. The superheat and the subcooling of the system are then determined at the suction line and at the liquid line, respectively, and the refrigerant charge level is calculated based on the determined subcooling, the determined superheat, and rated operating conditions of the system, including rated refrigerant charge level, rated liquid line subcooling, and rated suction line superheat.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Nano solid-liquid phase change energy storage composite material
InactiveCN101982518AHigh energy storage densityGood heat transfer performanceHeat-exchange elementsIndustrial wasteCorrosion
The invention relates to a nano solid-liquid phase change energy storage composite material, belonging to a phase change energy storage technology. The composite material comprises the following components in parts by weight: 88 to 98 parts of hydrated salt, 1 to 7 parts of a nano material and 1 to 5 parts of thickener. With regard to the nano solid-liquid phase change energy storage composite material, the hydrated salt is taken as a main body for phase change energy storage, thus having higher energy storage density and good heat transfer performance; the nano material is taken as nucleating agent, thereby reducing and even eliminating the degree of supercooling of the hydrated salt and having stable property and corrosion resistance; and a proper amount of the thickener is added to increase the viscosity of liquid hydrated salt, thereby preventing the phase separation of the hydrated salt and simultaneously strengthening the suspension stability of the nano material. The nano solid-liquid phase change energy storage composite material of the invention can be widely applied to the fields of solar thermal utilization, industrial waste heat recovery, air conditioning energy storage and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
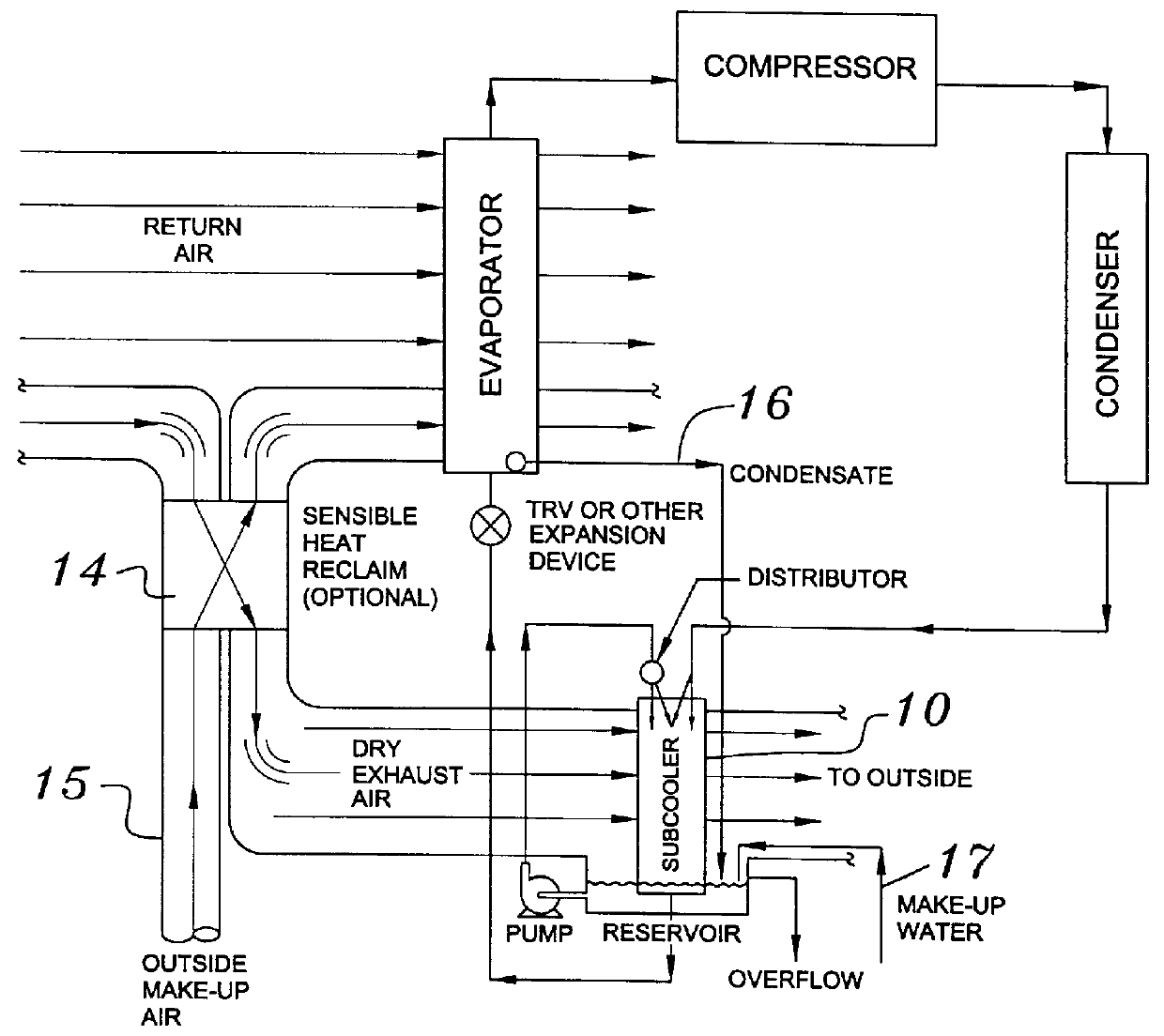
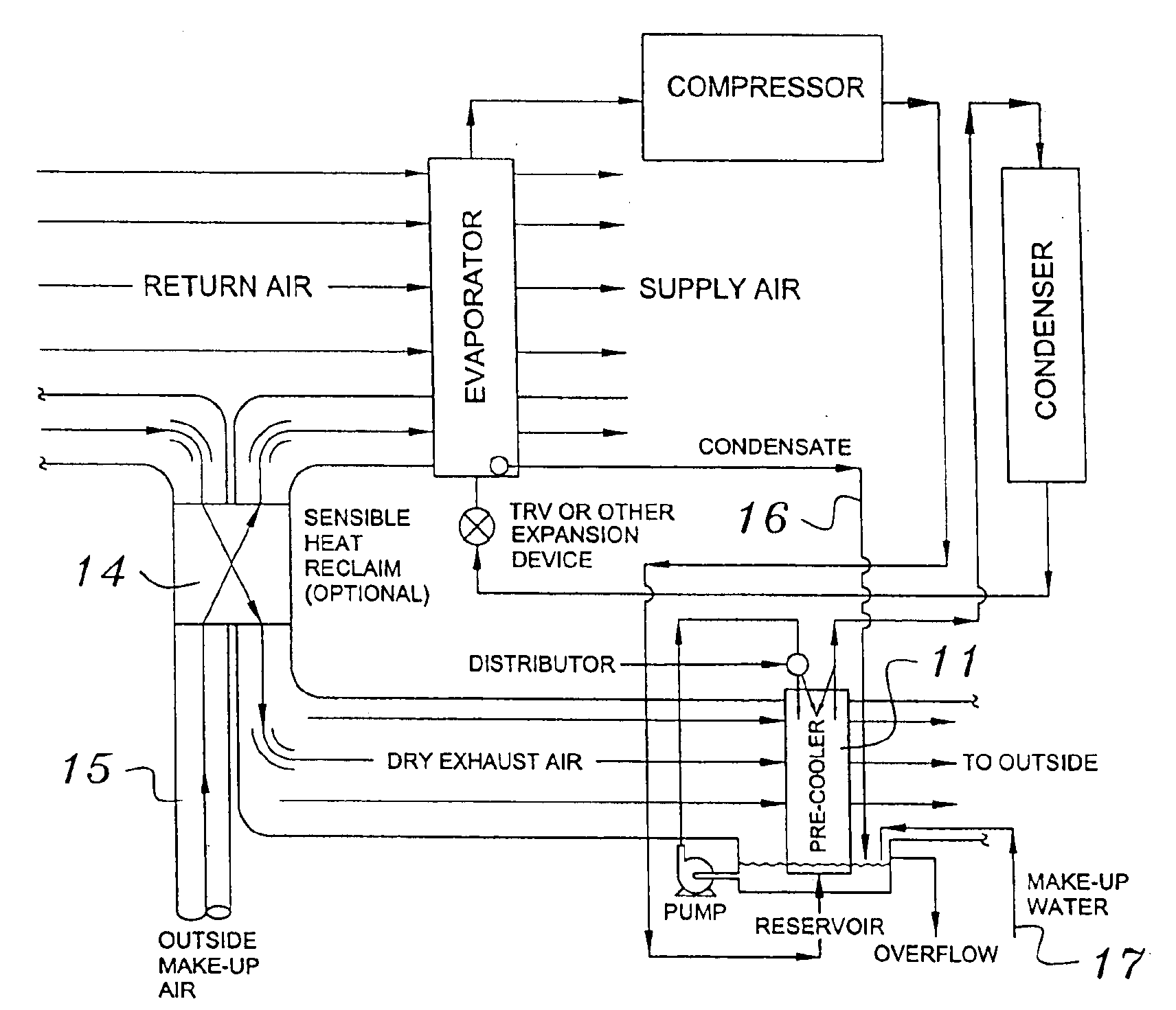
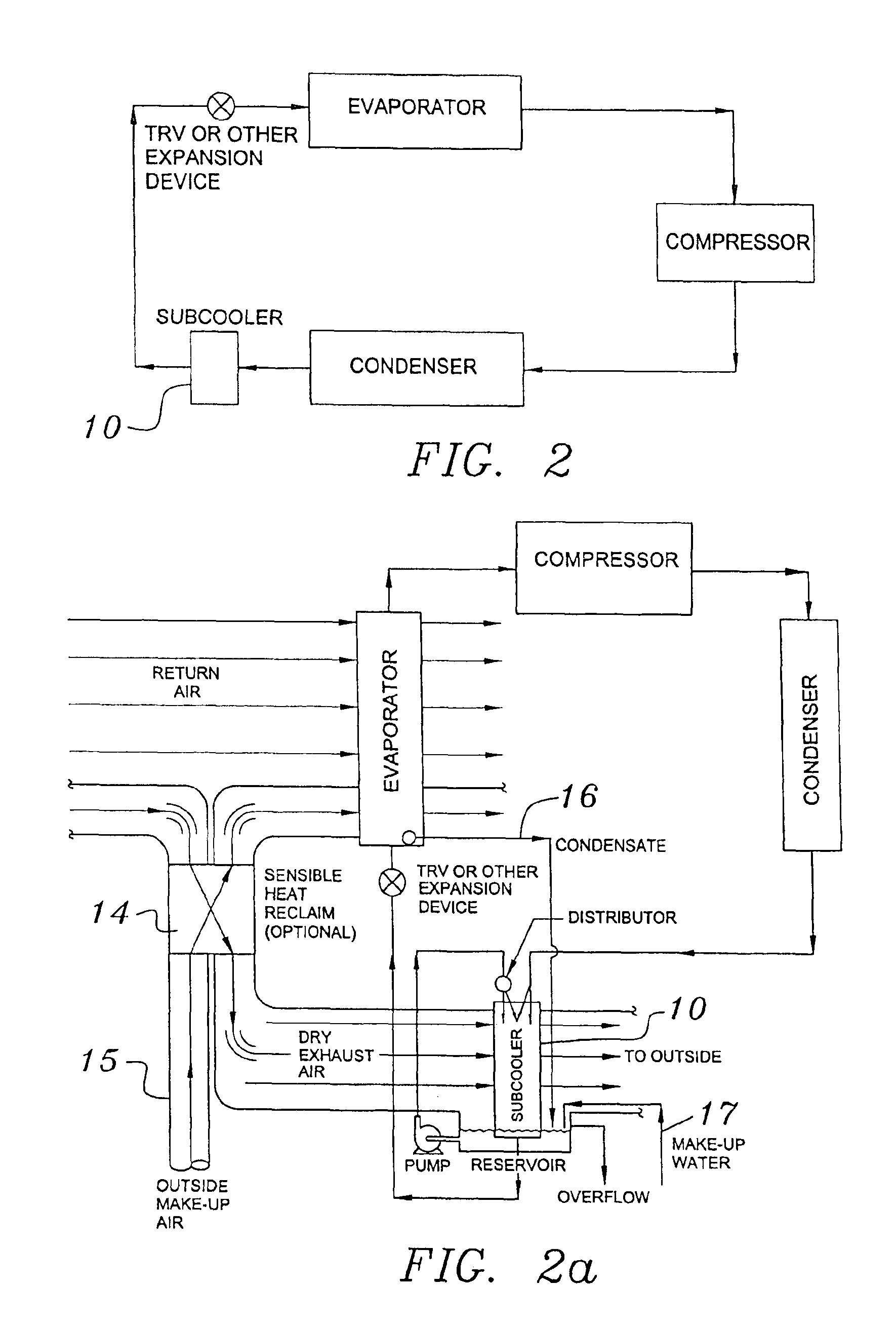
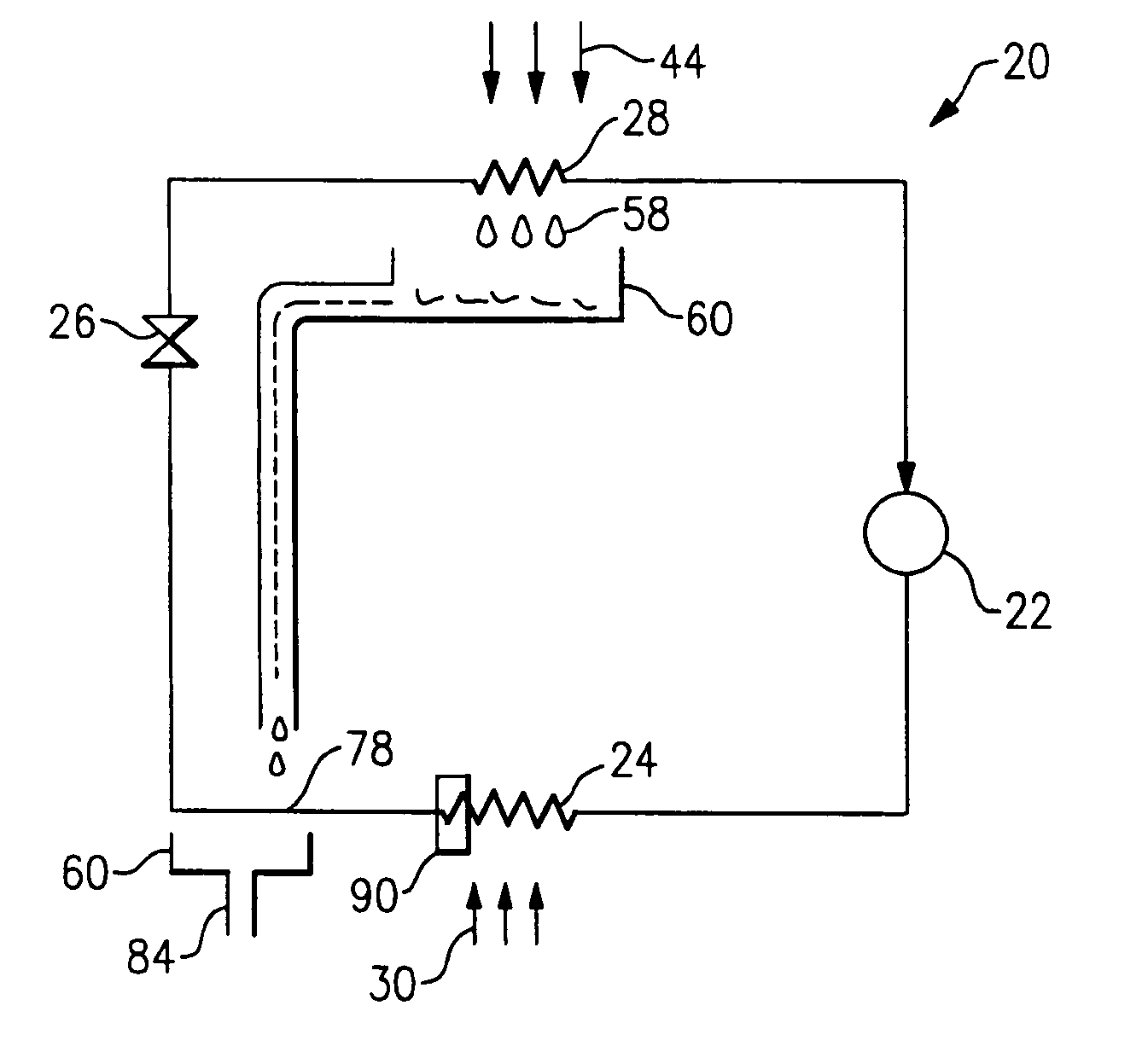
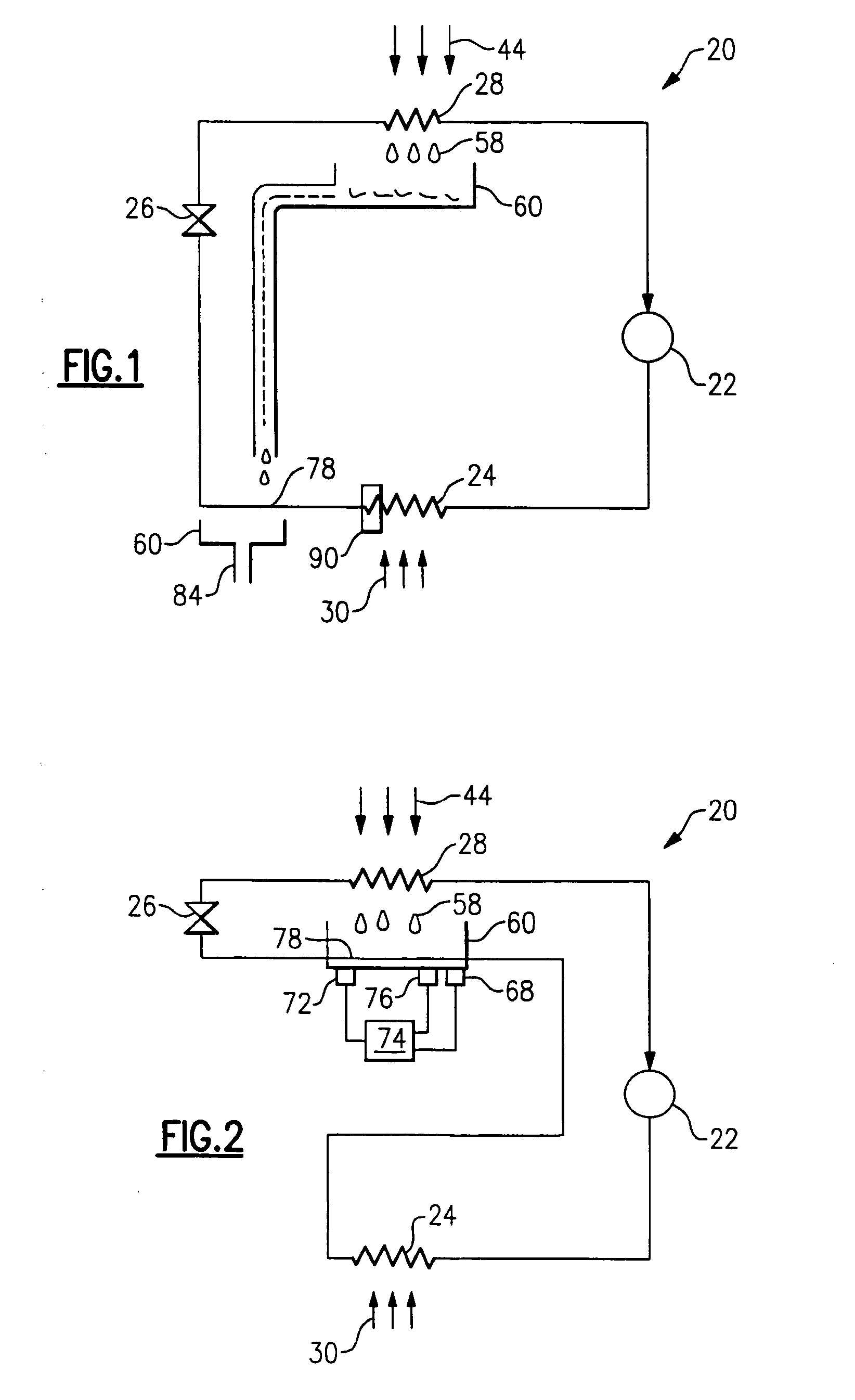
Building exhaust and air conditioner condenstate (and/or other water source) evaporative refrigerant subcool/precool system and method therefor
InactiveUS6070423AComprehensive understandingReduce the temperatureEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingHeat recovery systemsWater wetIndoor air quality
First, a system for providing liquid refrigerant subcooling, subsequent to that subcooling accomplished by the primary condenser of an air conditioner or heat pump, by means of evaporative cooling utilizing the condensate water of said air conditioner or heat pump system and / or some other water supply to wet the surface of the subcool heat exchanger and then passing the cold, dry building exhaust air required for good indoor air quality across the wetted surface of the subcool heat exchanger. Said exhaust air could be used after first undergoing a sensible heat exchange with the incoming make up air. Said subcooling providing for an increased refrigeration capacity, and efficiency of the system. Secondly, a system for providing hot gas discharge refrigerant precooling before said hot gas passes into the primary condenser of an air conditioner or heat pump, by means of evaporative cooling utilizing the condensate water of said air conditioner or heat pump system and / or some other water supply to wet the surface of the precool heat exchanger and then passing the cold, dry building exhaust air required for good indoor air quality across the wetted surface of the precool heat exchanger. Said precooler providing lower power consumption of the compressor, lower head pressure, increased mass flow of the refrigerant and improved efficiency of the primary condenser of the air conditioning or heat pump system. Said exhaust air could be used after first undergoing a sensible heat exchange with the incoming make up air on either the subcooler or precooler. Finally, a combination subcooler and precooler system where the cold dry exhaust air is first used to evaporatively subcool the liquid refrigerant in the water wetted subcooler and then subsequently used to conductively cool the hot gas refrigerant passing through a dry surface precooler or alternately used to evaporatively cool the wetted surface of the precooler thereby evaporatively precooling the hot gas refrigerant passing through the precooler.
Owner:GLOBAL ENERGY & ENVIRONMENT RES INC +1
Apparatus and method for determining refrigerant charge level
ActiveUS7631508B2Low-cost non-invasiveLow costThermometer applicationsRefrigeration safety arrangementLiquid lineMonitoring system
A method and apparatus for non-invasively determining a charge level of a refrigerant in a vapor-compression cycle system. The method and apparatus monitor the system while the system is operated to ascertain that the system is operating at approximately steady-state. The superheat and the subcooling of the system are then determined at the suction line and at the liquid line, respectively, and the refrigerant charge level is calculated based on the determined subcooling, the determined superheat, and rated operating conditions of the system, including rated refrigerant charge level, rated liquid line subcooling, and rated suction line superheat.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Exhaust heat recovery system
InactiveUS20110167818A1Easy to operateLow efficiencyInternal combustion piston enginesEngine componentsSuper coolingEngineering
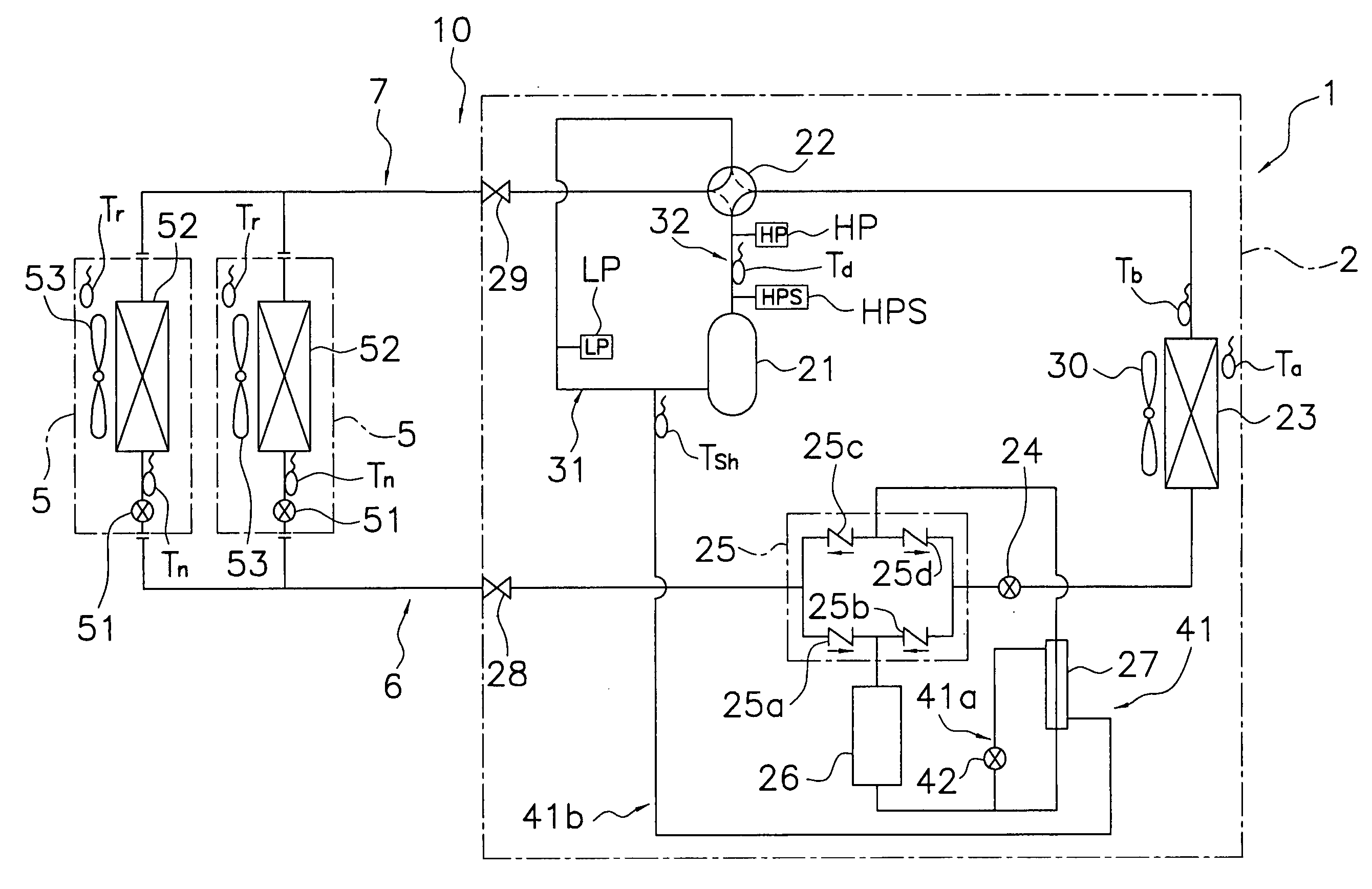
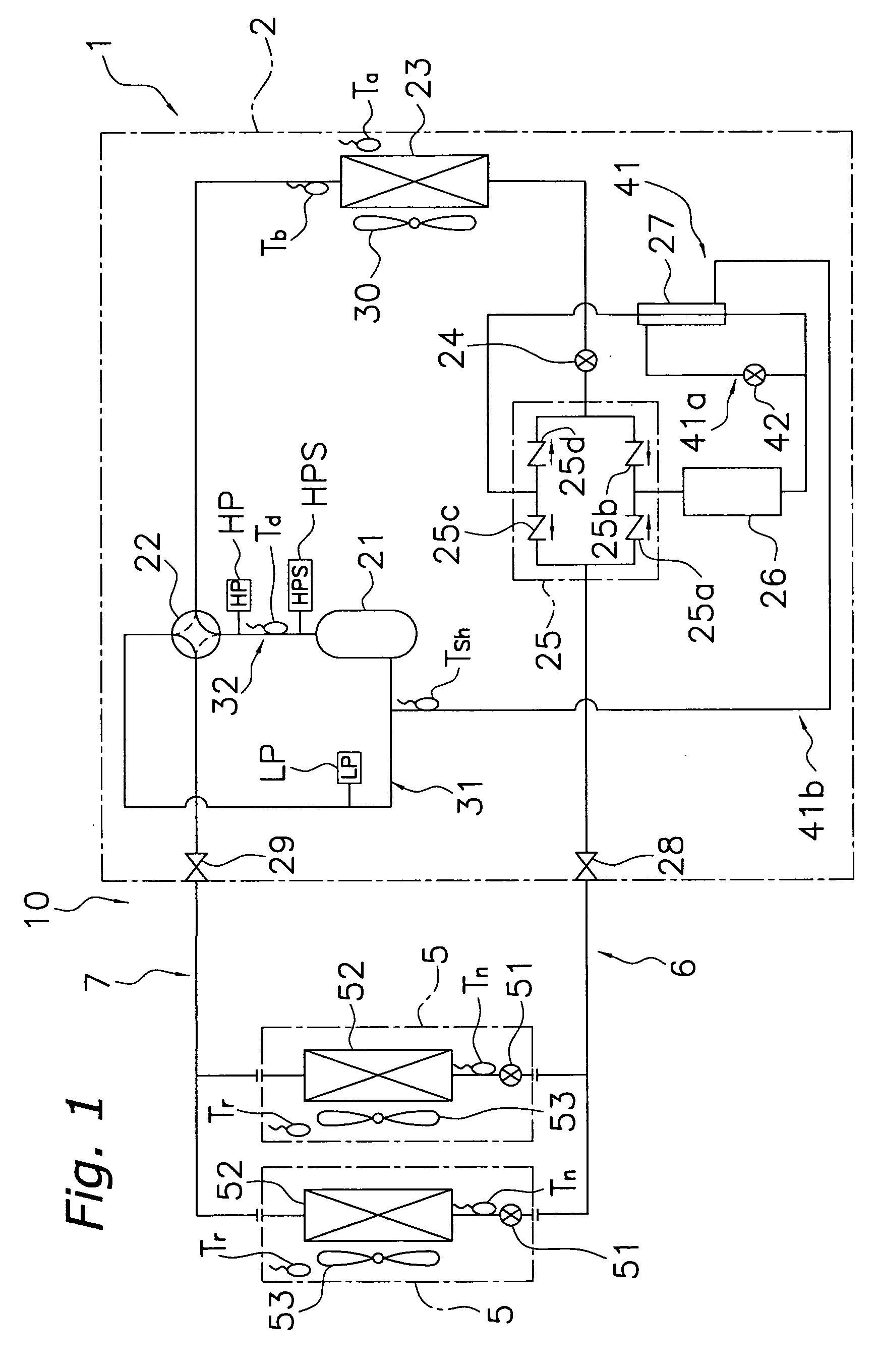
In a case of a refrigerant amount being short when a Rankine cycle starts operating, because the pressure difference does not occur across a refrigerant pump, refrigerant cannot be injected from a bypass circuit to the Rankine cycle, and therefore super-cooling degree cannot be controlled. An exhaust heat recovery system is provided that can adjust the super-cooling degree even in the case of the pressure difference not occurring across the refrigerant pump. The system includes a refrigerant tank, for storing refrigerant, which is connected by pipes to the low-pressure circuit side and the high-pressure circuit side of the Rankine cycle through a low-pressure-side valve and a high-pressure-side valve, respectively, and a temperature adjuster for adjusting internal temperature of the refrigerant tank.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Refrigeration monitoring system and method
ActiveCN101802521AEvaporators/condensersRefrigeration safety arrangementLiquid lineMonitoring system
A system is provided and may include a compressor having a motor and a refrigeration circuit including an evaporator and a condenser fluidly coupled to the compressor. The system may further include a first sensor producing a signal indicative of one of current and power drawn by the motor, a second sensor producing a signal indicative of a saturated condensing temperature, and a third sensor producing a signal indicative of a liquid-line temperature. Processing circuitry may processes the current or power signal to determine a derived condenser temperature and may compare the derived condenser temperature to the saturated condensing temperature received from the second sensor to determine a subcooling associated with a refrigerant charge level of the refrigeration circuit.
Owner:EMERSON CLIMATE TECH INC
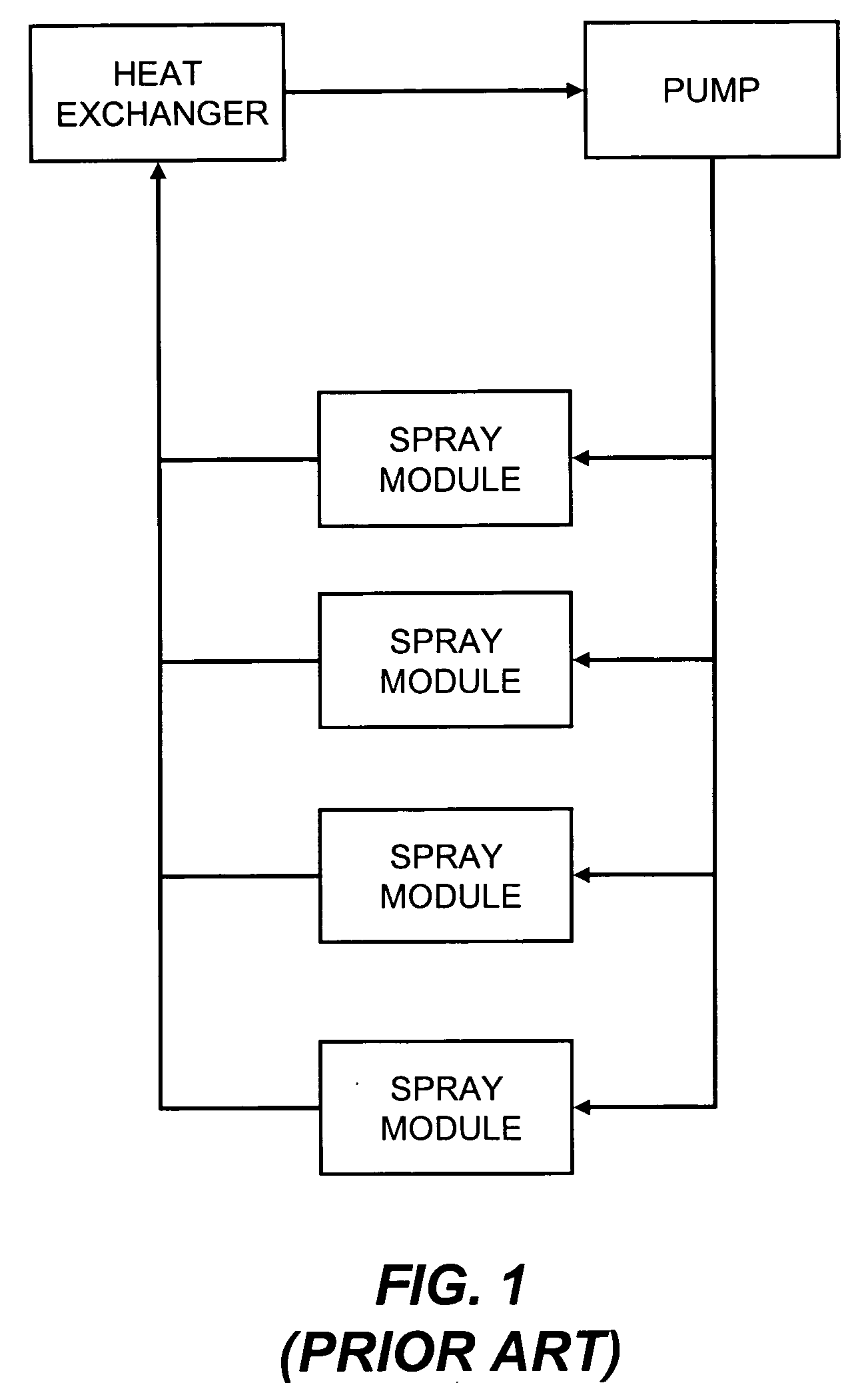
Heat exchanging fluid return manifold for a liquid cooling system
InactiveUS20080066889A1Safety devices for heat exchange apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNuclear engineeringLiquid cooling system
The present invention is a two-phase liquid cooling system that cools a plurality of electronic components connected in parallel. A pump delivers a cooling fluid, as a liquid, to a supply manifold wherein it splits into distinct branch lines. Preferably, the branch lines feed coolant to individual spray modules. The liquid coolant removes heat from the components to be cooled through evaporation. The resulting liquid and vapor mixture exits the spray modules via return branches. Each individual return branch feeds into a return manifold wherein the manifold is sized sufficiently for the separation of liquid and vapor under the influences of gravity. In addition, a heat exchanger is located within the return manifold and provides for the condensation of vapor. The heat exchanger may also provide liquid subcooling.
Owner:ISOTHERMAL SYST RES
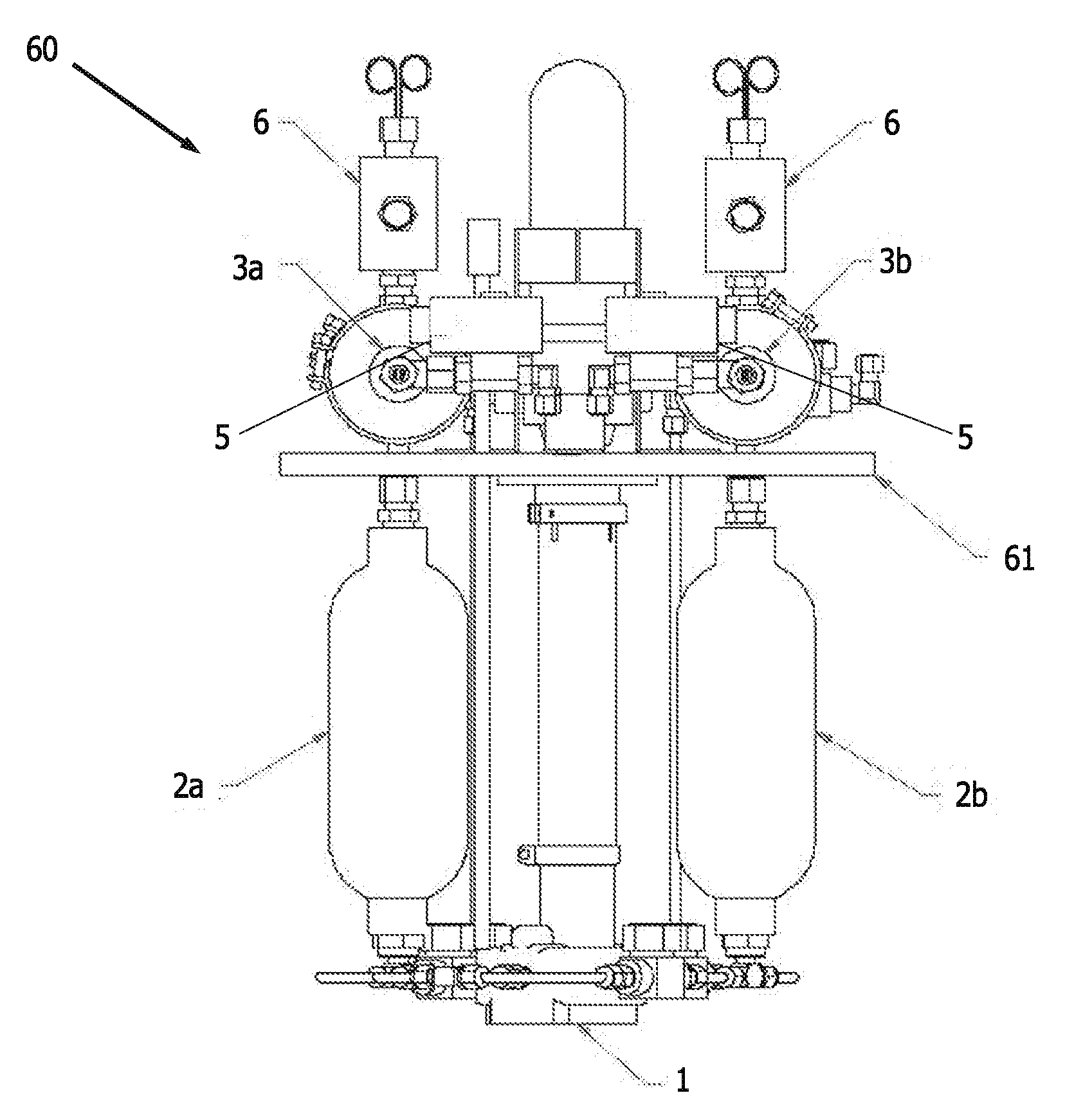
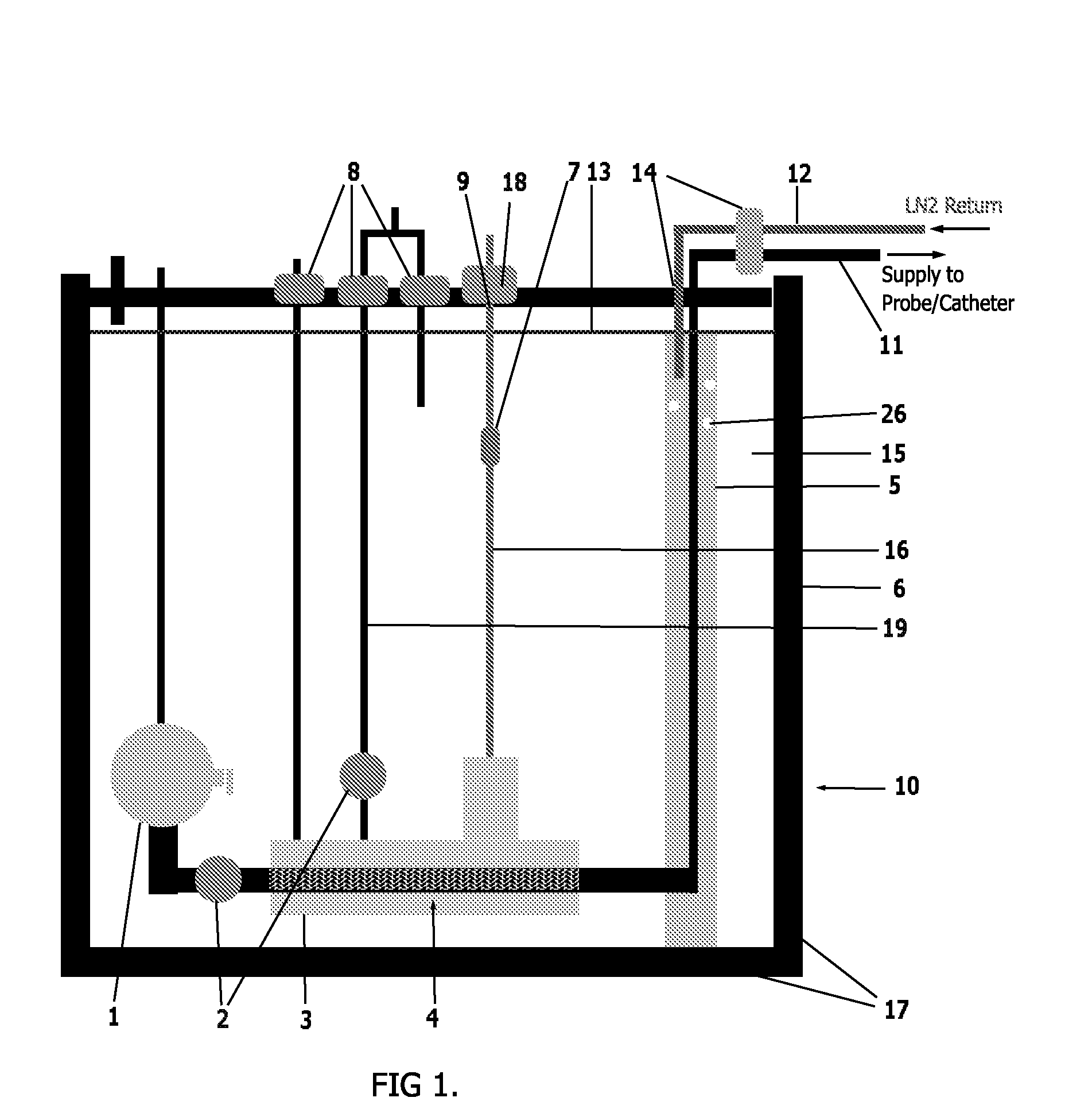
Modular pulsed pressure device for the transport of liquid cryogen to a cryoprobe
ActiveUS20100057067A1Shorten the timeReduced health costMedical devicesCatheterSubcoolingProcess engineering
A cryogenic medical device for delivery of subcooled liquid cryogen to various configurations of cryoprobes is designed for the treatment of damaged, diseased, cancerous or other unwanted tissues. The device is a closed or semi-closed system in which the liquid cryogen is contained in both the supply and return stages. The device is capable of generating cryogen to a supercritical state and may be utilized in any rapid cooling systems. As designed, the device comprises a number of parts including a vacuum insulated outer dewar, submersible cryogen pump, baffled linear heat exchanger, multiple pressurization cartridges, a return chamber, and a series of valves to control the flow of the liquid cryogen. The cryogenic medical device promotes the subcooling to any external cryogenic instrument.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Silicon dioxide coated phase-change microcapsules and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107513375AIncrease coverageReduce breakage rateHeat-exchange elementsMicroballoon preparationToxic materialSilicon dioxide
The invention discloses silicon dioxide coated phase-change microcapsules and a preparation method and an application thereof, wherein the phase-change microcapsules include a core material and a wall material; the core material includes a phase-change material, and the wall material is silicon dioxide; the enthalpy value retention rate of the silicon dioxide coated phase-change microcapsules is 20-99%; the average particle size of the microcapsules is 0.1-100 microns. Through a sol-gel reaction on an emulsion interface, the silicon dioxide coated phase-change material is obtained by one step; no toxic substances are generated in the preparation process, so the preparation process is green and environmentally friendly; the prepared phase-change energy-storage microcapsules are high in coating rate and low in damage rate, the supercooling degree of the phase-change material is effectively reduced, the obtained phase-change material has no volatile gases, the use is safe, and an application scope is expanded; the preparation method has the advantages of simple process, low cost, cheap and easily obtained used raw materials, and easily achieved industrialization. The phase-change energy-storage microcapsules can be widely applied to the fields of textile, building energy conservation, electronic part and component thermal management, waste heat recovery and the like.
Owner:中科世宇(北京)科技有限公司
Freezer apparatus
ActiveUS20060048539A1Increase flow rateIncrease subcoolingCompression machines with non-reversible cycleFluid circulation arrangementEngineeringRefrigeration
A refrigeration system to increase the subcooling degree of refrigerant flowing through a main refrigerant circuit is provided. The refrigeration system is configured such that a portion of the refrigerant flowing through the main refrigerant circuit can be made to bypass the remainder of the main refrigerant circuit in a bypass refrigerant circuit so as to be returned to the intake side of a compressor and to be used to cool the refrigerant flowing through the main refrigerant circuit to a subcooled state.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
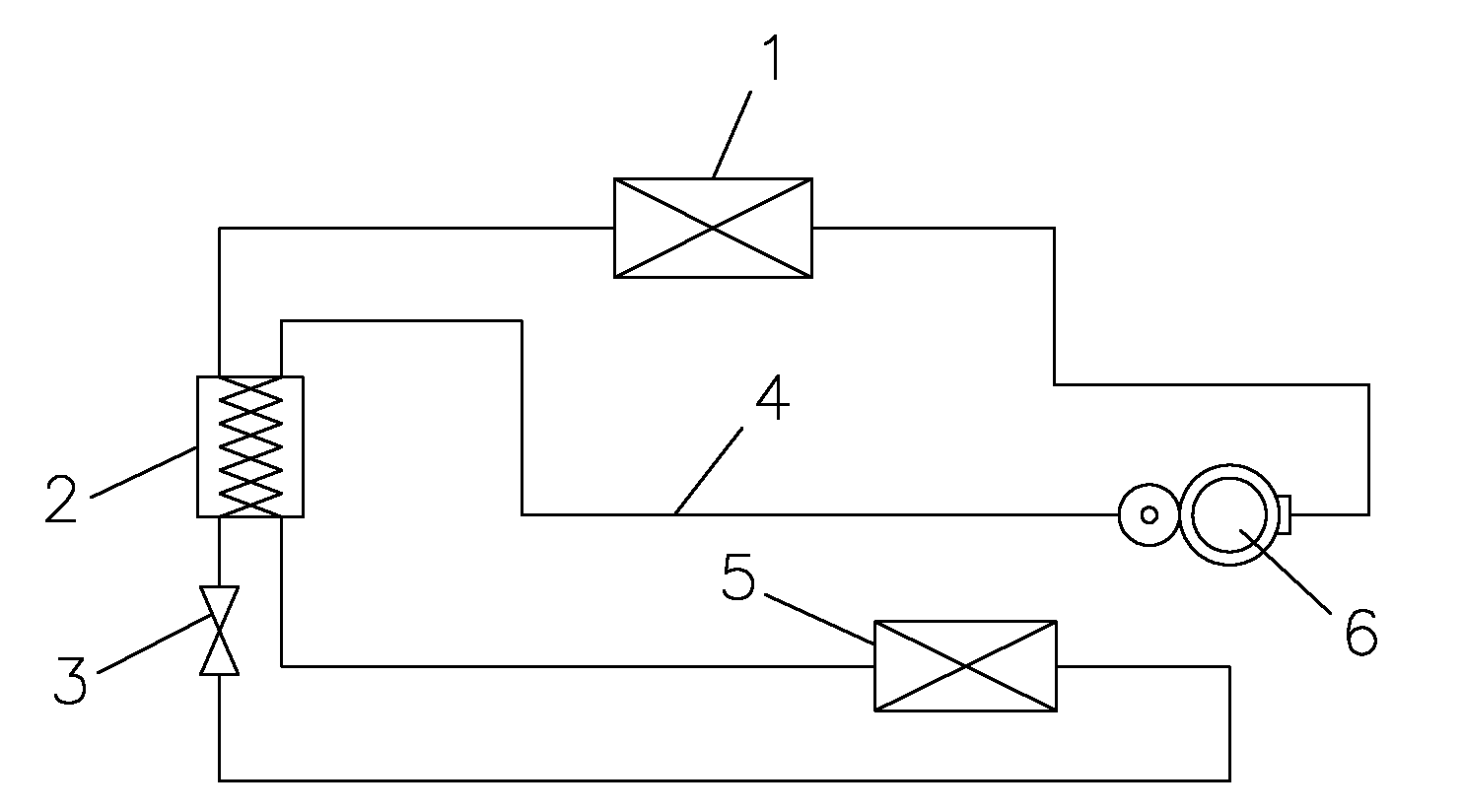
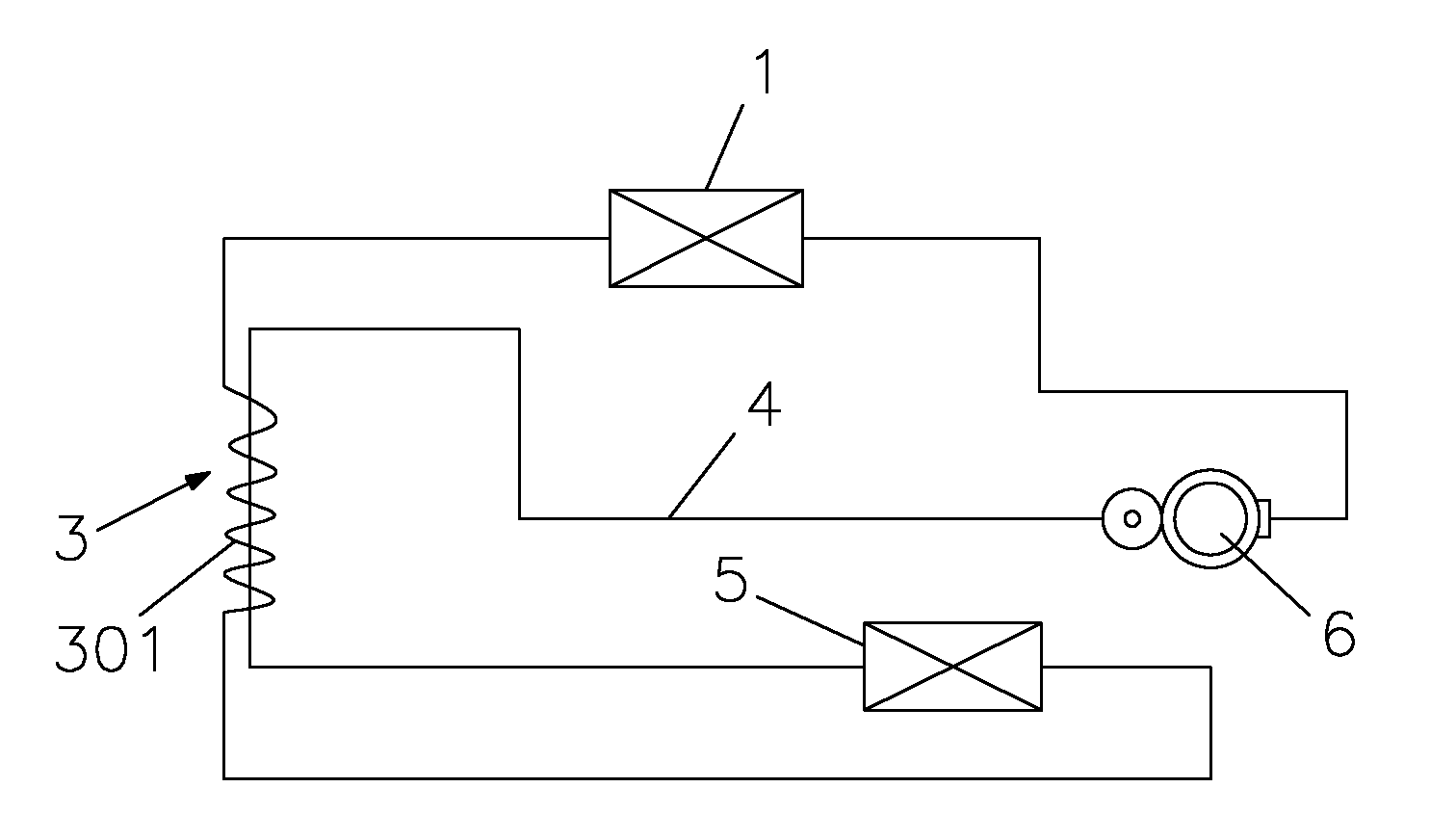
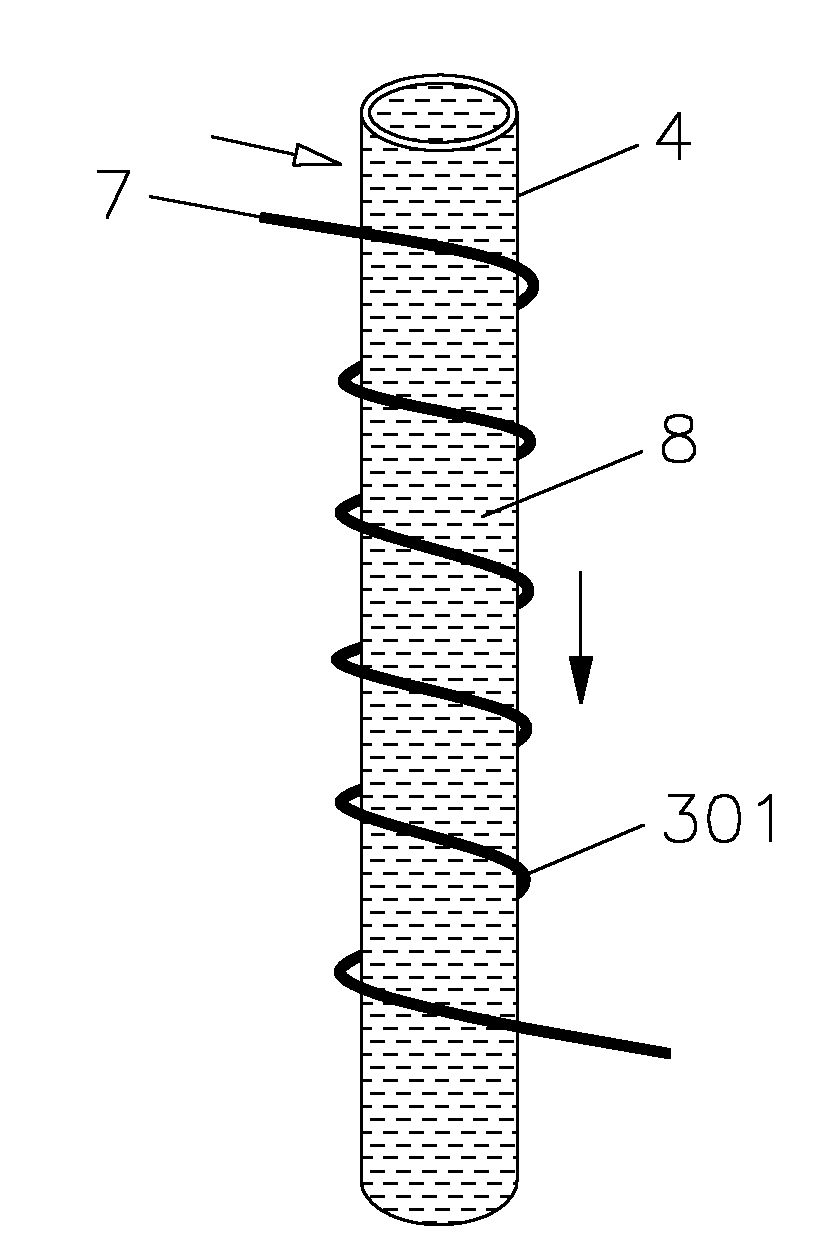
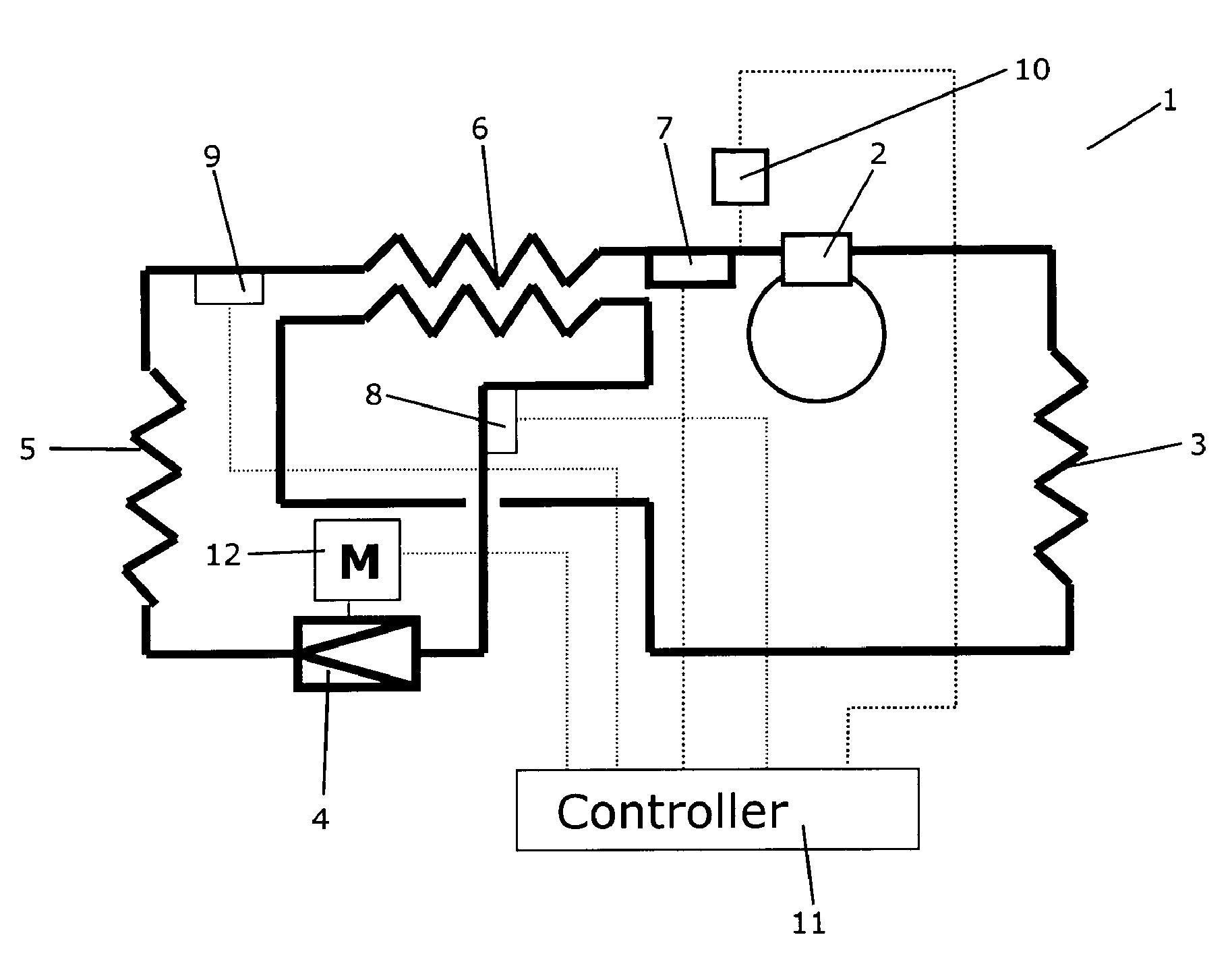
Refrigeration cycle device and method of controlling the same
ActiveUS20110083456A1Reduce the amount requiredLimited amountMechanical apparatusCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEngineeringControl valves
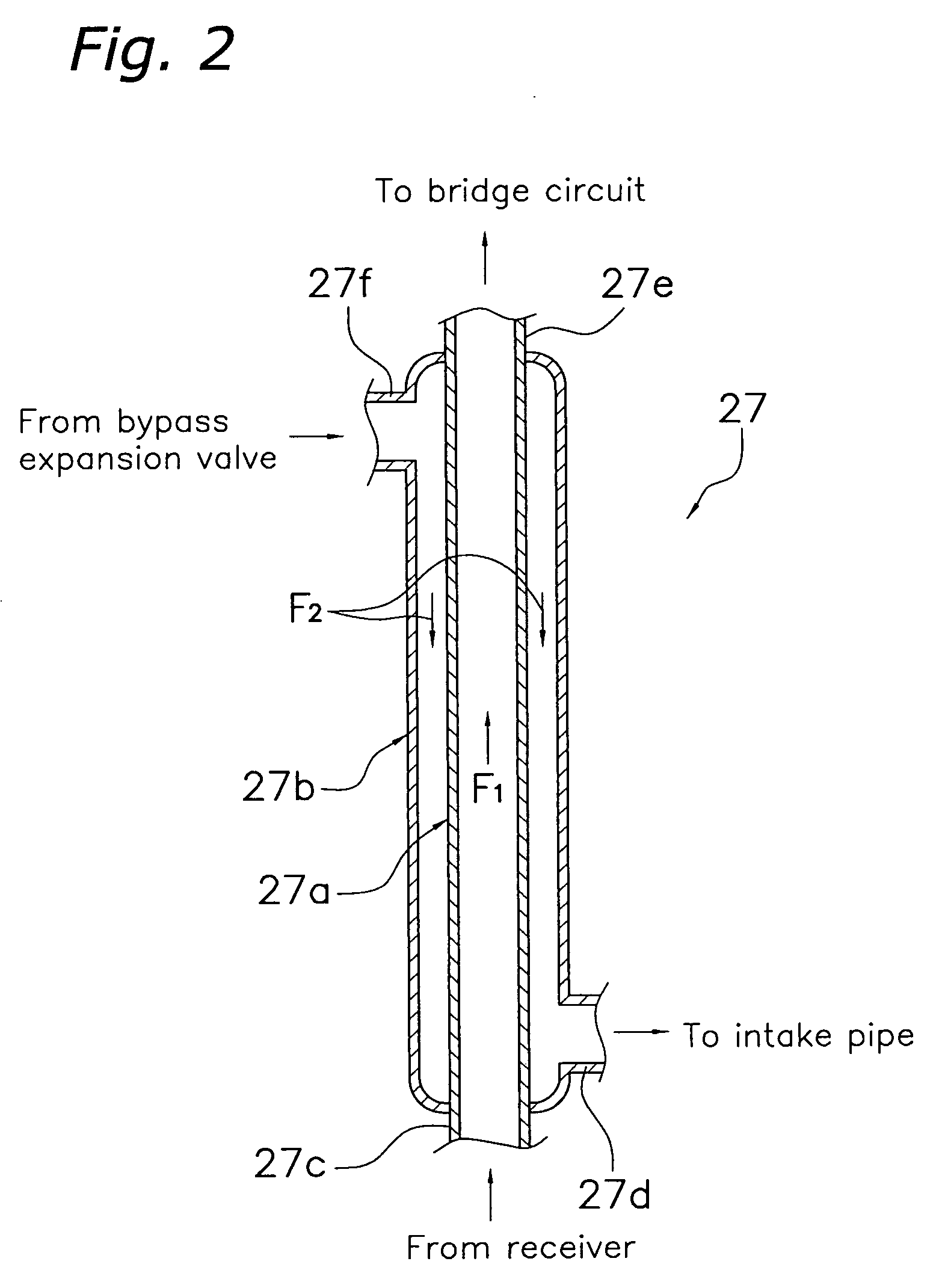
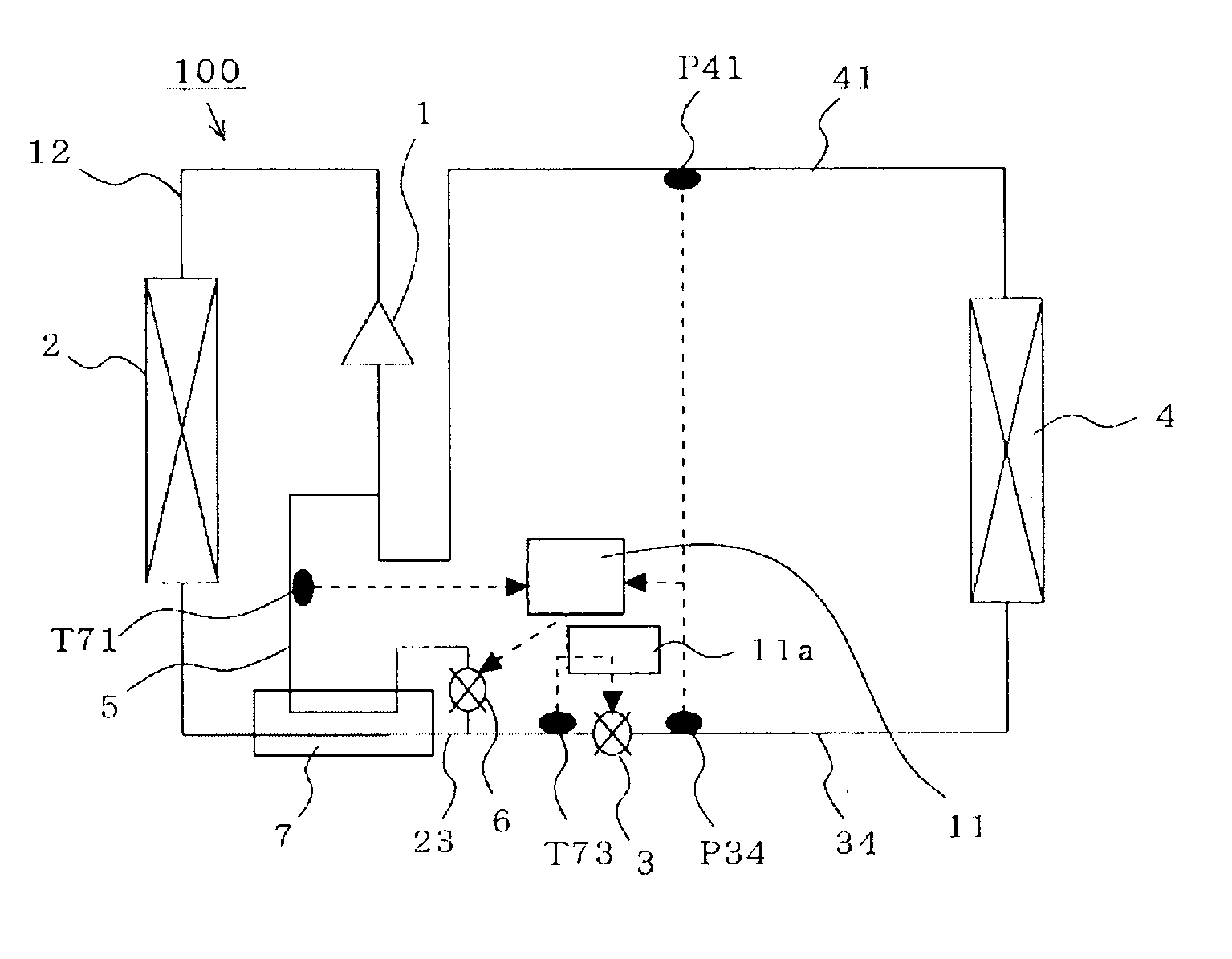
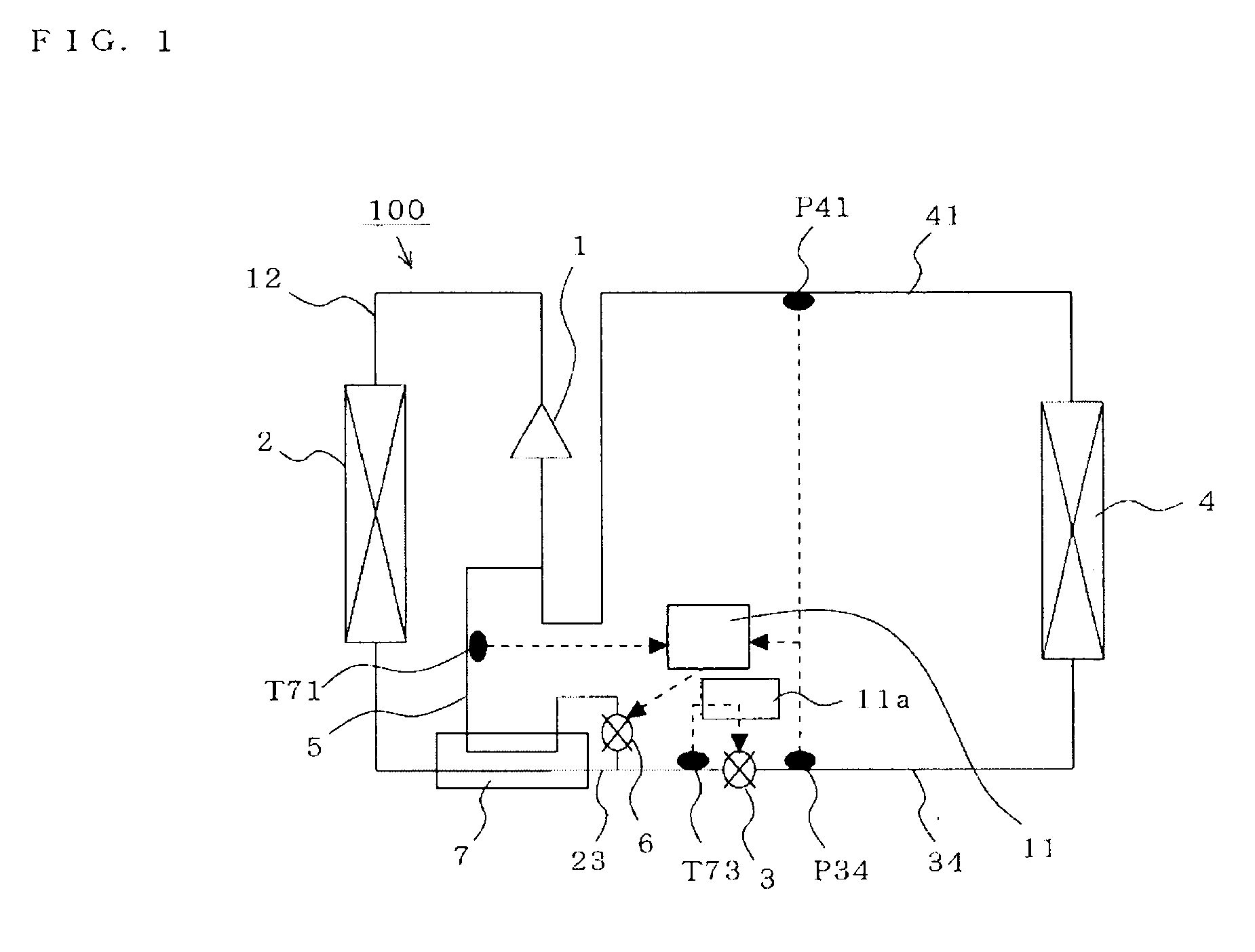
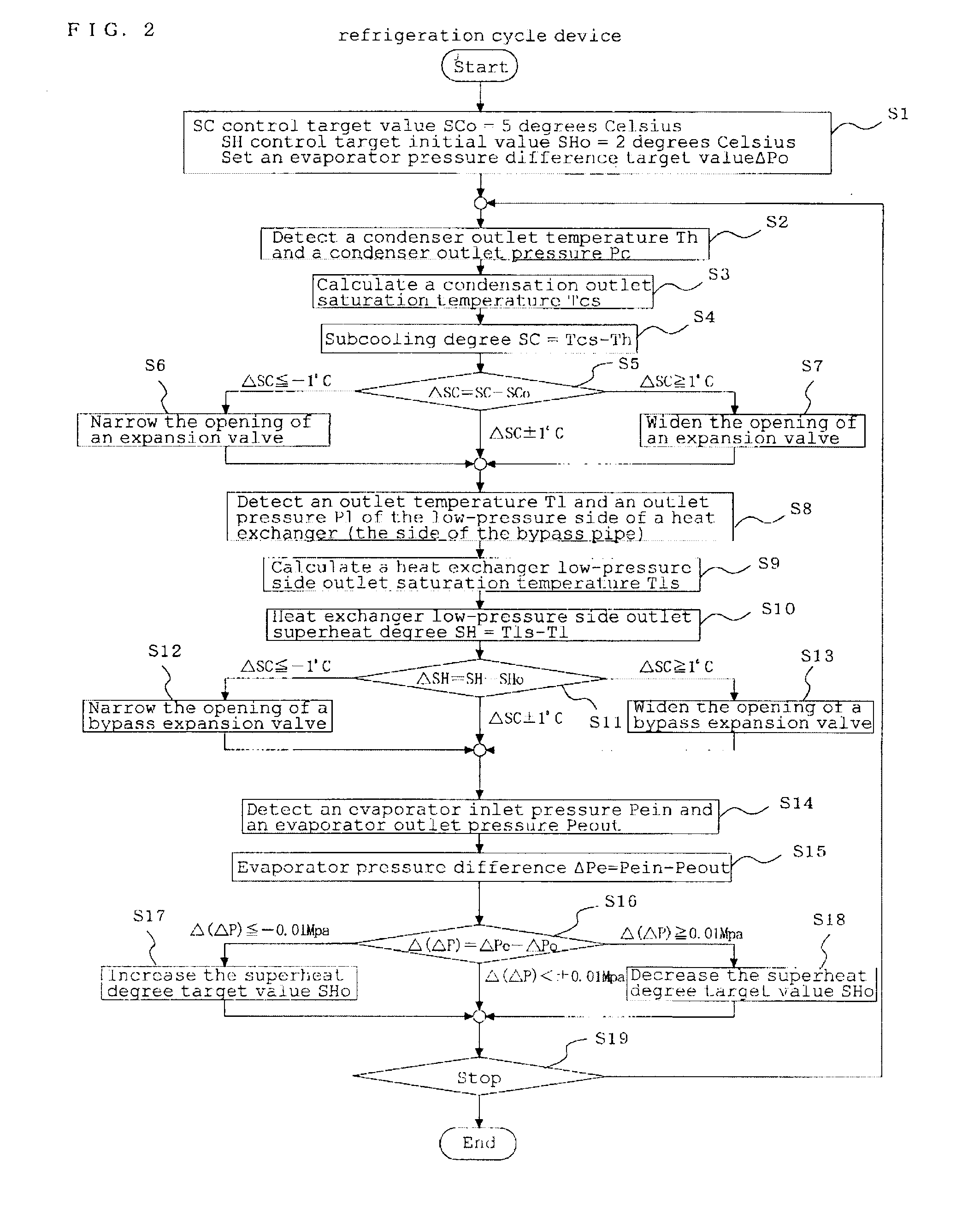
A refrigeration cycle device 100 where a combustible refrigerant circulates includes a bypass pipe 5 that is connected so that part of the refrigerant that flows through a circulation pipe extending from a condenser 2 to a flow control valve 3 bypasses the flow control valve 3 and an evaporator 4; a bypass flow control valve 6 that controls the amount of the refrigerant flowing through the bypass pipe 5; a heat exchanger 7 that allows heat exchange between the refrigerant that flows through the bypass pipe 5 after flowing out of the bypass flow control valve 6 and the refrigerant that flows through the circulation pipe after flowing out of the condenser 2; and a subcooling degree sensor T73 that detects the subcooling degree of the refrigerant at the inlet of the flow control valve 3. At least either the flow control valve 3 or the bypass flow control valve 6 is controlled so that the subcooling degree of the refrigerant at the inlet of the flow control valve 3 is equal to or greater than or a predetermined value.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
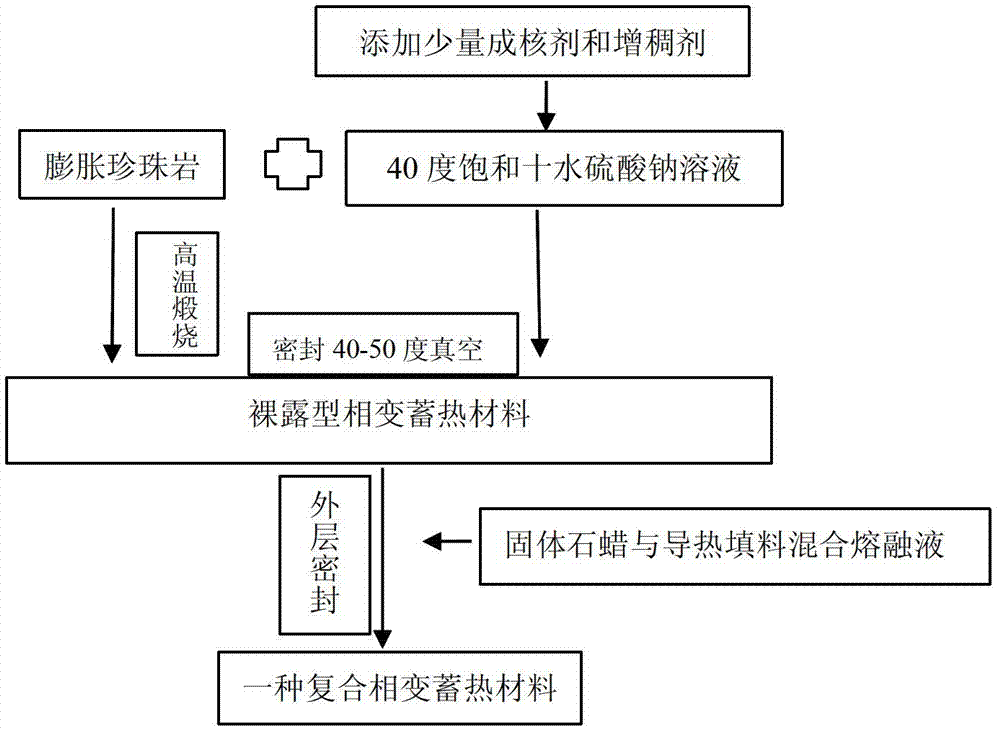
Composite phase change heat storage material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103194179AImprove overcoolingEasy to separateHeat-exchange elementsParaffin waxFluid phase
The invention discloses a composite phase change heat storage material and a preparation method thereof. The composite phase change heat storage material is characterized by comprising the following materials in parts by weight: 39.4-40.3 parts of saturated sodium sulfate decahydrate solution, 0.8-1.2 part of nucleating agent, 1.2-2 parts of thickening agent, 23.6-24.0 parts of solid paraffin, 1.2-2.4 parts of heat-conducting filler, 17.8-18.6 parts of expanded perlite and 13.6-13.9 parts of distilled water, wherein a 40 DEG C saturated sodium sulfate decahydrate solution containing the nucleating agent and the thickening agent is adsorbed into the expanded perlite by employing a vacuum absorption method and then is sealed by employing industrial solid paraffin after adsorption is finished, and the heat-conducting filler is added in the sealing process. The composite phase change heat storage material has the advantages that after being modified and micro-packaged, the composite phase change heat storage material has low supercooling degree, the solution is uniform and not layered during solid-liquid phase change, the performance is stable, the repeatability is high, the service life is prolonged, and the composite phase change heat storage material can be widely applied to actual building energy conservation engineering.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Backheating method and backheating structure for heat pump air conditioner
InactiveCN101979938AReduce the temperatureReduce vaporizationHeat recovery systemsFluid circulation arrangementEvaporationEngineering
The invention discloses a backheating method and a backheating structure for a heat pump air conditioner, which can improve the performance of the air conditioner. The backheating structure comprises heat exchangers A and B, a compressor, and a throttling element connected between the heat exchangers A and B, wherein the heat exchanger B is connected with the compressor by an air suction pipe of the compressor; and a higher-temperature coolant in the throttling element performs heat exchange with a lower-temperature coolant in the air suction pipe of the compressor. In the backheating method and the backheating structure, the temperature of the coolant in the throttling element can be reduced by performing backheating in a throttling process, thereby retarding the evaporation of the coolant and the change of the dryness of the coolant, making more stable the flow regime of the coolant and reducing inevitable loss; and the dryness of the coolant at an outlet of the throttling element is reduced, namely, the degree of subcooling of the air conditioner is increased, so the cooling capacity of the air conditioner can be improved. The backheating method and the backheating structure for the heat pump air conditioner can improve the cooling or heating performance of the heat pump air conditioner; and the backheating structure is simplified to a certain extent so as to be convenient to manufacture and save the cost.
Owner:四川长虹空调有限公司
Building exhaust and air conditioner condensate (and/or other water source) evaporative refrigerant subcool/precool system and method therefor
InactiveUS6857285B2Improve pumping efficiencyReduce power consumptionEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingHeat recovery systemsWater wetWater source
A system for providing liquid refrigerant subcooling, by means of evaporative cooling utilizing the condensate water of said air conditioner, refrigeration / heat pump system and / or some other water supply to wet the surface of the subcool heat exchanger and pass the dry exhaust air across the wetted surface of the subcool heat exchanger. A system for providing hot gas discharge refrigerant precooling into the primary condenser of an air conditioner, refrigation or heat pump system by evaporative cooling utilizing the condensate water of said system and / or other water supply to wet the surface of the precool heat exchanger and then passing the cold, dry exhaust air across the wetted surface of the precool heat exchanger. A combination subcooler / precooler system where the cold dry building exhaust air is used to evaporatively subcool the liquid refrigerant in the water wetted (or dry) subcooler and then used to conductively cool the hot gas refrigerant.
Owner:OLIVE TREE PATENTS 1
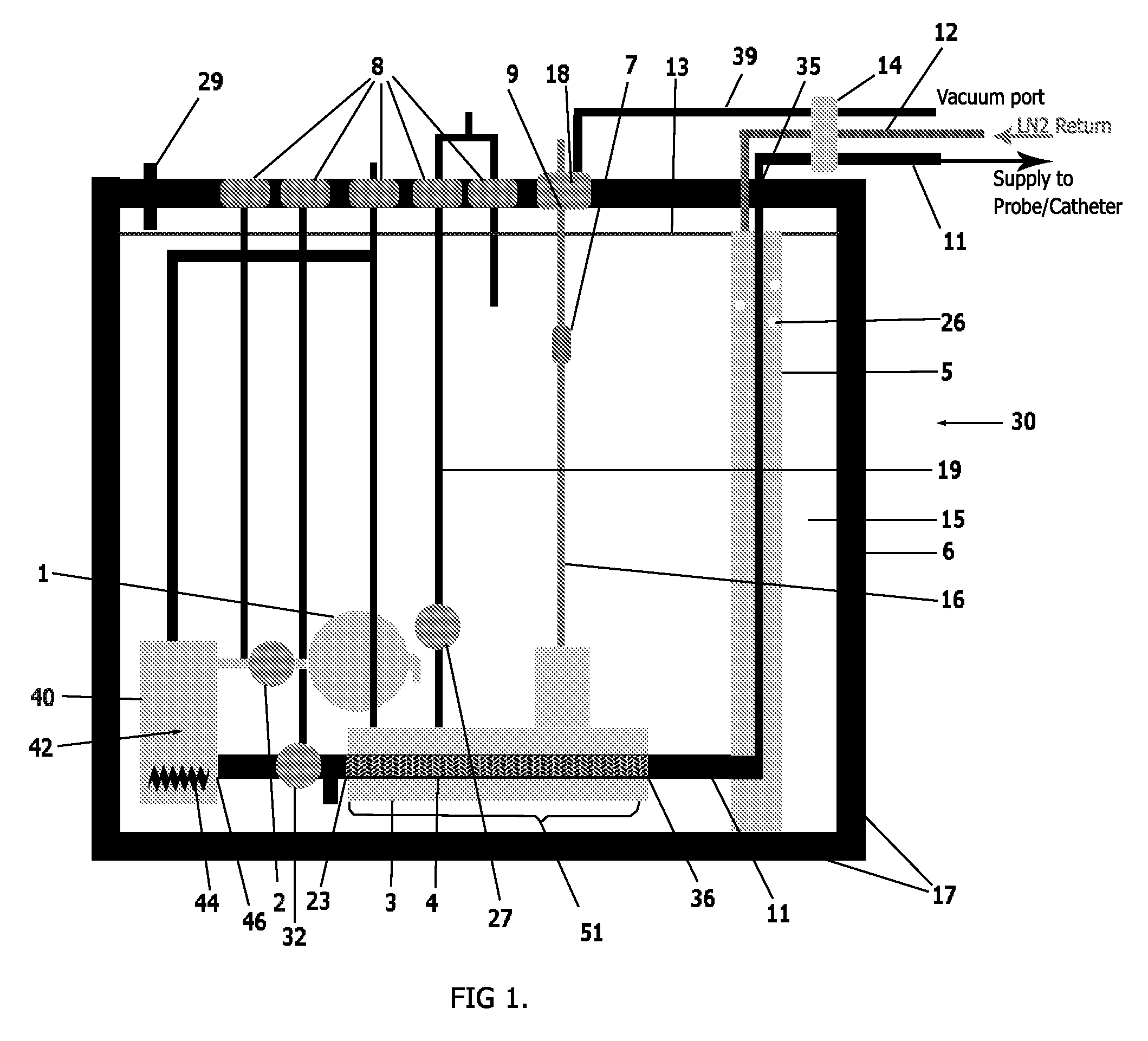
Medical Device for the Transport of Subcooled Cryogenic Fluid through a Linear Heat Exchanger
ActiveUS20100057064A1Increase surface areaReduce the temperatureCatheterSurgical instruments for coolingProcess engineeringMedical device
A cryogenic medical device for delivery of subcooled liquid cryogen to various configurations of cryoprobes is designed for the treatment of damaged, diseased, cancerous or other unwanted tissues. The device is a closed or semi-closed system in which the liquid cryogen is contained in both the supply and return stages. The device comprises a number of parts including a vacuum insulated outer dewar, submersible cryogen pump, baffled linear heat exchanger, return chamber, and a series of valves to control the flow of the liquid cryogen. The cryogenic medical device promotes the subcooling to any external cryogenic probe.
Owner:ENDOCARE
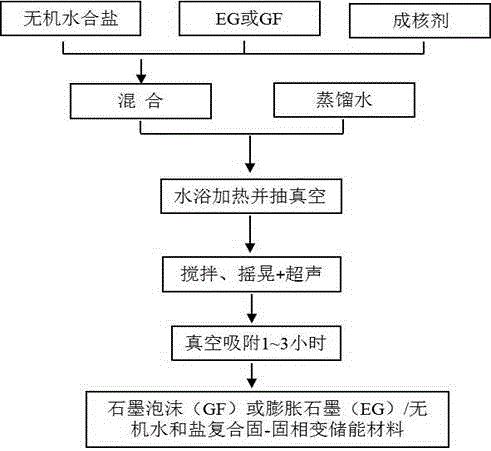
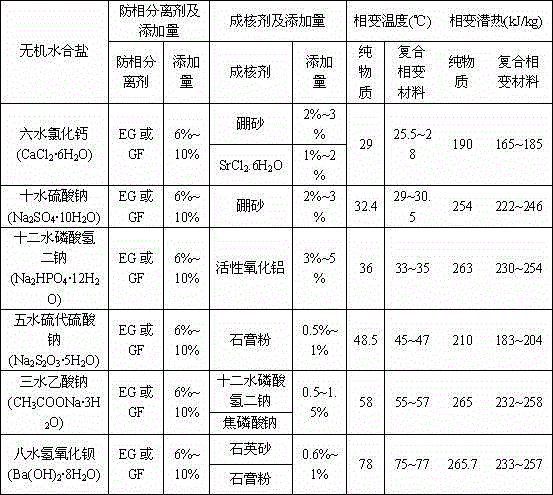
Preparation method of expanded-graphite-base hydrated salt composite solid-solid phase-change energy storage material
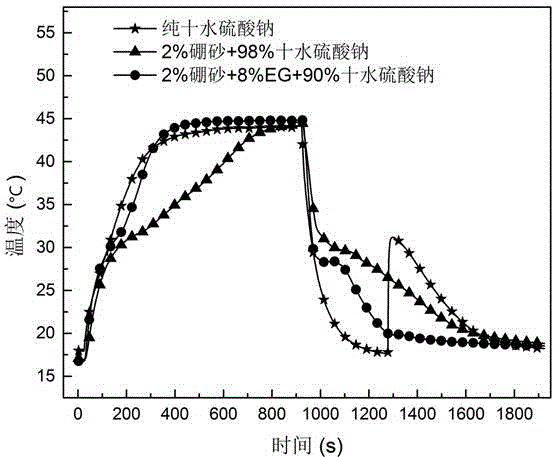
InactiveCN104531077AReduce subcoolingSmall volume changeHeat-exchange elementsPhysical chemistryDistilled water
The invention provides a preparation method of a graphite foam (GF) or expanded graphite (EG) / inorganic hydrated salt composite solid-solid phase-change energy storage material. The method comprises the following steps: adding 6-10 wt% of EG or GF into an inorganic hydrated salt phase-change material, adding distilled water which is 2 times by mass of the EG or GF, adding a corresponding nucleator, and carrying out vacuum adsorption in a water bath with the temperature of 5-20 DEG C higher than hydrated salt phase-change temperature for 1-3 hours while continuously stirring and vibrating or carrying out ultrasonic vibration. The composite solid-solid phase-change energy storage material thoroughly solves the problem of phase separation of the inorganic hydrated salt, has the characteristics of low degree of supercooling, favorable heat-conducting property, small phase-change volume change, stable performance and no leakage, and is convenient for packaging.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
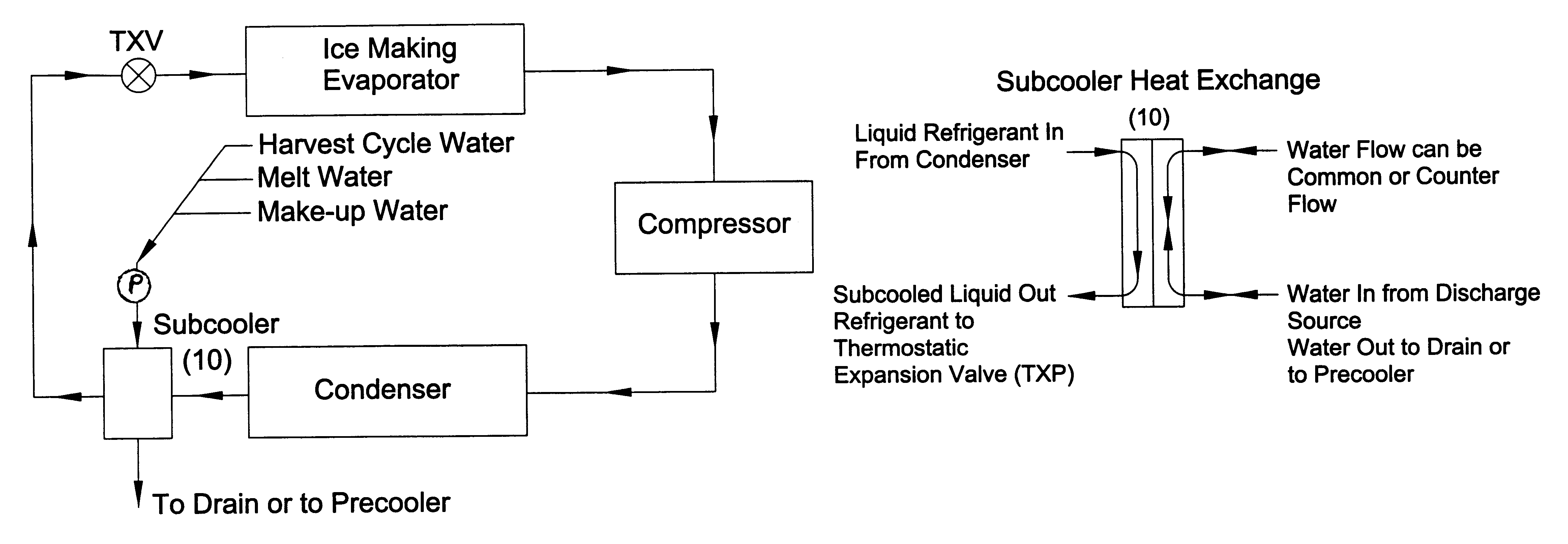
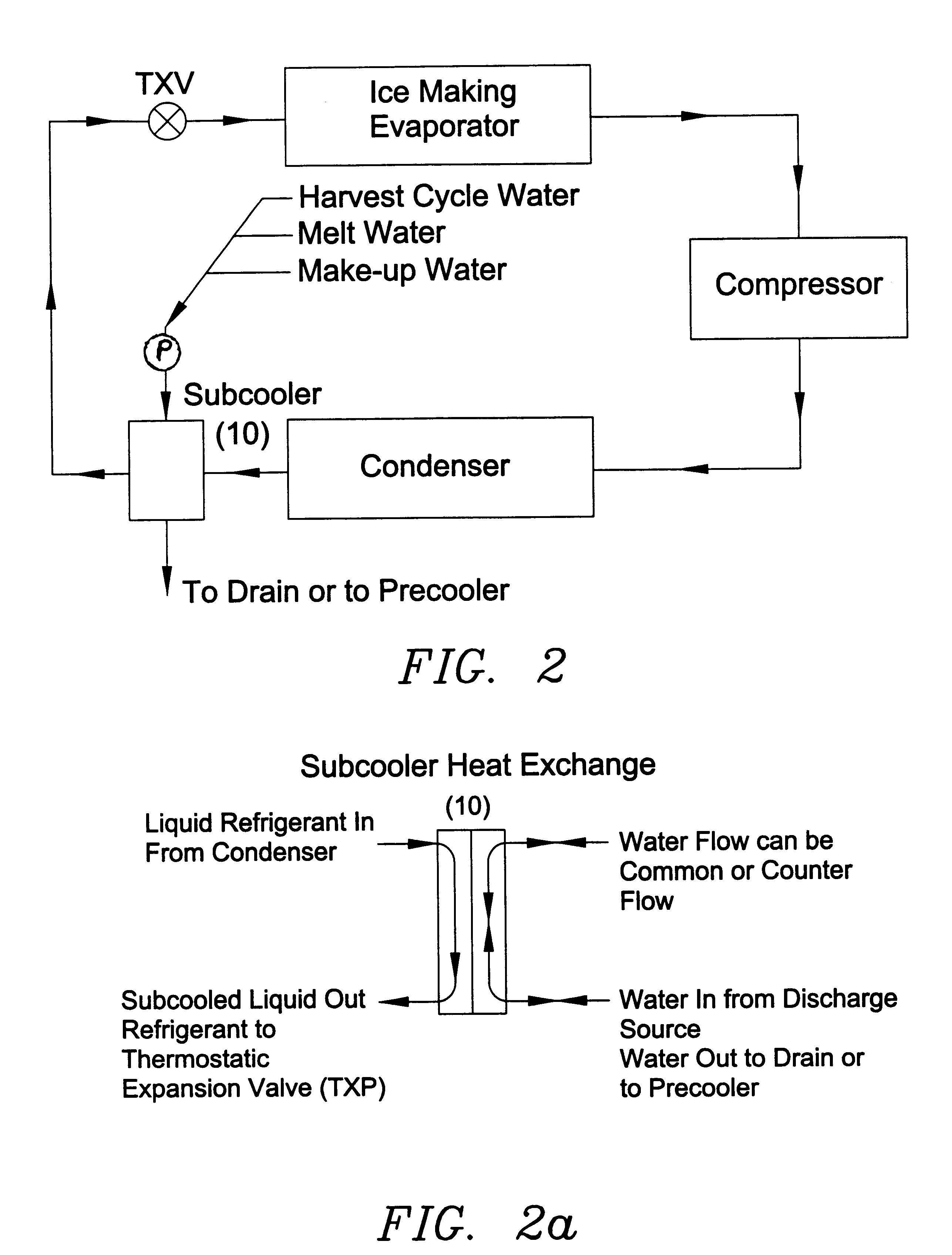
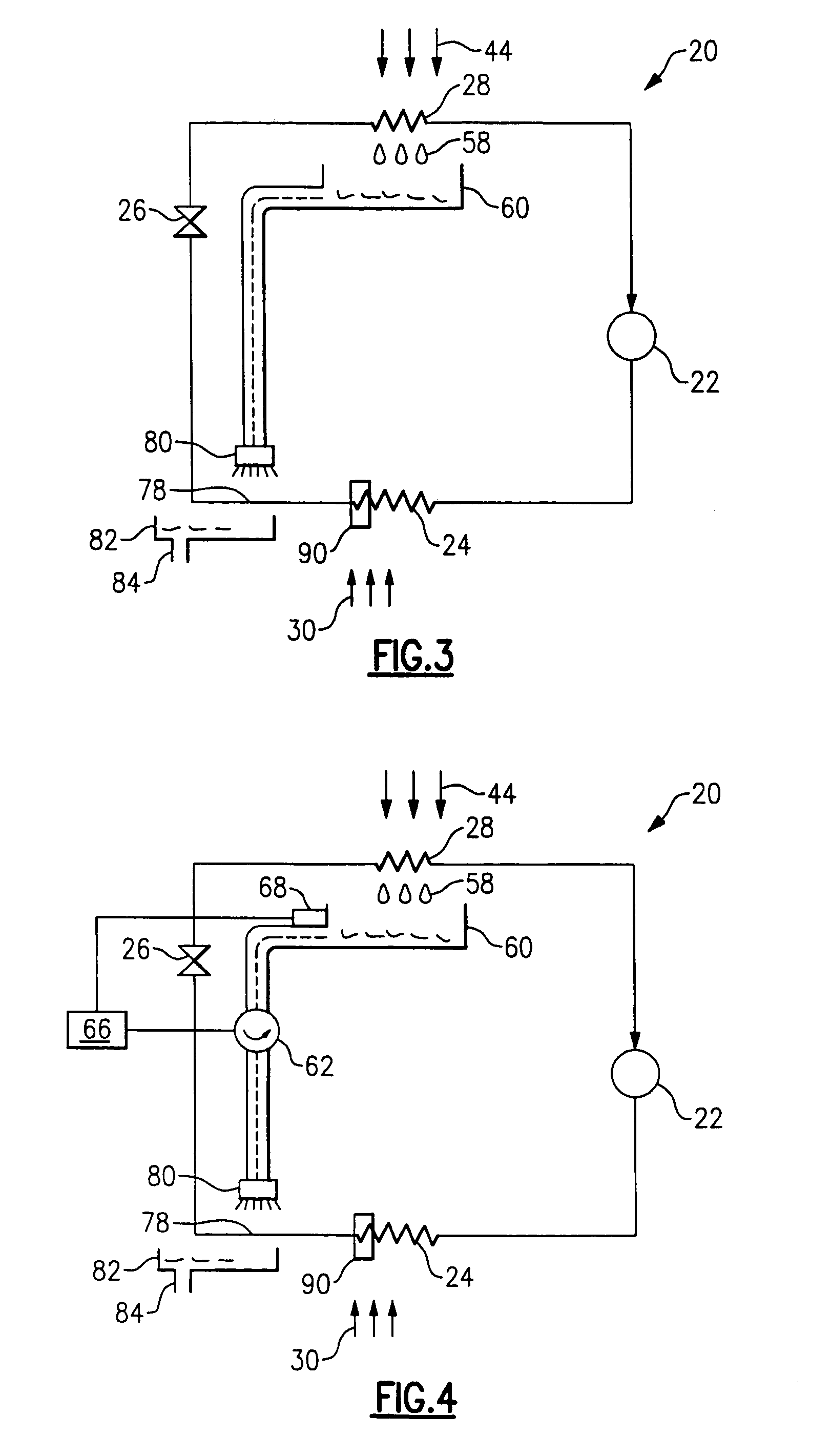
Utilization of harvest and/or melt water from an ice machine for a refrigerant subcool/precool system and method therefor
InactiveUS6237359B1Comprehensive understandingReduce heat dissipationSkin implantsFood processingCounter flowWater discharge
A system for providing liquid refrigerant subcooling, subsequent to that subcooling accomplished by the primary condenser of an ice machine, by means of utilizing cold harvest and / or melt water discharge from said ice machine. The subcooler is connected in fluid communication with the output of a pump that pumps stored ice machine discharge water to directly flow through the subcooler from a bottom portion to a top portion in a counter-flow direction and then to discharge such that the subcooler utilizes the pumped and flowing cold discharge water from the ice machine for providing maximum available subcooling to the liquid refrigerant of said ice machine
Owner:OLIVE TREE PATENTS 1 +1
Method for operating a vapour compression system using a subcooling value
ActiveUS20130074535A1Guaranteed uptimeMechanical apparatusCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEngineeringRefrigerant
A vapour compression system comprises a compressor, a condenser, an expansion device, e.g. in the form of an expansions valve, and an evaporator arranged along a refrigerant path. A method for operating the vapour compression system comprises the steps of: obtaining a superheat value being representative for the superheat of refrigerant entering the compressor; obtaining a subcooling value being representative for the subcooling of refrigerant entering the expansion device; and operating the expansion device on the basis of the obtained superheat value and on the basis of the obtained subcooling value. The subcooling value is taken into account when operating the expansion device, because variations in the subcooling value have significant influence on the refrigerating capacity of the evaporator at a given opening degree of the expansion device, thereby resulting in a more stable operation of the system. The system may further comprise an internal heat exchanger.
Owner:DANFOSS AS
Calcium chloride hexahydrate phase change energy storage material composition
InactiveCN102134473AHigh latent heat of phase changeGood temperature regulationHeat-exchange elementsCalcium Chloride HexahydrateEnergy storage
The invention discloses a calcium chloride hexahydrate phase change energy storage material composition, which comprises calcium chloride hexahydrate, a nucleating agent, a thickener, other functional additives and the like. The phase change temperature of the composition is 23 to 25 DEG C, the degree of supercooling is less than 3 DEG C, and the latent heat of phase change is more than 180kJ / kg. The composition has high phase change stability, passed 3,000 times of tests of cold and hot circulation and can keep the uniform distribution of the nucleating agent in a short time period.
Owner:益田润石(北京)化工有限公司
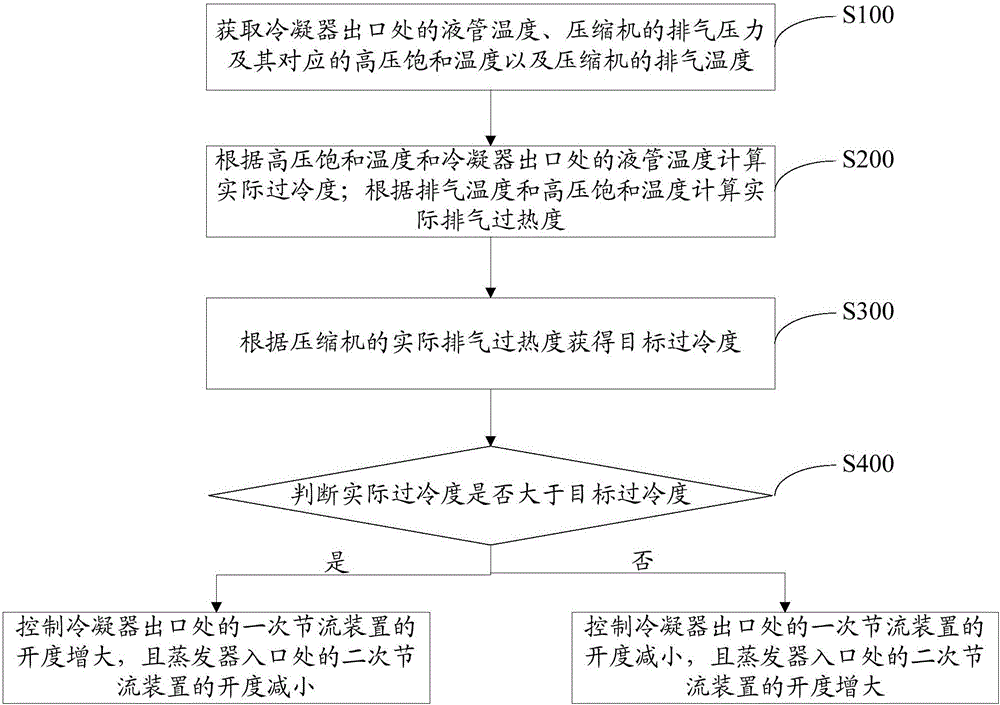
Control method of heat pump system and heat pump system
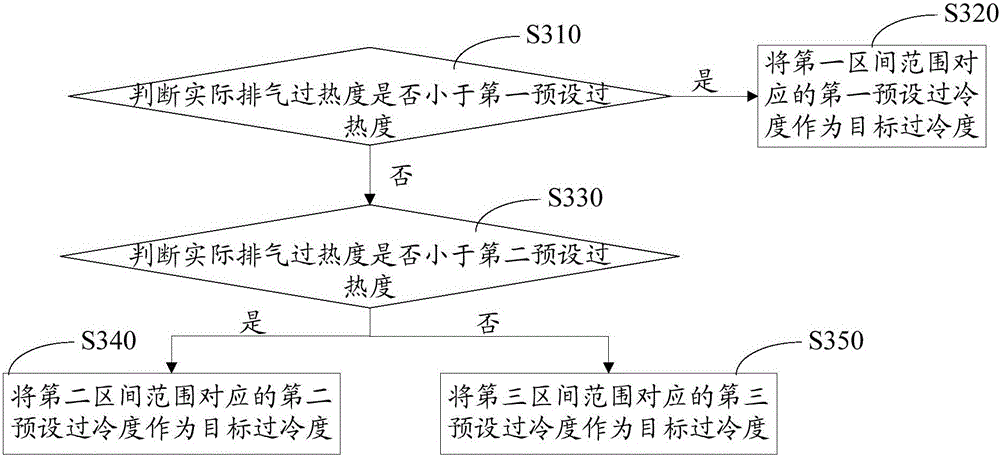
ActiveCN106196787APrevent liquid shockGuaranteed uptimeRefrigeration safety arrangementSuper coolingDischarge rate
The invention provides a control method of a heat pump system. The control method comprises steps as follows: the liquid pipe temperature at an outlet of a condenser, the discharge pressure of a compressor, the high-pressure saturation temperature corresponding to the discharge pressure and the discharge temperature of the compressor are acquired; the actual super-cooling degree is calculated according to the high-pressure saturation temperature and the liquid pipe temperature at the outlet of the condenser; the actual discharge superheat degree is calculated according to the discharge temperature and the high-pressure saturation temperature; the target super-cooling degree is acquired according to the actual discharge superheat degree of the compressor; whether the actual super-cooling degree is larger than the target super-cooling degree or not is judged, and if the actual super-cooling degree is larger than the target super-cooling degree, the actual super-cooling degree is reduced by adjusting the opening degree of a throttling device; and if the actual super-cooling degree is not larger than the target super-cooling degree, the actual super-cooling degree is increased by adjusting the opening degree of the throttling device. The invention further provides the heat pump system. With the control method of the heat pump system and the heat pump system, the accuracy of gas filling liquid detection and judgment of the system is improved, and the compressor is prevented from producing liquid impact, so that long-time reliable running of the compressor can be guaranteed.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Air-conditioning system and method for judging whether refrigerant perfused amount is proper
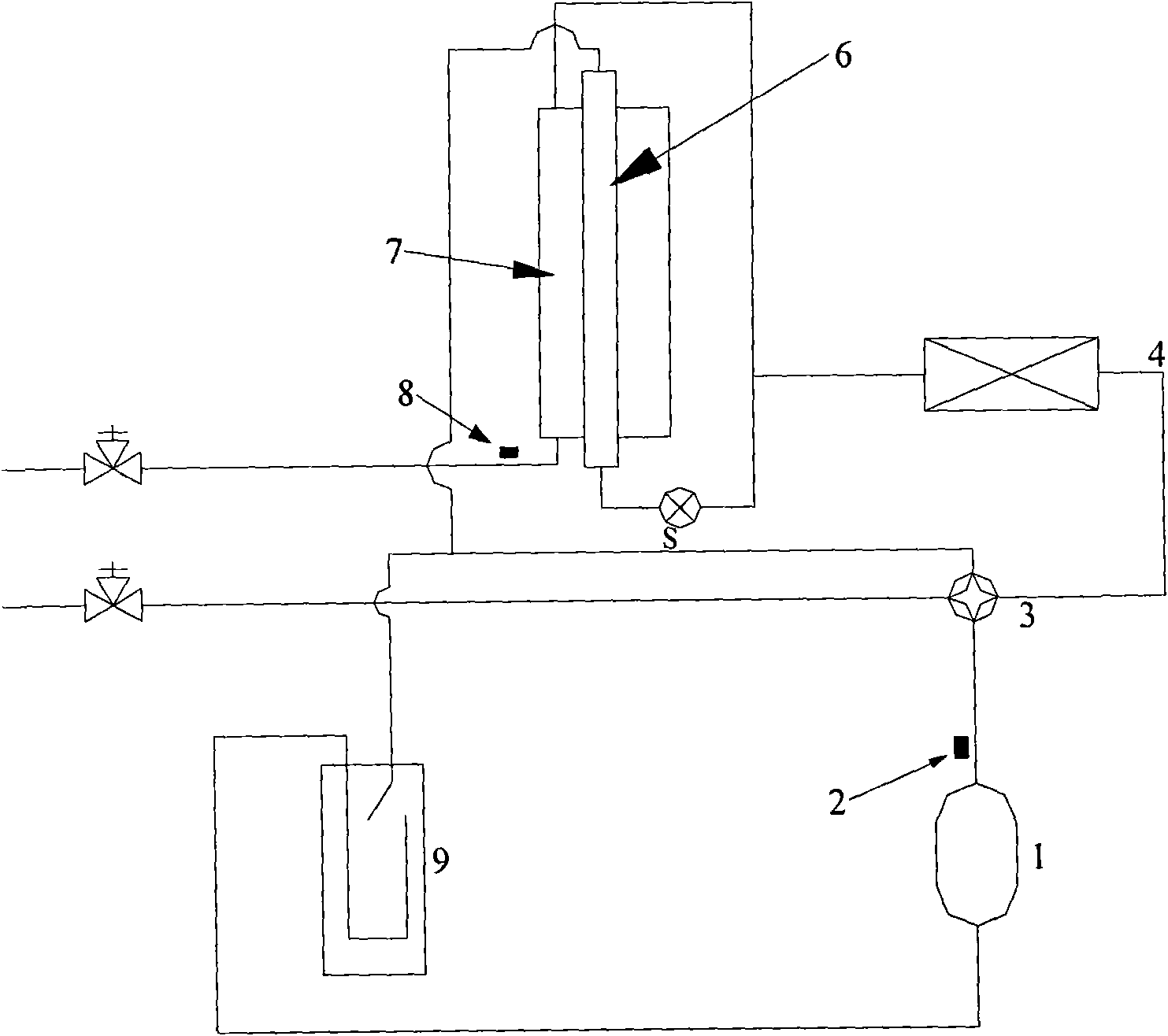
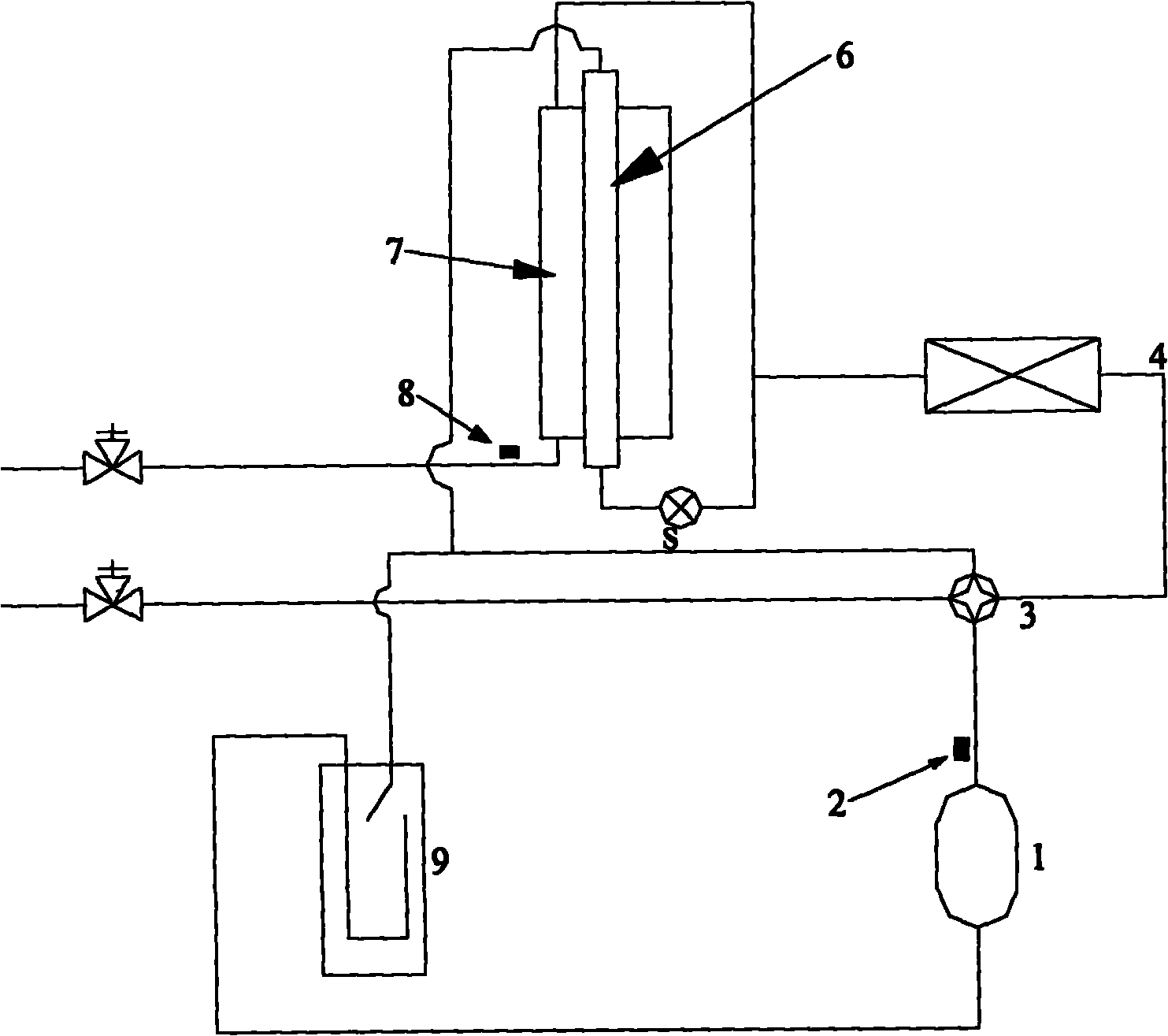
InactiveCN101839580AOvercoming indeterminationGuaranteed circulationCompression machines with several evaporatorsSubcoolersCondensation temperatureMaster controller
The invention provides an air-conditioning system with a subcooler, a temperature sensor is arranged on a pipeline between a subcooler liquid pipe and an indoor unit, a pressure sensor is arranged at the exhaust port of a compressor, and the temperature sensor and the pressure sensor are connected on a master controller. The invention also provides a method for judging whether the refrigerant perfused amount in the air-conditioning system with the subcooler is proper, comprising the following steps: calculating the difference between the high voltage condensation temperature of refrigerant at the exhaust port of the compressor and the temperature of the refrigerant at the liquid outlet of a high voltage side of the subcooler, namely obtaining an actual subcooling degree; and comparing the difference of the actual subcooling degree and a target subcooling degree with a judgment value, and judging whether the refrigerant perfused amount is proper according to the comparing result. The invention overcomes the problem that the refrigerant perfused amount can not be judged in the existing air-conditioning system with a subcooler, can ensure circulated operation of the air conditioning system with a proper refrigerant, improves the operation efficiency and service life of a unit and ensures the use effect for users.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Refrigerant subcooling by condensate
ActiveUS20050166614A1Facilitates subcoolingCondensate preventionEvaporators/condensersSystem capacityEngineering
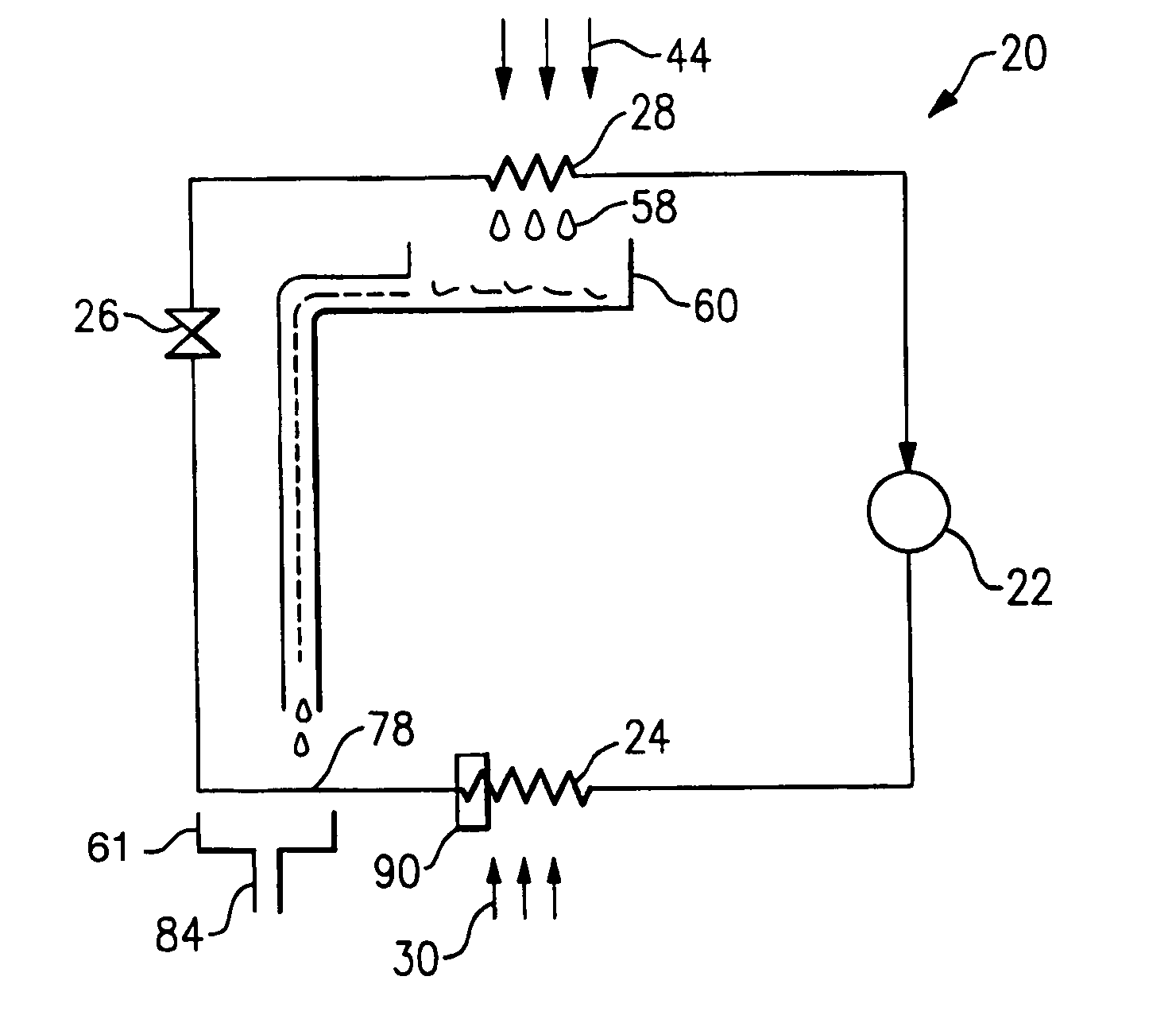
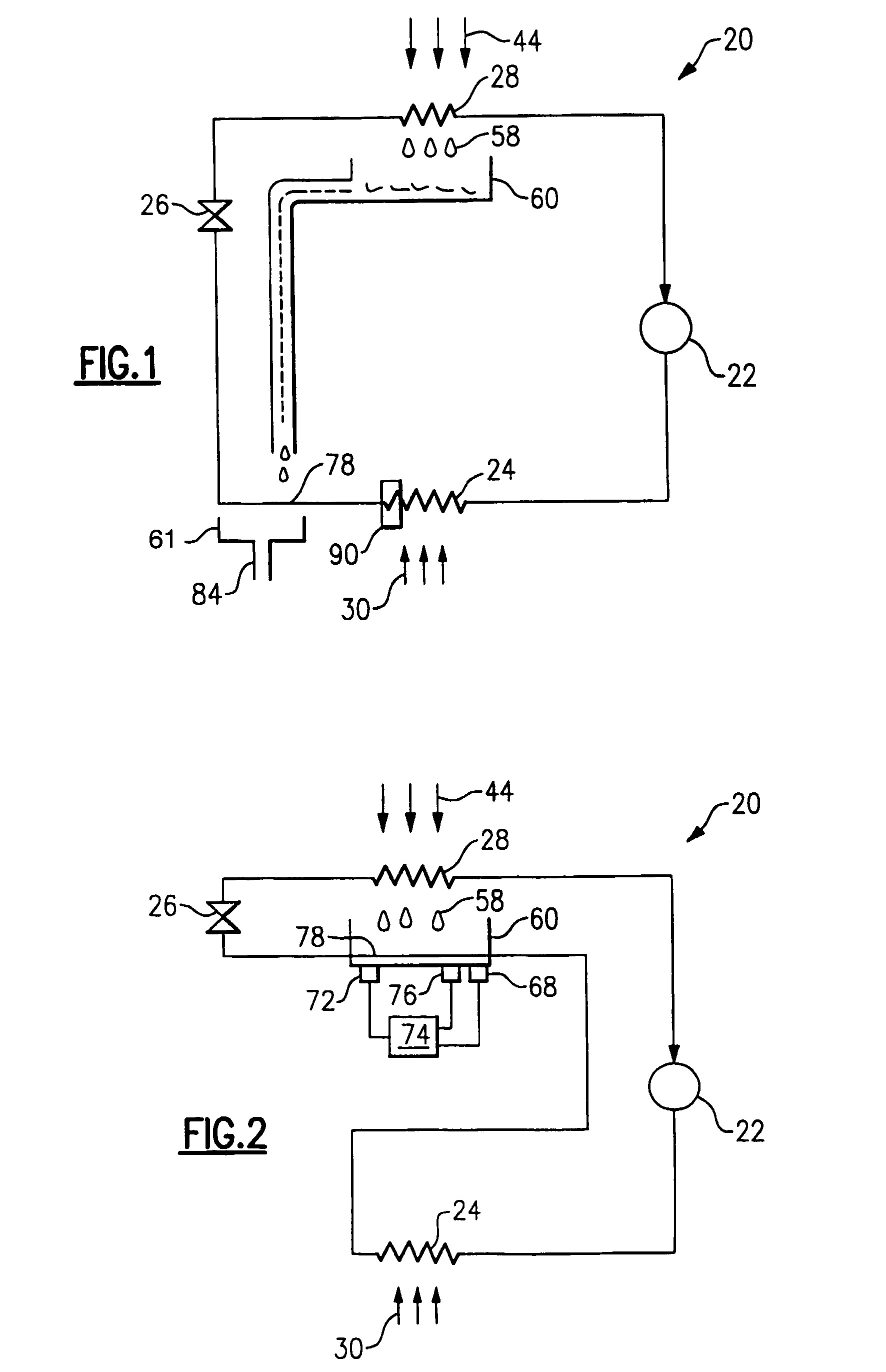
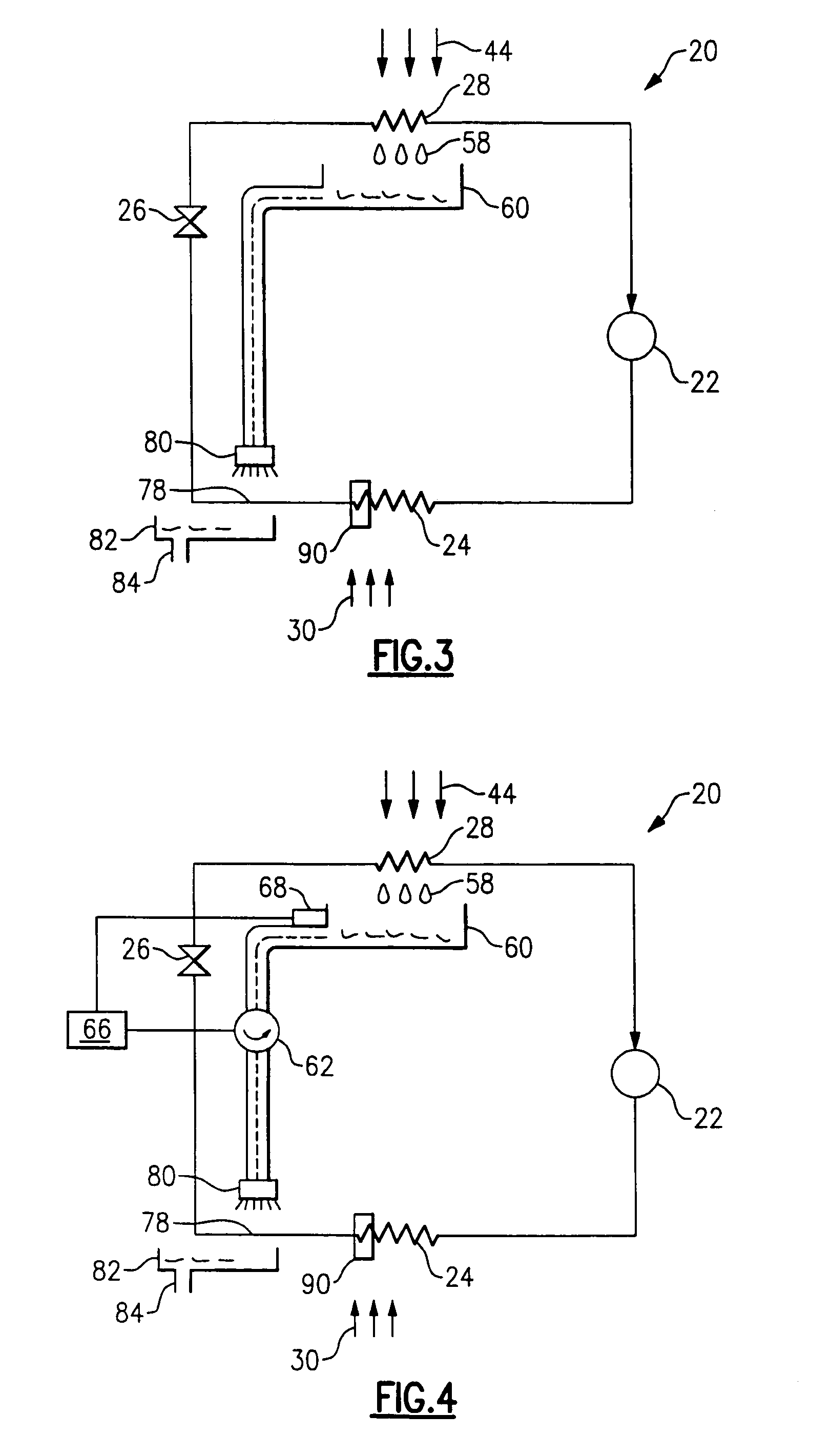
Refrigerant is circulated through a vapor compression system including a compressor, a condenser, an expansion device, and an evaporator. Cold condensate forms on the evaporator surfaces as the refrigerant accepts heat from an air stream. The cold condensate drips down from the evaporator coil and collects in a condensate pan. In one example, the cold condensate is directed into a condensate heat exchanger to subcool the refrigerant exiting the condenser. In another example, the refrigerant exiting the condenser flows through a refrigerant line located in the condensate pan. In another example, the cold condensate is sprayed on the refrigerant line exiting the condenser or on the subcooling portion of the condenser. By utilizing the condensate for further subcooling of the refrigerant, system capacity and efficiency are enhanced. Various control techniques and condensate flow methods are also disclosed.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
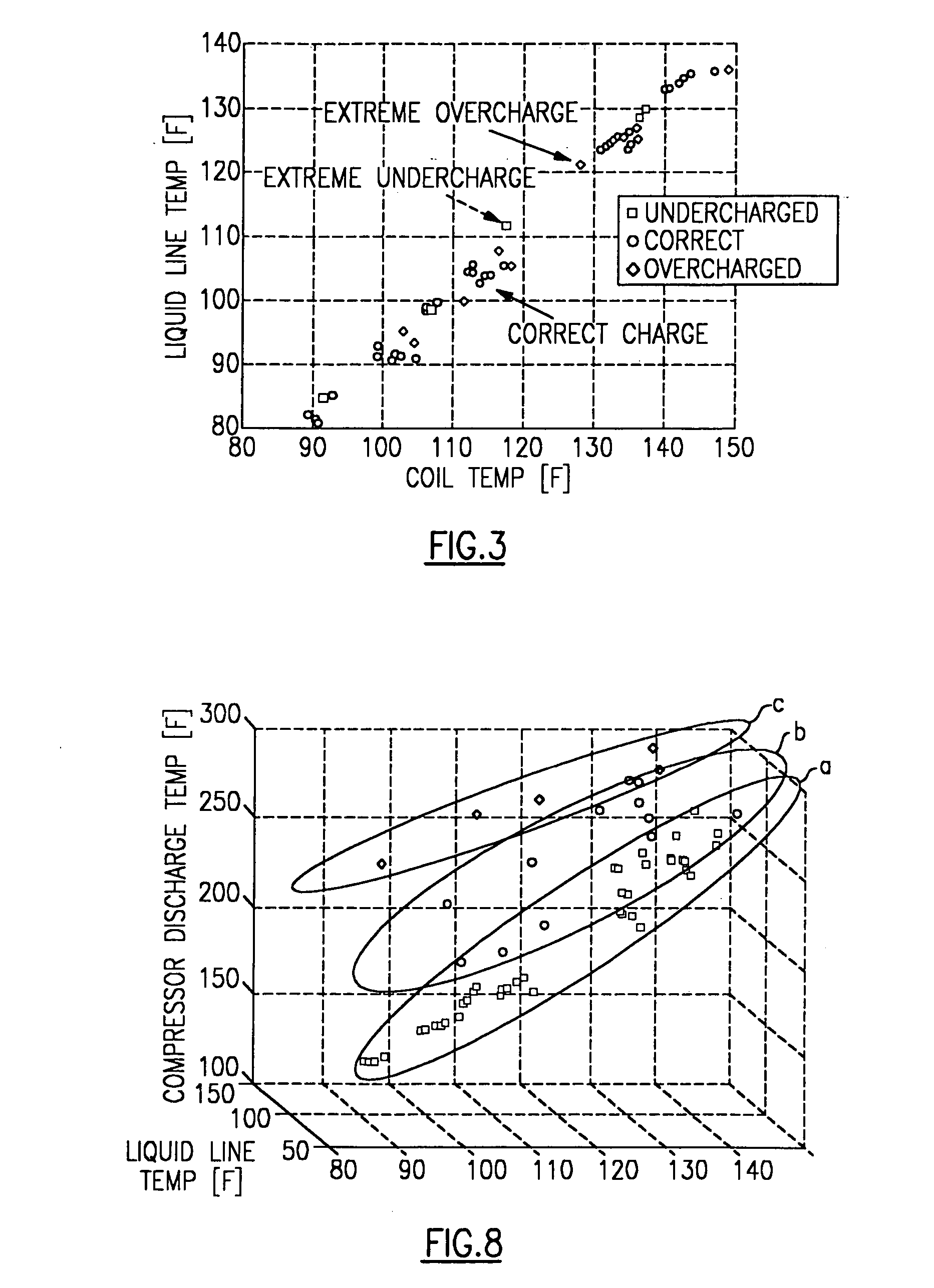
Detection of refrigerant charge adequacy based on multiple temperature measurements
InactiveUS20070125102A1Temperature measurement in air-conditioning systemsVehicle heating/cooling devicesLiquid lineTwo temperature
The refrigerant charge adequacy of an air conditioning system is determined by the sensing of two temperatures in the system, one being at a midpoint in a condenser coil and the other being the temperature in the liquid line of the condenser discharge, with the difference then being indicative of the degree of subcooling, which, in turn, may be indicative of refrigerant charge condition. The method is refined by measuring a third temperature at the compressor discharge, with the three temperature values then being used to calculate a pair of residual values which provide an indication of whether the two temperature approach is useful in determining charge adequacy under the existing conditions and if not, whether the system is overcharged or undercharged.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Hand Held Refrigeration Gauge
The present invention is a hand held gauge for use with refrigeration systems. The gauge includes a service port connector, a display screen, and user interfacing buttons. The gauge also includes electronic storage of the pressure-to-saturation temperature data for different refrigerants. The gauge allows for the measuring of temperature and pressure of refrigeration systems. After a user inputs a refrigerant type, the gauge uses the pressure and the saturation data to determine the saturation temperature. The saturation temperature is compared to the measured temperature to get the superheat or subcooling. These results may all be displayed on the display screen.
Owner:WEICK BRIAN K
Refrigerant flow regulating system of multi-connected air-conditioning heat exchanger and regulating method thereof
InactiveCN102345949AImprove cooling effectEfficient regulation technologiesFluid circulation arrangementEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention provides a refrigerant flow regulating system of a multi-connected air-conditioning heat exchanger. The opening of an electronic expansion valve at the outlet of the heat exchanger is controlled, and the supercooling degree or superheating degree at the outlet of each heat exchanger is detected and controlled so as to regulate the refrigerant flow of each heat exchanger. The regulating method comprises the following steps: (1) starting the system; (2) acquiring data; (3) calculating the temperature difference; (4) determining whether the temperature difference exceeds the range; (5) calculating the variation value of the electronic expansion valve; and (6) finishing the regulation and operating normally. According to the invention, the refrigerant flow of each heat exchanger is regulated effectively, and the whole refrigerating effect of the air-conditioning system is improved.
Owner:QINGDAO HISENSE HITACHI AIR CONDITIONING SYST
Refrigerant subcooling by condensate
ActiveUS7013658B2Facilitates subcoolingCondensate preventionEvaporators/condensersSystem capacityEngineering
Refrigerant is circulated through a vapor compression system including a compressor, a condenser, an expansion device, and an evaporator. Cold condensate forms on the evaporator surfaces as the refrigerant accepts heat from an air stream. The cold condensate drips down from the evaporator coil and collects in a condensate pan. In one example, the cold condensate is directed into a condensate heat exchanger to subcool the refrigerant exiting the condenser. In another example, the refrigerant exiting the condenser flows through a refrigerant line located in the condensate pan. In another example, the cold condensate is sprayed on the refrigerant line exiting the condenser or on the subcooling portion of the condenser. By utilizing the condensate for further subcooling of the refrigerant, system capacity and efficiency are enhanced. Various control techniques and condensate flow methods are also disclosed.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
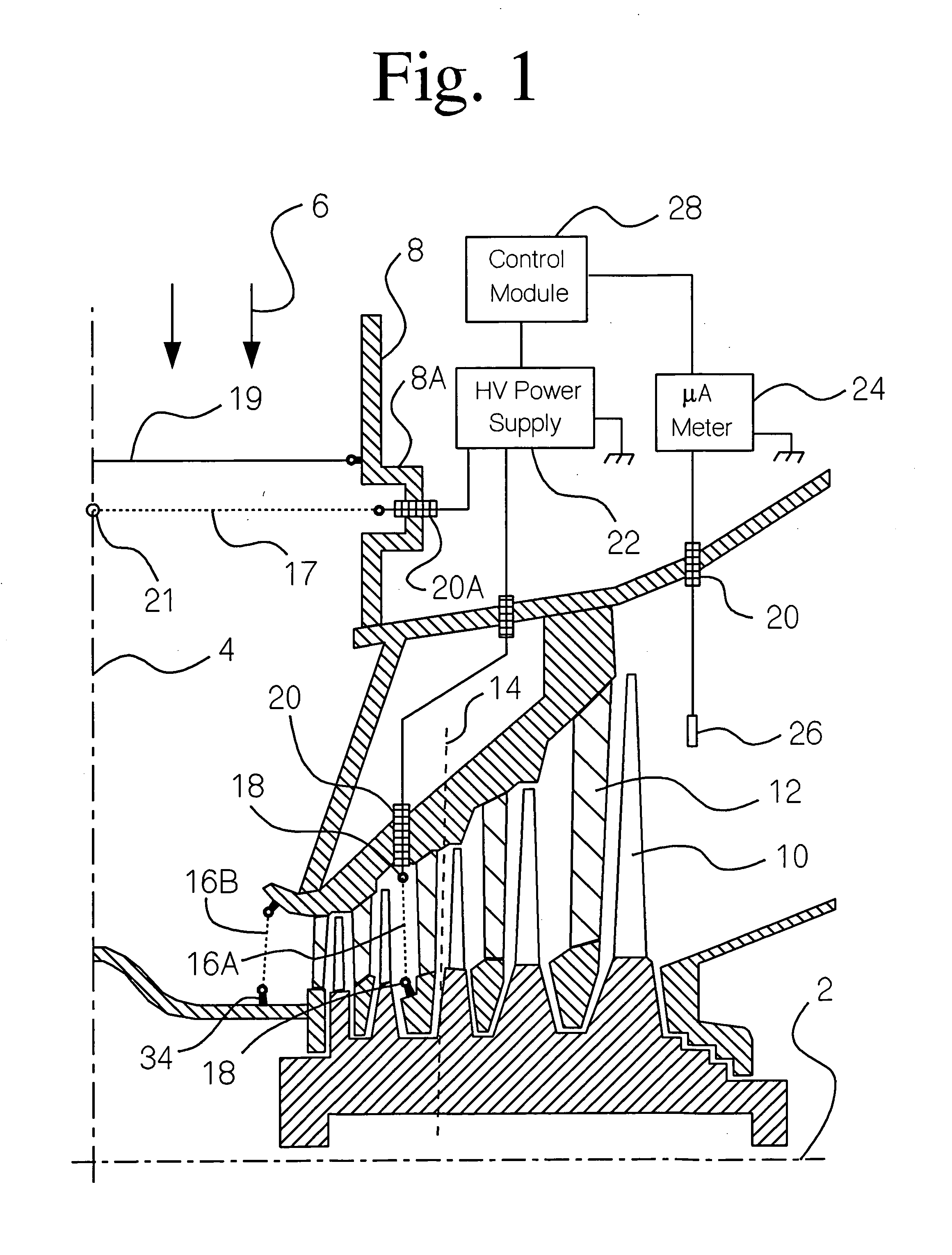
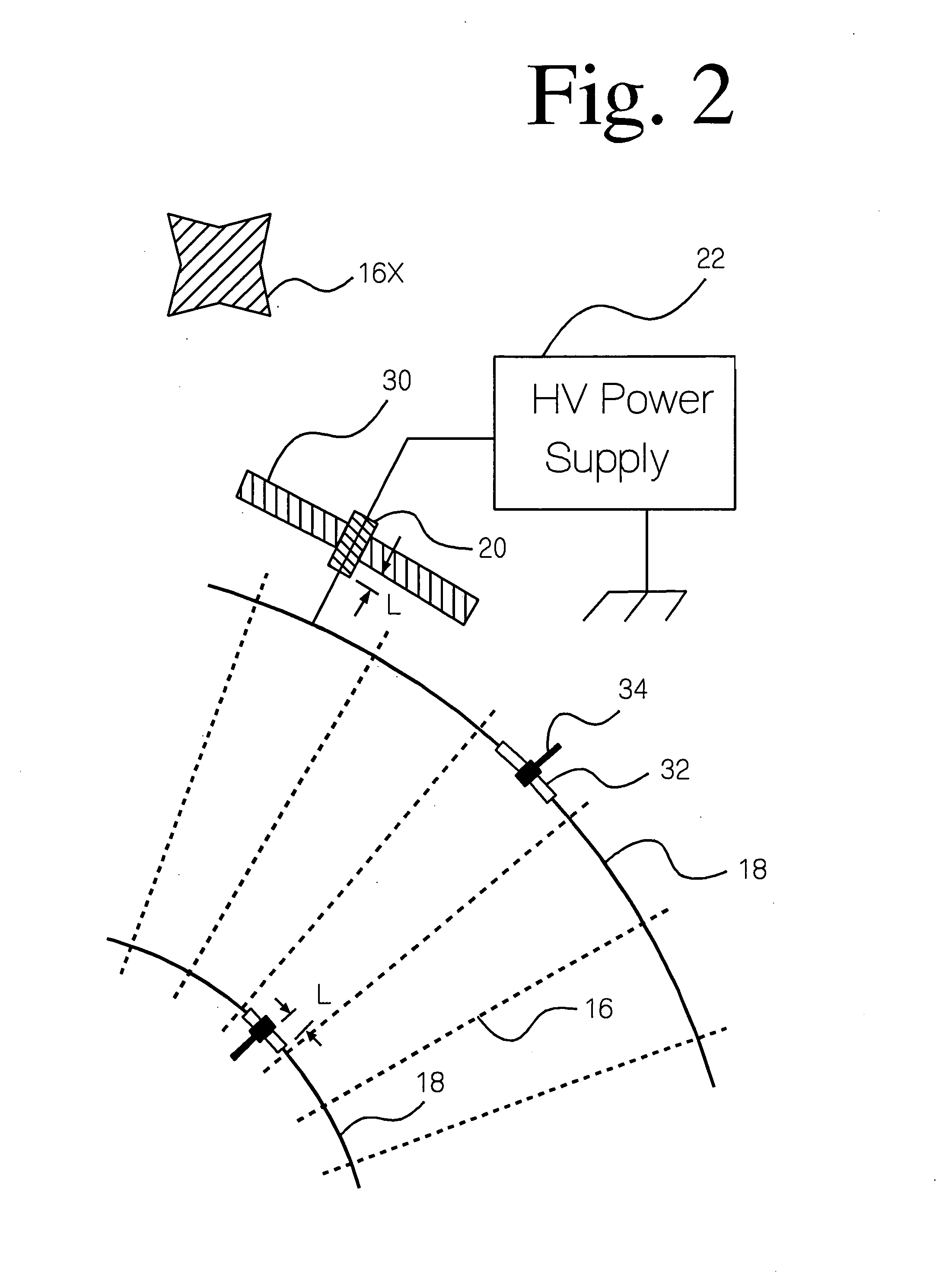
Electrostatic method and device to increase power output and decrease erosion in steam turbines
InactiveUS20050207880A1Easy to condenseSubcooling is decreasedPump componentsWorking fluid for enginesLiquid waterEngineering
The wet steam exiting a low pressure steam turbine does not rapidly attain thermodynamic equilibrium because insufficient condensation nuclei are present in the phase transition zone inside the turbine. Therefore, the steam is subcooled, decreasing the power generated by the turbine, and the liquid water carried by the steam consists of relatively coarse droplets which strike the surface of the turbine blades causing erosion. Corona electrodes installed inside the turbine before the saturation line create electrically charged particles which serve as condensation nuclei, decreasing subcooling, and producing a large number of fine droplets. Thereby, thermodynamic equilibrium is more closely approached, more power is generated, and smaller water droplets cause less erosion inside the turbine.
Owner:TARELIN ANATOLY OLEKSIOVYCH +2
Multiflow overcold condenser
A multi-flow subcooling condenser, comprising: a pair of headers, a plurality of flat heat transfer tubes connecting the pair of headers, and corrugated fins arranged alternately with the heat transfer tubes. The condenser includes a refrigerant condensing core section and a subcooling cooling core section. The lower part of one of the headers of the condenser, which serves as a liquid tank to collect liquid refrigerant for delivery to the subcooled cooling core section, also has a desiccant. A plug mechanism is provided to the end of the desiccant including the manifold, in the plug mechanism the plug can be arbitrarily fixed or removed, whereby the desiccant can be replaced.
Owner:SANDEN CORP
Preparation method of nanoparticle-enhanced refrigerant hydrate phase-change cold storage working medium
InactiveCN102295917AImprove effective utilizationEvenly dispersedHeat-exchange elementsRational useWorking fluid
A method for preparing nanoparticle-enhanced refrigerant hydrate phase-change cold storage refrigerants, using the solubilization effect of compound surfactants, dissolving refrigerants in water to prepare thermodynamically stable refrigerant microemulsions, and then dispersing nanoparticles In the refrigerant microemulsion, a refrigerant hydrate phase-change cold storage working substance strengthened by nanoparticles is prepared. By stably dispersing nanoparticles in the refrigerant microemulsion system to enhance heat and mass transfer, increase the reaction interface, and induce heterogeneous nucleation, thereby significantly reducing the induction time and subcooling degree of hydrate formation, effectively achieving crystallization effect. The product of the invention can be widely used in fields such as peak shifting of electric power, building energy saving, cold storage air conditioner, refrigeration and preservation of agricultural products and biological products, high and low temperature cold storage and refrigerated logistics, etc., and can achieve the purpose of effective cold storage and release of cold and rational use of energy.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com