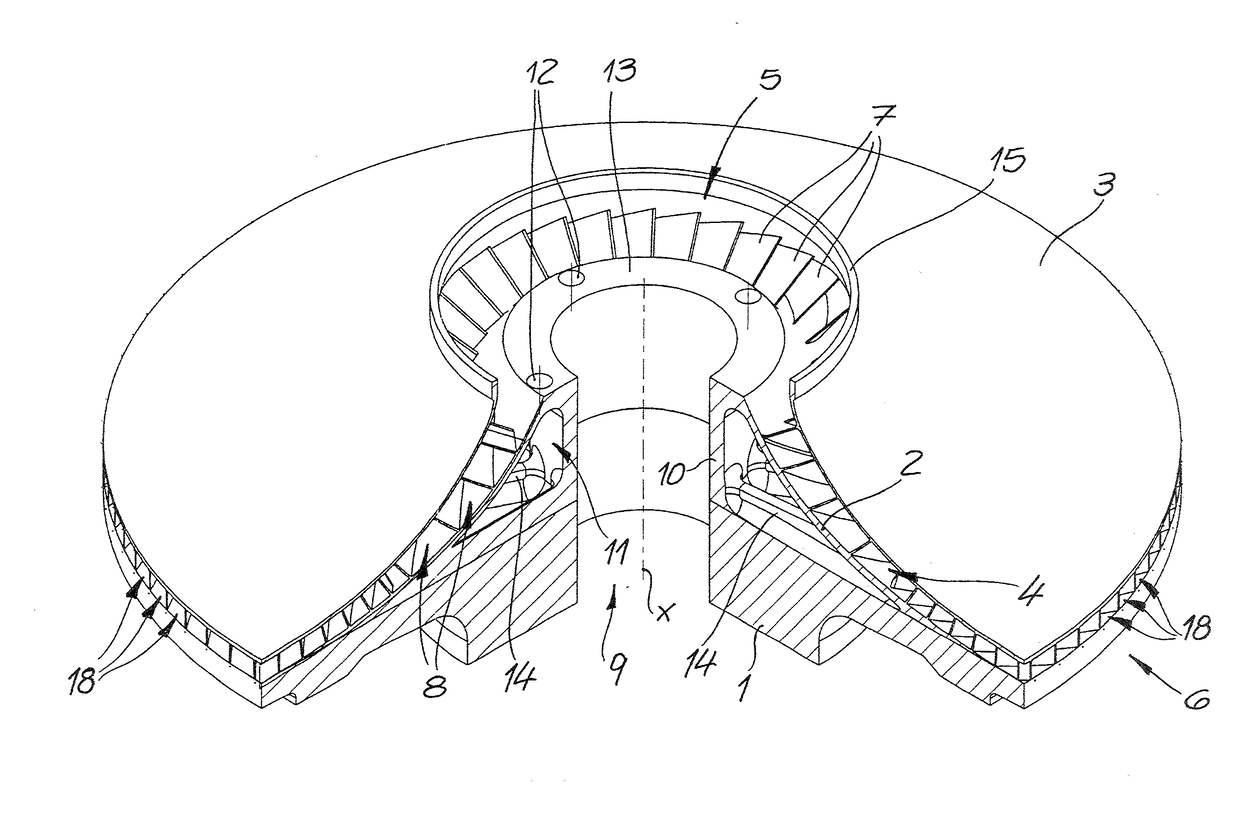
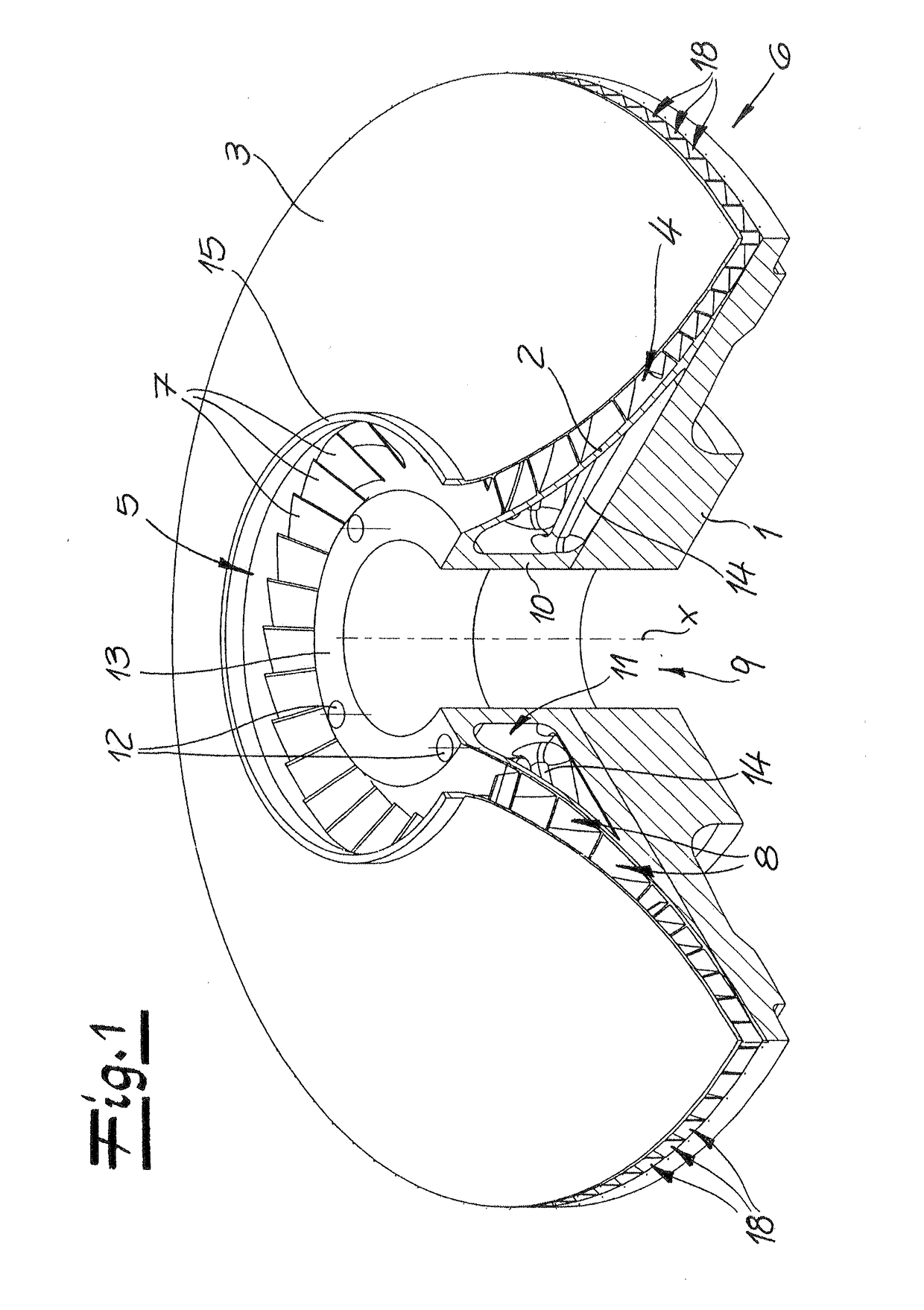
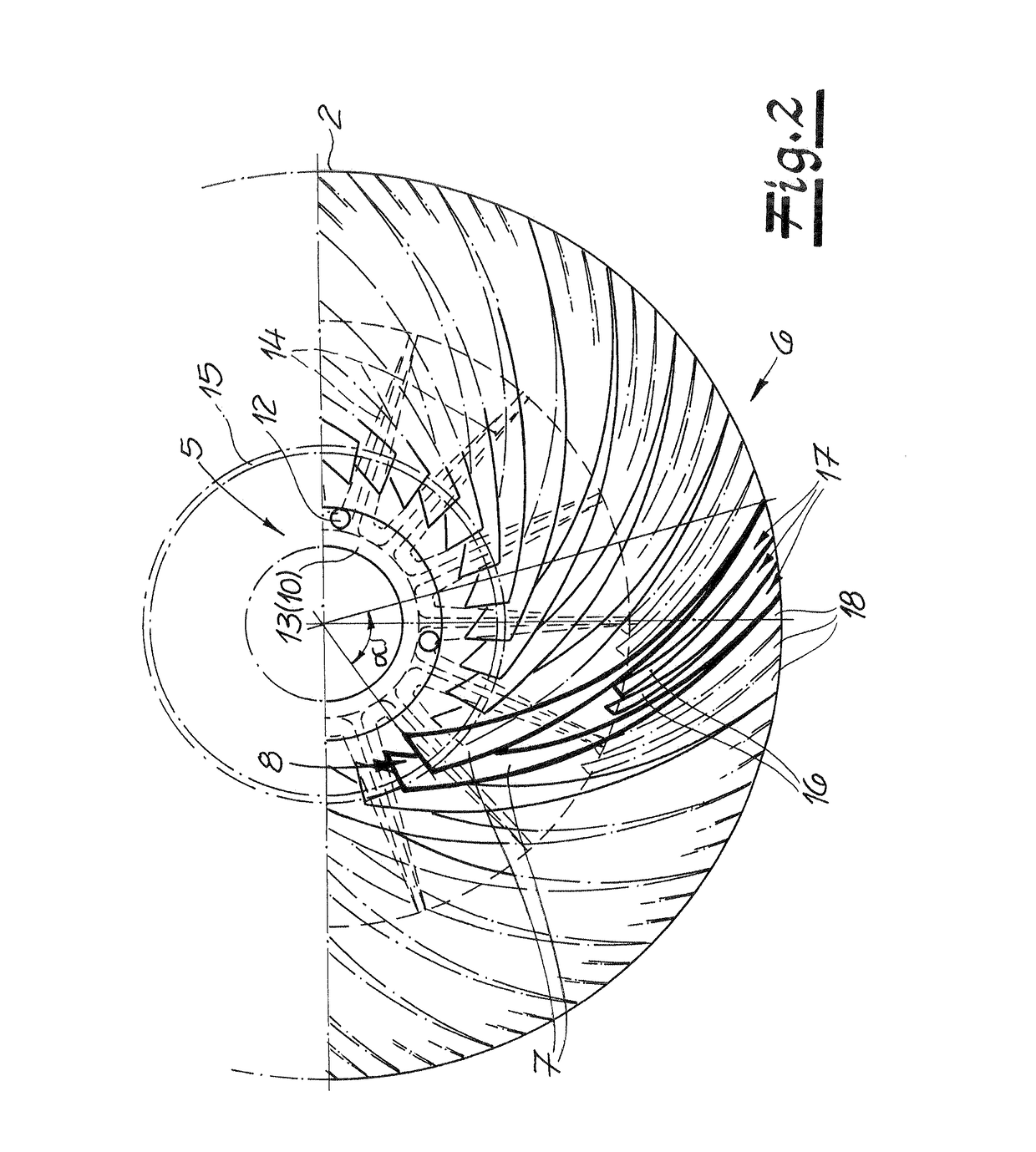
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
193 results about "Radial turbine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A radial turbine is a turbine in which the flow of the working fluid is radial to the shaft. The difference between axial and radial turbines consists in the way the fluid flows through the components (compressor and turbine). Whereas for an axial turbine the rotor is 'impacted' by the fluid flow, for a radial turbine, the flow is smoothly orientated perpendicular to the rotation axis, and it drives the turbine in the same way water drives a watermill. The result is less mechanical stress (and less thermal stress, in case of hot working fluids) which enables a radial turbine to be simpler, more robust, and more efficient (in a similar power range) when compared to axial turbines. When it comes to high power ranges (above 5 MW) the radial turbine is no longer competitive (due to heavy and expensive rotor) and the efficiency becomes similar to that of the axial turbines.
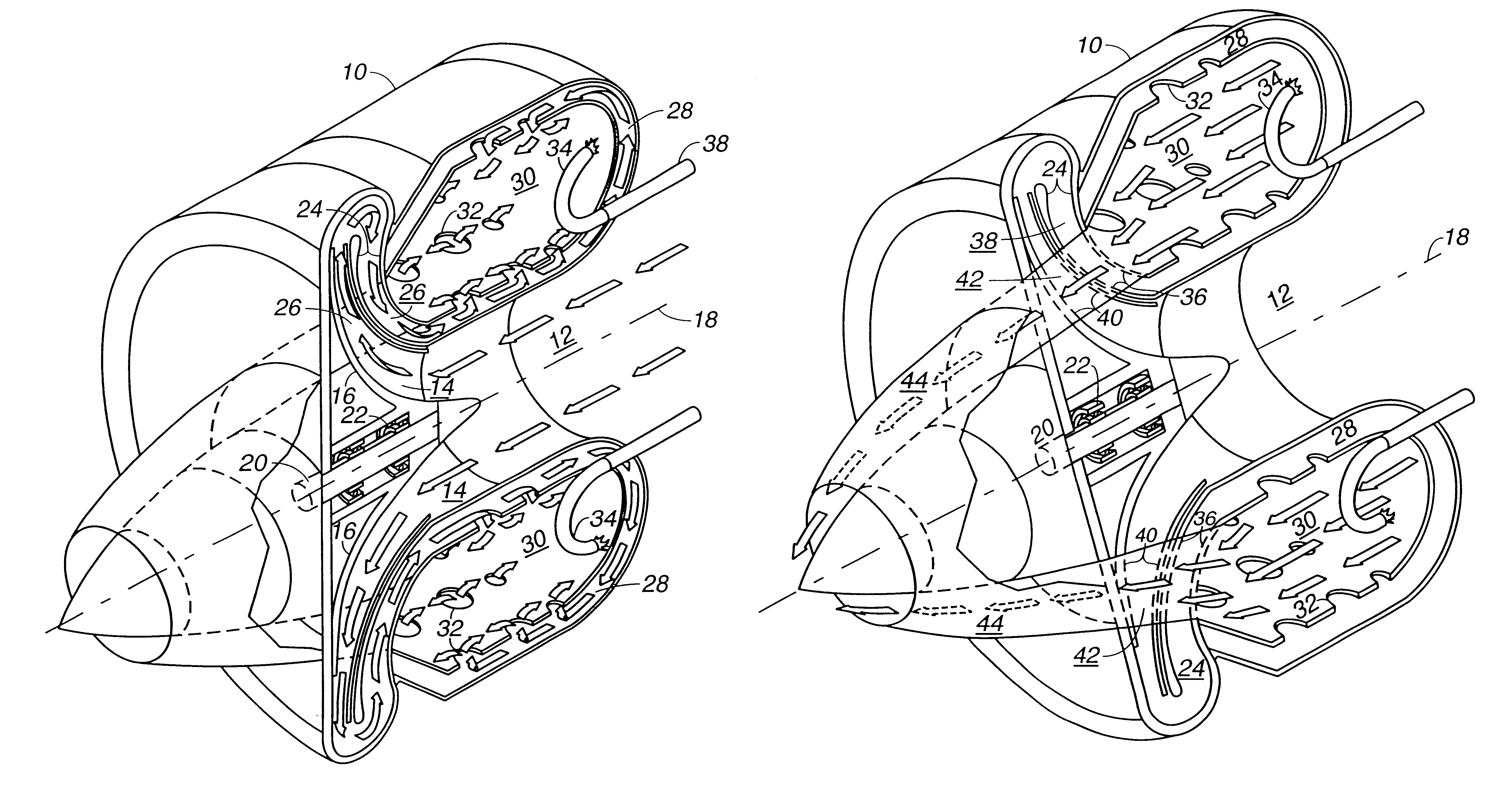
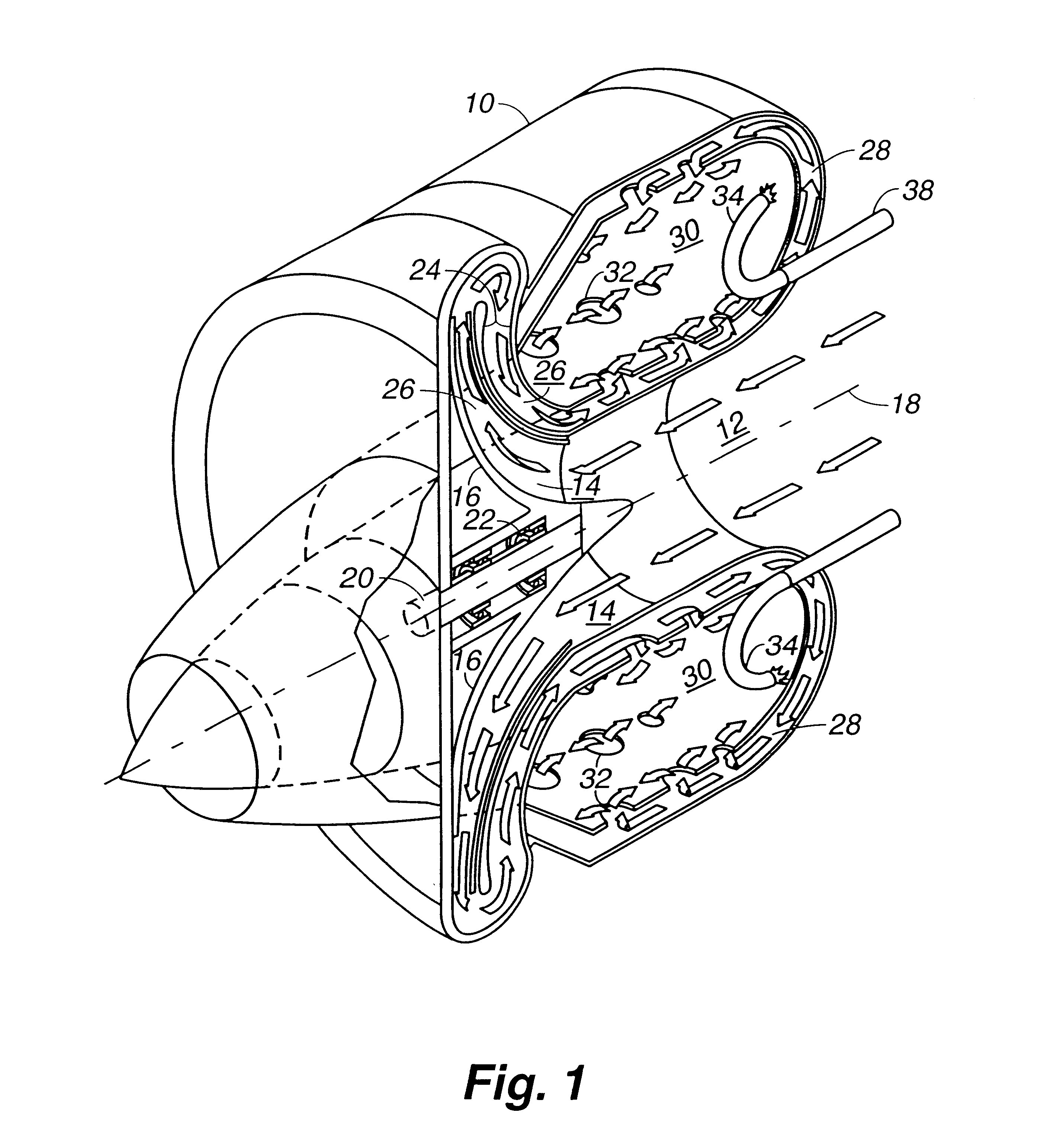
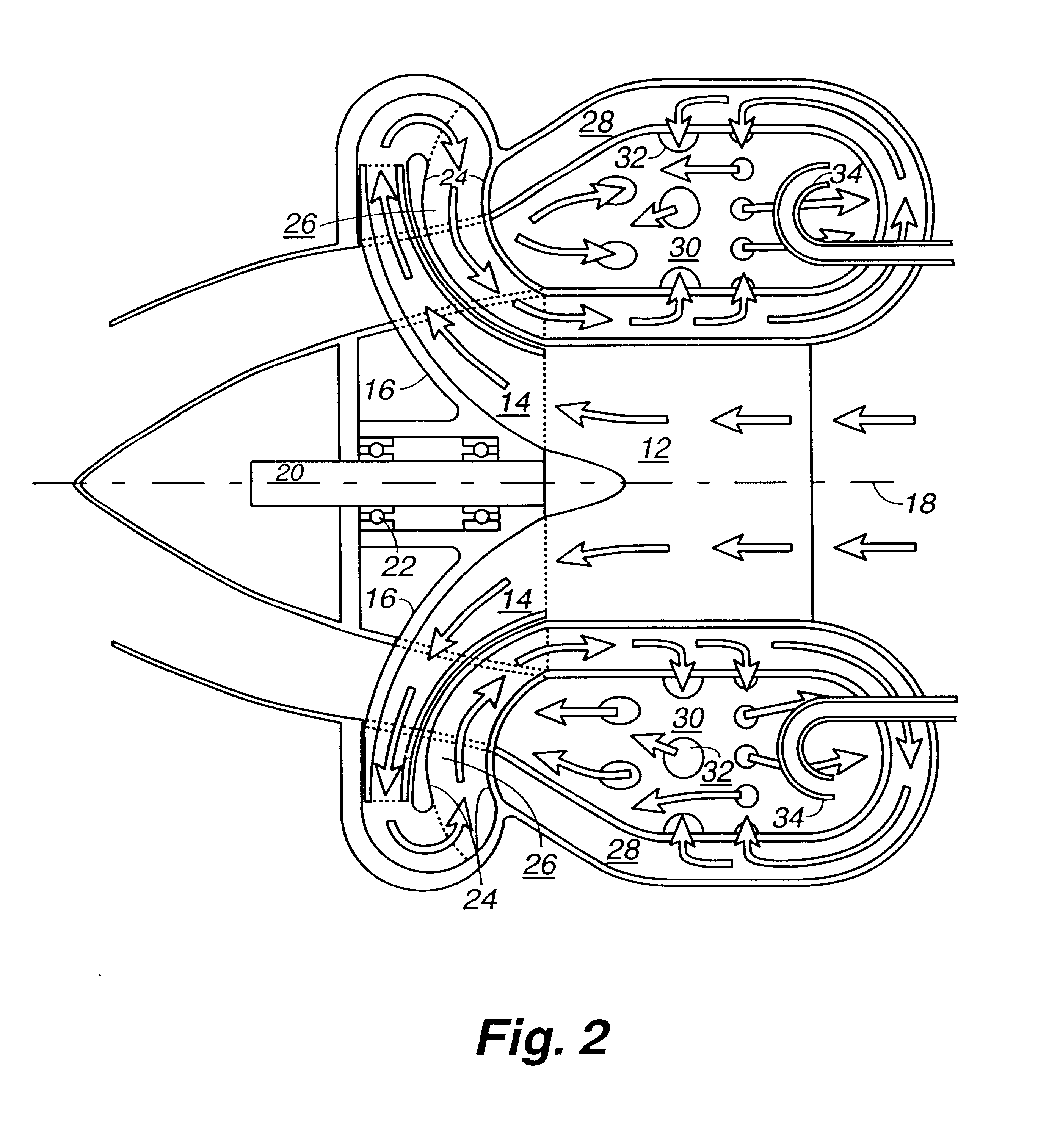
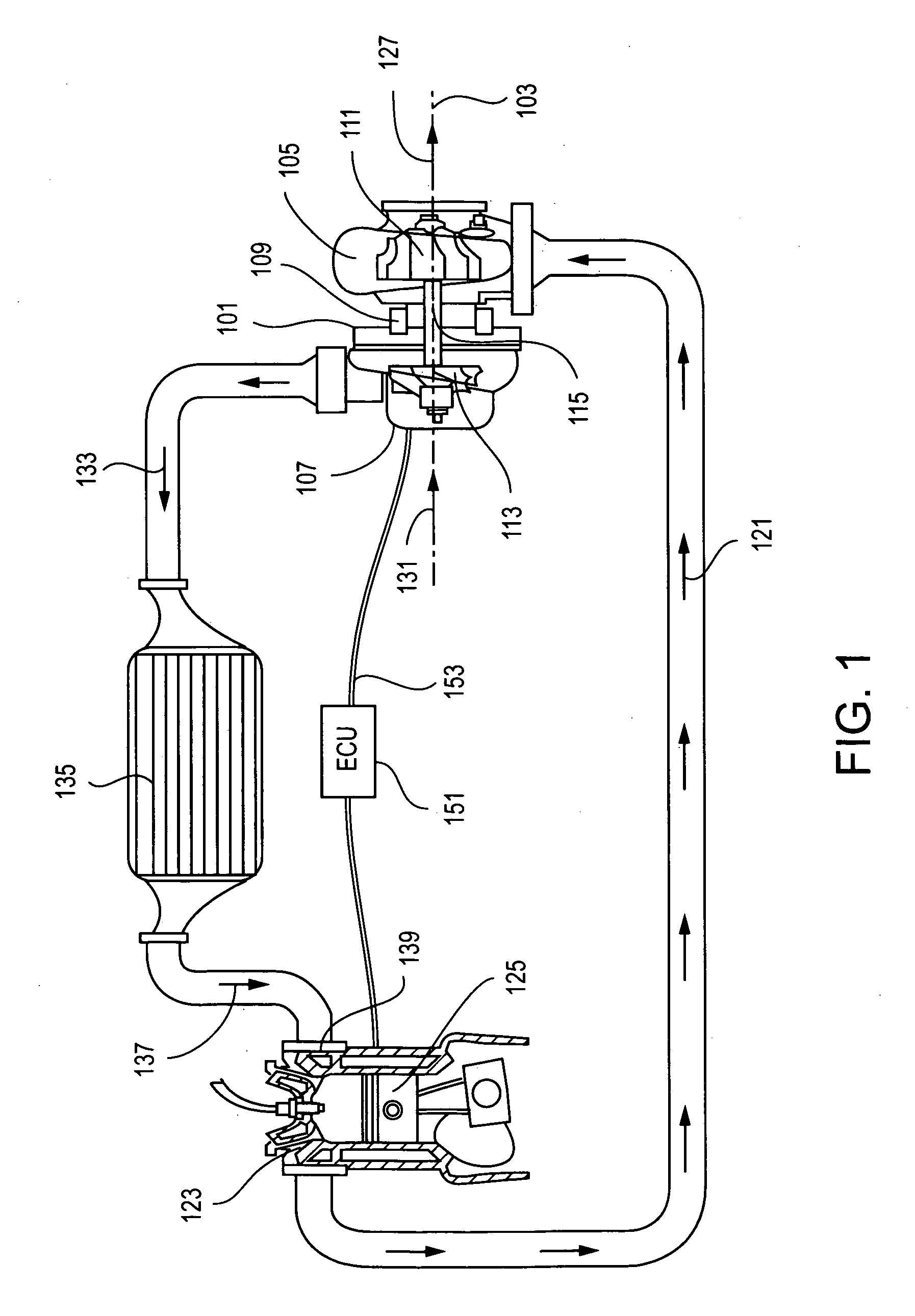
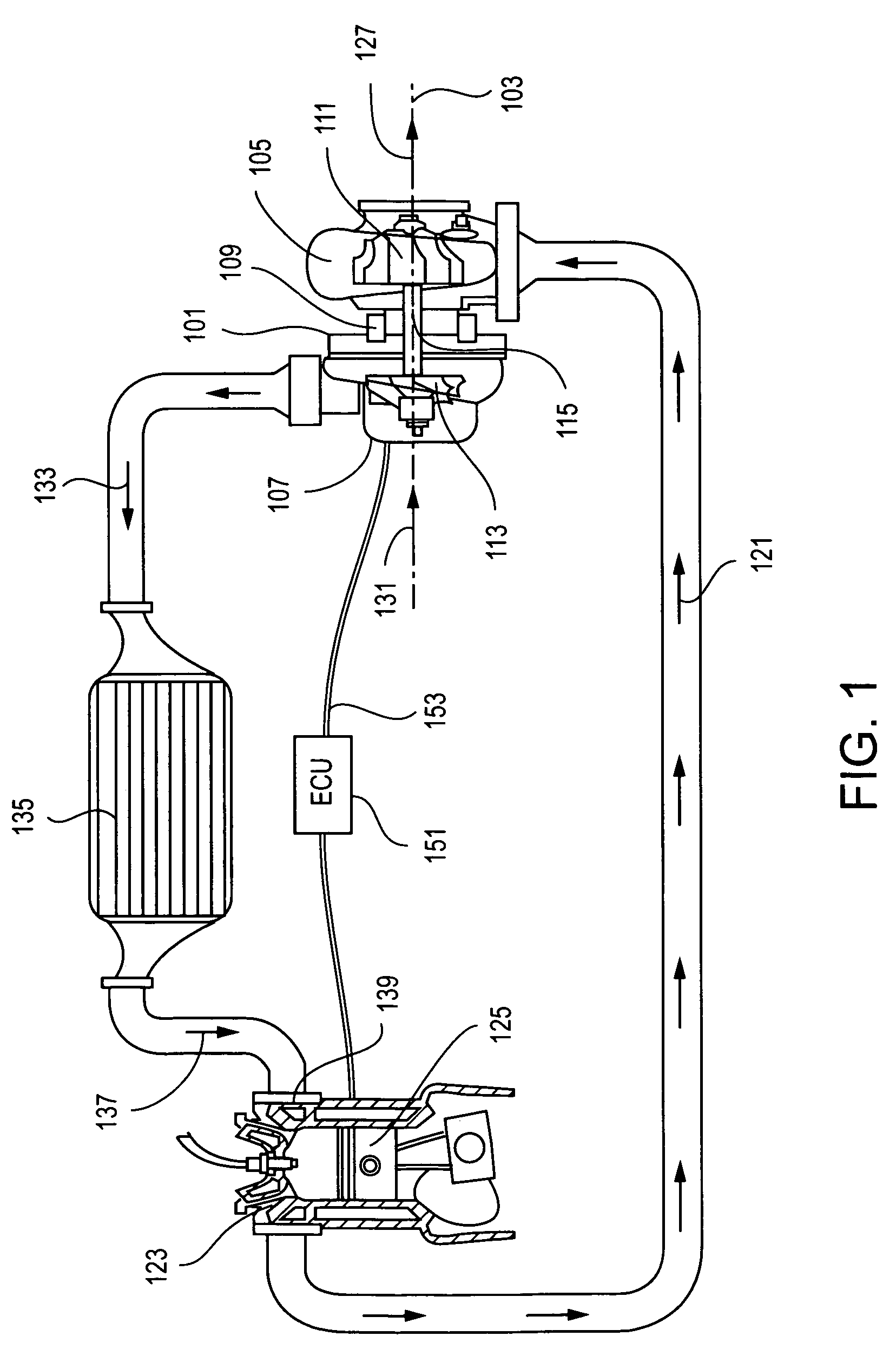
Single rotor turbine engine
There has been invented a turbine engine with a single rotor which cools the engine, functions as a radial compressor, pushes air through the engine to the ignition point, and acts as an axial turbine for powering the compressor. The invention engine is designed to use a simple scheme of conventional passage shapes to provide both a radial and axial flow pattern through the single rotor, thereby allowing the radial intake air flow to cool the turbine blades and turbine exhaust gases in an axial flow to be used for energy transfer. In an alternative embodiment, an electric generator is incorporated in the engine to specifically adapt the invention for power generation. Magnets are embedded in the exhaust face of the single rotor proximate to a ring of stationary magnetic cores with windings to provide for the generation of electricity. In this alternative embodiment, the turbine is a radial inflow turbine rather than an axial turbine as used in the first embodiment. Radial inflow passages of conventional design are interleaved with radial compressor passages to allow the intake air to cool the turbine blades.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Two-shaft turbocharger
InactiveUS20070204615A1Improve transient response timeReduce morbidityInternal combustion piston enginesCombination enginesAxial compressorTurbine blade
A turbocharger, having an axial compressor wheel and an axial turbine wheel mounted on a first shaft supported by a housing, and a radial compressor wheel and a radial turbine wheel mounted on a second shaft, the second shaft concentrically extending around the first shaft and being supported by the housing. The housing defines a first duct extending axially from the exducer of the axial compressor to the inducer of the radial compressor, and a second duct extending axially from the exducer of the radial turbine to the inducer of the axial turbine. A plurality of controllable compressor guide vanes extend through the first duct, and a plurality of controllable turbine stator vanes extend through the second duct. The housing is provided with variable diffuser vanes at the exducer of the radial compressor, and with variable turbine vanes at the inducer of the radial turbine. The variable turbine vanes and the turbine stator vanes are controlled to accurately control the rotation rate of the radial and axial turbines. The compressor guide vanes are controlled to minimize surge and maximize choke flow rate.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Radial turbine wheel with locally curved trailing edge tip
The present invention provides a turbine wheel with locally curved trailing edge blade tips on the blades of the turbine wheel. The locally curved trailing edge may increase the blade vibration mode natural frequency which may in turn result in longer blade fatigue lifetimes. It may also eliminate vortex shedding. Methods for increasing the blade vibration mode natural frequencies using the turbine wheel of the present invention are also provided.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Two-shaft turbocharger
InactiveUS7571607B2Easy to controlIncrease pressure ratioInternal combustion piston enginesCombination enginesAxial compressorImpeller
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Bladeless conical radial turbine and method
ActiveUS7192244B2Improve efficiencyIncrease speedEngine manufacturePump componentsEngineeringRadial turbine
Turbo-machinery and methods are disclosed for a bladeless conical radial turbine wherein fluid is directed axially within the pump body to produce an axial output. The rotor comprises a plurality of spaced apart conical elements. A plurality of spiraling flow paths may be provided to receive fluid to which fluid has been imparted by acceleration of the fluid through the spaces between the conical elements using boundary layer adhesion techniques. The fluid is smoothly directed to any number of subsequent boundary layer pumping stages which are axially positioned with respect to each other.
Owner:GRANDE III SALVATORE F +1
Bladeless conical radial turbine and method
ActiveUS20050214109A1Improve efficiencyIncrease speedEngine manufacturePump componentsEngineeringRadial turbine
Turbo-machinery and methods are disclosed for a bladeless conical radial turbine wherein fluid is directed axially within the pump body to produce an axial output. The rotor comprises a plurality of spaced apart conical elements. A plurality of spiraling flow paths may be provided to receive fluid to which fluid has been imparted by acceleration of the fluid through the spaces between the conical elements using boundary layer adhesion techniques. The fluid is smoothly directed to any number of subsequent boundary layer pumping stages which are axially positioned with respect to each other.
Owner:GRANDE III SALVATORE F +1
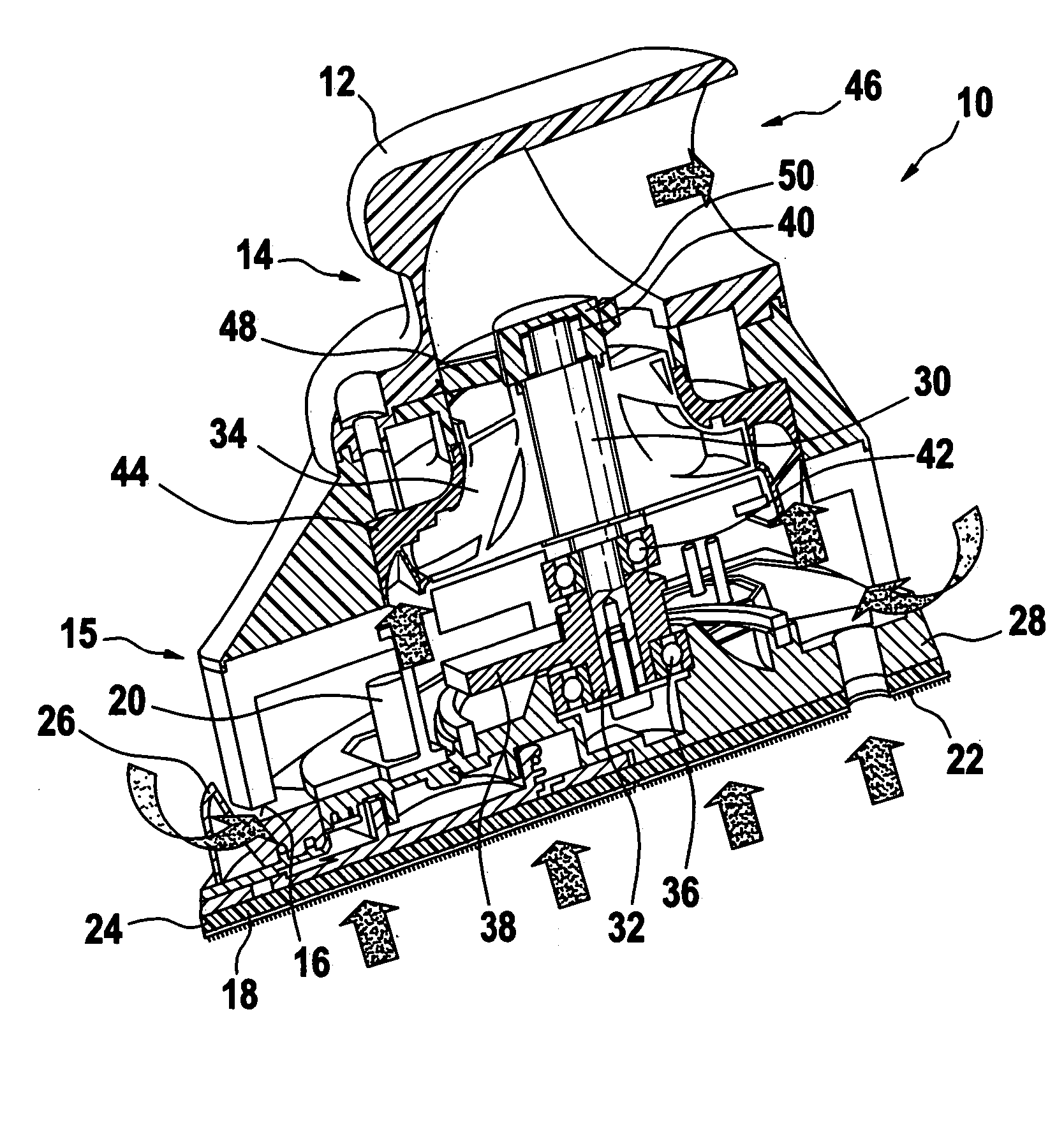
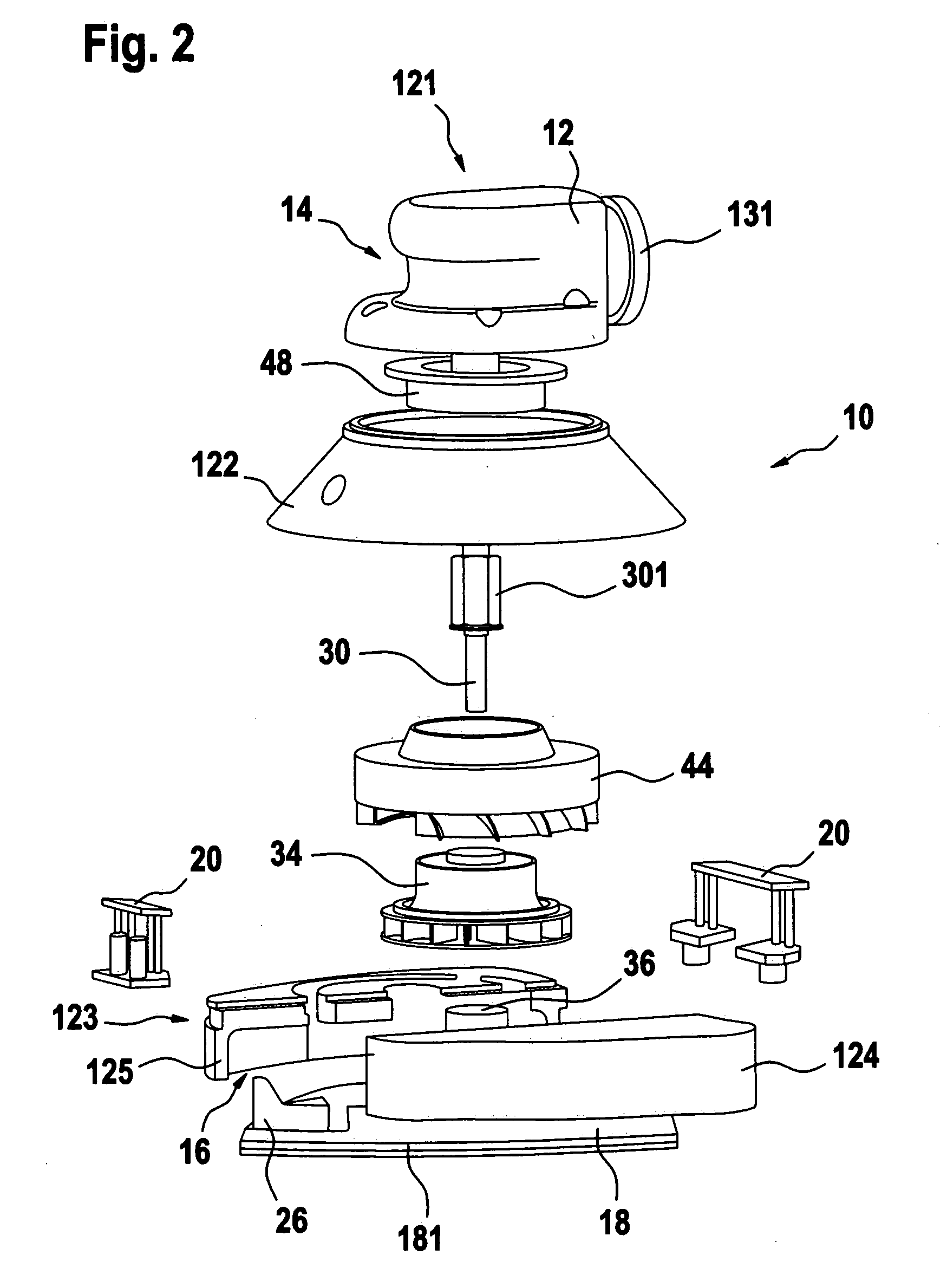
Power tool
InactiveUS20050221739A1Improve efficiencyEasy to operateGrinding drivesBelt grinding machinesImpellerAs Directed
A power tool with a housing (12) and a tool (18, 22) located thereon such that it is capable of being driven in a rotating and / or oscillating manner, the tool being operable as directed using vacuum flow, in particular using a vacuum cleaner. The power tool is made particularly powerful by the fact that a radial turbine wheel (34) with forward-guiding and rearward-guiding vane rows (44, 48) functions as the drive.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
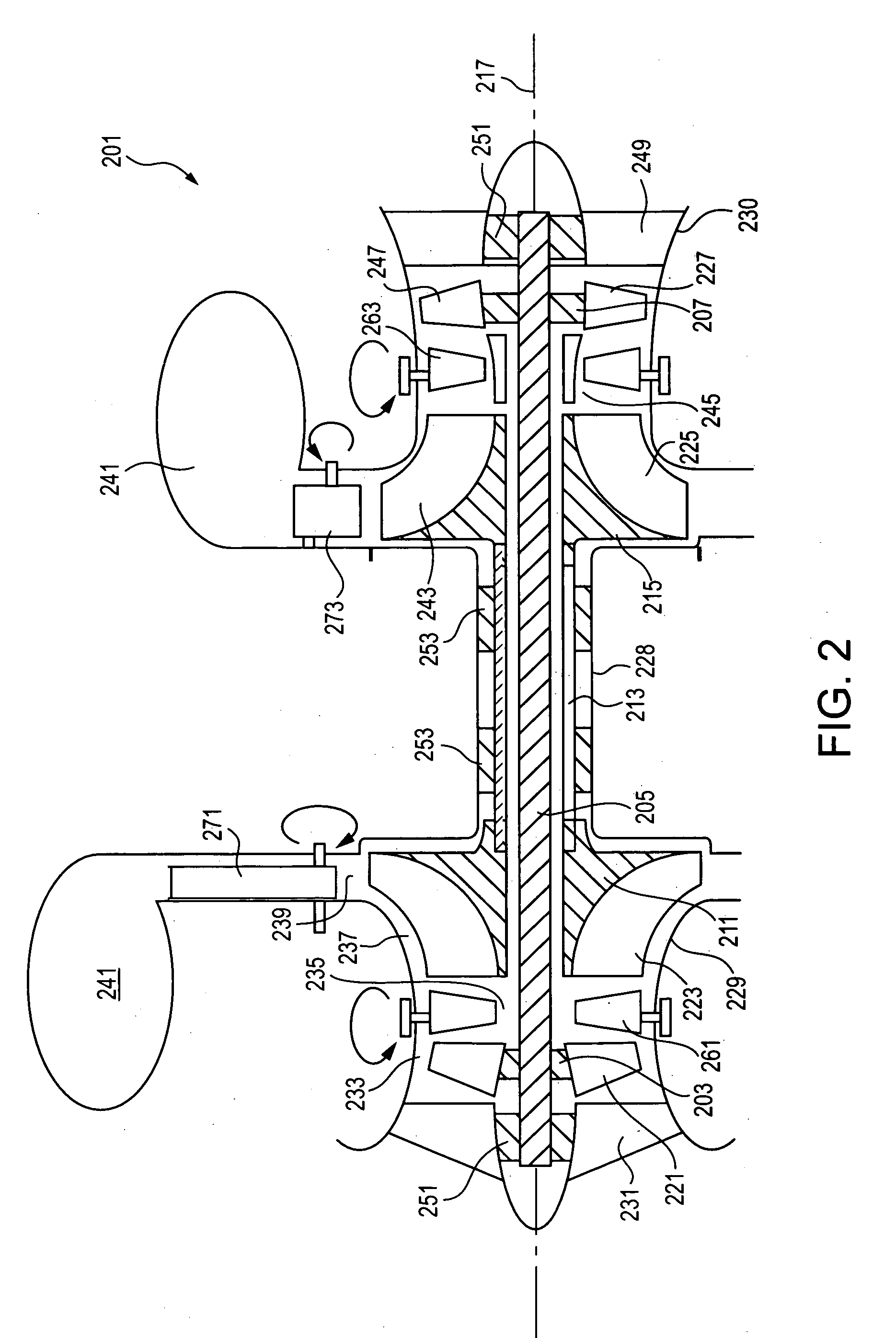
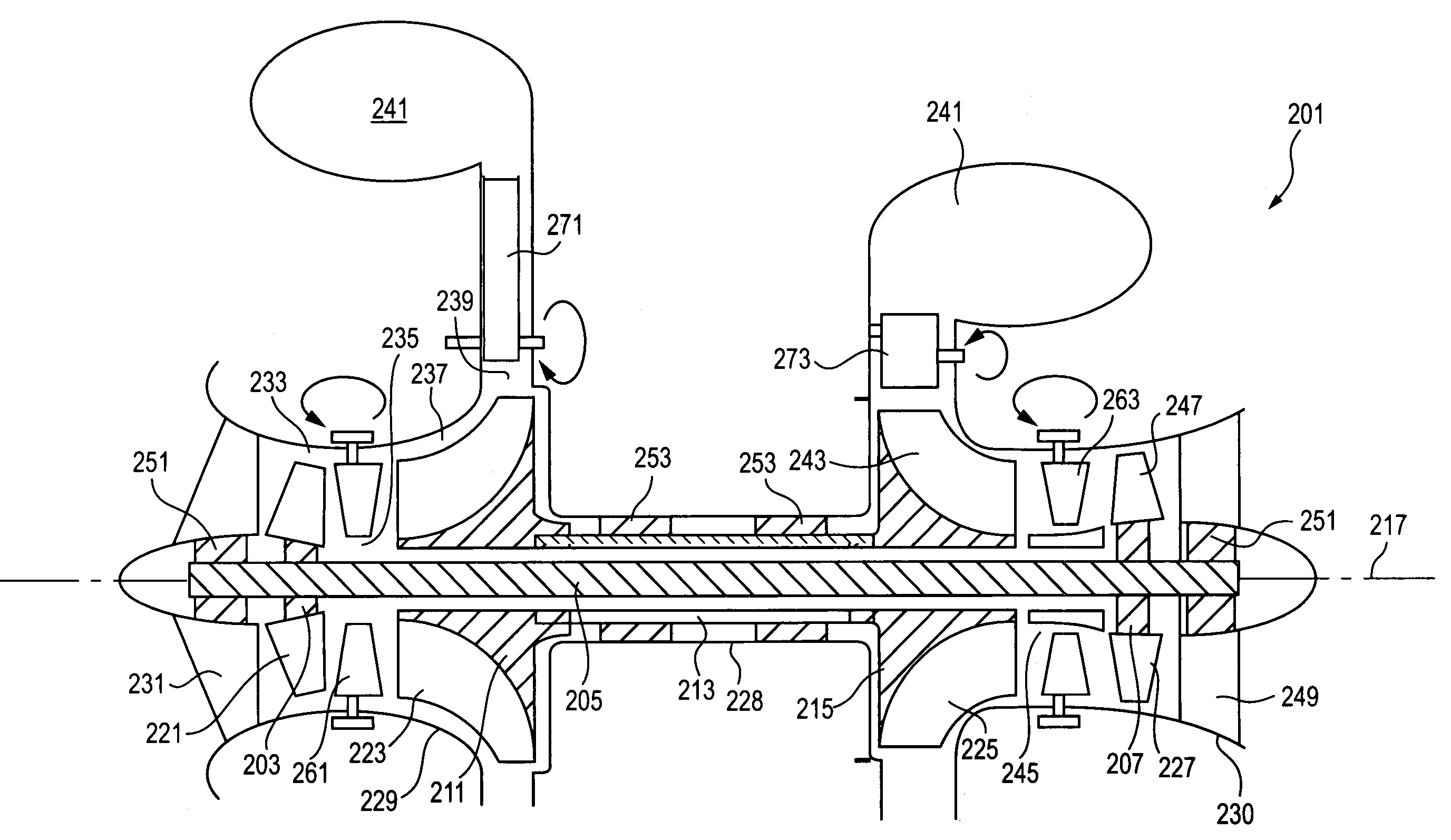
Radial-radial single rotor turbine
A rotor for use in turbine applications has a radial compressor / pump having radially disposed spaced apart fins forming passages and a radial turbine having hollow turbine blades interleaved with the fins and through which fluid from the radial compressor / pump flows. The rotor can, in some applications, be used to produce electrical power.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
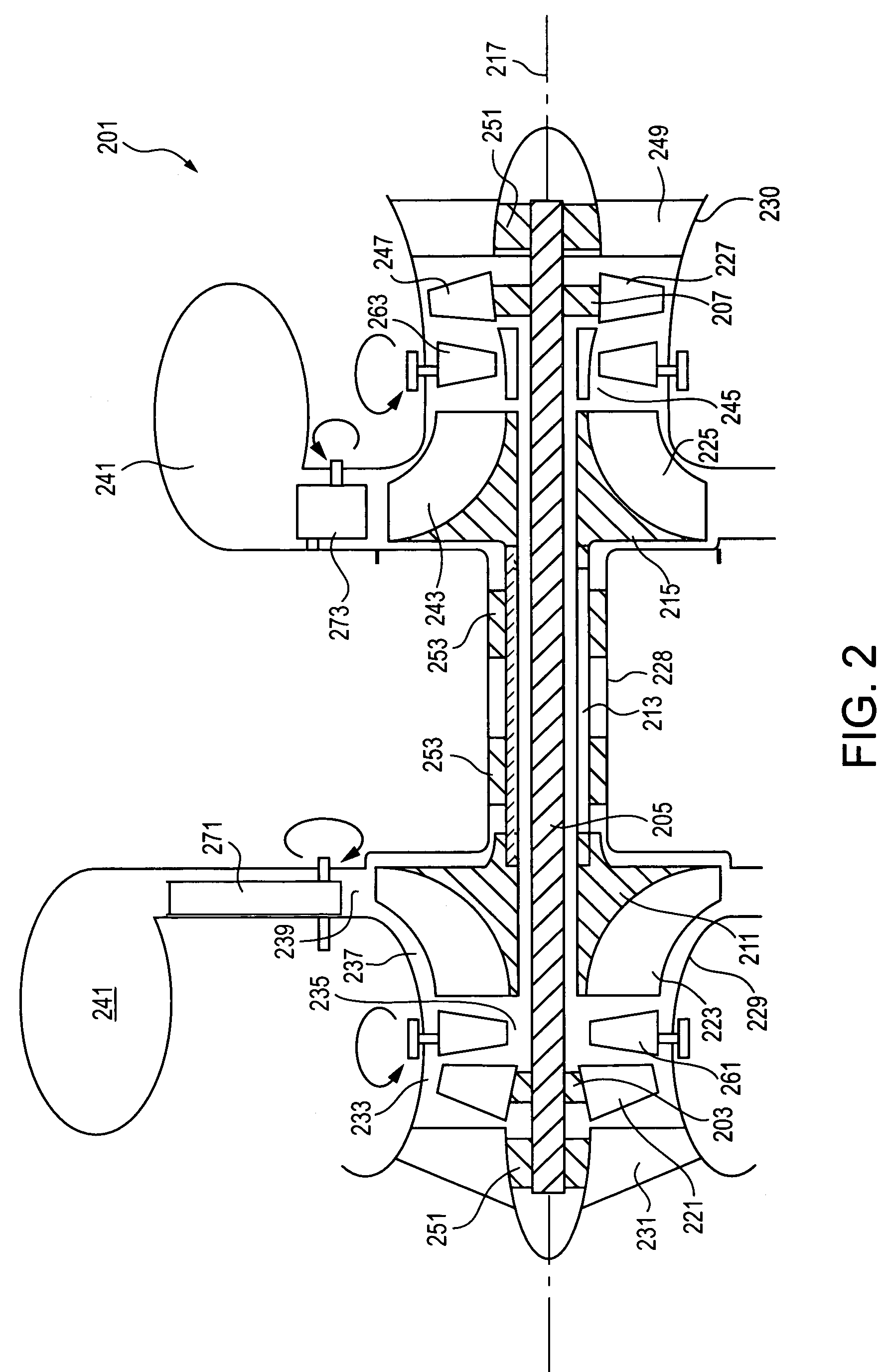
Intermediate floor for a radial turbine engine
InactiveUS20120230812A1High purityQuality improvementSpecific fluid pumpsEngine manufactureParticulatesEngineering
A radial turbomachine includes a radial diffuser channel with a diaphragm, a deflecting channel connecting to the radial diffuser channel downstream thereof, and a return flow channel connecting to the deflecting channel downstream thereof. The main flow direction of the radial diffuser channel runs radially from inside to outside. The main flow direction of the deflecting channel is deflected from radially outward to radially inward. The main flow direction of the return channel runs radially from outside to inside. The diaphragm comprises first, second and third outer surface sections. The first outer surface section has a convex shape for delimiting the deflecting channel. At least one consumption-gas removal channel is provided in the diaphragm so that, if the main flow in the deflecting channel comprises solid or liquid particles, a consumption gas can be discharged therefrom through the consumption-gas removal channel as low-particulate gas of a main flow.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Radial turbine
ActiveUS20130136590A1Reduce the number of partsReduce manufacturing costEngine manufacturePump componentsImpellerRadial turbine
A radial turbine includes a radial turbine wheel provided with a main pathway in which blade height progressively increases while curving toward an axial direction from a radial direction. A sub-let is formed on a shroud side of the radial turbine wheel at a position separated from the main inlet in the radial direction and the axial direction. Also, a blade shape that forms the sub-inlet is such that, in a plane orthogonal to the axial line of the radial turbine wheel, a center line of the blade is inclined at a predetermined angle toward the rotation direction with respect to the radial direction.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Turbine combined pulse detonation engine
The invention discloses a turbine combined pulse detonation engine (PDE). An air inlet device is positioned at the front tip of an engine shell; a gas compressor is positioned at the lower reaches of the air inlet device and is coaxial with the air inlet device; the gas compressor is coaxial with a radial turbine; a flow-guide casing is a smooth transition case between the gas compressor and the radial turbine; a guider is positioned between the flow-guide casing and the radial turbine; an inlet valve is positioned between the flow-guide casing and the inner wall of the engine shell; a diffusion cushion chamber ranges from the lower reaches of the gas compressor to the upper reaches of the inlet valve; a multi-tube detonation chamber is positioned at the lower reaches of the inlet valve; the outer annular wall surface of the multi-tube detonation chamber is part of the engine shell and the inner annular wall surface forms an inner annular wall; an inner flow passage is positioned at the lower reaches of the radial turbine; an ignition system is an ignition device of the multi-tube detonation chamber and the exit of the multi-tube detonation chamber is connected with a nozzle. The PDE is no longer than the length corresponding to the maximum external profile diameter of the gas compressor, thus greatly reducing coupling of detonation circulation and turbine operation, having high working frequency and conducing to power extraction.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
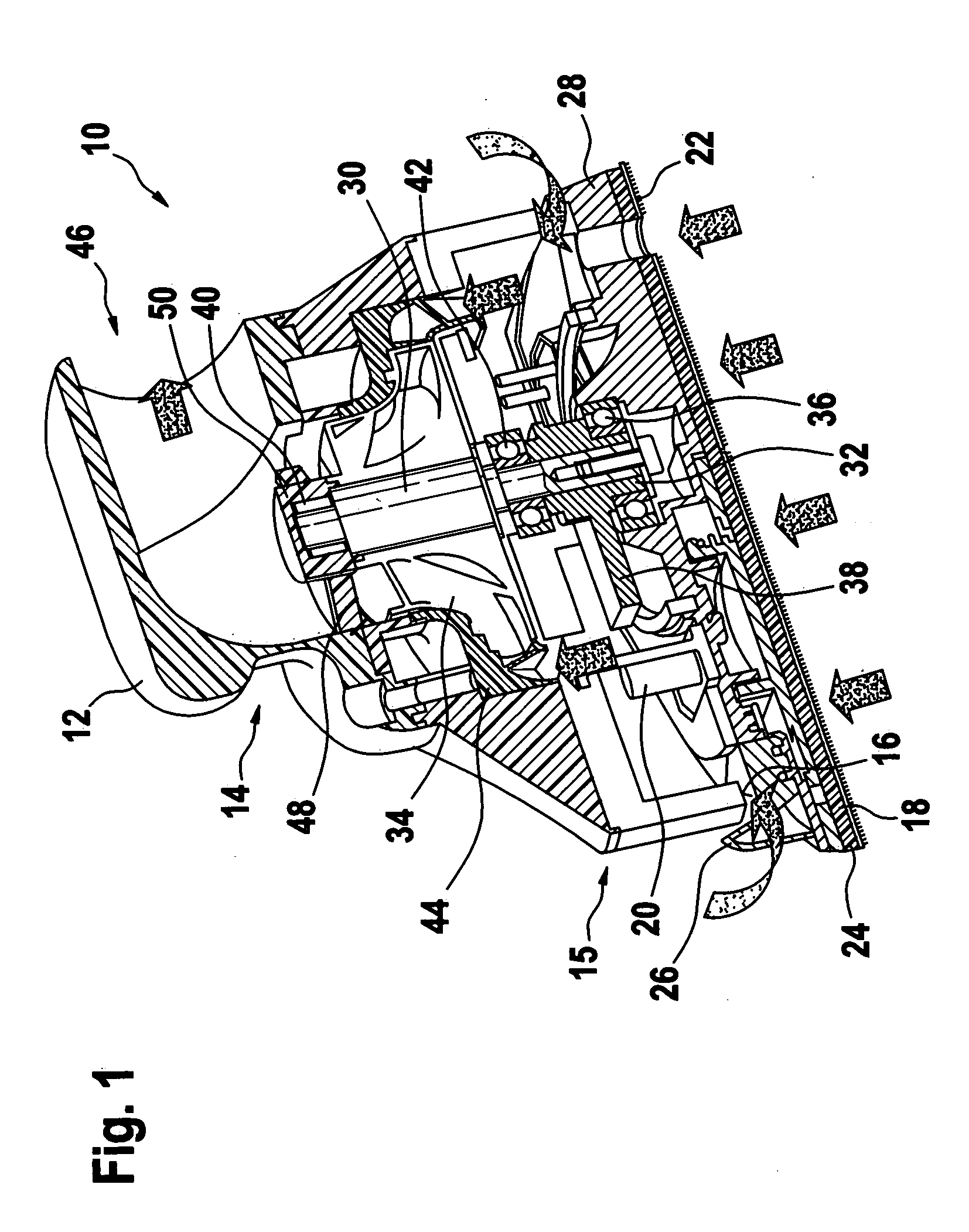
Power tool
InactiveUS7040972B2Level of efficiencyHigh degreeGrinding drivesBelt grinding machinesImpellerAs Directed
A power tool with a housing (12) and a tool (18, 22) located thereon such that it is capable of being driven in a rotating and / or oscillating manner, the tool being operable as directed using vacuum flow, in particular using a vacuum cleaner. The power tool is made particularly powerful by the fact that a radial turbine wheel (34) with forward-guiding and rearward-guiding vane rows (44, 48) functions as the drive.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Variable turbine cooling flow system
InactiveUS6931859B2Control flowOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngine manufactureAmbient pressureHigh pressure
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Turbine wheel for a radial turbine
InactiveUS20170107821A1High strengthEasy to manufactureTurbinesAdditive manufacturing apparatusImpellerTurbine wheel
A turbine wheel for a radial turbine includes a rotationally symmetrical base plate and a flow chamber delimited by a hub disk and a cover disk, wherein the flow chamber connects an axial inner opening to a radial outer opening and is subdivided by turbine blades into flow channels. In a method for producing such a turbine wheel, the hub disk, the turbine blades and the cover disk are integrally formed on the base plate using additive production methods.
Owner:ATLAS COPCO ENERGAS
Thermodynamic cycle operating at low pressure using a radial turbine
ActiveUS10082030B2Improve expansion propertiesAvoid condensationBlade accessoriesSteam engine plantsSingle stageAxial pressure
Expansion machines in thermodynamic cycles operate at low pressures, i.e. below 10 bar. The interplay among components including gas generator, expansion machine, heat exchangers and pressure reduction device (absorber or condenser) is optimized, resulting in configurations operating at the lowest achievable cost level. A single stage radial turbine characterized by a pressure ratio of 5-10, a dimensionless speed of about 0.7 and a loading coefficient of 0.7 is a preferred expansion machine for certain thermodynamic cycles involving CO2 gas to permit such radial turbines to operate close to their optimum design specification and highest efficiency level. Methods to handle liquids which may condense within or inside the turbine are also disclosed, as well as methods to handle axial pressure on bearings and methods to protect lubricant in bearings.
Owner:CLIMEON AB
Axially-split radial turbines and methods for the manufacture thereof
Embodiments of an axially-split radial turbine, as are embodiments of a method for manufacturing an axially-split radial turbine. In one embodiment, the method includes the steps of joining a forward bladed ring to a forward disk to produce a forward turbine rotor, fabricating an aft turbine rotor, and disposing the forward turbine rotor and the aft turbine rotor in an axially-abutting, rotationally-fixed relationship to produce the axially-split radial turbine.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Turbine wheel for a radial turbine
InactiveCN106593945ASave materialReduce manufacturing costTurbinesAdditive manufacturing apparatusImpellerTurbine wheel
The invention relates to a turbine wheel for a radial turbine. A turbine wheel for a radial turbine includes a rotationally symmetrical base plate (1) and a flow chamber (4) delimited by a hub disk (2) and a cover disk (3), wherein the flow chamber connects an axial inner opening (5) to a radial outer opening (6) and is subdivided by turbine blades (7) into flow channels (8). In a method for producing such a turbine wheel, the hub disk (2), the turbine blades (7) and the cover disk (3) are integrally formed on the base plate (1) using additive production methods.
Owner:ATLAS COPCO ENERGAS
Resonator silencer for a radial flow machine, in particular for a radial compressor
InactiveUS20140020975A1Easy to implementEasy to installEngine manufacturePump componentsEngineeringRadial compression
A volute for a radial turbomachine is proposed. The turbomachine includes a radial compressor or a radial turbine. The volute is in particular for a radial compressor. The volute has a substantially annular cavity which is delimited at least by a first radial side surface. At least one substantially annularly circumferential groove is formed in the side surface.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Cylinder head with turbine
InactiveUS20120055424A1Large amount of heatA large amountPump componentsEngine fuctionsCylinder headRadial turbine
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
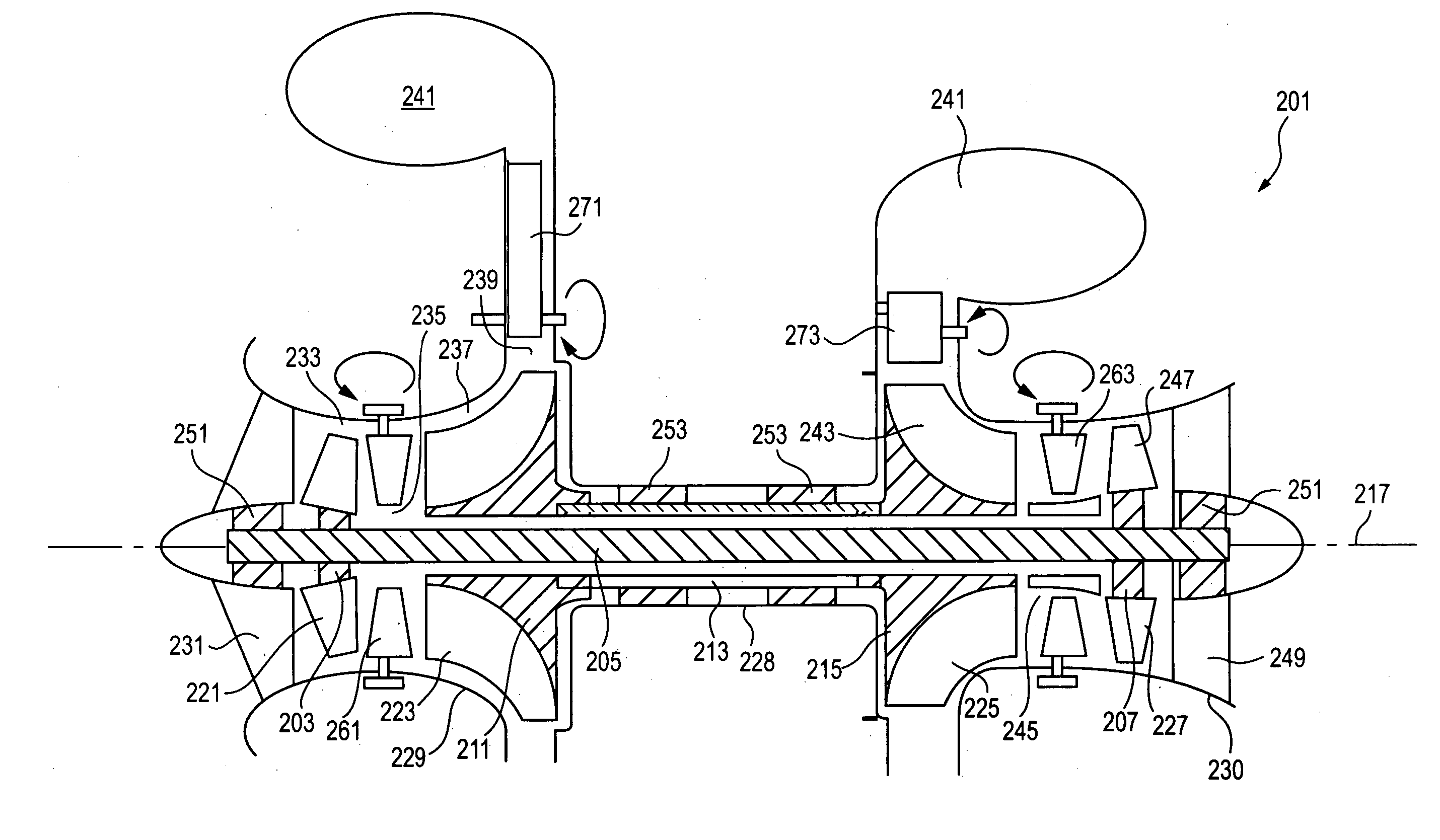
Single stage dual-entry centrifugal compressor, radial turbine gas generator
ActiveUS7628018B2Complete efficientlyHigh lossPump componentsWind motor controlBall bearingHigh pressure
Owner:OPRA TECH
Variable turbine cooling flow system
InactiveUS20050132711A1Control flowOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngine manufactureAmbient pressureHigh pressure
Cooling air to the blades and disks of a gas turbine may be modulated to provide a variable turbine cooling flow. A bellows may be extended by providing a high pressure compressor discharge flow to an interior of the bellows. The bellows may be compressed when the interior of the bellows communicates with ambient pressure air. The extension / compression of the bellows moves an arm over orifices in a cooling air flow path. The pressure inside of the bellows is metered to move the arm over at least one orifice, thereby restricting cooling air flow when the engine is running at low power. The pressure inside of the bellows is metered to move the arm to uncover all of the slots to provide maximum cooling flow when the engine is running at high power. The resulting variable cooling flow system results in less need for cooling air at low powers, thus reducing engine fuel consumption.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Axially-split radial turbine
An axially-split radial turbine includes a forward rotor section and an aft rotor section being mechanically and abuttingly coupled to one another along an annular interface that resides within a plane generally orthogonal to a rotational axis of the axially-split radial turbine. The axially-split radial turbine can be provided as part of a gas turbine engine.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Single stage dual-entry centrifugal compressor, radial turbine gas generator
ActiveUS20090232676A1Complete efficientlyHigh lossPump componentsWind motor controlBall bearingHigh pressure
A compact, single shaft gas turbine gas generator uses a high pressure ratio dual-entry single stage centrifugal compressor, can combustors, and a radial inflow turbine with the compressor configured to achieve an overall pressure ratio of about 12:1 or greater and Mach Numbers less than or equal to about 1.4. The radial inflow turbine is configured to provide an expansion ratio of about 4:1 to about 5:1, to provide partially expanded combustion gases to a free-power turbine or an expansion nozzle, in a work-producing engine configuration. A ball bearing assembly in front of the compressor is used in conjunction with a thrust piston assembly to take up turbine thrust load, while a radial tilt pad bearing assembly is used in front of the turbine. A collector with scroll-shaped sector portions collects compressed air from an annular vaned diffuser, and respective crossover ducts channel the collected diffused compressed air from each sector portion to a plenum feeding can combustors. Bleed systems at each compressor inlet provide increased diffuser stability margins. Gas turbine engines configured with the above gas generator may provide 30% thermal efficiency or more in a rated power range of about 4 Mw or less.
Owner:OPRA TECH
Wind-tracking twin-turbine system
ActiveUS8946923B2Improve adhesionReduce air resistanceWorking fluid for enginesMachines/enginesTurbineRadial turbine
Owner:DIRECTTECH GLOBAL GMBH
Mixed Flow Turbine or Radial Turbine
ActiveUS20100098548A1Optimal Rate of ChangeCut surfacePropellersEngine manufactureMixed flowFront edge
Intended is to provide a mixed flow turbine or a radial turbine, which can suppress an abrupt increase in a load to be applied to the front edge portion of a blade, thereby to reduce an incidence loss. The mixed flow turbine or the radial turbine comprises a hub (3), and a plurality of blades (7) arranged at substantially equal interval on the outer circumference (5) of the hub (3) and having a warpage (23) curved convexly in the rotating direction, as entirely viewed from the front edge side to the back edge side. Each blade (7) is provided, at its front edge portion, with an inflection point (K), at which the warpage (23) in the section along the outer circumference is curved concavely in the rotating direction.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Variable-pitch nozzle for a radial turbine, in particular for an auxiliary power source turbine
InactiveUS20140147278A1Limit deterioration in performanceDeterioration can be suppressedPropellersEngine manufactureLeading edgeTrailing edge
A radial turbine nozzle of a turbine engine rotating about a central axis includes a first annular array of fixed blades and a second annular array with a same number of variable-pitch blades. The blades have pressure and suction surfaces. Each variable-pitch blade is connected to cups and is configured to be rotated by a controller about a geometric axis connecting centers of the cups. Each variable-pitch blade is mounted at a distance from the axis of the cups such that this axis of rotation is positioned facing the suction surface of the blade and substantially closer to a trailing edge than to a leading edge of that blade. The nozzle can modify the reduced flow admitted by a radial turbine in accordance with requirements of a thermodynamic cycle and produce a seal in an area of maximum load of the nozzle blades.
Owner:SAFRAN HELICOPTER ENGINES
Dual-use radial turbomachine
InactiveUS20070277527A1Efficient use ofEasy to useEngine manufacturePump componentsHigh liftRadial turbine
The impeller is preferably modified to use back swept, radial or forward swept blades to accommodate relatively low, medium and high lift, respectively applications for both centrifugal compressor and turbine rotor use.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Axially-split radial turbines and methods for the manufacture thereof
Embodiments of an axially-split radial turbine, as are embodiments of a method for manufacturing an axially-split radial turbine. In one embodiment, the method includes the steps of joining a forward bladed ring to a forward disk to produce a forward turbine rotor, fabricating an aft turbine rotor, and disposing the forward turbine rotor and the aft turbine rotor in an axially-abutting, rotationally-fixed relationship to produce the axially-split radial turbine.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Integrated cantilever rotor structure
InactiveCN102434217ARealize direct connectionSimple structureBlade accessoriesGas turbine plantsFailure rateEngineering
The invention relates to an integrated cantilever rotor structure, which comprises a generator rotor, a centrifugal compressor impeller, sealed grate teeth and a radial turbine impeller which are arranged on a central pull rod in sequence. One side of the centrifugal compressor impeller is connected with the radial turbine impeller through the sealed grate teeth in end face matching mode, the centrifugal compressor impeller and the radial turbine impeller are arranged in back-to-back mode, and the other end of the centrifugal compressor impeller is connected with the generator rotor. The integrated cantilever rotor structure has the advantages of being simple in structure, small in volume and capable of enabling a unit structure to be simple, usage to be reliable, failure rate to be low and both manufacture cost and maintenance cost to be reduced.
Owner:HARBIN DONGAN ENGINE GRP
Radial turbine rotor blade
ActiveCN104854325AReduce impact lossImprove turbine efficiencyBlade accessoriesCombustion enginesRotational axisLeading edge
[Problem] To provide a radial turbine rotor blade whereby, even if a variable nozzle mechanism in a variable-geometry turbocharger is closed down, resulting in a flow field with a low turbine velocity ratio (U / C0), inflowing-gas impact losses at the leading edge of the rotor blade are reduced, improving turbine efficiency. [Solution] This radial turbine rotor blade is characterized in that: with respect to the direction of rotation (R) of the rotor blade (50), the hub-side corner (Pa) of the leading edge (51) of the rotor blade (50) is behind the shroud-side corner (Sc) of said leading edge (51); and in a radial view of the rotor blade (50), a line that connects the aforementioned shroud-side corner (Sc) to the hub-side corner (Pa) forms a 30-70° angle with a line that extends in the direction of the axis of rotation from the shroud-side corner (Sc) of the leading edge (51) to the surface of the hub (17).
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com