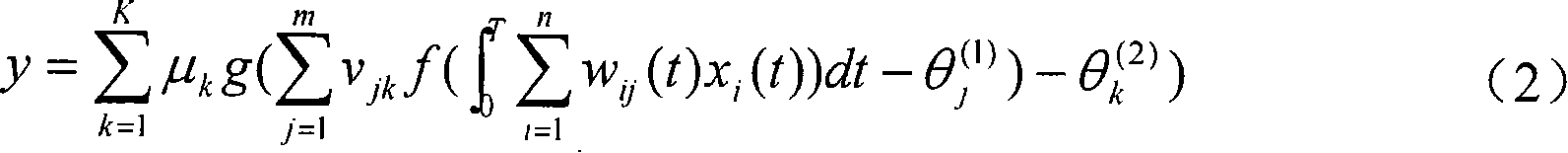Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
137 results about "Procedural modeling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Procedural modeling is an umbrella term for a number of techniques in computer graphics to create 3D models and textures from sets of rules. L-Systems, fractals, and generative modeling are procedural modeling techniques since they apply algorithms for producing scenes. The set of rules may either be embedded into the algorithm, configurable by parameters, or the set of rules is separate from the evaluation engine. The output is called procedural content, which can be used in computer games, films, be uploaded to the internet, or the user may edit the content manually. Procedural models often exhibit database amplification, meaning that large scenes can be generated from a much smaller amount of rules. If the employed algorithm produces the same output every time, the output need not be stored. Often, it suffices to start the algorithm with the same random seed to achieve this.
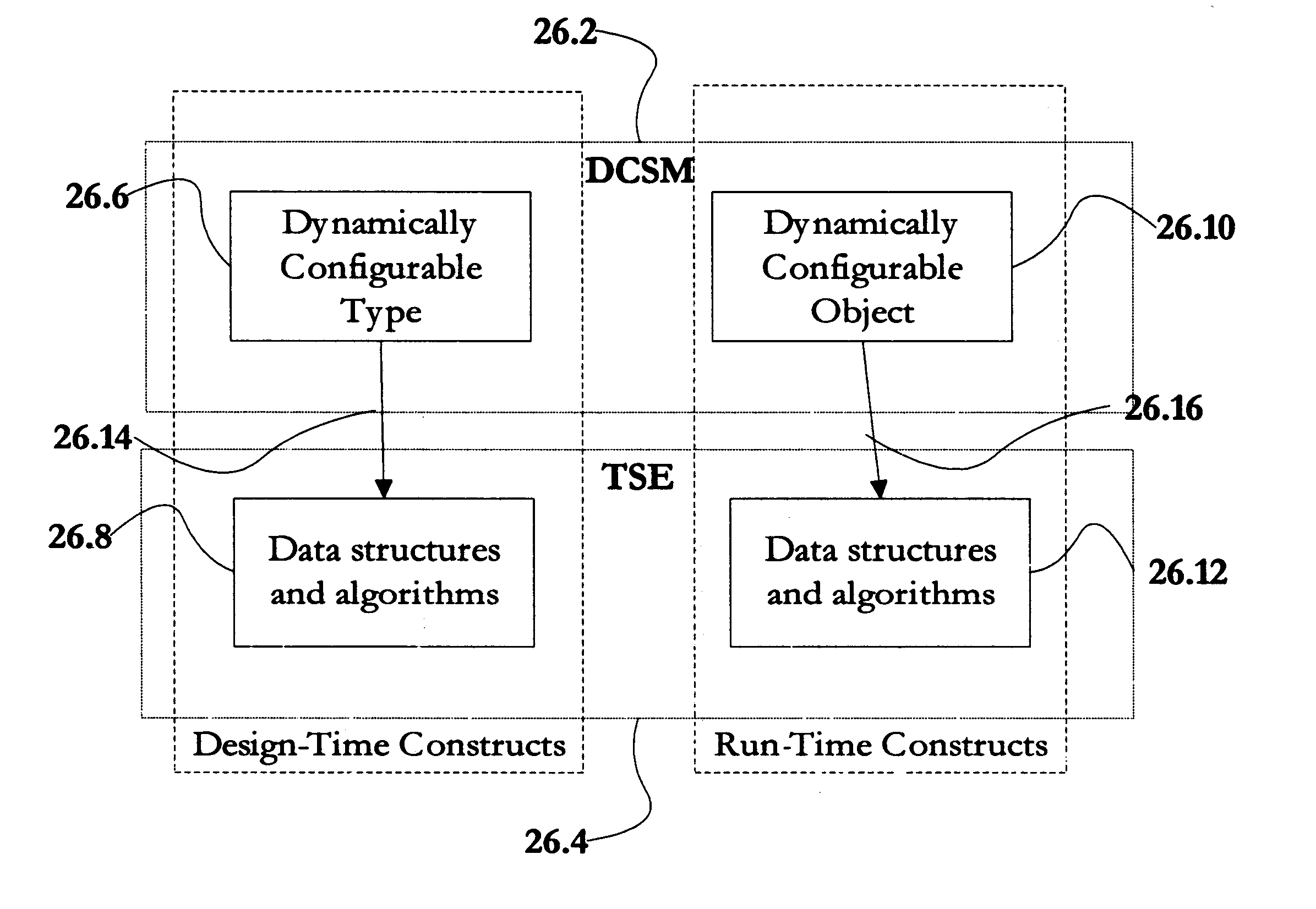
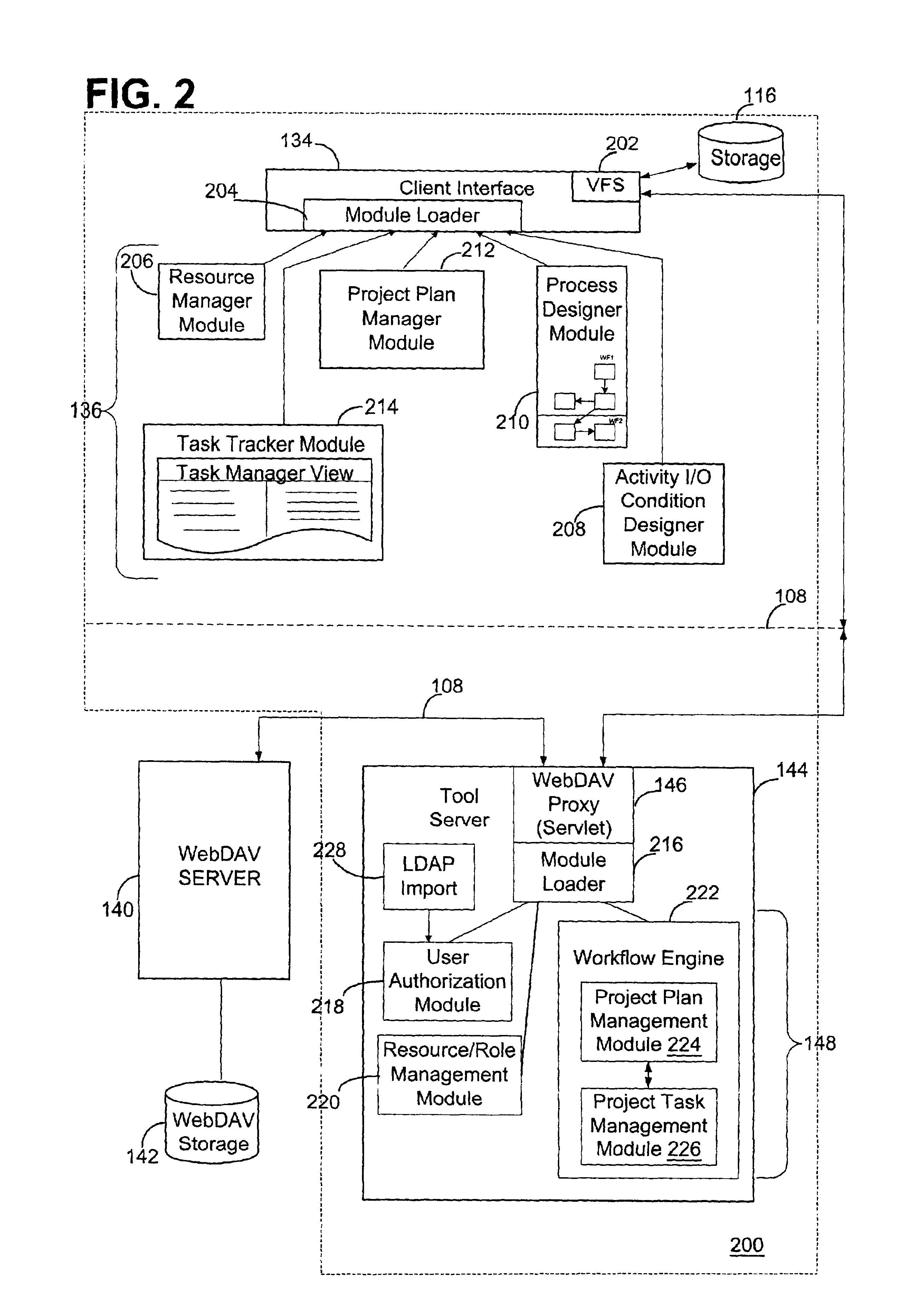
Method and apparatus for the development of dynamically configurable software systems
InactiveUS6269473B1Dynamic configurabilityImprove abilitiesData processing applicationsSoftware designSoftware systemSemantics
A software modeling environment is presented that supports the development and execution of software that can be dynamically configured. This is achieved by introducing a design-time object modeling construct called a dynamically configurable type (DCT) that supports the subdivision of an object into a plurality of subsets of semantics and allows dynamic merging of these semantic subsets together in different combinations in order to allow the resultant object to exhibit different semantics over time to serve different purposes. Specific process modeling constructs are included which take advantage of this semantic merging capability. Also included are other supporting design-time and run-time constructs and services. One embodiment of the present invention allows this software modeling environment to be integrated into a standard software development environment, enhancing the modeling capabilities already present.
Owner:EVOLVE SOFTWARE
Knowledge-engineering protocol-suite
InactiveUS6952688B1Improve efficiencyExtension of timeKnowledge representationSpecial data processing applicationsEnsemble simulationControl communications
A Knowledge-Engineering Protocol-Suite is presented that generally includes methods and systems, apparatus for search-space organizational validation, and appurtenances for use therewith. The protocol-suite includes a search-space organizational validation method for synergistically combining knowledge bases of disparate resolution data-sets, such as by actual or simulated integrating of lower resolution expert-experience based model-like templates to higher resolution empirical data-capture dense quantitative search-spaces. Furthermore, from alternative technological vantages, the suite relates to situations where this synergetic combining is beneficially accomplished, such as in control systems, command control systems, command control communications systems, computational apparatus associated with the aforesaid, and to quantitative modeling and measuring tools used therewith. The protocol-suite also includes facile algorithmic tools for use with the method and a process-modeling computer for use in a distributed asynchronous system of process modeling computers.
Owner:ADA ANALYTICS ISRAEL
Methods and systems for improving a workflow based on data mined from plans created from the workflow
Methods and systems consistent with the present invention provide an integrated process modeling and project planning tool that allows an enterprise affiliate to improve a workflow that models a process. To improve the workflow, the tool initiates execution of a plan created from the workflow such that an instance of the process is at least partially performed, receives a characteristic about the performance of the plan, and modifies the workflow to reflect the characteristic so that a subsequent plan created from the modified workflow has the received characteristic.
Owner:BORLAND
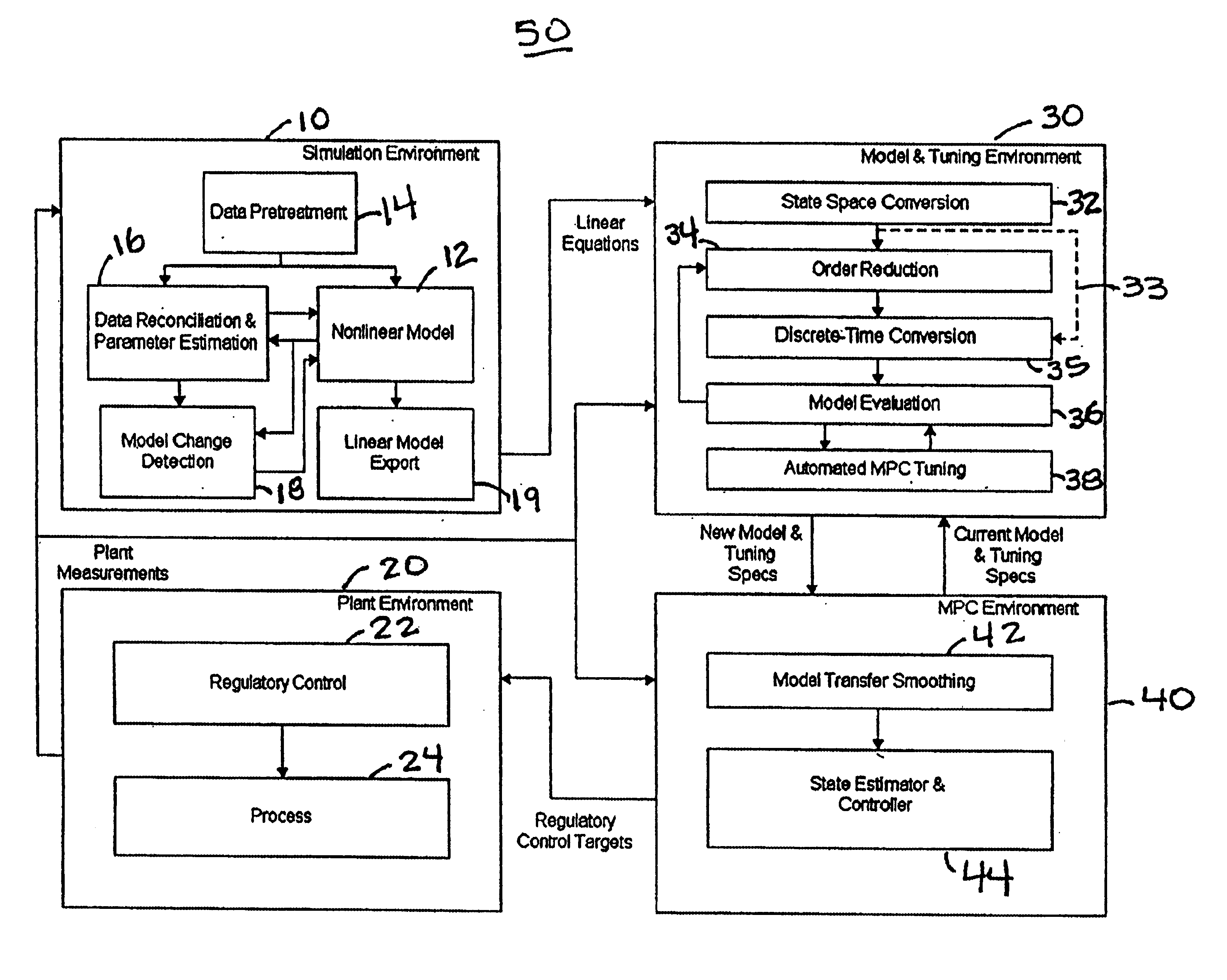
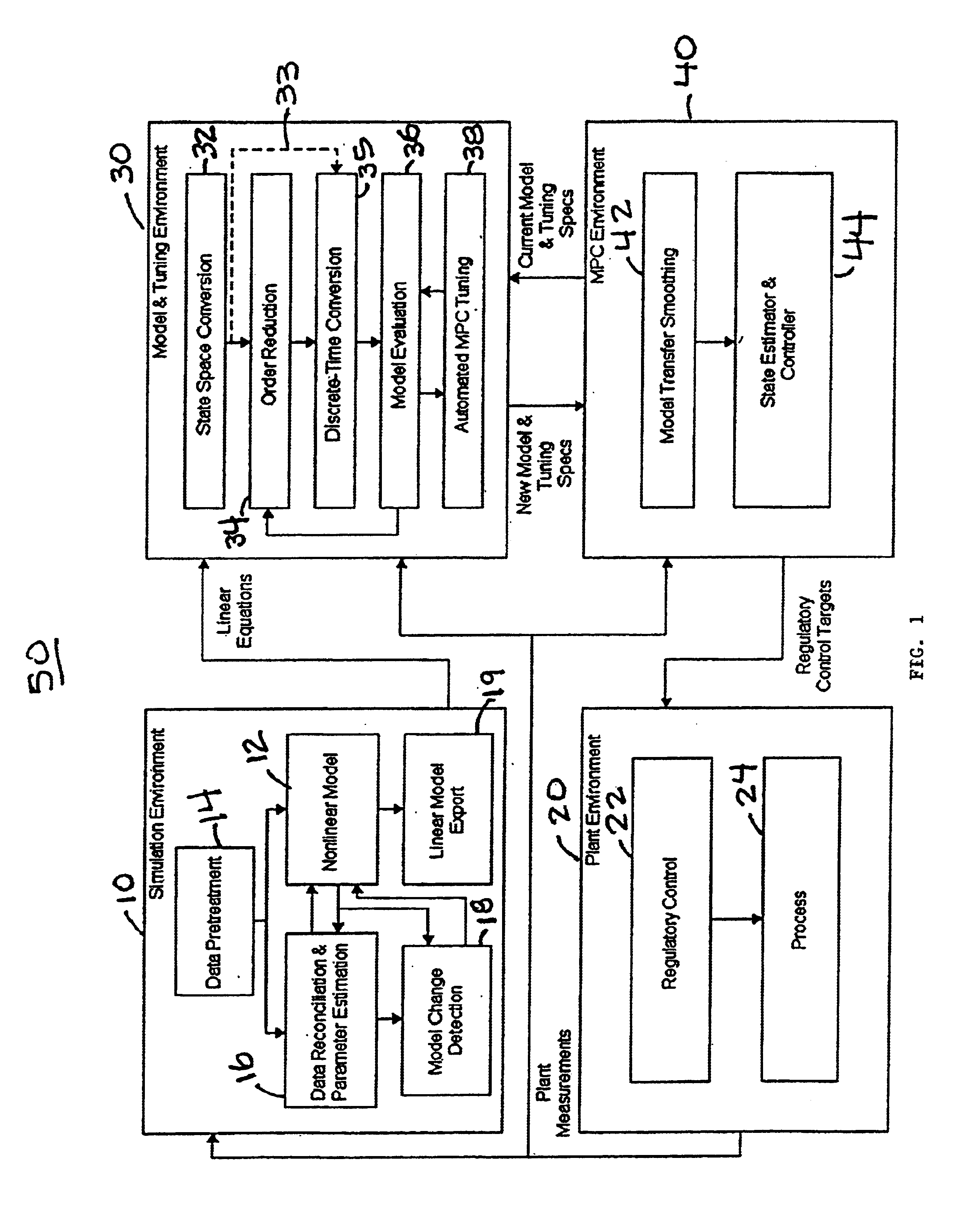
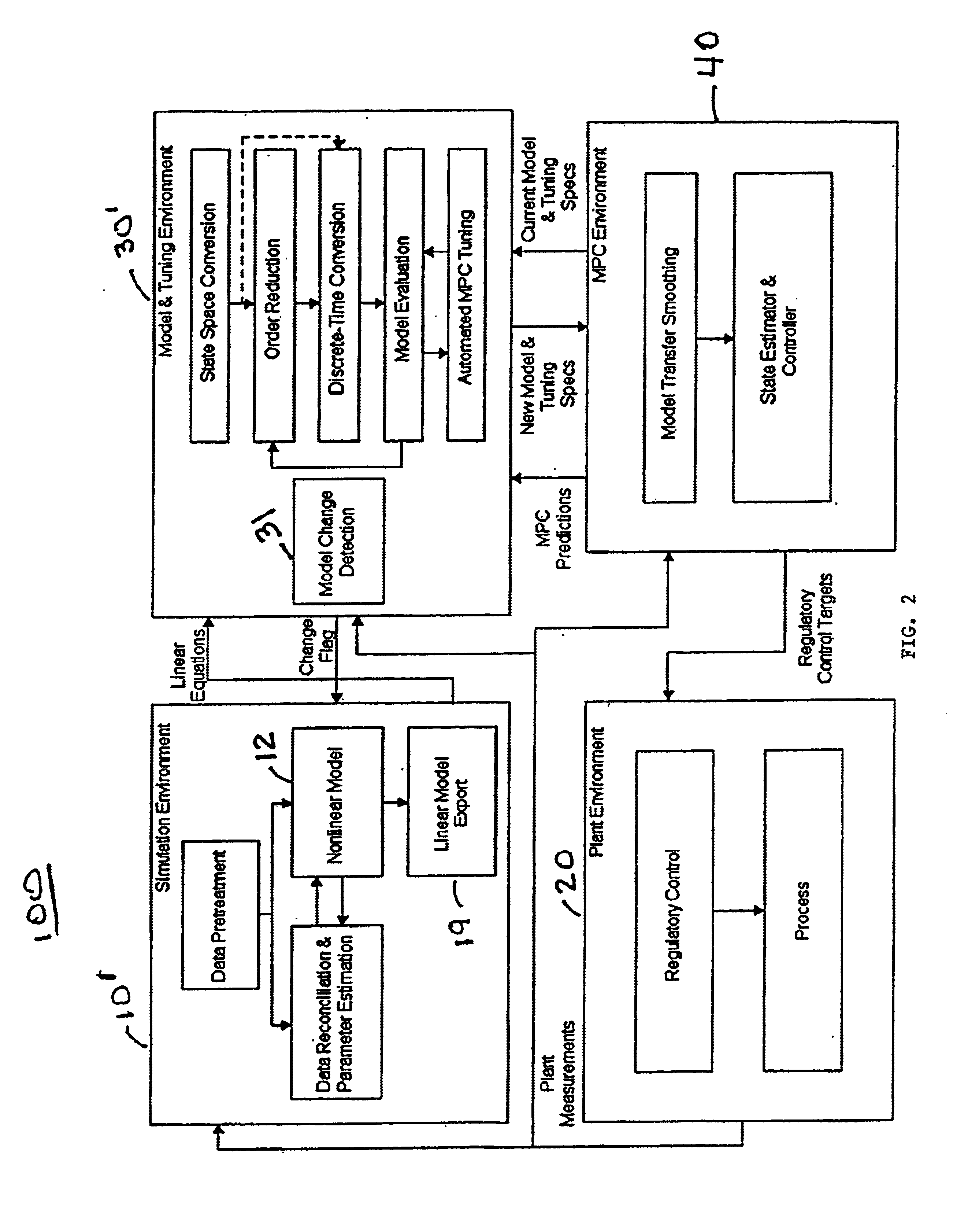
System and methodology and adaptive, linear model predictive control based on rigorous, nonlinear process model
InactiveUS6826521B1Analogue computers for chemical processesAdaptive controlSoftware systemPredictive controller
A methodology for process modeling and control and the software system implementation of this methodology, which includes a rigorous, nonlinear process simulation model, the generation of appropriate linear models derived from the rigorous model, and an adaptive, linear model predictive controller (MPC) that utilizes the derived linear models. A state space, multivariable, model predictive controller (MPC) is the preferred choice for the MPC since the nonlinear simulation model is analytically translated into a set of linear state equations and thus simplifies the translation of the linearized simulation equations to the modeling format required by the controller. Various other MPC modeling forms such as transfer functions, impulse response coefficients, and step response coefficients may also be used. The methodology is very general in that any model predictive controller using one of the above modeling forms can be used as the controller. The methodology also includes various modules that improve reliability and performance. For example, there is a data pretreatment module used to pre-process the plant measurements for gross error detection. A data reconciliation and parameter estimation module is then used to correct for instrumentation errors and to adjust model parameters based on current operating conditions. The full-order state space model can be reduced by the order reduction module to obtain fewer states for the controller model. Automated MPC tuning is also provided to improve control performance.
Owner:ABB AUTOMATION INC
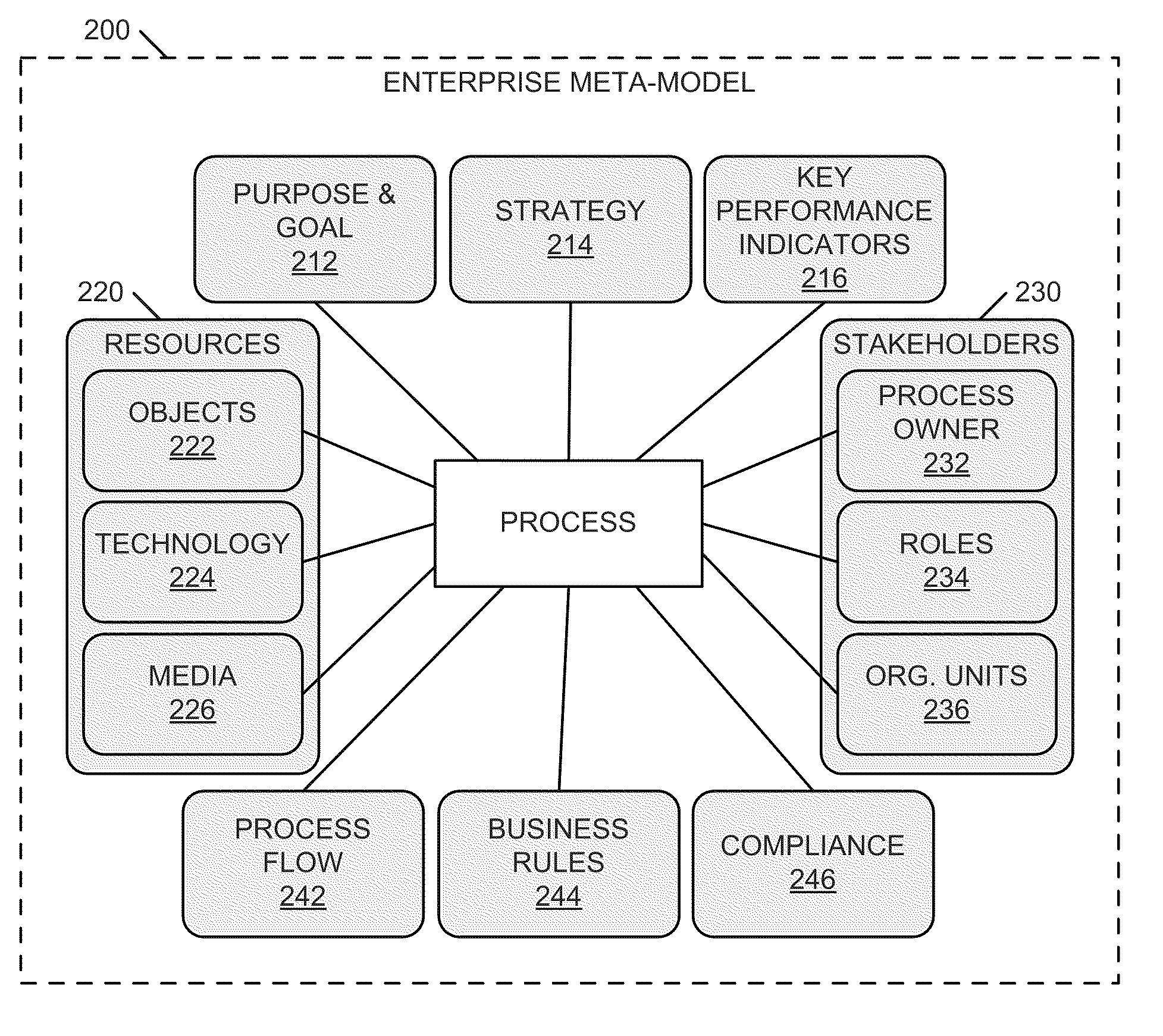
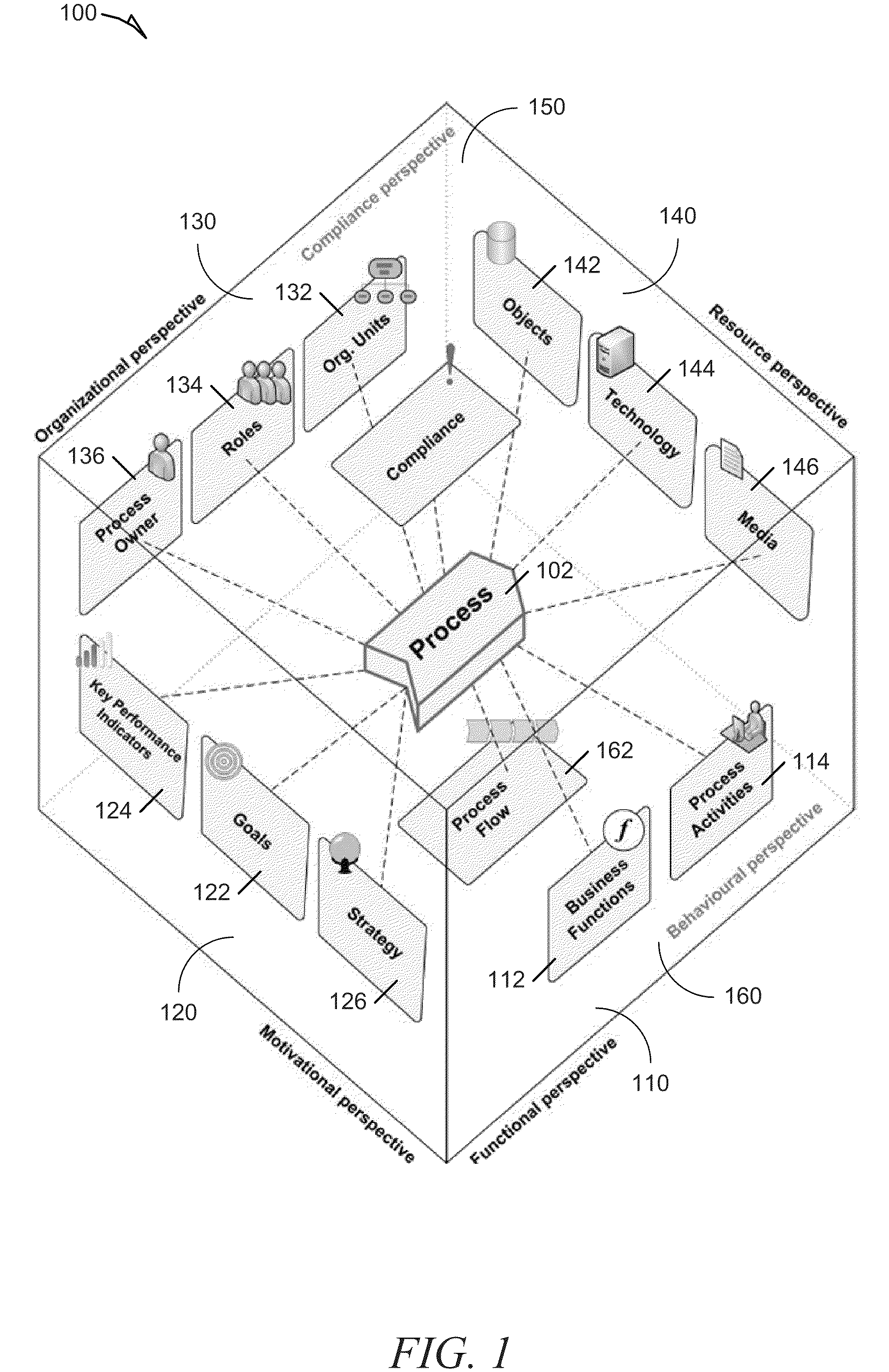
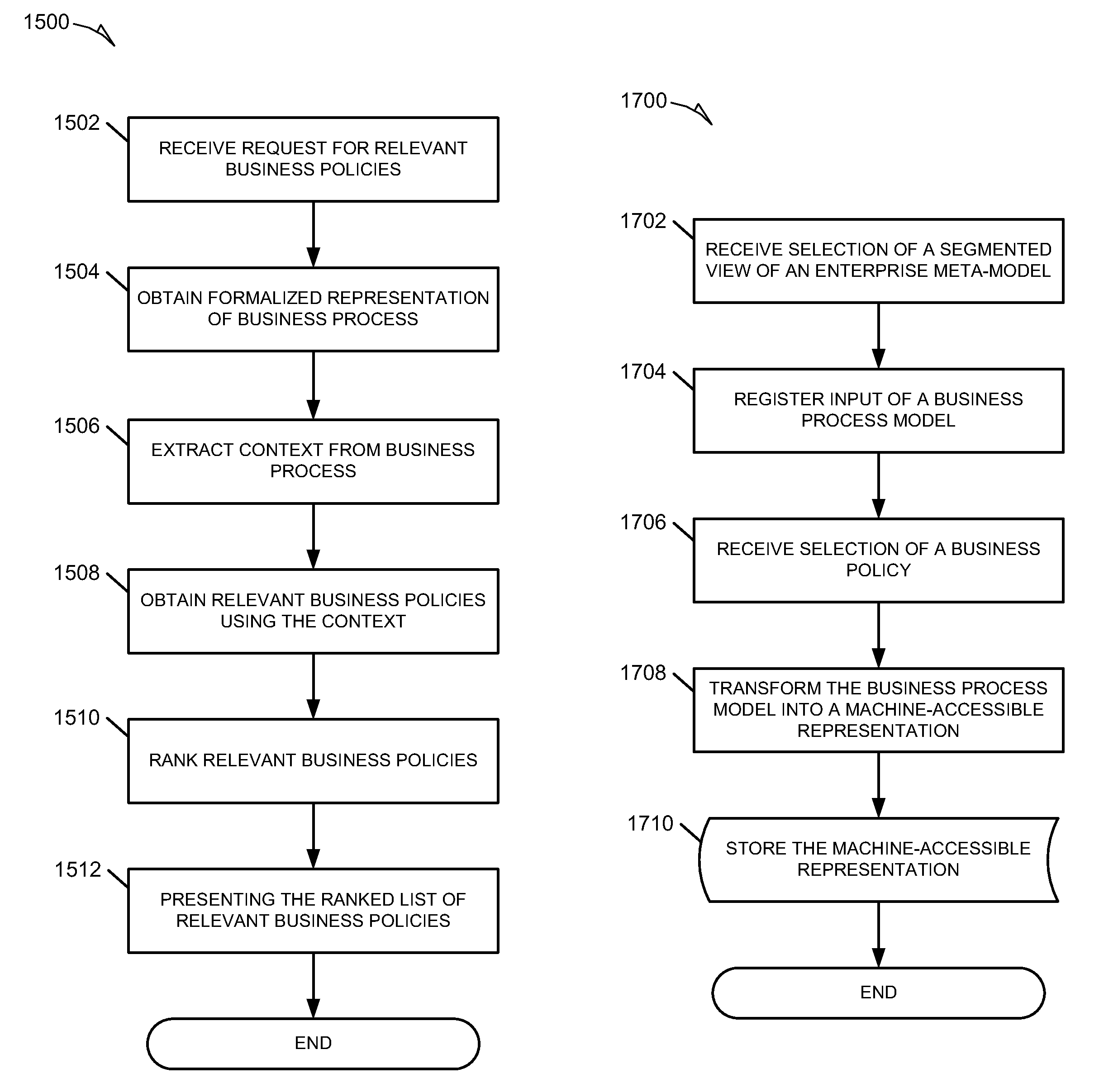
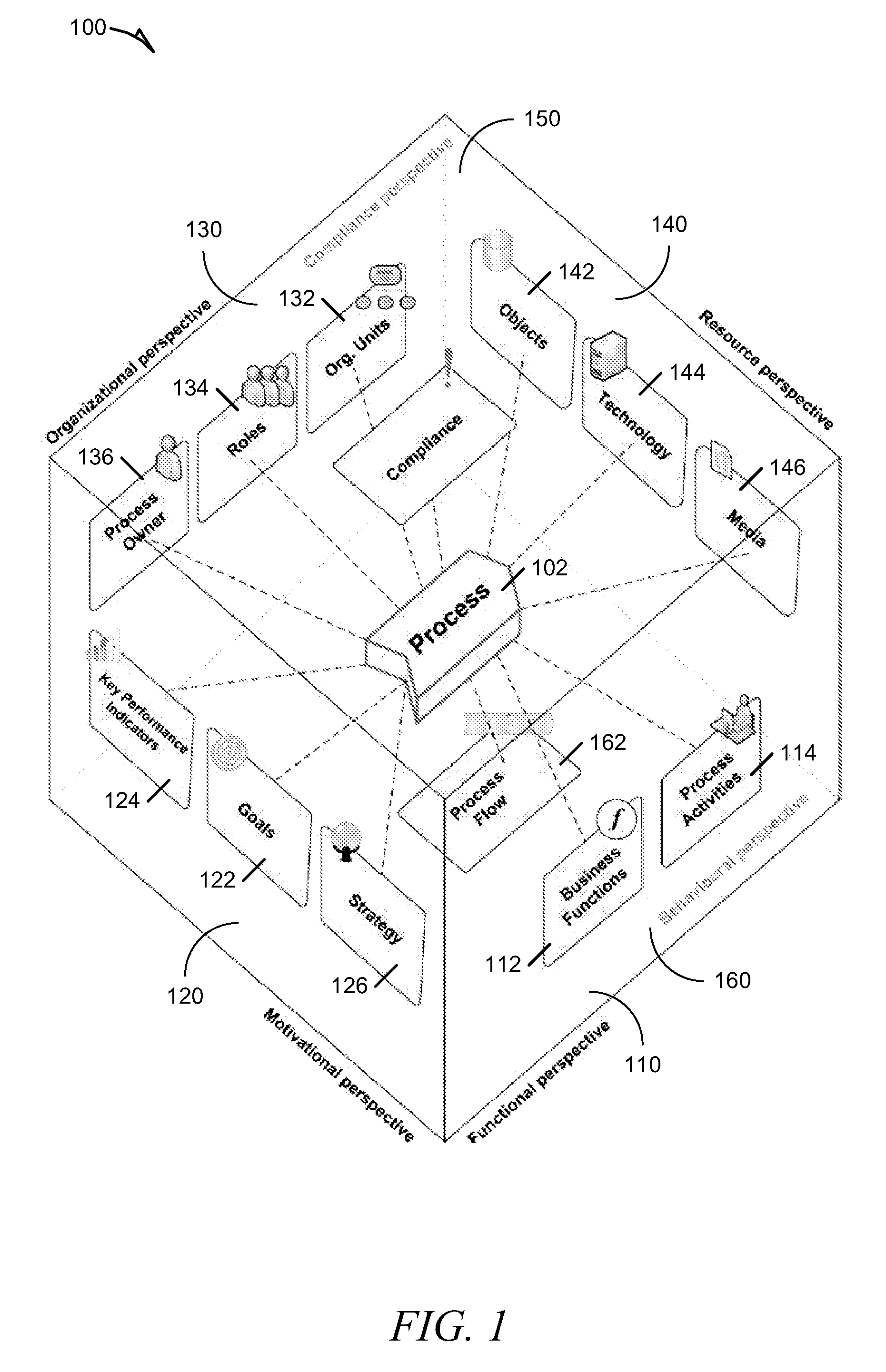
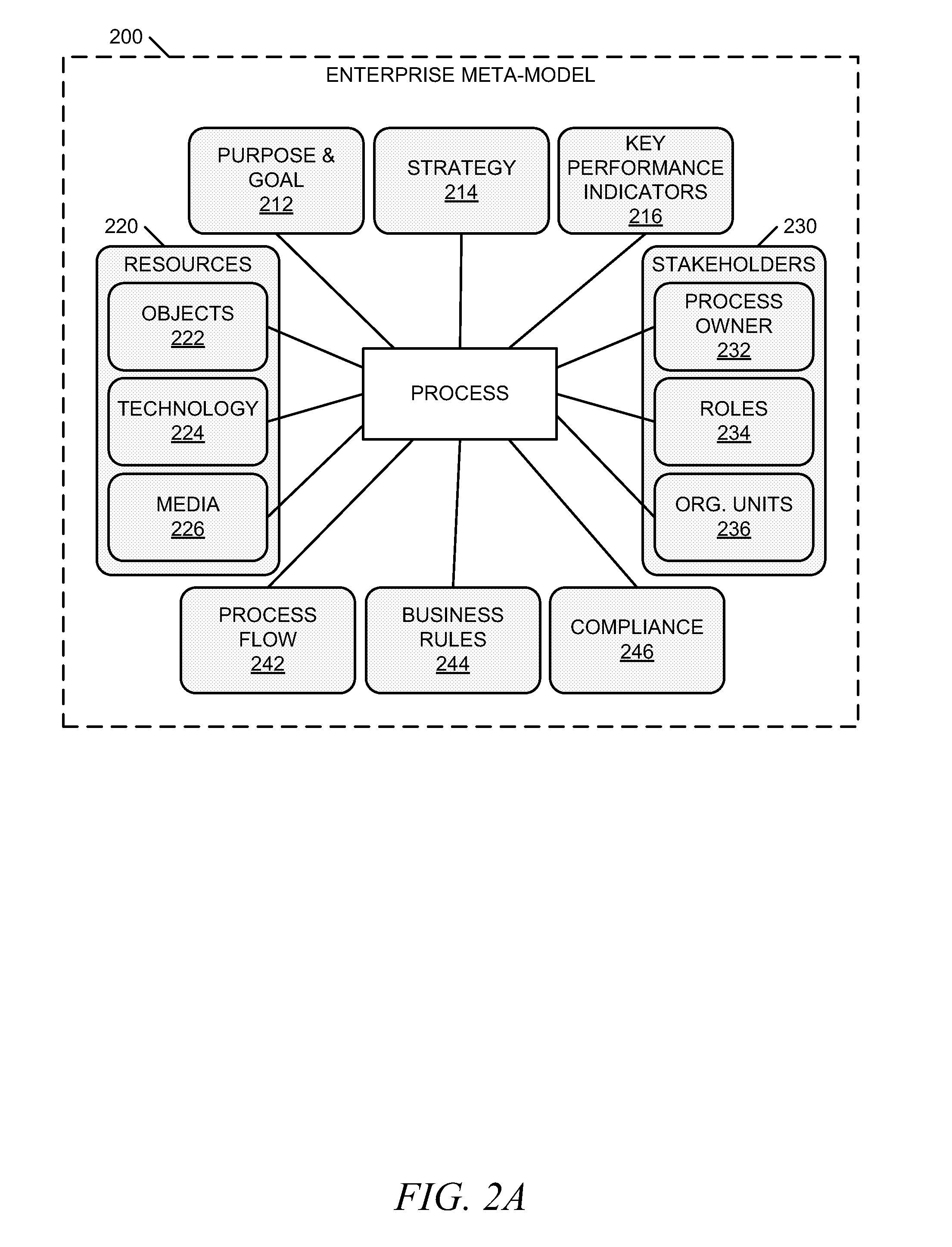
Systems and methods for integrating process perspectives and abstraction levels into process modeling
ActiveUS20110029947A1Office automationSpecific program execution arrangementsAbstraction layerEnterprise modelling
Methods and systems for integrating process perspectives and abstraction levels into business process modeling are described. In one example embodiment, modeling business processes for an enterprise can include selecting a segmented view of an enterprise meta-model. The segmented view is associated with a business process to be modeled. The enterprise meta-model is a machine-readable representation of business rules and policies for the enterprise. A business process model is created using a set of visual modeling tools, which are limited by the segmented view. A business policy having some relevance to the process being modeled can be selected for annotation to the business process. Once completed, the business process model is transformed into a machine-readable representation and stored in a repository.
Owner:SAP AG
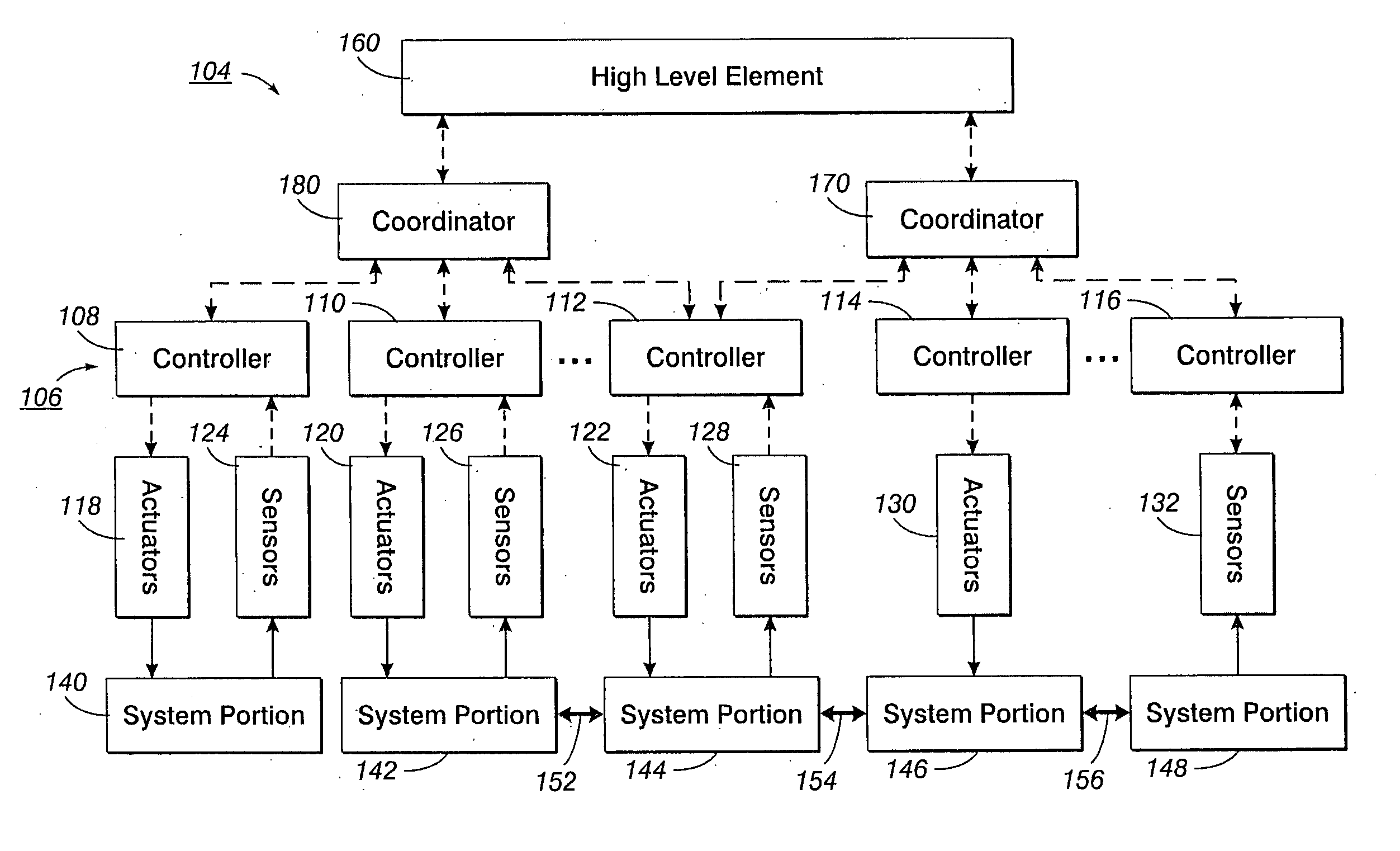
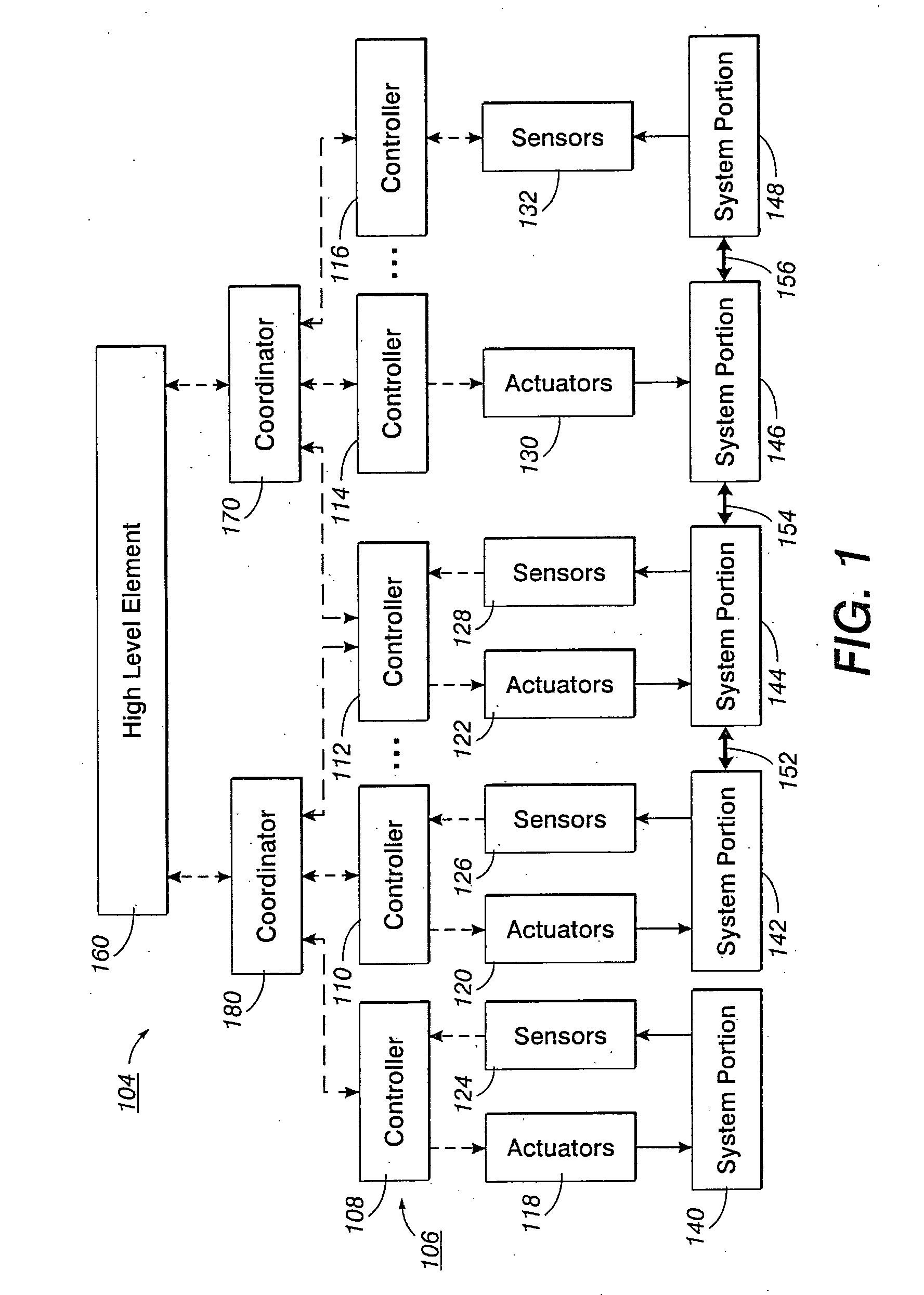
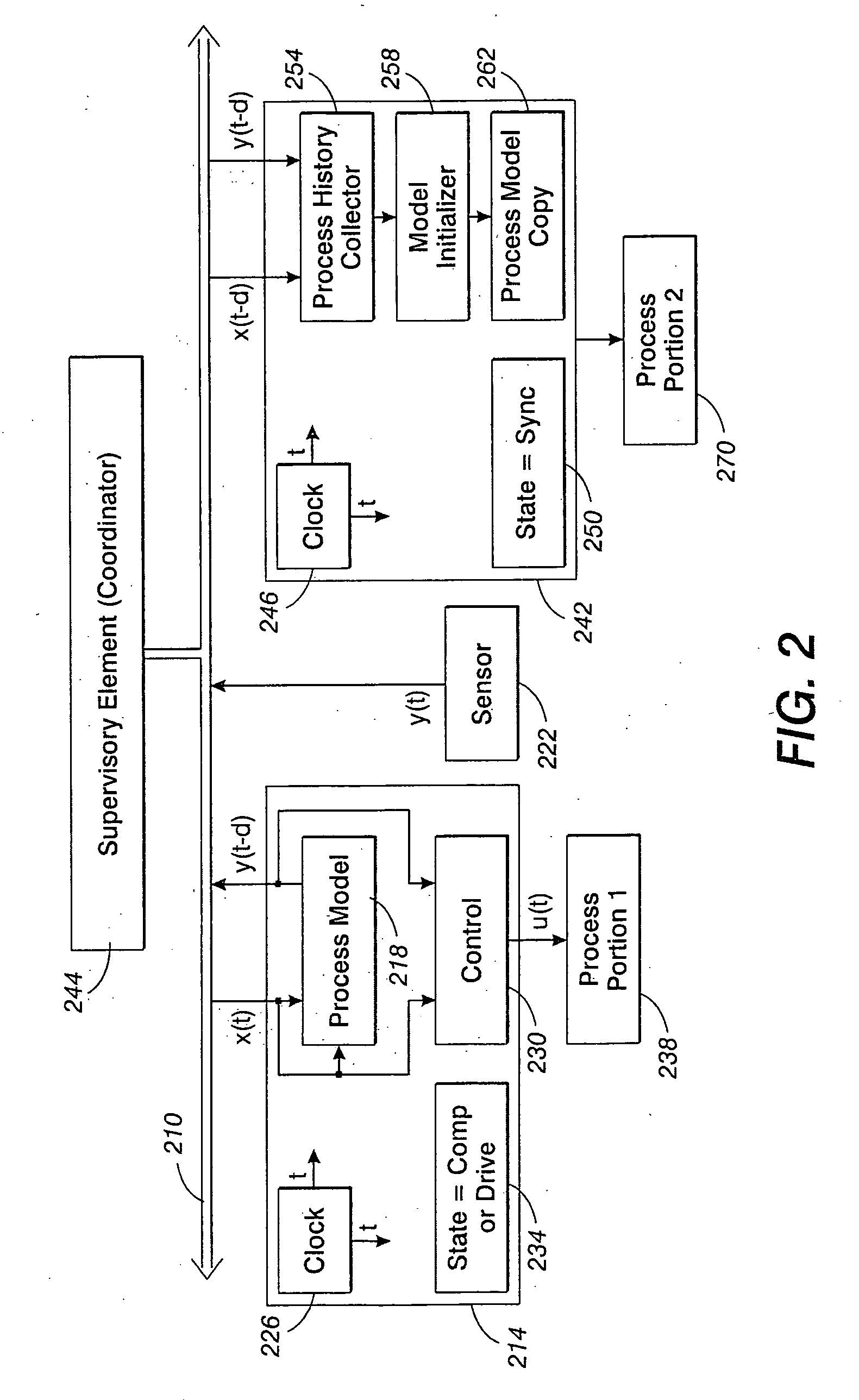
Synchronization in a distributed system
InactiveUS20060227350A1Programme controlDigitally marking record carriersPaper documentDocument preparation
A method for synchronizing the control efforts of a plurality of controllers includes determining an apply time for using updated information. The apply time can take into account worst case processing and / or communication delays across a system. Reacting to the updated information only after at the apply time ensures that all system elements are able to react to the updated information in concert. A time stamp indicates when the data was collected. The apply time indicates when the data can be used. Process modeling or simulation is used to estimate system status at the apply time based on the system status at the time of the time stamp, the updated information, and predetermined information regarding the behavior of the system over time. In a document processor, the method allows tightly coupled modules, such as sheet transportation modules, to behave in a cooperative manner when separate modules are in contact with the same sheet.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
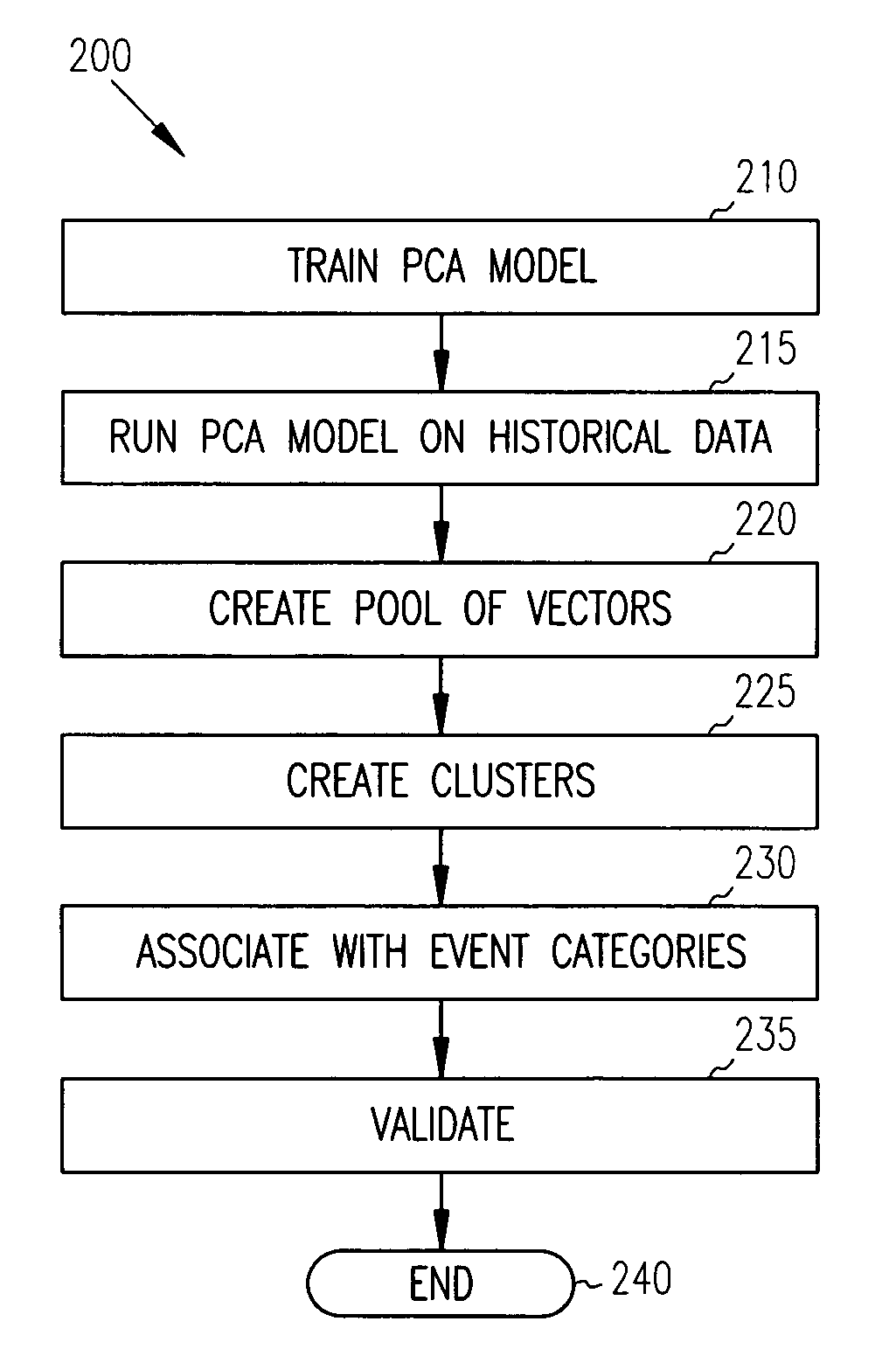
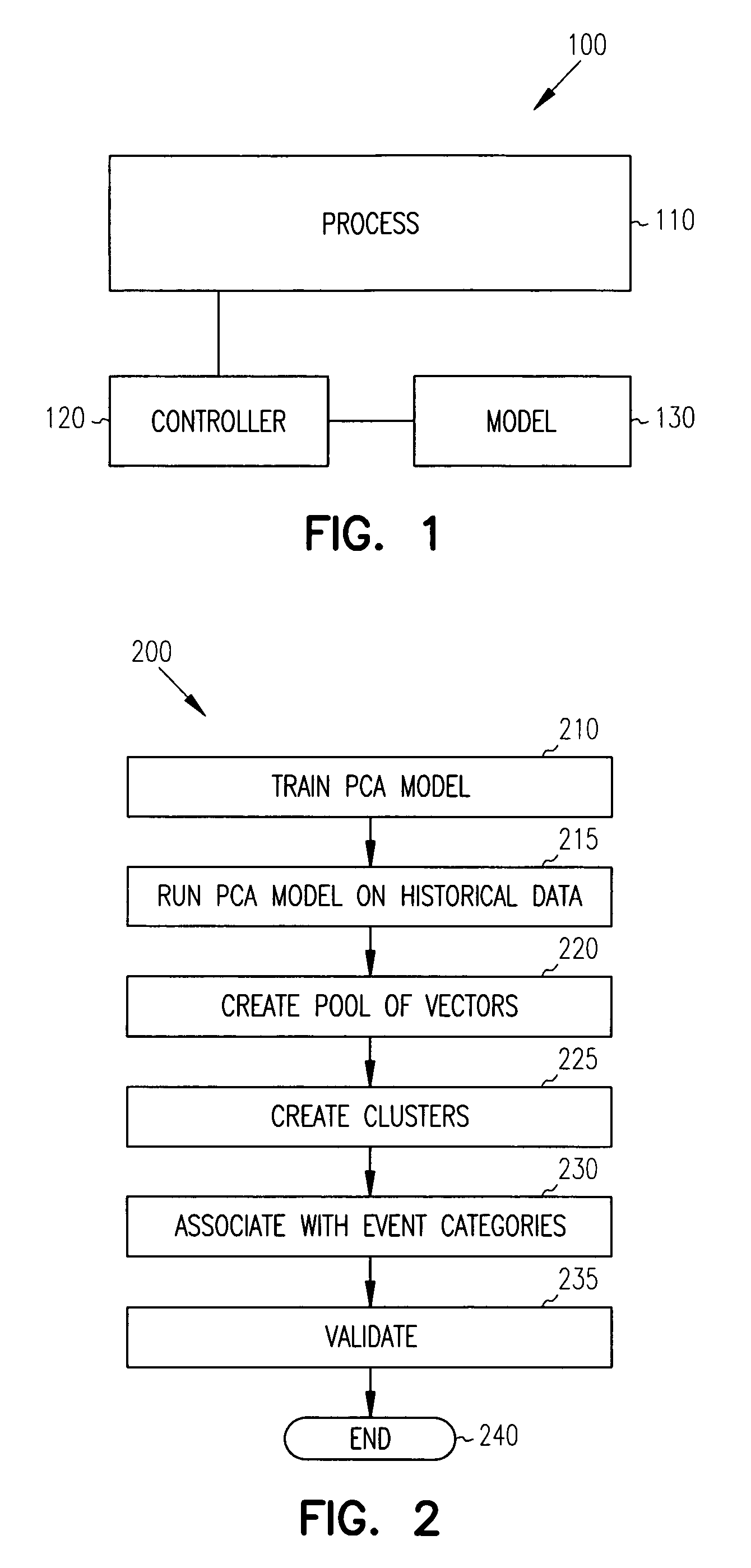
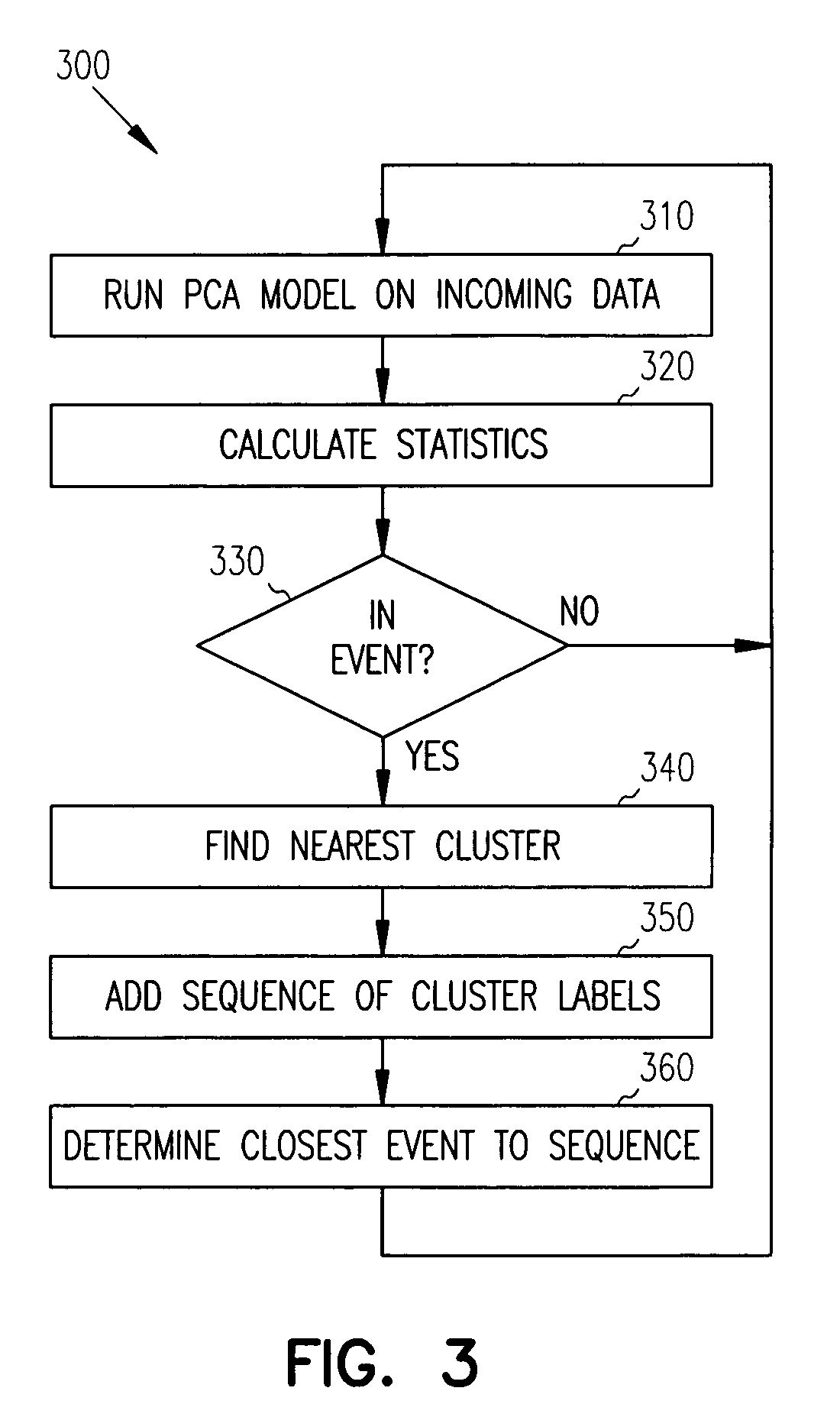
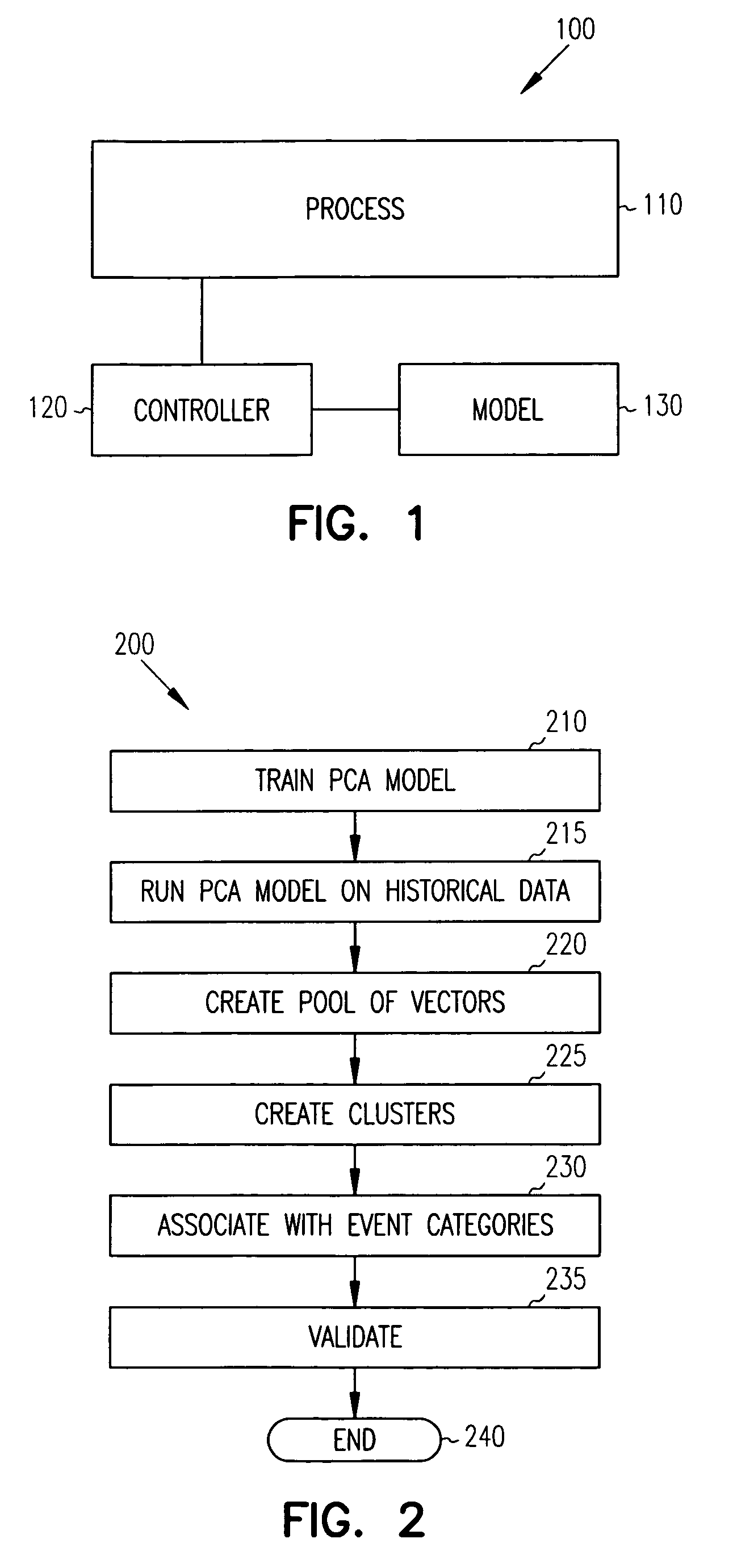
Principal component analysis based fault classification
ActiveUS7096153B2Electric testing/monitoringDigital computer detailsKernel principal component analysisPrincipal component analysis
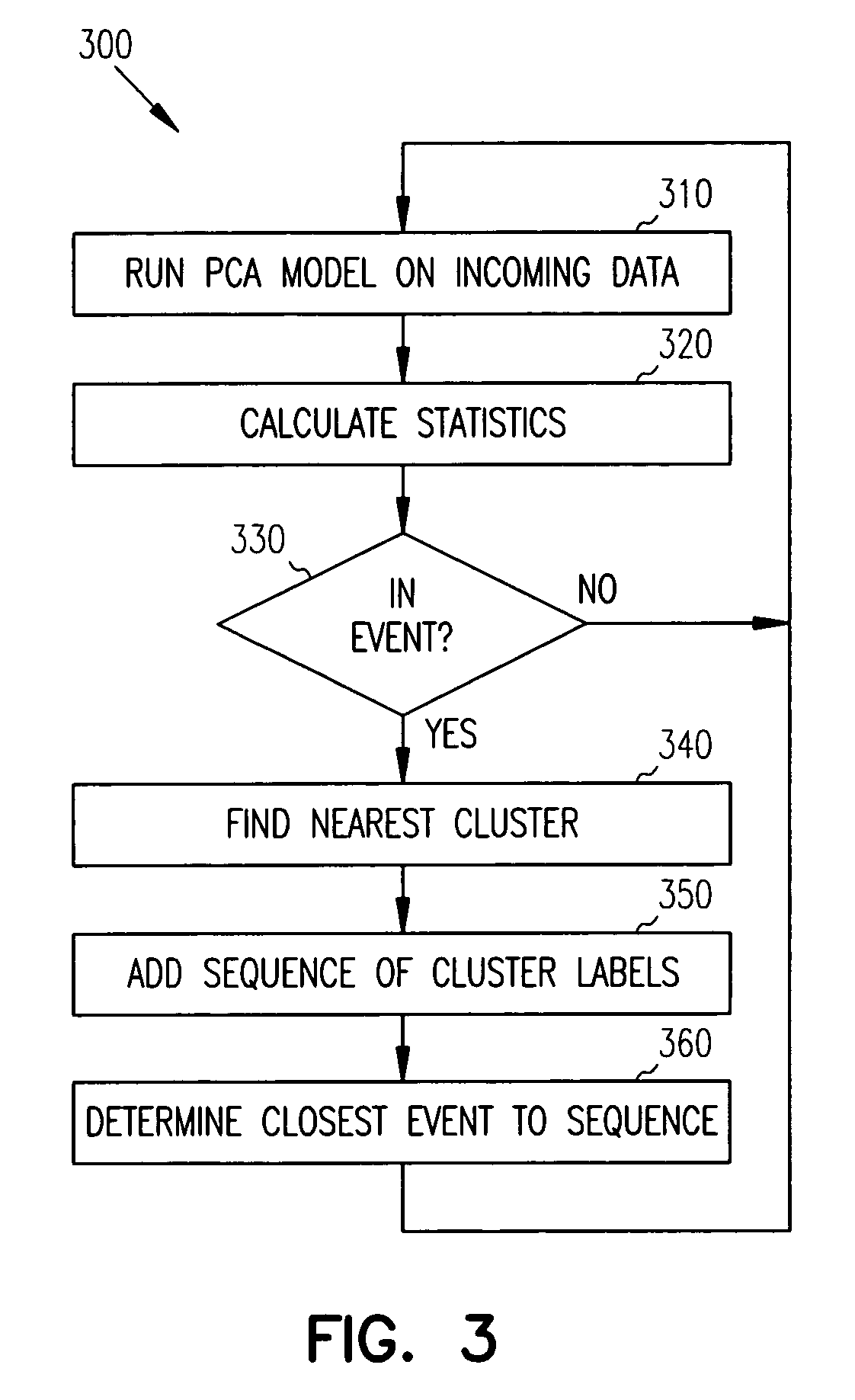
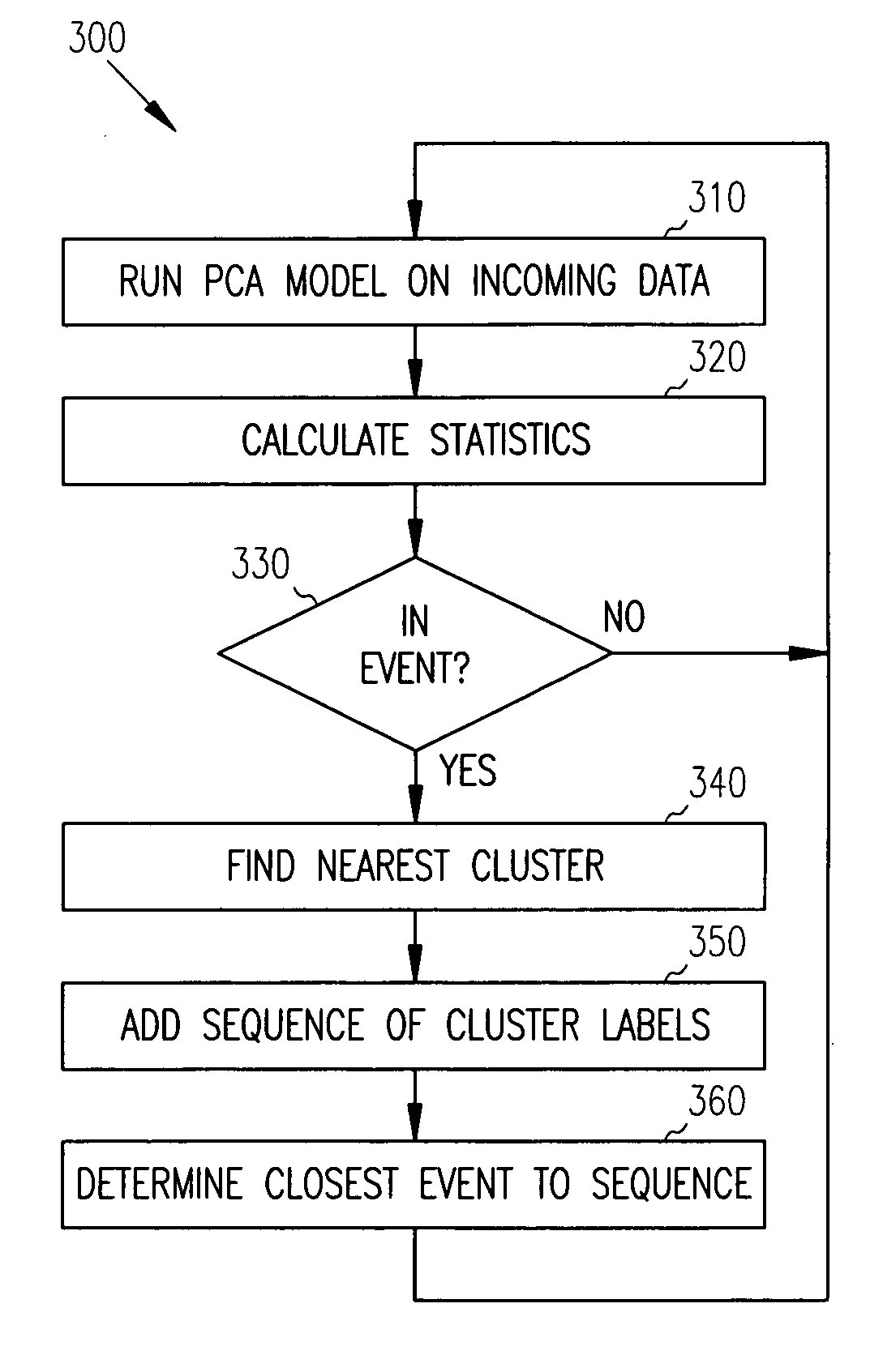
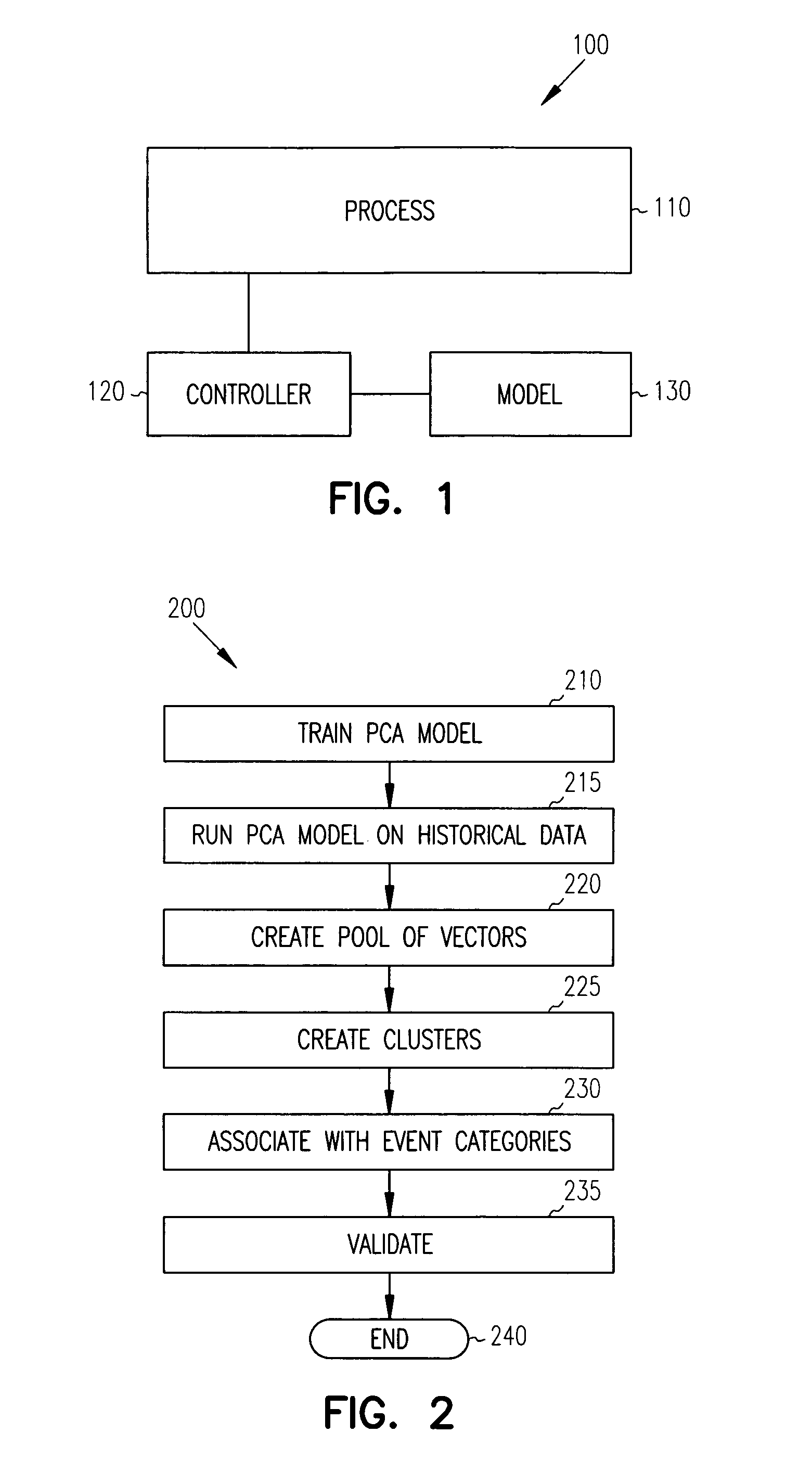
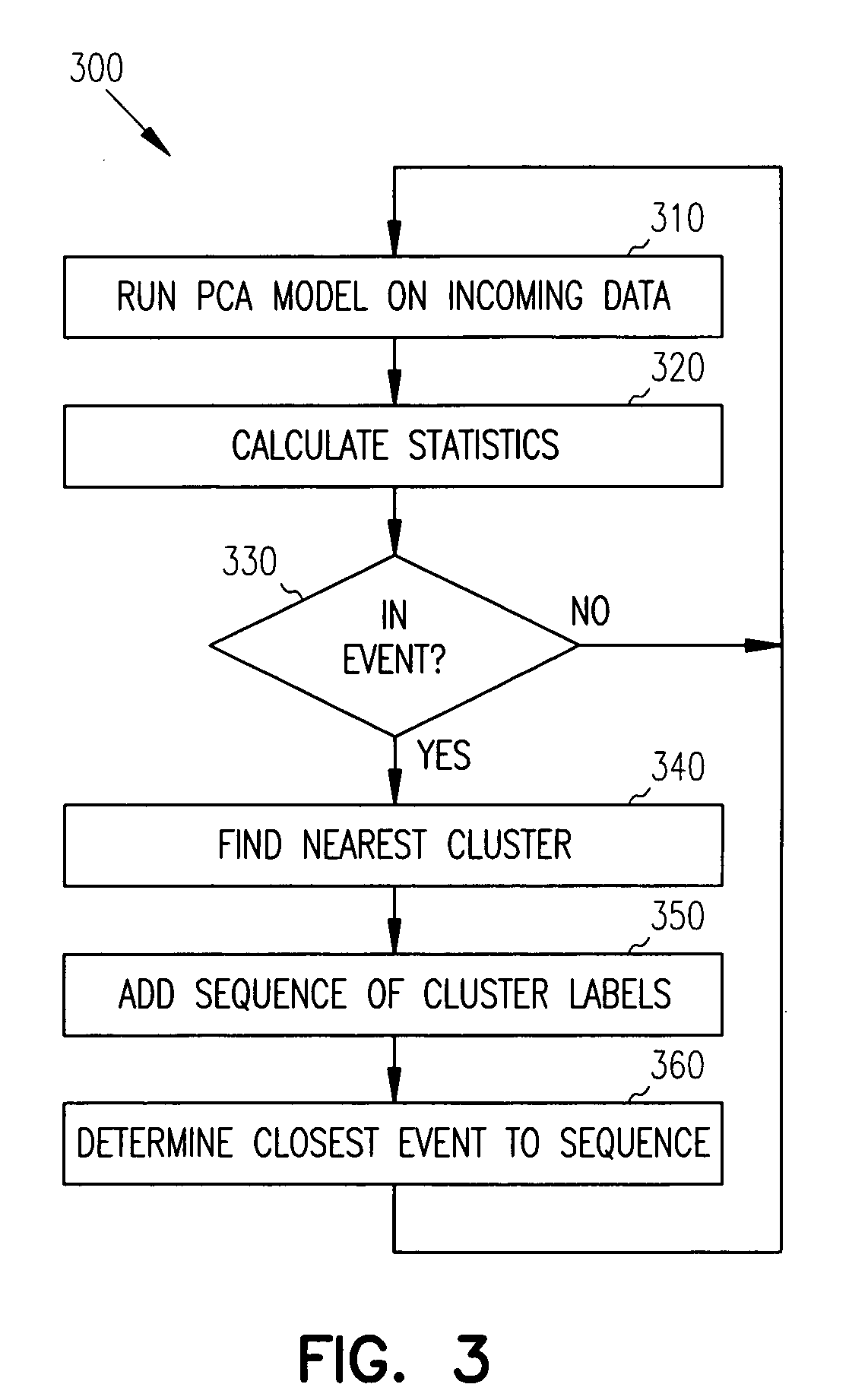
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is used to model a process, and clustering techniques are used to group excursions representative of events based on sensor residuals of the PCA model. The PCA model is trained on normal data, and then run on historical data that includes both normal data, and data that contains events. Bad actor data for the events is identified by excursions in Q (residual error) and T2 (unusual variance) statistics from the normal model, resulting in a temporal sequence of bad actor vectors. Clusters of bad actor patterns that resemble one another are formed and then associated with events.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
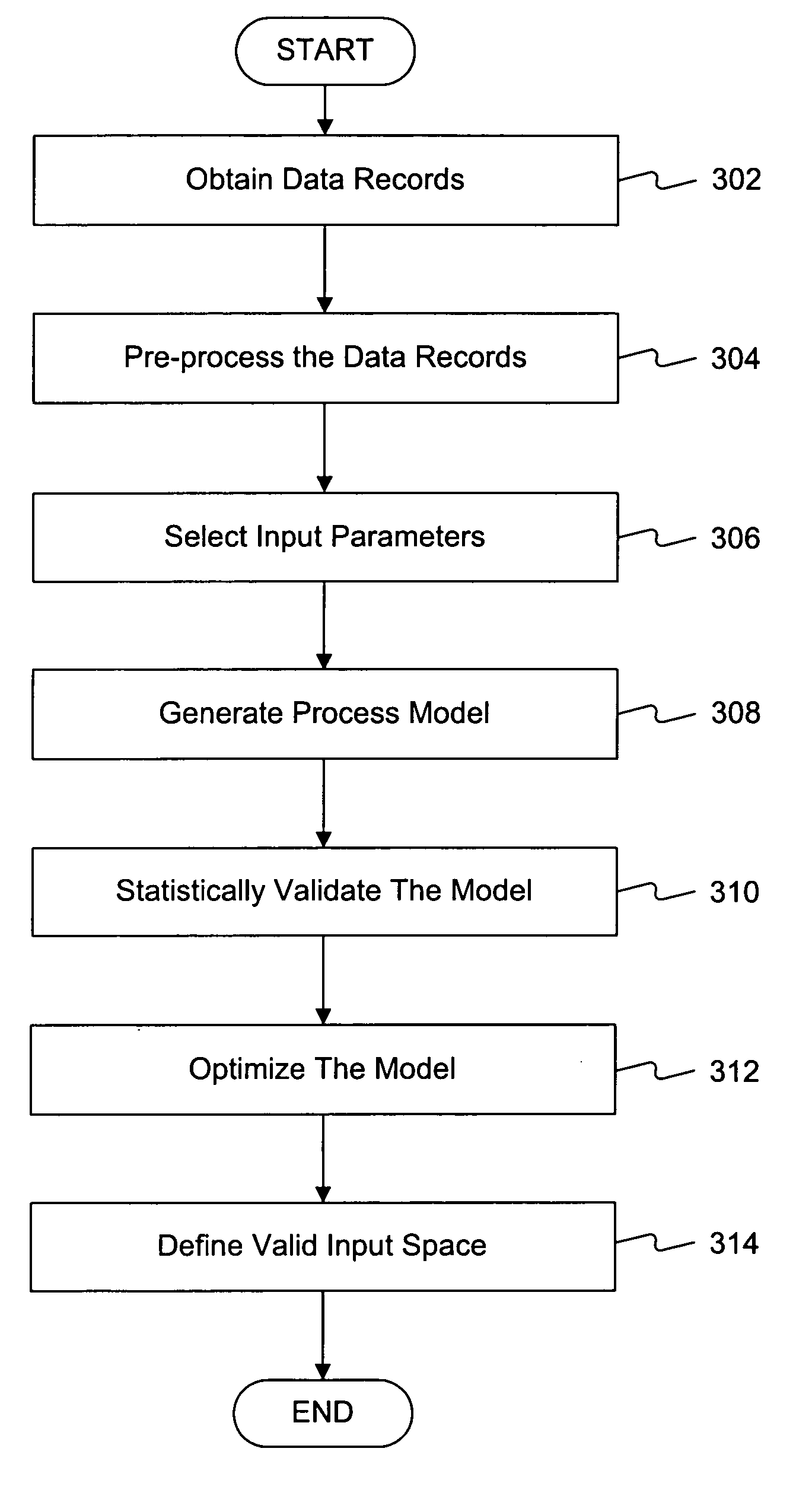
Batch statistics process model method and system
A method is provided for process modeling. The method may include obtaining batch statistics data records associated with one or more input variables and one or more output parameters and selecting one or more input parameters from the one or more input variables. The method may also include generating a computational model indicative of interrelationships between the one or more input parameters and the one or more output parameters based on the data records and determining desired respective statistical distributions of the input parameters of the computational model.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
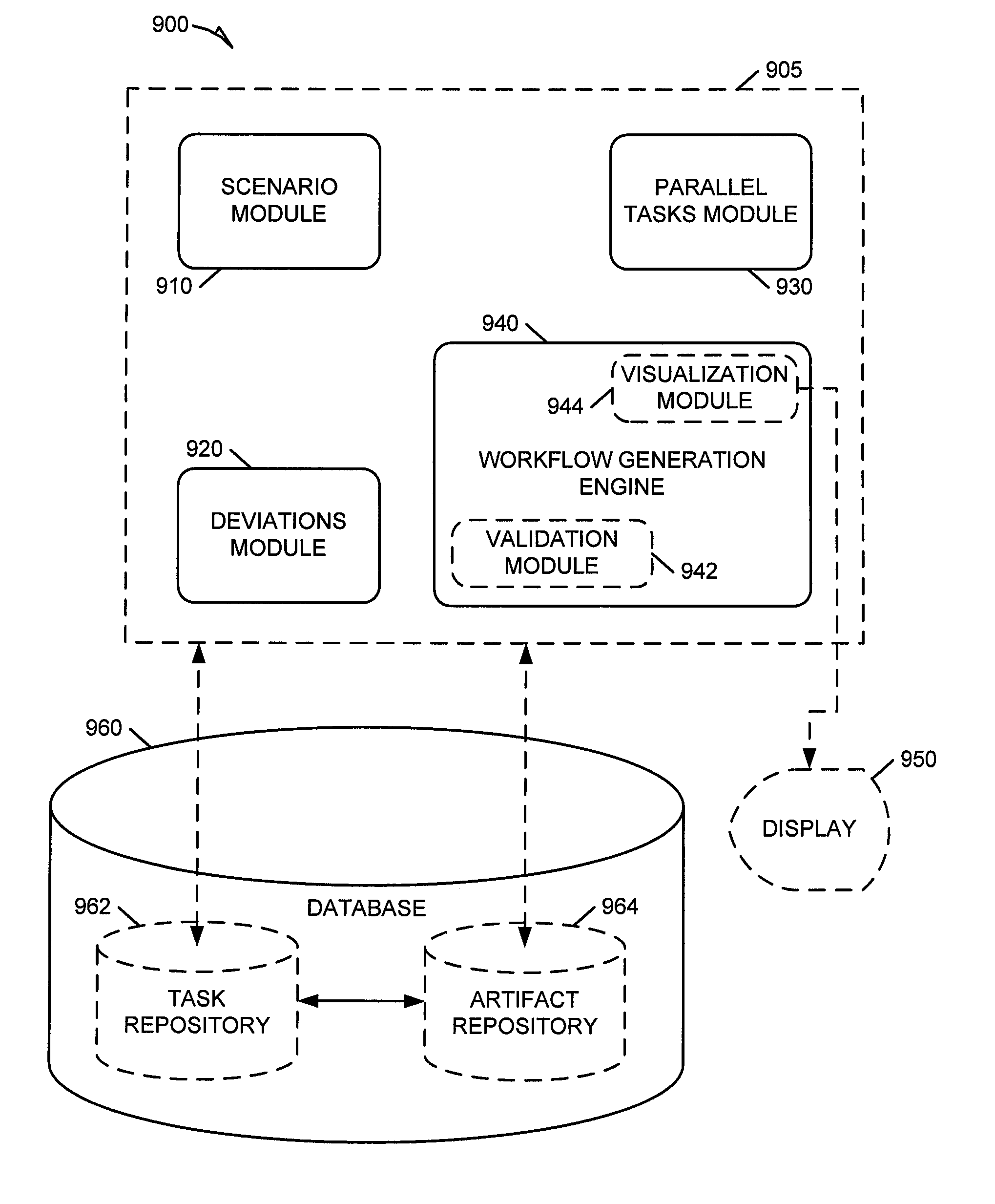
Systems and methods for scenario-based process modeling
Methods and systems for scenario-based process modeling are described. In one example embodiment, a system for scenario-based process modeling can include a scenario module, a deviations module, a parallel tasks module, and a workflow generation engine. The scenario module is to receive a series of tasks to define a standard process flow. The deviations module is to receive a deviation from the standard process flow. The parallel tasks module is to enable identification of one or more parallel tasks. The workflow generation engine is to generate a workflow model based on the standard process flow, deviation, and one or more parallel tasks.
Owner:SAP AG
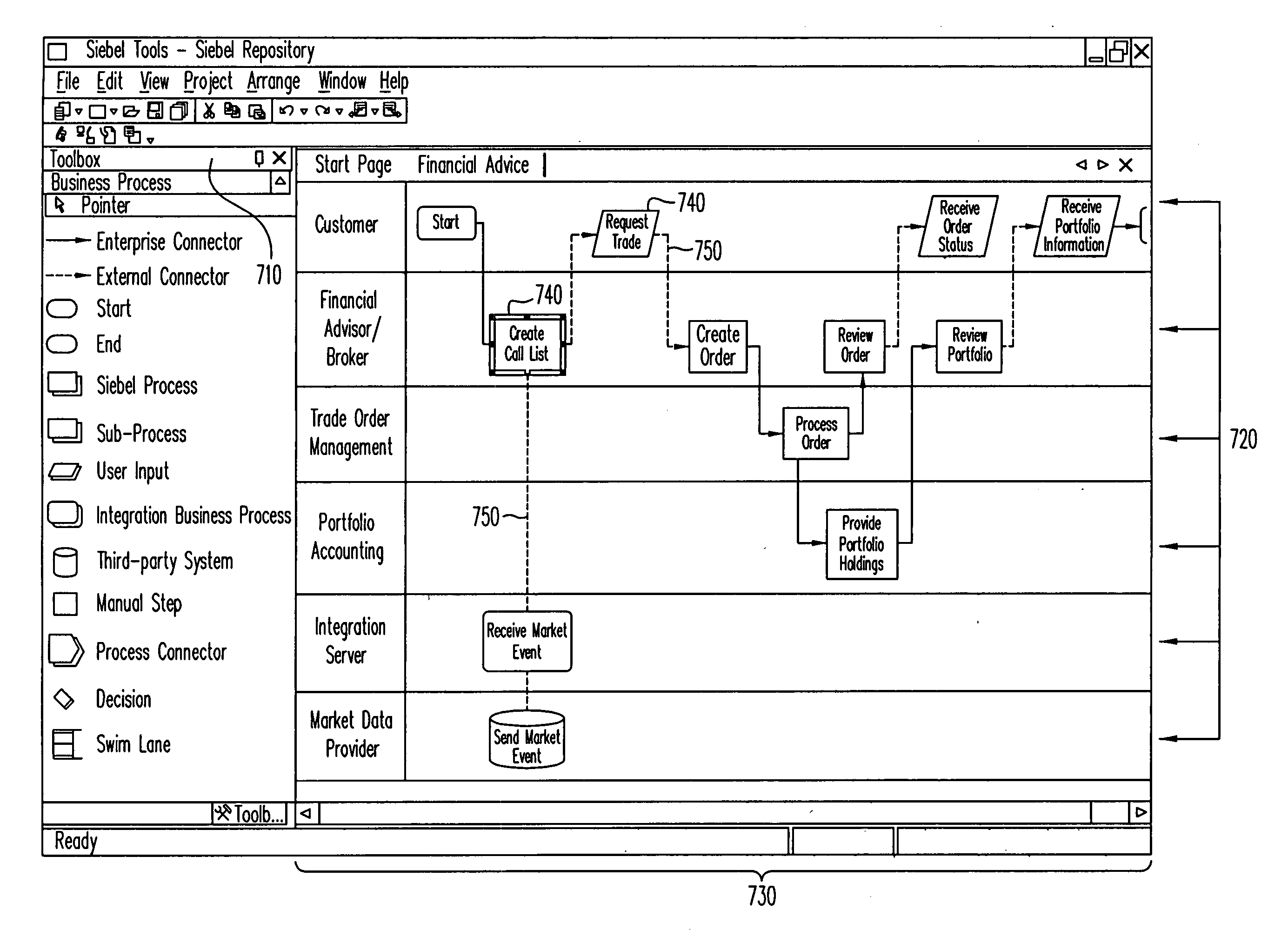
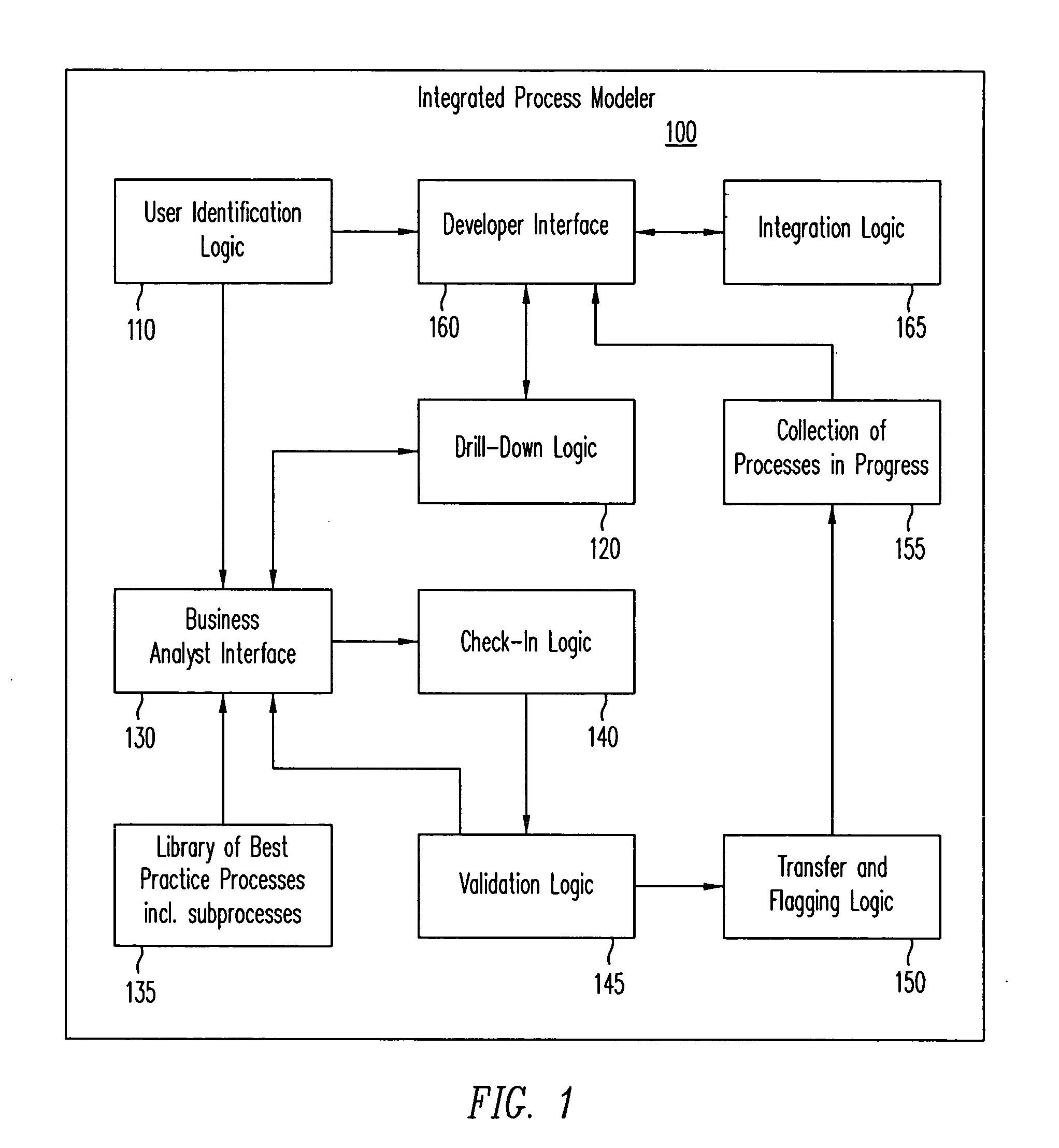
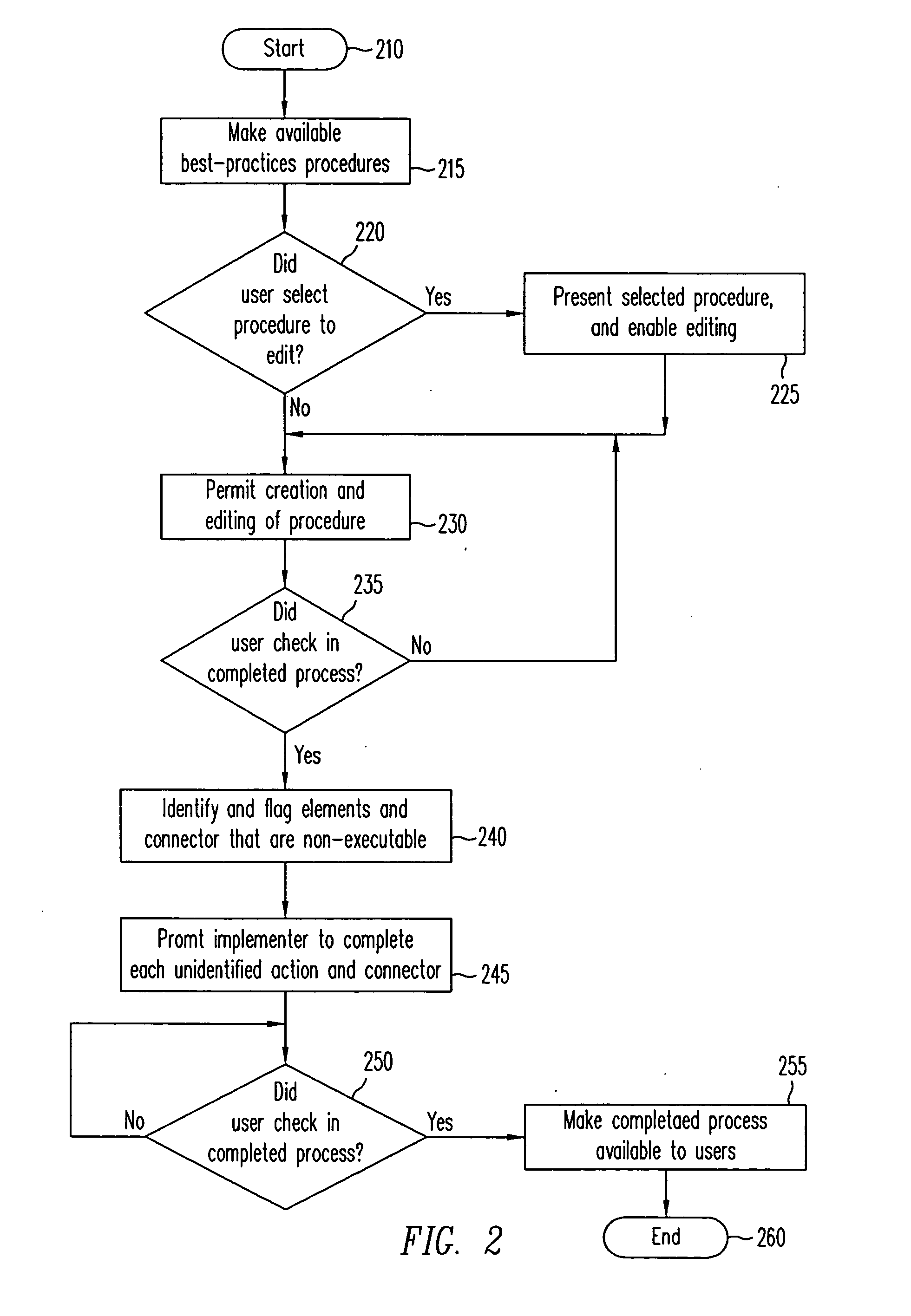
Method and apparatus to present an integrated process modeler
A method and apparatus for an integrated process modeler is described. The modeler comprises a non-technical interface to permit design of a business process by a non-technical use and a technical interface to implement substeps of the process to automate technical aspects of the process by a technical user, using the same process modeler. The resulting process designed to be used by non-technical employees, to automatically lead the non-technical employees through the business process.
Owner:SIEBEL SYST INC
Principal component analysis based fault classification
ActiveUS7447609B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceElectric testing/monitoringKernel principal component analysisPrincipal component analysis
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is used to model a process, and clustering techniques are used to group excursions representative of events based on sensor residuals of the PCA model. The PCA model is trained on normal data, and then run on historical data that includes both normal data, and data that contains events. Bad actor data for the events is identified by excursions in Q (residual error) and T2 (unusual variance) statistics from the normal model, resulting in a temporal sequence of bad actor vectors. Clusters of bad actor patterns that resemble one another are formed and then associated with events.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Principal component analysis based fault classification
ActiveUS20050141782A1Electric testing/monitoringDigital computer detailsKernel principal component analysisPrincipal component analysis
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is used to model a process, and clustering techniques are used to group excursions representative of events based on sensor residuals of the PCA model. The PCA model is trained on normal data, and then run on historical data that includes both normal data, and data that contains events. Bad actor data for the events is identified by excursions in Q (residual error) and T2 (unusual variance) statistics from the normal model, resulting in a temporal sequence of bad actor vectors. Clusters of bad actor patterns that resemble one another are formed and then associated with events.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
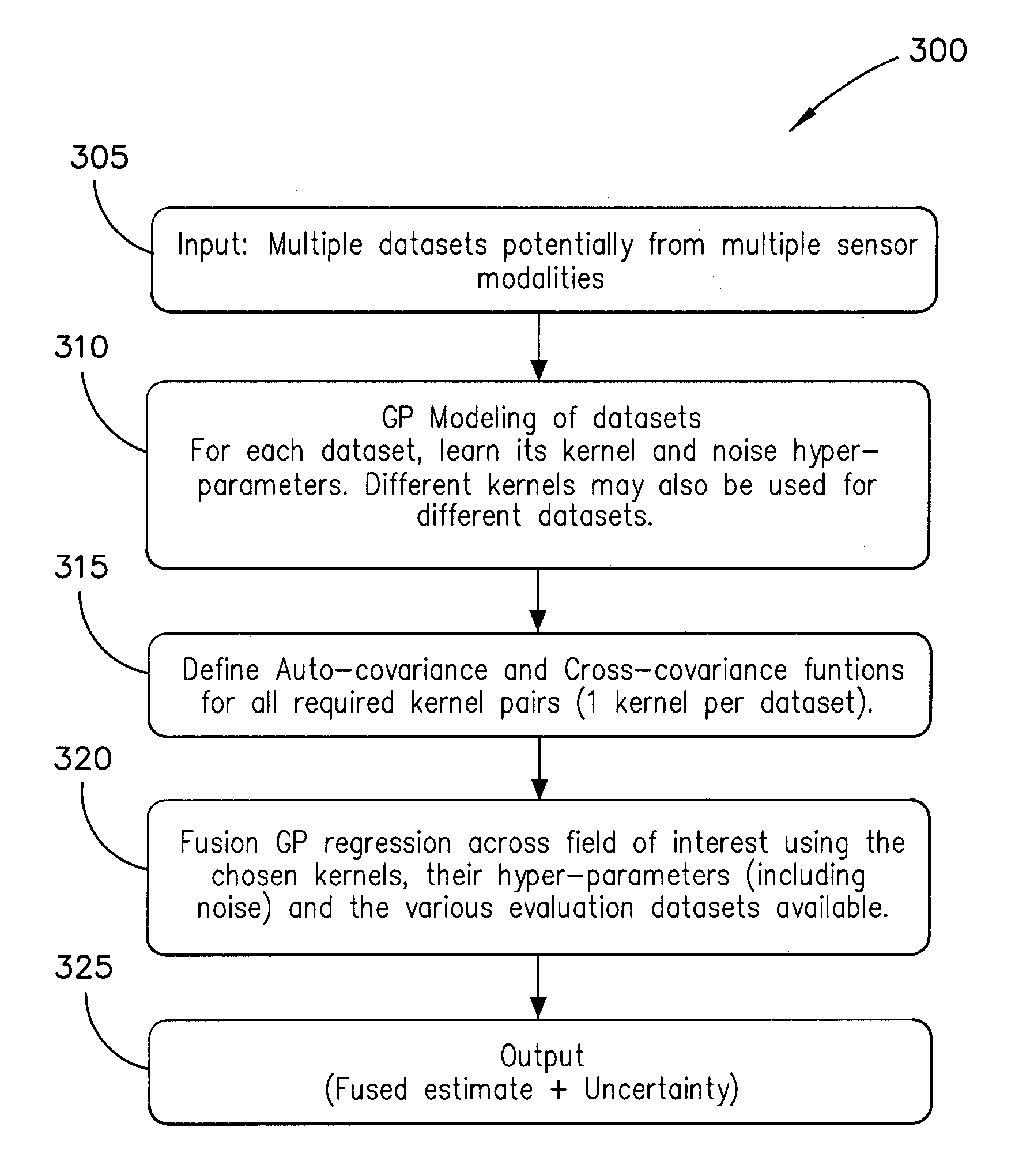
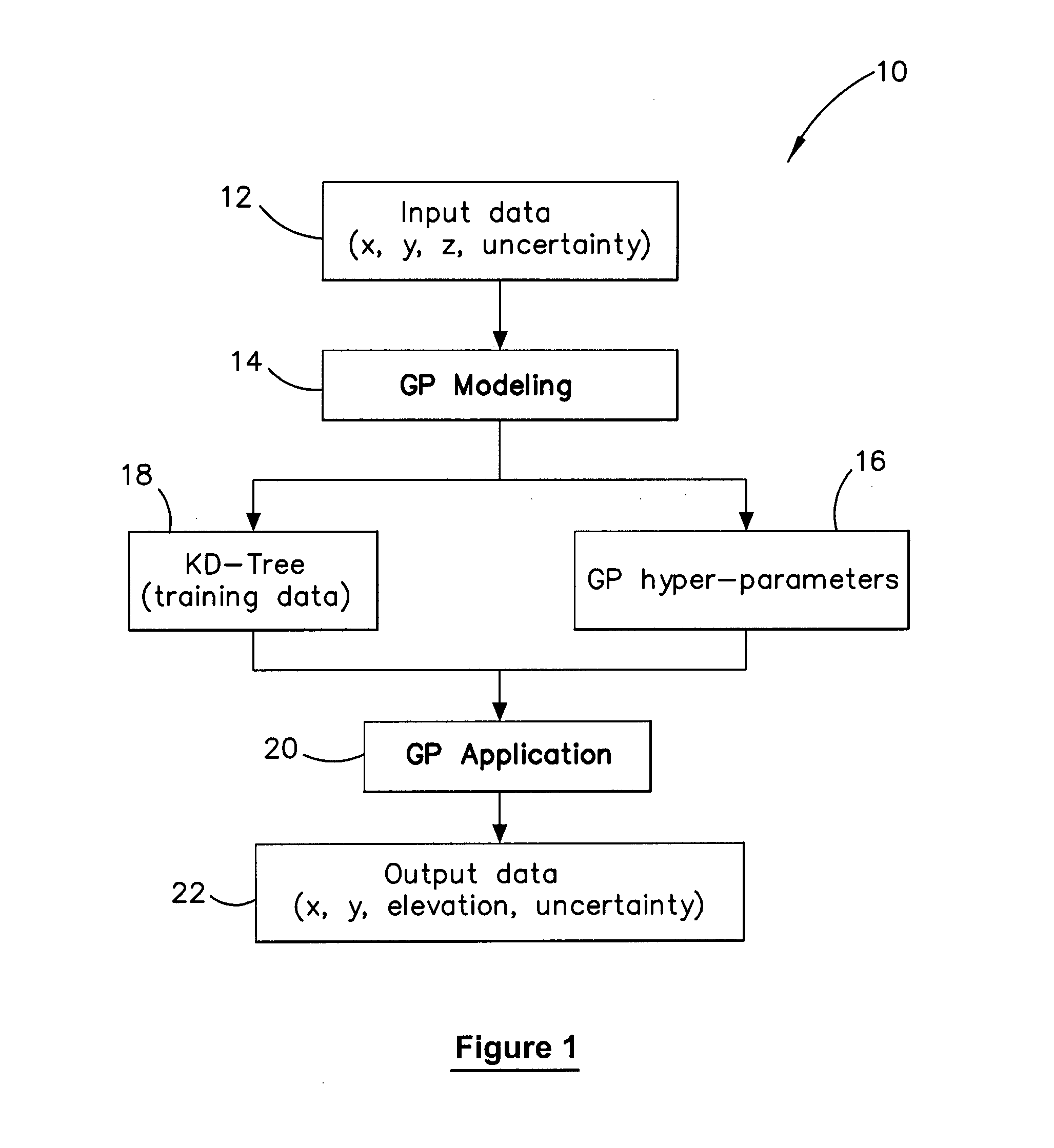
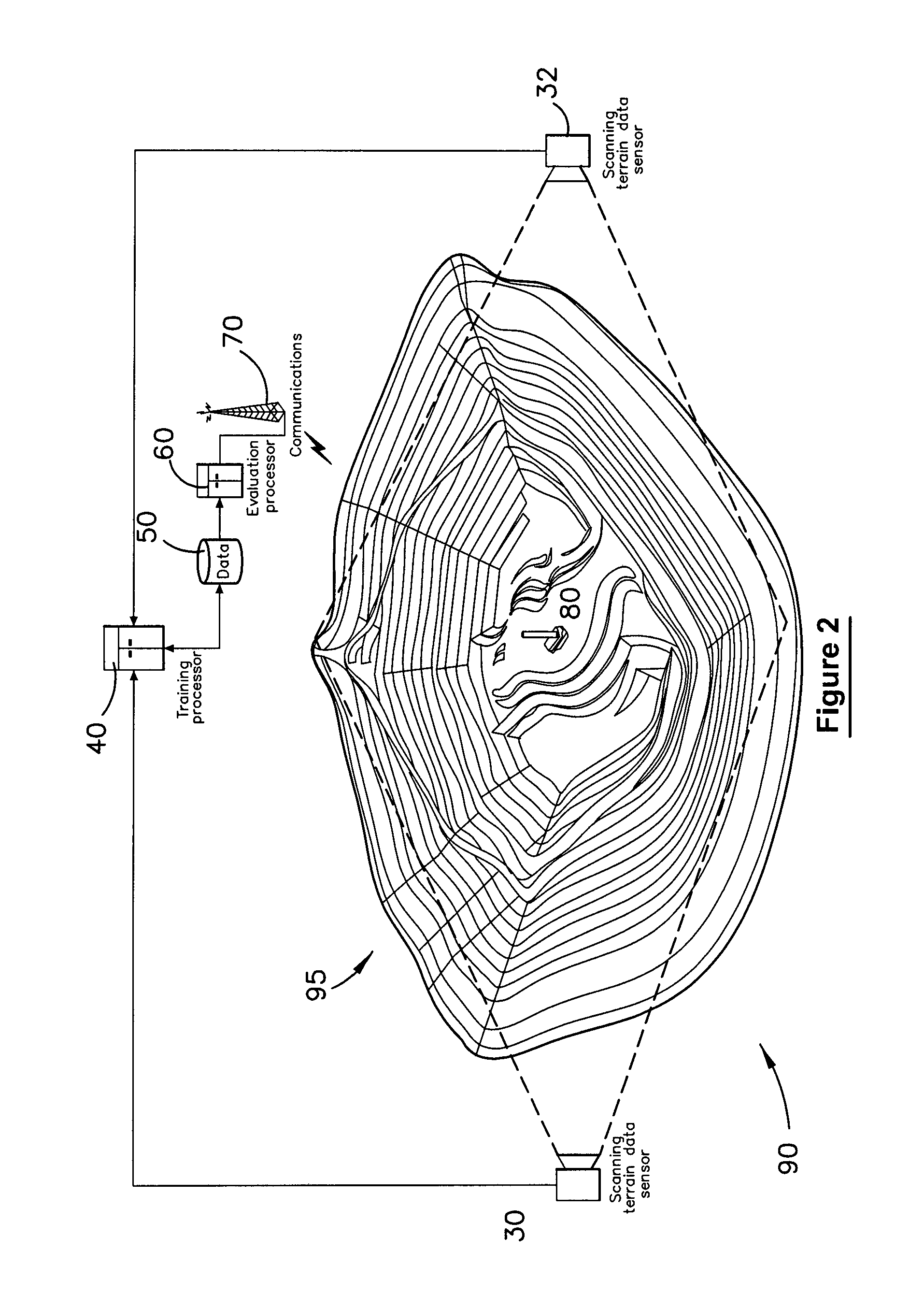
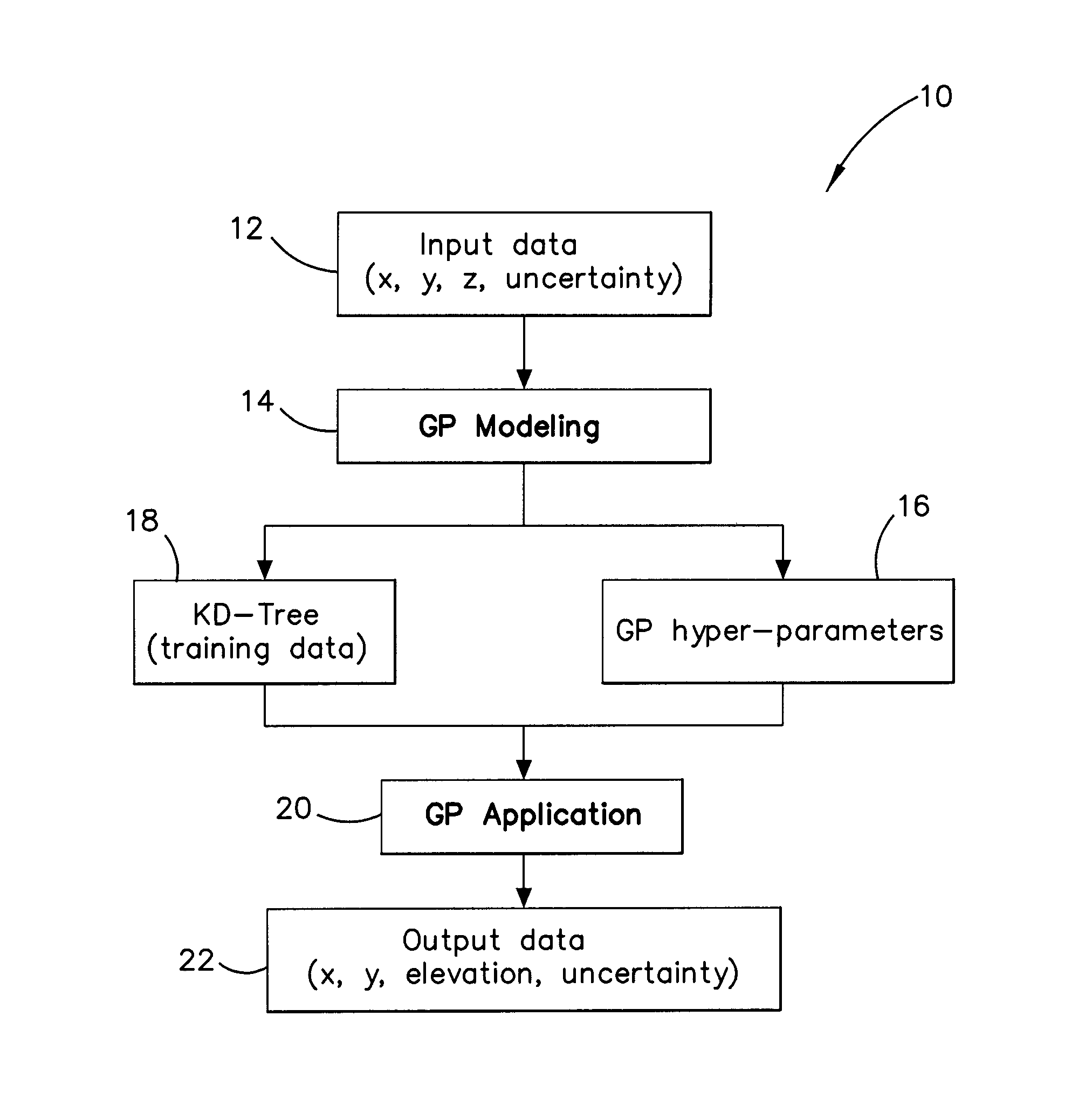
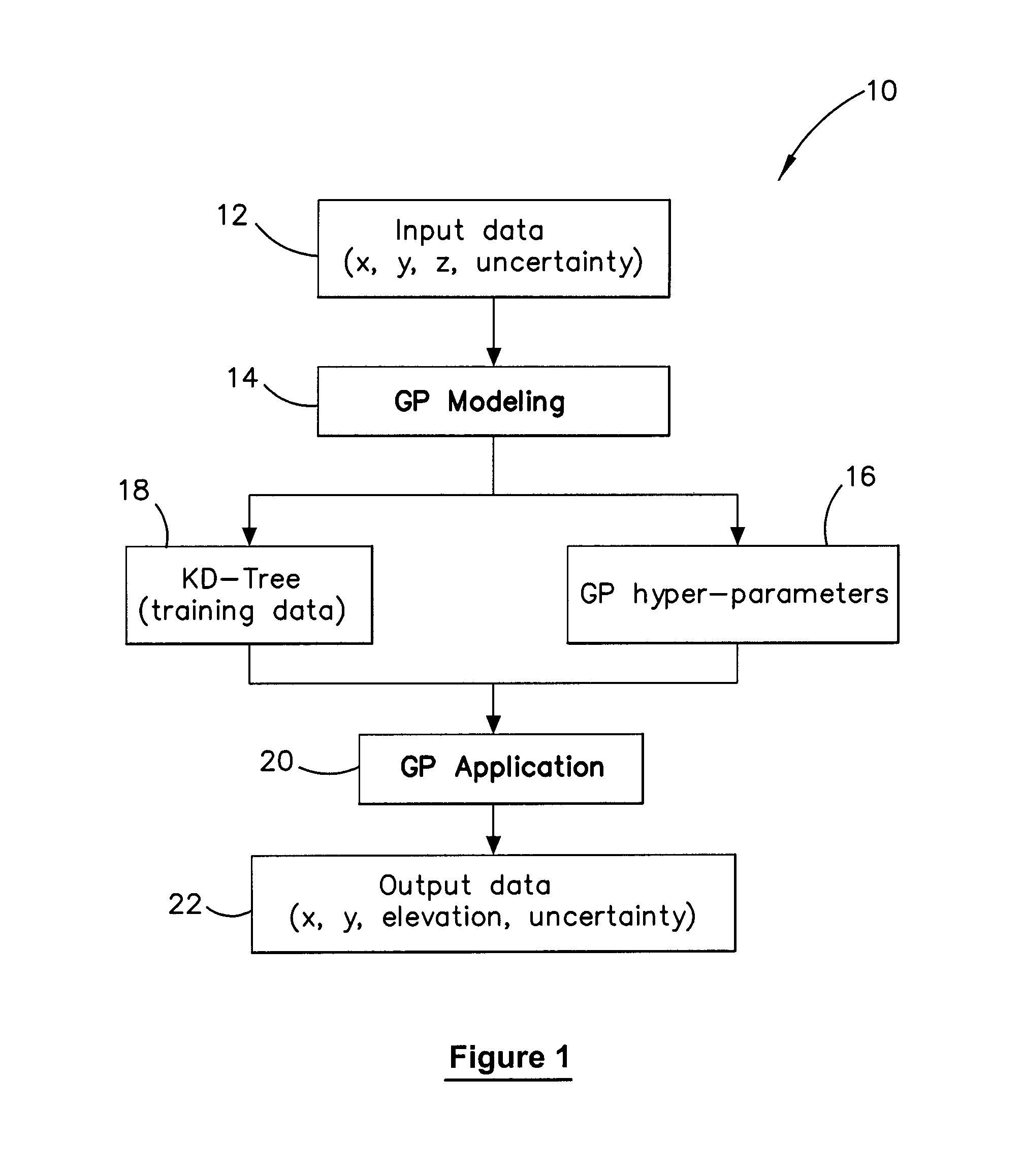
Method and system for multiple dataset gaussian process modeling
A method of computerised data analysis and synthesis is described. First and second datasets of a quantity of interest are stored. A Gaussian process model is generated using the first and second datasets to compute optimized kernel and noise hyperparameters. The Gaussian process model is applied using the stored first and second datasets and hyperparameters to perform Gaussian process regression to compute estimates of unknown values of the quantity of interest. The resulting computed estimates of the quantity of interest result from a non-parametric Gaussian process fusion of the first and second measurement datasets. The first and second datasets may be derived from the same or different measurement sensors. Different sensors may have different noise and / or other characteristics.
Owner:SYDNEY THE UNIV OF
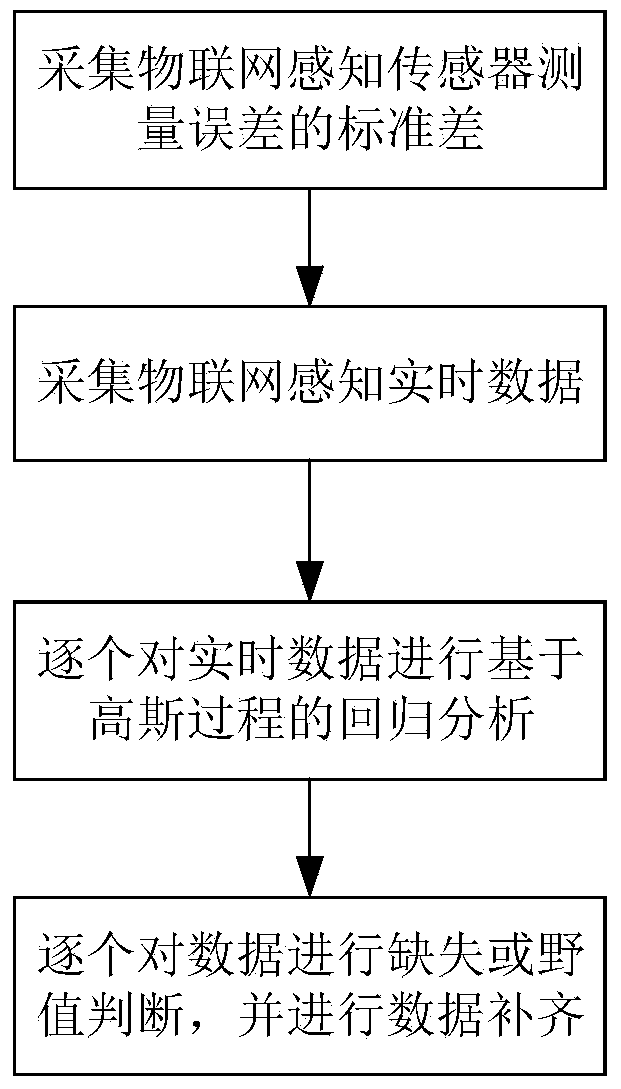
Internet of Things data uncertainty measurement, prediction and outlier-removing method based on Gaussian process
InactiveCN104200113ASimple methodReduce forecast errorData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsThe InternetPattern perception
The invention relates to an Internet of Things data uncertainty measurement, prediction and outlier-removing method based on the Gaussian process. The method is a dynamical system method of estimating and collecting the standard deviation of Internet of Things perception sensor measurement errors and combining the Gaussian process modeling theory with autoregression model representations; prediction values and uncertainty measurement of observation data effective time sequence data are given, whether the data are missing values or outlier data is judged according to the information, and data supplement is correspondingly carried out. The method is a non-parameterized probability prediction method. Due to the fact that training set learning has the feature of tracing system dynamic states, judgment, early-warning and data supplement can be carried out on data exception and data missing phenomena in time according to the prediction value uncertainty and the sensor calibration standard deviation, the prediction error is small, and the accuracy is high. The Internet of Things data uncertainty measurement, prediction and outlier-removing method is used for controlling the quality of Internet of Things automatic observation data, and can ensure accuracy of collected data.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Sparseness data process modeling approach
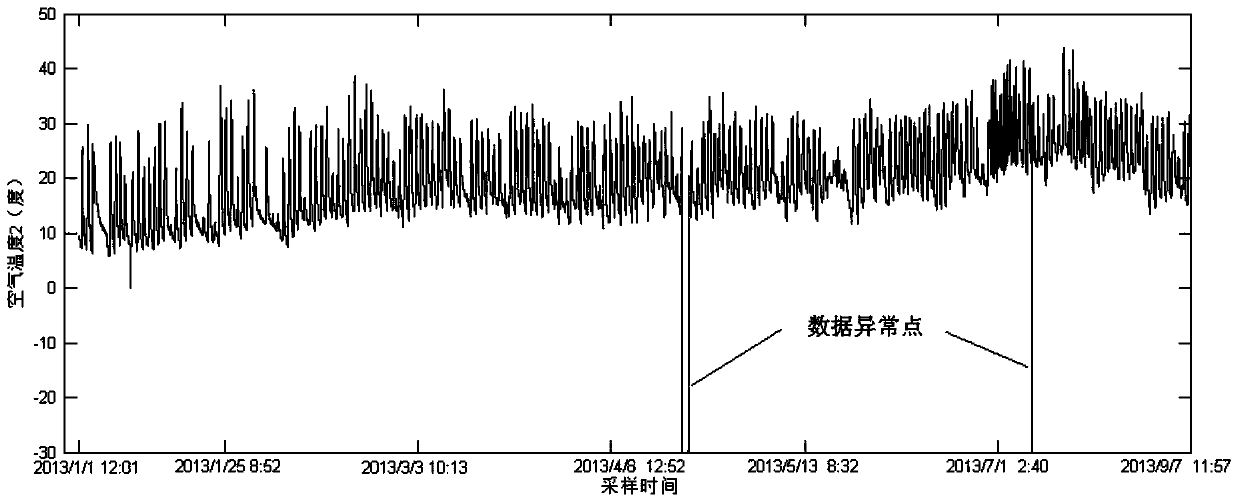
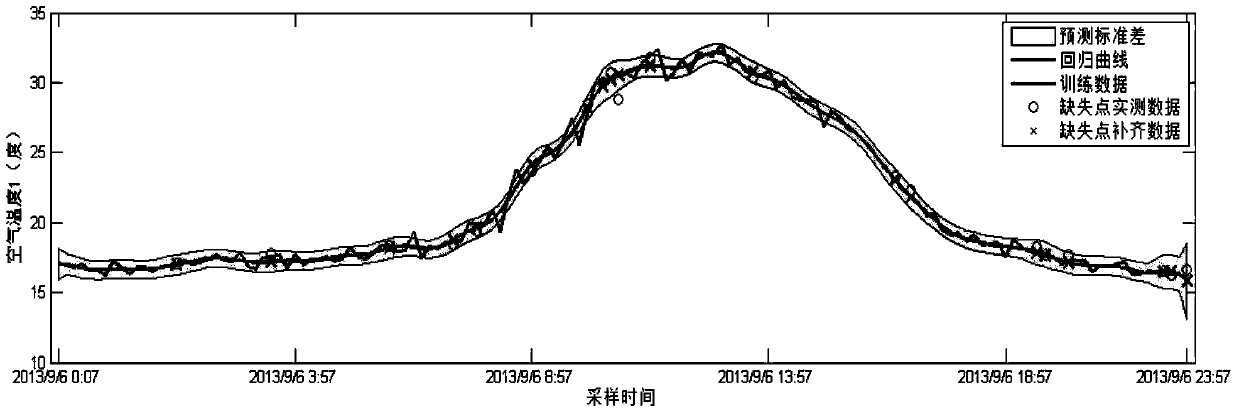
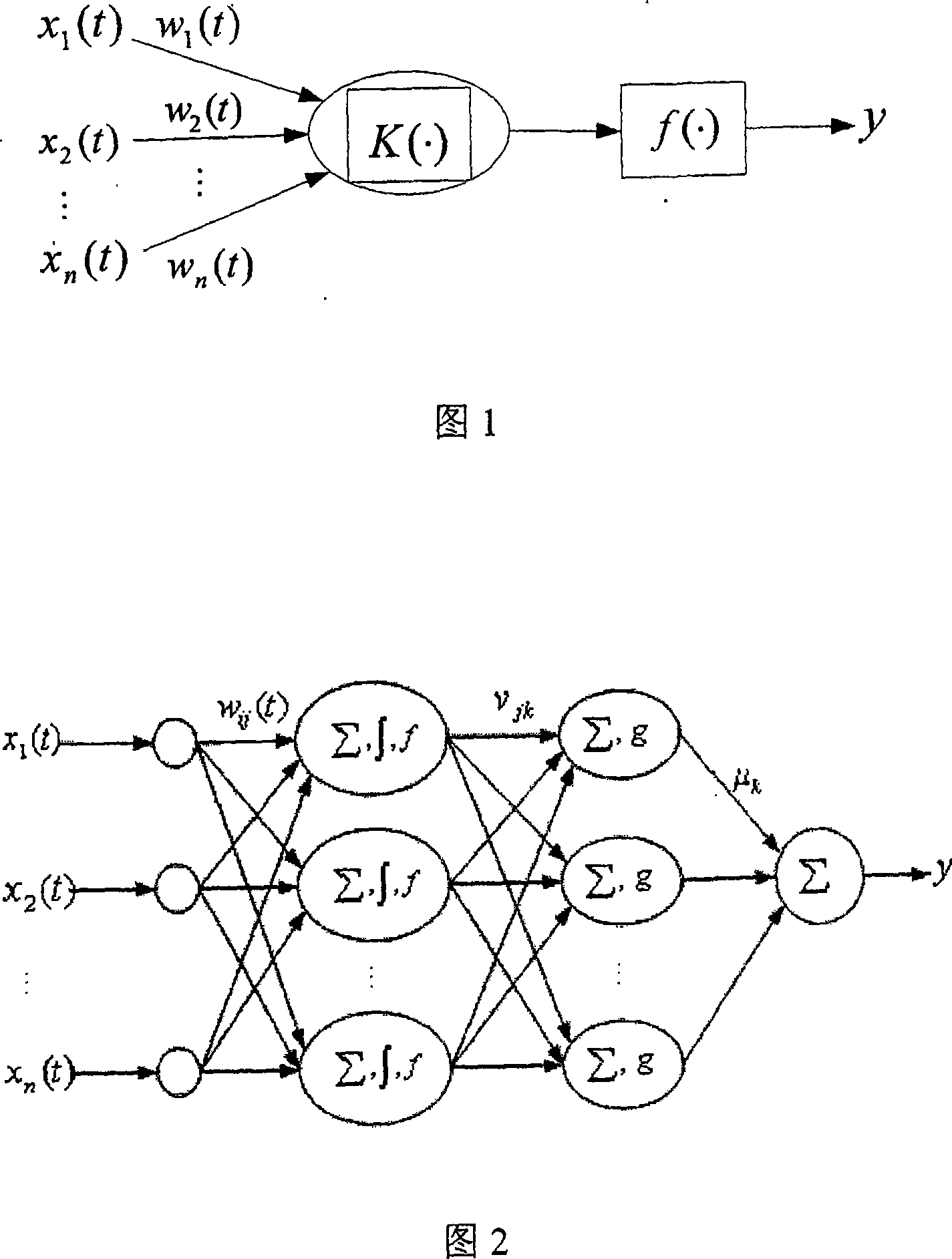
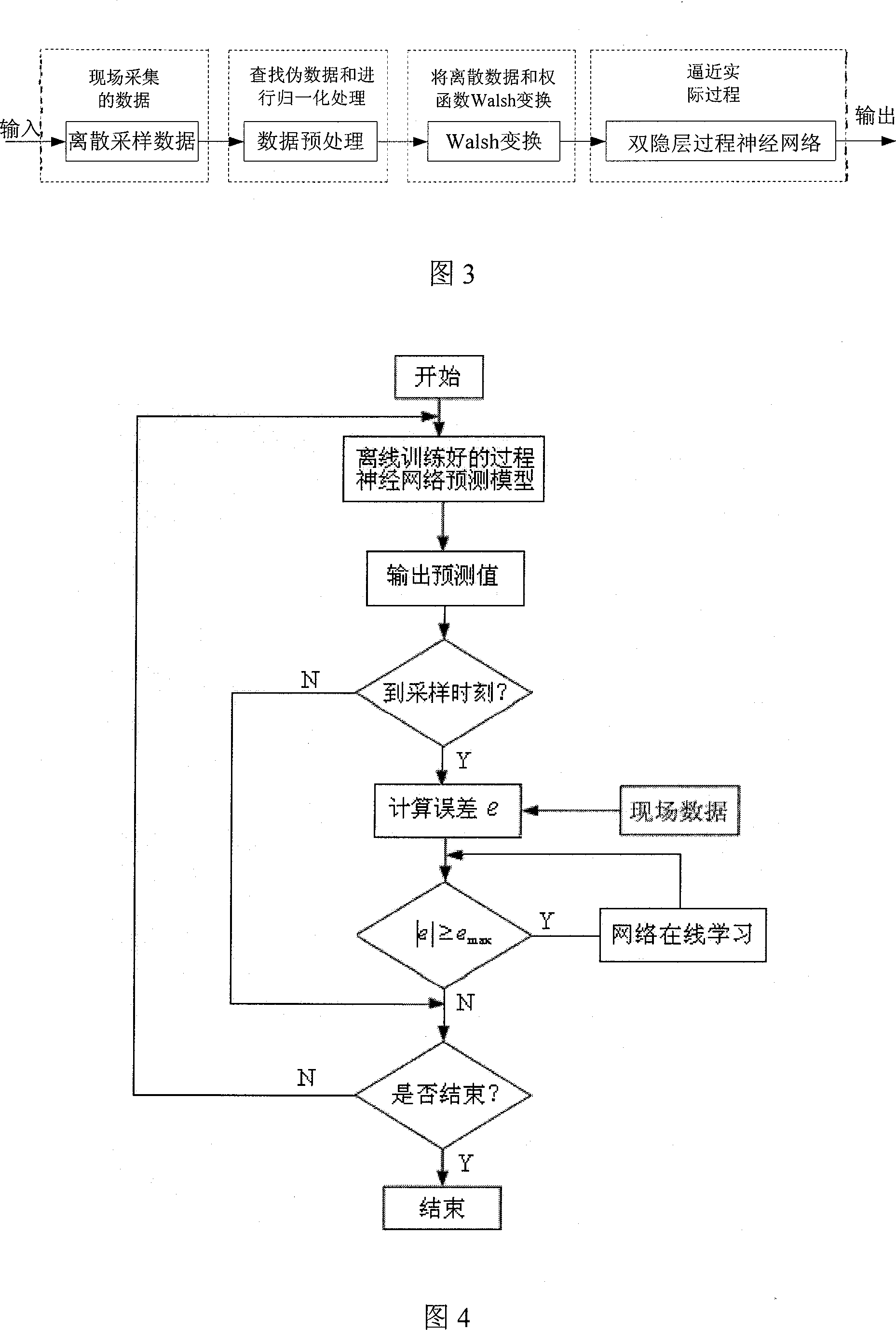
The present invention relates to a method applying a procedure neural network to establish a procedure predicting model for sparse data. On the basis of the pretreatment of the sparse sample data, a learning algorithm based upon the discrete Walsh transform is applied to increase the learning efficiency and the modeling precision of the procedure neural network. To ensure that the established procedure predicting model can amend the prediction deviations timely, a method of data sampling periodic network rolling learning is adopted based upon the characteristics of the sparse data procedure to conduct an on-line amendment to the network predicting model timely through up-to-date sampled data, thereby improving the accuracy of the predicting model further. The present invention provides an effective approach for solving the modeling problem related to a kind of sparse data procedure.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method and system for multiple dataset gaussian process modeling
A method of computerized data analysis and synthesis is described. First and second datasets of a quantity of interest are stored. A Gaussian process model is generated using the first and second datasets to compute optimized kernel and noise hyperparameters. The Gaussian process model is applied using the stored first and second datasets and hyperparameters to perform Gaussian process regression to compute estimates of unknown values of the quantity of interest. The resulting computed estimates of the quantity of interest result from a non-parametric Gaussian process fusion of the first and second measurement datasets. The first and second datasets may be derived from the same or different measurement sensors. Different sensors may have different noise and / or other characteristics.
Owner:SYDNEY THE UNIV OF
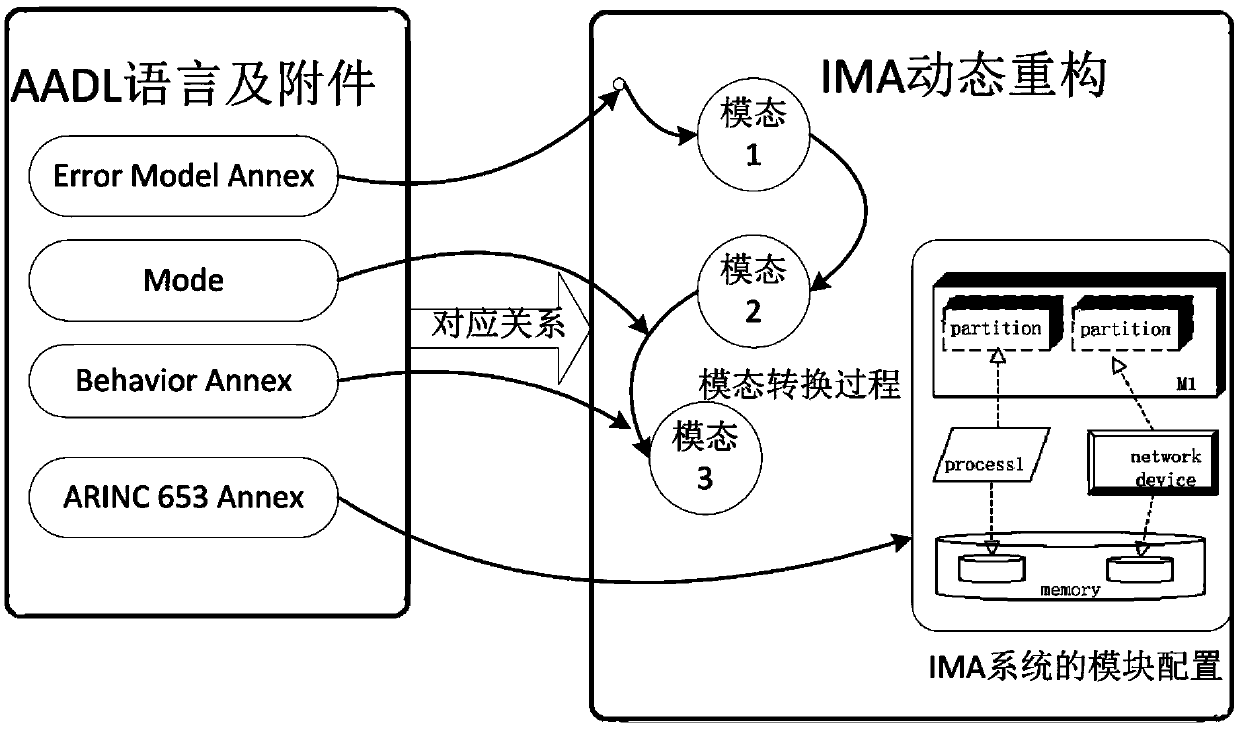
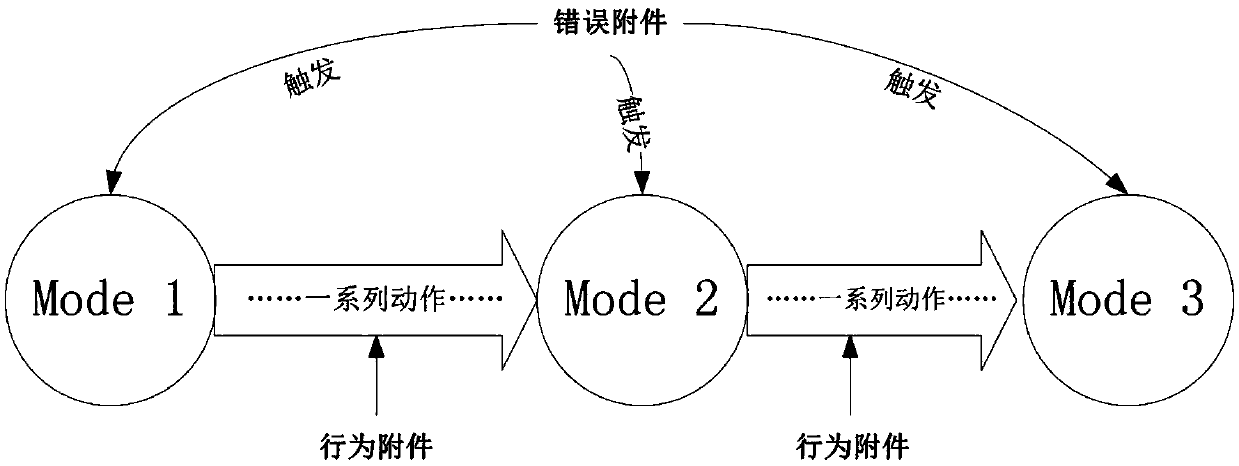
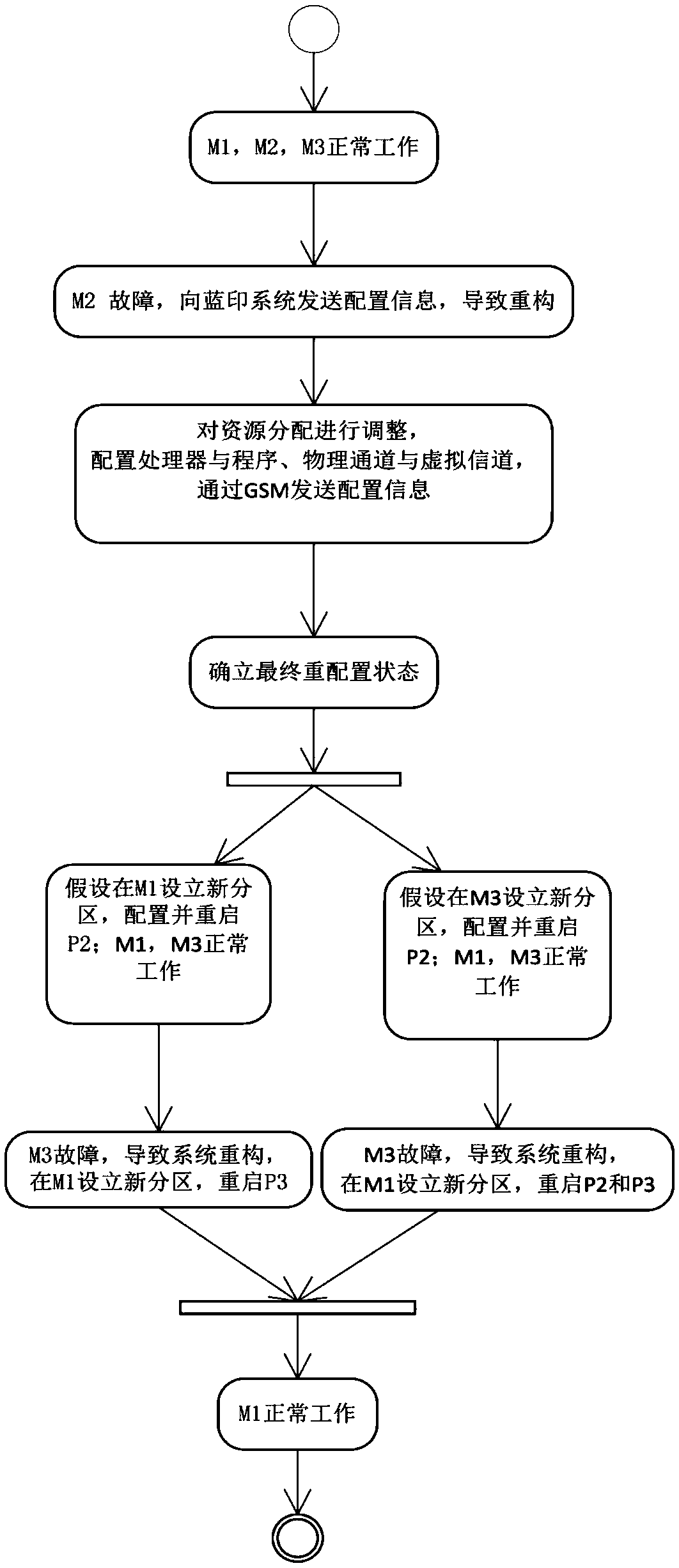
AADL based IMA dynamic reconfiguration modeling method
ActiveCN105373650ASecurity for easy analysisFacilitate analysis workSpecial data processing applicationsCAD numerical modellingComputer scienceHuman language
The invention discloses an AADL based IMA dynamic reconfiguration modeling method used for avionics system security modeling. The method comprises: determining dynamic reconfiguration process elements, decomposing a dynamic reconfiguration process into sub-states, and determining trigger and conversion actions required for conversion between each state configuration situation and a state; representing software and hardware constitution of IMA by utilizing ARINC653 accessories, describing the dynamic reconfiguration process by utilizing behavior accessories, describing a trigger behavior by utilizing error model accessories, and representing different configuration situations of the dynamic reconfiguration process by utilizing modes; determining IMA dynamic reconfiguration process model instances; describing a dynamic reconfiguration conversion process by utilizing combination of the AADL behavior accessories and the modes; and realizing and perfecting an established model by utilizing software. According to the method, the complicated dynamic reconfiguration process is modeled, so that the security of the dynamic reconfiguration process can be conveniently analyzed; and a brand-new process modeling method is constructed by combining a mature AADL language with the IMA dynamic reconfiguration process.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
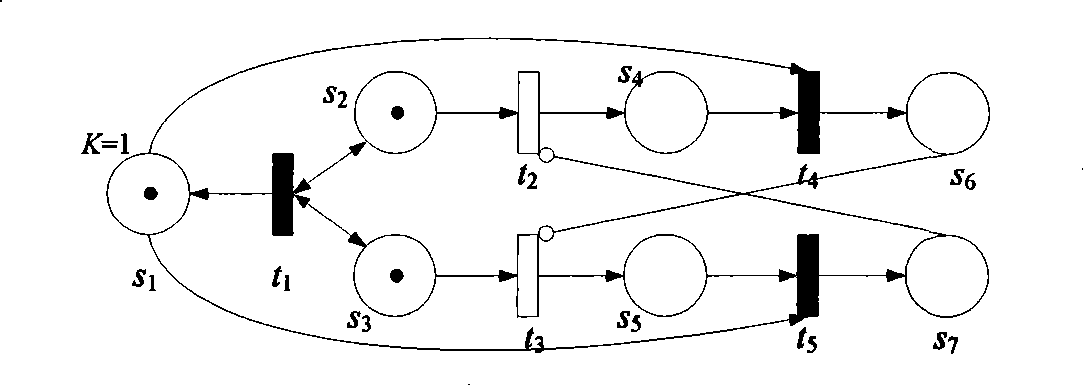
Simulation method for equipment maintenance and guarantee based on Petri network model
InactiveCN101477588AEvaluate work intensityOptimize quantitySpecial data processing applicationsSimulationNetwork model
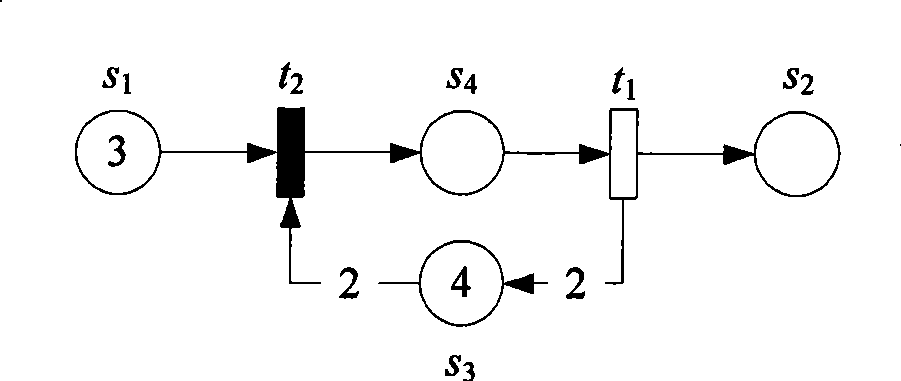
The invention discloses a method for simulating the equipment maintenance support based on Petri network model. The method comprises the following steps: the Petri network process modeling is performed through distributing given equipment use and maintenance process to each event occurrence time; the time and the simulation frequency are given on the basis of modeling; the simulation analysis is performed on the established Petri network model; and finally, the availability of system / equipment during the task period, the working strength of maintenance man or the task ending time is obtained, and the maintenance support scheme can be evaluated accordingly, so as to provide scientific basis for solution selection and resource allocation.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
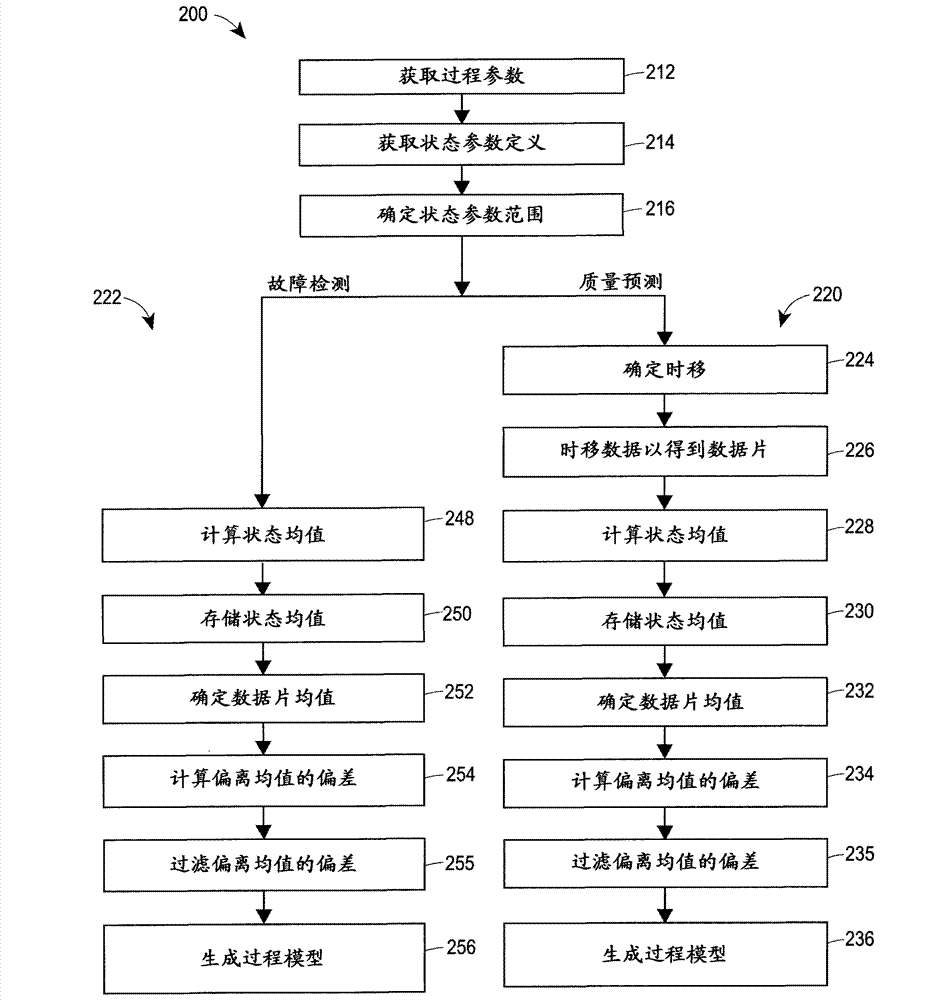
Inferential process modelling, quality prediction and fault detection using multi-stage data segregation
ActiveCN103019094AEasy to viewImprove forecast qualitySimulator controlElectric testing/monitoringSingle processProcedural parameter
A process modelling technique uses a single statistical model, such as a PLS, PRC, MLR, etc. model, developed from historical data for a typical process and uses this model to perform quality prediction or fault detection for various different process states of a process. Training data sets of various states of the process are stored and the training data divided into time slices. Mean and / or standard deviation values are determined for both the time slice parameters and variables and the training data. A set of deviations from the mean are determined for the time slice data and the model generated based on the set of deviations. The modeling technique determines means (and possibly standard deviations) of process parameters for each of a set of product grades, throughputs, etc., preferably compares on-line process parameter measurements to these means and use these comparisons in a single process model to perform quality prediction or fault detection across the various states of the process. Because only the means and standard deviations of the process parameters of the process model are updated, a single process model can be used to perform quality prediction or fault detection while the process is operating in any of the defined process stages or states. Moreover, the sensitivity (robustness) of the process model may be manually or automatically adjust each process parameter to tune or adapt the model over time. An alternative aspect is a method of displaying process alert information using a user interface having multiple screens.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
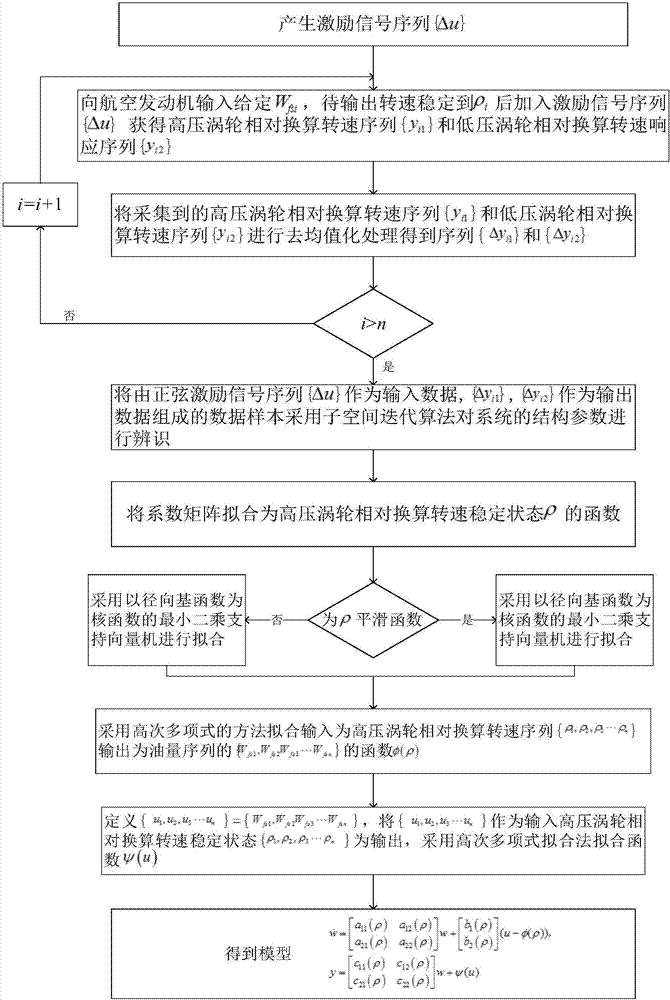
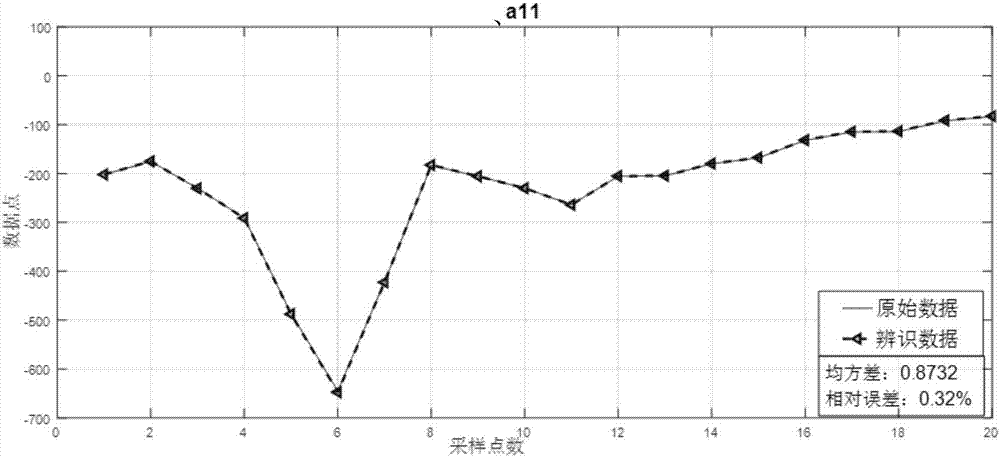
Modeling method of transient process of aero-engine
ActiveCN107239634AHigh precisionImprove dynamic performanceGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsAviationDynamic models
The invention provides a modeling method of the transient process of an aero-engine, and belongs to the field of modeling and simulating of the transient state of the aero-engine. By distinguishing a dynamic model of the aero-engine in different steady states and combining the dynamic model with a corresponding steady-state model, the transient process of the aero-engine is presented as a dynamic variable parameter model through methods of polynomial fitting and a least squares support vector machine. The approximate transient process of multiple discrete steady state points is improved, the dynamic characteristics are better, and the situation that by means of an existing method, error accumulation exists when modeling of the transient state is conducted through output accumulation is improved; meanwhile, single input multiple output is modeling through the method, universality is wider, modeling can be promoted to modeling of the transient process of multiple input multiple output aero-engine through proper adjustment.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
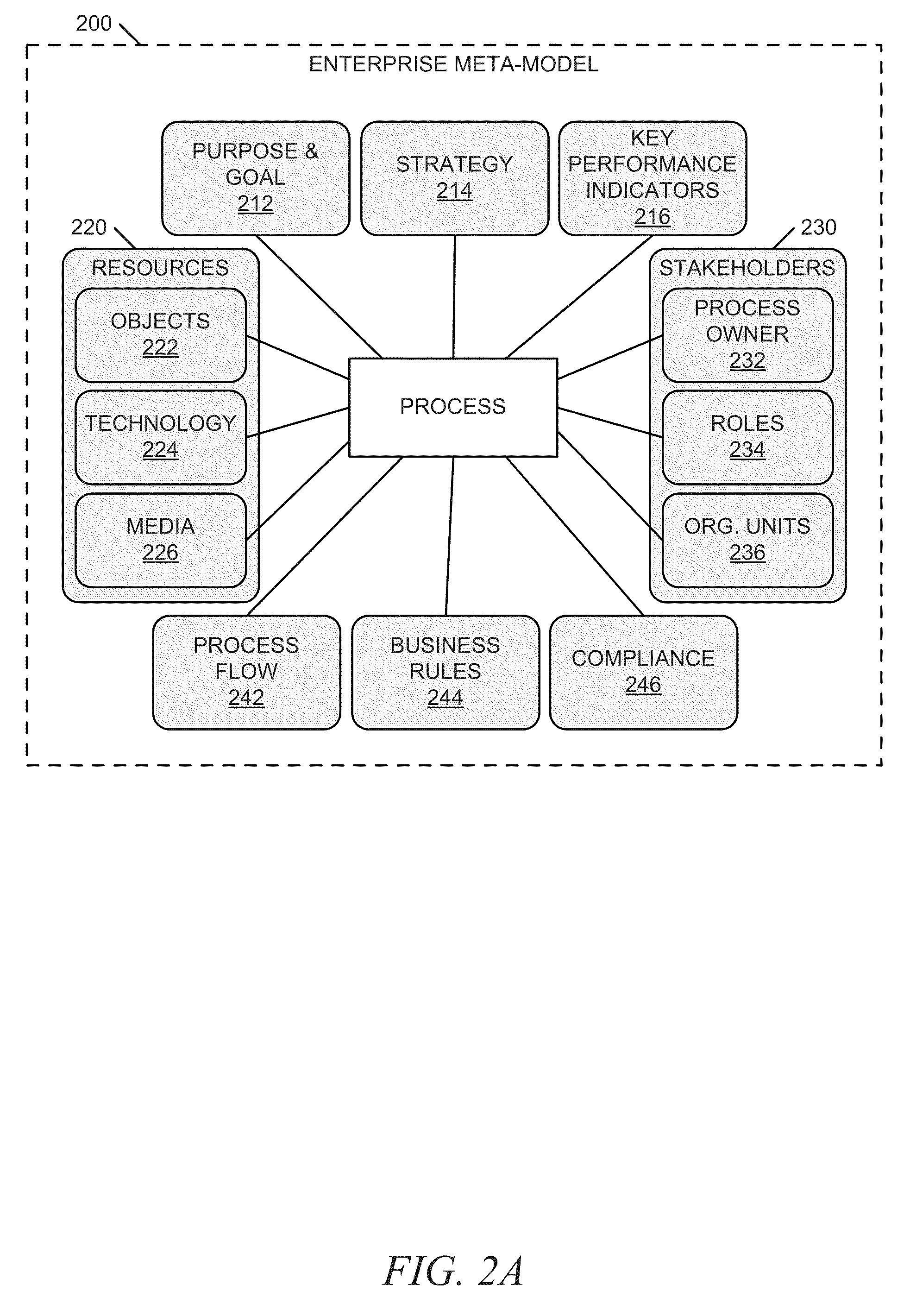
Systems and methods for integrating process perspectives and abstraction levels into process modeling
ActiveUS8468491B2Office automationSpecific program execution arrangementsAbstraction layerEnterprise modelling
Methods and systems for integrating process perspectives and abstraction levels into business process modeling are described. In one example embodiment, modeling business processes for an enterprise can include selecting a segmented view of an enterprise meta-model. The segmented view is associated with a business process to be modeled. The enterprise meta-model is a machine-readable representation of business rules and policies for the enterprise. A business process model is created using a set of visual modeling tools, which are limited by the segmented view. A business policy having some relevance to the process being modeled can be selected for annotation to the business process. Once completed, the business process model is transformed into a machine-readable representation and stored in a repository.
Owner:SAP AG
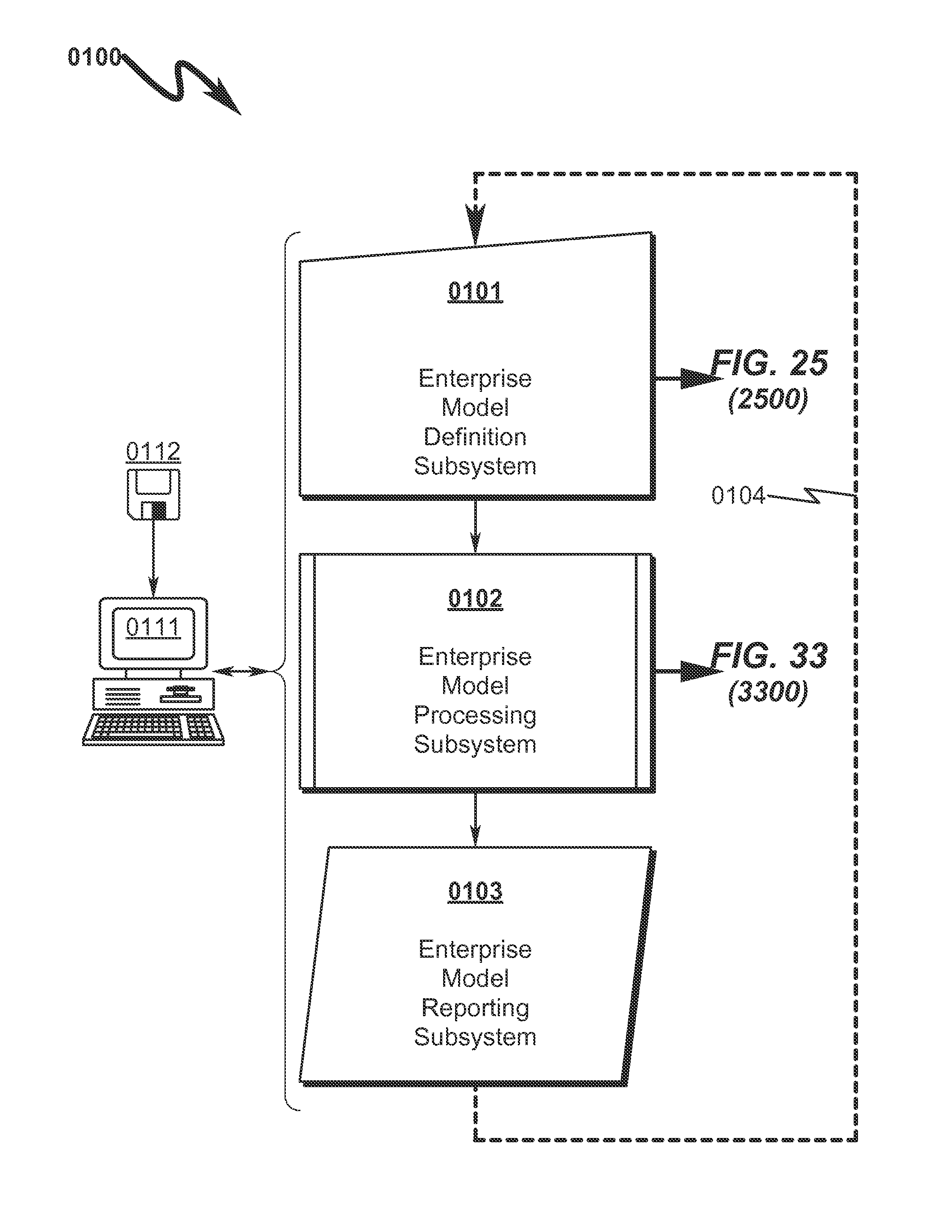
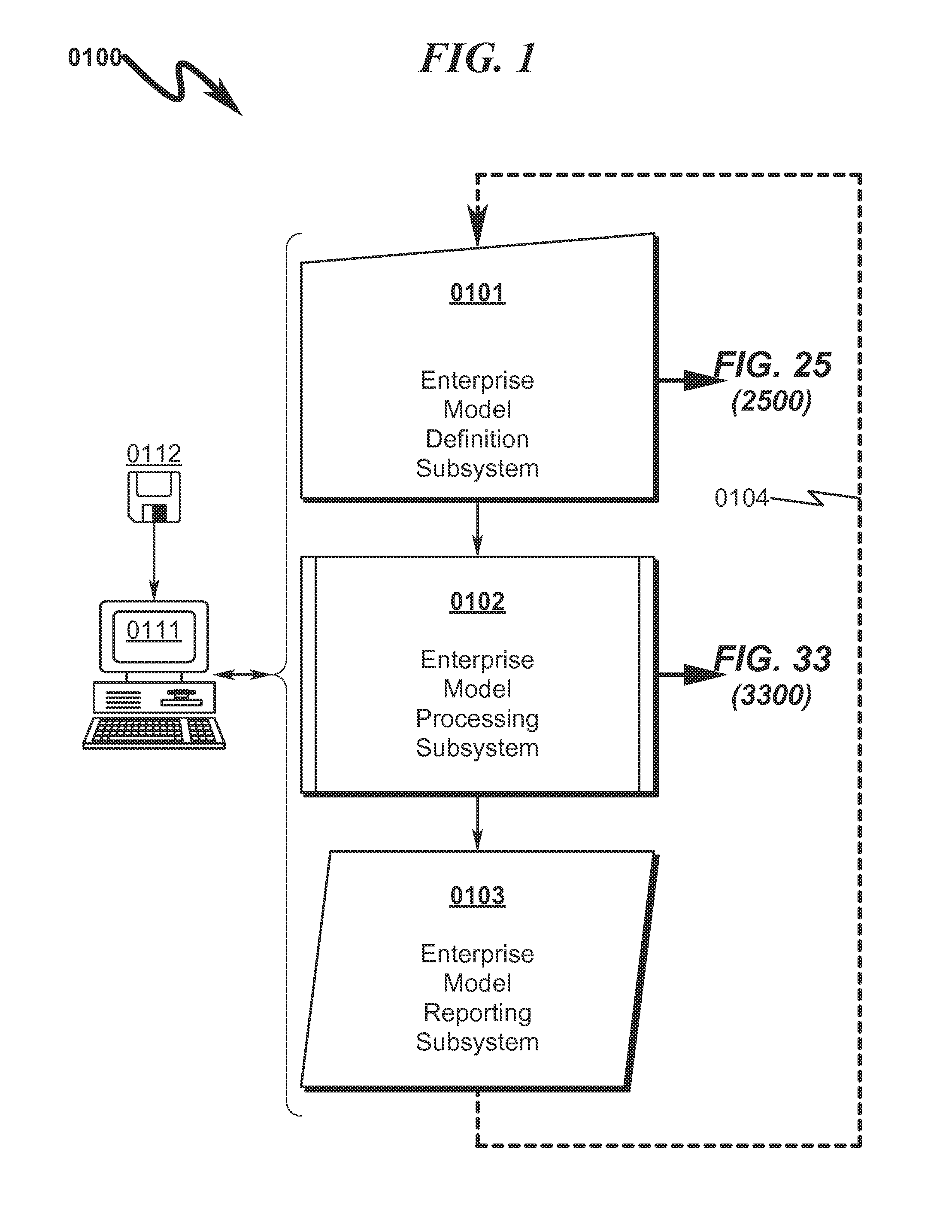
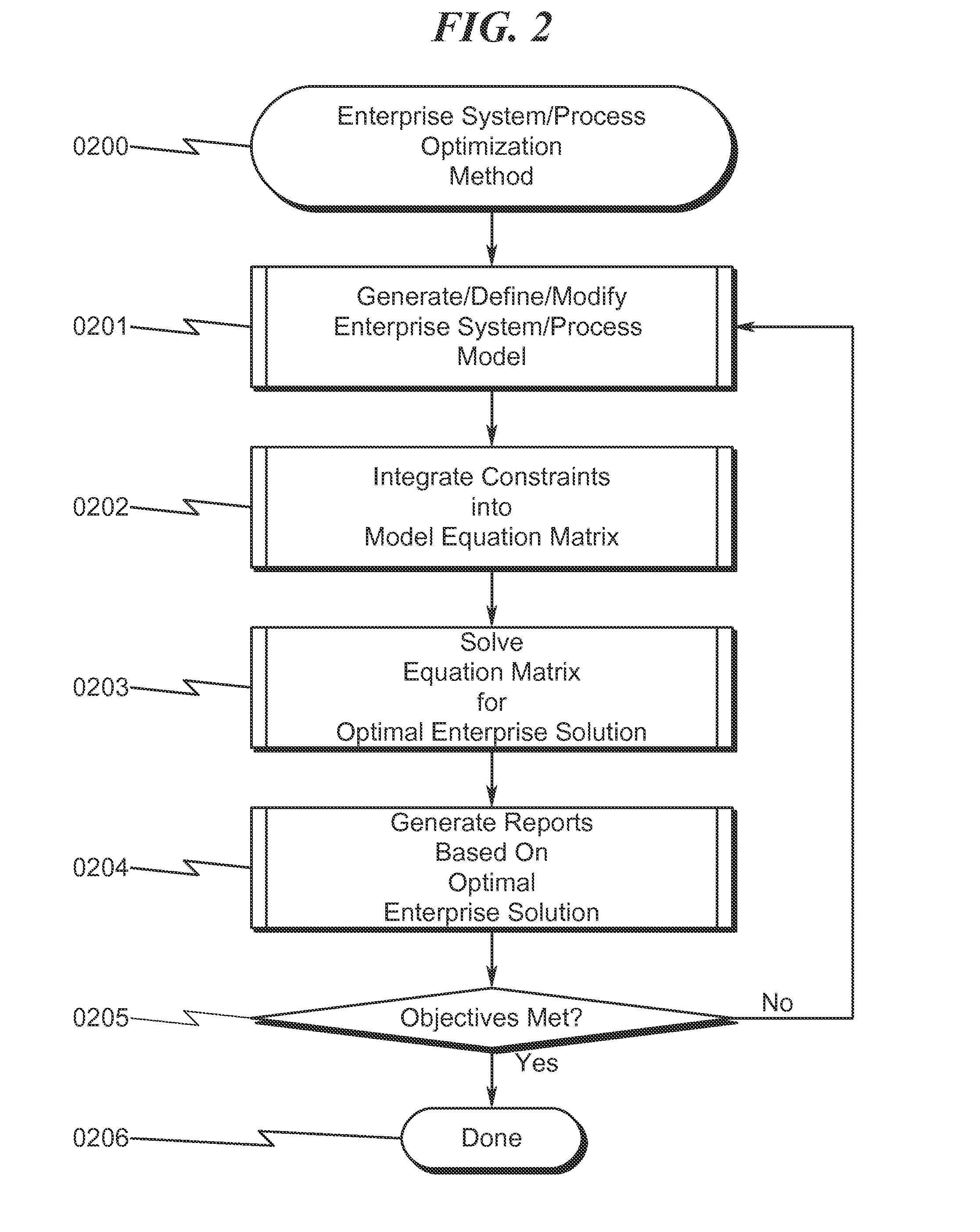
Enterprise System/Process Modeling System and Method
An enterprise system / process modeling (ESPO) system and method that permits efficient representation of enterprise systems / processes (ESP) and calculation of global solutions to models associated with these ESPs is disclosed. The system / method incorporates an enterprise system / process modeling definition subsystem (ESPD) in which an interconnected processes, resources, constraints, and objectives may be defined to describe a global enterprise system / process model (ESPO). This ESPO describes the enterprise to be modeled and the various boundaries within which enterprise modeling is to take place. This ESPO is translated and transformed into an intermediate indexed format by an enterprise global modeling subsystem (EGMS) for use in generating the coefficients of an equation matrix. The equation matrix is solved for a solution state space conforming to desired enterprise objectives and the results are presented for review by an enterprise model reporting subsystem (FSPR).
Owner:RIVER LOGIC
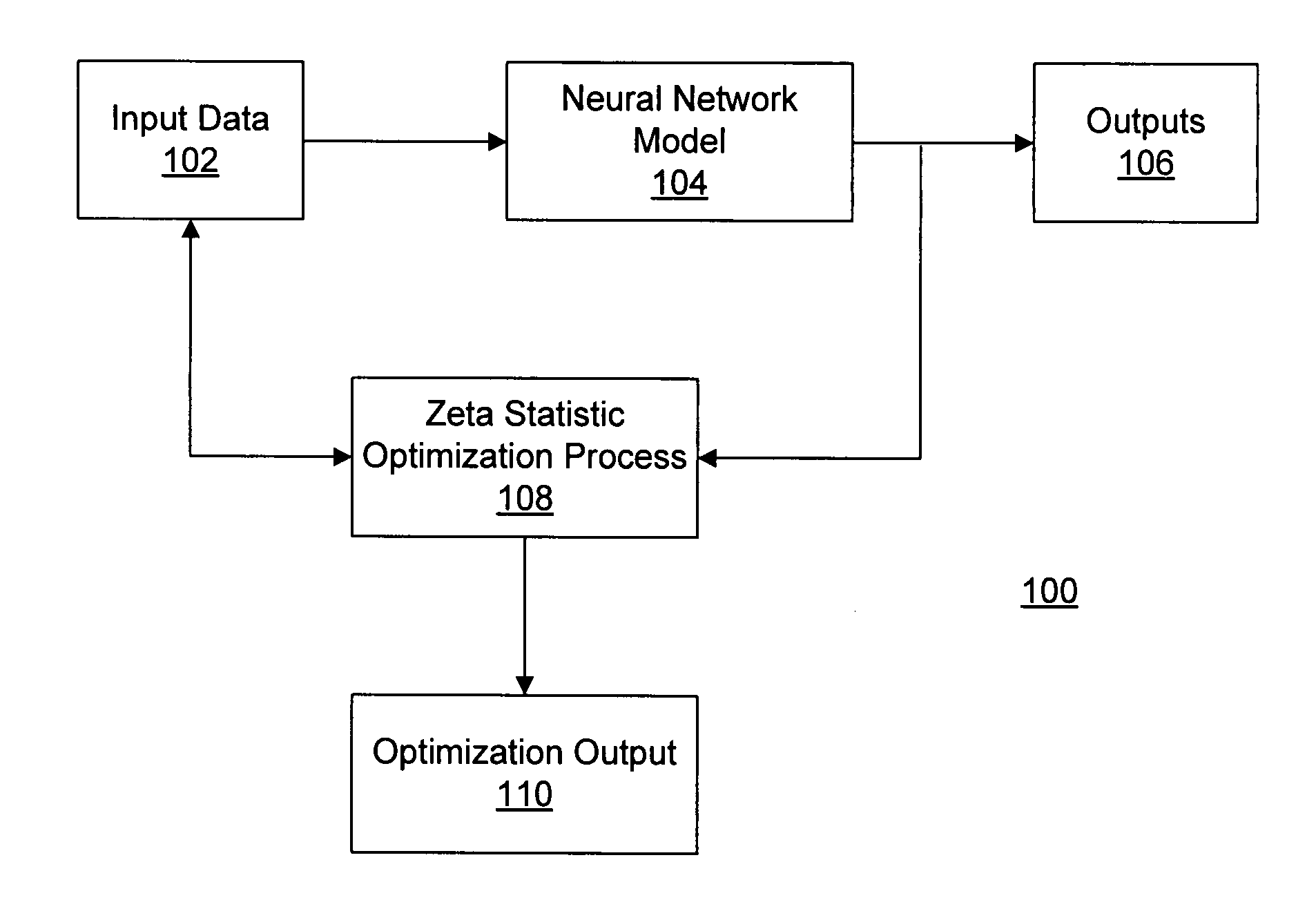
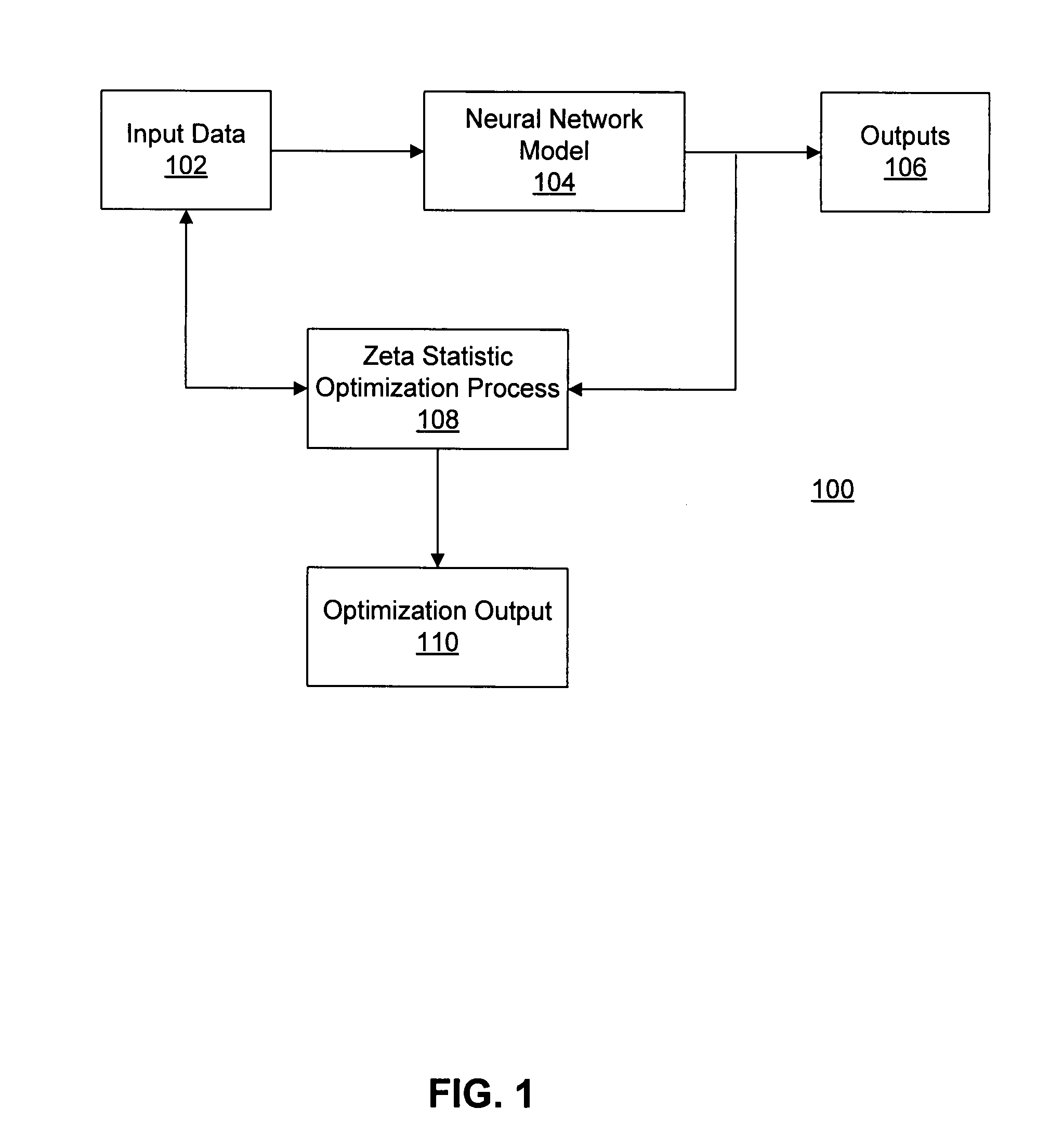
Process modeling and optimization method and system
ActiveUS20080021681A1Digital computer detailsComputation using non-denominational number representationProcedural modelingProcess modeling
A method is provided for model optimization. The method may include obtaining respective distribution descriptions of a plurality of input parameters to a model indicative of interrelationships between the input parameters and one or more output parameters. The method may also include specifying respective search ranges for the plurality of input parameters and simulating the model to determine a desired set of input parameters based on a zeta statistic of the model. Further, the method may include determining respective desired distributions of the input parameters based on the desired set of input parameters; determining significance levels of the input parameters in interacting with the output parameter based on the simulation and the desired distributions of the input parameters; and presenting the significance levels.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
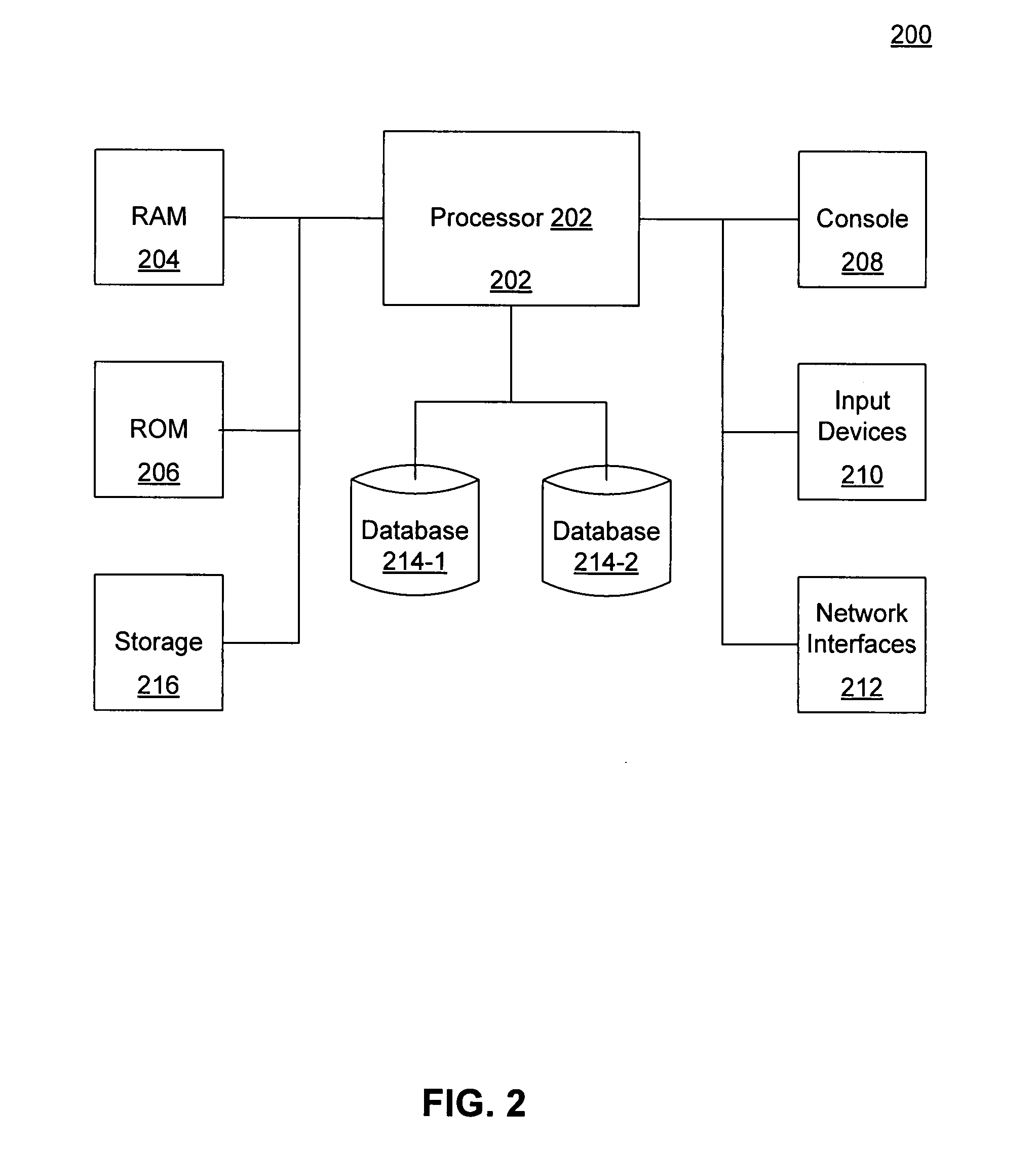
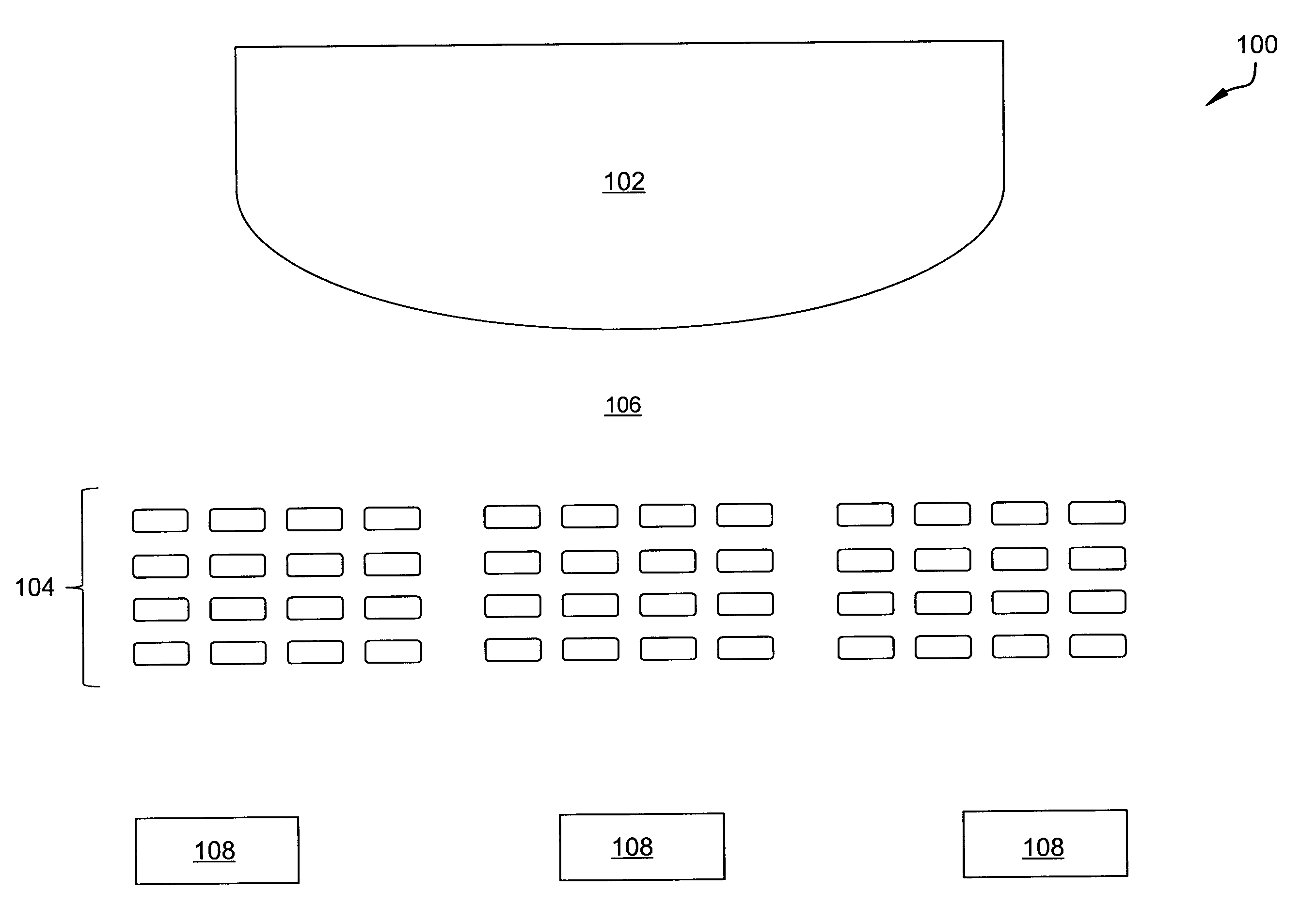
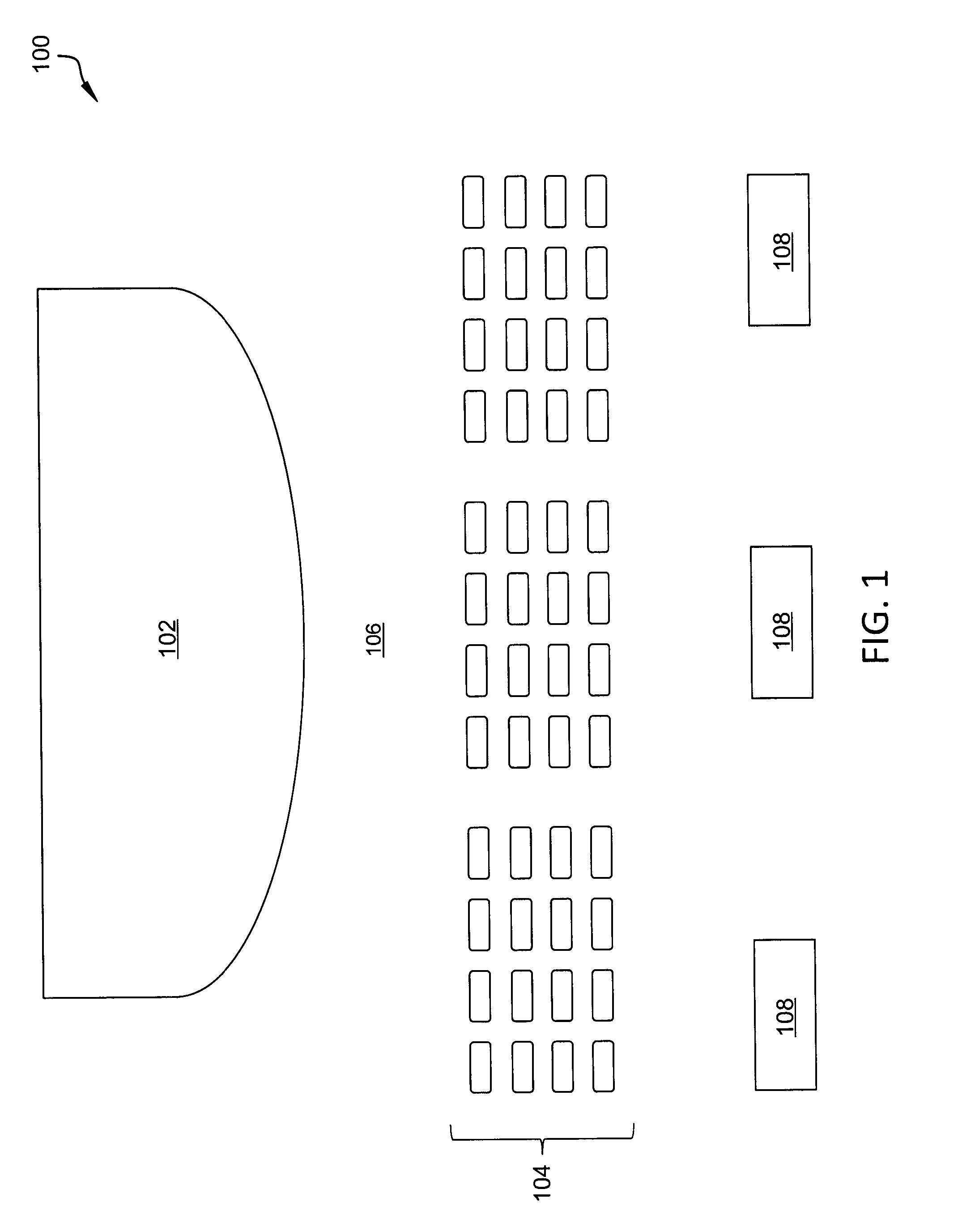
Automated ticket comparison and substitution recommendation system
Systems and methods for creating a recommendation engine of a process modeling server and automatically comparing tickets by the recommendation engine are disclosed. The recommendation engine may be generated by digitizing a seat map of a venue that characterizes one or more interrelationships between the seats. After creation, the process modeling server receives a notification that a ticket holder's ticket to an event taking place at a venue has been cancelled or become otherwise unavailable. The process modeling server compares one or more attributes of the now-unavailable ticket to one or more rules maintained by a recommendation engine of the process modeling server. The recommendation engine generates one or more substitute ticket alternatives based on the comparison for selection. The recommendation engine may refine the one or more rules over time based on actual customer selection.
Owner:STUBHUB
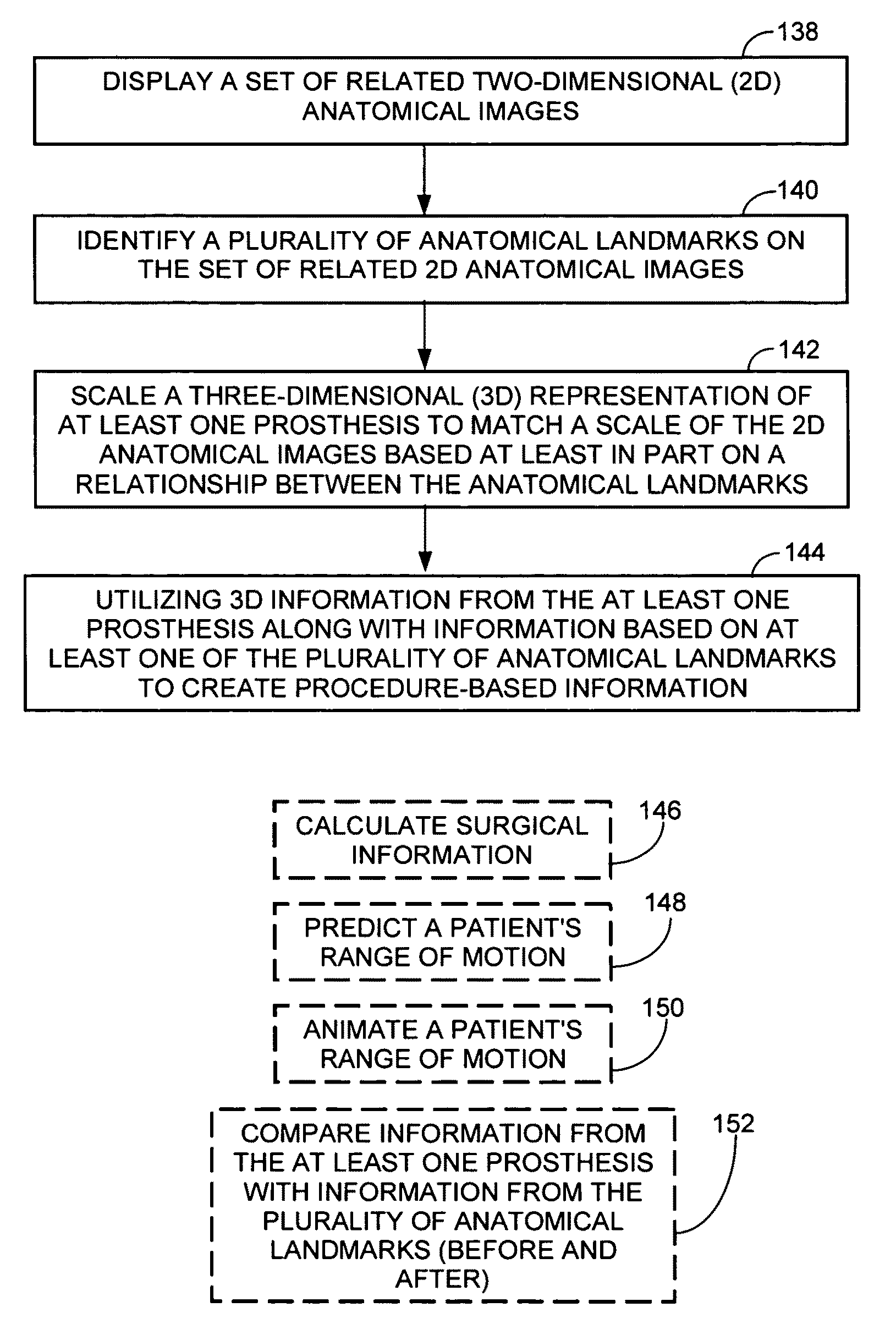
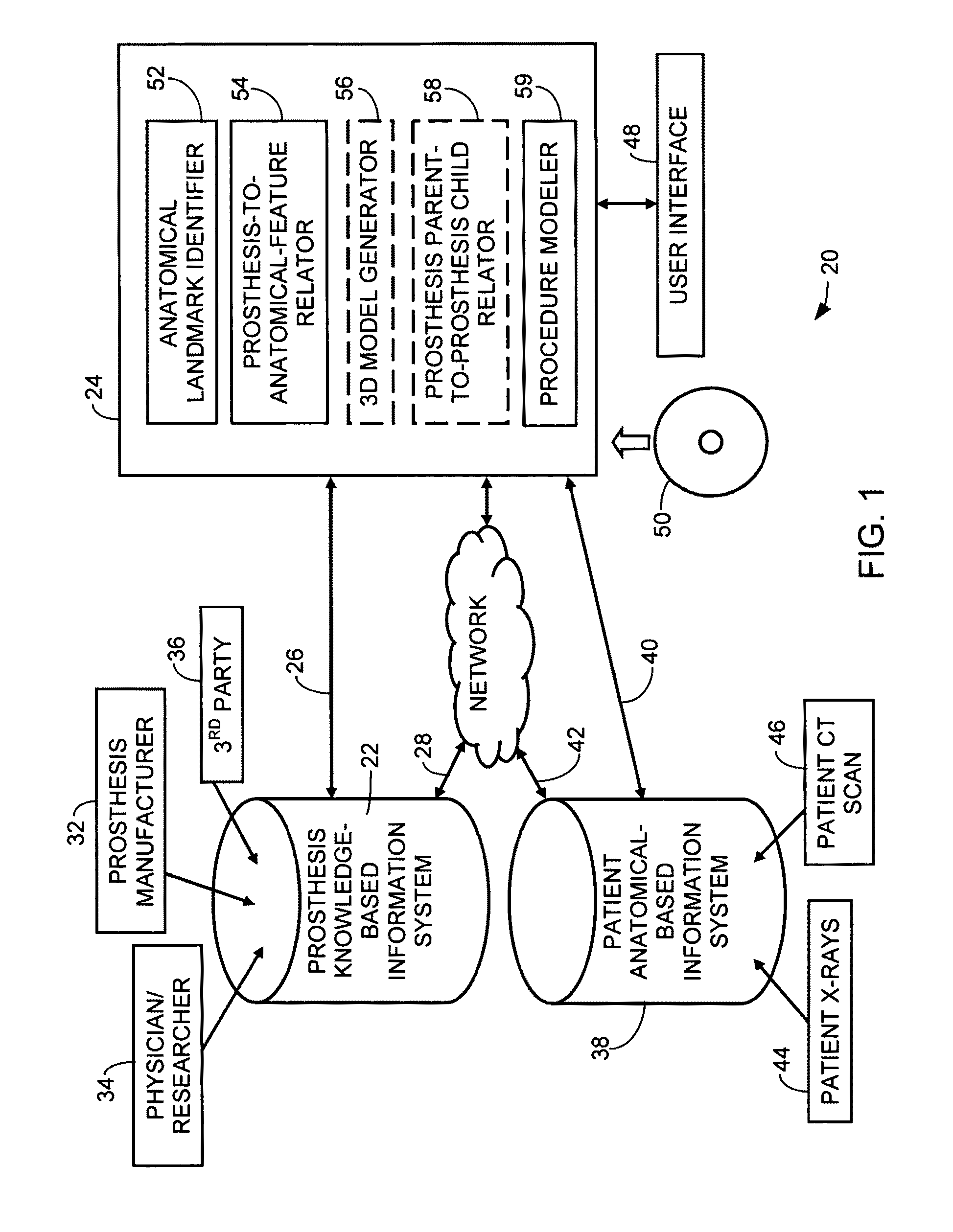
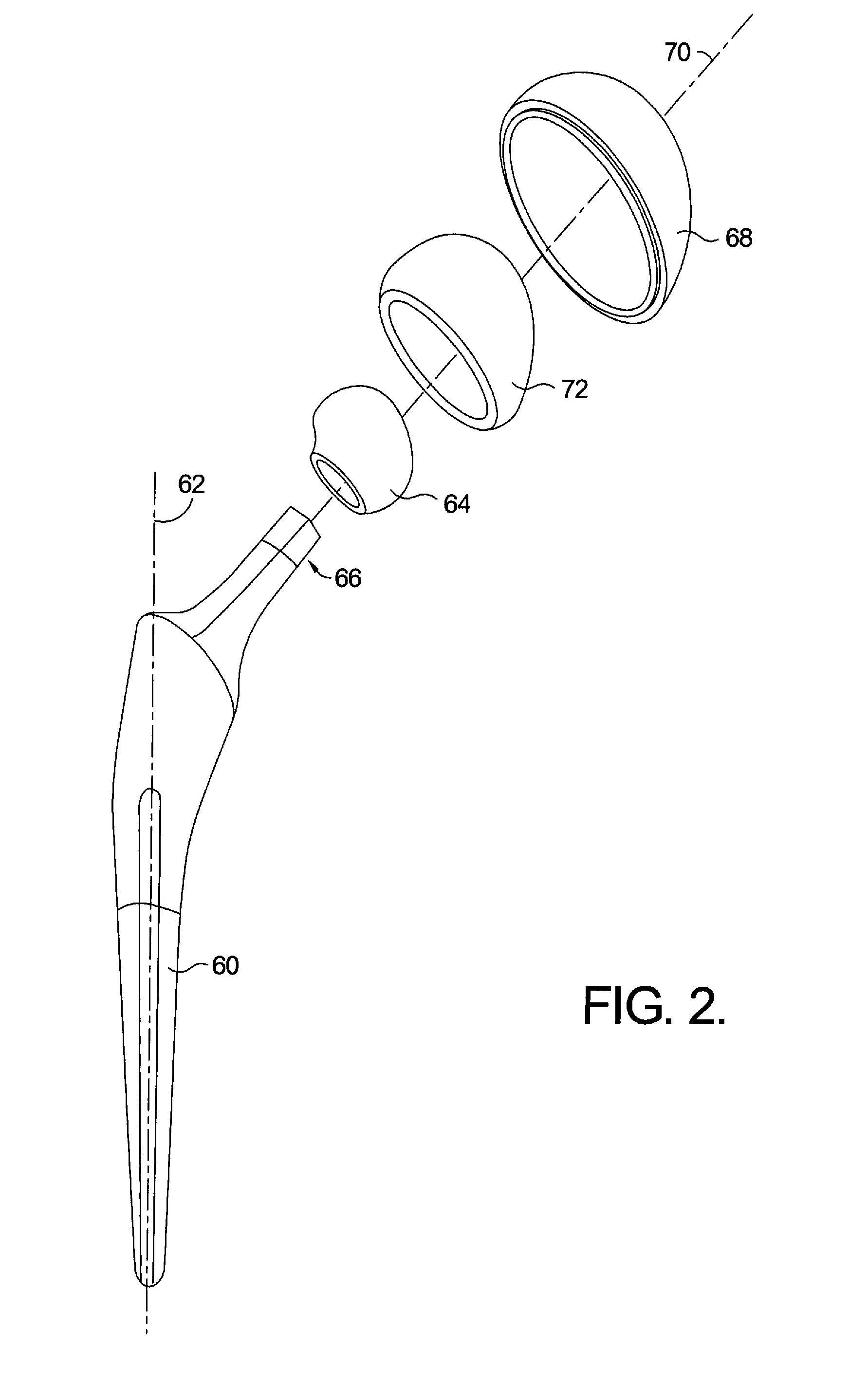
Method and system for surgical modeling
ActiveUS8160326B2Analogue computers for chemical processesJoint implantsAnatomical structuresAnatomical landmark
A method of surgical modeling is disclosed. A set of related two-dimensional (2D) anatomical images is displayed. A plurality of anatomical landmarks is identified on the set of related 2D anatomical images. A three-dimensional (3D) representation of at least one prosthesis is scaled to match a scale of the 2D anatomical images based at least in part on a relationship between the anatomical landmarks. 3D information from the at least one prosthesis along with information based on at least one of the plurality of anatomical landmarks is utilized to create procedure-based information. A system for surgical modeling is also disclosed. The system has a prosthesis knowledge-based information system, a patient anatomical-based information system, a user interface, and a controller. The controller has an anatomical landmark identifier, a prosthesis-to-anatomical-feature relator, and a procedure modeler.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
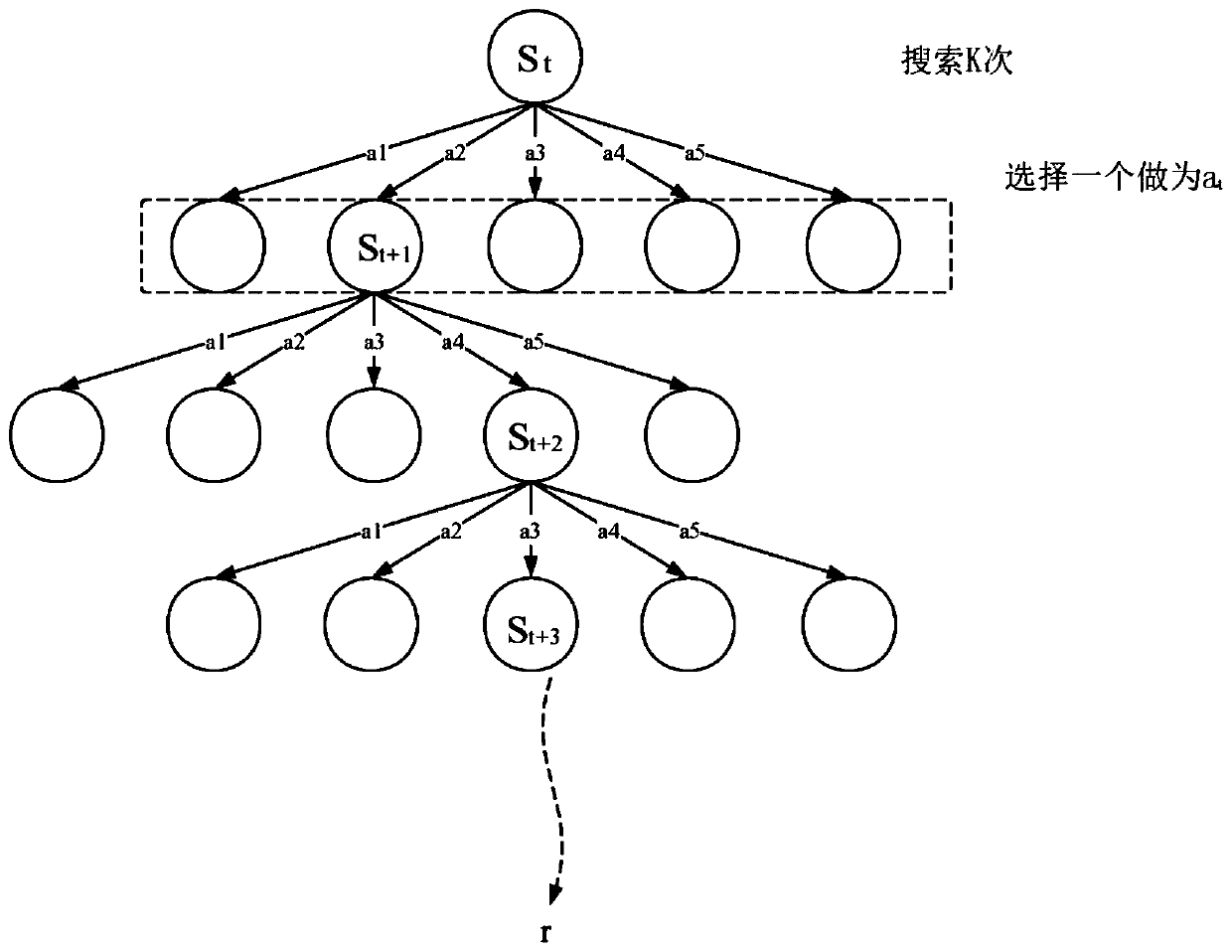
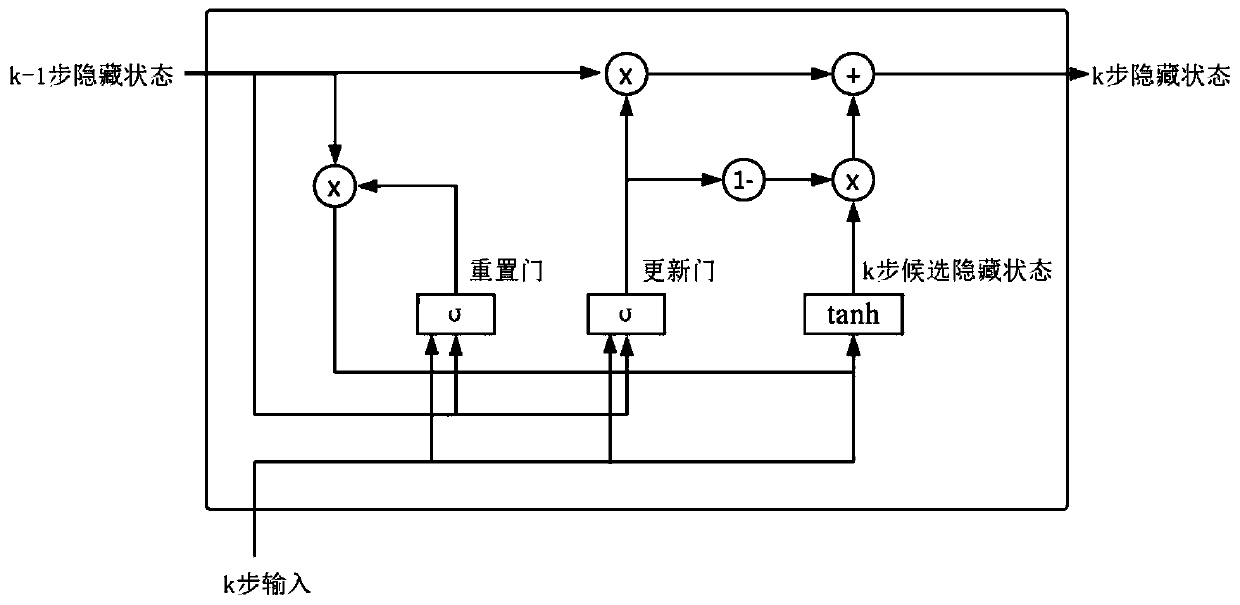
Method for identifying a named entity based on policy value network and tree search
ActiveCN110209770AText database queryingSpecial data processing applicationsInformation processingData set
The invention discloses a method for identifying a named entity based on a policy value network, and belongs to the field of information processing. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, modeling a labeling process of named entity recognition into a Markov decision process (MDP) so that a model for identifying the named entity based on enhanced learning is provided, namely MM-NER. MM-NER is the first to apply the Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) enhanced MDP model to named entity recognition (sequence tag task).A strategy value network is designed on the basis of an MDP state definition to obtain label probability and label sequence accuracy evaluation, and an MCTS is used for simulation, so that a label sequence with more global consciousness is searched out. In the inferenceprocess, the strategy value network is directly used to ensure that the identification effect is basically consistent with the tree search strategy, and the time complexity is greatly reduced. An experimental result of the present invention on the CoNLL2003 named entity identification data set demonstrates the effectiveness of the MM-NER with the K-step exploration decision mechanism.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Battle process modeling method for battle simulation and model scheduling method
ActiveCN104951631AReasonable process modelingReasonable descriptionSpecial data processing applicationsComputational problemModularity
The invention discloses a battle process modeling method for battle simulation. Battle processes are divided into different levels according to campaign, combat, operation and activity; each level is described through CSDs; battle process modeling in each level adopts CSDs integrating certainty and randomness. The invention further discloses a model scheduling method obtained based on the battle process modeling method. The model scheduling method comprises the following steps: searching an earliest initial module(s) from the set of modules to be run; running the earliest initial module if only one earliest initial module exists, otherwise, judging modules to be run according to module impacting levels, and driving the modules to run according to the running rule; removing a module from the set of modules to be run after the module is run, and searching another earliest initial module(s) again; conducting the steps in sequence circularly till the set of modules to be run is empty. The battle process modeling method and the model scheduling method have the advantages that efficiency models of various certainty and randomness configured to battle activities, so as to solve the problem in calculating efficiency indexes, and support the modularized encapsulation of the efficiency models to facilitate reuse of the models.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Example-Based Procedural Synthesis of Element Arrangements
ActiveUS20090058871A1Texturing/coloringCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer scienceProcedural modeling
Method and apparatus for synthesizing element arrangements from an example. Embodiments may synthesize element arrangement patterns from an example arrangement. Embodiments may combine a texture synthesis technique based on local neighborhood comparison of an example and a target with procedural modeling based on local growth. Given an example, connectivity of elements may be constructed to get neighborhoods information of each element. A synthesis process may start with a single seed and expand the synthesized pattern by placing new elements at seed locations one by one. A reference element may be selected from the example that has neighborhood features that are most similar to neighborhood features of the target seed in the synthesized pattern. A non-rotation mode, a rotation mode, and a flow field mode may be provided. A painting tool, a flow field tool, and a boundary tool may be provided.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
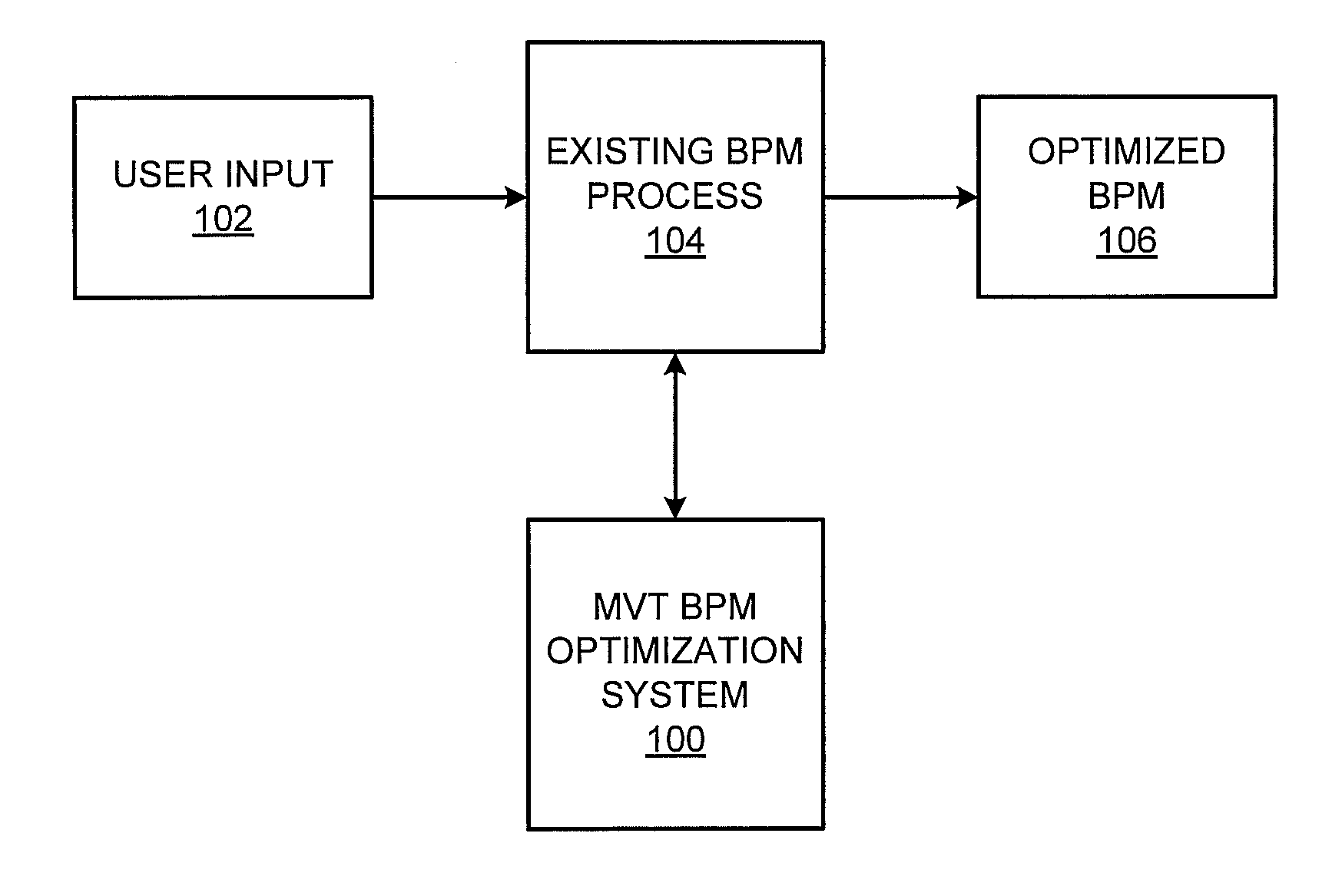
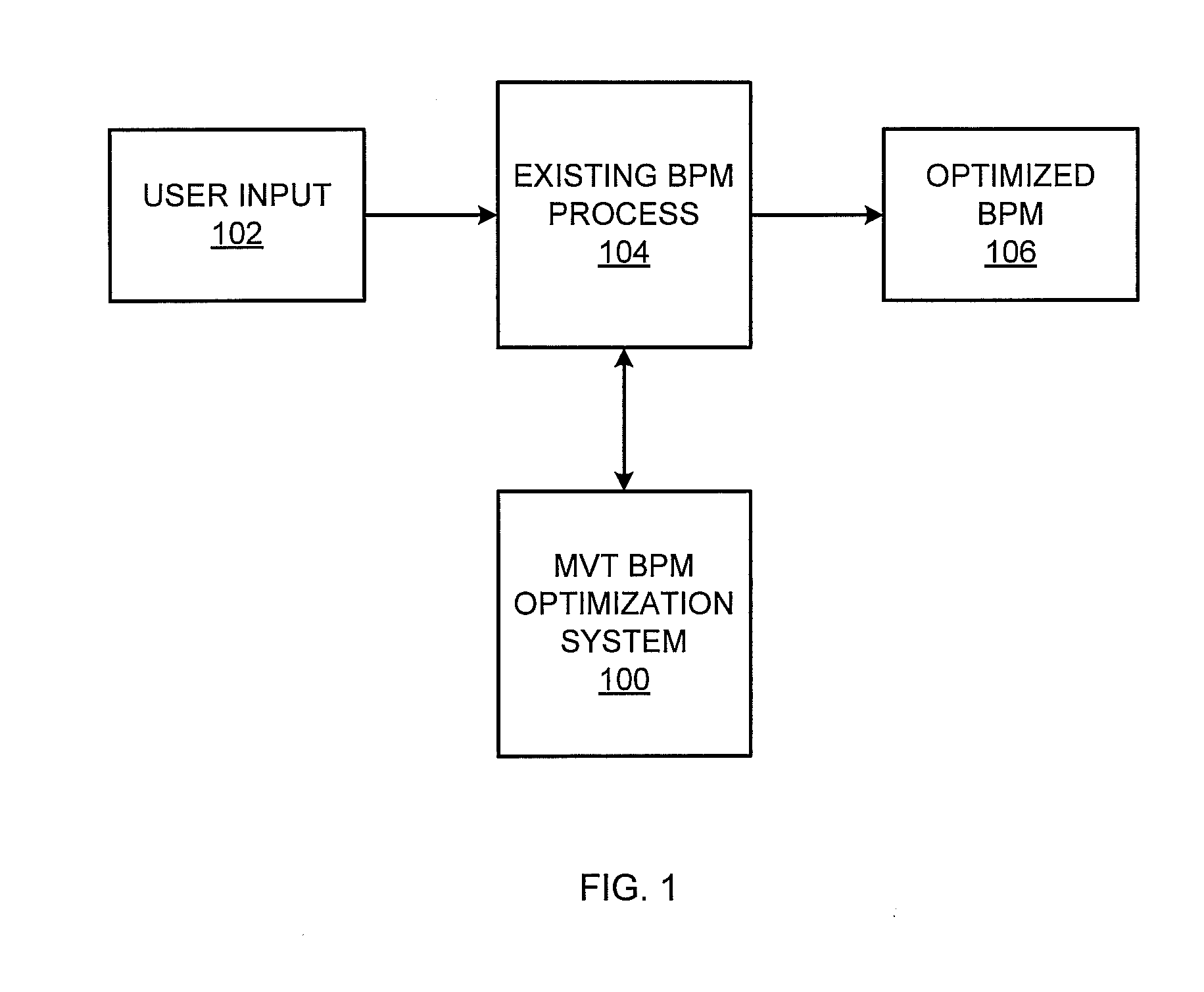
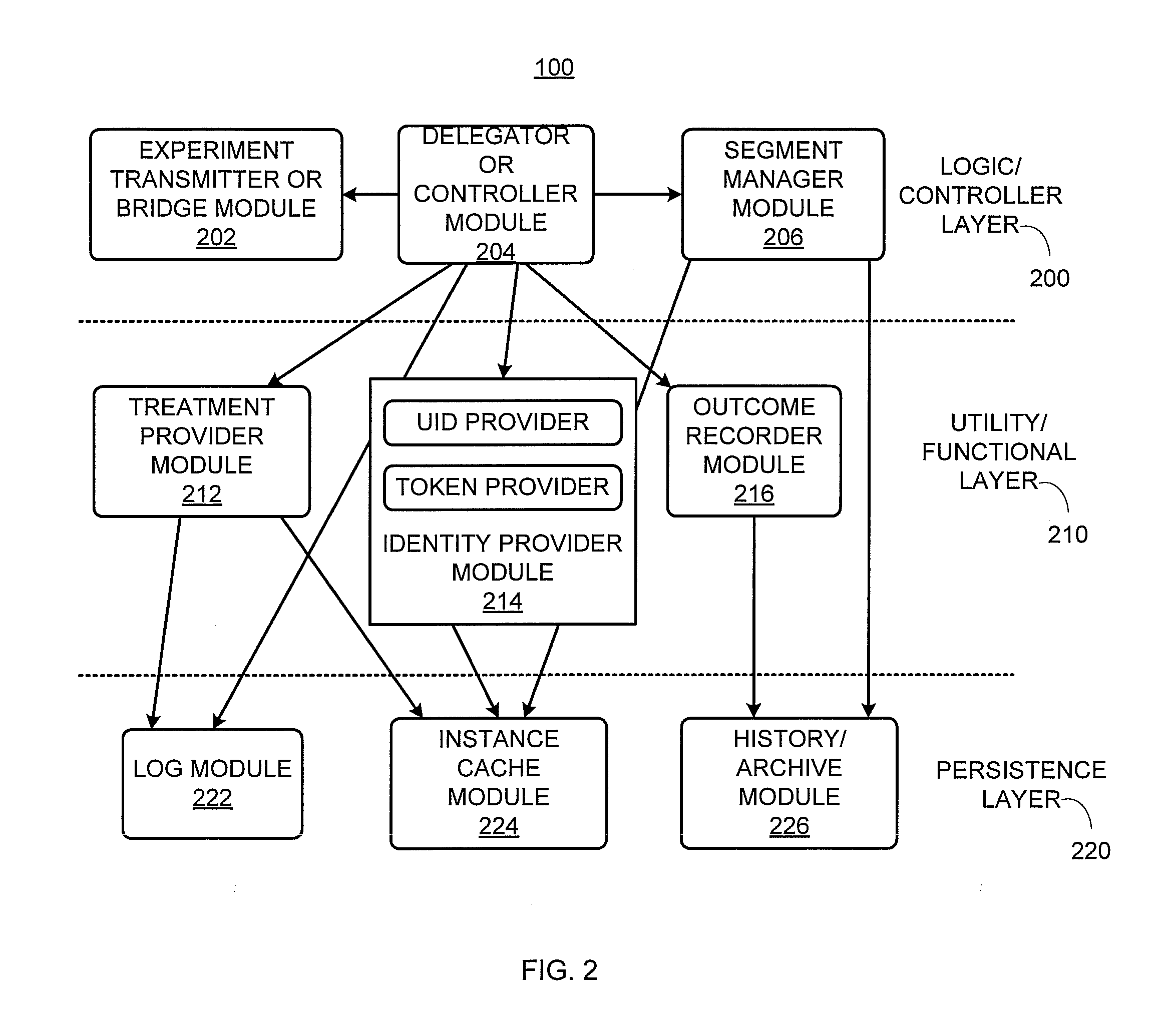
MVT optimization of business process modeling and management
A multivariate business process modeling or management (BPM) optimization system and method for optimizing a BPM system includes a logic layer to control operation of the BPM system, a utility layer to implement a randomized experimental treatment based on a hypothesis, and a persistence layer to collect data from application of the randomized experimental treatment to the BPM system. The multivariate BPM optimization system and method optimizes the BPM system by computerized testing of the hypothesis and generation of results to add, remove or modify a step or modify a point in a flow of the BPM system based on the data collected from application of the randomized experimental treatment.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
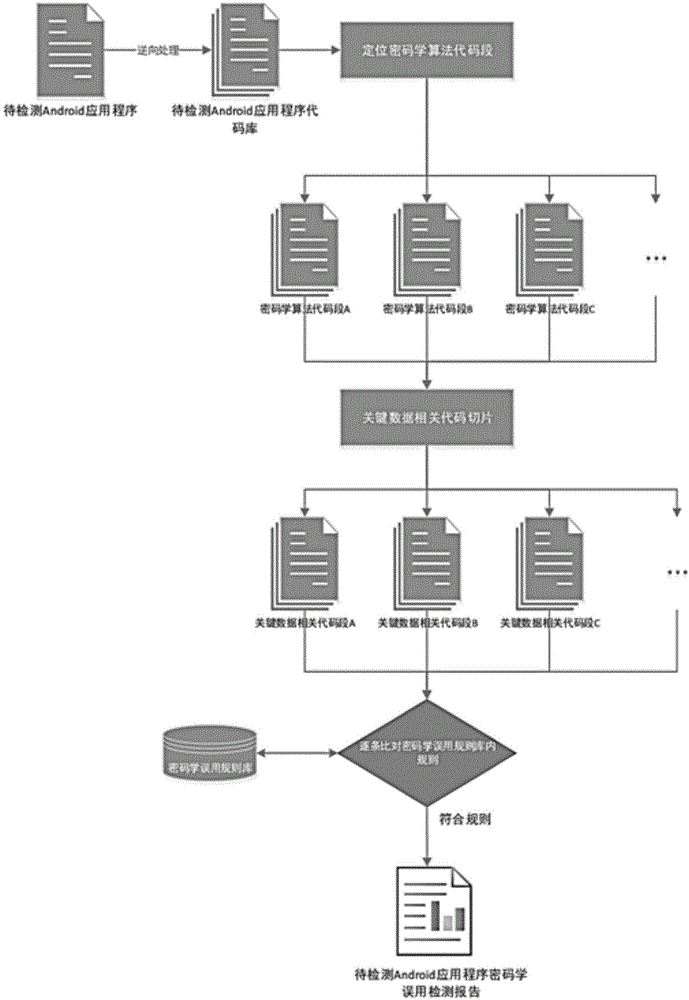
Method for detecting cryptology misuse of Android application programs
ActiveCN104484175ADigital data protectionSpecific program execution arrangementsData abstractionPattern matching
The invention discloses a method for detecting cryptology misuse of Android application programs. The method comprises the following steps of decompiling a to-be-detected program and generating a codebase; then, looking up code segments related with a cryptographic algorithm from the codebase; then, stripping the code segments related with the cryptographic algorithm out of an original program to obtain a complete cryptographic algorithm implementation process code; finally, performing data abstraction and process modeling processing on each cryptographic algorithm implementation process code segment obtained in the step 3; comparing the cryptographic algorithm implementation process code segments item by item through pattern matching and a cryptographic algorithm implementation rule appointed in advance, outputting items which do not meet the implementation rule and summarizing to form a safety analysis result. According to the method disclosed by the invention, through static analysis on an Android application program, a cryptographic algorithm type used in the application program can be automatically judged, and the code segments related with the cryptographic algorithm are automatically extracted; safety analysis is performed on the code segments so as to find out a problem link during a cryptographic algorithm implementation process, and the safety analysis result of the cryptology misuse of the application program is finally obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com