Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
214 results about "Parallel encoding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
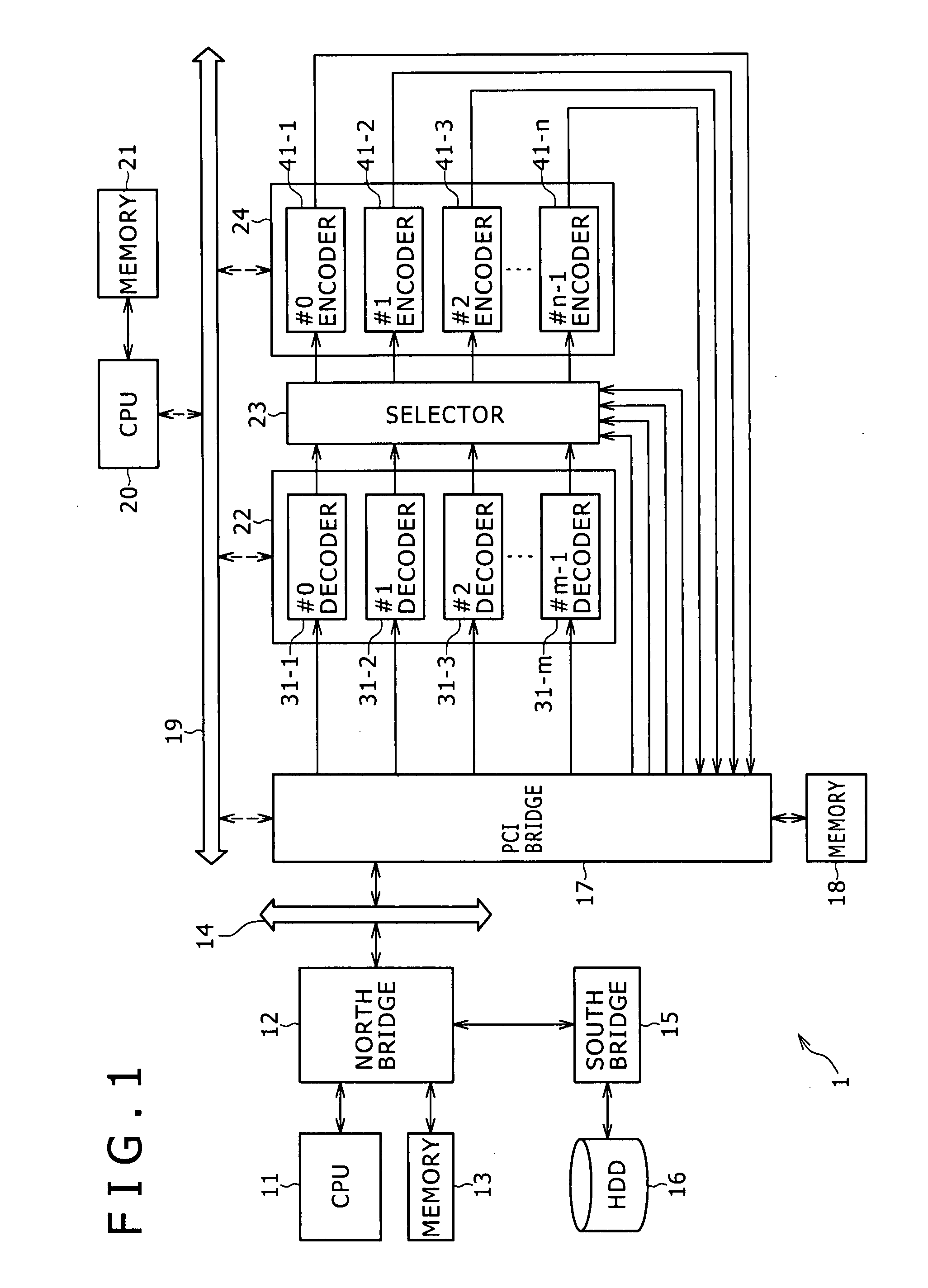
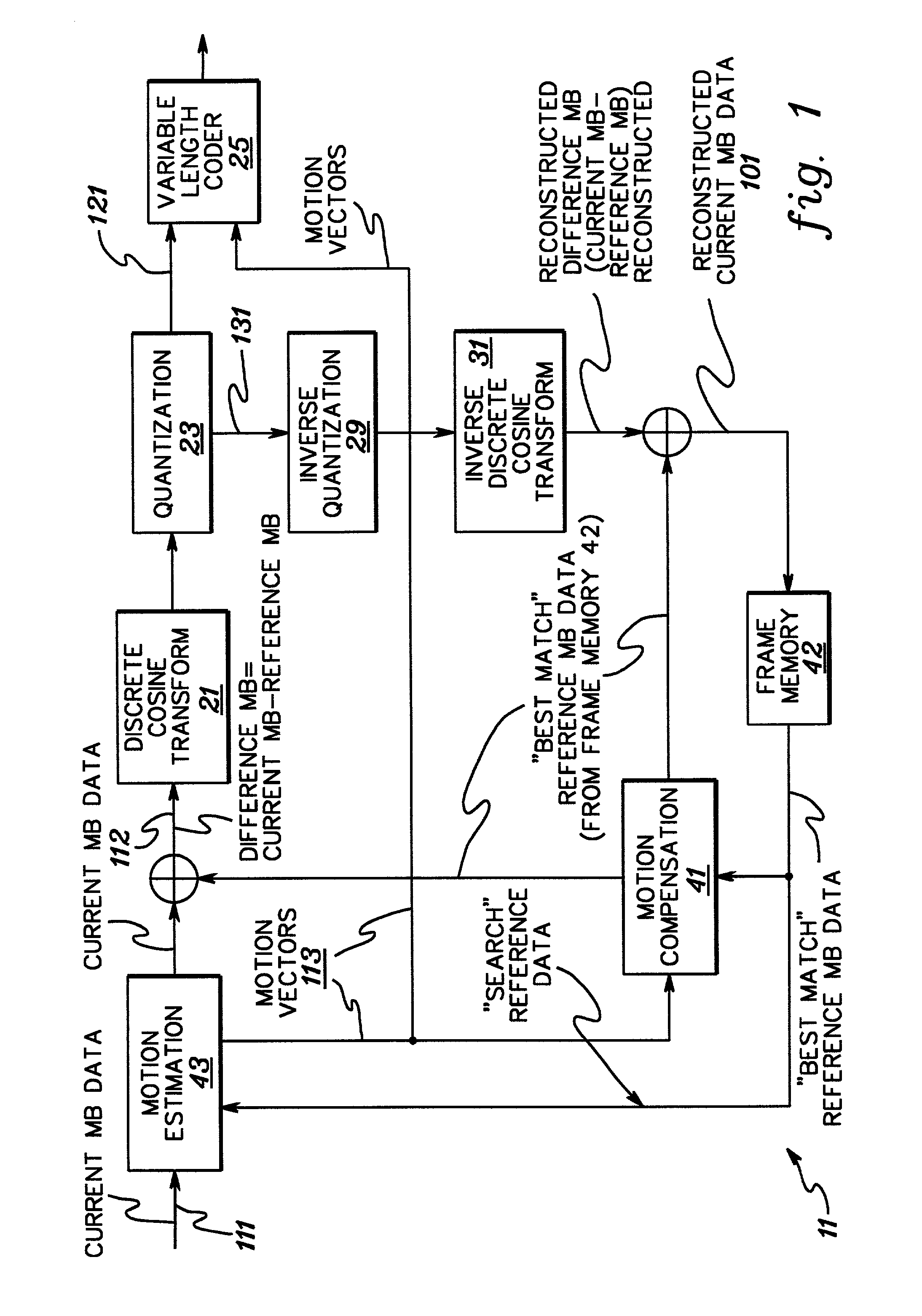
Method and Apparatus for Real Time Parallel Encoding
ActiveUS20080137736A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionParallel encodingVideo sequence
There are provided apparatus and methods for parallelizing an encoding process across multiple processors. An apparatus includes a computing resource balancer and a splitter. The computing resource balancer is for assigning encoder instances to respective ones of the multiple processors based on at least one of thread affinity and process affinity. The splitter is for temporally dividing an incoming video sequence into discrete GOPs such that each of the encoder instances is capable of encoding the incoming video sequence in parallel so that each of the discrete GOPs is encoded on a respective one of the multiple processors.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Method and system of single carrier block transmission with parallel encoding and decoding
ActiveUS20100146363A1High resolutionIncrease data rateAssess restrictionCode conversionTransmission systemParallel encoding
A Single Carrier Block Transmission (SCBT) system employs an inherently parallel approach to error correction processing. At the transmission system (200), an incoming data stream is split (210) into P parallel data streams, each having a data rate equal to a fraction of the incoming data stream's data rate. The parallel data streams are then each separately encoded (220) in P parallel encoding processes (beneficially, using P parallel encoders (222)). The P separately encoded data streams are then merged (330), interleaved (320), and mapped (310) into a single stream of encoded symbols, which are transmitted to the receiver using an arbitrary modulation (240) and transmission scheme. At the receiver (255), the received data stream is de-interleaved (350) and split into P encoded data streams, which are then decoded (285) using P parallel decoders. Then, the decoded data streams are combined or multiplexed (295) into a single data stream.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and system for implementing parallel encoding of high-definition video
InactiveCN101282478AMaintain a high degree of parallelismAvoid the problem of water bottleneckTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationComputer architectureParallel encoding
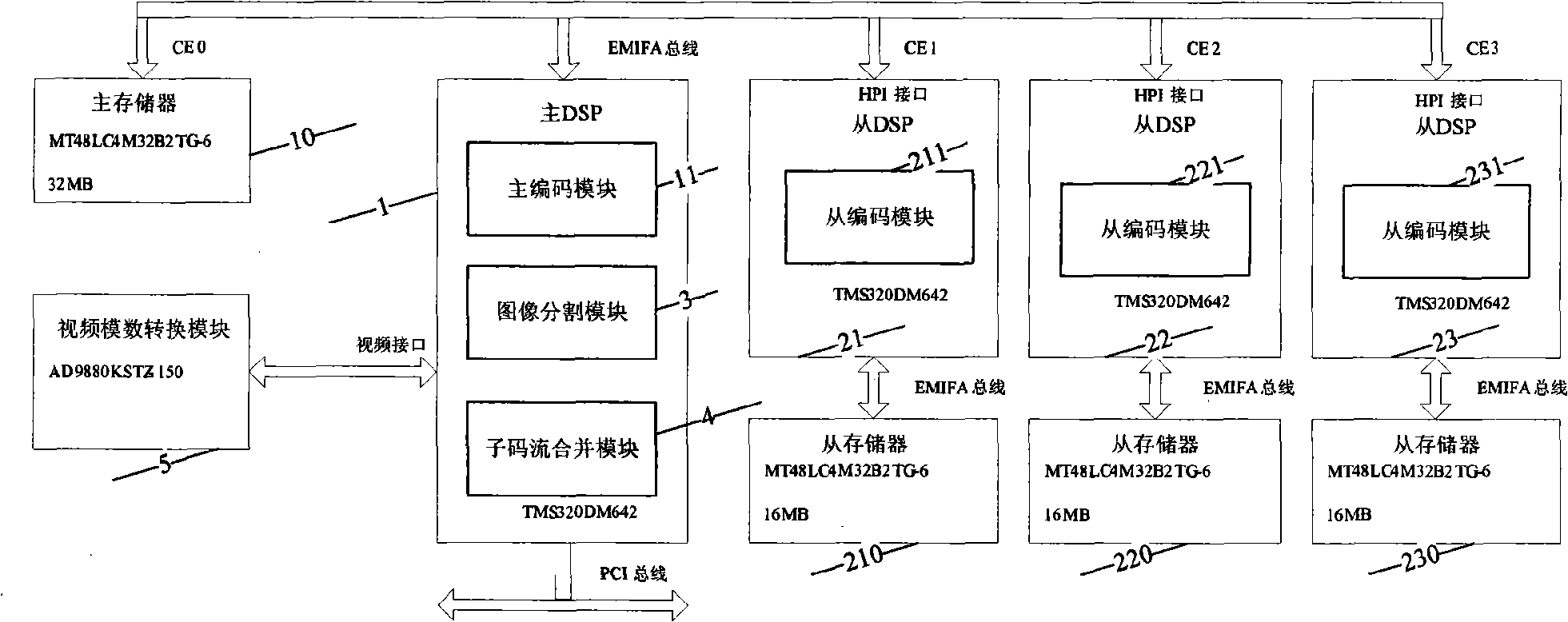
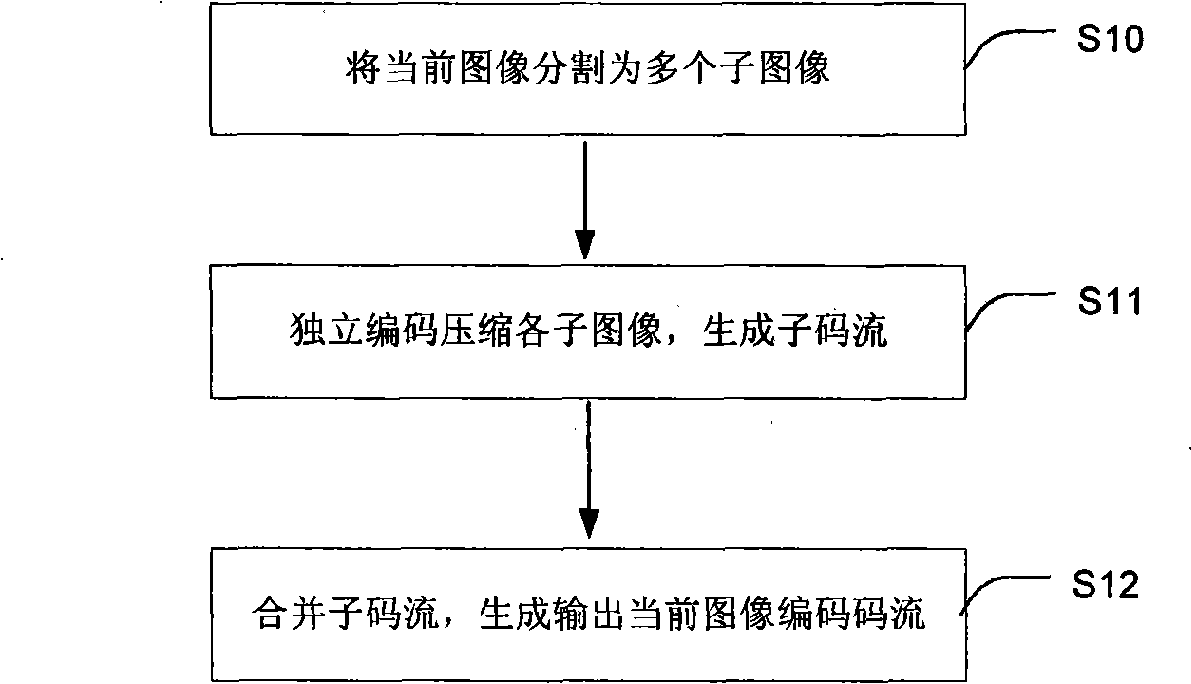
The invention discloses a system for realizing high-definition video parallel coding, which includes a image segmentation module, a subcode stream merge module, a storage module, a video modulus conversion module and several image coding modules; the video modulus conversion module is connected with at least one image coding module; the image coding module is connected with the image segmentation module and the storage module; the image segmentation module divides the current image into several sub-images; the image coding module independently encodes and compresses the divided sub-images to create subcode stream; the subcode stream merge module subsequently merges the sub-images to create and output coding stream of the current image. The method of dividing the coded image into sub-images for parallel coding of the invention avoids problem of flow bottleneck caused by over-load of some module in prior parallel method based on module flow, which can flexibly distribute sub-images with appropriate size according to processing capacity of target processor and keep high-parallelism of multiple processors, thereby upgrading performance of the whole system.
Owner:SHANGHAI AVCON INFORMATION TECH
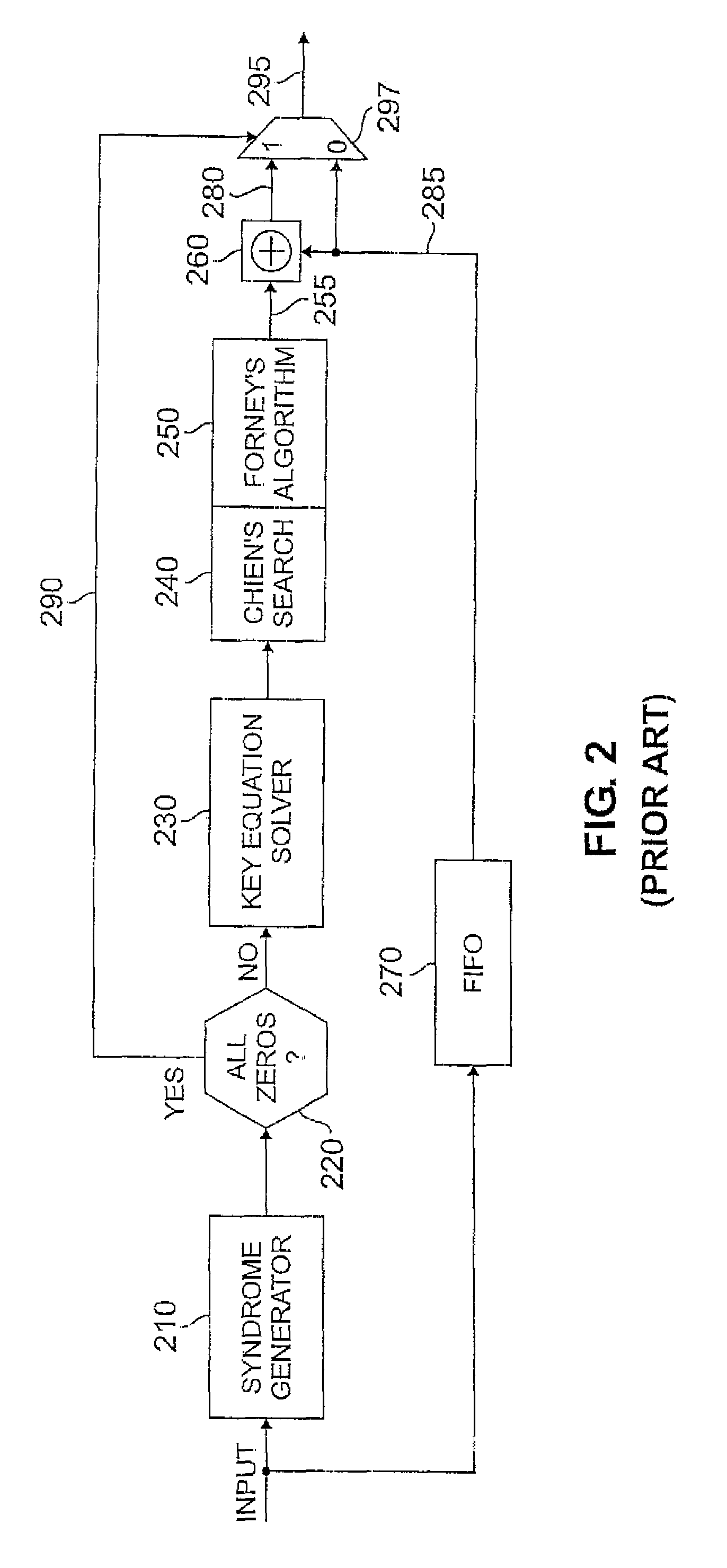
High speed syndrome-based FEC encoder and decoder and system using same
InactiveUS6990624B2Increase speedReduce complexityCode conversionCyclic codesComputer hardwareParallel encoding
A decoder, encoder and corresponding system are disclosed for providing fast Forward Error Correcting (FEC) decoding and encoding of syndrome-based error correcting codes. Three-parallel processing is performed by elements of the system. More particularly, in an illustrative embodiment, a decoder performs three-parallel syndrome generation and error determination and calculations, and an encoder performs three-parallel encoding. Low power and complexity techniques are used to save cost and power yet provide relatively high speed encoding and decoding.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Parallel video coding based on prediction type
InactiveUS20120014438A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureVideo encoding
Owner:SHARP KK
Parallel encoding and decoding processor system and method
InactiveUS6870883B2Simple configurationIncrease speedResource allocationPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVariable-length codeParallel encoding
Encoding and decoding systems for MPEG encoding and decoding at a high speed using a parallel processing system, wherein macroblocks to be processed are designated for first to third processors which are made to carry out all processings of encoding, variable length coding, and local decoding of those macroblocks; the variable length coding is carried out after confirming that the variable length coding with respect to the previous macroblock is ended; the variable length coding which was normally sequentially carried out at a specific processor is carried out at all of the processors; and the encoding and local decoding are carried out at all of the processors; whereby the loads are dispersed, the efficiency is improved as a whole, and the processing speed becomes fast.
Owner:SONY CORP
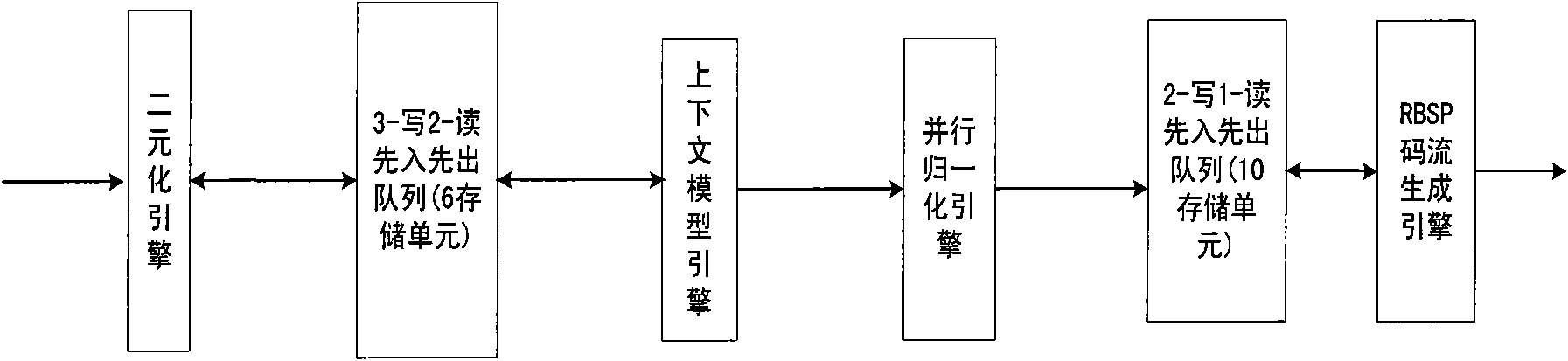
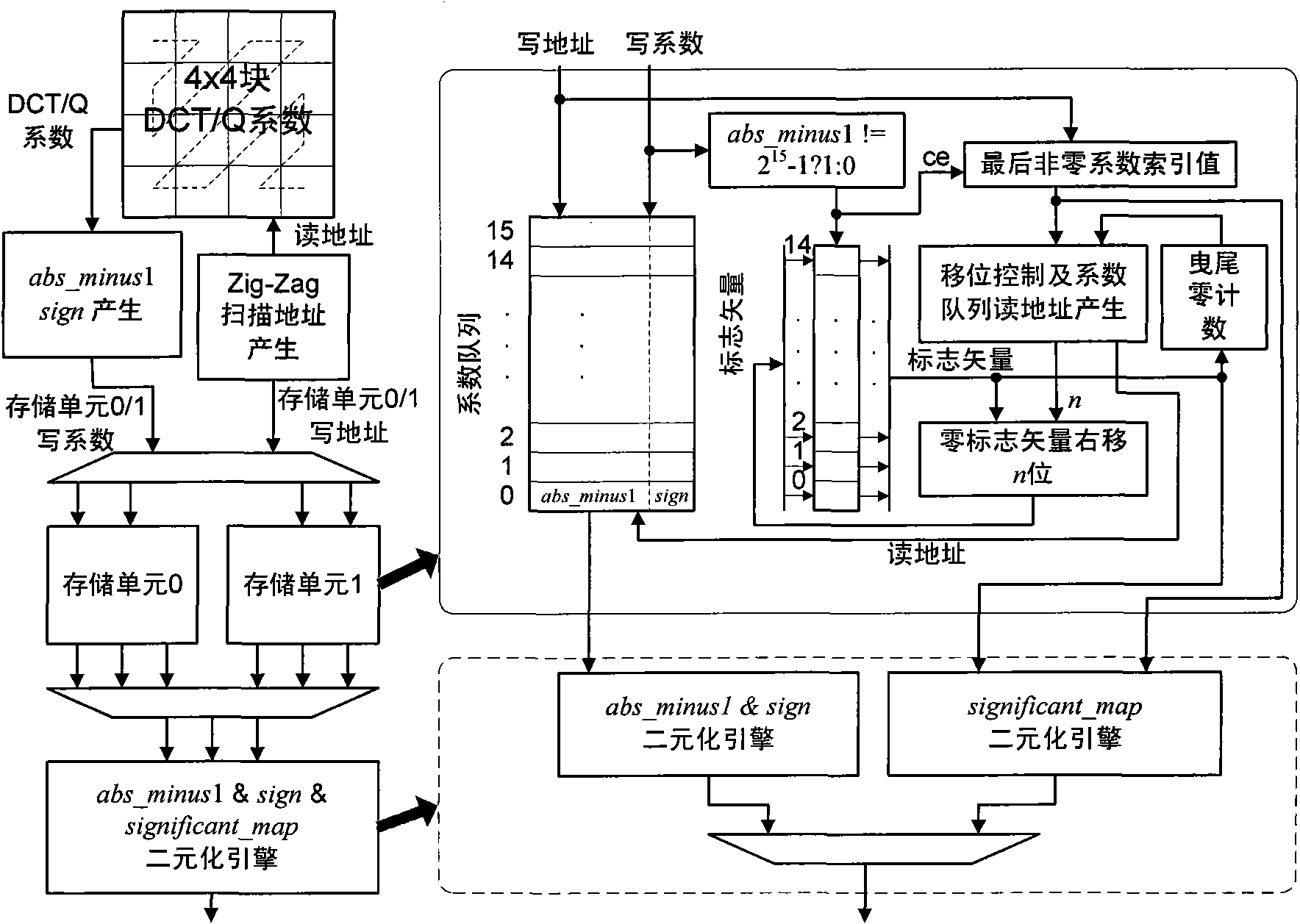
Parallel encoding realization circuit and encoding method based on CABAC (Context-based Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding) in H.264/AVC (Advanced Video Coding)
ActiveCN101951516AAvoid stagnationSolve Computational BottlenecksTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationParallel encodingContext model
The invention discloses a parallel encoding realization circuit and an encoding method based on CABAC (Context-based Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding) in H.264 / AVC (Advanced Video Coding). The parallel encoding realization circuit comprises a binary engine, a context model engine, a parallel normalization engine and an RBSP (Remote Batch Station Processor) code stream generation engine, wherein the binary engine is used for executing a parallel normalization operation; the context model engine is used for executing context read and updating operation of two bits per period; the parallel normalization engine is used for executing the normalization operation of two bits per period; and the RBSP is used for generating an RBSP output code stream. The binary engine and the context model engine are connected in a three-writing, two-reading and first-in, first-out queue; and the parallel normalization engine and the RBSP code stream generation engine are connected in a two-writing, one-reading and first-in, first-out queue. The invention ensures that processing speeds of the binary engine, the normalization engine and the RBSP code stream generation engine are matched, avoids productionline stagnancy and solves the problems of unbalanced throughput rates among various levels of processing engines and calculation bottleneck initiated by correlation of a coding interval, coding lowerlimit normalization and a code stream production process.
Owner:CERTUS NETWORK TECHNANJING
Parallel video coding based on block size
InactiveUS20120014436A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureParallel encoding
Owner:SHARP KK
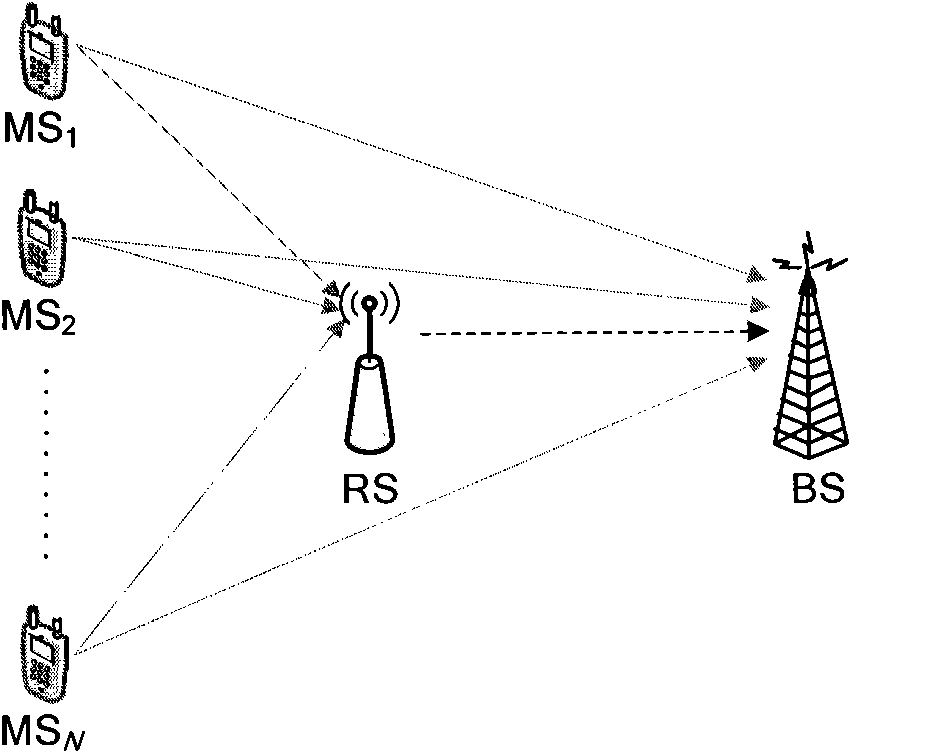
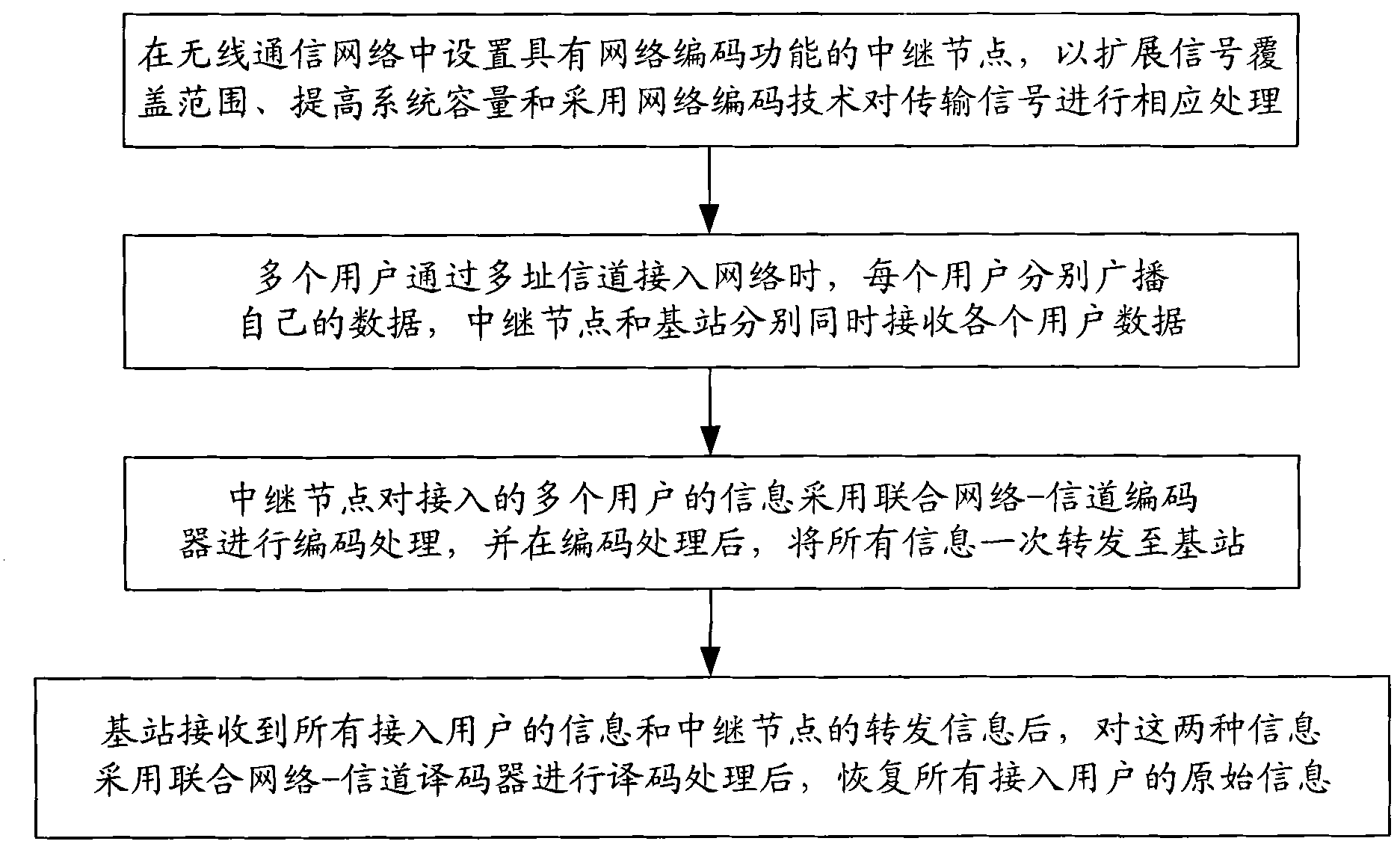
Multi-user network coding communication method with high-speed parallel encoding and decoding structure
InactiveCN101867451ASolve the problem of simultaneous network encodingGreat interleaving gainError preventionParallel encodingOriginal data
The invention discloses a multi-user network coding communication method with a high speed parallel encoding and decoding structure, which comprises the following steps: in a wireless relay network, multiple accessed user information is integrally interweaved by a relay node, serial / parallel conversion is carried out on the interweaved sequence, multiple groups of converted parallel data are input to a high speed parallel encoder to be encoded, and finally encoded data is broadcasted, thus realizing network encoding. A base station carries out teration decoding by means of a combined network-channel decoder according to original data broadcasted by users and data obtained by network encoding and channel encoding and forwarded by the relay node to obtain the original information of the users. The decoder of the base station comprises two parallel decoder groups, i.e. a user decoder group and a relay decoder group; iteration decoding is realized through transmitting soft information between two parallel decoder groups, thus not only recovering the original information of all accessed users but also improving decoding reliability and reducing decoding time delay. By adopting the method, the relay uplink transmission efficiency and the quality of transmission signal are improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
A device and method for low-density checksum LDPC parallel coding
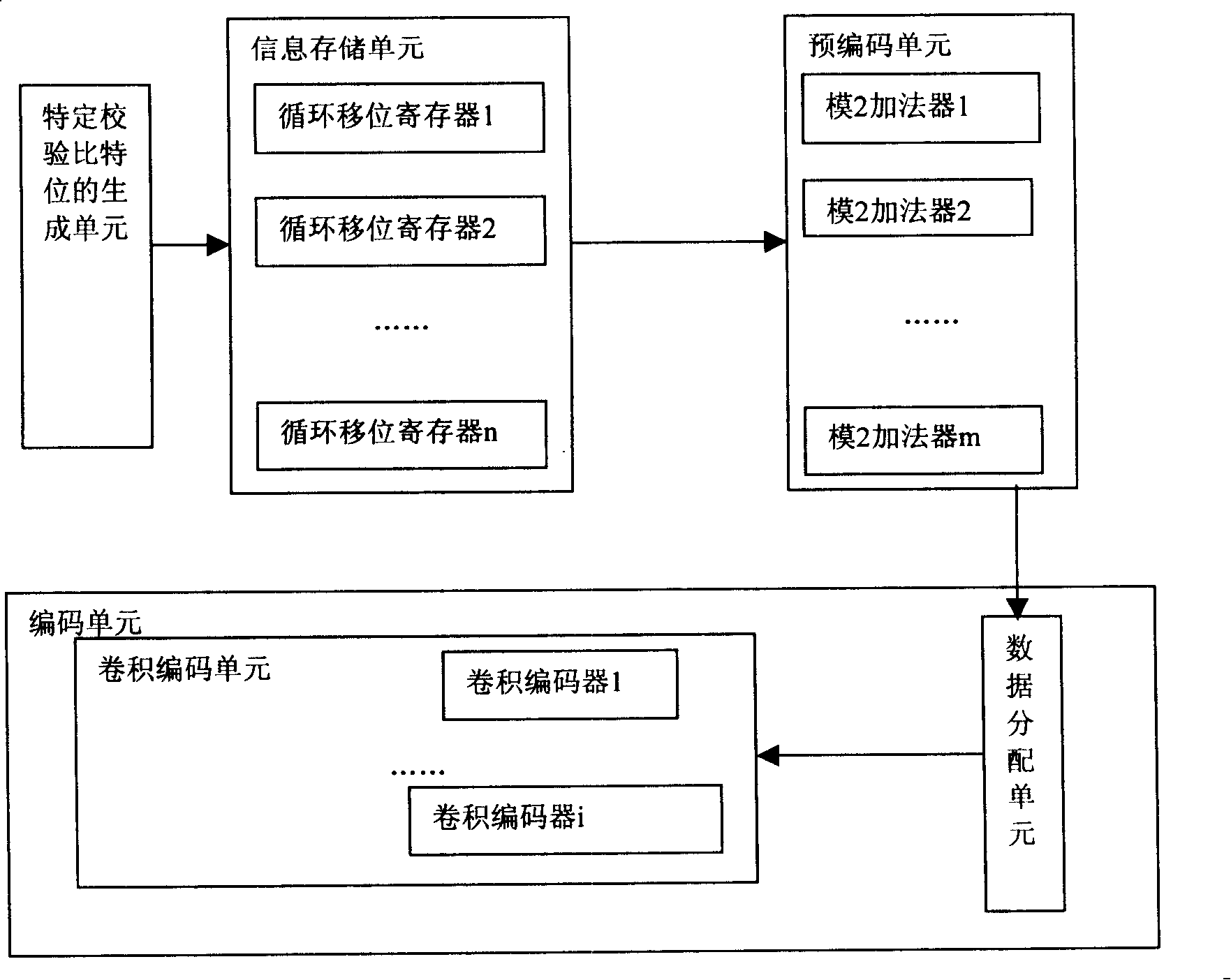
InactiveCN101192833AReduce complexityImprove scalabilityError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsShift registerParallel encoding
The invention relates to the communications field and provides parallel encoding device and a method for a low density parity-check code (LDPC). By adopting the practice of step-by-step encoding combined with the serial-parallel approach, a concatenated encoding scheme with linear complexity combining with pre-encoding and parallel convolution coding structures is provided thereby. The encoding device for realizing the encoding scheme mainly comprises an information storage unit, a pre-encoding unit and an encoding unit (comprising a data distribution unit and a convolution coding unit) as well as a v (0) verification bit generating unit. The encoding device of the invention adopts a circular shift register and a model 2 adder, which is easy to realize and avoid multiplication operation of vector and matrix. Complexity of the encoding device is reduced. The encoding device provided by the invention features good expansibility. A plurality of basic encoders are used for parallel encoding so that encoding efficiency can be improved by many times compared with the single basic encoding device. Therefore, when hardware complexity permits, parallel structures can be applied as much as possible, which greatly improves encoding efficiency.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Method and apparatus for coding bits of data in parallel
InactiveUS20030101401A1Reduce encoding delayIncrease delayError correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionComputer architectureCode point
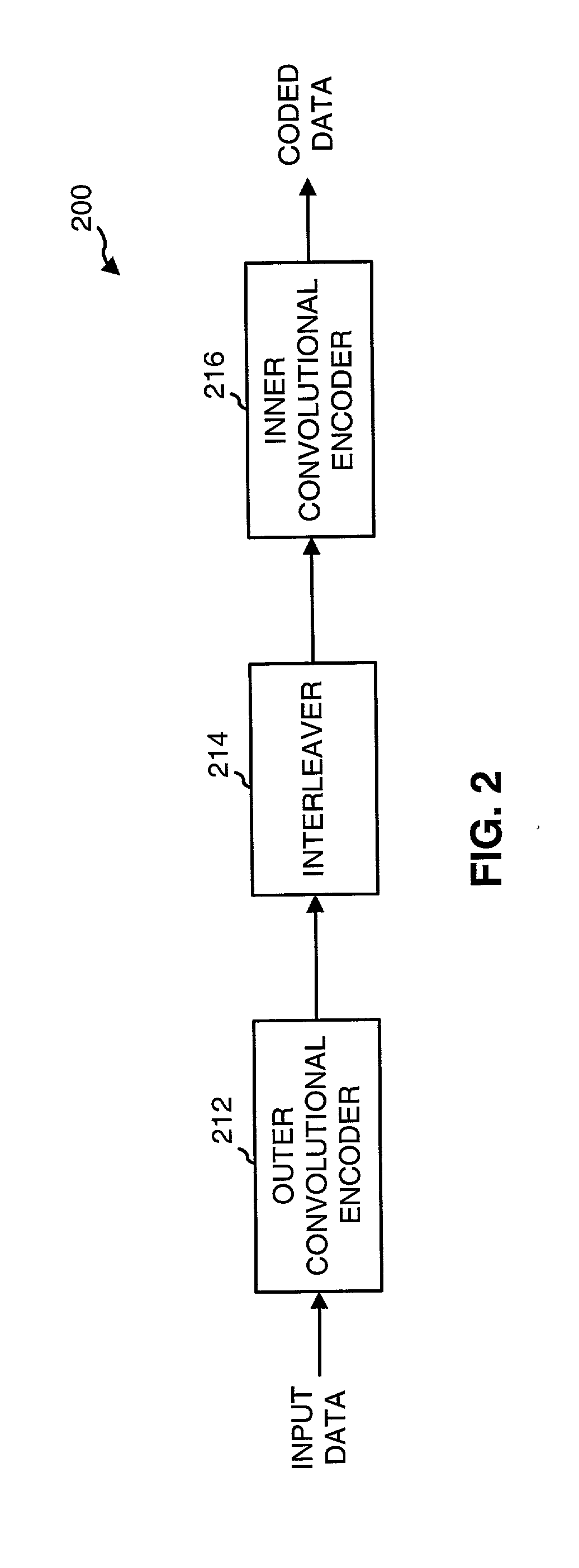
A concatenated encoder capable of coding multiple data bits in parallel and including a first (outer) encoder, a memory, and a second (inner) encoder coupled in cascade. The first encoder receives and codes M data bits in parallel in accordance with a first coding scheme to generate MR code bits. The memory receives and stores unpunctured ones of the MR code bits from the first encoder. The second encoder receives and codes N code bits in parallel in accordance with a second coding scheme to generate coded data. M and N can be any values (e.g., M>=8, N>=4). Each encoder can be a (e.g., a rate ½) convolutional encoder that implements a particular polynomial generator, and can be implemented with one or more look-up tables, a state machine, or some other design.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
CRC encoding circuit, CRC encoding method, data sending device and data receiving device
InactiveUS6934902B2Reduce the numberCode conversionError detection onlyParallel encodingParallel computing
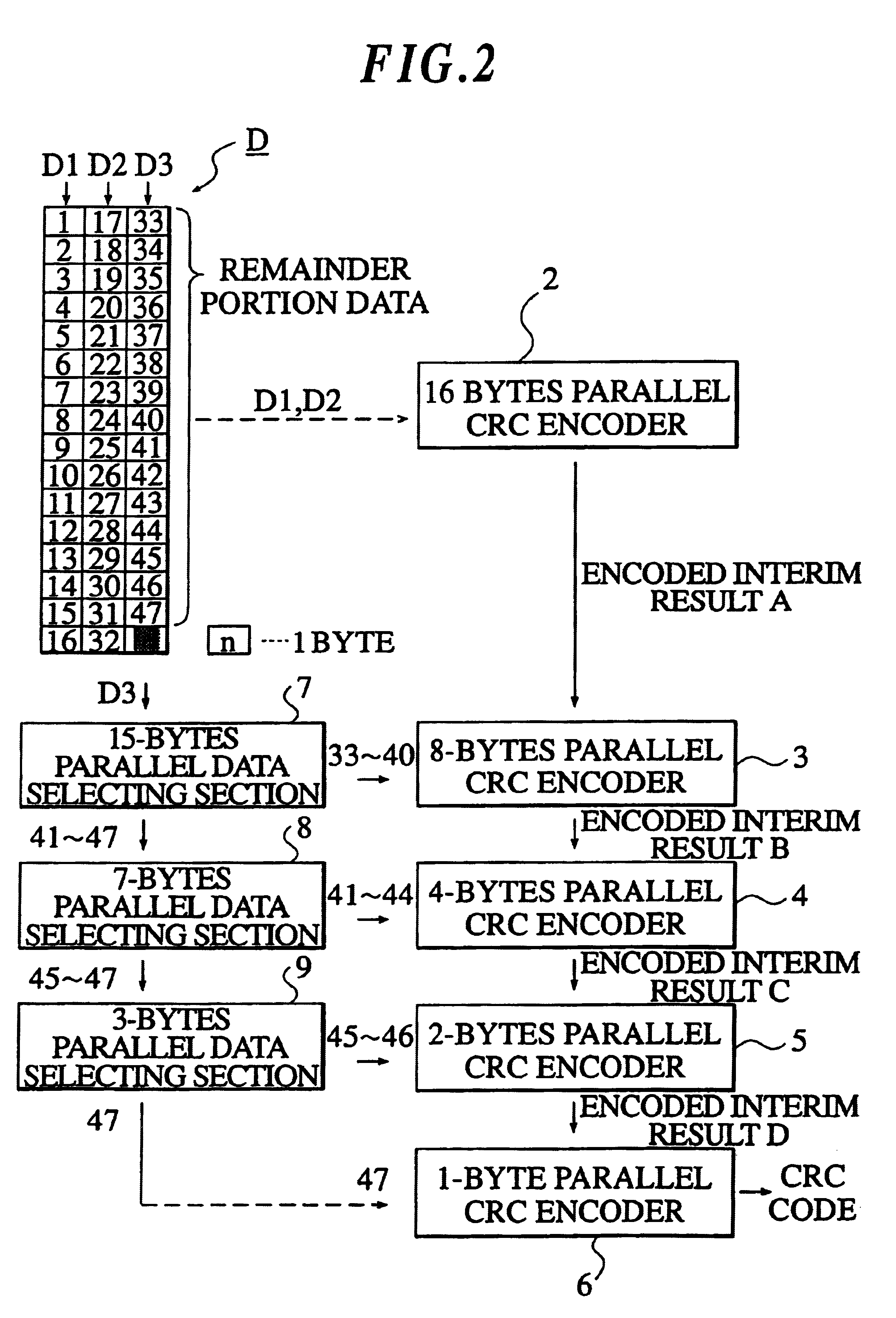
A CRC encoding circuit for generating CRC bits in accordance with initial parallel data having remainder portion data in a last column of the initial parallel data. A first parallel encoding unit is included for generating first CRC bits in accordance with the initial parallel data other than the remainder portion data. A CRC bits selector selects second CRC bits having predetermined number of bytes, from the first CRC bits generated by the first parallel encoding unit. A parallel data selector selects second parallel data having the same number of bytes as the second CRC bits, from the remainder portion data. A second parallel encoding unit generates third CRC bits in accordance with the second CRC bits and the second parallel data
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Parallel video coding based on scan order
InactiveUS20120014439A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureVideo encoding
Owner:SHARP KK
Precoders for partial response channels
InactiveUS6718502B1Increase the minimum Euclidean distanceComplexity and minimized and reducedModification of read/write signalsData representation error detection/correctionComputer hardwareBCJR algorithm
Precoders and their corresponding logic schemes, together with a method of using the precoders and their schemes to generate a media code sequence of symbols for data storage channels, with partial response equalization and a multilevel encoding / modulation scheme. Partial responses are defined by the classical and modified target polynomials, while the multilevel encoding / modulation schemes include: 1) Structured Set Partitions (SSP), 2) a set of conventional block codes with different error correcting capabilities, and 3) a variety of iterative decoding such as the List Trellis Decoder (LTD), the BCJR algorithm, and soft decoding of low-density parity check codes. The precoders are derived from the SSP's, and combined with conventional ECC encoders designed for error detection, or error correction, or both. A cascade of parallel ECC encoders, followed by an SSP precoder, increases the minimum Euclidean distance between different media code sequences of symbols, and as a result gives lower bit error rates after decoding.
Owner:DATA STORAGE INST
Information processing apparatus and information processing method
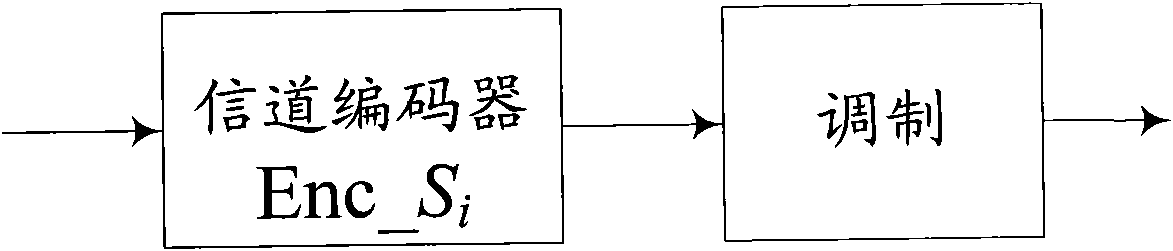
ActiveUS20080056358A1Easy data conversionBoost efficiency of data dataTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationInformation processingParallel encoding
An information processing apparatus for encoding a baseband signal, the information processing apparatus includes: a data splitting block; an encoder; a control block; and a splicing block. The data splitting block is configured to acquire the baseband signal before splitting it into predetermined encoding sections. The encoder is configured to generate encoded streams by parallelly encoding a continuous plurality of the encoding sections acquired by the data splitting block from the baseband signal. The control block is configured to control the encoder to perform the parallel encoding in a manner subject to predetermined constraints. The splicing block is configured to splice the encoded streams generated by the encoder.
Owner:SONY CORP
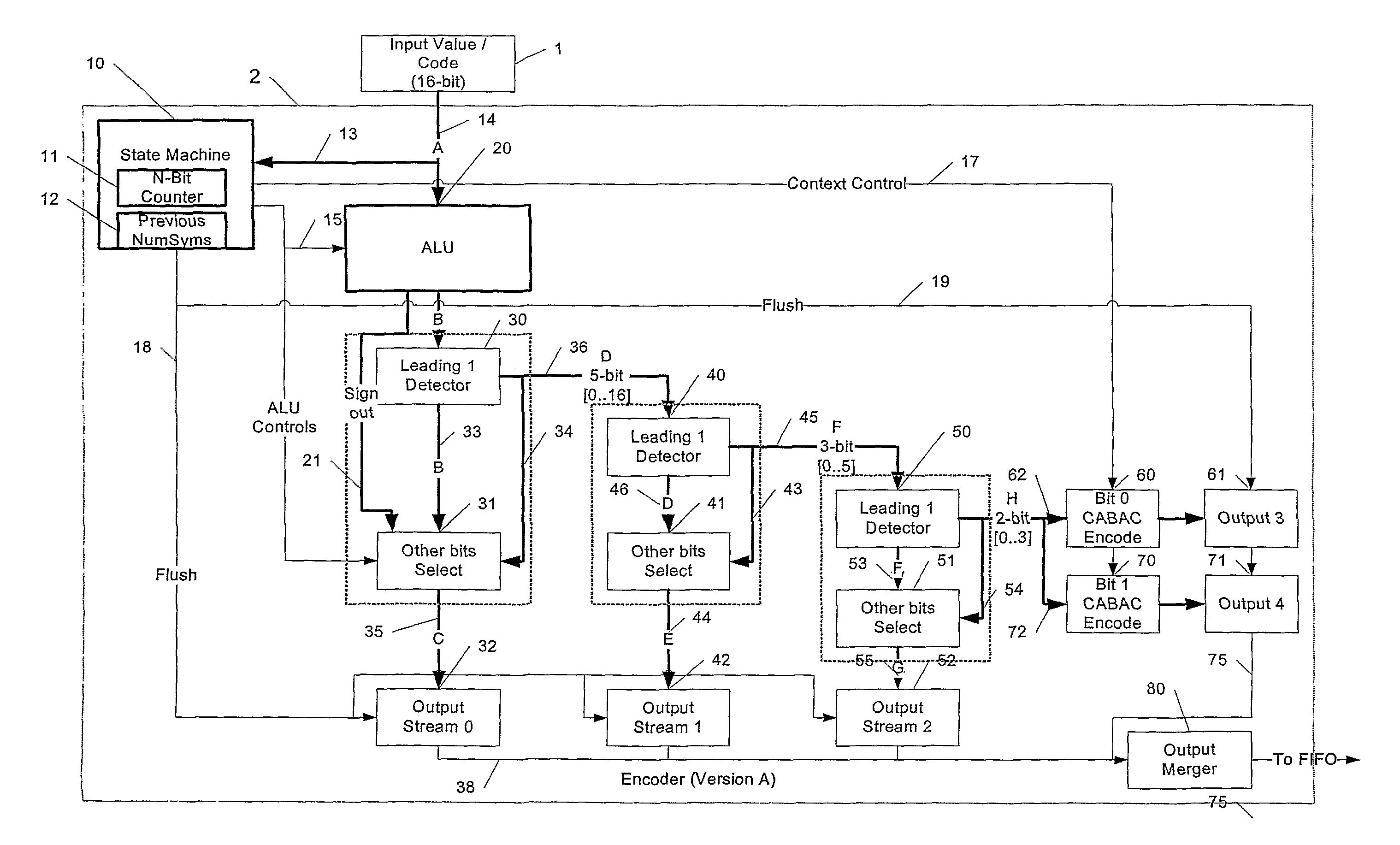
Method of decoding data and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS7796065B2Low costImproving pipeliningCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer hardwareParallel encoding
Incoming decoded data (1), for example from an H264 decoder, is fed to an encoder unit (2) that entropy encodes the decoded data using a parallel encoding scheme that includes context-based arithmetic encoding. The syntax is chosen so that the context does not depend on the immediately previously encoded symbol. The output of the encoder (2) is fed to a FIFO memory whose output is fed to a complimentary decoder (4) whose output produces a delayed copy of the incoming decoded data (1).
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
Apparatus and method for encoding moving picture
InactiveUS20120263225A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionParallel encodingComputer science
An apparatus and method for encoding a moving picture. Since the apparatus includes a plurality of central processing units (CPUs), the apparatus may perform parallel encoding even for a H.264 video encoder having high complexity. In particular, since the apparatus still uses information about blocks around a macroblock even at a boundary of a slice, the apparatus may improve the efficiency of a video codec.
Owner:MEDIA EXCEL KOREA
Method of coding and decoding images, coding and decoding device and computer programs corresponding thereto
ActiveUS20140016700A1Avoid large quantitiesEasy to compressColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionTheoretical computer scienceComputer program
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
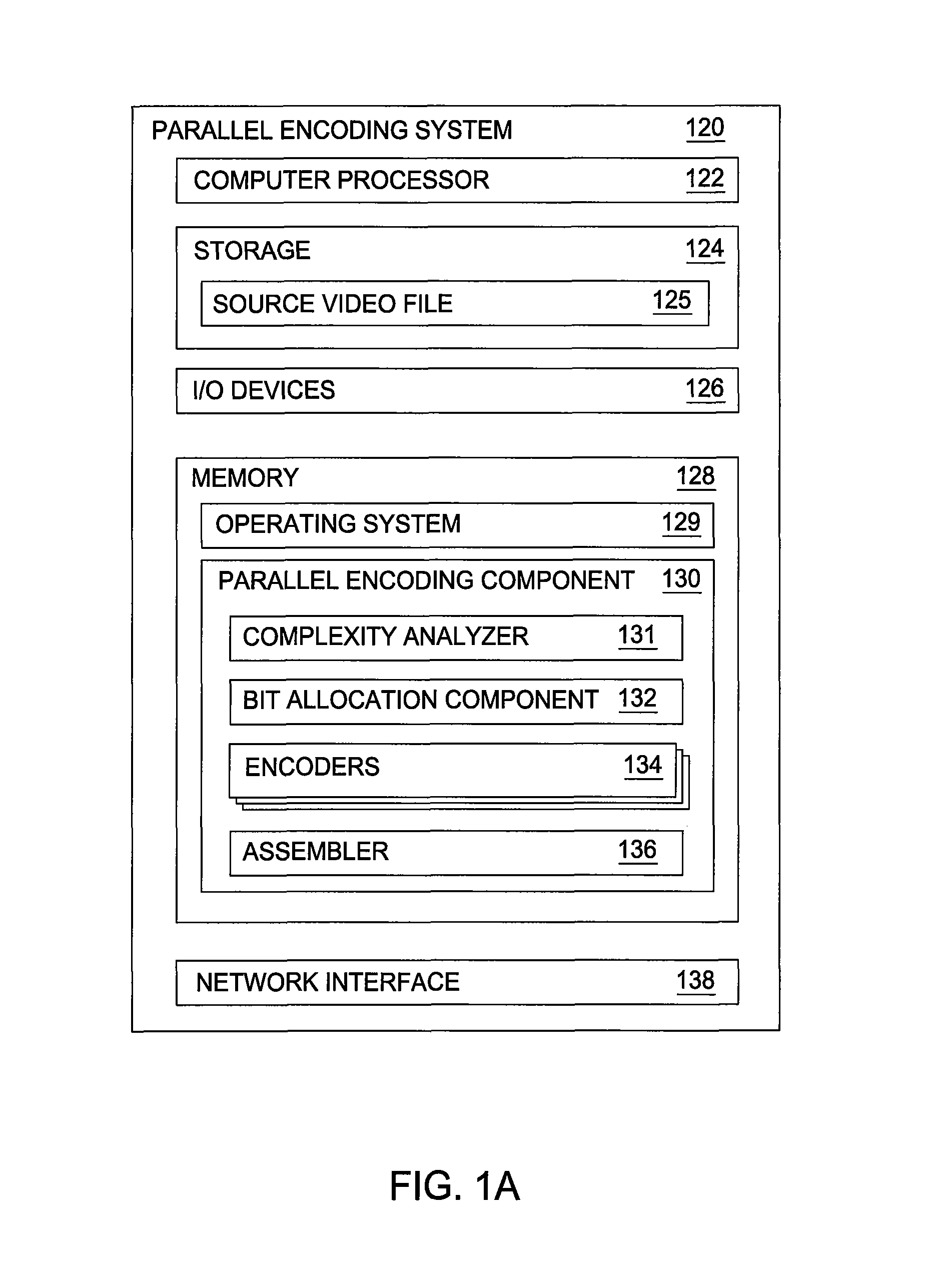
Parallel video encoding based on complexity analysis
ActiveUS8837601B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer graphics (images)Video encoding
Embodiments of the invention provide techniques for encoding chunks of a video file in parallel. Embodiments may divide a source video file into a plurality of chunks, and may encode each chunk at a rate based upon complexity data associated with the chunk. The encoded chunks may then be reassembled to produce an encoded video file.
Owner:NETFLIX
Multiple parallel encoders and statistical analysis thereof for encoding a video sequence
InactiveUS7072393B2Improve picture qualityIncrease the compression ratioTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionParallel encoding
System and method are provided for optimally encoding a sequence of video frames using image statistics collected from multiple encoders connected in parallel, each encoder employing a different set of encode parameters. The image statistics are used to select an optimum set of encode parameters for use in encoding the sequence of video frames in a subsequent encode subsystem stage. As an alternative, multiple buffers are connected to the outputs of the multiple, parallel connected encoders, with the encoded stream from the encoder employing the optimum set of encode parameters selected for output as the bitstream of encoded video data.
Owner:IBM CORP
Parallel video coding based on mapping
InactiveUS20120014440A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureParallel encoding
Owner:SHARP KK
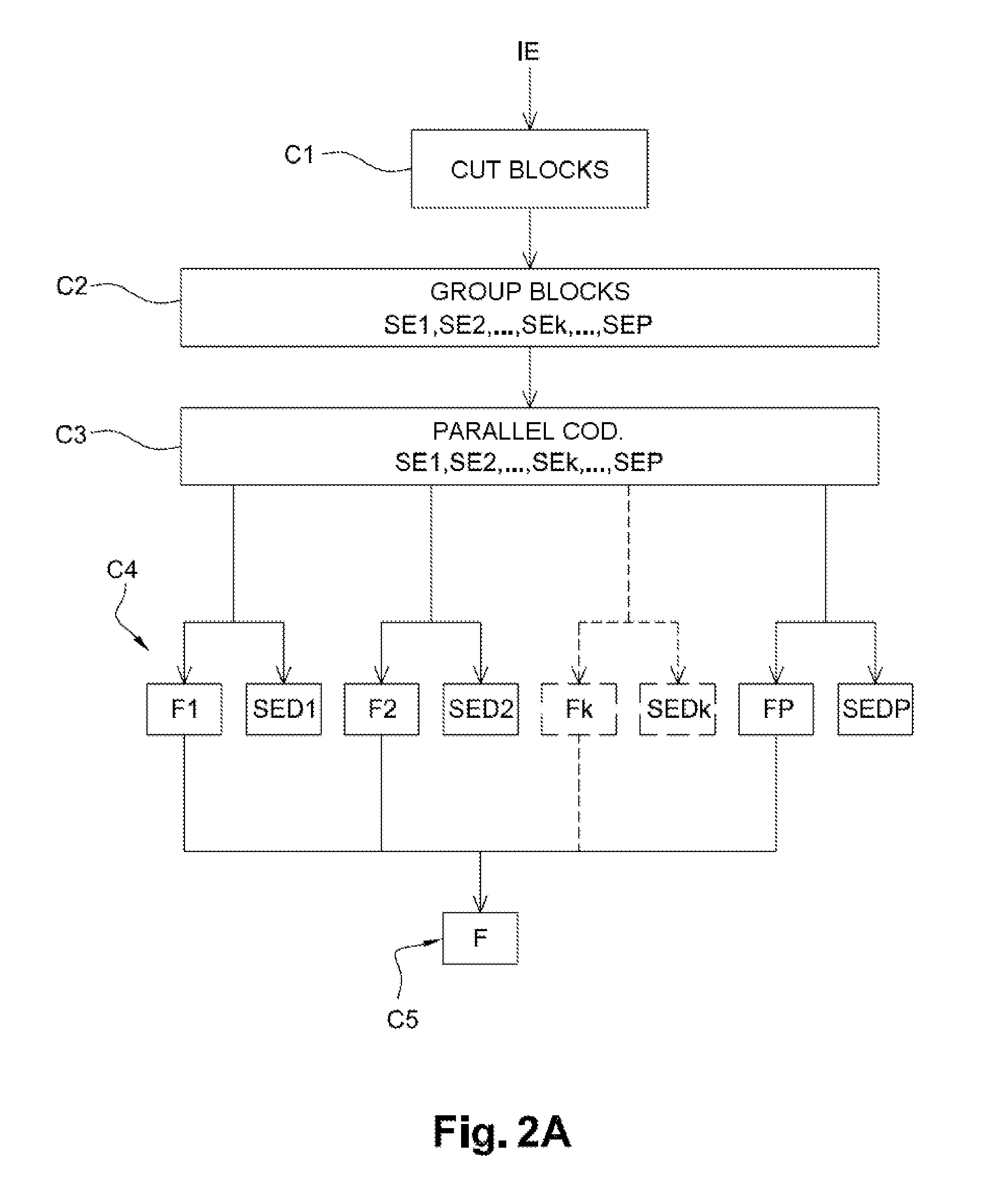
Segmented parallel encoding with frame-aware, variable-size chunking
ActiveUS9432704B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionParallel encodingTranscoding
The subject matter herein generally relates to transcoding content, typically audio / video files though not limited to such, from one version to another in preparation for online streaming or other delivery to end users. Such transcoding may involve converting from one format to another (e.g., changing codecs or container formats), or creating multiple versions of an original source file in different bitrates, frame-sizes, or otherwise. A transcoding platform is described herein that, in certain embodiments, leverages distributed computing techniques to transcode content in parallel across a platform of machines that are preferably idle or low-utilization resources of a content delivery network. The transcoding system also utilizes, in certain embodiments, improved techniques for segmenting the original source file so as to enable different segments to be sent to different machines for parallel transcodes.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
High speed syndrome-based FEC encoder and system using same
InactiveUS7509564B2Increase speedReduce complexityError preventionTransmission systemsComputer hardwareParallel encoding
A decoder, encoder and corresponding system are disclosed for providing fast Forward Error Correcting (FEC) decoding and encoding of syndrome-based error correcting codes. Three-parallel processing is performed by elements of the system. More particularly, in an illustrative embodiment, a decoder performs three-parallel syndrome generation and error determination and calculations, and an encoder performs three-parallel encoding. Low power and complexity techniques are used to save cost and power yet provide relatively high speed encoding and decoding.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
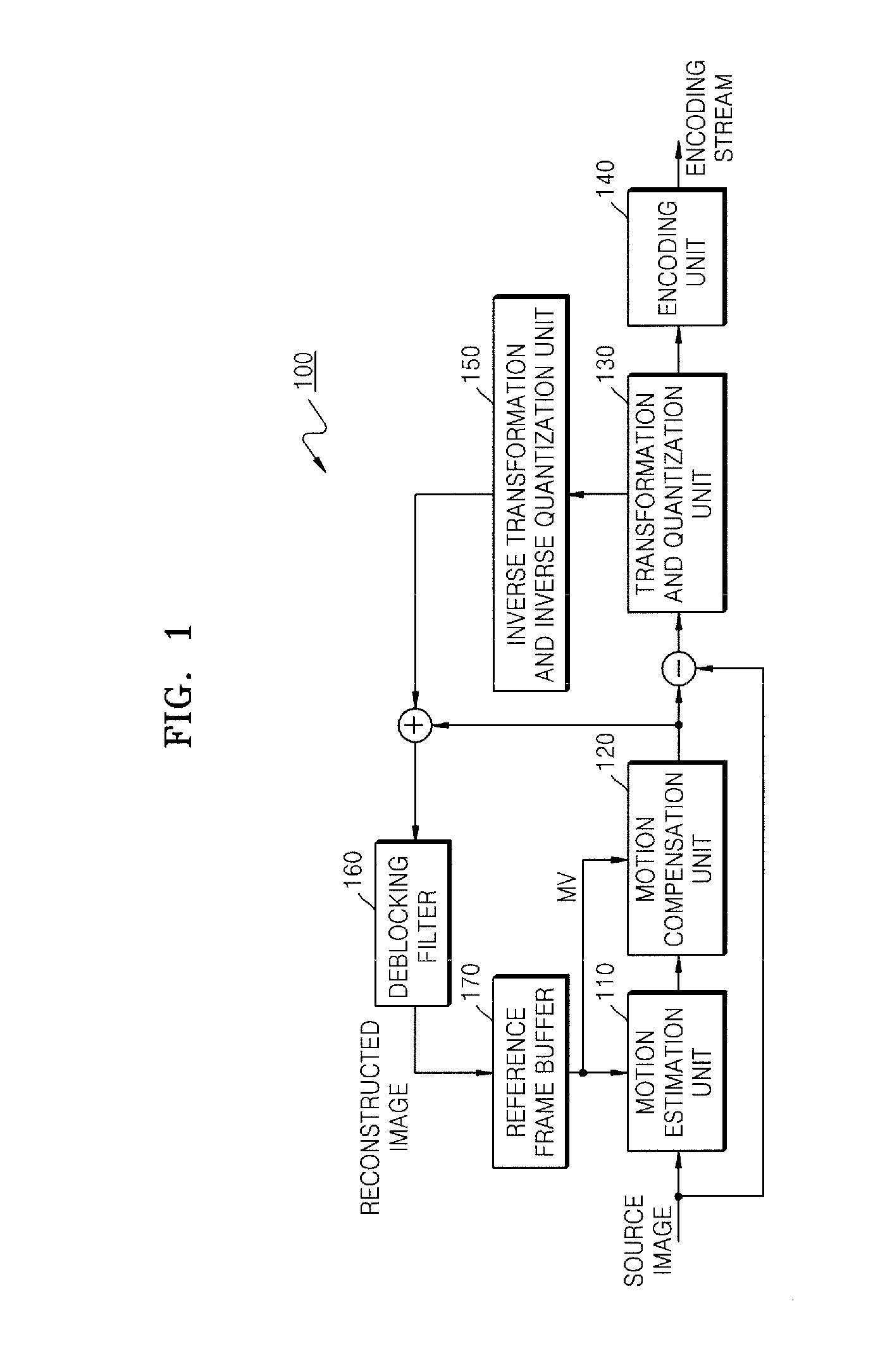
Image decoding device, image decoding method, image encoding device, and image encoding method
InactiveCN102550029ATelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationParallel encodingParallel processing
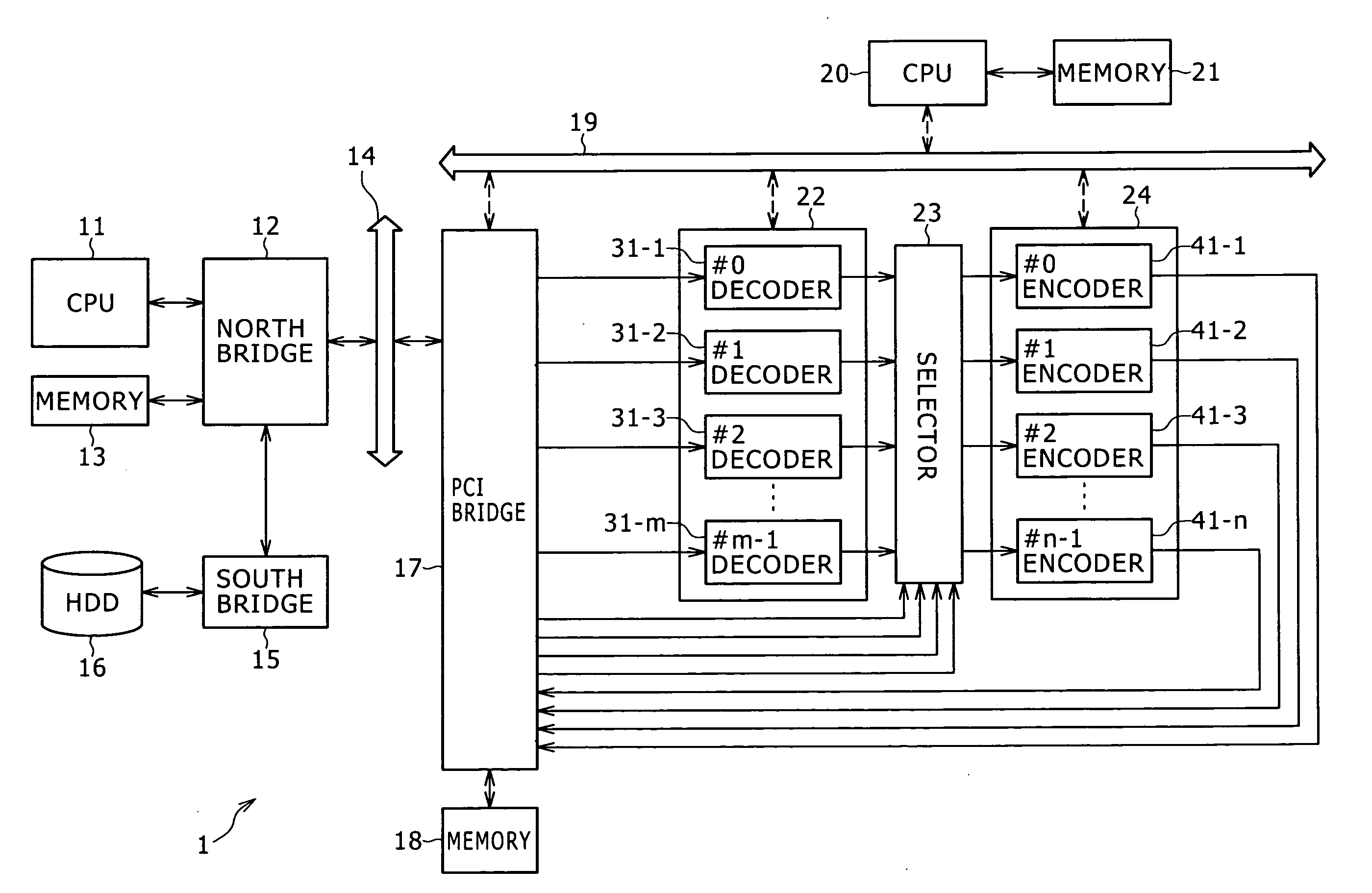
This image decoding device (100), which appropriately executes parallel encoding processing by a simple configuration, is provided with: a stream dividing control unit (140) that designates a region to be processed, and selects a portion of a divided stream on the basis of the disposition of the region to be processed; M stream dividing units (130) that generate MN divided streams by means of executing stream dividing processing in parallel with respect to M designated regions to be processed; and N decoding engines (120) that, in parallel, decode a portion of each of N divided streams that contain the selected portion. For each divided stream, the stream dividing units (130) reconfigure, as a new slice, a slice portion group comprising at least one slice portion allocated to the divided stream when a slice contained in the region to be processed is divided into a plurality of slice portions which are allocated to a plurality of divided streams.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Methods and apparatus for constant-weight encoding and decoding
InactiveUS6844833B2Lower latencyError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniques18-bitDriver circuit
Methods and apparatus for spreading and concentrating information to constant-weight encode of data words on a parallel data line bus while allowing communication of information across sub-word paths. In one embodiment, data transfer rates previously obtained only with differential architectures are achieved by only a small increase in line count above single ended architectures. For example, an 18-bit data word requires 22 encoded data lines for transmission, where previously, 16 and 32 lines would be required to transmit un-coded data with single-ended and differential architectures respectively. Constant-weight parallel encoding maintains constant current in the parallel-encoded data lines and the high and low potential driver circuits for the signal lines.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method of parallel video coding based on scan order
InactiveUS8879619B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureVideo encoding
Owner:SHARP KK
Parallel video coding based on same sized blocks
InactiveUS20120014437A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureVideo encoding
Owner:SHARP KK
Parallel entropy coding
ActiveUS20110235699A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionParallel encodingDigital image
Parallel coding of digital pictures is described. A digital picture is divided into two or more vertical sections. Two or more corresponding Stage 1 encoder units can perform a first stage of entropy coding on the two or more vertical sections on a row-by-row basis. The entropy coding of the vertical sections can be performed in parallel such that each Stage 1 encoder unit performs entropy coding on its respective vertical section and returns a partially coded Stage 1 output to a Stage 2 encoder unit. Each partially coded Stage 1 output includes a representation of data for a corresponding vertical section that has been compressed by a compression factor greater than 1. The Stage 2 encoder unit can generate a final coded bitstream from the partially encoded Stage 1 output as a Stage 2 output.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Method and circuit of high performance variable length coding and decoding for image compression
ActiveUS20080107349A1Improve performanceDecompressing in short timeCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionClock timeData stream
The differential value of the adjacent pixels is calculated firstly and is coded by a VLC coding. The VLC coding includes codes representing the Quotient and Remainder with a marker bit inserted in between. The divider is predicted with no code in the coded data stream. If three pixel components are presented in the same clock time, three VLC encoders and three VLD decoders are applied to encode and decode one pixel at a time. During encoding, both Remainder and Quotient of the same pixel component are encoded in parallel followed. During decoding, both Remainder and Quotient of the same pixel component are decoded in parallel and the results of the first pixel component are used a reference to decode the second pixel component which adopts the same decoding procedure and the decoded results of the second pixel component is used as reference to decode the third pixel component.
Owner:TAIWAN IMAGINGTEK
FPGA implementation method and apparatus of universal quasi-cyclic LDPC code encoder
ActiveCN108540139AOvercoming the problem of complex logical connectionsError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionComputer architectureParallel encoding
The invention discloses an FPGA implementation method and apparatus of a universal quasi-cyclic LDPC code encoder. According to the method disclosed by the invention, compromised quantitative calculation is performed according to the requirements of the number of cyclic blocks of a non-unit matrix portion of a generated matrix, the dimensionality of the cyclic block, a code length, a code rate, asystem clock and an encoding rate, so as to figure out the parallelism of a part of parallel encoding modules. The method not only has computational and configuration versatility, but also achieves good compromise between the coding rate and the number of consumed resources, thereby overcoming the problems that the encoding rate of a serial input encoder is too low, too many resources are consumedby a fully parallel input encoding circuit, it is not conducive to the reasonable use of the resources, and that the logic connection of a two-step encoding circuit is complicated.
Owner:ACADEMY OF BROADCASTING SCI STATE ADMINISTATION OF PRESS PUBLICATION RADIO FILM & TELEVISION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com