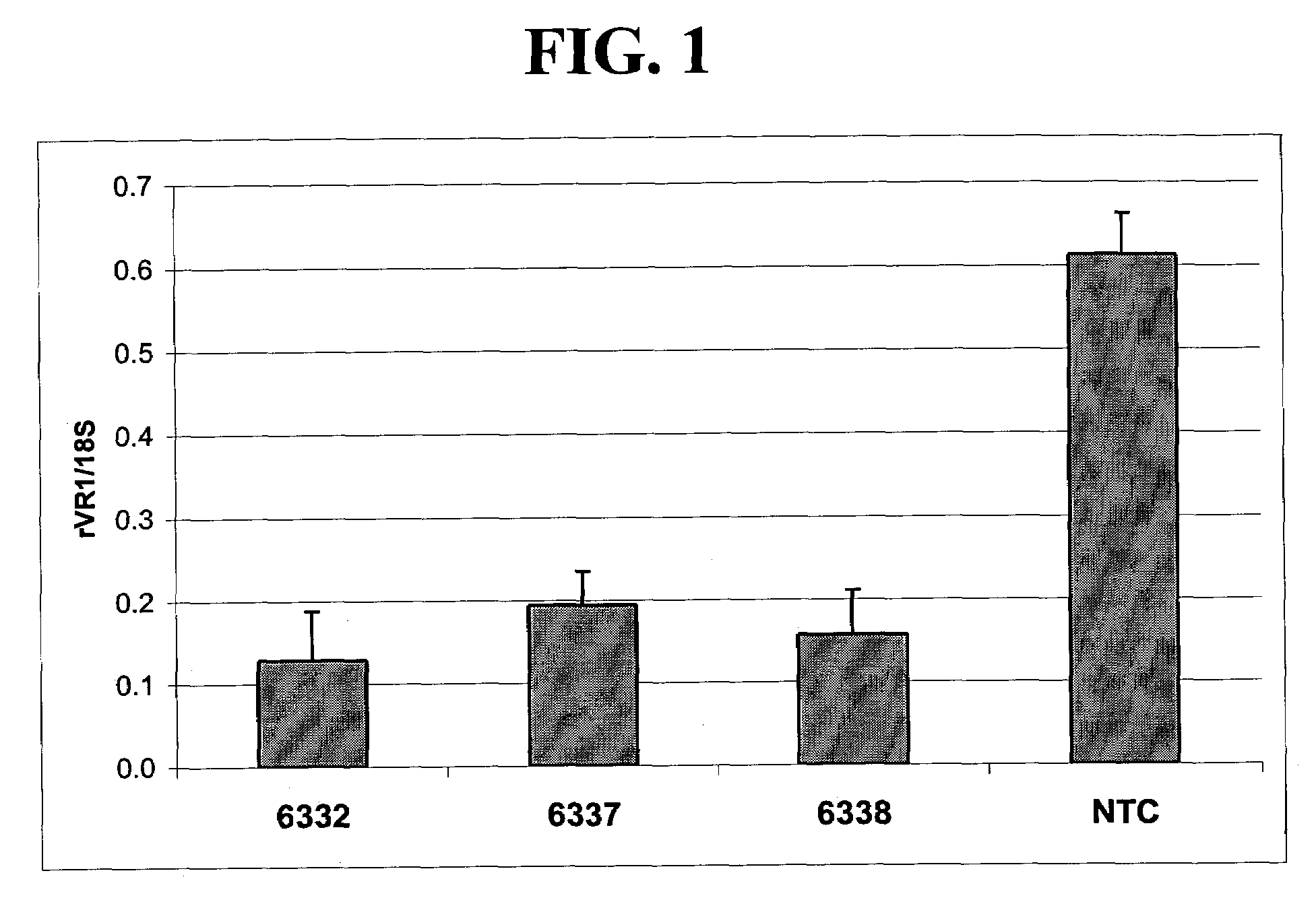
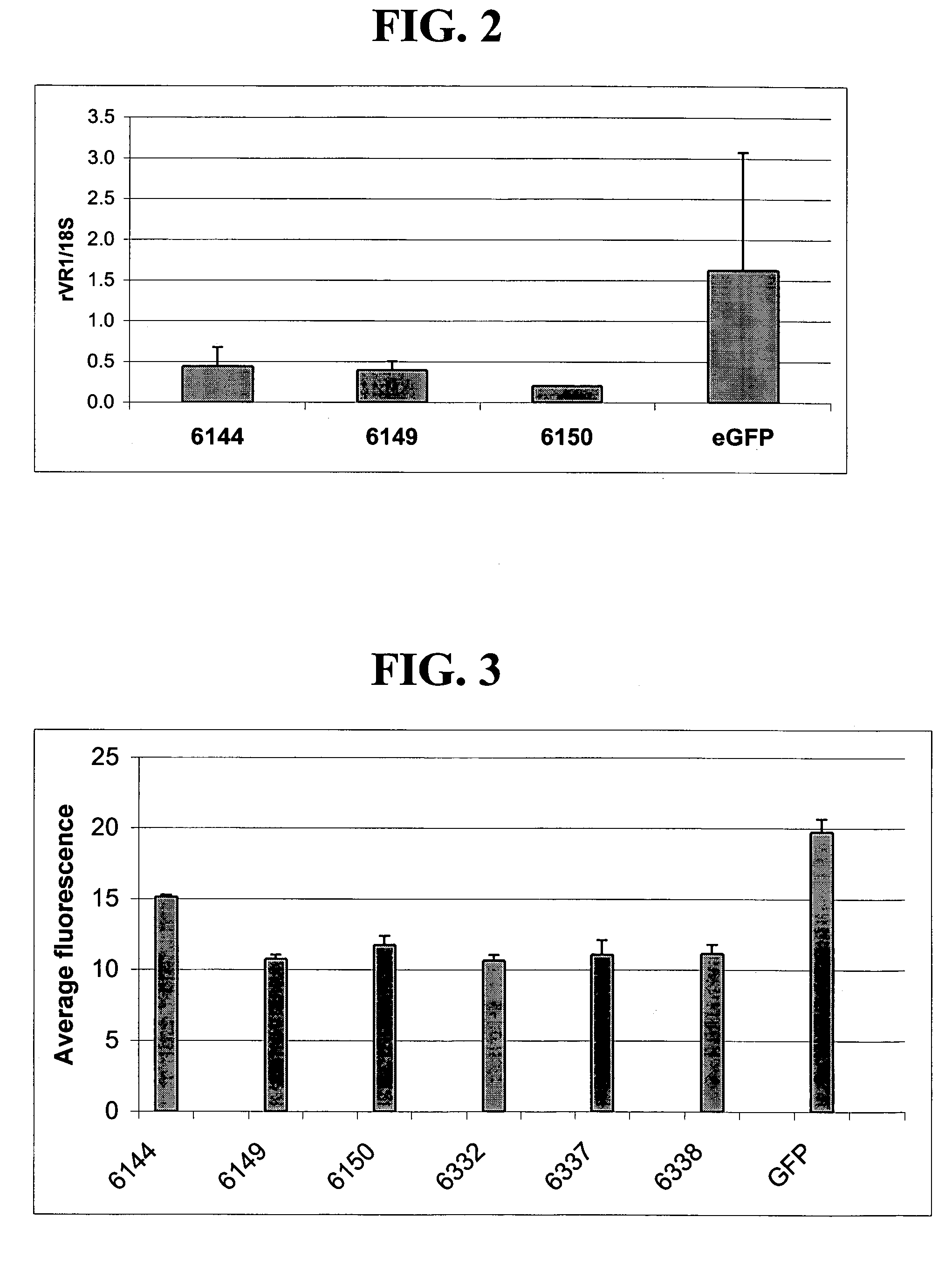
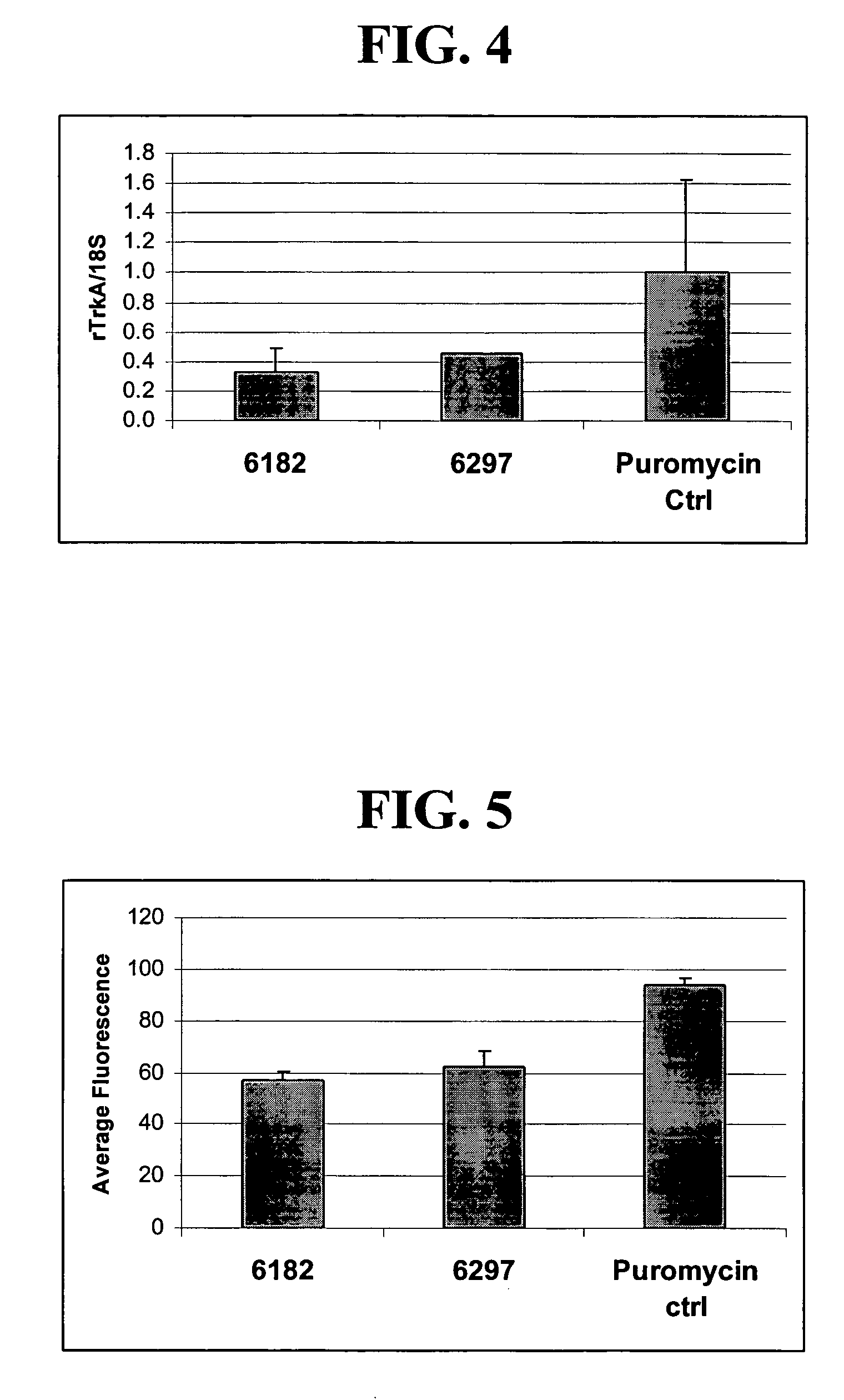
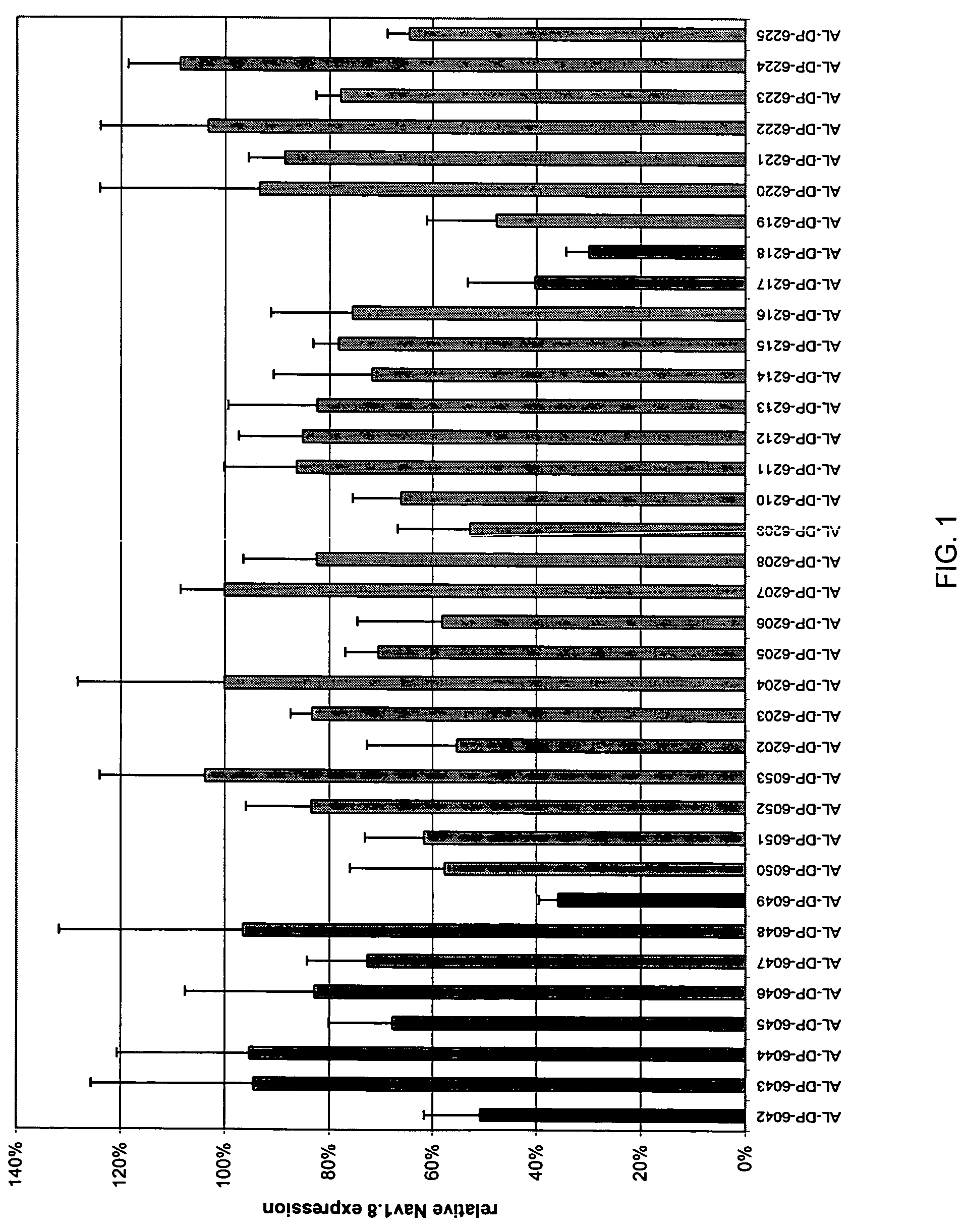
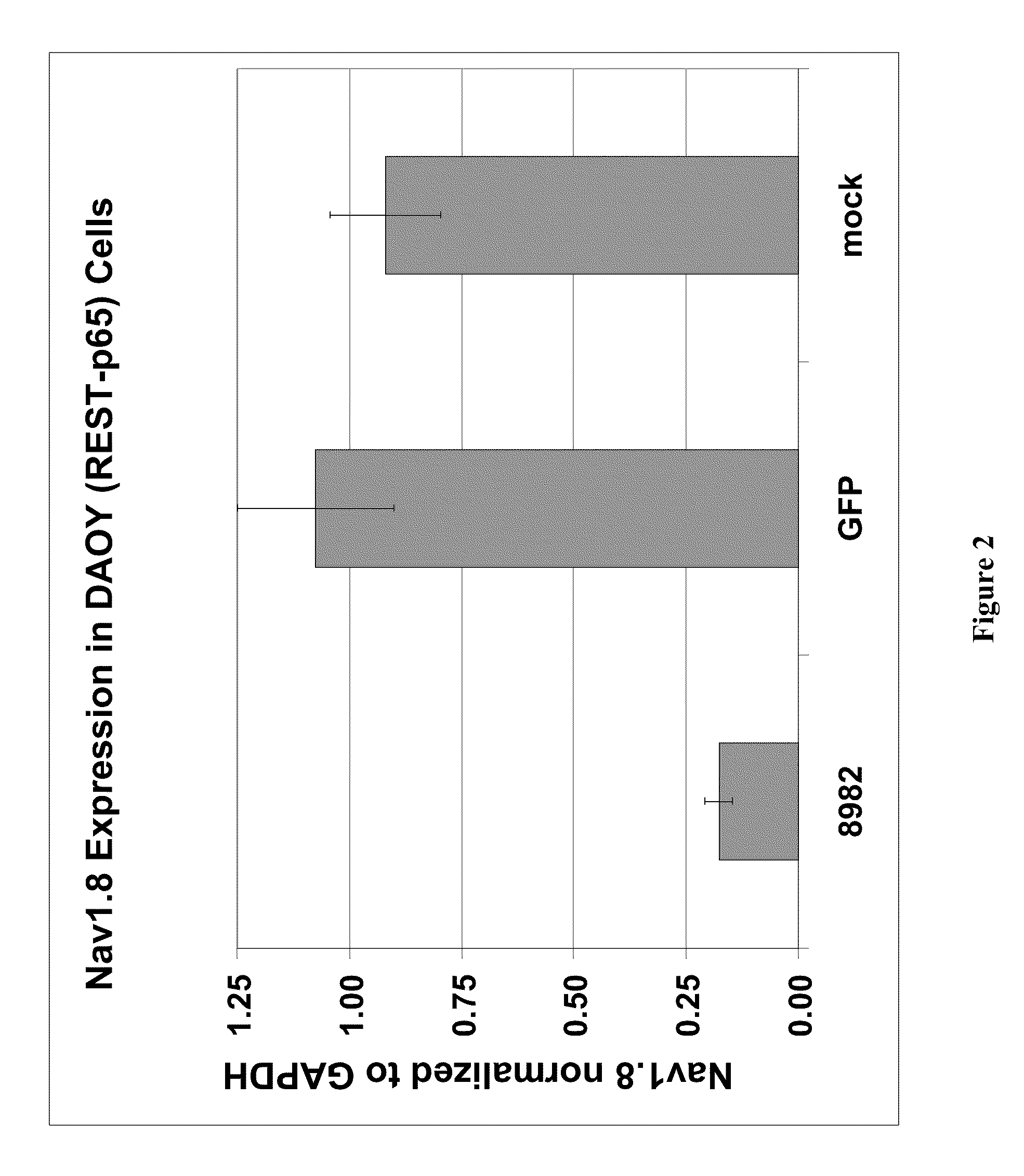
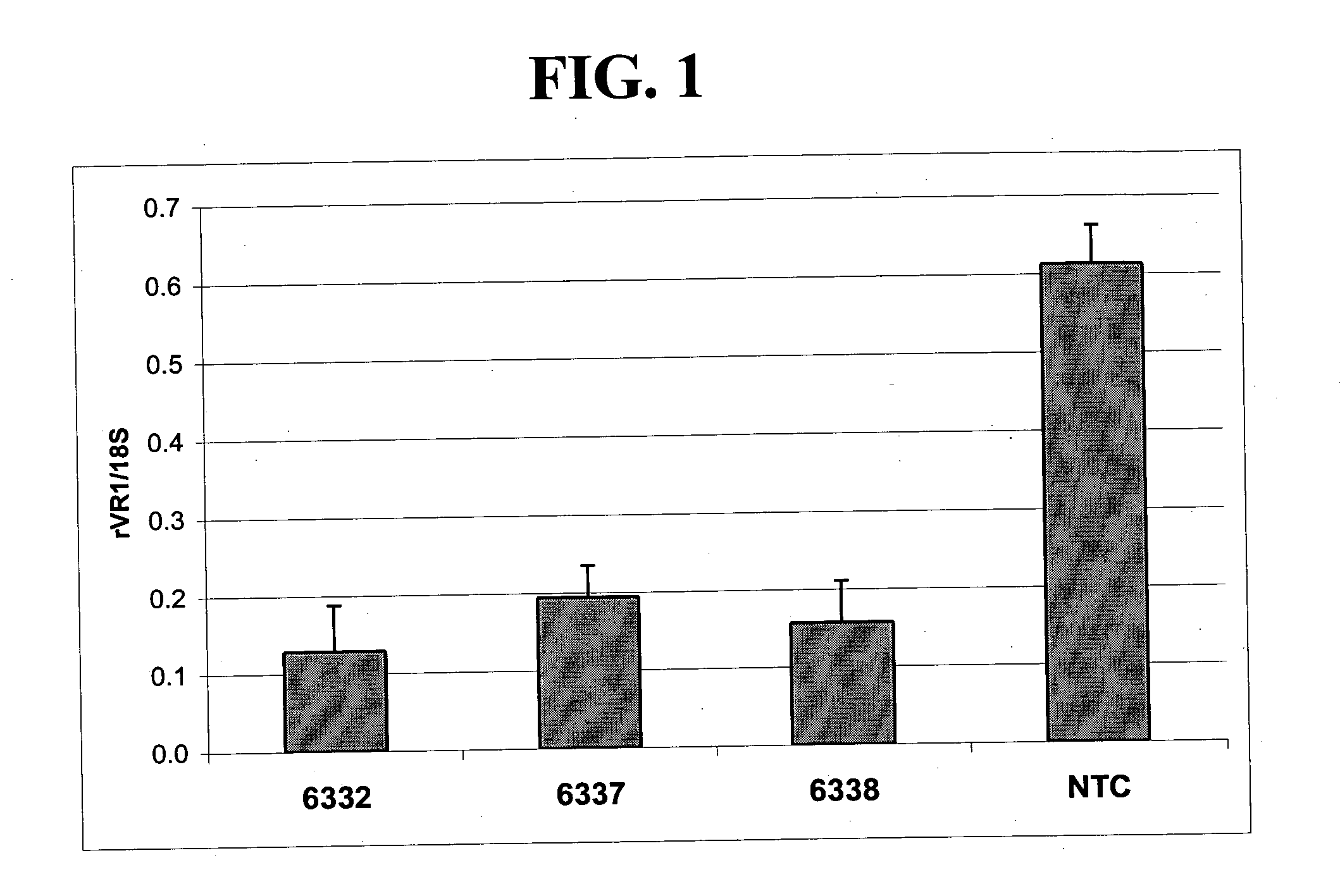
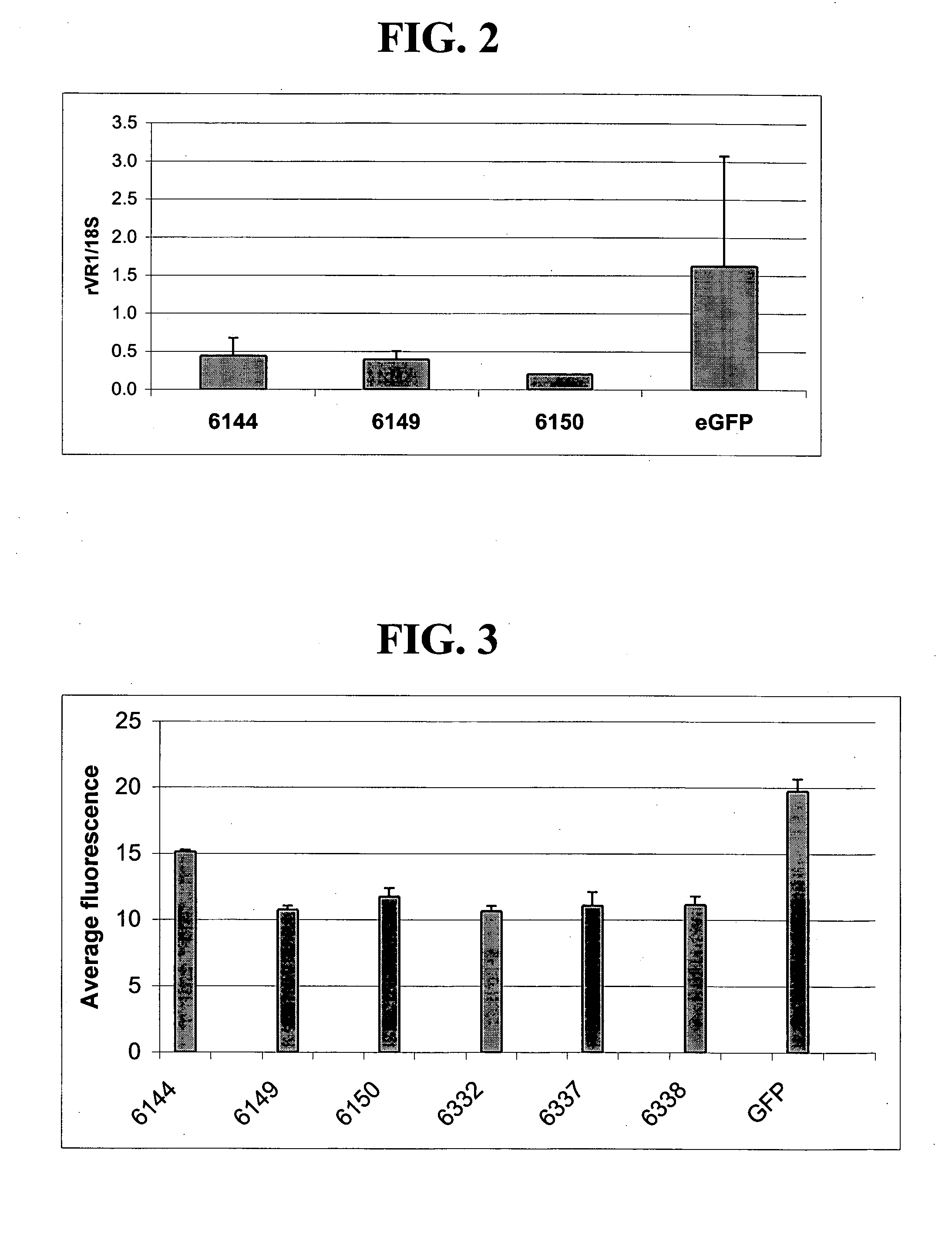
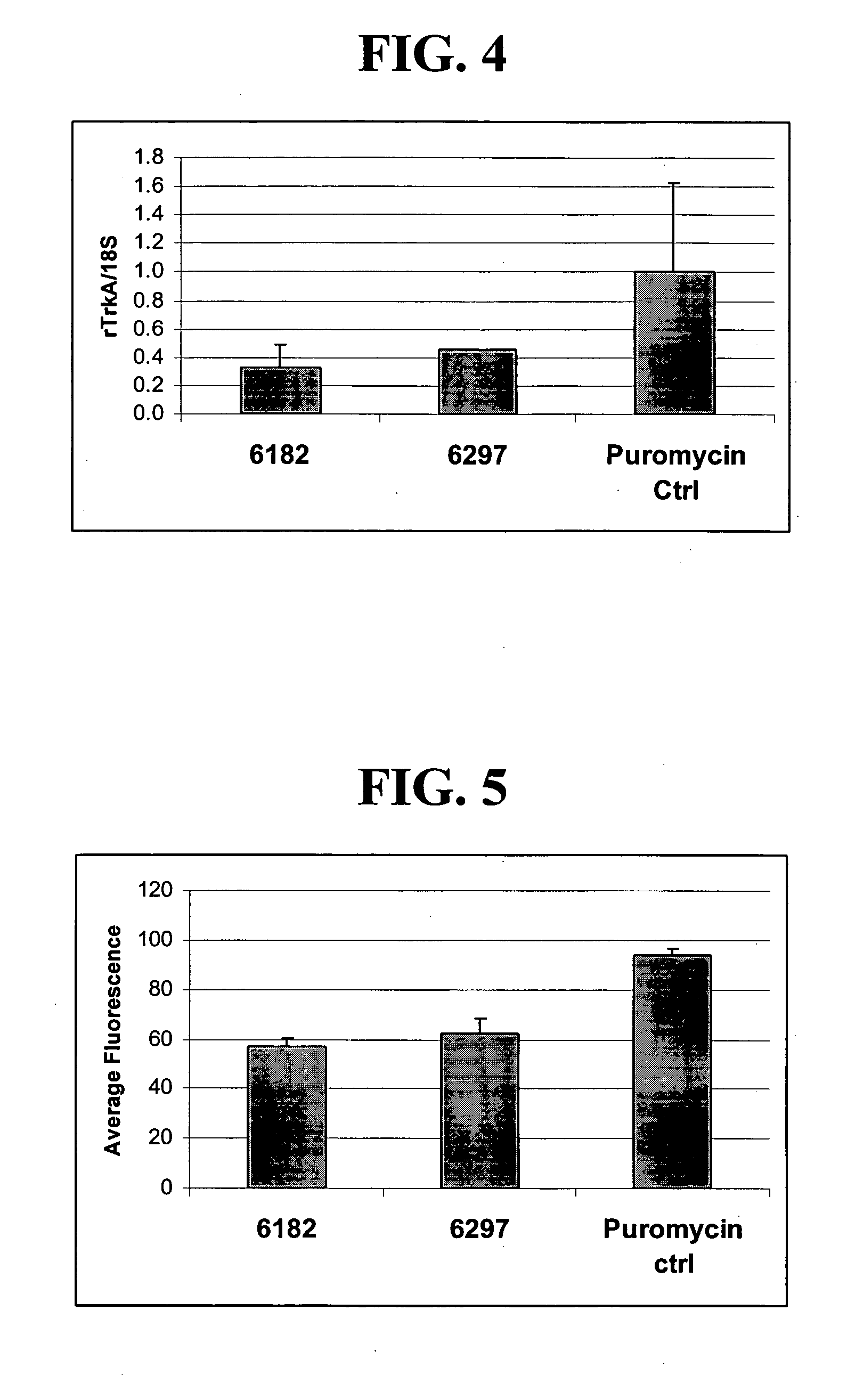
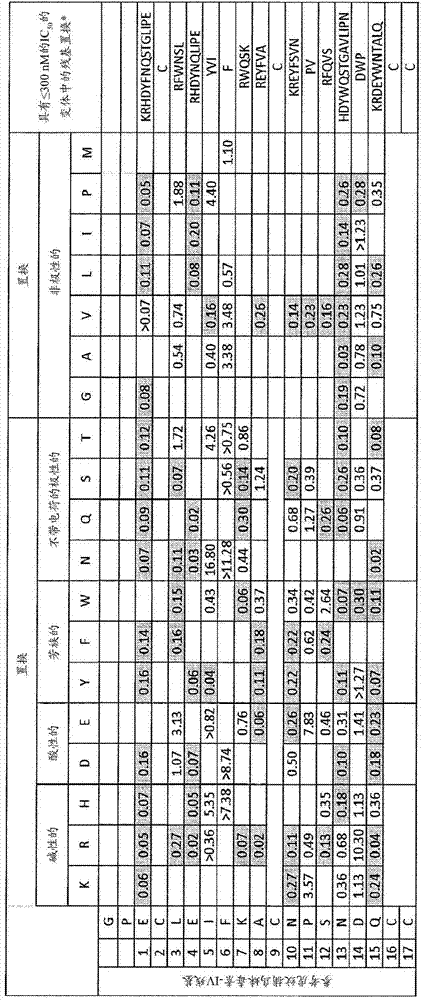
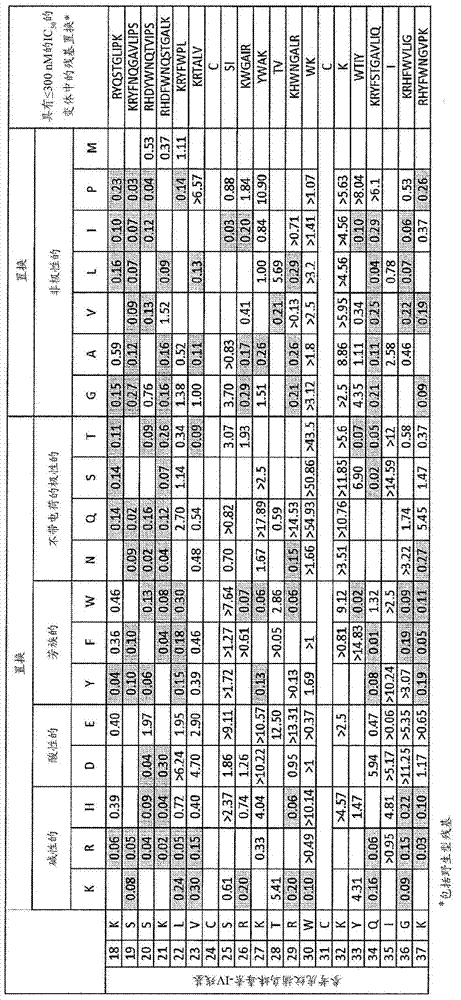
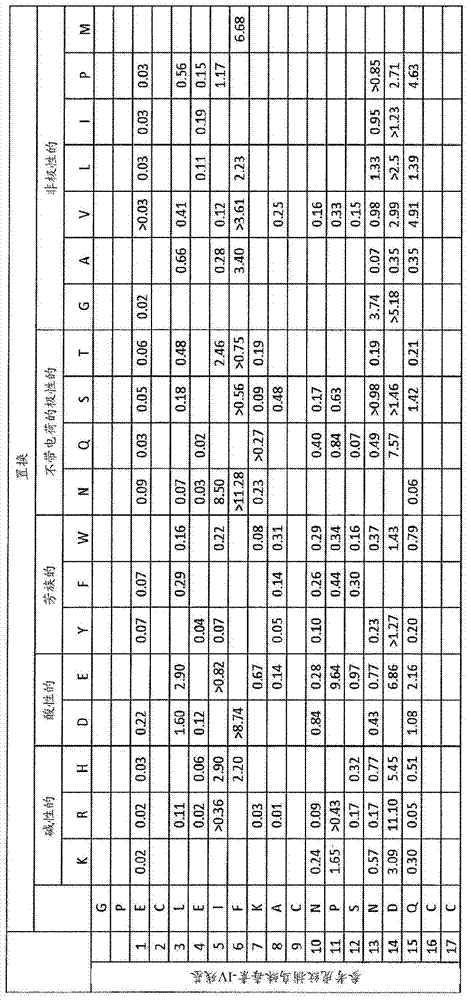
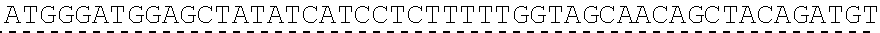Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73 results about "NAV1" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
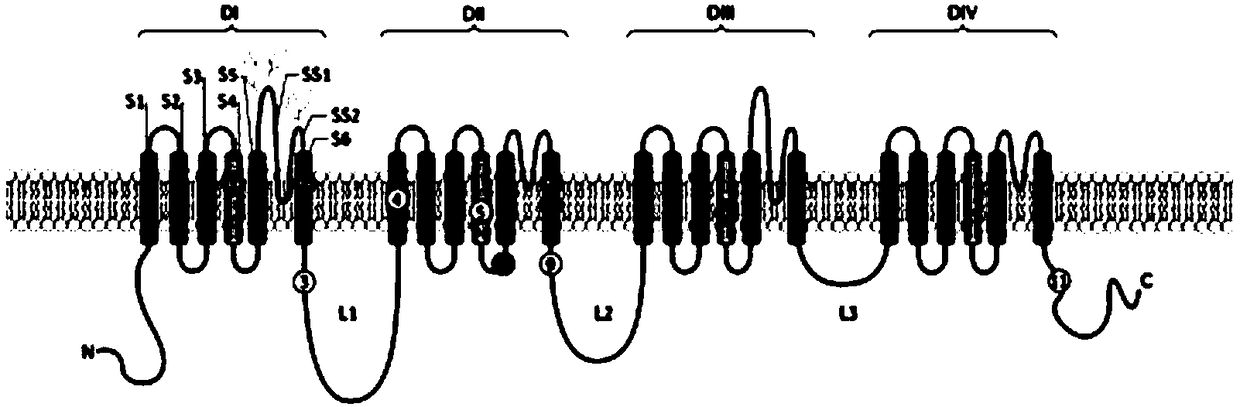
Neuron navigator 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NAV1 gene. This gene belongs to the neuron navigator family and is expressed predominantly in the nervous system. The encoded protein contains coiled-coil domains and a conserved AAA domain characteristic for ATPases associated with a variety of cellular activities. This gene is similar to unc-53, a Caenorhabditis elegans gene involved in axon guidance. The exact function of this gene is not known.
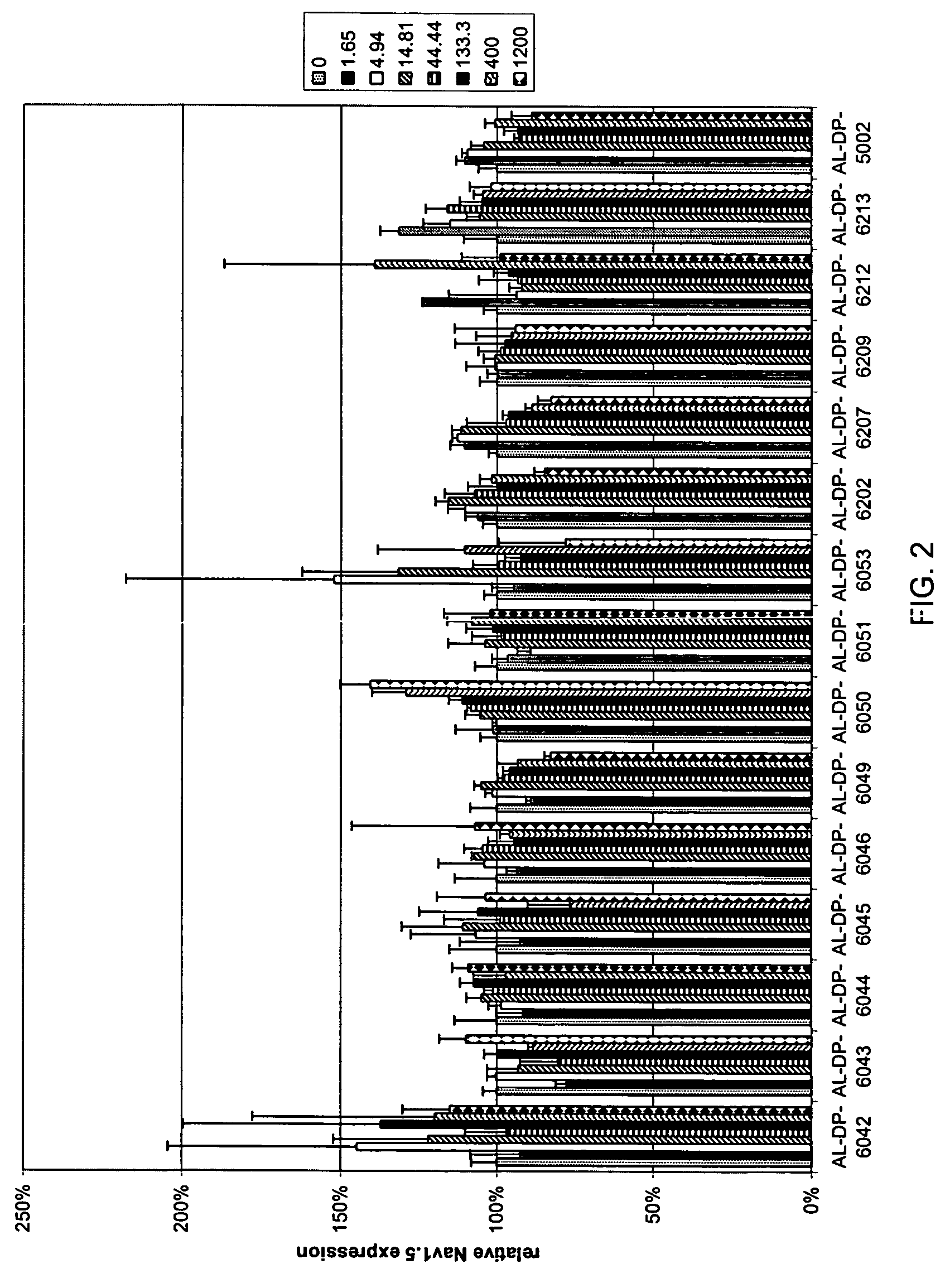
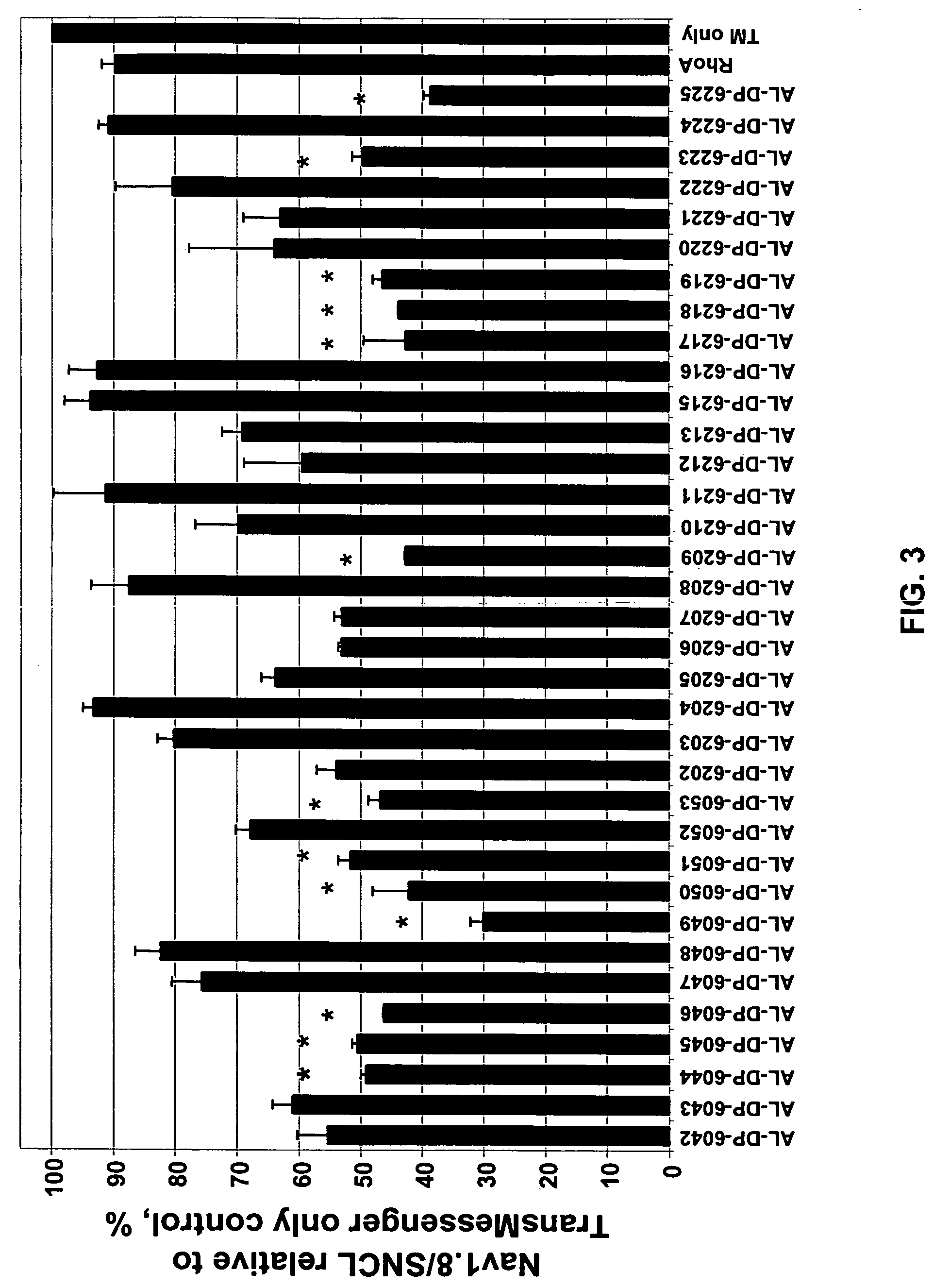
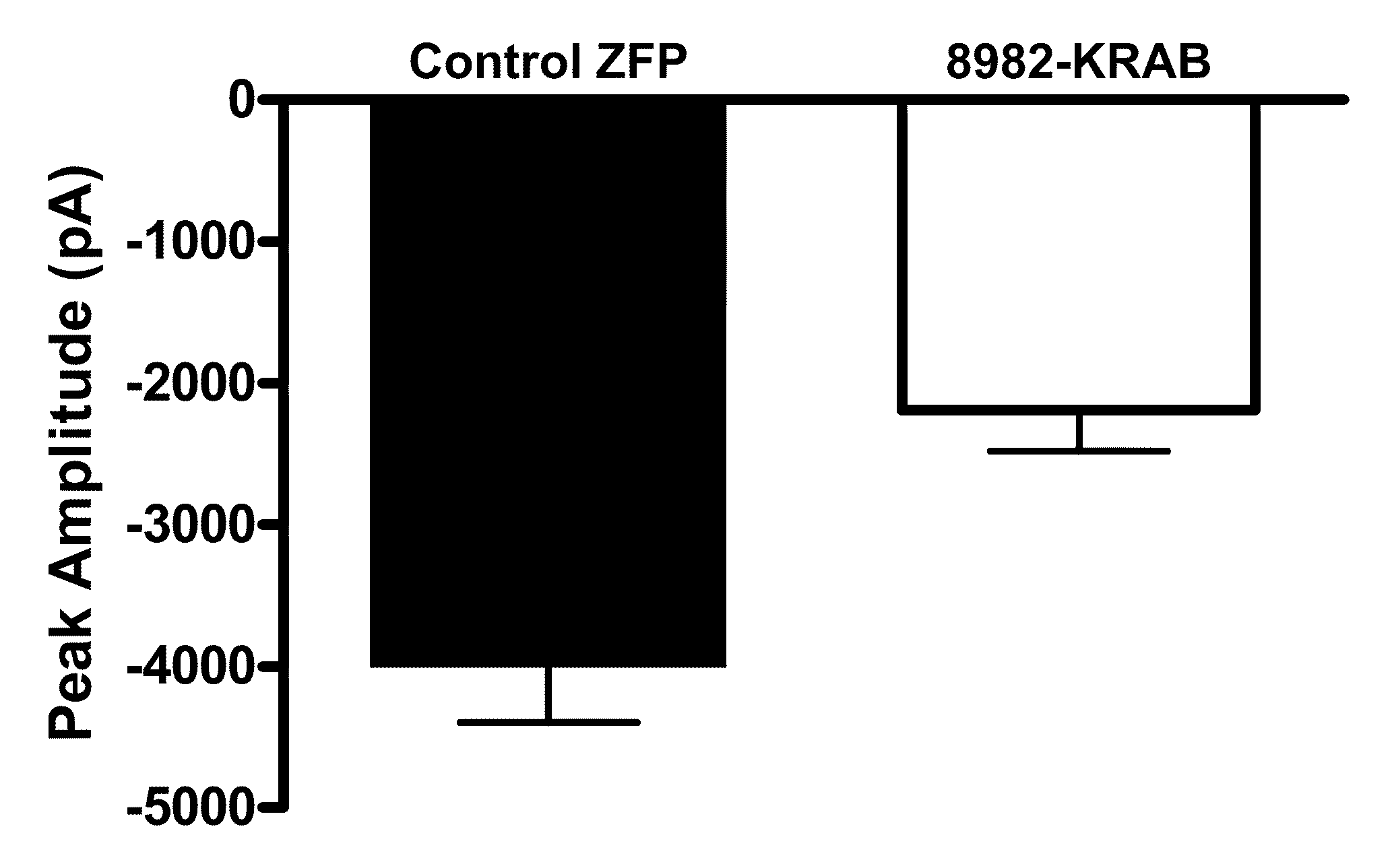
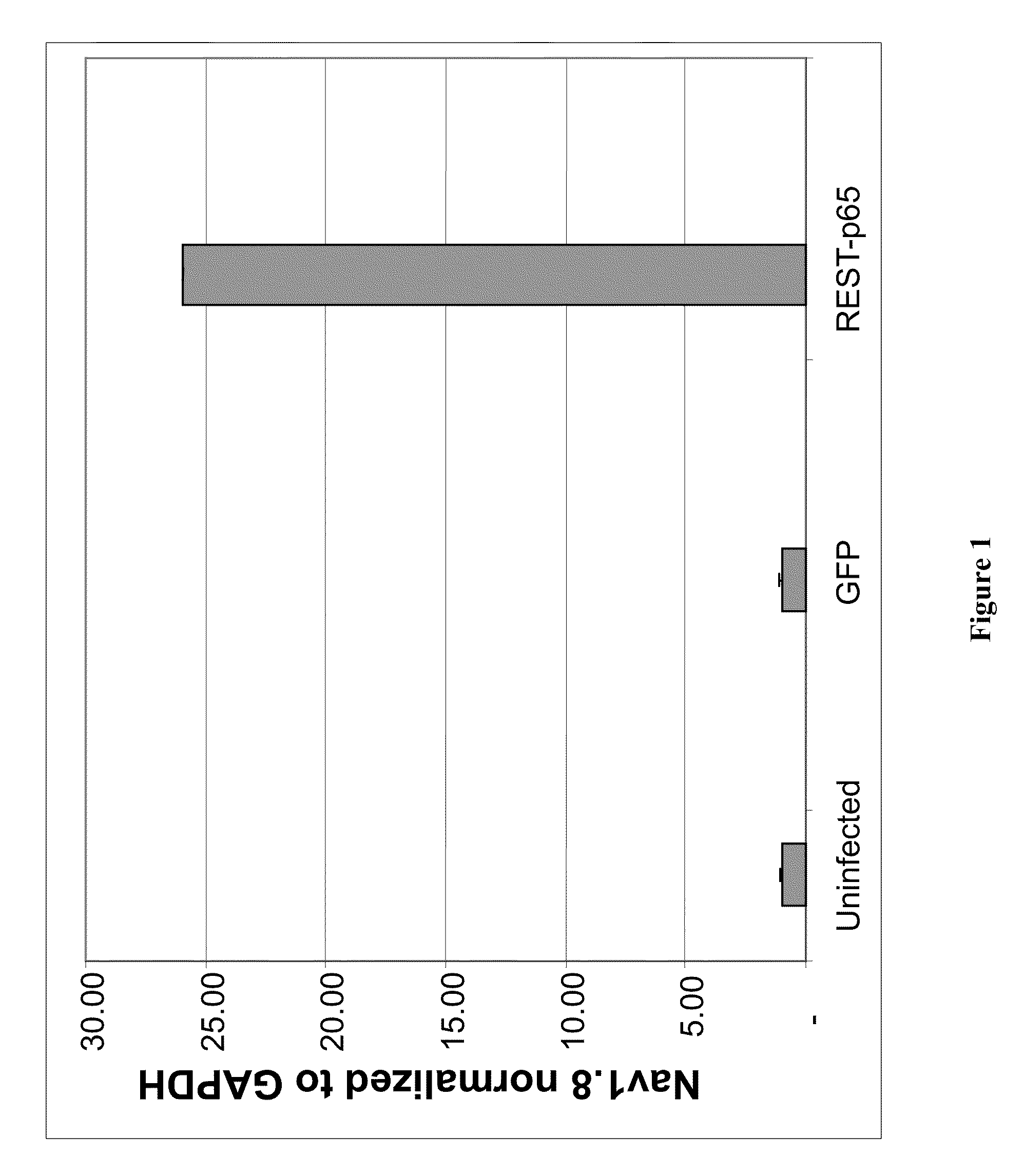
Treatment of neuropathic pain with zinc finger proteins
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
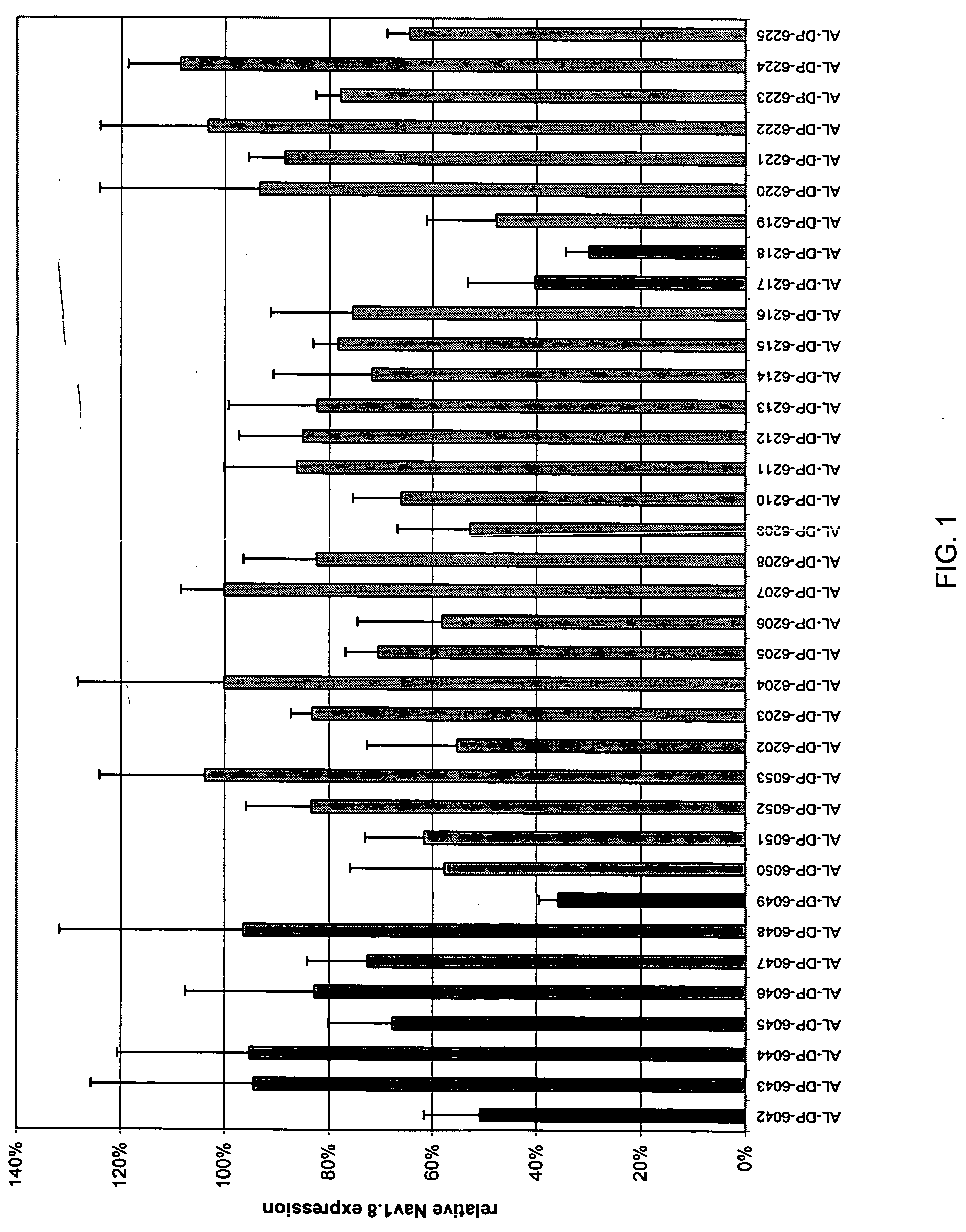
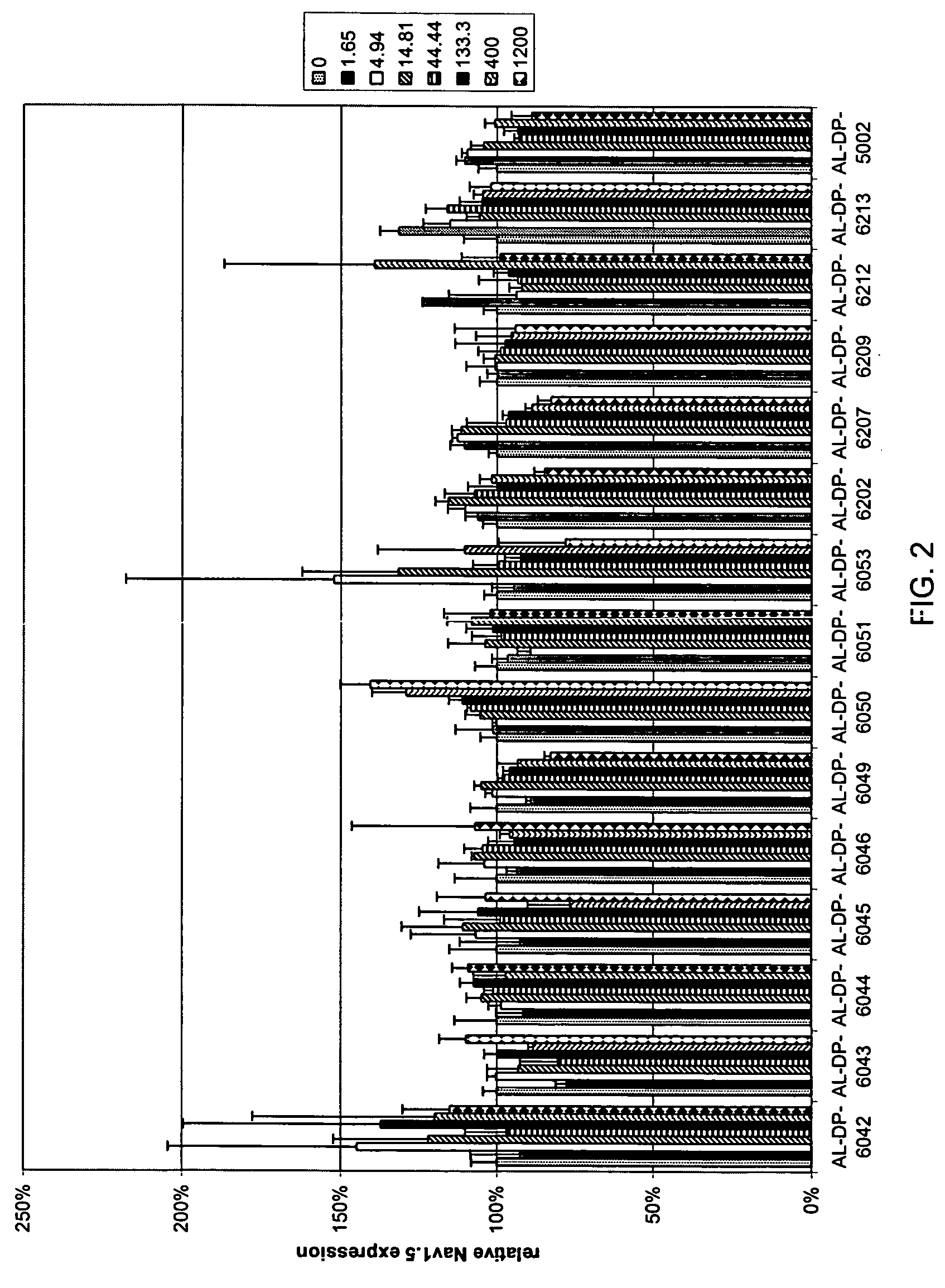
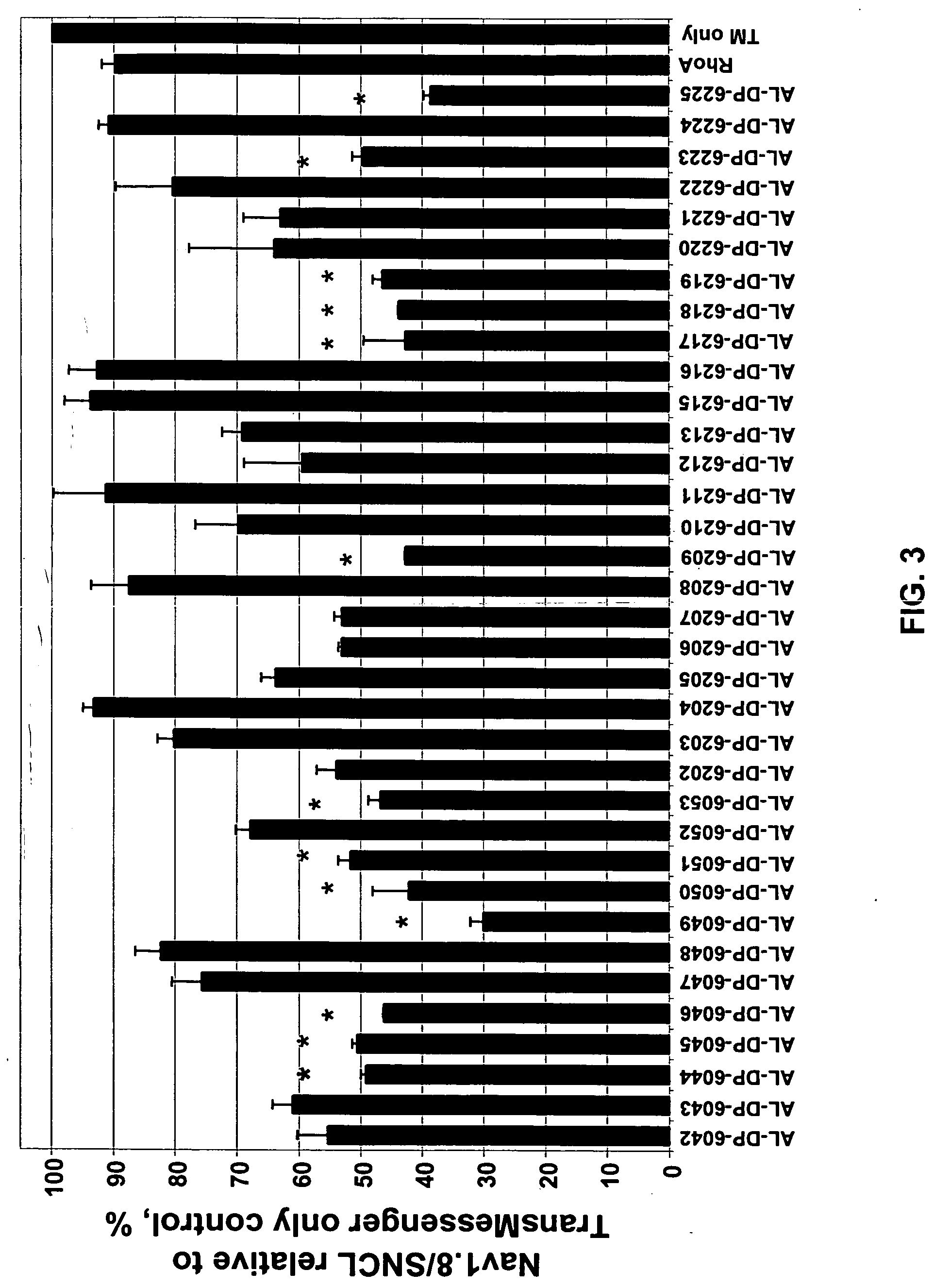
Compositions and methods for inhibiting expression of Nav1.8 gene
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
Treatment of chronic pain with zinc finger proteins
InactiveUS20090215878A1Suppress gene expressionModulate physiological processes correlatedOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNormal levelPain patient
A variety of zinc finger proteins (ZFPs) and methods utilizing such proteins are provided for use in treating chronic pain. ZFPs that bind to a target site in genes that are aberrantly expressed in subjects having chronic pain are described. In addition, ZFPs that bind to a target site in genes expressed at normal levels in subjects experiencing chronic pain, modulation of whose expression results in decreased pain perception, are also provided. For example, genes that are over-expressed in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) of pain patients (e.g., Nav1.8) can be repressed.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
Treatment of neuropathic pain with zinc finger proteins
InactiveUS20050245476A1Easy to produceNervous disorderFusion with DNA-binding domainNAV1Dorsal roots
A variety of zinc finger proteins (ZFPs) and methods utilizing such proteins are provided for use in treating neuropathic pain. ZFPs that bind to a target site in genes that are aberrantly expressed in subjects having neuropathic pain are described. In addition, ZFPs that bind to a target site in genes expressed at normal levels in subjects experiencing neuropathic pain, modulation of whose expression results in decreased pain perception, are also provided. For example, genes that are over-expressed in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) of pain patients (e.g., VR1, TRKA and / or Nav1.8) can be repressed, whereas genes that are under-expressed in the same populations can be activated.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
Compositions and methods for short interfering nucleic acid inhibition of NAv1.8
InactiveUS20060199779A1Inhibition of translationInhibit expressionNervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsChronic painCell membrane
The invention provides short interfering nucleic acids, either single-stranded or double-stranded, that cause RNAi-induced degradation of mRNA from the Nav1.8 sodium channel gene; to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such short interfering nucleic acids; recombinant vectors comprising such short interfering nucleic acids; a method for inhibiting translation of an mRNA; a method for inhibiting expression of a polypeptide; a method for blocking the membrane potential in a cell; a method for blocking the sodium current in a cell; and a method for inhibiting chronic pain.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP +1
Compositions and methods for inhibiting expression of Nav1.8 gene
InactiveUS20070105806A1Inhibit expressionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to a double-stranded ribonucleic acid (dsRNA) for inhibiting the expression of the Nav1.8 gene (Nav1.8 gene), comprising an antisense strand having a nucleotide sequence which is less that 25 nucleotides in length and which is substantially complementary to at least a part of the Nav1.8 gene. The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the dsRNA together with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier; methods for treating diseases caused by the expression of the Nav1.8 gene using the pharmaceutical composition; and methods for inhibiting the expression of the Nav1.8 gene gene in a cell.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
Potent and selective inhibitors of nav1.7
ActiveUS20150023988A1High potencyHigh selectivityPeptide/protein ingredientsAnaestheticsPreventing painNAV1
Disclosed is a composition of matter comprising an isolated polypeptide, which is a peripherally-restricted Nav1.7 inhibitor. In some disclosed embodiments, the isolated polypeptide is an inhibitor of Nav1.7. Other embodiments are conjugated embodiments of the inventive composition of matter and pharmaceutical compositions containing the inventive composition of matter. Isolated nucleic acids encoding some embodiments of inventive polypeptides and expression vectors, and recombinant host cells containing them are disclosed. A method of treating or preventing pain is also disclosed.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Antibodies to complex targets
InactiveUS20160207996A1Improve production yieldLow production costImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsWhole-cell/virus/DNA/RNA ingredientsEscherichia coliCamelid
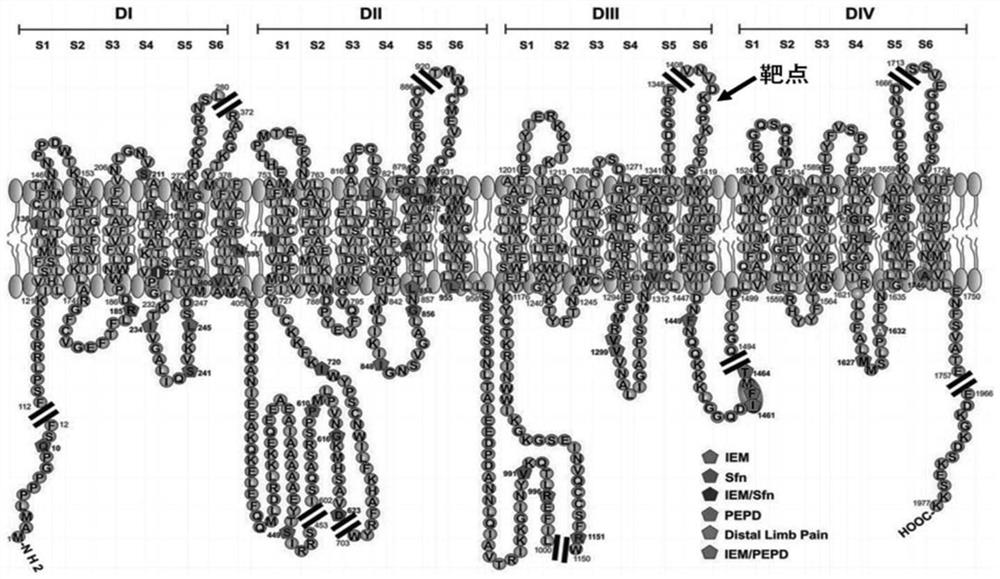
The present invention relates to antibodies and antigen binding fragments thereof derived from antibodies raised by DNA immunization of host animals, particularly camelids (e.g. llama). The antibodies and antigen binding fragments thereof bind to proteins which may be particularly large in size (at least 1115 amino acids in length), or have at least 8 transmembrane domains, or are naturally encoded by nucleotide sequences which are difficult to replicate in standard or common E. coli strains. The present invention also relates to antibodies and antigen binding fragments thereof which bind to ion channels, in particular the voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.7. Methods of raising antibodies against particular protein targets by a process of DNA immunization are also provided.
Owner:ARGENX BVBA
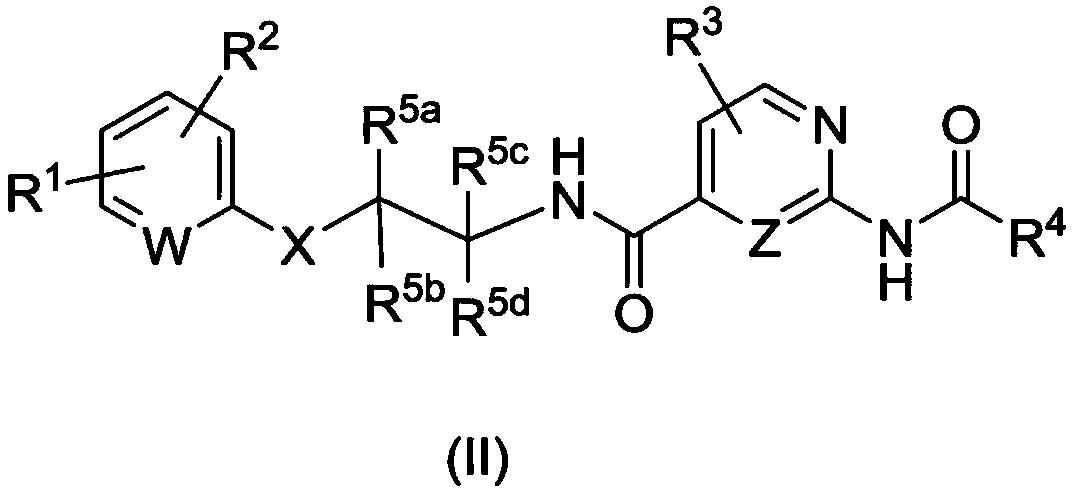
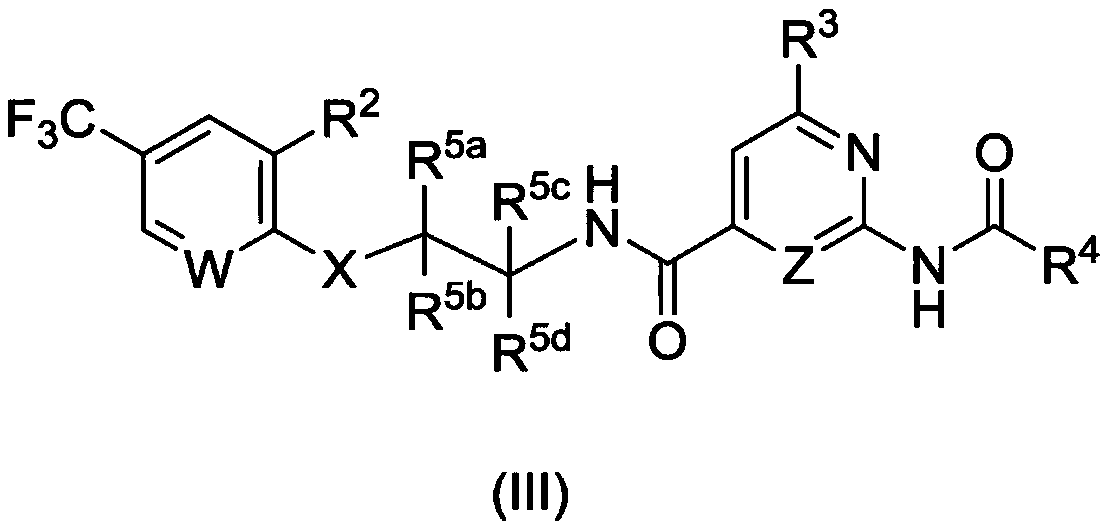
Heterocyclic compounds as NaV channel inhibitors and uses thereof
InactiveUS9676757B2Improve convenienceHigh specificity and stabilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNAV1Medicinal chemistry
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Heterocyclic compounds as nav channel inhibitors and uses thereof
InactiveUS20150266862A1Improve convenienceHigh specificity and stabilityBiocideNervous disorderNAV1Medicinal chemistry
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Huwentoxin-iv variants and methods of use
The present invention relates to Huwentoxin-IV variants, polynucleotides encoding them, methods of making and using the foregoing, and methods of alleviating pain with peptide inhibitors of Nav1.7.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Application of bulleyaconitine A in preparing medicament for treating Nav1.7 ache disease
The invention relates to an application of bulleyaconitine A used for preparing medicine for treating Nav1.7 pain, which belongs to medicine containing effective organic ingredients, in particular to medicine using the bulleyaconitine A for treating a disease. The medicine contains excipient which plays roles in padding, bond, disintegration and lubrication, the bulleyaconitine A and the excipient are mixed to be pressed into tablets, and each tablet of bulleyaconitine A contains 0.1mg to 0.5mg of the bulleyaconitine A. The invention has the characteristics of rapid absorption by oral administration, low content in the brain for the medicine distributed in a body, long half life period, little toxicity, and no tolerant phenomenon or addiction.
Owner:YUNNAN HAOPY PHARM LTD
Analgesic applications of snake toxin polypeptide
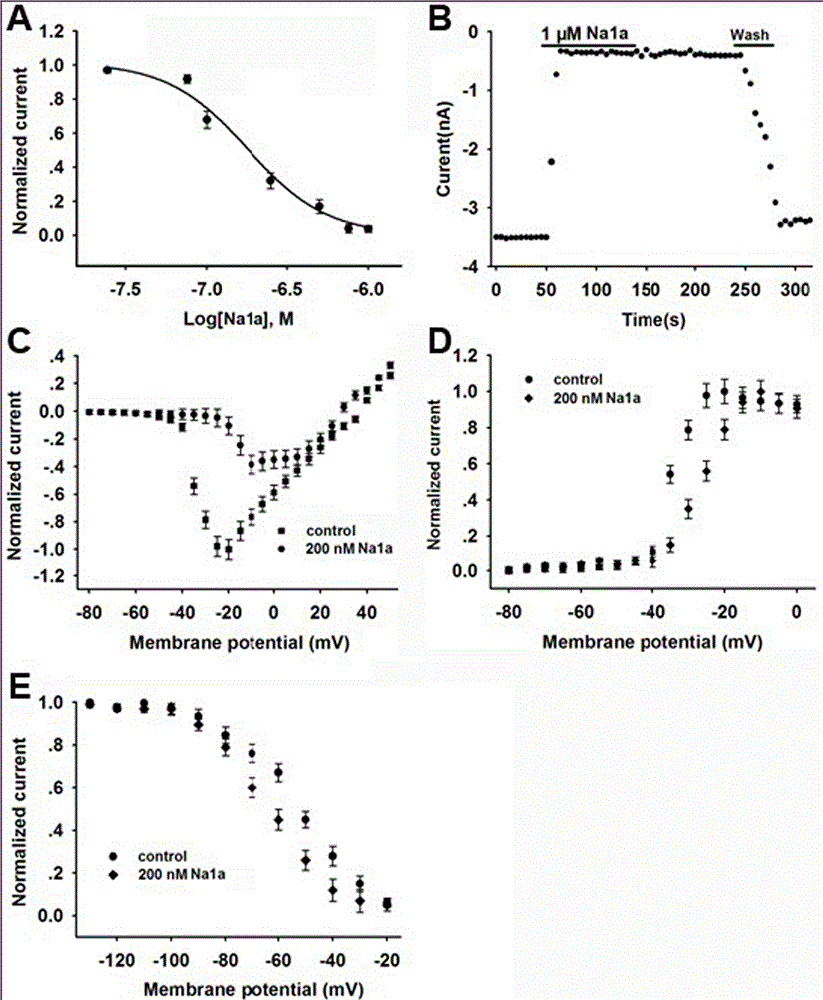
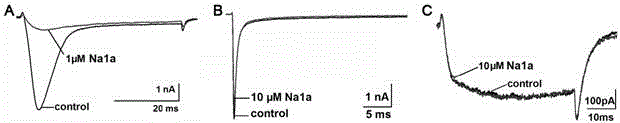
The present invention relates to analgesic applications of a polypeptide toxin mu-EPTX-Na1a (short for Na1a) from Naja atra. According to the present invention, the Na1a provides a strong inhibition effect for the voltage-gated sodium channel subtype Nav1.8, wherein the half-maximal inhibition concentration is 167 nM; the subtype selectivity shows that the Na1a is highly specific; the pharmacodynamics activity experiment results show that the Na1a provides stronger analgesic activities in acetic acid writhing pain models, formalin pain models and complete Freund's adjuvant pain models compared to morphine, and provides similar or slightly excellent analgesic activities in hot plate pain models and sciatic nerve ligation models compared to morphine; the evaluation results of the side effects of the Na1a show that the weak side effects are provided in the movement function, the cardiotoxicity, the hemolytic activity and the cytotoxic activity; and the Na1a is the analgesic polypeptide having the application value.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Nav1.7 knockout mice and uses thereof
Owner:AMGEN INC
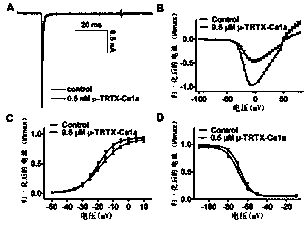
Application of sodium channel blocker mu-TRTX-Ca1a as analgesic drug
ActiveCN110713530AGood analgesic effectGood inhibitory effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticDisulfide bondingIonic Channels
The invention relates to an amino acid sequence and a gene sequence of cyriopagopus albostriatus toxin mu-TRTX-Ca1a, and application, and belongs to the field of biomedicine. The mu-TRTX-Ca1a contains38 amino acid residues, wherein six cysteines form three pairs of disulfide bonds, and the molecular weight is 4289.31 Da. The cyriopagopus albostriatus toxin mu-TRTX-Ca1a can preferentially inhibitsodium channel subtype Nav1.7. The cyriopagopus albostriatus toxin mu-TRTX-Ca1a can remarkably alleviate the pain caused by a mice formalin model, an acetic acid writhing model and a hot plate model,and can be used as a drug for treating pain.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Treatment of Neurological and Neurodevelopmental Diseases and Disorders Associated with Aberrant Ion Channel Expression and Activity
ActiveUS20180328915A1High transmission frequencyReduce the amplitudeOrganic active ingredientsCompound screeningDiseaseEctopic expression
Provided are methods for treating and / or reducing the symptoms of a neurological or neurodevelopmental disease or disorder characterized by ectopic expression of certain ion channels, in particular, the Nav1.8 subtype SCN10a sodium channel, or the KCNQ1 potassium channel, in neuronal cells of the central nervous system (CNS) of a subject by administering to a subject in need an antagonist of one or both of these ion channels, and in particular, an antagonist of SCN10a, to block, reduce, or suppress the aberrant CNS neuronal ion channel expression and / or activity and normalize behavioral and cognitive defects associated with the neurological and neurodevelopmental disease or disorder, so as to treat and / or reduce the symptoms of the neurological or neurodevelopmental disease or disorder. Examples of such diseases or disorders that may be treated by the described methods include, for example, Pitt-Hopkins Syndrome (PTHS), autism, autism spectrum disorder, schizophrenia, 18q syndrome and the like.
Owner:LIEBER INST
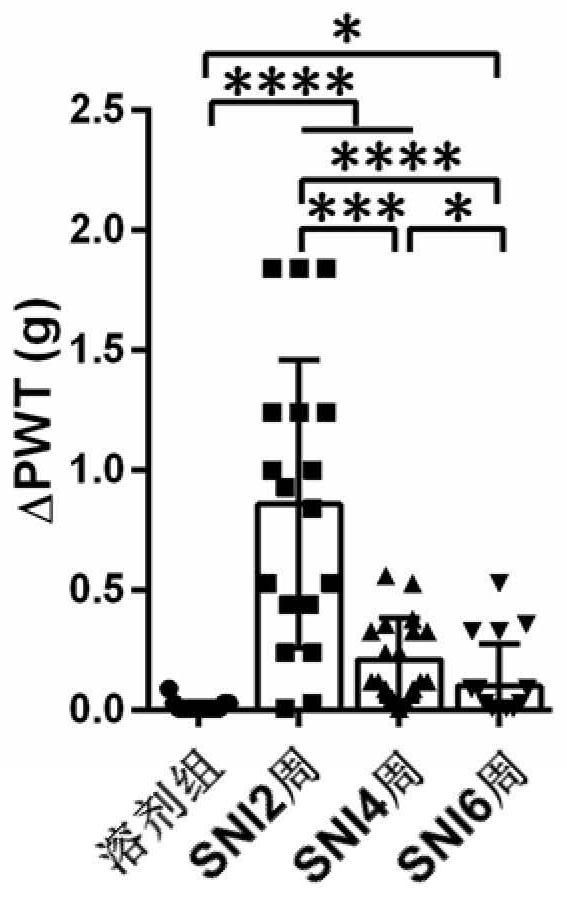
Target polypeptide of Nav1.9, antibody and antibody fragment bound with polypeptide, and related medicine composition
ActiveCN108530534AAvoid side effectsTreat and Relieve PainNervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody fragmentsNerve cells
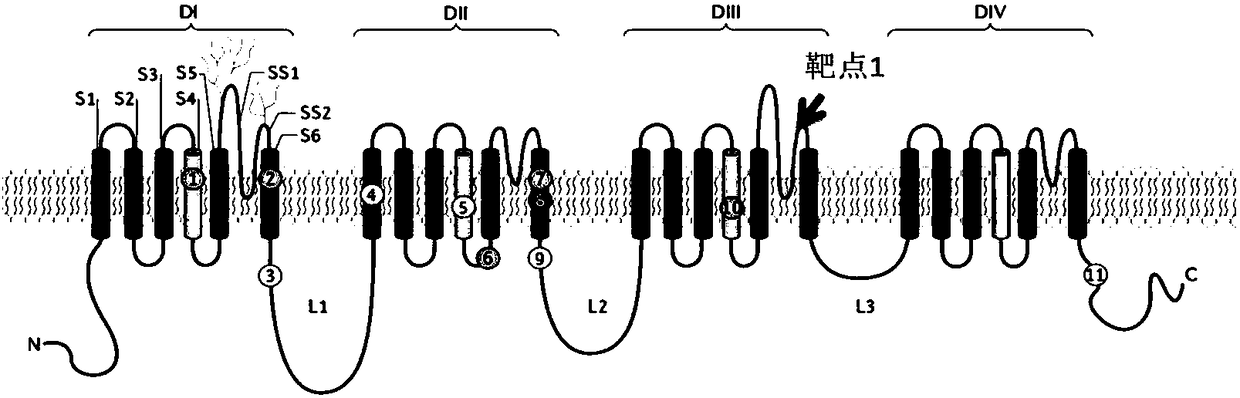
The invention provides target polypeptide of Nav1.9, an antibody and an antibody fragment bound with the polypeptide, and the related medicine composition. The target polypeptide is S3-4 ring of a voltage sensor paddle of a III-rd structural domain of a voltage gate sodium ion channel alpha subunit. The antibody of the antibody fragment can deactivate a voltage sensor valve and sodium ions cannotenter nerve cells normally, so that the effects of performing treatment and relieving pain are achieved.
Owner:POPULAS BIOPHARMACEUTICAL WUHAN LTD
Voltage-gating sodium ion channel structure modeling method based on development coupling analysis
ActiveCN107967408ADetermine the interactionReliable methodSystems biologySpecial data processing applicationsCrystallographyStructural biology
The invention relates to a voltage-gating sodium ion channel structure modeling method based on development coupling analysis, and belongs to the field of structural biology. The method includes the steps that through the rosetta membrane-protein homology modeling method, a eukaryon sodium ion channel NavPas (PDBid:5X0M) tertiary structure serves as a template, and four subunit structures of whicha Nav1.5 pore domain is composed are primarily established; through the development coupling analysis (DCA) method, the contact ratio between actual residue pairs and interaction residue pairs obtained after forecasting through DCA in the structures is evaluated; combined with a scoring function, the structures with the high score and the high contact ratio are selected as initiating structures of all structural domains; the four selected subunit structures are assembled and optimized; a structure capable of having the high interface contact ratio and the high RosettaMP score to meet the evaluation requirements is further selected from the optimized structures to serve as a final structure. According to the voltage-gating sodium ion channel structure modeling method based on development coupling analysis, the defects that in a traditional structure modeling method, transmembrane area information is not fully considered, the homology of a template is low, and the forecasting accuracy is poor are overcome, and the reliability is high.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
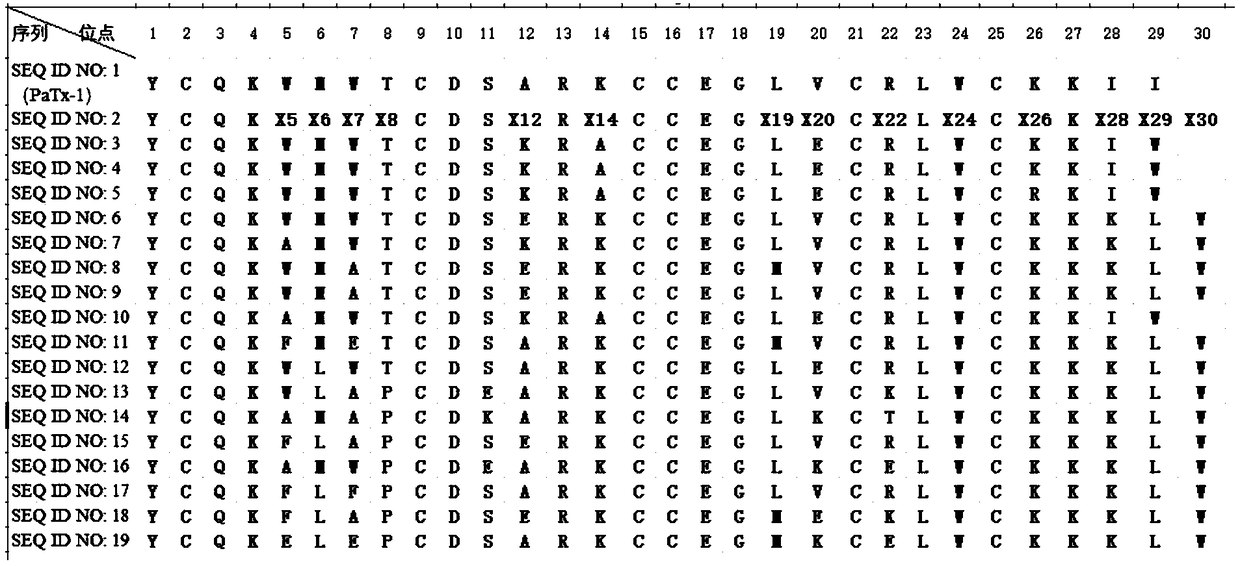
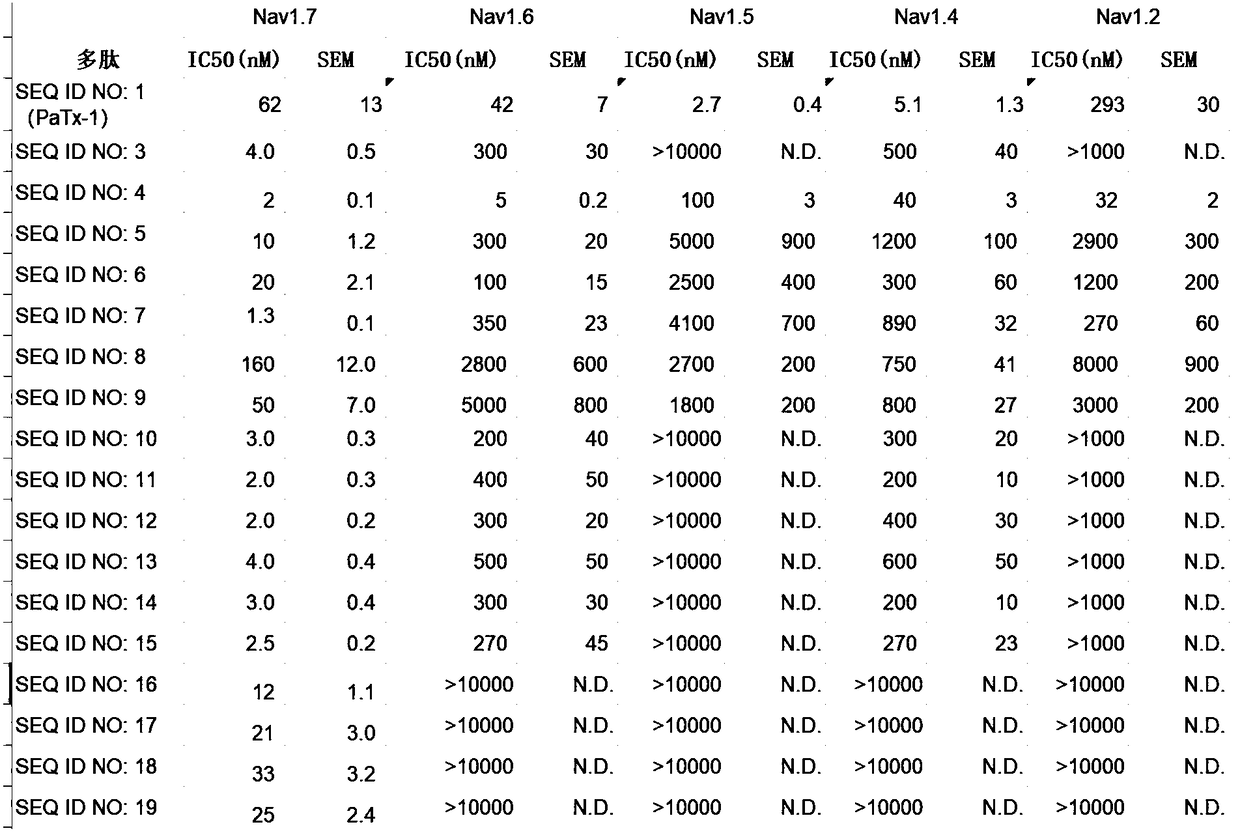
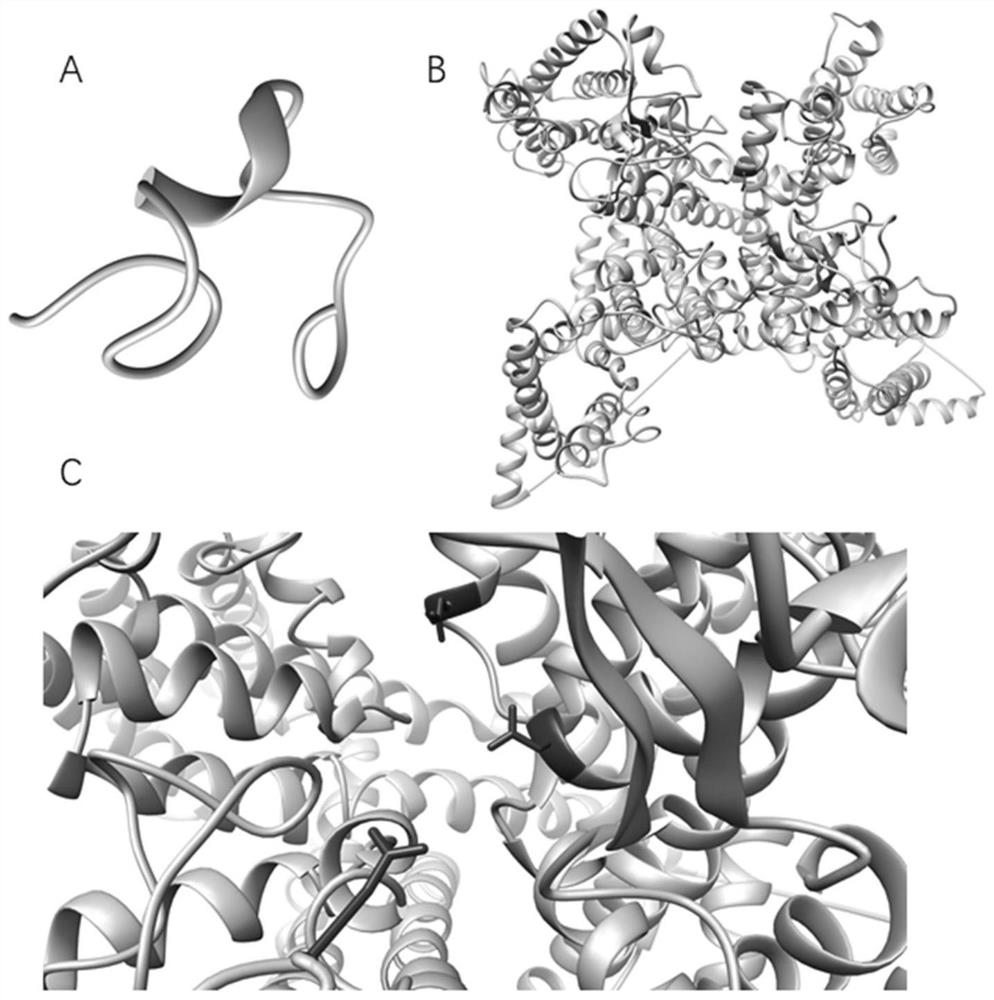
Phrixotoxin (PaTx-1) and application thereof
ActiveCN109369784AHigh selectivityAvoid side effectsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPhrixotoxinMedicine
The invention mainly relates to phrixotoxin (PaTx-1) extended polypeptide and application thereof. The polypeptide toxin can effectively and selectively block Nav1.7 (voltage-gated sodium channel alpha subunit group), and therefore the polypeptide toxin can serve as a selective sodium ion channel blocking agent so as to be applied to multiple aspects such as molecular mechanisms, neutral signal transmission and disease treatment relevant to Nav1.7 sodium ion channels.
Owner:广东帕派恩生物科技有限公司
Conotoxin, polypeptide composition as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN113549139AWeakened blockadeReduce manufacturing costCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsConotoxinCardiac muscle
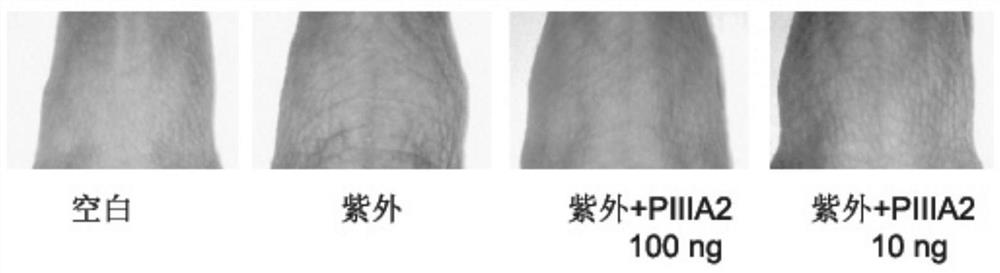
The invention discloses a conotoxin, a polypeptide composition as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of cosmetic preparation. The conotoxin has a sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. Amino acid residue mutation is performed on wild mu-conotoxin PIIIA, so that the retardation effect of the mu-conotoxin on a sodium channel is moderately weakened, and meanwhile, the stability is kept under acidic and alkaline conditions, and the isoelectric point stability and the target specificity are kept. The novel conotoxin provided by the invention has the characteristics of stability, low production cost and the like. The mutated conotoxin or salt thereof keeps a relatively strong anti-wrinkle function, and the mutated conotoxin can avoid facial muscle stiffness and paralysis caused by excessive inhibition of a skeletal muscle sodium channel Nav1.4, and meanwhile, the risk of inhibiting the myocardial sodium channel and a brain sodium channel is also remarkably reduced.
Owner:四川丽妍工坊生物科技有限公司
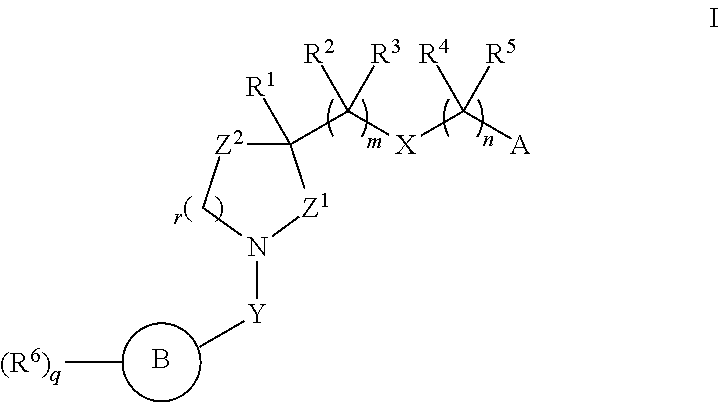
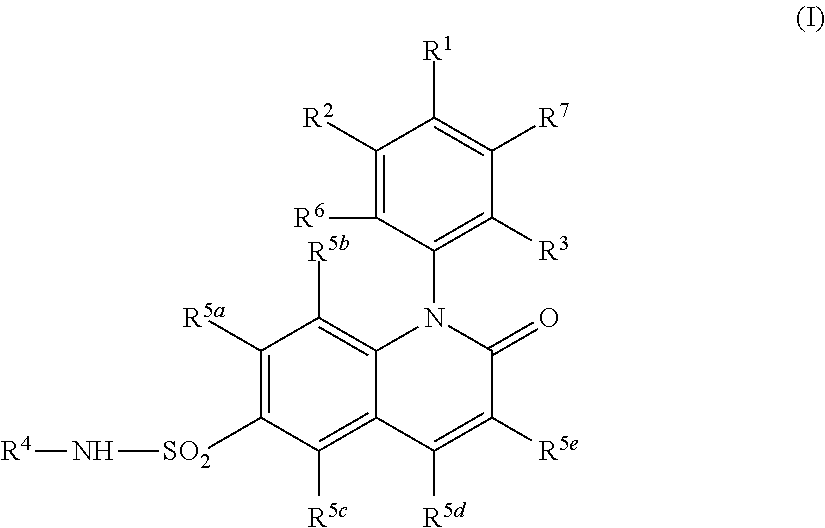
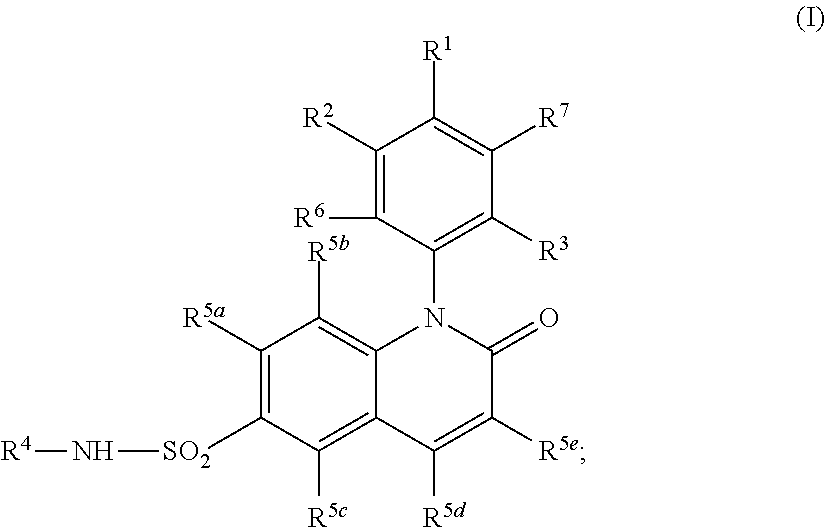
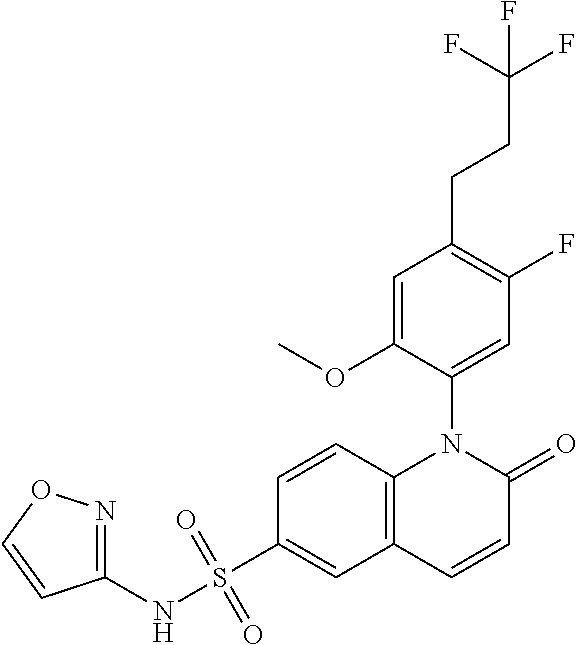
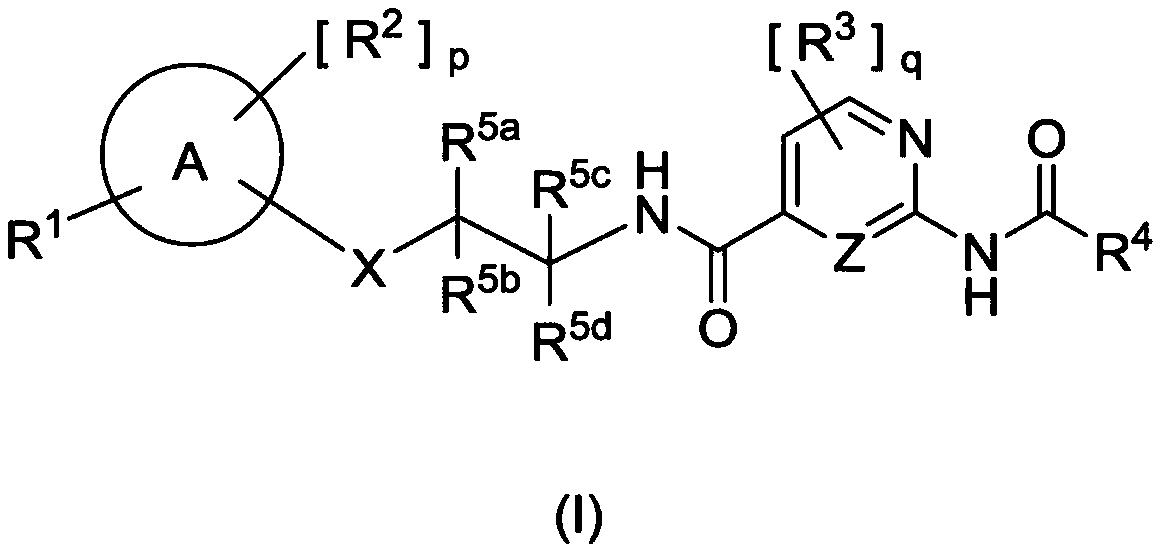
Alkyl dihydroquinoline sulfonamide compounds
The present invention provides compounds of Formula (I), and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, that are inhibitors of voltage-gated sodium channels, in particular Nav1.7. The compounds are useful for the treatment of diseases associated with the activity of sodium channels such as pain disorders, cough, and itch. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions containing compounds of the present invention.
Owner:AMGEN INC
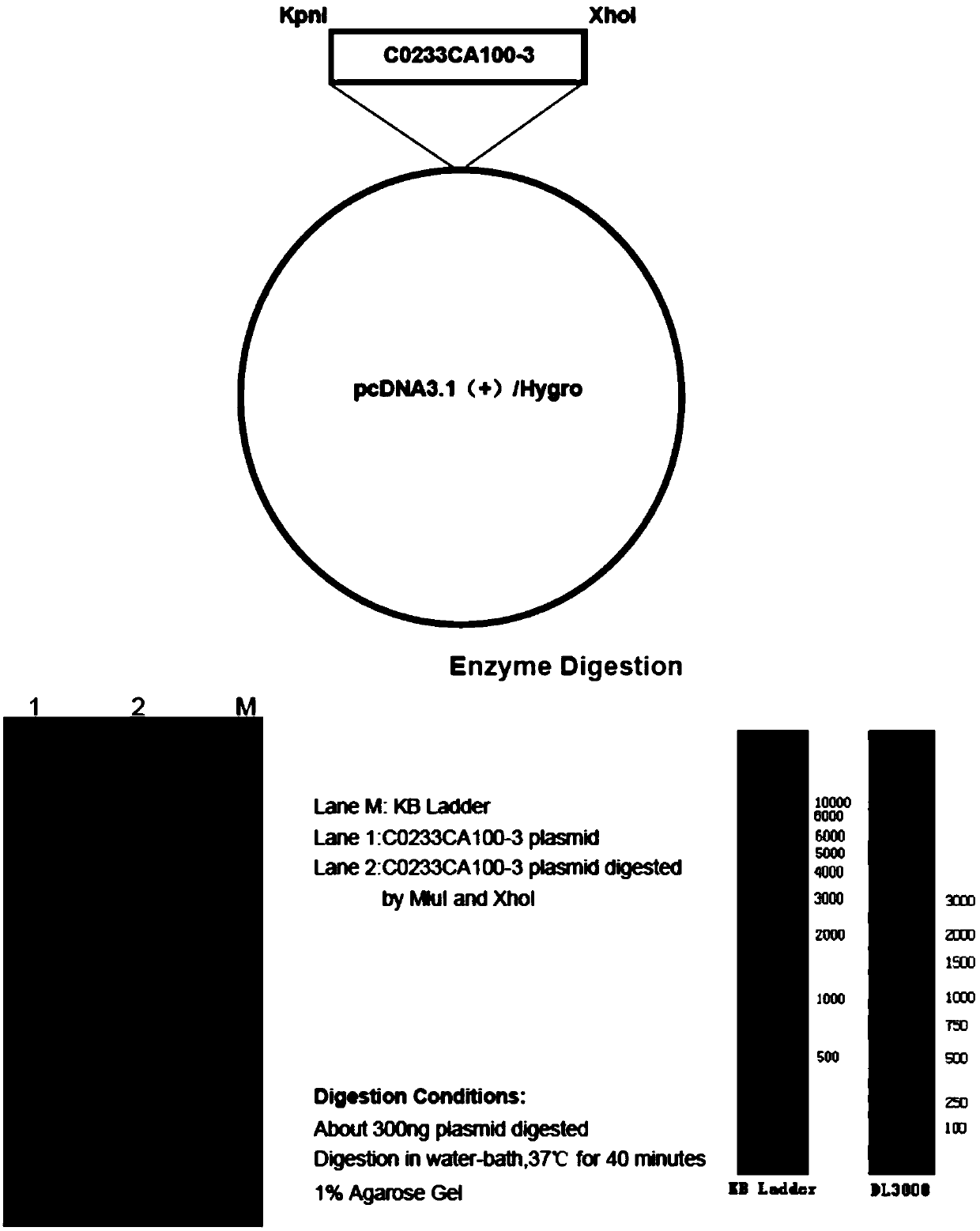
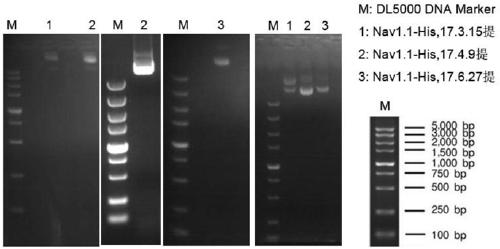
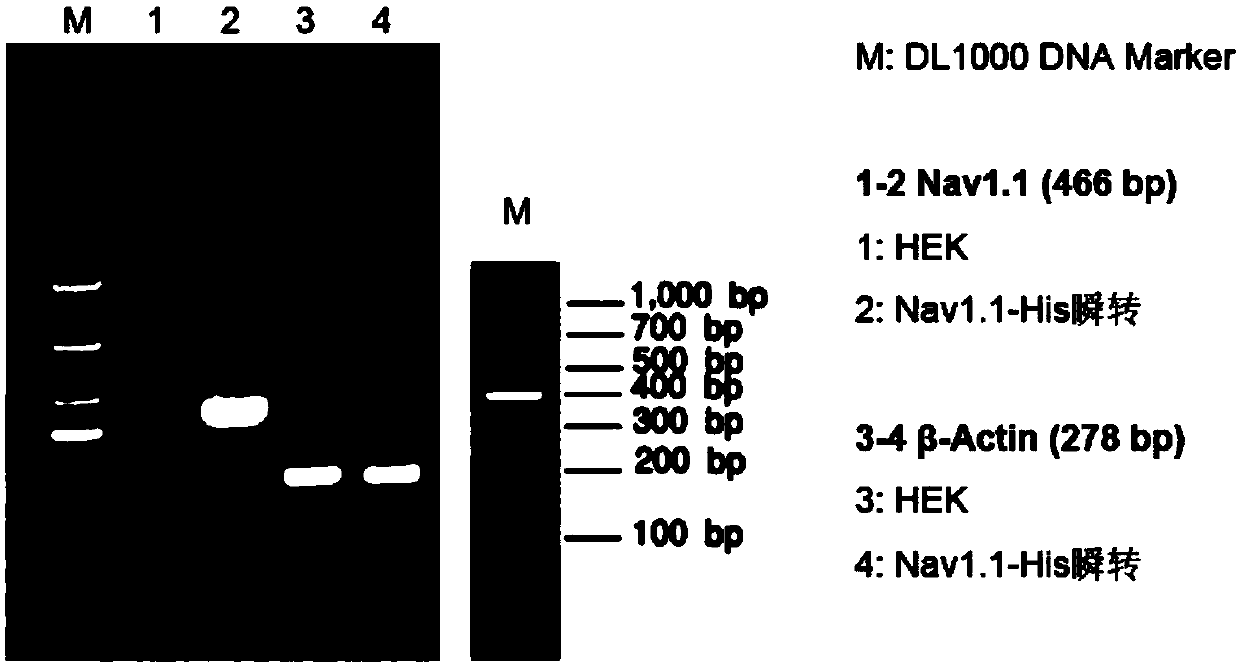
Cell line capable of stably expressing 6His-Nav1.1 fusion protein and construction
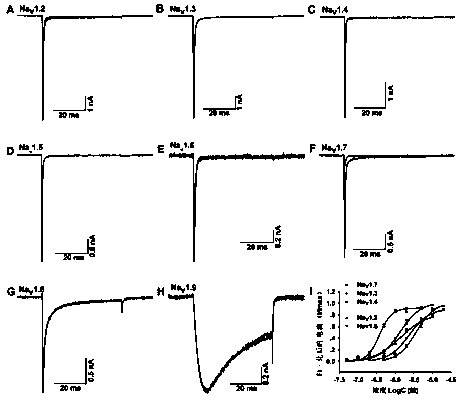
ActiveCN109593727AEasy to purifyEasy to enrichCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsGenetically modified cellsNAV1High-throughput screening
The invention provides a cell line capable of stably expressing 6His-Nav1.1 fusion protein and construction. The cell line is prepared by transfecting an HEK293 cell with a recombinant vector carryinga sequence shown in SEQ ID No.3. The cell line can stably express the 6His-Nav1.1 fusion protein with bioactivity, Nav1.1 is easier to purify and enrich by the aid of a 6His label carried by the protein, a biological recognition aglucone and a toxicity research target are provided for Nav1.1 ion channel research, high-throughput screening of new drugs and unknown toxins, and an important biological affinity material is provided for screening, separation and identification of nerve drugs and neurotoxins. Meanwhile, a core raw material is provided for development of biosensors and establishmentof a high-throughput screening technology.
Owner:CHINA NAT CENT FOR FOOD SAFETY RISK ASSESSMENT
AMIDE DERIVATIVES AS Nav1.7 and Nav1.8 BLOCKERS
Owner:RAQUALIA PHARMA INC
Antibody or antibody fragment specifically binding to voltage-gated sodium channel alpha subunit Nav1.7
ActiveCN113527479AAchieve therapeuticAchieve pain reliefAntipyreticAnalgesicsAntibody fragmentsIonic Channels
The invention provides an antibody or an antibody fragment of a targeted cell membrane voltage-gated sodium channel alpha subunit Nav1.7, and the specific binding target of the antibody or the antibody fragment is an ion-conducting pore module (PM) of an S3 structural domain of an IV structural domain (Domain IV) of the voltage-gated sodium channel alpha subunit. The antibody or the antibody fragment thereof can inactivate the ion-conducting pore module so that sodium ions cannot normally enter nerve cells, and the effect of treating and relieving pain is achieved.
Owner:POPULAS BIOPHARMACEUTICAL WUHAN LTD
Scn9a antisense pain killer
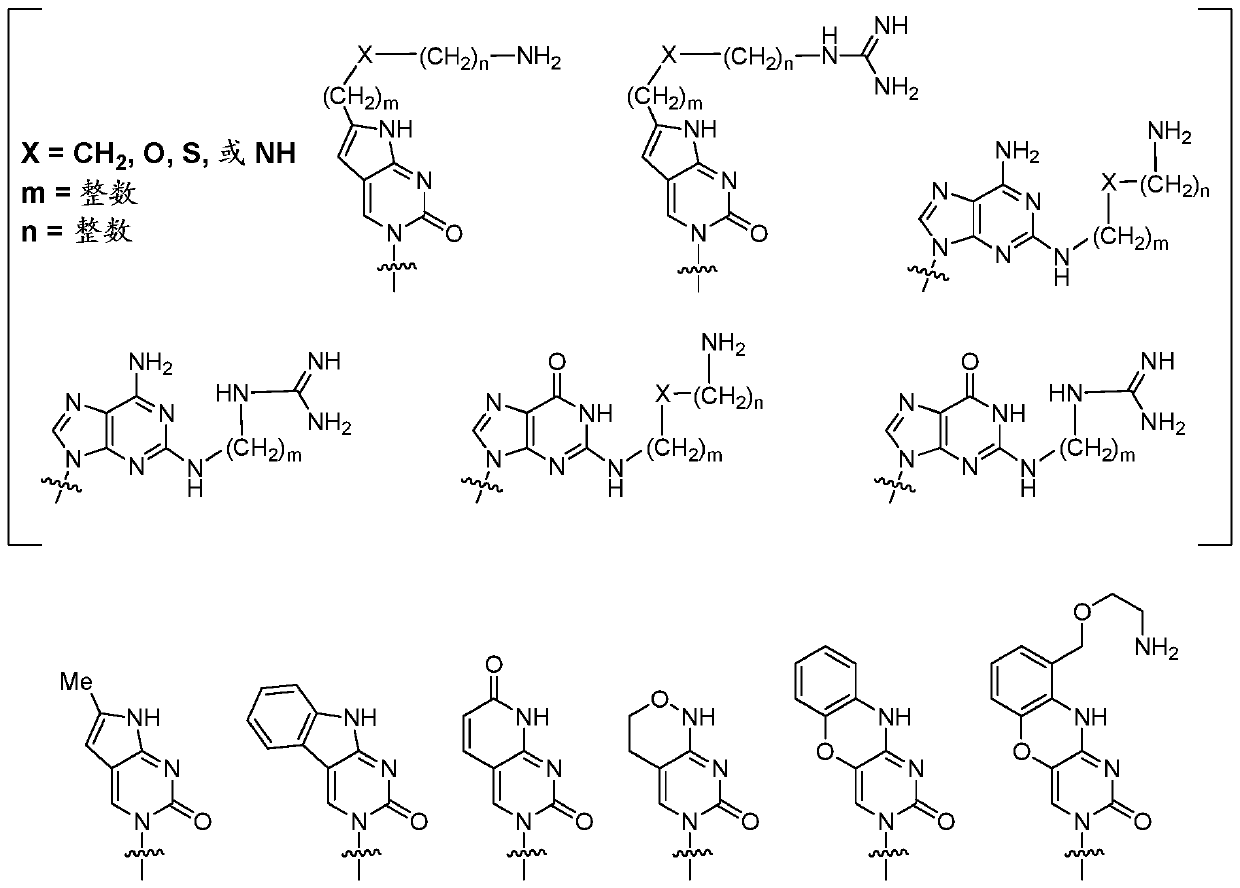
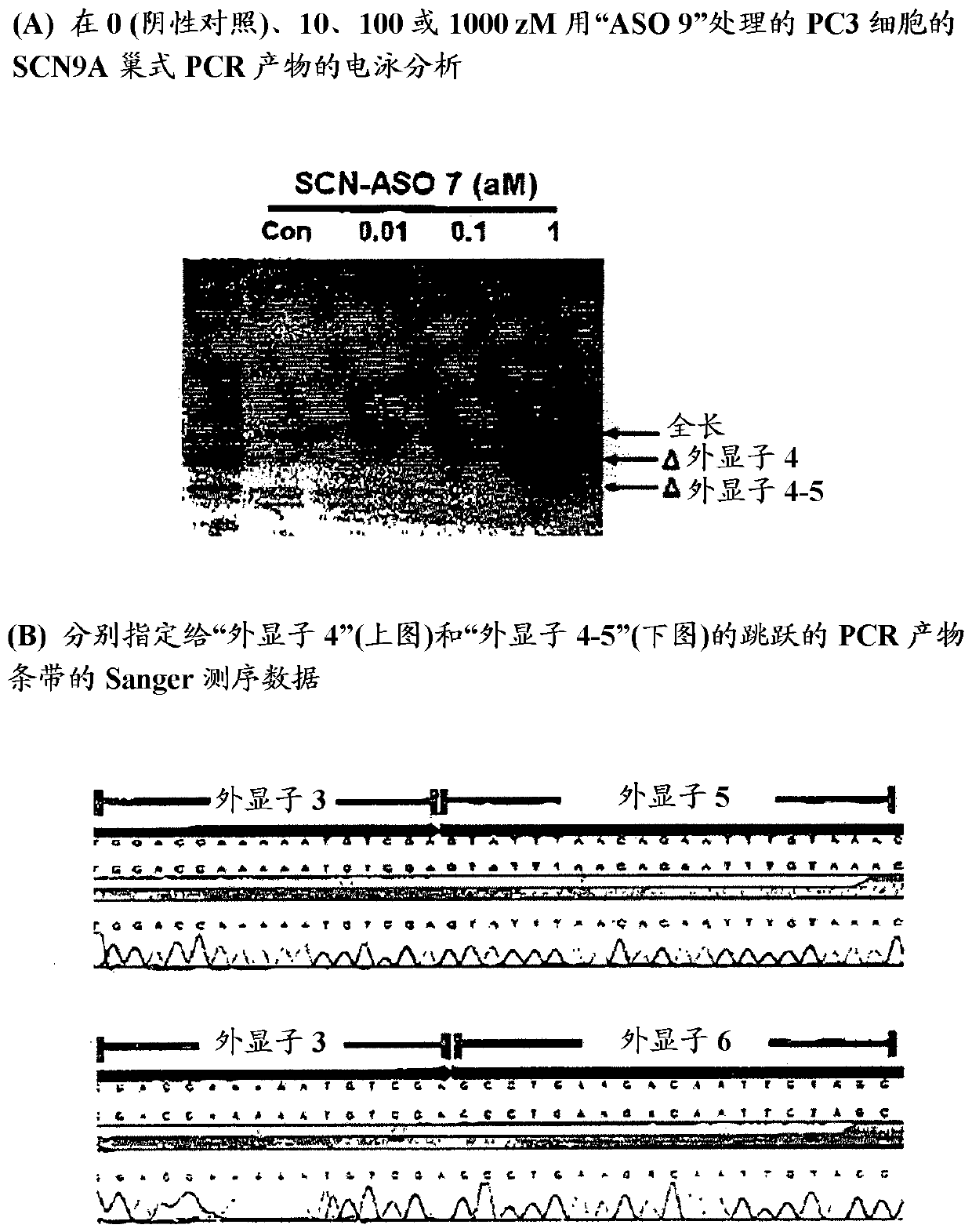
The current invention provides peptide nucleic acid derivatives targeting the 3' splice site of exon 4 in the human SCN9A pre-mRNA. The peptide nucleic acid derivatives potently induce SCN9A mRNA splice variant(s) lacking the SCN9A exon 4 in cells, and are useful to safely treat pains or conditions involving Nav1.7 activity.
Owner:OLIPASS CORP
Scn9a antisense oligonucleotides
The invention provides peptide nucleic acid derivatives targeting a part of the human SCN9A pre-mRNA. The peptide nucleic acid derivatives potently induce splice variants of the SCN9A mRNA in cells, and are useful to safely treat pains or conditions involving Nav1.7 activity.
Owner:OLIPASS CORP
Analgesic and antipruritic pharmaceutical composition and application method thereof
The invention discloses an analgesic and antipruritic pharmaceutical composition and an application method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of medical chemistry. The research of the invention finds that the analgesic effect generated by independently inhibiting the activity of Nav1.7 or Nav1.8 is reduced along with the time history of peripheral nerve injury, and also finds that a neuropathic pain mouse with poor response to the Nav1.7 small-molecule inhibitor has better response to the Nav1.8 small-molecule inhibitor. According to the discovery, the analgesic effect of combined administration of different Nav1.7 inhibitors and Nav1.8 inhibitors is researched, and it is found that the analgesic effect can be remarkably improved and the response rate can be increased to 100% by combined administration of appropriate doses of the Nav1.7 inhibitor PF-05089771 and the Nav1.8 inhibitor PF-04885614. Therefore, the composition of the PF-05089771 and the PF-04885614 can be used for treating diseases caused by too high activity of the Nav1.7 or the Nav1.8, and the diseases include but are not limited to intractable pain and itching.
Owner:上海瑞虎康医药合伙企业(有限合伙)
Nav1.9 target polypeptide, antibody and antibody fragment combined with same, and related pharmaceutical composition
ActiveUS20200157198A1Raise pain thresholdTreat painNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody fragmentsCell membrane
The present invention provides an antibody or antibody fragment thereof for a targeted cytomembrane voltage-gated sodium channel α subunit Nav1.9. The specific binding target is a S3-4 ring of a voltage sensor paddle of a domain II of the voltage-gated sodium channel α subunit. The antibody or antibody fragment thereof is able to inactivate a voltage sensor valve, to make sodium ions unable to enter nerve cells normally, thereby achieving the effect of treating and relieving pains.
Owner:POPULAS BIOPHARMACEUTICAL WUHAN LTD
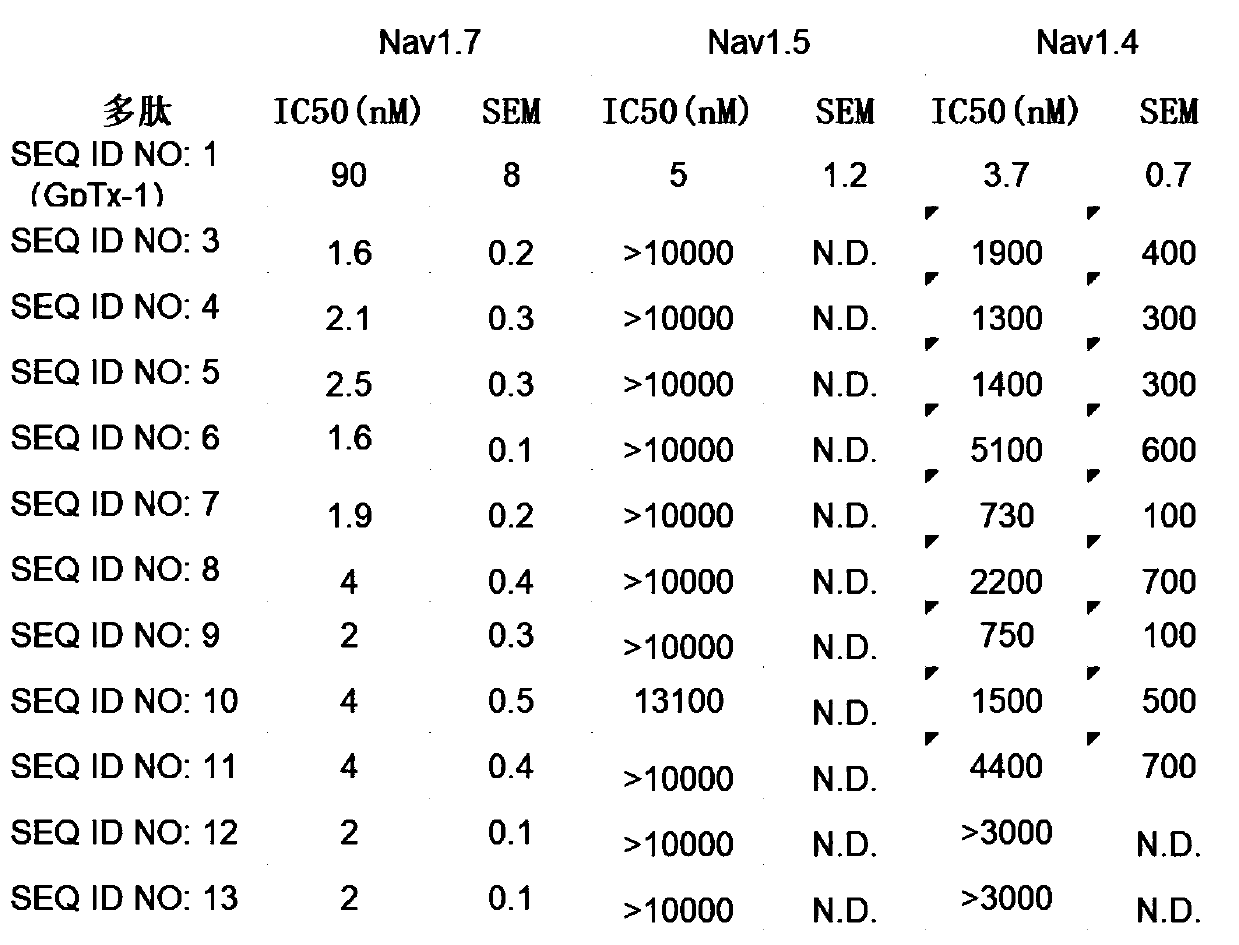
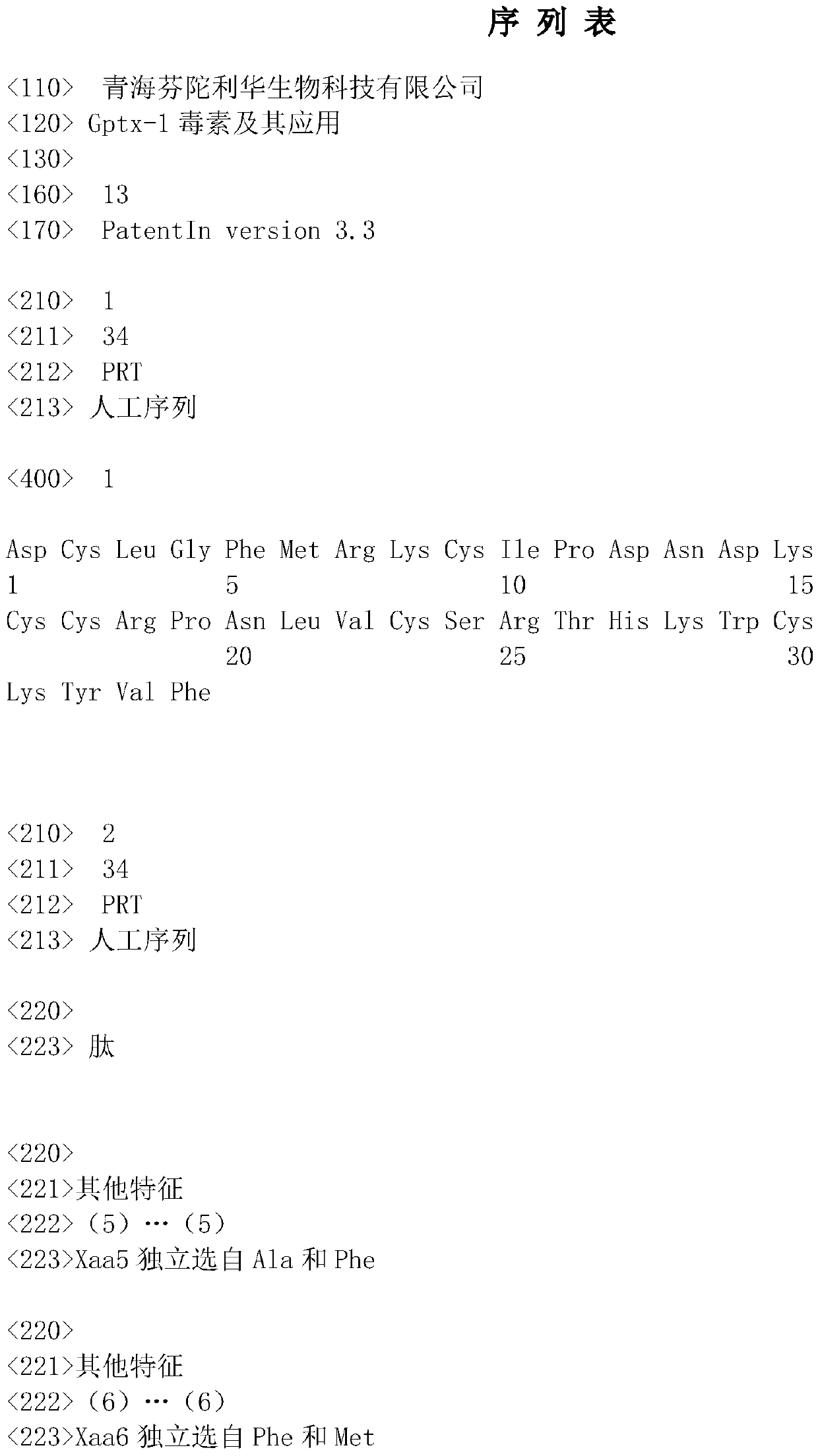
gptx-1 toxin and its application
ActiveCN109517041BHigh selectivityAvoid side effectsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticMedicineNAV1
The invention primarily relates to Grammostola porter(Gptx-1) toxin and an application thereof. The polypeptide toxin can block Nav1.7 (an alpha subunit family of a voltage-gated sodium channel) effectively and selectively, so that the toxin can be used as a selective sodium ion channel blocking agent which is applied to the fields of molecular mechanism of the related Nav1.7 sodium ion channel, neural signal transfer, disease treatment and the like.
Owner:广东帕派恩生物科技有限公司
Oligonucleotides for modulating scn9a expression
The present invention relates to oligonucleotides (oligomers) that are complementary to voltage-gated sodium ion channel encoding nucleic acids, such as SCN9A, which encodes the voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.7. The oligonucleotides of the invention are capable of inhibiting the expression of voltage-gated sodium ion channels, such as Nav1.7, and are useful in the prevention or the treatment ofpain.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com