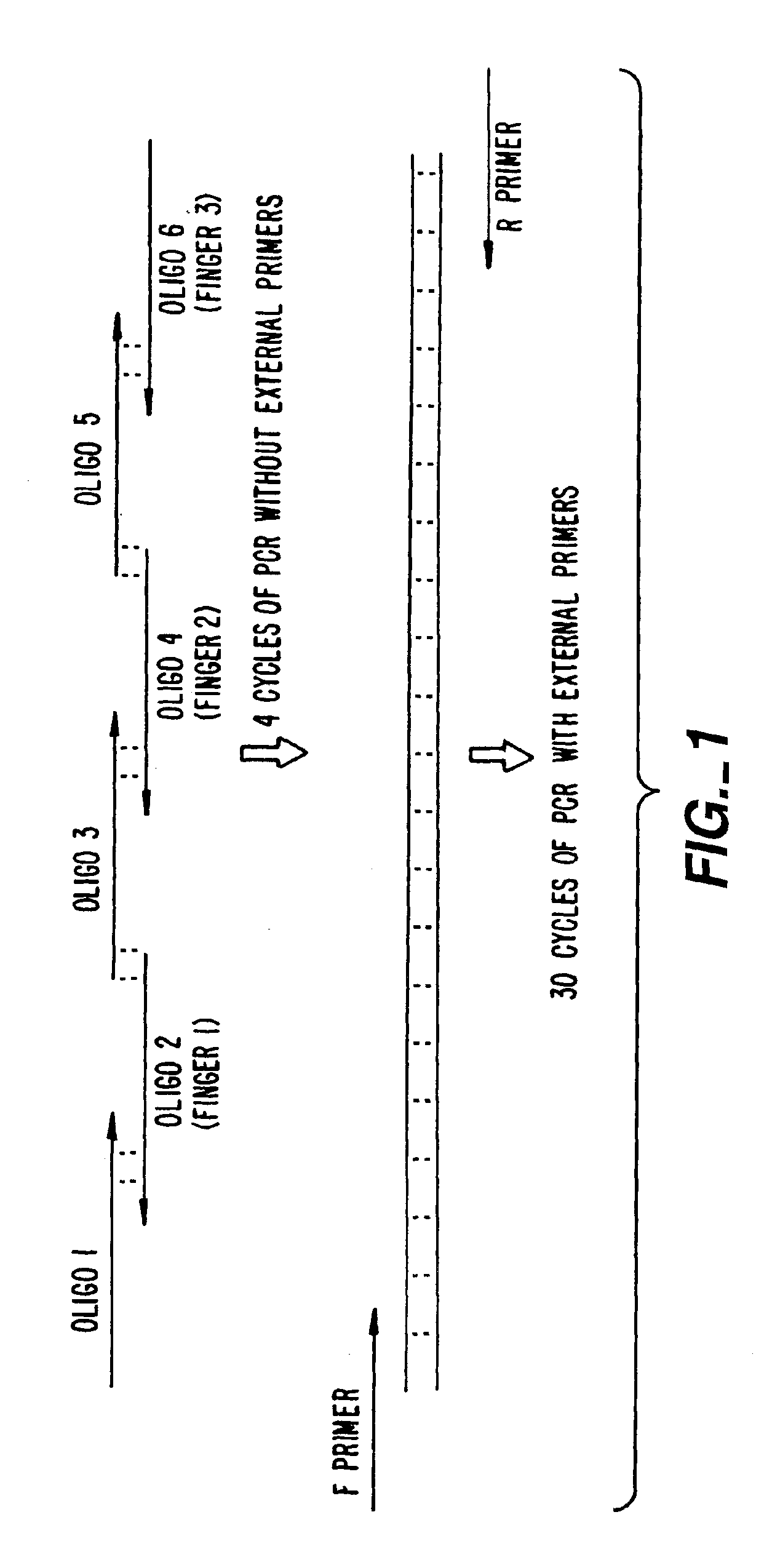
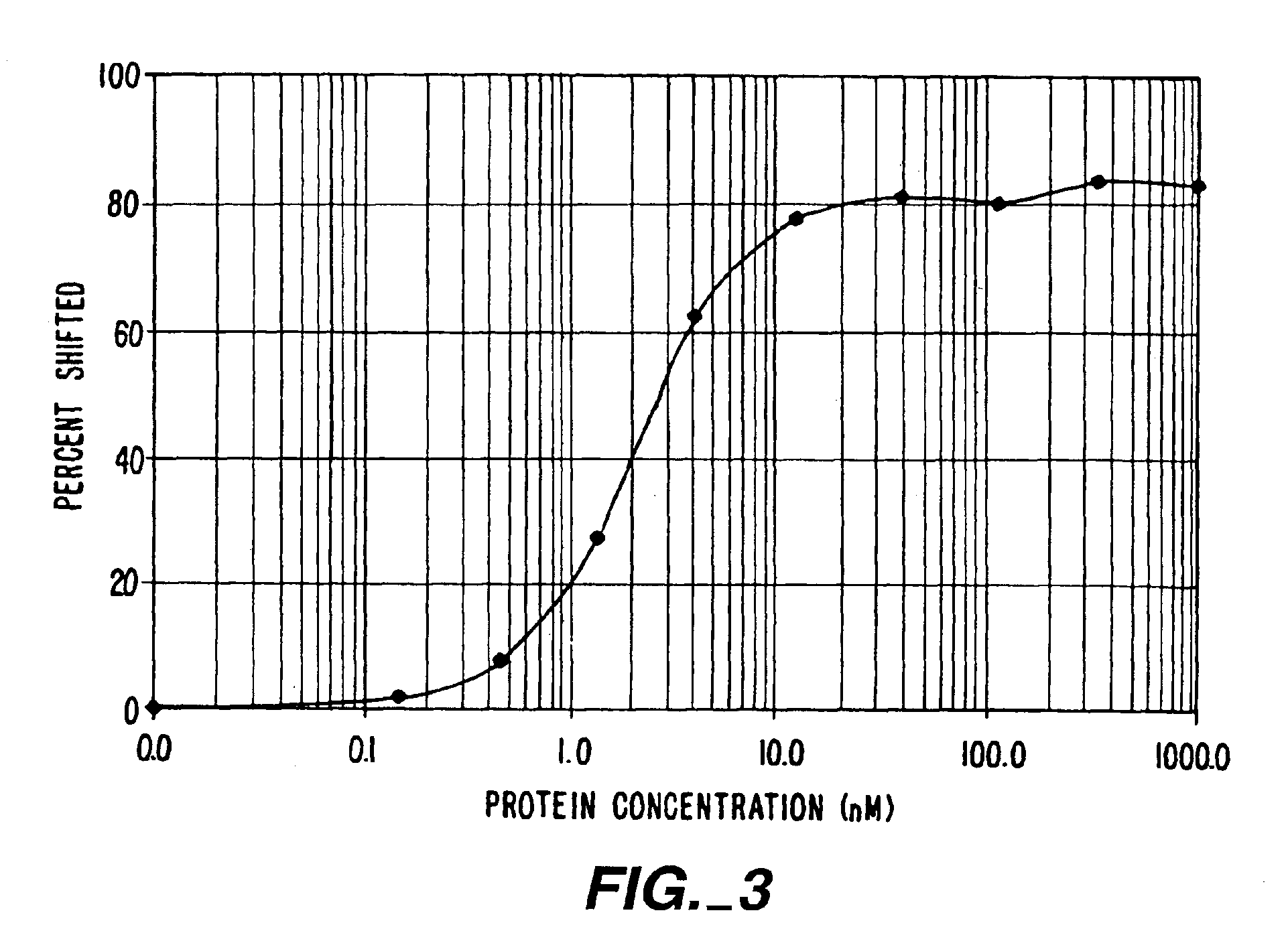
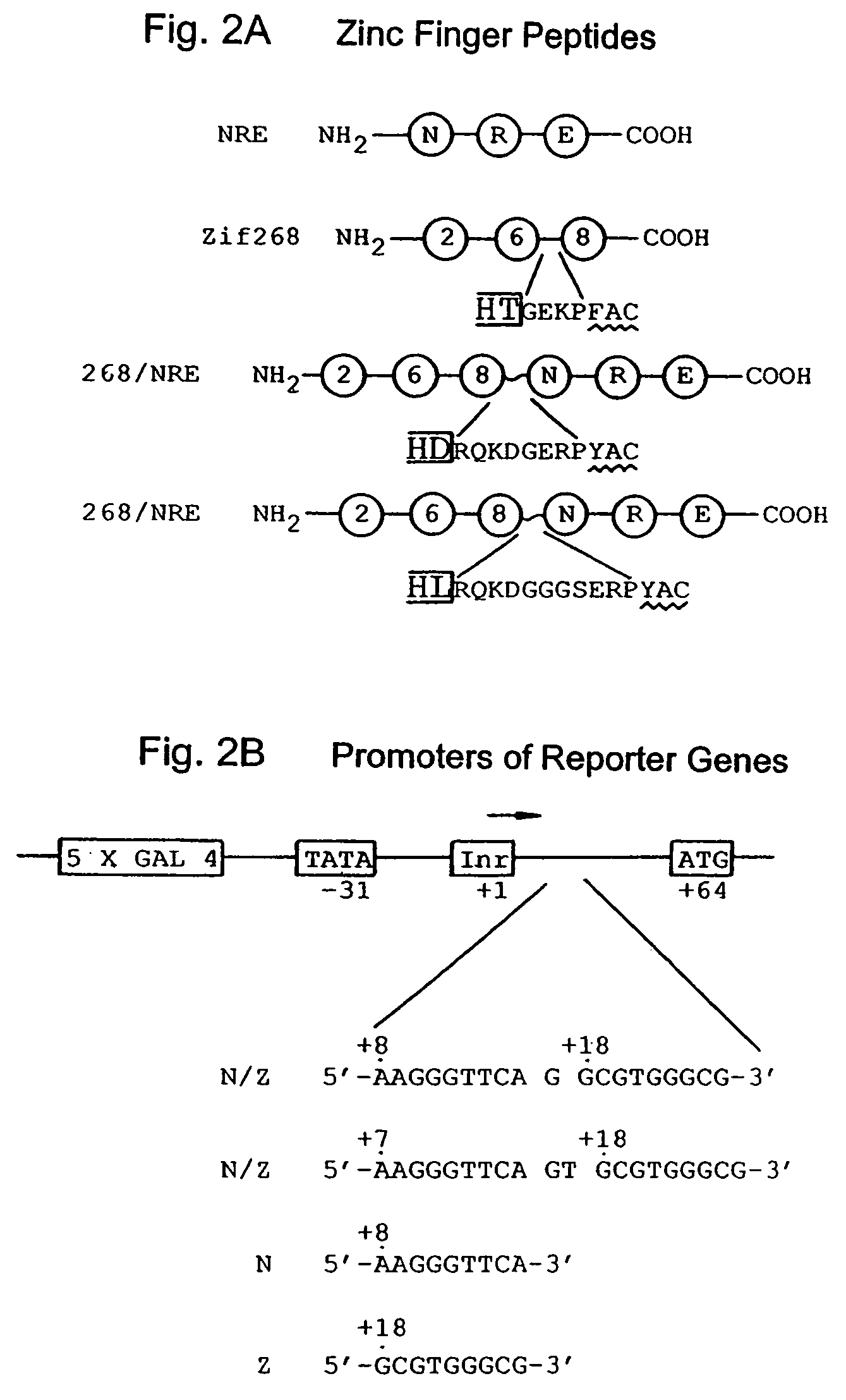
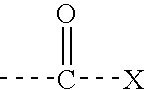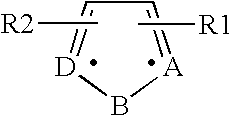Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
310 results about "Zinc finger" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
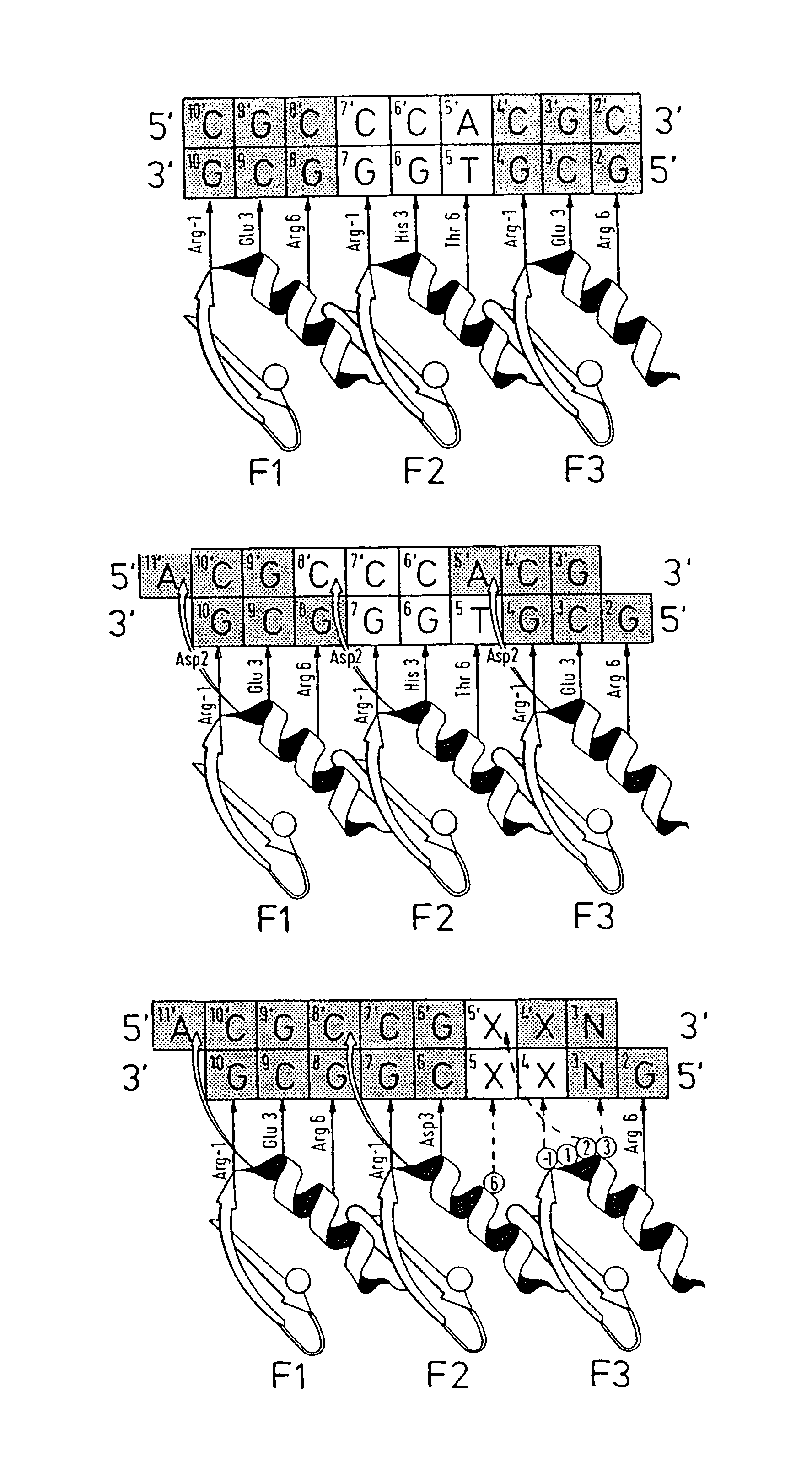
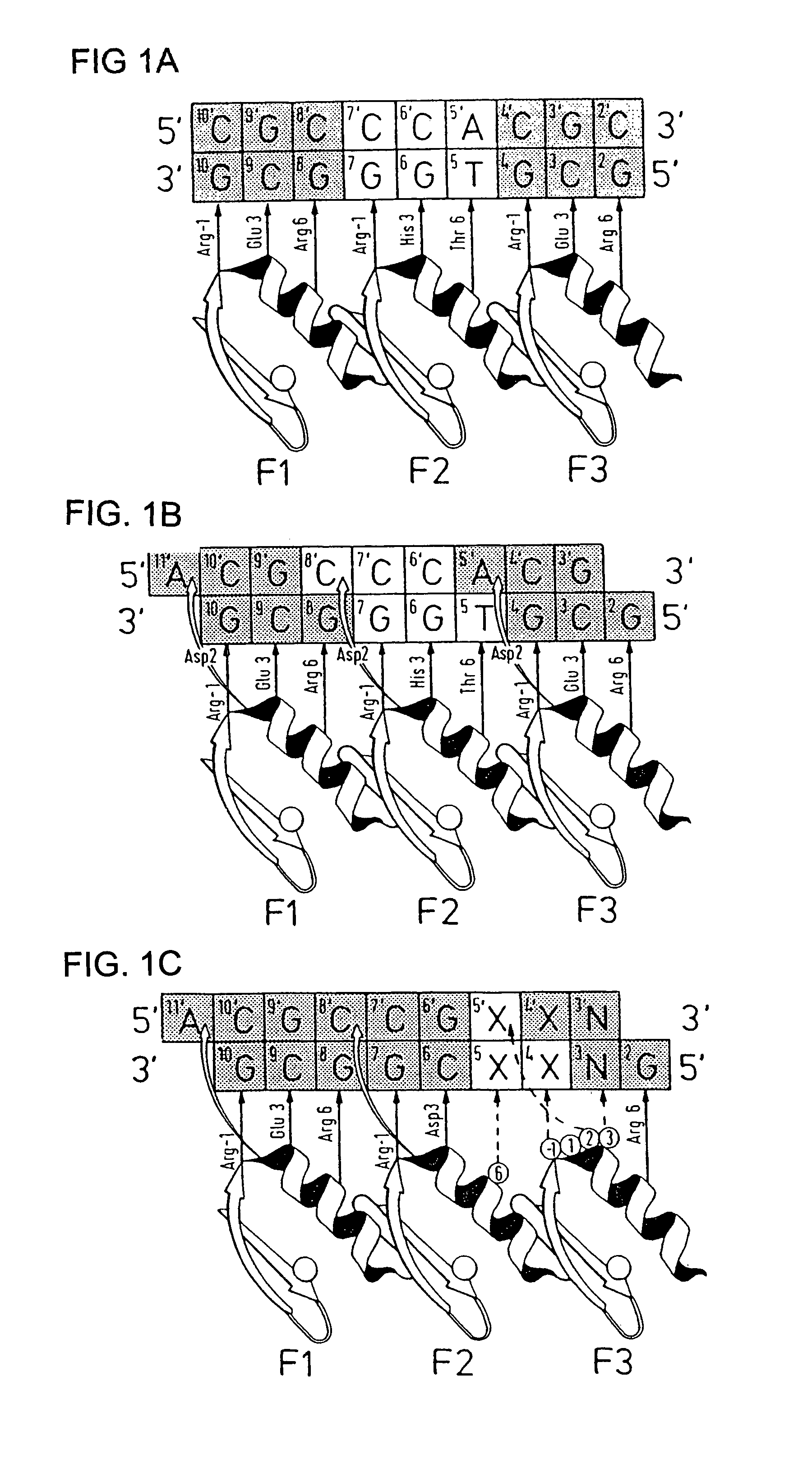
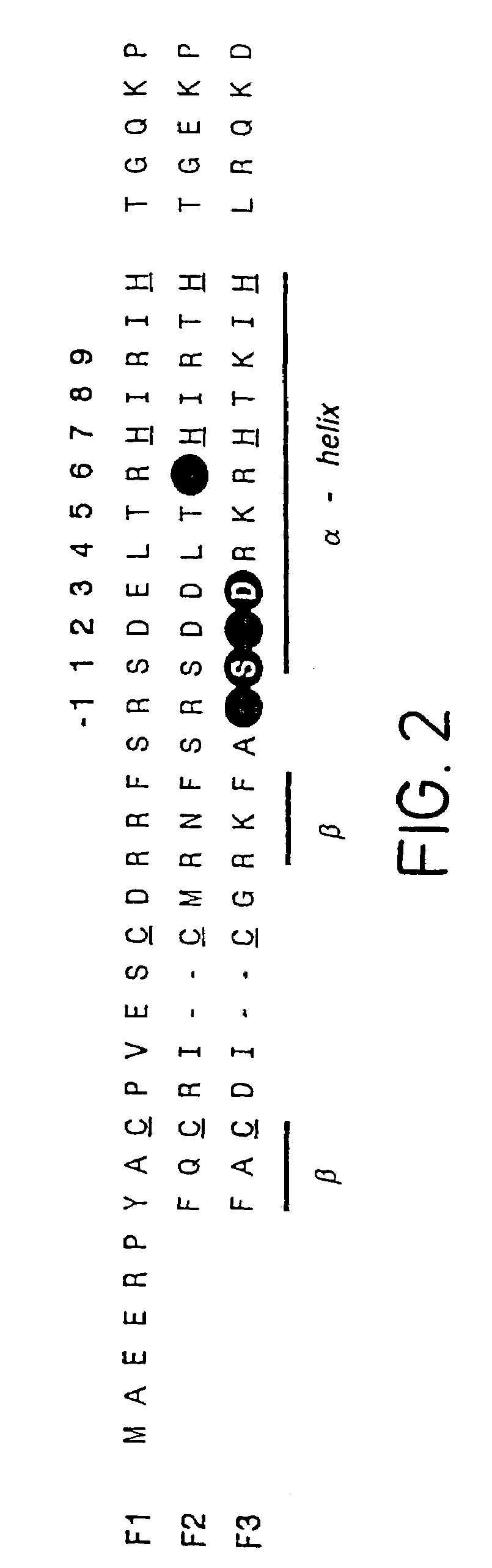
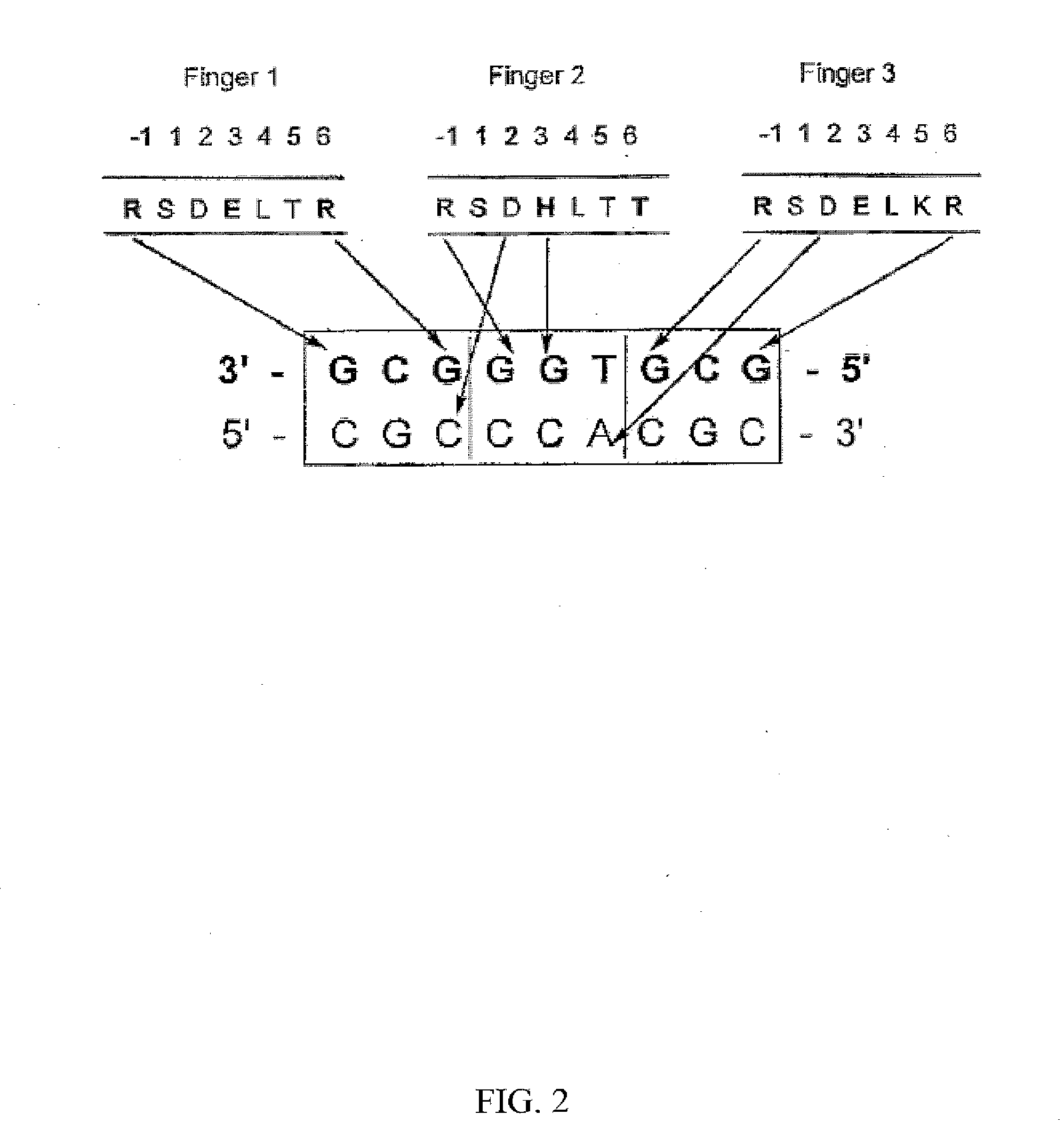
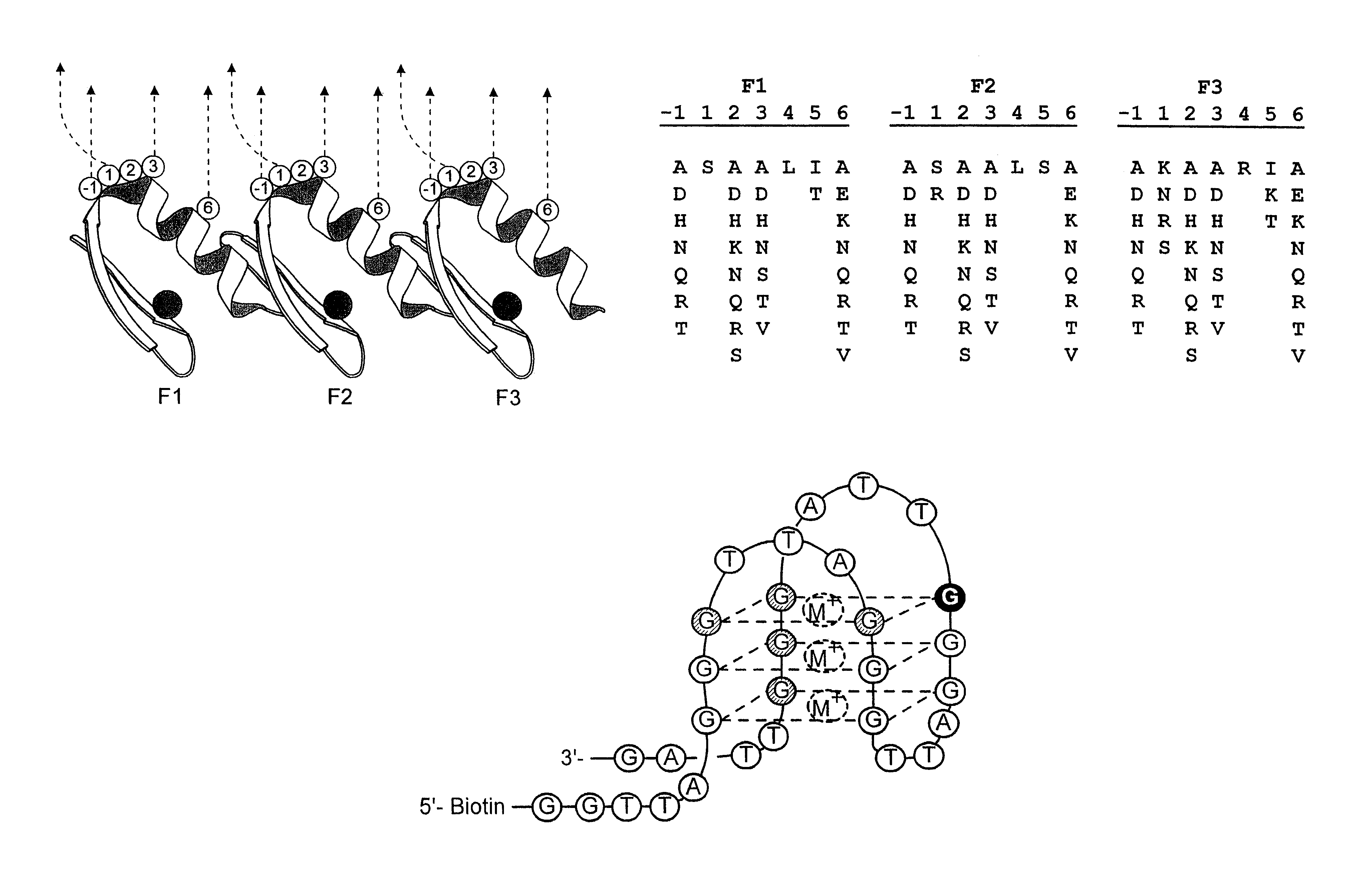
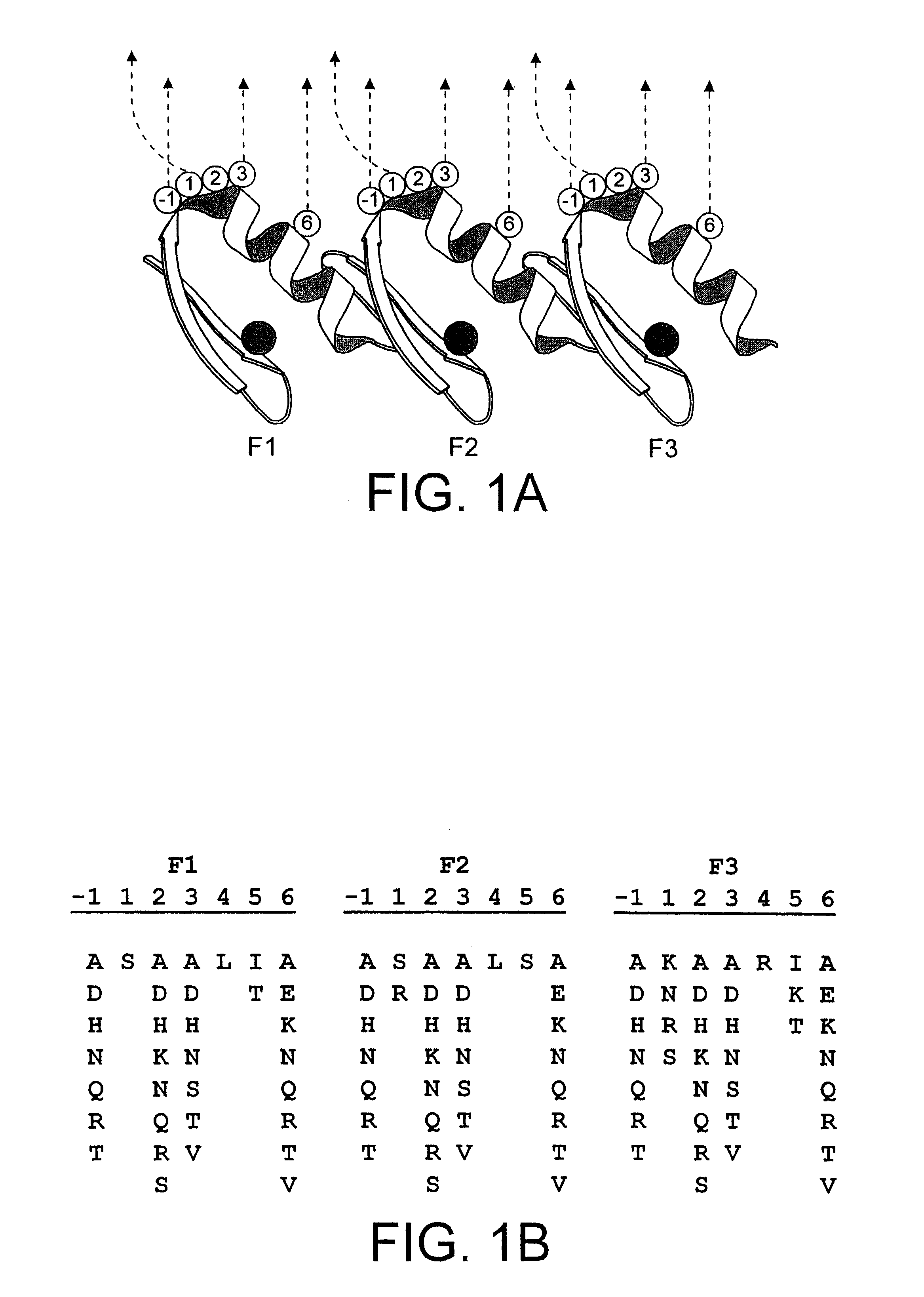
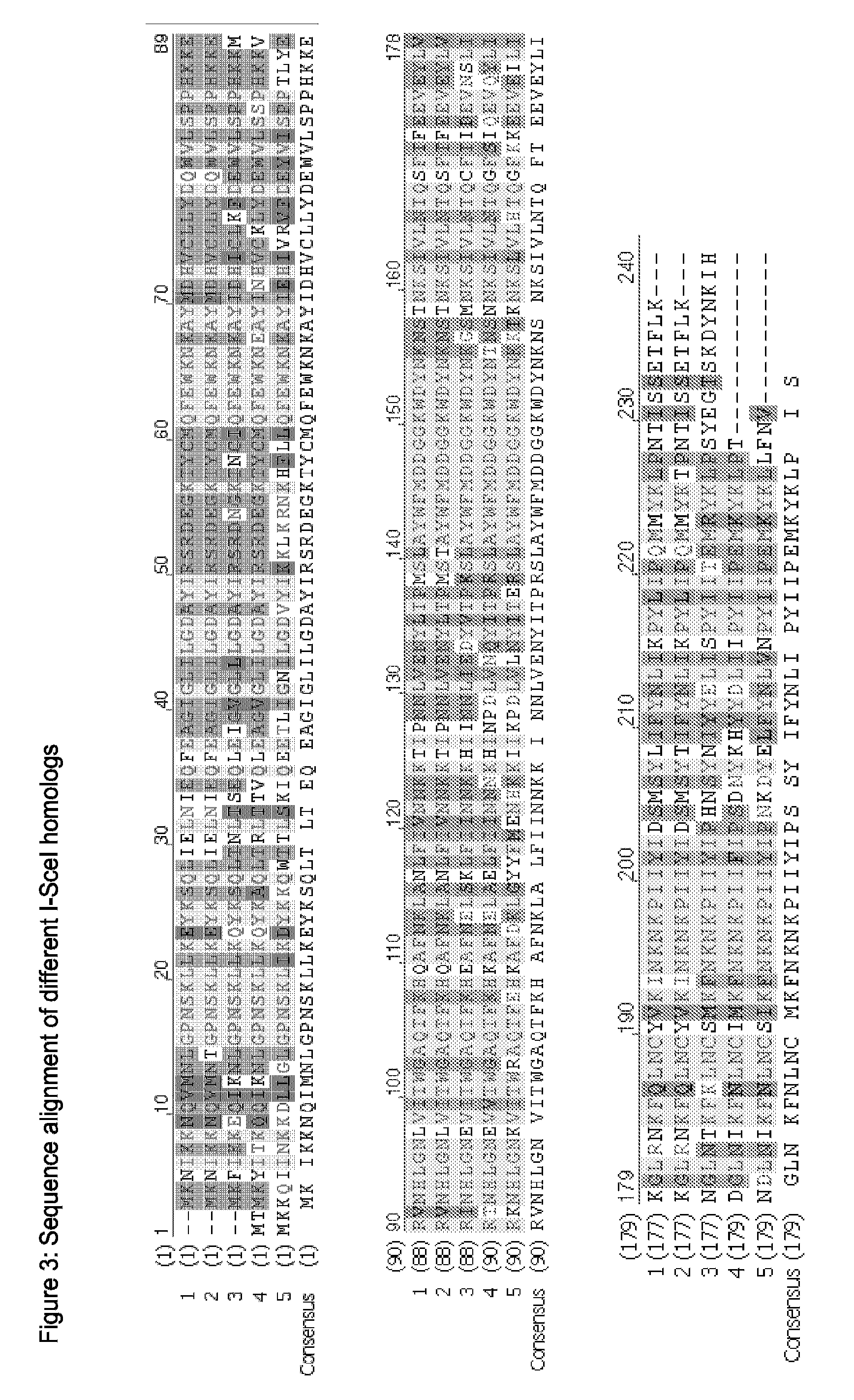
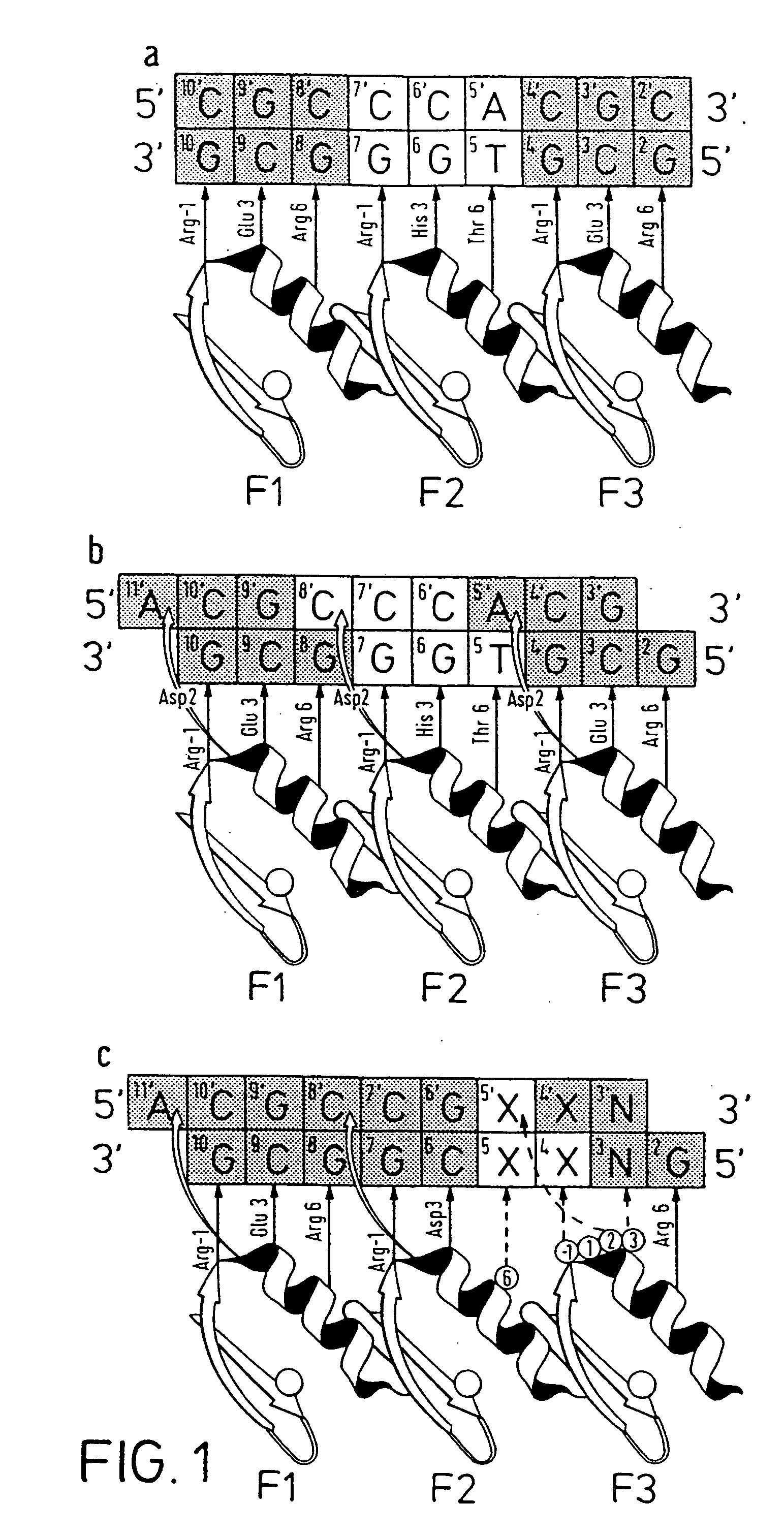
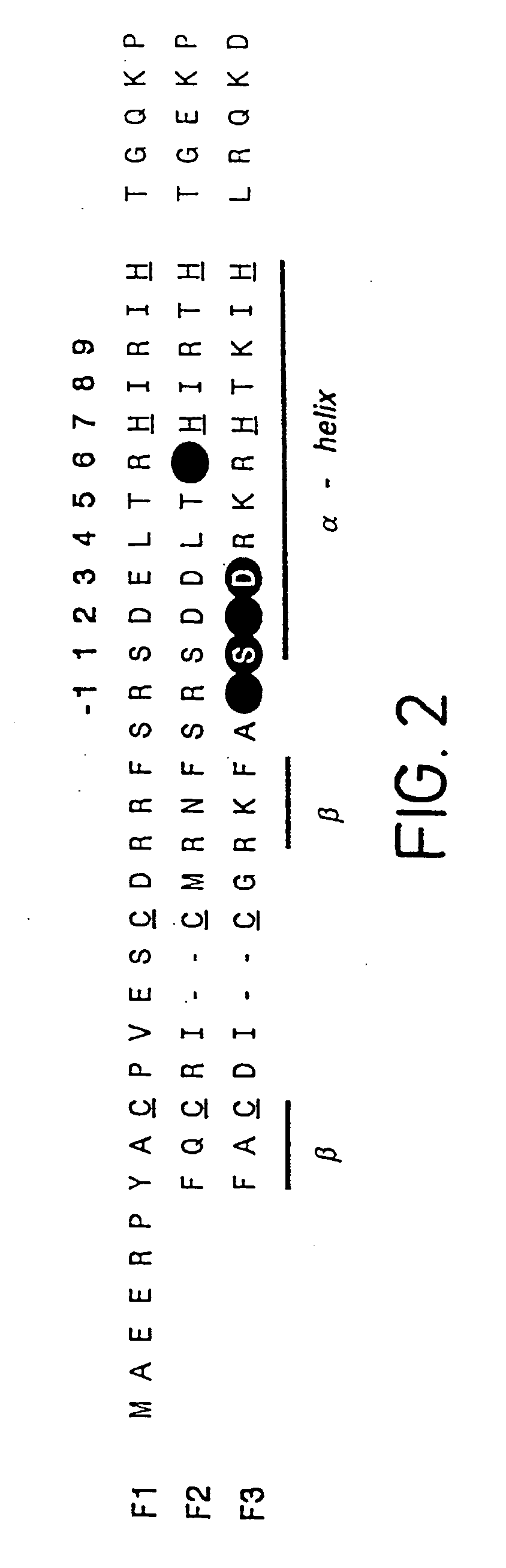
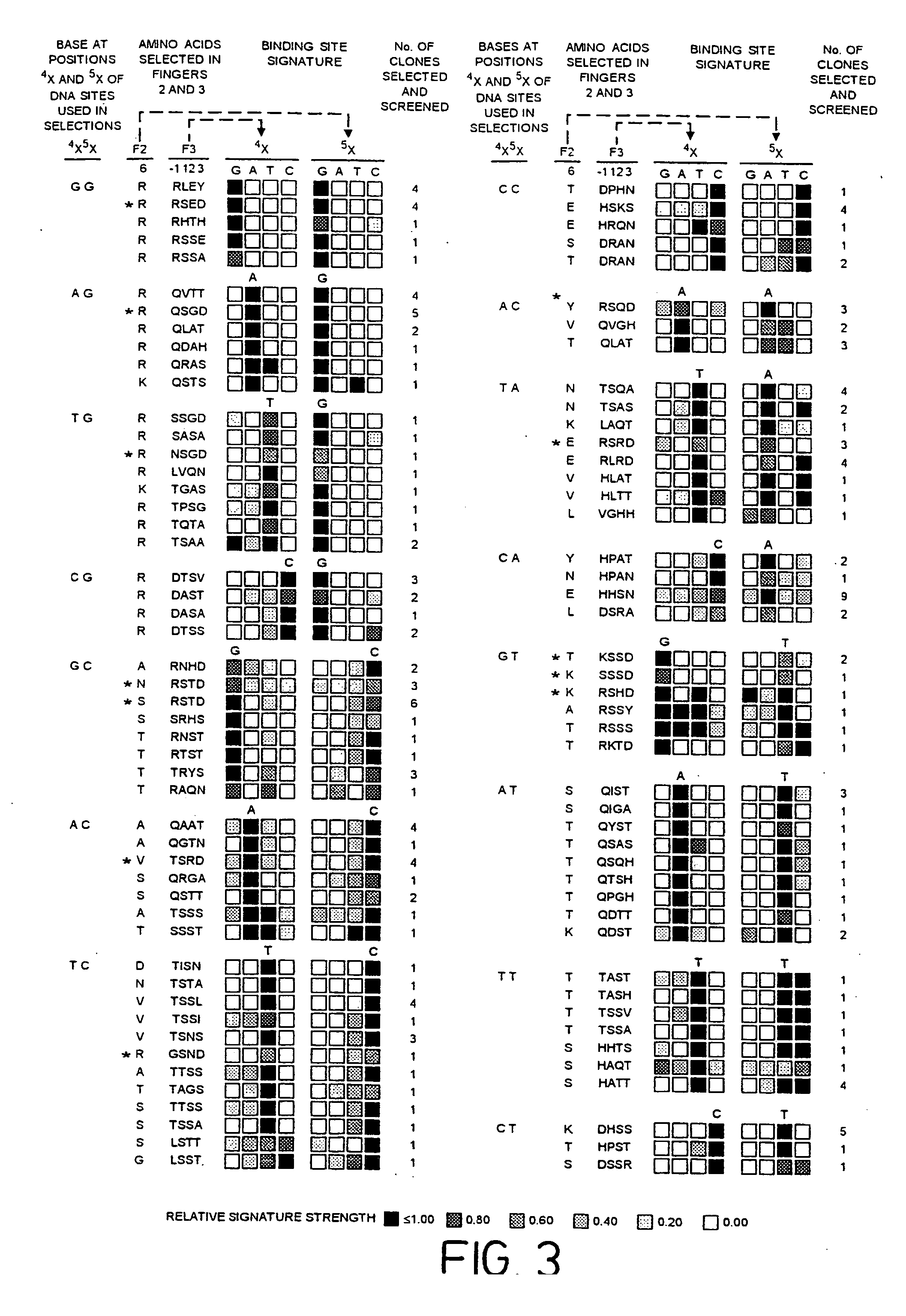
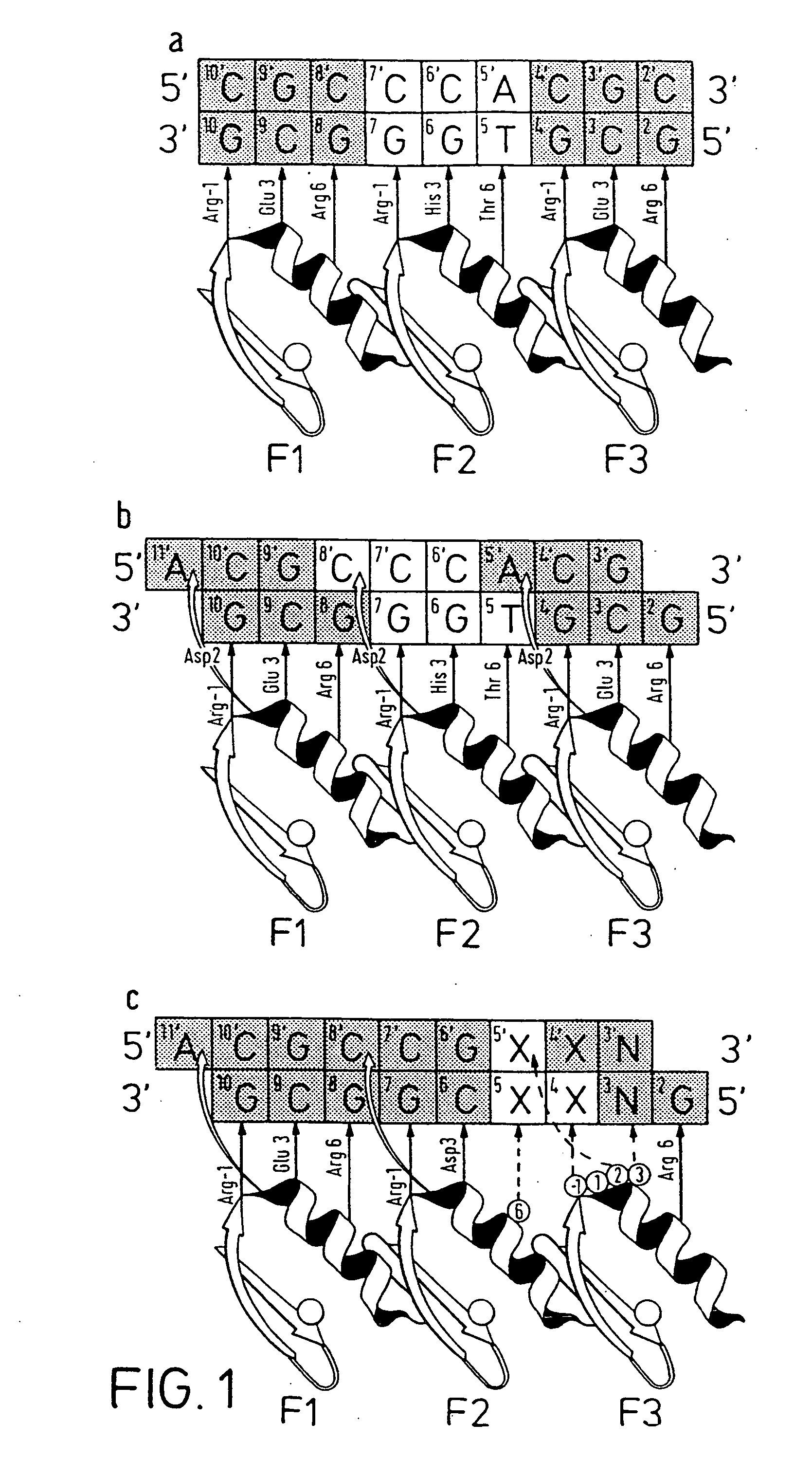
A zinc finger is a small protein structural motif that is characterized by the coordination of one or more zinc ions (Zn²⁺) in order to stabilize the fold. Originally coined to describe the finger-like appearance of a hypothesized structure from Xenopus laevis transcription factor IIIA, the zinc finger name has now come to encompass a wide variety of differing protein structures. Xenopus laevis TFIIIA was originally demonstrated to contain zinc and require the metal for function in 1983, the first such reported zinc requirement for a gene regulatory protein. It often appears as a metal-binding domain in multi-domain proteins.
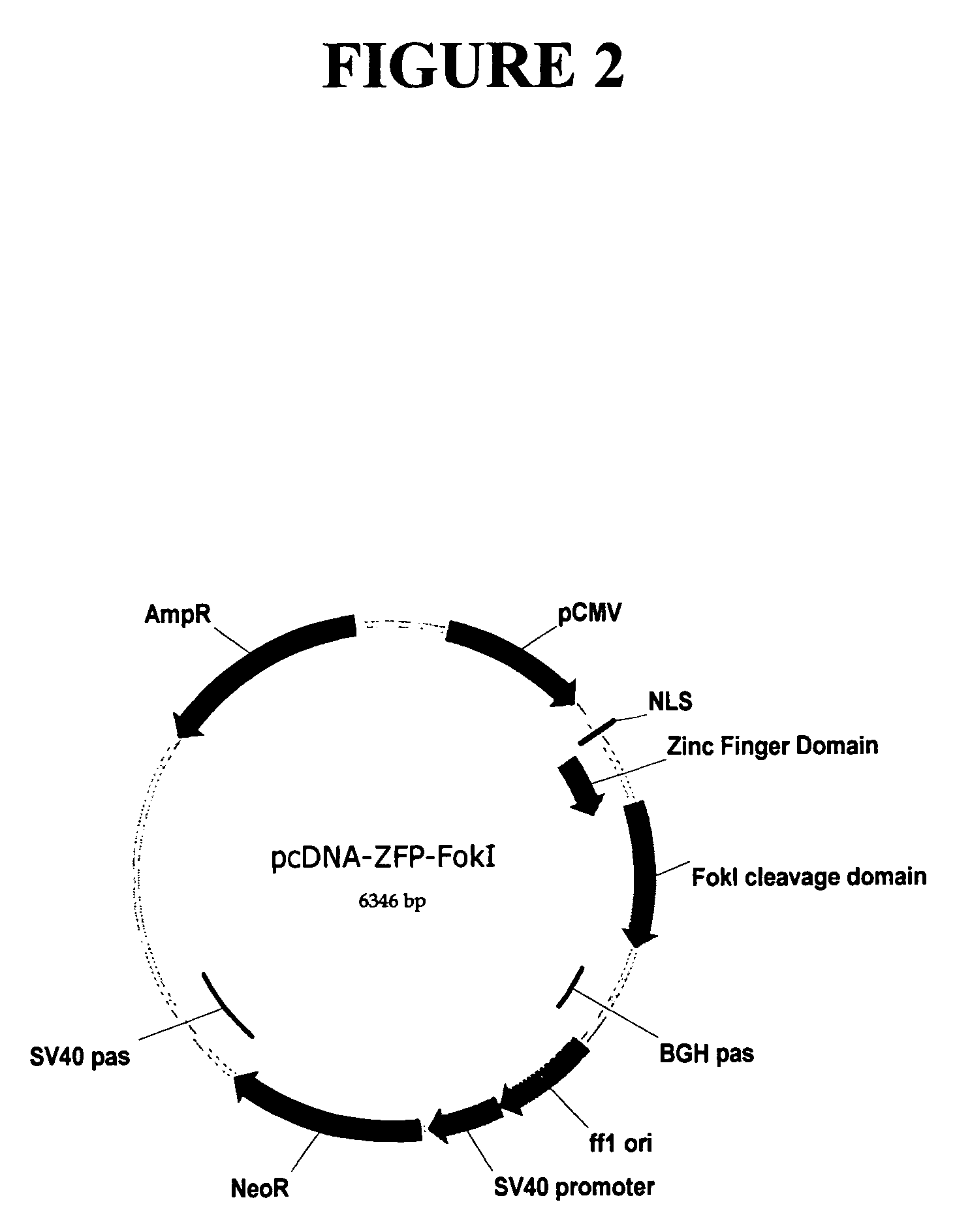
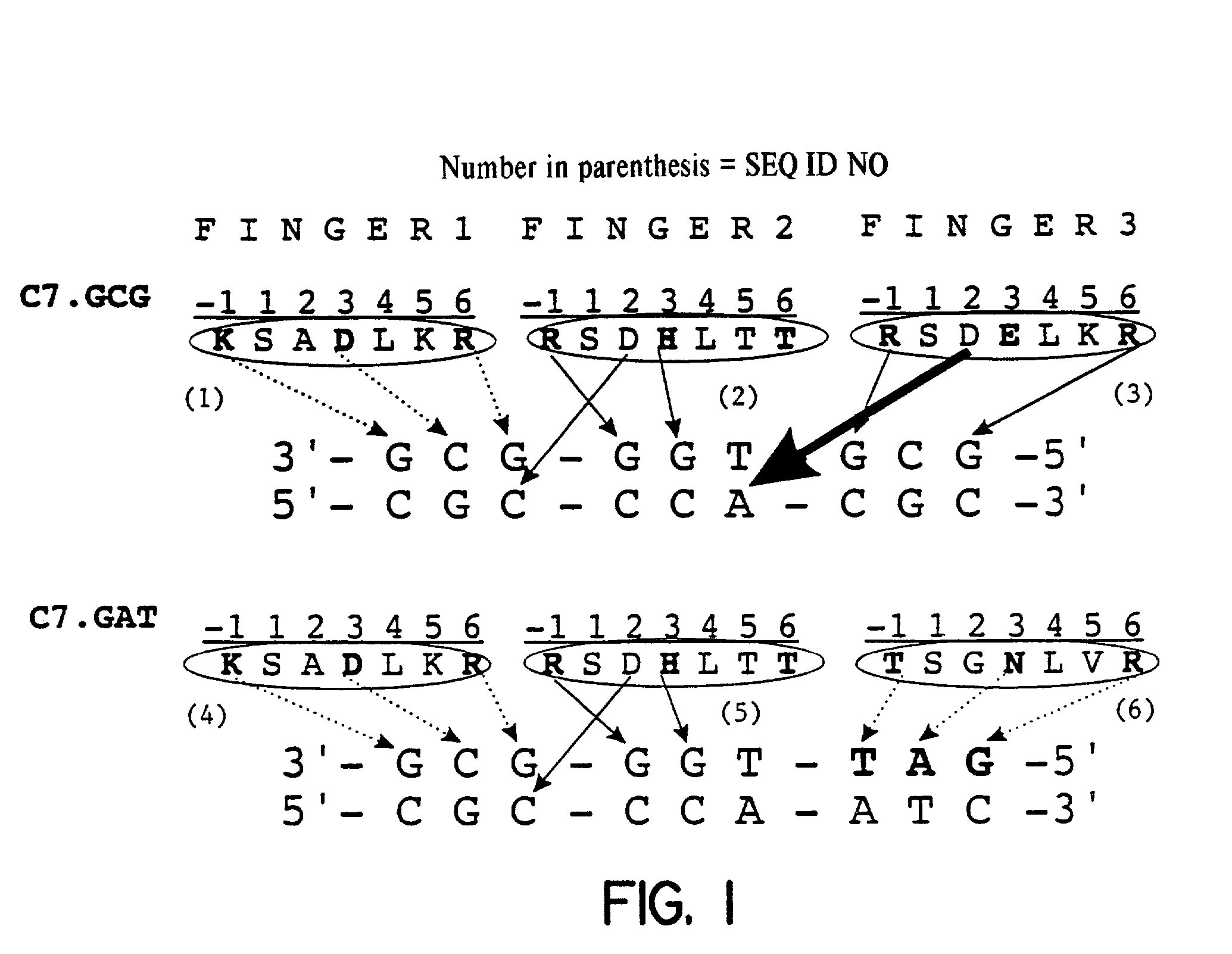
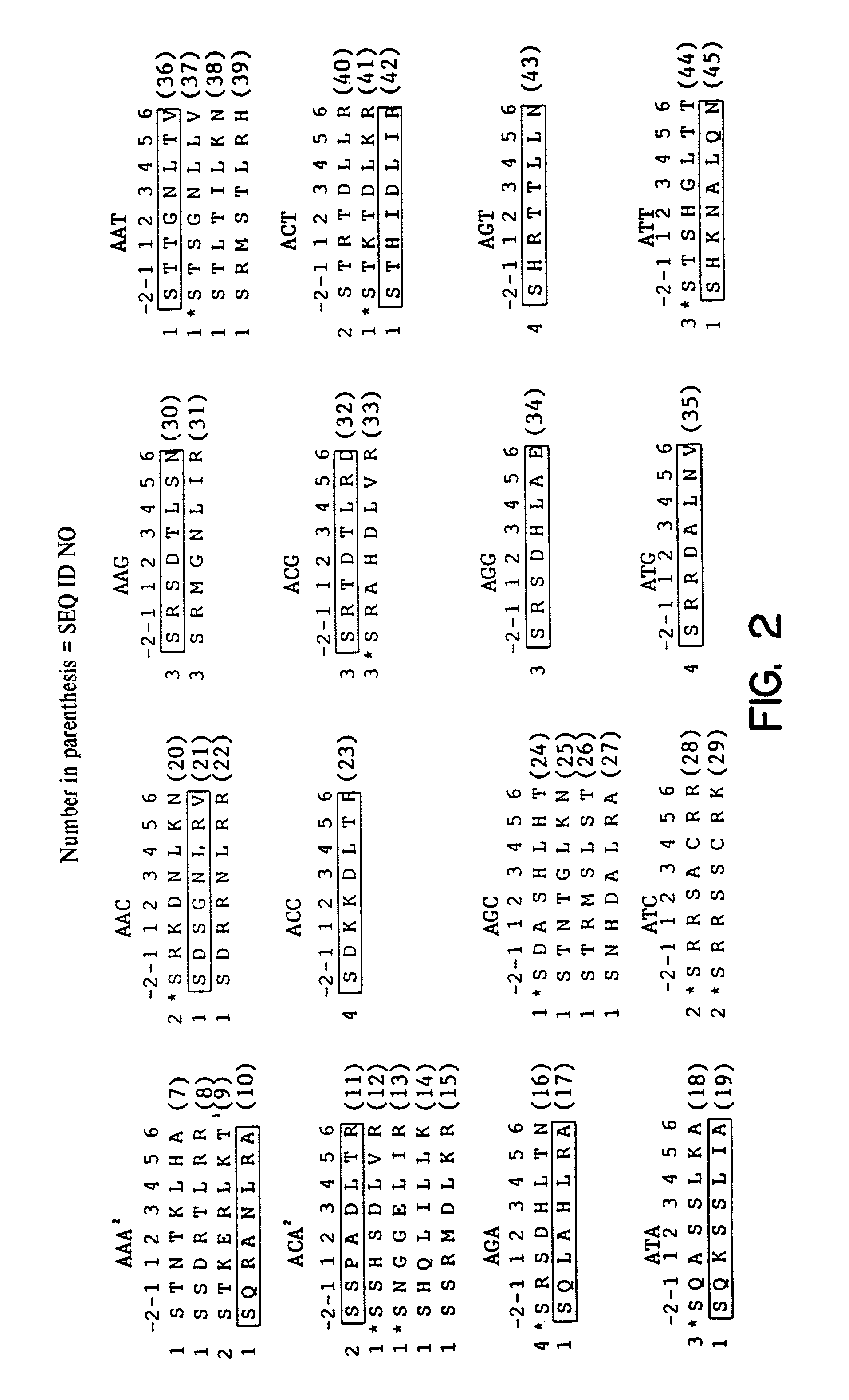
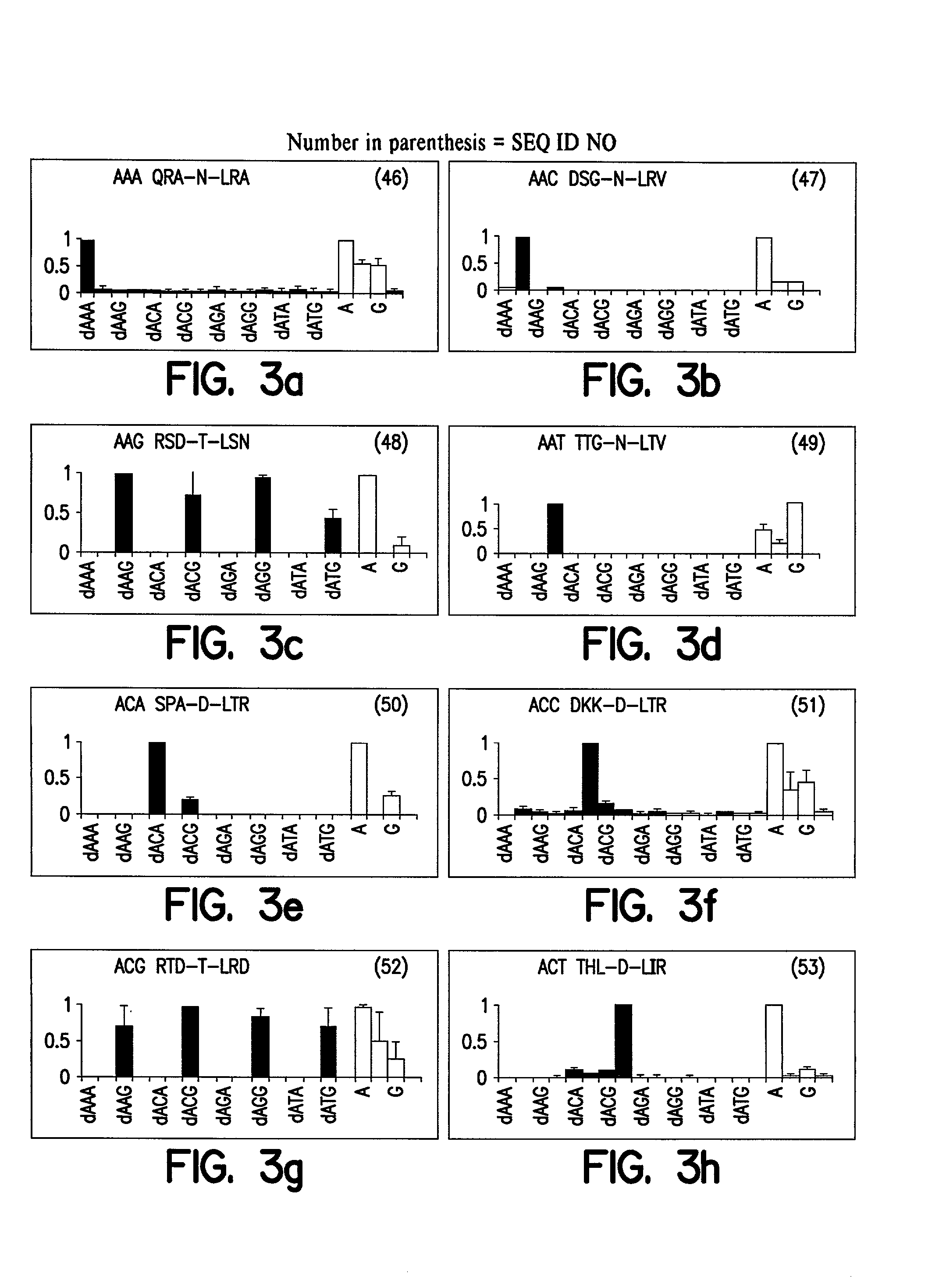
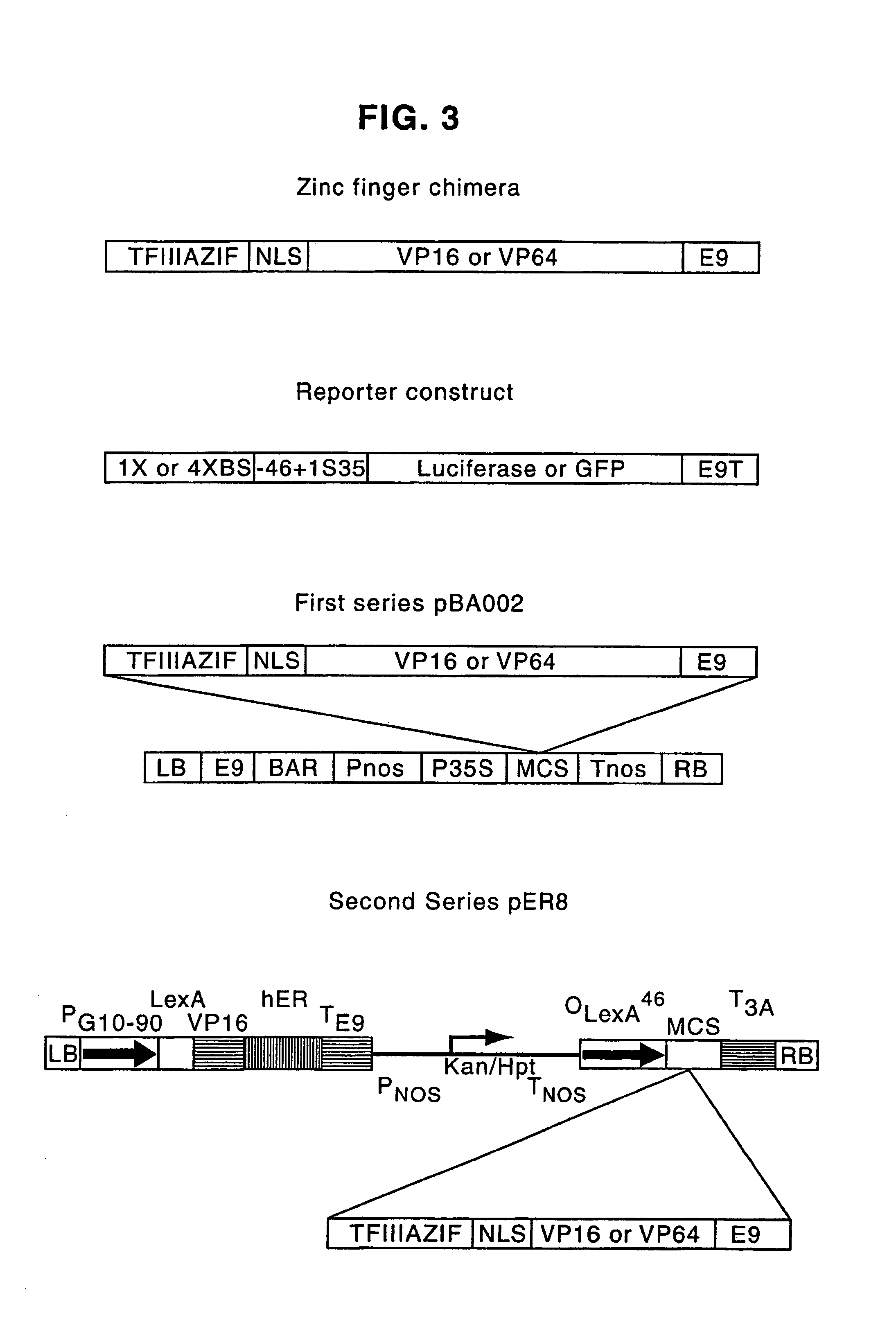
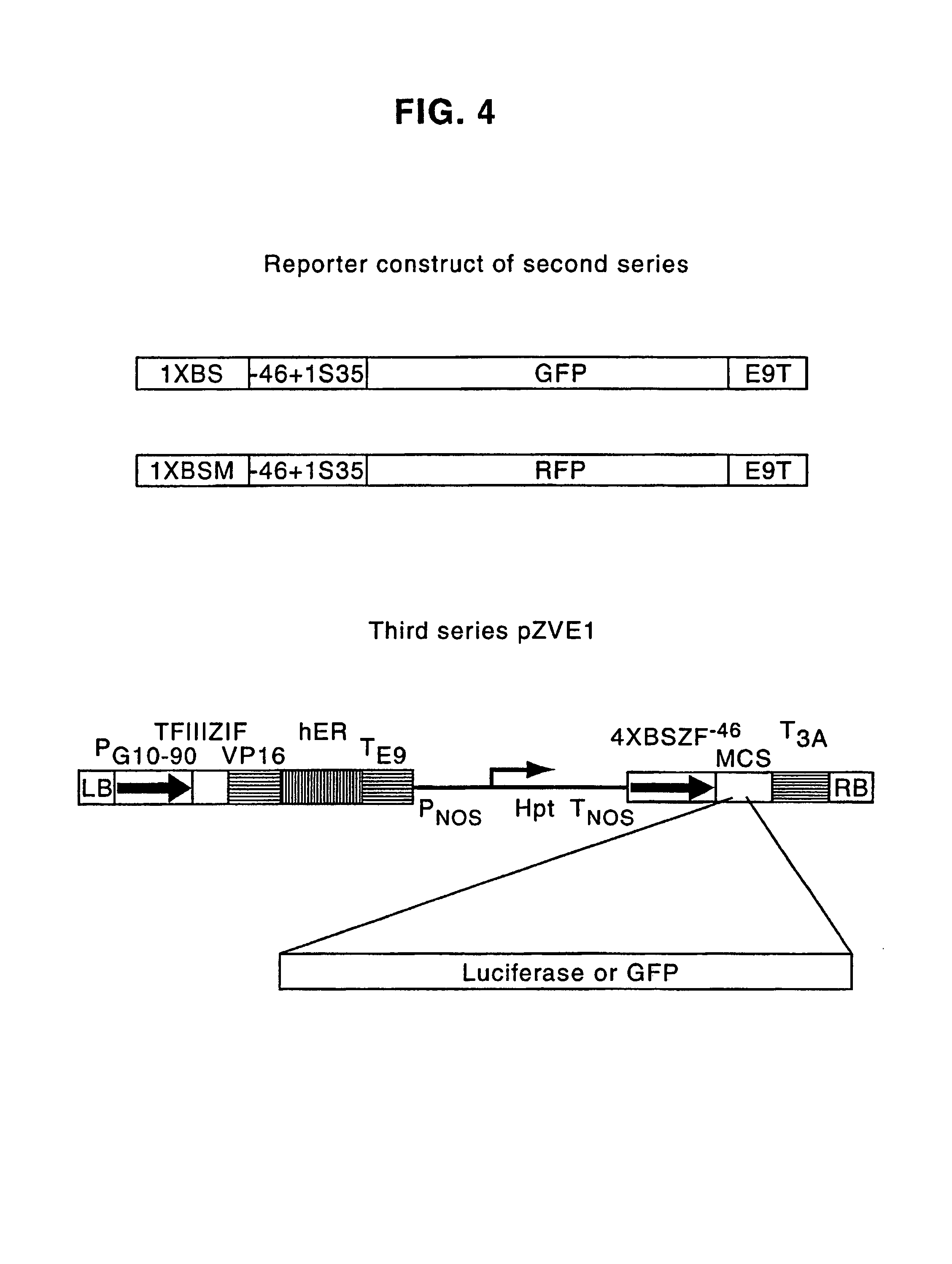
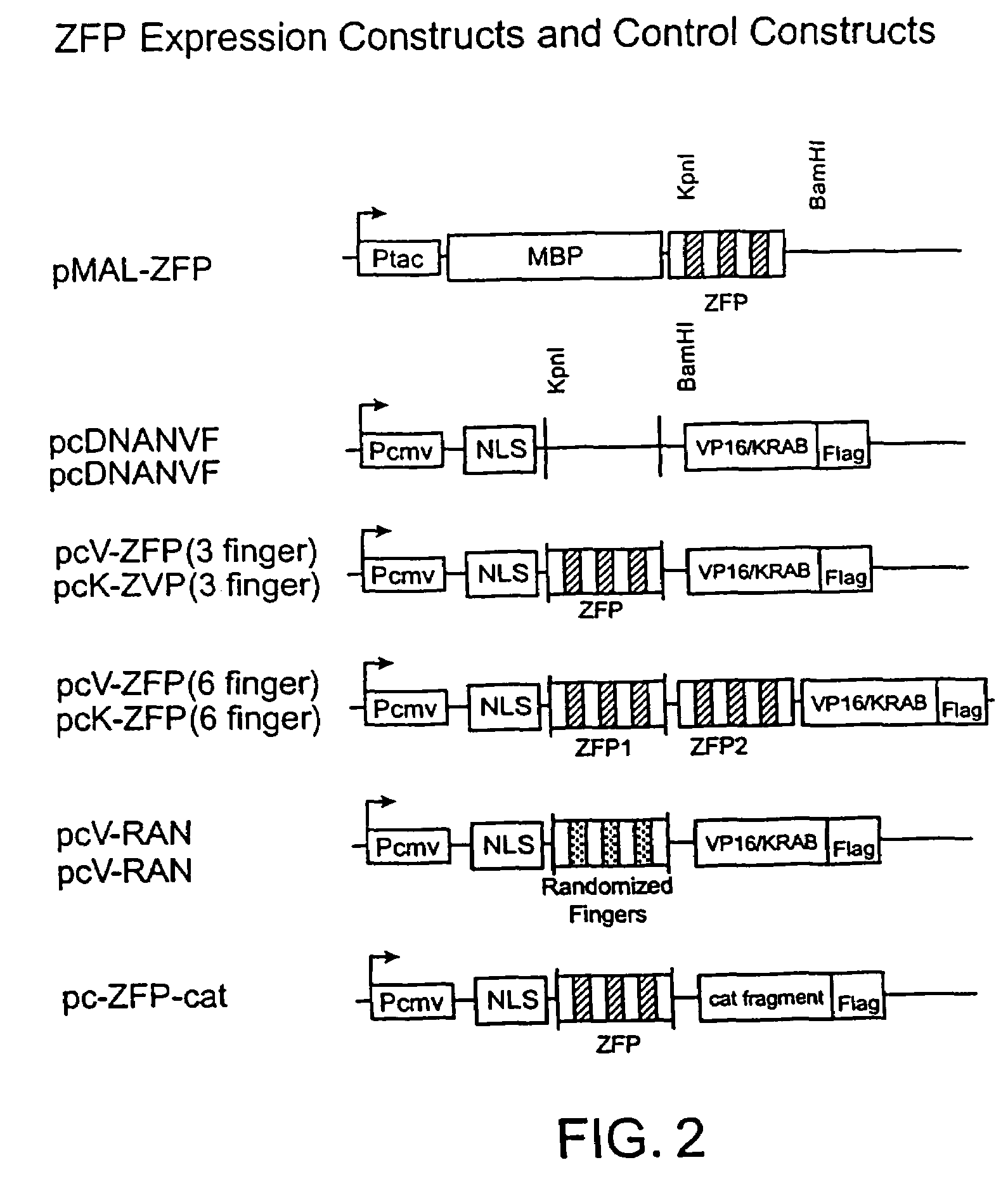
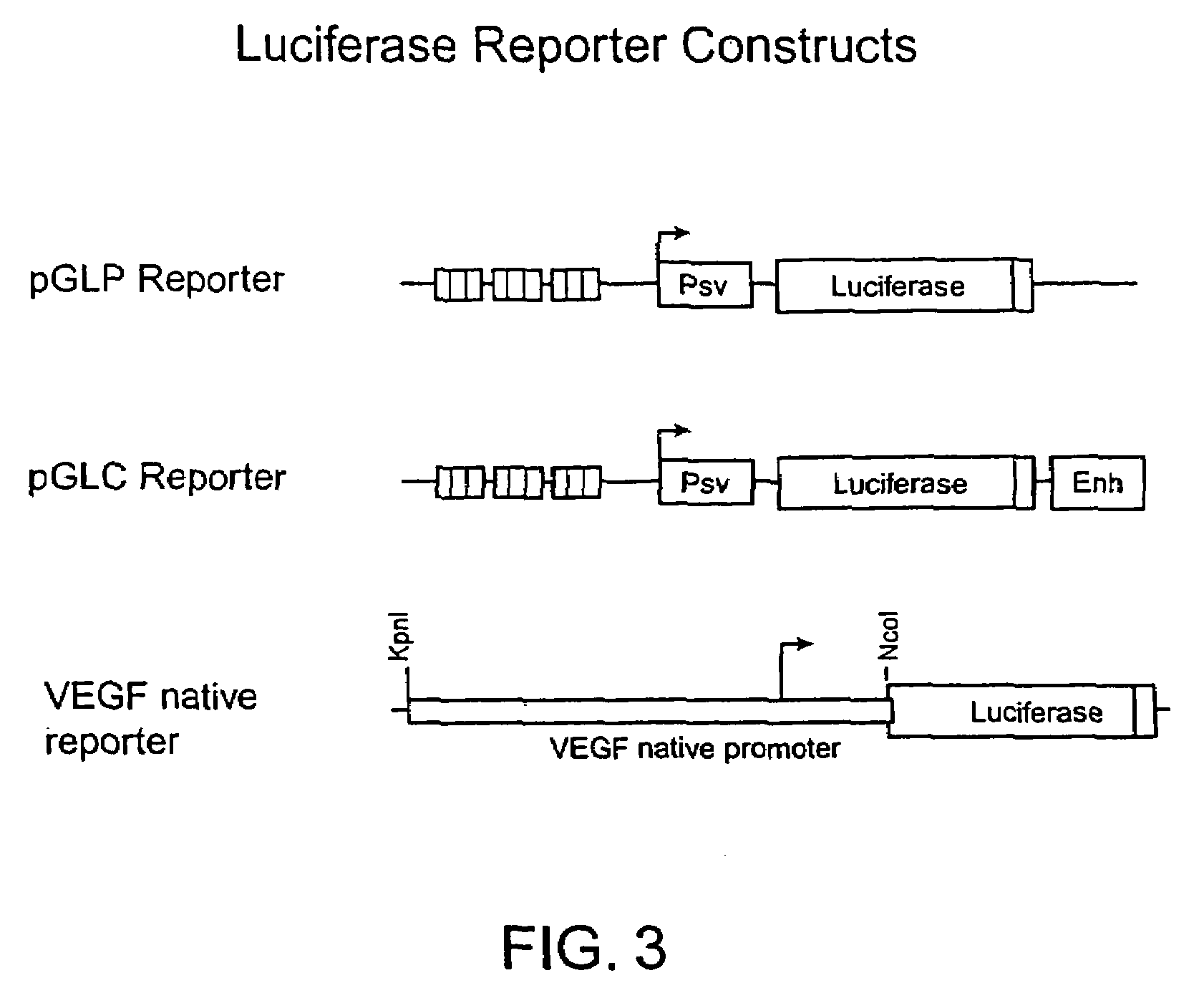
Regulation of endogenous gene expression in cells using zinc finger proteins
InactiveUS7013219B2Fusion with DNA-binding domainAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsZinc fingerGene expression
The present invention provides methods for modulating expression of endogenous cellular genes using engineered zinc finger proteins.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
Nucleic acid encoding poly-zinc finger proteins with improved linkers
InactiveUS7153949B2Enhanced affinity and specificityImprove the level ofPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDNA-binding domainNucleotide
Polynucleotides encoding chimeric proteins, and methods for their production and use are disclosed. The chimeric proteins comprise a flexible linker between two zinc finger DNA-binding domains, wherein the linker contains eight or more amino acids between the second conserved histidine residue of the carboxy-terminal zinc finger of the first domain and the first conserved cysteine residue of the amino-terminal zinc finger of the second domain.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
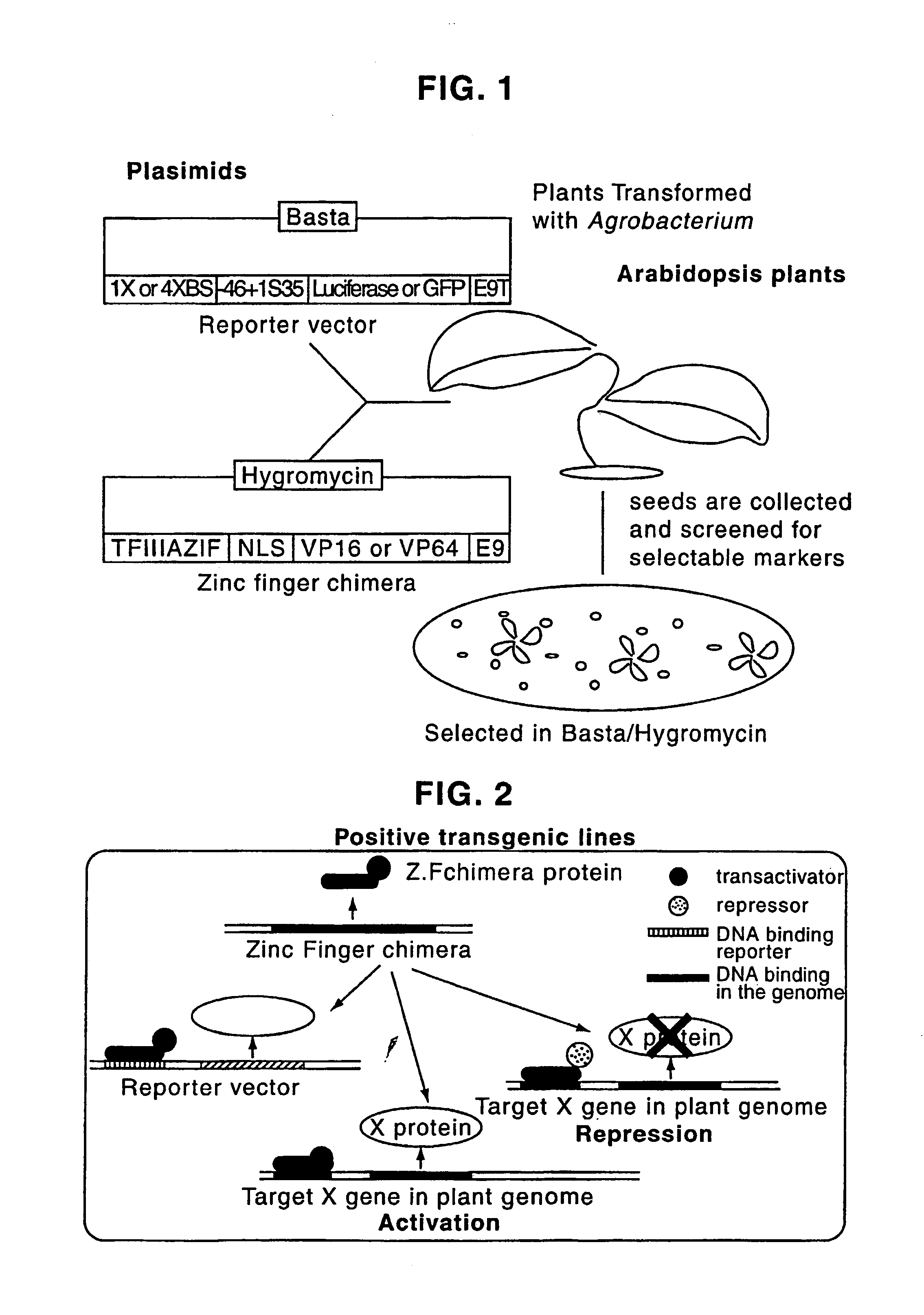
Zinc finger proteins for DNA binding and gene regulation in plants
InactiveUS7262054B2Alters compositionEasy to produceOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyZinc finger
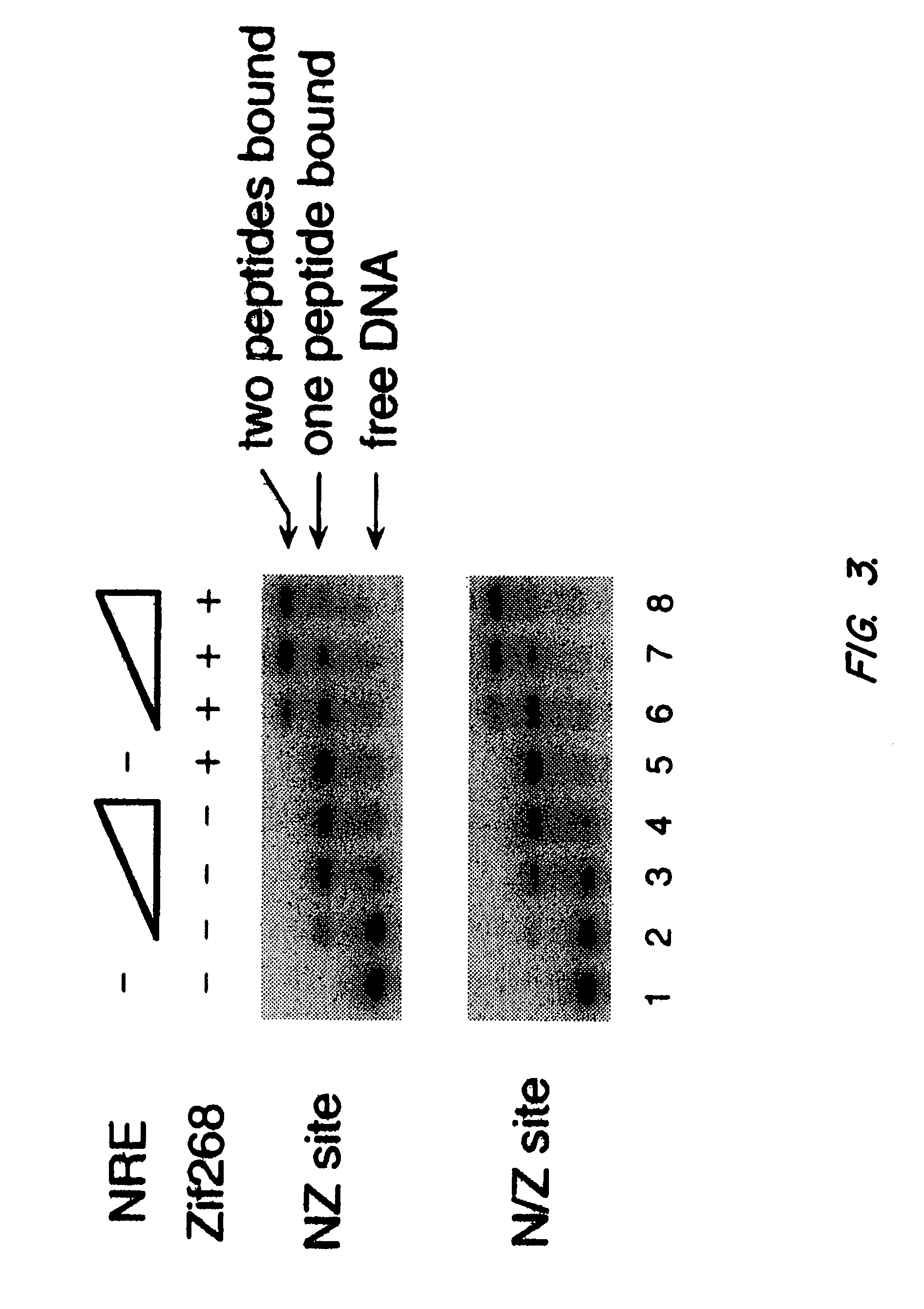
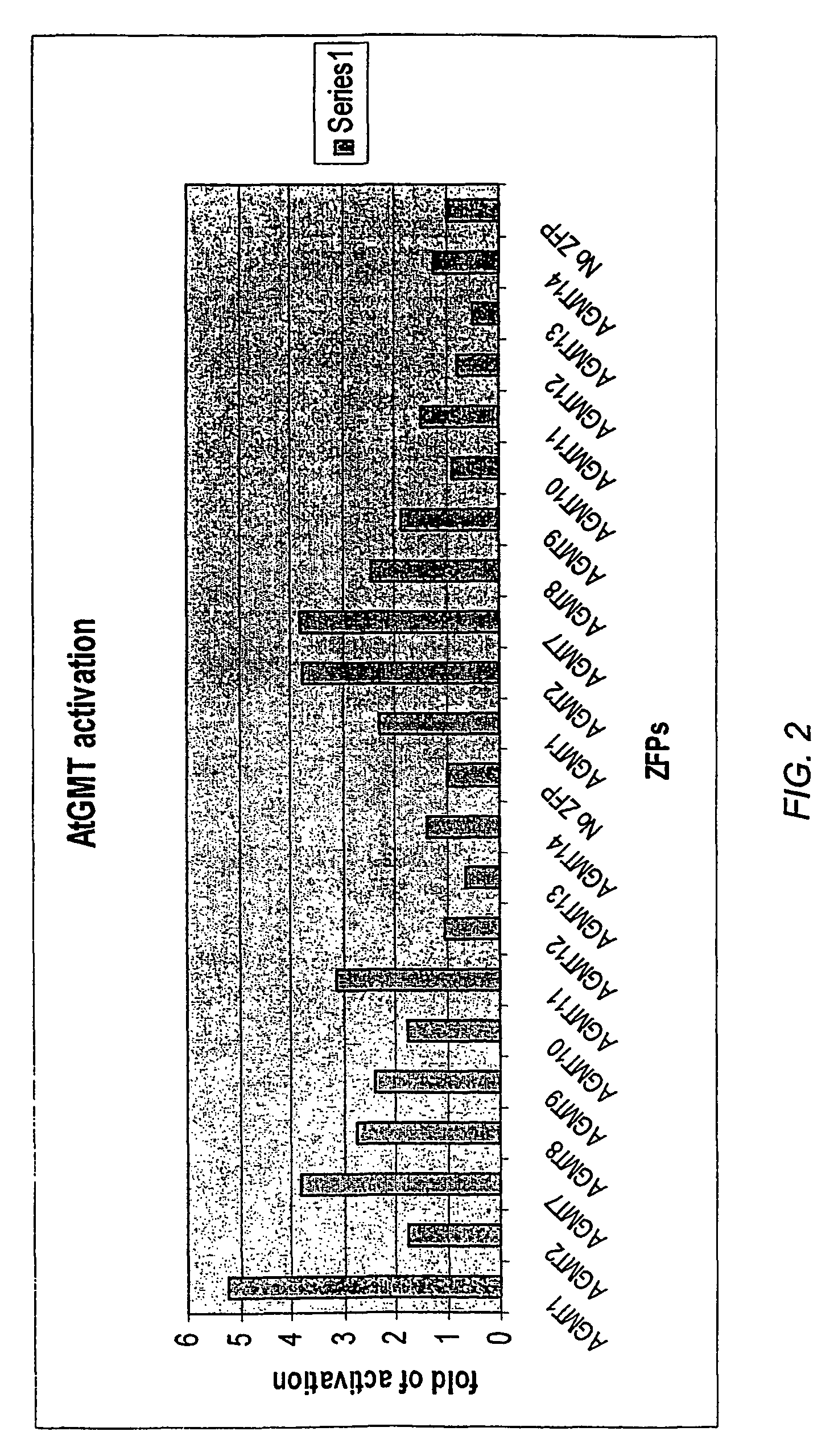
Disclosed herein are modified plant zinc finger proteins; compositions comprising modified plant zinc finger proteins and methods of making and using modified plant zinc finger proteins. The modified plant zinc finger proteins, in contrast to naturally-occurring plant zinc finger proteins, have a binding specificity that is determined by tandem arrays of modular zinc finger binding units.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
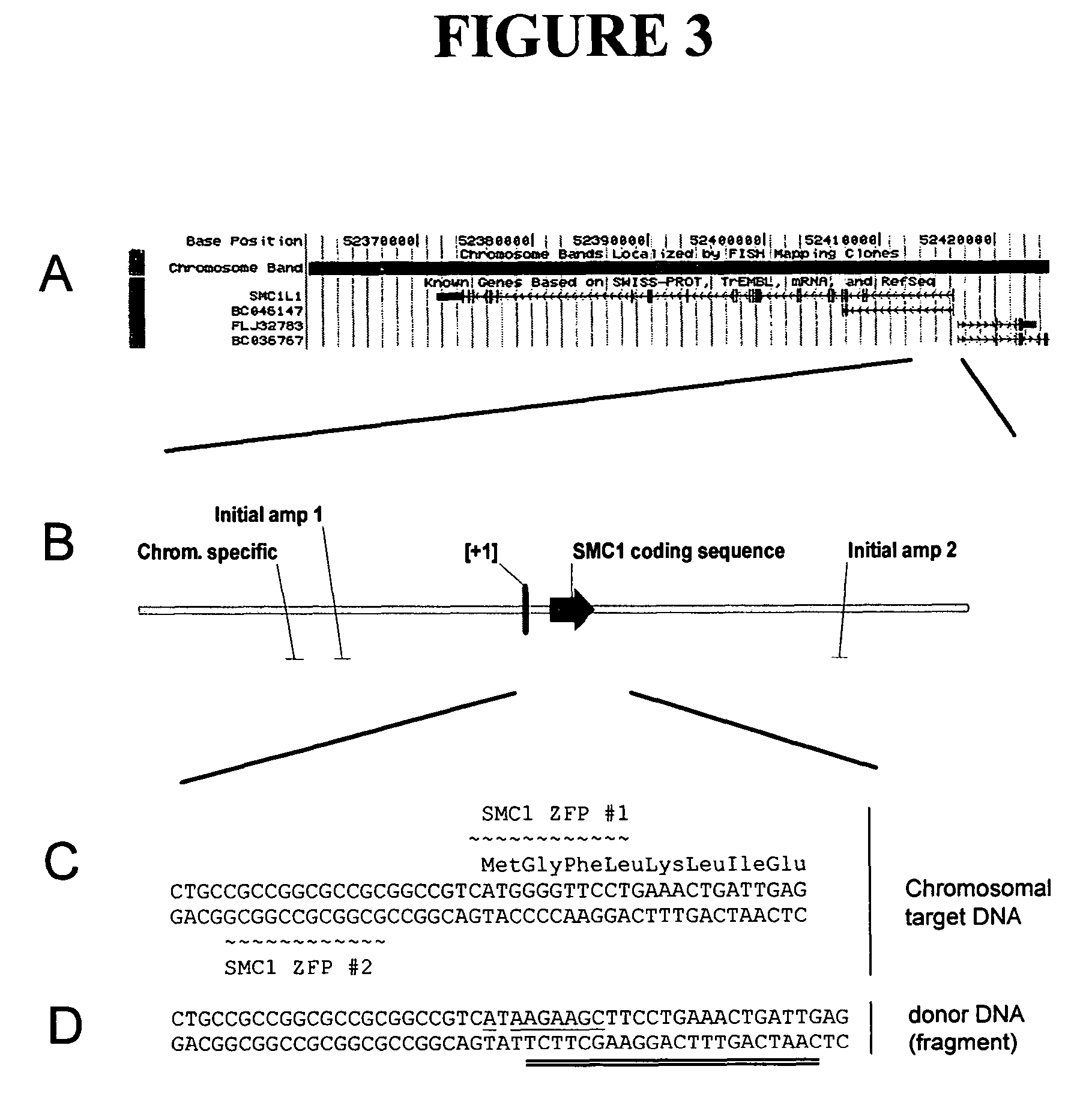
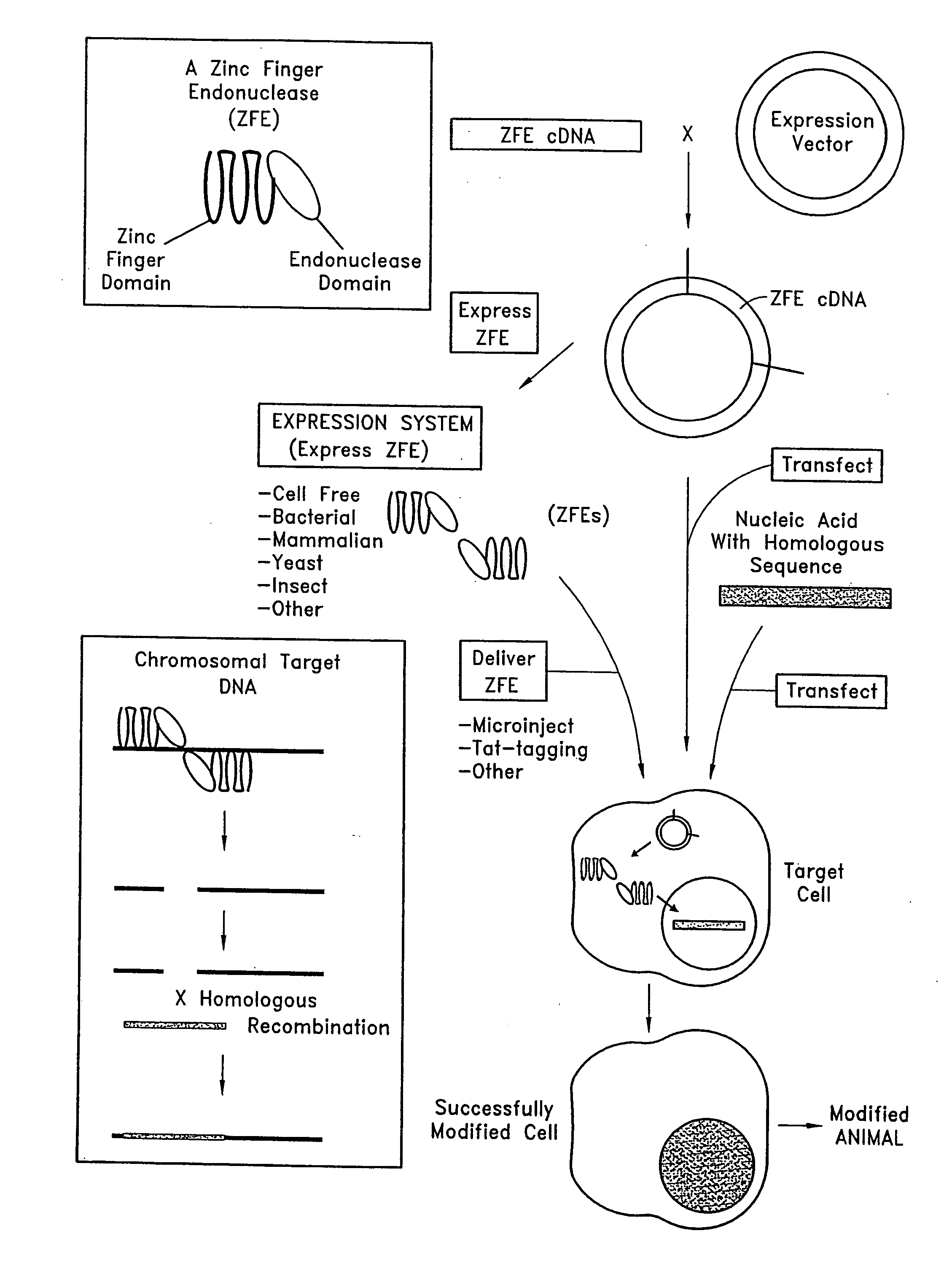
Methods and compositions for targeted cleavage and recombination
ActiveUS7888121B2High frequencyInhibitory activityFusion with DNA-binding domainHydrolasesPolynucleotideGenome
Disclosed herein are methods and compositions for targeted cleavage of a genomic sequence, targeted alteration of a genomic sequence, and targeted recombination between a genomic region and an exogenous polynucleotide homologous to the genomic region. The compositions include fusion proteins comprising a cleavage domain (or cleavage half-domain) and an engineered zinc finger domain and polynucleotides encoding same. Methods for targeted cleavage include introduction of such fusion proteins, or polynucleotides encoding same, into a cell. Methods for targeted recombination additionally include introduction of an exogenous polynucleotide homologous to a genomic region into cells comprising the disclosed fusion proteins.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
Treatment of neuropathic pain with zinc finger proteins
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
Nucleic acid binding proteins
Disclosed herein are methods for designing DNA binding proteins comprising a plurality of zinc fingers and methods for binding the proteins to target nucleotide sequences in cells.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
Screening system for zinc finger polypeptides for a desired binding ability
InactiveUS6733970B2Determining affinityDetermining specificitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingZinc
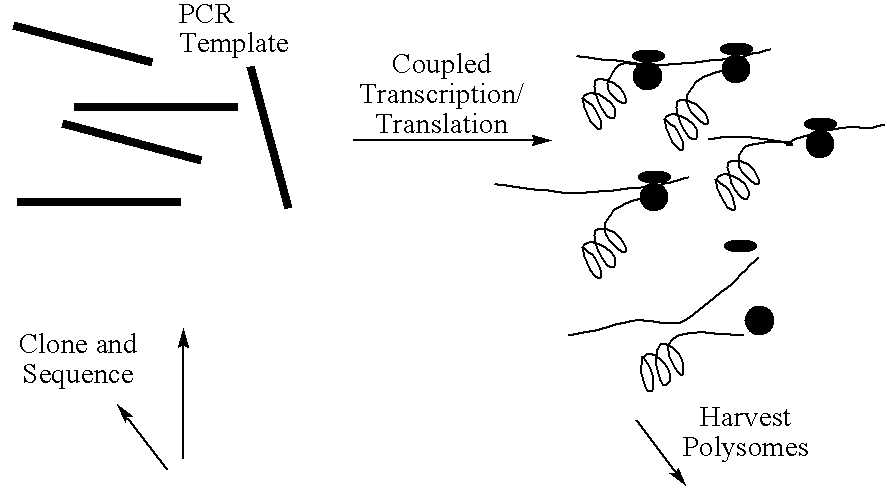
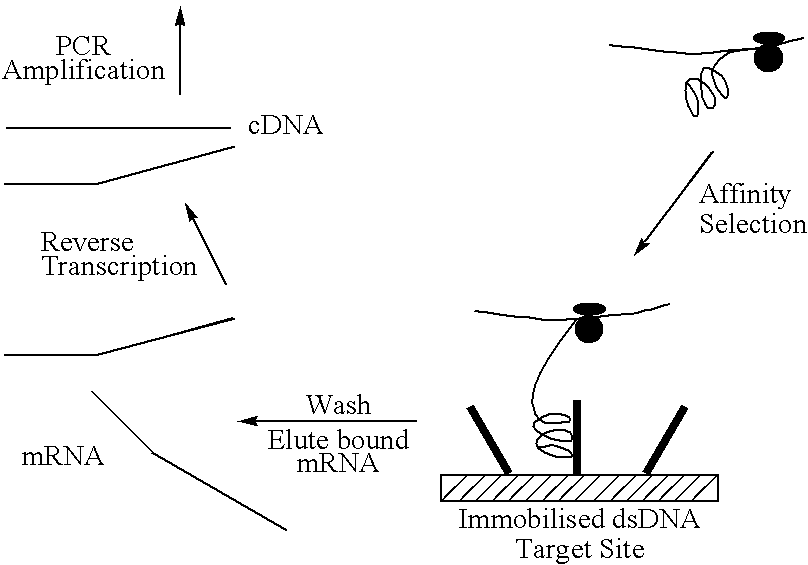
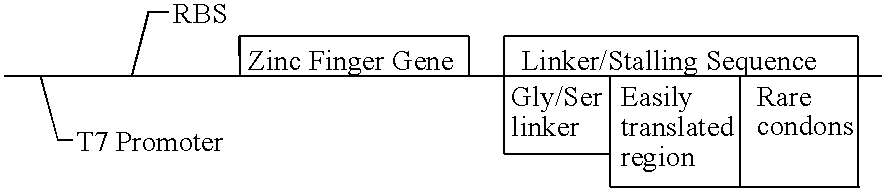
This invention relates to a method for producing a zinc finger nucleic acid binding protein comprising preparing a zinc finger protein according design rules, varying the protein at one or more positions, and selecting variants which bind to a target nucleic acid sequence by polysome display.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD +1
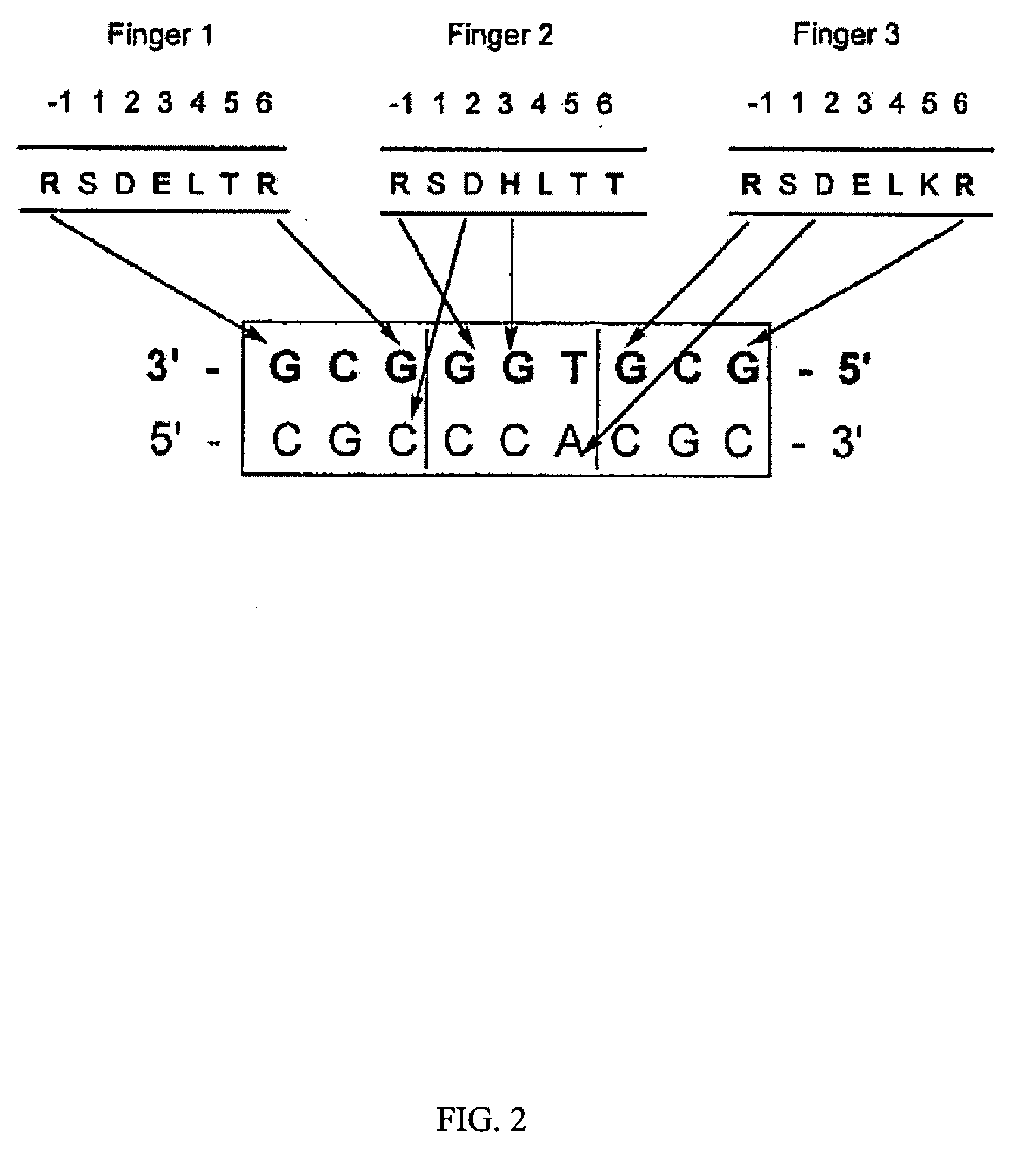
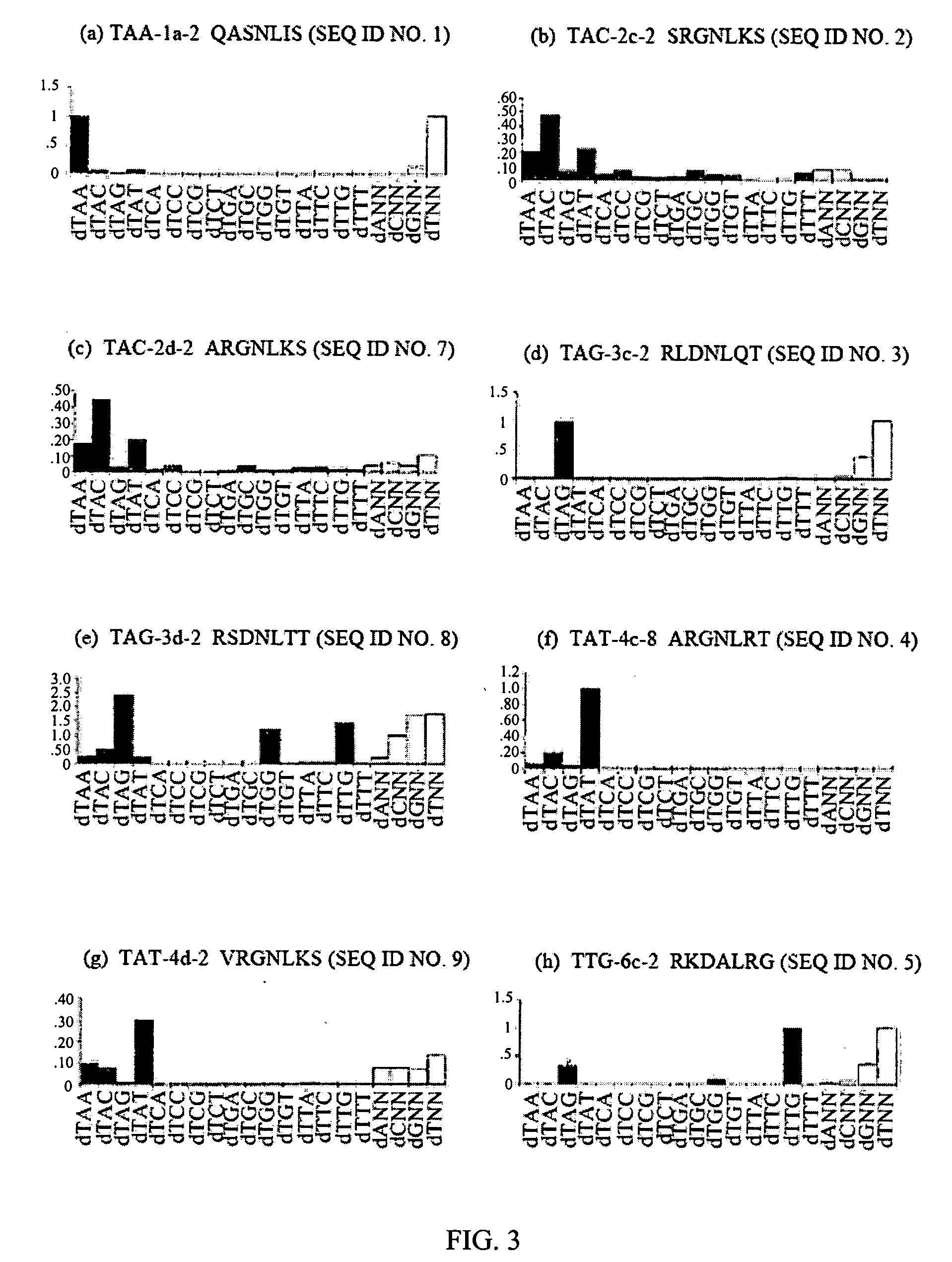
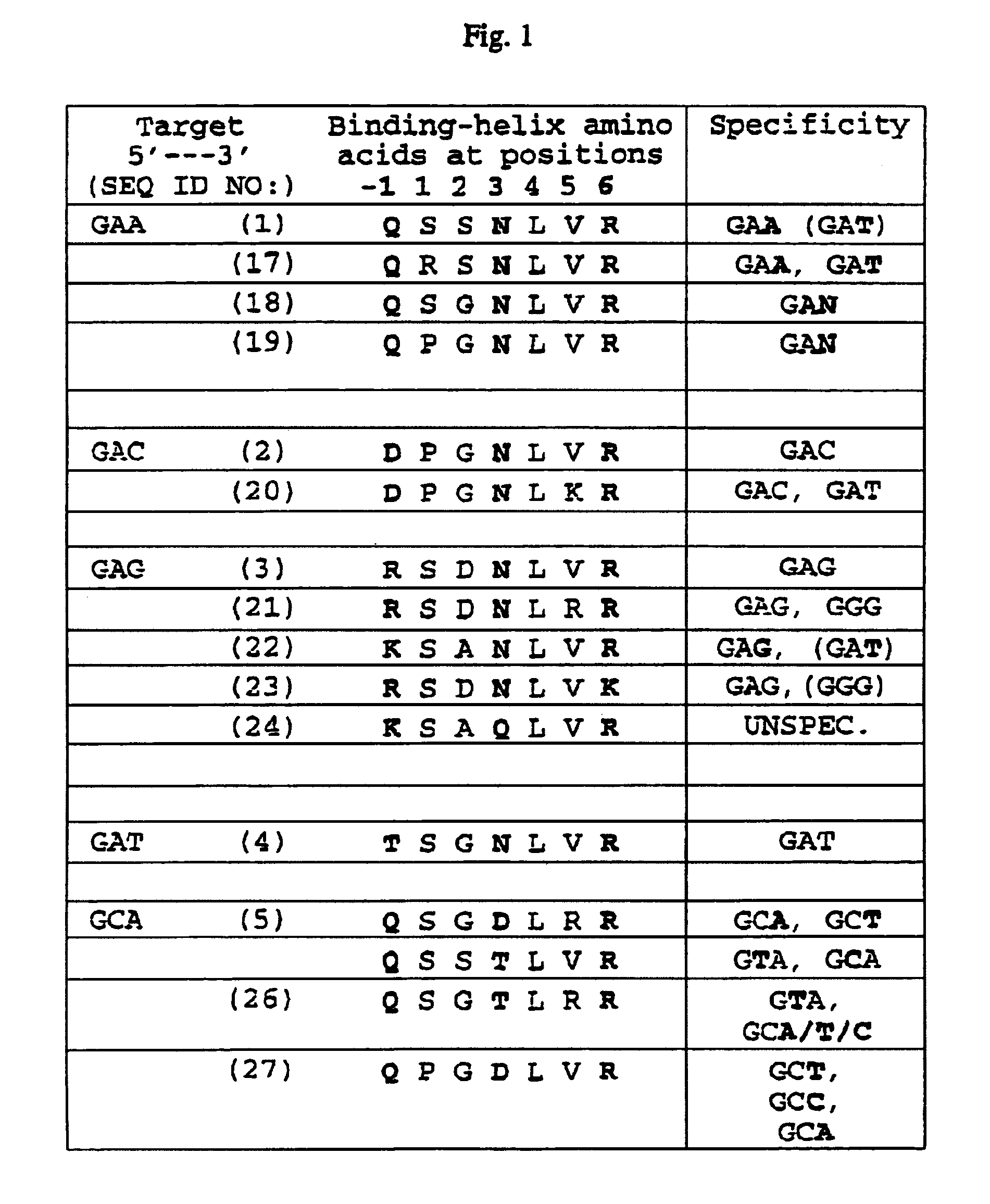
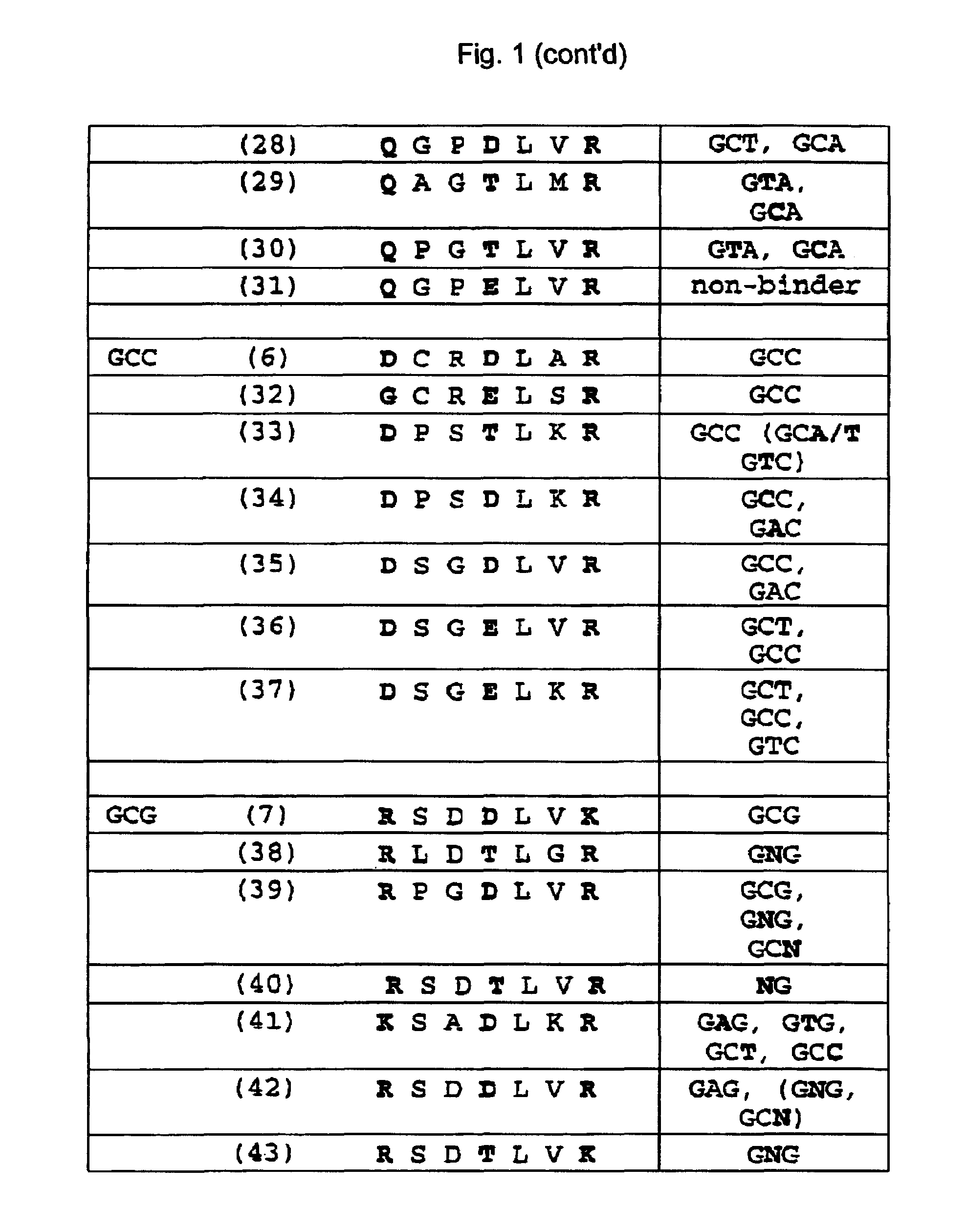
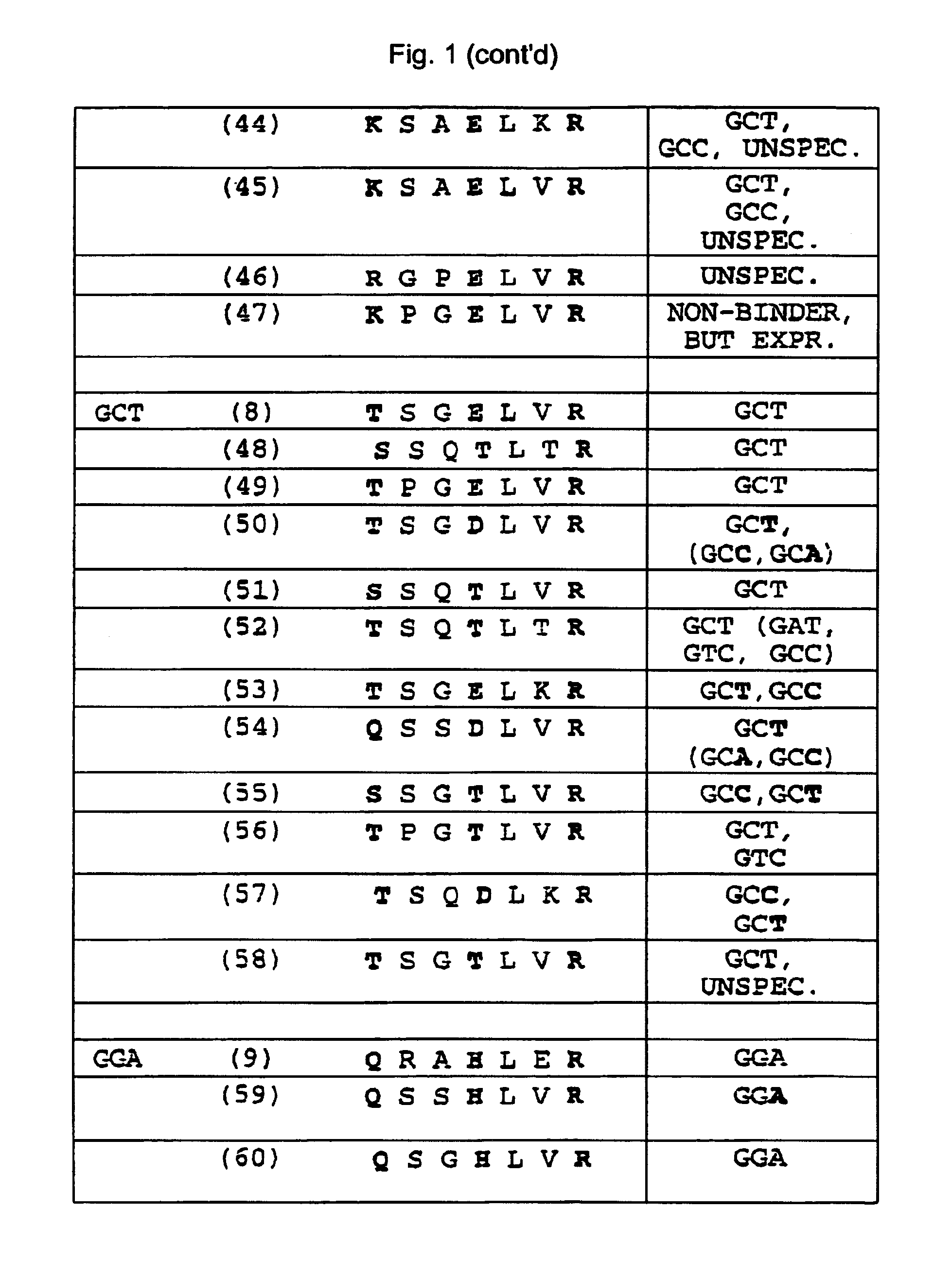
Zinc finger binding domains for nucleotide sequence ANN
InactiveUS7067617B2Exquisite binding specificityIncrease the number ofPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesBinding domainNucleotide sequencing
Polypeptides that contain from 2 to 12 zinc finger-nucleotide binding regions that bind to nucleotide sequences of the formula (ANN)2–12 are provided. Polynucleotides that encode such polypeptides and methods of regulating gene expression with such polypeptides and polynucleotides are also provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Zinc finger binding domains for tnn
Polypeptides that contain zinc finger-nucleotide binding regions that bind to nucleotide sequences of the formula TNN are provided. Compositions containing a plurality of polypeptides, isolated heptapeptides possessing specific binding activity, polynucleotides that encode such polypeptides and methods of regulating gene expression with such polypeptides, compositions and polynucleotides are also provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Methods and compositions for using zinc finger endonucleases to enhance homologous recombination
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
Regulated gene expression in plants
A method is provided of regulating transcription in a plant cell from a DNA sequence comprising a target DNA operably linked to a coding sequence, which method comprises introducing an engineered zinc finger polypeptide in said plant cell which polypeptide binds to the target DNA and modulates transcription of the coding sequence.
Owner:GENDAQ +1
Zinc finger domains specifically binding agc
Polypeptides that contain zinc finger-nucleotide binding regions that bind to nucleotide sequences of the formula AGC are provided. Compositions containing a plurality of polypeptides, isolated heptapeptides possessing specific binding activity, polynucleotides that encode such polypeptides and methods of regulating gene expression with such polypeptides, compositions and polynucleotides are also provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
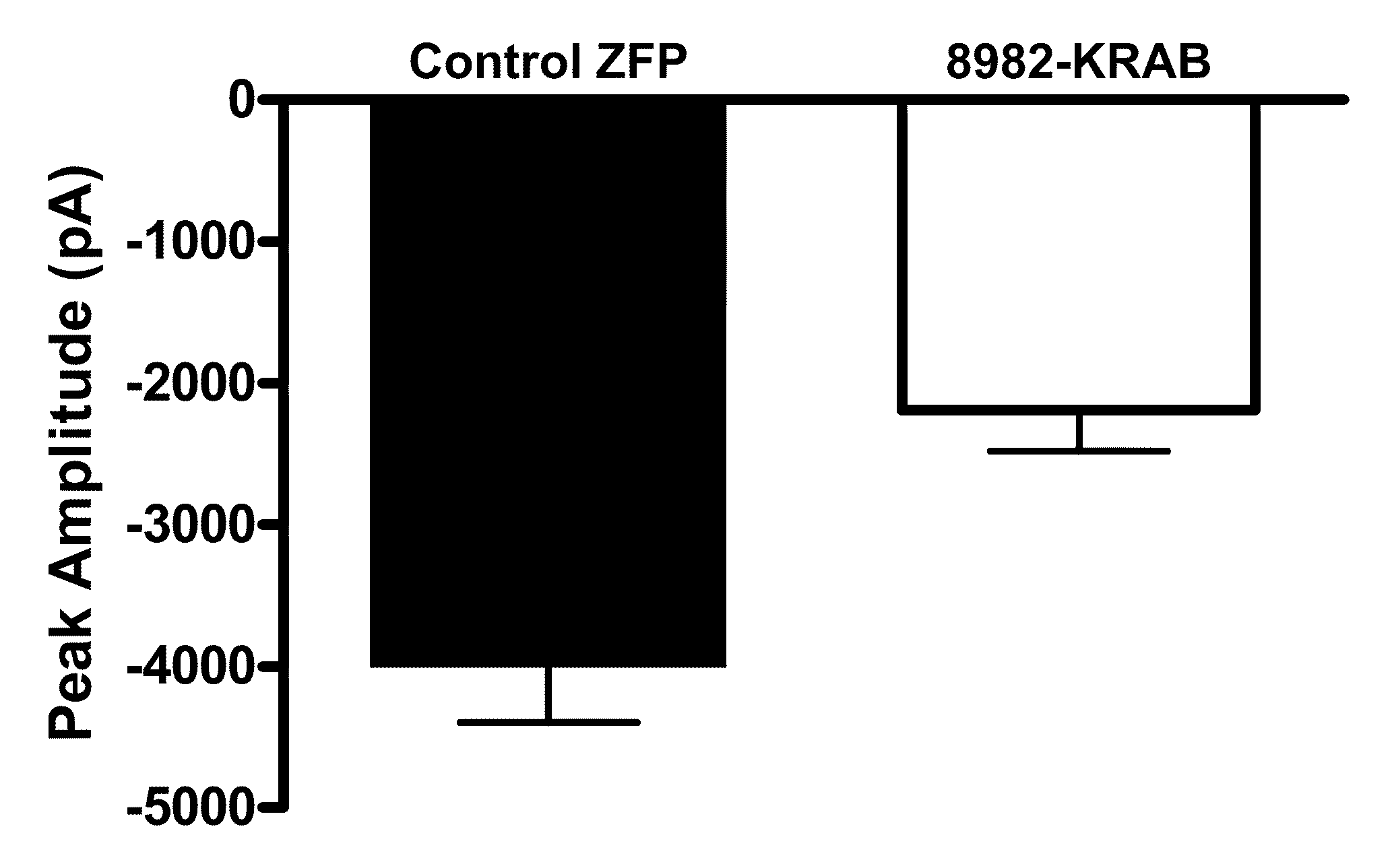
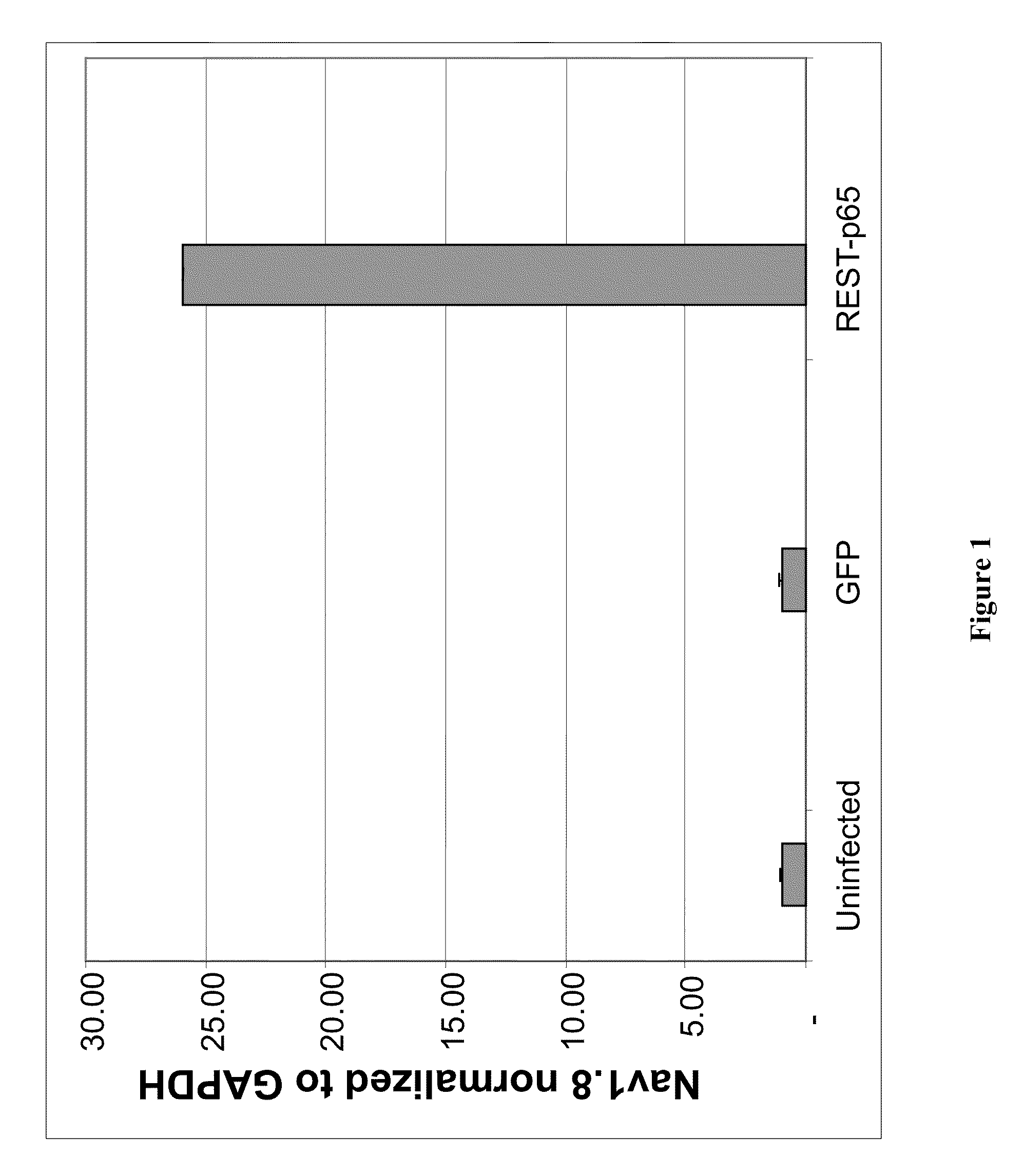
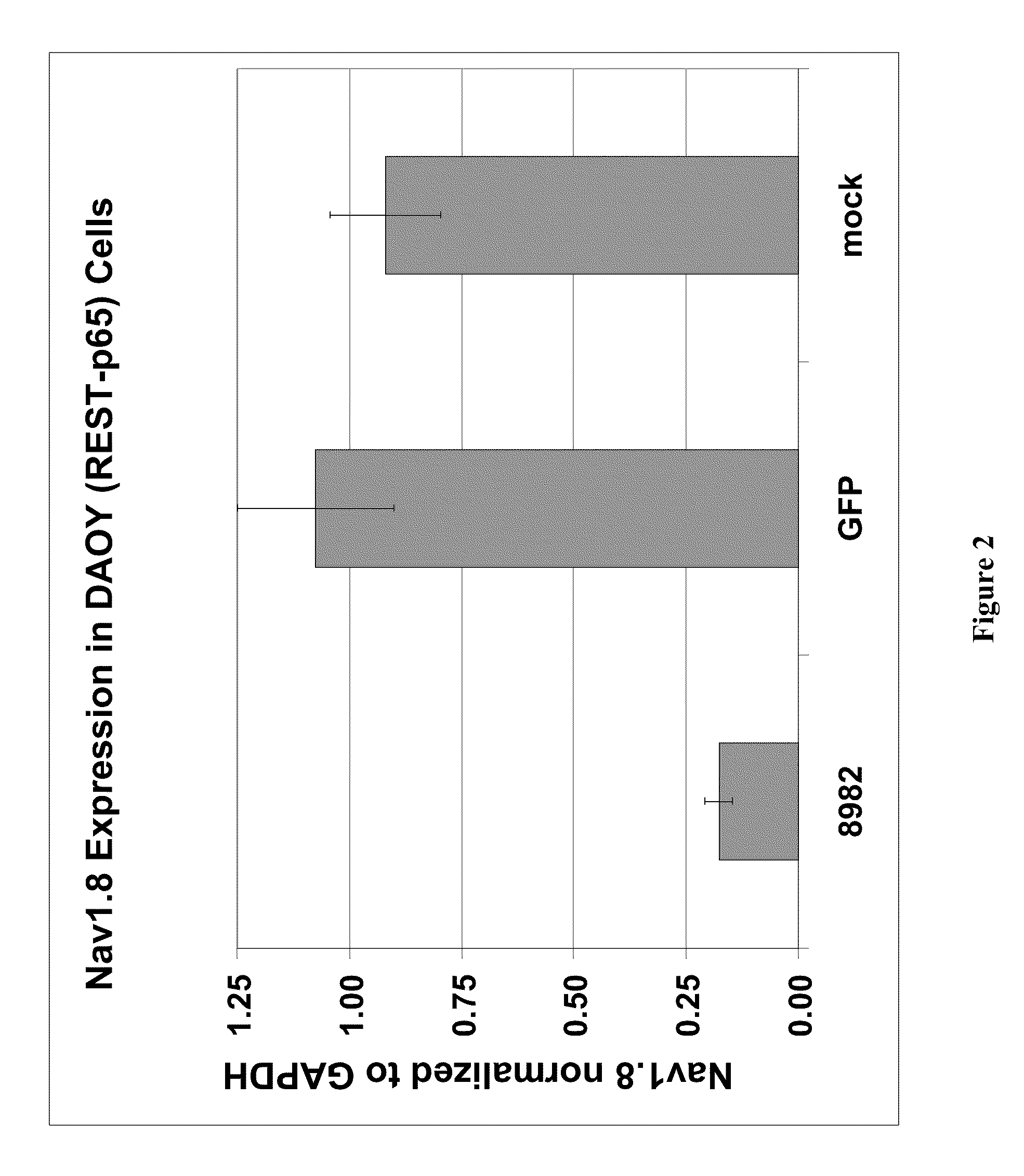
Treatment of chronic pain with zinc finger proteins
InactiveUS20090215878A1Suppress gene expressionModulate physiological processes correlatedOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNormal levelPain patient
A variety of zinc finger proteins (ZFPs) and methods utilizing such proteins are provided for use in treating chronic pain. ZFPs that bind to a target site in genes that are aberrantly expressed in subjects having chronic pain are described. In addition, ZFPs that bind to a target site in genes expressed at normal levels in subjects experiencing chronic pain, modulation of whose expression results in decreased pain perception, are also provided. For example, genes that are over-expressed in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) of pain patients (e.g., Nav1.8) can be repressed.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
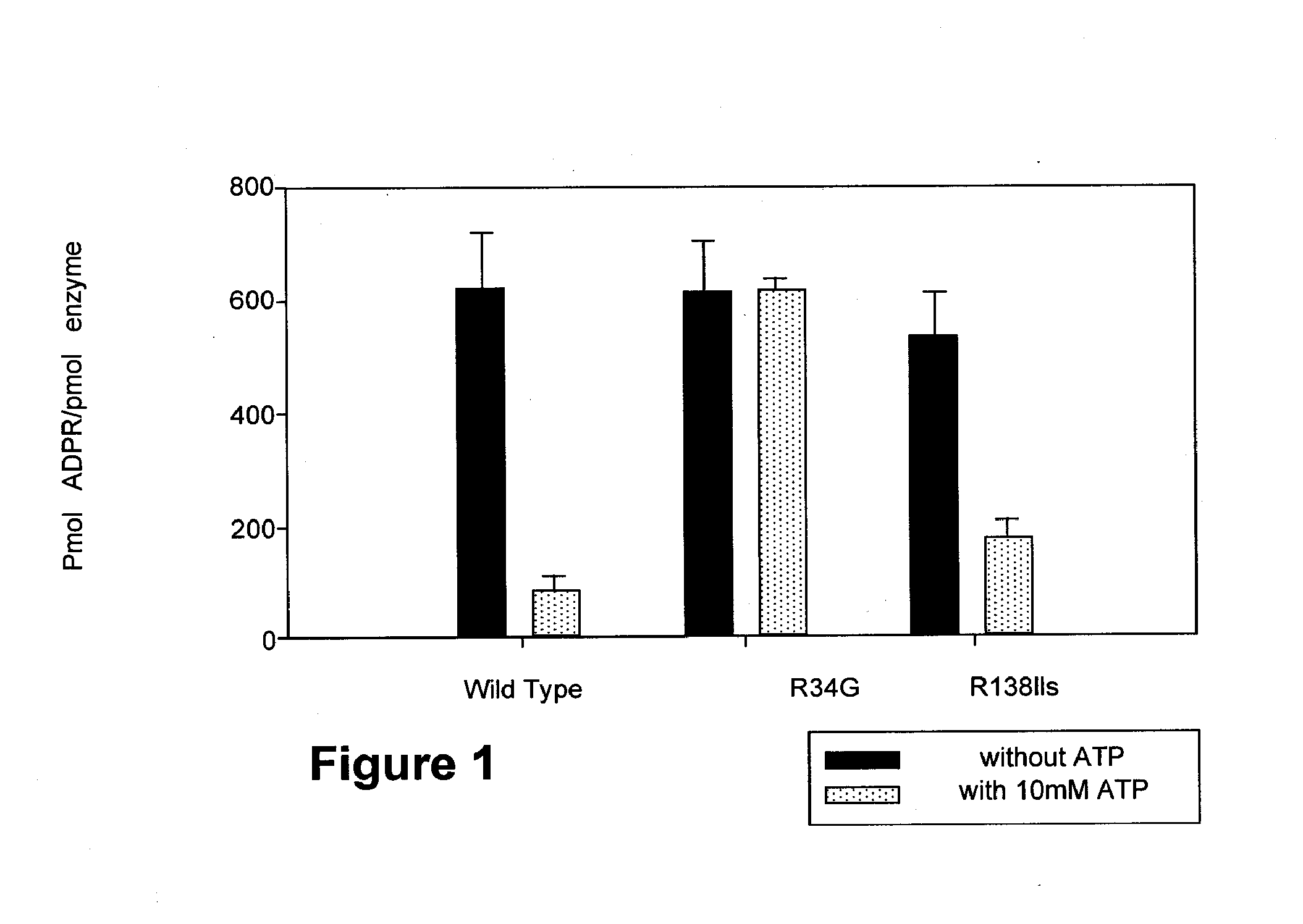
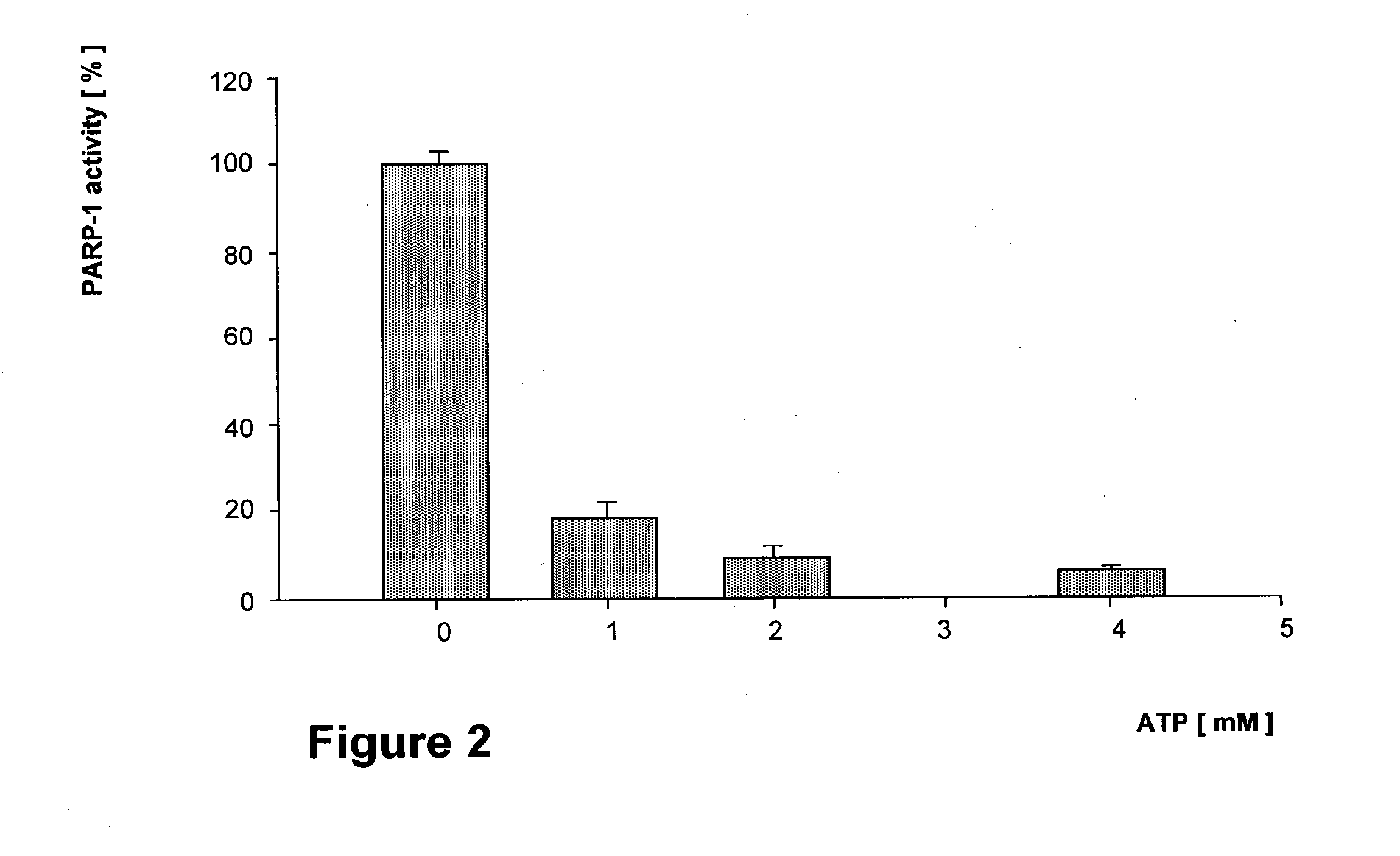
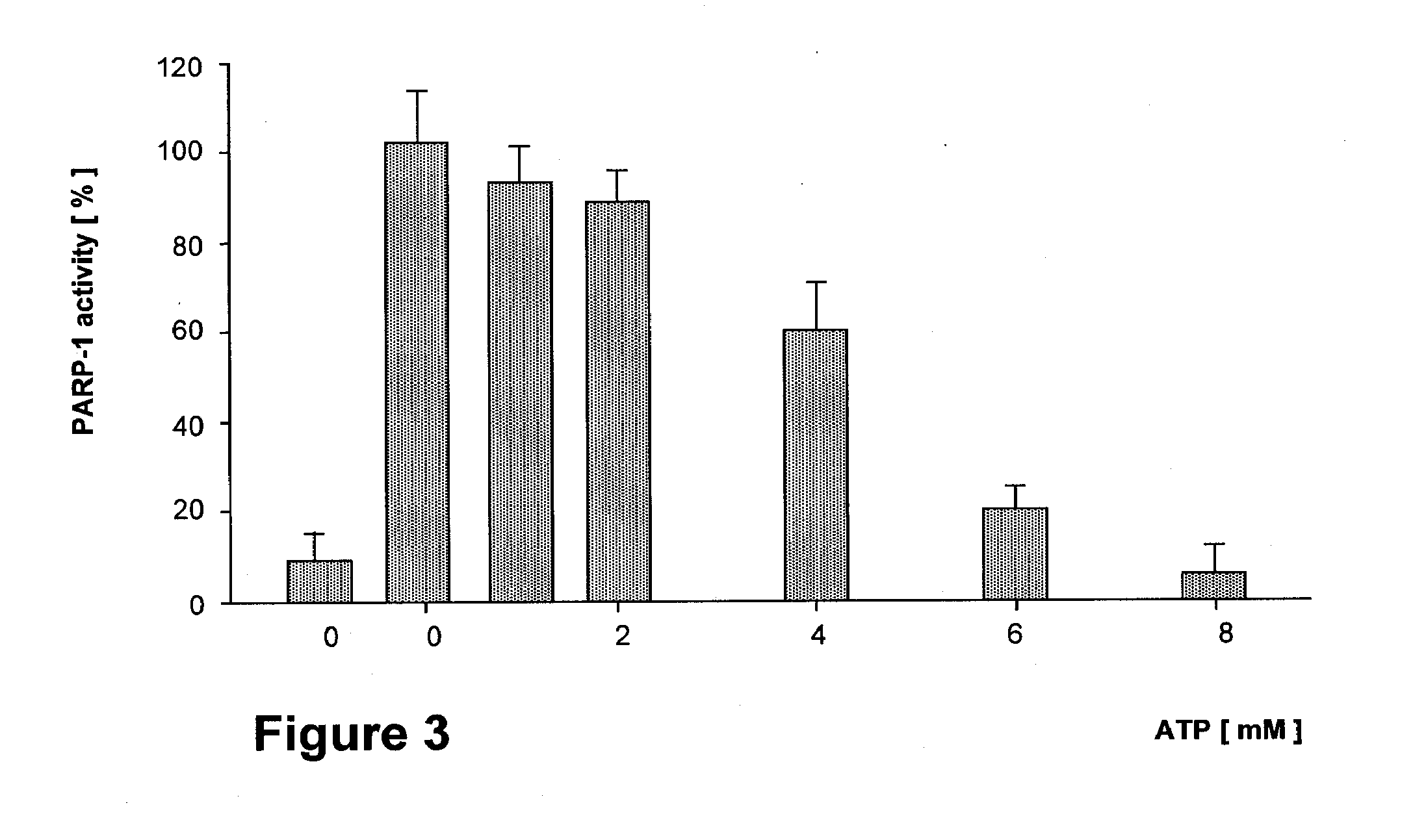
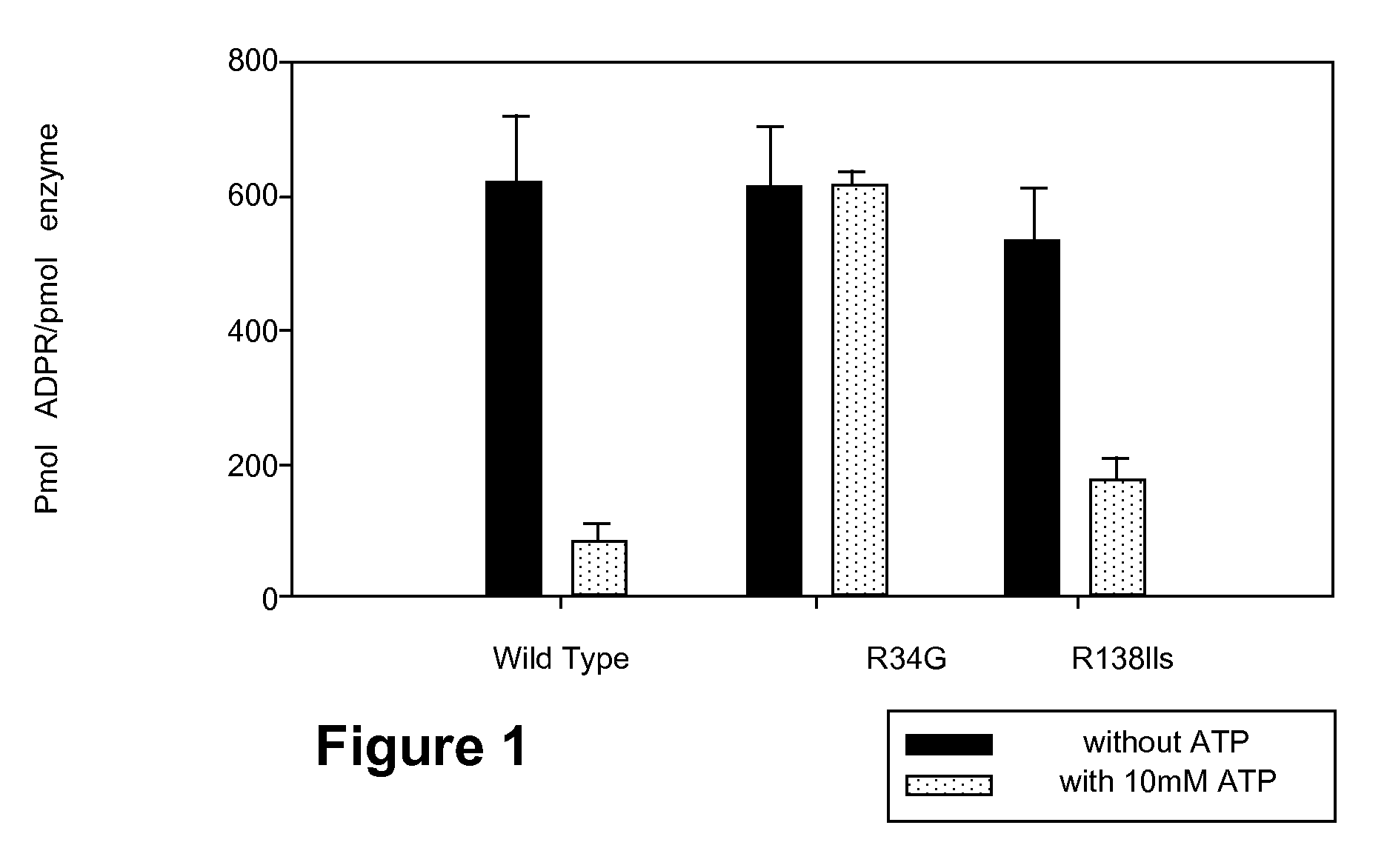
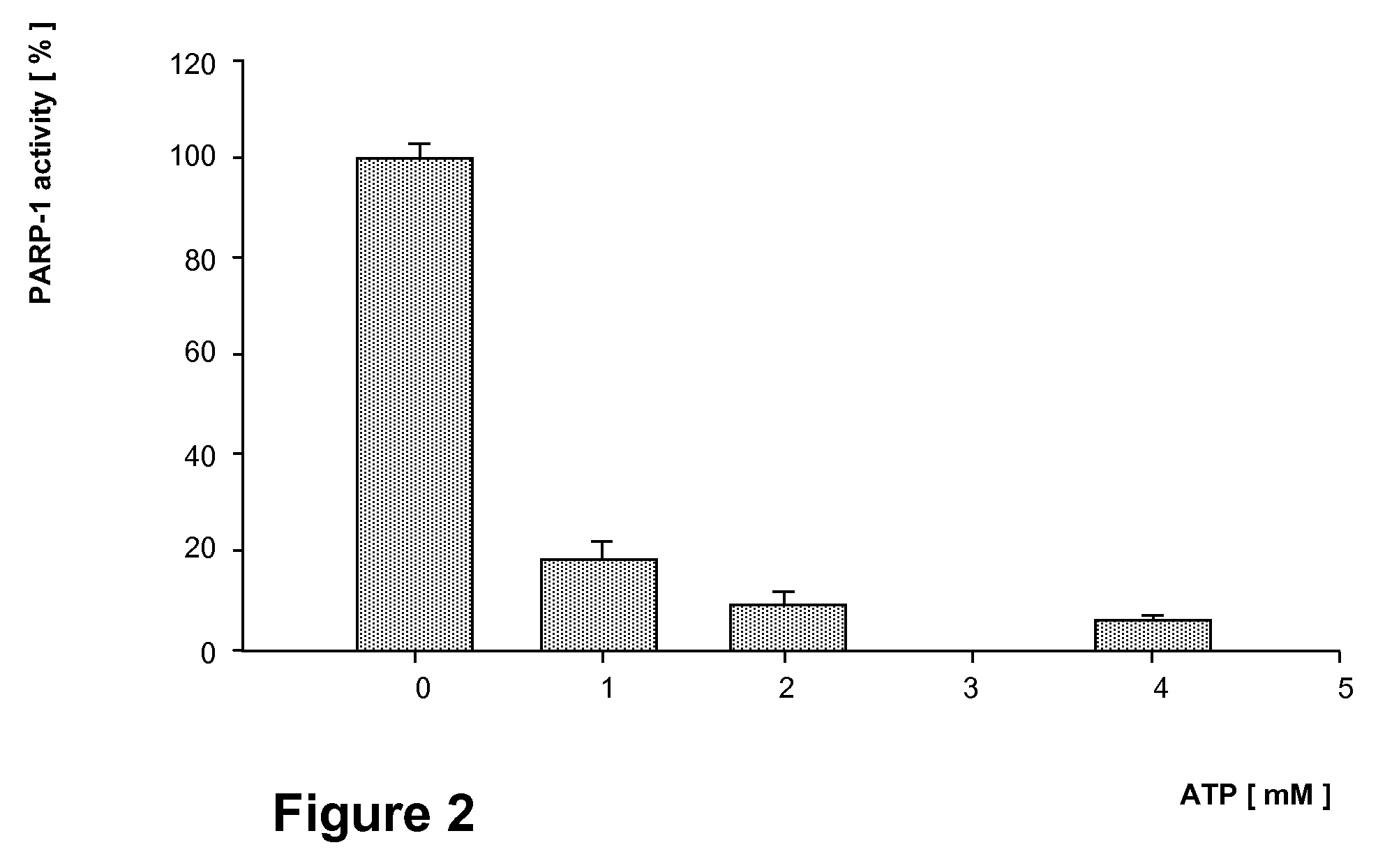
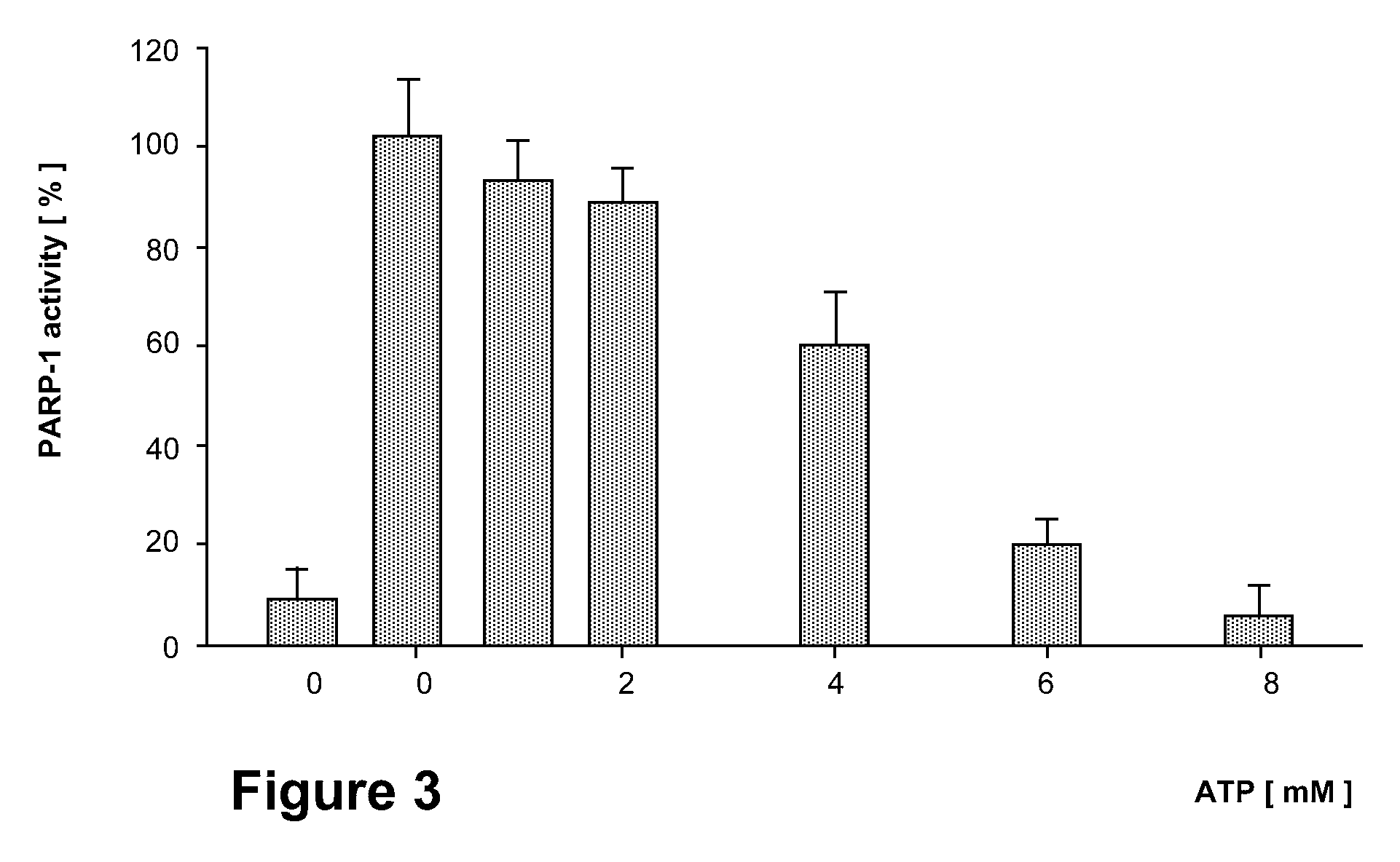
Parp Modulators and Treatment of Cancer
The invention relates to a method of modulating poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1 (PARP-1) activity in a mammal comprising administering to a mammal an effective amount of an organic aromatic compound having from 4 to about 35 carbon atoms, wherein said organic aromatic compound is capable of binding the arginine-34 moiety located in Zinc finger-1 of the PARP-1 enzyme and wherein said organic aromatic compound has electron donating capabilities such that it's π-electron system will interact with the positively charged (cationic) guanidinium moiety of the specific arginine-34 residue of the Zinc-1 finger of PARP-1 and does not contain benzamide or lactam substituents. In particular, substituted benzopyrones and substituted indoles and their pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds that modulate the activity of PARP-1, are described. The invention is also directed to the composition of matter, kits and methods for their therapeutic and / or prophylactic use in treating diseases and disorders described herein, by administering effective amounts of such compounds. Preferably, the compositions and methods provided herein inhibit PARP activity.
Owner:BIPAR SCI INC
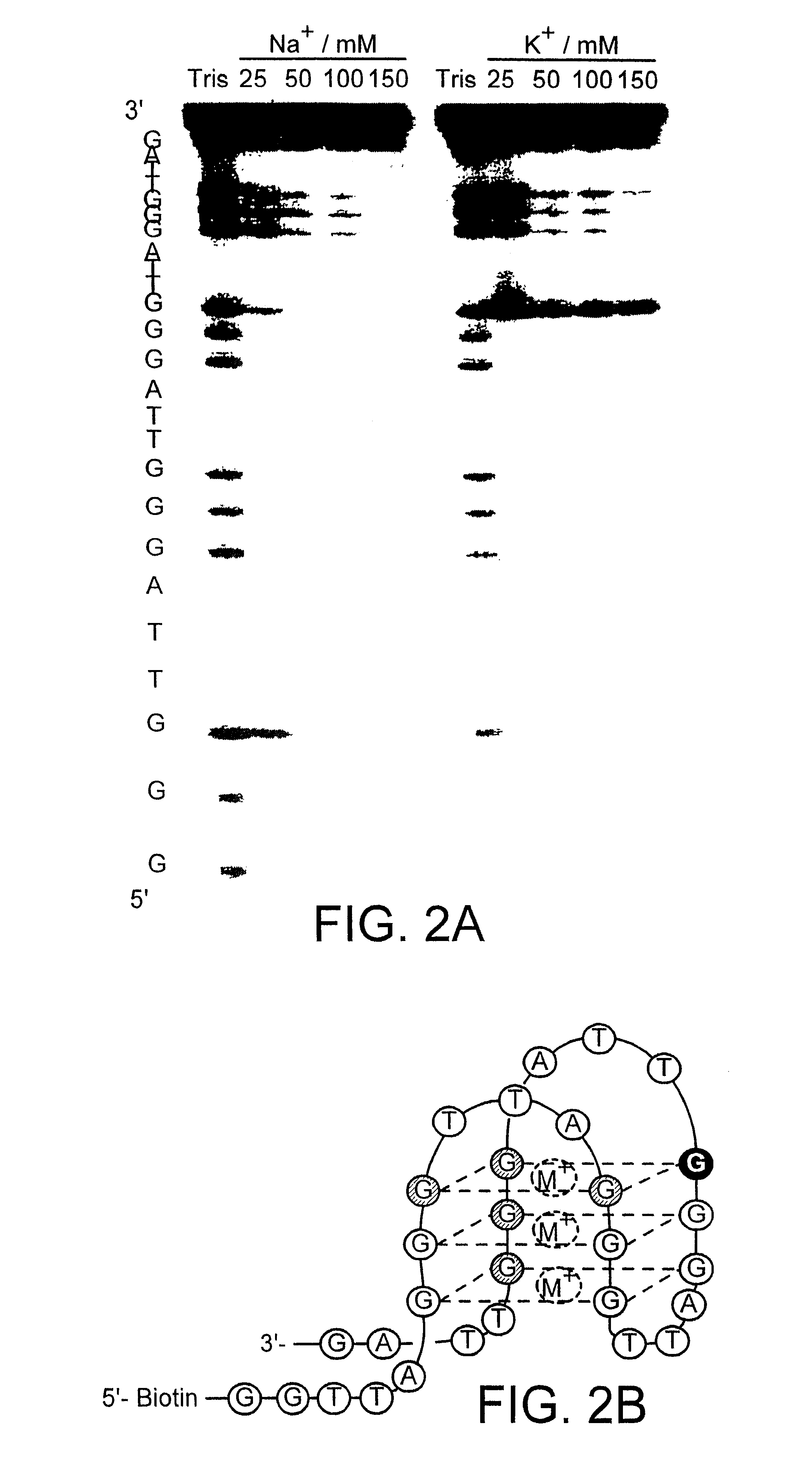
Zinc finger polypeptides capable of binding DNA quadruplexes
InactiveUS6492117B1Facilitates ELISA-based detectionRapid and easily automatedPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsZincZinc finger
The present invention relates to isolated or purified molecule(s) capable of binding to one or more of telomeric, G-quadruplex, or G-quartet nucleic acid(s).
Owner:GENDAQ +2
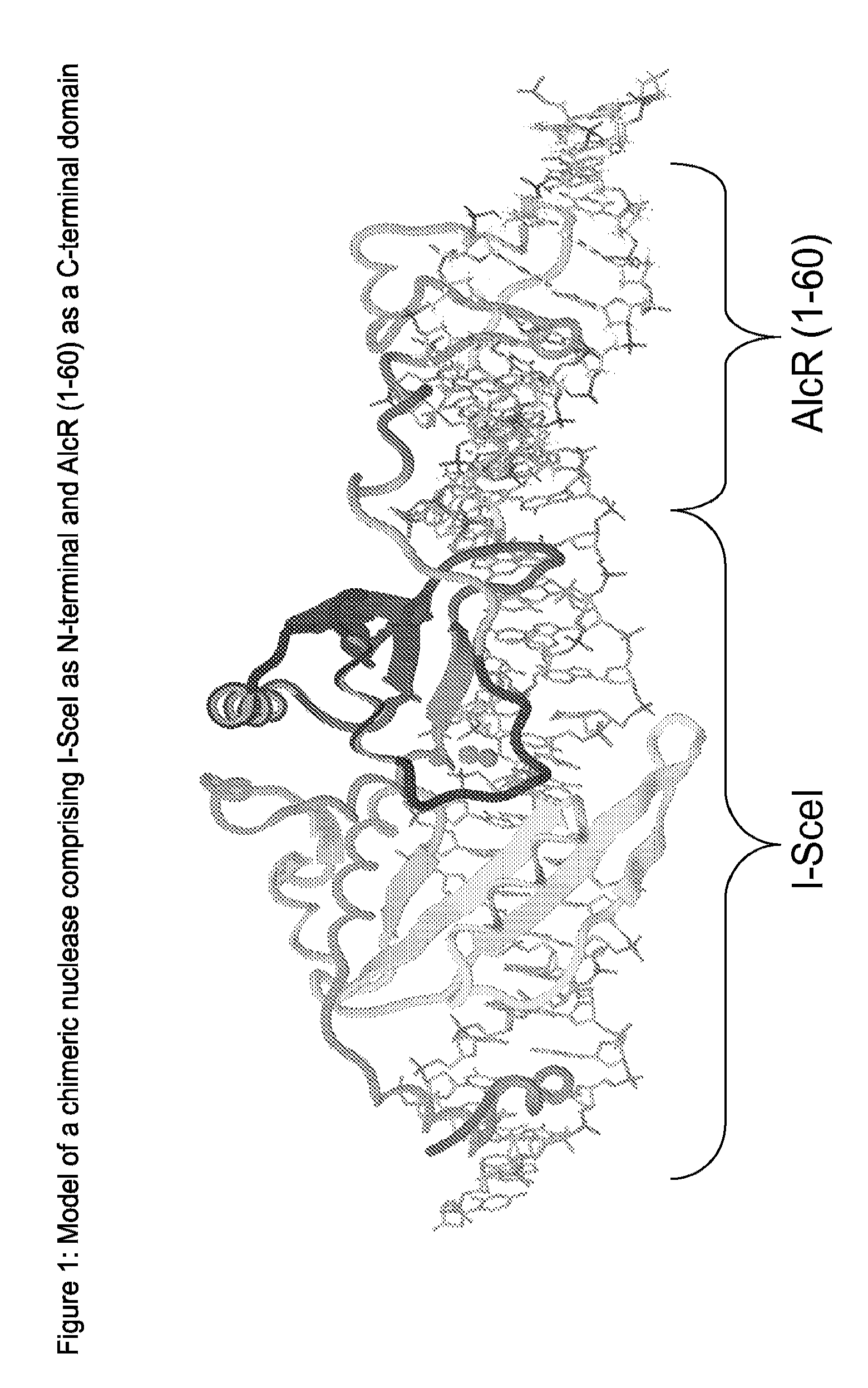
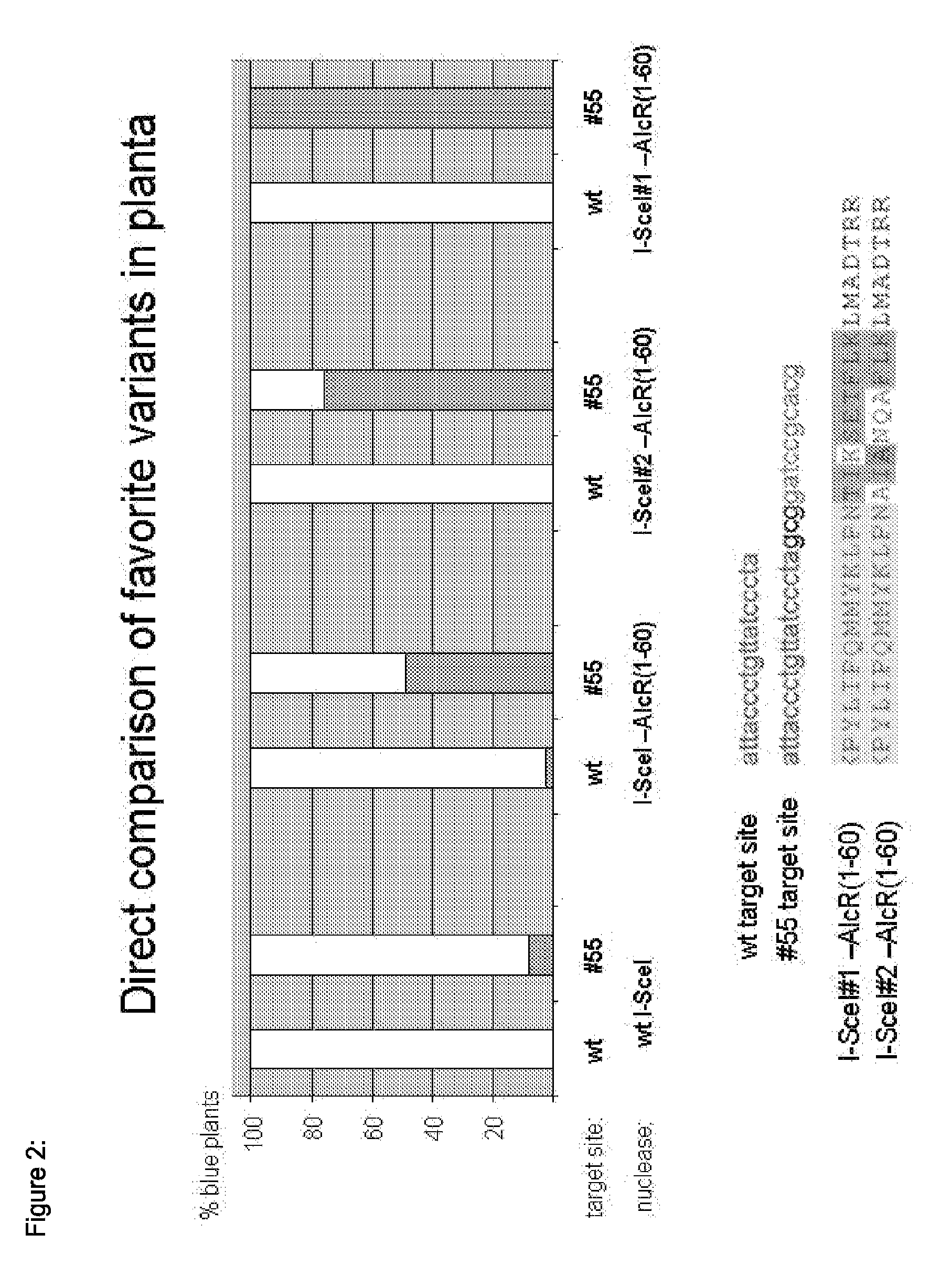
Chimeric Endonucleases and Uses Thereof
The invention relates to chimeric endonucleases, comprising a endonuclease and a heterologous DNA binding domain comprising one or more Zn2C6 zinc fmgers, as well as methods of targeted integration, targeted deletion or targeted mutation of polynucleotides using chimeric endonucleases.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Zinc finger binding domains for GNN
InactiveUS7101972B2Quick switchPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotideBinding domain
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Application of CRISPR/Cas 9 technology in obtaining of bombyx zinc finger protein gene mutation
InactiveCN107012174AGene editing achievedStable introduction of DNAPeptidesGene engineeringZinc finger
The invention relates to an application of CRISPR / Cas 9 technology in obtaining of bombyx zinc finger protein gene mutation, and belongs to the technical field of bombyx breeding and gene engineering. In the invention, the CRISPR / Cas 9 gene editing technology is applied to obtain bombyx zinc finger protein gene mutation, a set of method for performing gene edition on zinc finger protein and exploring the gene function is realized, and thus a set of effective method for the batch research and transcription factors in future is provided.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Functional genomics using zinc finger proteins
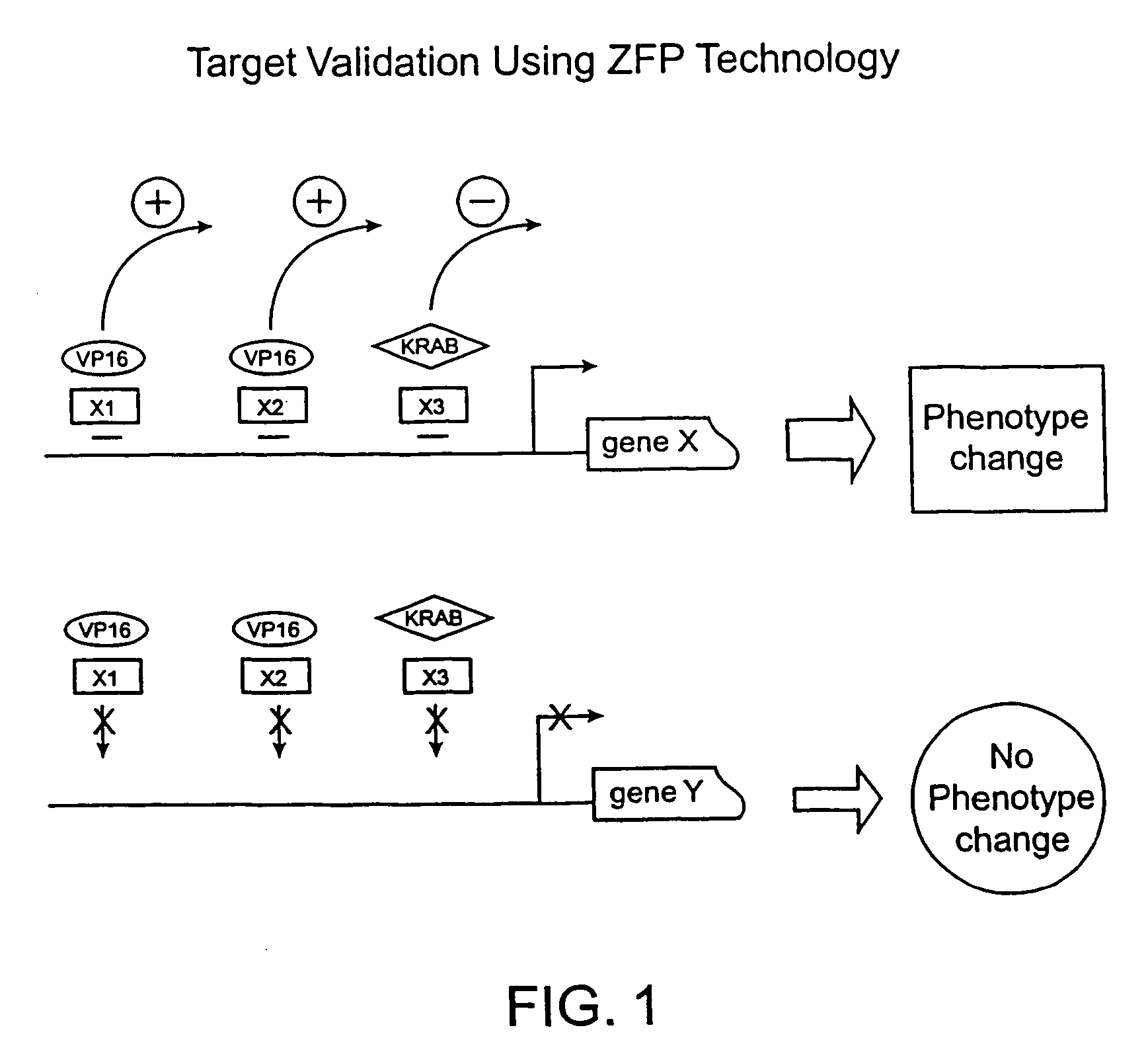
InactiveUS7235354B2Prevents repressionInhibition of activationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsZinc
The present invention provides methods of regulating gene expression using recombinant zinc finger proteins, for functional genomics and target validation applications.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
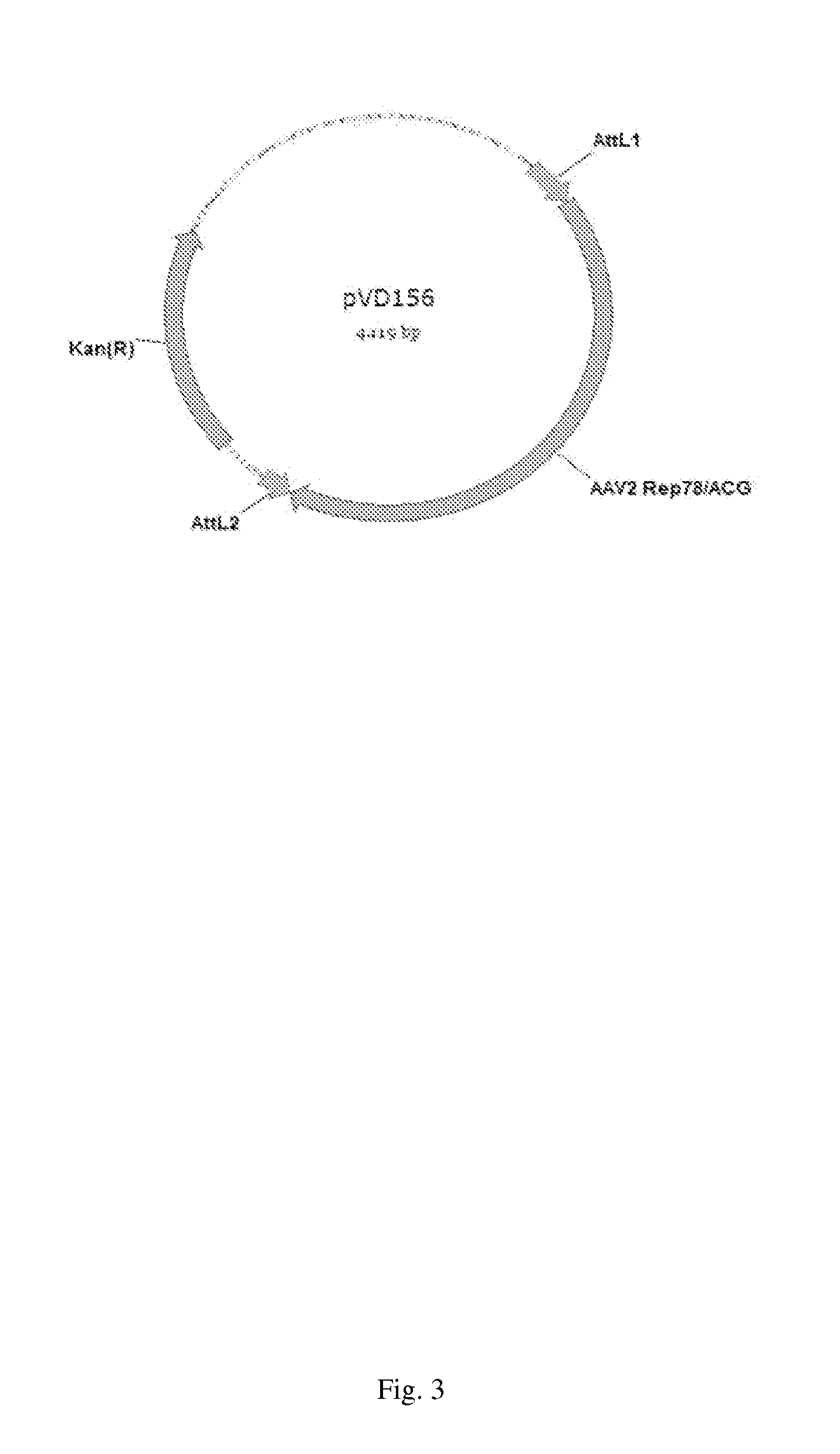
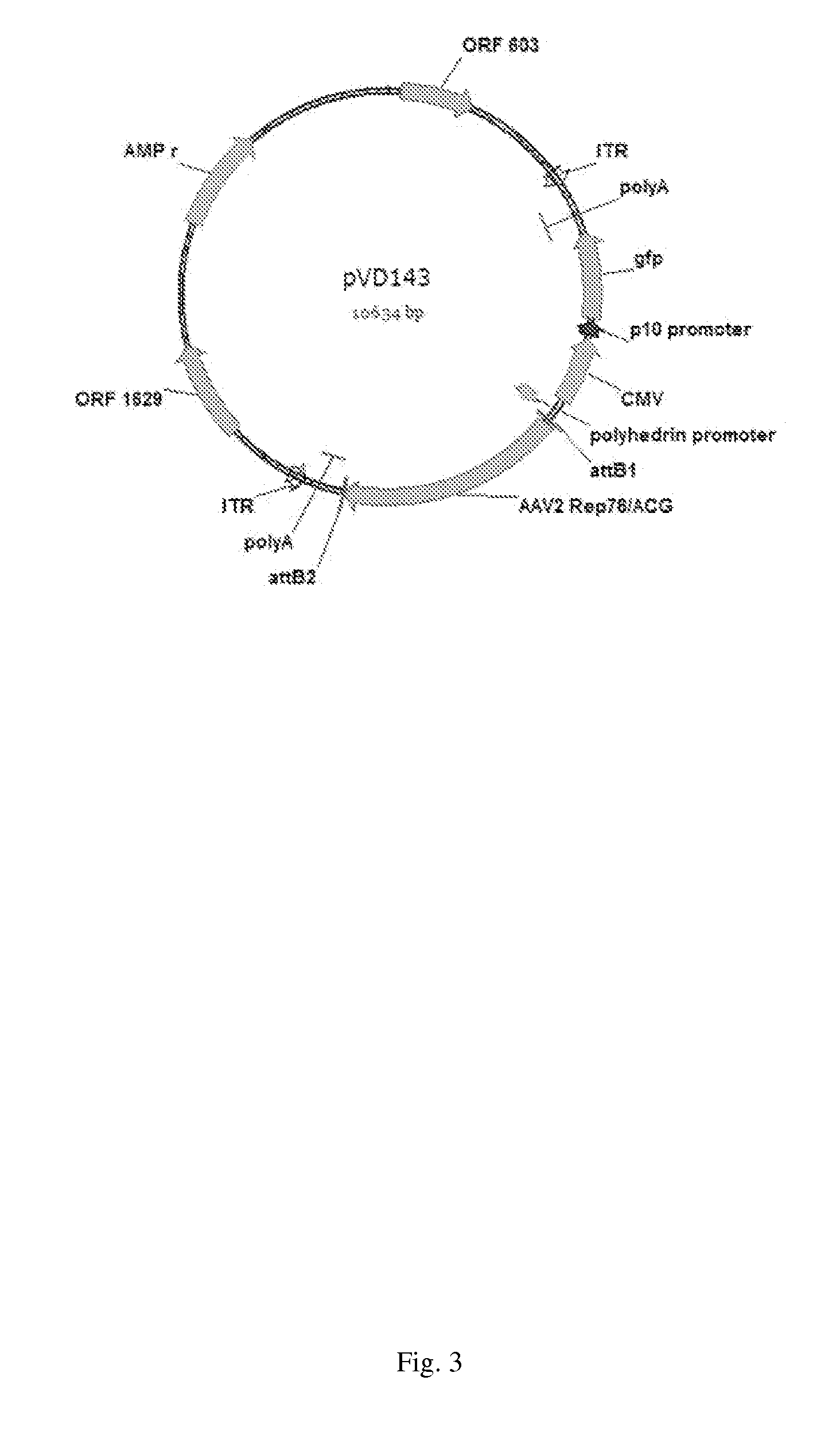
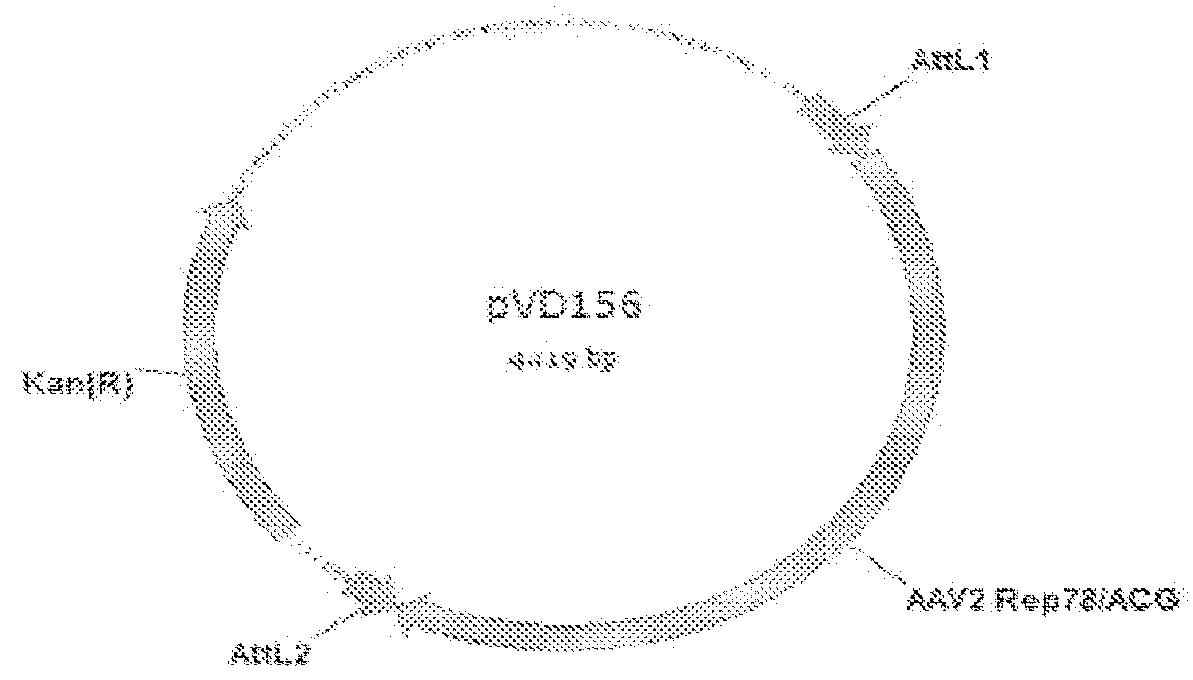
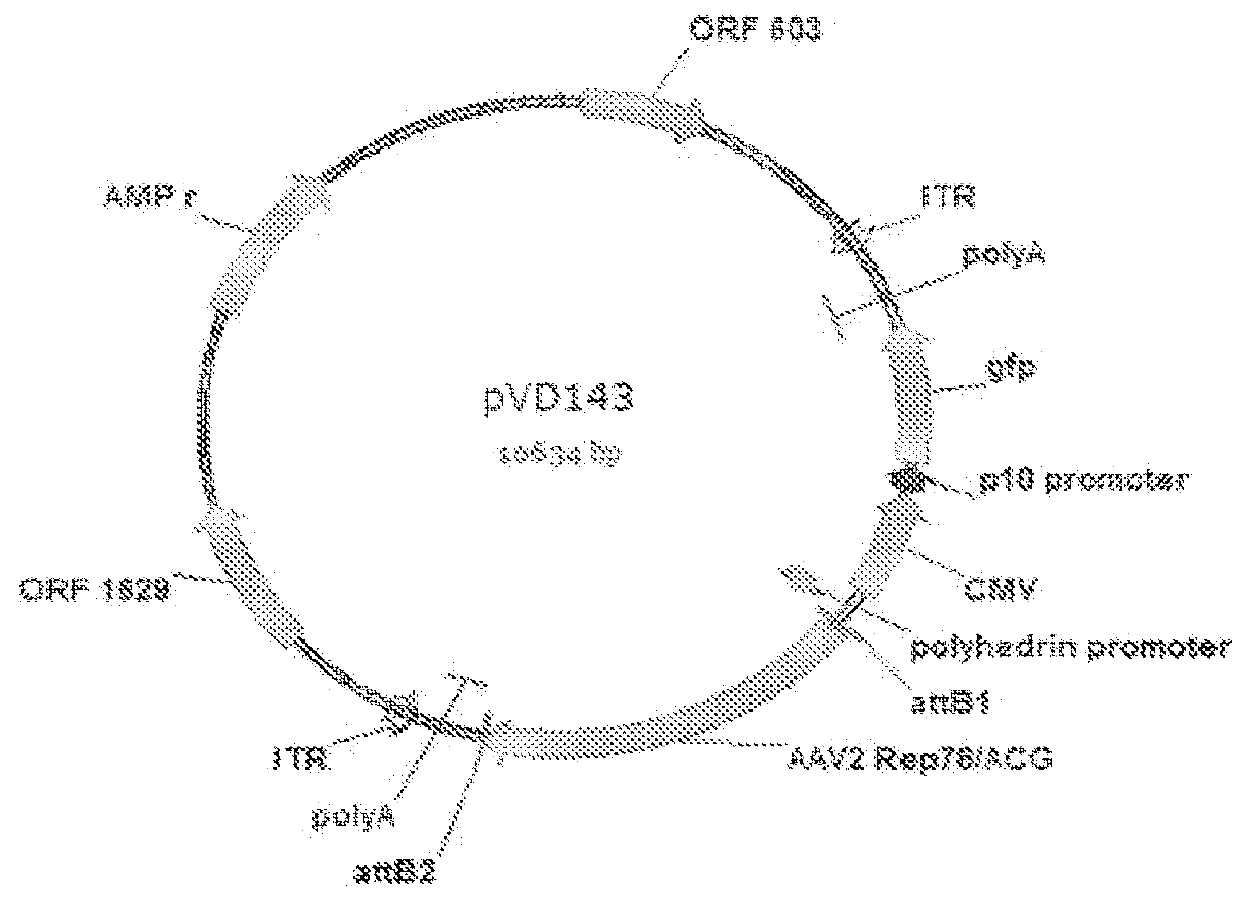
Mutated rep encoding sequences for use in aav production
ActiveUS20130023034A1Improve propertiesStable productionAnimal cellsSugar derivativesNucleotideWild type
The invention relates to a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a Parvoviral Rep protein, wherein a nuclear localization signal (NLS) in said Parvoviral Rep protein is mutated as compared with a corresponding wild type sequence. The invention also relates to a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a Parvoviral Rep protein, wherein the zinc finger domain in said Parvoviral Rep protein is mutated as compared with a corresponding wild type sequence. Further, the invention relates to a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a Parvoviral Rep protein, wherein an amino acid at position 43, 57, 79, 97, 120, 179, 305, 484, 493 or 571 of the said Parvoviral Rep protein is mutated in comparison to a corresponding wild type sequence, said amino acid position being defined with reference to SEQ ID NO: 2.
Owner:UNIQURE IP BV
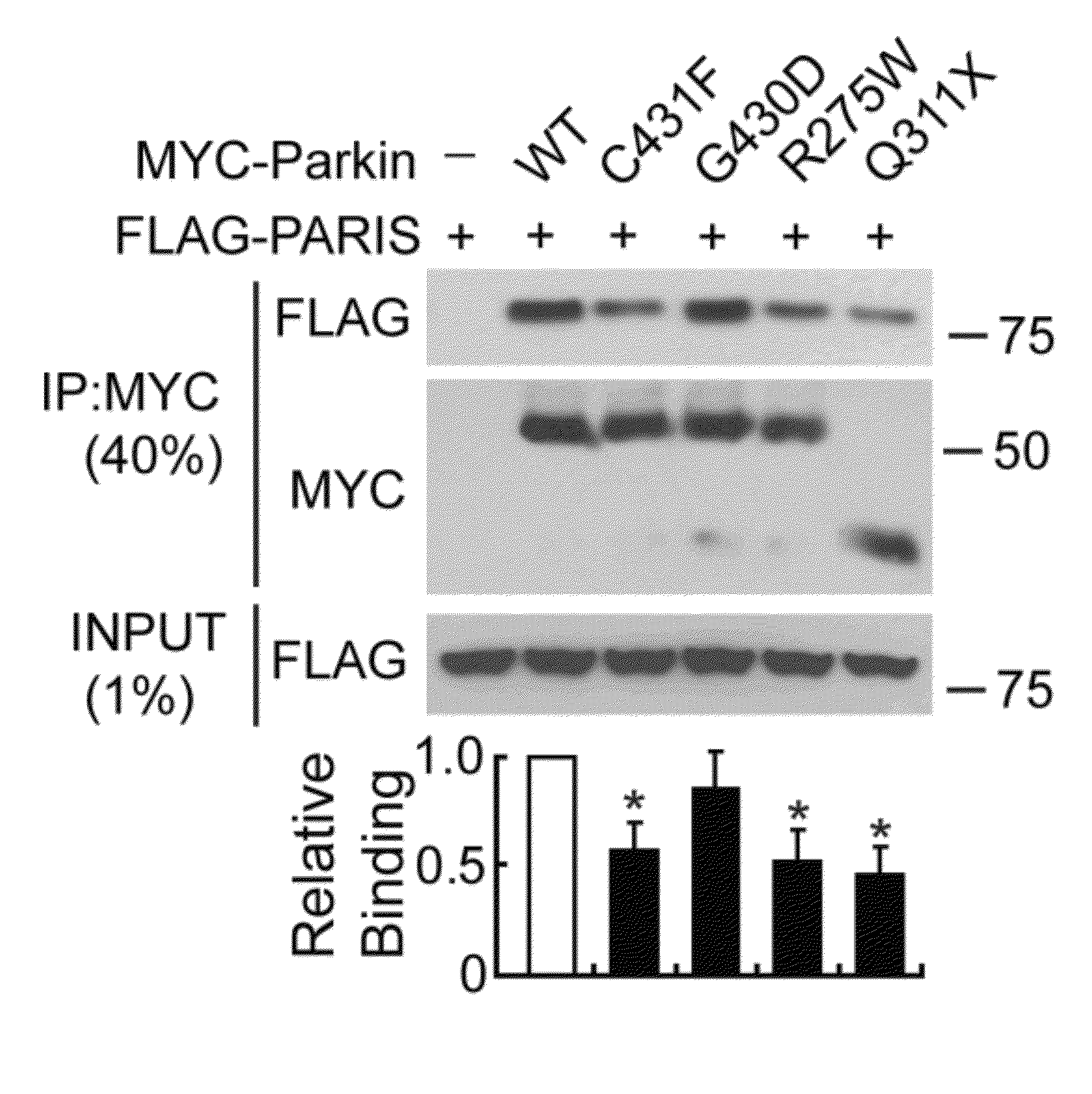
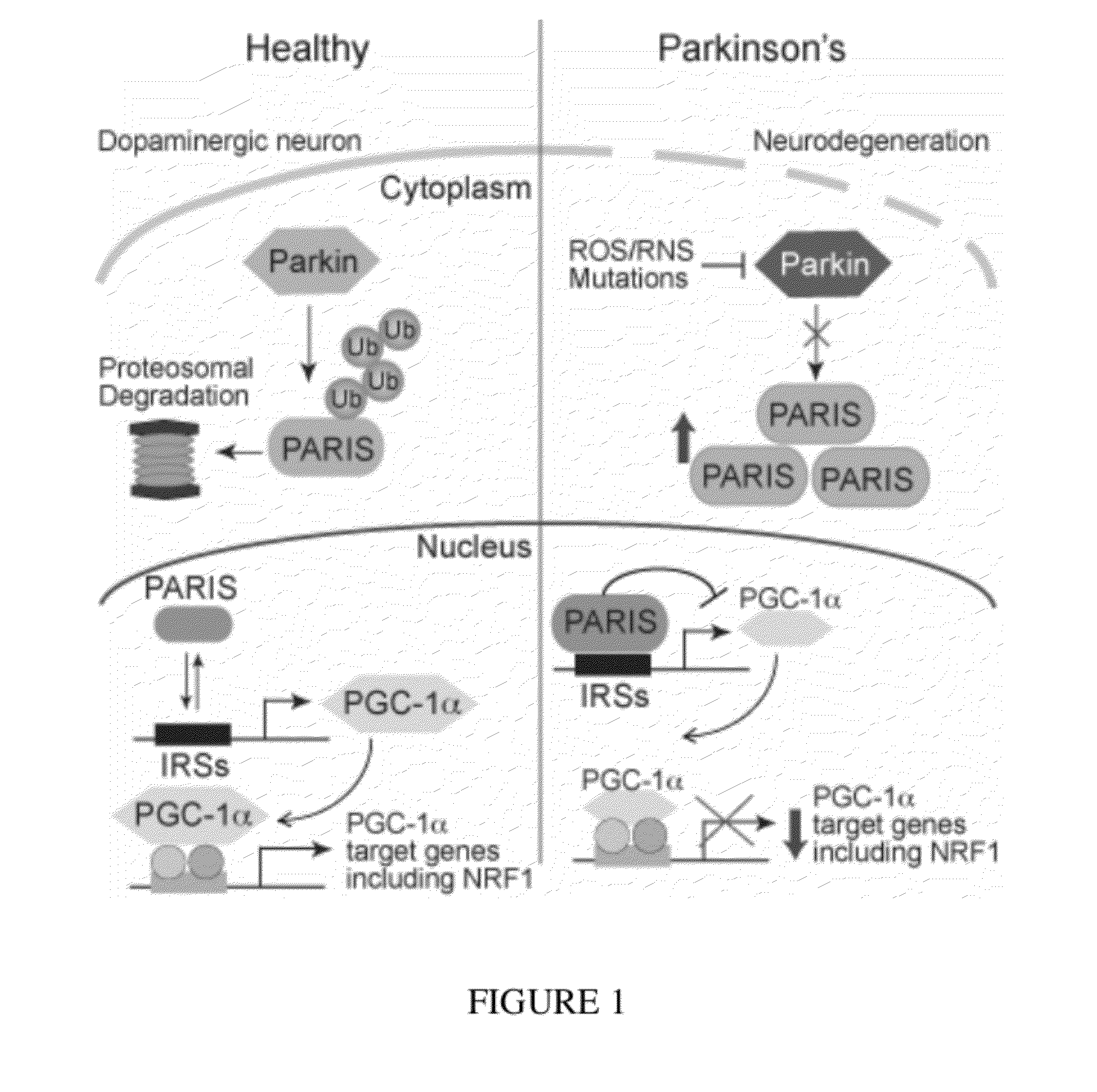
Transcriptional repression leading to parkinson's disease
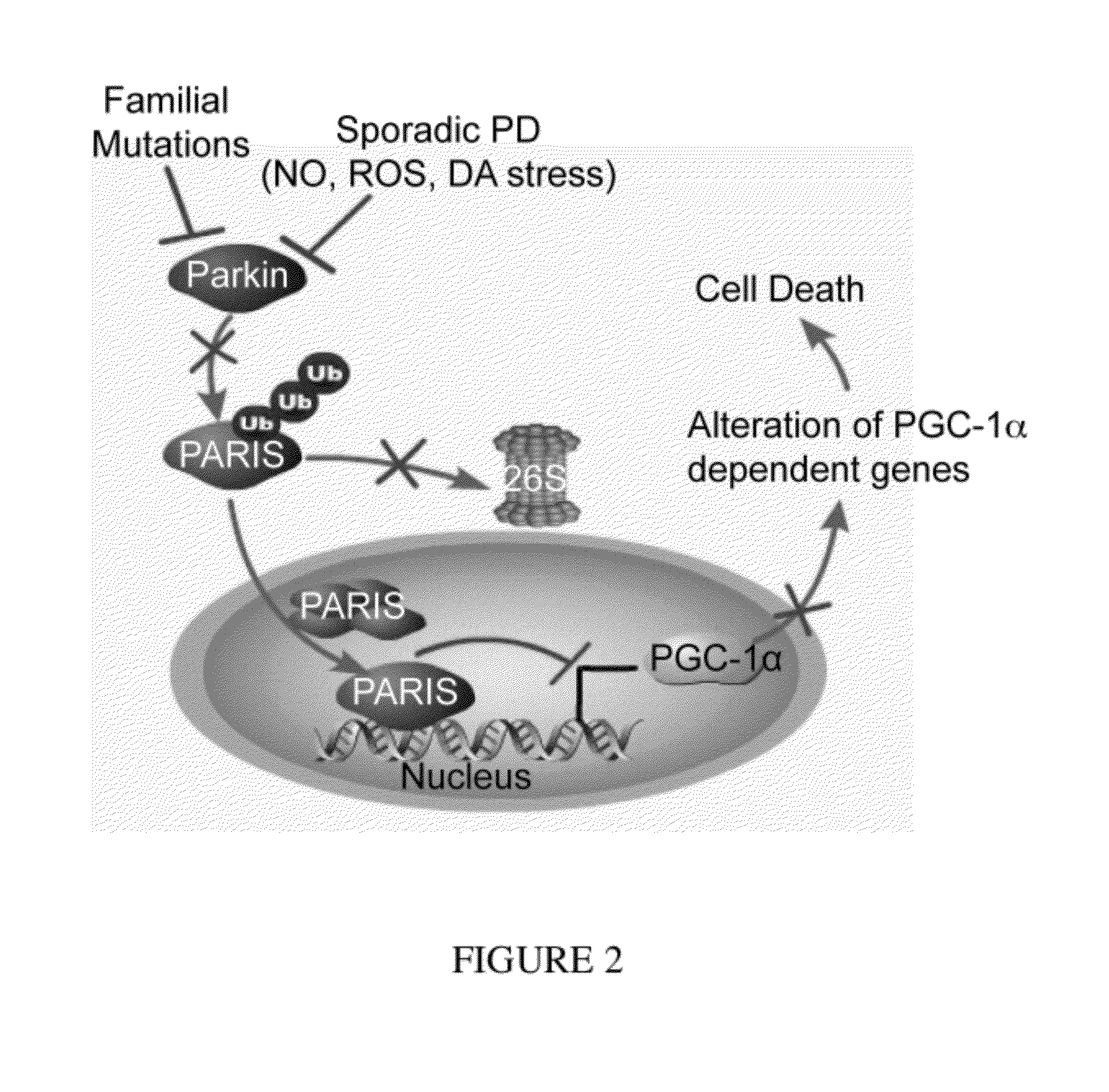
Parkinson's disease is caused by the preferential loss of substantia nigra dopamine neurons. A Parkin Interacting Substrate, PARIS (ZNF746) is identified. The levels of PARIS are regulated by the ubiquitin proteasome system via binding to and ubiquitination by the E3 ubiquitin ligase, parkin. PARIS is a KRAB and zinc finger protein that accumulates in models of parkin inactivation and in human brain Parkinson's disease patients. PARIS represses the expression of the transcriptional co-activator, PGC-1α and the PGC-1α target gene, NRF-1 by binding to insulin response sequences in the PGC-1α promoter. Conditional knockout of parkin in adult animals leads to progressive loss of dopamine (DA) neurons that is PARIS dependent. Overexpression of PARIS causes selective loss of DA neurons in the substantia nigra, which is reversed by either parkin or PGC-1α co-expression. The identification of PARIS provides a molecular mechanism for neurodegeneration due to parkin inactivation.
Owner:VALTED
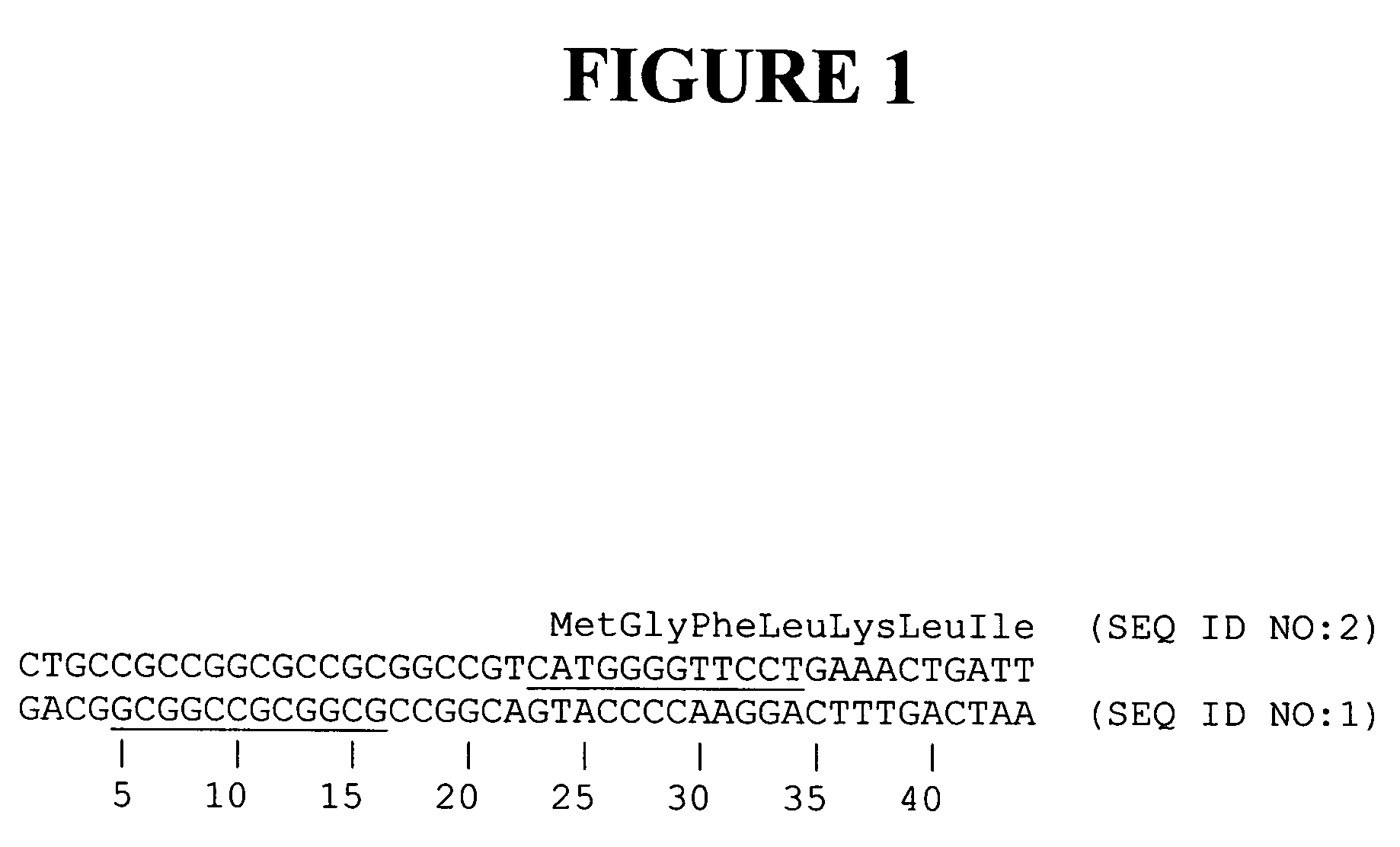
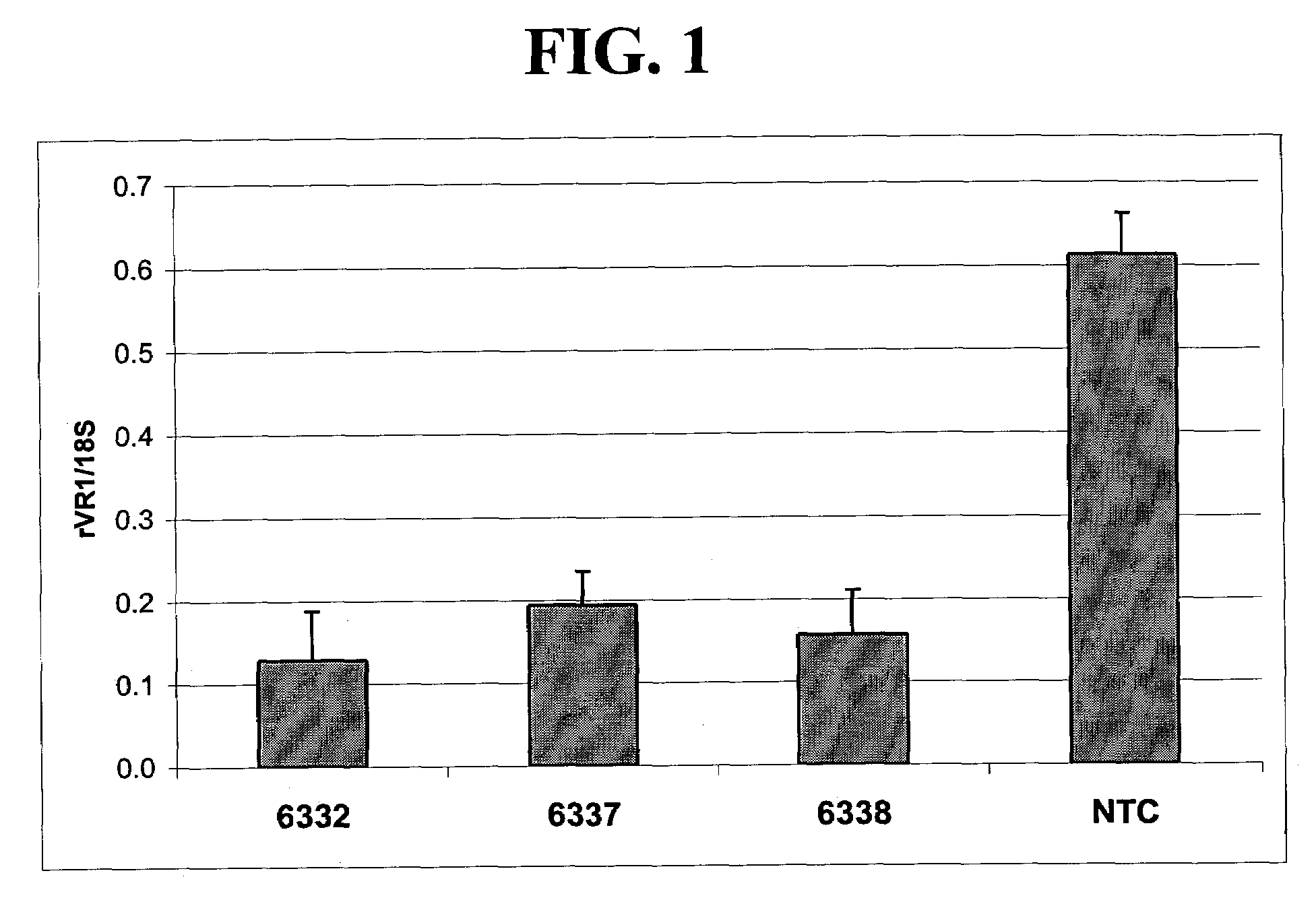
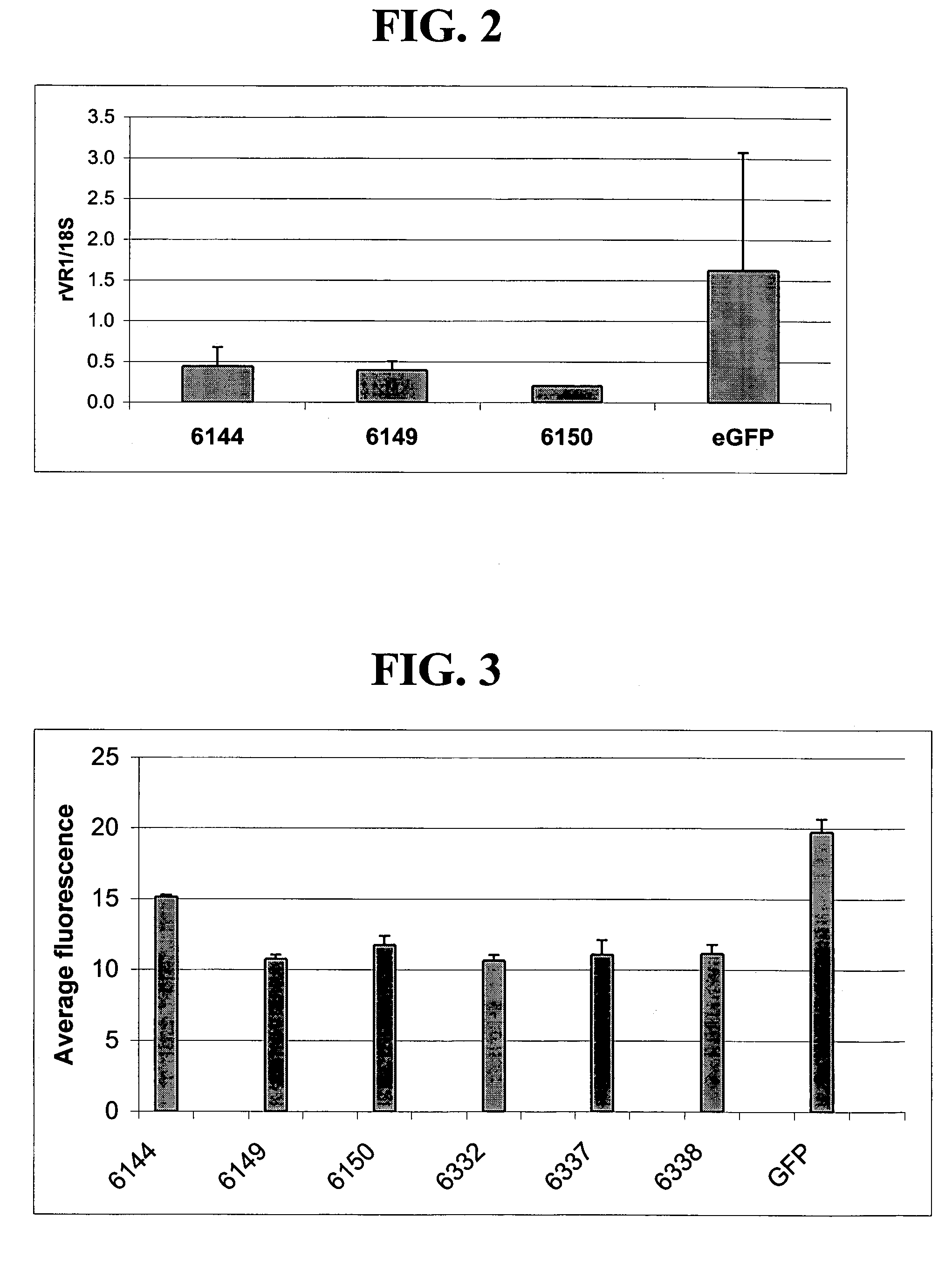
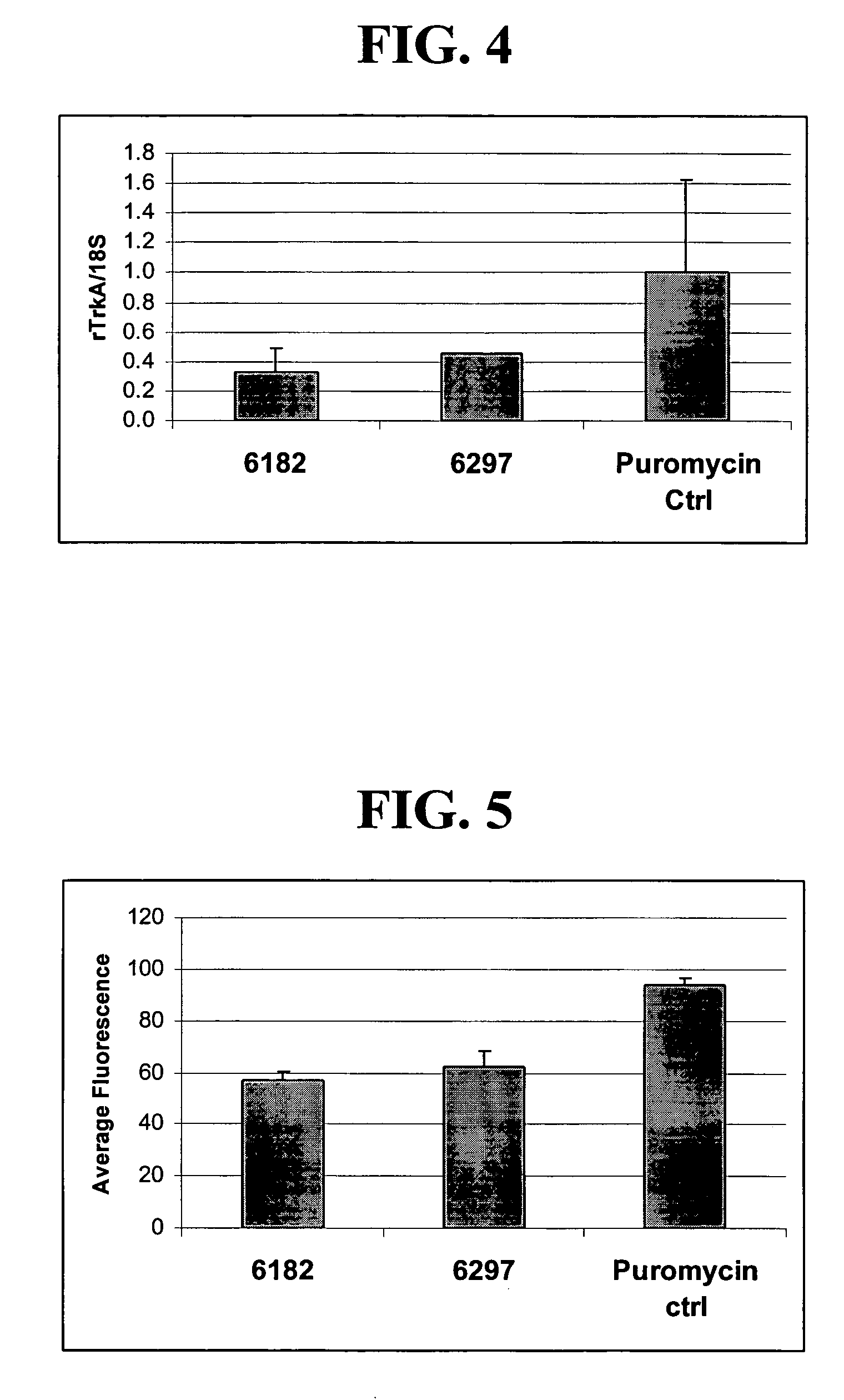
Treatment of neuropathic pain with zinc finger proteins
InactiveUS20050245476A1Easy to produceNervous disorderFusion with DNA-binding domainNAV1Dorsal roots
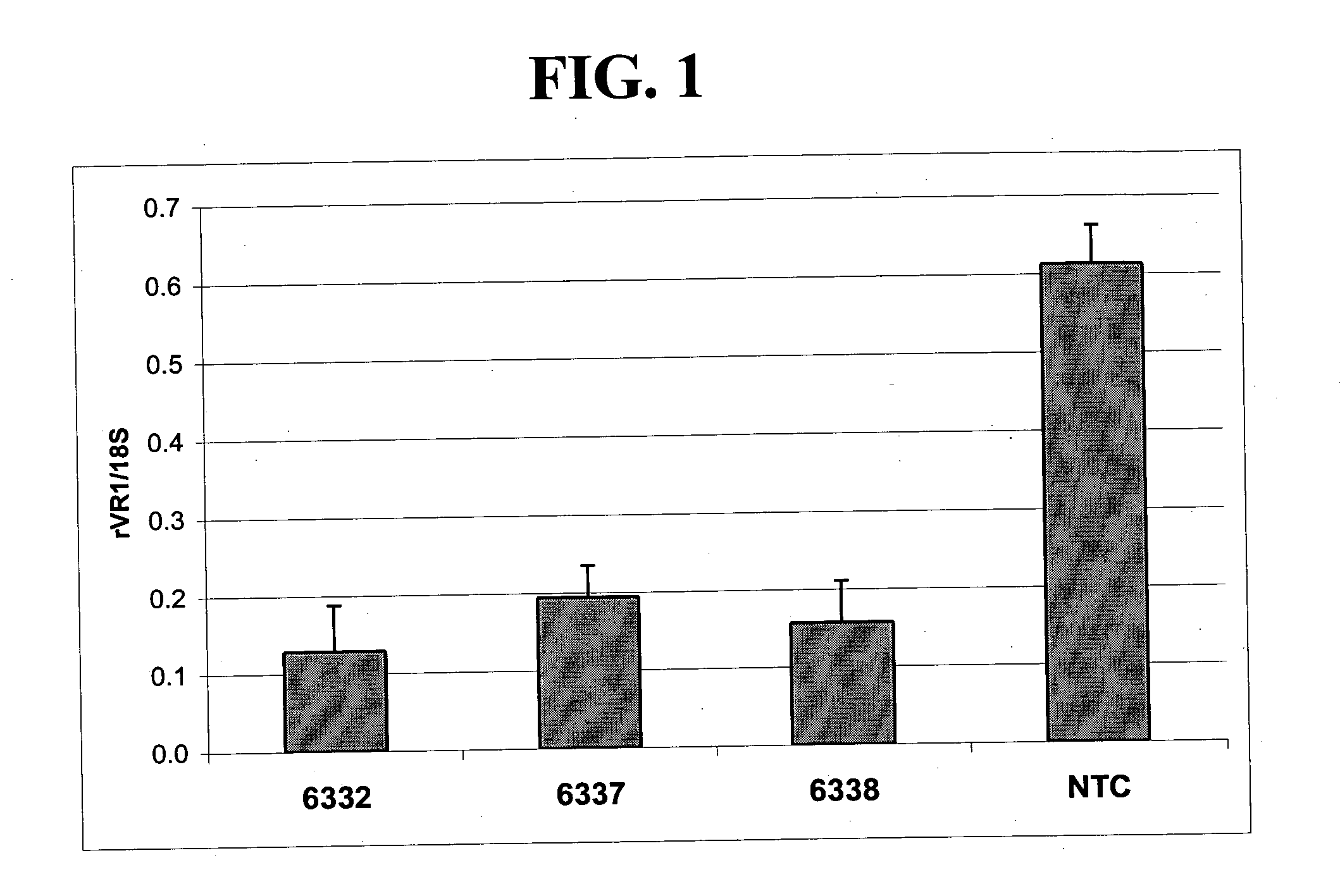
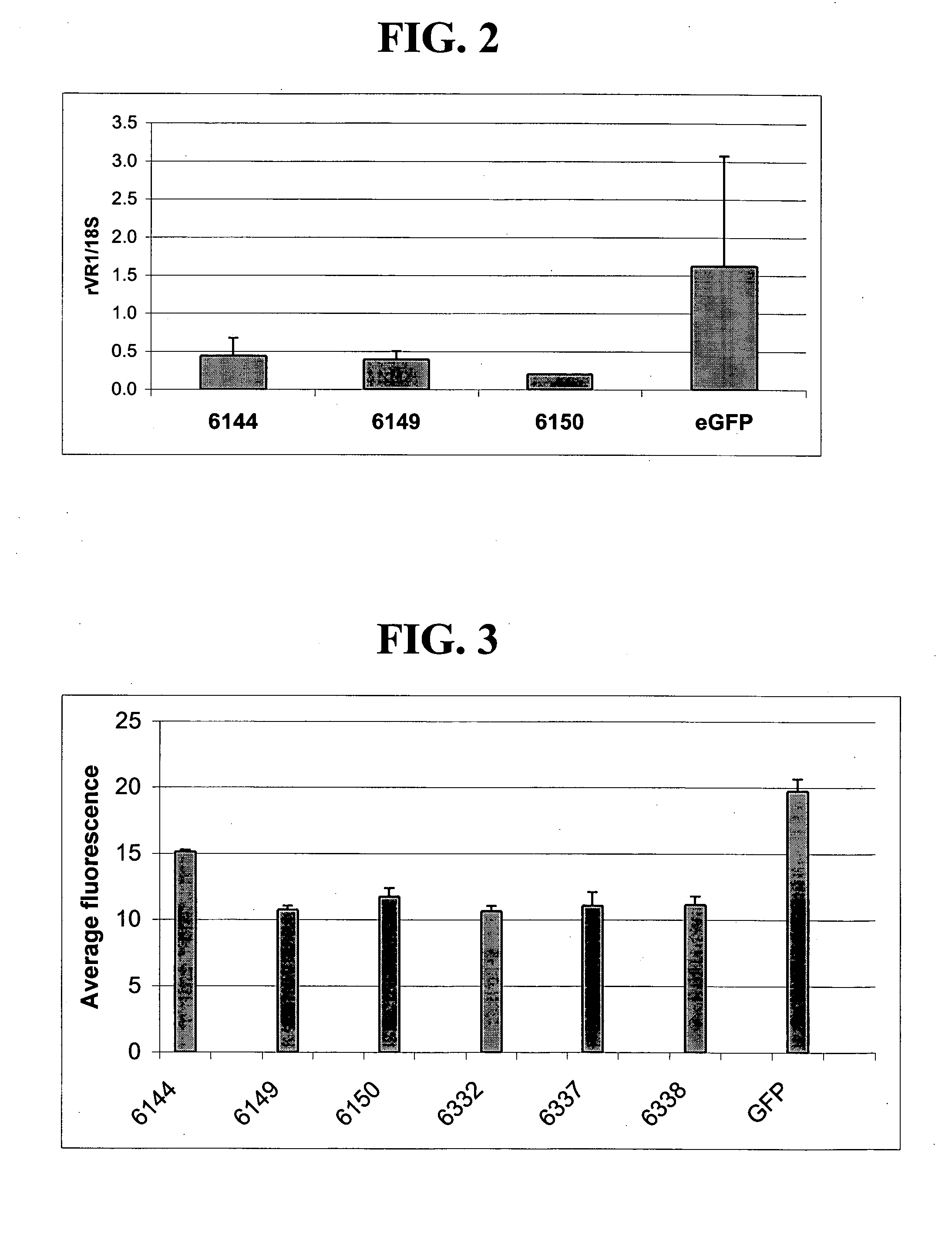
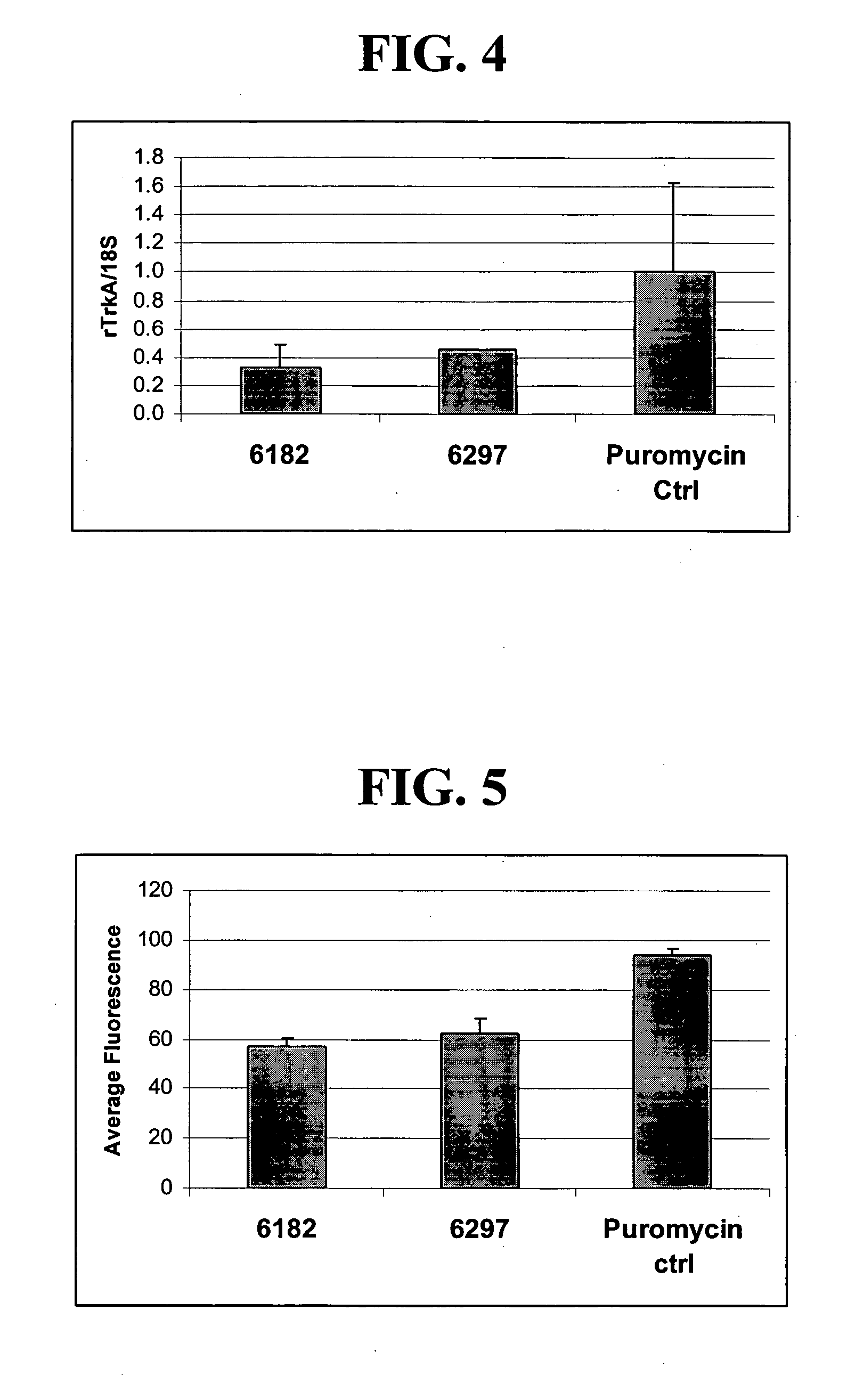
A variety of zinc finger proteins (ZFPs) and methods utilizing such proteins are provided for use in treating neuropathic pain. ZFPs that bind to a target site in genes that are aberrantly expressed in subjects having neuropathic pain are described. In addition, ZFPs that bind to a target site in genes expressed at normal levels in subjects experiencing neuropathic pain, modulation of whose expression results in decreased pain perception, are also provided. For example, genes that are over-expressed in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) of pain patients (e.g., VR1, TRKA and / or Nav1.8) can be repressed, whereas genes that are under-expressed in the same populations can be activated.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
Nucleic acid binding polypeptide library
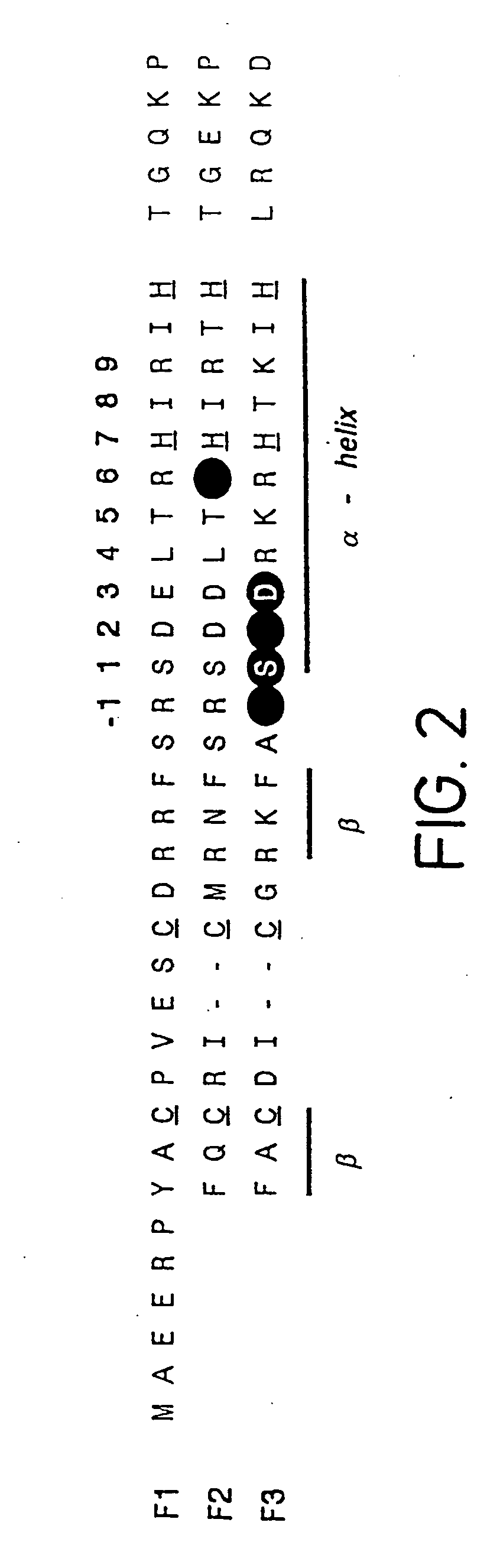
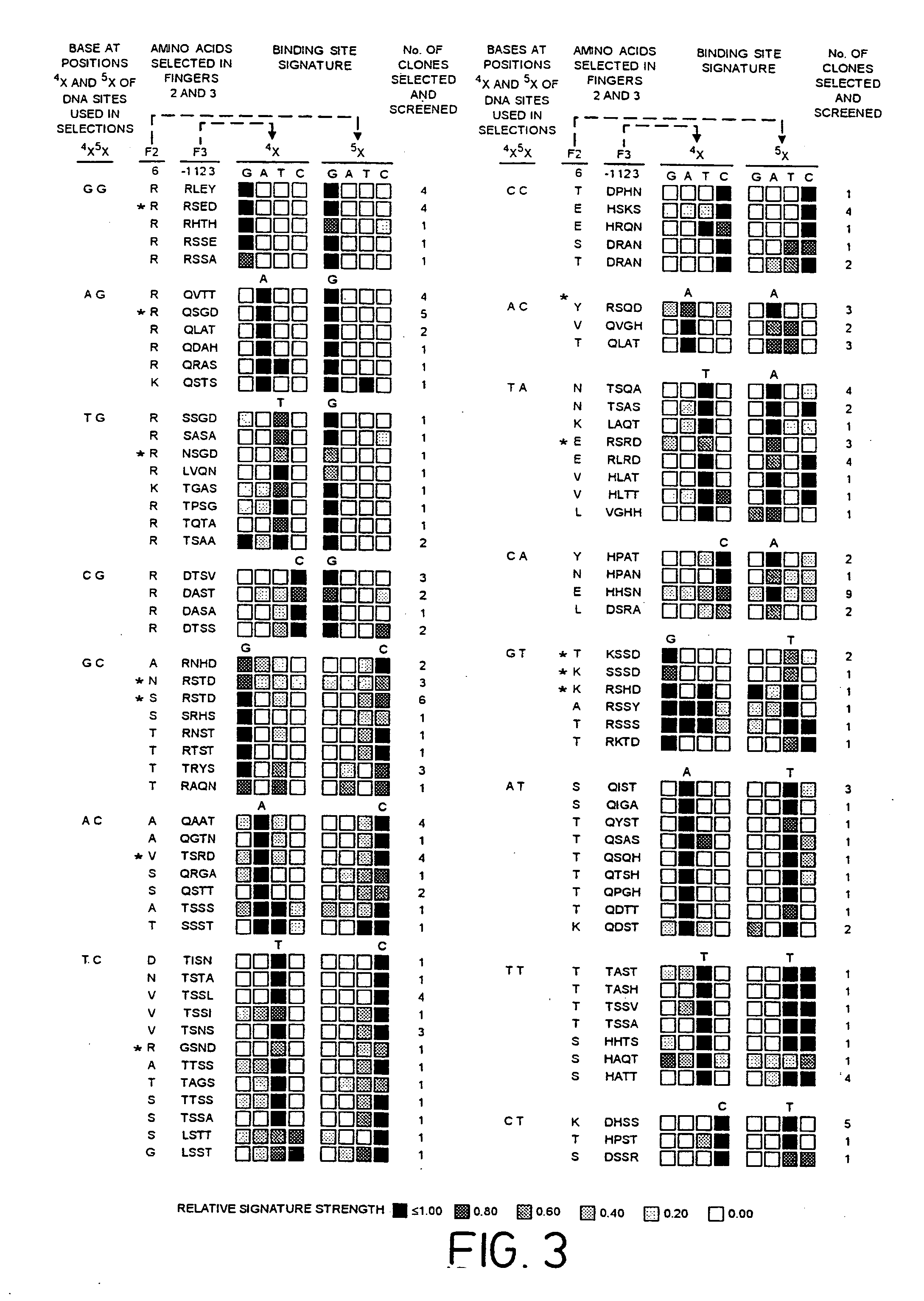
The invention relates to a zinc finger polypeptide library in which each polypeptide comprises more than one zinc finger which has been at least partially randomized, and to a set of zinc finger polypeptide libraries which encode overlapping zinc finger polypeptides, each polypeptide comprising more than one zinc finger which has been at least partially randomized, and which polypeptide may be assembled after selection to form a multifinger zinc finger polypeptide.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
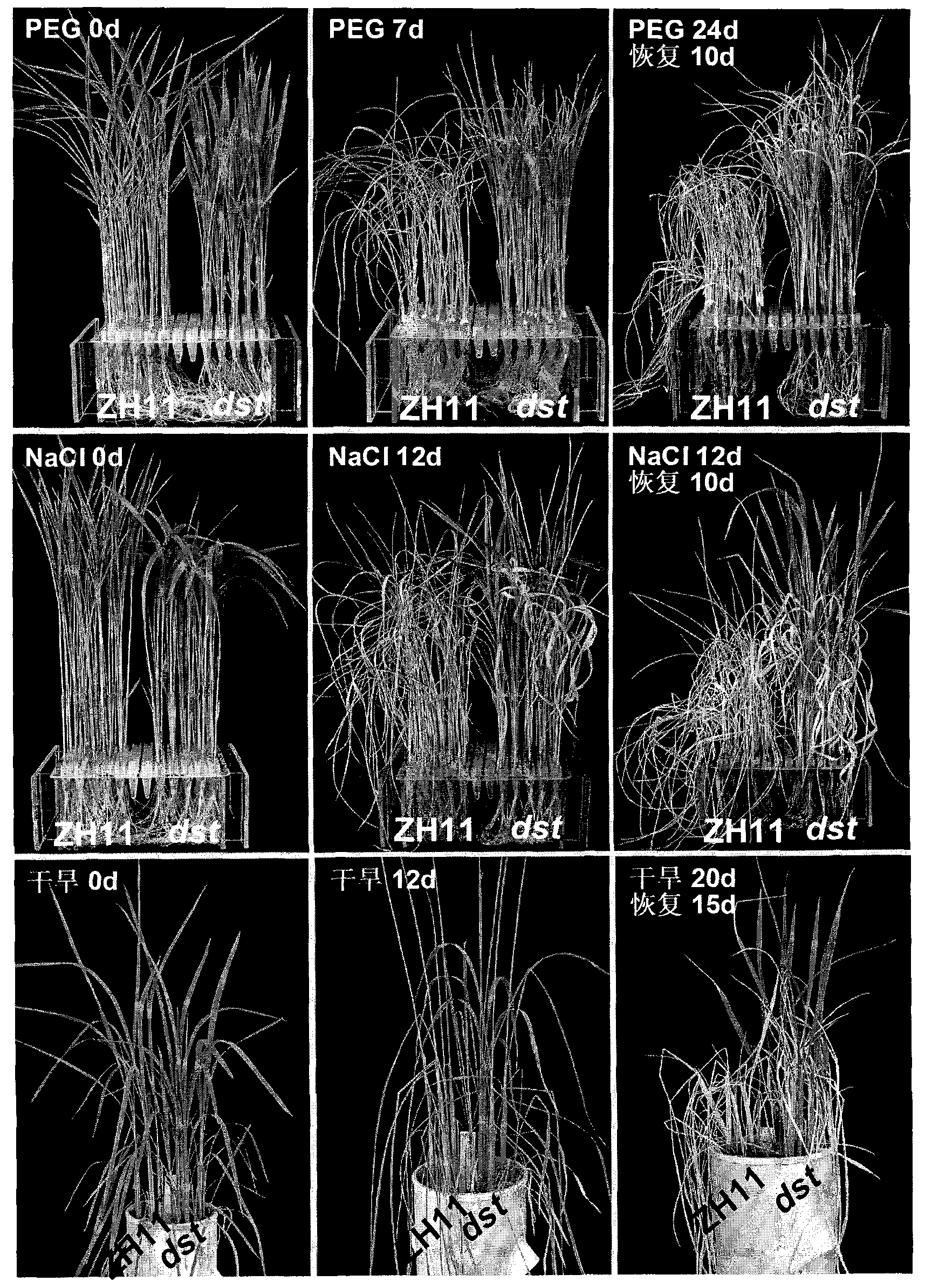
New gene for rice zinc-finger protein transcription factor and application thereof to drought resistance and salt tolerance
ActiveCN101875689AImproved resistance to salt or drought stressRaw materials are simpleFungiBacteriaAgricultural scienceCis-regulatory element
The invention relates to a new gene for the rice zinc-finger protein transcription factor and the application thereof to drought resistance and salt tolerance, in particular to the rice zinc-finger protein transcription factor, a coding sequence thereof, a carrier or host, a cis-acting element and antagonist of the rice zinc-finger protein transcription factor or the coding sequence. The rice zinc-finger protein transcription factor comprises polypeptide, and the polypeptide can be the polypeptide having the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2, the conservative variant polypeptide or the homologous polypeptide separated from the same; the carrier or host includes the coding sequence; and the cis-acting element is combined with the rice zinc-finger protein transcription factor. The invention also relates to a method for improving the drought resistance and the salt tolerance of the rice and a method for sieving the rice with high drought resistance and salt tolerance. The novel method for improving and studying the drought resistance and the salt tolerance of the rice has wide application prospect.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Nucleic acid binding polypeptide library
The invention relates to a zinc finger polypeptide library in which each polypeptide comprises more than one zinc finger which has been at least partially randomized, and to a set of zinc finger polypeptide libraries which encode overlapping zinc finger polypeptides, each polypeptide comprising more than one zinc finger which has been at least partially randomized, and which polypeptide may be assembled after selection to form a multifinger zinc finger polypeptide.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
PARP Modulators and Treatment of Cancer
The invention relates to a method of modulating poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1 (PARP-1) activity in a mammal comprising administering to a mammal an effective amount of an organic aromatic compound having from 4 to about 35 carbon atoms, wherein said organic aromatic compound is capable of binding the arginine-34 moiety located in Zinc finger-1 of the PARP-1 enzyme and wherein said organic aromatic compound has electron donating capabilities such that it's π-electron system will interact with the positively charged (cationic) guanidinium moiety of the specific arginine-34 residue of the Zinc-1 finger of PARP-1 and does not contain benzamide or lactam substituents.In particular, substituted benzopyrones and substituted indoles and their pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds that modulate the activity of PARP-1, are described. The invention is also directed to the composition of matter, kits and methods for their therapeutic and / or prophylactic use in treating diseases and disorders described herein, by administering effective amounts of such compounds. Preferably, the compositions and methods provided herein inhibit PARP activity.
Owner:BIPAR SCI INC
Mutated rep encoding sequences for use in AAV production
ActiveUS9228174B2Stable productionQuality improvementAnimal cellsSugar derivativesNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
Nucleic acids encoding Parvoviral Rep proteins with a mutated nuclear localization signal (NLS) are provided. Also provided is a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a Parvoviral Rep protein with a mutated zinc finger domain and a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a Parvoviral Rep protein comprising an amino acid mutation at position 43, 57, 79, 97, 120, 179, 305, 484, 493 or 571 with reference to SEQ ID NO: 2. Nucleic acid constructs and cells, such as insect cells, comprising the nucleic acids are provided as well as a method for producing a recombinant Parvoviral virion using the nucleic acids.
Owner:UNIQURE IP BV
Pharmacological agents and methods of treatment that inactivate pathogenic prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and viruses by attacking highly conserved domains in structural metalloprotein and metalloenzyme targets
The invention relates to the treatment of viral, bacterial, parasitic, proliferative diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, inflammatory diseases, immunological diseases, transplanted organ rejection, and diseases produced by intoxication with heavy metals. The invention relates to the use of specific metal chelating agents including, furoic acid, 2-thiophenecarboxylic acid and their derivatives, analogs and structurally related chemicals as pharmacological agents that can be used effectively to disrupt and inactivate specific transition metal ion containing zinc finger structural motifs in metalloproteins and specific transition metal ion containing catalytic sites in metalloproteinases, which in turn, inactivate the pathogenic virus, pathogenic prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells which produces disease conditions. The preparations can be administered topically or for systemic use. The preparations are novel wide-spectrum antibiotics which have antiviral, antiproliferative, antineoplastic, antiangiogenic, antibacterial, antiparasitic, antiinfective, and anti-inflammatory effects and can be used in the treatment and prevention of diseases such as AIDS, cancers, untoward angiogenesis, pulmonary anthrax, malaria, inflammatory responses, Alzheimer's disease and other diseases.
Owner:POLS LAB BIOTECH
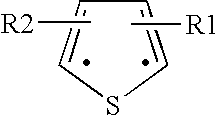
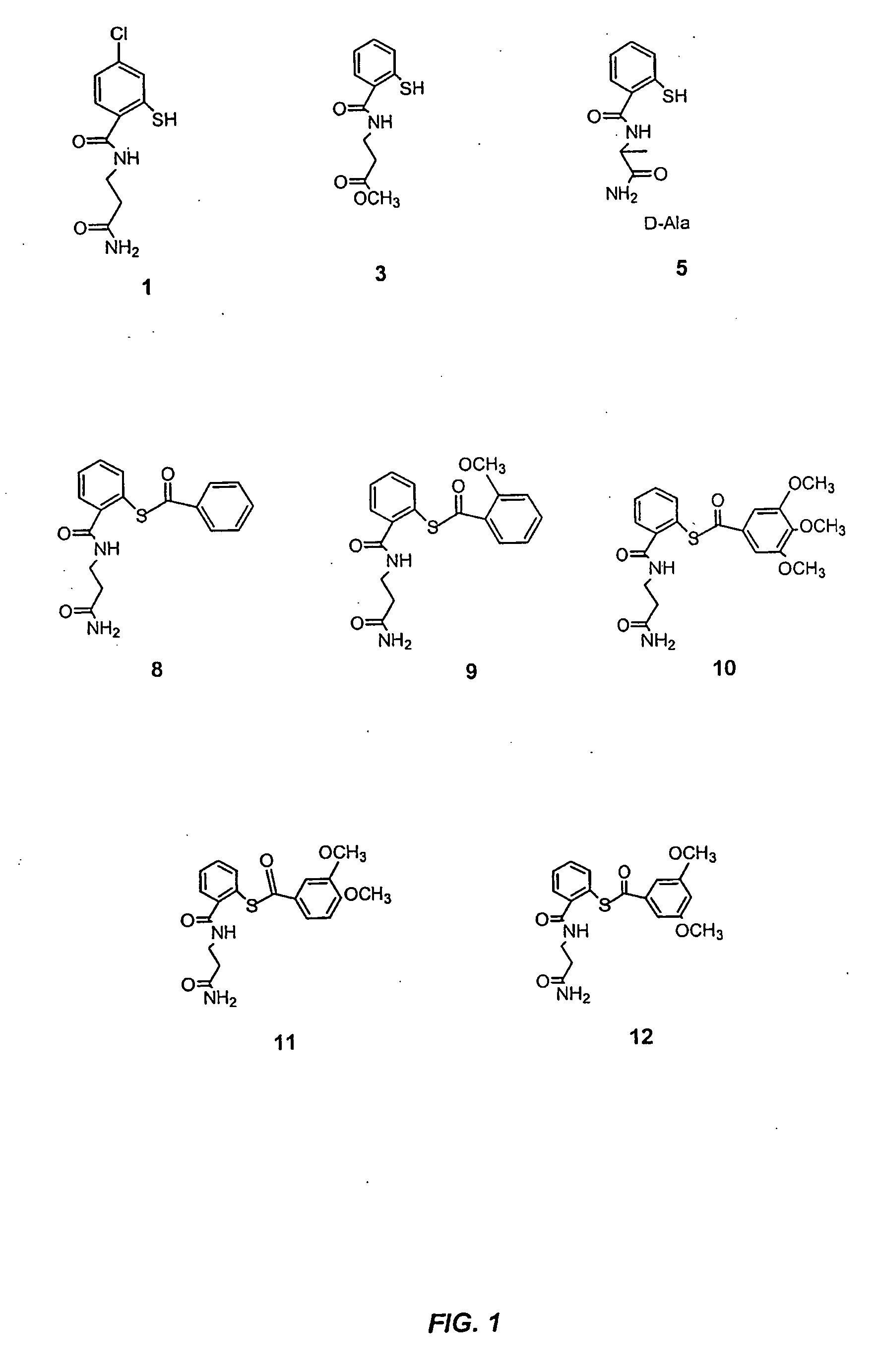
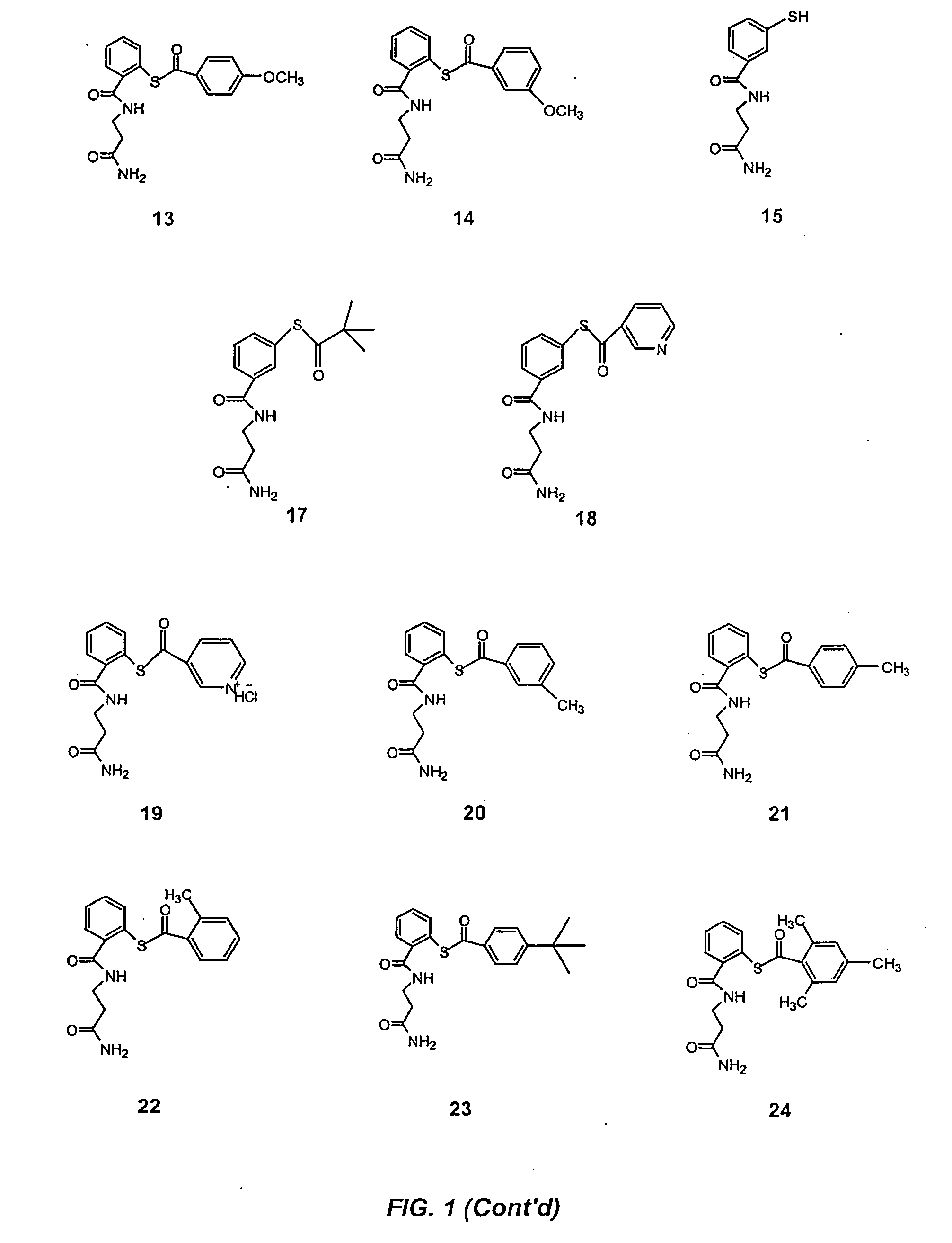
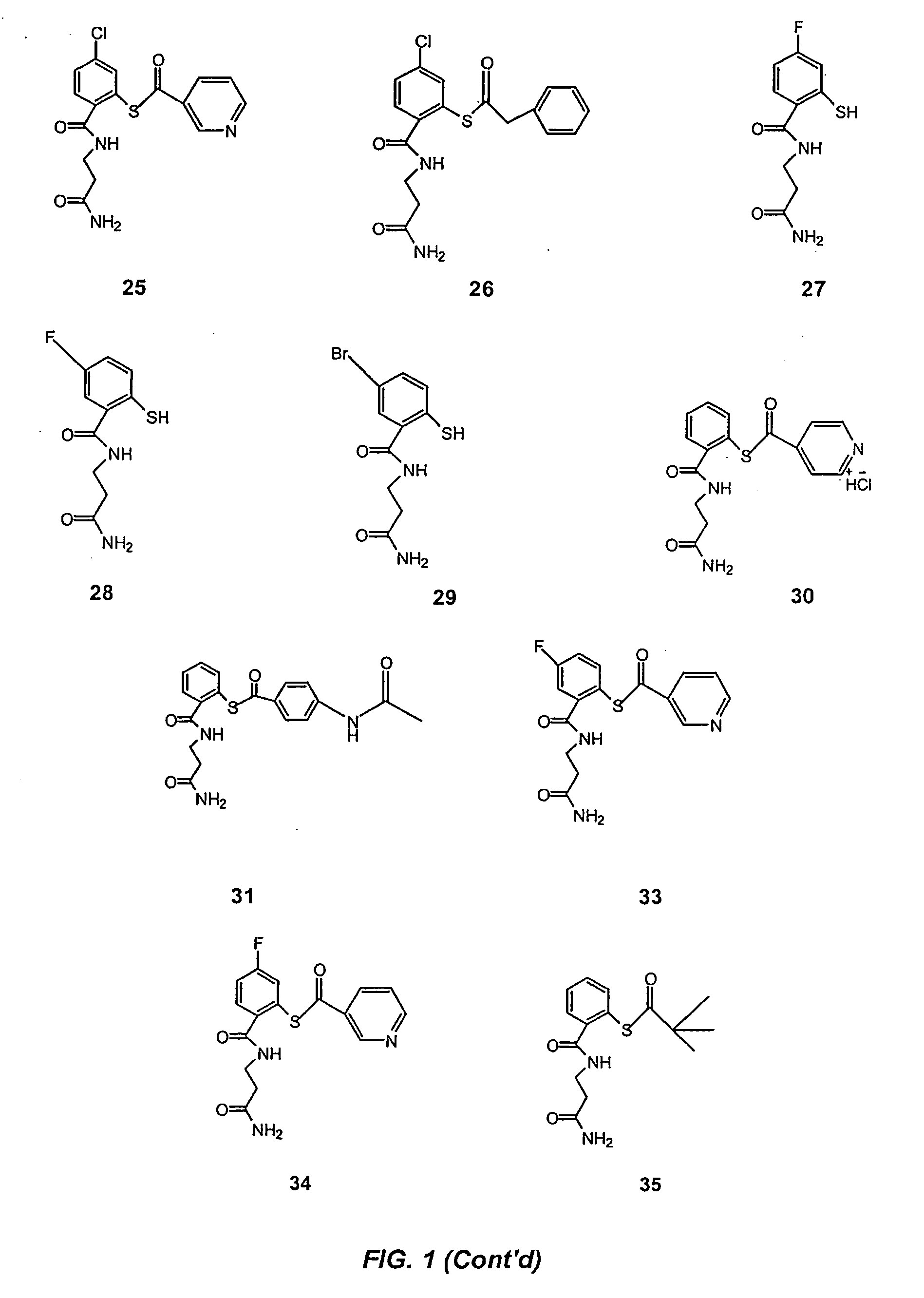
Acylthiols and component thiol compositions as anti-hiv and anti-retroviral agents
Certain thiol and acylthiol compounds inhibit retrovirus growth by attacking the highly conserved zinc finger regions of essential viral proteins. These compounds, compositions containing them, and methods of using them to treat retroviral infections such as HIV are described. These compounds are also useful for preparation of vaccines comprised of inactivated retroviruses such as HIV, prevention of the transmission of such retroviruses, and detection of retroviral proteins.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Regulation of endogenous gene expression in cells using zinc finger proteins
InactiveUS20050215502A1Inhibition of activationInhibit expressionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsZinc fingerCell biology
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com