Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
213 results about "Internal time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Internal Time is an accessible, up-to-date overview of a subject that is important to all of us. With its remarkable depth and breadth of coverage, this book should be of interest to a wide and diverse audience.
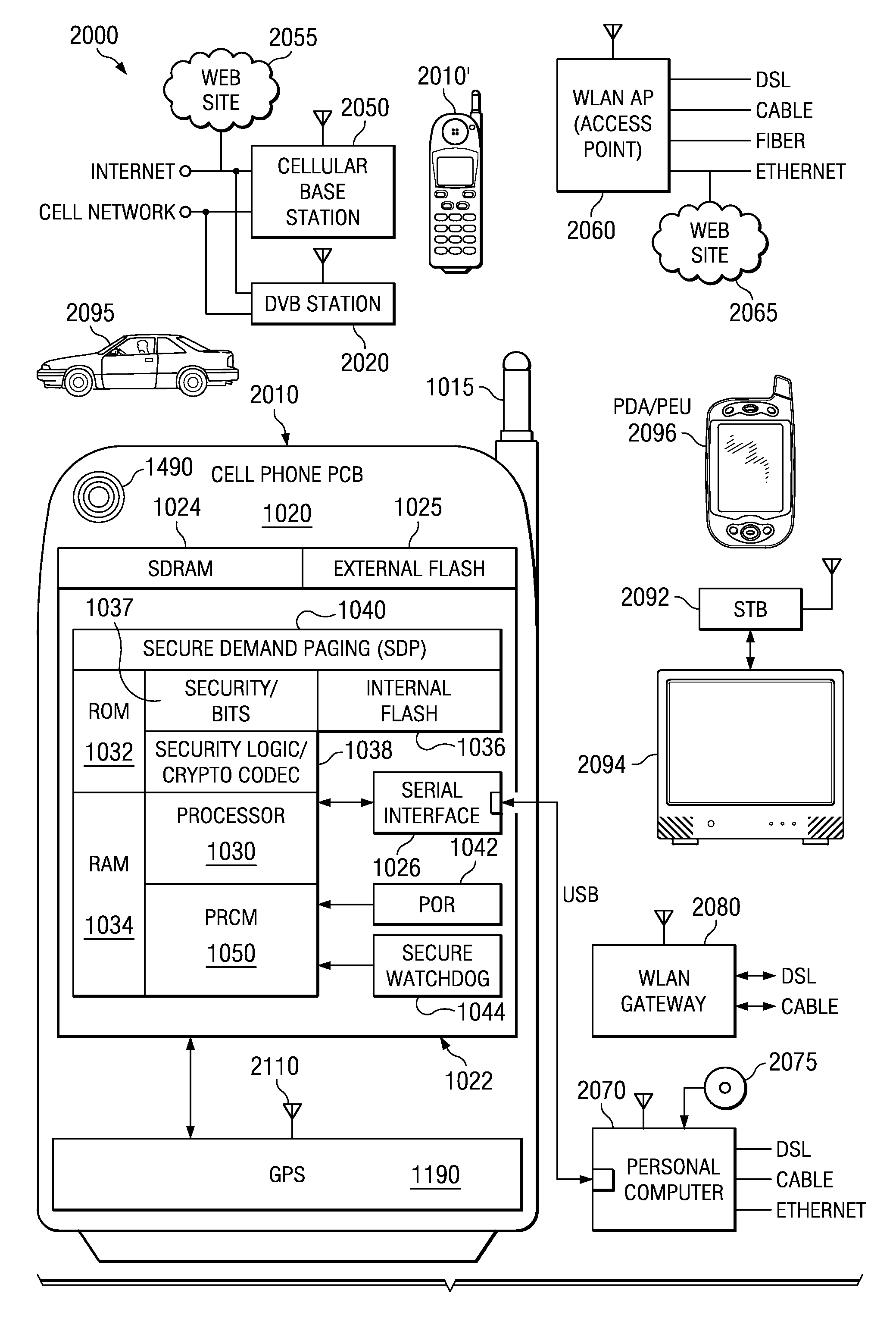
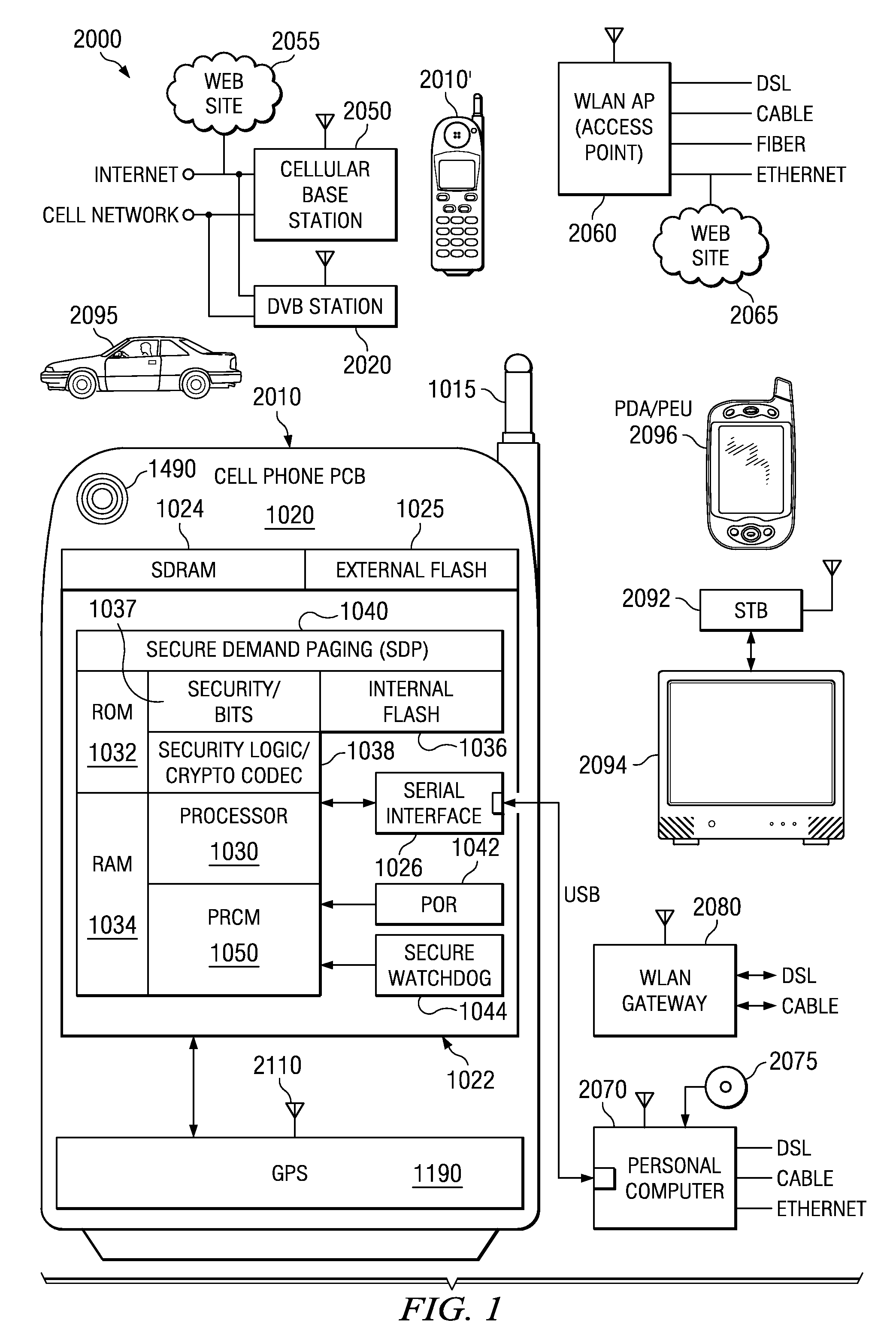
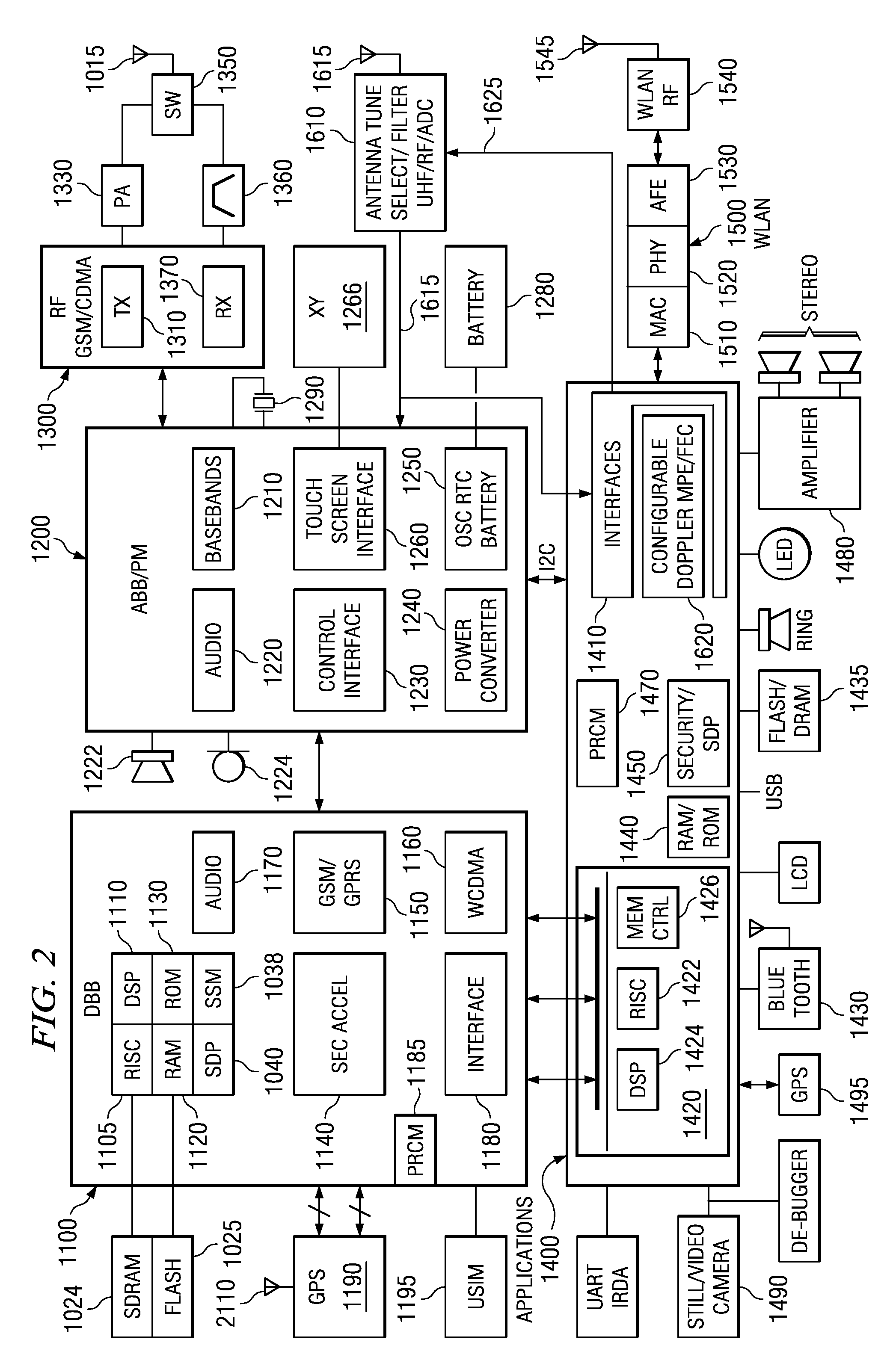
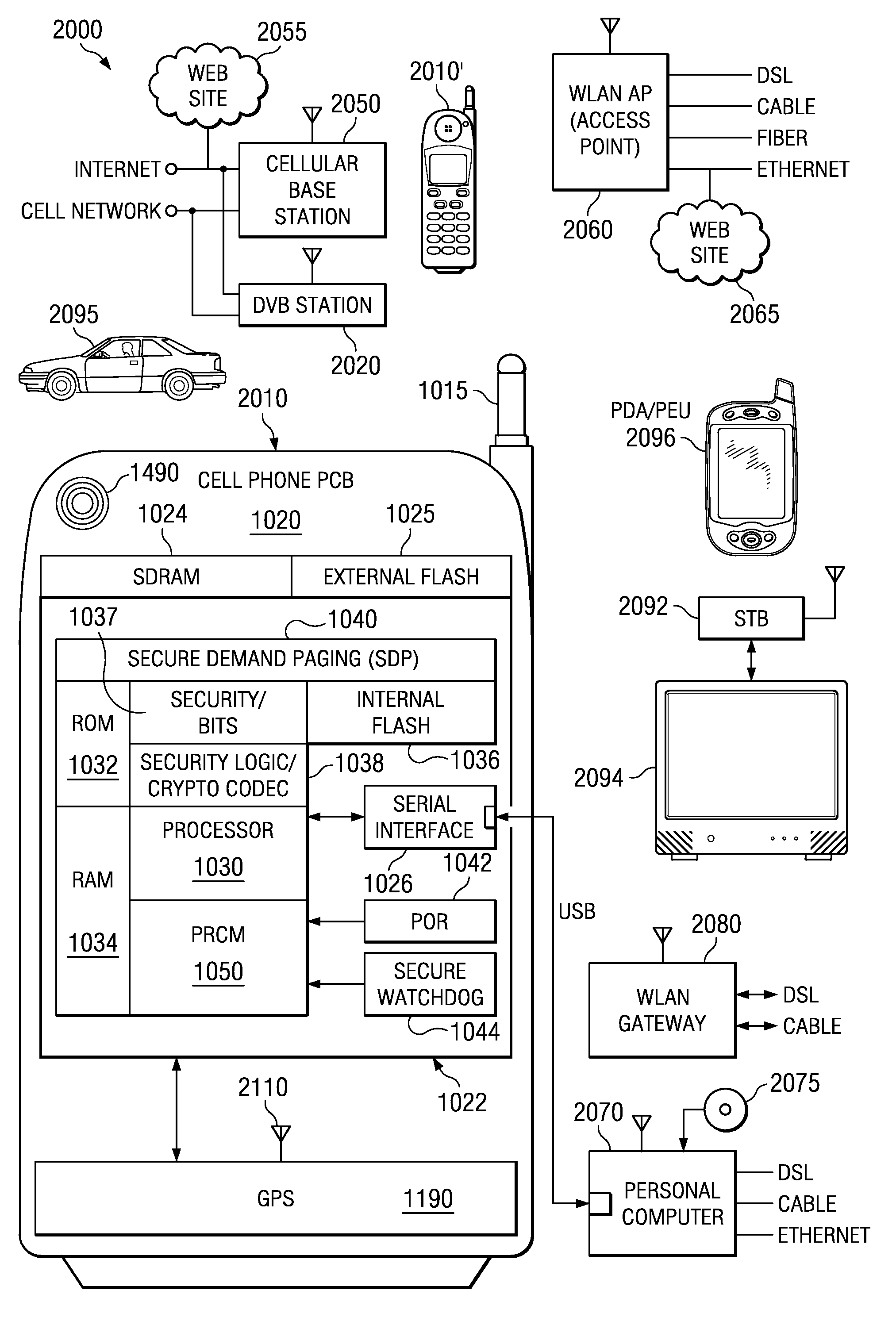
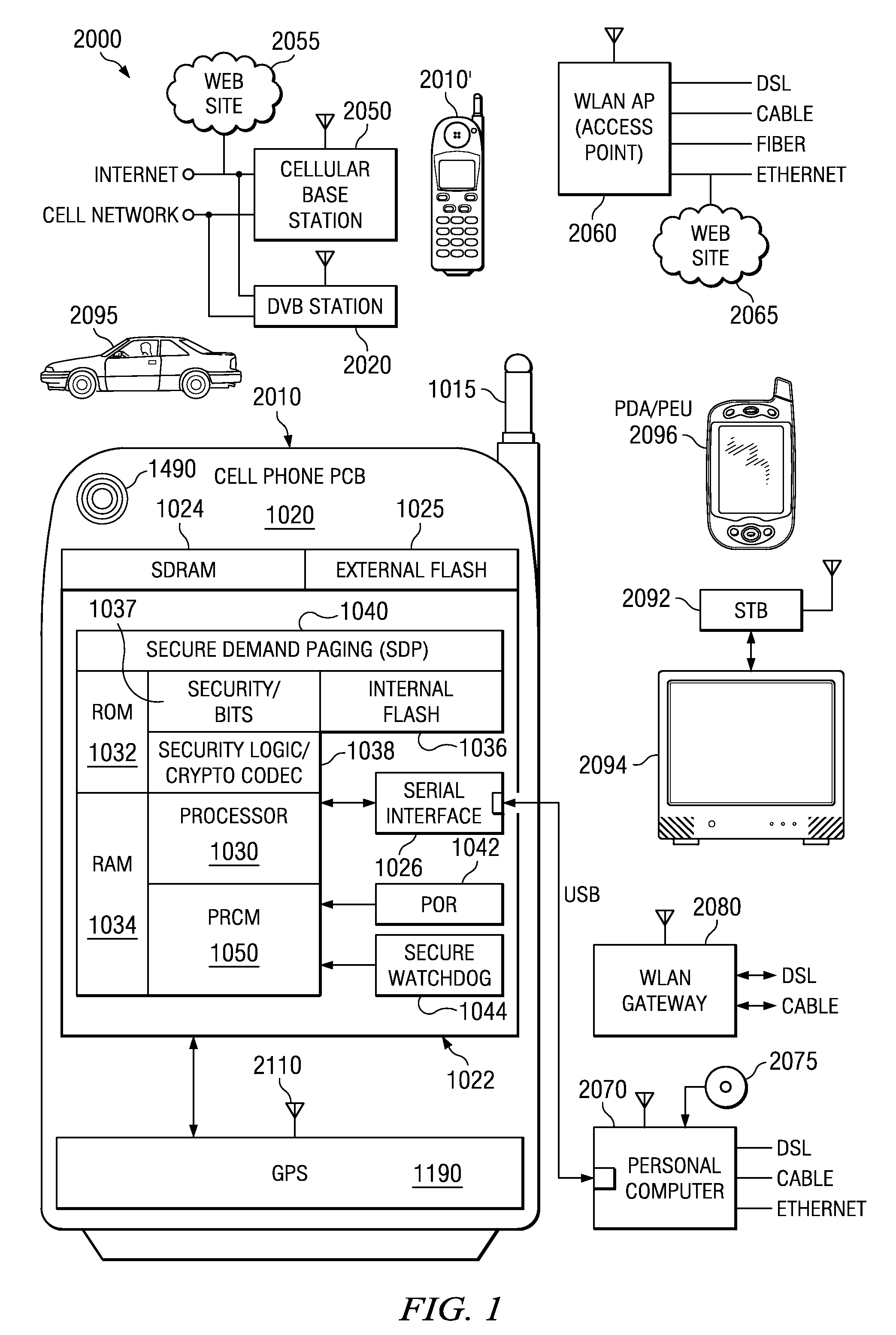
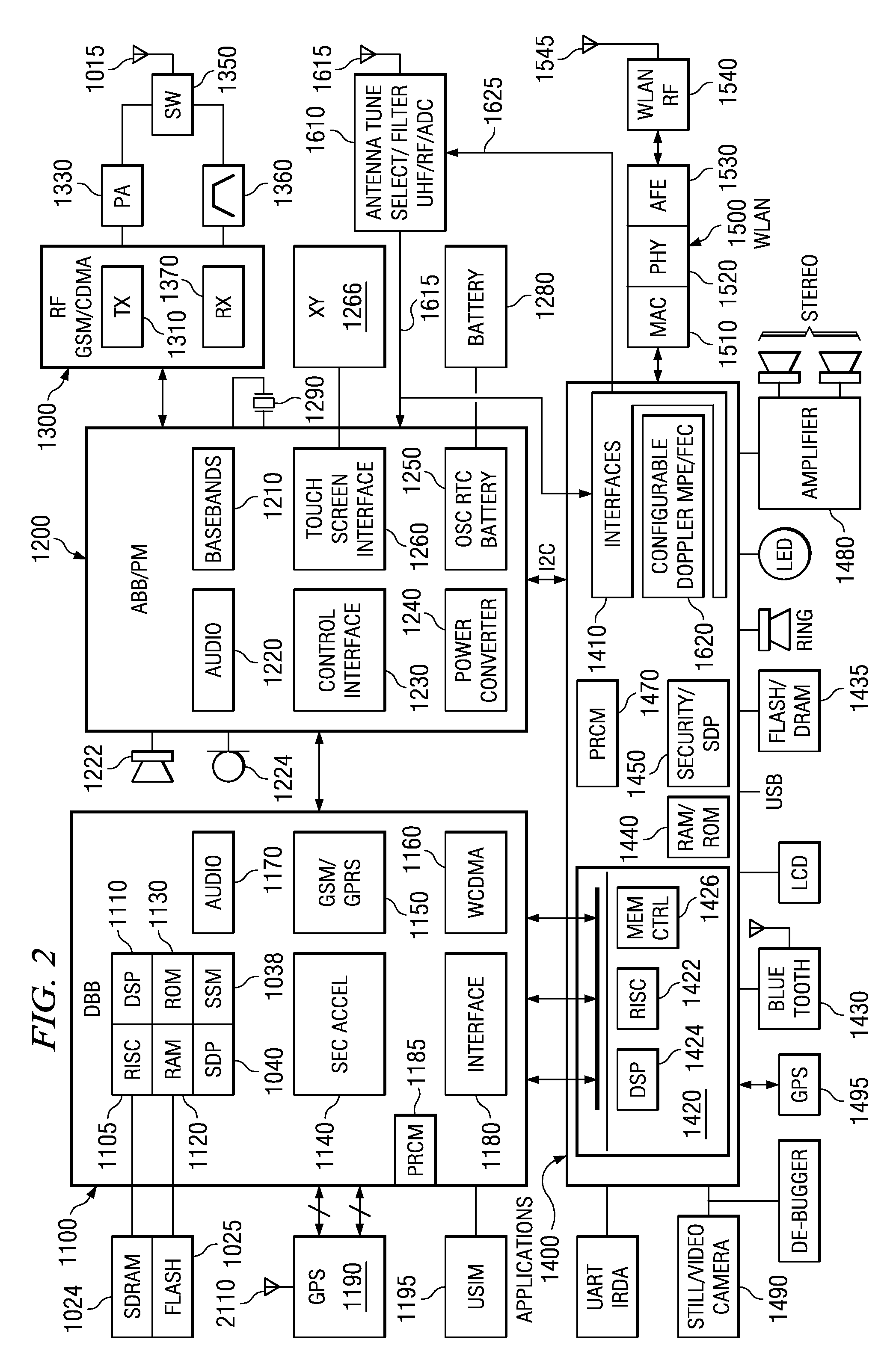
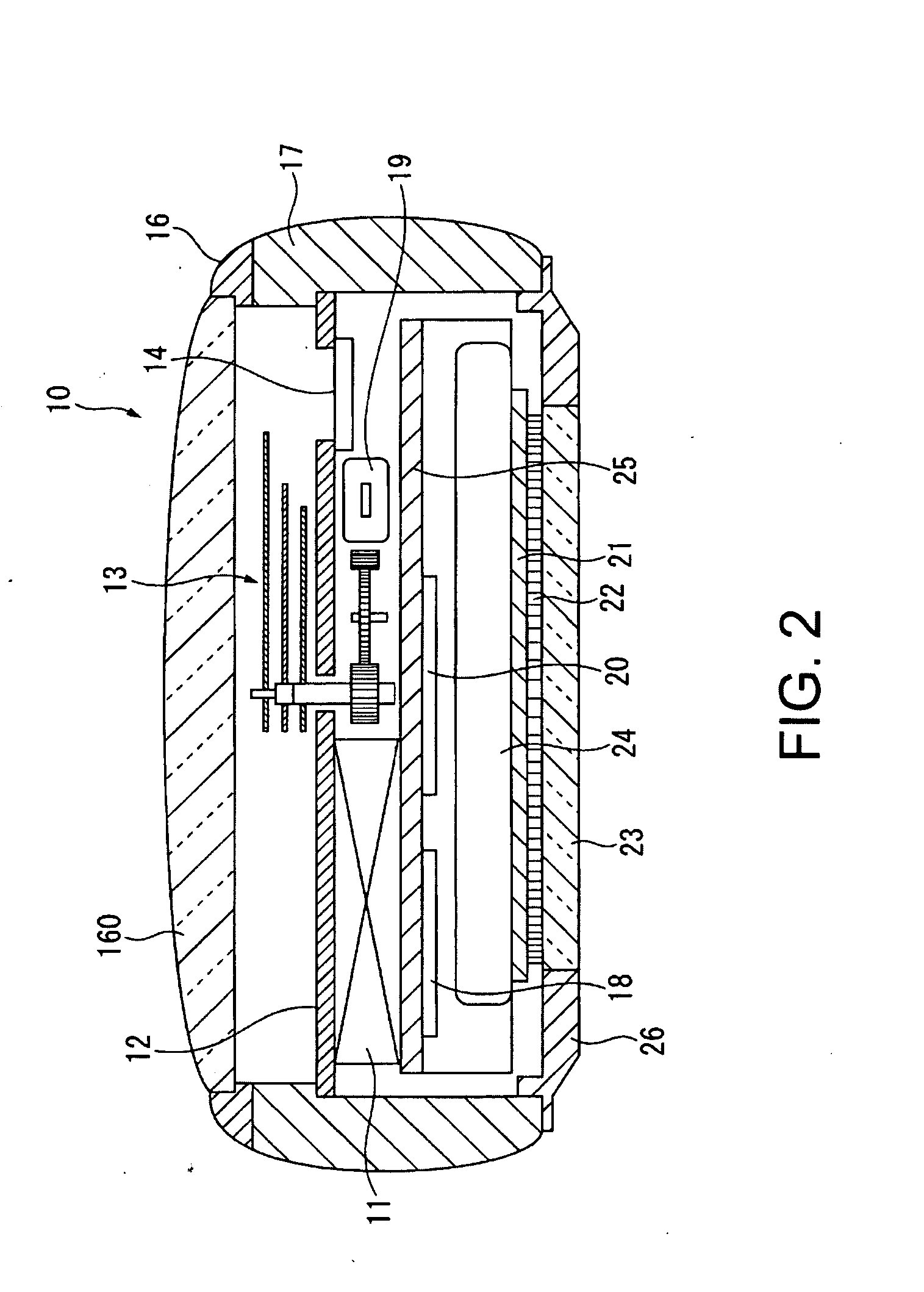
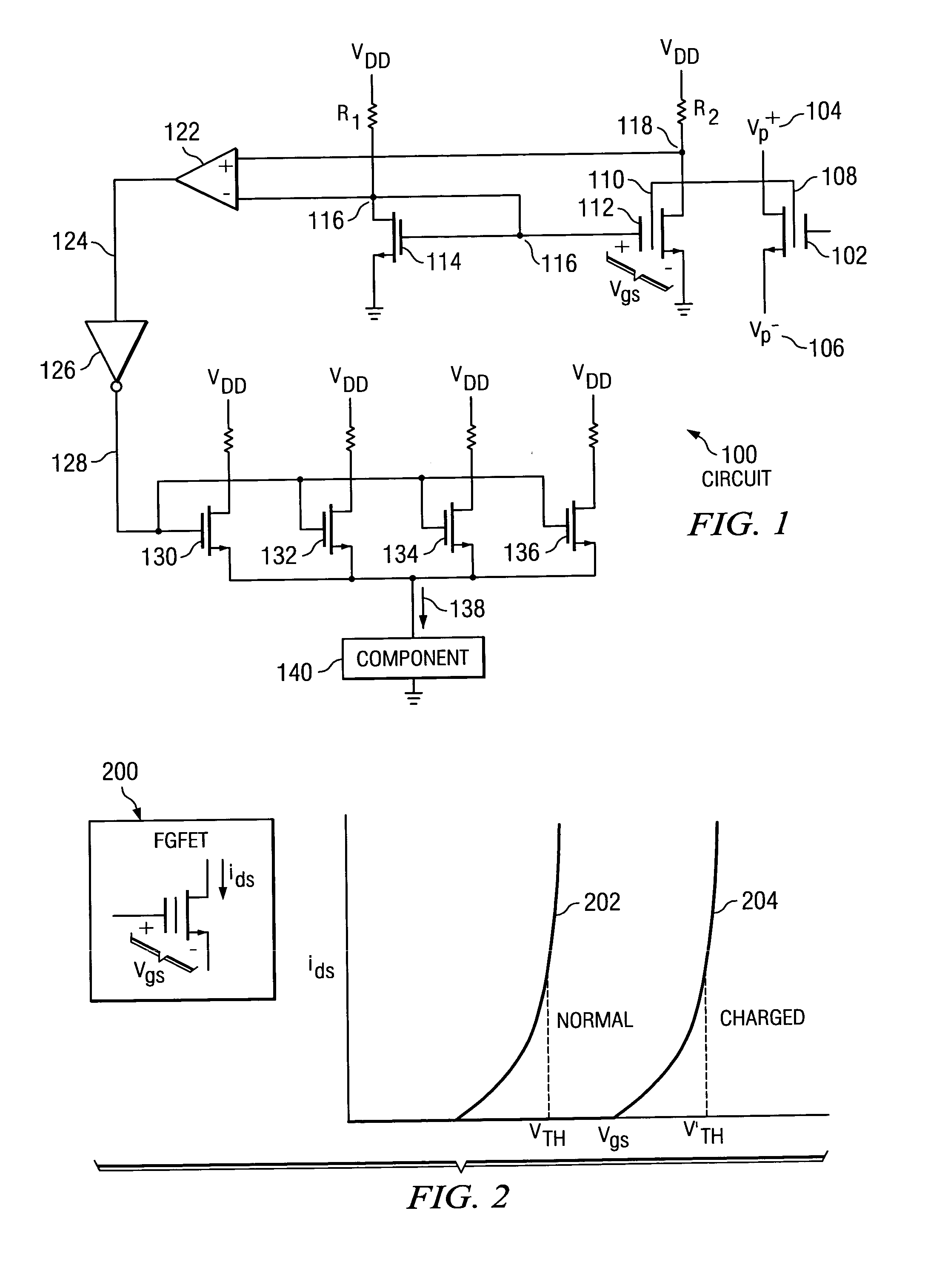
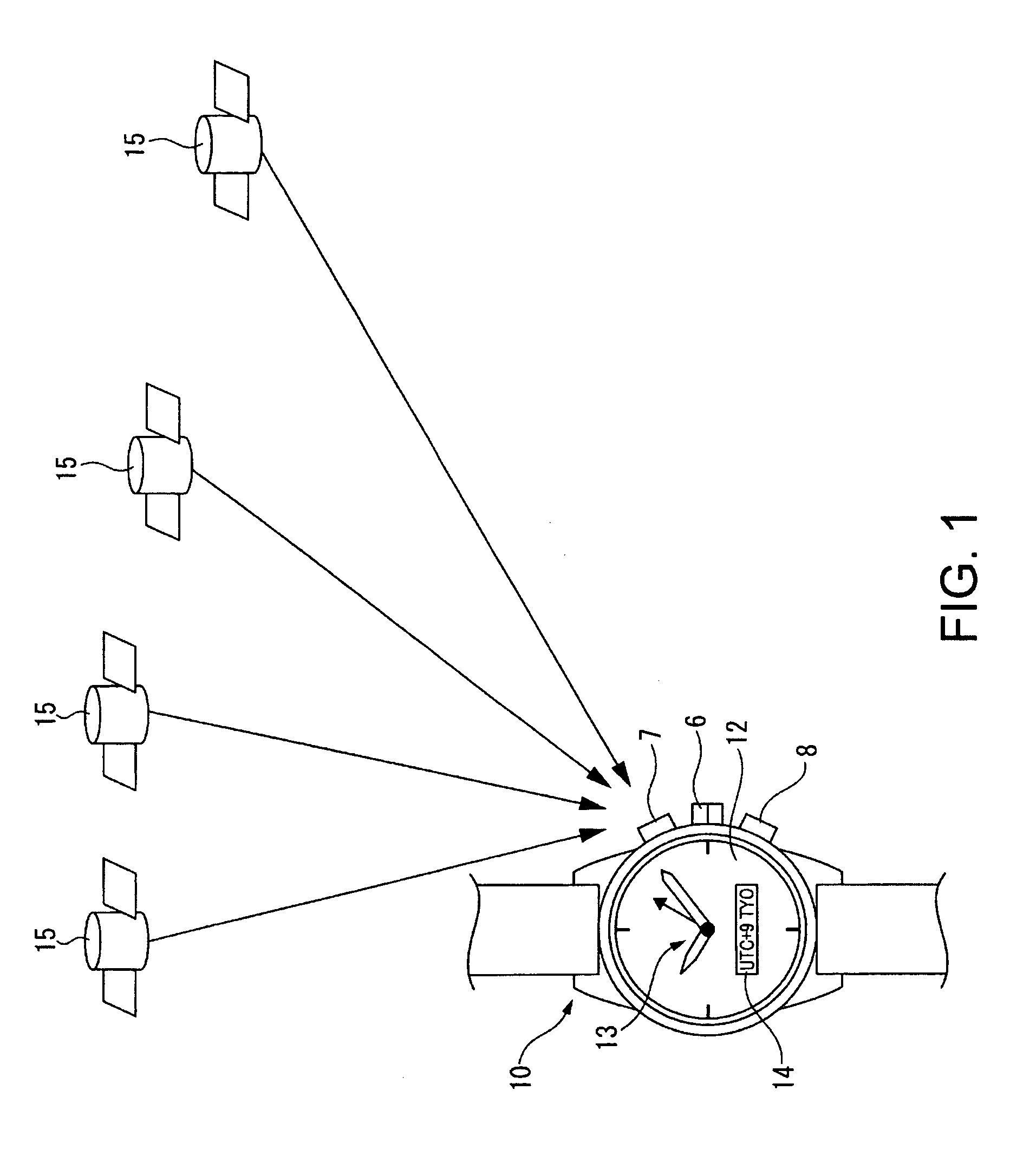
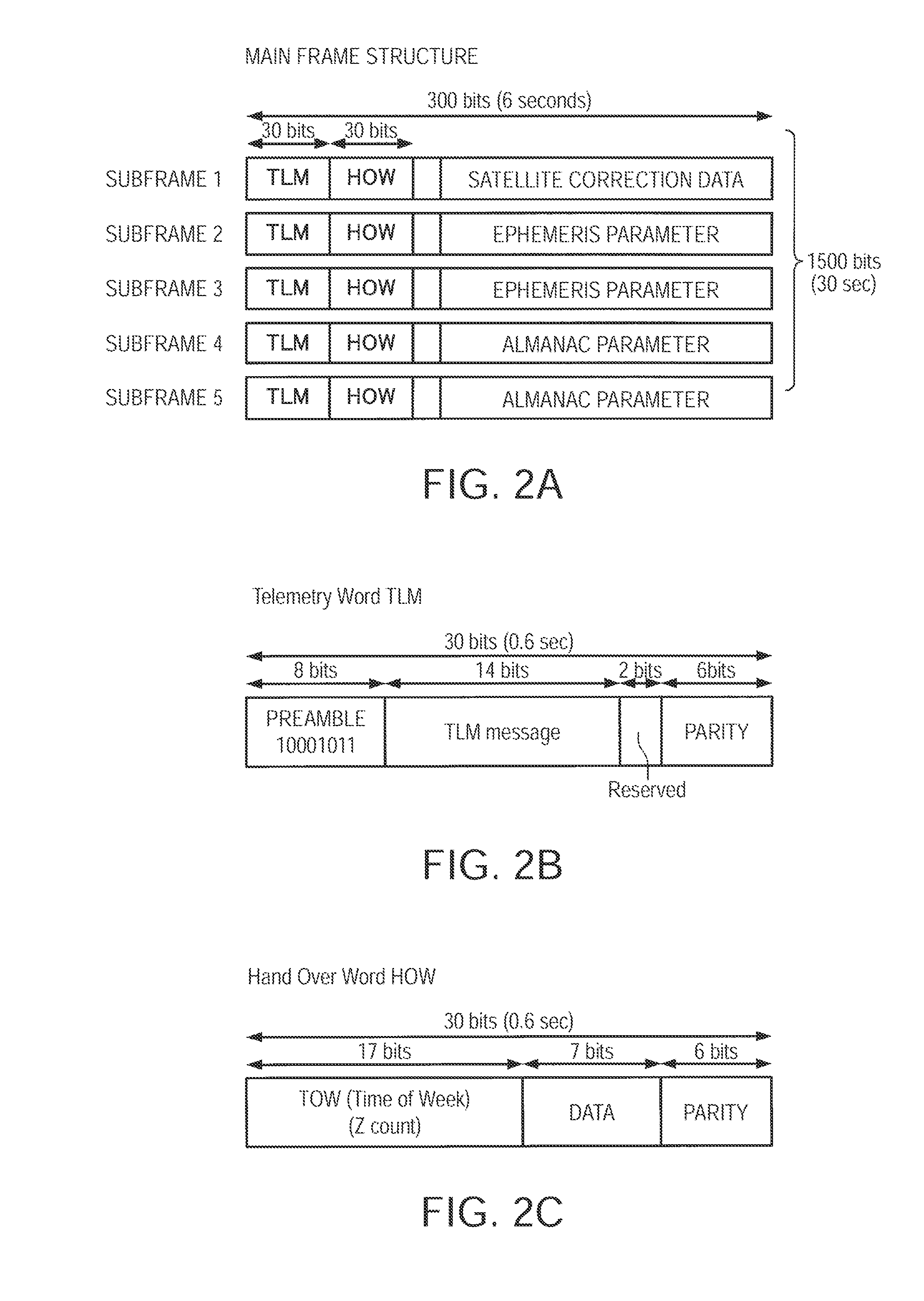
Satellite (GPS) assisted clock apparatus, circuits, systems and processes for cellular terminals on asynchronous networks
ActiveUS20090054075A1Fixed lengthRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionAsynchronous networkComputer terminal
A wireless circuit (1100, 1190) for tracking an incoming signal and for use in a network (2000) having handover from one part (Cell A) of the network to another part (Cell B). The wireless circuit includes a processor (CE 1100) responsive to the incoming signal, the processor (CE 1100) operable to generate pulse edges representing network-based receiver synchronization instances (RSIs), and a timekeeping circuitry (2420, 2430, 2450) including an oscillator circuitry (2162), the timekeeping circuitry (2420, 2430) operable to maintain a set of counter circuitries (2422-2428) including a counter circuitry (2422) operable to maintain at least one network time component based on the RSIs and another counter circuitry (2428) operable at least during handover and during loss of network coverage for maintaining at least one internal time component (NC) based on the oscillator circuitry (2162), the set of counter circuitries (2422-2428) operable to account for elapsing time substantially gaplessly and substantially without overlap between the time components during a composite of network coverage, loss of network coverage and handover, and the timekeeping circuitry further including a time generator (2450) for combining the time components from the set of counter circuitries (2422-2428) to generate an approximate absolute time (SGTB). Other electronic circuits, positioning systems, methods of operation, and processes of manufacture are also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Technique for scheduling execution of jobs for or by network-connected devices
ActiveUS20020198923A1Limitations of prior art device management systems are avoidedAvoid restrictionsResource allocationMemory systemsCascading failureStart time
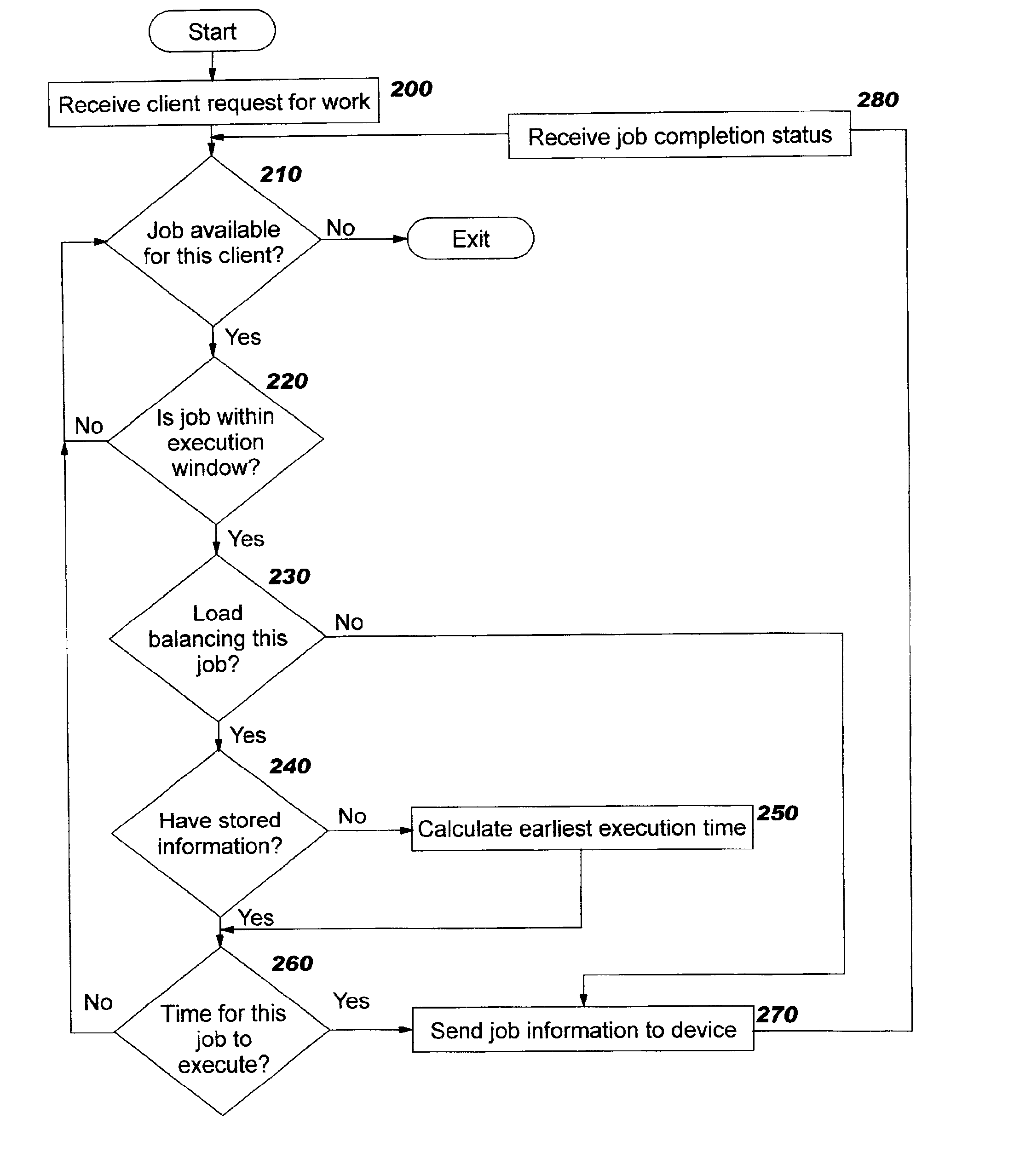
Methods, systems, computer program products, and methods of doing business by improving the scheduling of execution of jobs for or by network-connected devices, thereby enabling the job execution process to scale more easily, efficiently, and effectively to support large numbers of devices and / or users. Examples of jobs include, but are not limited to, distribution of resources (including software, configuration information, images, and other types of content) to a device, fetching a device's inventory information, backing up a device's contents, and so forth. Jobs are programmatically scheduled based upon a specified time internal, according to a class of the requester. Only if an earliest start time after which the job may be executed for this requester has been reached will the job be executed; otherwise, the job execution is delayed. The disclosed techniques lessen the need for additional servers to handle spikes in processing load, reduce the likelihood of reaching system overload, and reduce the likelihood of cascading failures that may occur when systems are overloaded.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Power Reforming Methods and Associated Multiphase Lights
InactiveUS20100320927A1Good colorImprove cooling effectDc network circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionPower factorColor mixing
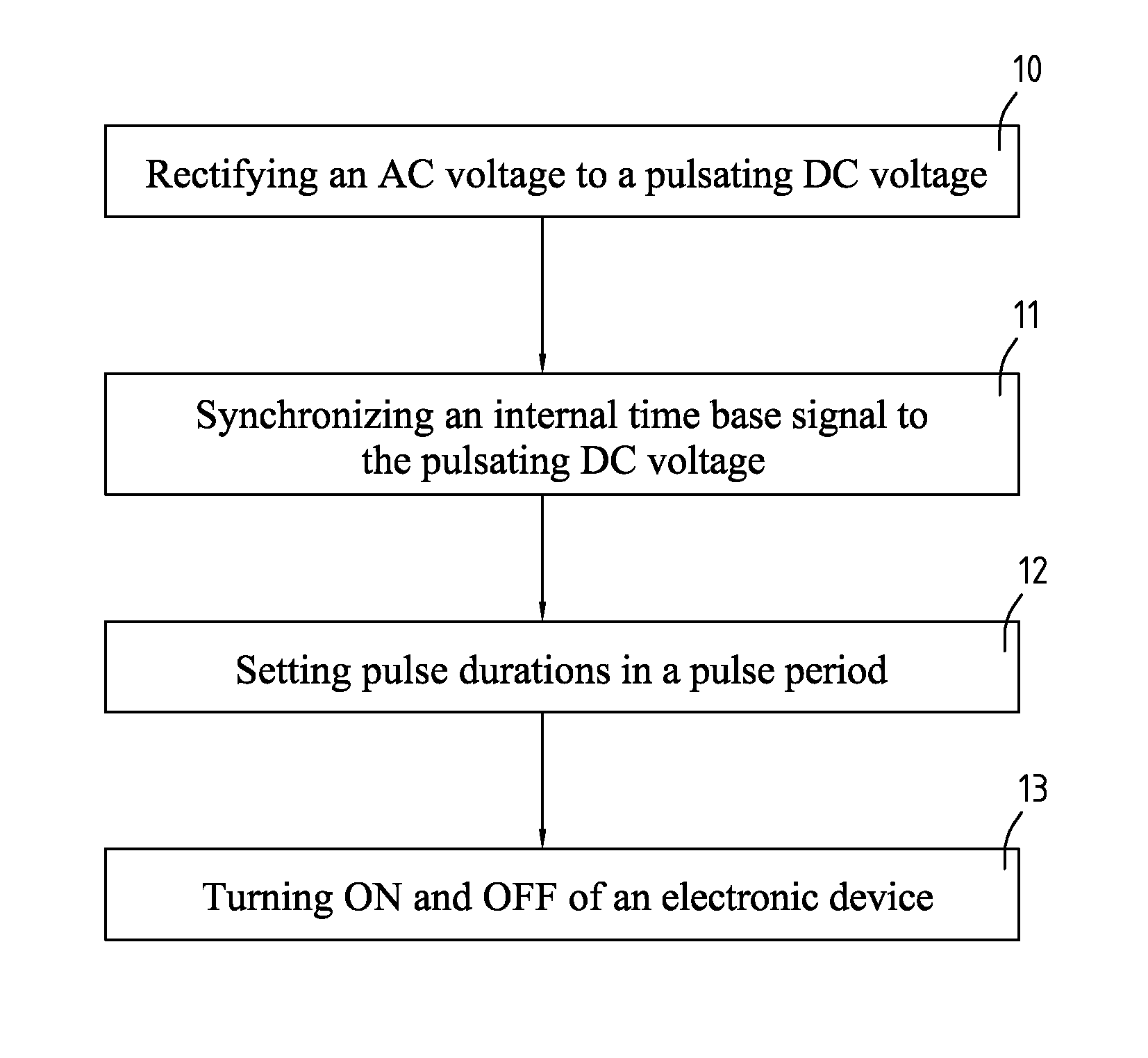
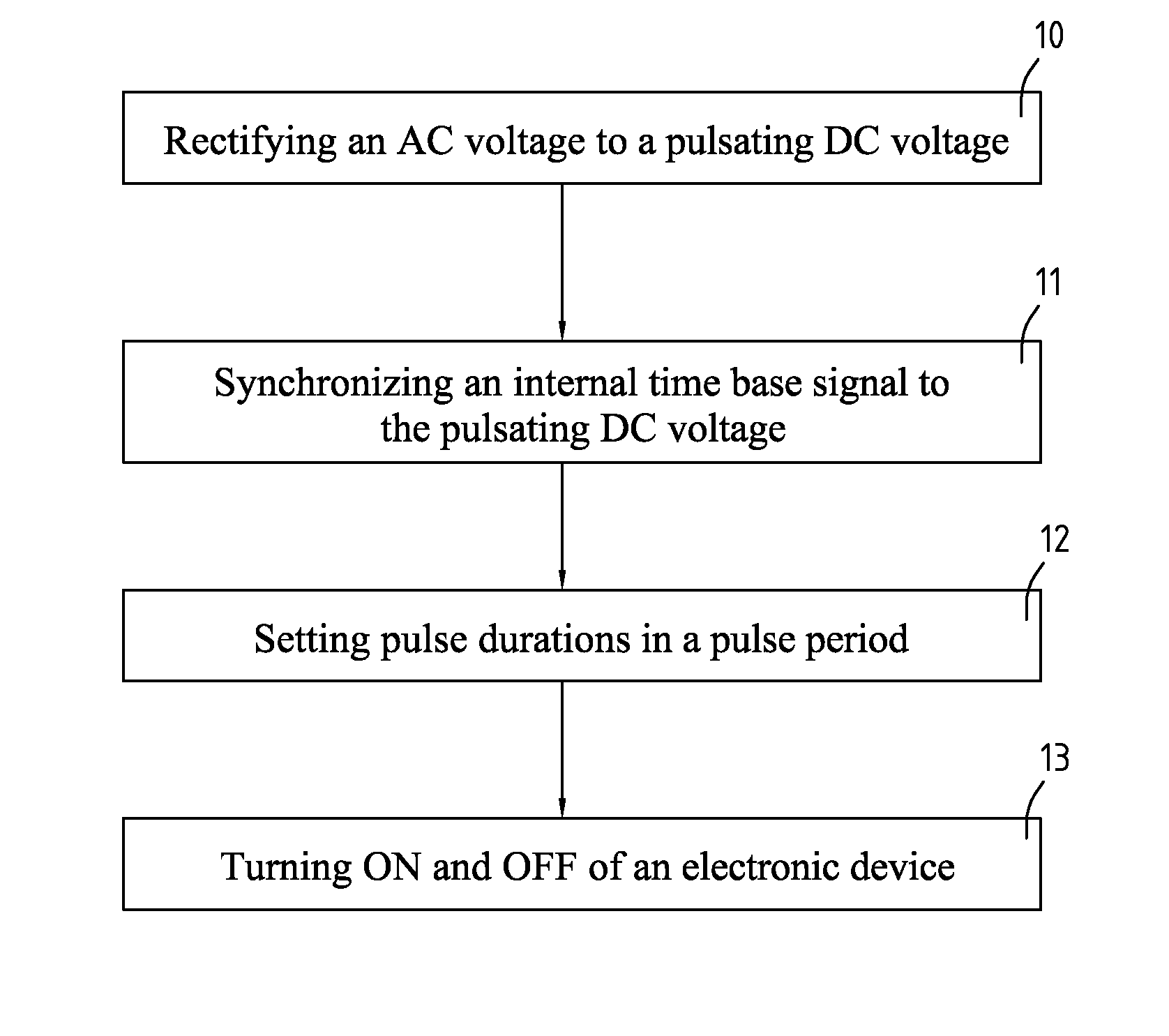
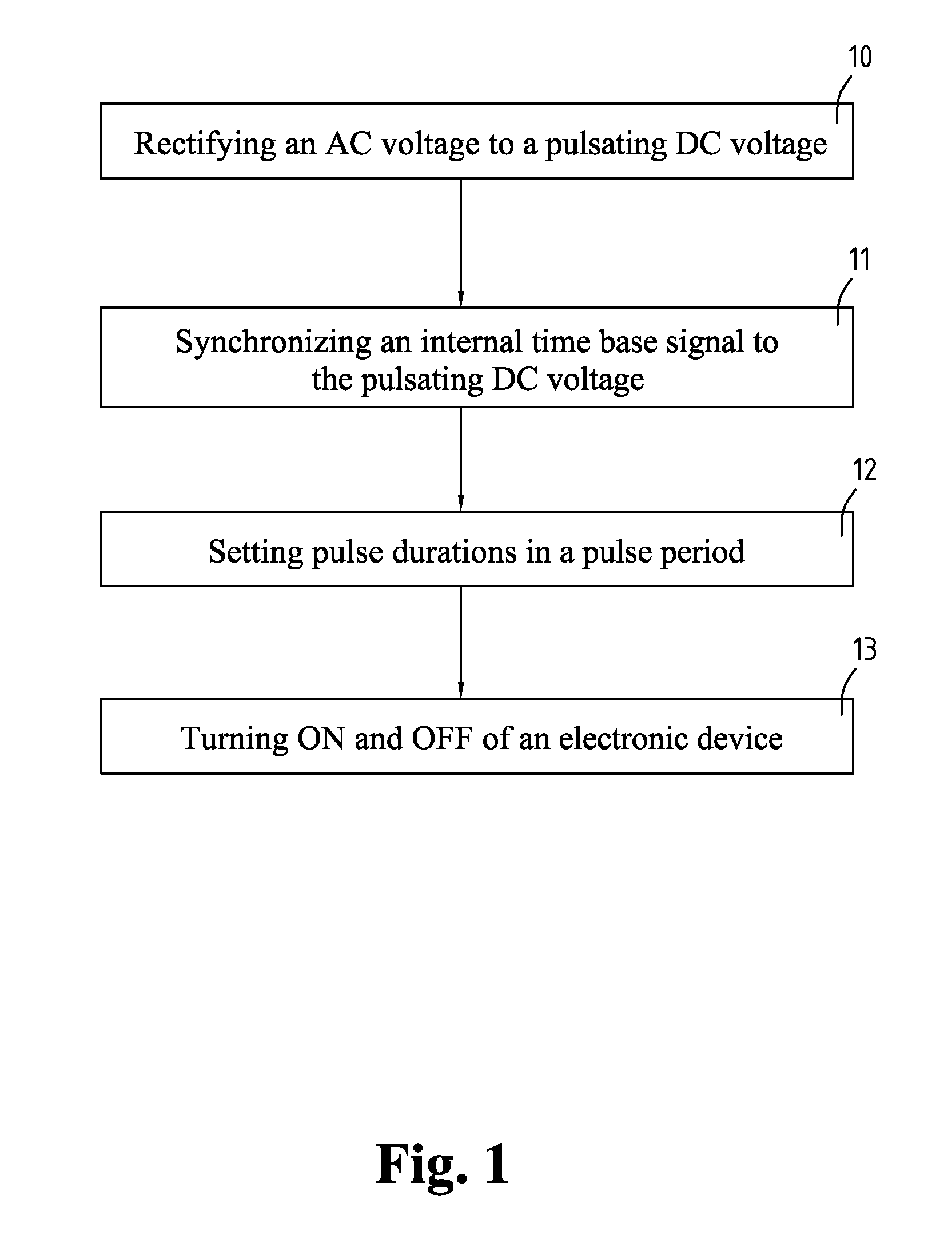
The present invention relates to power reforming methods and associated multiphase lights, especially to power reforming methods and associated multiple lights that selectively turn ON and OFF to reform current to follow voltage appropriately, which provides better heat dissipation, improving power factor and color mixing capability. The method comprises acts of rectifying an AC voltage to a pulsating DC voltage, synchronizing an internal time base signal to the pulsating DC voltage, setting pulse duration in a pulse period and turning ON and OFF of an electronic device. The device comprises at least two loads, a rectifier, at least two drivers and a controller.
Owner:GRAY RICHARD LANDRY
Technique for scheduling execution of jobs for or by network-connected devices
InactiveUS6993763B2Avoid limitationsImprove schedulingResource allocationMemory systemsCascading failureStart time
Methods, systems, computer program products, and methods of doing business by improving the scheduling of execution of jobs for or by network-connected devices, thereby enabling the job execution process to scale more easily, efficiently, and effectively to support large numbers of devices and / or users. Examples of jobs include, but are not limited to, distribution of resources (including software, configuration information, images, and other types of content) to a device, fetching a device's inventory information, backing up a device's contents, and so forth. Jobs are programmatically scheduled based upon a specified time internal, according to a class of the requester. Only if an earliest start time after which the job may be executed for this requester has been reached will the job be executed, otherwise, the job execution is delayed. The disclosed techniques lessen the need for additional servers to handle spikes in processing load, reduce the likelihood of reaching system overload, and reduce the likelihood of cascading failures that may occur when systems are overloaded.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Satellite (GPS) assisted clock apparatus, circuits, systems and processes for cellular terminals on asynchronous networks
ActiveUS8249616B2Fixed lengthRadio transmissionSatellite radio beaconingAsynchronous networkComputer terminal
A wireless circuit (1100, 1190) for tracking an incoming signal and for use in a network (2000) having handover from one part (Cell A) of the network to another part (Cell B). The wireless circuit includes a processor (CE 1100) responsive to the incoming signal, the processor (CE 1100) operable to generate pulse edges representing network-based receiver synchronization instances (RSIs), and a timekeeping circuitry (2420, 2430, 2450) including an oscillator circuitry (2162), the timekeeping circuitry (2420, 2430) operable to maintain a set of counter circuitries (2422-2428) including a counter circuitry (2422) operable to maintain at least one network time component based on the RSIs and another counter circuitry (2428) operable at least during handover and during loss of network coverage for maintaining at least one internal time component (NC) based on the oscillator circuitry (2162), the set of counter circuitries (2422-2428) operable to account for elapsing time substantially gaplessly and substantially without overlap between the time components during a composite of network coverage, loss of network coverage and handover, and the timekeeping circuitry further including a time generator (2450) for combining the time components from the set of counter circuitries (2422-2428) to generate an approximate absolute time (SGTB). Other electronic circuits, positioning systems, methods of operation, and processes of manufacture are also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
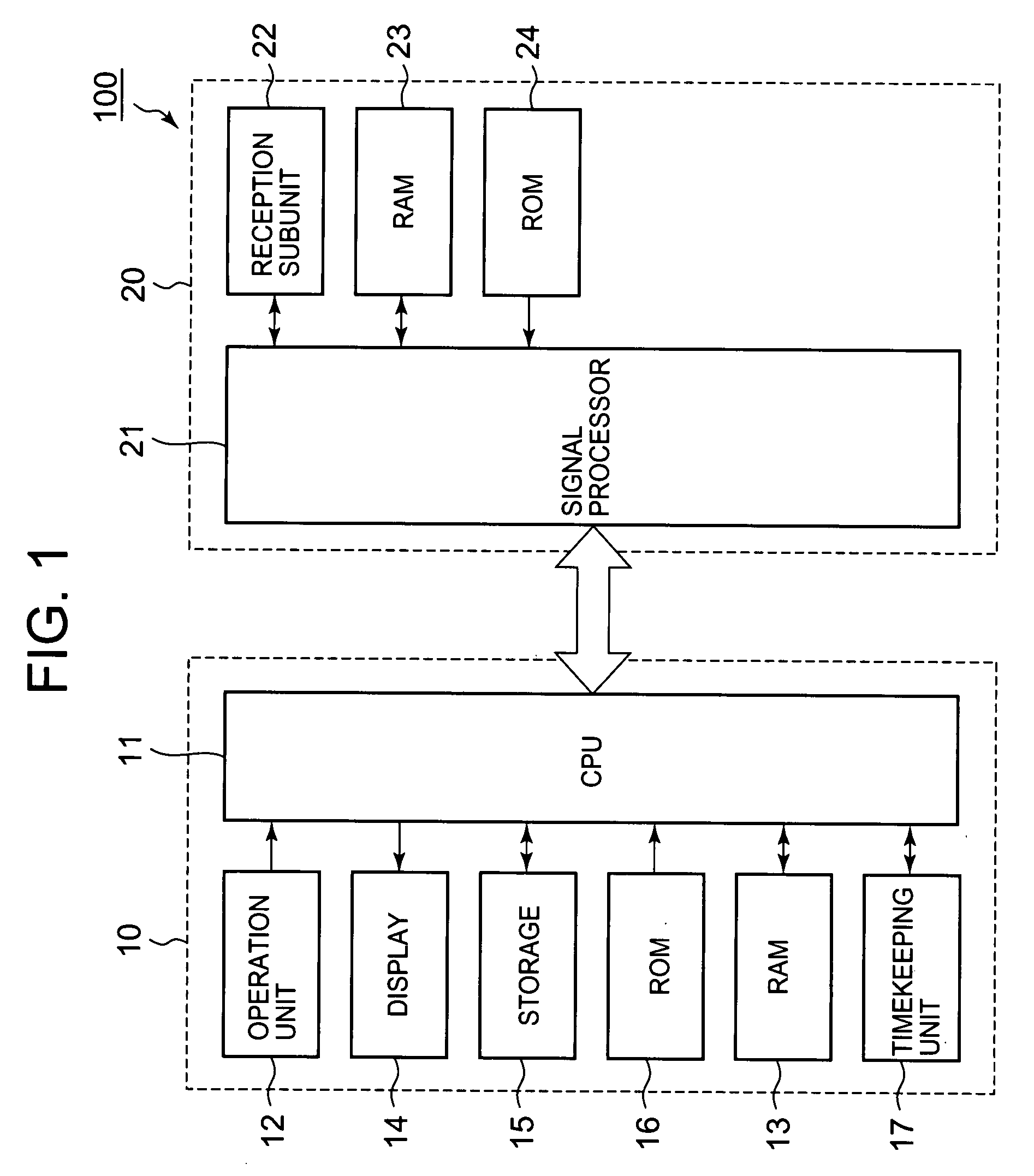
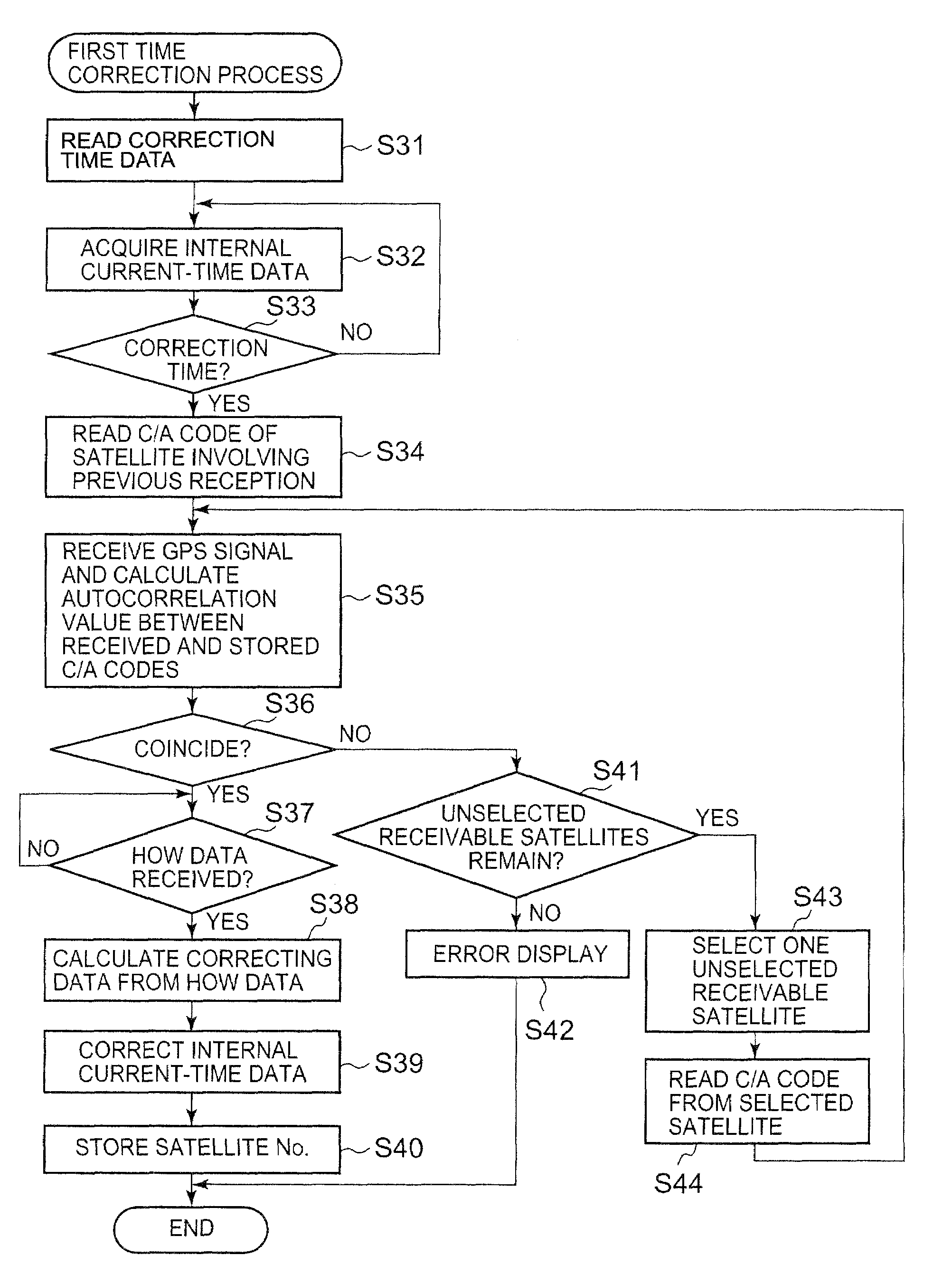
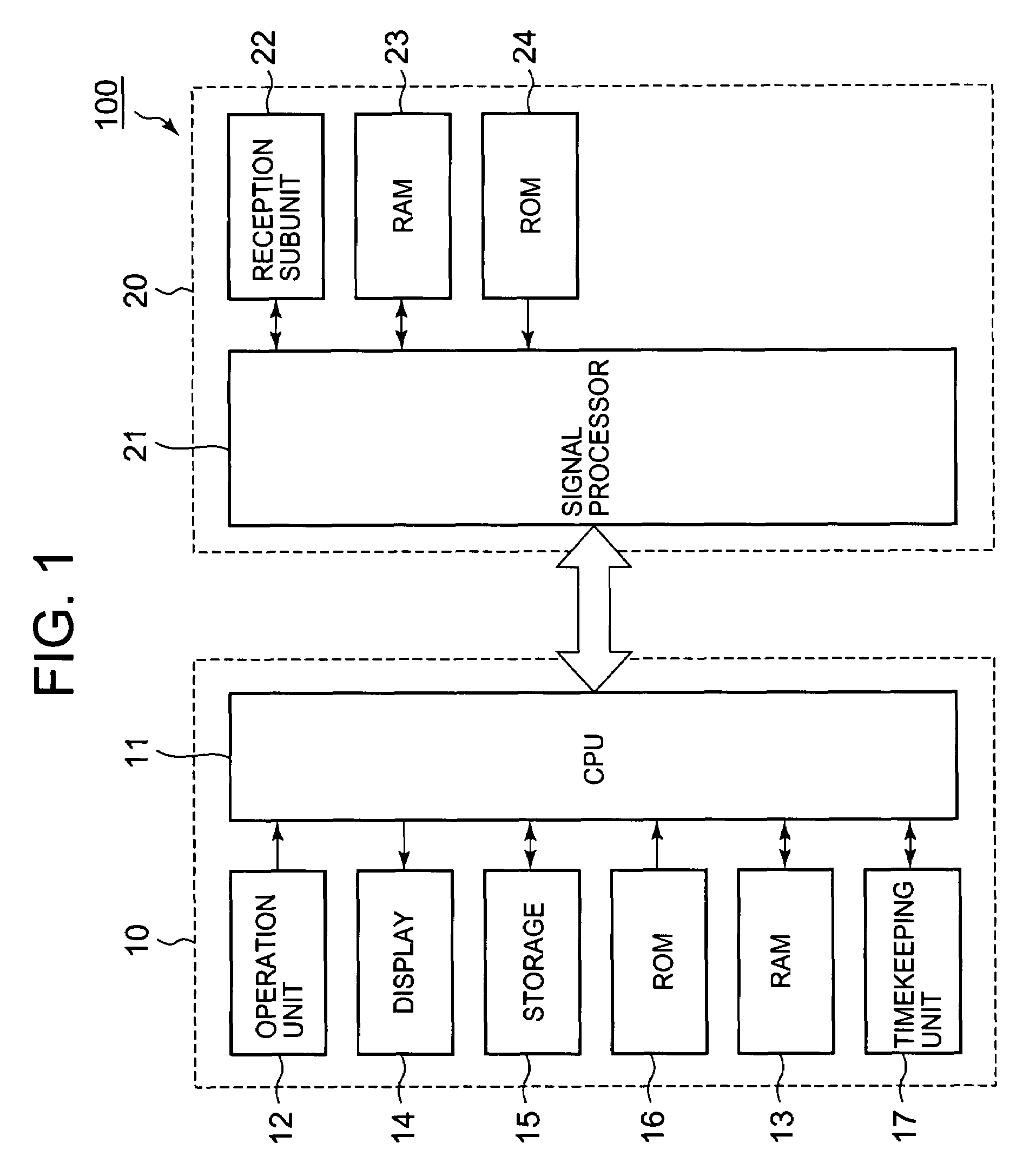
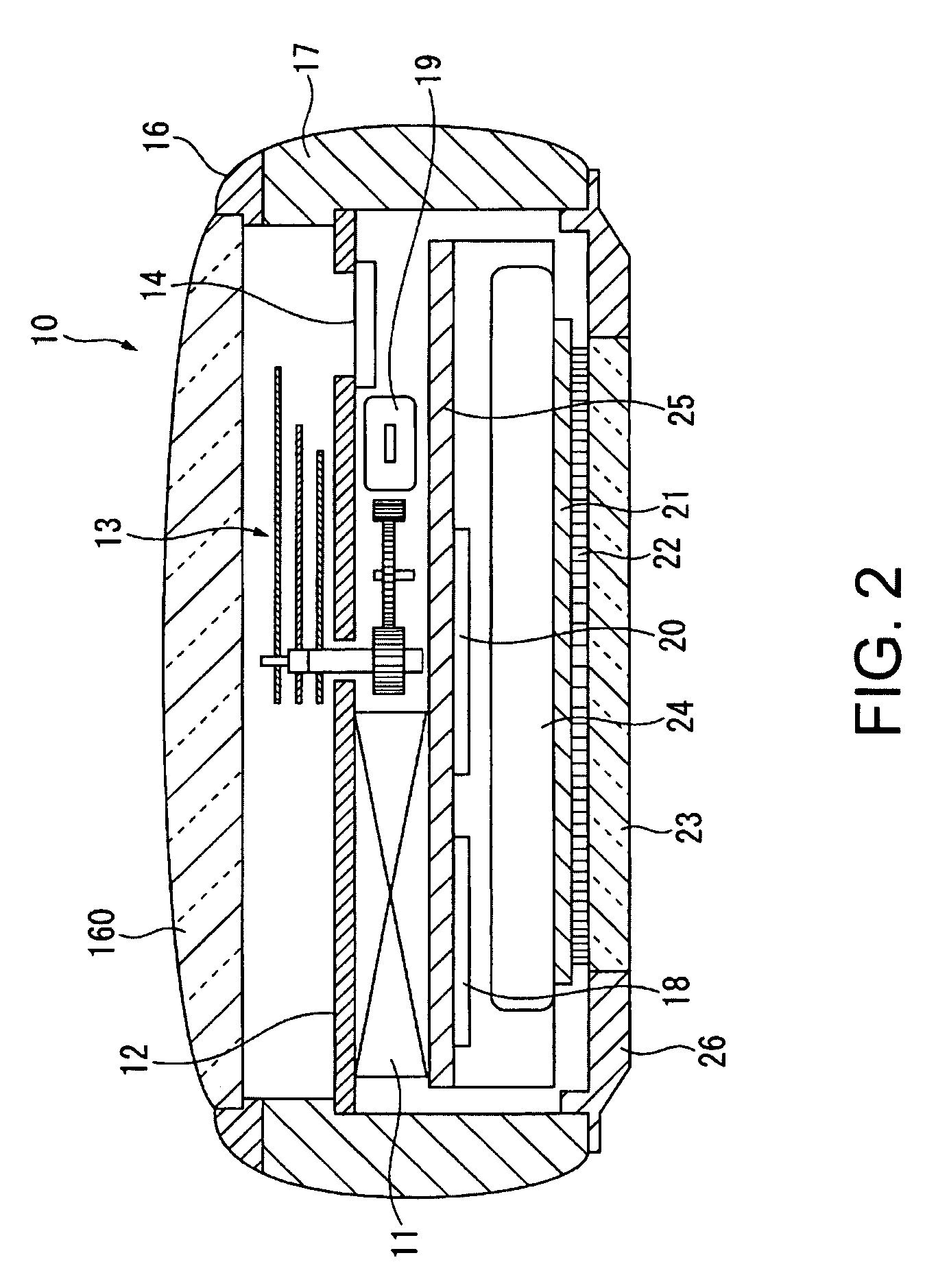
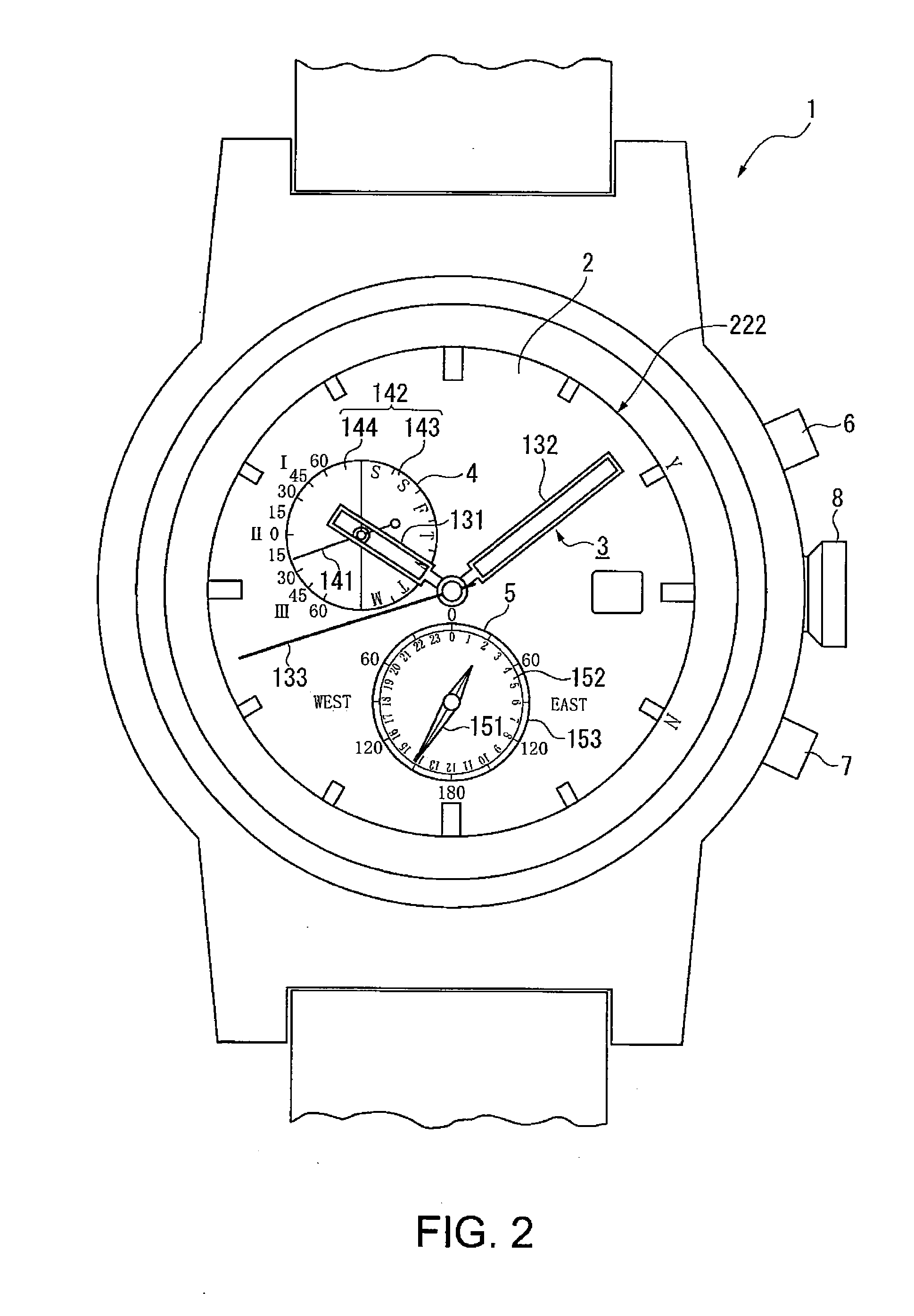
Timepiece and time correction method
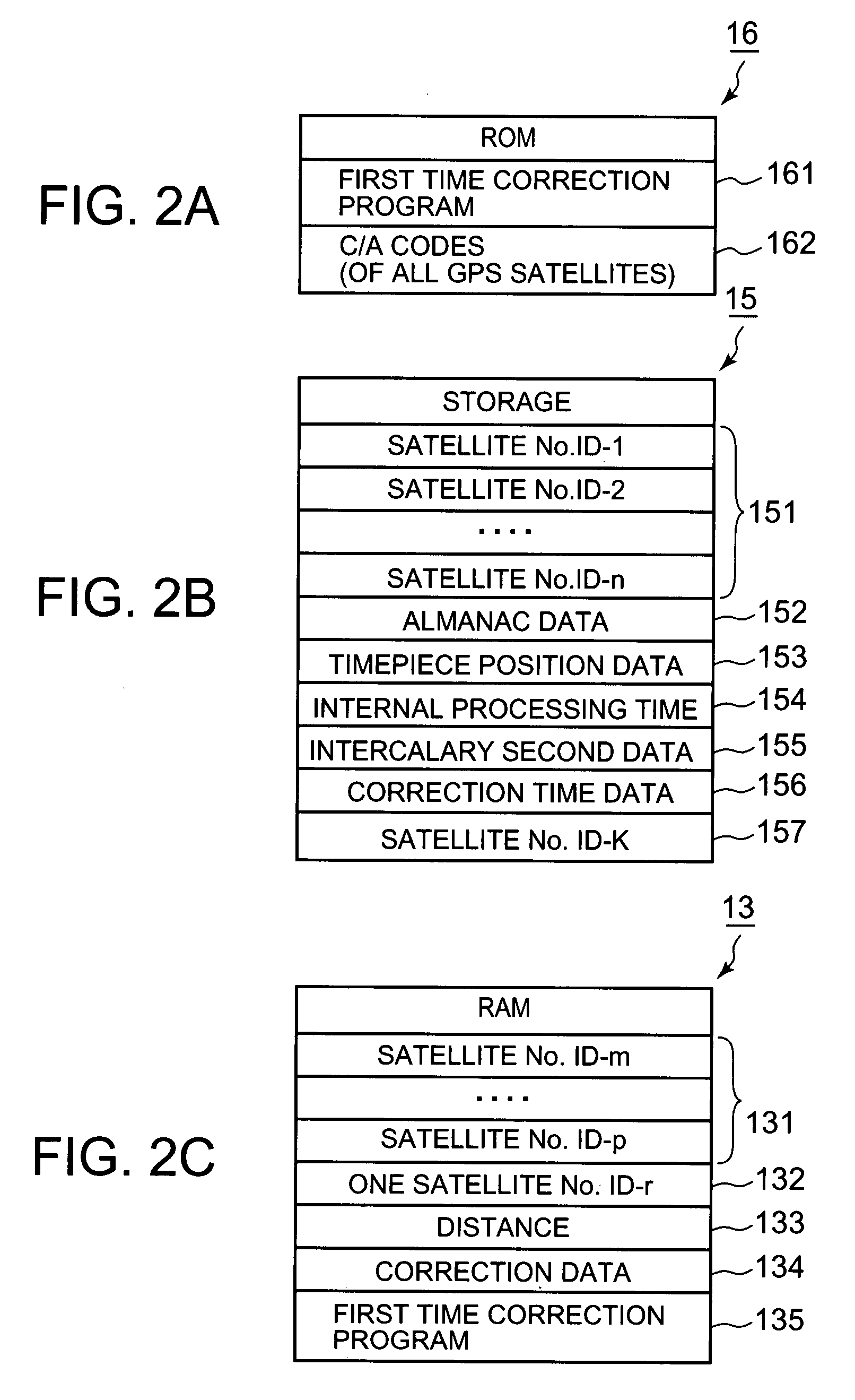
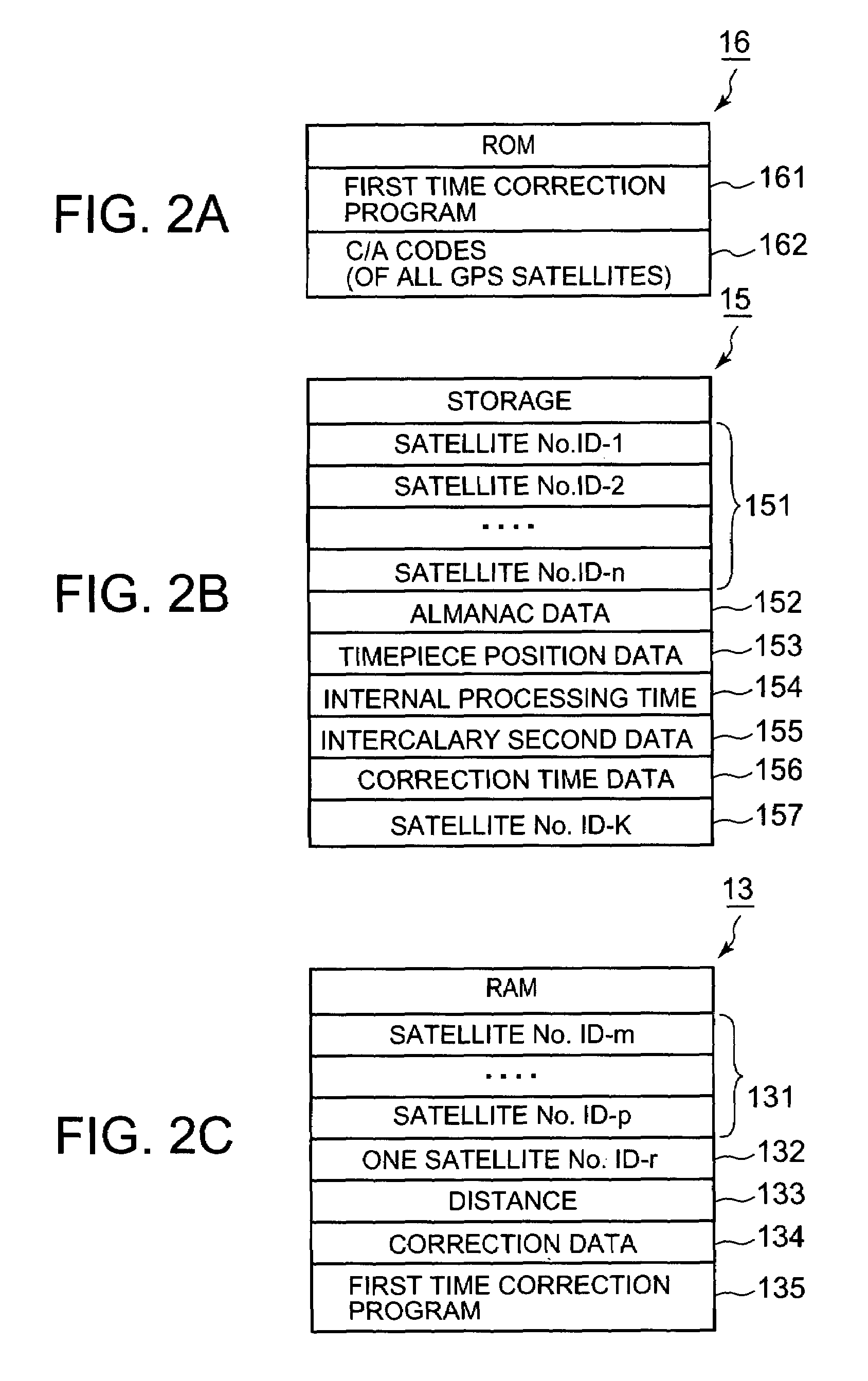
A timepiece comprises a reception subunit, a timekeeping unit that holds internal time data indicative of the current time, storage, and a CPU. The CPU determines whether the internal time data acquired from the timekeeping unit matches correction time data stored in storage, selects a GPS satellite represented by satellite identification data stored in the storage when the determination is affirmative, acquires GPS time data included in navigation data which in turn is included in a GPS signal obtained from the selected GPS satellite, corrects the internal time data based on the GPS time data, and stores the correction time data in correspondence to the satellite identification data representing that GPS satellite.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
Electronic timepiece and control method for an electronic timepiece
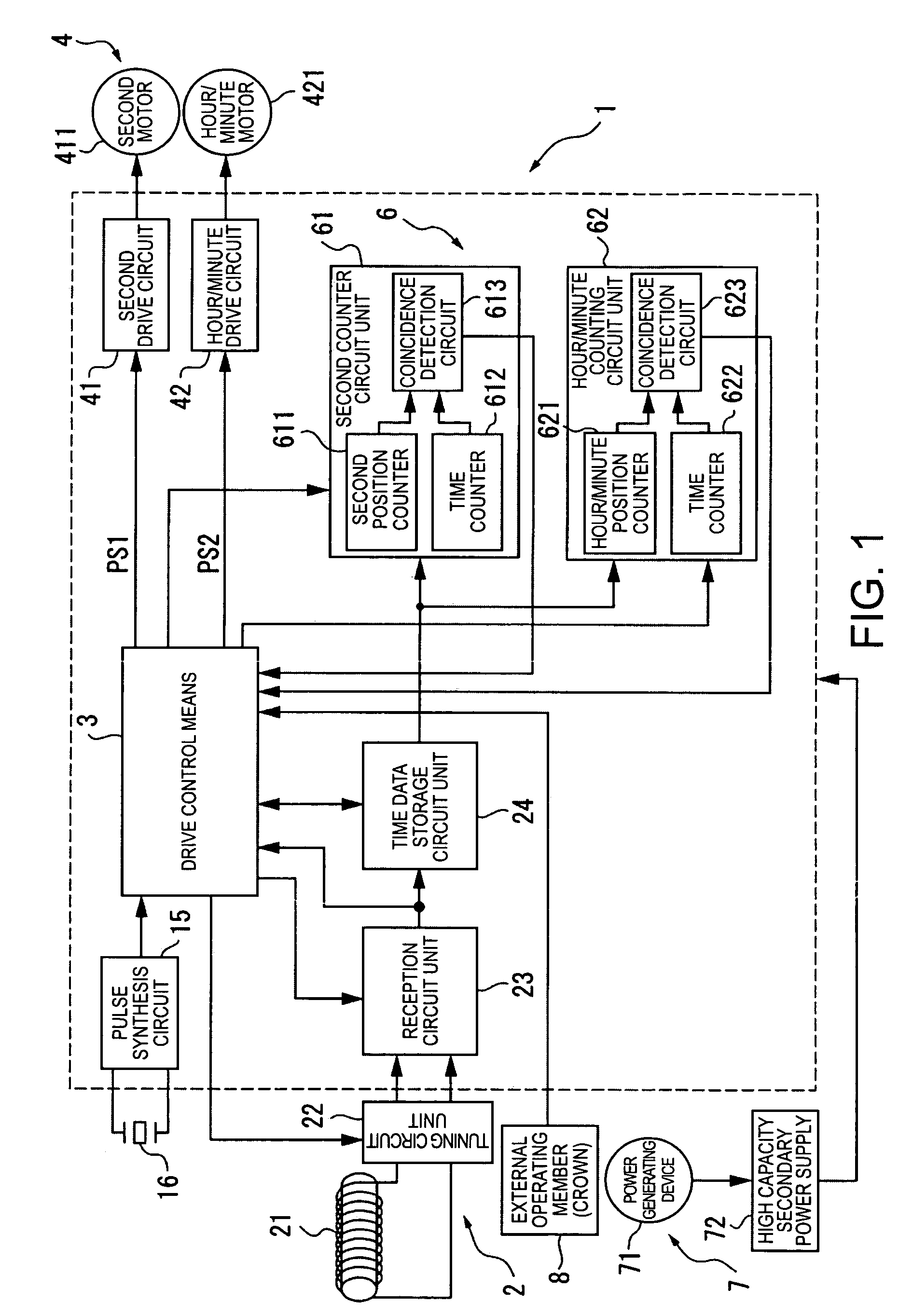
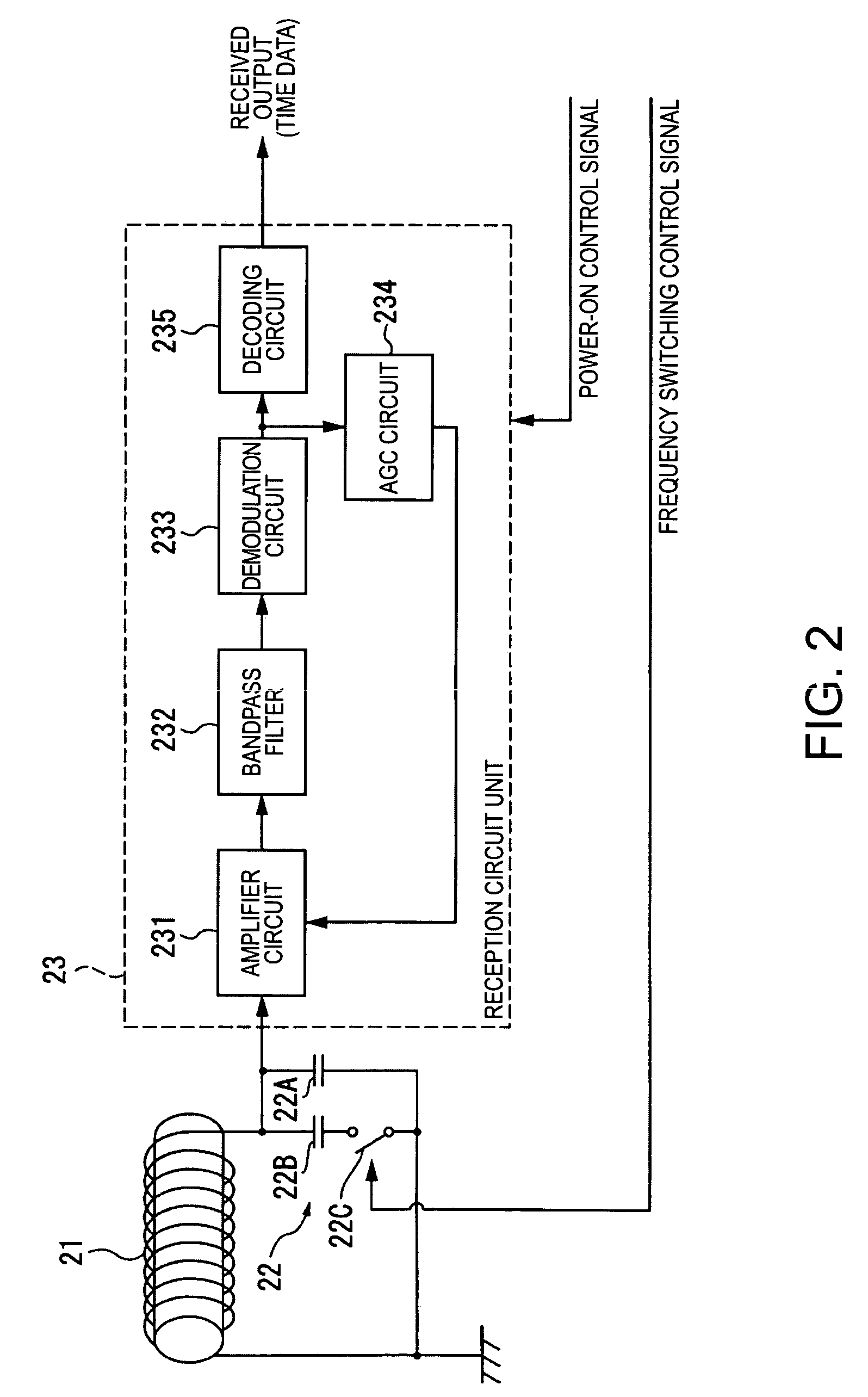
ActiveUS7983116B2Reduce power consumptionIntuitive adjustmentSynchronous motors for clocksMaster clocksTime informationEngineering
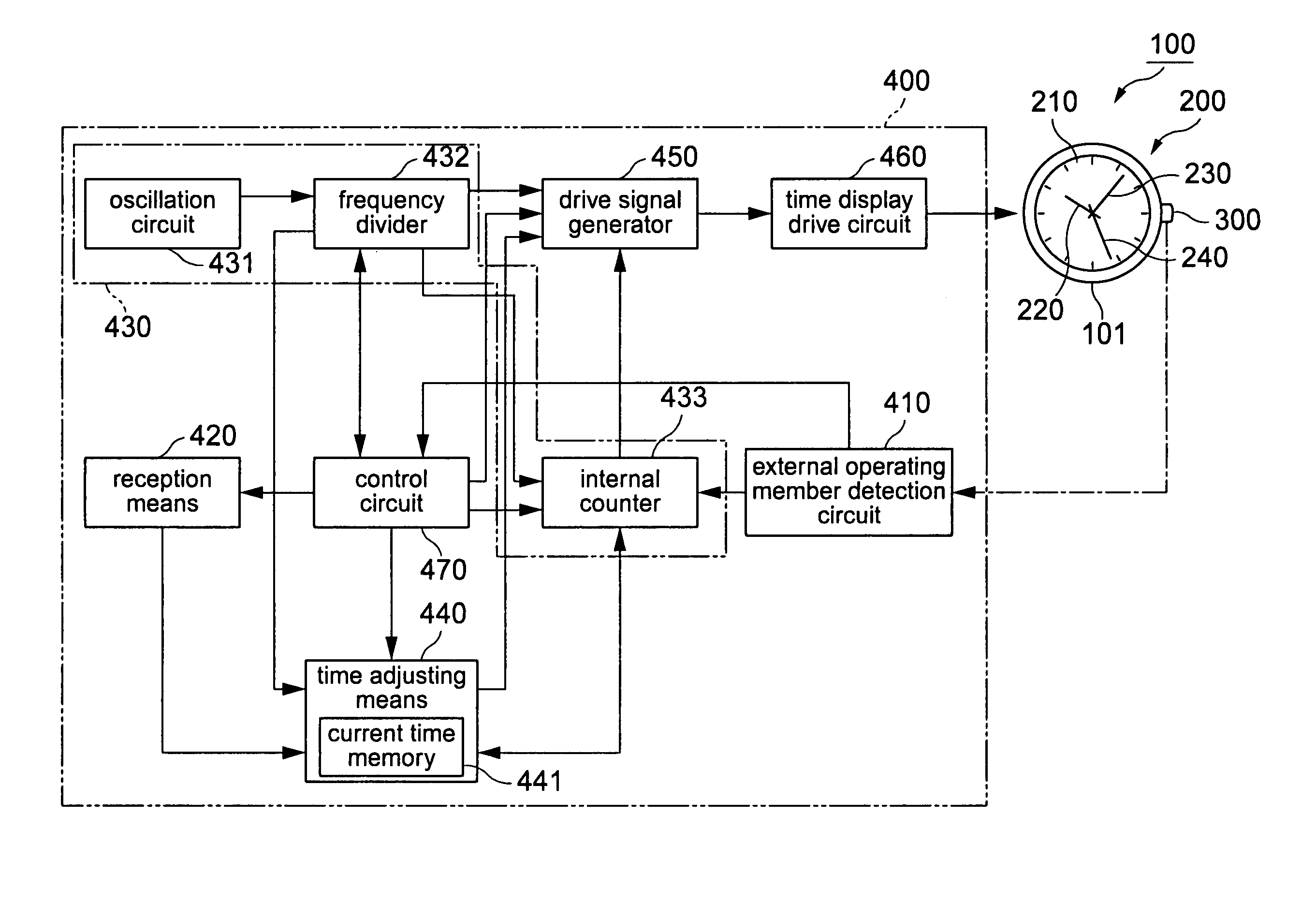
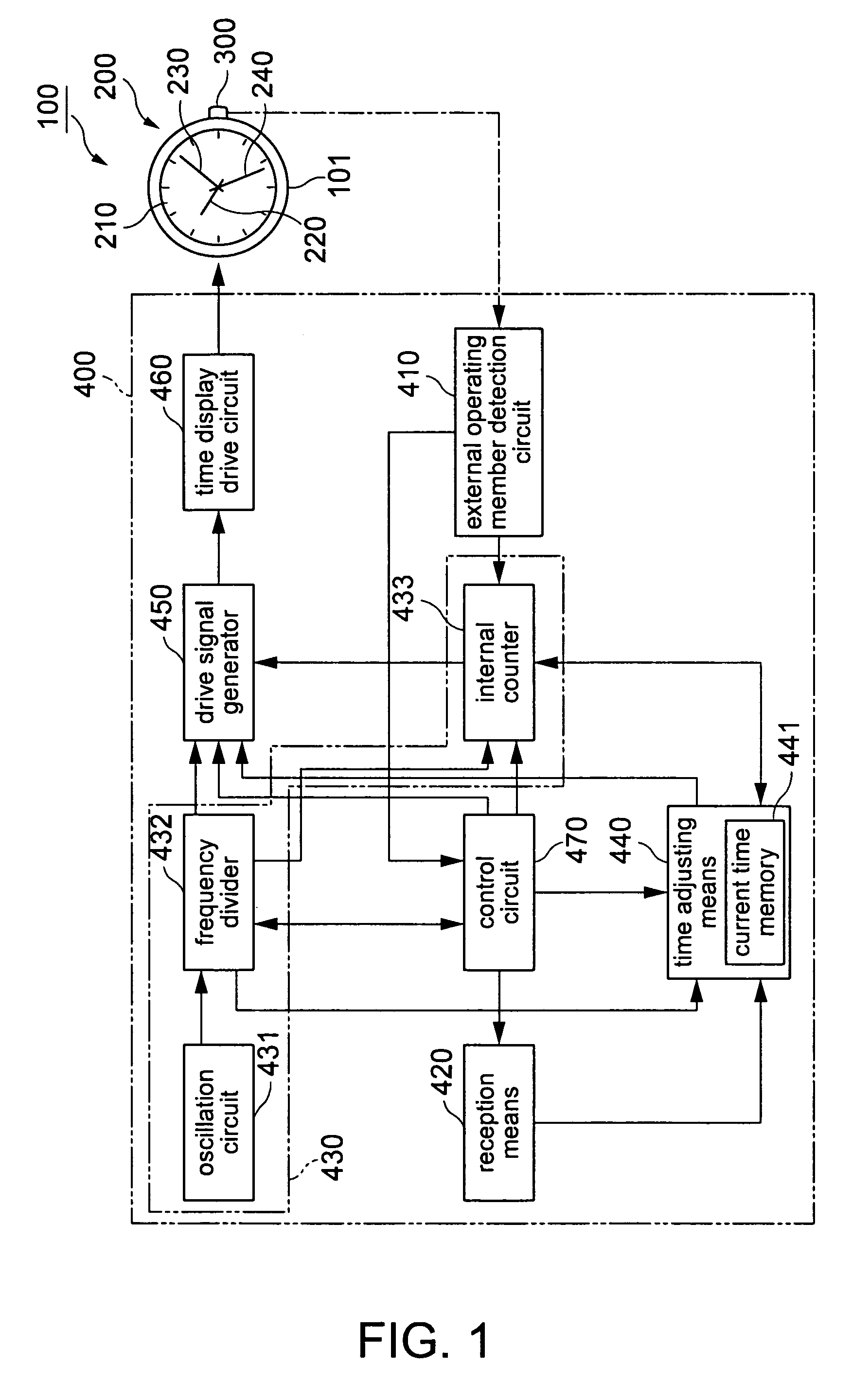
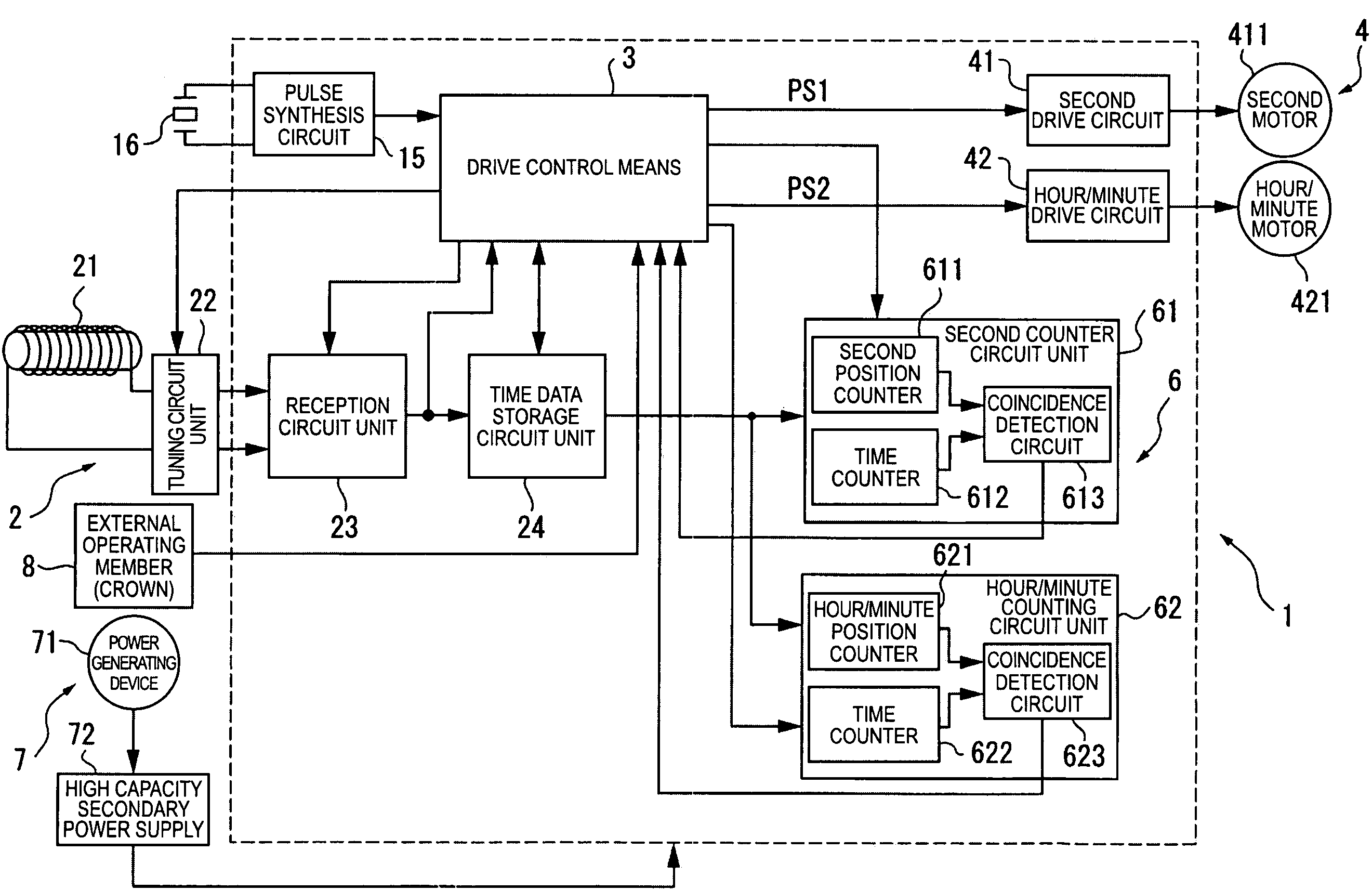
An electronic timepiece includes a reception unit that receives satellite signals transmitted from positioning information satellites; a time information generating unit that generates an internal time; a manual reception process unit that starts operation of the reception unit and executes a manual reception process when an external operating member is operated; an automatic reception process unit that automatically operates the reception unit and executes an automatic reception process when a predetermined condition is satisfied; a simple time adjustment process unit that executes a simple time adjustment process to receive a satellite signal from one positioning information satellite by means of the reception unit, acquire time information from the received satellite signal, and adjust the internal time; and a high precision time adjustment process unit that executes a high precision time adjustment process to receive satellite signals from a plurality of positioning information satellites by means of the reception unit, acquire time information and positioning information from the received satellite signals and determine the location, and adjust the internal time to the time acquired based on the positioning result. The automatic reception process unit executes the simple time adjustment process by means of the simple time adjustment process unit when the automatic reception process executes, and the high precision time adjustment process unit executes the high precision time adjustment process only when the manual reception process is executed by the manual reception process unit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
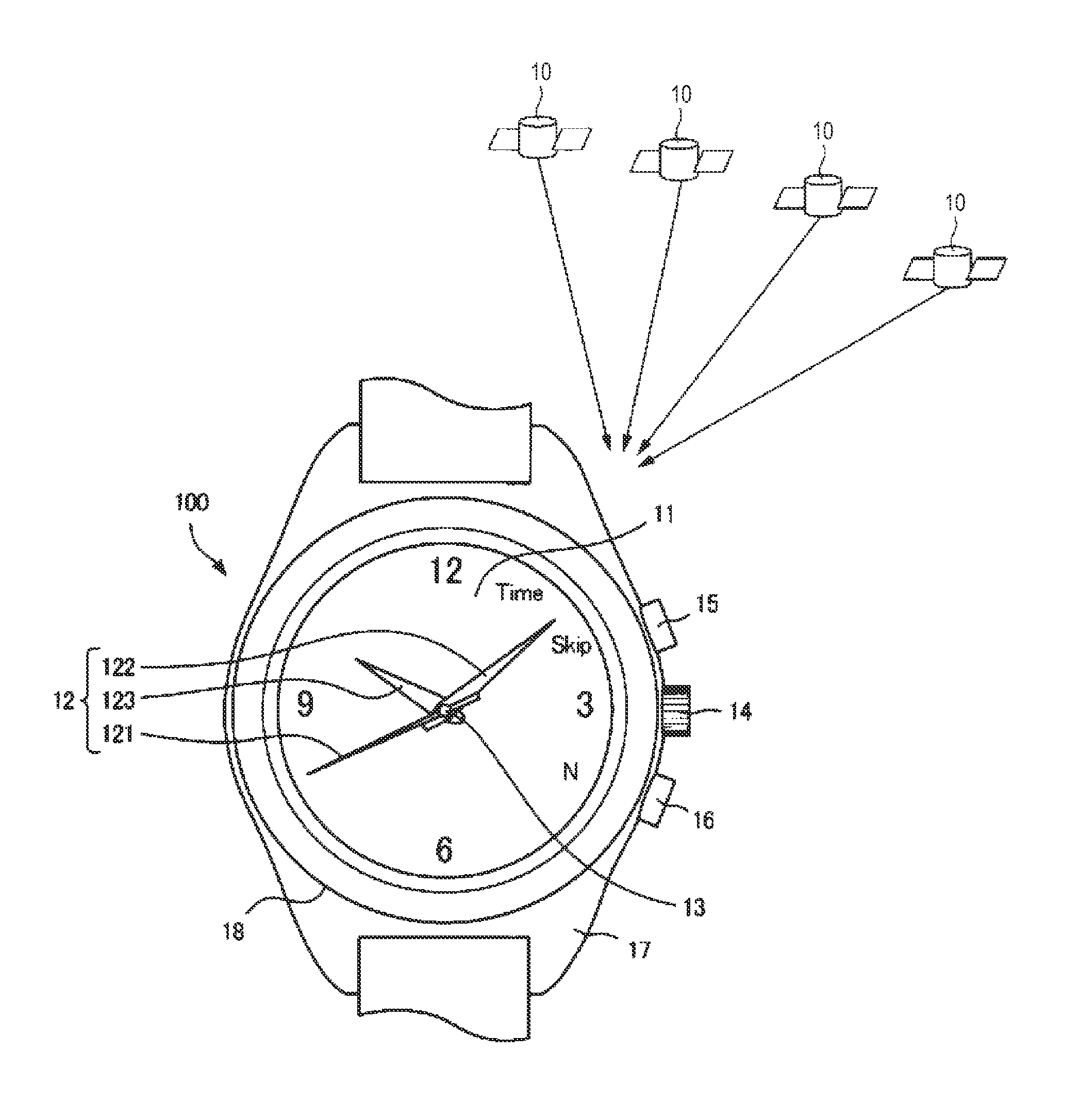
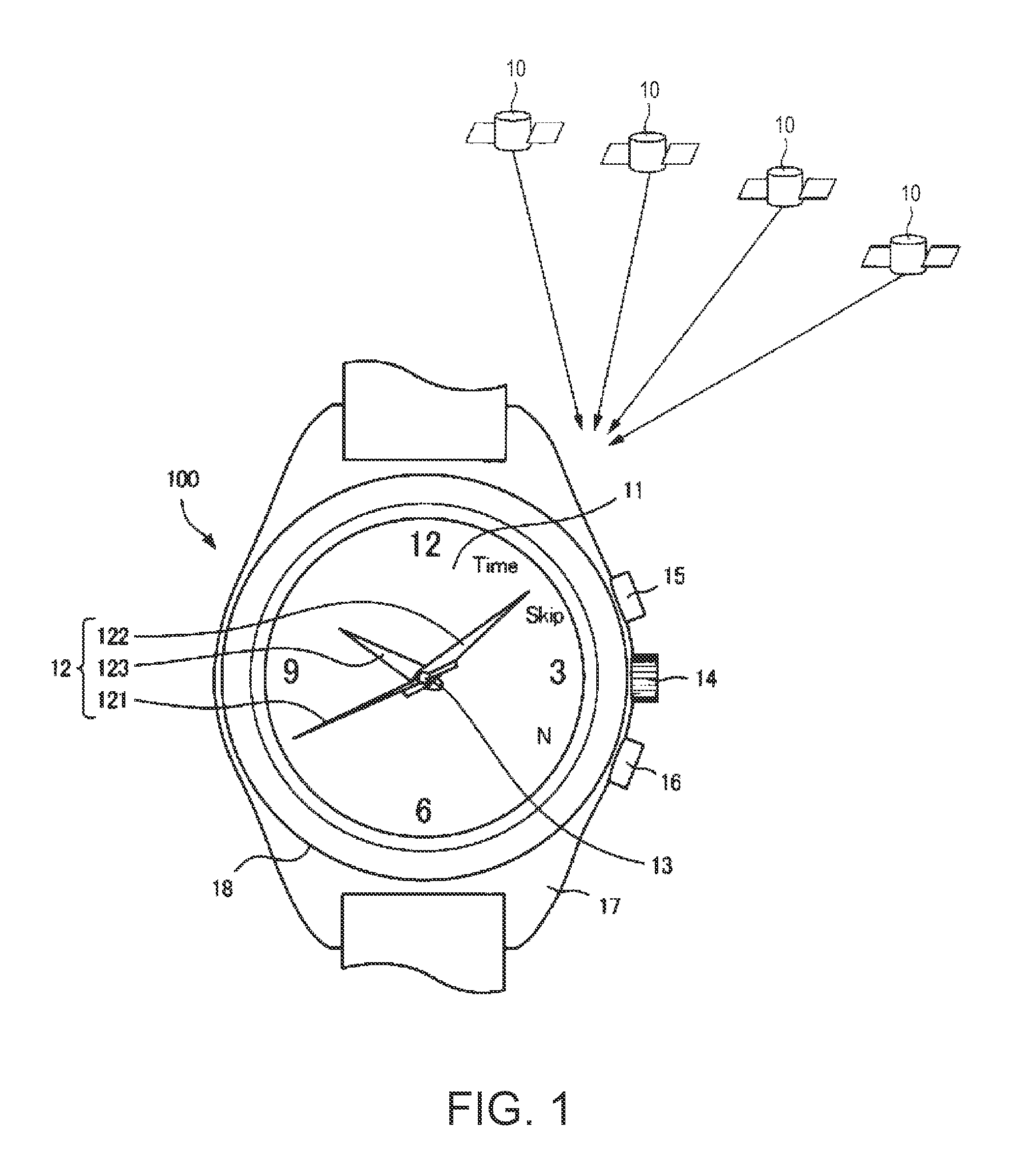
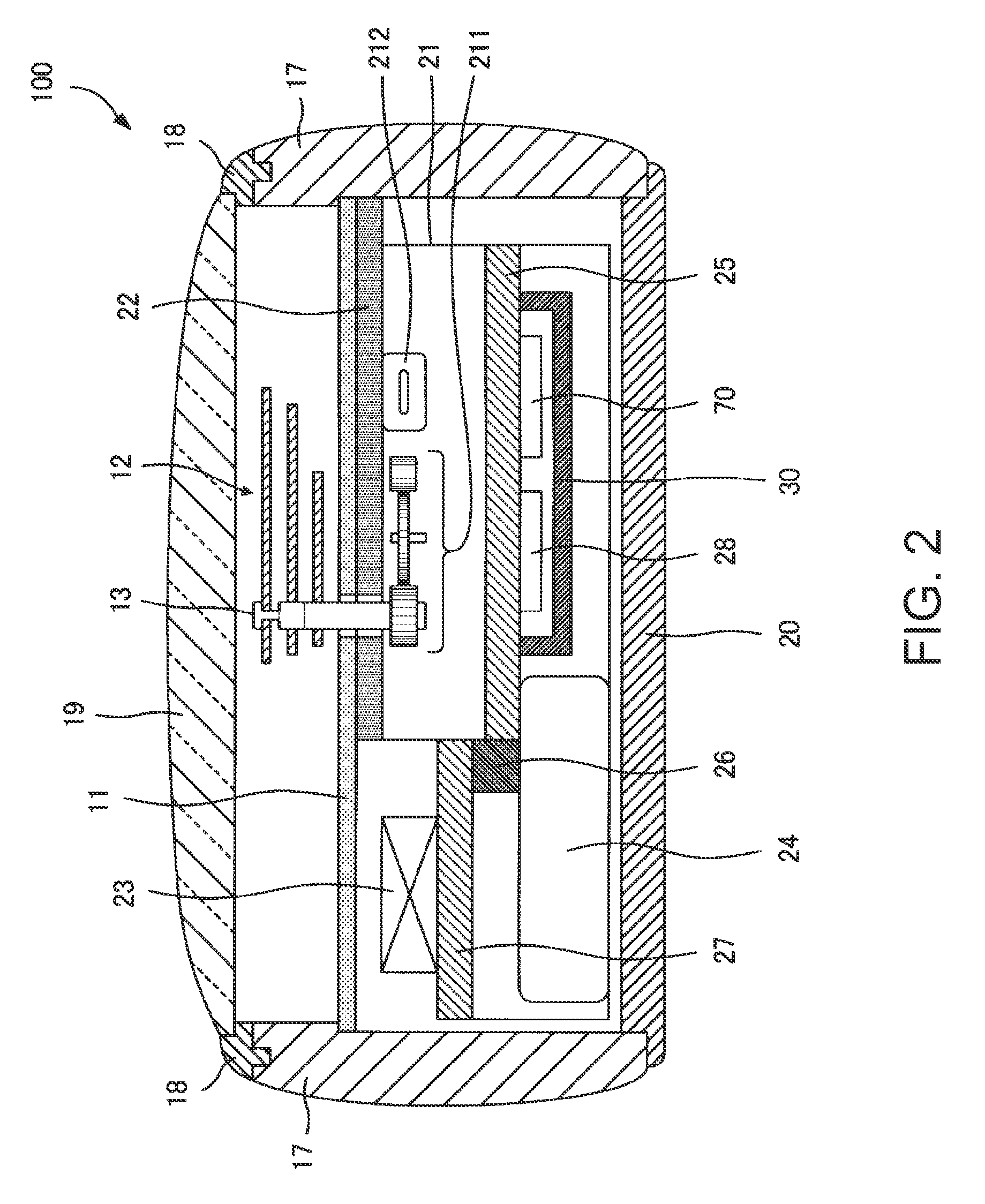
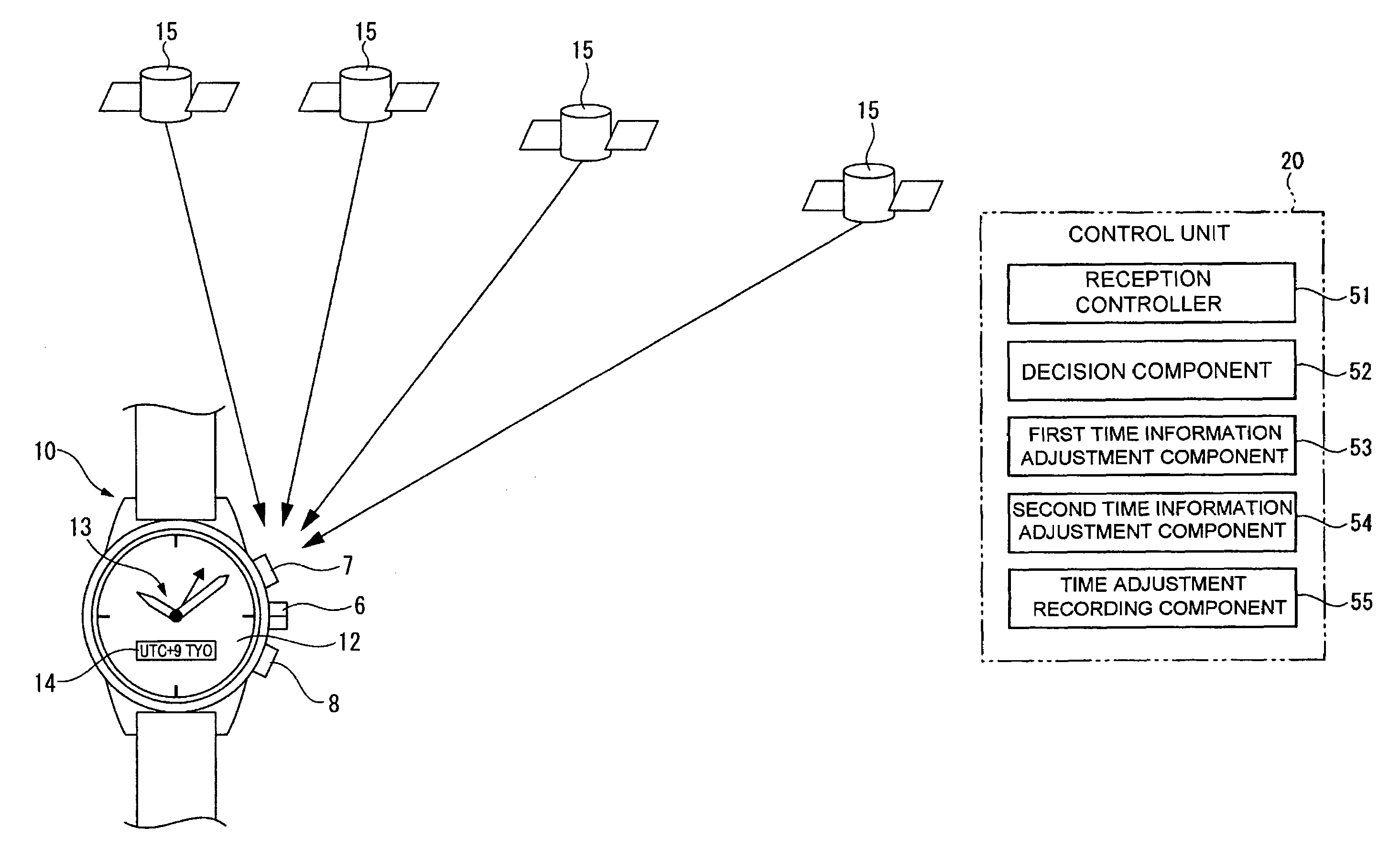
Time Adjustment Device, Timepiece with a Time Adjustment Device, and a Time Adjustment Method
InactiveUS20090129206A1Short timeReduce power consumptionMechanical clocksElectric windingTime informationEngineering
A time adjustment device having a reception unit that receives satellite signals transmitted from positioning information satellites; a time information generating unit that generates internal time information; a time information adjustment component that corrects the internal time information; and a reception controller that controls operation of the reception unit; wherein the satellite signal contains satellite time information that is kept by the positioning information satellite; the reception unit can select a first reception mode for receiving first information including the hour, minute, and second data in the satellite signal, and a second reception mode for receiving second information including the hour, minute, and second data, week information for the current year, month, and day, and satellite health information in the satellite signal; the time information adjustment component includes a time adjustment recording component that records whether or not the time was adjusted using the second information received in the second reception mode after the internal time information was initialized, a first time information adjustment component that controls the reception unit by way of the reception controller in the first reception mode to receive the first information, and sets the hour, minute, and second values of the internal time information based on the received first information, and a second time information adjustment component that controls the reception unit in the second reception mode to receive the second information, and sets the year, month, day, hour, minute, and second values of the internal time information using the received second information; the first time information adjustment component operates when it is recorded in the time adjustment recording component that the time was adjusted using the second information; and the second time information adjustment component operates when it is not recorded in the time adjustment recording component that the time was adjusted using the second information.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
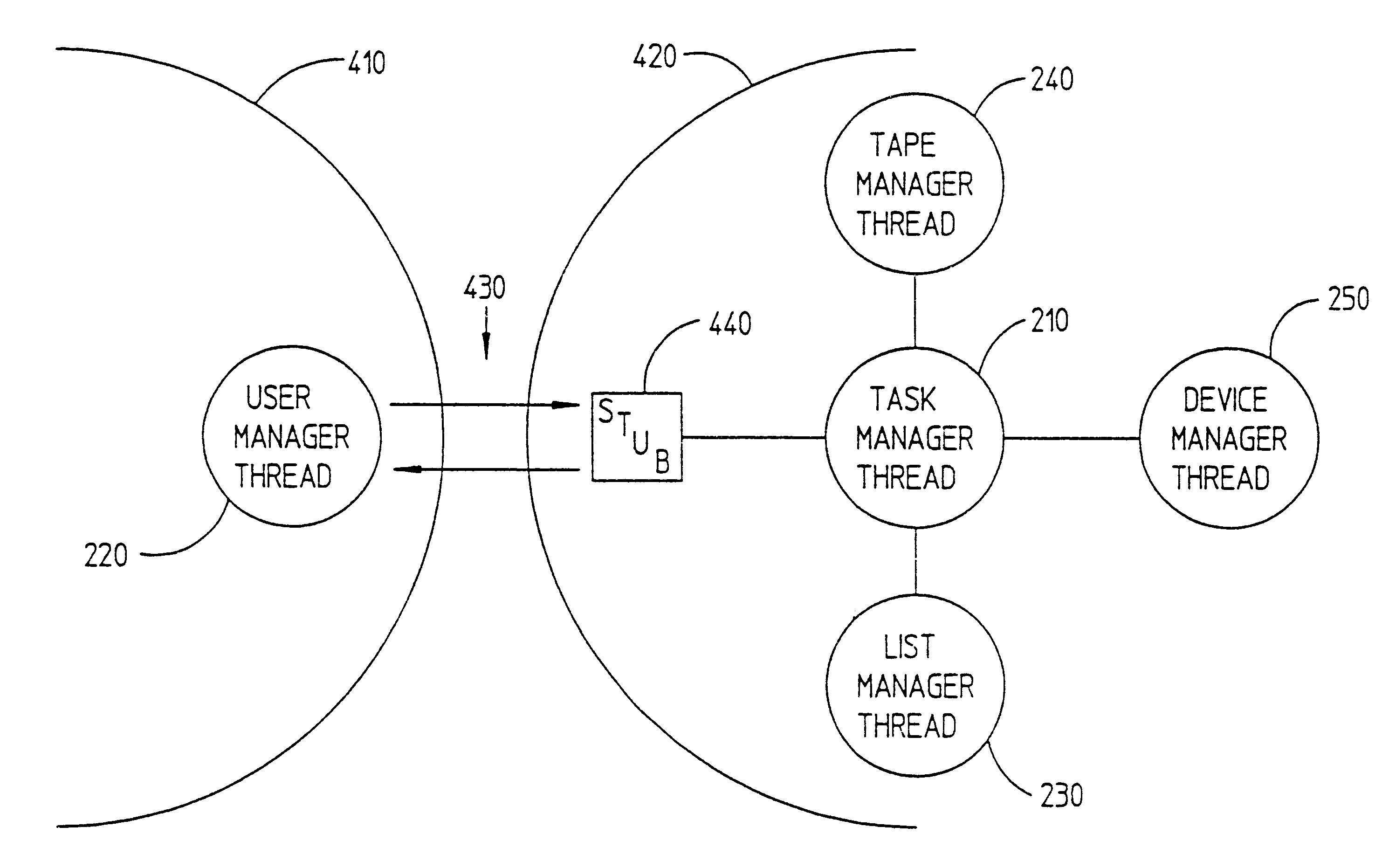
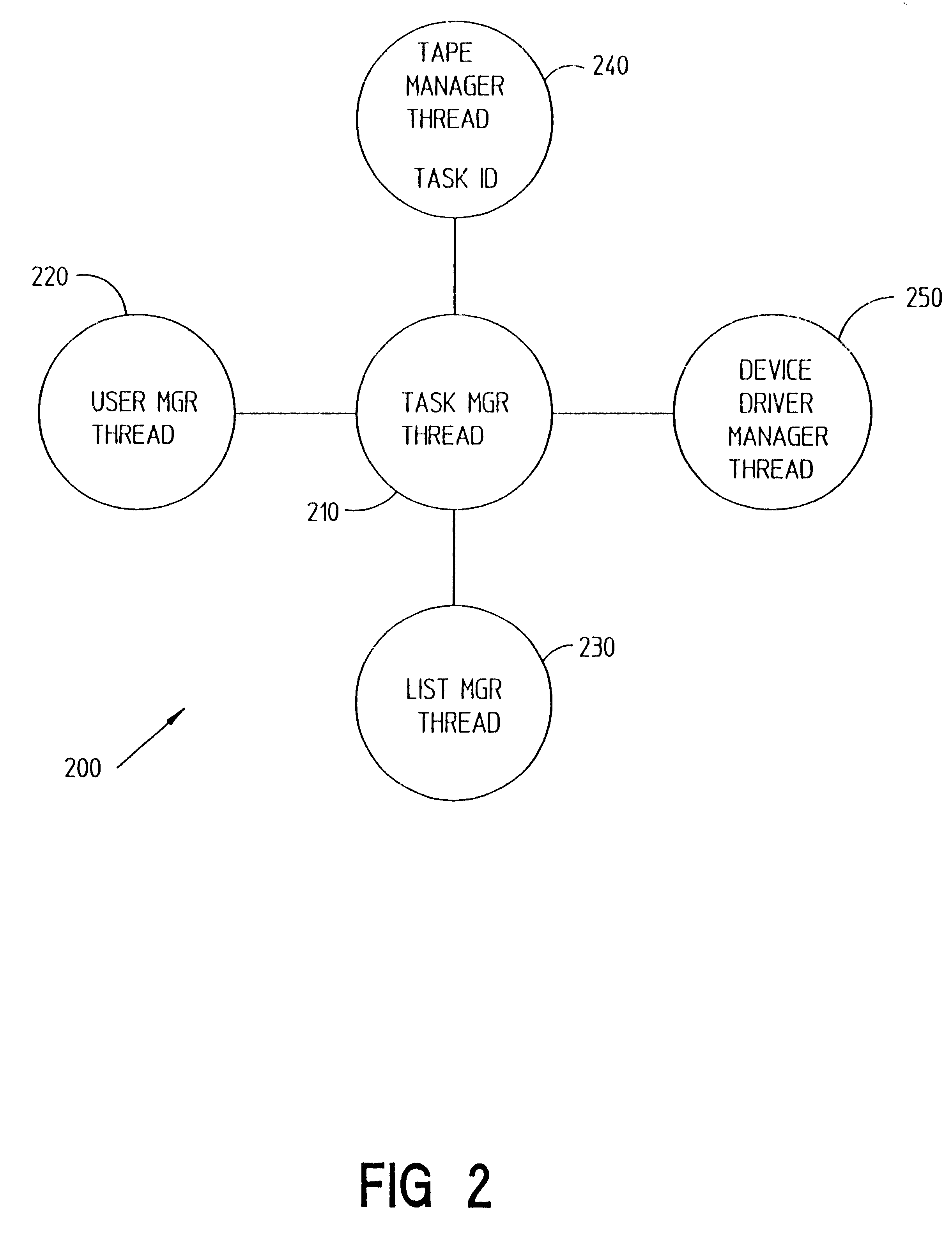
System and method for avoiding deadlock in a non-preemptive multi-threaded application running in a non-preemptive multi-tasking environment
A system and method for avoiding deadlock in a non-preemptive multi-tasking application program, wherein the application program operates in an operating system that provides a non-preemptive multi-tasking environment. All components of the application program that require resources from other components within the application program, and that will not yield to internal timeslicing within the application program, are placed in separate executables (i.e., application programs). Thus allowing maximum background processing and the avoidance of deadlock.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
System for measuring a time offset and method of measuring a time offset
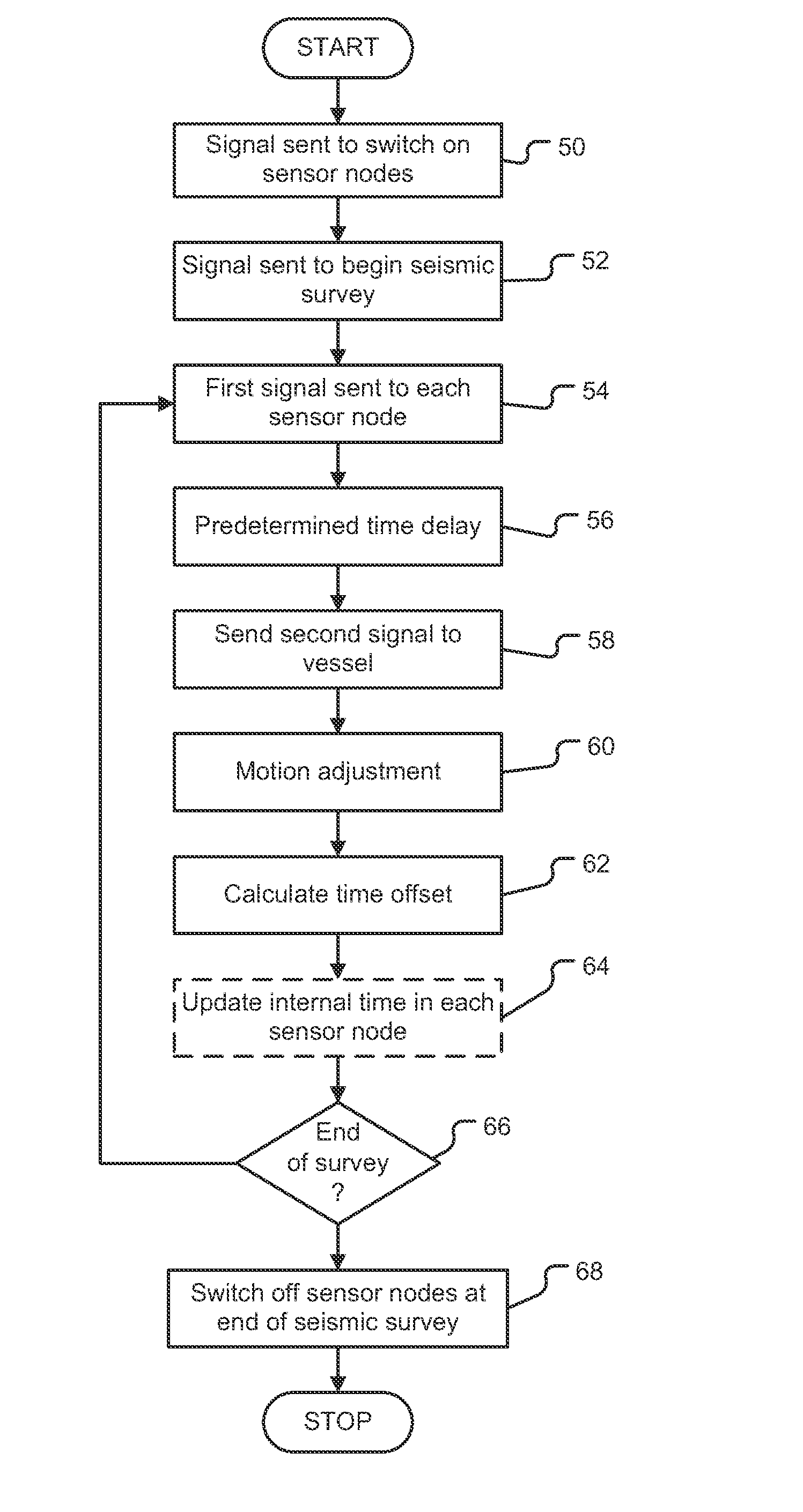
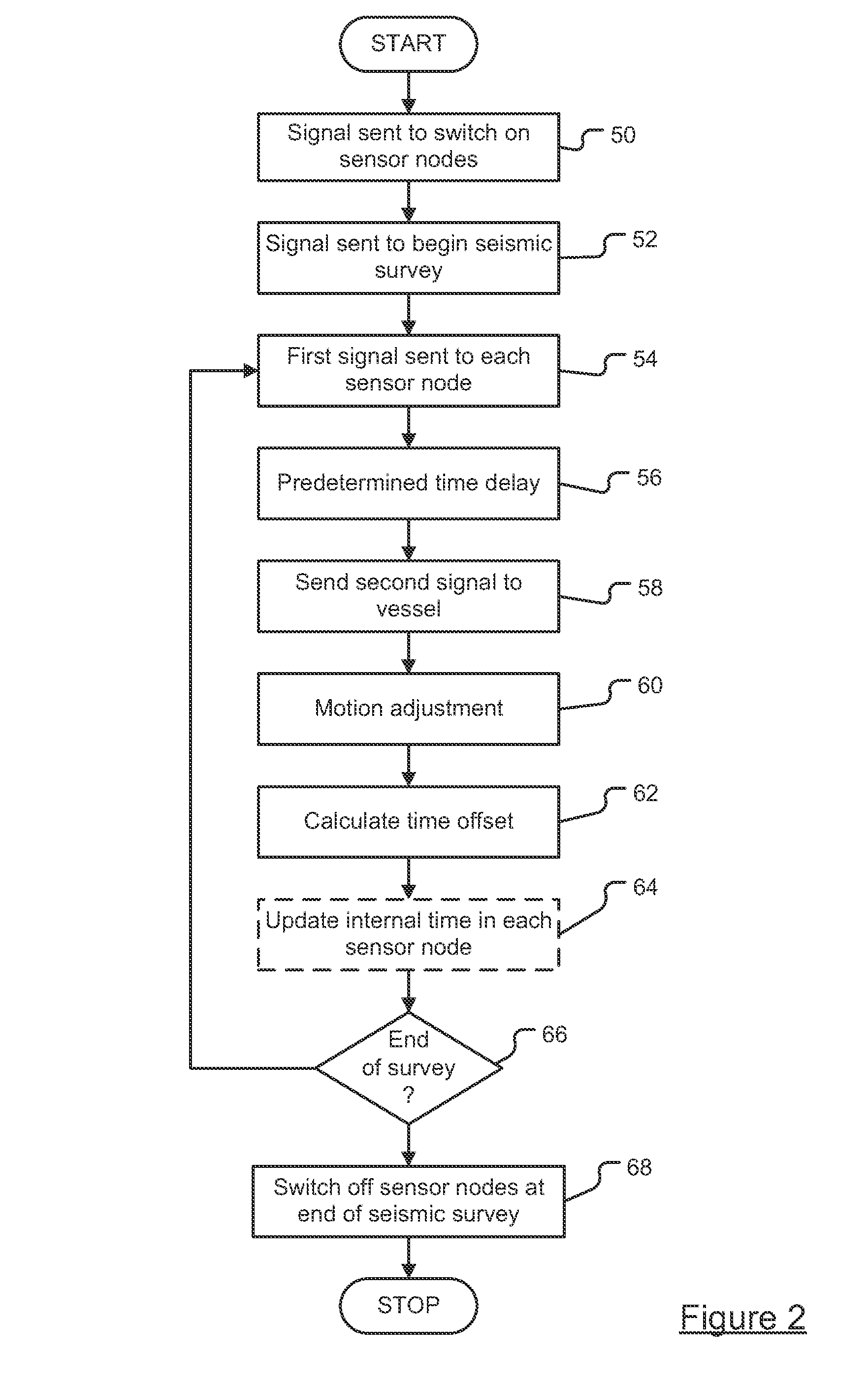
ActiveUS20120294112A1Improve convenienceImprove energy efficiencySonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionSeismic signal transmissionTransceiverTime delays
A system and method measures the time offsets of a plurality of acoustic sensor nodes relative to a reference time. The system includes an acoustic transceiver arranged to transmit a first signal to each acoustic sensor node and a processing resource arranged to record the transmission time of the first signal relative to the reference time. The acoustic sensor nodes receive the first signal and transmit a return second signal to the acoustic transceiver after a predetermined time delay, the second signal including the current acoustic sensor node internal time. The acoustic transceiver receives the second signal, and the processing resource records the time at which the second signal was received relative to the reference time and records also the combined time of flight of the first and second signal. From this data the time offset between the sensor node internal time and the reference time is calculated.
Owner:SONARDYNE INT LTD
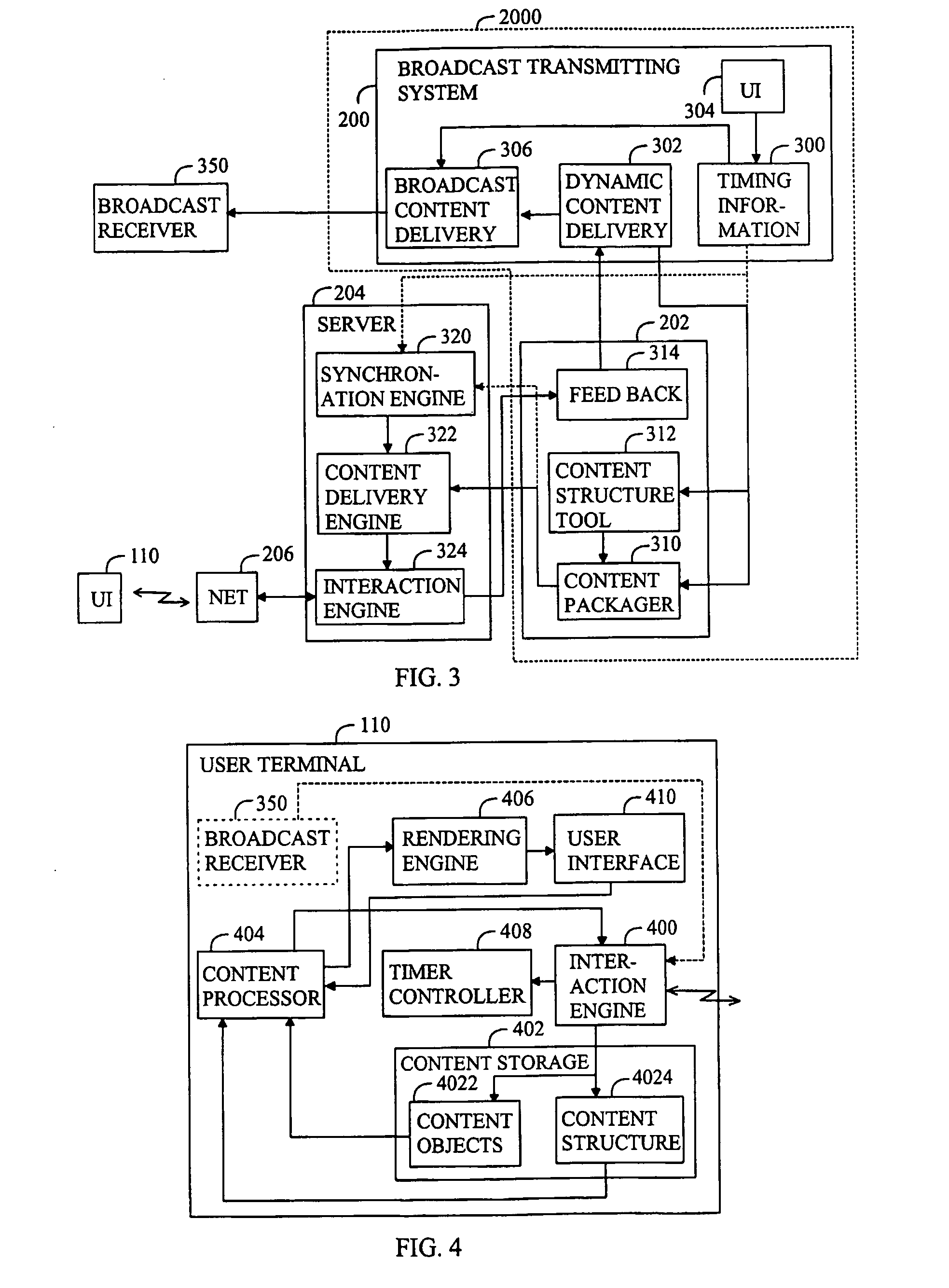
Media system, user terminal and method of providing content items relating to broadcast media stream
The invention relates to a media system, a user terminal and a method of providing one or more content items to at least one user terminal, the content item being related to a broadcast media stream. The method comprises: attaching the content item to a broadcasting time line of the broadcast media stream by a broadcasting system; broadcasting the broadcast media stream by the broadcasting system; synchronizing an internal time of the user terminal with the internal time of the broadcasting system; sending the content item attached to the broadcasting time line from the radio system to the user terminal; and presenting the received content item in the user terminal at a given moment in time that is based on the attachment and on the synchronization.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Electronic Timepiece and Control Method for an Electronic Timepiece
ActiveUS20090180356A1Reduce power consumptionIntuitive adjustmentSynchronous motors for clocksMaster clocksTime informationEngineering
An electronic timepiece includes a reception unit that receives satellite signals transmitted from positioning information satellites; a time information generating unit that generates an internal time; a manual reception process unit that starts operation of the reception unit and executes a manual reception process when an external operating member is operated; an automatic reception process unit that automatically operates the reception unit and executes an automatic reception process when a predetermined condition is satisfied; a simple time adjustment process unit that executes a simple time adjustment process to receive a satellite signal from one positioning information satellite by means of the reception unit, acquire time information from the received satellite signal, and adjust the internal time; and a high precision time adjustment process unit that executes a high precision time adjustment process to receive satellite signals from a plurality of positioning information satellites by means of the reception unit, acquire time information and positioning information from the received satellite signals and determine the location, and adjust the internal time to the time acquired based on the positioning result. The automatic reception process unit executes the simple time adjustment process by means of the simple time adjustment process unit when the automatic reception process executes, and the high precision time adjustment process unit executes the high precision time adjustment process only when the manual reception process is executed by the manual reception process unit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Time synchronization method in mobile station based on asynchronous scheme and system using the same
ActiveUS20060233132A1Reliable informationTime-division multiplexPipe elementsTime informationMobile station
Disclosed is a system and a method for setting an internal time corresponding to a standard time at a current location in a mobile station of an asynchronous scheme. The mobile station of the asynchronous scheme uses a Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP), which is an application of a Network Time Protocol (NTP), allowing the mobile station to easily update internal time information using a synchronized time. The SNTP can provide a time value which can be used to accurately reset an internal time of the mobile station of the asynchronous scheme. By using the SNTP, the mobile station of the asynchronous scheme can obtain exact time information as in a CDMA network and update the mobile station's internal time with the time corresponding to an area in which a standard time is changed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Timepiece and time correction method
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
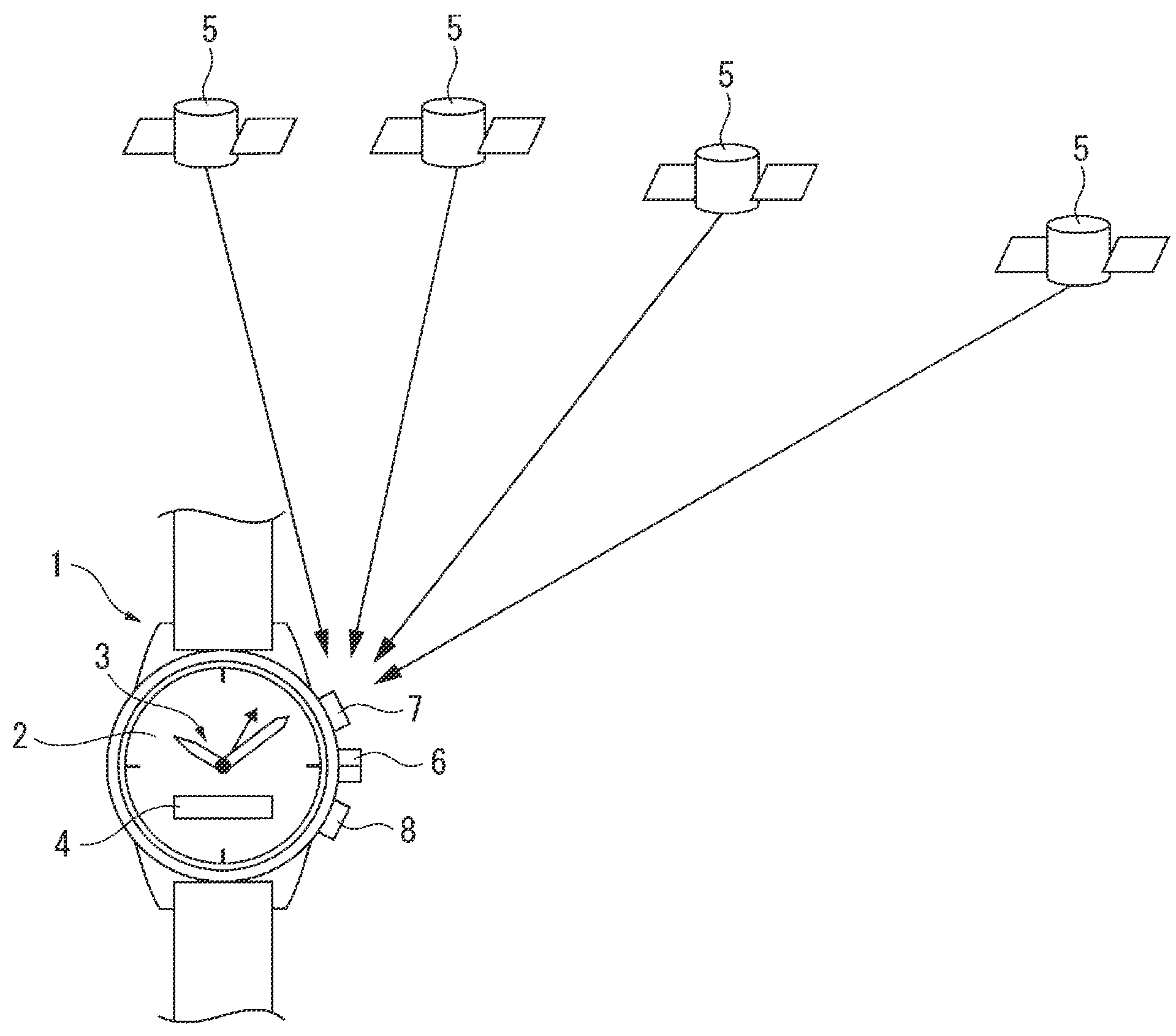
Radio-controlled timepiece and control method for the same
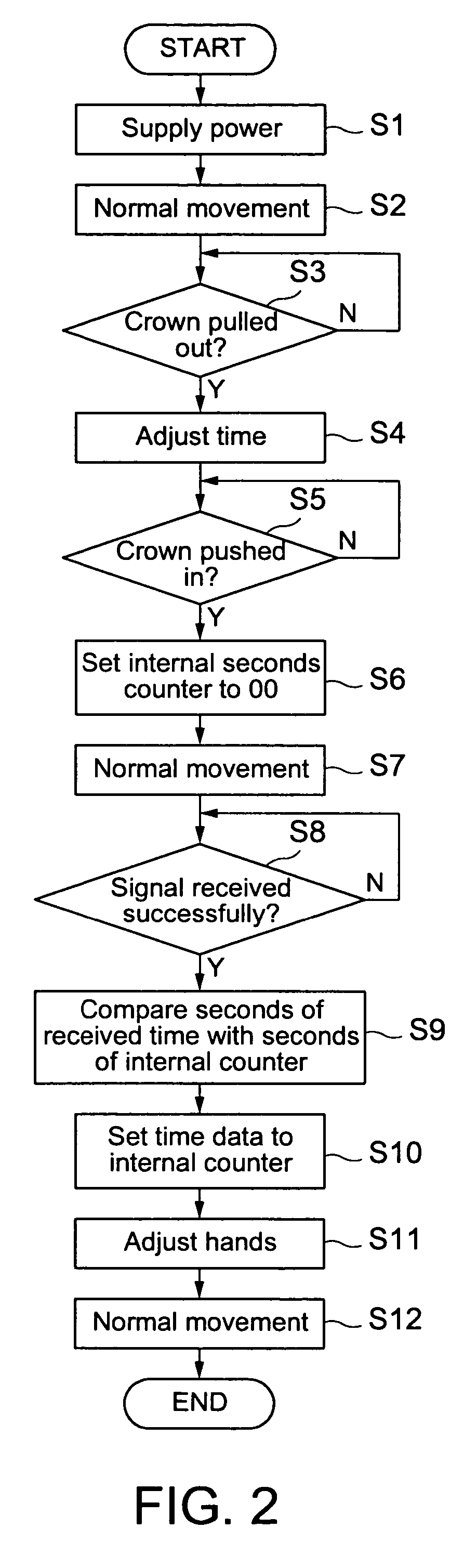
ActiveUS7075859B2Easy to adjustEasy constructionSynchronous motors for clocksDwelling equipmentTime differenceTime data
A watch has a crown for manual time adjustment, a receiver for receiving current time update signals by radio transmission, an internal counter for counting the passage of time according to an internal oscillator, and time display hands. The watch preferably does not have a means for determining the position of its time display hands and therefore relies on user intervention for roughly correlating its time display hands to its internal counter. Preferably, the user begins a manual time correction operation when the second hand is at a predetermined position between 0-60 seconds. When the crown is pushed in, the seconds count value of the internal counter is reset to the predetermined position, and the watch waits for reception of a current time radio signal. When a radio signal is successfully received, the received seconds value is compared to the seconds count in the internal counter. If the time difference is within +30 seconds, the internal time is deemed to be advanced by the difference, and if the time difference is within −30 seconds, the internal time is deemed to be delayed by the difference. The received time data is written into the internal counter, and the time display hands are moved according to the deemed time difference.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method and device for calibrating time
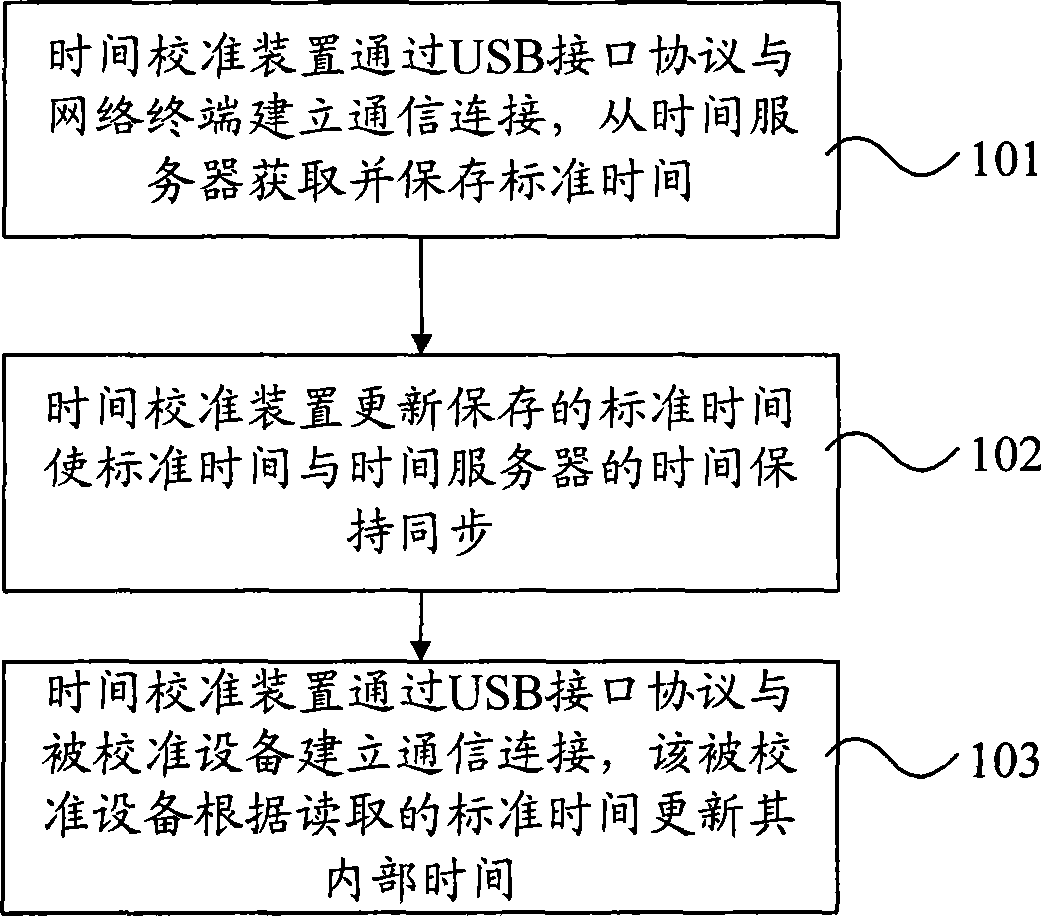
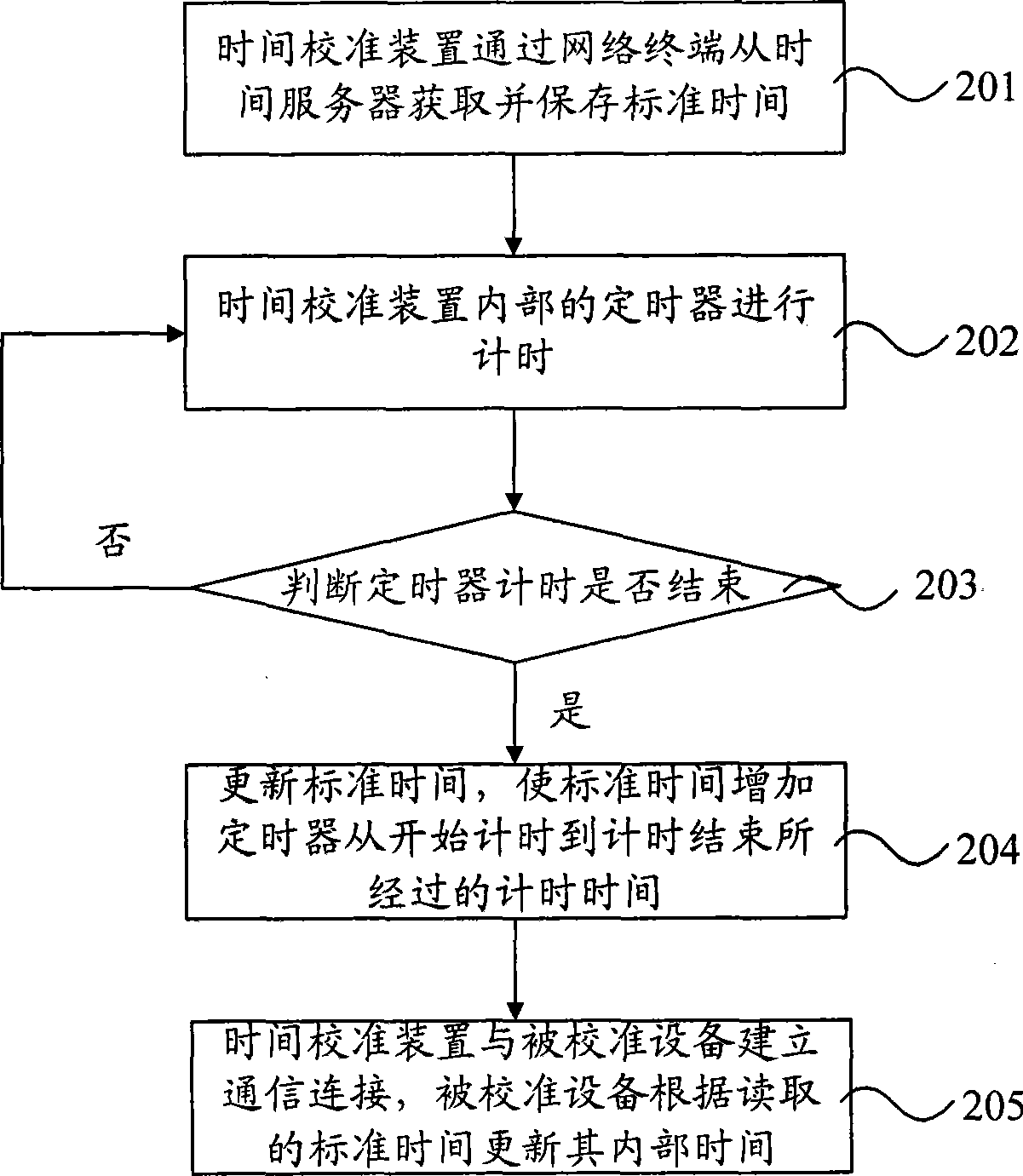
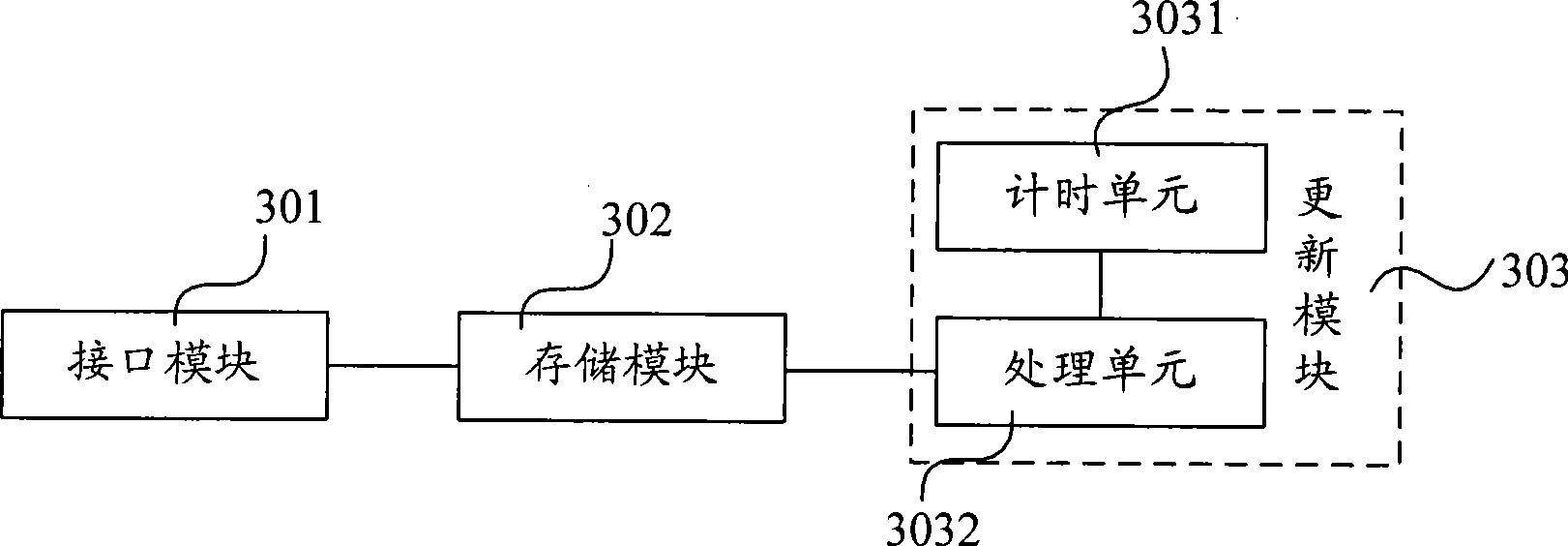
InactiveCN101546169AEasy to implementImprove calibration accuracySetting time indicationNetwork terminationInterface protocol
The invention discloses a method and a device for calibrating time, wherein the time-calibrating method comprises the following steps that: the time-calibrating device establishes a communication link with a network terminal through a USB interface protocol, acquires and saves standard time from a time server through the network terminal; the time-calibrating device updates the standard time to keep the standard time synchronous with the time of the time server; the time-calibrating device establishes the communication link with calibrated equipment through the USB interface protocol; and the calibrated equipment updates the internal time thereof according to the read standard time. The invention has the advantage that the internal time of the calibrated equipment is synchronized with the time of the time server, and a proposal for calibrating an internal clock of the equipment is easy to implement, is not limited by regions, and is economical and effective.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Radio-controlled timepiece and method of adjusting the time kept by a radio-controlled timepiece
ActiveUS7307919B2Improve accuracySynchronous motors for clocksTime-pieces with integrated devicesTime informationEngineering
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Electronically expiring device
InactiveUS7048195B2Record carriers used with machinesTime interval measurement without driving mechanismStopped workTime segment
The present invention relates to a method and system for expiring a device after a predetermined time period has elapsed. A device, which contains its own internal time cell, is designed to stop working or self-destruct after a predetermined time period has expired. The device uses its own time cell so that the elapsed time period is not altered through an external time source. After the predetermined time period has elapsed, the device or a component of the device self-destructs when connected to a power source.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
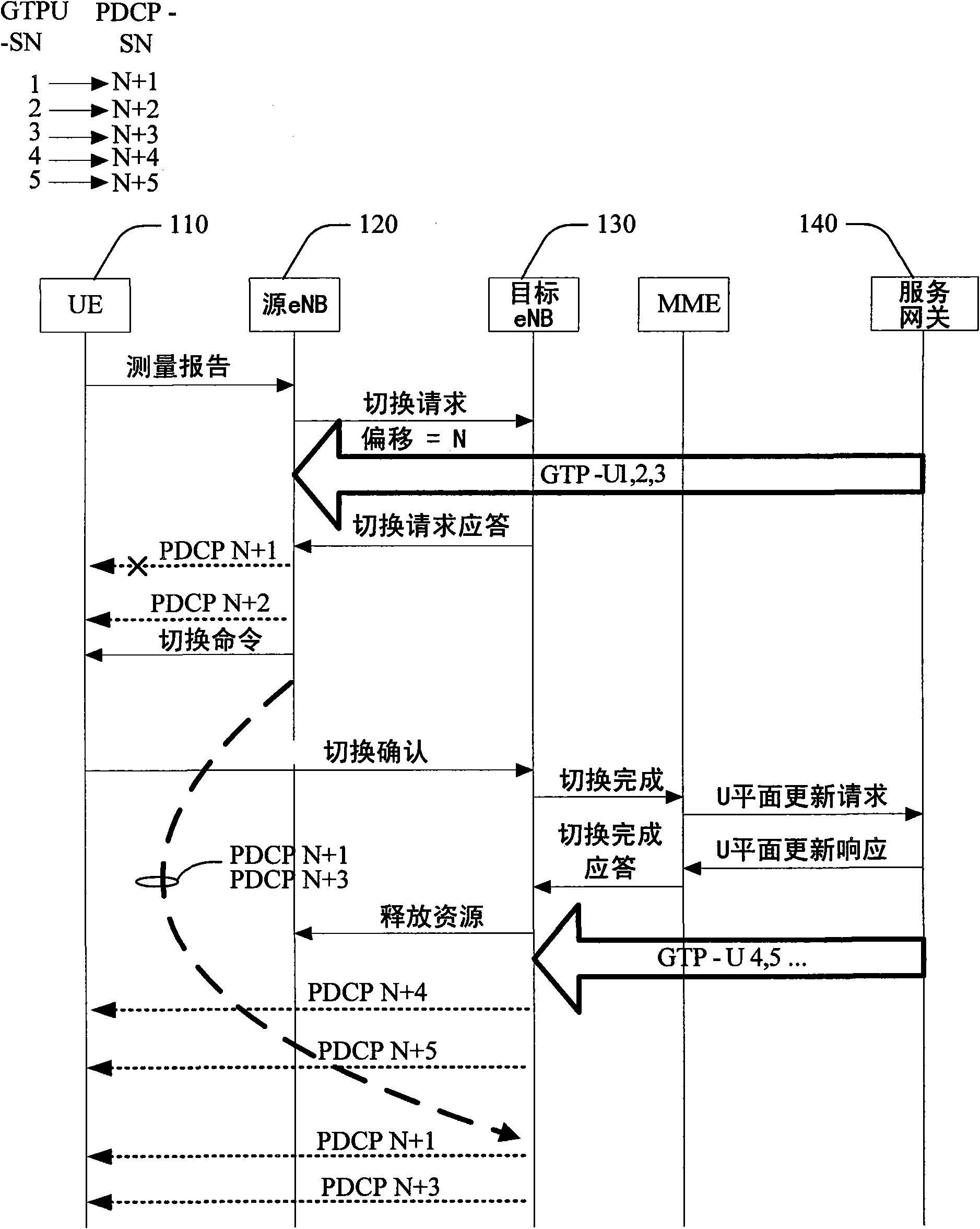
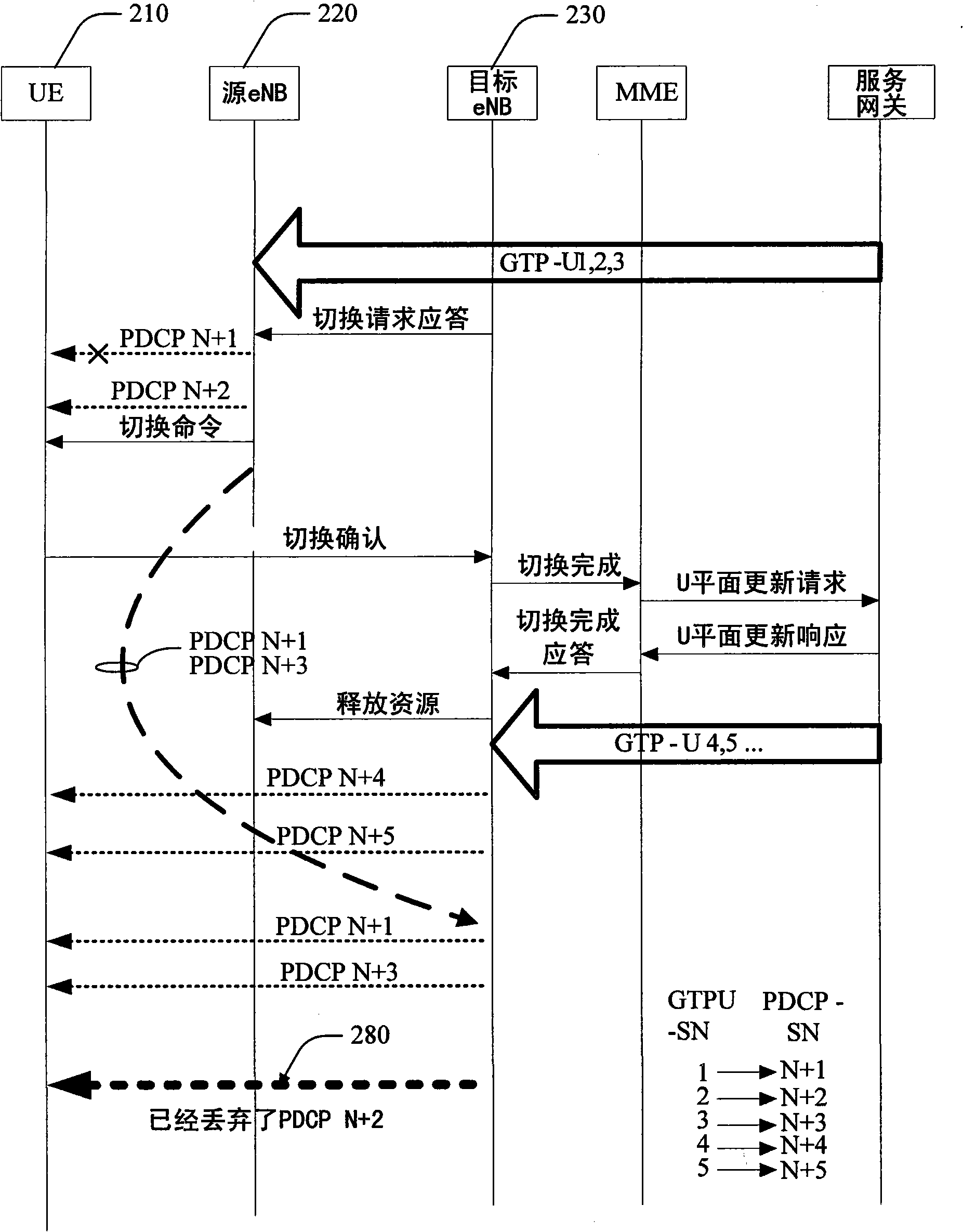
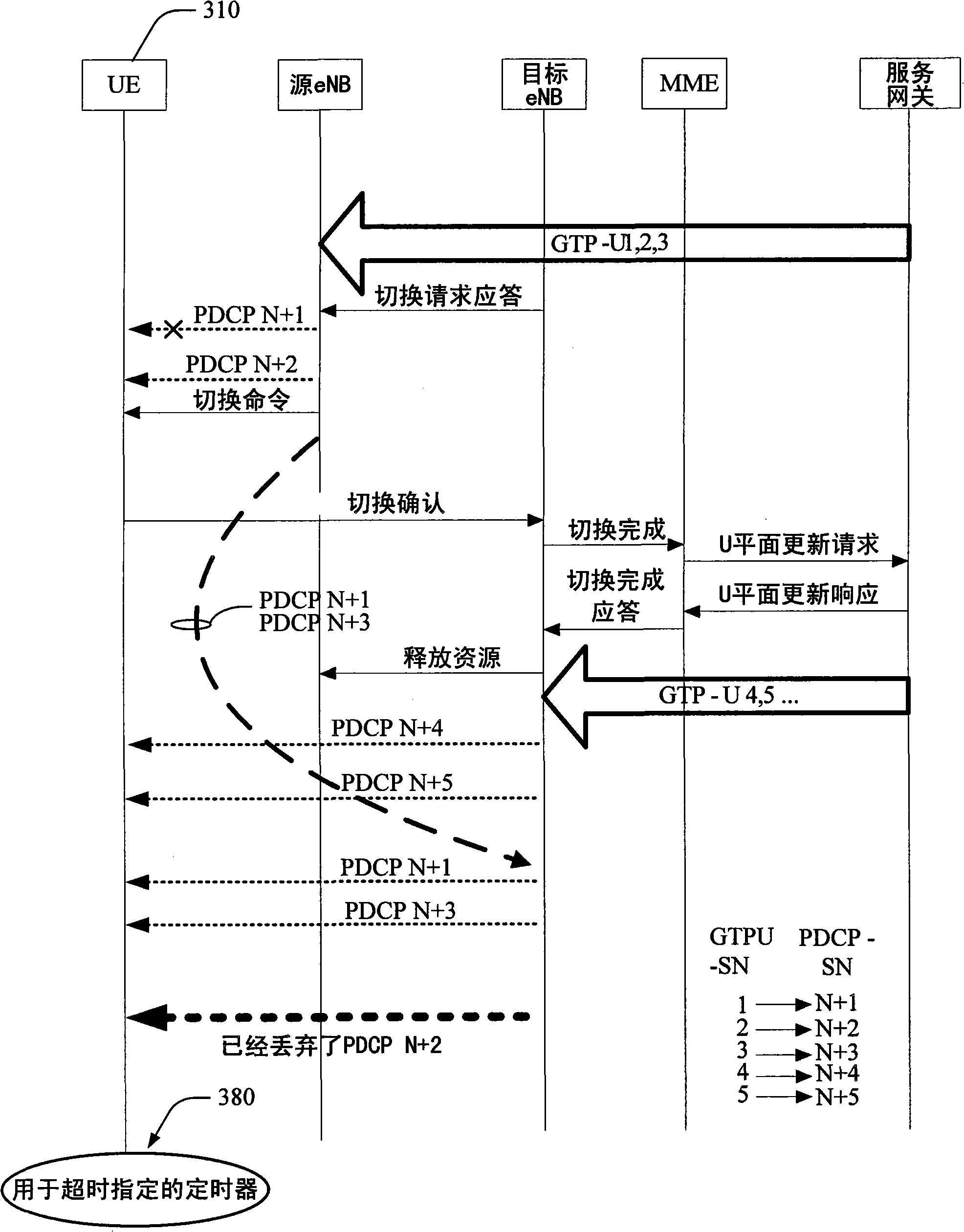
In-order delivery of packet data convergence protocol (PDCP) service data units in downlink during handover
Systems and methods that manage effects of discarded SDUs during handover. Aspects of the subject innovation maintain order for arrival of PDCP SDUs when a UE encounters a lost PDCP, which has resulted from a dropped SDU at the source eNB - before assignment of an associated PDCP SN. By initially assigning all SDUs corresponding PDCP SNs, a PDCP SN gap or hole can then be encountered upon dropping of a PDCP SDU. To manage PDCP SN gaps or holes thus generated, an internal time out can be designated to terminate an associated UE's delay for such SN hole(s) via a time out. Other aspects enable the source eNB to send a PDCP Status Message to the UE (via the target eNB) to abort the SN gaps or holes resulting from a dropped PDCP SN.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Electronically expiring device
InactiveUS20050001040A1Record carriers used with machinesTime interval measurement without driving mechanismStopped workTime segment
The present invention relates to a method and system for expiring a device after a predetermined time period has elapsed. A device, which contains its own internal time cell, is designed to stop working or self-destruct after a predetermined time period has expired. The device uses its own time cell so that the elapsed time period is not altered through an external time source. After the predetermined time period has elapsed, the device or a component of the device self-destructs when connected to a power source.
Owner:IBM CORP
Power reforming methods and associated multiphase lights
InactiveUS8674613B2Improve power factorShorten the timeElectric signal transmission systemsDc network circuit arrangementsPower factorEngineering
The present invention relates to power reforming methods and associated multiphase lights, especially to power reforming methods and associated multiple lights that selectively turn ON and OFF to reform current to follow voltage appropriately, which provides better heat dissipation, improving power factor and color mixing capability. The method comprises acts of rectifying an AC voltage to a pulsating DC voltage, synchronizing an internal time base signal to the pulsating DC voltage, setting pulse duration in a pulse period and turning ON and OFF of an electronic device. The device comprises at least two loads, a rectifier, at least two drivers and a controller.
Owner:GRAY RICHARD LANDRY
Electronic Timepiece and Reception Control Method for an Electronic Timepiece
ActiveUS20120201101A1Reduce processor loadEasy to getSynchronous motors for clocksSetting time indicationData miningLeap second
An electronic timepiece can easily acquire a leap second information reception time with minimal processor load. A first table groups leap second information reception times expressed by hour, minute, second, and day values into plural minute-second patterns of minute-second combinations that are common to plural hours, and relates numbers identifying these minute-second patterns to the day and hour values. The minute-second combinations are grouped by number in a second table. The number corresponding to the day and hour of the internal time is found from the first table (S1). A minute-second combination that is later than the internal time is found from the minute-second combinations corresponding to the acquired number (S2). And leap second reception time is calculated. If the resulting leap second reception time matches the internal time is determined (S9). If the times match, the leap second information is received (S10, S11).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Time adjustment device, timepiece with a time adjustment device, and a time adjustment method
InactiveUS7649812B2Short timeReduce power consumptionMechanical clocksSynchronous motors for clocksTime informationEngineering
A time adjustment device having a reception unit that receives satellite signals transmitted from positioning information satellites; a time information generating unit that generates internal time information; a time information adjustment component that corrects the internal time information; and a reception controller that controls operation of the reception unit; wherein the satellite signal contains satellite time information that is kept by the positioning information satellite; the reception unit can select a first reception mode for receiving first information including the hour, minute, and second data in the satellite signal, and a second reception mode for receiving second information including the hour, minute, and second data, week information for the current year, month, and day, and satellite health information in the satellite signal; the time information adjustment component includes a time adjustment recording component that records whether or not the time was adjusted using the second information received in the second reception mode after the internal time information was initialized, a first time information adjustment component that controls the reception unit by way of the reception controller in the first reception mode to receive the first information, and sets the hour, minute, and second values of the internal time information based on the received first information, and a second time information adjustment component that controls the reception unit in the second reception mode to receive the second information, and sets the year, month, day, hour, minute, and second values of the internal time information using the received second information; the first time information adjustment component operates when it is recorded in the time adjustment recording component that the time was adjusted using the second information; and the second time information adjustment component operates when it is not recorded in the time adjustment recording component that the time was adjusted using the second information.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
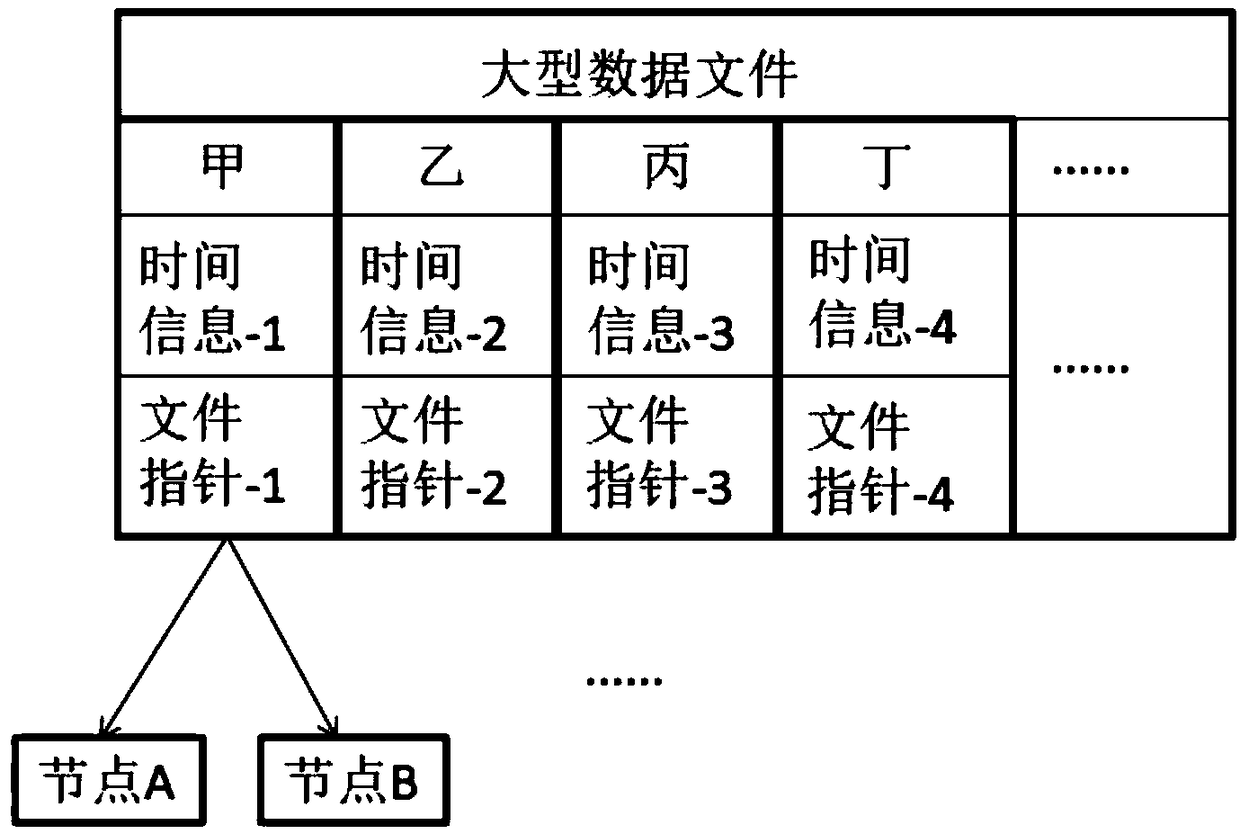
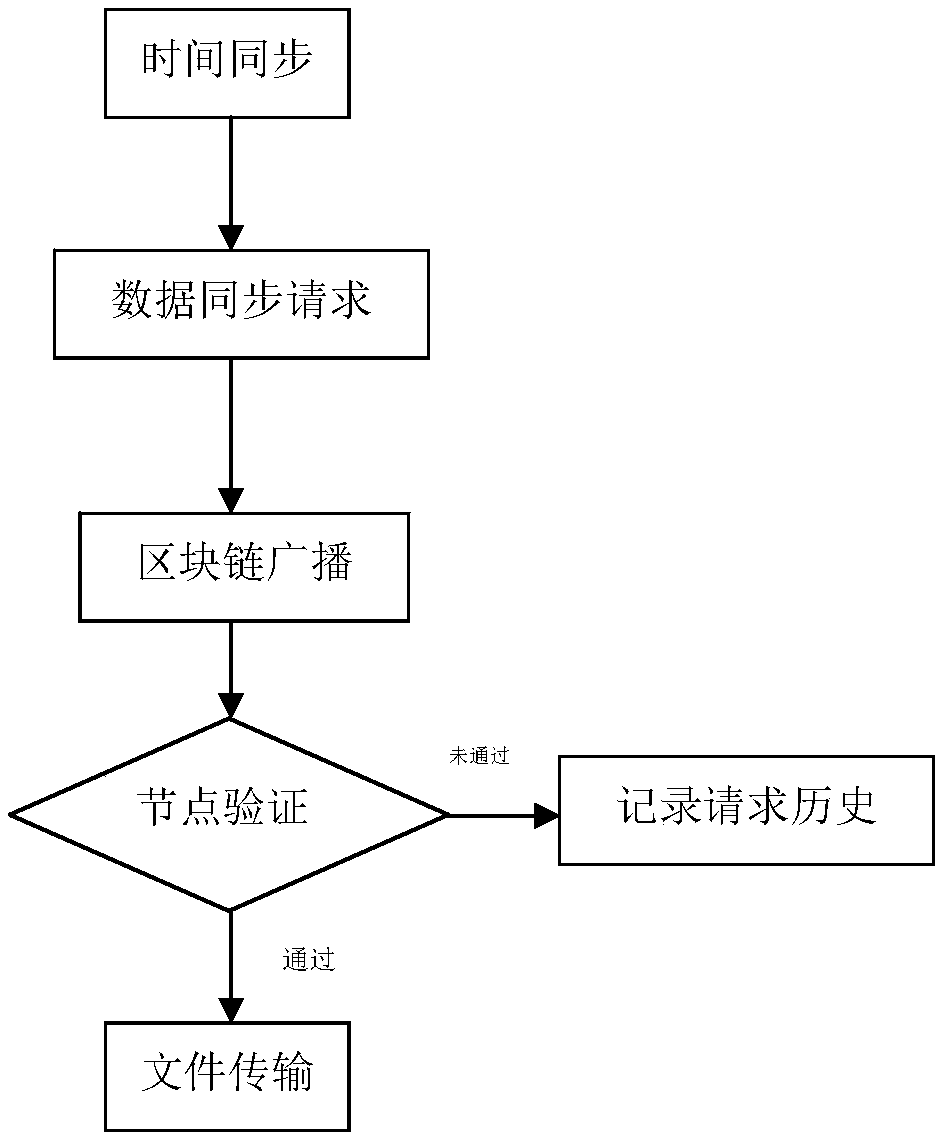
A node data synchronization method in block chain
InactiveCN108984697AEfficient use ofImprove transmission efficiencyPayment protocolsTransmissionData synchronizationData file
The invention provides a node data synchronization method in a block chain, which is used for solving the problems of concurrently synchronizing large-scale data files of multiple nodes, and differentaccess rights and access order in the switching process of a private chain and a public chain. Through splitting of large data files, node s the private chain are stored in a specific format, a synchronization mechanism of private chain internal time management is adopted to ensure that access order of private chain internal node, the data synchronization request is issued by block chain broadcast of synchronization request, and the data transmission is controlled by key verification. The account books of each node are recorded according to the file for the request and the transmission record, so the traceability of the operation record is ensured. The security of the whole private link file storage is improved through the partitioned backup node storage of large files, and the file transfer mode of P2P is adopted to improve the transfer speed. The method is applicable to the field of large-scale file security management transmission and use.
Owner:JIANGSU HENGBAO INTELLIGENT SYST TECH CO LTD
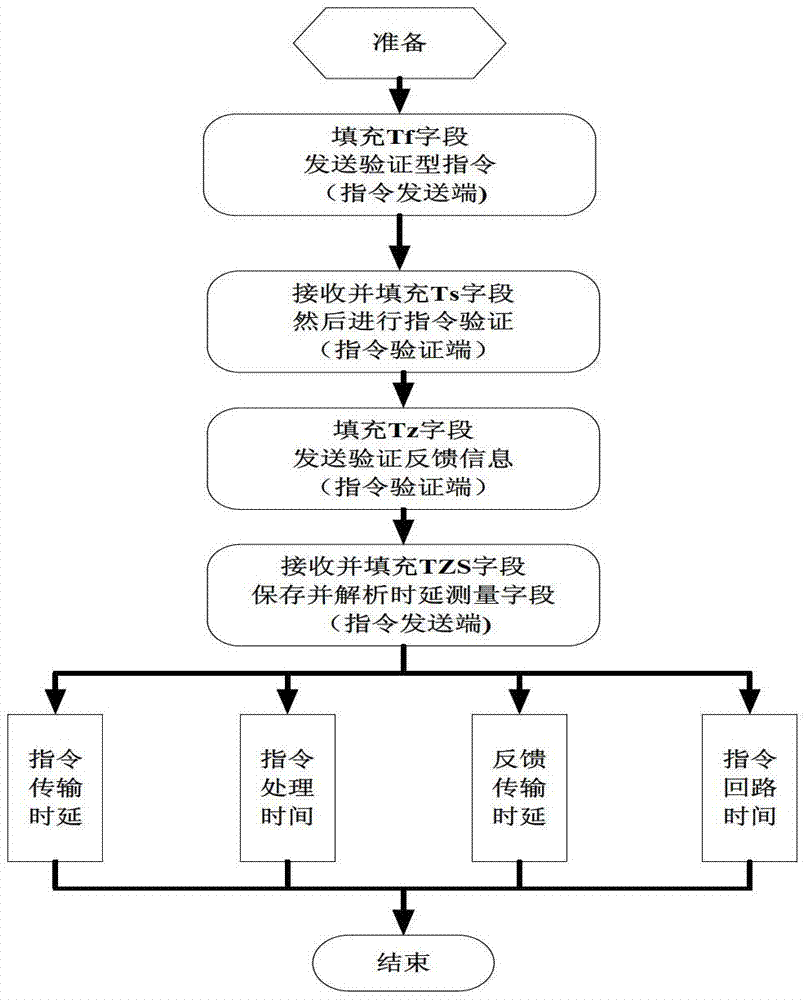
Measuring method of space teleoperation command time delay
InactiveCN103117816AImprove accuracyAnalyze Latency DistributionTransmission systemsTransmission monitoringInformation transmissionTransmission time delay
The invention relates to a measuring method of space teleoperation command time delay and aims at time delay measurement and analysis problems. The measuring method improves accuracy of measurements and analysis of teleoperation control command in each section of time delay in a system through measures of developing a high-precision timing system, adding time delay measuring fields in sub-system inside information, and the like. The measuring method has the advantages of being capable of conducting system internal time delay measurements on the teleoperation control command, analyzing precision of command transmission time delay, command executing time, command feedback time delay, command circuit time, two-machine synchronous time, and the like. The measuring method can be popularized to time delay measurement in other information transmission processes, is capable of adding time delay measurement fields in every point of a router, and fills corresponding fields through an information source and an information sink, thereby further analyzing time delay distribution conditions inside a system.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
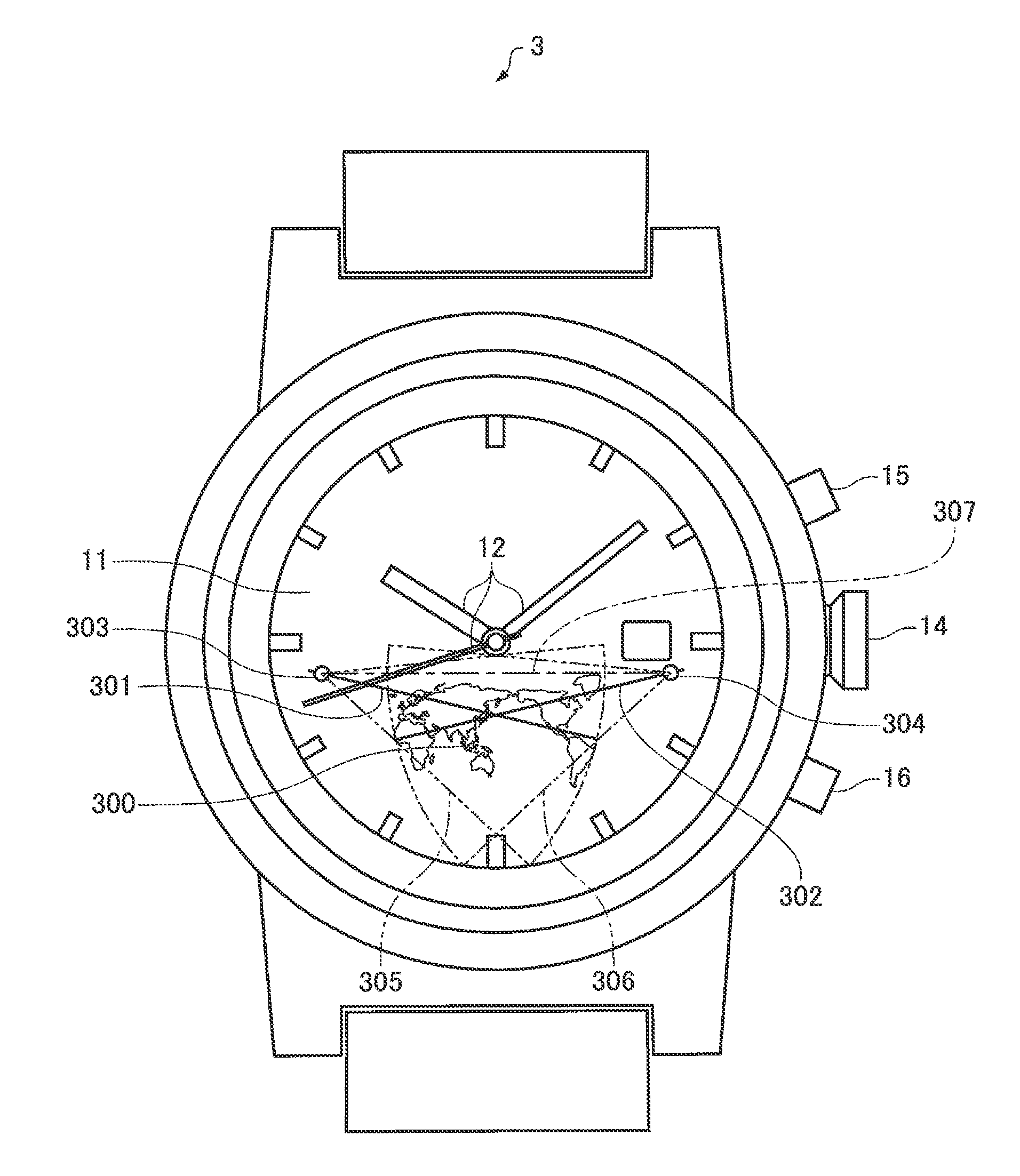
Electronic Timepiece and Time Difference Correction Method for an Electronic Timepiece
An electronic timepiece has a function for receiving satellite signals transmitted from positioning information satellites, and includes a reception unit that receives the satellite signal and acquires satellite information from the received satellite signal, a satellite search unit that executes a process of searching for a capturable positioning information satellite based on the received satellite signal and capturing the found satellite signal, a positioning calculation unit that selects a specific number of positioning information satellites from among the positioning information satellites captured by the satellite search unit, executes a positioning calculation based on the satellite information contained in the satellite signals sent from the selected positioning information satellites, and generates positioning information, a time information adjustment unit that corrects internal time information based on the satellite information, a time information display unit that displays the internal time information, a storage unit that stores time difference information defining the time difference in each of a plurality of areas into which geographical information is divided, and a time difference evaluation unit that calculates an assumed positioning region based on the positioning information, and determines based on the time difference information if the assumed positioning region contains a time difference boundary. The time information adjustment unit correcting the internal time information based on the time difference in the assumed positioning region when the time difference evaluation unit determines that the assumed positioning region does not contain a time difference boundary, The positioning calculation unit reselecting the specific number of positioning information satellites and continuing the positioning calculation when the time difference evaluation unit determines that the assumed positioning region contains a time difference boundary. The reception unit terminates satellite signal reception when the time difference evaluation unit determines that the assumed positioning region does not contain a time difference boundary.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
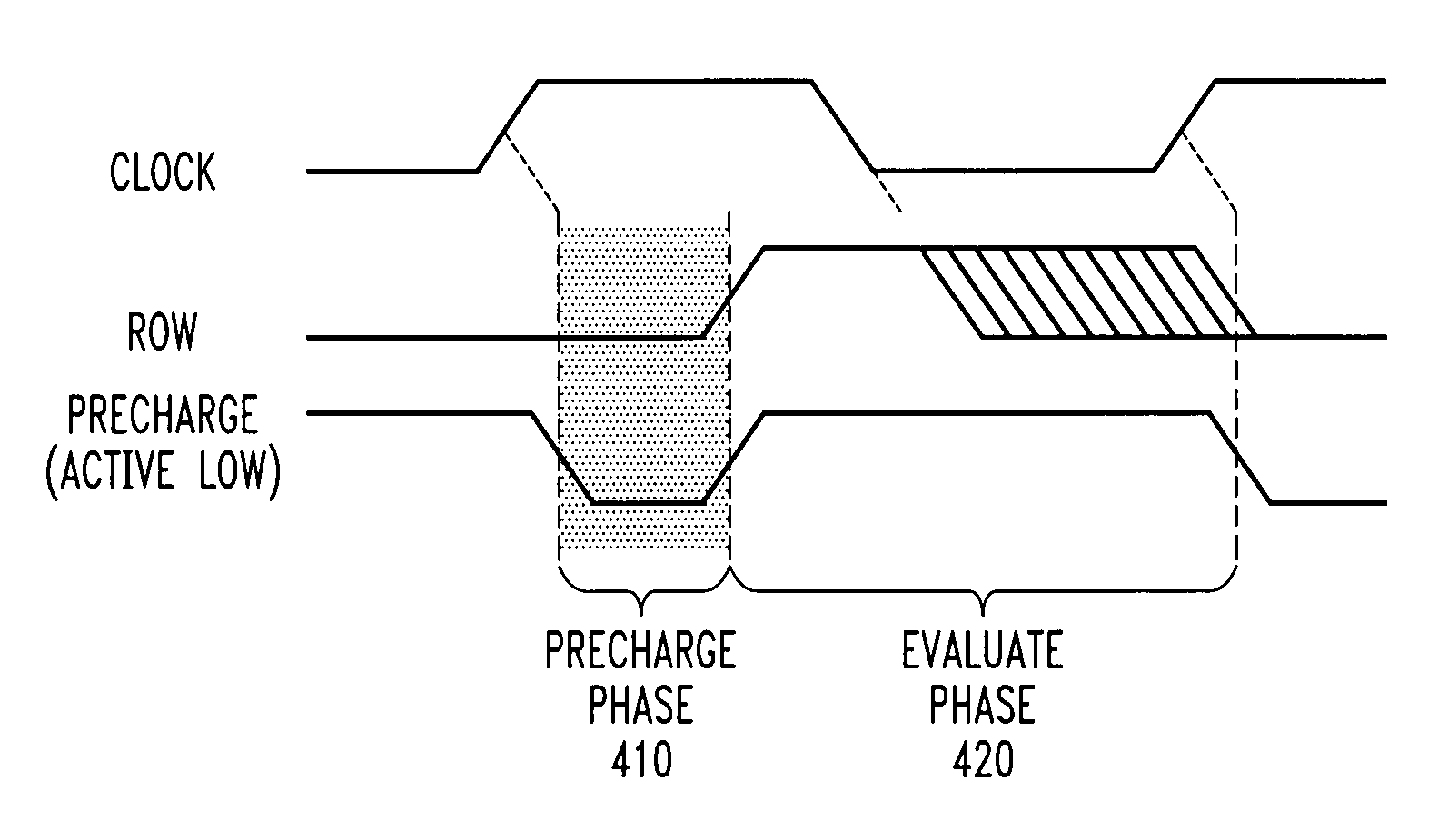
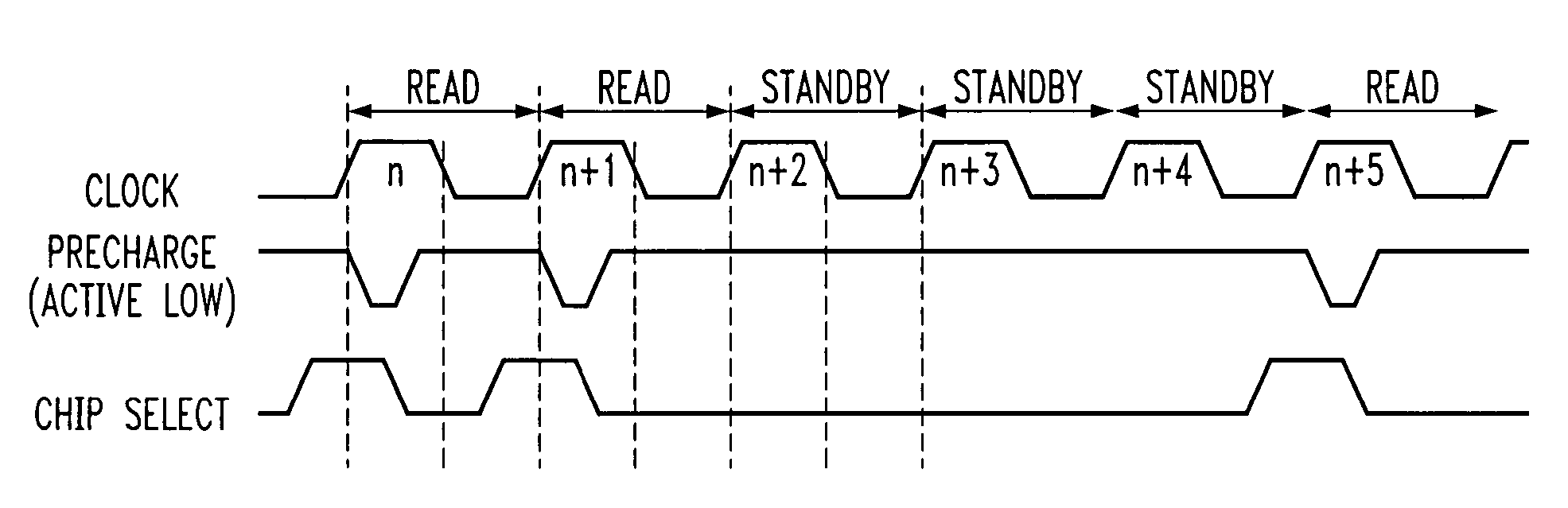
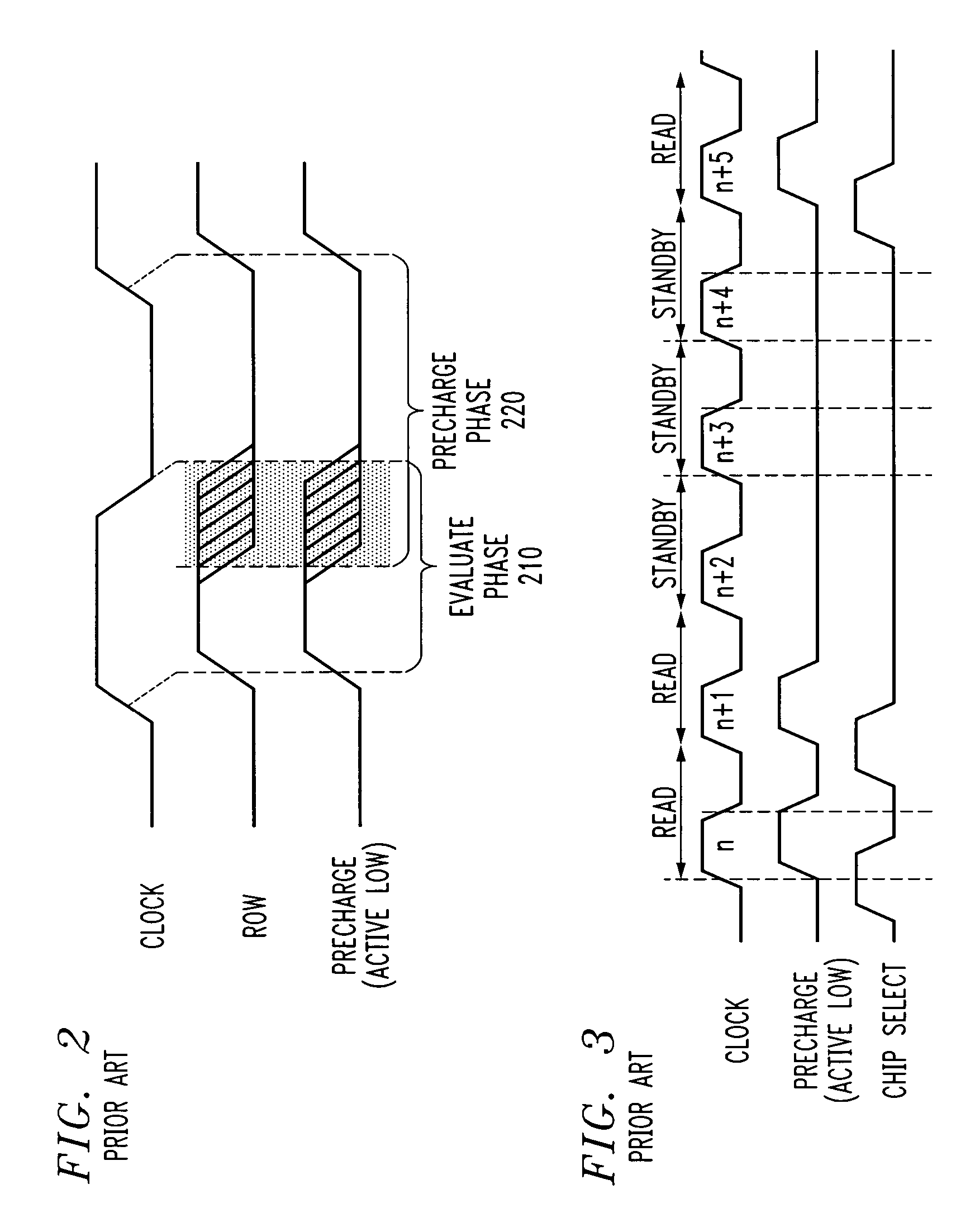
Method and apparatus for reducing leakage current in a read only memory device using shortened precharge phase
InactiveUS20050162951A1Reduce leakage currentShorten the construction periodRead-only memoriesDigital storageTime segmentDrain current
A method and apparatus are provided for reducing leakage current in a read only memory device. Leakage current is reduced by reducing the duration of the precharge cycle during each read cycle so that the associated leakage current will flow for a shorter time period during each cycle. The precharge phase is positioned at the beginning of each read cycle, prior to the evaluation phase. The precharge phase is terminated by a subsequent clock edge or by an internal time out prior to a subsequent clock edge. The time interval between when the columns reach their precharge voltage and the evaluation phase begins is reduced.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
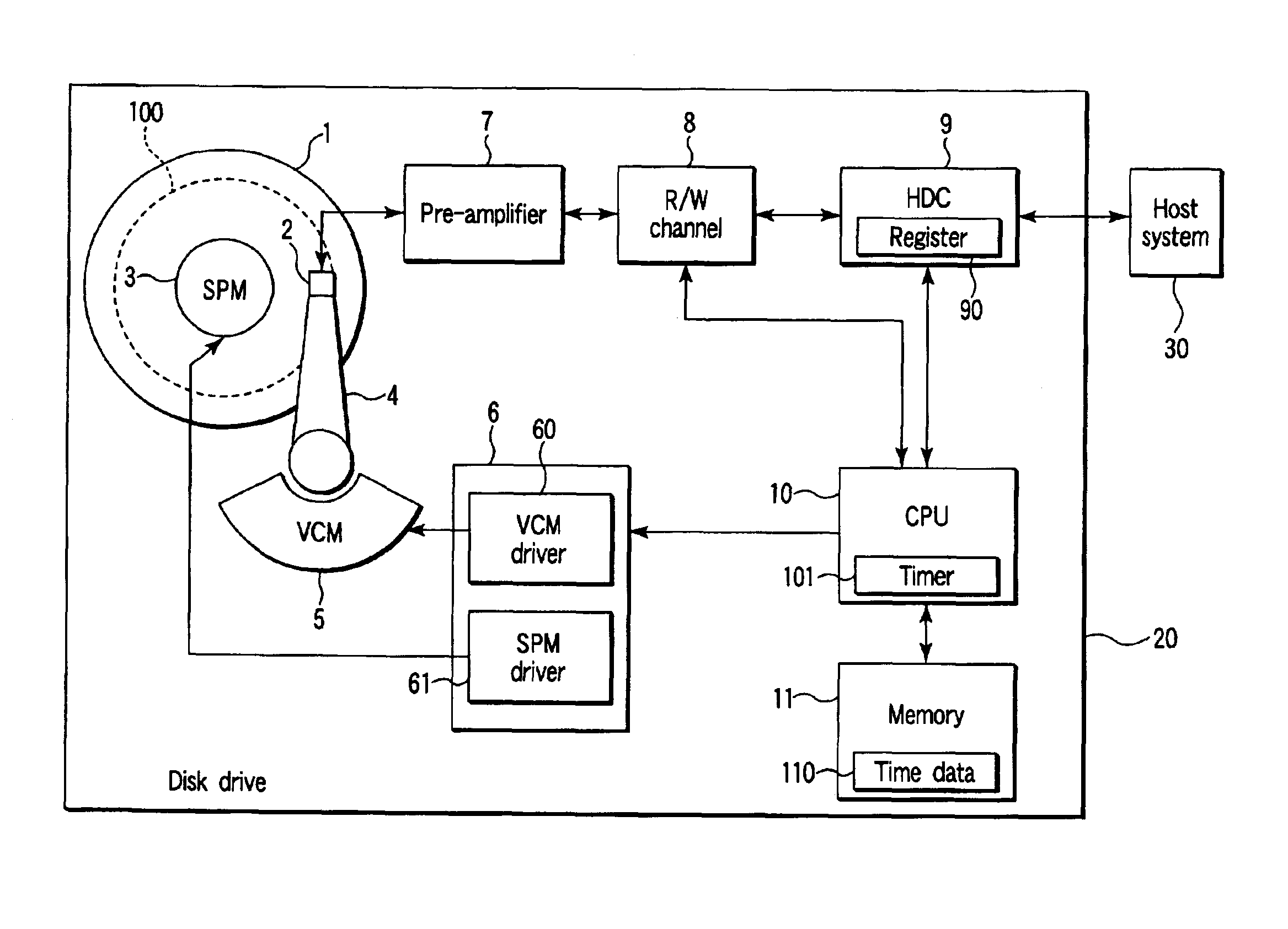
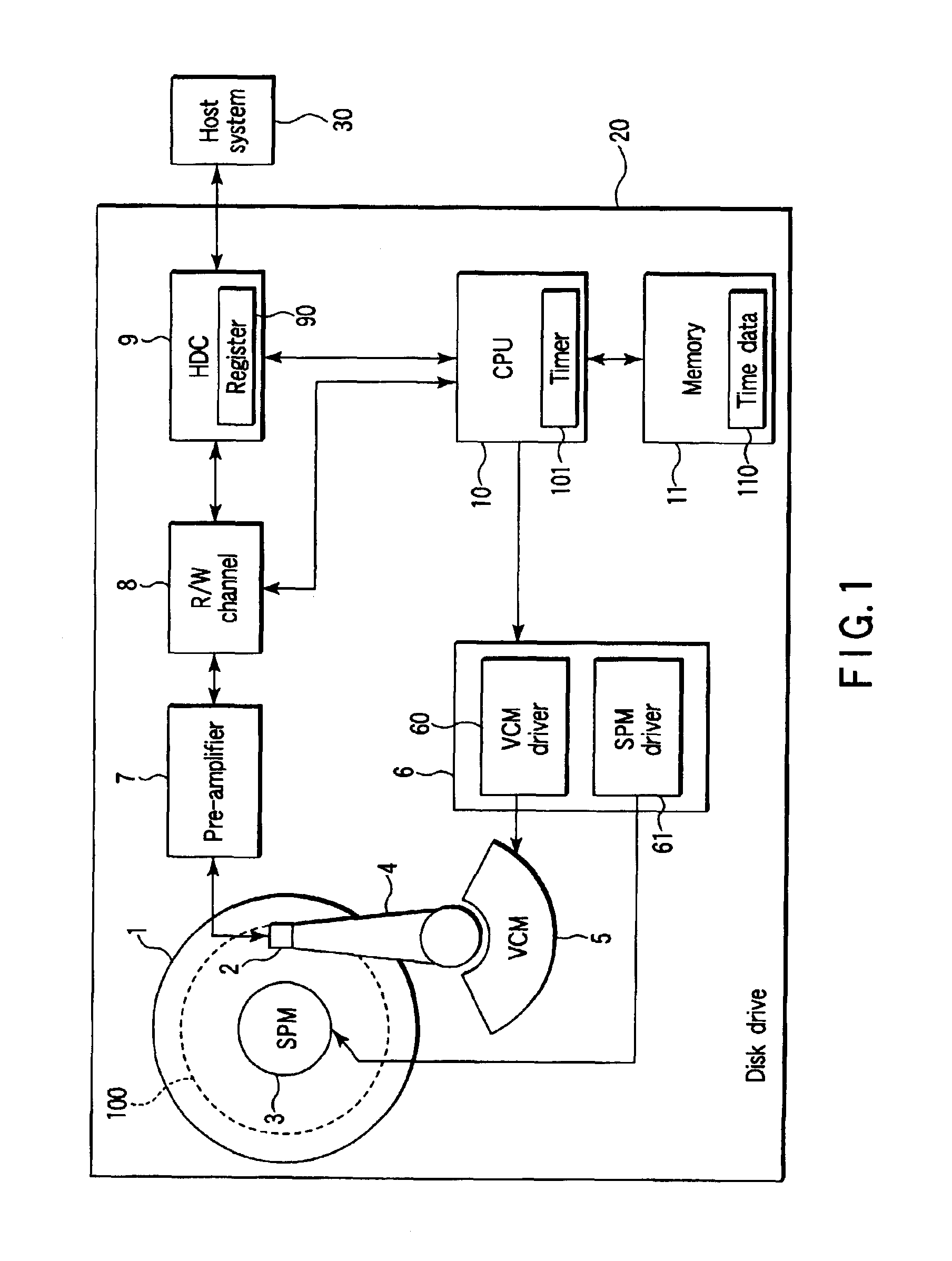
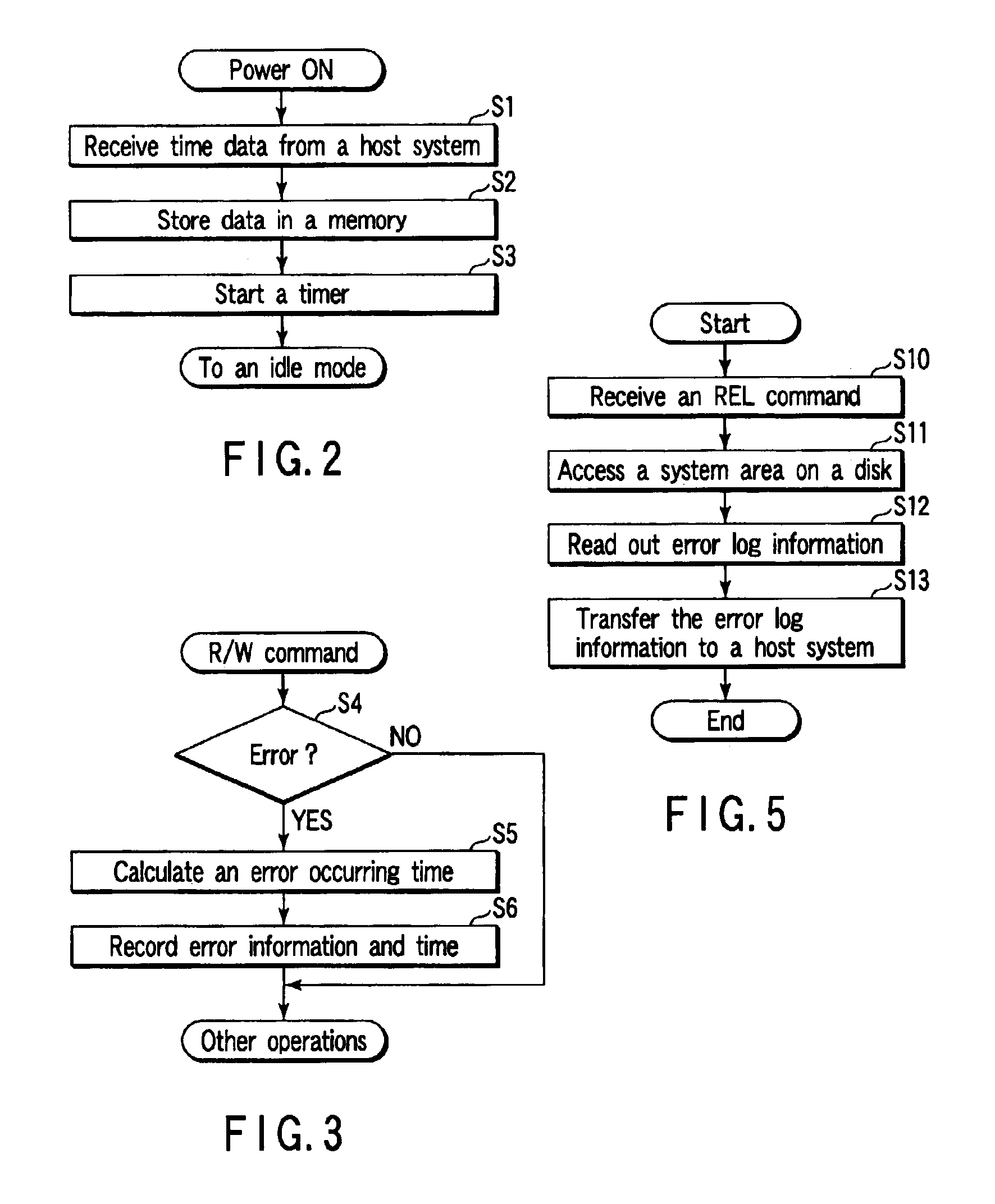
Method and apparatus for event management in a disk drive
A disk drive is disclosed which has an event management function. At an event occurring time such as an error generation, the disk drive records the event information together with time data. A CPU of the disk drive is configured to, at a power ON time, allow the time data which is received from a host system to be stored in a memory. At the time of an error occurring, the CPU, while using the time measured by an internal timer and time data, generates time data which is synchronized with the internal time of the host system.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Electronic Timepiece and Electronic Device
ActiveUS20130051186A1Easy to checkImprove usabilityVisual indicationsSynchronous motors for clocksTime informationEngineering
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com