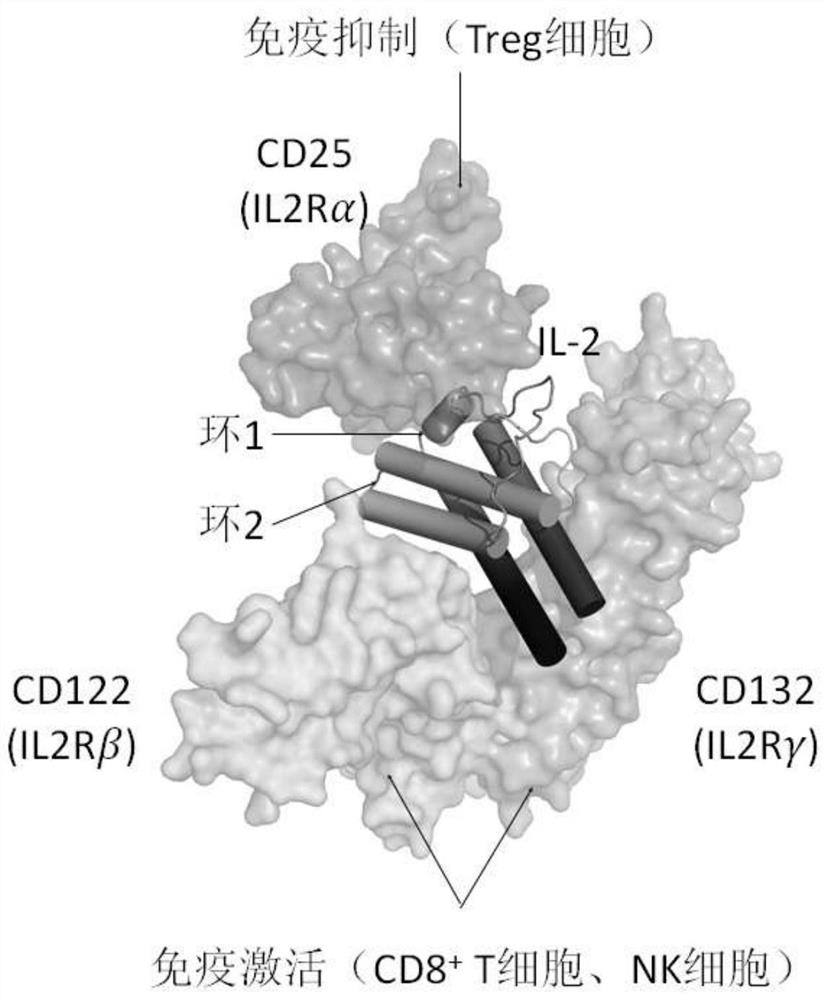
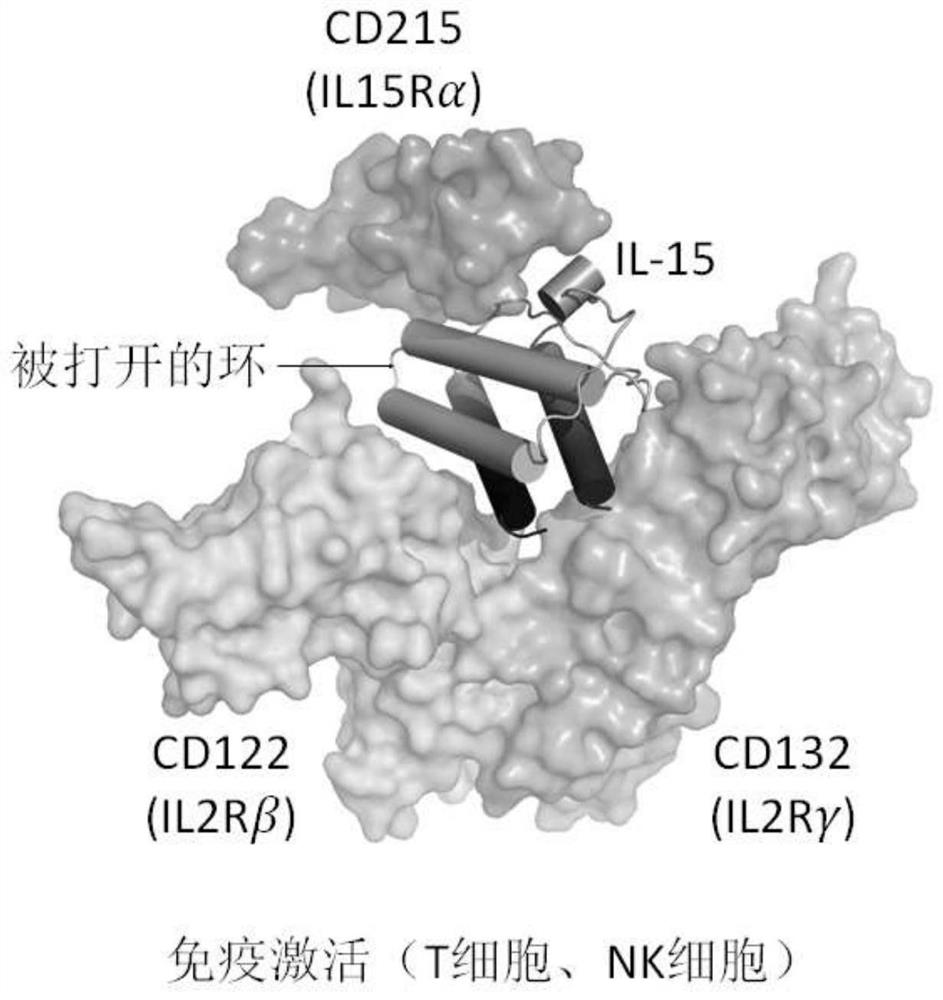
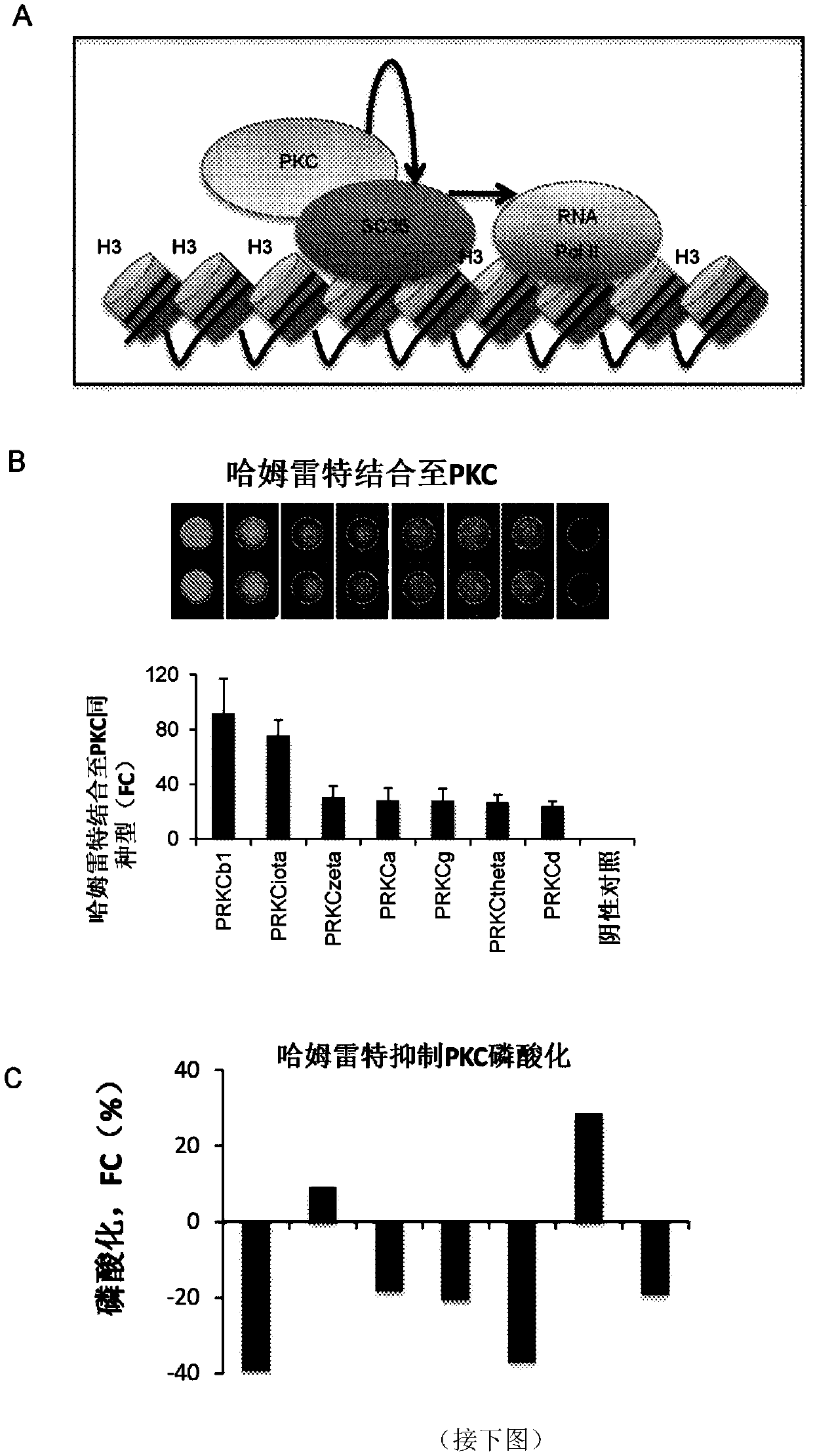
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "HECT domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In molecular biology, the HECT domain is a protein domain found in ubiquitin-protein ligases. The name HECT comes from 'Homologous to the E6-AP Carboxyl Terminus'. Proteins containing this domain at the C terminus include ubiquitin-protein ligase, which regulates ubiquitination of CDC25. Ubiquitin-protein ligase accepts ubiquitin from an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in the form of a thioester, and then directly transfers the ubiquitin to targeted substrates. A cysteine residue is required for ubiquitin-thiolester formation. Human thyroid receptor interacting protein 12 (TRIP12), which also contains this domain, is a component of an ATP-dependent multisubunit protein that interacts with the ligand binding domain of the thyroid hormone receptor. It could be an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase. Human ubiquitin-protein ligase E3A interacts with the E6 protein of the cancer-associated Human papillomavirus type 16 and Human papillomavirus type 18. The E6/E6-AP complex binds to and targets the p53 tumour-suppressor protein for ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis.
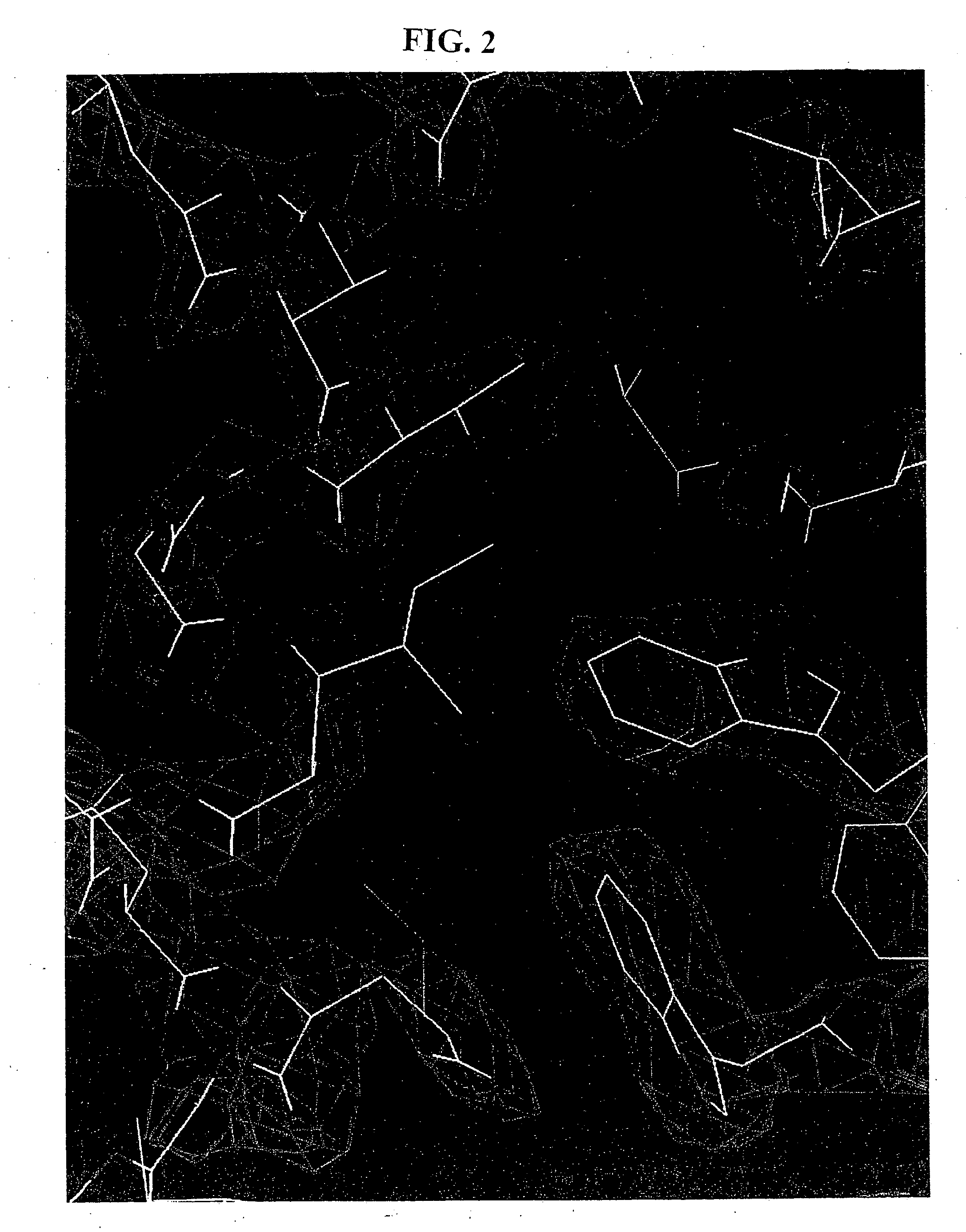
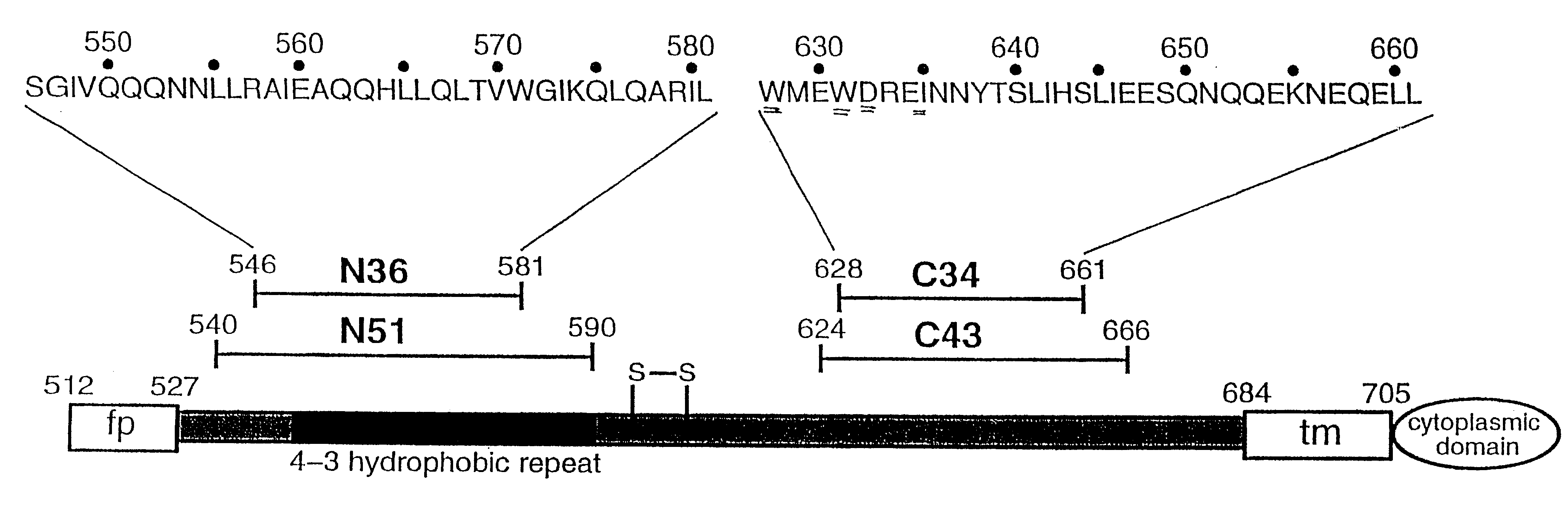
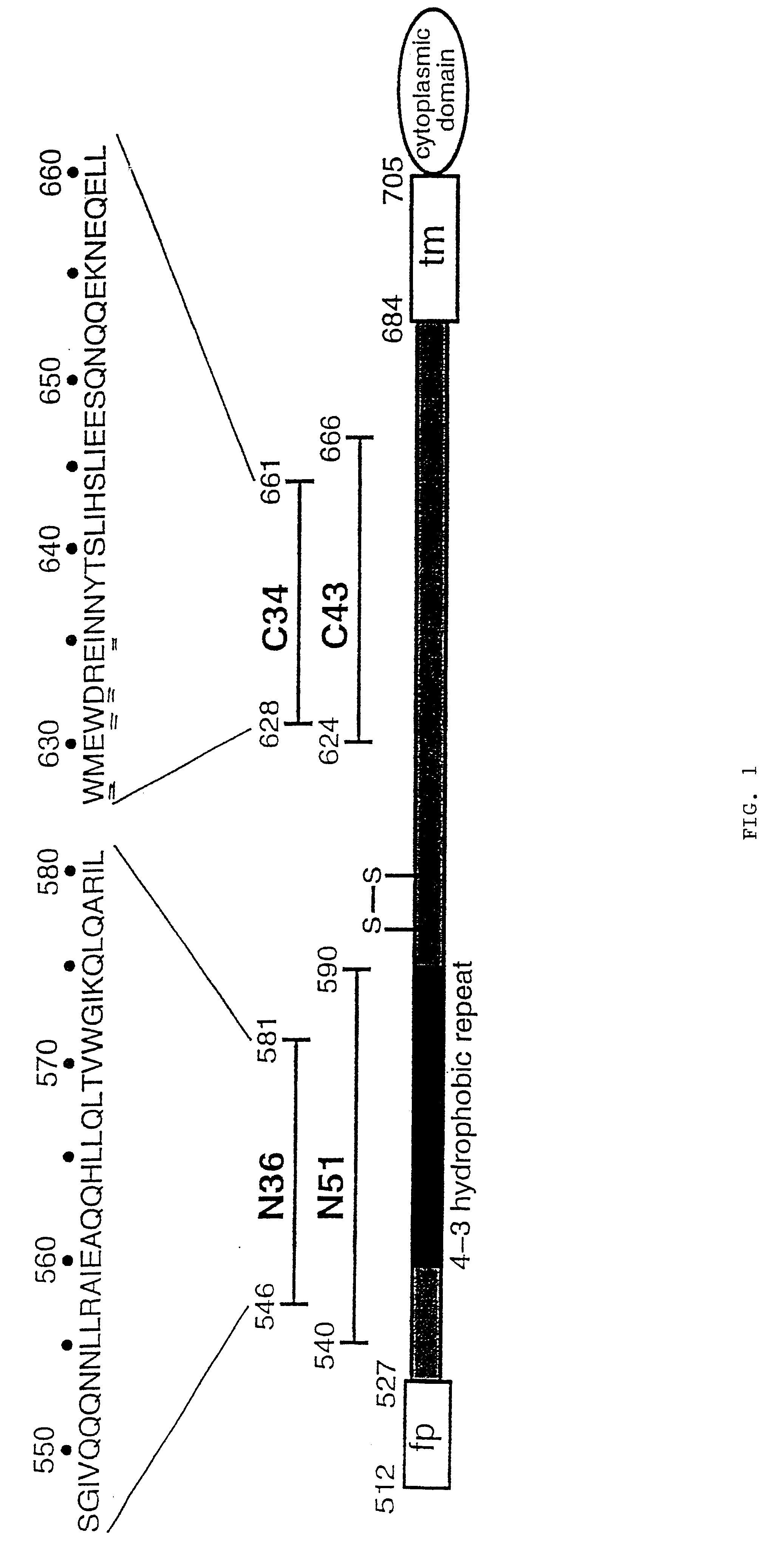
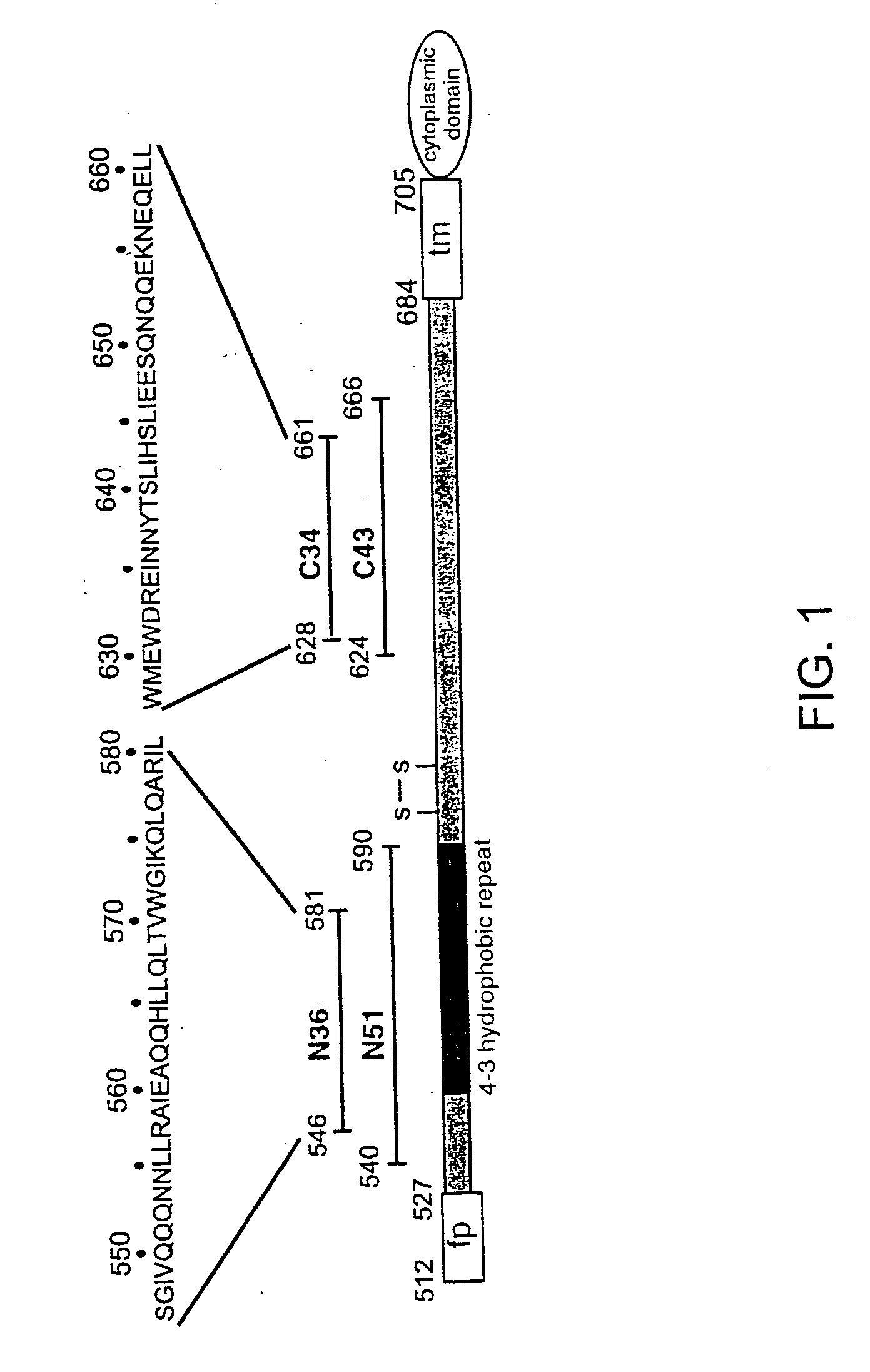
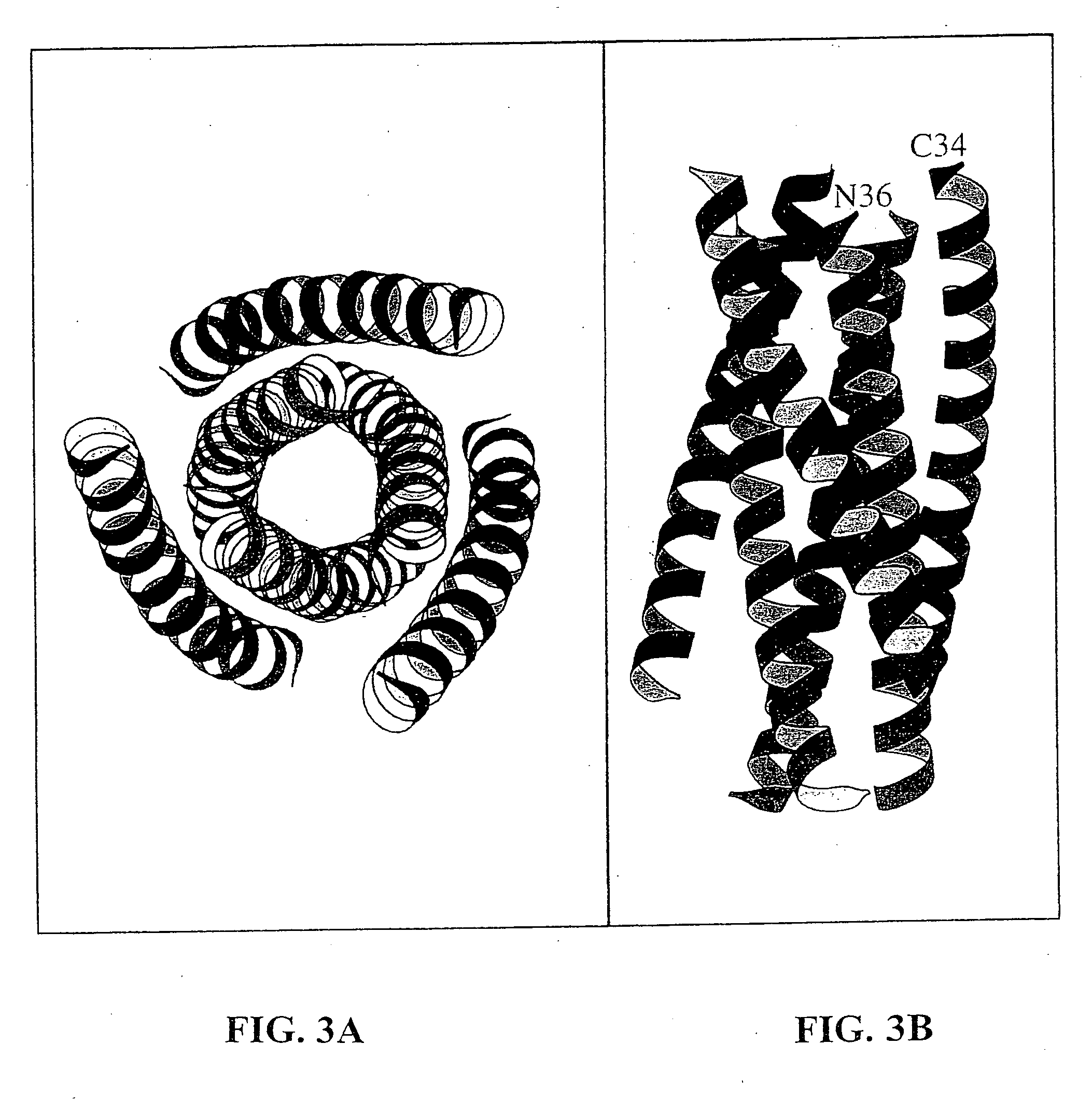
Core structure of gp41 from the HIV envelope glycoprotein
InactiveUS6506554B1Increase infectivityHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementHiv envelopeDesigning drug
Described are the crystal structure of the alpha-helical domain of the gp41 component of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein which represents the core of fusion-active gp41, methods of identifying and designing drugs which inhibit gp41 function and drugs which do so.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
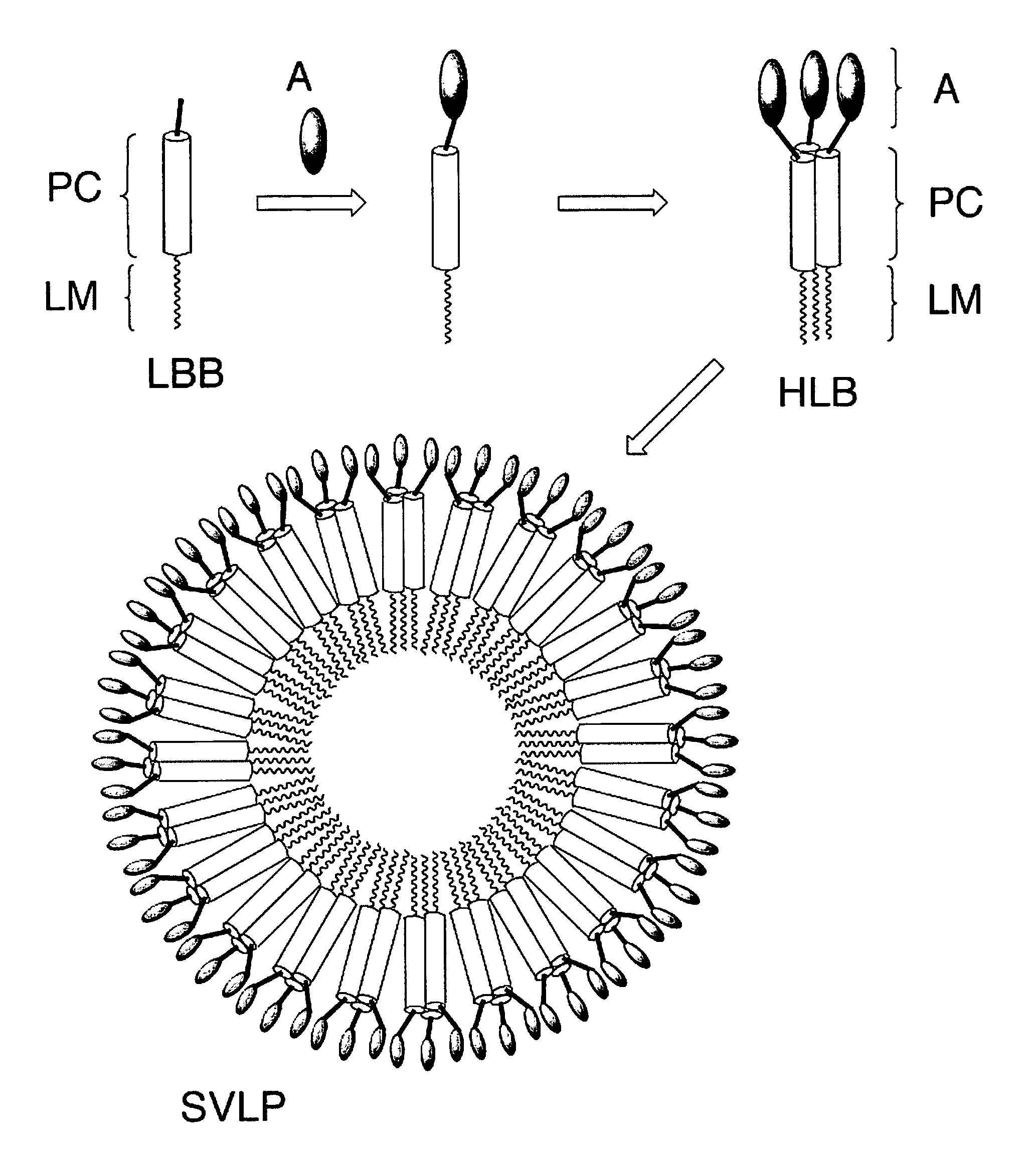
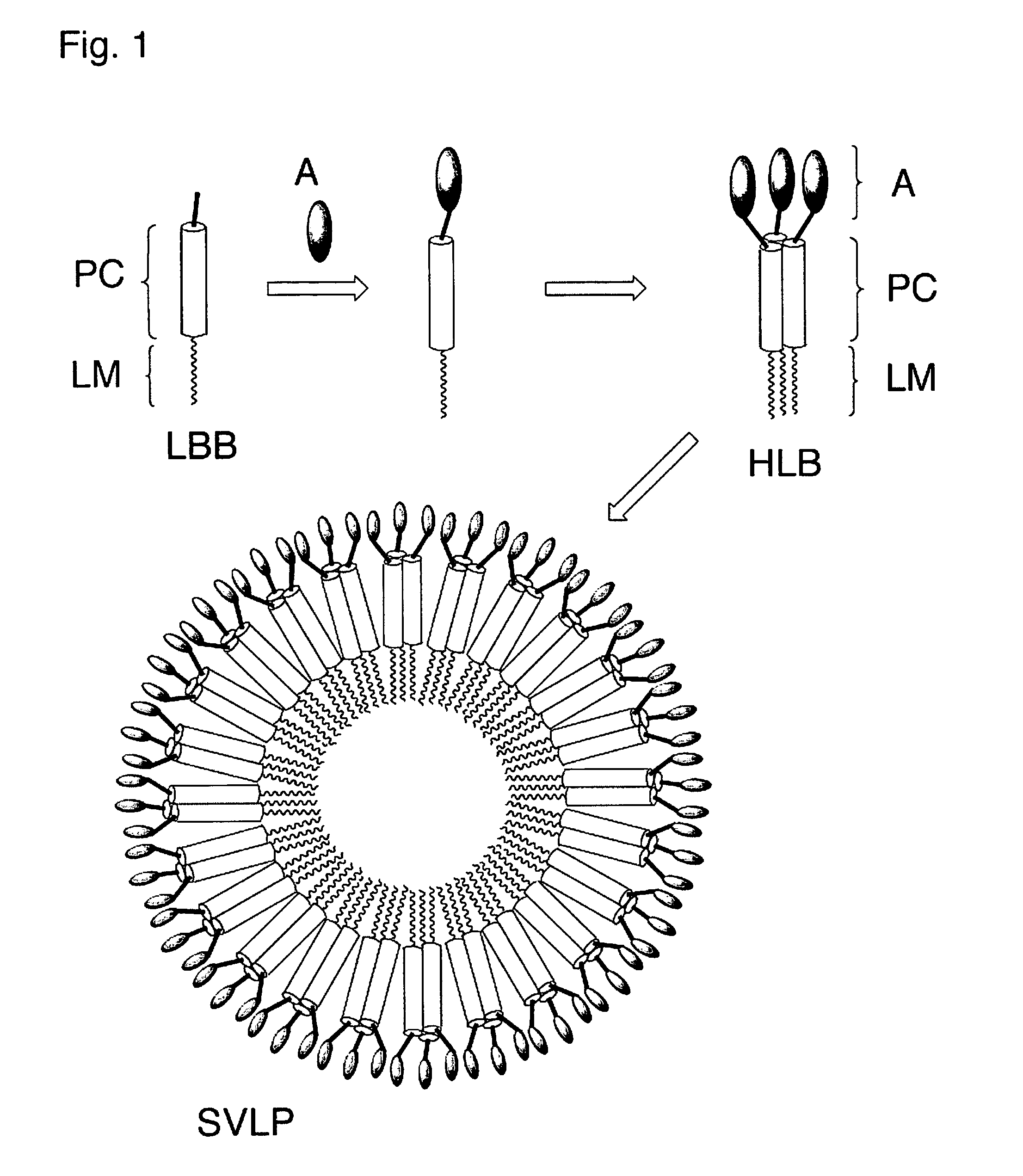
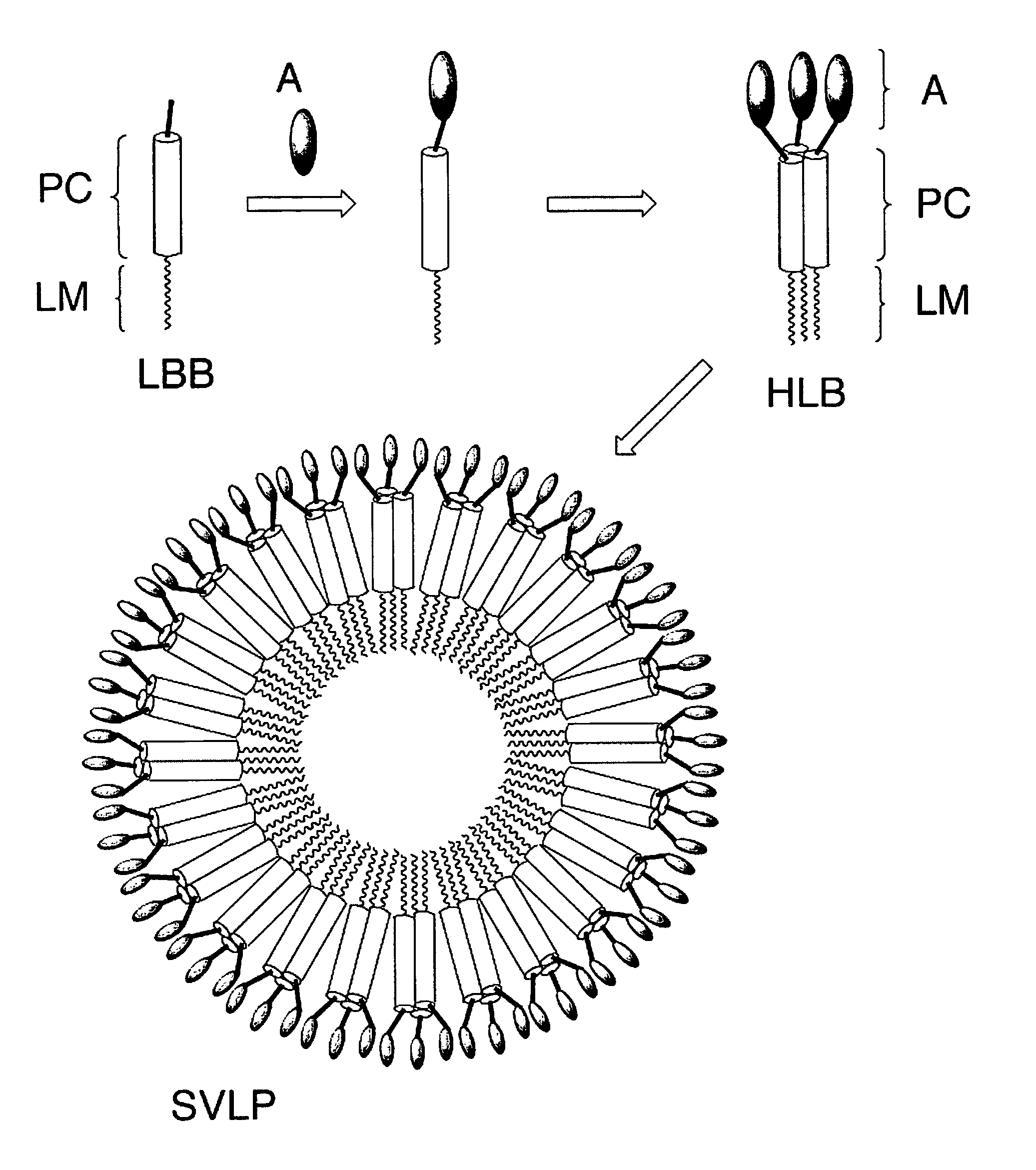
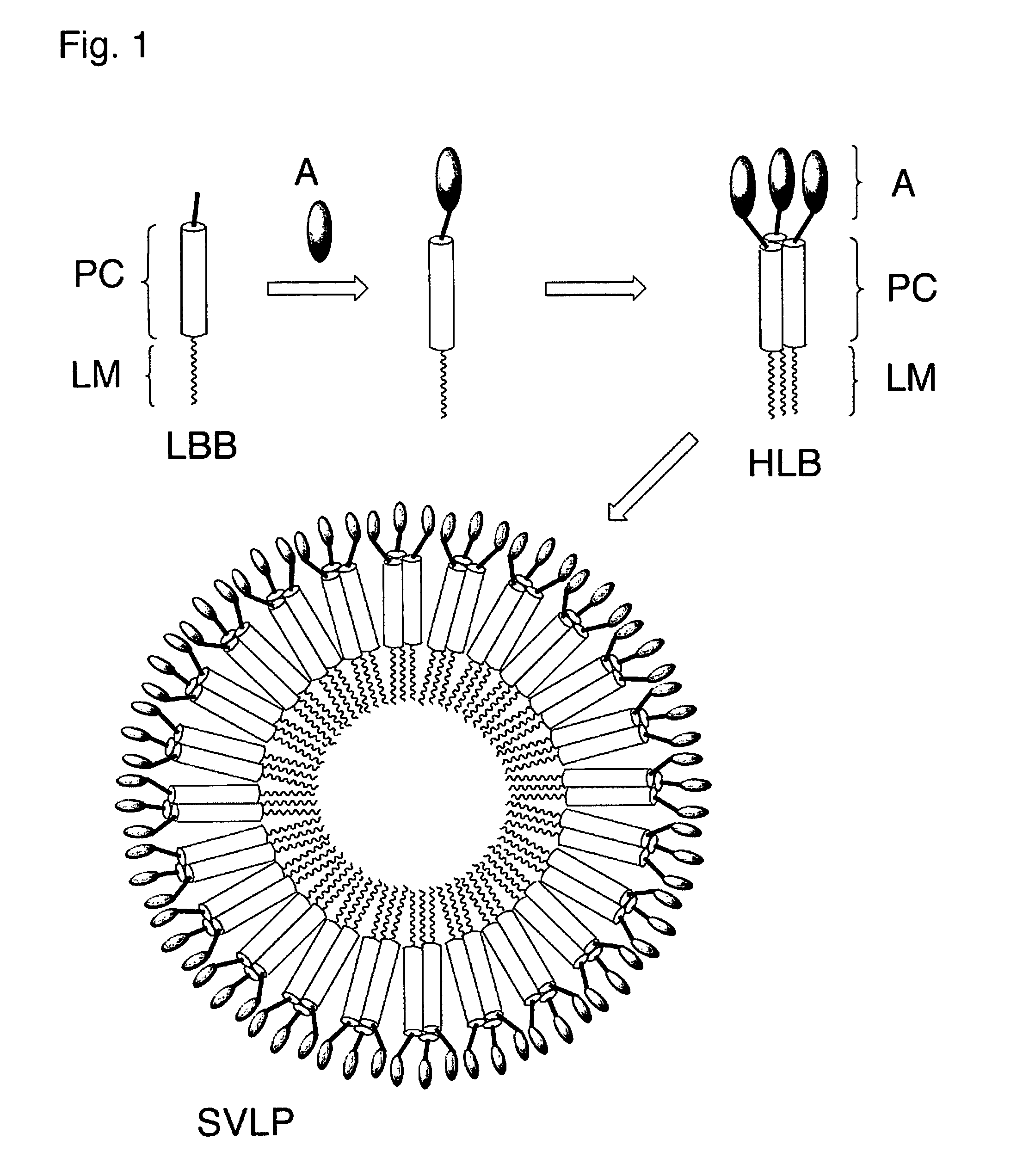
Coiled-coil lipopeptide helical bundles and synthetic virus-like particles
ActiveUS20100015173A1Efficient inductionVirus peptidesSaccharide peptide ingredientsChemical synthesisCoiled coil
The invention relates to lipopeptide building blocks consisting of a peptide chain comprising a coiled-coil domain, linked covalently to a lipid moiety comprising long alkyl or alkenyl chains, and optionally linked to an antigen; and to helical lipopeptide bundles and synthetic virus-like particles formed by aggregation. The nanometer size and shape of these bundles and particles, their stability under aqueous physiological conditions, their chemical composition, the possibility to incorporate B- and T-cell epitopes, and their production by chemical synthesis, make them highly suitable as vaccine delivery vehicles.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
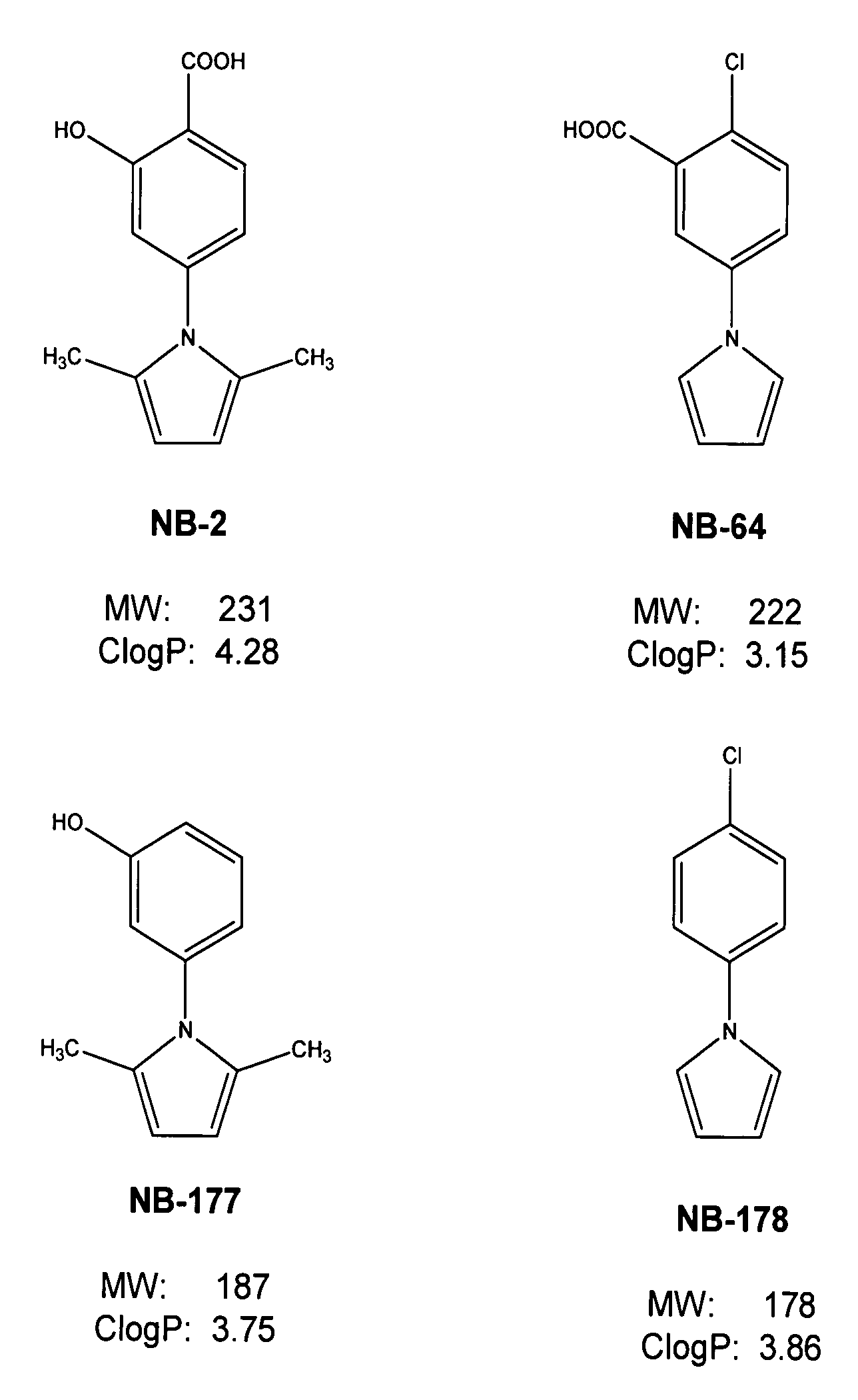
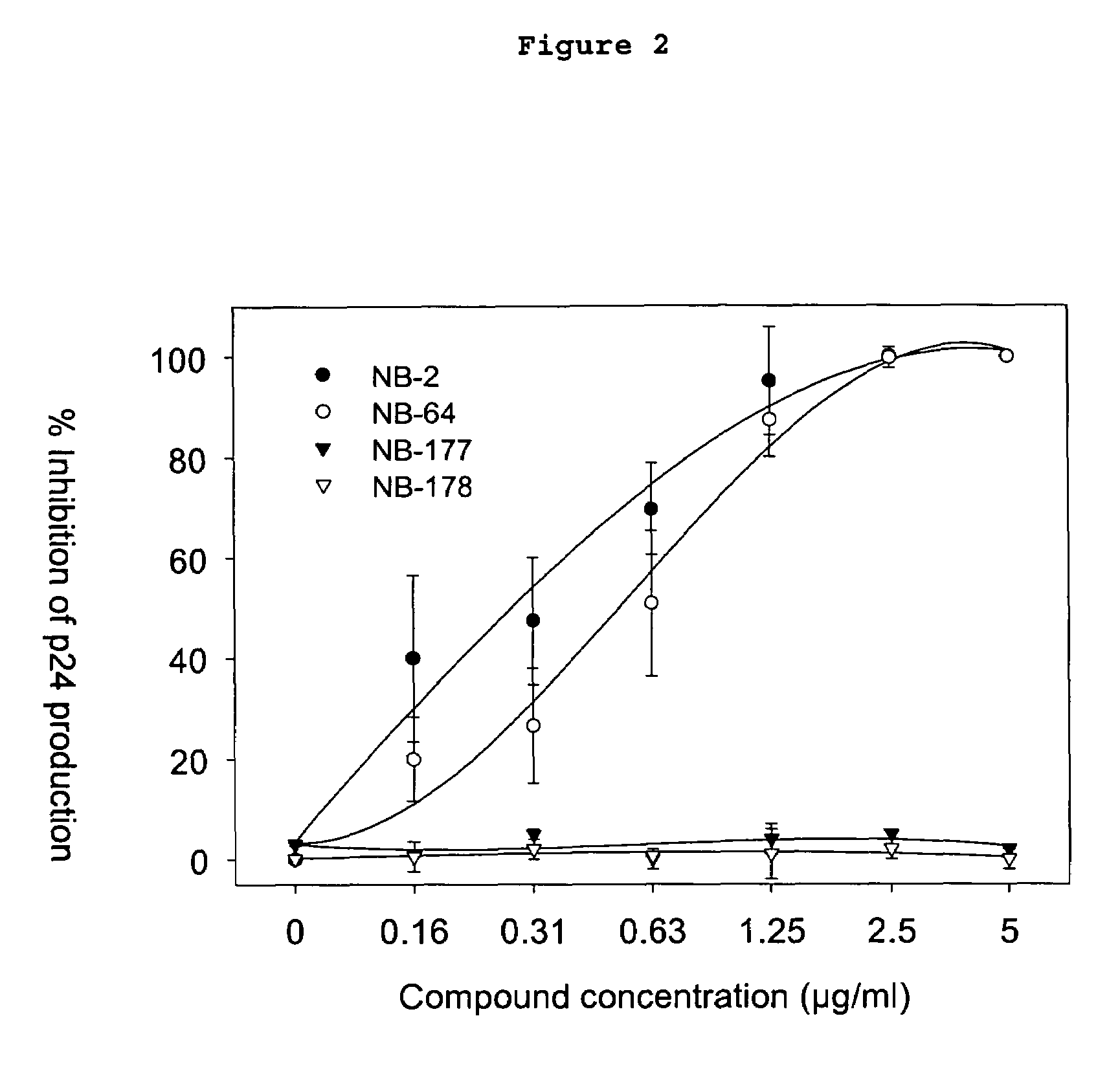
Compounds for inhibition of HIV infection by blocking HIV entry
ActiveUS7241803B2Potent anti-HIV activityInhibit HIV replicationBiocideOrganic chemistryFluorescenceCoiled coil
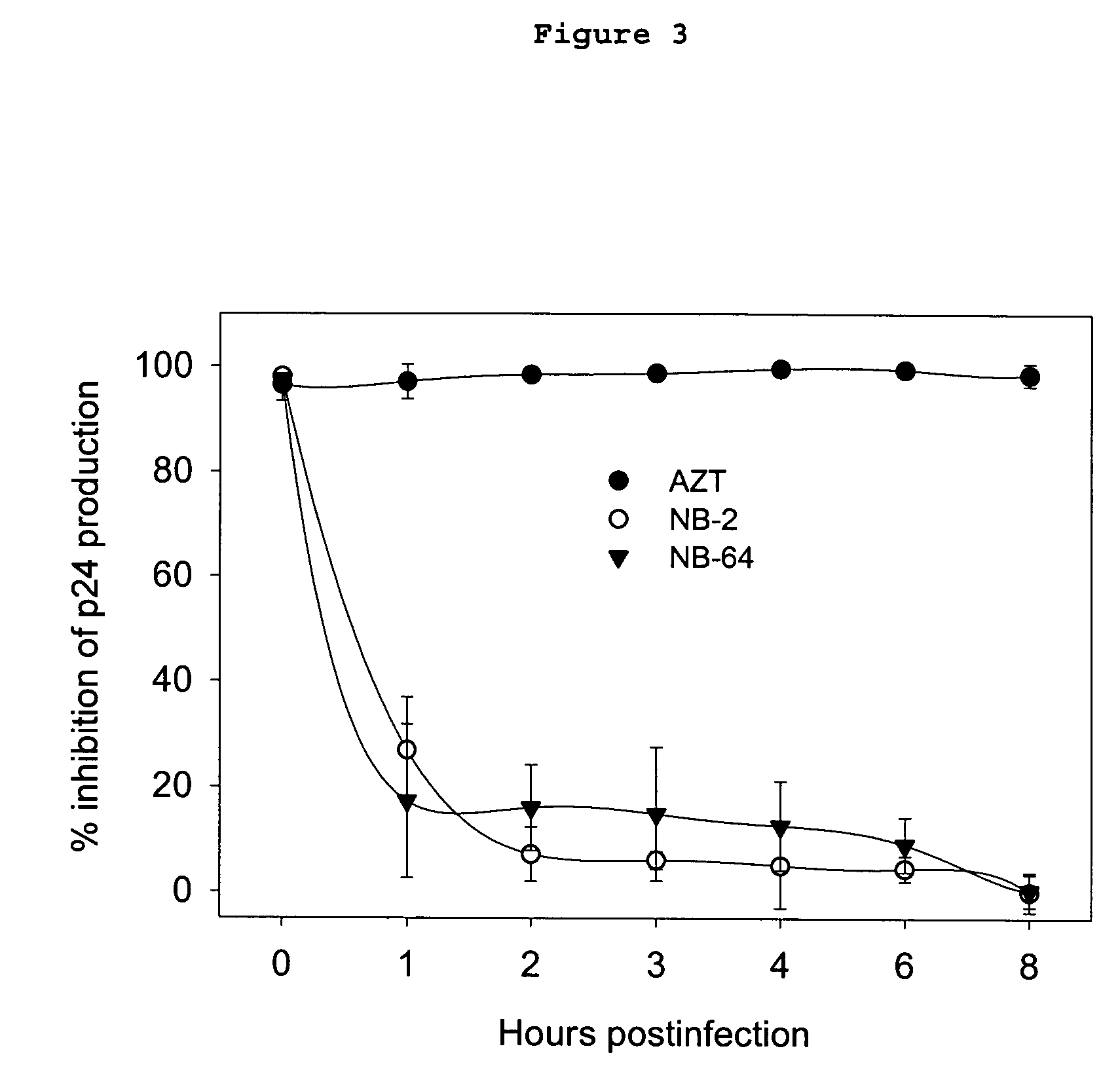
A group of compounds that inhibit HIV replication by blocking HIV entry was identified. Two representative compounds, designated NB-2 and NB-64, inhibited HIV replication (p24 production) with IC50 values <0.5 μg / ml. It was proved that NB-2 and NB-64 are HIV entry inhibitors by targeting the HIV gp41 since: 1) they inhibited HIV-mediated cell fusion; 2) they inhibited HIV replication only when they were added to the cells less than one hour after virus addition; 3) they did not block the gp120-CD4 binding; 4) they did not interact with the coreceptor CXCR4 since they failed to block anti-CXCR4 antibody binding to CXCR4-expressing cells; 5) they blocked the formation of the gp41 core that is detected by sandwich enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using a conformation-specific MAb NC-1; 6) they inhibited the formation of the gp41 six-helix bundle revealed by fluorescence native-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (FN-PAGE); and 7) they blocked binding of D-peptide to the hydrophobic cavity within gp41 coiled coil domain, modeled by peptide IQN17. These results suggested that NB-2 and NB-64 may interact with the hydrophobic cavity and block the formation of the fusion-active gp41 coiled coil domain, resulting in inhibition of HIV-1 mediated membrane fusion and virus entry.
Owner:NEW YORK BLOOD CENT
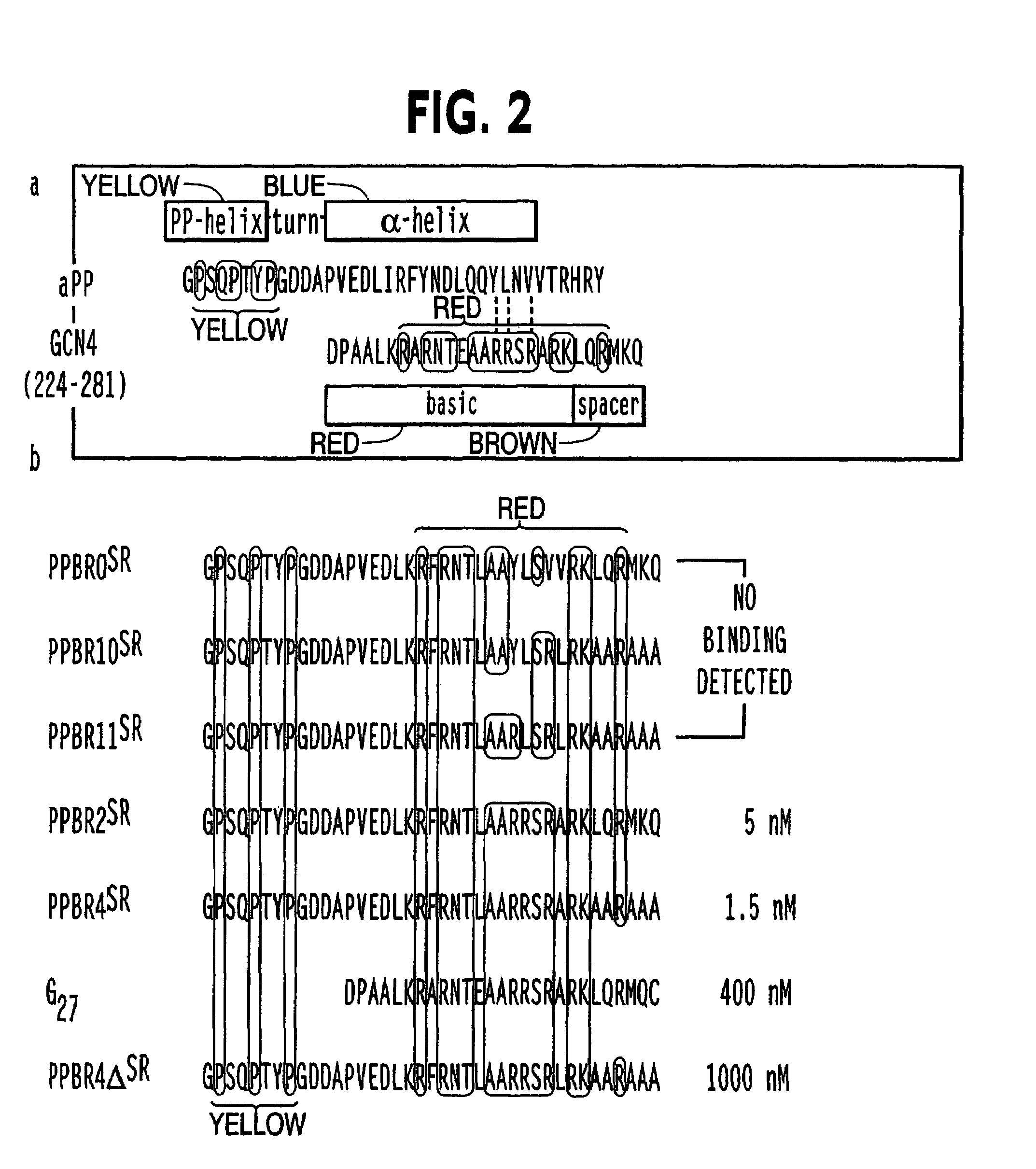
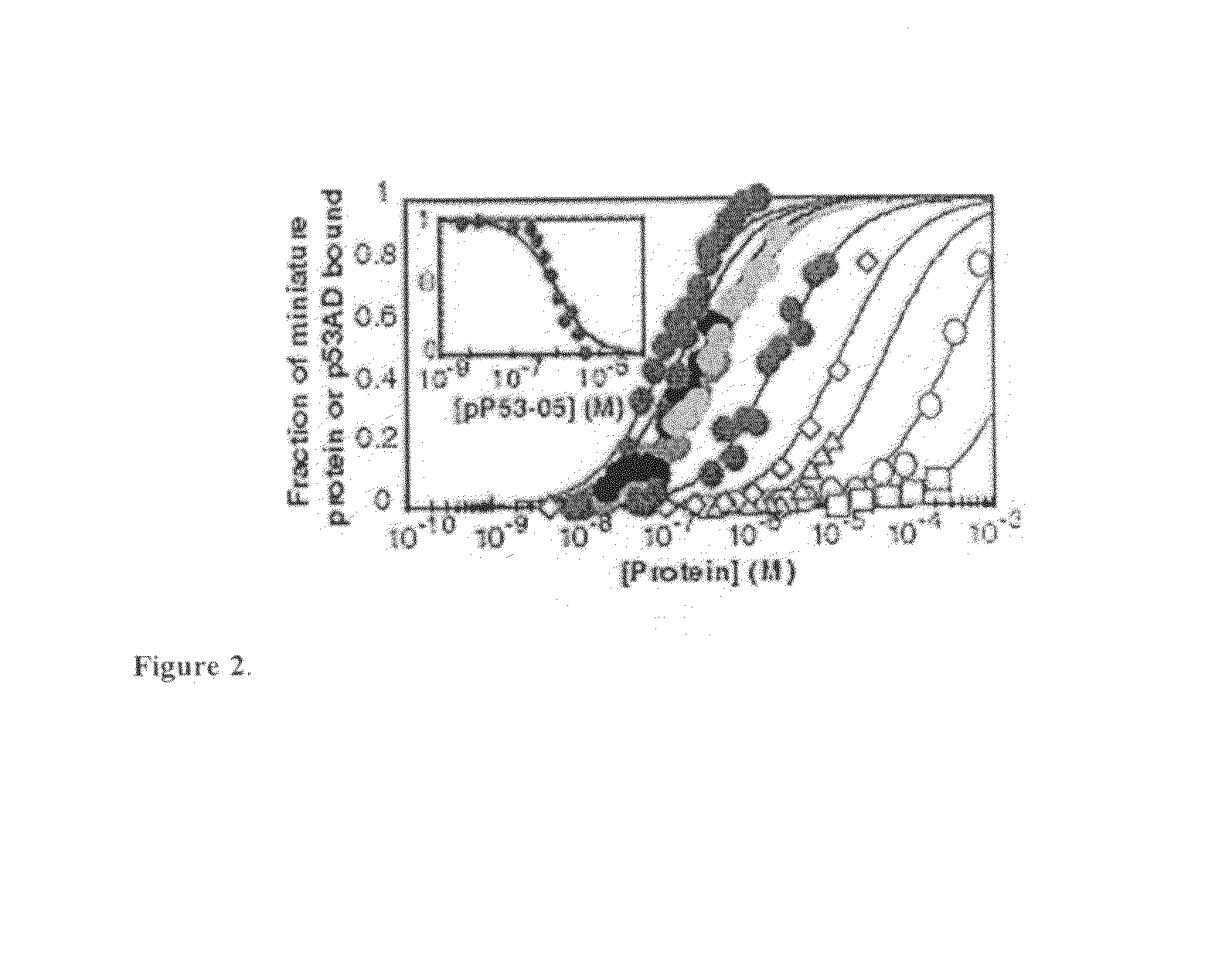
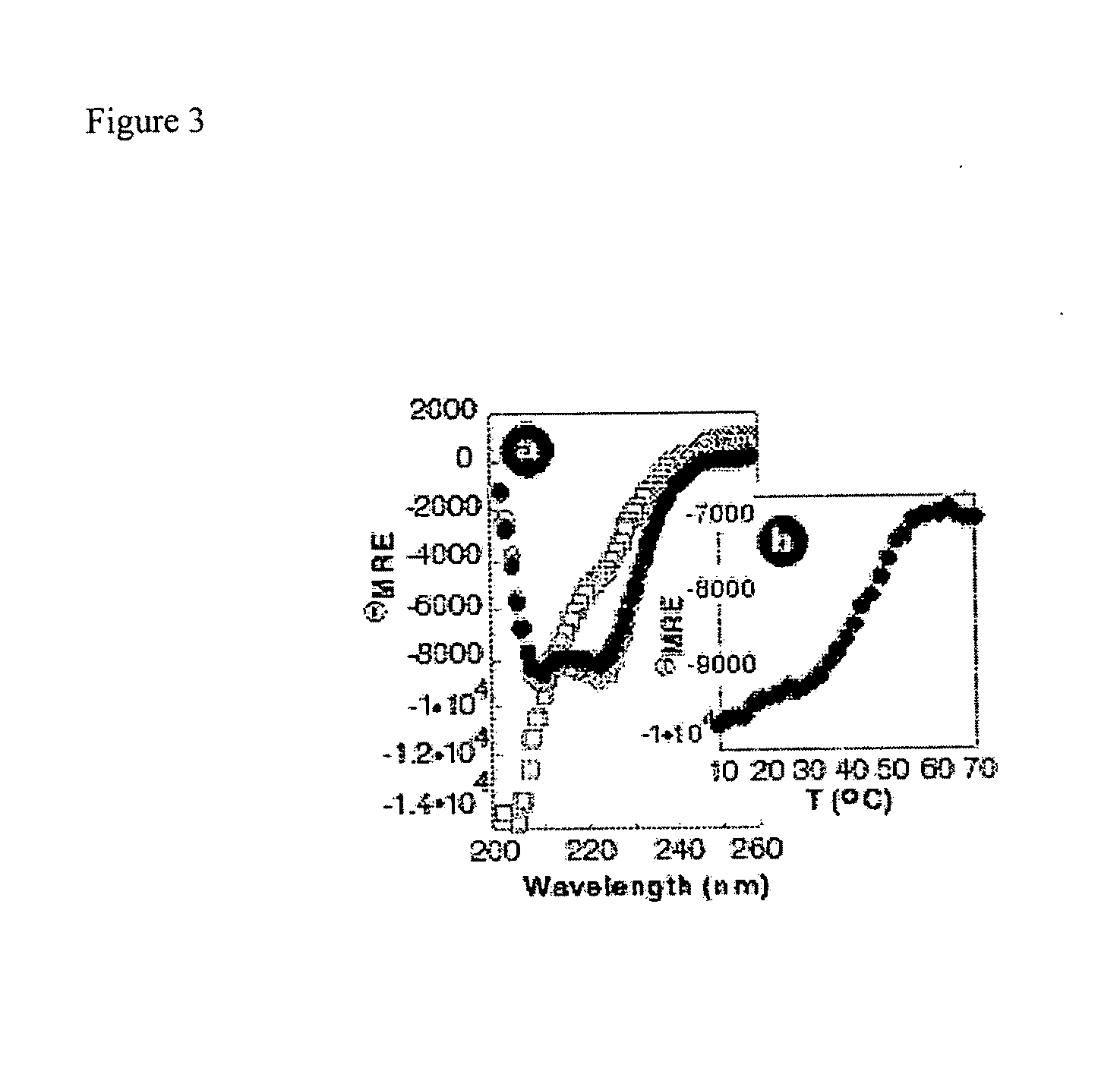
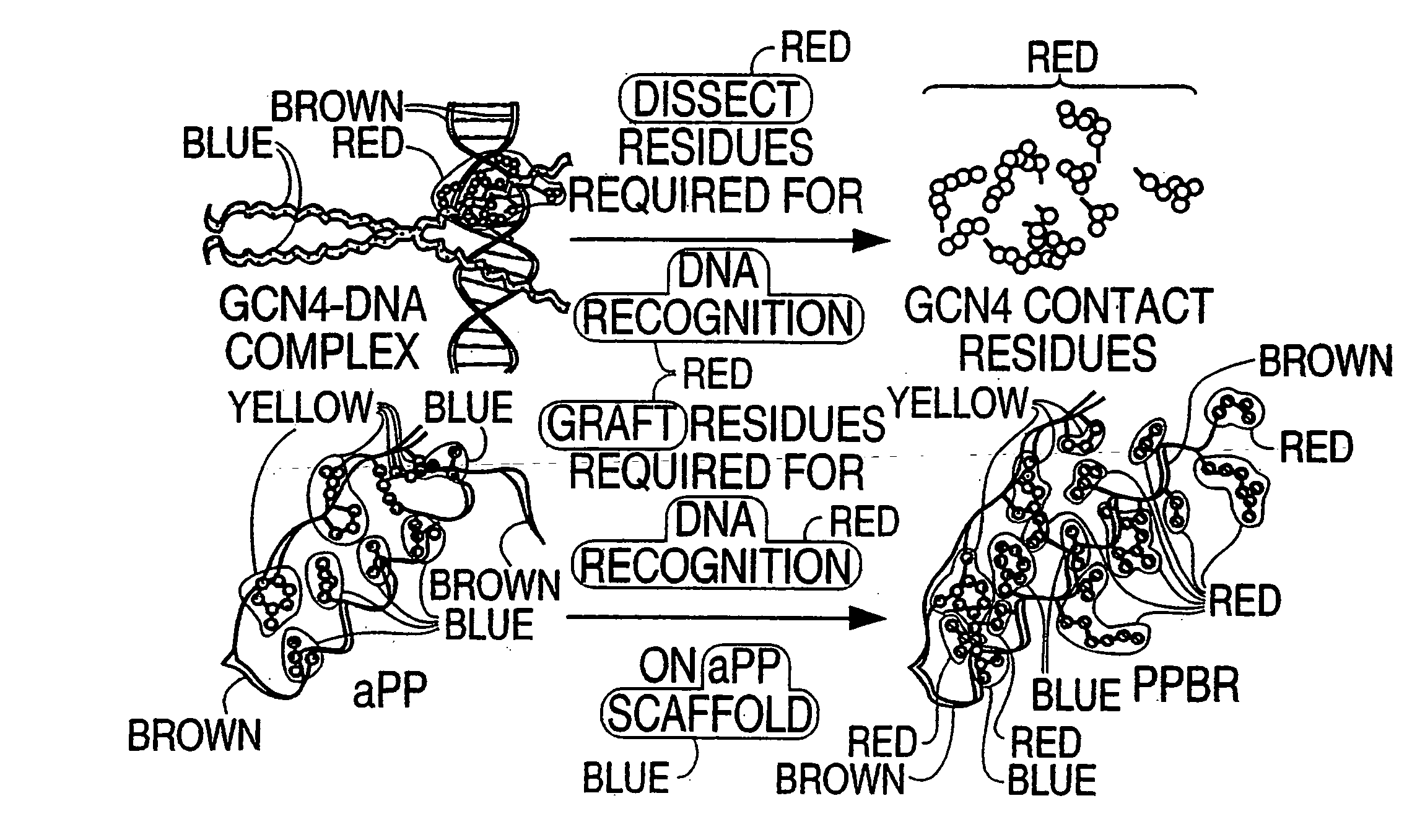
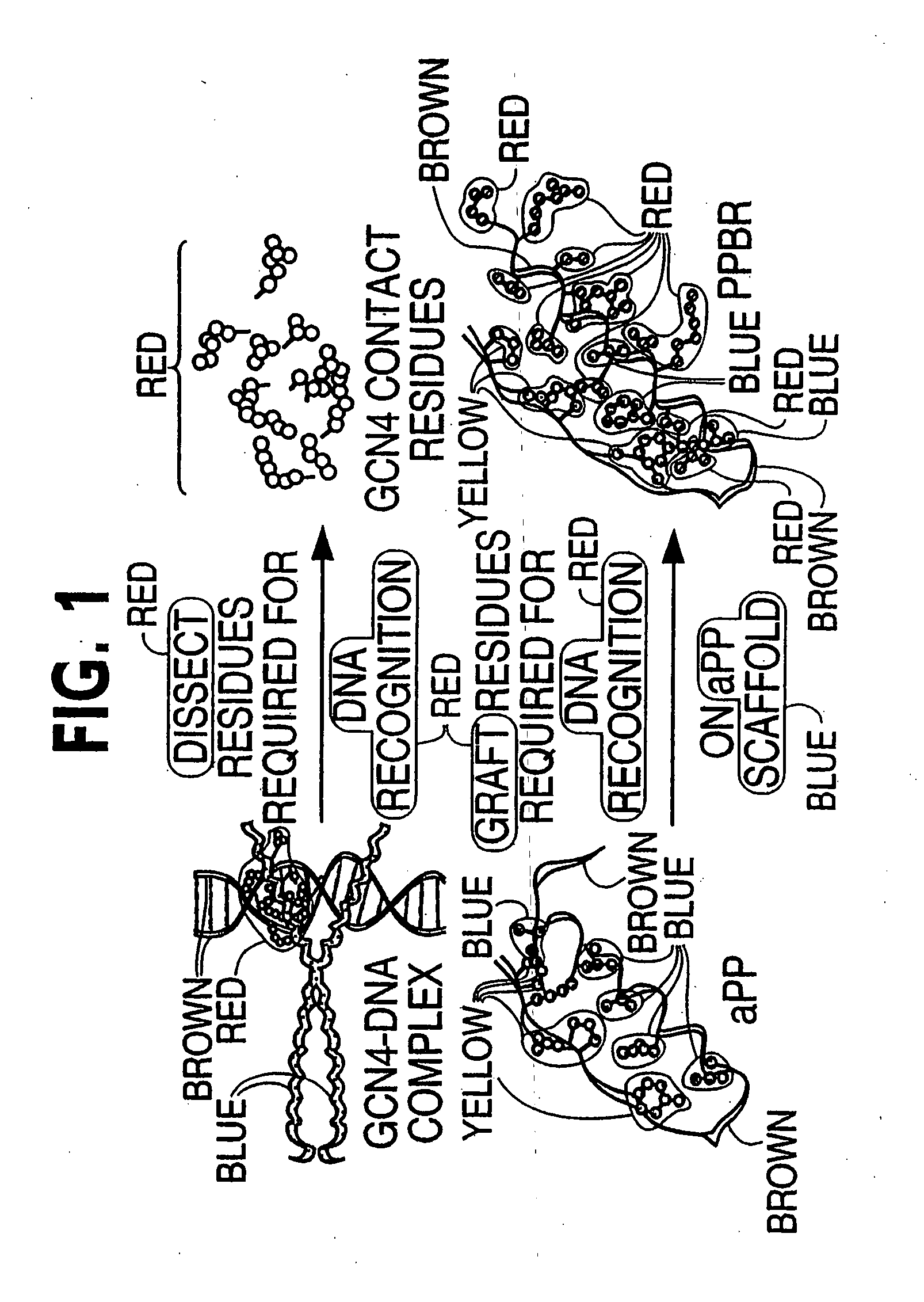
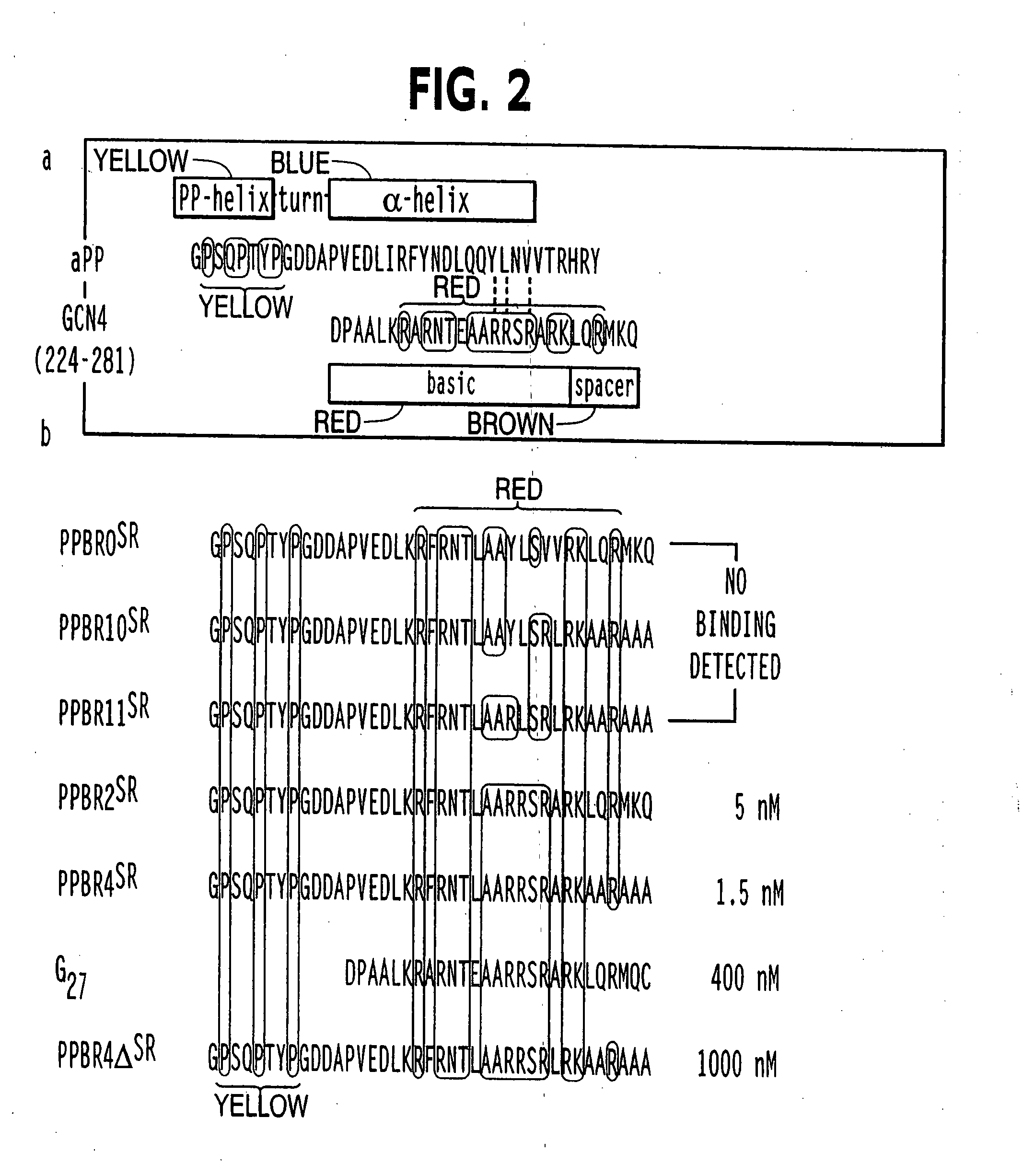
Modified avian pancreatic polypeptide miniature binding proteins
The present invention provides a protein scaffold, such as an avian pancreatic polypeptide, that can be modified by substitution of two or more amino acid residues that are exposed on the alpha helix domain of the polypeptide when the polypeptide is in a tertiary form.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Multi-domain amphipathic helical peptides and methods of their use
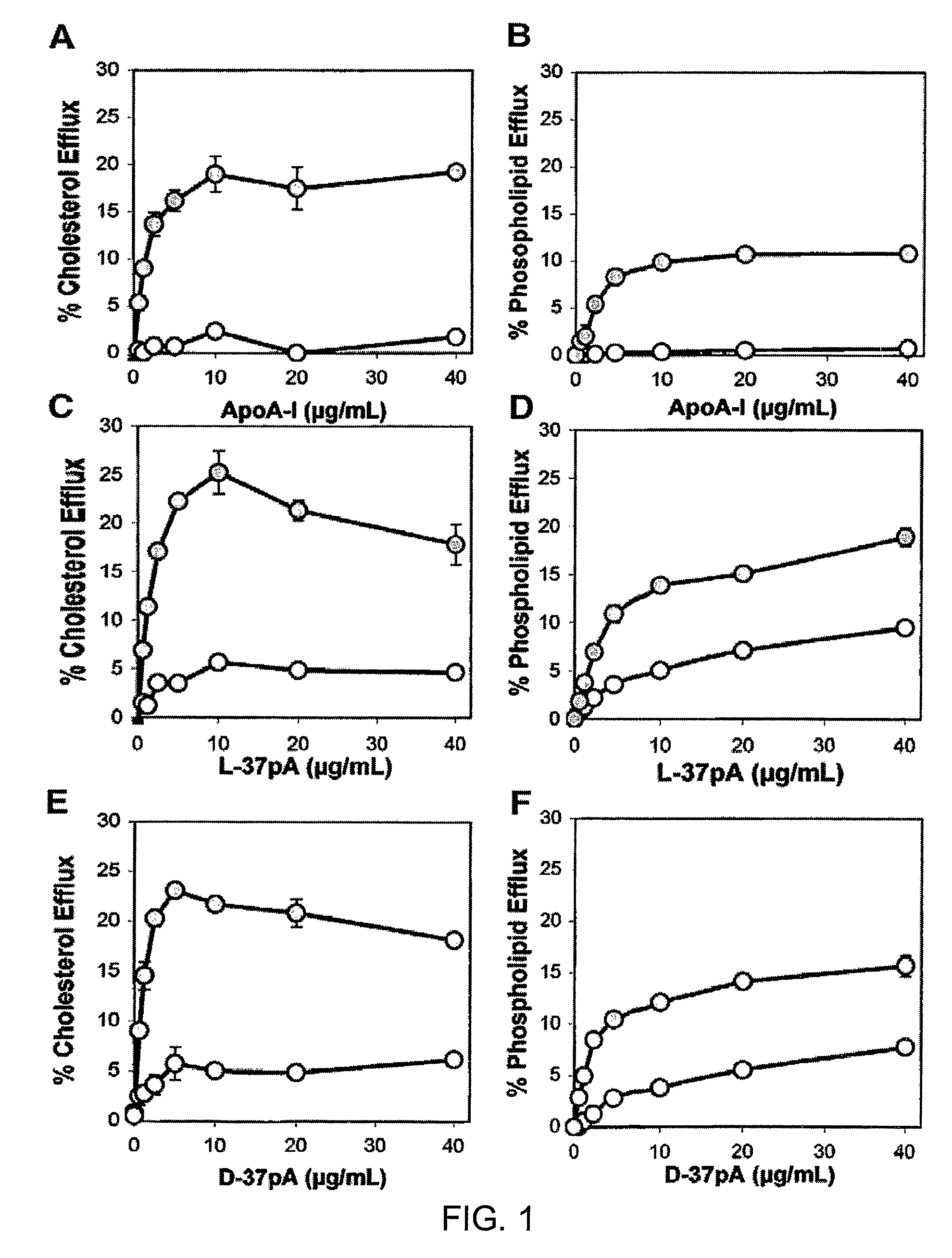
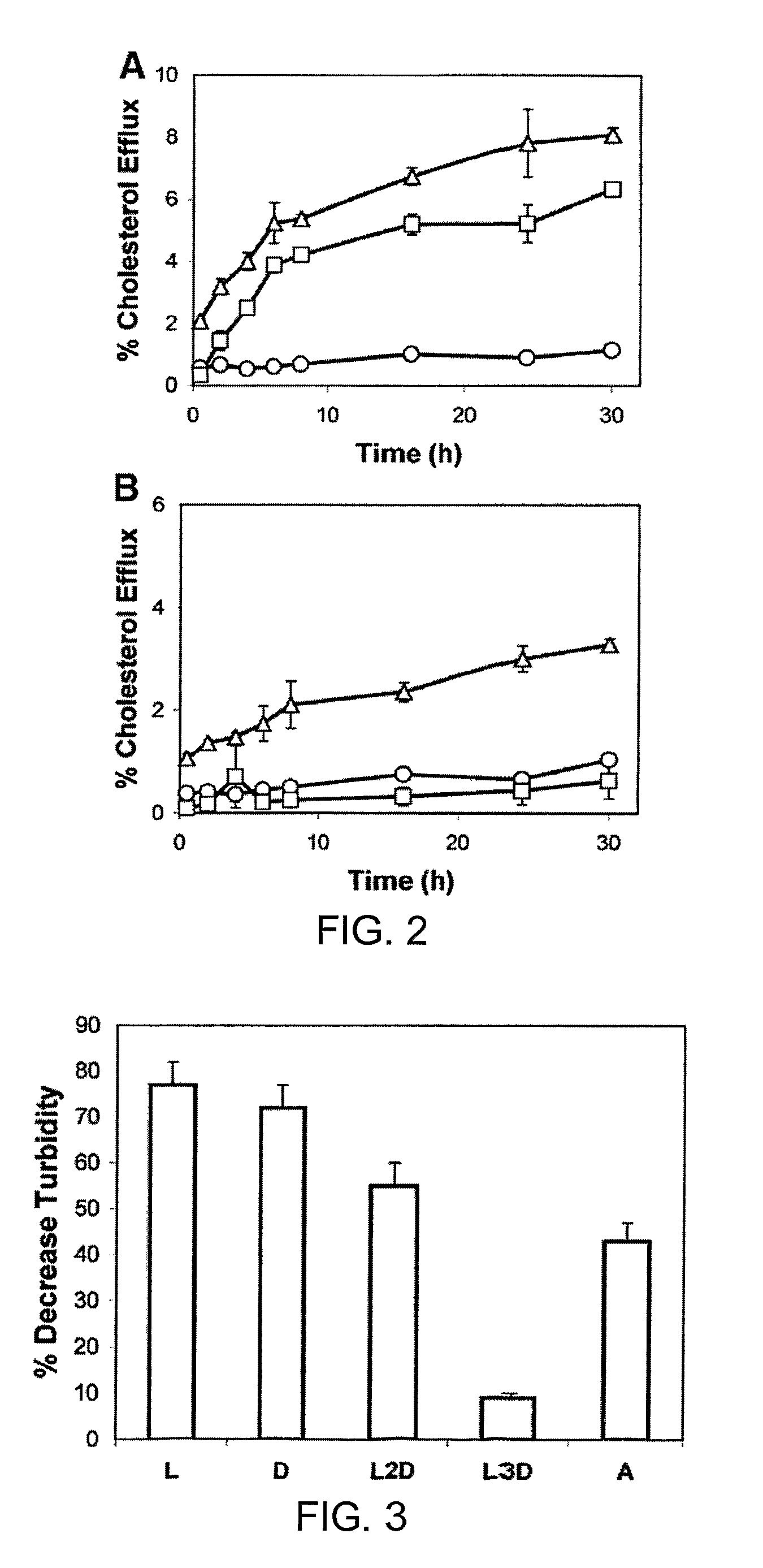
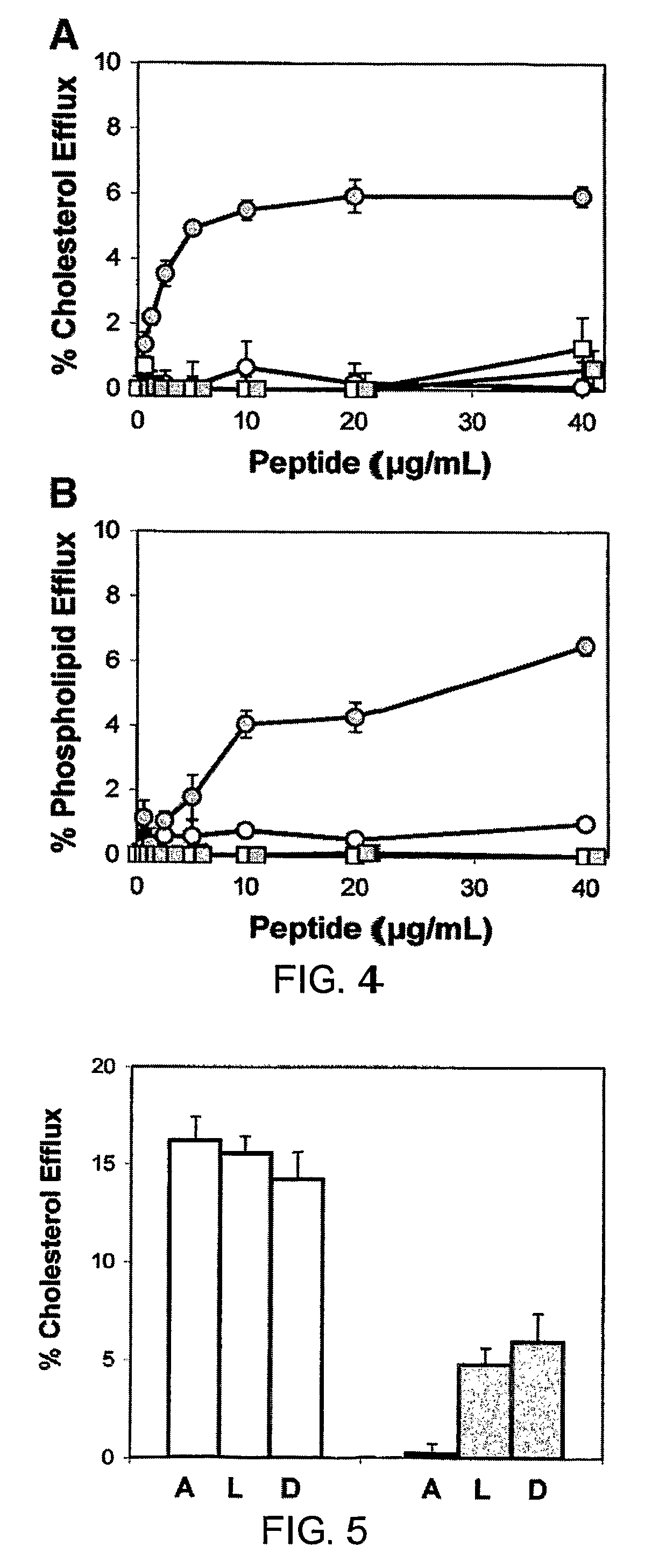
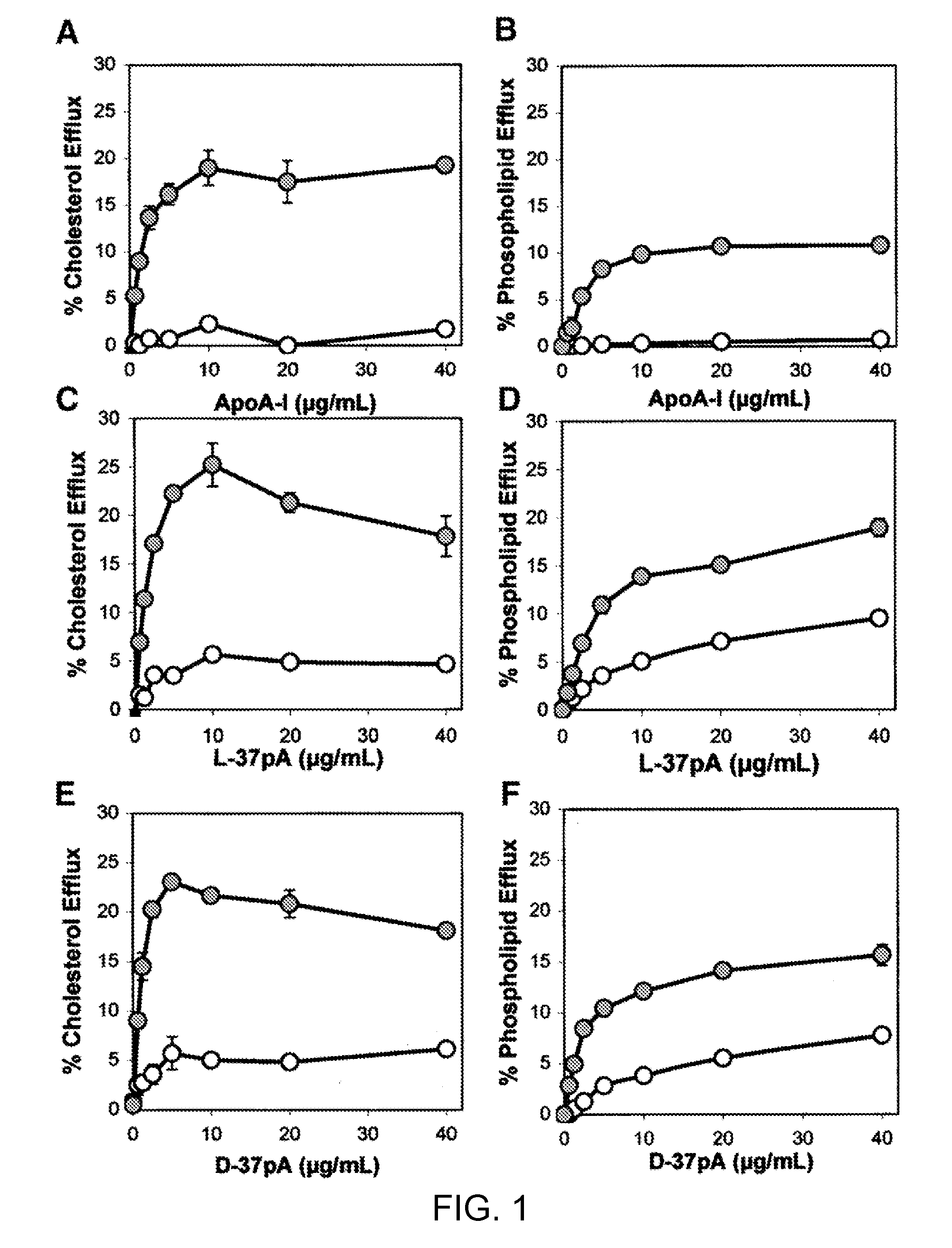
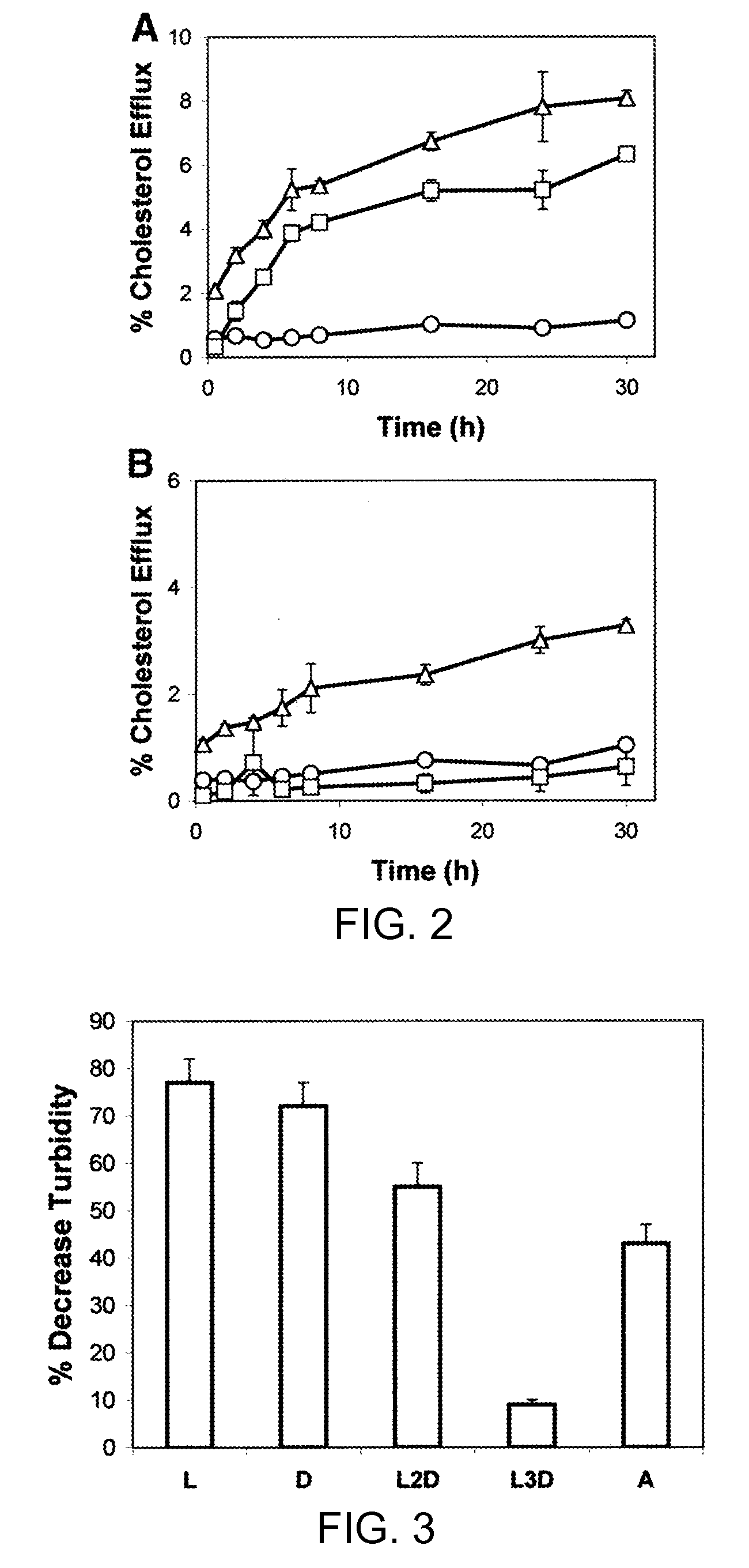
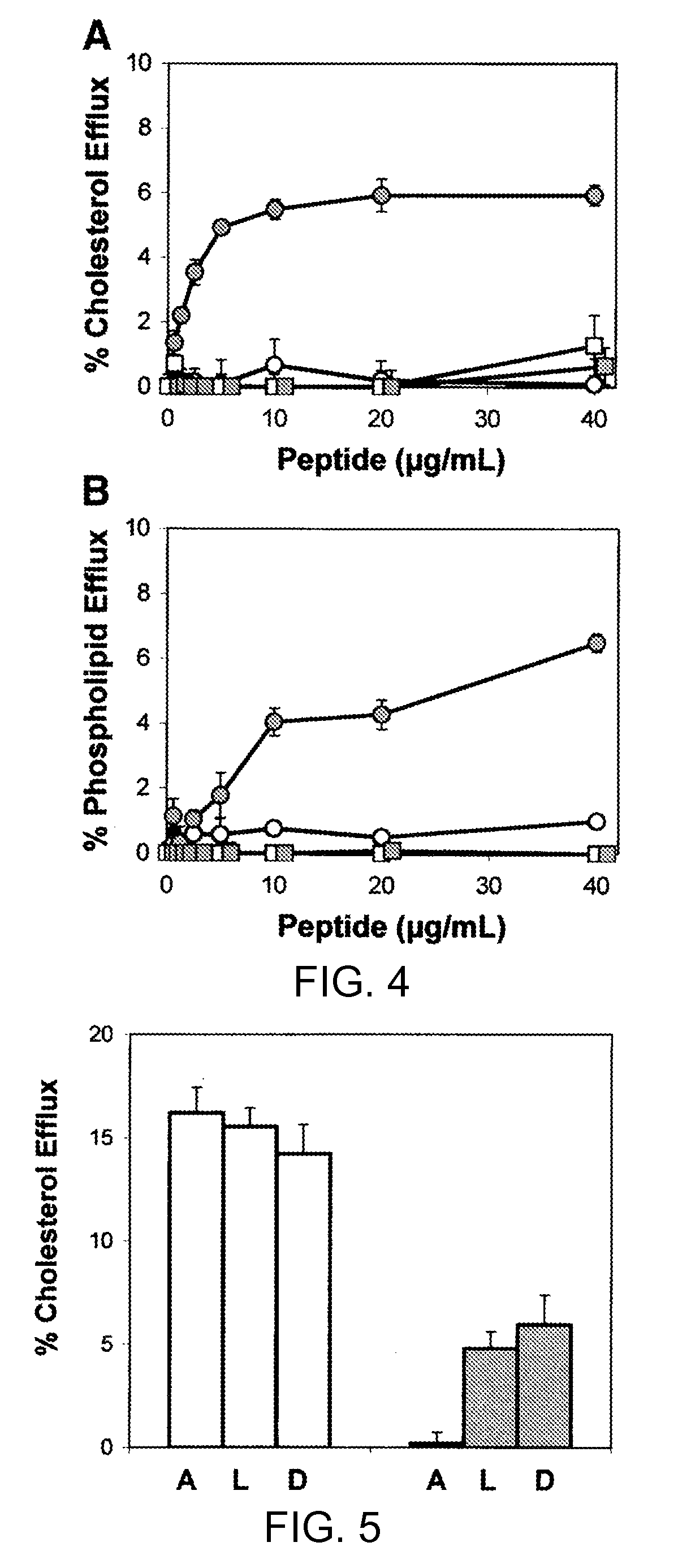
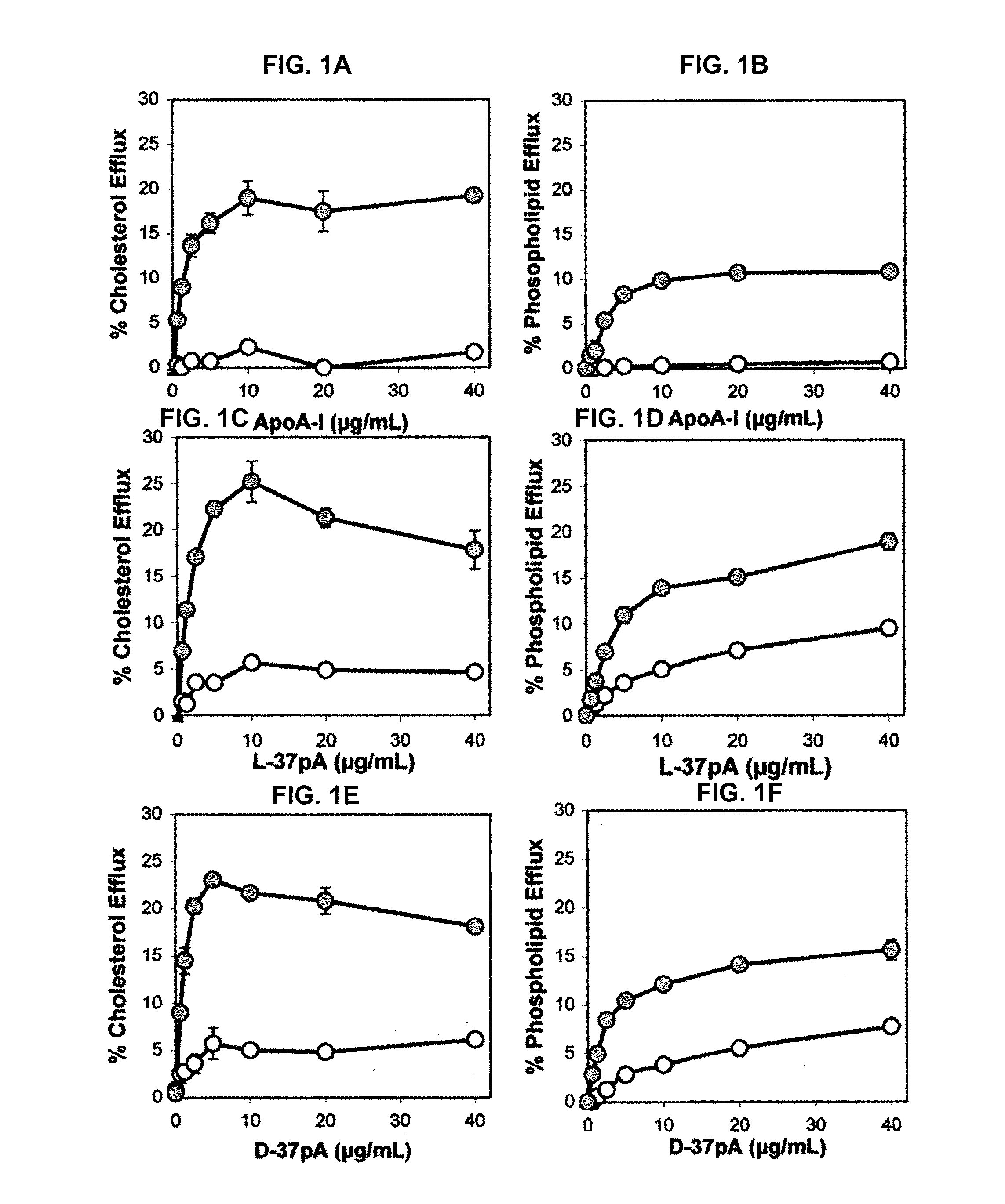
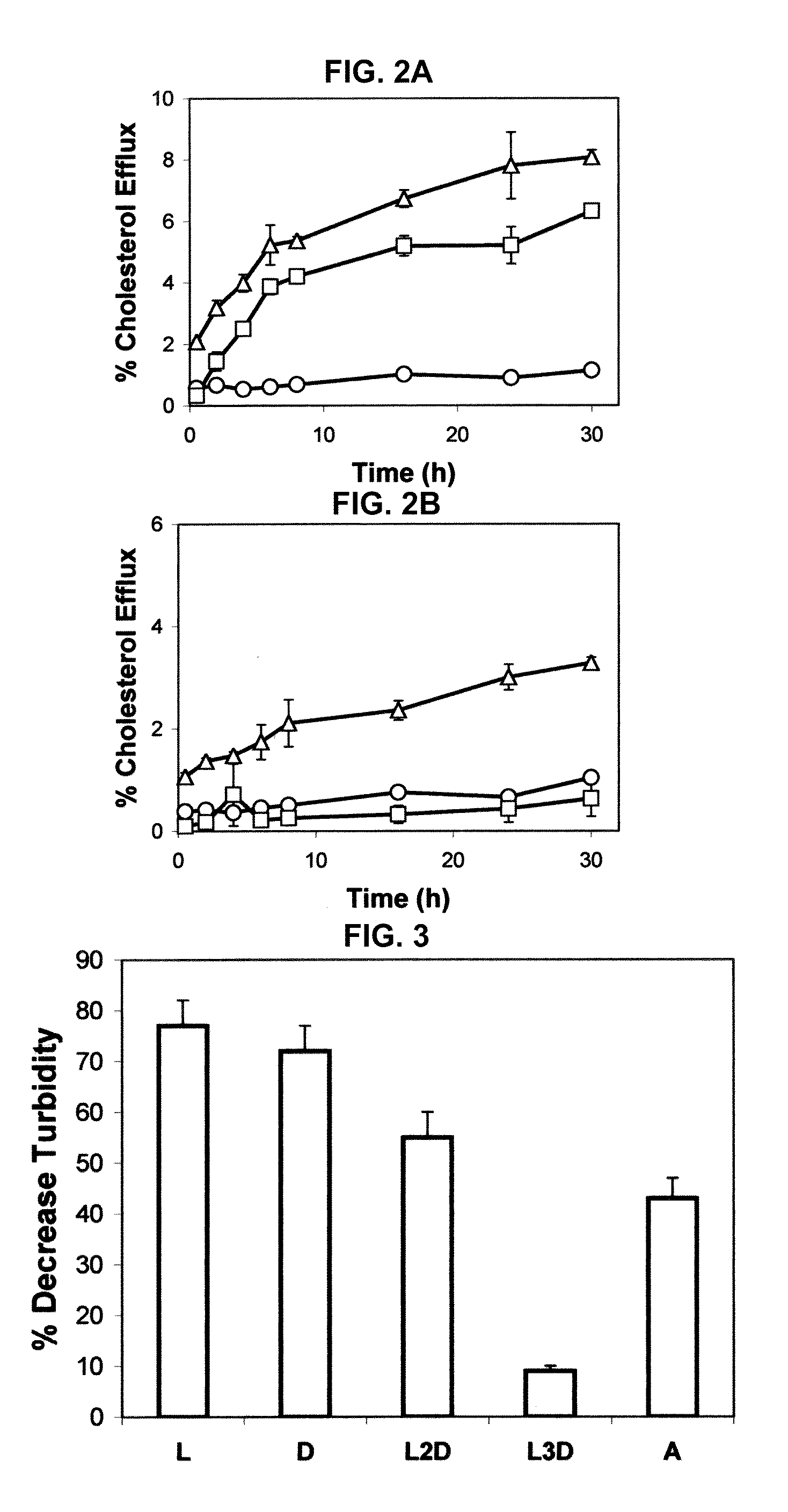
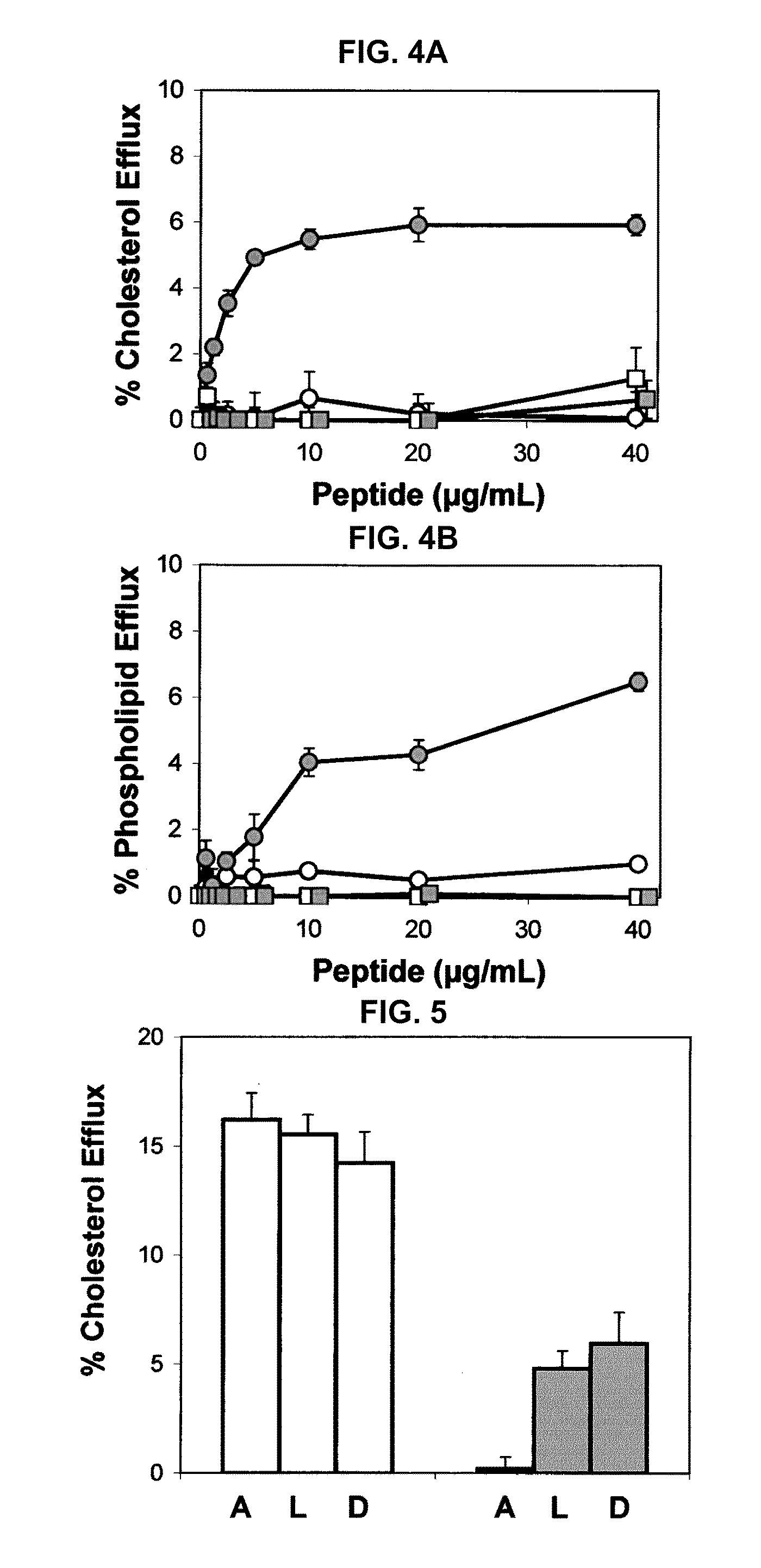
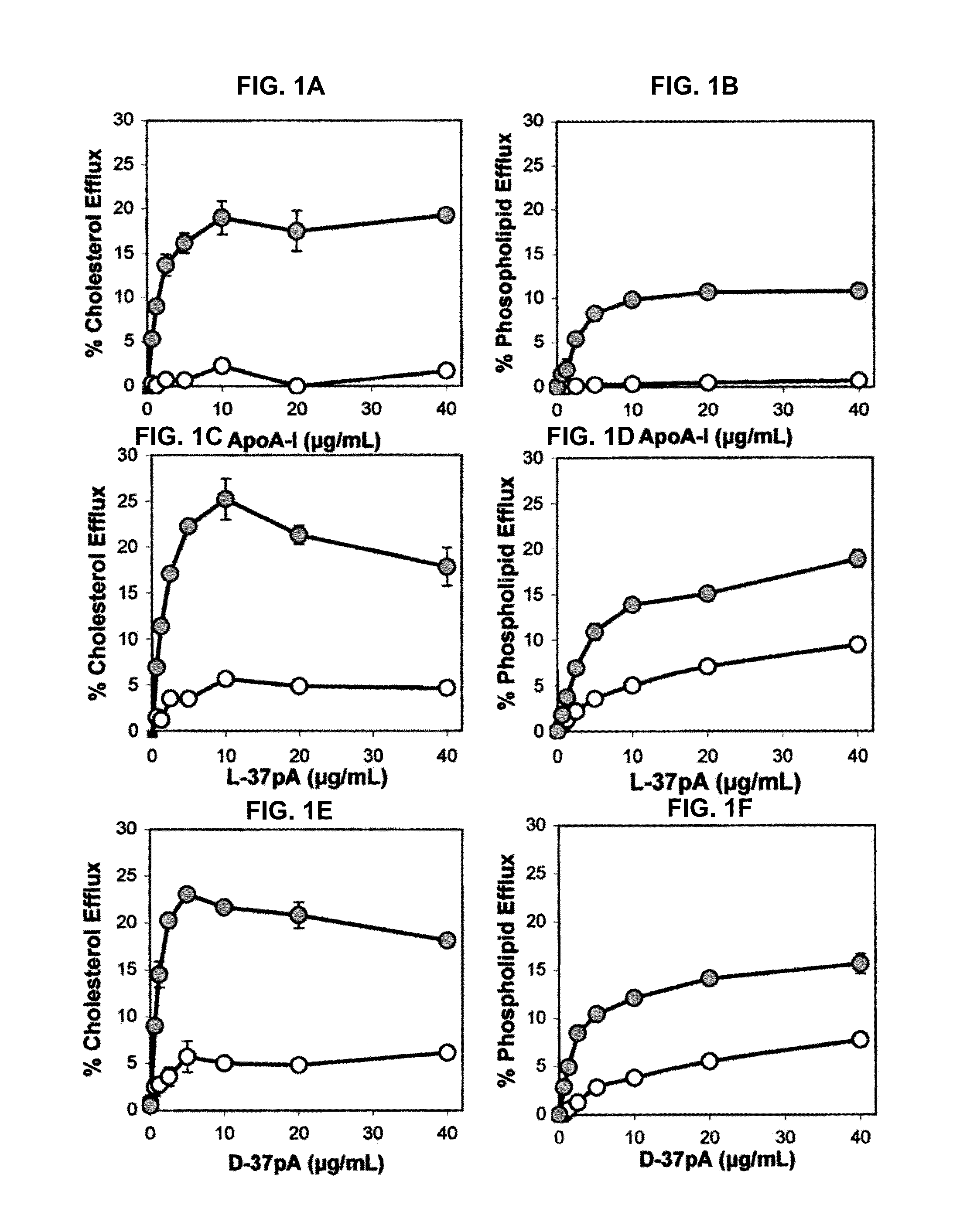
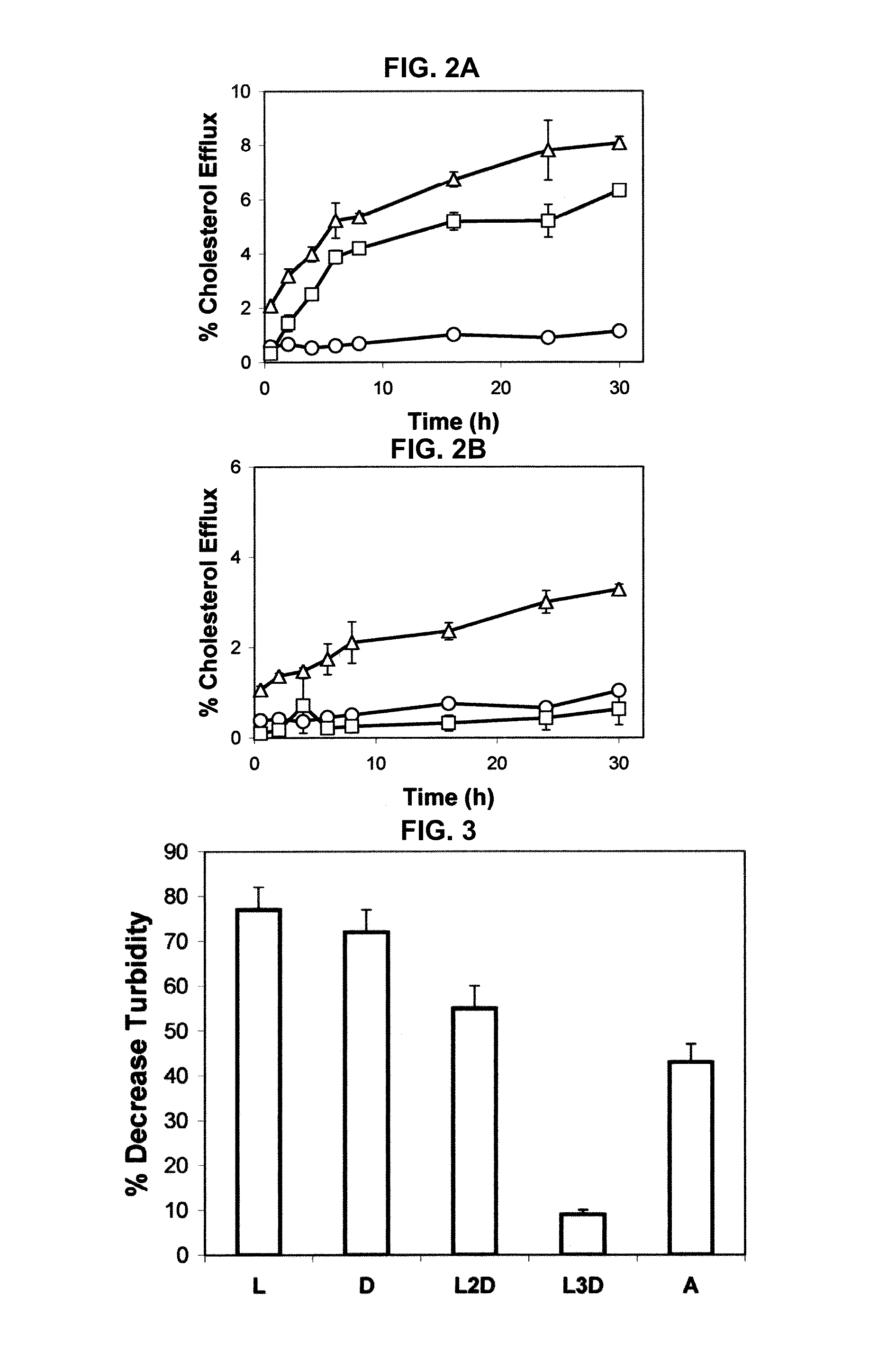
Disclosed herein are peptides or peptide analogs with multiple amphipathic α-helical domains that promote lipid efflux from cells via an ABCA1-dependent pathway. Also provided herein are methods of using multi-domain amphipathic α-helical peptides or peptide analogs to treat or inhibit dyslipidemic disorders. Methods for identifying non-cytotoxic peptides that promote ABCA1-dependent lipid efflux from cells are also disclosed herein.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
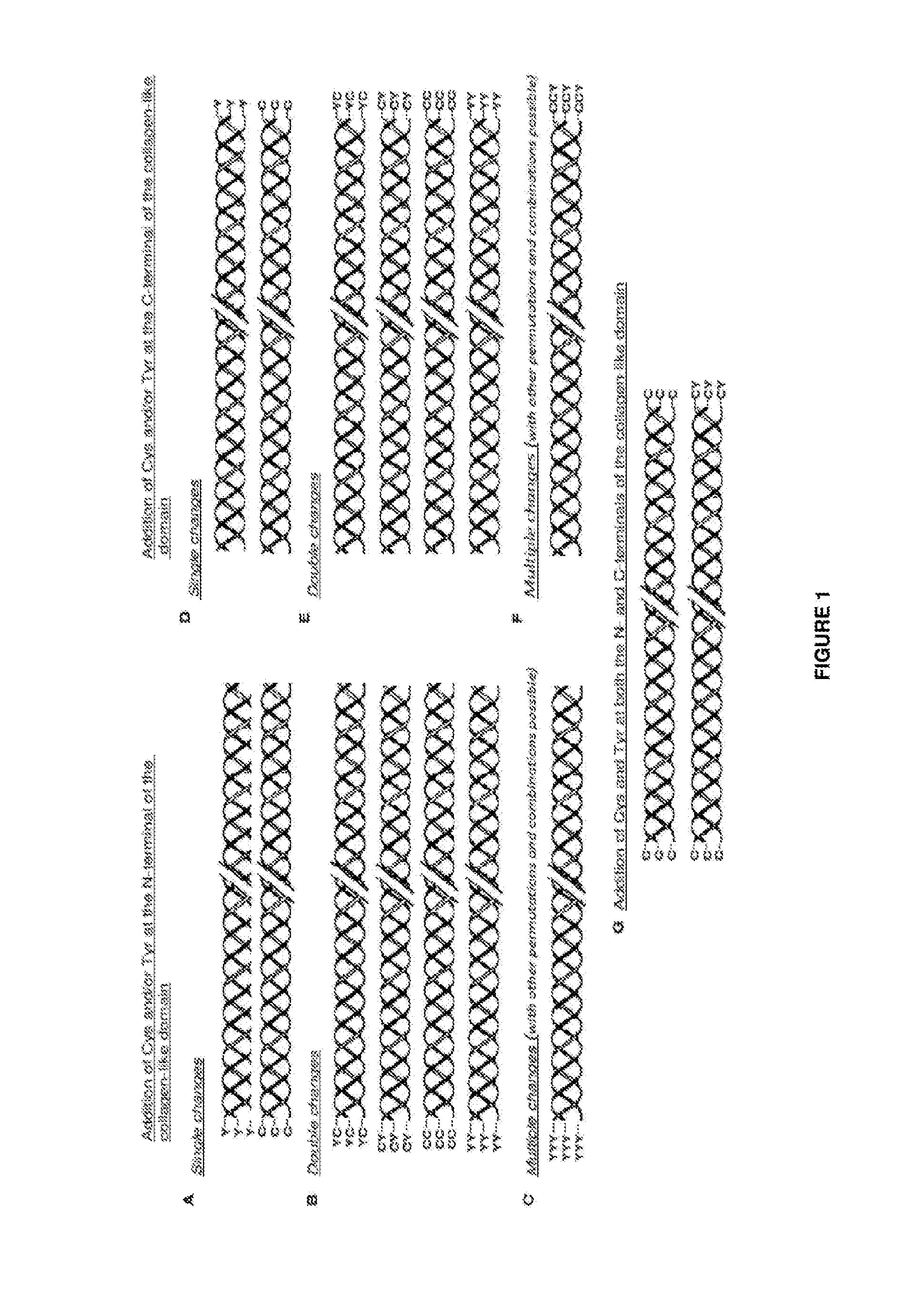
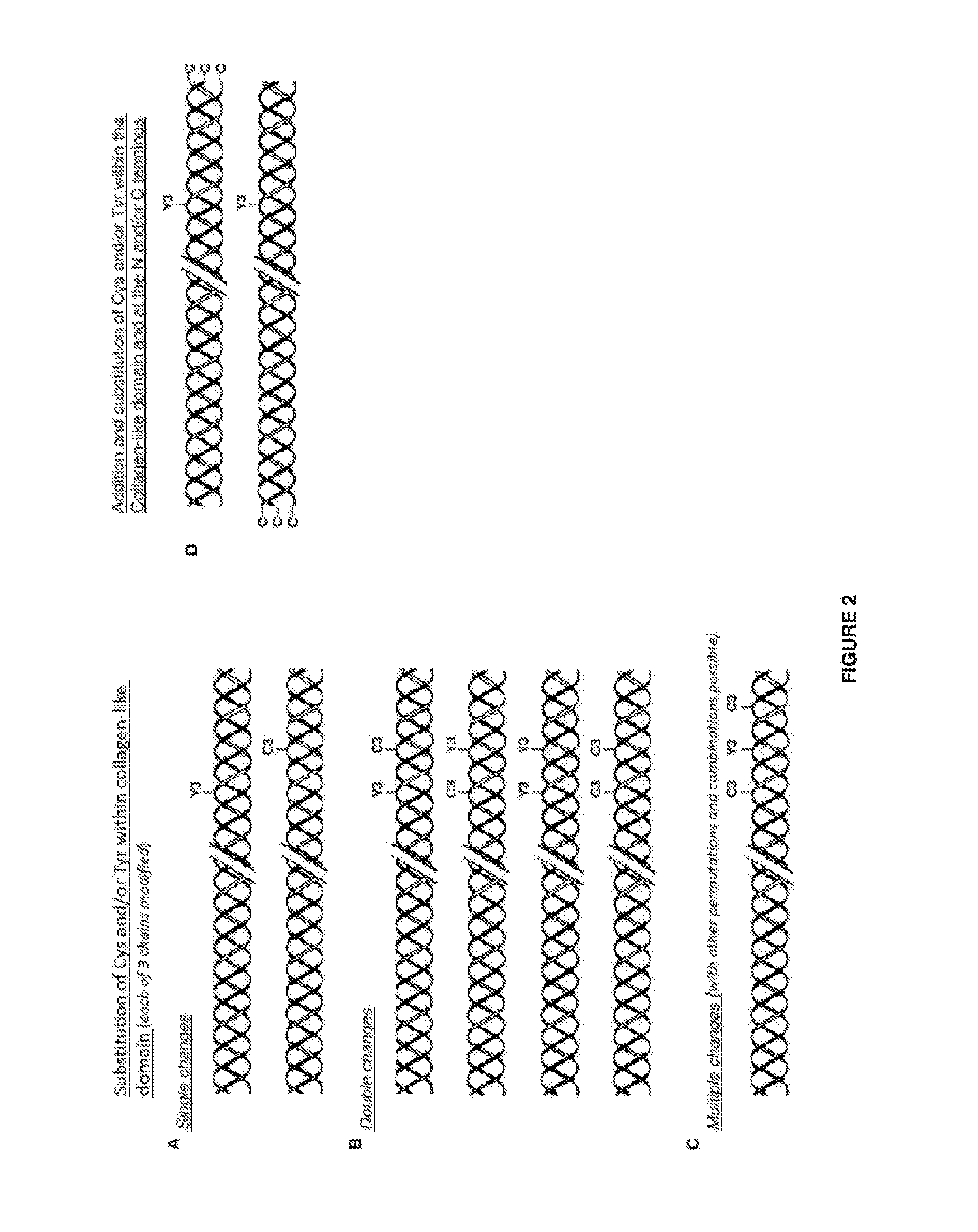
Modified bacterial collagen-like proteins
ActiveUS10155793B2Easy to oxidizeFacilitate cross-linkingCosmetic preparationsConnective tissue peptidesBiotechnologyBacteroides
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Core structure of gp41 from the HIV envelope glycoprotein
Described are the crystal structure of the α-helical domain of the gp41 component of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein which represents the core of fusion-active gp41, methods of identifying and designing drugs which inhibit gp41 function and drugs which do so.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Multi-domain amphipathic helical peptides and methods of their use
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
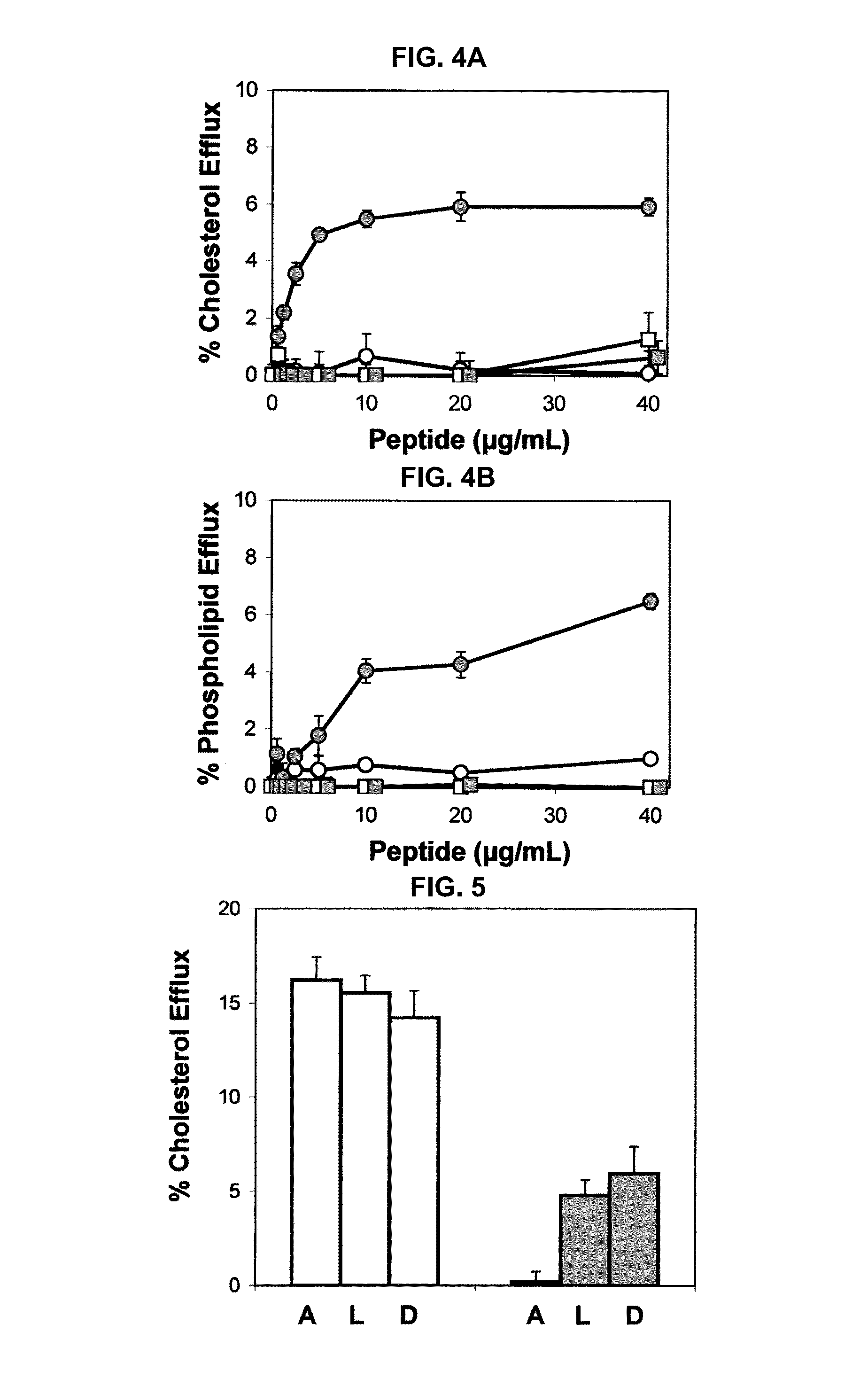
Peptides promoting lipid efflux via abca1 and activating a lipoprotein lipase
ActiveUS20110033518A1Promote lipid effluxImprove lipophilicityOrganic active ingredientsApolipeptidesDiseaseA lipoprotein
Disclosed herein are peptides and peptide analogs with multiple amphipathic α-helical domains that promote lipid efflux from cells via an ABCA1-dependent pathway, as well as peptides that activate lipoprotein lipase, and compositions comprising such peptides or combinations thereof. Also provided herein are methods of using multi-domain amphipathic α-helical peptides or peptide analogs to treat or inhibit dyslipidemic disorders. Methods for identifying non-cytotoxic peptides that promote ABCA1-dependent lipid efflux from cells and activate lipoprotein lipase within cells are also disclosed herein.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
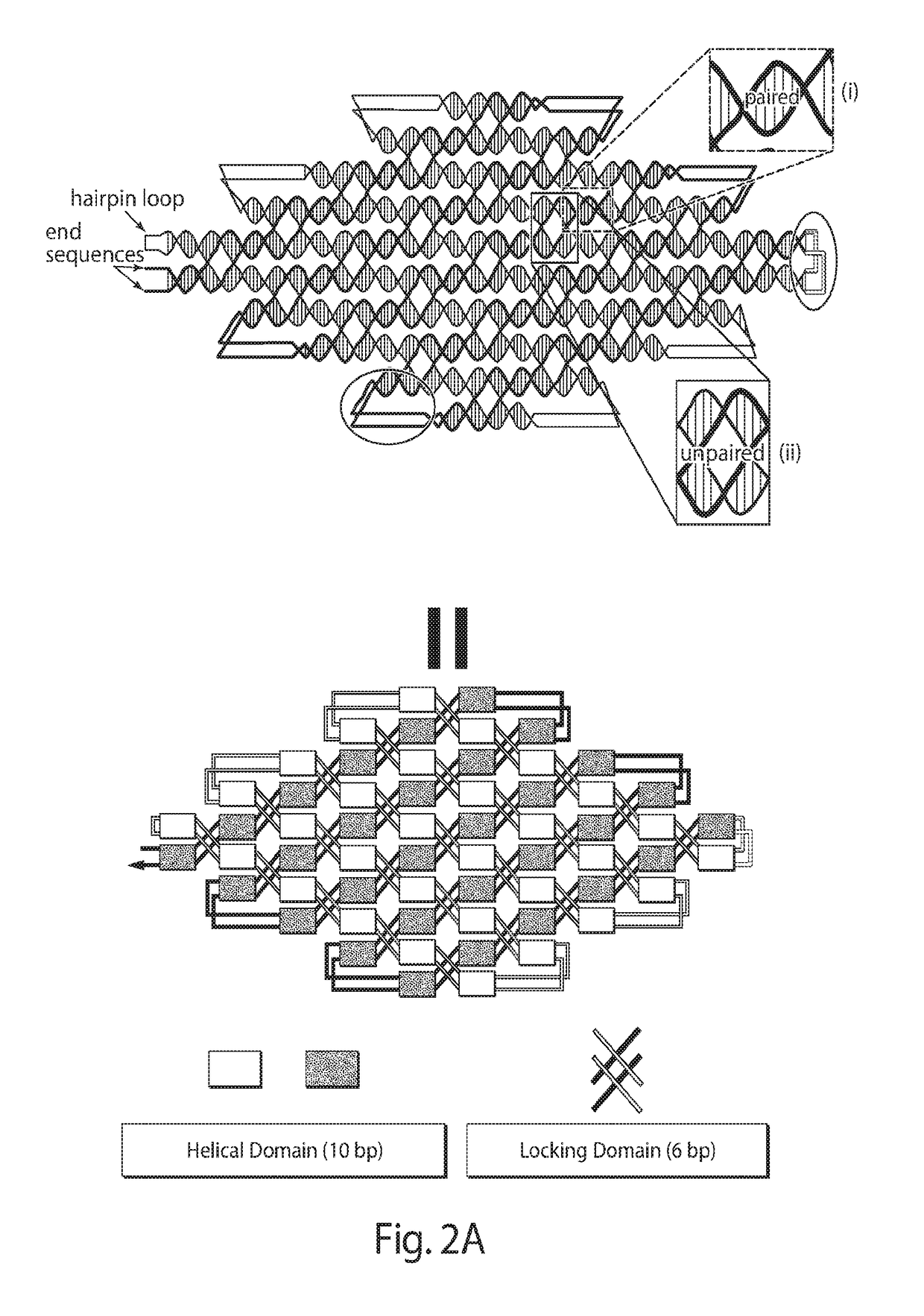
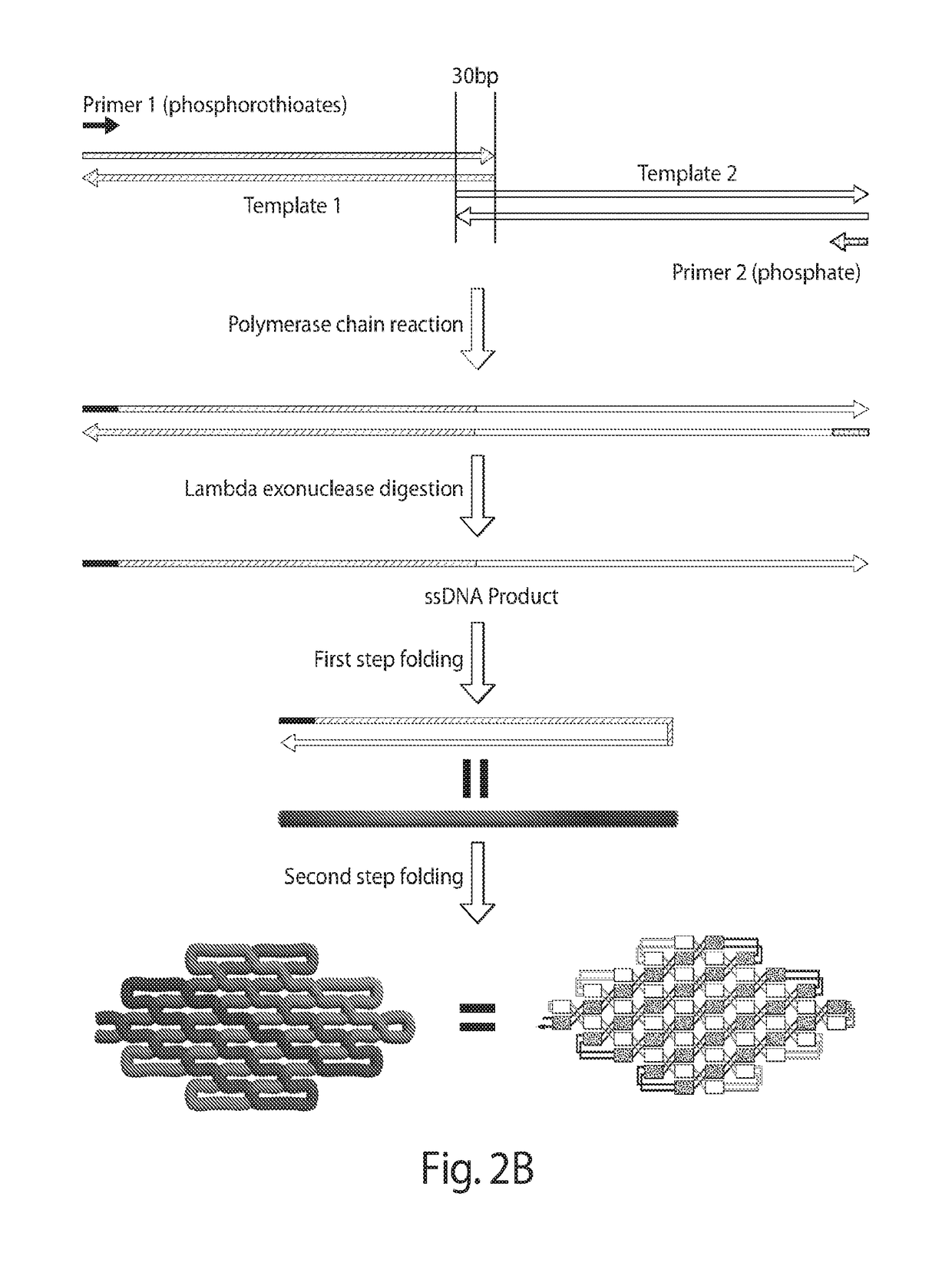
Single-stranded DNA nanostructures
ActiveUS20180044372A1Robust assemblyRobust replicationSugar derivativesHydrolasesSingle strandSingle strand dna
The present disclosure relates to nanostructures assembled from nucleic acid consisting of a single strand of DNA rationally-designed to self-assemble into a hairpin loop, helical domains, and locking domains.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Protein binding miniature proteins
InactiveUS20050287542A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPancreatic polypeptidomaAlpha helix
The present invention provides a protein scaffold, such as an avian pancreatic polypeptide, that can be modified by substitution of two or more amino acid residues that are exposed on the alpha helix domain of the polypeptide when the polypeptide is in a tertiary form.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Malaria vaccine of self-assembling polypeptide nanoparticles
The invention is directed to functionalized self-assembling polypeptide nanoparticles, and to methods of using these nanoparticles to vaccinate against malaria. The functionalized SAPN comprises a self-assembling core, and at least one epitope fused to the self-assembling core. The self-assembling core comprises a pentameric coiled-coil domain, a trimeric coiled-coil domain, and a linker. The linker joins the pentameric coiled-coil domain and the trimeric coiled-coil domain. Particular sequences of the epitopes used in the vaccine are from the Plasmodium parasite.
Owner:LANAR DAVID +1
Interparticle spacing material including nucleic acid structures and use thereof
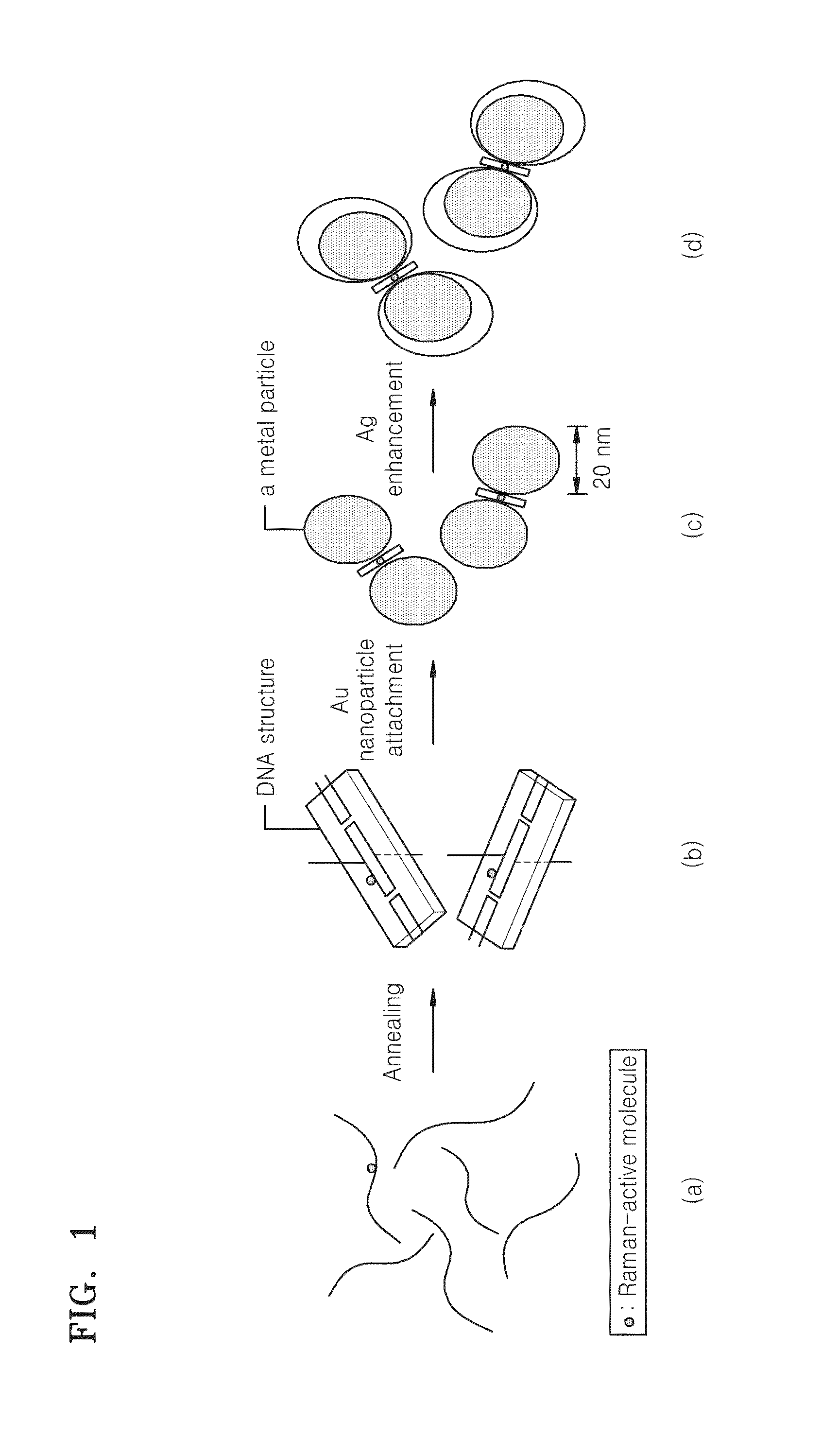
InactiveUS20140356857A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid structureMetal particle
Provided is an interparticle spacing material comprising a nucleic acid structure which comprises at least one nucleic acid lattice comprising a double helix domain; and at least one metal particle which is in contact with a plane of the nucleic acid lattice, in a direction extending obliquely or perpendicularly away from the plane; wherein the double helix domain comprises a hybridization area in which a single strand is hybridized with another single strand.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
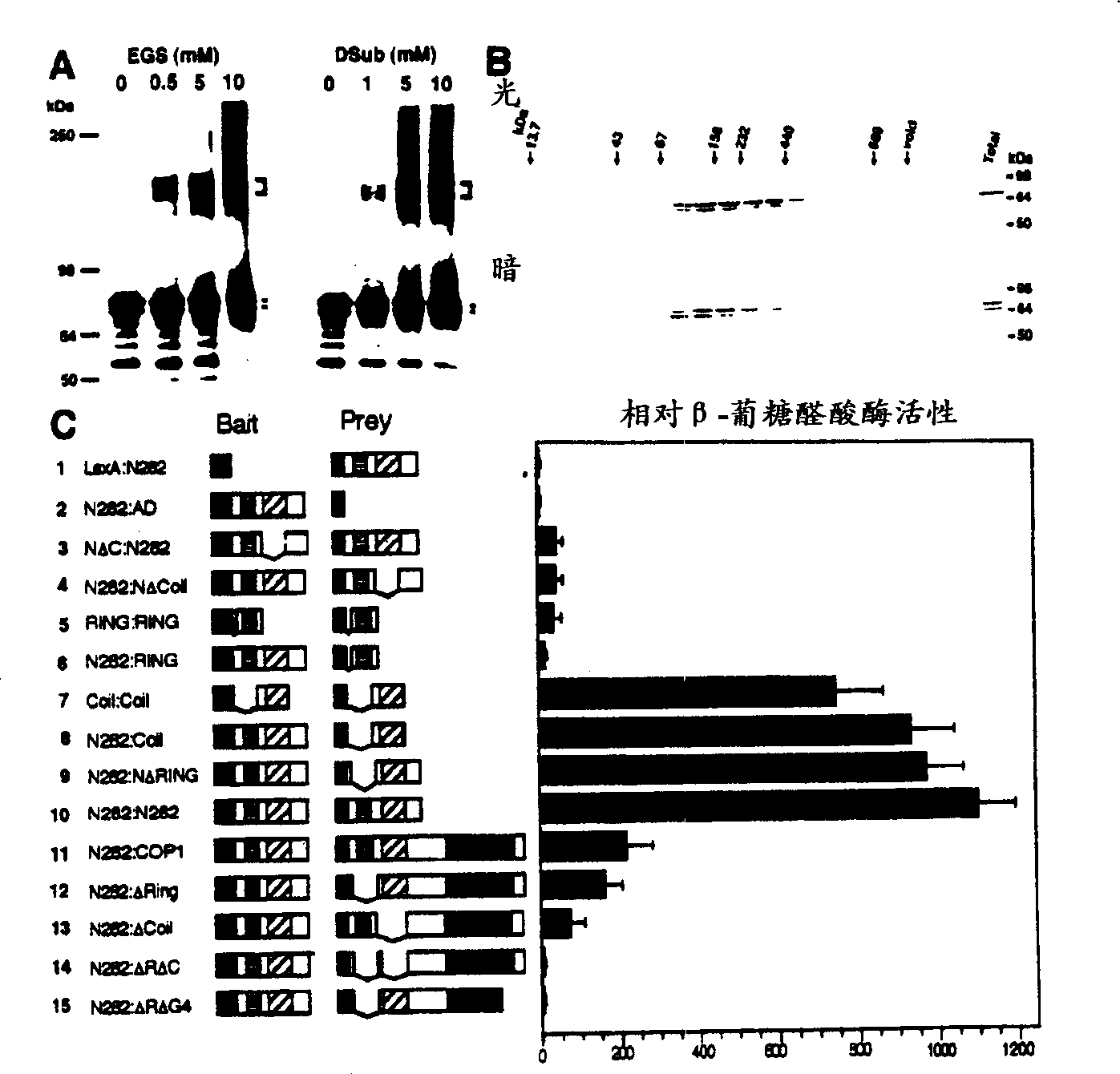
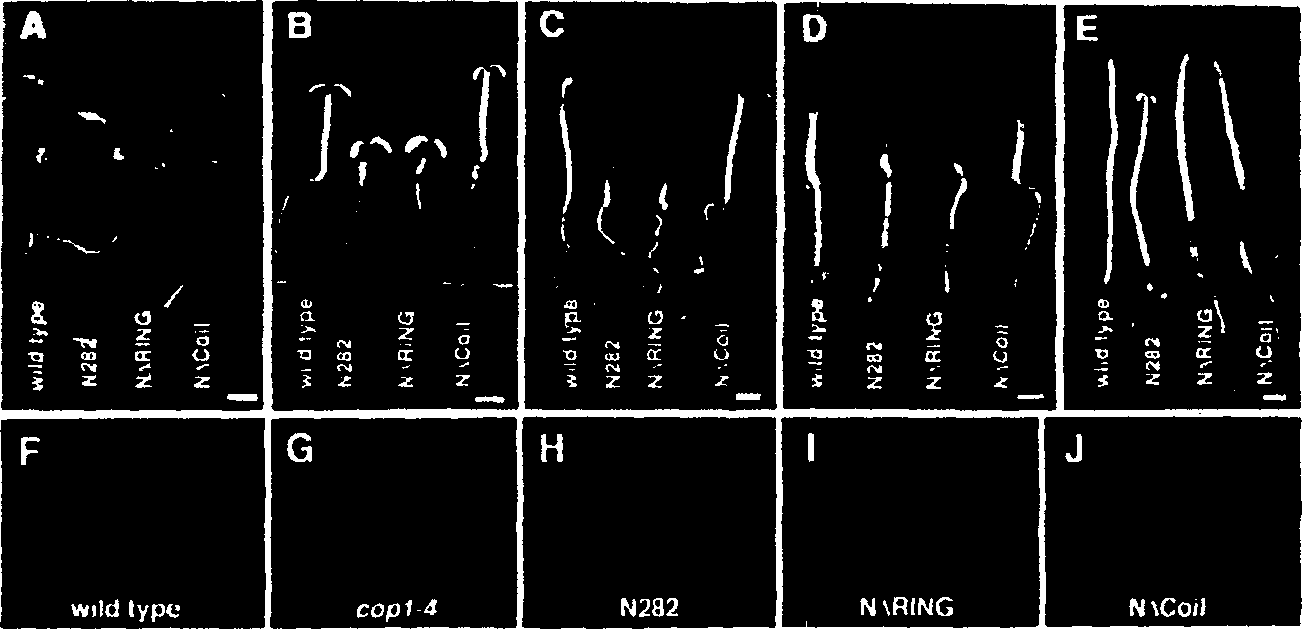
Plants and plants cells encoding wild type COP1 gene and coil domain thereof
InactiveCN1329670AReduce accumulationInhibitory activityClimate change adaptationMicroorganism based processesWild typePlant cell
The present invention relates to a seedling which exhibits better germination characteristics when grown in the dark and whose growth is improved under conditions of low light levels. More specifically, the present invention relates to the preparation of plant cells and whole plants which contain a nucleotide sequence encoding a helical domain, together with a sequence encoding a wild-type COP1 gene. The plant of the present invention will form unopened and compact leaves when seedlings germinate in the dark, and the chlorosis phenomenon of seedlings grown under low light conditions after germination will be weakened. The present invention also relates to breeding methods that enable the transfer of these desirable traits into wild-type plants.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Modified bacterial collagen-like proteins
ActiveUS20160376326A1Improve propertiesSpecific functionalityCosmetic preparationsConnective tissue peptidesBiotechnologyBacteroides
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Peptides promoting lipid efflux
Disclosed herein are peptides and peptide analogs with multiple amphipathic α-helical domains that promote lipid efflux from cells via an ABCA1-dependent pathway, as well as peptides that activate lipoprotein lipase, and compositions comprising such peptides or combinations thereof. Also provided herein are methods of using multi-domain amphipathic α-helical peptides or peptide analogs to treat or inhibit dyslipidemic disorders. Methods for identifying non-cytotoxic peptides that promote ABCA1-dependent lipid efflux from cells and activate lipoprotein lipase within cells are also disclosed herein.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
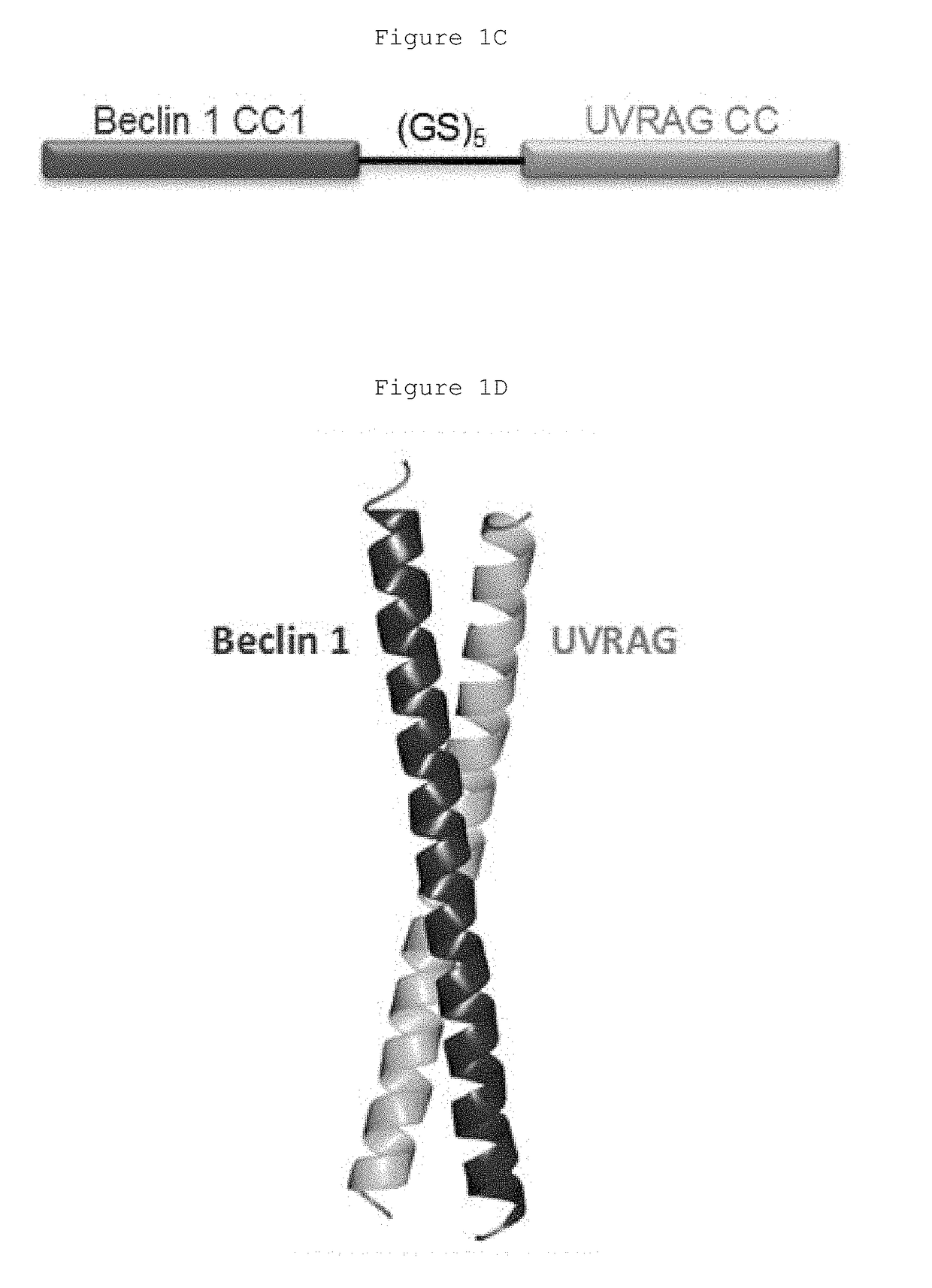
Hydrocarbon-stapled polypeptides for enhancement of endosome-lysosomal degradation
InactiveUS20180002381A1High trafficExcessive degradationPeptide/protein ingredientsApoptosis related proteinsAutophagic deathPhysical interaction
The present invention relates to a Beclin1-UVRAG complex structure which reveals a tightly packed coiled coil assembly with Beclin 1 and UVRAG residues complementing each other to form a stable dimeric complex. This potent physical interaction is critical for UVRAG-dependent EGFR degradation but less critical for autophagy. Targeting the Beclin coiled coil domain with rationally designed stapled peptides leads to enhanced autophagy activity and EGFR degradation in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines, suggesting translational value for these compounds.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Optimized polypeptide for a subunit vaccine against avian reovirus
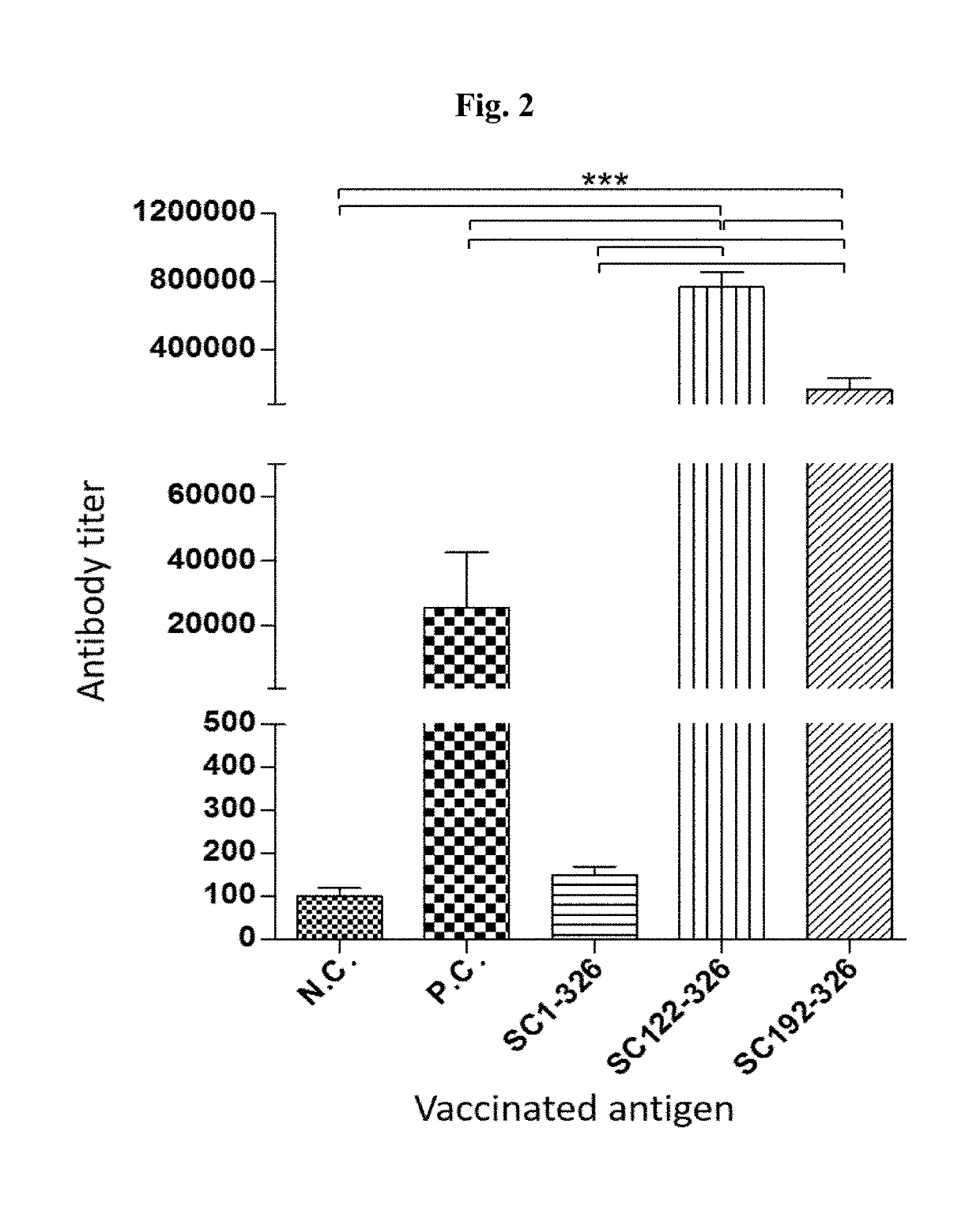
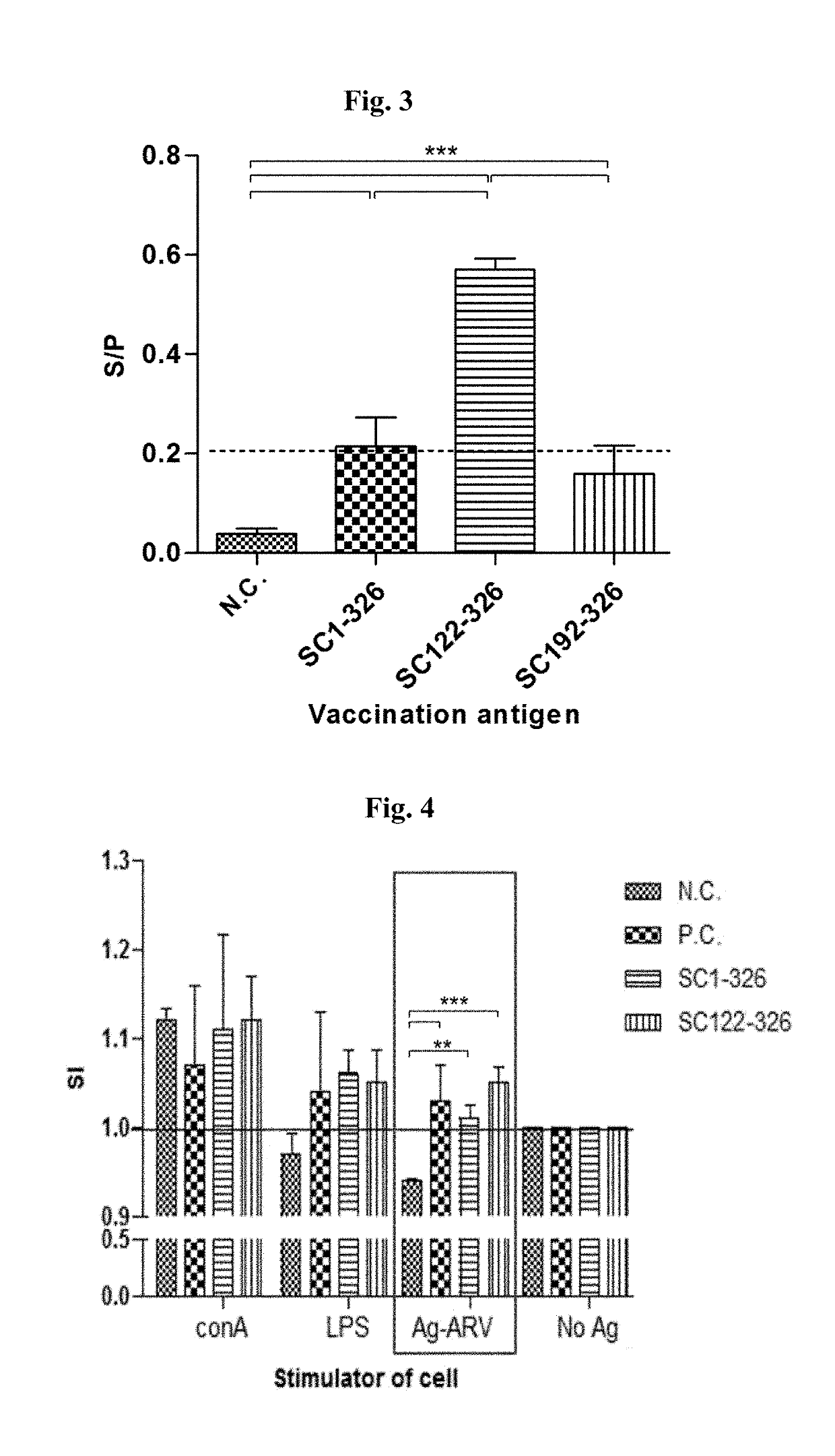
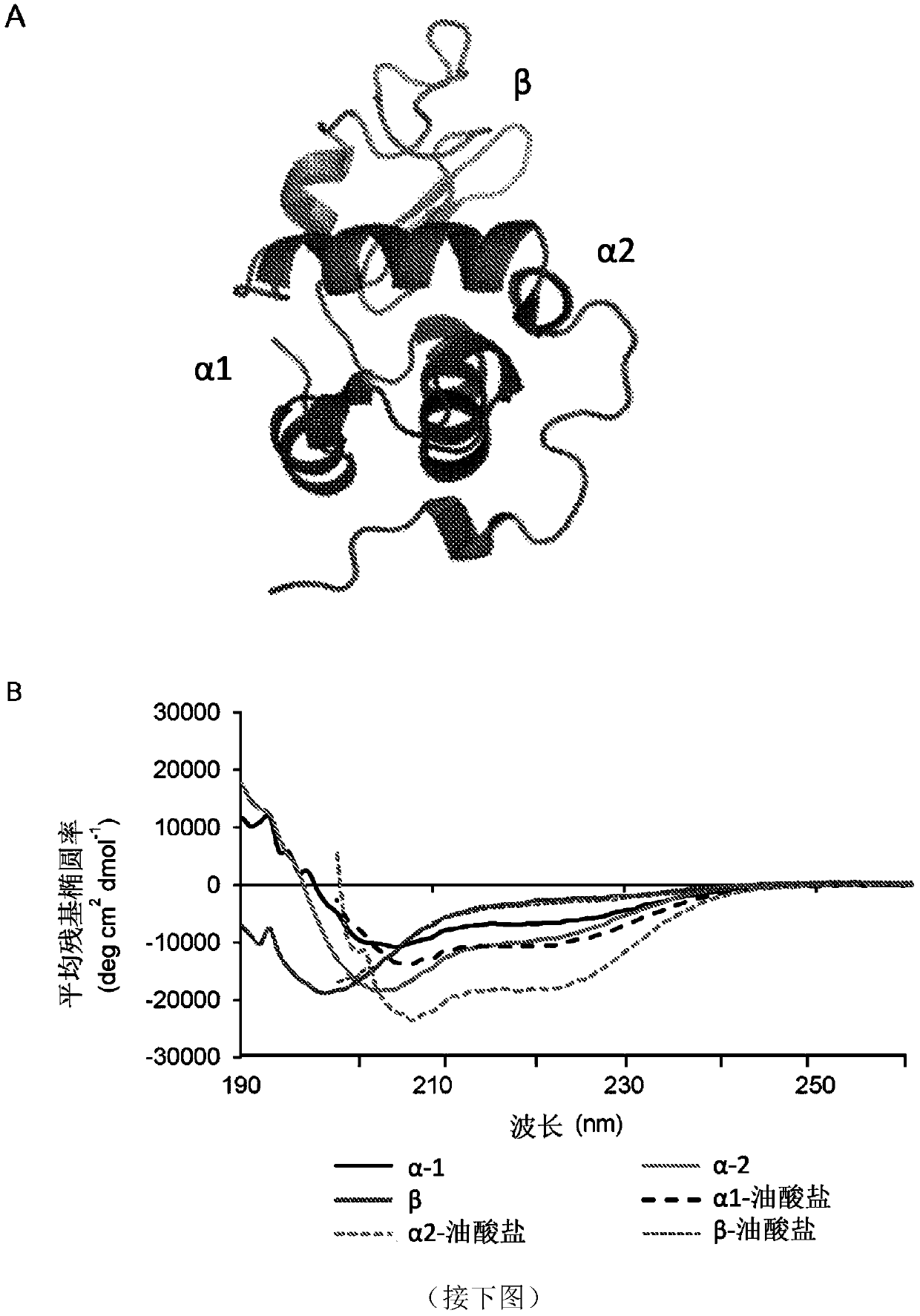
An isolated polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence corresponding to the amino acid residues forming a full or partial alpha-helical domain, the hinge domain, the beta-triple spiral domain and afull or partial globular head domain of an avian reovirus sigma C protein, and lacking the amino acid sequence that is N-terminal to said alpha-helical domain is provided. Furthermore, a vaccine comprising, or a viral vector expressing, at least one of the isolated polypeptides of the present invention is provided.
Owner:GAVISH GALILEE BIO APPL
Modified coiled coil type proteins having improved properties
ActiveUS9388225B2Improve bindingImproving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses negative-senseArginineCarrier protein
The present application is related to a modified protein comprising a protein having a coiled coil domain and a peptide having the sequence such as shown in SEQ ID NO 1: ZXBBBBZ that is linked to the coiled coil domain wherein:Z is any amino acid or is absent;X is any amino acid;B is an arginine (R) or a lysine (K).Said modified protein is in particular an antigen or a carrier protein, associated to an antigen. This modified protein has an increased affinity for negatively charged polymers such as nucleic acids or heparin, and shows an increased immunogenicity.
Owner:OSIVAX SAS
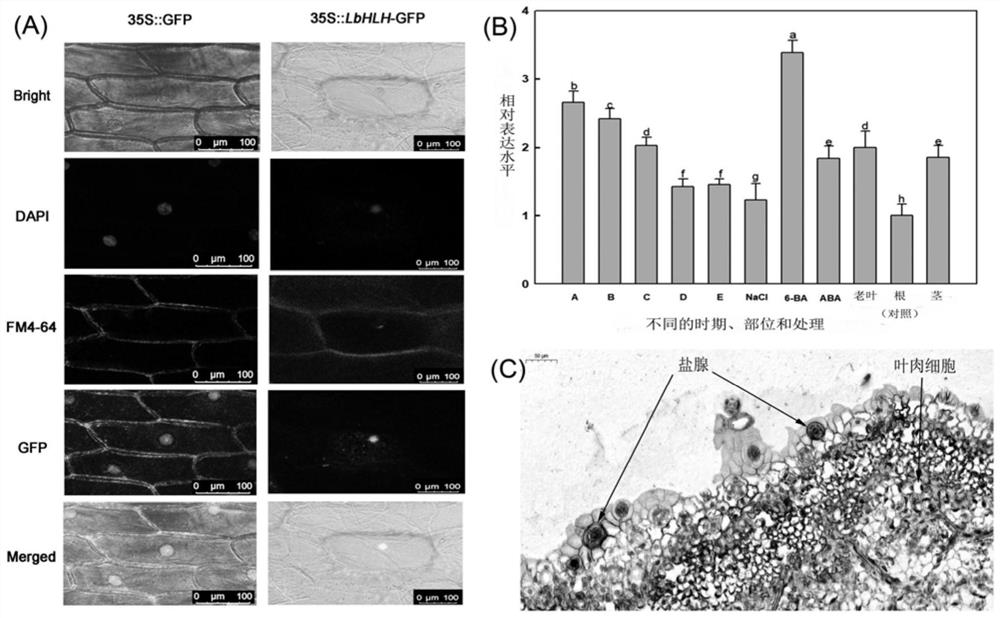
Two-color sea lavander herb gene LbHLH and application thereof
InactiveCN113355335AReduce developmentImprove salt tolerancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyHeterologous
The invention provides a two-color sea lavander herb gene LbHLH and application thereof. According to the invention, the full length of the gene LbHLH is obtained by performing cloning on a salt-secreting halophyte two-color sea lavander herb. The gene LbHLH comprises an open reading frame of 2067 bp, and is used for coding a protein consisting of 688 amino acids. The gene LbHLH has a typical helix-loop-helix (HLH) structural domain between amino acids 480-526. Experiments show that an arabidopsis thaliana plant for heterologous expression of the gene has the effects of promoting epidermal hair development, reducing root hair development and enhancing salt tolerance. A yeast two-hybrid experiment also shows that the gene LbHLH can interact with AtGL1, so that the gene LbHLH can play an important role in differentiation and salt resistance of hairy bodies and root hairs.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Therapeutically active complexes
InactiveUS20200009222A1Avoid componentsInhibition of activationOrganic active ingredientsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsLactalbuminAmino acid
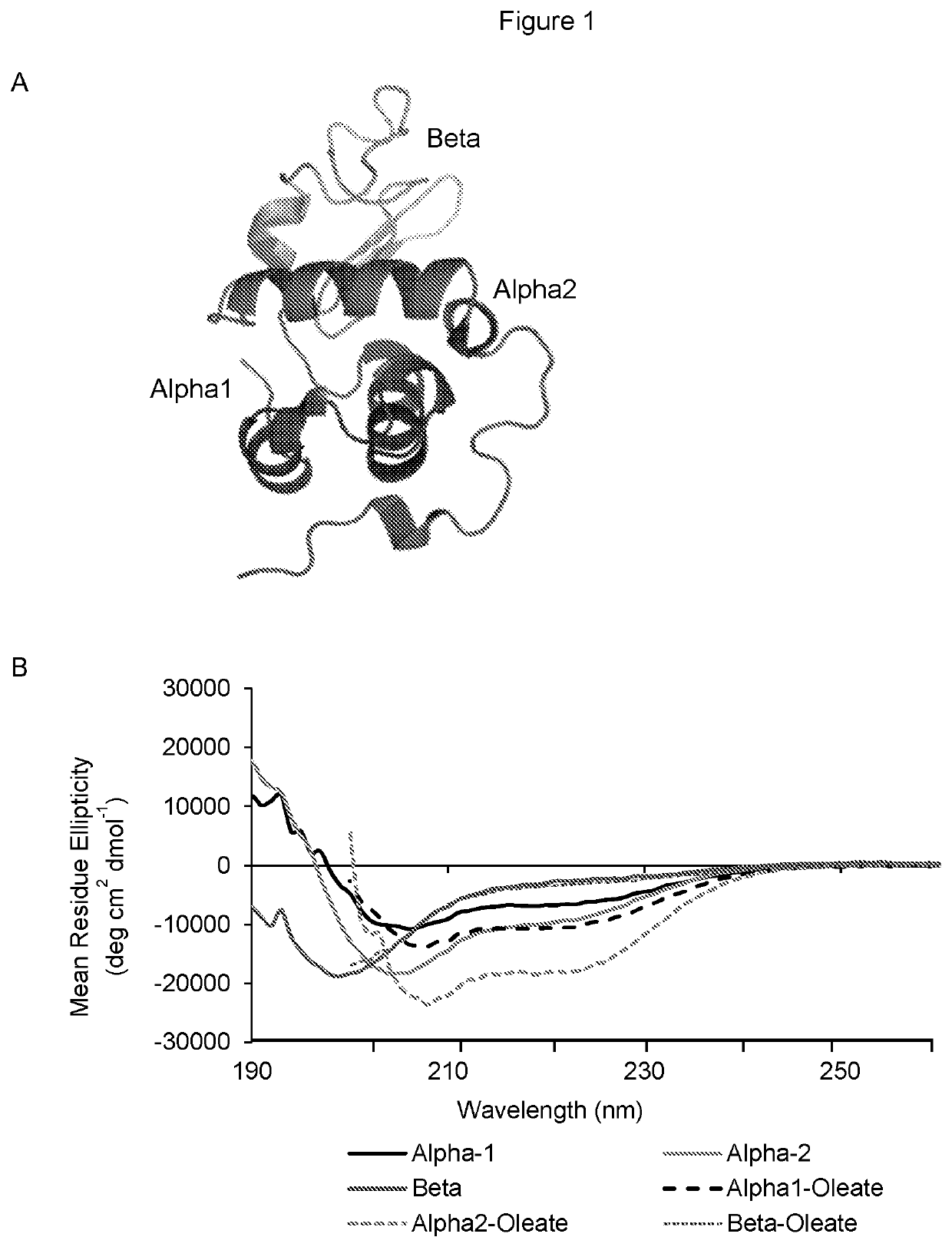
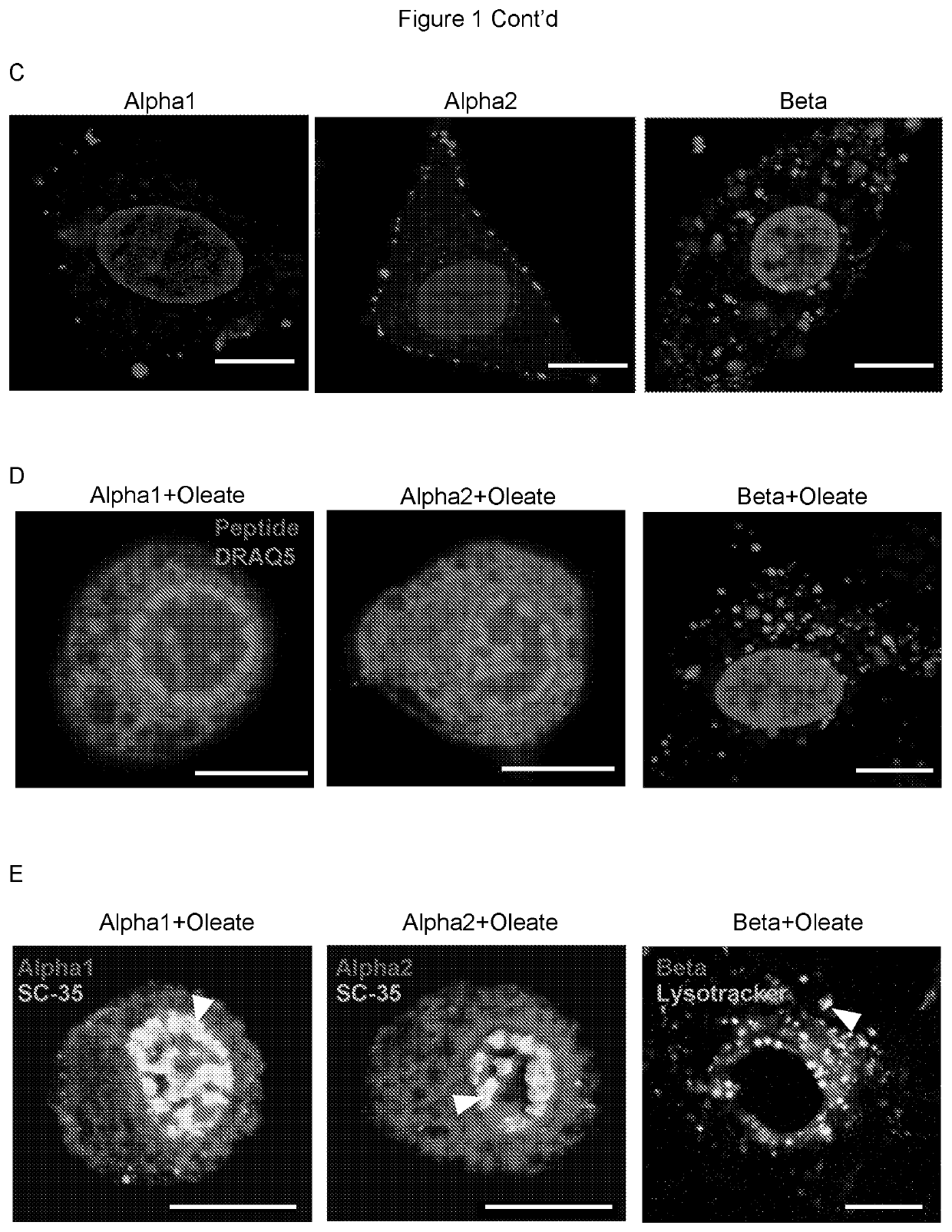
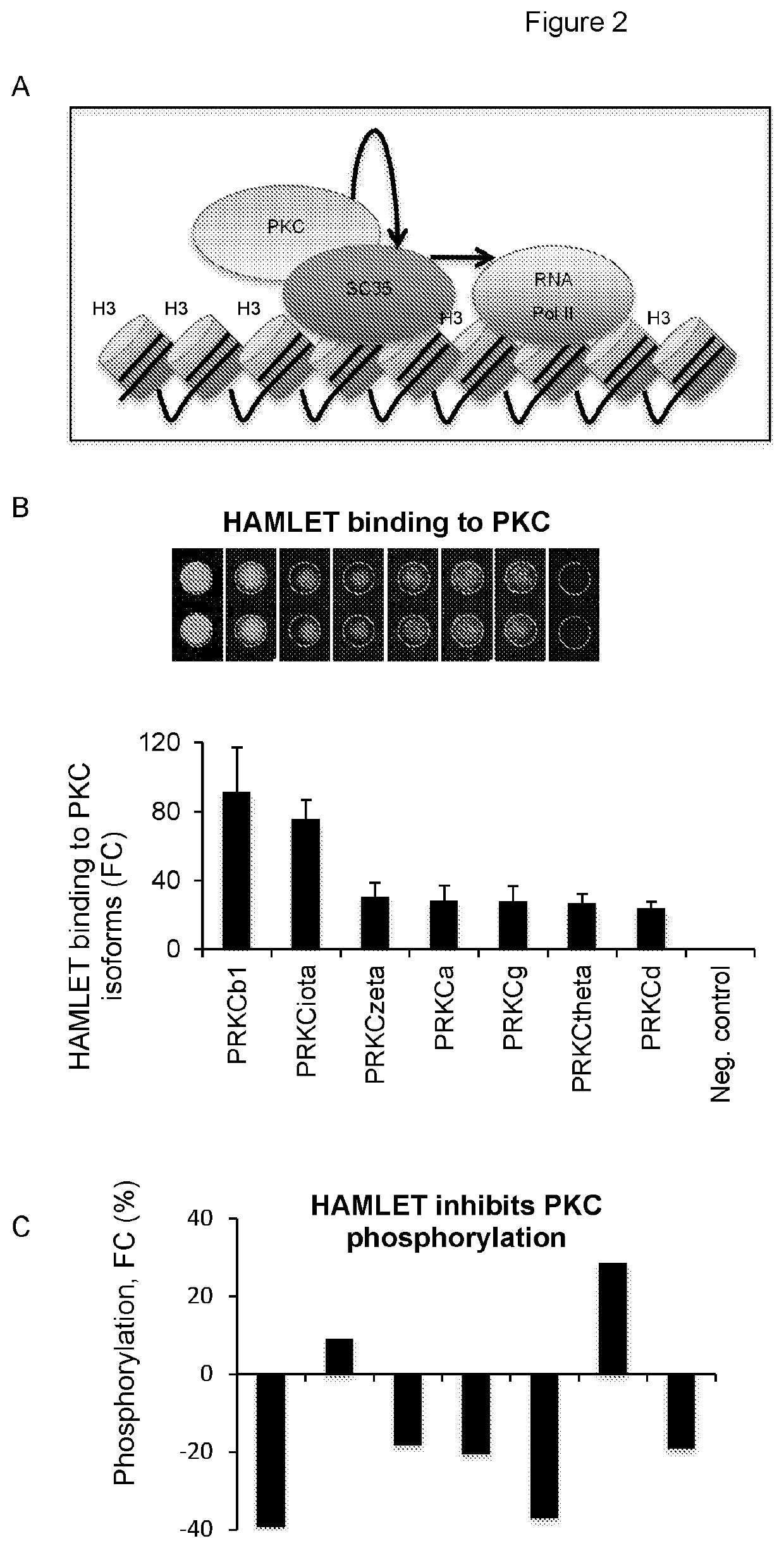
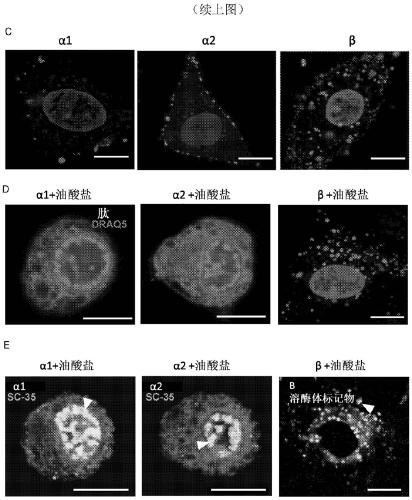
A biologically active complex comprising a peptide of up to 50 amino acids in length which comprises an alpha-helical domain of a protein which has membrane perturbing activity or a variant thereof which lacks cysteine residues, and oleic acid or a salt thereof, provided the protein is other than alpha-lactalbumin. Complexes of this type are useful in therapy, in particular cancer therapy.
Owner:HAMLET PHARMA AB
Methods and compositions for regulating adipogenesis
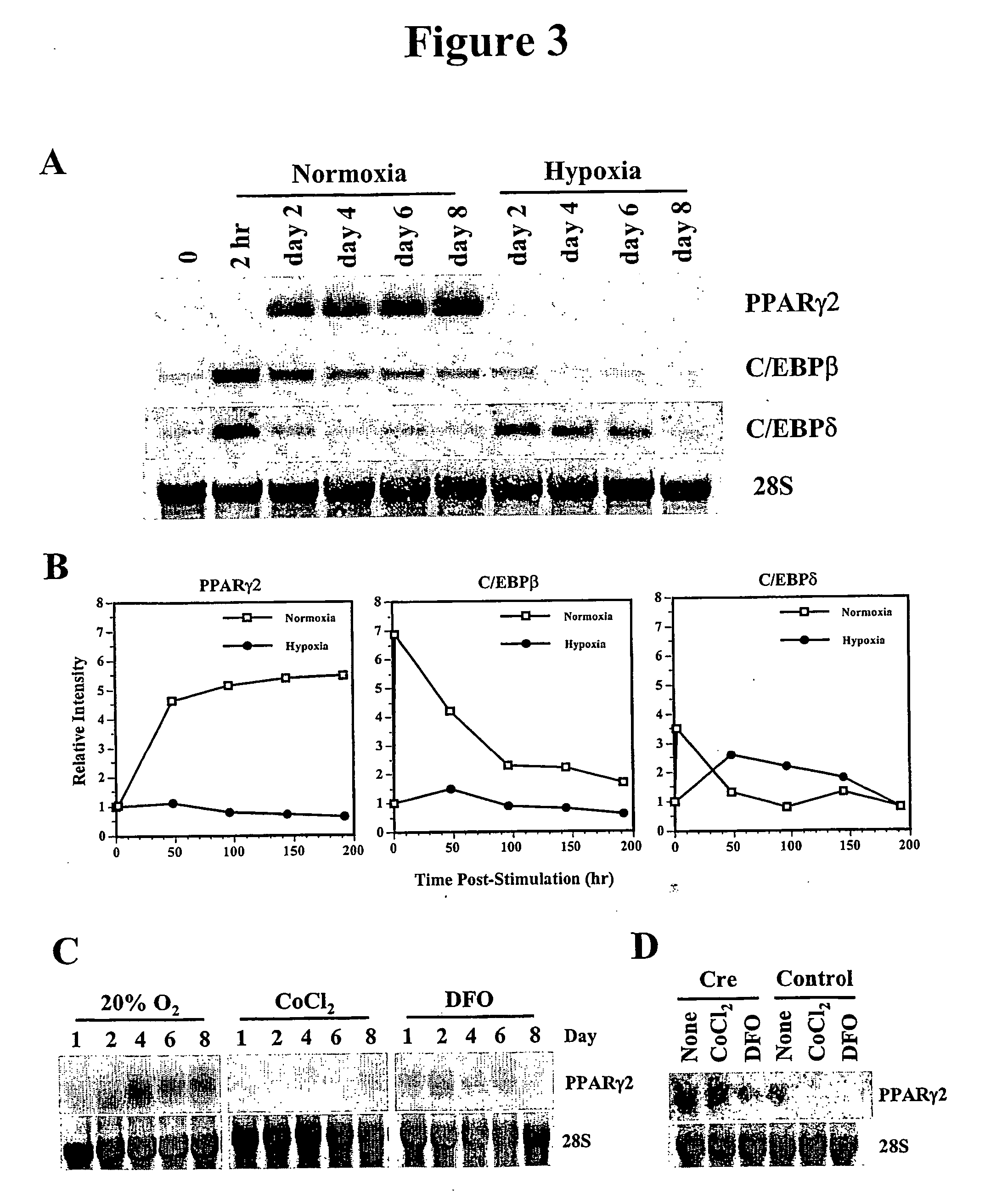
InactiveUS20050282167A1Increase probabilityEnhanced colony-forming capabilityCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesAbnormal tissue growthDEC1
According to the disclosure hypoxia-mediated adipogenic inhibition involves the repression of PPARγ2 expression and its activity is a common mechanism for adipogenic inhibition by a variety of stimuli. The present disclosure relates to methods and compositions for regulating adipogenesis. The disclosure provides compositions comprising one or more DEC1 / Stra13 fragments of capable of inhibiting PPARγ2 promoter activity. These fragments, e.g. the basic helix loop helix domain or amino acids 1-141, have substantially the same PPARγ2 promoter repressing activity as the full length polypeptide. The present disclosure provides methods of inhibiting adipogenesis comprising contacting a cell with a fragment of DEC1 / Stra13. The invention further relates to methods and compositions of inhibiting angiogenesis in a tumor comprising contacting a tumor or tumor cell with a DEC1 / Stra13 agonist.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Protein binding miniature proteins
The present invention provides a protein scaffold, such as an avian pancreatic polypeptide, that can be modified by substitution of two or more amino acid residues that are exposed on the alpha helix domain of the polypeptide when the polypeptide is in a tertiary form.
Owner:YALE UNIV
DNA & protein binding miniature proteins
InactiveUS20080108789A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAlpha helixADAMTS Proteins
The present invention provides a protein scaffold, such as an avian pancreatic polypeptide, that can be modified by substitution of two or more amino acid residues that are exposed on the alpha helix domain of the polypeptide when the polypeptide is in a tertiary form.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Coiled-coil lipopeptide helical bundles and synthetic virus-like particles
ActiveUS8450284B2Efficient inductionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical synthesisCoiled coil
The invention relates to lipopeptide building blocks consisting of a peptide chain comprising a coiled-coil domain, linked covalently to a lipid moiety comprising long alkyl or alkenyl chains, and optionally linked to an antigen; and to helical lipopeptide bundles and synthetic virus-like particles formed by aggregation. The nanometer size and shape of these bundles and particles, their stability under aqueous physiological conditions, their chemical composition, the possibility to incorporate B- and T-cell epitopes, and their production by chemical synthesis, make them highly suitable as vaccine delivery vehicles.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
Fusion polypeptides and uses thereof
PendingCN113912734APeptide/protein ingredientsFusions for plasma life prolongingA-siteCarrier protein
The present invention relates to a fusion polypeptide comprising a carrier protein and a polypeptide of interest, the carrier protein has a plurality of helical domains linked by a loop, the polypeptide of interest is inserted into the loop of the carrier protein, the carrier protein obscuring a site of interest on the polypeptide of interest, therefore, the accessibility of the site is blocked. The invention also relates to polynucleotides and carriers encoding the fusion polypeptides, as well as host cells comprising the polynucleotides and / or carriers. Further, the invention also relates to application of the fusion polypeptide of the invention in the treatment of cancer and / or activation of immune cells.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Killer cell antibiosis polypeptide activated by lymphokine and its application
InactiveCN1194988CEnhanced inhibitory effectGood killing effectAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsESCHERICHIA COLI ANTIGENHigh activity
An antibacterial polypeptide HLP-3P21, which is separated from the kytoplasm of the killer cell activated by human lymphokine, is disclosed. Its cDNA sequence and amino acid sequence are measured. It has high activity to pathogenic colibacillus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Optimized polypeptide for a subunit vaccine against avian reovirus
An isolated polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence corresponding to the amino acid residues forming a full or partial α-helical domain, the hinge domain, the β-triple spiral domain and a full or partial globular head domain of an avian reovirus sigma C protein, and lacking the amino acid sequence that is N-terminal to said α-helical domain is provided. Furthermore, a vaccine comprising, or a viral vector expressing, at least one of the isolated polypeptides of the present invention is provided.
Owner:GAVISH GALILEE BIO APPL
Therapeutically active complexes
InactiveCN110234321AOrganic active ingredientsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsLactalbuminAmino acid
A biologically active complex comprising a peptide of up to 50 amino acids in length which comprises an alpha-helical domain of a protein which has membrane perturbing activity or a variant thereof which lacks cysteine residues, and oleic acid or a salt thereof, provided the protein is other than alpha-lactalbumin. Complexes of this type are useful in therapy, in particular cancer therapy.
Owner:HAMLET PHARMA AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com