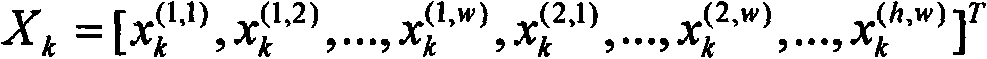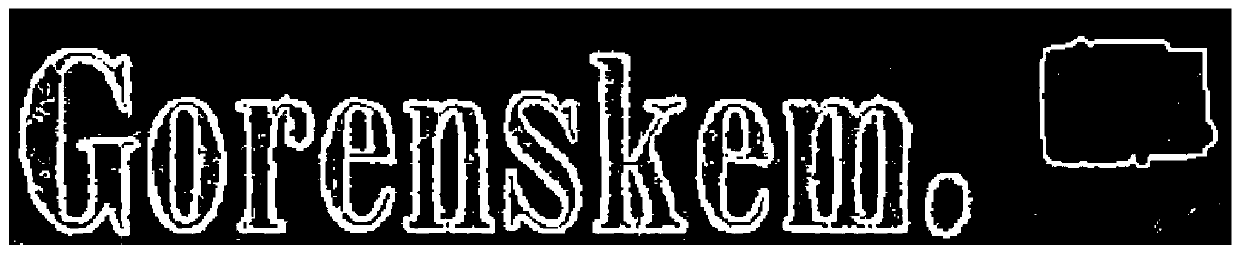Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Gradient noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
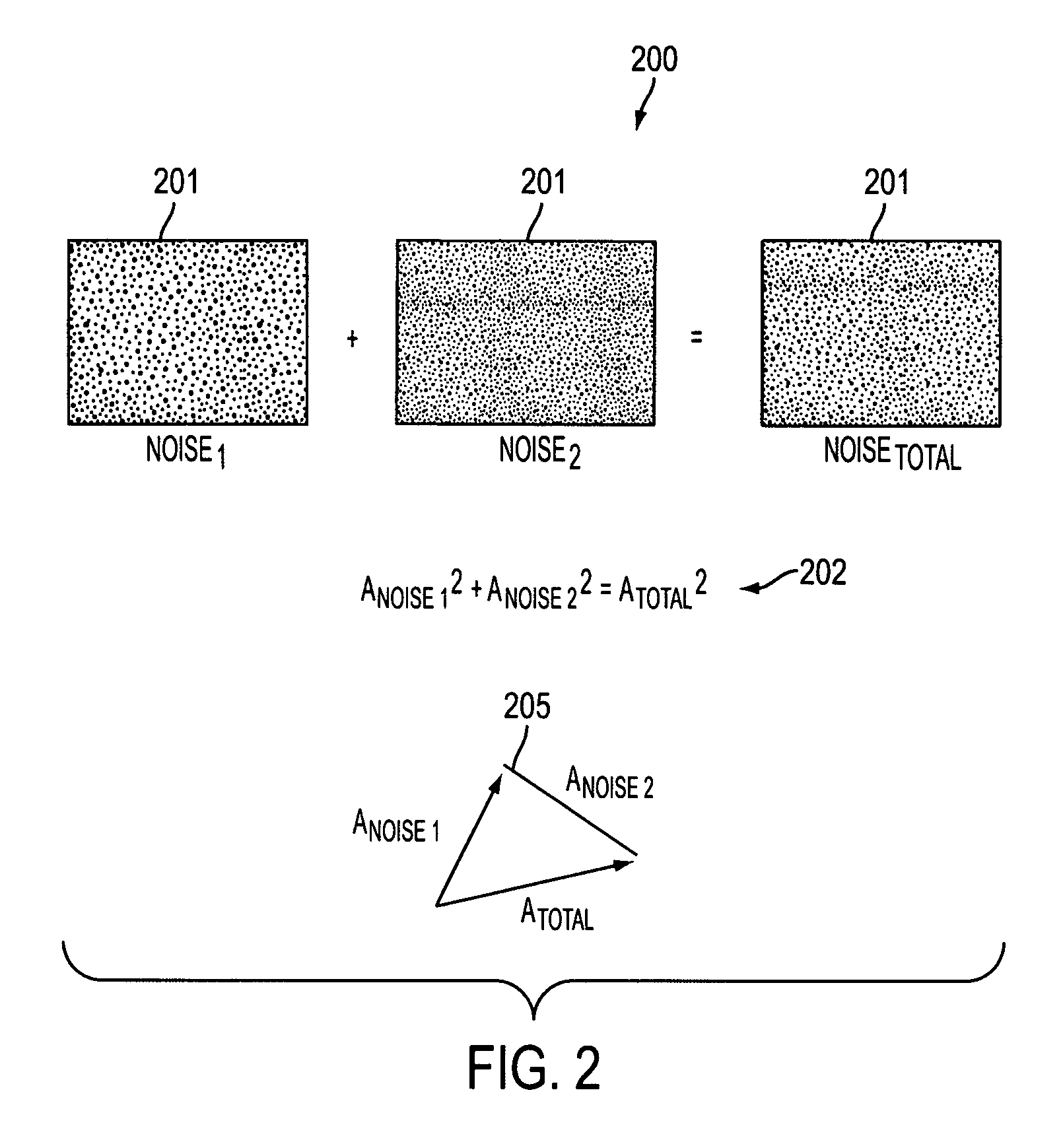
Gradient noise is a type of noise commonly used as a procedural texture primitive in computer graphics. It is conceptually different, and often confused with value noise. This method consists of a creation of a lattice of random (or typically pseudorandom) gradients, dot products of which are then interpolated to obtain values in between the lattices. An artifact of some implementations of this noise is that the returned value at the lattice points is 0. Unlike the value noise, gradient noise has more energy in the high frequencies.
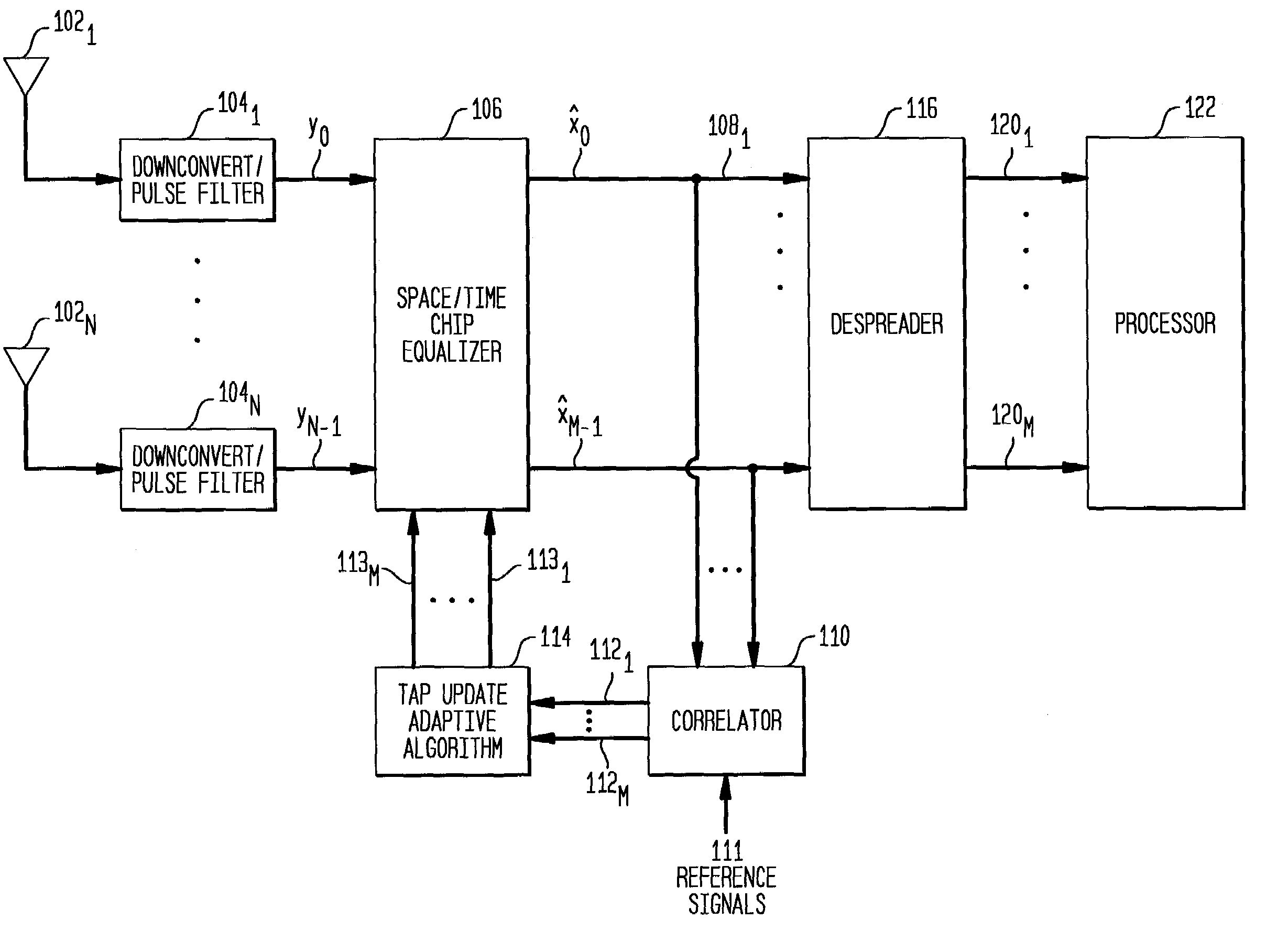
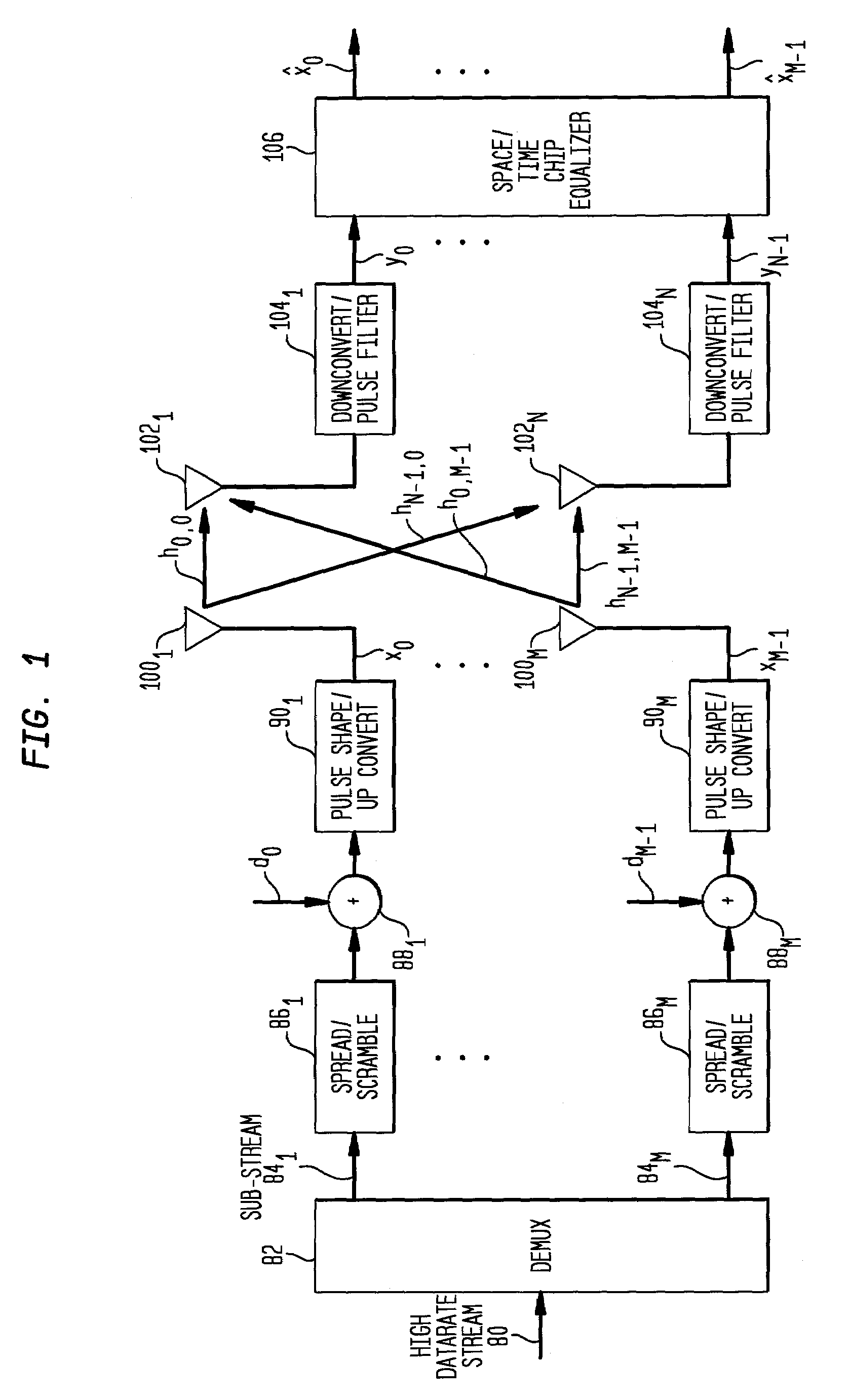
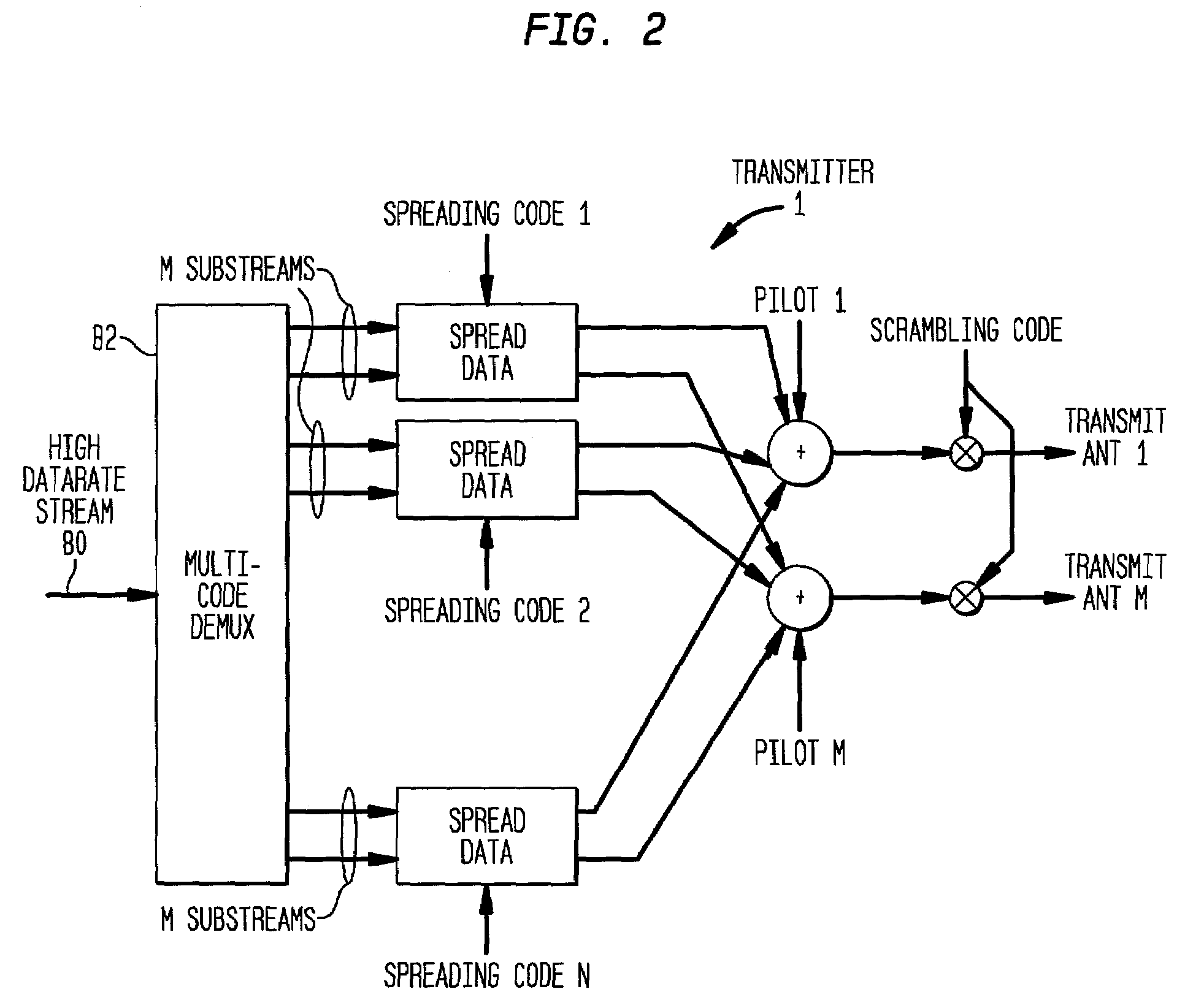
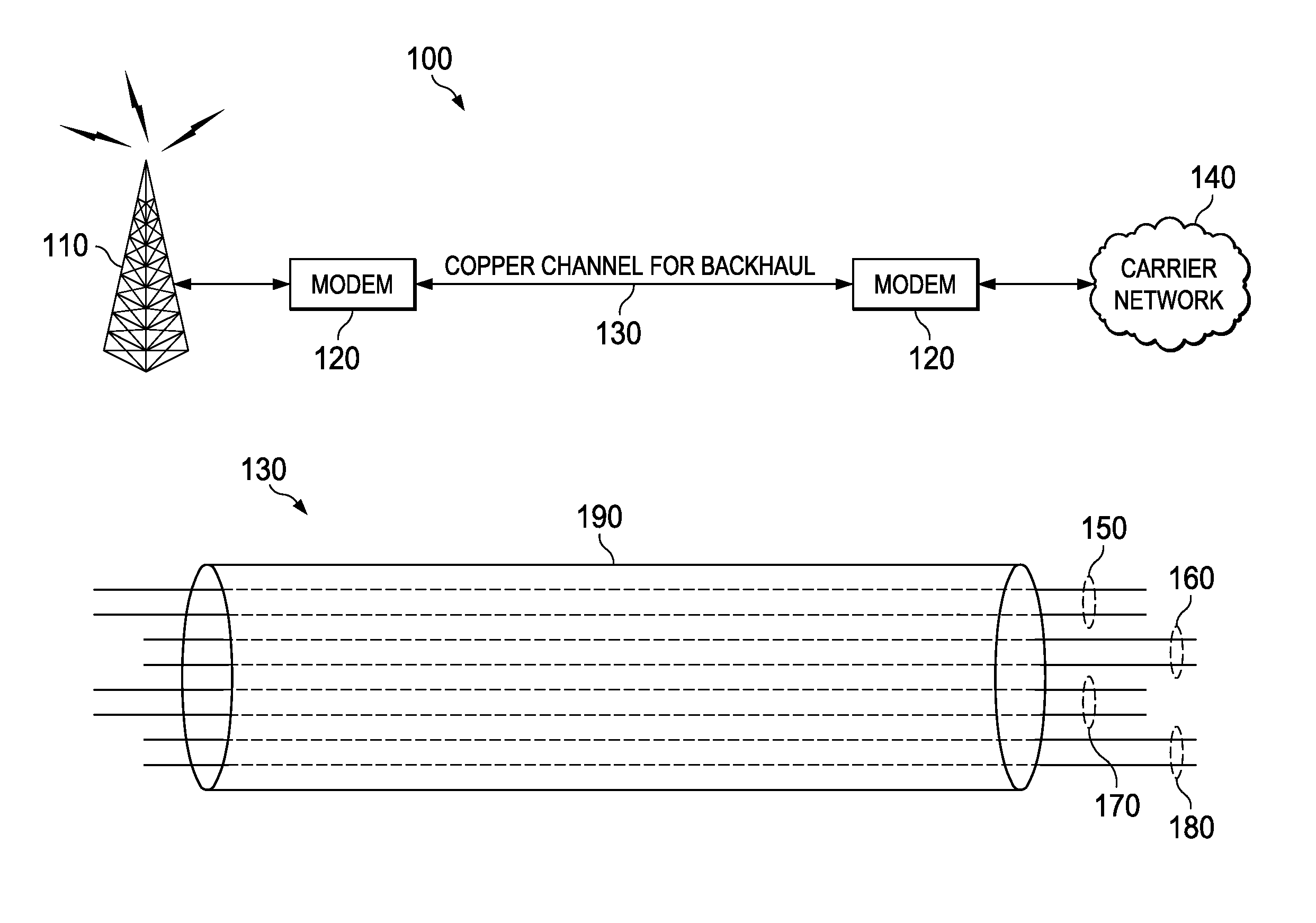
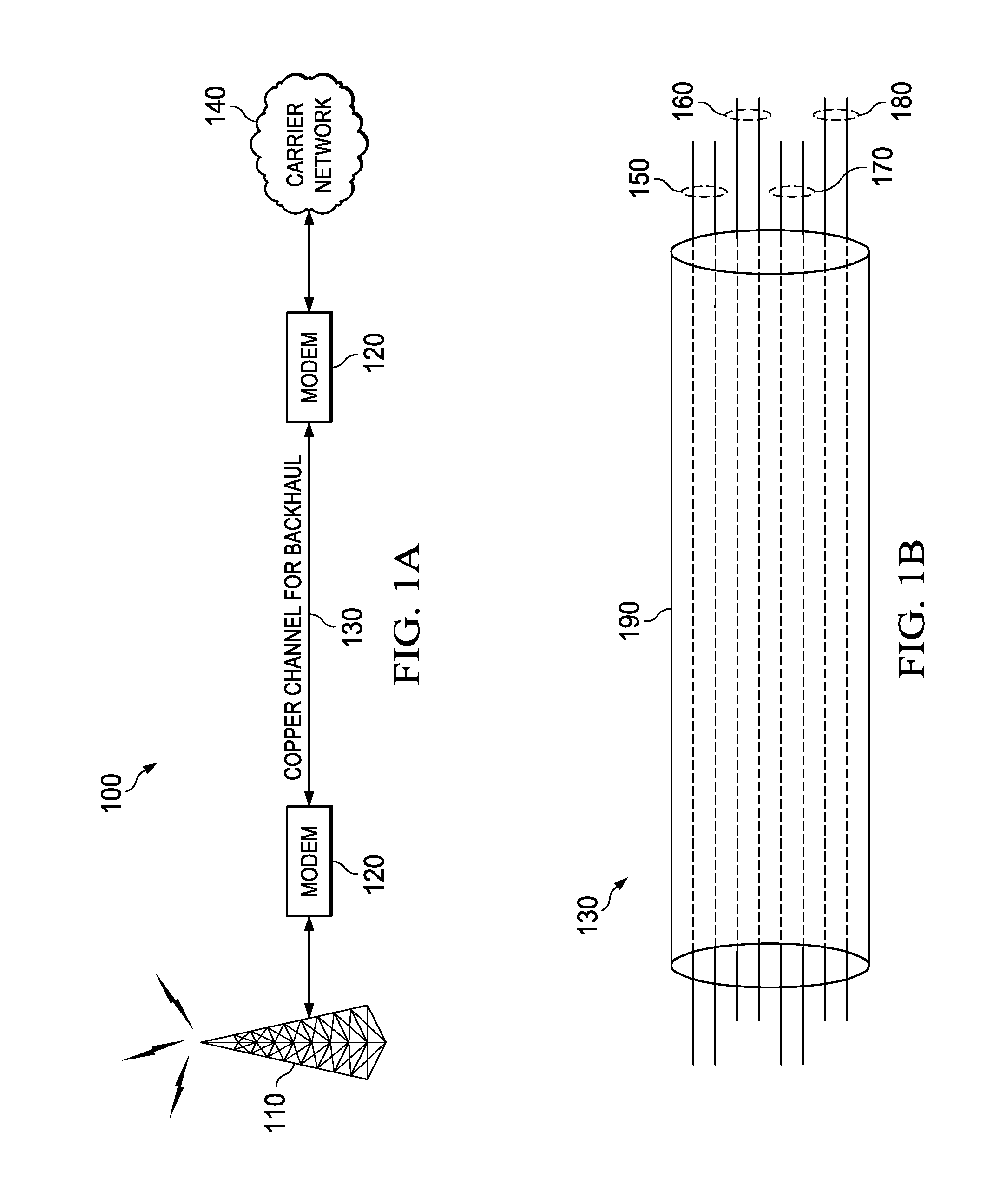
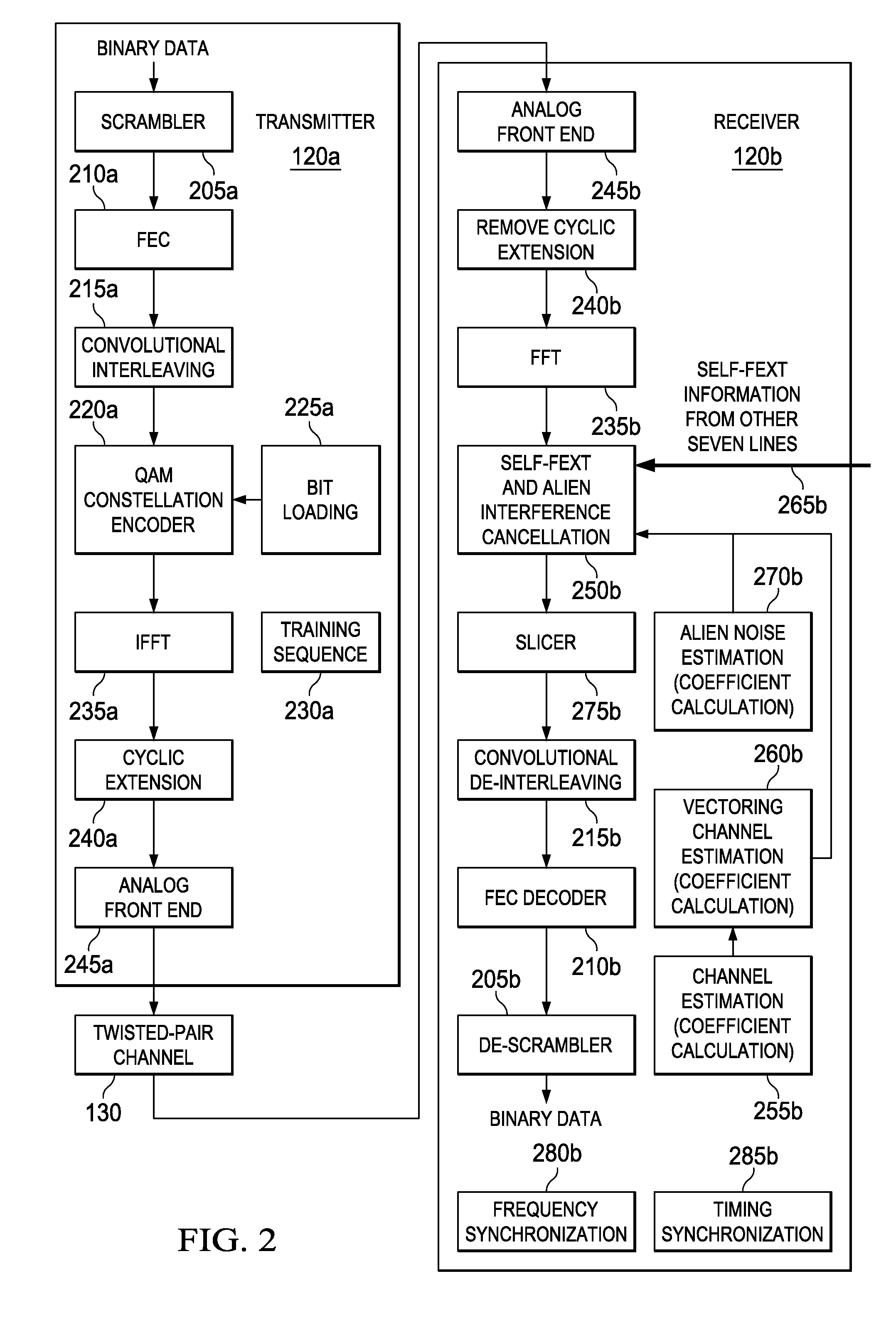
Equalizer and method for performing equalization in a wireless communications system
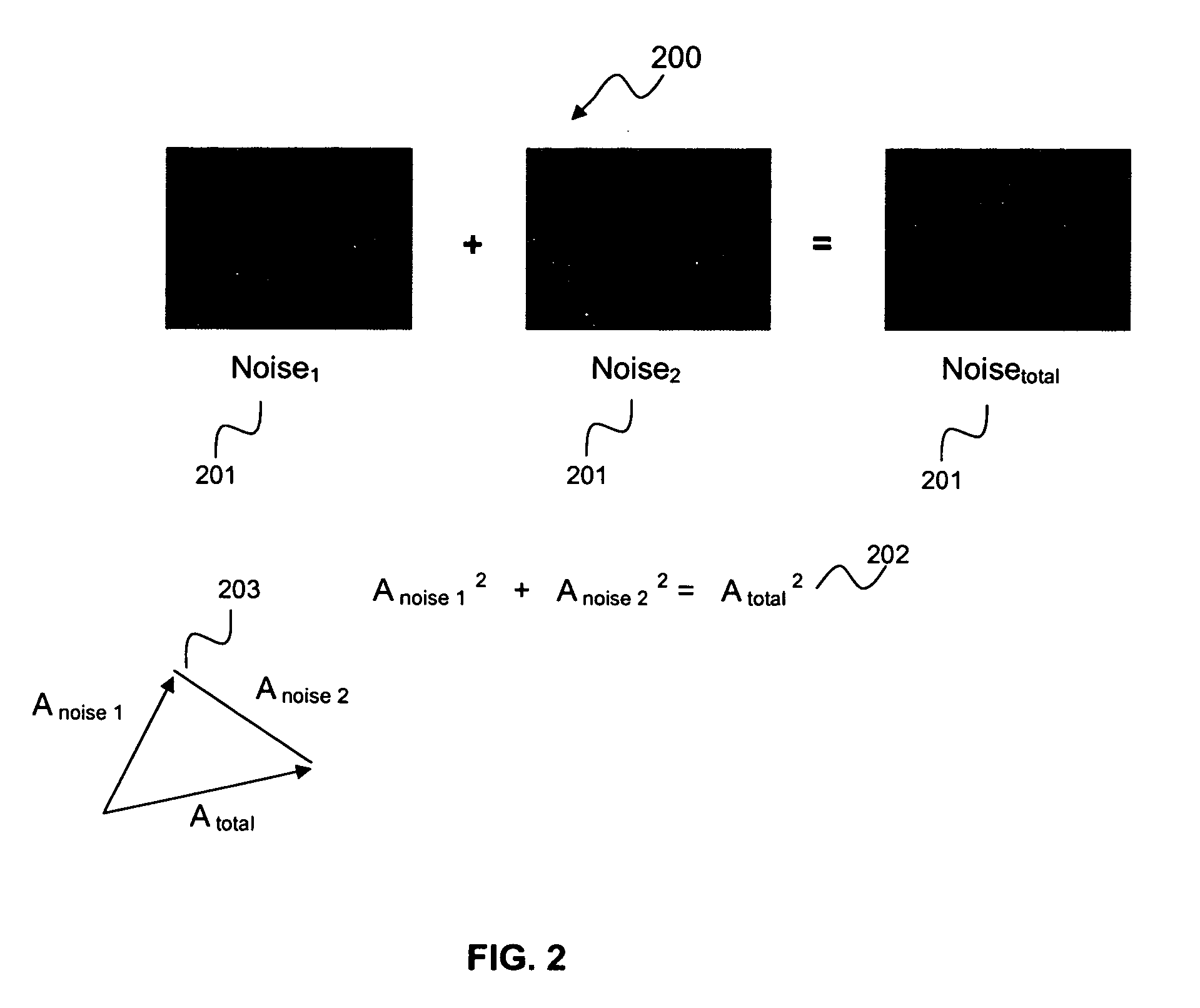
InactiveUS7167507B2Reduce adaptation noiseReduce noiseError prevention/detection by using return channelMultiple-port networksCommunications systemPulse shaping
A receiver, system, and method for performing equalization. The receiver includes a multi-channel chip equalizer for receiving a plurality of receive baseband signals and restoring chip pulse shapes of a plurality of transmit baseband signals transmitted by a plurality of transmit antenna to produce a plurality of equalized output streams and a correlator for correlating the plurality of equalized output streams with a correlation signal to reduce gradient noise in the plurality of equalized output streams. The method of equalizing includes receiving a plurality of receive baseband signals and restoring chip pulse shapes of a plurality of transmit baseband signals transmitted by a plurality of transmit antenna to produce a plurality of equalized output streams and correlating the plurality of equalized output streams with a correlation signal to reduce gradient noise in the plurality of equalized output streams.
Owner:LGS INNOVATIONS
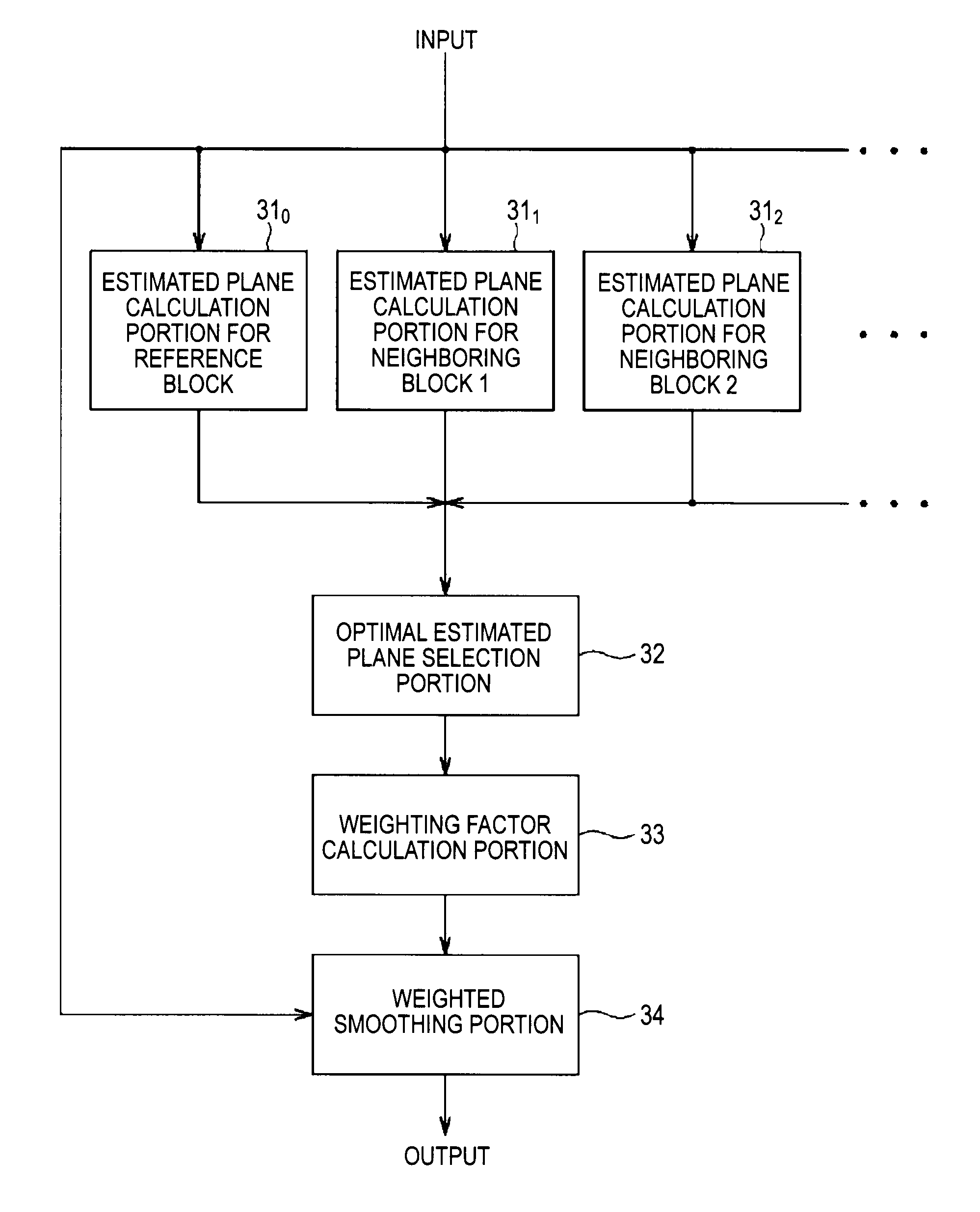
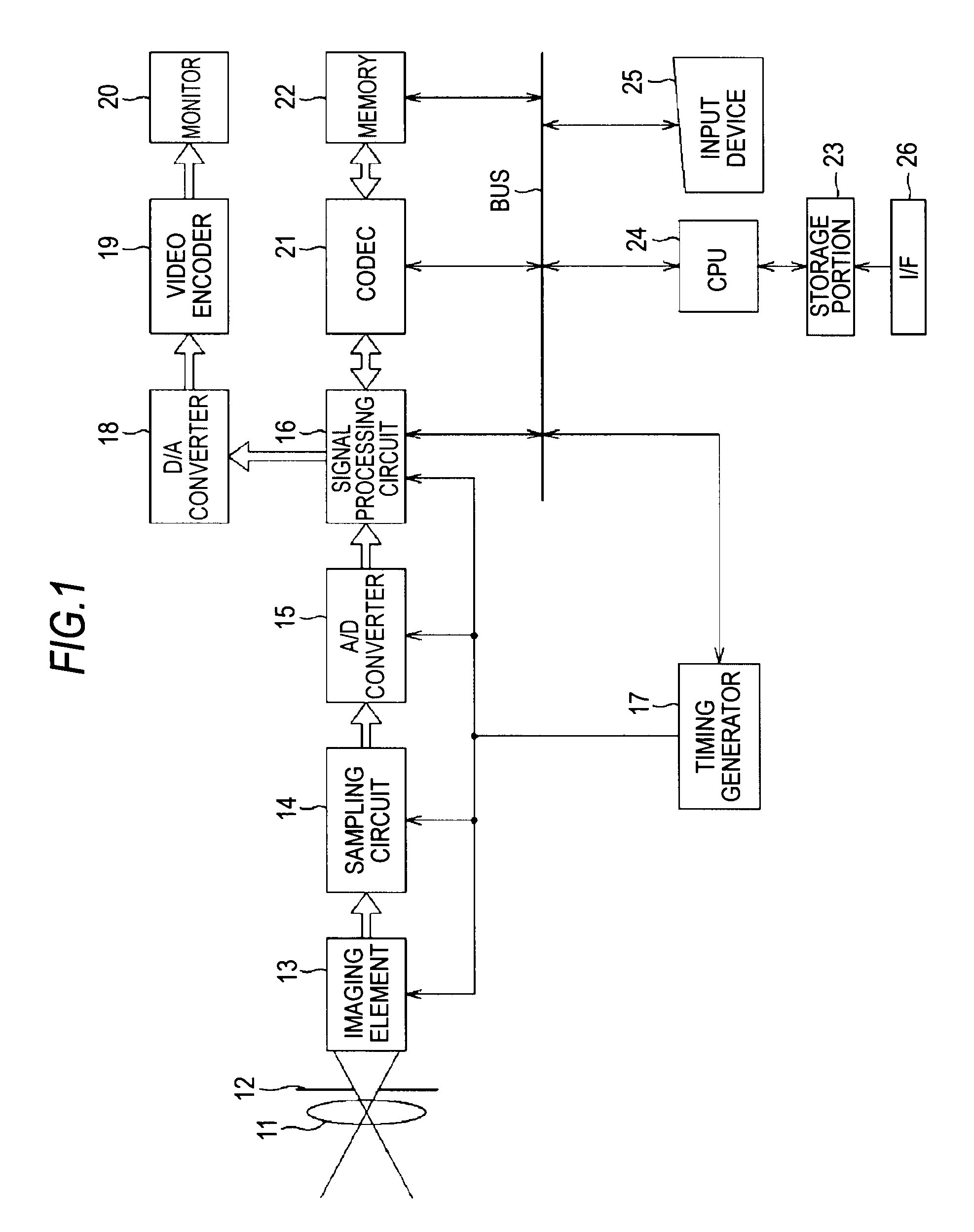
Image processing device and associated methodology of processing gradation noise
InactiveUS8411992B2Improve denoising effectAchieve denoisingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsComputational scienceImaging processing
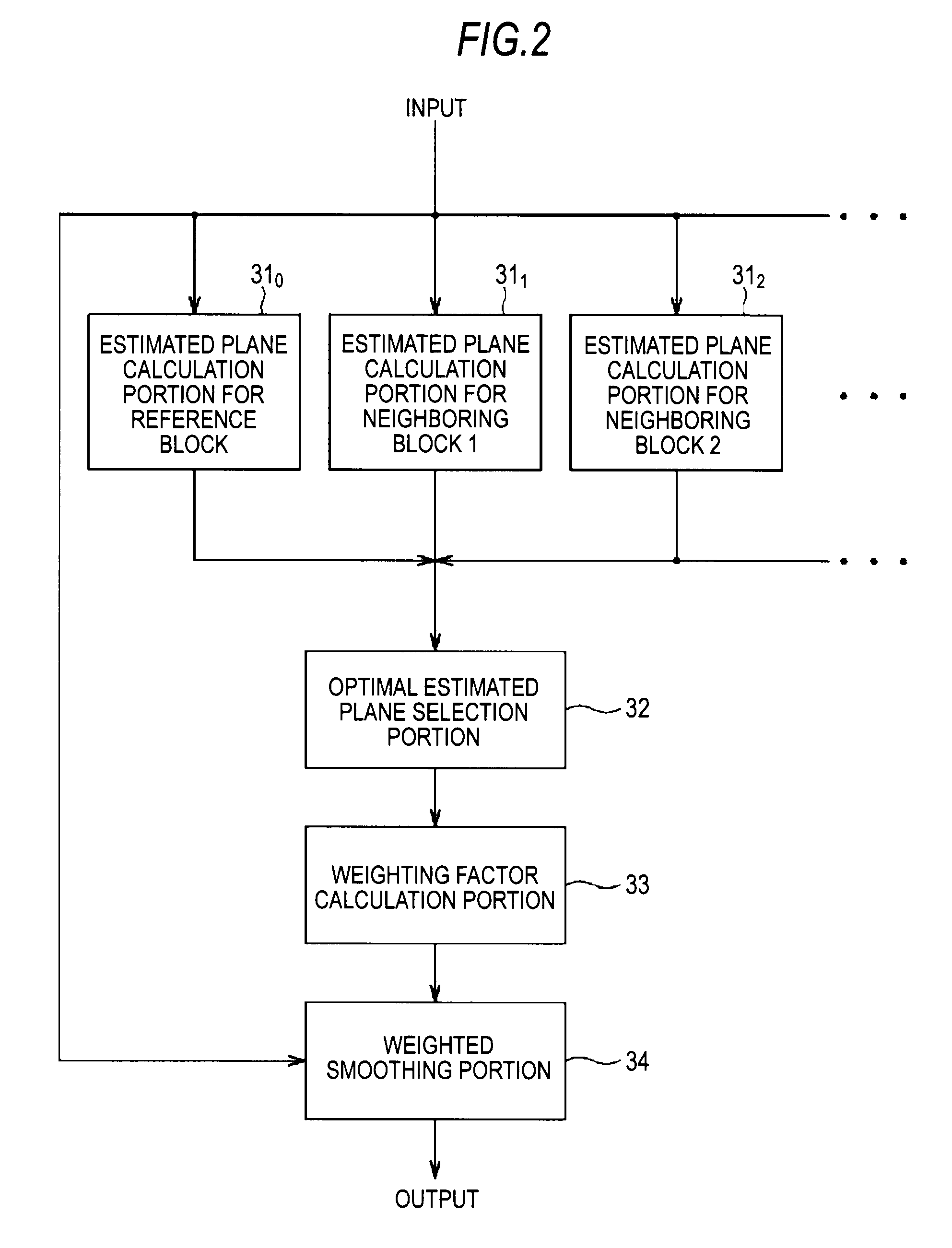
An image processing device includes: an estimated plane calculation portion calculating, for inputted image data, estimated planes defined by luminance values in blocks each containing a predetermined number of pixels including a reference pixel; an optimal estimated plane selection portion selecting an optimal estimated plane having a least summation of errors between luminance values of respective pixels in a block and an estimated plane among the estimated planes; a weighting factor calculation portion calculating a weighting factor for the reference pixel base on luminance values of the reference pixel and in the optimal estimated plane; and a weighted smoothing portion computing a sum of products of relative luminance differences between the luminance values of the respective pixels in the block and in the optimal estimated plane and the weighting factor for the reference pixel and adding a luminance value in the optimal estimated plane at a reference pixel position to a result of computation.
Owner:SONY CORP
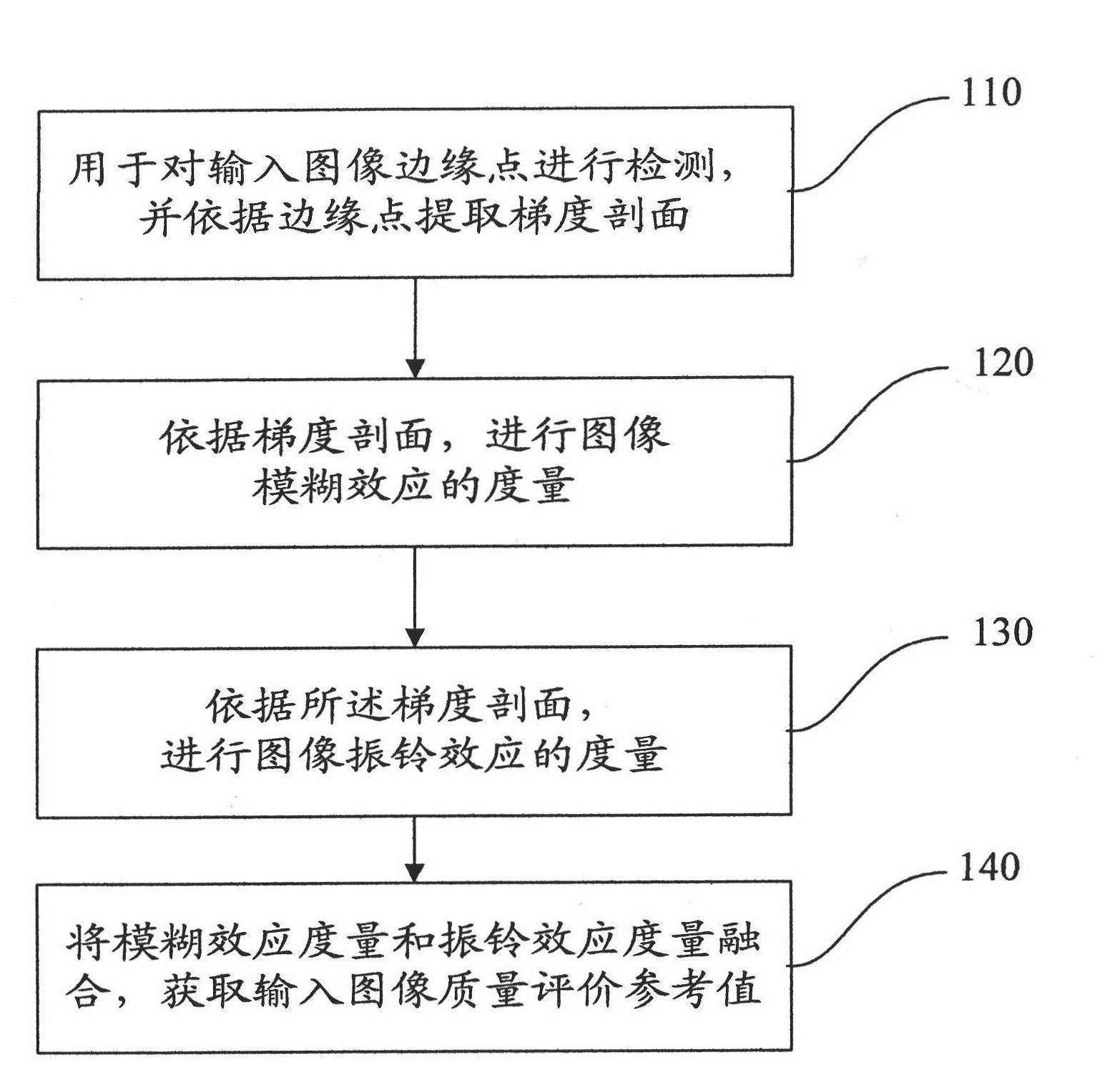
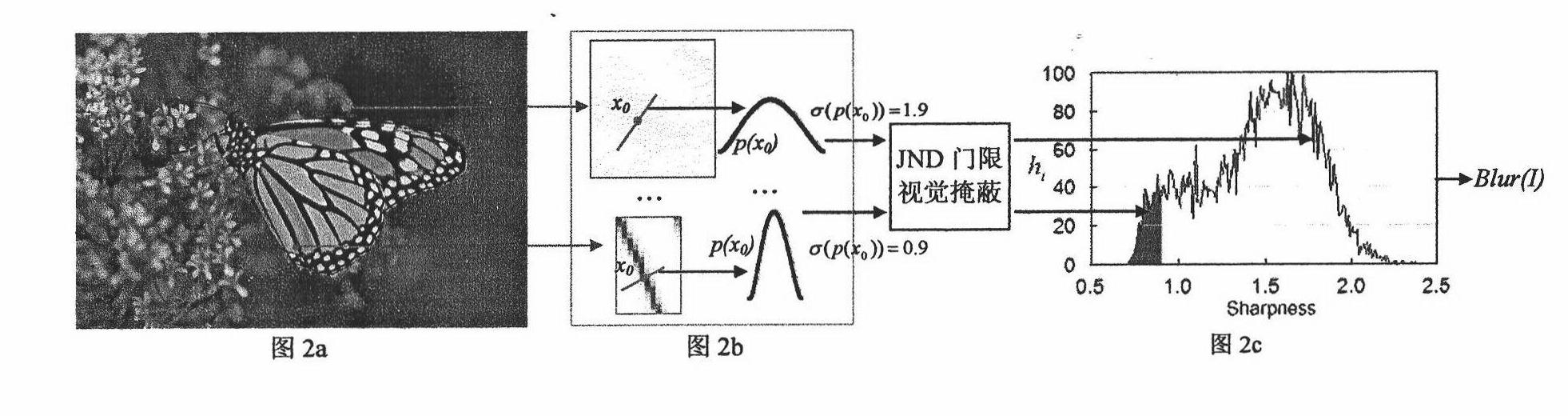
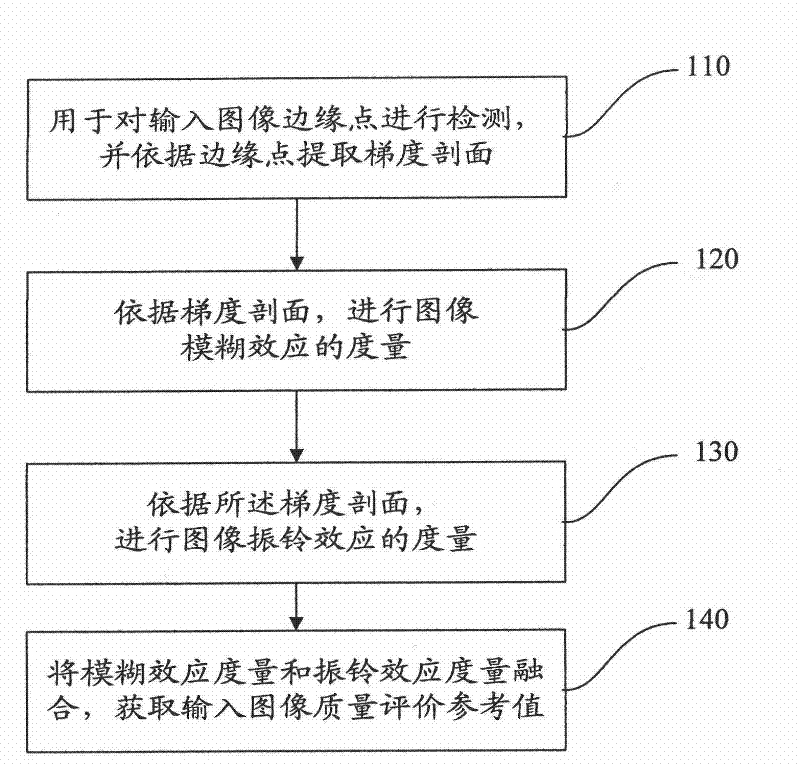
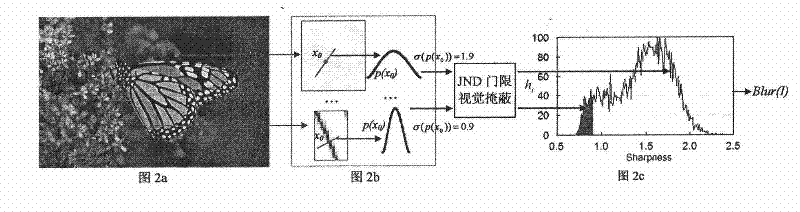
Image reference-free quality evaluation method and system based on gradient profile
The invention discloses image reference-free quality evaluation method and system based on a gradient profile. The image reference-free quality evaluation system comprises a gradient profile extraction device, a blurring effect evaluation device, a ringing effect evaluation device and an integrated evaluation device, wherein the gradient profile extraction device is used for detecting input image edge points and extracting the gradient profile according to the edge points; the blurring effect evaluation device is used for measuring the blurring effect of images according to the gradient profile; the ringing effect evaluation device is used for measuring the ringing effect of the images according to the gradient profile; and the integrated evaluation device is used for fusing the blurring effect measurement and the ringing effect measurement to acquire a quality evaluation reference value of input images. Based on the invention, the quality evaluation can be carried out on various types of natural images; and especially, the invention has favorable robustness for partially-blurred images due to the defocusing, the motion and other reasons.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
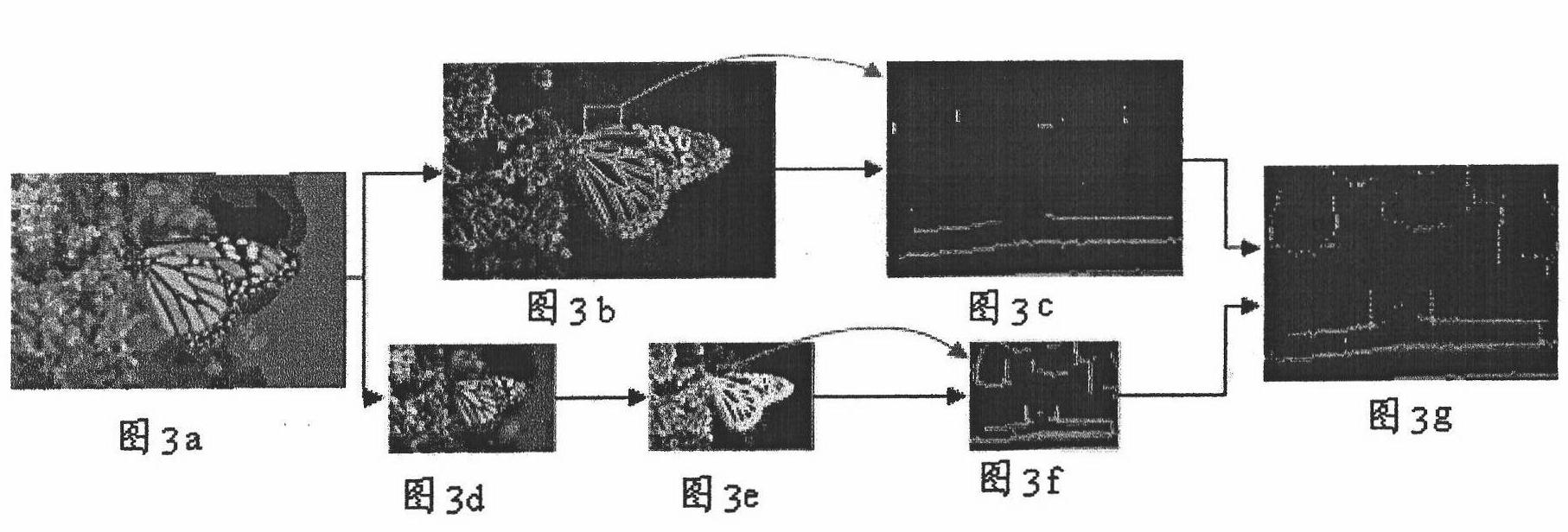
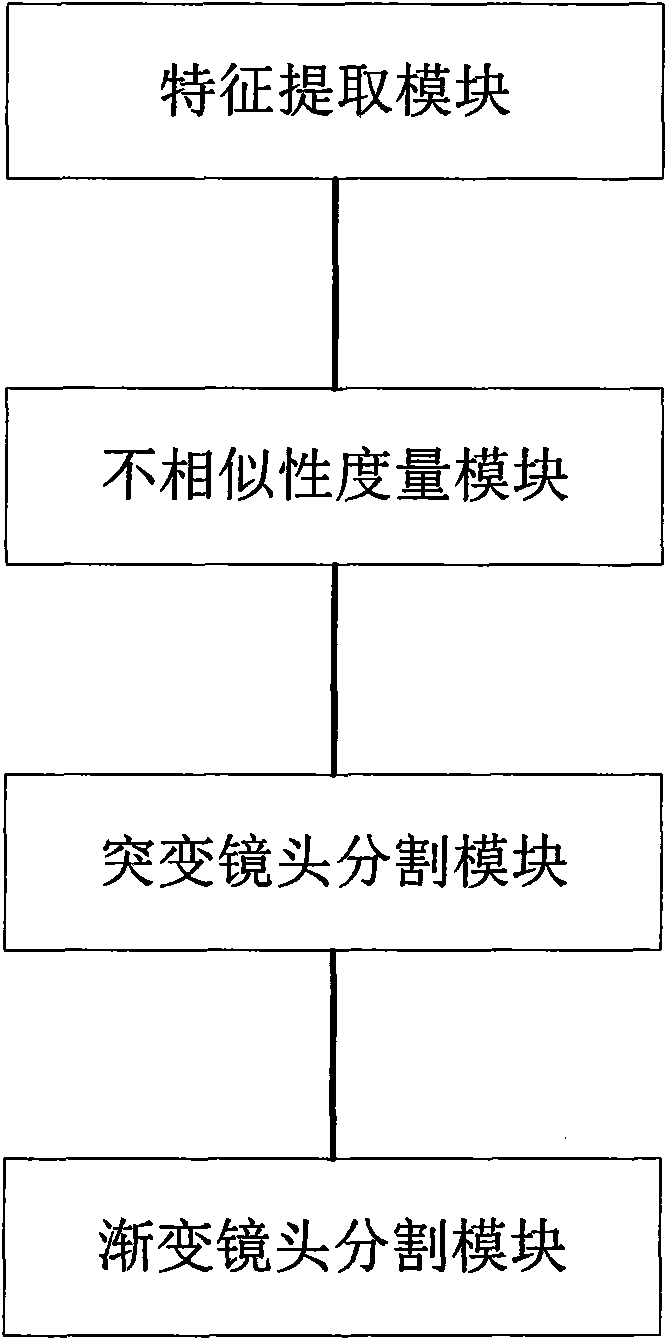
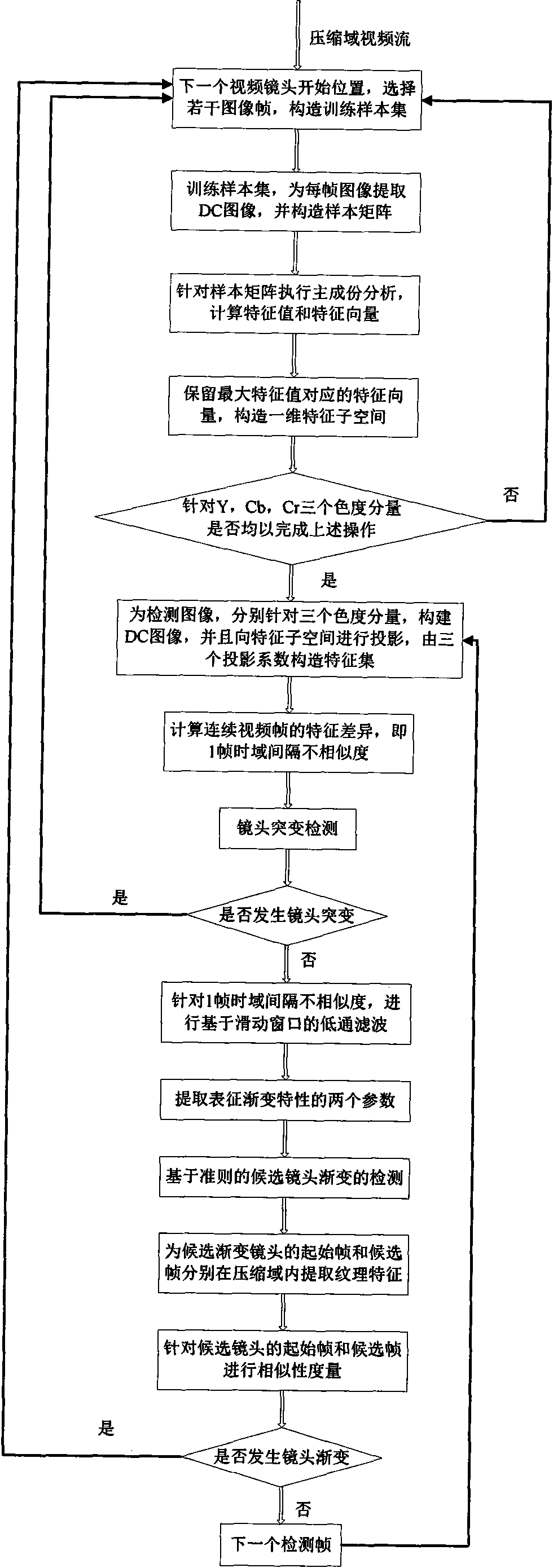
Compressed domain video lens mutation and gradient union automatic segmentation method and system
InactiveCN101650830AImprove Segmentation AccuracyImprove robustnessImage analysisTime domainAutomatic segmentation
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
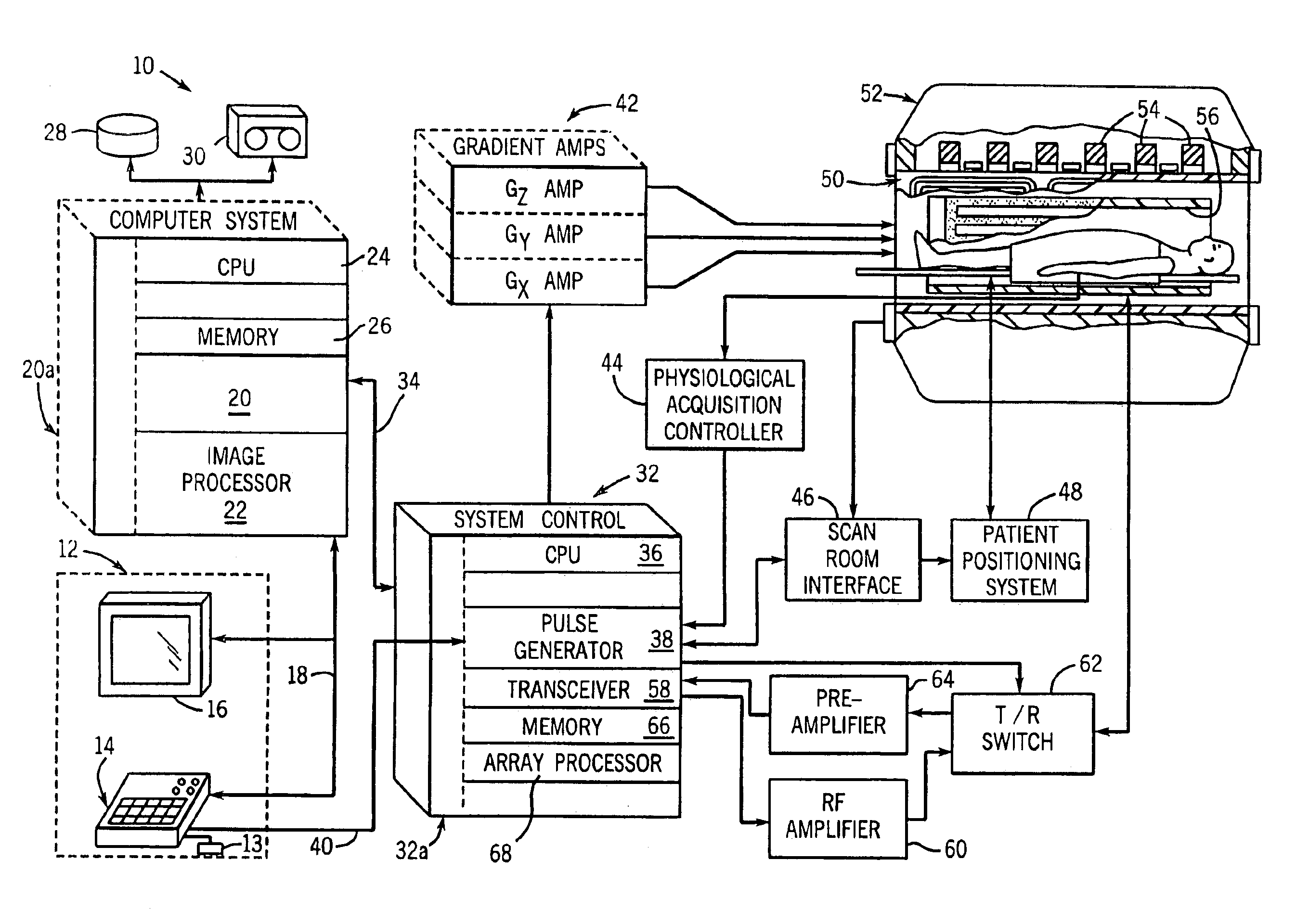
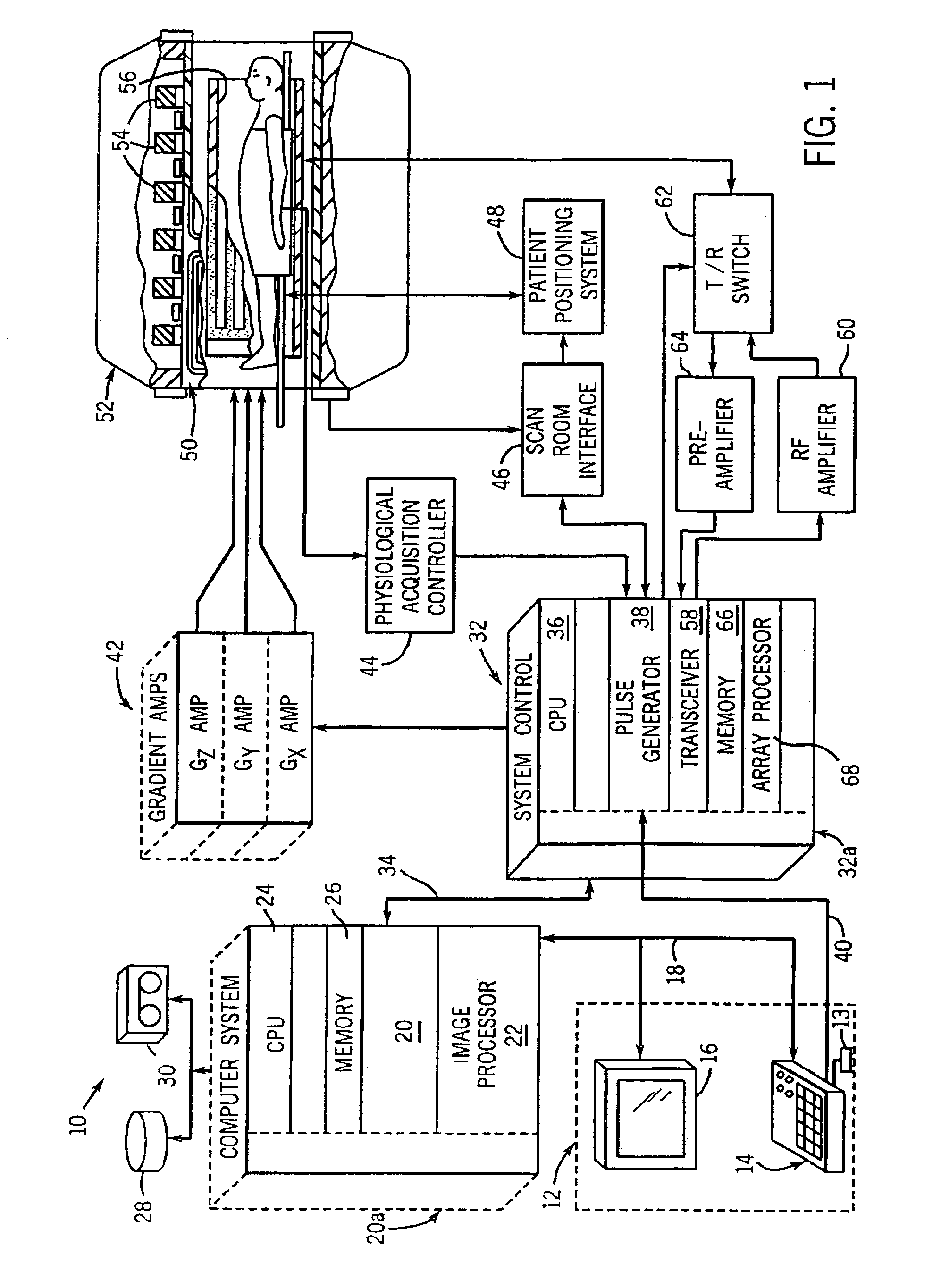
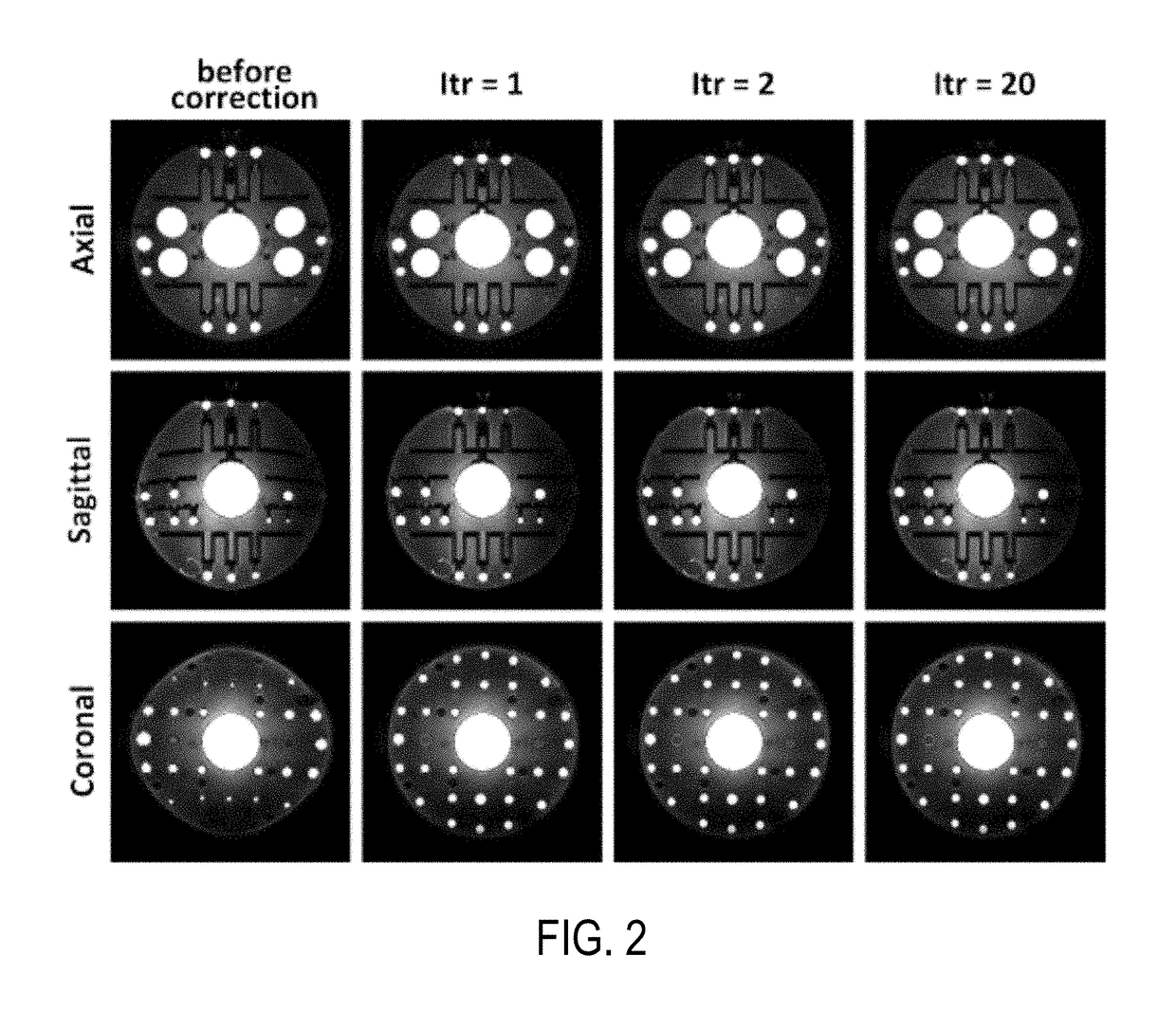
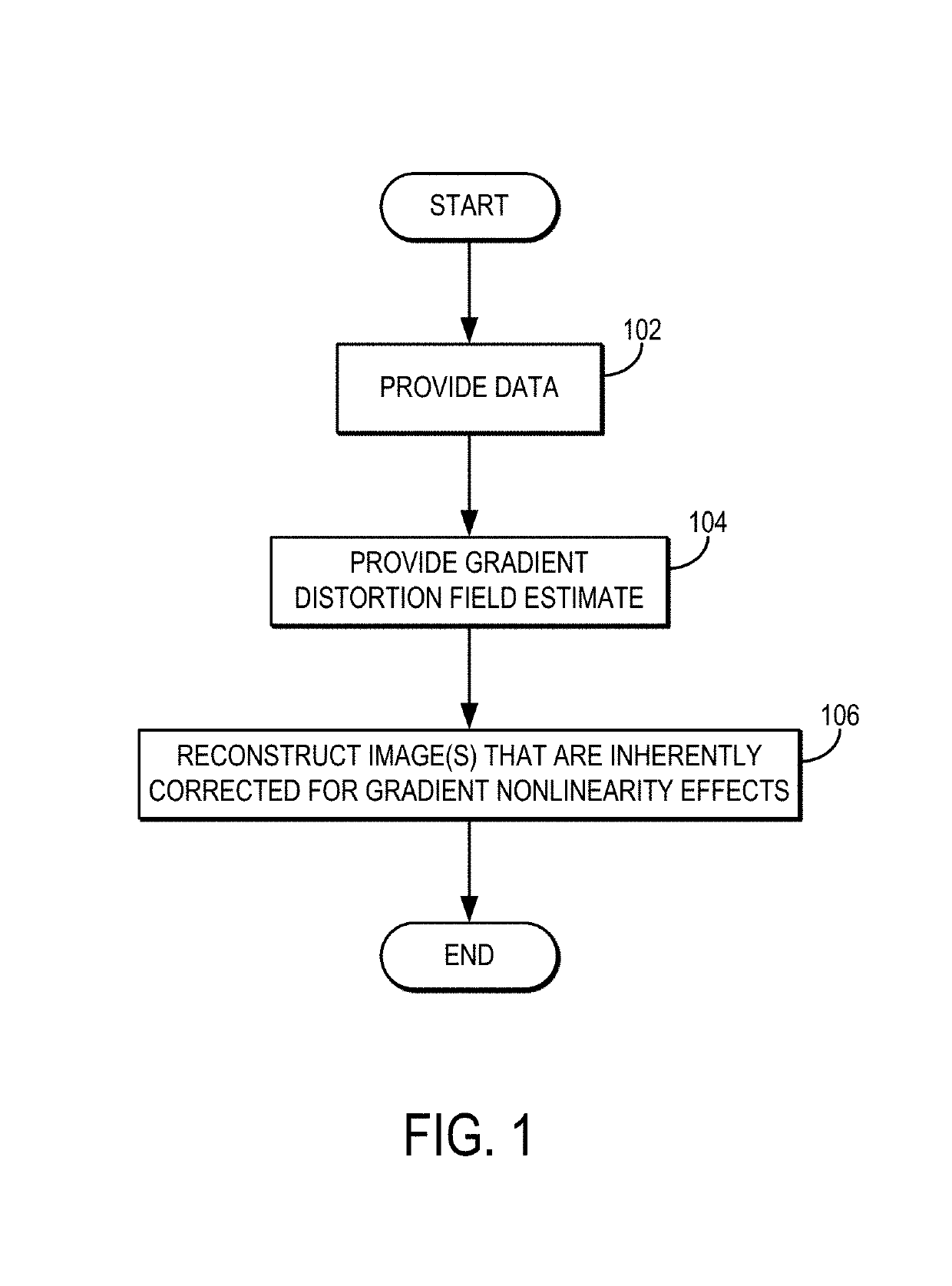
Gradient non-linearity compensation in moving table MRI
InactiveUS6967479B2Quantity minimizationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsData acquisitionComputer science
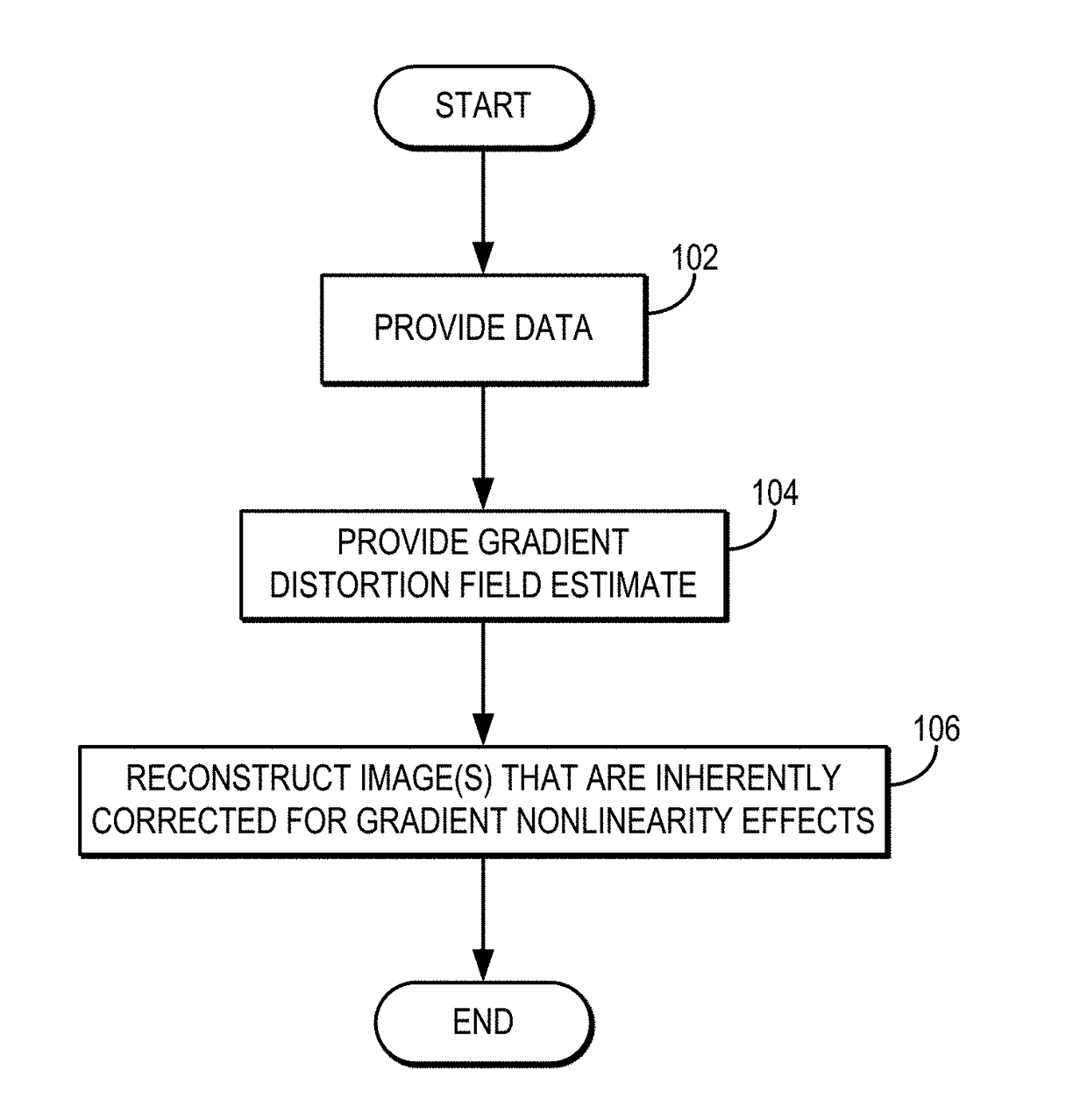
The present invention includes a method and apparatus to correct for gradient field distortions. The invention is particularly applicable in moving table imaging where a single extended image is desirable. The invention includes acquiring MR data in motion in the presence of gradient non-linearities, transforming the MR data acquired into the image domain, and then applying a warping correction function to the transformed MR data. The warp-corrected MR data is then corrected for motion induced during the MR acquisition. The data may be acquired point-by-point, line-by-line, or another sub-portion of the entire MR data acquired, and processed to minimize the amount of motion correction needed. Based on table velocity or acquisition sequence applied, the data is partitioned based on a common motion correction factor, and after correcting for motion, the data is accumulated to build up a final image.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES +2
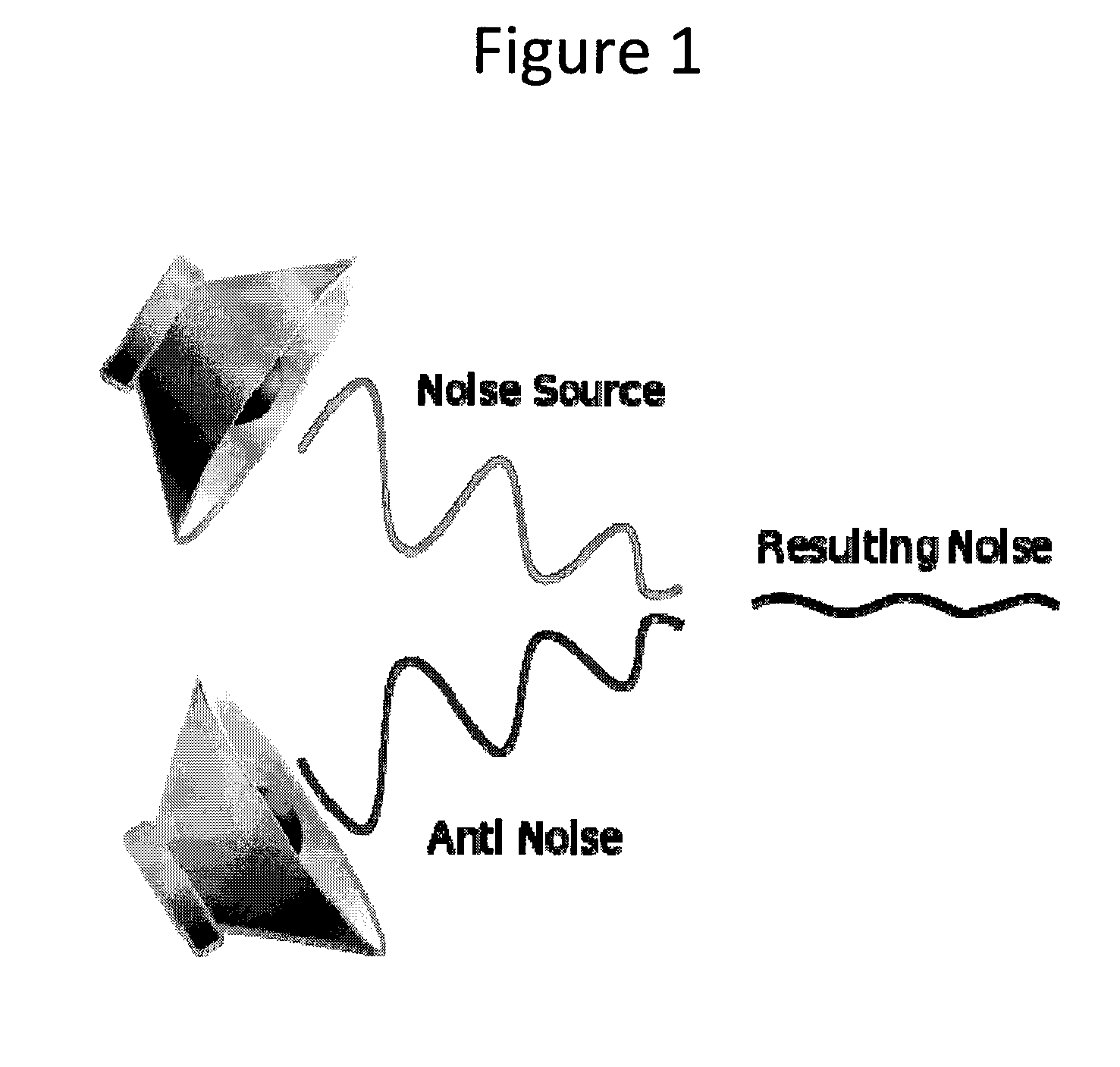
Active noise cancellation method for automobiles
InactiveUS20150003626A1Reduce cancellationReduce noiseMicrophonesEar treatmentNegative phaseEngineering
A Noise Cancellation Process for enclosed cabins is disclosed. According to one embodiment, an input audio source corresponding to sound received from multiple microphones situated equidistantly in both directions in a two dimensional plane, is converted to a digital signal via an analog to digital (A / D) convertor. The A / D converted audio is analyzed for content to identify ambient noise. The frequency, amplitude and phase of the identified ambient noise is subsequently determined. A Noise correction sound wave is generated with negative phase of that corresponding to the identified ambient noise. The noise correction sound wave is added to the identified noise to create a noise corrected sound.
Owner:MAX SOUND CORP
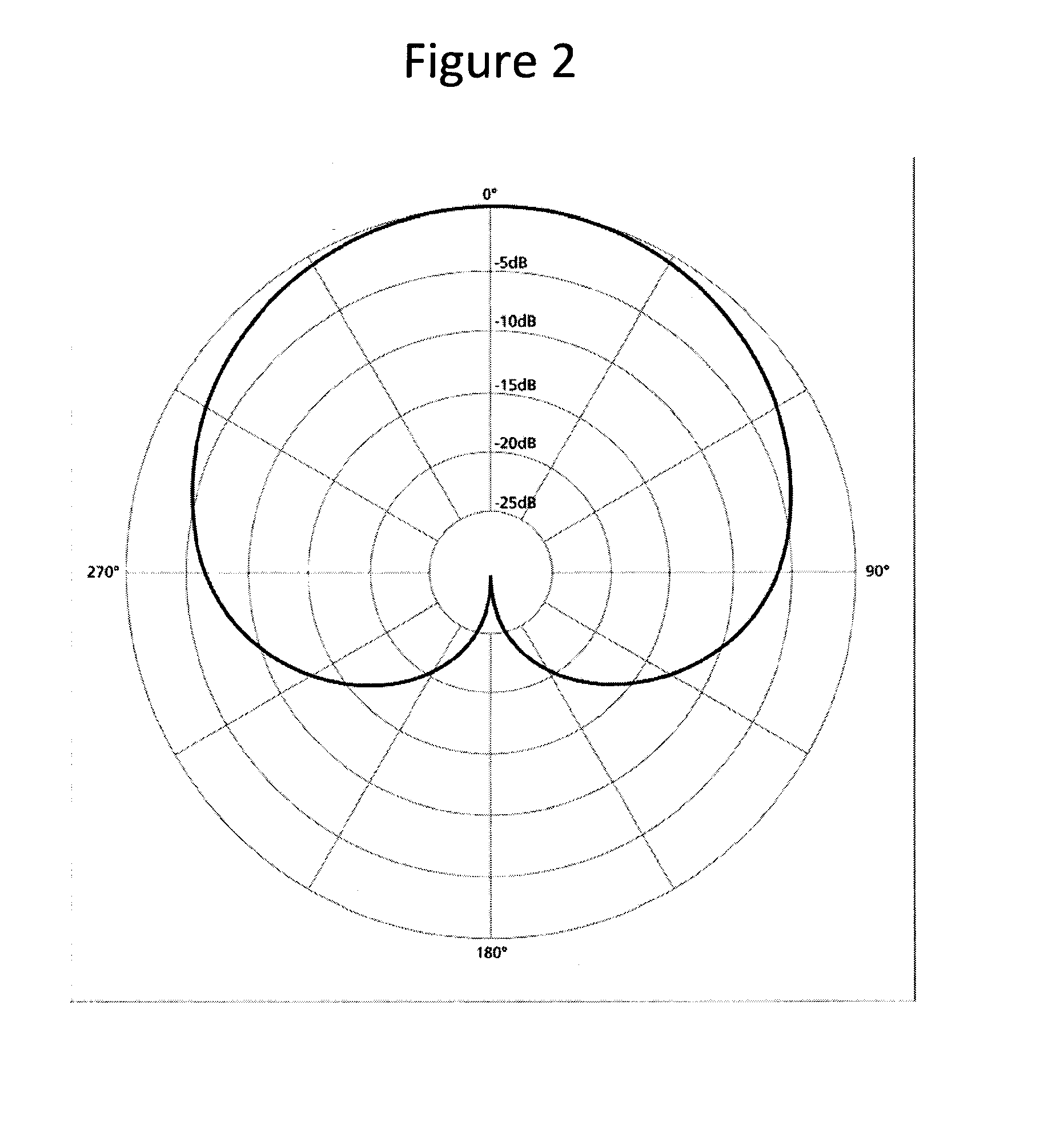
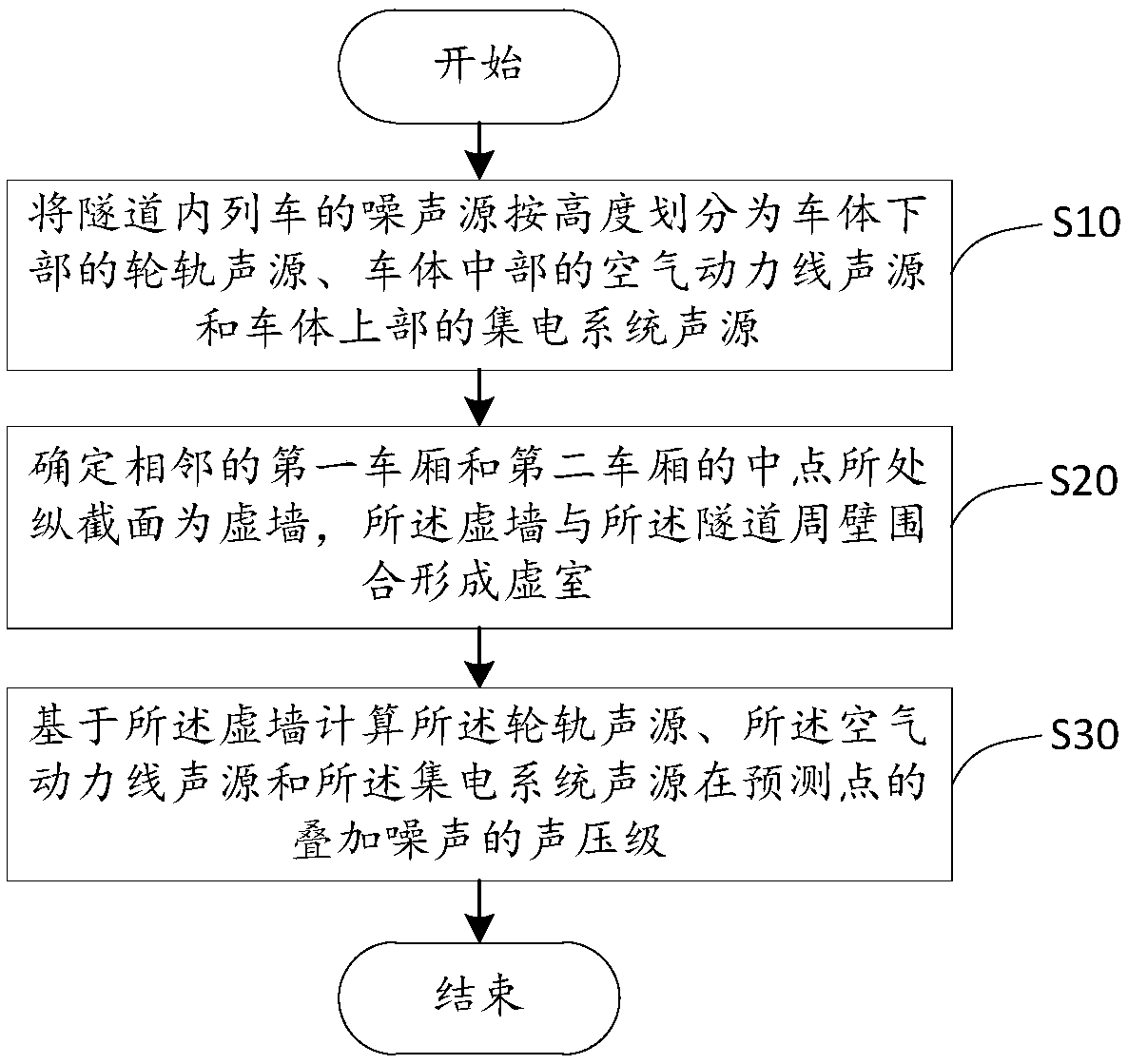
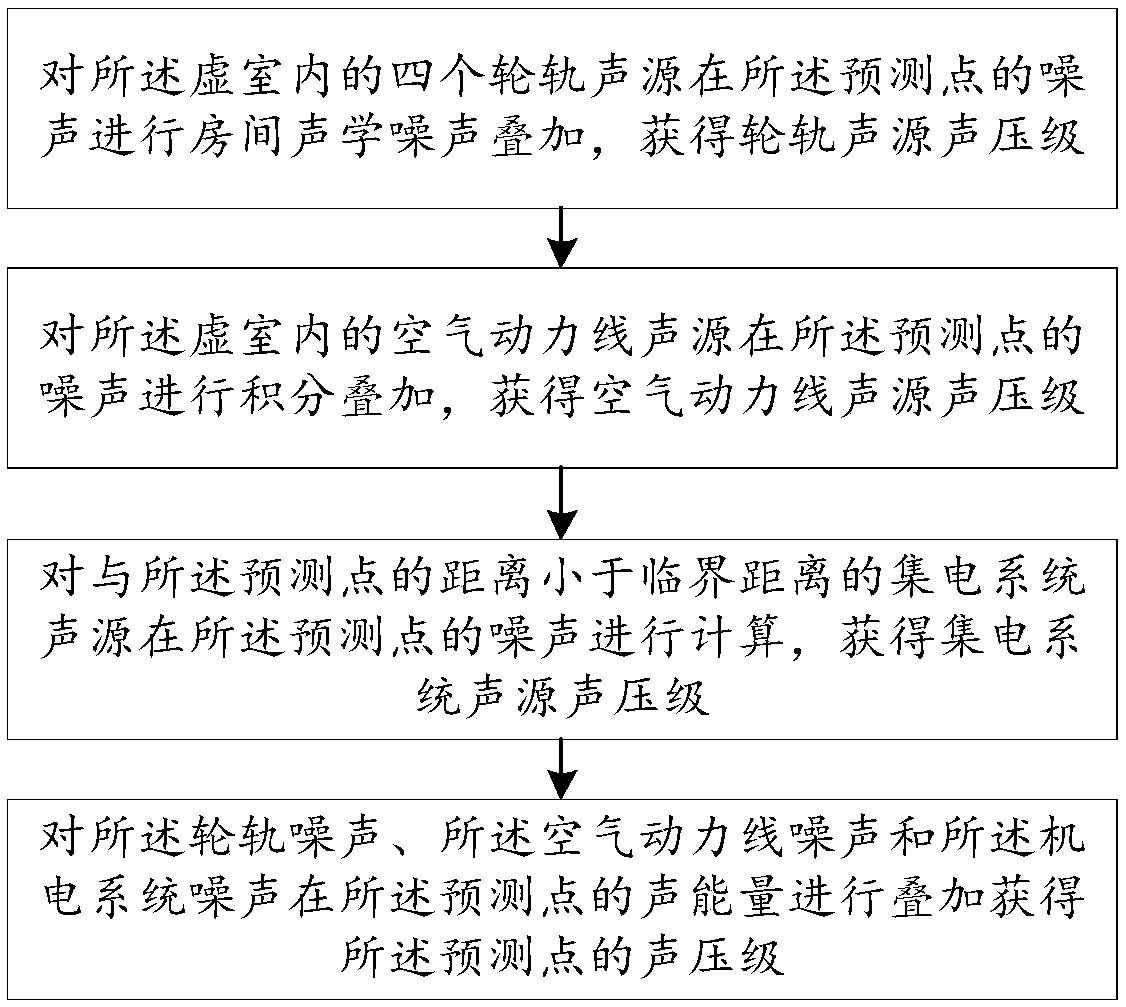
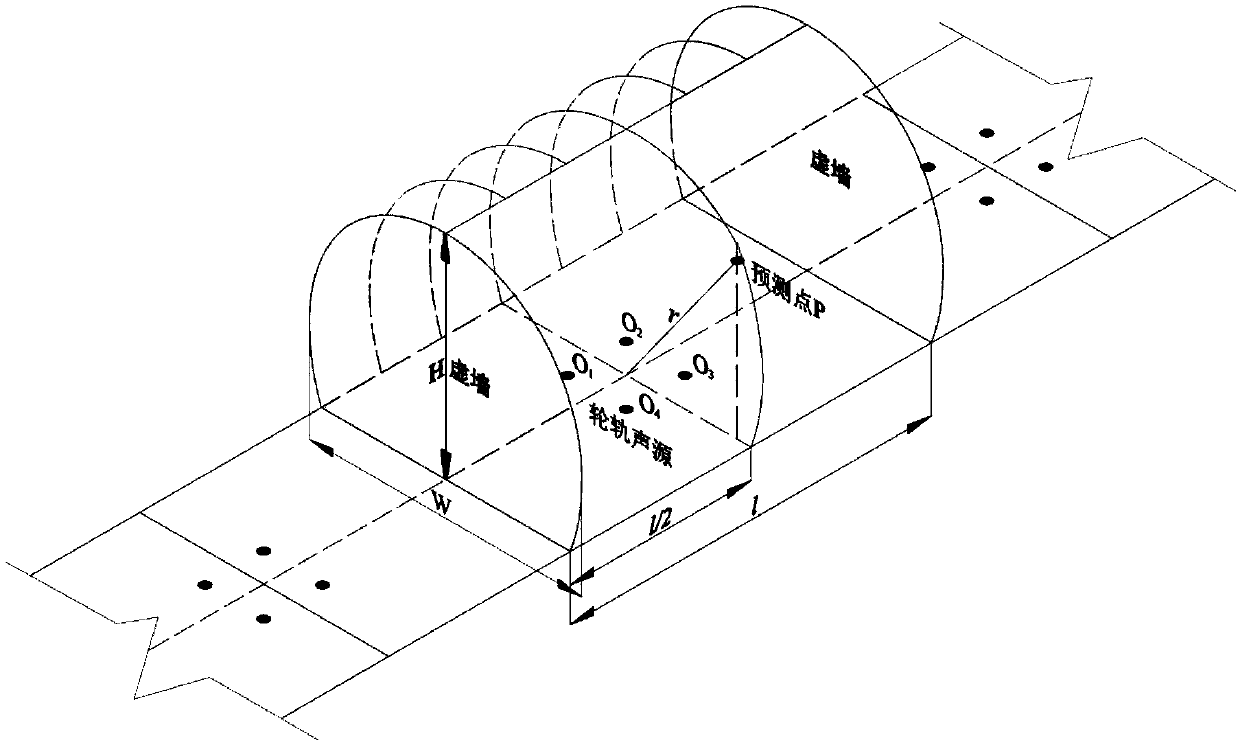
Method and apparatus for measuring and calculating train noise in tunnel and storage medium
InactiveCN108680249AHigh precisionImprove accuracySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSound sourcesCollection system
The invention provides a method and apparatus for measuring and calculating train noise in a tunnel and a storage medium and relates to the technical field of high speed train noise prediction. The method for measuring and calculating train noise in the tunnel comprises the following steps: train noise sources in the tunnel are divided into wheel-rail sound sources in a lower part of the vehicle body, aerodynamic line sound sources in a middle part of the vehicle body, and a current collection system sound source in an upper part of the vehicle body; a longitudinal section where a middle pointbetween adjacent first and second carriages is positioned is determined as a virtual wall, and a virtual room is formed via enclosure of the virtual wall and a surrounding wall of the tunnel; a soundpressure level of superimposed noise of the wheel-rail sound sources, the aerodynamic line sound sources, and the current collection system sound sources at a prediction point is calculated based onthe virtual wall. According to the method for measuring and calculating train noise in the tunnel, a plurality of sound source on a train are regarded as point sound sources via arrangement of the virtual room, the sound pressure level is obtained after noise of the point sound sources is superimposed at the prediction point, and prediction accuracy is improved when a noise measurement and calculation quantity is small.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Low-impact noise acquisition magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS7112965B2Nature differentQuality differentMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonancePulse sequence
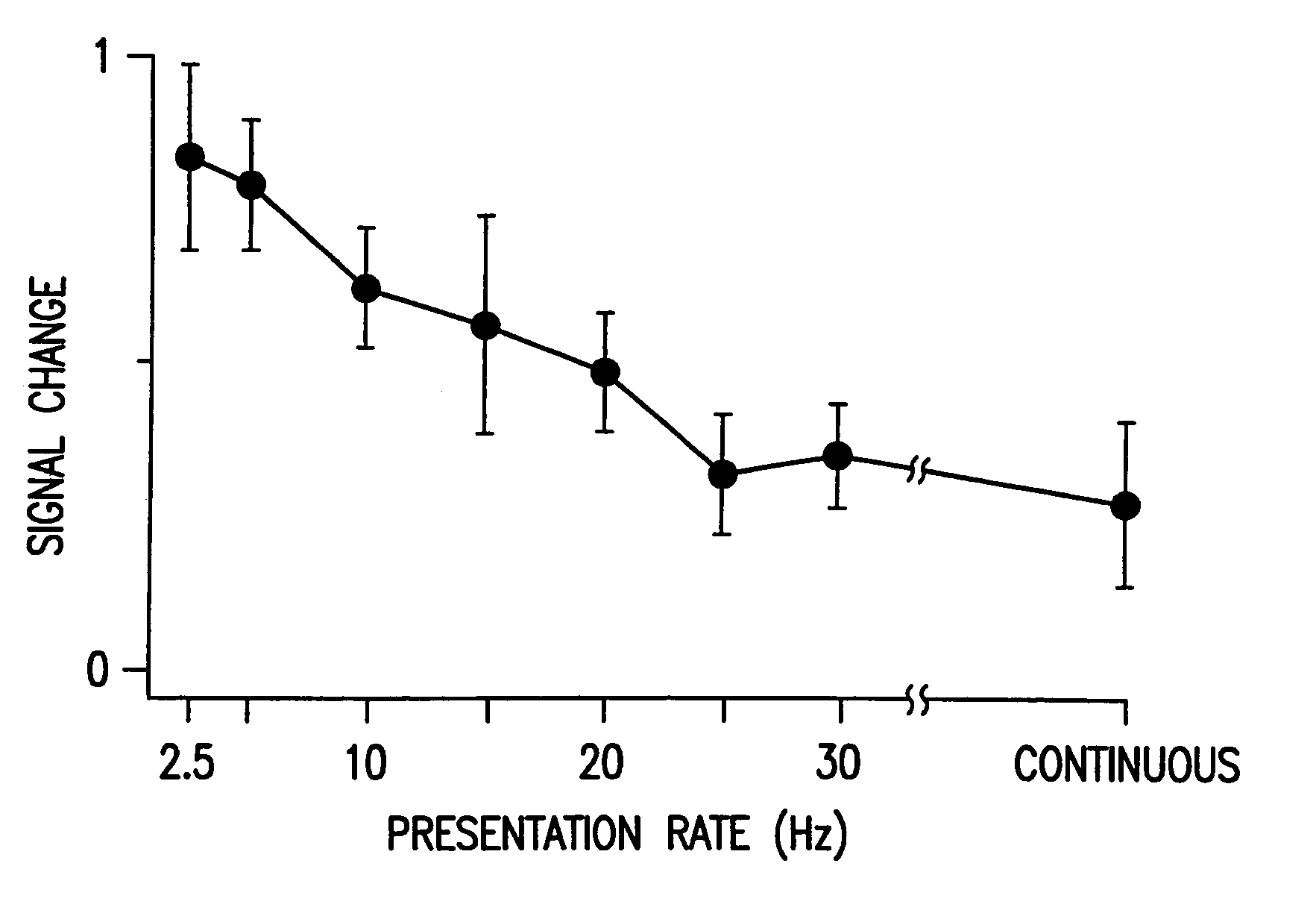
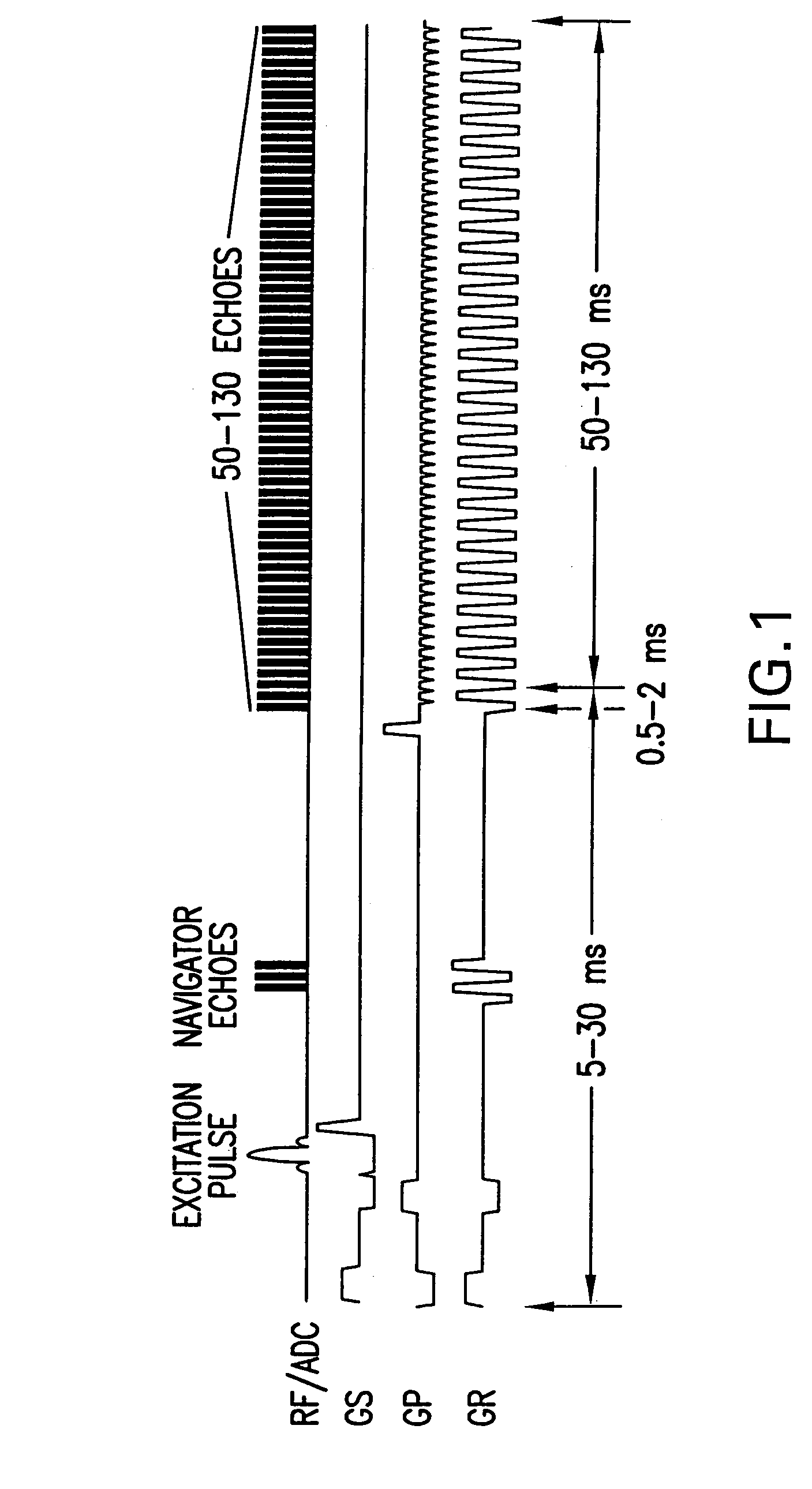
A nuclear magnetic resonance imaging method that utilizes a LINA-EPI gradient pulse sequence, comprising the steps of: generating a LINA-EPI gradient pulse sequence comprising a read gradient, a RF excitation pulse, a slice gradient, and a phase encoding gradient; generating substantially monotonous gradient noise as a result of generating the LINA-EPI gradient pulse sequence, wherein the substantially monotonous gradient noise is substantially without banking and minimizes confounding BOLD effects during imaging; and imaging a test subject using the LINA-EPI gradient pulse sequence.
Owner:BASEL UNIV OF +1
Reference-free image objective quality evaluation method based on gradient self-similarity
InactiveCN107146216AImprove relevanceReflects the degree of image distortionImage enhancementImage analysisObjective qualityStatistical analysis
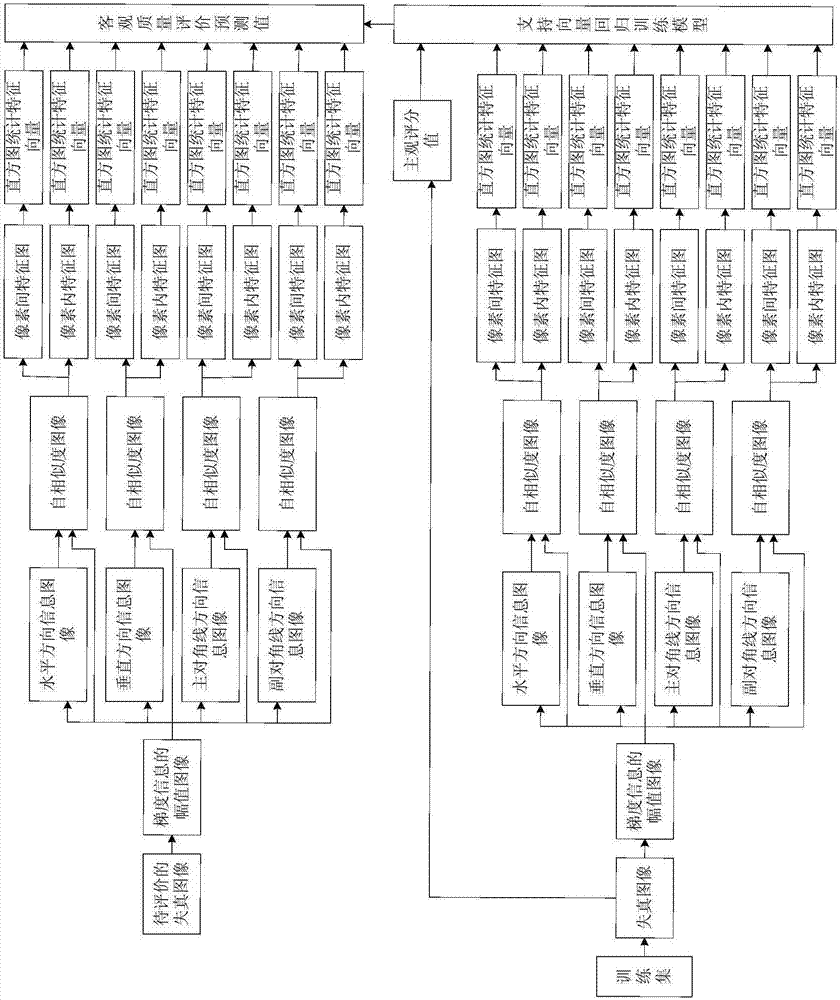
The invention discloses a reference-free image objective quality evaluation method based on gradient self-similarity. According to the process of the method, first, gradient filtering is performed on a to-be-evaluated distorted image to obtain an amplitude image of gradient information; second, information images in four directions are obtained according to the amplitude image of the gradient information, and a self-similarity image between the information image in each direction and the amplitude image is calculated; third, inter-pixel feature extraction method operation and intra-pixel feature extraction method operation are performed on the self-similarity images to obtain an inter-pixel feature graph and an intra-pixel feature graph; fourth, a histogram statistical method is adopted to perform statistical analysis on the inter-pixel feature graph and the intra-pixel feature graph; and last, support vectors are adopted to perform regression prediction on an objective quality evaluation predicted value of the to-be-evaluated distorted image according to histogram statistical feature vectors. The method has the advantages that influences of changes of image gradient self-similarity on visual quality can be fully considered, and therefore the correlation between an objective evaluation result and subjective perception can be effectively improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
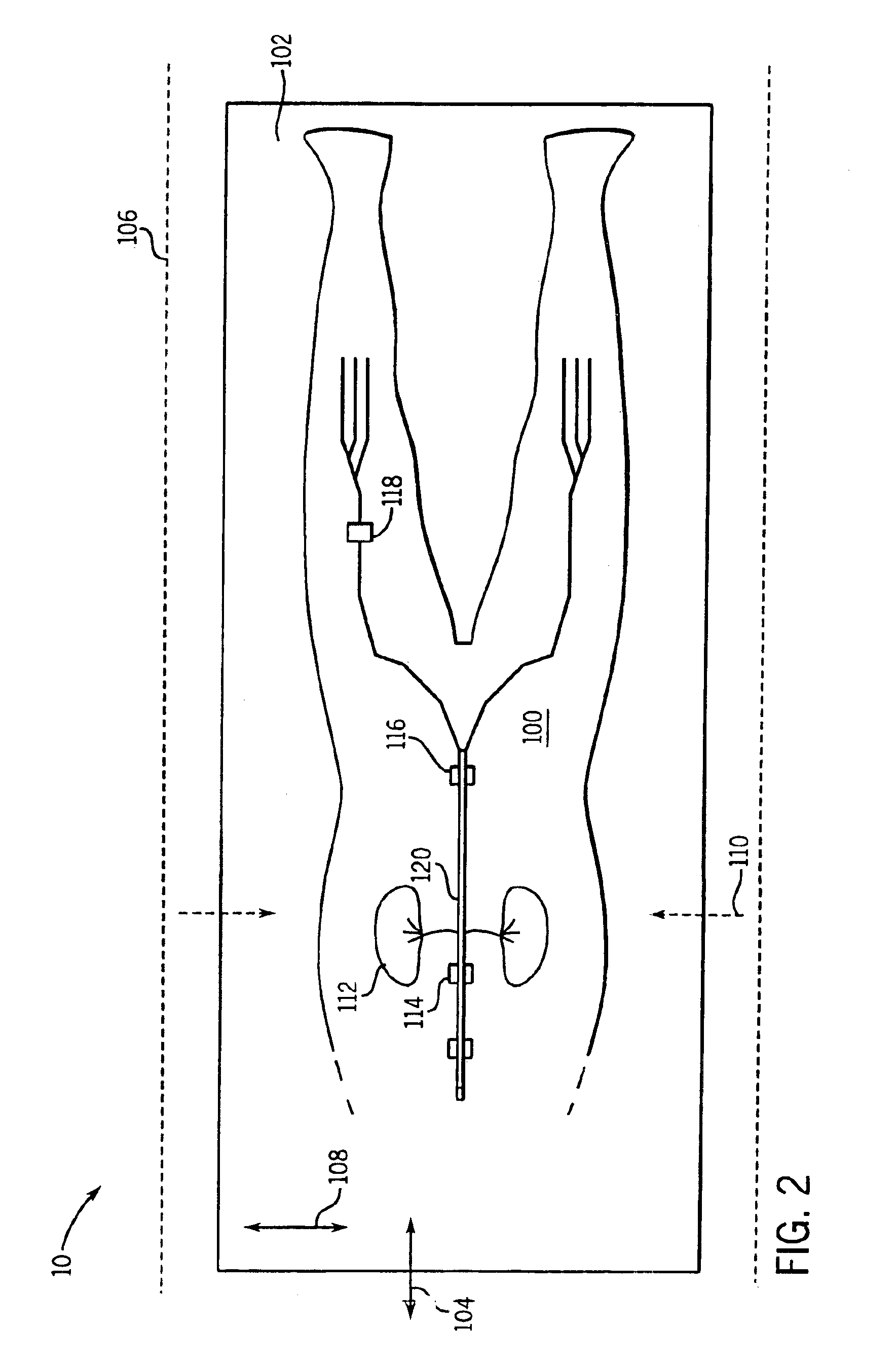
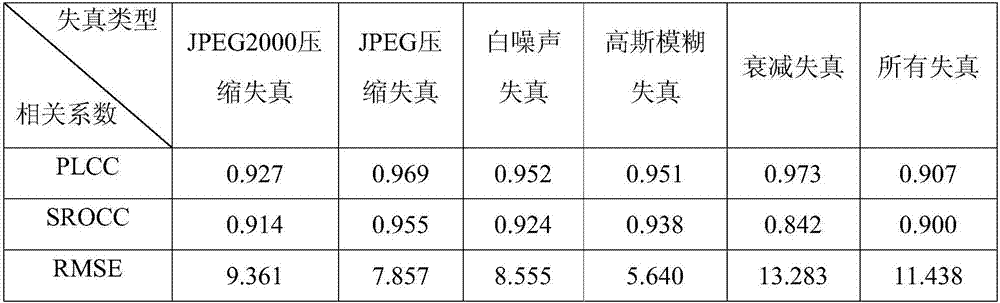
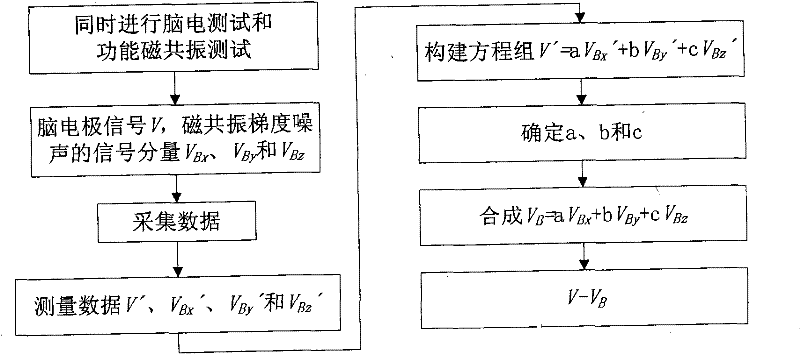
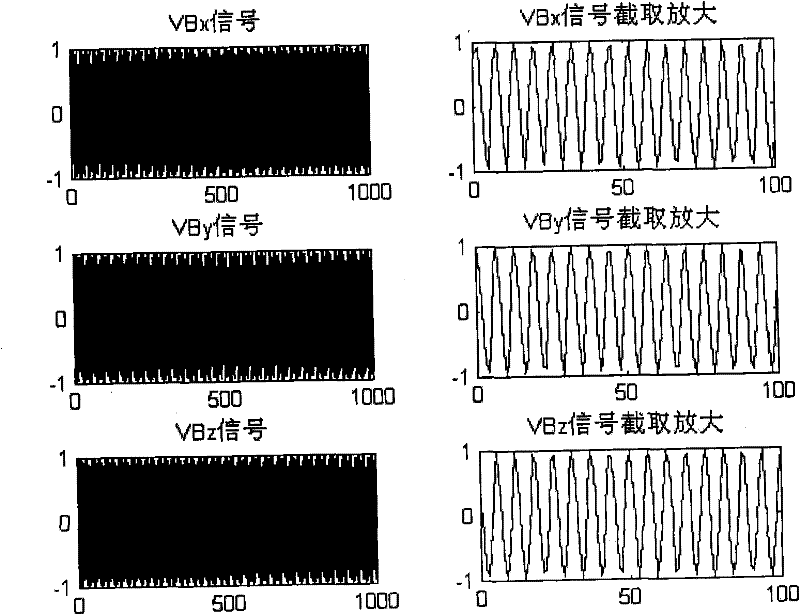
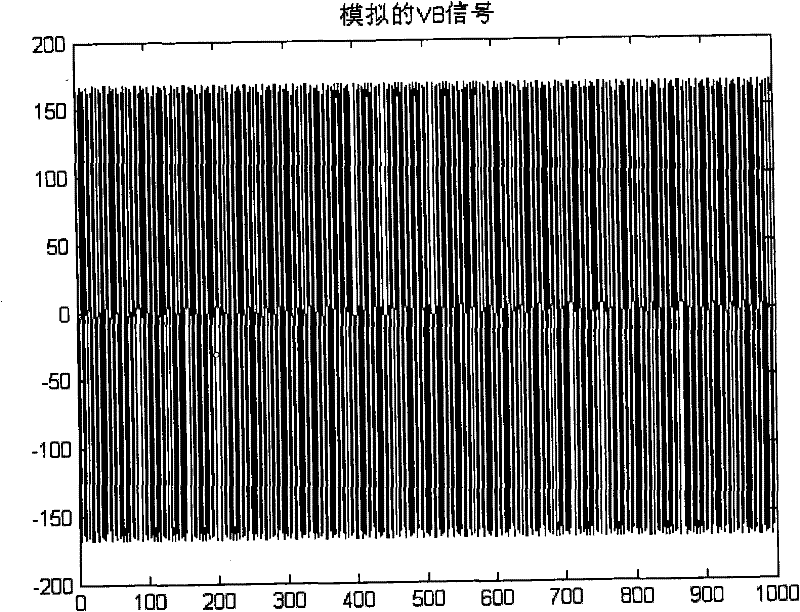
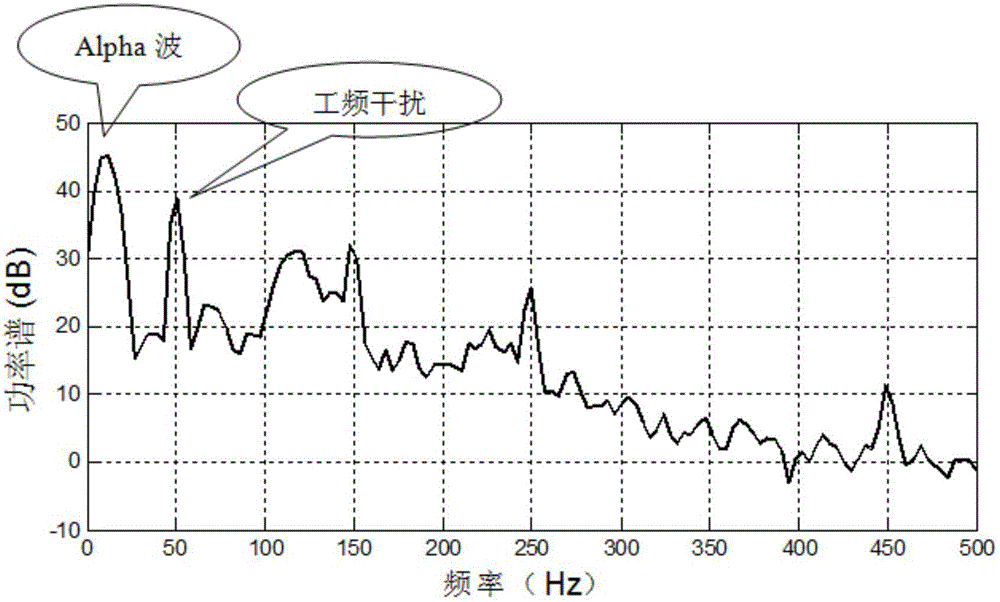
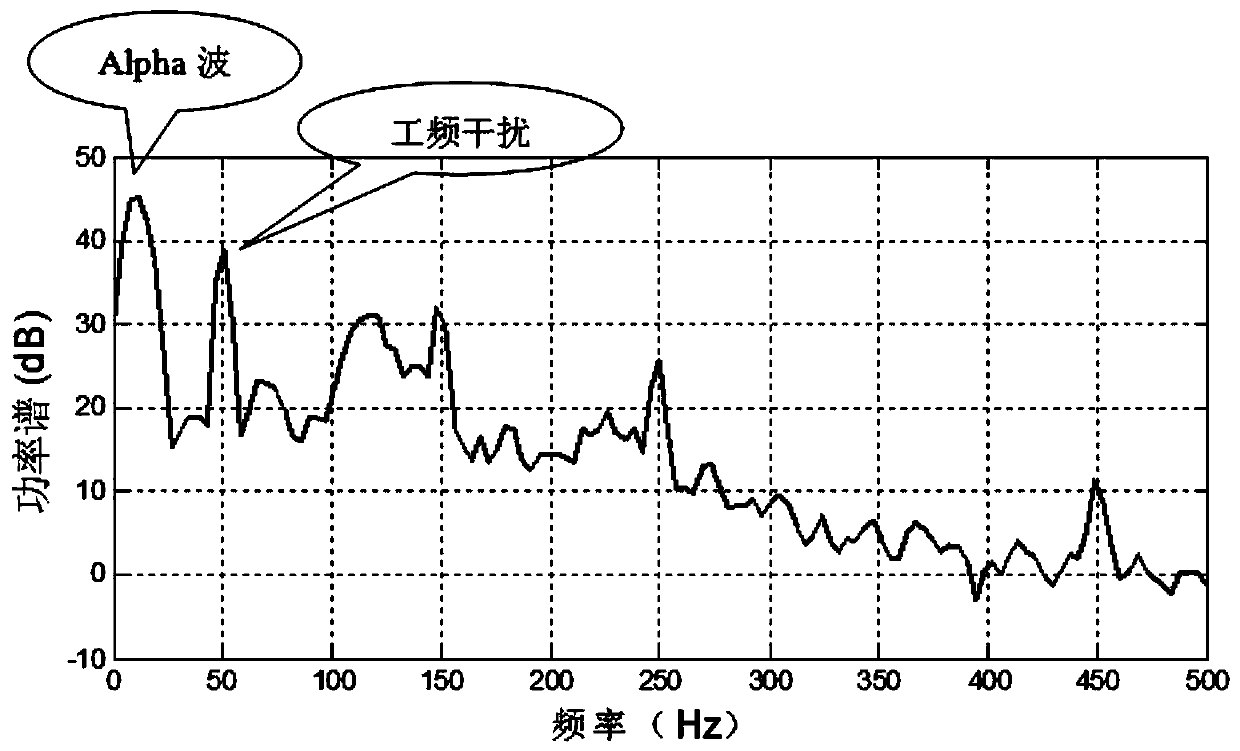
Method for removing magnetic resonance gradient noise in electroencephalograph signal
InactiveCN101744619AGood removal effectImprove real-time performanceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiseaseResonance
The invention provides a method for removing magnetic resonance gradient noise in an electroencephalograph signal, and belongs to the technical field of biological information. In the method, on the premise that electroencephalograph testing and functional magnetic resonance testing are carried out synchronously, three mutually perpendicular coils are adopted to measure signal components VBx, VBy and VBz on the electroencephalograph position while the electroencephalograph signal V is measured; a linear equation set that V' equals to aVBx' plus bVBy' and cVBz' is constructed by using a group of measured data V' of the electroencephalograph signal V and three groups of measured data VBx', VBy' and VBz' of the signal components VBx, VBy and VBz of the magnetic resonance gradient noise so as to obtain coefficients a, b and c; a magnetic resonance gradient noise signal that VB equals to aVBx plus VBy and VBz is synthesized by using the coefficients a, b and c and the signal components VBx, VBy and VBz of the magnetic resonance gradient noise; and finally, the signal VB of magnetic resonance gradient signal is reduced from the electroencephalograph signal V to acquire the magnetic resonance gradient noise removed electroencephalograph signal. The method has the characteristics of clock synchronization and real-time calculation, does not require hardware reforming on magnetic resonance equipment, and can be applied to research and diagnosis on human brain and diseases related to human brain.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Intelligent gradient noise reduction system
InactiveCN101689373AMaintain speech-to-noise level ratiosLittle change in levelSpeech analysisNoise levelVoice activity
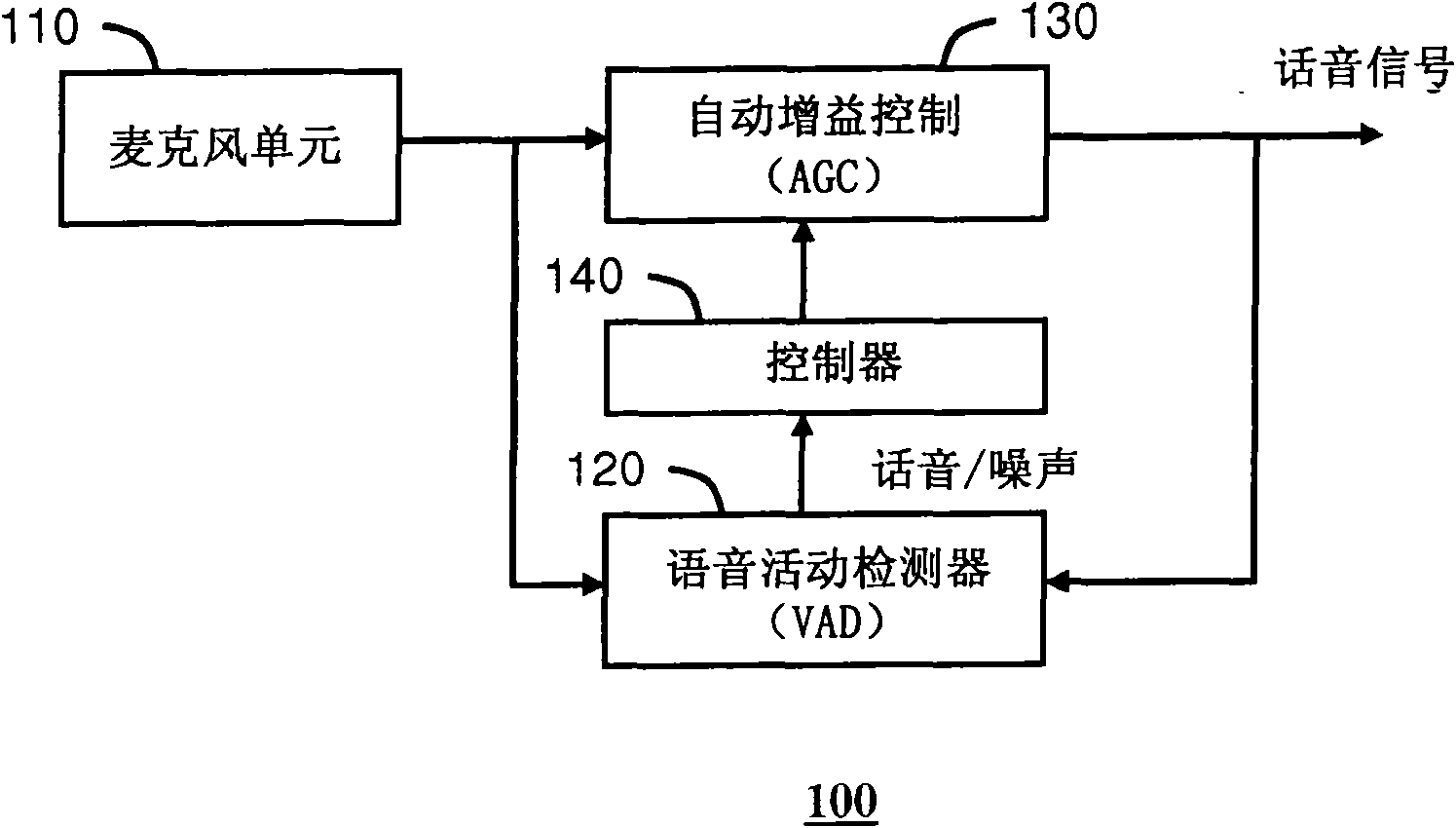
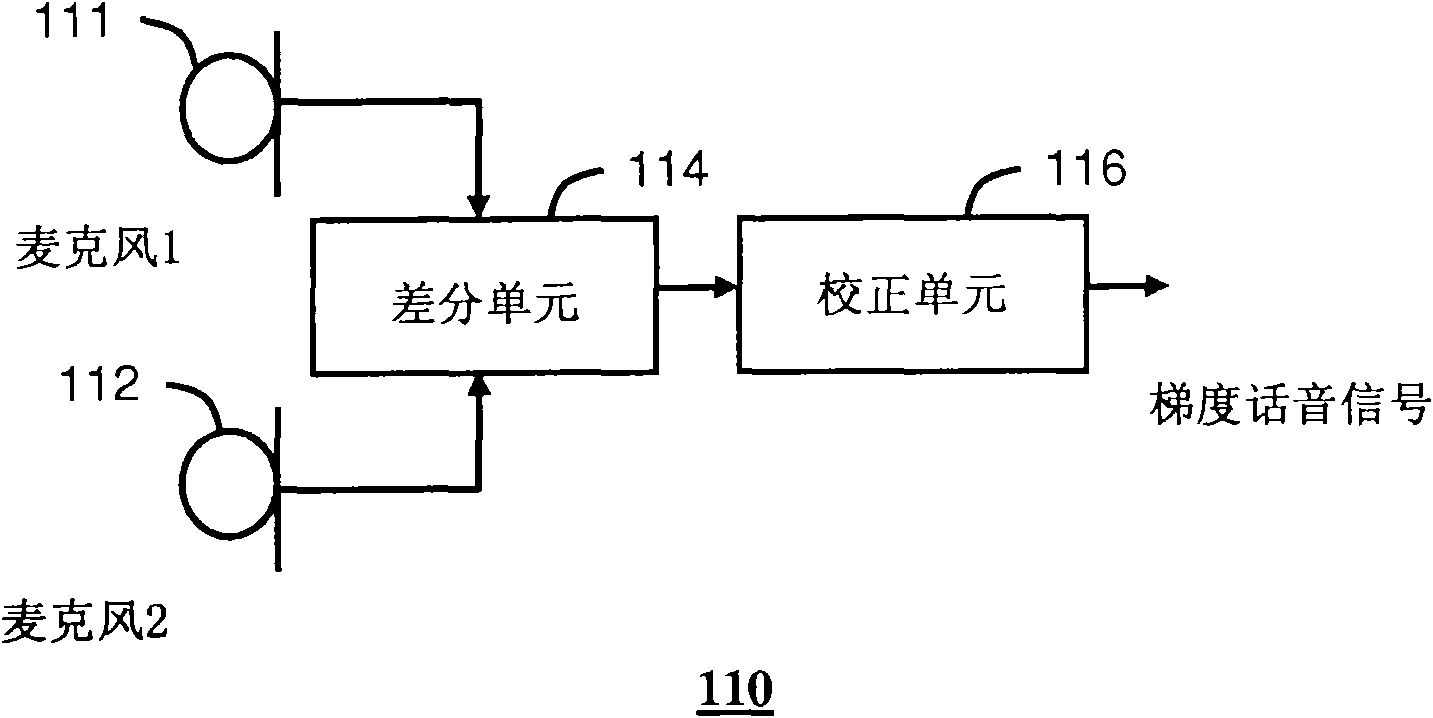
An intelligent noise reduction system (100) is provided. The system can include a gradient microphone (110) to produce a gradient speech signal, a correction unit (116) to de-emphasize a high frequency gain imparted by the gradient microphone, a Voice Activity Detector 120 (VAD) to determine portions of speech activity (701) and portions of noise activity (702) in the gradient speech signal, an Automatic Gain Control 130 (AGC) unit to adapt a speech gain (740) of the gradient speech signal to minimize variations in speech signal levels, and a controller (140) to control the speech gain appliedby the AGC to the portions of noise activity to preserve a speech to noise level ratio between speech activity and noise activity in the gradient speech signal.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
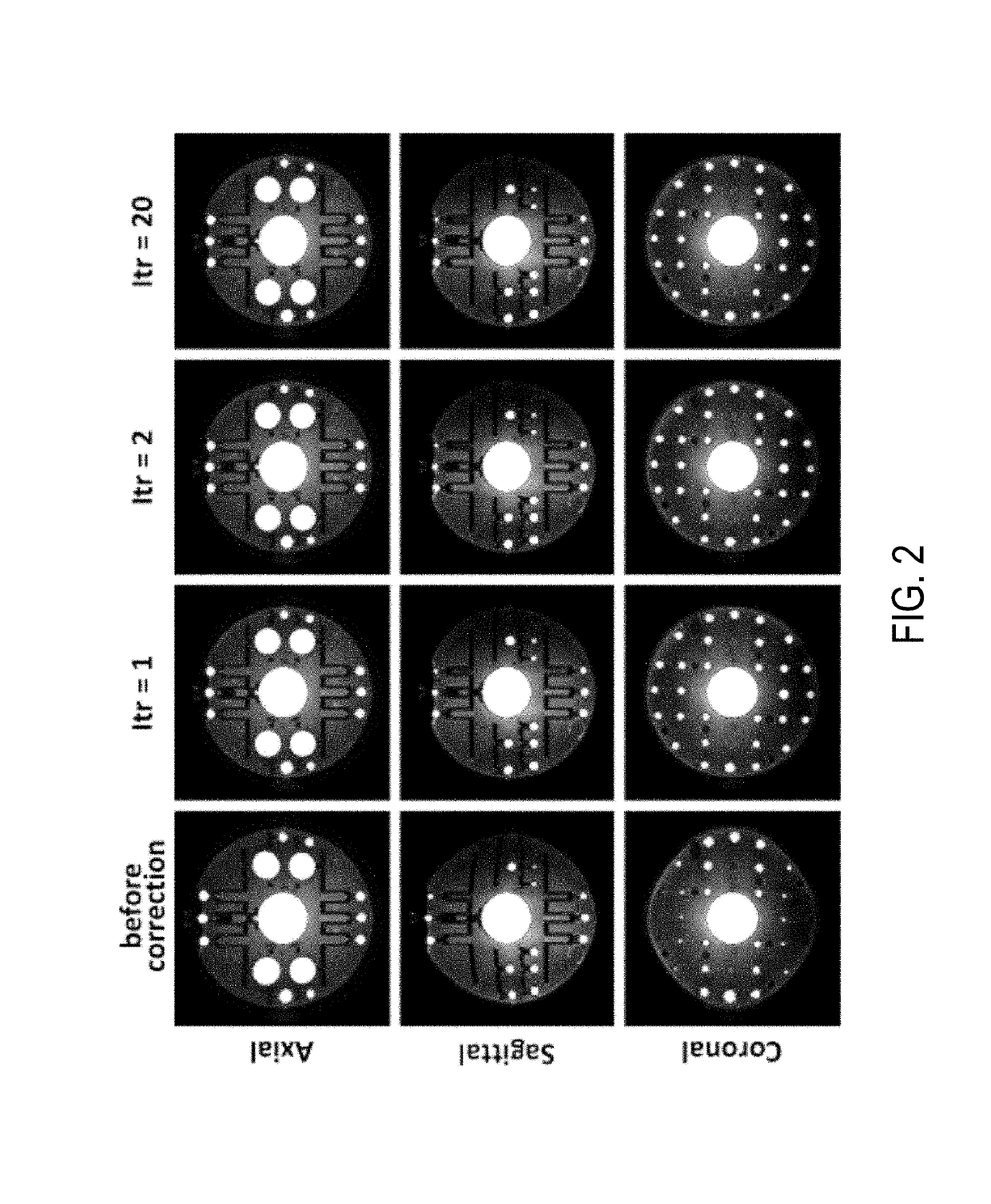
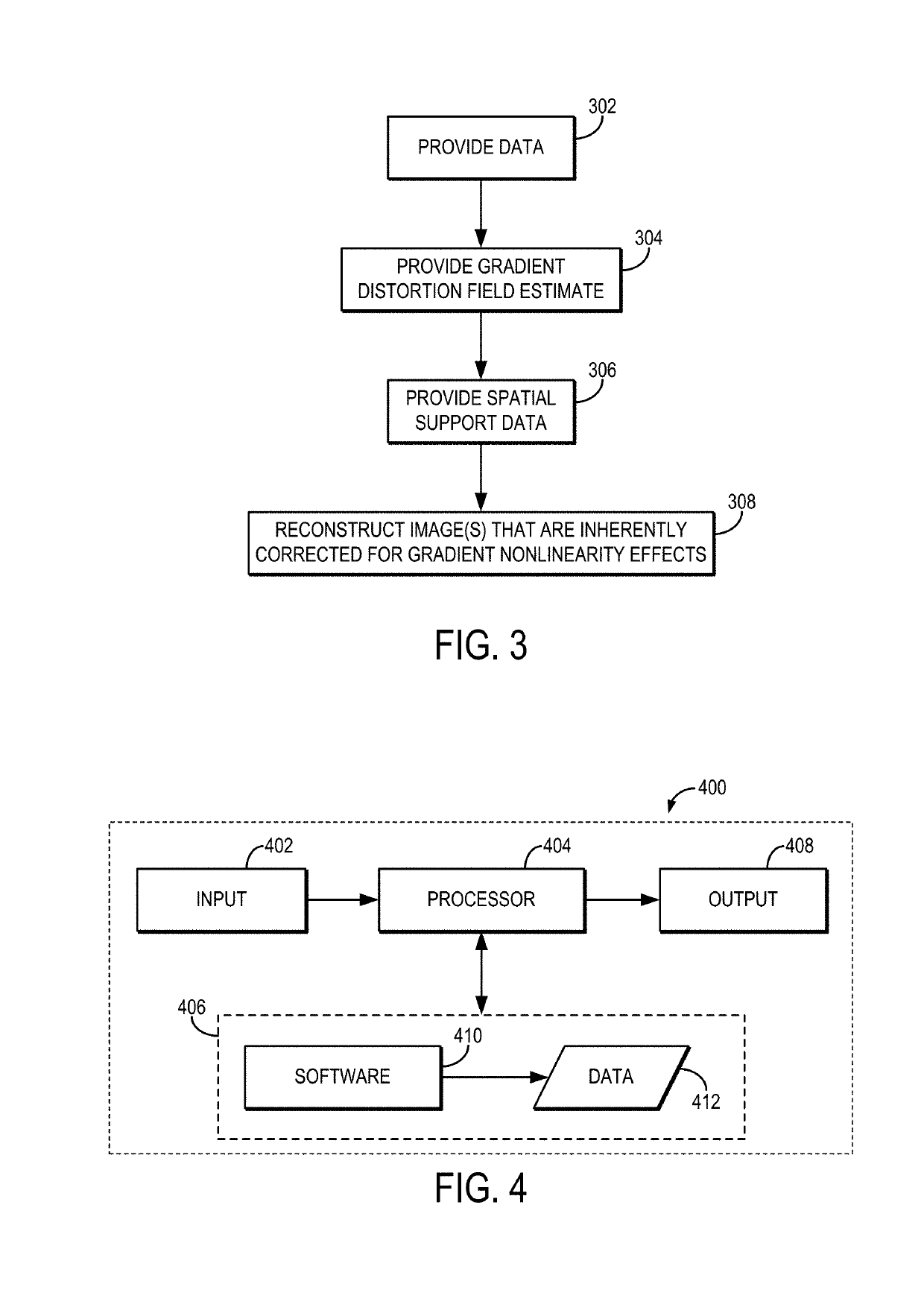
Integrated image reconstruction and gradient non-linearity correction with spatial support constraints for magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20180238988A1The effect is accurateMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceComputational physics
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Method and computer for local correction of gradient non-linearities
ActiveUS20180348325A1Quickly and efficiently takesMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceComputer science
In a method and magnetic resonance (MR) apparatus for generating an approximated trace-weighted MR image of a subject, at least three diffusion-weighted MR images of the subject are created, based on different diffusion encoding directions and diffusion gradient fields with essentially equal diffusion encoding strengths. A weighting factor is determined by an optimization method based on spatial inhomogeneities of the diffusion gradient fields for each image point of the at least three diffusion-weighted MR images. Based on the weighting factors, the at least three diffusion-weighted MR images are combined to generate the approximated trace-weighted MR image. Furthermore, an ADC map is determined based on approximated trace-weighted images and the effective diffusion encoding strength. Furthermore, a trace-weighted MR image is synthesized with nominal diffusion encoding strength based on a trace-weighted image with effective diffusion encoding strength.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Brain signal online denoising method in nuclear magnetic resonance environment
ActiveCN107981862AMeet data processing speed requirementsLower requirementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceSlide window
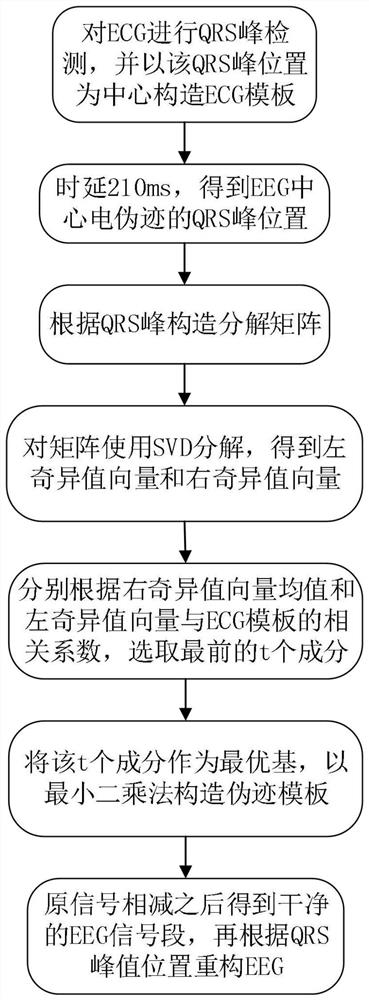
The invention discloses a brain signal online denoising method in a nuclear magnetic resonance environment. The method comprises the steps of 1) conducting high-pass filtering on collected brain electrical signals; 2) conducting up-sampling on the filtered signals and synchronizing the brain electrical signals with markers sent by a fMRI device; 3) constructing a sliding window to construct a noise template Atau for preliminary denoising; 4) slicing a signal Sh mixed with noise into a slice with a length of T*w points, fitting the noise template with slice date through least squares to obtainfitting parameters ytau, and subtracting ytau*Atau from the Sh to obtain a signal Sr with residual artifacts; 5) conducting PCA on the signal Sr, sorting each component according to degree of relevance, taking the largest m components as an optimal base betaj(j=1,2,...,m) of gradient noise, fitting the optimal base with the Sr through the least squares to obtain fitting parameter aj(j=1,2,...,m),subtracting N from the Sr, and conducting denoising through the construction of a gradient noise template and denoising through the PCA to eventually eliminate the gradient noise. The brain signal online denoising method in the nuclear magnetic resonance environment has the advantages that real-time denoising can be conducted on the signals to meet demands of data processing speed of an online experiment.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GUANGDA INNOVATION TECH CO LTD
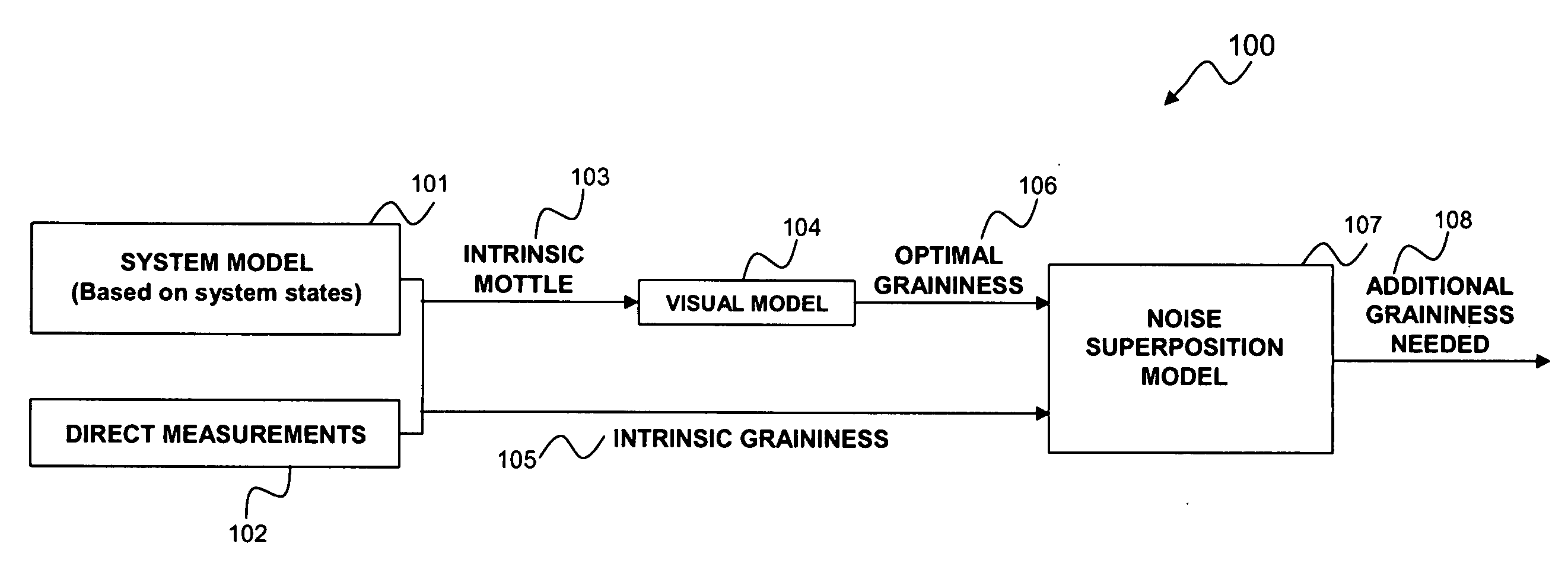
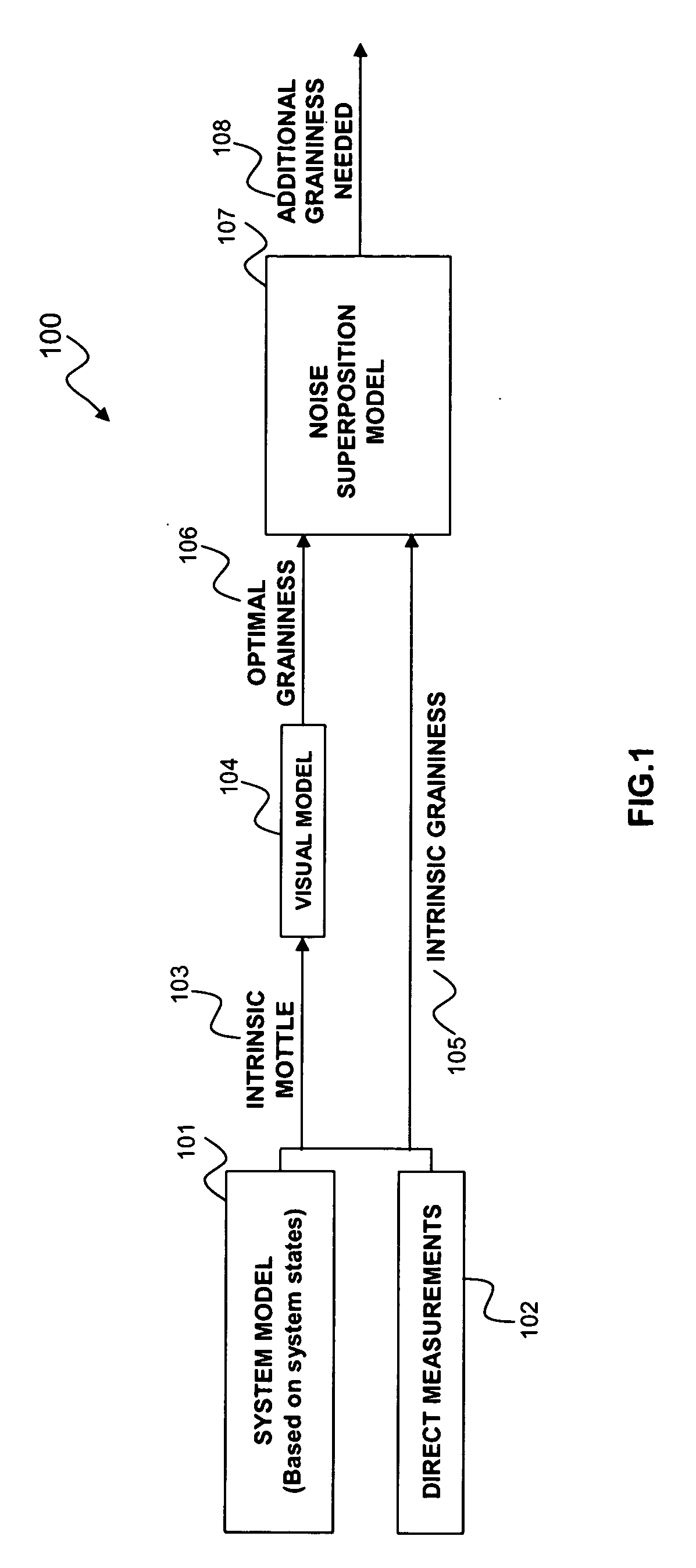
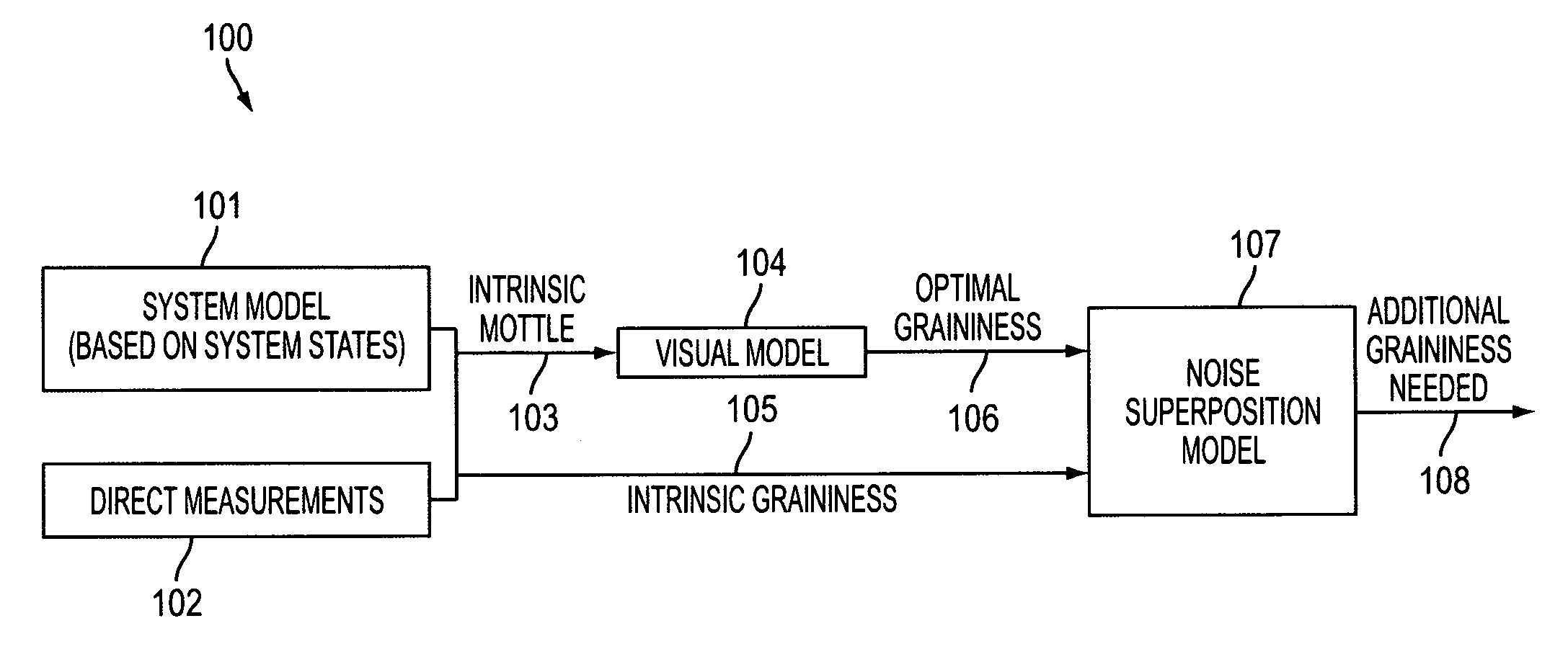
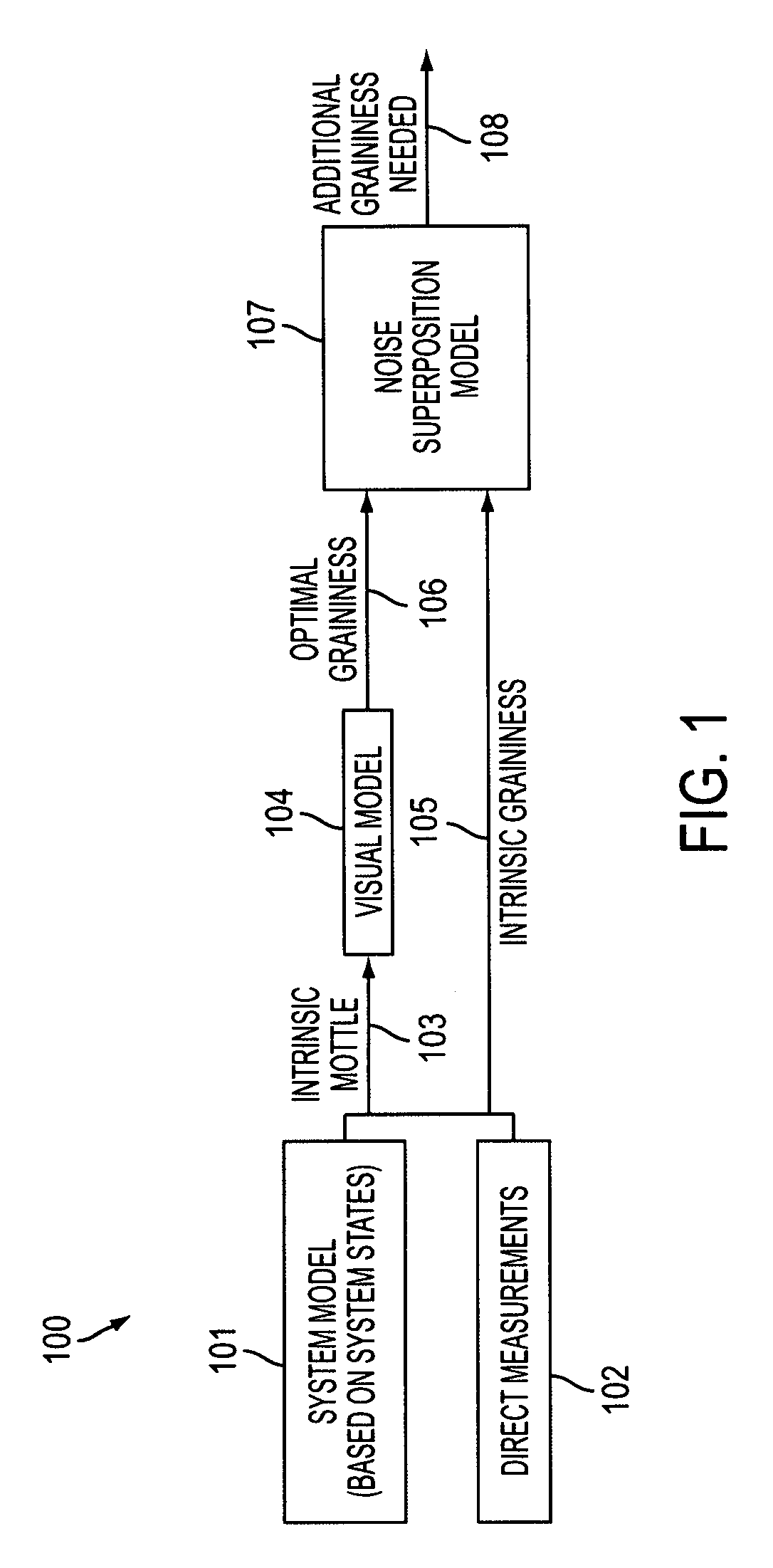
Automatic grainy noise control for optimal macro uniformity appearance
InactiveUS20070286513A1Improve image processing capabilitiesExcellent appearance uniformityImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionNoise controlPredictive systems
A system's intrinsic mottle & graininess levels are either measured or predicted based on the knowledge of system states including material states and actuator states. The optimal amount of total graininess is then calculated based on established visual models or customer surveys. The difference between this optimal graininess and the machine's intrinsic graininess is then used to calculate the required addition of grainy noise to the print. This additional amount of grainy noise can be added to the print either through textured halftone screens or through noise injection into the input digital (contone) image.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method for electroencephalogram signal extraction under magnetic resonance environment
ActiveCN106361328AQuality improvementImprove effectivenessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonanceBroadband
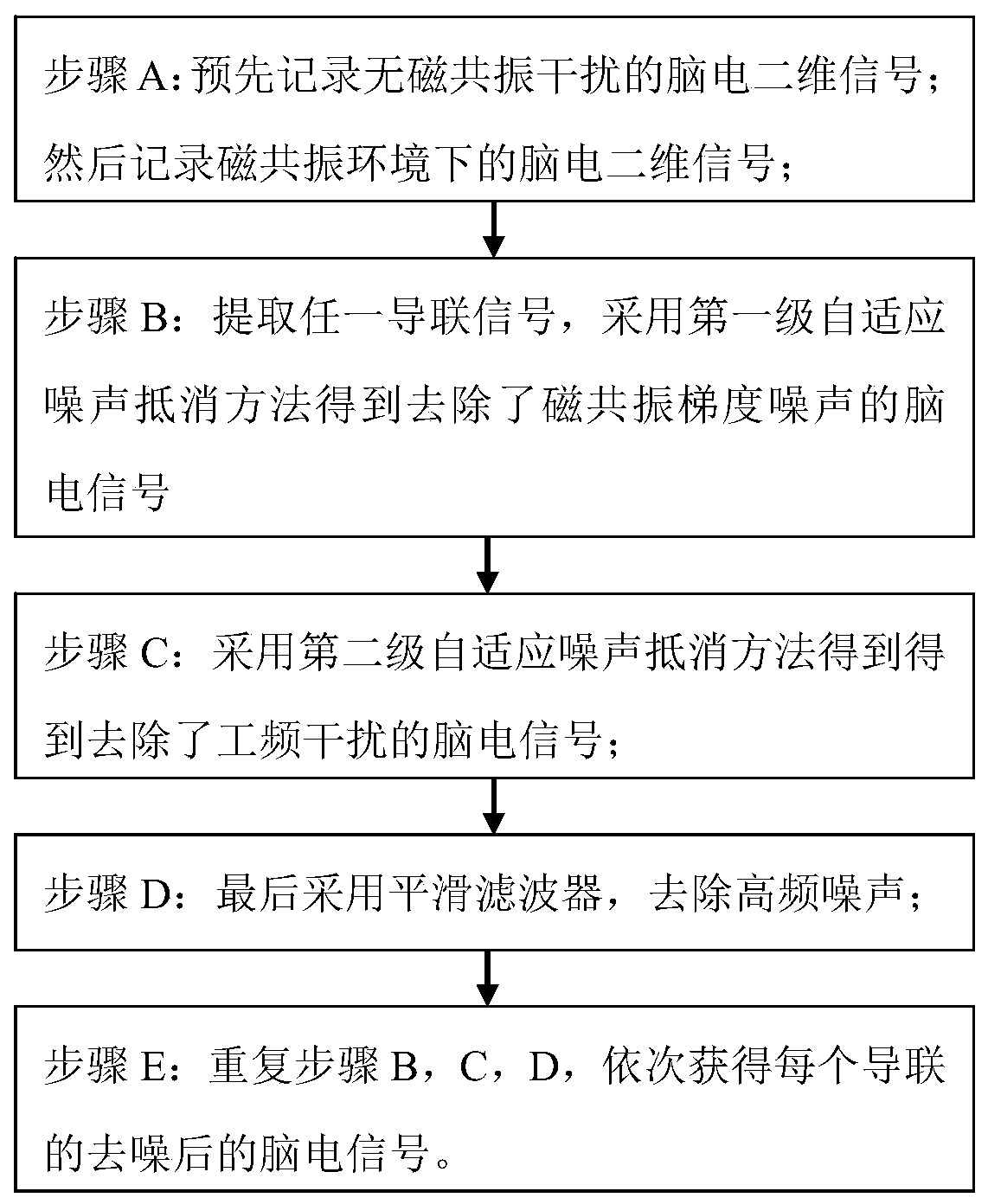
The invention belongs to the technical field of neural information, relates to an electroencephalogram signal extraction method and specifically provides a method for electroencephalogram signal extraction under a magnetic resonance environment. The method is used for improving efficiency and precision of extracting weak electroencephalogram signals, wide-band electroencephalogram information is reserved so that the electroencephalogram information can be widely used for clinical application and scientific research. According to the method, first electroencephalogram signals free of magnetic resonance interference are pre-recorded, the electroencephalogram signals under the magnetic resonance environment are recorded, magnetic resonance gradient noises and power line interference are sequentially removed through two-stage self-adaption noise offset, finally high-frequency noises are removed through a smoothing filter, and high-quality electroencephalogram signals are obtained. According to the electroencephalogram signal extraction method, the magnetic resonance gradient noises, the power line interference and the high-frequency noises of an instrument can be effectively removed, the high-quality electroencephalogram signals are extracted, and the signal extraction efficiency and precision are greatly improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Processor, modem and method for cancelling alien noise in coordinated digital subscriber lines
Owner:GRINDSTONE CAPITAL
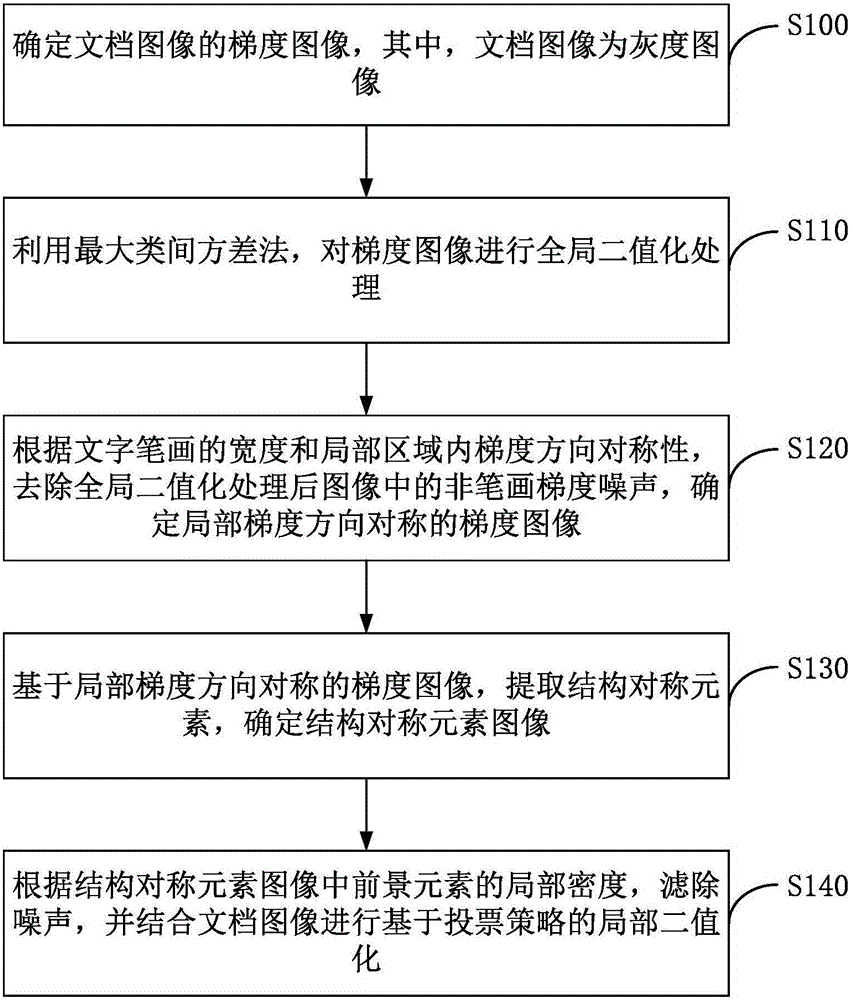
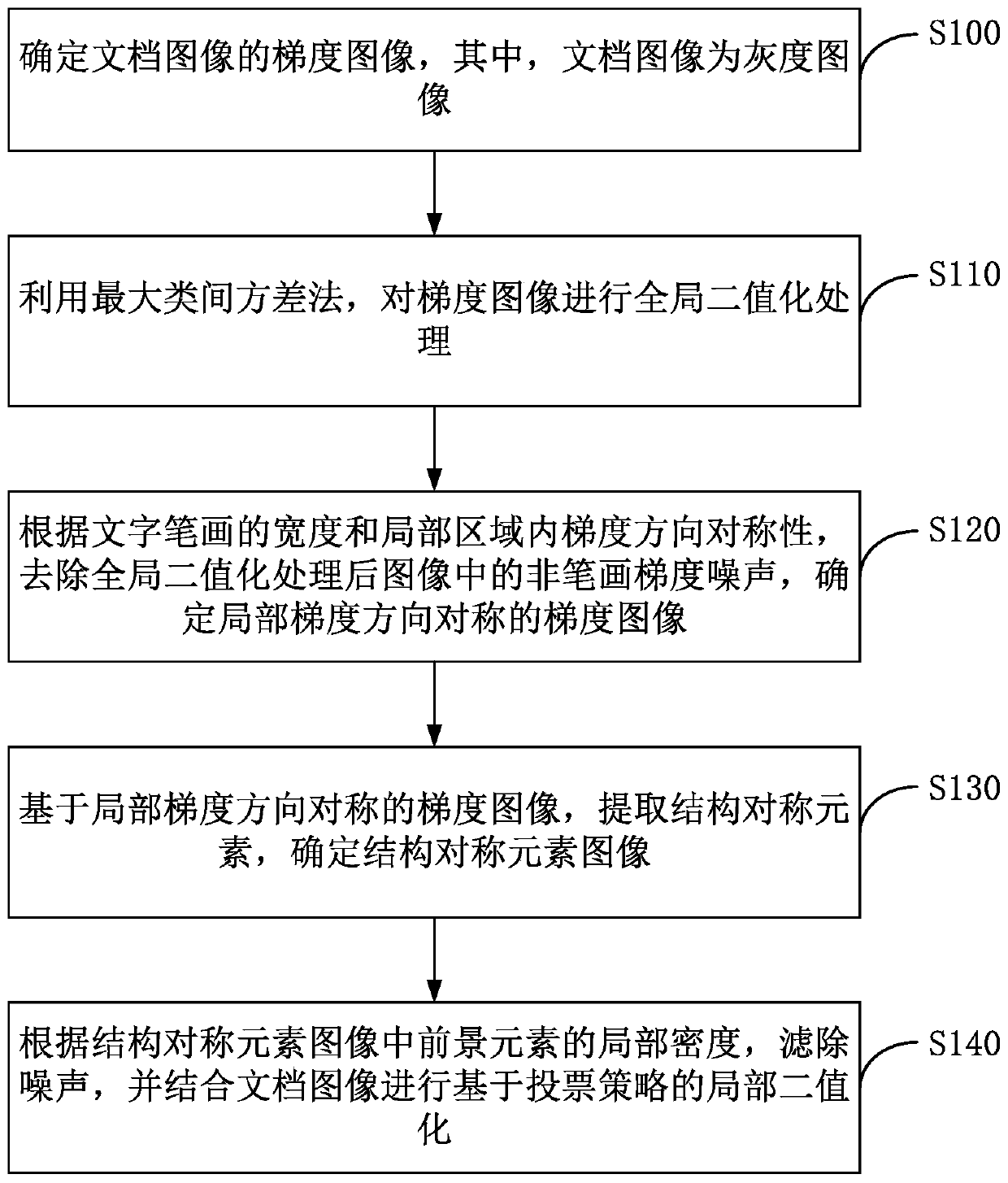
Document image binarization method based on stroke structural symmetry
ActiveCN106203434AExcellent binarizationStrong local adaptabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionStructural symmetry
The invention discloses a document image binarization method based on stroke structural symmetry. The method includes the following steps: determining the gradient image of a document image, wherein the document image is a grayscale image; utilizing the OTSU method to conduct global binarization processing on the gradient image; based on the width of character strokes and the regional gradient symmetry, removing non-stroke gradient noise of the image which undergoes the global binarization processing, and determining a gradient image being regional gradient symmetrical; based on the gradient image being regional gradient symmetrical, determining a structural symmetry element image; based on the local intensity of foreground elements of the structural symmetry element image, filtering noise, and conducting local binarization processing based on voting strategy in combination with the document image. According to the invention, the embodiments increase the adaptability of character extraction from document image.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
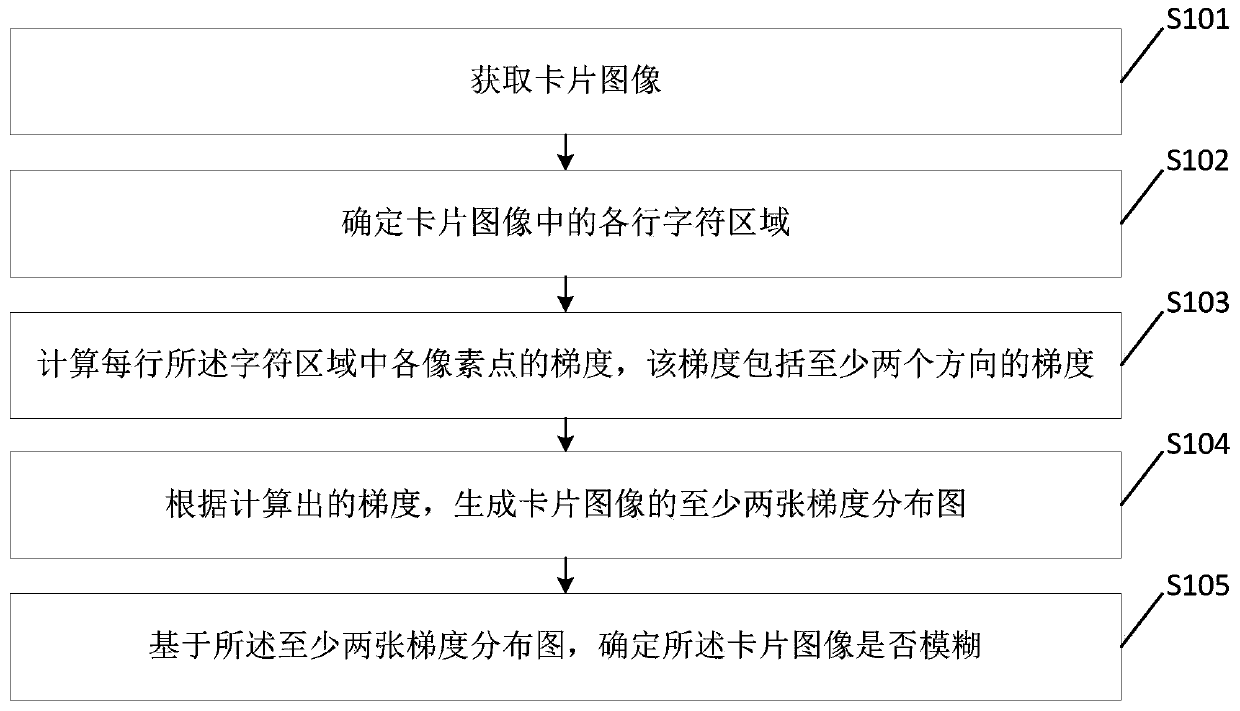
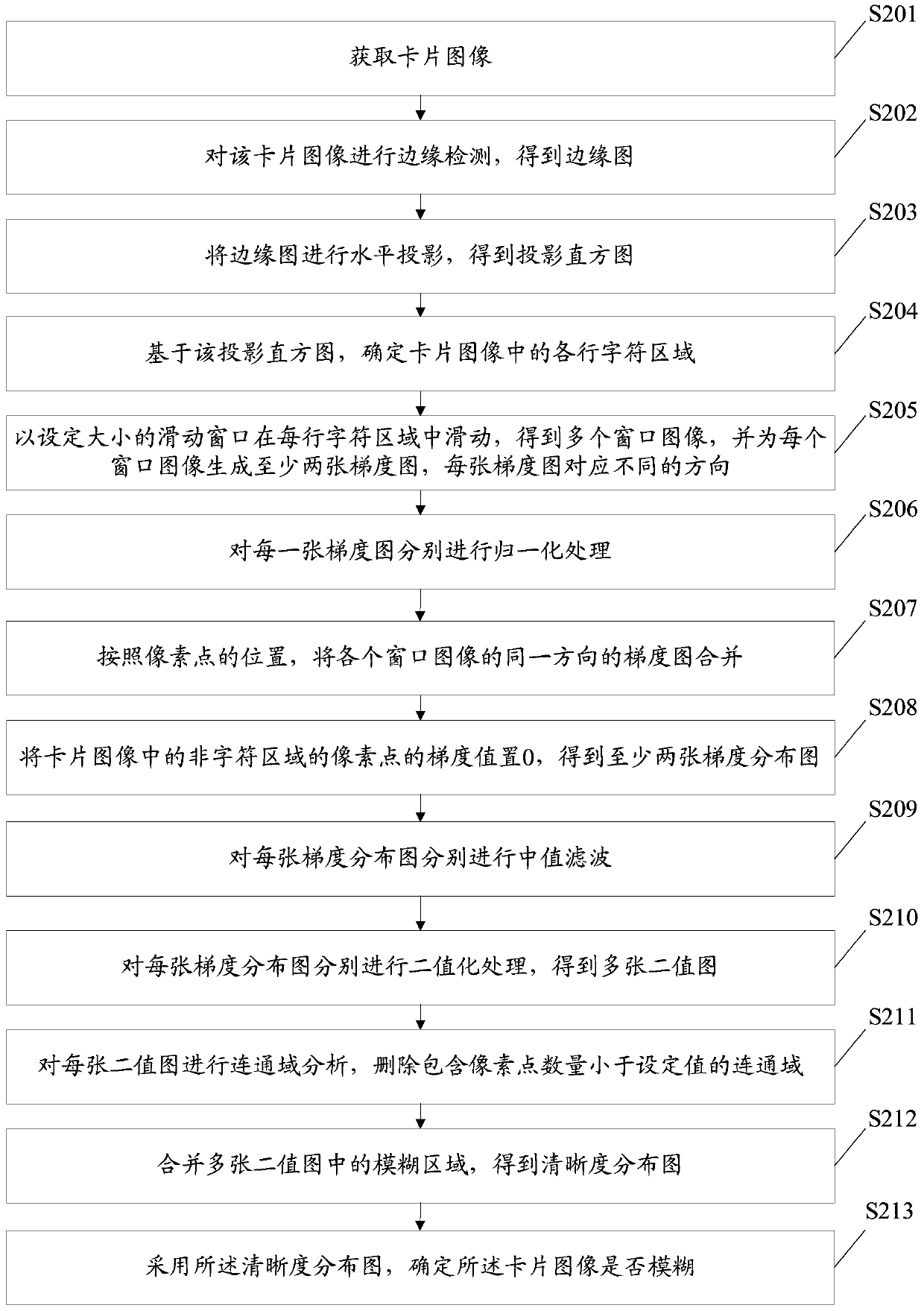
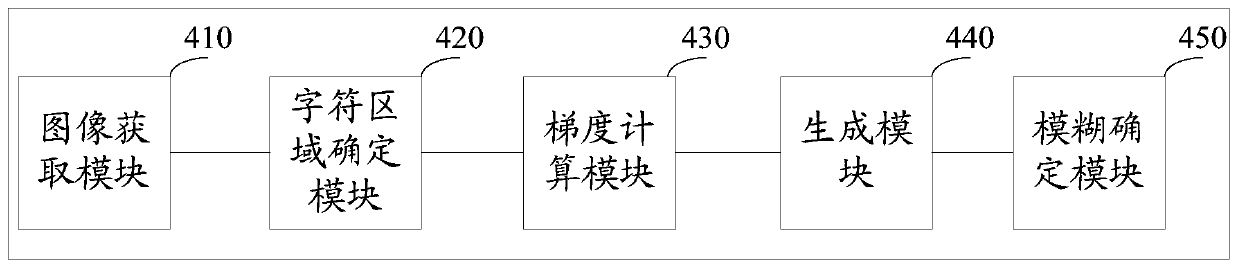
Card image fuzzy detection method and device
ActiveCN106296665BAccurate identificationImprove detection accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingCard image
The disclosure relates to a card image blur detection method and device, and belongs to the technical field of image processing. The method includes: acquiring a card image; determining each line of character areas in the card image; calculating the gradient of each pixel in each line of the character area, the gradient including gradients in at least two directions; according to the calculated the gradient, generating at least two gradient distribution maps of the card image, each gradient distribution map corresponding to one of the at least two directions; based on the at least two gradient distribution maps, determining whether the card image is blurred . The device includes an image acquisition module, a character area determination module, a gradient calculation module, a generation module and a blur determination module. The embodiments of the present disclosure can effectively detect whether the card image is blurred.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
Integrated image reconstruction and gradient non-linearity correction with spatial support constraints for magnetic resonance imaging
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Automatic grainy noise control for optimal macro uniformity appearance
InactiveUS7623271B2Improve image processing capabilitiesExcellent appearance uniformityImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionNoise controlIntrinsics
Owner:XEROX CORP
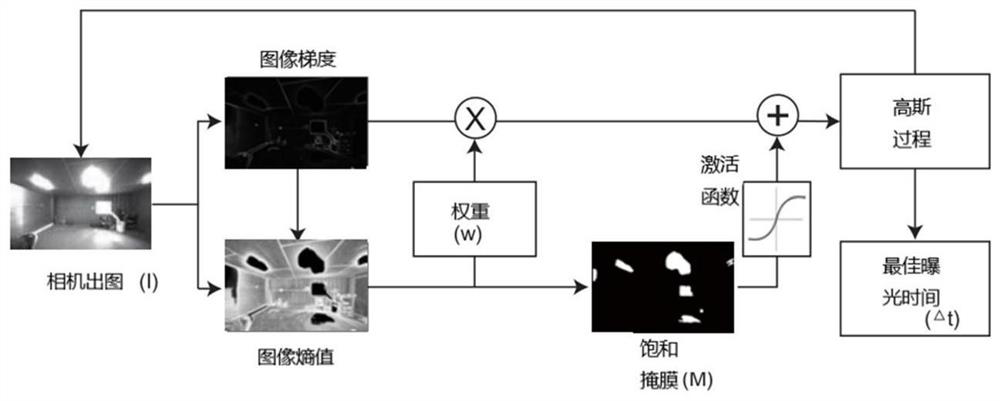
Bayesian optimization exposure control method based on entropy weight image gradient
ActiveCN114339064AReduce lossesPreserve detailed featuresTelevision system detailsInternal combustion piston enginesPattern recognitionShutter
The invention discloses a Bayesian optimization exposure control method based on entropy weight image gradient, and relates to the technical field of vehicle-mounted cameras. According to the Bayesian optimization exposure control method based on the entropy weight image gradient, the entropy weight gradient is added on the basis of the gradient information of the original image, so that on one hand, gradient noise in the original image can be minimized, and on the other hand, a saturated mask can be established; therefore, the information loss of the original image is reduced to the maximum extent by reducing the overexposure or underexposure area, and the detail features of the original image are reserved; meanwhile, in order to avoid overlong exposure stabilization time of the camera, a Bayesian optimization algorithm is added in the exposure control method, and the optimal shutter time is obtained. The Bayesian optimization exposure control method is suitable for many computer vision target detection fields, such as scenes of lane detection, vehicle detection, pedestrian detection and the like.
Owner:南京仙电同圆信息科技有限公司
Image reference-free quality evaluation method and system based on gradient profile
The invention discloses image reference-free quality evaluation method and system based on a gradient profile. The image reference-free quality evaluation system comprises a gradient profile extraction device, a blurring effect evaluation device, a ringing effect evaluation device and an integrated evaluation device, wherein the gradient profile extraction device is used for detecting input imageedge points and extracting the gradient profile according to the edge points; the blurring effect evaluation device is used for measuring the blurring effect of images according to the gradient profile; the ringing effect evaluation device is used for measuring the ringing effect of the images according to the gradient profile; and the integrated evaluation device is used for fusing the blurring effect measurement and the ringing effect measurement to acquire a quality evaluation reference value of input images. Based on the invention, the quality evaluation can be carried out on various types of natural images; and especially, the invention has favorable robustness for partially-blurred images due to the defocusing, the motion and other reasons.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Online removal method for nuclear magnetic artifacts in synchronous EEG-fMRI data acquisition
ActiveCN113040789ASmall amount of calculationMeet processing speed requirementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsLow-pass filterMedicine
The invention discloses an online removal method for nuclear magnetic artifacts in synchronous EEG-fMRI data acquisition. The online removal method comprises the following steps that (1), pulse artifacts are filtered from acquired noise-containing electroencephalogram signals through a low-pass filter with designed parameters; (2), up-sampling is carried out on the filtered signal in the step (1), and the electroencephalogram signals with a mark sent by fMRI equipment are synchronized, namely synchronizing is carried out by using a synchronization box to obtain a signal Sh; and (3), the electroencephalogram signals are random signals, the gradient noise takes a slice scanning time T as a period, and the shape of the noise in each period is similar, so that a sliding window is constructed by using N slices to construct a gradient noise formwork. The adaptive SVD denoising used in the method considers the morphological characteristics of the electrocardiographic artifacts, so that the signal-to-noise ratio of the collected signal is better improved; and compared with PCA-based OBS denoising, the denoising method has the advantages that the effective electroencephalogram signals are better reserved while the artifacts are removed, and the accuracy is higher.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Adversarial sample generation method and device
PendingCN114169409AIncreaseHigh strengthCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsAlgorithmNetwork model
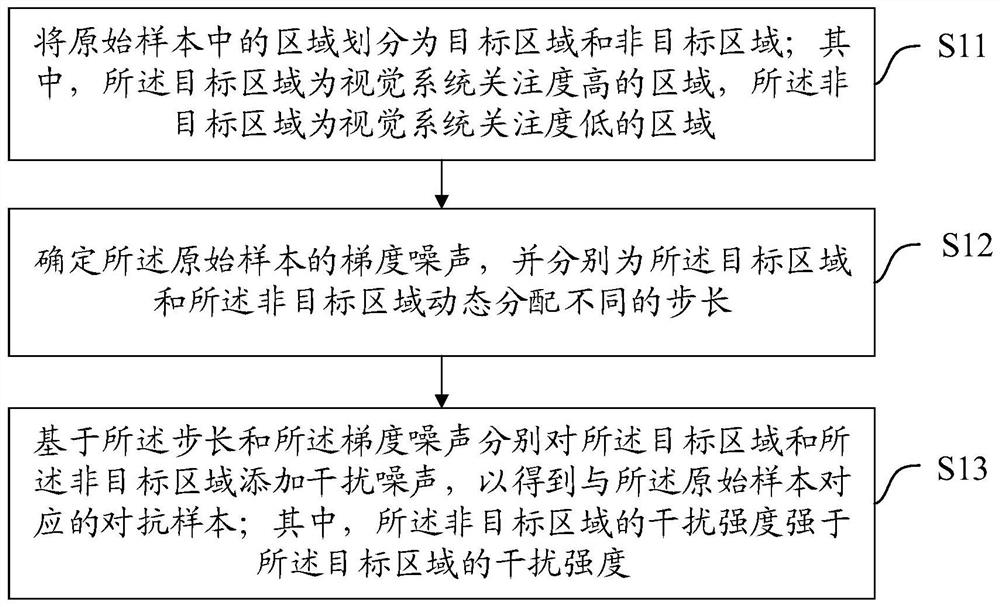
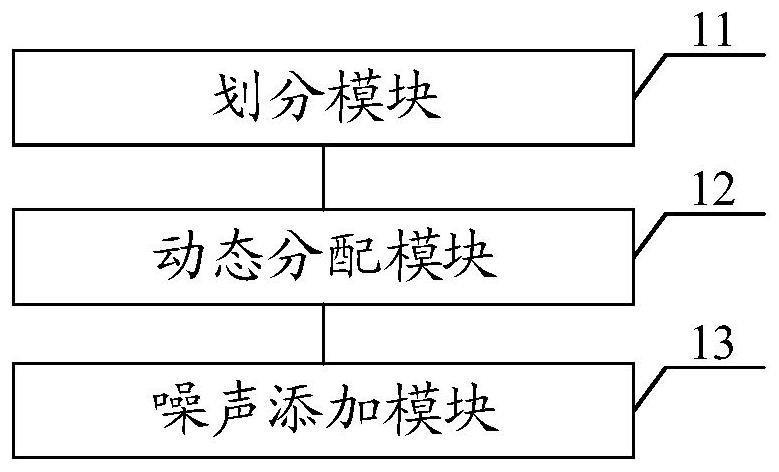
The invention discloses an adversarial sample generation method and device. The adversarial sample generation method comprises the steps of dividing a region in an original sample into a target region and a non-target region; the target area is an area with high attention of a visual system, and the non-target area is an area with low attention of the visual system; determining gradient noise of the original sample, and dynamically distributing different step lengths for the target area and the non-target area respectively; respectively adding interference noise to the target area and the non-target area based on the step length and the gradient noise to obtain an adversarial sample corresponding to the original sample; the interference intensity of the non-target area is higher than that of the target area. According to the method, the disturbance noise amplitude and the noise information energy intensity can be increased under the condition that human eyes are not easy to perceive through small disturbance in the target area and high disturbance in the non-target area, so that the aggressiveness of the adversarial sample is improved, and the trained network model has higher robustness.
Owner:INSPUR BEIJING ELECTRONICS INFORMATION IND
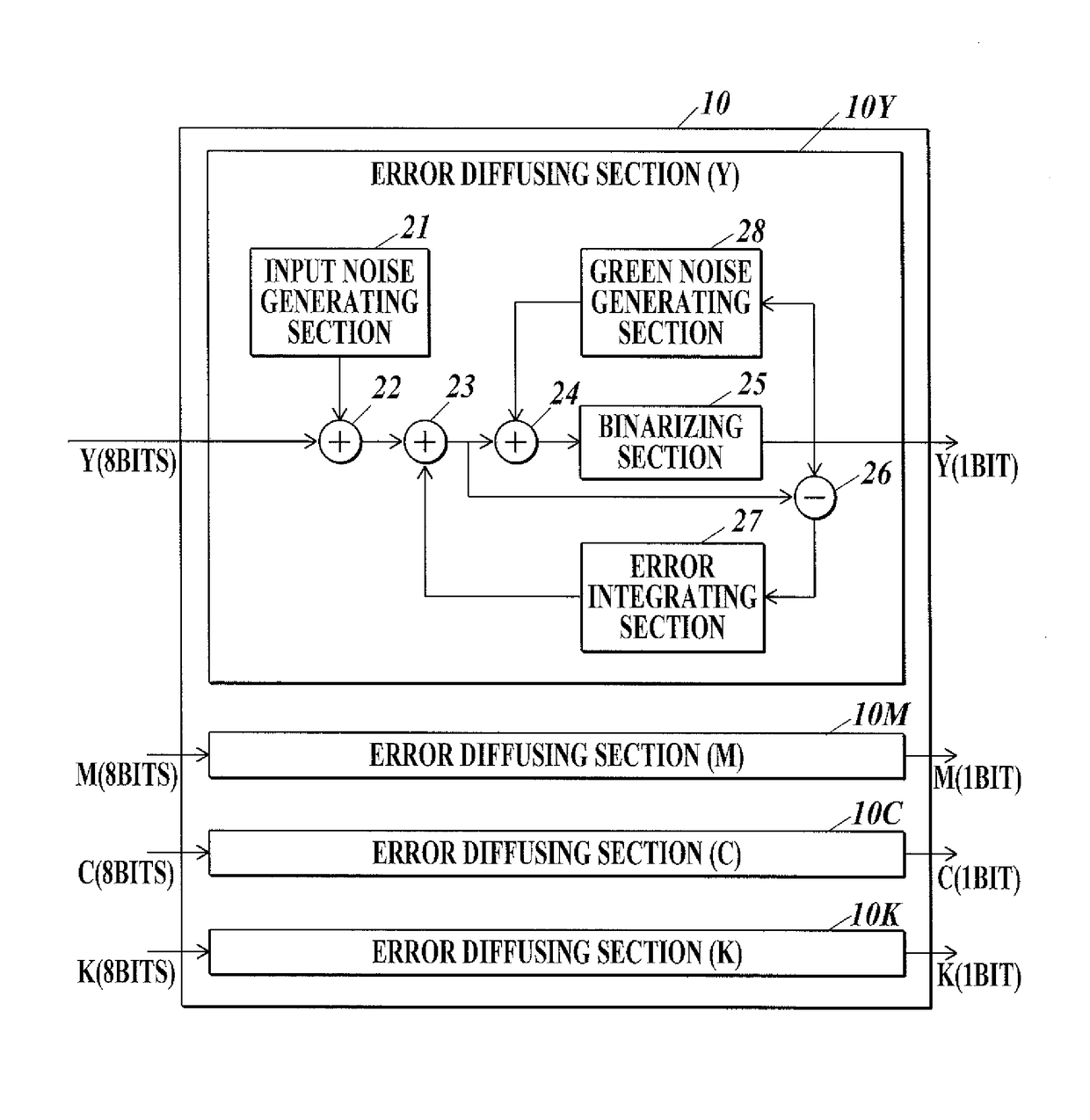
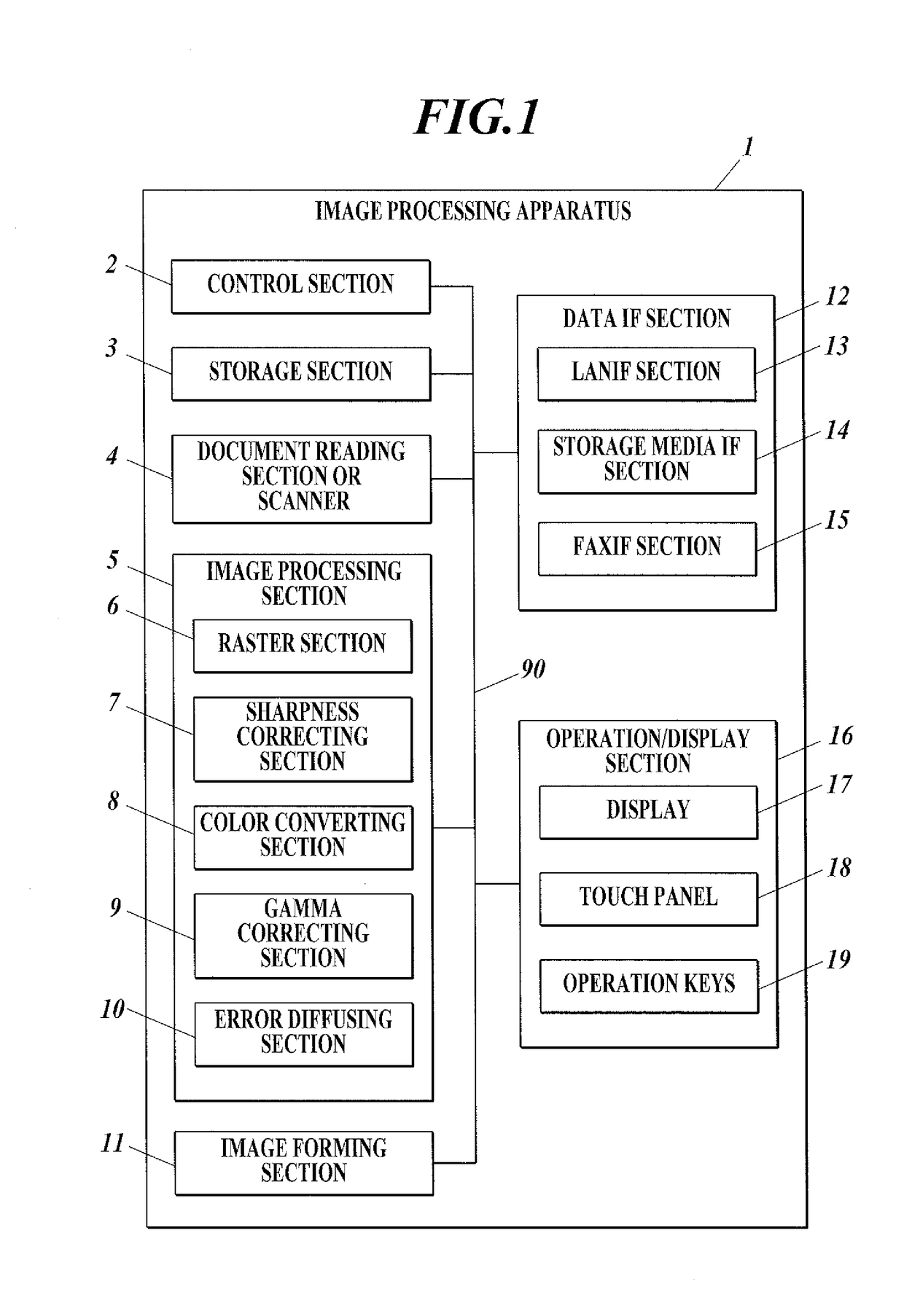
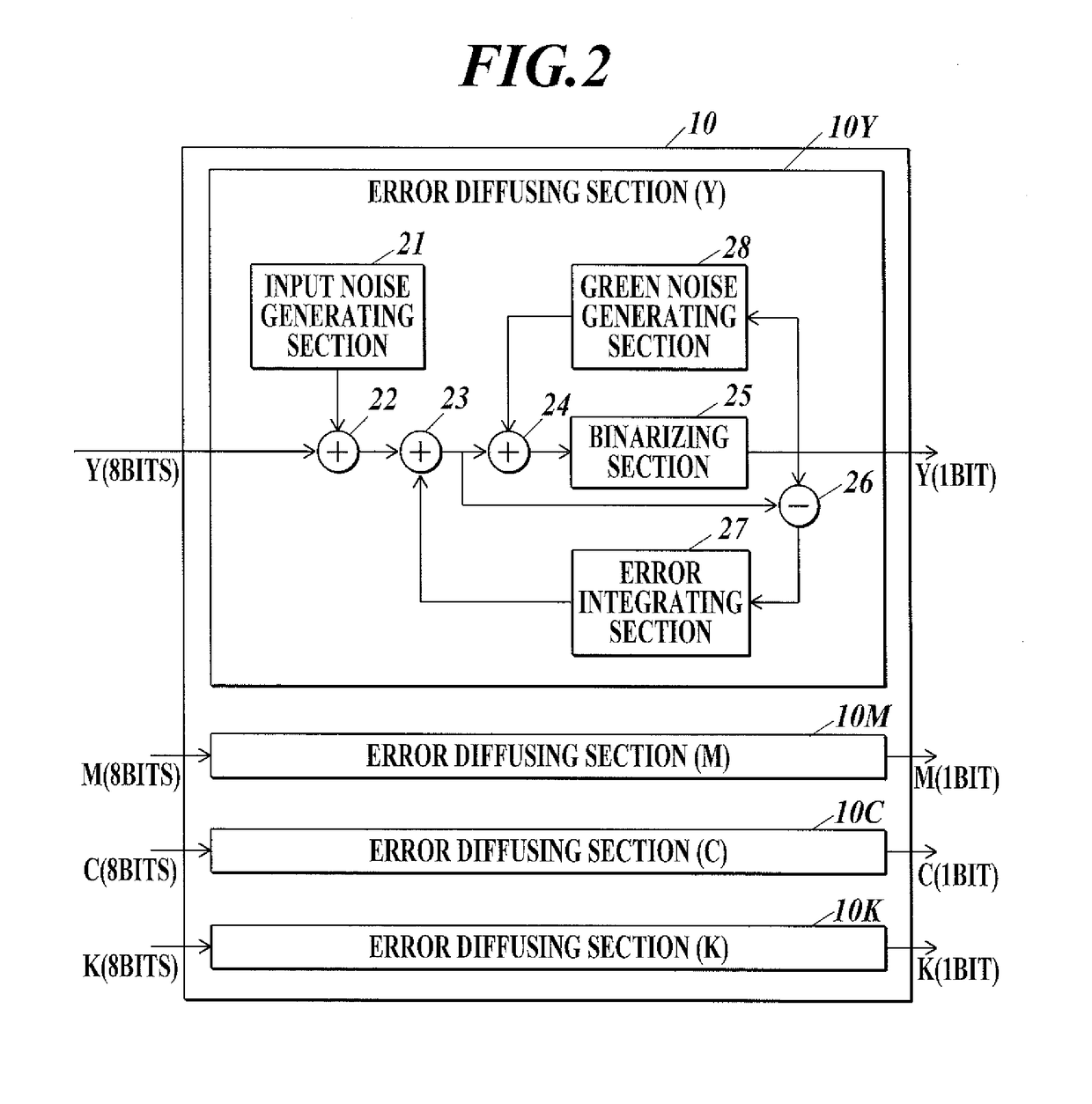
Image processing apparatus, control method, and computer-readable recording medium configured to perform error diffusion process having and adder to add an error intergrated value diffused to the target pixel, the green noise and the predetermined noise, to the pixel value of the target pixel
ActiveUS9681024B2Image can be preventedReproductivity can be improvedImage enhancementVisual presentation using printersImaging processingAlgorithm
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
A method for extracting EEG signals in a magnetic resonance environment
ActiveCN106361328BQuality improvementImprove effectivenessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonanceBroadband
The invention belongs to the technical field of neural information, relates to a method for extracting EEG signals, and specifically provides an extraction method for EEG signals in a magnetic resonance environment, which is used to improve the efficiency and accuracy of extracting weak EEG signals while retaining wide-band EEG signals. Electrical information, so that it can be widely used in clinical and scientific research; the invention first records the EEG signals without magnetic resonance interference, and then records the EEG signals in the magnetic resonance environment, and then uses two-stage adaptive noise cancellation to remove the magnetic resonance signals in turn. Gradient noise and power frequency interference, and finally a smoothing filter is used to remove high-frequency noise to obtain high-quality EEG signals. The invention can effectively remove magnetic resonance gradient noise, power frequency interference, and high-frequency noise of instruments, extract high-quality EEG signals, and greatly improve signal extraction efficiency and precision.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Document Image Binarization Method Based on Symmetry of Stroke Structure
ActiveCN106203434BExcellent binarizationStrong local adaptabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionImage extractionStructural symmetry
The invention discloses a document image binarization method based on the symmetry of stroke structure. Wherein, the method includes: determining the gradient image of the document image, wherein the document image is a grayscale image; using the maximum inter-class variance method to perform global binarization processing on the gradient image; according to the width and The symmetry of the gradient direction in the local area, remove the non-stroke gradient noise in the image after global binarization processing, and determine the gradient image with symmetric local gradient direction; determine the structural symmetry element image based on the gradient image with symmetric local gradient direction; The local density of foreground elements in the structurally symmetric element image is used to filter out noise, and combined with the document image to perform local binarization based on a voting strategy. The embodiment of the invention solves the technical problem of how to enhance the adaptability to document image text extraction.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
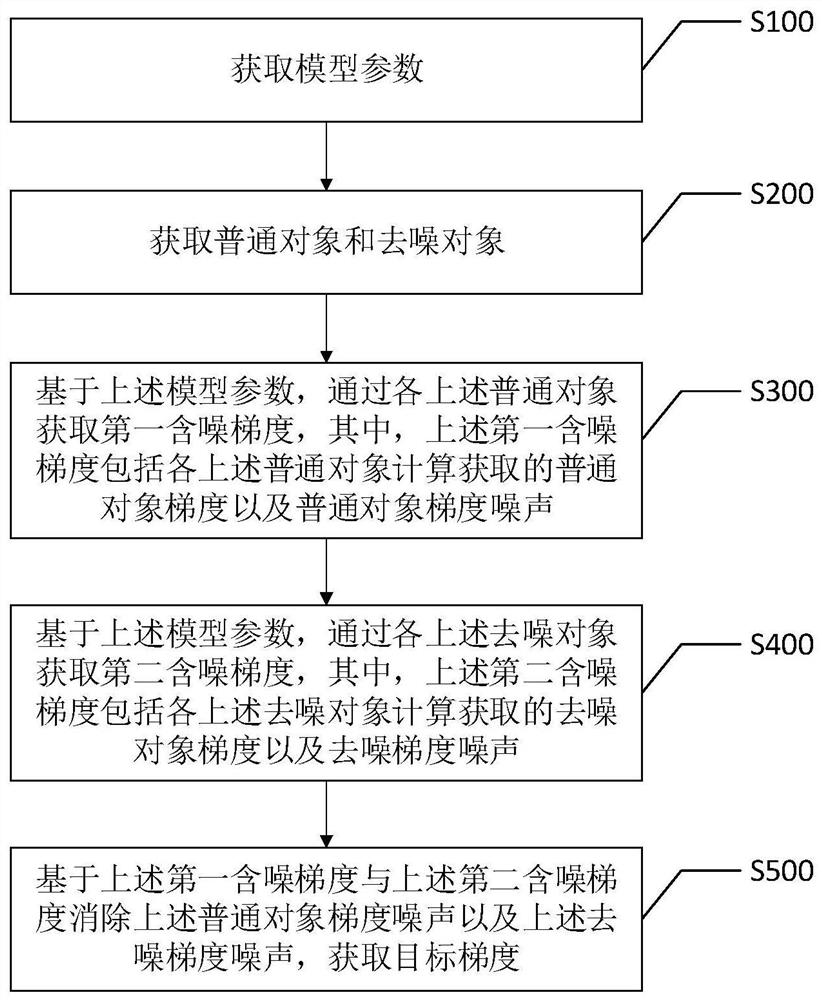
Federation recommendation gradient acquisition method and device, intelligent terminal and storage medium
PendingCN112287231AHigh precisionImprove recommendation effectDigital data information retrievalMachine learningAlgorithmEngineering
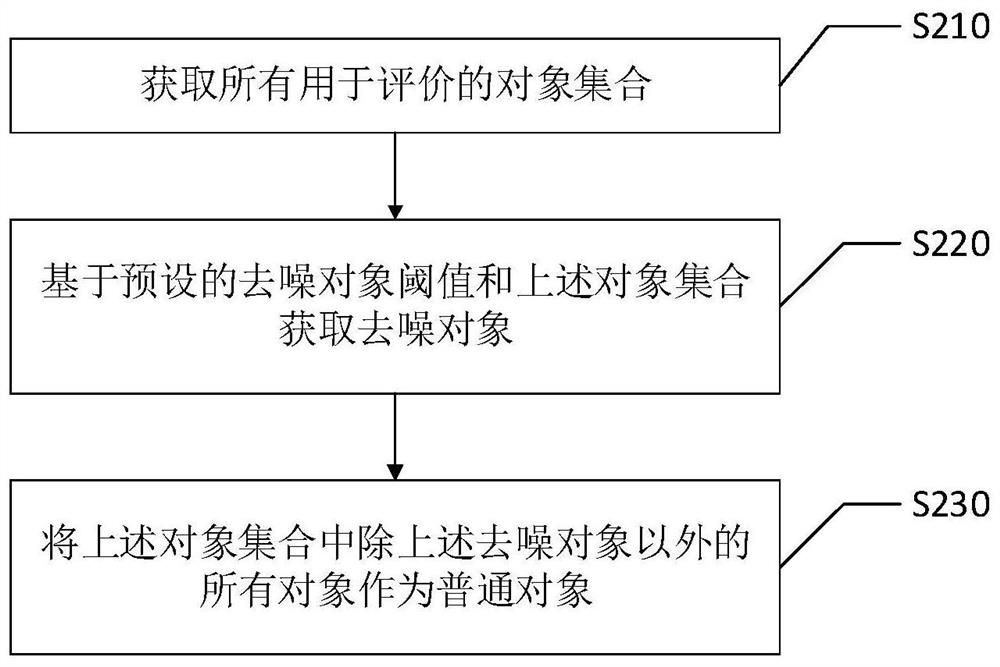
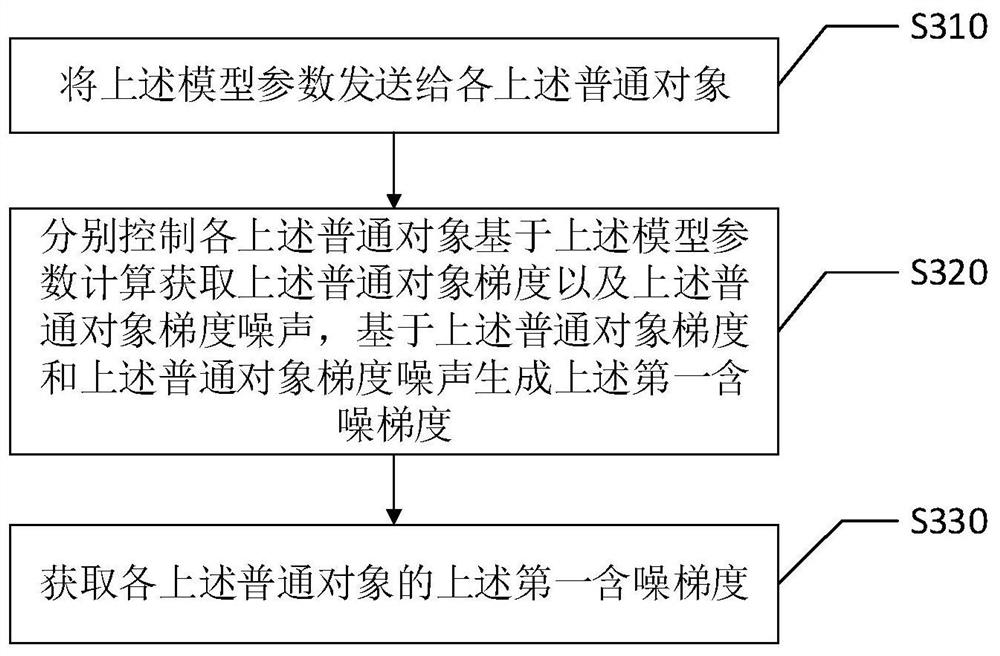
The invention discloses a federation recommendation gradient obtaining method and device, an intelligent terminal and a storage medium, and the federation recommendation gradient obtaining method comprises the steps: obtaining common objects and denoising objects; based on the model parameters, obtaining a first noise-containing gradient through each common object; based on the model parameters, obtaining a second noise-containing gradient through each denoising object; and based on the first noise-containing gradient and the second noise-containing gradient, eliminating the common object gradient noise and the denoised gradient noise, and obtaining a target gradient. In this way, the first noise-containing gradient and the second noise-containing gradient both contain corresponding gradient noise, and the scoring behavior of the user can be protected; meanwhile, corresponding gradient noise can be eliminated after the first noise-containing gradient and the second noise-containing gradient are obtained, and the target gradient without the gradient noise is obtained. Therefore, according to the scheme, gradient noise can be eliminated while user scoring behaviors are protected, andthe accuracy of the model in the federation recommendation process is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
An Online Denoising Method of Brain Signals in MRI Environment
ActiveCN107981862BMeet data processing speed requirementsLower requirementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a brain signal online denoising method in a nuclear magnetic resonance environment. The method comprises the steps of 1) conducting high-pass filtering on collected brain electrical signals; 2) conducting up-sampling on the filtered signals and synchronizing the brain electrical signals with markers sent by a fMRI device; 3) constructing a sliding window to construct a noise template Atau for preliminary denoising; 4) slicing a signal Sh mixed with noise into a slice with a length of T*w points, fitting the noise template with slice date through least squares to obtainfitting parameters ytau, and subtracting ytau*Atau from the Sh to obtain a signal Sr with residual artifacts; 5) conducting PCA on the signal Sr, sorting each component according to degree of relevance, taking the largest m components as an optimal base betaj(j=1,2,...,m) of gradient noise, fitting the optimal base with the Sr through the least squares to obtain fitting parameter aj(j=1,2,...,m),subtracting N from the Sr, and conducting denoising through the construction of a gradient noise template and denoising through the PCA to eventually eliminate the gradient noise. The brain signal online denoising method in the nuclear magnetic resonance environment has the advantages that real-time denoising can be conducted on the signals to meet demands of data processing speed of an online experiment.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GUANGDA INNOVATION TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com