Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
520 results about "Entrance channel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
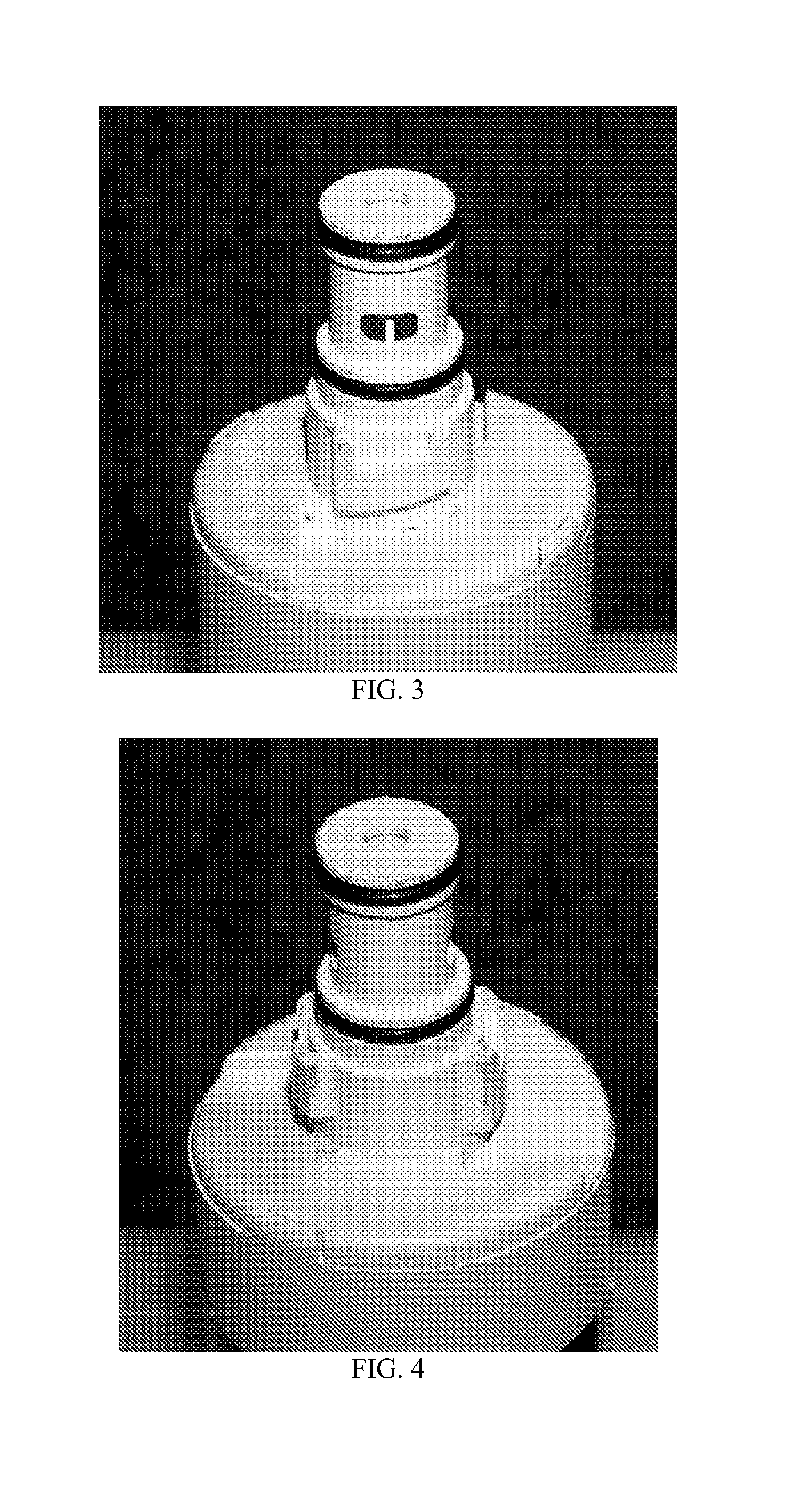
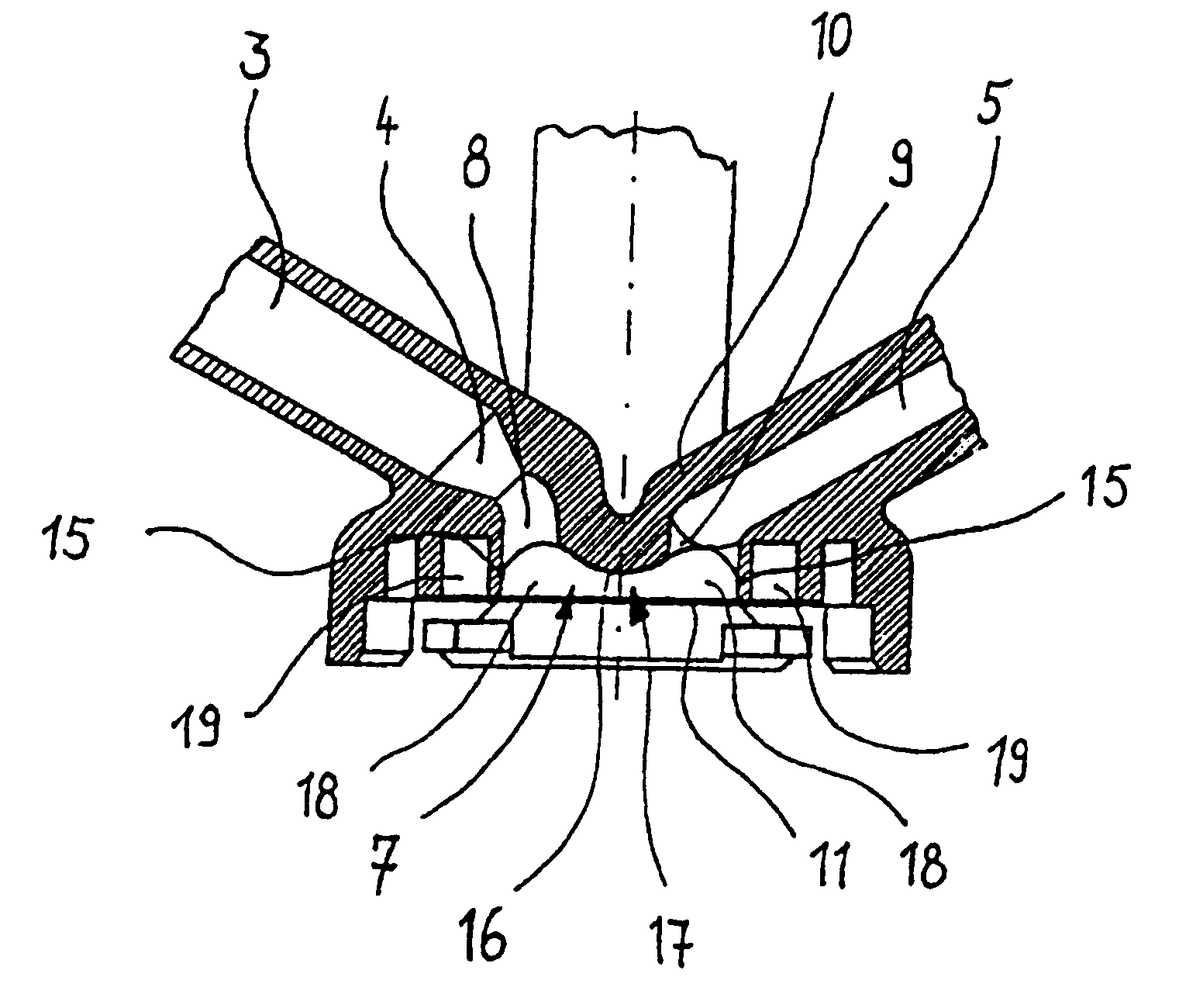
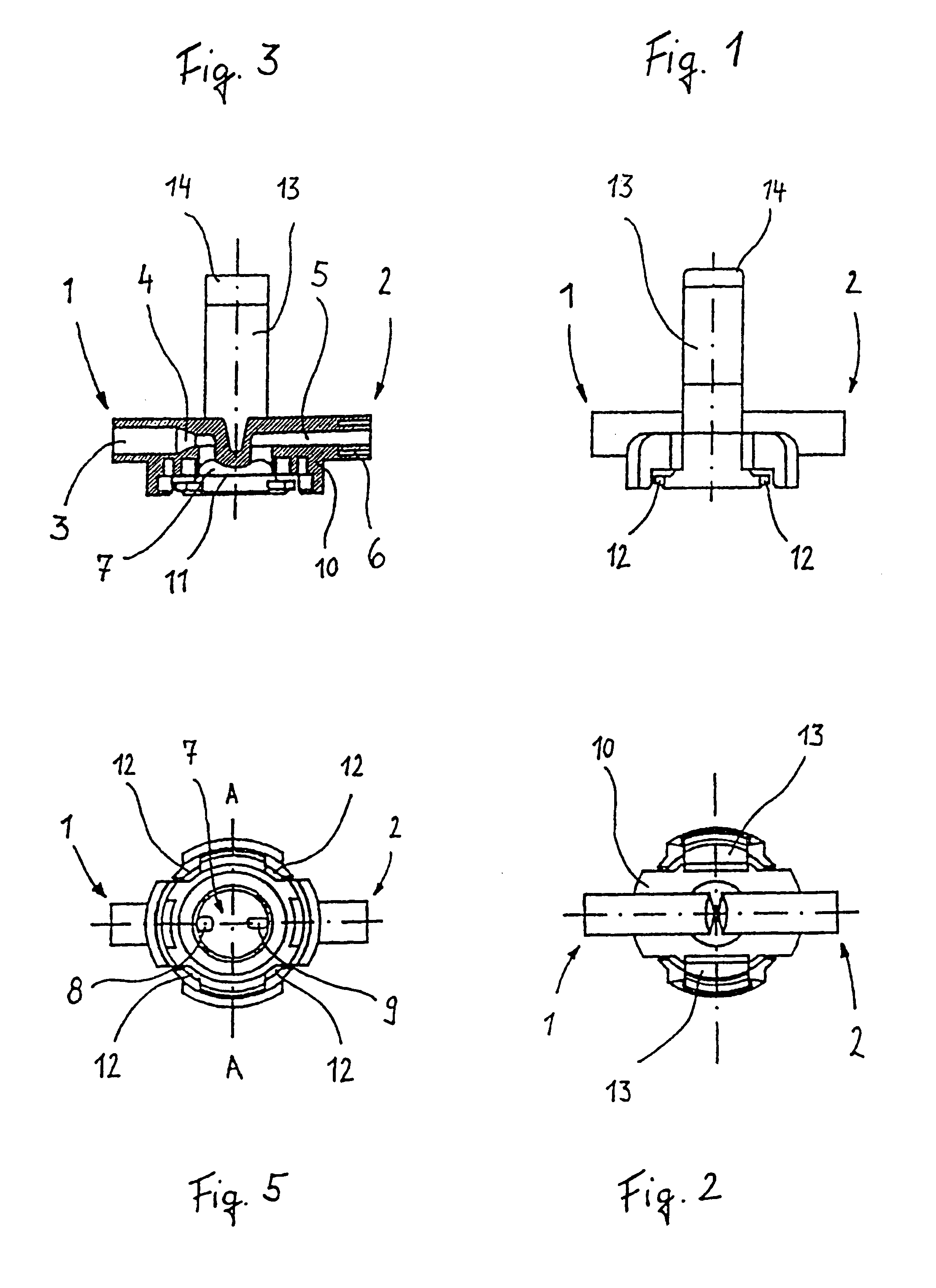
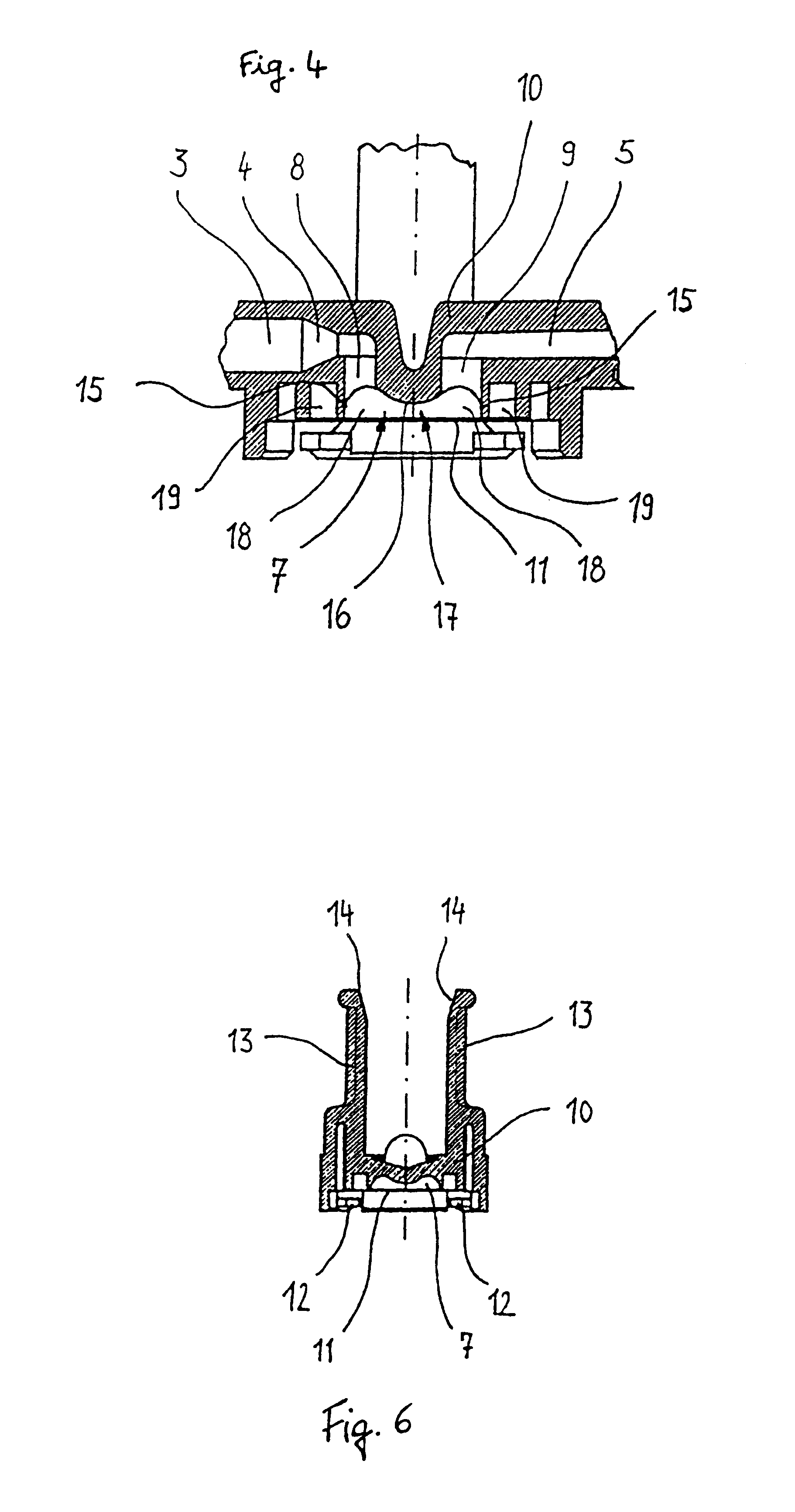
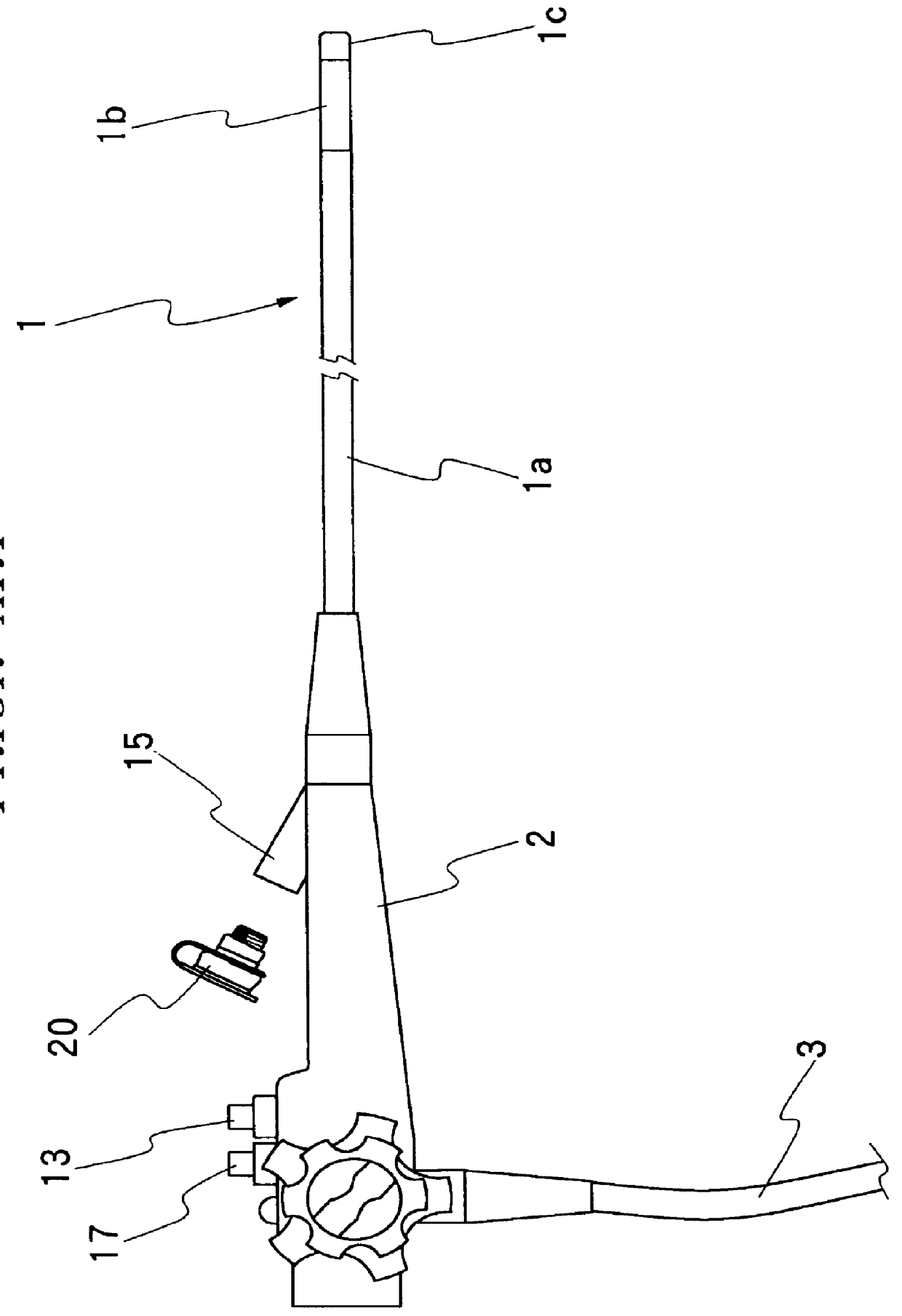
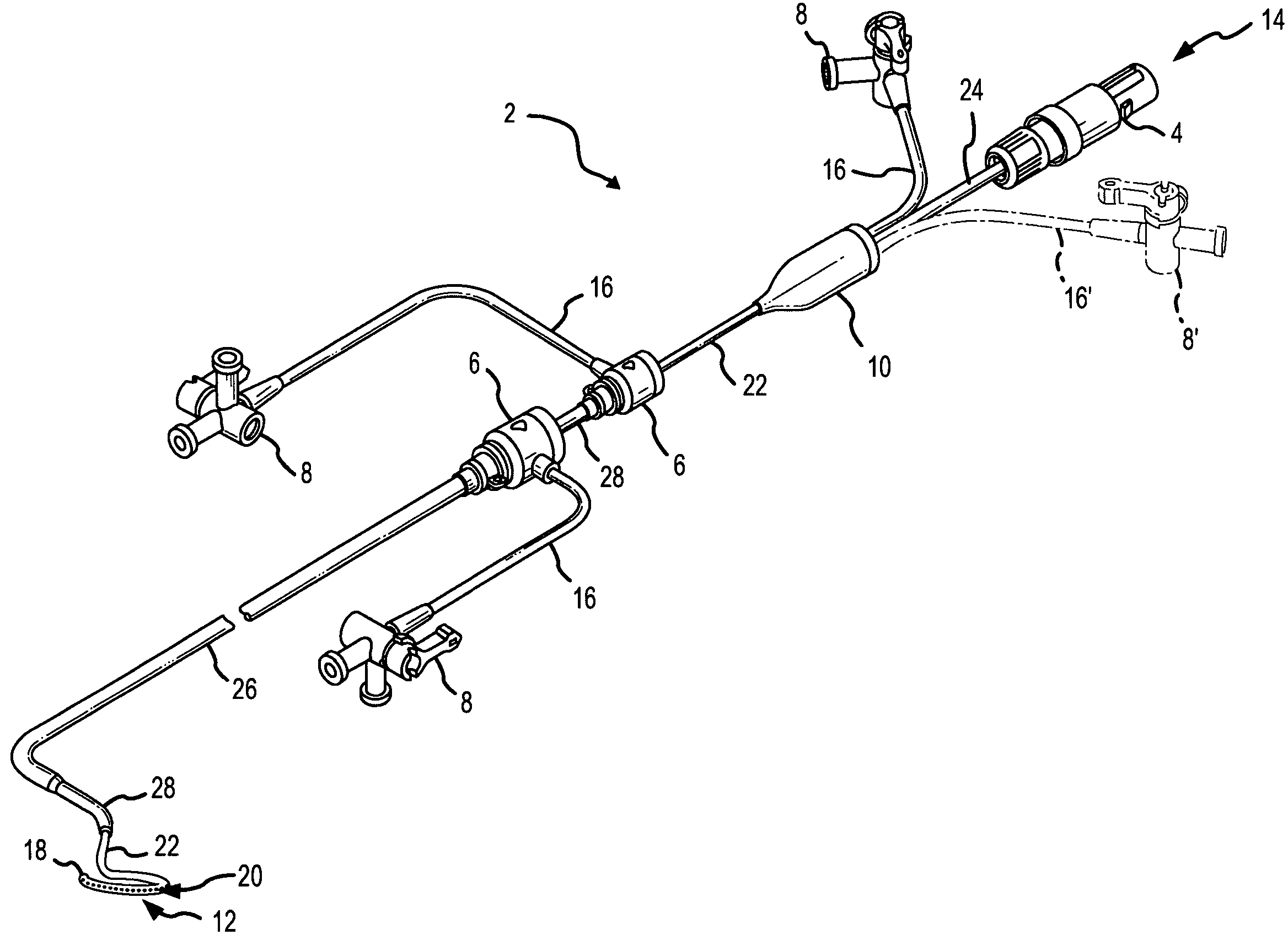
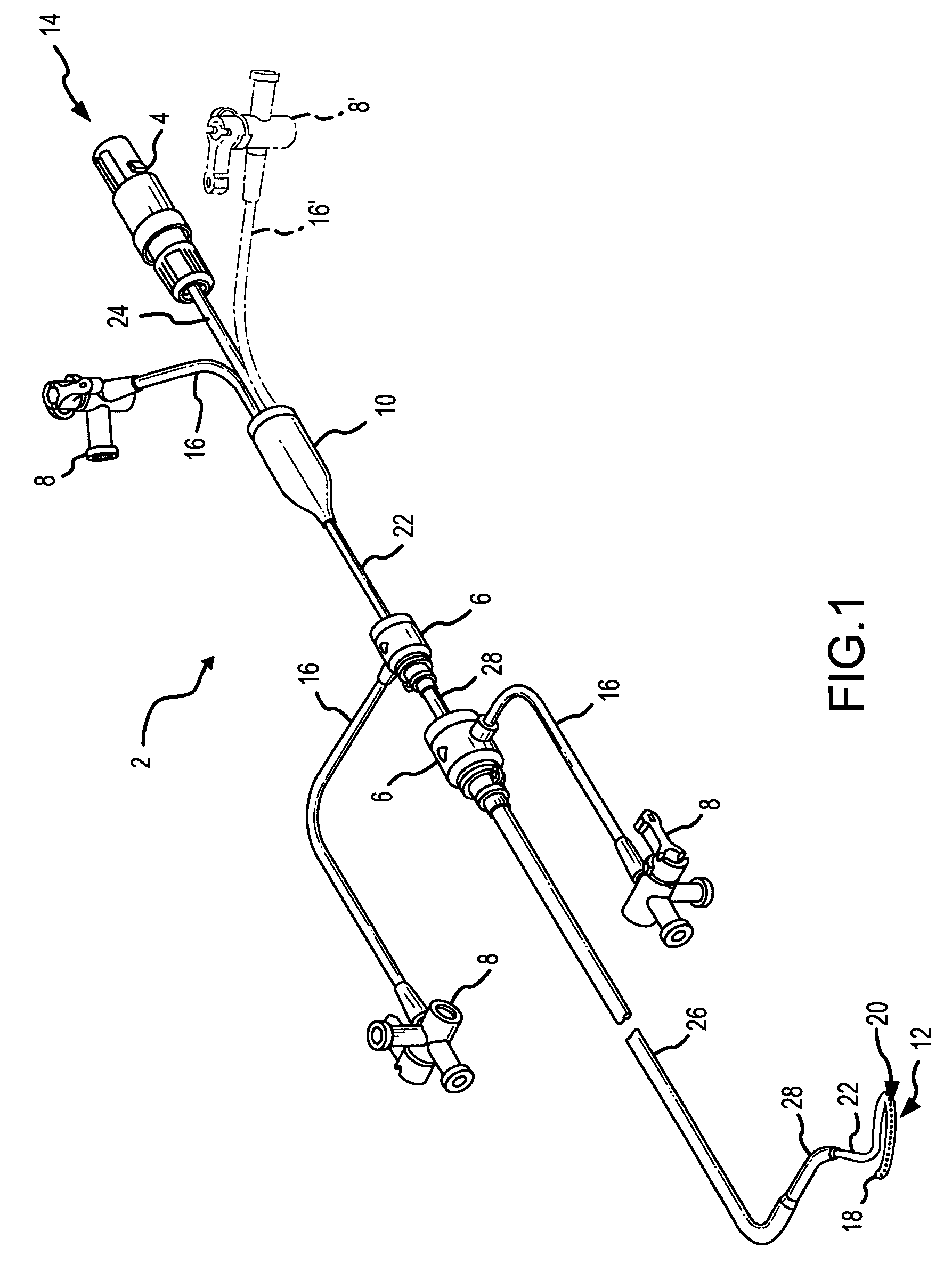
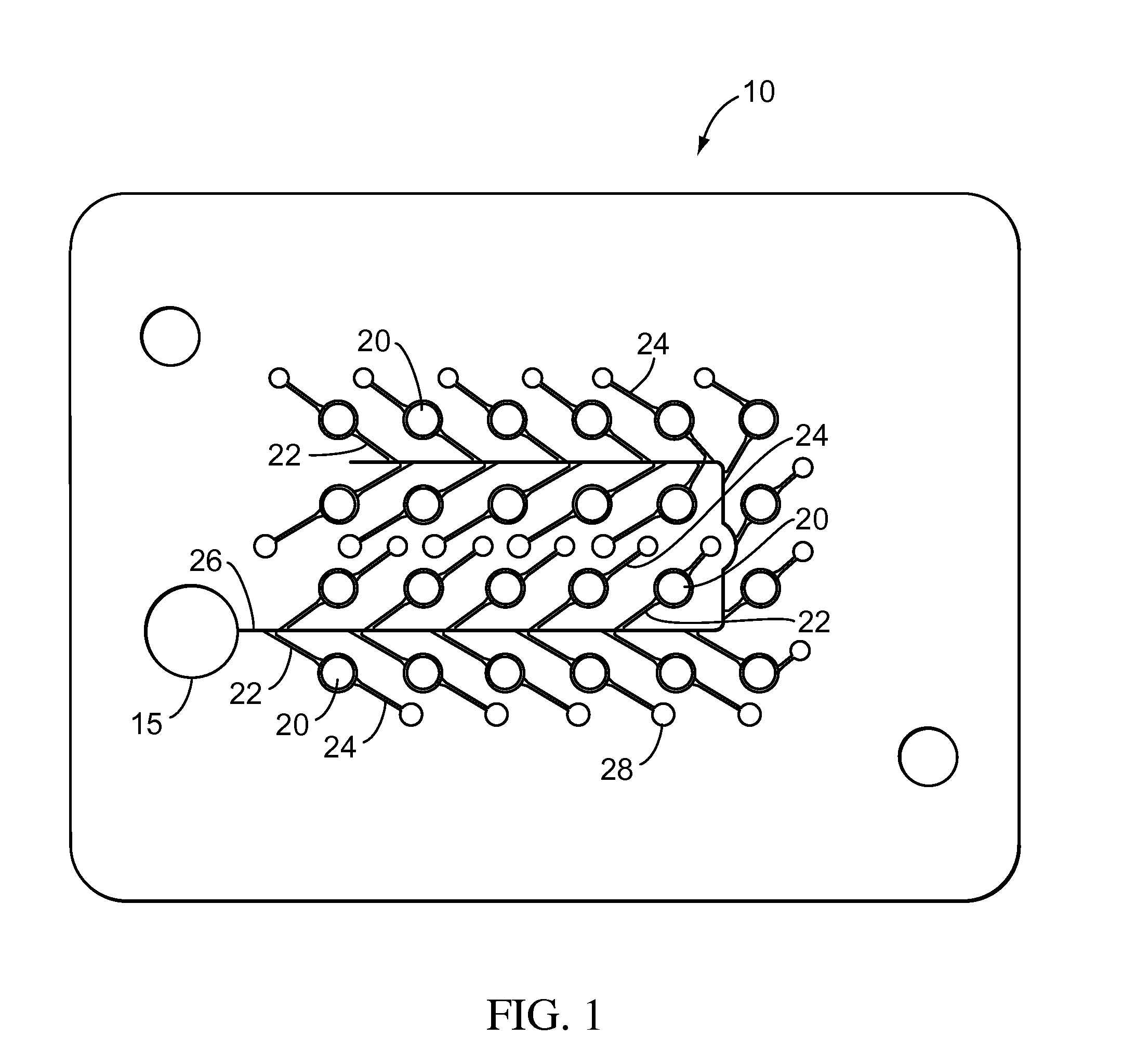
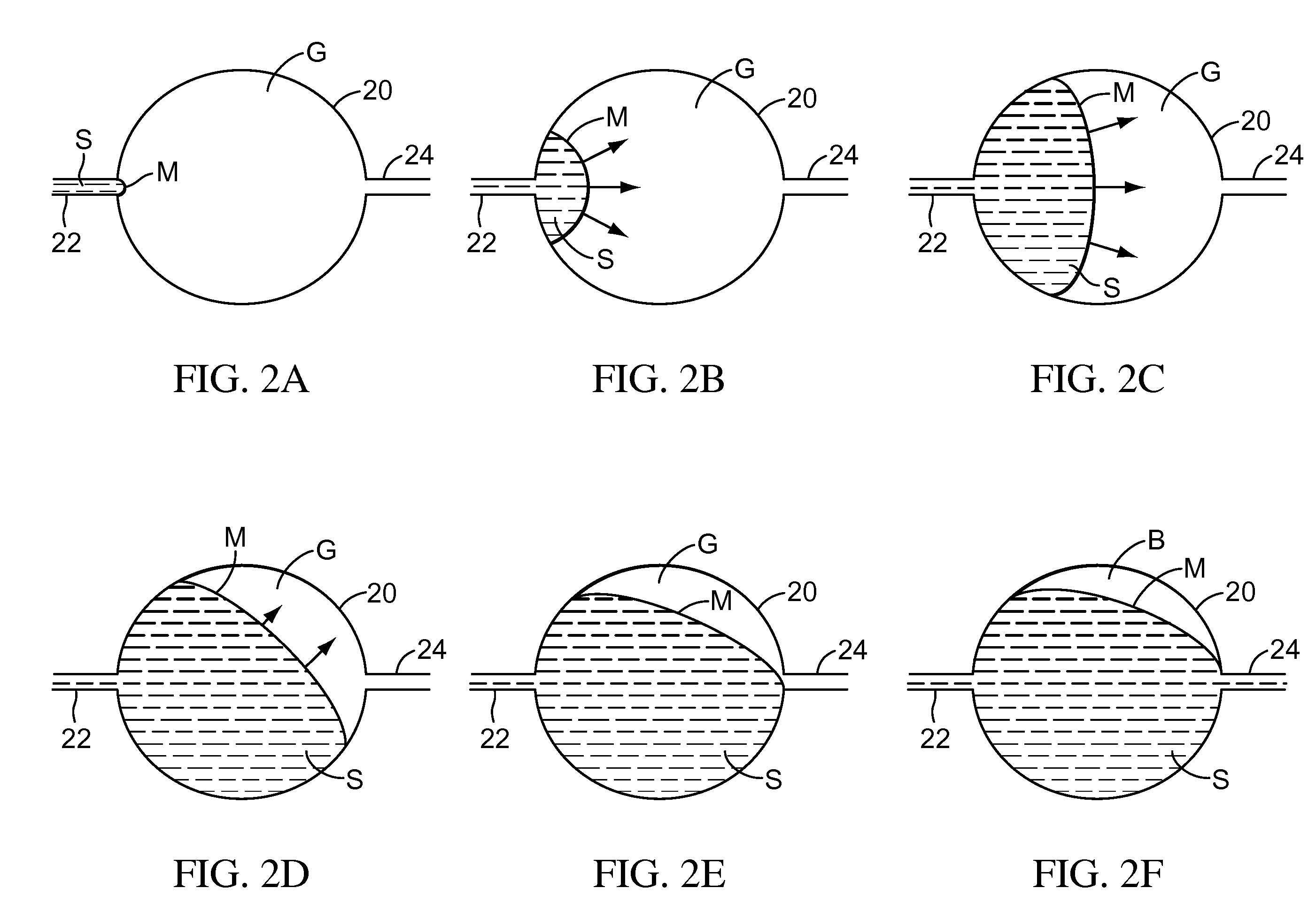
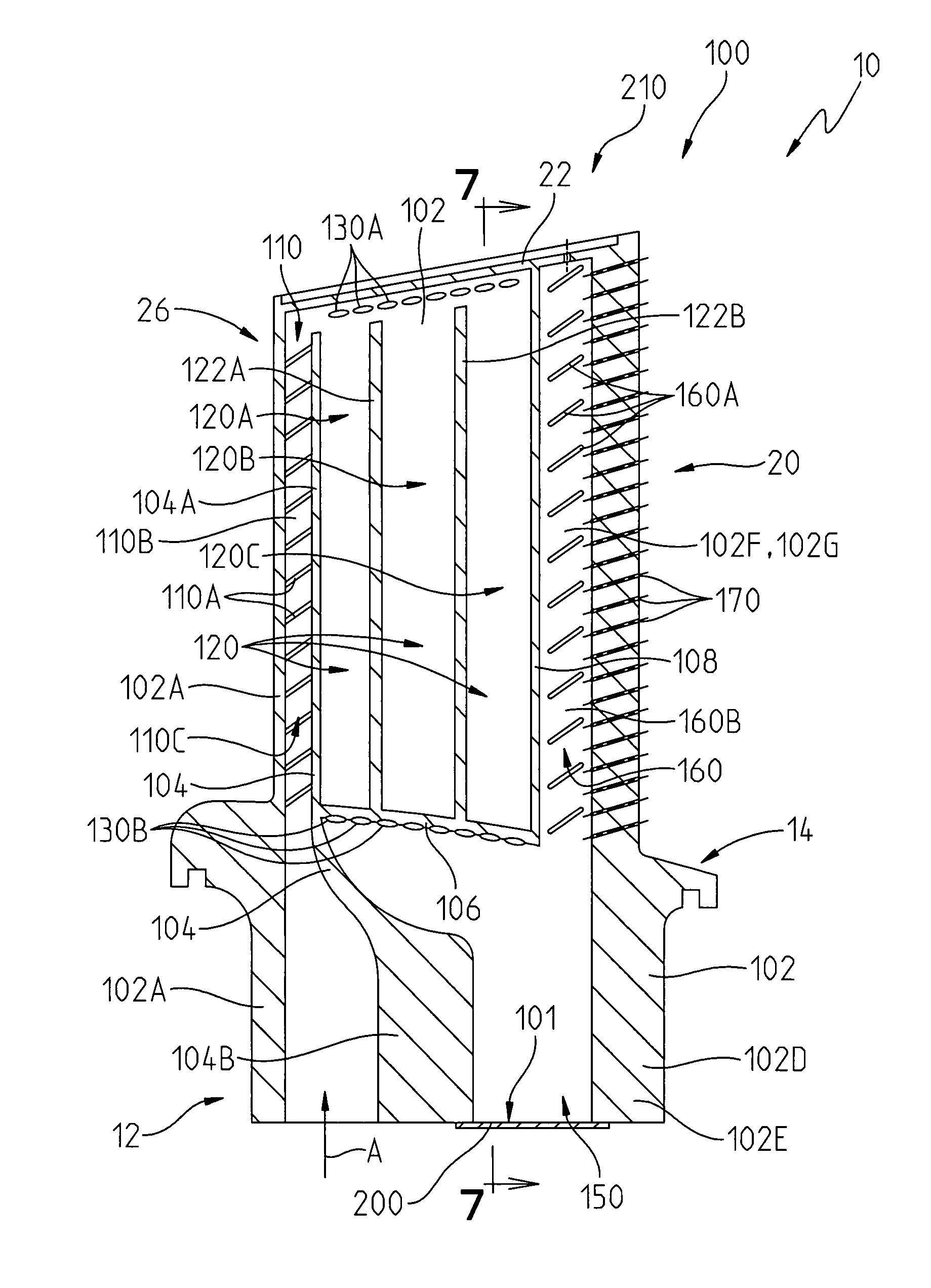
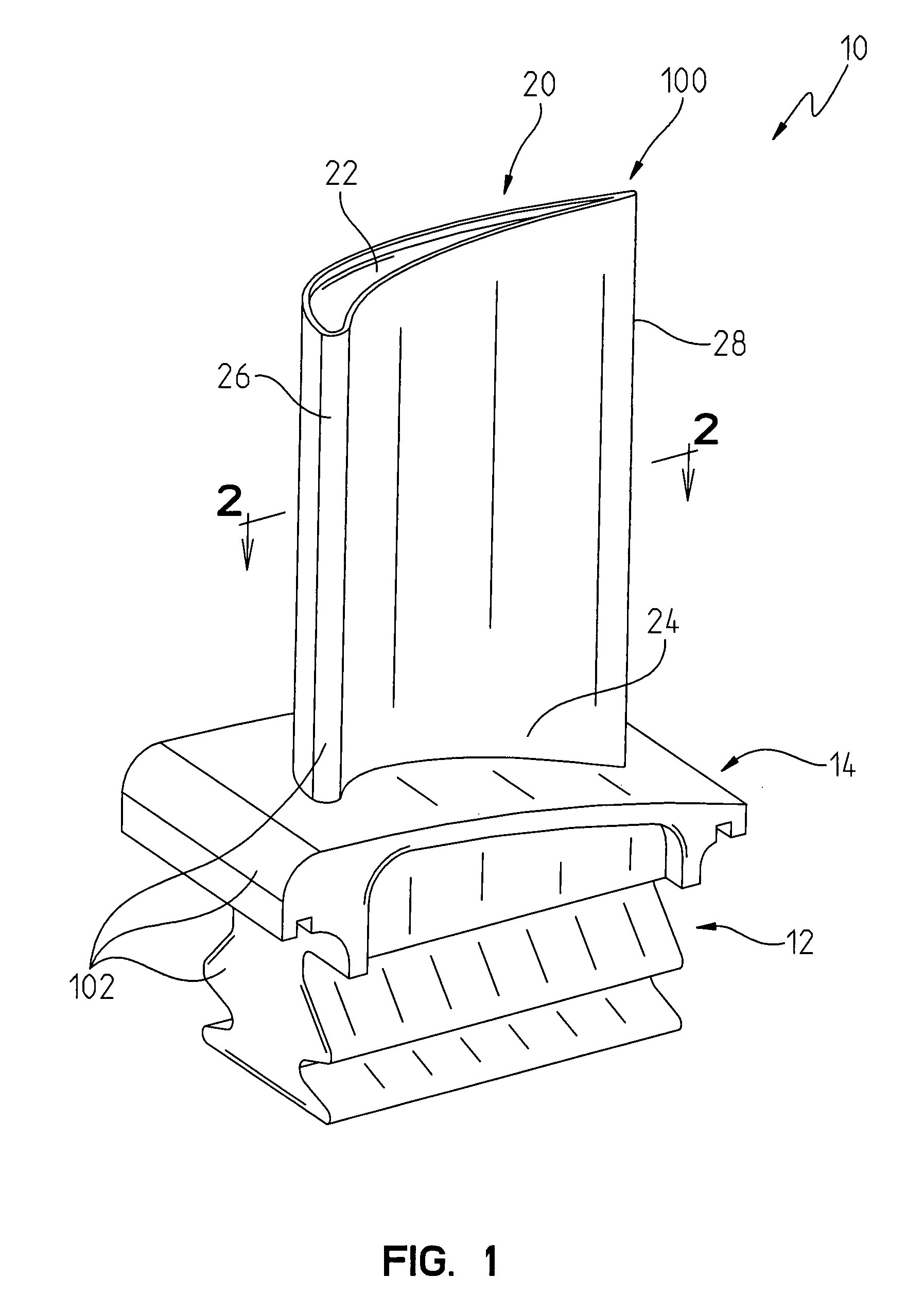
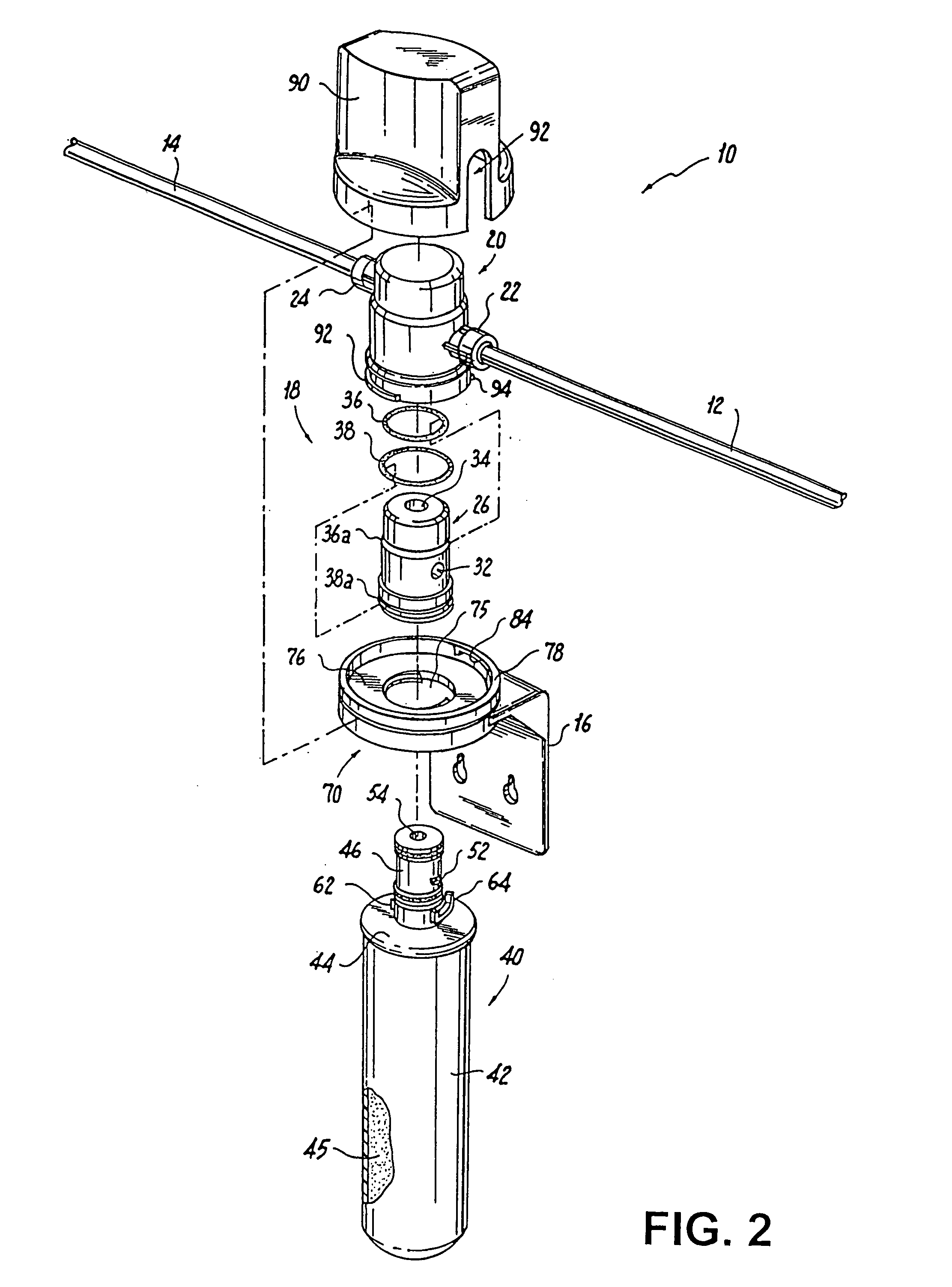
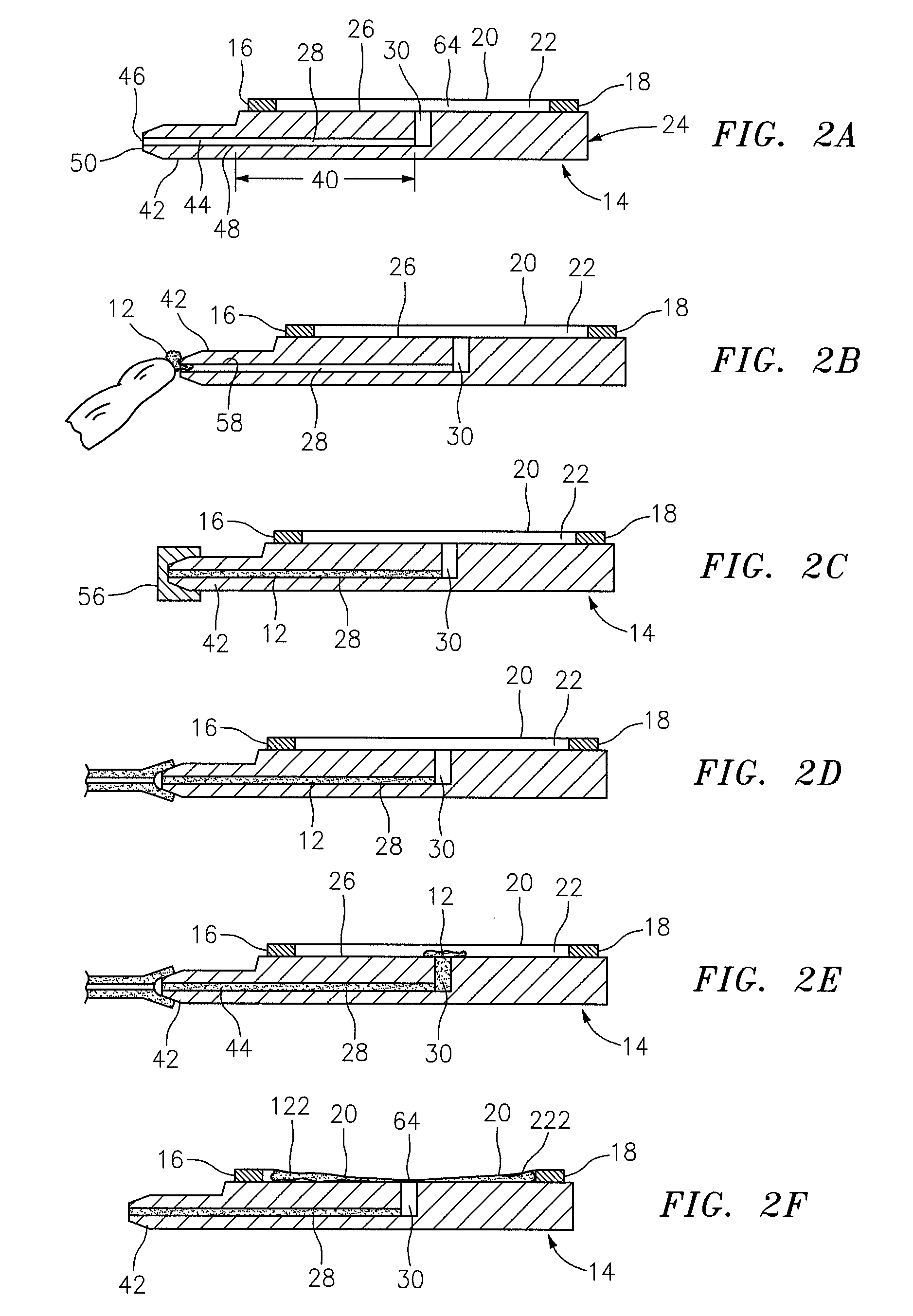
Pressure dome for connecting a transducer with a sealed fluid system
InactiveUS6725726B1Improve compromiseCatheterFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsInlet channelTransducer
The invention relates to a pressure dome for connecting a transducer with a fluid system comprising an inlet channel and an outlet flow as well as a measuring chamber in which a fluid is able to circulate and which has a measuring membrane. To improve fluid irculation and simplify handling, the measuring chamber ceiling is configured in the shape of a calotte and the pressure dome is removably coupled to the transducer housing by means of a snap connection.
Owner:MANFRED ADOLFS +1
Plug device for endoscopic instrument channel
A plug device for use in an entrance passage which is provided on a manipulating head of an endoscope to guide a treating instrument like forceps into an instrument channel of the endoscope. The plug device includes a metallic outer shell, and a pressure relief member formed of a resilient material and fitted in the outer shell member, the pressure relief member having: a valve portion including a slit which is normally closed and openable on insertion of a treating instrument into the entrance passage; a pressure relief chamber; and throttle portions including apertures of different size located on the inner and outer sides of the pressure relief chamber within the entrance passage to the instrument channel of the endoscope. An auxiliary or secondary pressure relief chamber is formed between the valve member and the pressure relief member.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
In situ micromachined mixer for microfluidic analytical systems
The present invention relates to an in situ micromachined mixer for microfluidic analytical systems. In a preferred embodiment, a 100 pL mixer for liquids transported by electroosmotic flow (EOF) is described. Mixing was achieved in multiple intersecting channels with a bimodal width distribution and varying lengths. Five .mu.m width channels ran parallel to the direction of flow whereas larger 27 .mu.m width channels ran back and forth through the network at a 45.degree. angle. All channels were approximately 10 .mu.m deep. It was observed that little mixing of confluent streams occurred in the 100 .mu.m wide mixer inlet channel where mixing would be achieved almost exclusively by diffusion. In contrast, mixing was complete after passage through the channel network in the .apprxeq.200 .mu.m length mixer. Solvent composition was altered by varying the voltage on solvent reservoirs. The high efficiency attained in this mixer was attributed to the presence of a 2 pL vortex in the center of the mixer. Video tracking of fluorescent particles with a fluorescence microscope allowed the position and volume of this vortex to be determined.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
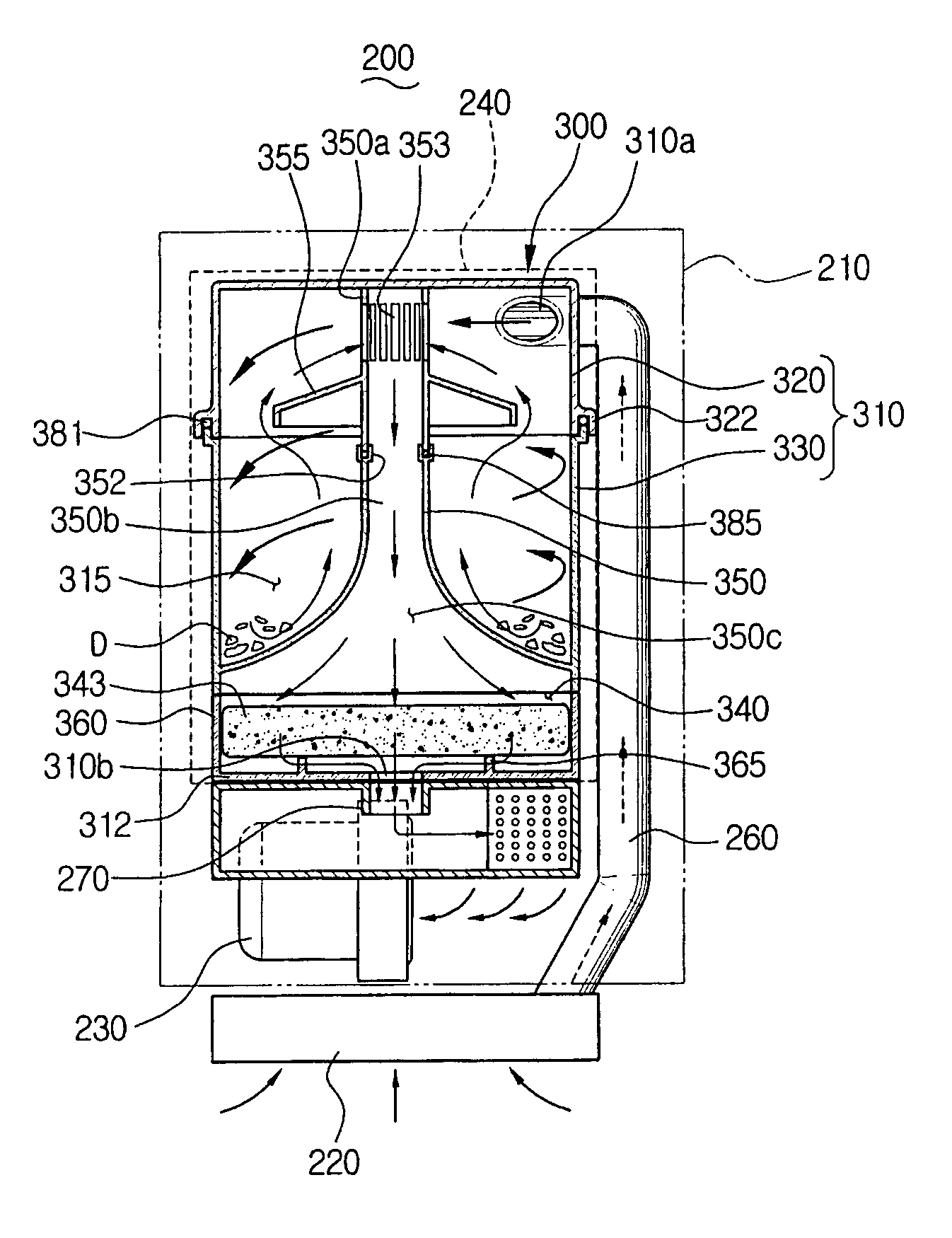
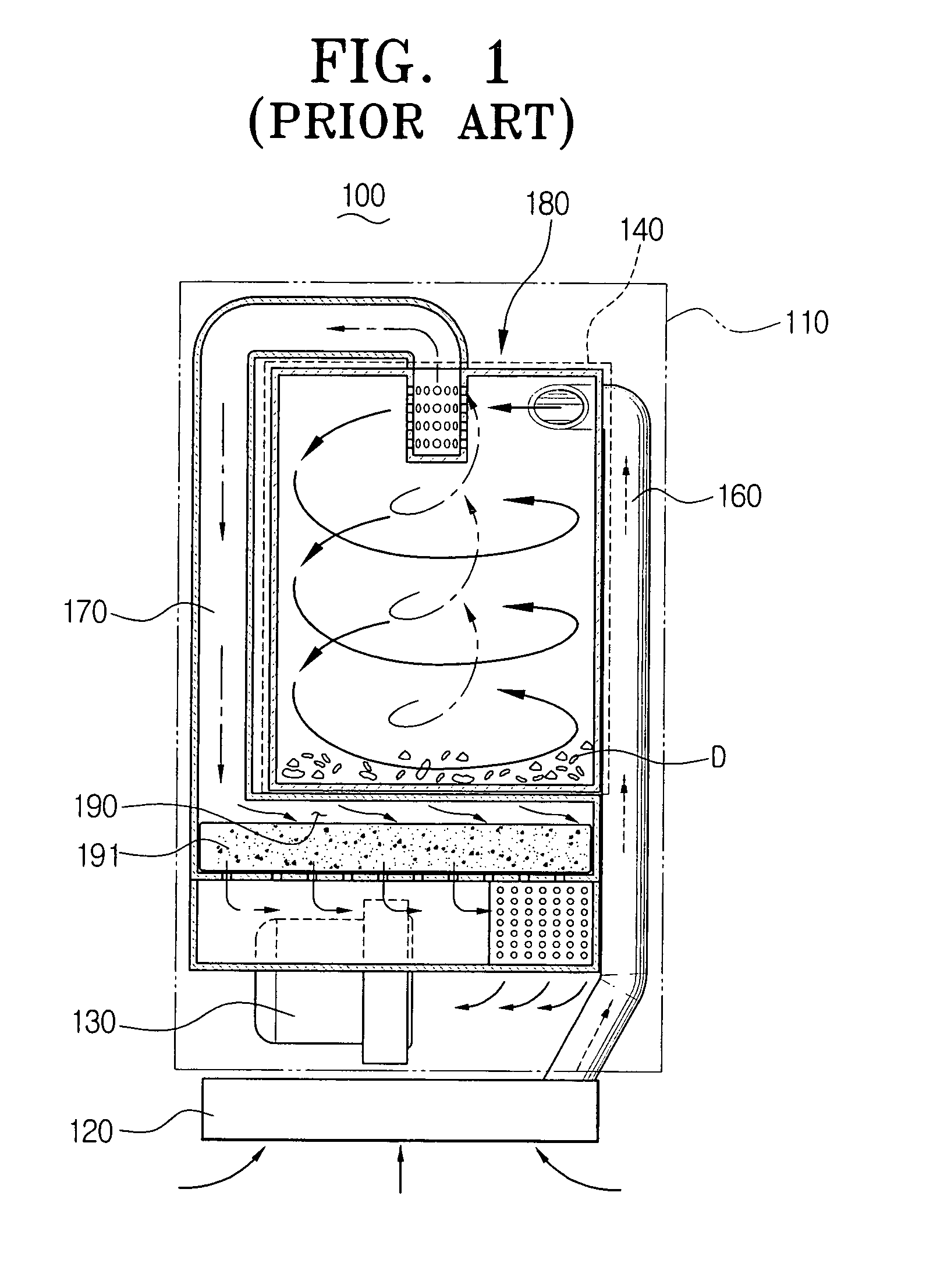
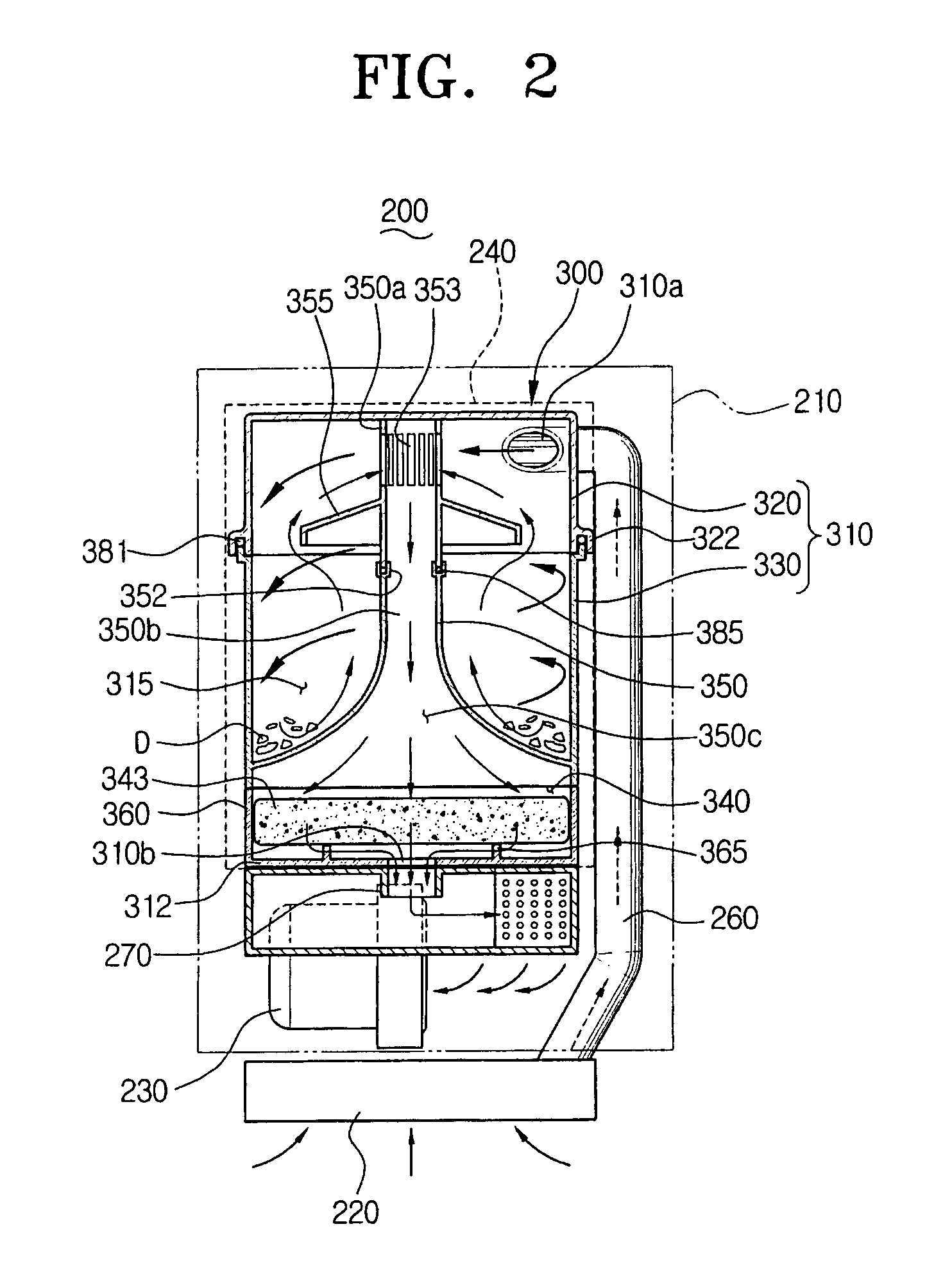
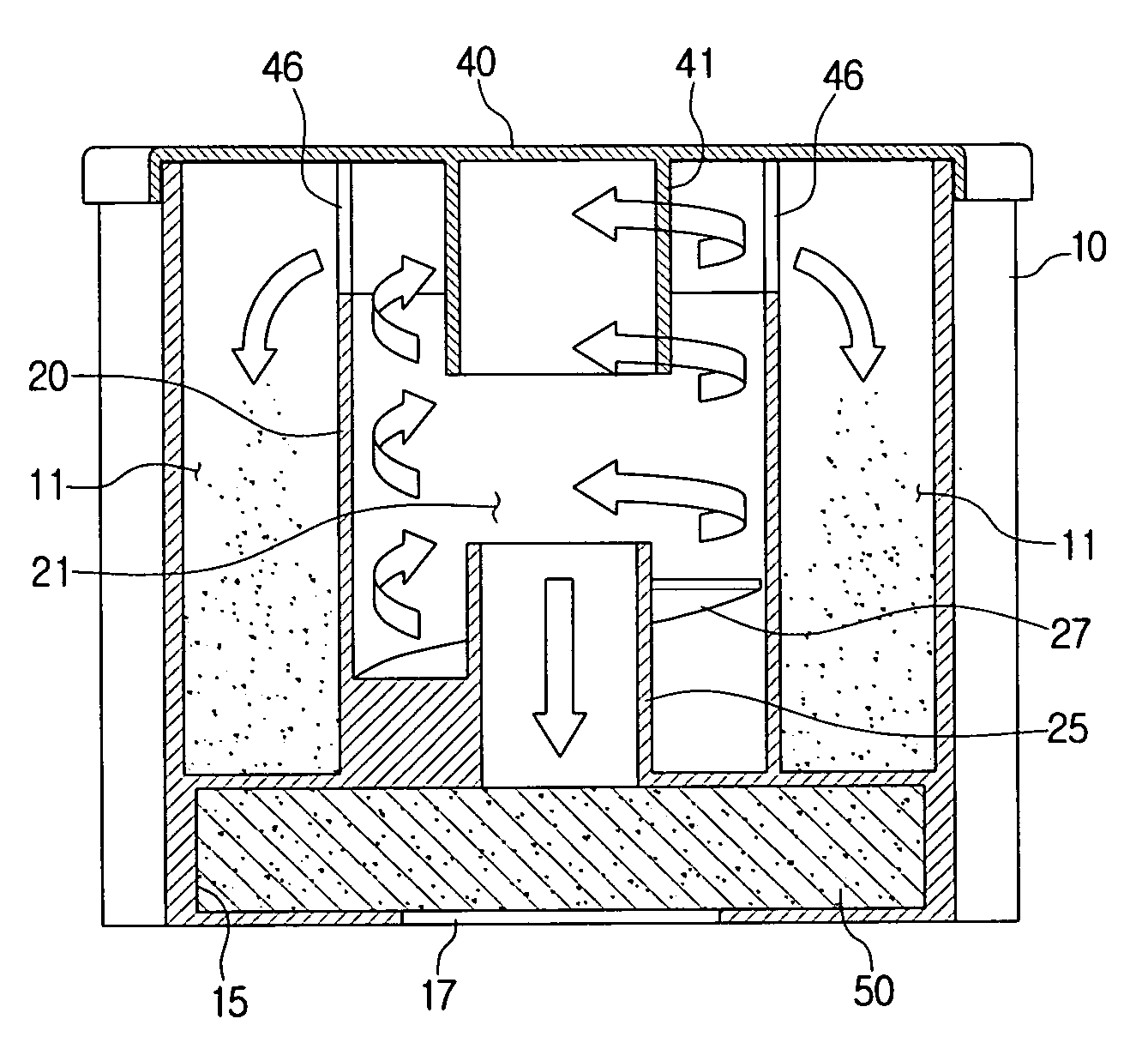
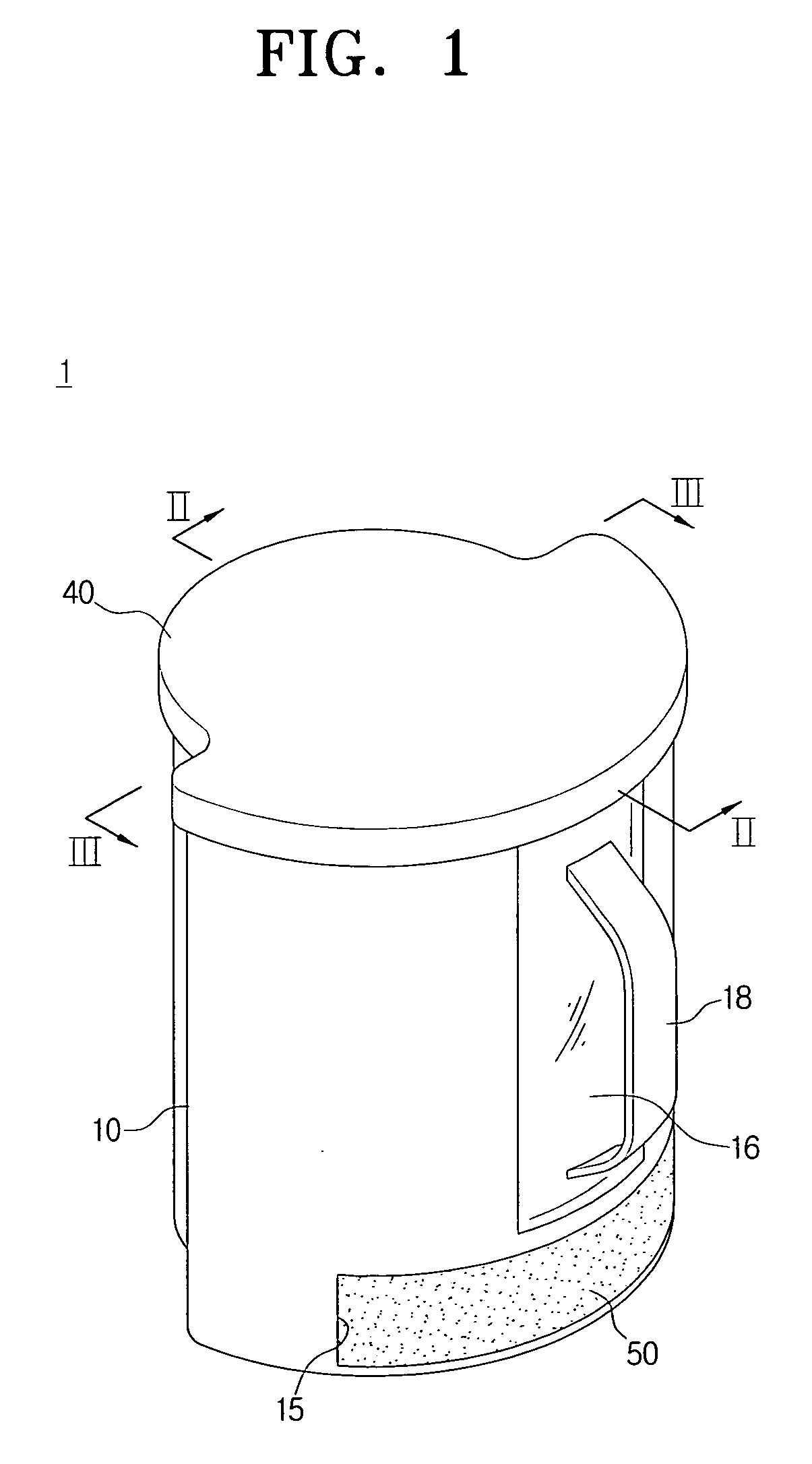
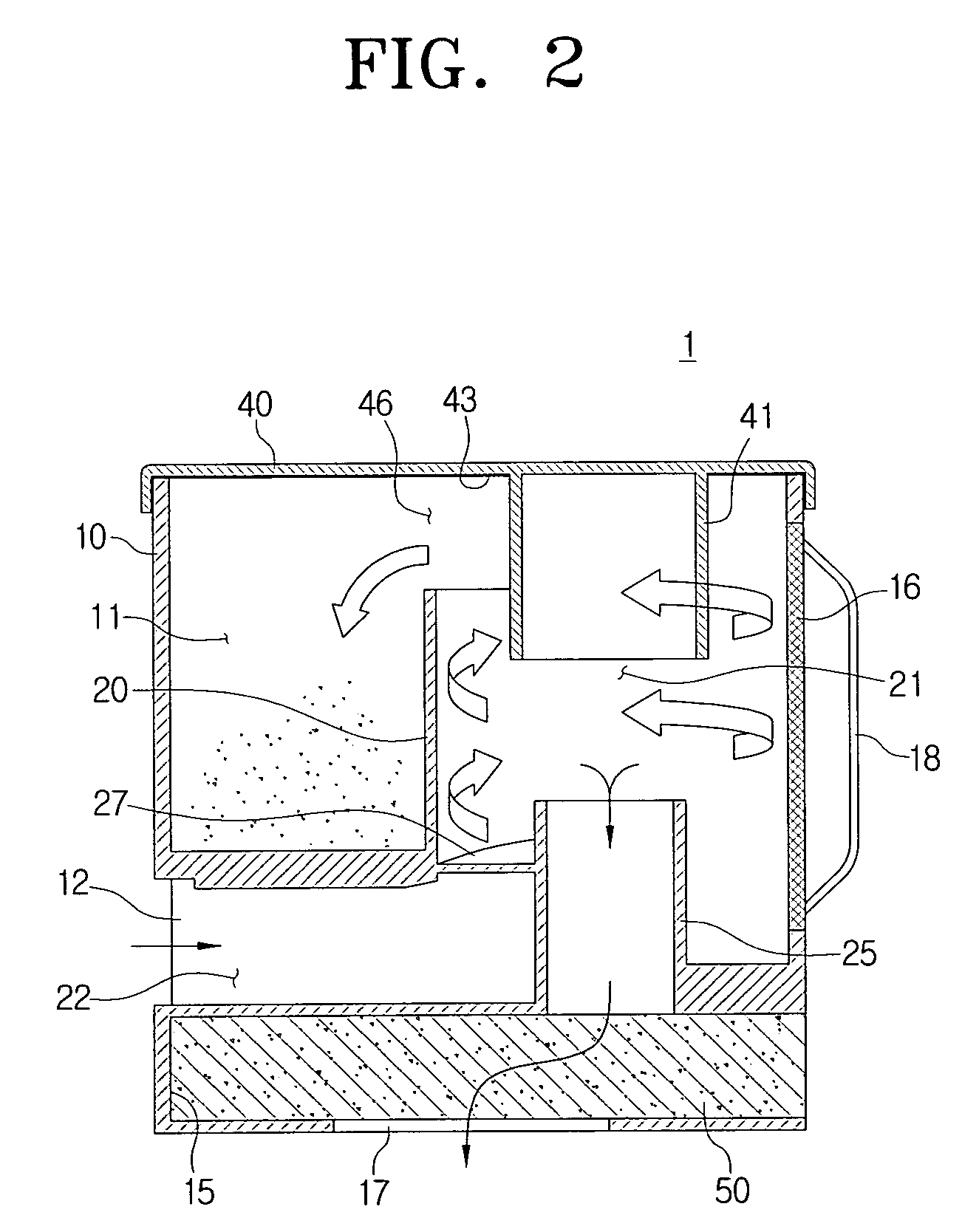
Cyclone dust collecting device and vacuum cleaner having the same
InactiveUS7395579B2Less spaceEasy to manufactureCleaning filter meansCombination devicesVacuum cleanerDust collector
The vacuum cleaner having a suction port assembly and a dust collecting chamber includes a first air inlet path to connect the suction port assembly and the dust collecting chamber, a second air inlet path to connect a lower end of the dust collecting chamber and a vacuum generator, a cyclone dust collecting device detachably mounted in the dust collecting chamber so that an upper end is connected to the first air inlet path and a lower end is connected to the second air inlet path, and a filtering chamber integrally formed with the cyclone dust collecting device and having a filter member detachably disposed. As the second air inlet path requires less space, it is feasible to easily manufacture the vacuum cleaner and maintain the filtering chamber and the cyclone dust collecting device at a time. Therefore, maintenance of the vacuum cleaner becomes more convenient.
Owner:SAMSUNG GWANGJU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Dust collecting apparatus for vacuum cleaner
ActiveUS20070289266A1Improve visibilitySmall sizeCleaning filter meansCombination devicesMechanical engineeringVacuum cleaner
A dust collecting apparatus which is removably connected to a cleaner body is provided. The apparatus includes a cyclone body which forms a cyclone chamber and is in fluid communication with an air inlet passage on one side thereof; an exit pipe which is protruded from a bottom of the cyclone body to an upper side of the cyclone chamber; and a dust canister body which forms a dust collection chamber between the cyclone body and the dust canister body. The cyclone body is arranged eccentrically within the dust collection chamber so that a portion of the cyclone body has a common portion in contact with a portion of the dust canister body. The common portion is made of transparent materials to see through the cyclone chamber.
Owner:SAMSUNG GWANGJU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Rotary valve assembly for fluid filtration system
A valve assembly is disclosed for use in conjunction with a replaceable filter cartridge system. The valve assembly includes a head member having an interior valve chamber defining a central axis, and inlet and outlet passages extending parallel to and communicating with the interior valve chamber. The valve assembly further includes a valve member having an inlet path and an outlet path, adapted for rotation within the interior valve chamber of the head member between a filter position wherein the inlet path of the valve member is in communication with the inlet passage of the head member and a bypass position wherein the inlet path of the valve member is out of communication with the inlet passage of the head member. The valve assembly further includes a seal member seated in an upper surface of the valve member and positioned to seal against an opposing surface of the interior valve chamber. The seal member sealingly isolates untreated and treated fluid streams flowing through the inlet and outlet paths of the valve member, respectively, when the valve member is in the filter position, and sealingly isolates the inlet and outlet passages of the head member from the atmosphere when the valve member is in the bypass position to permit fluid to flow therebetween.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Devices and Methods for Controlling Bubble Formation in Microfluidic Devices
InactiveUS20070280856A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionInlet channelEngineering
A microfluidic device may include a sample distribution network including a plurality of sample chambers configured to be loaded with biological sample for biological testing of the biological sample while in the sample chambers, the biological sample having a meniscus that moves within the sample chambers during loading. The sample distribution network may further include a plurality of inlet channels, each inlet channel being in flow communication with and configured to flow biological sample to a respective sample chamber, and a plurality of outlet channels, each outlet channel being in flow communication and configured to flow biological sample from a respective sample chamber. At least some of the sample chambers may include a physical modification configured to control the movement of the meniscus so as to control bubble formation within the at least some sample chambers. At least some of the sample chambers may include a dried reagent positioned within the at least some sample chambers proximate the inlet channels in flow communication with the at least some sample chambers.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
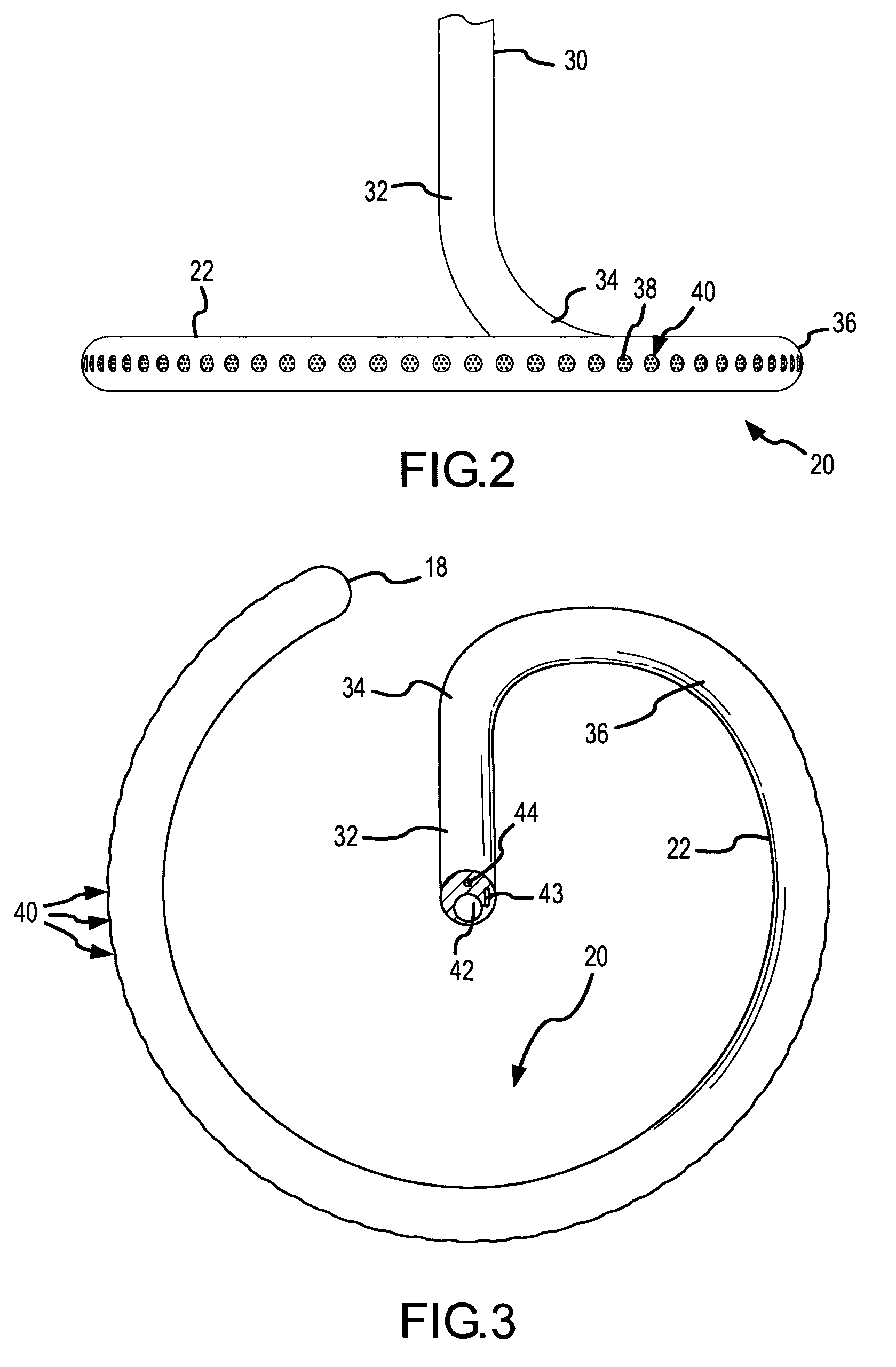
Ablation catheter with adjustable virtual electrode
An ablation catheter has a virtual electrode tip including a fluid manifold structure for operably varying the active area of the virtual electrode. An array of apertures in the distal end of the catheter form the virtual electrode structure. A movable plug slides within the fluid manifold and seals against the interior walls of the fluid manifold. Conductive fluid cannot flow past the plug to fill the fluid manifold on the side of the plug opposite a fluid inlet channel into the fluid manifold. An electrode is positioned within the fluid manifold between the plug and the end wall of the fluid manifold adjacent the channel. By moving the plug within fluid manifold, only those portholes between the plug and the inlet channel will emit energized fluid. The effective length of an active ablation section of the virtual electrode is changed by repositioning the plug within the fluid manifold.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Devices and Methods for Positioning Dried Reagent In Microfluidic Devices
InactiveUS20070280857A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementInlet channelEngineering
A microfluidic device may include a sample distribution network including a plurality of sample chambers configured to be loaded with biological sample for biological testing of the biological sample while in the sample chambers, the biological sample having a meniscus that moves within the sample chambers during loading. The sample distribution network may further include a plurality of inlet channels, each inlet channel being in flow communication with and configured to flow biological sample to a respective sample chamber, and a plurality of outlet channels, each outlet channel being in flow communication and configured to flow biological sample from a respective sample chamber. At least some of the sample chambers may include a physical modification configured to control the movement of the meniscus so as to control bubble formation within the at least some sample chambers. At least some of the sample chambers may include a dried reagent positioned within the at least some sample chambers proximate the inlet channels in flow communication with the at least some sample chambers.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Component separation device
ActiveUS8273302B2High collecting percentageEfficient separationElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentInlet channelSolid particle
A component separating device includes a flow channel, an acoustic wave generator for generating an acoustic wave in the flow channel, a first inlet channel for introducing a fist solution containing solid particles into the flow channel, a second inlet channel for introducing a second solution, and outlet channels for discharging a solution from the flow channel. A density grade generator is provided at the first inlet channel for forming a density grade of the solid particles. This component separating device extracts the solid particles into a high-purity solution at a high collecting rate.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Branching passage assembly for endoscopic biopsy channel
Mounted internally of a casing of a manipulating head assembly of an endoscope is a branching passage member to connect a base end of a biopsy channel with a biopsy channel entrance way and a suction passage. The branching passage member is retained in position by threaded engagement with a biopsy channel entrance pipe which is fitted in the biopsy channel entrance way. Further, the branching passage member is provided with restrictive members thereby to restrict movements of the branching member except a movement toward the biopsy channel entrance pipe when the branching member is pulled into the biopsy channel entrance way for engagement with the entrance pipe.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Fuel-water separator unit with parallel flow
InactiveUS6939464B1Minimize back flushingMembrane filtersLoose filtering material filtersMechanical engineeringFilter element
A filter assembly includes a housing and an inner post with a fluid inlet passage extending in the housing. An outer post surrounds the inner post to define a fluid outlet passage. A filter cartridge is received around the inner post and the outer post. The filter cartridge includes a filter element. A first endplate, which defines a first opening, is attached to a first end of the filter element. A first seal is received in the first opening to seal between the inner post and the first endplate. A second endplate, which defines a second opening, is attached to a second end of the filter element. A seal is received in the second opening to seal the outer post with the second endplate. The housing and the filter cartridge define an outer cavity. The fluid inlet passage opens into the outer cavity to minimize back flushing of contaminants.
Owner:FLEETGUARD INC
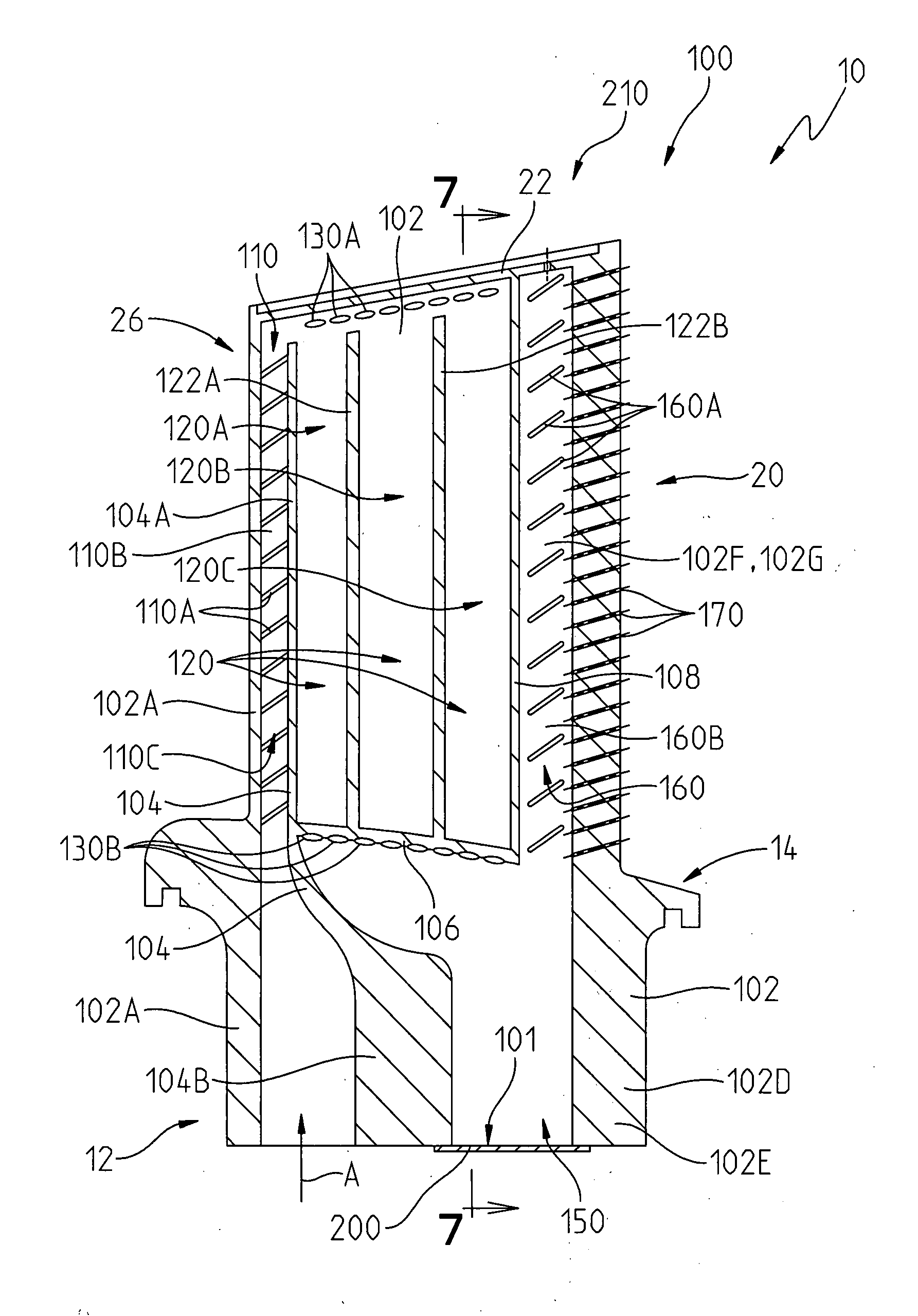
Turbine BOAS with edge cooling
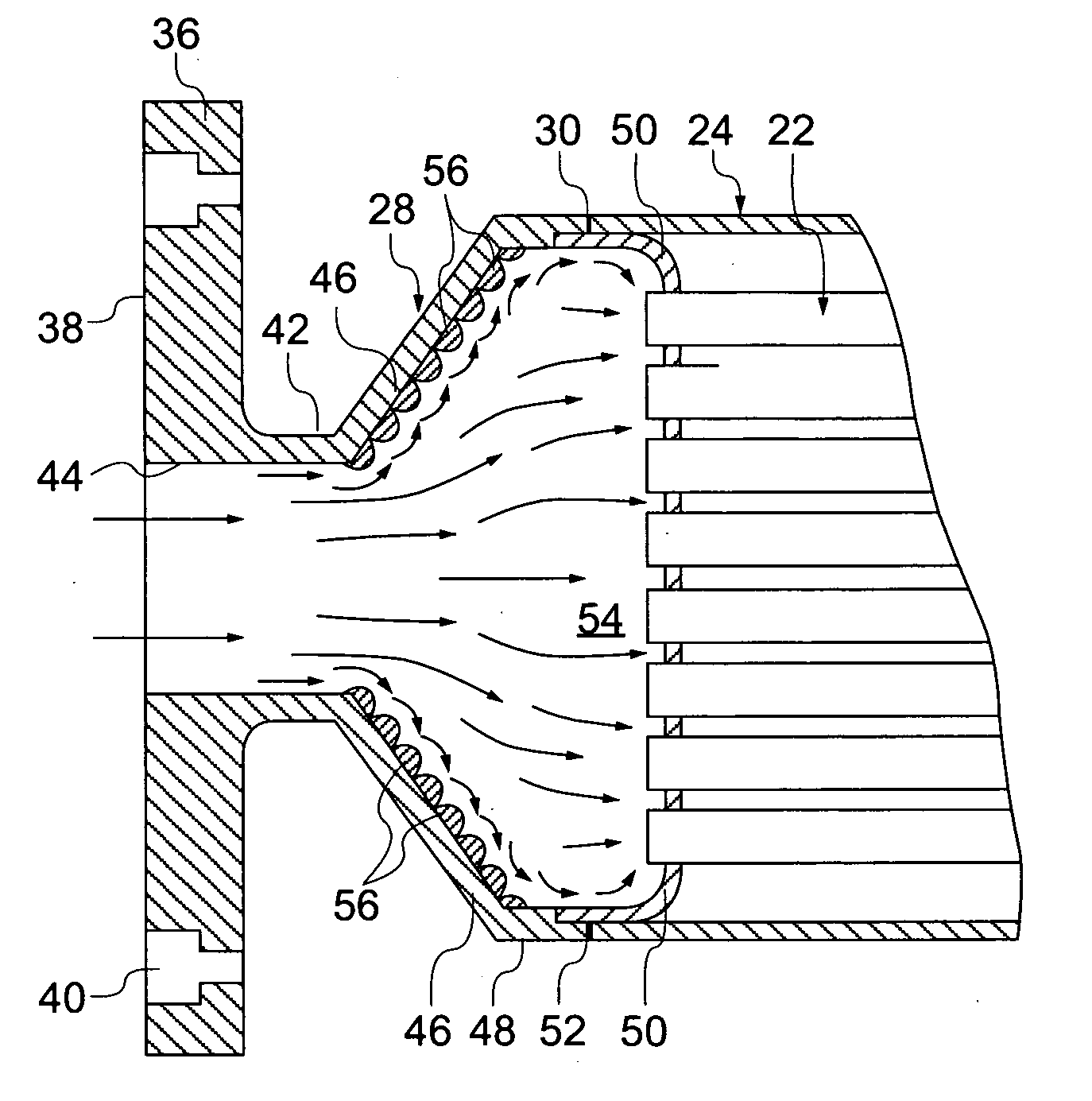
A cooling hole having an inlet passage forming an inward spiral flow path and an outlet passage forming an outward spiral flow path in which the two paths are counter flowing in order to improve the heat transfer coefficient. The spiral cooling hole is used in a blade outer air seal (BOAS) for a turbine in which the edges of the shroud segments include a counter flowing micro serpentine flow cooling circuit with thin diffusion discharge cooling slots for the BOAS edges. The total BOAS cooling air is impingement from the BOAS cooling air manifold and metered through the impingement cooling holes to produce impingement cooling onto the backside of the BOAS. The spent cooling air is then channels into the multiple micro serpentine cooling flow circuits located around the four edges of the shroud segments. This cooling air then flows in a serpentine path through the horizontal serpentine flow channels and then discharged through the thin diffusion cooling slots as peripheral purge air for the mate faces as well as the spacing around the BOAS or shroud segments. Trip strips are used in the serpentine flow channels for the augmentation of internal heat transfer cooling capability. The micro serpentine flow cooling air circuits spaced around the four edges of the shroud segments are formed into the shroud segments during the casting process of the shroud segments.
Owner:FLORIDA TURBINE TECH
Blade for a gas turbine
A blade is provided for a gas turbine. The blade comprises a main body comprising a cooling fluid entrance channel; a cooling fluid collector in communication with the cooling fluid entrance channel; a plurality of side channels extending through an outer wall of the main body and communicating with the cooling fluid collector and a cooling fluid cavity; a cooling fluid exit channel communicating with the cooling fluid cavity; and a plurality of exit bores extending from the cooling fluid exit channel through the main body outer wall.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Rotary valve assembly for fluid filtration system
A valve assembly is disclosed for use in conjunction with a replaceable filter cartridge system. The valve assembly includes a head member having an interior valve chamber defining a central axis, and inlet and outlet passages extending parallel to and communicating with the interior valve chamber. The valve assembly further includes a valve member having an inlet path and an outlet path, adapted for rotation within the interior valve chamber of the head member between a filter position wherein the inlet path of the valve member is in communication with the inlet passage of the head member and a bypass position wherein the inlet path of the valve member is out of communication with the inlet passage of the head member. The valve assembly further includes a seal member seated in an upper surface of the valve member and positioned to seal against an opposing surface of the interior valve chamber. The seal member sealingly isolates untreated and treated fluid streams flowing through the inlet and outlet paths of the valve member, respectively, when the valve member is in the filter position, and sealingly isolates the inlet and outlet passages of the head member from the atmosphere when the valve member is in the bypass position to permit fluid to flow therebetween.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Blade for a gas turbine
A blade is provided for a gas turbine. The blade comprises a main body comprising a cooling fluid entrance channel; a cooling fluid collector in communication with the cooling fluid entrance channel; a plurality of side channels extending through an outer wall of the main body and communicating with the cooling fluid collector and a cooling fluid cavity; a cooling fluid exit channel communicating with the cooling fluid cavity; and a plurality of exit bores extending from the cooling fluid exit channel through the main body outer wall.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
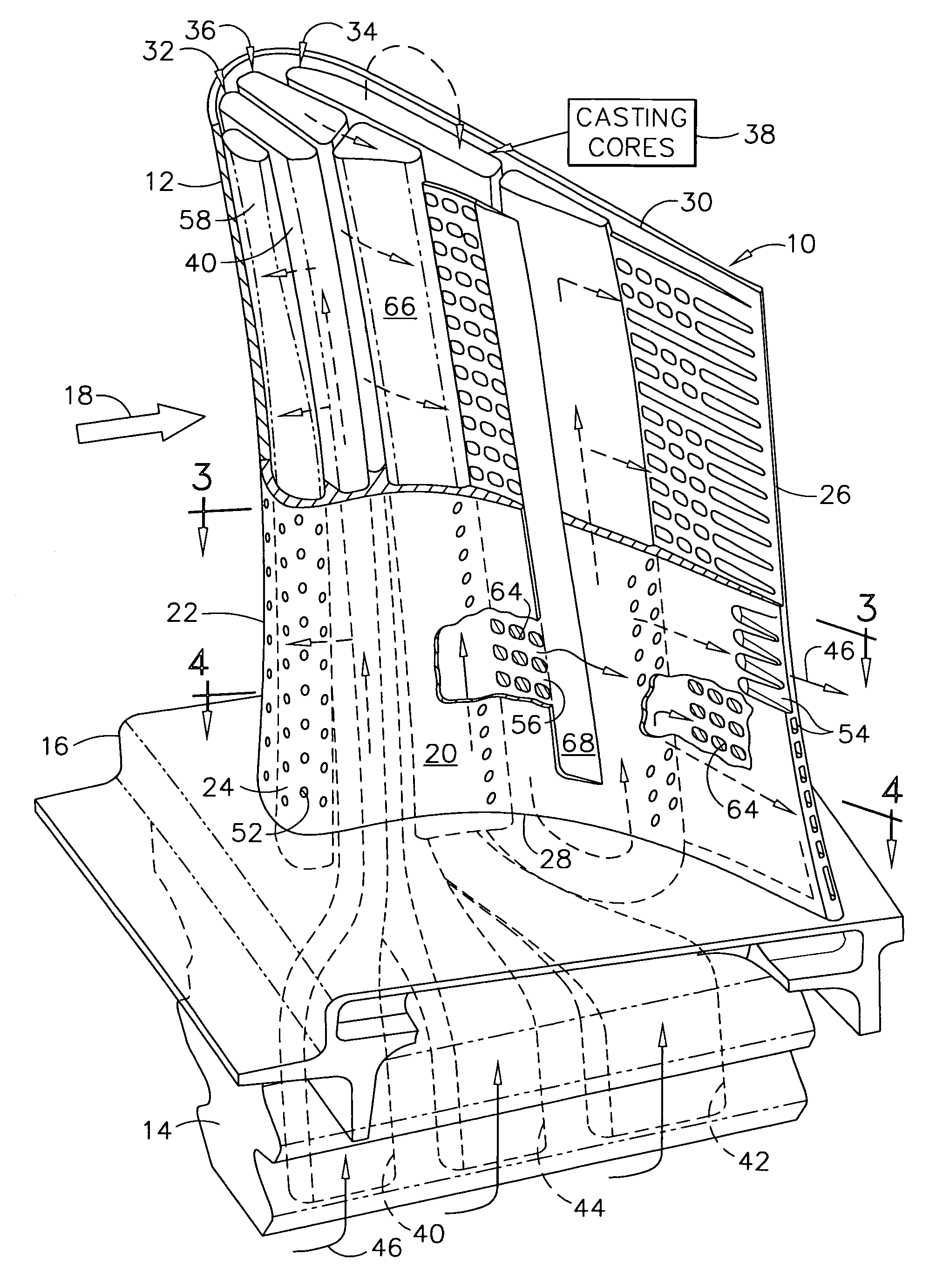
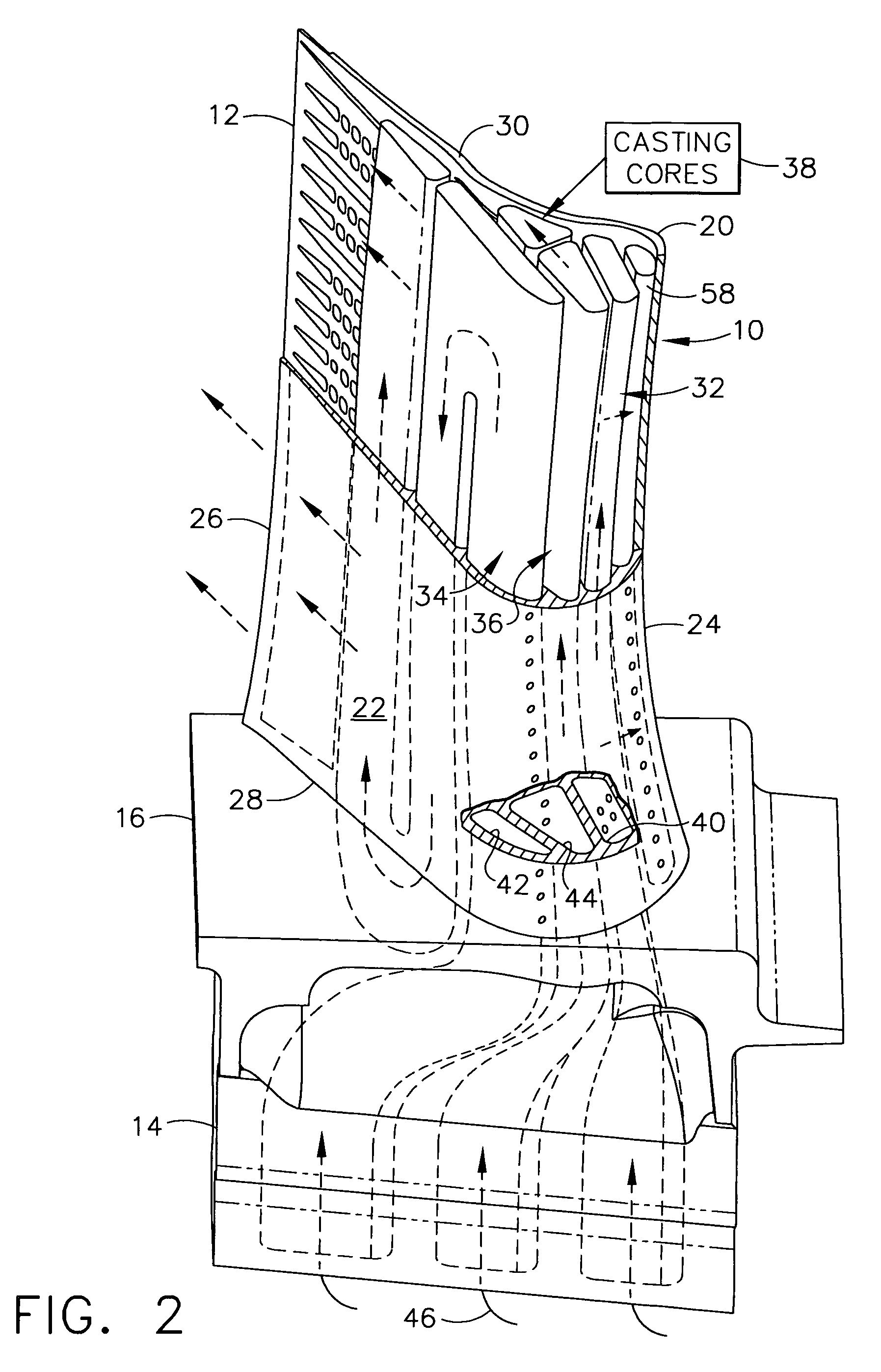
Triple circuit turbine blade
A turbine blade includes an airfoil having pressure and suction sidewalls extending between leading and trailing edges, and from root to tip. A dovetail is joined to the airfoil root at a platform. Three internal cooling circuits extend in span inside the airfoil, and each circuit includes a respective inlet channel commencing in axially adjacent alignment in the dovetail. The inlet channels twist together from the dovetail, through the platform, and into the airfoil behind the leading edge in transverse adjacent alignment across the sidewalls.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multi-functional regulator
InactiveUS20080023662A1Reduce number and sizeReduce complexityOperating means/releasing devices for valvesCheck valvesDifferential pressureInlet pressure
A multifunctional regulator provides a housing having an inlet passage joined with an outlet passage through a poppet valve. The housing has a control diaphragm separating the control chamber into a first volume and a second volume and depending on the differential pressure between the two volumes, the diaphragm will push open the poppet valve. Pressurizing and depressurizing valves join the first volume with the inlet and outlet passages, whereby, with an inlet pressure level within the inlet passage greater than an outlet pressure level within the outlet passage, and with the pressurizing valve admitting the inlet pressure level to the first volume, the diaphragm is displaced into the second volume thereby forcing the poppet valve to open and thereby raising the outlet pressure toward the inlet pressure with fluid flow from the inlet to outlet passages.
Owner:STANDFORD MU
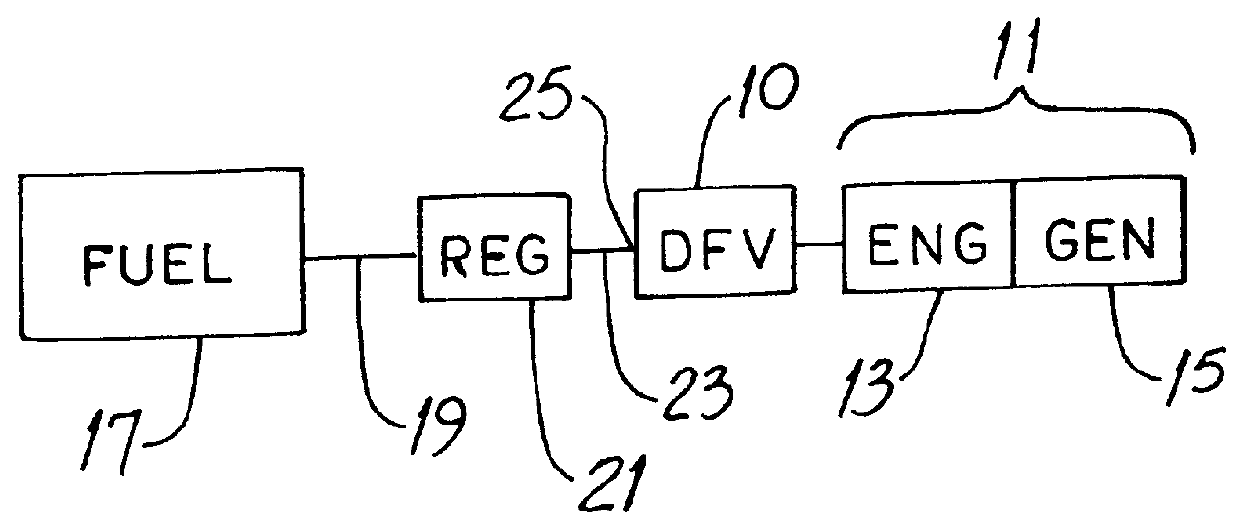
Dual-fuel valve
InactiveUS6068017APrevent movementPrevent inadvertent movementInternal combustion piston enginesFuel supply apparatusInlet channelEmission standard
A valve for flowing gaseous fuel, i.e., natural gas or propane gas, to an internal combustion engine includes a valve body having an inlet passage and first and second outlet paths in parallel with one another and in flow communication with the inlet passage. A plug-type adjustment member is threaded into the body and an annular seat in the body coacts with the adjustment member to form an orifice in the first outlet path. A stop mechanism limits movement of the adjustment member between a first position at which the orifice area is smaller and a second position at which the orifice area is larger. The valve permits adjustment of fuel flow to small engines so that such engines provide maximum power without exceeding applicable emission standards. And the valve is tamper-resistant.
Owner:GENERAC POWER SYSTEMS
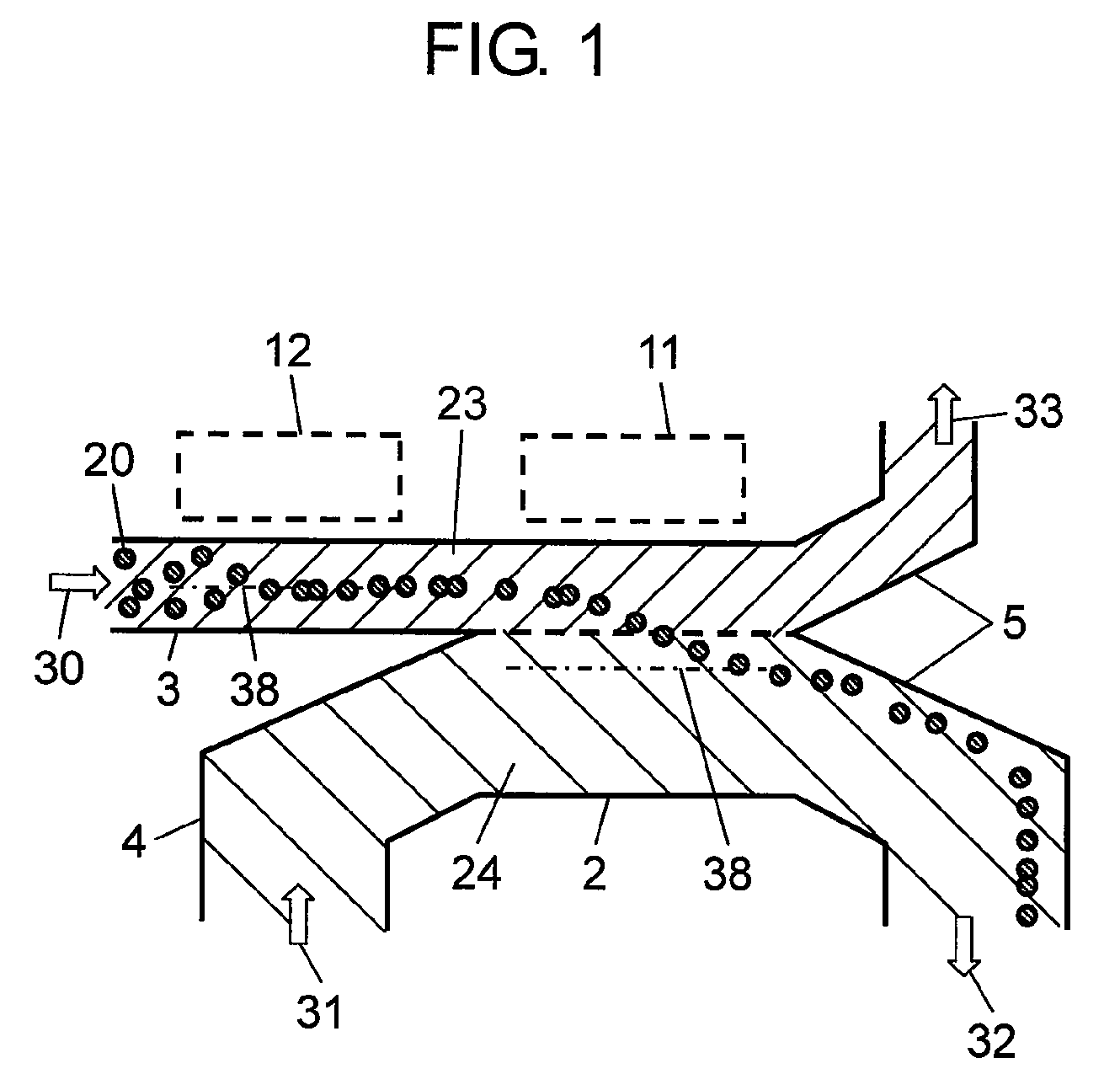
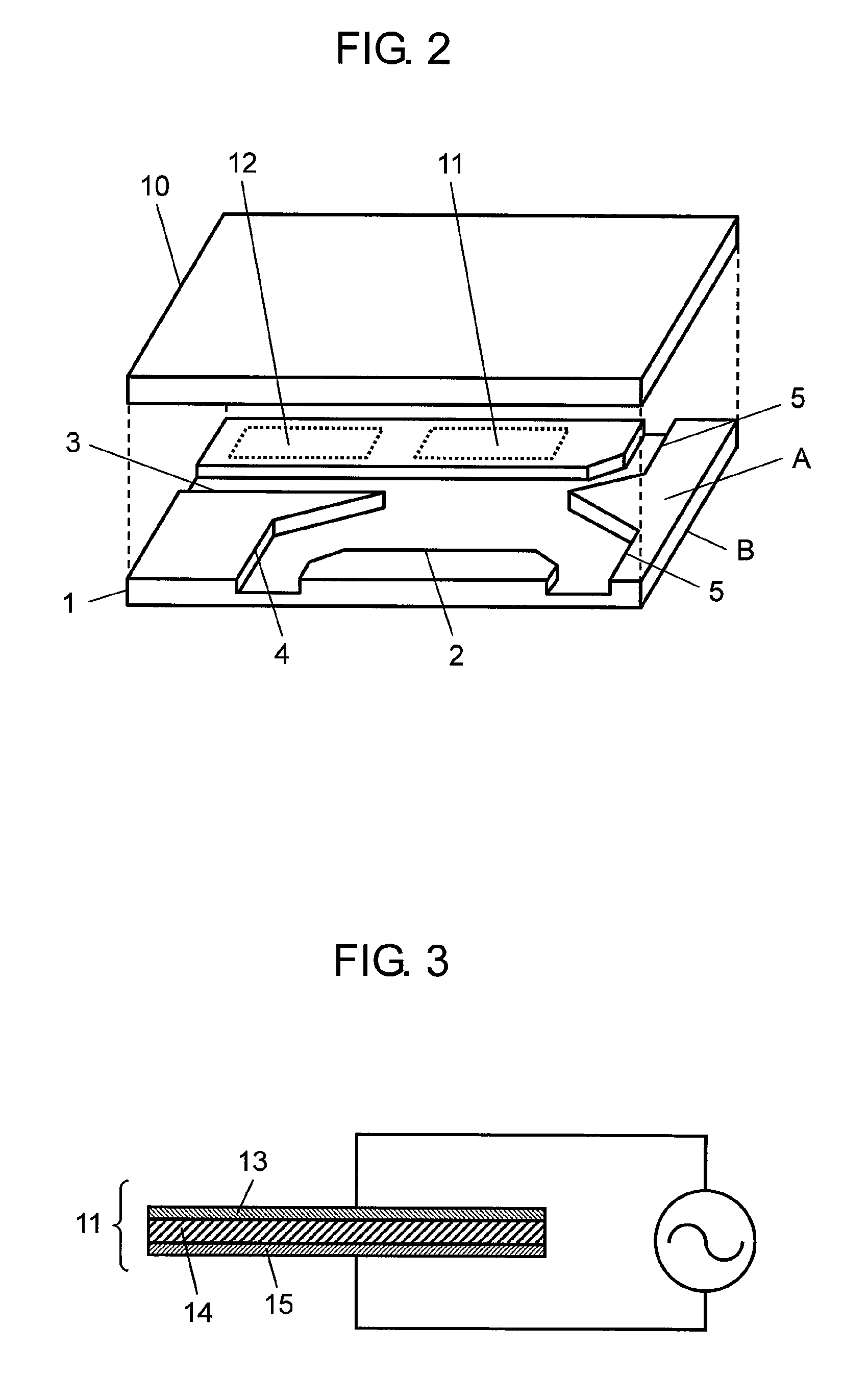
Combined thermal protection and surface temperature control system
ActiveUS20080105402A1Cosmonautic environmental control arrangementAir-treating devicesTemperature controlControl system
The invention relates to a combined thermal protection and surface temperature control apparatus. In one embodiment, a combined thermal protection and surface temperature control apparatus comprises a porous member having an entrance side, and a separate exit side. One or more coolant entrance channels extend through the entrance side, extend part-way through the porous member, and end within the porous member before reaching the exit side. Conversely, one or more coolant exit channels begin within the porous member, extend through a portion of the porous member, and extend through the exit side. The coolant entrance and exit channels may be parallel and may alternate. The channels may only extend across a portion of the thickness of the porous member.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Security checking cabin and method
A secured checking cabin for checking people entering closed public regions has an entrance passage between two armored walls defining a gap dimensioned to prevent more than a single person at a time to walk between the walls side by side. At least one armored capturing unit coupled to the entrance passage admits a person coming from the entrance passage, and is in communication with a closed public space. An entrance mechanism allows the entrance of one person at a time to the entrance passage, and a no-return mechanism prevents him from returning therethrough. An exit mechanism releases a person from the capturing unit to the closed public space, and a locking mechanism locks both the entrance and exit mechanisms upon demand. At least one detector is located in the entrance passage or in the capturing unit for detecting a material suggestive of a potential danger.
Owner:MESINGER JOSHUA
Method of manufacturing a handle for a beverage dispensing head
InactiveUS7658006B2Lower time per unit costLiquid flow controllersLiquid transferring devicesValve actuatorEngineering
In a method of manufacturing a beverage dispensing head, a first section is molded to include an exit channel and a first portion of a valve bore. A second section is molded to include an entry channel, a passage through the second section, and a second portion of the valve bore. A third section is molded to include a passage through the third section and a third portion of the valve bore. The first section is mated with the second section and the second section is mated with the third section to form a handle including a passageway therethrough. The mating of the first section with the second section and the second section with the third section aligns the first portion with the second portion and the second portion with the third portion to form the valve bore for the passageway. In addition, the entry channel is sealed to form a fluid entry aperture and a fluid entry conduit for the passageway. Further, the exit channel is sealed to form a portion of a fluid exit conduit for the passageway. Still further, the exit channel aligns with the passages to form a portion of the fluid exit conduit and to provide a fluid exit aperture for the passageway. After forming the handle, a valve assembly is placed within the valve bore, and a valve actuator assembly is mounted onto the handle. A nozzle is secured to the handle such that the fluid exit aperture communicates with the nozzle.
Owner:TAPRITE FASSCO MFG INC
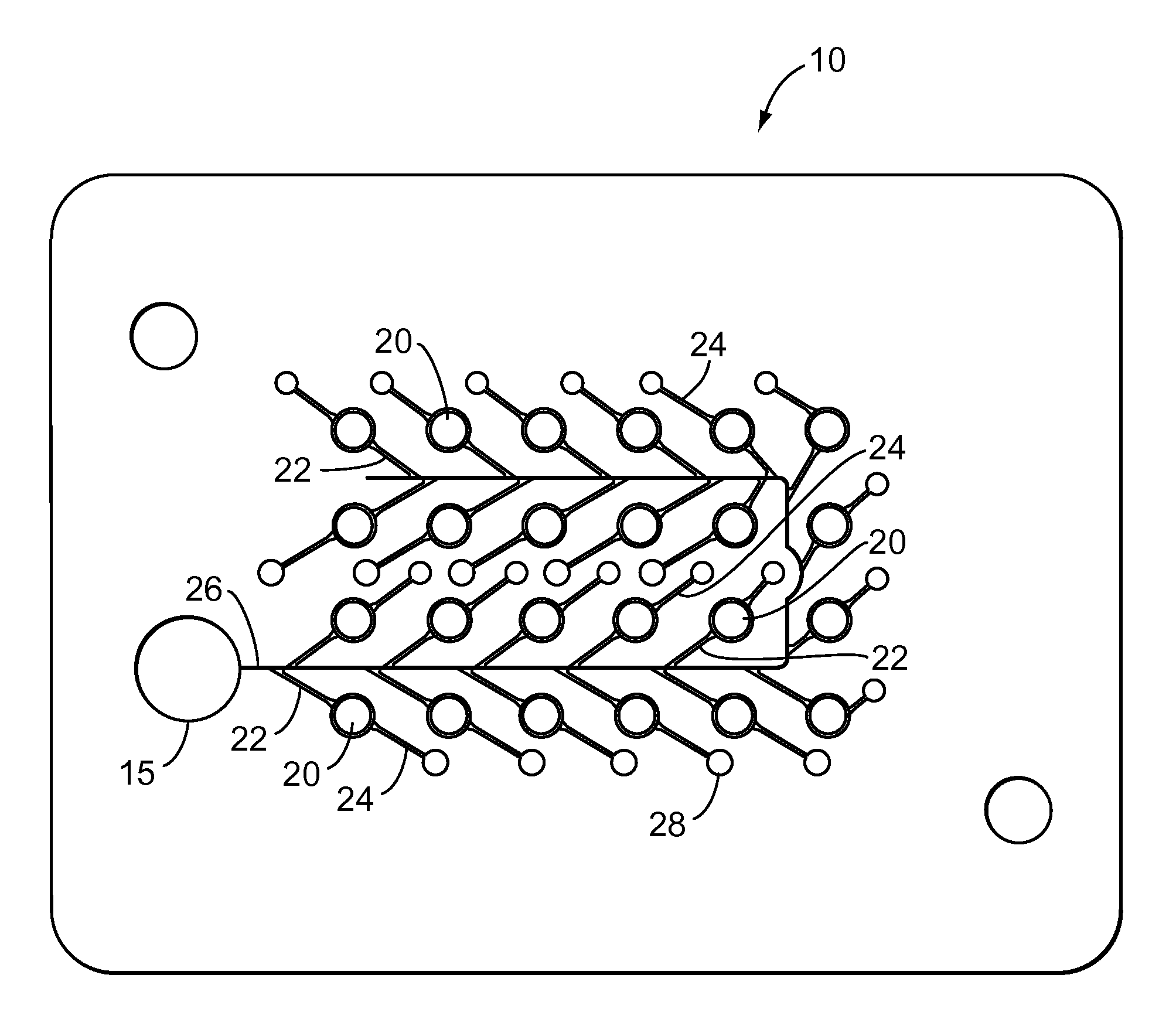
Biologic fluid analysis cartridge with deflecting top panel
A cartridge for analyzing a biologic fluid sample is provided that includes a base plate, a sample inlet port, a first chamber wall, a second chamber wall, and an optically transparent cover panel disposed in contact with the first and second chamber walls. The base plate has a body with a chamber surface, a body passage, and a chamber entry passage. The body passage is in fluid communication with the chamber entry passage, and the chamber entry passage extends through to the chamber surface. The sample inlet port has an inlet passage in fluid communication with the body passage. The first and second chamber walls each have a height extending outwardly from the chamber surface, and the two walls are spaced apart from one another. The cover panel is sufficiently flexible to deflect and contact a central region of the chamber surface.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
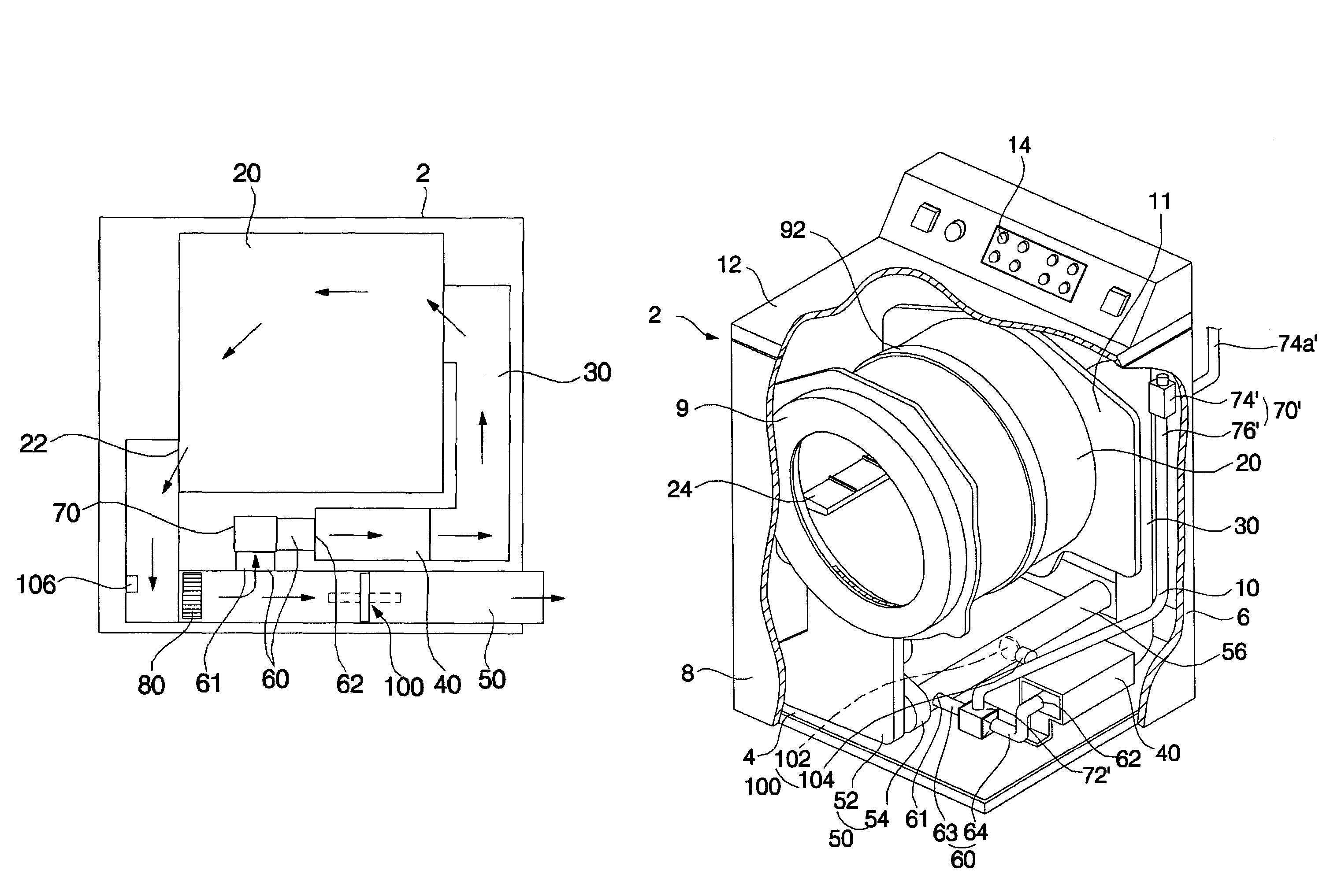
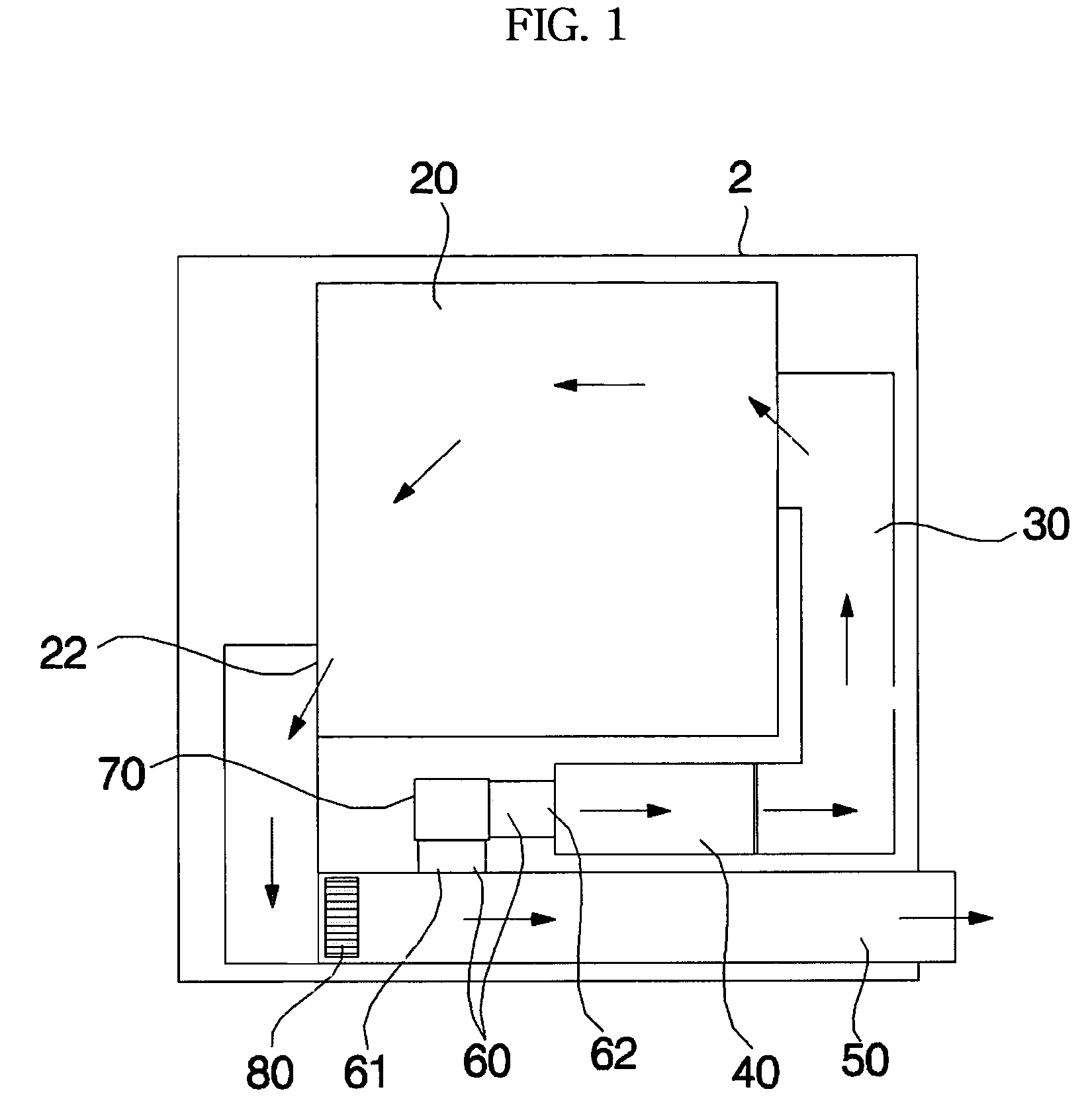
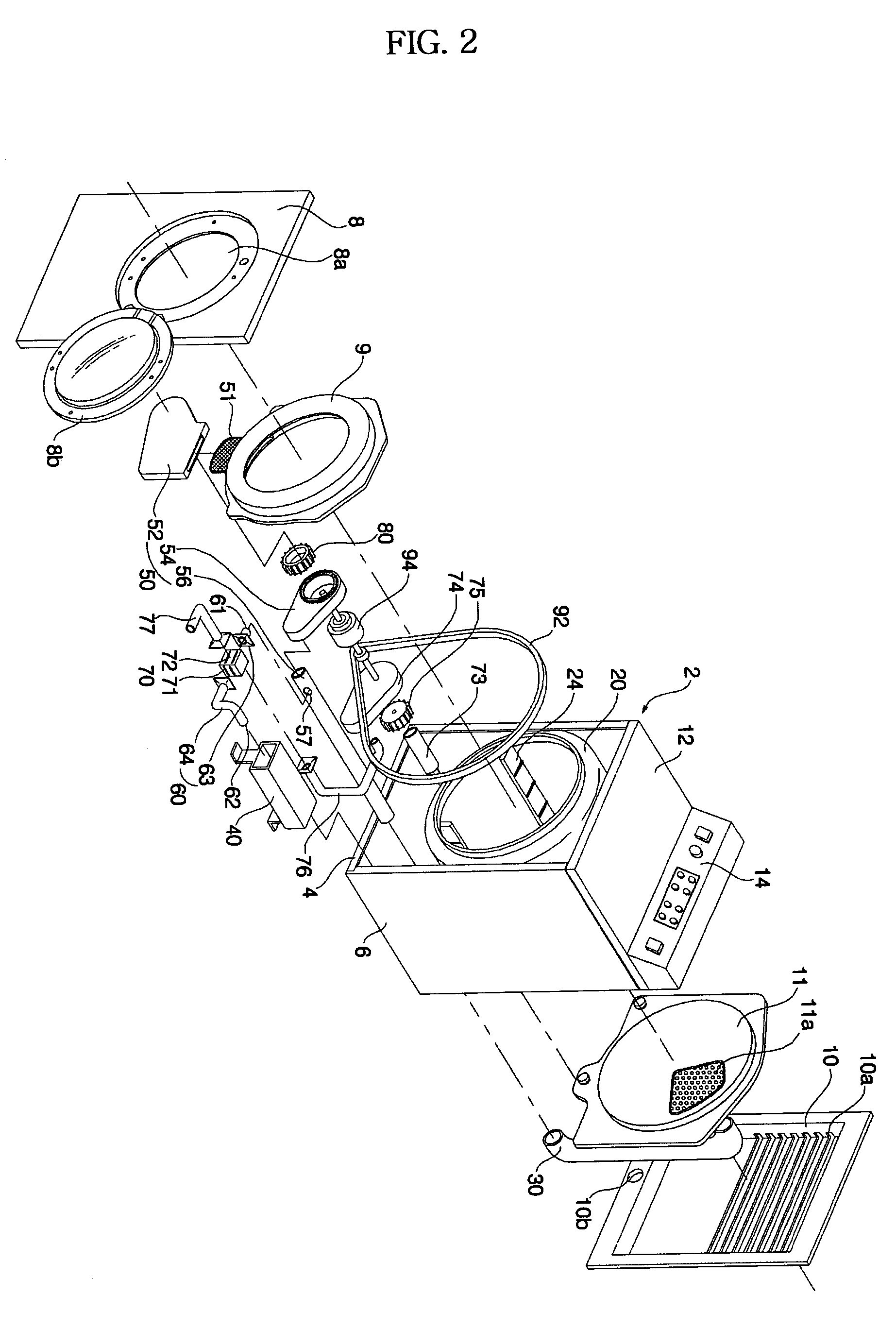
Drying machine and drying machine with washing function and method of controlling the same
InactiveUS7228647B2Adequate flowShorten the timeDrying gas arrangementsOther washing machinesInlet channelPulp and paper industry
Disclosed herein is a drying machine or a drying machine with washing function. The drying machine or the drying machine with washing function comprises a heater for heating air introduced into an inlet channel of a drum, an outlet channel for allowing air in the drum to be discharged out of the drying machine or the drying machine with washing function therethrough, and a circulating channel connected between the outlet channel of the drum and the heater. When the exhaust resistance of air at the outlet channel is large, some of air, passing through the outlet channel, is guided to the heater through the circulating channel. Consequently, the drying machine or the drying machine with washing function according to the present invention has an effect in that air flow rate sufficient to dry the laundry is obtained and time necessary to dry the laundry is reduced.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
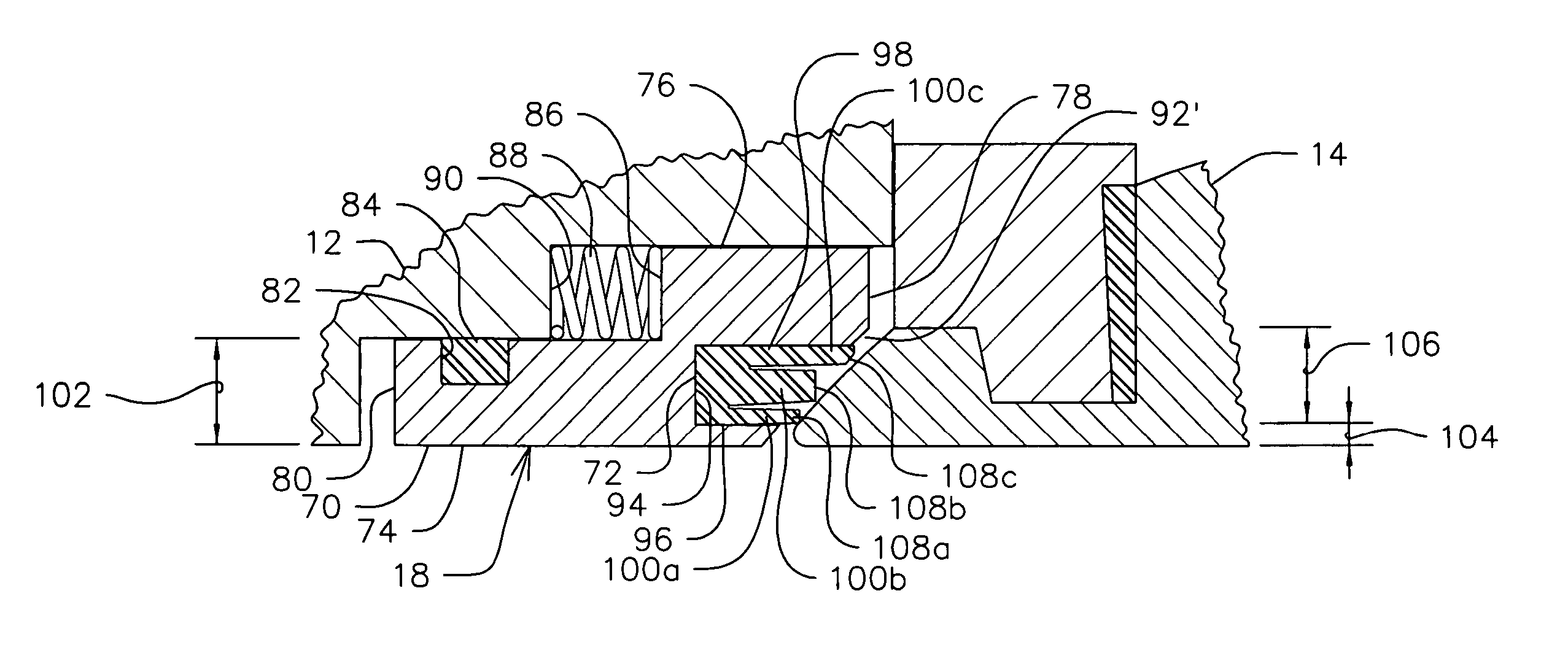
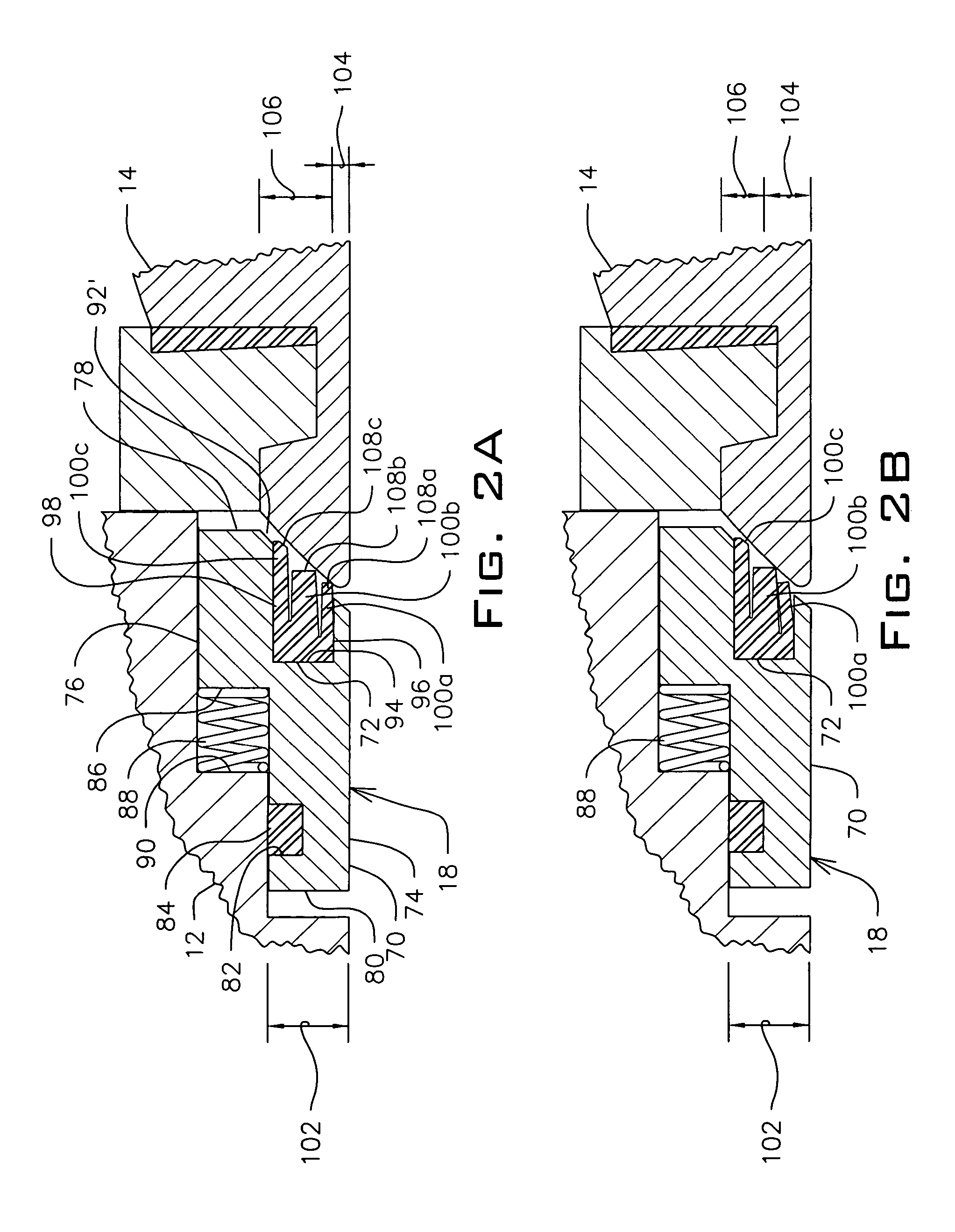
Valve with pressure adaptable seat
A seat assembly extending about an inlet passage of a valve and engaging a valve member is disclosed. The seat assembly includes an annular seat carrier having an annular groove formed therein, and a seat positioned in and extending from the annular groove of the seat carrier. The seat has an inner side, an outer side, and a plurality of spaced apart, concentric seal rings extending from the inner side of the seat to the outer side thereof. The seal ring nearest the inner side of the seat is engageable with the valve member to provide an innermost seal when the seat assembly is acted upon by a pressure within a pressure range and the seal ring nearest the inner side of the seat is deflectable in a radially outward direction and out of sealing engagement with the valve member when the pressure exceeds the pressure range to cause the adjacent seal ring to provide the innermost seal.
Owner:VALVE INNNOVATIONS L L C
Component separation device
ActiveUS20100126922A1High collecting percentageEfficient separationSludge treatmentElectrostatic separatorsInlet channelSolid particle
A component separating device includes a flow channel, an acoustic wave generator for generating an acoustic wave in the flow channel, a first inlet channel for introducing a fist solution containing solid particles into the flow channel, a second inlet channel for introducing a second solution, and outlet channels for discharging a solution from the flow channel. A density grade generator is provided at the first inlet channel for forming a density grade of the solid particles. This component separating device extracts the solid particles into a high-purity solution at a high collecting rate.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Replaceable ink container for inkjet printer
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Heat exchanger with modified diffuser surface
InactiveUS20070062679A1Minimize formationSpeed up gas flowHeat exchanger casingsHeat transfer modificationPlate heat exchangerEngineering
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
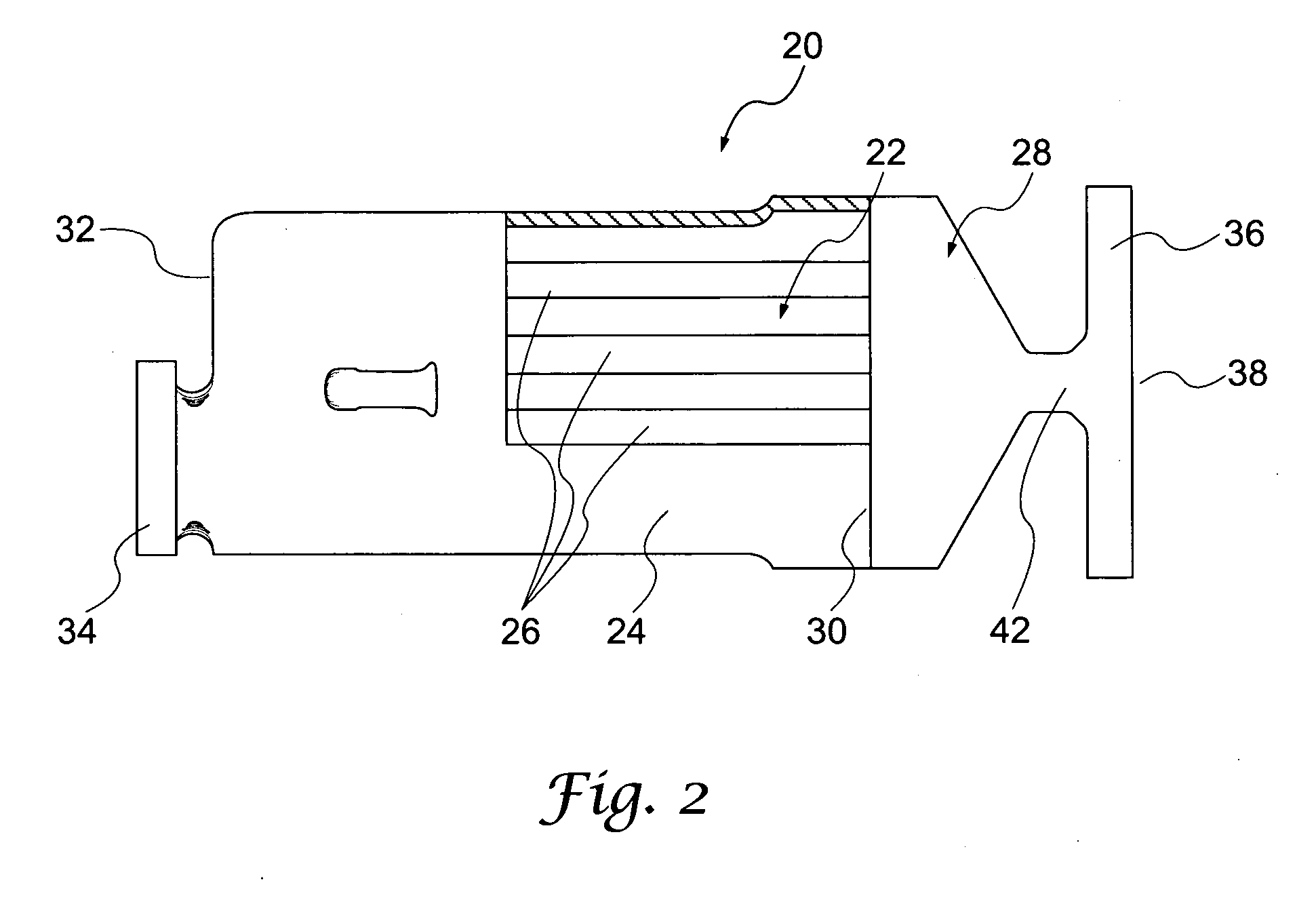
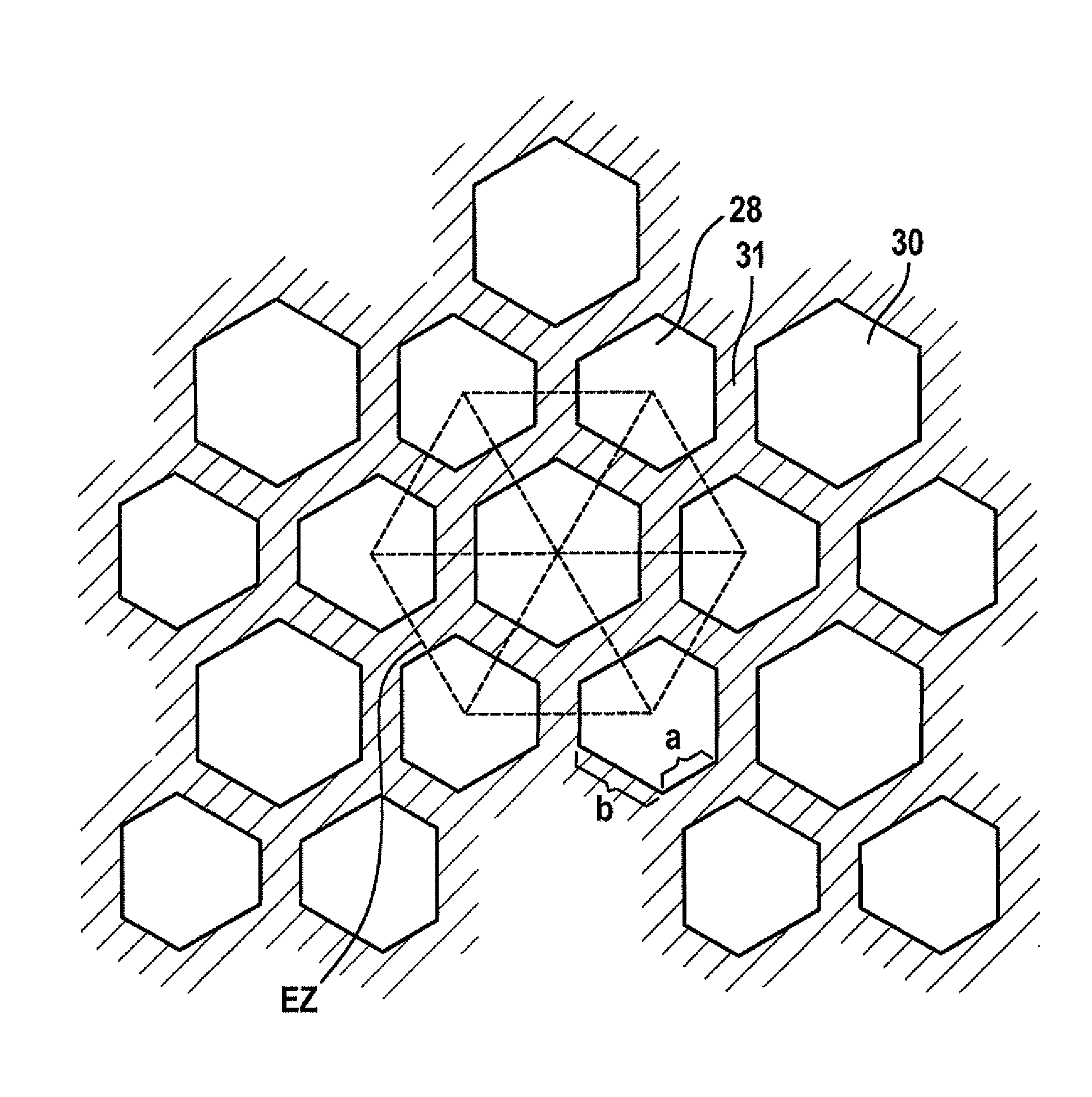
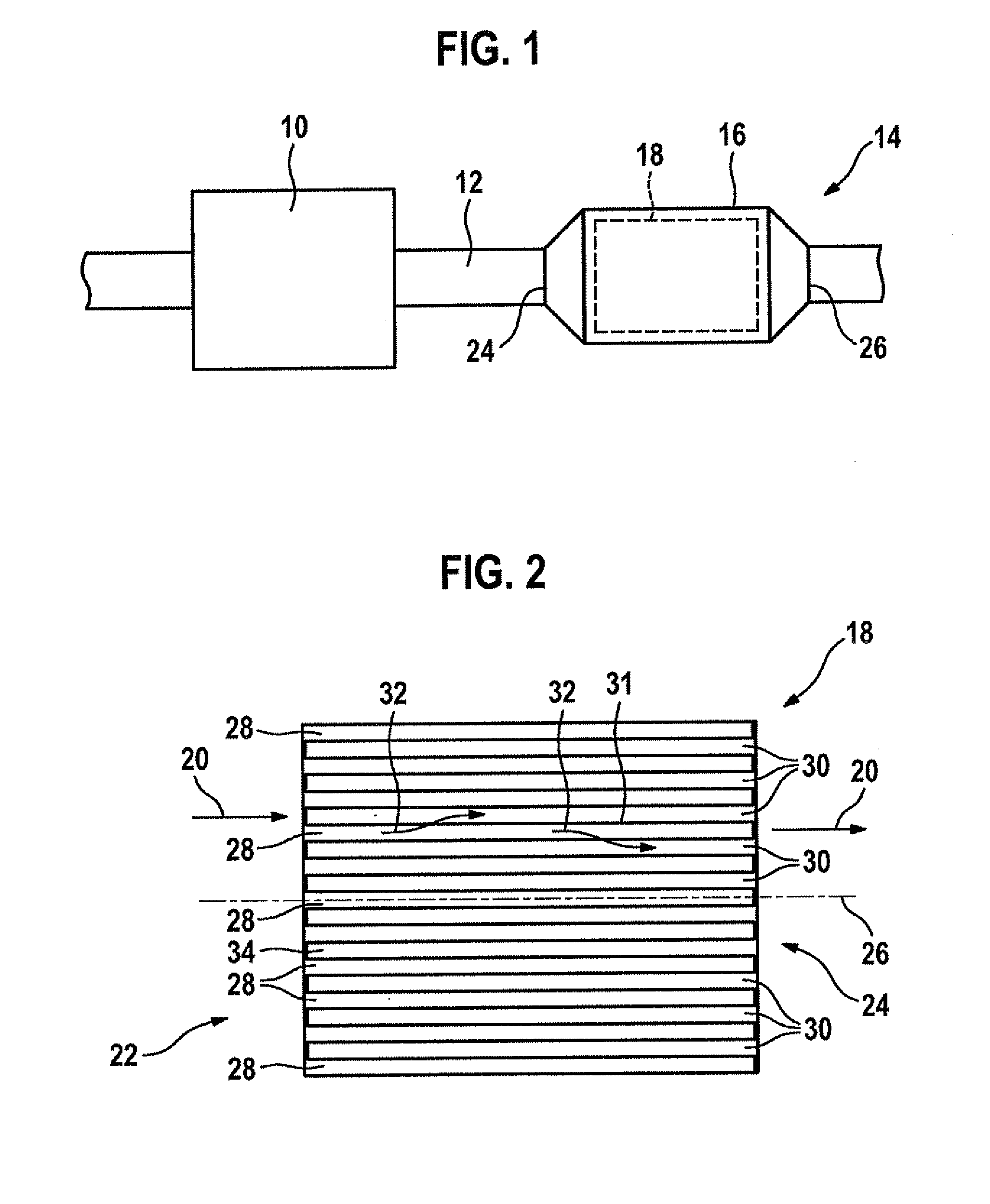
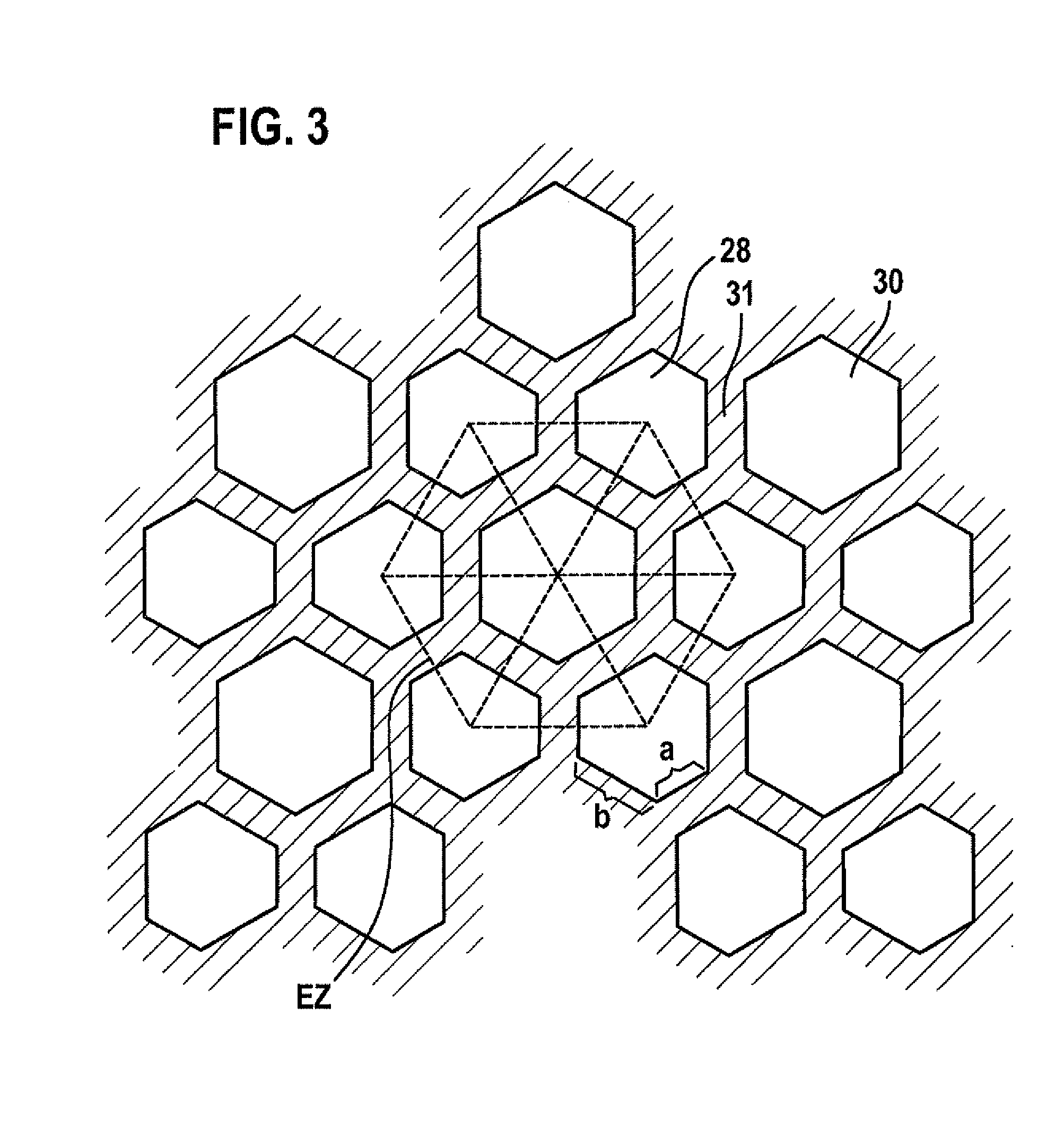
Filter device in particular for an exhaust system of an internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20090205301A1Promote absorptionIncrease intervalCombination devicesInternal combustion piston enginesInlet channelExternal combustion engine
Cross-sectional geometries of filter elements for soot particle filters are described, allowing uniform loading of the filter element with soot. Starting with hexagonal cell shapes, other polygonal shapes are arranged around them. All the cross-sectional geometries have in common the fact that the cross-sectional area of all inlet channels is larger than the cross-sectional area of all outlet channels.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
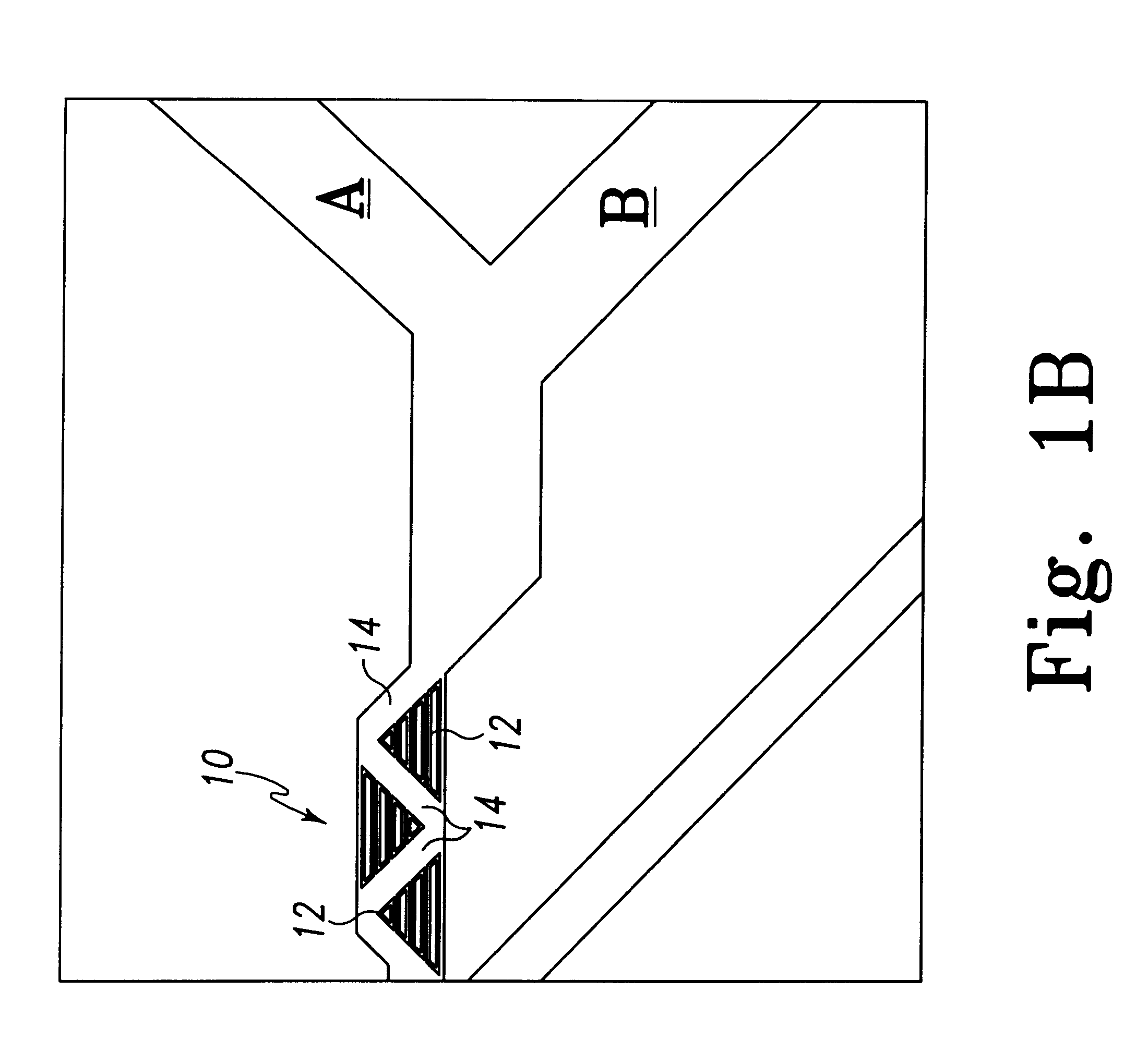
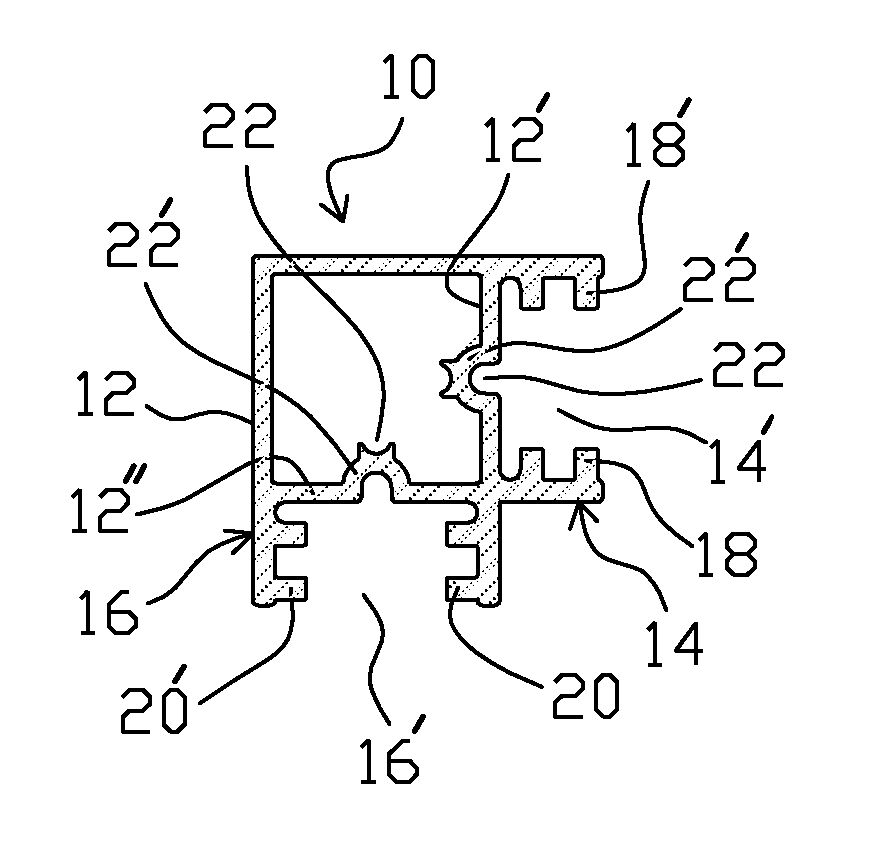
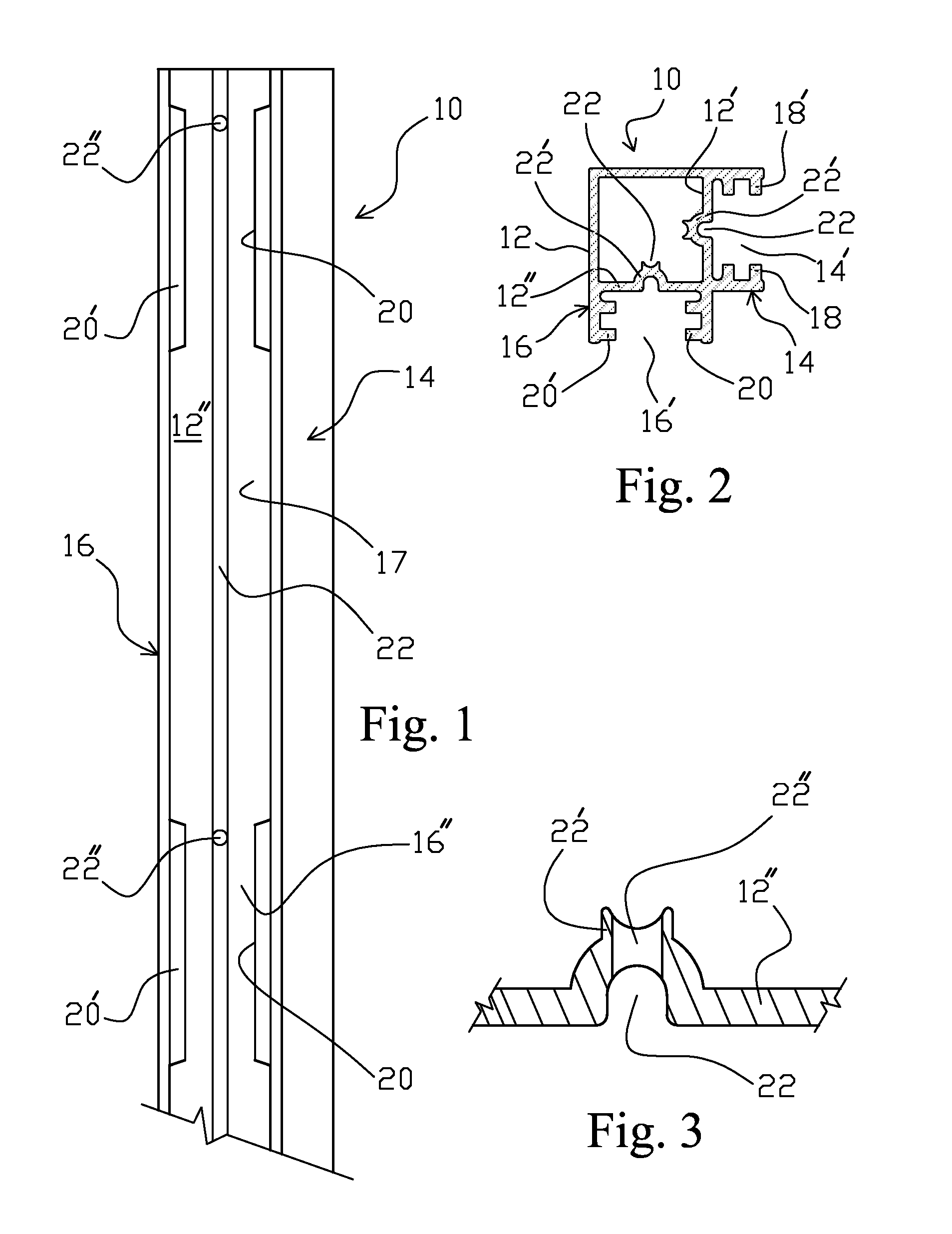
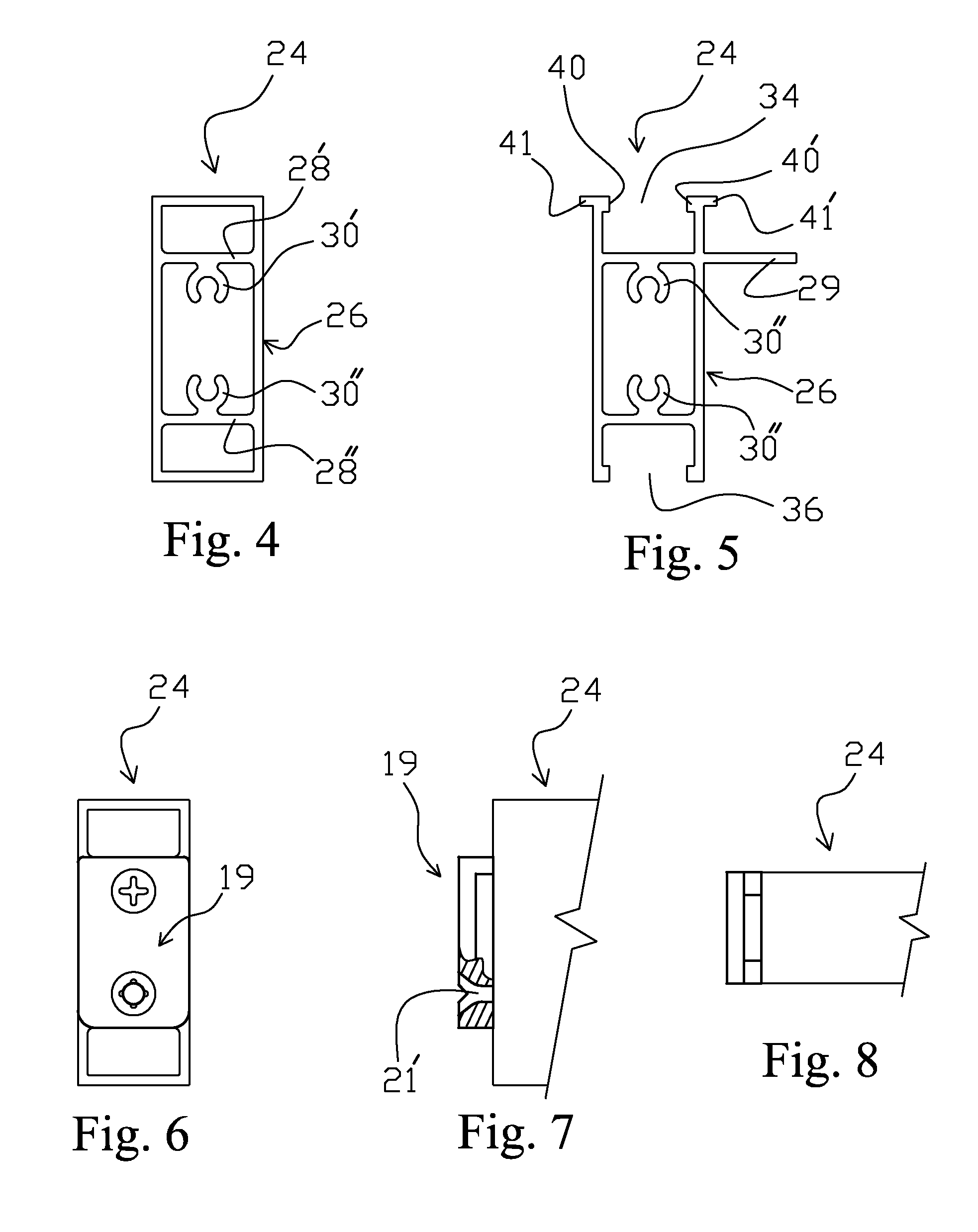
Frame system with releasable couplers
Structure and method for assembling a structural frame for use in erecting temporary or permanent structures, which structural frame has a first component having at least one auxiliary elongated web section with an elongated entrance channel opening for allowing insertion into the hollow interior of a coupler component to which is attached a second component. The channel opening defines a wider gap portion through which a coupler component is inserted, and a narrower gap portion that secures the coupler therein attaching the coupler component to an end of the second component. The first and second components are firmly, yet removable, secured together by first inserting the first wider section of the coupler through the wider gap section of the entrance channel opening of the first component, and then sliding the coupler along the hollow interior of the first component until the wider section is located at and within the narrower gap section of the entrance channel opening of the first component.
Owner:HOWE IAN +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com