Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
74 results about "Dipole magnet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
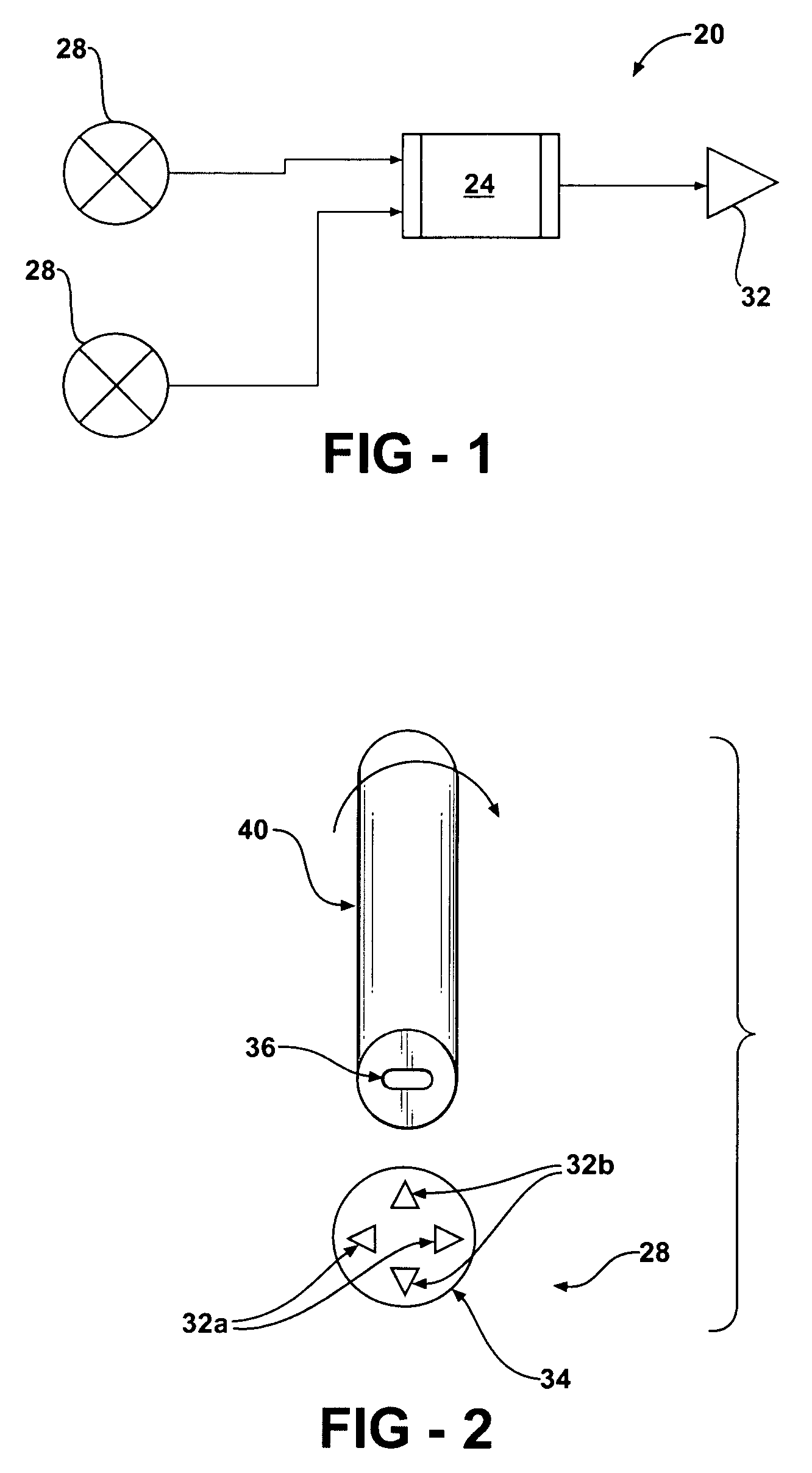
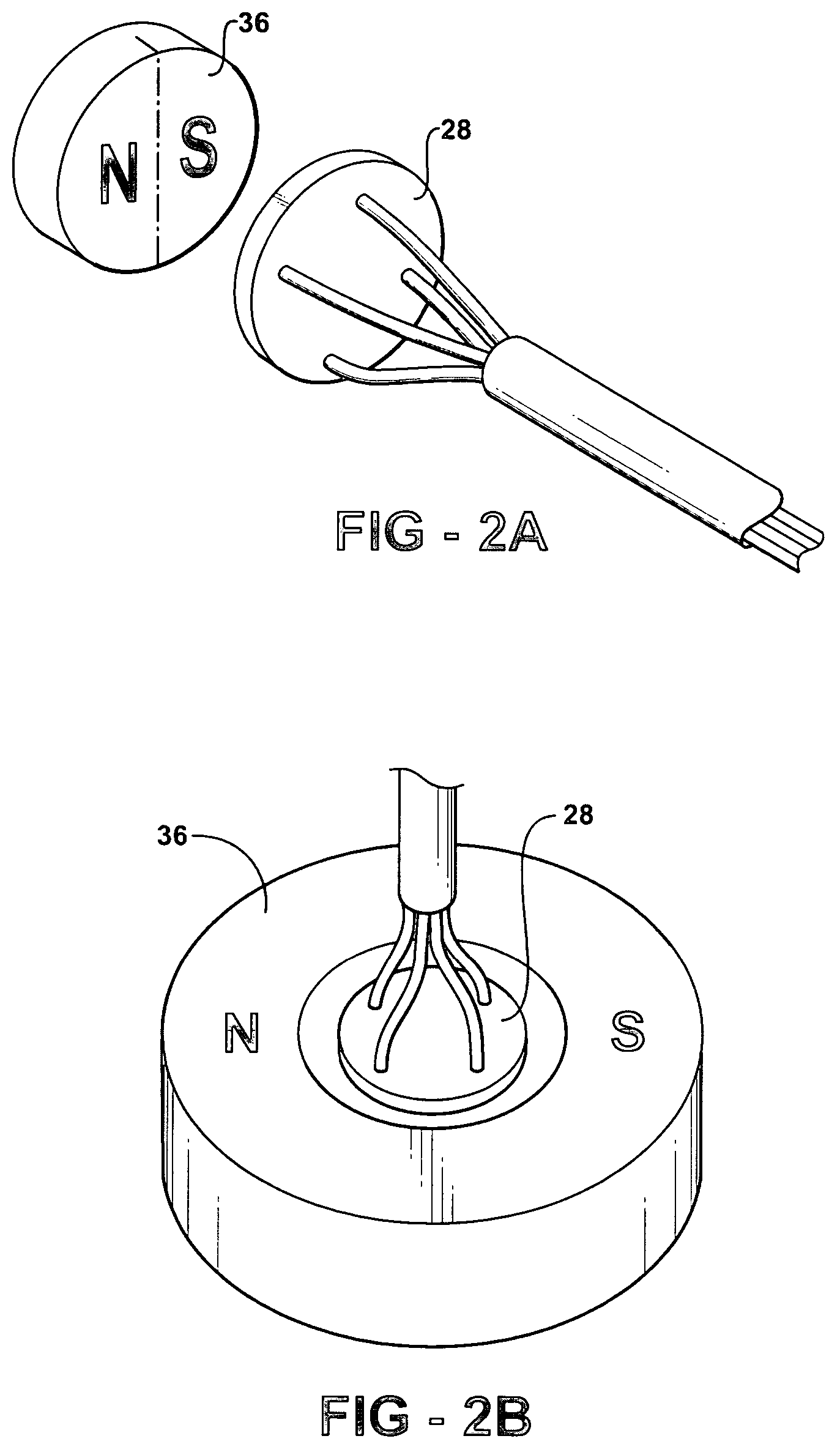
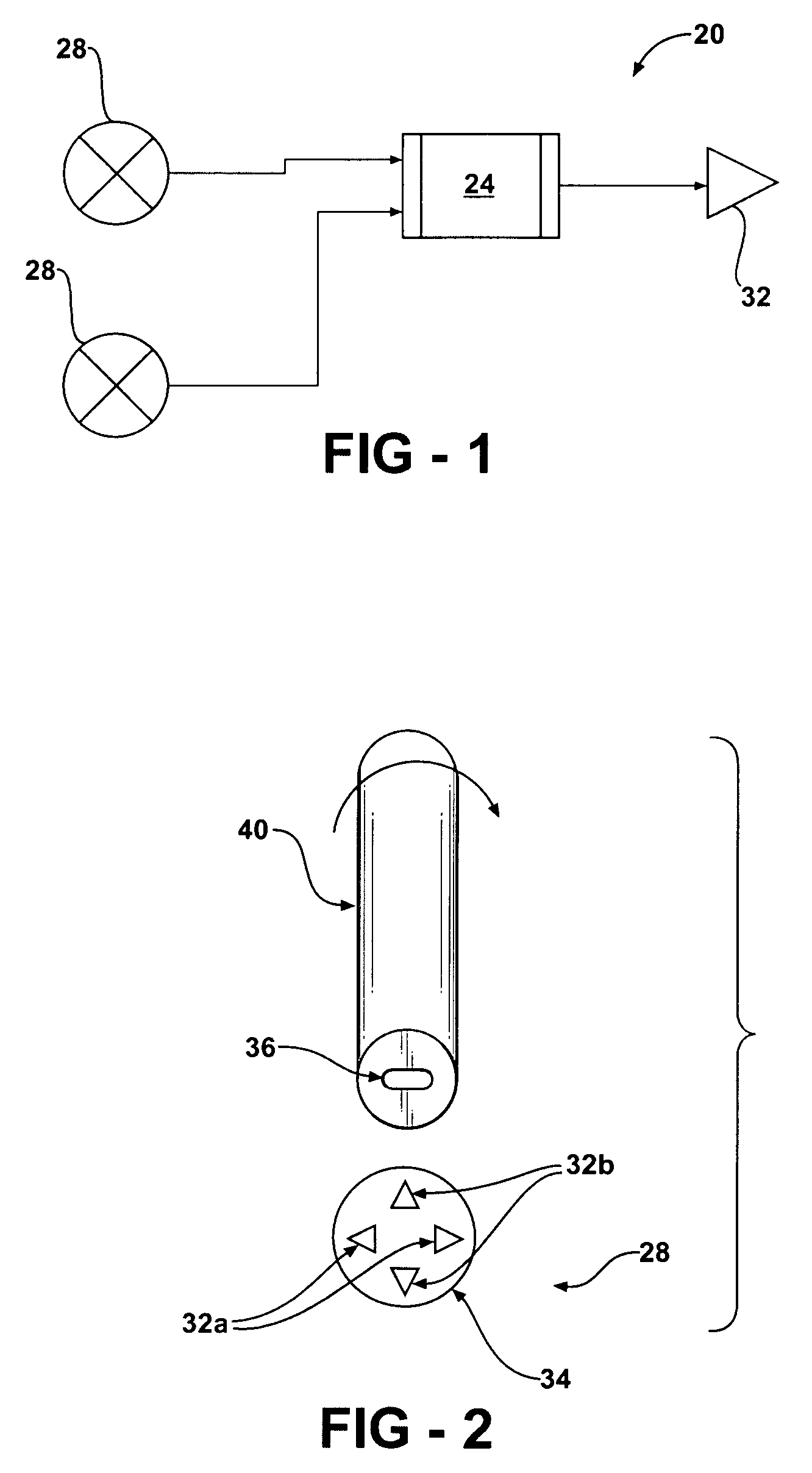
A dipole magnet is a magnet in which opposite poles (i.e., North and South poles) are on opposite sides of the magnet. The simplest example of a dipole magnet is a bar magnet.
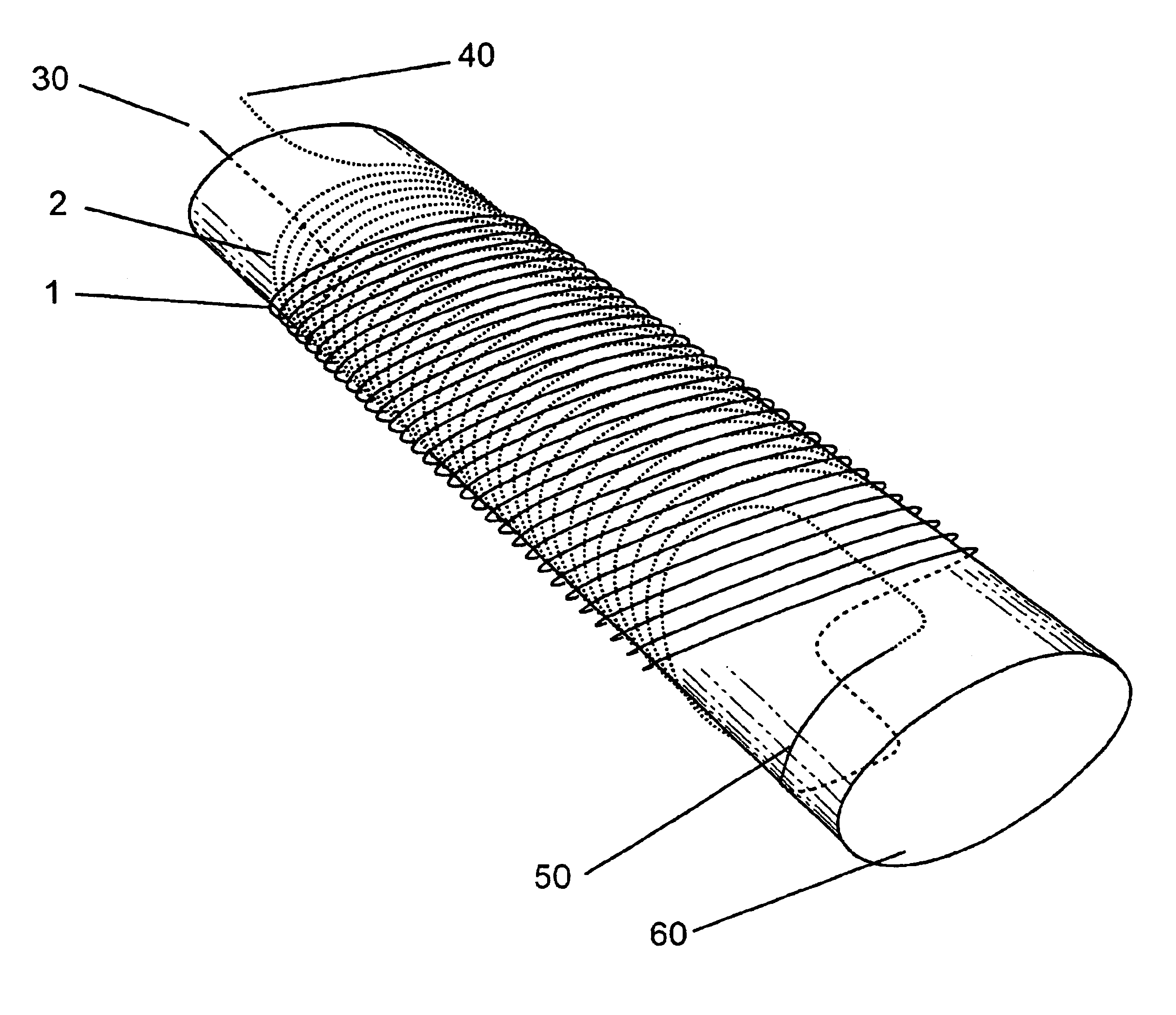
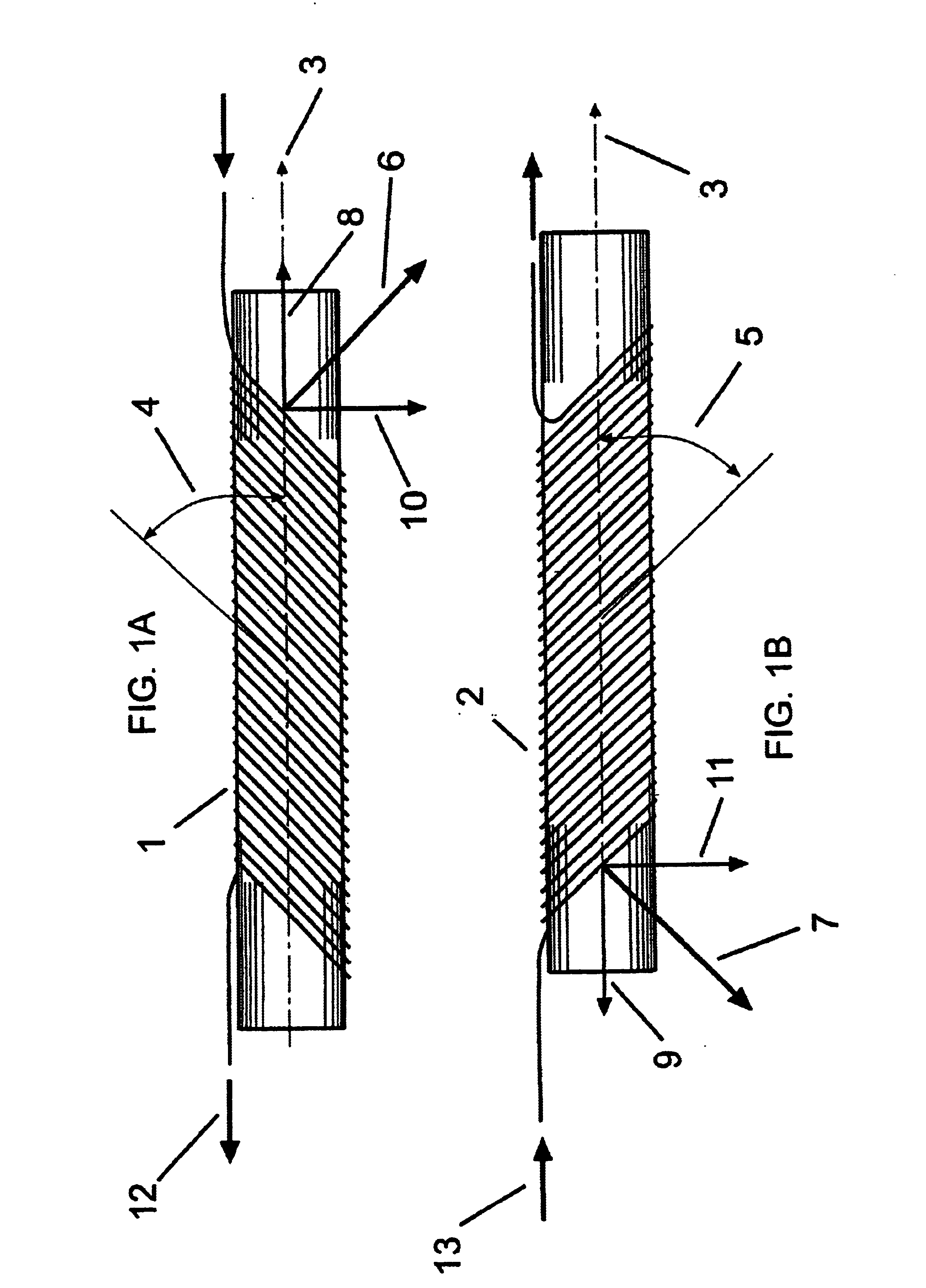
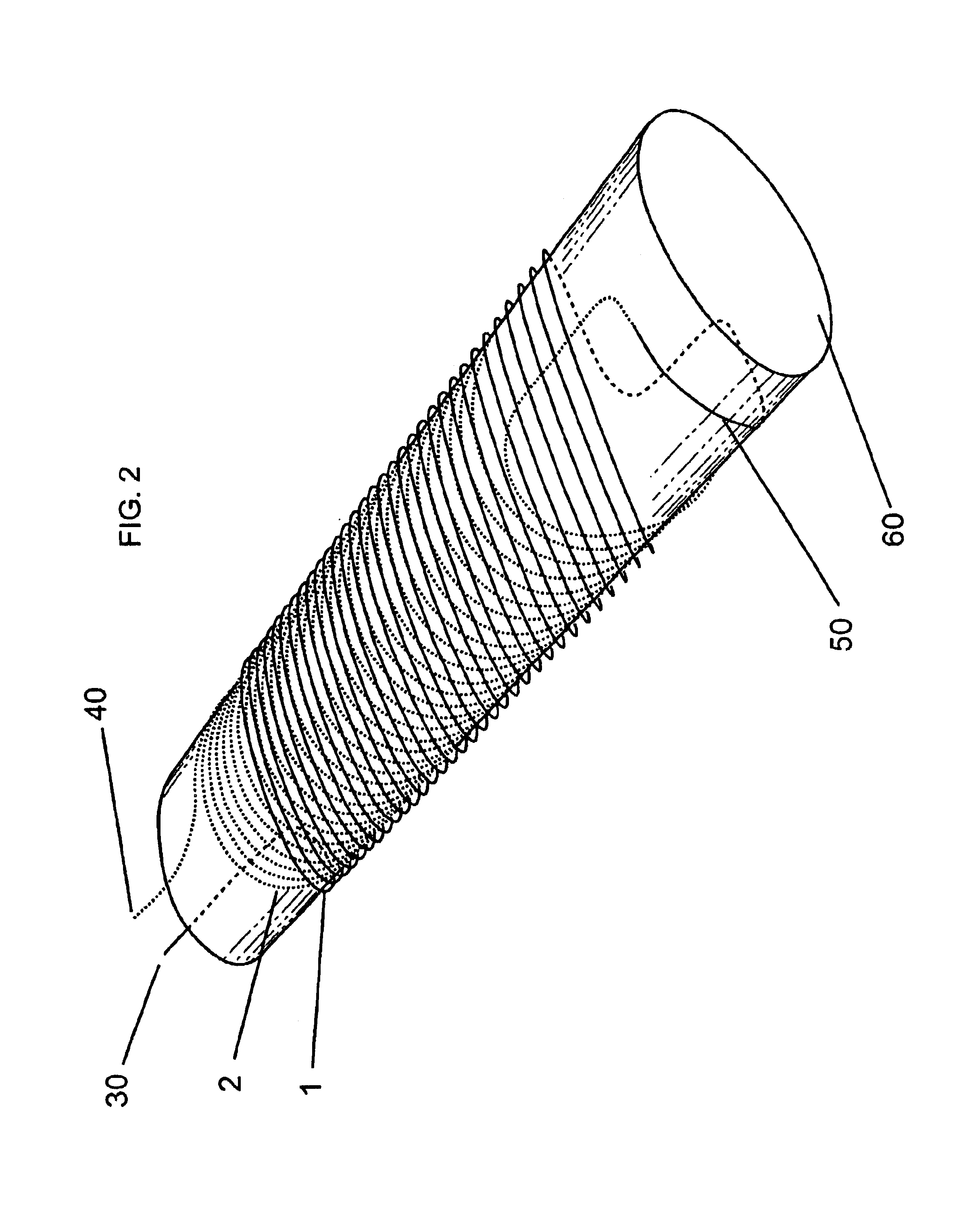
Concentric tilted double-helix dipoles and higher-order multipole magnets
InactiveUS6921042B1Simple processLess costlyElectromagnets without armaturesFilament handlingElectric machineryMagneto hydrodynamic
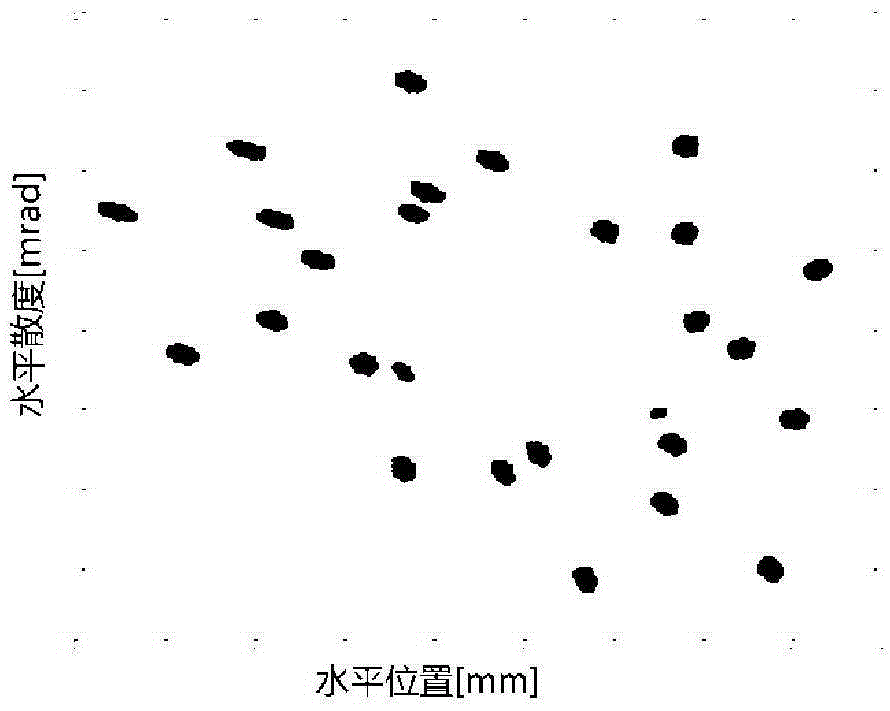
Concentric tilted double-helix magnets, which embody a simplified design and construction method for production of magnets with very pure field content, are disclosed. The disclosed embodiment of the concentric tilted double-helix dipole magnet has the field quality required for use in accelerator beam steering applications, i.e., higher-order multipoles are reduced to a negligibly small level. Magnets with higher multipole fields can be obtained by using a simple modification of the coil winding procedure. The double-helix coil design is well-suited for winding with superconducting cable or cable-in-conduit conductors and thus is useful for applications that require fields in excess of 2 T. The coil configuration has significant advantages over conventional racetrack coils for accelerators, electrical machinery, and magneto-hydrodynamic thrusting devices.
Owner:GOODZEIT CARL L +2
High efficiency, inductive vibration energy harvester
InactiveUS7569952B1Reducing magnetic field fringing effectHigh materialMagnetsMechanical energy handlingHigh fluxThin layer
An inductive energy harvester comprises a permanent magnet magnetic field source attached by a pair of compact spiral disk springs to an induction coil. The springs position the magnet so that the induction coil surrounds one end of the magnet where the flux density is greatest. In addition, the magnetic flux emerging from that end of the magnet is enhanced by a disk of magnetic material having high permeability and high flux density. In another embodiment, the magnetic field source comprises two dipole magnets arranged in opposing flux relationship with a thin layer of high flux density, high magnetic permeability material located in a gap between the magnets.
Owner:FERRO SOLUTIONS
Magnetic switch
A magnetically activated switch includes a flexible metallic strip on the inside of a sealed encasement, having first and second ends. The first end provides for an electrical contact and extends through the wall of the sealed encasement, with the strip being firmly secured by the wall of the encasement at the exit point, leaving the second end unsupported and having a magnetic responsive element attached. A first dipole magnet is coupled to the flexible metallic strip and located within the sealed encasement, intermediate the first and second ends. Second and third dipole magnets are diametrically opposed and separate to each other where each of the second and third dipole magnets are fixedly coupled to the inside surface of the sealed encasement. Two electrical terminals coupled respectively to the second and third dipole magnets extending through the sealed encasement. A magnetic activation device in sliding engagement with the outside surface of the sealed encasement effects the movement of the magnetic contact by sliding to first and second positions corresponding to alignment of the second and third dipole magnets creating an electrical circuit flowing from the flexible metallic strip to one of said two electrical terminals.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
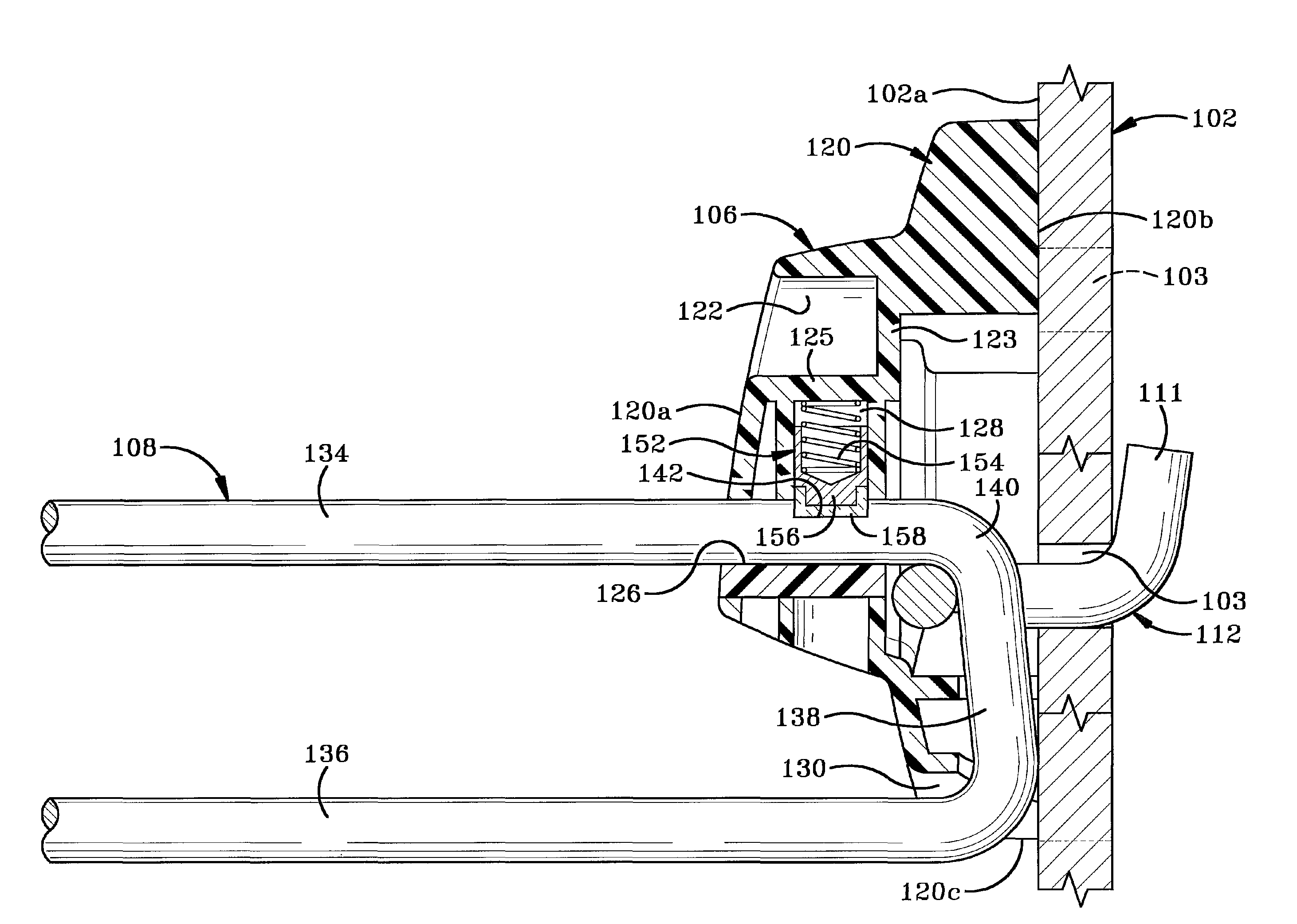
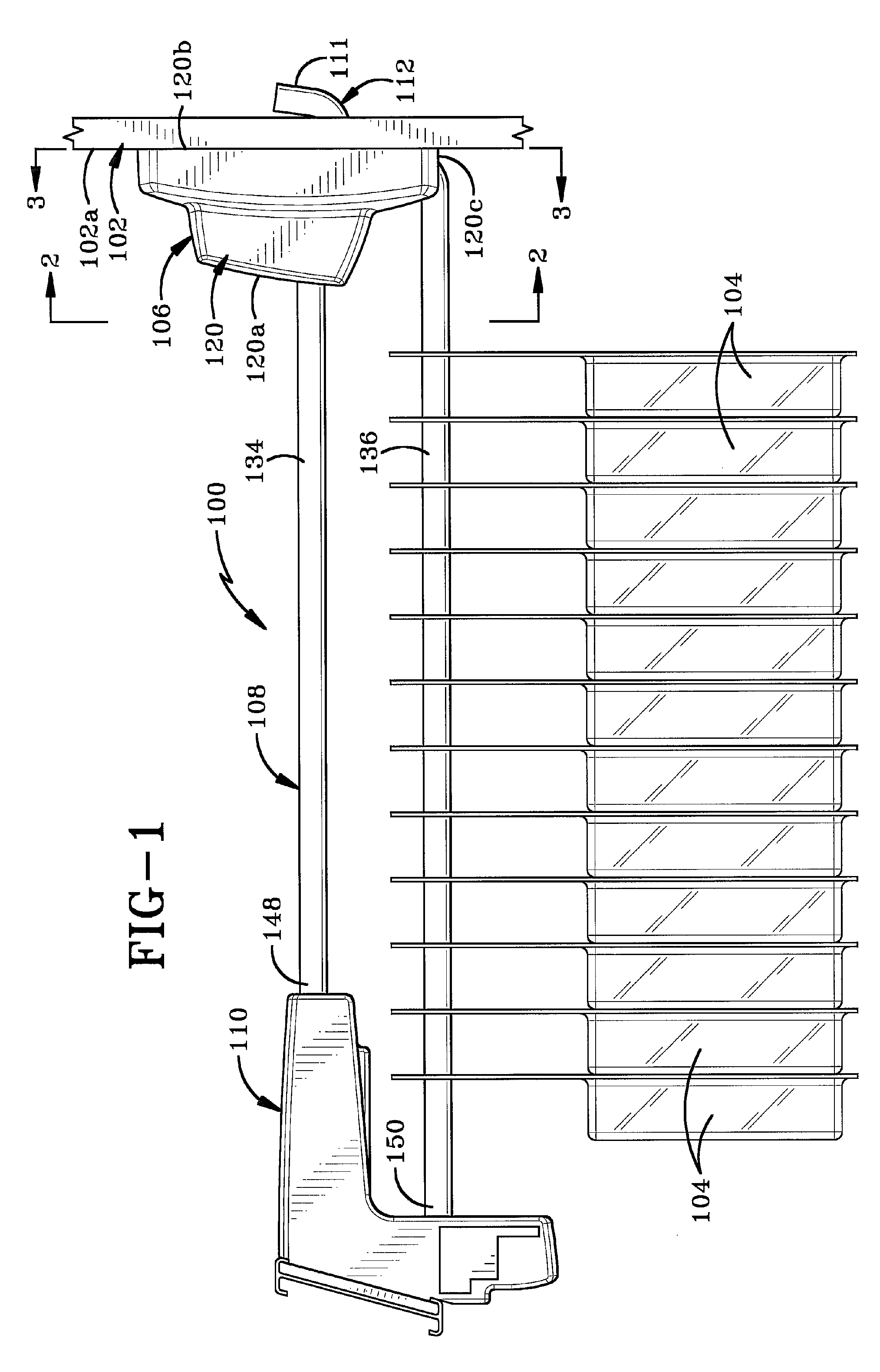
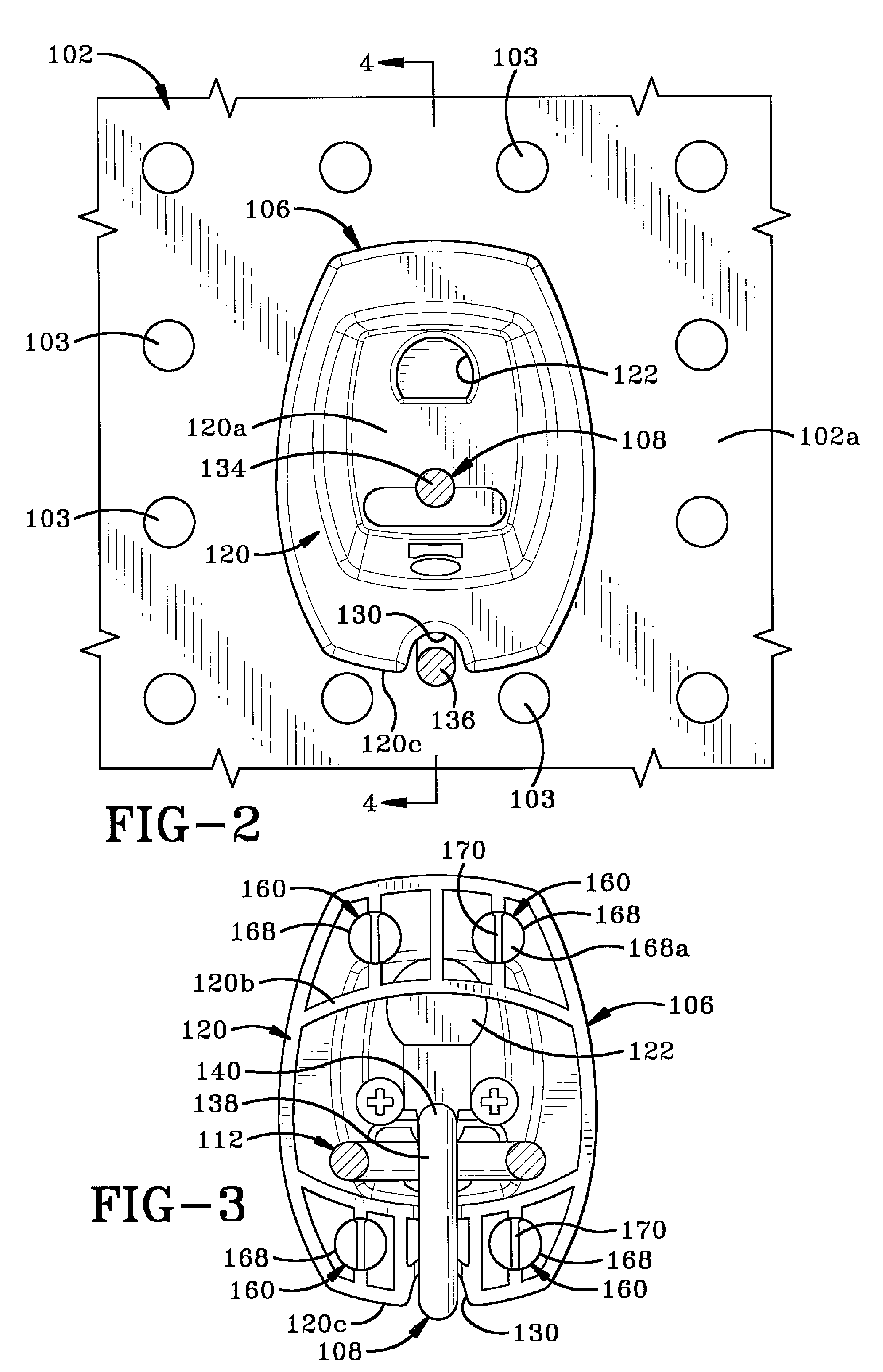
Display hook assembly having a secure free end
InactiveUS7703308B2Prevent removalLocks for portable objectsNon-mechanical controlsLinear motionDisplay board
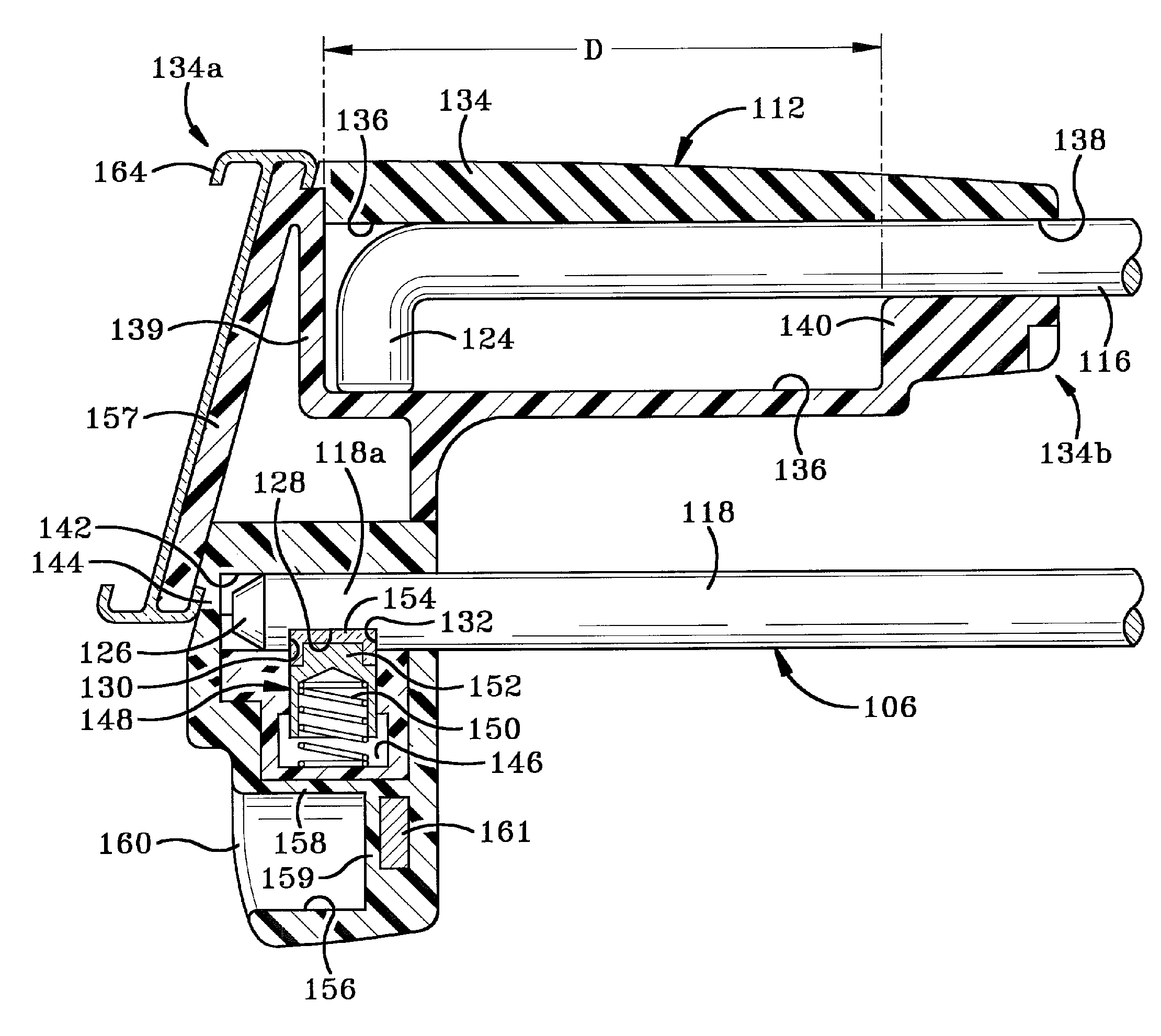
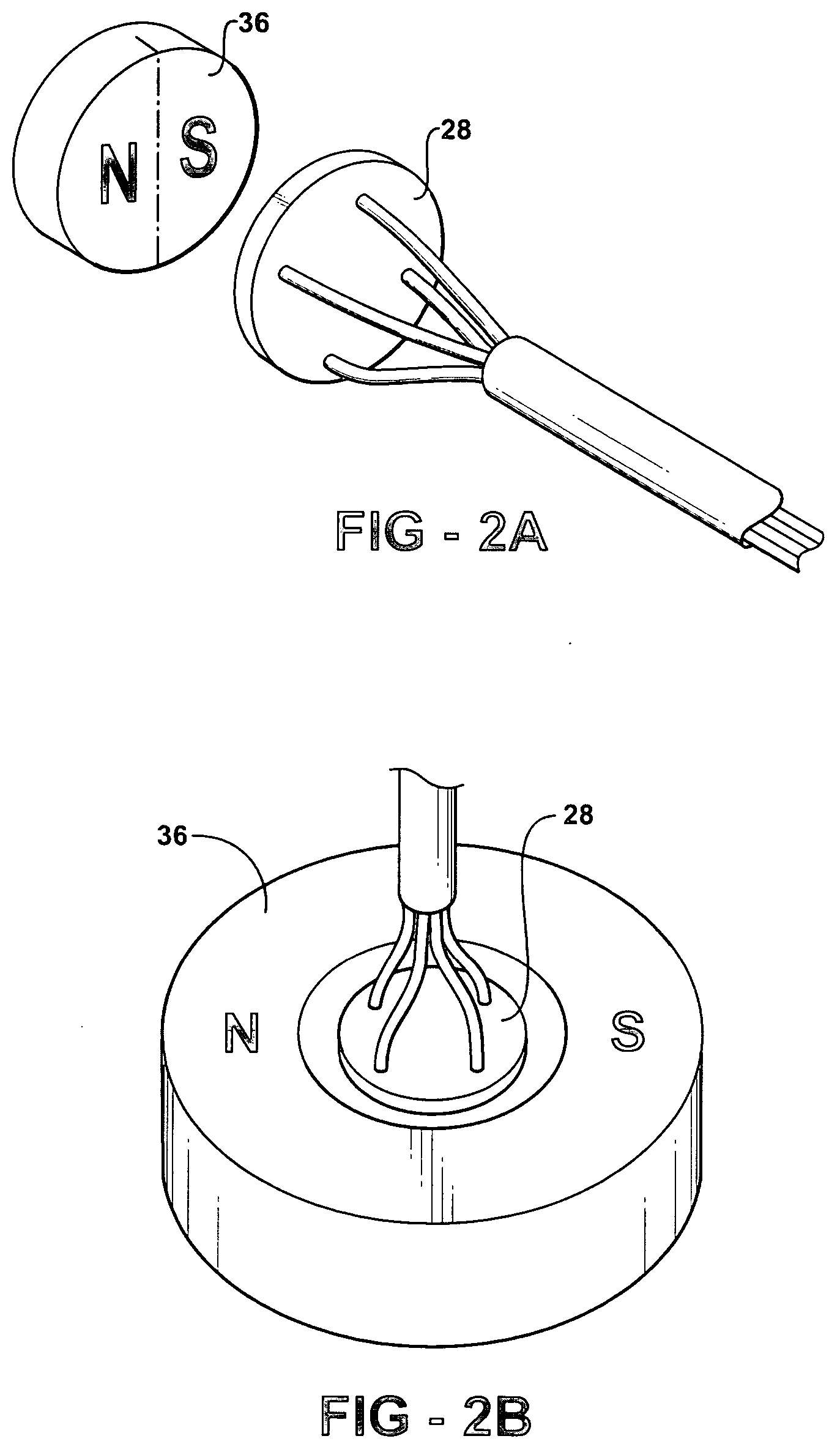
A securable system for displaying items of merchandise on a display board. The display system includes a lockable end assembly that engages the free end of at least one rod of a merchandise display therein. The end assembly is slidable along the rod between an unlocked position where items of merchandise may be removed therefrom and a locked position where items of merchandise cannot be removed therefrom. The end assembly is lockingly engaged with the rod by a locking mechanism that is linearly moveable within an interior chamber of the end assembly. The end assembly is provided with a specially shaped recess in its outer wall which is positioned perpendicular to the linear motion of the locking mechanism. A complementary dipole magnet key is inserted into the recess to unlock the locking mechanism.
Owner:INVUE SECURITY PROD INC
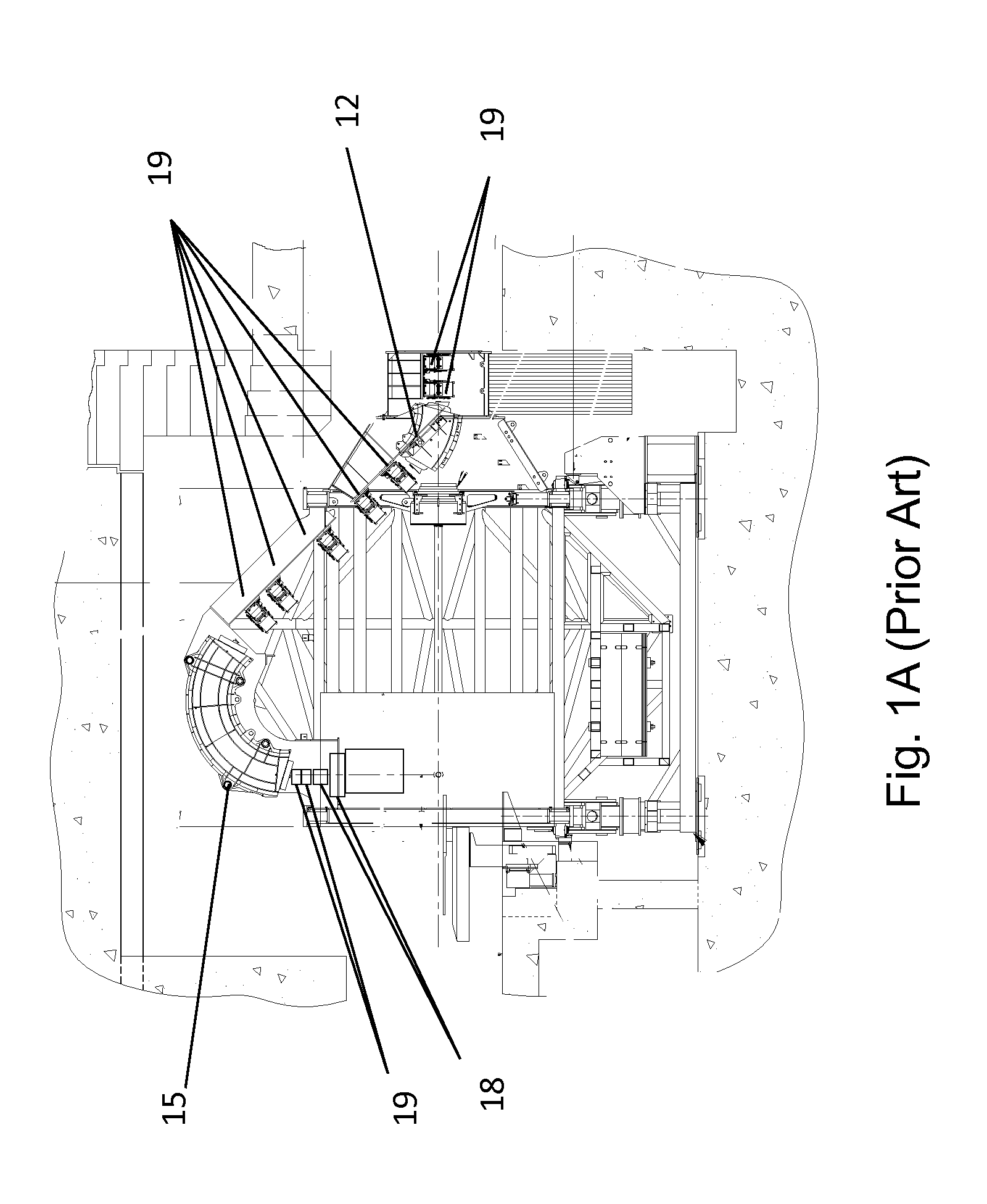
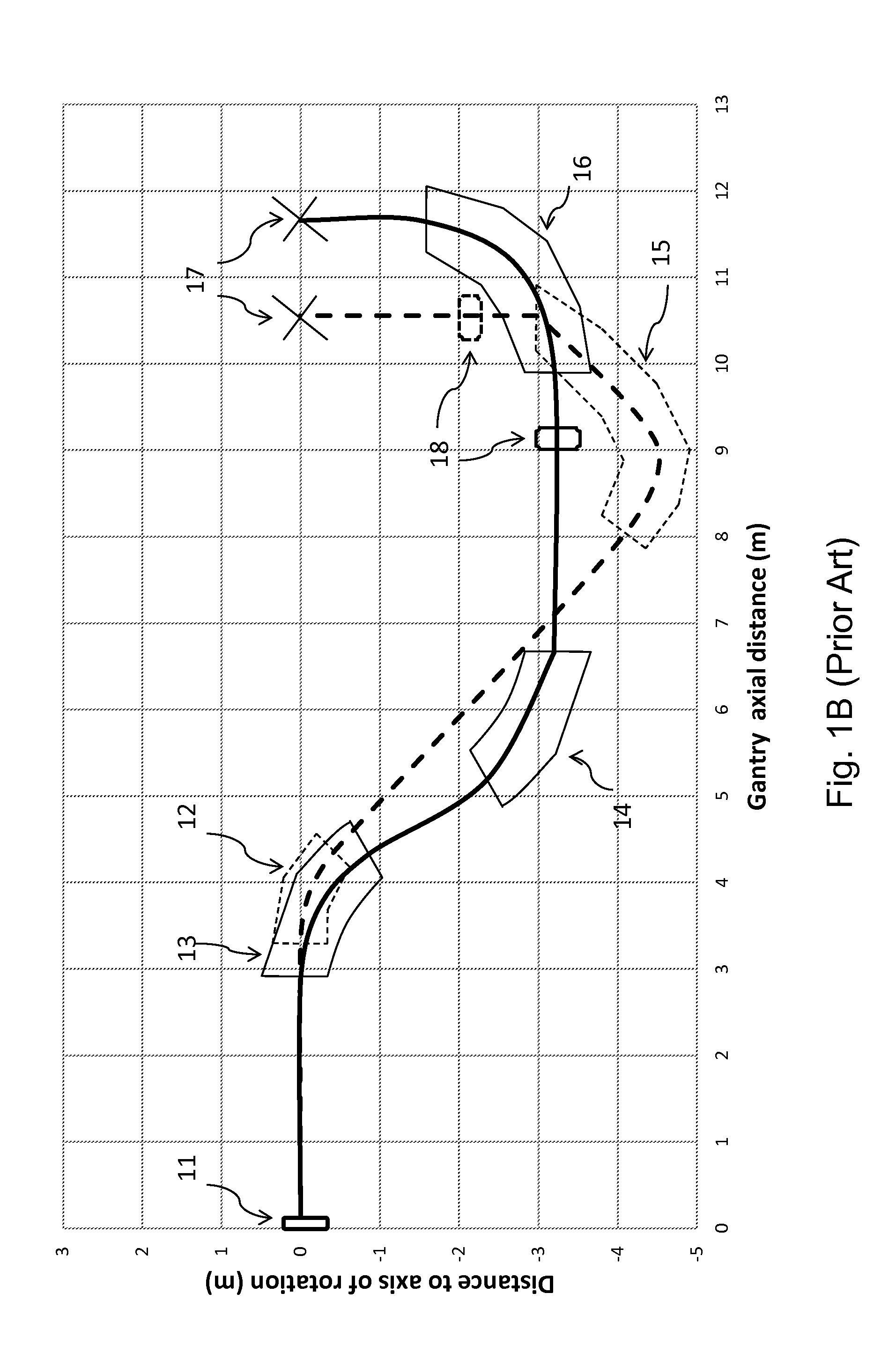
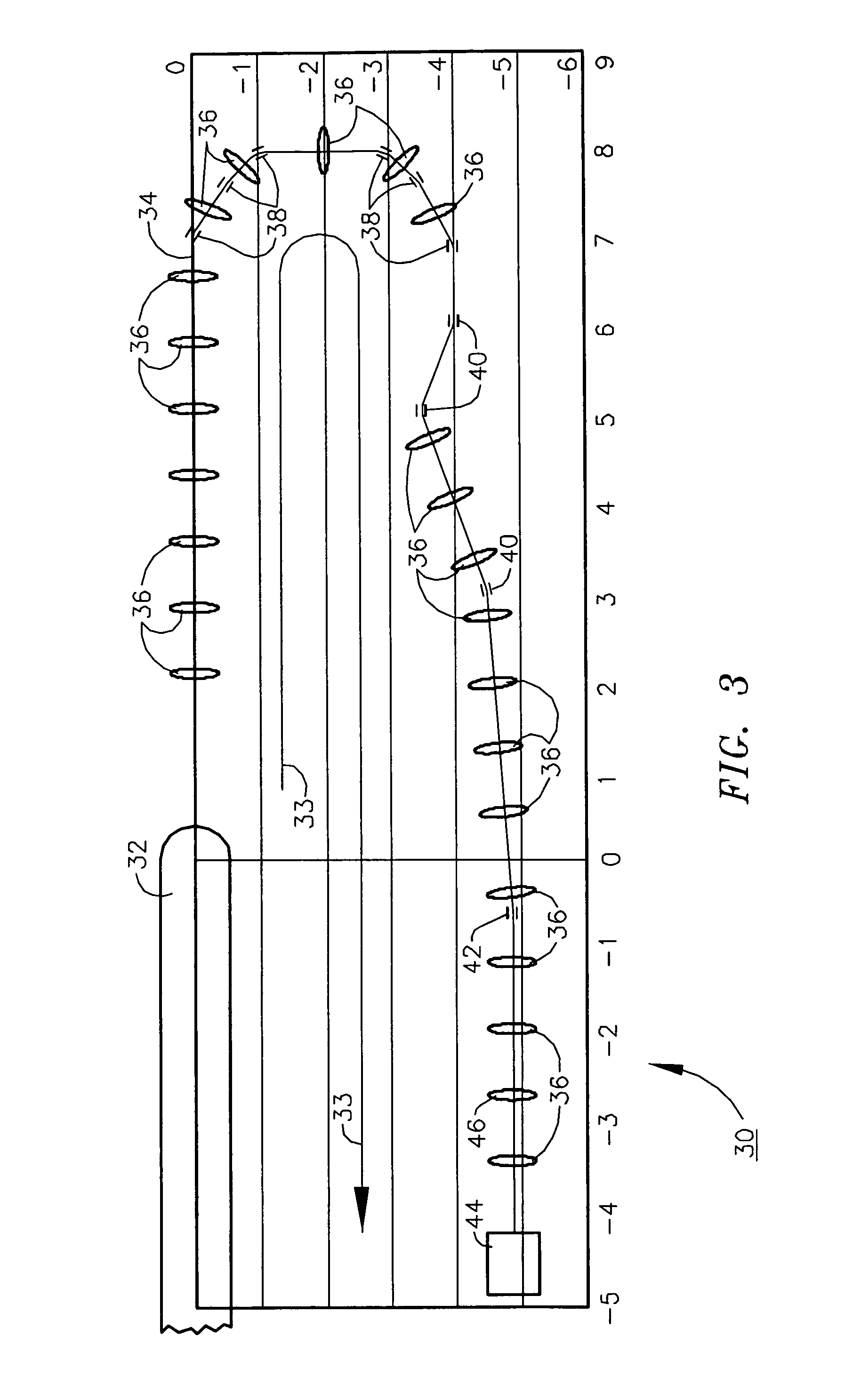
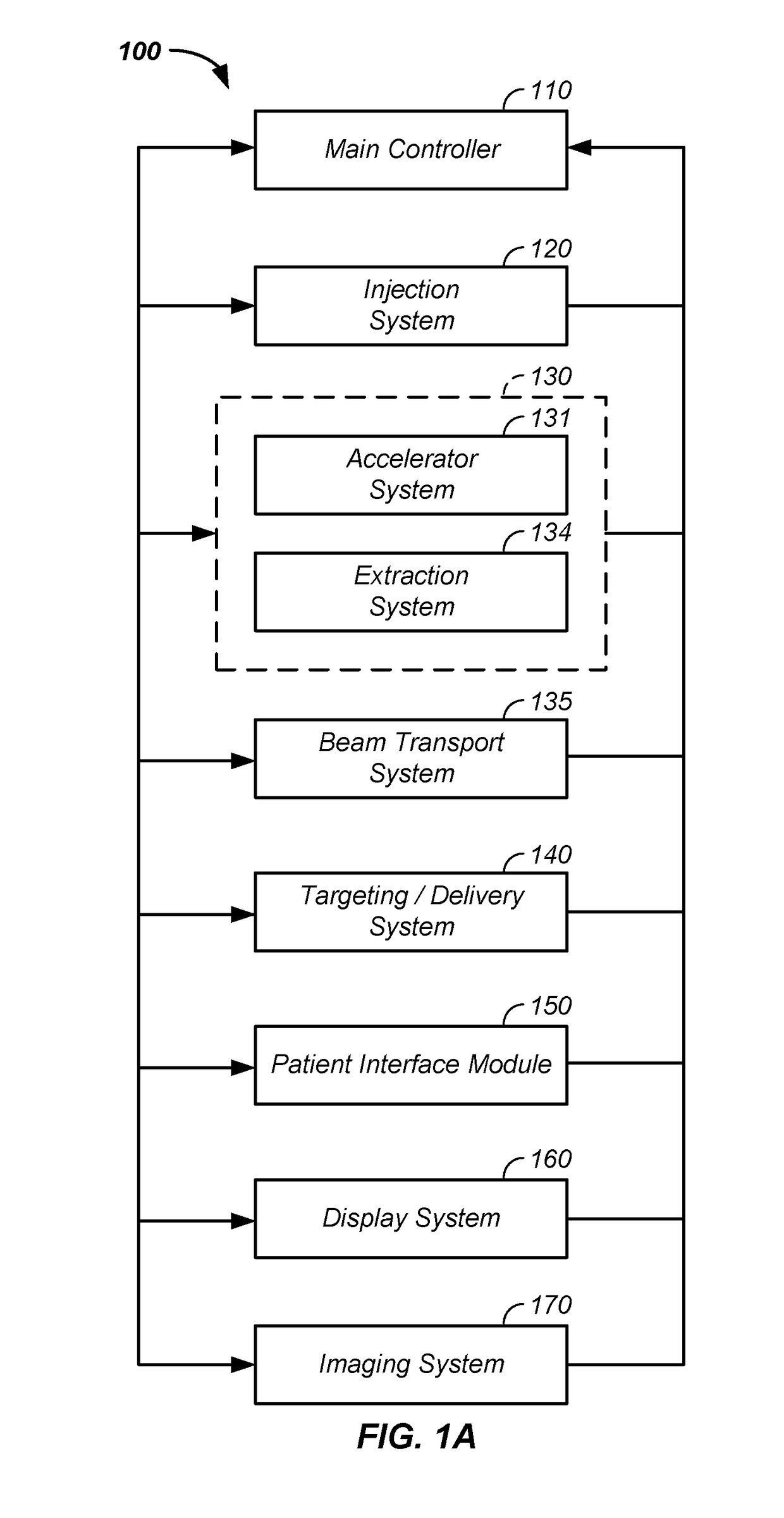
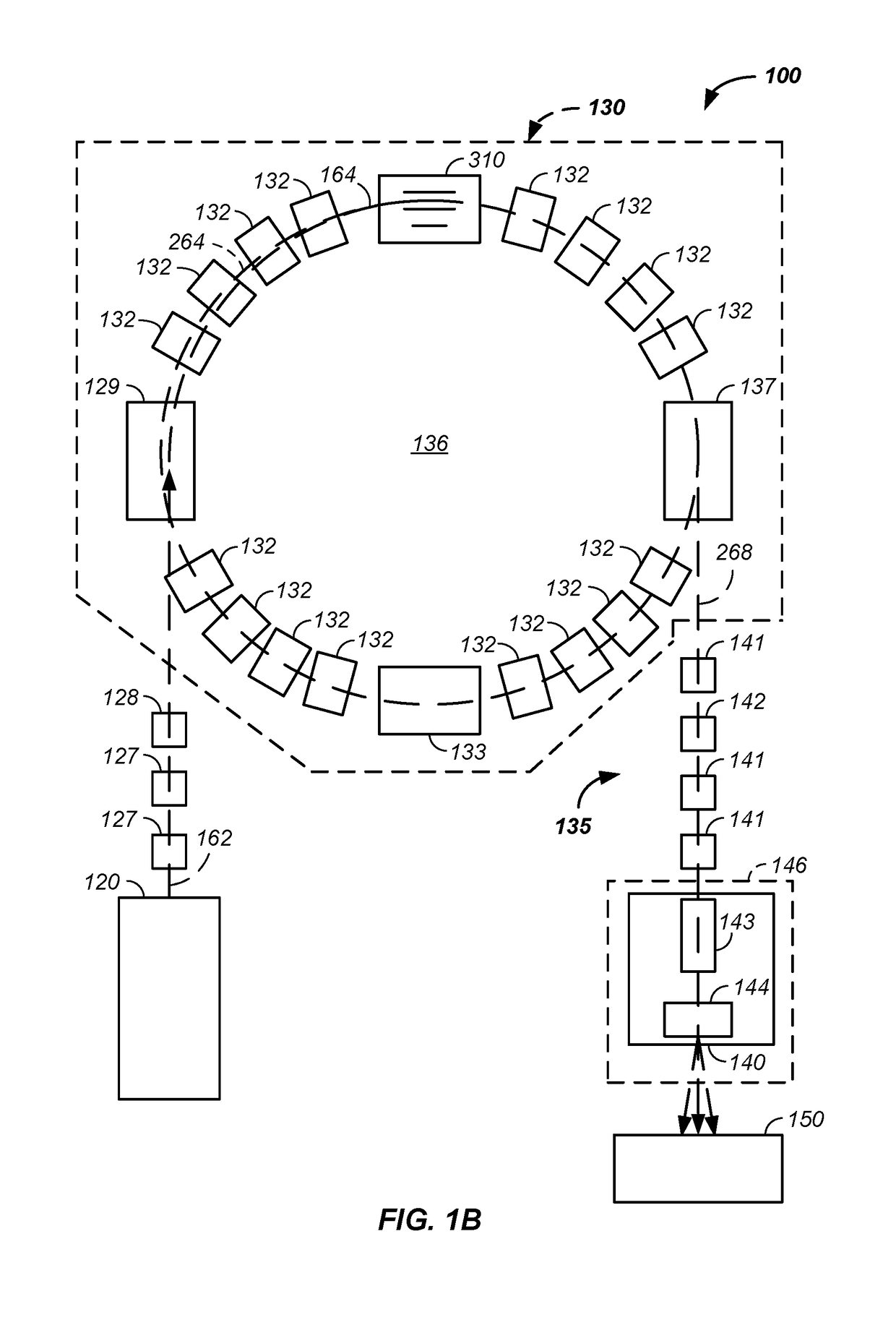
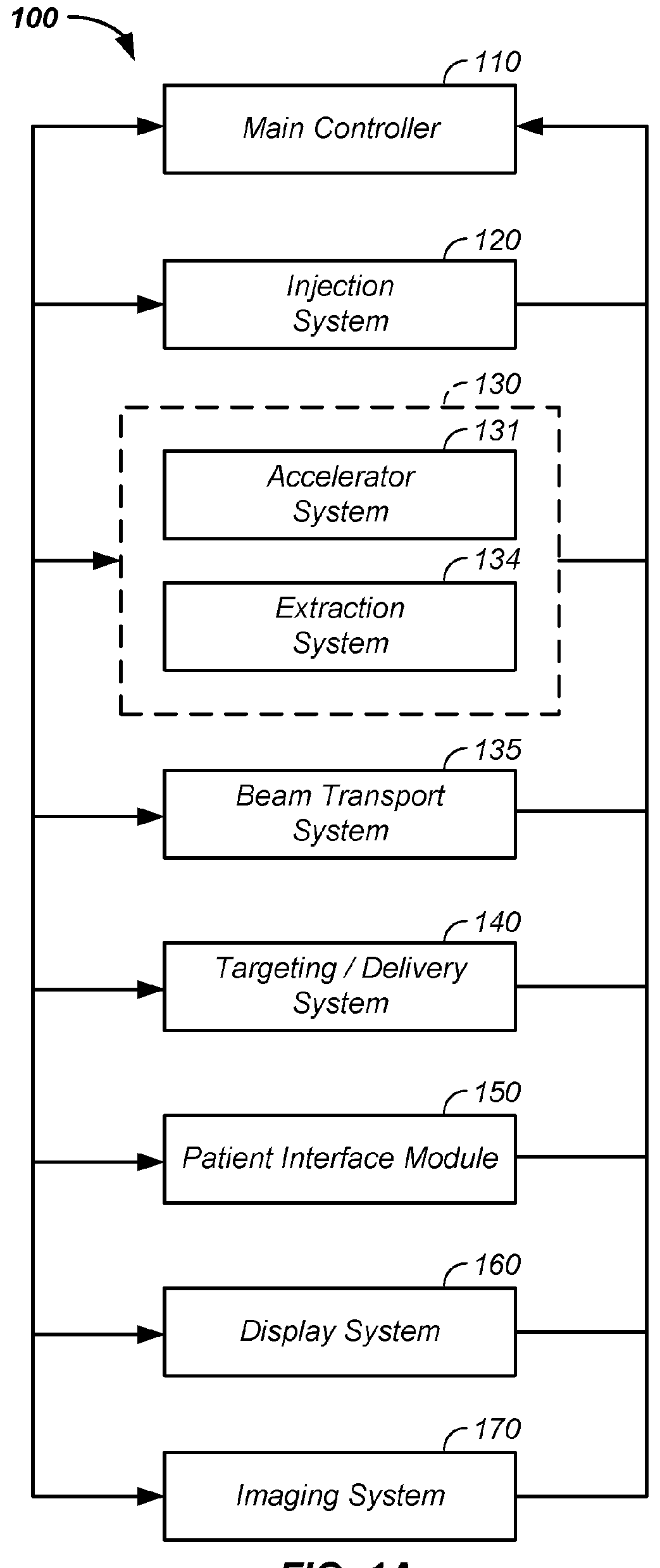
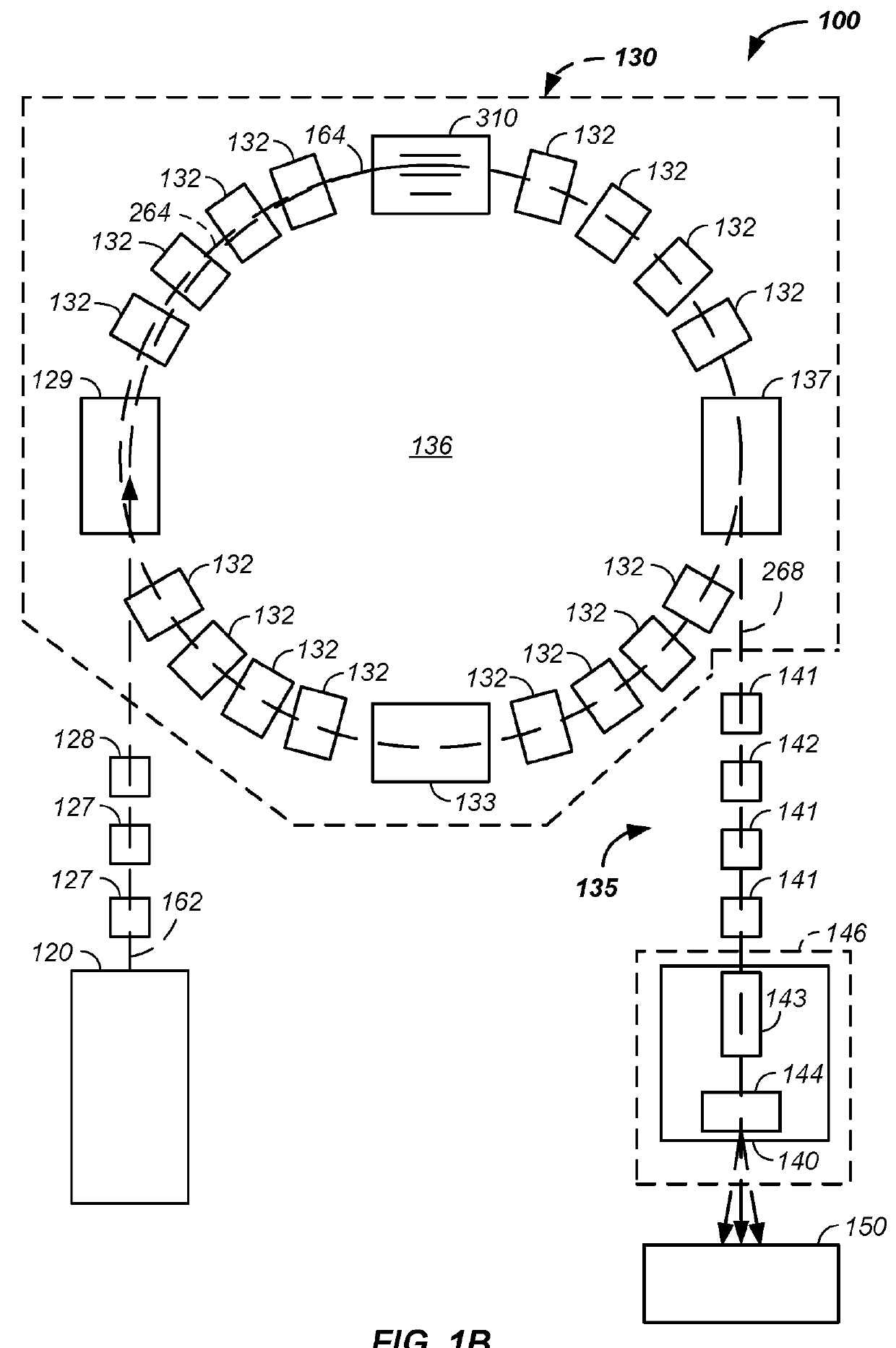
Compact proton therapy system with energy selection onboard a rotatable gantry
ActiveUS9012866B2Reduced cost and dimensionConsumption of costThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersBeam energyParticle beam
Systems and apparatuses for providing particle beams for radiation therapy with a compact design and suitable to a single treatment room. The radiation system comprises a stationary cyclotron coupled to a rotating gantry assembly through a beam line assembly. The system is equipped with a single set of dipole magnets that are installed on the rotating gantry assembly and undertakes the dual functions of beam energy selection and beam deflection. The energy degrader may be exposed to the air pressure. The beam line assembly comprises a rotating segment and a stationary segment that are separated from each other through an intermediate segment that is exposed to an ambient pressure.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +1
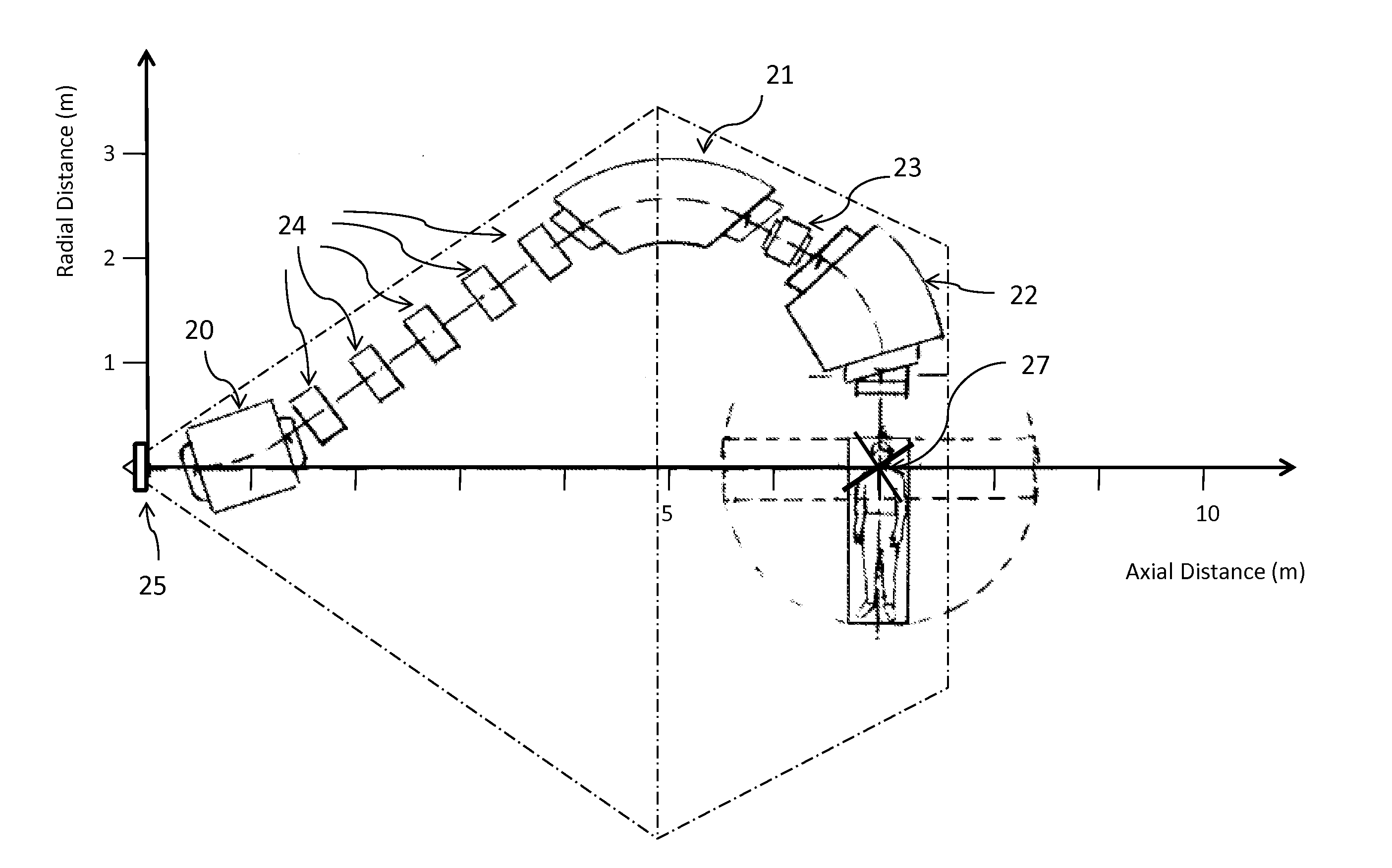
Compact gantry for particle therapy
ActiveUS20130001432A1Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsParticle beamDipole magnet
The present invention relates to a particle therapy apparatus used for radiation therapy. More particularly, this invention relates to a compact isocentric gantry for delivering particle beams perpendicularly to a rotation axis of the gantry. The gantry comprises three dipole magnets. The angle of the last dipole magnet is smaller than 90° and a most preferred bending angle for this last dipole magnet is 60°.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Compact proton therapy system with energy selection onboard a rotatable gantry
ActiveUS20140275699A1Low costReduced dimensionChemical conversion by chemical reactionIrradiation devicesBeam energyParticle beam
Systems and apparatuses for providing particle beams for radiation therapy with a compact design and suitable to a single treatment room. The radiation system comprises a stationary cyclotron coupled to a rotating gantry assembly through a beam line assembly. The system is equipped with a single set of dipole magnets that are installed on the rotating gantry assembly and undertakes the dual functions of beam energy selection and beam deflection. The energy degrader may be exposed to the air pressure. The beam line assembly comprises a rotating segment and a stationary segment that are separated from each other through an intermediate segment that is exposed to an ambient pressure.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +1
Magnetic key for use with a security device
InactiveUS20080168811A1Strong magnetismReduce the chance of chippingNon-mechanical controlsKeysLocking mechanismMagnetic poles
A key for unlocking a magnetically attractable locking mechanism retained within the interior of an anti-theft security device. The key comprises a housing which retains a dipole magnet therein. The dipole magnet is of a specifically designed cross-sectional shape configured to be complementary to a recess in the body of the security device. The shape of the magnet permits it to only enter the recess in one orientation and to bring only the appropriate one of the north or south magnetic poles into the proximity of the locking mechanism. The dipole magnet is movable in the housing between an extended position where at least a portion thereof protrudes from the housing, and a retracted position where the magnet is withdrawn entirely into the housing. The magnet is mounted on a spring-biased slide in the housing that is activated to move the magnet between the extended and retracted positions.
Owner:INVUE SECURITY PROD INC
Beam line architecture for ion implanter
ActiveUS20080078954A1Facilitate uniform and precise implant property across waferImprove filtering effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIsotope separationLight beamIon beam
A parallelizing component of an ion implantation system comprises two angled dipole magnets that mirror one another and serve to bend an ion beam traversing therethrough to have a substantially “s” shape. This s bend serves to filter out contaminants of the beam, while the dipoles also parallelize the beam to facilitate uniform implant properties across the wafer, such as implant angle, for example. Additionally, a deceleration stage is included toward the end of the implantation system so that the energy of the beam can be kept relatively high throughout the beamline to mitigate beam blowup.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES
Security device for attaching a peg hook to a peg support
Owner:INVUE SECURITY PROD INC
Angular position sensor-based engine controller system
An engine controller system employs angular position sensors which are operable to very accurately determine the position of rotating engine members. Information about the angular position of the engine members is used to alter operation of the engine for improved efficiency and / or reduced emissions from the engine. The angular position of the crankshaft and camshafts can be determined by affixing a dipole magnet to each of them such that the magnet field of the magnet rotates with the rotating member and then placing a angular position sensor adjacent each rotating member to detect the rotation of each magnetic field. In another embodiment, the angular position of each end of at least one of the rotating members is determined to allow the processor to determine the torsional deflection of the member and the engine controller system is responsive to that determined deflection to further alter operation of the engine.
Owner:LITENS AUTOMOTIVE INC
Angular position sensor-based engine controller system
An engine controller system employs angular position sensors which are operable to very accurately determine the position of rotating engine members. Information about the angular position of the engine members is used to alter operation of the engine for improved efficiency and / or reduced emissions from the engine. The angular position of the crankshaft and camshafts can be determined by affixing a dipole magnet to each of them such that the magnet field of the magnet rotates with the rotating member and then placing a angular position sensor adjacent each rotating member to detect the rotation of each magnetic field. In another embodiment, the angular position of each end of at least one of the rotating members is determined to allow the processor to determine the torsional deflection of the member and the engine controller system is responsive to that determined deflection to further alter operation of the engine.
Owner:LITENS AUTOMOTIVE INC
Compact gantry for particle therapy
ActiveUS20130187060A1Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsParticle beamDipole magnet
The present invention relates to a particle therapy apparatus used for radiation therapy. More particularly, this invention relates to a compact isocentric gantry for delivering particle beams perpendicularly to a rotation axis of the gantry . The gantry comprises three dipole magnets. The angle of the last dipole magnet is smaller than 90° and a most preferred bending angle for this last dipole magnet is 60°.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Heavy ion or proton synchrotron with medical deflection magnetic focusing structure
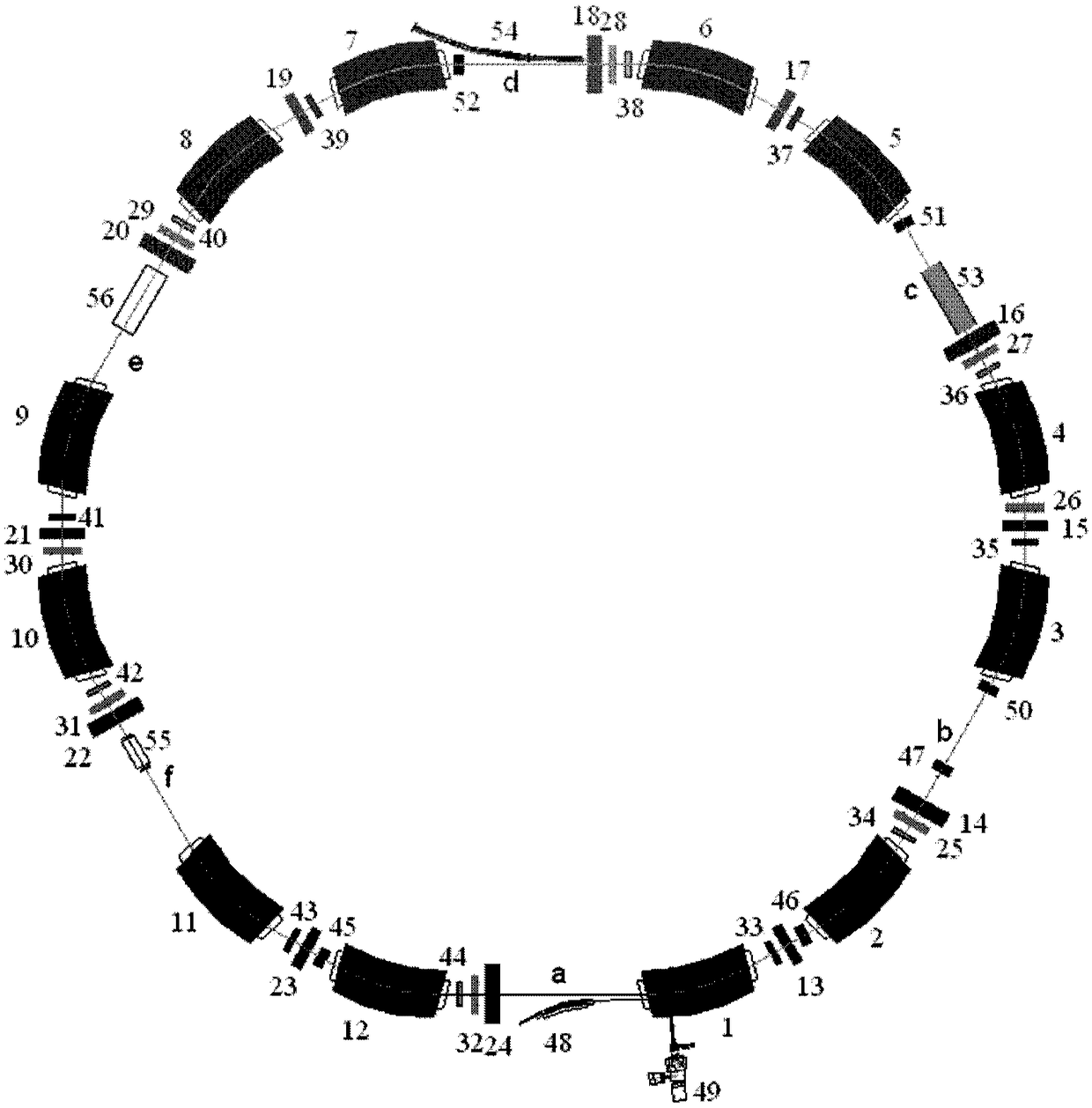
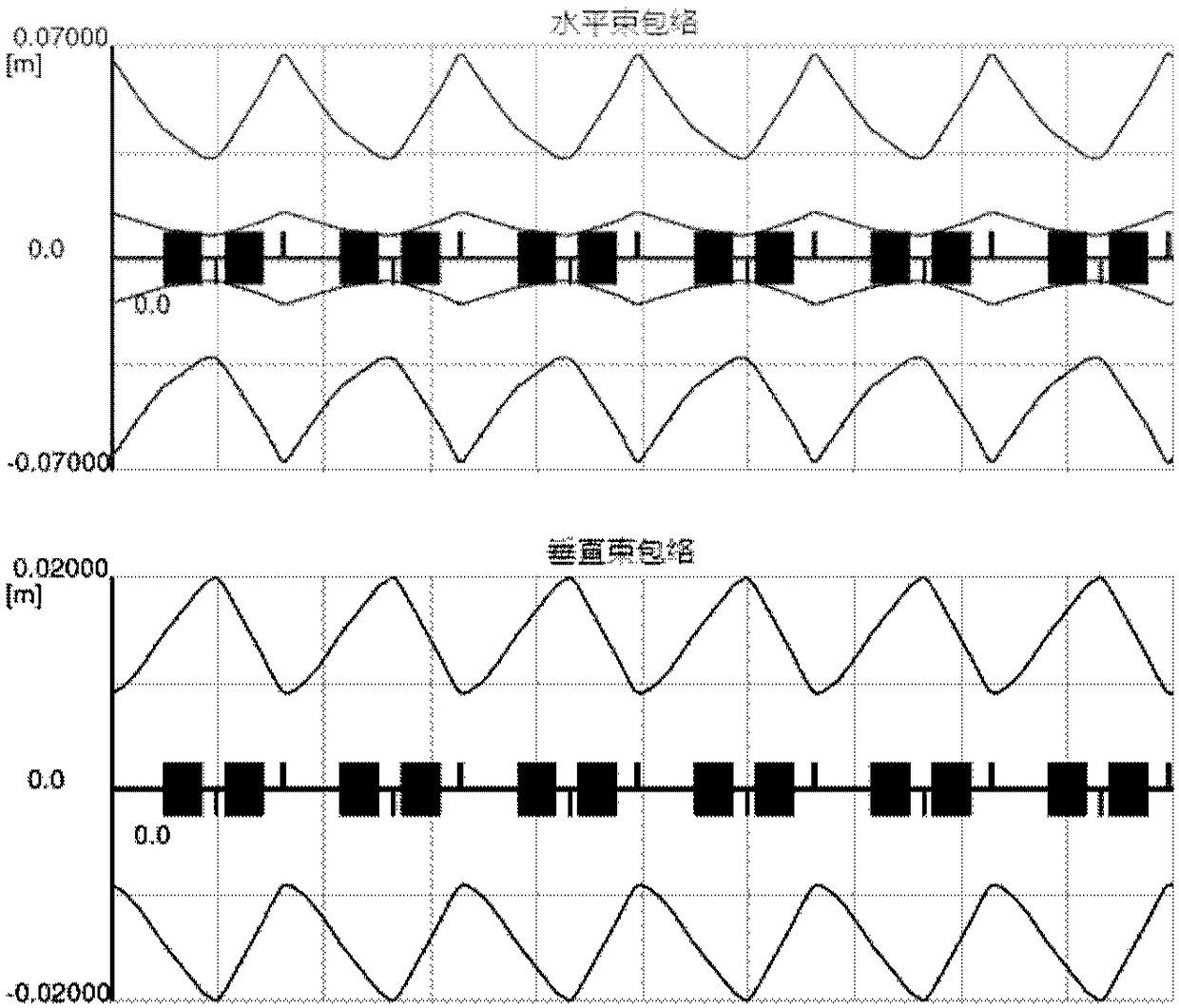
ActiveCN101917815AReduce manufacturing costReduced space required for installationMagnetic resonance acceleratorsManufacturing cost reductionSynchrotron
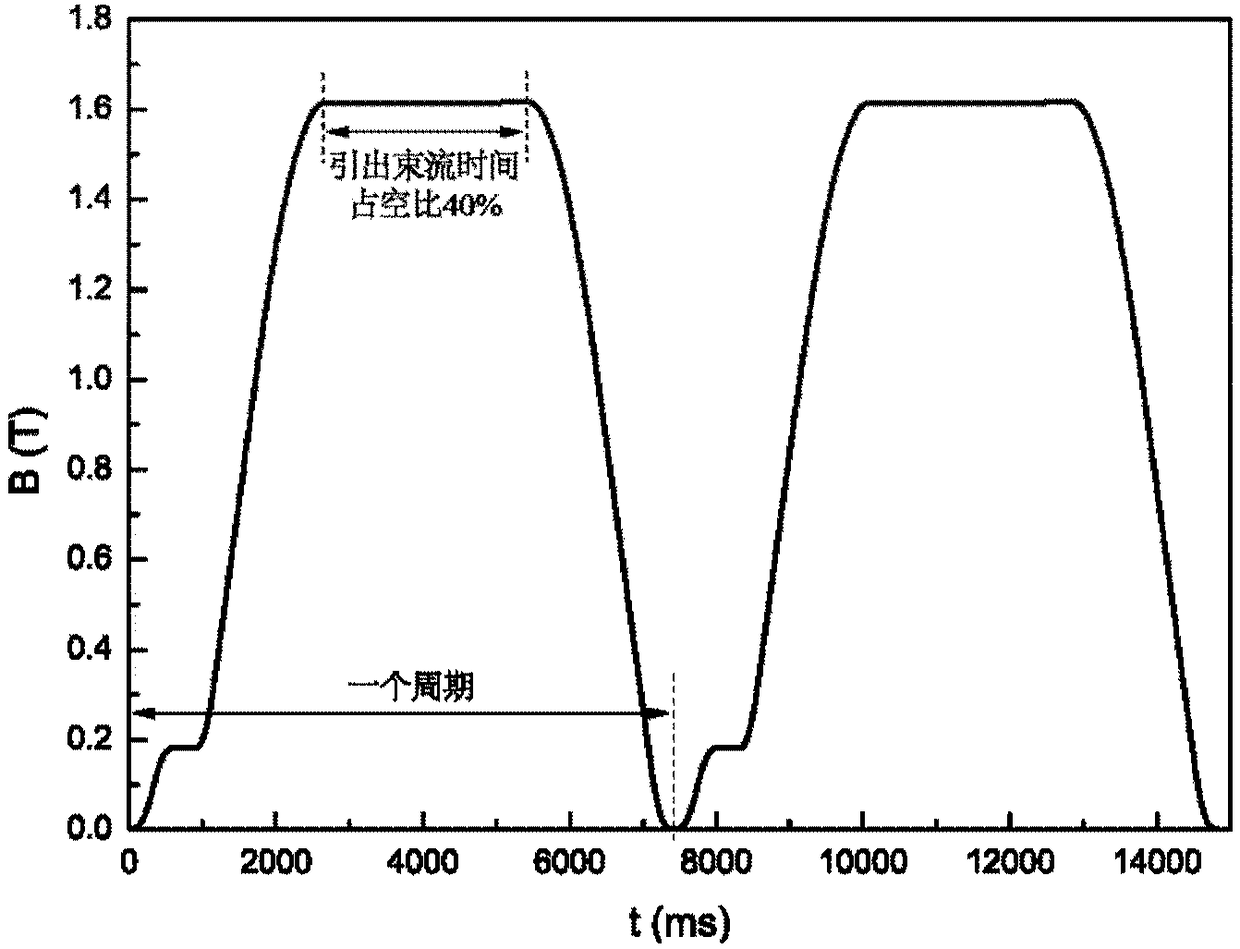
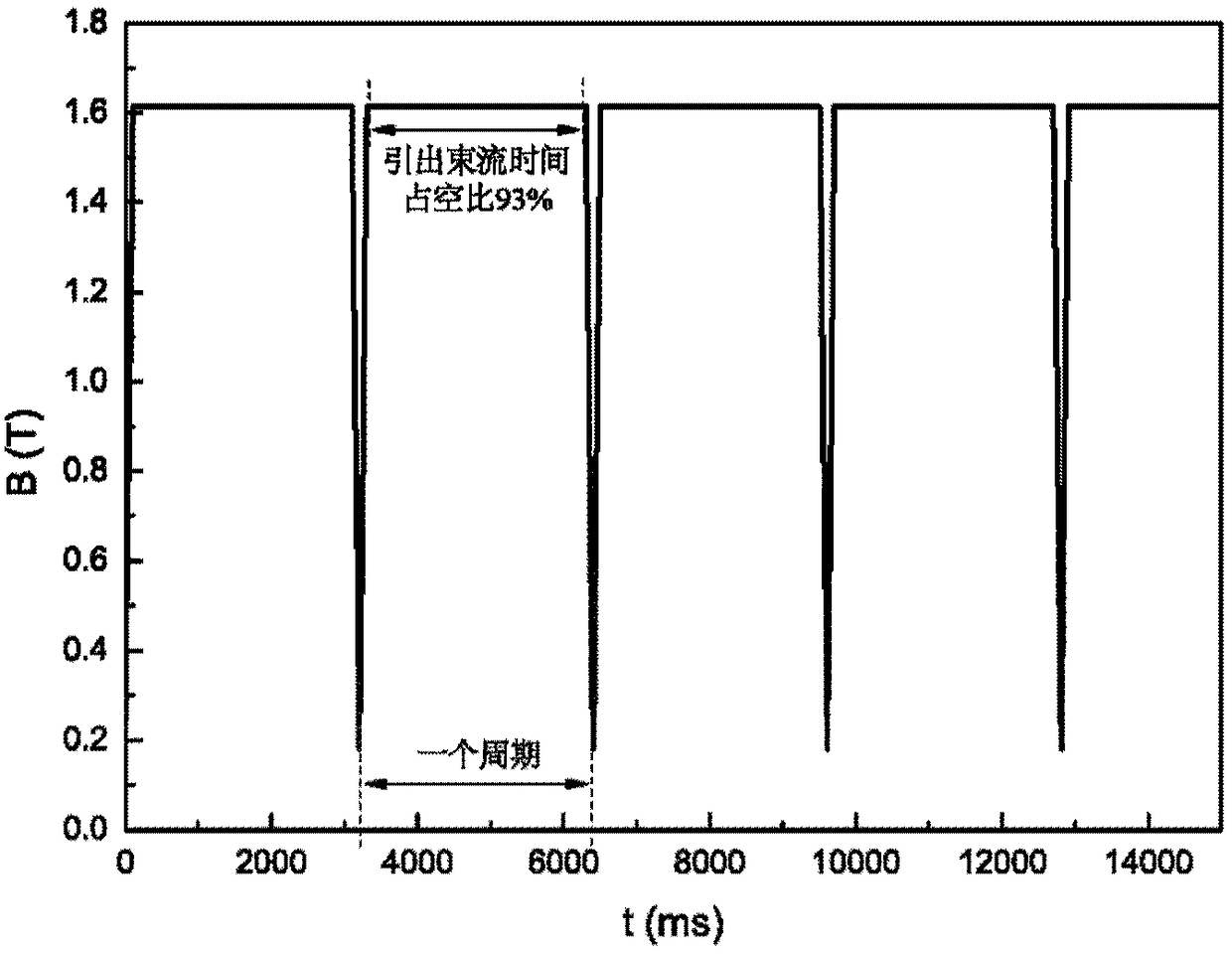
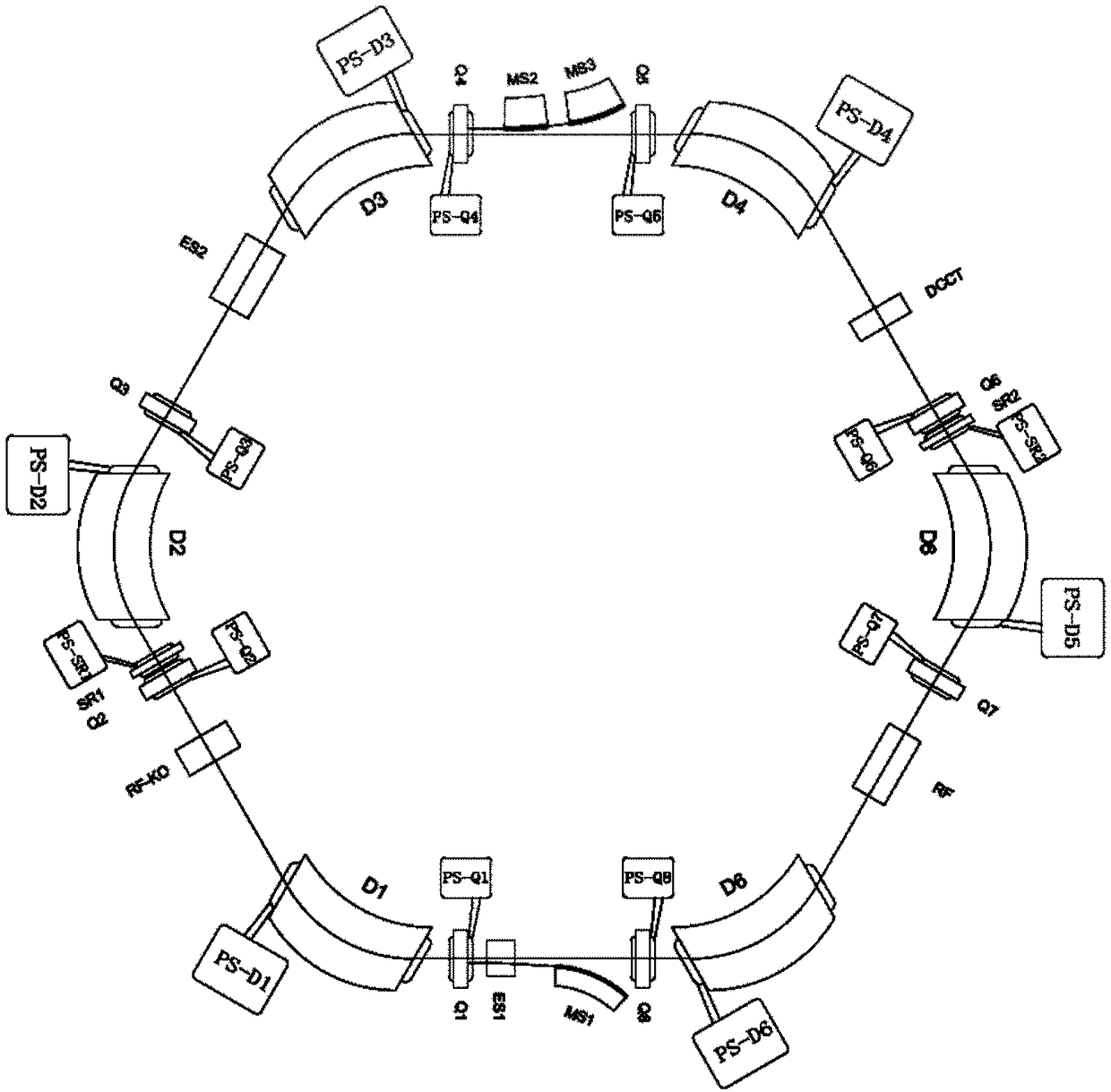
The invention relates to the technical field of design methods for a magnetic focusing structure of a medical electrified particle synchrotron, in particular to a heavy ion or proton synchrotron with a medical 45-degree deflection magnetic focusing structure. The synchrotron comprises eight deflection dipole magnets and eight synchrotron linear sections, wherein the eight deflection dipole magnets and the eight synchrotron linear sections are alternatively connected in turn through an annular vacuum pipeline; the eight deflection dipole magnet is 45-degree deflection dipole magnet; and the 45-degree deflection magnetic focusing structure comprises the annular vacuum pipeline in which electrified particles run and a magnet element, an acceleration element and an injection and extraction element which are arranged on the annular pipeline. The synchrotron has the advantages of effectively utilizing the space of the synchrotron, realizing the function of the medical heavy ion / proton synchrotron by arranging as few elements as possible, reducing manufacturing cost and installation space to the maximum extent, improving therapeutic efficiency and lowering treatment cost.
Owner:国科离子医疗科技有限公司
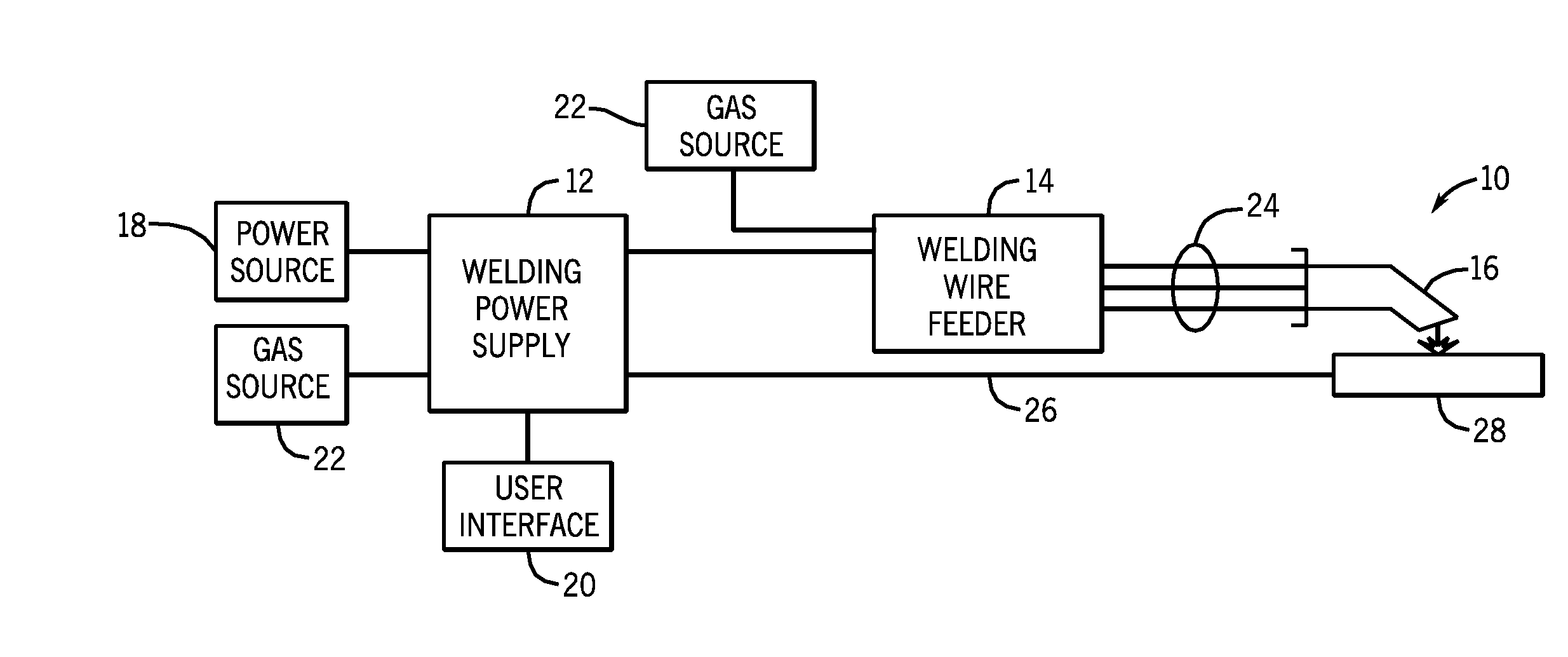
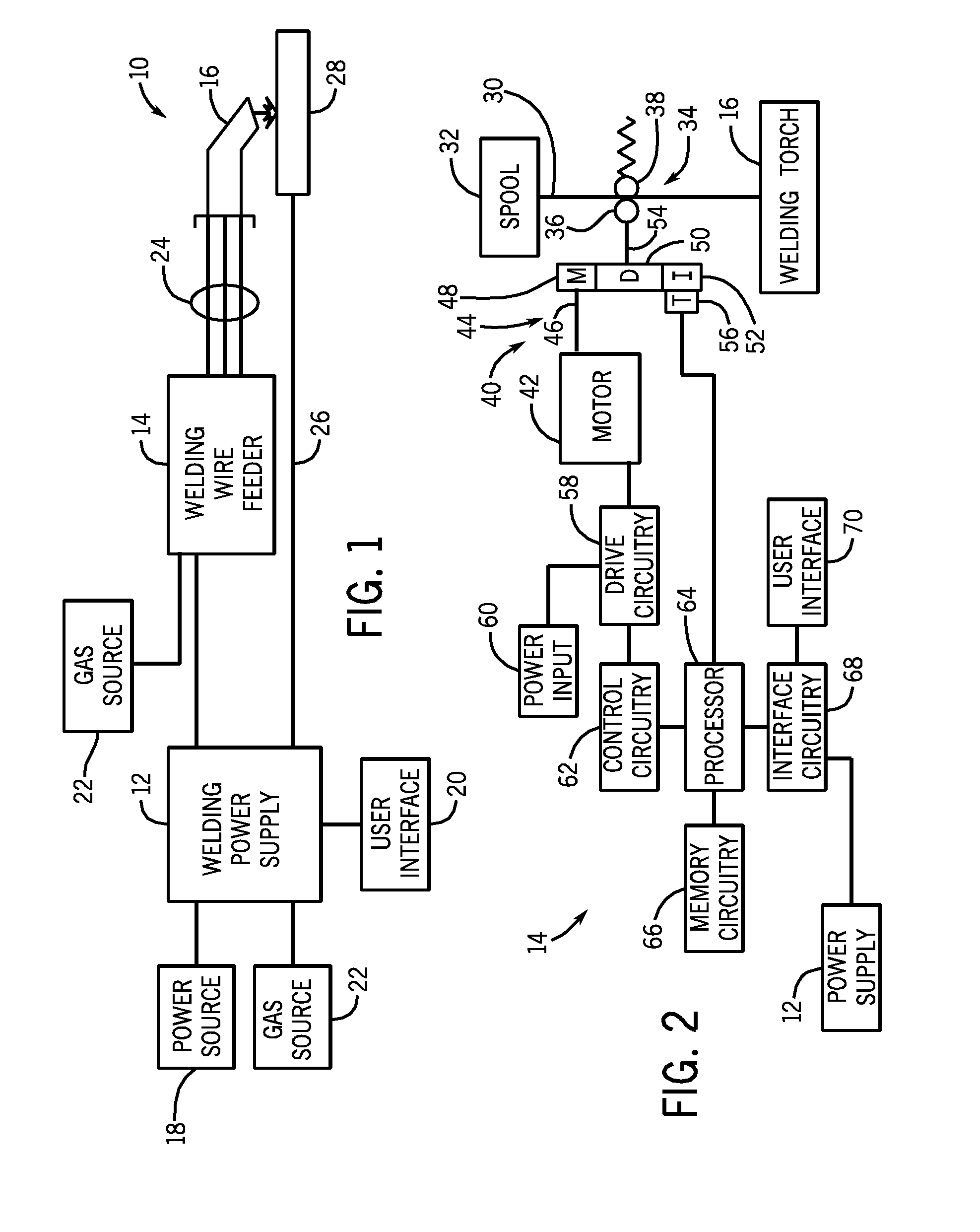
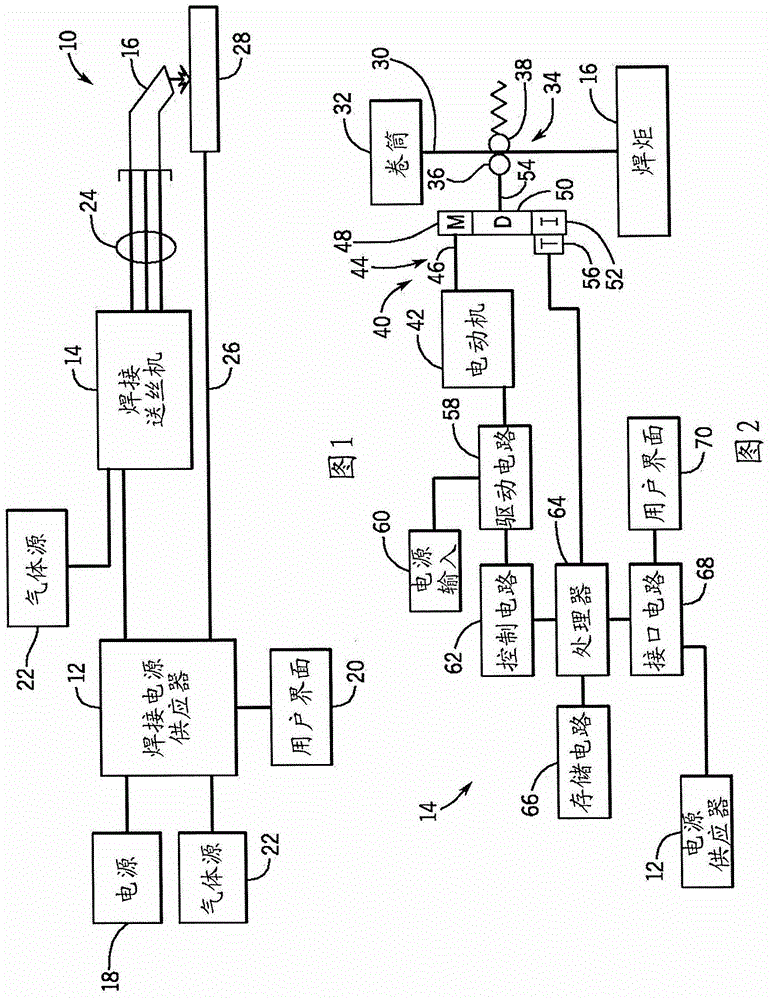
Welding wire feeder with magnetic rotational speed sensor
A welding wire feeder includes a magnetic rotational sensor system configured to measure a parameter indicative of a wire feed speed of the welding wire feeder. The magnetic rotational sensor system includes a dipole magnet coupled to a gear driven by an electric motor of the welding wire feeder and a magnetic sensor disposed adjacent to the dipole magnet and configured to measure an angular position of the dipole magnet. The magnetic rotational sensor system also includes a processor configured to receive signals of the angular position measured by the magnetic sensor and to calculate a wire feed speed of the welding wire feeder based upon the angular position signals and configuration parameters of the welding wire feeder.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Beam line architecture for ion implanter
ActiveUS7507978B2Facilitate uniform and precise implant property across waferImprove filtering effectRadiation/particle handlingMaterial analysis by optical meansIon beamLight beam
A parallelizing component of an ion implantation system comprises two angled dipole magnets that mirror one another and serve to bend an ion beam traversing therethrough to have a substantially “s” shape. This s bend serves to filter out contaminants of the beam, while the dipoles also parallelize the beam to facilitate uniform implant properties across the wafer, such as implant angle, for example. Additionally, a deceleration stage is included toward the end of the implantation system so that the energy of the beam can be kept relatively high throughout the beamline to mitigate beam blowup.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES
Method of controlling coherent synchroton radiation-driven degradation of beam quality during bunch length compression
InactiveUS8217596B1Prevent degradationQuick compressionLaser detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsTransport systemLight beam
A method of avoiding CSR induced beam quality defects in free electron laser operation by a) controlling the rate of compression and b) using a novel means of integrating the compression with the remainder of the transport system: both are accomplished by means of dispersion modulation. A large dispersion is created in the penultimate dipole magnet of the compression region leading to rapid compression; this large dispersion is demagnified and dispersion suppression performed in a final small dipole. As a result, the bunch is short for only a small angular extent of the transport, and the resulting CSR excitation is small.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
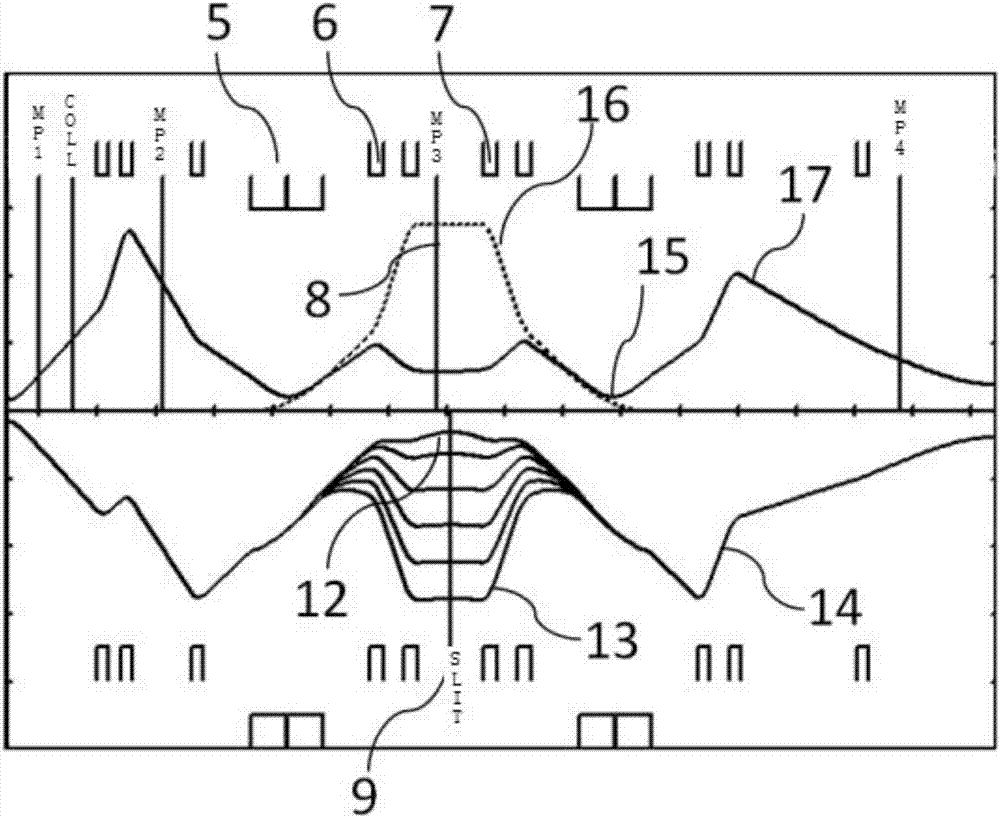
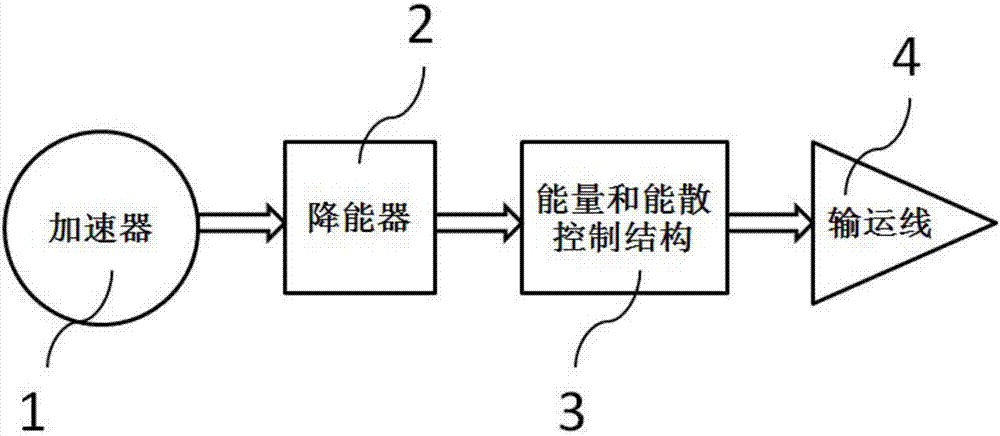
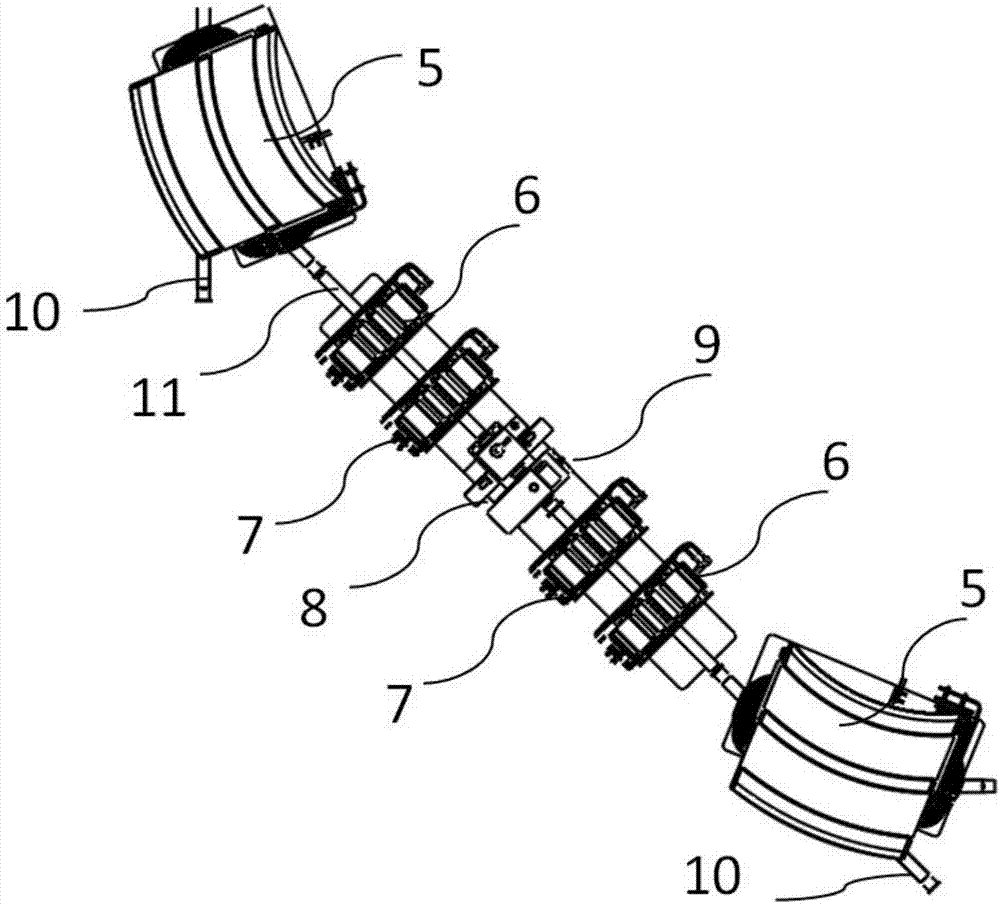
A compact type proton beam energy and energy spread control structure
ActiveCN107018619AReduced air gap heightReduce the numberAcceleratorsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyBeam energyProton
The invention discloses a compact type proton beam energy and energy spread control structure composed of two rectangular dipole magnets, two defocused quadrupole magnets, two focused quadrupole magnets, a beam measuring system, a selection slit and a vacuum tube. The two rectangular dipole magnets are arranged in a symmetrical manner at 45 degrees. One rectangular dipole magnet is connected in turn by means of the vacuum tube with one defocused quadrupole magnet, one focused quadrupole magnet, the beam measuring system and the selection slit, and then sequentially connected to the other defocused quadrupole magnet, the other focused quadrupole magnet and the other rectangular dipole magnet. The compact type proton beam energy and energy spread control structure of the invention can safely and efficiently transmit the mass beam with a transmission divergence of less than 2% and energy of 70-235MeV according to the treatment requirement, and realize the beam energy and energy spread control structure composed of the two rectangular dipole magnets arranged in a symmetrical manner at 45 degrees and the four quadrupole magnets; the compact type proton beam energy and energy spread control structure has characteristics of safety, high efficiency and high precision, and promotes the development and wide application of proton treatment technology in the future.
Owner:HEFEI CAS ION MEDICAL & TECHNICAL DEVICES CO LTD
Continuous wave slow extraction synchronous accelerator
PendingCN108124374AFlexible regulation of energyHigh energy cost performanceMagnetic resonance acceleratorsCapacitanceConstant power
The invention provides a continuous wave slow extraction synchronous accelerator. Multiple magnets used for synchronously accelerating heavy ions and / or protons comprise dipole magnets, quadrupole magnets and sextupole magnets, wherein the dipole magnets are used for turning of ion beam current, the quadrupole magnets are used for focusing of the ion beam current, and the sextupole magnets are used for matching of a phase space during slow extraction; each magnet is provided with at least one power unit electrically connected with the magnet, and each power unit comprises a voltage source andan energy storage capacitor; the voltage source is connected with the two ends of the energy storage capacitor and used for charging the energy storage capacitor; and multiple power units are connected in a series-parallel manner and then are electrically connected with the magnets and provide energy required in an ascent stage of a current waveform pulse for the magnets. By applying the continuous wave slow extraction synchronous accelerator provided by the invention, forward and reverse high pulsed power does not need to be extracted from a power grid, only forward constant power is needed,no interference is produced to the power grid, and power distribution capacity demand is reduced while beam current stability is improved.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Double dipole cancer therapy treatment beam scanning apparatus and method of use thereof
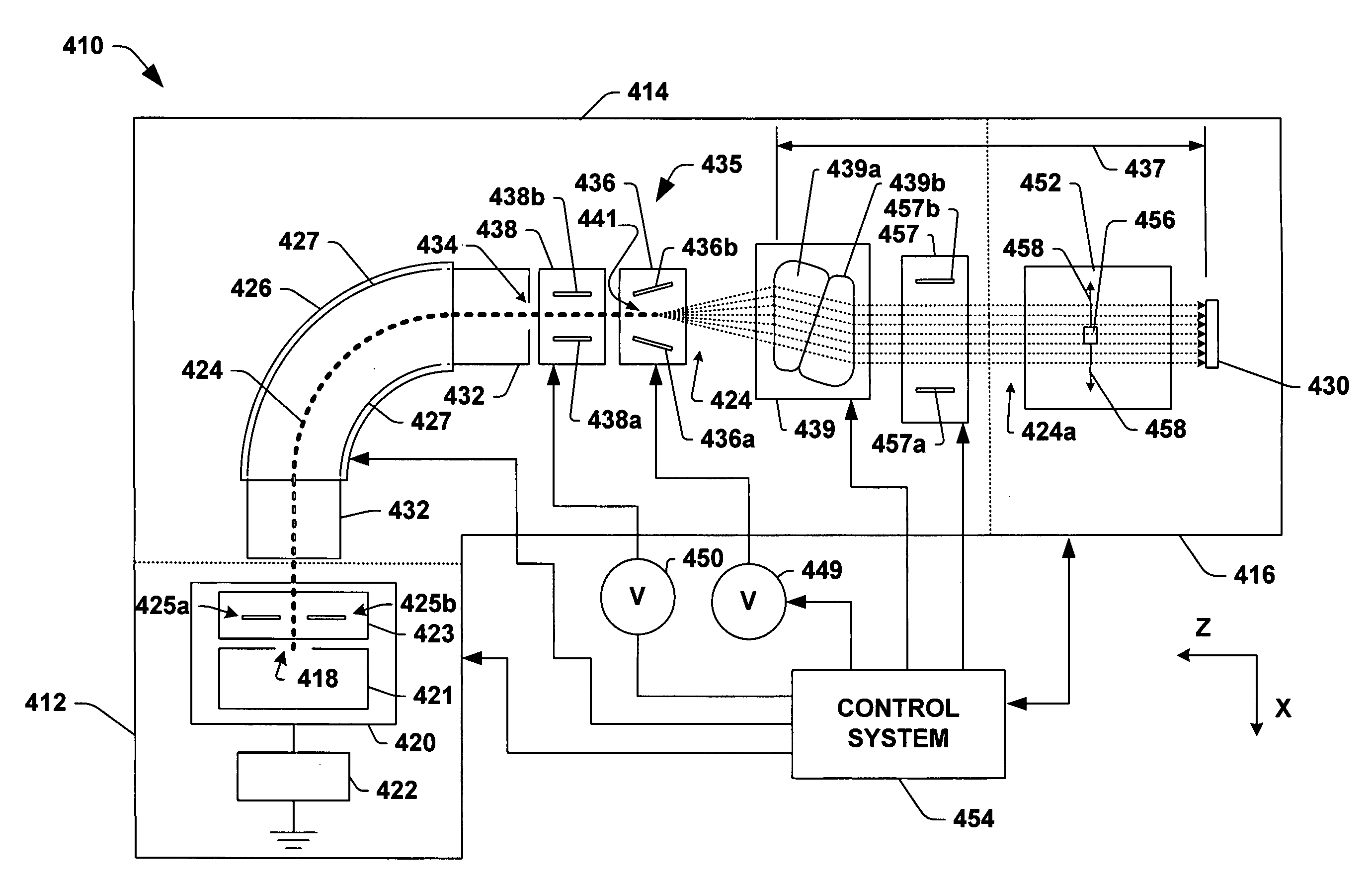
The invention comprises a method and apparatus for steering / scanning charged particles, comprising: a double dipole scanning system, comprising: (1) a beam path chamber comprising an entrance side and an exit side, the entrance side comprising a smaller area than the exit side; (2) a first dipole magnet, the first dipole magnet comprising a first coil and a third coil on first opposite sides of the beam path chamber; and (3) a second dipole magnet, the second dipole magnet comprising a second coil and a fourth coil on second opposite sides of the beam path chamber, the beam path chamber further comprising a truncated square / rectangle pyramid shape, the smaller entrance side of the charged particles comprising a top of the truncated pyramid shape, the exit side of the charged particles comprising a larger bottom of the truncated pyramid shape.
Owner:ELGART FAYE HENDLEY +4
Orthogonal double dipole cancer therapy treatment beam scanning apparatus and method of use thereof
InactiveUS20180104510A1Electric discharge tubesMagnetic resonance acceleratorsBeam scanningCancer therapy
The invention comprises a method and apparatus for scanning charged particles in a cancer therapy system, comprising the steps of: (1) providing a first and second dipole magnet system and a gap, the gap comprising a common gap length, along a path of the charged particles, within both the first and second dipole magnet systems, the gap comprising a progressively increasing x / y-plane cross-section area from an entrance area of the charged particles into the double dipole magnet system to an exit area of the double dipole magnet system, the x / y-plane perpendicular to a z-axis from a center of the entrance area to a center of the exit area; (2) scanning the positively charged particles along a first axis of the x / y-plane using the first dipole magnet system; and (3) scanning the positively charged particles along a second axis of the x / y-plane using the second dipole magnet system.
Owner:PROTOM INT HLDG CORP
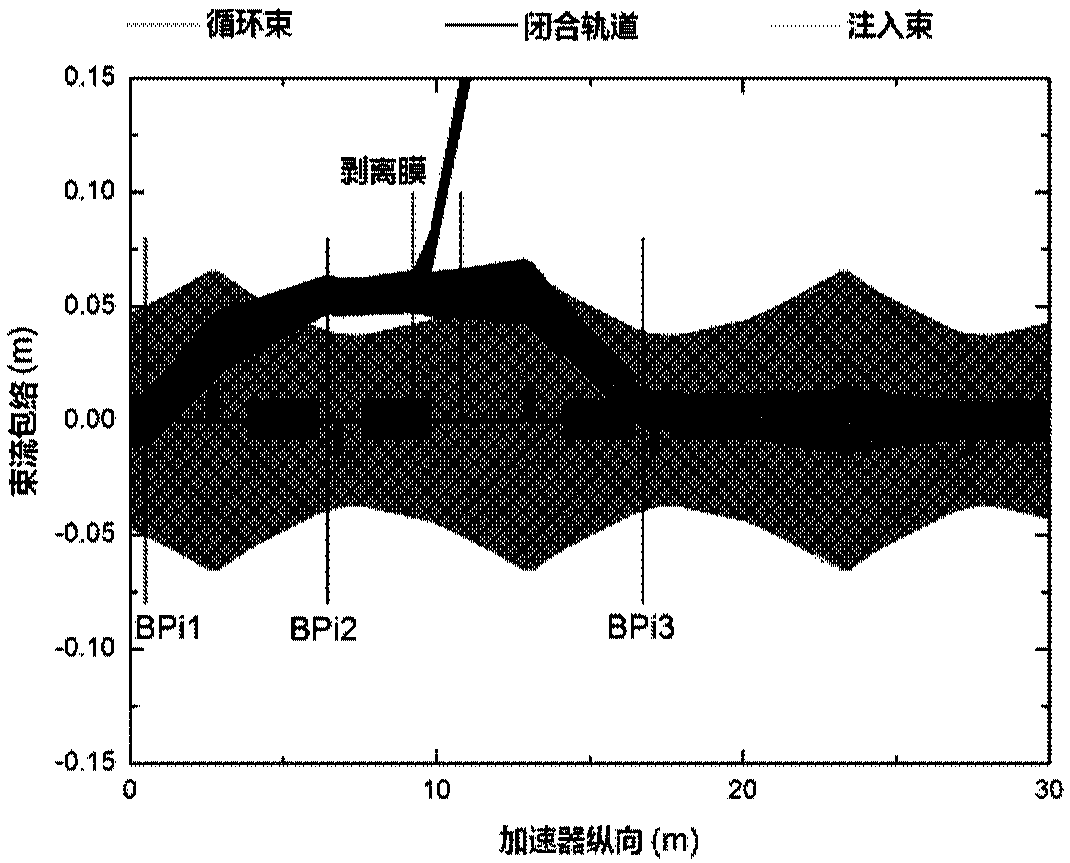
Injection device and injection method for medical proton synchrotron
ActiveCN105357856AReduce biasIncrease the number of proton storesMagnetic resonance acceleratorsMedical devicesPhase spaceEngineering
The invention relates to an injection device and an injection method for medical proton synchrotron. The device comprises a first straight section, a first deflection dipole magnet, a second straight section, a second deflection dipole magnet and a third straight section, which are sequentially connected with one another. According to the injection device and the injection method, the injection function of the medical proton synchrotron is achieved by utilizing as few elements as possible; and maximum filling of phase spaces of the horizontal emittance and the vertical emittance of the proton synchrotron is achieved, so that the proton storage number of the proton synchrotron is effectively increased, and a multi-level energy lead-out technology within a single cycle can be supported. The adopted elements are small in number and simple to control; the construction cost of the device and a building can be reduced to the maximal extent; and the treatment cost is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI AIPUQIANG PARTICLE EQUIP
Systems comprising a mechanically actuated magnetic on-off attachment device
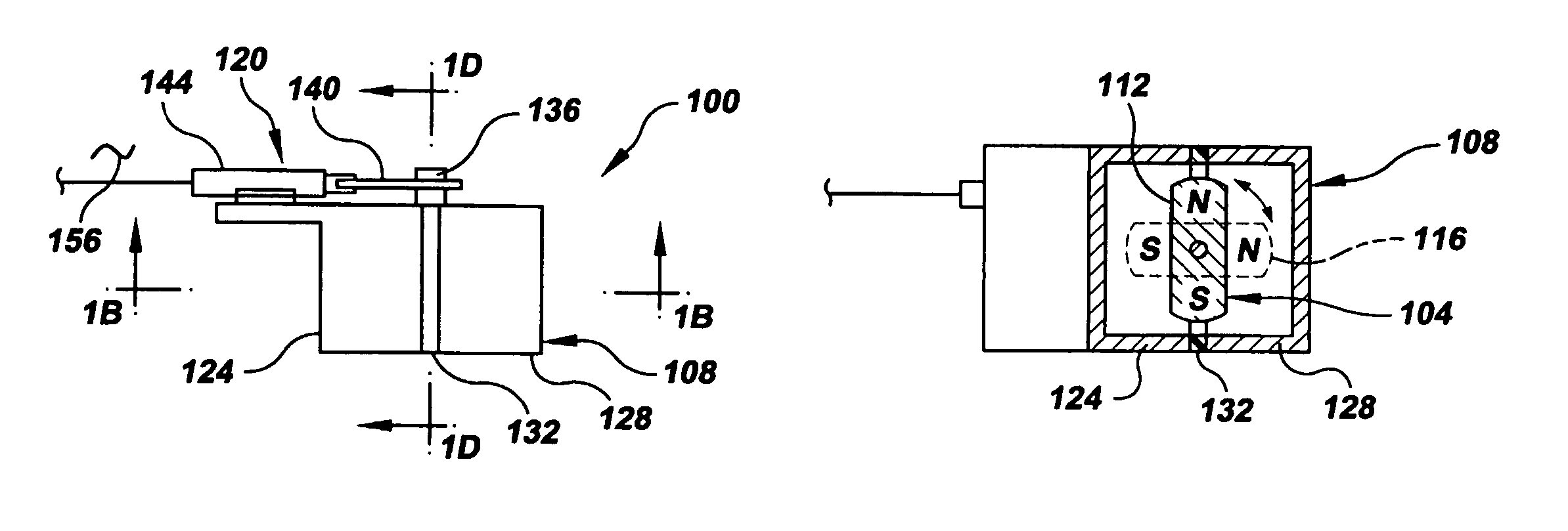
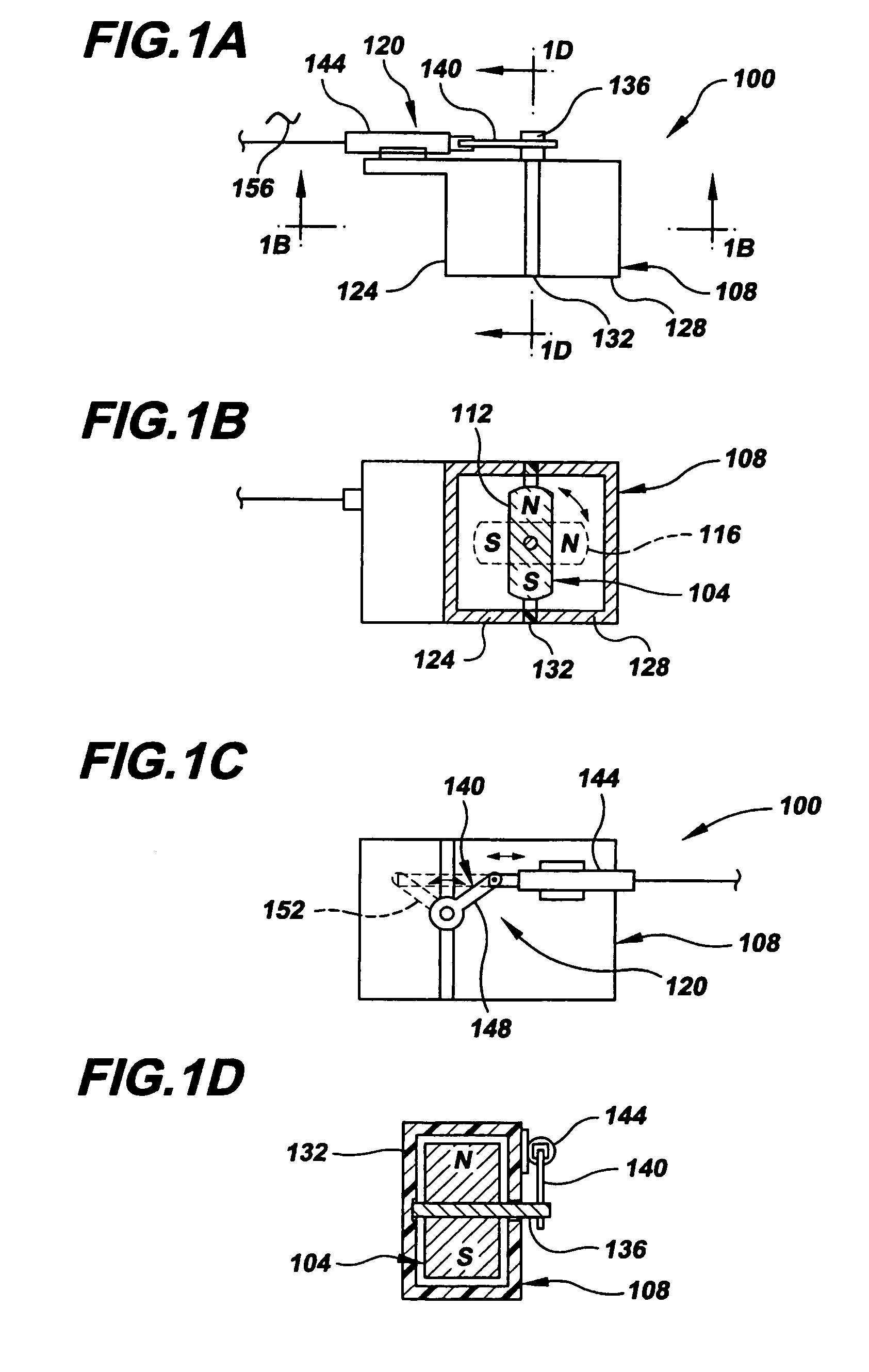
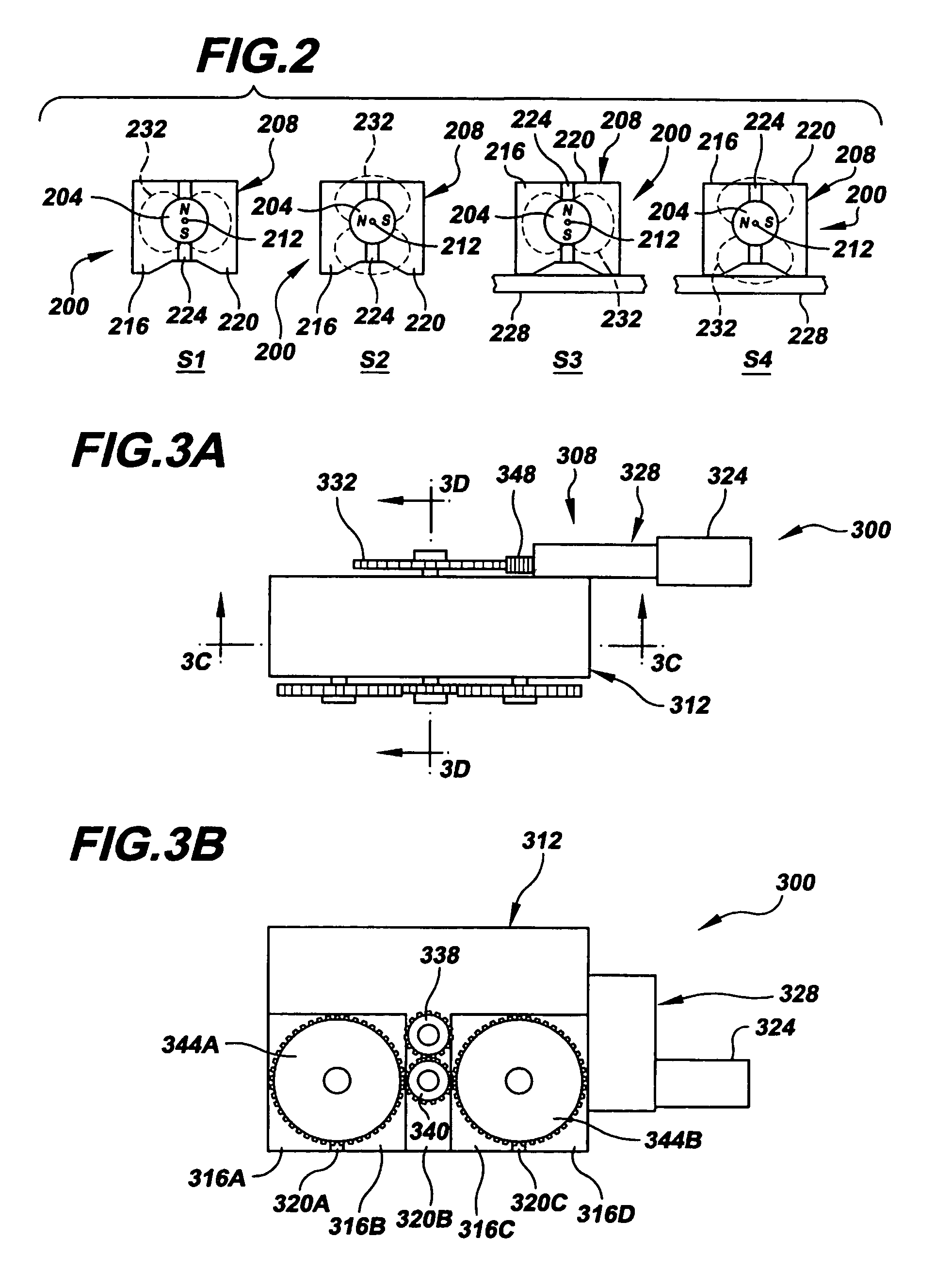
A magnetic on-off robotic attachment device (MOORAD) (100, 300, 400, 624, 624′, 660, 676, 804) is used to make a number of systems, such as a mobile apparatus (608, 644, 668, 700, 700′), a belt mechanism (800) and a sensor device (504, 508, 656). The MOORAD allows the respective system to be removably magnetically attached to a ferromagnetic structure / object (228, 420, 604, 604′, 720A-B, 720A′-B′, 848). Each MOORAD generally includes a dipole magnet (104, 304A-B, 404) movable relative to first and second ferromagnetic portions (112, 116, 316A-D, 408, 412) that are separated by corresponding magnetically insulating portions (120, 320A-C, 416) so as to change that MOORAD between off and on states.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VERMONT
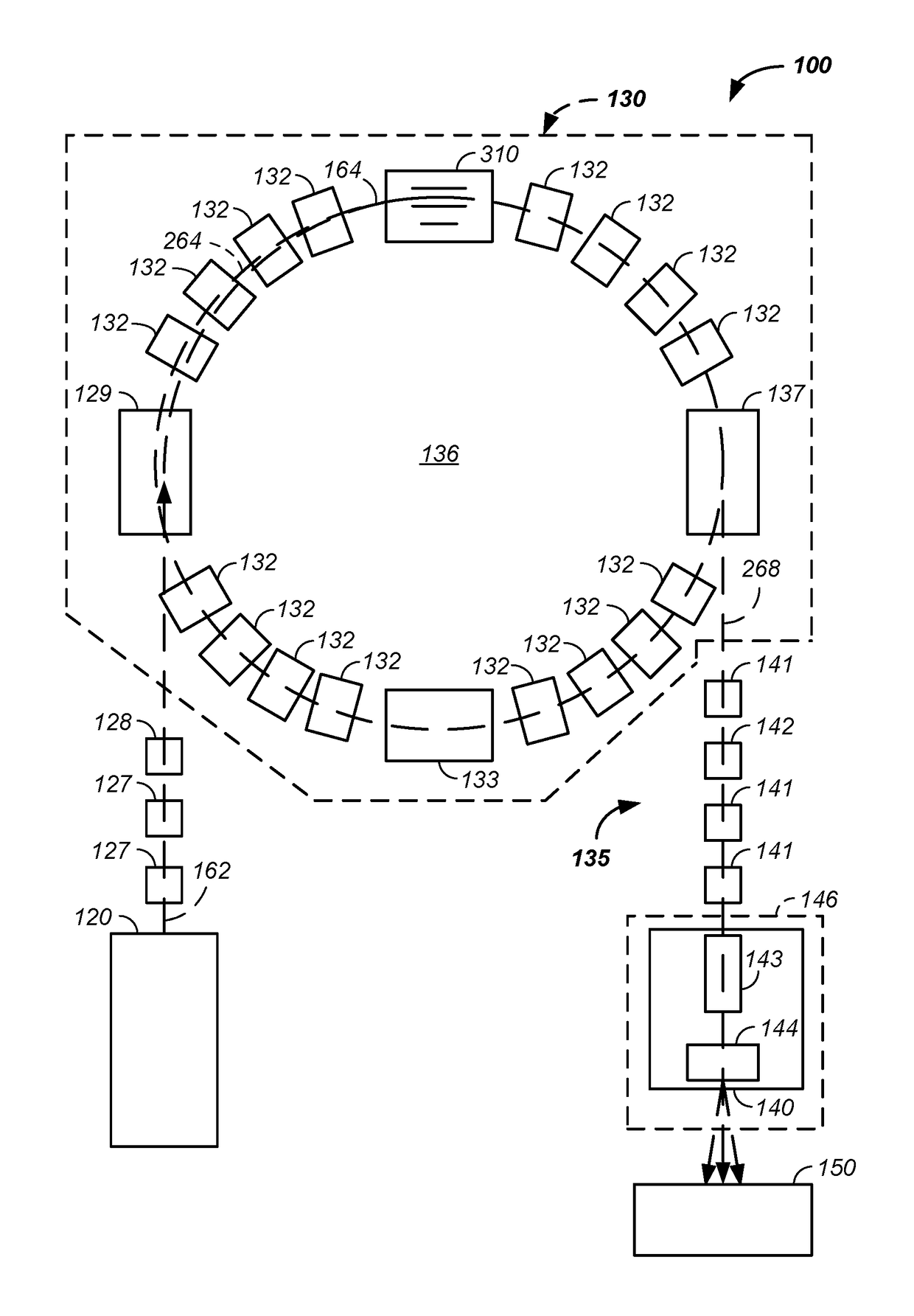
Particle Beam Transport Apparatus And Method Of Transporting A Particle Beam With Small Beam Spot Size
ActiveUS20110210263A1Electric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansParticle beamField strength
An apparatus for transporting a charged particle beam is provided. The apparatus may include: means for scanning the charged particle beam on a target, a dipole magnet arranged upstream of the means for scanning, at least three quadrupole lenses arranged between the dipole magnet and the means for scanning, and means for adjusting the field strength of at least three quadrupole lenses in function of the scanning angle of the charged particle beam. The apparatus can be made at least single achromatic.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Rotation magnetic bearing with permanent magnets, preferably for a wind turbine
InactiveUS20110062716A1Simple and robustBending stabilityMachines/enginesWind energy generationRotational axisMagnetic bearing
An apparatus (1) for rotational motion about a rotational axis (14) of a first member (2) relative to a second member (3), the first member having an outer surface being rotational symmetric about the rotational axis, and the second member having a corresponding rotational symmetric cavity with an inner surface accommodating at least part of the first member with an interspace between the outer surface of the first member and the inner surface of the second member. A repulsive magnetic field (4) between the first and the second member prevents contact between the outer surface of the first member and the inner surface of the second member. This magnetic field is achieved by a plurality of permanent dipole magnets (6, 13) arranged in the first member and in the second member with identical polarity (7) directed towards the interspace between the first and the second member. By using a plurality of magnetic dipoles an arbitrary shape can be provided with a surface having only north or south poles of magnets. The inventions is especially suited for rotational support of Darrieus-type wind turbines (20).
Owner:ZEUTHEN KRISTOFFER +2
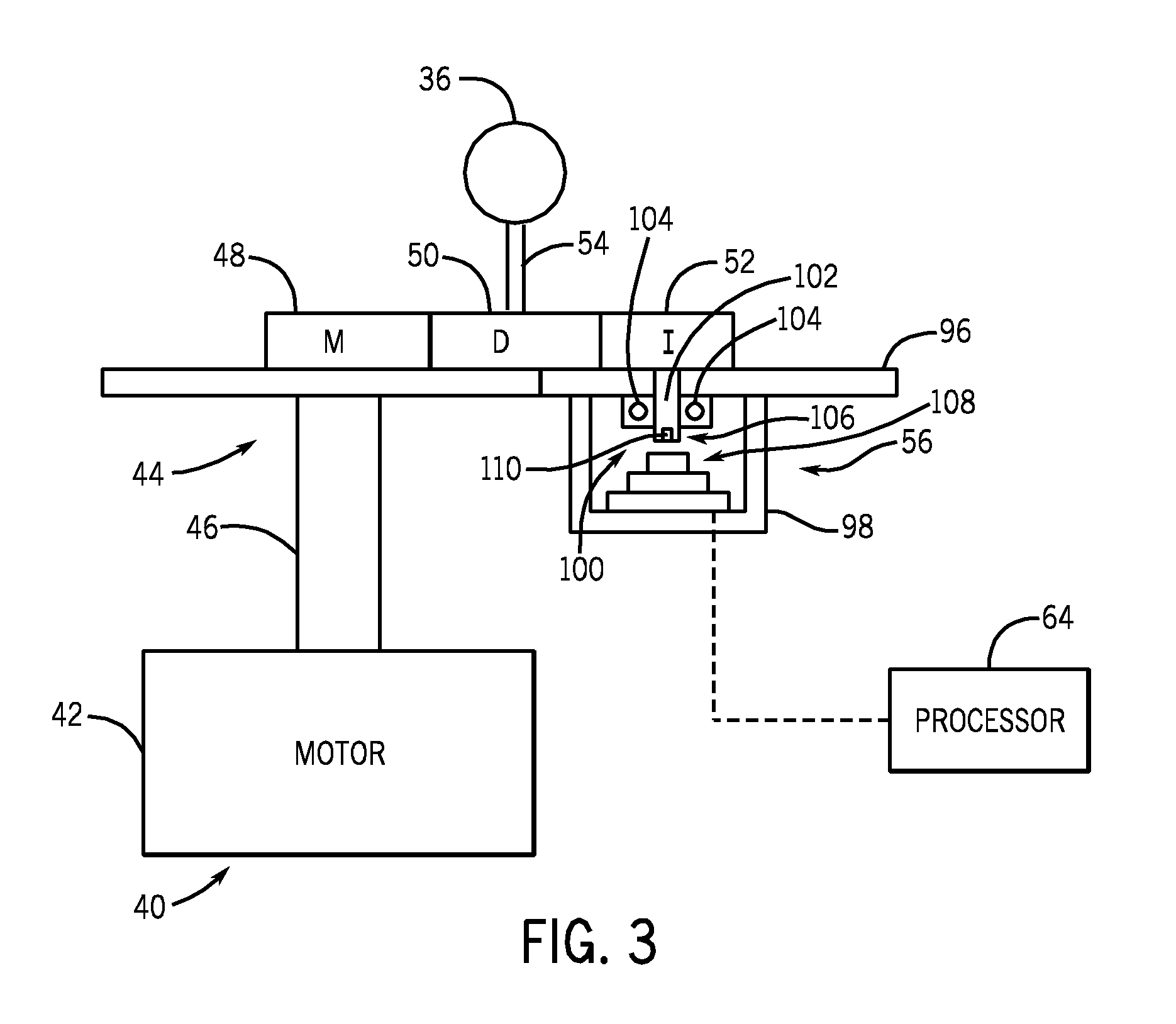
Welding wire feeder with magnetic rotational speed sensor
A welding wire feeder (14) includes a magnetic rotational sensor system (56) configured to measure a parameter indicative of a wire feed speed of the welding wire feeder. The magnetic rotational sensor system includes a dipole magnet (110) coupled to a gear (52) driven by an electric motor (42) of the welding wire feeder and a magnetic sensor (108) disposed adjacent to the dipole magnet and configured to measure an angular position of the dipole magnet. The magnetic rotational sensor system also includes a processor (64) configured to receive signals of the angular position measured by the magnetic sensor and to calculate a wire feed speed of the welding wire feeder based upon the angular position signals and configuration parameters of the welding wire feeder.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Contact magnetic printing of magnetic media using actuated magnet poles and stampers
InactiveUS6950253B2Apply evenlyHigh strengthRecord information storageRe-recordingElastomerMagnetic media
A magnetic printing apparatus includes a dipole magnet that supplies a magnetic field to a magnetic media, a holder for holding the magnetic media, a set of stampers with servo patterns and a press for pressing the magnetic media firmly against the stampers while the magnetic media and stampers are being exposed to a magnetic field and a set of elastomer pads to distribute and equalize the force of the press on the magnetic media. Servo formatting, using the contact magnetic printing apparatus, is done by positioning the magnetic media against the stampers. A force is then applied to the magnetic media and stamper so that the two are in firm contact with each other. A sequence of magnetic fields is then applied to the stampers and magnetic media which duplicates the servo patterns of the stamper onto the magnetic media.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Increased ion beam throughput with reduced beam divergence in a dipole magnet
InactiveUS6323493B1Reduce beam divergenceImproved plasma and/or electron confinementElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansIon beamLight beam
Spreading of an ion beam when passing through a dipole magnet is reduced or suppressed by electrostatic ion beam confinement which supplements magnetic confinement which may be provided. The magnetic confinement is enhanced by the provision of a magnetic mirror through concentration and localized increase of the dipole field with a concave profile of the pole pieces faces and / or provision of permanent magnets or localized regions of material of increased permeability to form magnetic cusps. Pitch and geometry of convex portions of the pole piece faces are adjusted to increase the mirror ratio and the location of the maximum mirror field relative to the thickness of a graphite or insulating liner which may be employed. Electrostatic confinement elements in the form of negatively charged electrodes and / or electrically isolated electrodes or insulators which assume a negative charge. Ionization of plasma between the pole pieces may be enhanced by application of a VHF / UHF field having a frequency of about 40 MHz to 100 MHZ or higher.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
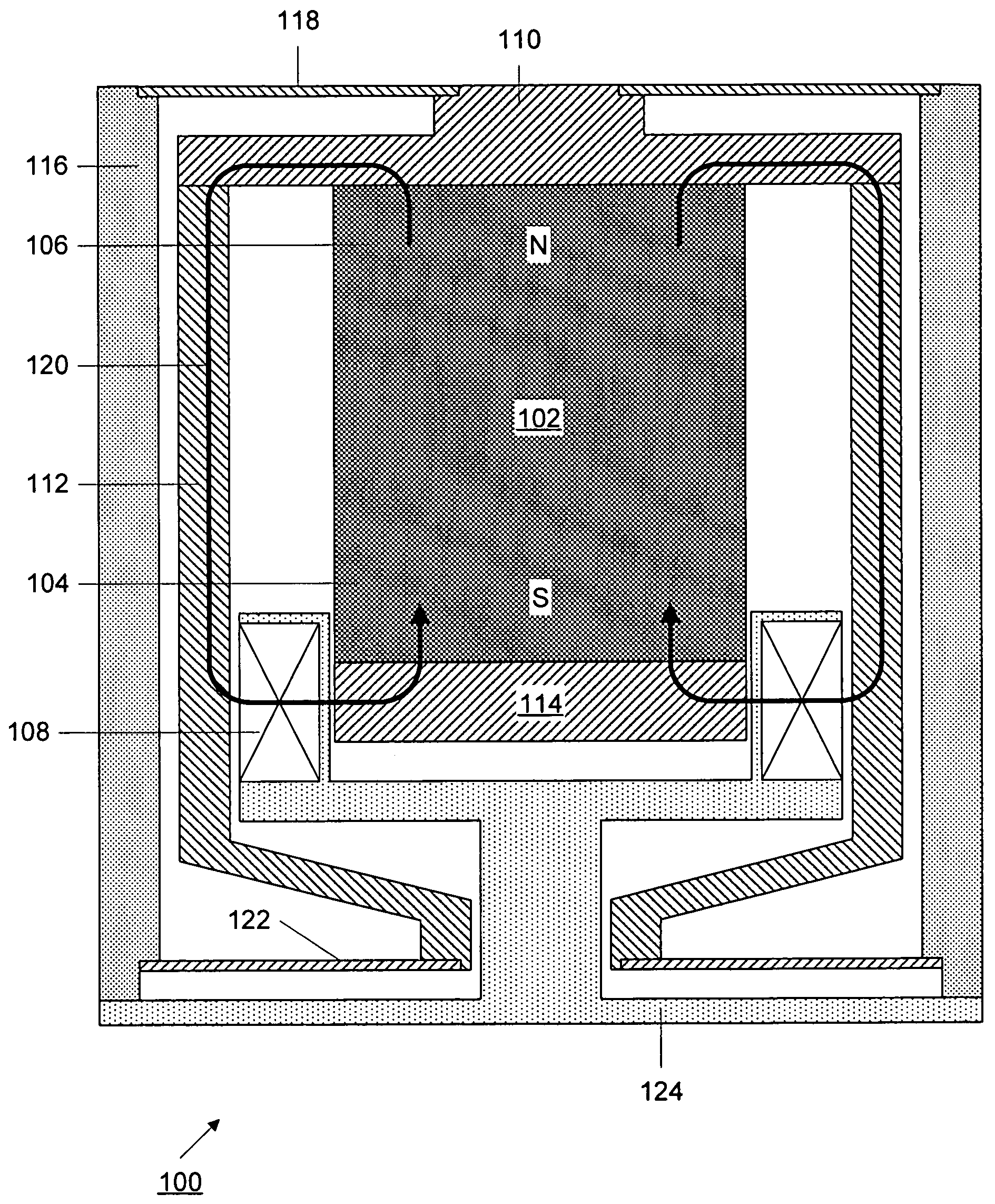
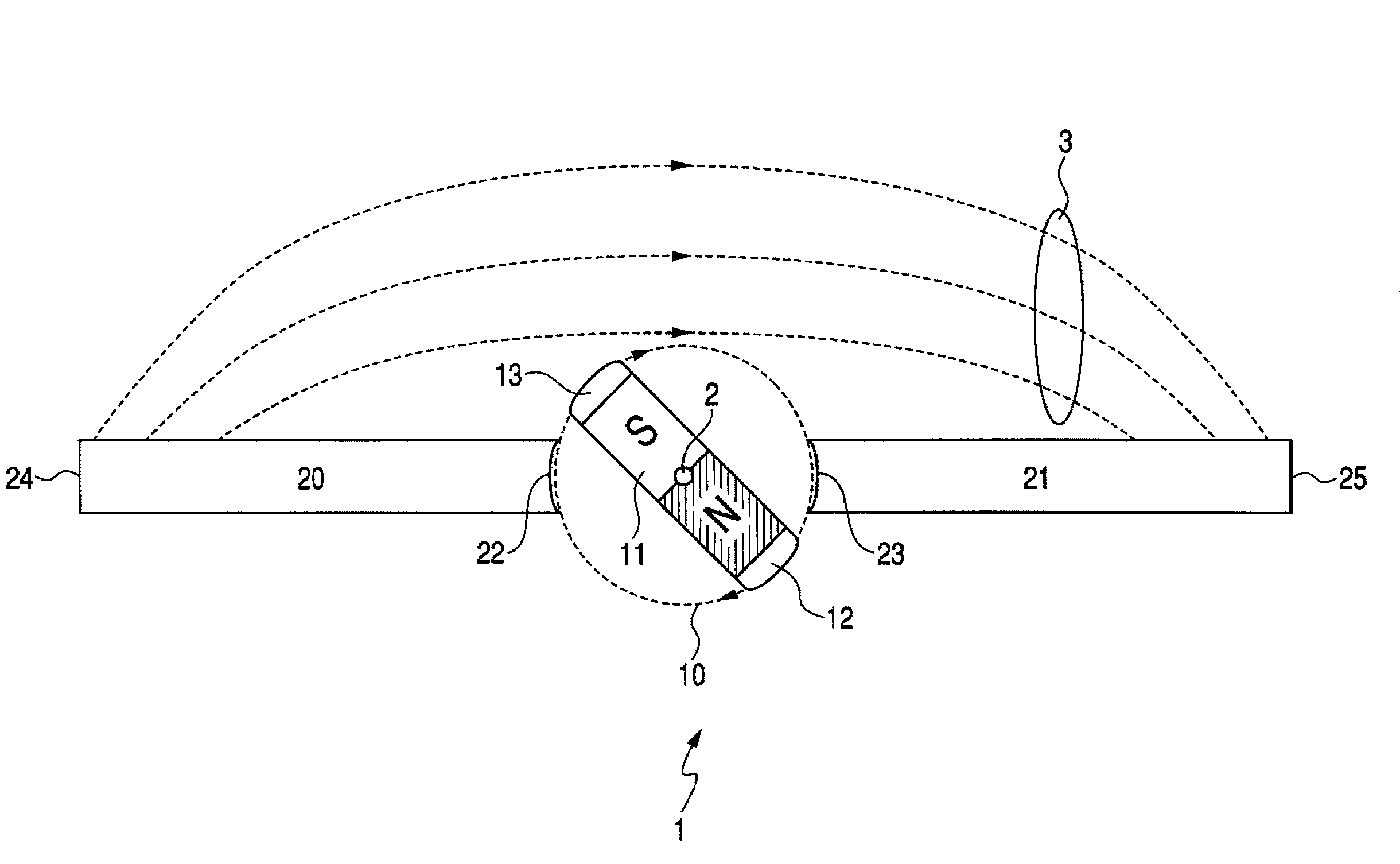
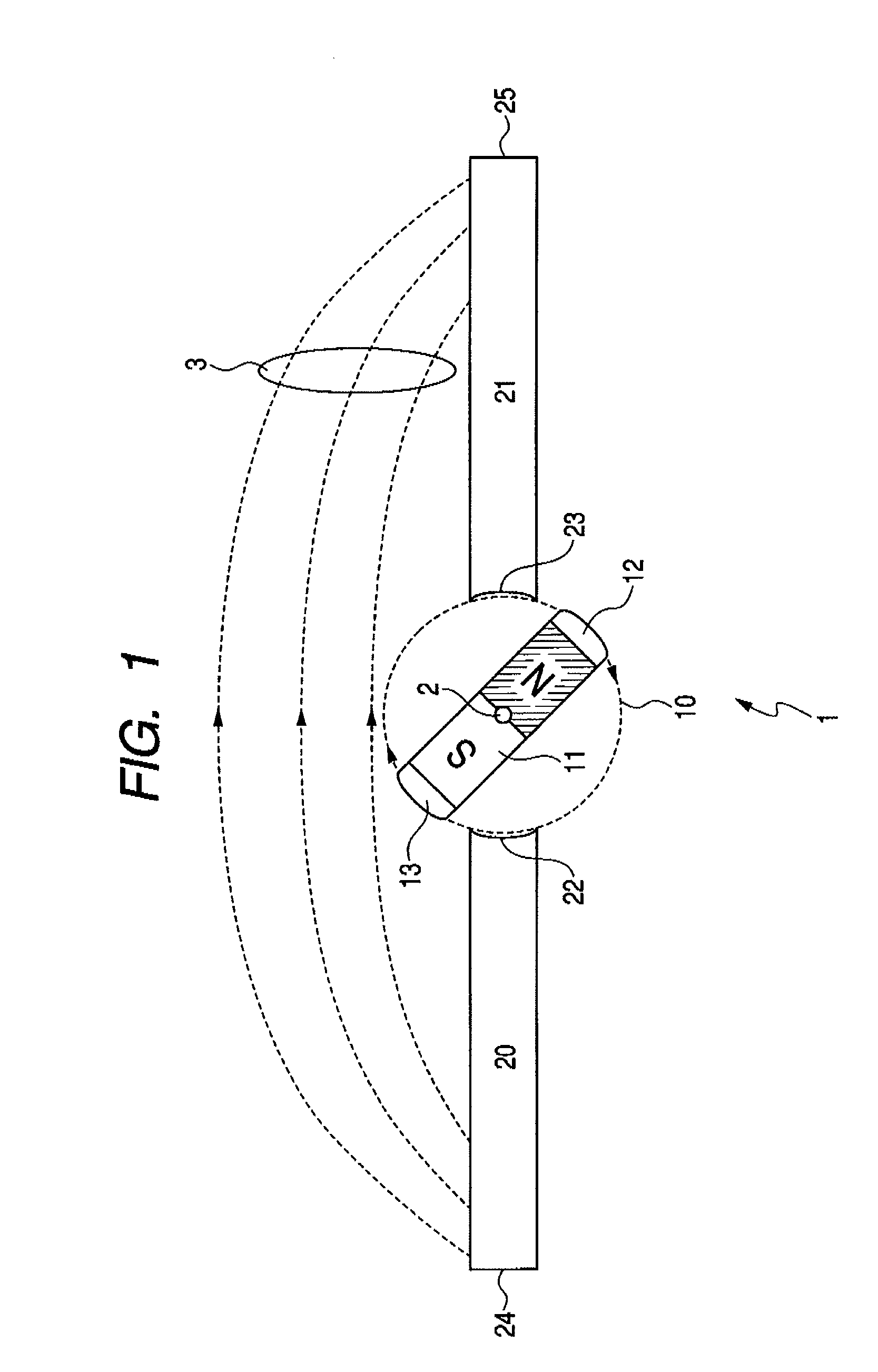
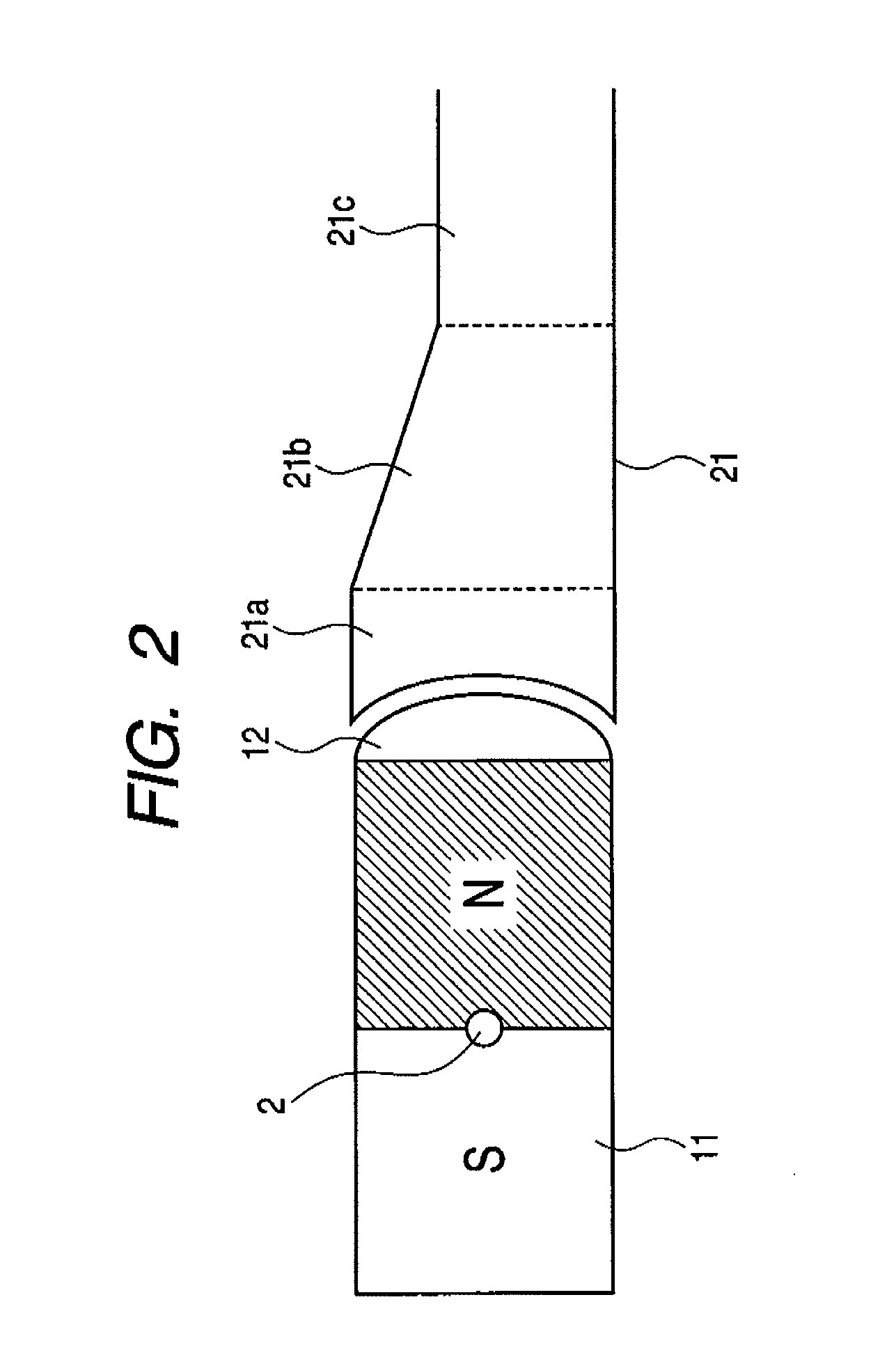
Magnet assembly capable of generating magnetic field having direction that is uniform and can be changed and sputtering apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20090078571A1Construction of assembly can be simplifiedLow costCellsElectric discharge tubesDipole magnetAtomic physics
The magnet assembly includes one rotatable dipole magnet subassembly, which is formed from a permanent magnet and a magnetically permeable convex end portion coupled to each of both ends of the permanent magnet, and at least two magnetically permeable flux guide subassemblies, which are configured so as to be magnetically coupled to the dipole magnet subassembly. The flux guide subassembly has a concave end portion that fits into the convex end portion. The flux guide assemblies guide a flux from the dipole magnet subassembly and generate a flux outside. The condition of fitting into the flux guide subassemblies is reversed by rotating the dipole magnet subassembly, whereby it is possible to easily reverse the direction of a magnetic field generated outside.
Owner:CANON ANELVA CORP
Heavy ion synchroaccelerator
ActiveCN108112154AMagnetic focusing structure is simpleEasy beam debuggingMagnetic resonance acceleratorsHeavy ion synchrotronIon beam
A heavy ion synchroaccelerator comprises an annular vacuum pipeline, the annular vacuum pipeline has a plurality of linear ion beam sections and a plurality of curve ion beam sections, the linear ionbeam sections and the curve ion beam sections are alternately arranged, heavy ions are injected from a first linear ion beam section and are led out from another linear ion beam section, each curve ion beam section comprises one first dipole magnet and one second dipole magnet which are connected in series, the heavy ions are moved from the first dipole magnets to the second dipole magnets, vertical correcting magnets and vertical focusing quadrupole magnets are arranged in order between the first dipole magnets and the second dipole magnets, the linear ion beam sections at the downstreams ofthe second dipole magnets are provided with horizontal correcting magnets, hexapole magnets and horizontal correcting quadrupole magnets in order. The heavy ion synchroaccelerator is simple in structure, can save processing cost, facilitate installation and debugging of the device, is easier to achieve high accumulation flow intensity, and can fully utilize transverse acceptability of the synchroaccelerator.
Owner:惠州离子科学研究中心 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com