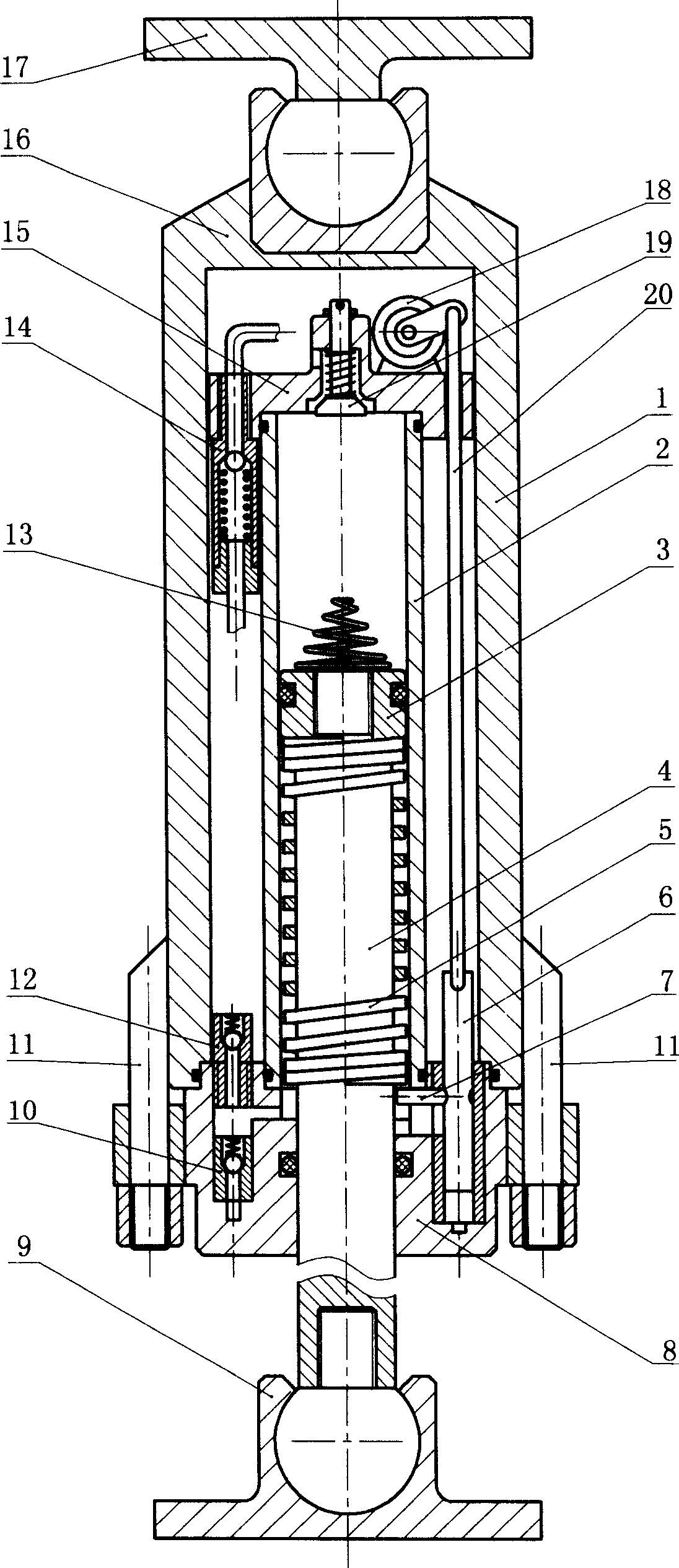
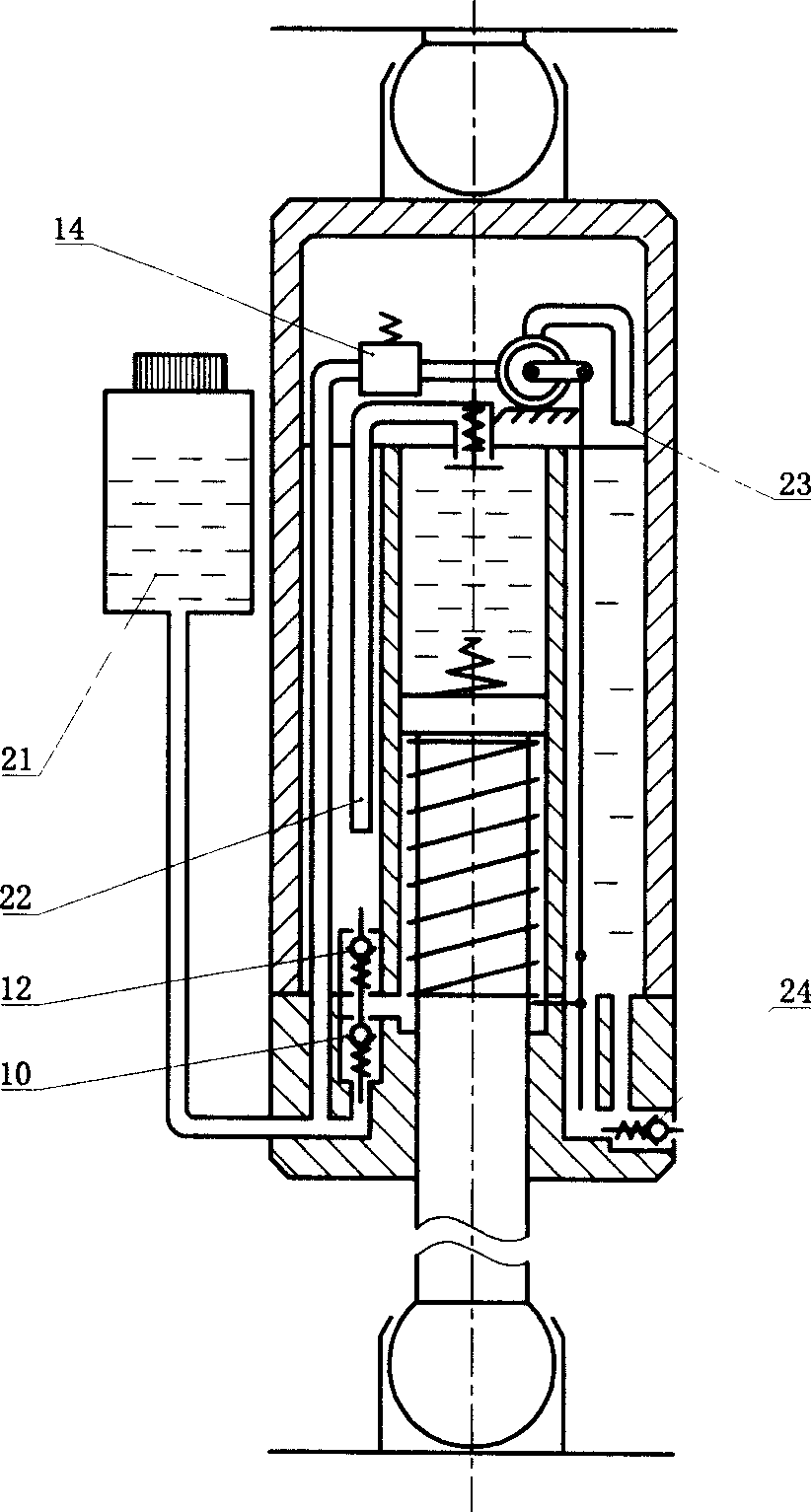
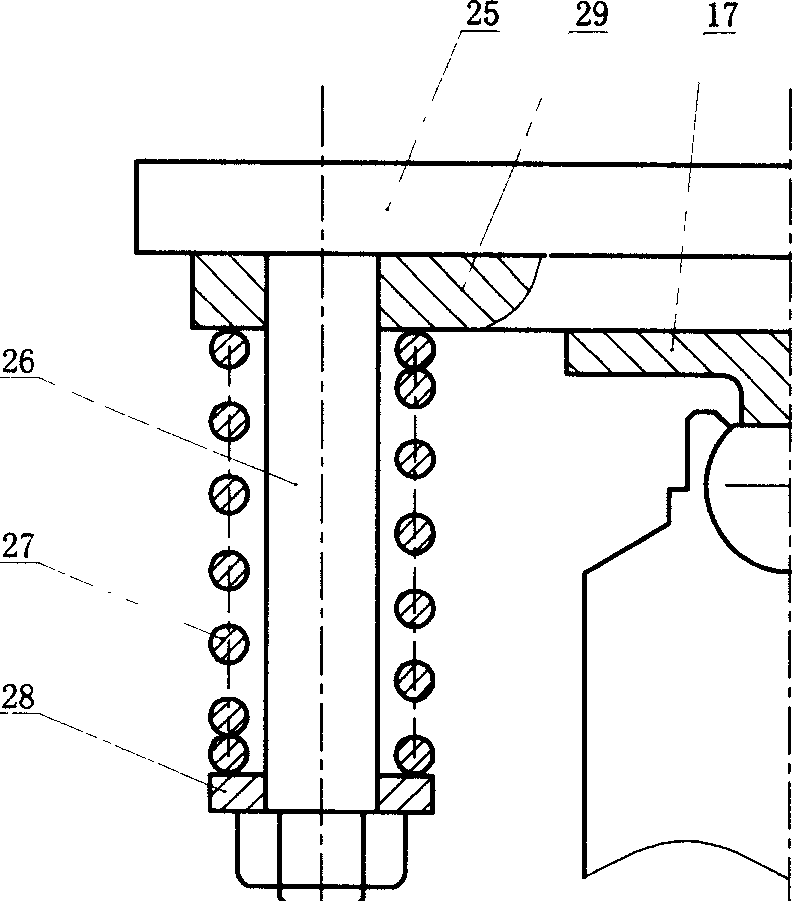
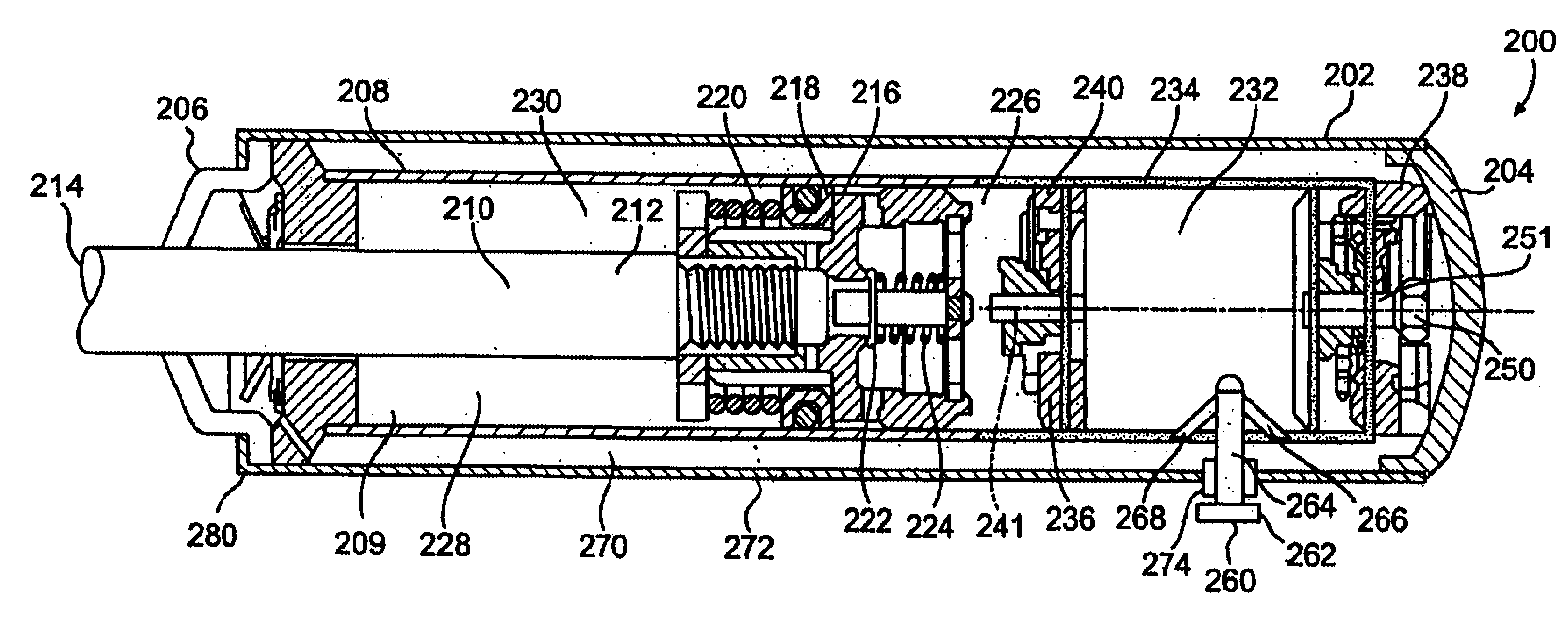
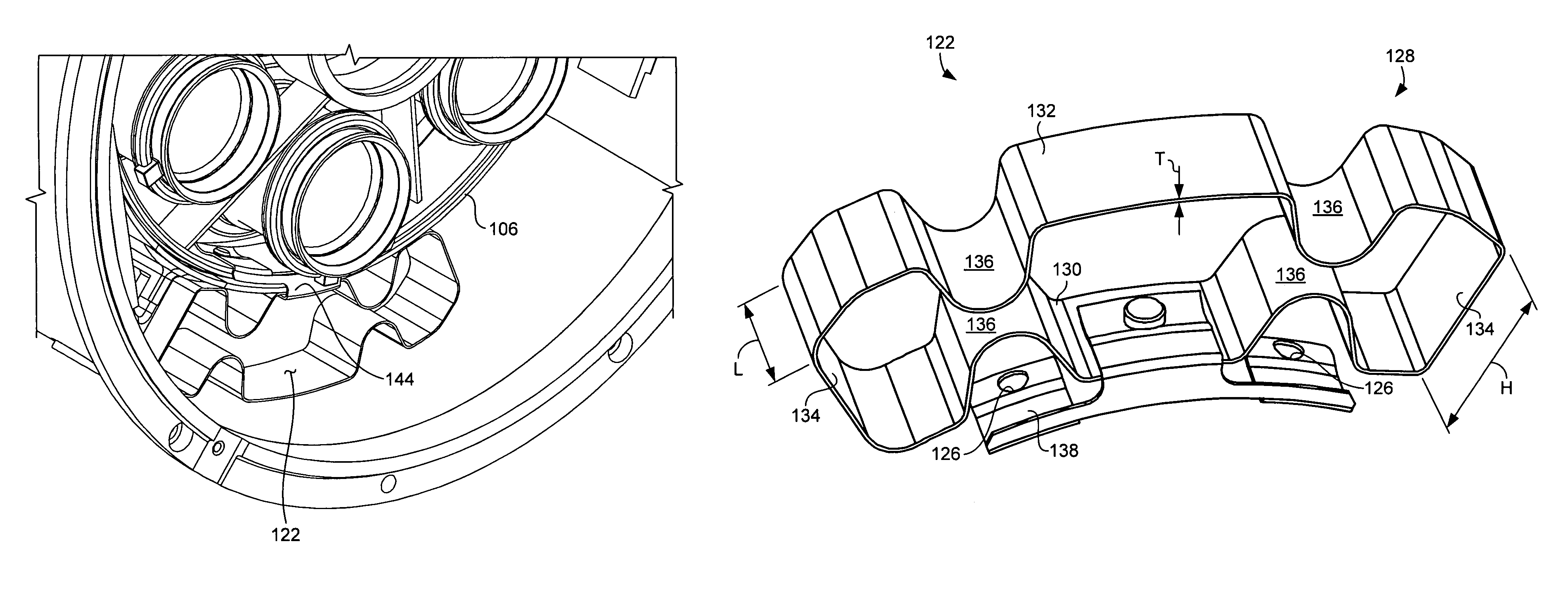
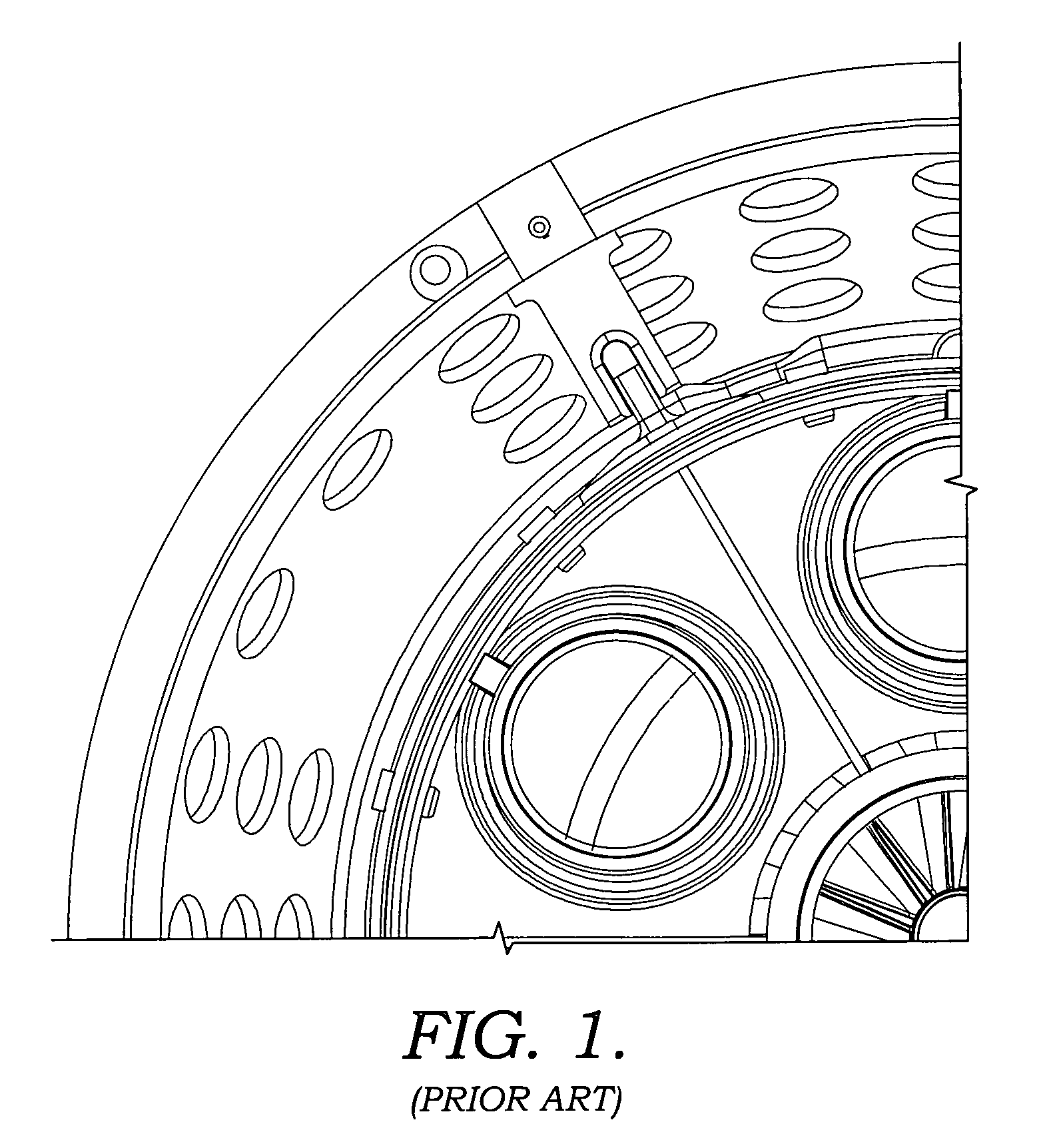
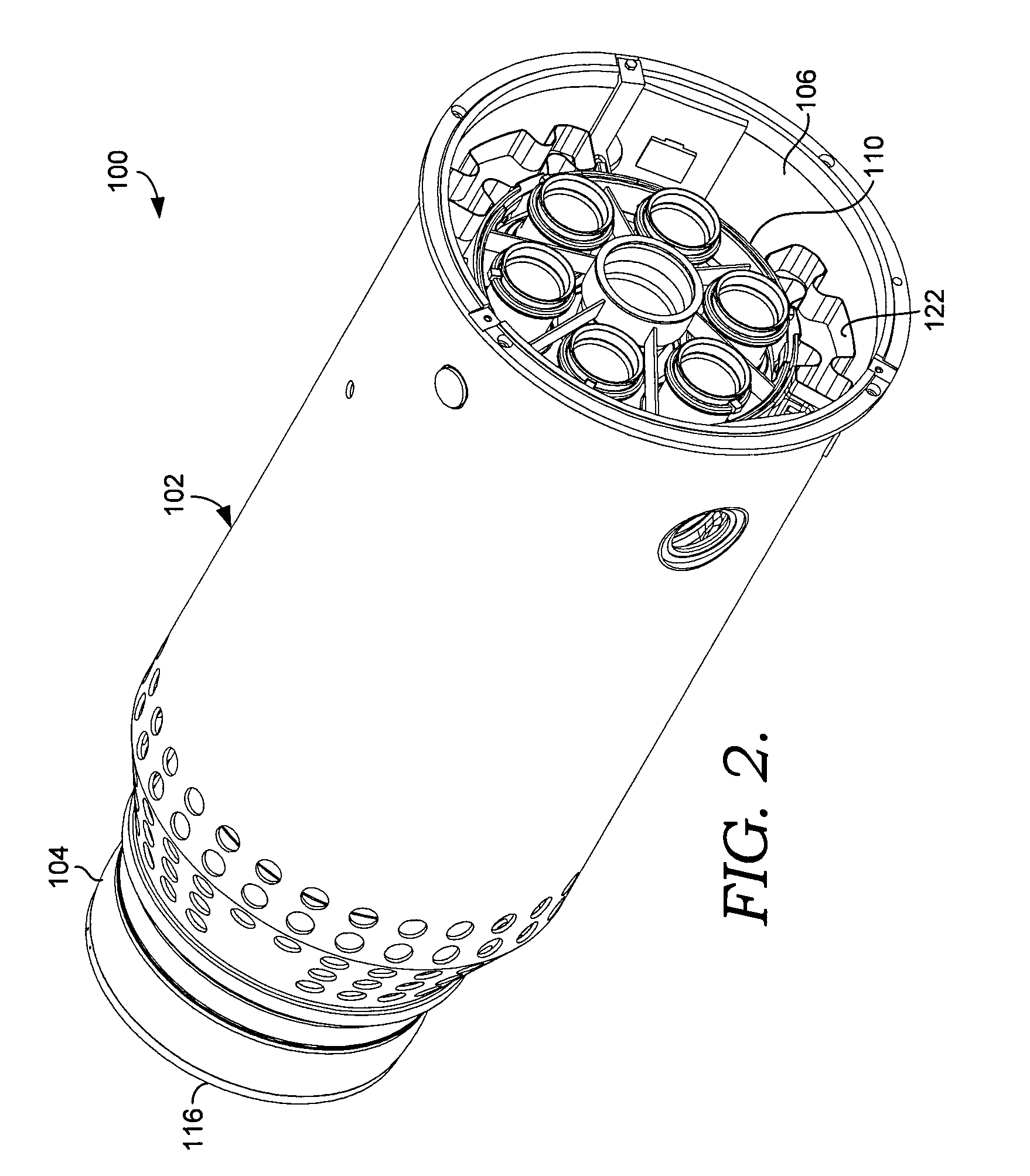
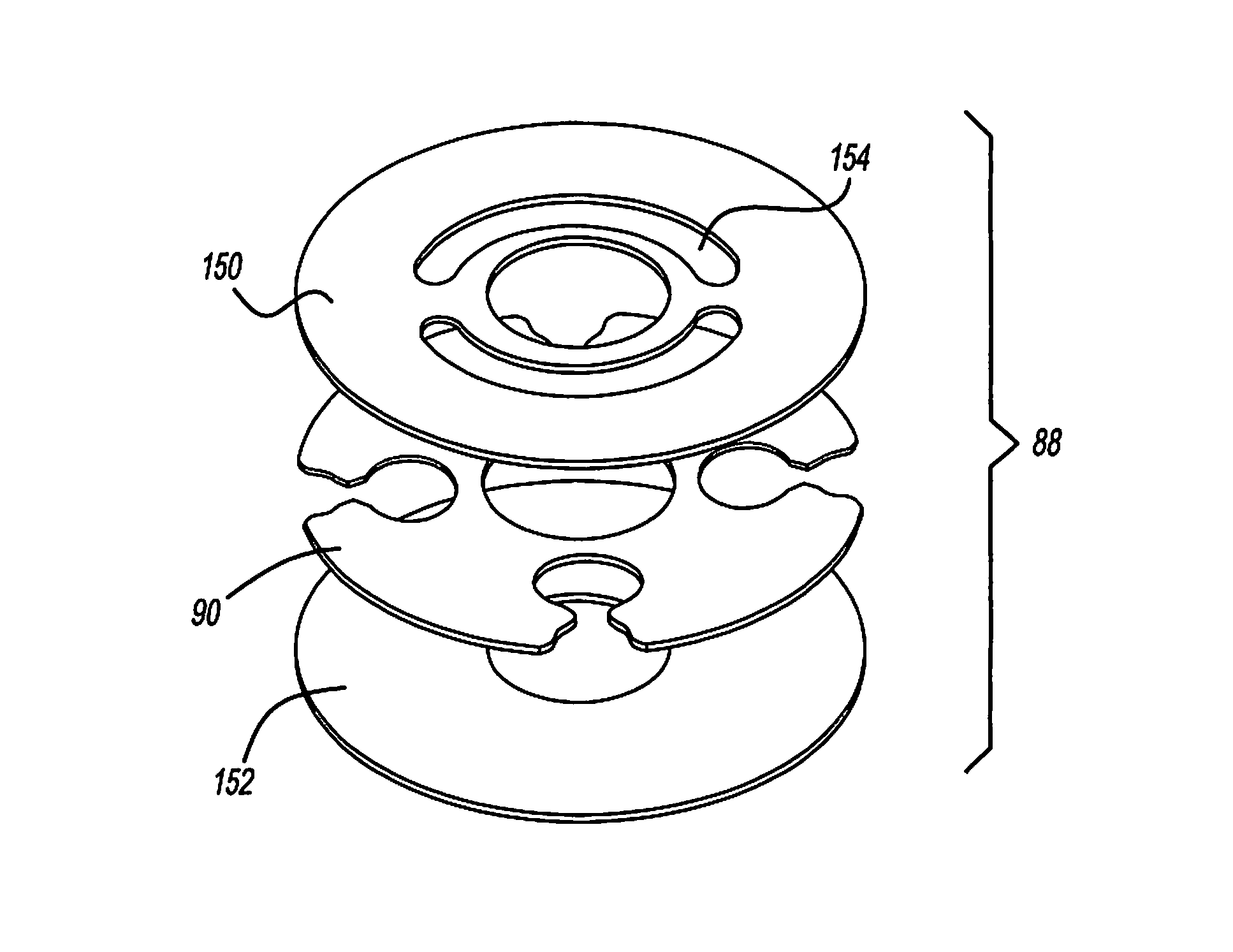
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
158 results about "Blast damper" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
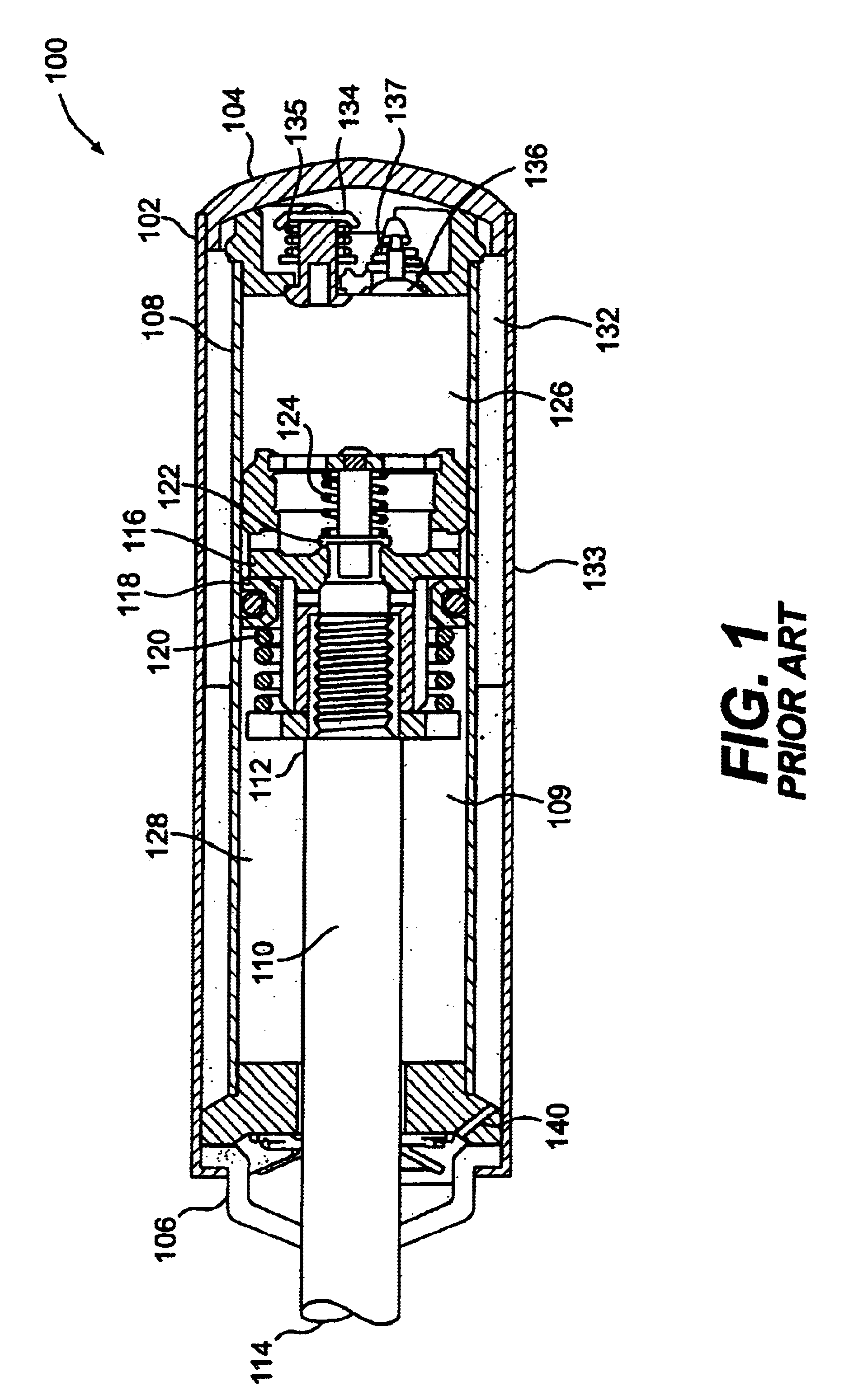
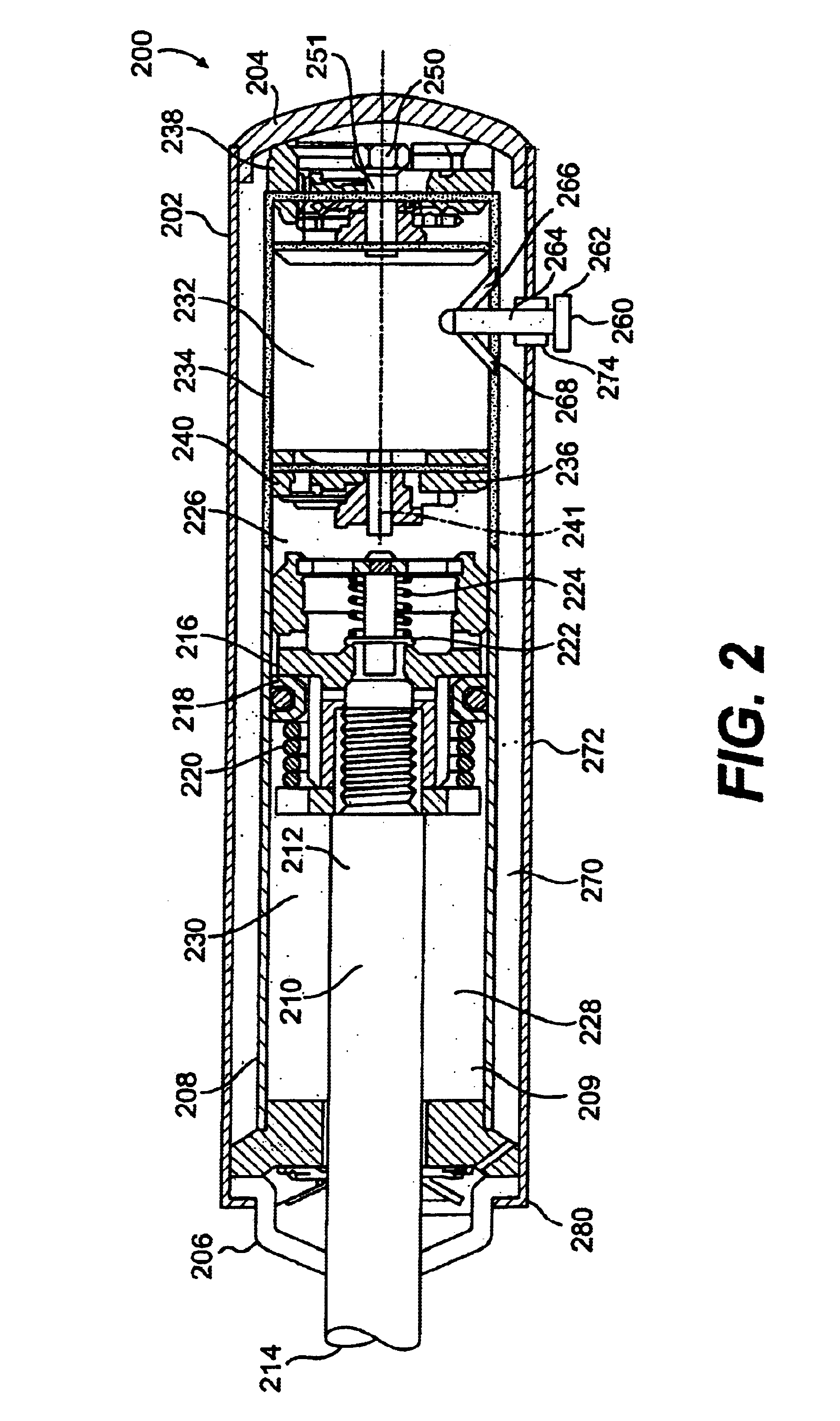
A blast damper is used to protect occupants and equipment of a structure against overpressures resultant of an explosion. The blast dampers normally protect air inlets and exhaust penetrations in an otherwise hardened structure. Blast dampers are related or identical to blast valves, the latter name is generally used to describe blast mitigation devices as they relate to nuclear explosions.
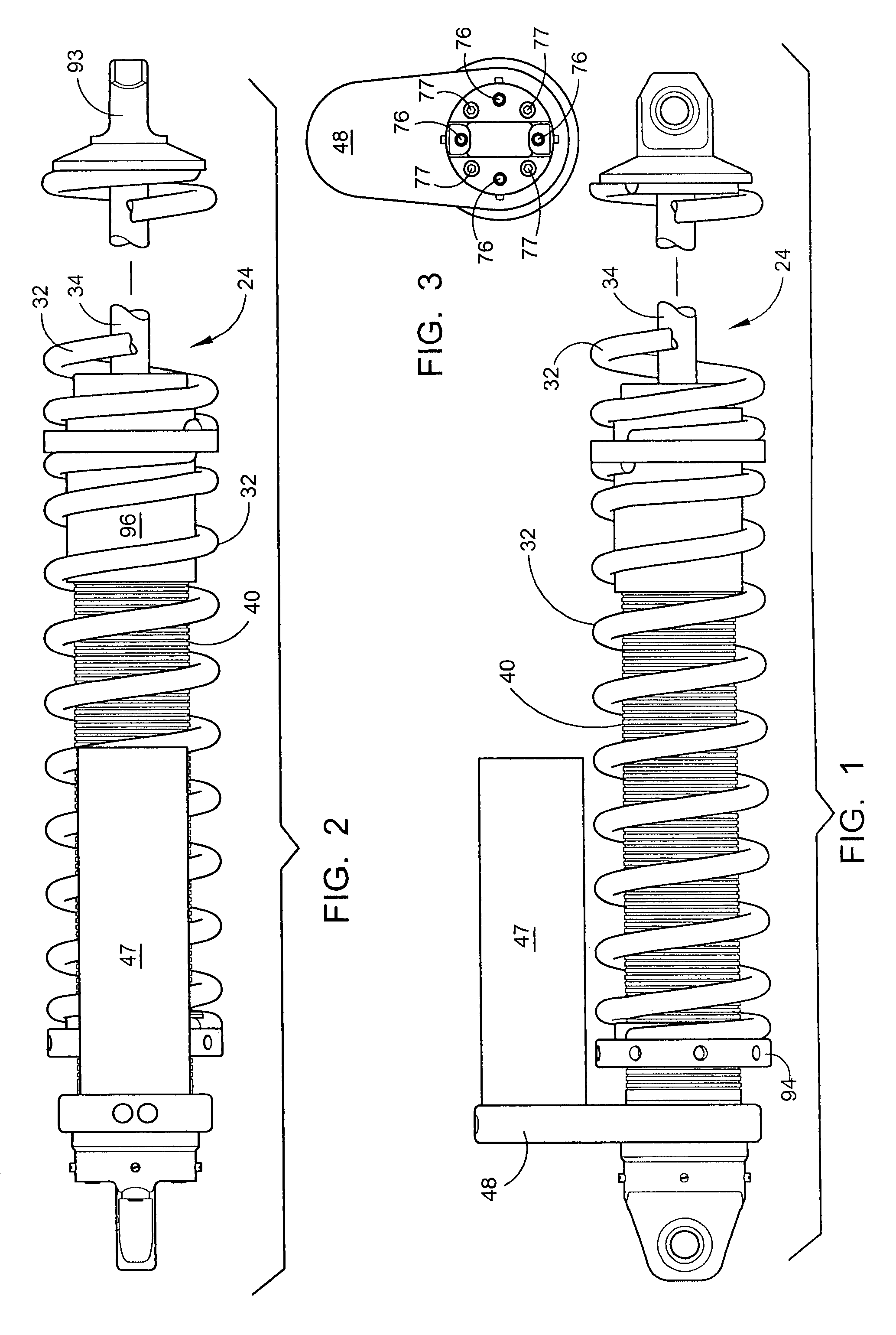
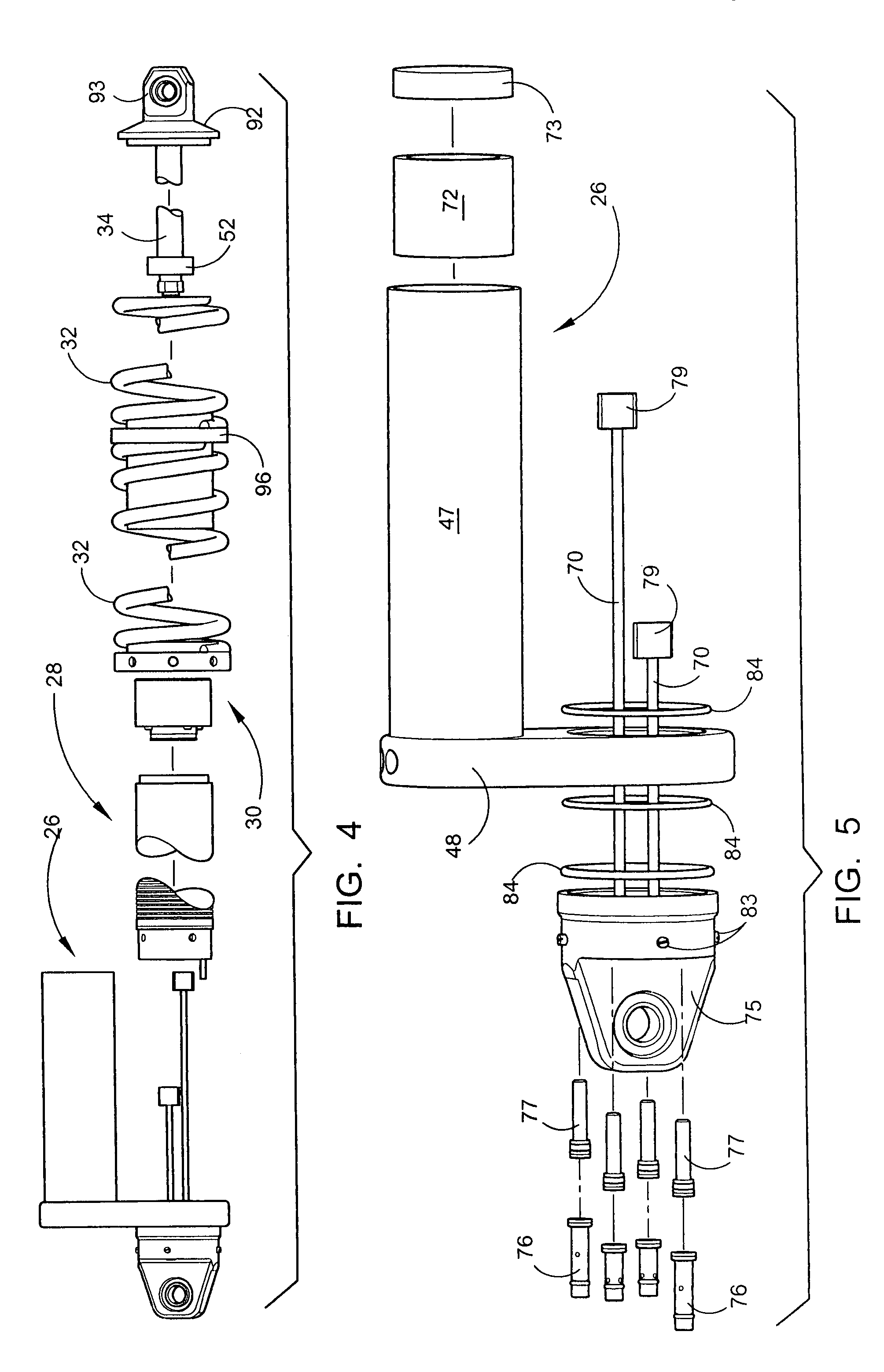
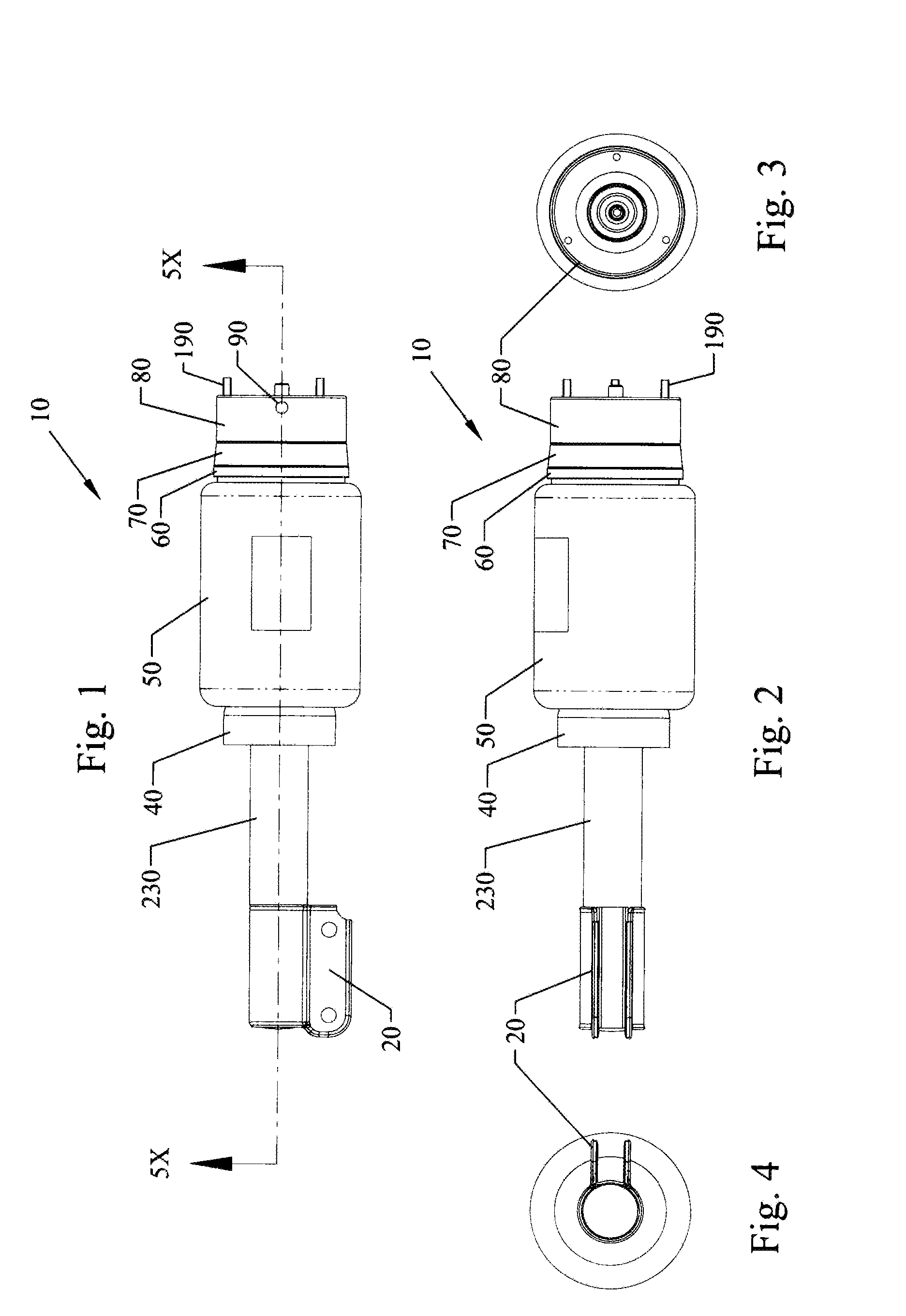
Shock absorber and suspension apparatus
ActiveUS20120305347A1Wide rangeKeeping energy conservationSpringsLiquid based dampersWorking fluidForce generation
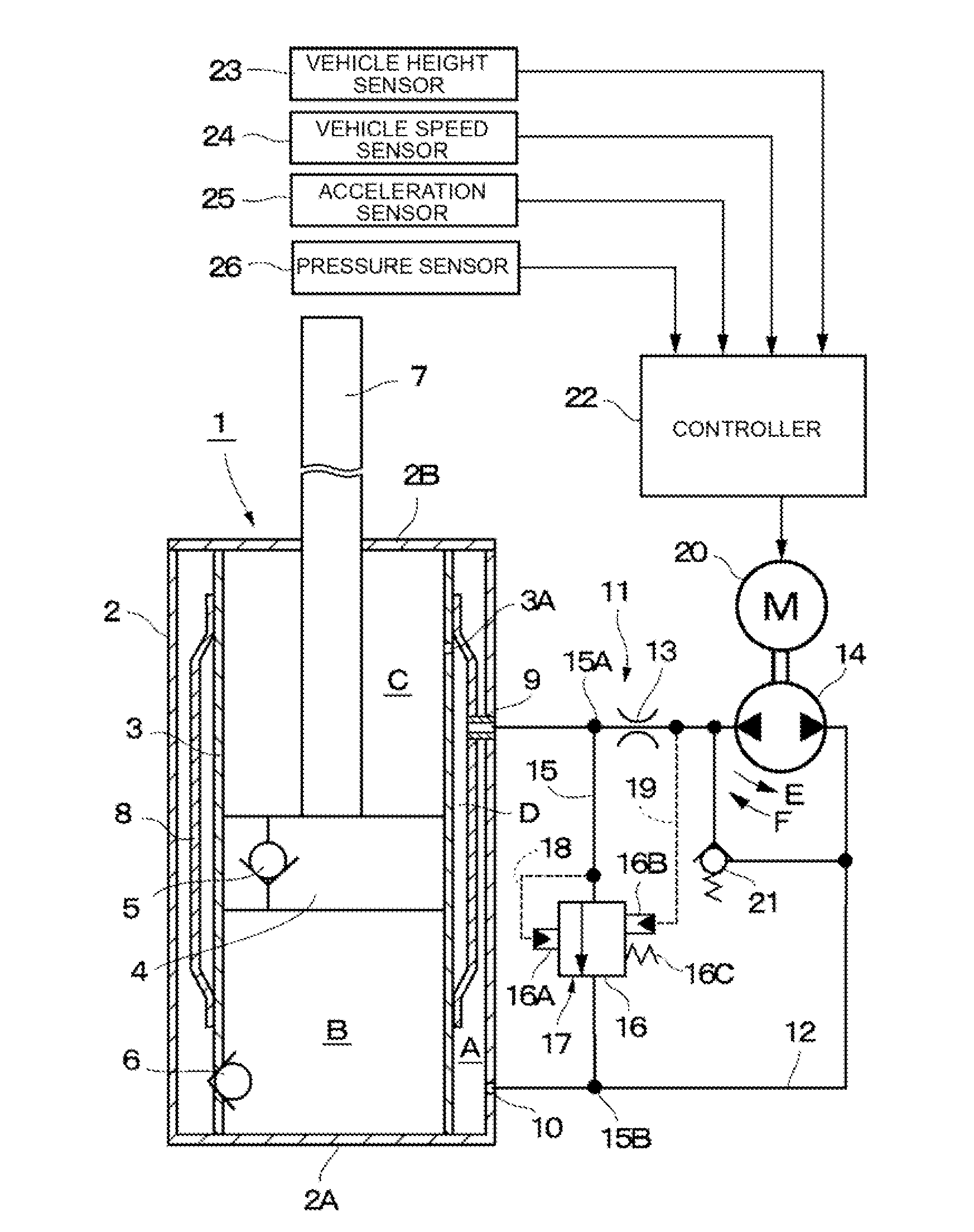
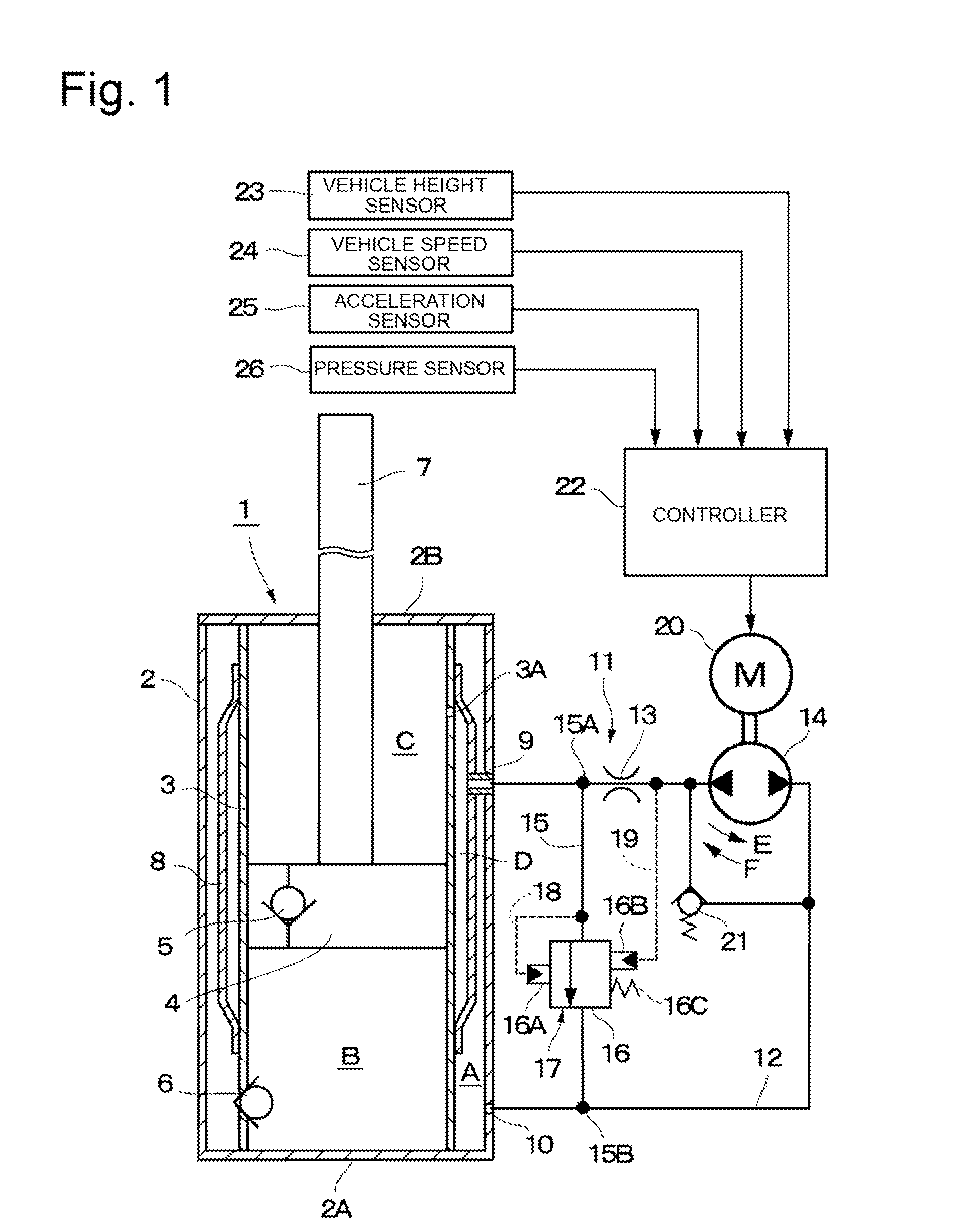
A shock absorber includes: at least one cylinder apparatus including a cylinder sealingly containing operating fluid, a piston slidably fittedly inserted in the cylinder to divide an interior of the cylinder into two chambers, and a piston rod coupled to the piston and extending to an outside of the cylinder; and at least one damping force generation mechanism connected to the cylinder apparatus, and capable of generating a damping force to be applied to a flow of the operating fluid caused by a movement of the piston and adjusting the damping force from the outside. The damping force generation mechanism includes a damping valve for generating the damping force, a pilot chamber for applying a pilot pressure by the operating fluid to the damping valve, and a pump for at least supplying or discharging the operating fluid to or from the pilot chamber.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
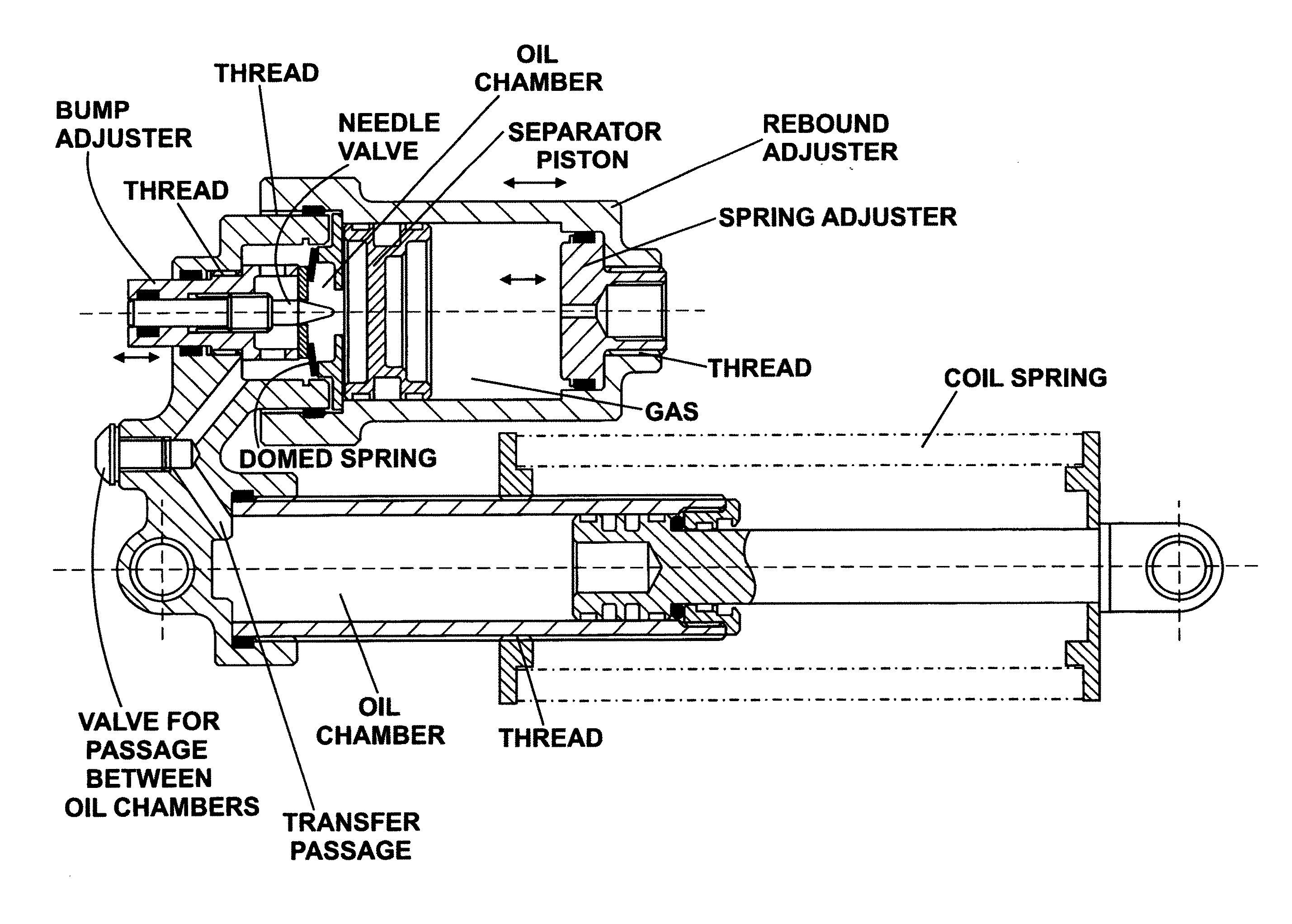
Externally adjustable internal bypass shock absorber
ActiveUS7270222B1Characteristic variesReduce the overall diameterSpringsShock absorbersReciprocating motionCoil spring
A shock absorber that combines both the suspension function and the shock absorbing function in one unit. It has an elongated shock body filled with hydraulic fluid and a piston mounted on a piston rod that reciprocally travels within the shock body. The shock body is telescopically received in a bypass cylinder body having a greater diameter that produces an annular chamber between the outer surface of the shock body and the inner surface of the bypass cylinder body. A coil spring is mounted on the outside surface of the bypass cylinder body to provide a suspension function by the shock absorber. A plurality of bypass tubes are associated with longitudinally spaced ports in the shock body. Adjuster rods are telescopically received inside the respective bypass tubes for controlling whether the individual ports are closed, partially open, or fully open. These adjuster rods would be manipulated externally of the shock absorber assembly.
Owner:AYMAR BRANDON
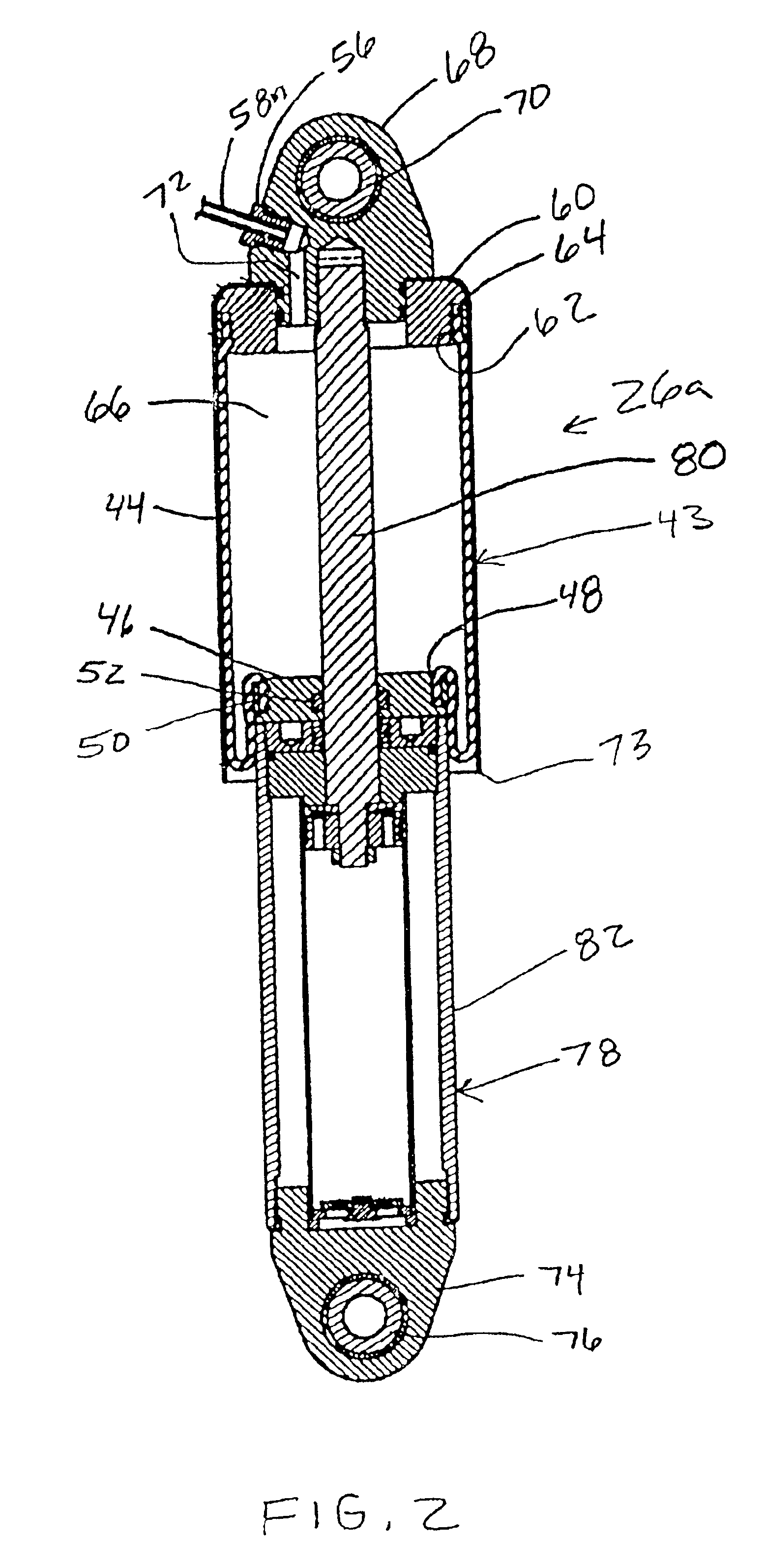
Landing gear shock absorber with variable viscosity fluid
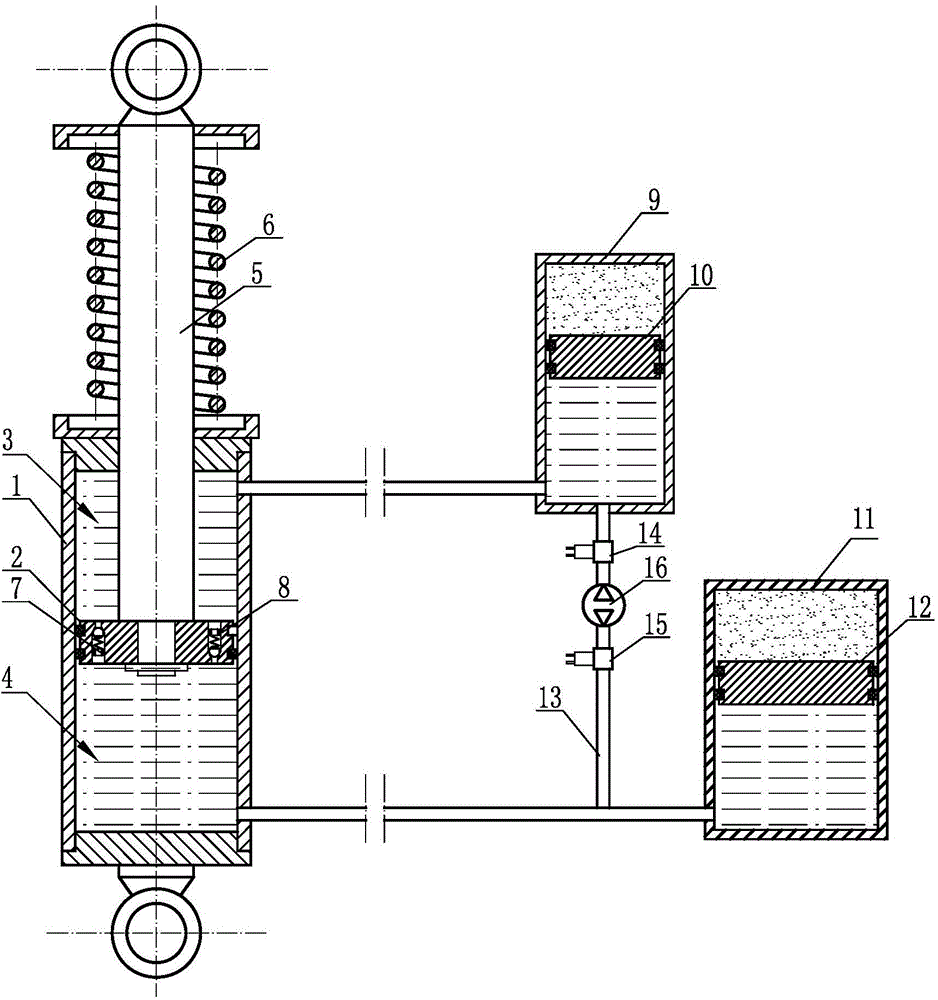
An aircraft landing gear includes a sealed cylinder divided by a cylinder head to define an upper chamber and a lower chamber. The lower chamber is further divided by a piston having a piston rod passing in a sealed manner through the lower cylinder end. The cylinder head includes one or more orifices, the opening of each containing an electromagnetic coil configured to control the viscosity of the magneto-rheological oil passing therethrough. The electrical current through the electromagnetic coil is continually controlled by a microcomputer with attached sensors for piston position and pressure between the desired piston and the cylinder head, such that the pressure between the piston and the cylinder head decelerates the aircraft evenly throughout the desired piston stroke. The pressure also is limited to a desired maximum level so that, in a severe crash, the shock absorber will absorb significant energy before it fails structurally.
Owner:JAUNT AIR MOBILITY LLC
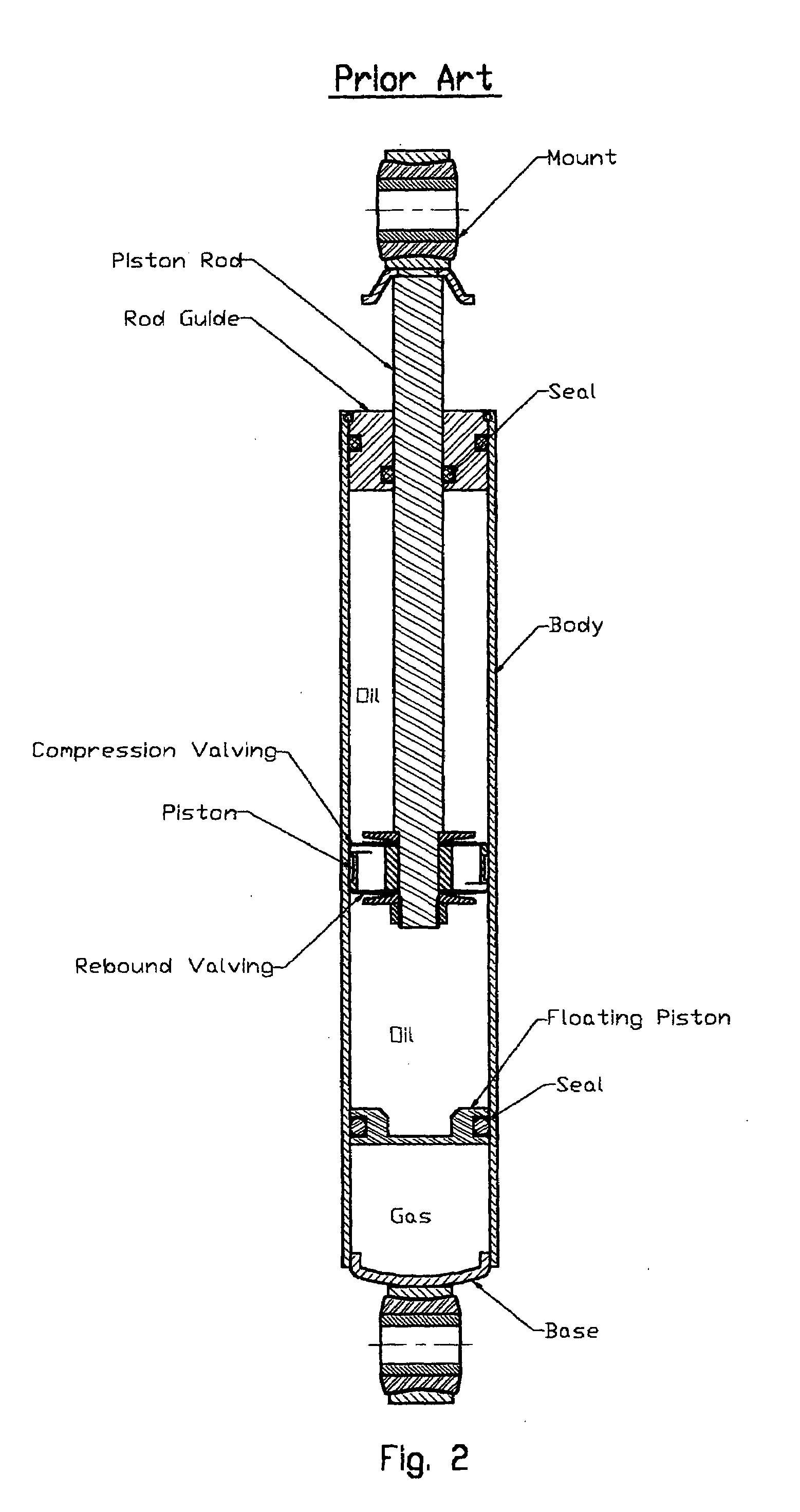
Rod guide and seal system for gas filled shock absorbers
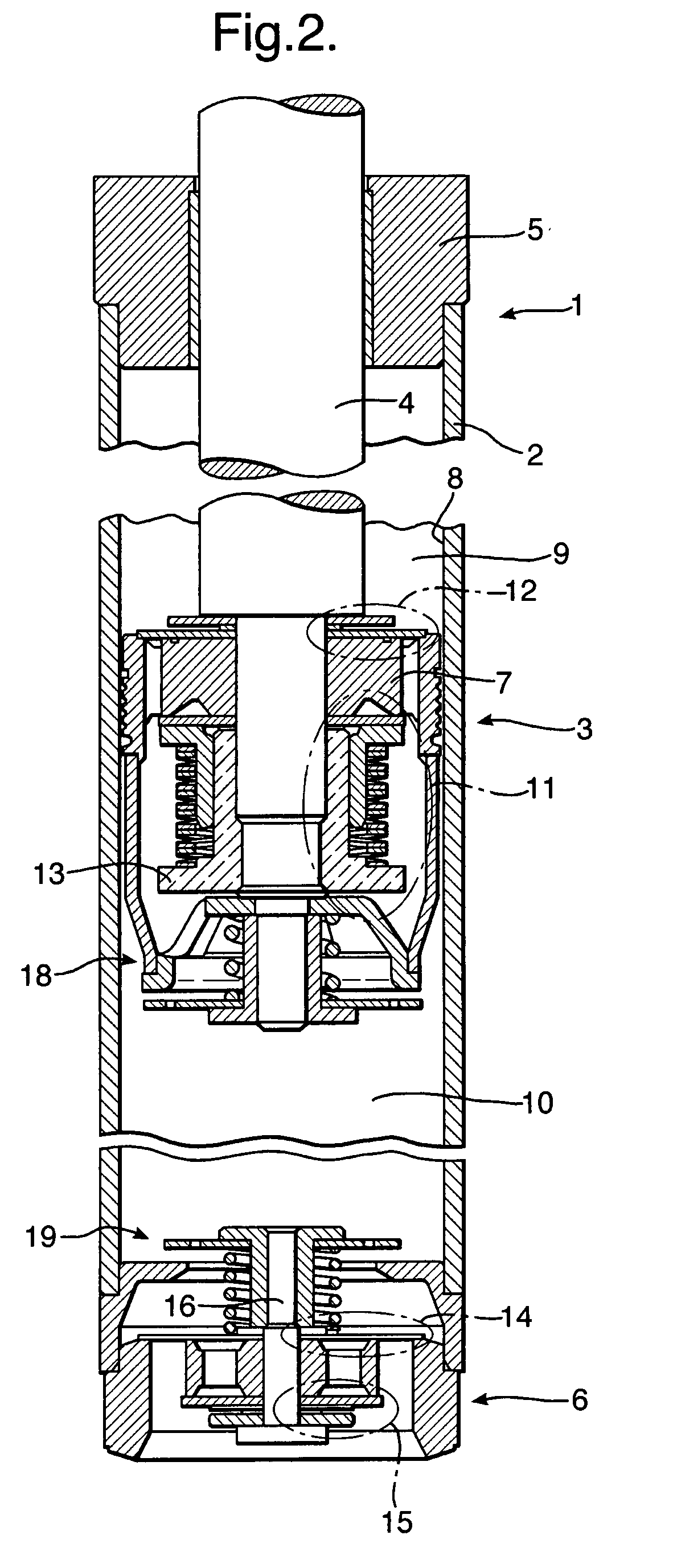
A gas shock absorber has a pressure tube which defines a working chamber. A piston assembly divides the working chamber into an upper working chamber and a lower working chamber. A plurality of extension passages extend through the piston assembly and are opened and closed by an extension valve assembly. A plurality of compression passages extend through the piston assembly and are opened and closed by a compression valve assembly. A rod guide assembly is located between the pressure tube and the piston rod. The rod guide assembly includes an oil chamber for sealing and lubricating the piston rod. An axially movable piston maintains the pressure within the oil chamber equal to the pressure in the upper working chamber.
Owner:TENNECO AUTOMOTIVE OPERATING CO INC
Oil-gas spring
InactiveCN1699780AFew leaksEasy to useResilient suspensionsGas and liquid based dampersAutomatic controlGas spring
The invention discloses a gas oil spring, especially a gas oil spring that can control the extension length and change pressure and support force automatically as the spring element on the vehicle suspensions. The outer cylinder store the oil and high pressure air, the inner cylinder is used as working cylinder; pressing the oil out of the outer cylinder to improve the oil, air is compressed or expansion and has the function of spring. When the piston moves up and down, draw the outside oil into the outer cylinder to enhance the extension distance and attenuate part of the extension power to play the function of buffer. When the extension distance get the limit height, the decompression valve is driven to exhaust the additional oil in the outer cylinder, make the extension height and support force adapt the load status under the function of the oil cycling.
Owner:仇恒超
Shock absorber with adjustable valving
InactiveUS6851528B2Simple and cost-effectiveImprove featuresSpringsLiquid based dampersCompressed fluidReservoir fluid
A shock absorber includes a shock rod and piston which are disposed within a fluid chamber within a shock body. The piston separates the shock body fluid chamber into a compression fluid chamber and a rebound fluid chamber. A reservoir fluid chamber accommodates the entry of the shock rod into the fluid chamber as the shock absorber compresses under shock forces. The compression fluid chamber is in fluid communication with the reservoir fluid chamber through a third chamber or passage. A first valve may control passage of fluid from the compression fluid chamber into the passage. Second and third valves may be disposed within the passage in parallel with each other and in series with the first valve. The third valve may include an easily accessible knob disposed outside the shock body.
Owner:BOMBARDIER RECREATIONAL PROD INC
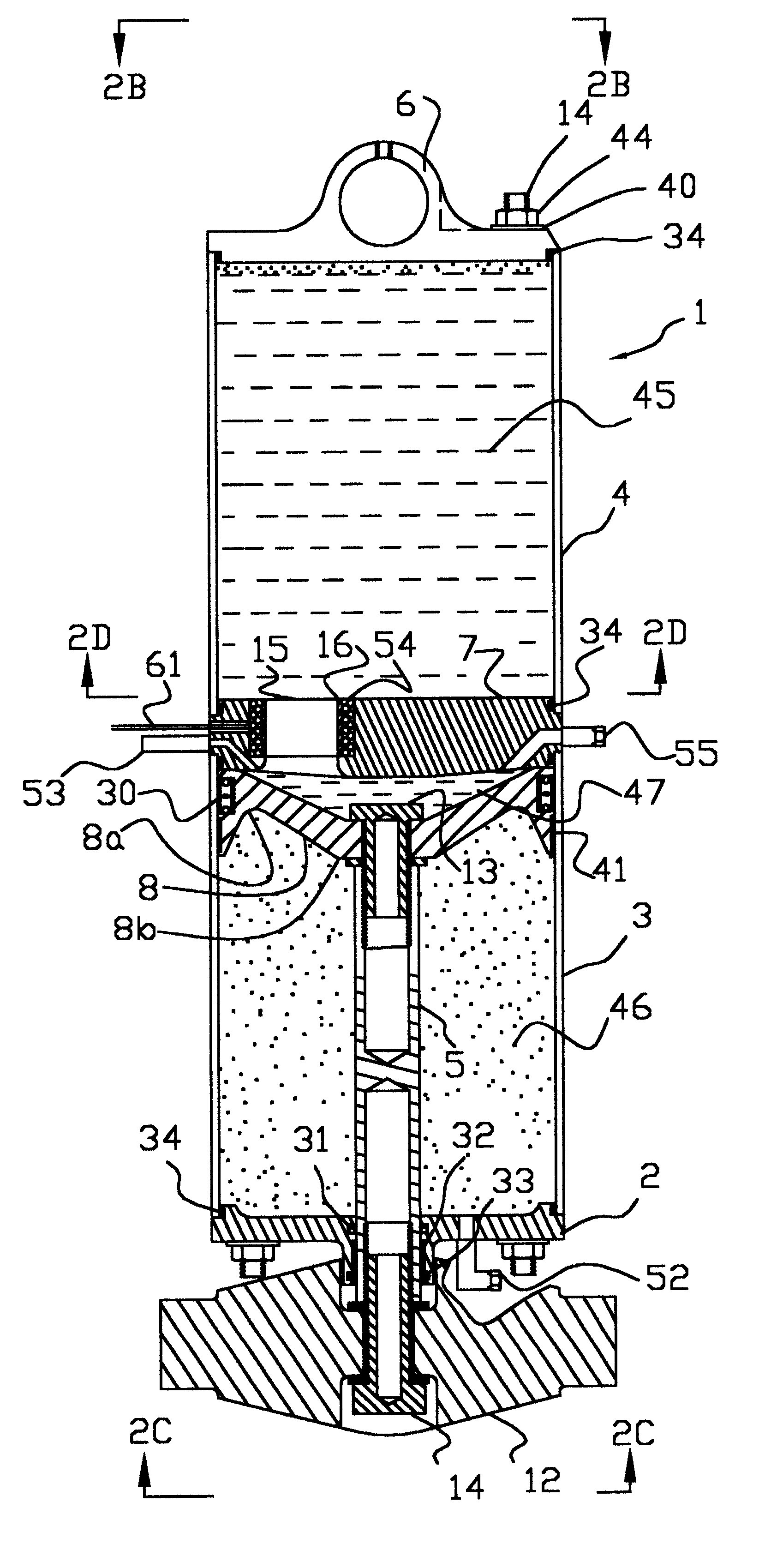
Hydraulic suspension damper
InactiveUS20080121478A1Minimize production specific lossLow costSpringsShock absorbersEngineeringPiston rod
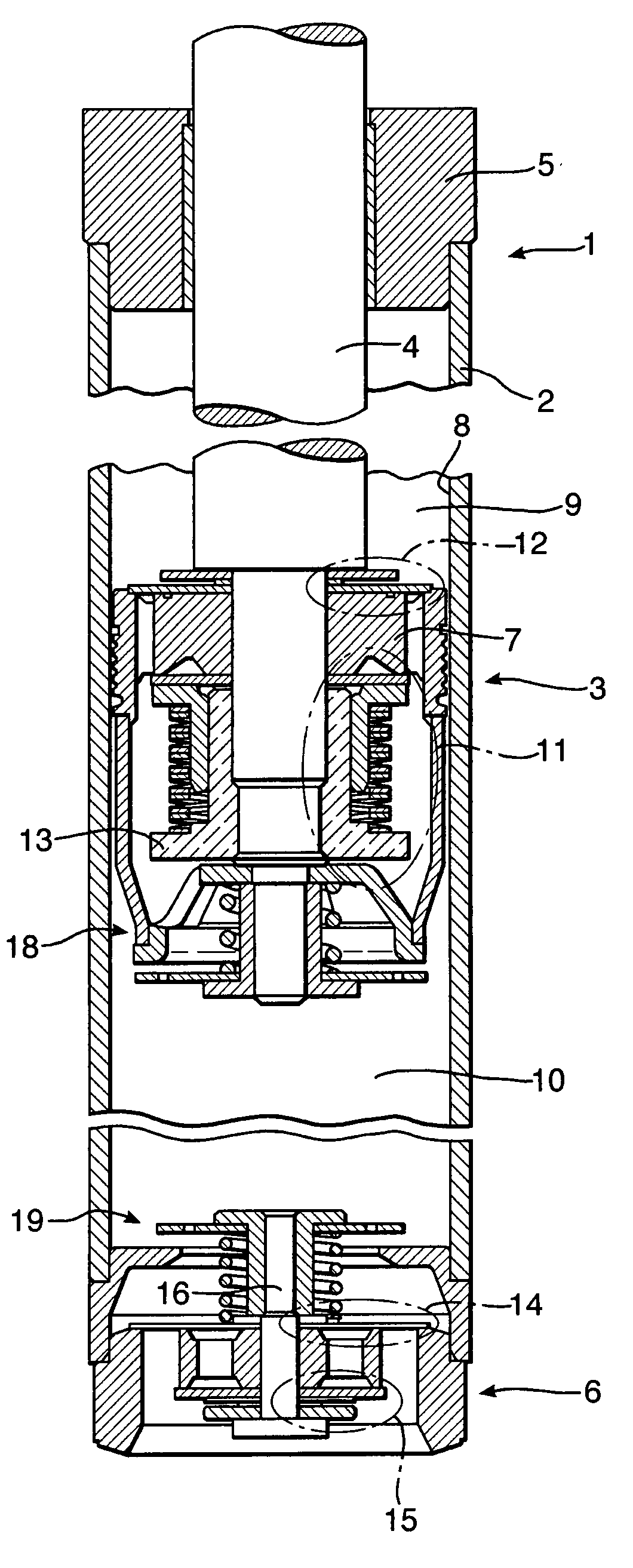
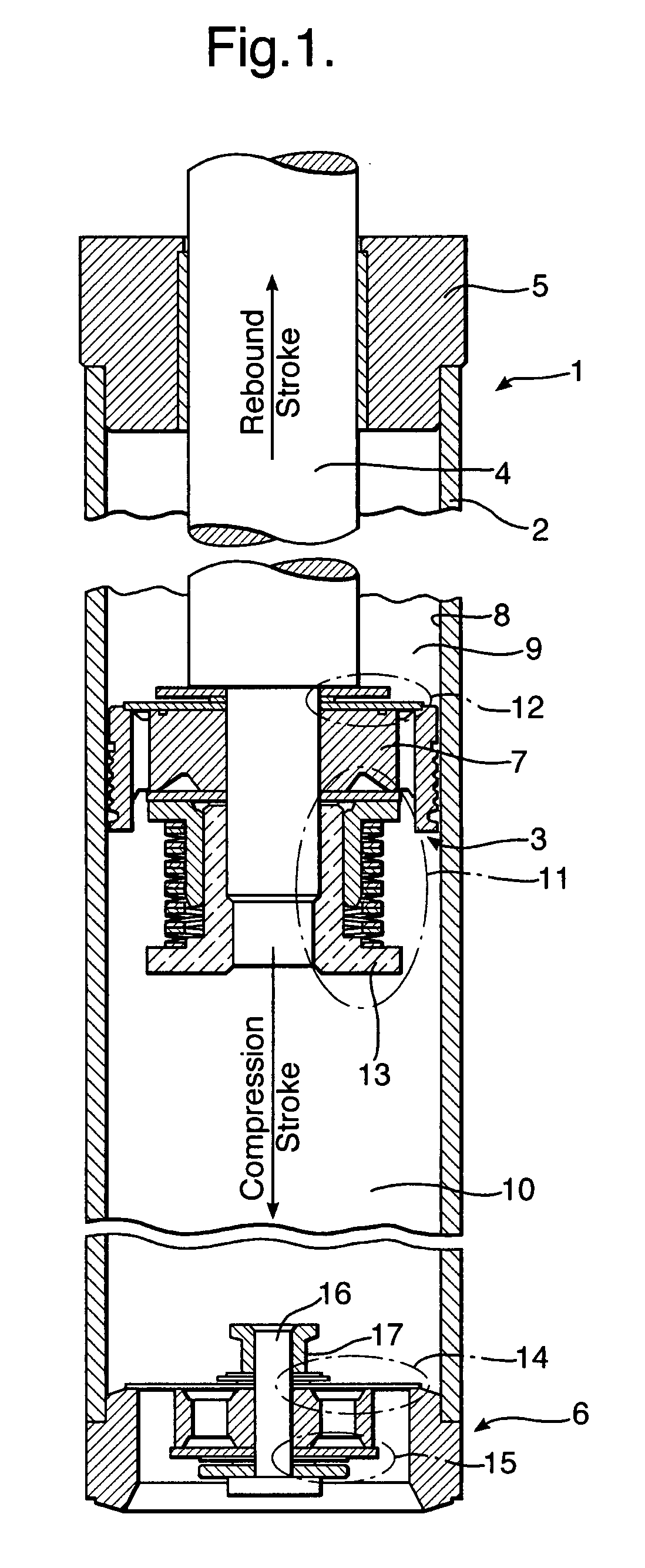
The invention relates to a suspension hydraulic damper (1) comprising a tube (2) filled with working liquid, inside of which a slidable piston assembly (3), provided with compression (12) and rebound (11) valve assemblies and attached to a piston rod led outside the damper, is placed, and at least one additional compression valve system (18, 19). To increase an amount of dissipated energy during extremely fast compression strokes the compression valve system (18, 19) comprises at least one substantially thin closing element, preferably in a form of a flat floating disc (24, 34), having an outside diameter less than the inner diameter of the tube (2) and being axially slidable with respect to the piston rod (4) axis, a spring (23, 33) surrounding the piston rod (4) axis and pressing the closing element against a retainer (26, 35) into open position, an abutting surface (28, 38) for the closing element (24, 34) in closed position, and at least one passage (25, 31) for the flow of damping medium in closed position.
Owner:BWI +1
Air spring and shock absorber assembly for use in suspension systems
An air spring and shock absorber unit for use in vehicle suspension systems or cab suspension systems comprising a shock absorber mounted within an air spring. The lower end of the air spring bellows is attached to the air spring piston in such a manner which enables the lower end of the bellows to be disconnected from the air spring piston without damaging the crimp ring which connects the bellows to the piston.
Owner:LINK MFG
Suspension systems
A shock absorber assembly comprises a piston and cylinder arrangement, a damping-fluid chamber and a damping valve arrangement which is located in the damping fluid chamber and serves to divide the chamber into sub-chambers. The assembly is such that in use the valve arrangement regulates the flow of fluid between the sub-chambers.
Owner:HUNTER
Air-bag suspension system
InactiveUS6905126B1Prevents bottoming-outEasy to replacePassenger cyclesChildren cyclesSolenoid valveOn board
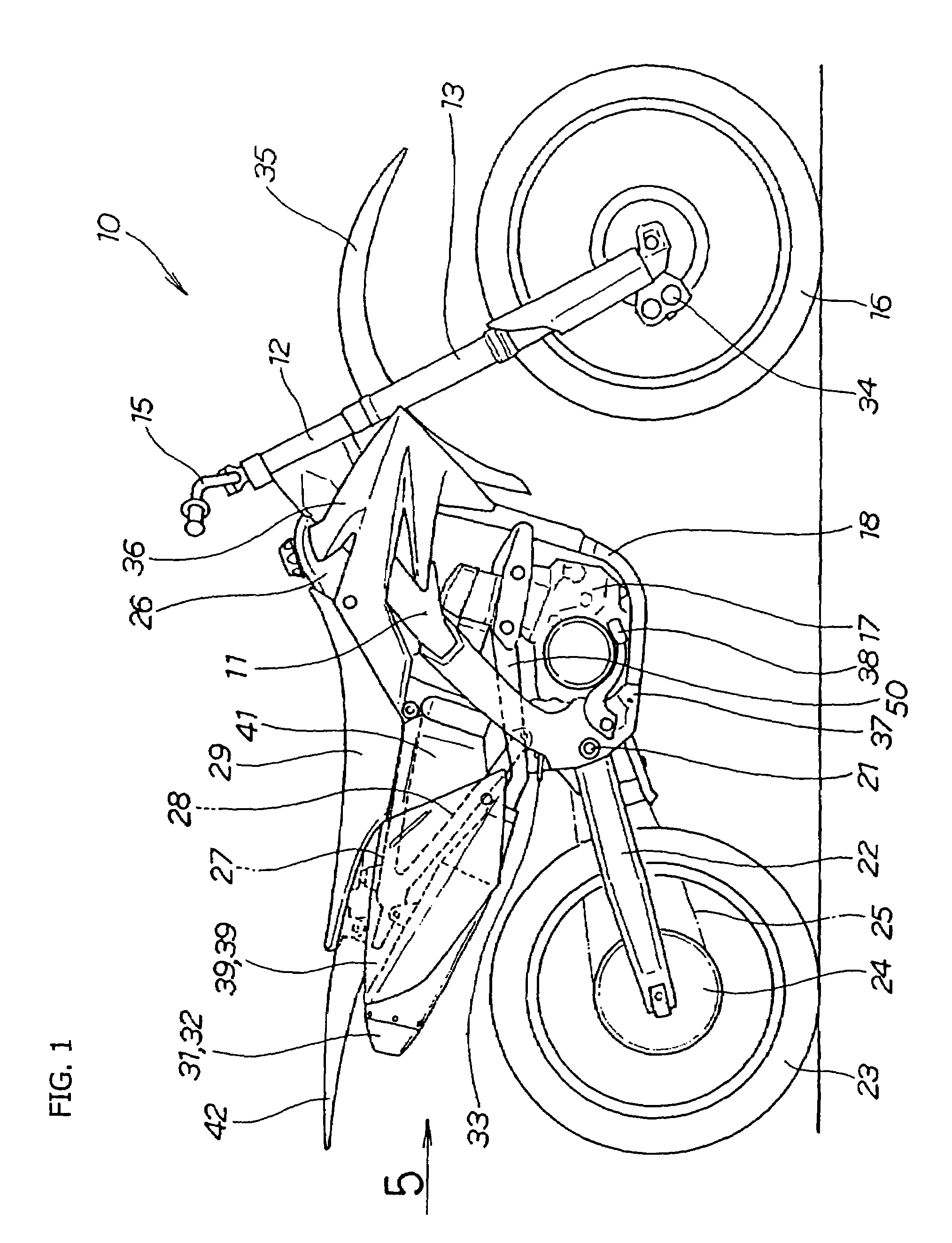
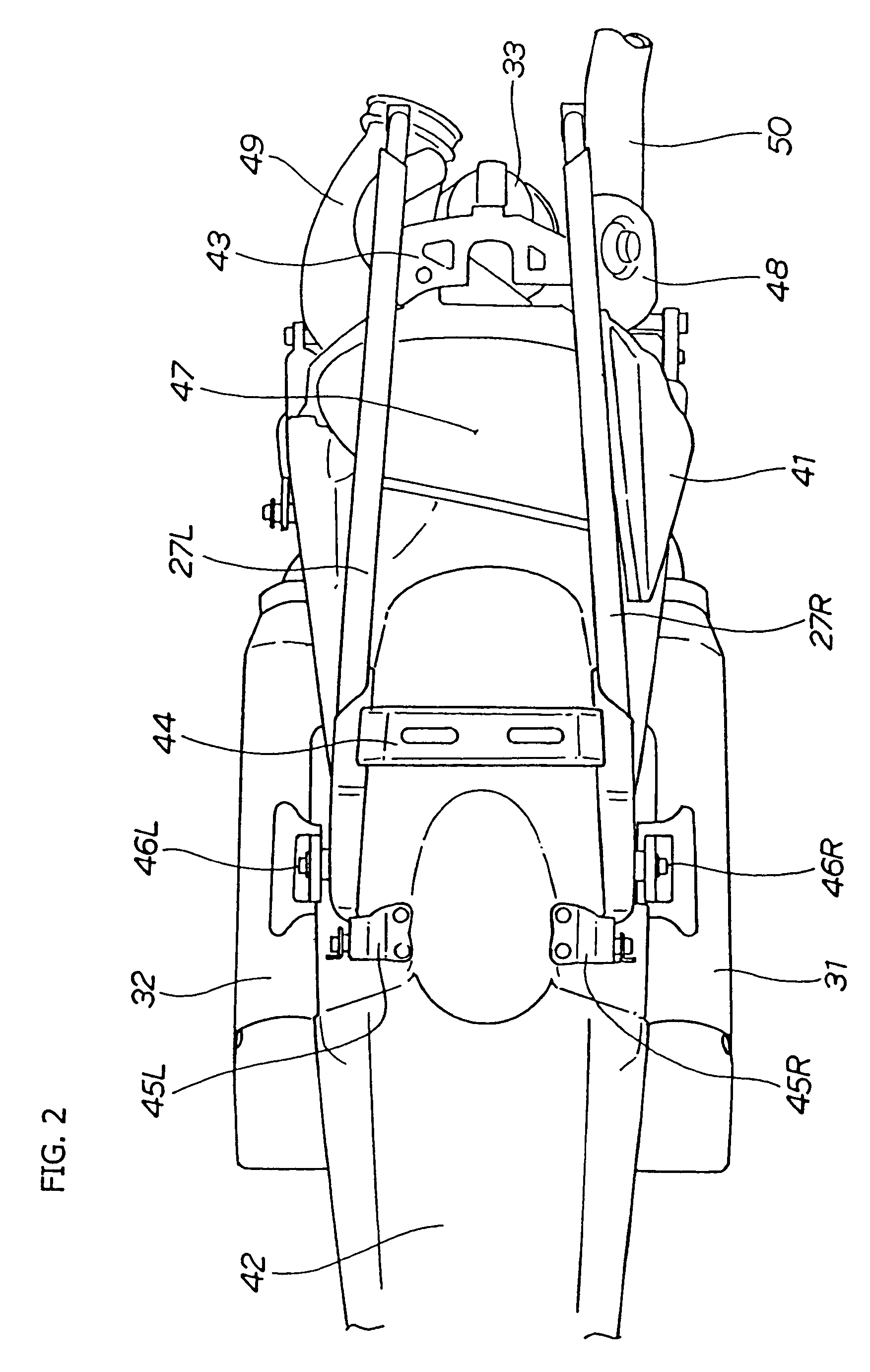
An air-bag suspension system for a motorcycle having a motorcycle main frame, fender struts extending outwardly from the main frame, and a swing arm pivotally mounted to the main frame about a pivot axis. The air-bag suspension system includes shock absorber assemblies each having an air-bag. The air in the air-bags is generated by an on-board compressor and released through a solenoid valve. The air-bag suspension system replaces the standard coil spring hydraulic suspension commonly found on motorcycles and provides a greater range of adjustment, remotely controlled, while the motorcycle is in use. The air-bag suspension system accommodates heavier loads than the stock suspension systems when the air-bags are fully inflated; and when deflated completely, provide an aesthetically pleasing stance. The range of wheel travel provided allows the rider to adjust the suspension to provide the smoothest ride coupled with an increased load capacity or adverse road conditions.
Owner:AFCO PERFORMANCE GRP LLC
Servicing of landing gear shock absorbers
A method and portable apparatus for servicing a shock absorber on a landing gear assembly of an aircraft in a weight-on-wheels state is disclosed. The shock absorber includes at least one chamber containing both hydraulic fluid and a gas in fluid communication with each other. The apparatus includes a source of gas and a source of hydraulic fluid. The amount of hydraulic fluid in the chamber is corrected, preferably such that the chamber is then filled with a known amount of degassed hydraulic fluid. A pre-set mass of gas is then delivered into the chamber under the control of a gas delivery system of the portable apparatus. More accurate servicing of a shock absorber may thus be provided since account is additionally taken of gas dissolved in hydraulic fluid. By delivering a pre-set mass of gas into the chamber, there is no need to rely on a measure of gas pressure or H-dimension (h) when servicing the shock absorber.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Automobile active self-adaption type shock absorber
The invention discloses an automobile active self-adaption type shock absorber comprising a hydraulic oil cylinder, a piston, a piston rod and a shock absorption spring. The hydraulic oil cylinder is spaced by the piston into an upper oil cavity and a lower oil cavity. The piston is provided with an upstream one-way damping pressure valve and a downstream one-way damping pressure valve. The upper oil cavity is communicated with an upper oil cavity energy accumulator. The lower oil cavity is communicated with a lower oil cavity energy accumulator. A pressure regulating device is connected between the upper oil cavity energy accumulator and the lower oil cavity energy accumulator. When an automobile body vibrates downwards, hydraulic oil in the lower oil cavity flows back to the lower oil cavity energy accumulator through an oil tube, the shock absorption effect of an air spring is played, the upstream one-way damping pressure valve is opened, and vibration energy of the automobile body is absorbed through damping of the upstream one-way damping pressure valve, so that the bearing capacity of the air spring reaches the maximum and will not increase any more, the peak of impact of the shock absorber system on an automobile frame is reduced remarkably, and vibration of the automobile body is absorbed actively; when the automobile body vibrates upwards and tires leave the automobile frame, the process is contrary, active self-adaption shock absorption is achieved, and vibration of the automobile body is reduced effectively.
Owner:刁久新
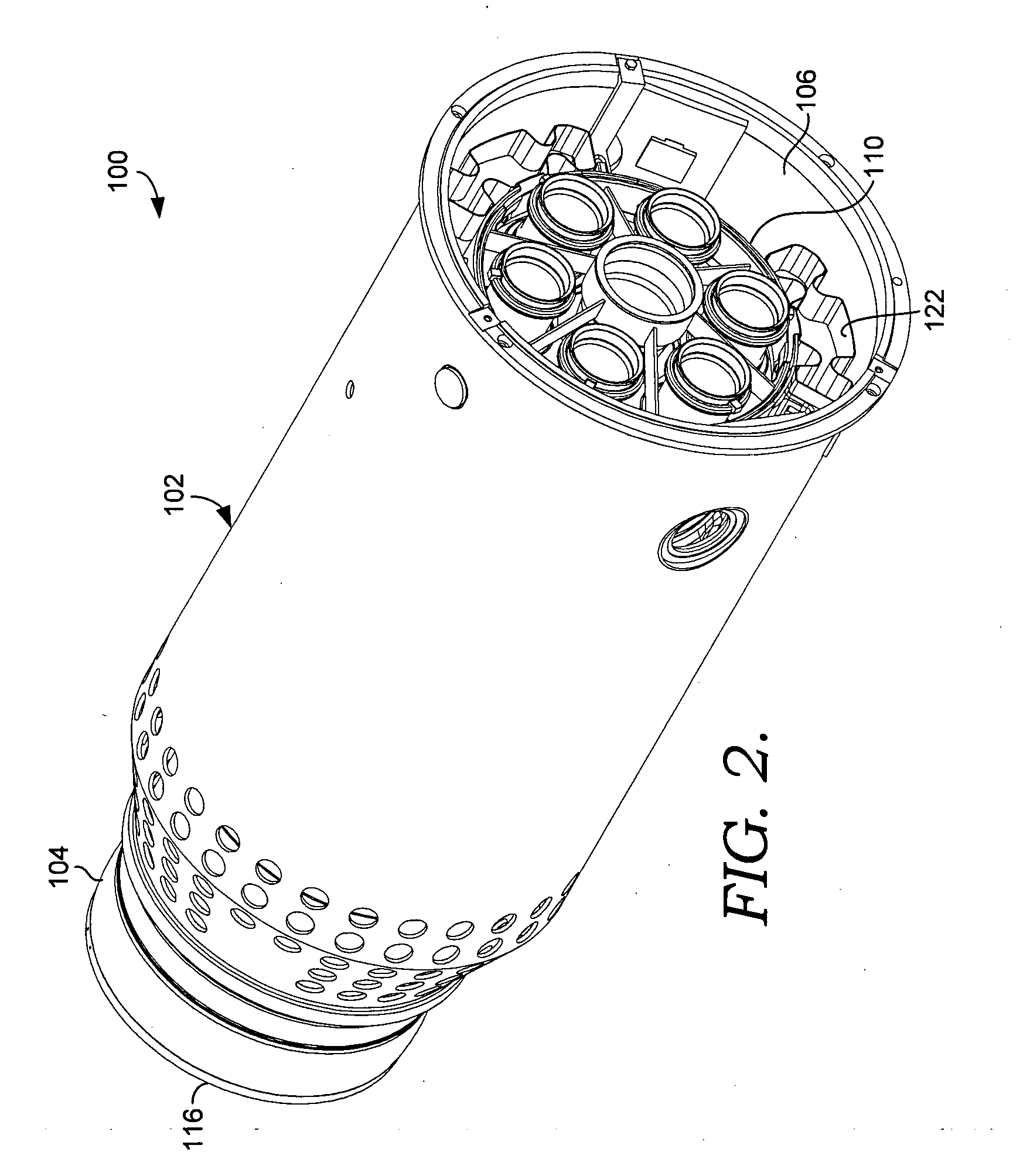
Exhaust system for a motorcycle, and motorcycle including same
ActiveUS7364010B2Increase in the allowable marginExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusMufflerShock absorber
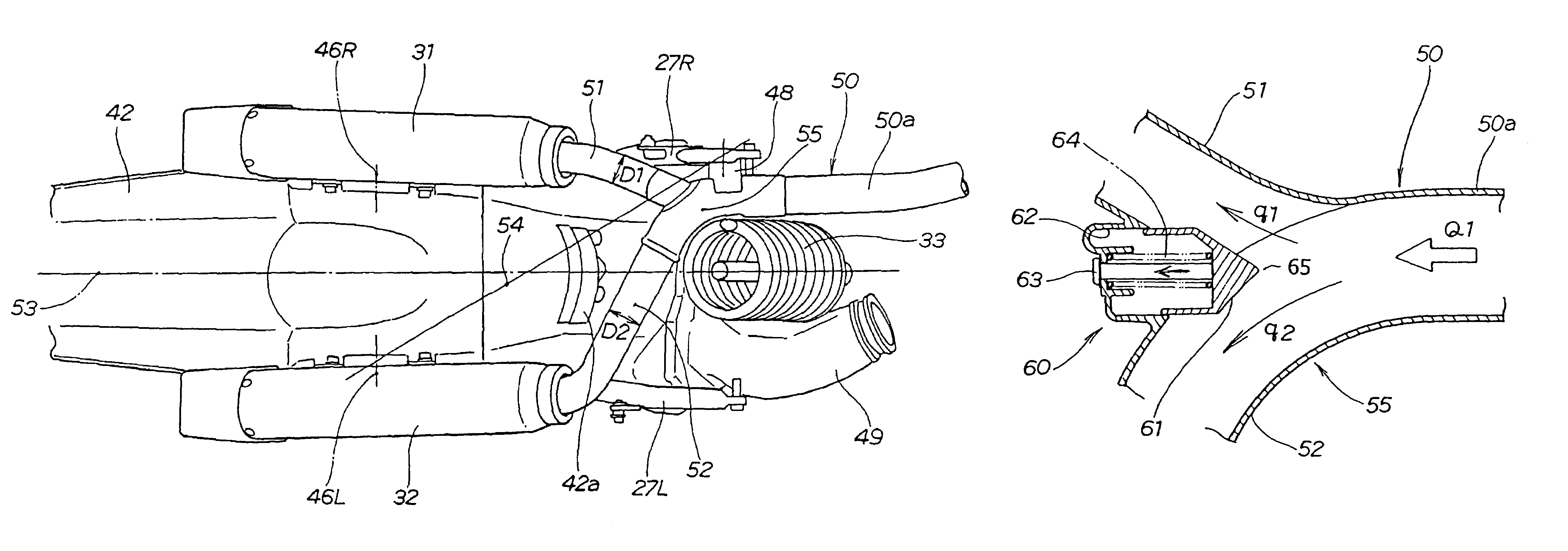
A motorcycle, having both left and right mufflers, has an exhaust structure which enables an increase in the allowable margin through which the rear wheel is permitted to rise. A main exhaust pipe extends from an engine to one side of a shock absorber disposed on the rear side of the engine. The main exhaust pipe is branched in the vicinity of the shock absorber into a first branch pipe and a second branch pipe. The first branch pipe is connected to a first muffler disposed on the same side as the main exhaust pipe, and the second branch pipe is connected to a second muffler after passing between the shock absorber and a rear wheel to the opposed side of the vehicle body. The second branch pipe does not interfere with the rising motion of the rear wheel, and a sufficient allowable margin is secured for the rear wheel.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
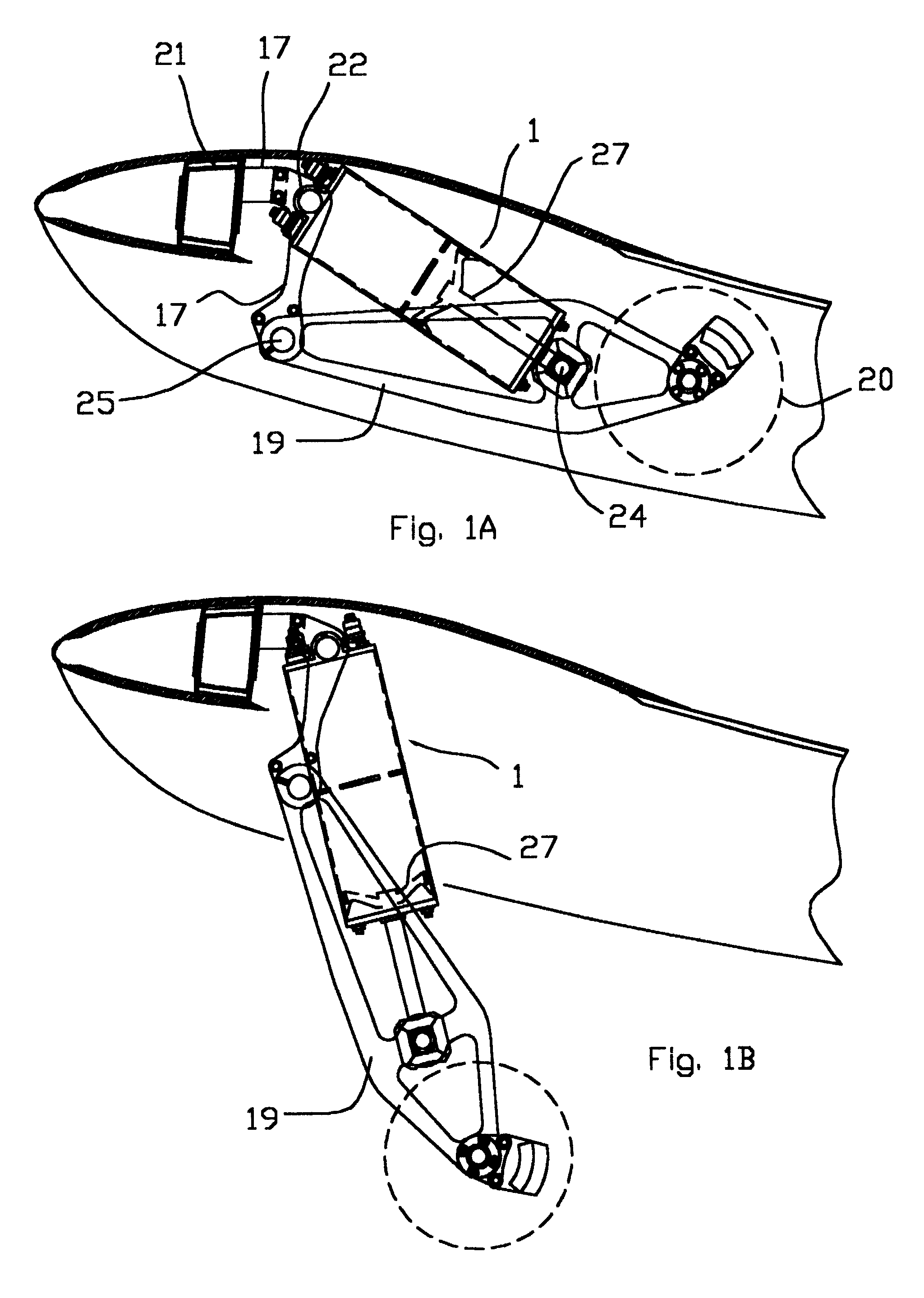
Vehicle steering damper, steering damper kit for motorcycle, and motorcycle incorporating same
InactiveUS7021433B2Efficient use ofEffective of gapLiquid resistance brakesSpringsHydraulic fluidControl valves
A steering damper in a motorcycle includes a vane partitioning a chamber in a damper housing into two oil chambers, wherein hydraulic fluid flows between the two chambers to generate attenuating force. The steering damper also includes a damper shaft connected to the vane and supporting the vane for rocking motion with respect to the housing, and a hydraulic pressure control valve. The housing is attached to a head pipe, and the damper shaft is attached to a steering system. When the head pipe is to be attached to the housing, the housing is extended rearwardly behind a top bridge, and a linear solenoid for driving and controlling the hydraulic pressure control valve is attached to the housing and disposed below the extension thereof.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
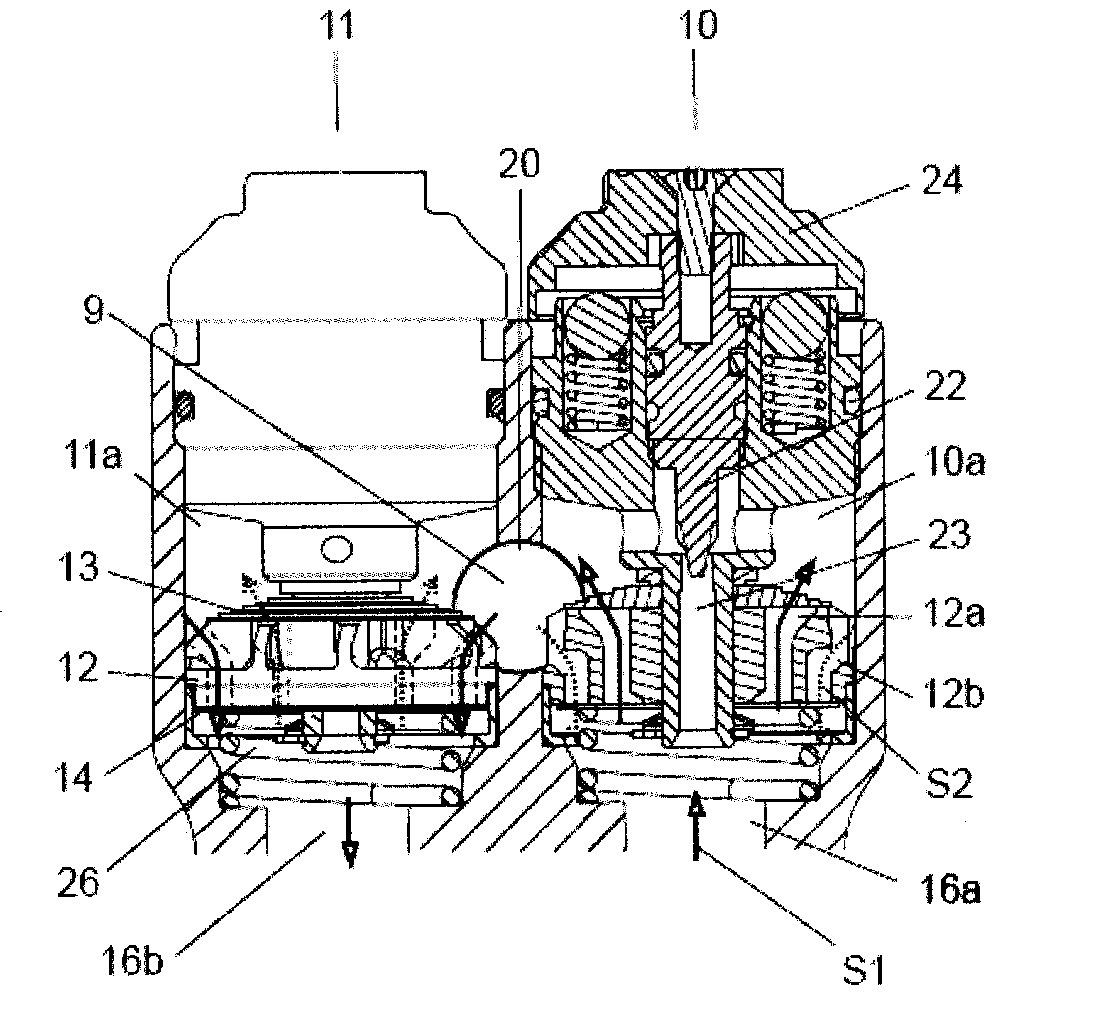
Solenoid valve of shock absorber
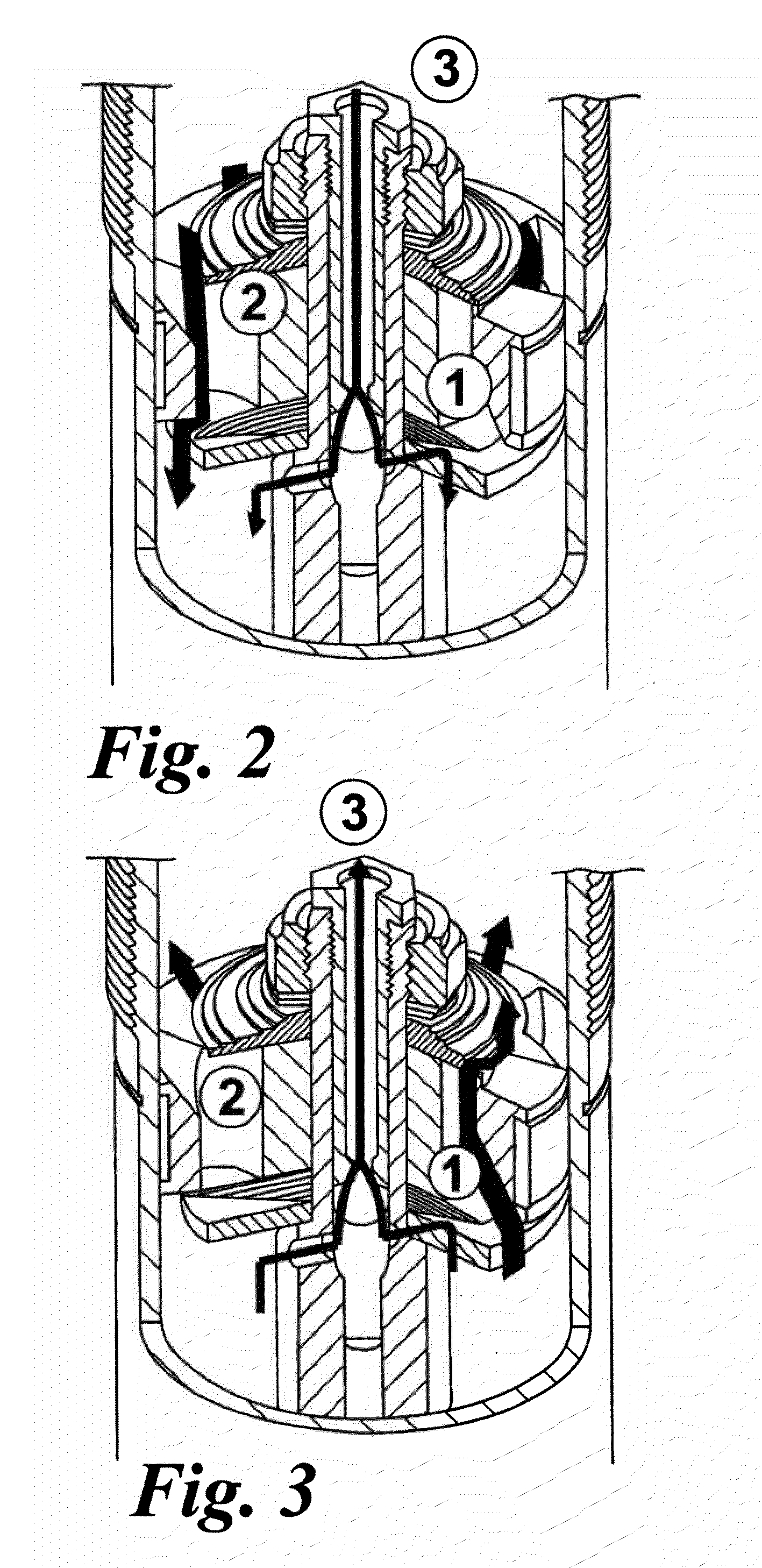
The present invention relates to a solenoid valve configured to be mounted to a shock absorber of a vehicle to adjust damping force. solenoid valve of a shock absorber in which a damping force is adjusted through adjustment of back pressure against a disc valve. The solenoid valve includes a back pressure chamber for generating back pressure against the disc valve by a fluid introduced through a back pressure adjusting flow passage, and a spool moved in a spool guide by operation of a solenoid to control opening / closing or opening rate of the back pressure adjusting flow passage. The back pressure adjusting flow passage includes a variable orifice with an opening rate of the variable orifice being adjusted by the spool and the spool guide, the back pressure chamber, and a fixed orifice formed on the disc valve.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Pneumatic tire with noise damper
ActiveUS7188652B2Avoid thermal failureHigh speed conditions can be effectively preventedSpecial tyresInflatable tyresEngineeringCellular material
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
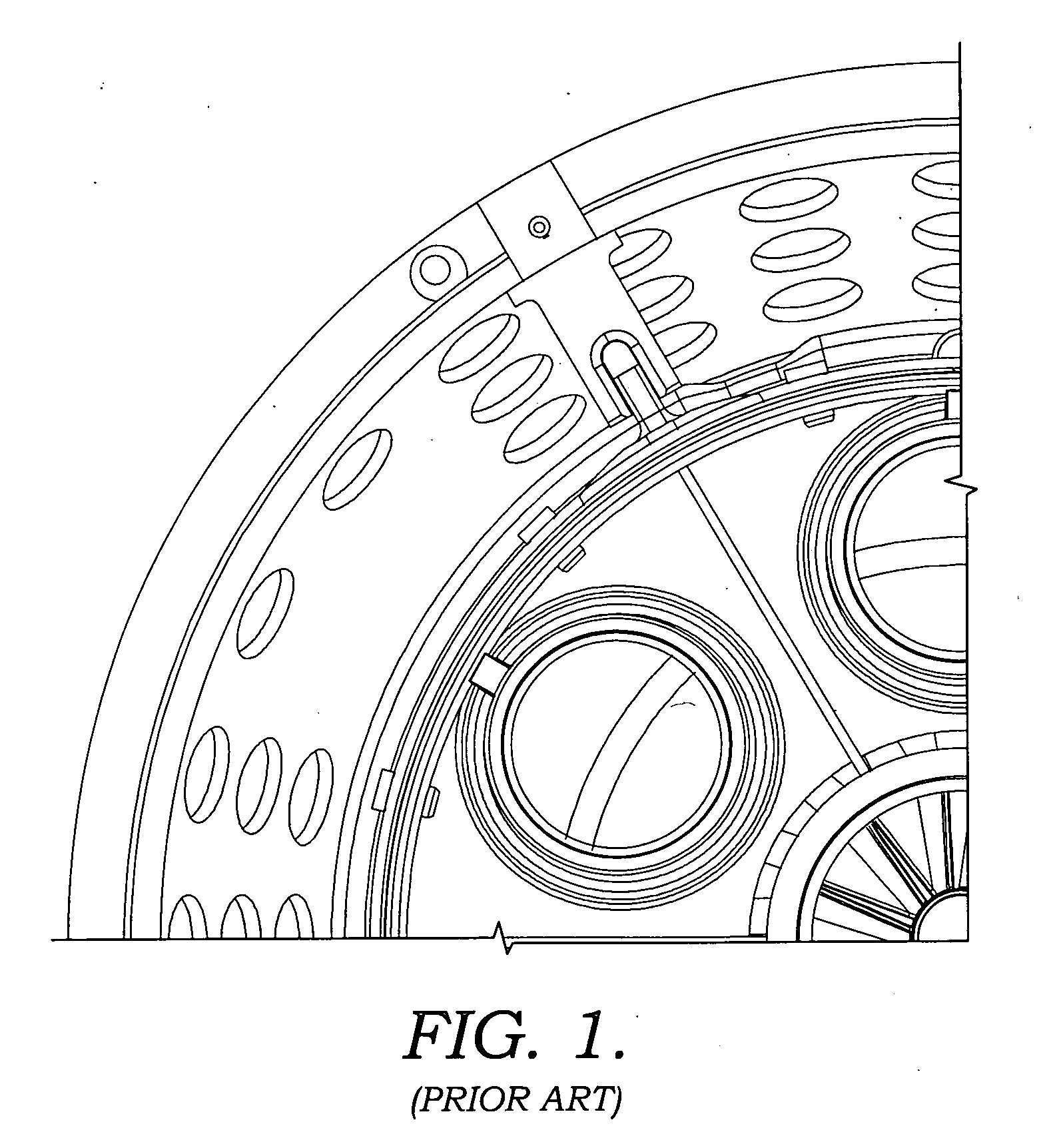
Combustion liner damper
ActiveUS20100089068A1Reduce vibrationReduce the overall heightPortable framesContinuous combustion chamberCombustorEngineering
The present invention are directed towards a system and method for providing a way of reducing the vibrations and wear between mating components of a gas turbine combustor. The gas turbine combustor includes a flow sleeve having a plurality of liner stops and a combustion liner located radially within the flow sleeve. Spring dampers are positioned between the combustion liner and the flow sleeve to restrict the relative movement between the flow sleeve and the combustion liner and dampen vibrations at their assembly location. The spring dampers are capable of compressing to permit thermal growth between the combustion liner and flow sleeve.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA SWITZERLAND AG
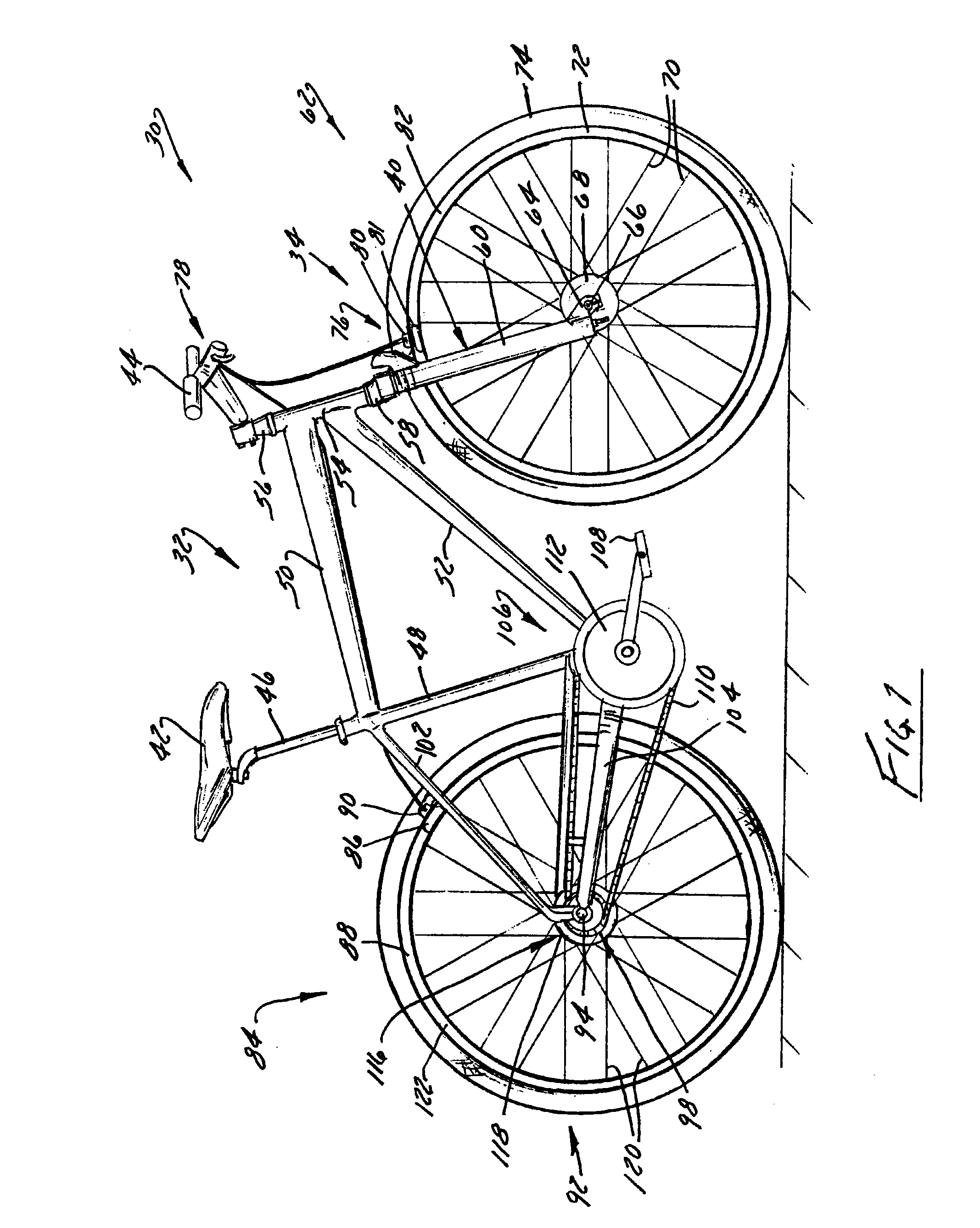
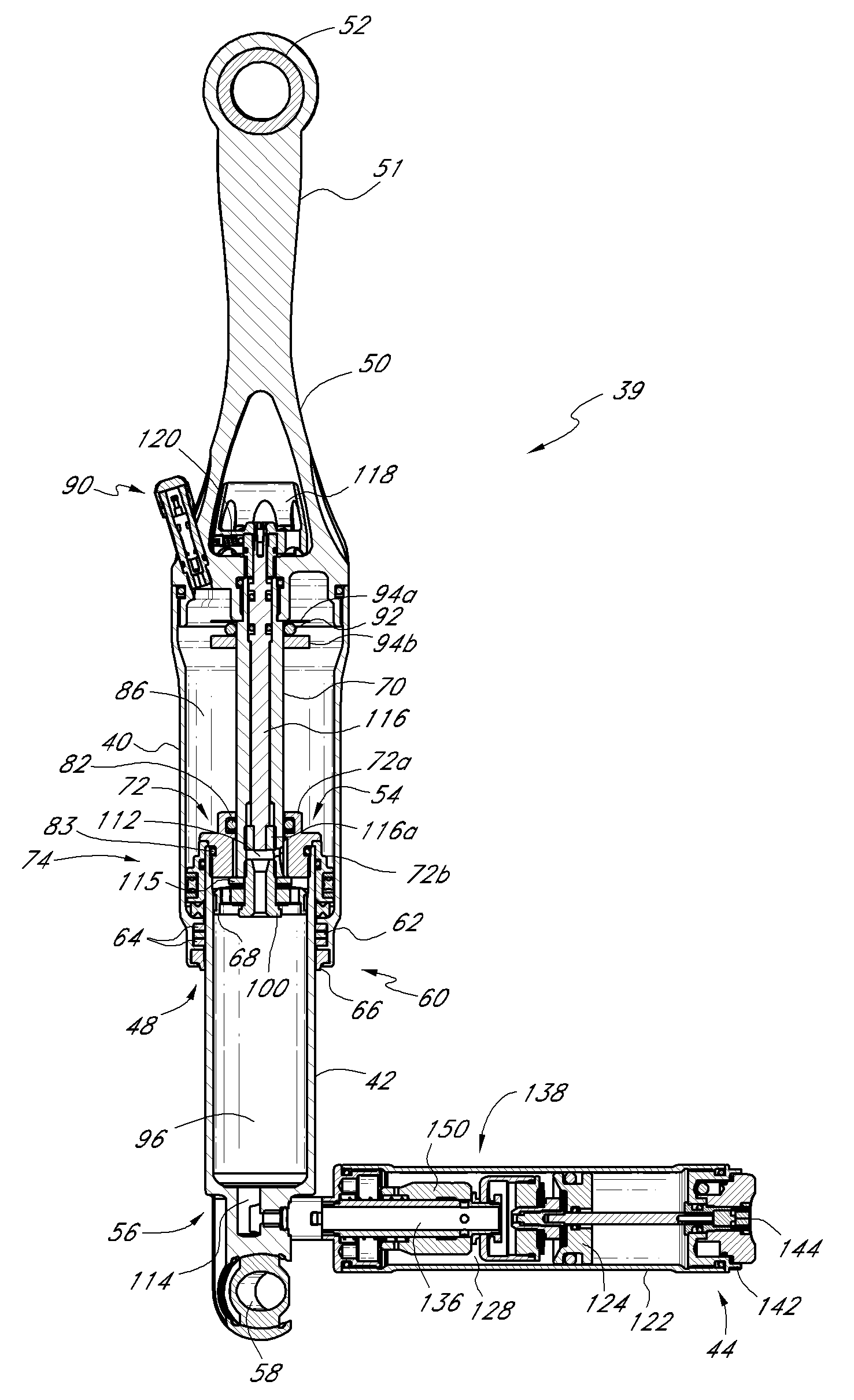
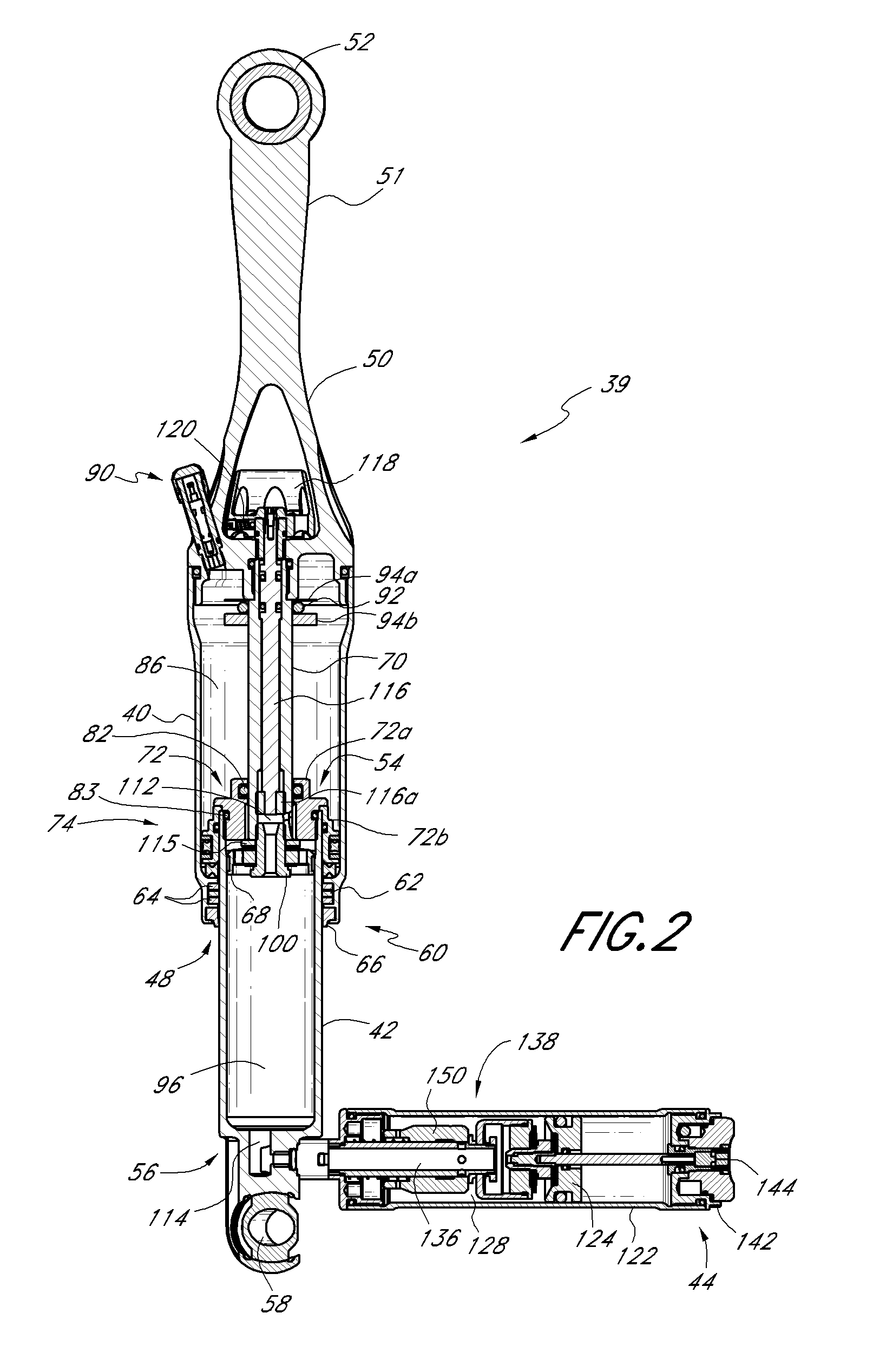
Bicycle shock assemblies with plunger operated valve arrangement
ActiveUS20100314209A1Alter performance of shockOvercomes drawbackWheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionEngineeringPiston
A shock absorber, which is particularly applicable to bicycles, includes a secondary chamber whose volume selectively contributes to a volume associated with a primary chamber of the shock. A piston is supported by a compression rod and cooperates with a shock tube to define the primary chamber. The secondary chamber is fluidly isolated from the primary chamber by a valve arrangement positioned proximate the piston. A plunger extends along a longitudinal length of the shock and forms or interacts with the valve arrangement such that the secondary chamber is selectively fluidly connected to the primary chamber so the primary and secondary chambers of the shock assembly contribute to the performance of the shock for a selected portion of shock travel.
Owner:TREK BICYCLE CORPORATION
Hydraulic locating type damping changing impact damper
InactiveCN101178108AGood cushioning propertiesReduce vibration energySpringsLiquid based dampersDamping functionInlet valve
The invention relates to an automobile suspension damper hydraulic position limit technology, in particular to a hydraulic position limit variable damper which can have the function of a normal damper and also can replace an elastic position limiter made of rubber in a normal suspension. The invention comprises a damper working cylinder, an oil storage cylinder sleeved at the external side of the damper working cylinder, a main piston matched with the damper working cylinder, and a compressed unloading valve and an oil inlet valve arranged on a bottom valve seat of the damper working cylinder. The invention is characterized in that a floating piston with an axial perforated oil liquid main passage at the middle part is arranged between the main piston and the bottom valve seat; the periphery of the floating piston oil liquid main passage is provided with a position limit damping hole; a position limit spring is arranged between the bottom valve seat and the floating piston. The invention can generate normal damping function, and can replace the elastic position limiter in the normal suspension made of rubber. The invention has better damping characteristic compared with the rubber position limiter.
Owner:郭孔辉
Damping force adjustable fluid pressure shock absorber
InactiveUS20090272611A1Stable damping forceAvoid drastic changesSpringsShock absorbersInternal pressureEngineering
A first piston and a second piston coupled to a piston rod are fitted in a cylinder, and an intermediate chamber is formed between the first and second pistons. A compression-side check valve and an extension-side check valve are provided at the first piston and the second piston. An extension-side main valve and a compression-side main valve are disposed in the intermediate chamber. A downstream side of a damping force adjusting valve is connected to the intermediate chamber. Inner pressures of an extension-side backpressure chamber and a compression-side backpressure chamber are adjusted by the damping force adjusting valve, whereby valve opening of the extension-side and compression-side main valves is controlled. Hydraulic fluid of the downstream side of the damping force adjusting valve is first sent into the intermediate chamber, and then is sent to a cylinder upper chamber or a cylinder lower chamber. Due to this arrangement, it is possible to prevent a sudden drastic change in a hydraulic fluid pressure and thereby to generate a stable damping force.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Rotary-actuated exhaust gas recirculation valve having a seating force attenuator
InactiveUS7461642B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringActuator
Means for attenuating the seating force of a cam-actuated poppet valve such as an exhaust gas recirculation valve in an internal combustion engine including a shock-absorber disposed between the valve stem and valve head. In a currently preferred embodiment, the shock-absorber is a wave washer disposed around the valve stem and captured between the valve stem and the valve head, between which axial motion is allowed. After the valve head engages the valve seat to close the valve, any further travel of the actuator cam and valve stem is absorbed by compression of the wave washer, thus attenuating additional force on elements of the valve actuation train. In opening the valve, the reverse occurs, in that initial motion of the actuator cam and valve stem serves to relieve compression of the wave washer, followed by removal of the valve head from the valve seat.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Shock absorber having a continuously variable valve with base line valving
A shock absorber includes an external control valve which controls the damping characteristics of the shock absorber. The external control valve controls the flow of fluid between the lower working chamber of the shock absorber and the reservoir chamber and between the upper working chamber of the shock absorber. The damping characteristics are dependent on the amount of current being applied to a solenoid valve which controls a fluid valve assembly. A soft fluid valve assembly is disposed in series with the fluid valve assembly to allow for the tuning of the damping forces at low current levels provided to the solenoid valve.
Owner:TENNECO AUTOMOTIVE OPERATING CO INC
Non-pressurized monotube shock absorber
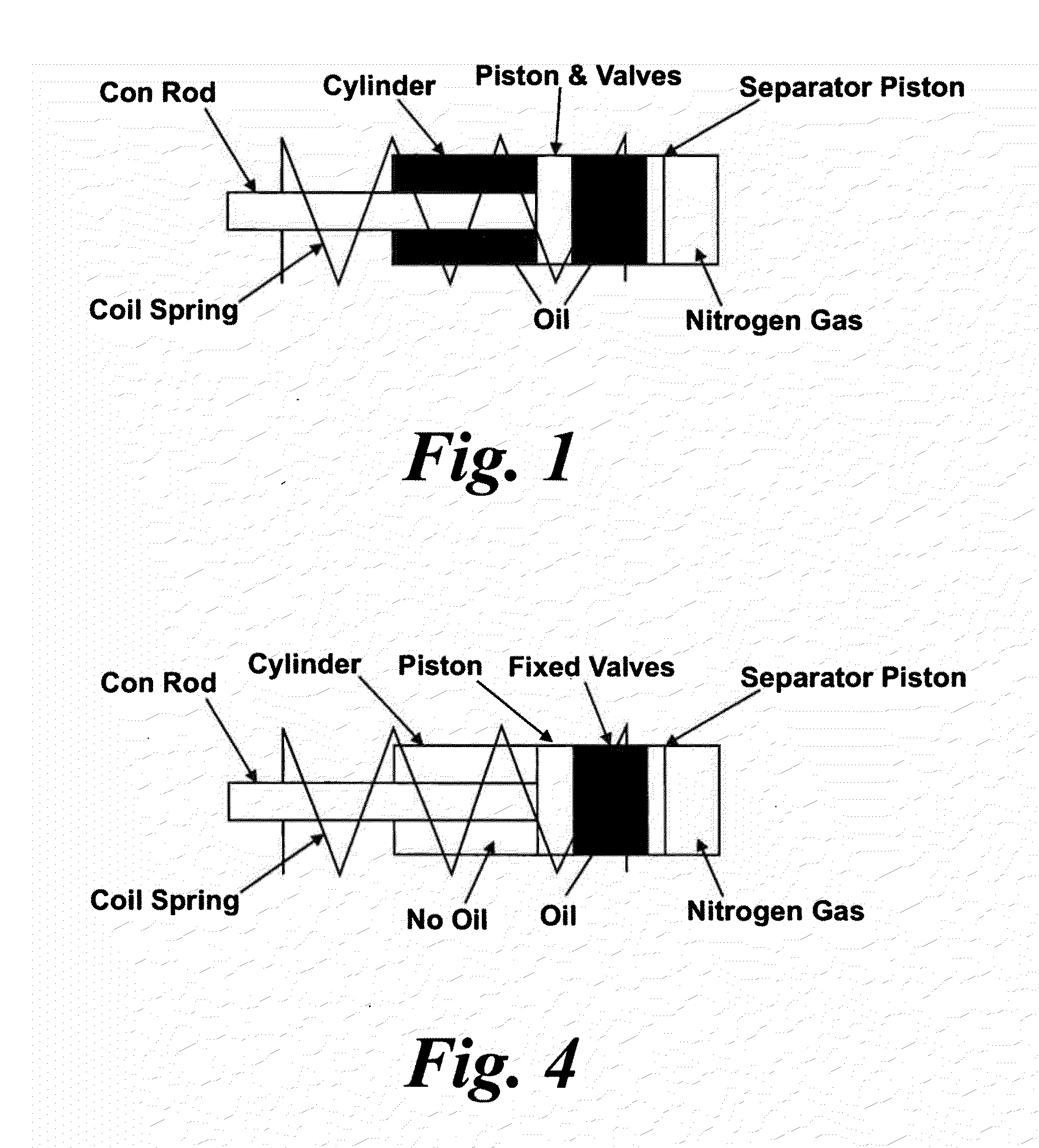
A shock absorber of a monotube type utilizes a mechanically fixed base valve to regulate oil flow between the compression and compensation chambers, and a compressible bladder in the compensation chamber to allow volume compensation, which, together, eliminate the need for pressurized gas and a floating piston found in conventionally known monotube dampers.
Owner:LEIPHART TROY +1
Shoe Ventilation and Shock Absorbtion Mechanism
An article of footwear has ventilation and shock absorption provided by a mechanism which may be constructed within or added to the footwear. A first chamber beneath the heel draws external air through a conduit which includes a one-way valve. As a wearer walks, the heel compresses the first chamber, forcing the air through a special second valve causing directional airflow to a second chamber in a controlled manner thereby absorbing the shock of the heel strike in the same manner a shock absorber functions in an automobile. As weight is transferred from the heel to the ball of the foot, further cushioning is provided by the second chamber. Specifically designed vents connected to the second chamber allow air to be forced into the region of the shoe around the foot. Expansion of the air from these vents affects cooling and drying of the foot through evaporation and convection.
Owner:RIDINGER MICHAEL R
Bicycle damper
A damper for a bicycle, having a primary unit including a damper tube, a piston rod that supports a main piston, a reservoir tube that is outside of the compression chamber of the primary tube, and an inertial valve within the reservoir tube. The damper also includes a flow path connecting the reservoir fluid chamber and the compression chamber of the primary tube. The damper also may have a damping valve in the reservoir tube. When the inertia valve is open, the damping valve opens before flow through the inertia valve is maximized. The main piston and the damper tube at least partially define a compression chamber and a rebound chamber. The main piston is movable within the damper chamber of the primary unit. The reservoir tube includes a reservoir fluid chamber. The inertial valve is responsive to terrain-induced forces and not responsive to rider-induced forces when the shock absorber is assembled to the bicycle.
Owner:SPECIALIZED BICYCLE COMPONENTS INC
Shock absorber with hydraulic flow ducts
ActiveUS20100018818A1Simple and short damperSpringsShock absorbersHolographic Data Storage SystemPhotopolymer
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for a multilayer optical articles. A method comprises forming a first multilayer article with a first substrate, first adherent, and second substrate using a first holder and a second holder. The method further comprises forming a second multilayer article with the first multilayer article, a second adherent, and a third substrate using the first holder and second holder to grasp the second multilayer article. After removal of the first and second holders, the first and second adherent maintains the second multilayer article in a posture at which the second multilayer article was held by the first and second holders, wherein the first and second adherent comprise a photopolymer such that the article is capable of storing data in a reflective holographic data storage system.
Owner:OHLINS
Combustion liner damper
ActiveUS8104290B2Reduce vibrationReduce the overall heightPortable framesContinuous combustion chamberCombustorEngineering
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA SWITZERLAND AG
Orifice disc for regulating flow in damper
A shock absorber for a vehicle includes a pressure tube that defines a fluid chamber. A piston disposed within the fluid chamber divides the fluid chamber into an upper working chamber and a lower working chamber. The piston defines a compression passage and a rebound passage which extend through the piston between the upper working chamber and the lower working chamber. A valve disc assembly engages the piston and controls the flow of fluid between the upper working chamber and the lower working chamber. The valve disc assembly includes a bleed disc that defines an orifice with a substantially non-linear contour. The orifice extends to an outer diameter of the bleed disc, and forms a bleed channel between the upper working chamber and the lower working chamber.
Owner:TENNECO AUTOMOTIVE OPERATING CO INC
Circulating lubrication type shock absorbing structure
The invention relates to a circulating lubrication type shock absorbing structure. The circulating lubrication type shock absorbing structure comprises a connecting rod, a connecting cylinder and shock absorbing springs. A blind hole is formed in the upper end face of the connecting rod. Positioning column heads are arranged in the shock absorbing springs in a penetrating mode. A cross rod locatedabove the connecting rod is arranged at the connecting cylinder. The upper ends of the positioning column heads are connected with the cross rod. A compression plate isolates a connecting rod portionoil chamber and an oil hopper located above an oil storing cavity in the blind hole. Oil discharging holes penetrating through the connecting rod portion oil chamber is formed in the lateral wall ofthe blind hole. The oil discharging hole is internally provided with a plug and an oil discharging hole closing spring driving the plug to move to the connecting rod portion oil chamber to seal the oil discharging hole. A connecting seat is provided with an oil return hole communicating an annular oil collecting groove with the connecting rod portion oil chamber. The oil return hole is internallyprovided with a connecting rod portion one-way valve opened to the interior of the connecting rod portion oil chamber. The circulating lubrication type shock absorbing structure has the advantages that shaking is little and automatic lubricating is achieved, and is used for solving the problem that an existing shock absorbing machine is liable to shake in the radial direction between two moving components.
Owner:JIANGSHAN XINGCHENG TECH INFORMATION CONSULTING SERVICES CO LTD
Mount and bearing for shock absorber
ActiveUS8292306B1Less-expensive and efficientLess expensiveSpringsVehicle cleaning apparatusTerrainLine tubing
Improved mount and bearing height adjustable air suspension shock absorber devices, apparatus, systems and methods, for use with sport utility vehicles(SUVs) such as Range Rovers®, and the like. Air lines run through an upper mount into an upper opening of an inflatable and deflatable airbag. The airlines have not external lines such as the nylon type tubing used in the prior art, and are not prone to failure which occurs more frequently with the external tubing air lines. Inflating and deflating the air springs / airbags (bladders) allows for the shock absorbers in the devices to be adjusted to different riding conditions over different types of terrains giving the rider a customized ride over different types of on road and off-road terrains. An internal air line machined into the head of the air suspension device provides a direct passageway for compressed air to pass into and out of the airbag without using external tubes. Sealing members such as O-rings provide airtight seals between the moving members of the head components of the air suspension devices.
Owner:ARNOTT T&P HLDG LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com