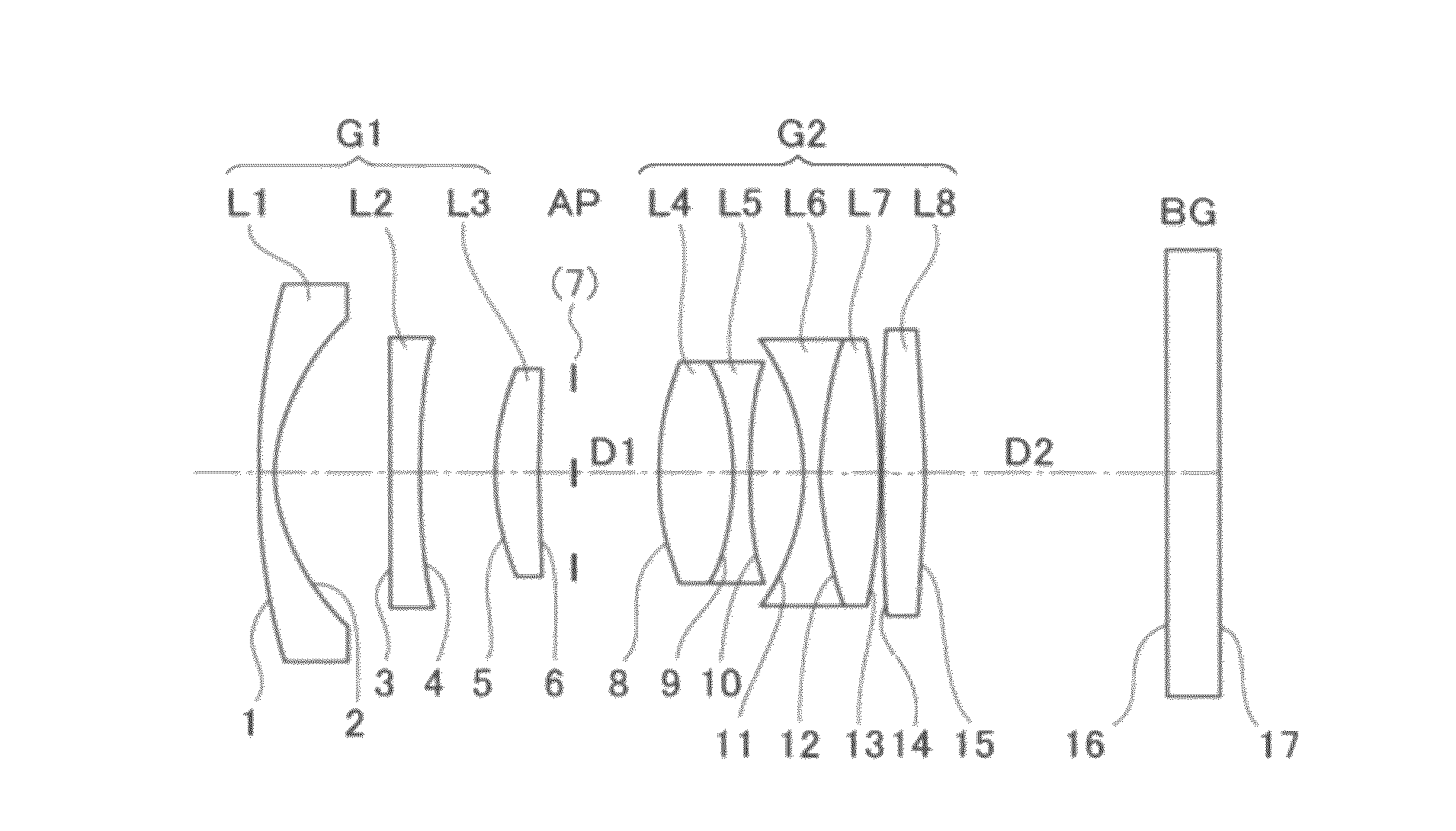
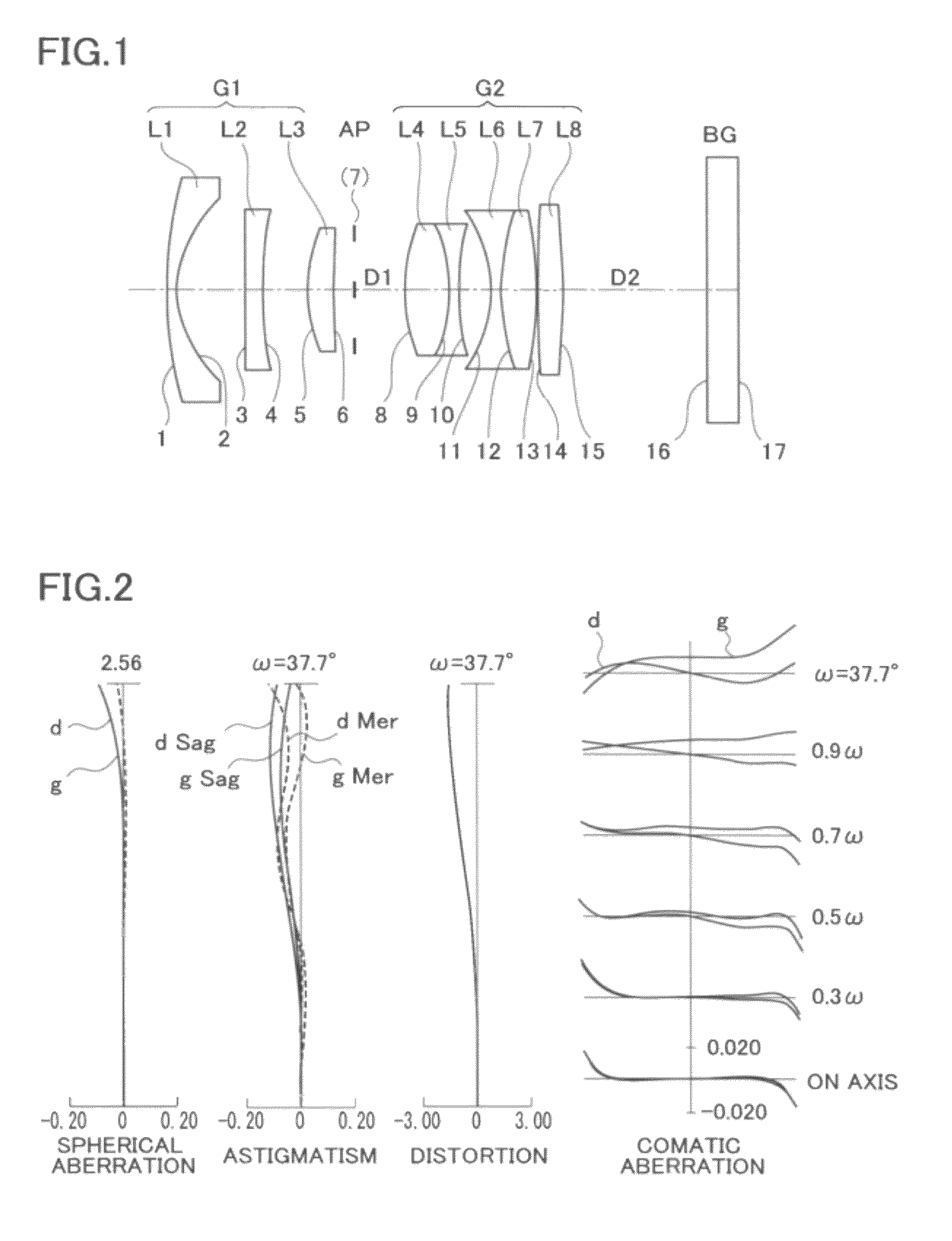
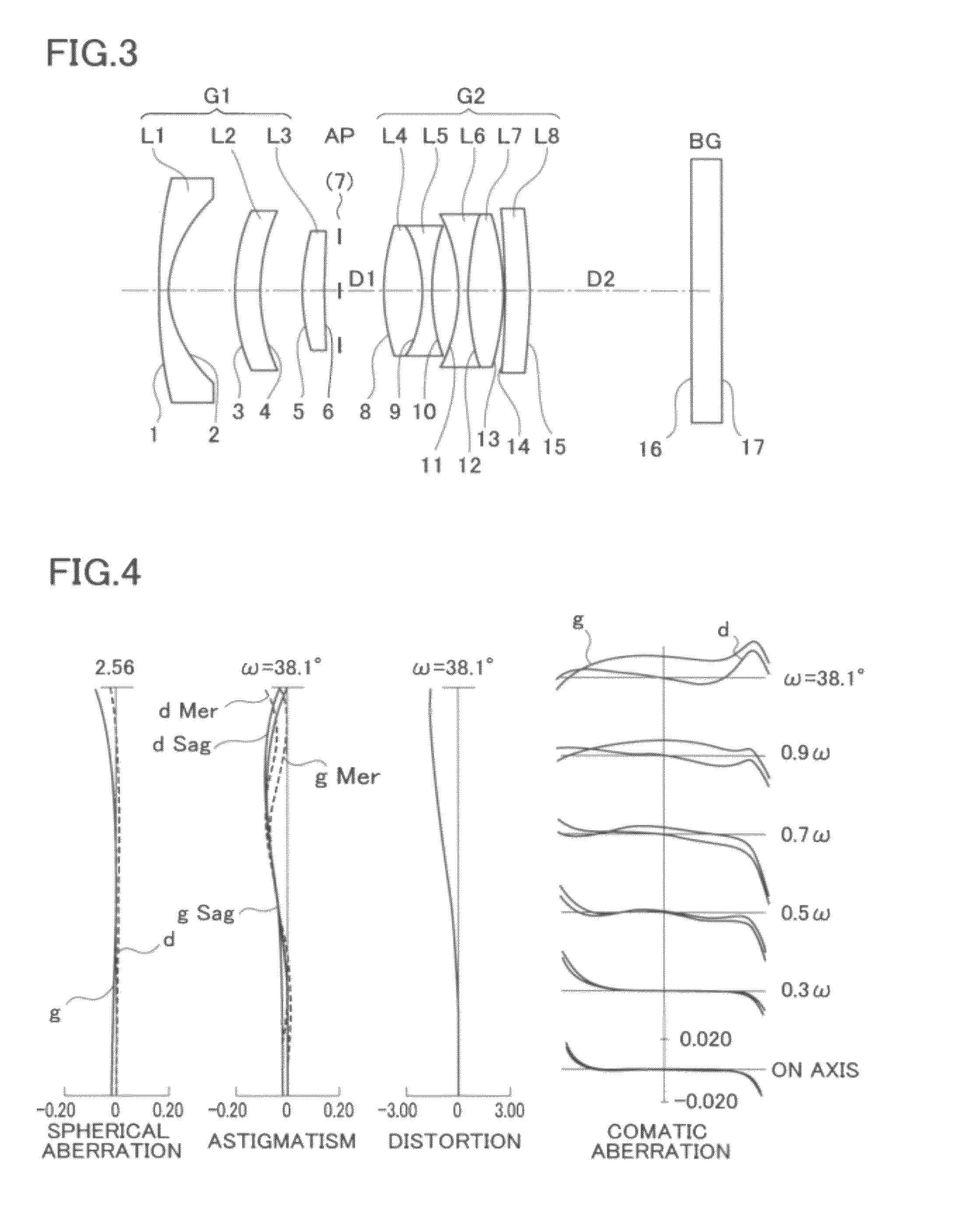
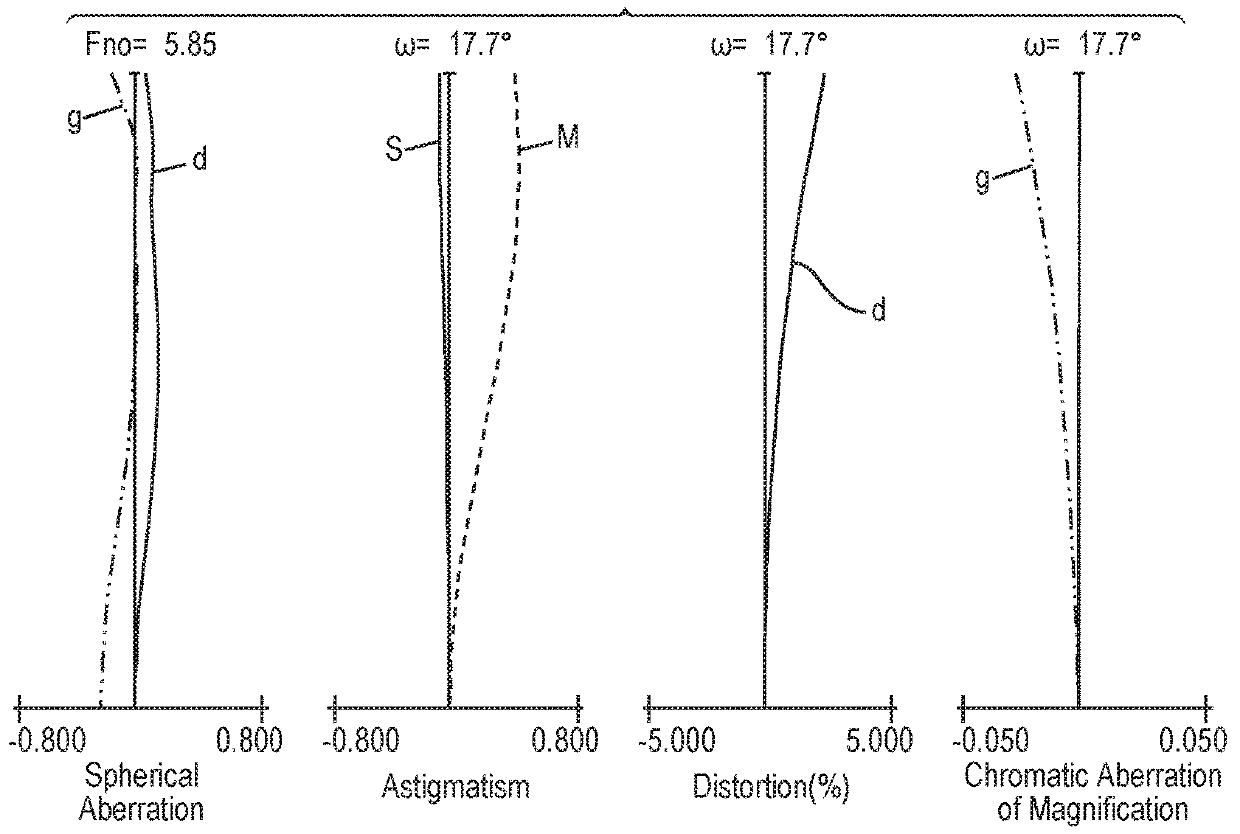
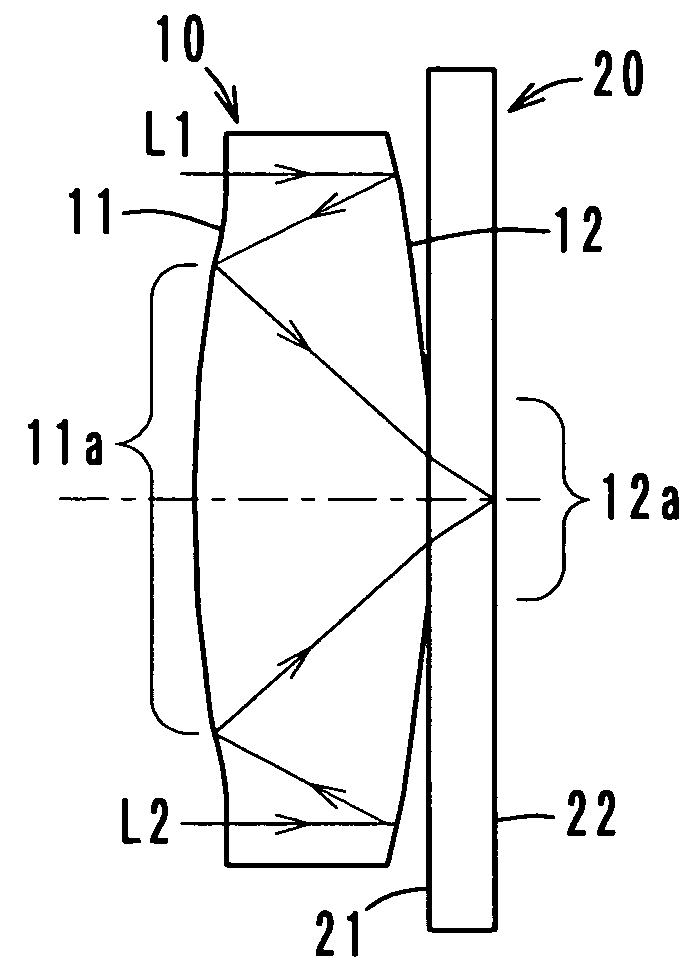
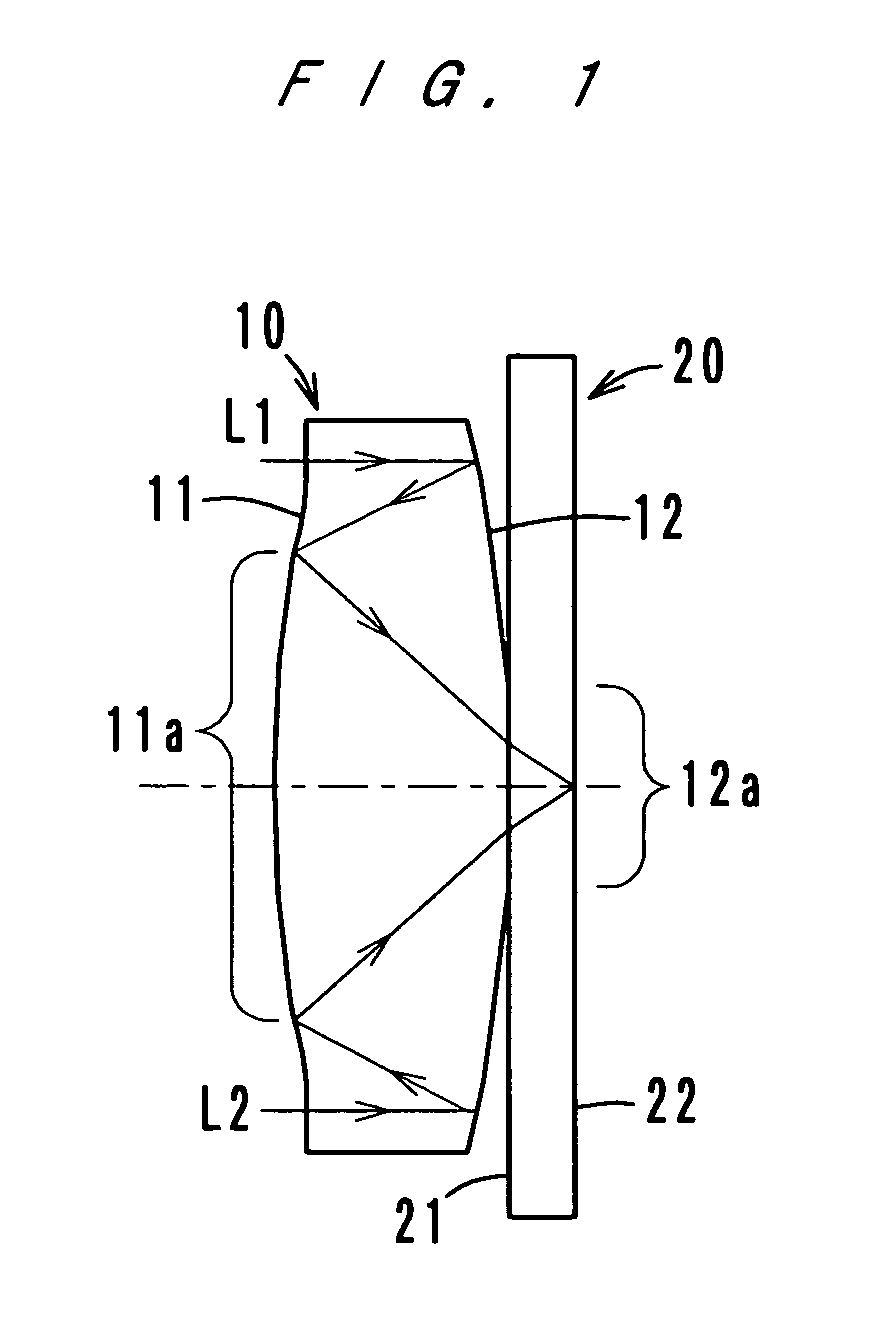
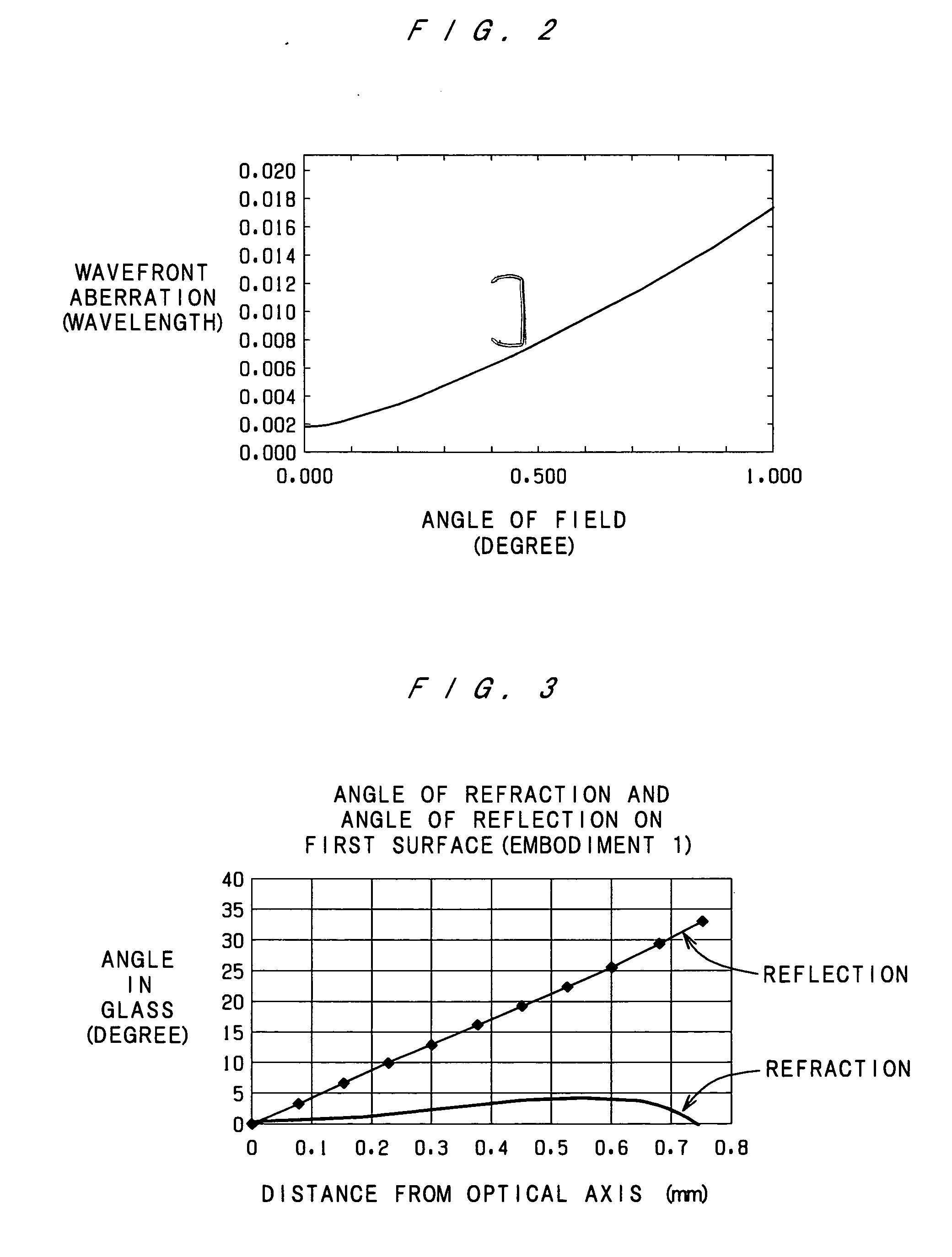
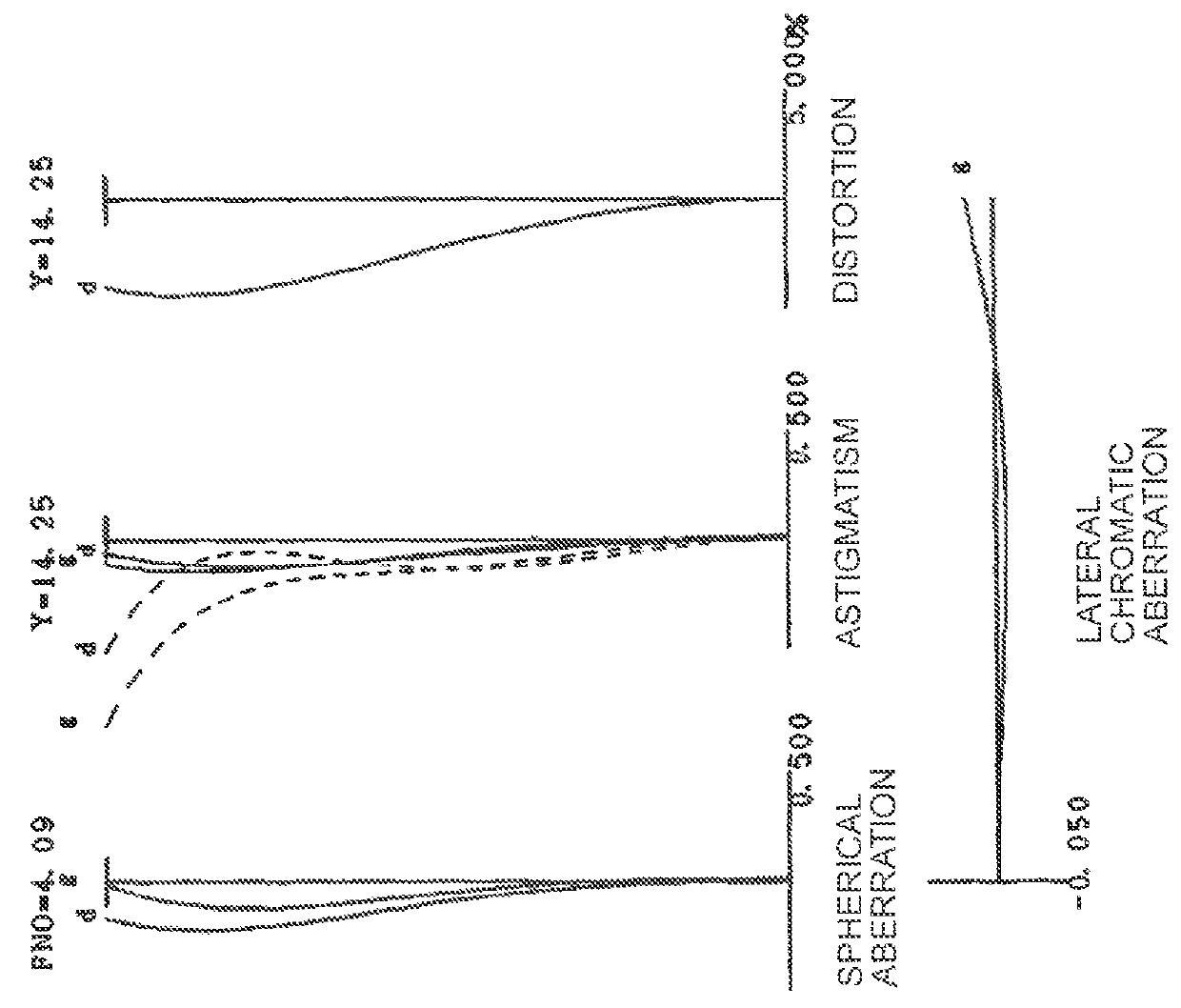
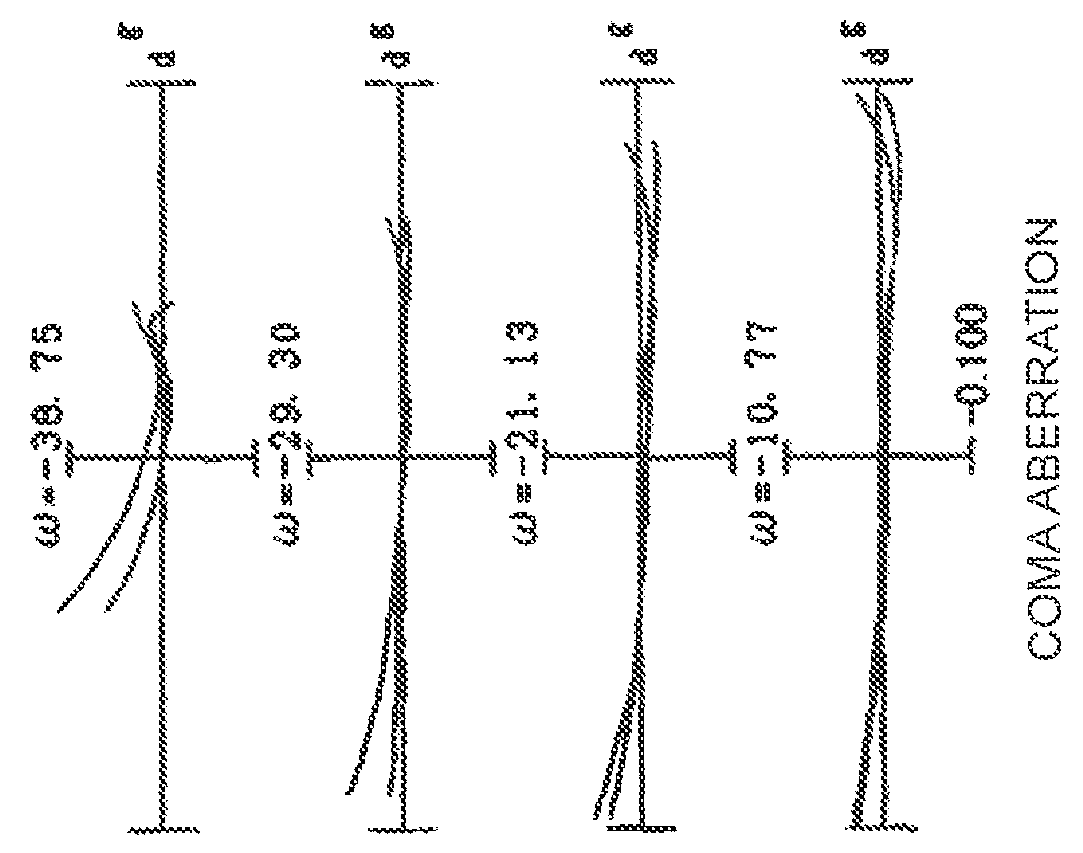
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34results about How to "Small aberration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
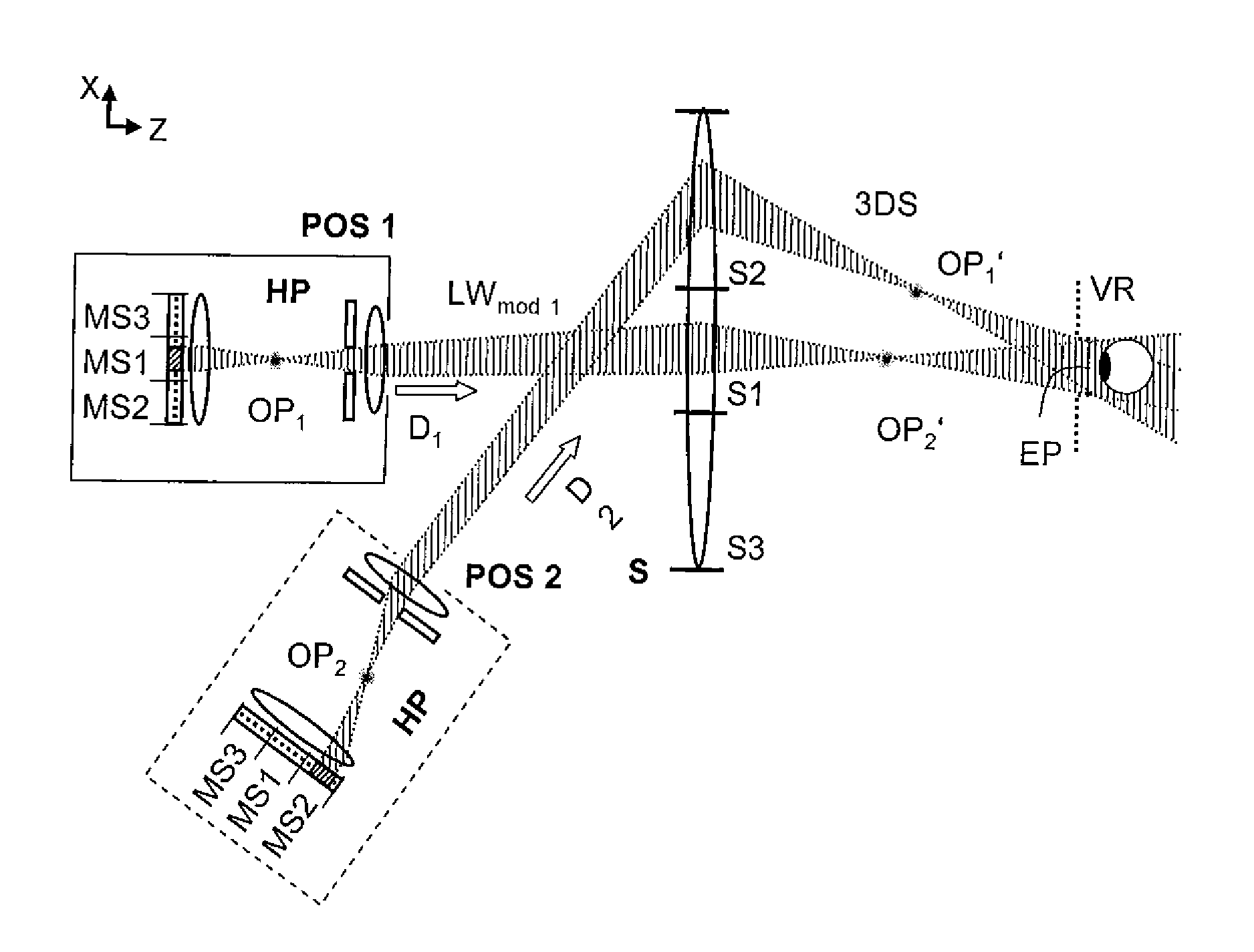
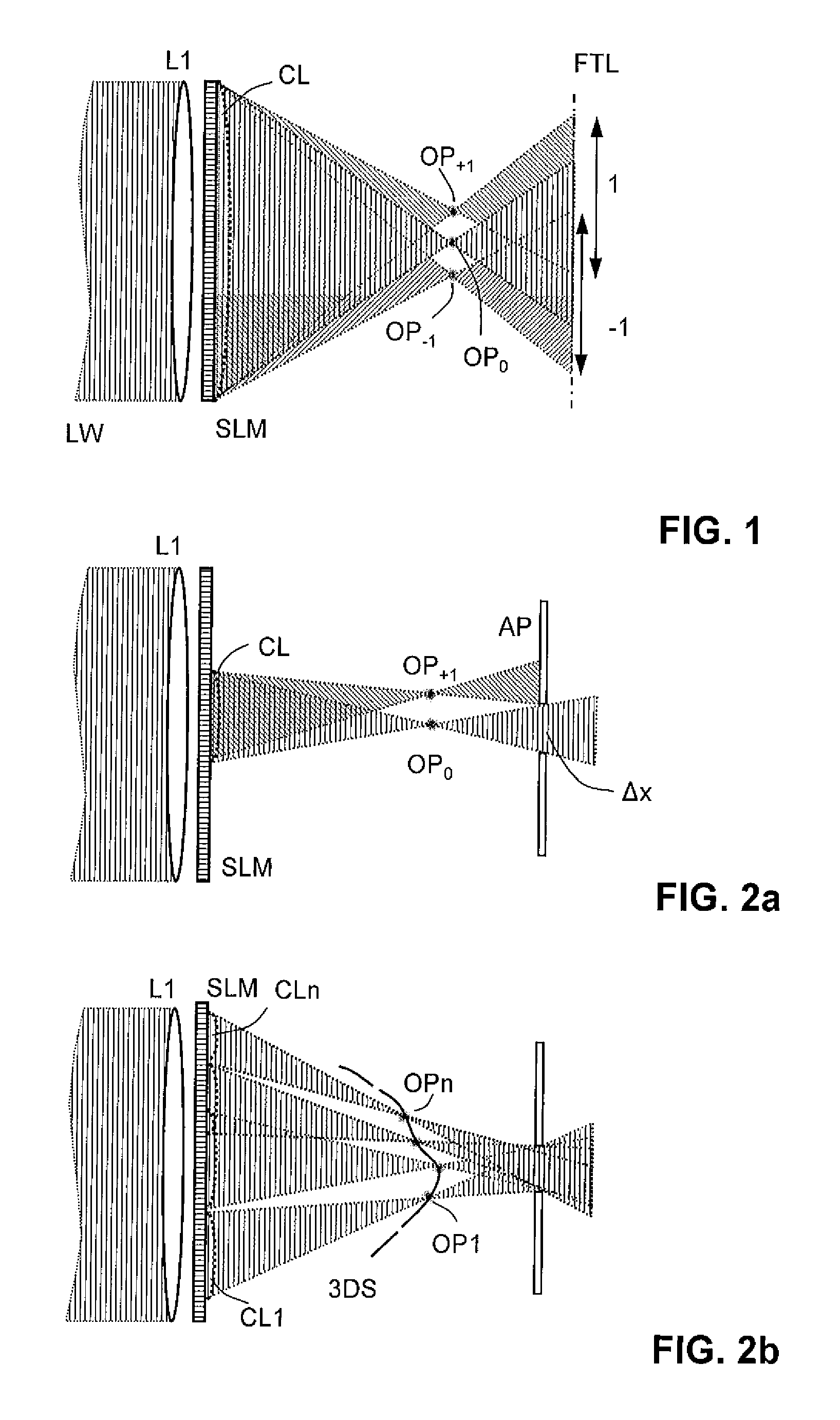
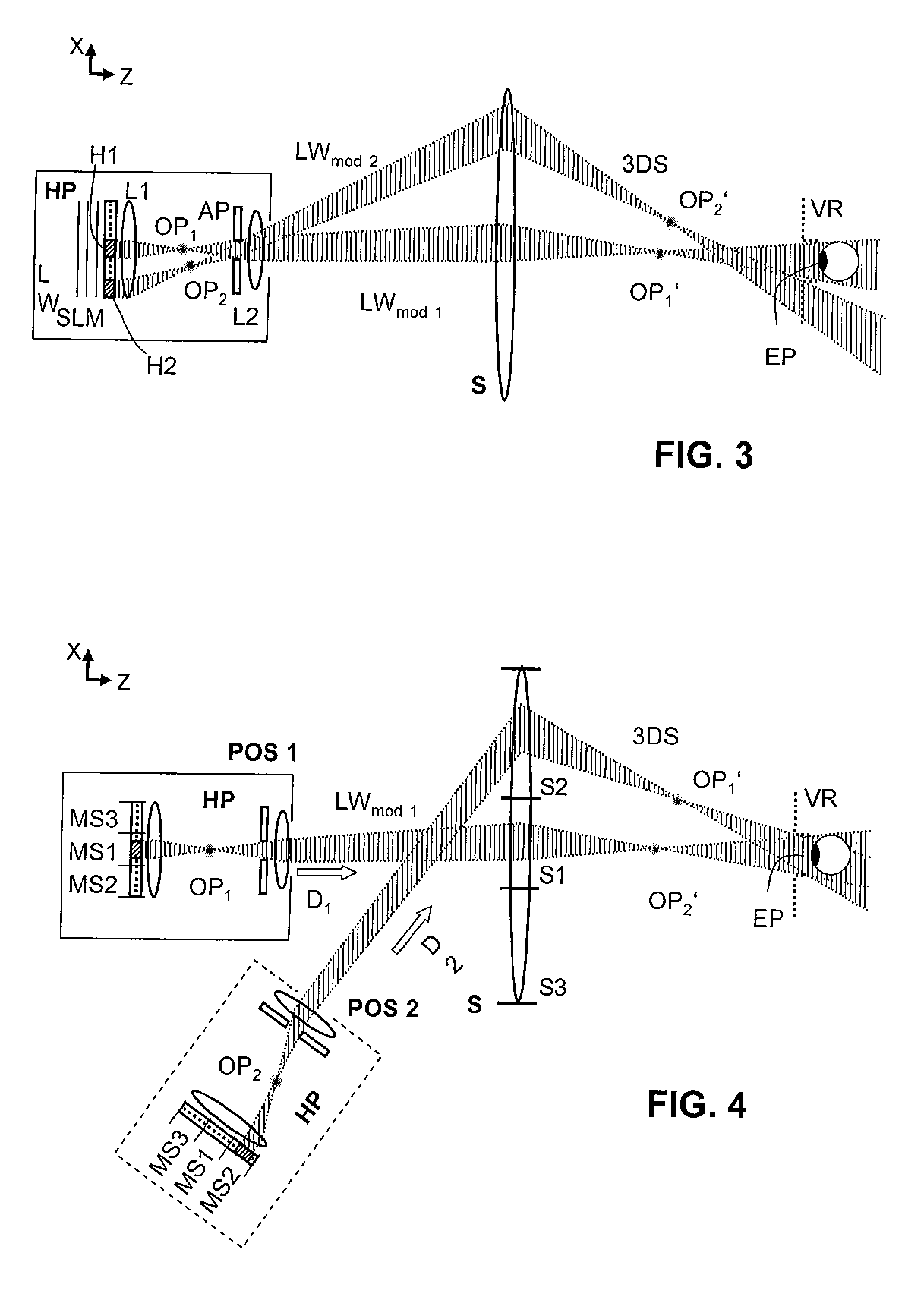
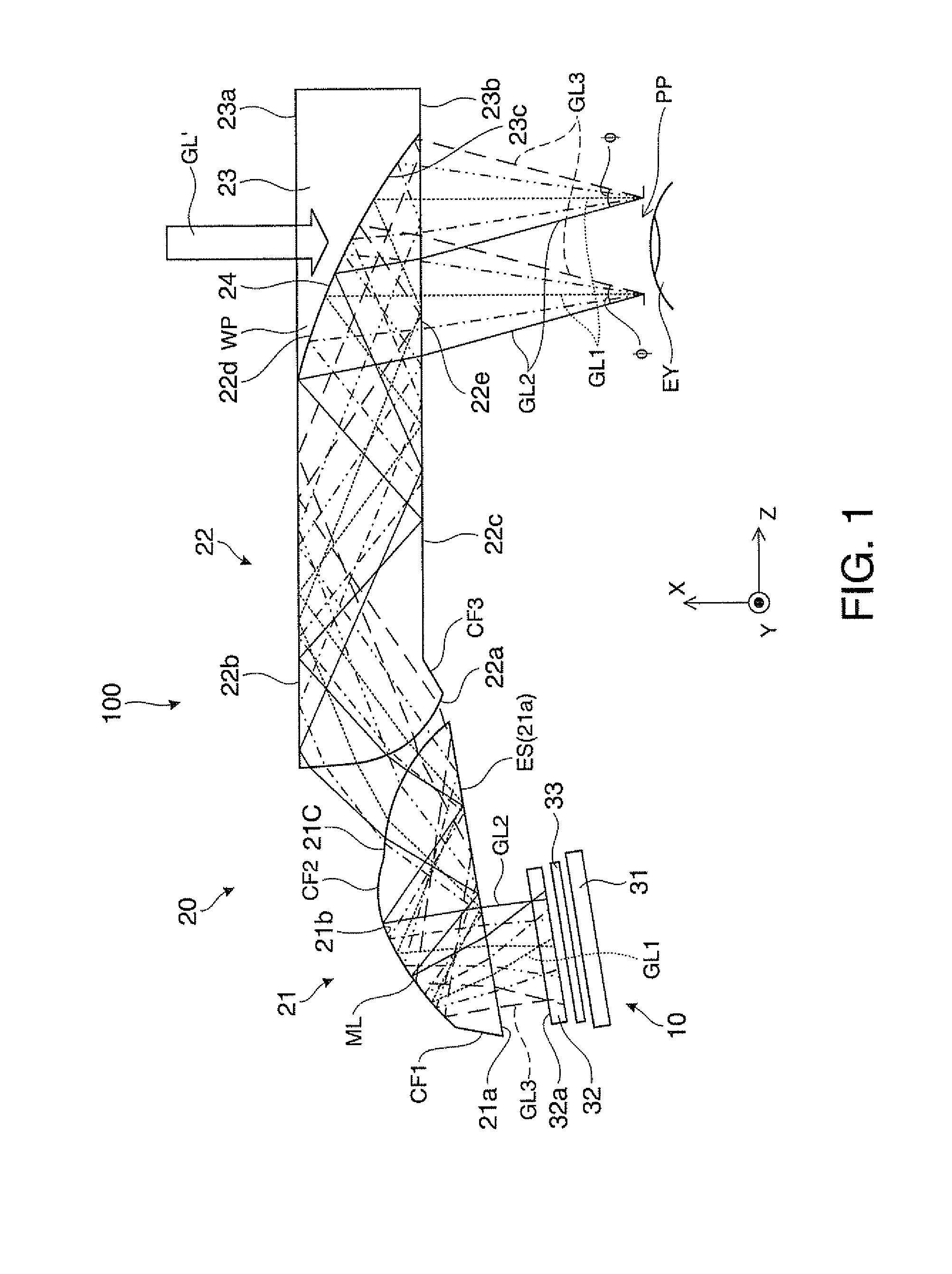
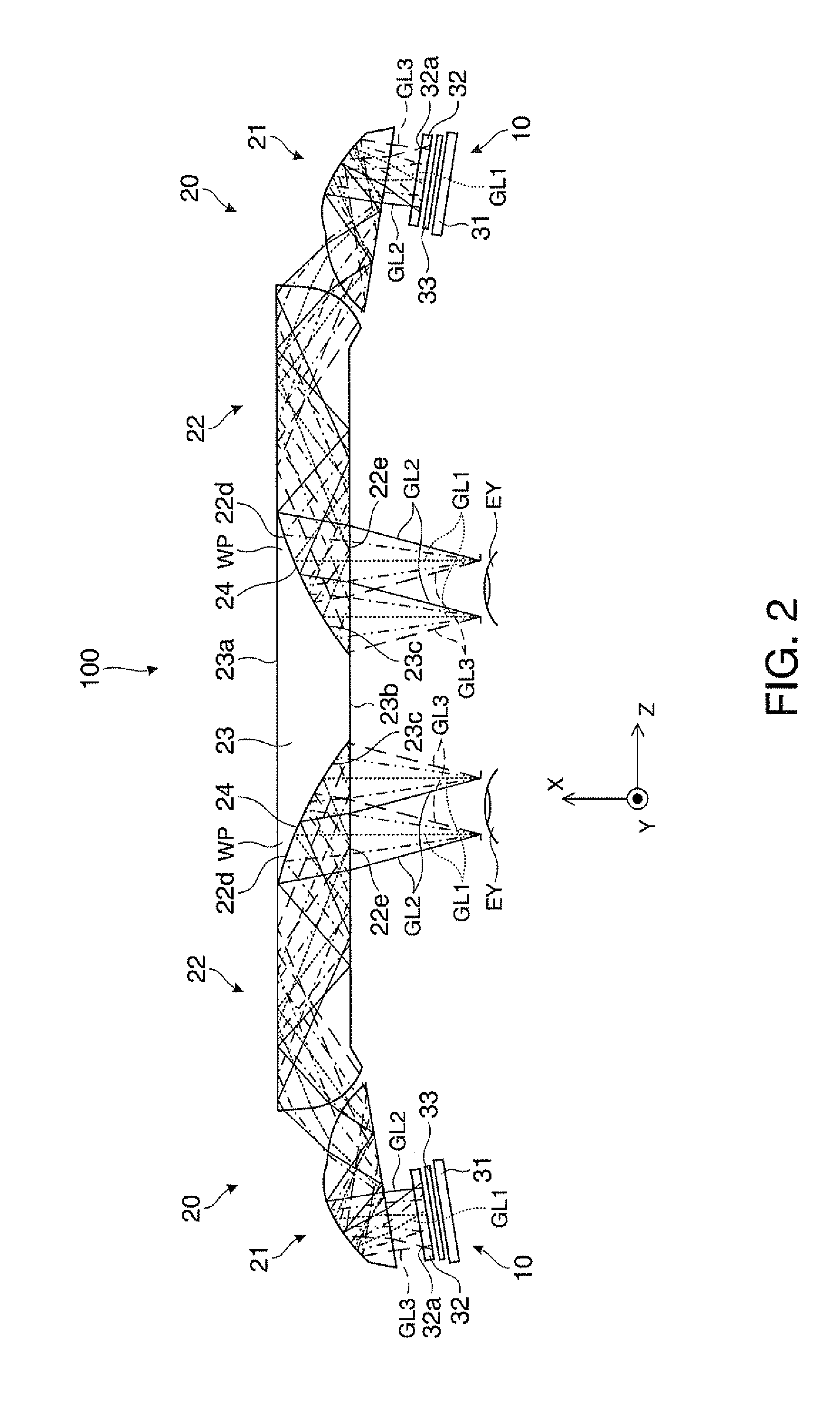
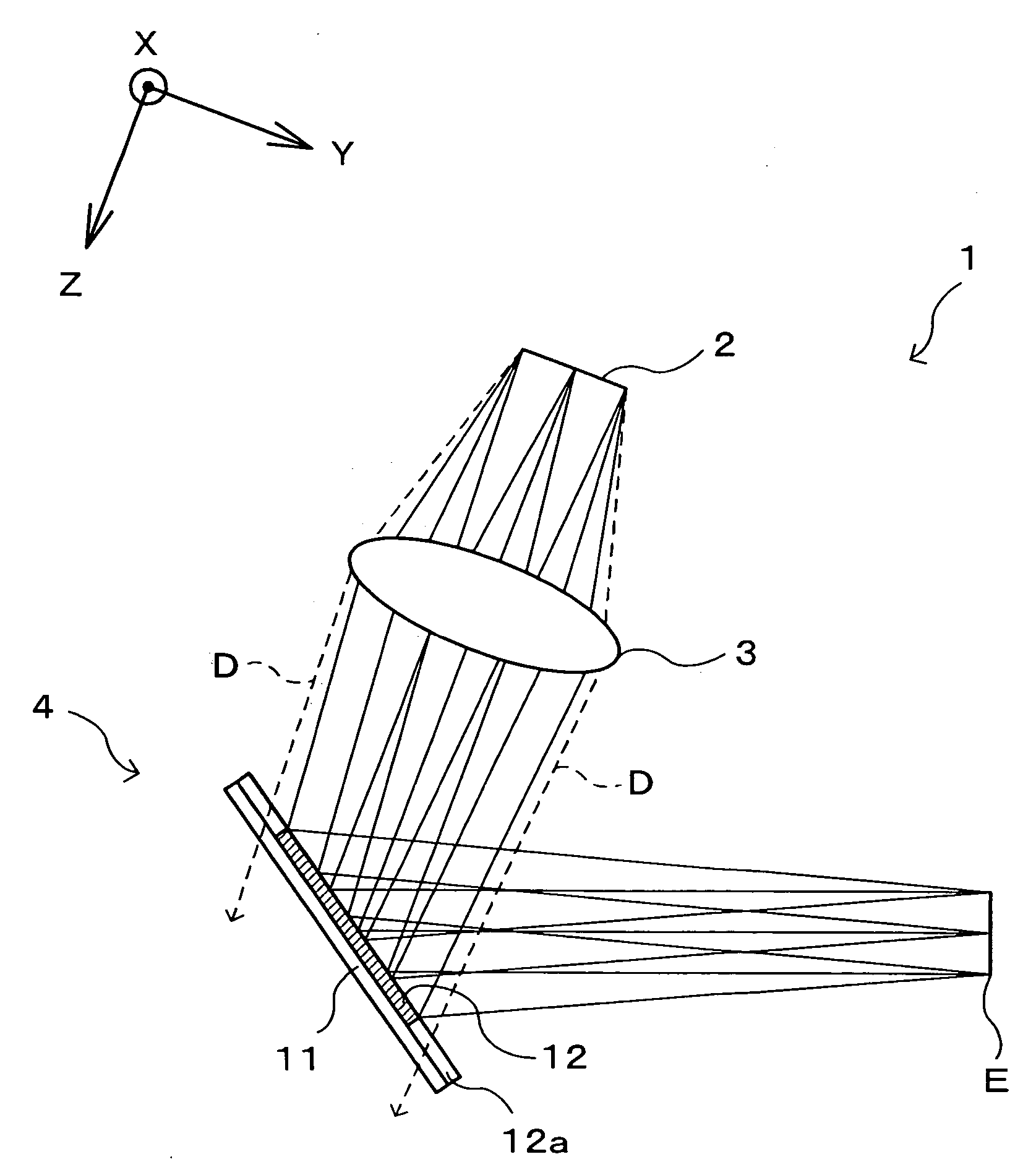
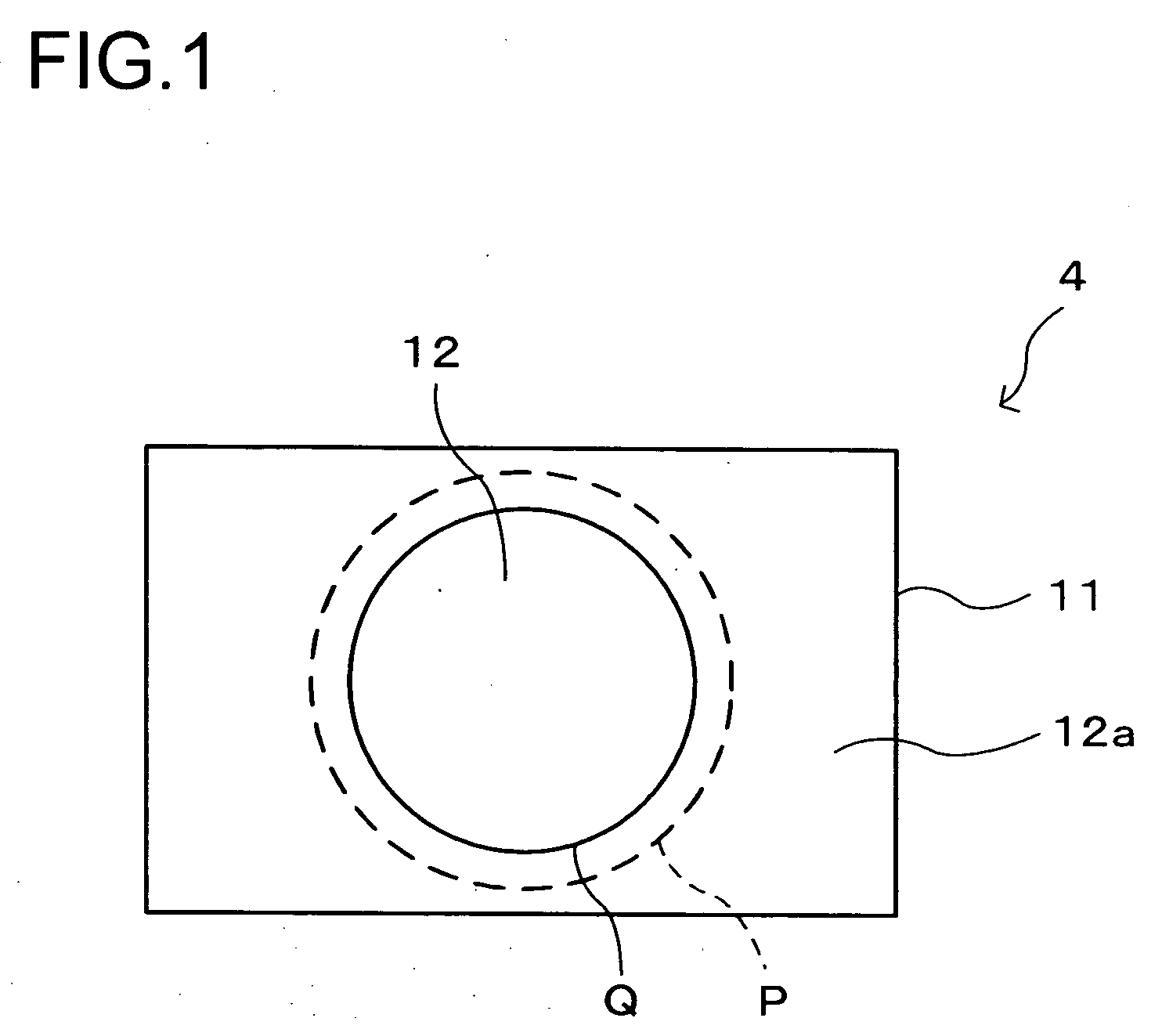
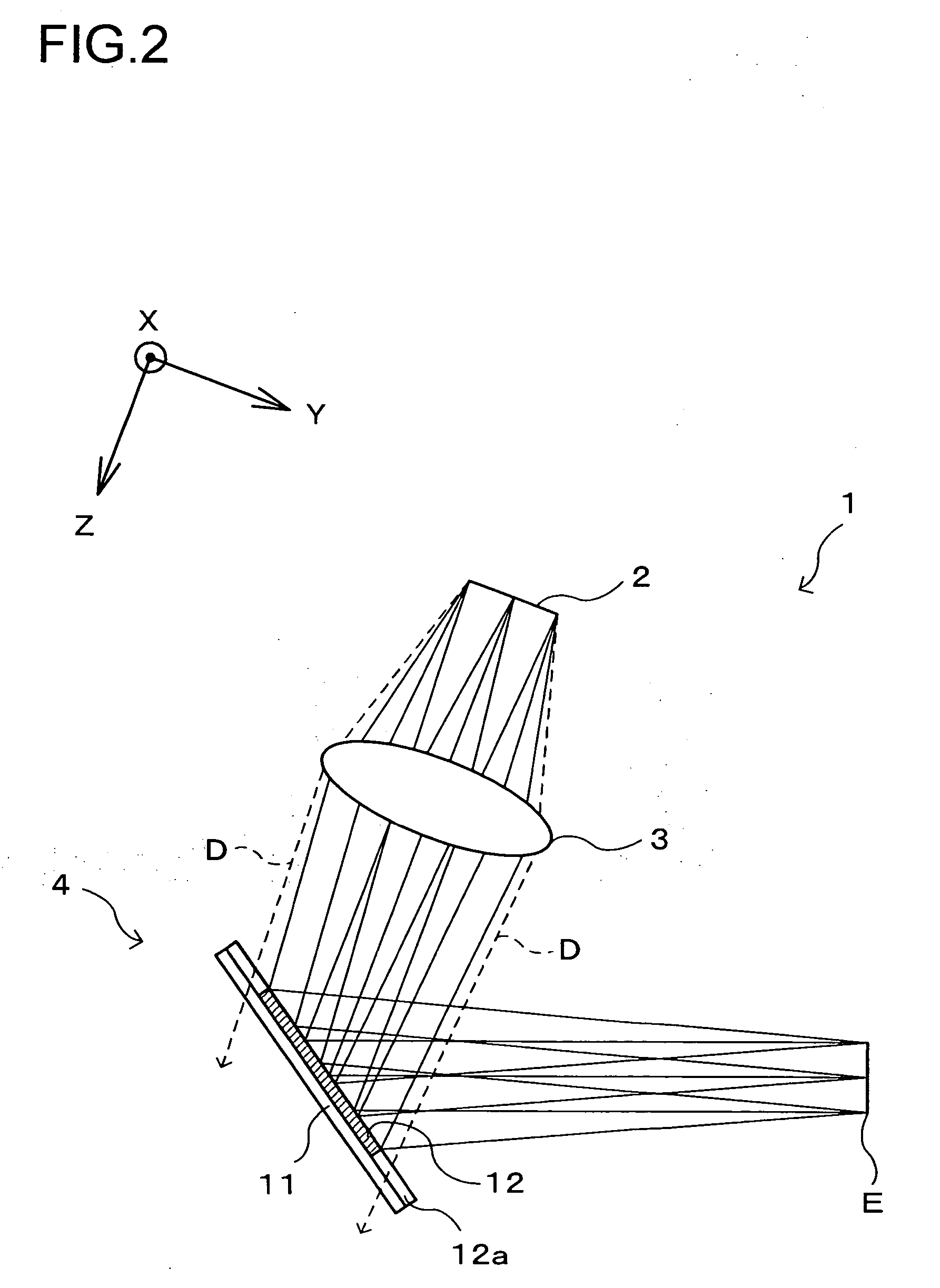
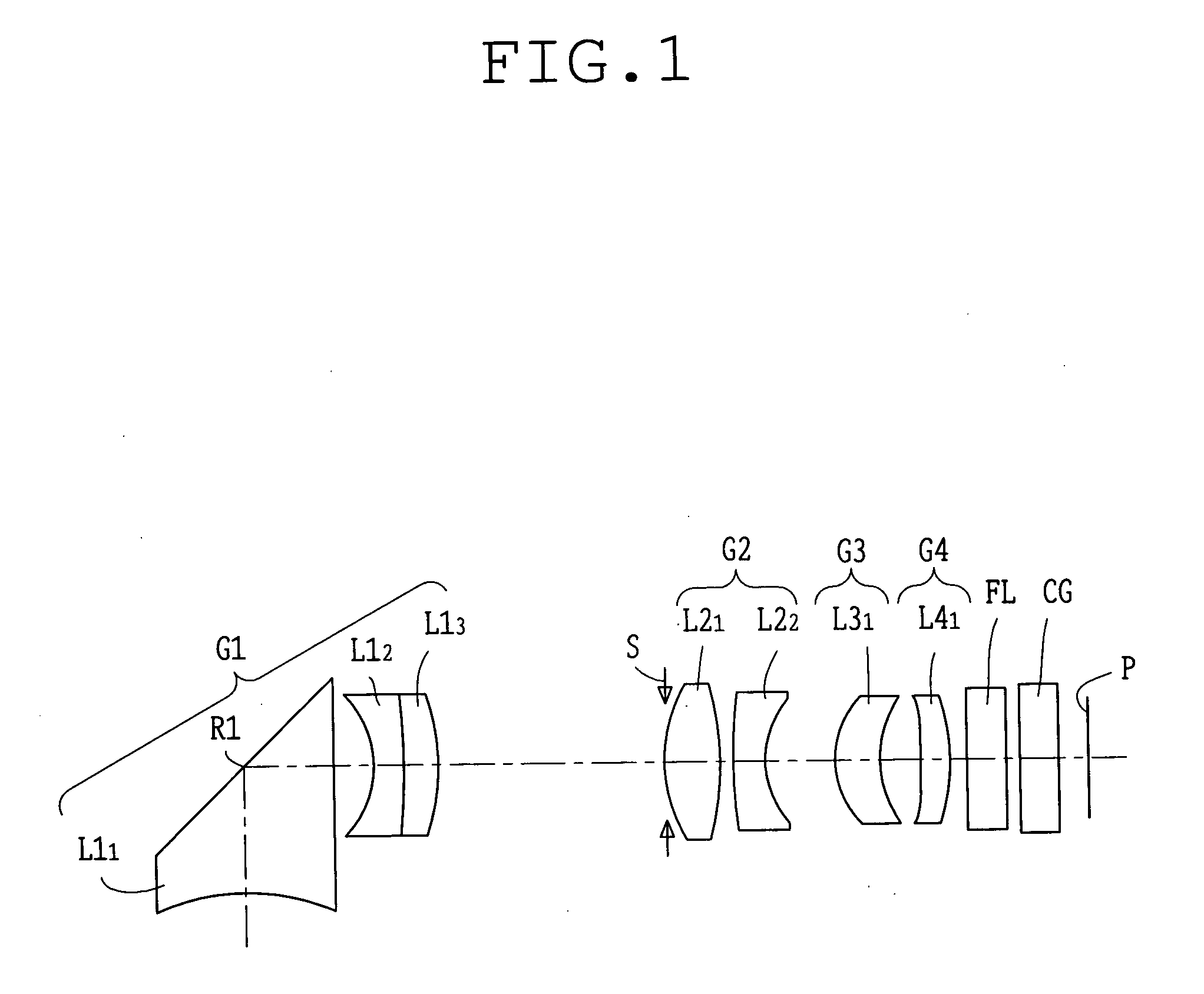
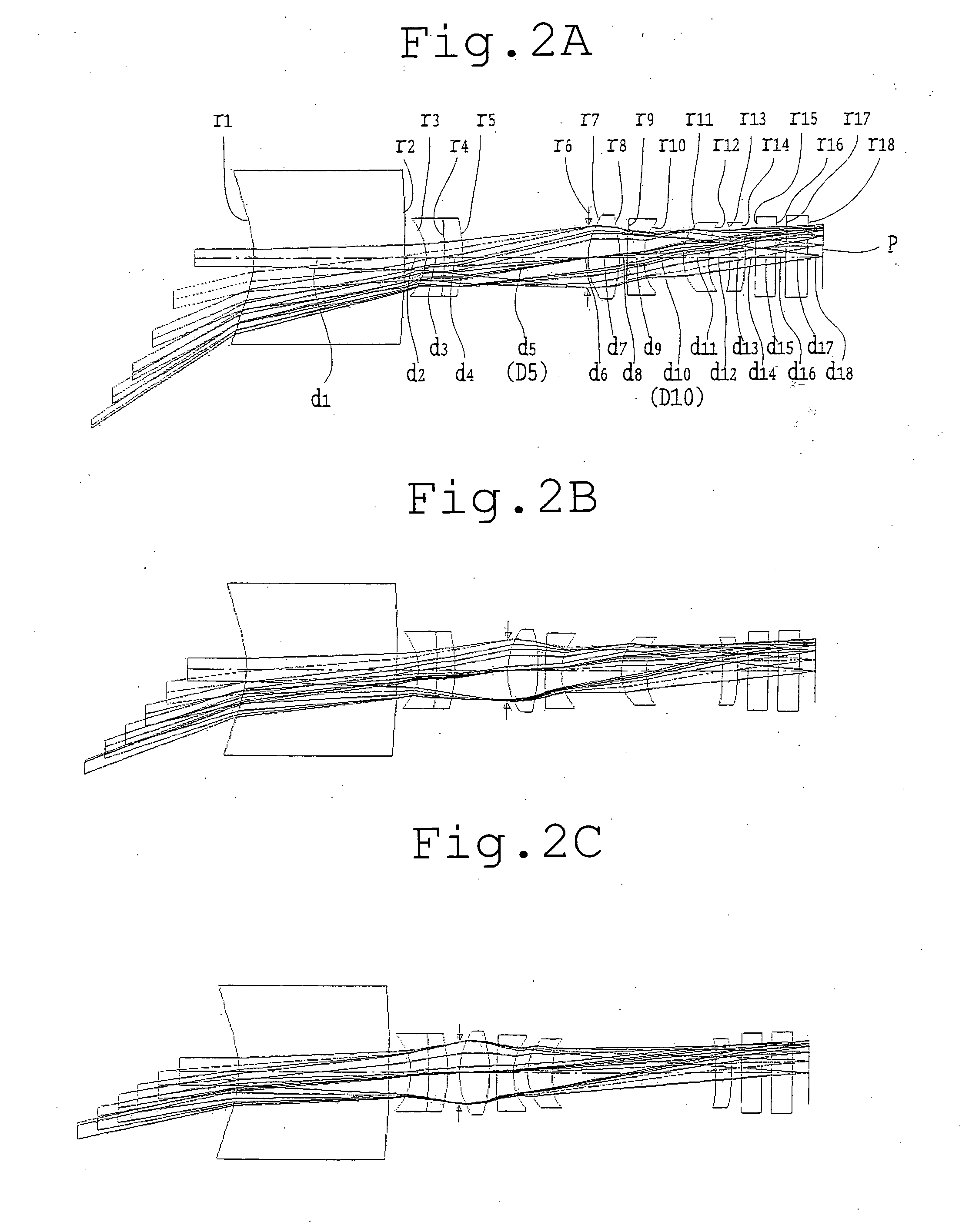
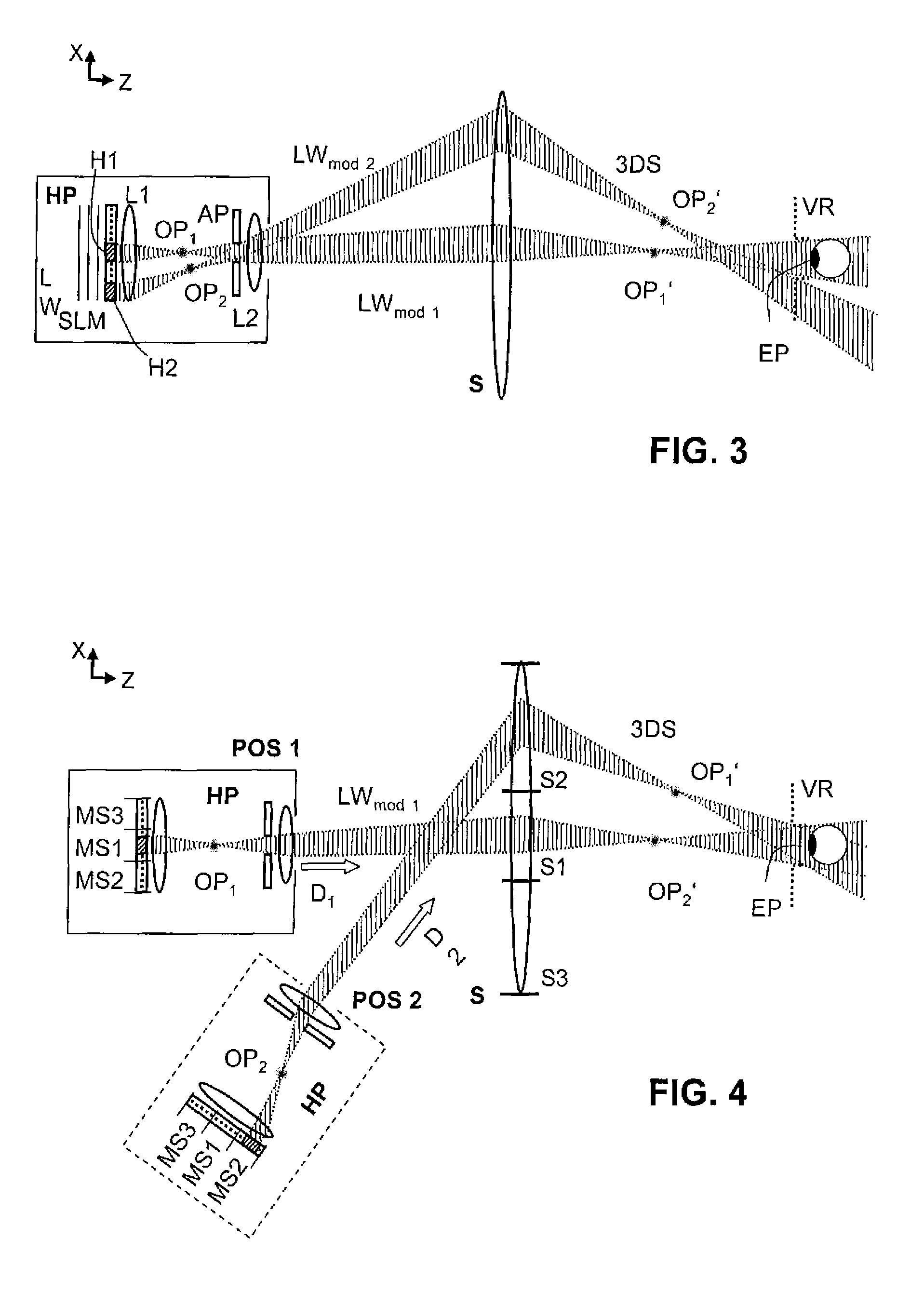
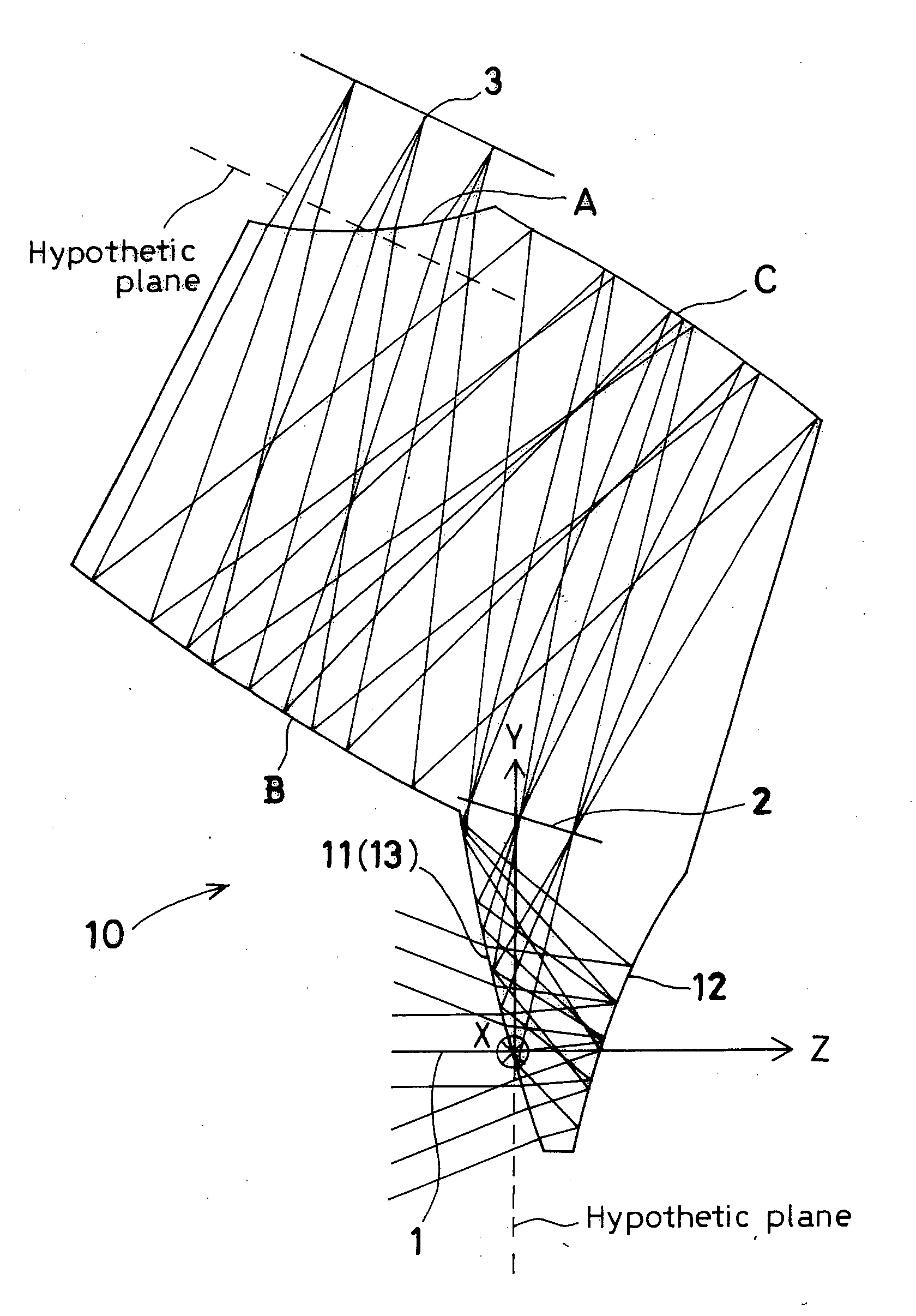
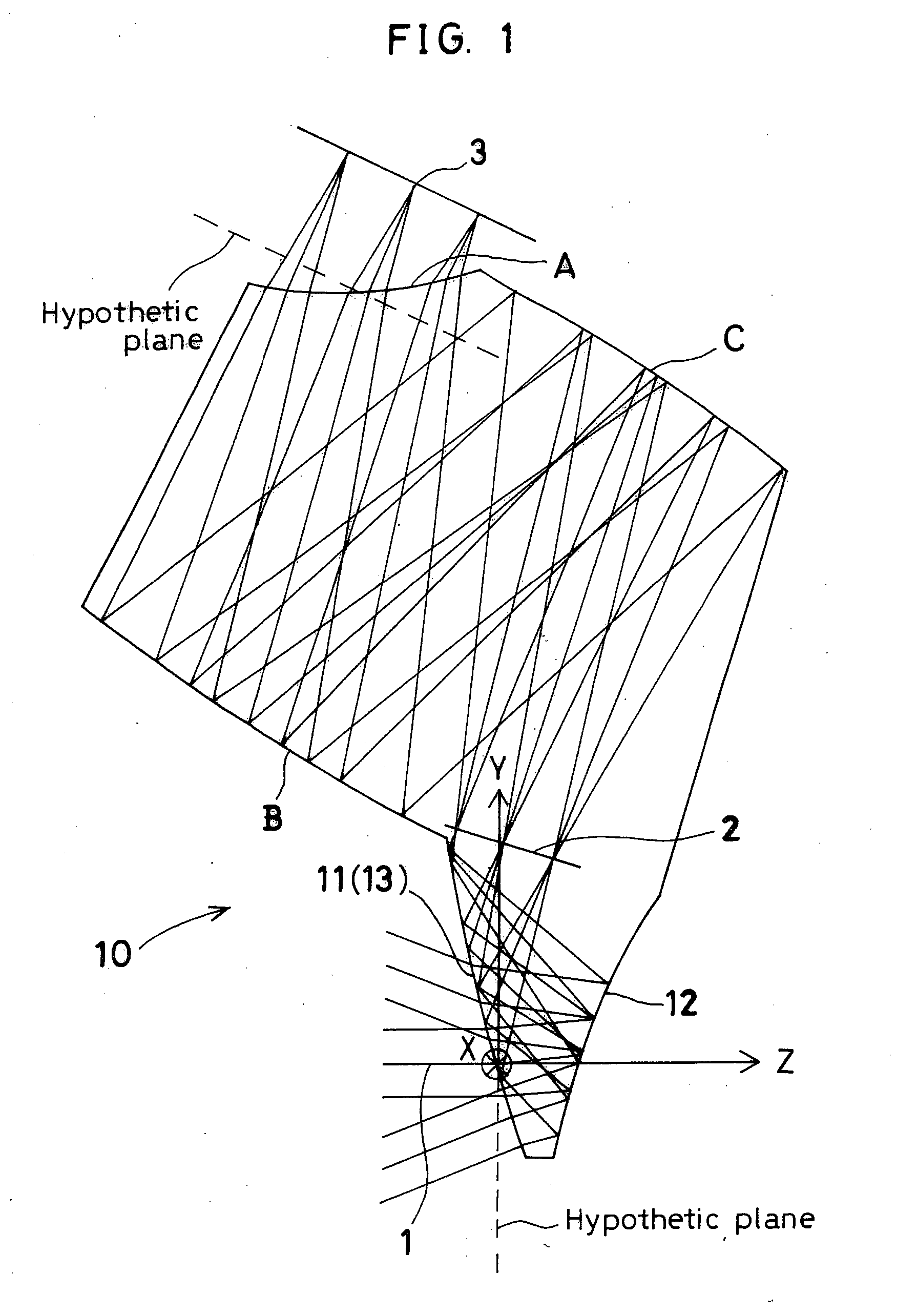
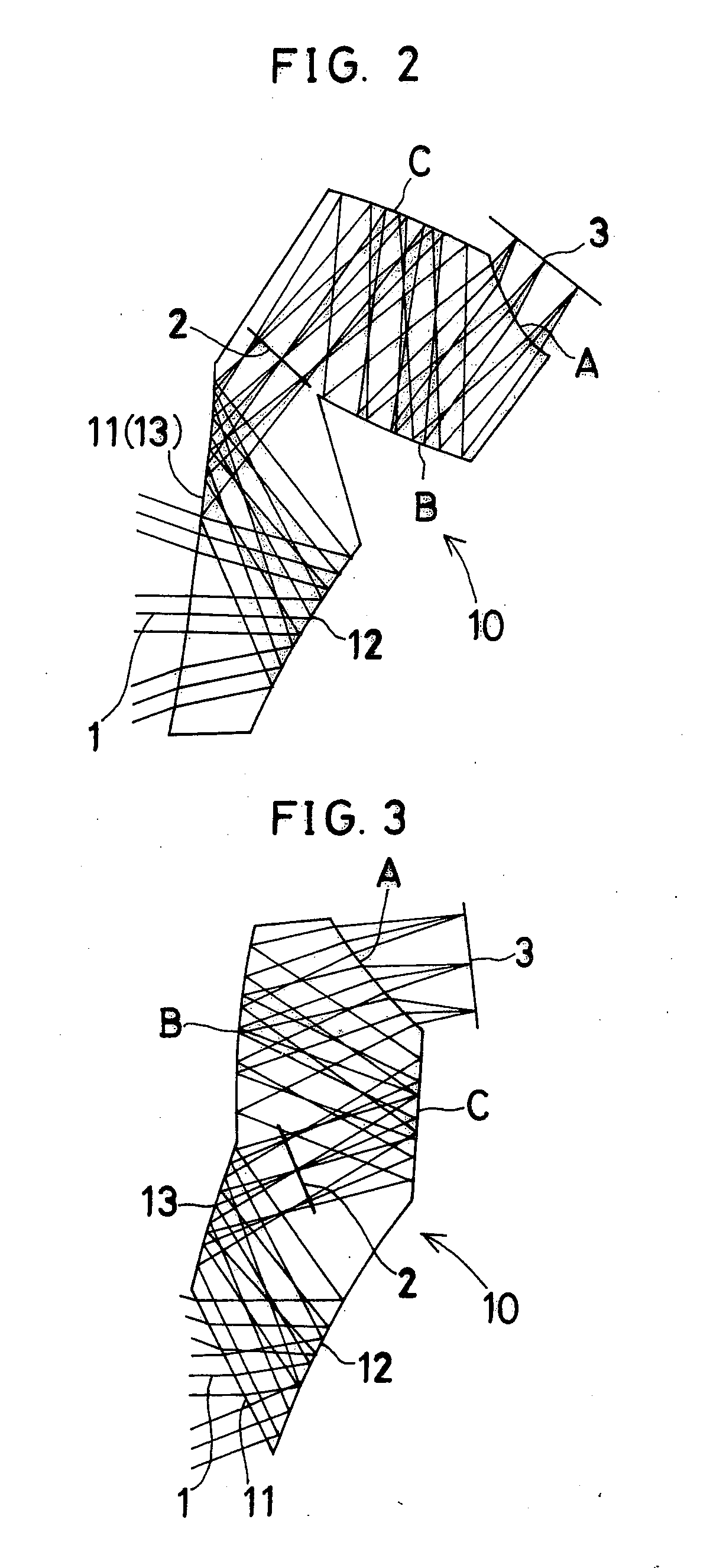
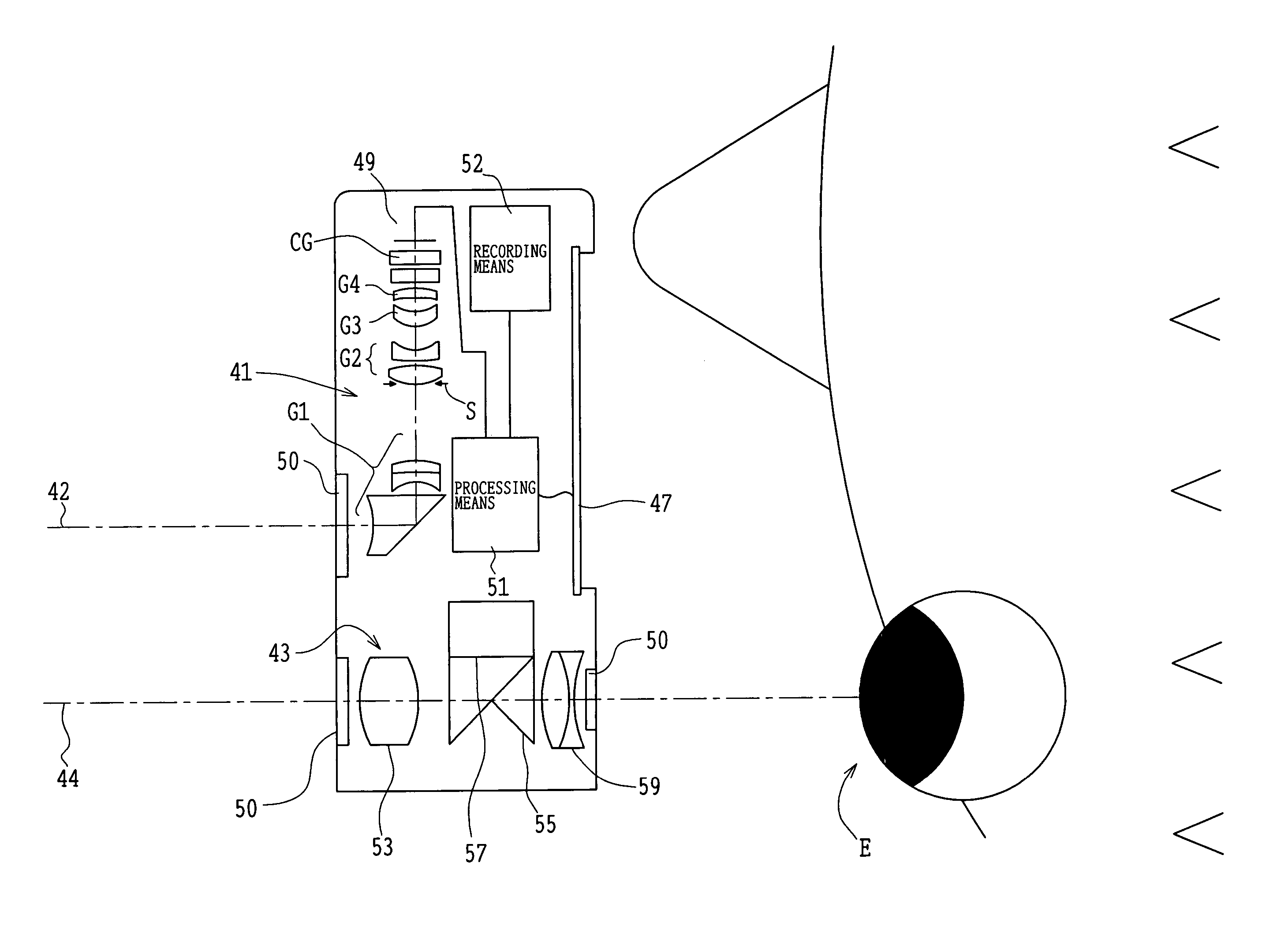
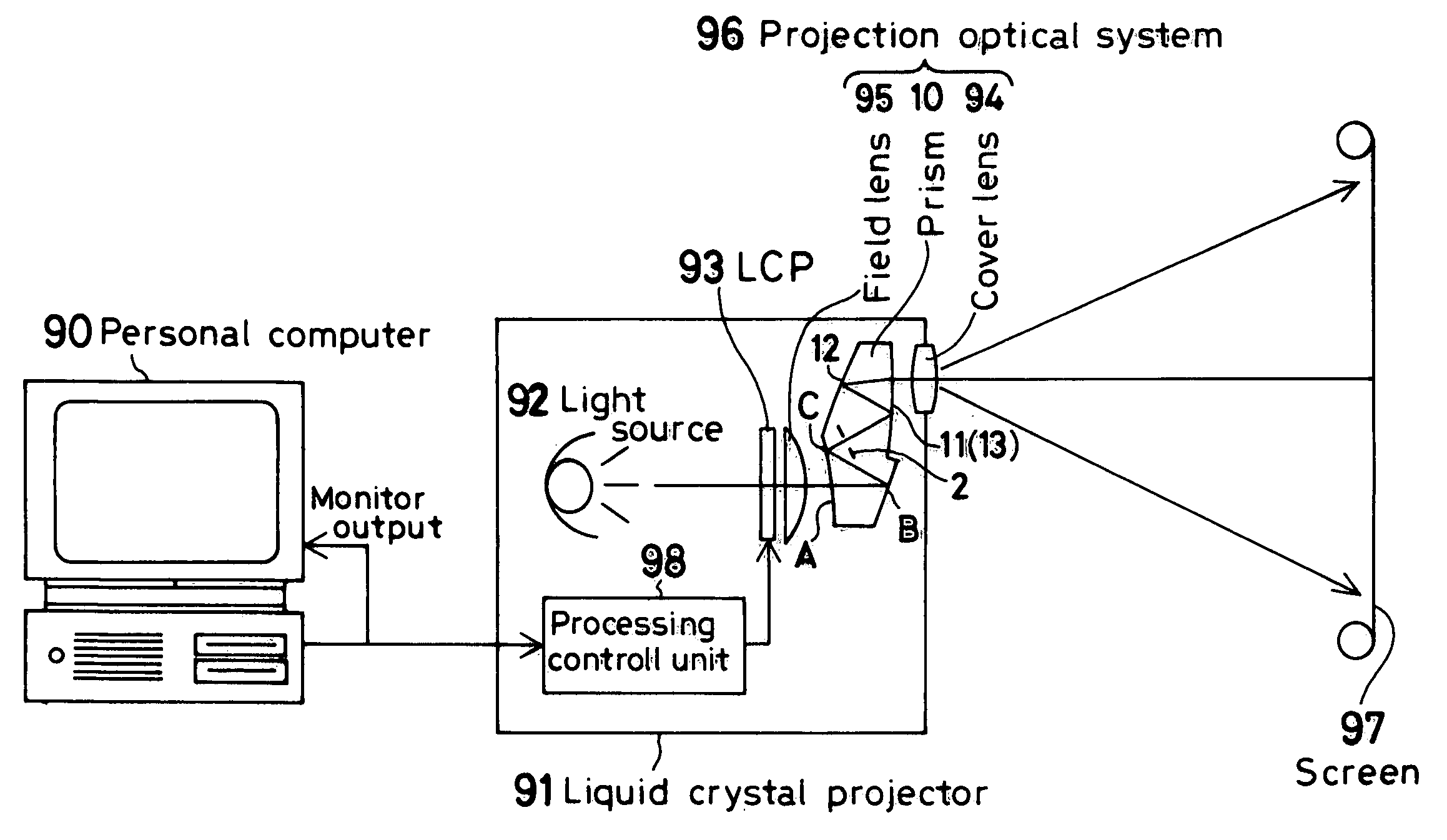
Holographic Projection System with Optical Wave Tracking and with Means for Correcting the Holographic Reconstruction
ActiveUS20100103246A1Reduce the effect of aberrationSmall aberrationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVisibilityProjection system
A holographic projection system with a display screen and an optical wave tracking means for controlling the direction of propagation of a modulated wave uses a position controller and an eye finder. An extremely wide tracking range is realised in the projection system for simultaneous viewing of the reconstruction by multiple observers, which are situated beside one another. The reconstruction of the scene is reconstructed for each eye position of an observer such that the entire scene is visible in the visibility region in a large tracking range with minimal errors. The projection system reconstructs the scene with the help of modulated partial waves. Projection means direct these partial waves with separately holographically reconstructed segments of the scene at the desired eye position through a structure of screen segments which are at least horizontally staggered on the display screen.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
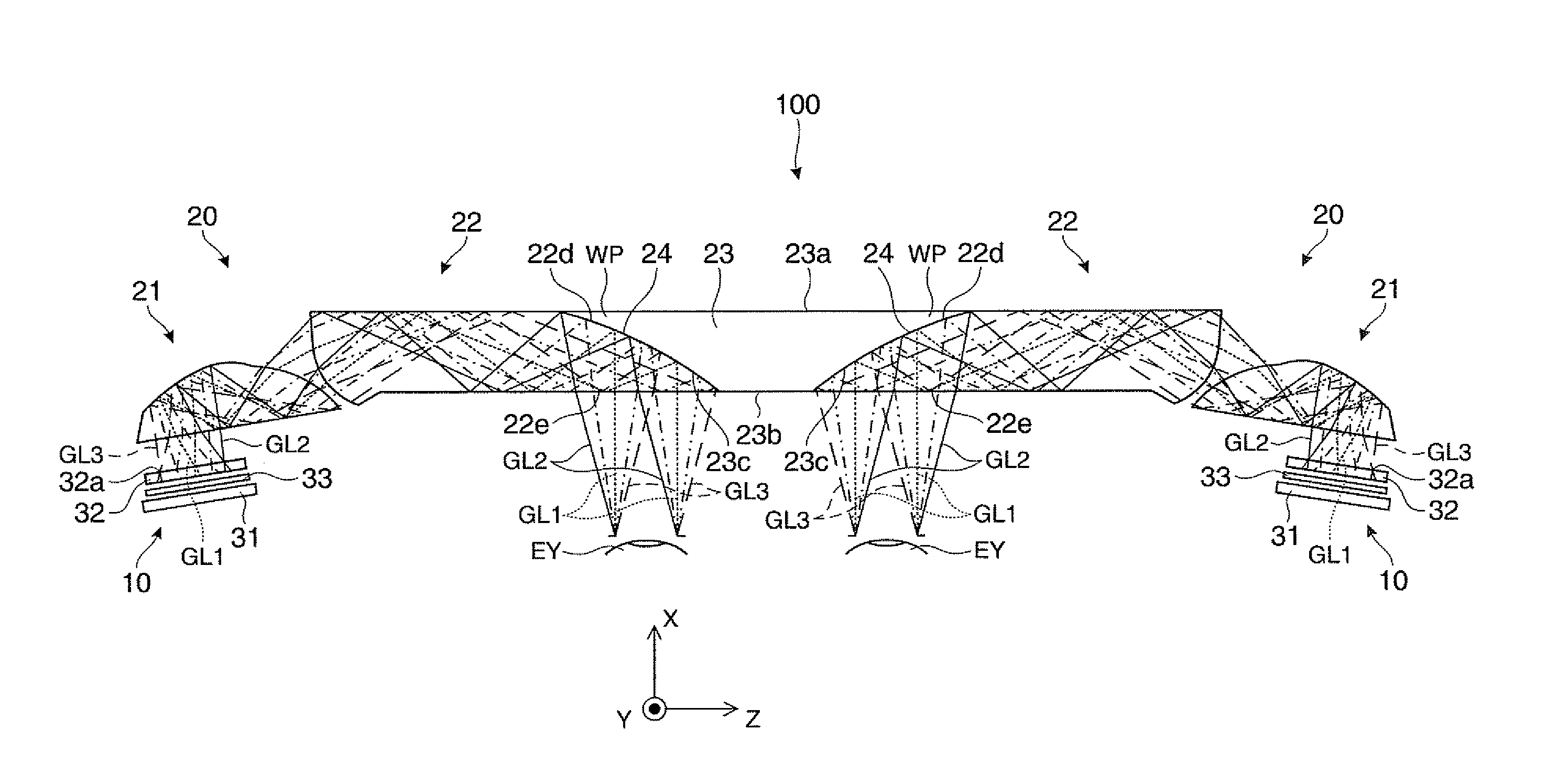
Image relay optical system and virtual image display device including the same
ActiveUS20120243102A1Small aberrationReduce aberrationPlanar/plate-like light guidesVirtual imageOptoelectronics
An image relay optical system is provided with an optical coupling member before incidence of image light on a light guide member. Among a first light incident surface, a coupling member reflecting surface, and a first light emitting surface provided in the optical coupling member, the coupling member reflecting surface and the first light emitting surface are curved surfaces. Therefore, a large bright virtual image with reduced aberration can be displayed.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
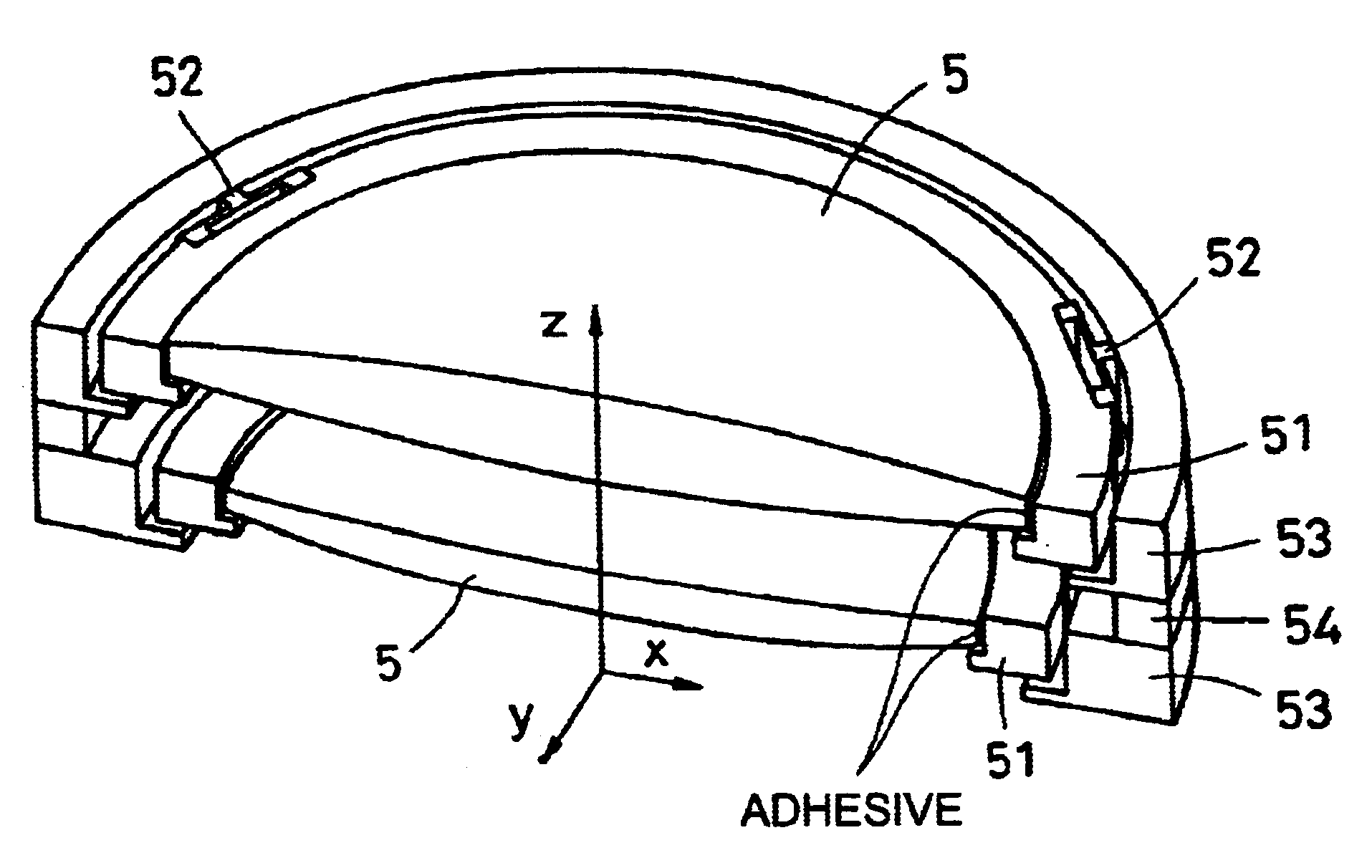
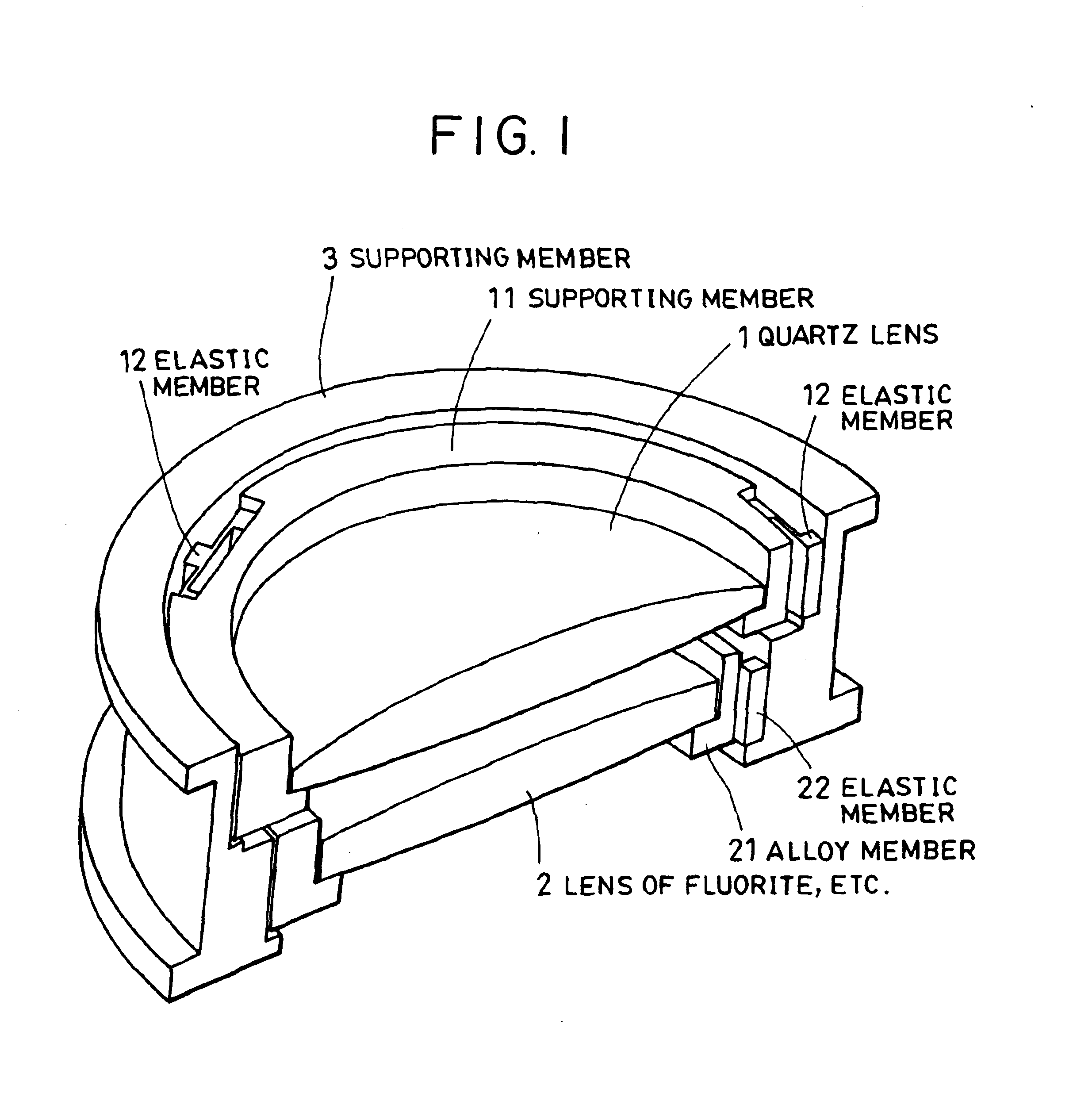
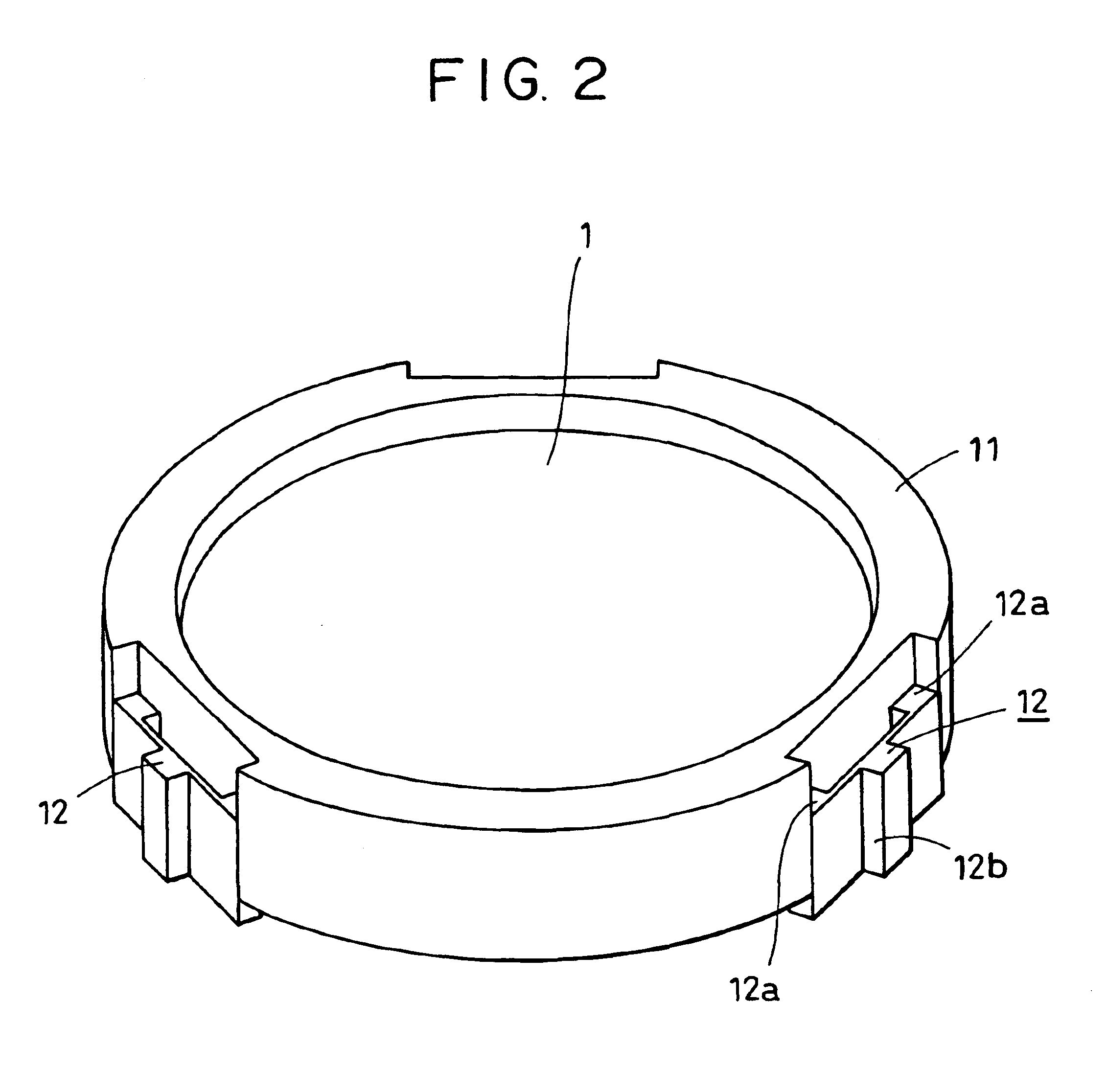
Supporting structure of optical element, exposure apparatus having the same, and manufacturing method of semiconductor device
InactiveUS6867848B2Reduce surface deformationHigh resolutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
A supporting structure for supporting an optical element. The supporting structure includes a first supporting member for supporting the optical element, a second supporting member arranged in an outer diameter side of the first supporting member for supporting the first supporting member, and an elastic member placed between the first supporting member and the second supporting member in the radial direction of the optical element. The inner diameter side of the elastic member is connected to the first supporting member while an outer diameter side of the elastic member is connected to the second supporting member. The elastic member is elastically deformable in the radial direction.
Owner:CANON KK
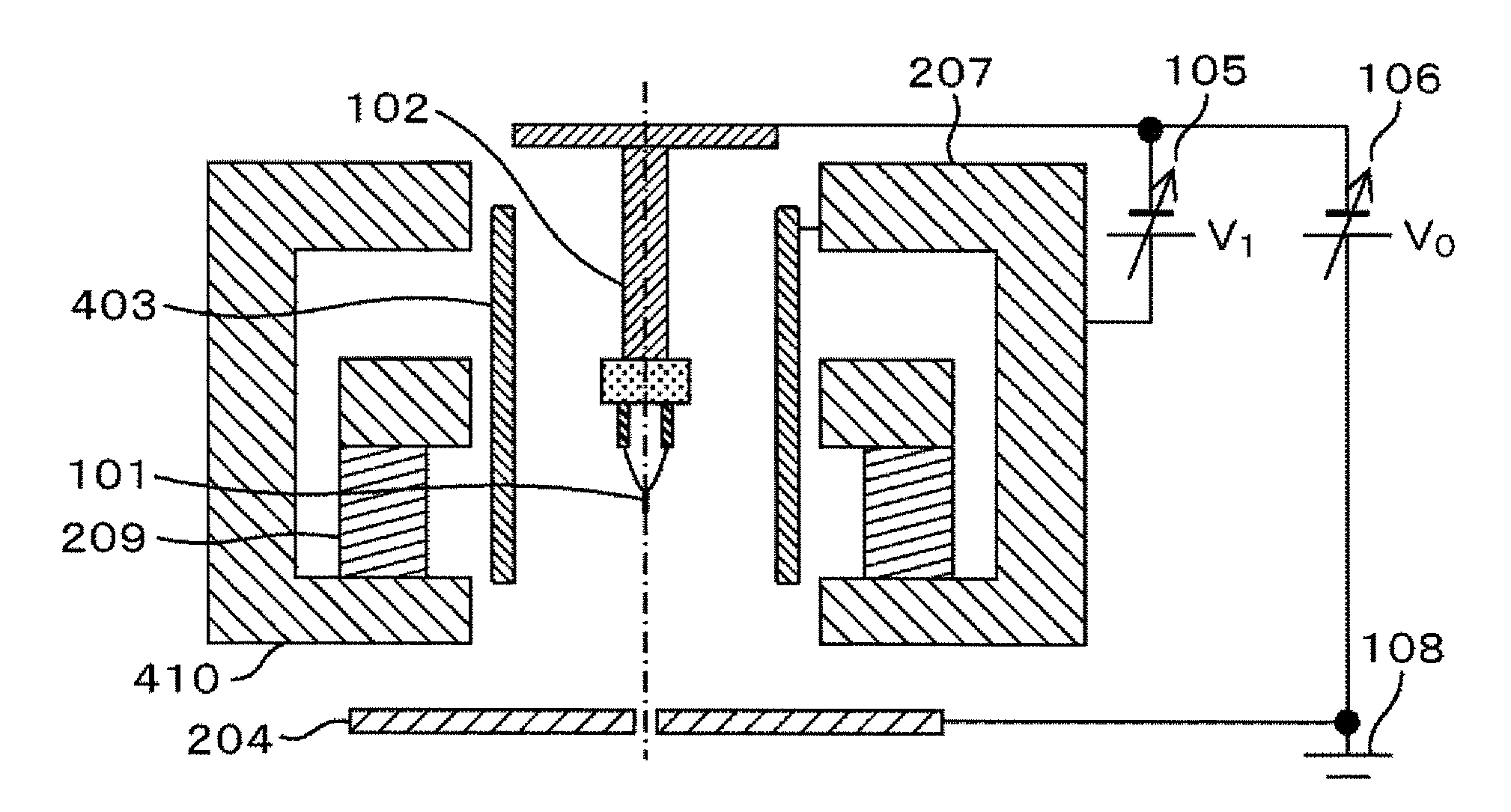
Electron Lens and Charged Particle Beam Apparatus
InactiveUS20080067396A1High resolutionSmall aberrationElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansRare earthMagnetic poles
The present invention provides a compact electron lens causing little aberration, and a charged particle beam apparatus such as a scanning electron microscope that is super compact and offers a high resolution. An upper magnetic pole and a sample-side magnetic pole are magnetically coupled to the respective poles of a permanent magnet that is made of a highly strong magnetic material such as a rare-earth cobalt system or a neodymium-iron-boron system, that is axially symmetrical, and that has a hole in the center thereof. An inner gap is created on the side of a center axis. Thus, a magnetic lens is formed axially. Moreover, a semi-stationary magnetic path that shields an outside magnetic field and has the magnetic reluctance thereof regulated is disposed outside. The sample-side magnetic pole and magnetic path defines a region where magnetic reluctance is the highest outside the permanent magnet. A space defined by the permanent magnet, upper magnetic pole, sample-die magnetic pole, and semi-stationary magnetic path is filled with a filling made of a non-magnetic material. Thus, an objective lens is constructed.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Optical device, image display device and head mounted display
A hologram optical element is formed on a substrate so as to make an optical device. The hologram optical element is formed in an area smaller than an irradiation area of a beam for reproduction such as image light or object light on the substrate. Supposing that the beam for reproduction is made of a center beam having intensity higher than 50% of center intensity and other peripheral beam, the hologram optical element is formed on the substrate in a size for diffracting only the center beam so that a flare or a ghost can be relieved without using additional optical elements such as a shading plate.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA PHOTO IMAGING
Electronic imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20050030405A1Thin depthSmall aberrationTelevision system detailsPrismsOptic systemElectron
An electronic imaging apparatus of the present invention comprises a photographing optical system, in order from an object side, a first lens group having negative refracting power, which has a reflecting component having a reflecting surface for bending an optical path of an incident light from the object side and at least two positive lens groups arranged at an image side of the first lens group, wherein the photographing optical system is a zoom optical system and the following condition is satisfied: −1.75<f1 / fw<−0.8 where f1 is a focal length of the first lens group, and fw is a focal length at the wide angle end at the photographing optical system.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
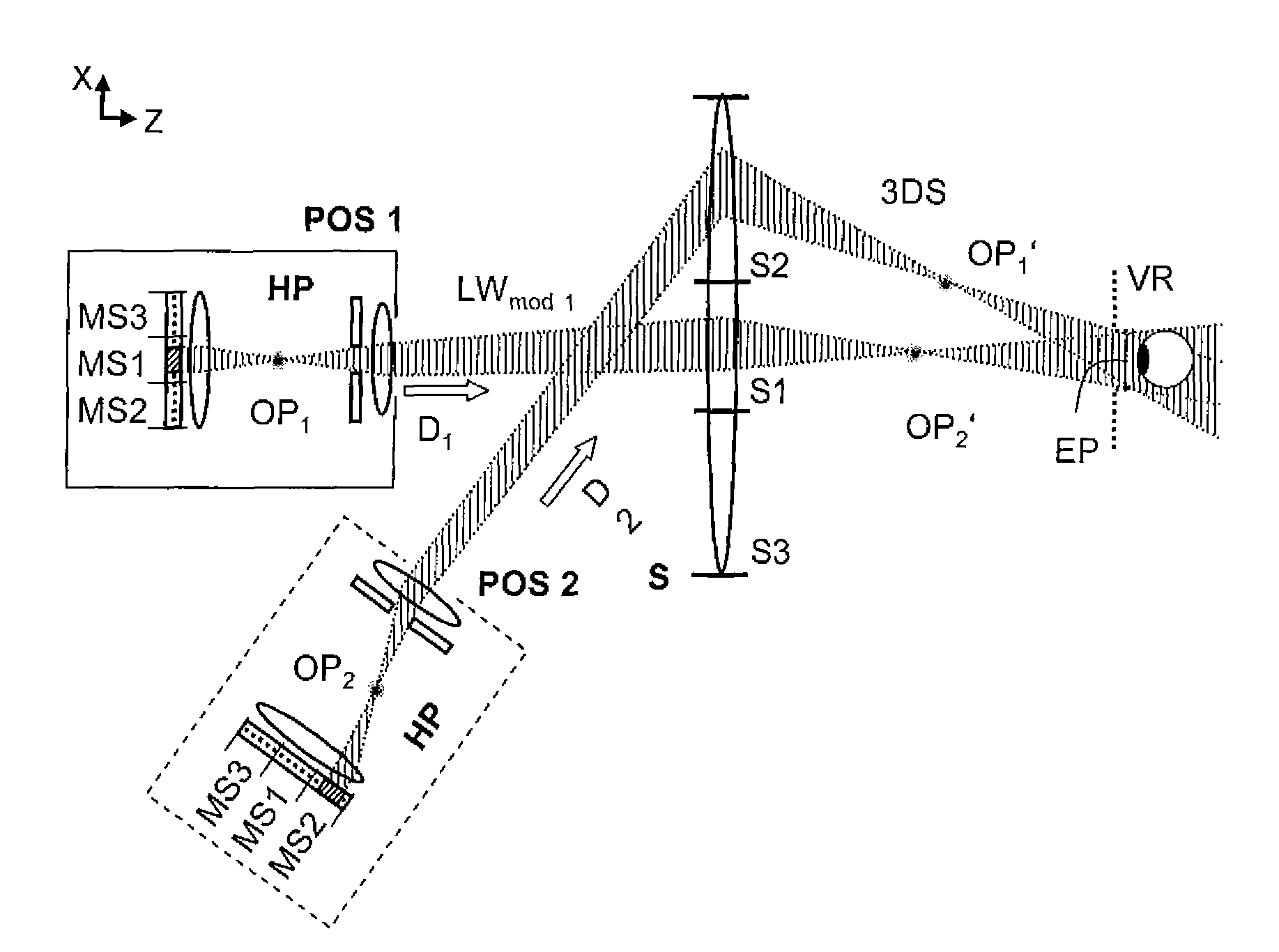
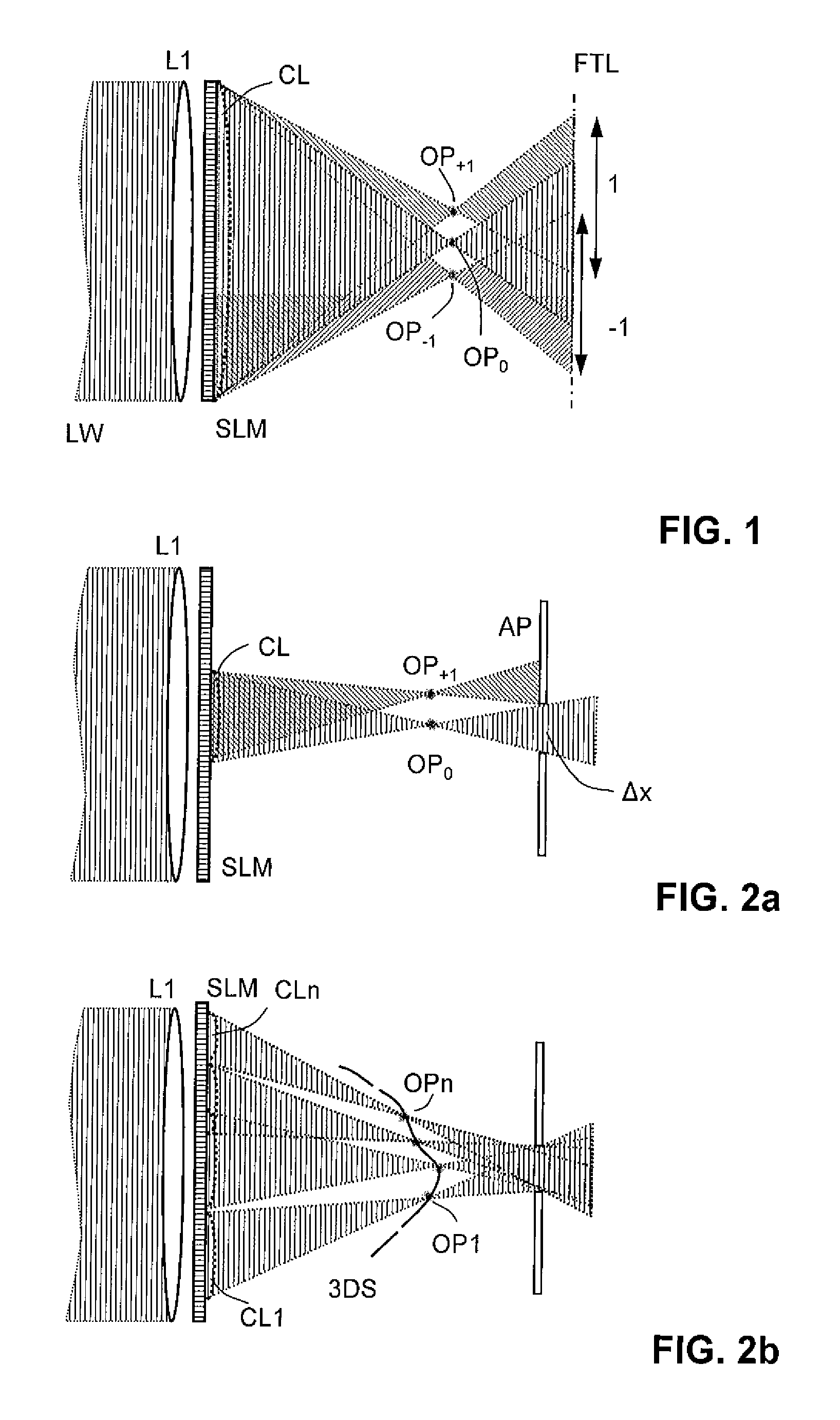
Holographic projection system with optical wave tracking and with means for correcting the holographic reconstruction
ActiveUS8395833B2Reduce the effect of aberrationSmall aberrationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVisibilityProjection system
A holographic projection system with a display screen and an optical wave tracking element for controlling the direction of propagation of a modulated wave uses a position controller and an eye finder. An extremely wide tracking range is realized in the projection system for simultaneous viewing of the reconstruction by multiple observers, which are situated beside one another. The reconstruction of the scene is reconstructed for each eye position of an observer such that the entire scene is visible in the visibility region in a large tracking range with minimal errors. The projection system reconstructs the scene with the help of modulated partial waves. Projection element(s) direct these partial waves with separately holographically reconstructed segments of the scene at the desired eye position through a structure of screen segments which are at least horizontally staggered on the display screen.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
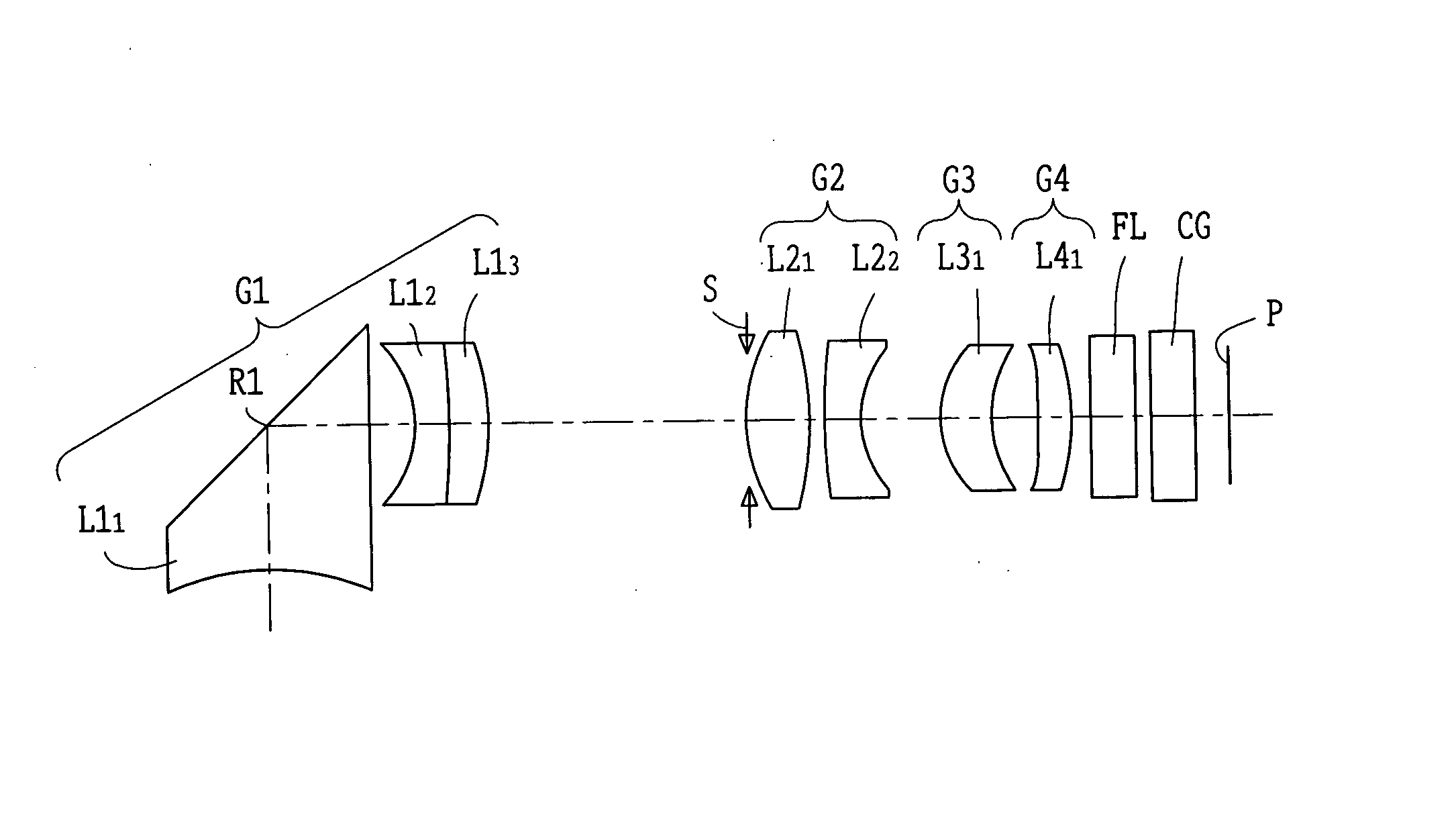
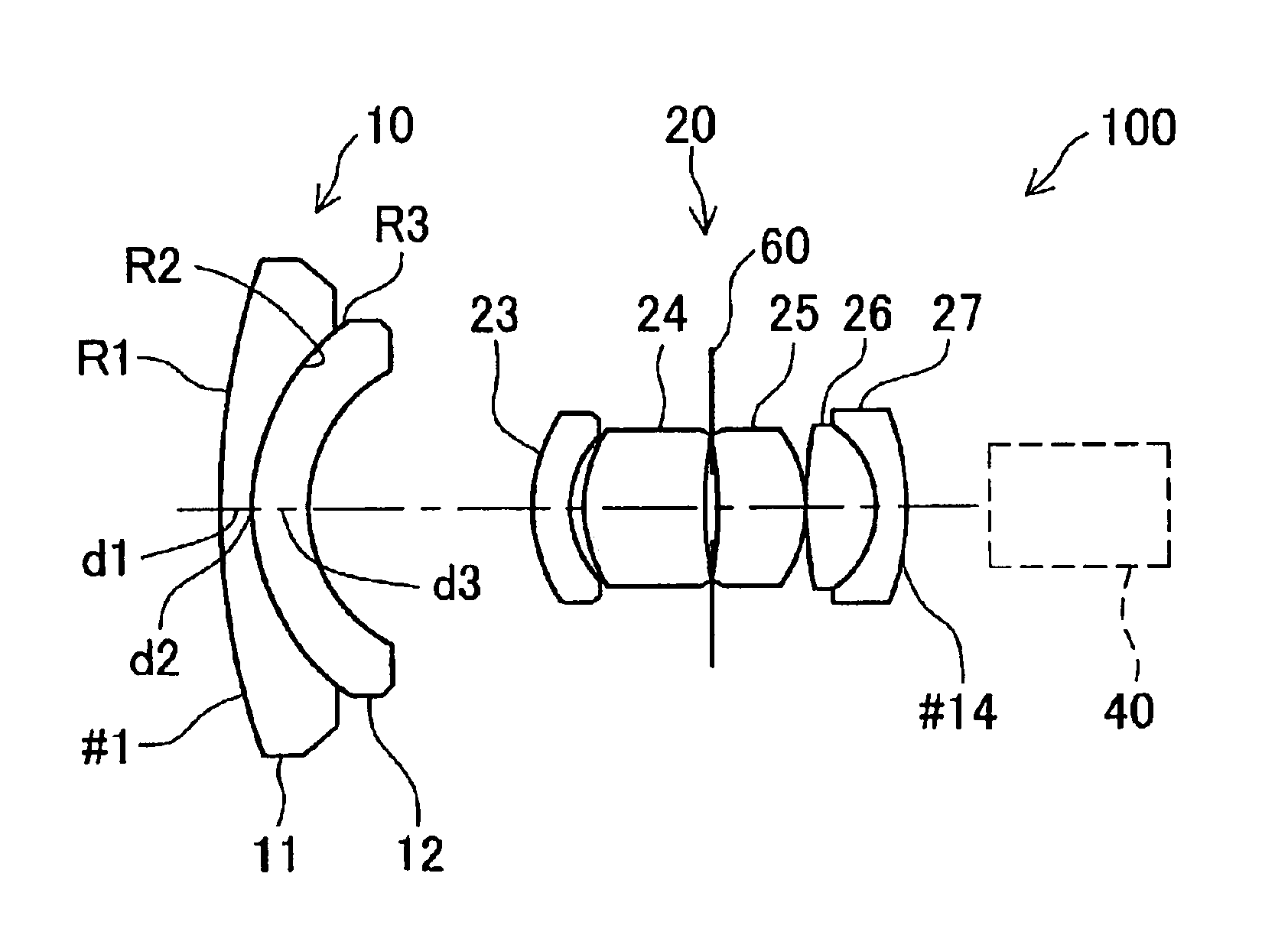
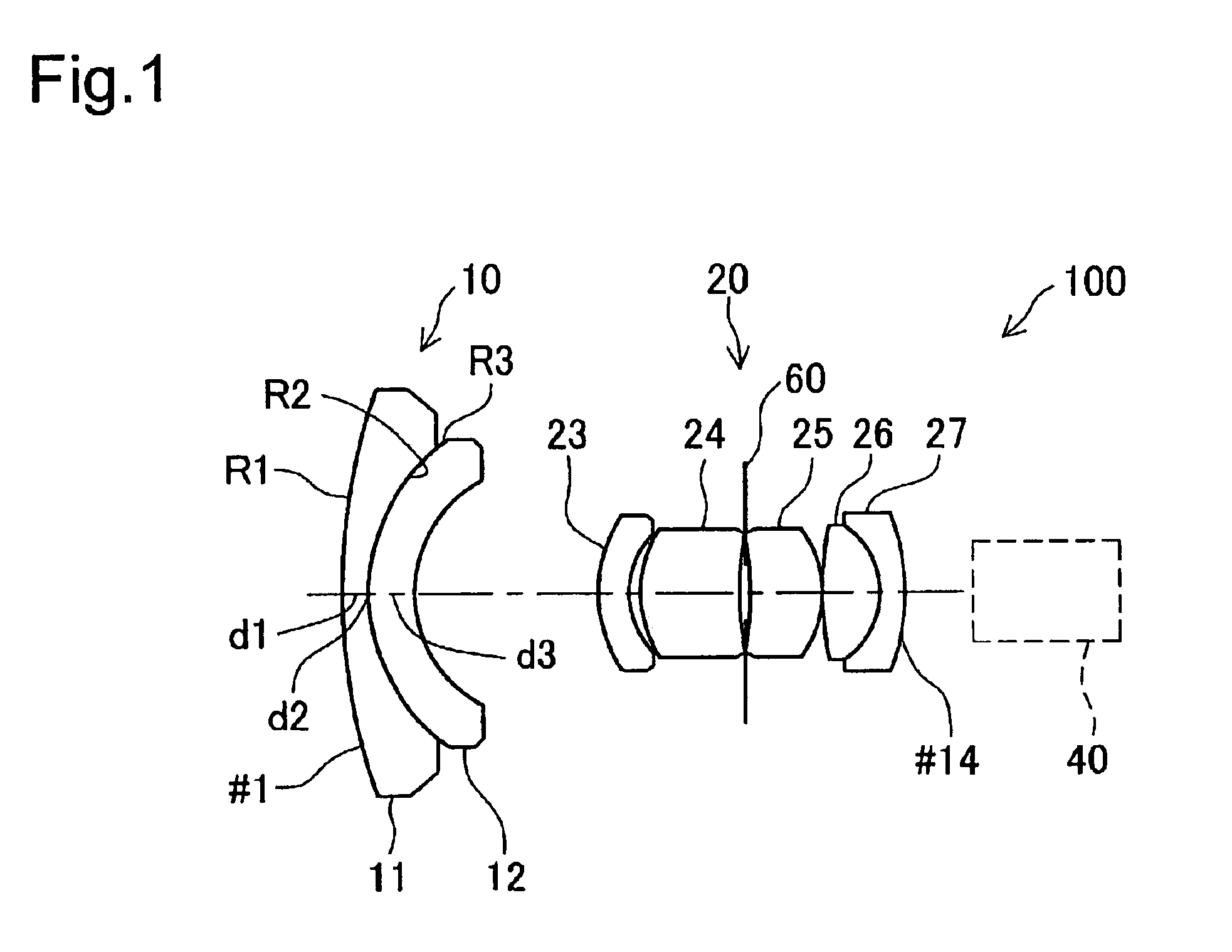
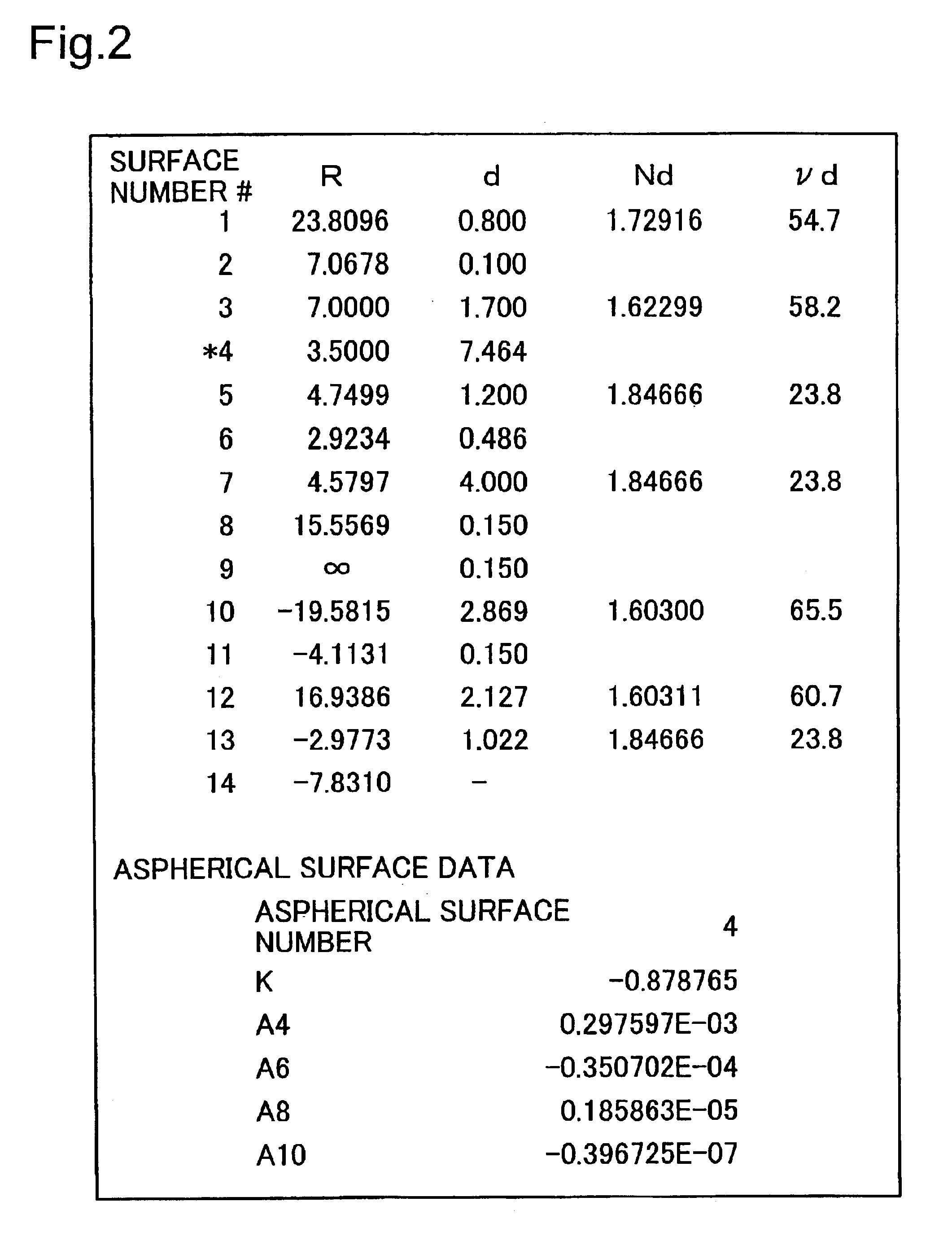
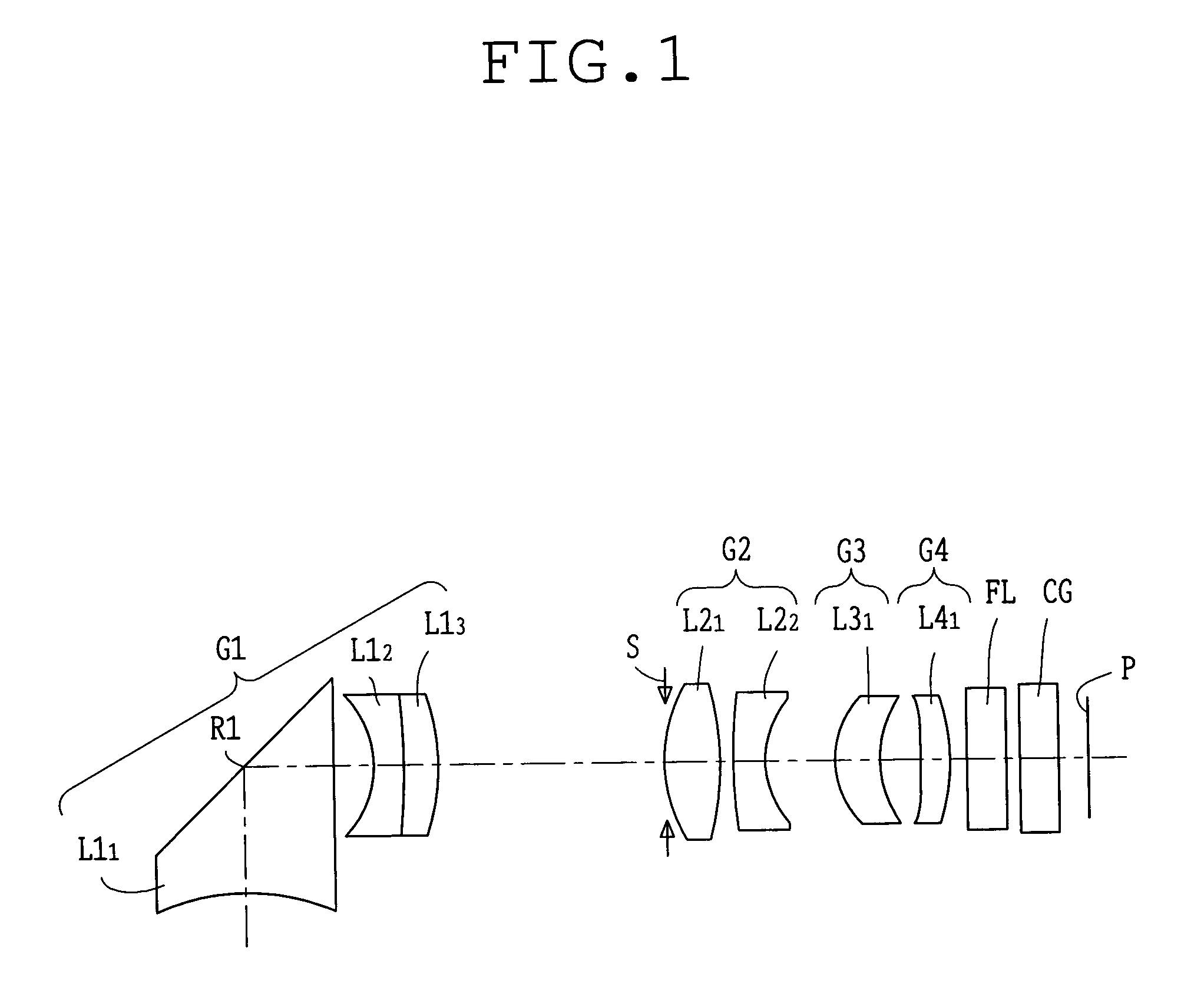
Wide-angle lens system
A wide-angle lens system having a long back focal length, disposed in front of a ⅓″ CCD camera and the focal length (f) for all lens groups is 3.0 mm, the F-number is 3.0 and the half-field angle is 46°. The following conditions are met by the first lens group: 1≦d / d3<1.2; R3 / R2=0.99; and d2 / f=0.03. Here, (d) indicates the thickness of the second lens along the normal line at a given distance from the optical axis within the maximum effective diameter of the object side convex surface of the lens. d3 is the thickness of the second lens along the optical axis.
Owner:ELMO CO LTD
Image-forming optical system
InactiveUS20080165424A1Aberration performanceIncrease degreeTelevision system detailsPrismsOptical pathPrism
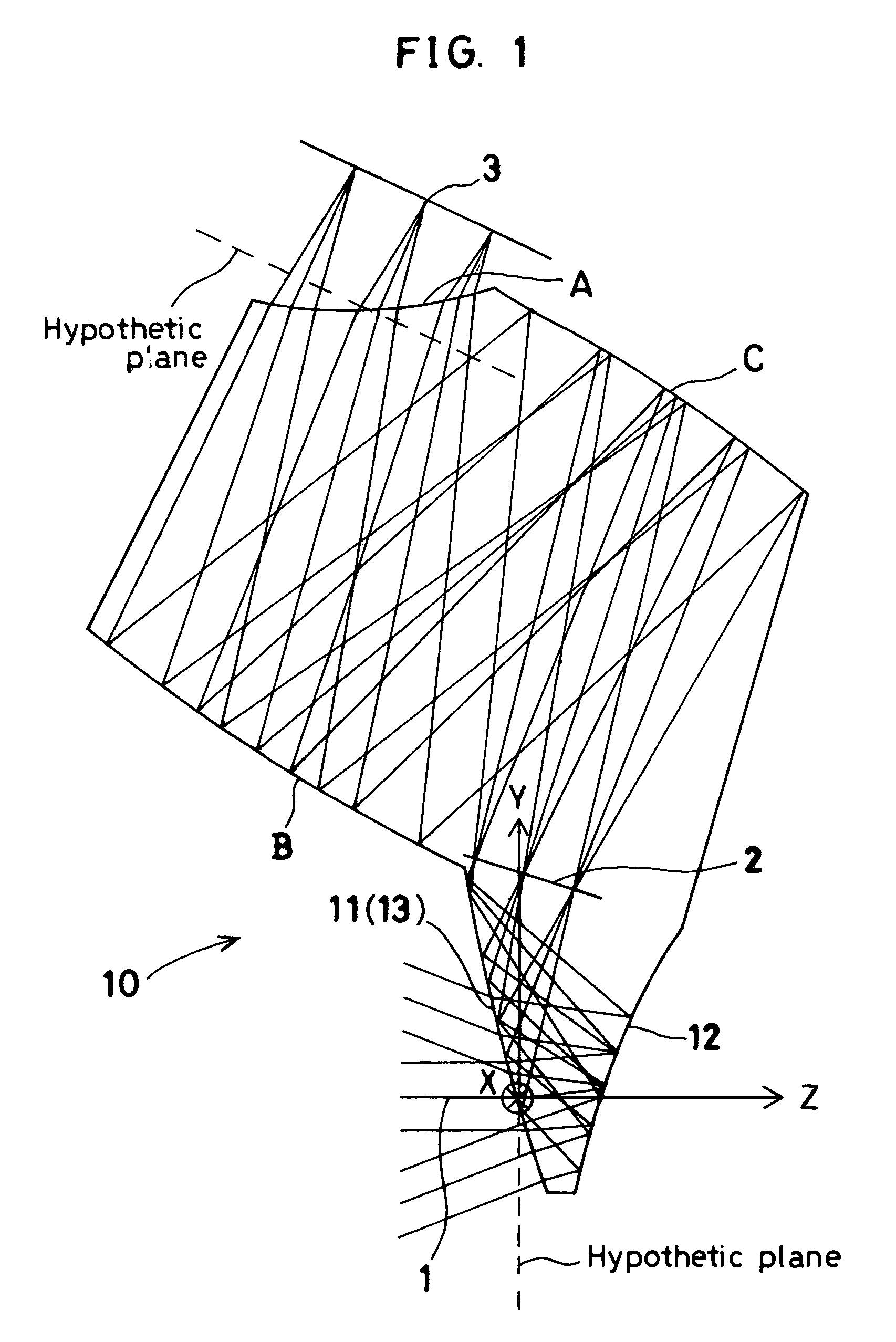
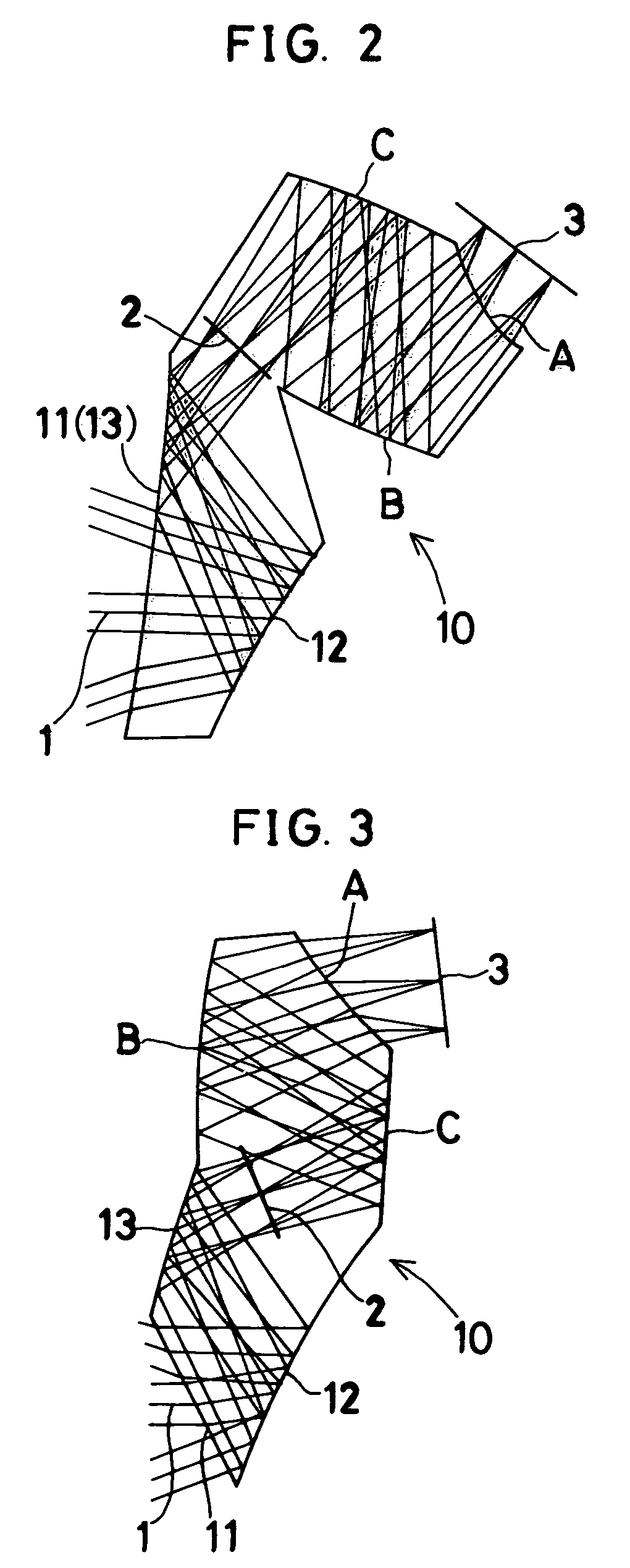
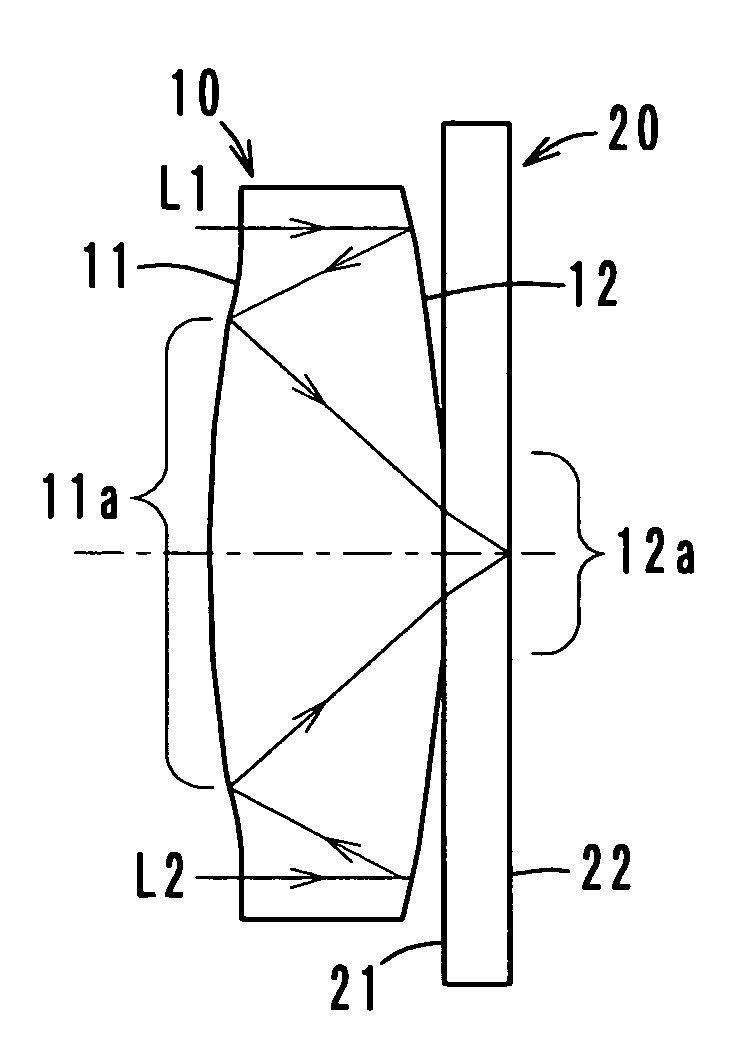
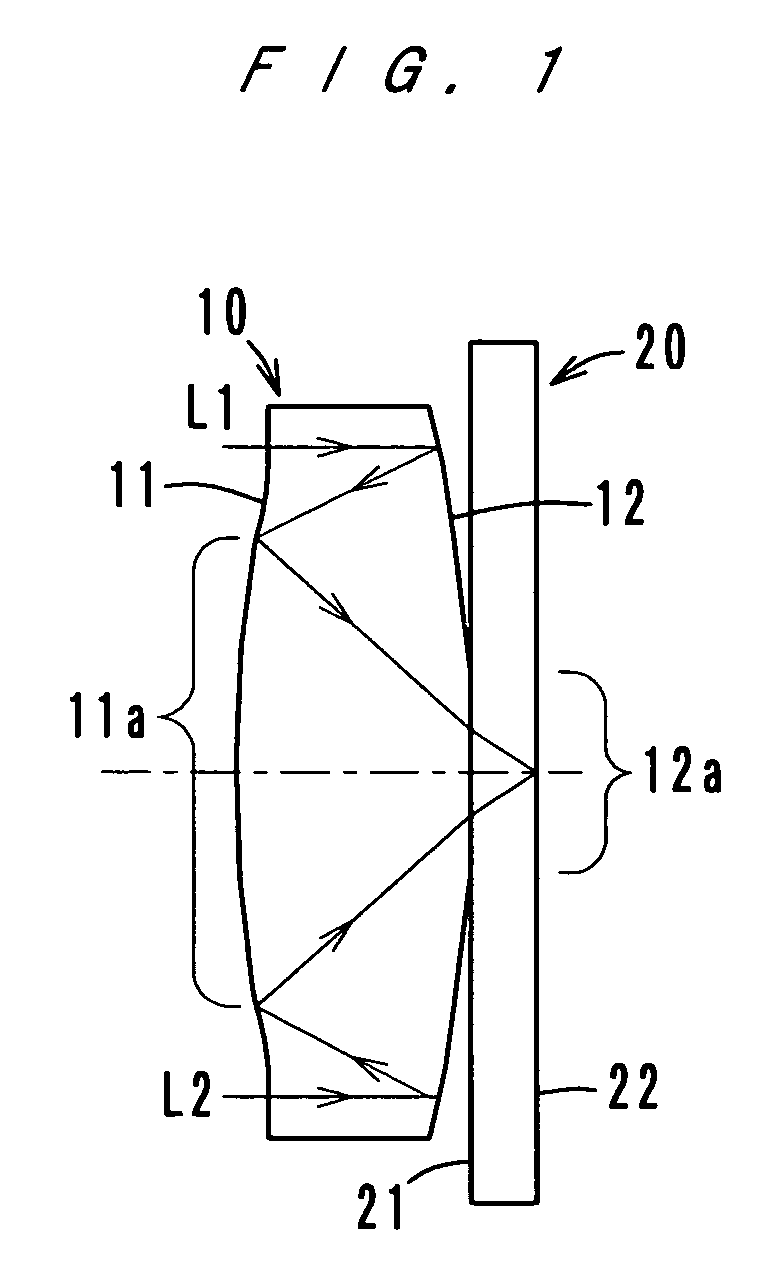
A high-performance image-forming optical system made compact and thin by folding an optical path using reflecting surfaces arranged to minimize the number of reflections. The image-forming optical system has a single prism. When image-side three surfaces of the prism are defined as a surface A, a surface B and a surface C in order from the image plane side thereof, at least one of the surfaces B and C has a rotationally asymmetric curved surface configuration that gives a power to a light beam and corrects aberrations due to decentration. The optical system leads light rays from an object to the image plane without forming an image in the prism and has a pupil in the prism. The surface A is a transmitting surface through which rays exit from the prism. The surfaces B and C are internally reflecting surfaces, which are positioned to face each other to form a Z-shaped optical path.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Electron gun
InactiveUS20120062094A1Reduce incidental electrostatic lens actionSmall aberrationElectrode and associated part arrangementsDischarge tube main electrodesPower flowElectrostatic lens
The present invention has an object to provide a cold cathode field-emission electron gun with low aberration, to thereby provide a high-brightness electron gun even in the case of a large current. The present invention provides a field-emission electron gun which extracts an electron beam from a cathode and converges the extracted electron beam, the field-emission electron gun including: a magnetic field lens which is provided such that the cathode is disposed inside of a magnetic field of the lens; and an extraction electrode for extracting electrons from the cathode, the extraction electrode being formed into a cylindrical shape without an aperture structure. The present invention can provide an electron gun having a function of converging an electron beam using a magnetic field, the electron gun which is capable of reducing an incidental electrostatic lens action and has small aberration and high brightness.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
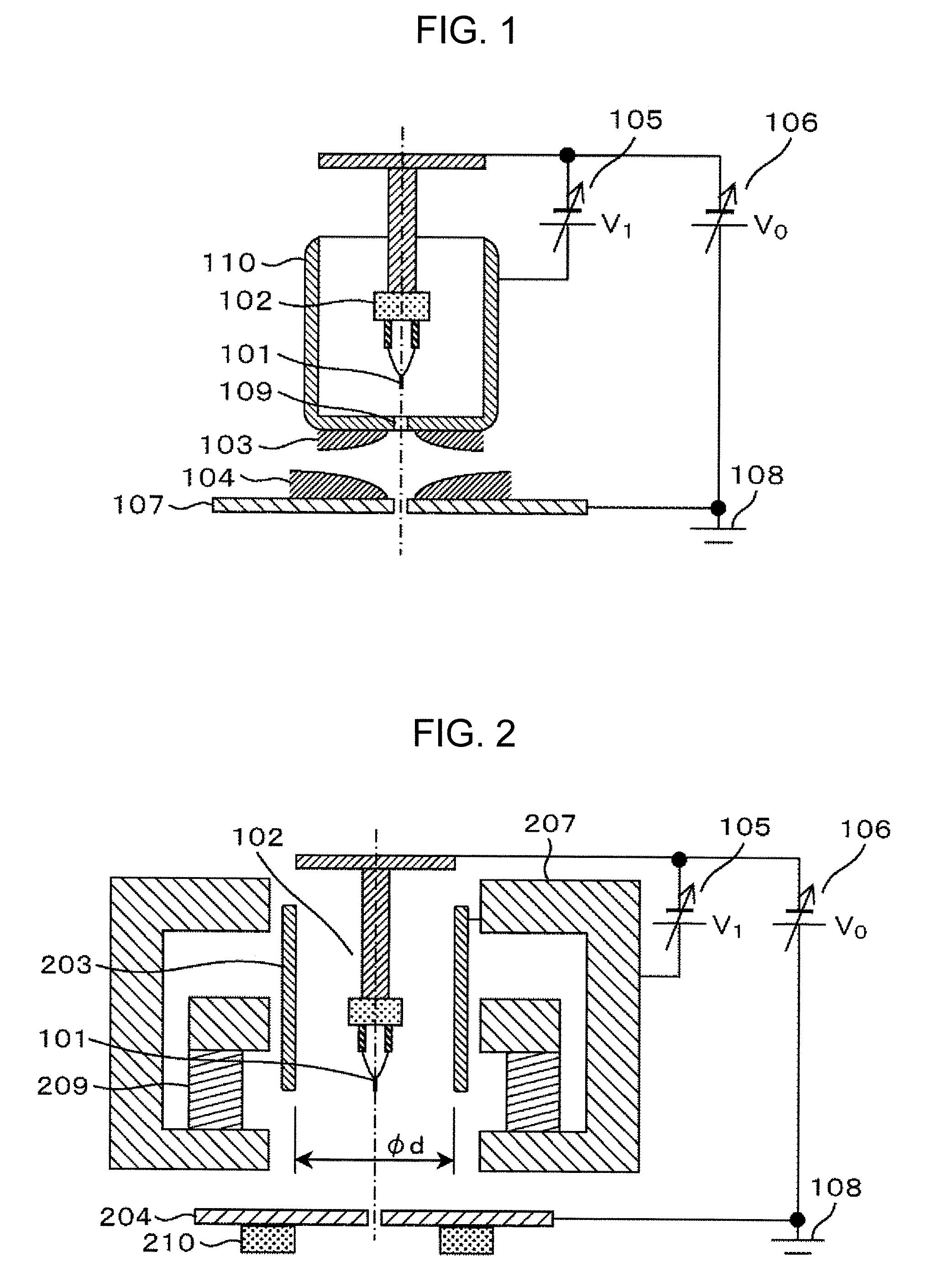
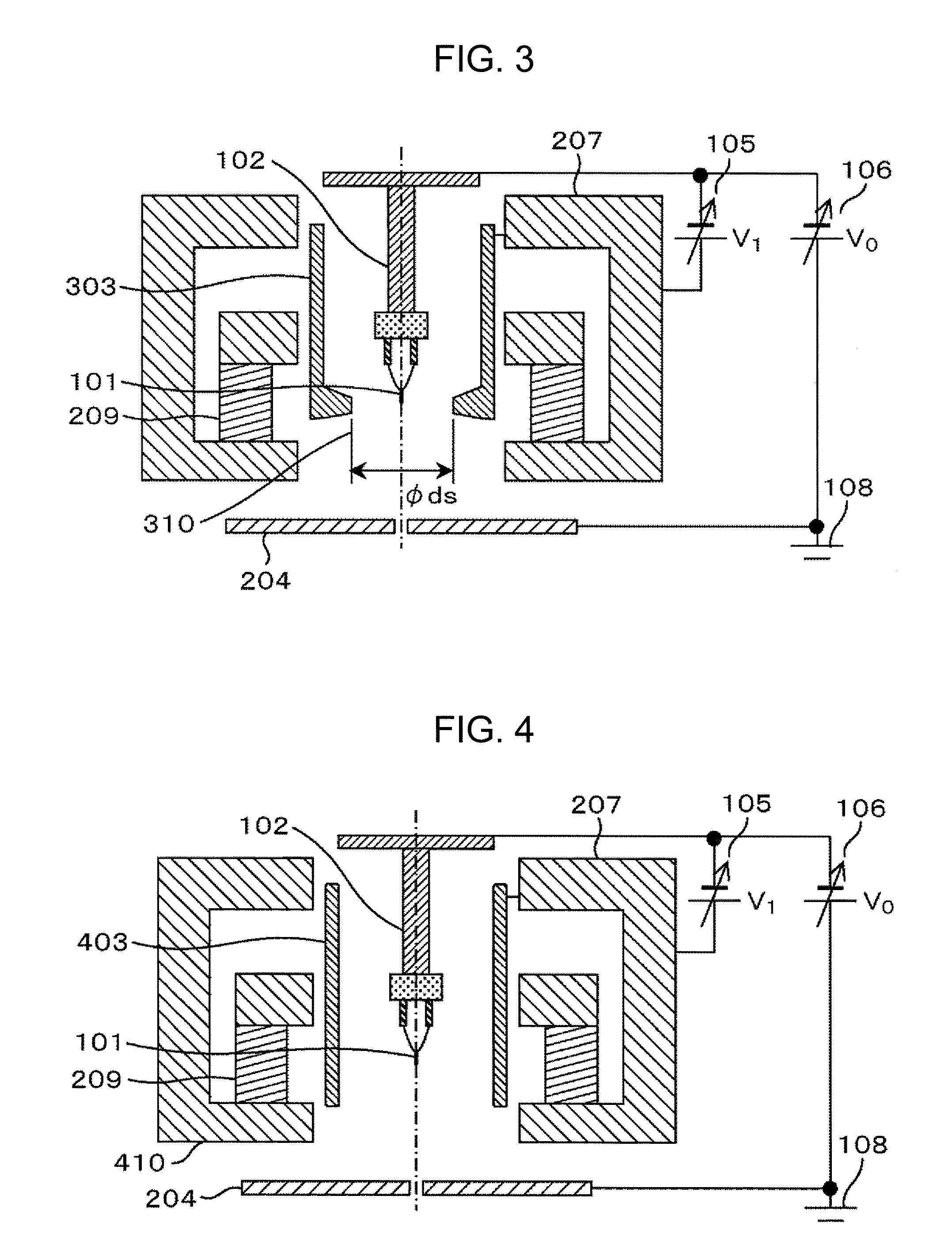
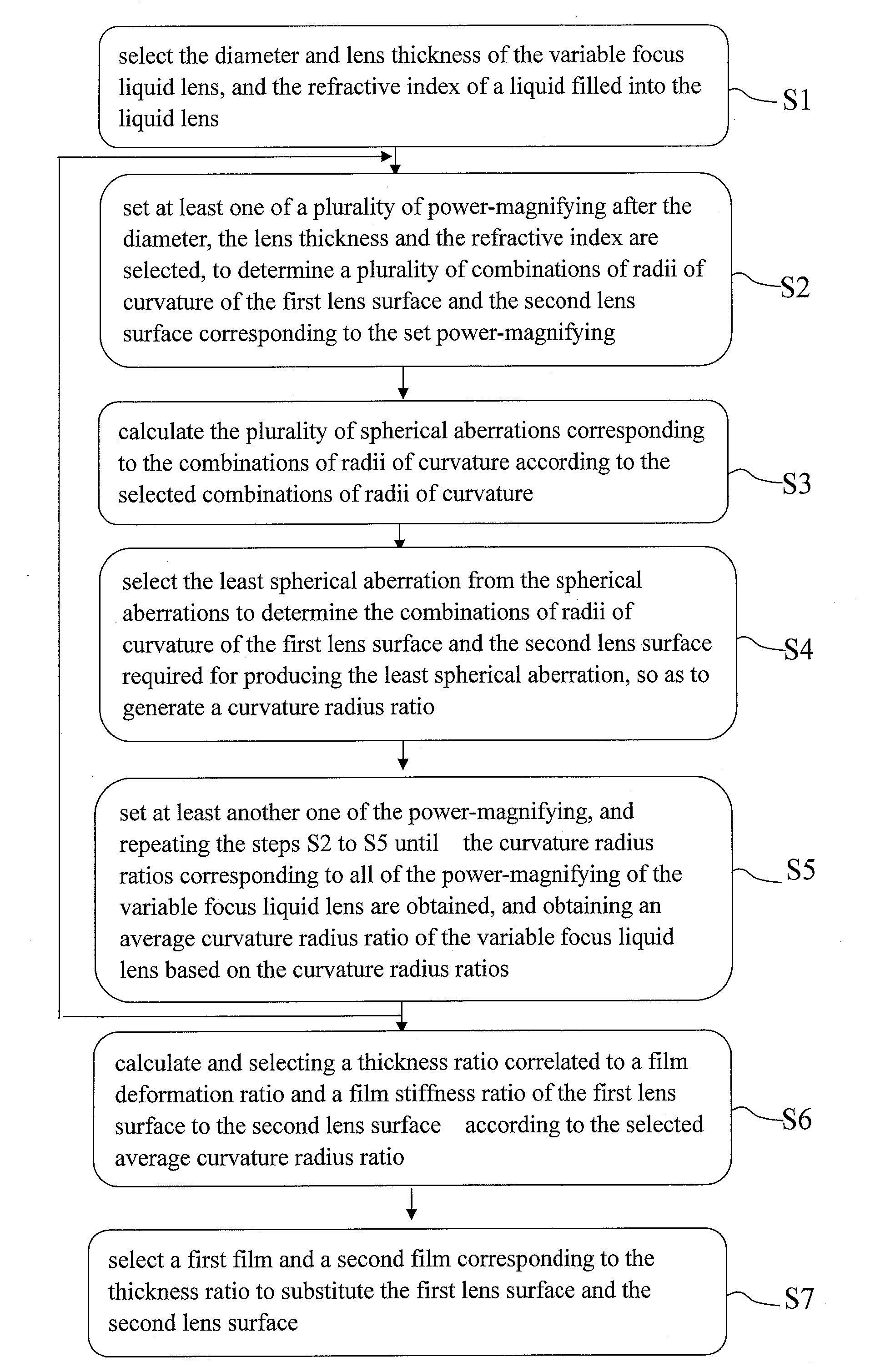
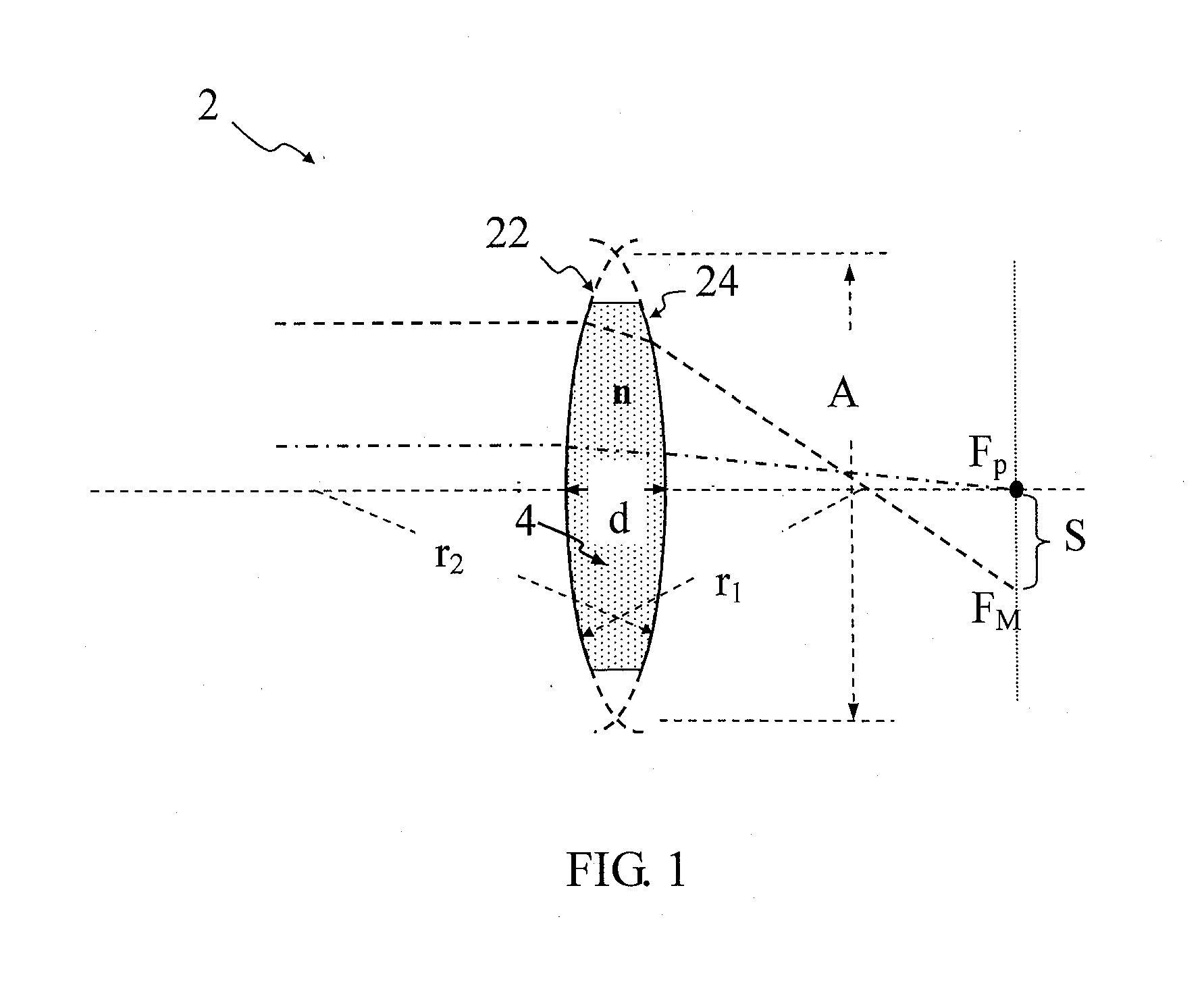
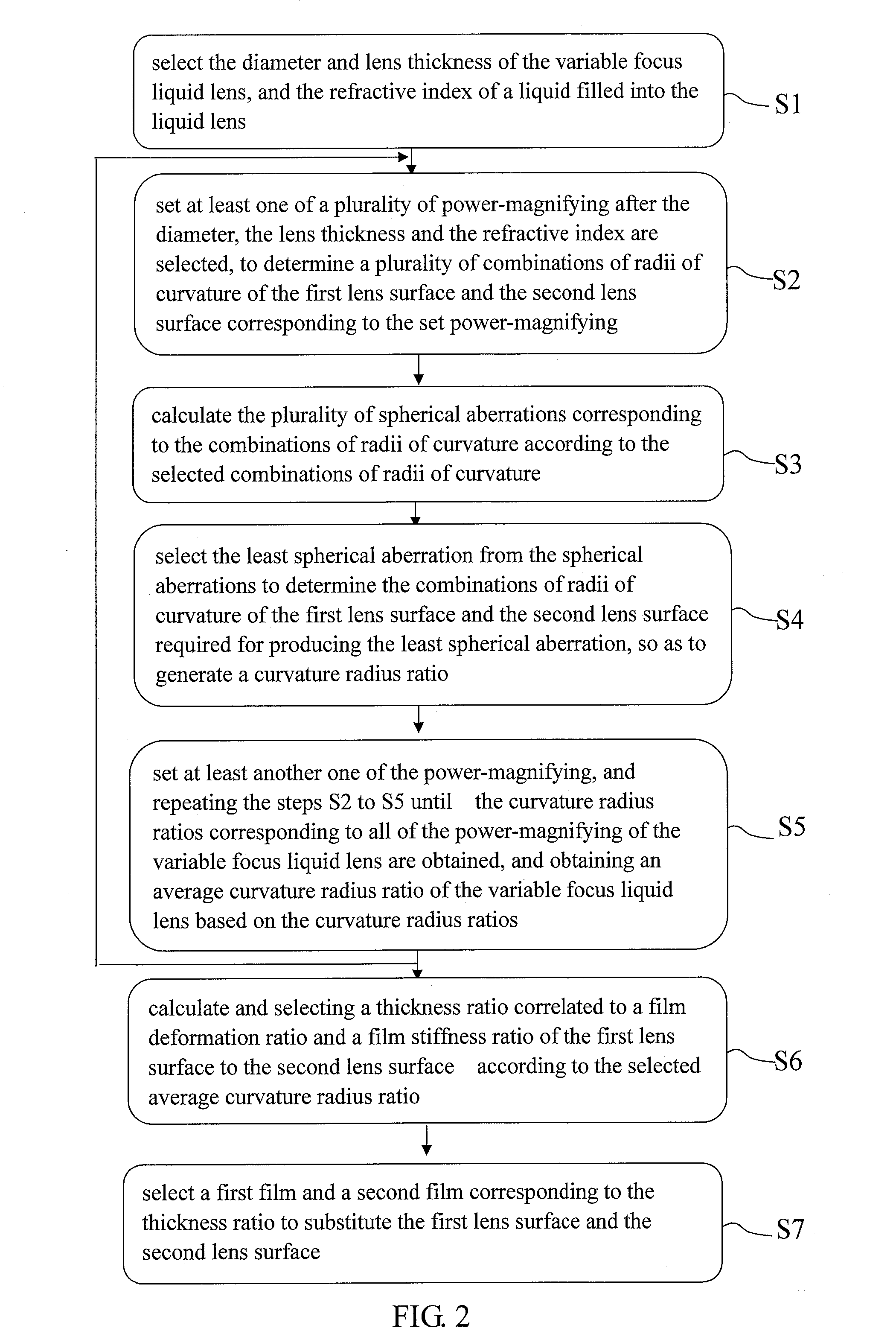
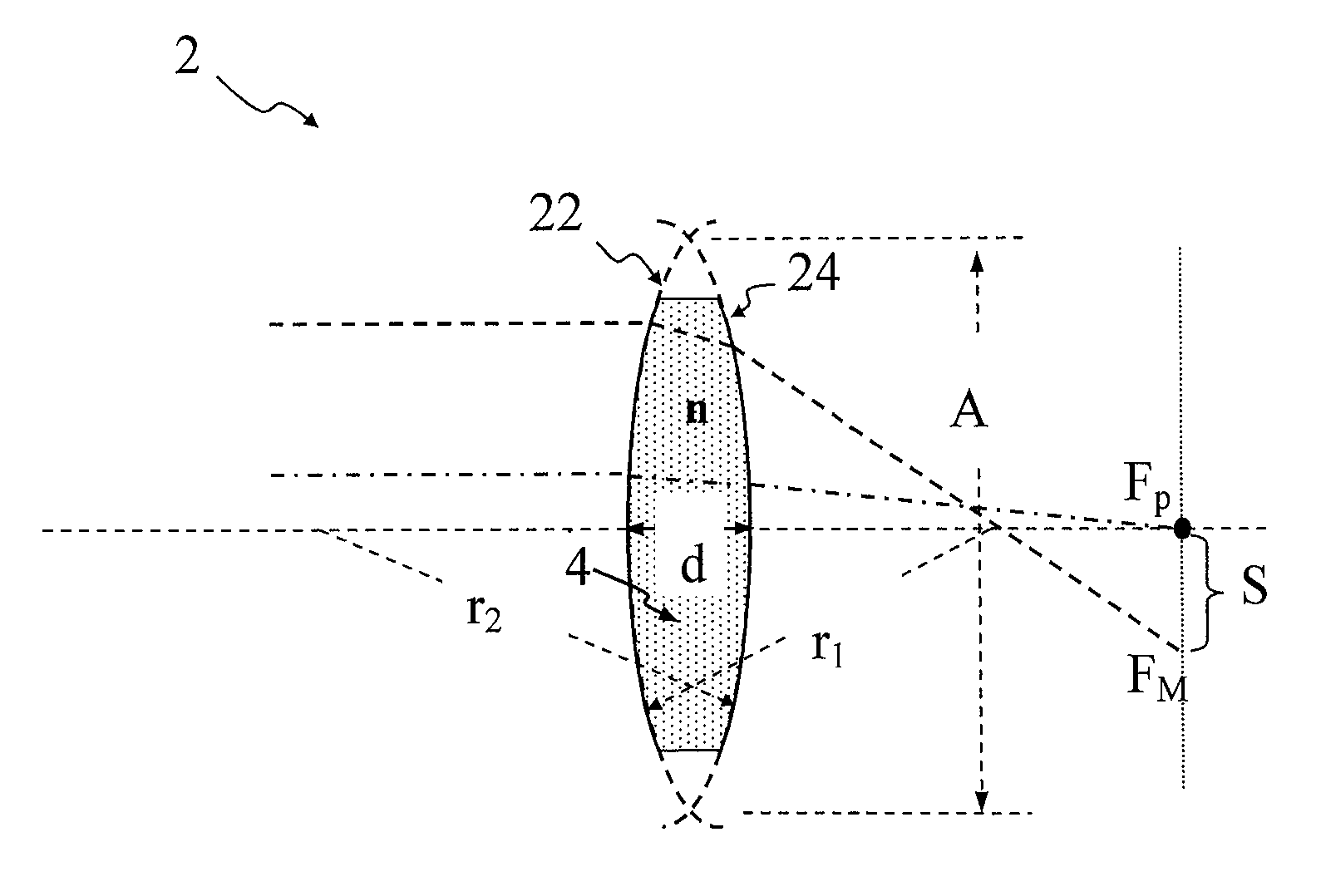
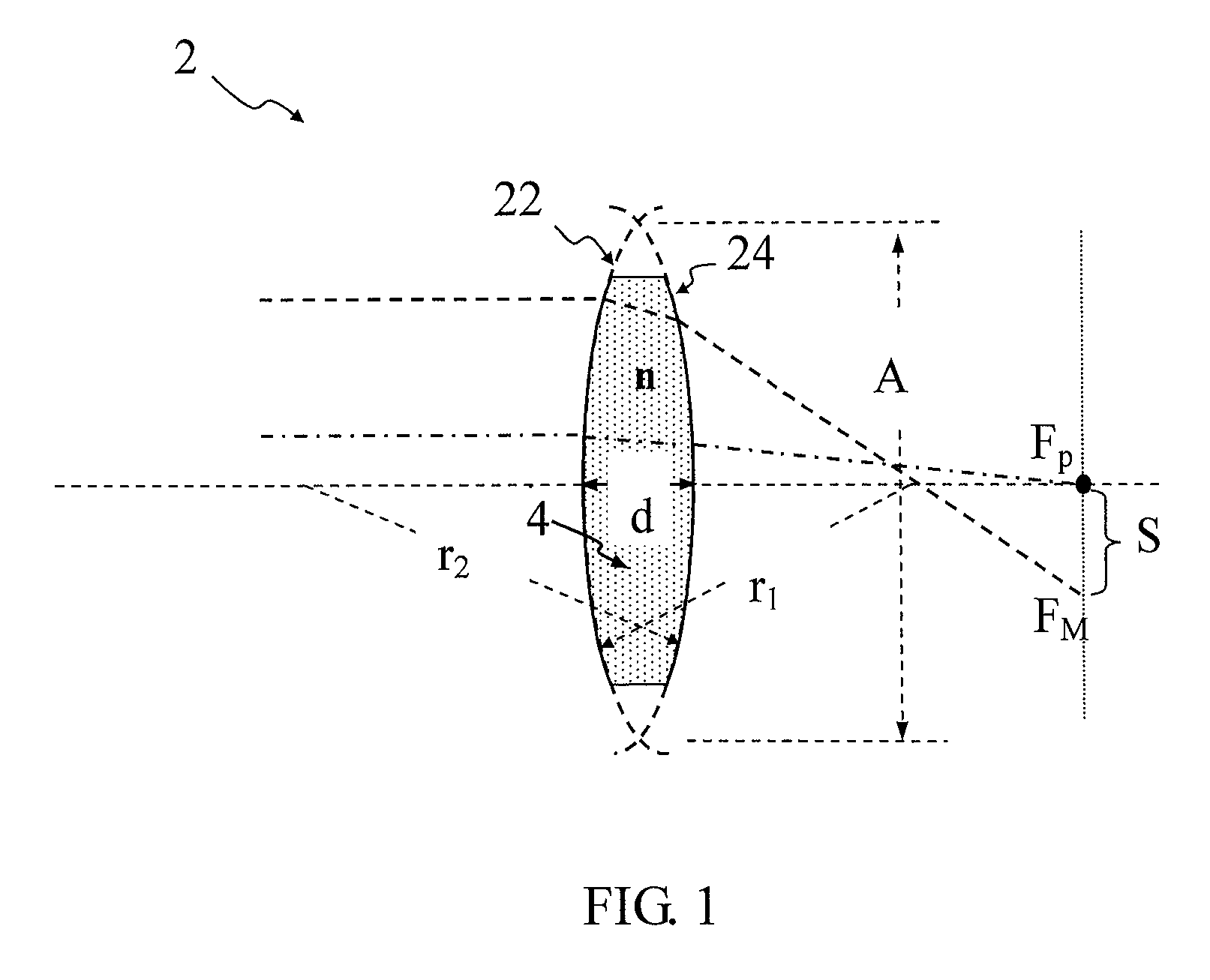
Method for compensating aberration of variable focus liquid lens
A method for compensating an aberration of a variable focus liquid lens is configured to compensate the aberration associated with a first lens surface and a second lens surface of the liquid lens. The first lens surface is of a first radius of curvature. The second lens surface is of a second radius of curvature.
Owner:NAT TAIPEI UNIV OF TECH
Variable magnification optical system and imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20190265449A1Small fluctuationFavorable optical performanceOptical elementsOphthalmologyConditional expression
A variable magnification optical system consists of, in order from an object side, a first optical system remaining stationary during changing magnification and a second optical system including a plurality of lens groups moving during changing magnification. The first optical system includes a first mirror and a second mirror having reflective surfaces arranged to face each other. The first mirror has a reflective surface concave toward the object side. The second mirror has a reflective surface convex toward the image side. An intermediate image is formed between the second mirror and the second optical system. Predetermined conditional expressions relating to the partial dispersion ratios of the lenses included in the second optical system are satisfied.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Imaging lens, imaging device and information device
An imaging lens includes an optical system having in order from an object side to an image side a first lens group having a positive refractive power and a second lens having a positive refractive power to image an optical image of an object, the first lens group and the second lens group being displaced in an extending amount different from one another to be focused on an object of a finite distance, the first lens group including a negative meniscus lens having a convex surface on the object side, a lens having a weak refractive power, and a lens having a positive refractive power, and the second lens group including four lenses or less or five lenses or less having at least one pair of a cemented lens.
Owner:RICOH KK
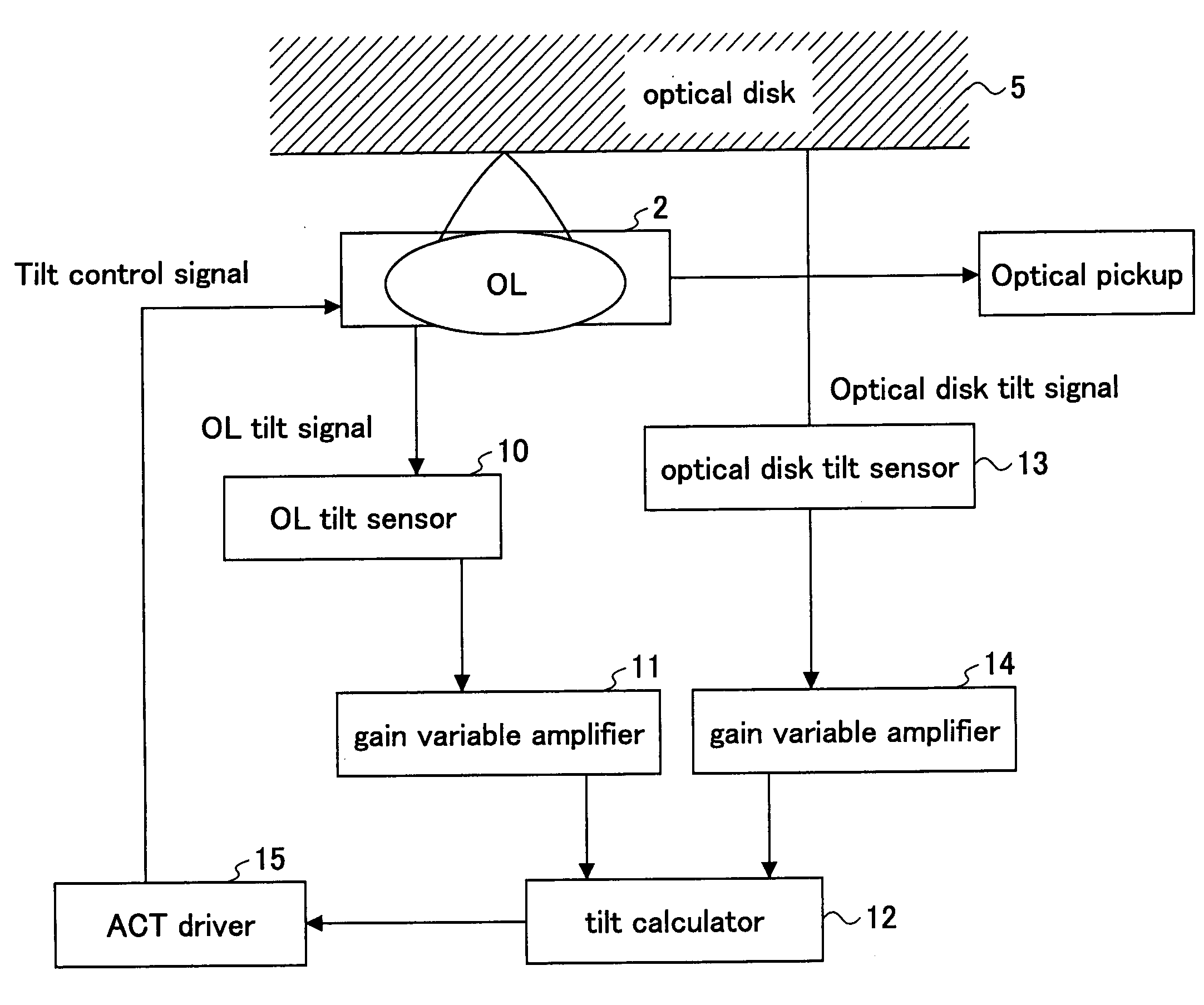
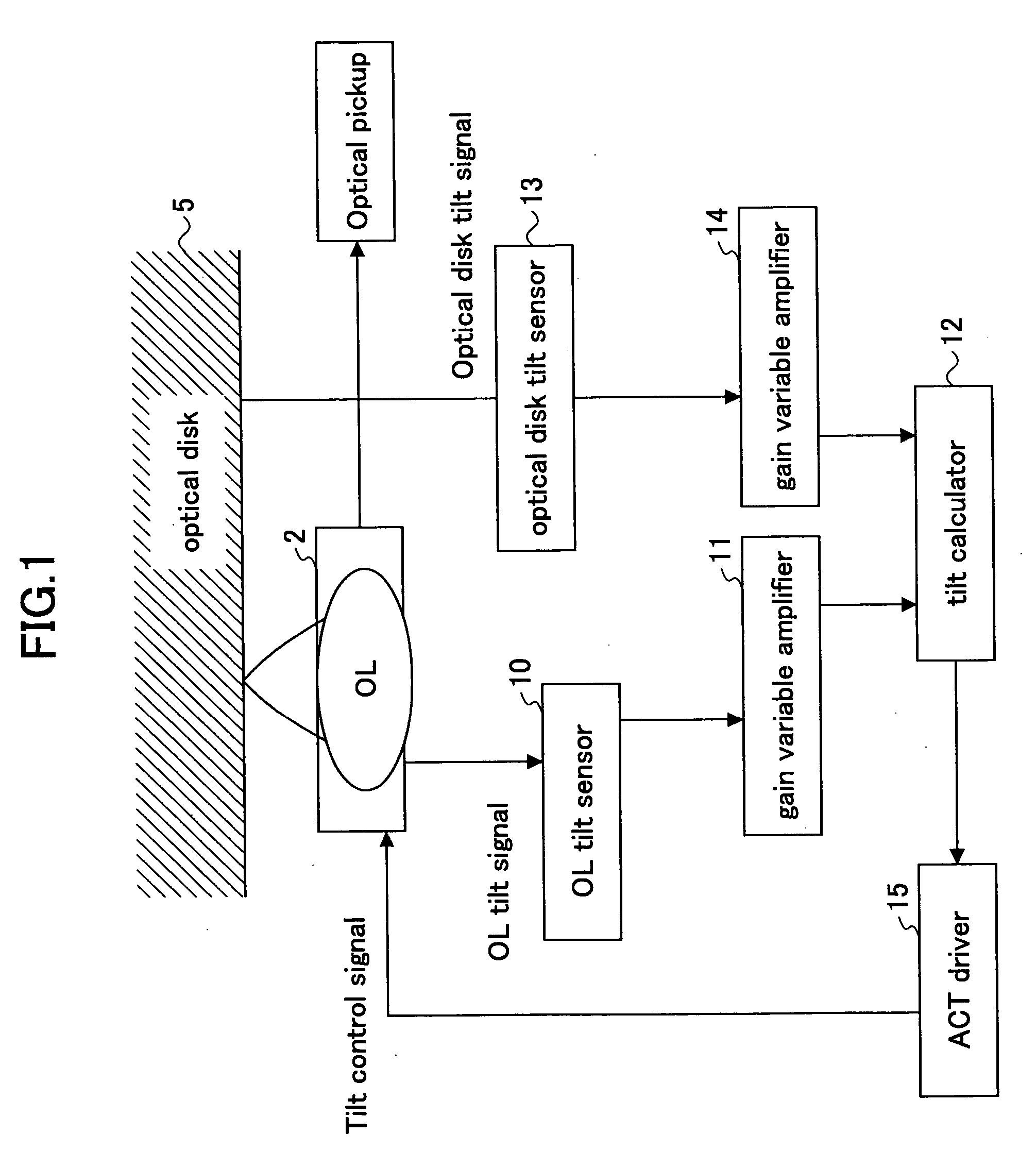
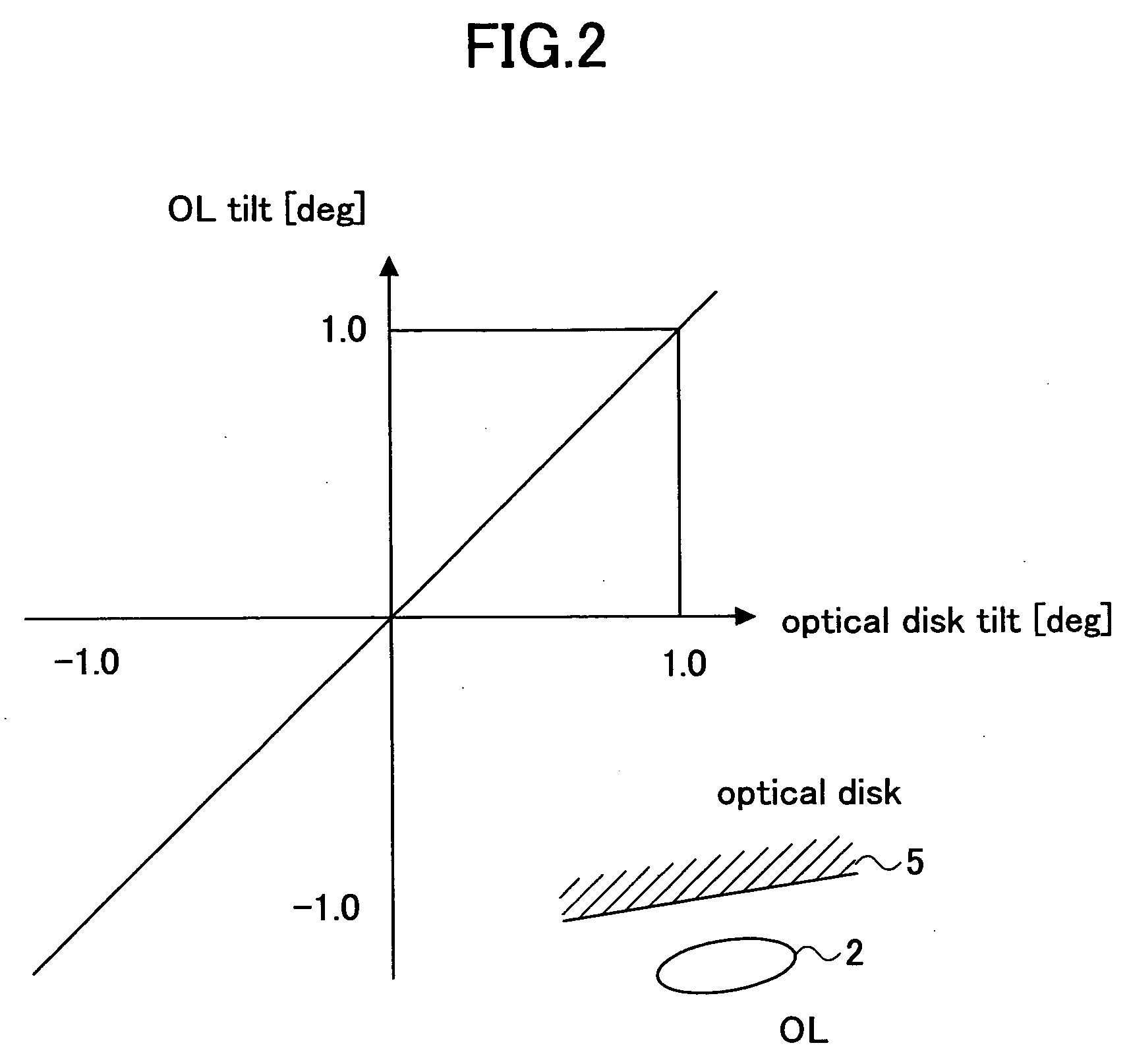
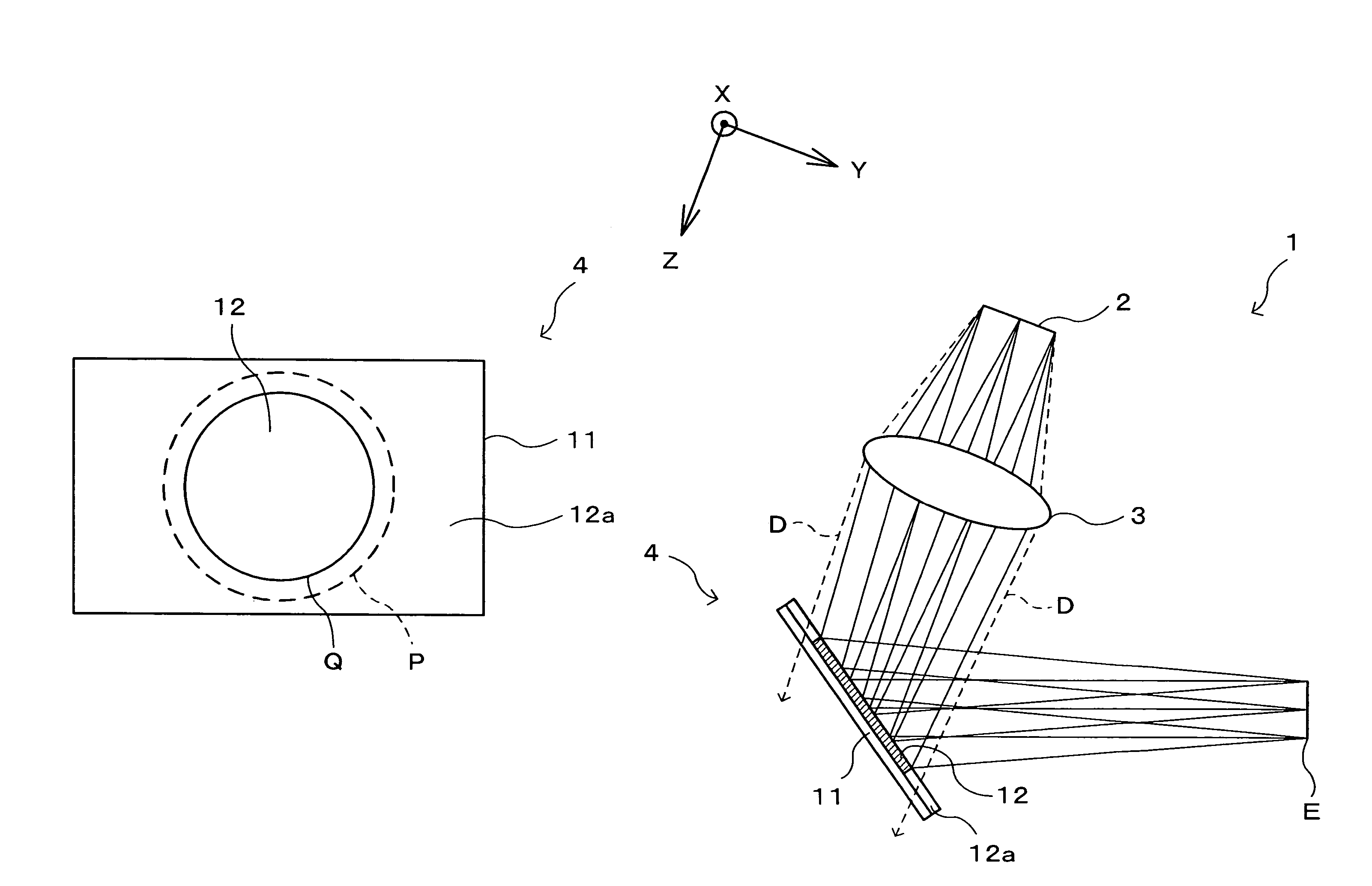
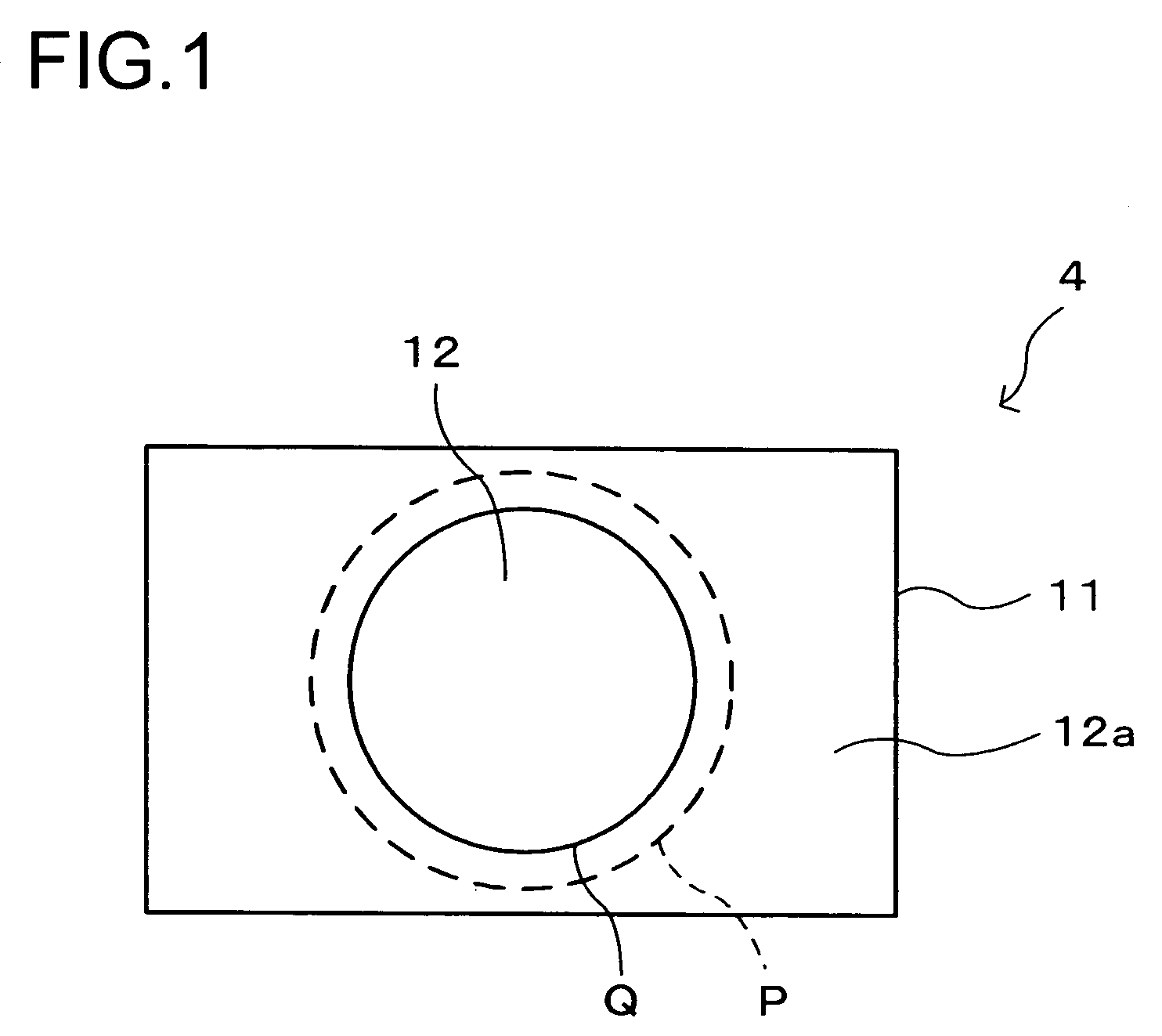
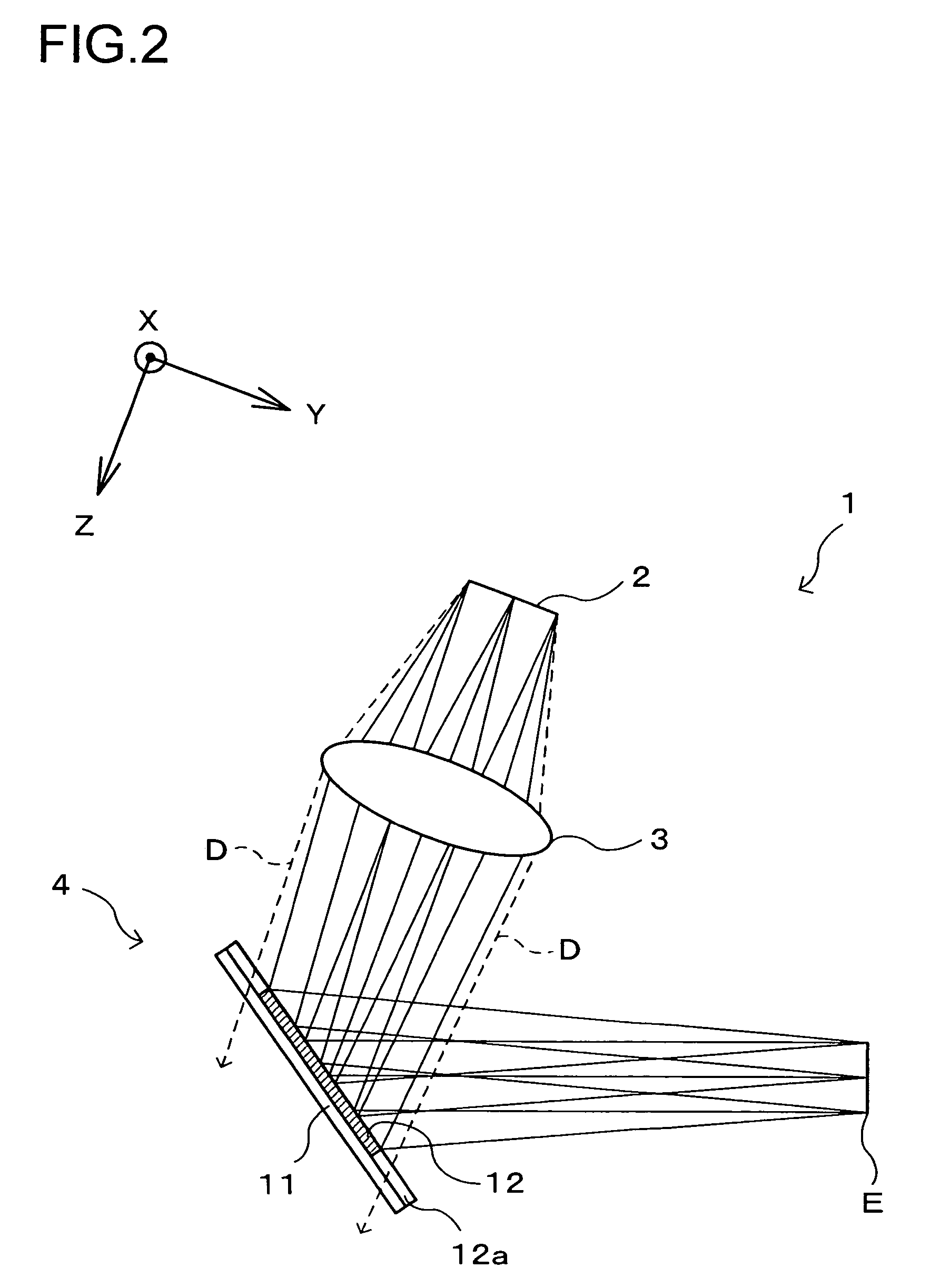
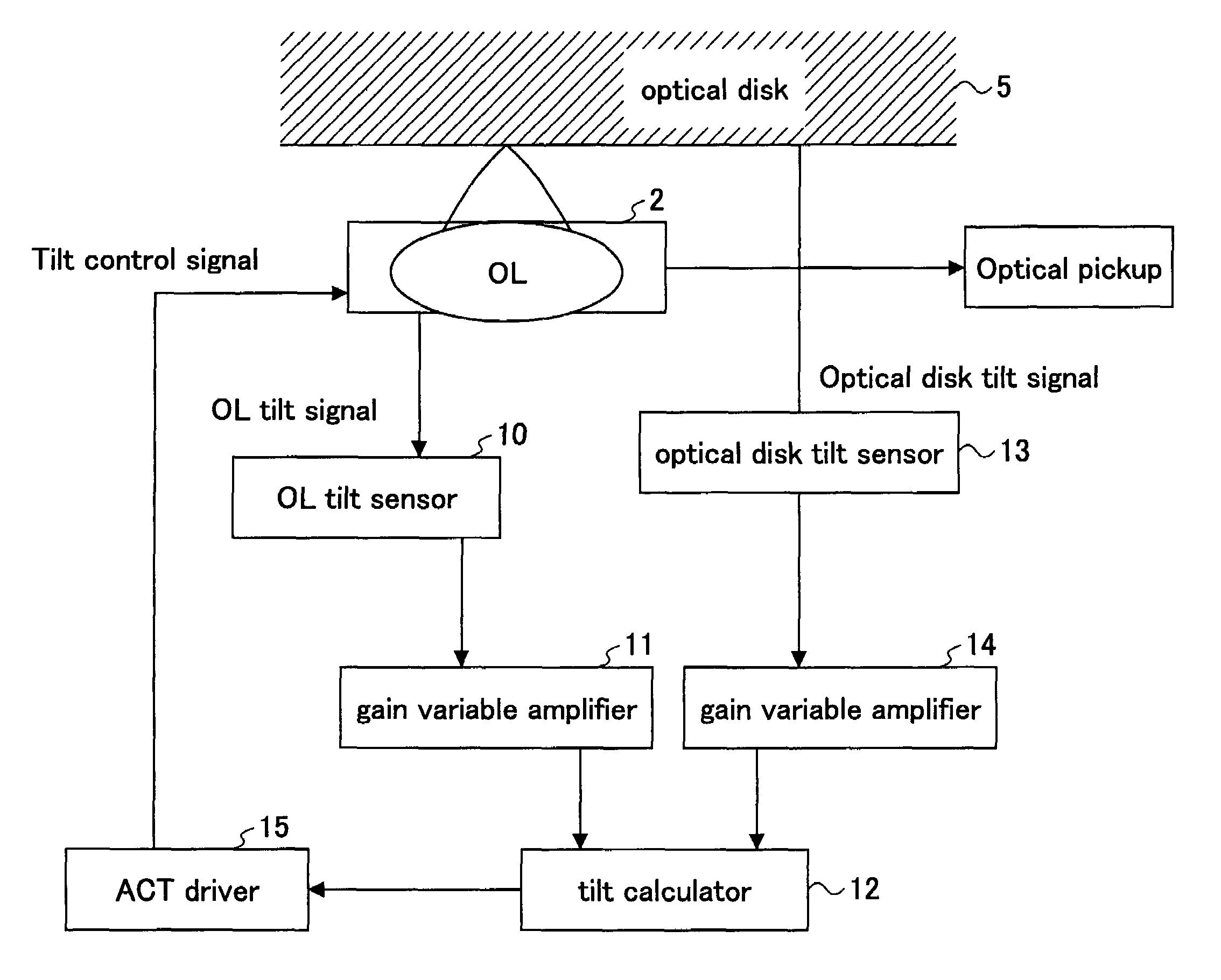
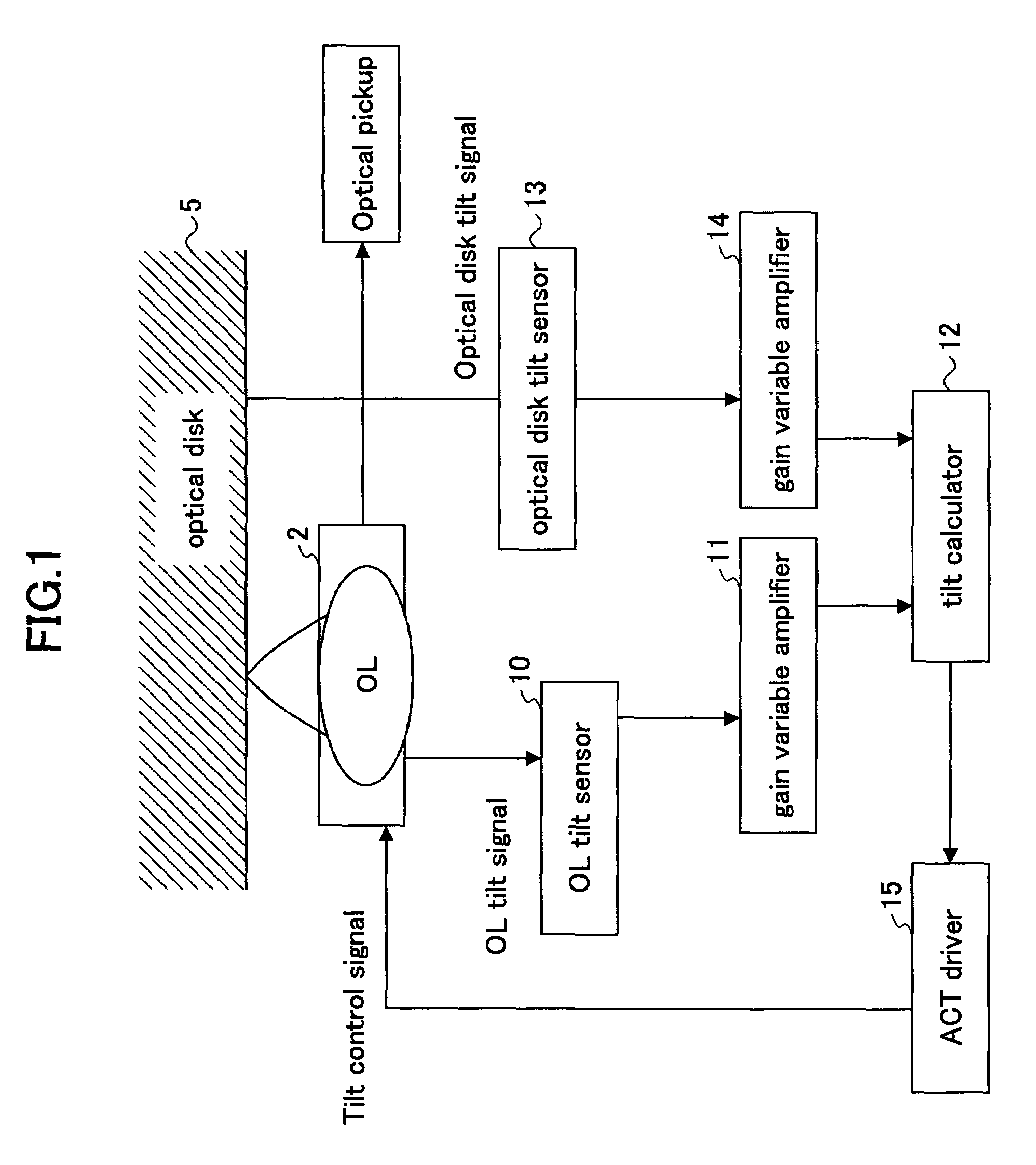
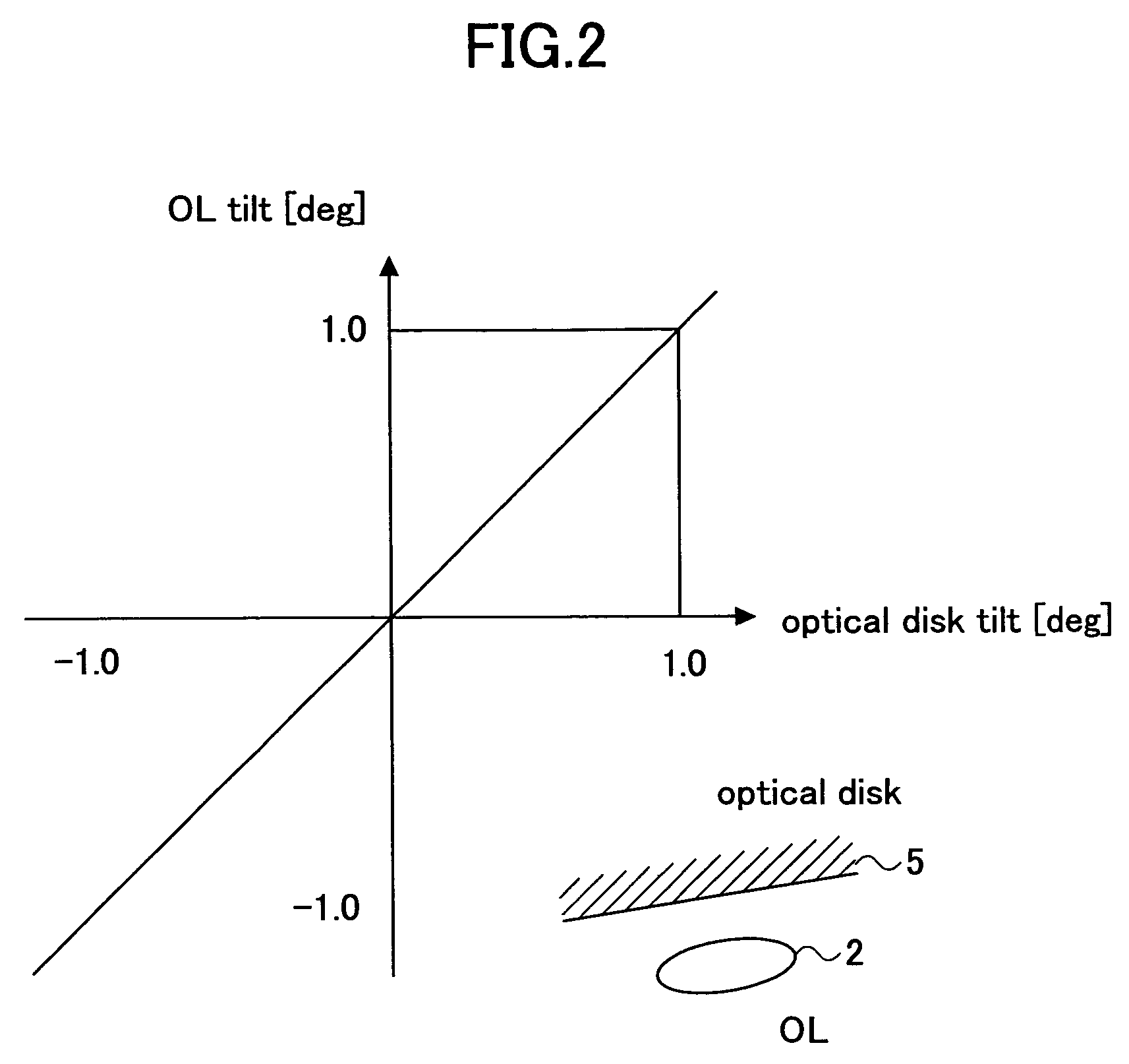
Optical recording medium tilt compensation device, tilt compensation method, and optical information recording apparatus
InactiveUS20060215507A1Minimum aberrationSmall aberrationCombination recordingRecord information storageActuatorOptical aberration
An optical recording medium tilt compensation device having a tilt compensation unit is disclosed that is able to compensate for a tilt error in servo control when recording or reproducing data in an optical recording medium. The optical recording medium tilt compensation device includes an object lens that condenses light from a light source on a recording surface of an optical recording medium; an object lens tilt actuator that controls a tilt of the object lens; an object lens tilt sensor that detects a tilt of the object lens; an optical recording medium tilt sensor that detects a tilt of the optical recording medium; a control unit that controls the tilt of the object lens in accordance with a tilt value from the optical recording medium tilt sensor so that an aberration of the spot condensed on the recording surface is minimum by driving the object lens tilt actuator; a gain variable unit that changes the magnitude of an output signal from the object lens tilt sensor or the optical recording medium tilt sensor.
Owner:RICOH KK
Lens manufacturing method, lens, and lens holding device
ActiveUS20170182621A1Good light transmission performanceSmall transmission wave surface aberrationOptical surface grinding machinesGrinding feed controlCamera lensEngineering
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Quasi-periodic optical metasurface imaging element
InactiveCN111722399AAchieve achromatic adaptationVersatile and strongOptical elementsNanopillarLight beam
The invention provides a quasi-periodic optical metasurface imaging element. The quasi-periodic optical metasurface imaging element comprises a substrate and a plurality of cuboid nanorods generated on the substrate, the nanorods are divided into a first size and a second size which respectively correspond to a first wavelength lambda 1 and a second wavelength lambda 2; the first size of nanorodsand the second size of nanorods are alternately arranged in a gold spiral shape at intervals; the length and the width of the nanorod are coupled with the wavelength of an incident light beam; and therotation angle of the nanorod is coupled with the wavelength, focal length, additional phase modulation value and position of the incident light beam, so that the focal length of the element to the parallel incident light with two wavelengths is the same. By adjusting the length, the width and the rotation angle of the nanorod, adaptation to incident beams with various wavelengths can be achieved, the incident beams are focused at the same point and have the quasi-periodic characteristic, and the universality of the design scheme is greatly higher than that of an existing scheme.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Optical holographic device with a hologram optical element on an area smaller than an irradiation area, holographic image display device and head mounted display with a hologram optical element on an area smaller than an irradiation area
A hologram optical element is formed on a substrate so as to make an optical device. The hologram optical element is formed in an area smaller than an irradiation area of a beam for reproduction such as image light or object light on the substrate. Supposing that the beam for reproduction is made of a center beam having intensity higher than 50% of center intensity and other peripheral beam, the hologram optical element is formed on the substrate in a size for diffracting only the center beam so that a flare or a ghost can be relieved without using additional optical elements such as a shading plate.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA PHOTO IMAGING
Optical recording medium tilt compensation device, tilt compensation method, and optical information recording apparatus
InactiveUS7577070B2Minimum aberrationSmall aberrationCombination recordingRecord information storageOptical recordingActuator
An optical recording medium tilt compensation device having a tilt compensation unit is disclosed that is able to compensate for a tilt error in servo control when recording or reproducing data in an optical recording medium. The optical recording medium tilt compensation device includes an object lens that condenses light from a light source on a recording surface of an optical recording medium; an object lens tilt actuator that controls a tilt of the object lens; an object lens tilt sensor that detects a tilt of the object lens; an optical recording medium tilt sensor that detects a tilt of the optical recording medium; a control unit that controls the tilt of the object lens in accordance with a tilt value from the optical recording medium tilt sensor so that an aberration of the spot condensed on the recording surface is minimum by driving the object lens tilt actuator; a gain variable unit that changes the magnitude of an output signal from the object lens tilt sensor or the optical recording medium tilt sensor.
Owner:RICOH KK
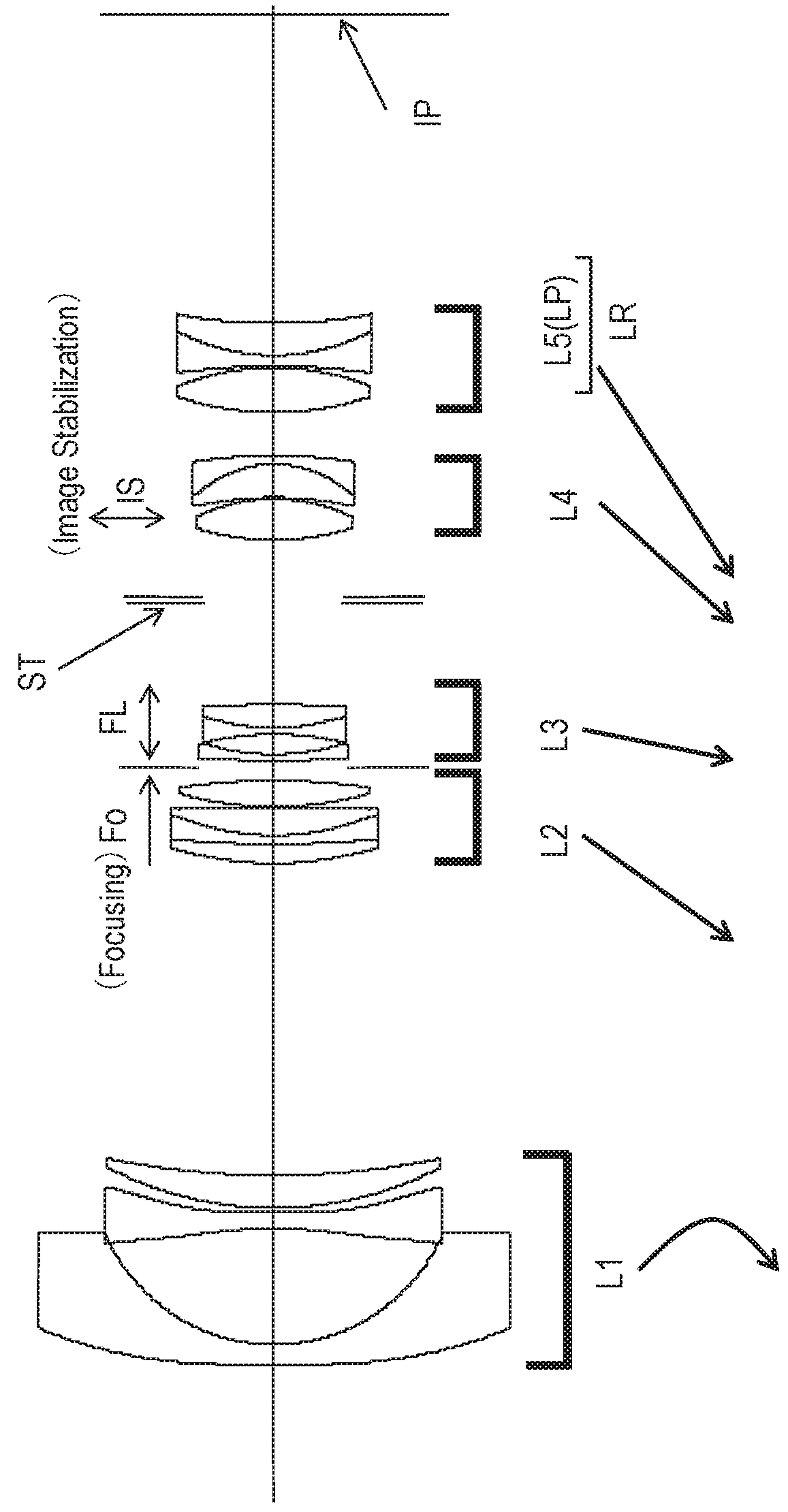
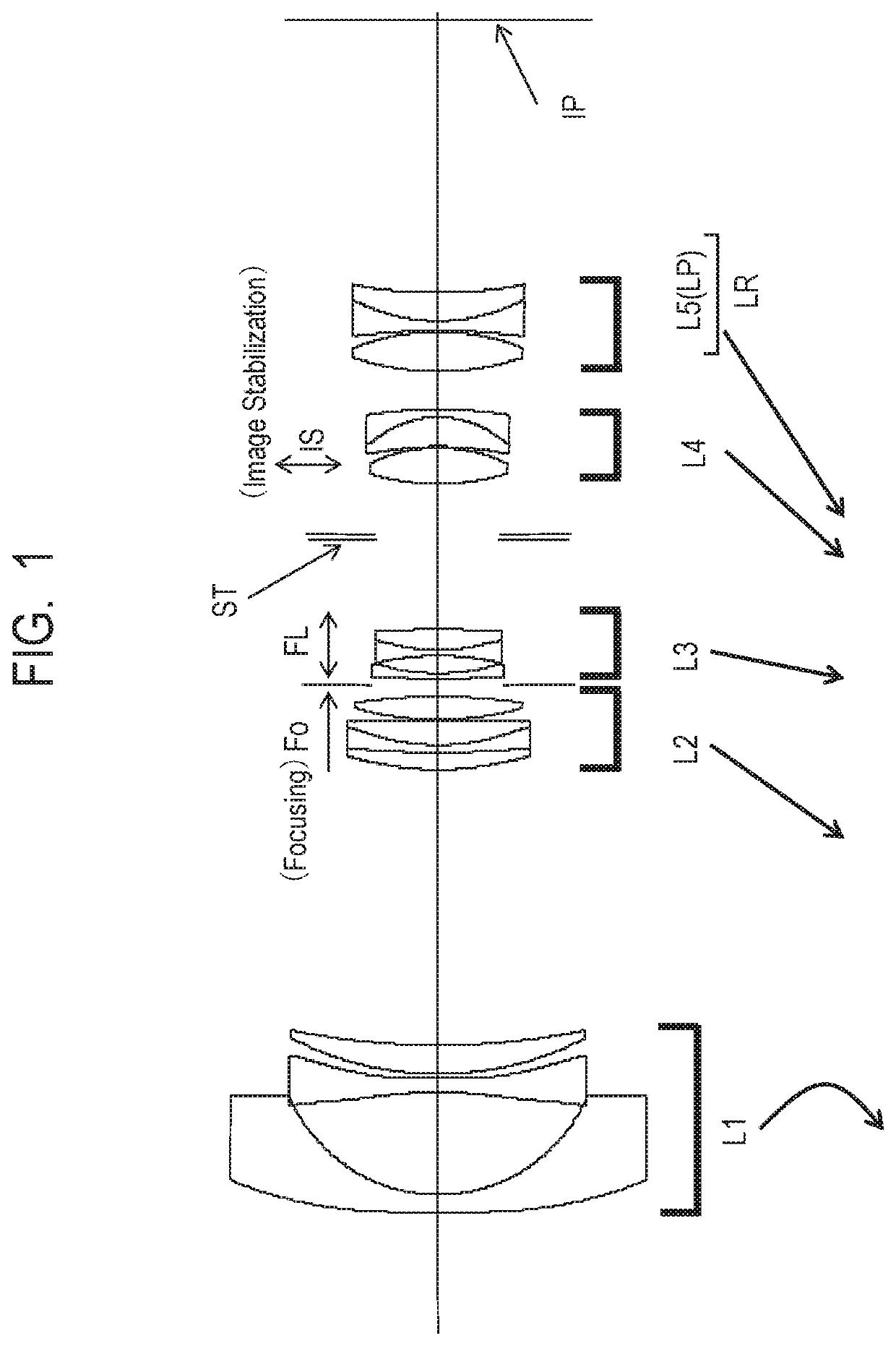
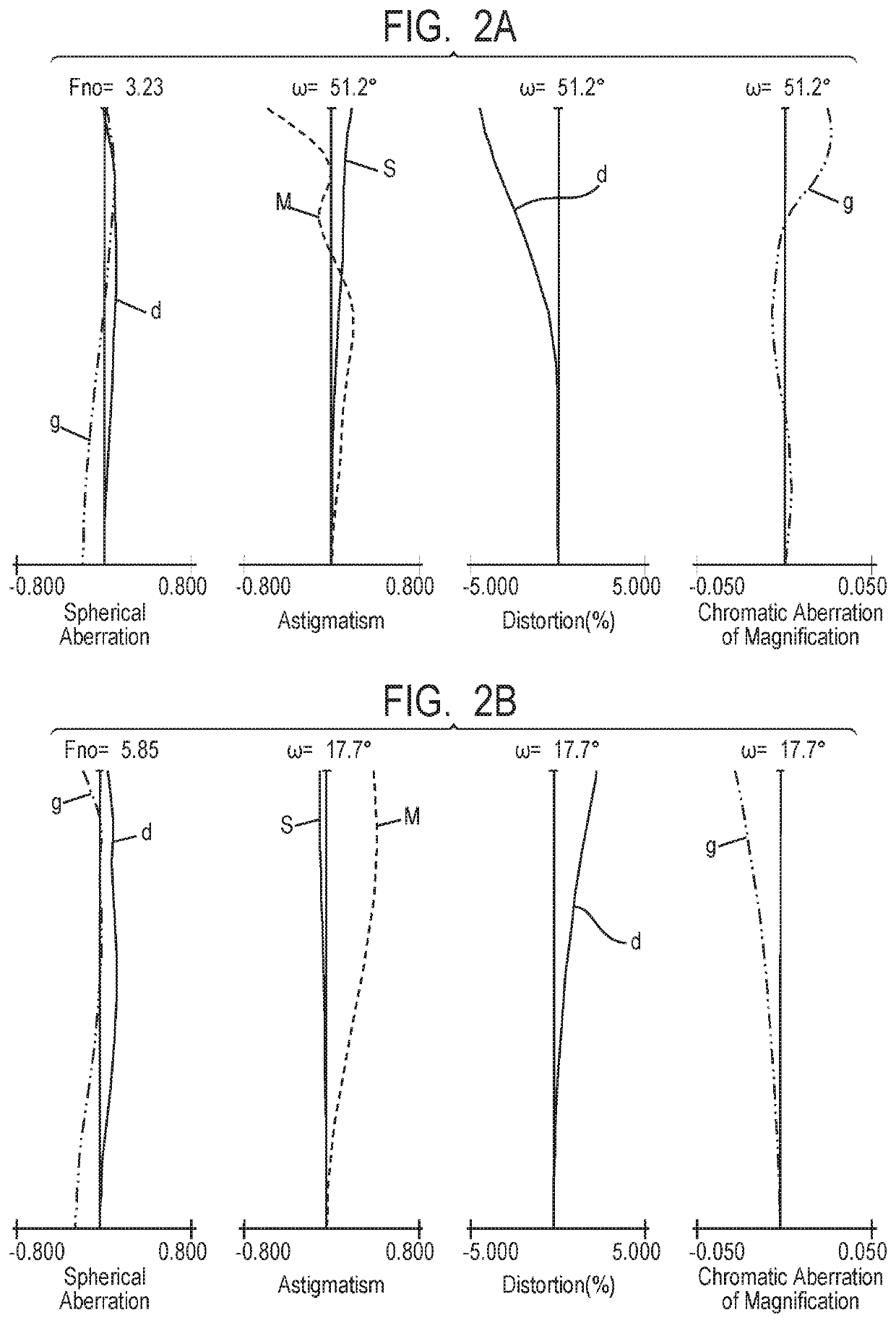
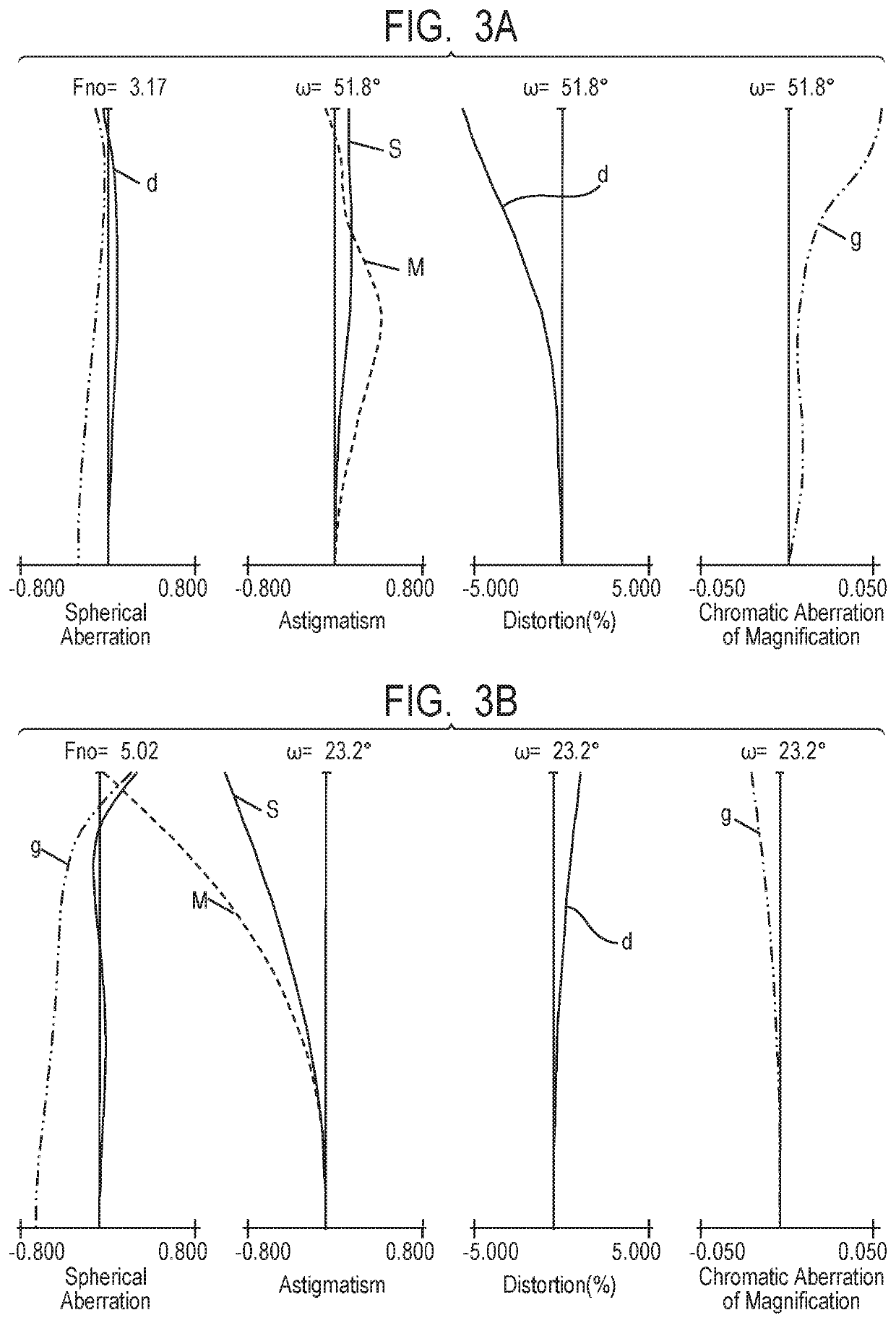
Zoom lens and image pickup apparatus
ActiveUS20180275370A1Small variationHigh optical performanceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPhysicsImage stabilization
Provided is a zoom lens including, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens unit having a negative refractive power; a second lens unit having a positive refractive power; a third lens unit having a negative refractive power; a fourth lens unit having a positive refractive power; and a rear lens group including at least one lens unit, the first lens unit, the second lens unit, the third lens unit, the fourth lens unit, and the rear lens group having an interval between each pair of adjacent lens units changed for zooming. The third lens unit is configured to move for focusing, and at least a part of the fourth lens unit forms a lens system IS, which is configured to move in a direction including a component of a direction perpendicular to an optical axis for image stabilization.
Owner:CANON KK
Catadioptric objective system and objective system
InactiveUS20050094540A1Good optical performanceSmall thicknessRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansOptical powerPhysics
A catadioptric objective system used for storage and / or reproduction of information by use of an optical near field. The catadioptric objective system is composed of a catadioptric objective lens and a light transmitting plate. The lens has a first surface and a second surface. The first surface has a positive optical power and transmits incident rays. The second surface has a positive optical power and reflects incident rays, and a plane portion is formed in the center of the second surface. The light transmitting plate has a third surface and a fourth surface which are substantially parallel to each other, and the third surface is bonded to the second surface. Incident rays pass through the first surface and are reflected by the second surface. Thereafter, the rays enter into the first surface again and are reflected by the first surface. Then, the rays pass through the plane portion of the second surface, and the rays are converged in vicinity of the fourth surface.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Electronic imaging apparatus
InactiveUS7453507B2Thin depthSmall aberrationTelevision system detailsPrismsElectronElectronic imaging
An electronic imaging apparatus of the present invention comprises a photographing optical system, in order from an object side, a first lens group having negative refracting power, which has a reflecting component having a reflecting surface for bending an optical path of an incident light from the object side and at least two positive lens groups arranged at an image side of the first lens group, wherein the photographing optical system is a zoom optical system and the following condition is satisfied:−1.75<f1 / fw<−0.8where f1 is a focal length of the first lens group, and fw is a focal length at the wide angle end at the photographing optical system.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Zoom lens and imaging apparatus
A zoom lens includes, in order from the object side: a positive first lens group; a negative second lens group; a positive third lens group; a negative fourth lens group; and a positive fifth lens group. The distance between the first and second lens groups constantly increases, the distance between the second and third lens groups constantly decreases, the distance between the third and fourth lens groups constantly changes, and the distance between the fourth and fifth lens groups constantly increases when changing magnification from the wide angle to the telephoto end. The first lens group includes, in order from the object side, a negative lens, a positive lens, and a positive lens. The fourth lens group includes, in order from the object side, a negative lens, a negative lens, and a positive lens, and moves toward the image side when focusing from a far distance to a close distance.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Imaging optical system
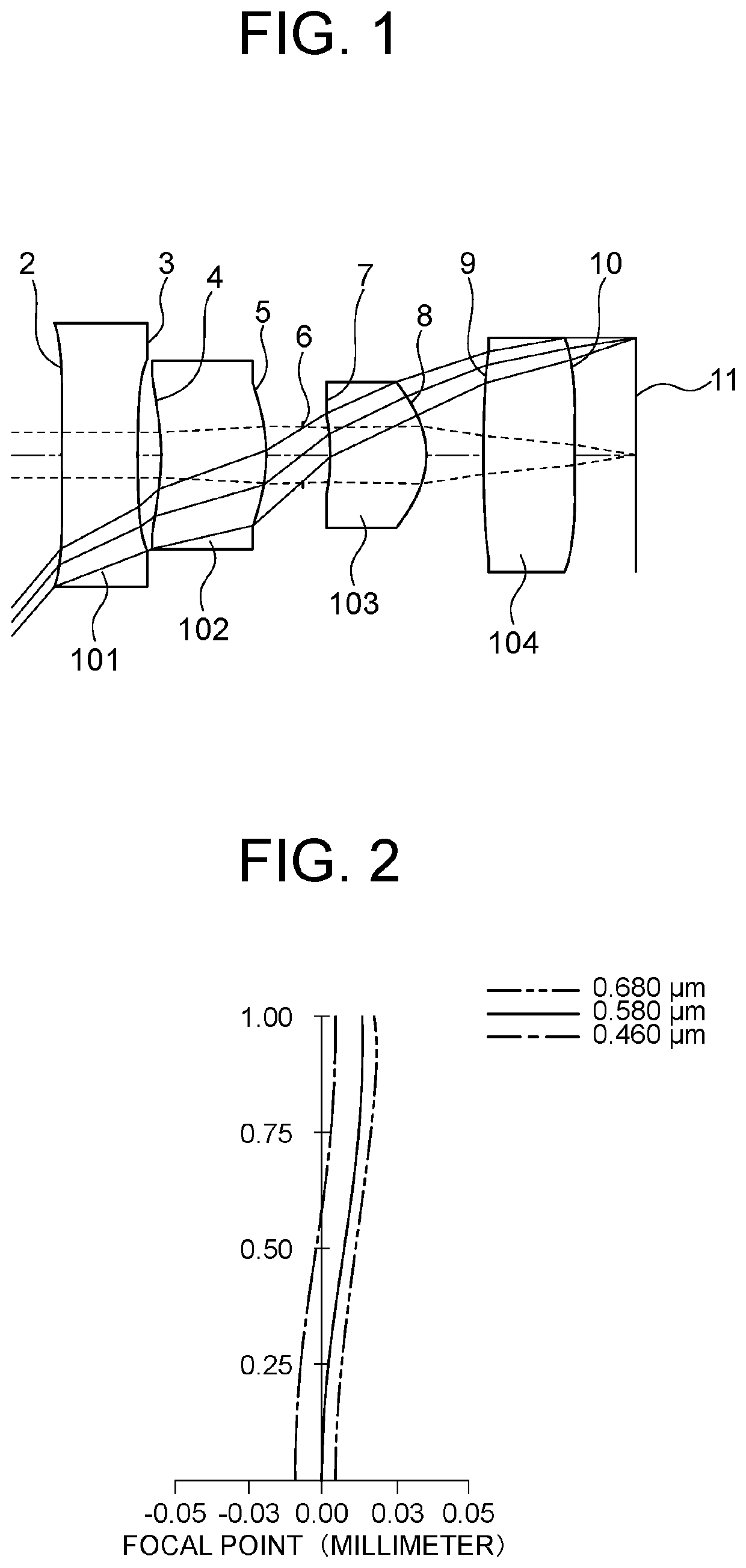
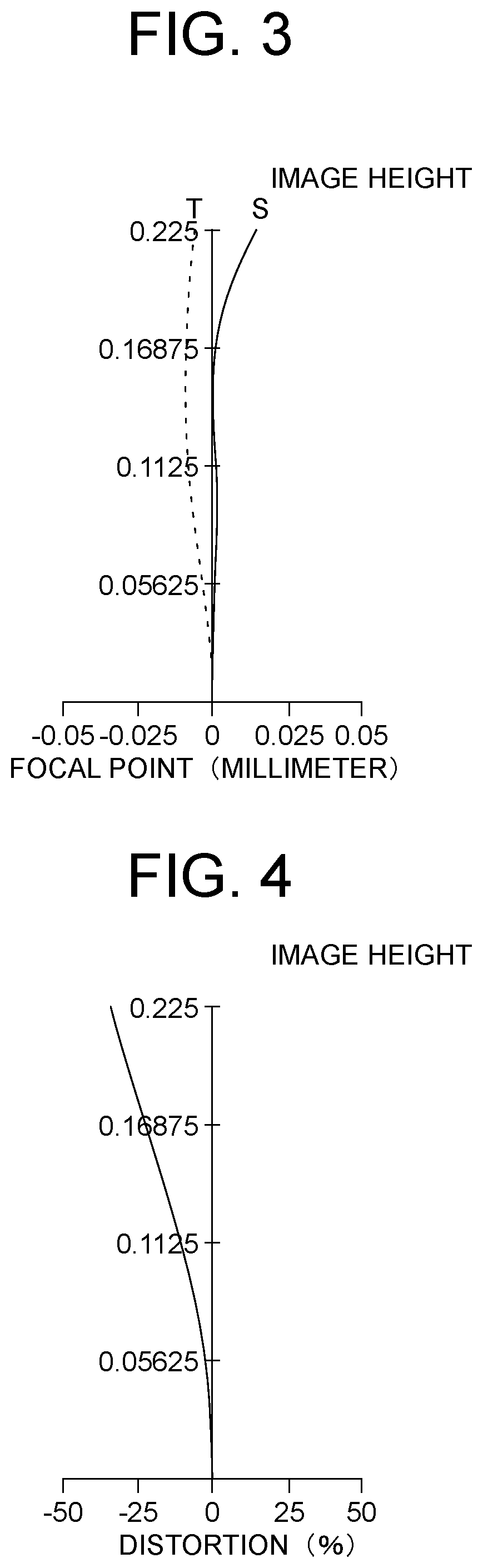
PendingUS20220326485A1Small aberrationReduce off-axis aberrationsOptical elementsOphthalmologyOptical axis
An imaging optical system wherein the number of lenses is three to seven, one to four lenses, each of which is an aspheric lens in which radius of curvature of each of both surfaces is infinity in the paraxial region and which has a power of the third-order aberration region in the peripheral area are provided, the first lens from the object side is a negative lens or the aspheric lens, the relationship0.18<(∑i=1i=n<semantics definitionURL="">❘<annotation encoding="Mathematica">"\[LeftBracketingBar]"< / annotation>< / semantics>1fi<semantics definitionURL="">❘<annotation encoding="Mathematica">"\[RightBracketingBar]"< / annotation>< / semantics>)·fn<0.9is satisfied where i represents a natural number, fi represents focal length of the i-th lens from the object side, f represents focal length of the whole system and n represents the number of the lenses, and the relationship40°<HFOV<80°is satisfied where HFOV represents angle that the principal ray of bundle of rays that enters the imaging optical system and reaches the maximum value of image height forms with the optical axis.
Owner:IKEMORI KEIJI +1
Electron gun
InactiveUS8669535B2Small aberrationIncrease brightnessStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationCold cathodeAtomic physics
The present invention has an object to provide a cold cathode field-emission electron gun with low aberration, to thereby provide a high-brightness electron gun even in the case of a large current. The present invention provides a field-emission electron gun which extracts an electron beam from a cathode and converges the extracted electron beam, the field-emission electron gun including: a magnetic field lens which is provided such that the cathode is disposed inside of a magnetic field of the lens; and an extraction electrode for extracting electrons from the cathode, the extraction electrode being formed into a cylindrical shape without an aperture structure. The present invention can provide an electron gun having a function of converging an electron beam using a magnetic field, the electron gun which is capable of reducing an incidental electrostatic lens action and has small aberration and high brightness.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Method for compensating aberration of variable focus liquid lens
A method for compensating an aberration of a variable focus liquid lens is configured to compensate the aberration associated with a first lens surface and a second lens surface of the liquid lens. The first lens surface is of a first radius of curvature. The second lens surface is of a second radius of curvature.
Owner:NAT TAIPEI UNIV OF TECH
Image-forming optical system
InactiveUS7524071B2Easy to correctReduce deteriorationTelevision system detailsProjectorsLight beamPrism
A high-performance image-forming optical system made compact and thin by folding an optical path using reflecting surfaces arranged to minimize the number of reflections. The image-forming optical system has a single prism. When image-side three surfaces of the prism are defined as a surface A, a surface B and a surface C in order from the image plane side thereof, at least one of the surfaces B and C has a rotationally asymmetric curved surface configuration that gives a power to a light beam and corrects aberrations due to decentration. The optical system leads light rays from an object to the image plane without forming an image in the prism and has a pupil in the prism. The surface A is a transmitting surface through which rays exit from the prism. The surfaces B and C are internally reflecting surfaces, which are positioned to face each other to form a Z-shaped optical path.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Catadioptric objective system and objective system
InactiveUS7359307B2Simple structureSmall aberrationRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansOptical powerPhysics
A catadioptric objective system used for storage and / or reproduction of information by use of an optical near field. The catadioptric objective system is composed of a catadioptric objective lens and a light transmitting plate. The lens has a first surface and a second surface. The first surface has a positive optical power and transmits incident rays. The second surface has a positive optical power and reflects incident rays, and a plane portion is formed in the center of the second surface. The light transmitting plate has a third surface and a fourth surface which are substantially parallel to each other, and the third surface is bonded to the second surface. Incident rays pass through the first surface and are reflected by the second surface. Thereafter, the rays enter into the first surface again and are reflected by the first surface. Then, the rays pass through the plane portion of the second surface, and the rays are converged in vicinity of the fourth surface.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Image reading apparatus and image reading method
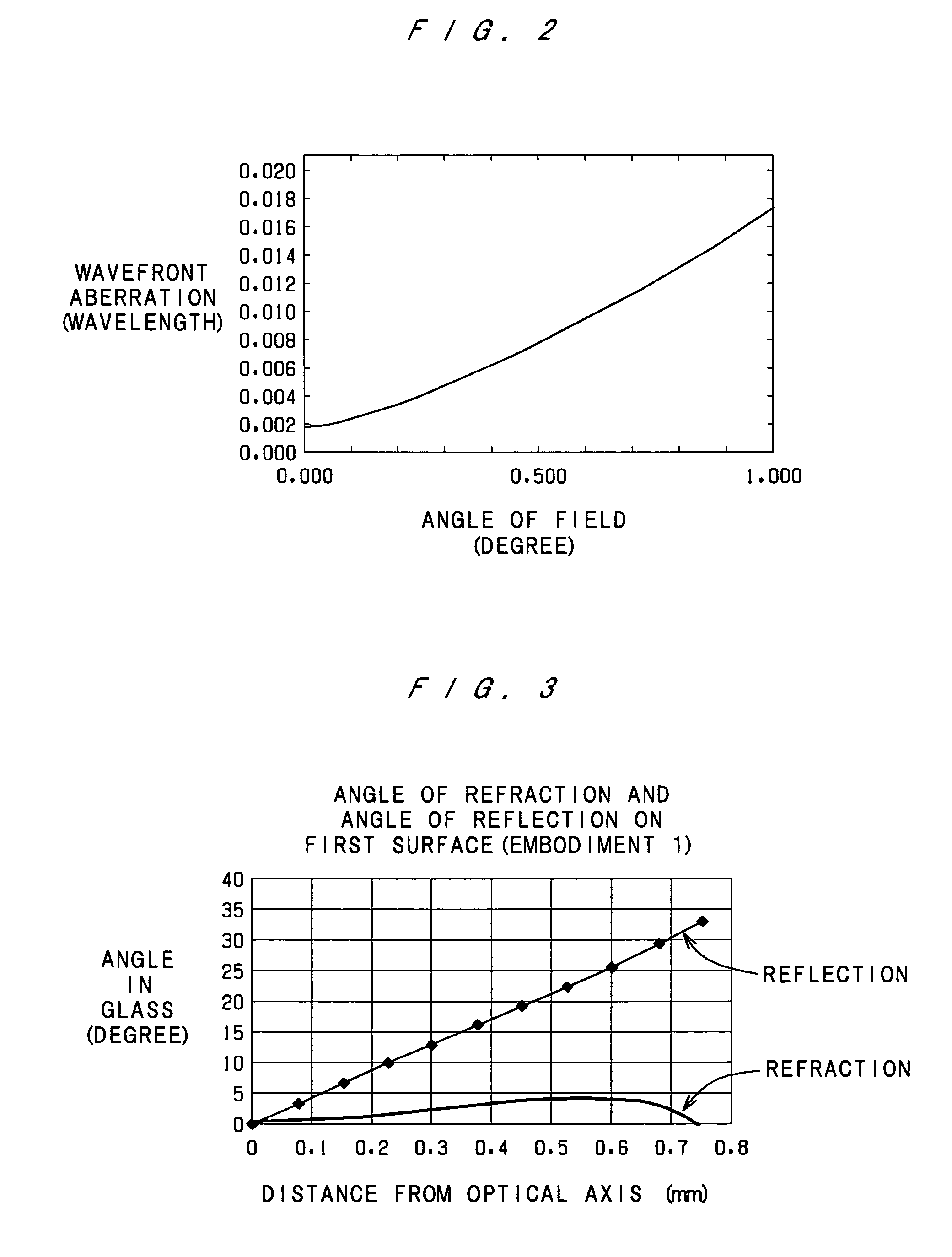
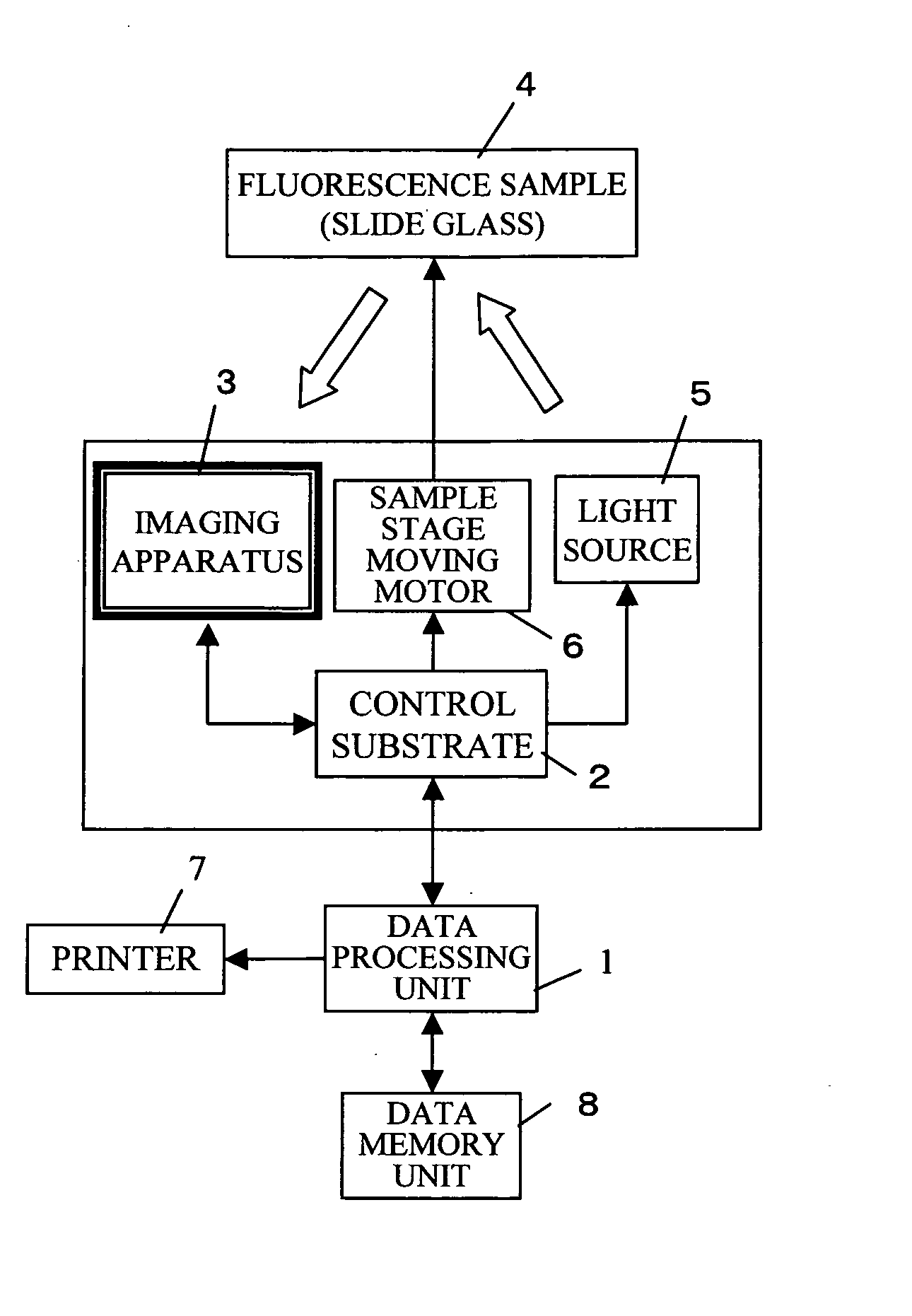
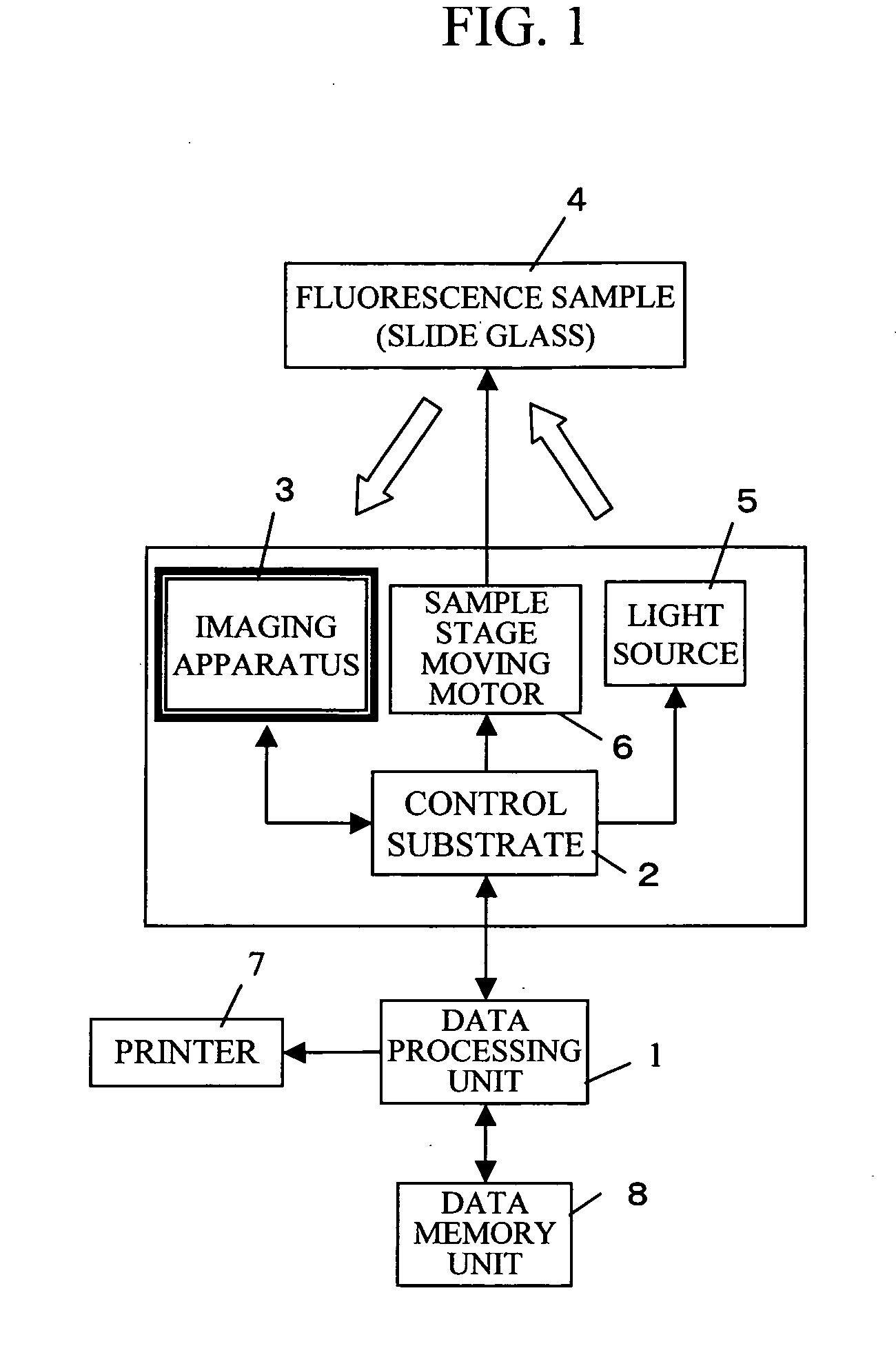
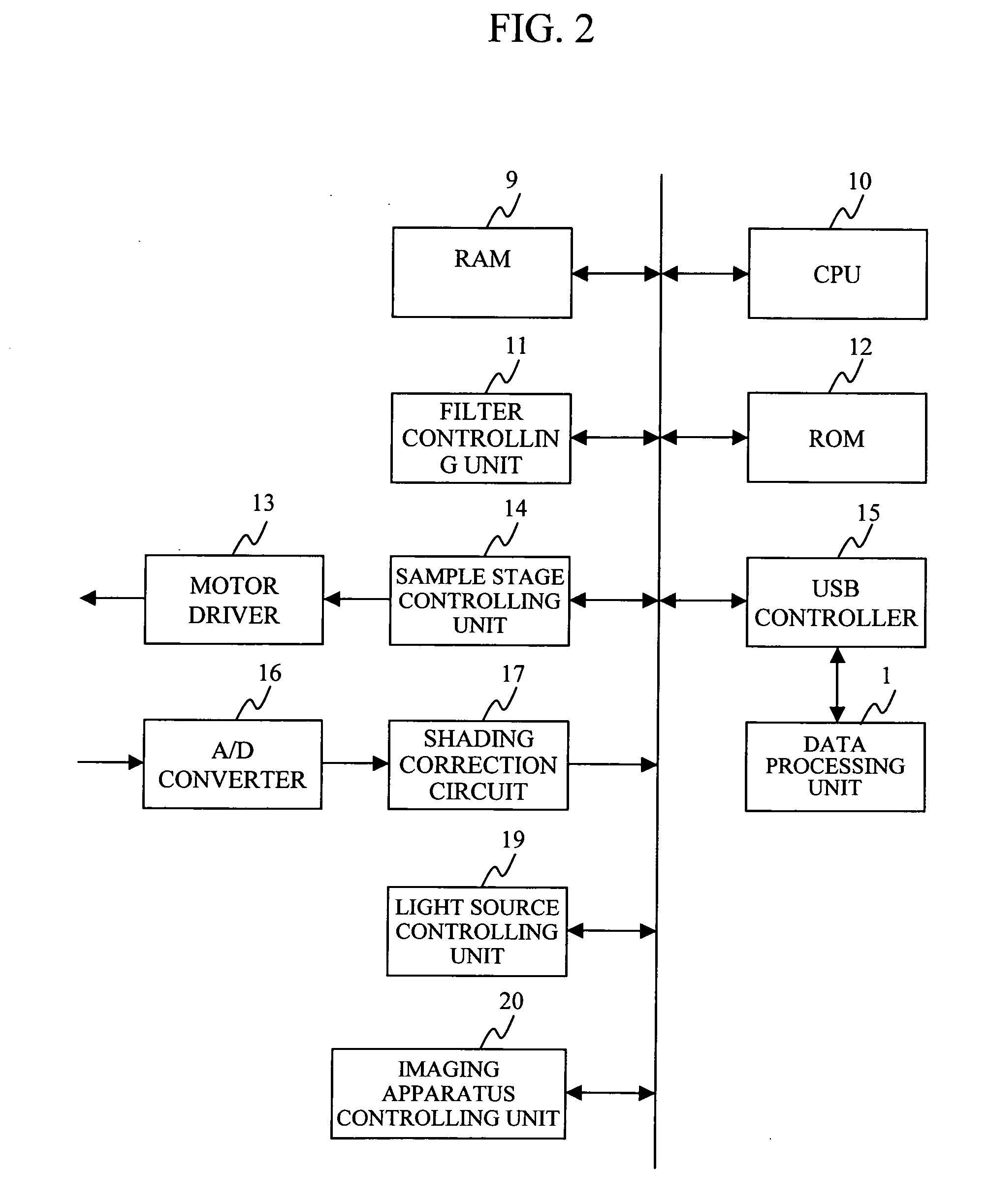
InactiveUS20050135696A1High resolutionLow noiseTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionDistortionImage resolution
Sensitivity error, image distortion, and background noise upon synthesizing images obtained by an imaging apparatus, and lack of resolution upon reading the entire area of a sample at a time are solved. While moving the sample by the distance that corresponds to the resolution, the sample is read using all the scanning lines of the imaging apparatus, and then an entire image is obtained by synthesizing each line. The imaging apparatus is located such that the scanning lines are parallel to the short side of the sample, and the short side direction is resolved by the maximum resolution of the imaging apparatus.
Owner:HITACHI SOFTWARE ENG
Zoom lens and image pickup apparatus
ActiveUS10495861B2Small decentering aberrationSmall aberrationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisImage stabilization
Provided is a zoom lens including, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens unit having a negative refractive power; a second lens unit having a positive refractive power; a third lens unit having a negative refractive power; a fourth lens unit having a positive refractive power; and a rear lens group including at least one lens unit, the first lens unit, the second lens unit, the third lens unit, the fourth lens unit, and the rear lens group having an interval between each pair of adjacent lens units changed for zooming. The third lens unit is configured to move for focusing, and at least a part of the fourth lens unit forms a lens system IS, which is configured to move in a direction including a component of a direction perpendicular to an optical axis for image stabilization.
Owner:CANON KK
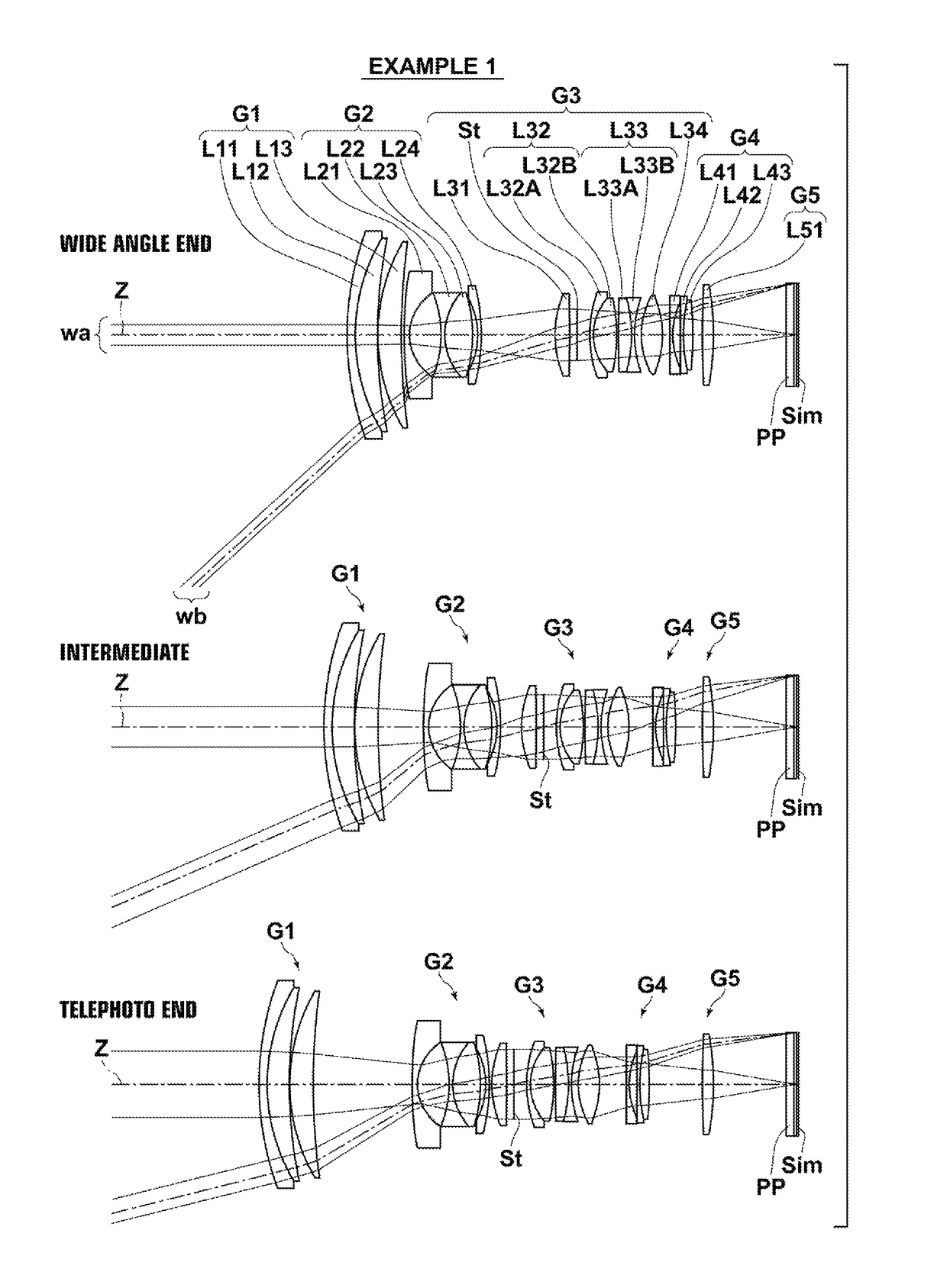
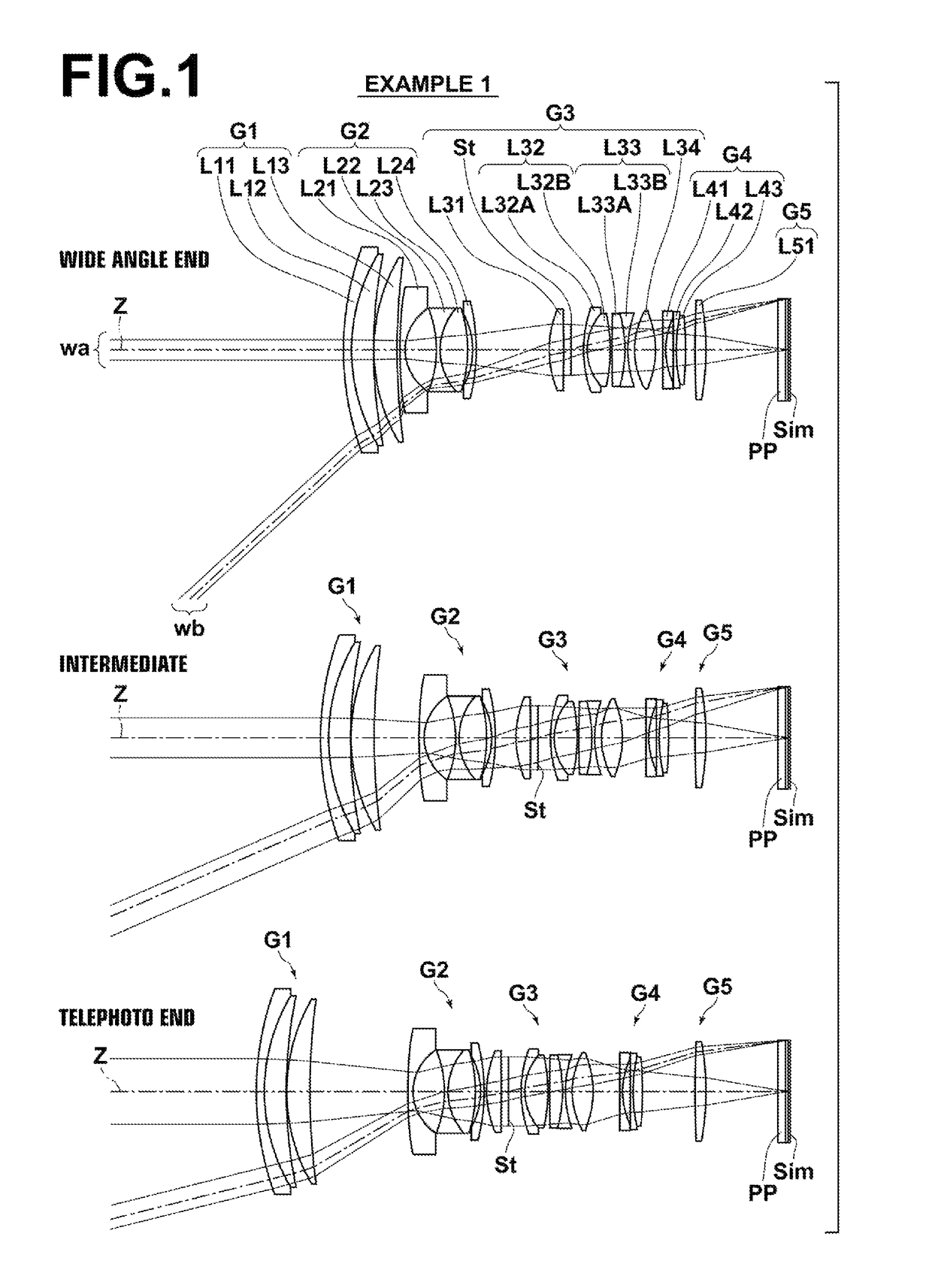
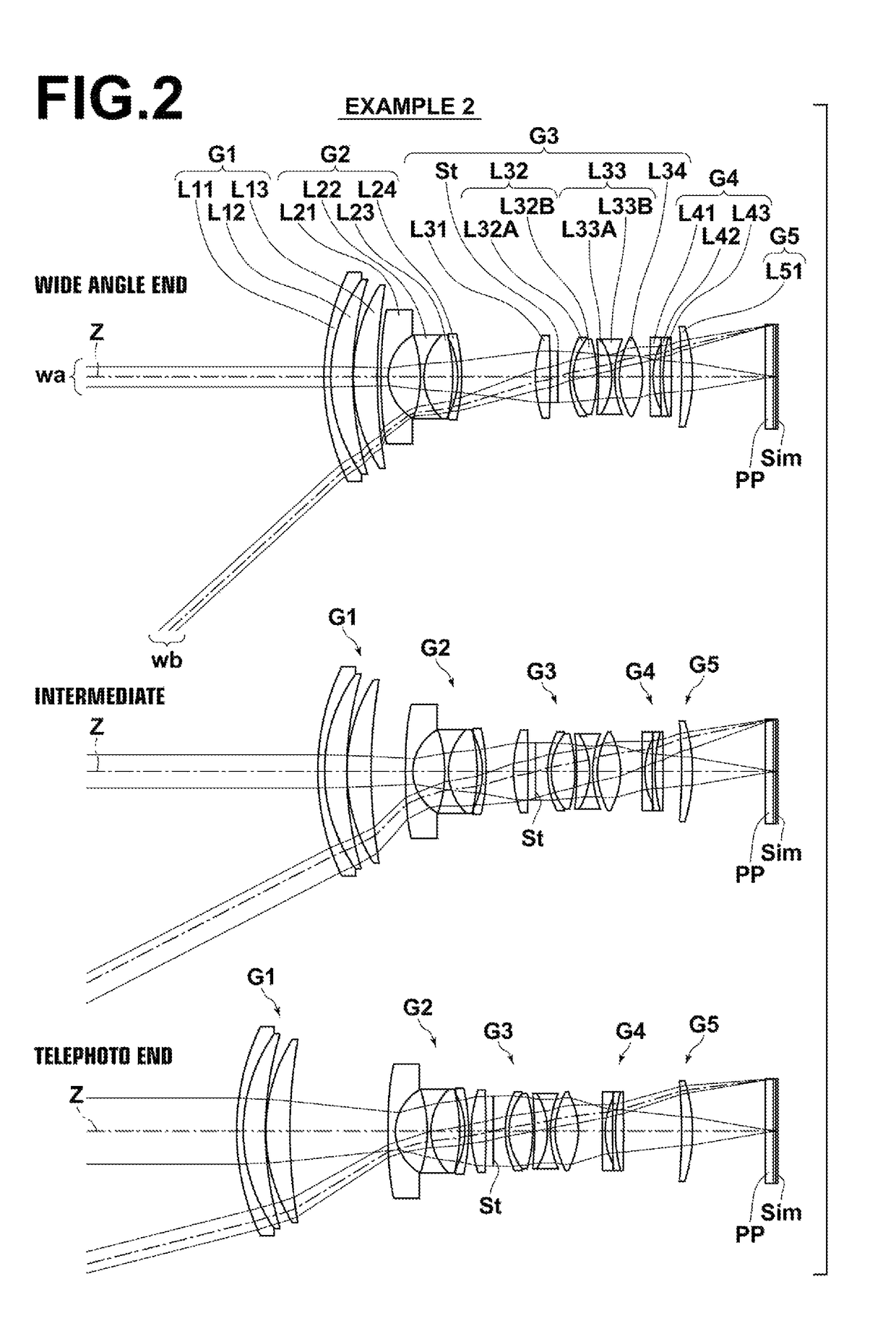
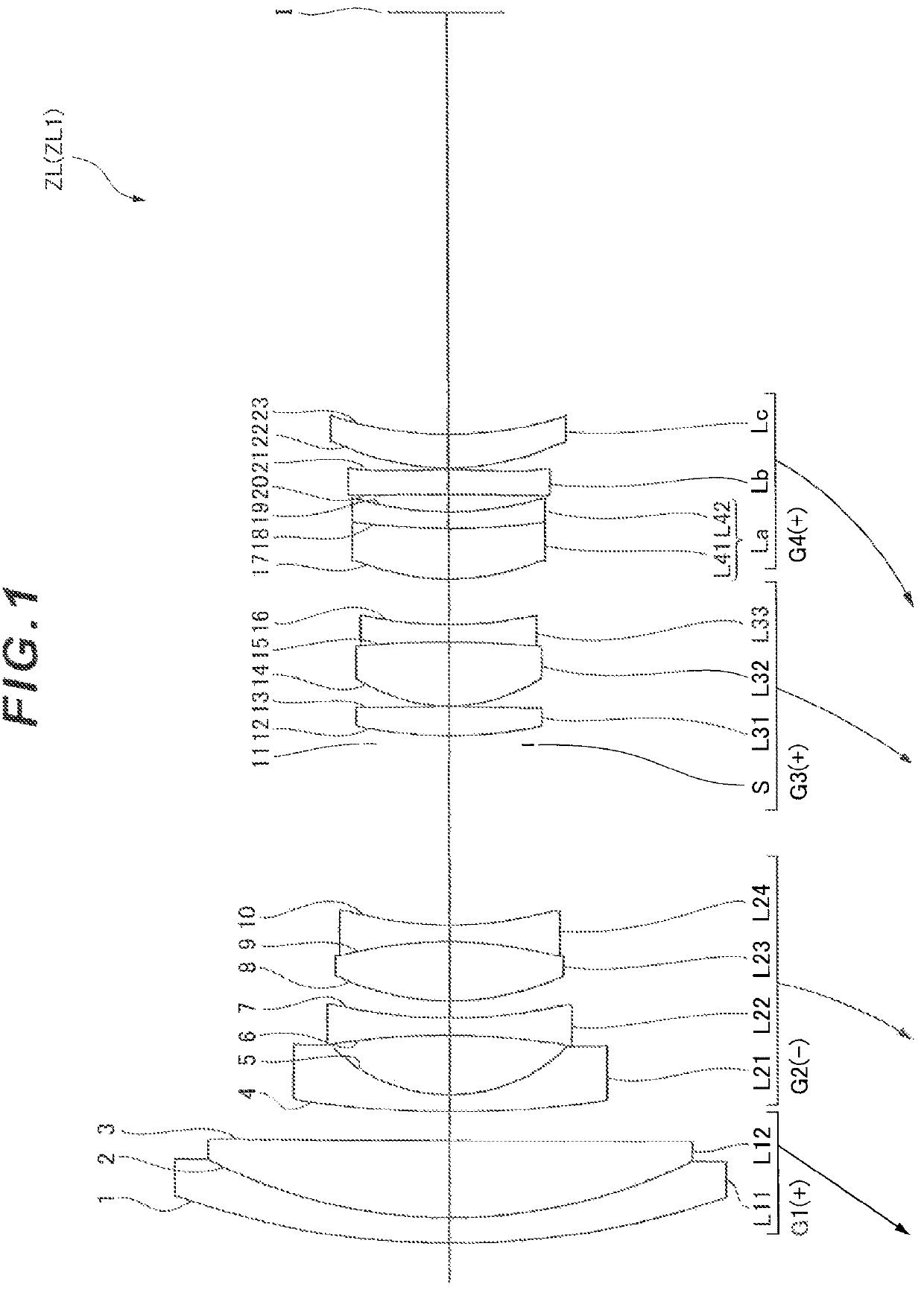
Zoom lens, imaging device and method for manufacturing the zoom lens
ActiveUS9341829B2Improve performanceSmall aberrationMetal working apparatusOptical elementsConditional expressionZoom lens
A zoom lens has, in order from an object, a first lens group (G1) having positive refractive power; a second lens group (G2) having negative refractive power; a third lens group (G3) having positive refractive power; and a fourth lens group (G4) having positive refractive power. Zooming is performed by changing an air gap between the lens groups. The fourth lens group (G4) includes, in order from the object, a lens component (La) having positive or negative refractive power, a positive lens component (Lb), and a positive lens component (Lc) having a convex surface facing the object. Specified conditional expressions are satisfied.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com