Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40results about How to "Simple arithmetic processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
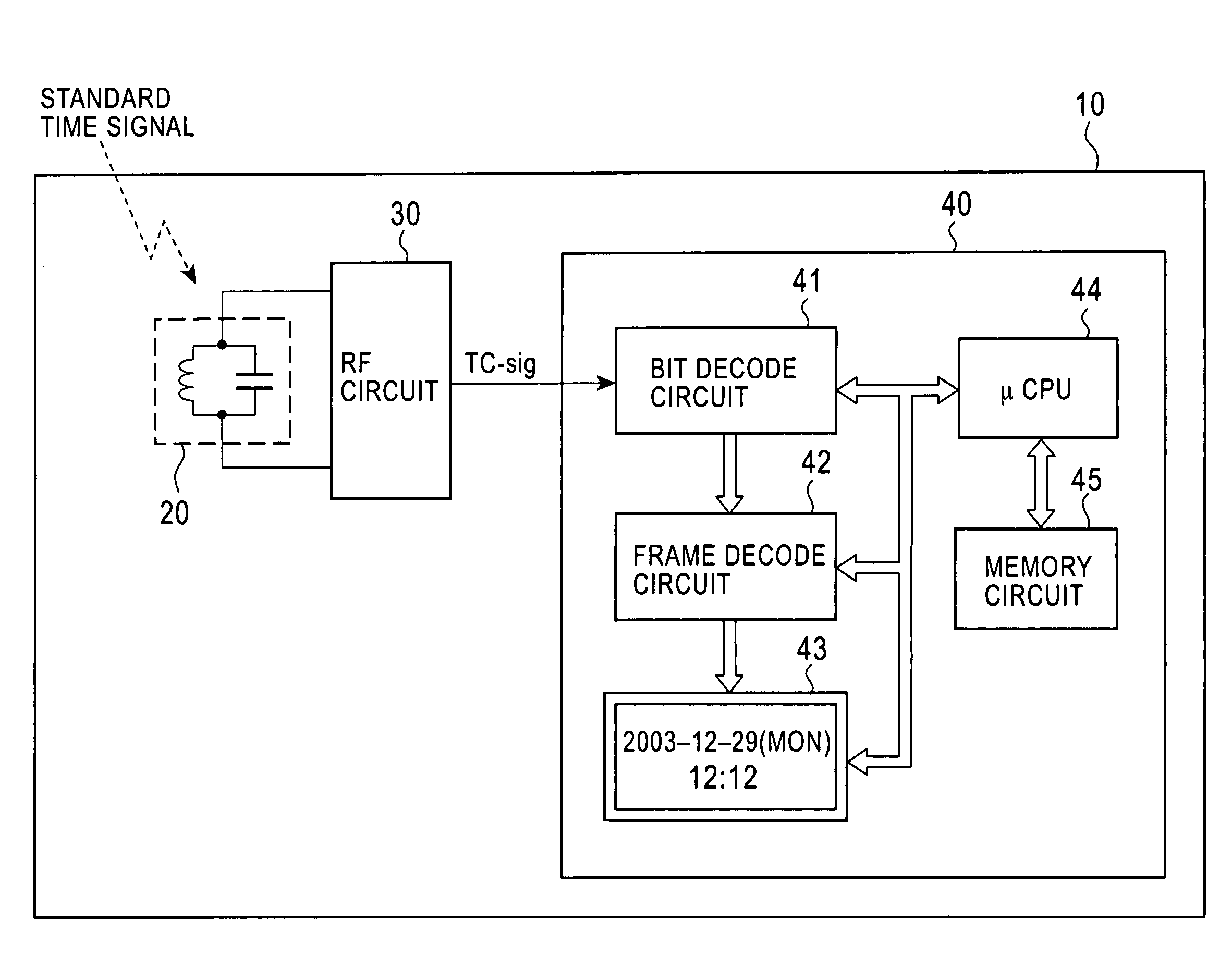
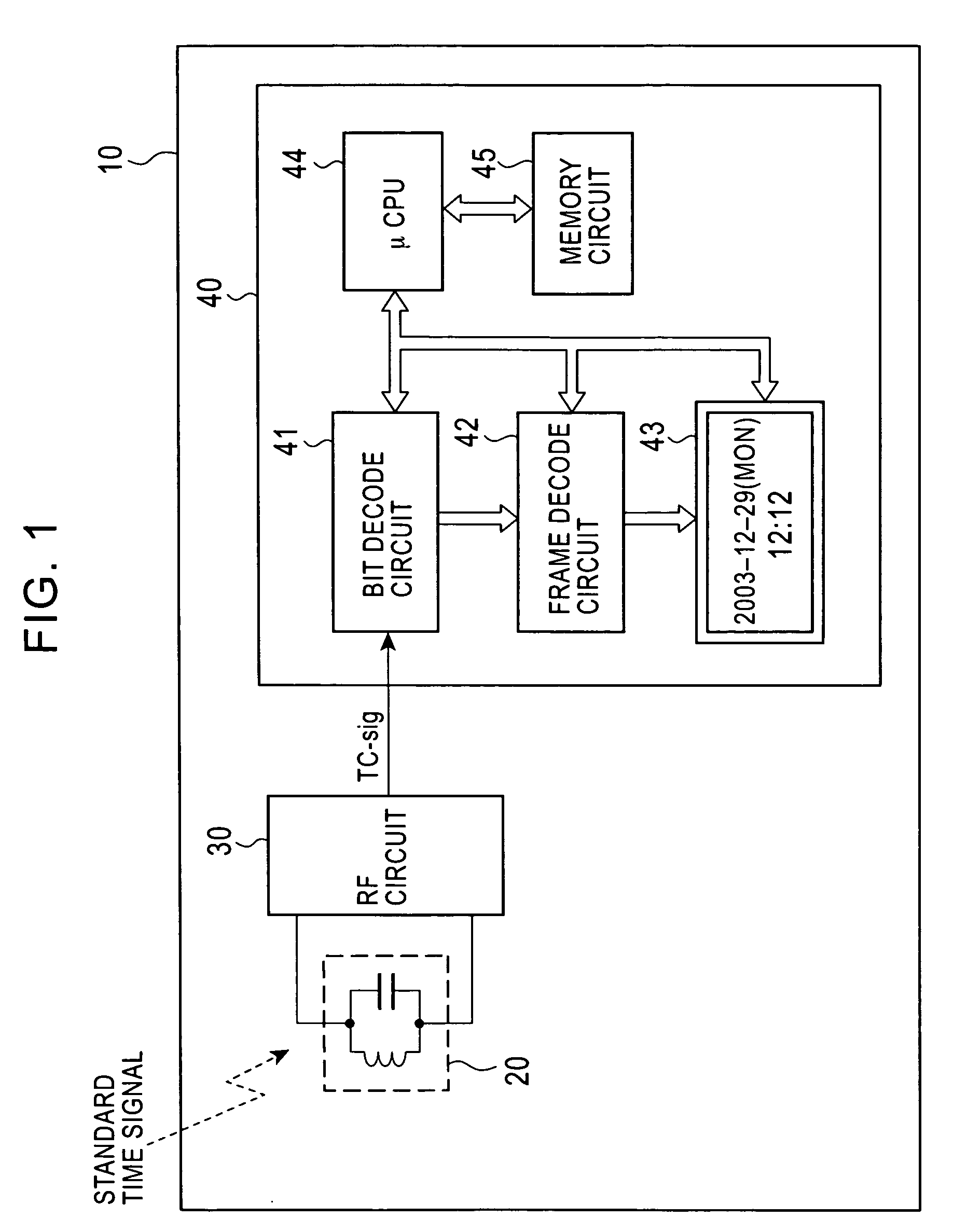
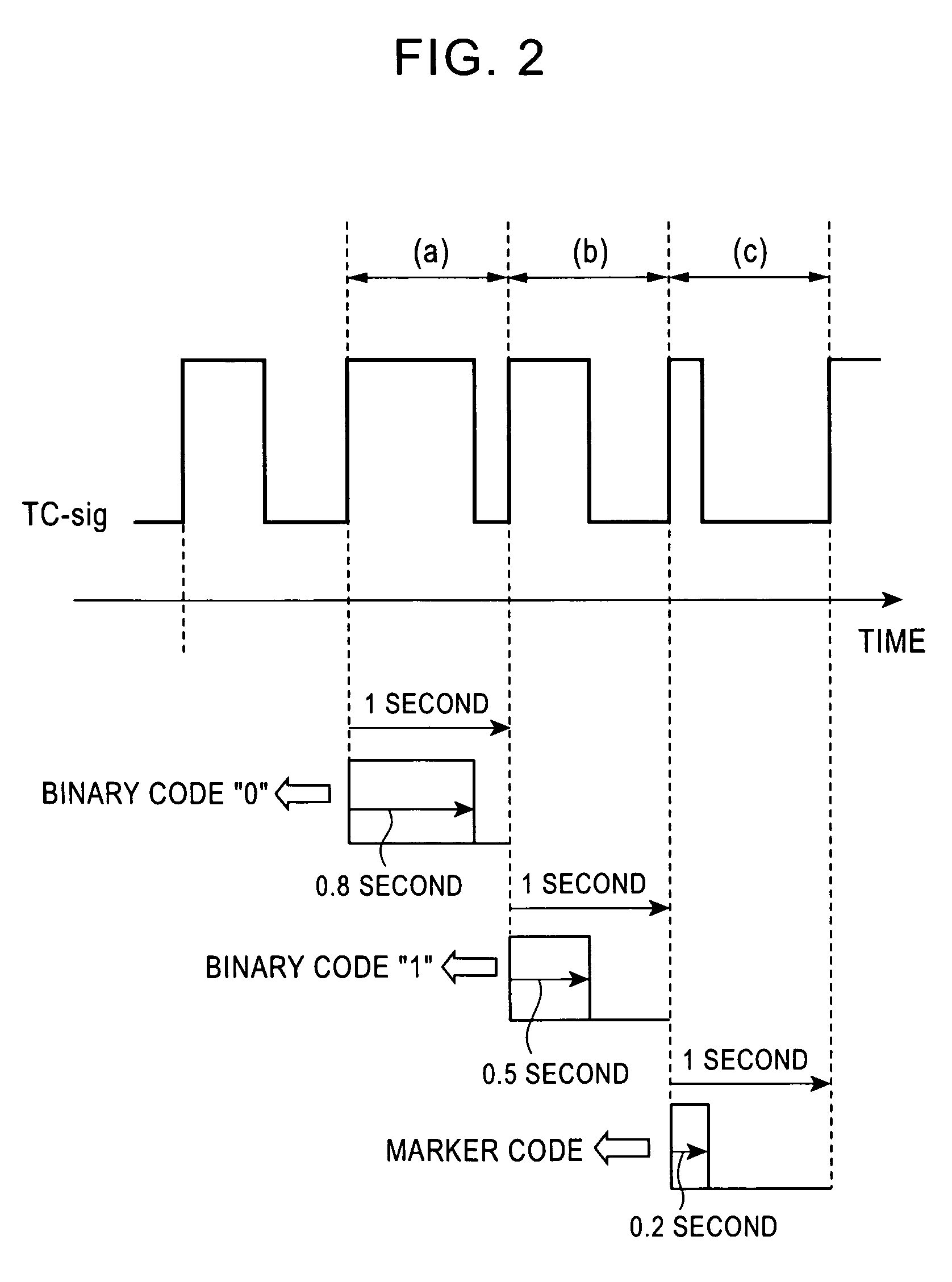
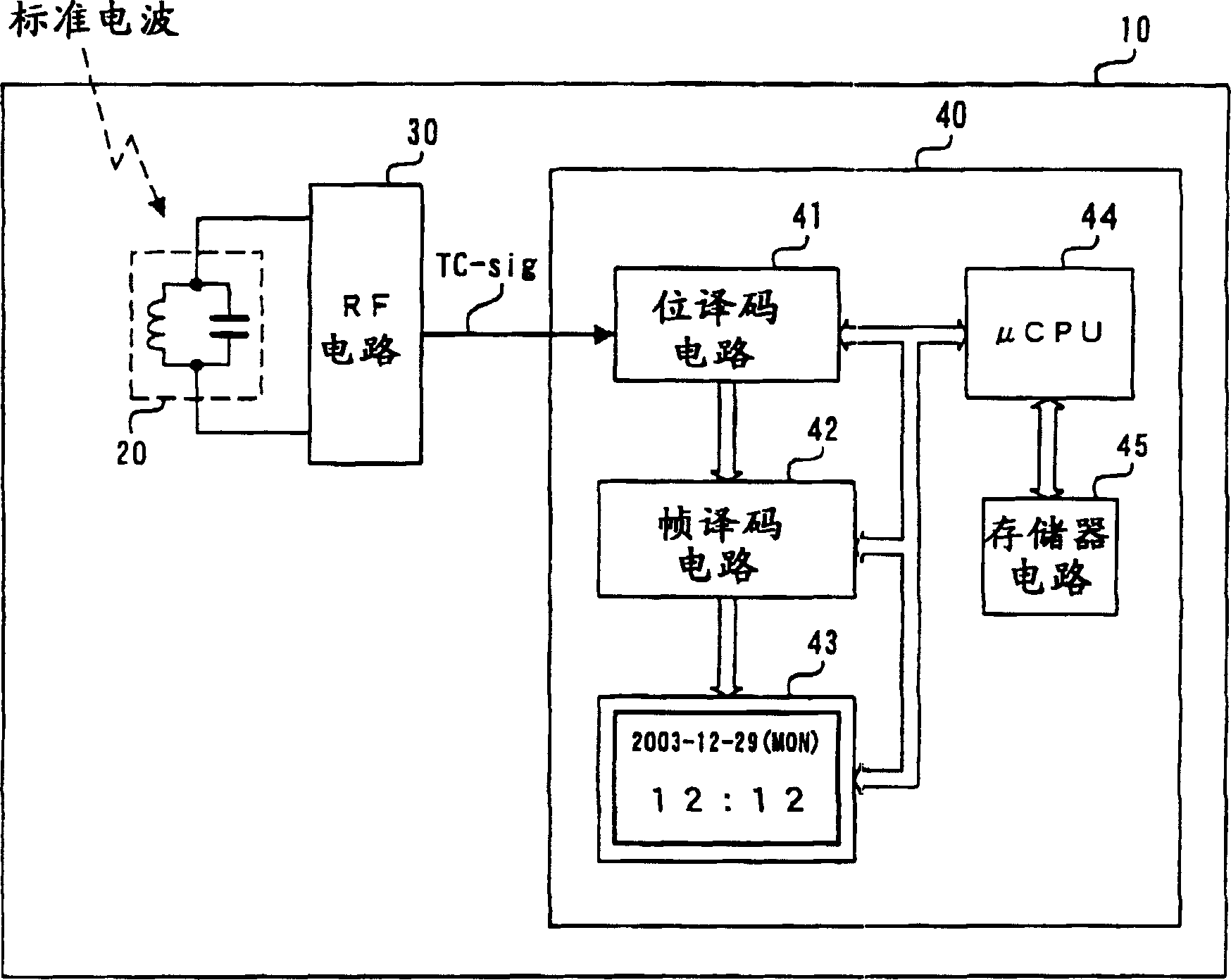
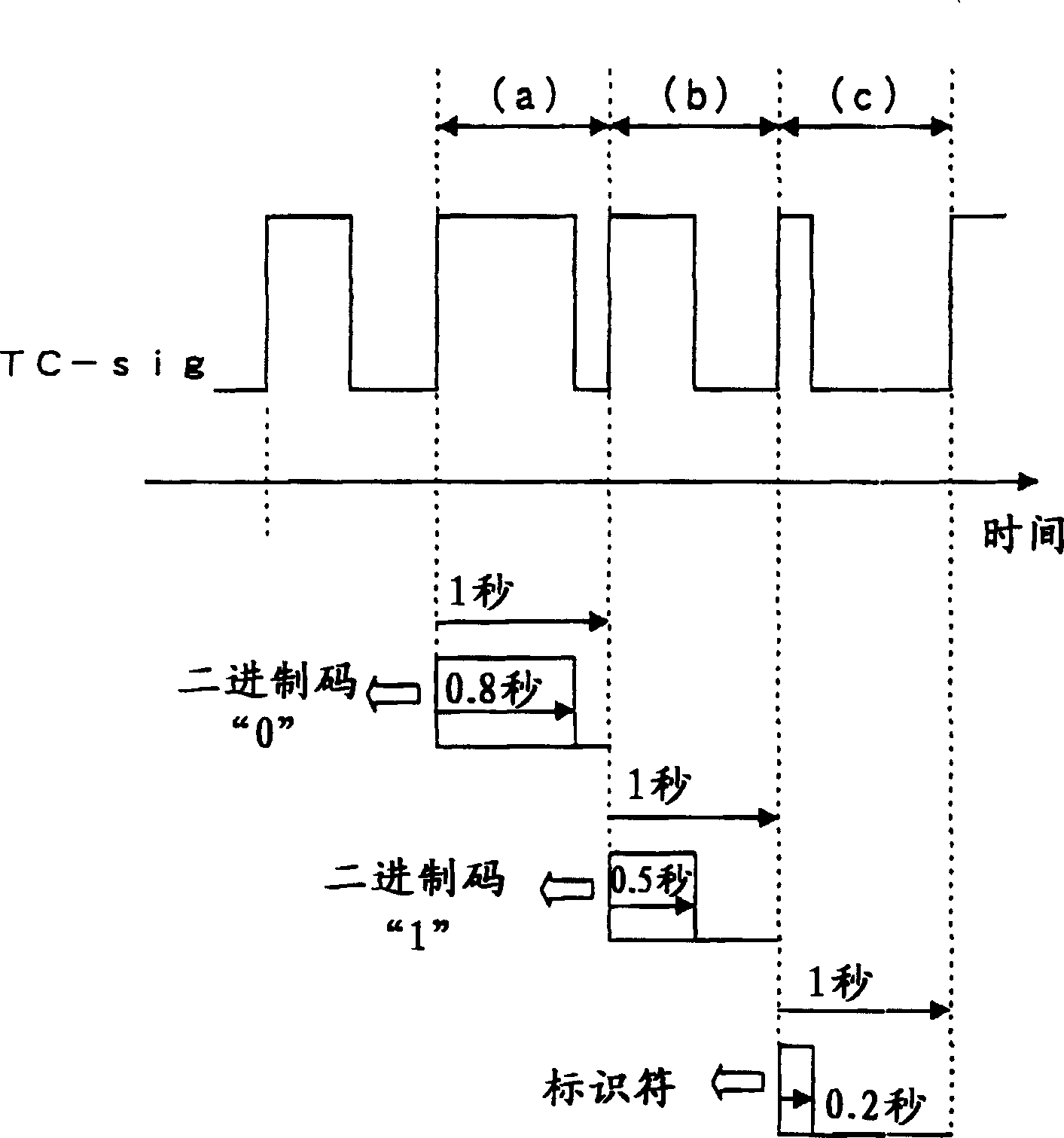
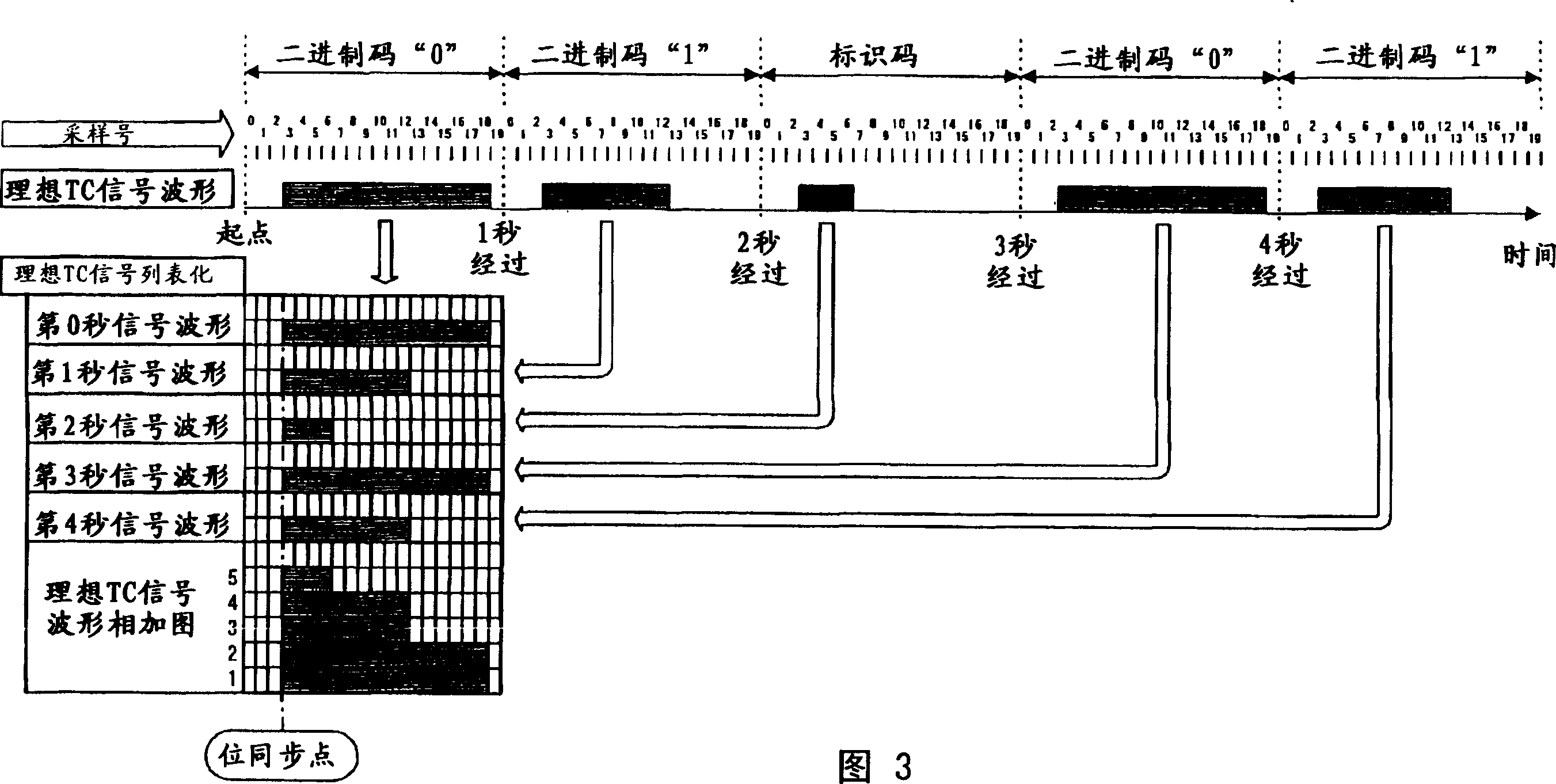
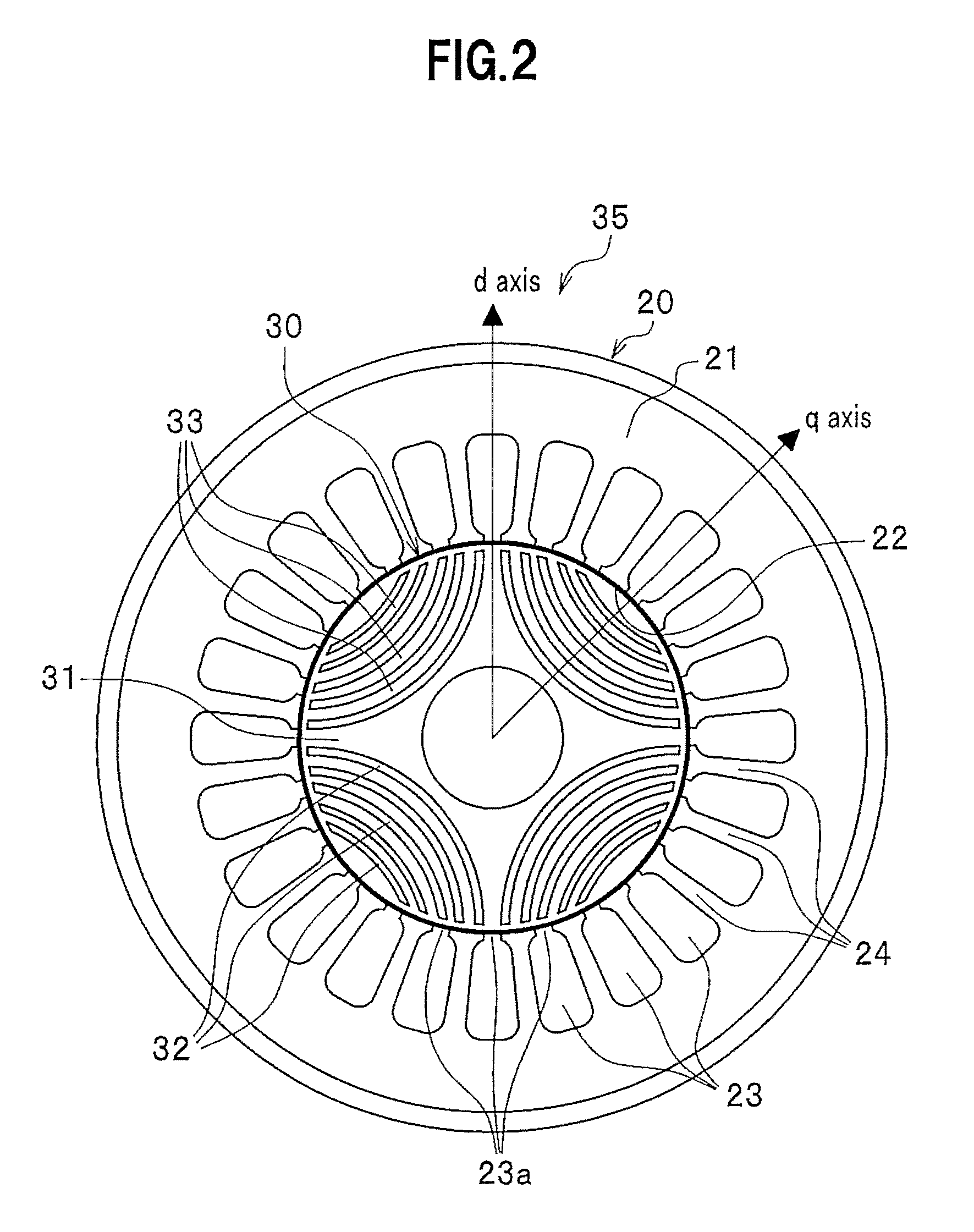
Standard time signal receiving time device and decoding method of time code signal
InactiveUS20050195690A1Accurate decodingSimple arithmetic processingSetting time indicationRadio-controlled time-piecesDecoding methodsComputer science
In a radio controlled clock and a decoding method of a time code signal, the time code signal can be accurately decoded irrespective of the mixture of noises and the deterioration of a radio wave signal receiving situation, and arithmetic processing is simple. A standard time signal is received and the time code signal superposed on this standard time signal is sampled at an interval of 50 ms and is stored to a memory. The stored sampling data are formed as a list in a data group every one second (20 samples). The plurality of data groups formed as a list are added every each sampling point, and a point for maximizing an increase change of the adding result is set to a synchronizing point of the sampling. Further, the correlation of the sampling data group and a code template pattern is calculated and a code shown by the sampling data group is judged.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Touch panel and method of detecting press operation position thereon
InactiveUS20100207907A1Reduce in quantityAvoid shapeInput/output processes for data processingBand shapeEngineering
In a touch panel, one of conductive layers on a bottom of an upper substrate and on a top of a lower substrate is formed of belt-shaped conductive layers. The other is a single conductive layer facing the belt-shaped conductive layers. The single conductive layer is provided with a pair of electrodes in positions corresponding to both ends in a direction where the belt-shaped conductive layers extend. When the upper substrate is pressed while a voltage is applied between the pair of electrodes, the top and lower conductive layers contact with each other. Then, a voltage value corresponding to the pressed position in the direction where the belt-shaped conductive layers extend is generated from any of the belt-shaped conductive layers. From the voltage value and the position of the belt-shaped conductive layer from which the voltage value is generated, a pressed position on the upper substrate can be detected.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
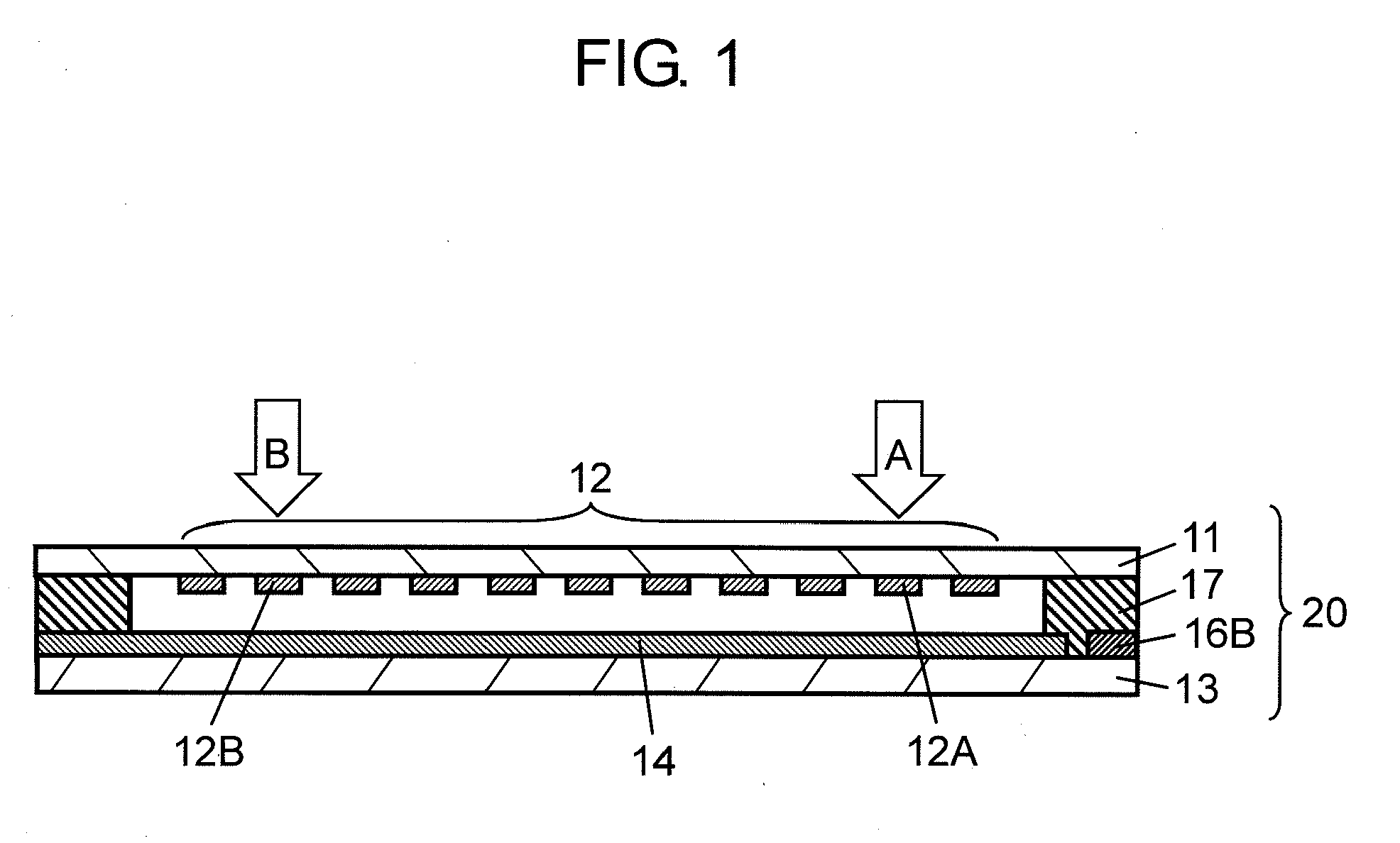
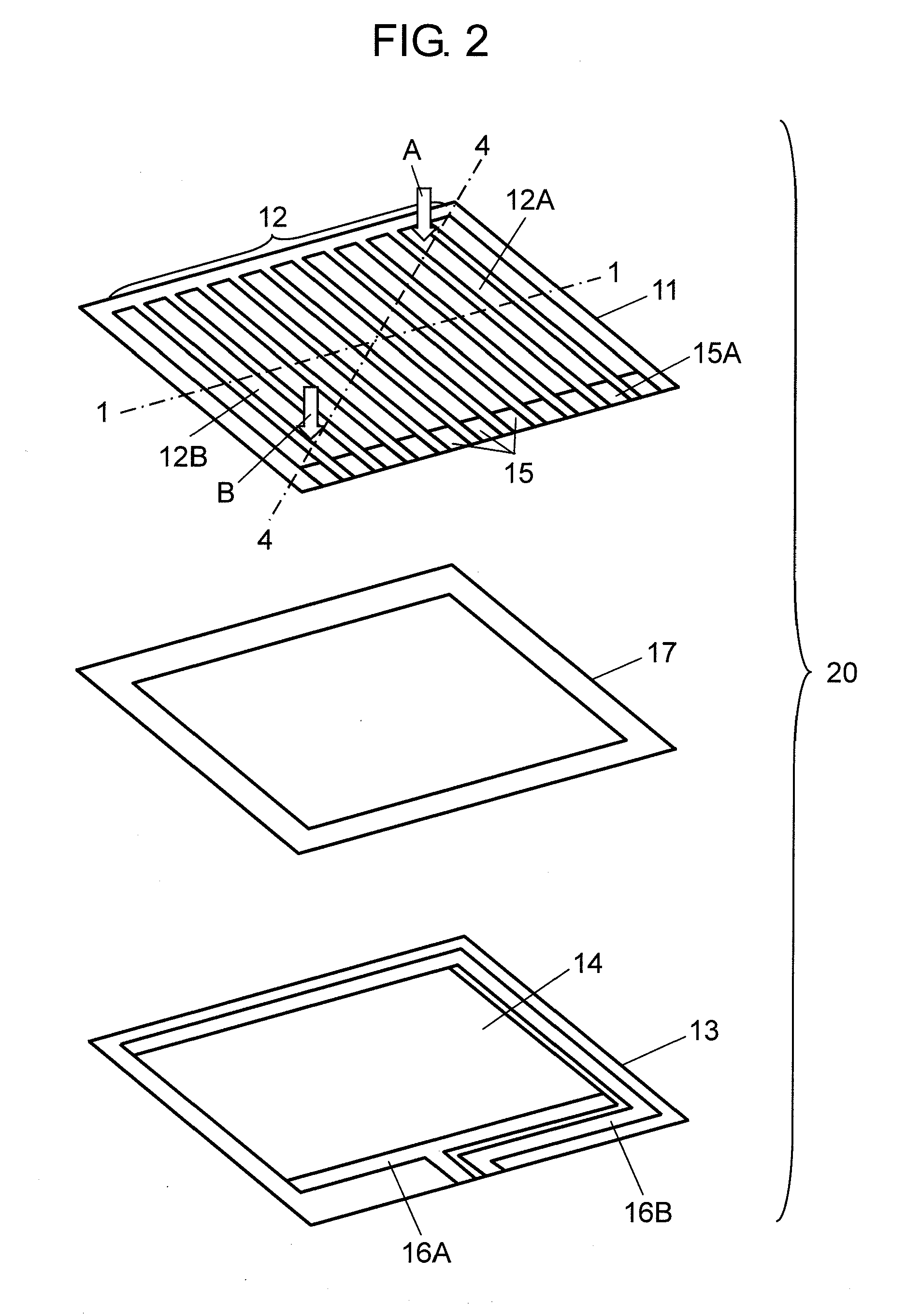
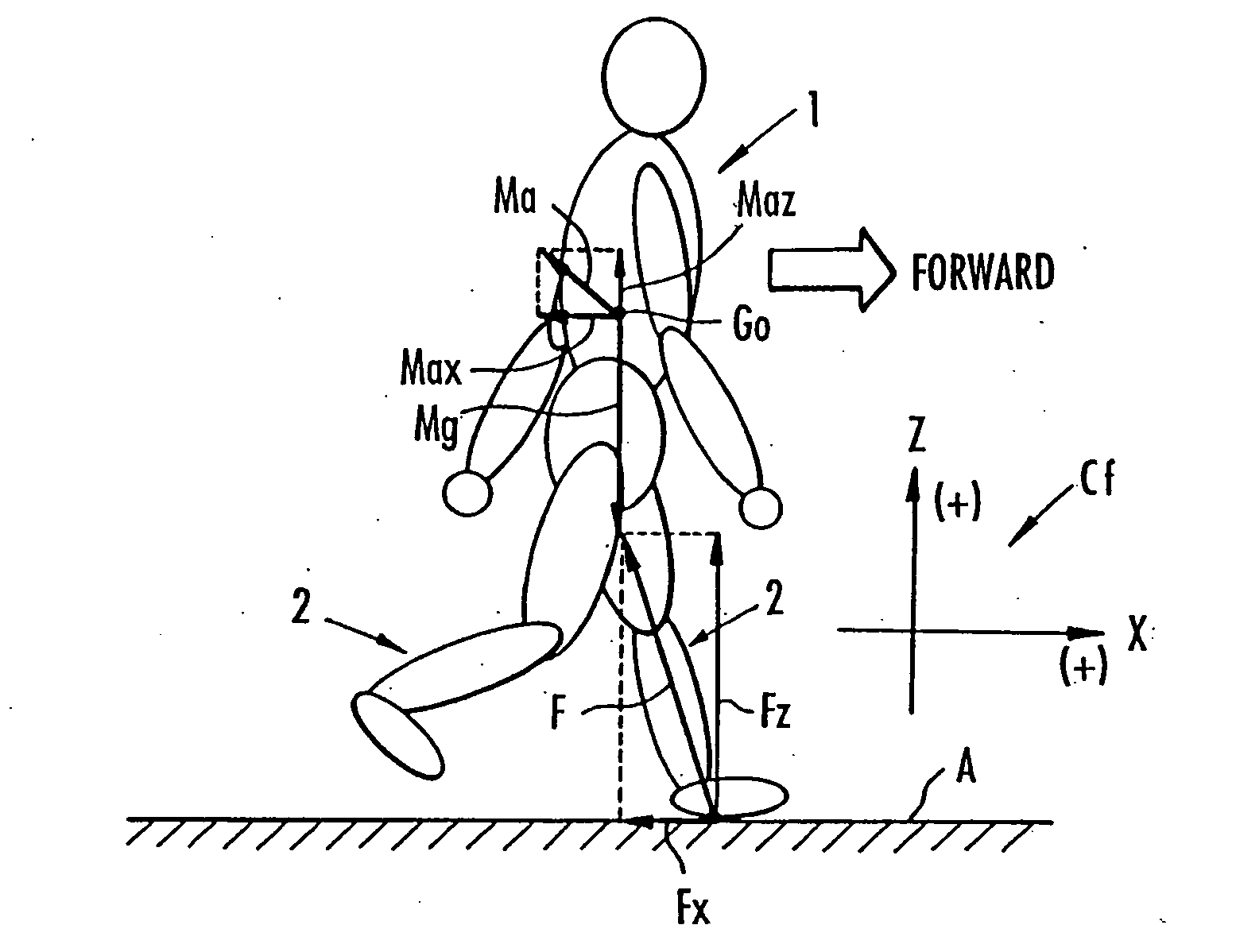
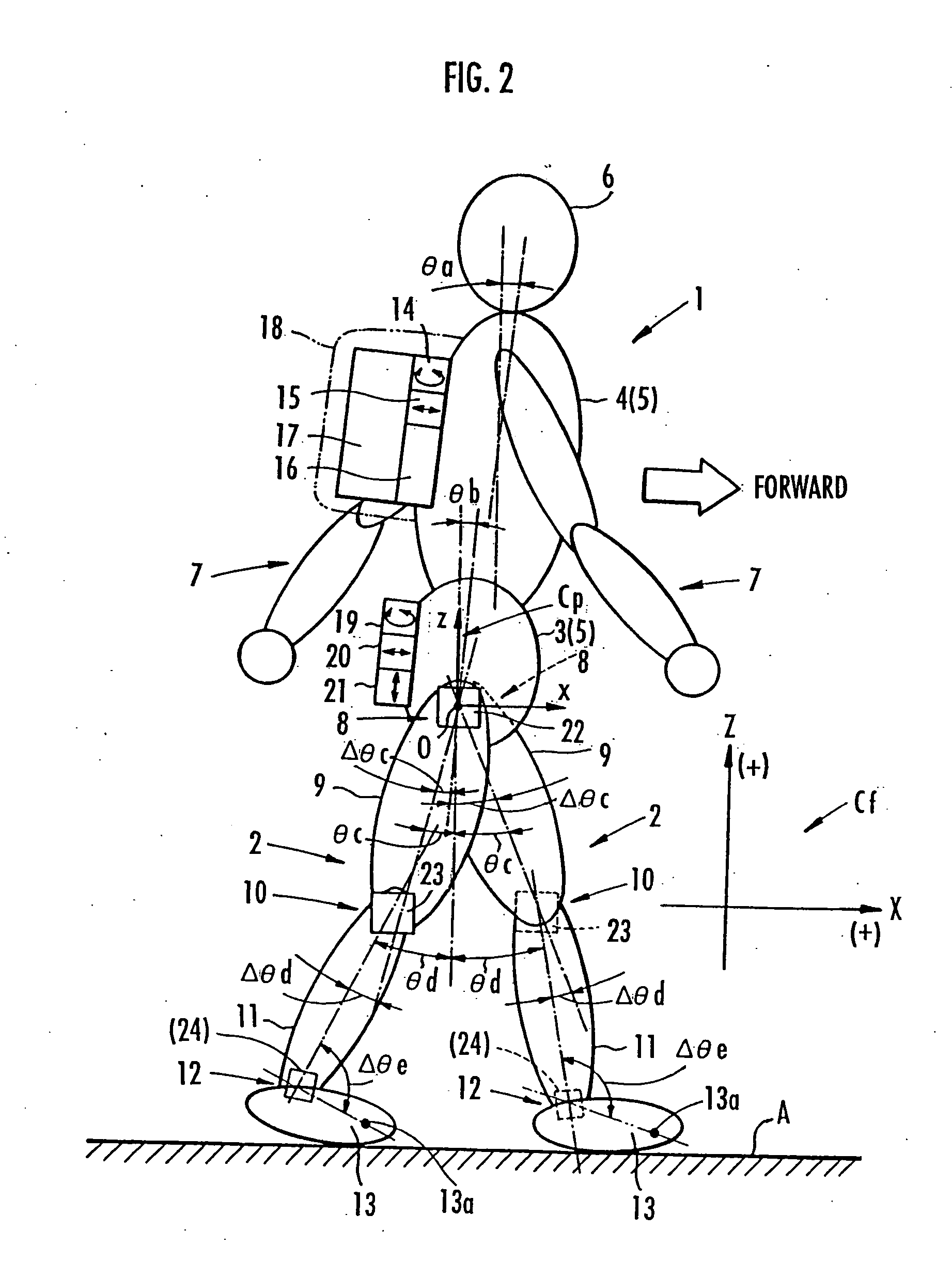
Method of assuming acting point of floor reaction force to biped walking mobile body and method of assuming joint moment of biped walking mobile body
InactiveUS20060197485A1Simple arithmetic processingGood estimateProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlGround contactEngineering
While a biped walking mobile body is in a motion, including level-ground walking, the position of the center of gravity (G0) of the biped walking mobile body, the position of an ankle joint (12) of each leg (2), and the position of a metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) of a foot (13) are successively grasped, and the horizontal position of a floor reaction force acting point of the leg (2) in contact with the ground is estimated on the basis of the relative positional relationship among the aforesaid positions. Depending on whether the center of gravity (G0) is behind the ankle joint (12), between the ankle joint (12) and the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a), or before the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) with respect to the advancing direction of the biped walking mobile body, the horizontal position of the ankle joint (12), the center of gravity (G0), or the metatarsophalangeal joint (13a) is defined as the horizontal position of a floor reaction force acting point. The vertical position of the floor reaction force acting point is estimated on the basis of the vertical distance from the ankle joint (12) to a ground contact surface.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
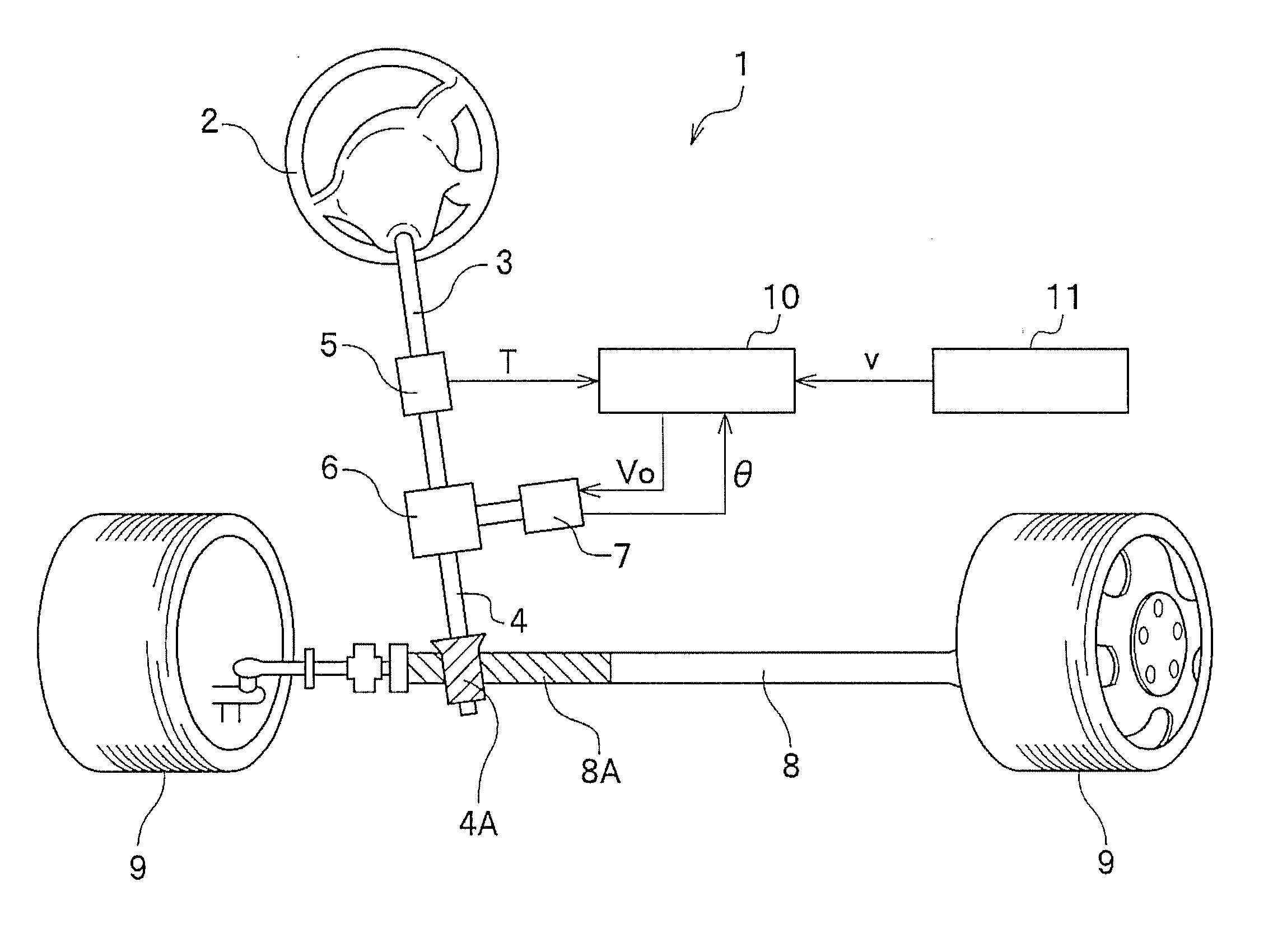
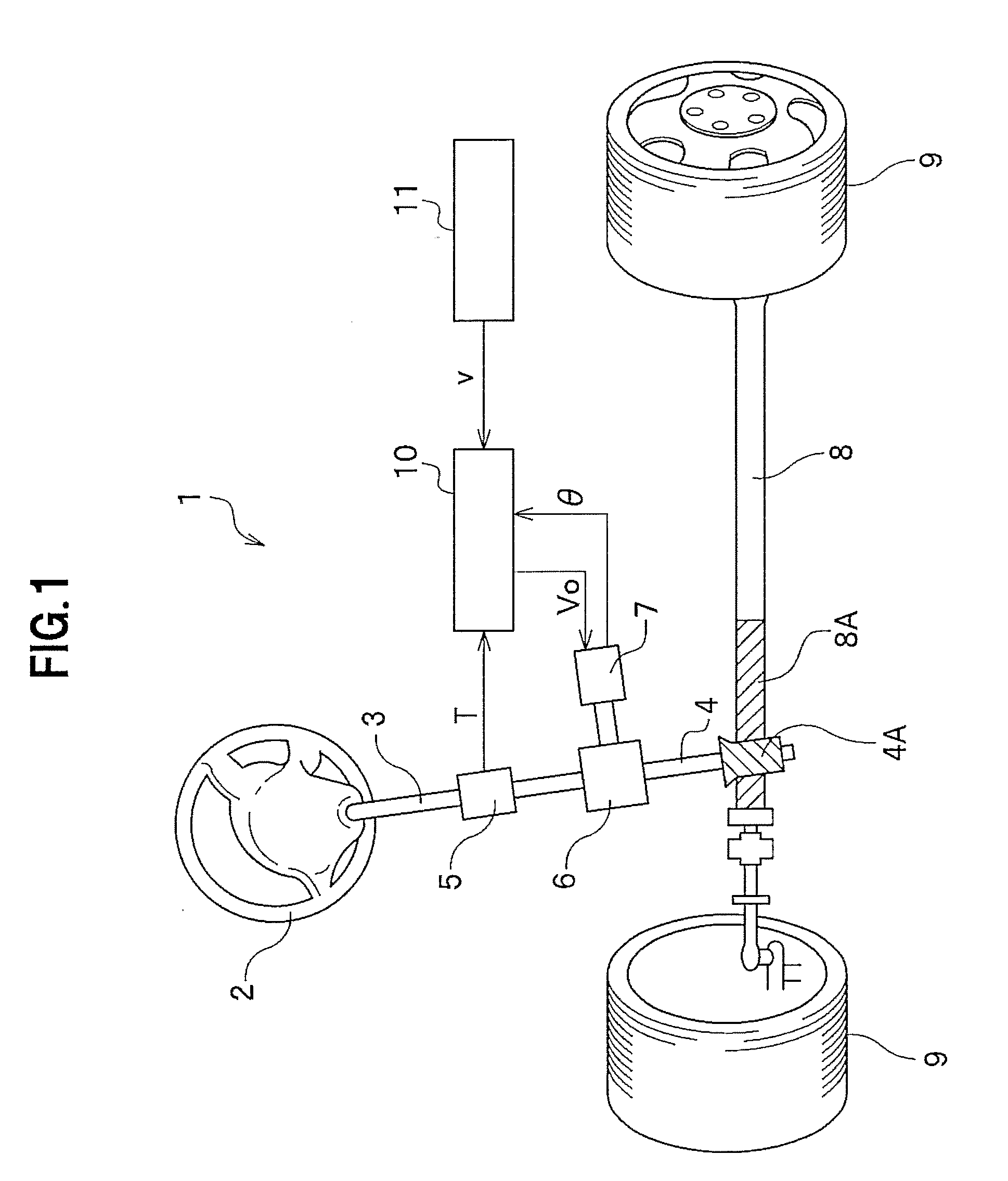
Electric power steering device
InactiveUS20110166750A1Good torque controlSimple arithmetic processingDigital data processing detailsField acceleration method controlTask controlThree-phase
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Real-time control method for artificial limb based on single-point acquiring muscle signals
The invention relates to a real-time control method for an artificial limb based on single-point acquiring muscle signals. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the muscle signals through a sound sensor; acquiring a forearm grabbing sound signal generated by carrying out grabbing actions with hands through a data acquisition card; wiping off the noise of the forearm grabbing sound signal; converting the sound signal into a digital signal; dividing the acquired digital signal into short timeframes; carrying out variance calculation on each frame signal; if the variance of each frame signal excesses a first threshold, intercepting the subsequent data segment to be used as an actuating signal segment; if the variances of the three continuous frames excess a second threshold, intercepting the subsequent data segment to be used as an actuating signal segment; extracting the time domain features of actuating signals in the actuating signal segment; inputting the time domain feature into a linear classification model to obtain an action discriminating result; and converting the action discriminating result into an electrical signal used for controlling the grabbing action of the artificial limb. The invention has the advantages of low cost, less interference, low hardware requirements and simple operation, and is not easy to be interfered.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
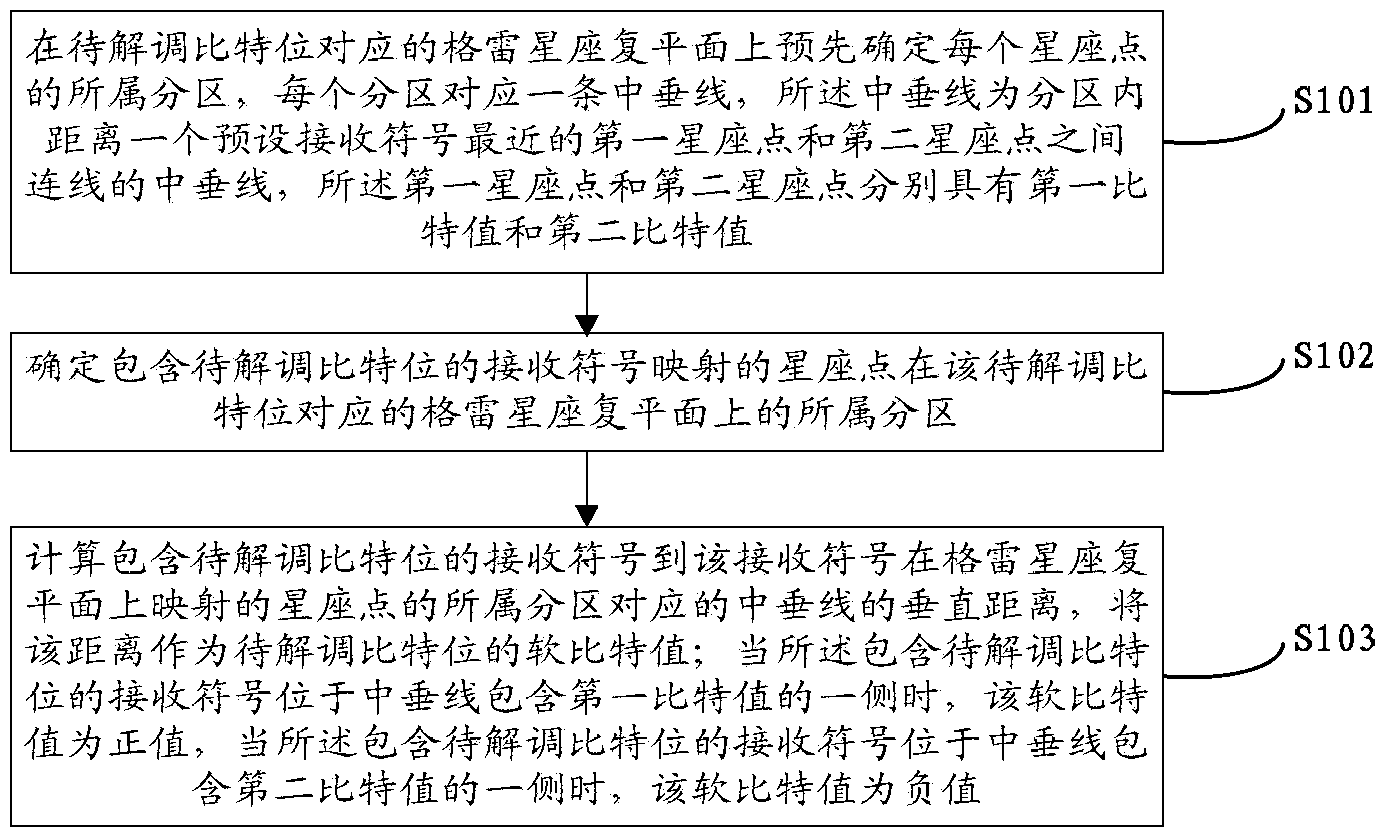
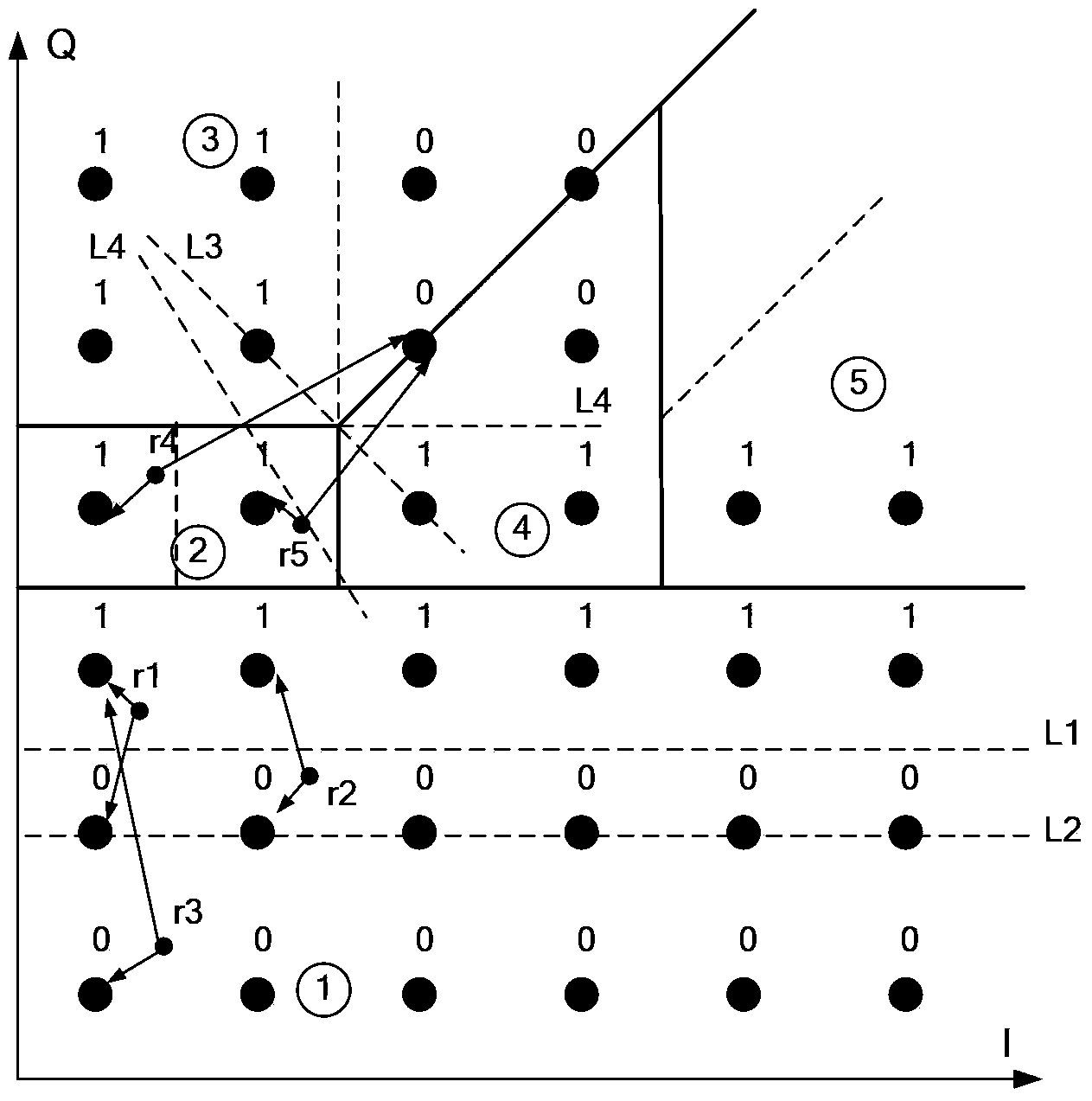
Quadrature amplitude modulation qubit demodulation method and device
ActiveCN104283835AThe operation process is simpleReduce computationMultiple carrier systemsQuadrature amplitude modulationConstellation
The embodiment of the invention discloses a quadrature amplitude modulation qubit demodulation method. The method includes the steps of predetermining a sub-area which each constellation point belongs to on a gray constellation complex plane corresponding to a bit position to be demodulated, wherein each sub-area corresponds to a perpendicular bisector; determining a sub-area which each constellation point containing the corresponding bit position to be demodulated and mapped by a received symbol on the gray constellation complex plane corresponding to the bit position to be demodulated; calculating the perpendicular distance between each received symbol containing the corresponding bit position to be demodulated and the corresponding perpendicular bisector, and making the distances serve as the qubit values of the bit position to be demodulated, wherein the qubit values are positive when each received symbol containing the corresponding bit position to be demodulated is located on the side, with the first bit value, of the corresponding perpendicular bisector, and the qubit values are negative when each received symbol containing the corresponding bit position to be demodulated is located on the side, with the second bit value, of the corresponding perpendicular bisector. The invention further discloses a quadrature amplitude modulation qubit demodulation device. By means of the quadrature amplitude modulation qubit demodulation method and device, the qubit demodulation efficiency can be improved.
Owner:大唐联诚信息系统技术有限公司
Planar display apparatus
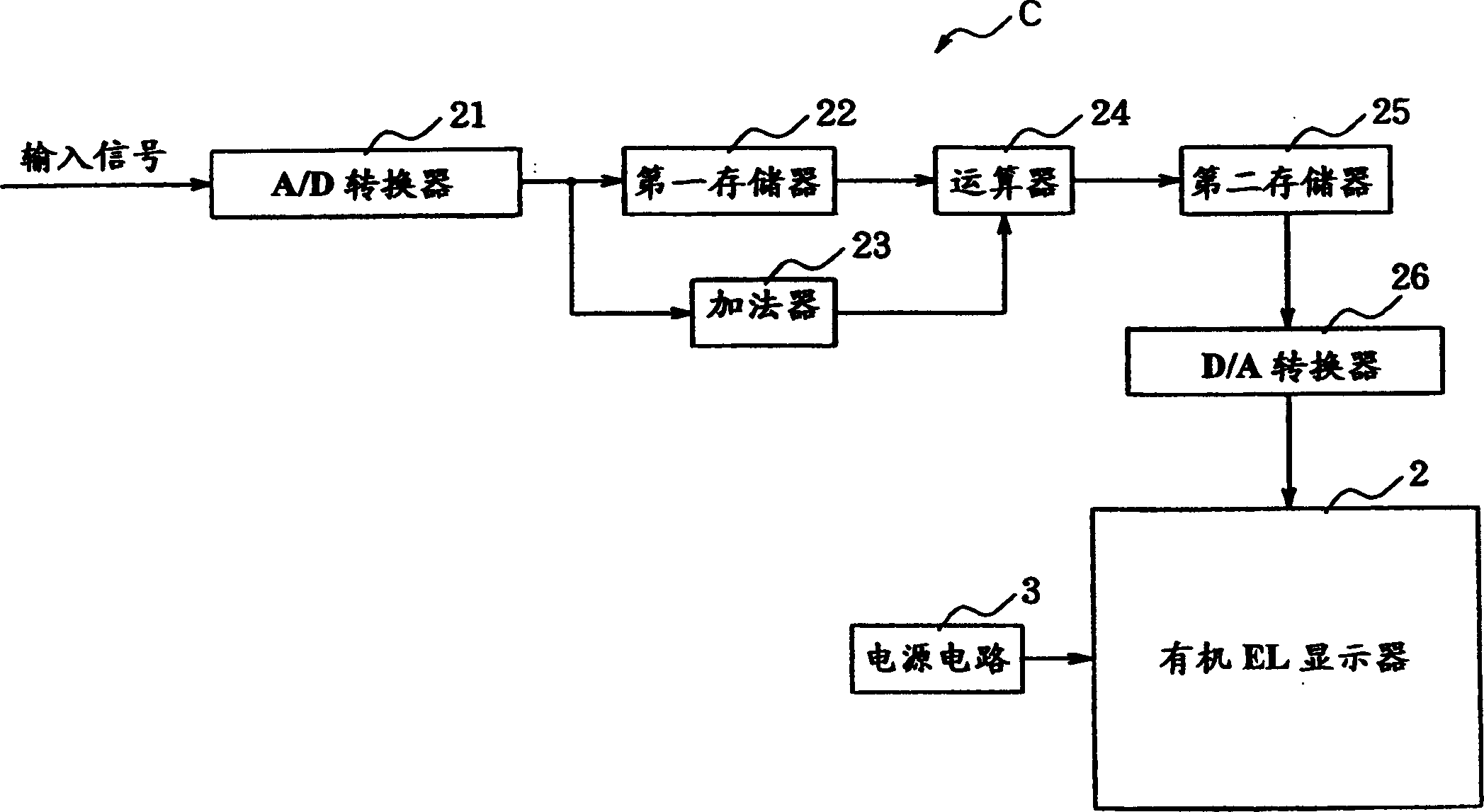
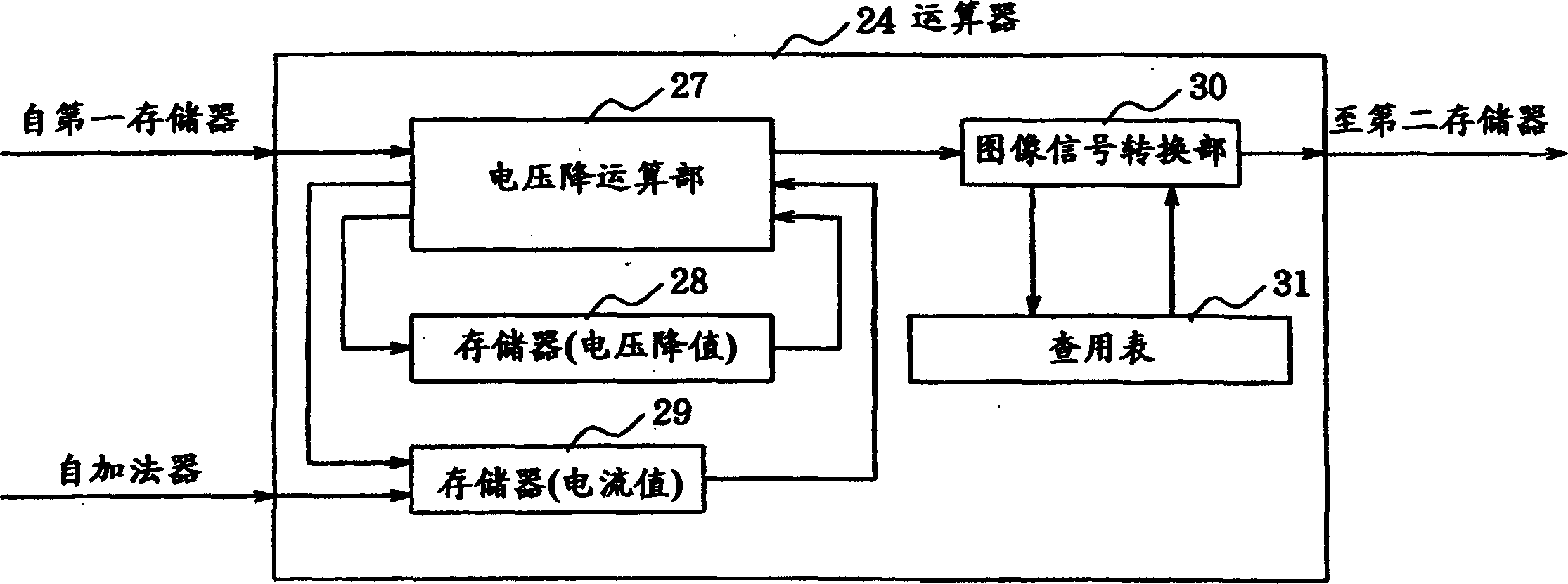
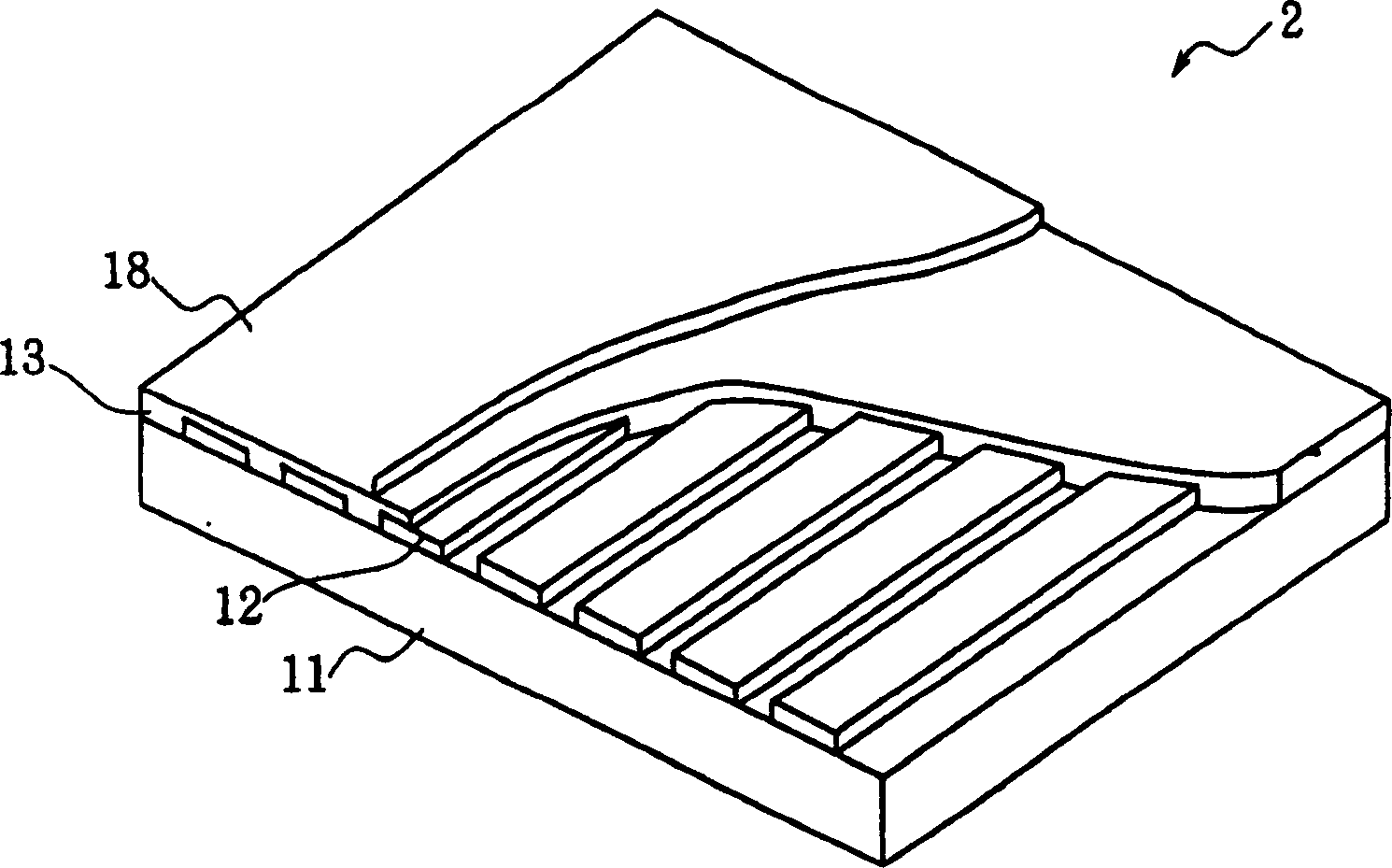
InactiveCN1556977ANo crosstalkSimple arithmetic processingStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceVoltage drop
The invention provides a flat display device which comprises for pixels arranged along drive lines a voltage drop calculator 27 for calculating a voltage drop occurring in accordance with the position of each pixel, and a video signal converter 30 and a lookup table 31 for correcting the input signal to be supplied to the pixel in accordance with the magnitude of the calculated voltage drop, whereby crosstalk due to the voltage drop is prevented.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Rollover Judging Device
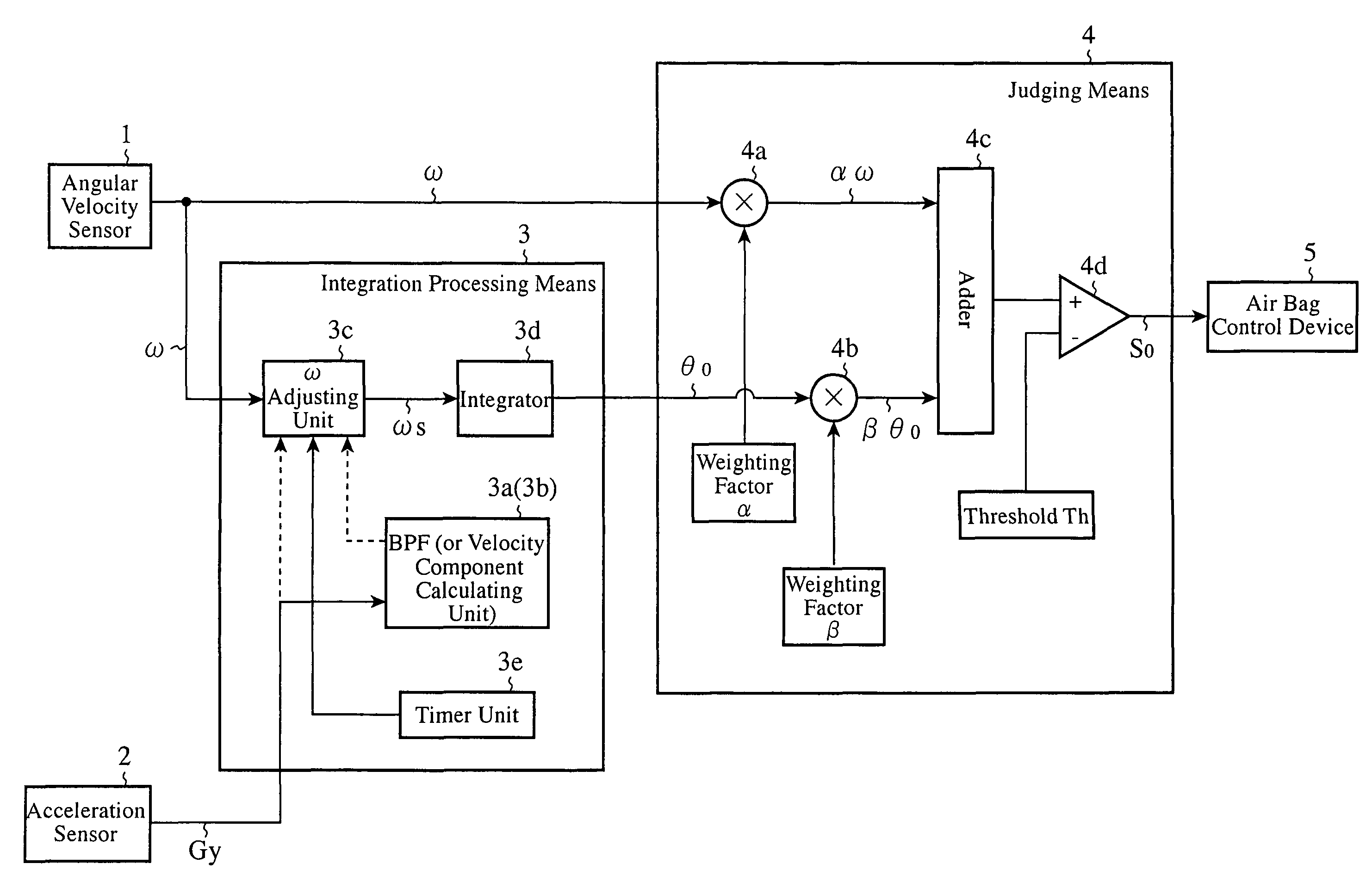
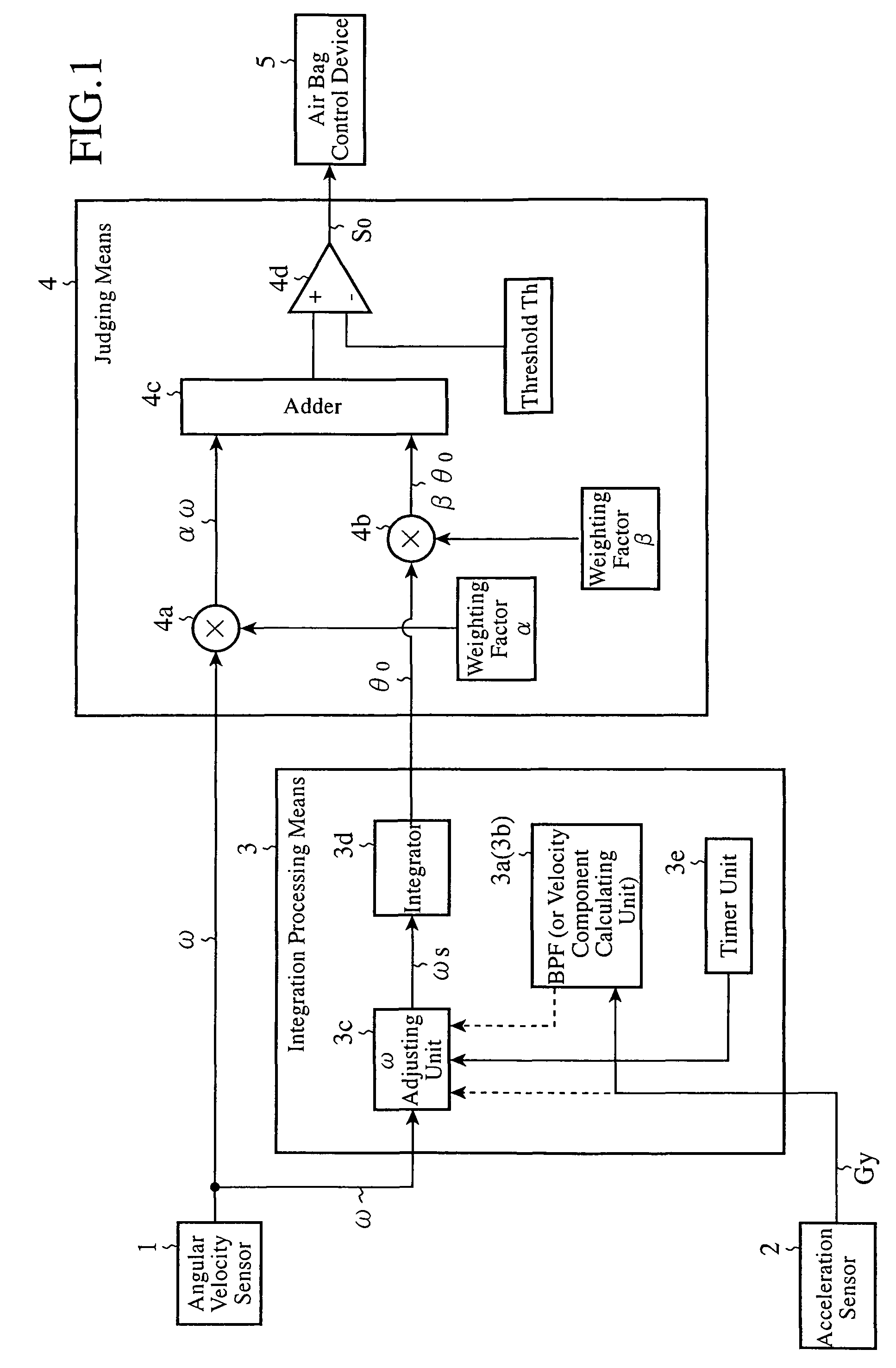
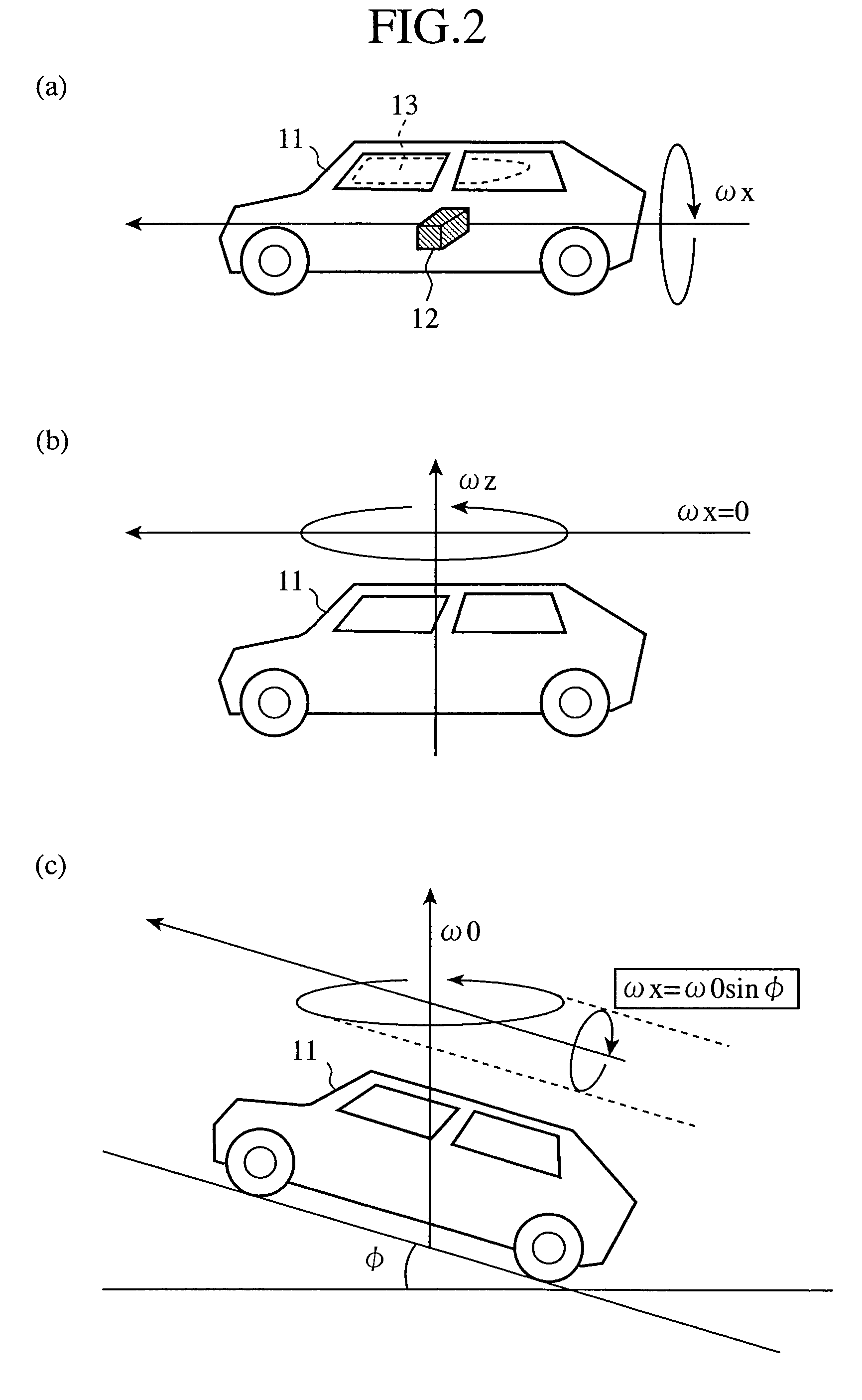
ActiveUS20090118892A1Simple arithmetic processingImprove reliabilityVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesIntegratorAngular velocity
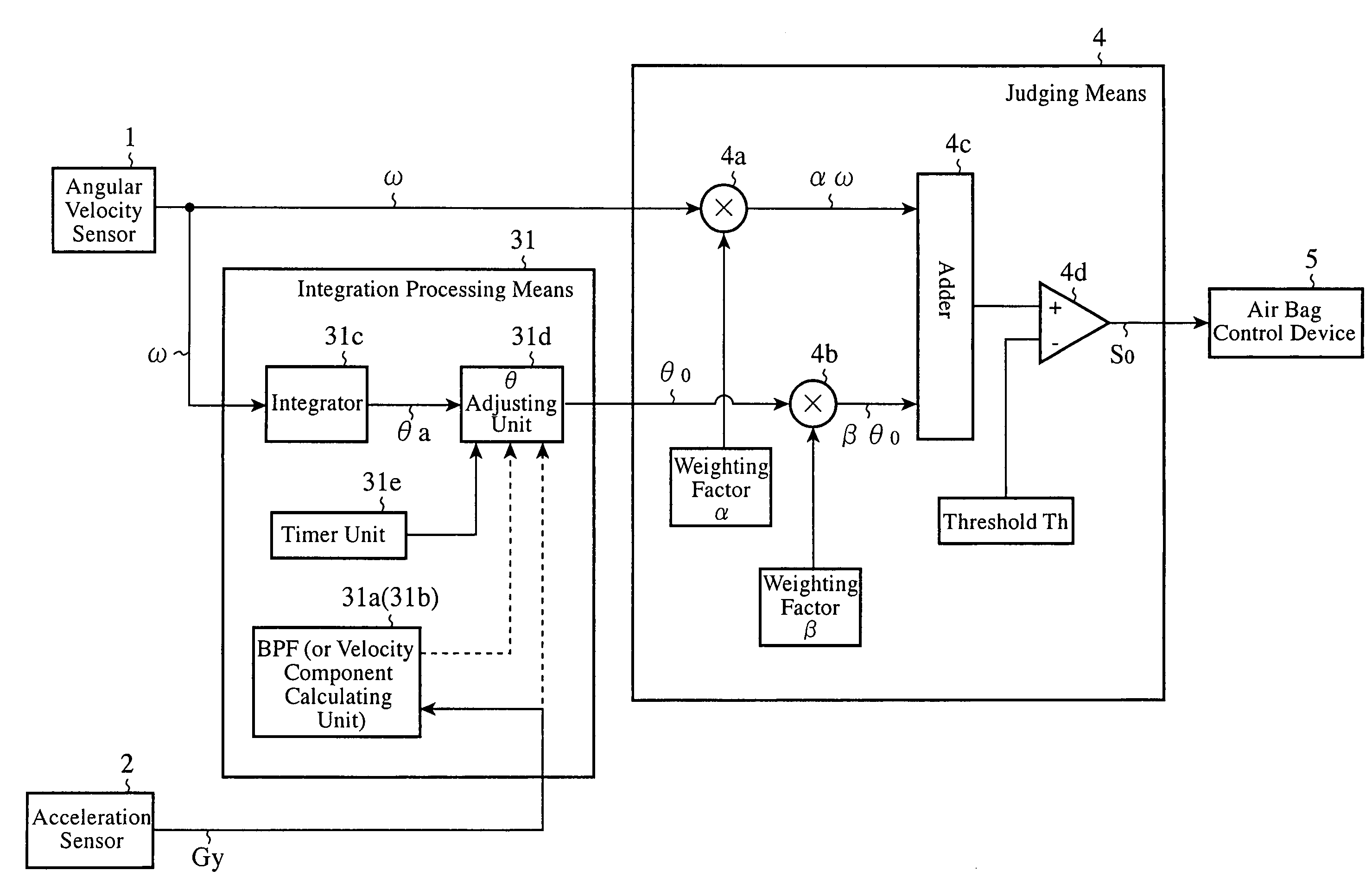
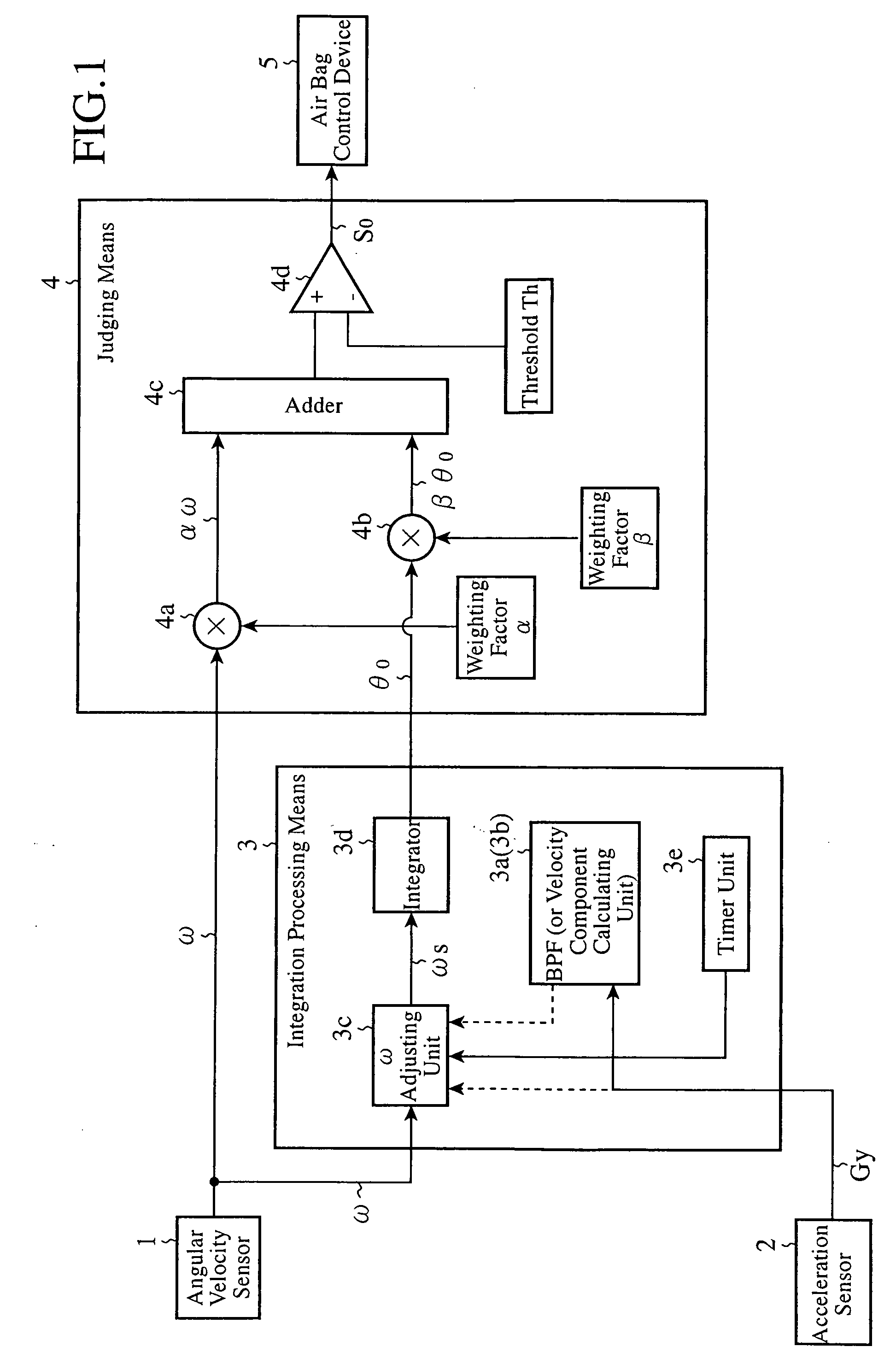
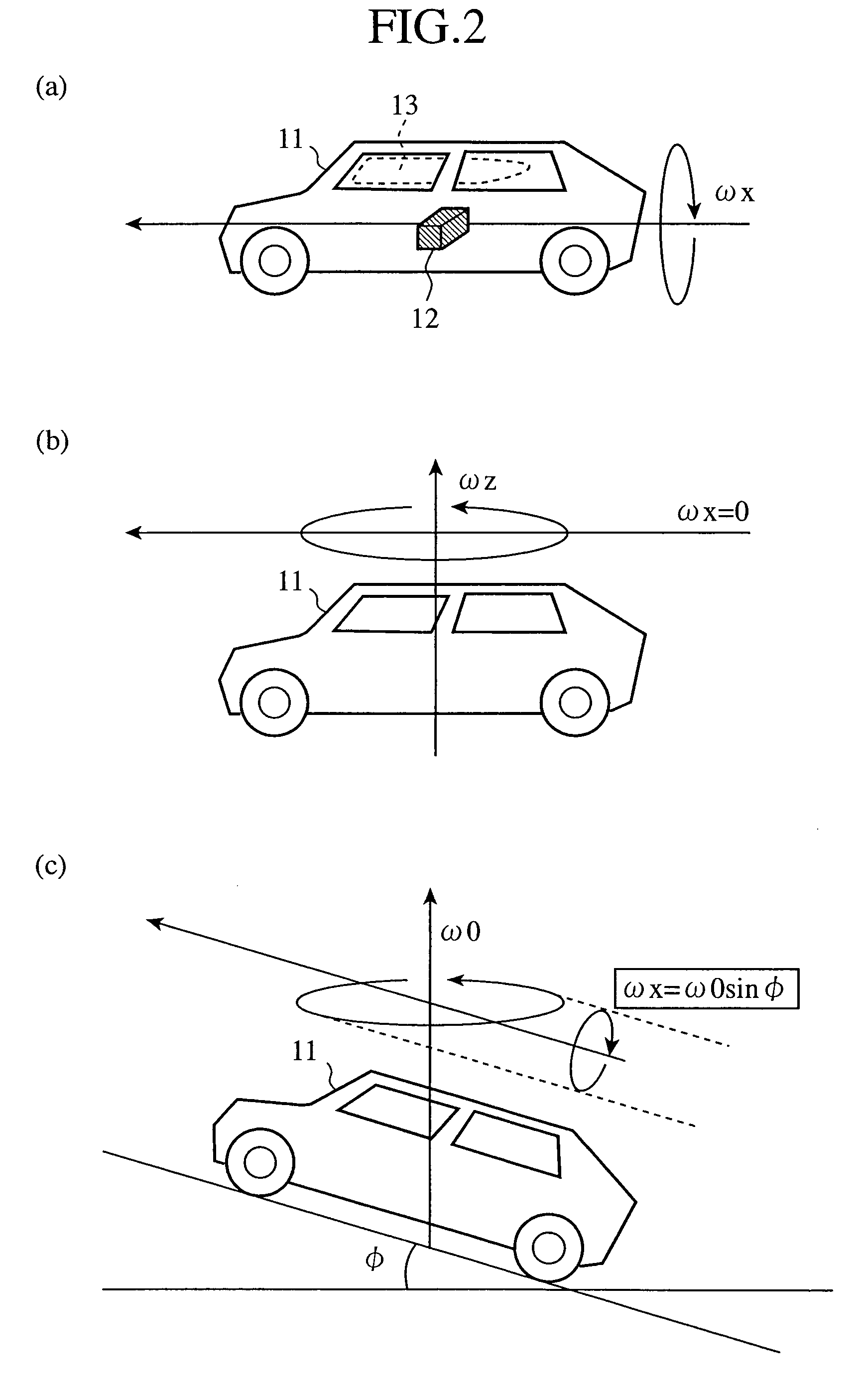
A rollover judging device adjusts the magnitude of an angular velocity component ω of a vehicle in a direction of a rollover, which is measured by an angular velocity sensor 1, by using an ω adjusting unit 3c on the basis of an acceleration component of the vehicle in its rightward or leftward direction or in its upward or downward direction, which is measured by an acceleration sensor 2, calculates an angle component θo by integrating with respect to time this adjusted angular velocity component ωo by using an integrator 3d, carries out predetermined multiplication and addition processes by using a judging means 4 on the basis of this angle component θo and the measured angular velocity component ω, and, when the result of this addition process exceeds a preset threshold Th, outputs a signal indicating judgment of occurrence of a rollover to an air bag control device 5.
Owner:NEXGEN CONTROL SYST LLC
Friction stir welding apparatus
ActiveCN103658966ASimple structureIncrease freedomWelding/soldering/cutting articlesNon-electric welding apparatusMechanical engineeringFriction stir welding
The present invention provides a friction stir welding apparatus which is vertically movable with respect to a processing target side surface of a processing target member, The friction stir welding apparatus is provided with a displacement detecting device that detects displacement of the welding tool caused by deformation of the fitting jig, at a time of performing friction stir welding in which the arm is moved to move the welding tool with respect to the processing target member, while stirring the processing target member by rotating the probe with respect to the processing target member and pressing the probe to intrude into the processing target member, in which the fitting jig can be deformed more than the arm at the time of performing friction stir welding, and in which the displacement detecting device has a displacement sensor fixed to the welding tool, and a reference member fixed to a fixing portion between the fitting jig and the arm to provide a reference position at a time of detecting the displacement to the displacement sensor.
Owner:F TECH INC +1
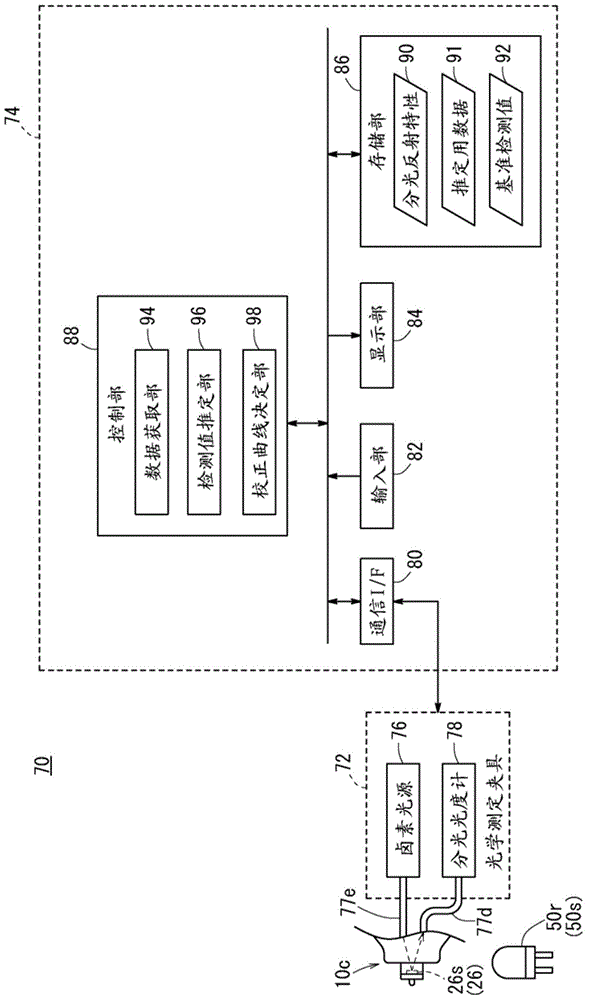
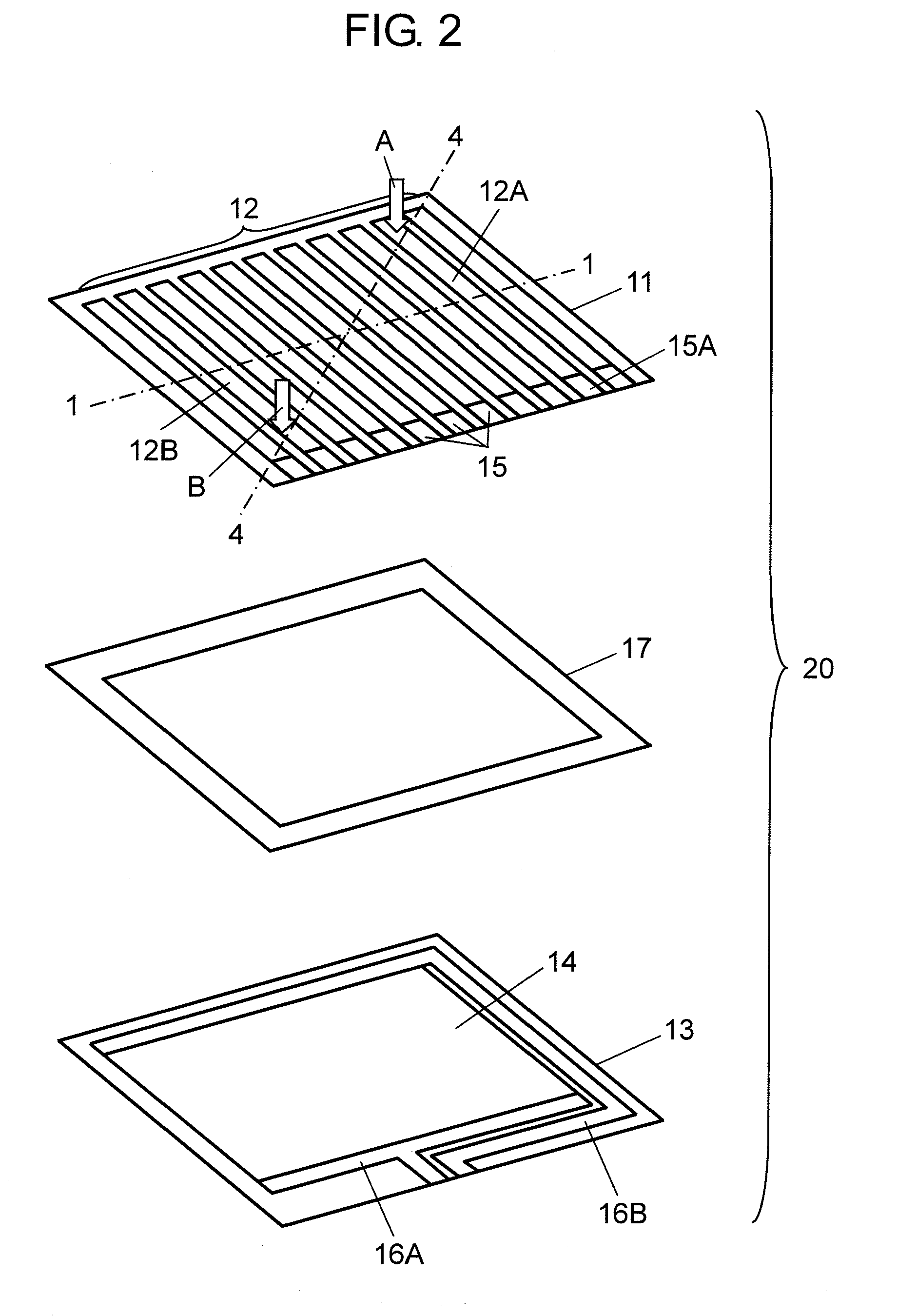
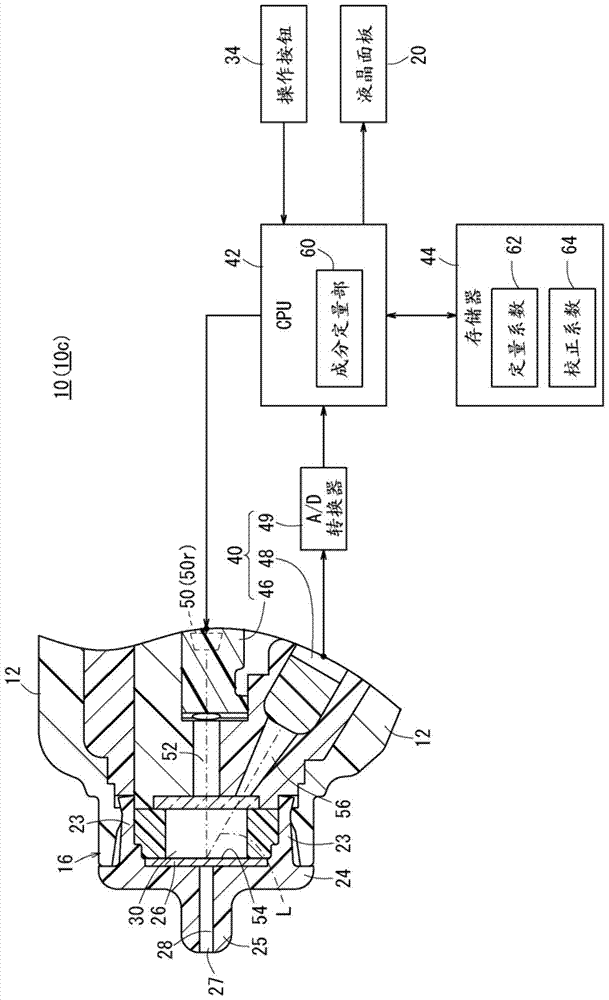
Calibration method, device, and program, and bodily-fluid component measurement device calibrated using said method
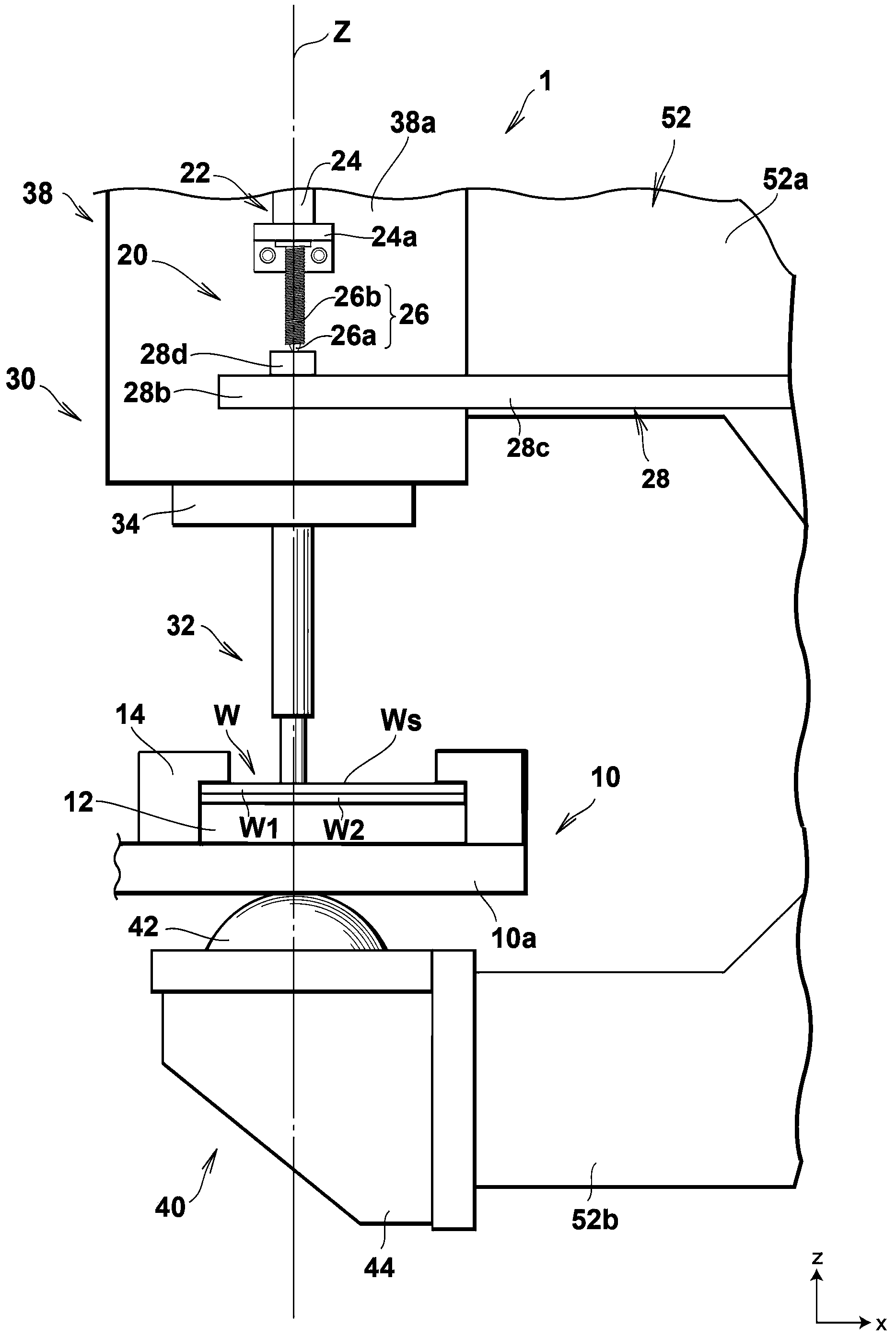
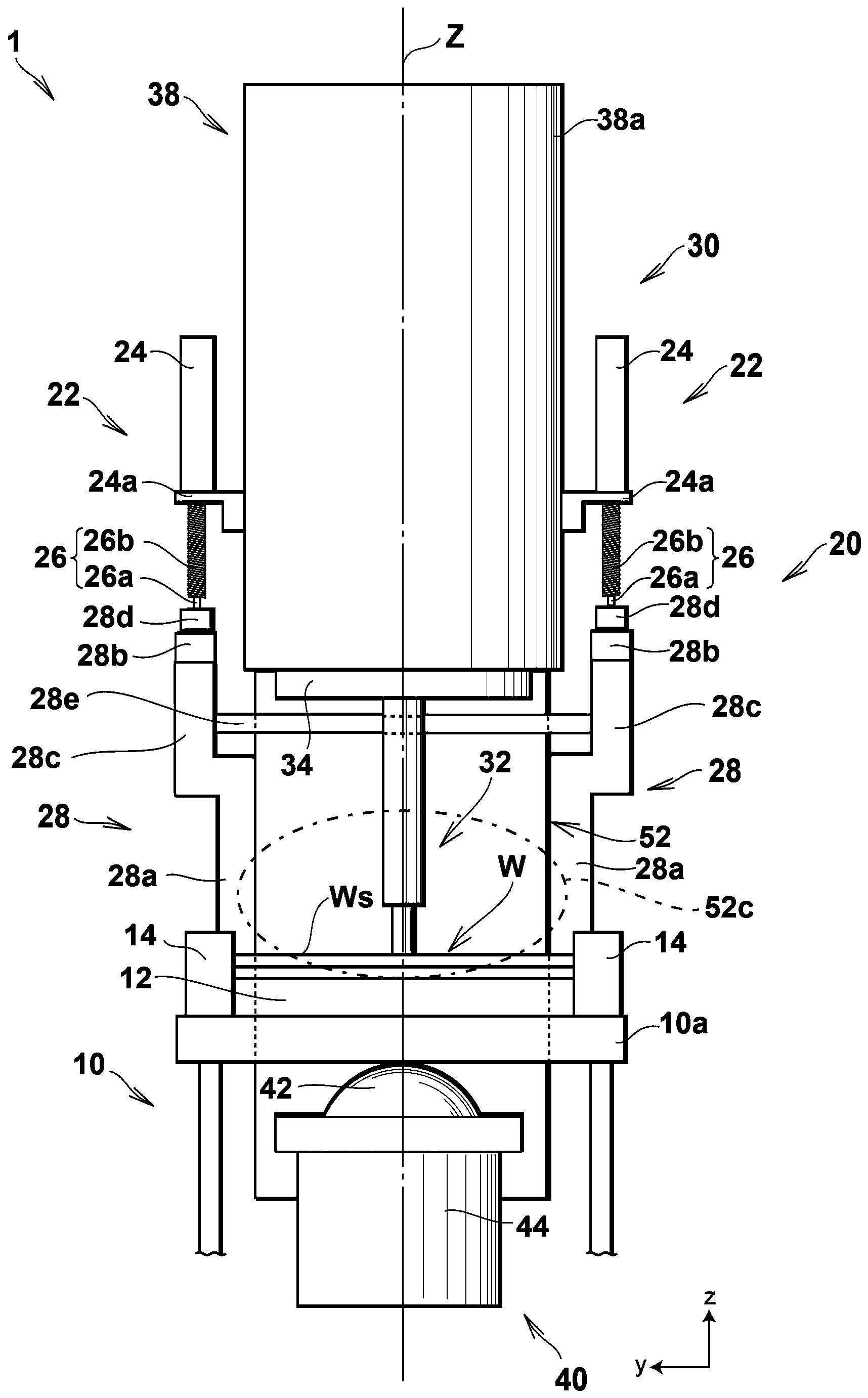
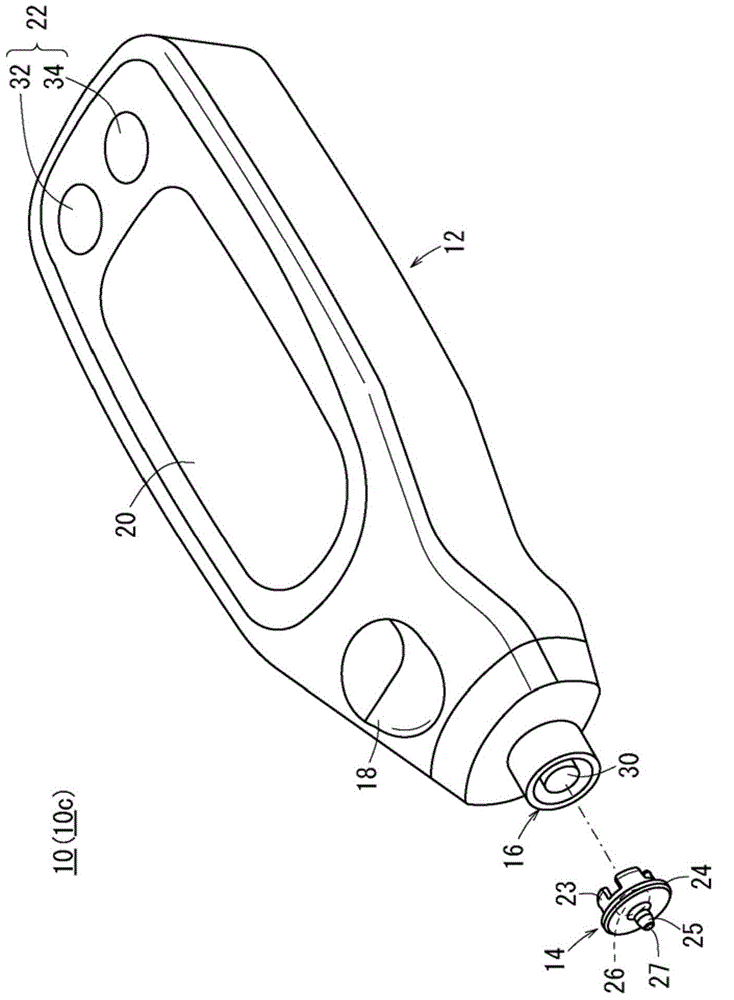
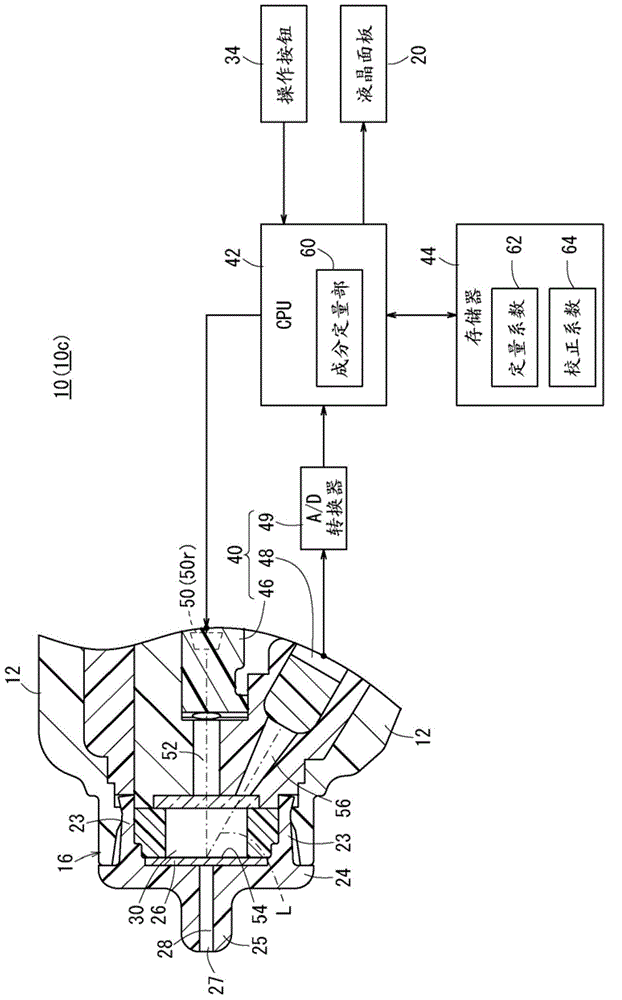
ActiveCN104937397AGuaranteed measurement accuracySimple arithmetic processingMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyEngineeringBody fluid
The present invention pertains to the following: a calibration method, device, and program; and a bodily-fluid component measurement device calibrated using said method. For each of a number of samples (26s), a reference detected value that would be obtained using a reference light source (50s) and an individual detected value that would be obtained using an individual light source (50r) that is of the same type as the reference light source (50s) and is to be installed in a device being calibrated (10c) are estimated. A calibration curve that converts detected values obtained from test strips (26) using the device being calibrated (10c) with the aforementioned individual light source (50r) installed therein to detected values that would have been obtained using the reference light source (50s) is determined on the basis of the relationships between the per-sample (26s) pairs of estimated reference detected values and individual detected values.
Owner:TERUMO KK
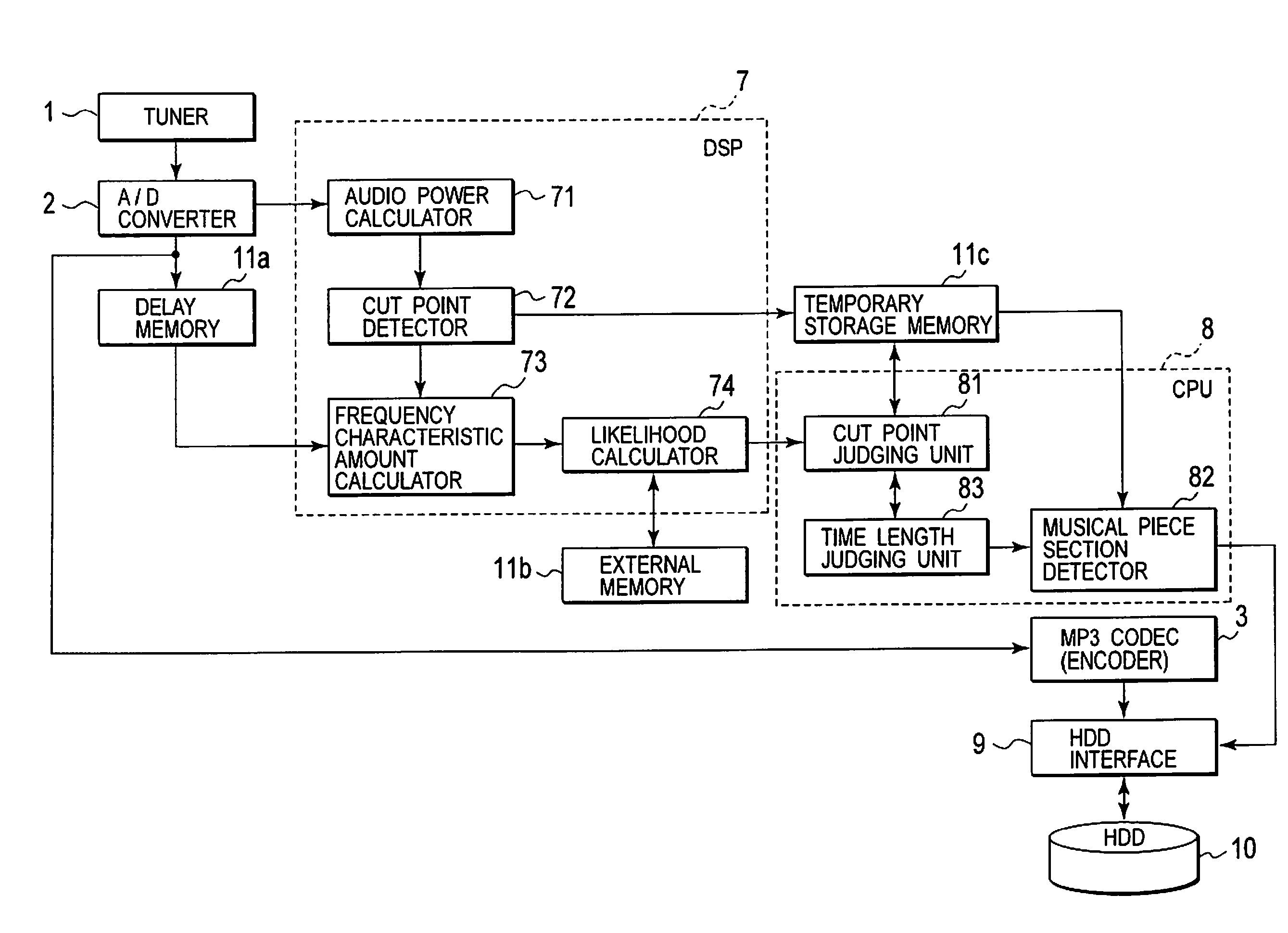
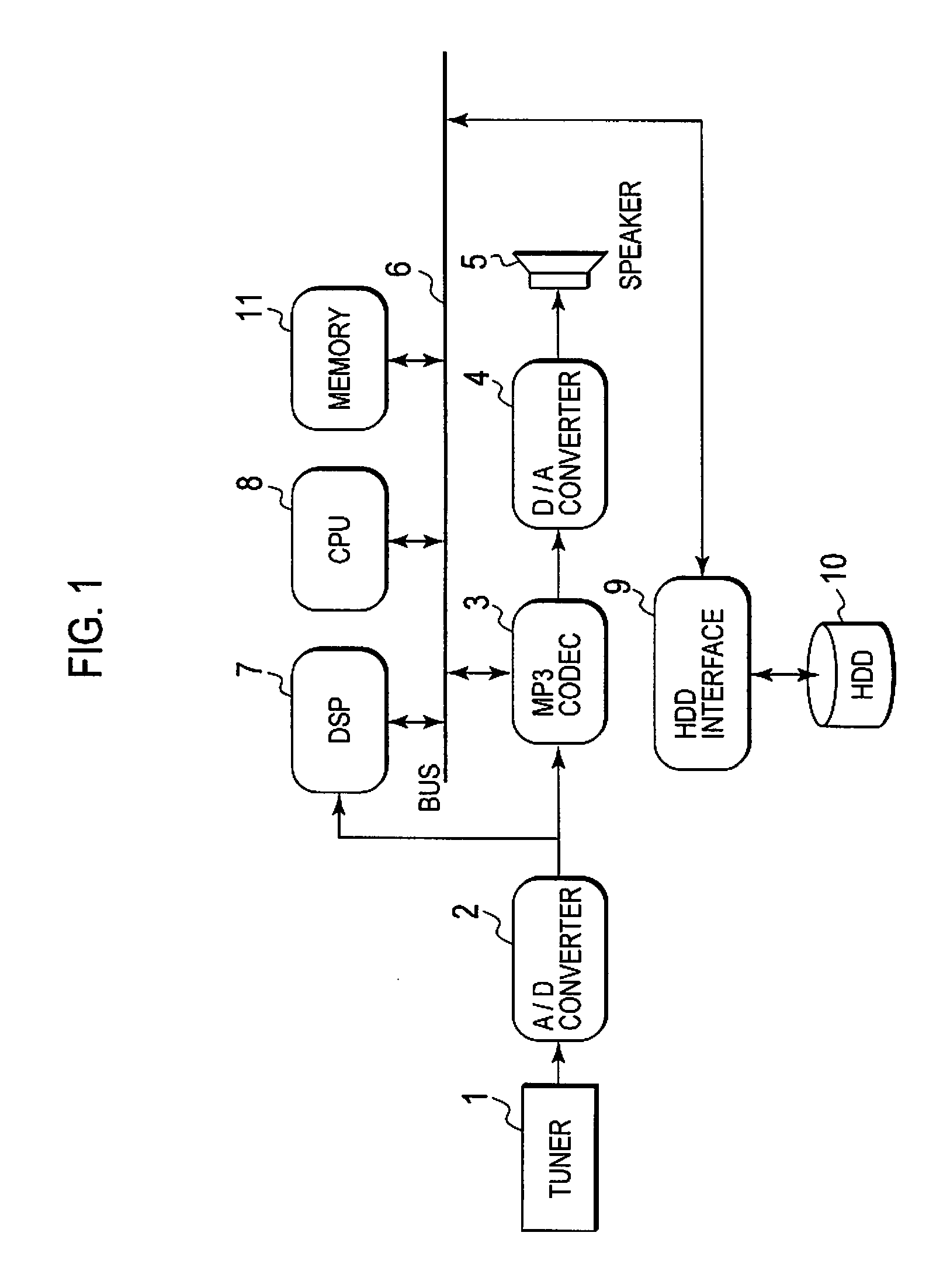
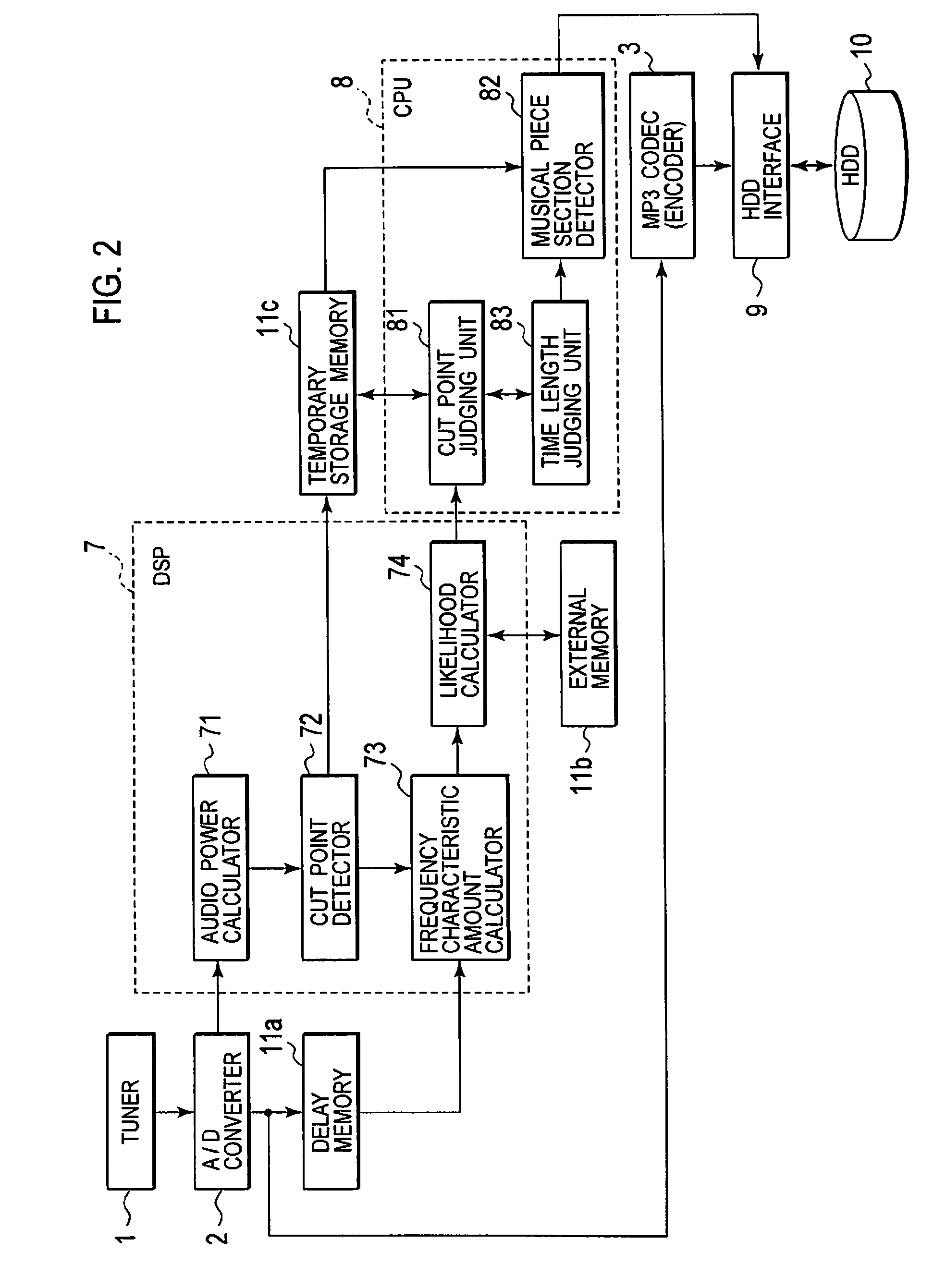
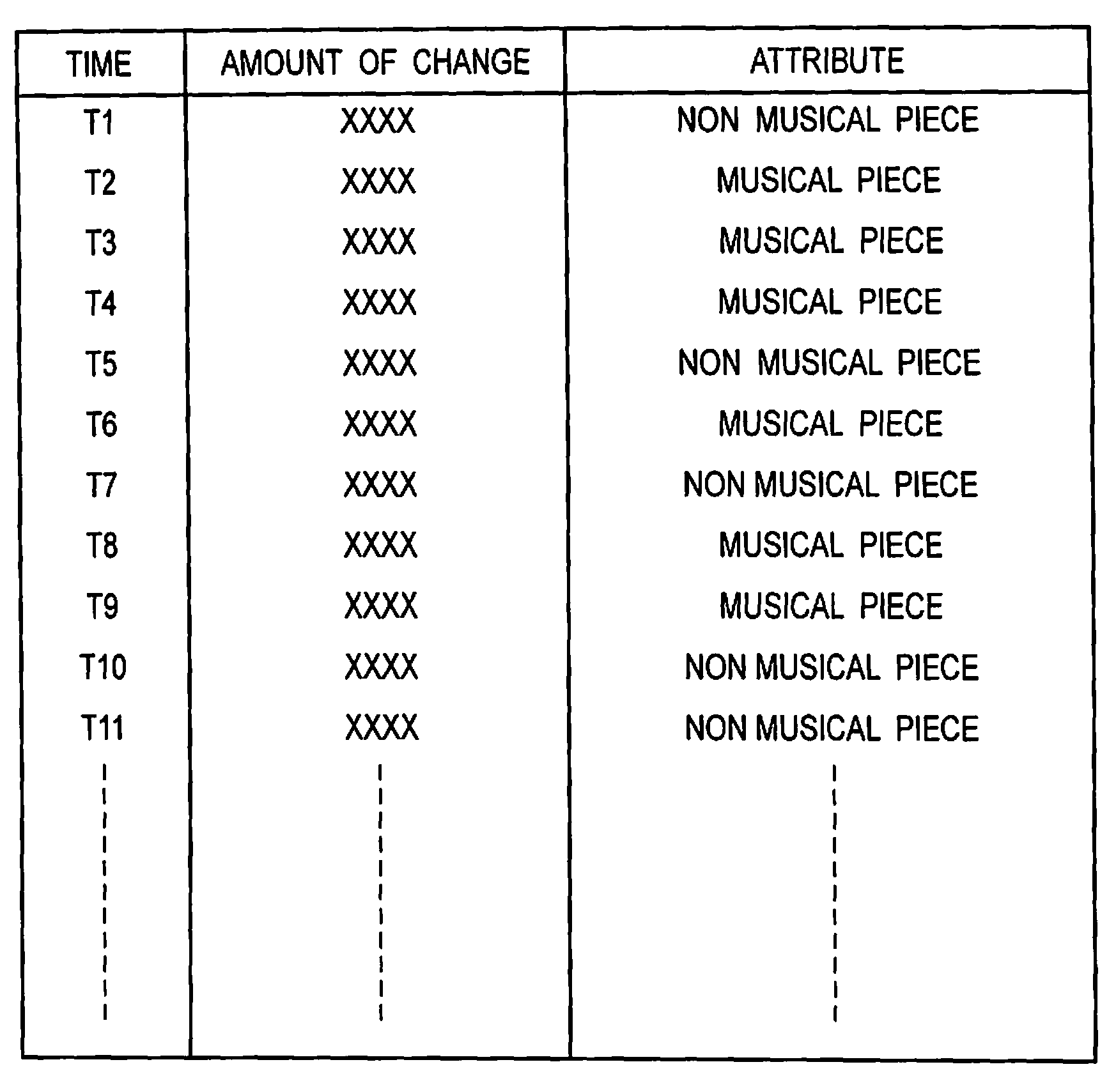
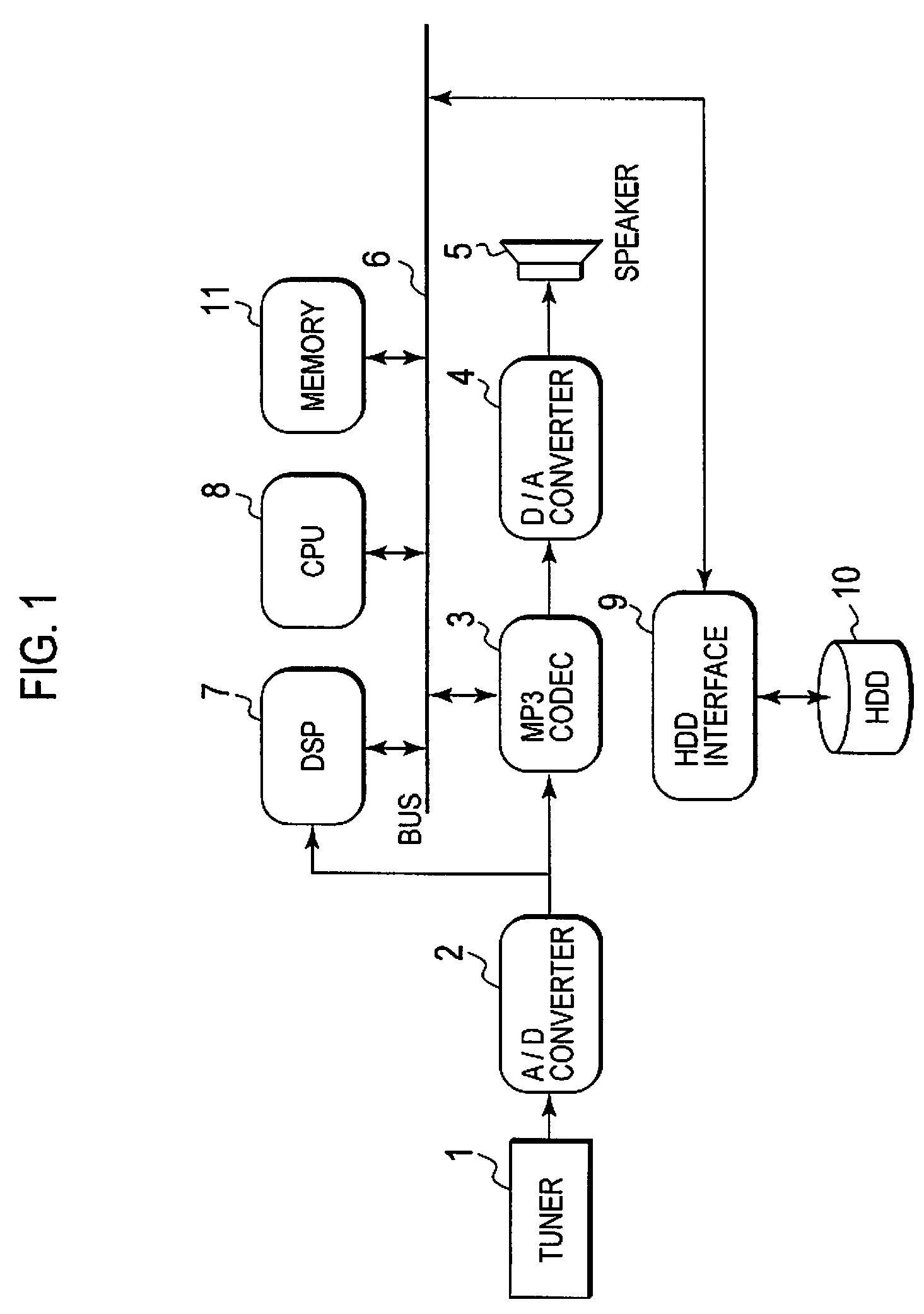
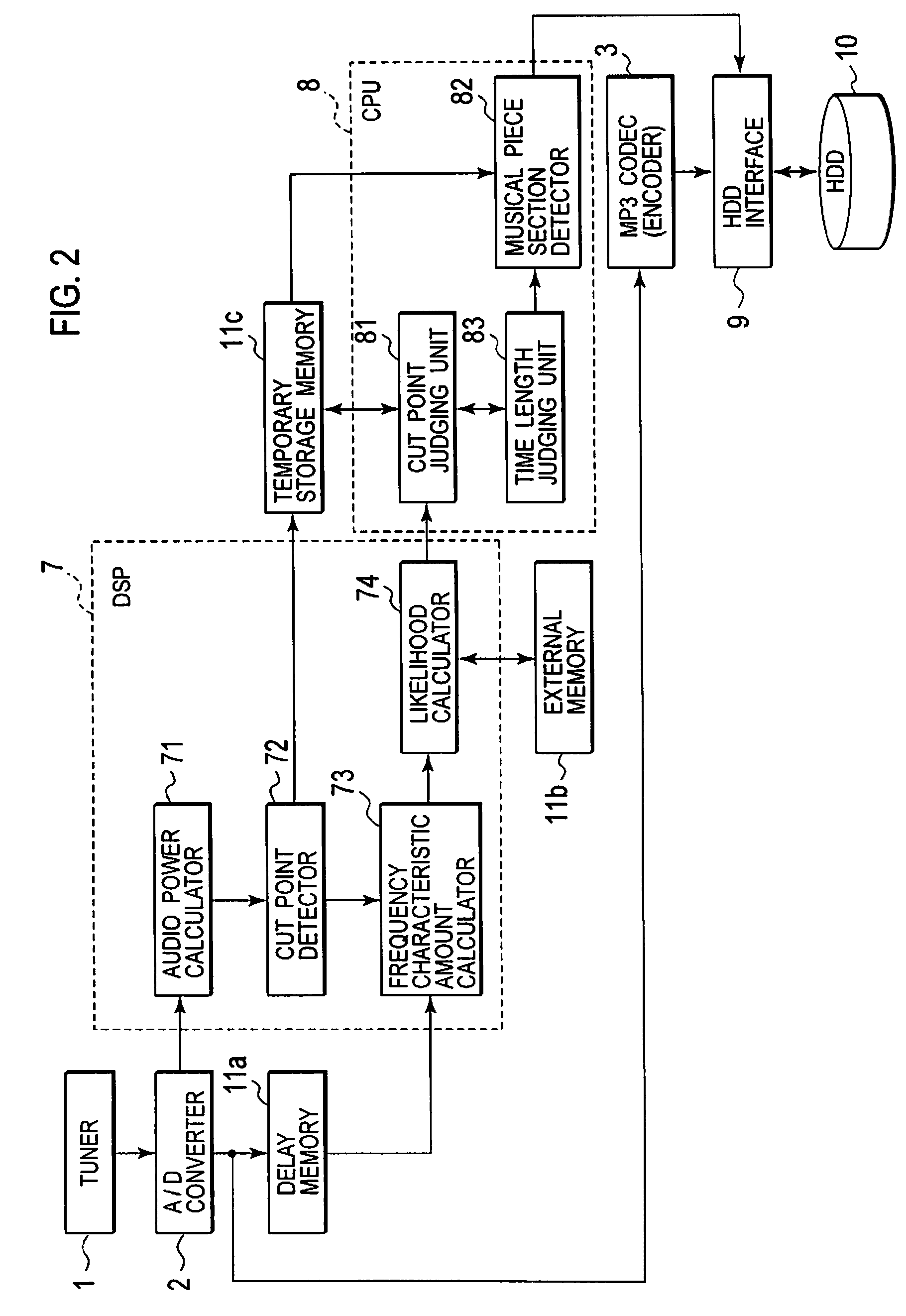
Recording or playback apparatus and musical piece detecting apparatus
InactiveUS20080236368A1Simple arithmeticSimple arithmetic processingElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisPoint detectorFrequency characteristic
Provided is a recording or playback apparatus capable of separating a musical piece from an audio including the musical piece and a speech through a simple arithmetic process. A cut point detector detects, as a cut point, a time point at which an audio signal level or an amount of change in the audio signal level is not lower than a predetermined value. A frequency characteristic amount calculator calculates a characteristic amount in a frequency area of the audio signal only at each cut point and in its proximity. A cut point judging unit judges an attribute of the cut point on a basis of the calculated characteristic amount of the frequency. A music section detector detects a start and end points of each music section on a basis of the attribute and an interval between sampling points.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Standard time signal receiving time device and decoding method of time code signal
InactiveCN1664724ADecoded correctlySimple arithmetic processingSynchronous motors for clocksElectric windingDecoding methodsComputer science
In a radio controlled clock and a decoding method of a time code signal, the time code signal can be accurately decoded irrespective of the mixture of noises and the deterioration of a radio wave signal receiving situation, and arithmetic processing is simple. A standard time signal is received and the time code signal superposed on this standard time signal is sampled at an interval of 50 ms and is stored to a memory. The stored sampling data are formed as a list in a data group every one second (20 samples). The plurality of data groups formed as a list are added every each sampling point, and a point for maximizing an increase change of the adding result is set to a synchronizing point of the sampling. Further, the correlation of the sampling data group and a code template pattern is calculated and a code shown by the sampling data group is judged.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
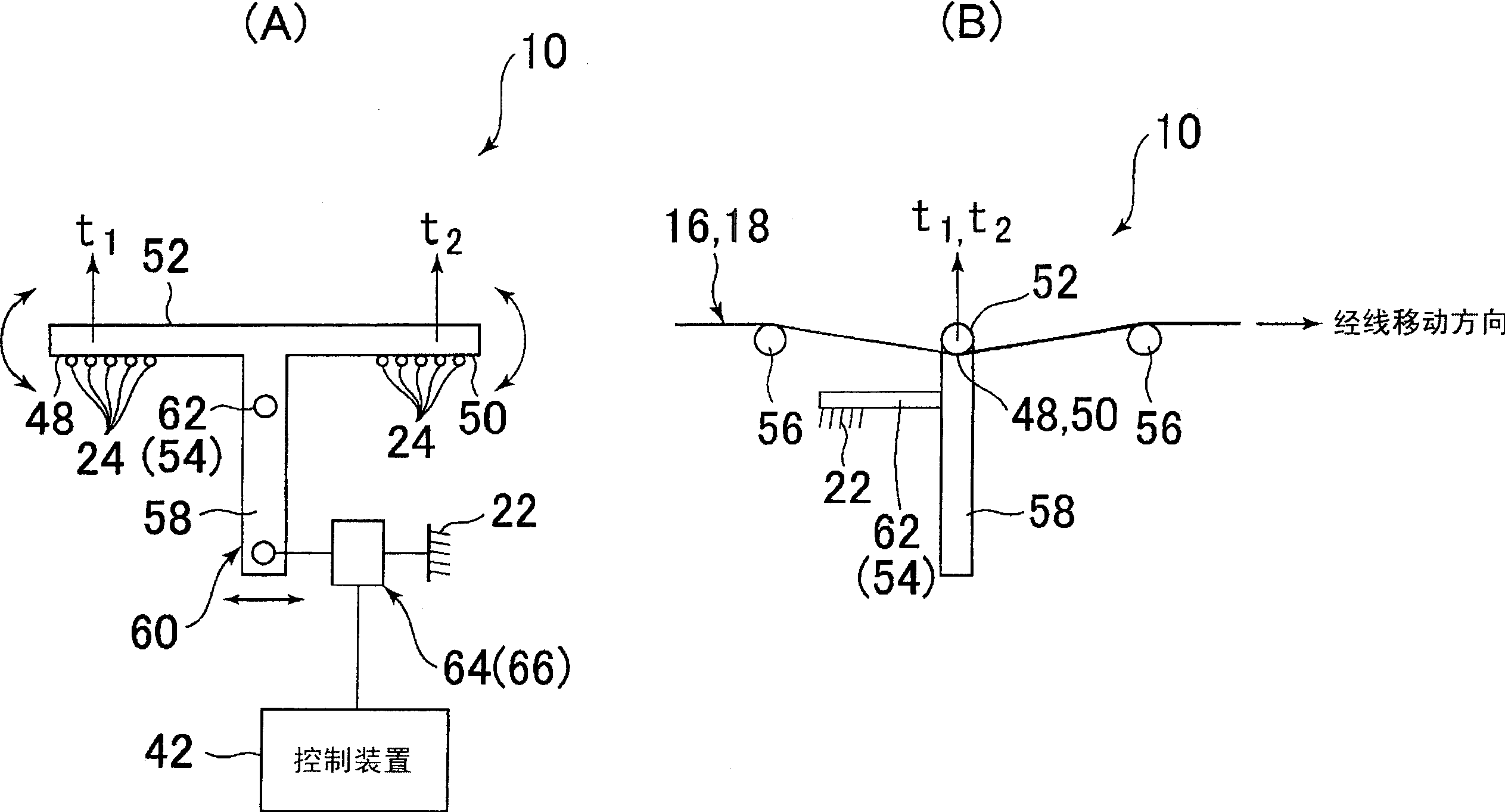
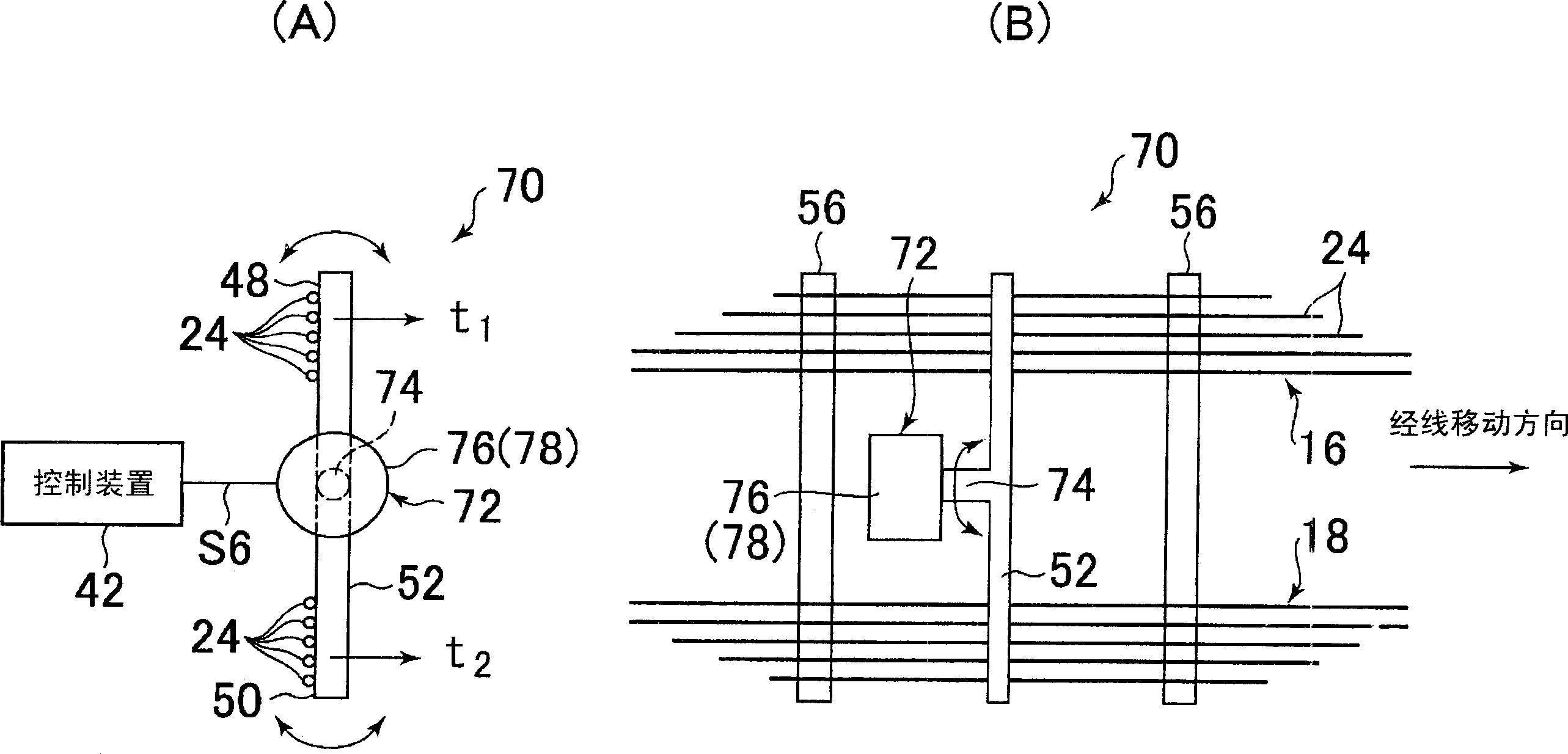
Device for detecting difference in warp tension of a loom
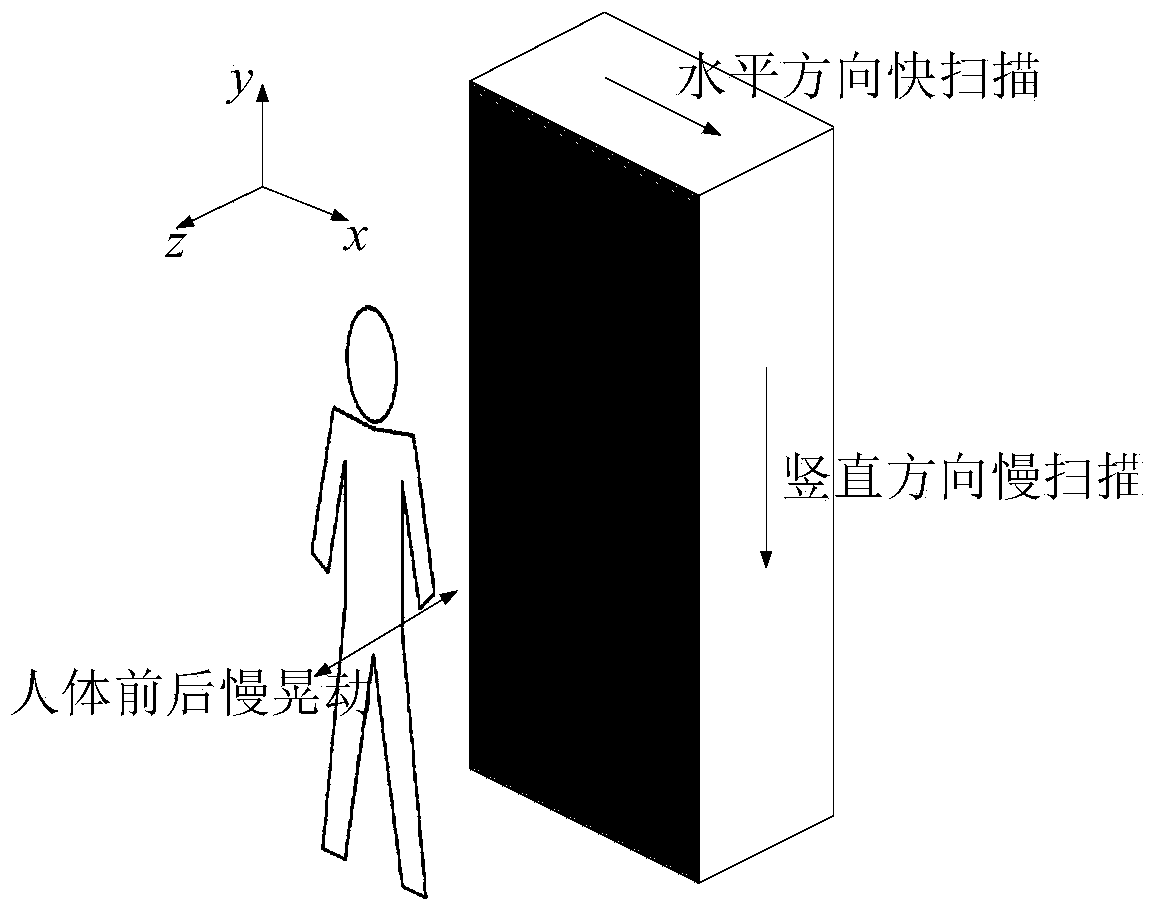
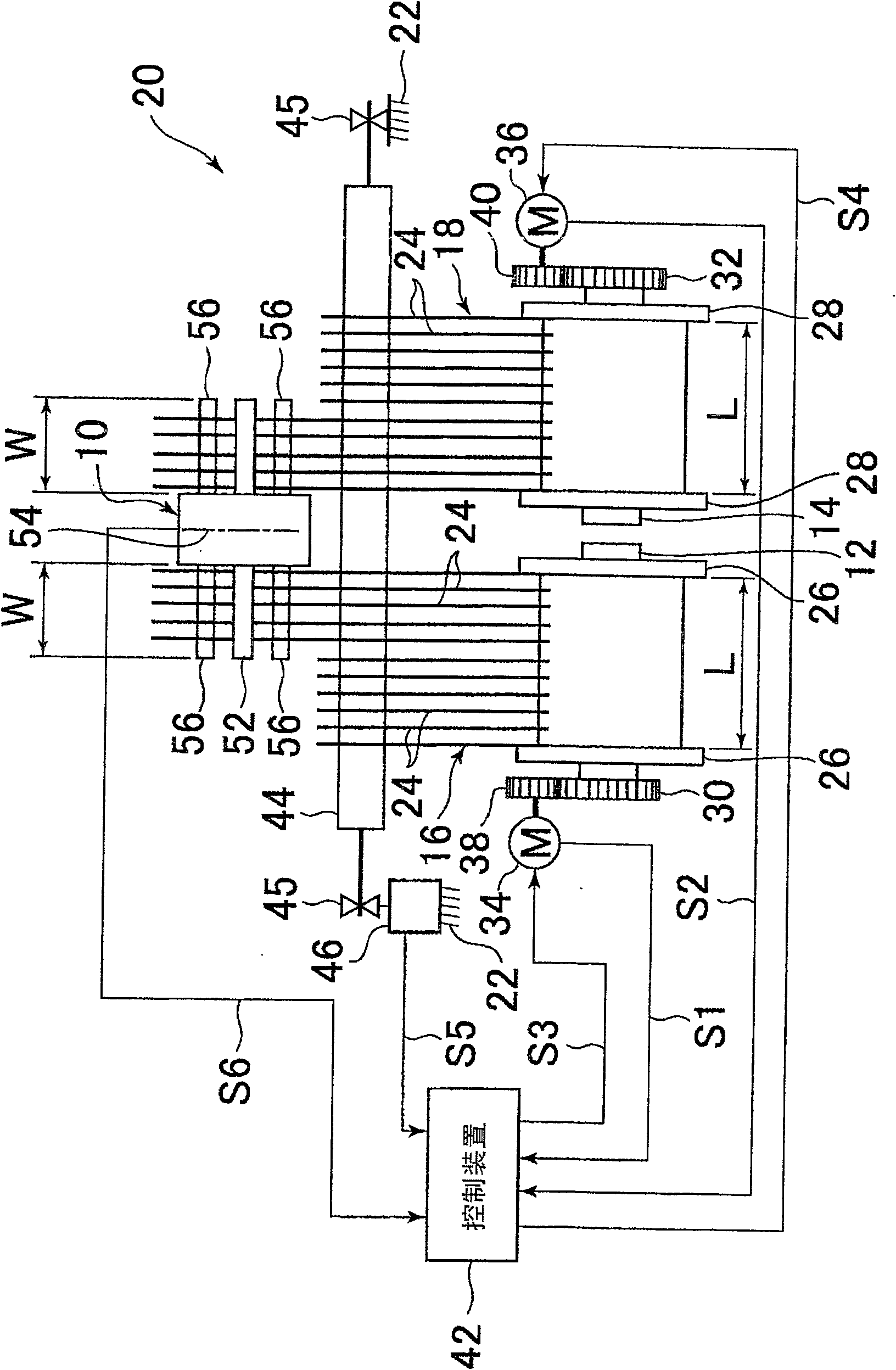
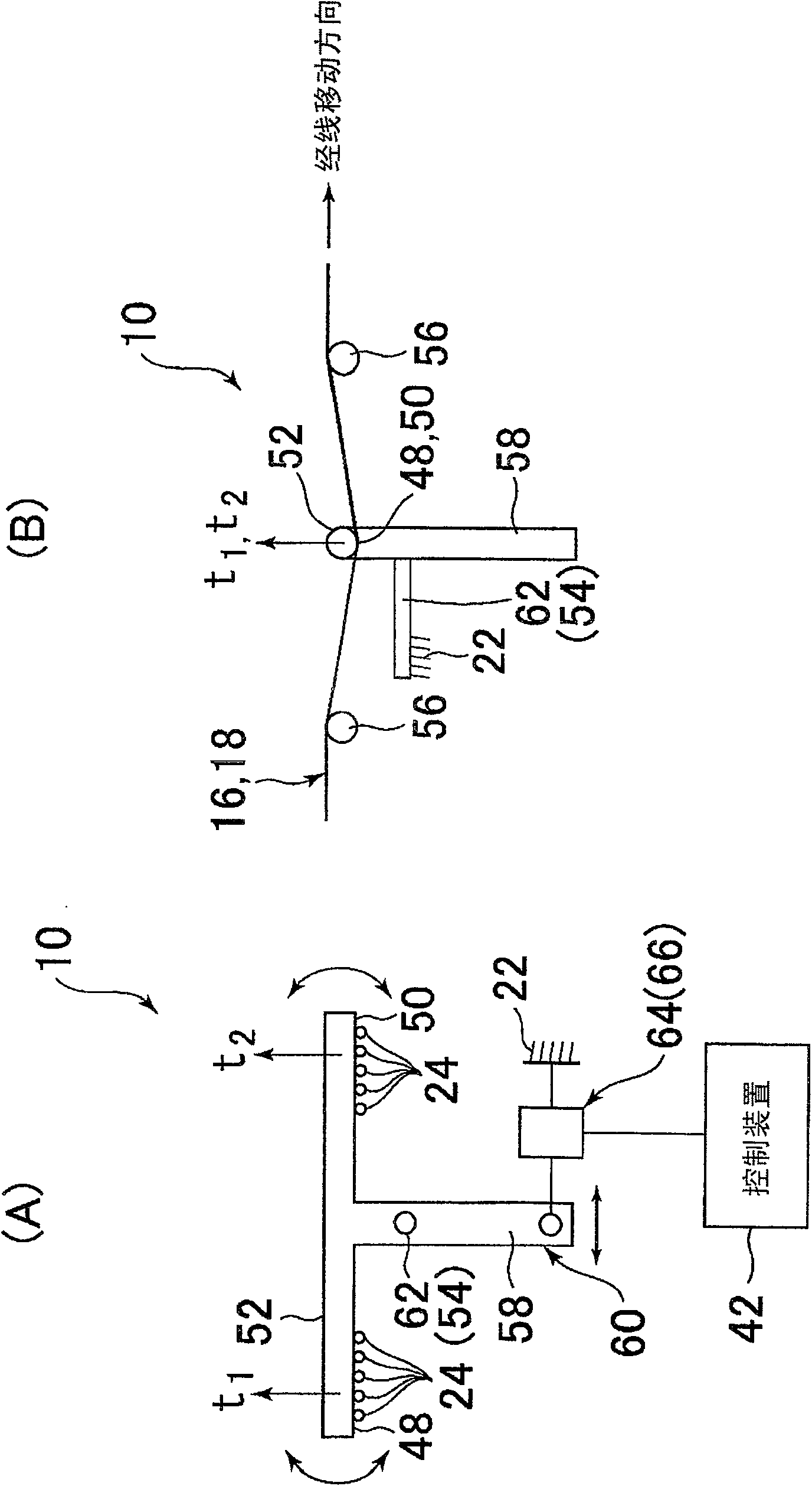
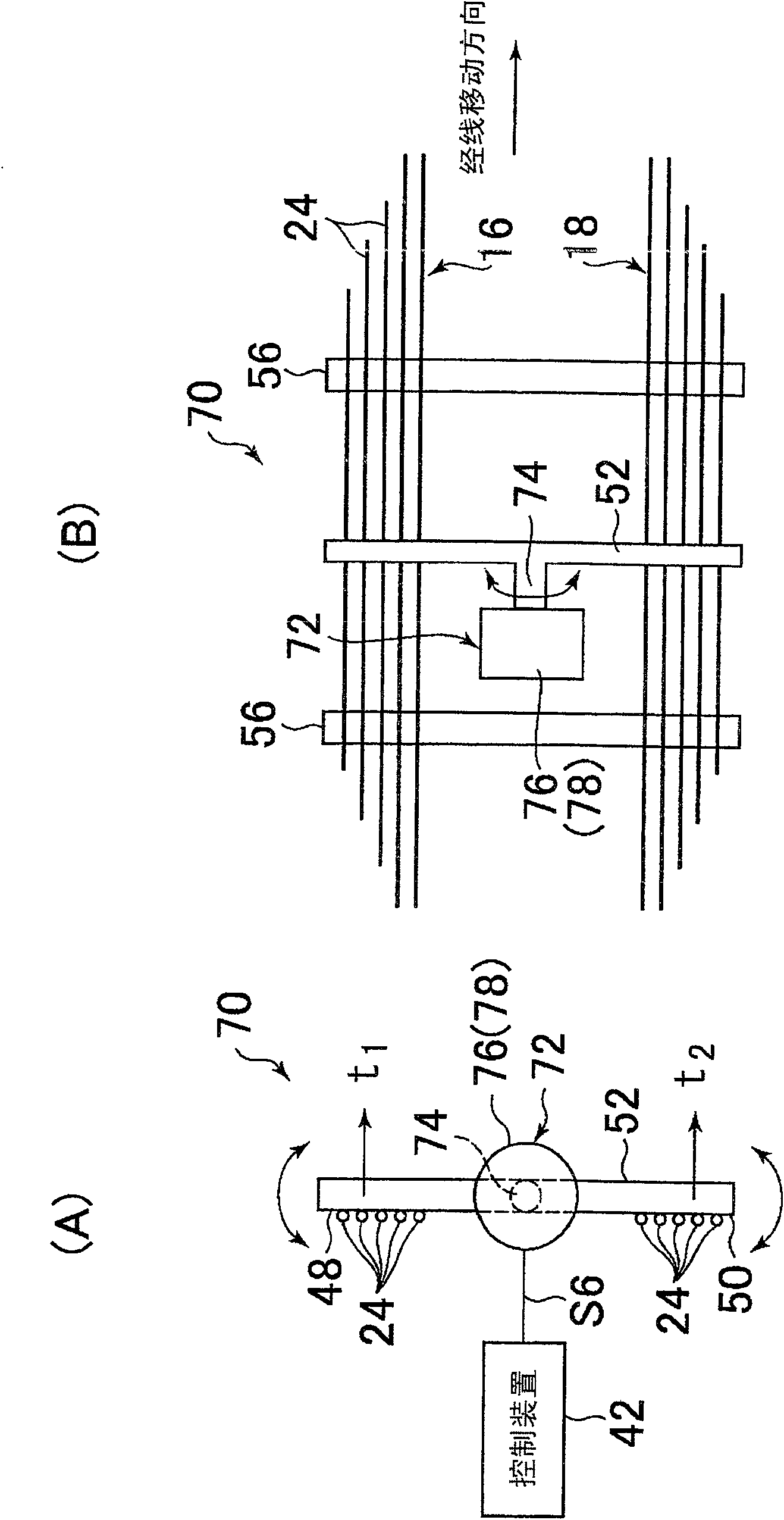
InactiveCN1550595AAccurate detectionReduce the numberMultiple loomsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A device for detecting difference in warp tension of a plurality of warp sheets let off side by side from different warp beams in the weft inserting direction detects a tension receiver having a plurality of contact faces which are individually in contact with the boundary side end portions of adjoining warp sheets at intervals in the weft inserting direction, and detects an angular rotational displacement or angular rotational force of the tension receiver around the axis extending in the warp moving direction.
Owner:TSUDAKOMA KOGYO KK
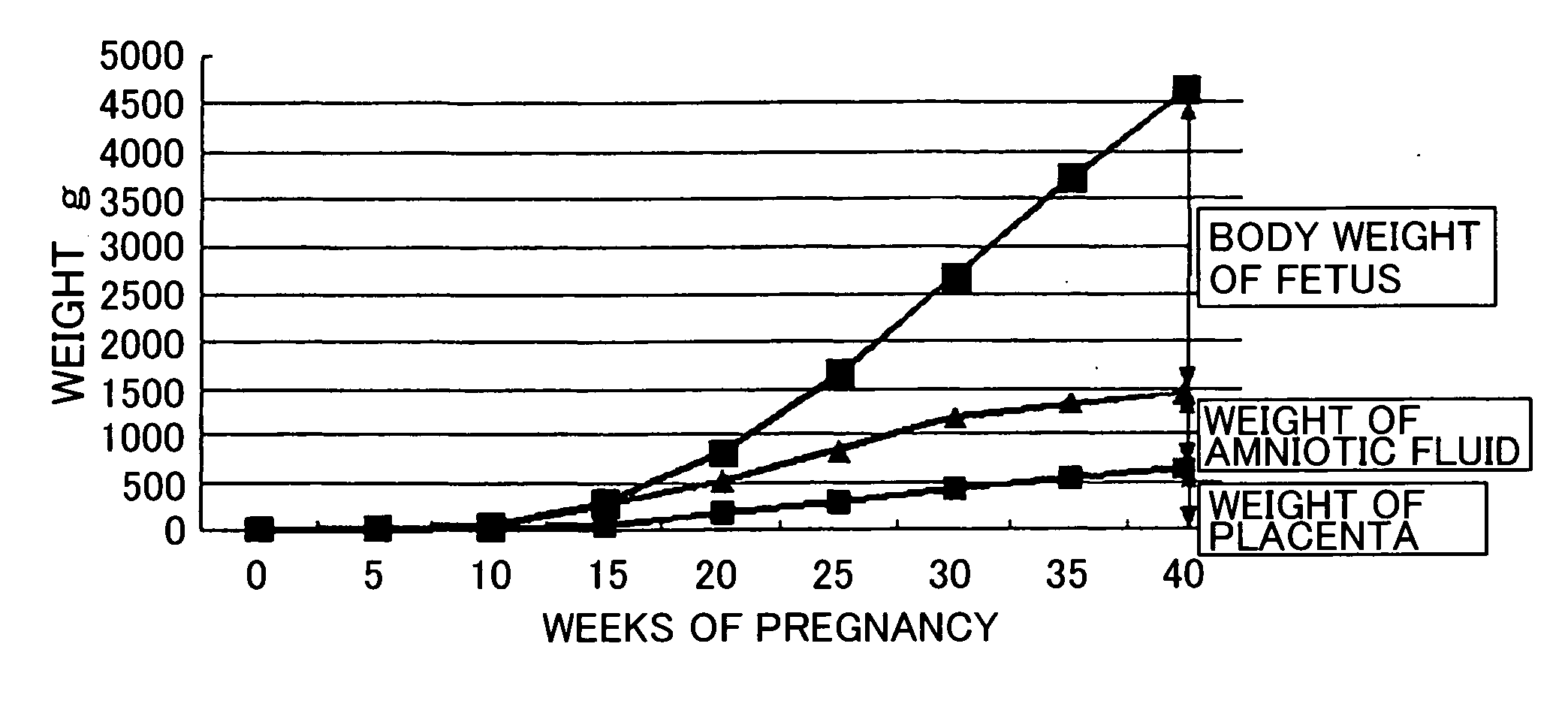
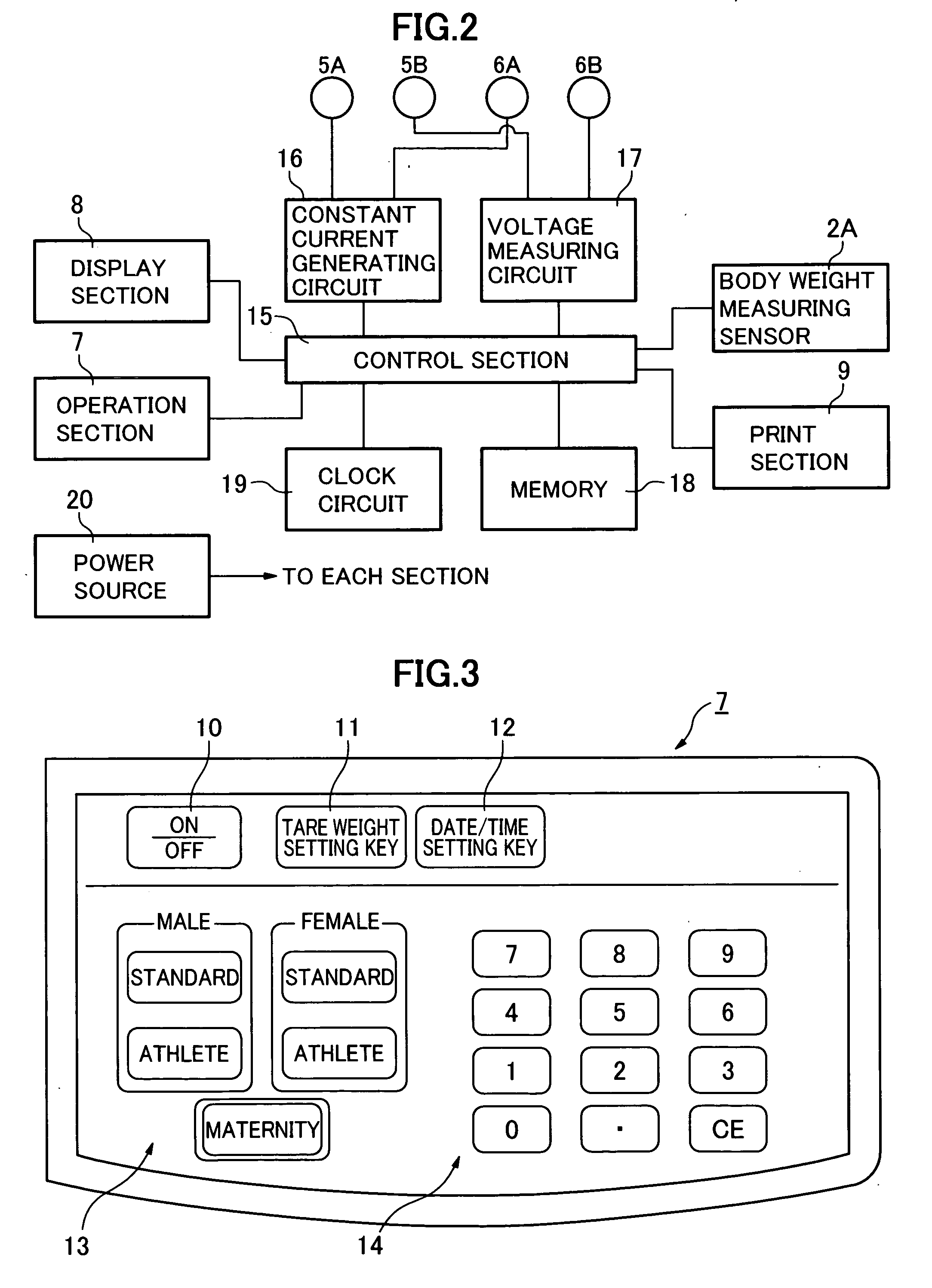
Basal metabolic rate measuring device
InactiveUS20060167373A1Easy to useSimple arithmetic processingSensorsErgometryFetal partsBody height
A basal metabolic rate measuring device capable of measuring the basal metabolic rate of a pregnant woman easily and accurately is provided by improving a known basal metabolic rate measuring device capable of calculating a basal metabolic rate based on the fat free mass data and age data of a subject. The basal metabolic rate measuring device calculates the fat free mass data of the body of a pregnant subject and calculates the basal metabolic rate of the subject based on at least the fat free mass data and age data. The fat free mass data of the body of the subject is calculated based on at least the body height data, body weight data, impedance data and fetal part weight data of the subject by a known basal metabolic rate measuring device provided with fetal part weight data acquiring means.
Owner:TANITA CORP
Fuel oil detecting device
InactiveCN104343535ASimple arithmetic processingReduce investment and maintenance costsEngine testingMachines/enginesTraffic volumeFuel oil
The invention discloses a fuel oil detecting device. The fuel oil detecting device comprises a pipeline, wherein a pressure sensor and a flow sensor are installed on the pipeline; the middle of the pipeline is a U-shaped section; two sides of the pipeline are a first horizontal section and a second horizontal section; the free end of the first horizontal section serves as an oil return pipe connecting end; a gas quick connector is arranged at the free end of the second horizontal section; probes of the pressure sensor and the flow sensor enter an oil path and are connected with a data acquisition processor, a data display and an alarm through conducting wires to form an operating circuit. The fuel oil detecting device realizes lubricating pipeline fault monitoring by monitoring the pressure and the flow value in the pipeline and performing simple operation processing, is relatively low in investment and maintenance cost, and has a high practical value.
Owner:TIANJIN HAIBIN FUEL INJECTION MAINTENANCE SERVICECO
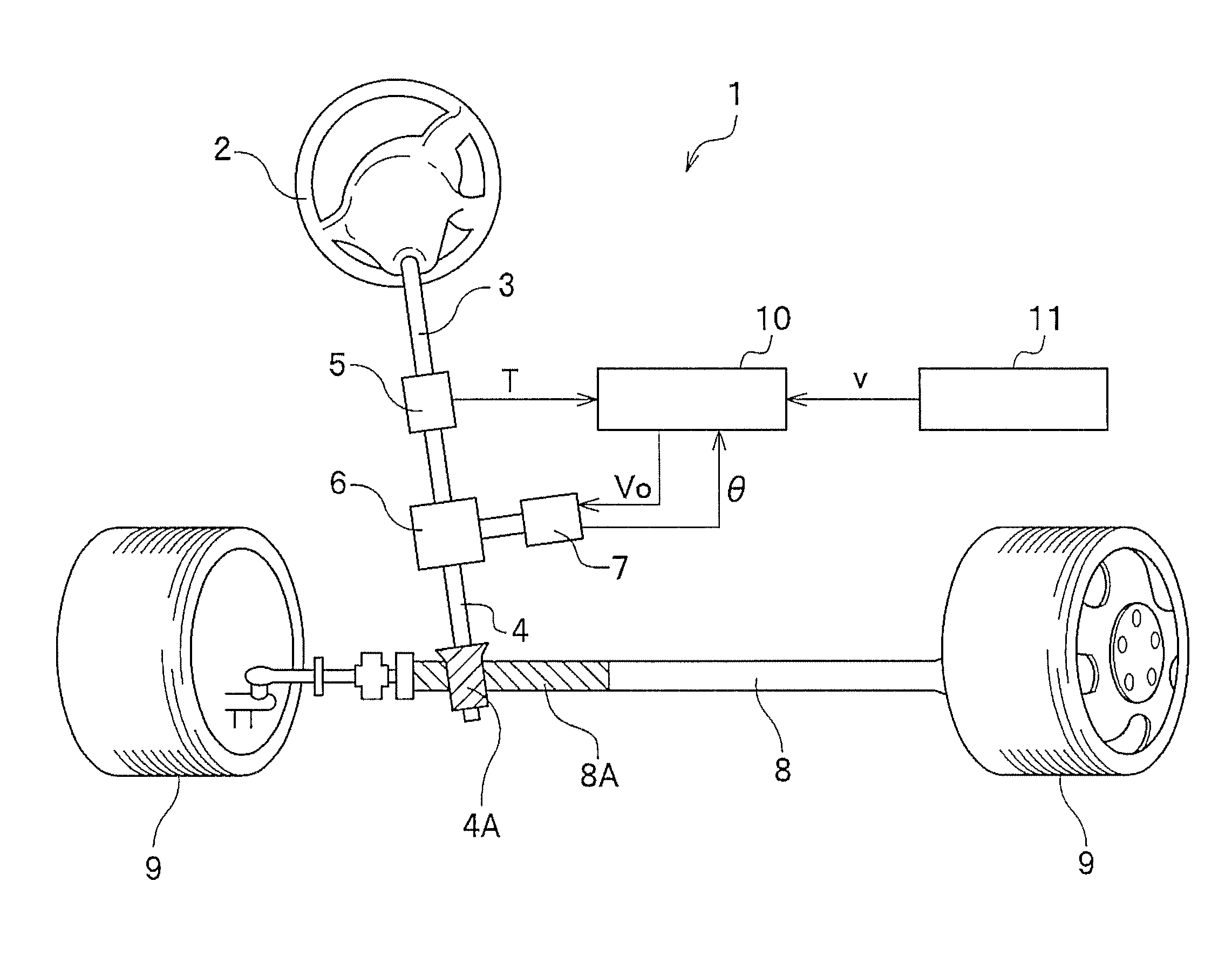
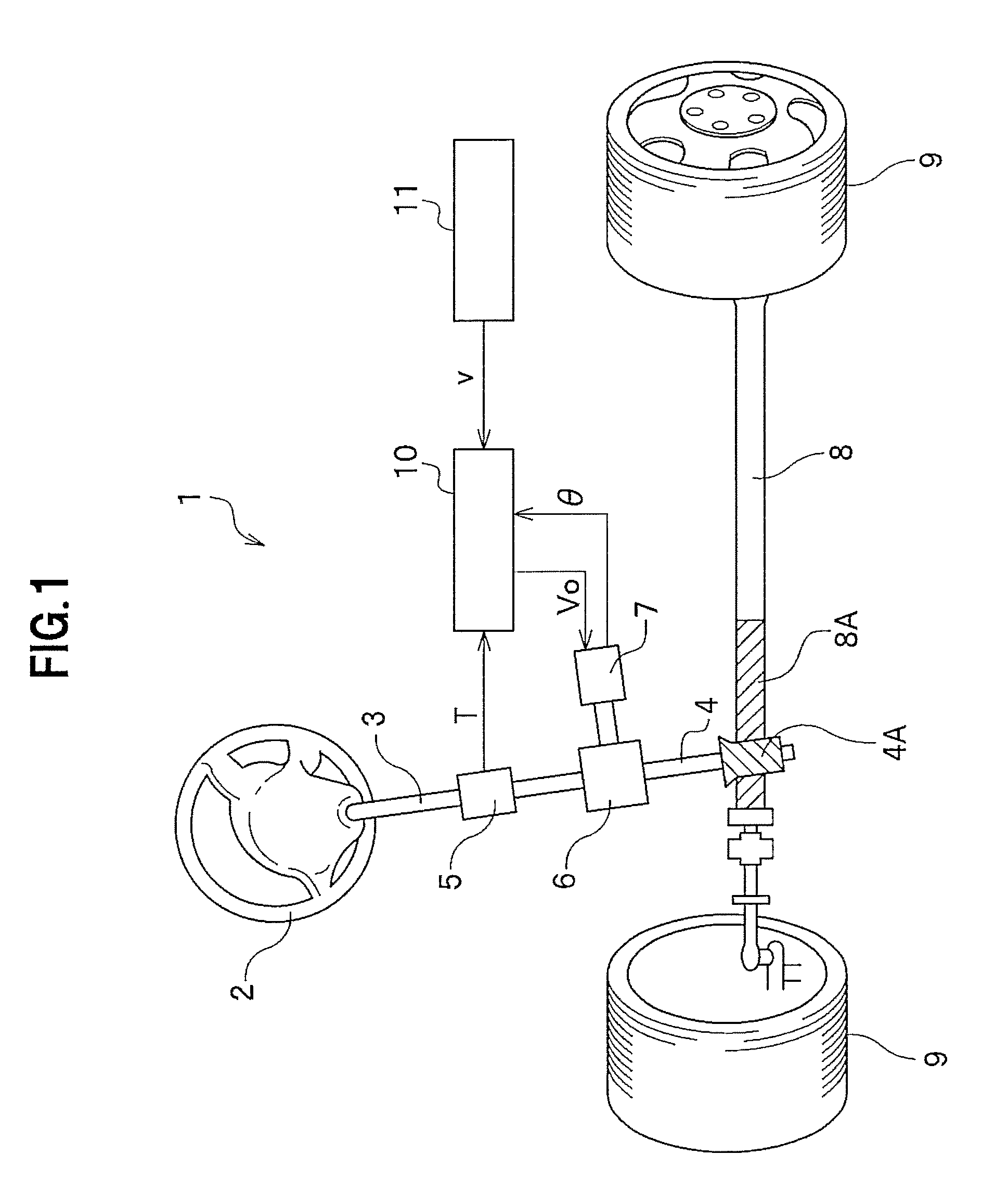
Electric power steering device
InactiveUS8606462B2Improved torque controlSimple arithmetic processingDigital data processing detailsField acceleration method controlElectric power steeringMaximum torque
There is provided a electric power steering device which can perform torque control through a simple arithmetic process using a synchronous reluctance motor having a nonlinear current / torque characteristic. A target torque is transmitted from an EPS control unit 41 to a motor control unit 51. The motor control unit 51 calculates a target-current effective value I and a target-current phase θ from the input target torque. Based on the calculated target-current effective value I and target-current phase θ, calculation is changed whether to perform calculation so that the maximum torque (the maximum torque obtainable at the minimum current effective value) can be obtained, or to perform calculation so that the maximum output (the maximum output obtainable at the minimum current effective value) can be obtained in accordance with a duty ratio of an output by a PWM converting unit 57 comprising a three-phase inverter. Next, a three-phase biaxial converting unit 53 calculates a target q-axis current Iq and a target d-axis current Id from the target-current effective value I and the target-current phase θ, and the PWM converting unit 57 performs duty control in order to control the torque of a motor 58.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
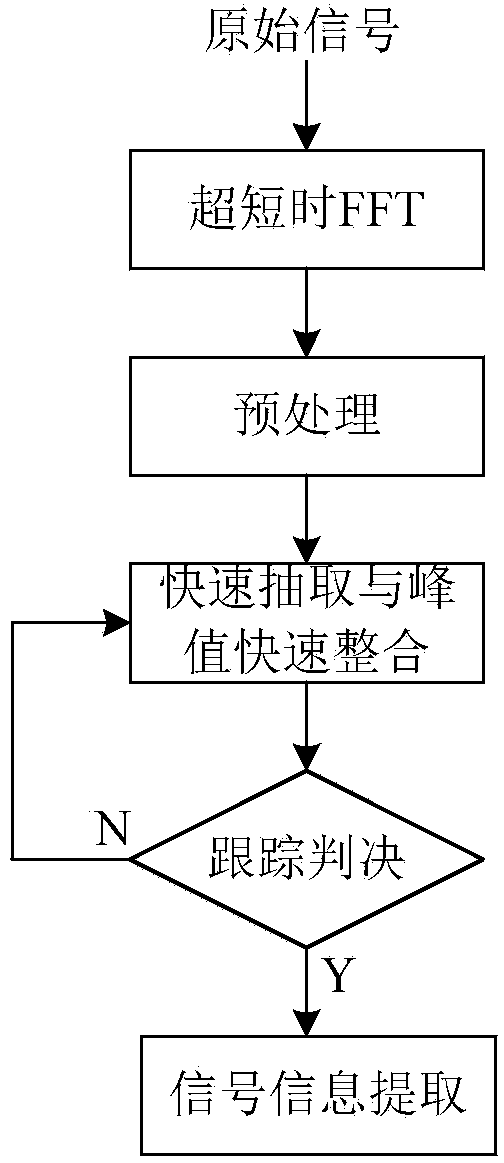
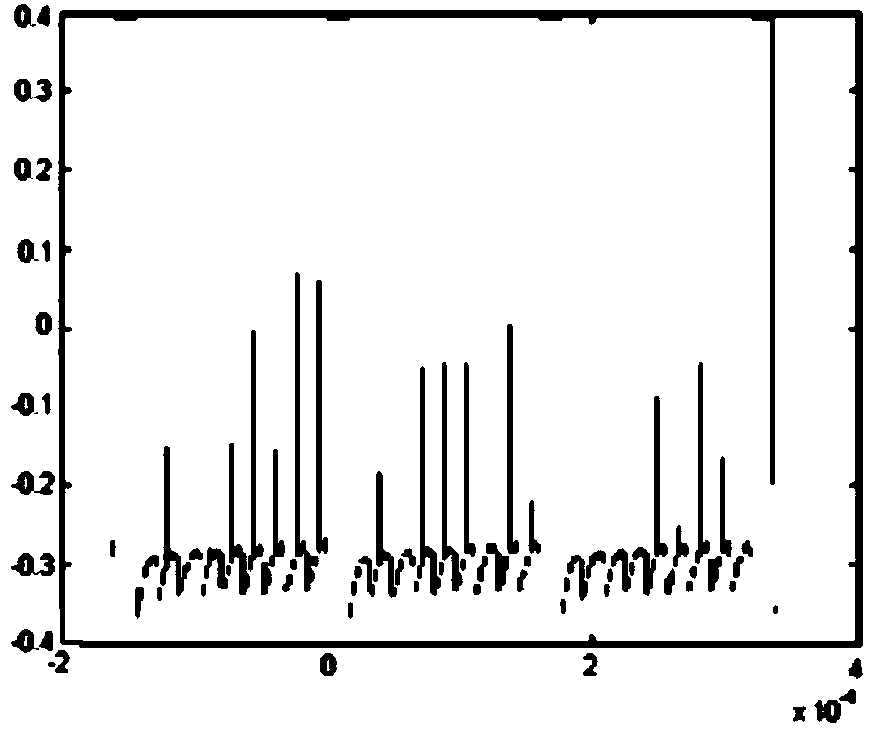
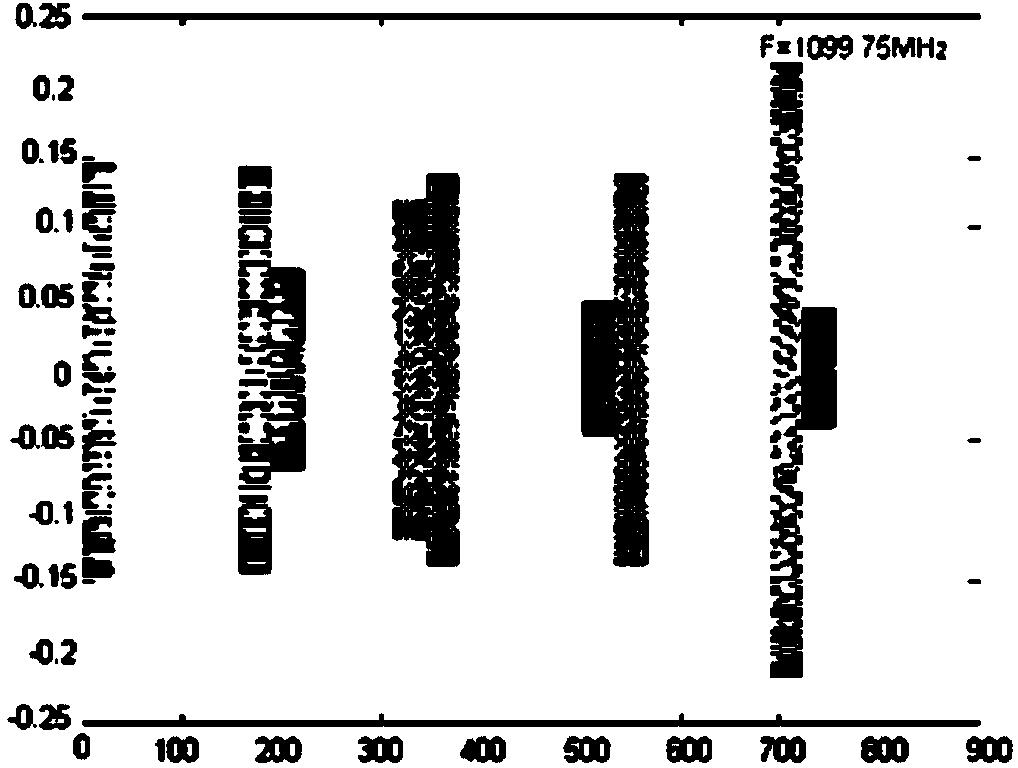
Short-time FFT (fast Fourier transform) based signal processing method for acousto-optic passive receiver
InactiveCN104215942AShorten judgment timeImprove real-time performanceWave based measurement systemsVIT signalsAcousto-optics
The invention provides a short-time FFT (fast Fourier transform) based signal processing method for an acousto-optic passive receiver. The acousto-optic passive receiver performs short-time Fourier transform on an initial signal to acquire a transformed signal after receiving the initial signal, and performs integral accumulation and high-speed synchronous sampling on the transformed signal to acquire an intermediate signal matrix; the intermediate signal matrix is finally subjected to restoration and tracking correlation, and a time frequency function is created; a data table inquiry mode is adopted, the type of the time frequency function is judged, all parameters of the time frequency function are restored, and a restored signal is taken as a final output signal of the acousto-optic passive receiver and is sent to a user. Real-time performance can be guaranteed by the method, a filter is not needed during overall signal processing, and the process is simple.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP NO 26 RES INST
Recording or playback apparatus and musical piece detecting apparatus
InactiveUS7745714B2Simple arithmetic processingElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisPoint detectorFrequency characteristic
Provided is a recording or playback apparatus capable of separating a musical piece from an audio including the musical piece and a speech through a simple arithmetic process. A cut point detector detects, as a cut point, a time point at which an audio signal level or an amount of change in the audio signal level is not lower than a predetermined value. A frequency characteristic amount calculator calculates a characteristic amount in a frequency area of the audio signal only at each cut point and in its proximity. A cut point judging unit judges an attribute of the cut point on a basis of the calculated characteristic amount of the frequency. A music section detector detects a start and end points of each music section on a basis of the attribute and an interval between sampling points.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
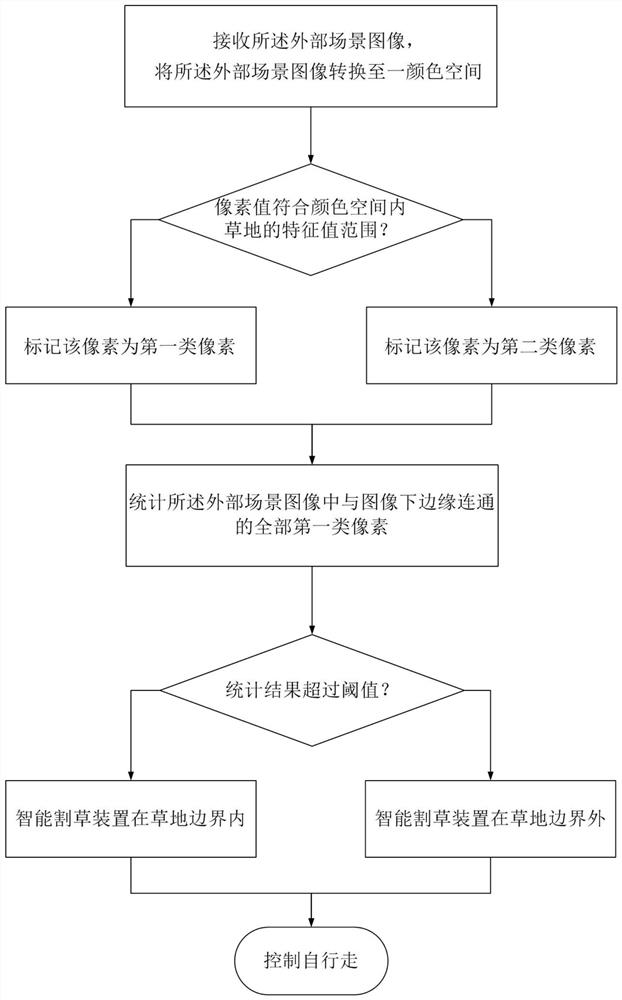
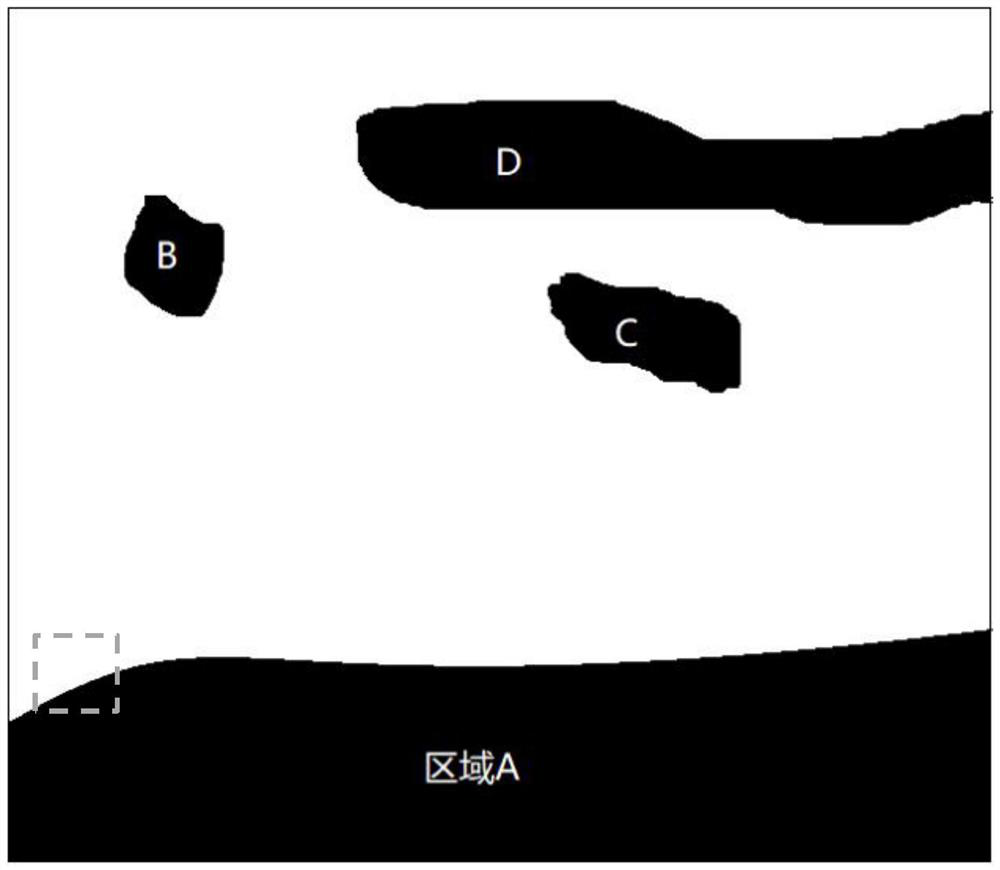
Grassland Boundary Recognition Method and Intelligent Mowing Device Using It
ActiveCN109584258BReduce computational overheadControl the cost of useImage enhancementImage analysisAgricultural engineeringComputer vision
A grassland boundary recognition method and an intelligent mowing device using the method, which determines the eigenvalue range of the grassland according to the brightness of the working environment, and screens the pixels in the acquired external scene image according to the eigenvalue range, and compares them with the external scene image after statistical screening. Connected pixels at the lower edge of the scene image to determine whether the intelligent mowing device is within the boundary of the grass. The invention realizes the identification and judgment of the grass boundary by simply screening and counting the pixel values of the image itself, and the calculation and processing of the image is relatively simple, thus effectively reducing the hardware cost and calculation overhead of the intelligent mowing device. The invention can improve the recognition efficiency of the grass boundary under the premise of ensuring the recognition accuracy.
Owner:NANJING SUMEC INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
An inspection device
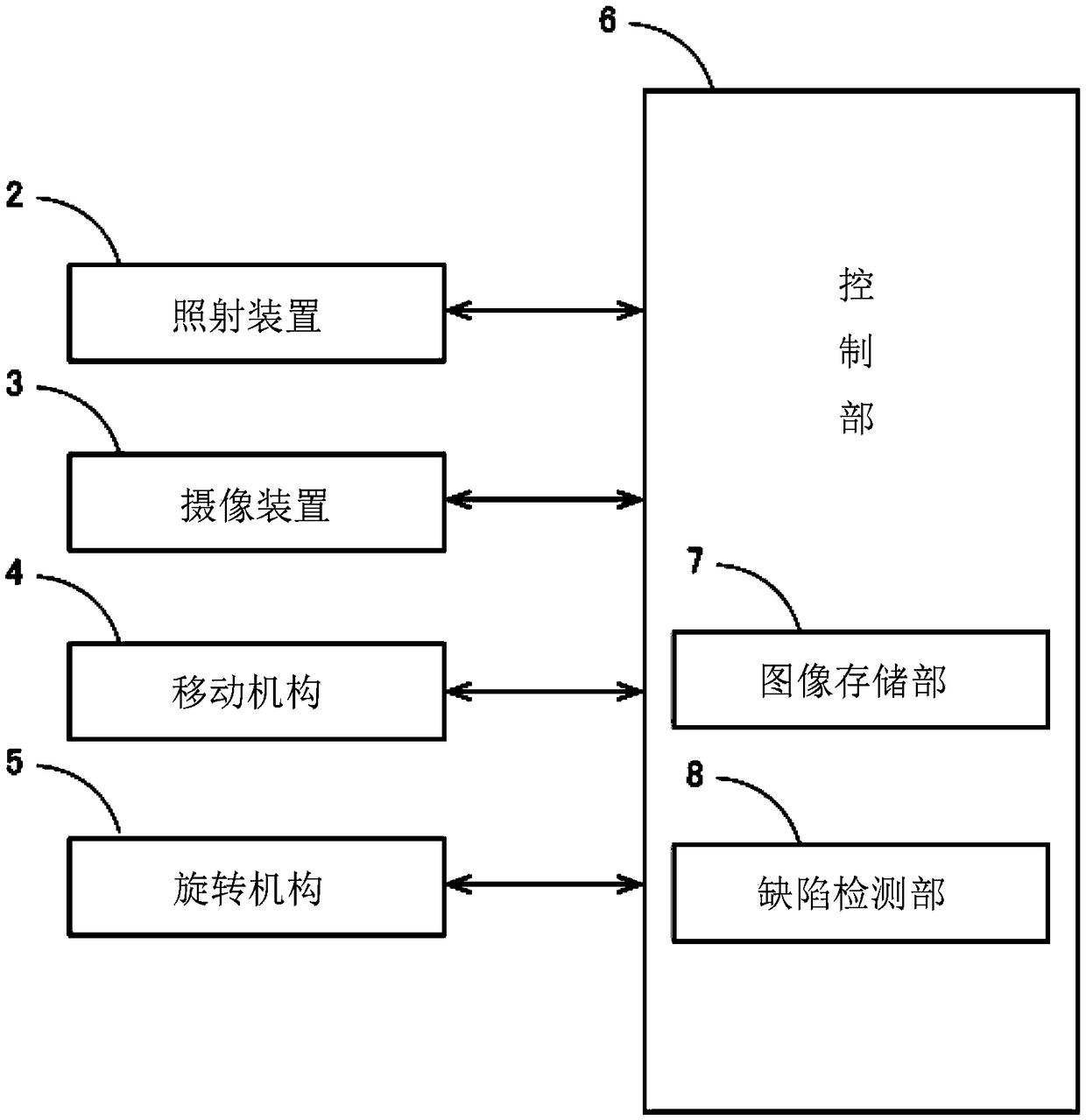
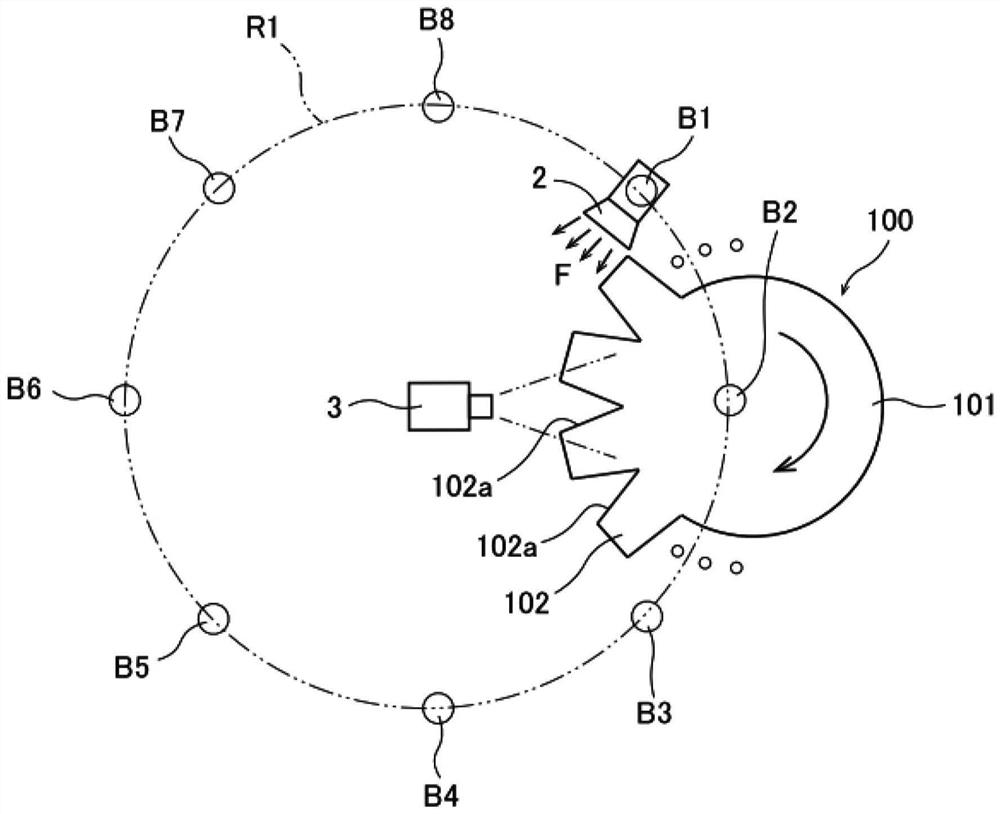
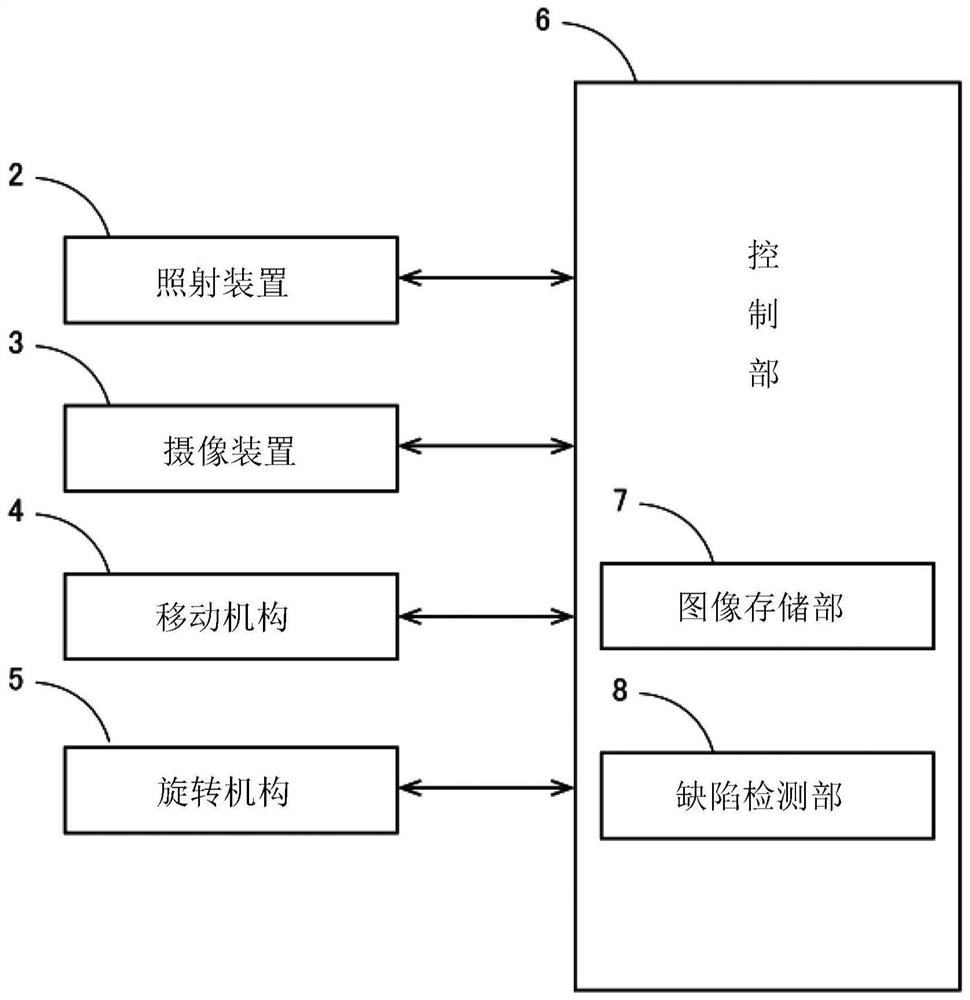
ActiveCN109211915ASimple arithmetic processingOptically investigating flaws/contaminationImage storageImage capture
An inspection device is provided. This inspection device is a device that performs visual inspection of the surface to be inspected included in the inspection object. The inspection device includes anirradiation device, an imaging device, an image storage unit, and a defect detecting unit. The illuminating device moves on an imaginary plane along the surface of the object to be inspected, and illuminates the surface of the object to be inspected toward the object to be inspected. The imaging device includes the inspection surface of the inspection object in the imaging range, receives the light reflected at the inspection surface, and generates a luminance distribution image as an imaging result. The image storage unit stores a plurality of brightness distribution images captured by the imaging device at a plurality of timings in which the positions of the irradiation devices are different and the inspection surface, the imaging device, and the irradiation device are not arranged in astraight line. The defect detecting unit detects a defect on the surface to be inspected based on a plurality of different brightness distribution images.
Owner:NIDEC TOSOK CORP
Rollover judging device
ActiveUS7925395B2Simple arithmetic processingImprove reliabilityVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesRolloverIntegrator
Owner:NEXGEN CONTROL SYST LLC
Die supply device
ActiveCN104871659ASimple arithmetic processingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical componentsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:FUJI KK
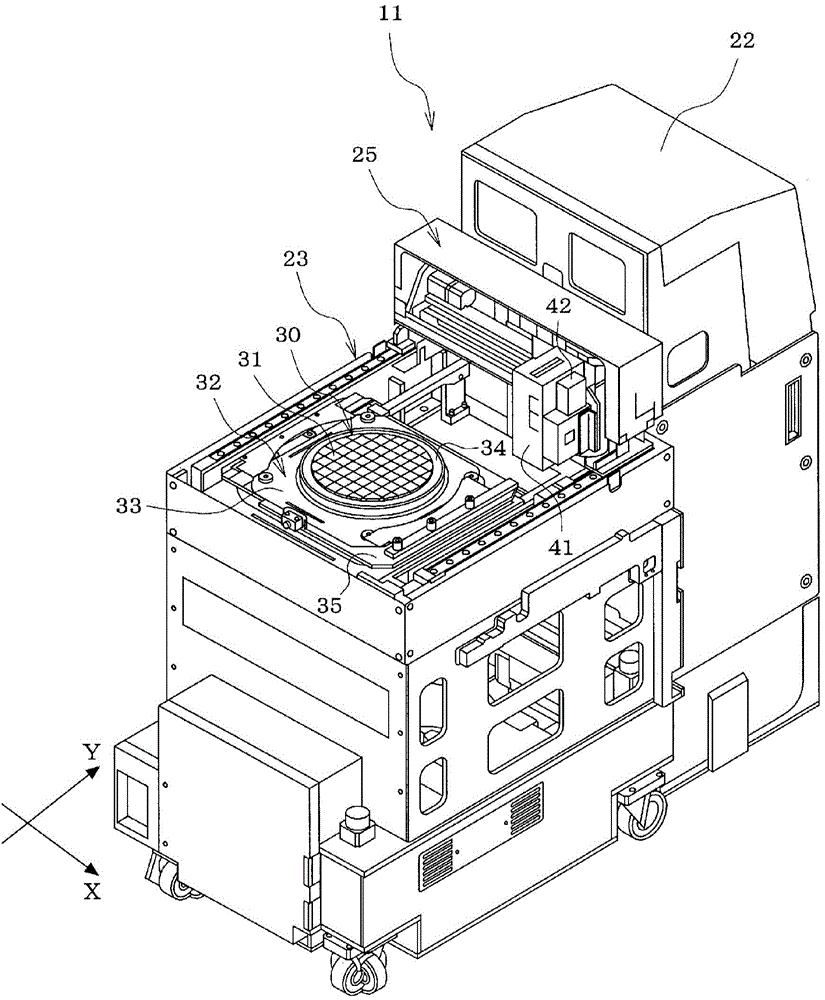
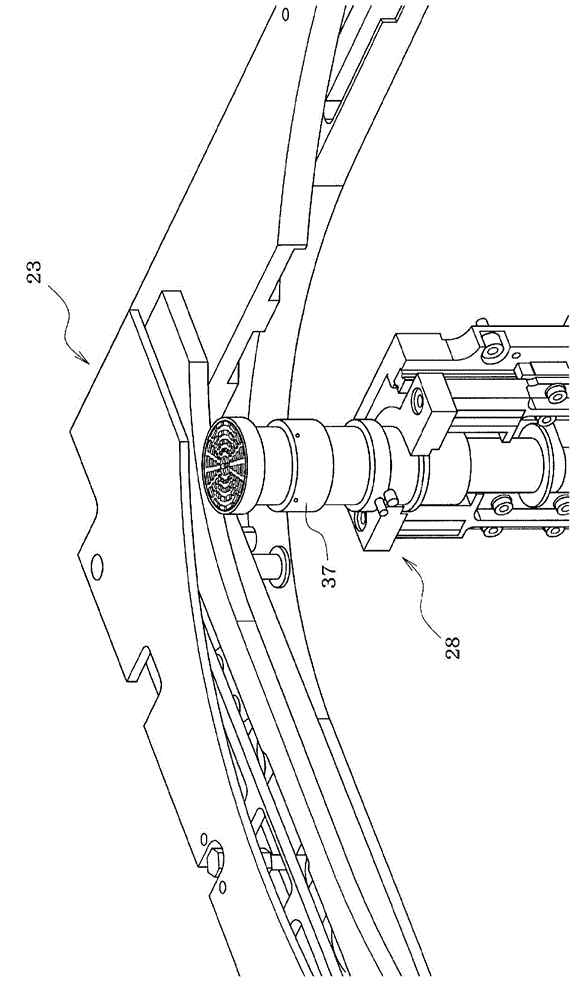
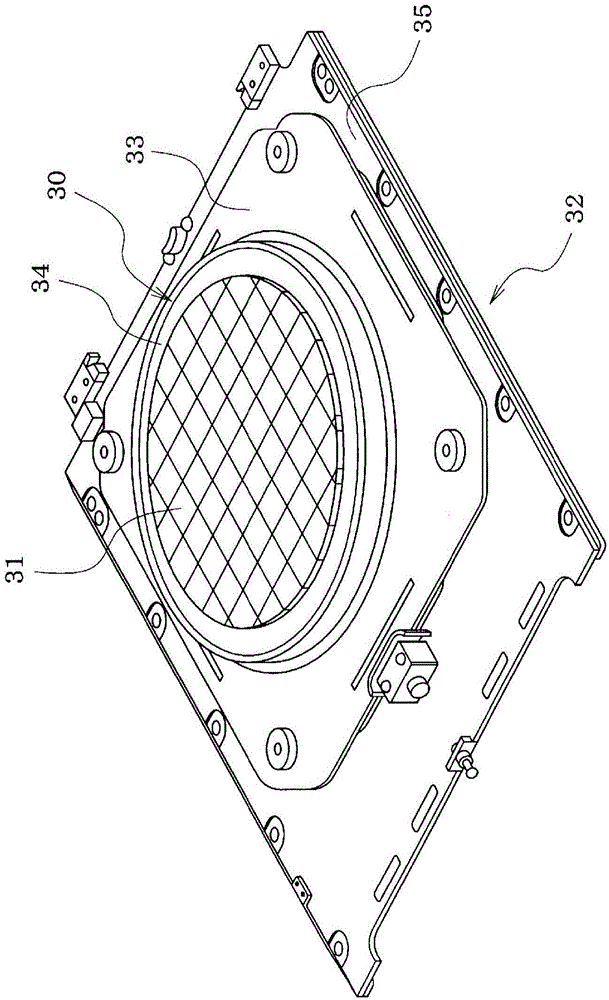
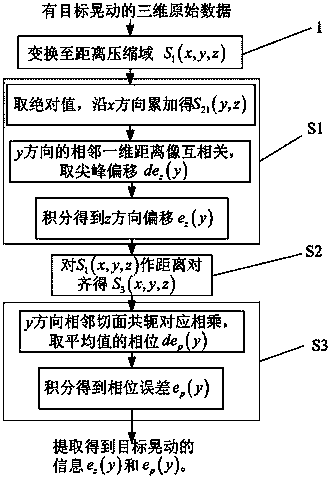
Method for extracting relative shake information of target in three-dimensional image
ActiveCN104237858ASimple arithmetic processingFast implementationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionComputer scienceInitial phase
The invention relates to a method for extracting relative shake information of a target in a three-dimensional image. The method includes the steps of converting original echo into a distance compressed domain according to the form of transmitted signals to obtain signals S1 (x, y and z); acquiring absolute values of the signal S1 (x, y and z), and accumulating the absolute values in an x-direction to obtain an accumulated signal S21 (y and z); subjecting two adjacent sequences of the signal S21 (y, z) in a y-direction to related processing, and marking a signal at a peak as a signal dez (y); subjecting the signal dez (y) to y-directional integration to obtain a relative movement displacement signal ez (y) of the target; enveloping and aligning the signals S1 (x, y and z) through the relative movement signal ez (y) to obtain signals S3 (x, y and z); acquiring two two-dimensional sequences in the y-direction from the signals S1 (x, y and z) or the signal S3 (x, y and z), conjugating one two-dimensional sequence, multiplying the same by the other two-dimensional sequence, and acquiring a phase, marked as dep (y), of an average result of a product; subjecting the phase dep (y) to y-directional integration to obtain a relative movement initial-phase signal ep (y) of the target.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device for detecting difference in warp tension of a loom
InactiveCN100582340CAccurate detectionReduce the numberMultiple loomsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A device for detecting difference in warp tension of a plurality of warp sheets let off side by side from different warp beams in the weft inserting direction detects a tension receiver having a plurality of contact faces which are individually in contact with the boundary side end portions of adjoining warp sheets at intervals in the weft inserting direction, and detects an angular rotational displacement or angular rotational force of the tension receiver around the axis extending in the warp moving direction.
Owner:TSUDAKOMA KOGYO KK
State of charge estimation method for secondary battery, state of charge estimation system for secondary battery, and abnormality detection method for secondary battery
PendingCN113646948ALess learning dataHigh-precision estimated capacityCircuit monitoring/indicationSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsState of chargeEngineering
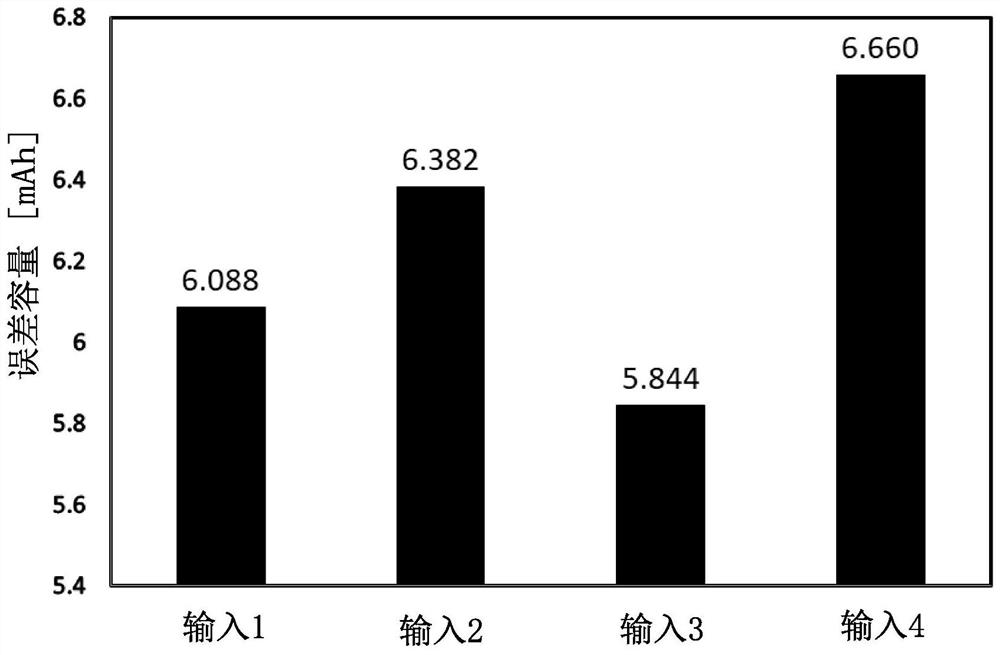
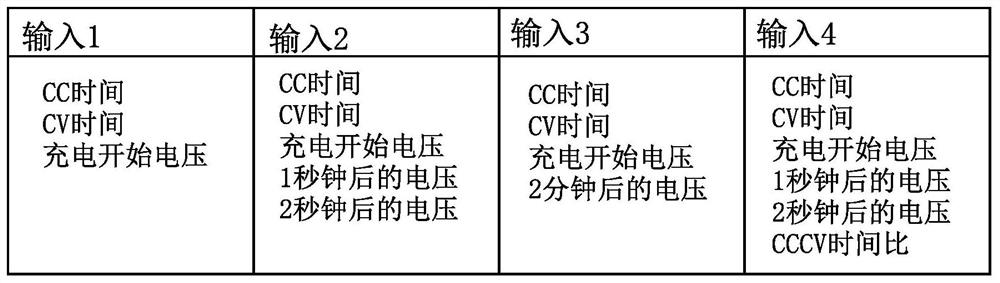
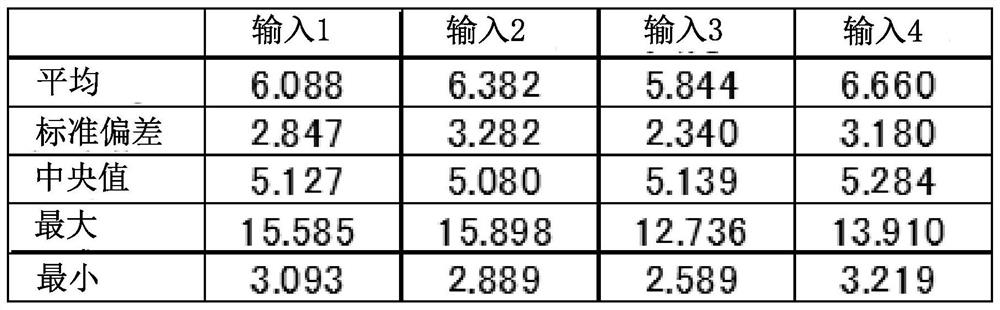
Provided is a state of charge (SOC) estimation method for a secondary battery, the method realizing highly precise estimation even if the deterioration of the secondary battery is advanced. Also provided is a capacity measurement system for the secondary battery, the system achieving highly precise estimation of SOC that can be performed in a short time and at a low cost. If the capacity of the second battery can be estimated with high precision, abnormal detection can be performed on the basis of that estimated value. Further provided is a novel abnormality detection method for a secondary battery. In a CCCV charging method, the CC time and the CV time are used as learning parameters for constructing a learning model. If the learning model is used, a highly precise estimated-capacity can be obtained by using, as the minimum input data, two parameters which are CC time and CV time, or three parameters which are CC time, CV time and a charge initiation voltage.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Check device
ActiveCN109211915BSimple arithmetic processingOptically investigating flaws/contaminationVisual inspectionEngineering
An inspection device is provided. This inspection apparatus is an apparatus that performs an appearance inspection of the surface to be inspected included in the object to be inspected. This inspection device includes an irradiation device, an imaging device, an image storage unit, and a defect detection unit. The irradiation device moves on an imaginary plane along the surface of the object to be inspected, and irradiates light toward the surface to be inspected of the object to be inspected. The imaging device includes the inspection surface of the inspection object in the imaging range, receives light reflected by the inspection surface, and generates a luminance distribution image as an imaging result. The image storage unit stores a plurality of luminance distribution images captured by the imaging device at a plurality of timings when the positions of the irradiation devices are different and the surface to be inspected, the imaging device and the irradiation device are not aligned in a straight line. The defect detection unit detects defects on the surface to be inspected based on a plurality of different luminance distribution images.
Owner:NIDEC TOSOK CORP
Die feeder
ActiveCN104871659BSimple arithmetic processingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical componentsPush upsEngineering
Owner:FUJI KK
Apparatus, system and method for extracting E1 access time division multiplex data
InactiveCN101227662BAffect processing powerTake advantage ofTransmission path multiple useData ingestionData abstraction
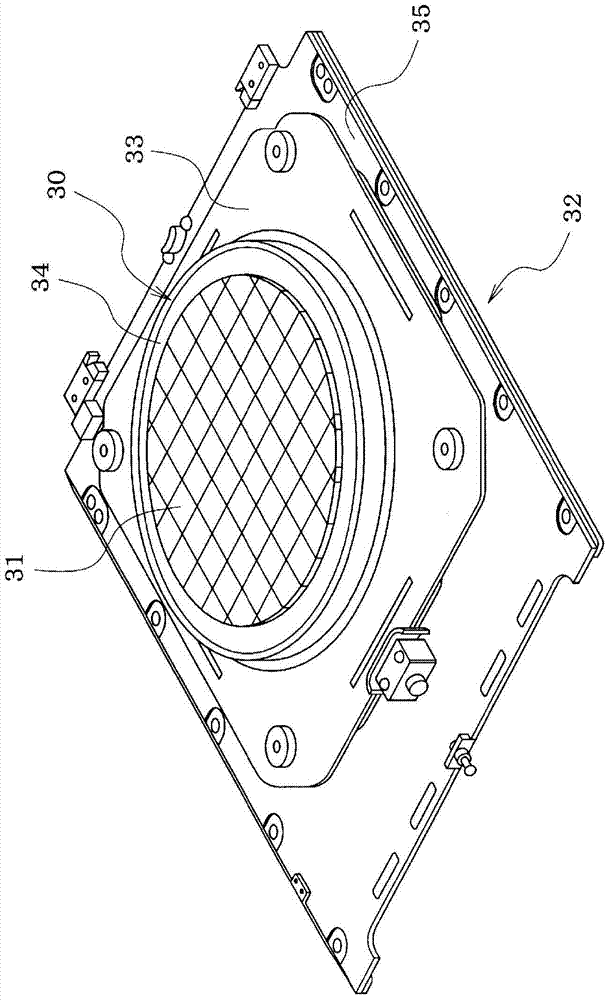
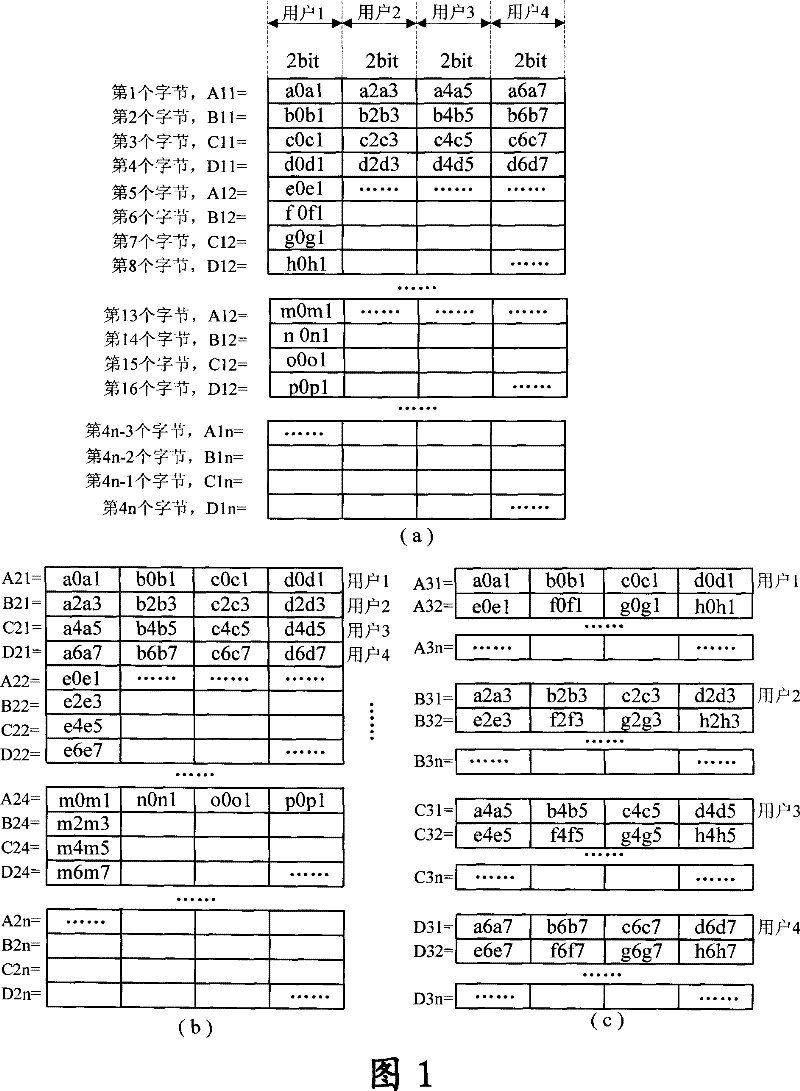
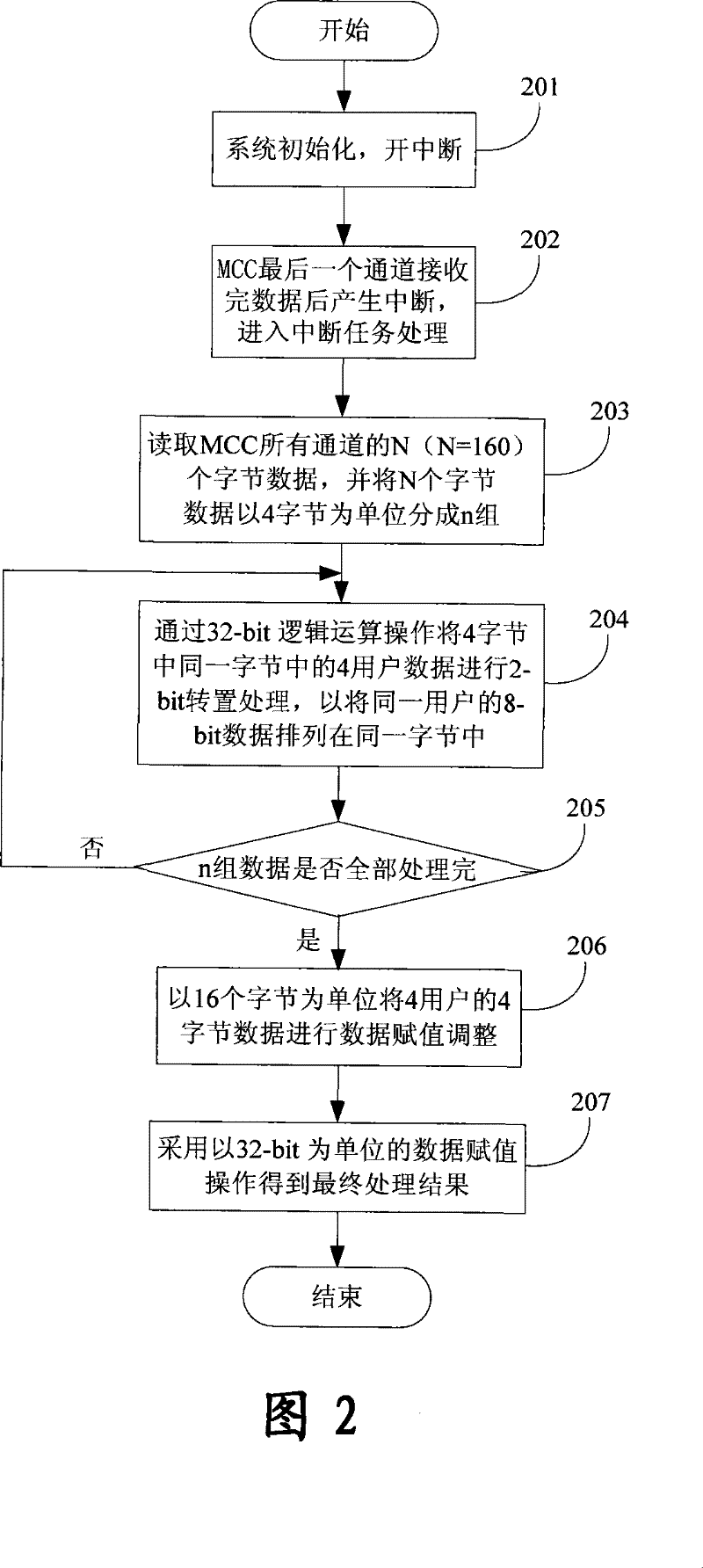
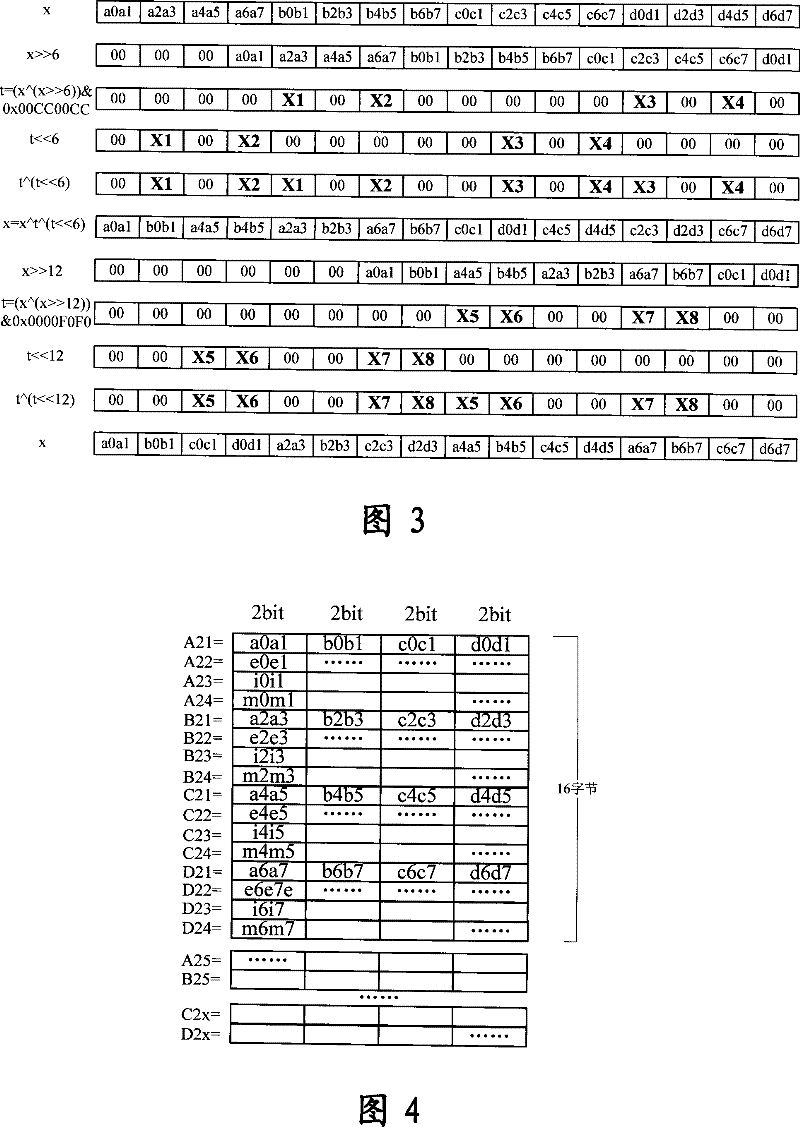
An extraction process of E1 switch-in time division multi-plexing data comprises the following steps that first producing the interrupt after the last channel of a multi-channel controller MCC having been received the data, processing the bit data with N number (N is the positive integer which is integer multiple relationship with 4) which receives the all channels of the MCC through the interrupt, and dividing the N bit data into n groups using 4 bits as a unit, secondly conducting the 2-bit transposition processing for the four users data in a same bit by each group data through the 32-bit logic calculus in order to array in turn the 8-bit of a same user in the 4 bits into a same bit, thirdly repeating the third step until the 2-bot transposition processing of the n groups is finished, conducting data evaluation operation to obtain the data abstraction results using 32-bit as a unit after conducted the data evaluation regulation for the 4 bit data using 16 bit as a unit. The invention fully utilizes the resource of a CPU and significantly increases the extraction rate of the data.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Touch panel and method of detecting press operation position thereon
InactiveUS8508492B2Reduce in quantityAvoid shapeInput/output processes for data processingBand shapeTouch panel
In a touch panel, one of conductive layers on a bottom of an upper substrate and on a top of a lower substrate is formed of belt-shaped conductive layers. The other is a single conductive layer facing the belt-shaped conductive layers. The single conductive layer is provided with a pair of electrodes in positions corresponding to both ends in a direction where the belt-shaped conductive layers extend. When the upper substrate is pressed while a voltage is applied between the pair of electrodes, the top and lower conductive layers contact with each other. Then, a voltage value corresponding to the pressed position in the direction where the belt-shaped conductive layers extend is generated from any of the belt-shaped conductive layers. From the voltage value and the position of the belt-shaped conductive layer from which the voltage value is generated, a pressed position on the upper substrate can be detected.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Calibration method and device, and body fluid composition measurement device calibrated using the method
ActiveCN104937397BSimple arithmetic processingGuaranteed measurement accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyMeasuring instrumentBody fluid
The present invention relates to a calibration method, device and program, and a body fluid component measurement device calibrated using the method. Estimation of the reference detection value in each sample (26s) when the reference light source (50s) is used respectively, and when a single light source (50r) of the same type as the reference light source (50s) is used and incorporated into the device to be calibrated (10c) single detection value. Based on the reference detection value estimated for each sample (26s) and the relationship of each group of individual detection values, the detection in the test paper (26) obtained by assembling the calibration object device (10c) with a single light source (50r) is determined. Values are converted into calibration curves of detection values when using a reference light source (50s).
Owner:TERUMO KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com