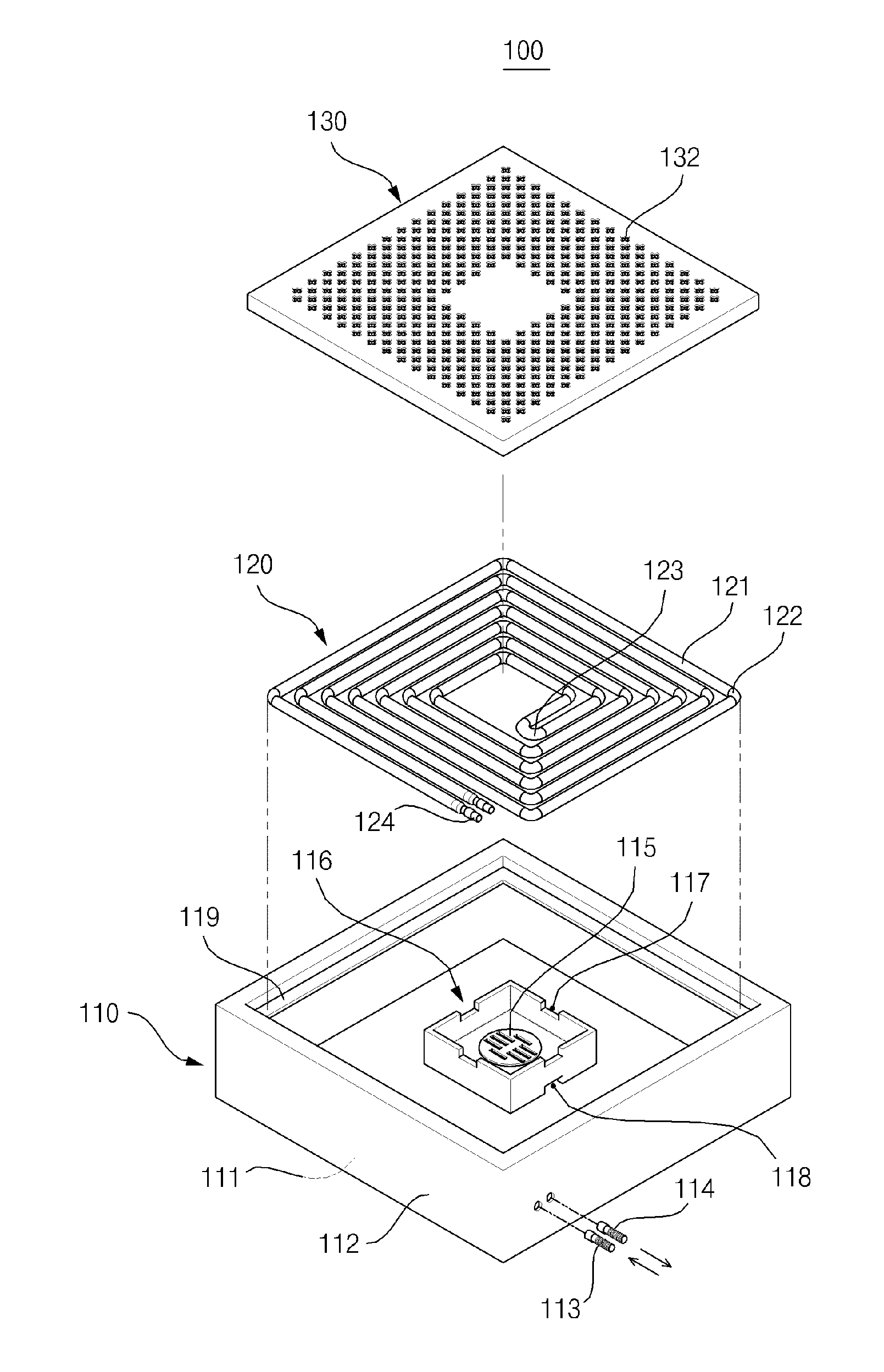
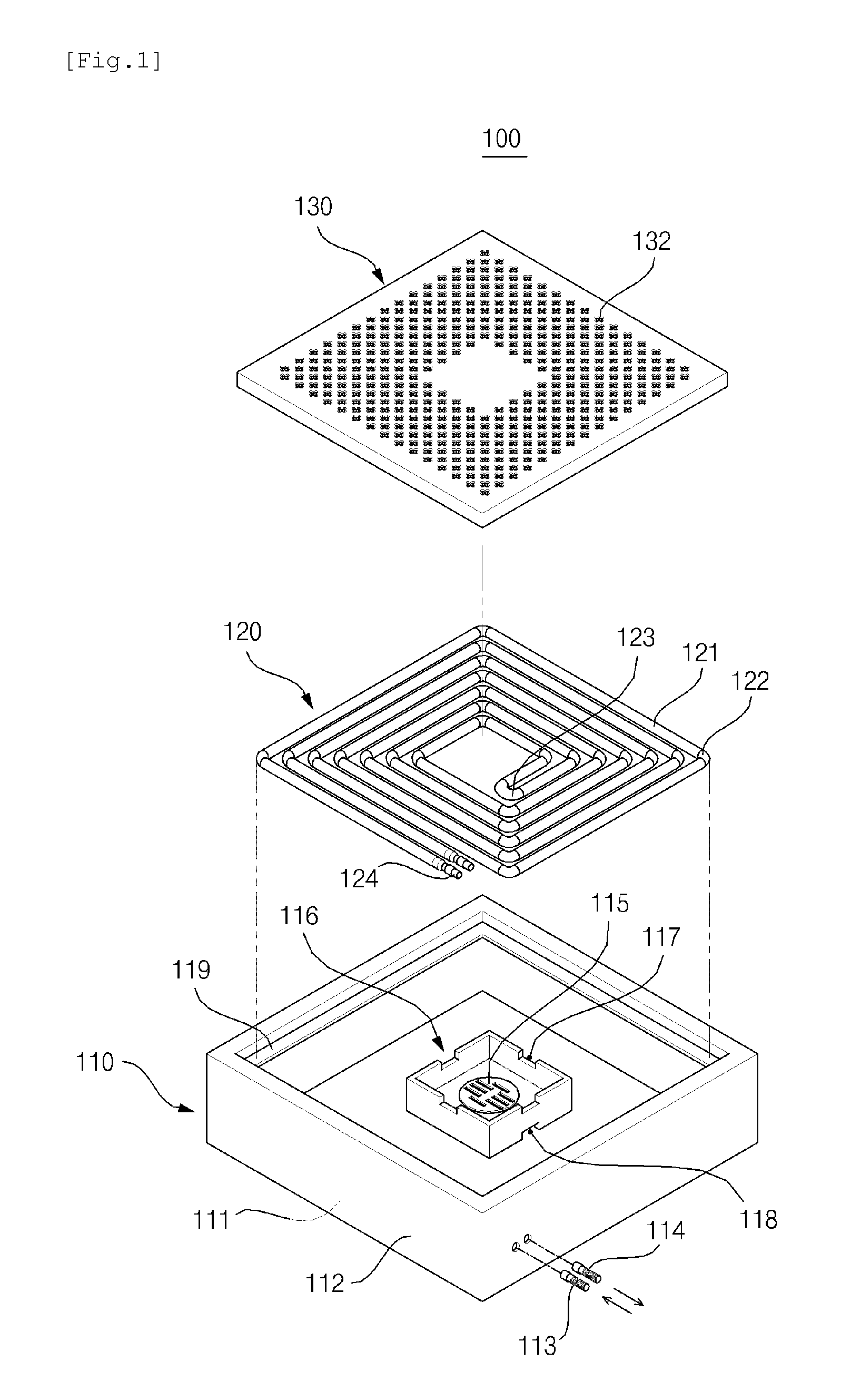
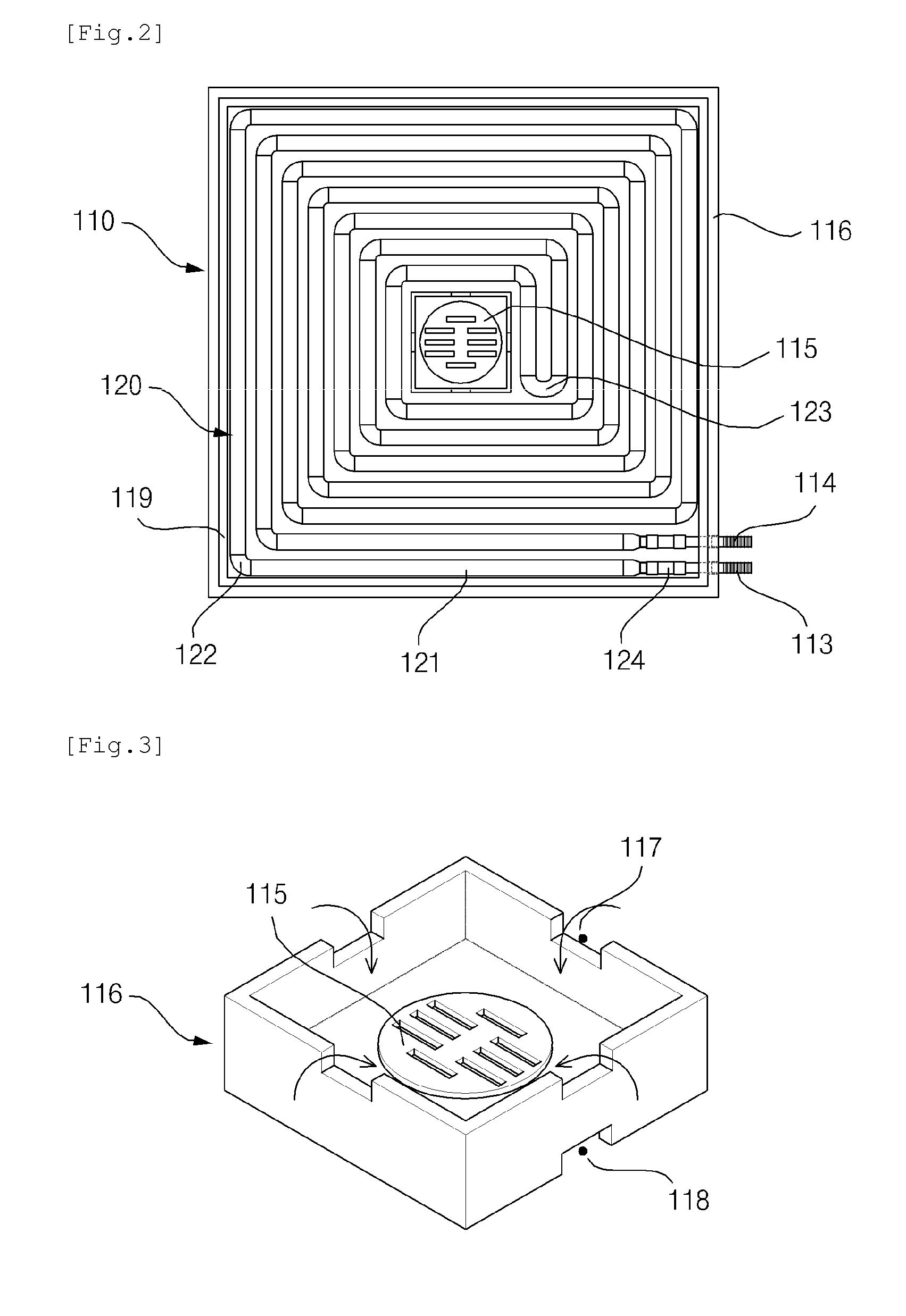
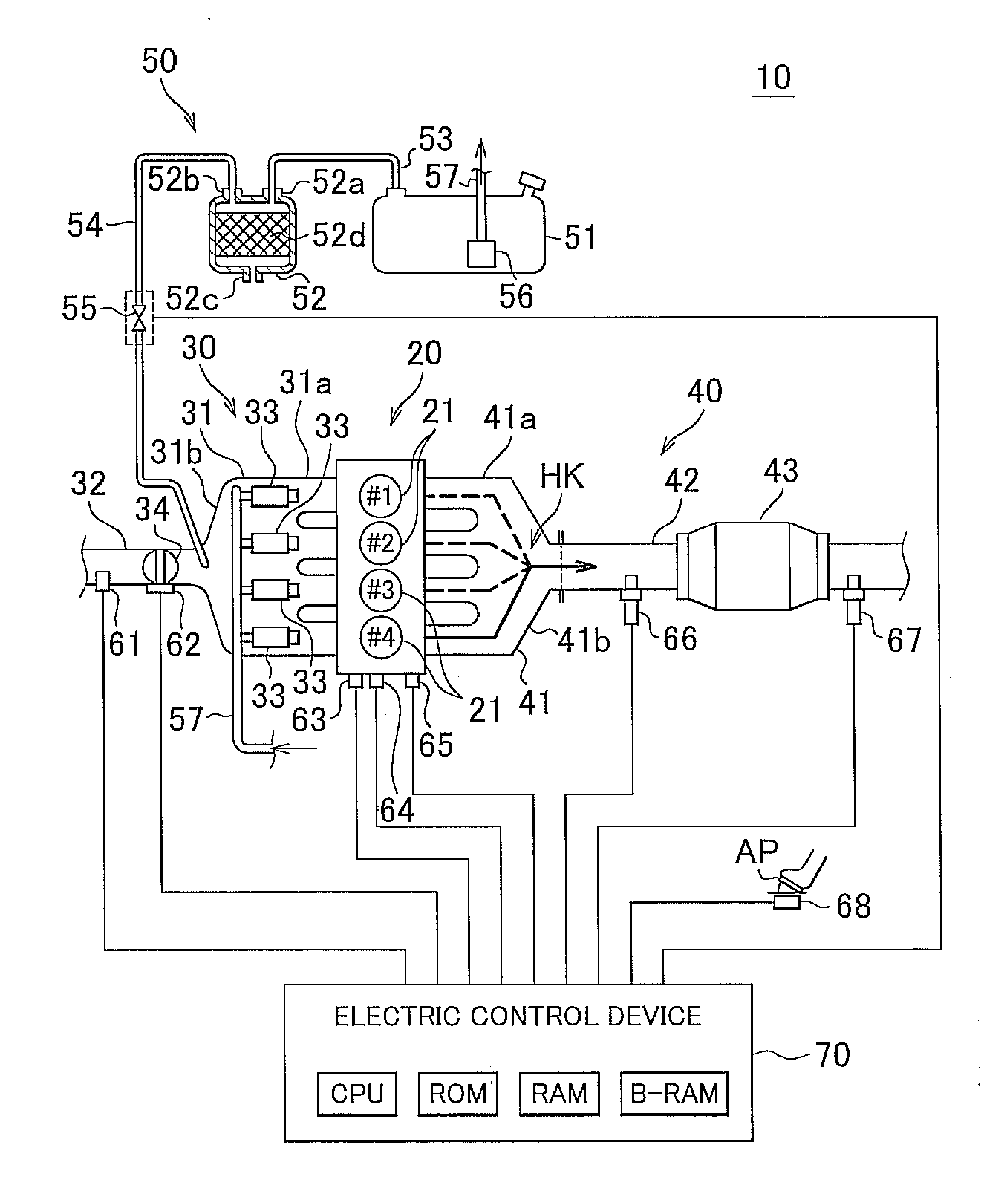
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
305results about How to "Reduce the amount of fuel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
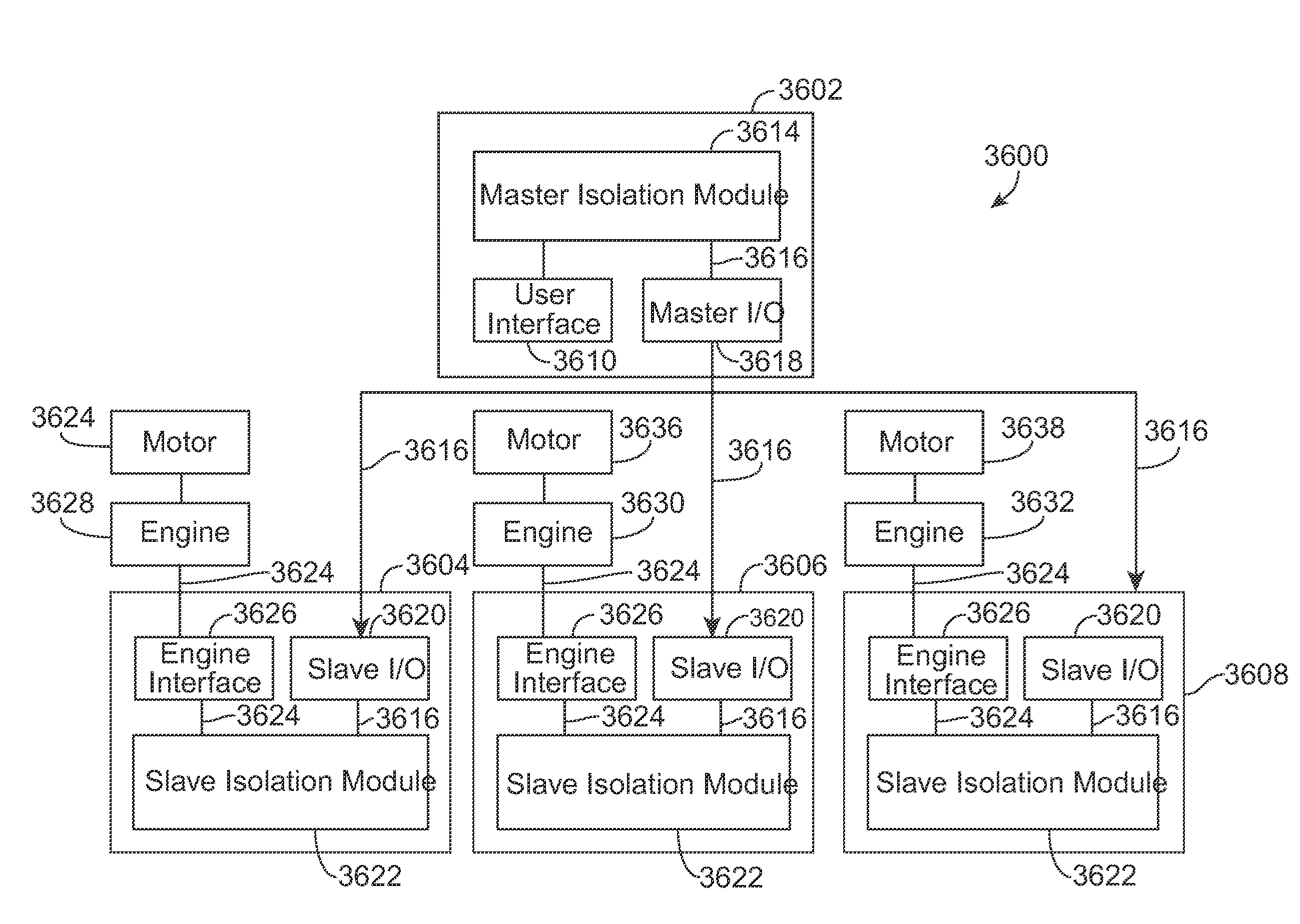
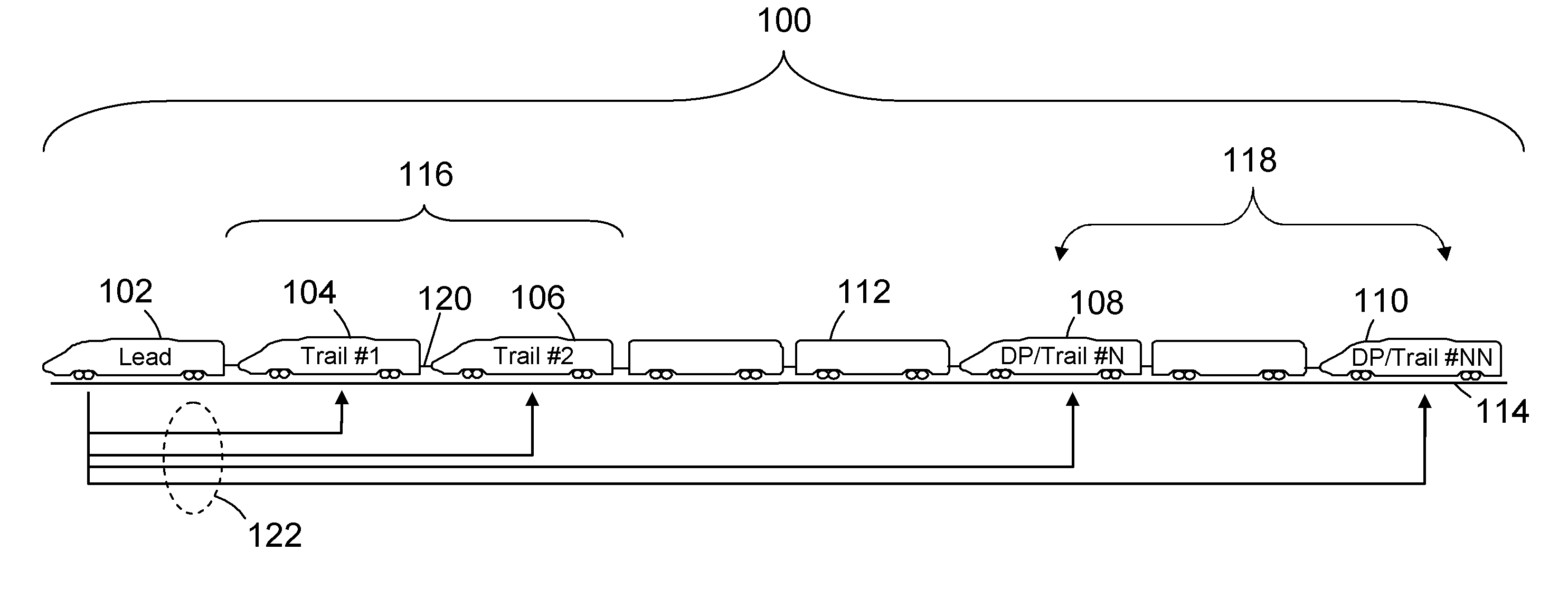
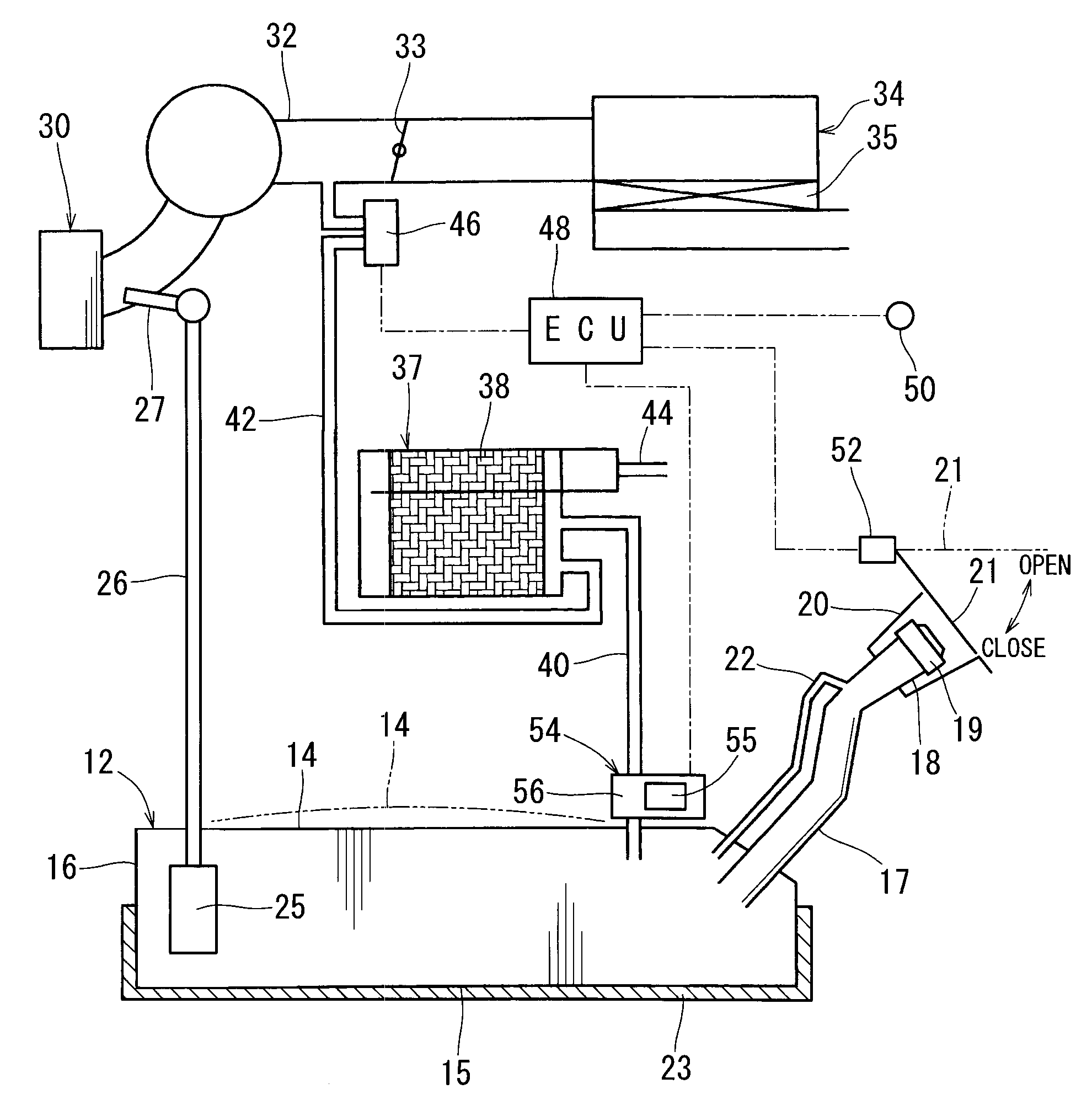
Control system and method for remotely isolating powered units in a vehicle system
ActiveUS20140094998A1Reduce amount of fuel consumeReduce the amount of fuelDigital data processing detailsSignalling indicators on vehicleAutomotive engineeringPower unit
A control system includes an energy management system and an isolation control system. The energy management system generates a trip plan that designates operational settings of a vehicle system having powered units that generate tractive effort to propel the vehicle system. The energy management system determines a tractive effort capability of the vehicle system and a demanded tractive effort of a trip. The energy management system identifies a tractive effort difference between the tractive effort capability of the vehicle system and the demanded tractive effort of the trip and selects at least one of the powered units based on the tractive effort difference. The isolation module remotely turns the selected powered unit to an OFF mode such that the vehicle system is propelled along the route during the trip by the powered units other than the selected powered unit.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
Apparatus for controlling automotive vehicle having a plurality of drive power sources
InactiveUS6484832B1Length of timeReduce total powerInternal combustion piston enginesDigital data processing detailsMobile vehicleMotorized vehicle
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
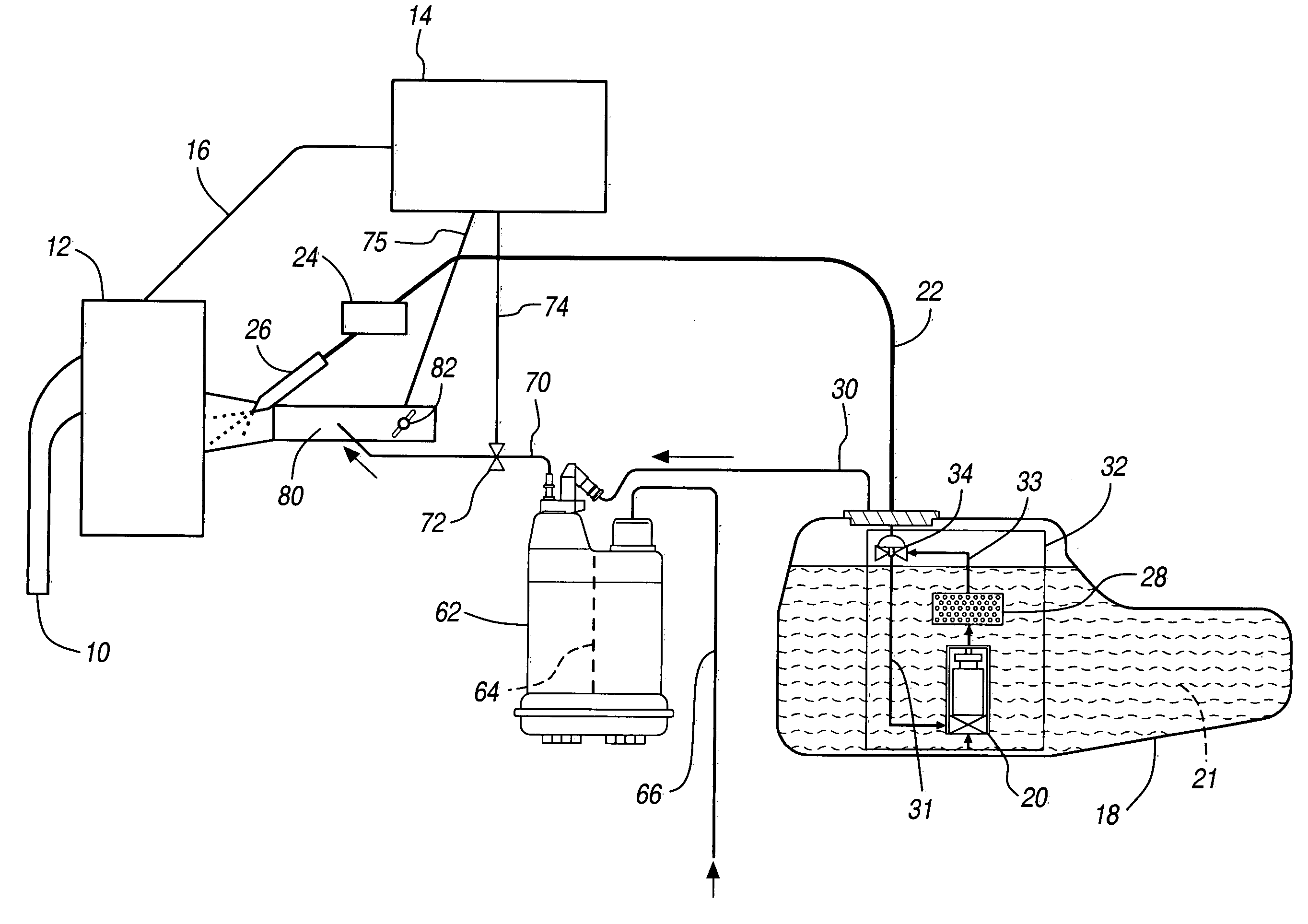
Hydrocarbon adsorpotion method and device for controlling evaporative emissions from the fuel storage system of motor vehicles
ActiveUS20070113831A1Reducing vapor releasedReduce the amount of fuelGas treatmentNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHydrocotyle bowlesioidesSlurry
The present invention is directed to an evaporative emissions control apparatus for minimizing fuel vapor emissions from a fuel storage system in a vehicle with an internal combustion engine. More specifically, the present invention is directed to an evaporative emissions control apparatus comprising a canister filled with a hydrocarbon adsorbent. The present invention is also directed an evaporative emissions control apparatus comprising a support substrate, which is coated with a hydrocarbon adsorbent slurry.
Owner:BASF CATALYSTS LLC
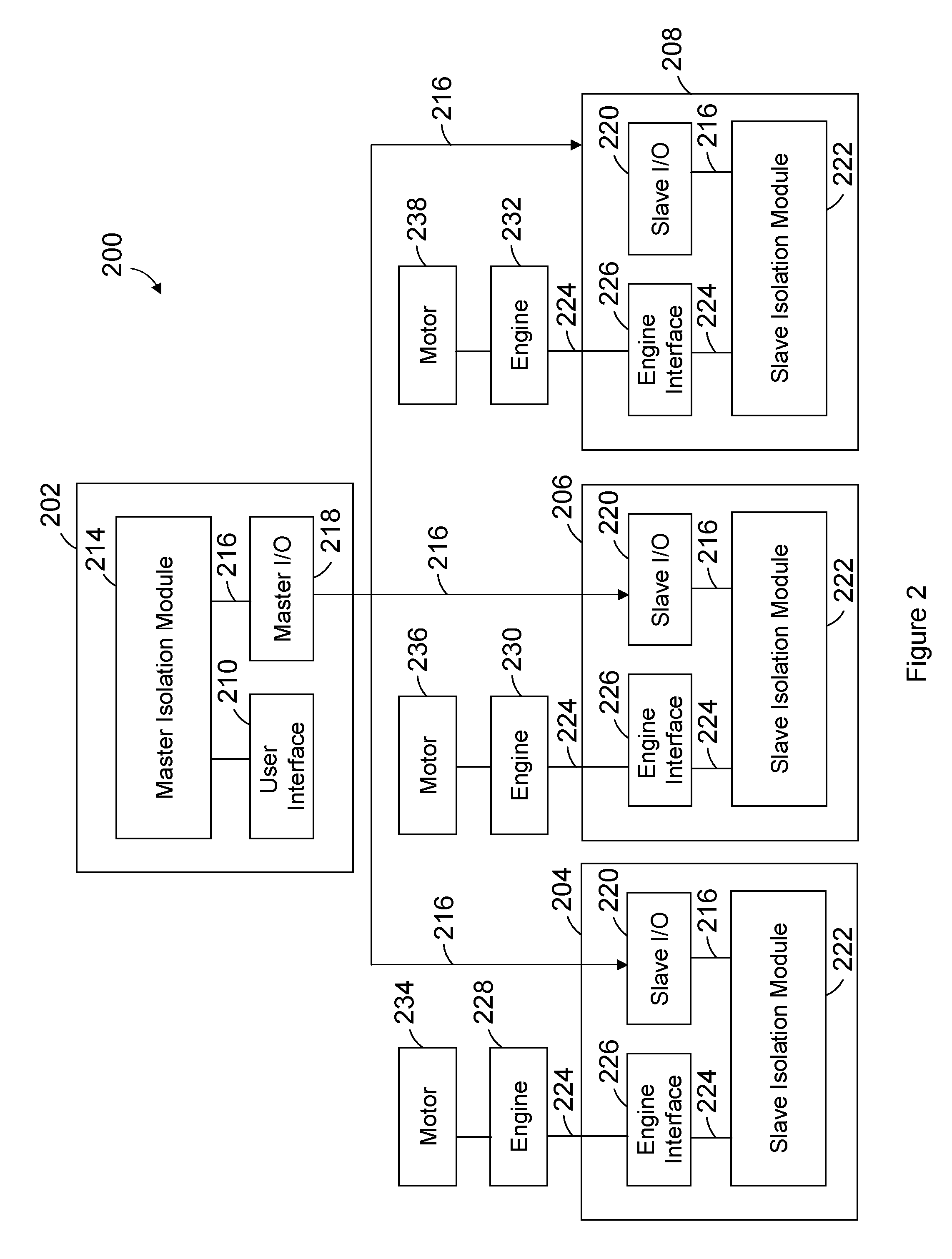
Control system and method for remotely isolating powered units in a rail vehicle system
ActiveUS20110060486A1Reduce the amount of fuelAnalogue computers for vehiclesReciprocating combination enginesControl systemComputer module
A control system for a rail vehicle system including a lead powered unit and a remote powered unit is provided. The system includes a user interface, a master isolation module and a slave controller. The user interface is disposed in the lead powered unit and is configured to receive an isolation command to turn on or off the remote powered unit. The master isolation module is configured to receive the isolation command from the user interface and to communicate an instruction based on the isolation command. The slave controller is configured to receive the instruction from the master isolation module. The slave controller causes the remote powered unit to supply tractive force to propel the rail vehicle system when the instruction directs the slave controller to turn on the remote powered unit. The slave controller causes the remote powered unit to withhold the tractive force when the instruction directs the slave controller to turn off the remote powered unit.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
LED Renewable Energy Lighting Unit having a Polygonal Solar Panel Configuration about a Horizontal or Vertical Pole
ActiveUS20150043200A1Enhance lighting systemReduce the amount of fuelMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceStreet lightLed illumination
The present invention discloses an improved renewable energy and rechargeable LED lighting unit having a roadway / street light pole with a polygonal frame member configuration disposed there about. A plurality of solar panels affixed to the polygonal configuration. The solar panels include a plurality of electrical modules that are affixed directly to an interior wall of at least one of the solar panels without interfering with the polygonal frame member when attached. A two-part closure plate arrangement are attached directly to the polygonal frame member and completely enclose and seal the plurality of electrical modules between the frame member and the at least one of the solar panels.
Owner:WILSON OSWALD A
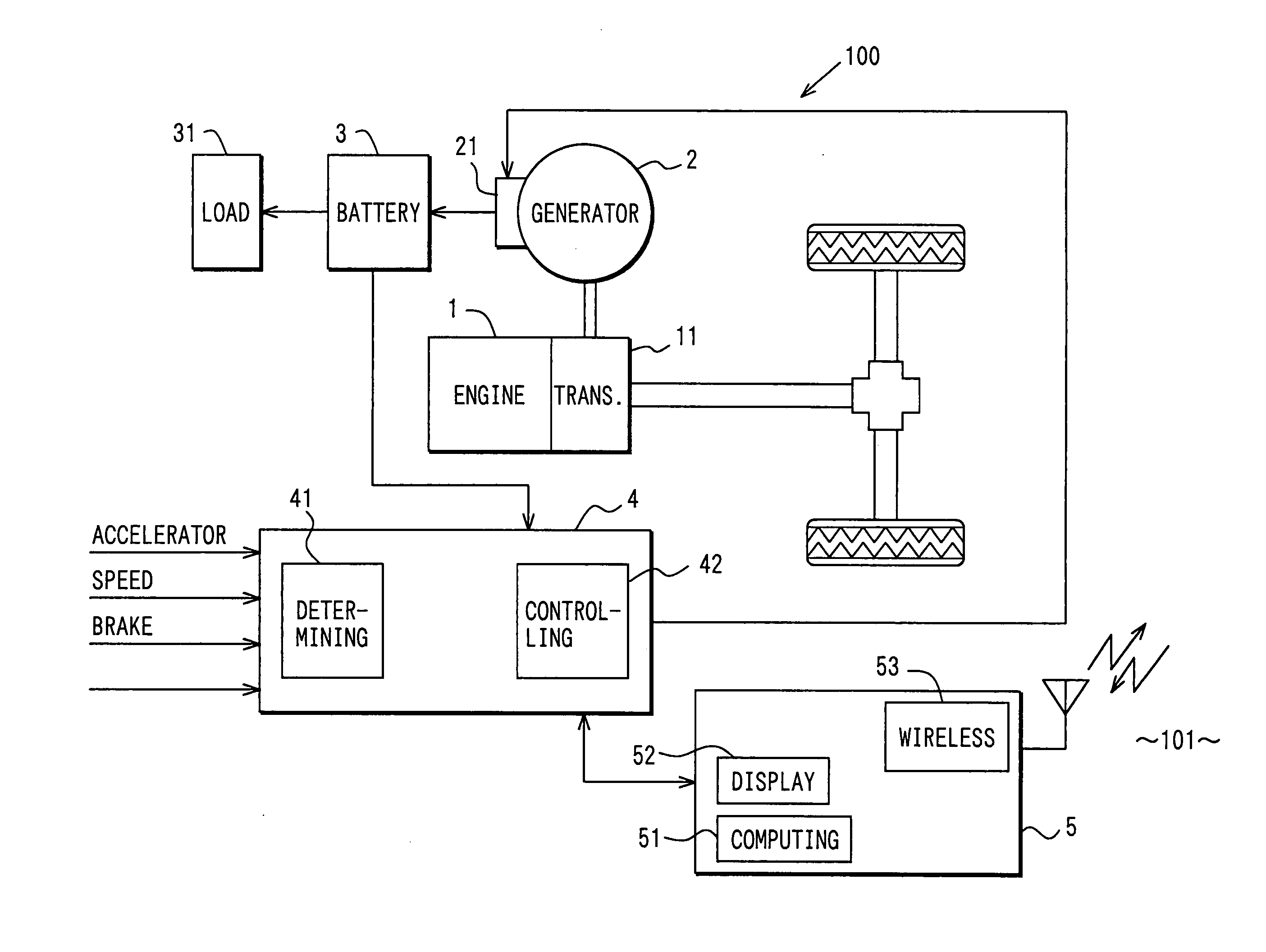
Environment conservation contribution system
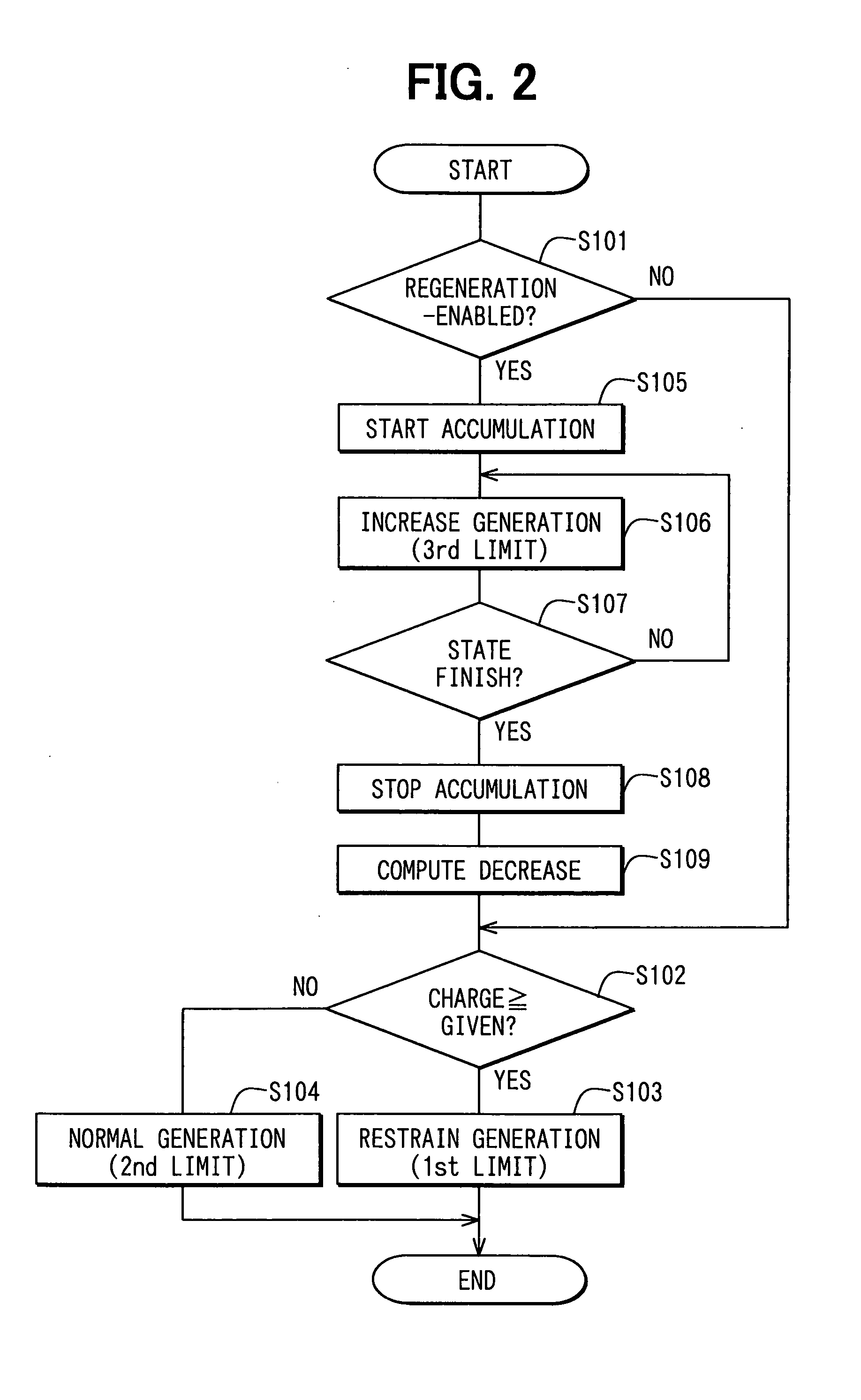
InactiveUS20050021191A1Decrease amount of fuel consumeDecrease amount of decreaseHybrid vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsExhaust gasIn vehicle
An in-vehicle generator is caused to start regenerative generation when the regenerative generation is possible. This regenerative generation can decrease a generation amount under a vehicle traveling state where fuel is consumed and exhaust gas is emitted, thereby decreasing a load of an engine and amounts of fuel consumption and exhaust emission. The fuel consumption or exhaust emission to be decreased is computed and transmitted to a managing center via an in-vehicle wireless terminal. The managing center provides a driver with a reward such as a service corresponding to the decreased amount of fuel consumption or exhaust emission that is computed in the relevant vehicle. This system enables the regenerative generation to be returned to the driver as an economic value, motivating the driver to decrease the fuel consumption or exhaust emission. This thereby contributes to the conservation of global environment.
Owner:DENSO CORP
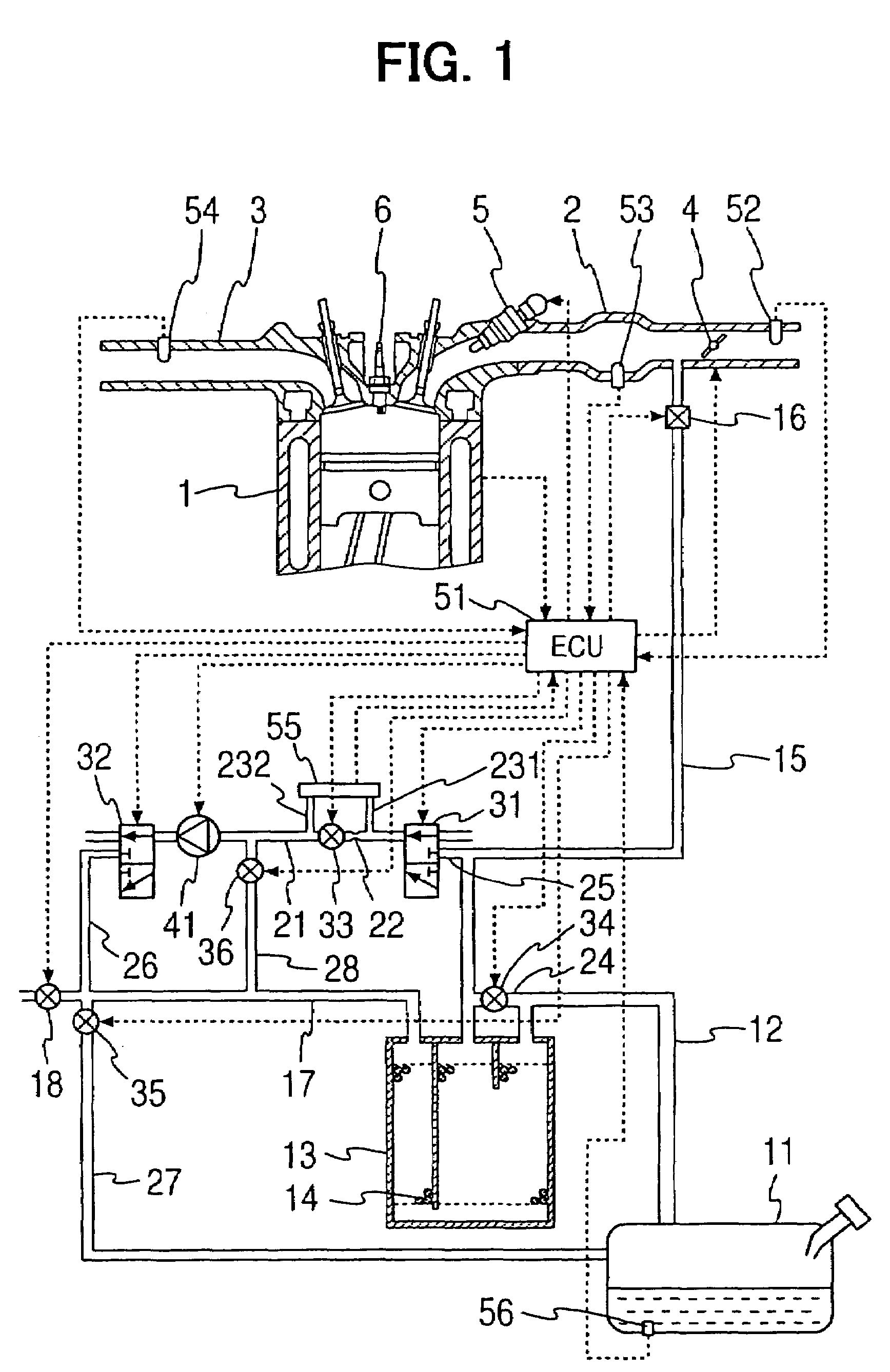
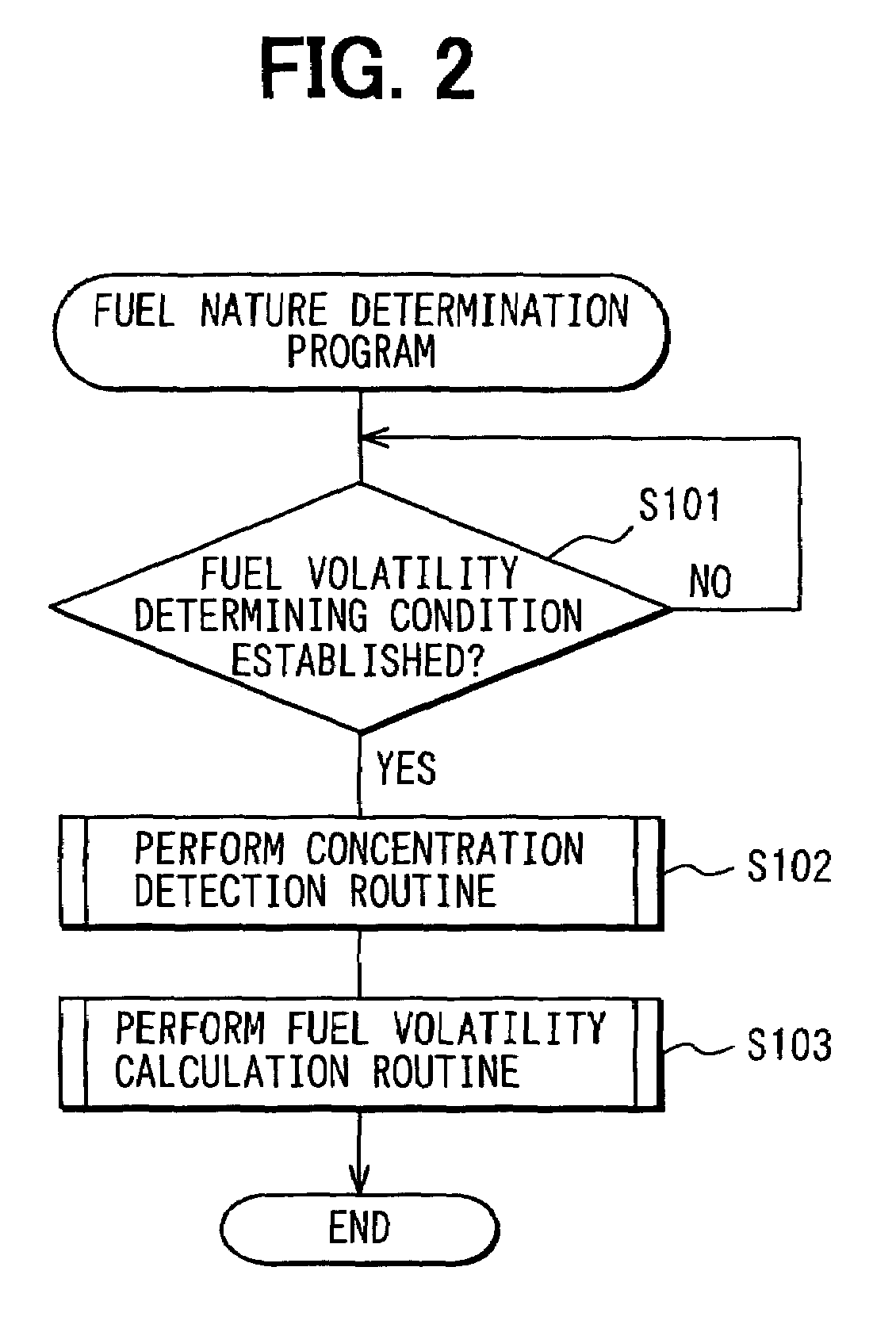
Fuel nature measuring device of internal combustion engine and internal combustion engine having the same
ActiveUS20060031000A1Reduce the amount of fuelReduce exhaust emissionsAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlDifferential pressureFuel tank
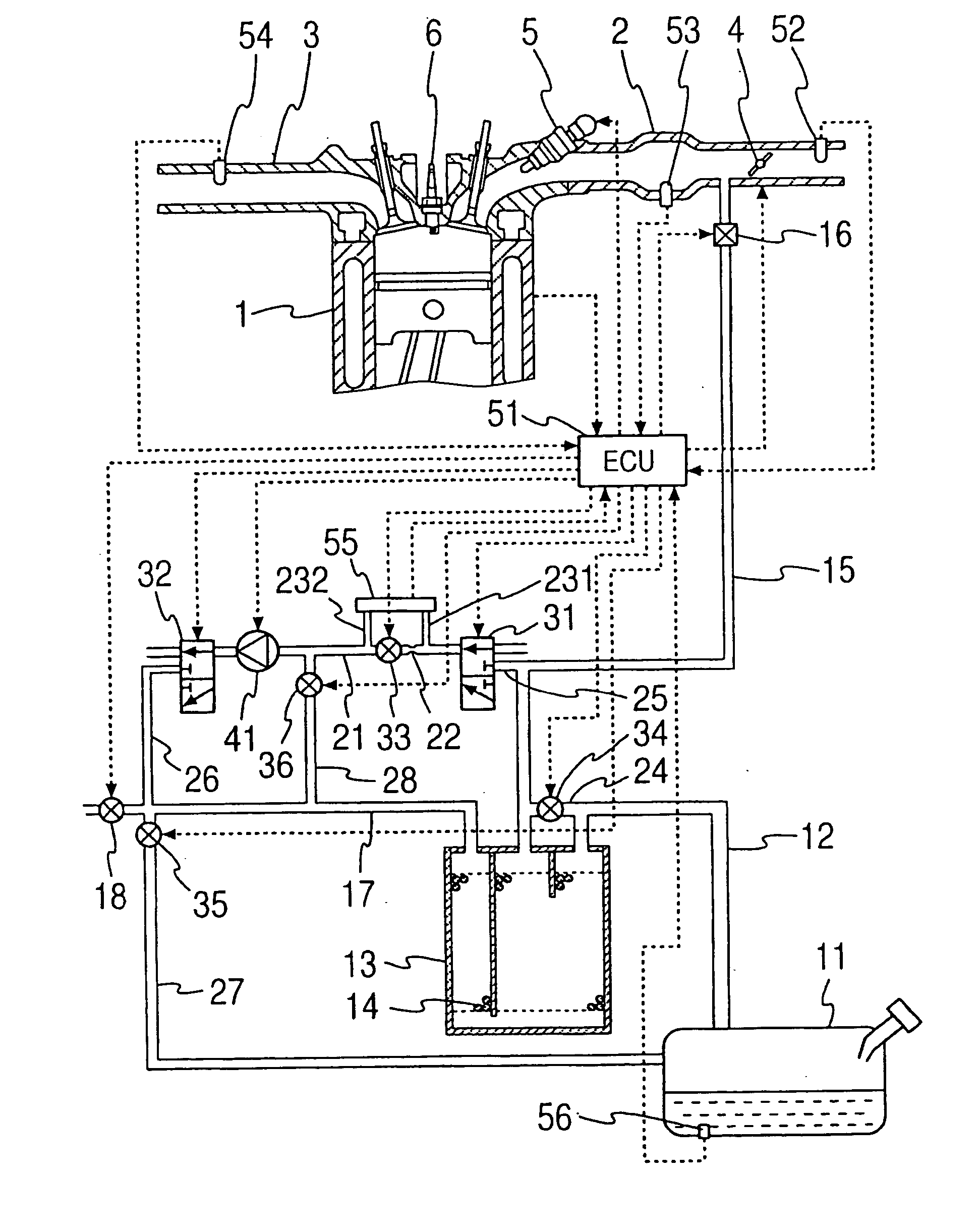
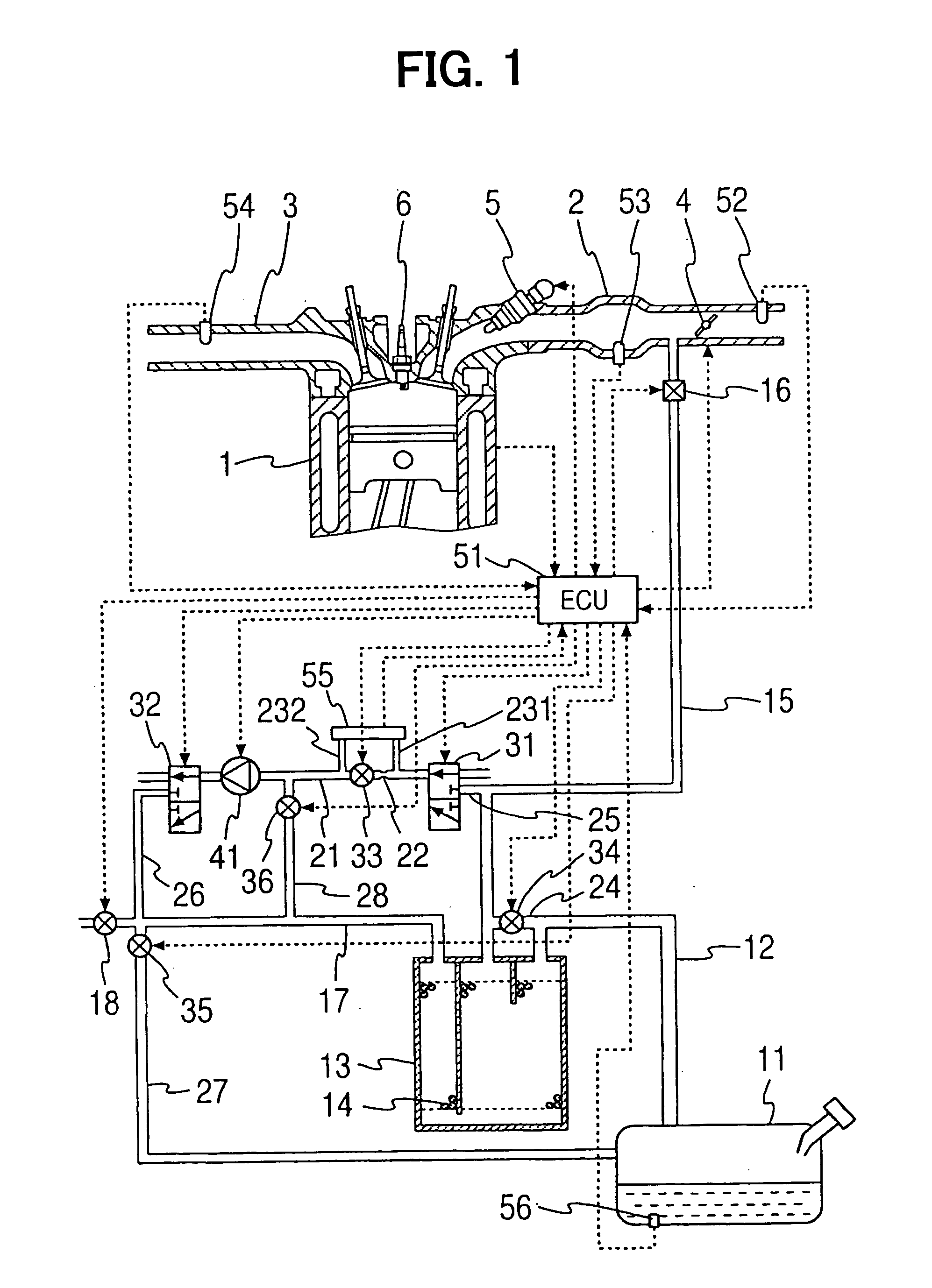
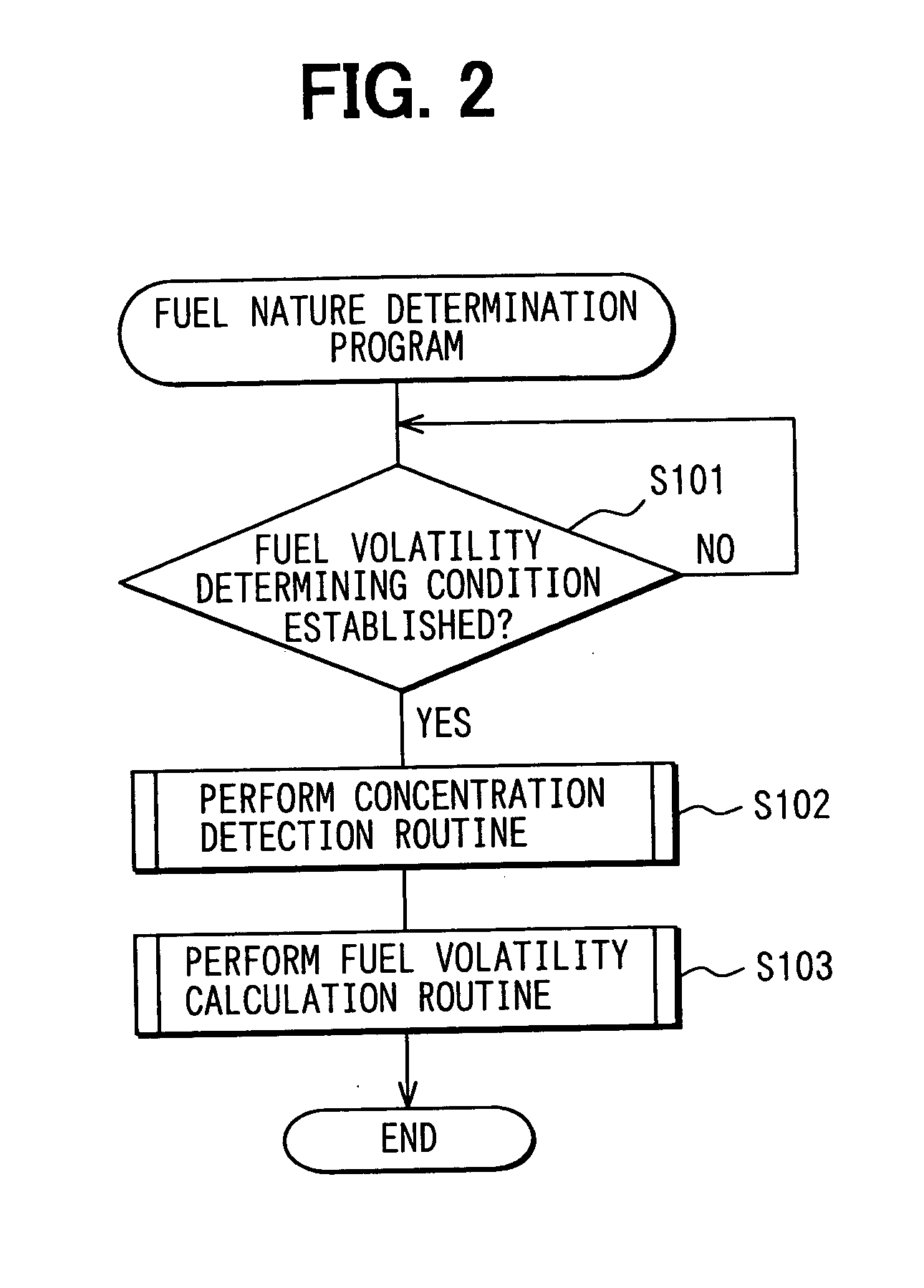
A fuel nature measuring device for measuring the nature of fuel stored in a fuel tank includes a measurement passage, a gas flow generator, a pressure detector, an concentration operator, a temperature detector, and a volatility calculator. The measurement passage has an orifice. The gas flow generator generates gas flow in the measurement passage. The pressure detector detects a differential pressure between opposite ends of the orifice. The concentration operator determines a concentration of evaporated fuel in the fuel tank based on the differential pressure detected when the opposite ends of the measurement passage communicate with the fuel tank and the fuel flows in the measurement passage. The temperature detector determines a temperature of the fuel in the fuel tank. The volatility calculator calculates a volatility of the fuel in the fuel tank based on the concentration of the evaporated fuel and the temperature of the fuel in the tank.
Owner:NIPPON SOKEN +1
Fuel vapor control devices
ActiveUS20090025694A1Volume of fuel tankReduce the amount of fuelElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEvaporationEngineering
A fuel vapor control device include a fuel tank for storing fuel, a canister for adsorbing fuel vapor produced in the fuel tank, and an evaporation path communicating between the fuel tank and the canister. The tank has a resiliently deformable wall portion that can resiliently deform in response to an amount of the fuel vapor in the fuel tank, so that volume of the fuel tank can be varied. A pressure regulating valve can perform a relief function for opening the evaporation path during the expansion of volume of the fuel tank to a set volume. The pressure regulating valve closes the evaporation path if pressure inside the fuel tank is lower than the set value. On the other hand, the pressure regulating valve opens the evaporation path if the pressure inside the fuel tank is equal to or higher than the set value.
Owner:AISAN IND CO LTD
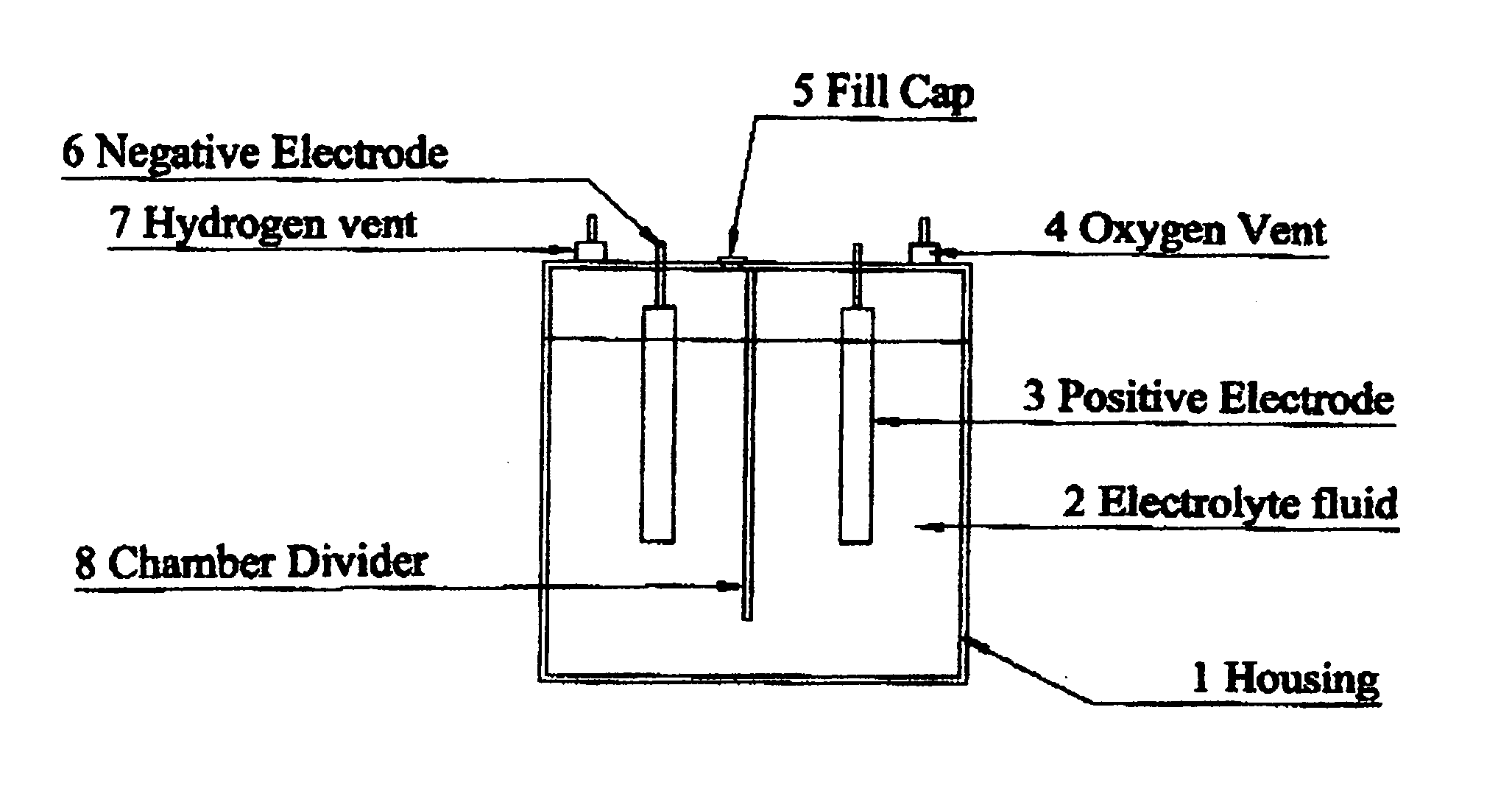
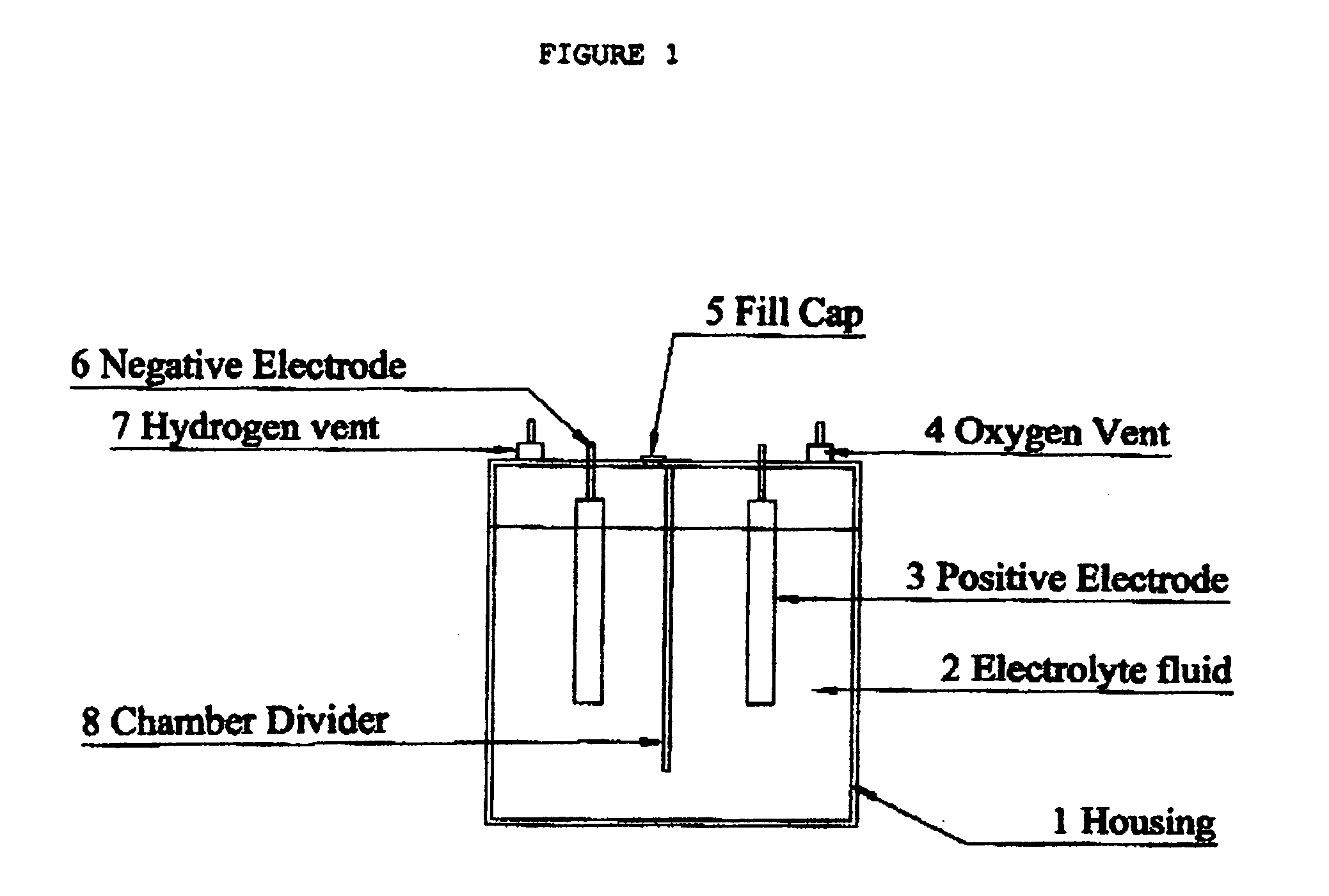
Device for generating hydrogen for use in internal combustion engines
InactiveUS20070246351A1Improve internal efficiencyLow costCellsNon-fuel substance addition to fuelElectrolysisCombustion
An electrolysis conversion system for converting water into hydrogen and oxygen, includes a housing in which are housed electrodes. The electrodes are immersed in an electrolyte and are connected to a positive and negative sides of an energy source. The housing is a non conductive material that has chambers to separate the hydrogen and the oxygen The present invention further discloses a method of utilizing the electrolyzer in conjunction with the fuel system of an internal combustion engine to improve the efficiency of said internal combustion engine.
Owner:SMOLA MATTHEW M +1
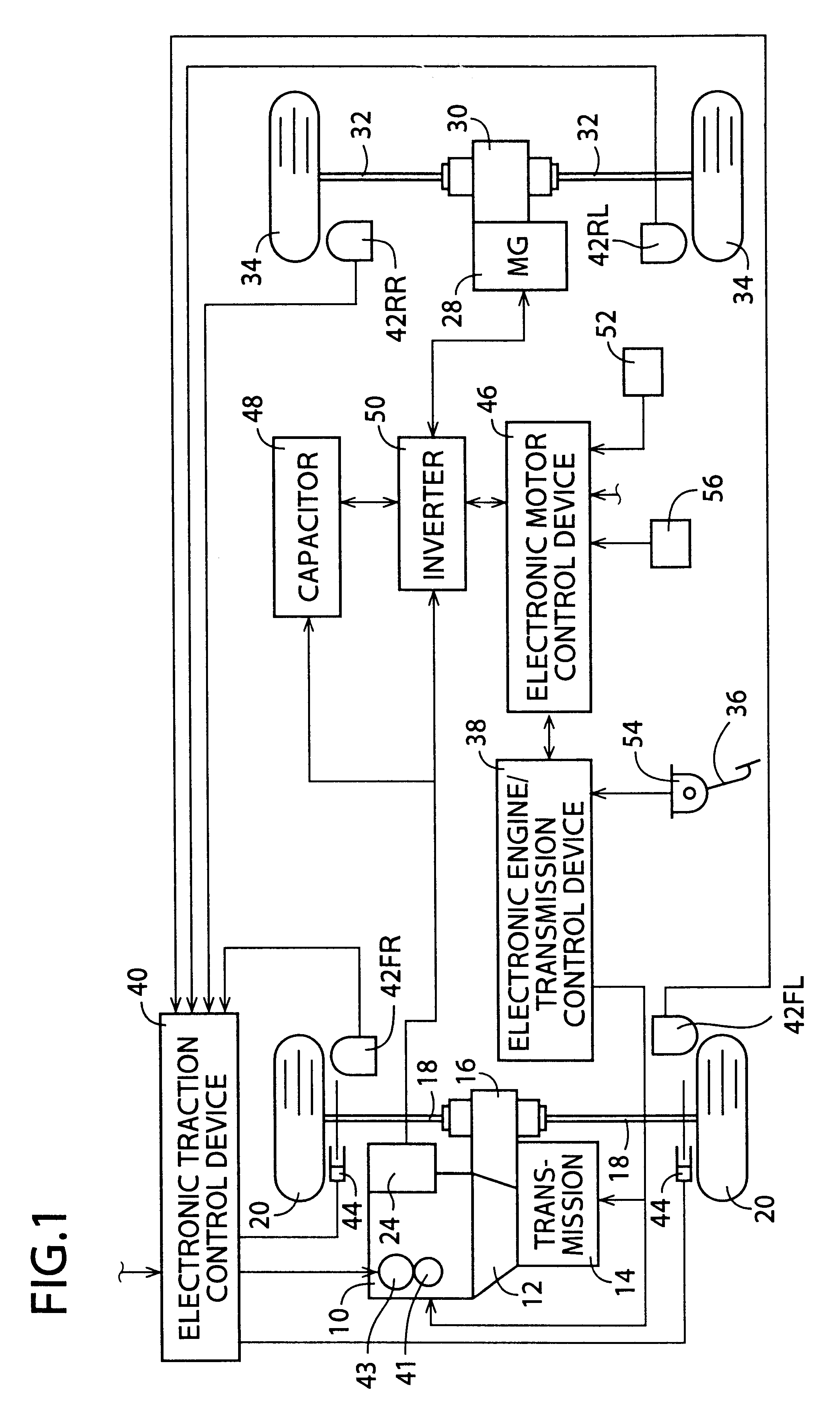
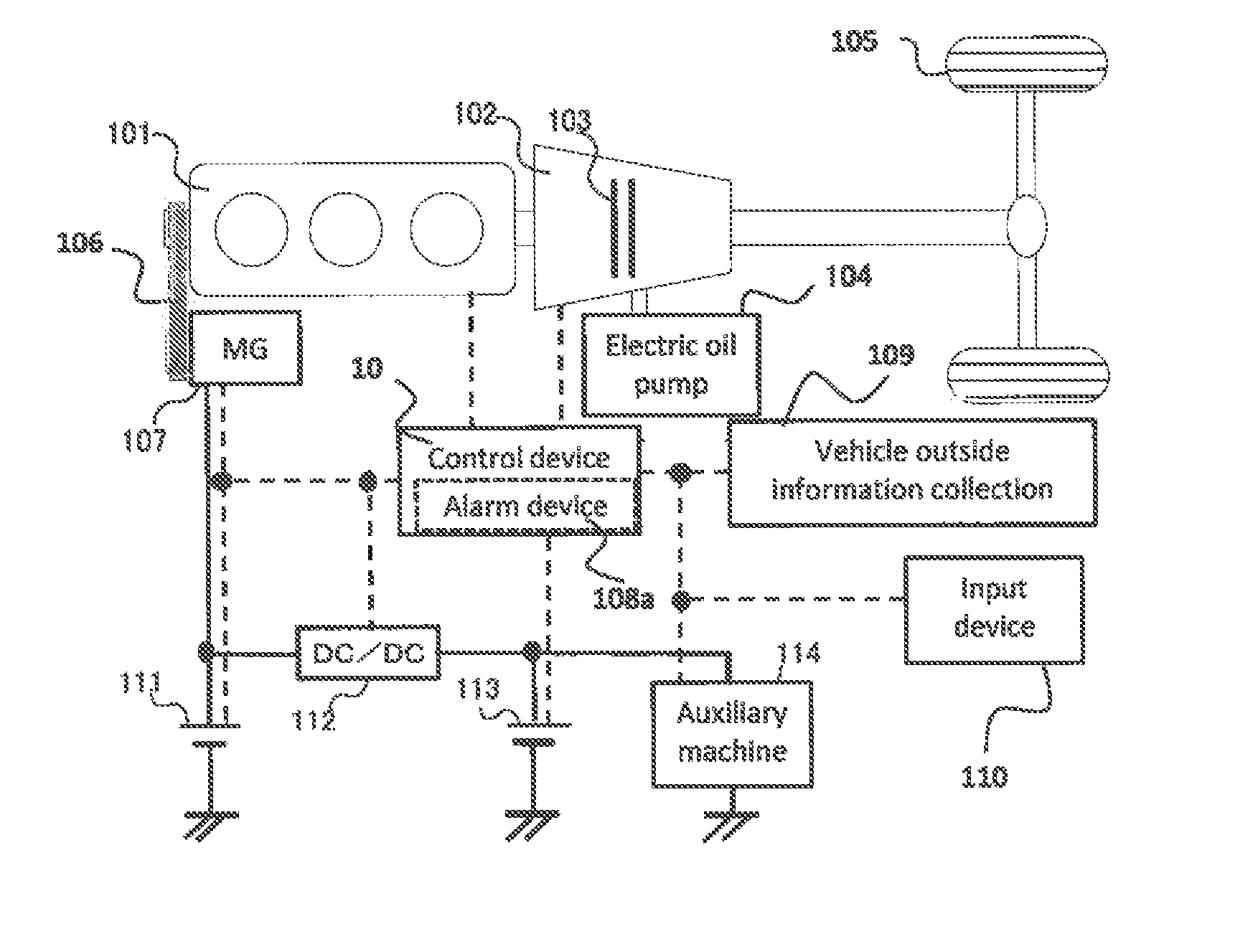
Vehicle control apparatus
ActiveUS20150088349A1Improve fuel economyBetter fuel economyHybrid vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesClutchDrive wheel
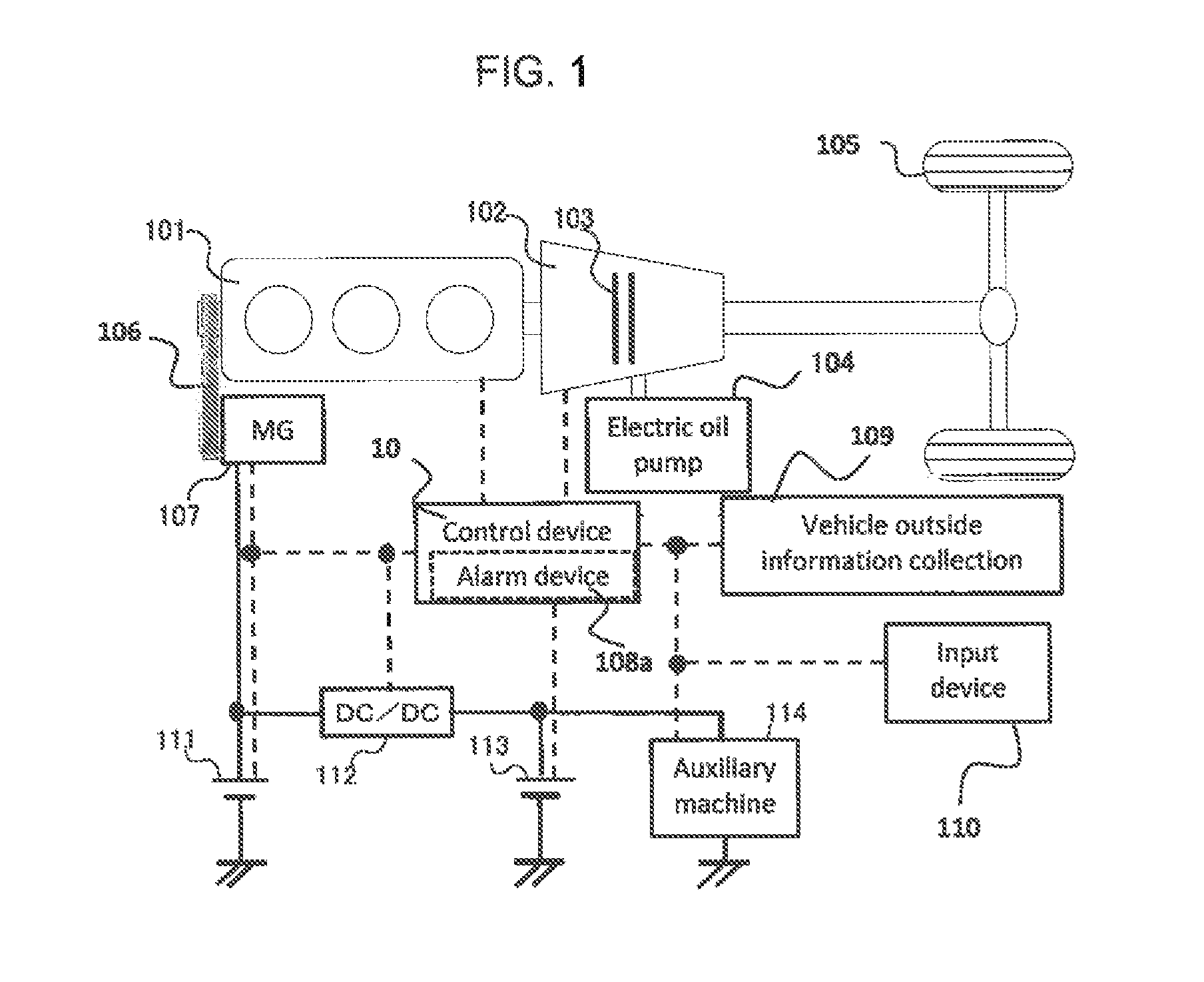
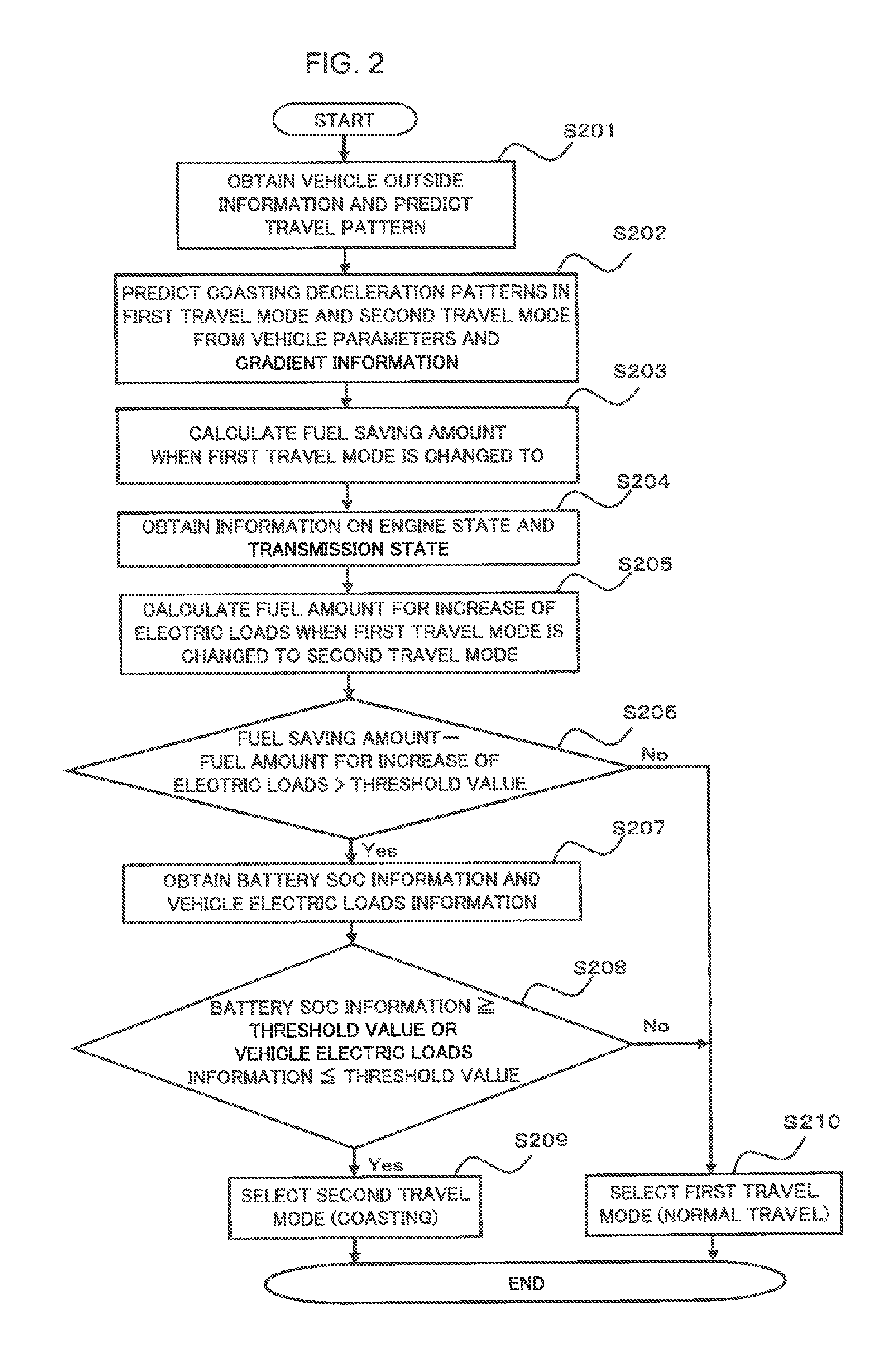
An object is to provide a vehicle control apparatus capable of enhancing fuel economy when coasting is performed by disconnecting a clutch disposed between an engine and drive wheels of the vehicle. A travel path and a travel pattern of a vehicle are predicted by a vehicle outside information collection device, such as a navigation system. Also, amounts of fuel consumption by normal traveling and coasting are predicted and compared, so that coasting control is performed in a case where an amount of fuel consumption can be reduced by performing the coasting control.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method for judging system condition in fuel cell system
A method for rapidly judging abnormalities, such as a decrease in a residual fuel amount and valve leakage, using only one pressure detecting device, includes a step of detecting a pressure change per unit time by the pressure detecting device after switching the fuel cutoff device from a cutoff state to a flow state, and a step of judging, by a pressure state judging device, whether the fuel amount in a fuel tank is smaller than a predetermined residual amount by comparing the pressure change per unit time detected by the pressure detecting device with a predetermined pressure change.
Owner:CANON KK
Ventilating device for fuel tank
InactiveUS20090236350A1Prevent outflowSimple designOperating means/releasing devices for valvesLarge containersInternal pressurePositive pressure
The fuel tank ventilating device includes a fuel cutoff device, and a connector pipe connecting the fuel cutoff device with a canister. The fuel cutoff device includes a first fuel cutoff valve, a second fuel cutoff valve, and a positive pressure valve; the first flow pipe and the second flow pipe are connected to a third flow pipe by a connecting part, and are connected to the canister. With the first fuel cutoff valve in a first submersion state, fuel that has collected in the first flow pipe will be returned to the fuel tank on the basis of a differential pressure between tank internal pressure and the pipe internal pressure bearing on the fuel inside the first flow pipe. With the first fuel cutoff valve in a submersion state, fuel that has leaked into the second flow pipe will not reach the connecting part.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Fuel injection control device
InactiveUS6076508AReduce impact noiseEasy to openElectrical controlNoise reducing fuel injectionLow loadEngineering
During the low load operation, this fuel injection control device reduces the initial armature displacement speed of the solenoid actuator that drives the open-close valve against the low fuel pressure in the balance chamber, thereby lowering impact noise produced in the solenoid portions. When the engine is determined to be idling, a command pulse width which energizes the solenoids of the solenoid actuator is calculated according to the target injection amount, the common rail pressure, and the target fuel injection timing. Since the initial period of the command pulse width, i.e., pull-in current conduction period, is set shorter than the pull-in current conduction period for the high load operation of the engine, the initial armature displacement speed of the solenoid becomes relatively slow reducing the impact noise of the armature abutting against the stopper.
Owner:ISUZU MOTORS LTD
Humid air turbine, humid air turbine control system, and humid air turbine control method
ActiveUS20080229755A1Guaranteed flame stabilityReduce the amount of fuelTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsGas turbine plantsCombustorControl system
The present invention provides a humid air turbine having a compressor, a humidificator for generating humid air by adding moisture to compressed air supplied from the compressor, a combustor, a turbine, a recuperator for effecting heat exchange between exhaust from the turbine and the humid air, an economizer for effecting heat exchange between exhaust from the recuperator and water, and a system for supplying the water heated by the economizer to the humidificator. The humid air turbine includes a temperature measurement device for measuring the temperature of gas discharged from the economizer, and a control device for adjusting the amount of moisture to be supplied to the humidificator in accordance with a temperature signal from the temperature measurement device. The present invention assures low NOx of combustor and flame stability before and after water addition to the humid air turbine.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Heating element for an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20090107974A1Inhibition releaseSave automobile users moneyVehicle heating/cooling devicesOhmic-resistance heating detailsEngineeringInternal combustion engine
The present invention provides a method and apparatus to quickly raise the temperature of an internal combustion engine and the temperature of the ambient air in a passenger compartment of a vehicle. The apparatus comprises a heating element that quickly realizes a temperature of approximately 300 degrees F. Heating system fluid flows across this heating element which raises the temperature of the heating system fluid. This now heated heating system fluid flows through heater core tubes which are connected to heater core fins, thus raising the ambient temperature air which is blown over the heater core fins and into the passenger compartment. The heated heating system fluid also flows over the engine thus helping to raise the operating temperature of the engine.
Owner:TESTA MATTHEW
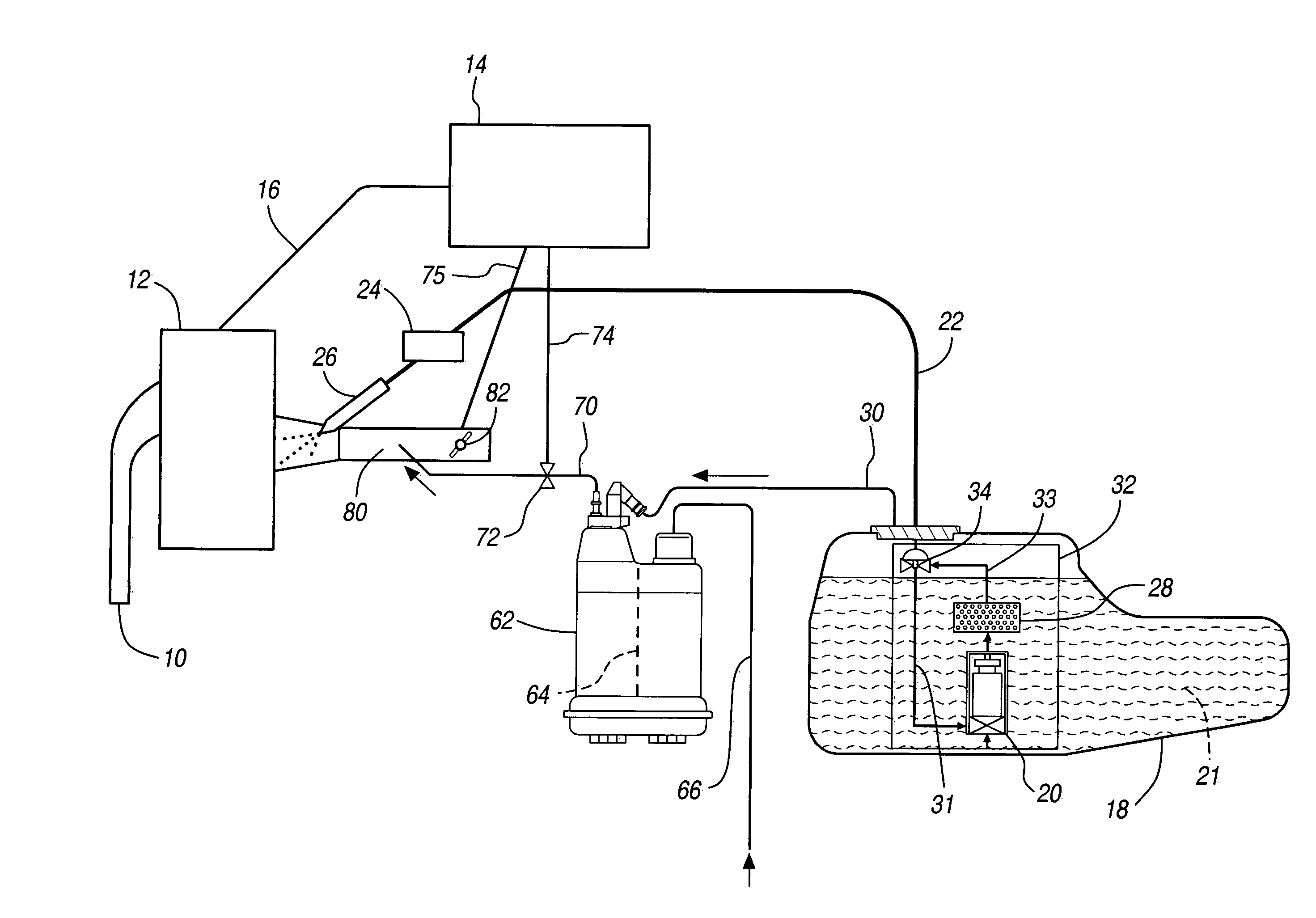
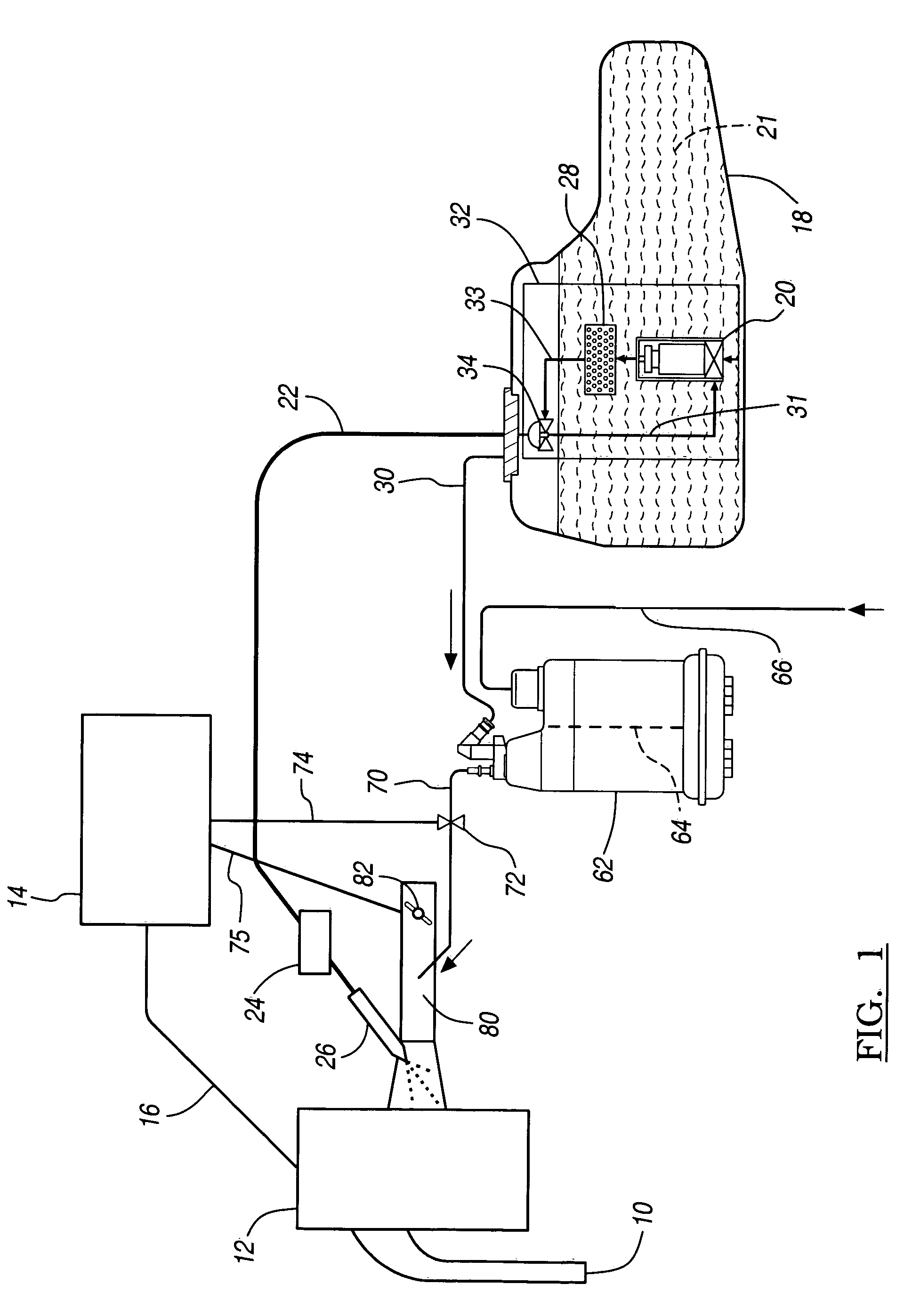
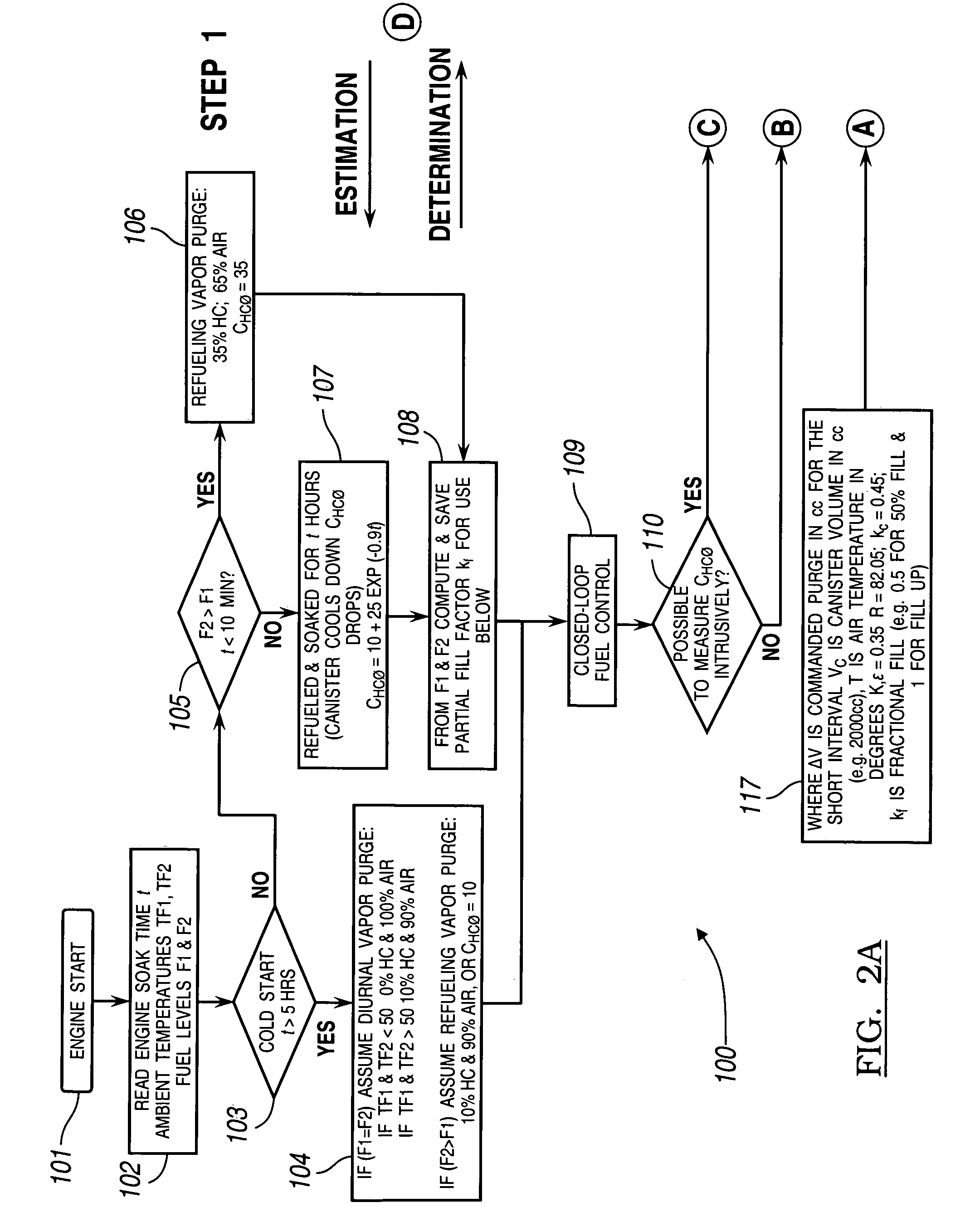
Evap canister purge prediction for engine fuel and air control
ActiveUS20050240336A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove fuel efficiencyElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelWell controlFuel vapor
In a system and a method for purging a vapor storage canister having adsorbed fuel vapor (or hydrocarbon vapor) by drawing air through the storage canister the storage canister being coupled with an engine having a system for controlling the amount of fuel provided to the engine, the amount of fuel vapor in the purge is estimated using a model that predicts fuel vapor concentration in the purge vapor. The engine controller uses the estimated amount of fuel vapor and air brought into the engine from the evaporative vapor storage canister for better control of engine air and fuel during purging.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
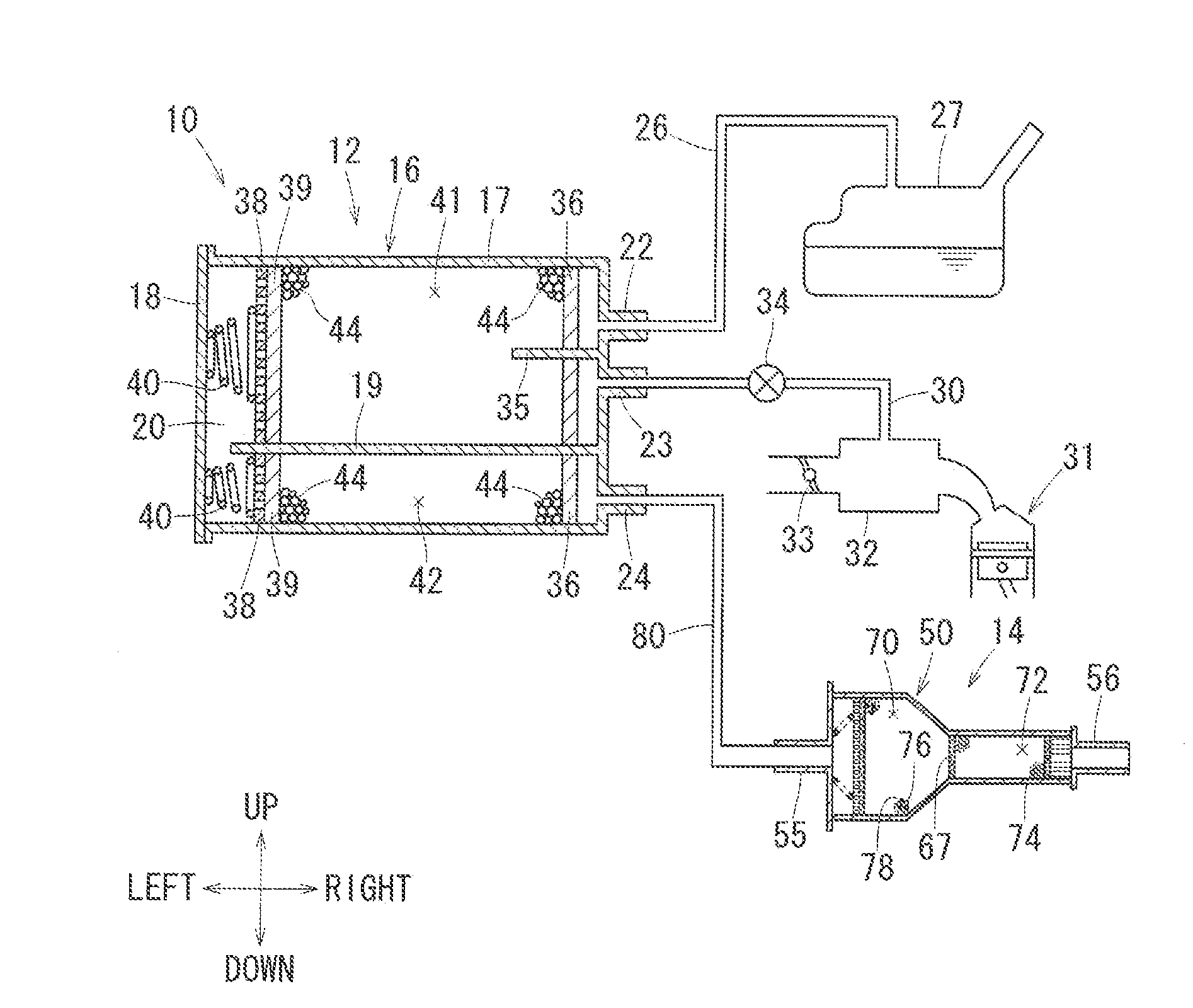
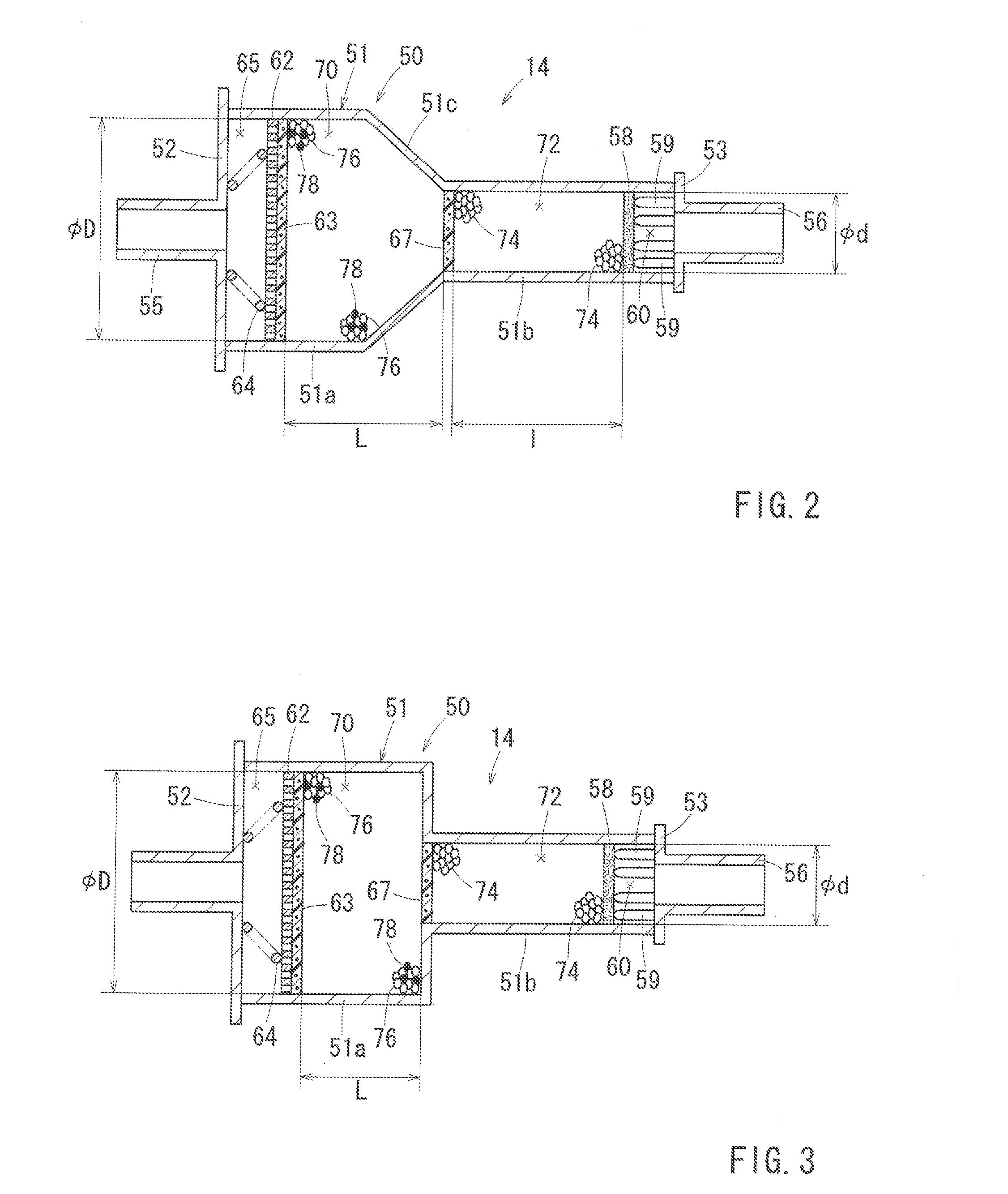
Trap canister capturing fuel vapor
InactiveUS20130186375A1Reduce the amount of fuelReduce pressure lossNon-fuel substance addition to fuelMachines/enginesNuclear engineeringFuel vapor
A trap canister is configured to capture fuel vapor contained in breakthrough gas discharged from an adsorbent canister. The trap canister has a housing defining an adsorption chamber therein, a breathable partition member disposed in the housing and dividing the adsorption chamber into a first chamber and a second chamber, an adsorbent filled in the first chamber and the second chamber, and a latent heal storage material tilled in the first chamber in a mixed manner with the adsorbent. The first chamber is configured to receive breakthrough gas, while the second chamber is configured to communicate with the atmosphere. The first chamber has a cross-sectional area larger than that of the second chamber.
Owner:AISAN IND CO LTD
Intake air control device and internal combustion engine mounting the same
InactiveUS20010027776A1Easy to manufactureEasily dismountedElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
A main passage mounting a throttle valve and an air bypass flow passage for reducing HC emission by promoting atomization of the fuel spray injected from the assembly pipe fuel injector are integrated in a body of an intake air control device arranged upstream of an assembly pipe in one-piece structure to form a unit. Thereby, the intake air control device can be easily manufactured, and easily mounted on and dismounted from the intake air system. An amount of HC emitted at warming-up operation of an internal combustion engine is reduced by efficiently supplying fuel spray injected from an assembly pipe fuel injector at starting and warming-up operations to the internal combustion engine.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Hydrocarbon adsorption method and device for controlling evaporative emissions from the fuel storage system of motor vehicles
ActiveUS7753034B2Reduce releaseReduce the amount of fuelGas treatmentNon-fuel substance addition to fuelSlurryEngineering
The present invention is directed to an evaporative emissions control apparatus for minimizing fuel vapor emissions from a fuel storage system in a vehicle with an internal combustion engine. More specifically, the present invention is directed to an evaporative emissions control apparatus comprising a canister filled with a hydrocarbon adsorbent. The present invention is also directed an evaporative emissions control apparatus comprising a support substrate, which is coated with a hydrocarbon adsorbent slurry.
Owner:BASF CATALYSTS LLC
Evap canister purge prediction for engine fuel and air control
ActiveUS7305975B2Reduce the amount requiredImprove fuel efficiencyElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelWell controlFuel vapor
In a system and a method for purging a vapor storage canister having adsorbed fuel vapor (or hydrocarbon vapor) by drawing air through the storage canister the storage canister being coupled with an engine having a system for controlling the amount of fuel provided to the engine, the amount of fuel vapor in the purge is estimated using a model that predicts fuel vapor concentration in the purge vapor. The engine controller uses the estimated amount of fuel vapor and air brought into the engine from the evaporative vapor storage canister for better control of engine air and fuel during purging.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
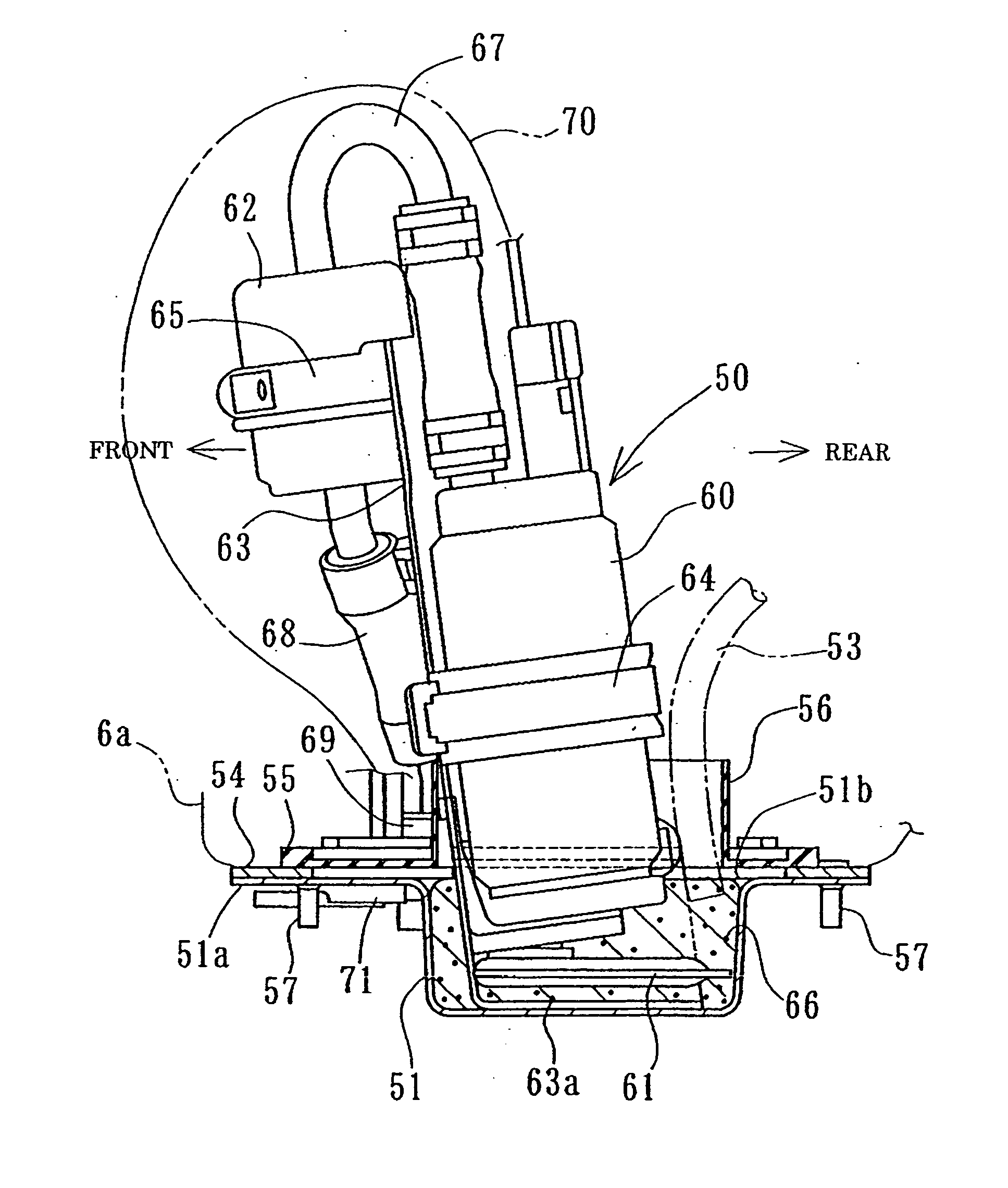
Fuel tank for motorcycle
ActiveUS20050279330A1Reduce the amount of fuelLow costTank vehiclesUsing liquid separation agentFuel tankEngineering
A fuel tank is provided for a motorcycle having a main body part and a downward swelling part that is opened upward and attached to a bottom part of the fuel tank. The inside of the downward swelling part is connected to the inside of the main body part, thereabove. A fuel pump is provided having a suction part disposed in the downward swelling element and a portion above the suction part installed in the main body part of the fuel tank. A fuel retaining member is also provided in the downward swelling part, whereby fuel retained by the fuel retaining member is sucked by the suction part.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
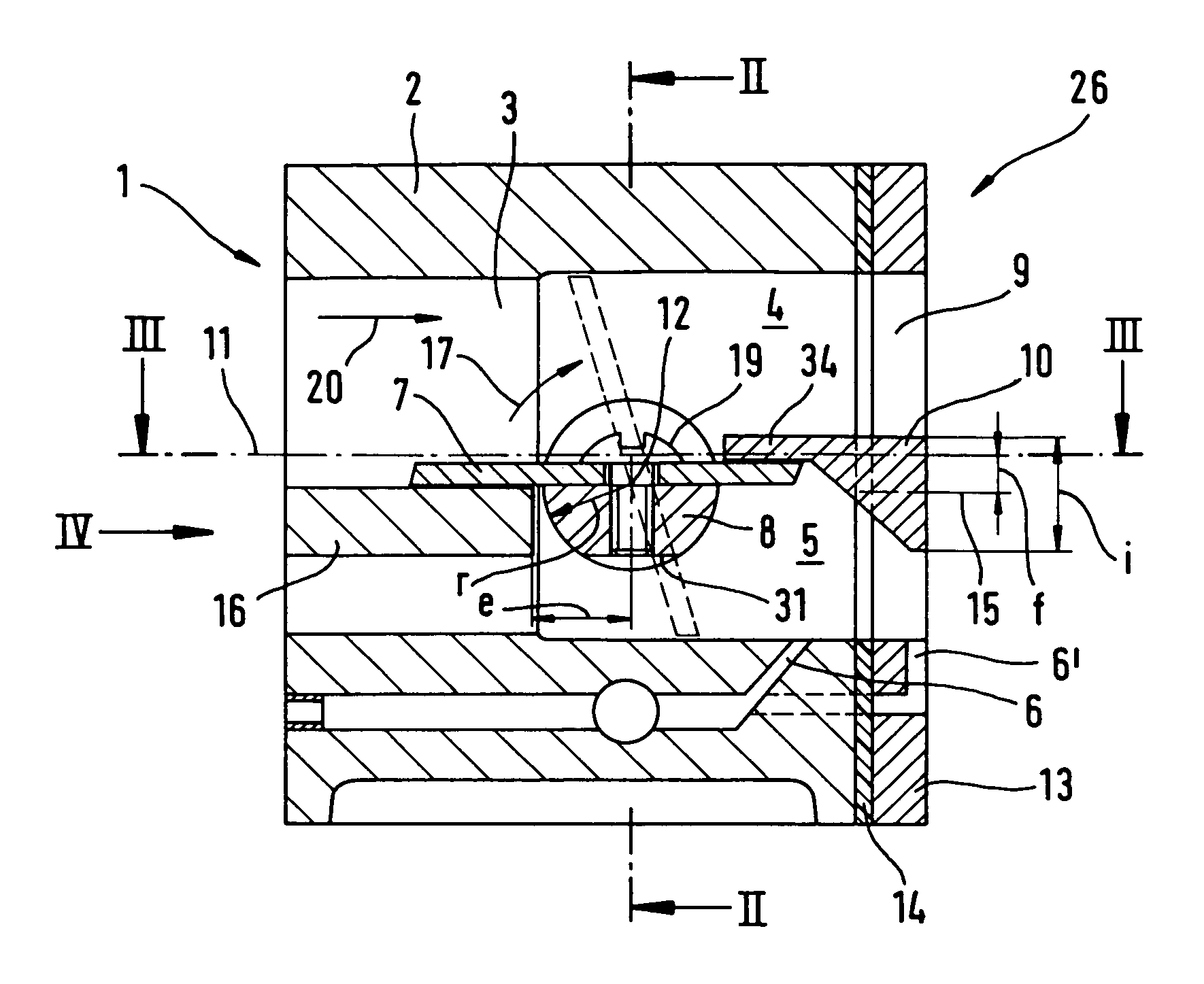
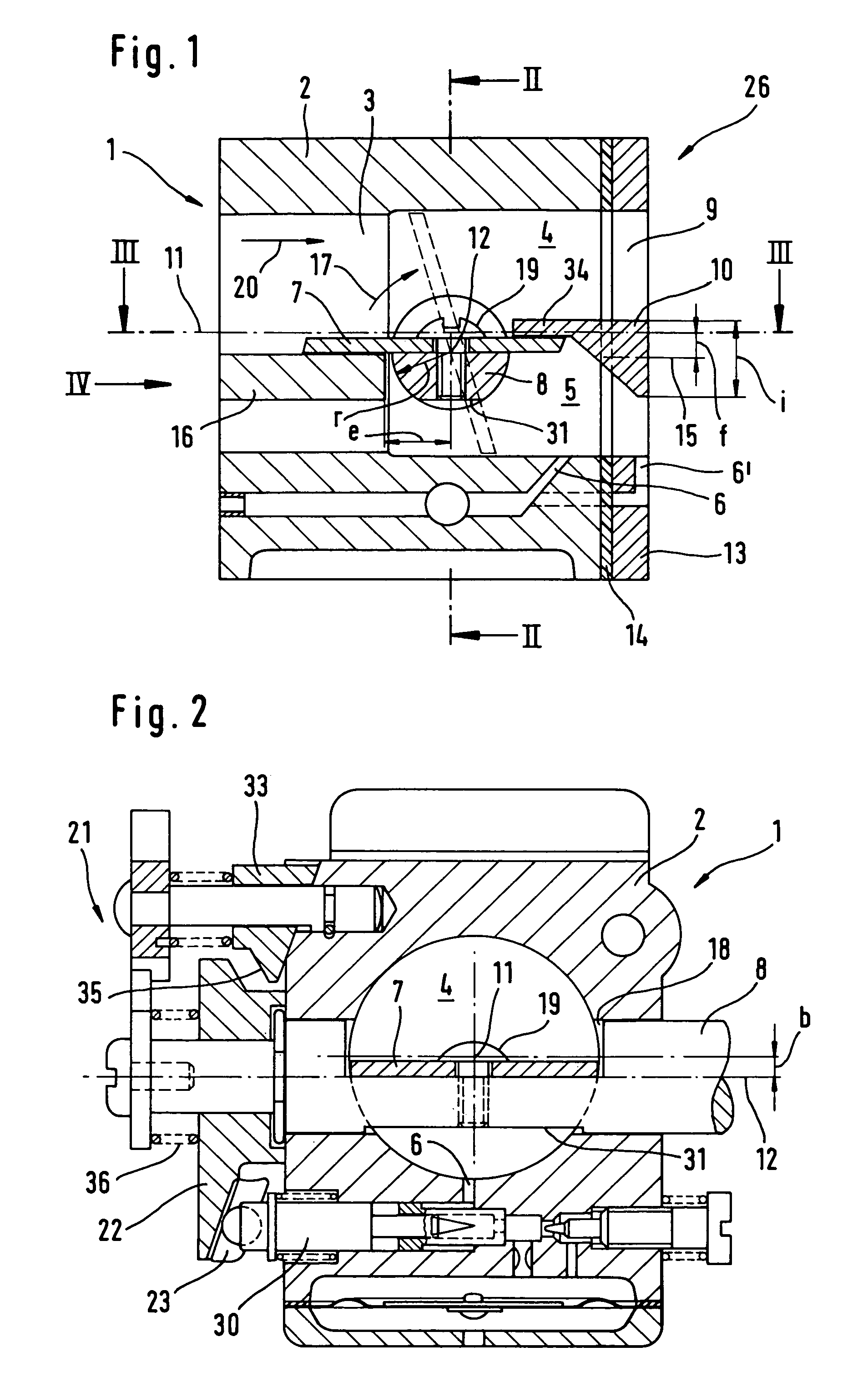
Intake device
ActiveUS7011298B2Improve sealingEasy to assembleLighting and heating apparatusUsing liquid separation agentEngineeringButterfly valve
An intake device having an intake channel that includes an intake channel section is provided. A butterfly valve is pivotably mounted in the intake channel section. A dividing wall is disposed downstream of the butterfly valve and divides the intake channel section into an air duct and a mixture duct. The air duct has a flow cross-section that is greater than the flow cross-section of the mixture duct. A fuel jet opens into the mixture duct.
Owner:ANDREAS STIHL AG & CO KG
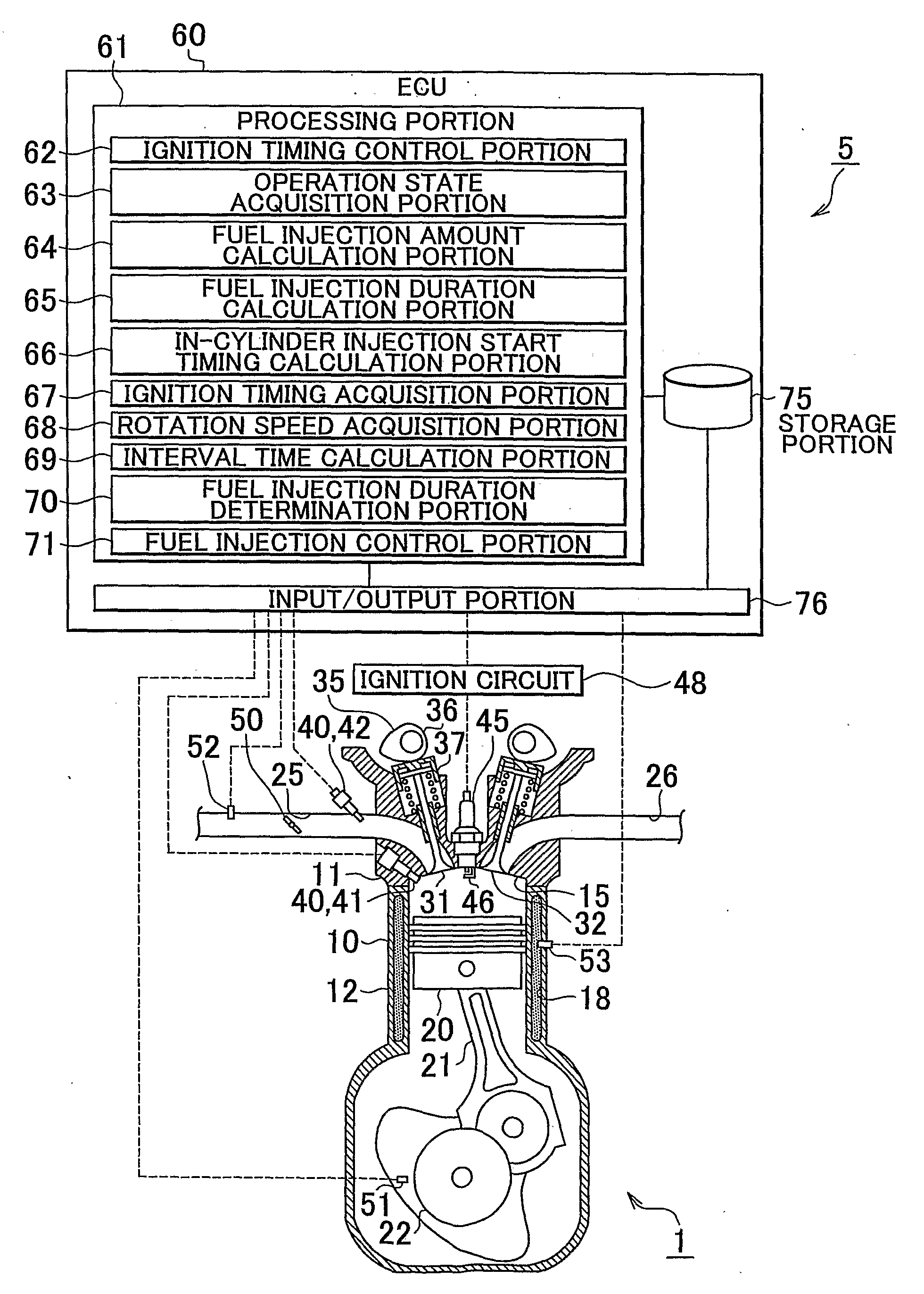
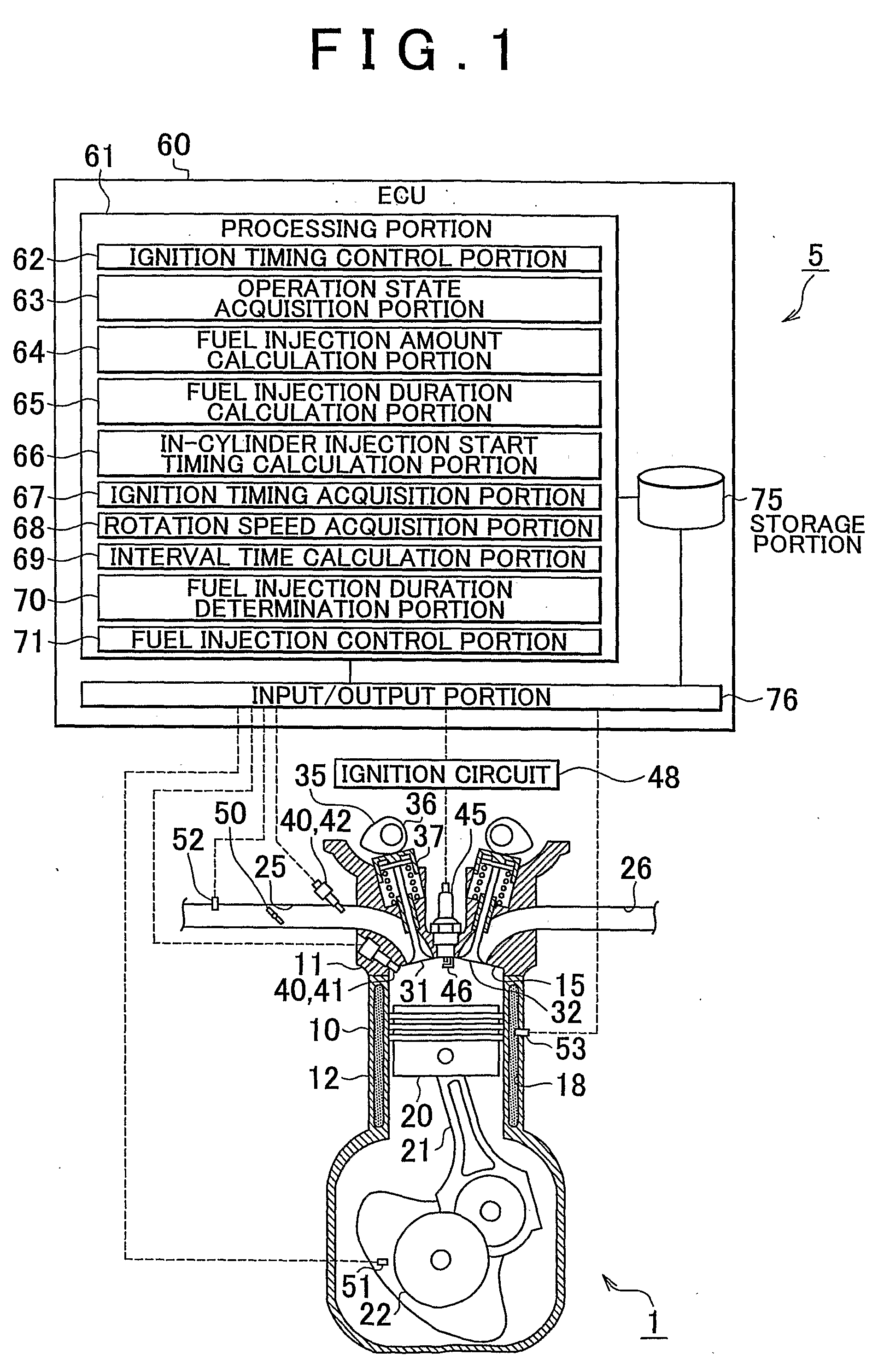
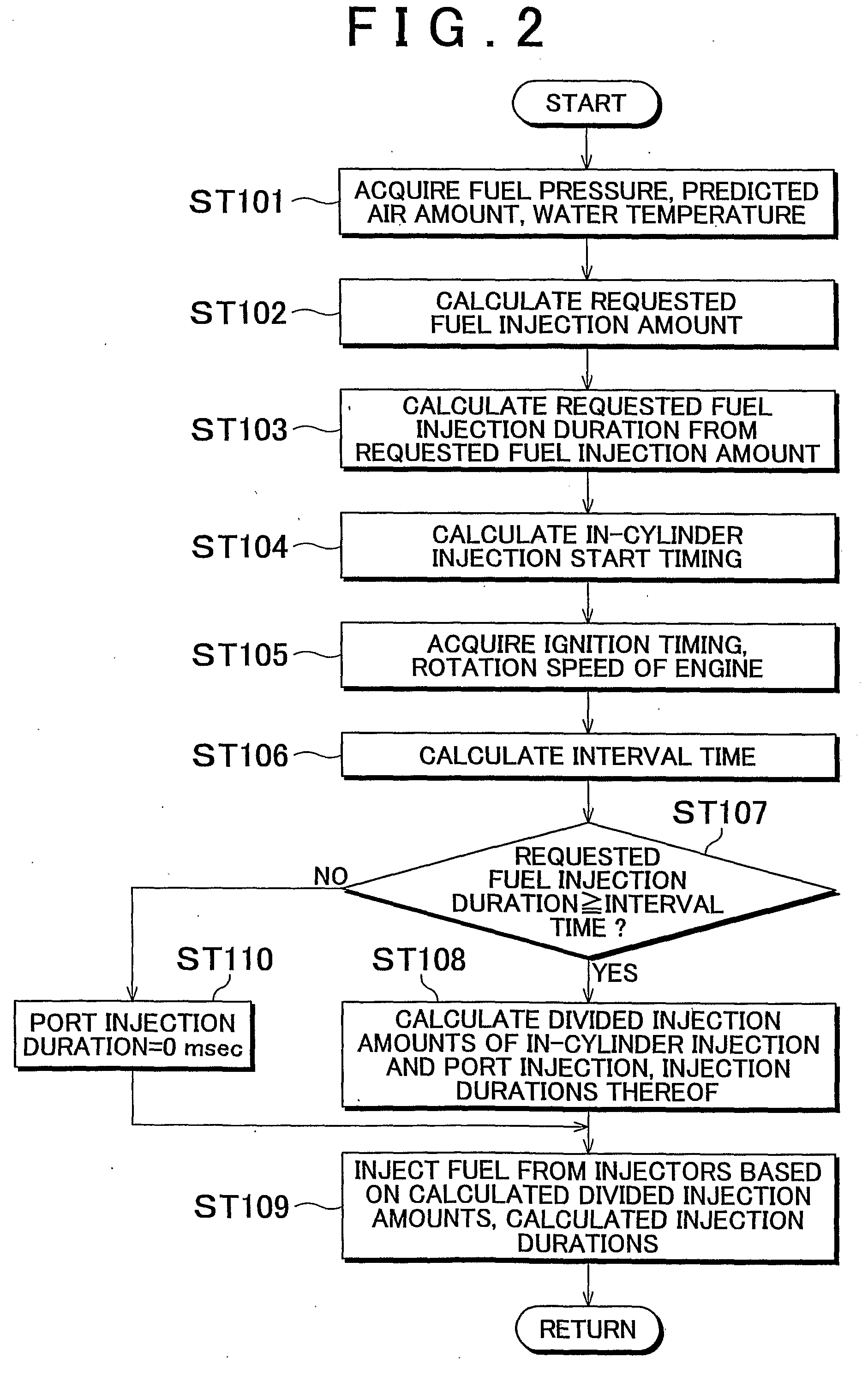
Fuel injection control device of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20090099756A1Emission reductionReduce the amount of fuelElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine including an in-cylinder injection injector and an intake port-injection injector. An ECU includes a fuel injection duration calculation portion that calculates a requested fuel injection duration and a fuel injection control portion that causes the in-cylinder injection injector to inject fuel during the compression stroke during the cold start of the engine, and that causes fuel to be injected also in a manner other than the fuel injection performed by the in-cylinder injection injector during the compression stroke if the requested fuel injection duration is longer than or equal to an interval time. Therefore, even if the requested fuel injection duration is longer than or equal to the interval time, the emissions can be reduced while a startability during a cold start of the internal combustion engine is secured.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
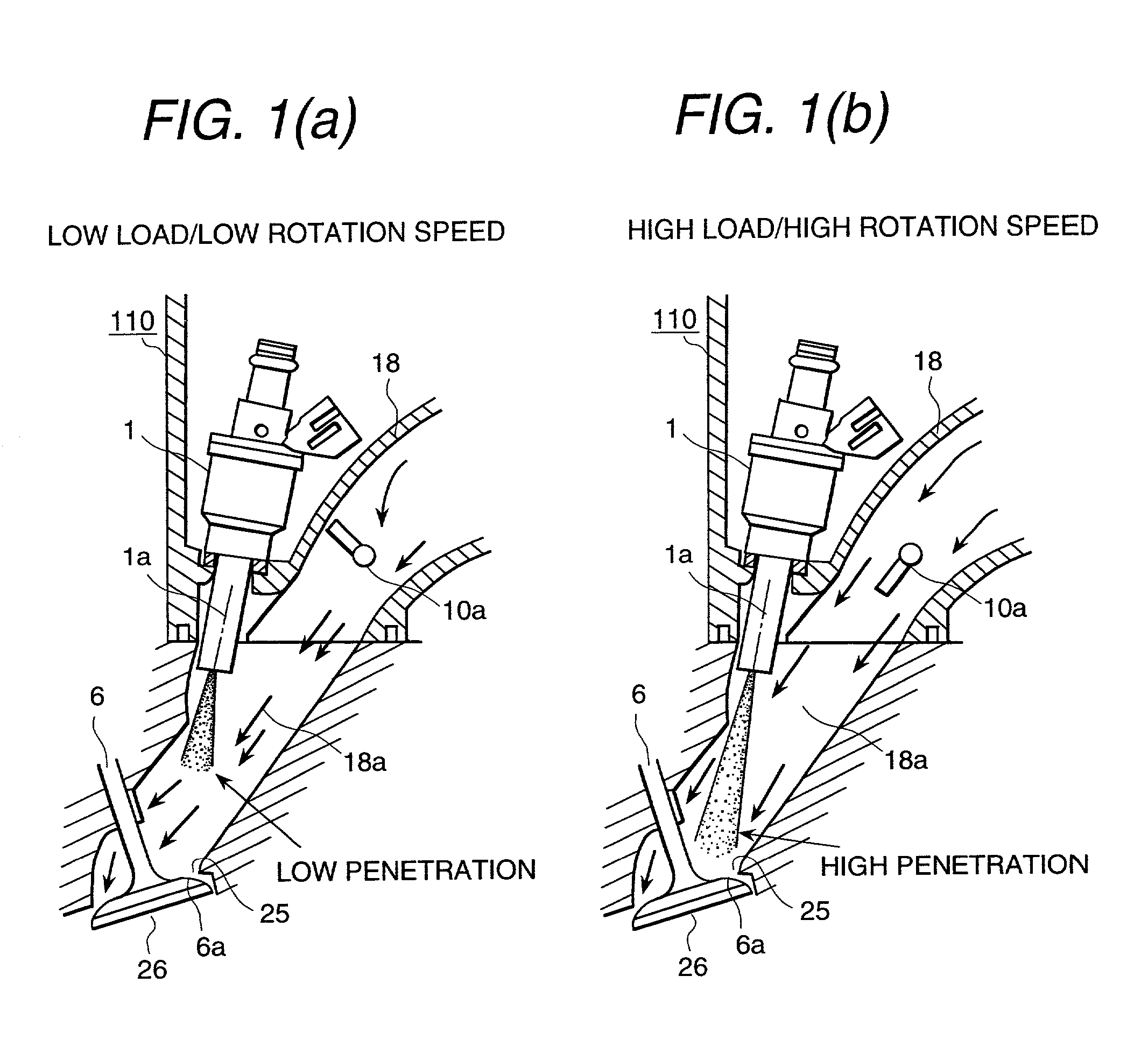
Fuel injection system for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20010023686A1Large penetration forceImprove permeabilityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesPort fuel injectionLow load
In a port fuel injection lean burn engine, attaching of fuel spray onto a wall surface, which is a problem at atomizing injected fuel, is reduced, and the quality and shaping state of the mixed gas in cylinders of the engine is improved. The engine comprises a fuel injector 1; an intake valve 6 for opening and closing an intake port; and an intake air flow control device 10. The injected fuel is shaped in a low penetration fuel spray when the engine is operated in a low load and low rotation speed, and the injected fuel is shaped in a high penetration fuel spray when the engine is operated in a high load and high rotation speed. The fuel is injected in synchronism with the intake stroke of the engine, and is transported by the air flow flowing through the intake air flow control device 10 to suppress attaching of fuel spray onto a wall surface.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Gorski rotary engine
InactiveUS7073477B2Reduce the amount of fuelNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesPower stationCombustion chamber
A rotary engine is provided with solid vanes which extend through the rotor and engage opposing interior wall portions of the stator housing. A series of grooves in the interior wall permit the expanding exhaust gases to by-pass the minimal surface area of vanes proximate to the combustion chamber to engage the larger surface area of a vane which is protruding more significantly from the rotor. This robust rotary engine is preferably made of cast iron, having internal portions coated with ceramic so that it readily can operate at temperatures exceeding 850° F. The heat energy is utilized to obtain maximum productive work rather than being discarded as a waste product as is typical with most state of the art power plants, resulting in an efficiency rating exceeding 60%.
Owner:GORSKI RAYMOND W
Apparatus for recycling wasted heat using waste hot water
InactiveUS20100270009A1Environmentally friendlyReduce the amount of fuelRecuperative heat exchangersSewerage structuresCharge and dischargeWater supply
The present invention relates to an apparatus for recycling wasted heat using waste hot water that includes: a tub that charges and discharges waste hot water; a heat exchange unit that transfers the heat of waste hot water to cold water supplied to a shower bat; and an upper cover that the open upper portion of the tub, and is friendly to the environment by reducing the amount of fuel consumed to supply hot water and it is possible to reduce the fuel cost by the reduced amount of fuel consumption.
Owner:GOMYUNG ENERTECH
Abnormality determination system for multi-cylinder internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20120022772A1Increase opportunitiesReliably determinedElectrical controlDigital data processing detailsExternal combustion engineFuel tank
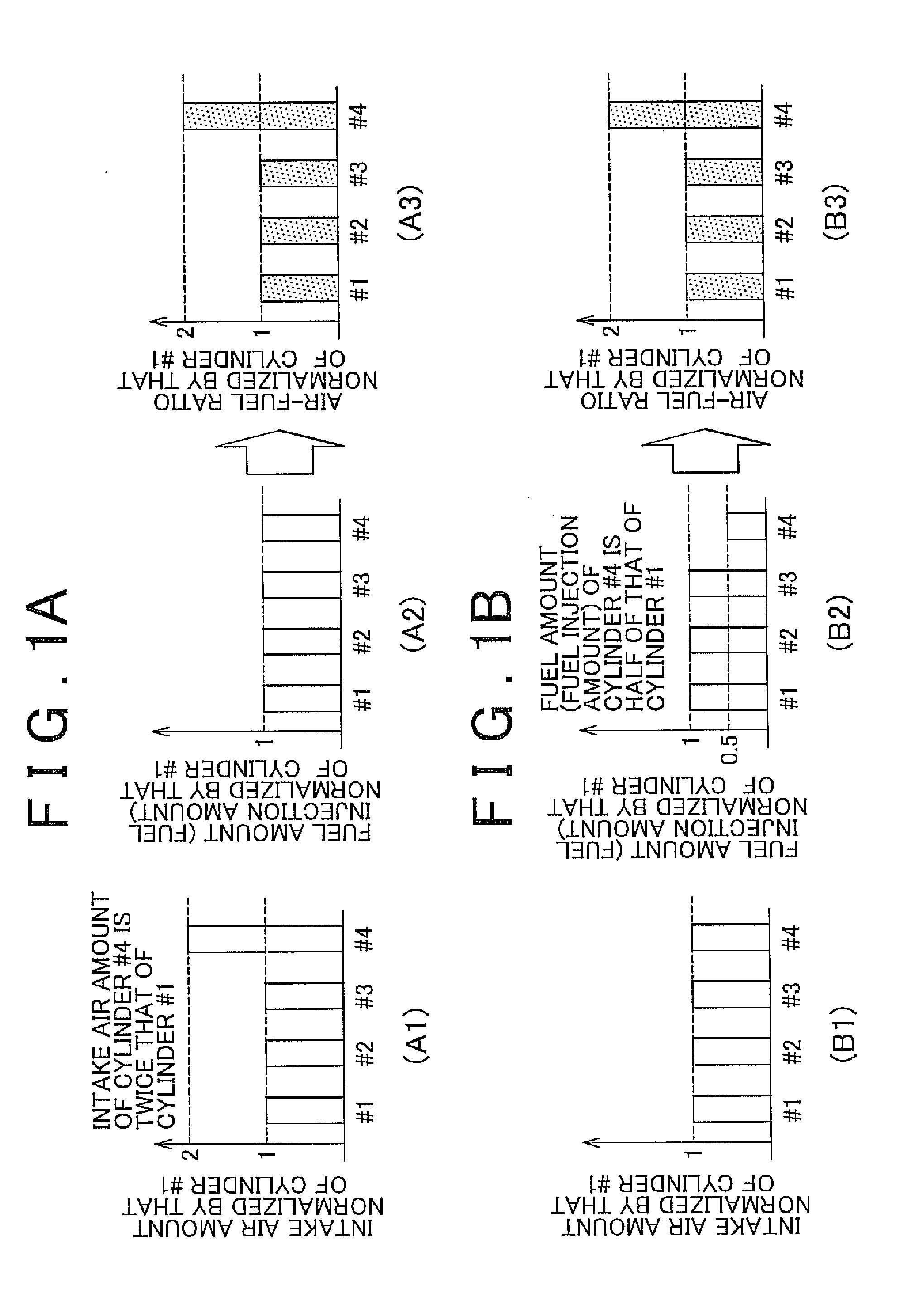
When the ratio of the amount of vaporized fuel (purge amount) to be introduced into an intake passage of an engine from a fuel tank through a purge passage pipe, a purge control valve, etc. to the total amount of fuel (total fuel amount) to be supplied to the engine is large, an abnormality determination system acquires, as a parameter Pon, the air-fuel ratio imbalance index value that increases as the difference between the air-fuel ratios of the respective cylinders increases. When the purge amount is small relative to the total fuel amount, the determination system acquires the air-fuel ratio imbalance index value as a parameter Poff. When the difference between the parameters Pon and Poff is less than a predetermined value and at least one of these parameters is greater than a predetermined threshold value, the determination system determines that an inter-cylinder air intake amount variation abnormality is occurring.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Fuel pressure control apparatus of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6450147B2Suppress or avoid so-called "ovReduce the amount of fuelElectrical controlLow-pressure fuel injectionExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Fuel nature measuring device of internal combustion engine and internal combustion engine having the same
ActiveUS7272485B2Reduce the amount of fuelReduce exhaust emissionsAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlMeasurement deviceDifferential pressure
A fuel nature measuring device for measuring the nature of fuel stored in a fuel tank includes a measurement passage, a gas flow generator, a pressure detector, an concentration operator, a temperature detector, and a volatility calculator. The measurement passage has an orifice. The gas flow generator generates gas flow in the measurement passage. The pressure detector detects a differential pressure between opposite ends of the orifice. The concentration operator determines a concentration of evaporated fuel in the fuel tank based on the differential pressure detected when the opposite ends of the measurement passage communicate with the fuel tank and the fuel flows in the measurement passage. The temperature detector determines a temperature of the fuel in the fuel tank. The volatility calculator calculates a volatility of the fuel in the fuel tank based on the concentration of the evaporated fuel and the temperature of the fuel in the tank.
Owner:NIPPON SOKEN +1
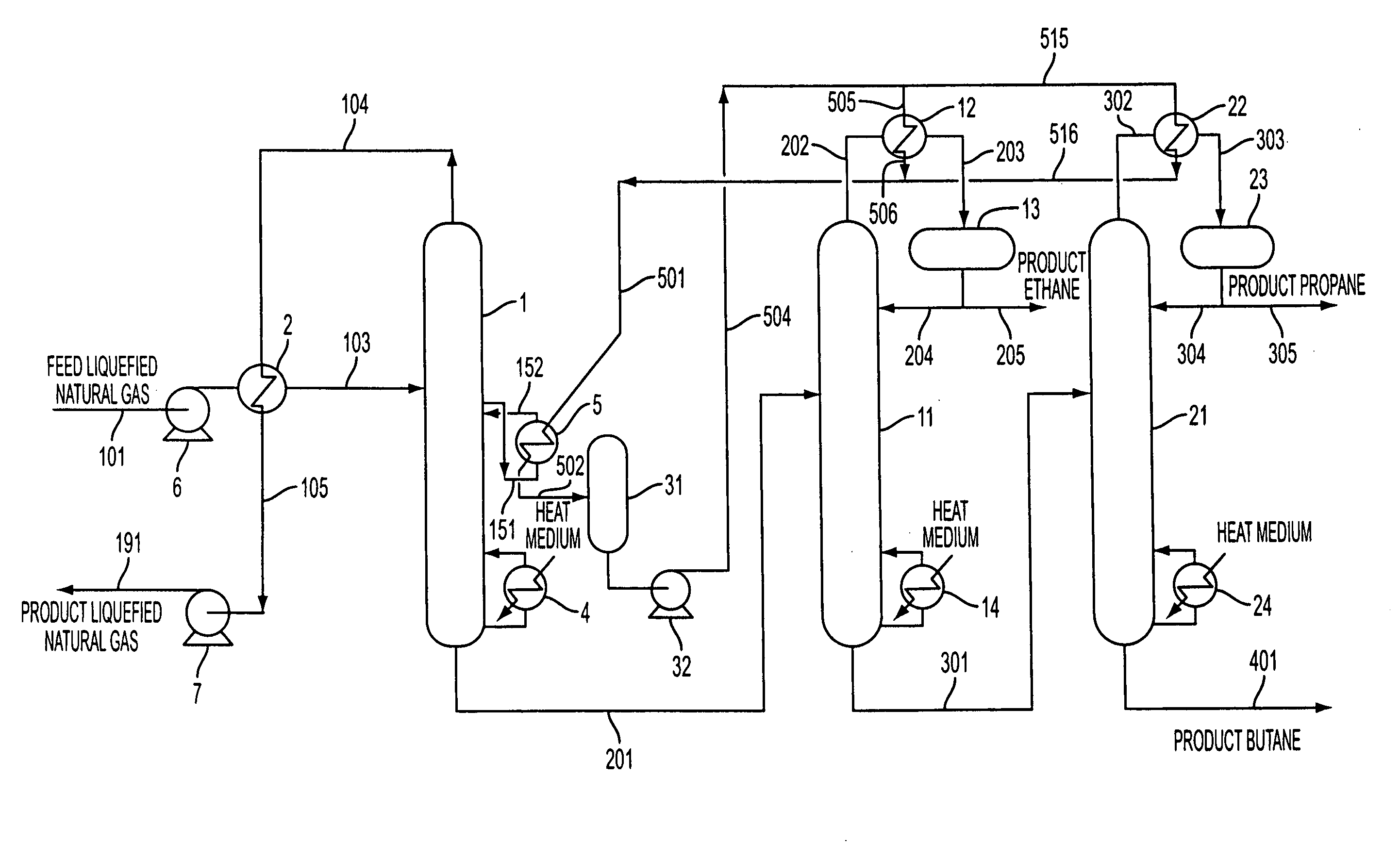
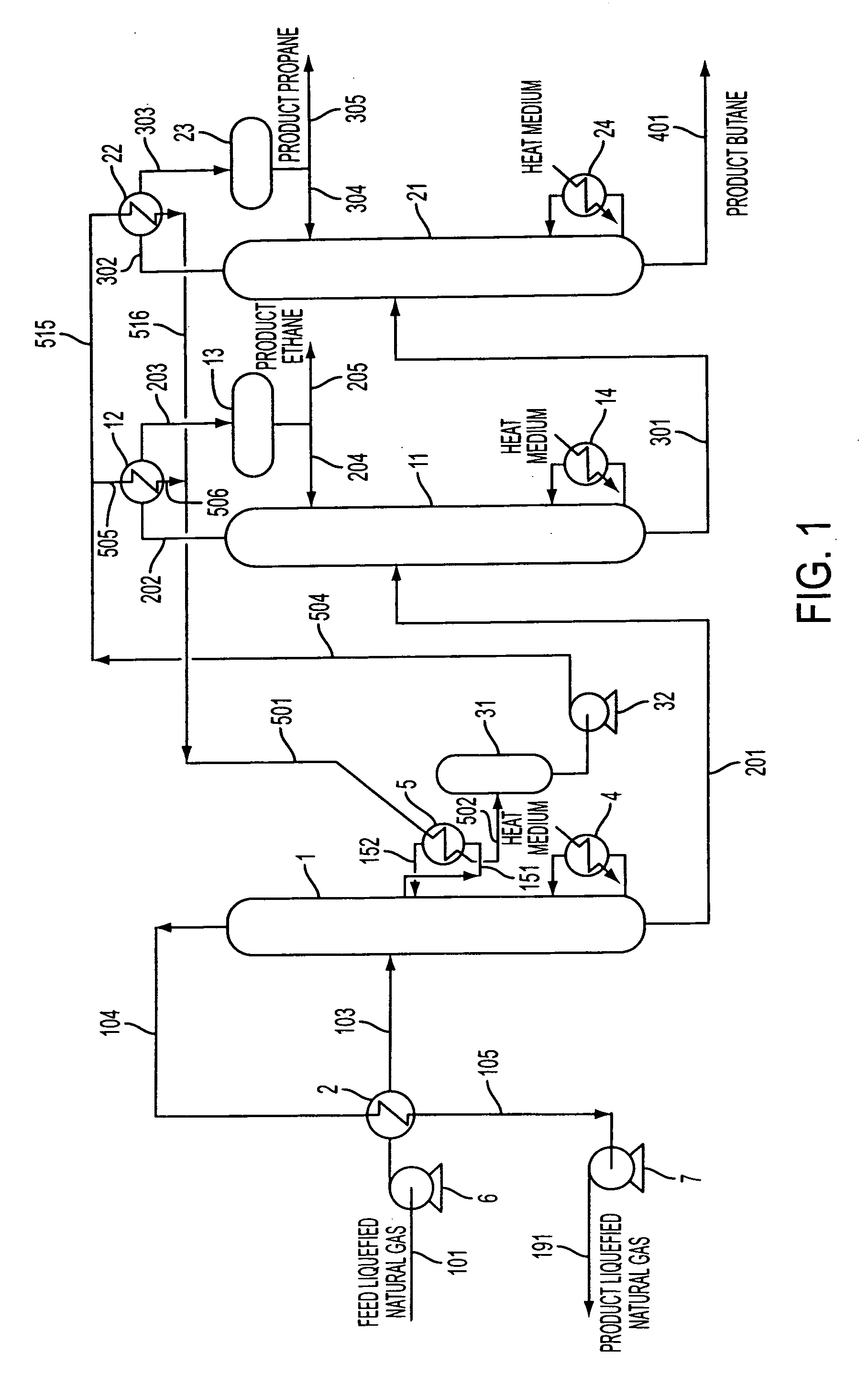
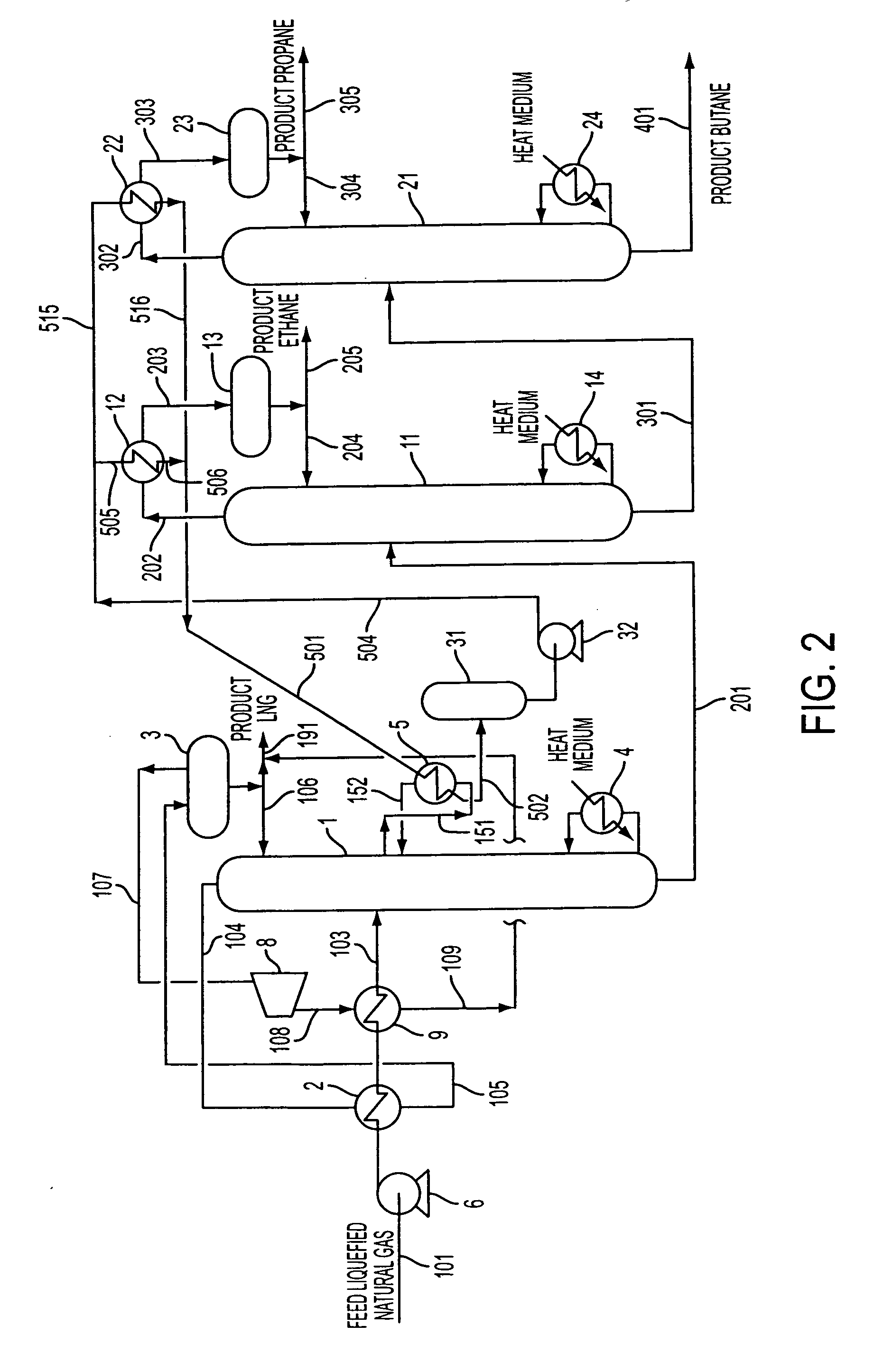
Process and apparatus for separation of hydrocarbons from liquefied natural gas
ActiveUS20060277943A1Weaken energyReduce the amount of fuelSolidificationLiquefactionDistillationHydrocarbon
A process for separating hydrocarbons from an LNG, including the steps of: distilling a feed LNG in a first distillation column to separate it into a fraction enriched with methane and a fraction enriched with components heavier than methane; distilling the fraction enriched with components heavier than methane in a second distillation column to separate it into a fraction enriched with ethane and a fraction enriched with components heavier than ethane; recovering the cryogenic heat of the feed LNG to be fed into the first distillation column or of the liquid inside the first distillation column by using a heat transfer medium; and cooling the overhead gas of the second distillation column by using the heat transfer medium which has recovered the cryogenic heat to condense at least part of the overhead gas of the second distillation column. An apparatus for carrying out this process.
Owner:TOYO ENG CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com