Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
69results about How to "Reduce Optical Noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
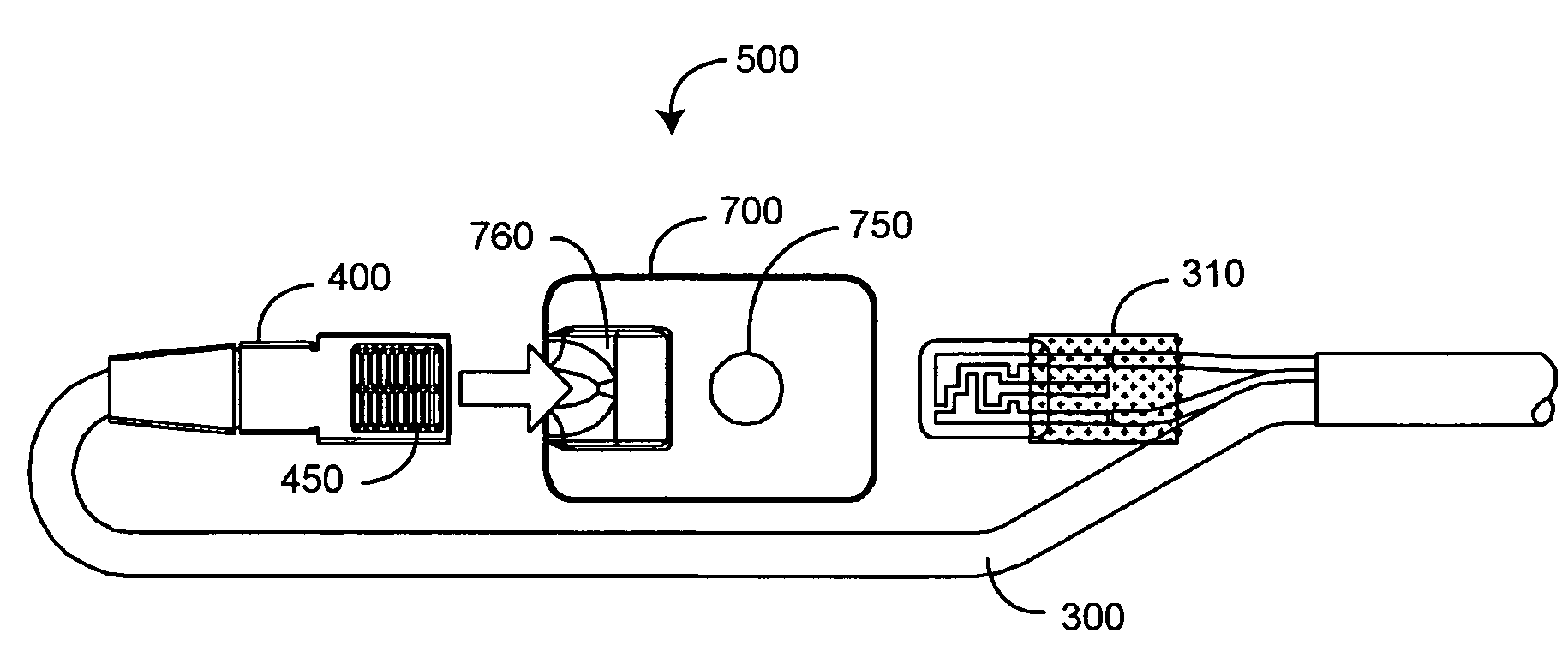
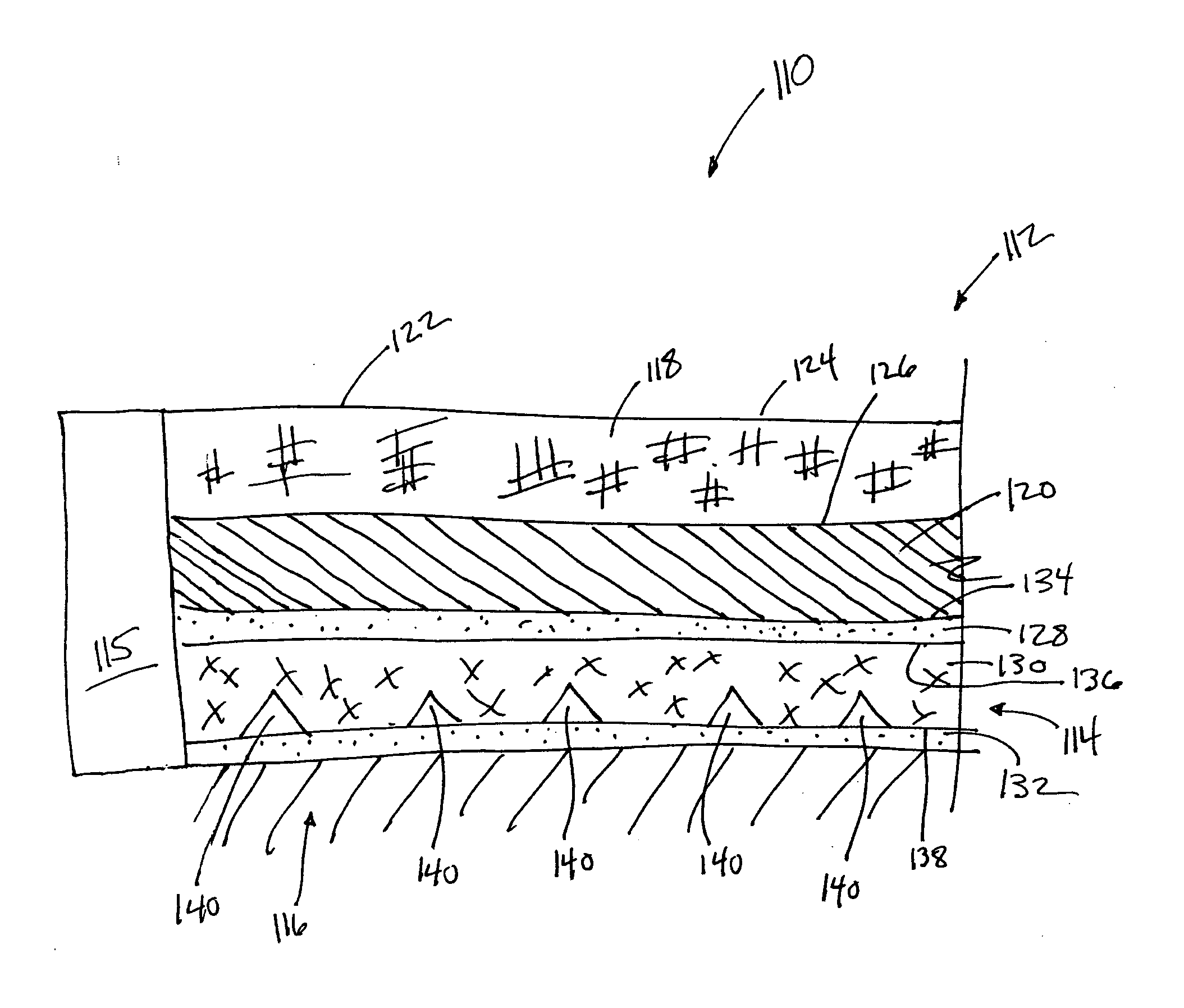
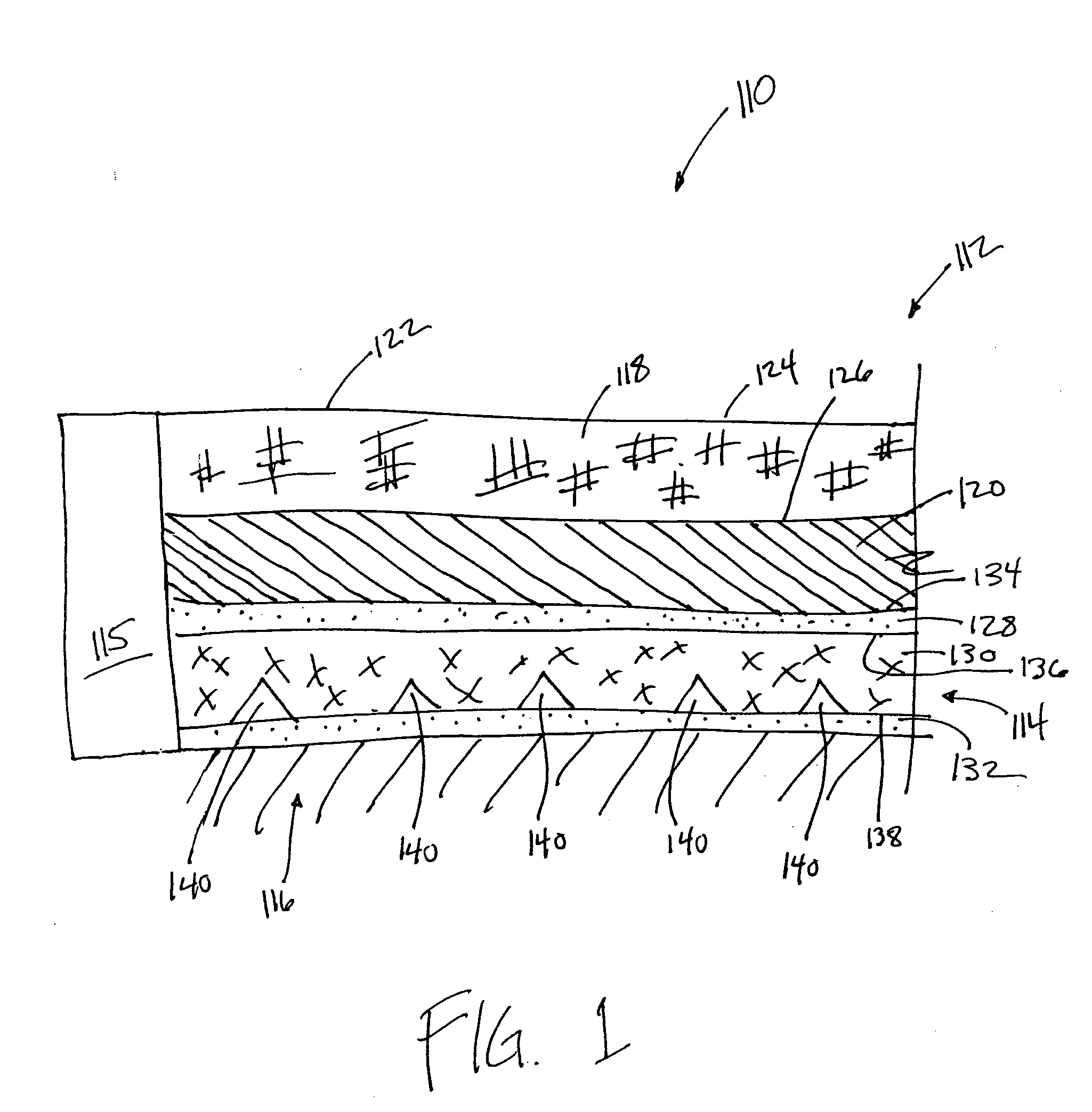
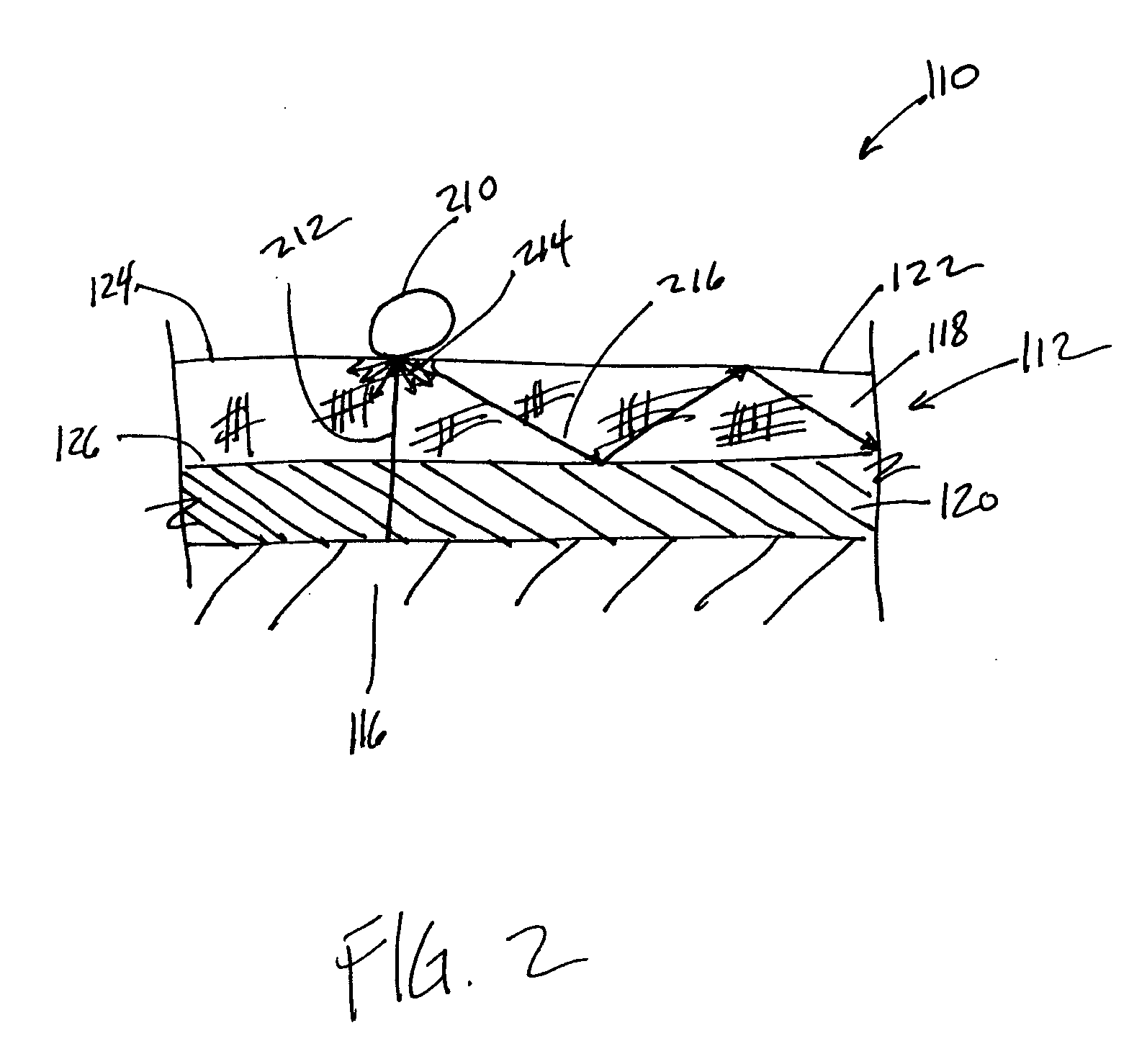
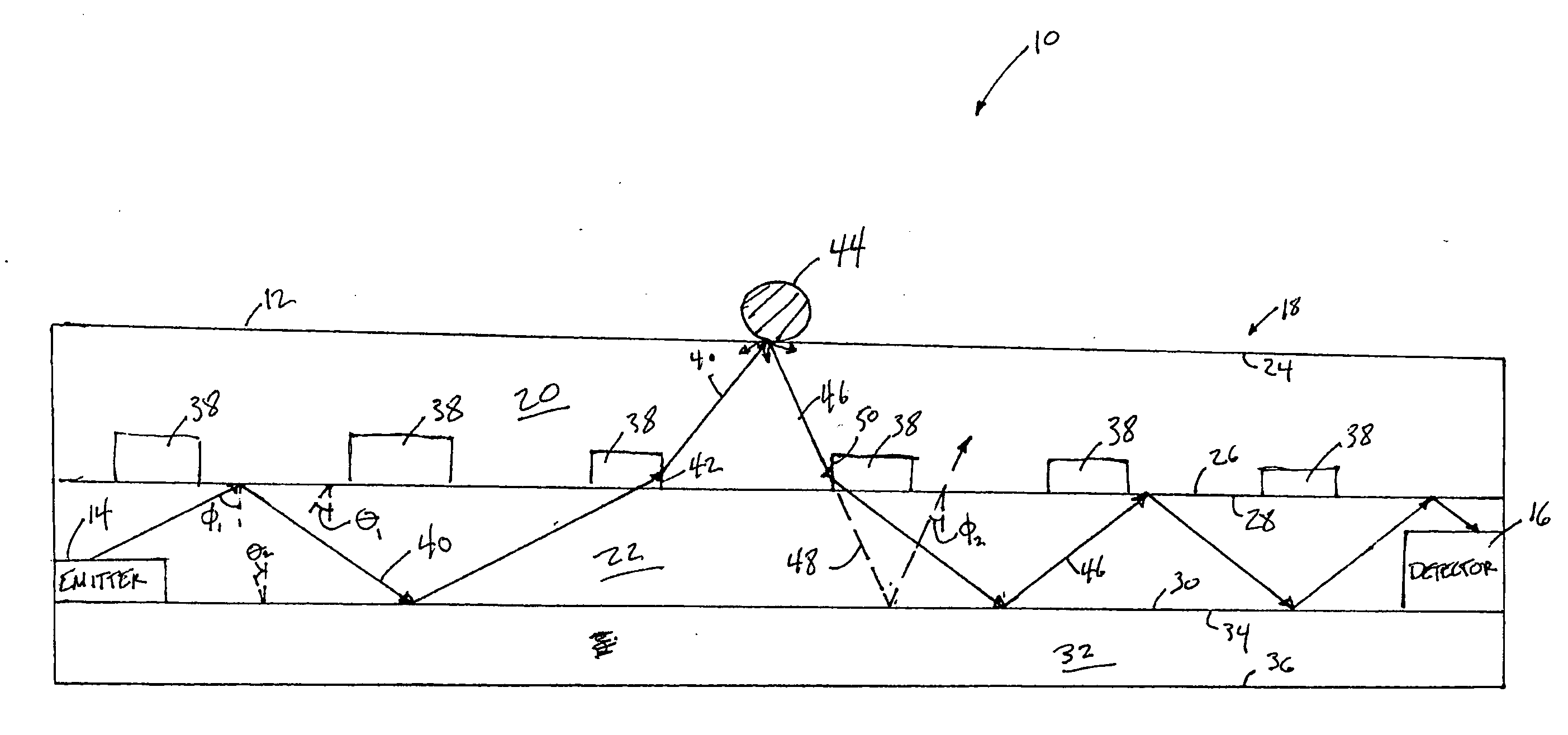
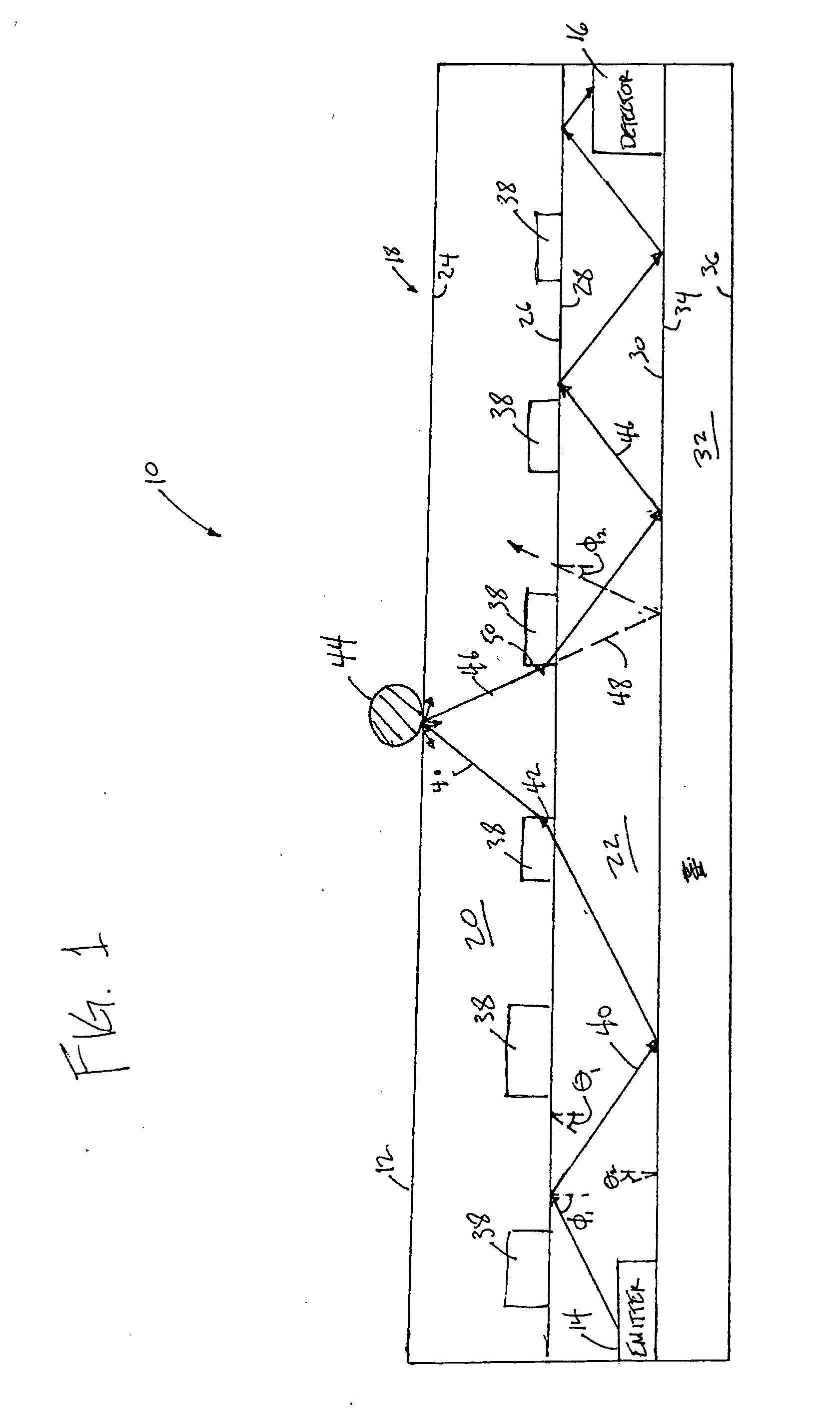
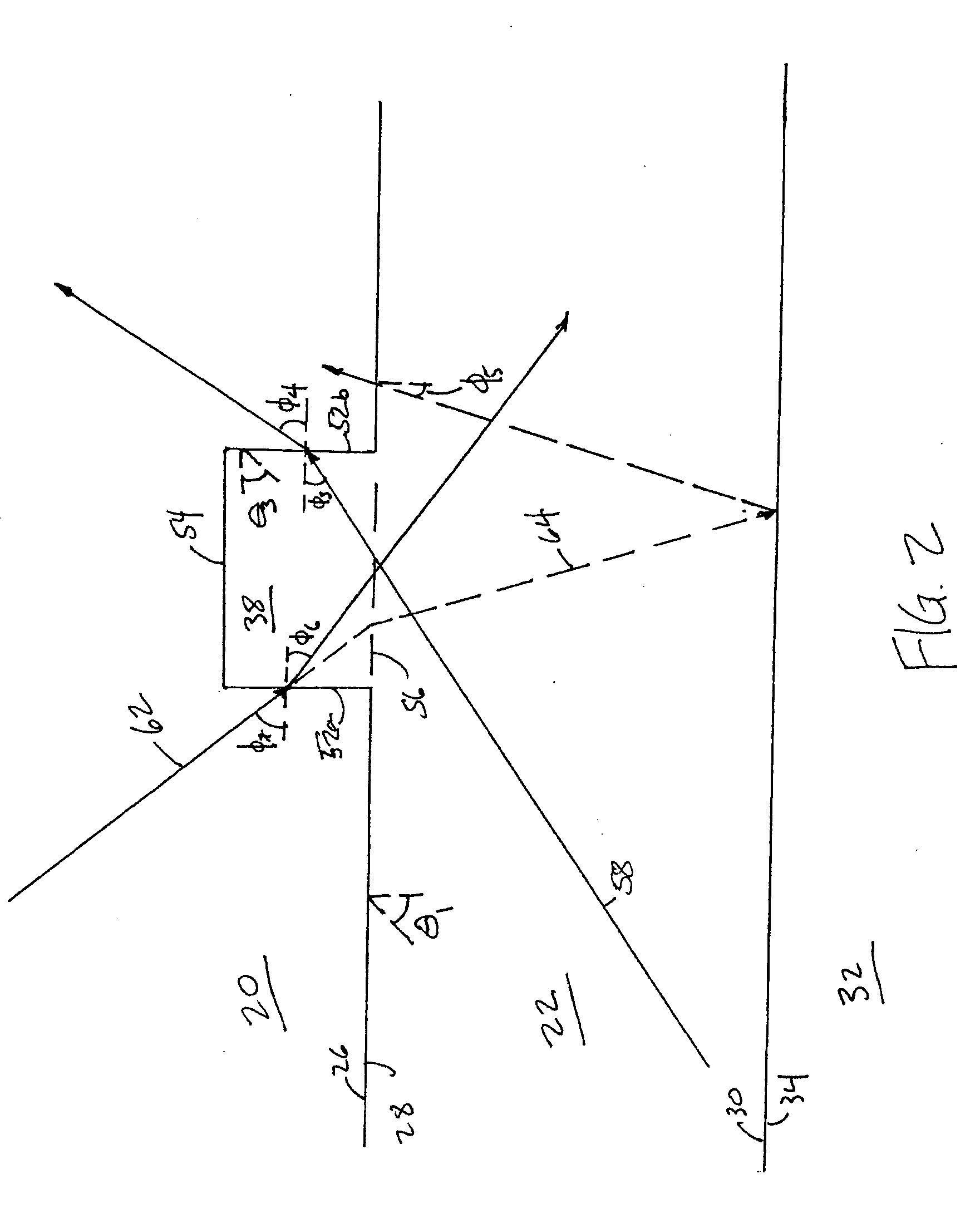
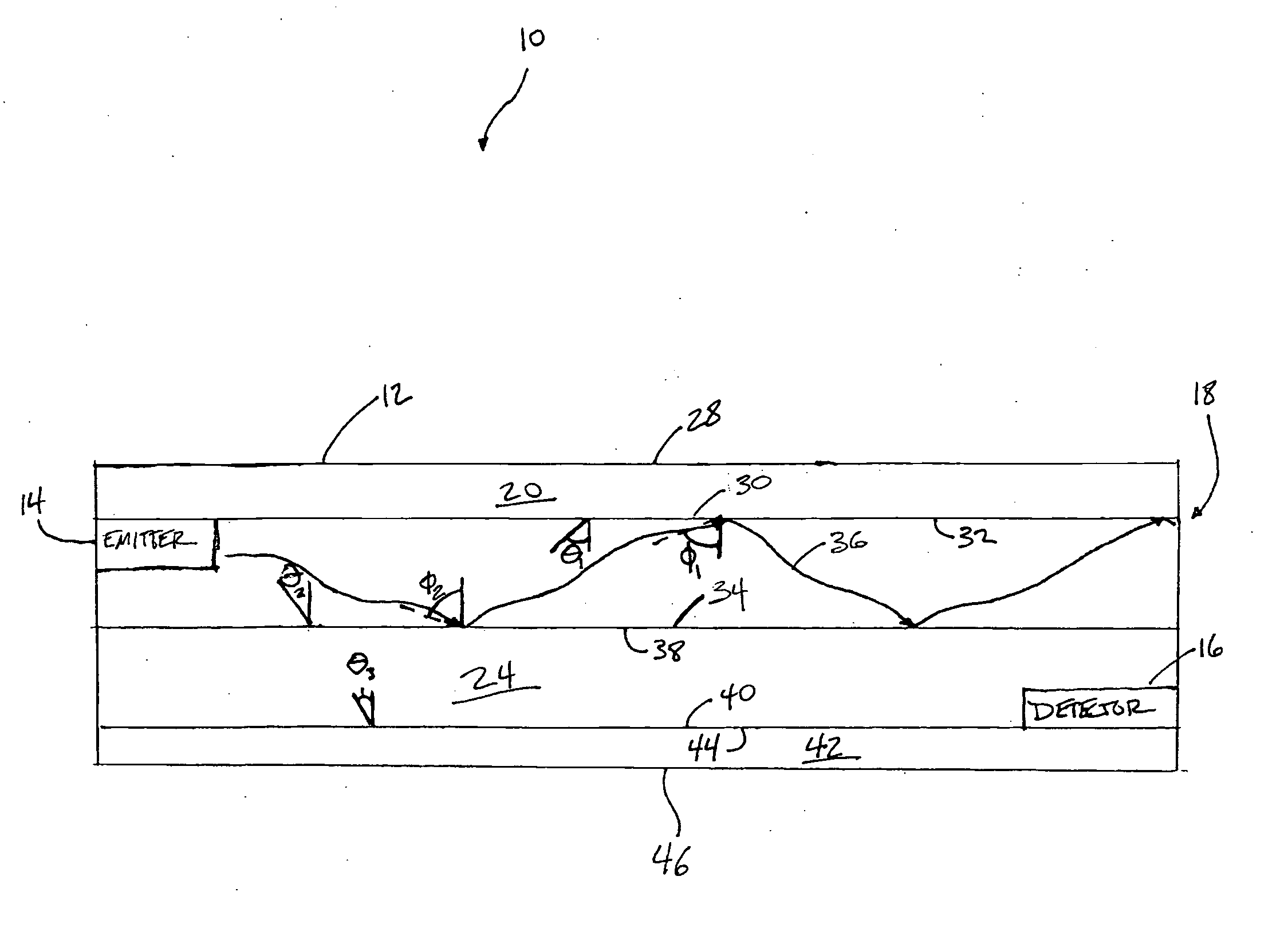
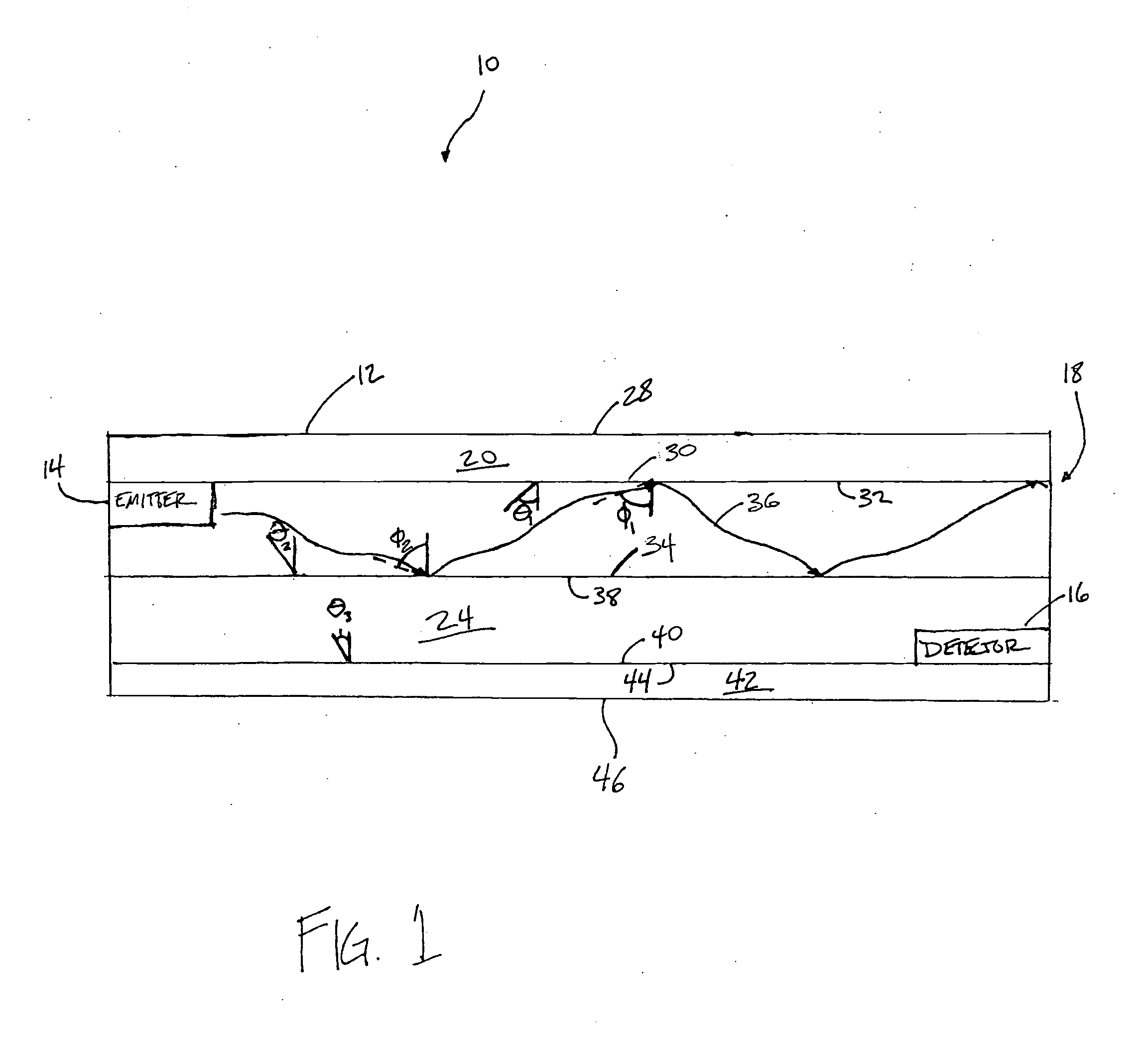
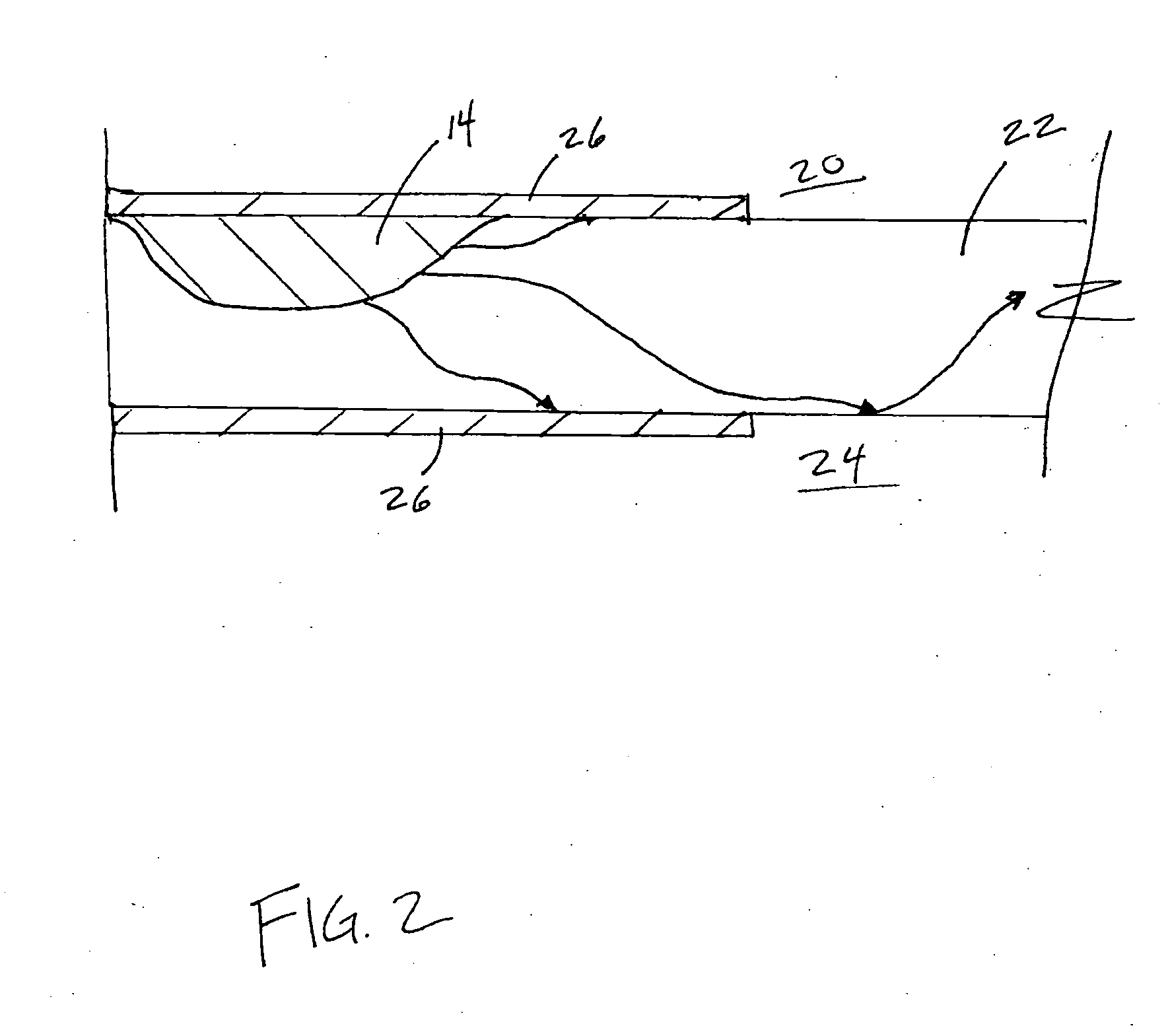
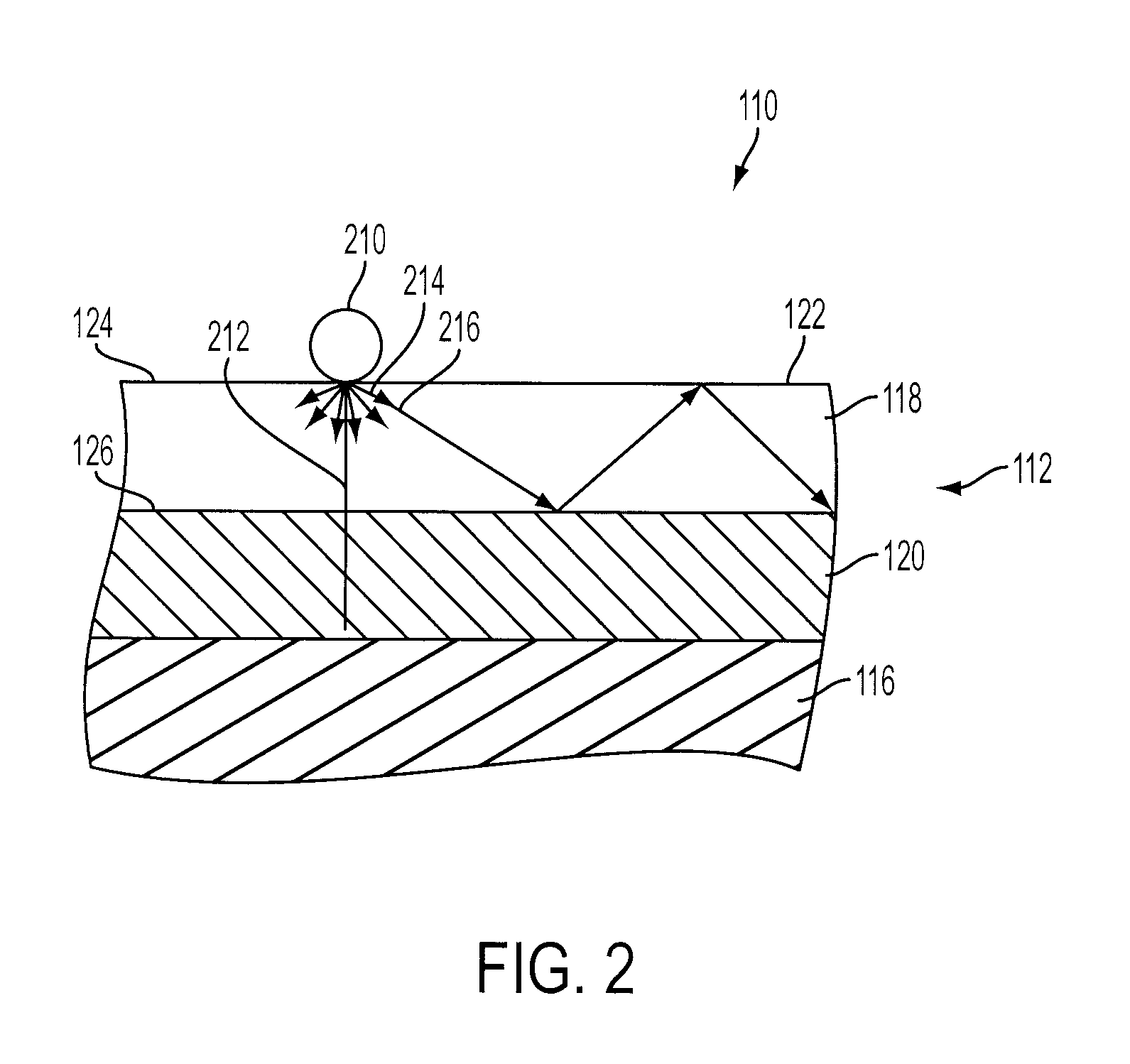
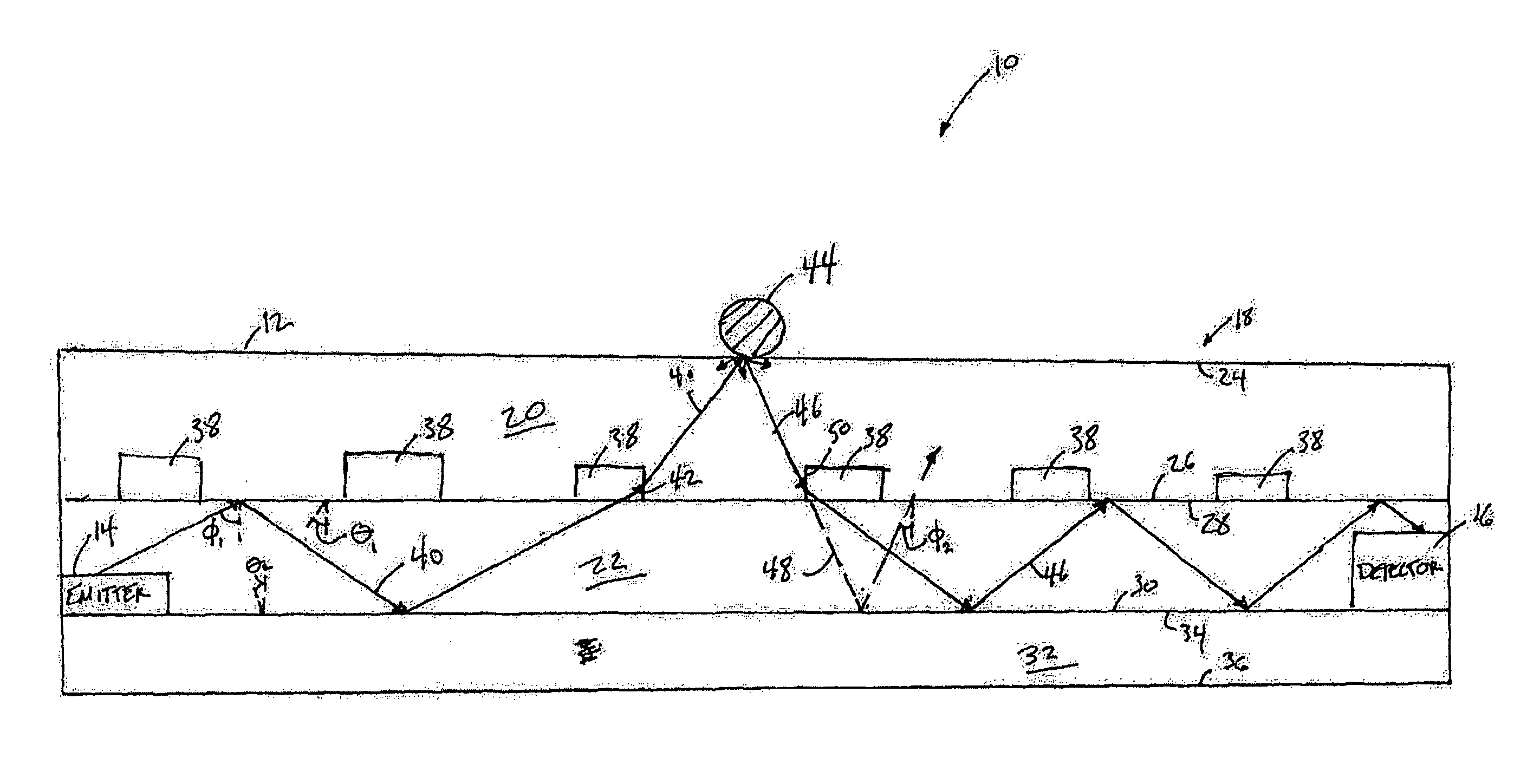
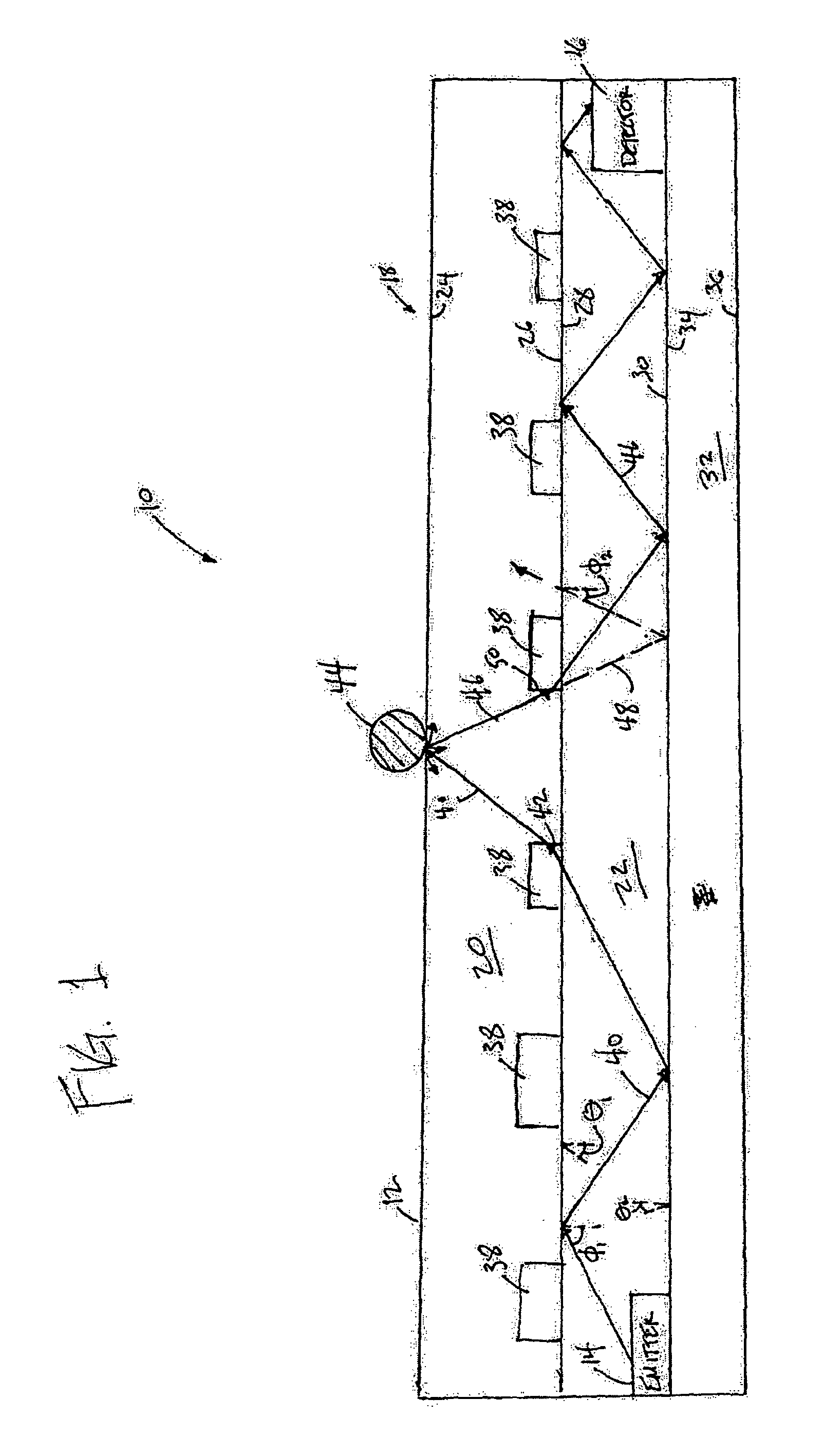
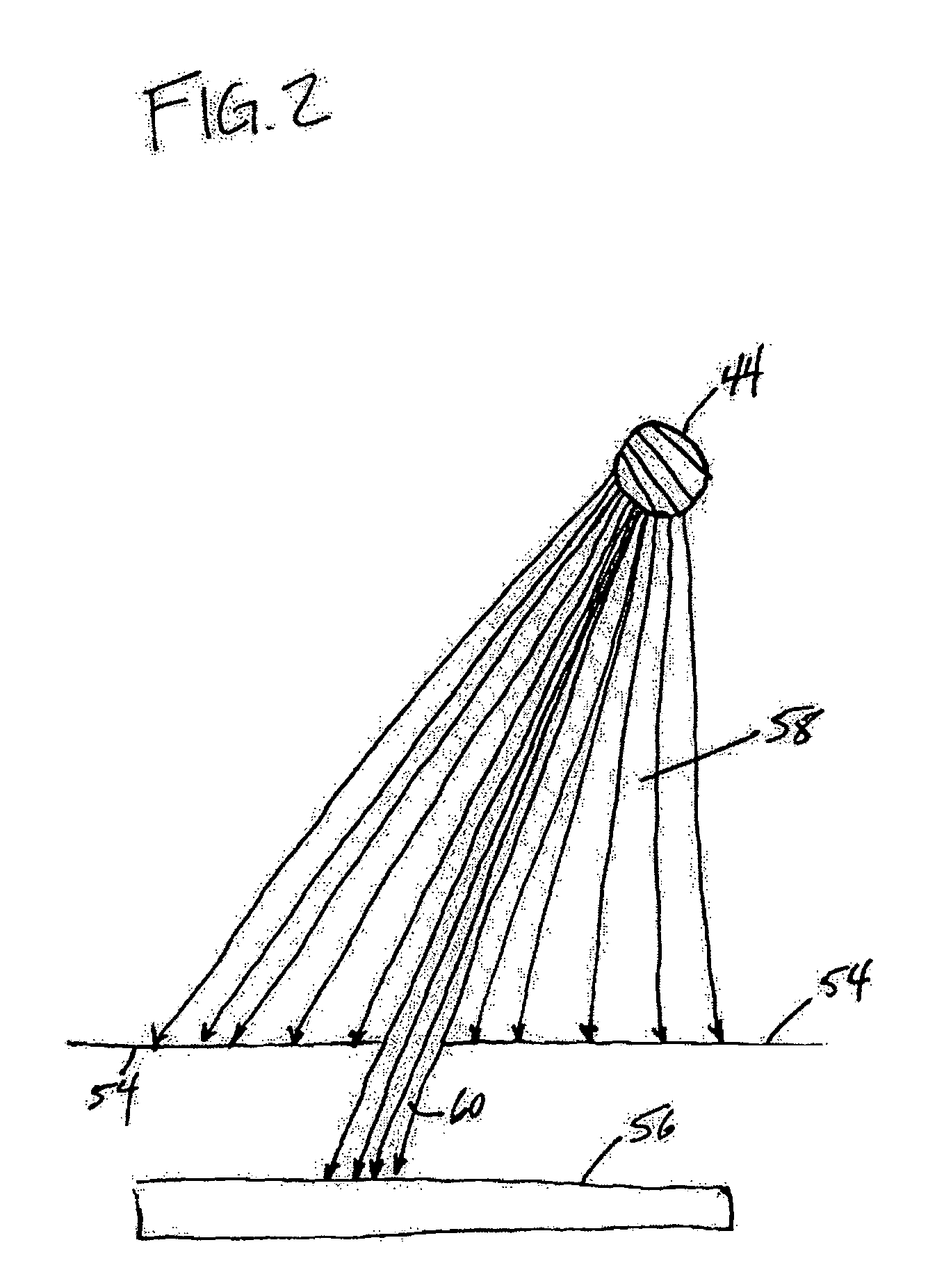
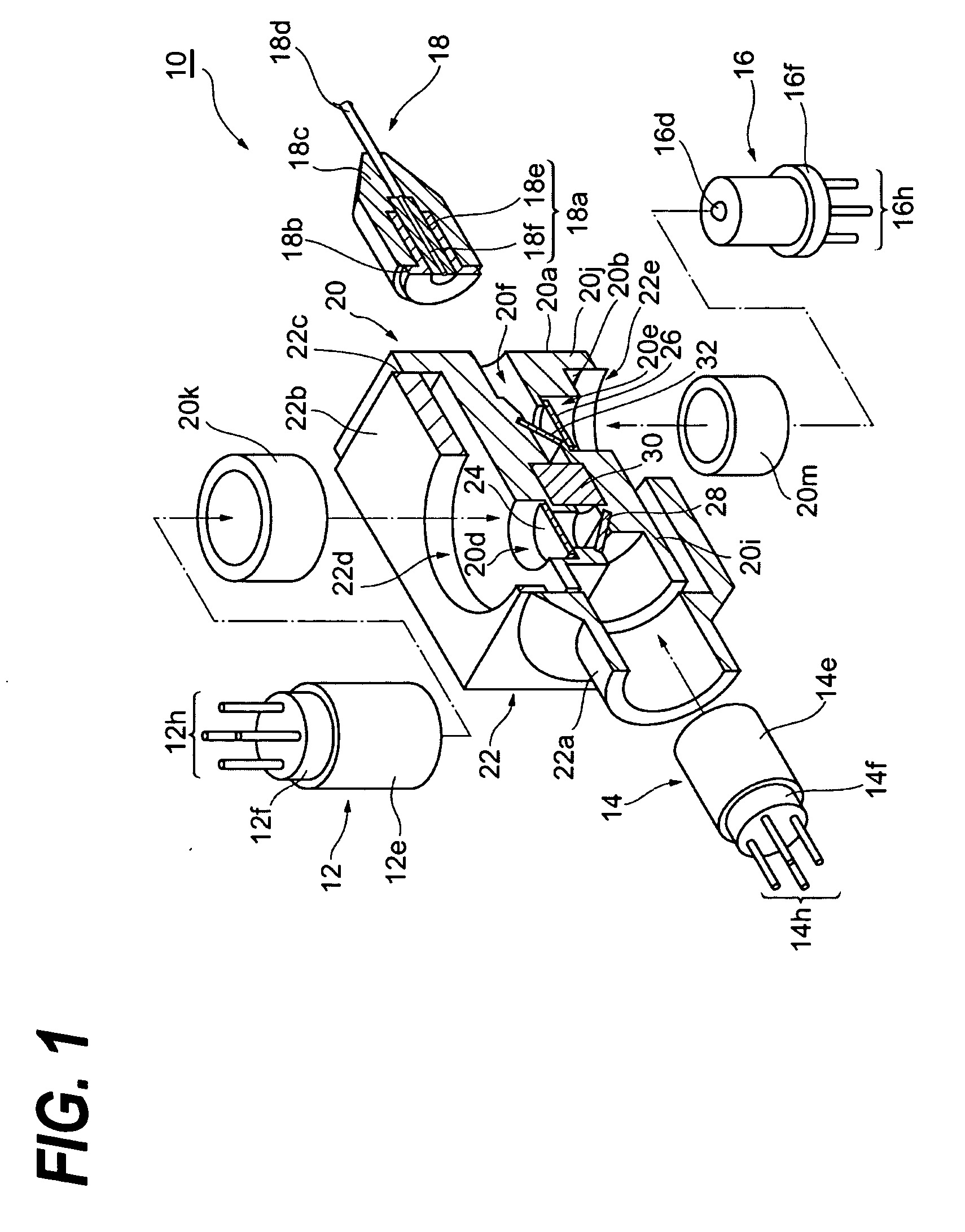
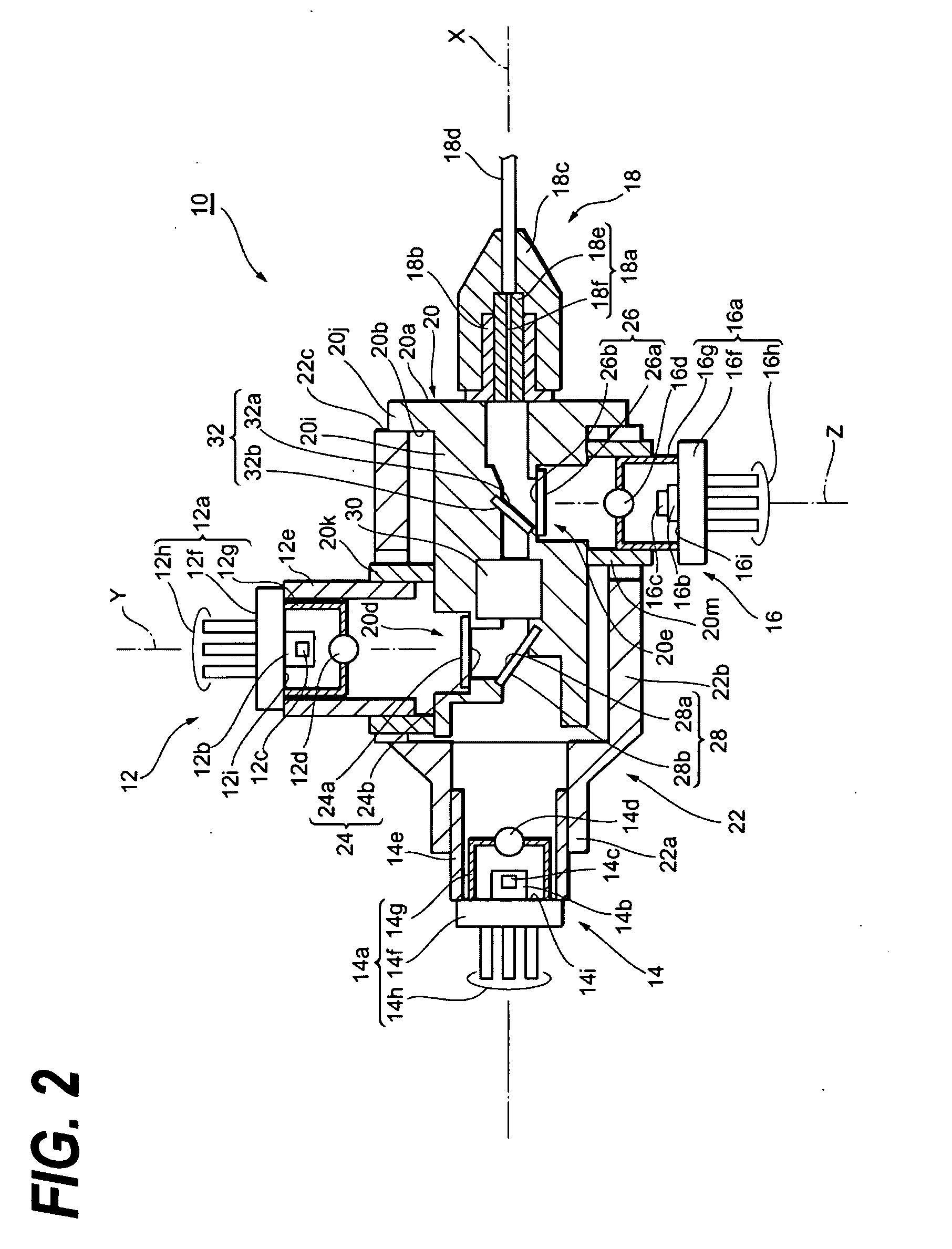
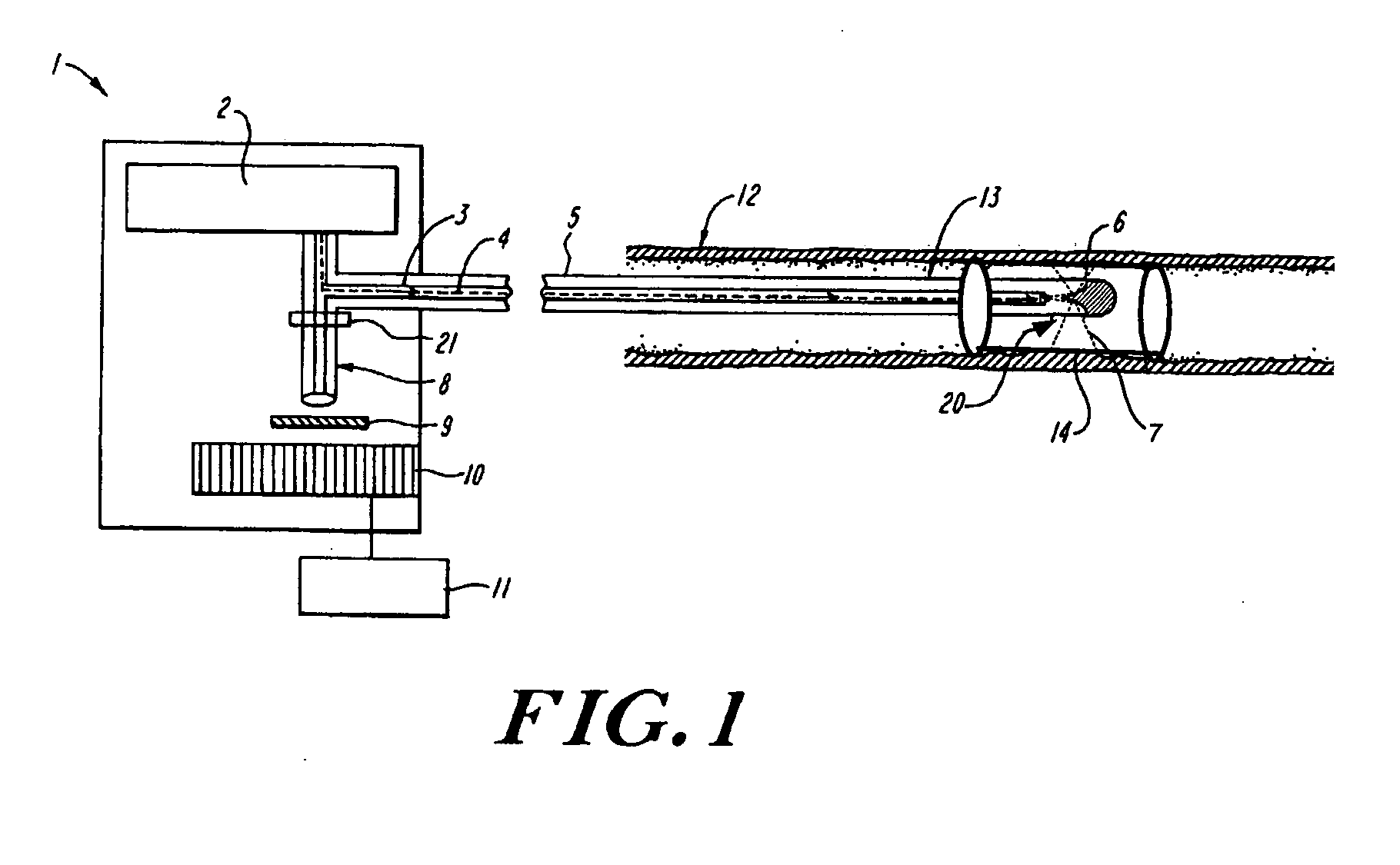
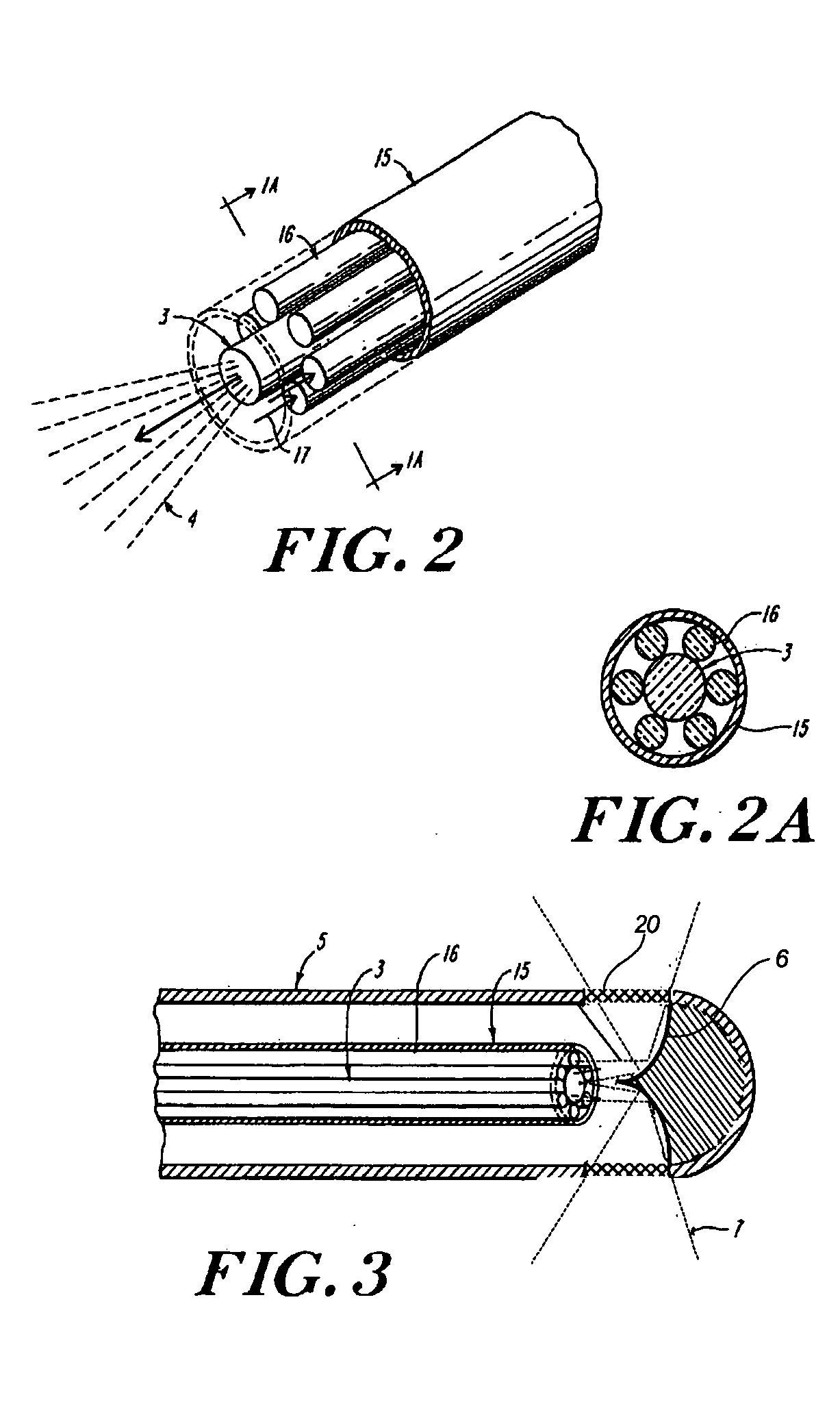
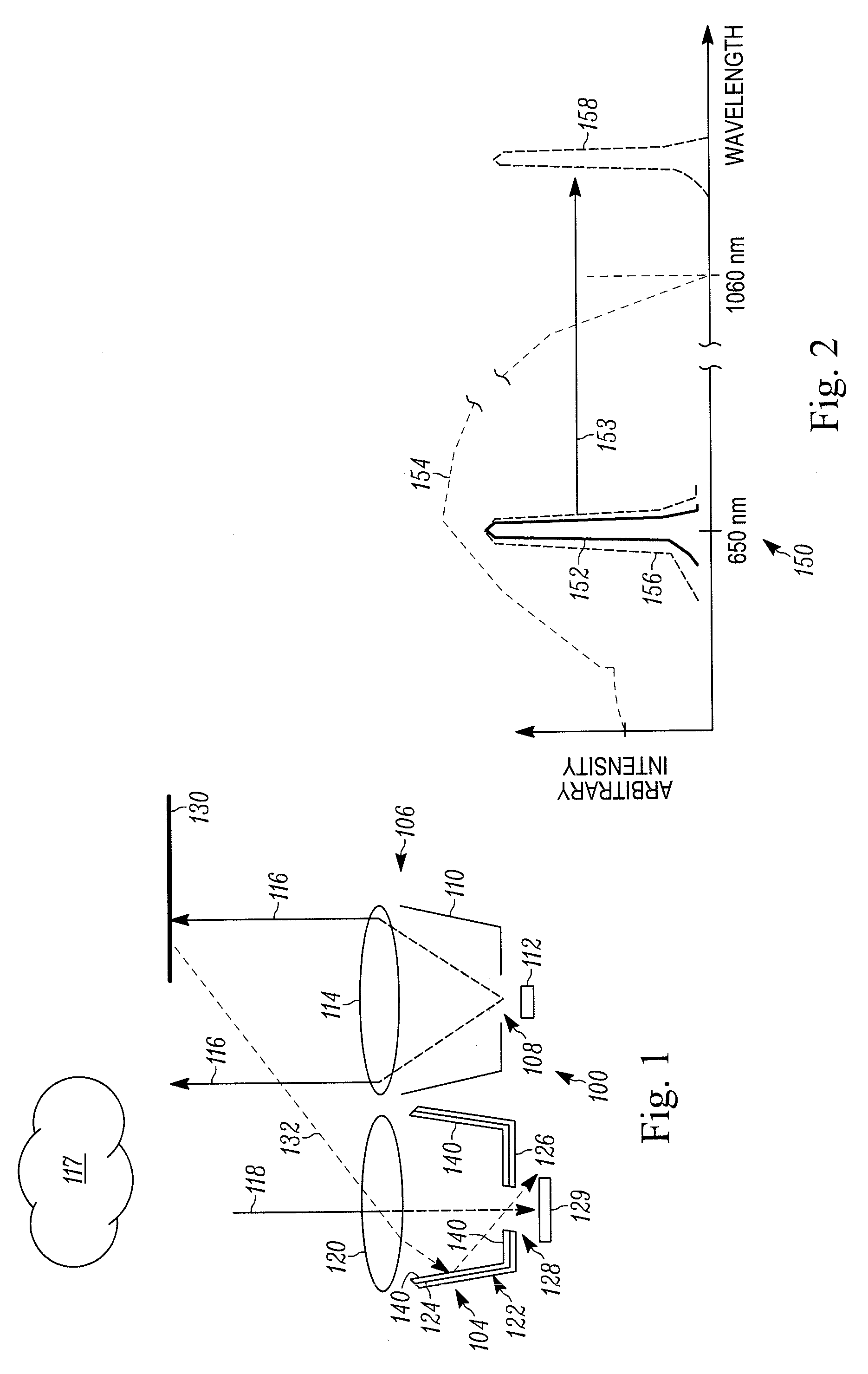
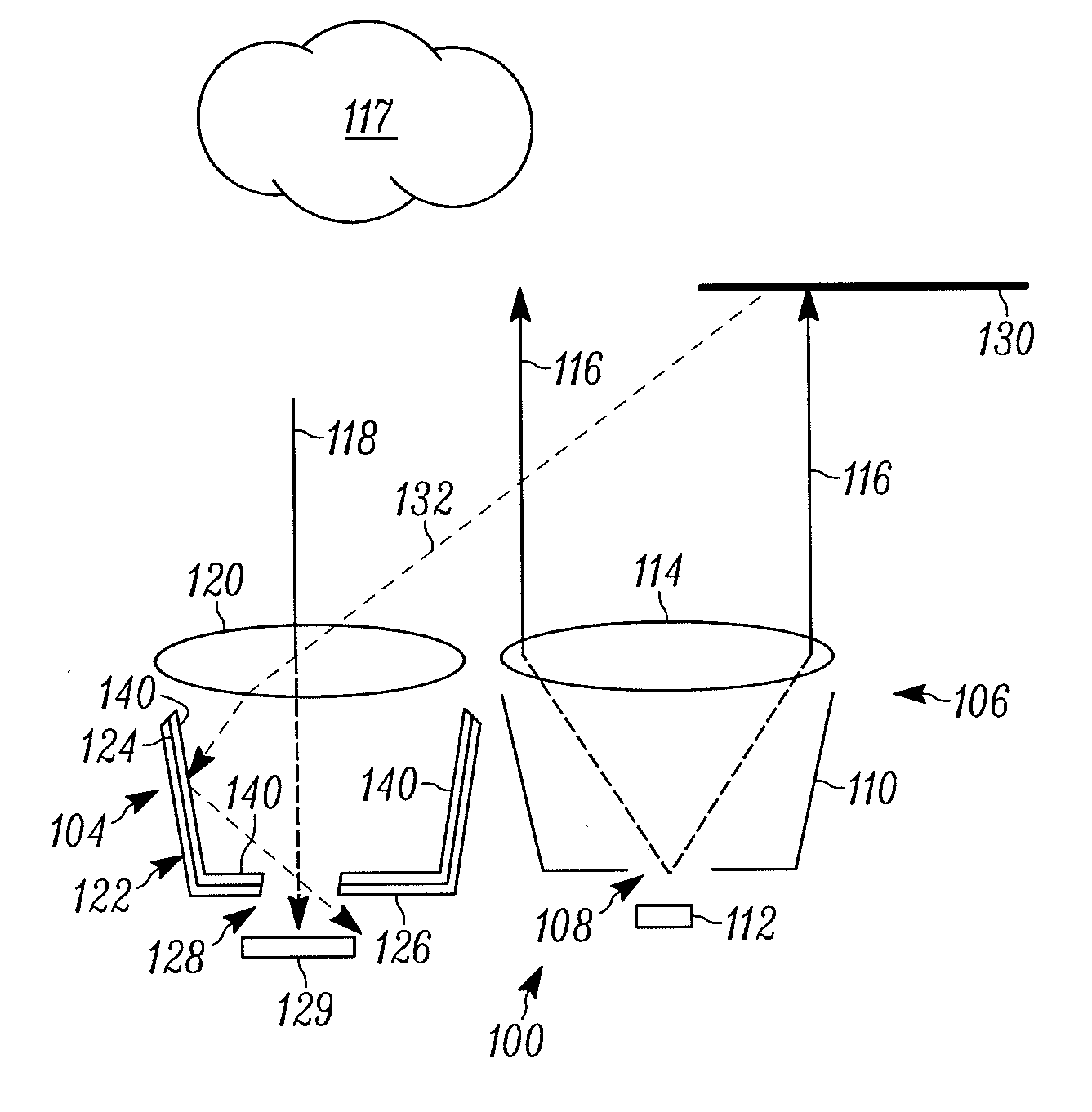
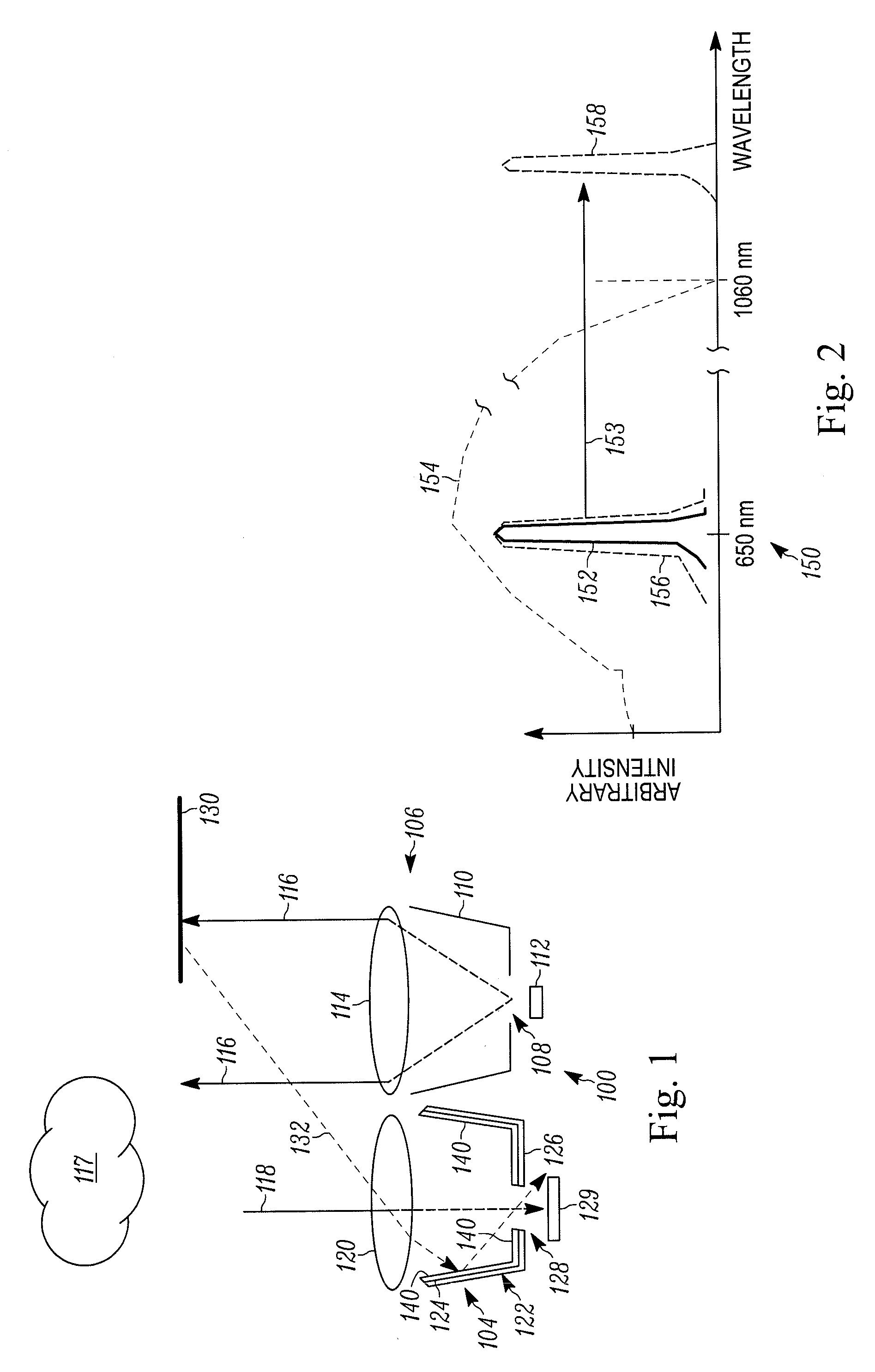
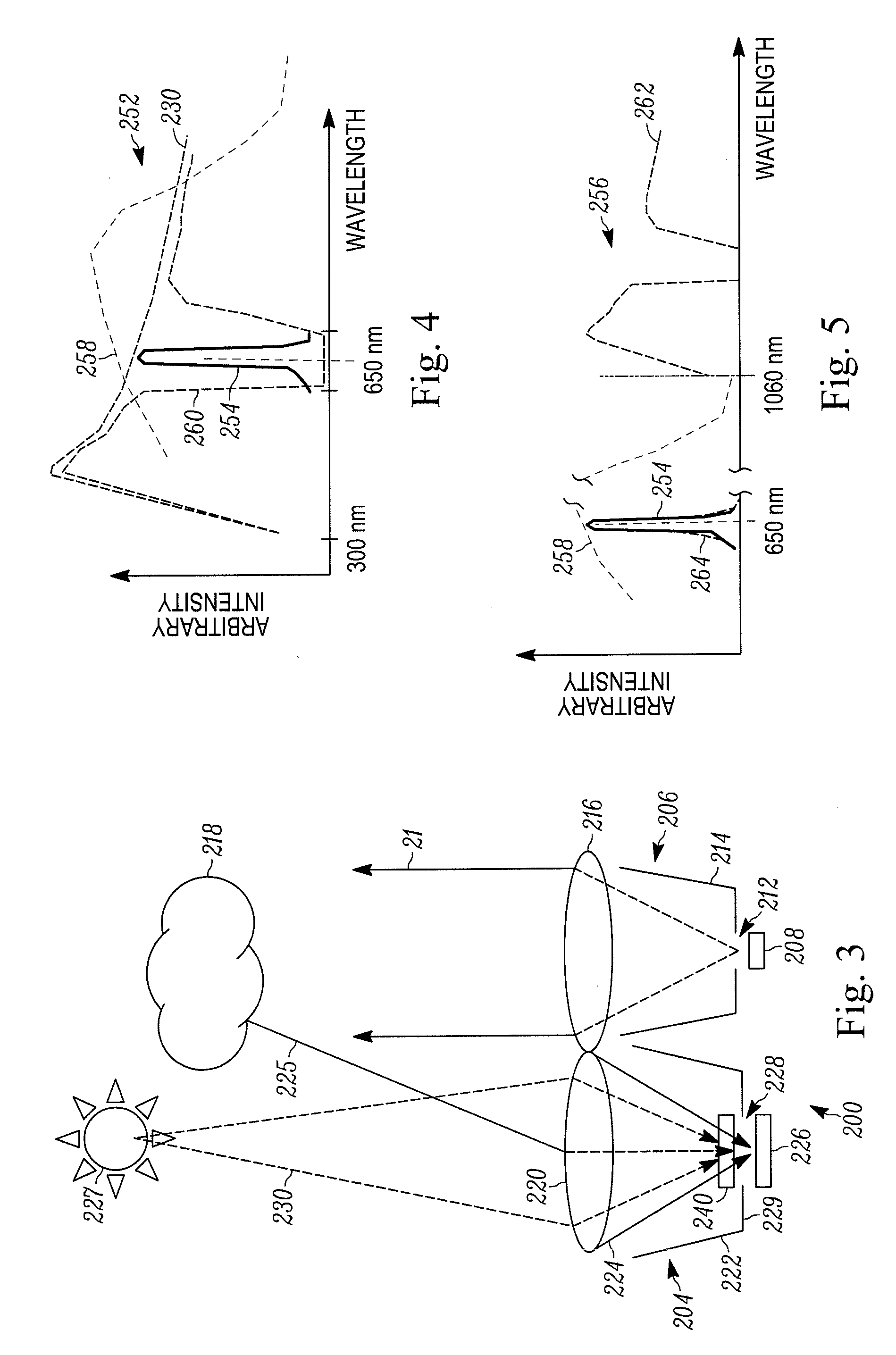
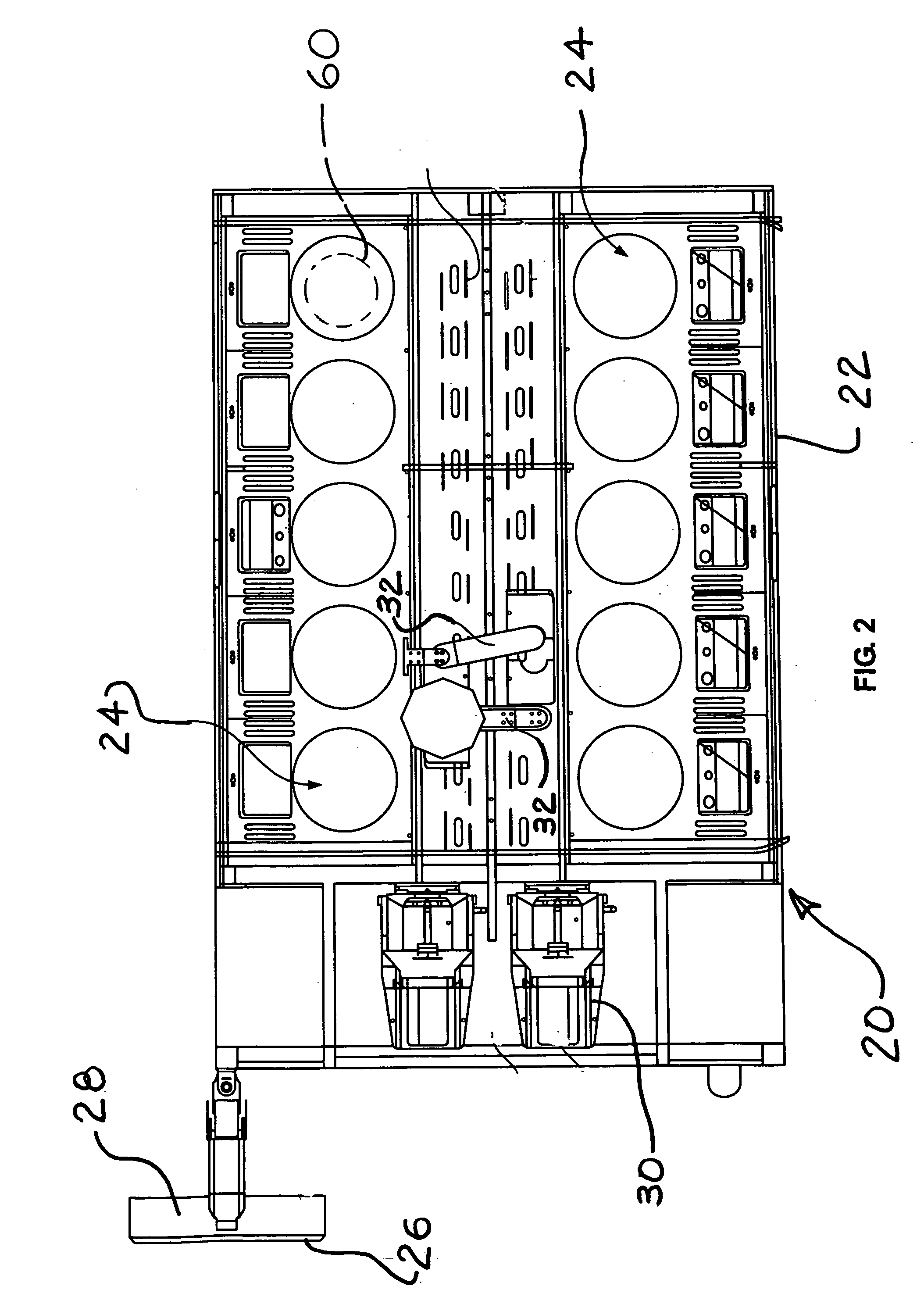
Pulse oximetry sensor
ActiveUS7280858B2Reduce Optical NoiseDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsOptical radiationPulse oximetry
A pulse oximetry sensor has an emitter adapted to transmit optical radiation of at least two wavelengths into a tissue site and a detector adapted to receive optical radiation from the emitter after tissue site absorption. A tape assembly is adapted to attach the emitter and detector to the tissue site. A flexible housing is disposed around and optically shields the detector.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Optical touch pad with multilayer waveguide
InactiveUS20070152985A1Reduce Optical NoiseInput/output processes for data processingTouchpadEngineering
An optical touch pad that includes a multilayer waveguide optically coupled to at least one electromagnetic radiation detector. Based on electromagnetic radiation directed from an object to the detector by the multilayer waveguide, information related to an object proximate to (e.g., hovering above) and / or in contact with the optical touch pad may be determined. For example, the information related to the object may include position information, object-type information, and / or other information related to the object.
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
Optical touchpad system and waveguide for use therein
InactiveUS20080007541A1Easy to controlReduce Optical NoiseElectronic switchingInput/output processes for data processingInter layerRefractive index
An optical touchpad system that includes a waveguide having a plurality of waveguide layers. For example, the waveguide may include an intervening layer, a signal layer, and / or other layers. The intervening layer may be defined by a first surface, a second surface and a substantially transparent material having a first index of refraction disposed between the first and the second surface of the interface layer. The signal layer may be defined by a first surface, a second surface and a substantially transparent material having a second index of refraction that is greater than the first index of refraction.
Owner:O PEN
Optical touchpad system and waveguide for use therein
InactiveUS20080007540A1Enhance frame rateReduce optical noiseInput/output processes for data processingMulti materialEngineering
An optical touchpad system is disclosed that may be easily integrated into a variety of applications. One feature of the optical touchpad system that may contribute to this versatility may be the ability of the optical touchpad system to function in the same manner independent from a topology and / or opacity of an interface surface of the optical touchpad system. This may enable the interface surface to be composed of any of a variety of materials. This may further enable the interface surface to include various topologies adapted for the application in which the optical touchpad system may be employed.
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
Systems and methods for transmitting quantum and classical signals over an optical network
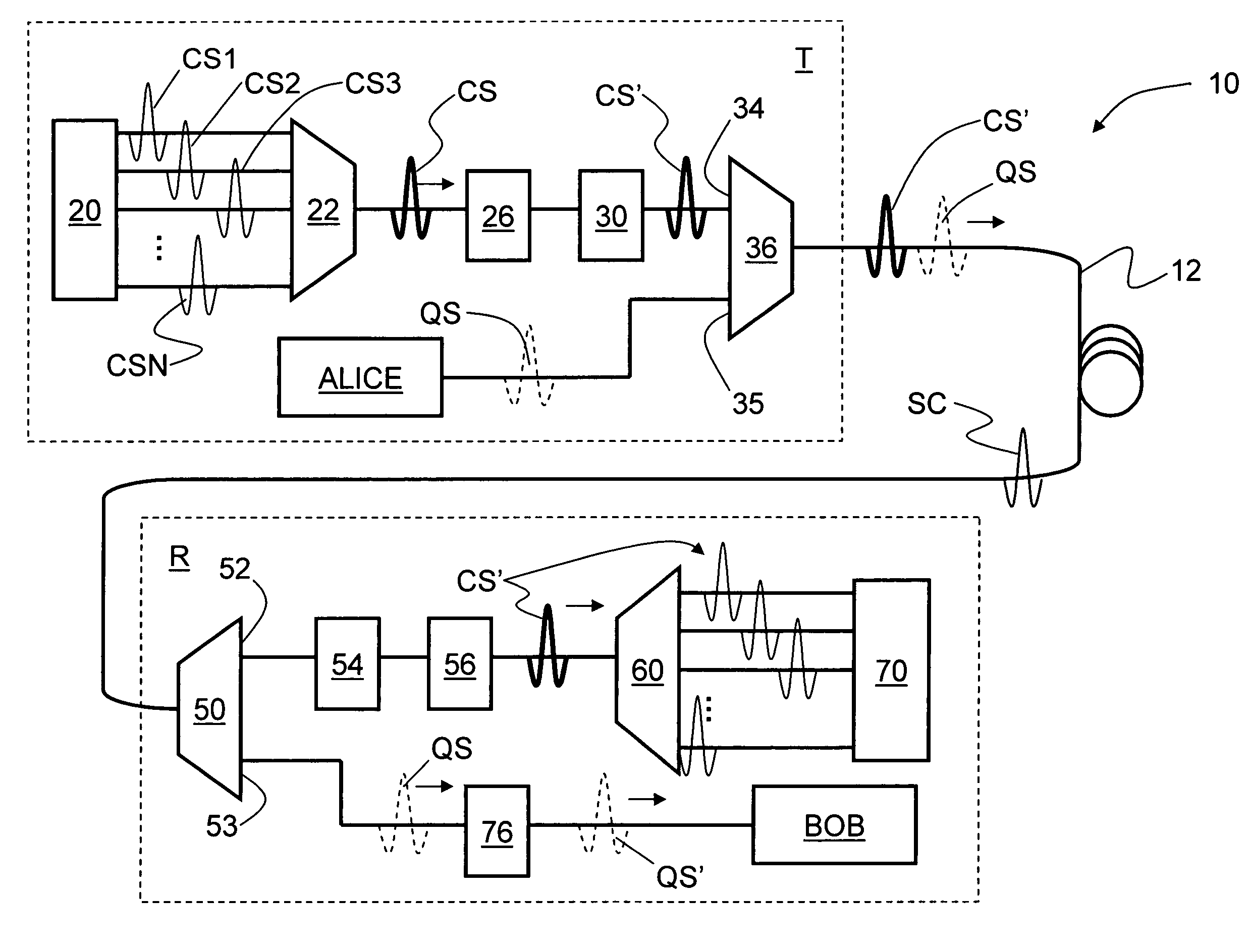
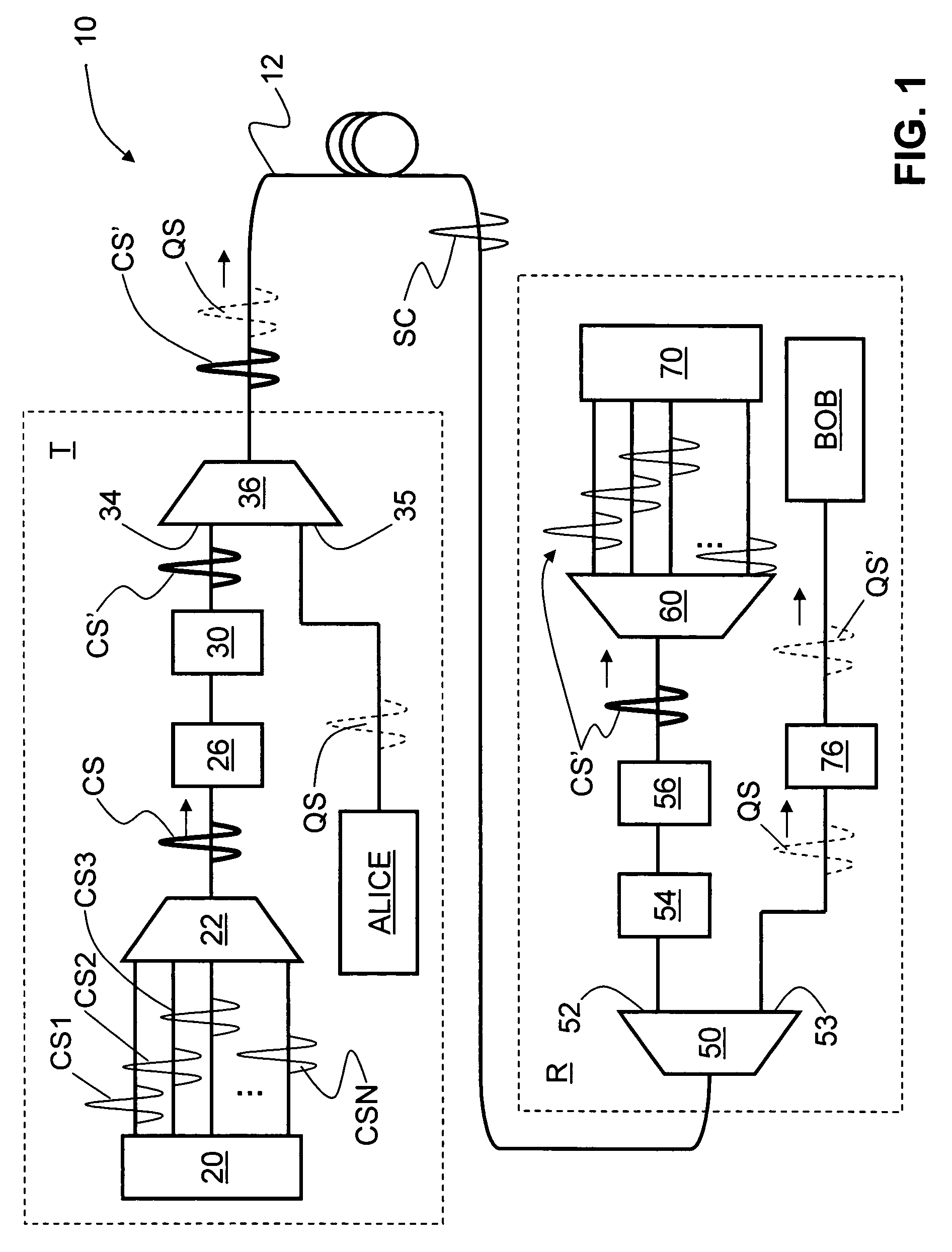
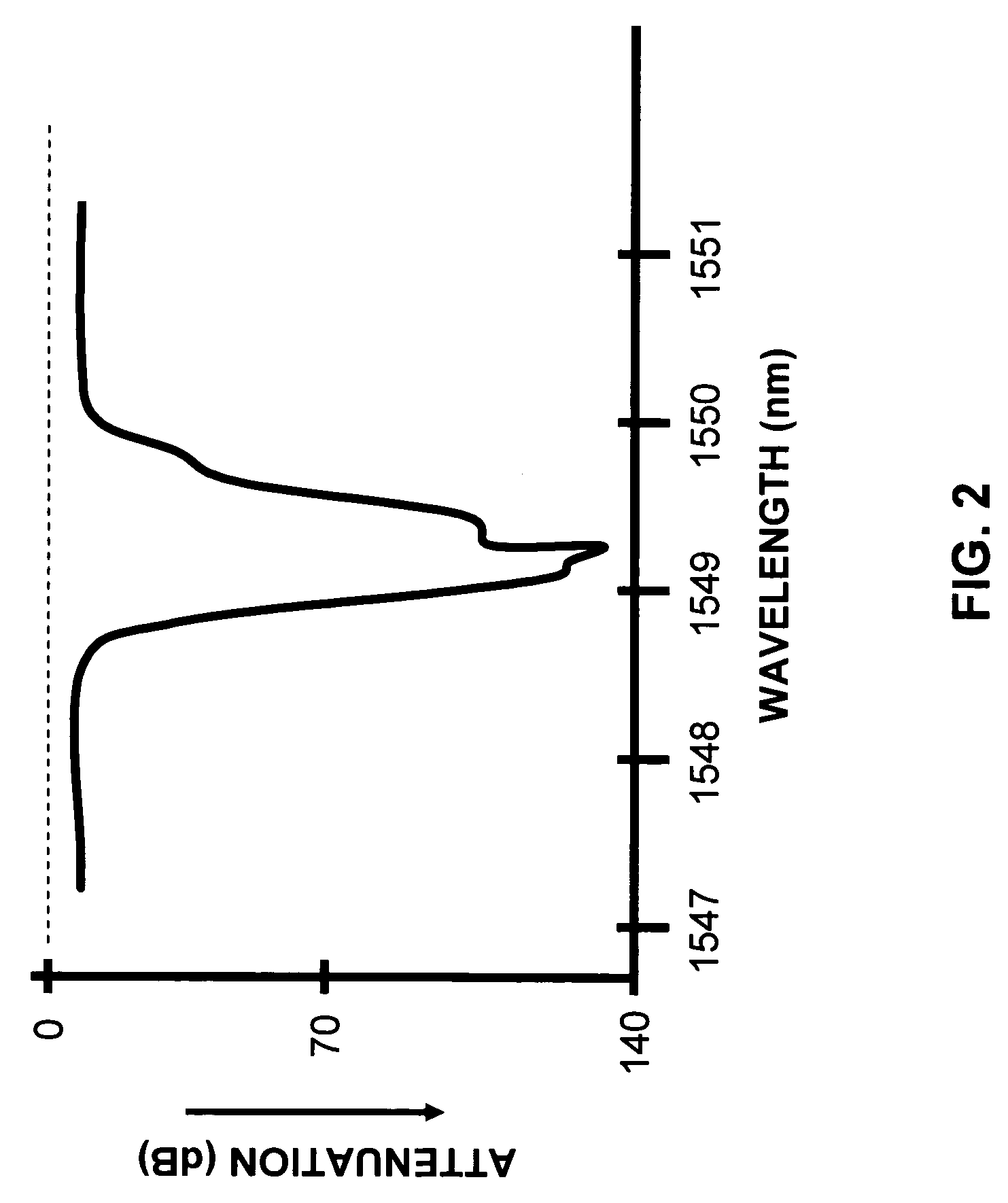
ActiveUS7248695B1Reduce Optical NoiseKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationMultiplexingLength wave
Systems and methods for transmitting quantum and classical signals over an optical network are disclosed, wherein the quantum signal wavelength either falls within the classical signal wavelength band, or is very close to one of the classical signal wavelengths. The system includes a deep-notch optical filter with a blocking bandwidth that includes the quantum signal wavelength but not any of the classical signal wavelengths. The deep-notch optical filtering is applied to the classical signals prior to their being multiplexed with the quantum signals to prevent noise generated by the classical signals from adversely affecting transmission of quantum signals in the transmission optical fiber. Narrow-band filtering is also applied to the quantum signals prior to their detection in order to substantially exclude spurious non-quantum-signal wavelengths that arise from non-linear effects in the optical fiber. The present invention allows for the quantum and classical signals to have wavelengths within just a few nanometers of one another, which has benefits for both classical and quantum signal transmission on a common transmission optical fiber.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
Optical touch pad with multilayer waveguide
InactiveUS8013845B2Reduce Optical NoiseInput/output processes for data processingTouchpadElectromagnetic radiation
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
Optical touchpad system and waveguide for use therein
InactiveUS8031186B2Increased durabilityIncrease frame rateInput/output processes for data processingTouchpadEngineering
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
Optical touchpad with three-dimensional position determination
InactiveUS8094136B2Easy to controlReduce Optical NoiseTransmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsInformation opticsOphthalmology
An optical touchpad that may be able to provide accurate, reliable information about the position of an object in three-dimensions. The optical touchpad may enable a determination as to whether the object is engaged with the touchpad or hovering just above the touchpad. When the object is in contact with the optical touchpad, the optical touchpad may enable a determination of the force applied by the object to the optical touchpad. The optical touchpad may enable a determination of an object type of the object. These and other determinations of information related to the object may enhance the control provided by the touchpad system to the user as an electronic interface. The operation of the optical touchpad may further enable an enhanced frame rate, reduced optical noise in the optical signal(s) guided to the one or more sensors, augment the ruggedness of the optical touchpad, an enhanced form factor (e.g., thinner), and / or provide other advantages.
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
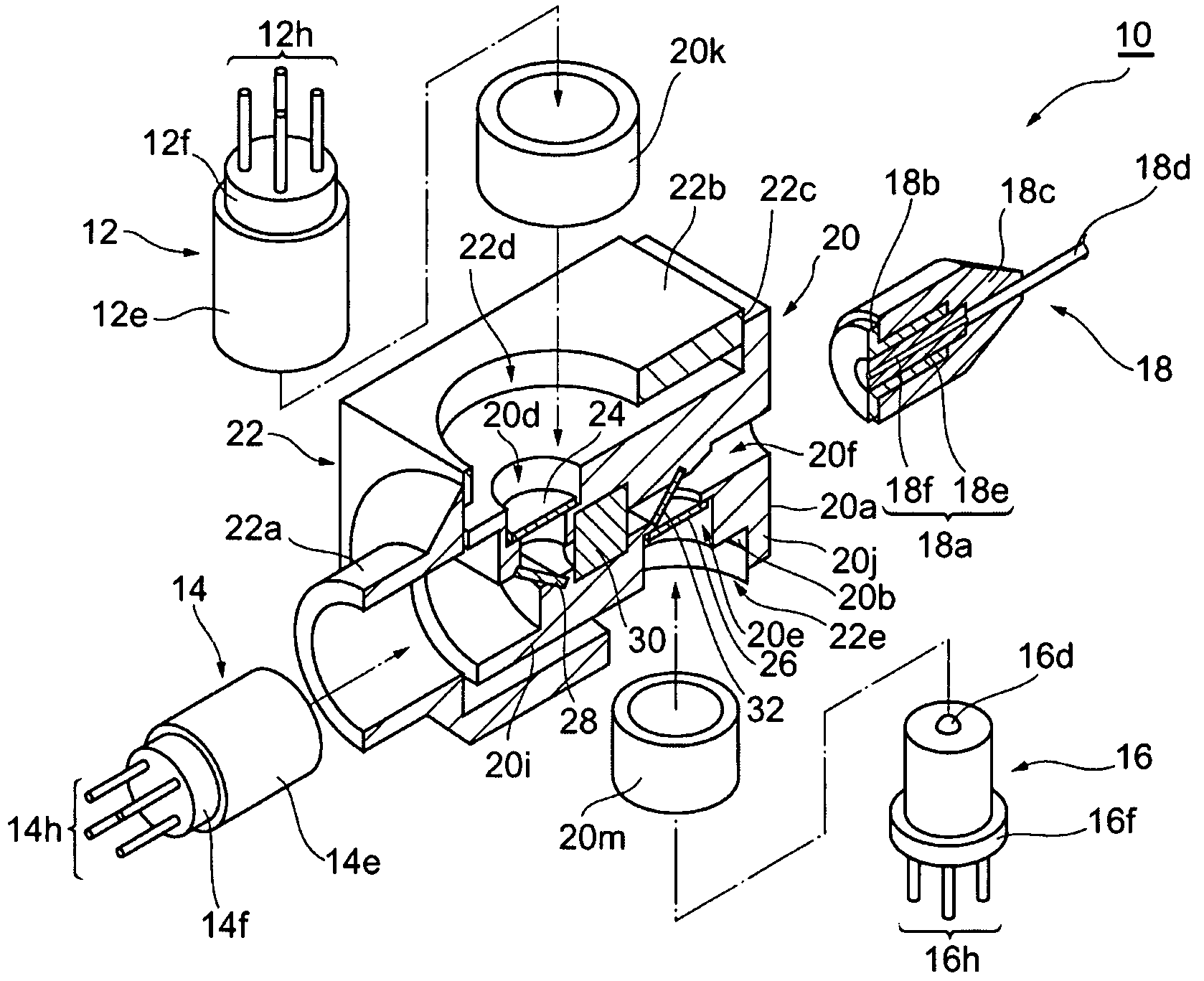
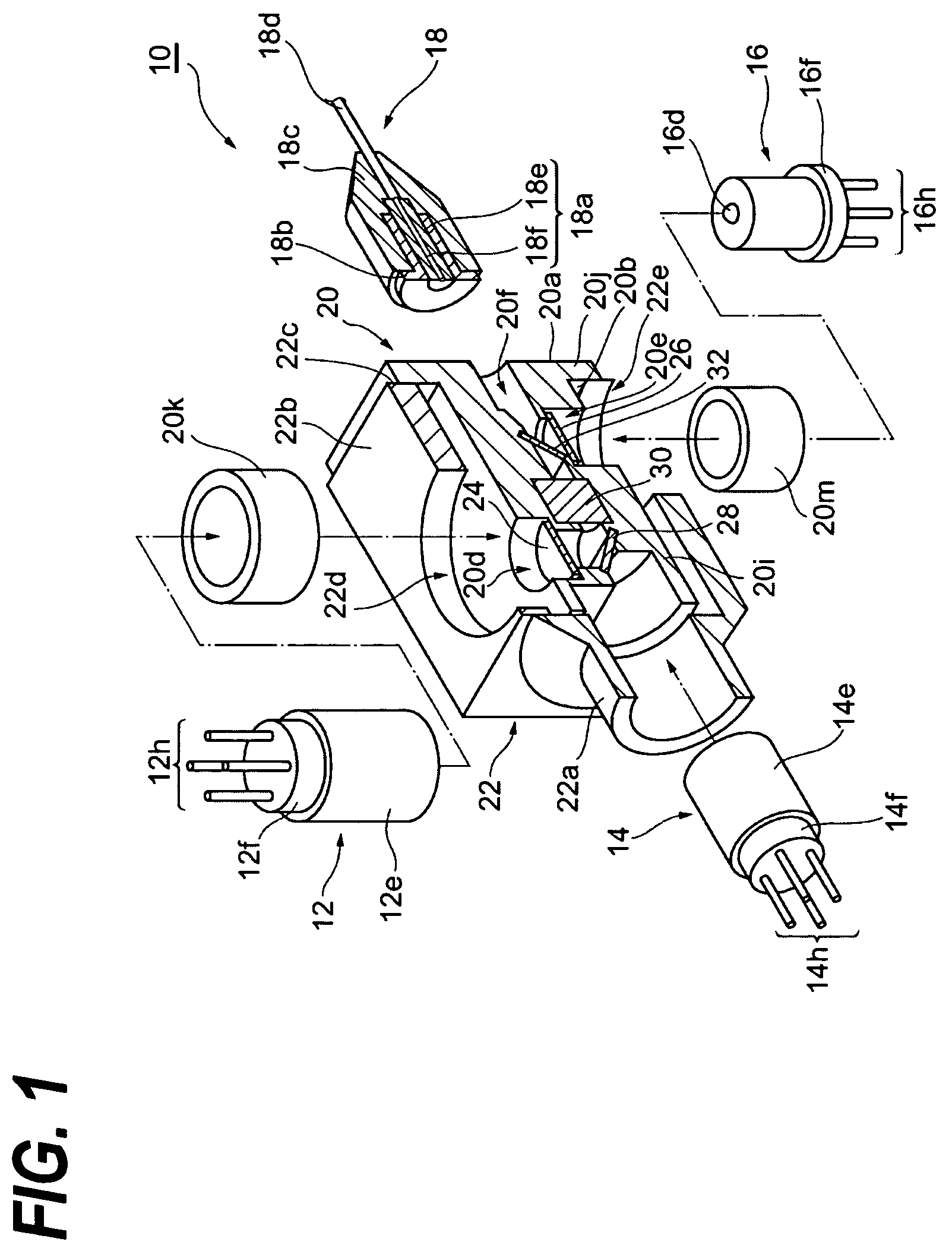
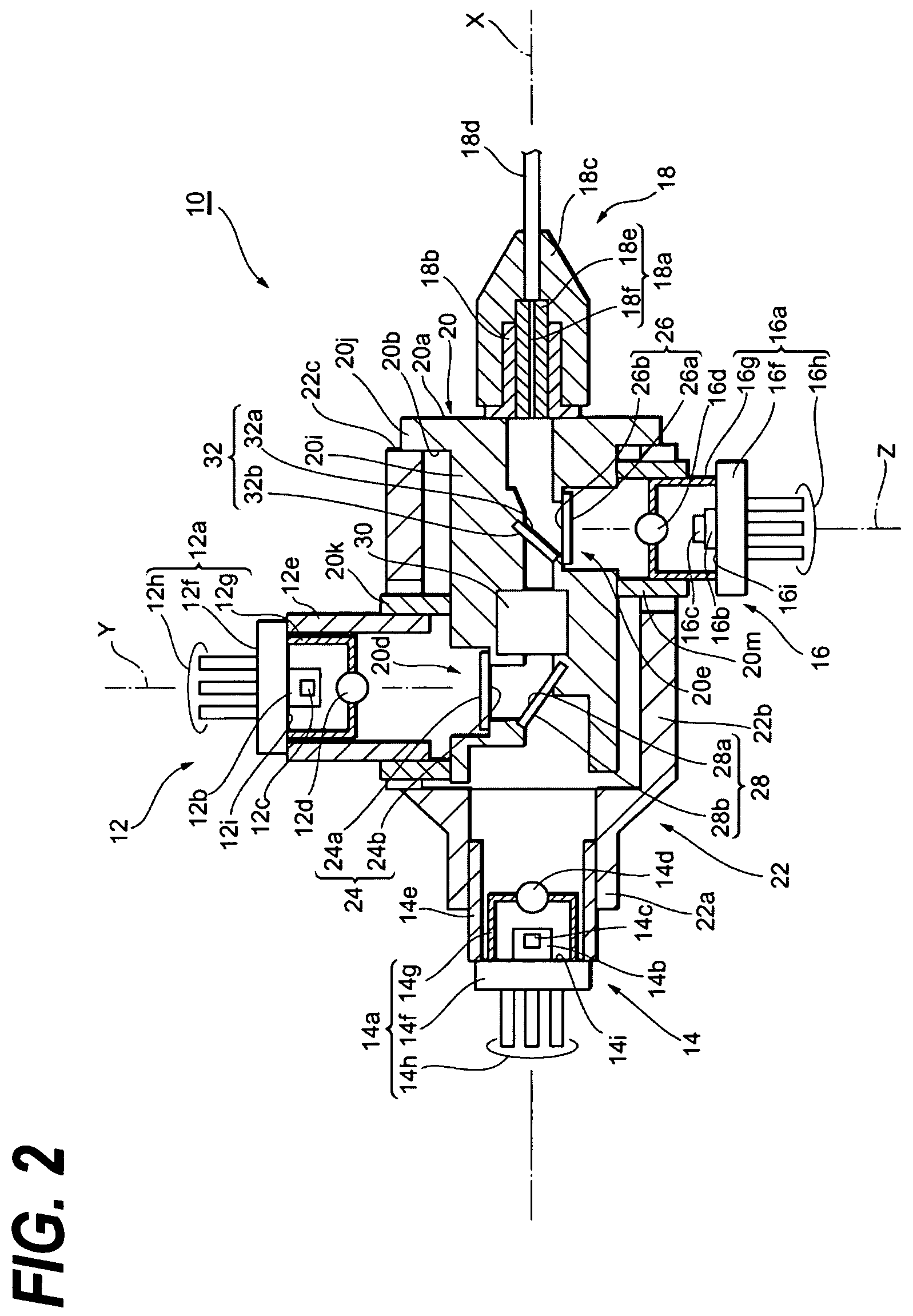
Bidirectional optical assembly and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20070122154A1Superior optical coupling efficiencyReduce Optical NoiseWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesEngineeringOptical coupling
The present invention provides a bi-direction optical assembly with two optical transmitting channels by a small-sized package and relatively low cost. In the bi-directional optical assembly, the first transmitting optical subassembly (TOSA) and the receiving optical subassembly (ROSA) are optically coupled with the optical fiber via the inner housing. While the second transmitting optical subassembly is optically coupled with the optical fiber via the outer housing slidable to the inner housing.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
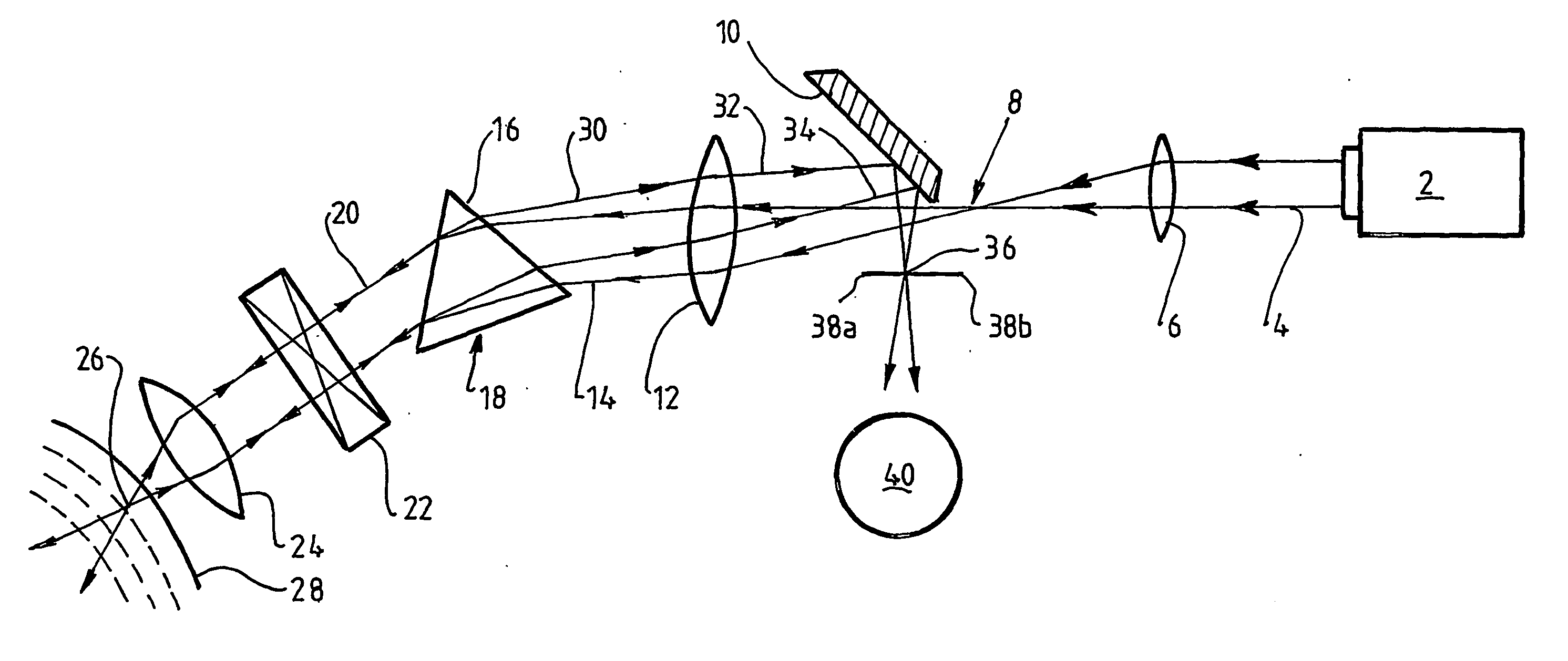
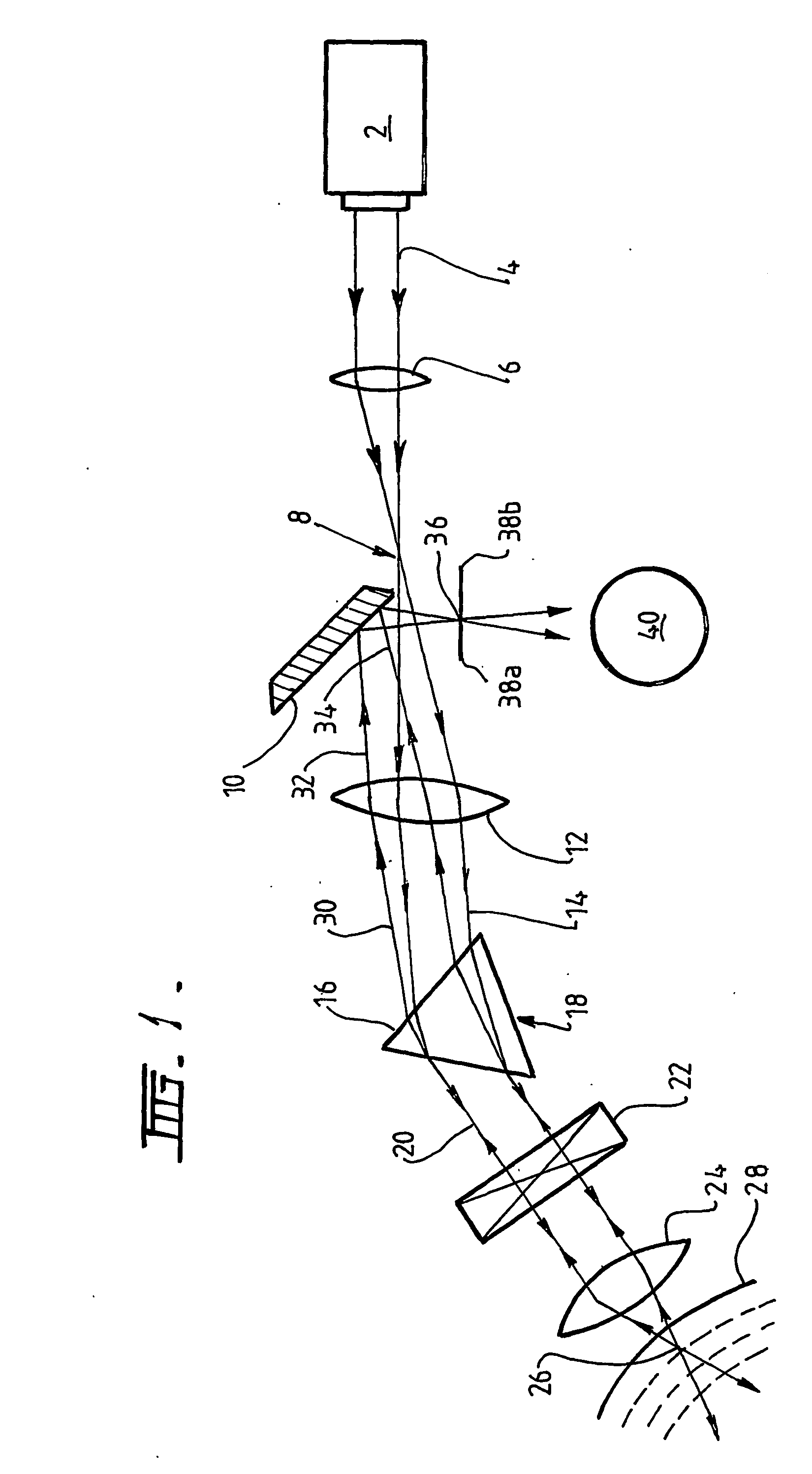
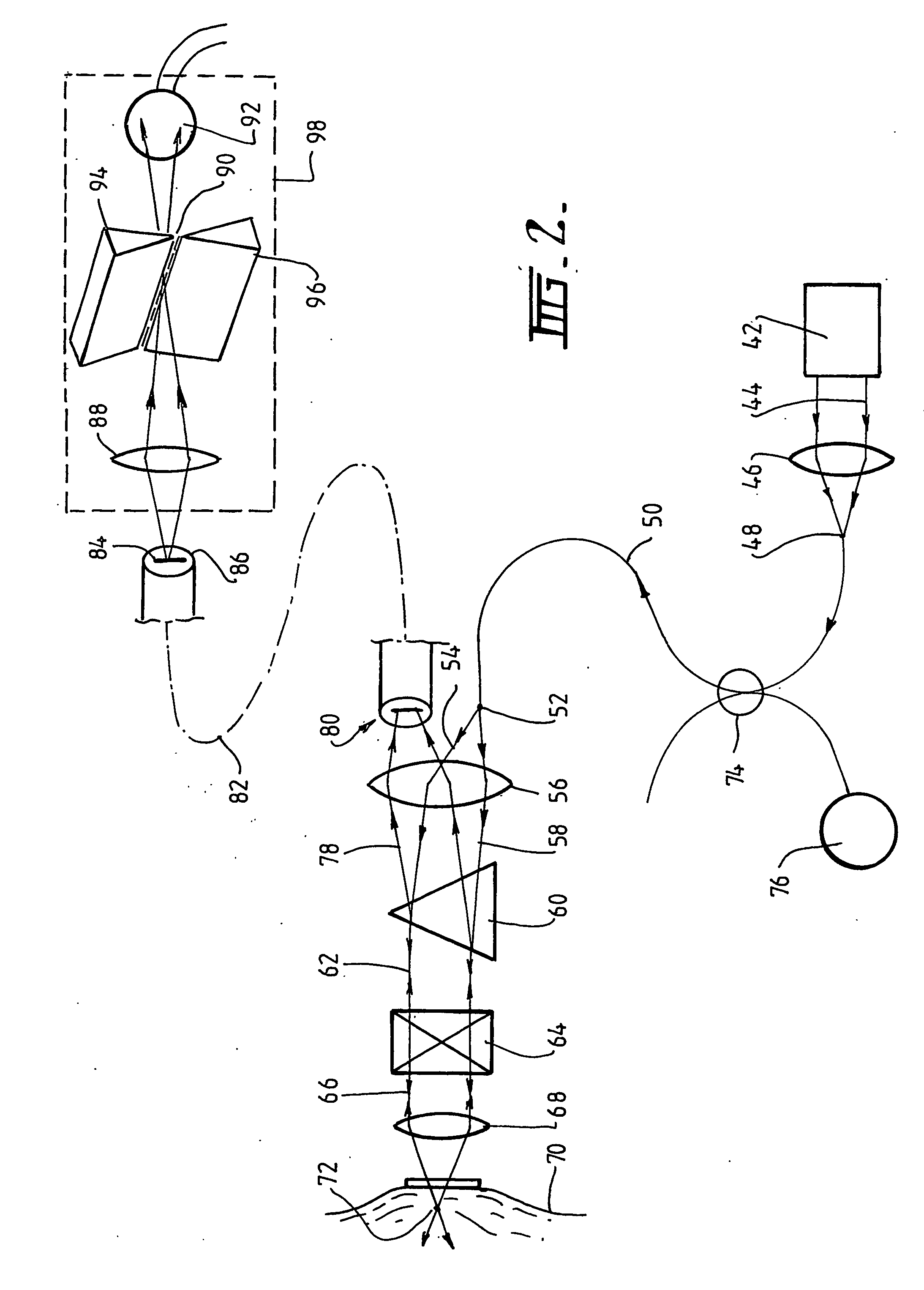
Laser scanning confocal microscope with fibre bundle return
ActiveUS20050174425A1Improve focal plane isolationReduce Optical NoiseRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFiber bundleFluorescence
The invention provides a confocal microscope or endoscope, having a source of coherent light for illuminating a sample, and an imaging optical fibre bundle (82) for receiving return light, whereby the fibre bundle (82) provides a return channel for fluorescent return light (78). The optical fibre bundle (82) preferably preserves, between entry and exit ends of the bundle, the relative spatial coordinates of the cores of individual fibres constituting the bundle.
Owner:OPTISCAN
Bidirectional optical assembly and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7556439B2Reduce Optical NoiseEnhanced couplingWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesTransmission channelEngineering
The present invention provides a bi-direction optical assembly with two optical transmitting channels by a small-sized package and relatively low cost. In the bi-directional optical assembly, the first transmitting optical subassembly (TOSA) and the receiving optical subassembly (ROSA) are optically coupled with the optical fiber via the inner housing. While the second transmitting optical subassembly is optically coupled with the optical fiber via the outer housing slidable to the inner housing.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Fluorescence microscope and observation method using the same
ActiveUS7297961B2Easy to getReduce Optical NoisePhotometryPhase-affecting property measurementsMicroscopic observationRefractive index
The present invention relates, in general, to a fluorescence microscope and method of observing samples using the microscope and, more particularly, to a fluorescence microscope and method of observing samples using the microscope, which can reduce optical noise and obtain images with higher sensitivity, thus obtaining precise information about the density, quantity, location, etc. of a fluorophore, and which can simultaneously process separate images even when a plurality of fluorophores having different excitation and fluorescent wavelength ranges is distributed, thus easily obtaining information about the fluorophores. The fluorescence microscope of the present invention includes an objective lens, and first and third medium units. The first medium unit has a refractive index of n1 to accommodate one or more micro-objects including fluorophores and provide a path of excitation light to excite the fluorophores. The third medium unit has a refractive index of n3, and is placed between the first medium unit and the objective lens to totally reflect the excitation light incident through the first medium unit at an interface of the third medium unit coming into contact with the first medium unit. The refractive indices of the third and first medium units satisfy a relationship of n1>n3.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Raman spectroscopy for monitoring drug-eluting medical devices
InactiveUS20050171436A1Suitable for measuringReduce Optical NoiseDiagnostics using spectroscopyCatheterSpectral patternImage resolution
The present invention provides low-resolution Raman spectroscopic systems and methods for in situ monitoring of drug-eluting devices in a lumen of a subject. A preferred system can employ multi-mode radiation in making in situ Raman spectroscopic measurements of the lumen and / or device. For example, a system can include a light source such as a multi-mode laser, and a light detector to measure spectral patterns and differentiates spectral features of drugs released in a target region. Drug-release curves can be extrapolated or otherwise predicted using the Raman spectrum taken during or subsequent to device insertion and / or activation.
Owner:PRESCIENT MEDICAL
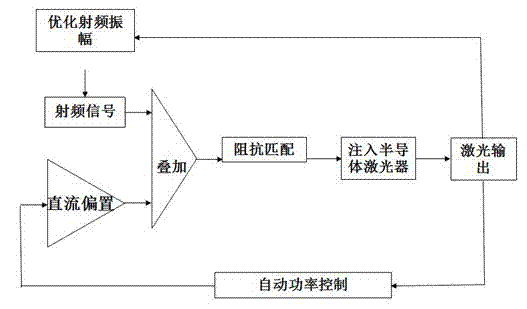
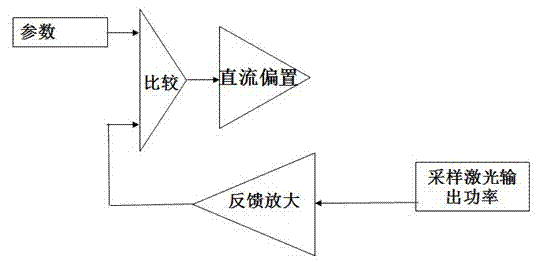
A method of producing stable full-time low-noise laser output
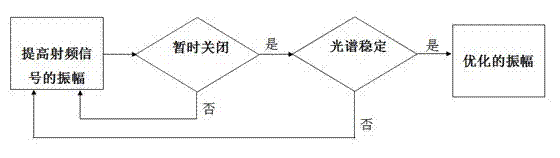
ActiveCN102290706AIncrease amplitudeOptimizing RF modulationLaser detailsLaser output parameters controlLow noiseImpedance matching
The invention discloses a method for generating stable, full-time low noise laser output. The method includes the following steps: regulating and maintaining a semiconductor laser operating temperature by means of a thermoelectric controller (TEC) attached on the laser; generating a direct-current bias from a direct-current generator; generating an amplitude-modulatable radio frequency signal from a local oscillator; superposing the radio frequency signal onto the direct-current bias to generate amplitude-modulatable drive current; injecting the amplitude-modulatable drive current into the semiconductor laser by way of input-coupled impedance matching; regulating the direct-current bias by means of an automatic power control circuit; and optimizing the amplitude of the radio frequency signal. By modulating the driving of the semiconductor laser diode, the method effectively overcomes the mode hopping phenomenon, the method is applicable to laser diodes with various wavelengths, the generated laser output has the advantages of low coherence, low noise, little speckles, long-time stable output power and long-time uniform beam illumination, and the method is particularly suitable forbiomedicine and medical diagnosis and clinic.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION CORP SUZHOU
Passive optical network system using time division multiplexing
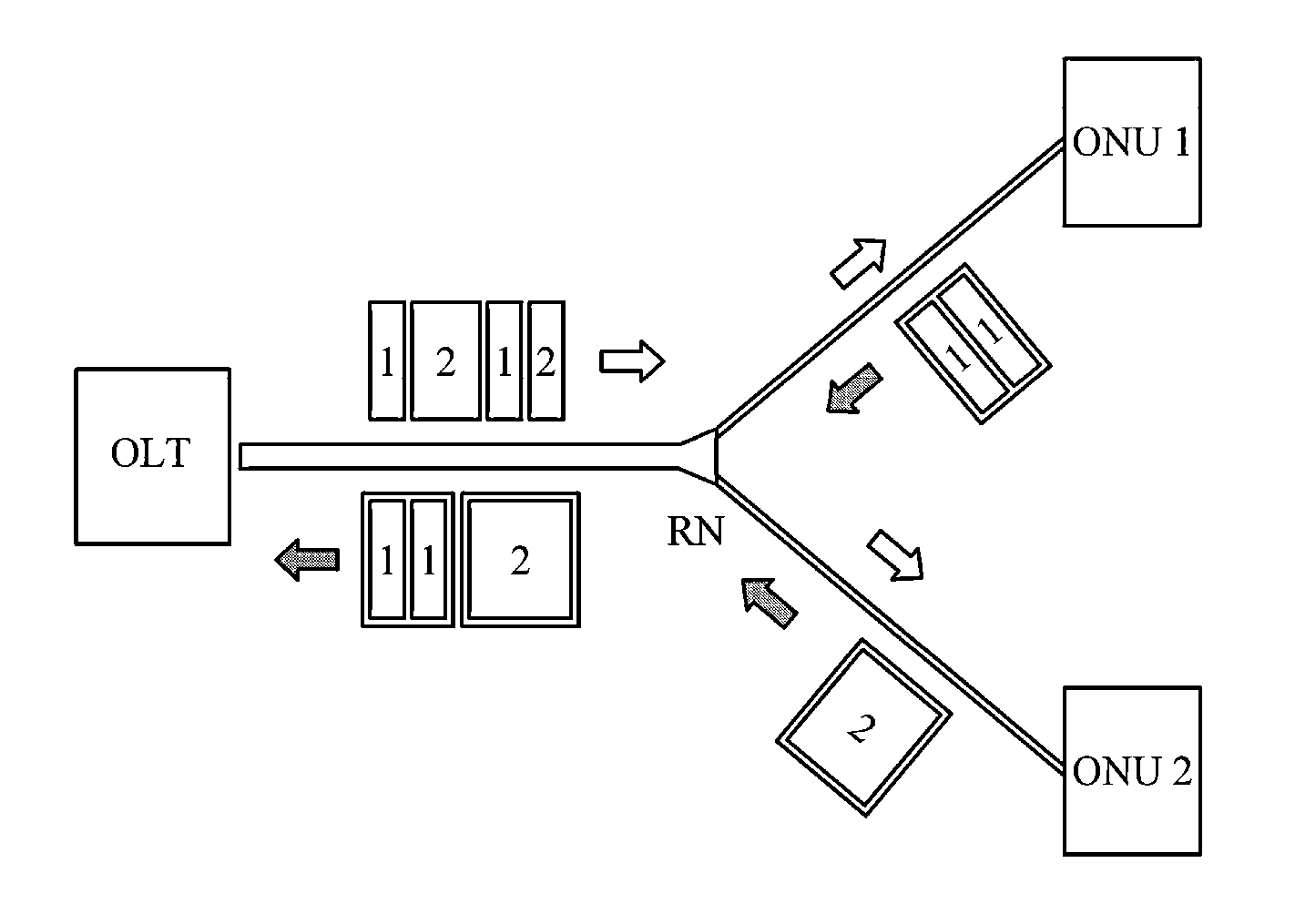
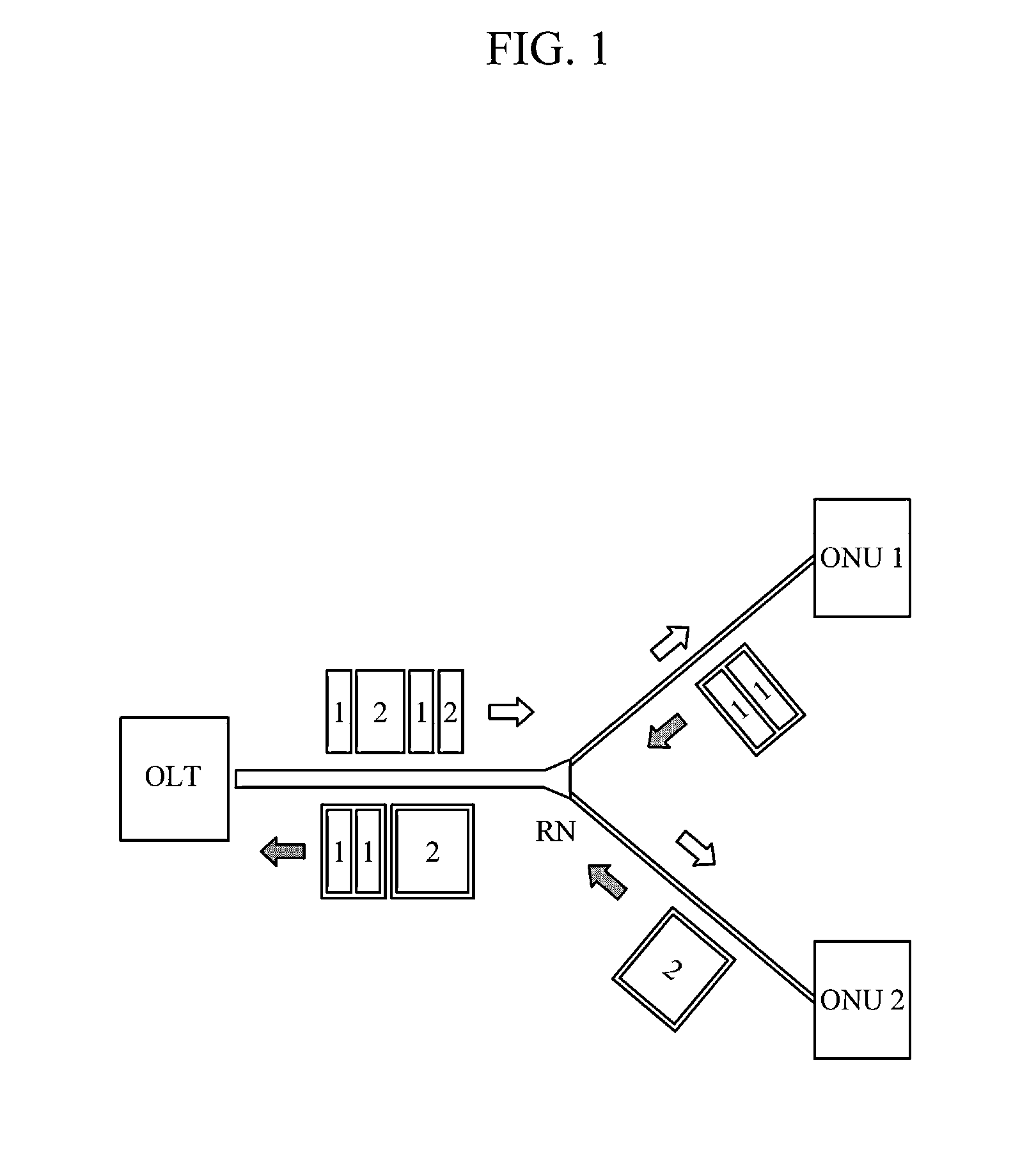
InactiveUS20150055956A1Avoid quality lossPerformance deteriorationTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical time division multiplexingEngineering
Disclosed is a passive optical network system using a time division multiplexing scheme. According to one exemplary embodiment, the passive optical network system includes a plurality of optical network units (ONUs); an optical line terminal (OLT) to be connected to the plurality of ONUs for communication and to transmit and receive an optical signal to and from the plurality of ONUs using a time division multiplexing (TDM) scheme, wherein each of the plurality of ONUs includes a light source that generates an optical signal with a predetermined intensity even in burst-off state; and an optical filter disposed on a receiving path of an optical receiver of the OLT to filter out an optical noise signal received from an ONU in burst-off state among the plurality of ONUs.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Signal light noise reduciton apparatus and signal light noise reduction method
InactiveUS20050129382A1Reduce signal light noiseReducing signal light noiseLaser using scattering effectsNanoopticsCarbon nanotubeSignal light
An increase in the span of the transmission distance is aimed at by reducing unwanted ASE generated during optical communication. A carbon nanotube is employed as a saturable absorber 15 and this saturable absorber constitutes a noise reduction apparatus that has the function of cutting off or reducing transmission of unwanted ASE or the like which is of weak signal light intensity and of allowing transmission of signal light of strong light intensity. This noise reduction apparatus is arranged for example in the transmission path of signal light of a bidirectional excitation type EDFA, more precisely the apparatus is inserted in the latter stage of the EDF 40. In this way, carbon nanotubes having a saturable absorption function can be utilized in the field of optical communication.
Owner:ALNAIR LABS CORP +1
Fluorescence microscope and observation method using the same
ActiveUS20050092934A1Efficiently blocking unnecessary fluorescenceReduce working spacePhotometryPhase-affecting property measurementsMicroscopic observationRefractive index
The present invention relates, in general, to a fluorescence microscope and method of observing samples using the microscope and, more particularly, to a fluorescence microscope and method of observing samples using the microscope, which can reduce optical noise and obtain images with higher sensitivity, thus obtaining precise information about the density, quantity, location, etc. of a fluorophore, and which can simultaneously process separate images even when a plurality of fluorophores having different excitation and fluorescent wavelength ranges is distributed, thus easily obtaining information about the fluorophores. The fluorescence microscope of the present invention includes an objective lens, and first and third medium units. The first medium unit has a refractive index of n1 to accommodate one or more micro-objects including fluorophores and provide a path of excitation light to excite the fluorophores. The third medium unit has a refractive index of n3, and is placed between the first medium unit and the objective lens to totally reflect the excitation light incident through the first medium unit at an interface of the third medium unit coming into contact with the first medium unit. The refractive indices of the third and first medium units satisfy a relationship of n1>n3.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
System and method for optics detection
ActiveUS8731240B1Reduces ambient optical noiseImprove abilitiesDefence devicesSighting devicesDiscriminatorOptics
An optics detection system is disclosed. The optics detection system includes a sensor module and a processor. The sensor module is configured to illuminate a field of regard with a plurality of light pulses and to capture reflections of the plurality of light pulses in a plurality of frames, respectively. The processor is configured to process the plurality of frames to locate and identify optics within the field of regard using a plurality of discriminators.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
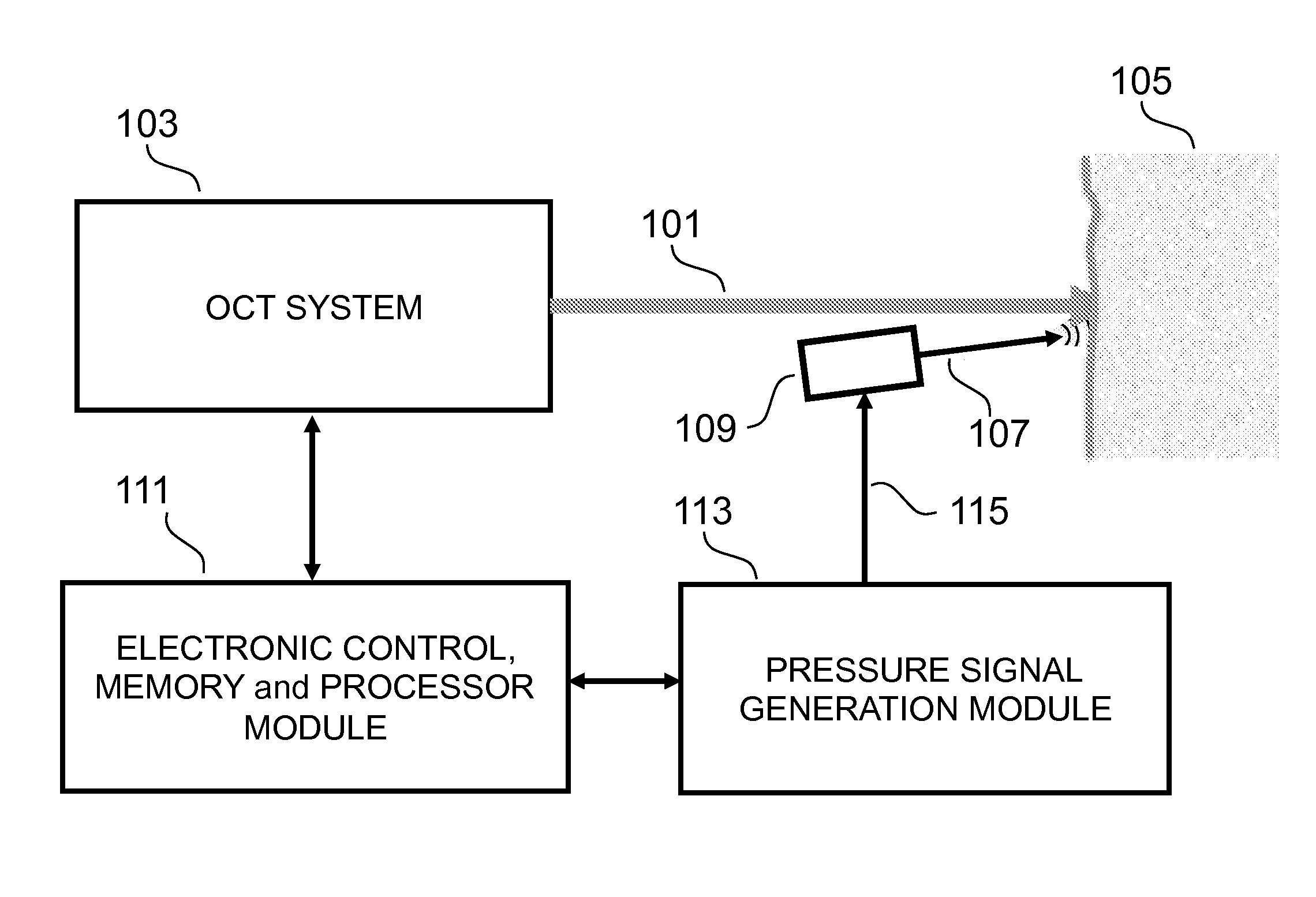
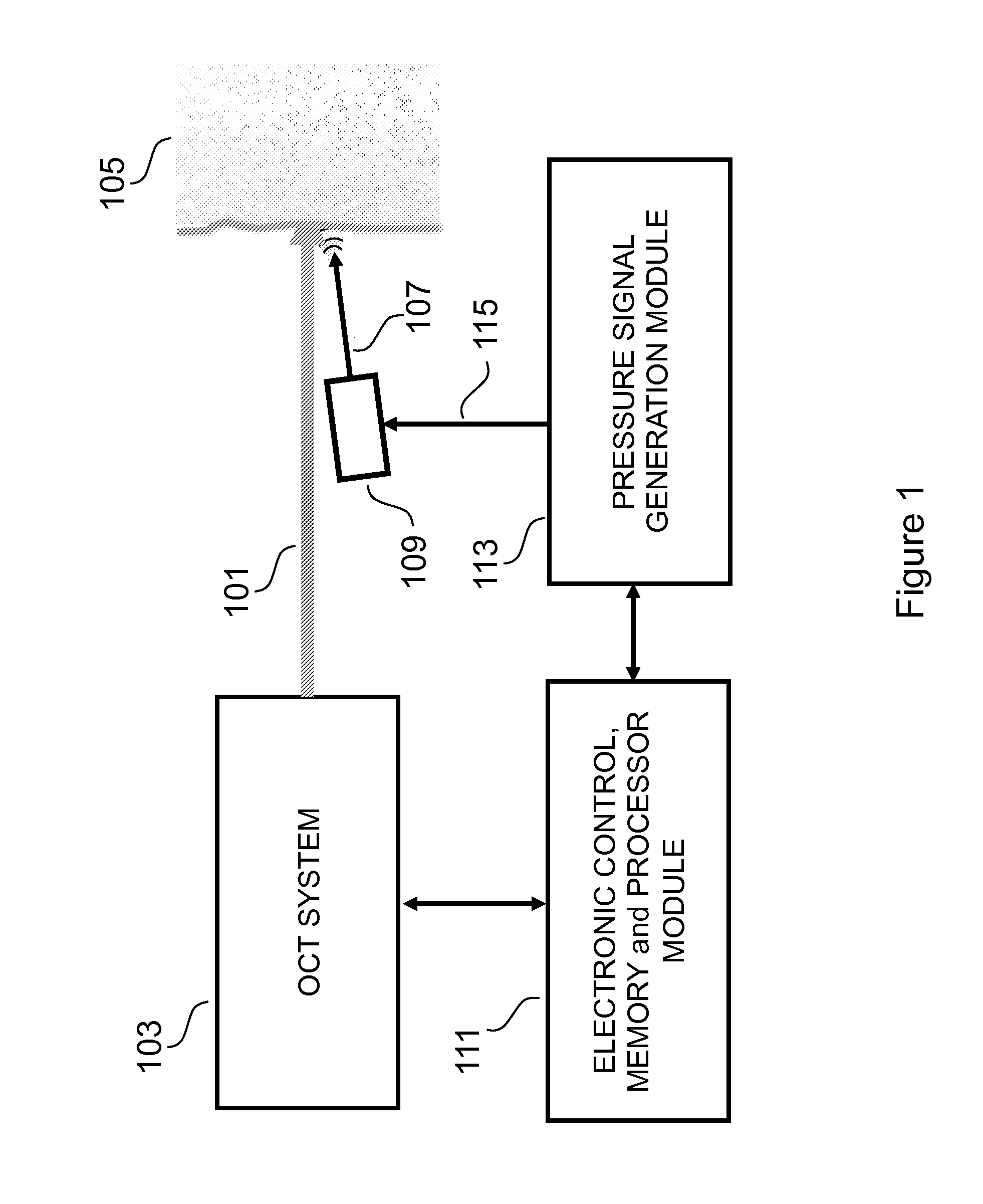
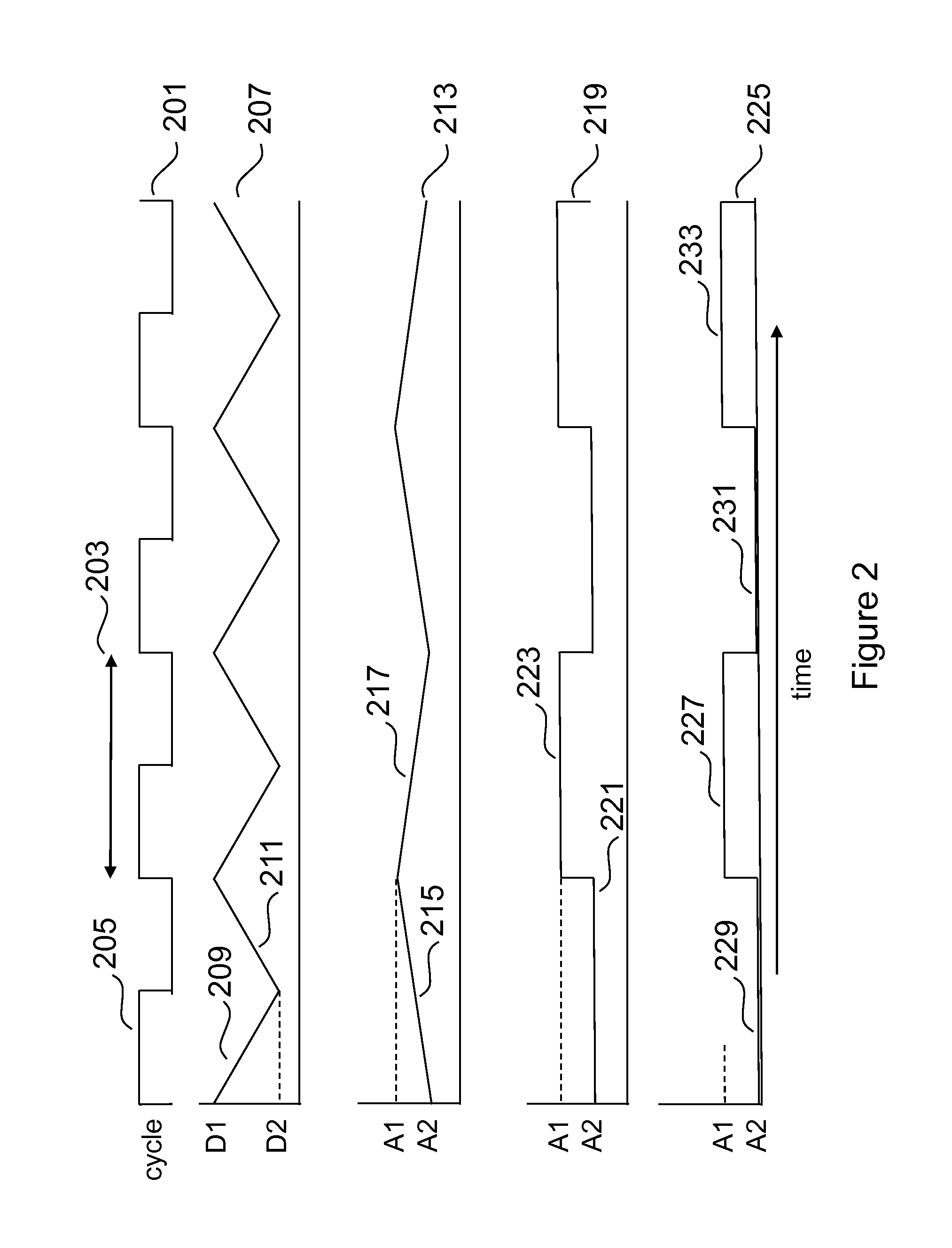
Enhanced OCT Measurement and Imaging Apparatus and Method
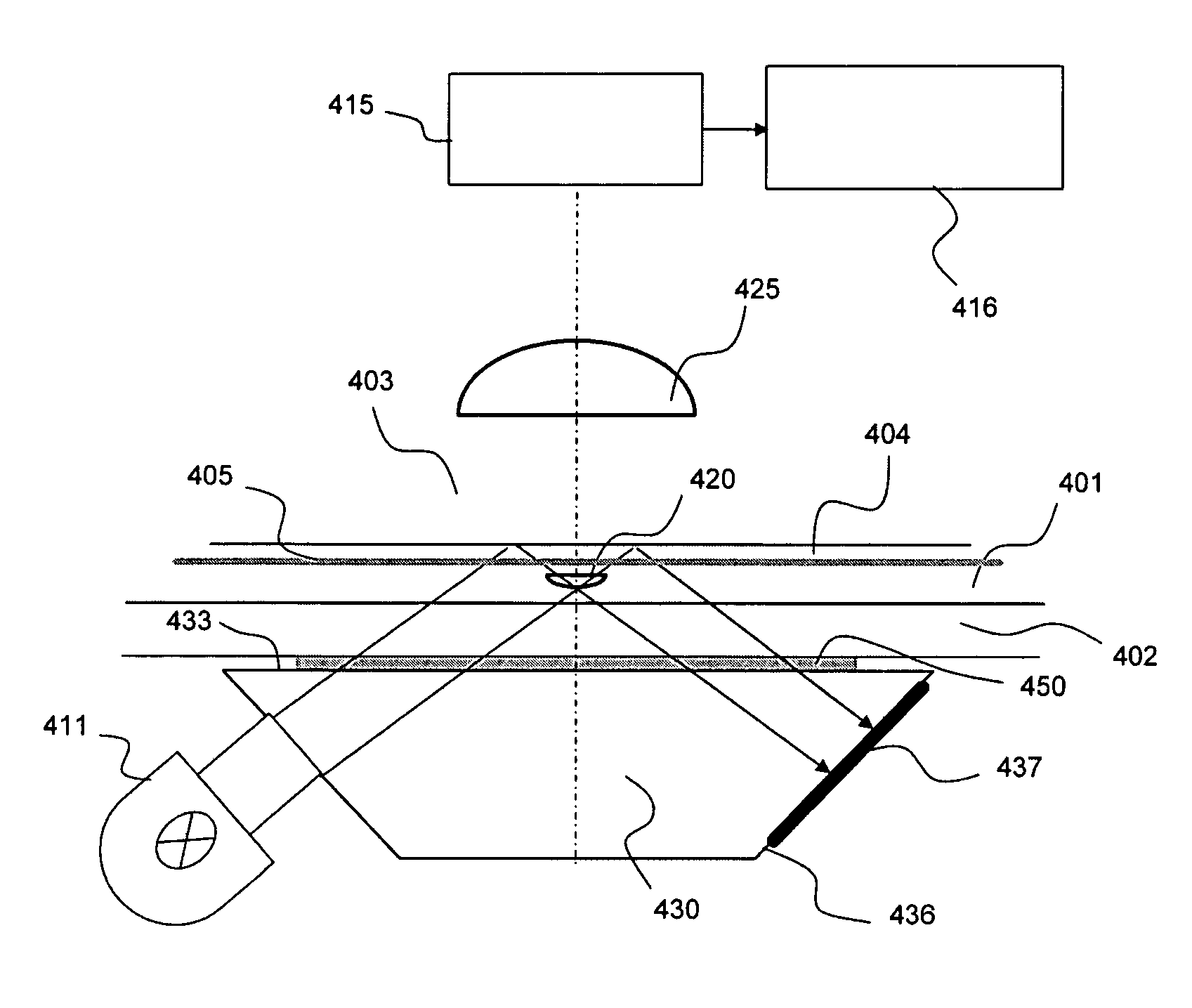
InactiveUS20150233701A1Enhanced OCT measurement and imagingReduce impactDiagnostics using vibrationsMaterial analysis by optical meansDifferential signalingConcentrations glucose
The invention teaches a method, apparatus and system for enhancing measurement and imaging using optical coherence tomography (OCT) by using a pressure wave, such as ultrasound, in conjunction with OCT to make measurements and generate images of a target. The pressure signal modulates the refractive index of the target at high speed, thereby disrupting the generation of a constant speckle noise pattern and thereby reducing speckle noise. The pressure signal can also be switched between at least two states at high speed which enables acquiring a high speed differential signal related weak scattering sites thereby enabling enhanced measurement and imaging of targets such as tissue. In the particular case of measurement of the concentration of glucose in tissue, differential signals enhance the accuracy with which the glucose concentration can be measured.
Owner:HOGAN JOSH
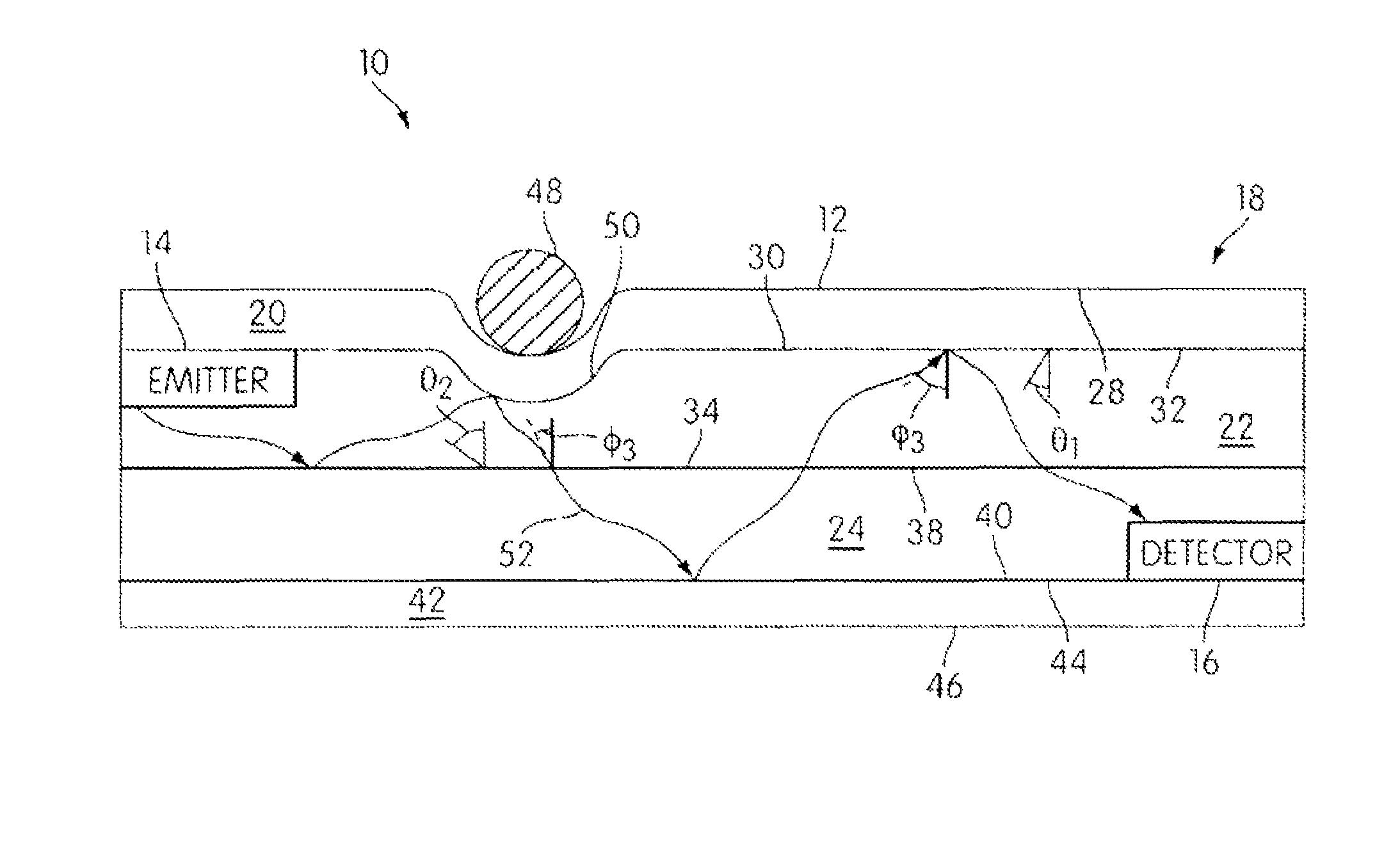
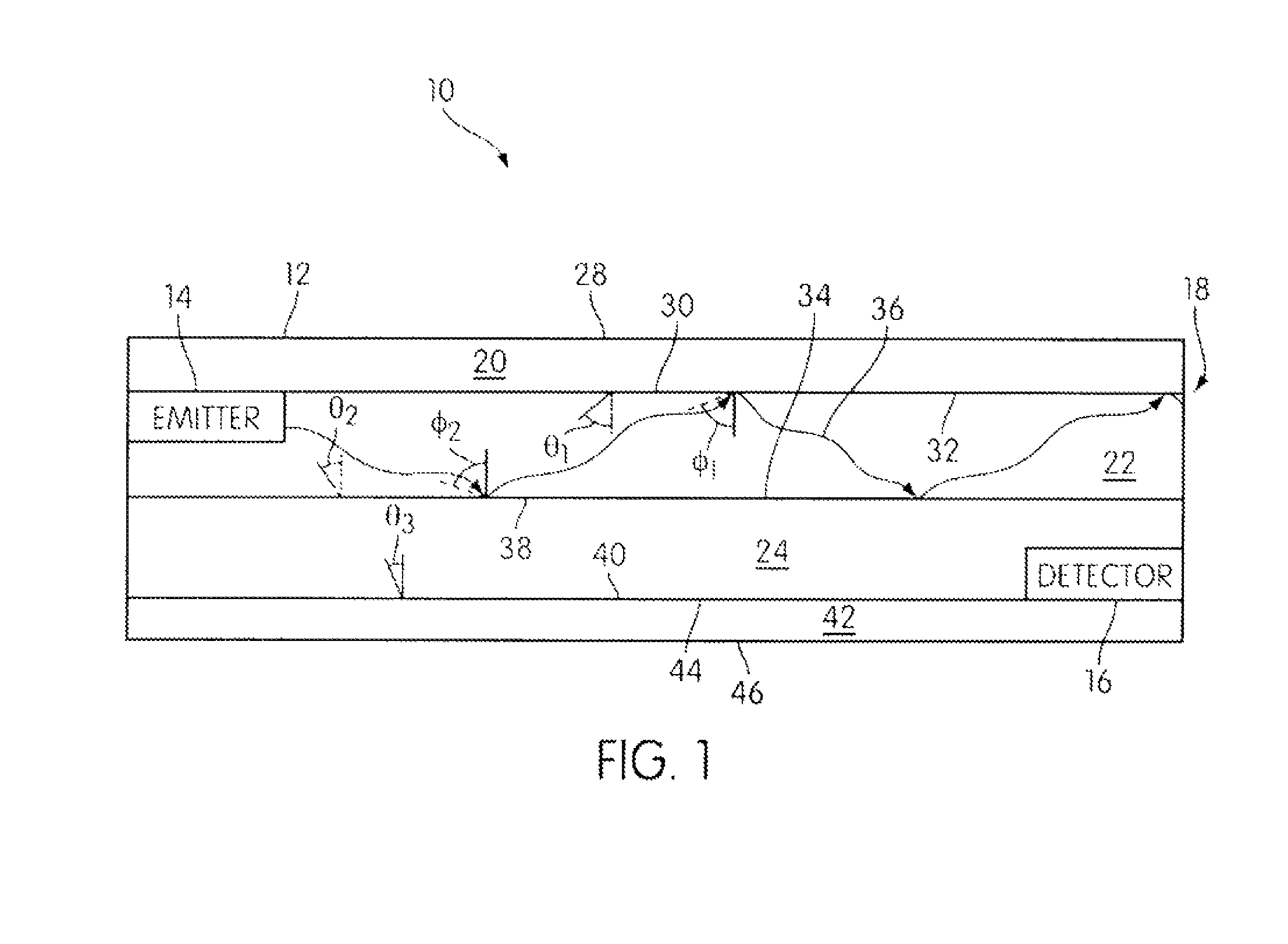
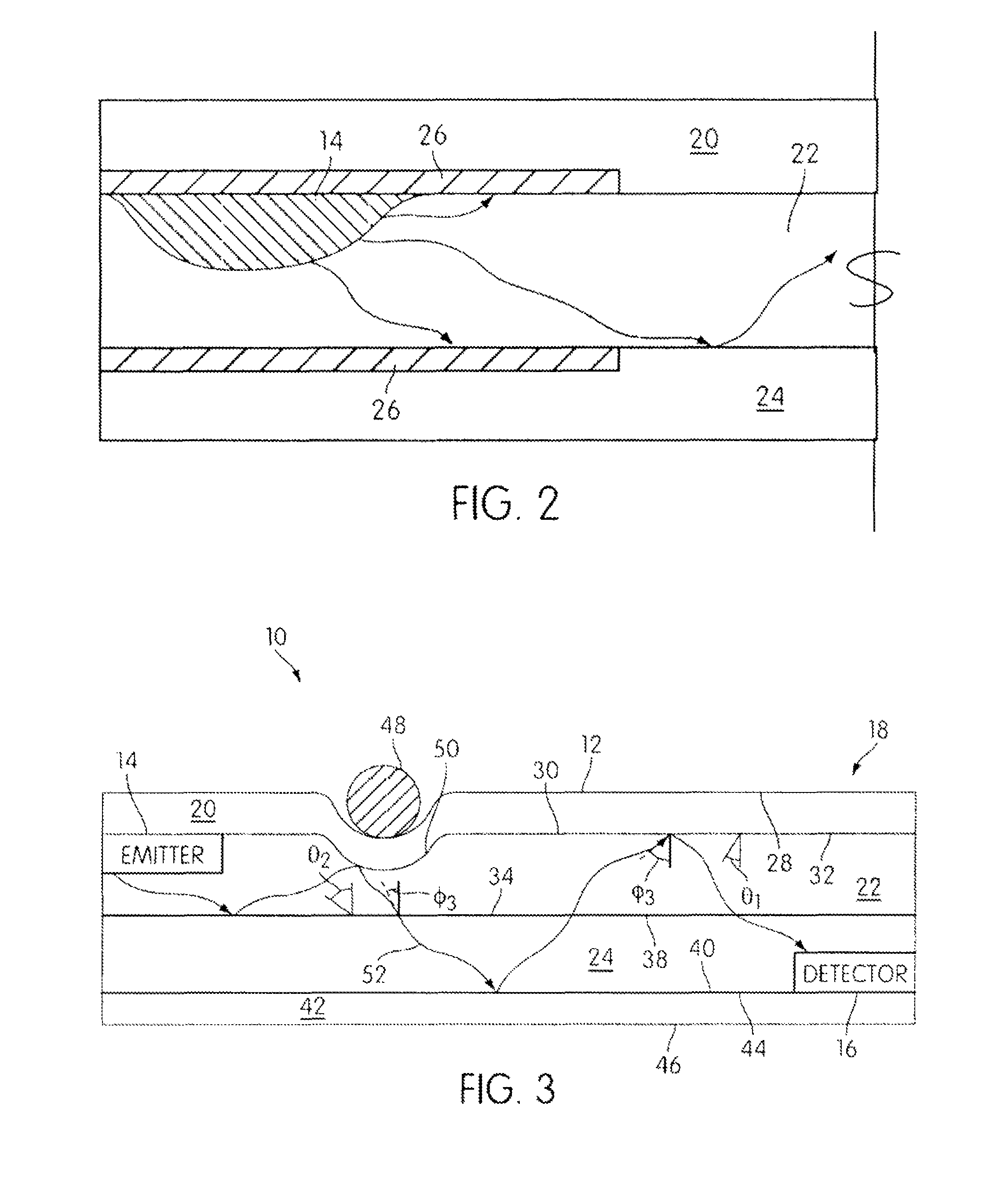
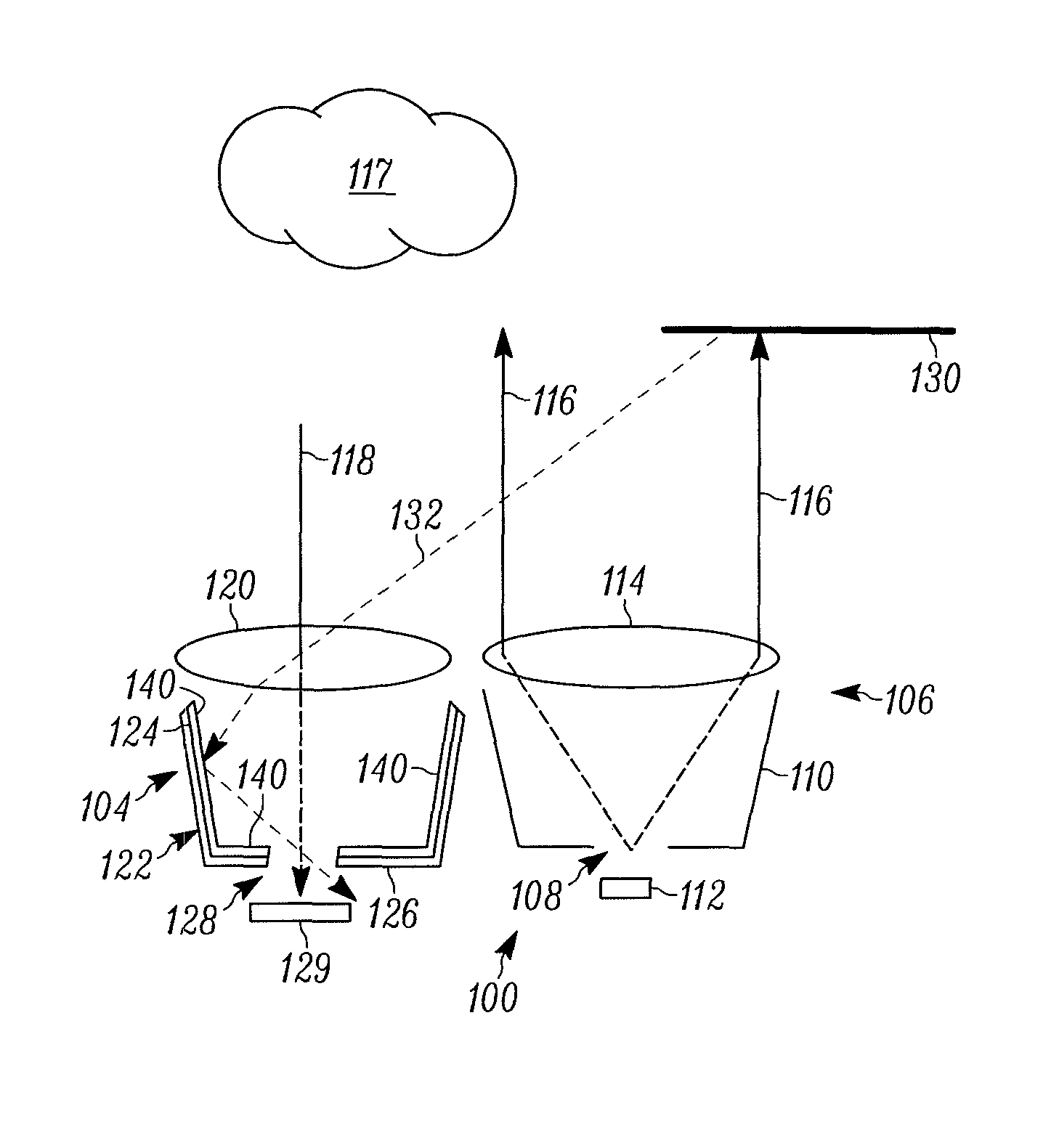
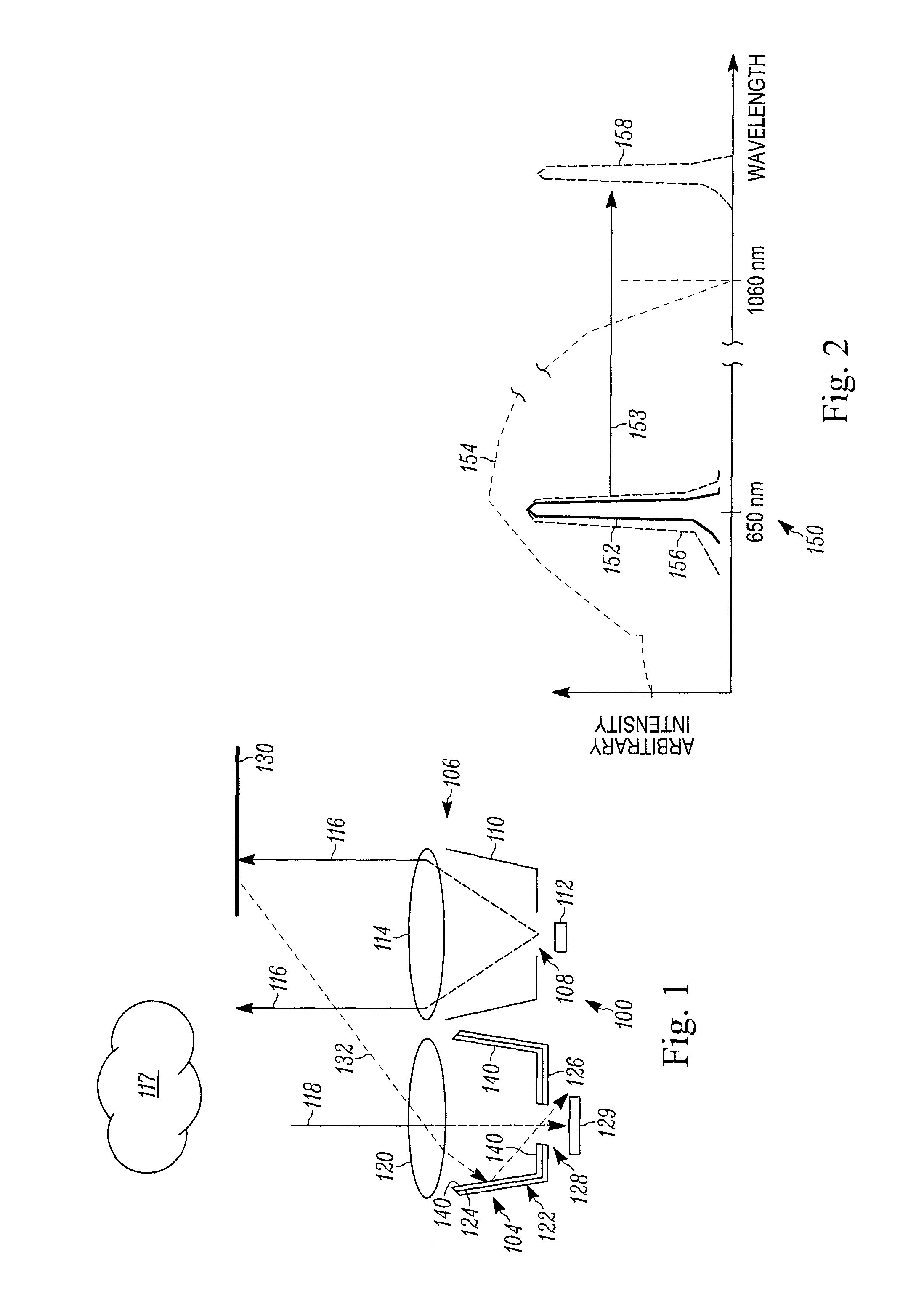
System and method for reduction of optical noise
ActiveUS8480246B2Improve performanceReduce Optical NoisePhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansPhosphorLength wave
A variety of methods and systems are described that relate to reducing optical noise. In at least one embodiment, the method includes, emitting a first light having a selected wavelength from a light source, receiving a reflected first light onto a phosphor-based layer positioned inside a receiver, the reflected first light being at least some of the emitted first light that has been reflected by an object positioned outside of a desired target location. The method further includes, shifting the wavelength of the received reflected first light due to an interaction between the received reflected first light and the phosphor-based layer, and passing the received reflected first light with respect to which the wavelength has been shifted through a light detector without detection.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
System and method for reduction of optical noise
ActiveUS20120314410A1Improve sensor performanceImprove performanceMechanical apparatusPhotometryPhysicsOptical noise
A variety of methods and systems are described that relate to reducing optical noise. In at least one embodiment, the method includes, emitting a first light having a selected wavelength from a light source, receiving a reflected first light onto a phosphor-based layer positioned inside a receiver, the reflected first light being at least some of the emitted first light that has been reflected by an object positioned outside of a desired target location. The method further includes, shifting the wavelength of the received reflected first light due to an interaction between the received reflected first light and the phosphor-based layer, and passing the received reflected first light with respect to which the wavelength has been shifted through a light detector without detection.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
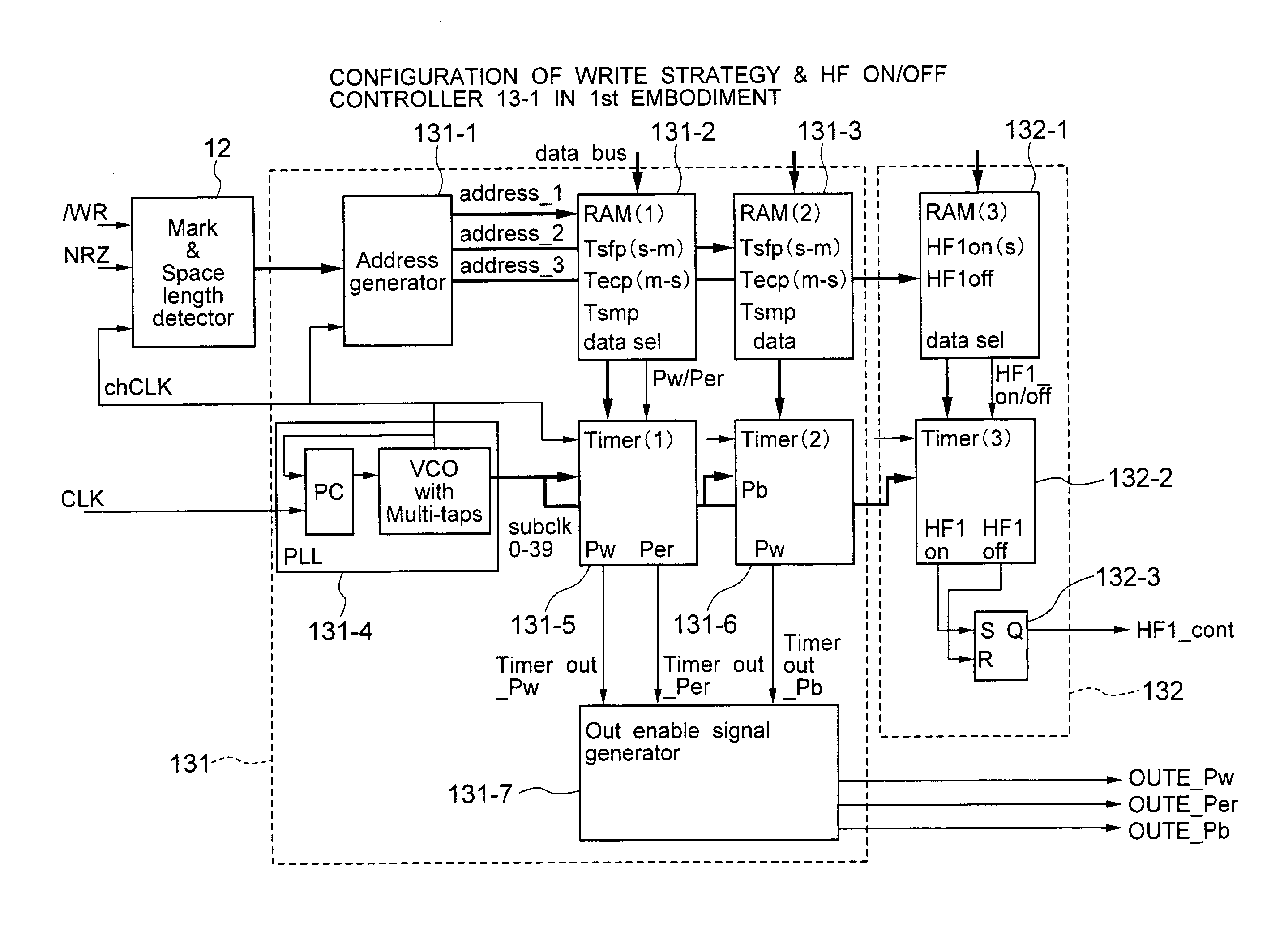
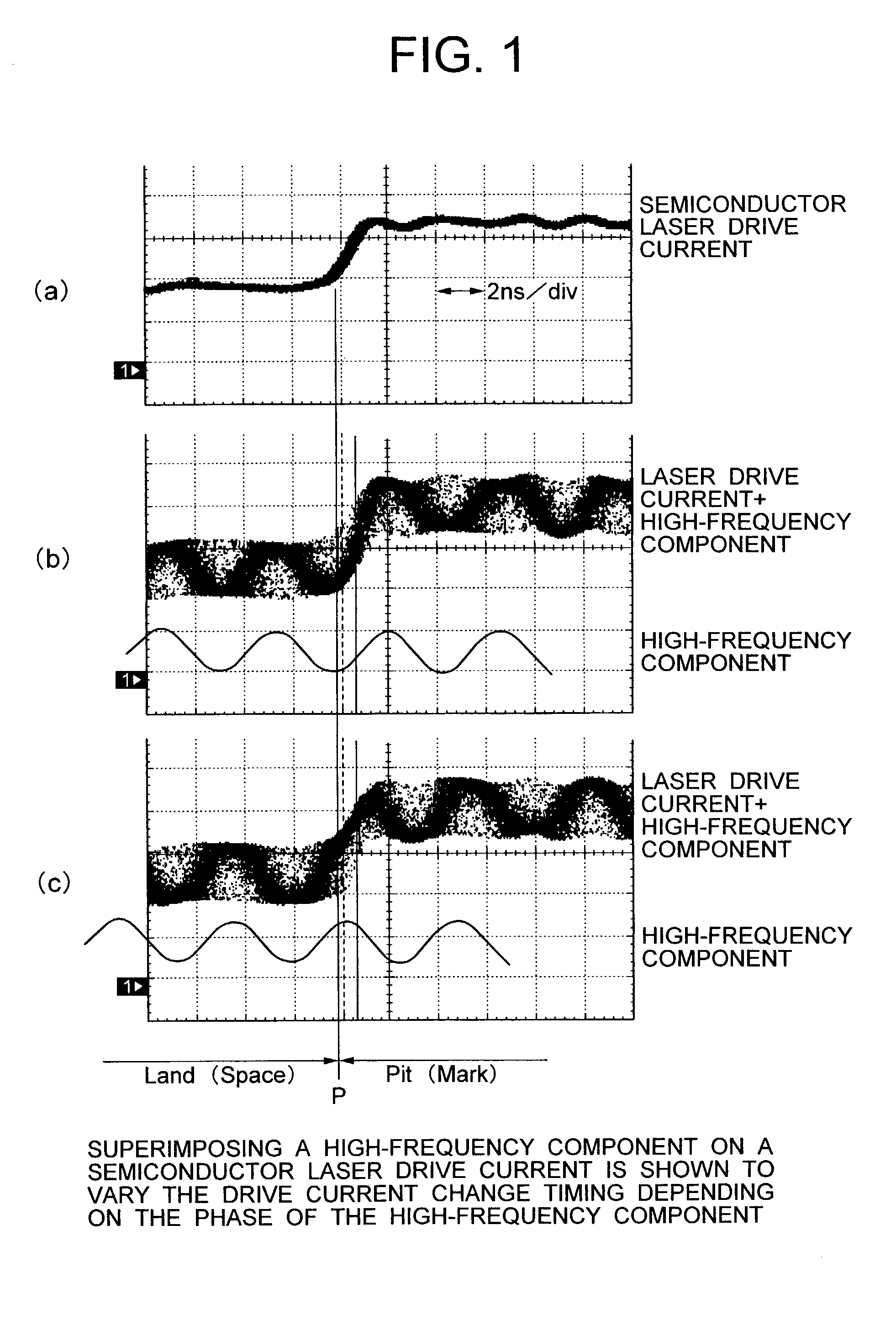
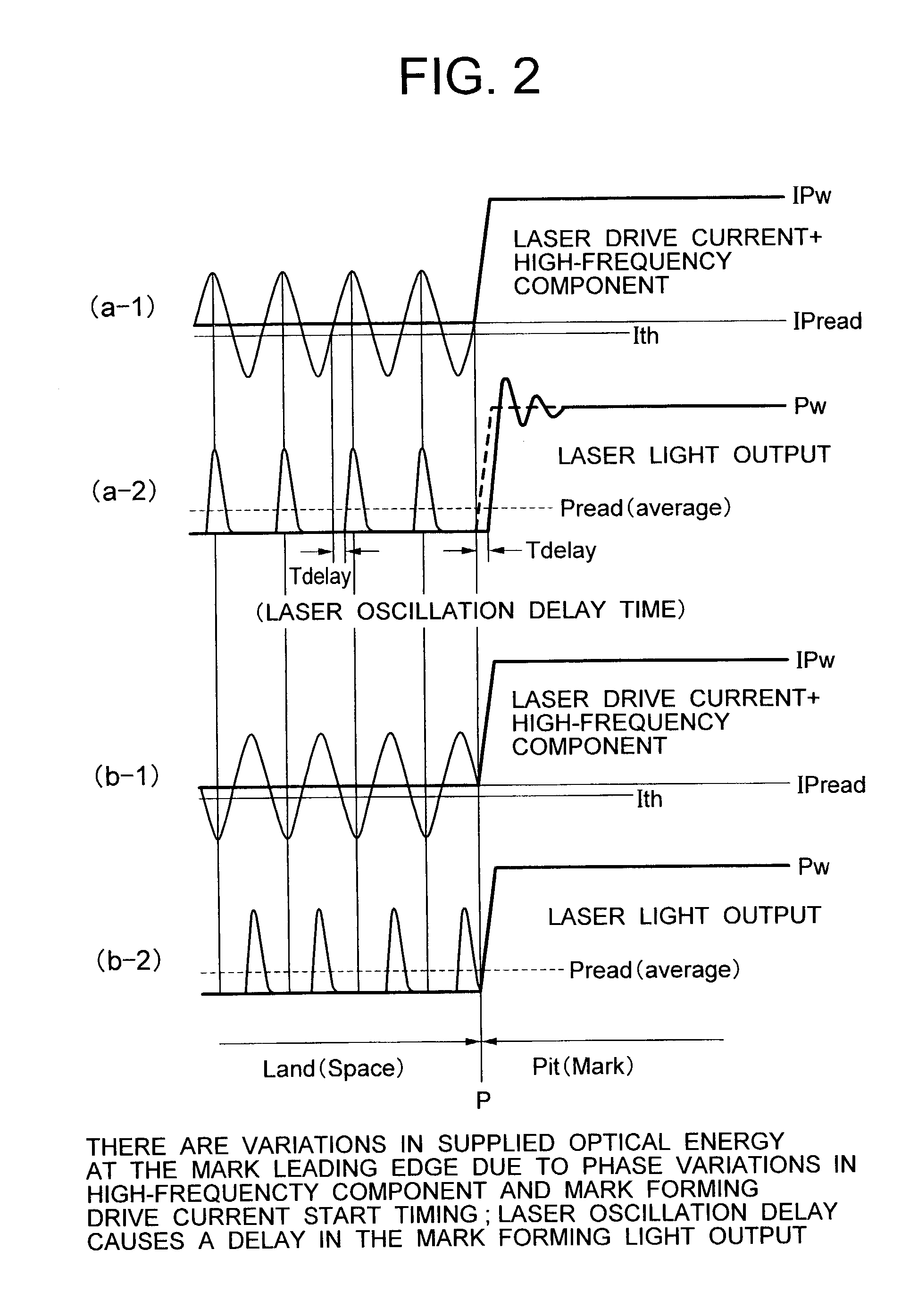
High-frequency superimposing method and optical disk apparatus using it
ActiveUS7038989B2Reduce noiseReduce adverse effectsTelevision system detailsRecording strategiesDriving currentSuperimposition
Owner:HITACHI-LG DATA STORAGE +1
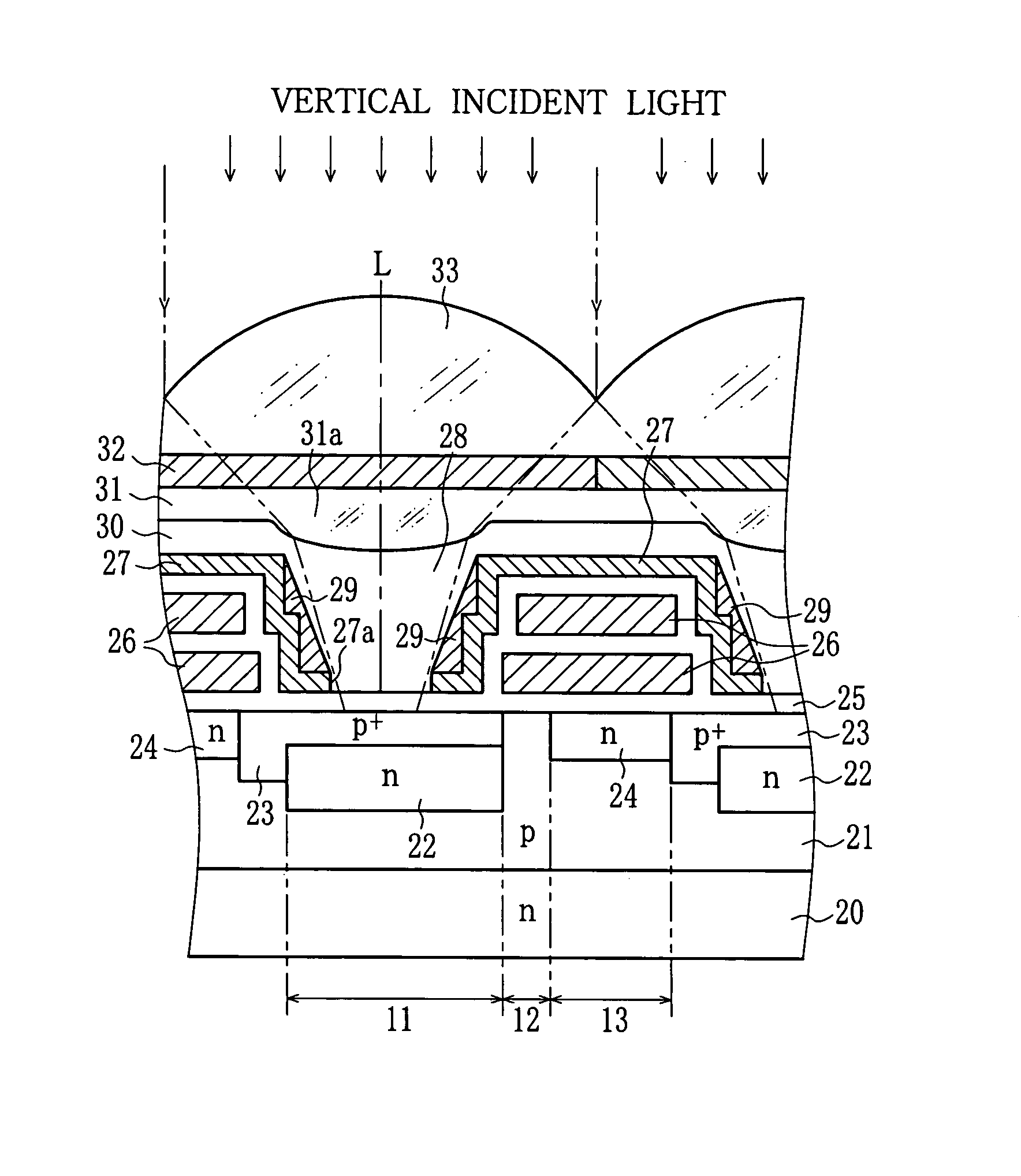
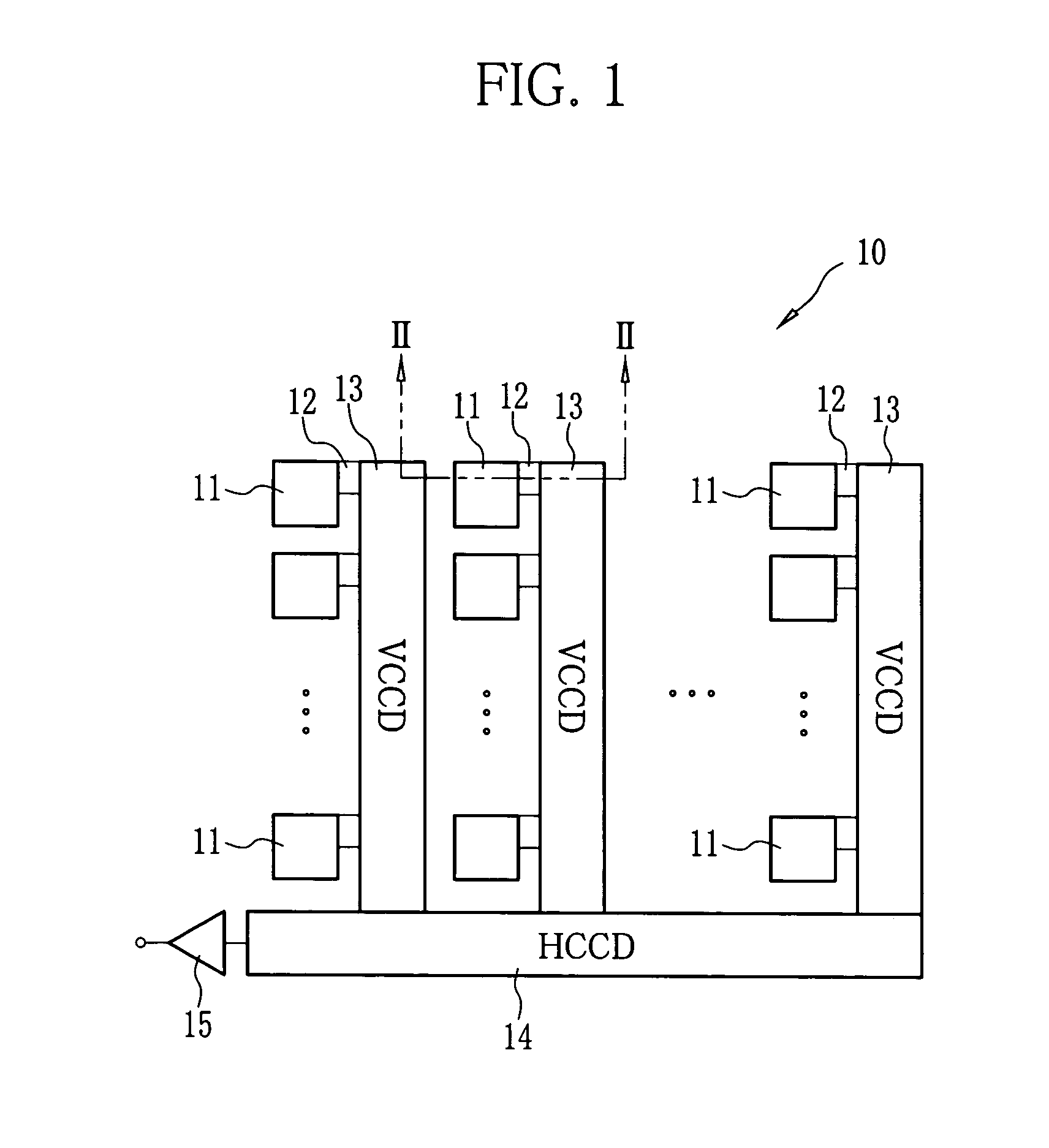
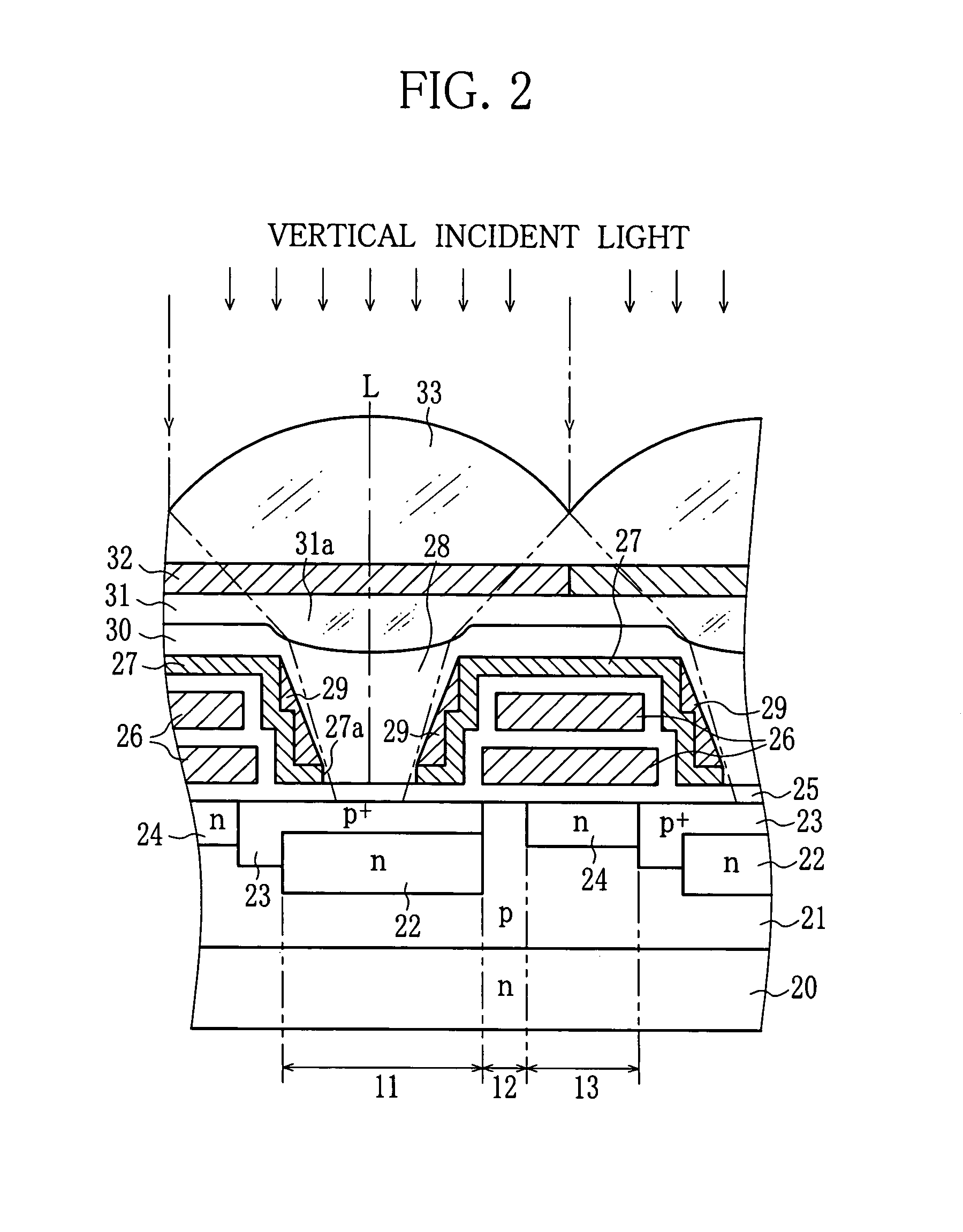
Solid state imaging device
InactiveUS7446356B2Reduce noiseReduce Optical NoiseTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesOptical axisPhotodiode
A CCD image sensor includes photodiodes, vertical transfer CCDs for transferal of signal charge of the photodiodes, and a light shielding layer for protection of the vertical transfer CCDs from light. The light shielding layer covers over recesses disposed above the photodiodes, and each of the recesses has an opening on the bottom to expose a light receiving surface of the photodiode. A light diffusion layer is formed on the light shielding layer in each recess. Since the incident light oblique to an optical axis of a microlens is diffused by the light diffusion layer, the vertical CCDs hardly receive the light coming from around the edges of the opening.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
System and method for reduction of optical noise
ActiveUS8421037B2Improve performanceReduce Optical NoisePhotometryHandling using diaphragms/collimetersPhosphorLength wave
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Wavelength Division Multiplexing Passive Optical Network System
InactiveUS20140355990A1Increasing upstreamIncreasing downstream data bandwidth streamWavelength-division multiplex systemsRadio-over-fibreAudio power amplifierEngineering
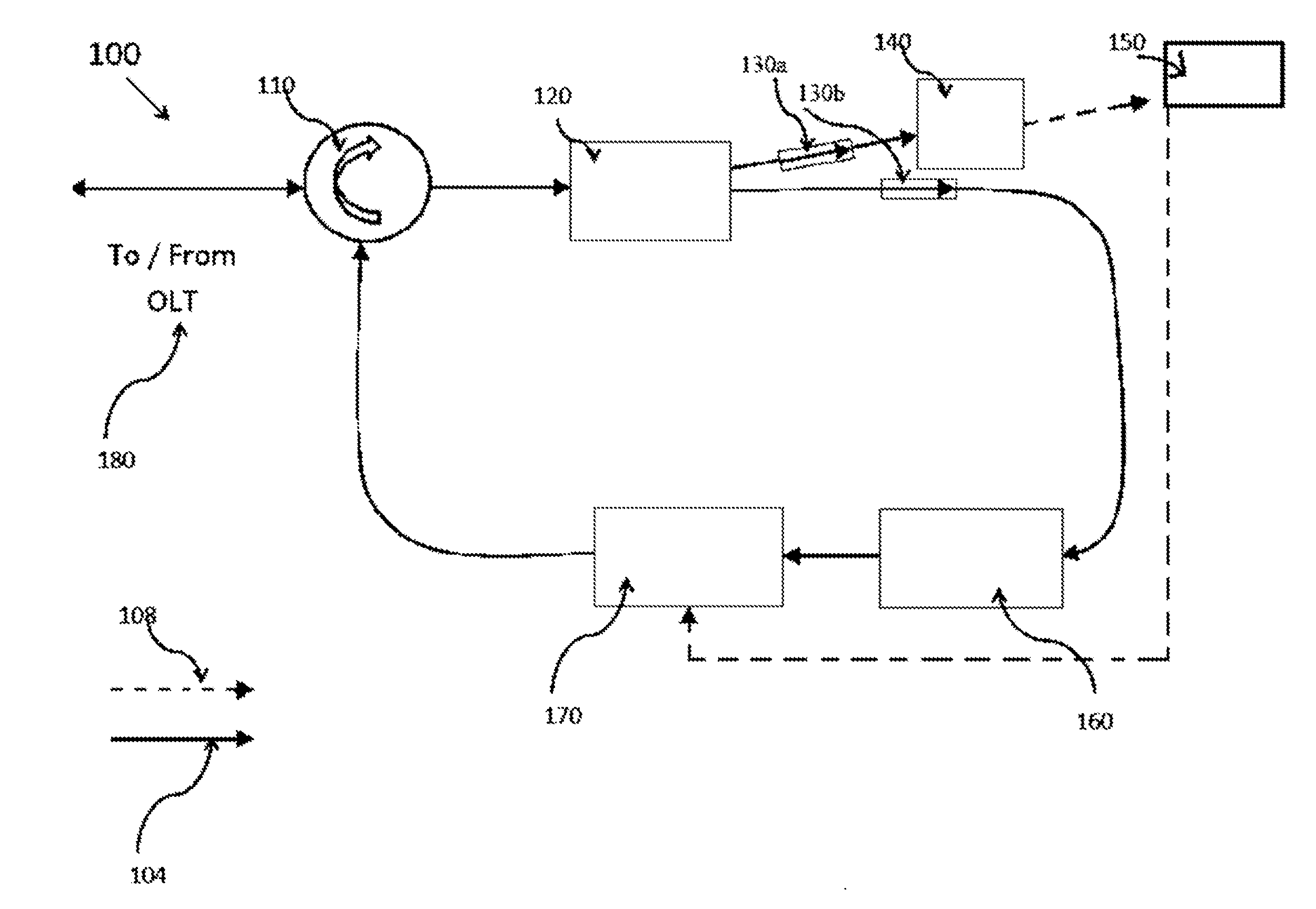
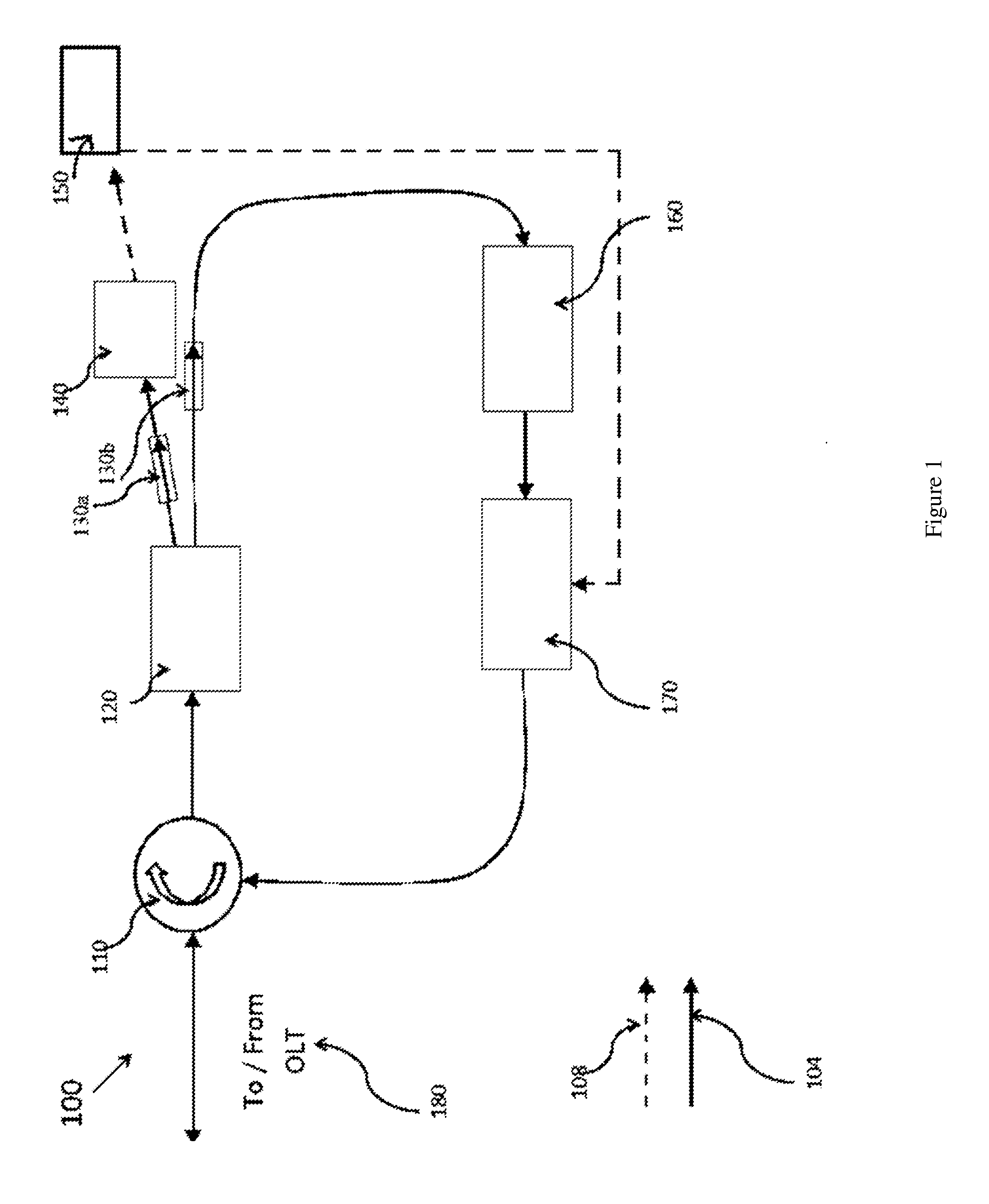
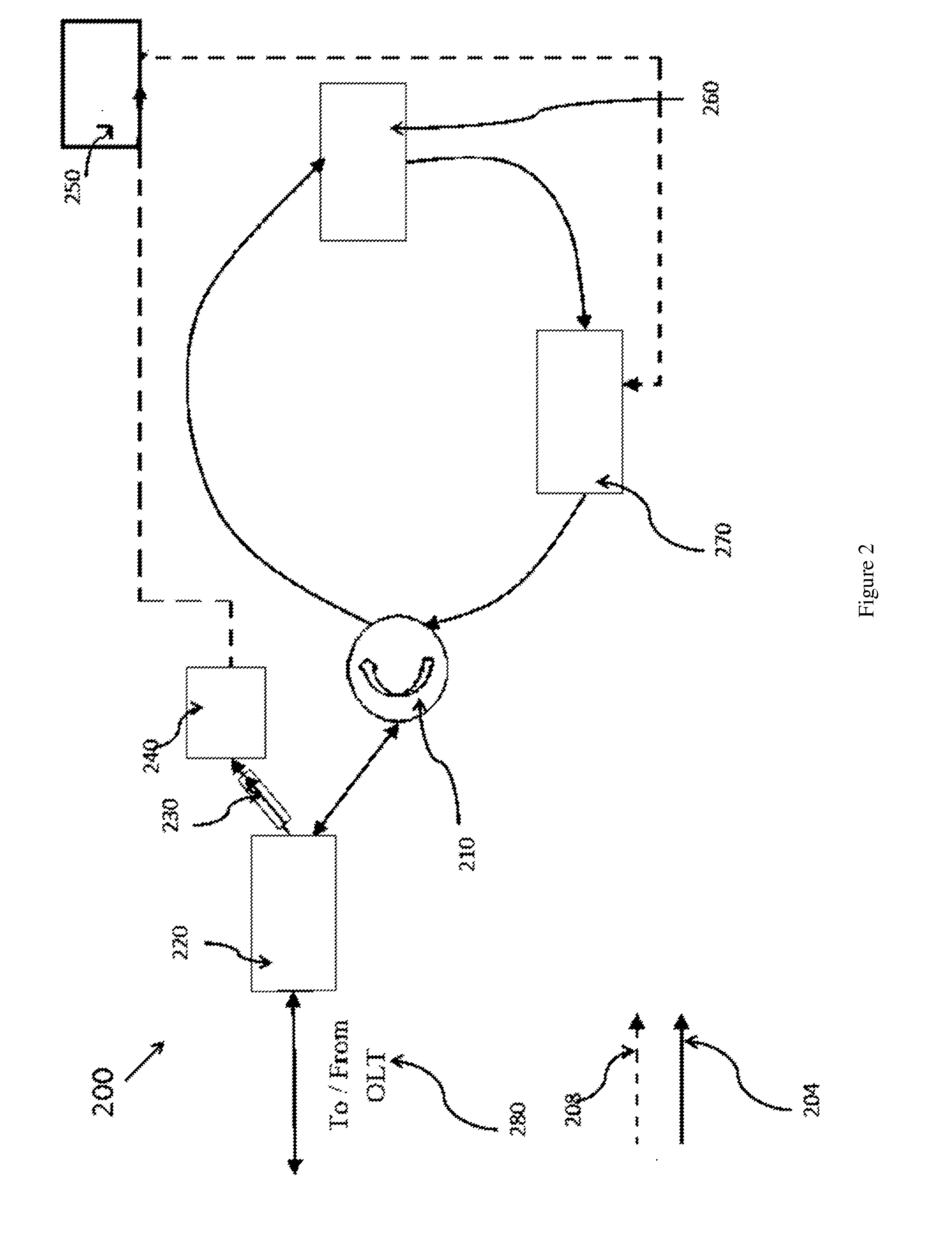
This disclosure describes a wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network system (100) comprising an optical line terminal (180) for controlling transmission of data that are carried by optical signals across the optical network system along an upstream or downstream path; a signal modulating loop circuit including a circulator (110) connected to the optical line terminal (180) for determining the transmission paths of the optical signals; a splitter (120) connected to the circulator (110) for splitting the optical signals into a first portion of optical signals and a second portion of optical signals according to a predetermined ratio; an amplifier (160) connected to the splitter (120) for amplifying the second portion of optical signals; and a modulator (170) connected in between the amplifier (160) and the splitter (120) for modulating the amplified second portion of optical signals to be transmitted to the circulator (110); a converter (140) connected to the splitter (130) for converting the first portion of optical signals into electrical signals; and one or more optical network units (150) connected in between the converter (140) and modulator (170) for receiving the electrical signals from the converter (140), and transmitting electrical signals to the modulator (170) for converting the electrical signals into optical signals to be transmitted together with the amplified second portion of optical signals to the optical line terminal (180); wherein the circulator (110) directs the optical signals received from the modulator (170) to the splitter (120) for being transmitted back into the signal modulating loop circuit and / or towards the optical network units along the downstream path, or towards the optical line terminal along the upstream path.
Owner:TELEKOM MALAYSIA BERHAD
Monolithic integrated optical accelerometer based on phase detection
ActiveCN110133321AReduce volumeImprove reliabilityAcceleration measurementSpeed/acceleration/shock instrument detailsElectricityAccelerometer
The invention discloses a monolithic integrated optical accelerometer based on phase detection. The monolithic integrated optical accelerometer comprises a wide-spectrum light source, a spot size converter, a photoelectric detector, a one-way isolator, 2:1 and 1:2 type Y waveguides, a spring vibrator structure, upper, middle and lower electrodes, a waveguide reflector, a lithium niobate single crystal film layer, a silicon dioxide buffer layer, a silicon substrate, a refrigerating piece, a magnetic force feedback module and a packaged shell; the spring vibrator structure is located between thetwo branch ends of the 1:2 type Y waveguide; the upper electrode and the lower electrode are located on the outer sides of the two branches of the 1:2 type Y waveguide; the middle electrode is located on the upper surface of a mass block of the spring vibrator structure; light is coupled into the 2:1 type Y waveguide through the spot size converter and then enters the 1:2 type Y waveguide throughthe one-way isolator to realize light splitting; and two beams of the light are reflected by the waveguide reflector, are coupled into the branches of the 2:1 type Y waveguide and then are directly coupled into the photoelectric detector. The monolithic integrated optical accelerometer disclosed by the invention is high in detection precision, small in size, simple in preparation process and highin reliability and environmental adaptability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
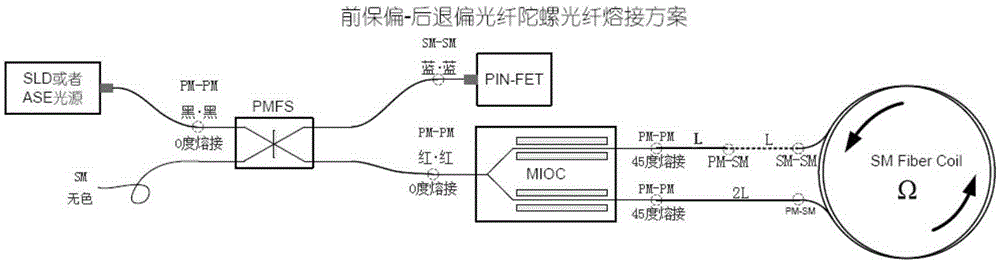
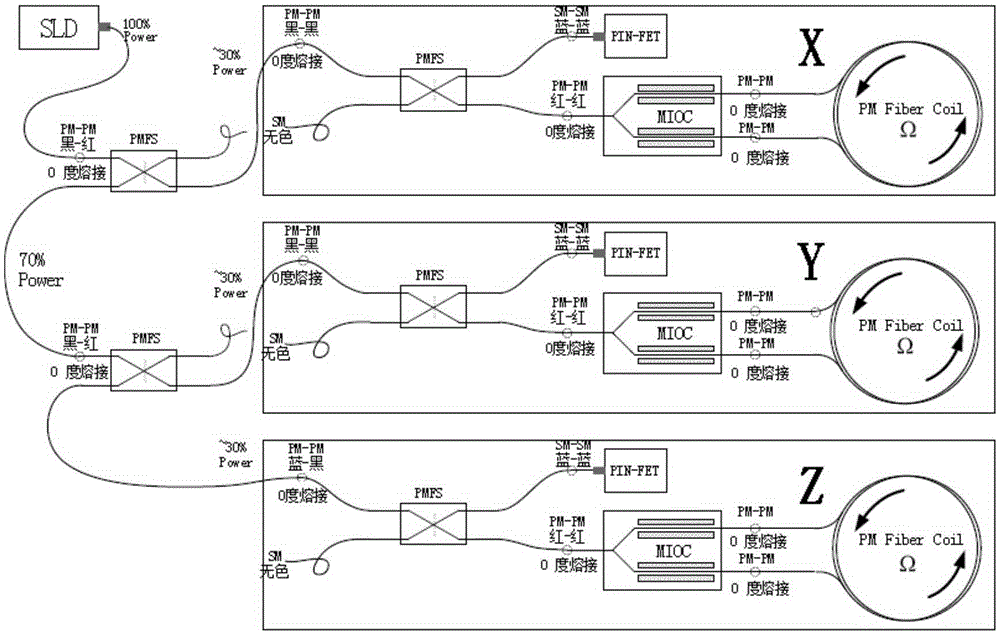
Optical device matching scheme for fiber-optic gyroscopes
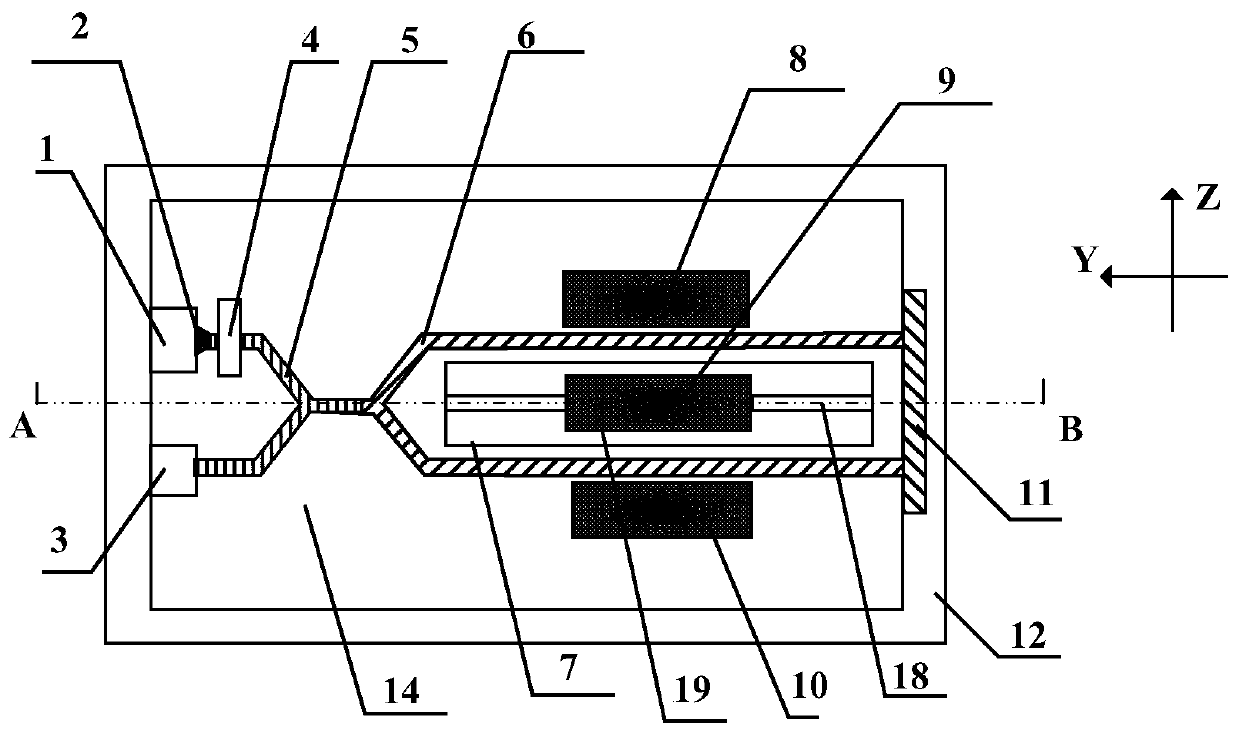
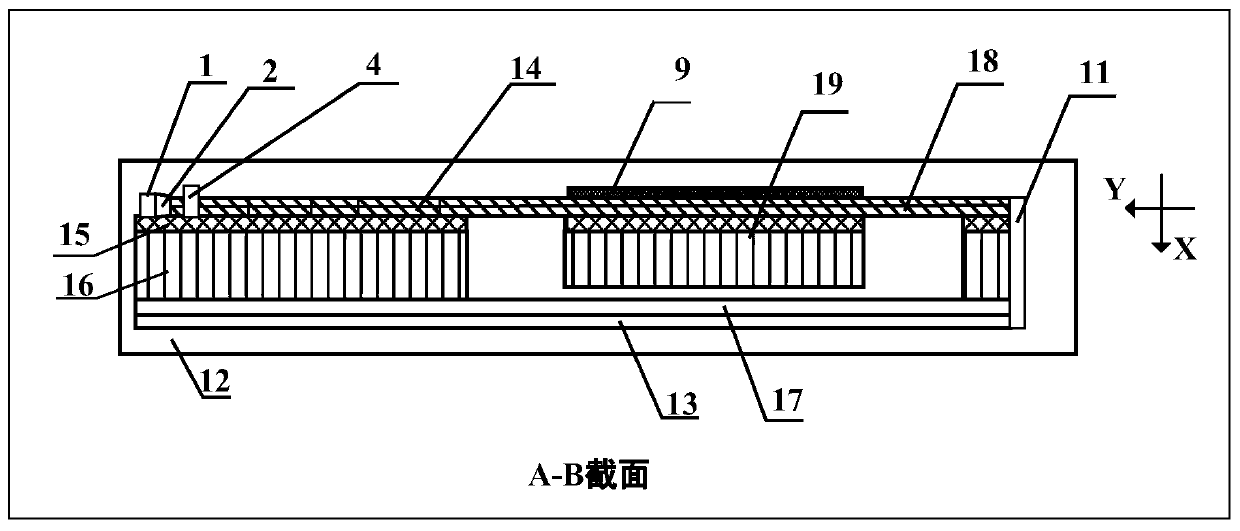
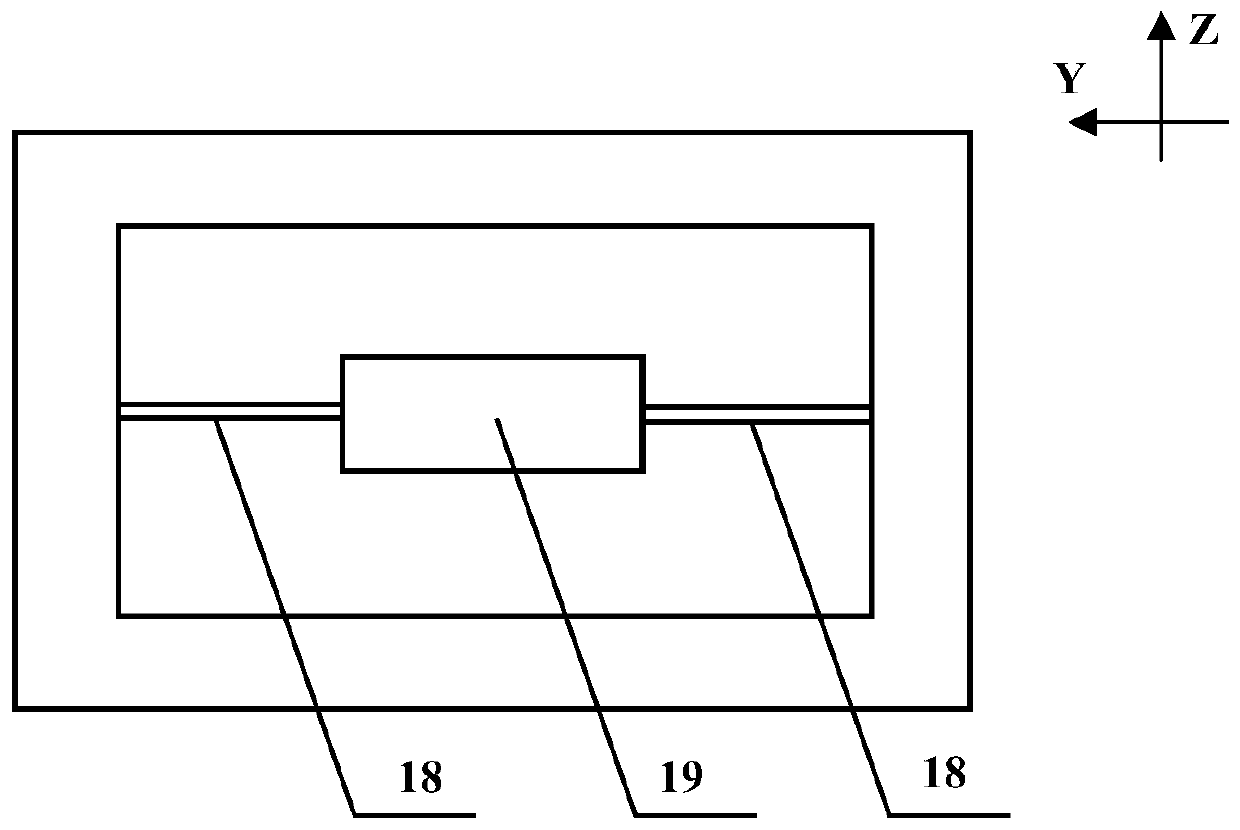
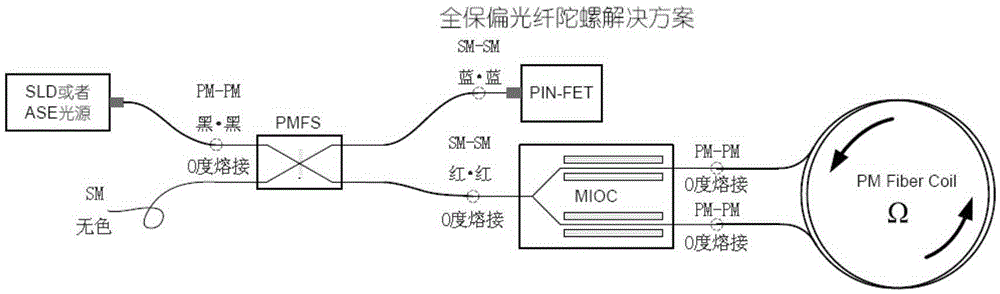
InactiveCN106556387AReduce Optical NoiseImprove first-pass yieldSagnac effect gyrometersFiberGyroscope
The invention relates to an optical device matching scheme for fiber-optic gyroscopes. The matching technology adopts an interferometric fiber optic gyroscope optical path design theory, realizes optical fiber type matching, optical power matching, optical polarization matching and spectrum matching, well solves the problems of low finished product rate, low performance index, unstable process, low production efficiency and other difficulty problems that are caused by optical device mismatching and trouble the fiber-optic gyroscope industry for years from theory, engineering, technology, product quality and other levels.
Owner:北京浦丹光电股份有限公司
End point detection in workpiece processing
ActiveUS20070121123A1Reduce Optical NoiseAccurate detectionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesUltimate tensile strengthOptical noise
In a workpiece process end point detection system, light is diffused and then light intensity or color is sensed. Optical noise is greatly reduced and more accurate end point detection can be made. A light emitter and a light sensor may be located within a workpiece process chamber. A housing around the light emitter and the light sensor seals out process fluids and also diffuses light passing through. The diffused light may be optically filtered before reaching the light sensor.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
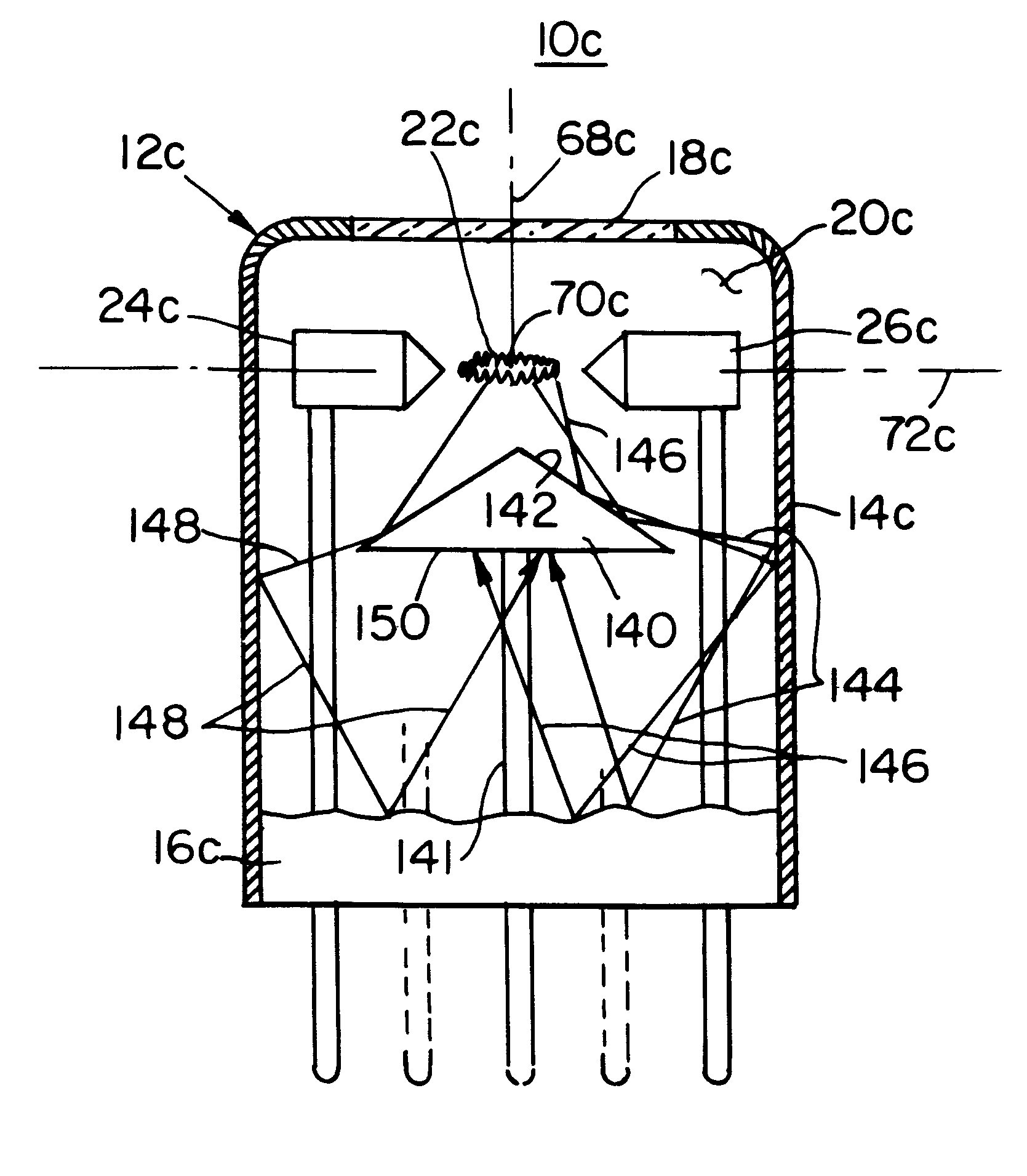
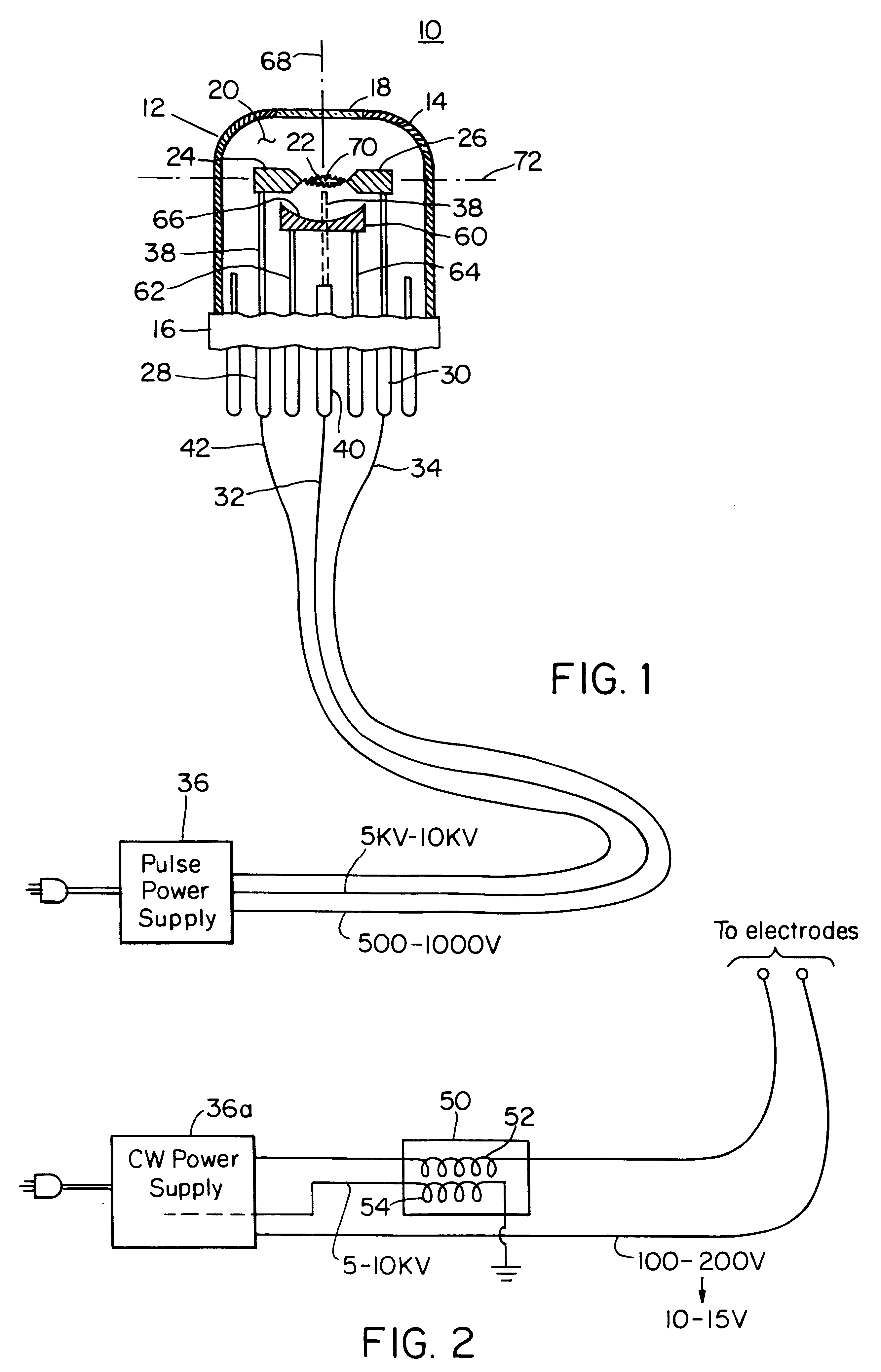
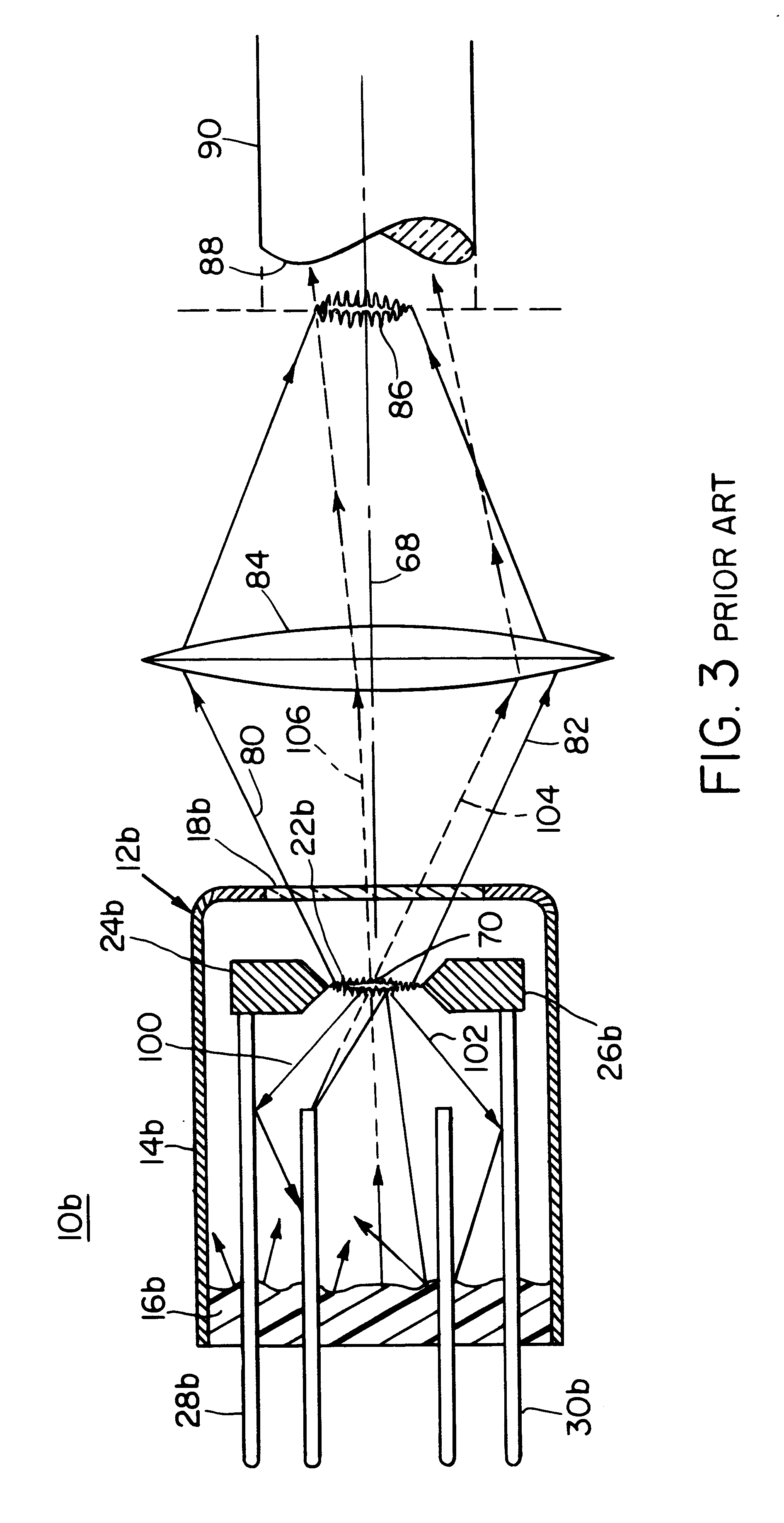
Arc lamp
InactiveUS6274970B1Reduce Optical NoiseReduce heat lossIncadescent screens/filtersElectric discharge tubesArc lampAcoustics
An arc lamp includes a housing; an inert gas in the housing; a pair of spaced electrodes in the housing for establishing an arc in the gas to generate a radiation output; a window in the housing for transmitting forward radiation generated by the arc; and a spherical reflector on the opposite side of the electrodes from the window and having its center disposed in the arc for redirecting rearward radiation through the center to add to the forward radiation transmitted through the window.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
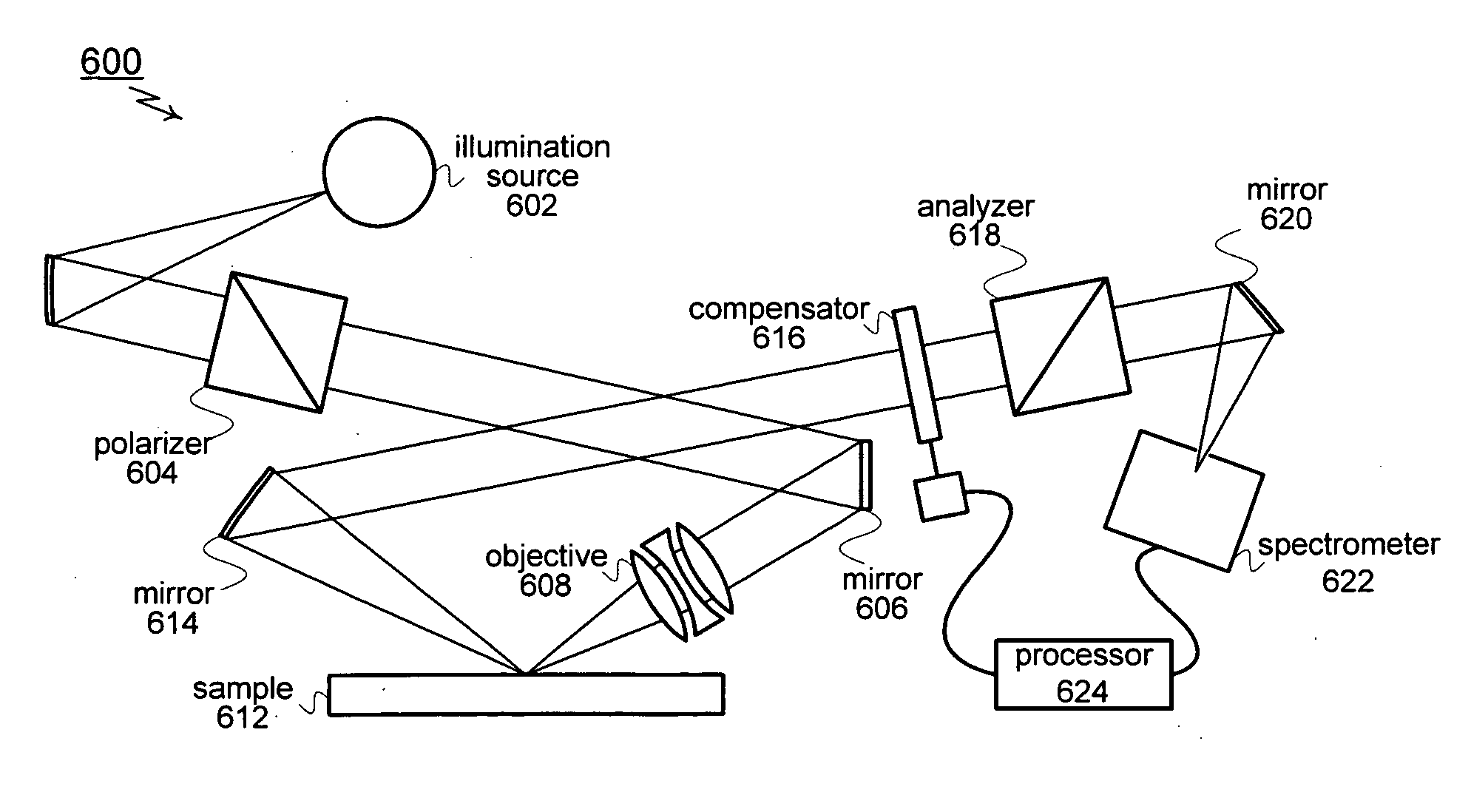
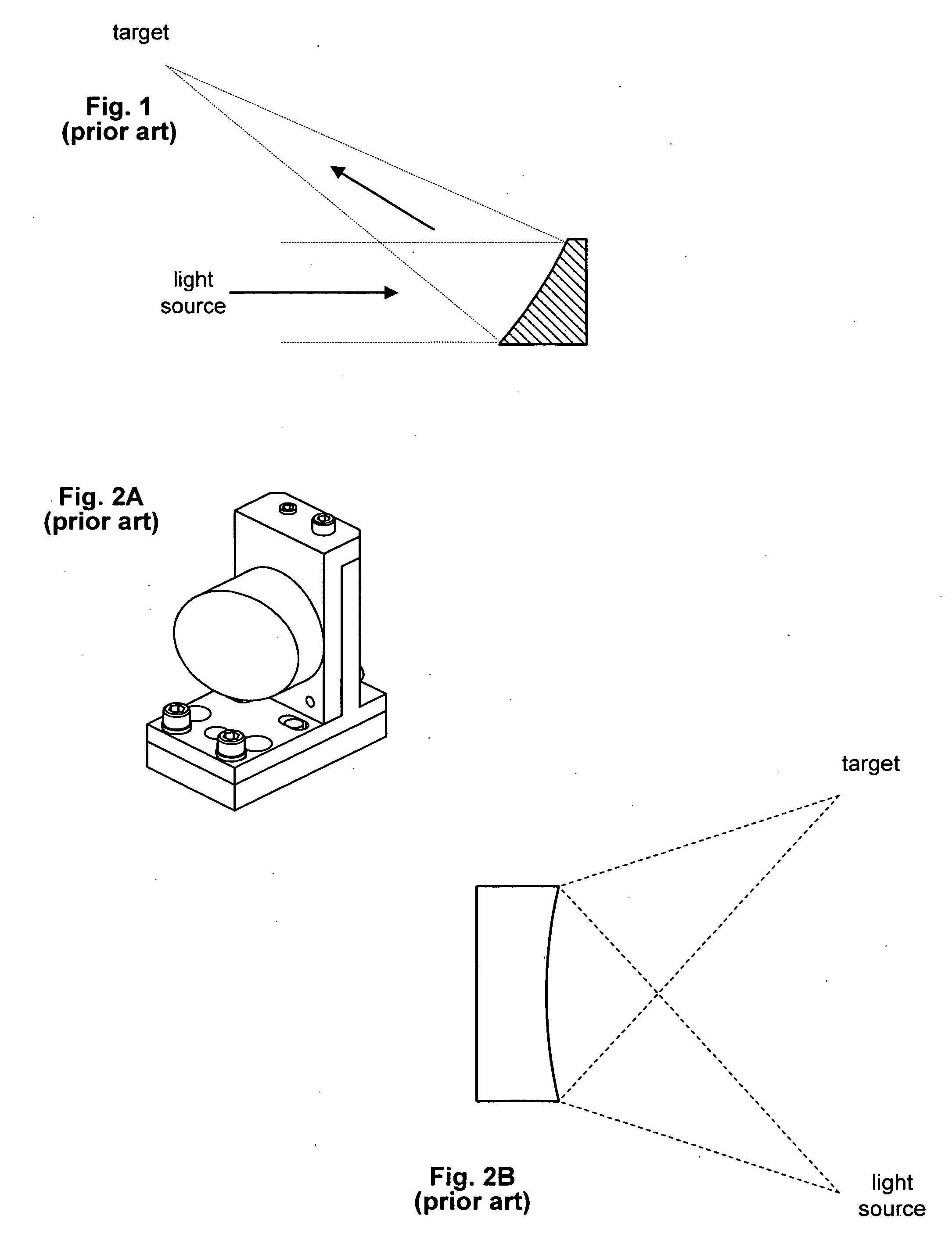
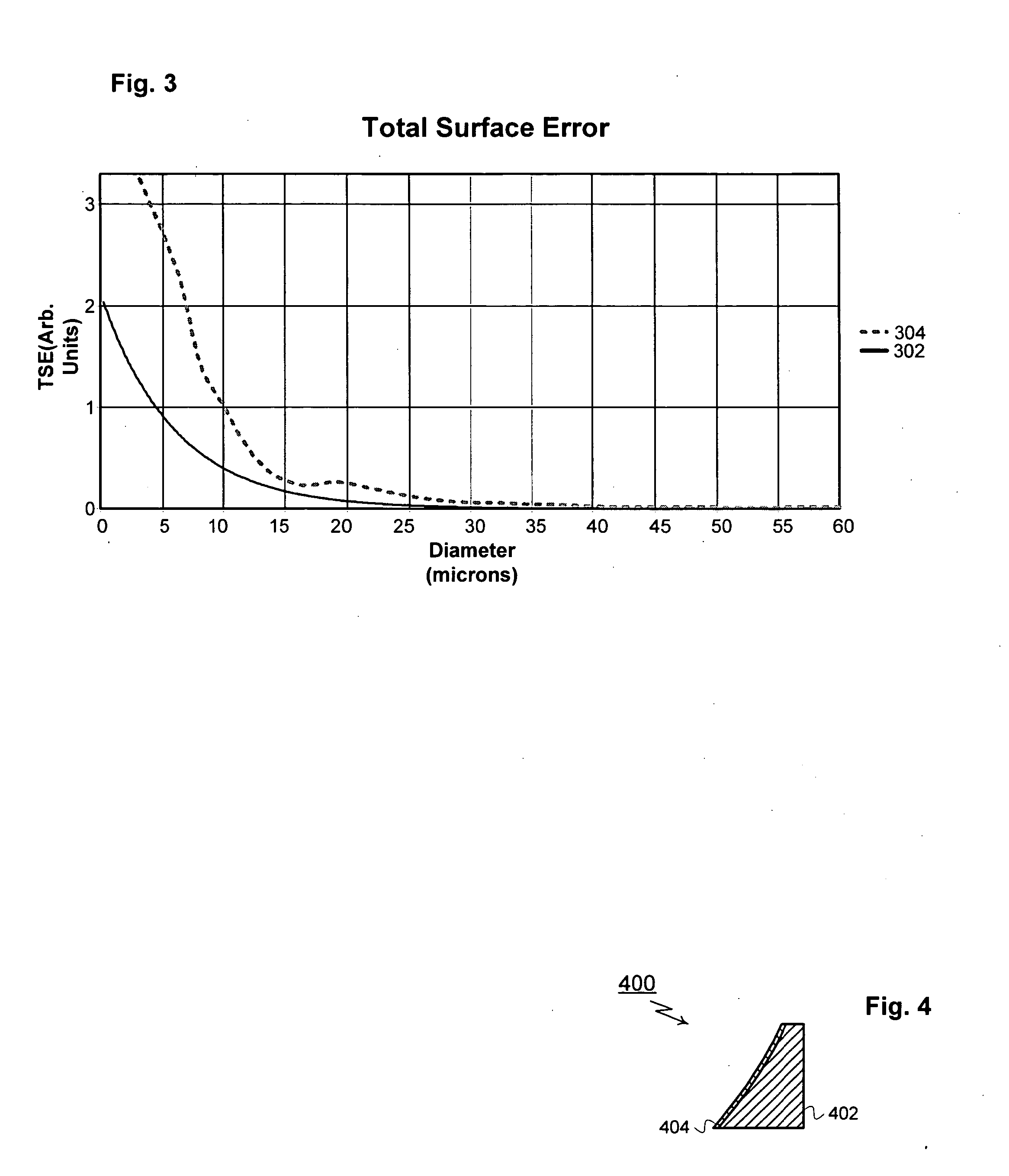
Techniques for reducing optical noise in metrology systems
InactiveUS20070121104A1Improved metrology system performanceReduce scattered lightMirrorsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationLow noiseDiamond turning
A first method for fabricating low-noise optical components for use in optical metrology systems includes shaping a glass substrate to obtain a desire shape and then coating the glass substrate with a reflective coating. A second method includes shaping a glass master die to a desired shape and then using the glass master to form a glass substrate to the desire shape. A third method includes diamond turning a substrate to a desired shape and then polishing the substrate to meet two surface conditions which in turn ensures that the scattered light is minimized and the metrology instruments performance is greatly increased. These conditions relate to a measurement of encircled energy compared to an ideal diffraction limited component of the same focal length and diameter.
Owner:THERMA WAVE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com