Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40results about How to "Minimize connection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
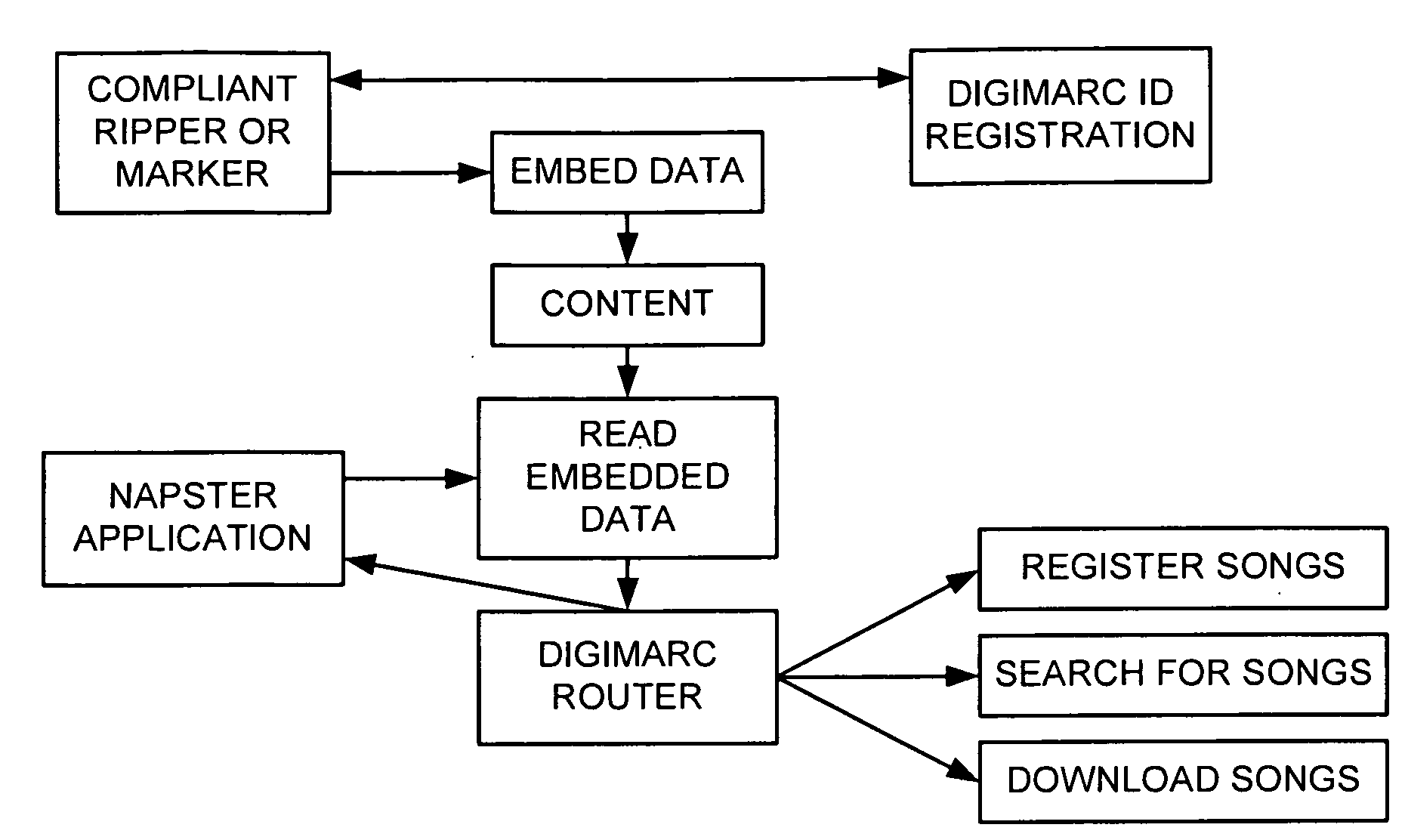
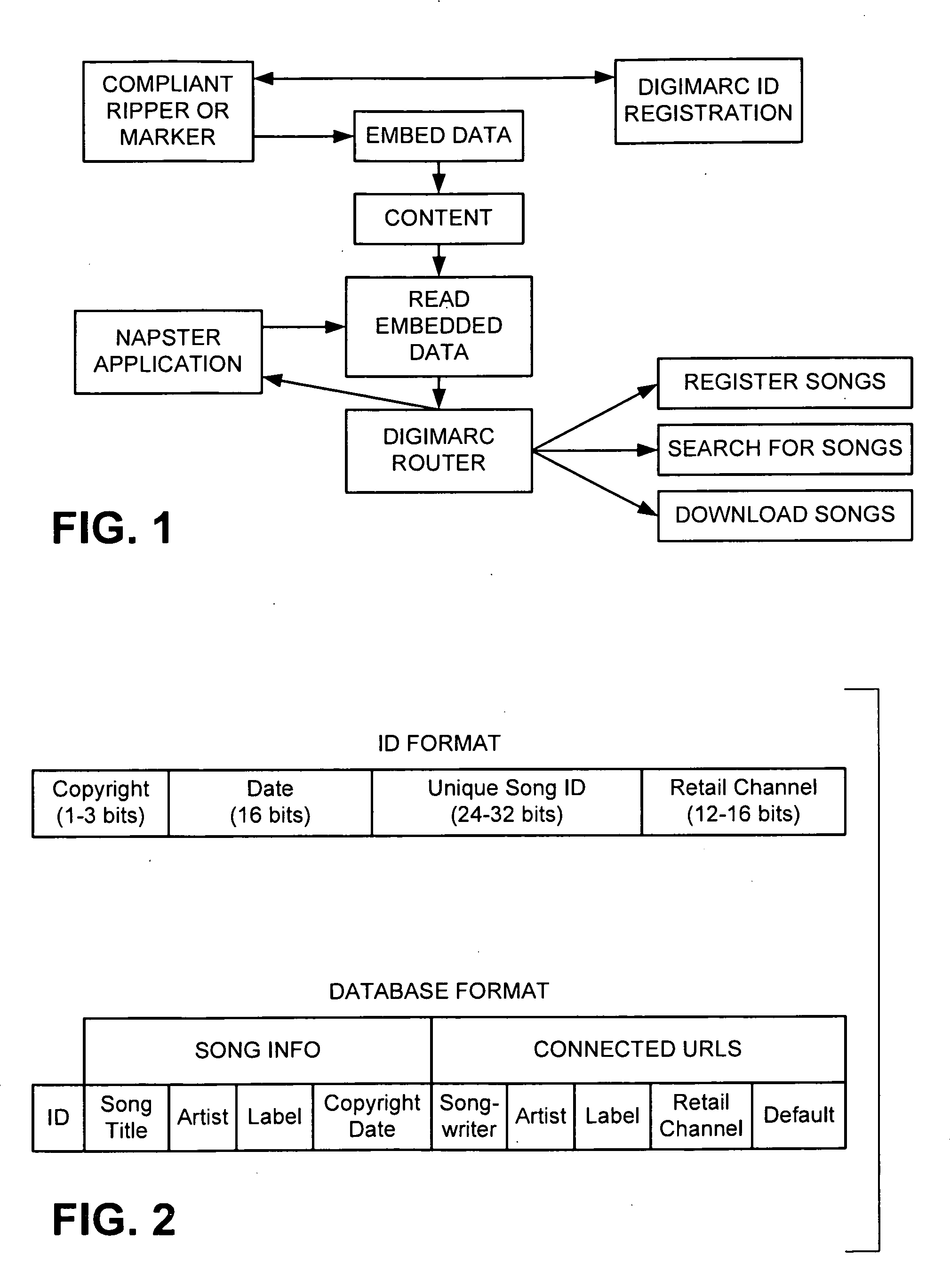
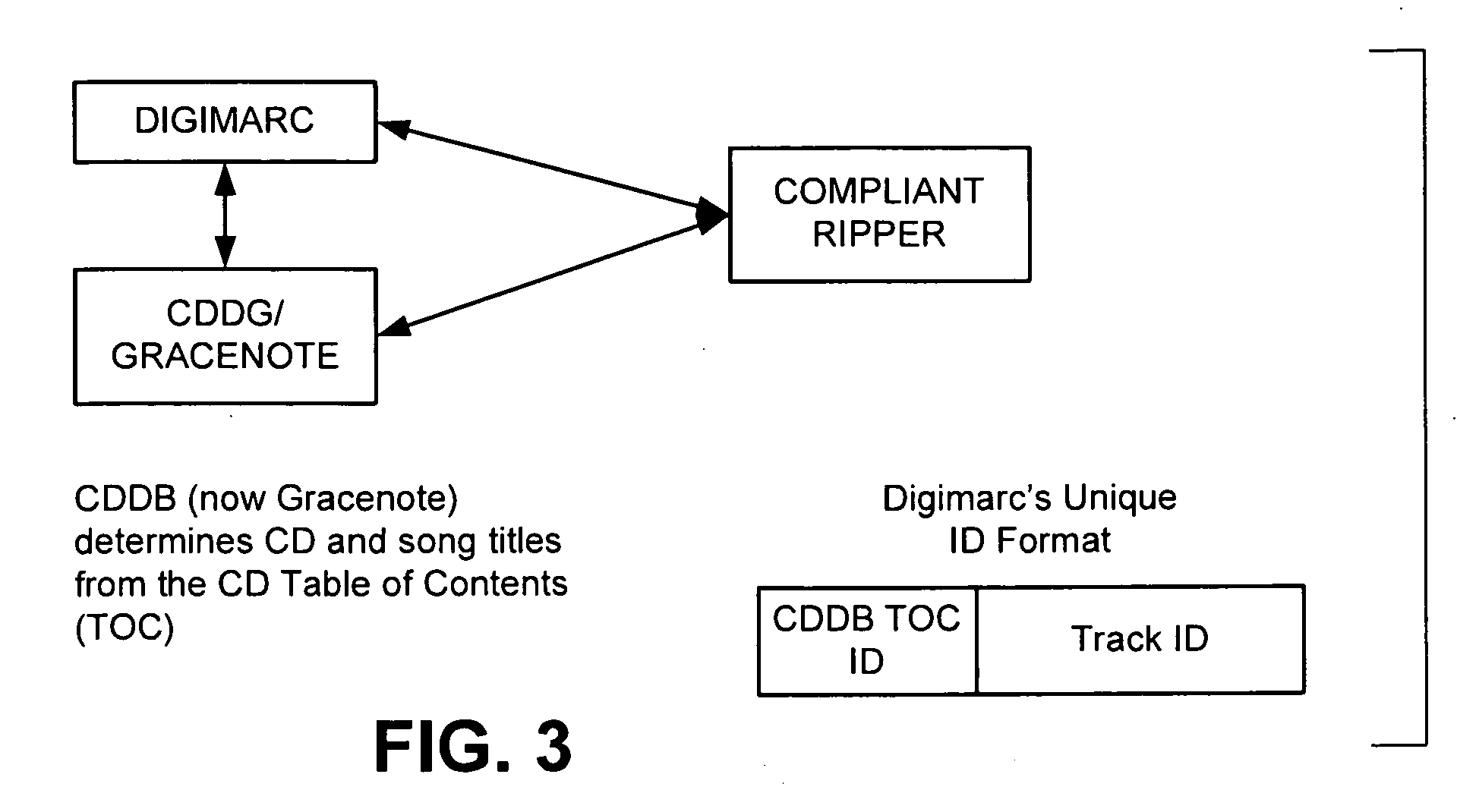
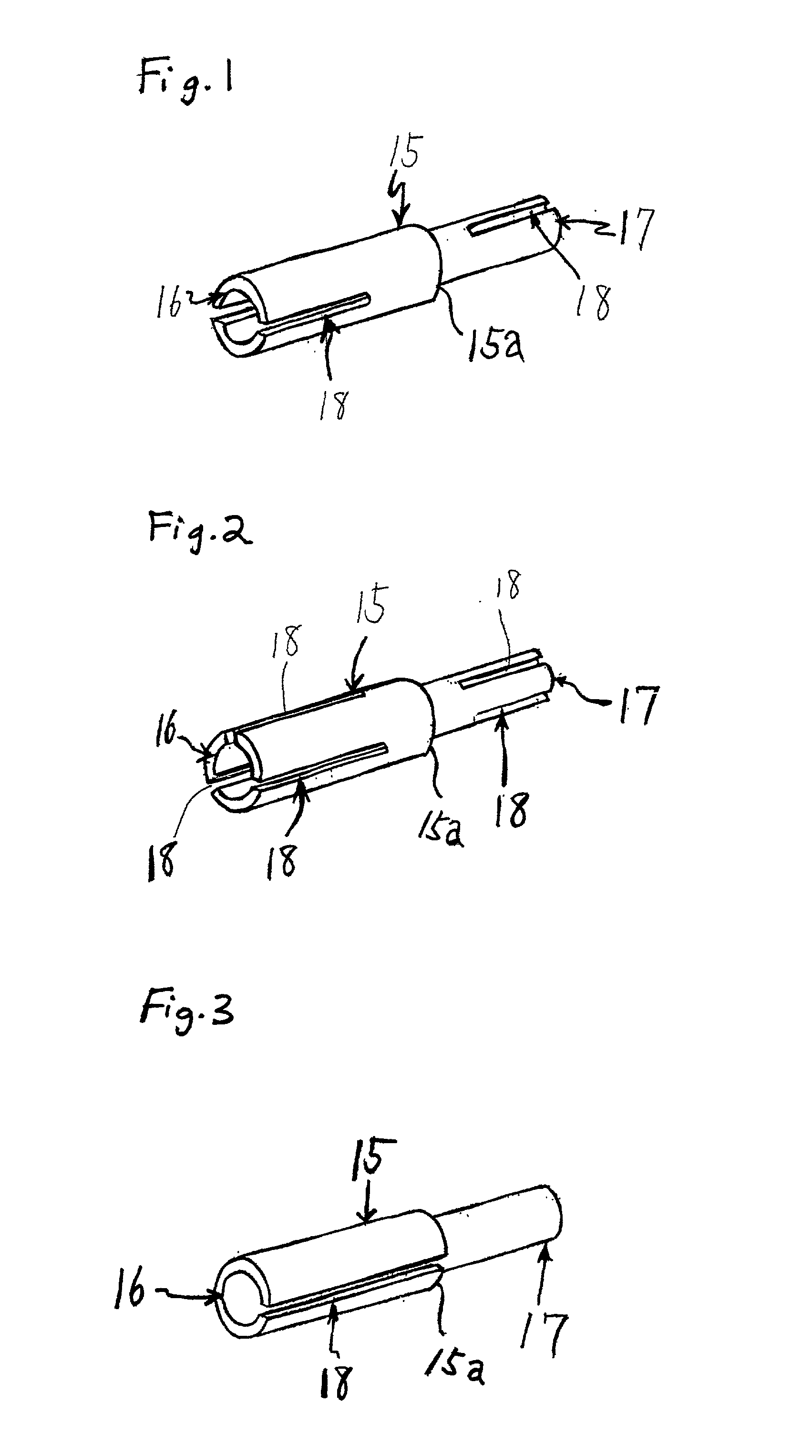
Media Methods and Systems
InactiveUS20090158318A1Good effectImprove service reliabilityTelevision system detailsDigital data authenticationBroadcastingFingerprint
Several novel watermarking and fingerprinting applications—and related improvements—are disclosed. Some relate to advertising. These include techniques for replacing broadcast advertising with other advertising; inserting advertising based on a viewer's ad-viewing history; triggering insertion of advertising based on fingerprint data derived from compressed video content; and discontinuing advertising when a threshold amount of advertising has apparently been viewed. A great number of other features and technologies are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
System and Method for Cryptographic Identification of Interchangeable Parts
InactiveUS20090327715A1Improve securityPart can be usedUser identity/authority verificationEndoscopesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
An anti-counterfeiting identification system for a medical tubing system, including a tubing assembly having upstream and downstream tubing portions removably connected to one another in a mechanically coupled state and a mechanically uncoupled state. The mechanically coupled state is a reliable fluid tight connection of the upstream and downstream portions for fluids passing there through from the upstream portion to the downstream portion. A two-part encrypted identification assembly has a first part connected to the upstream portion and a second part connected to the downstream portion. The first and second parts are electrically connected only through one lead and ground and are electrically connected to one another only in the mechanically coupled state. Also provided are methods for identification, anti-piracy, and inventory.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
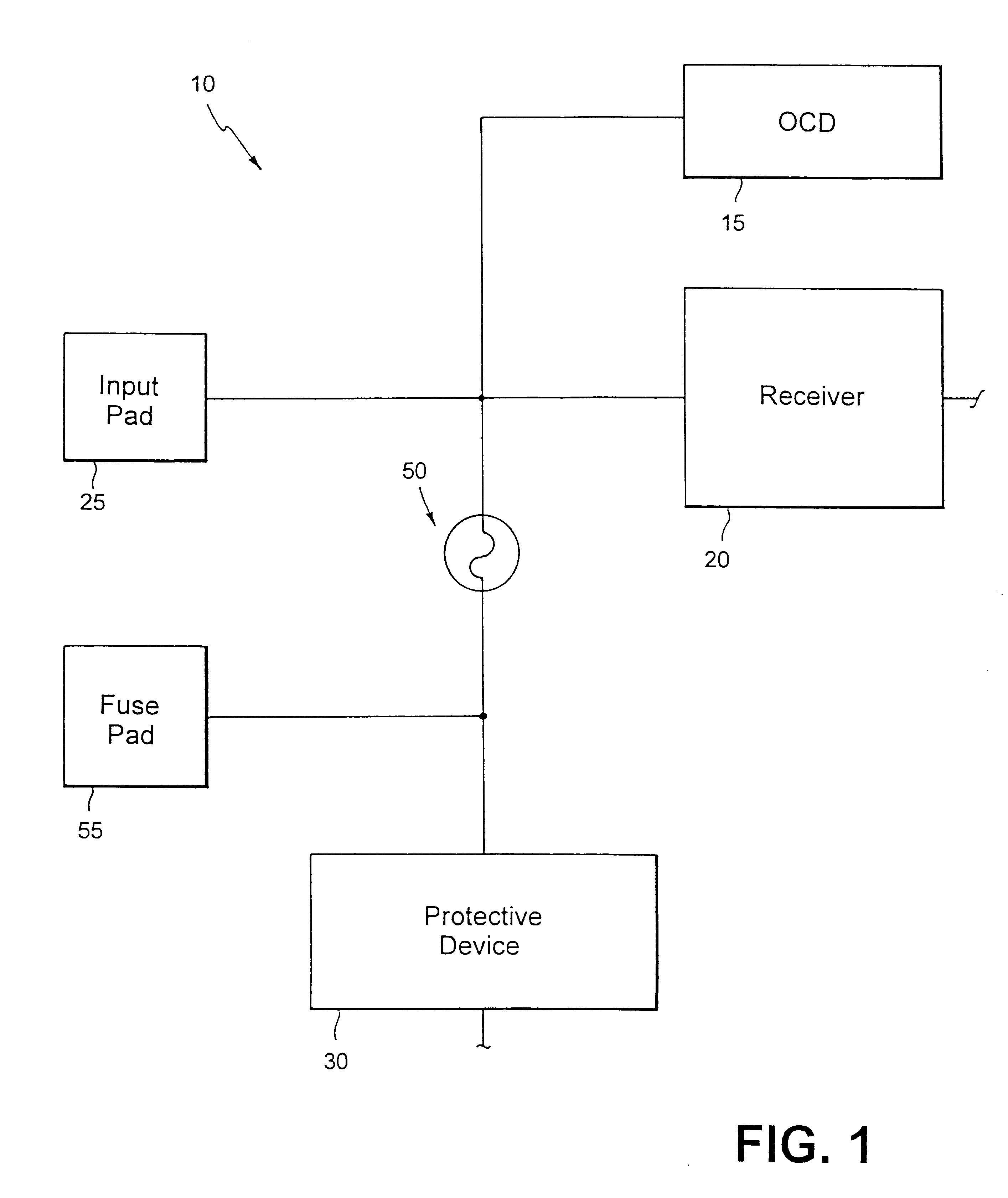
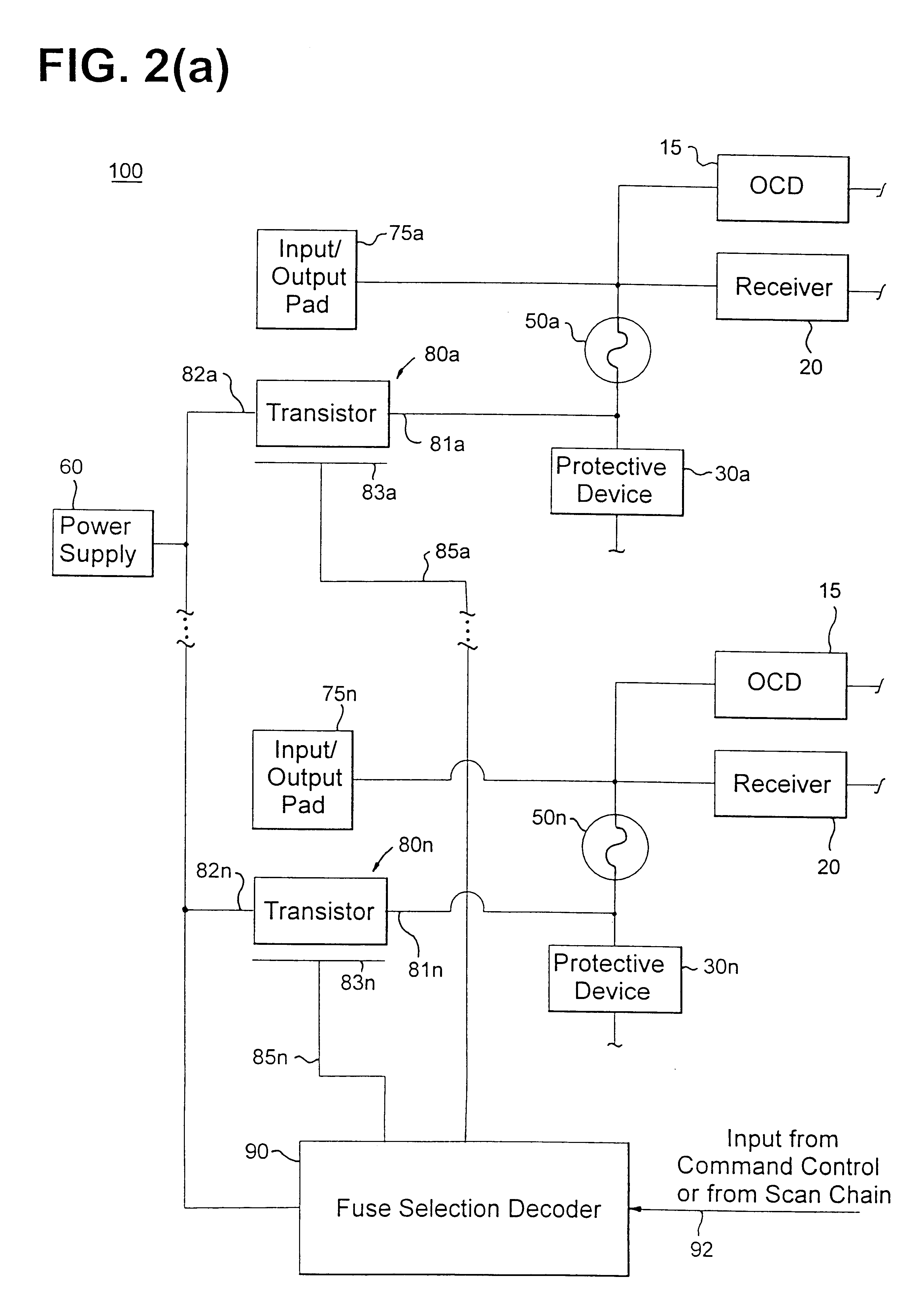
Impedance control using fuses
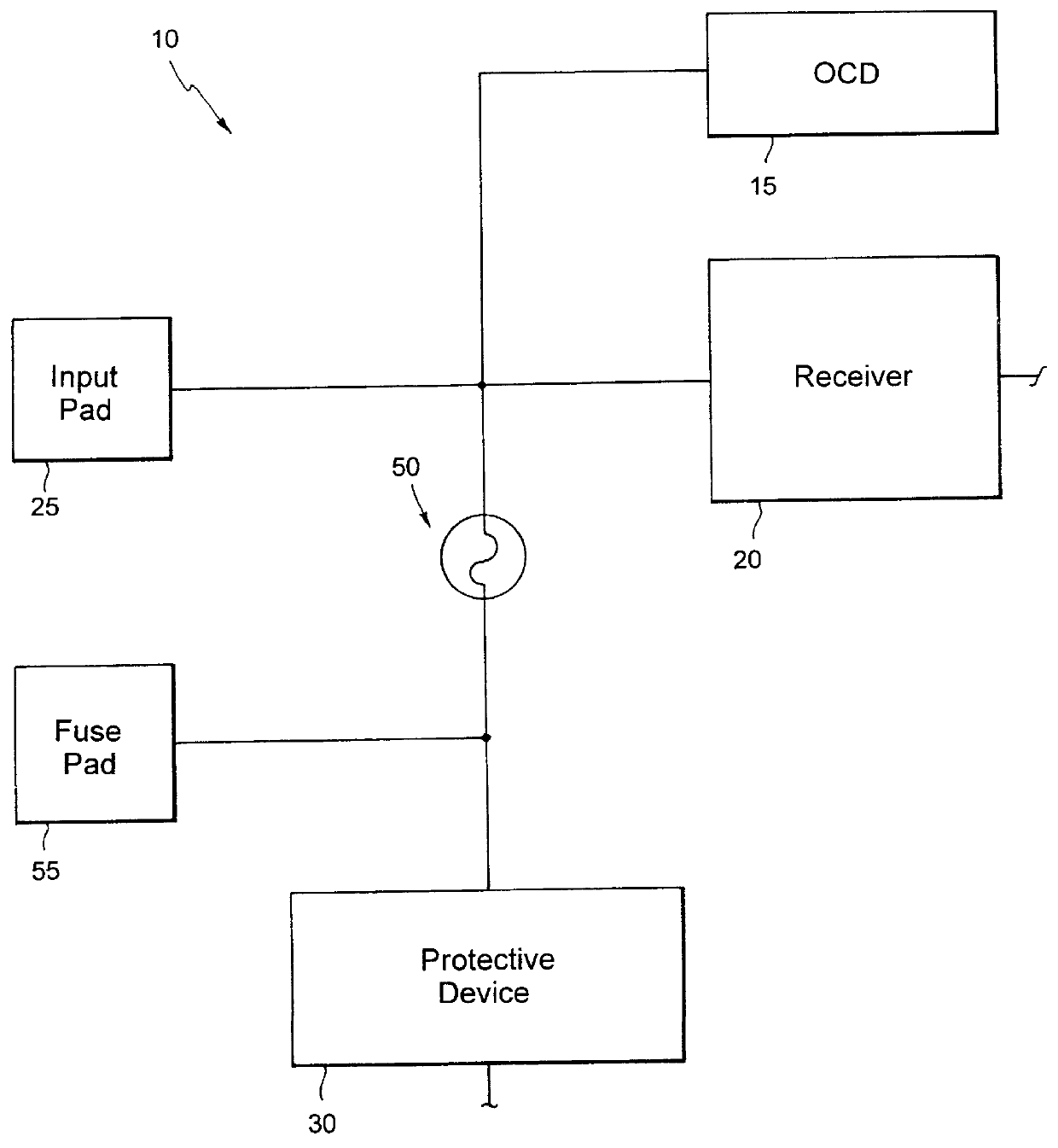
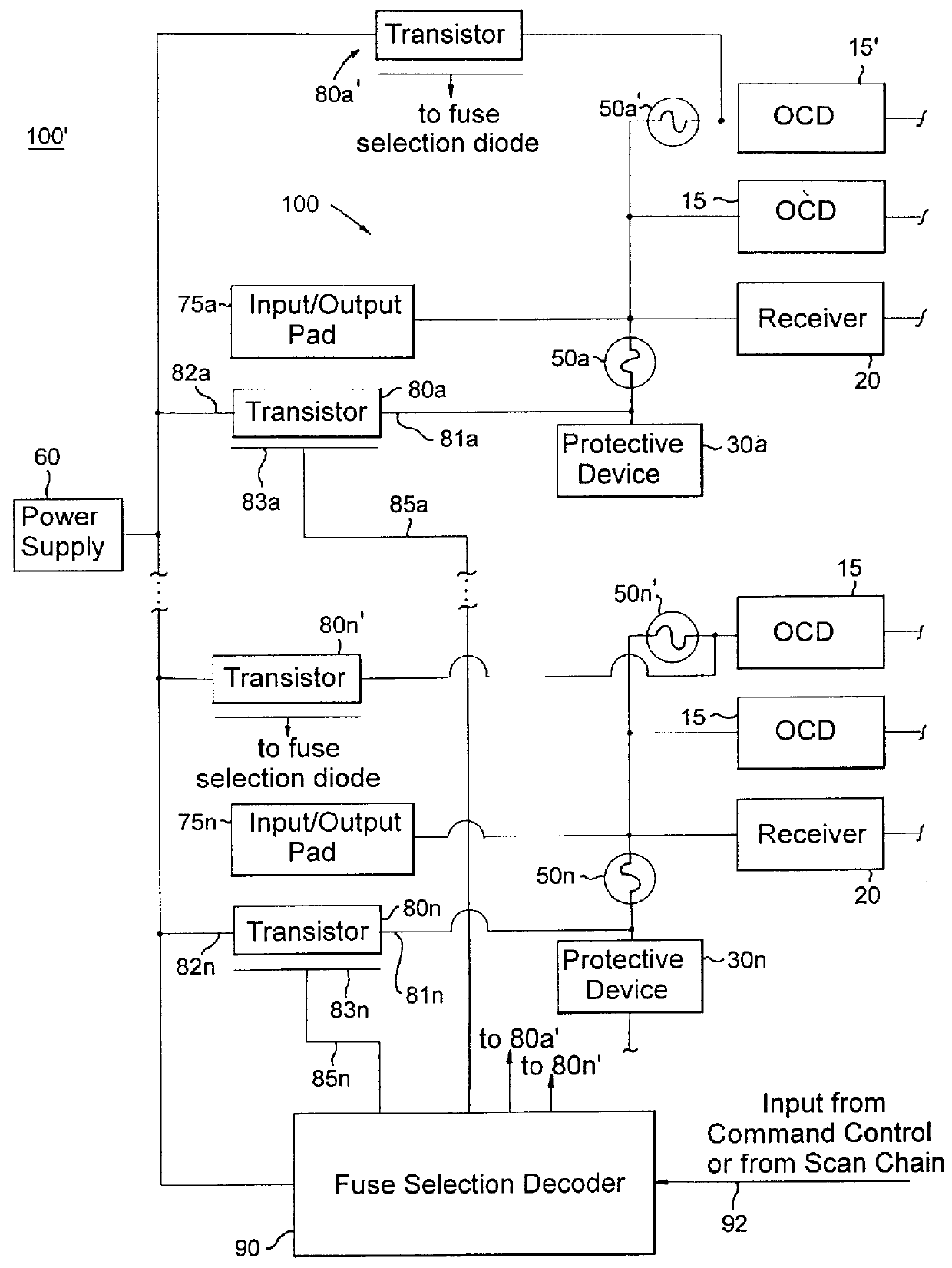
InactiveUS6141245ALower latencyHigher-bandwidth operationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMemory chipElectricity
A system and method for reducing impedance loading of semiconductor integrated circuit devices implementing protective device structures that contributes to impedance loading at an I / O pad connection. The method comprises providing a fuse device between the I / O pad connection and the protective device; connecting a current source device associated with each fuse device in the integrated circuit, the current source device connected to one end of the fuse device; providing fuse selection circuit for activating current flow through a selected fuse device between the current source and the I / O connection, the current flow being of an amount sufficient for blowing the fuse and disconnecting the protective device from the circuit structure, thereby reducing impedance loading at the I / O connection. Such a system and method is employed in a memory system comprising integrated circuit chips disposed in a stacked relation, with each chip including: a layer of active circuitry formed at a first layer of each chip; a plurality of through conducting structures disposed substantially vertically through each chip for enabling electronic connection with active circuitry at the first layer; second conducting device disposed at an end of the through conducting structure at an opposite side of a chip for connection with a corresponding through conductive structure of an adjacent stacked chip, the stacked chip structure formed by aligning one or more through conducting structures and second conducting devices of adjacent chips, whereby a chip of the stack is electronically connected to active circuitry formed on other chips of the stack. The stacked chip structure is ideal for reducing data access latency in memory systems employing memory chips such as DRAM.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
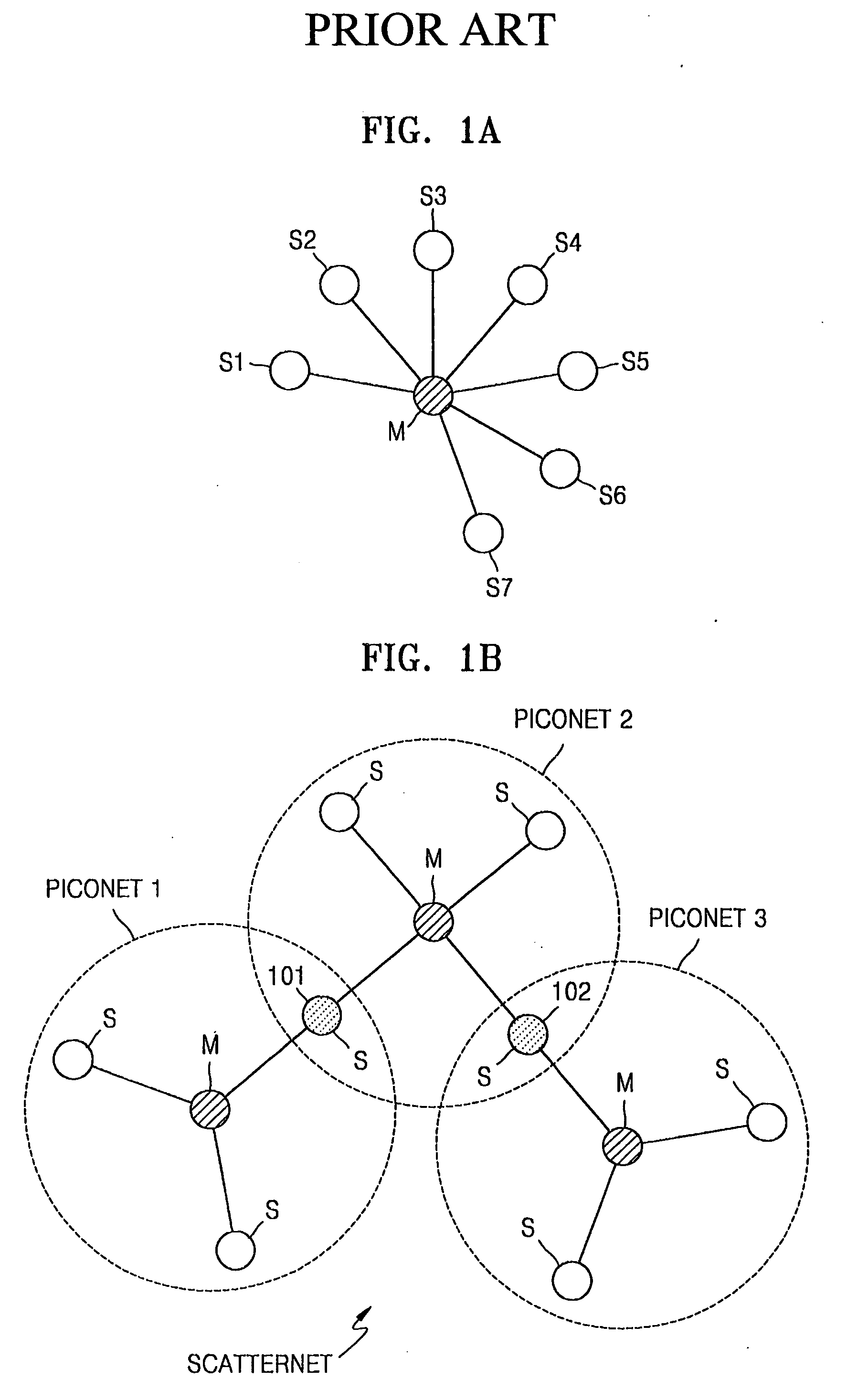
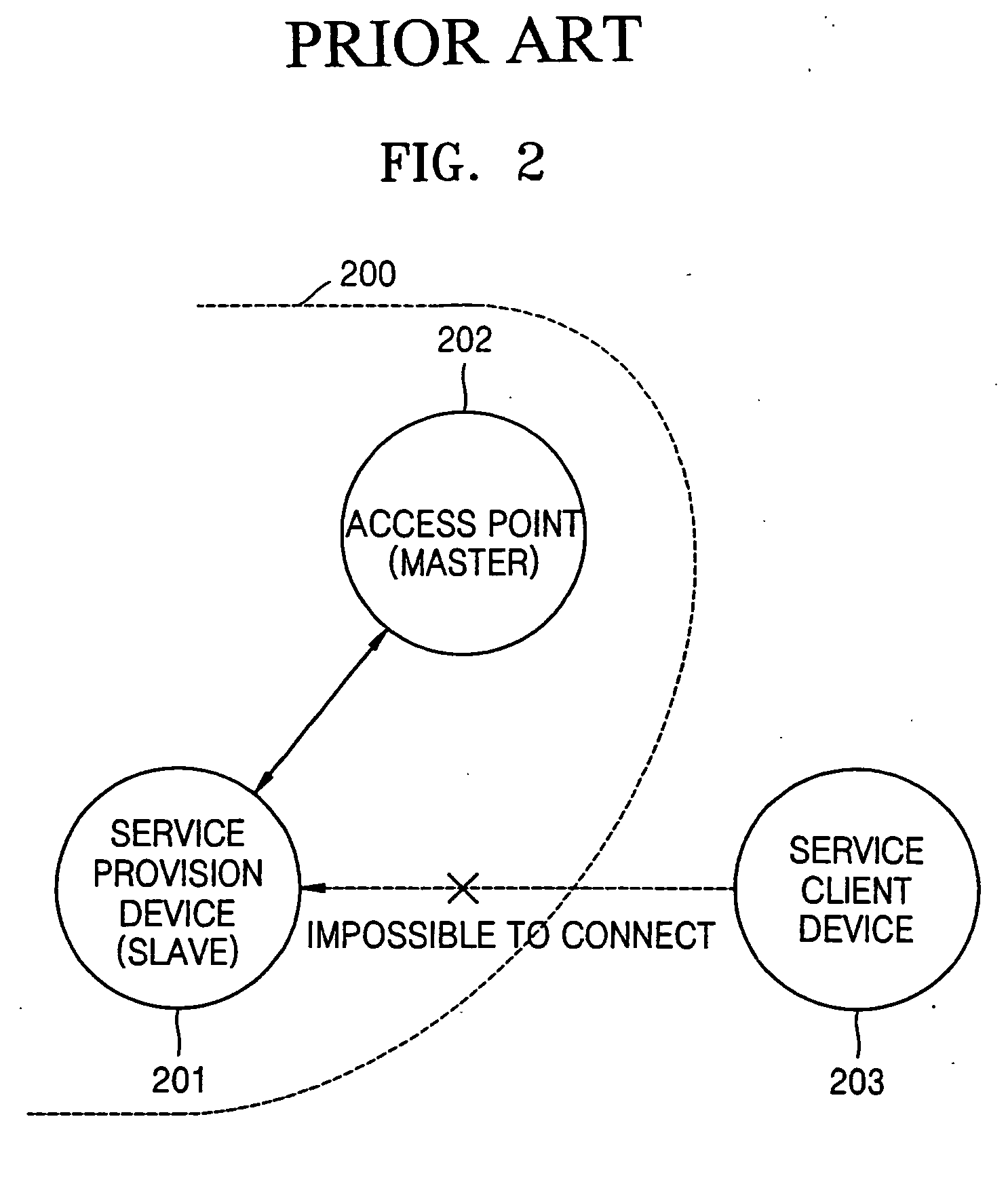
Method of relaying connection requests between wireless devices in wireless network and apparatus therefor
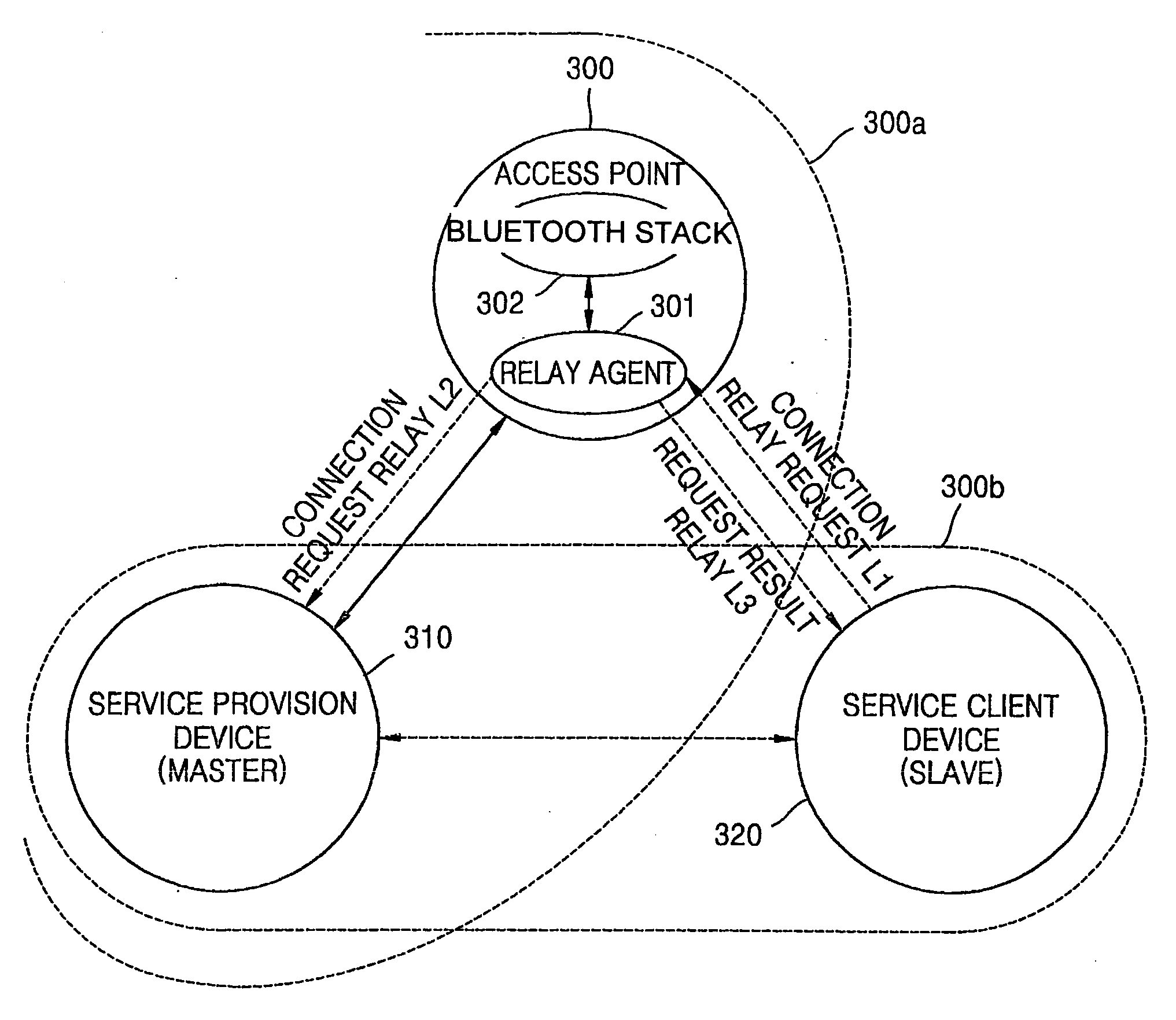
InactiveUS20050107102A1Minimize connection waiting timeMinimize connectionNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationTrunkingWireless network
An apparatus to relay connection requests between wireless devices in a wireless network including at least one piconet having a master device and one or more slave devices, the apparatus including a connection request relay unit in the master device to relay to a first wireless device a request from a second wireless device to connect to the first wireless device, wherein the first wireless device is one of the oner or more slave devices, and the second wireless device is outside the at least one piconet having the master device, and a method of relaying the connection requests.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
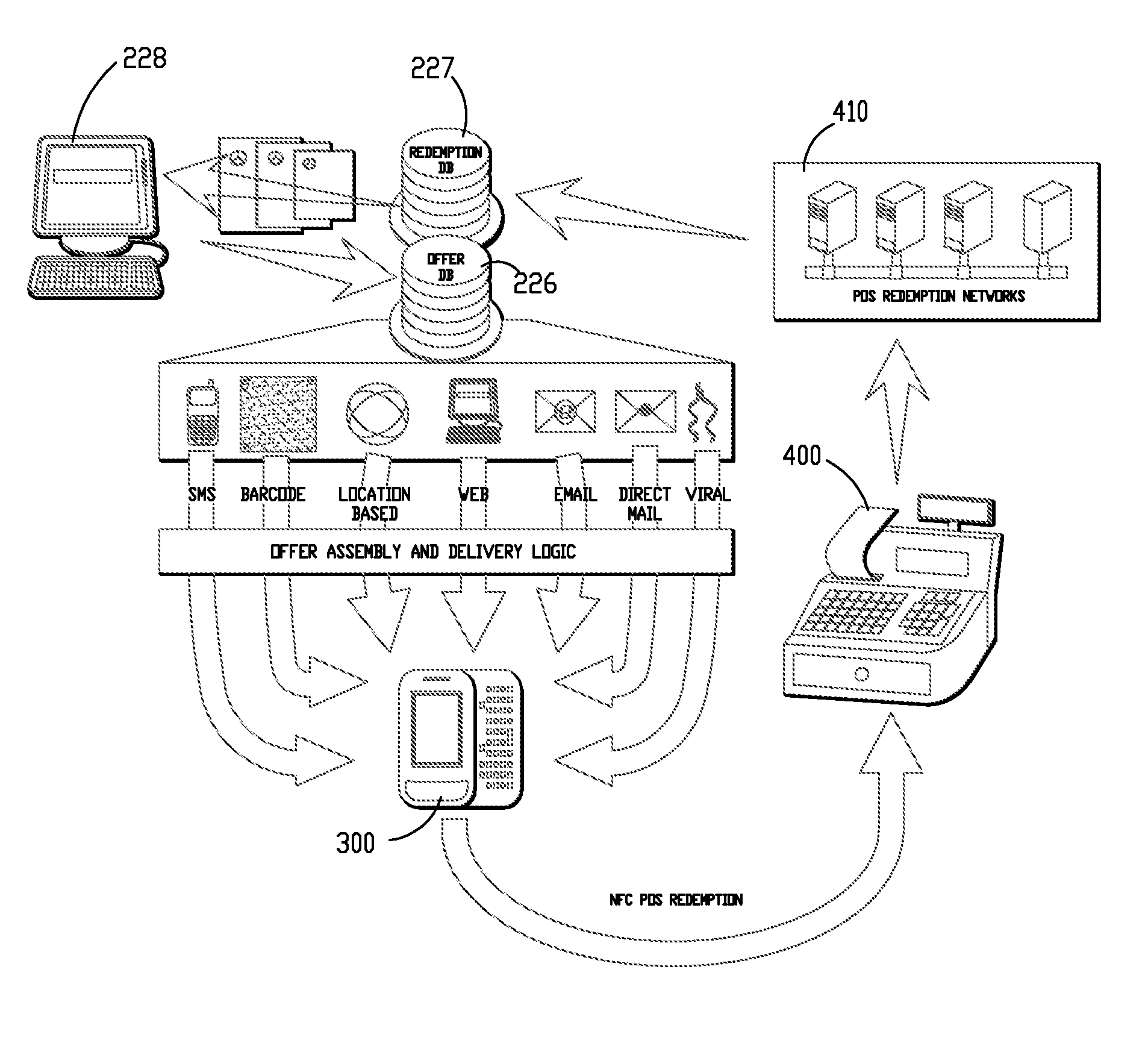
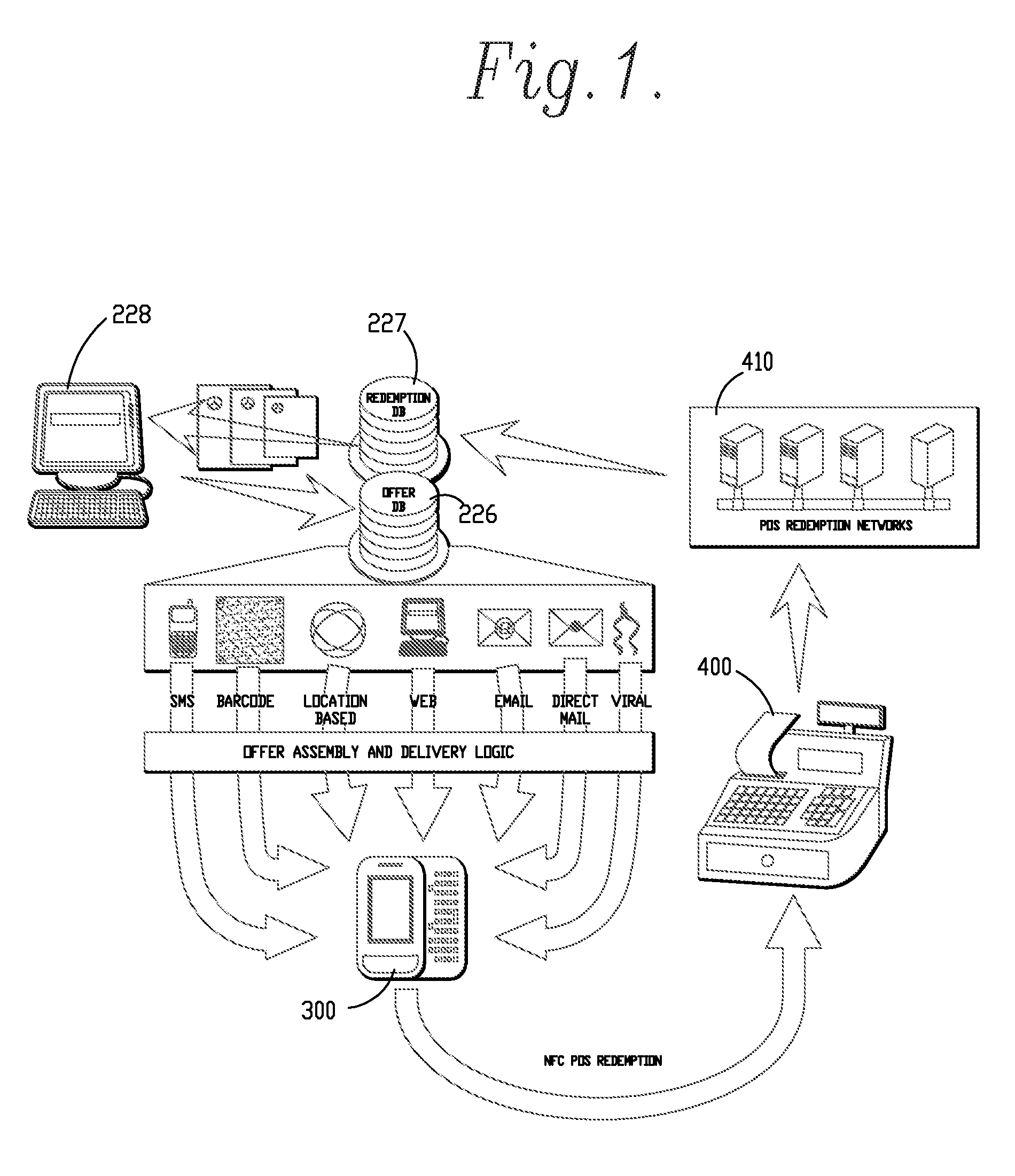
Methods and systems for creation and distribution of promotional materials and gathering of consumer data
InactiveUS20110087529A1Quick displayMinimizing necessary connectionNear-field transmissionMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsUnique identifierMobile device
A system and methods for the creation and / or distribution of promotional materials, such as coupons, to consumers is provided. A promotional material item is created electronically and a copy of the item is distributed to mobile devices, or other electronic devices, of consumers. Each copy of the promotional material item includes a unique identifier for redemption and tracking purposes.
Owner:SAEPIO TECH
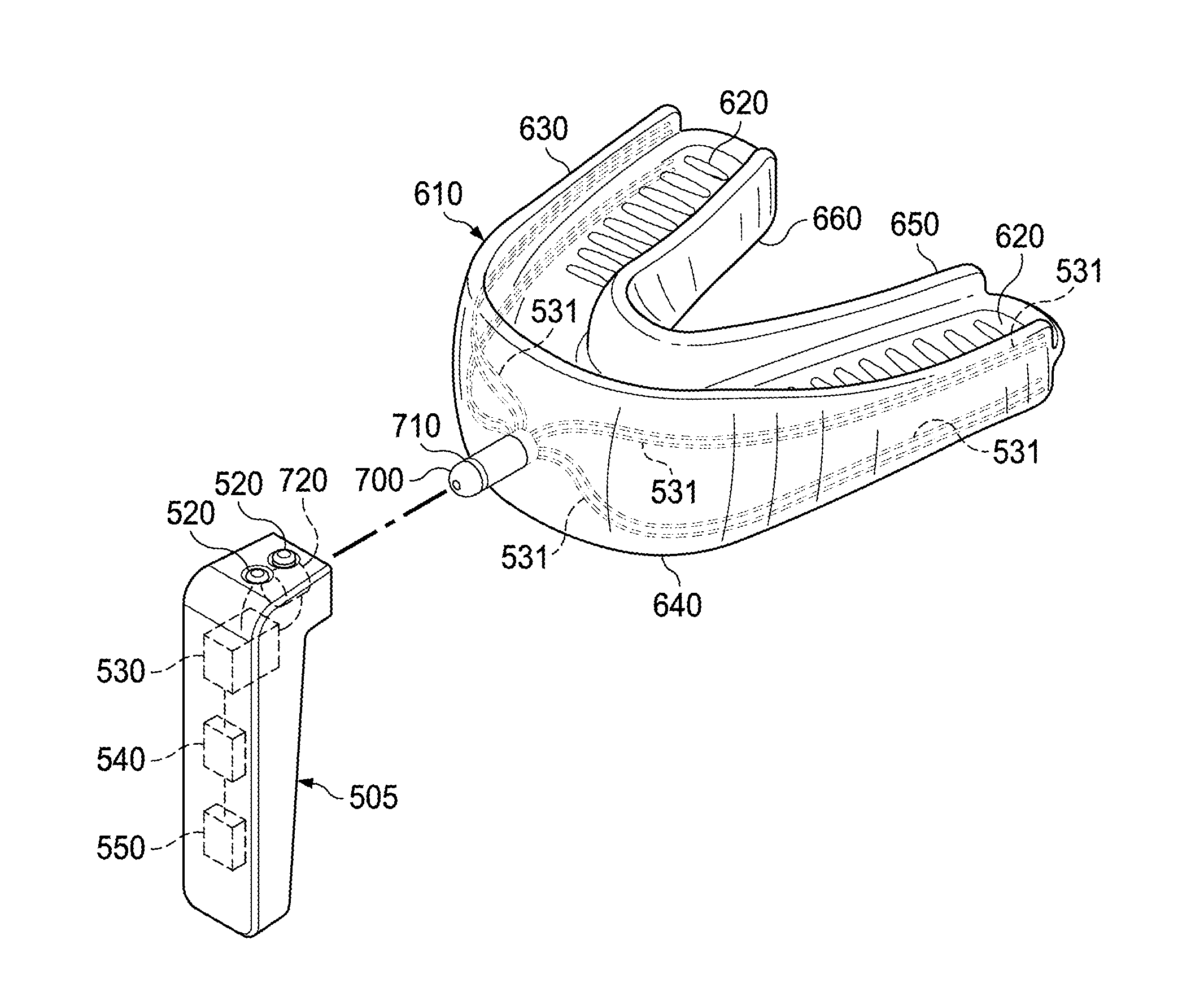
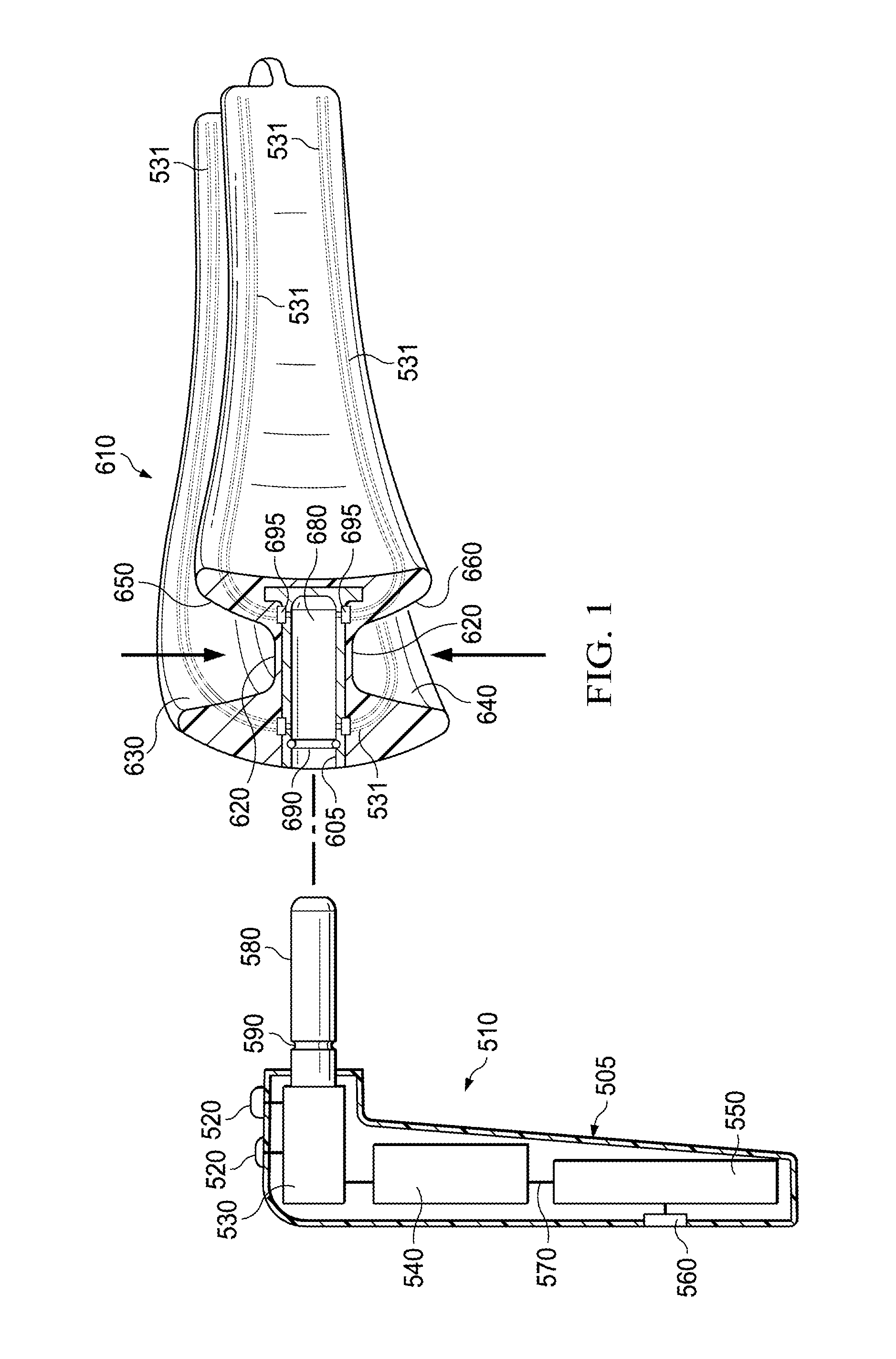
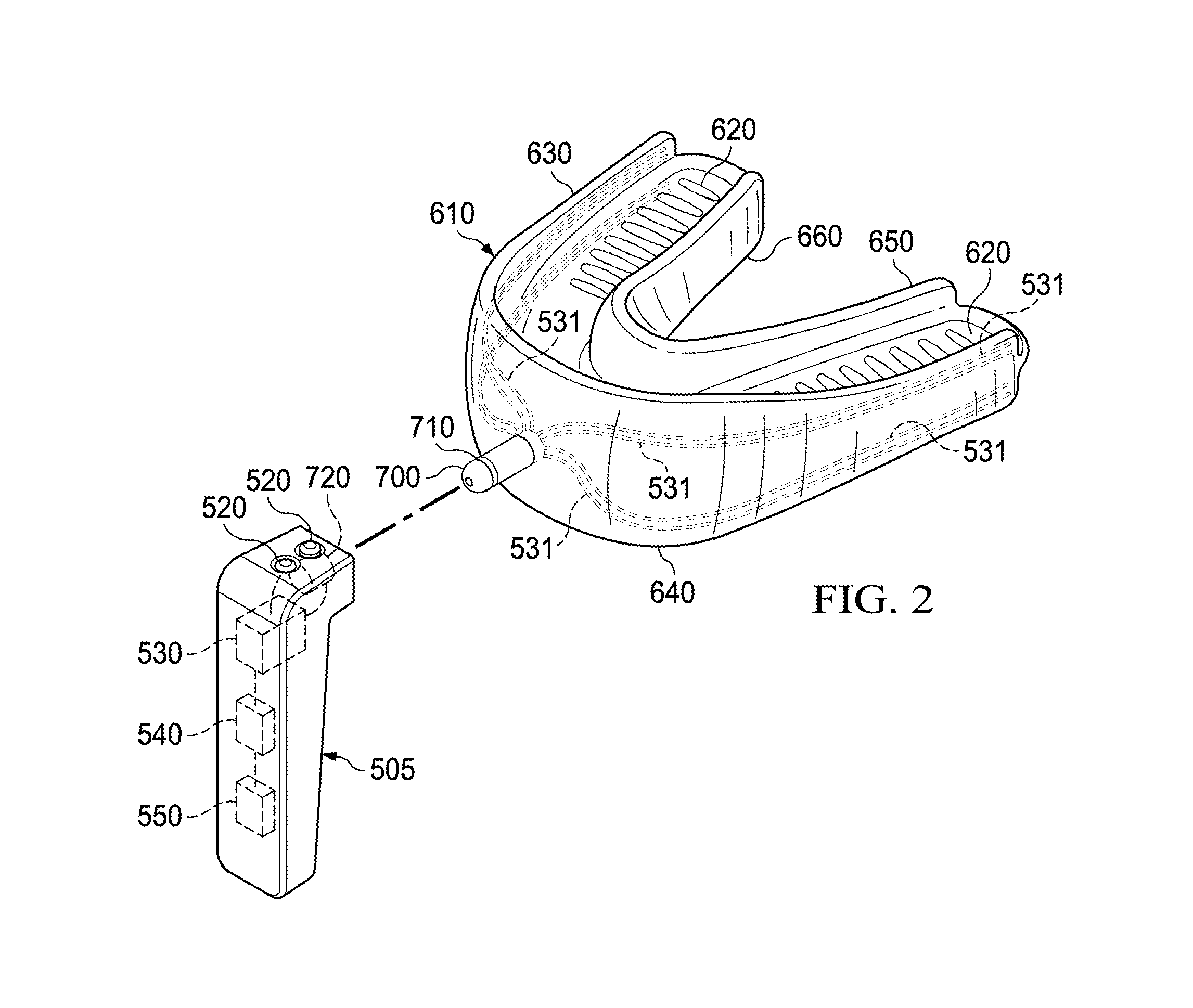
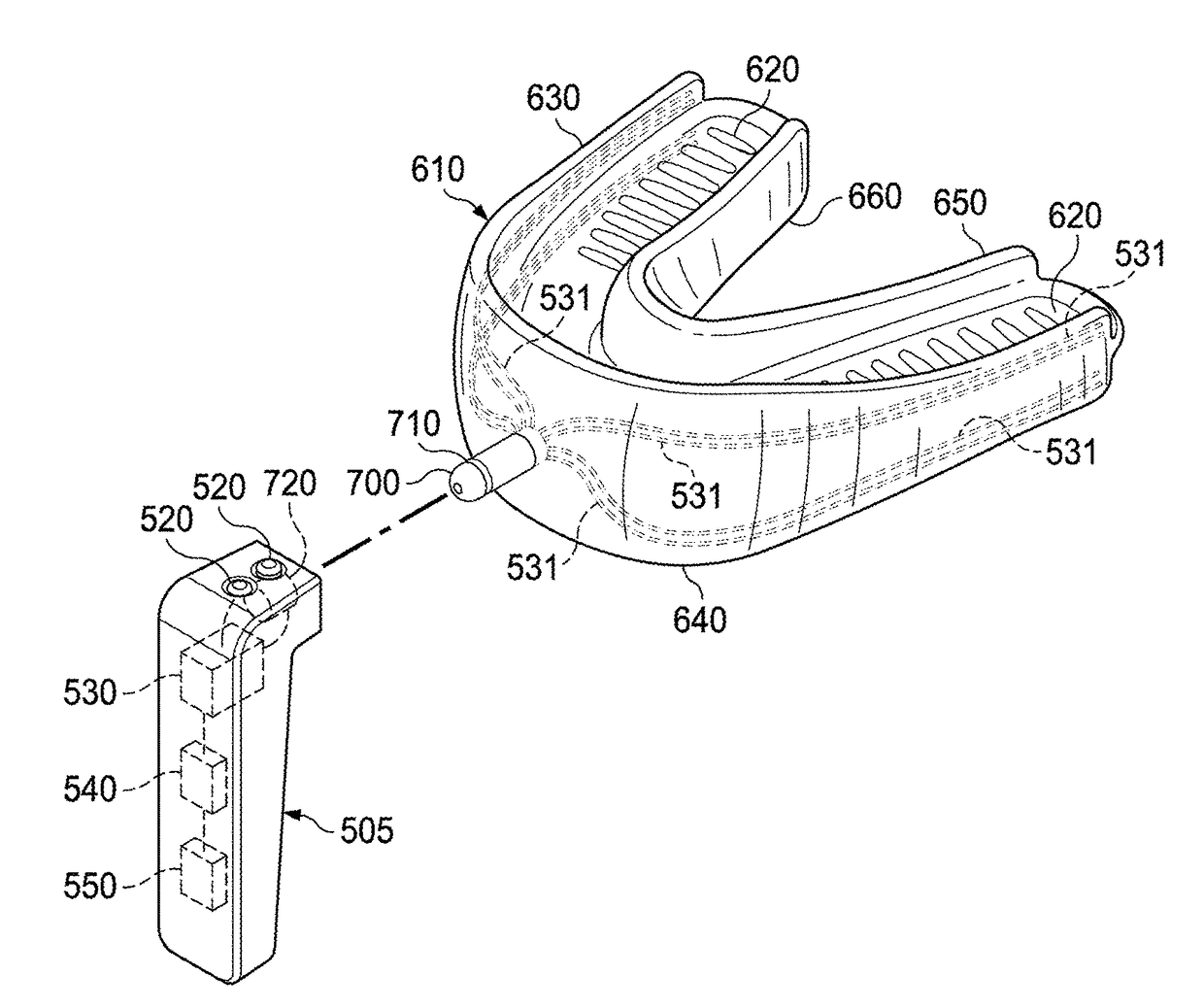
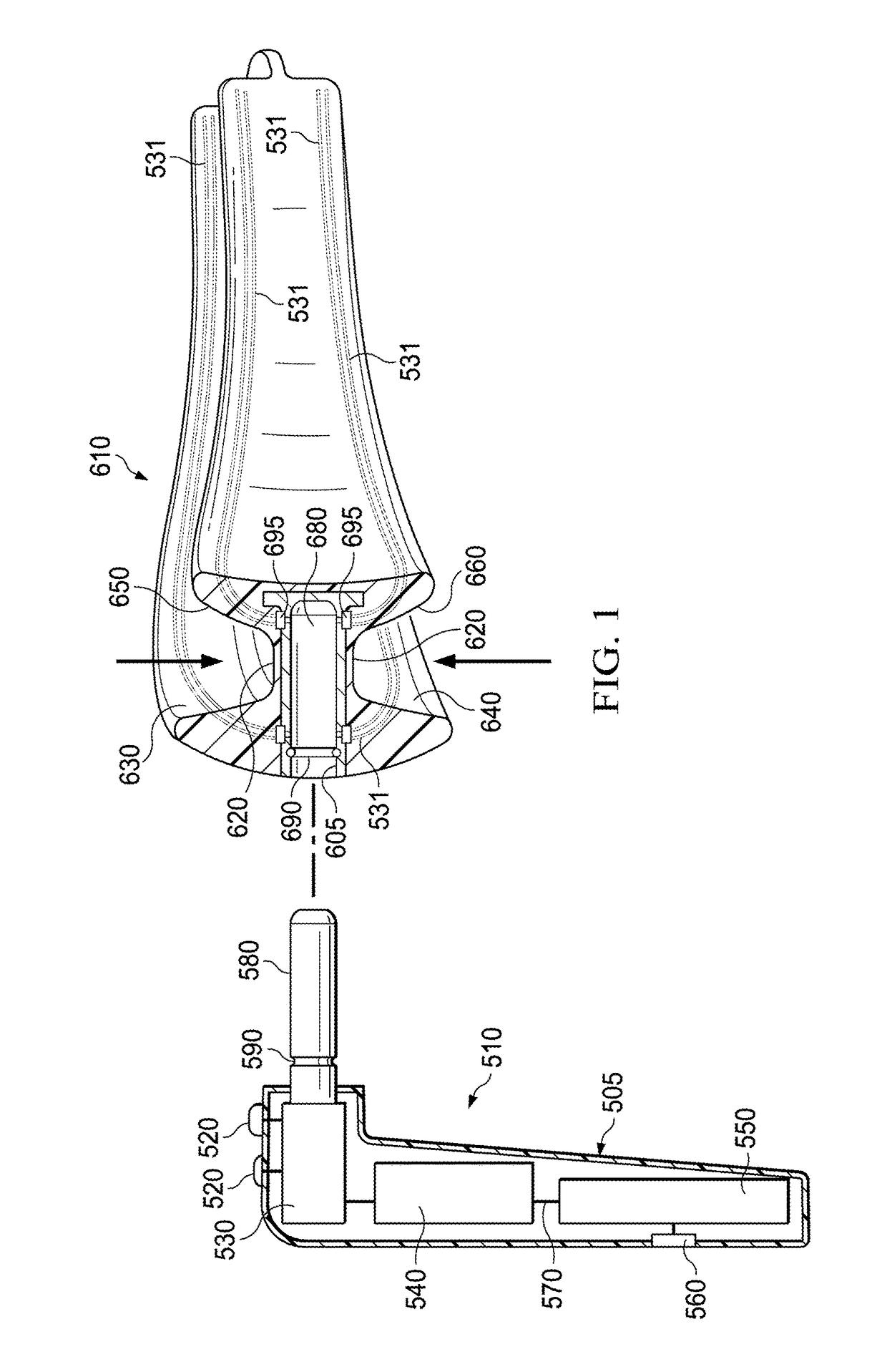
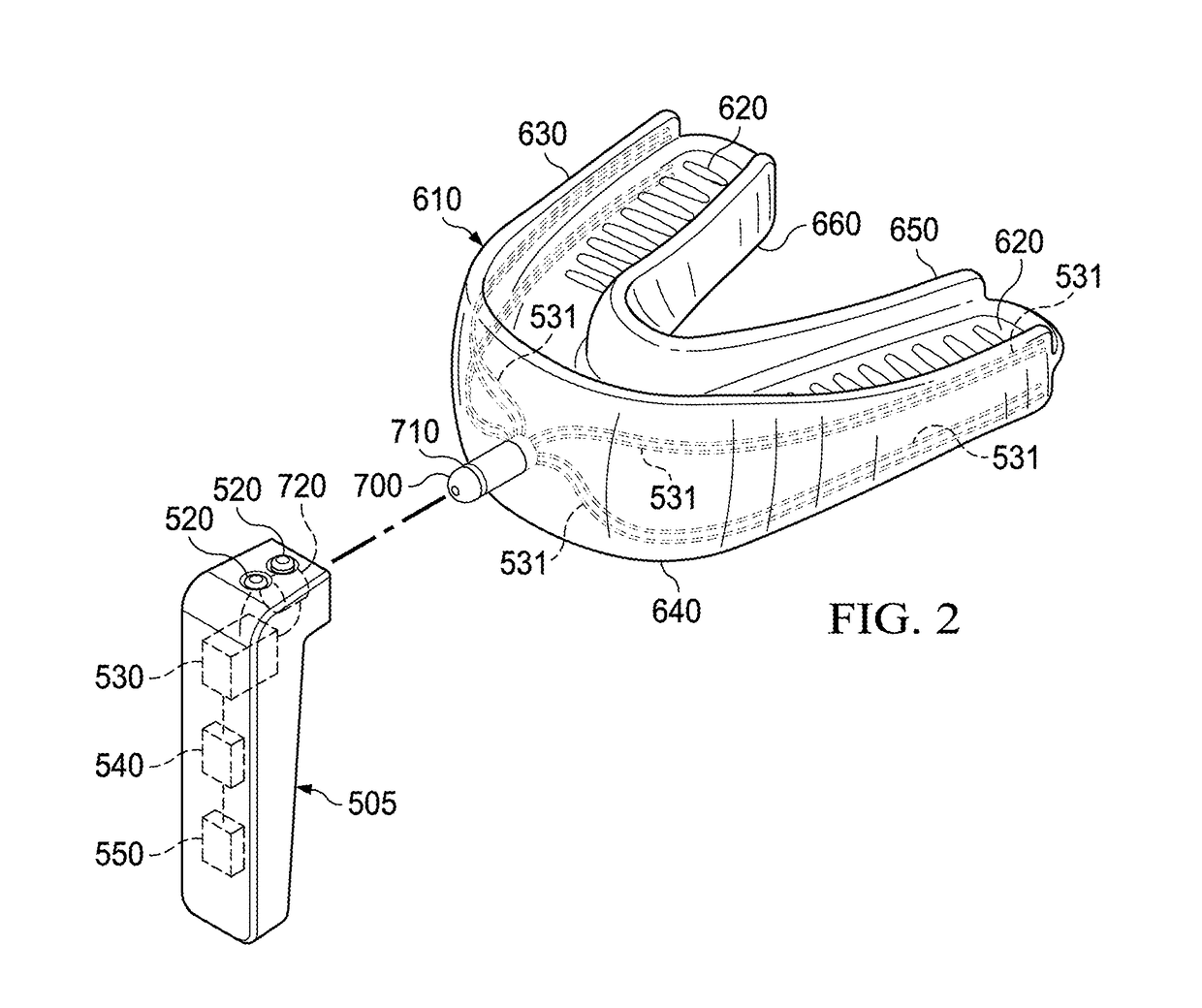
Electro-orthodontic device
ActiveUS20140023983A1Minimize connectionEasy to buildAdditive manufacturing apparatusOthrodonticsElectricityDental Gingiva
An electro-orthodontic appliance is provided that helps accelerate orthodontic tooth movement through the application of a controlled electrical current to gum and teeth, thus stimulating osteogenesis.
Owner:ADVANCED ORTHODONTICS & EDUCATION ASSOC LLC
Method and system for centrally allocating addresses and port numbers
InactiveUS20060259625A1Minimized connection blockingImprove scalabilityDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsCommunication interfaceComputer network
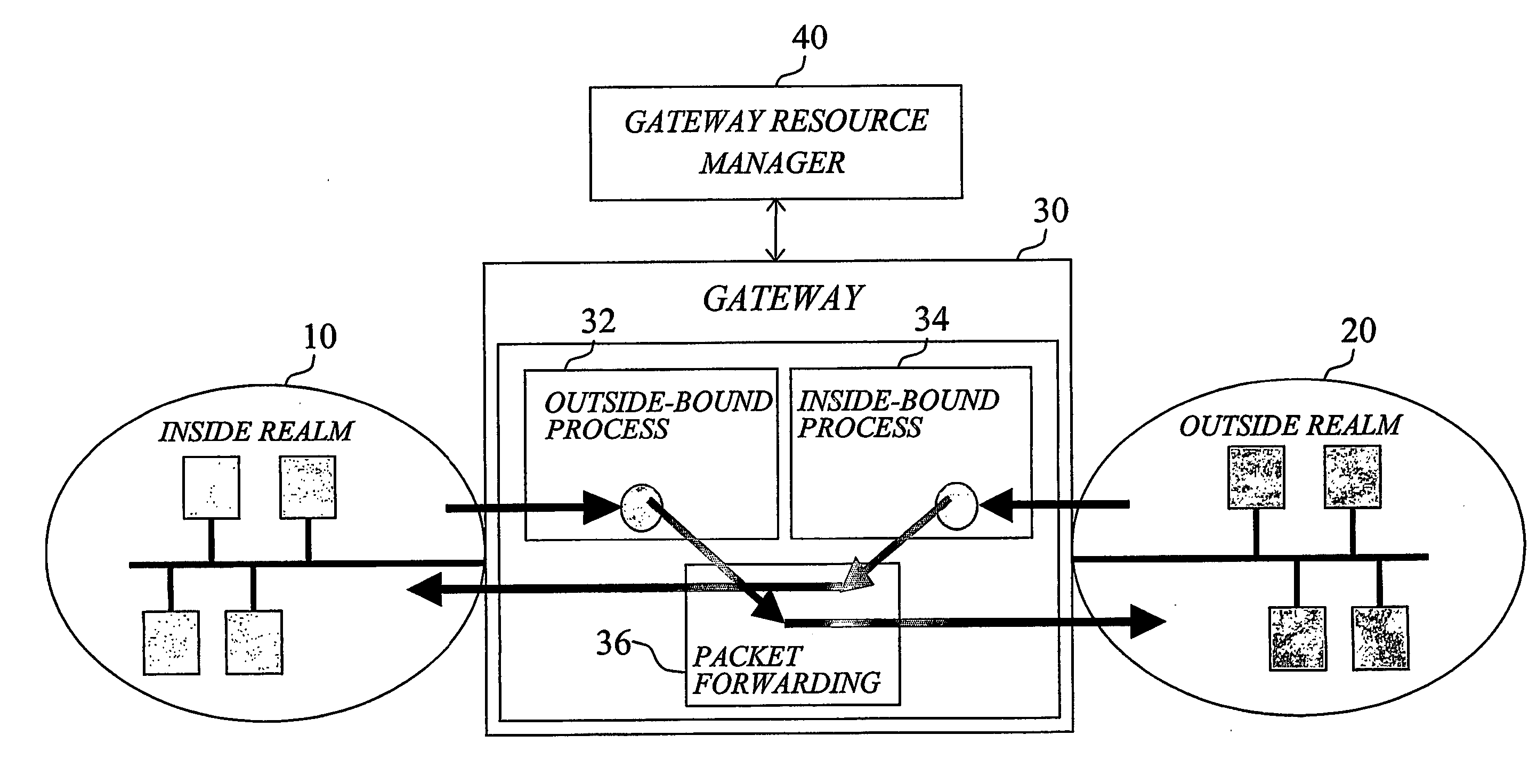
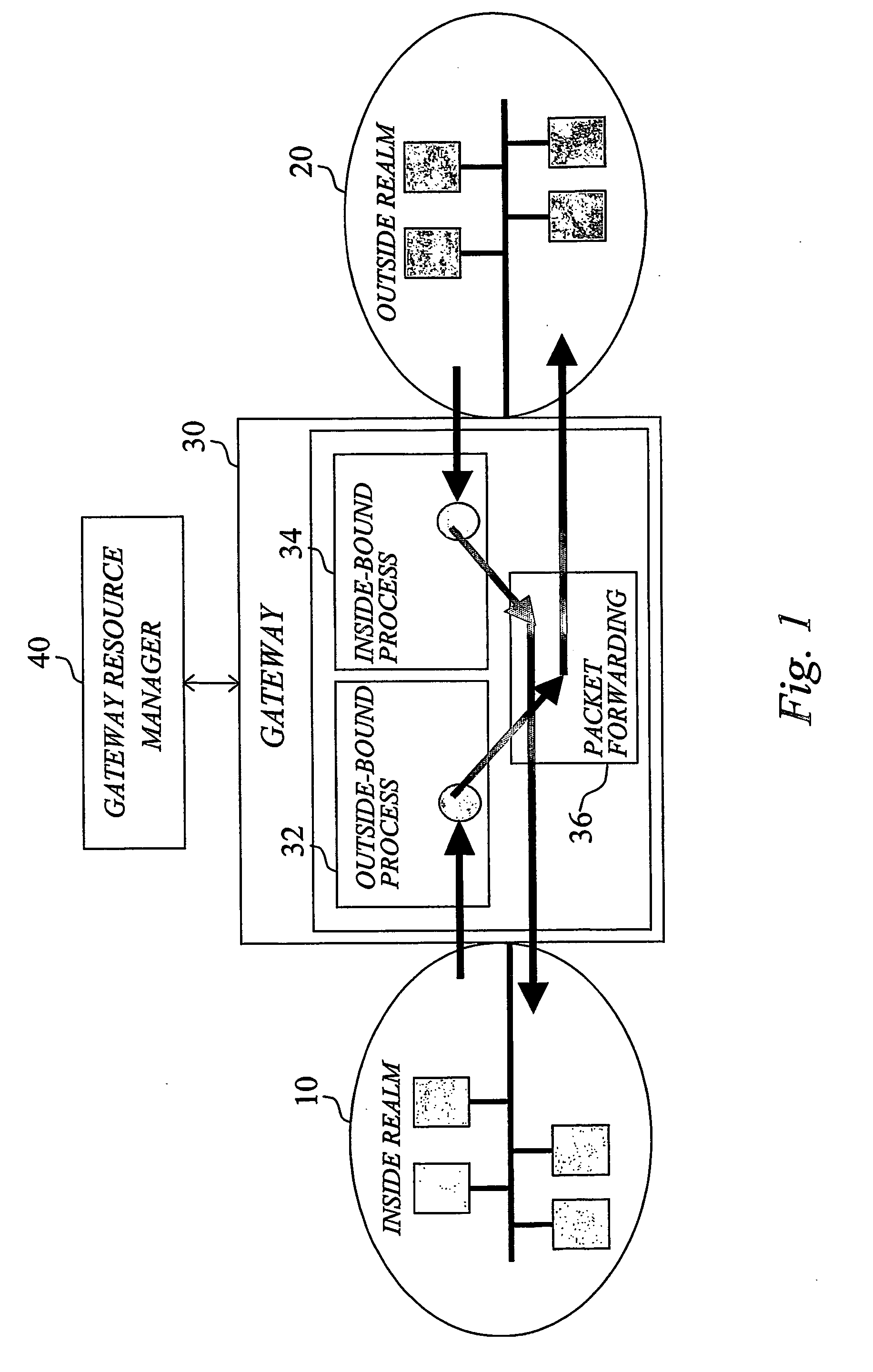
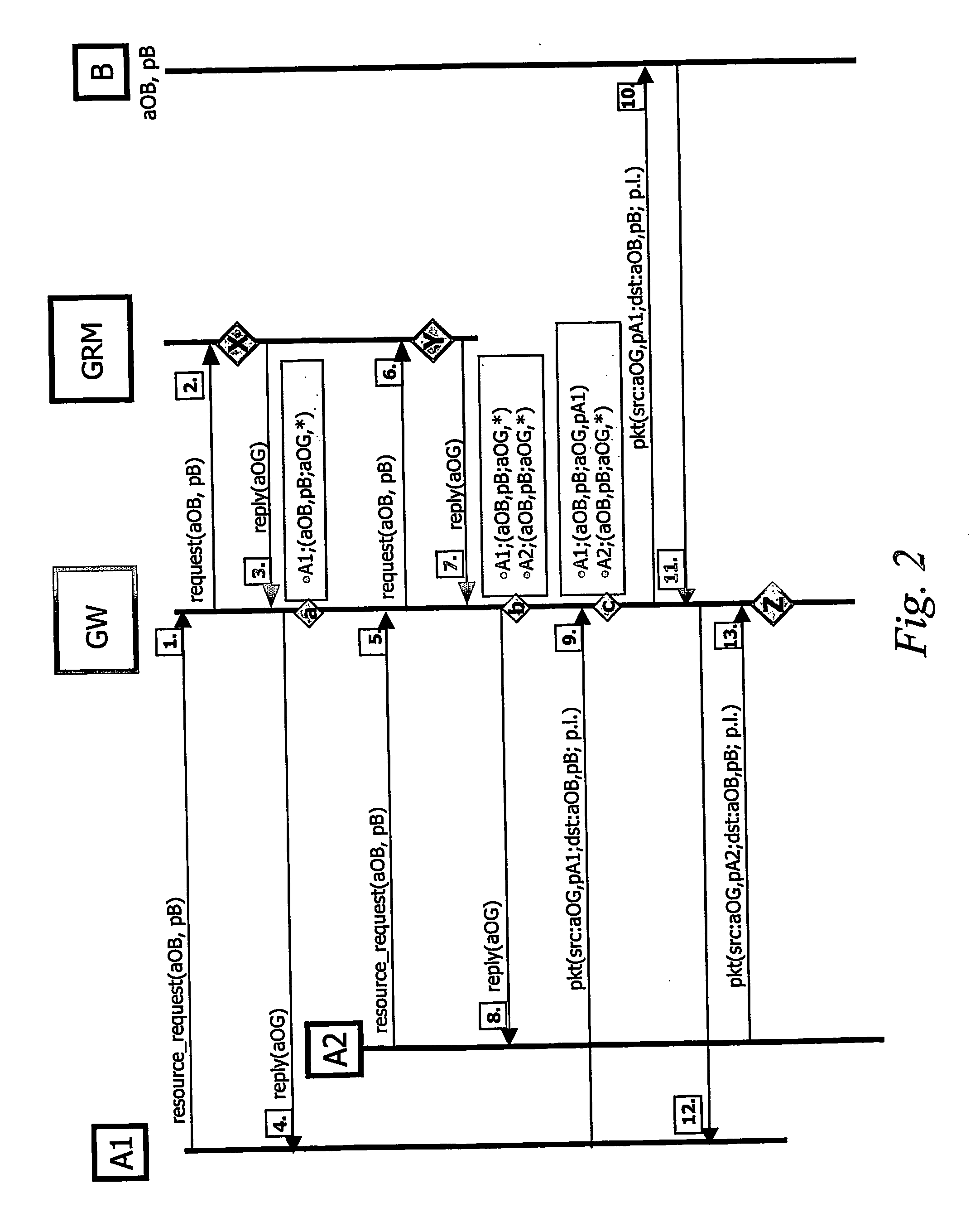
An inside-realm node (A) attempting to connect to an outside-realm node (B) through an intermediate gateway (30) requests central configuration from a gateway resource manager (40). In response to the configuration request initiated from the inside-realm node, an outside-realm gateway address and an inside node port number are centrally allocated to the inside-realm node by resource allocation logic (42). Establishment of the connection is initiated at least partly based on the allocated address and port number by means of appropriate signaling with the gateway (30). The allocated address and port number are signaled back to the requesting inside-realm node in a configuration reply, allowing inside-realm node to configure its communication interface accordingly. The central allocation of socket parameters for the inside-realm node is preferably performed based on predetermined connection information, which is included in or derivable, for example by means of the name-to address translator (50), form the initial configuration request.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Impedance control using fuses
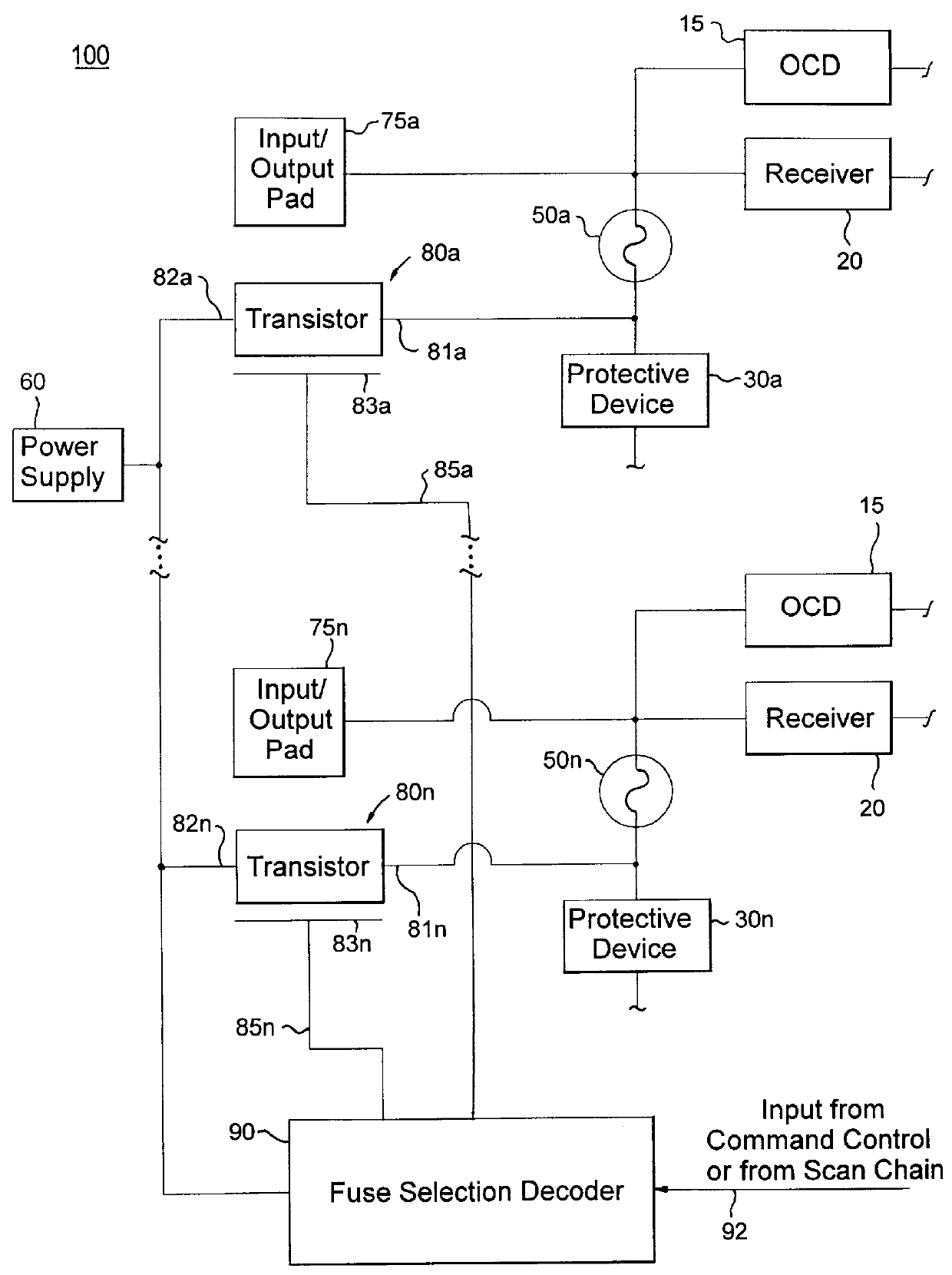
InactiveUS6243283B1Reduce capacityRemove loadSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMemory chipElectricity
A system and method for reducing impedance loading of semiconductor integrated circuit devices implementing protective device structures that contributes to impedance loading at an I / O pad connection. The method comprises providing a fuse device between the I / O pad connection and the protective device; connecting a current source device associated with each fuse device in the integrated circuit, the current source device connected to one end of the fuse device; providing fuse selection circuit for activating current flow through a selected fuse device between the current source and the I / O connection, the current flow being of an amount sufficient for blowing the fuse and disconnecting the protective device from the circuit structure, thereby reducing impedance loading at the I / O connection. Such a system and method is employed in a memory system comprising integrated circuit chips disposed in a stacked relation, with each chip including: a layer of active circuitry formed at a first layer of each chip; a plurality of through conducting structures disposed substantially vertically through each chip for enabling electronic connection with active circuitry at the first layer; second conducting device disposed at an end of the through conducting structure at an opposite side of a chip for connection with a corresponding through conductive structure of an adjacent stacked chip, the stacked chip structure formed by aligning one or more through conducting structures and second conducting devices of adjacent chips, whereby a chip of the stack is electronically connected to active circuitry formed on other chips of the stack. The stacked chip structure is ideal for reducing data access latency in memory systems employing memory chips such as DRAM.
Owner:MARVELL INT LTD
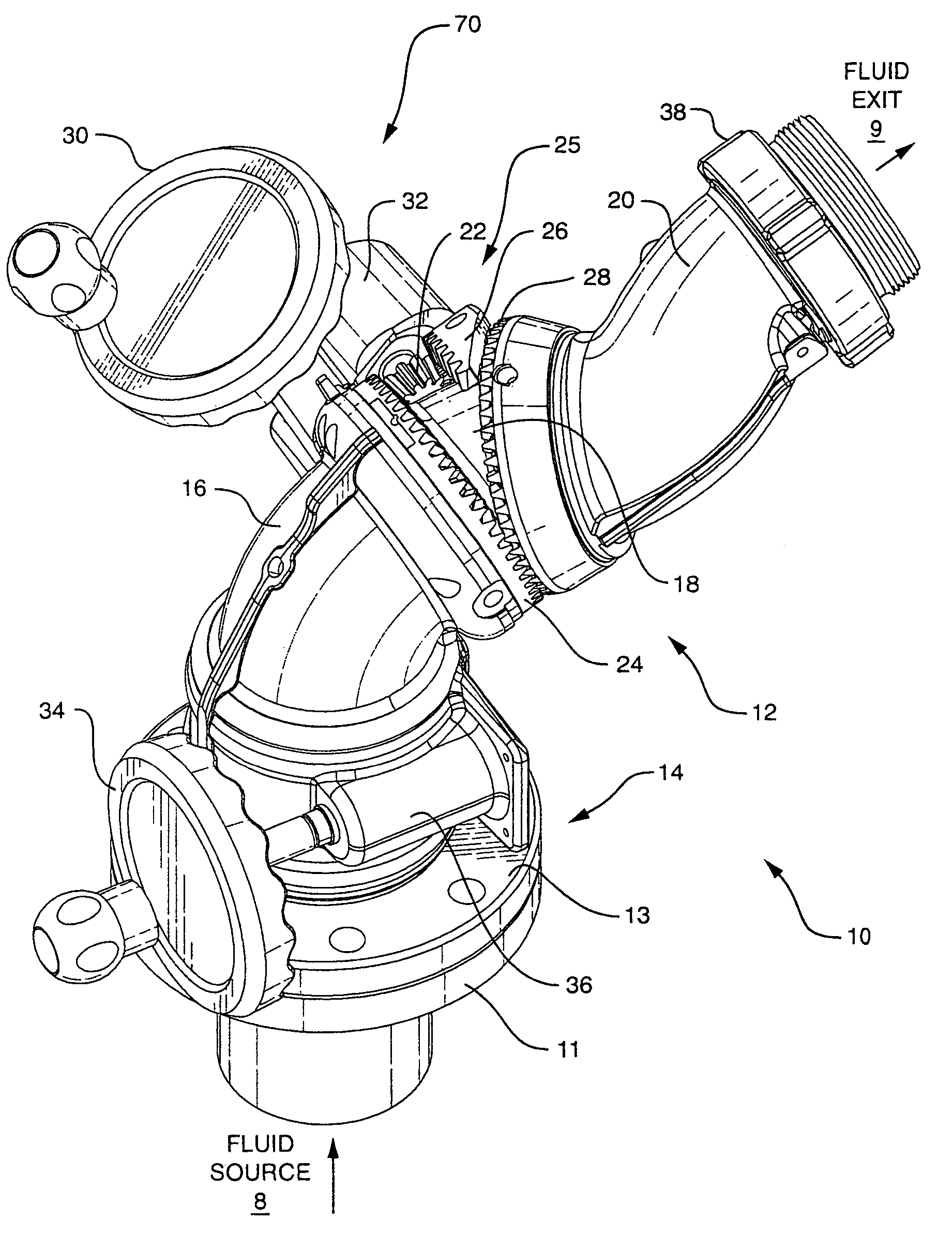
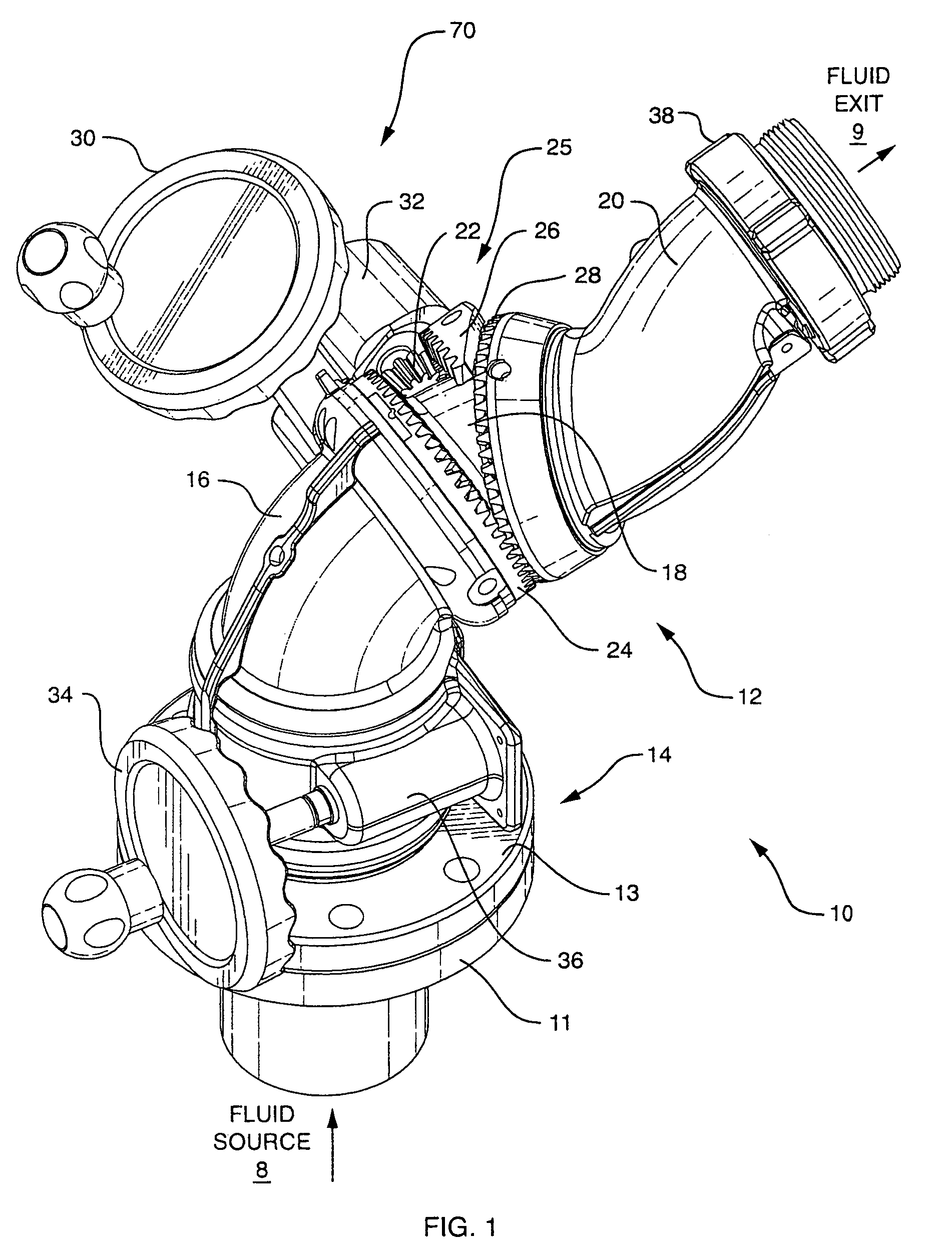
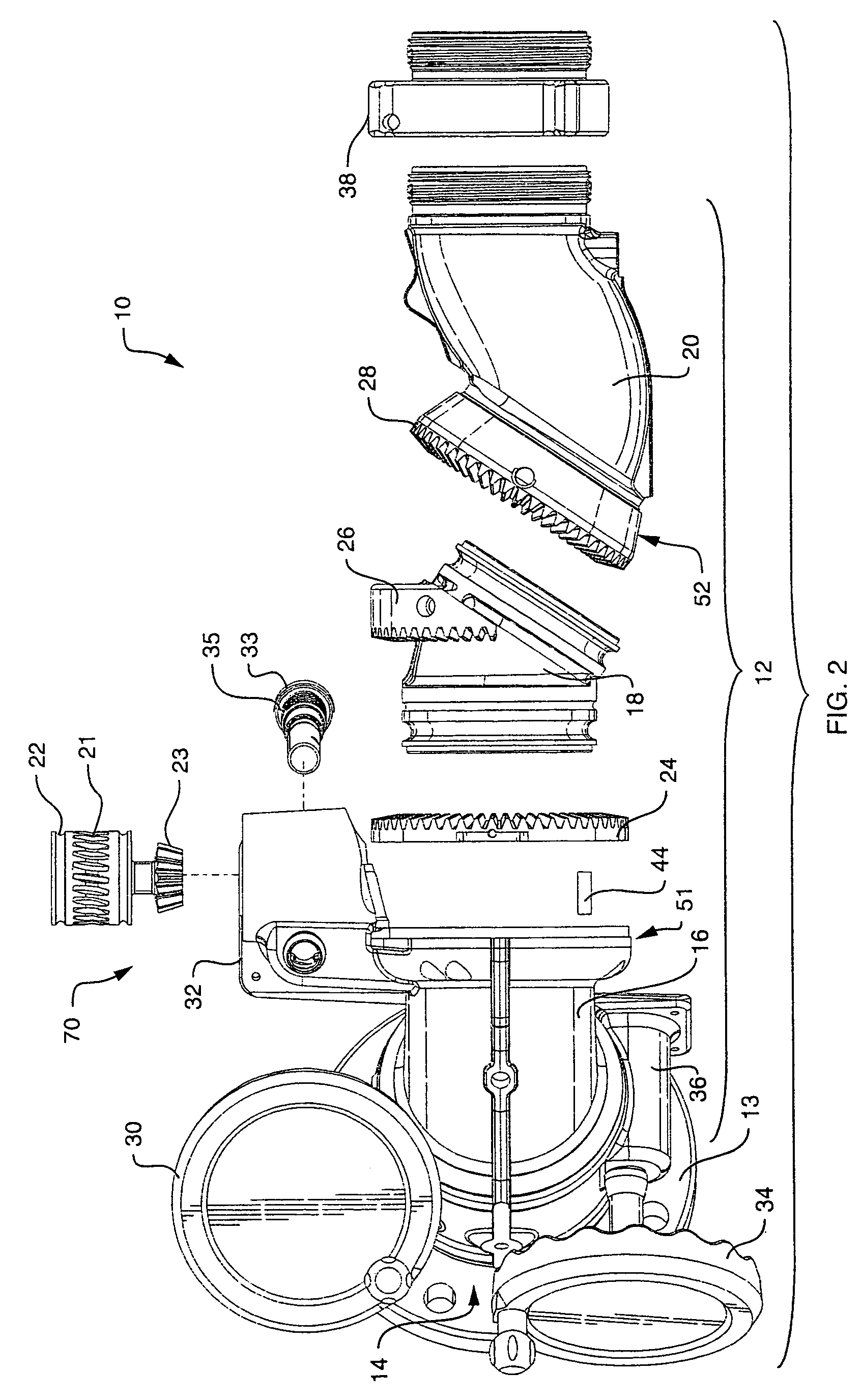
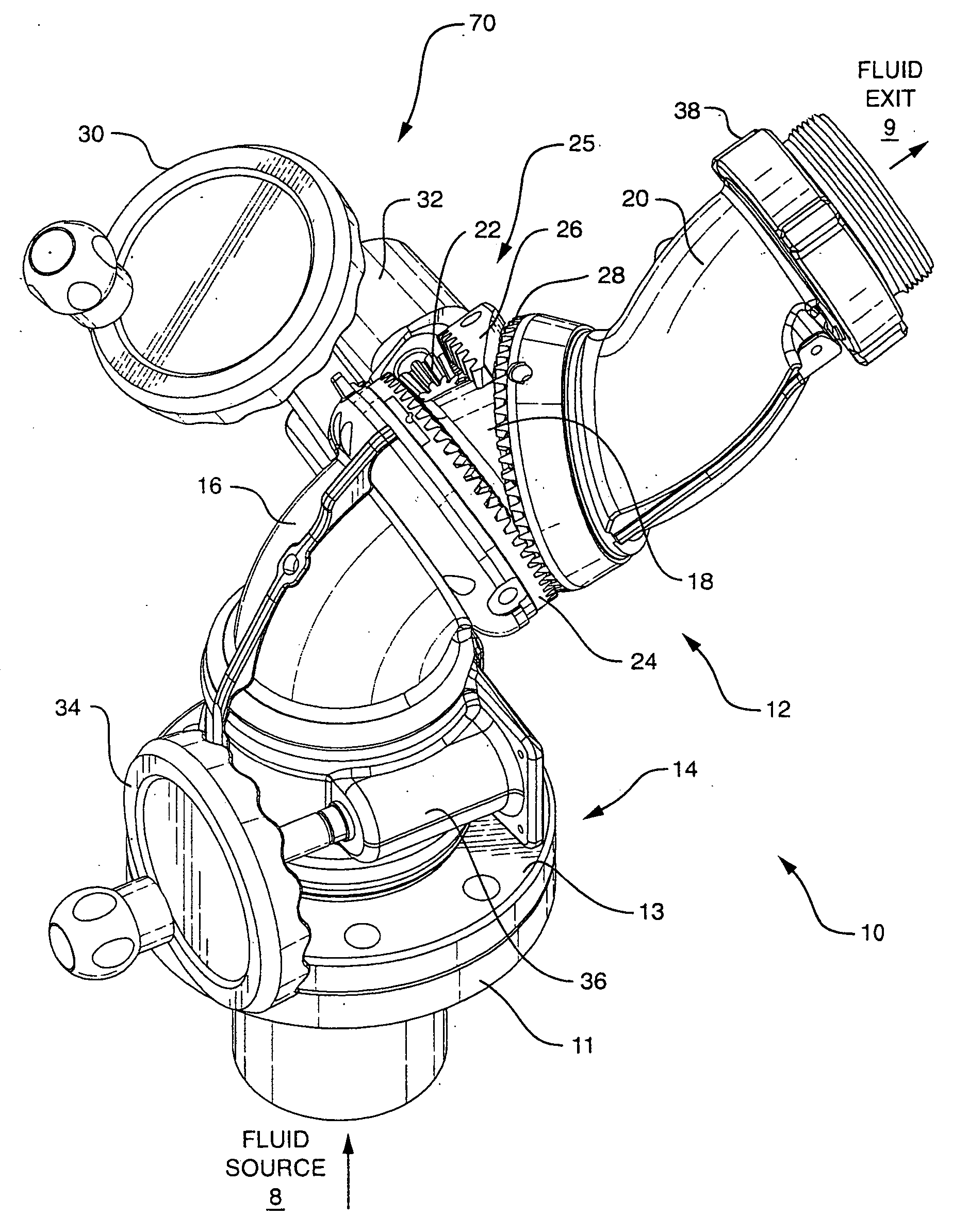
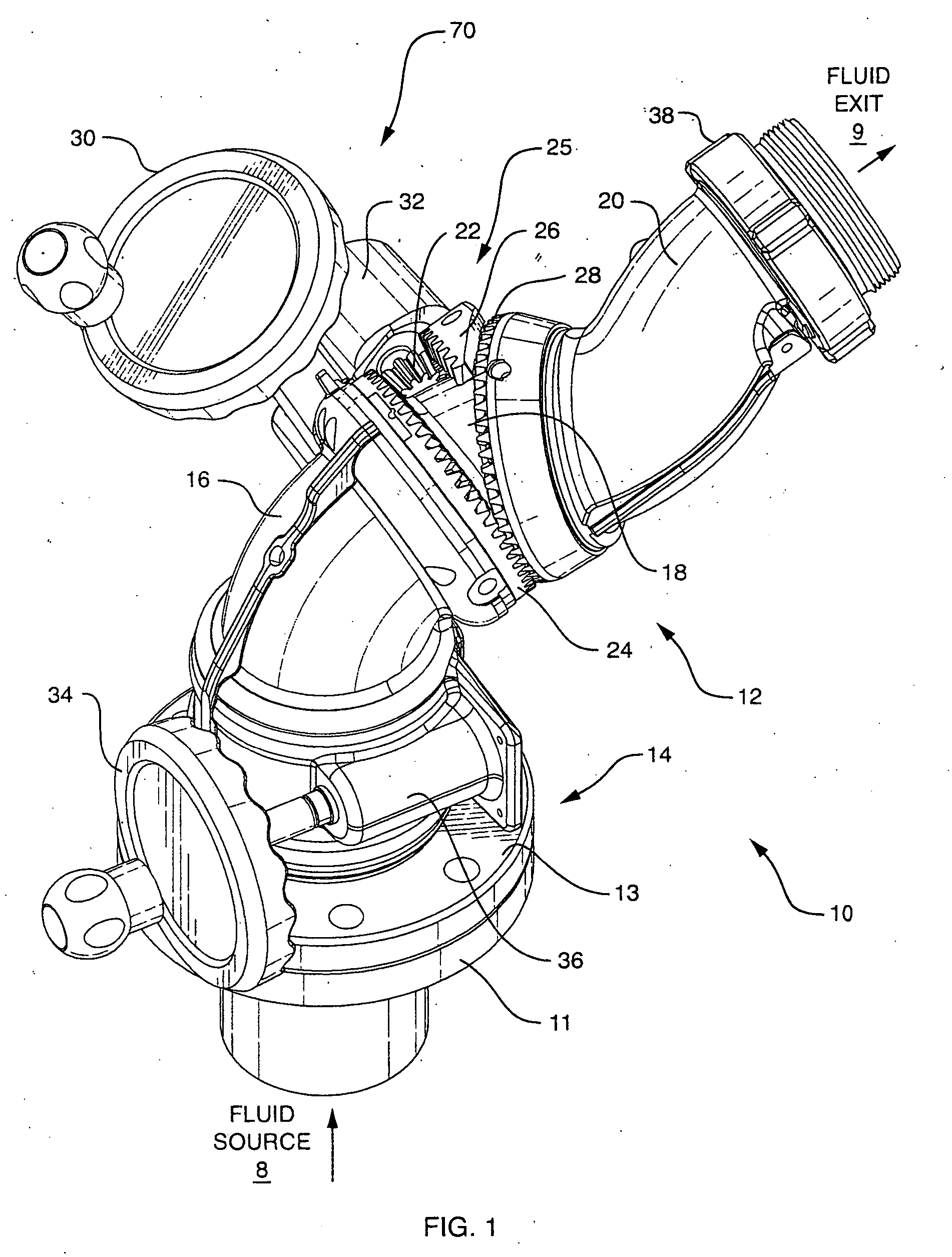
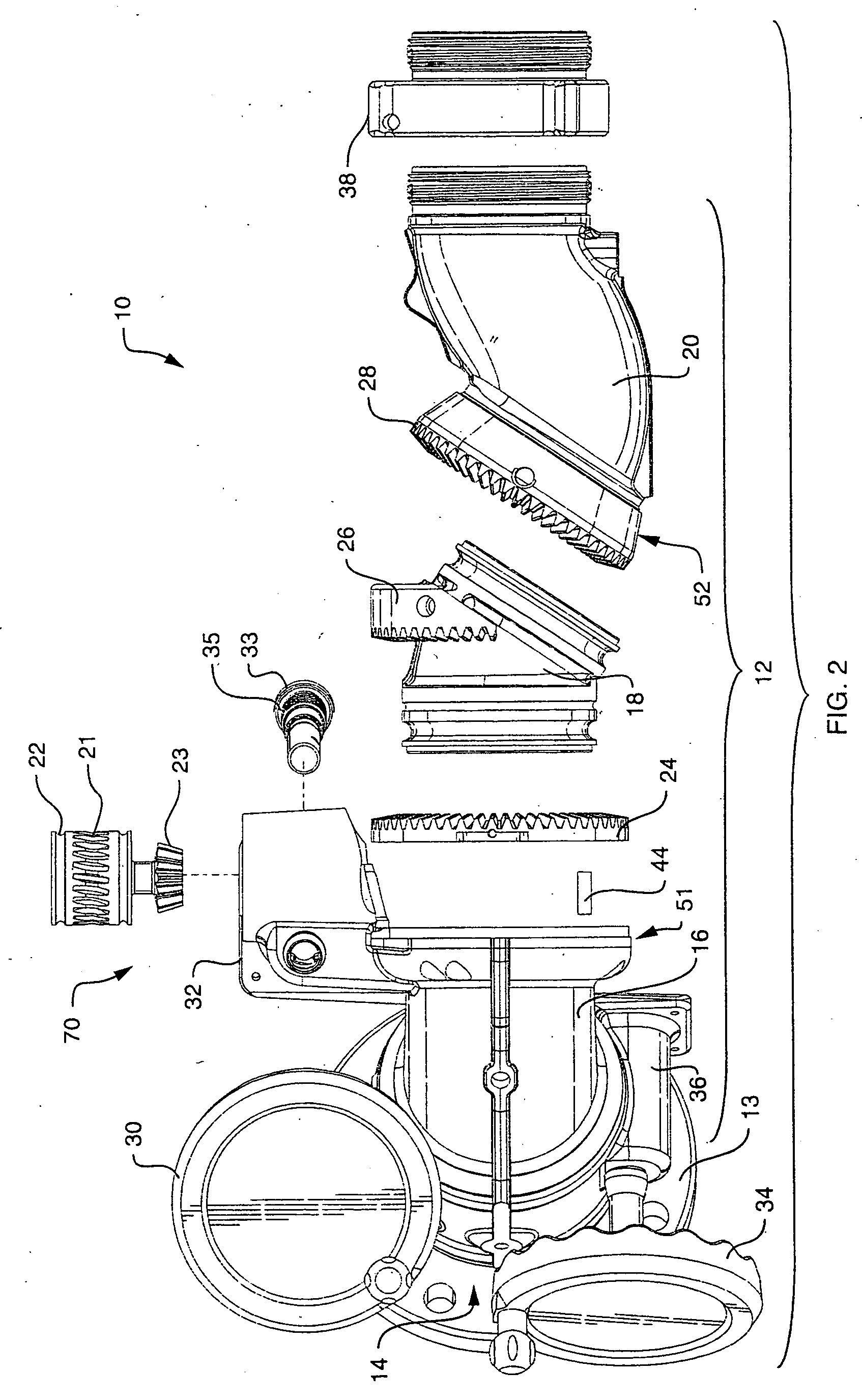
Segmented monitor
ActiveUS7137578B2Minimum turbulence and friction lossConvenient distanceSpray nozzlesAdjustable jointsDisplay deviceEngineering
A firefighting segmented monitor for redirecting a trajectory of a pressurized fluid discharge towards a target comprises a flowpath with minimum convolutions. The monitor flowpath comprises in series a stationary segment and three rotating segments including a lower segment, a middle segment and an upper segment connected in series each of which comprises a predetermined curvature. The lower segment swivels in one axis about the stationary segment. A nonorthogonal swivel is arranged on each end of the middle segment at the interfaces with the lower segment and the upper segment, and the swiveling of the middle and upper segments are synchronized with a single rotary input to produce an approximately planar elevational motion of the fluid discharge end of the monitor.
Owner:TASK FORCE TIPS
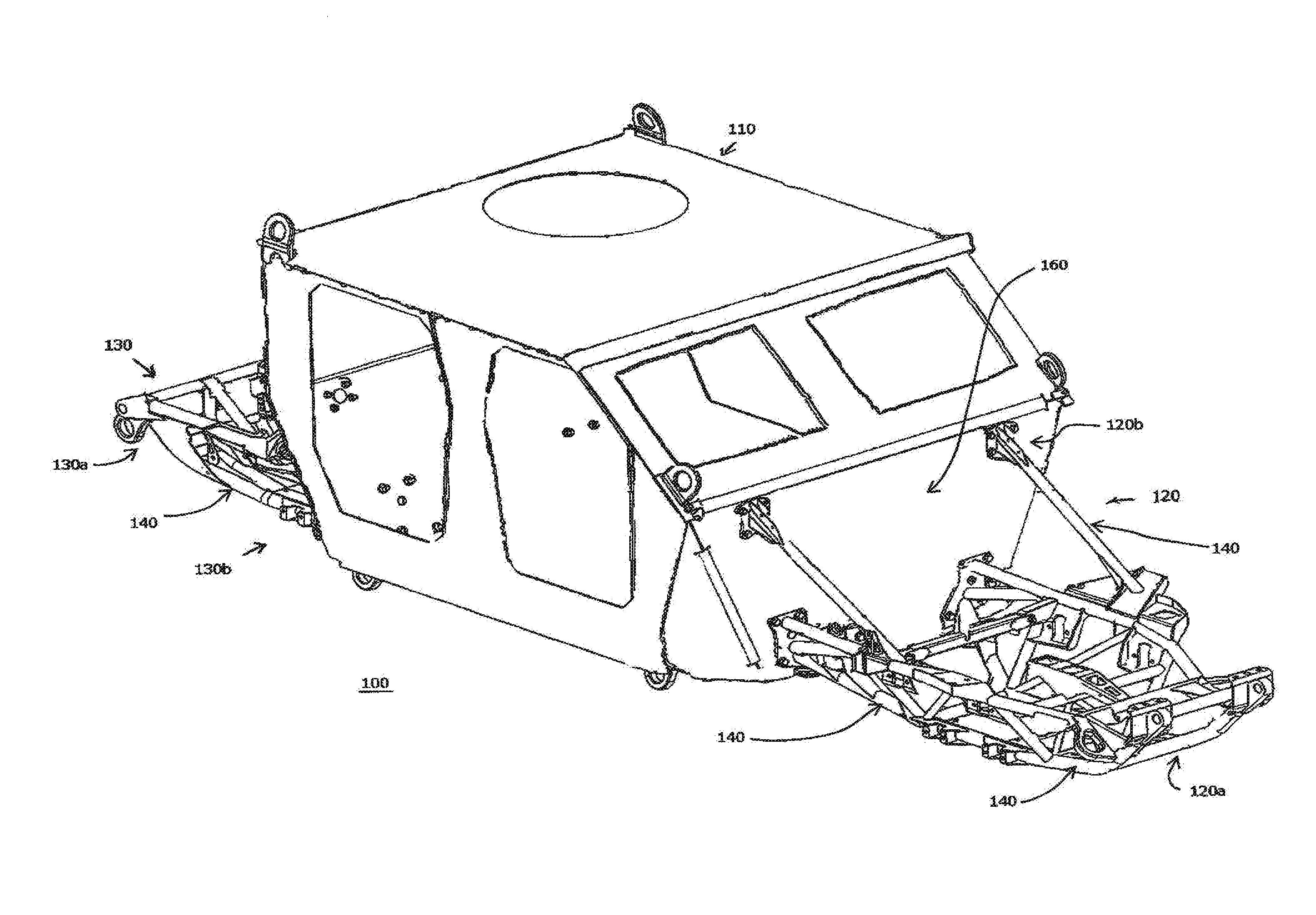
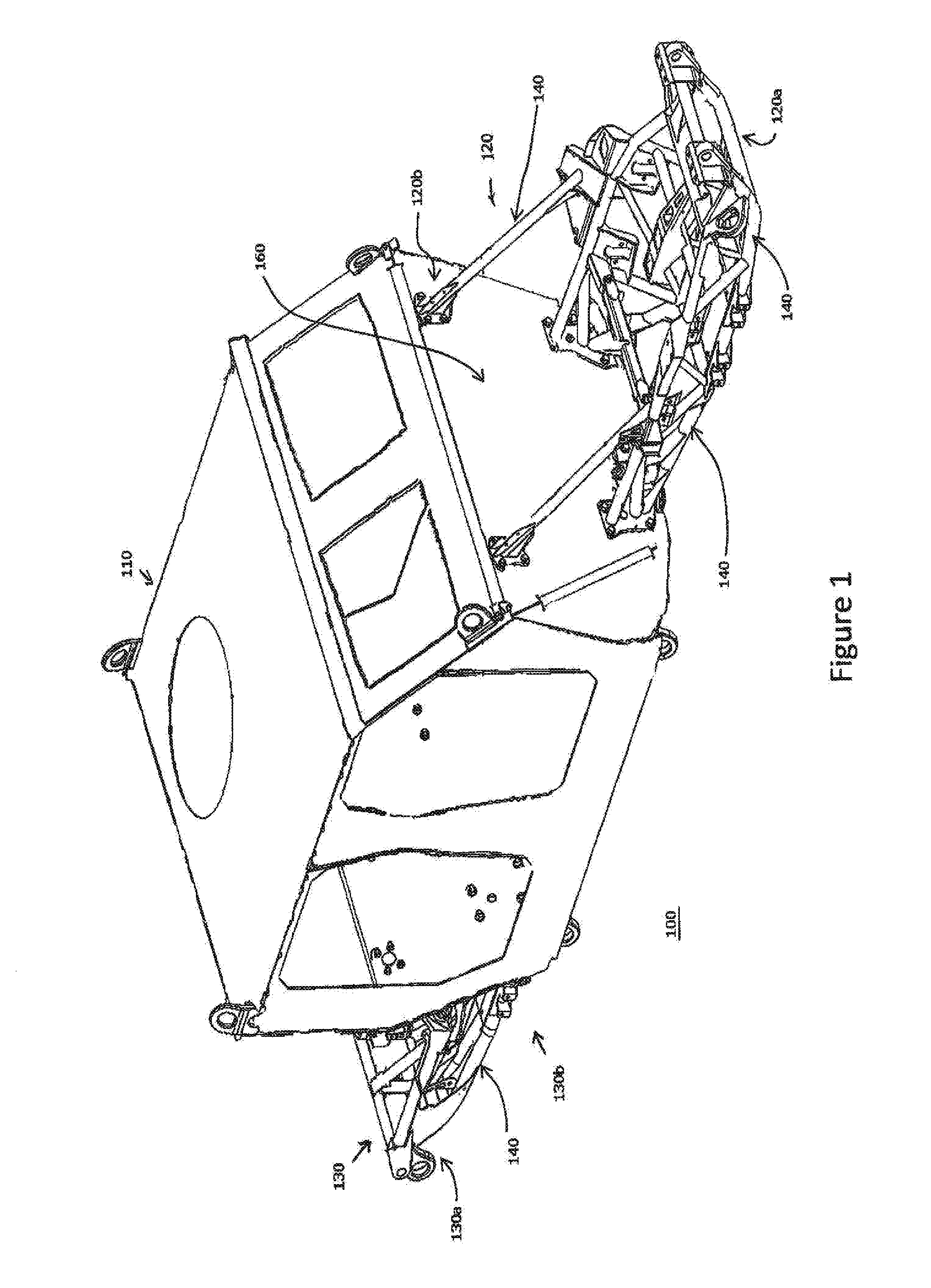
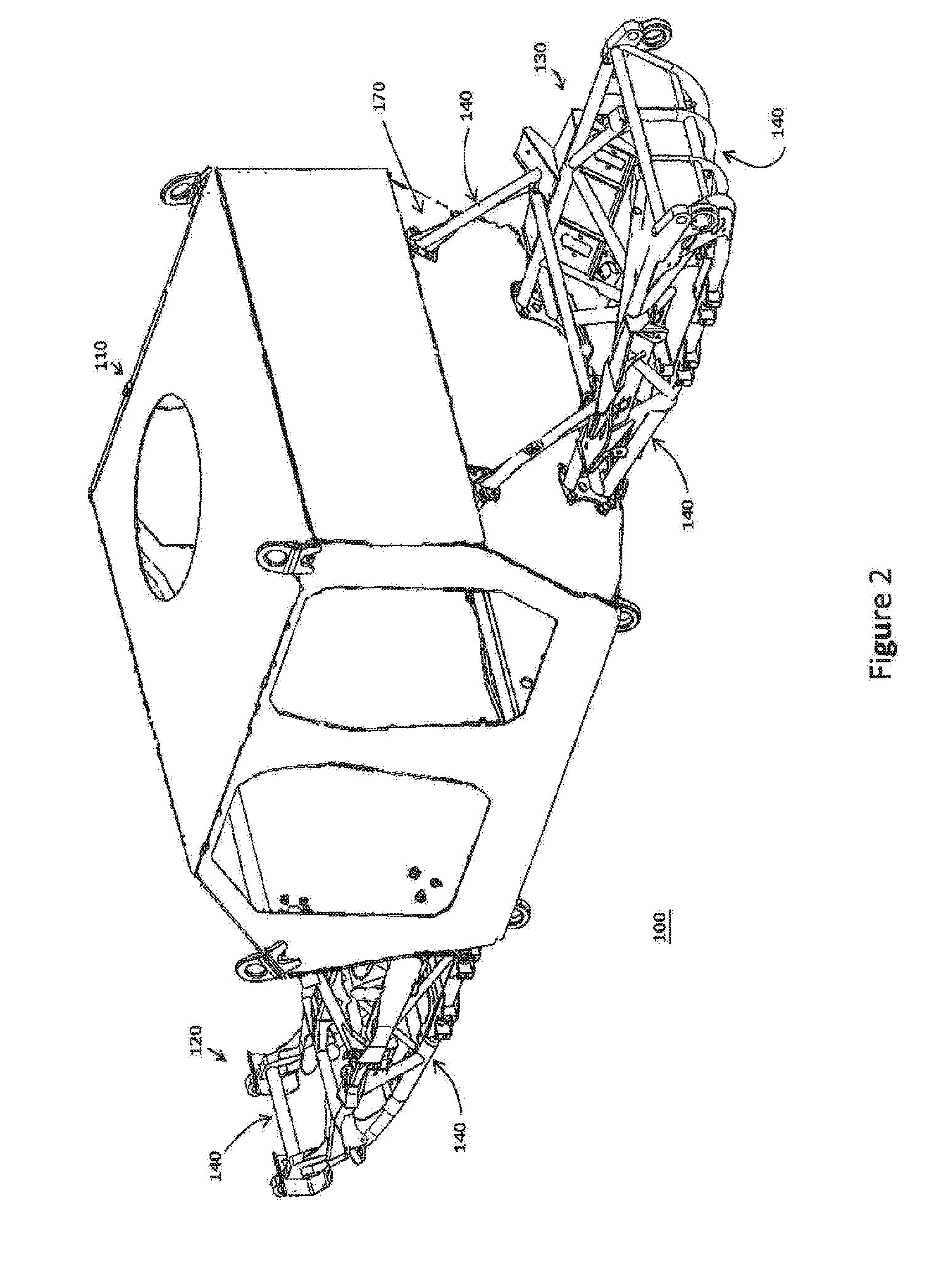
Modular Vehicle Architecture
InactiveUS20160257360A1Minimize connectionDissipating shearing loadsAgricultural vehiclesArmoured vehiclesModularityEngineering
The present invention relates to the field of mechanical engineering, in particular, vehicles. In one form, the invention relates to military or defence industry protected (armoured) vehicles with a modular vehicle architecture comprising: a capsule adapted for accommodating at least one occupant; at least one sub-frame detachably operatively connected to the capsule; wherein at least the sub-frame construction comprises members of tubular structure having a cross section corresponding to a conic section.
Owner:THALES AUSTRALIA
Segmented monitor
ActiveUS20050145727A1Minimize connectionMinimize rotational torqueSpray nozzlesAdjustable jointsConvolutionUpper segment
A firefighting segmented monitor for redirecting a trajectory of a pressurized fluid discharge towards a target comprises a flowpath with minimum convolutions. The monitor flowpath comprises in series a stationary segment and three rotating segments including a lower segment, a middle segment and an upper segment connected in series each of which comprises a predetermined curvature. The lower segment swivels in one axis about the stationary segment. A nonorthogonal swivel is arranged on each end of the middle segment at the interfaces with the lower segment and the upper segment, and the swiveling of the middle and upper segments are synchronized with a single rotary input to produce an approximately planar elevational motion of the fluid discharge end of the monitor.
Owner:TASK FORCE TIPS
Convertible multi-diameter sleeve for optical fiber connectors
InactiveUS20030044124A1Minimize connectionEliminate stressCoupling light guidesPrinted circuitsOptical fiber connectorElectric cables
This invention is a convertible multi-diameter sleeve for optical fiber connectors to allow optical fiber cables with plug ferrules of different internal and external diameters to be pushed into the sleeve and connected with precise core alignment keeping stable conditions. The sleeve has at least one slot extending part way along the length of the sleeve.
Owner:TONAMI ELECTRONICS CORP +1
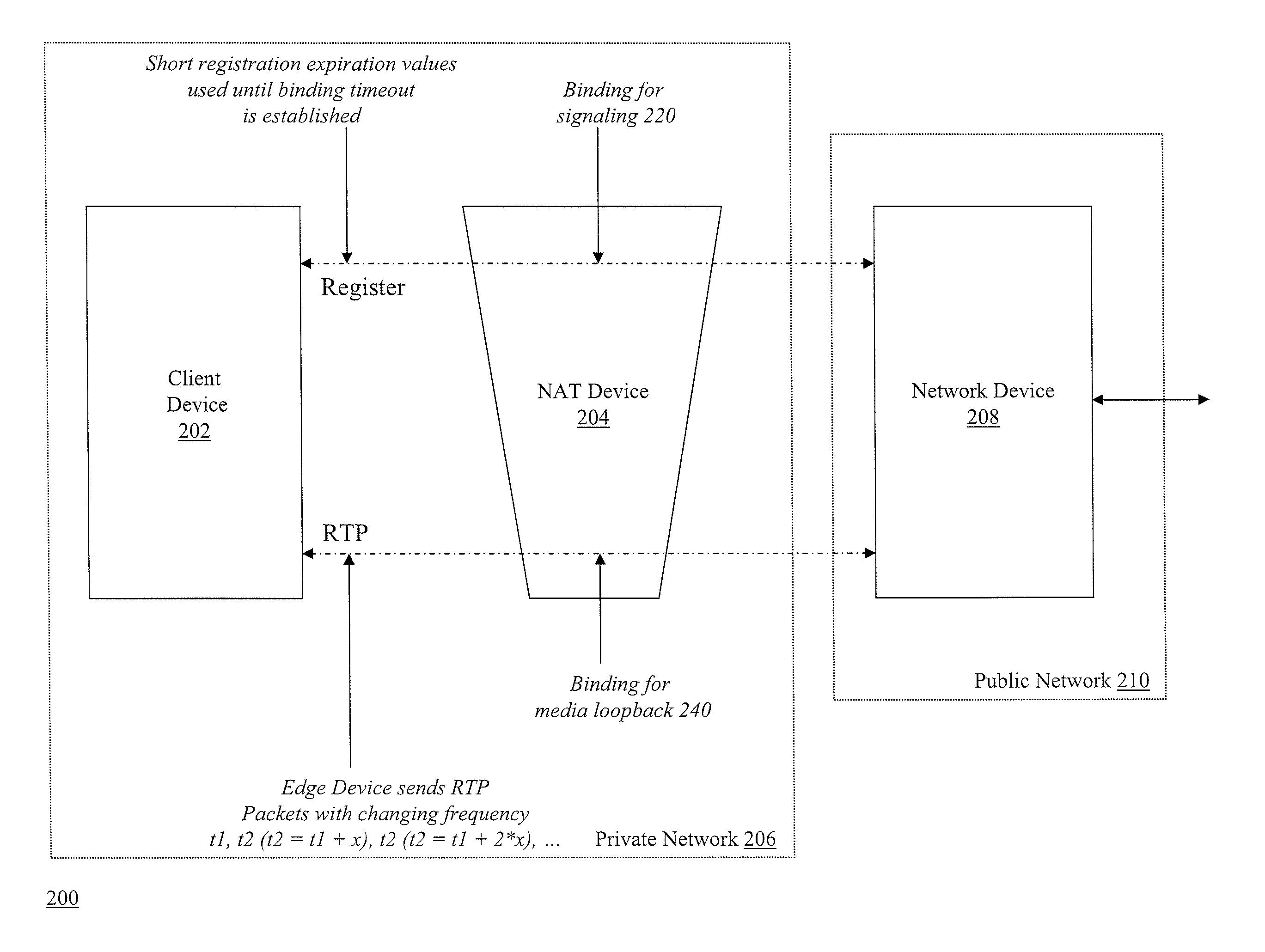
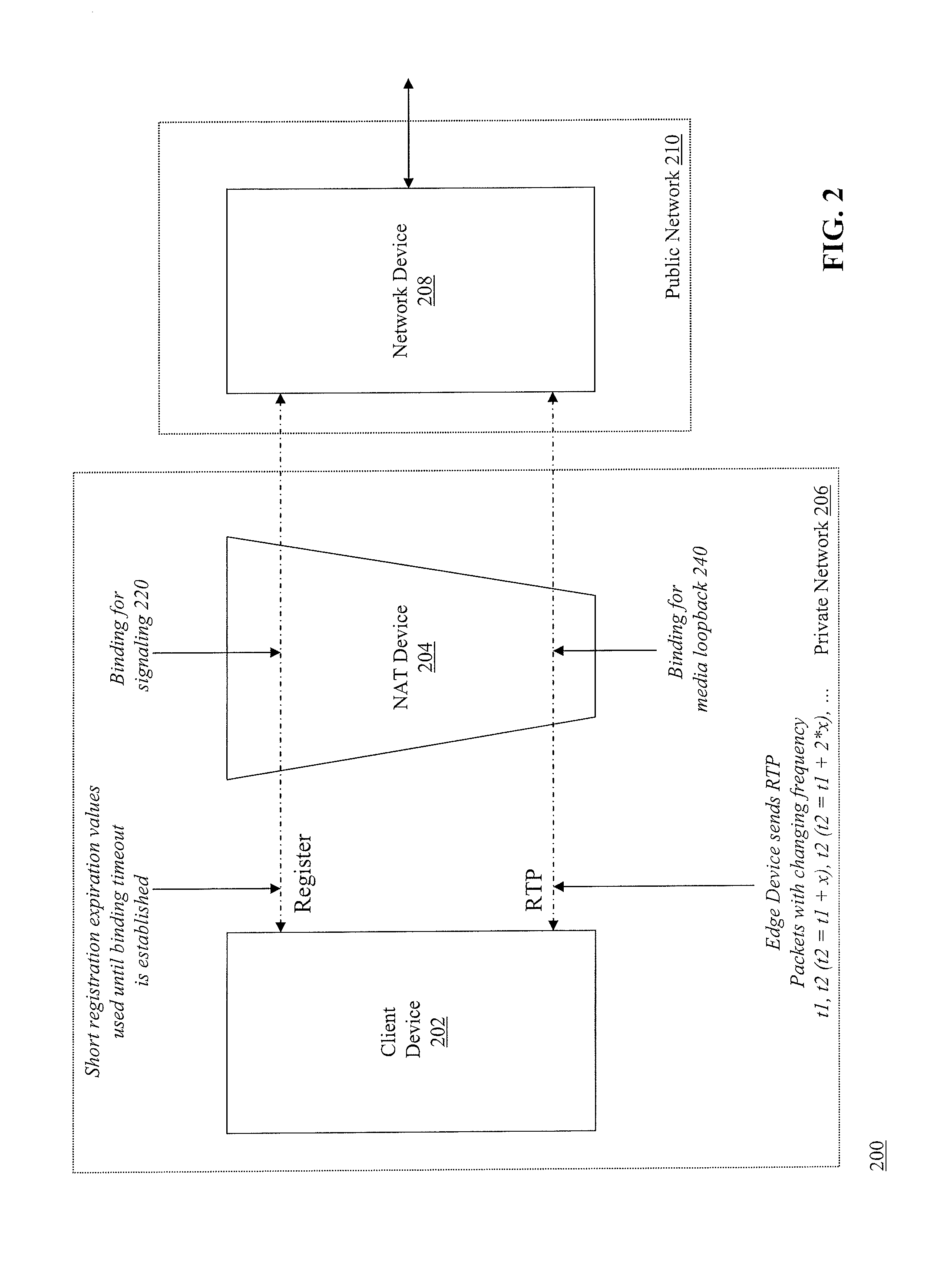
Determining expiration time of bindings for network address translation devices
ActiveUS20130054762A1Reduce network bandwidth usageMinimizes connection interruptionDigital computer detailsTransmissionExpiration TimeIp address
Methods and apparatuses, including computer program products, are described for determining expiration time of bindings for NAT devices. A first device receives a first request including a first source IP address / port pair of a first NAT binding, and transmits a response. The first device receives a second request including a second source IP address / port pair of a second NAT binding, and transmits a response. The first device sets a refresh time T1 of the first NAT binding to be shorter than an expected minimum expiration time of the first NAT binding, transmits one or more messages via the second NAT binding where a sending interval time T2 of the second NAT binding is longer than T1, increments T2 when a response is received, and if a response to any of the messages is not received, sets T1 equal to the last T2 value for which a response was received.
Owner:RIBBON COMM OPERATING CO INC
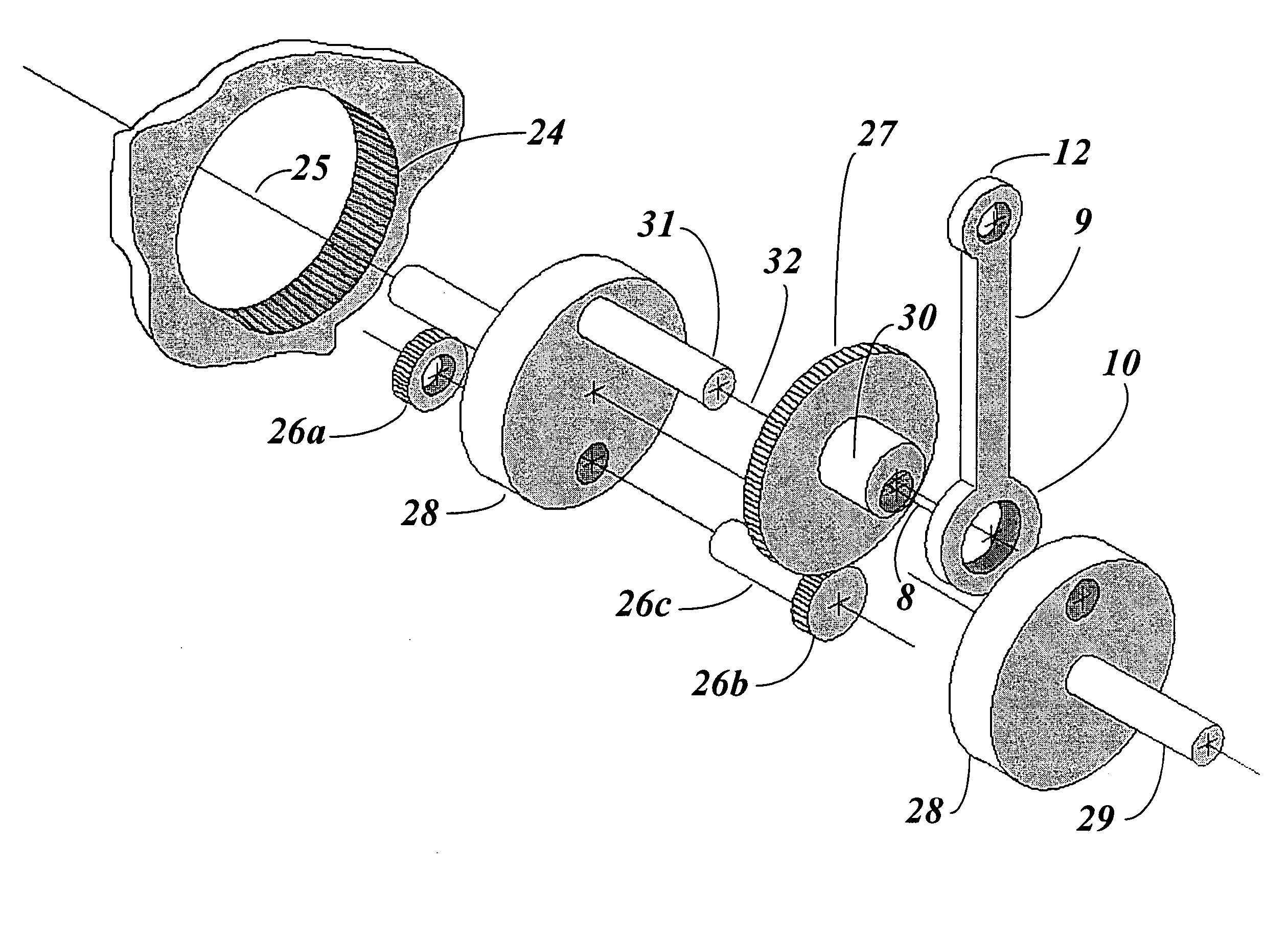
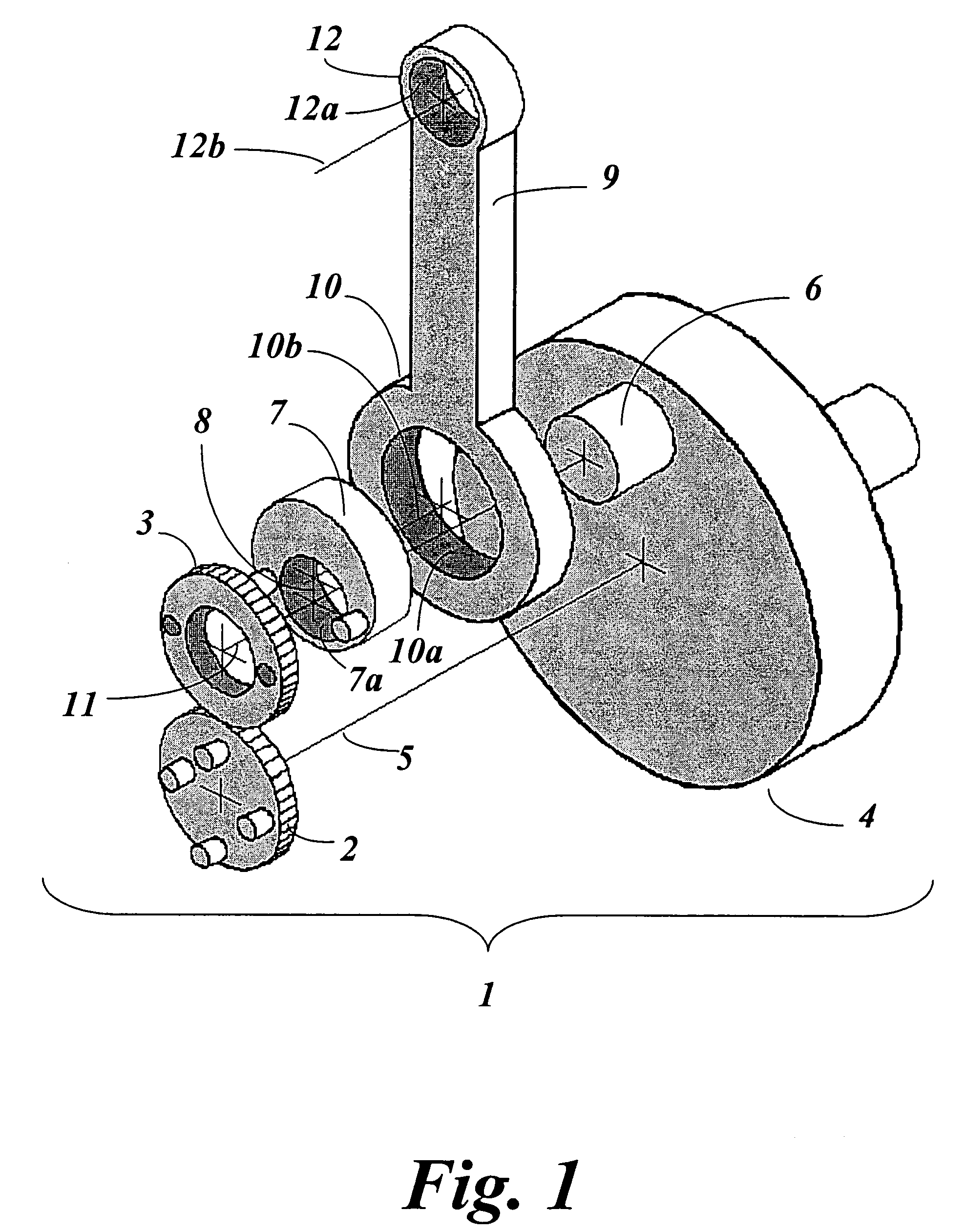
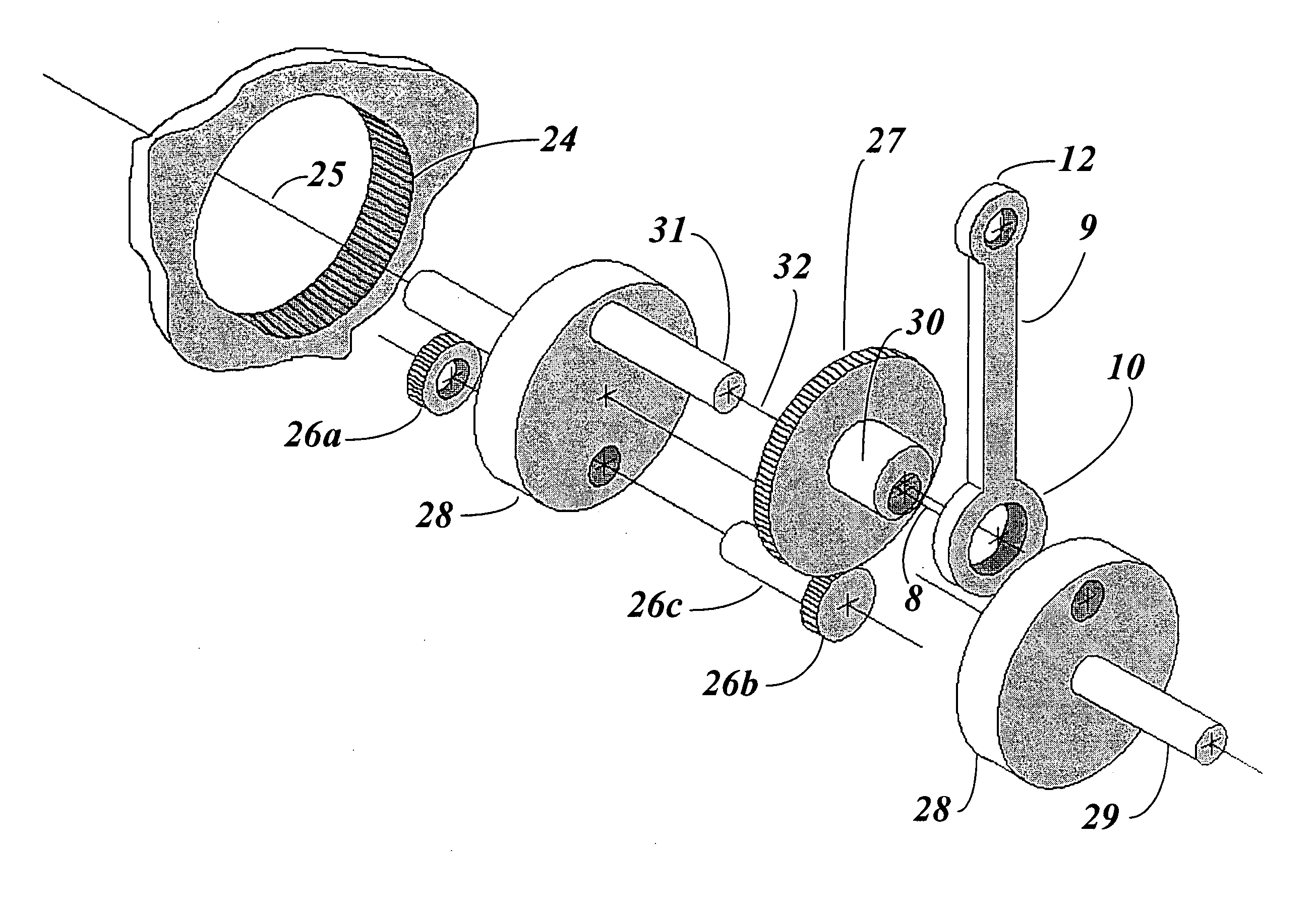
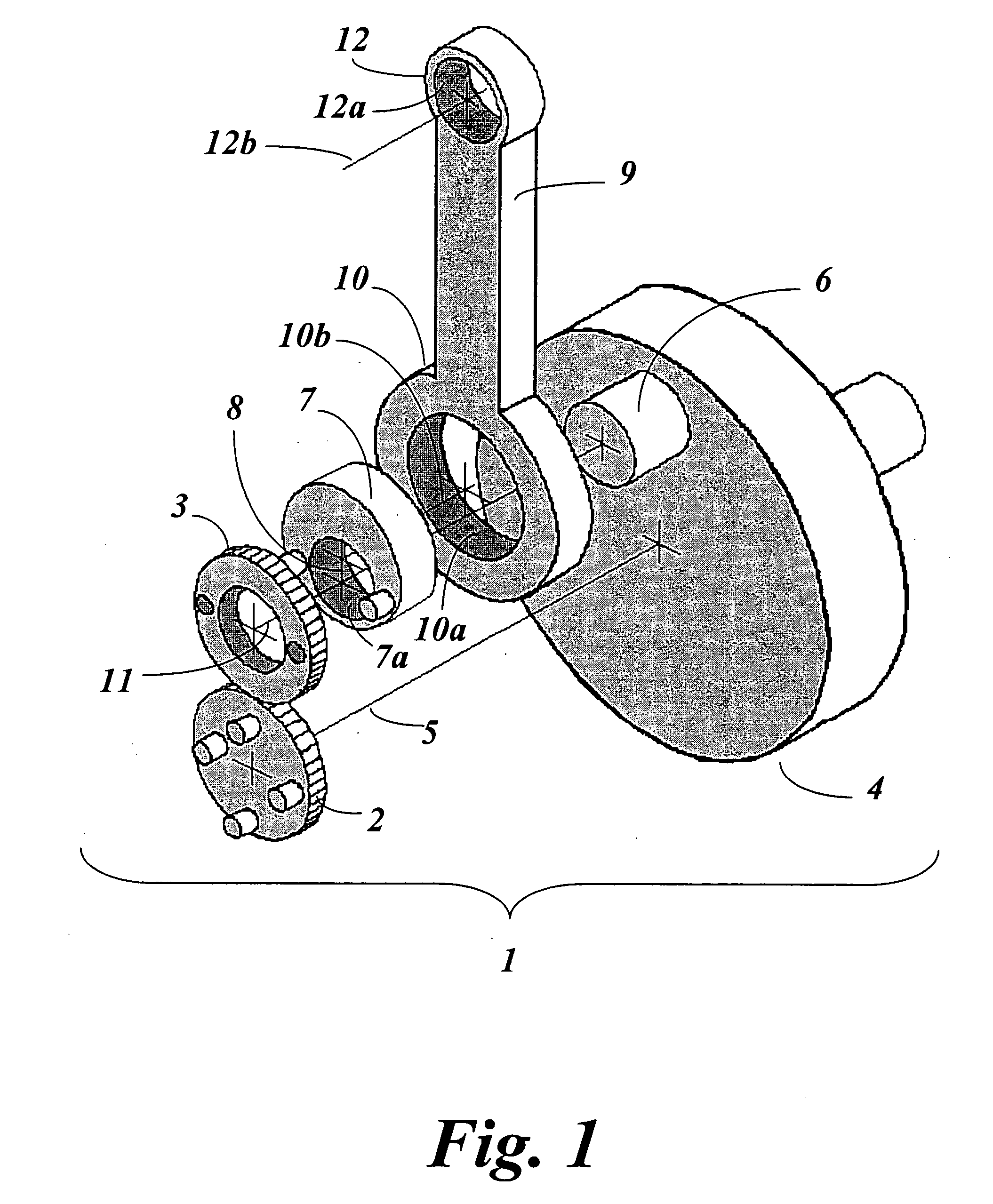
Epitrochoidal crankshaft mechanism and method
ActiveUS7185557B2High power outputImprove efficiencyRotary bearingsGearingFour-stroke engineInternal combustion engine
This invention relates to a mechanism and method for enhancing the performance of both two stroke and four stroke cycle reciprocating piston internal combustion engines, reciprocating piston pumps and compressors by generating an Epitrochoidal path of travel for the lower end of the connecting rod. The piston, attached to the upper end of the connecting rod, will be made to dwell at the lower part of its travel, enhancing the output of the engine, pump or compressor through better utilization of the available cylinder pressure.
Owner:MAROZZI
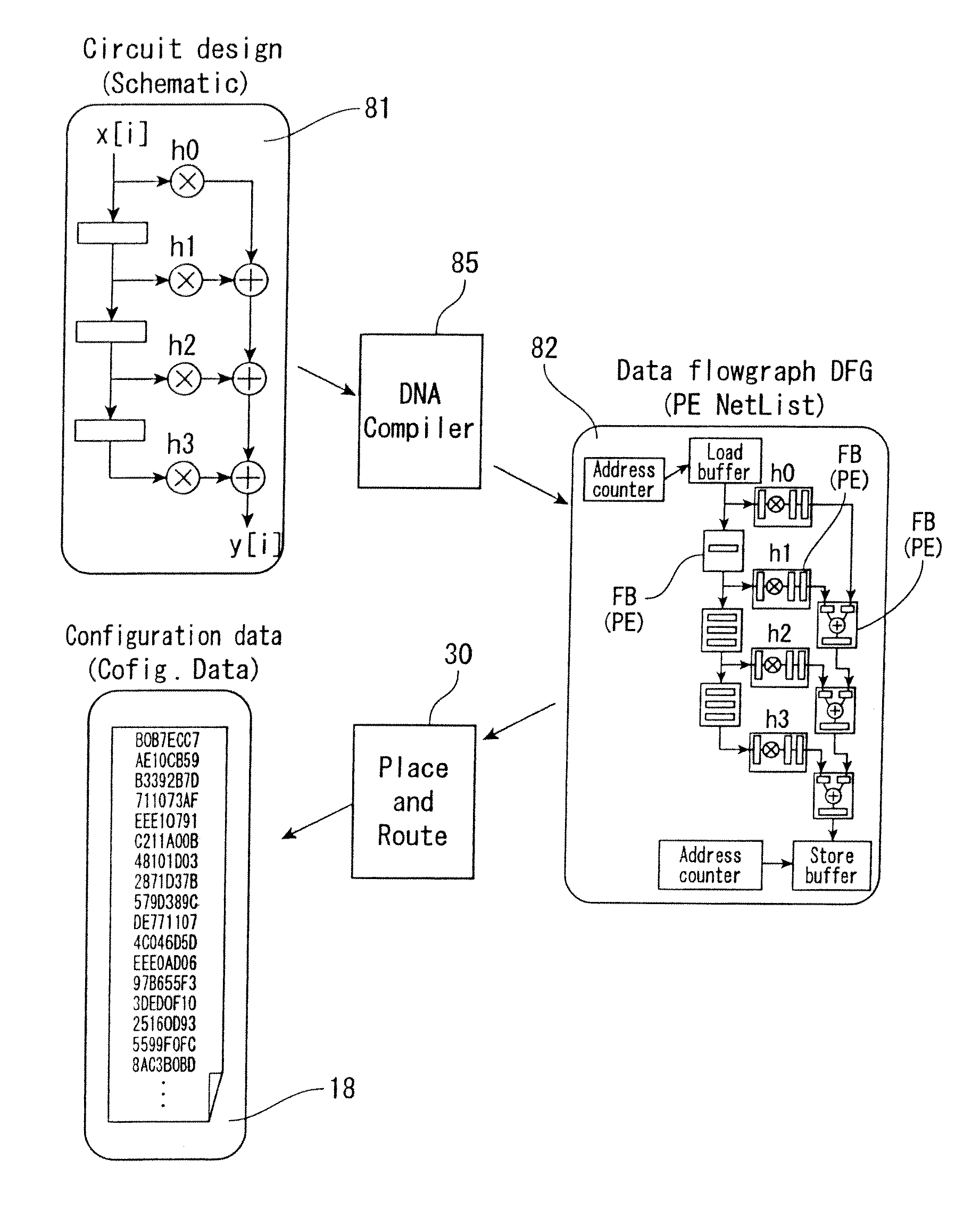
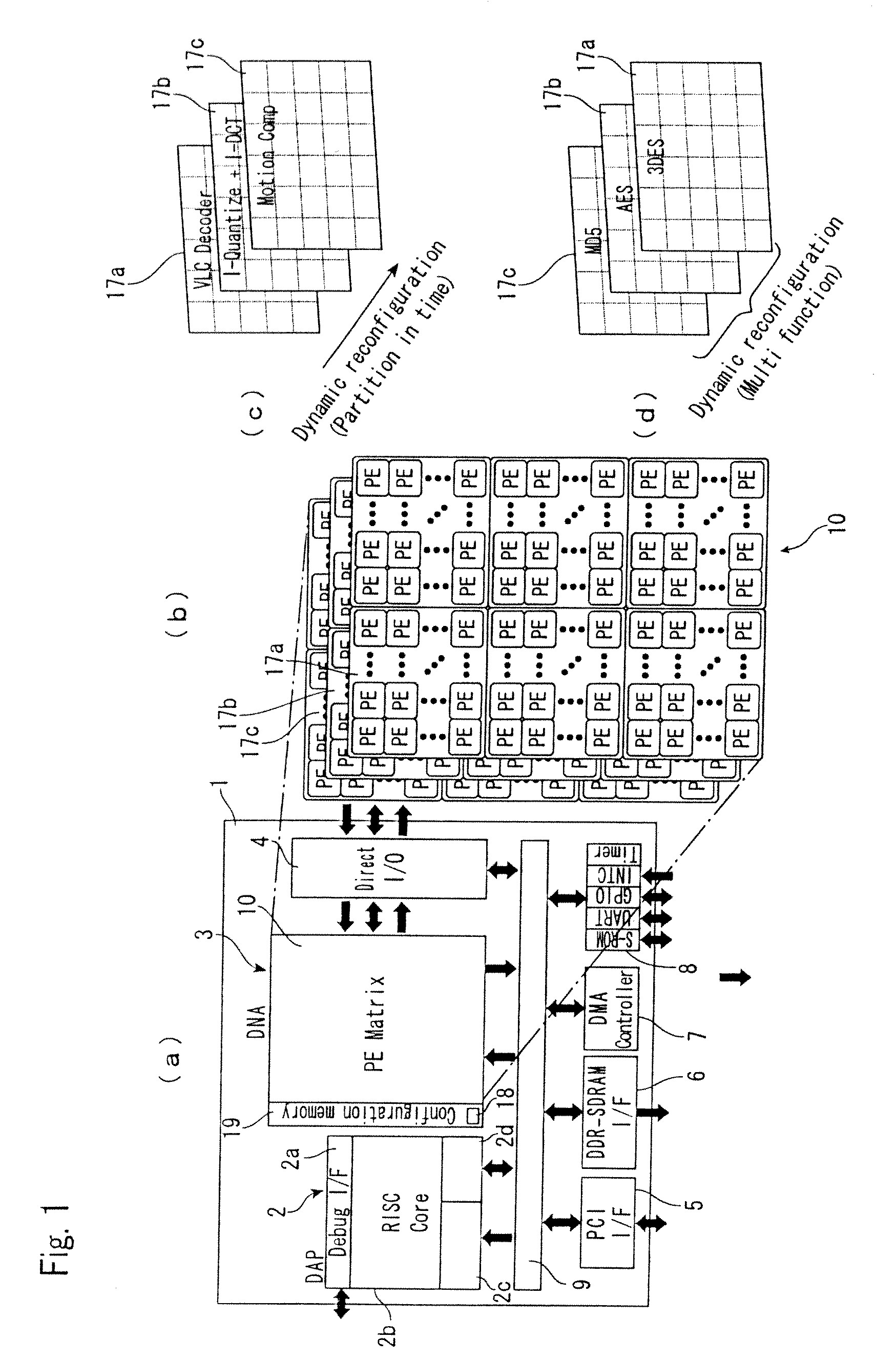
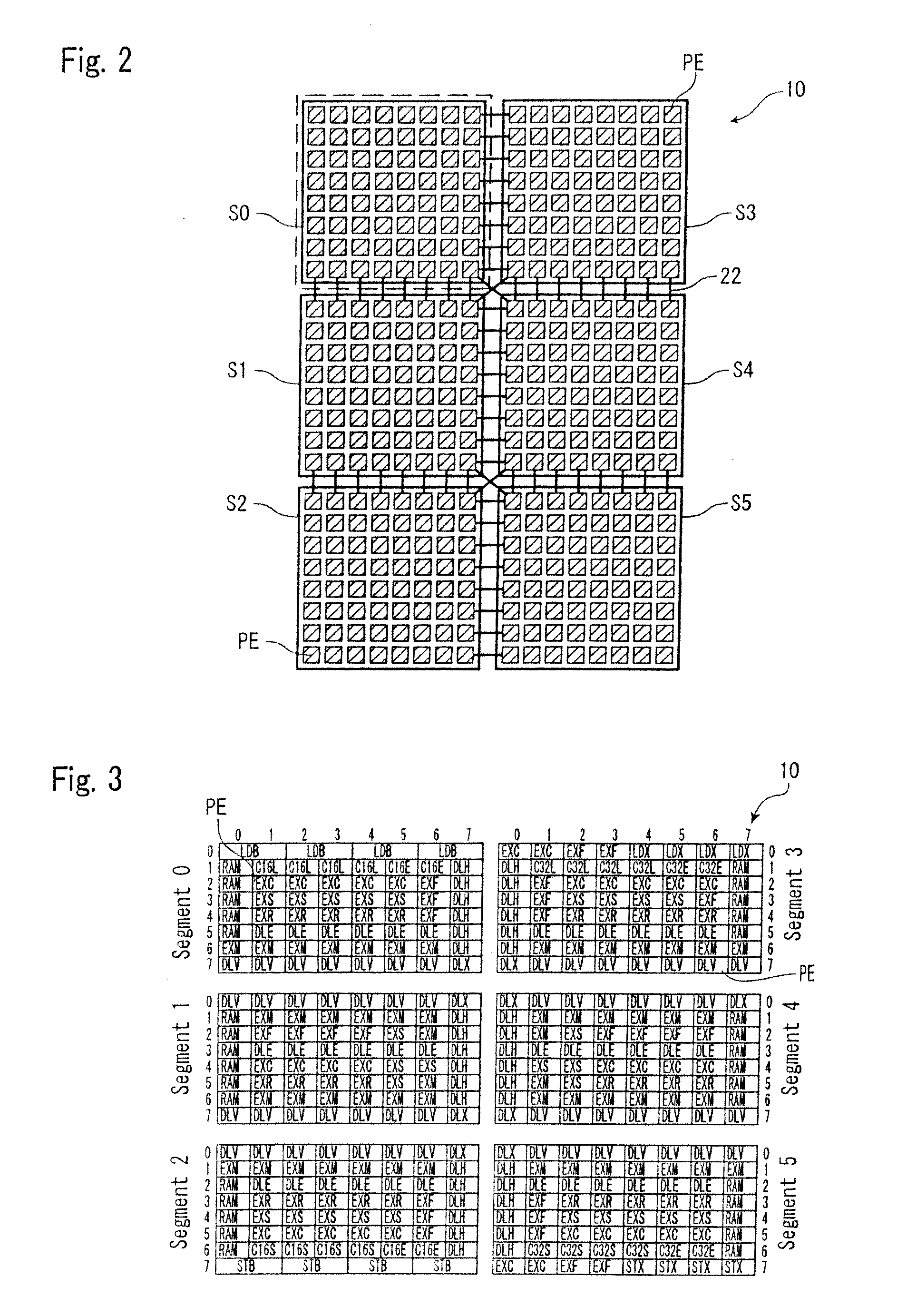
Method and system for mounting circuit design on reconfigurable device
InactiveUS20100017774A1Minimize cost functionMinimizing useCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringComputer hardware
There is provided a system for generating configuration data for implementing a circuit design in a segmented reconfigurable device. A placement and routing design aiding system (30) includes a database (31) for storing hardware information (89) including data of PEs included in each segment and data of a first-level and second-level routing matrix and an apparatus (33) for mapping the circuit design onto the PEs. The mapping apparatus (33) generates mappings of the circuit design onto the PEs by carrying out an iterative algorithm that minimizes a cost function based on the hardware information (89). The cost function includes an item that minimizes usage of the second-level routing matrix (22) that connects between the segments.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Film bulk acoustic wave resonator, its fabrication method and film bulk acoustic wave resonator filter using the resonator
InactiveUS7986075B2ConnectionLeakage of bulk acoustic waves towards the insulation substrate can be suppressedPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorResonator filter
The film bulk acoustic wave resonator includes a laminate structure composed of a piezoelectric layer, and first and second electrode layers interposing at least part of the piezoelectric layer, in which the first metal electrode is dispersively formed on an electrode plane facing the second metal electrode, and a gap is formed in a substrate correspondingly to the laminate-structured resonance part. Except for an area of a wire electrode electrically connected to the first electrode layer and an area of a wire electrode electrically connected to the second electrode layer, the piezoelectric layer, first electrode layer and second electrode layer do not come in contact with the insulating substrate but are supported on a hollow. Also, a prop is formed in the gap to support the laminate structure.
Owner:HITACHI MEDIA ELECTORONICS CO LTD
Epitrochoidal crankshaft mechanism and method
ActiveUS20060053964A1High outputIncrease distanceRotary bearingsGearingFour-stroke engineInternal combustion engine
This invention relates to a mechanism and method for enhancing the performance of both two stroke and four stroke cycle reciprocating piston internal combustion engines, reciprocating piston pumps and compressors by generating an Epitrochoidal path of travel for the lower end of the connecting rod. The piston, attached to the upper end of the connecting rod, will be made to dwell at the lower part of its travel, enhancing the output of the engine, pump or compressor through better utilization of the available cylinder pressure.
Owner:MAROZZI
Electro-orthodontic device
ActiveUS9662183B2Minimize connectionEasy to buildAdditive manufacturing apparatusOthrodonticsPower flowElectrical current
An electro-orthodontic appliance is provided that helps accelerate orthodontic tooth movement through the application of a controlled electrical current to gum and teeth, thus stimulating osteogenesis.
Owner:ADVANCED ORTHODONTICS & EDUCATION ASSOC LLC
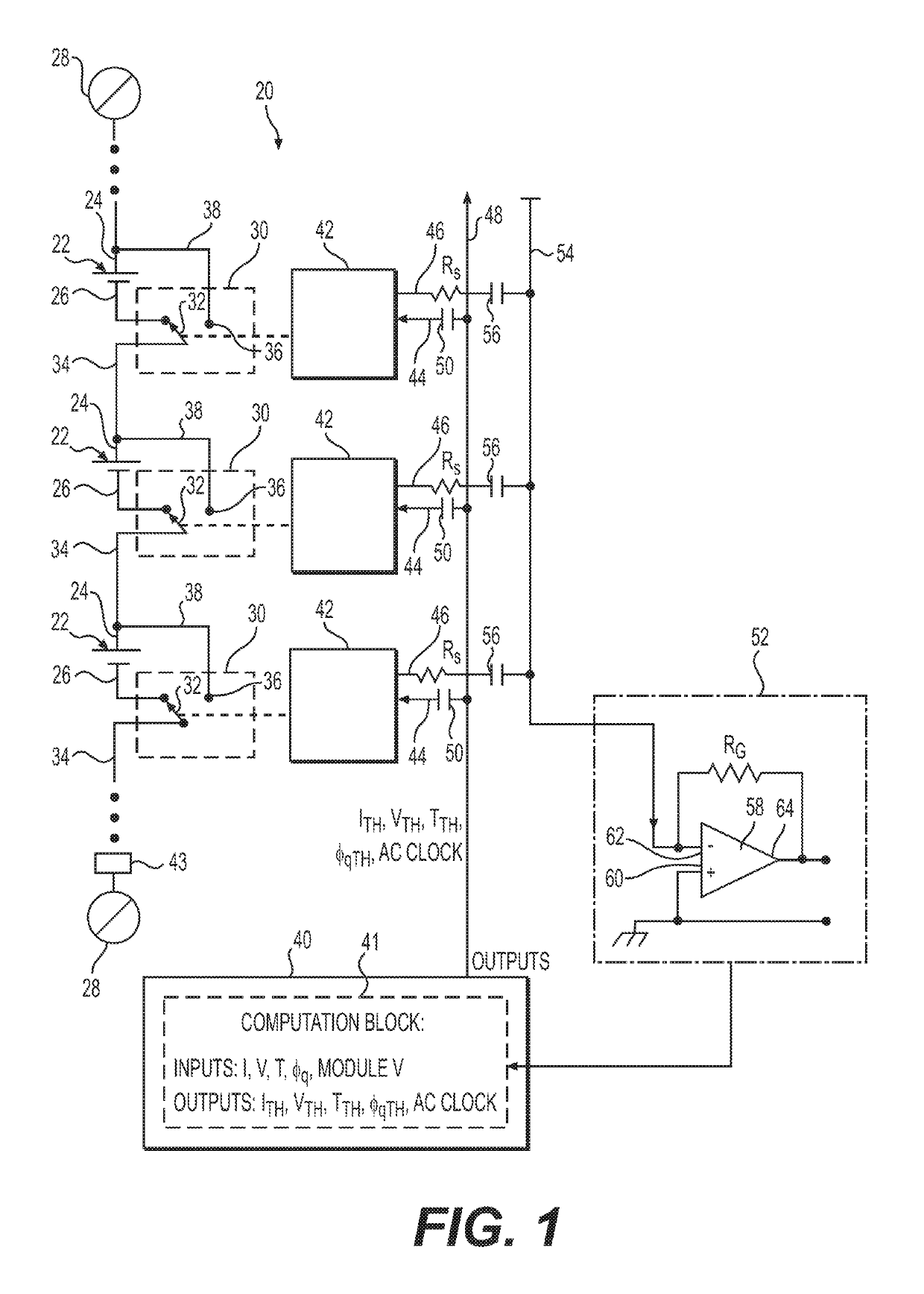
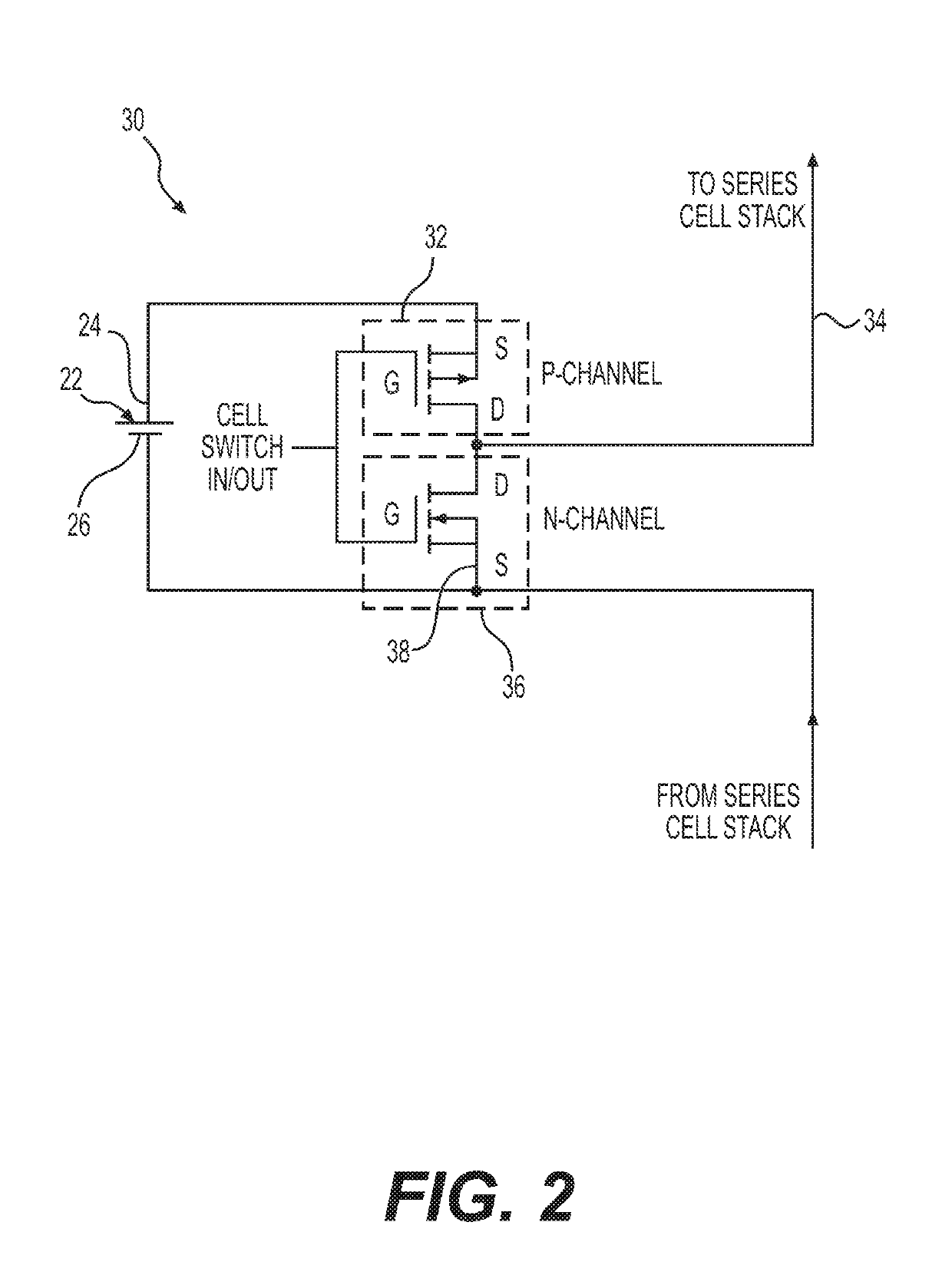
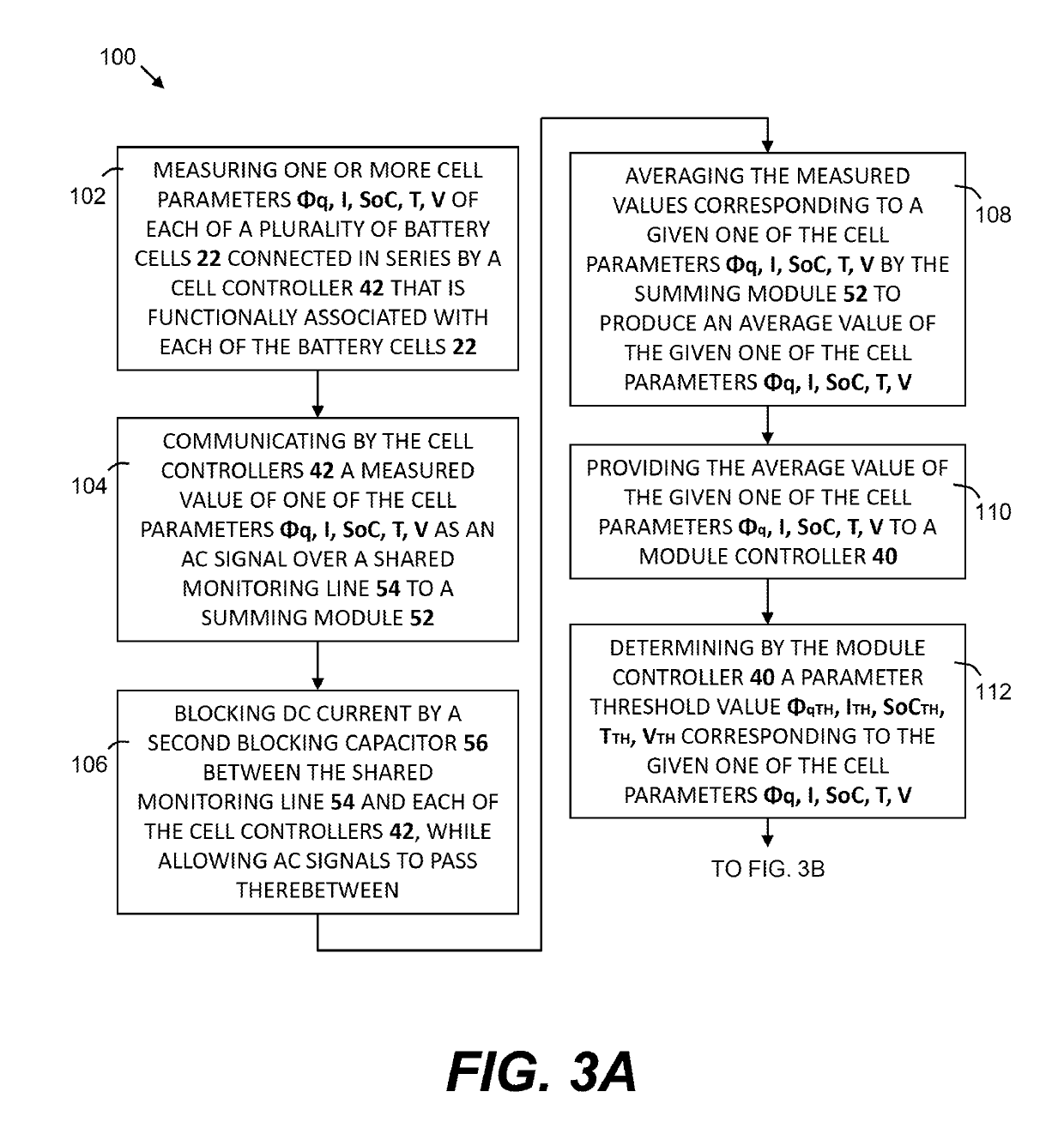
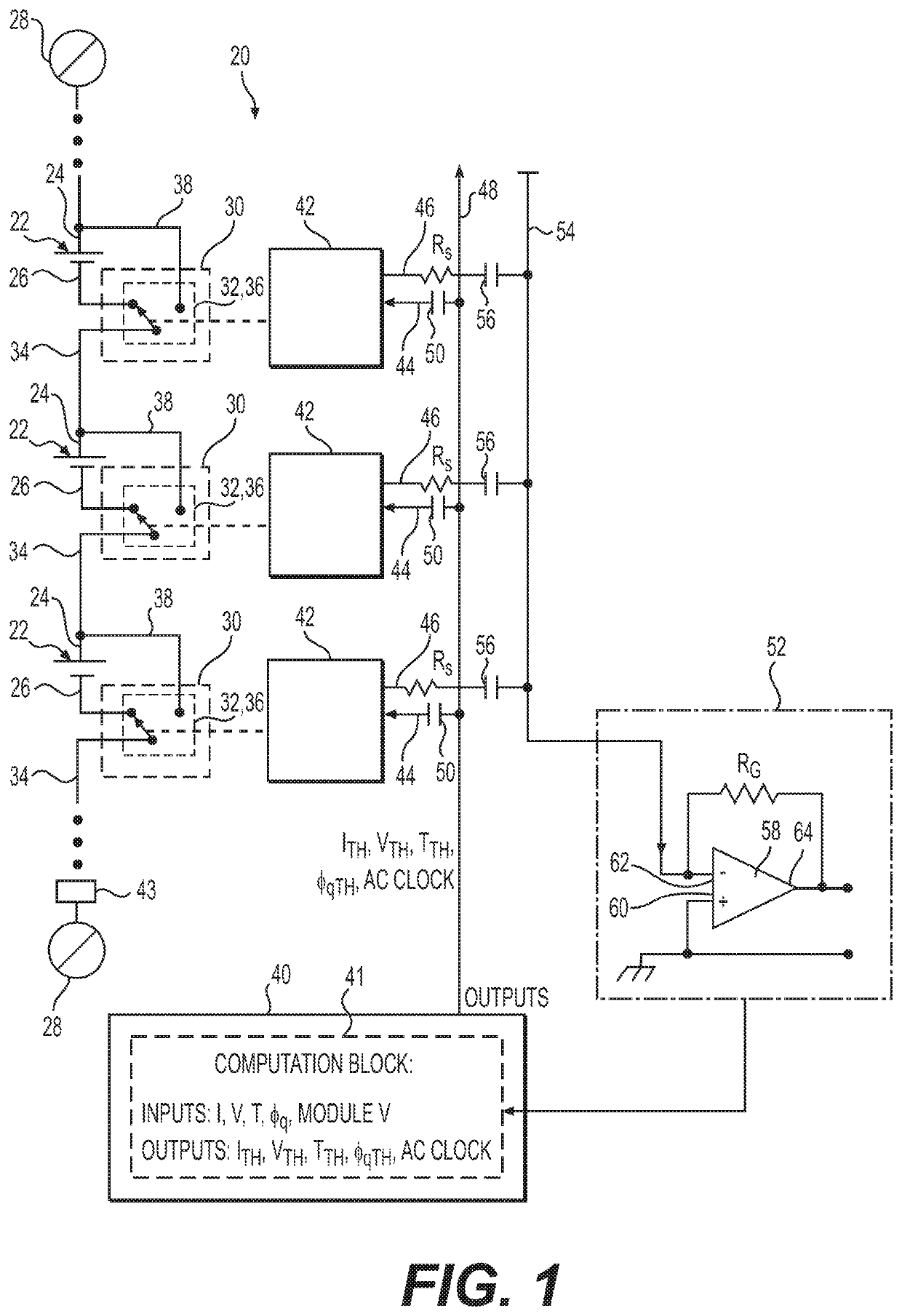
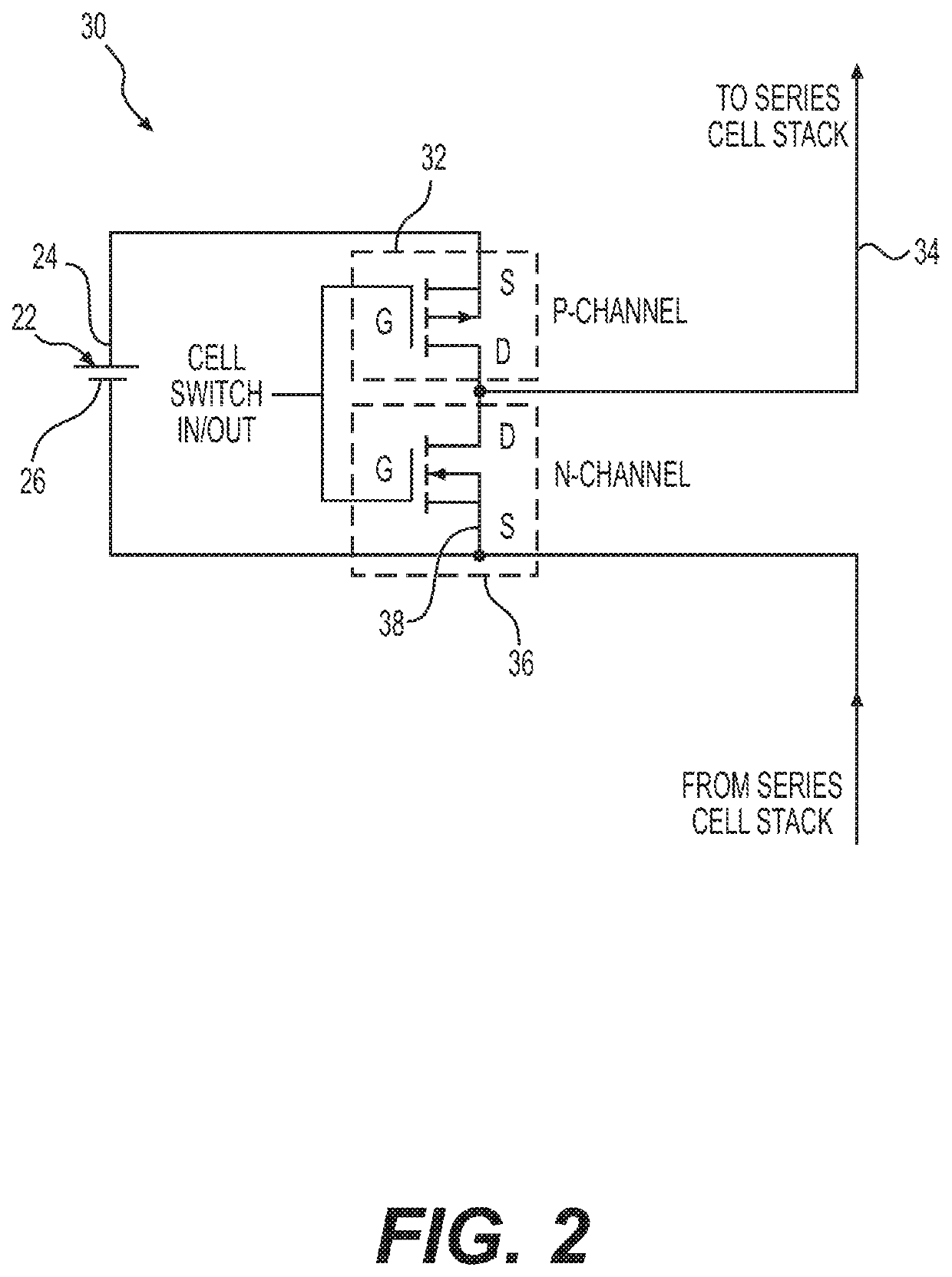
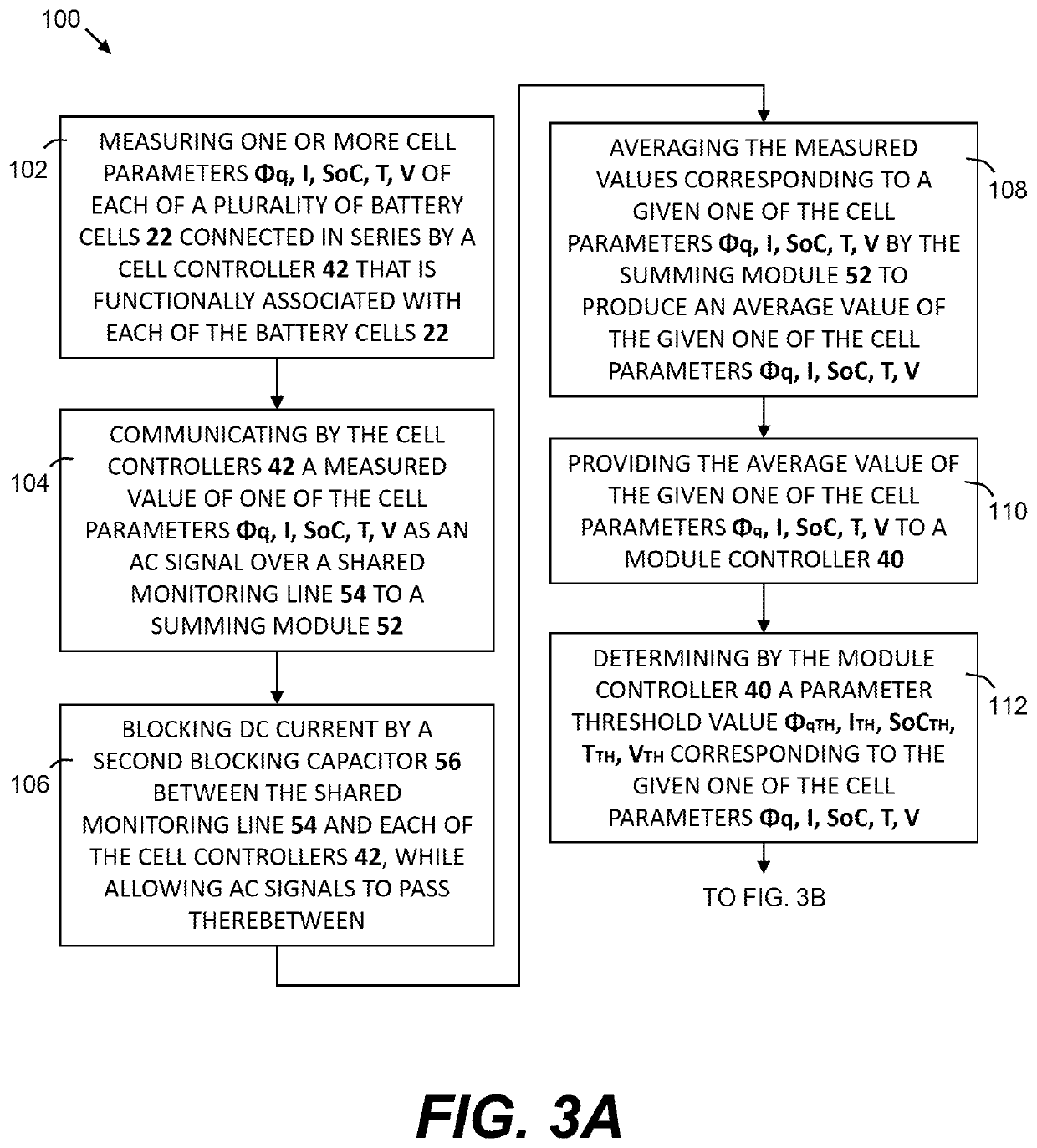
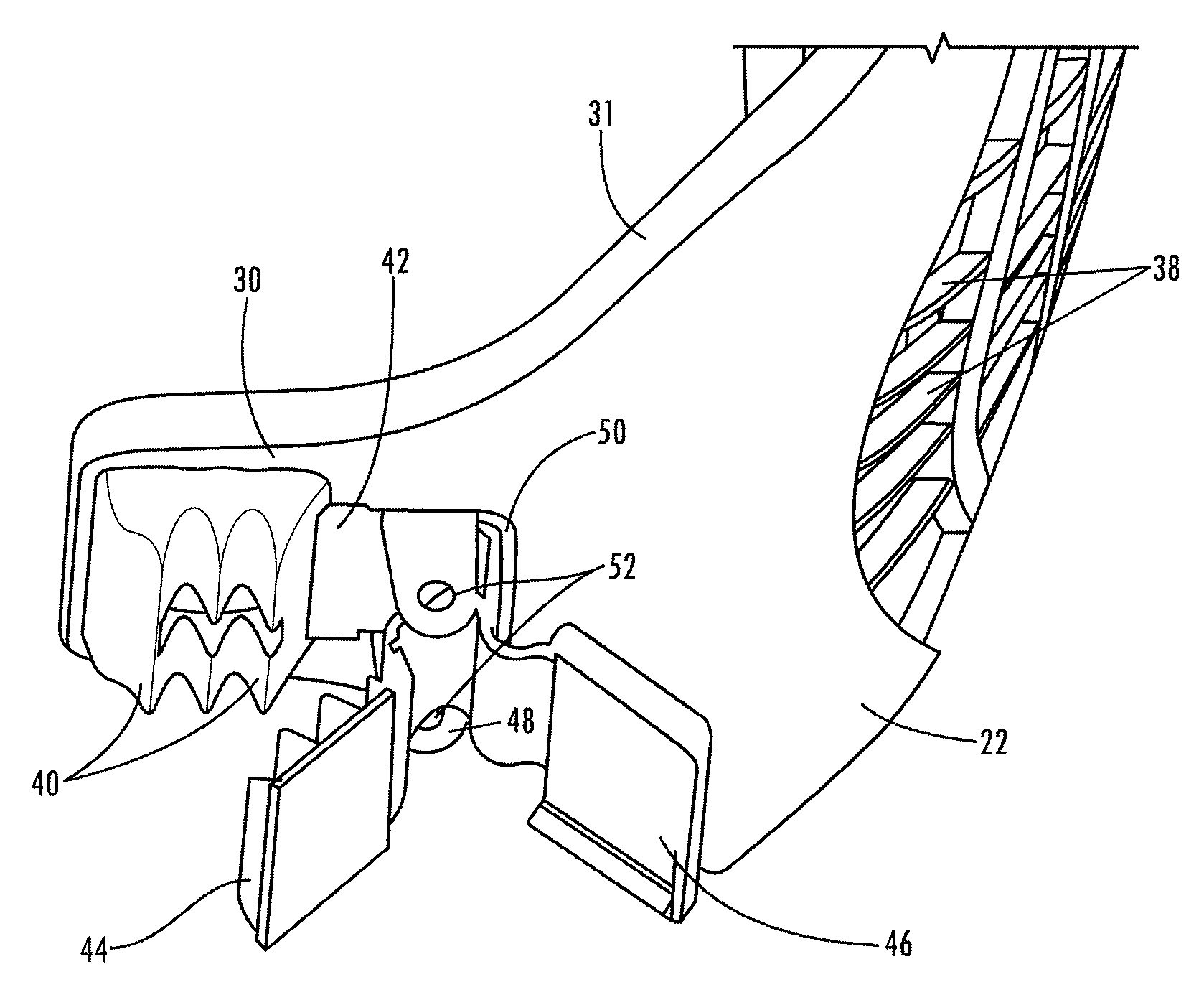
Cell balancing with local sensing and switching
ActiveUS20190148952A1Avoid damageAccurate balanceCharge equalisation circuitCircuit monitoring/indicationControl lineCell controller
A system and method for cell balancing within a battery module includes local sensing and switching at each of the battery cells. A switching circuit is associated with each one of the battery cells to connect or functionally disconnected the battery cell from the battery module. A module controller generates one or more parameter threshold values as maximum operating values for each of the battery cells. Each cell has a cell controller associated therewith to monitor one or more cell parameters, which are communicated to a summing module via a shared monitoring line, averaged, and communicated to the module controller. The cell controllers each receive a parameter threshold value via a shared control line and command the associated switching circuit to functionally disconnect and to bypass the battery cell if the cell parameter exceeds the corresponding parameter threshold value. Methods of checking the battery module are also provided.
Owner:NEAPCO INTPROP HLDG LLC
Performance monitoring modules and apparatus
InactiveUS20120252530A1Facilitate convenient useIncrease in dead-loadSwimming detailsGymnastic exercisingCommunication interfaceComputer module
Owner:DAYTON TECH
Convertible multi-diameter sleeve for optical fiber connectors
InactiveUS6616462B2Minimize connectionEliminate stressCoupling light guidesPrinted circuitsOptical fiber connectorElectric cables
This invention is a convertible multi-diameter sleeve for optical fiber connectors to allow optical fiber cables with plug ferrules of different internal and external diameters to be pushed into the sleeve and connected with precise core alignment keeping stable conditions. The sleeve has at least one slot extending part way along the length of the sleeve.
Owner:TONAMI ELECTRONICS CORP +1
Method and system for mounting circuit design on reconfigurable device
InactiveUS8136076B2Use minimizedMinimize cost functionCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureCircuit design
There is provided a system for generating configuration data for implementing a circuit design in a segmented reconfigurable device. A placement and routing design aiding system (30) includes a database (31) for storing hardware information (89) including data of PEs included in each segment and data of a first-level and second-level routing matrix and an apparatus (33) for mapping the circuit design onto the PEs. The mapping apparatus (33) generates mappings of the circuit design onto the PEs by carrying out an iterative algorithm that minimizes a cost function based on the hardware information (89). The cost function includes an item that minimizes usage of the second-level routing matrix (22) that connects between the segments.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
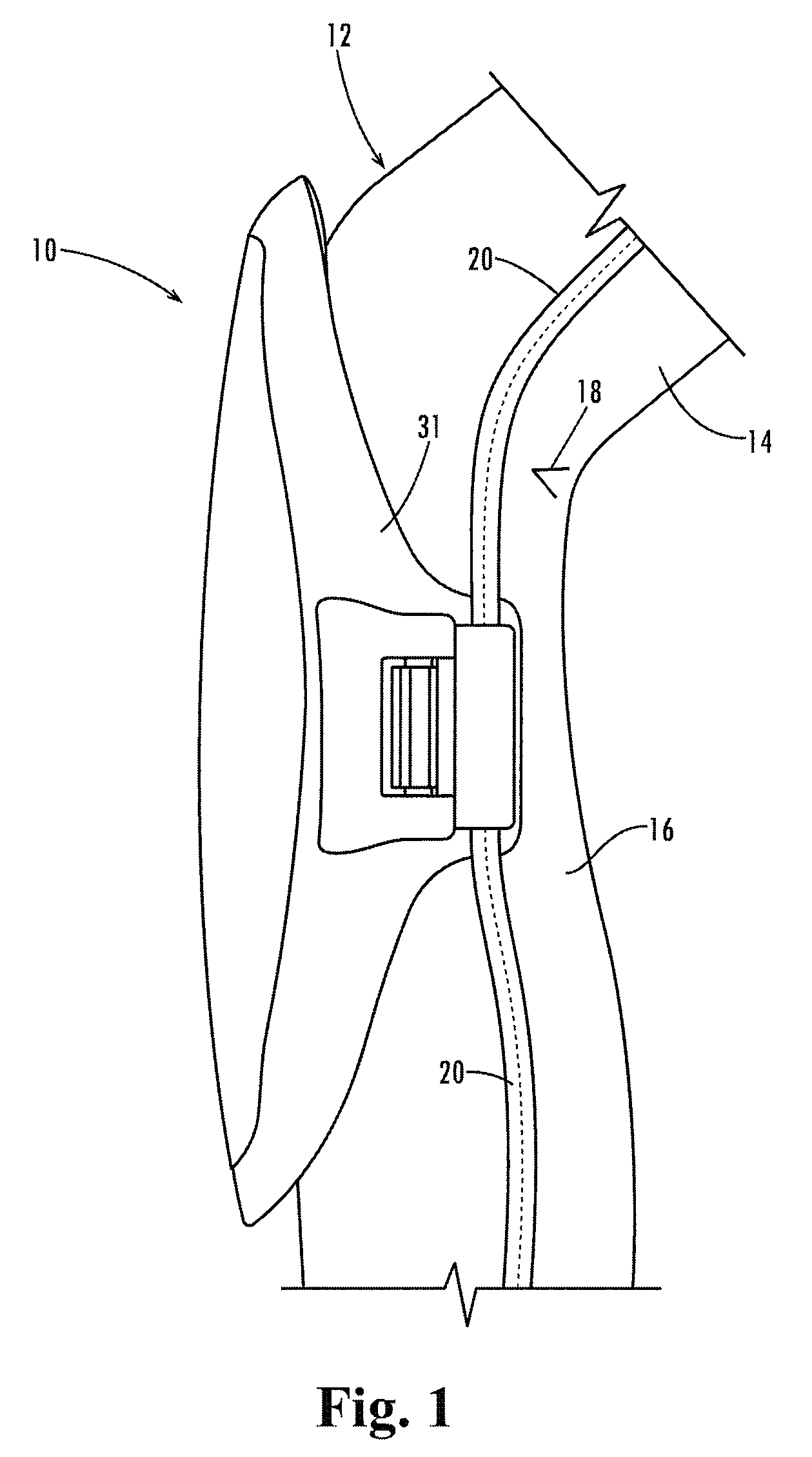
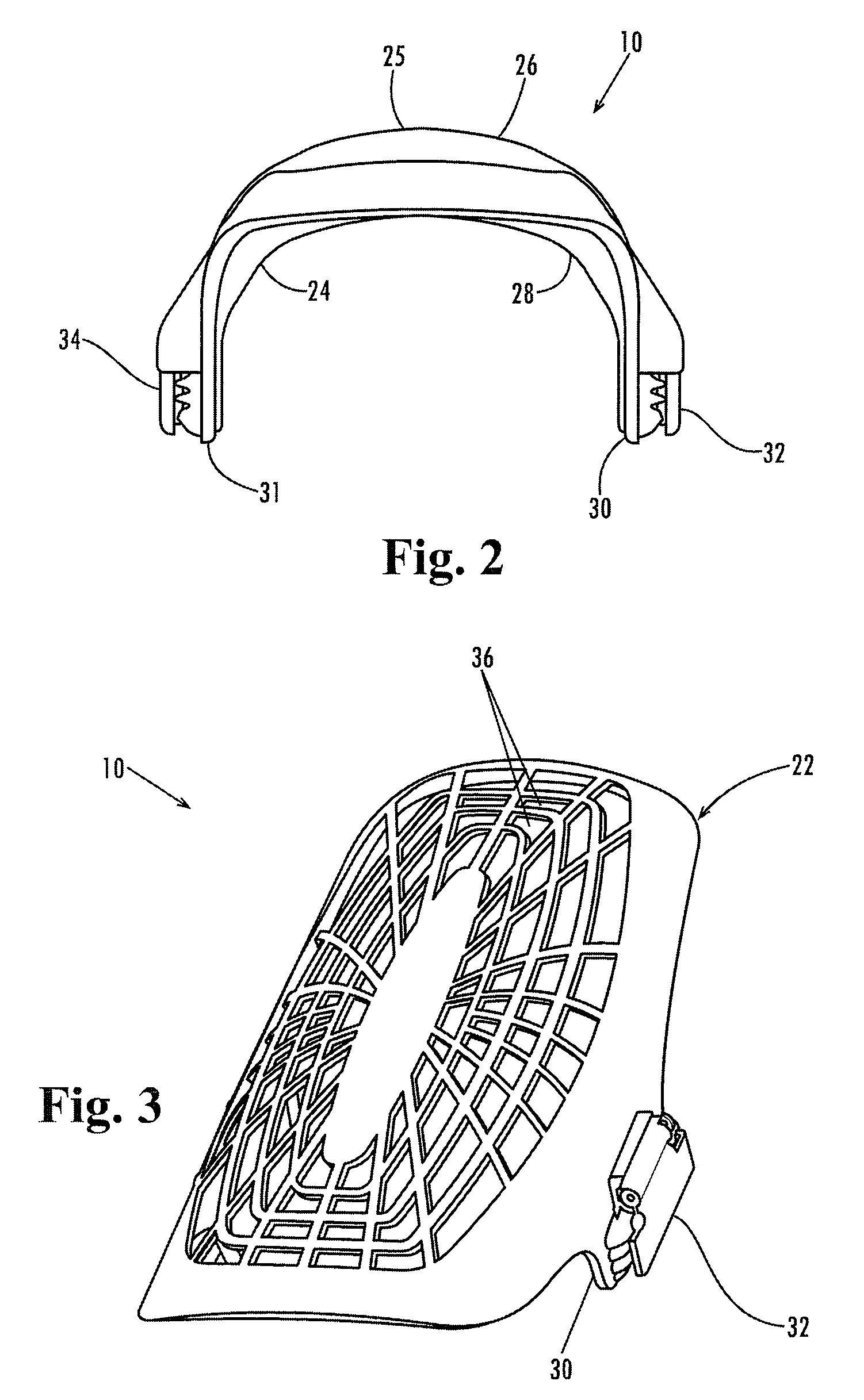
Clip-On Protective Kneepad
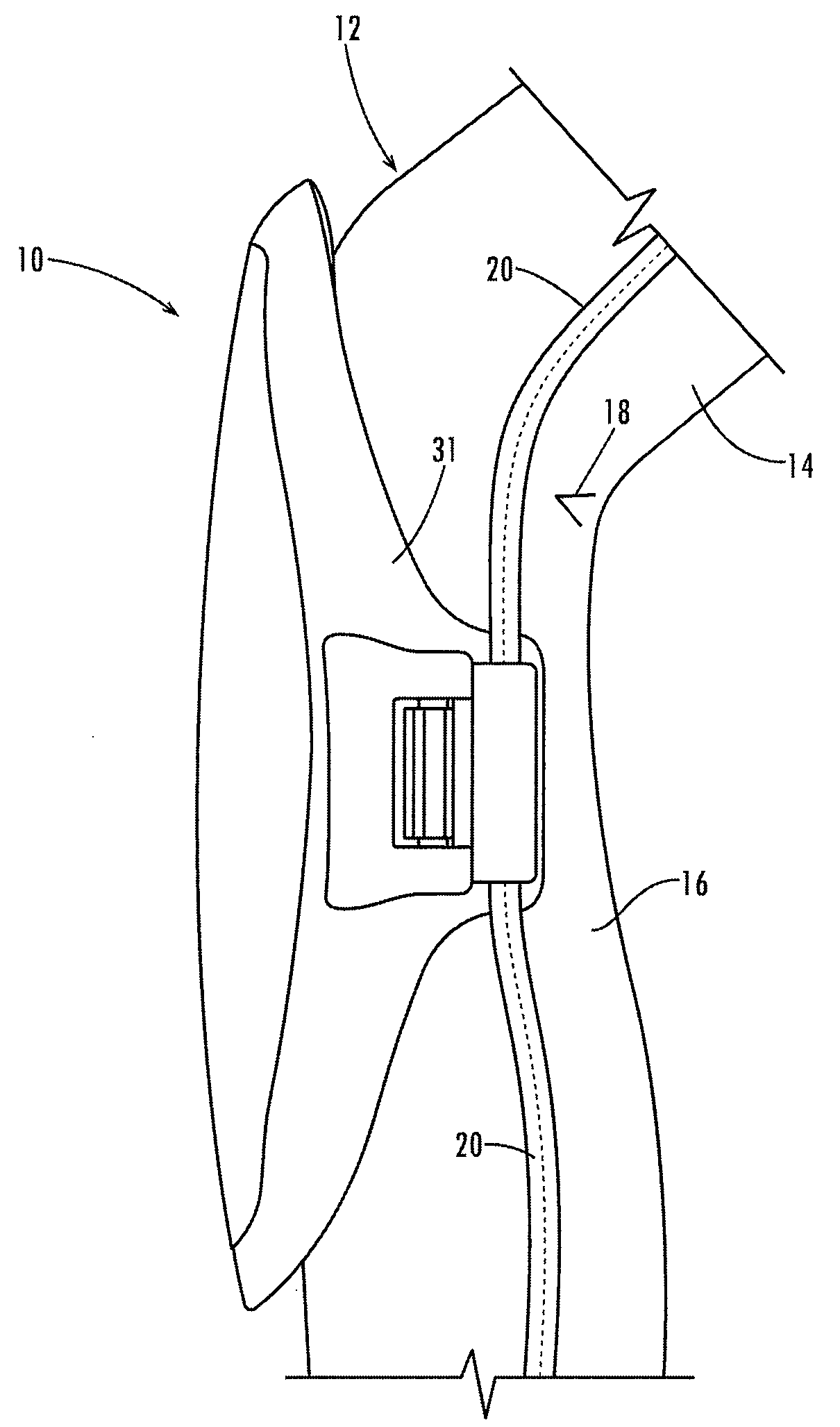
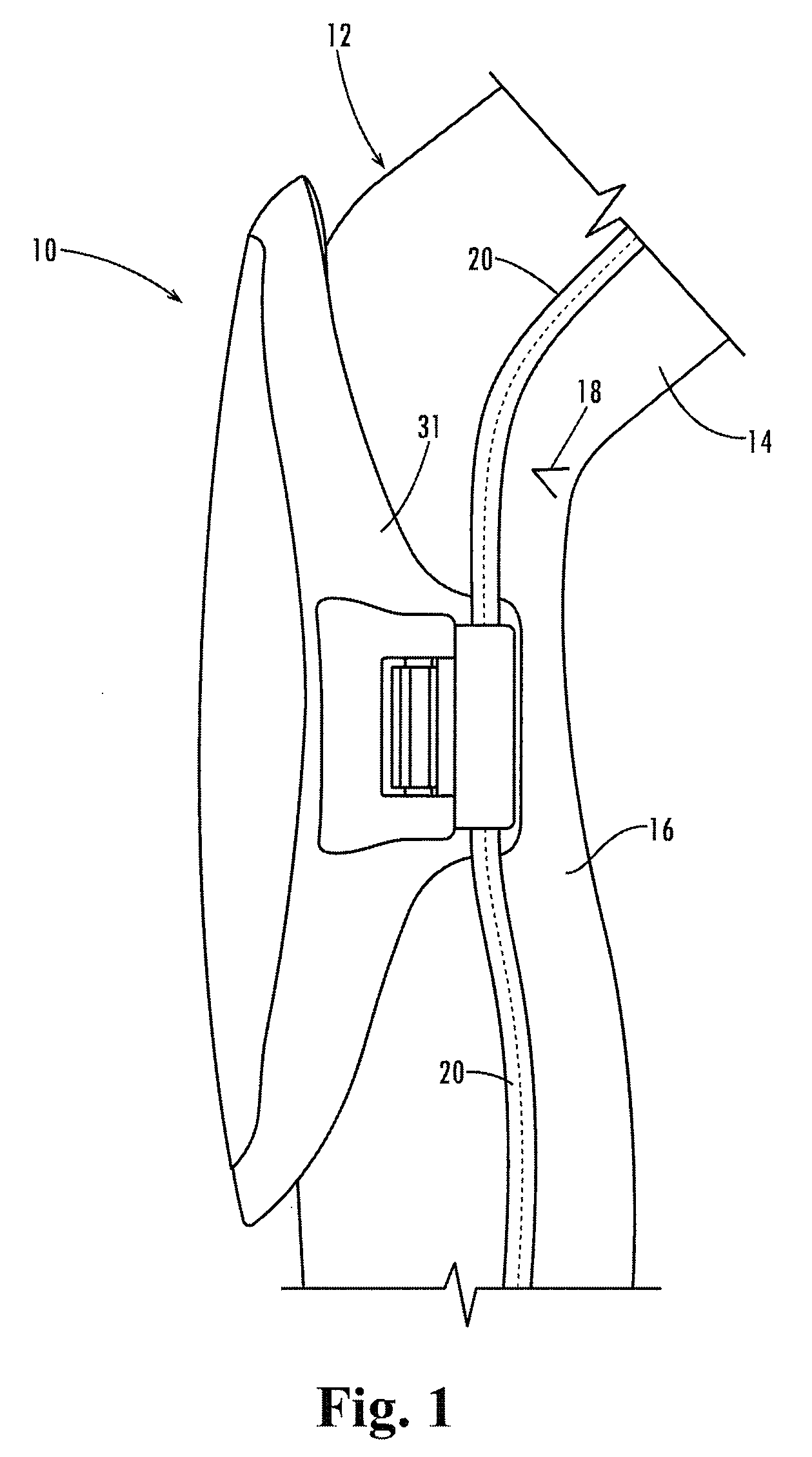
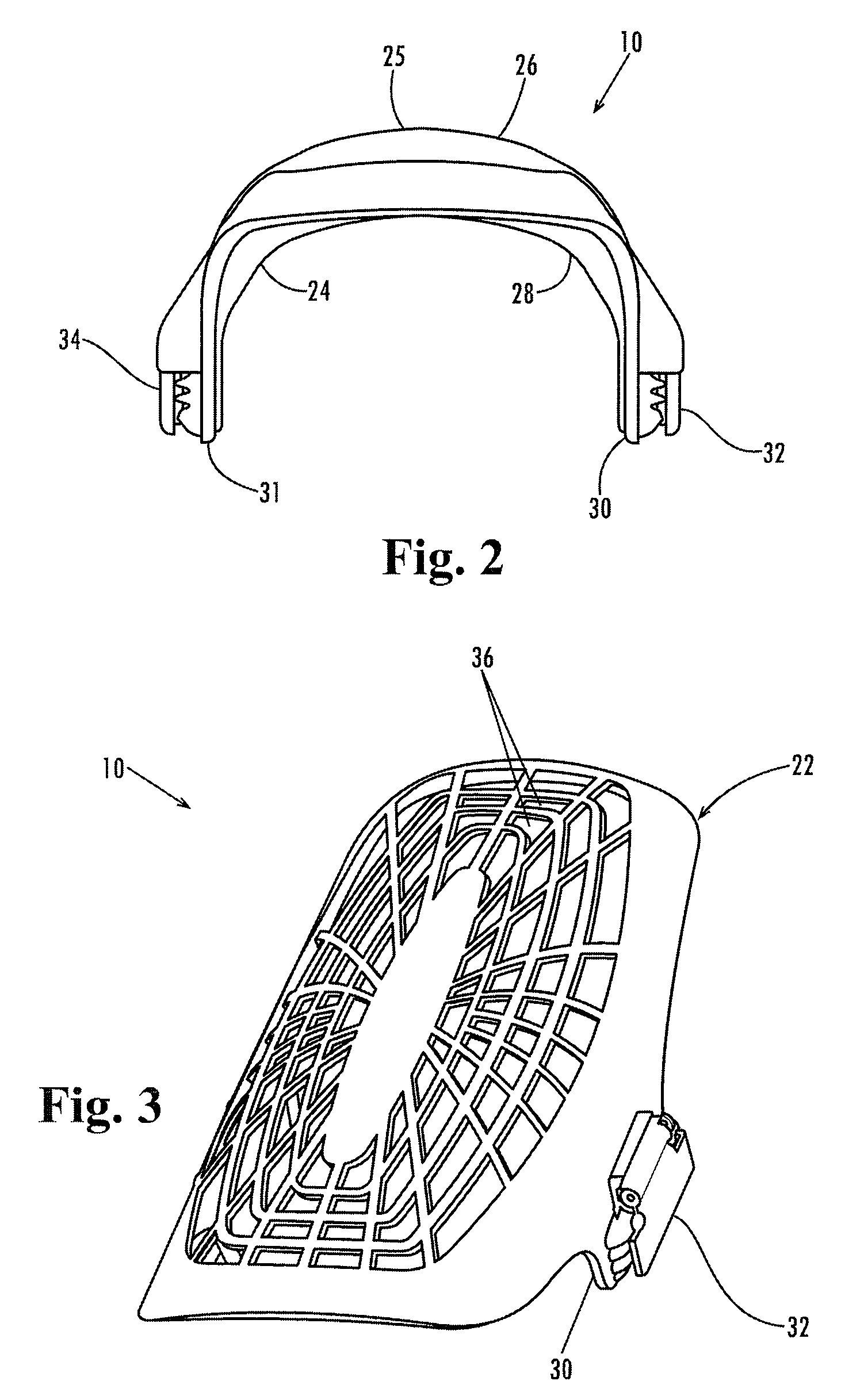
ActiveUS20080222767A1Avoid less flexibilityMore protective effectProtective garmentEngineeringMechanical engineering
A kneepad includes connectors (32 and 34) at its lower side edges (30 and 31) below the position of articulation of the joint. The connectors are biased toward a plurality of ribs (40) integrally formed in the external side surface of the outer hard shell (22) for trapping the side seams of the pant leg against the ribs and holding the kneepad firmly in place.
Owner:WILLIAMS JR JAMES D
Processing device, a system and a method for providing a message to a user
InactiveUS20090070159A1Reduce disadvantagesEffective guidanceMarket predictionsAdvertisementsComputer terminalWorld Wide Web
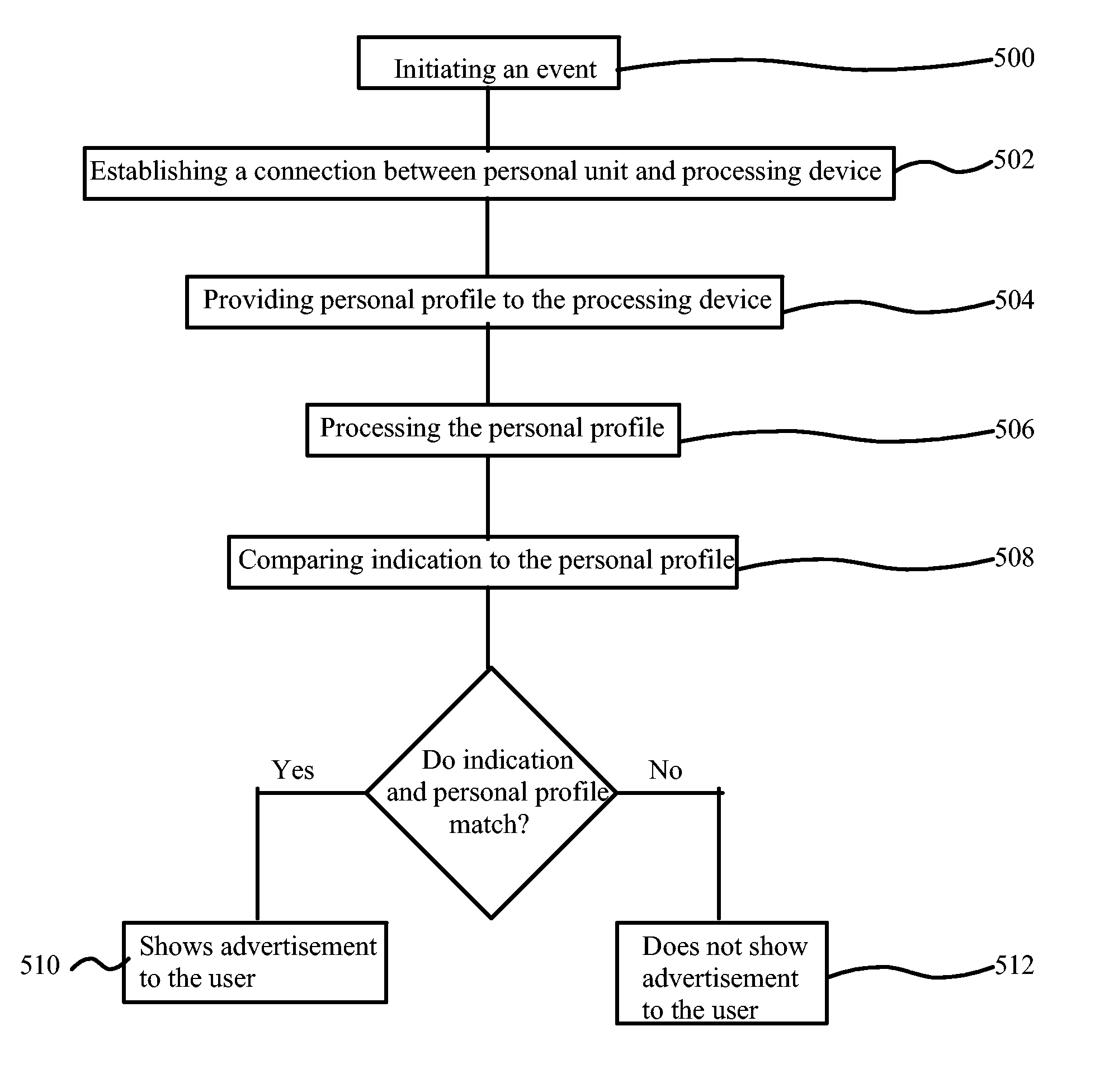
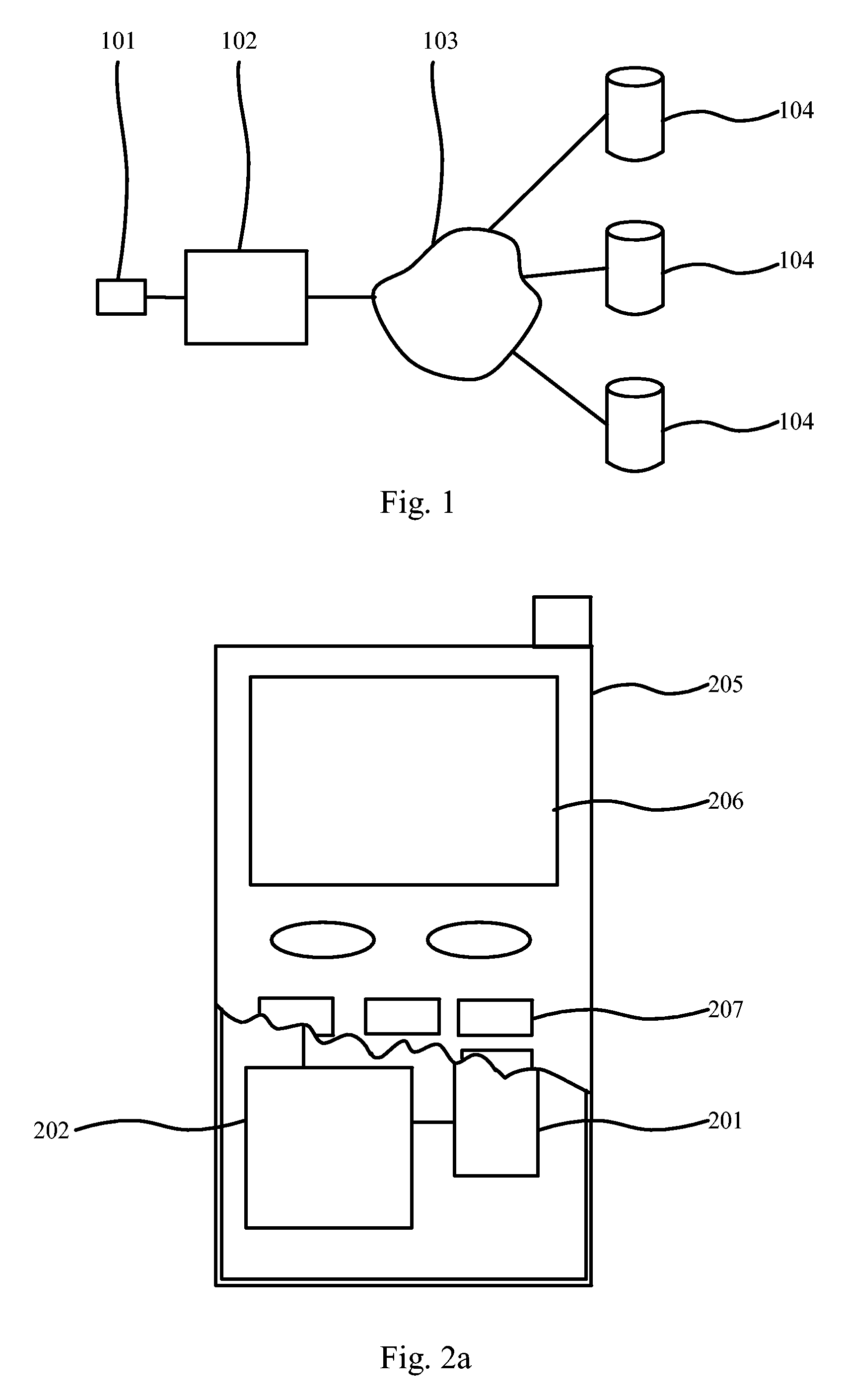
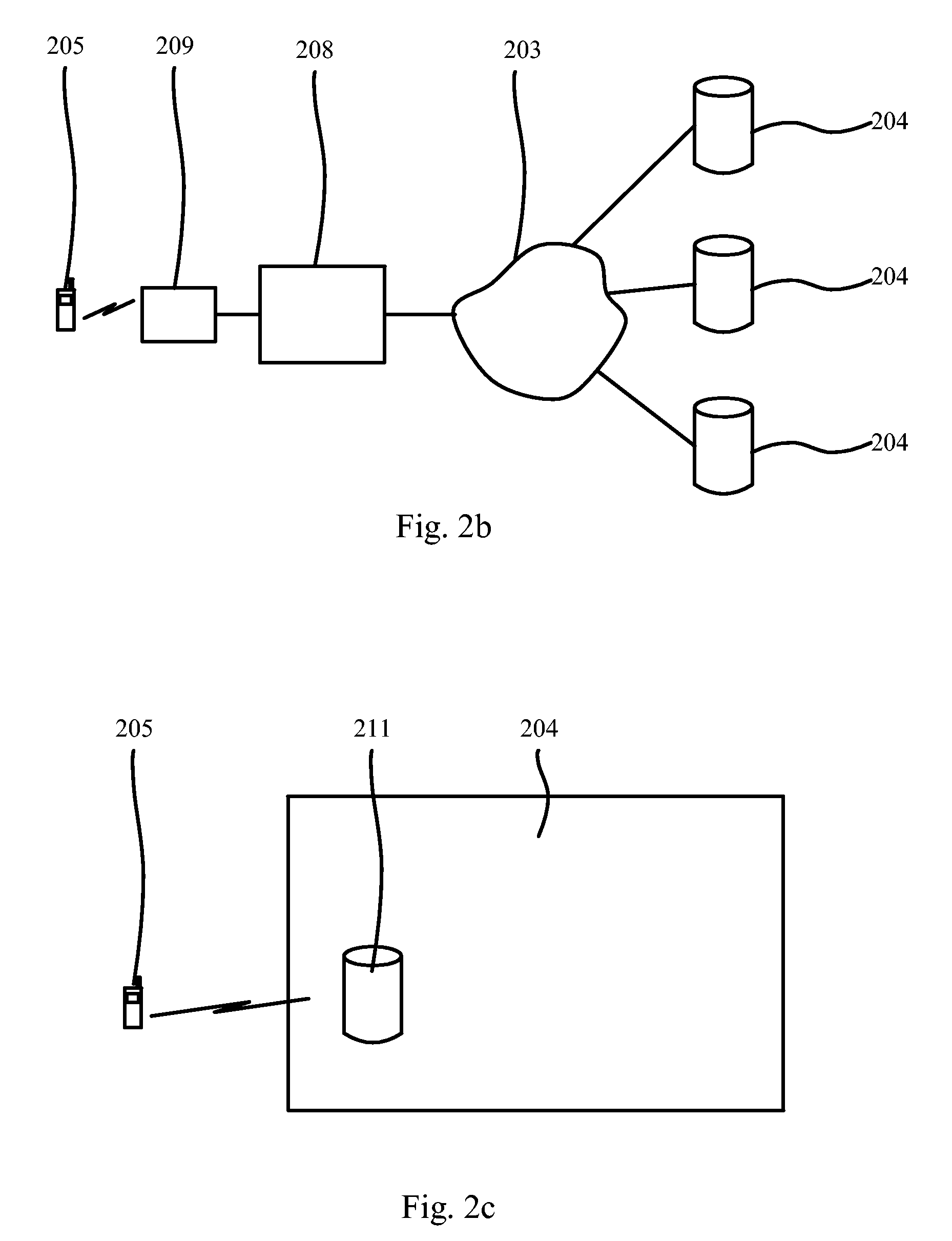
The present invention relates to a method, a processing device, and a system for providing message(s) to a user of e.g. a mobile terminal. The method comprises receiving a message(s) including an indication in a processing device and retrieving a personal file, which is stored in a personal unit, in the processing device. After receiving the message(s) and the personal profile, the processing device compares the personal profile and the indication. Therefore, in case the personal profile and the indication match, showing the message(s) to the user or in case the personal profile and the indication do not match, not showing the message(s) to the user.
Owner:XTRACT
Apparatus and Method for Sensing a Time Varying Ionic Current in an Electrolytic System
ActiveUS20090194429A1Reduce capacitanceHigh sensitivityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCapacitanceElectrolysis
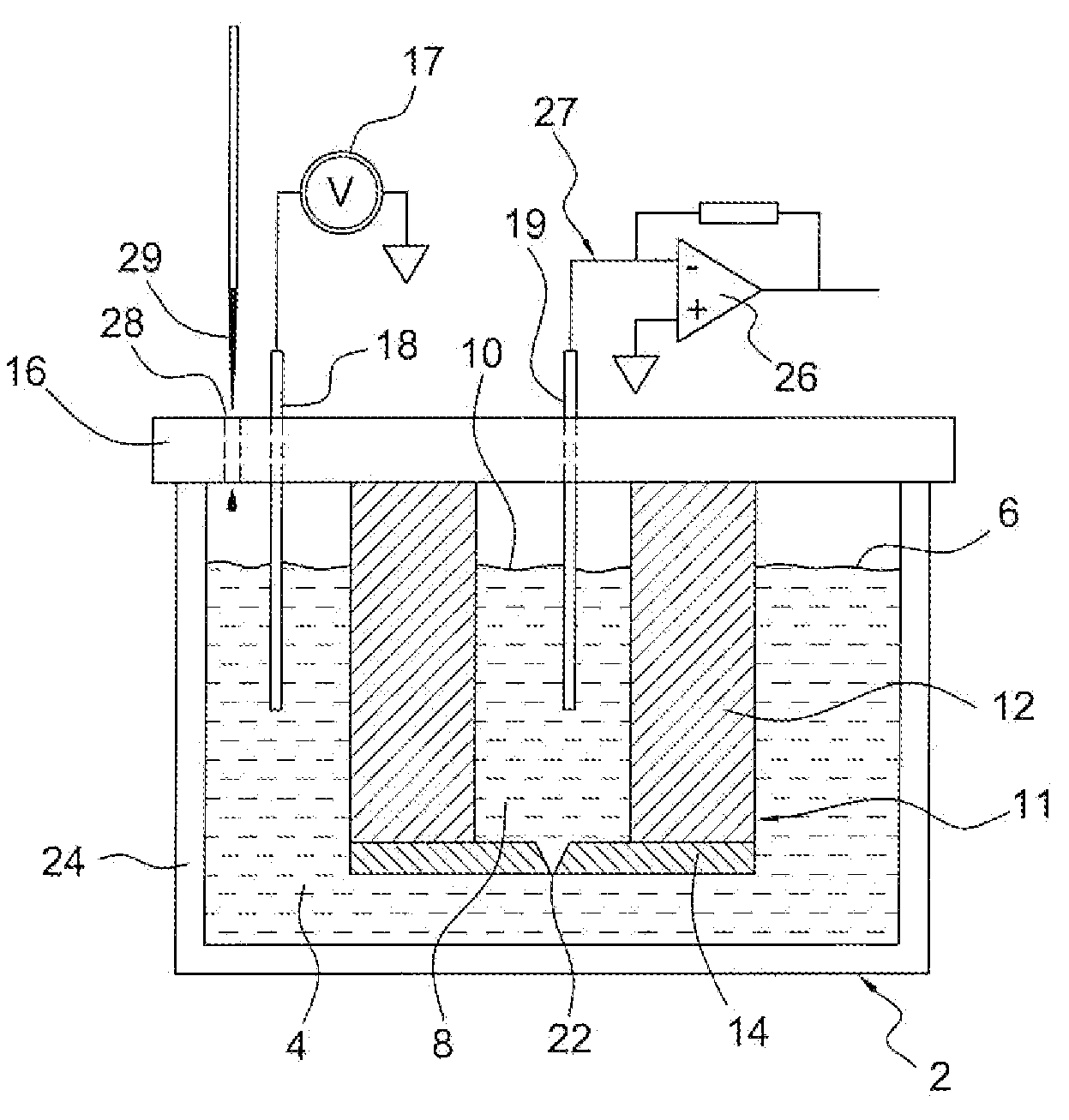
An apparatus and method for sensing time varying ionic current in an electrolytic system having a first fluid chamber and a second fluid chamber separated by a barrier structure is provided, wherein the barrier structure includes thick walls and a substrate having an orifice therein, with the first and second fluid chambers being in communication via the orifice. A potential is applied between electrodes in respective first and second fluid chambers, thus driving an electrical current between them and through the orifice. Total capacitance of the system is less than 10 pF. Analytes are added to one of the first and second fluid chambers and time varying ionic current that passes across the orifice is measured. An amplifier proximal to the barrier structure and electrodes amplifies the ionic current signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS BIOSCI
Thermal seal between manifold and nozzle
A seal is provided between a nozzle and a manifold. The seal provides a melt channel between an outlet of the manifold and a nozzle channel. The seal has higher thermal expansion coefficient than both the nozzle and the manifold to provide an improved seal between the manifold and the nozzle when the injection molding apparatus is at an operating temperature.
Owner:MOLD MASTERS 2007
Cell balancing with local sensing and switching
ActiveUS10833512B2Accurate balanceMinimize connectionCharge equalisation circuitCircuit monitoring/indicationControl engineeringComputer science
A system and method for cell balancing within a battery module includes local sensing and switching at each of the battery cells. A switching circuit is associated with each one of the battery cells to connect or functionally disconnected the battery cell from the battery module. A module controller generates one or more parameter threshold values as maximum operating values for each of the battery cells. Each cell has a cell controller associated therewith to monitor one or more cell parameters, which are communicated to a summing module via a shared monitoring line, averaged, and communicated to the module controller. The cell controllers each receive a parameter threshold value via a shared control line and command the associated switching circuit to functionally disconnect and to bypass the battery cell if the cell parameter exceeds the corresponding parameter threshold value. Methods of checking the battery module are also provided.
Owner:NEAPCO INTPROP HLDG LLC
Clip-on protective kneepad
ActiveUS7950067B2Minimize connectionMinimize any “droop” of the kneepadProtective garmentEngineeringMechanical engineering
A kneepad includes connectors (32 and 34) at its lower side edges (30 and 31) below the position of articulation of the joint. The connectors are biased toward a plurality of ribs (40) integrally formed in the external side surface of the outer hard shell (22) for trapping the side seams of the pant leg against the ribs and holding the kneepad firmly in place.
Owner:WILLIAMS JR JAMES D
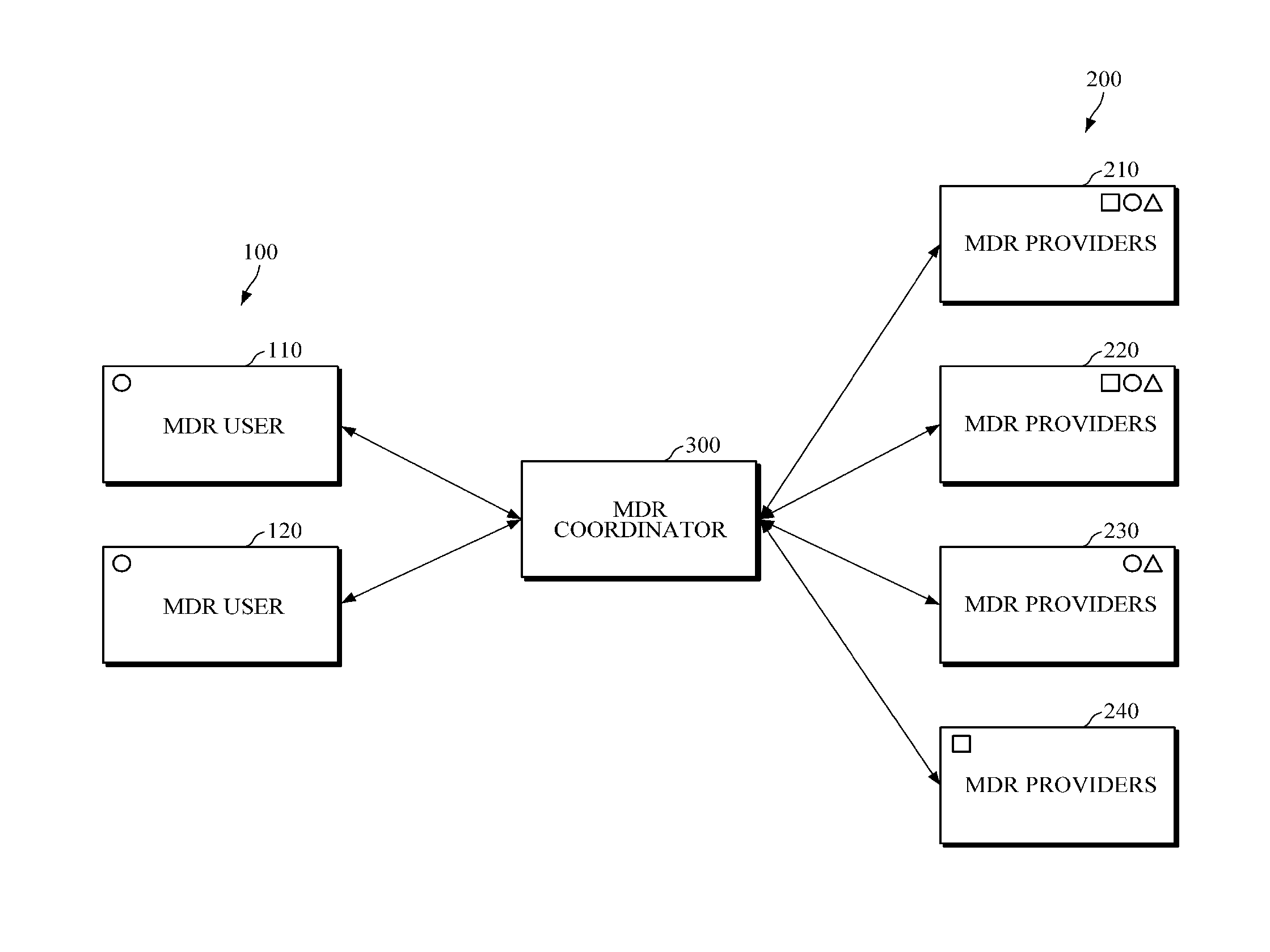
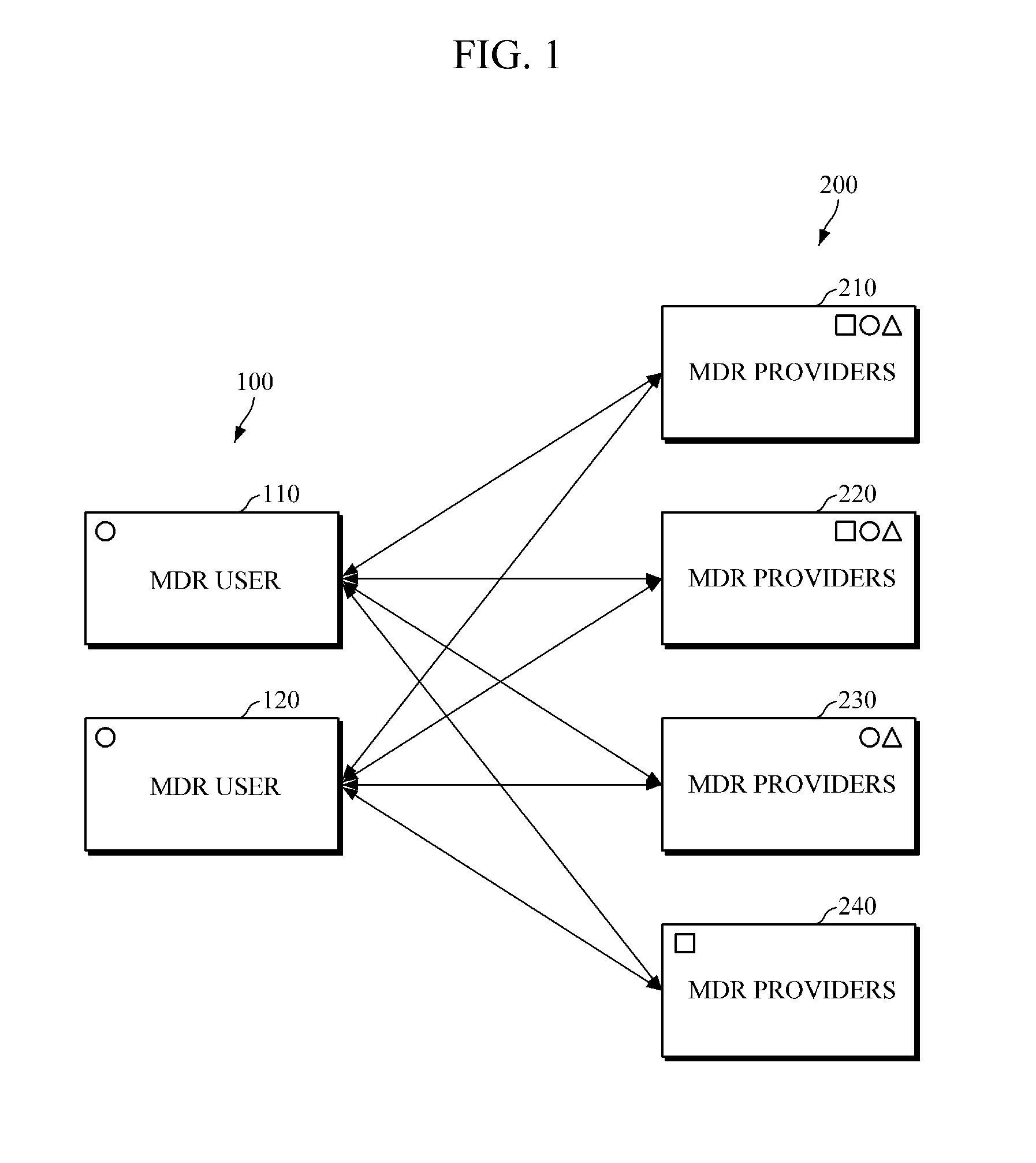
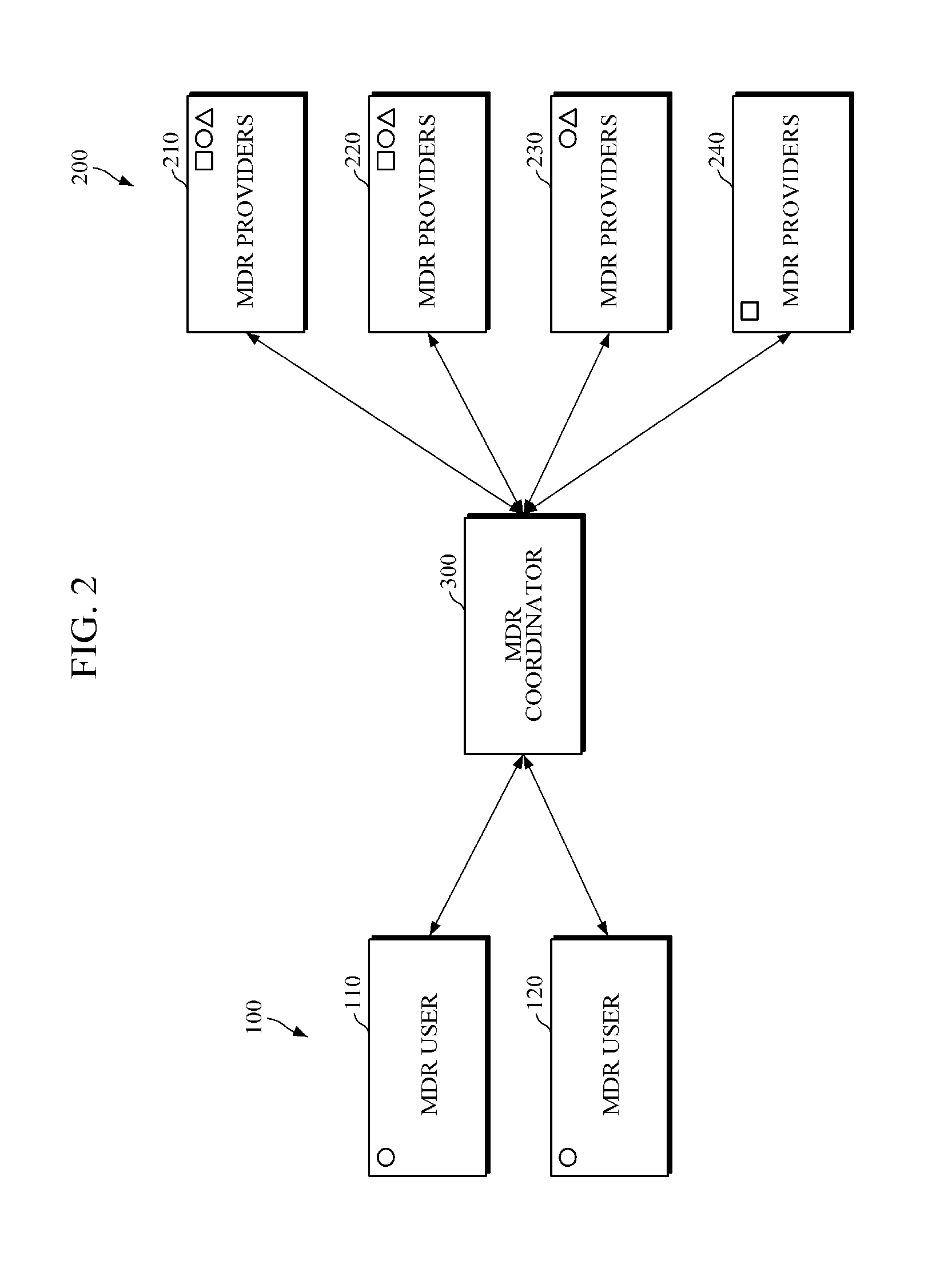
Equipment for mobile cloud cooperation and system including the equipment
InactiveUS20150142979A1Conveniently receiveMinimize connectionService provisioningDigital computer detailsMobile cloudReal-time computing
Provided are an apparatus for mobile cloud cooperation and a system including the apparatus. The system may include a mobile device resource (MDR) user which intends to use a mobile device resource of a different mobile device; a plurality of MDR providers each of which provides one or more owned MDRs; and an MDR coordinator configured to register and manage MDRs provided by the plurality of MDR providers. In response to receiving from the MDR user a request for use of a particular MDR, the MDR coordinator allows a requested MDR among the registered MDRs to be provided to the MDR user.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
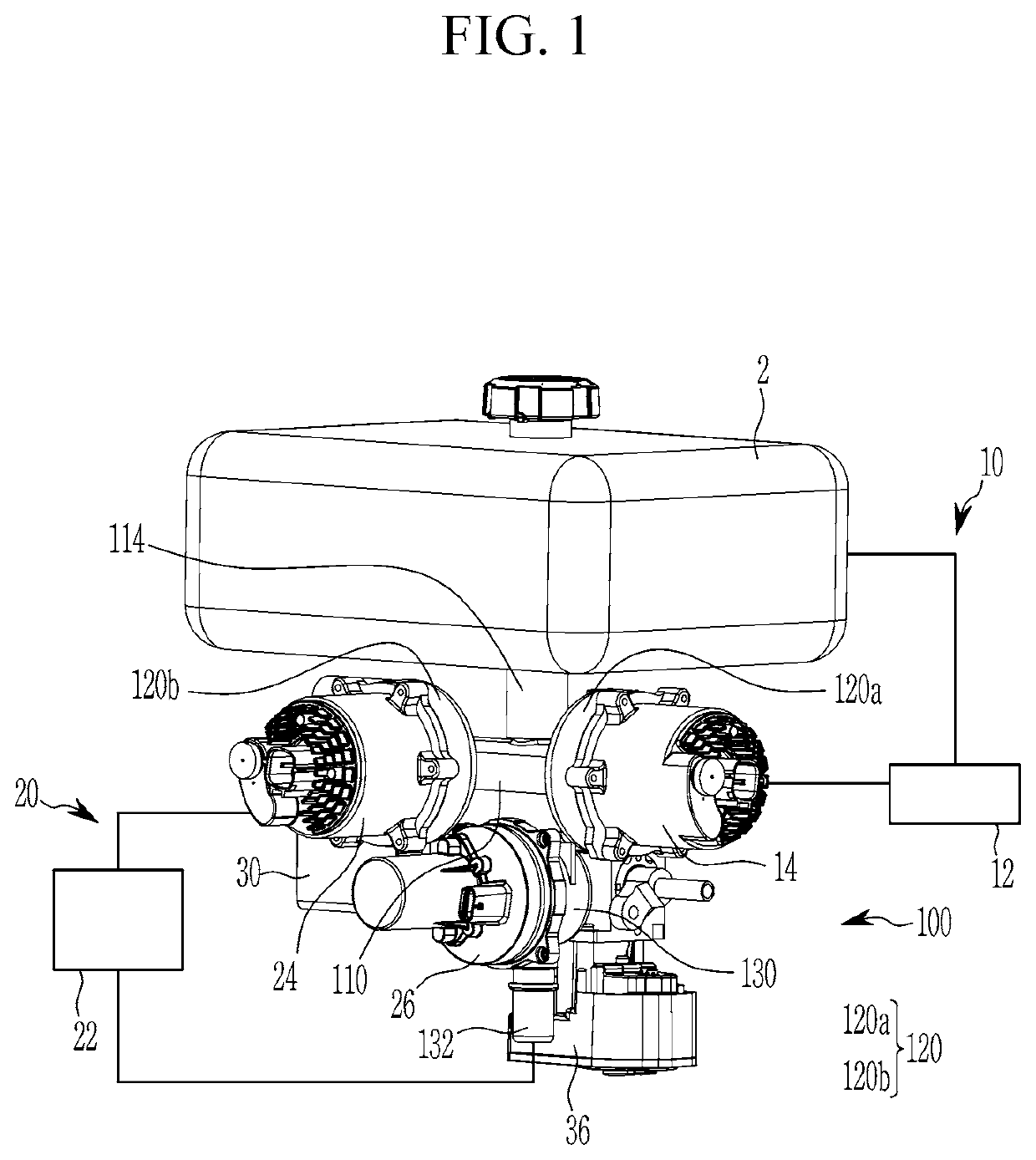
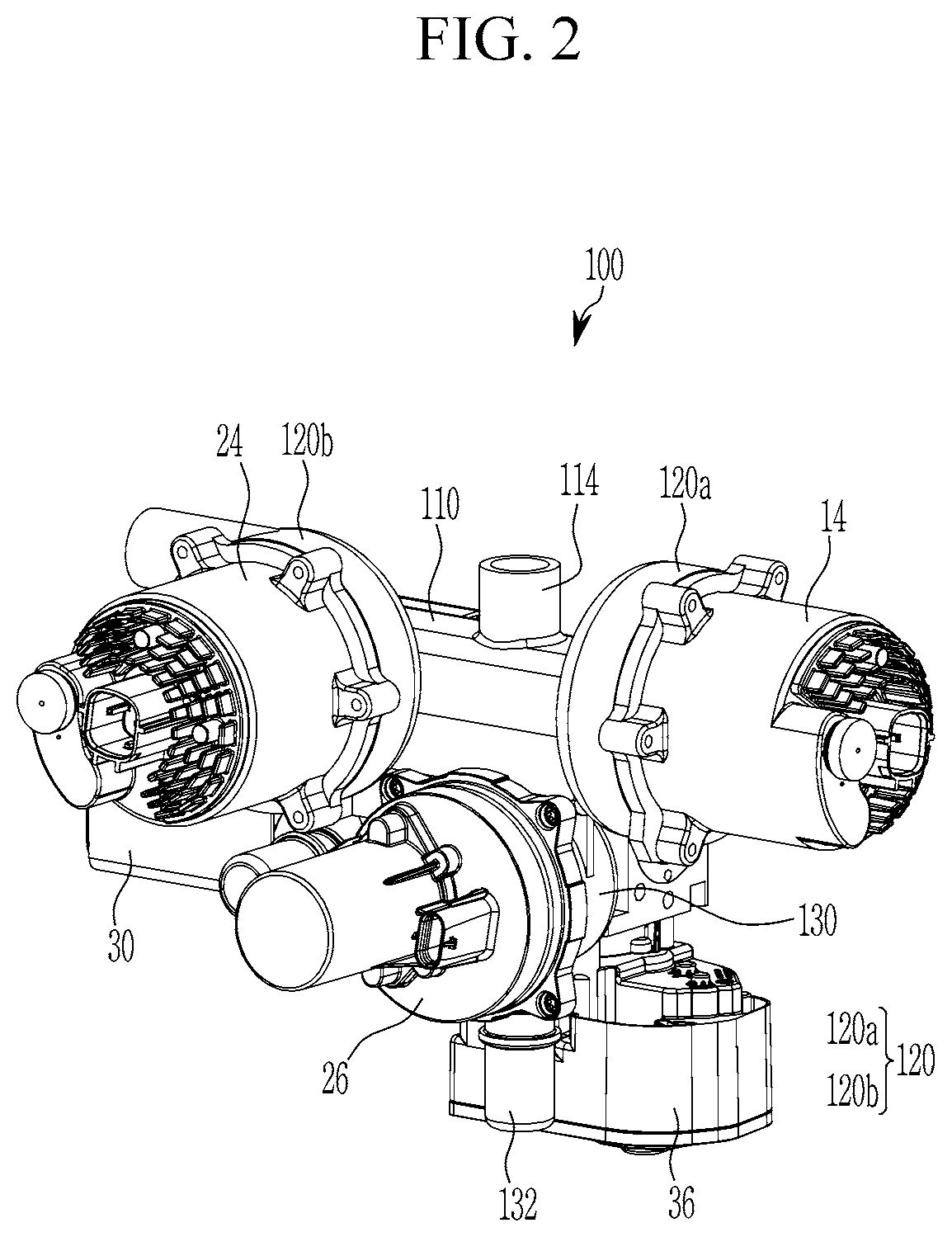
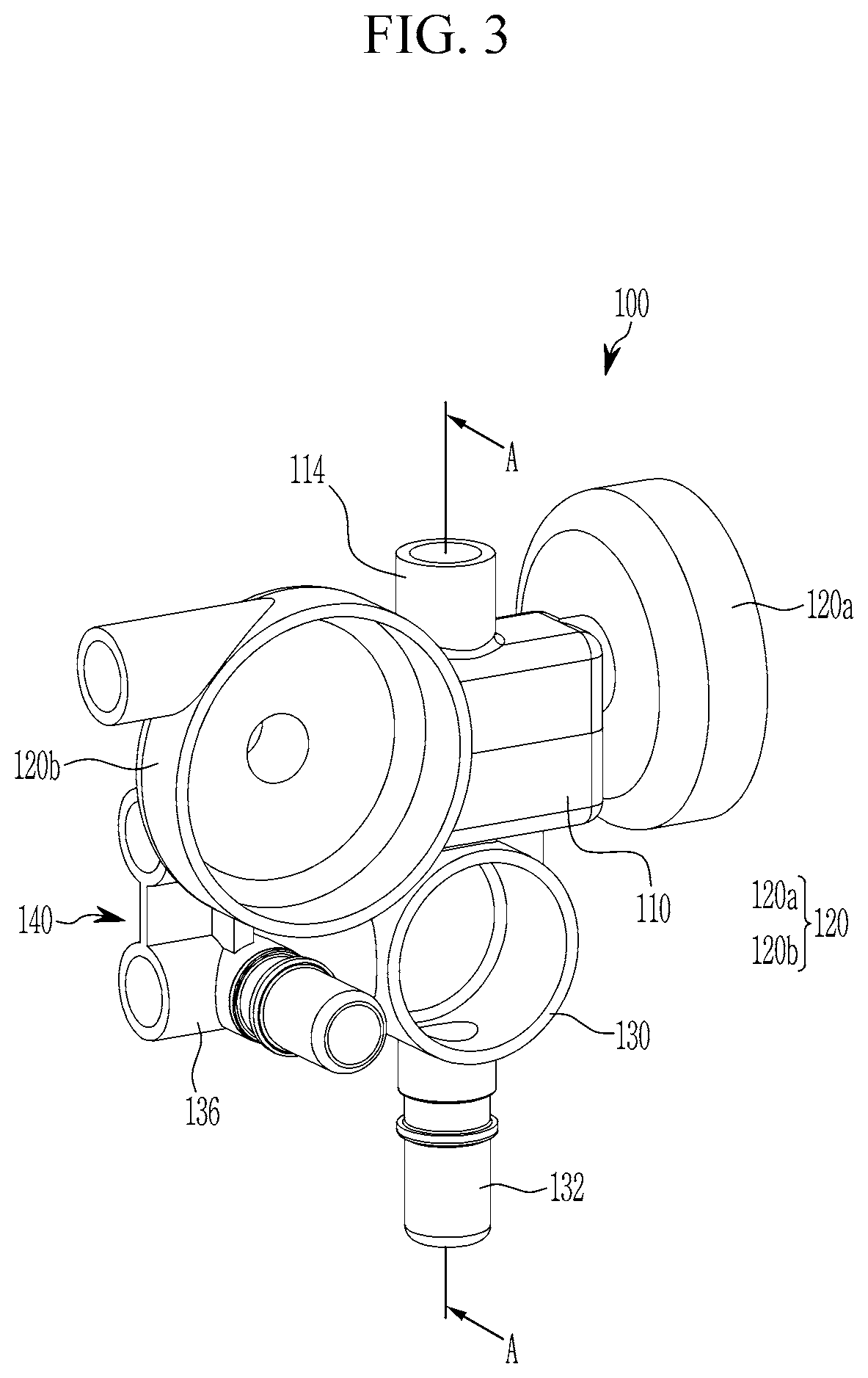
Coolant supplying module
ActiveUS20210219466A1Easy to installImprove space utilizationCoolant flow controlElectric propulsion mountingElectrical batteryProcess engineering
A coolant supplying module for supplying a coolant stored in a shared reservoir tank to an electrical component cooling circuit and a battery cooling circuit includes a main body connected to the shared reservoir tank, at least one water pump mounting portion formed at the main body to mount at least one water pump included in the electrical component cooling circuit and the battery cooling circuit, and a valve mounting portion formed at the main body to mount a coolant valve included in the battery cooling circuit.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com