Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38results about How to "Maximize data transfer rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
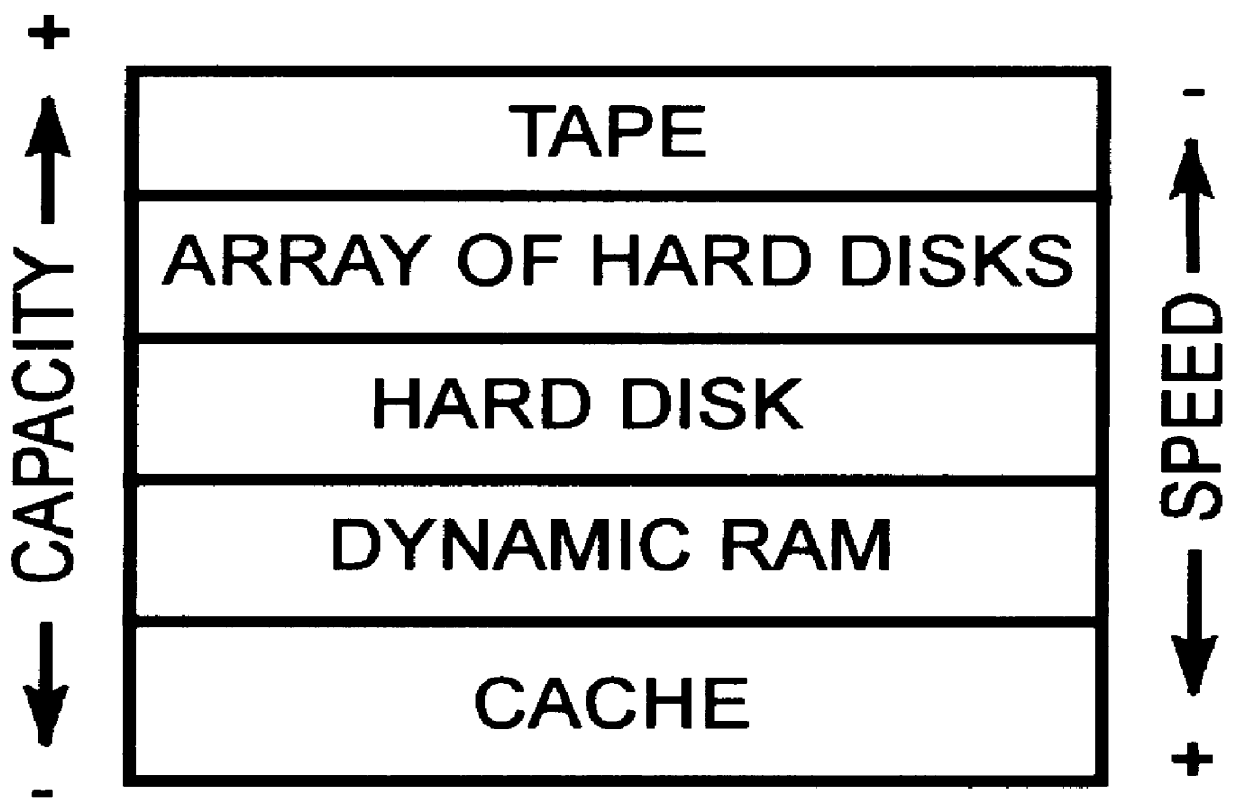
Modular disk memory apparatus with high transfer rate
InactiveUS6112276AIncrease chanceLarge capacityInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsFiberHard disc drive
A modular disk memory apparatus provides a modularly expandable, multi-gigabyte auxiliary memory for a computer or other host electronic device, and includes multiple, parallel serial data channels to maximize bidirectional data transfer rates between the apparatus and the host device. Maximization of READ / WRITE data transfer rates within the apparatus is achieved by utilizing a large number of small hard disk drives, typically eight 2.5-inch drives on each of a plurality of Disk Storage Modules, each including a plug-in printed circuit board capable of holding two 5-+E,fra 1 / 4+EE inch drives, thereby increasing the maximum data transfer rate per unit volume of the modules by a factor of two. Maximization of bidirectional data transfer rates between the apparatus and host device over that attainable using a single serial data channel such as a coaxial, quadaxial or fiber optic cable, is achieved by parsing or demultiplexing data to be transmitted from a single parallel channel onto p paralleled cables, thereby increasing the maximum transmittal rate by p. Data received over the parallel data channels is multiplexed or concatenated to comprise a data stream on a single parallel channel. Reconstruction data is embedded in data contained in the p parallel data channels specifying the number q of channels employed, where 1< / =q< / =p thereby configuring the demultiplexer to concatenate that number of data channels onto a single parallel data bus.
Owner:SIGNATEC
System and apparatus for interference suppression using macrodiversity in mobile wireless networks
InactiveUS20080318613A1Reduce amountMaximize data transfer rateSite diversityModulated-carrier systemsMobile wirelessWireless network
In a wireless network, plural downlink signals from plural base stations are transmitted to a terminal. The plural downlink signals all carry the same information to the terminal. The terminal provides feedback on the downlink channels. The feedback provides information on the taps of the channels. The amount of information fed back is constrained. Based on the feedback, transmission parameters of the downlink signals are adjusted. The process of transmitting, providing feedback, and adjusting the parameters continue so that the energy of the downlink signal is enhanced at the terminal location and suppressed elsewhere. Beam forming can be used to further suppress the energy signature at locations other than the terminal location.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
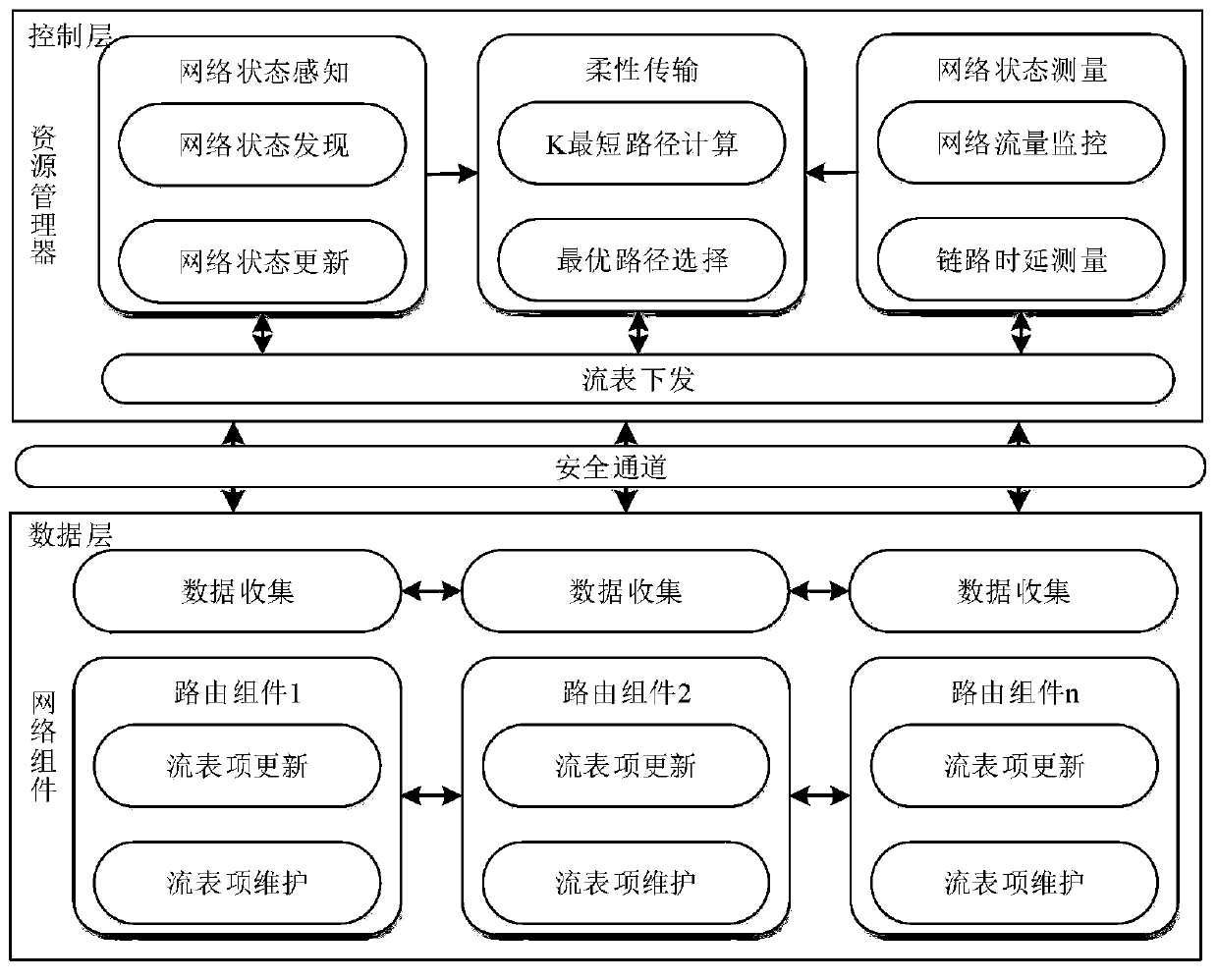
Flexible data transmission system based on SINET
ActiveCN108600102AFast data transferAvoid network congestionData switching networksData transmission systemsService resource
The invention provides a flexible data transmission system based on an SINET (Smart Identifier NETwork), comprising a resource management unit and a network assembly unit, wherein the resource management unit comprises a network state sensing module, a network state measuring module and a flexible transmission module, the flexible transmission module is used for calculating K shortest transmissionpaths and determining the optimal transmission path based on a network topology state and a network resource update state obtained by the network state sensing module as well as a network state linkmaximum available bandwidth and delay information measured by the network state measuring module. Through adoption of the flexible data transmission system of the invention, under centralized and unified control of an SINET control plane, the network state and the network assembly behavior are sensed, in combination with parameters such as routing hops, residual bandwidth and link delay, the optimal transmission path can be determined to achieve dynamic adaption and transmission of service resources, and data transmission reliability, network throughput, resource utilization rate are improved,link load balancing is achieved, so as to make up for the deficiency of a shortest routing method.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
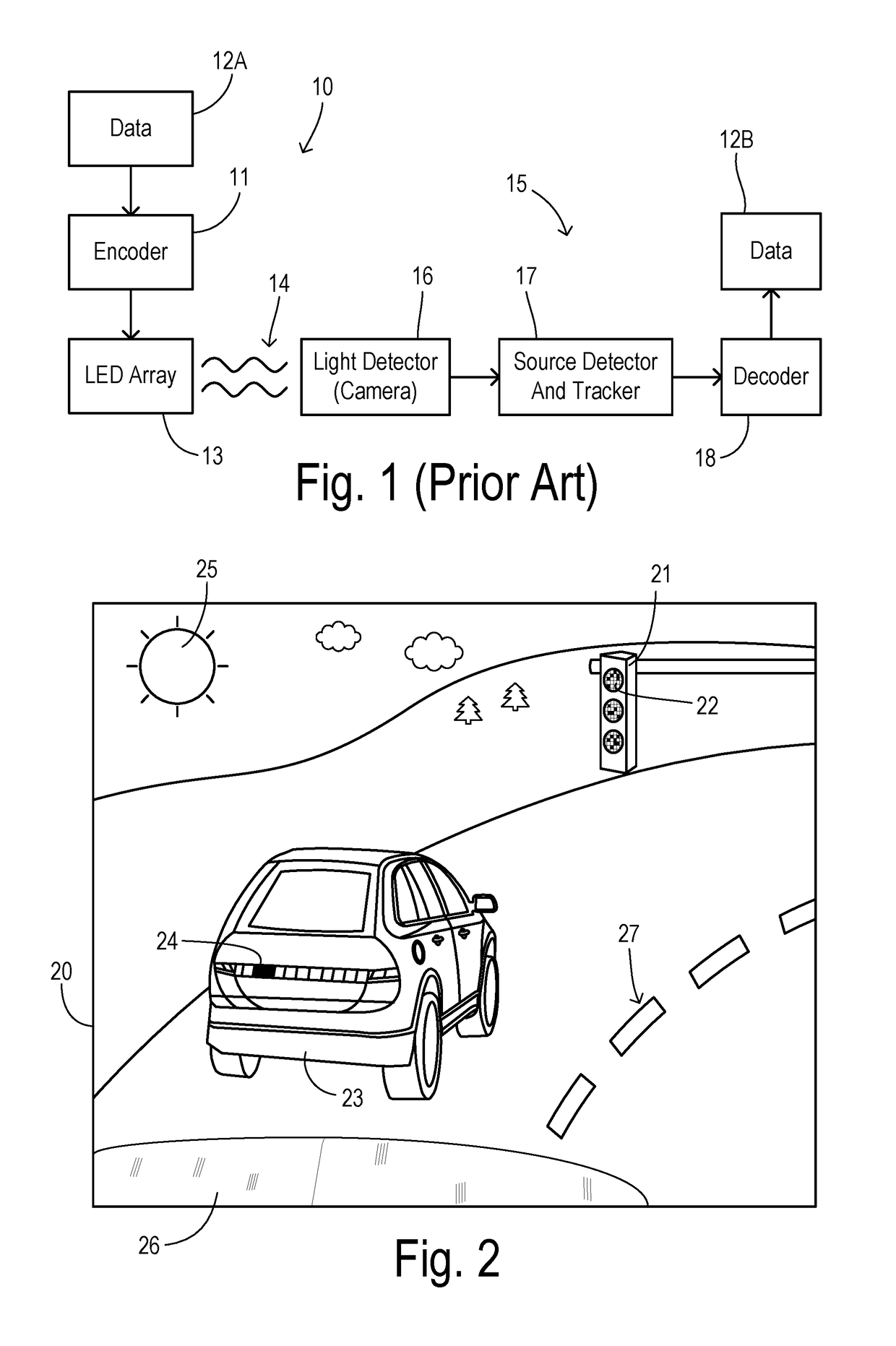
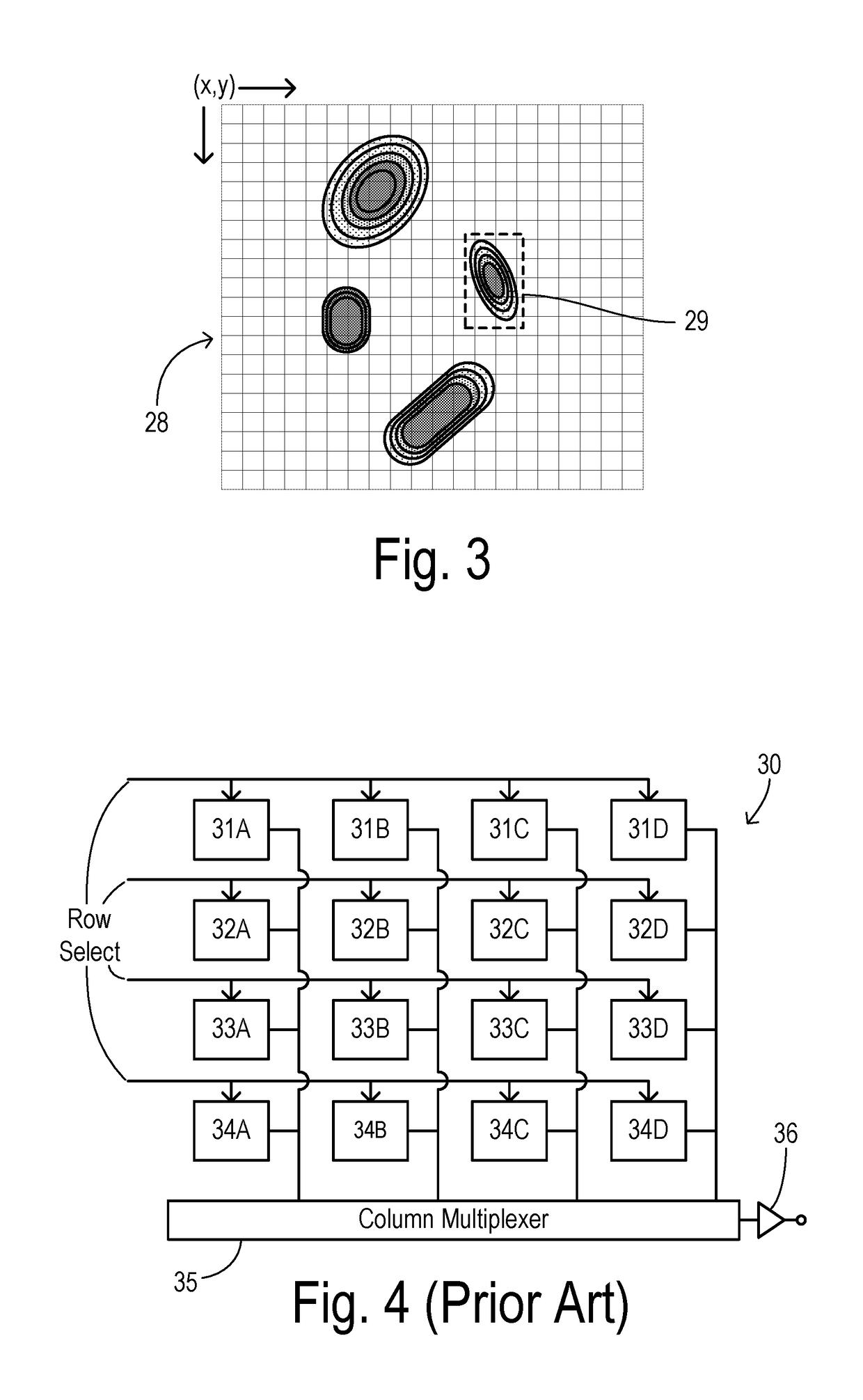
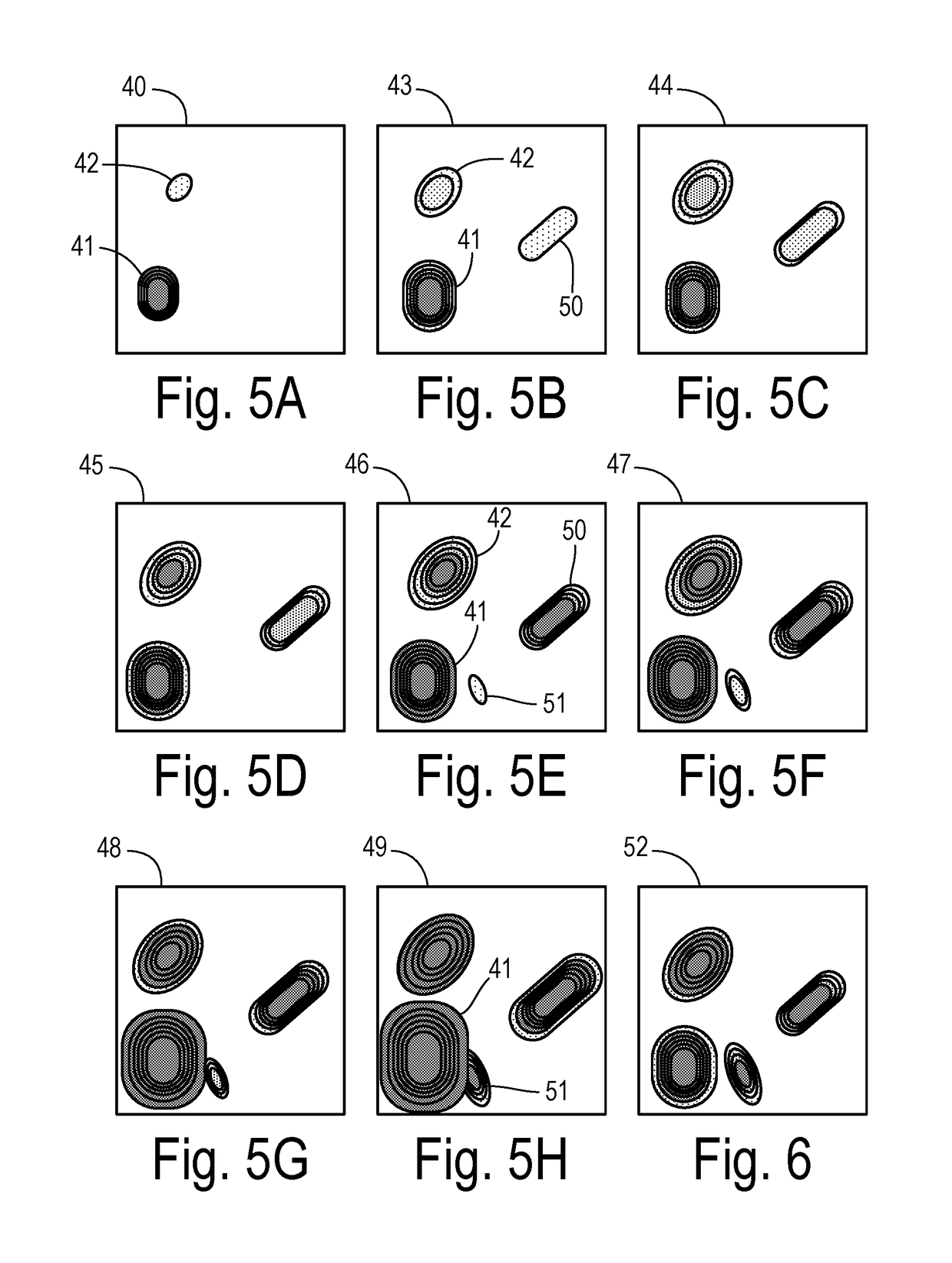
Detection of visible light communication sources over a high dynamic range
ActiveUS10193627B1High imagingGood durationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLed arrayLight signal
A visible light communication (VLC) receiver captures frames of a scene with a camera to detect flashing light signals from a VLC transmitter such as an array of LEDs. The method assembles an enhanced dynamic range image sequence from the frames. At least one VLC source is detected in the enhanced sequence, wherein the source occupies a respective subwindow within the scene. An imaging exposure such as the exposure time used for capturing images at the subwindow is optimized according to a brightness of the respective VLC source. Then a plurality of subwindow images are captured using the optimized exposure. VLC data visible in the subwindow images is then decoded.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
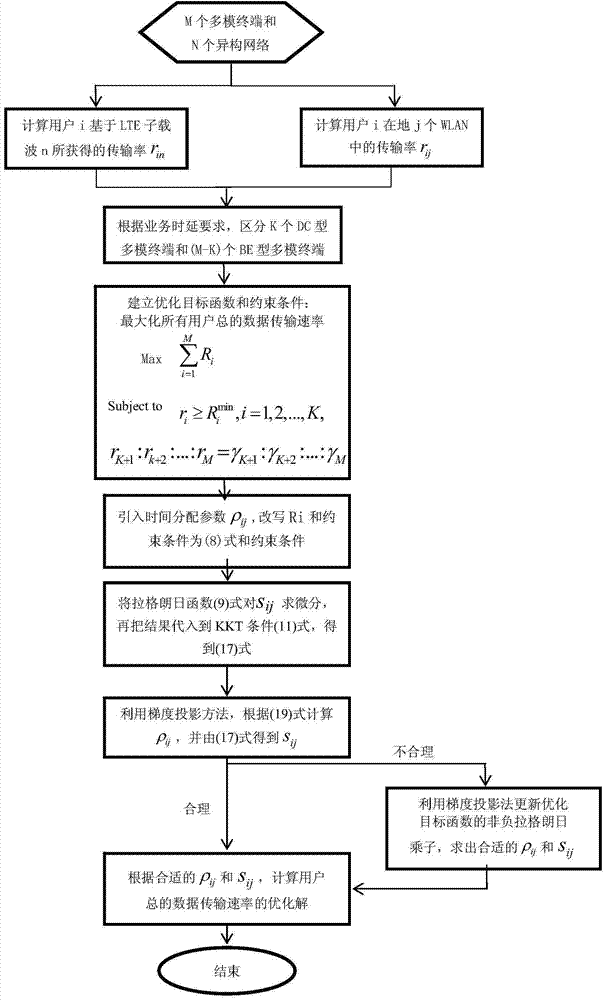
Optimization wireless resource method based on time delay differentiated services and proportionality rate constraints
ActiveCN103687023AMaximize data transfer rateMaximum throughputMulti-frequency code systemsWireless communicationTime-sharingData transmission
The invention discloses an optimization wireless resource method based on time delay differentiated services and proportionality rate constraints. The method divides services into two types from a physical layer: a time Delay-Constraint (DC) type service and a Best-Effort (BE) type service. Specifically, the method classifies optimization resource distribution to a linearity problem. Through introducing time sharing parameters, an index-grade mixing integer program problem is converted into a convex problem for solving; a Lagrange differential is then solved on a result to obtain an optimum performance response of bandwidth, whether the result is reasonable is verified, if the result is not reasonable, a decision is modified forwards, and if the result is reasonable, other network distribution parameters are calculated. Generally speaking, the method provided by the invention overcomes the disadvantage of a conventional wireless resource management method that the fairness between service types and users are not taken into consideration, the diversified demands for quality of service (QoS) of different types of services can be satisfied, the maximization of a data transmission rate can be realized, and the system total data transmission rate is improved to the maximum.
Owner:南京华睿智光信息科技研究院有限公司
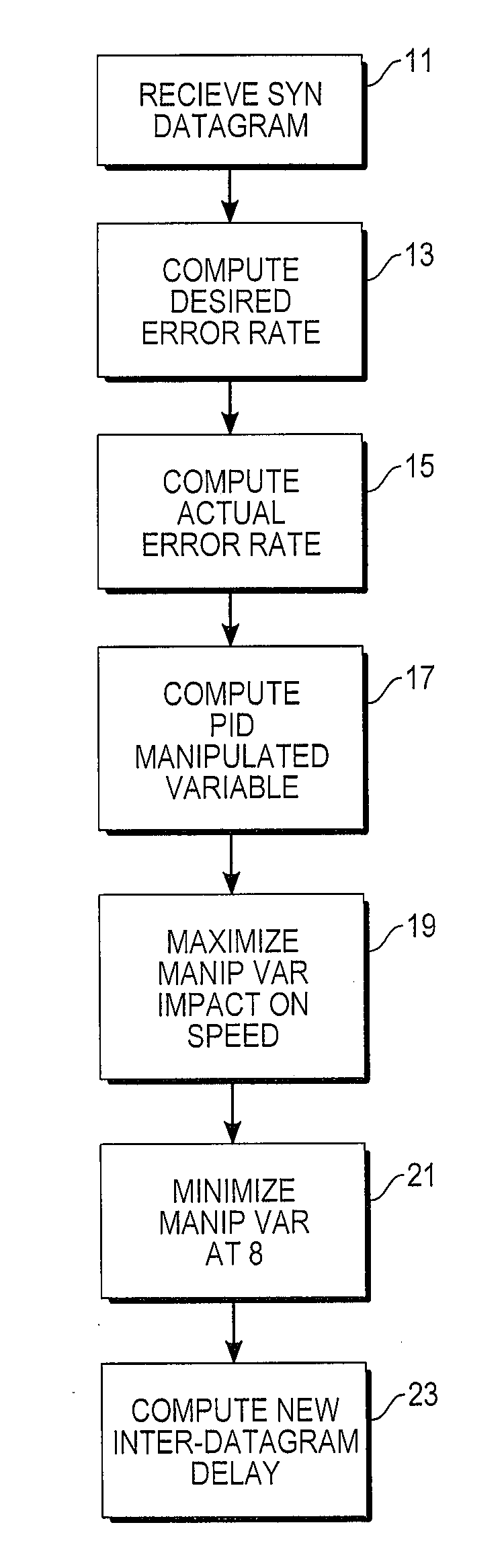
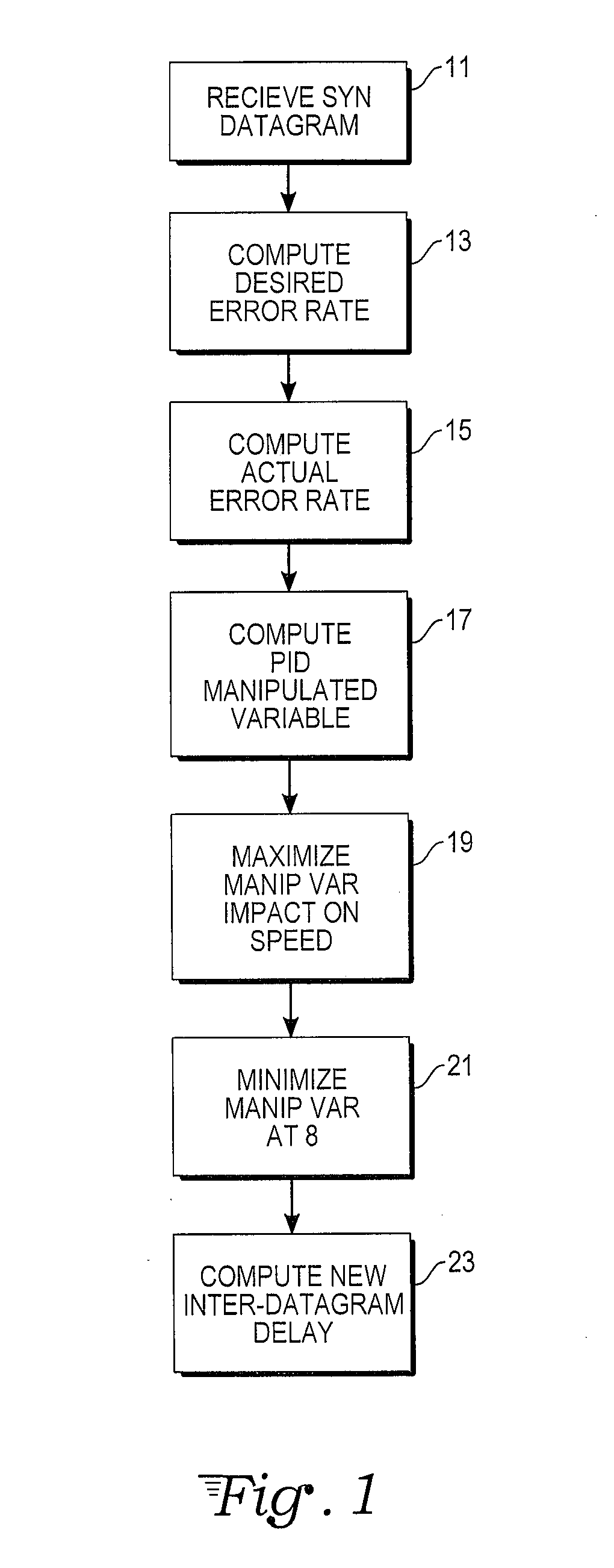
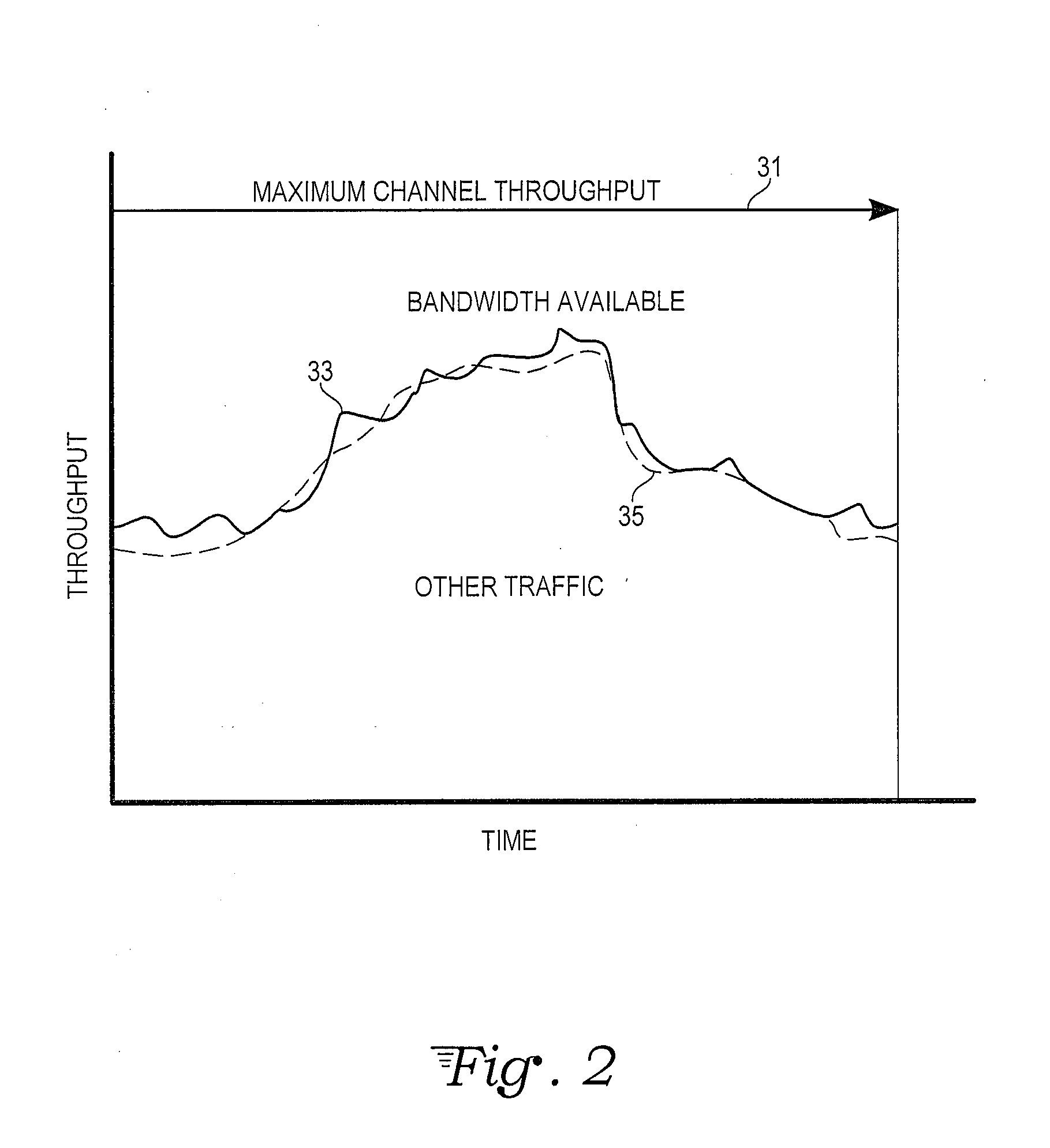
Telecommunications protocol with PID control of data transmission rate
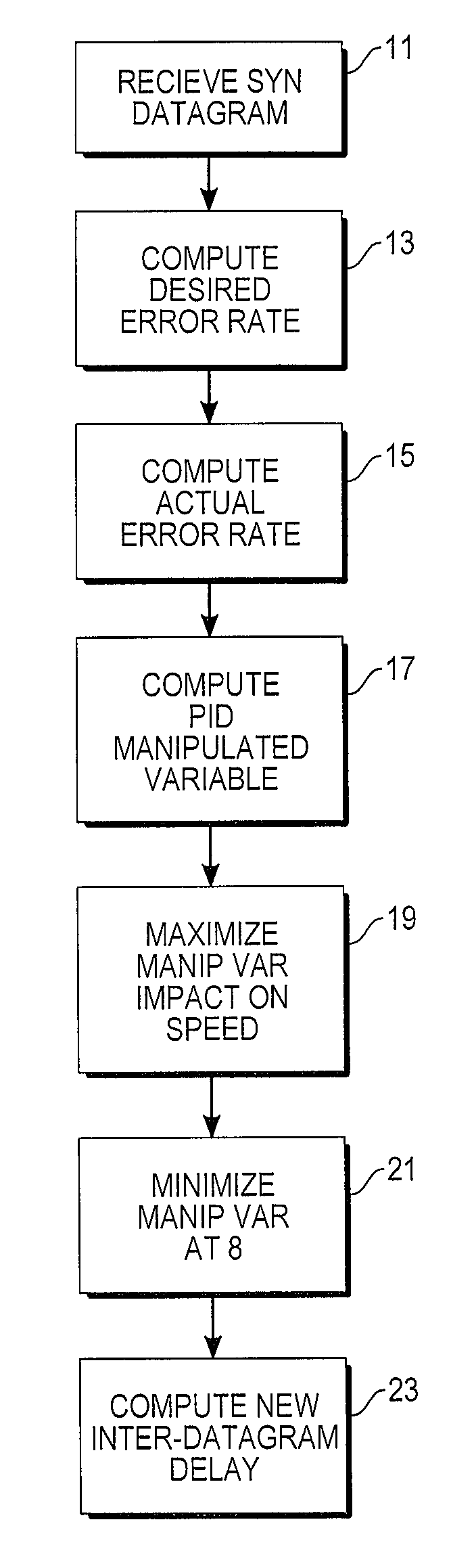
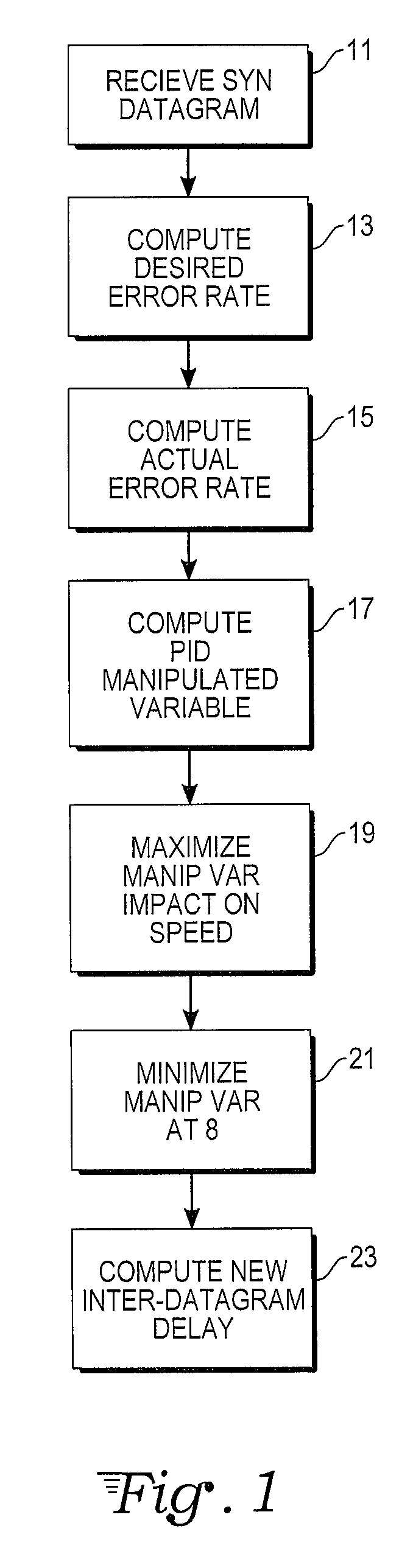
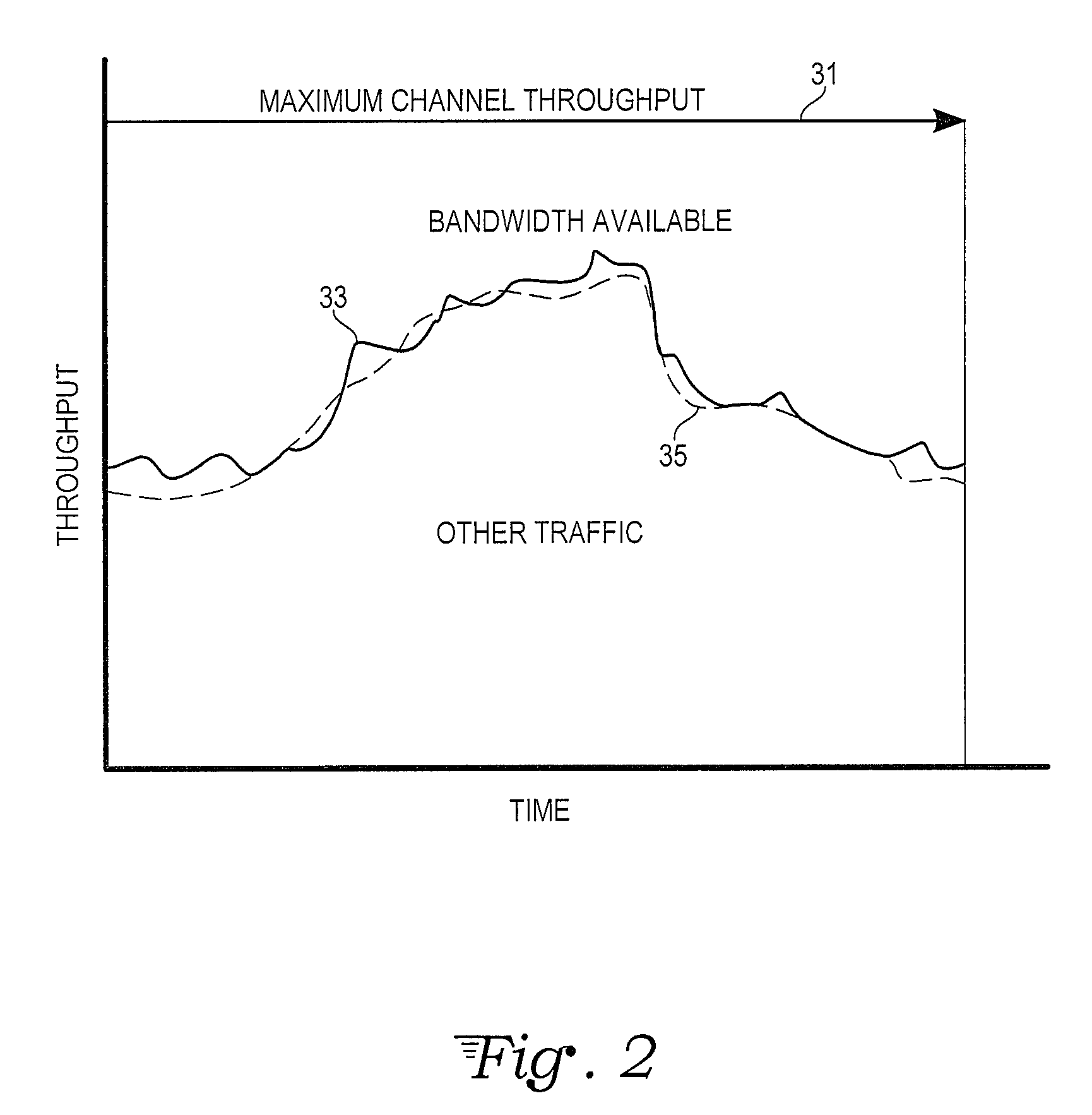
ActiveUS20120259989A1Minimizes overuseEasy to controlMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionData compressionData source
A computer data transmission system is provided with proportional-integral-derivative (PID) control over a data transmission rate so as to maximize use of available bandwidth of a datagram-based network. A data channel and a separate feedback channel are established between the sender and receiver units of the system. The sender unit coupled to the data and feedback channels sends datagrams over the data channel to the receiver continuously until a source of data is exhausted or paused by the receiver unit. The receiver unit sends acknowledgment messages over the feedback channel to the sender unit at predetermined intervals. A PID controller in the sender unit uses the information provided in the acknowledgment messages to track unsuccessfully transmitted datagrams and to adapt the data transmission rate to any changing network transfer conditions. In particular, the rate of datagram loss may be used as a PID process variable to control an inter-datagram delay of the sender. There may also be absolute speed and transmission rate acceleration / deceleration limits constraining the PID control. PID control may also be adapted for data compression control, datagram block sizes, and degree of redundancy in the datagrams sent.
Owner:SARATOGA DATA SYST
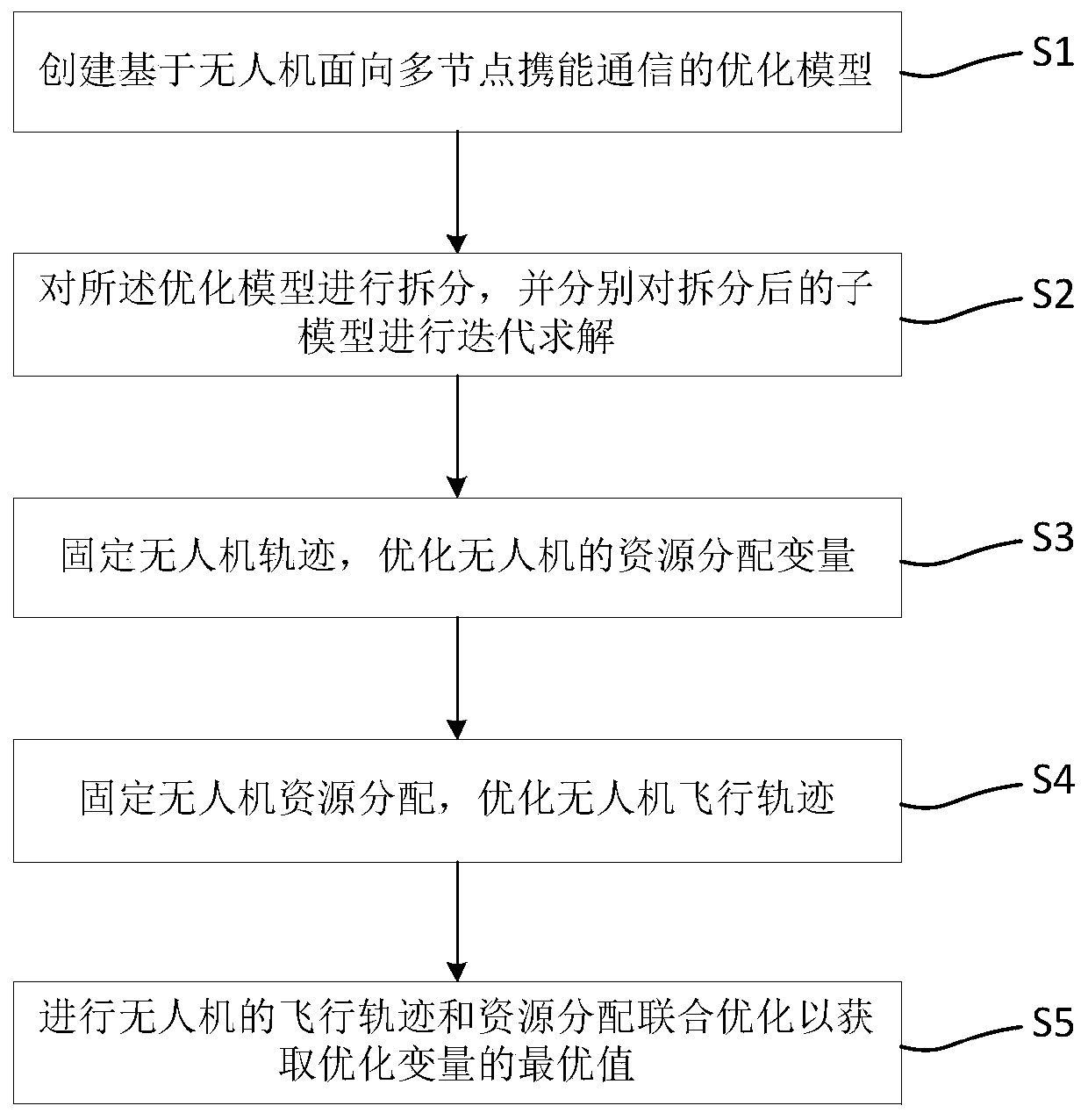
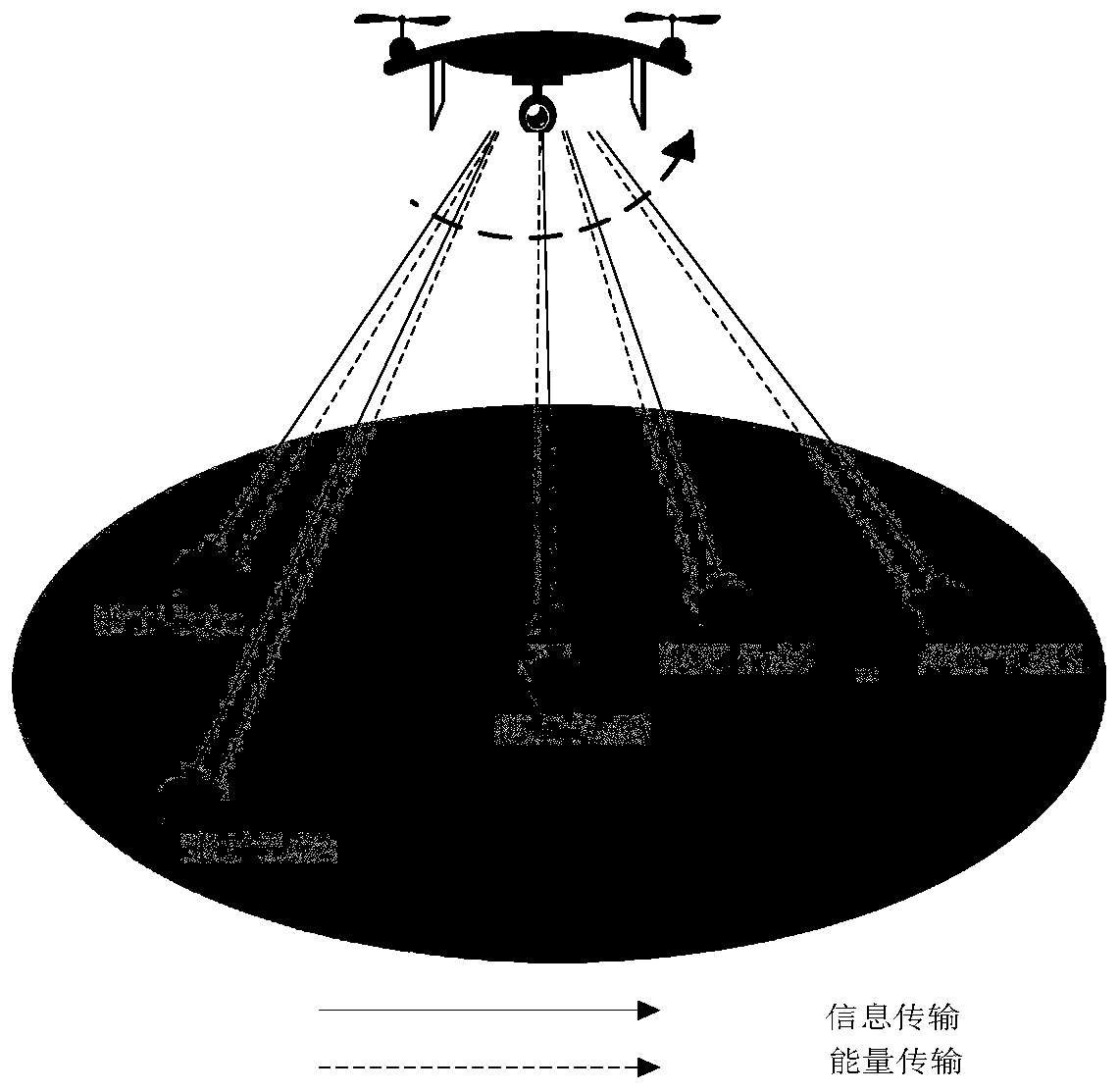
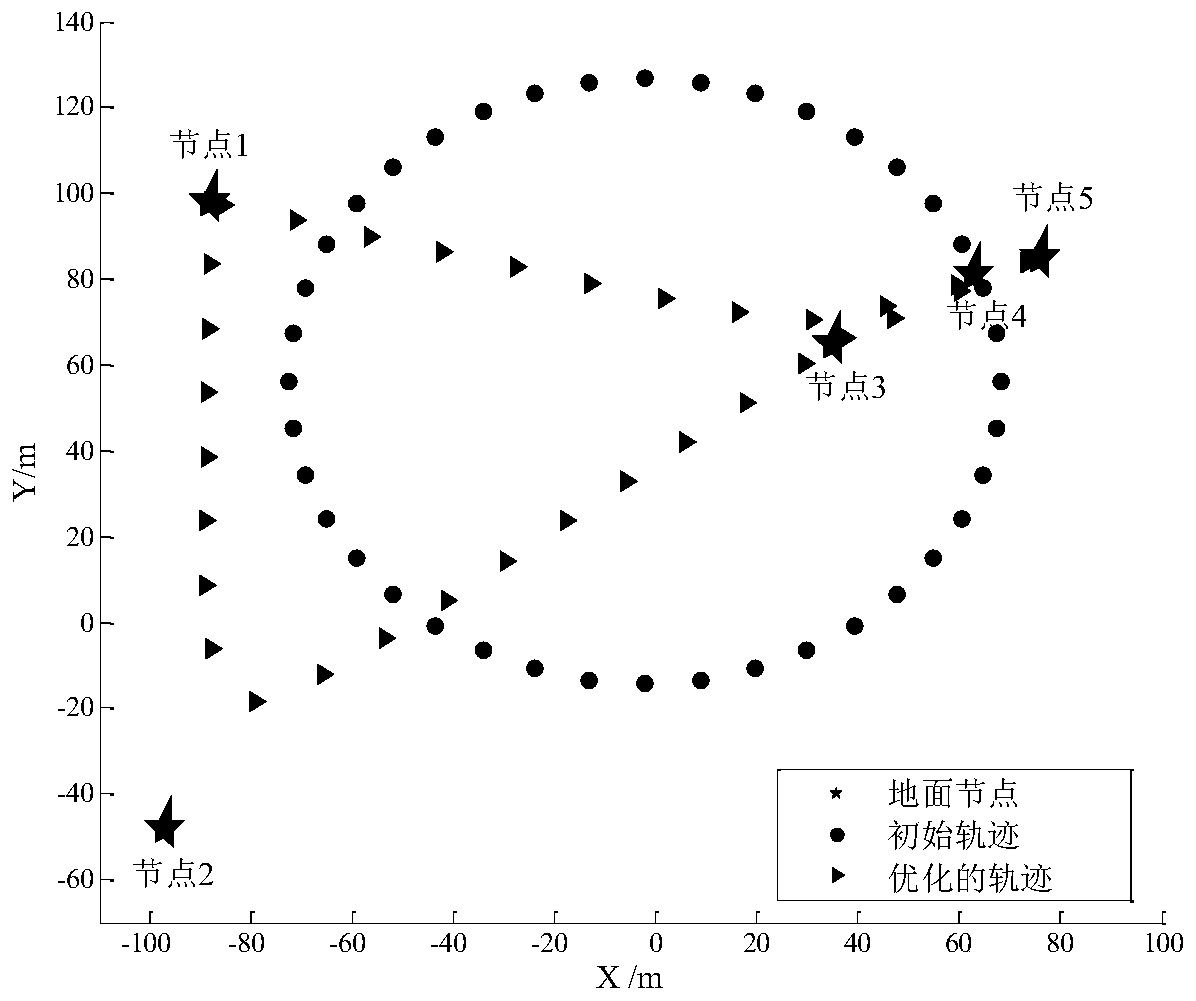
Unmanned aerial vehicle track and resource allocation joint optimization method for multi-carrier communication
ActiveCN110730031AOptimize flight pathSimultaneous transmissionPower managementInternal combustion piston enginesTelecommunications linkSimulation
The embodiment of the invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle trajectory and resource allocation joint optimization method for multi-carrier wireless communication. The method comprises the following steps: S1, creating an optimization model for multi-node energy-carrying communication based on an unmanned aerial vehicle; S2, splitting the optimization model, and respectively carrying out iterative solution on split sub-models; S3, fixing the trajectory of the unmanned aerial vehicle, and optimizing the resource allocation variable of the unmanned aerial vehicle; S4, fixing unmanned aerial vehicle resource allocation, and optimizing the flight path of the unmanned aerial vehicle; and S5, performing flight path and resource allocation joint optimization of the unmanned aerial vehicleto obtain an optimal value of the optimization variable. According to the invention, simultaneous transmission of information and energy of a plurality of ground nodes by the unmanned aerial vehicleis realized; the problems of node information interaction and endurance time of the Internet of Things are solved, and meanwhile, the design complexity of the receiver can be effectively reduced; andthe communication link is improved through the flight path of the unmanned aerial vehicle, the wireless resource utilization rate is improved, and the maximization of the data transmission rate is realized.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Machine to machine communications
InactiveUS20110045818A1Reduce loadImprove efficiencyMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsWireless commuication servicesTelecommunications networkCellular data
In a cellular telecommunications network a method for facilitating communications comprises receiving information elements from a cellular data communications device, said information elements being in a format conforming with a session-based message protocol, each information element including a header portion and a plurality of payload portions; extracting machine information from at least at least one of said payload portions; and generating an output message corresponding to at least one of said payload portions. The cellular data communications device generates information elements using information gathered from one or more information sensing, actuating and / or locating components.
Owner:VODAFONE IP LICENSING
Devices and methods for specialized machine-to-machine communication transmission network modes via edge node capabilities
ActiveUS10306442B1Improve network efficiencyImprove rendering capabilitiesTransmissionMachine-to-machine/machine-type communication serviceTransport systemEdge node
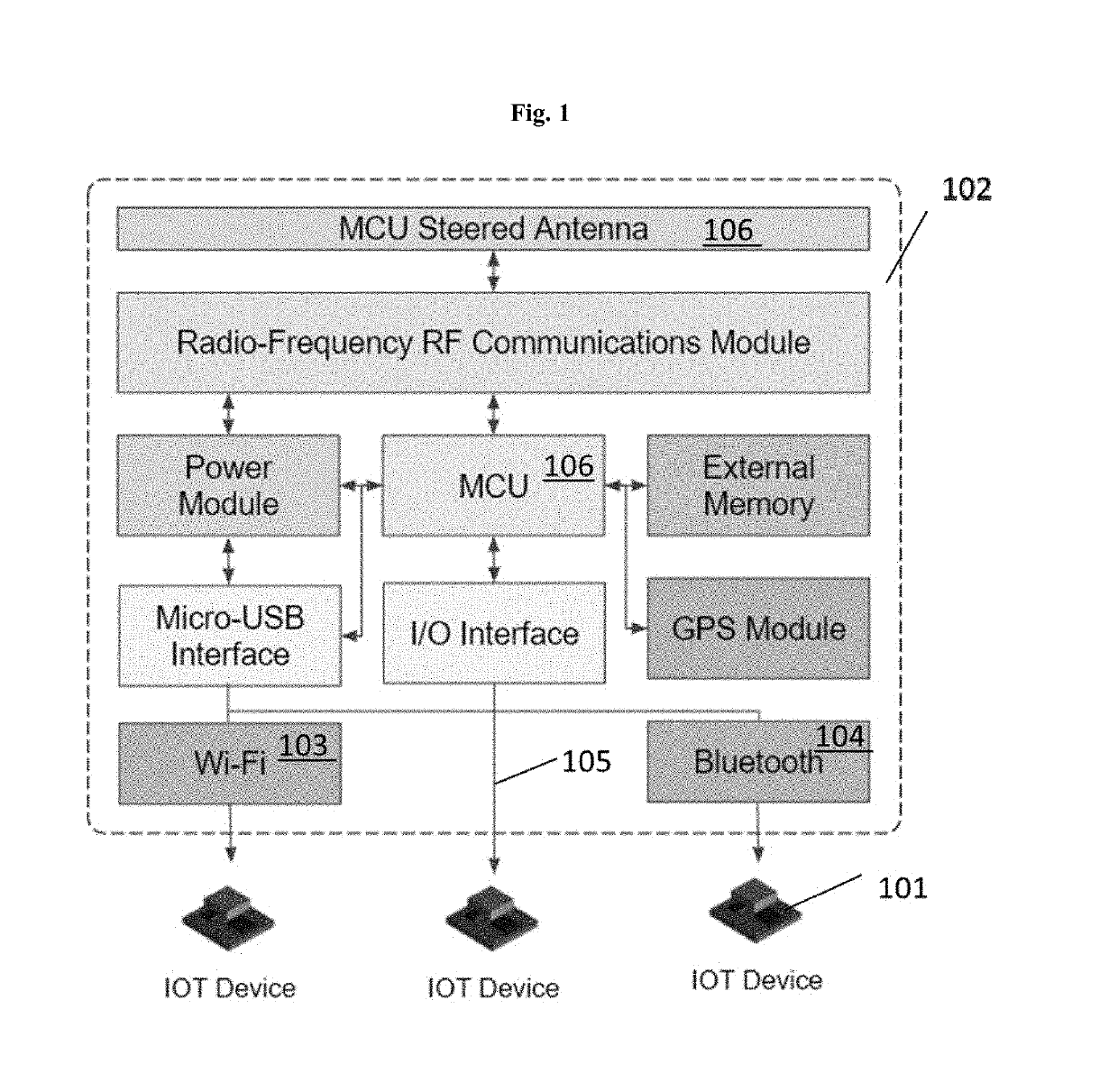
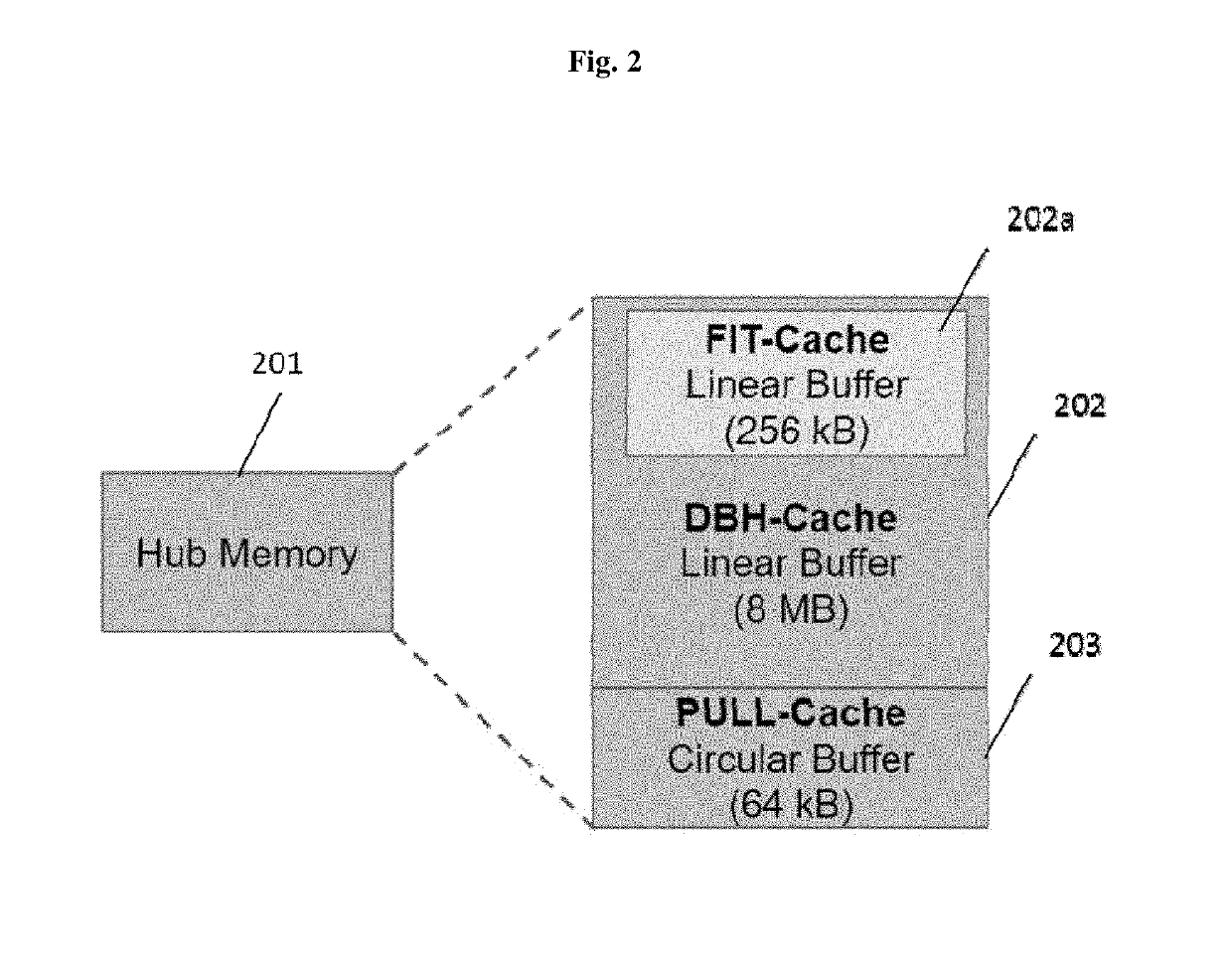
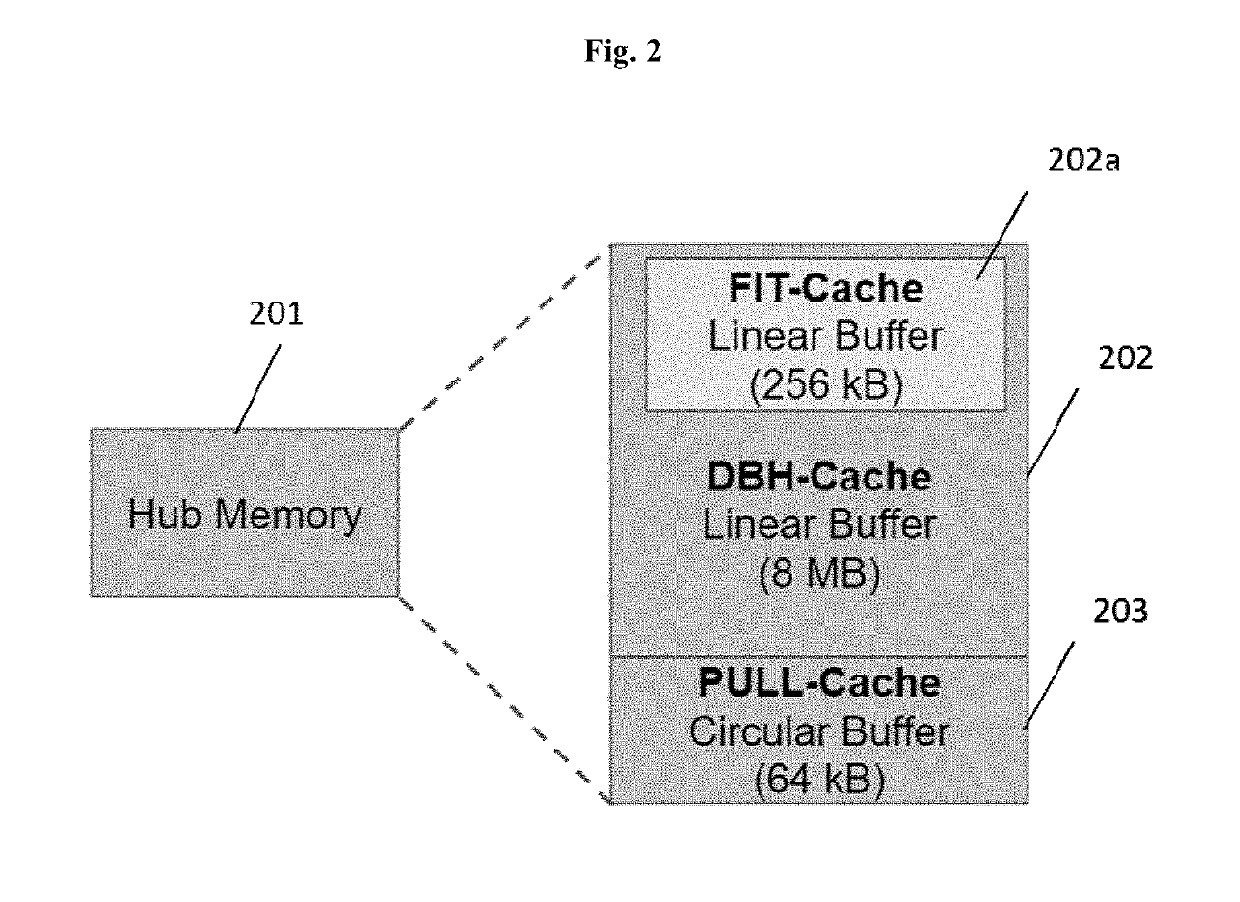
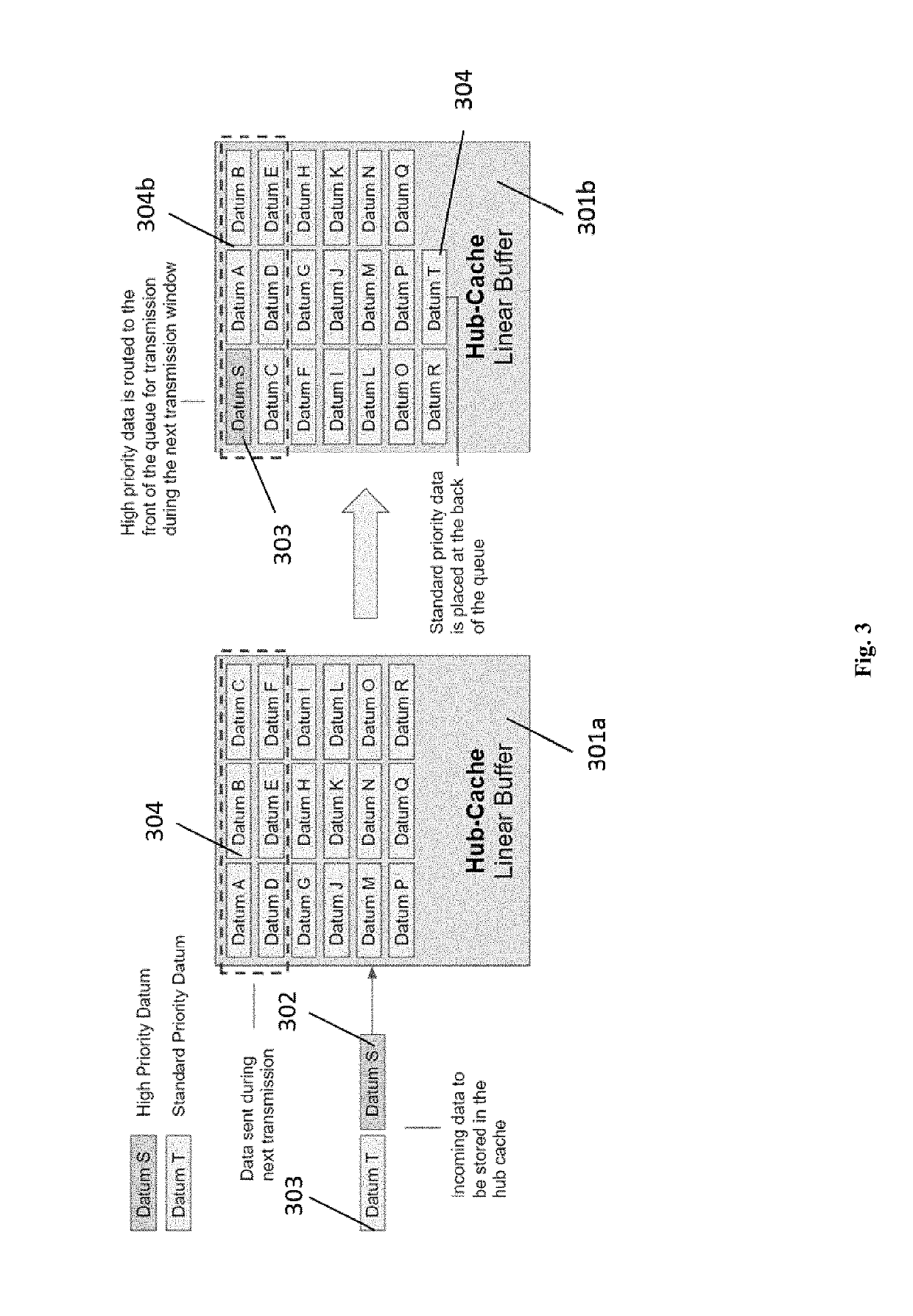
Disclosed herein are hub devices for a machine-to-machine (M2M) communications network that enables multiple communication modes for data source nodes, the hub comprising a processor, a local connectivity system configured to communicate data with the data source nodes via an interface, a data processing and caching system comprising a local memory and configured to receive and store user-defined data routing and processing functions, prioritize the data based on the user-defined functions; and route the prioritized data to the local memory for storage or to the data transmission system for immediate transmission based on the priority, and a data transmission system configured to dynamically assign an M2M upload mechanism to the routed data selected from: a real-time transmission mechanism, a fixed interval mechanism, a data backhaul mechanism, and a user pull mechanism; and transmit the data to a network backhaul link for delivery to a host point.
Owner:SKYLO TECH INC
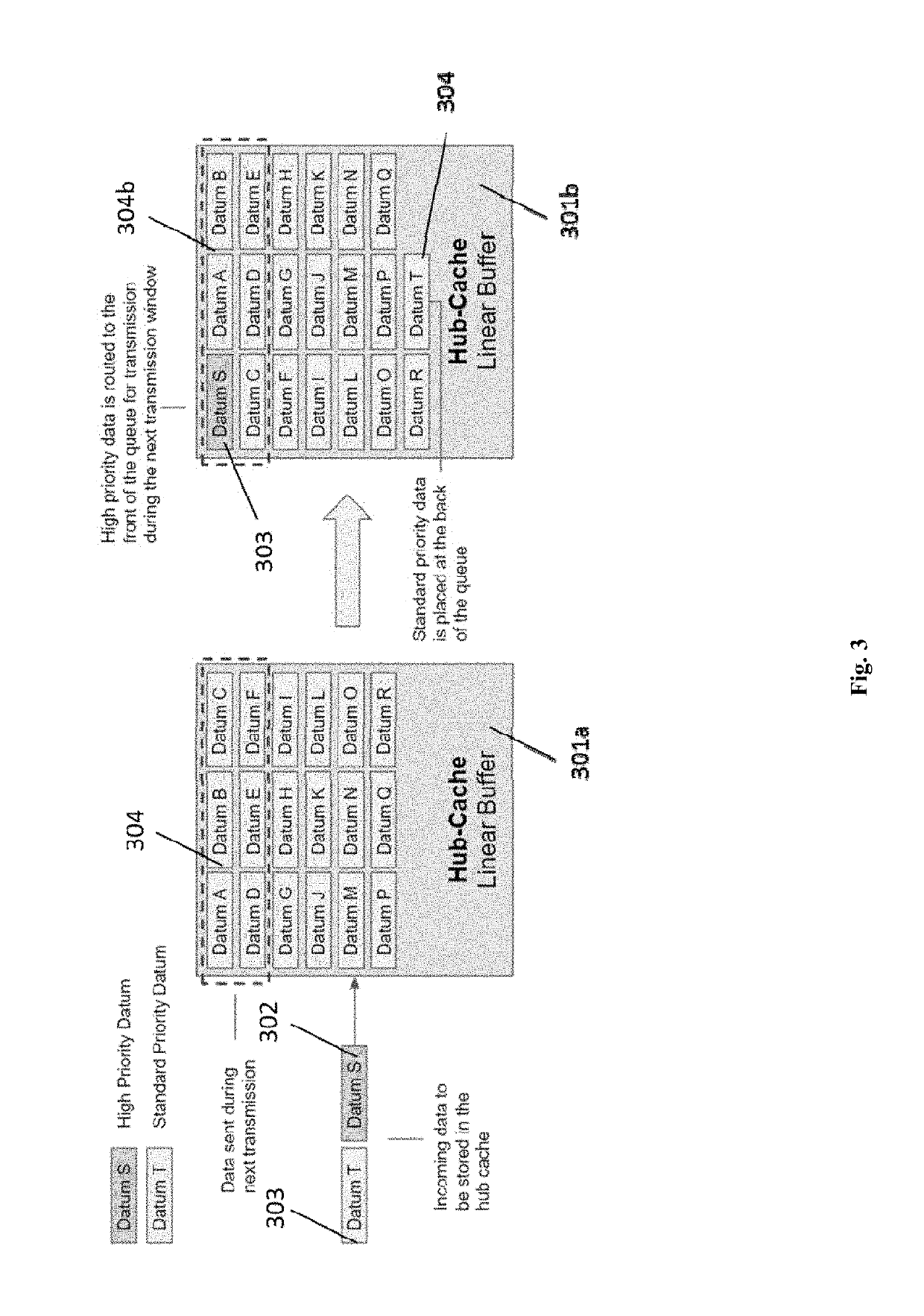
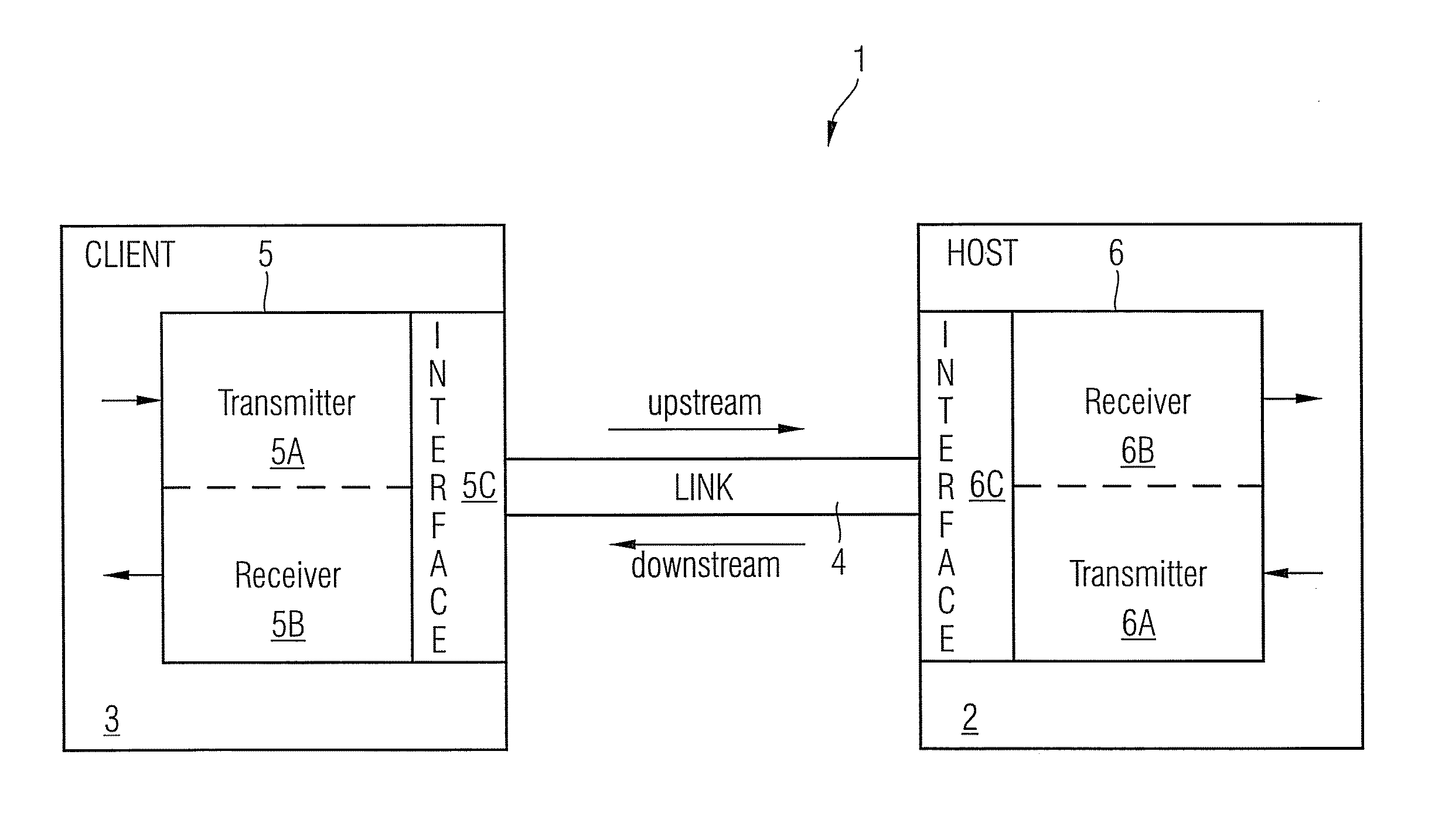
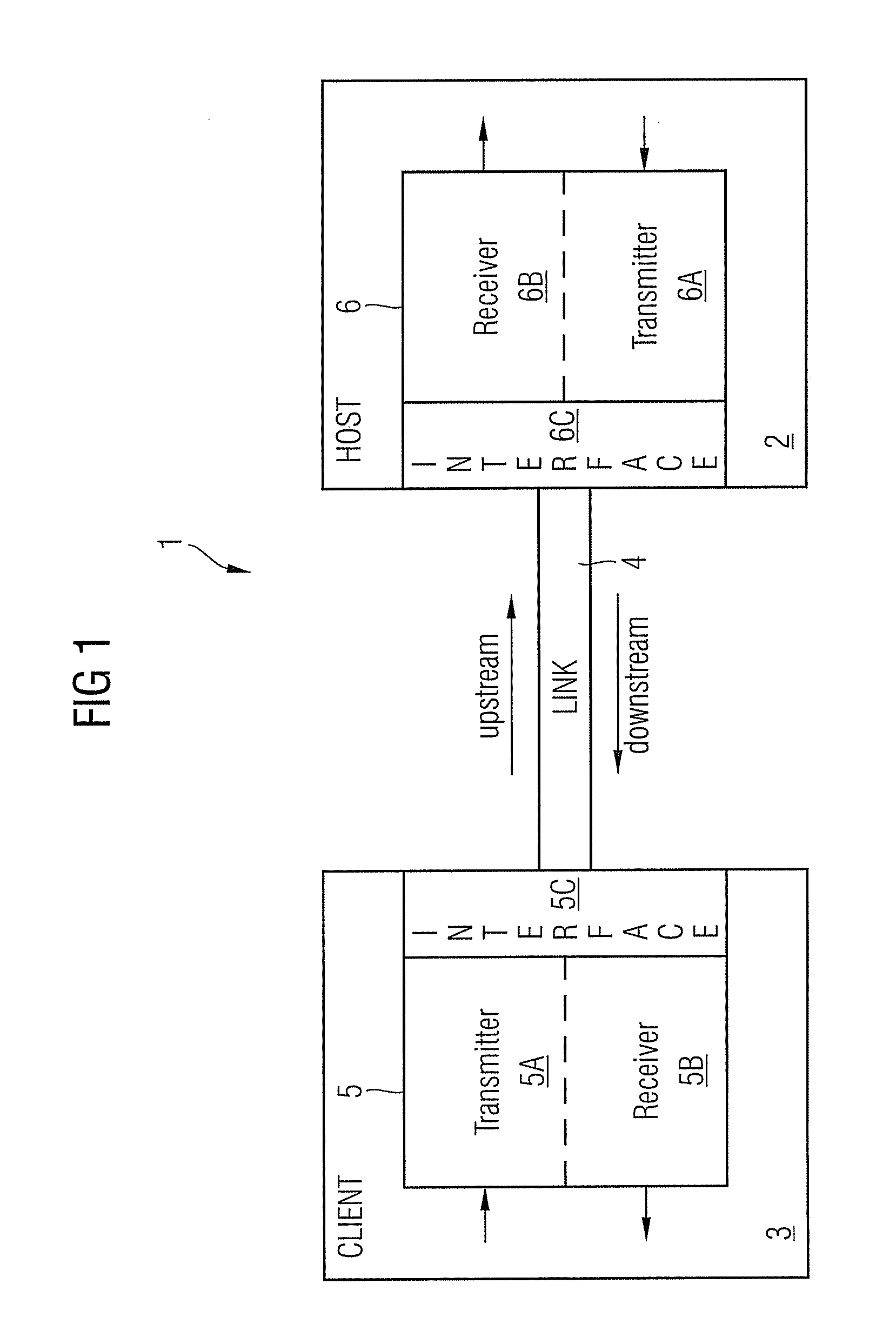
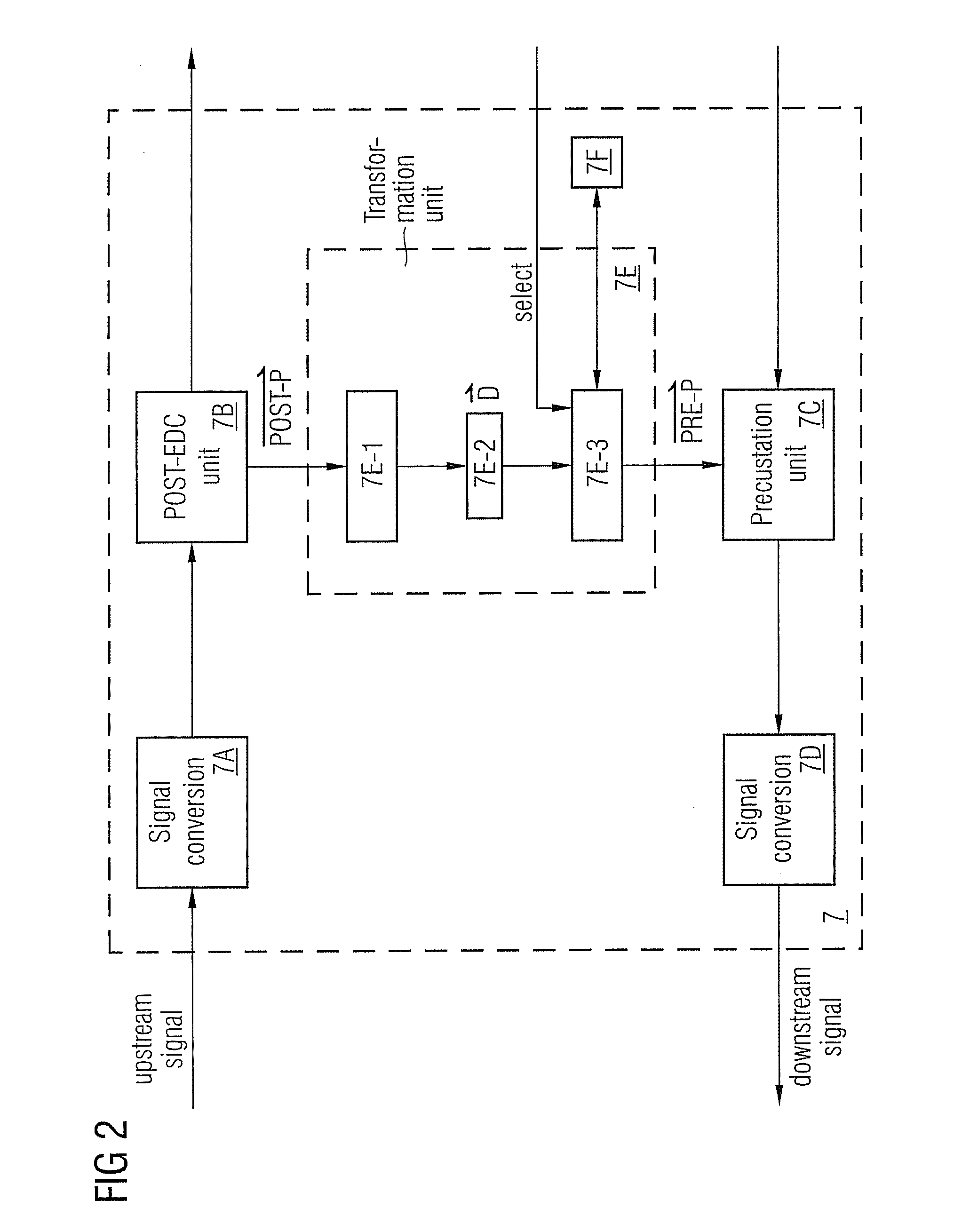
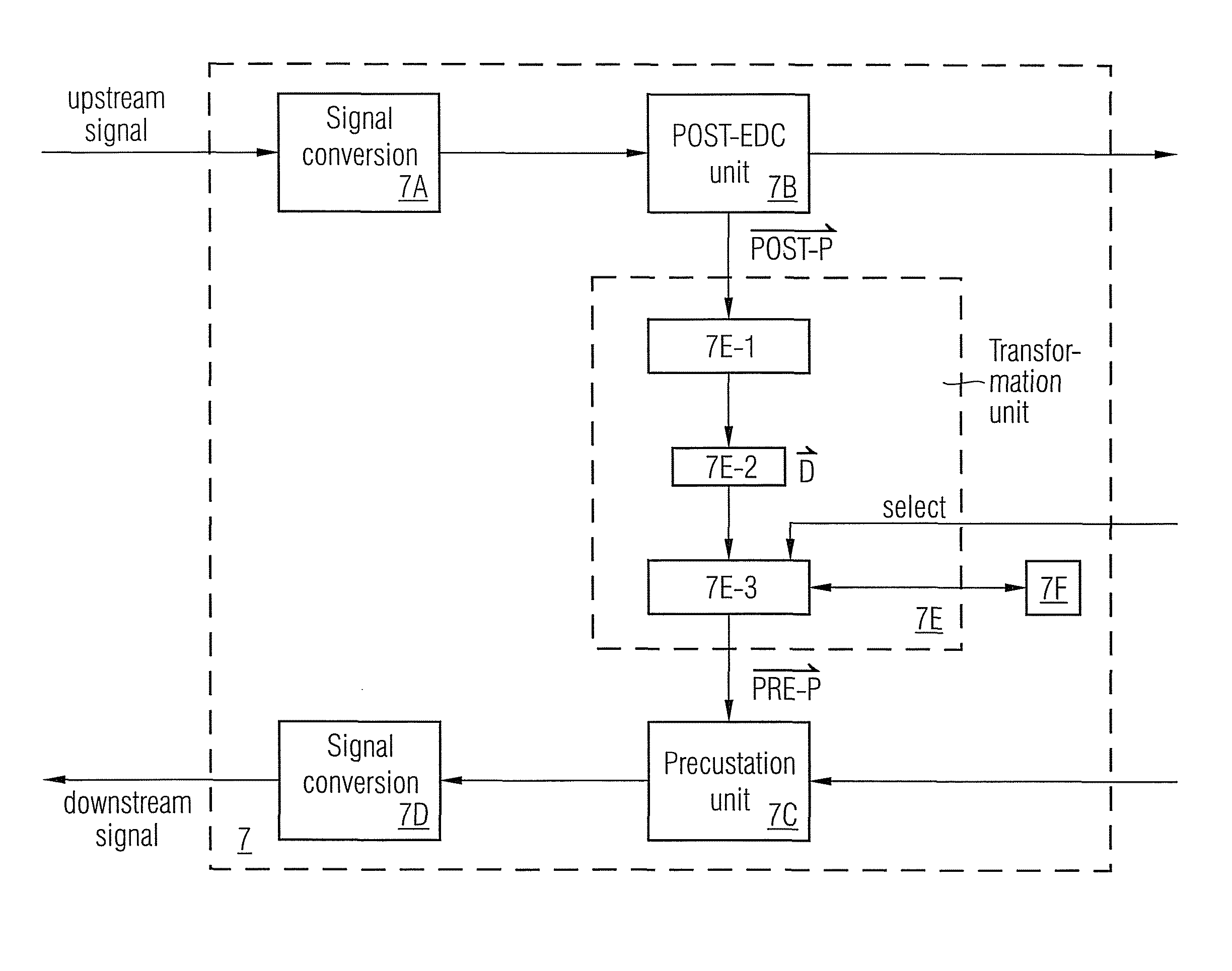
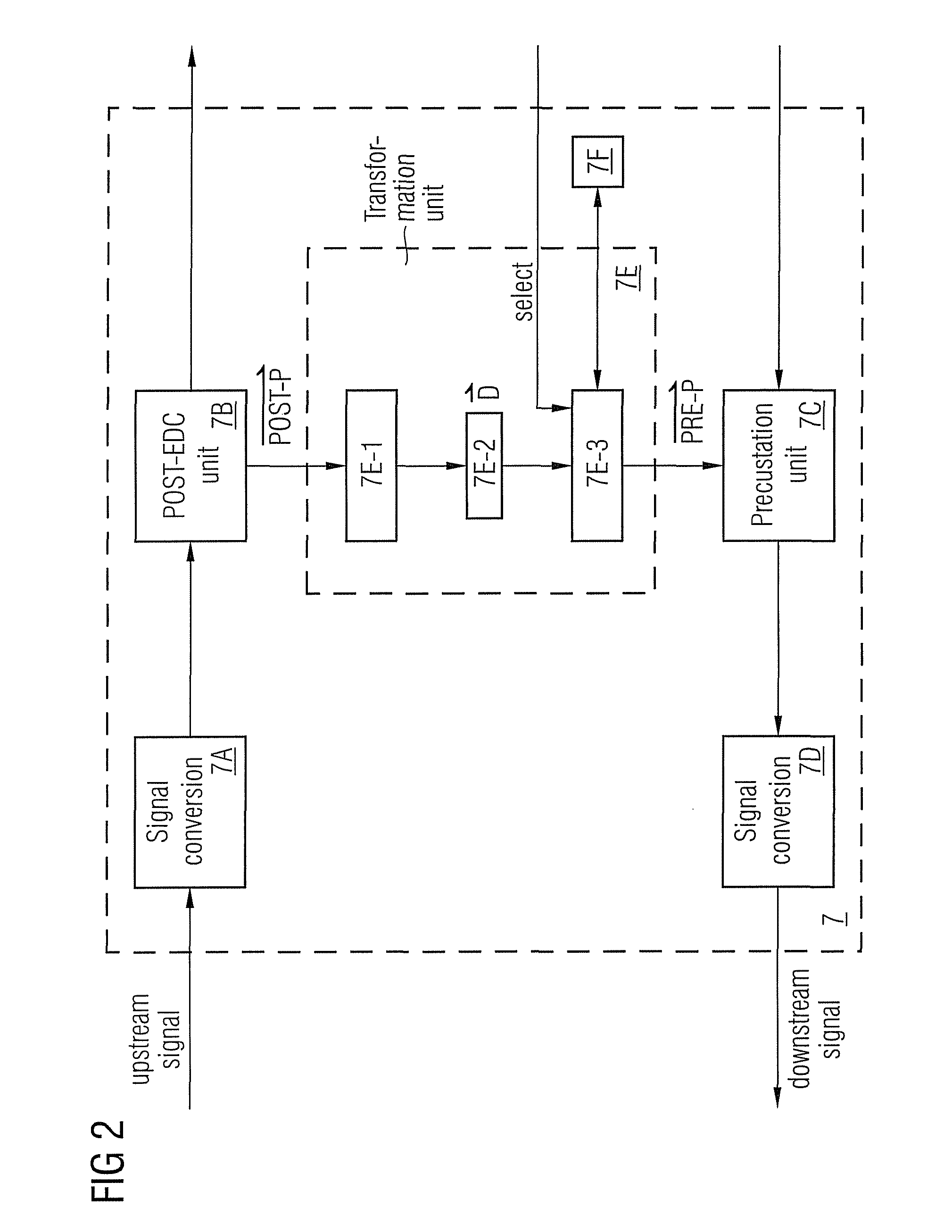
Method and a system with distortion compensation
ActiveUS20110206382A1Maximize data transfer rateMinimizing and maximizing target value of targetDistortion/dispersion eliminationTransmission noise suppressionEngineeringPre distortion
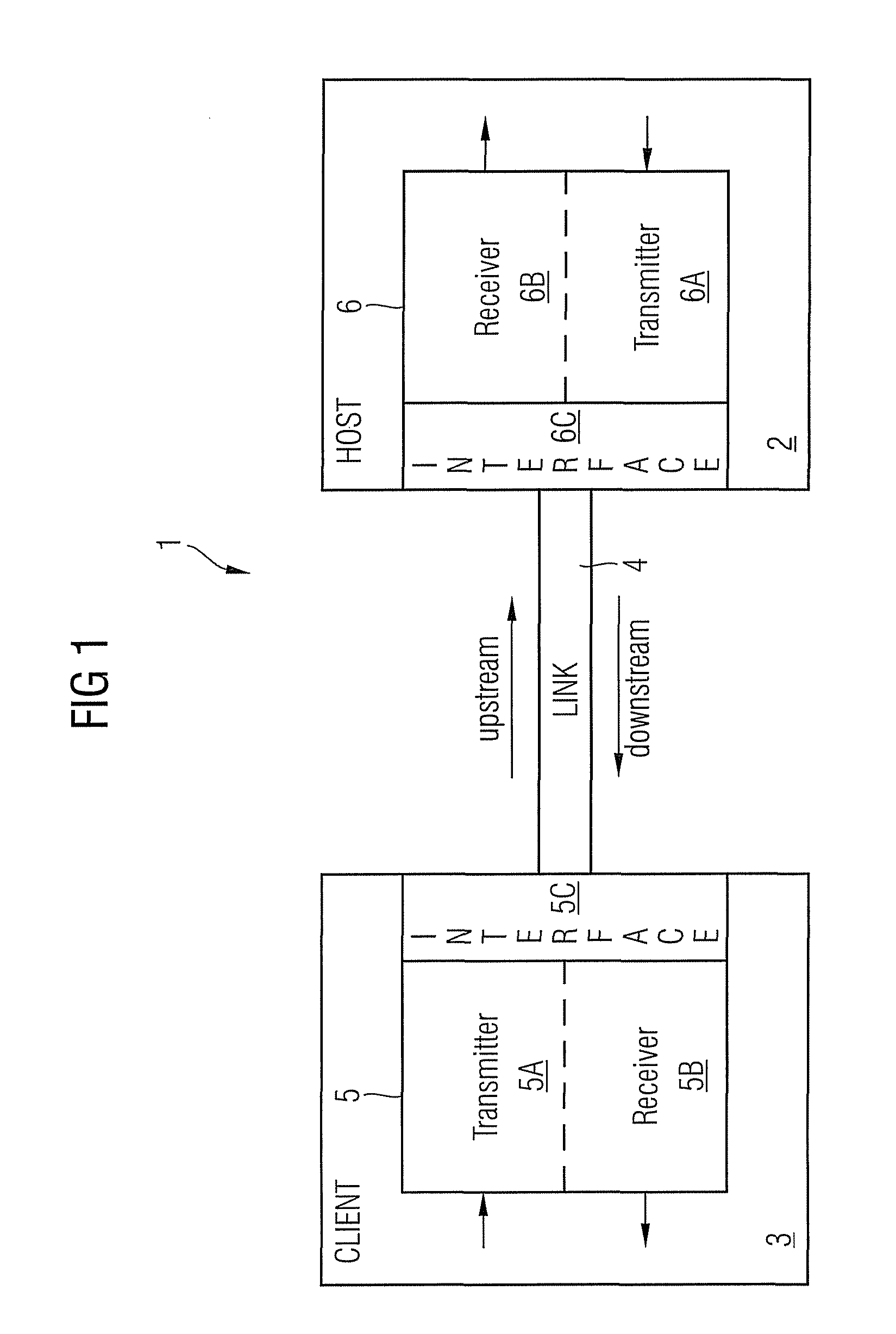
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for distortion compensation of signals transmitted via a bidirectional link between a client device and a host device, said method comprising the steps of performing a post-distortion-compensation for an upstream signal received by the host device on said bidirectional link by adjusting post-compensation parameters of a post-compensation unit of said host device and transforming the adjusted post-compensation parameters into pre-compensation parameters of a pre-compensation unit of said host device which performs a pre-distortion compensation for a downstream signal transmitted by said host device via said bidirectional link to said client device.
Owner:ADVA OPTICAL NETWORKING SE
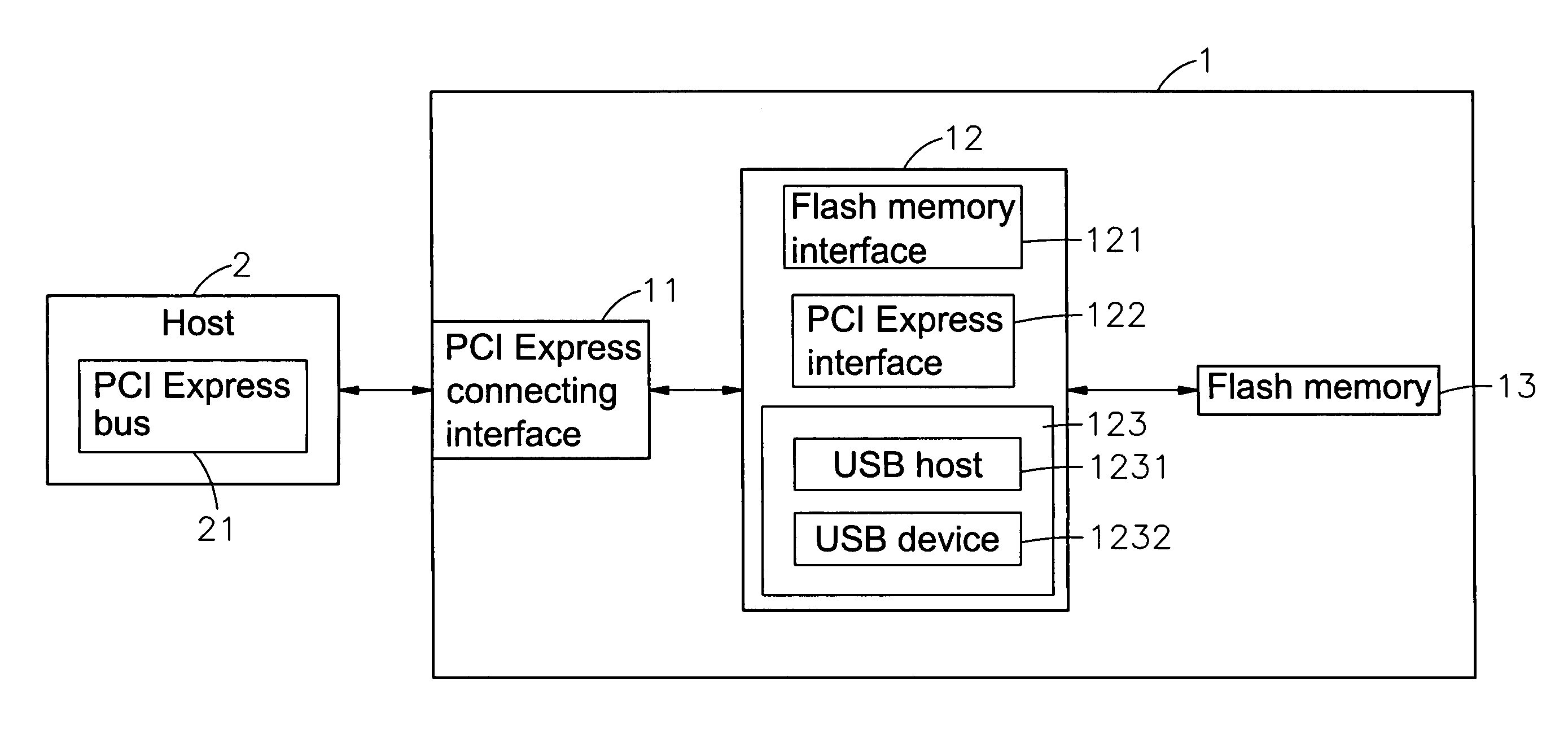
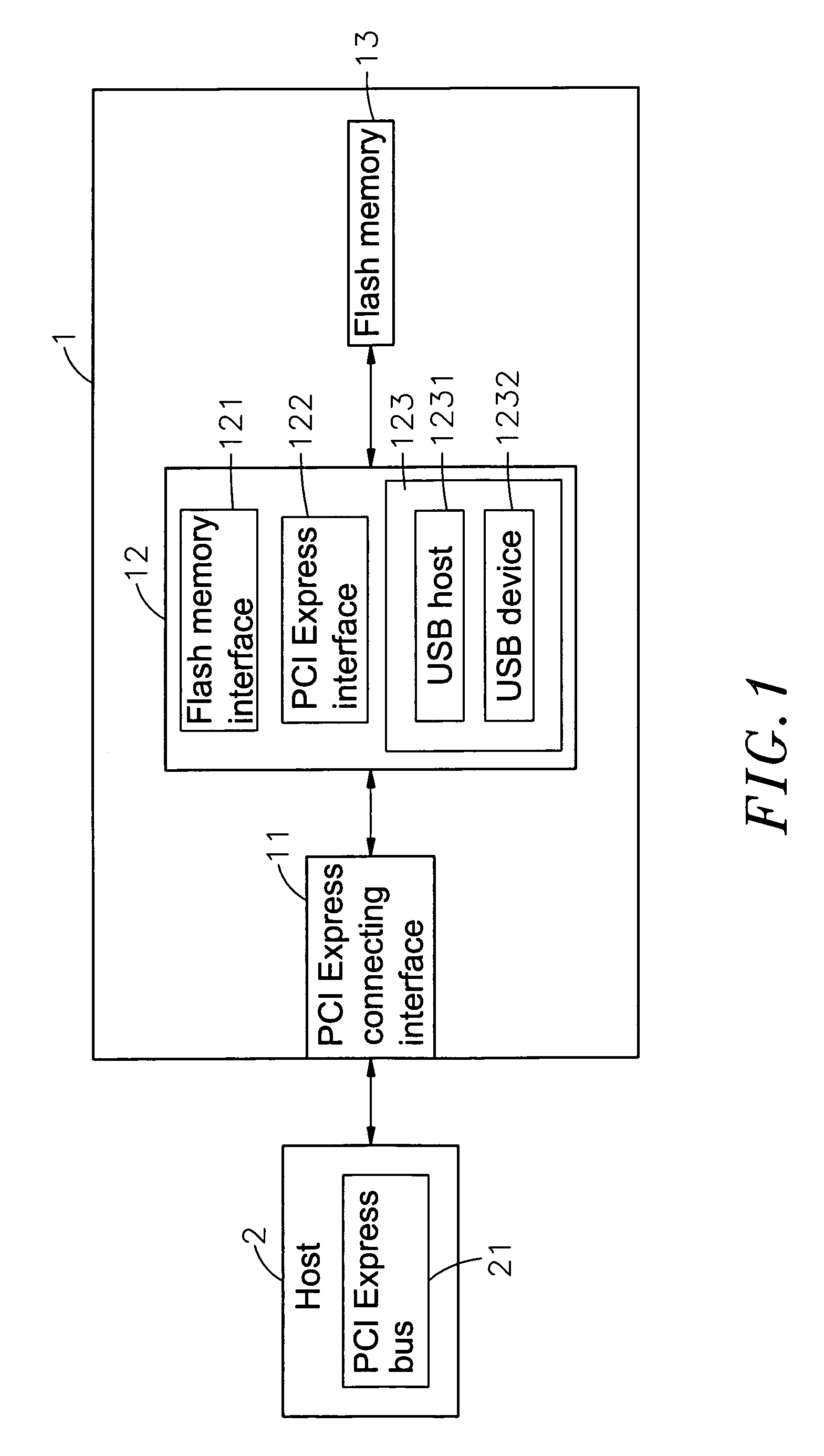
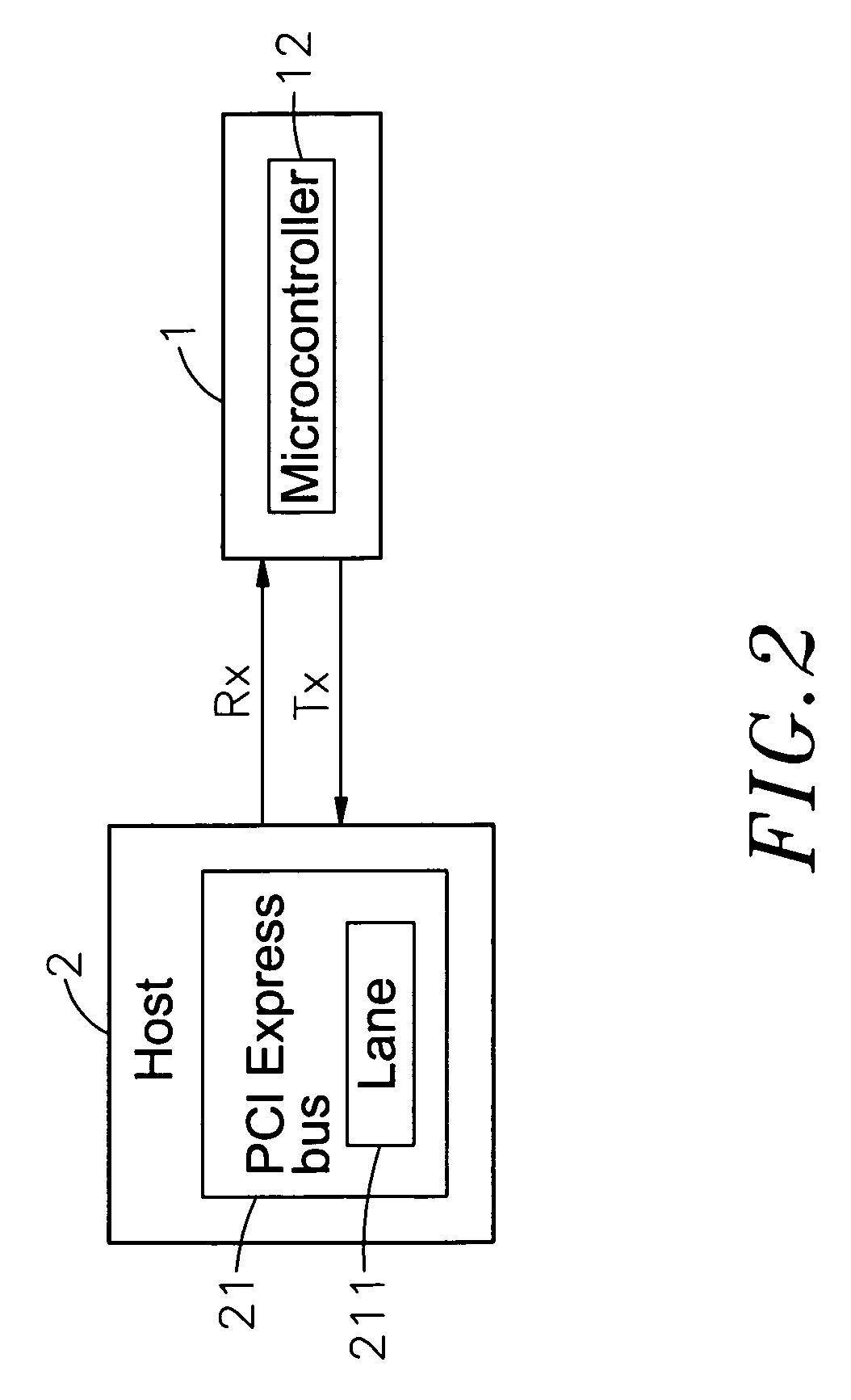
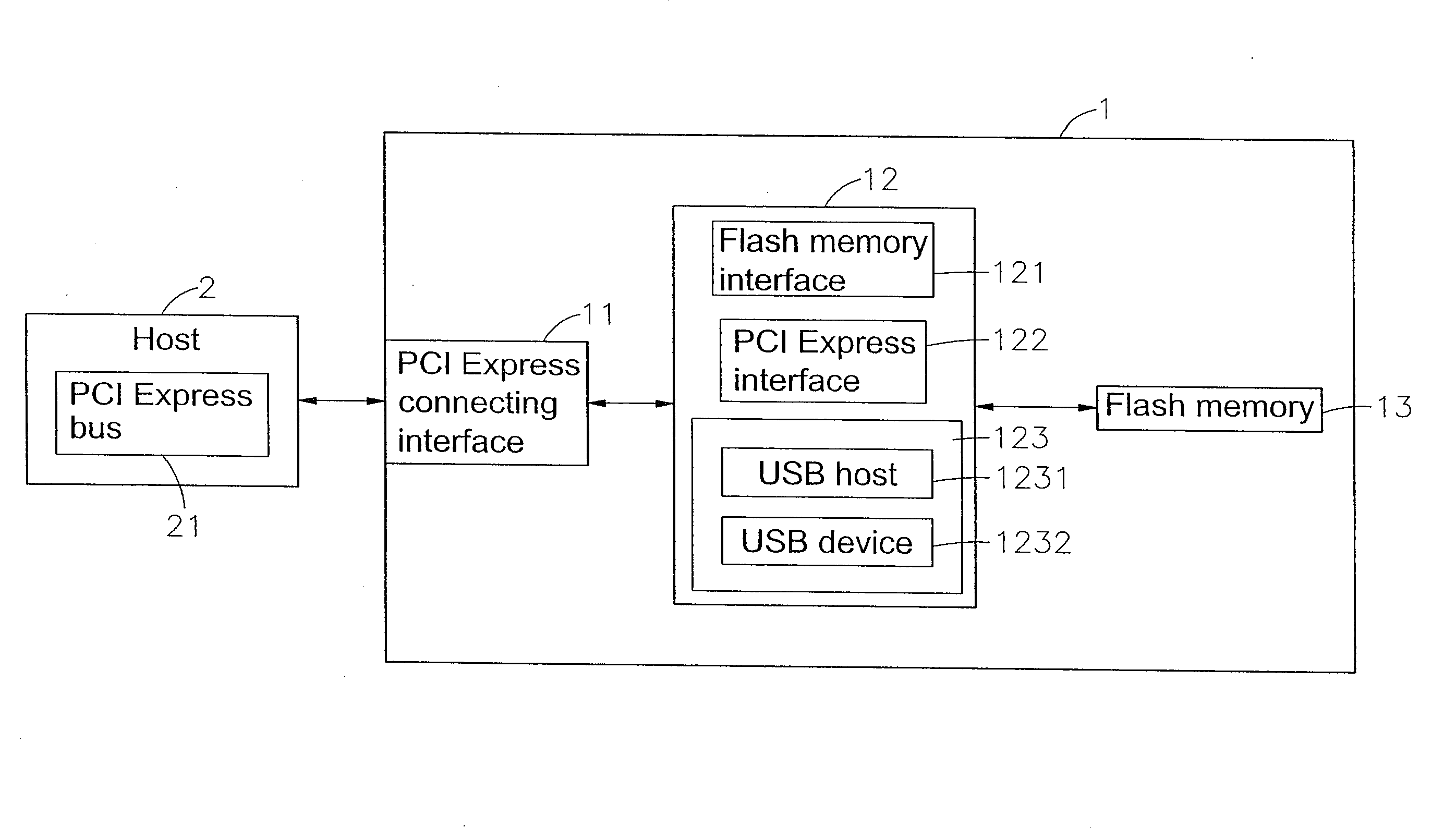
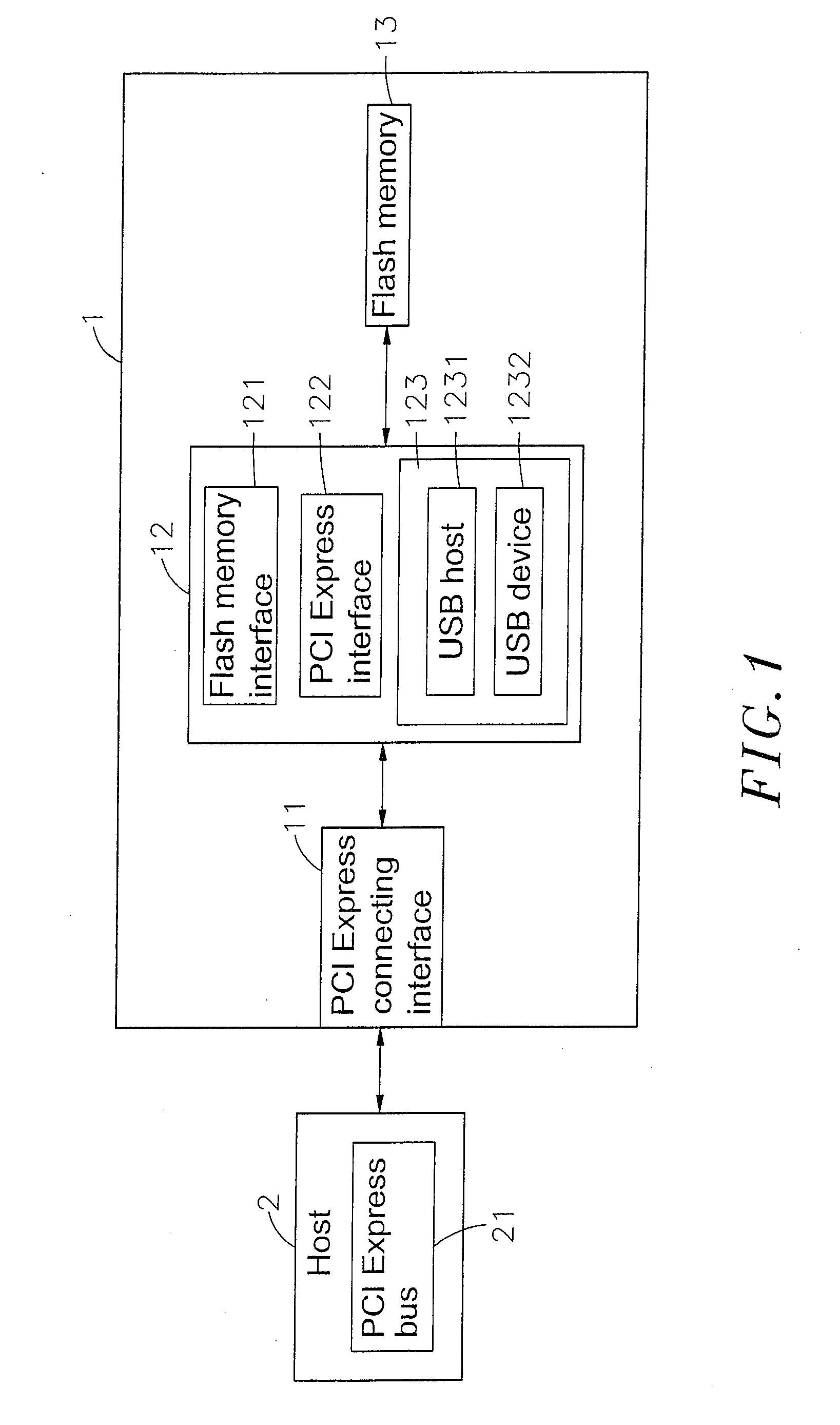
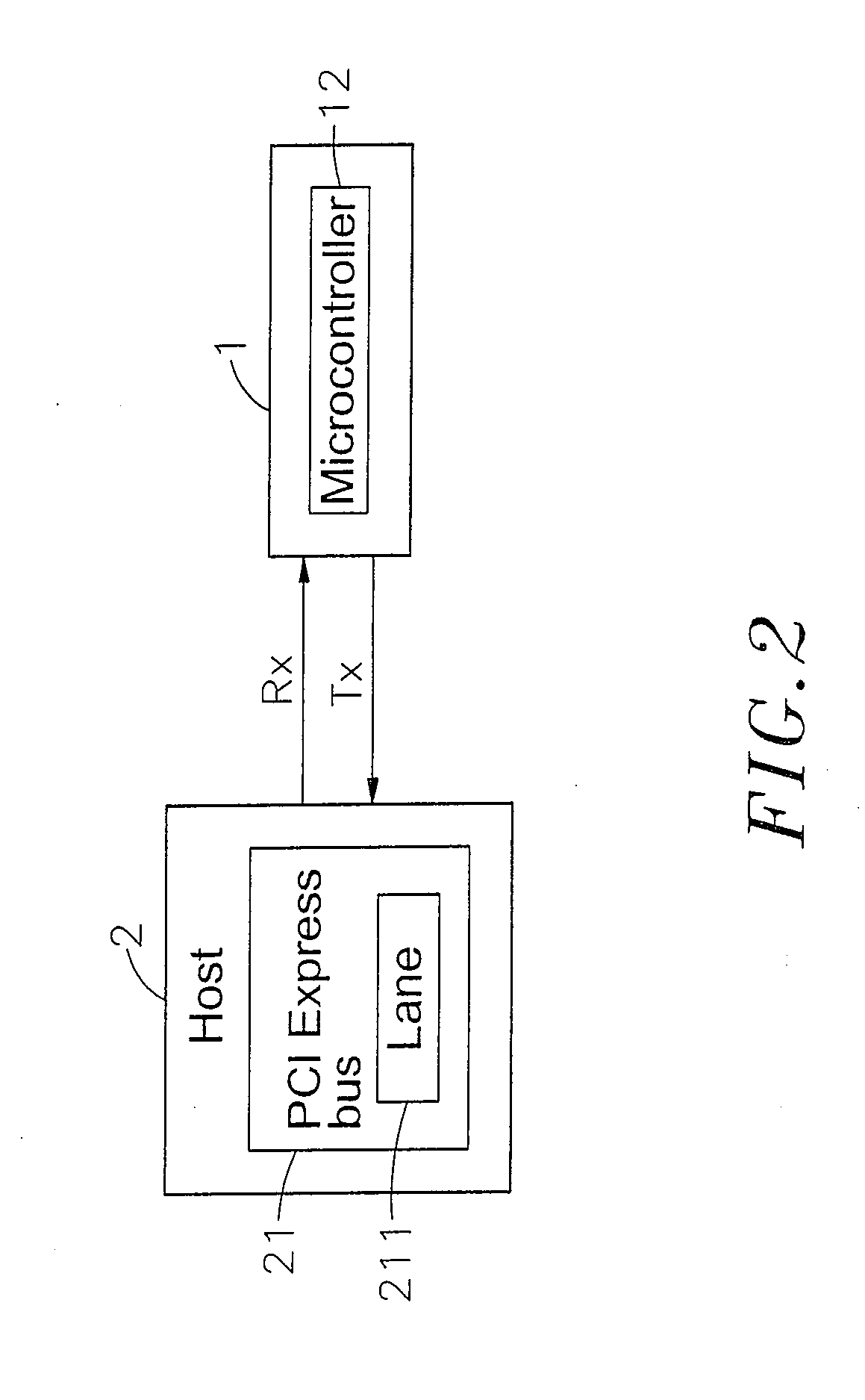
Virtual USB flash memory storage device with PCI express interface
ActiveUS7222211B2Maximize total data transmittedMaximize data transfer rateMemory systemsMicrocontrollerPCI Express
A virtual universal serial bus (USB) flash memory storage device with a peripheral component interconnect (PCI) Express including a microcontroller connected separately to a flash memory and PCI Express connecting interface, and the microcontroller has a flash memory interface, a PCI Express interface and a virtual USB module and the virtual USB module includes a USB host and a USB device. If a host gives a USB instruction for saving or reading to the storage device, the USB instruction will be sent to and executed by the virtual USB module and the required data processing for saving or reading will be completed through the flash memory interface and the flash memory. The data in the storage device can be transmitted with a PCI Express standard transmission rate, and the host considers the storage device as a USB device instead of a pure PCI Express device.
Owner:PHISON ELECTRONICS
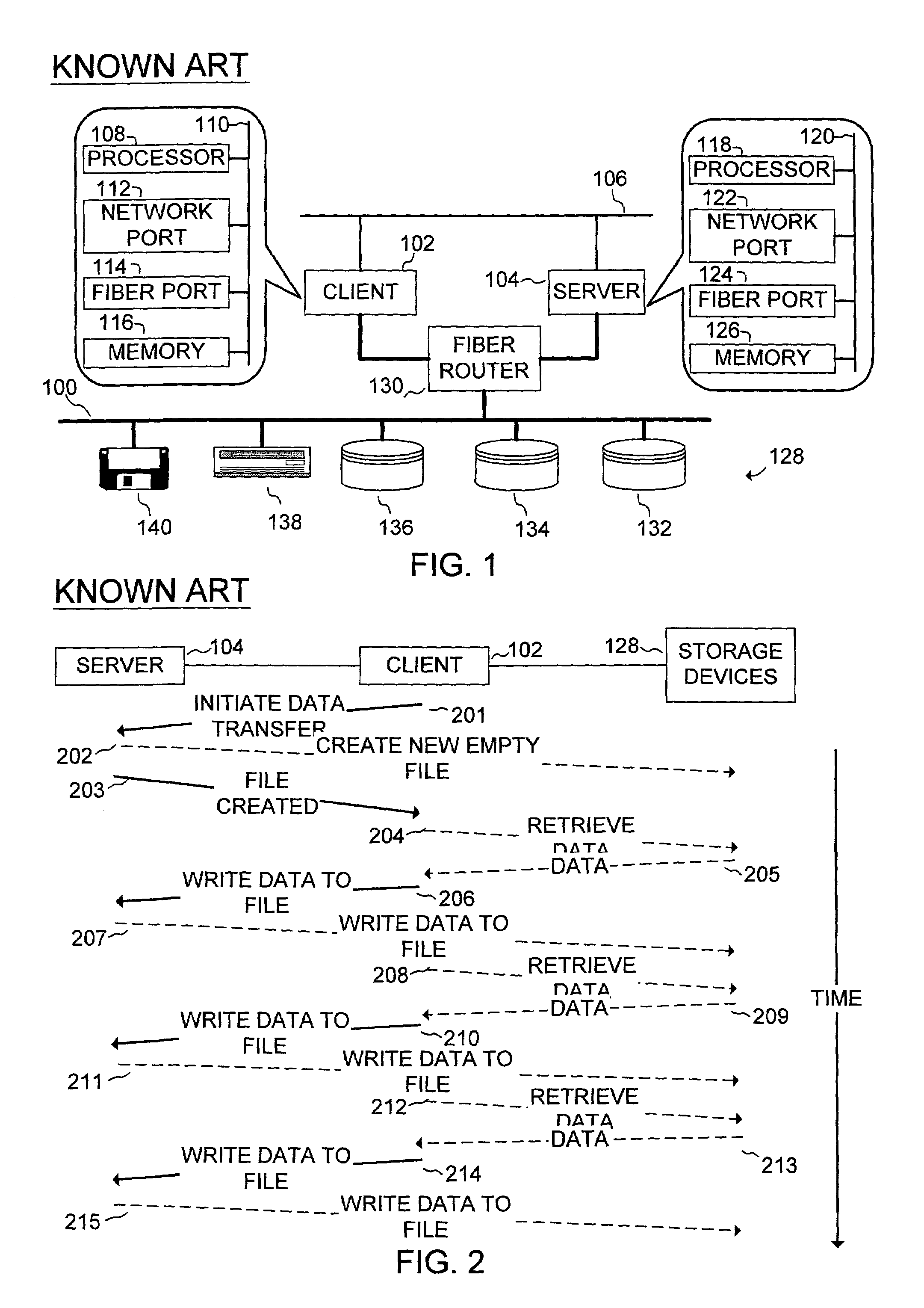
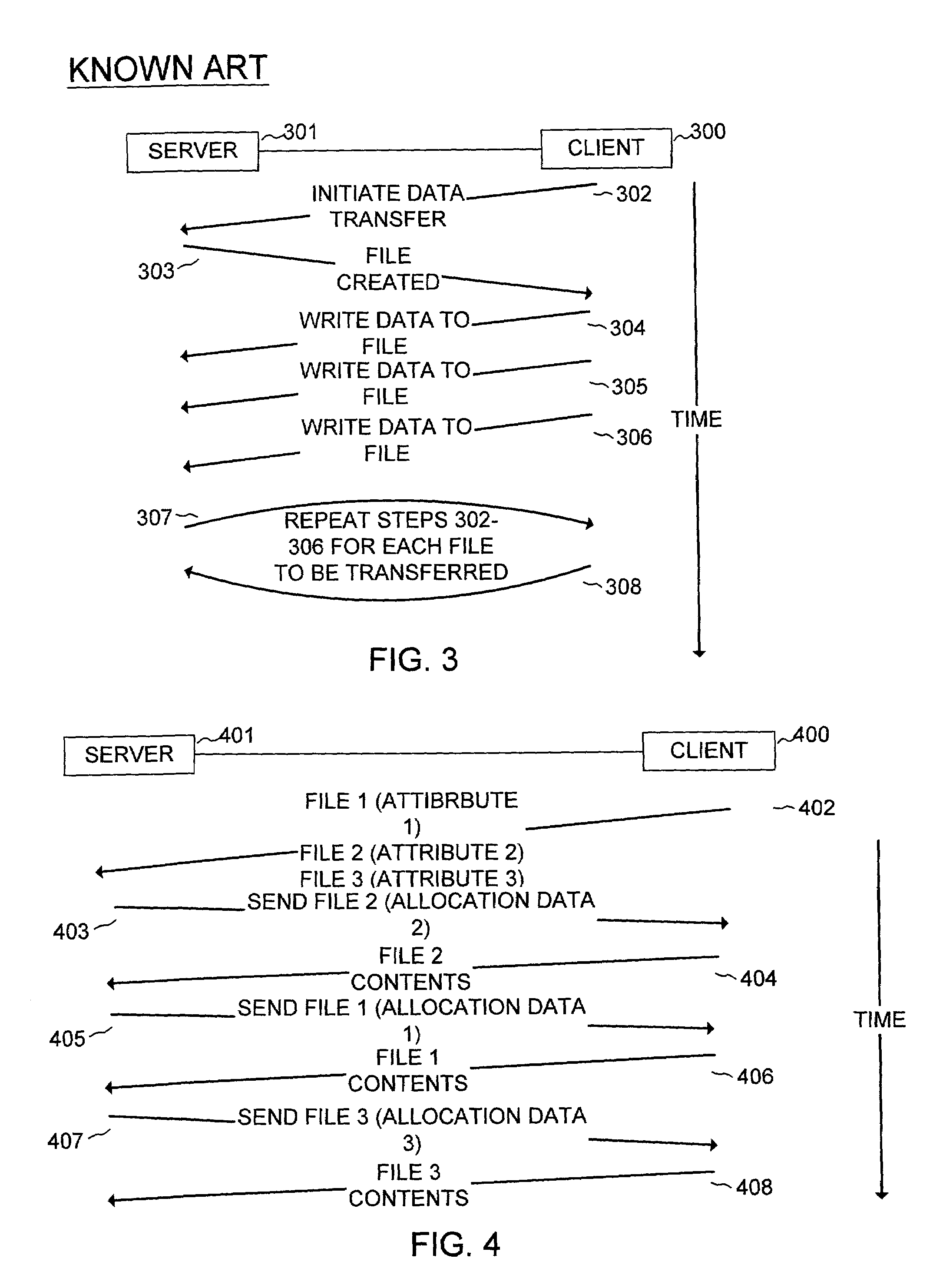
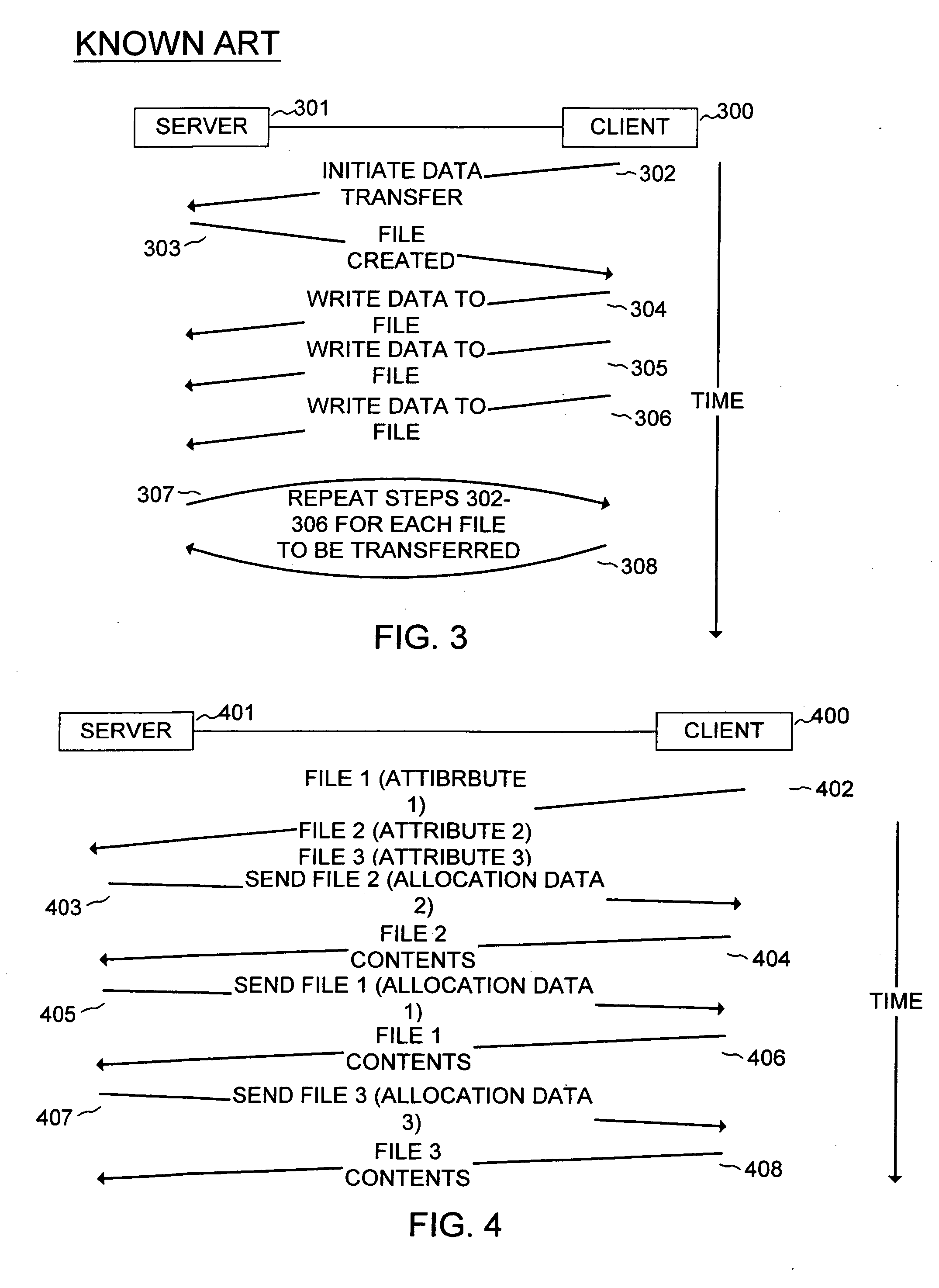
Network file sharing method and system
ActiveUS7103637B2Improve data transfer rateRelieving client loadMultiple digital computer combinationsMemory systemsData transportClient-side
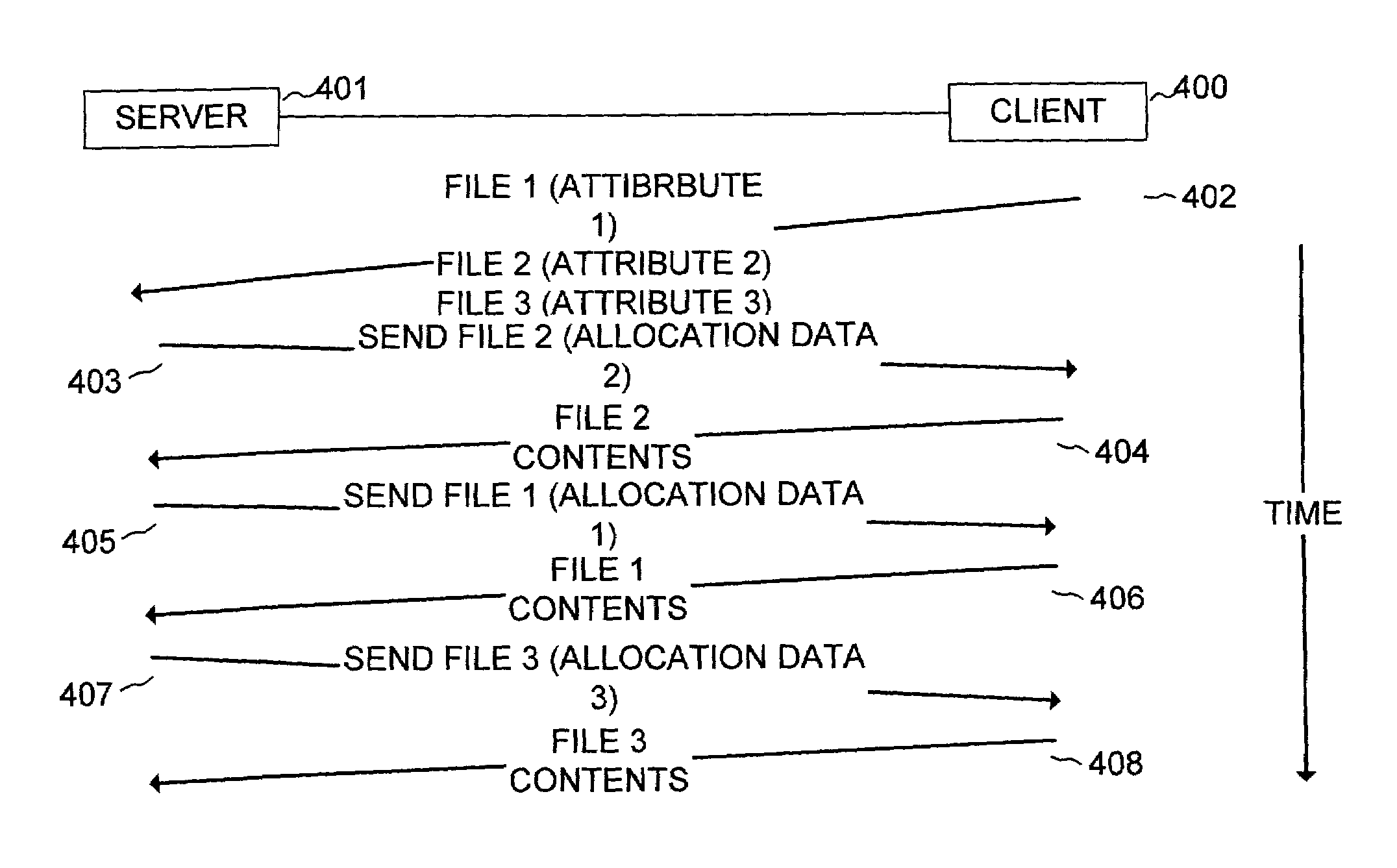
A method for writing file data from client to server which comprises writing file data from a client to a server, wherein the client issues to the server a file transfer proposal that includes the names of a plurality of files to be transferred and attributes of each of the plurality of files. The server determines optimum memory locations for the plurality of files and optimum sequence and size of data transfer and issues to the client a request to transfer the plurality of files in a sequence that is optimized for memory location and minimal number of data transfers, thereby maximizing data transfer rate from the client to the server. Client computer, server computer, and network apparatus that are configured to implement the method are also disclosed.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
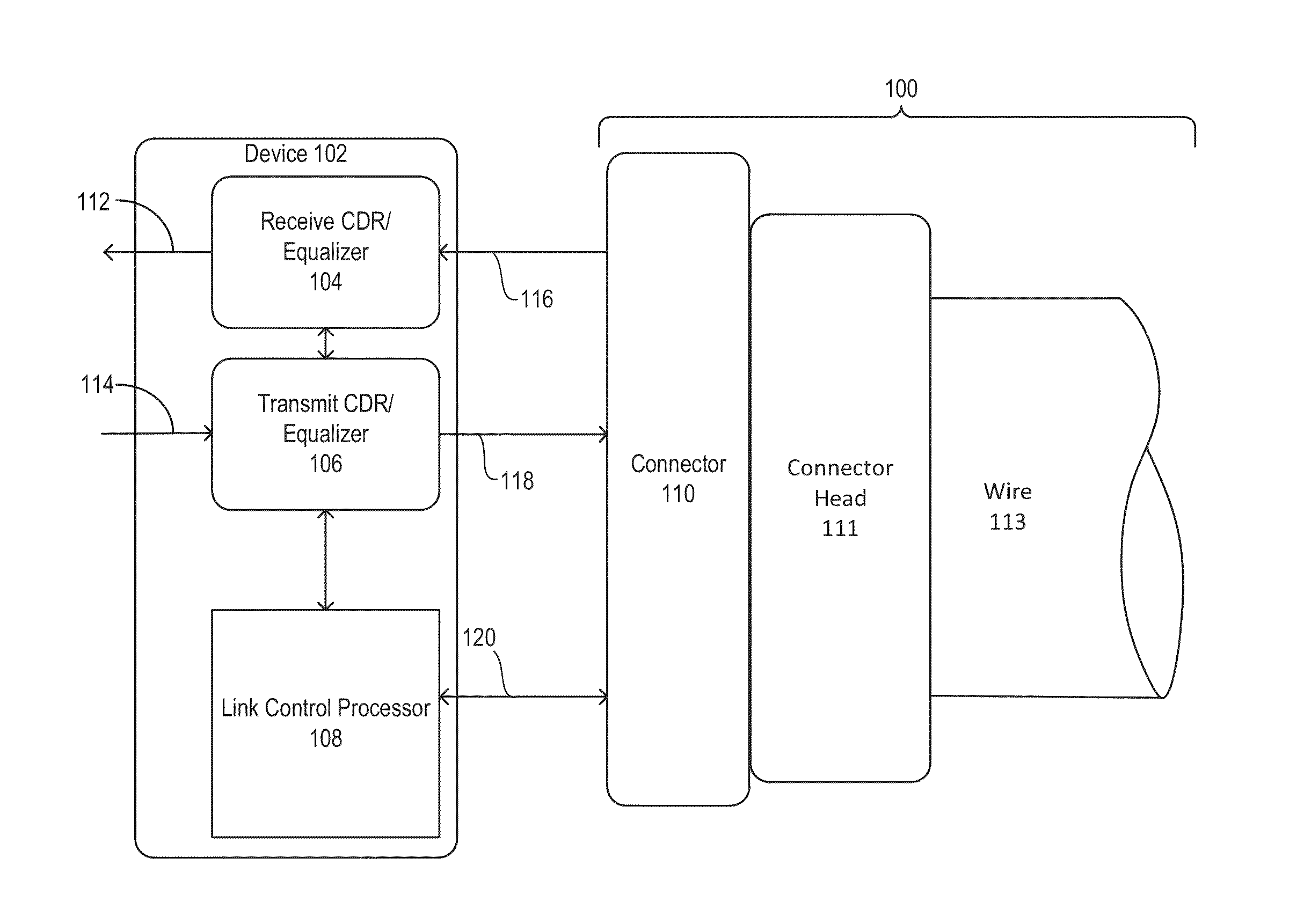
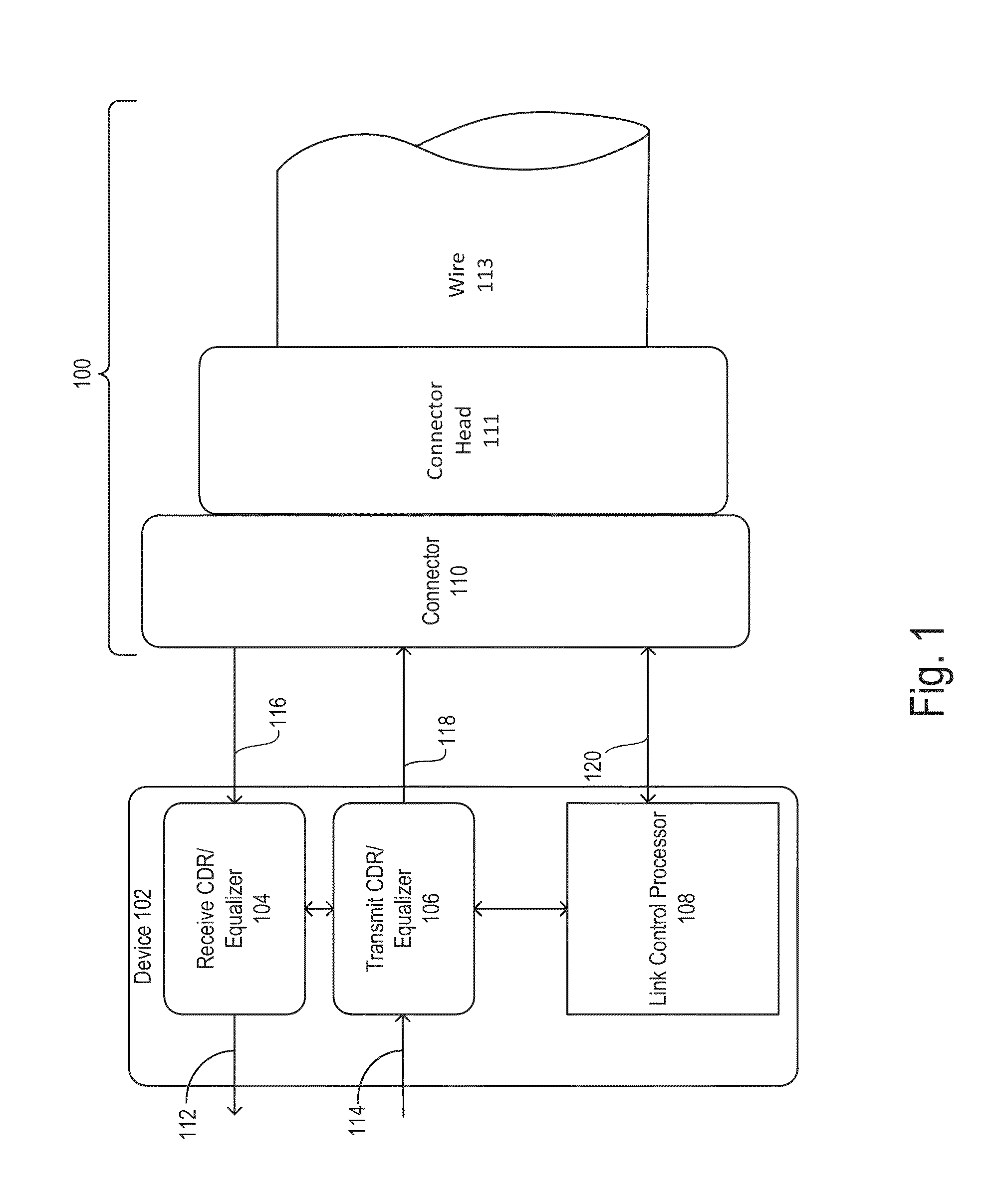
Data transfer cable system and method
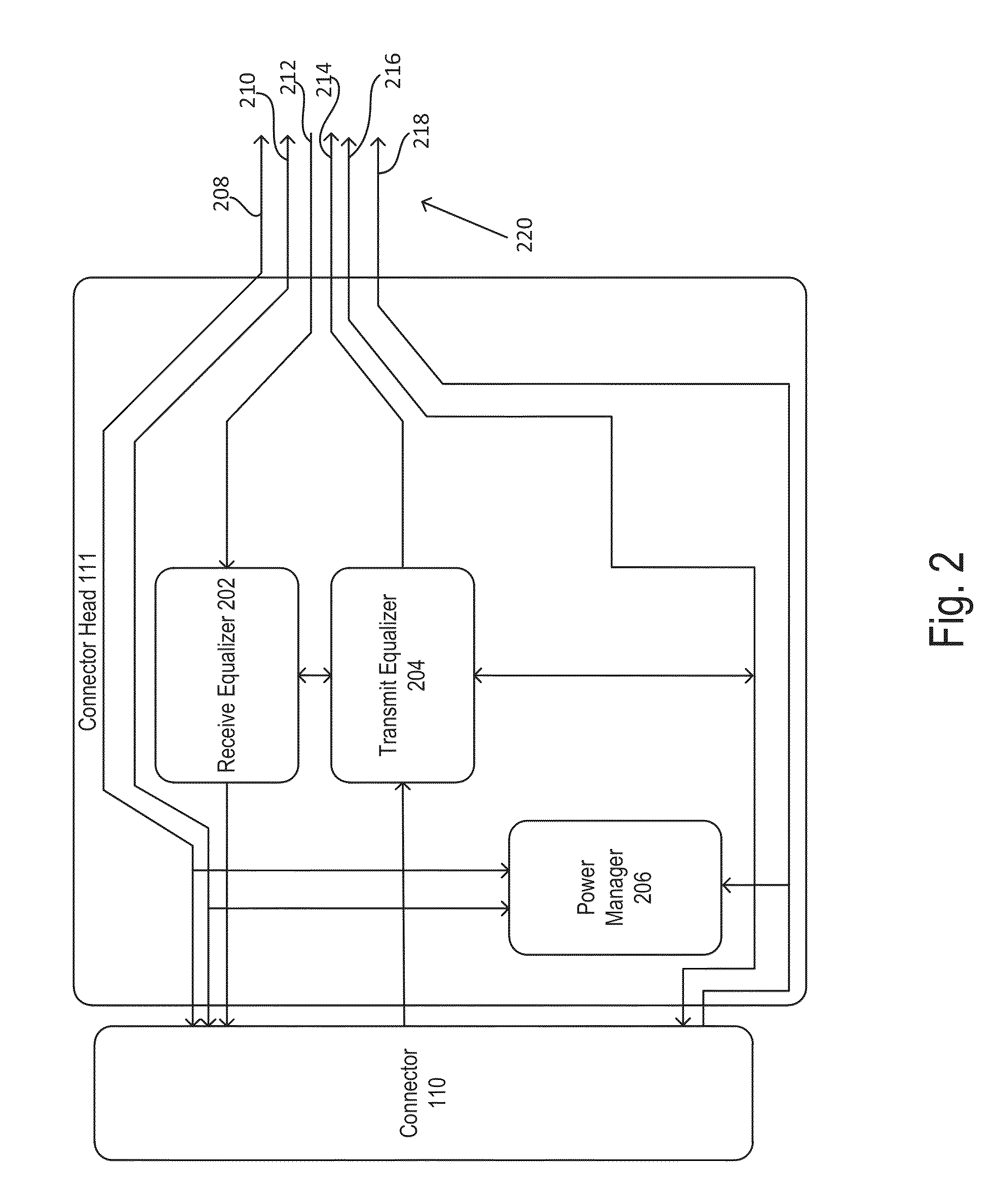
InactiveUS20130202016A1MaximizingReduce decreaseMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationData transmissionMulti rate
Embodiments of a device include a receive multi-rate CDR unit communicatively coupled to a processor, the receive multi-rate CDR configured to receive signals from a cable and perform clock and data recovery on signals and a transmitter multi-rate CDR unit communicatively coupled to a processor, the transmit multi-rate CDR configured to send signals to the cable after performing clock and data recovery on the signals. Embodiments of the cable include a receiver equalizer configured to receive signals from a wire and a transmitter equalizer configured to receive signals from a connector of the cable and configured to transmit an equalized signal to the wire.
Owner:ENSPHERE SOLUTIONS
Devices and methods for specialized machine-to-machine communication transmission network modes via edge node capabilities
ActiveUS20190239048A1Improve rendering capabilitiesImprove efficiencyTransmissionMachine-to-machine/machine-type communication serviceTransport systemEdge node
Disclosed herein are hub devices for a machine-to-machine (M2M) communications network that enables multiple communication modes for data source nodes, the hub comprising a processor, a local connectivity system configured to communicate data with the data source nodes via an interface, a data processing and caching system comprising a local memory and configured to receive and store user-defined data routing and processing functions, prioritize the data based on the user-defined functions; and route the prioritized data to the local memory for storage or to the data transmission system for immediate transmission based on the priority, and a data transmission system configured to dynamically assign an M2M upload mechanism to the routed data selected from: a real-time transmission mechanism, a fixed interval mechanism, a data backhaul mechanism, and a user pull mechanism; and transmit the data to a network backhaul link for delivery to a host point.
Owner:SKYLO TECH INC
Method and a system with distortion compensation
ActiveUS8755694B2Maximize data transfer rateMinimizing and maximizing target value of targetSecret communicationDistortion/dispersion eliminationPre distortionEngineering
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for distortion compensation of signals transmitted via a bidirectional link between a client device and a host device, said method comprising the steps of performing a post-distortion-compensation for an upstream signal received by the host device on said bidirectional link by adjusting post-compensation parameters of a post-compensation unit of said host device and transforming the adjusted post-compensation parameters into pre-compensation parameters of a pre-compensation unit of said host device which performs a pre-distortion compensation for a downstream signal transmitted by said host device via said bidirectional link to said client device.
Owner:ADTRAN NETWORKS SE
Method for managing distributed dynamic spectrums in digital subscriber line uplink system
InactiveCN102752020AMaximize data transfer rateIncrease data transfer rateTelephonic communicationCross-talk reductionDigital subscriber lineFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a method for managing distributed dynamic spectrums in a digital subscriber line uplink system. By utilizing the characteristic that the interference of strong users on weak users is mainly at low frequency, redistribution is performed on the strong subscriber by utilizing bit movement based on bits subjected to iterative water injection predistribution. Due to the fact that each modulator-demodulator maximizes self data transmission rate and neglects crosstalk disturbance on other users when the bits are subjected to the predistribution through an iterative water injection method, the strong users seriously interfere the weak users, the data transmission rate of the weak users is low, and then serious unfairness is caused. According to the method, the bits loaded in low-frequency sub-channels of the strong users are transferred to high-frequency sub-channels as many as possible through the bit movement, so that the crosstalk disturbance is effectively inhibited, the data transmission rate of the weak users is maximized while the requirement of a target data transmission rate of the strong users is met, and the data transmission rate of the digital subscriber line system is increased.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Network file sharing method and system
InactiveUS20060242264A1Improve data transfer rateRelieve loadMultiple digital computer combinationsMemory systemsData transportClient-side
A method for writing file data from client to server which comprises writing file data from a client to a server, wherein the client issues to the server a file transfer proposal that includes the names of a plurality of files to be transferred and attributes of each of the plurality of files. The server determines optimum memory locations for the plurality of files and optimum sequence and size of data transfer and issues to the client a request to transfer the plurality of files in a sequence that is optimized for memory location and minimal number of data transfers, thereby maximizing data transfer rate from the client to the server. Client computer, server computer, and network apparatus that are configured to implement the method are also disclosed.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
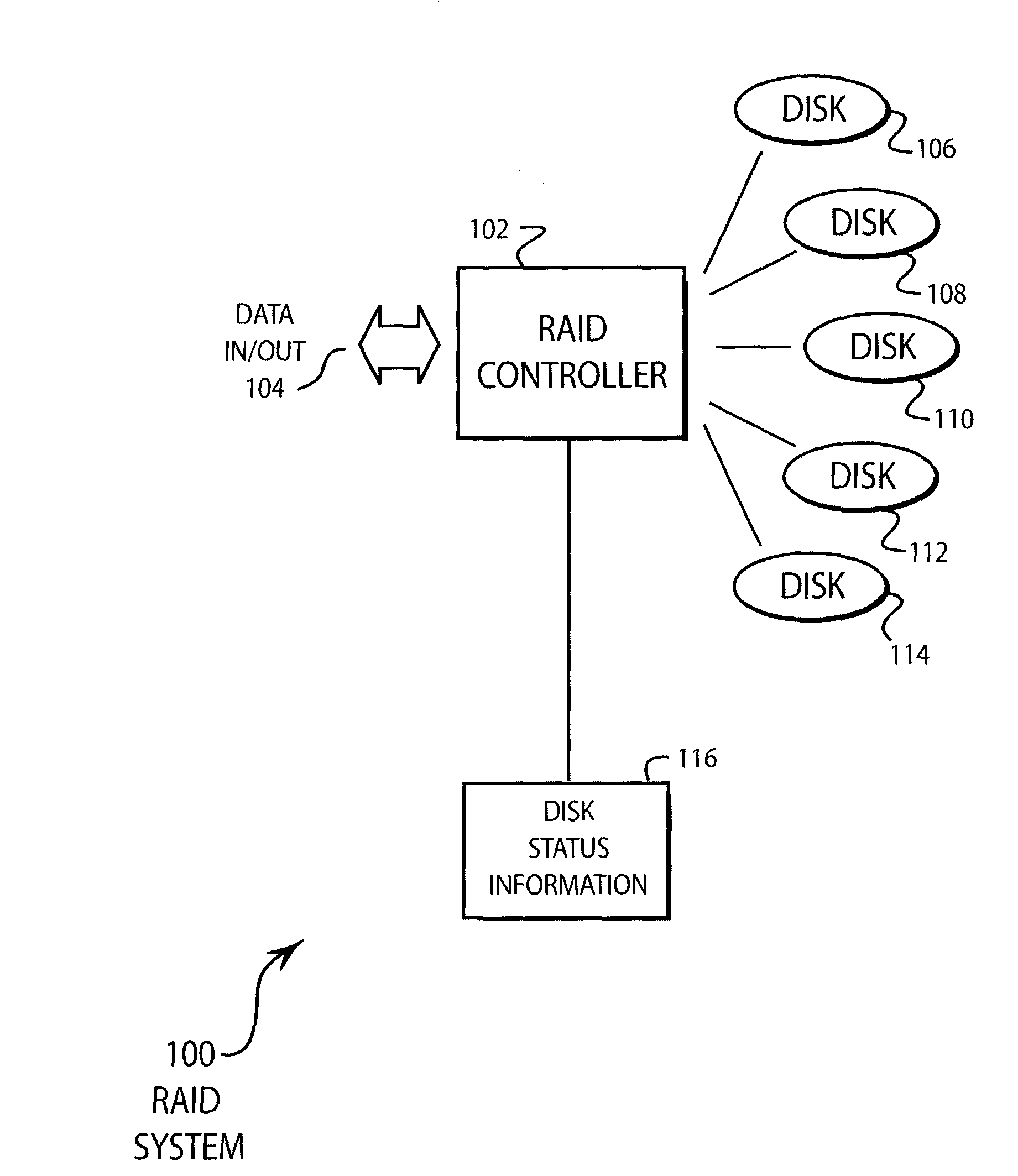
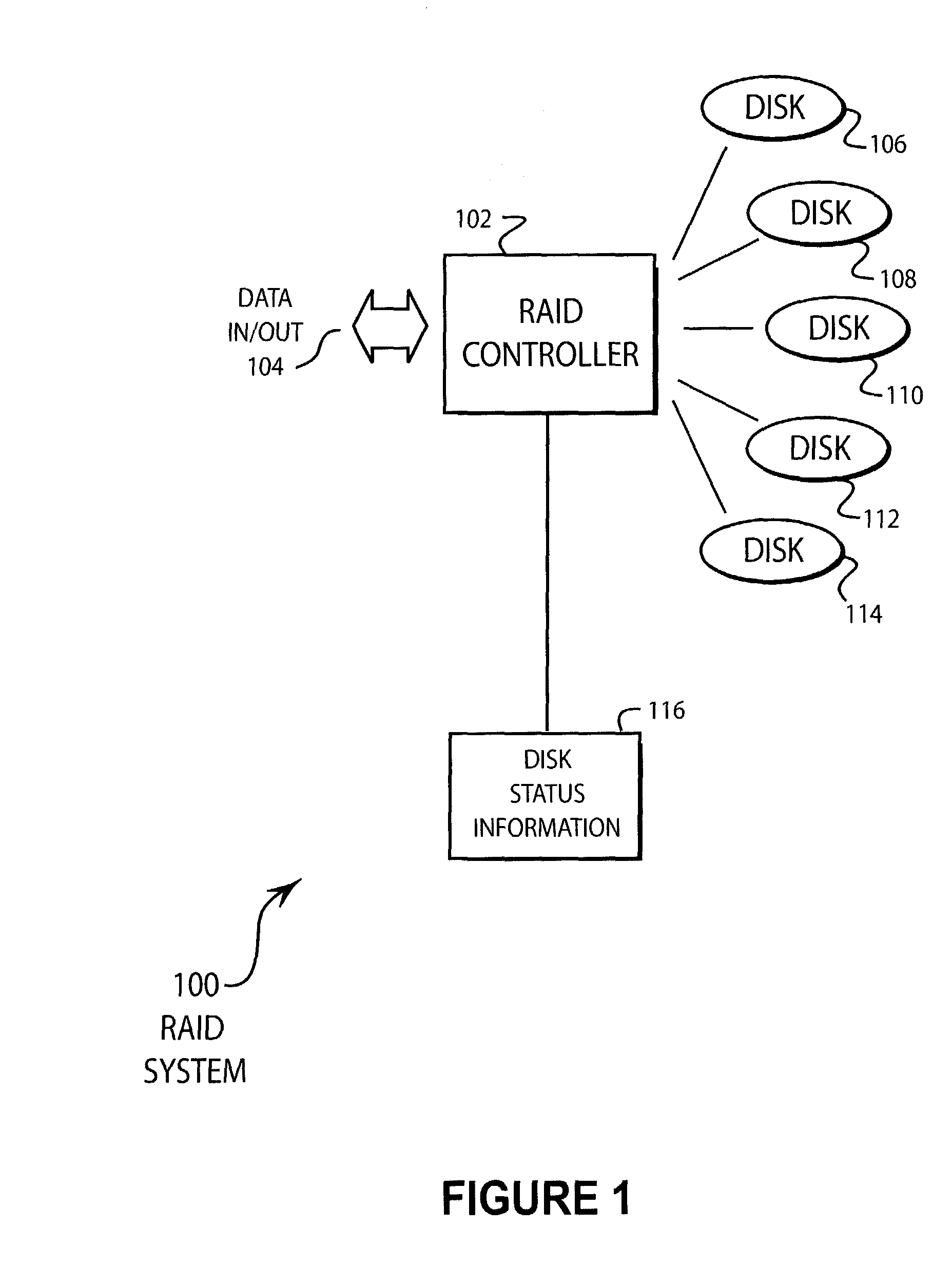
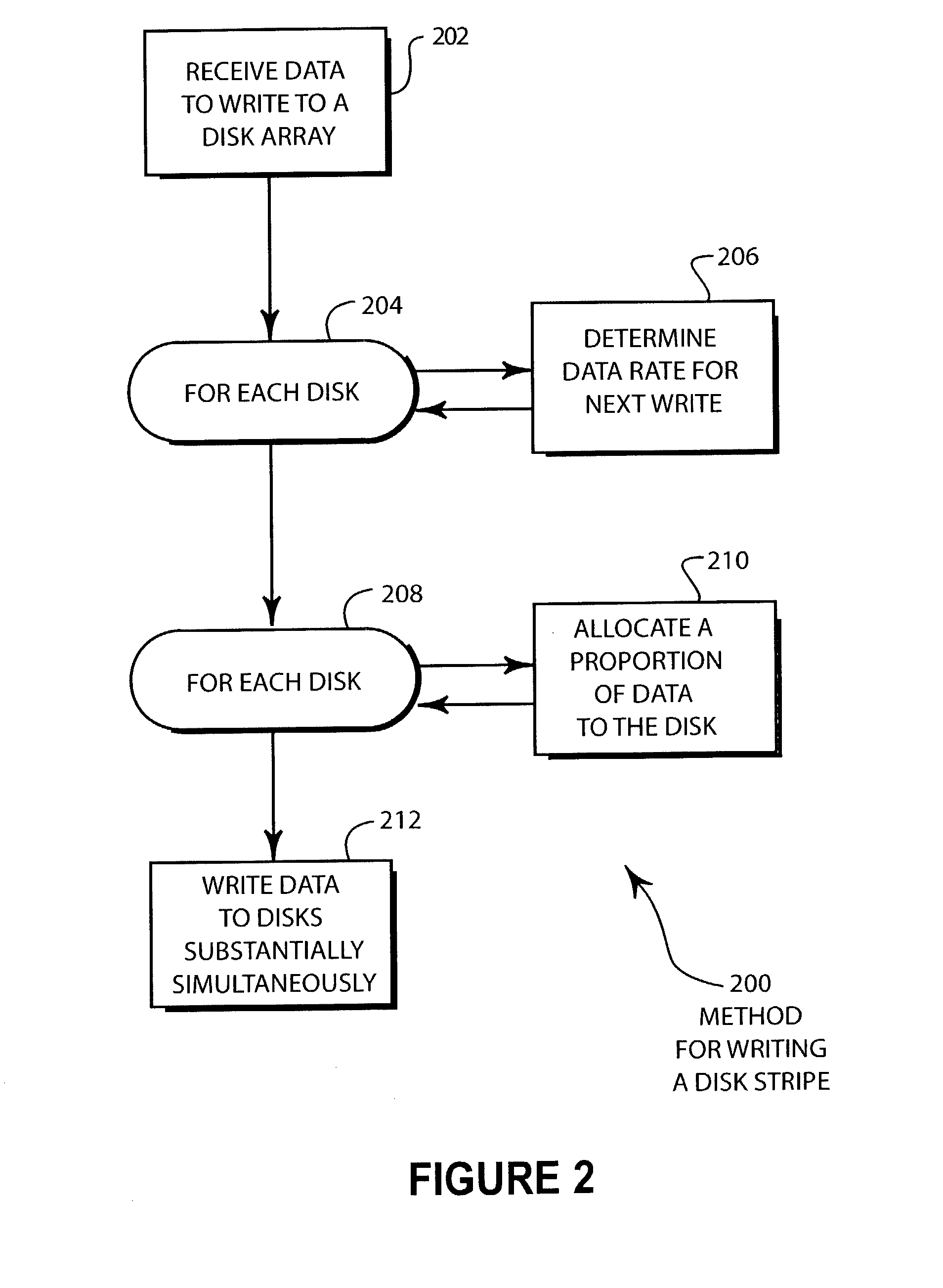
Method for minimizing RAID 0 data transfer rate variability
ActiveUS7073023B2Minimum data transfer rateMaximize data transfer rateInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsData transmissionMagnetic disks
A RAID 0 disk array has an optimizing algorithm for allocating the amount of data stored to each drive in a disk array. The algorithm allocates a proportion of the data for each stripe to the various disk drives based at least in part on the data transfer rate for each drive. The disk array may be constructed such that about half of the disk drives write to the outside tracks of the drives while the remaining disks write to the inside tracks. Using the algorithm, the minimum data transfer rate for the disk array may be maximized.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Improvements in data storage and manipulation
InactiveCN101317219AMaximize data transfer rateTransistorMultiplex system selection arrangementsData retrievalData storing
A data storage device comprises: a data member comprising means for storing data on a surface thereof; and a data retrieval member. The data retrieval member comprises: a plurality of heads for reading data from the data member; and a plurality of storage buffers each arranged to store data read from one of more of said heads. The retrieval member is arranged so as to output the contents of a plurality of said storage buffers sequentially. This allows fast and efficient reading of the data stored. Also disclosed is a telecommunications switch which may employ such a storage device. The switch dynamically assigns data packets to nodes as an output path becomes available to minimise queuing delays.
Owner:查尔斯·F·J·巴恩斯 +1
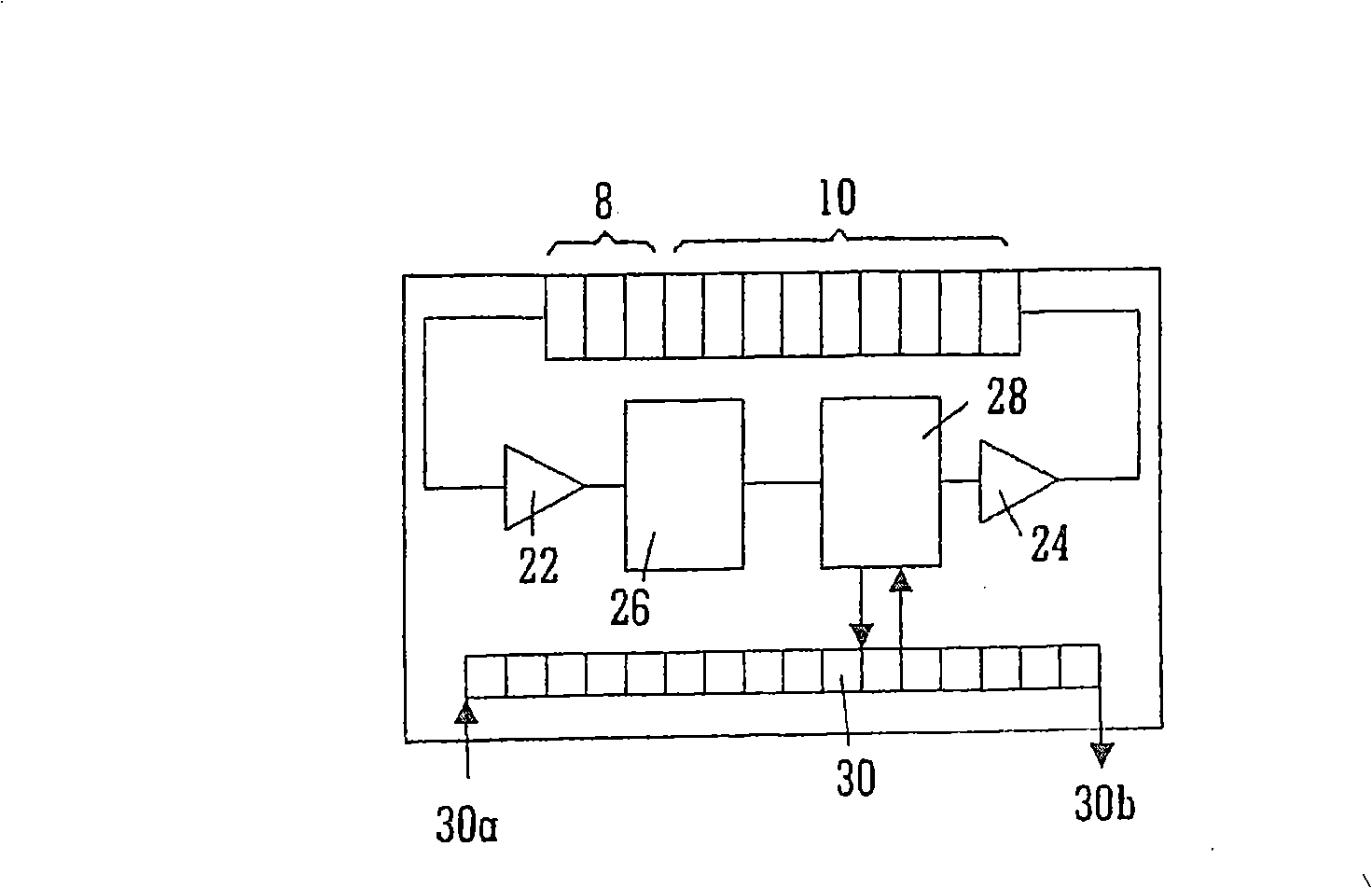
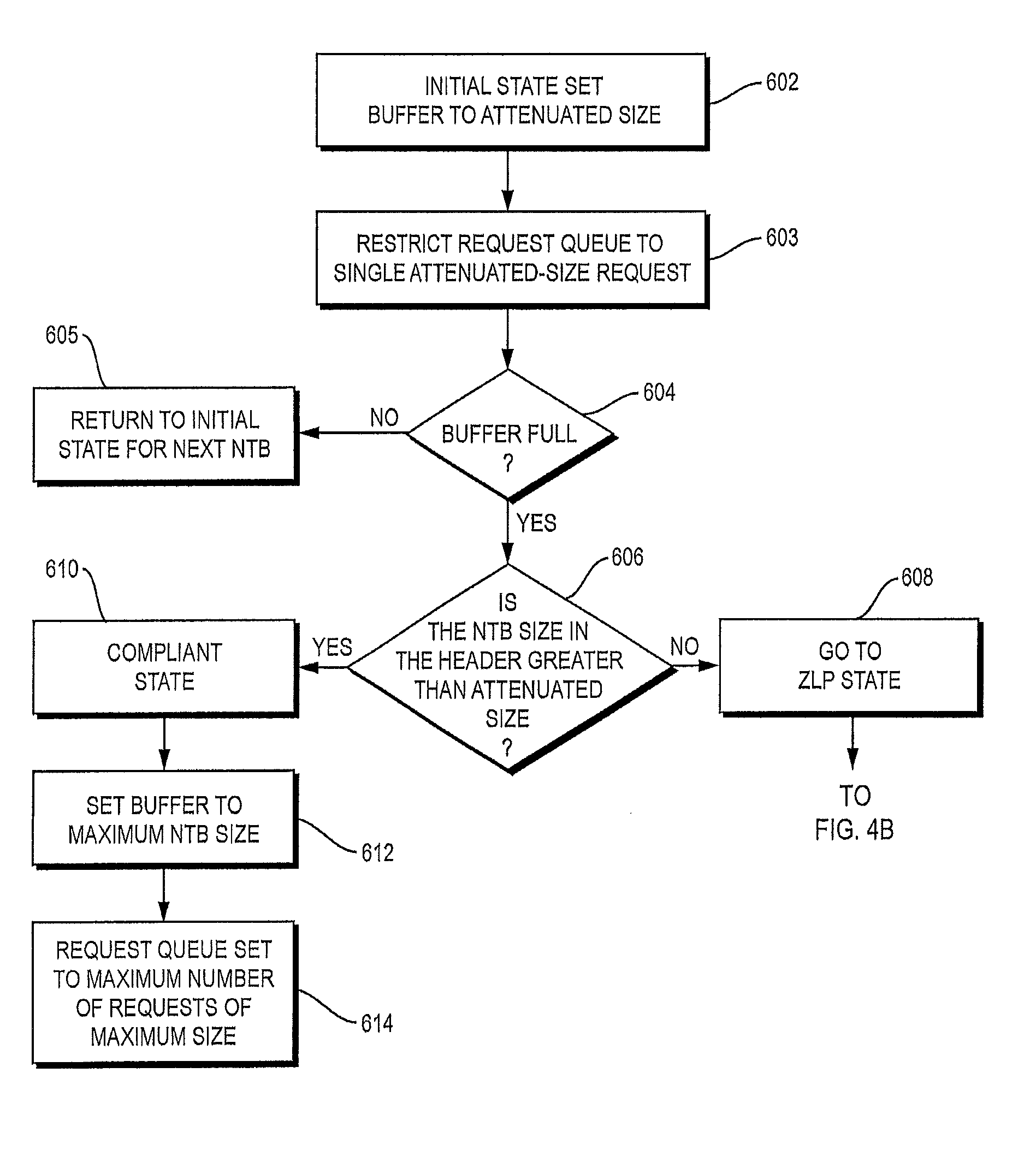
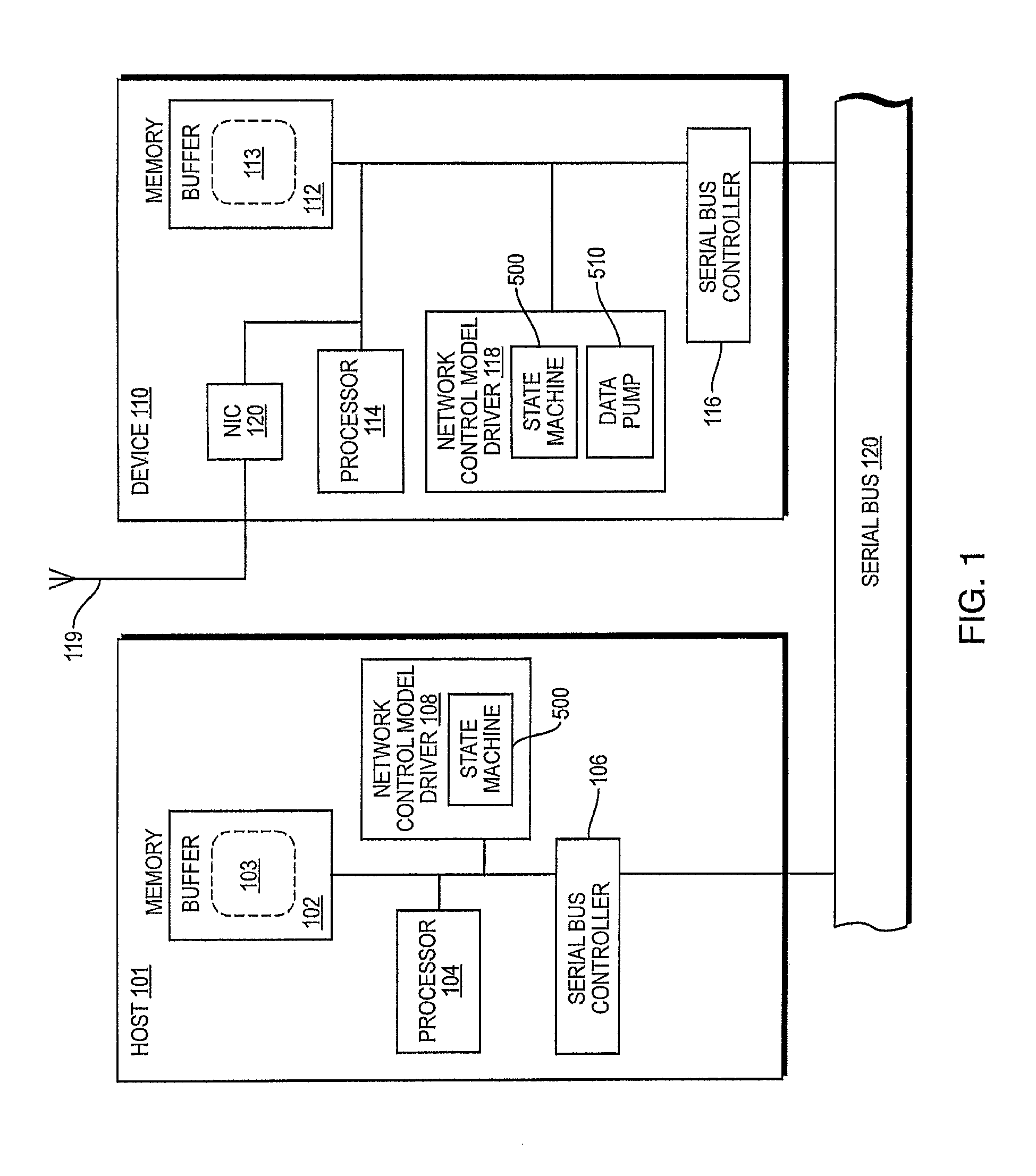
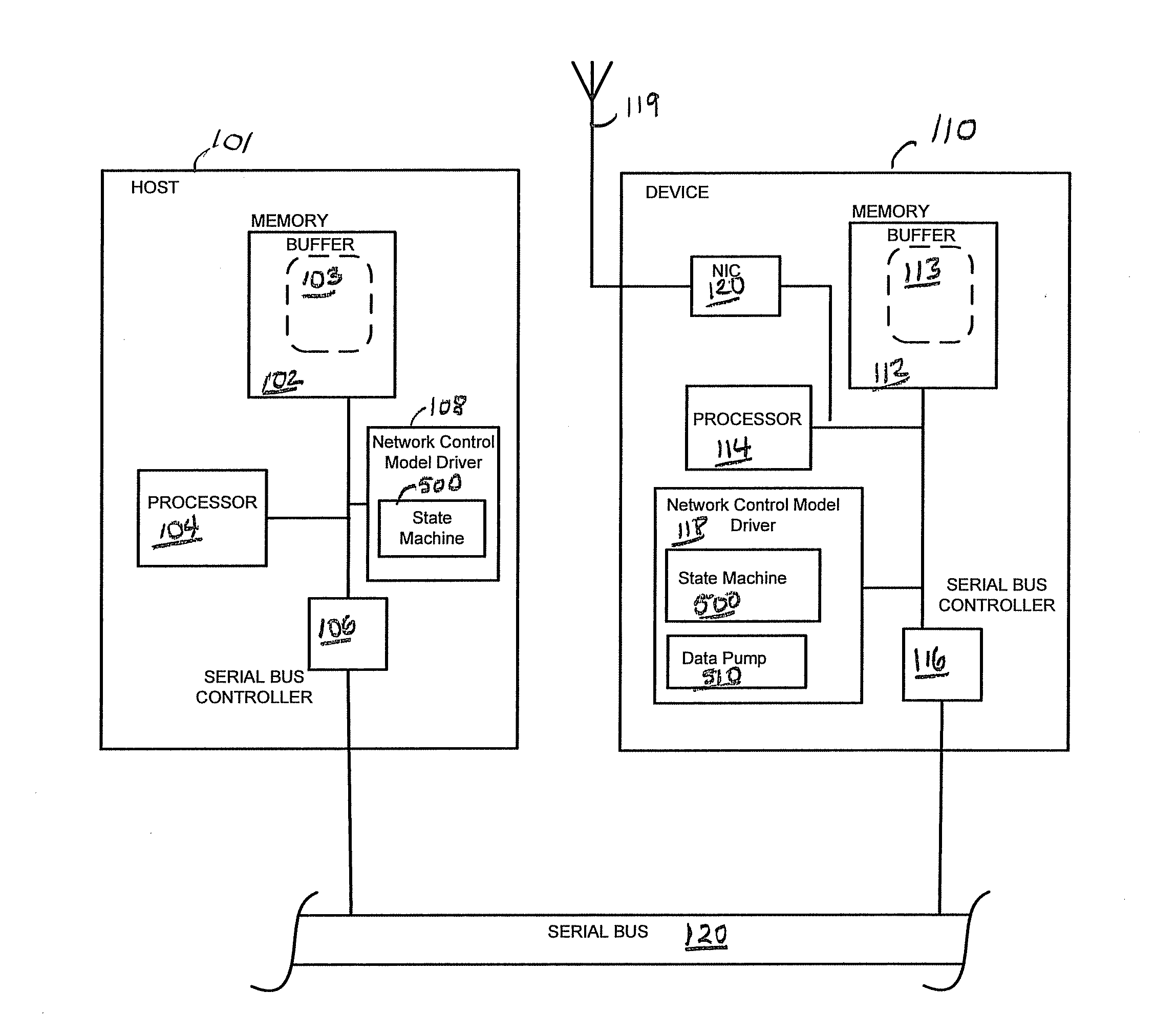
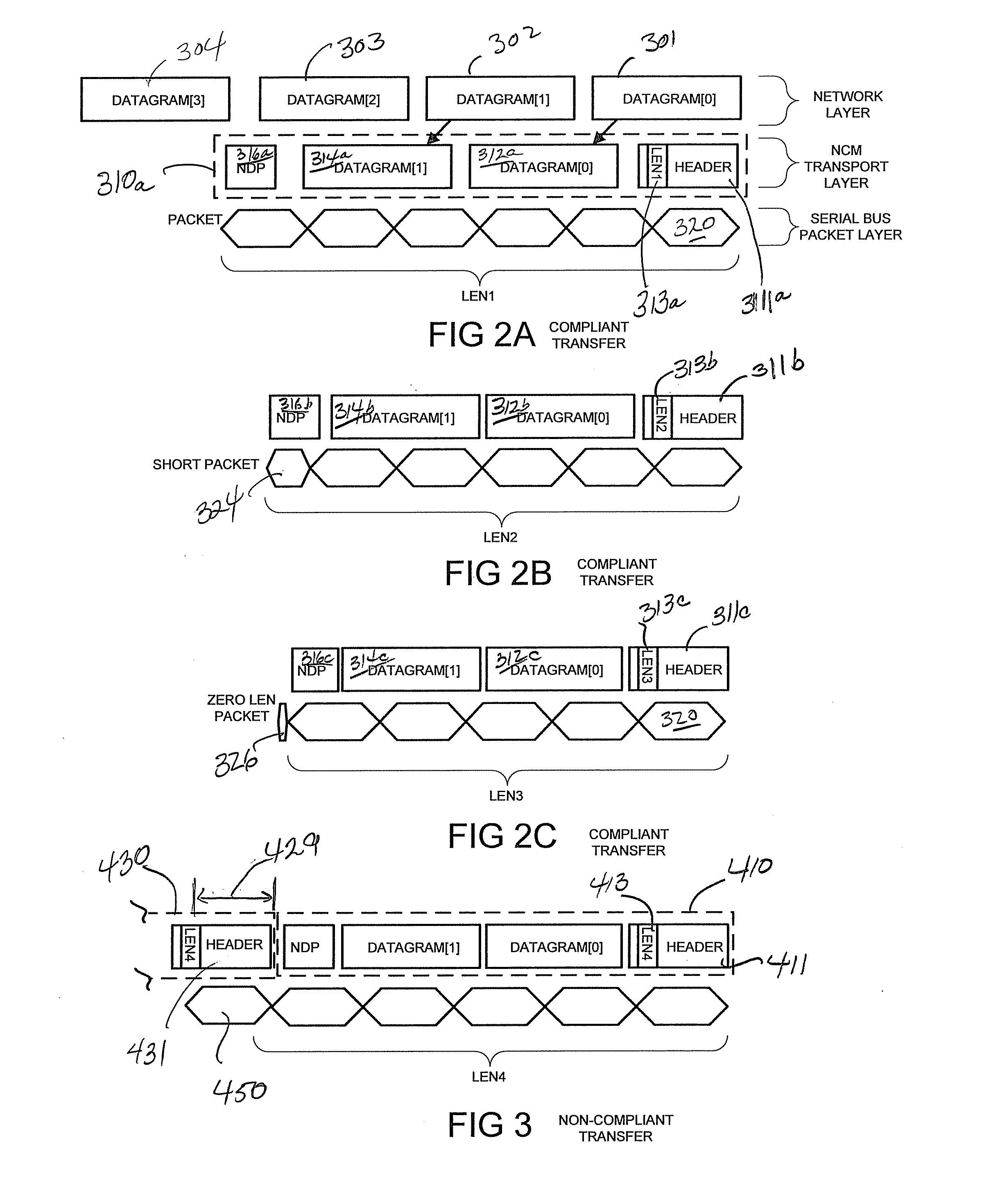
Network control model driver
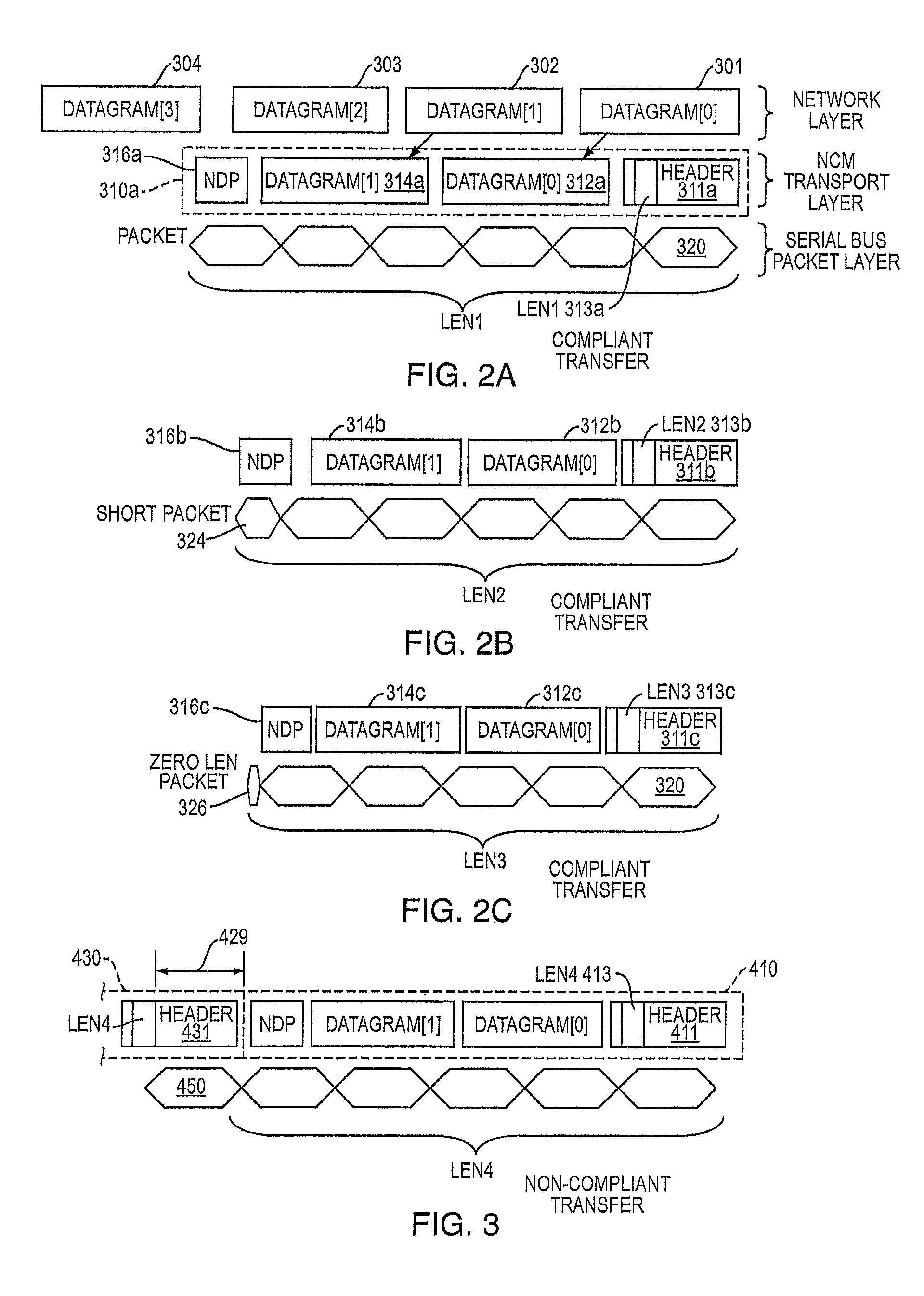
ActiveUS8904062B2Request queueMaximize data transfer rateData switching networksInput/output processes for data processingNetwork controlComputer science
A method and apparatus of operating a Universal Serial Bus device to determine if a host sending Network Control Model Transfer Blocks (NTBs) is compliant with end of transfer rules for NTBs and to then determine appropriate operations at the device to complete transactions with a non-compliant host.
Owner:MCCI CORP
Efficient rank extraction method in MIMO receiver and apparatus therefor
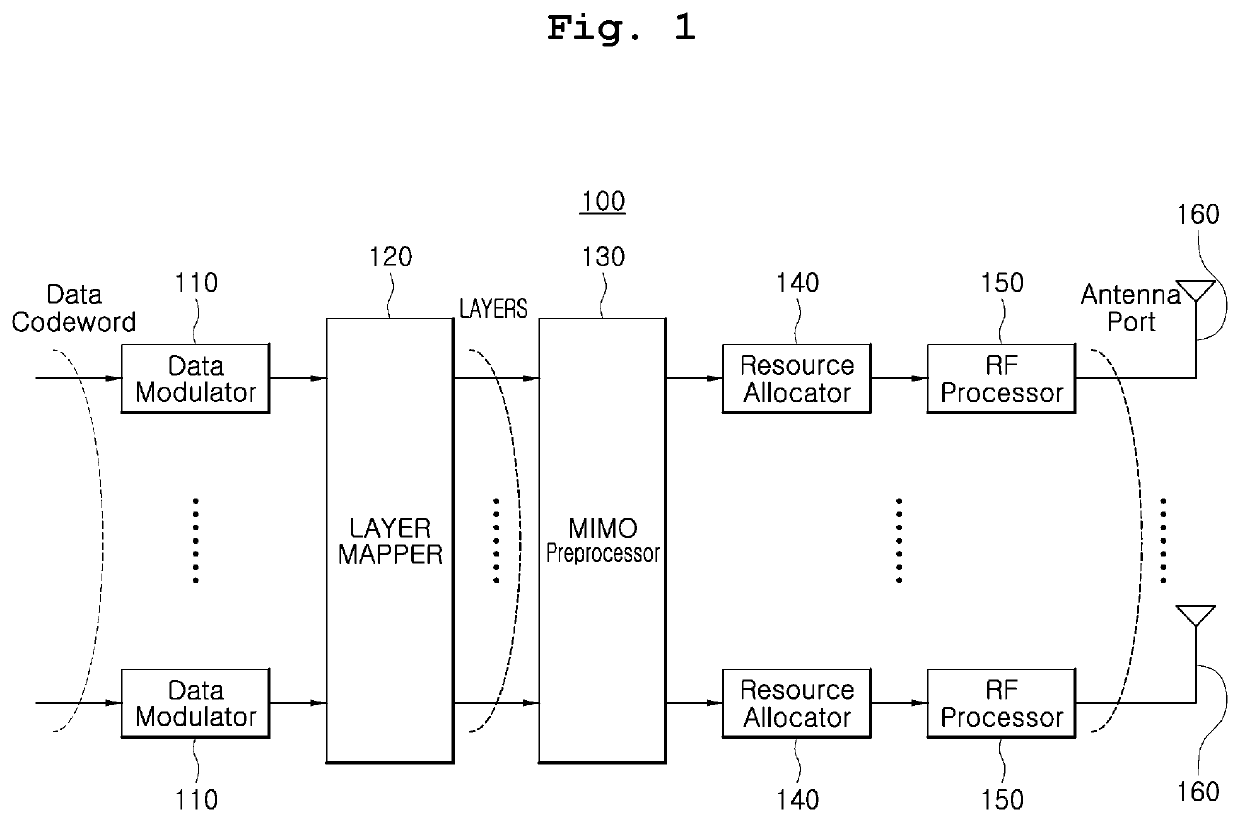
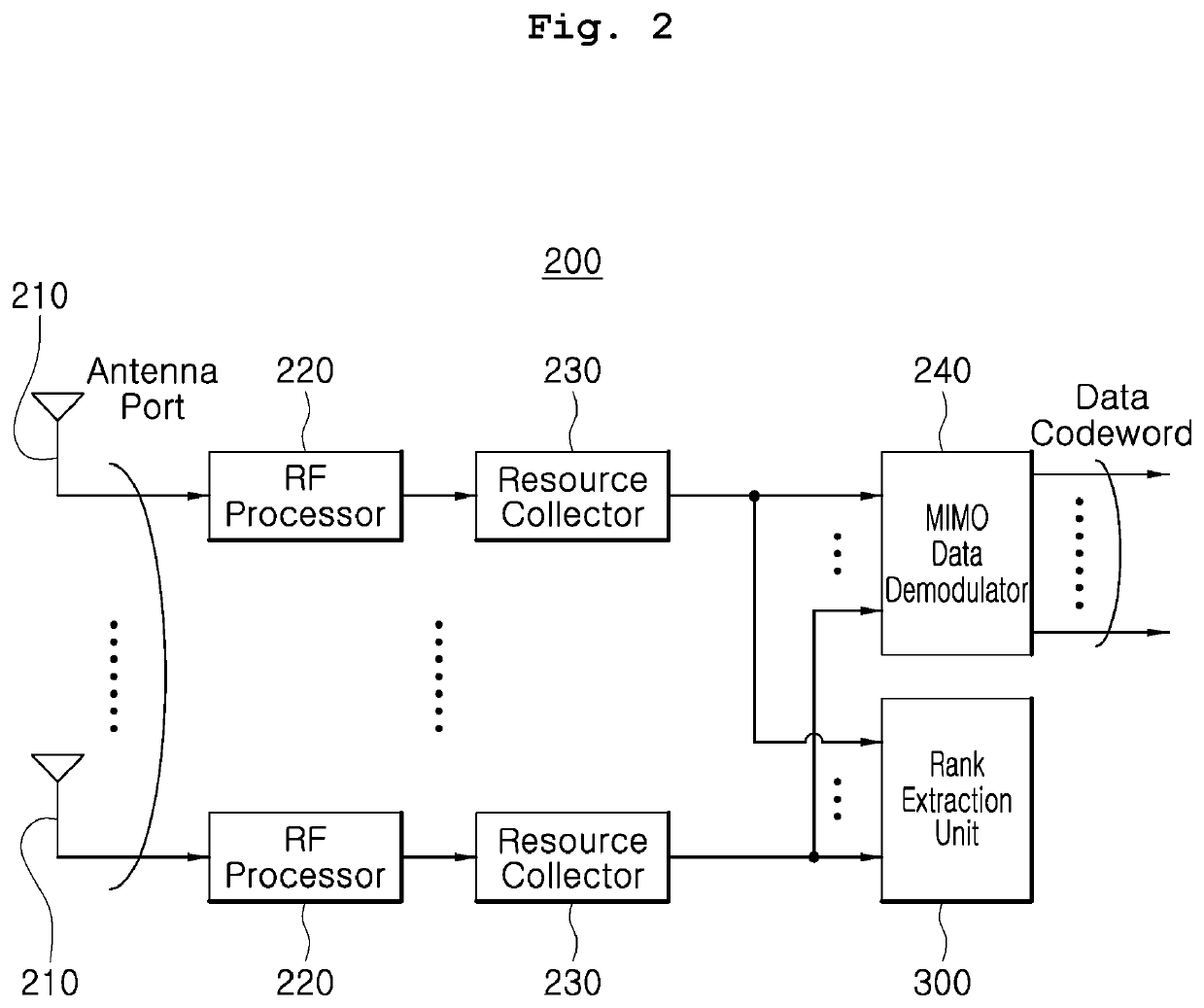
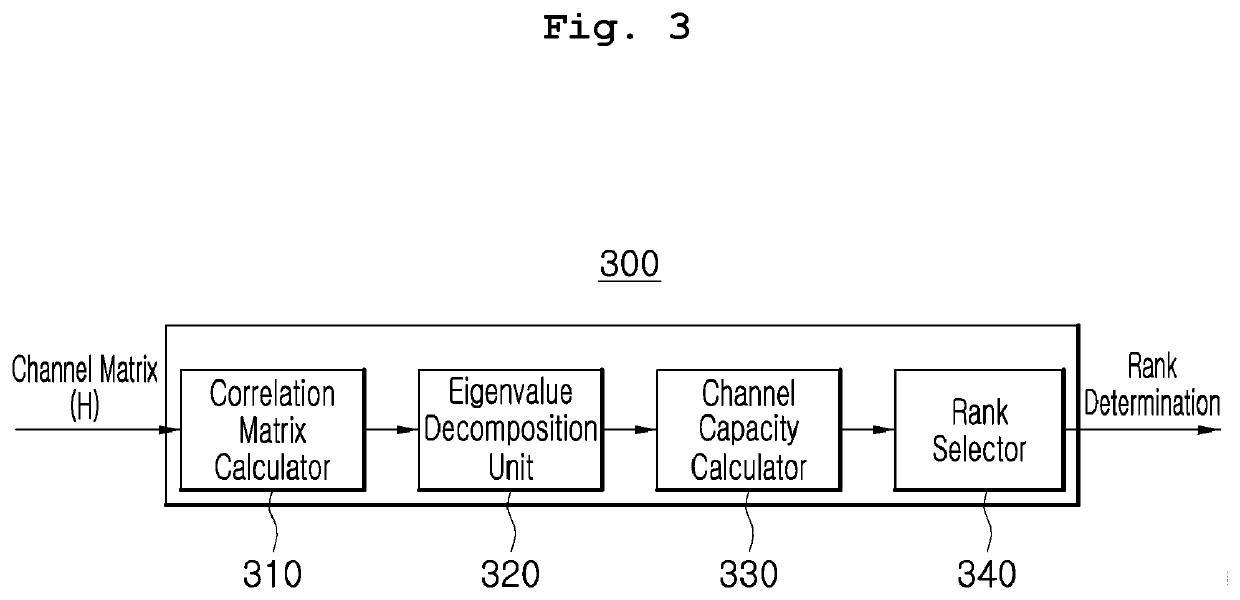
ActiveUS20200204232A1Reduce the amount of calculationMaximize data transfer rateRadio transmissionMulti inputControl theory
The present invention relate to a method of extracting an optimum rank without considering a precoding matrix indicator (PMI) in a multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) receiver, the method including calculating a correlation matrix from a MIMO channel matrix between a base station antenna and an MIMO receiver antenna; obtaining an eigenvalue from the correlation matrix; calculating channel capacity for each rank on the basis of the obtained eigenvalue; and selecting a rank corresponding to a channel capacity having a maximum value among the calculated channel capacities for each rank as an optimum rank.
Owner:GCT RES
Virtual USB flash memory storage device with PCI express interface, controller and method thereof
ActiveUS20070214306A1Maximize total data transmittedMaximize data transfer rateComponent plug-in assemblagesMemory systemsMicrocontrollerPCI Express
A virtual universal serial bus (USB) flash memory storage device with a peripheral component interconnect (PCI) Express interface including a microcontroller connected separately to a flash memory and a PCI Express connecting interface, and the microcontroller has a flash memory interface, a PCI Express interface and a virtual USB module and the virtual USB module includes a USB host and a USB device. If a host gives a USB instruction for saving or reading to the storage device, the USB instruction will be sent to and executed by the virtual USB module and the required data processing for saving or reading will be completed through the flash memory interface and the flash memory. The data in the storage device can be transmitted with a PCI Express standard transmission rate, and the host considers the storage device as a USB device instead of a pure PCI Express device.
Owner:PHISON ELECTRONICS
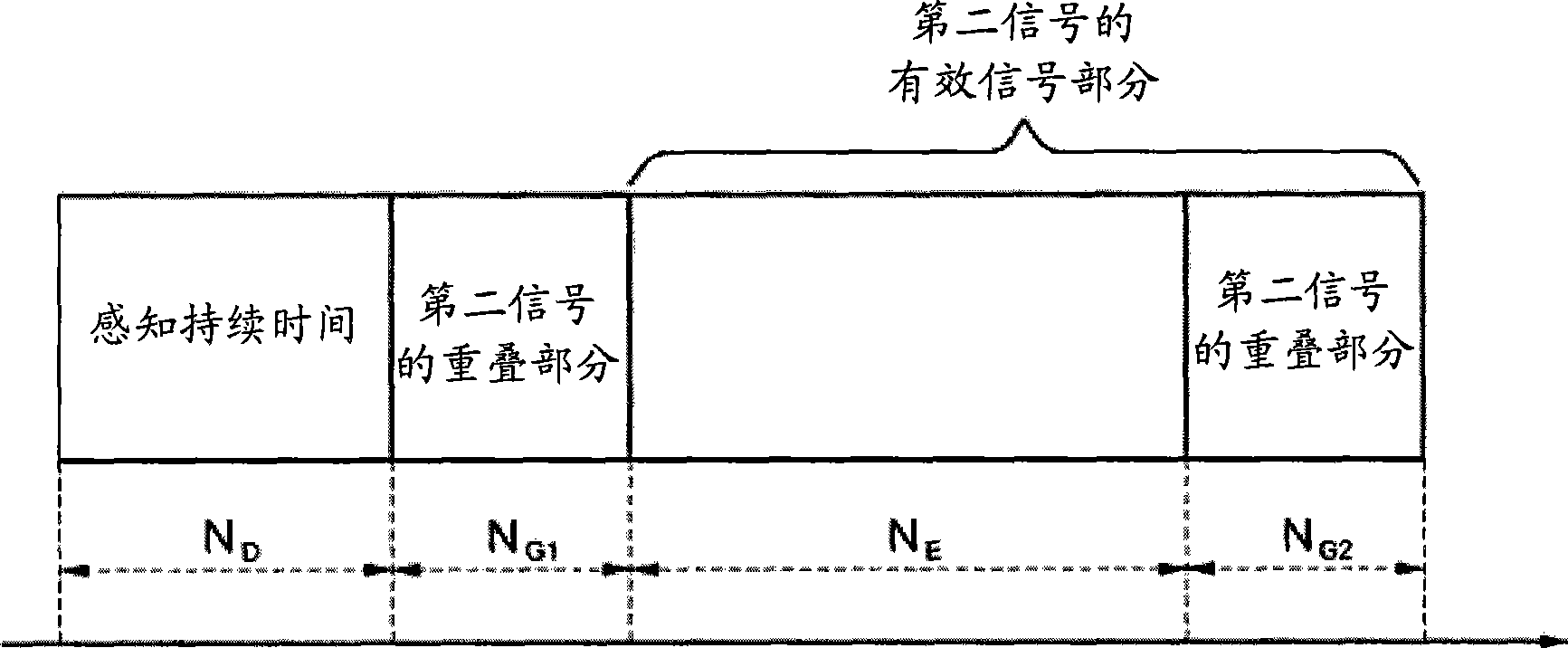
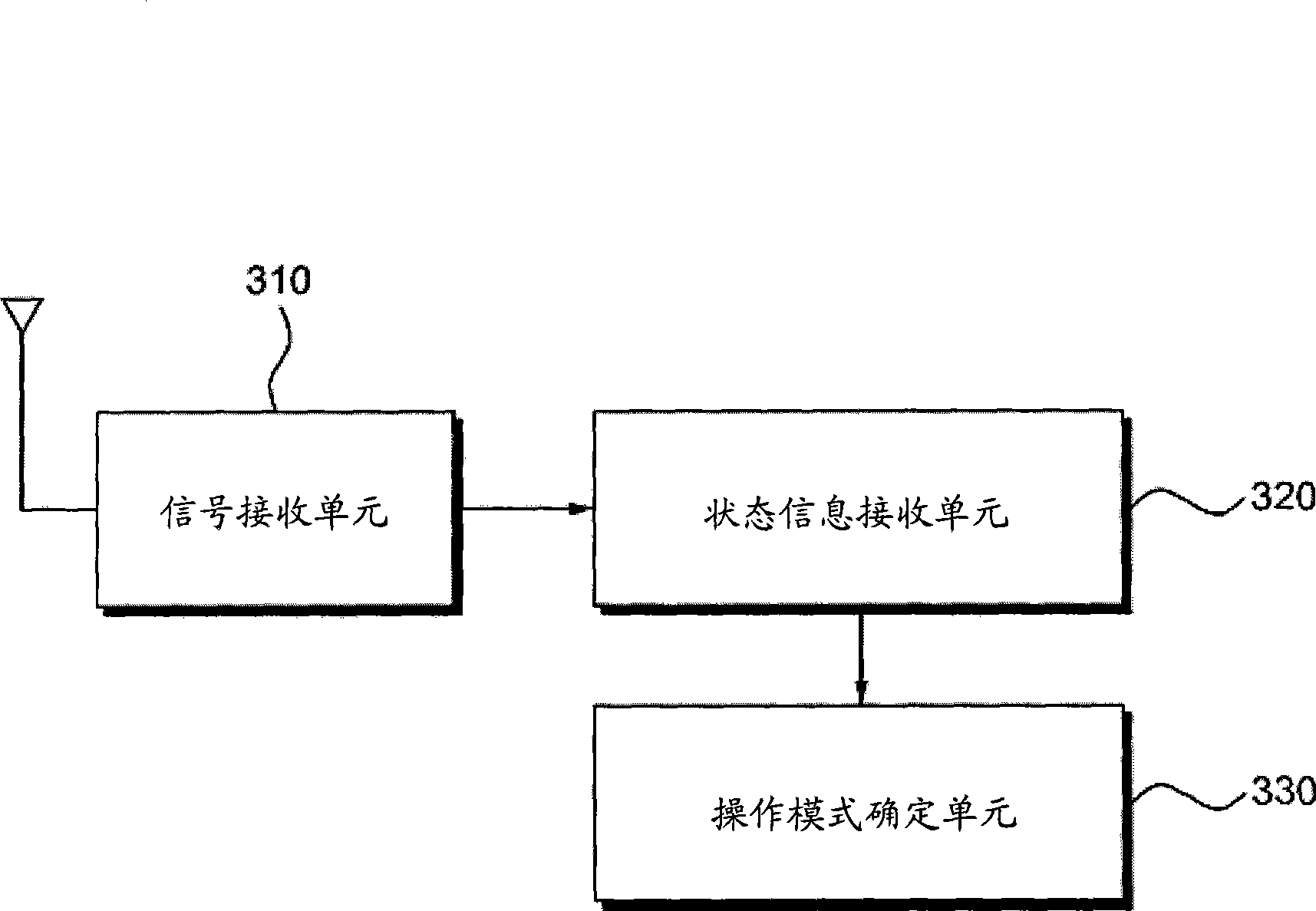
Cognitive radio communication device using overlapped signal and method thereof
InactiveCN101426273AMaximize data transfer rateEasy to useTransmission monitoringRadio transmission for post communicationTelecommunications equipmentGenerating unit
Disclosed is a cognitive communication device. A cognitive radio communication device includes a signal receiving unit that receives a first signal of a primary network and a second signal of a secondary network, the second signal including two or more overlapped portions where the same signal is repeated; a status information generating unit that uses the sameness between signals included in the overlapped portions to generate status information related to whether the first signal exists; and an operational mode determining unit that determines a communication operational mode of a communication device belonging to the secondary network, on the basis of the status information.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUNDATION YONSEI UNIV
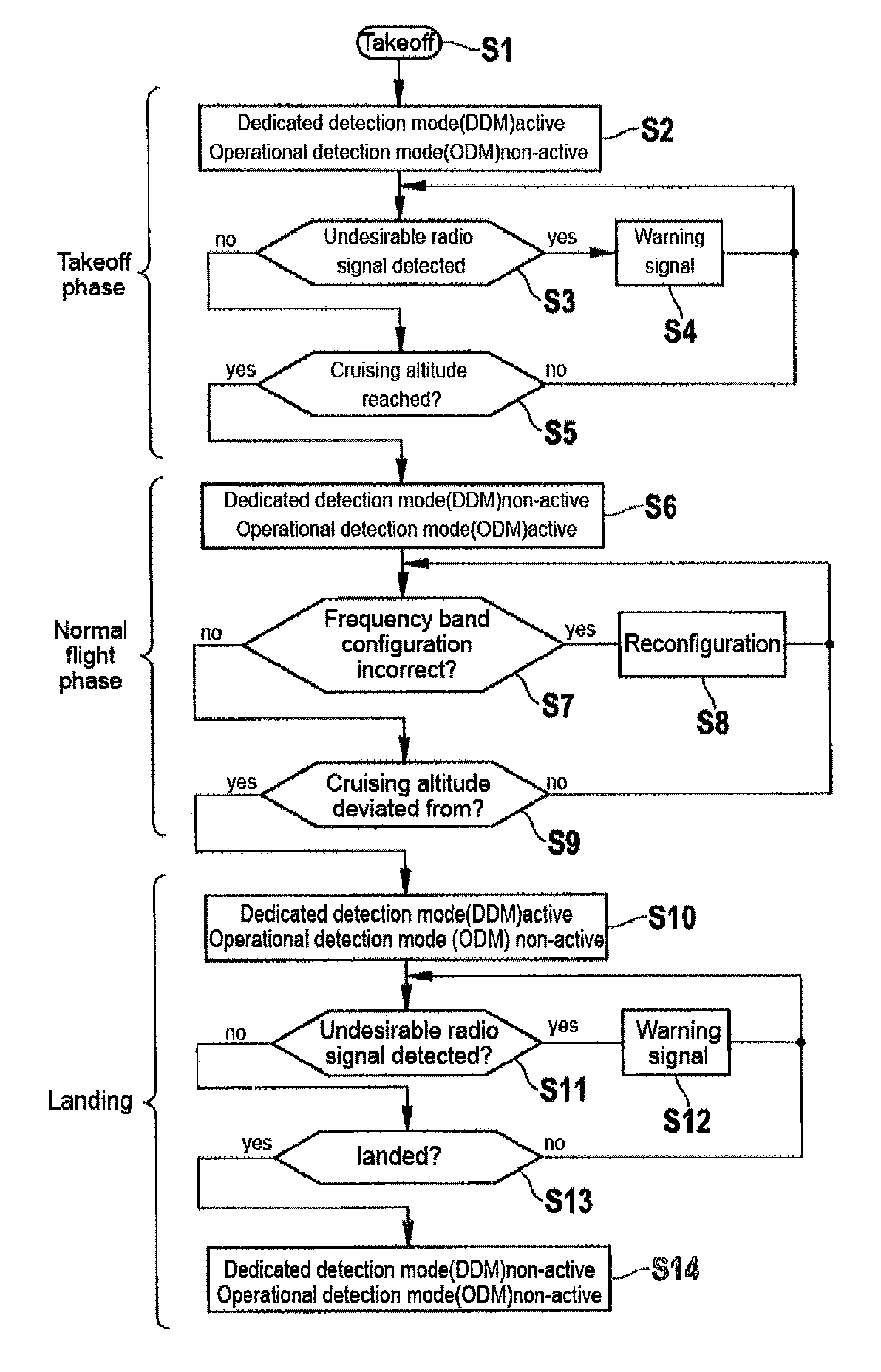
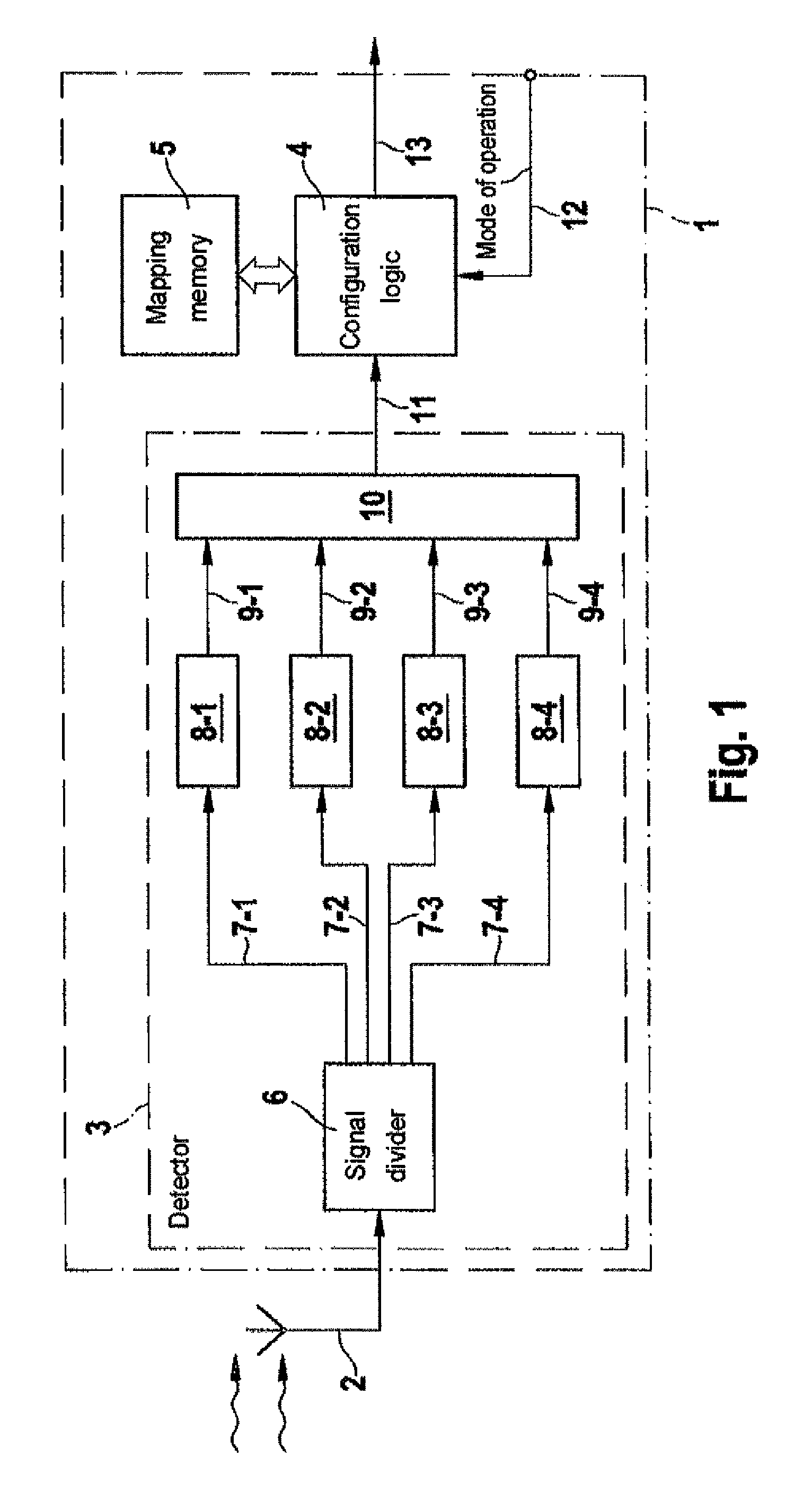
Apparatus and a method for detecting a communication channel
ActiveUS9369197B2Maximize total data transmittedMaximize data transfer rateRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesEngineeringWide band antenna
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Telecommunications protocol with PID control of data transmission rate
ActiveUS9185043B2Maximize useMaximize data transfer rateMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksData compressionTransmitter
A computer data transmission system is provided with proportional-integral-derivative (PID) control over a data transmission rate so as to maximize use of available bandwidth of a datagram-based network. A data channel and a separate feedback channel are established between the sender and receiver units of the system. The sender unit coupled to the data and feedback channels sends datagrams over the data channel to the receiver continuously until a source of data is exhausted or paused by the receiver unit. The receiver unit sends acknowledgment messages over the feedback channel to the sender unit at predetermined intervals. A PID controller in the sender unit uses the information provided in the acknowledgment messages to track unsuccessfully transmitted datagrams and to adapt the data transmission rate to any changing network transfer conditions. In particular, the rate of datagram loss may be used as a PID process variable to control an inter-datagram delay of the sender. There may also be absolute speed and transmission rate acceleration / deceleration limits constraining the PID control. PID control may also be adapted for data compression control, datagram block sizes, and degree of redundancy in the datagrams sent.
Owner:SARATOGA DATA SYST
Network control model driver
ActiveUS20130007313A1Maximize data transfer rateRequest queueTransmissionInput/output processes for data processingNetwork controlEmbedded system
A method and apparatus of operating a Universal Serial Bus device to determine if a host sending Network Control Model Transfer Blocks (NTBs) is compliant with end of transfer rules for NTBs and to then determine appropriate operations at the device to complete transactions with a non-compliant host.
Owner:MCCI CORP
A flexible data transmission system based on intelligent collaborative network
ActiveCN108600102BAvoid congestionMaximize data transfer rateData switching networksPathPingNetwork topology
The flexible data transmission system based on the intelligent collaborative network according to the present invention includes a resource management unit and a network component unit. The resource management unit includes a network state perception module, a network state measurement module and a flexible transmission module. The flexible transmission module is based on the network state perception module. The obtained network topology status and network resource update status, as well as the maximum available bandwidth and delay information of the network status link measured by the network status measurement module, calculate the K shortest transmission paths, and determine the optimal transmission path. Under the centralized and unified control of the intelligent collaborative network control plane, the present invention perceives the network status and network component behavior, and combines parameters such as routing hops, remaining bandwidth, and link delay to determine the optimal transmission path to meet the dynamics of service resources. Adaptation and transmission, improve data transmission reliability, network throughput, resource utilization, link load balancing, etc. to make up for the shortcomings of the shortest route method.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Uplink resource allocation method and cognitive small cell network system for executing same
ActiveUS10524211B2Maximize data transfer ratePower managementConnection managementPreference relationUplink transmission
Owner:JOLLY SEVEN SERIES 70 OF ALLIED SECURITY TRUST I
Electronic device comprising antenna
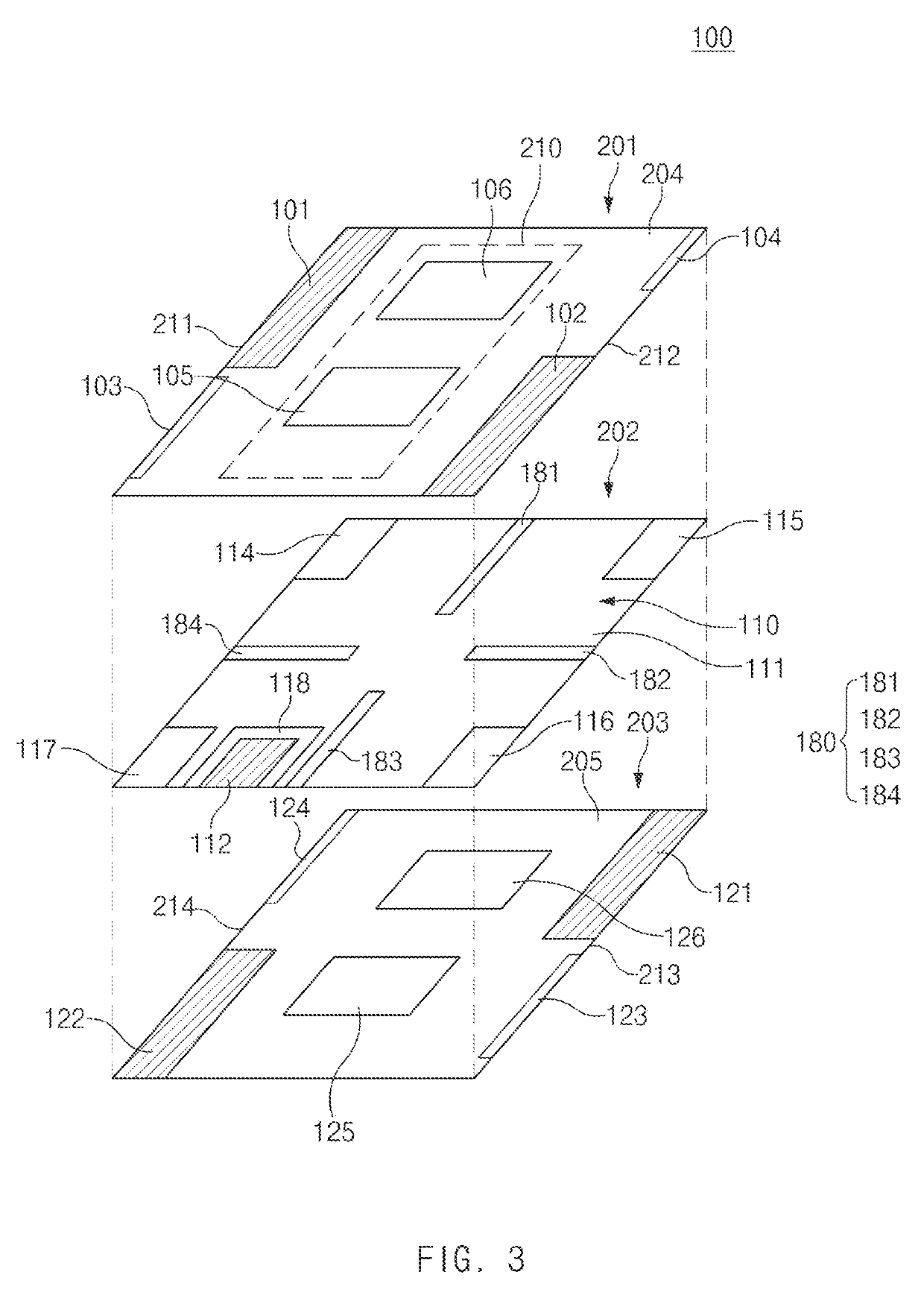
ActiveUS10411335B2Efficiently in vehicleReduce electromagnetic mutual couplingSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringCommunication circuits
An antenna assembly in a vehicle is provided. The antenna assembly includes a first plane including a first edge and a second edge extending in parallel to each other in a first direction, a second plane spaced apart from the first plane that overlaps the first plane and including a third edge extending along the first edge, and a fourth edge extending along the second edge, a non-conductive layer interposed between the first plane and the second plane, and a plurality of wireless communication circuits electrically connected to the antenna assembly, wherein the first conductive pattern and the second conductive pattern are positioned diagonally at opposing corners with each other when viewed from above the first plane, and wherein the third conductive pattern and the fourth conductive pattern are positioned diagonally against each other without overlapping with the first and second conductive patterns, when viewed from above the first plane.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
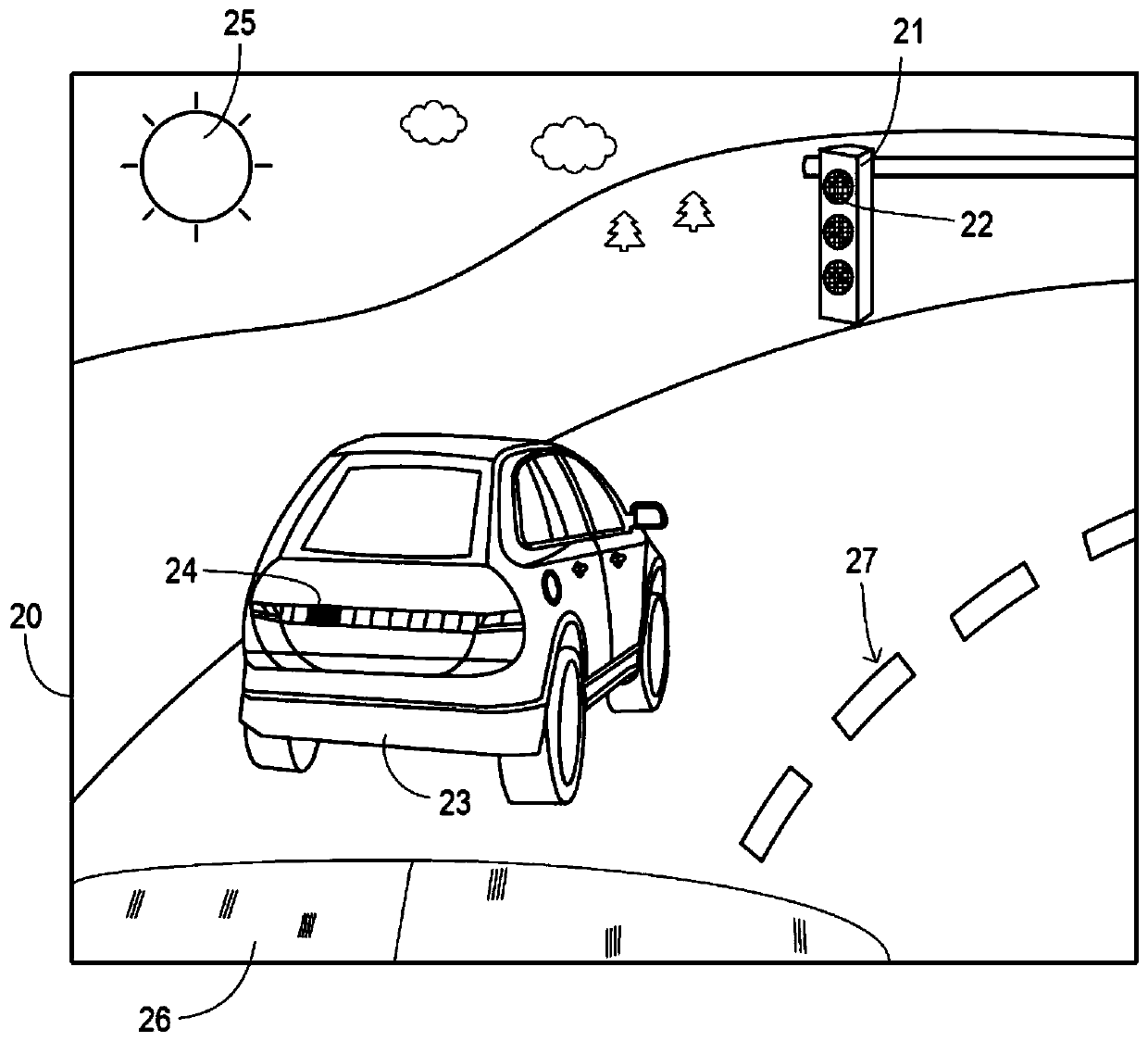
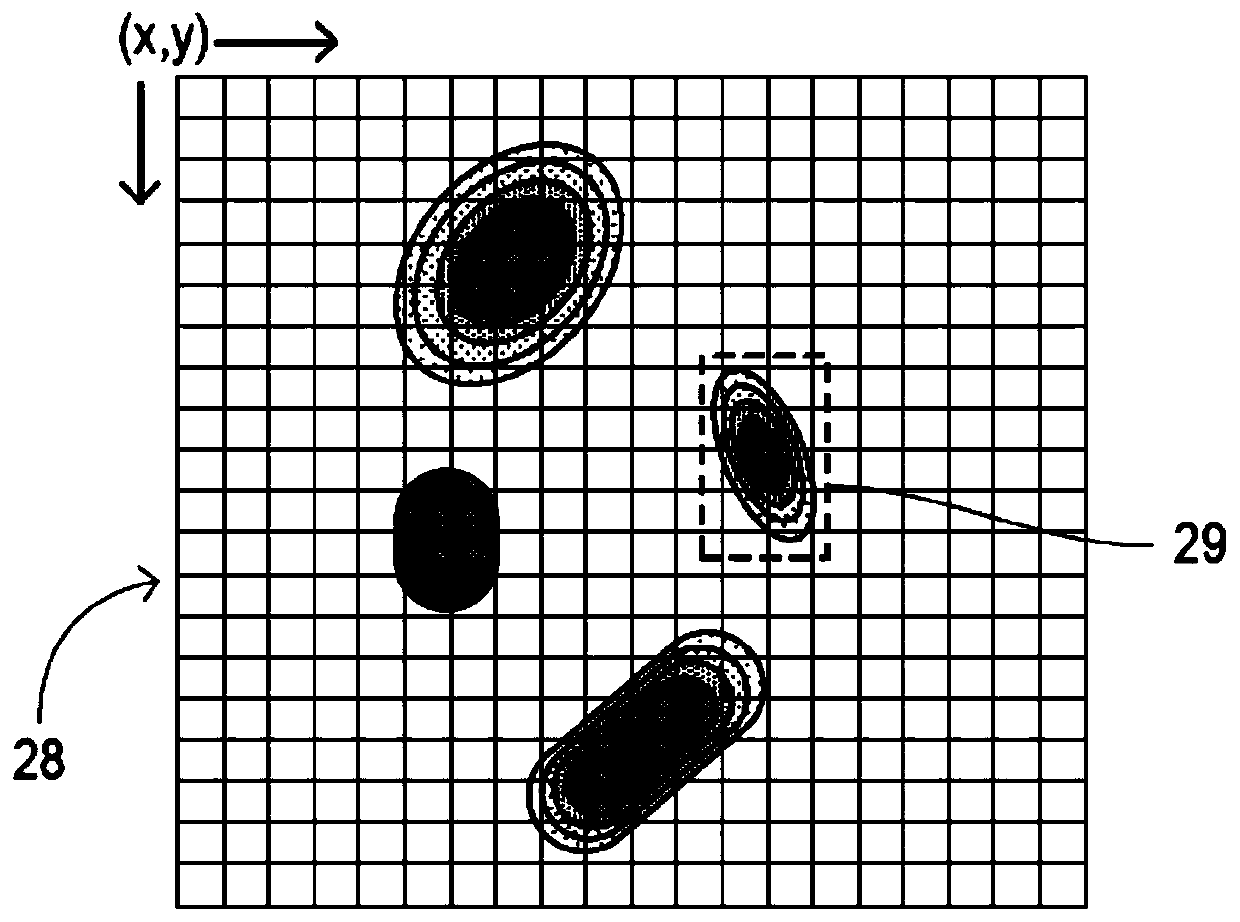
Detection of visible light communication sources over high dynamic range
PendingCN110557574AIncrease frame rateHigh image capture rateTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLed arrayLight signal
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com