Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40results about How to "Large amount of data processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
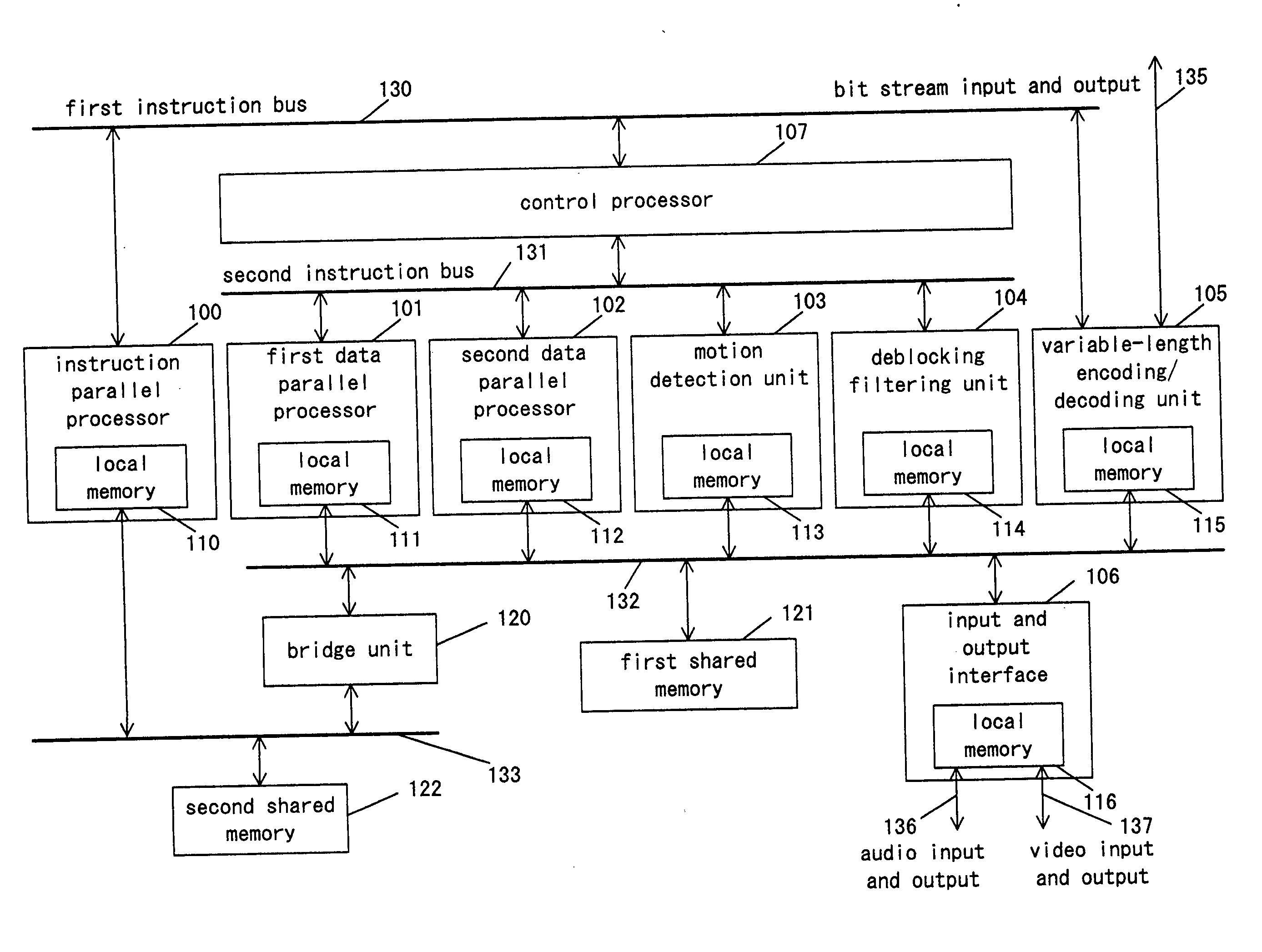
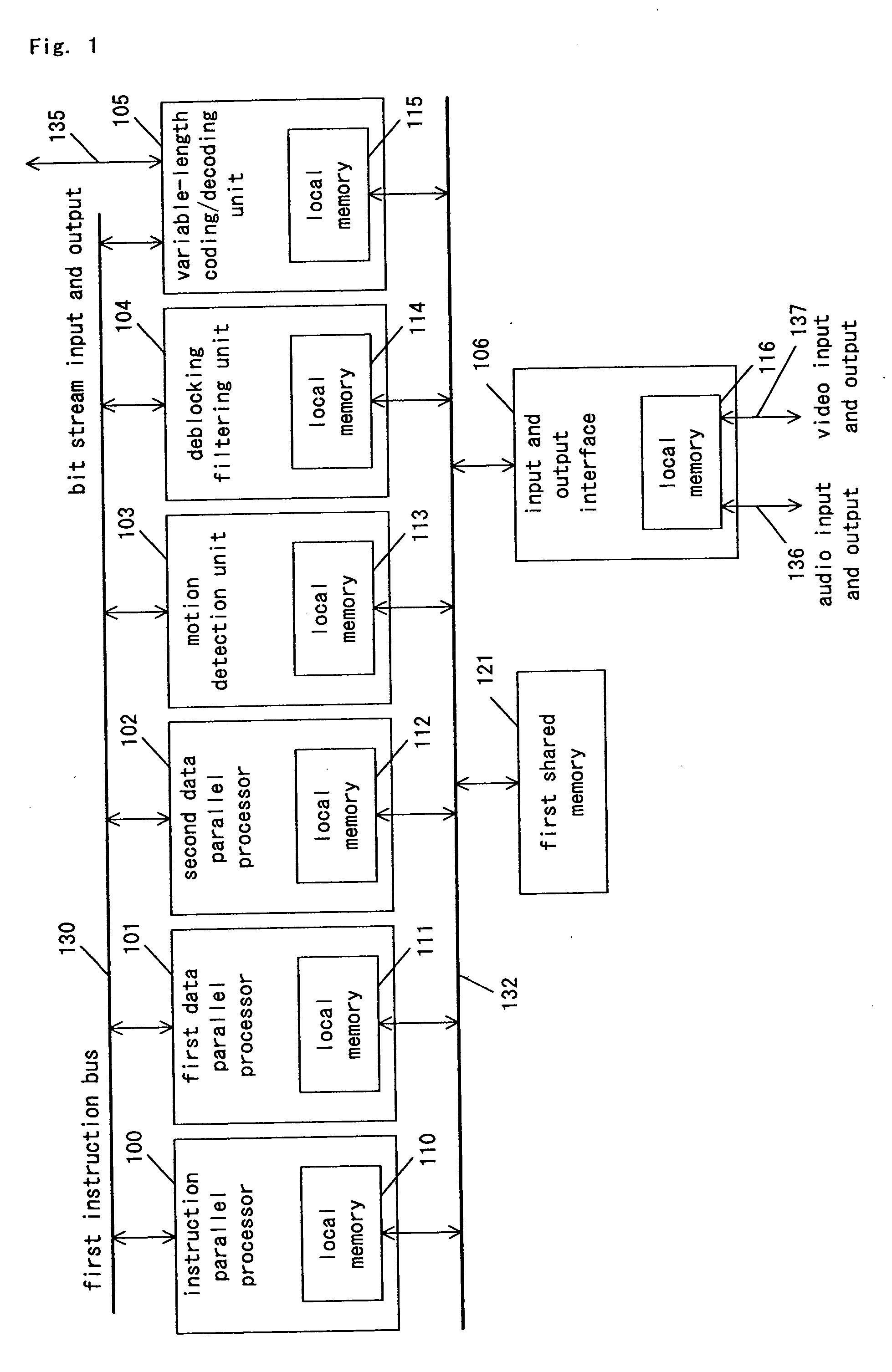
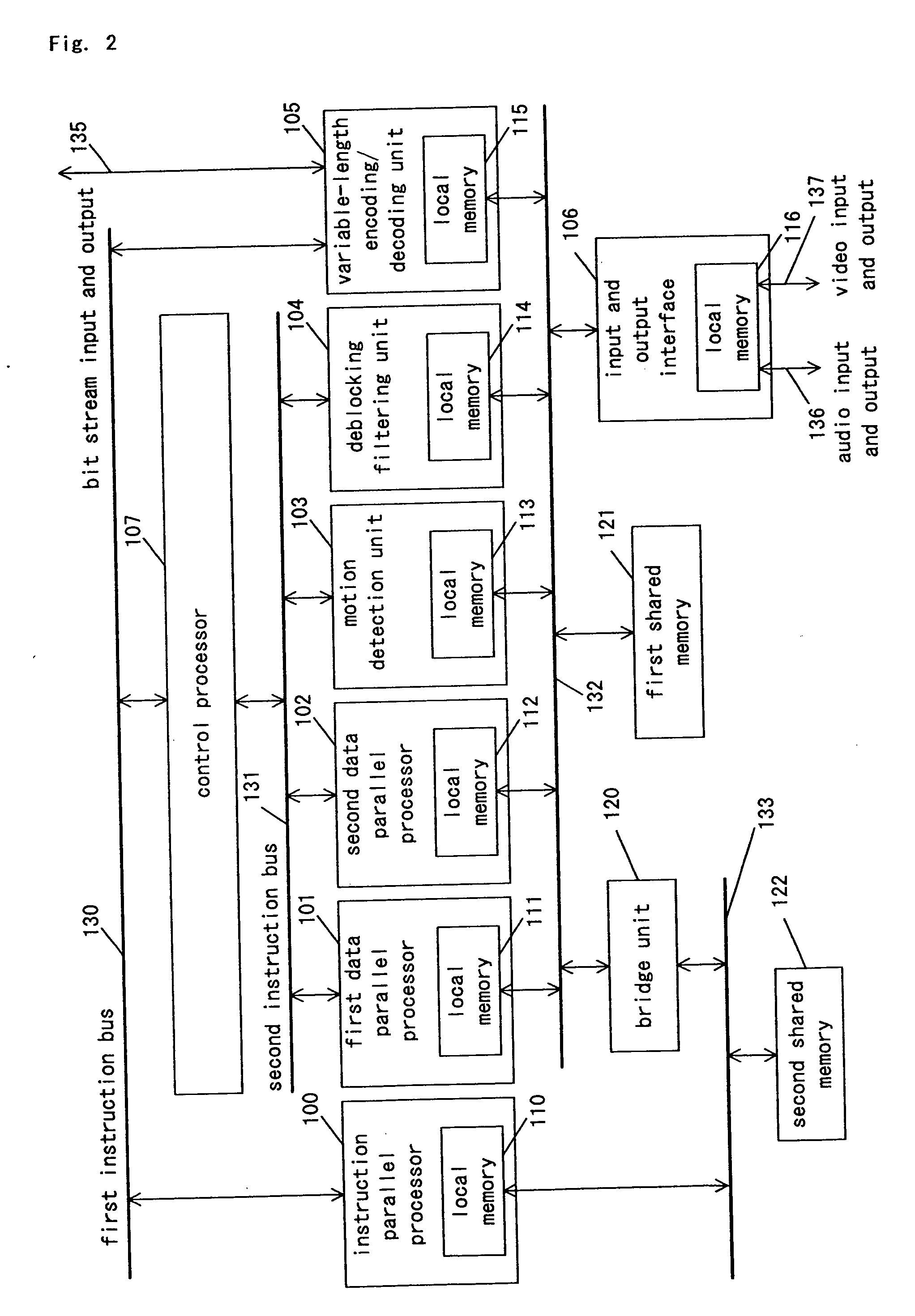
Signal-processing apparatus and electronic apparatus using same
InactiveUS20050062746A1High-performance and high-efficiency image processingLarge amount of data processingTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionImage compressionVariable length
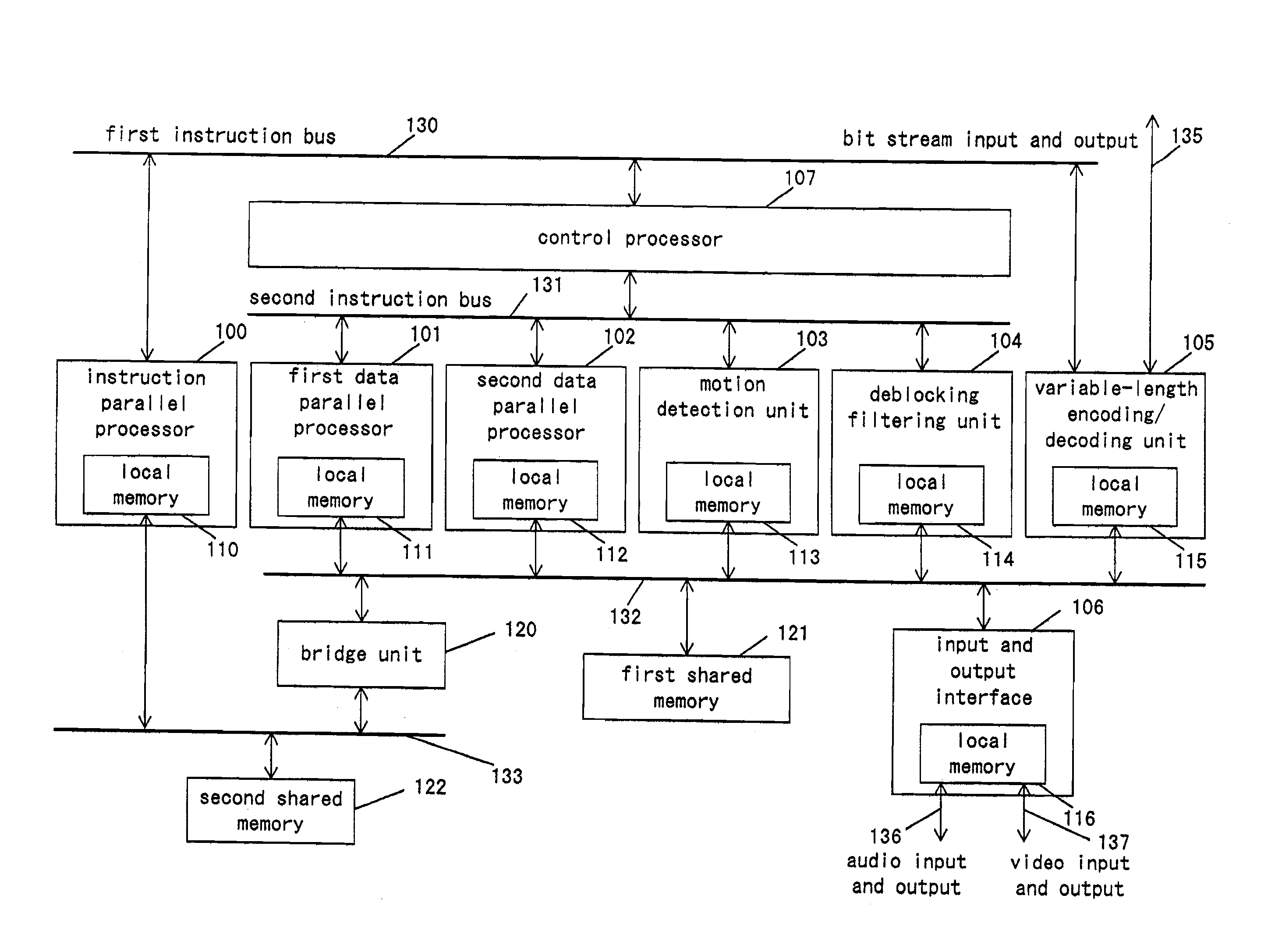
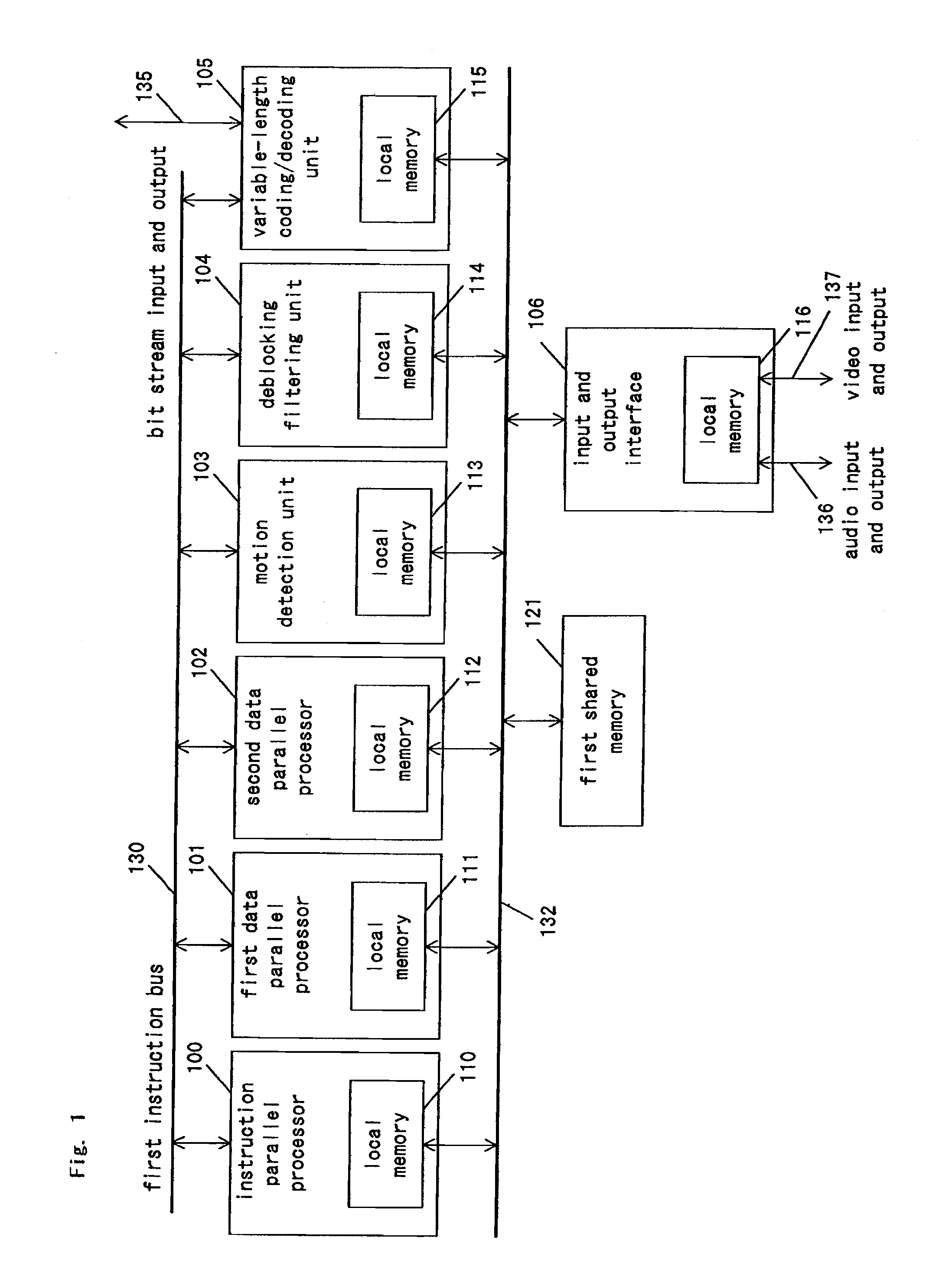
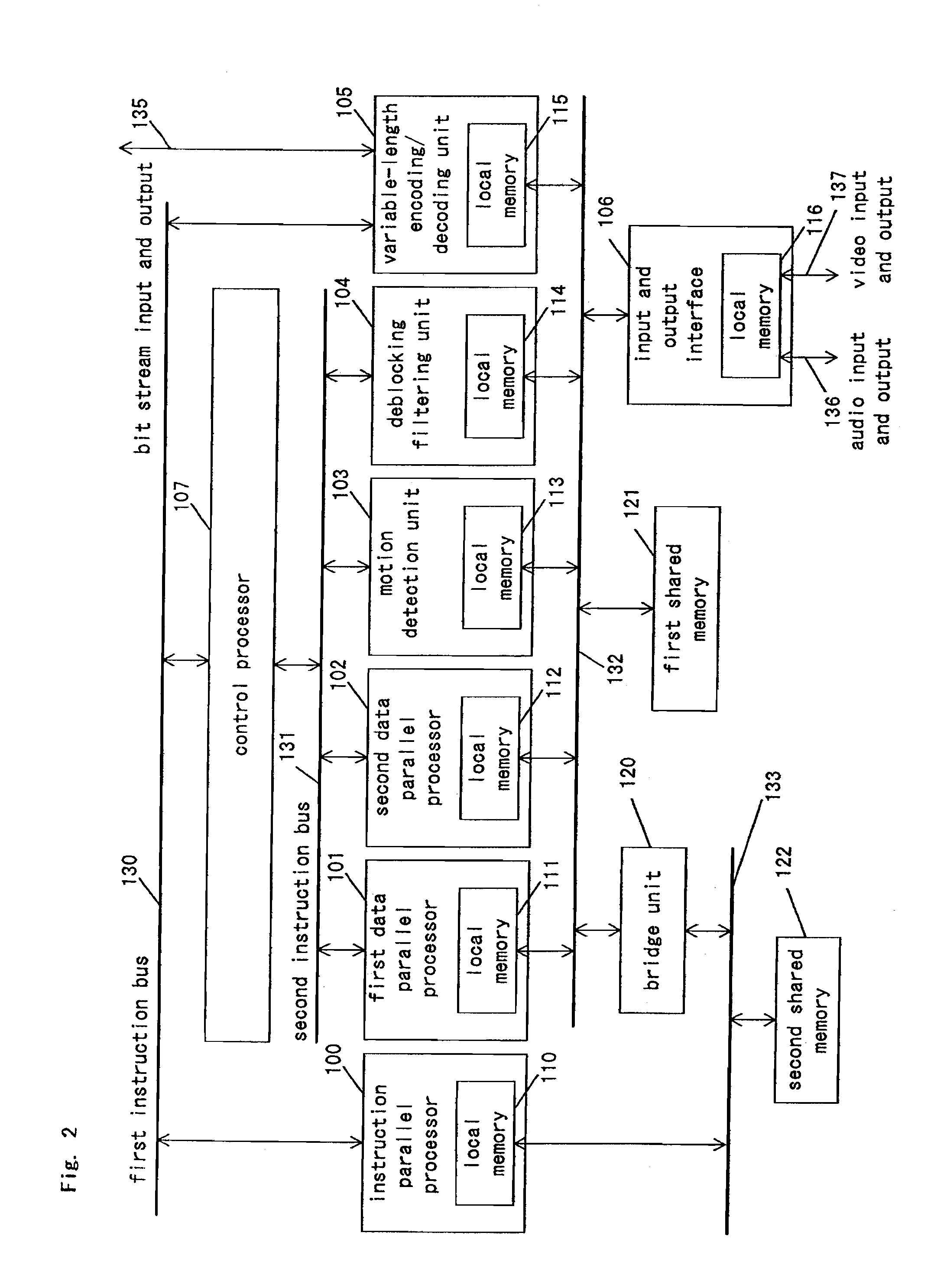
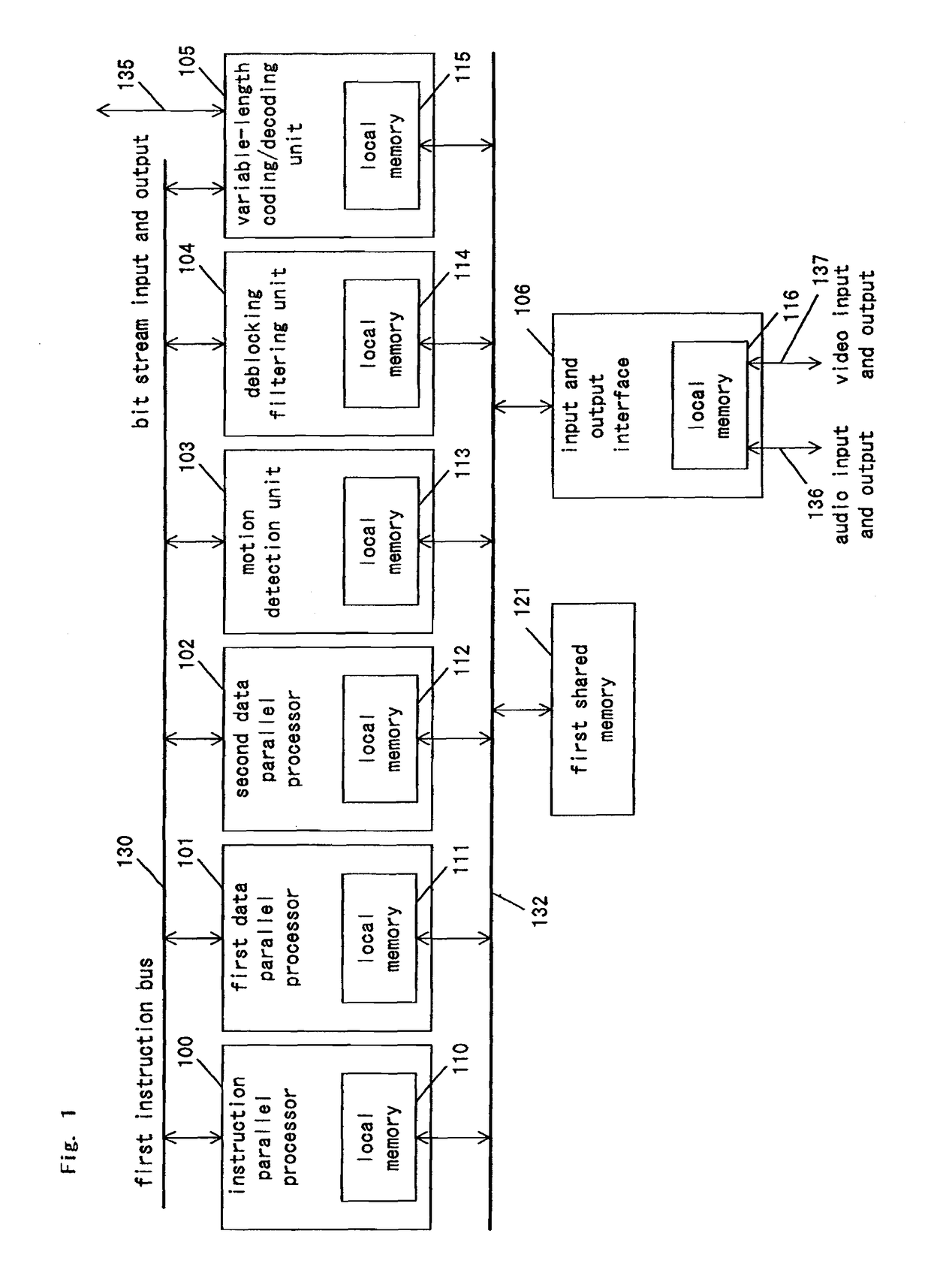
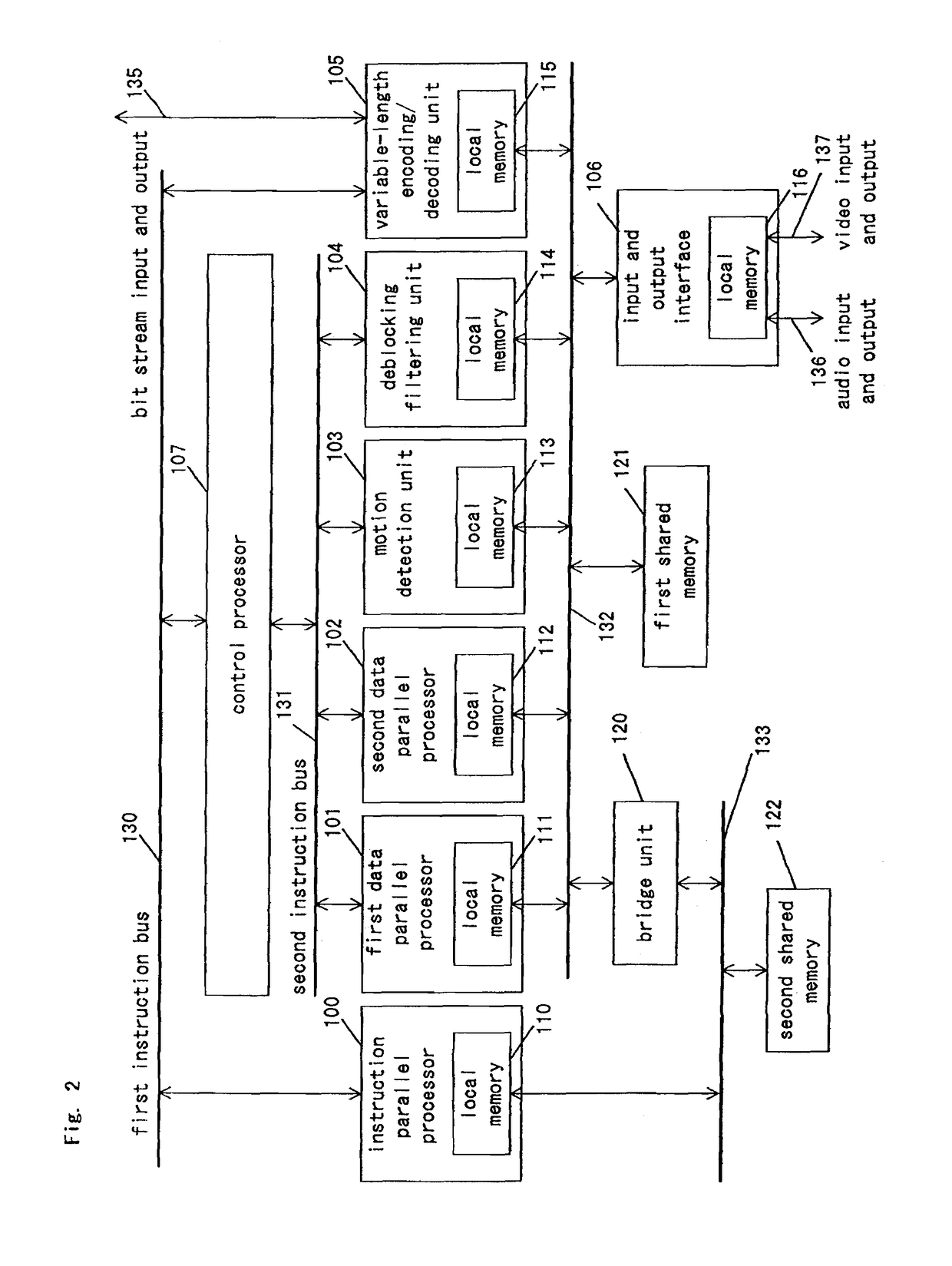
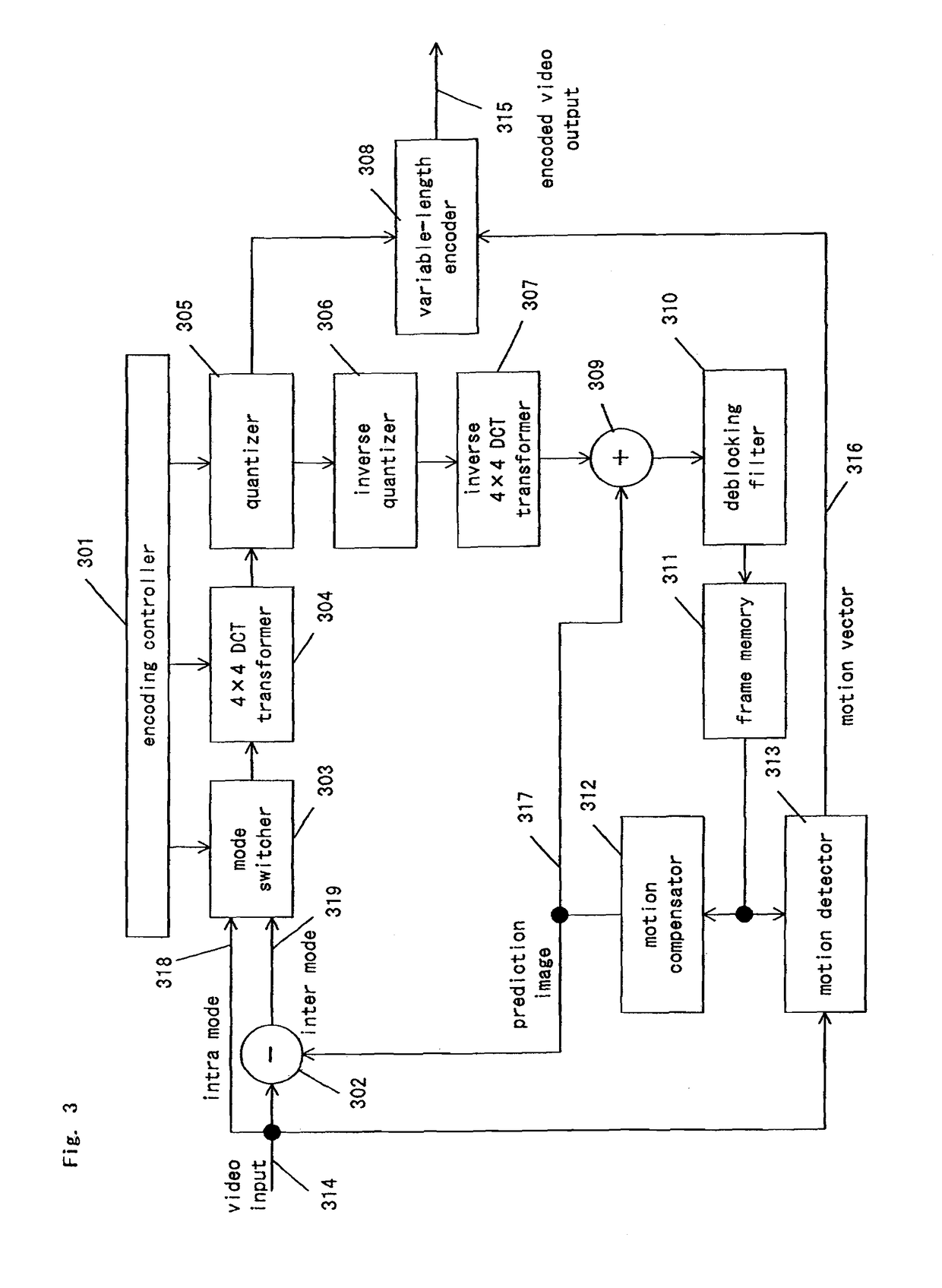
A signal-processing apparatus comprises an instruction-parallel processor, a first data-parallel processor, a second data-parallel processor, and a motion detection unit, a de-blocking filtering unit and a variable-length coding / decoding unit which are dedicated hardware. With this structure, in signal processing of an image compression and decompression algorithm with a large processing amount, the load is distributed between software and hardware, so that the signal-processing apparatus can realize high processing capability and flexibility.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
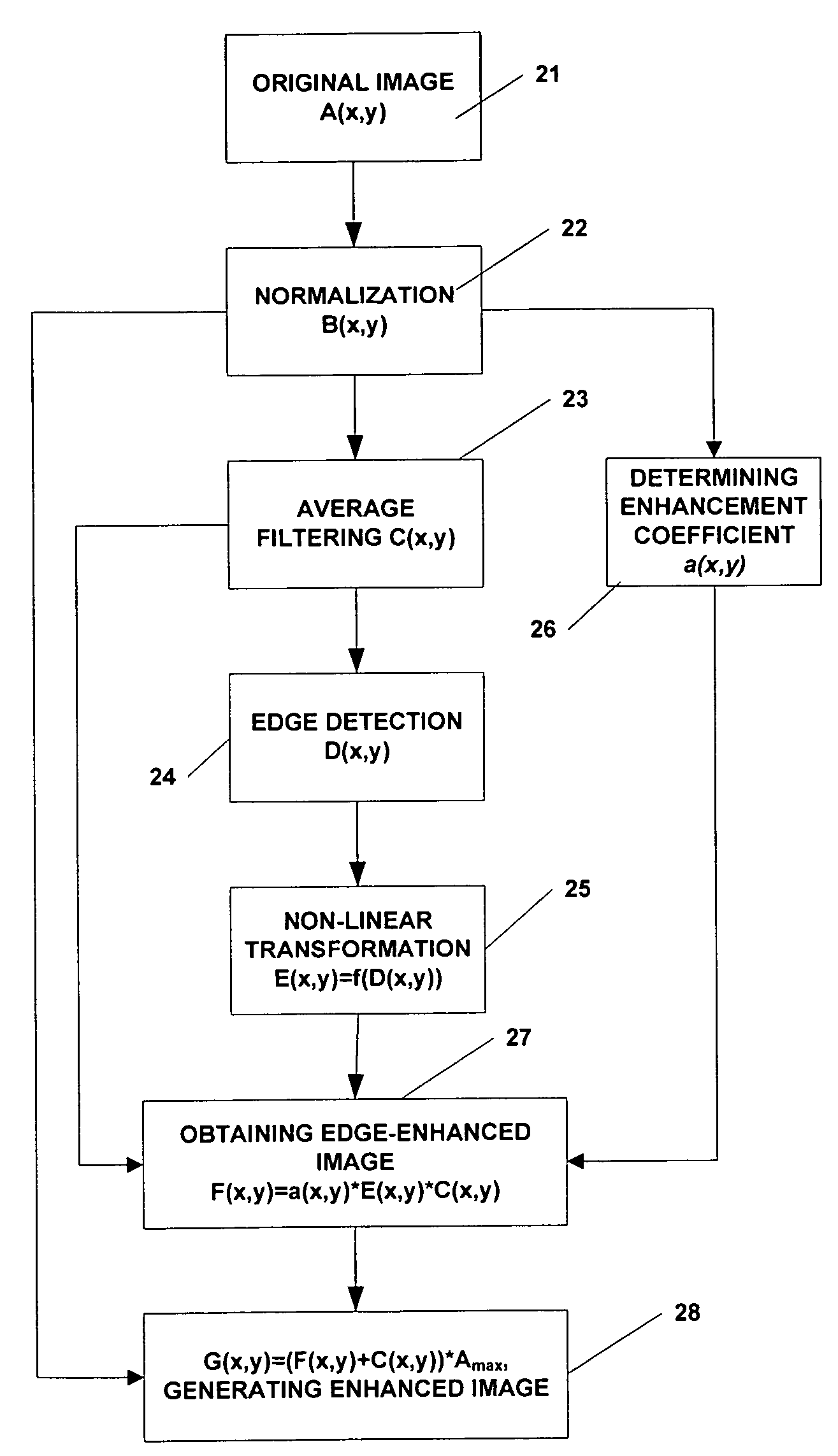
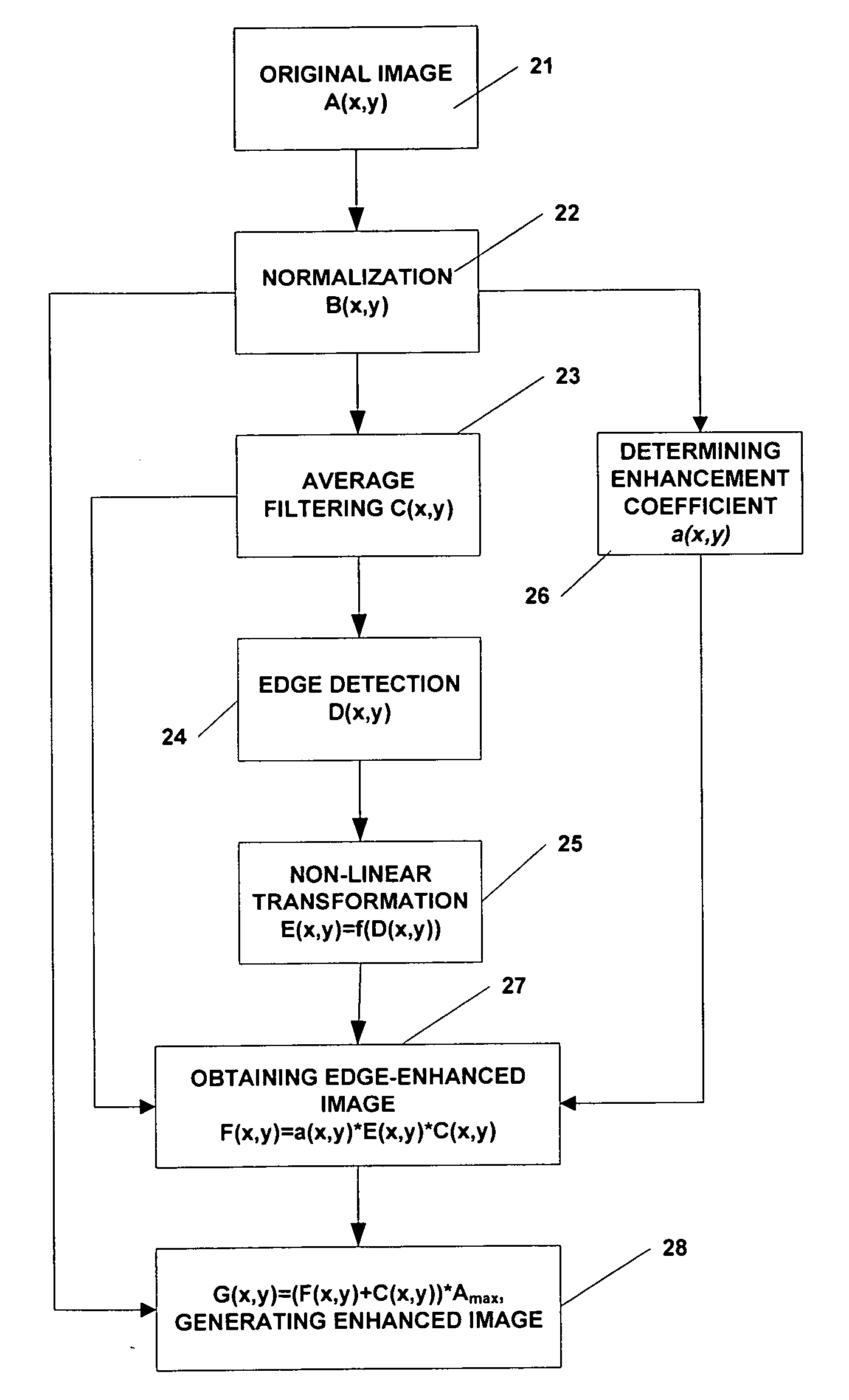
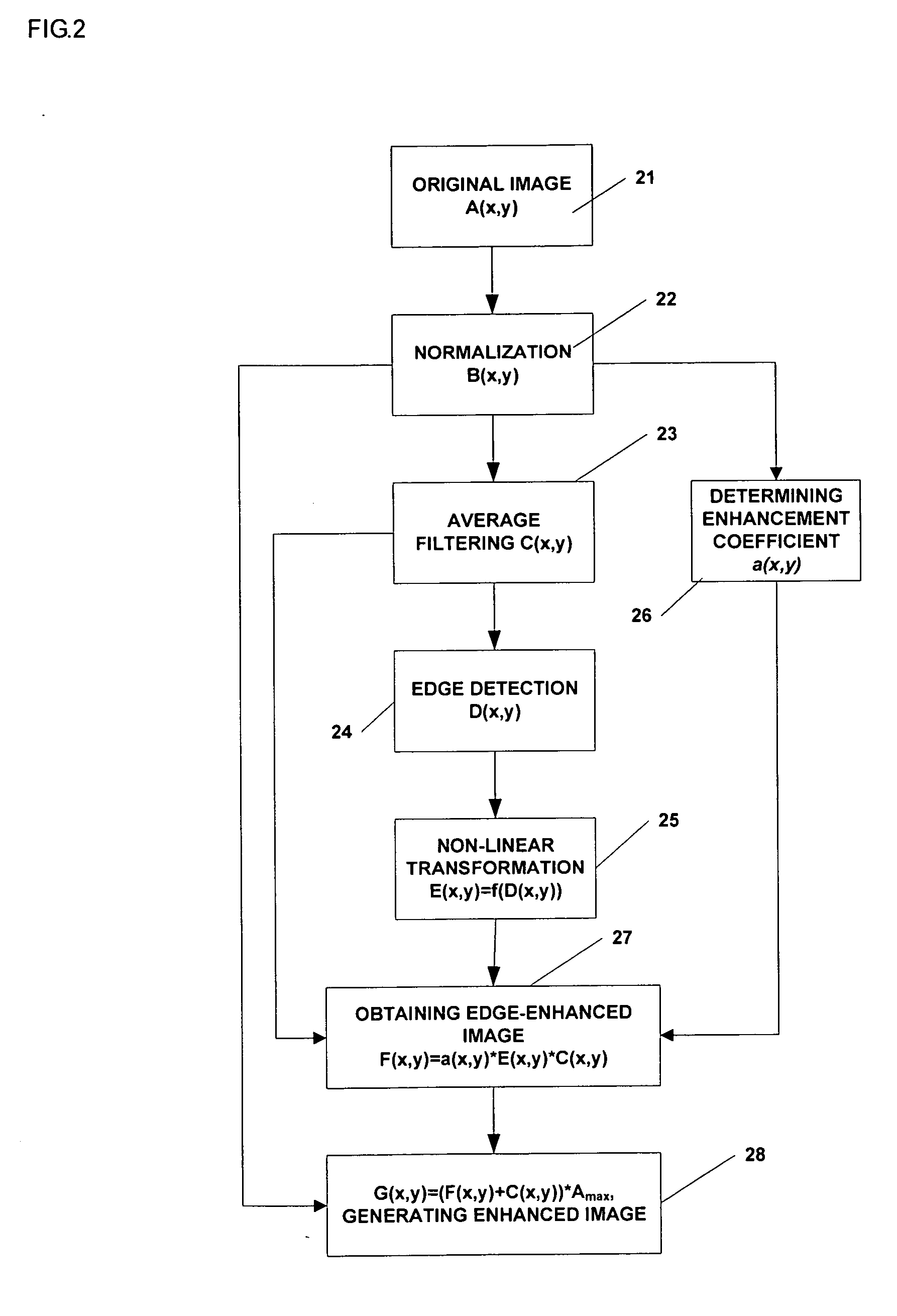
Method and apparatus for enhancing image acquired by radiographic system
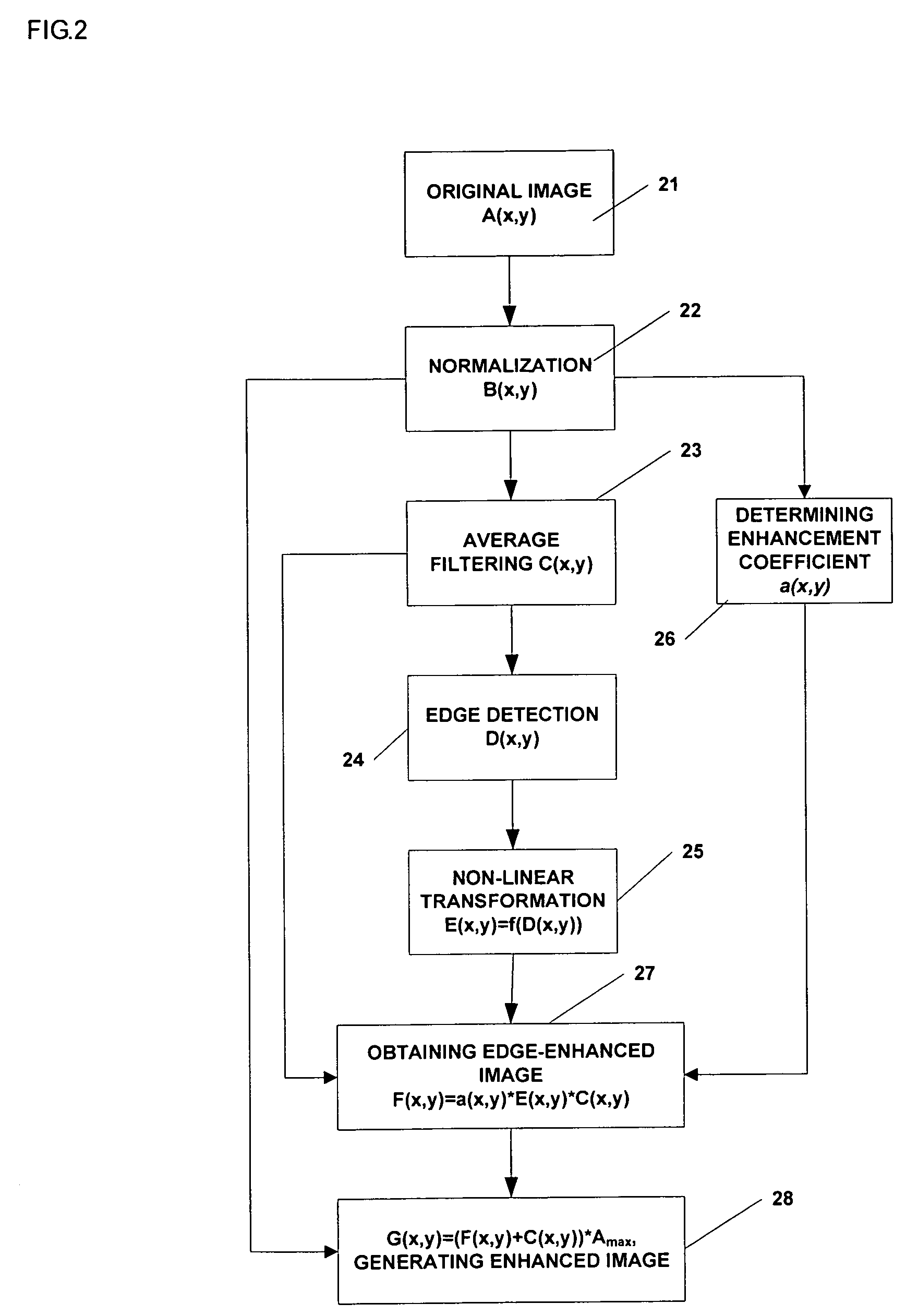
ActiveUS7689055B2Enhanced informationRemove image noiseImage enhancementImage analysisInformation processingLow-pass filter
A method of image information enhancement in radiography relates to image information processing techniques in radiography. The method comprising steps of: normalizing an acquired image A(x,y) to form a normalized image B(x,y); filtering the normalized image B(x,y) by a low-pass filter to obtain an filtered image C(x,y); calculating a relative standard deviation for each pixel in the image A(x,y), three times the relative standard deviation being an edge threshold for each pixel; thresholding a difference image obtained by subtracting the filtered image C(x,y) from the normalized image B(x,y) by using the edge threshold for each pixel to form a threshold-processed image D(x,y); enhancing a contrast of the threshold-processed image D(x,y) by using a non-linear function to form a contrast-enhanced image E(x,y); determining a enhancement coefficient a(x,y); obtaining a edge-enhanced image F(x,y) by multiplying the enhancement coefficient a(x,y), the contrast-enhanced image E(x,y) and the filtered image C(x,y); and generating a resulting image by multiplying a sum of the edge-enhanced image F(x,y) and the filtered image C(x,y) with the maximum value Amax As compared with the prior arts, the inventive method has a fast processing speed for image information enhancement and a simple algorithm, images clearly, eliminates noises in the images, and satisfies the requirements of relatively more enhancement to the contrast of the dark regions in the scanned images.
Owner:NUCTECH CO LTD +1
Frequency domain analysis method of bridge fatigue life on the basis of dynamic weighing system
ActiveCN105005694APrevent deviationThe calculation result is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsInfluence lineLoad time
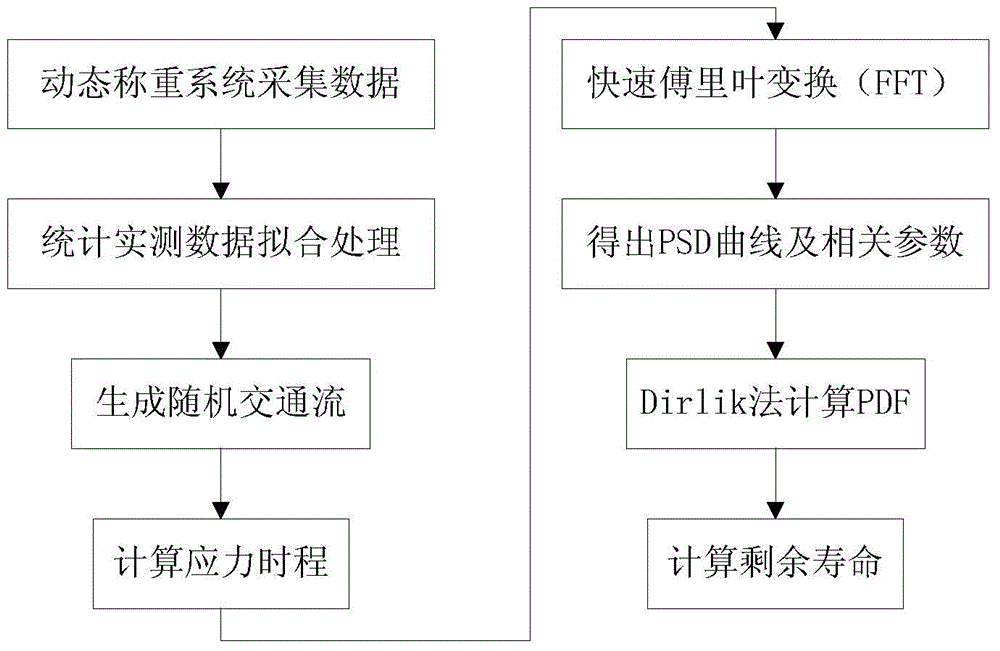
The invention relates to a frequency domain analysis method of bridge fatigue life on the basis of a dynamic weighing system. The frequency domain analysis method comprises the following steps: collecting data including the vehicle weight, the vehicle speed and the axle distance of each vehicle which passes through a bridge; calculating the collected data, and carrying out curve fitting; according to a fitting probability density curve, establishing a cellular automata simulation model of the vehicle, and generating a random traffic flow; simulating load time history under different vehicle flow density conditions, and loading the load time history to a bridge influence line to obtain stress time history data; carrying out FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) on the stress time history, obtaining PSD (Power Spectral Density), and calculating relevant parameters; using a Dirlik method to establish an experience form of a PDF (Probability Distribution Function); and calculating residual service life. Calculation time is greatly shortened.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Signal-processing apparatus and electronic apparatus using same
ActiveUS20080307198A1High-performance and high-efficiencyLarge amount of data processingTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionImage compressionVariable length
A signal-processing apparatus includes an instruction-parallel processor, a first data-parallel processor, a second data-parallel processor, and a motion detection unit, a de-blocking filtering unit and a variable-length coding / decoding unit which are dedicated hardware. With this structure, during signal processing of an image compression and decompression algorithm needing a large amount of processing, the load is distributed between software and hardware, so that the signal-processing apparatus can realize high processing capability and flexibility.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
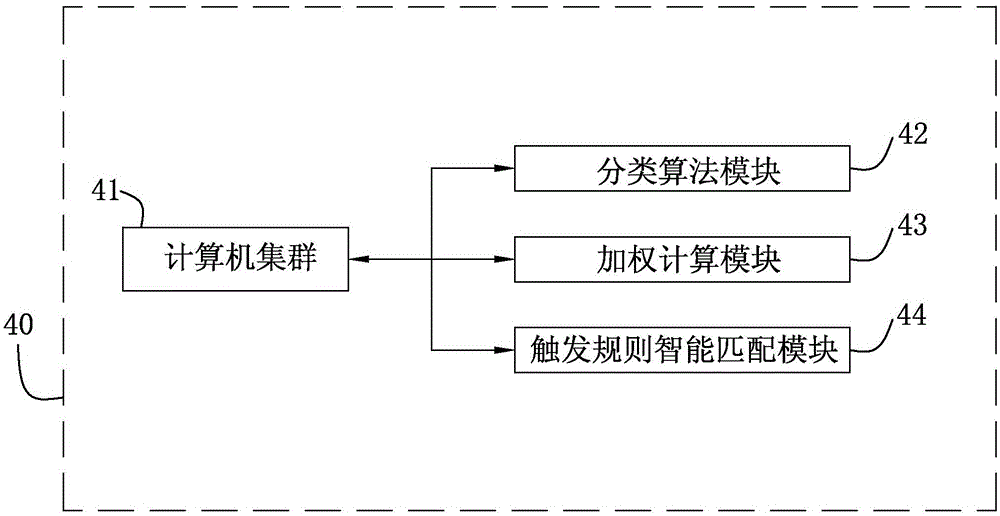
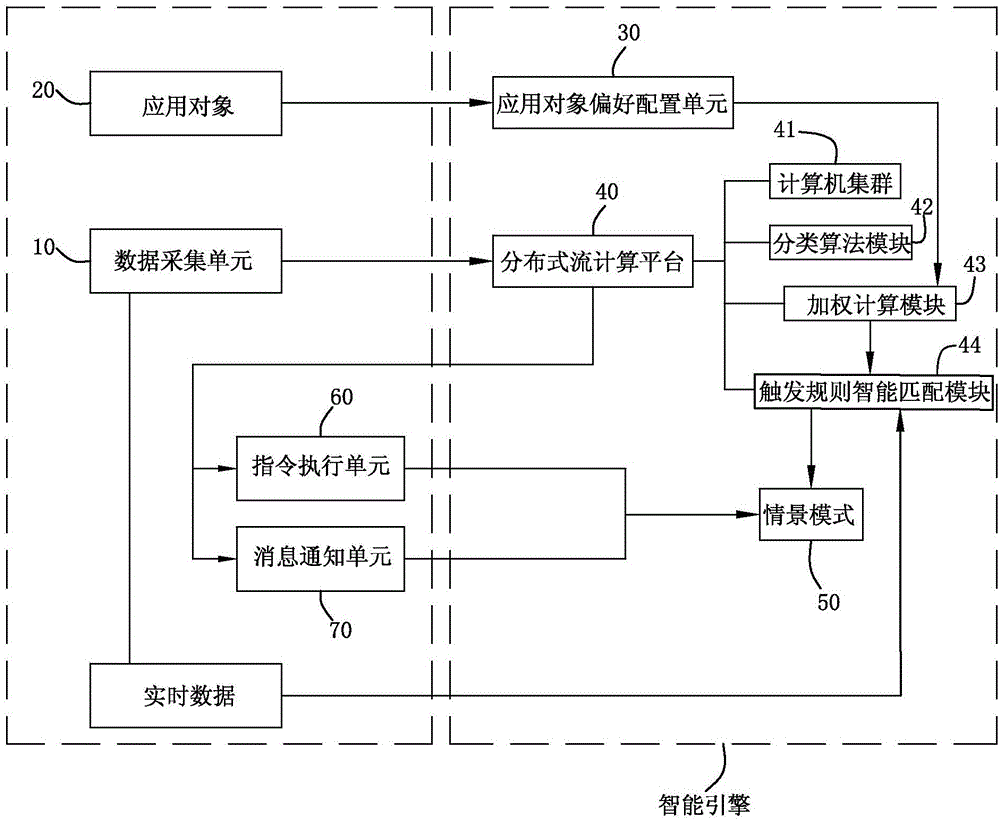
Intelligent engine system capable of automatically triggering intelligent home and intelligent life scenes and method
ActiveCN105005204AMake reasonableLarge amount of data processingComputer controlTotal factory controlPersonalizationReal-time data
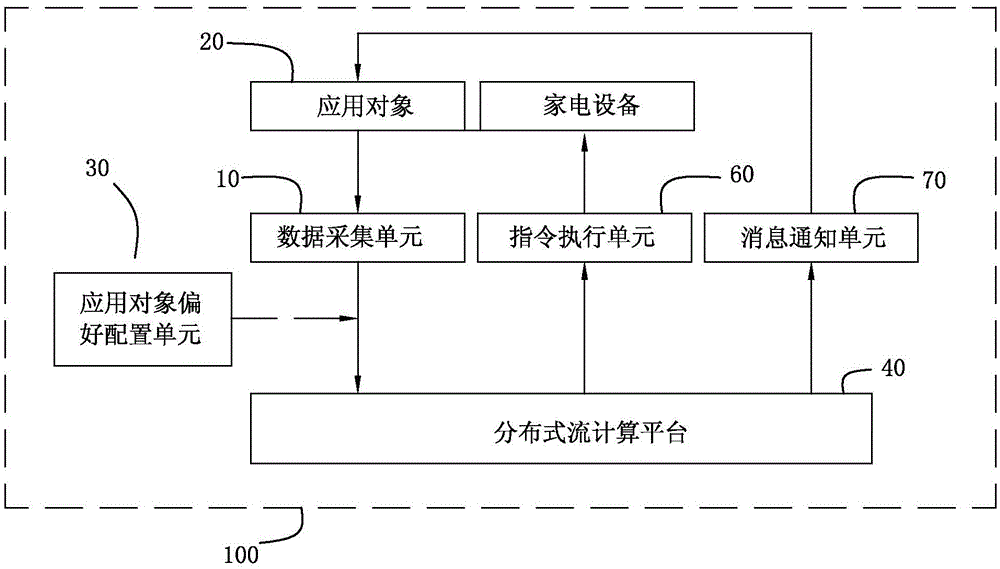
The invention discloses an intelligent engine system capable of automatically triggering intelligent home and intelligent life scenes and a method. The system comprises a data acquisition unit, an application object preference configuration unit, a distributed stream computing platform, an instruction execution unit and a message notification unit. The method comprises the steps that a, the data acquisition unit acquires environment factor data, behavioral data and physical condition data of an application object; b, the data are processed to form an environment scene mode; c, the application object sets or automatically generates personal preferences; d, weighting computing is carried out on the environment scene mode and the personal preferences, and a personalized scene mode and a scene trigger rule are developed; e, real-time data acquired by the data acquisition unit match the trigger rule of the application object; and f, if a trigger condition is met, the scene mode corresponding to the trigger rule is issued and applied to the life environment of the application object. According to the invention, the system has the advantages of being unattended, rich data source, being objective and true, scientific and compact data processing and control method and the like.
Owner:深圳广田智能科技有限公司
Method and apparatus for enhancing image acquired by radiographic system
ActiveUS20060291742A1Advanced image informationClear scanned imageImage enhancementImage analysisInformation processingRelative standard deviation
A method of image information enhancement in radiography relates to image information processing techniques in radiography. The method comprising steps of: normalizing an acquired image A(x,y) to form a normalized image B(x,y); filtering the normalized image B(x,y) by a low-pass filter to obtain an filtered image C(x,y); calculating a relative standard deviation for each pixel in the image A(x,y), three times the relative standard deviation being an edge threshold for each pixel; thresholding a difference image obtained by subtracting the filtered image C(x,y) from the normalized image B(x,y) by using the edge threshold for each pixel to form a threshold-processed image D(x,y); enhancing a contrast of the threshold-processed image D(x,y) by using a non-linear function to form a contrast-enhanced image E(x,y); determining a enhancement coefficient a(x,y); obtaining a edge-enhanced image F(x,y) by multiplying the enhancement coefficient a(x,y), the contrast-enhanced image E(x,y) and the filtered image C(x,y); and generating a resulting image by multiplying a sum of the edge-enhanced image F(x,y) and the filtered image C(x,y) with the maximum value Amax As compared with the prior arts, the inventive method has a fast processing speed for image information enhancement and a simple algorithm, images clearly, eliminates noises in the images, and satisfies the requirements of relatively more enhancement to the contrast of the dark regions in the scanned images.
Owner:NUCTECH CO LTD +1
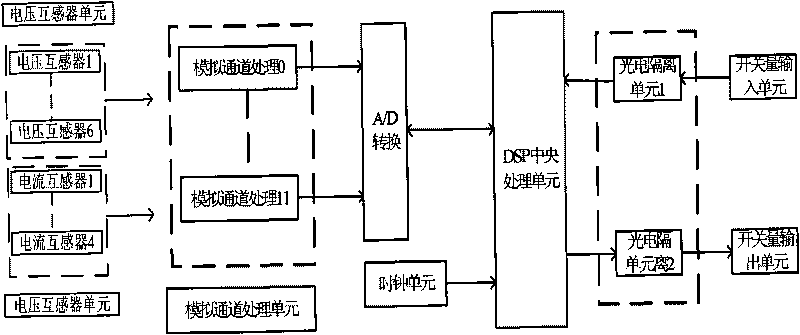
Short circuit detection and protection system based on DSP
InactiveCN101710687AOvercome susceptibility to other fault current waveformsImprove accuracyElectrical testingArrangements responsive to excess currentSystem structureProtection system
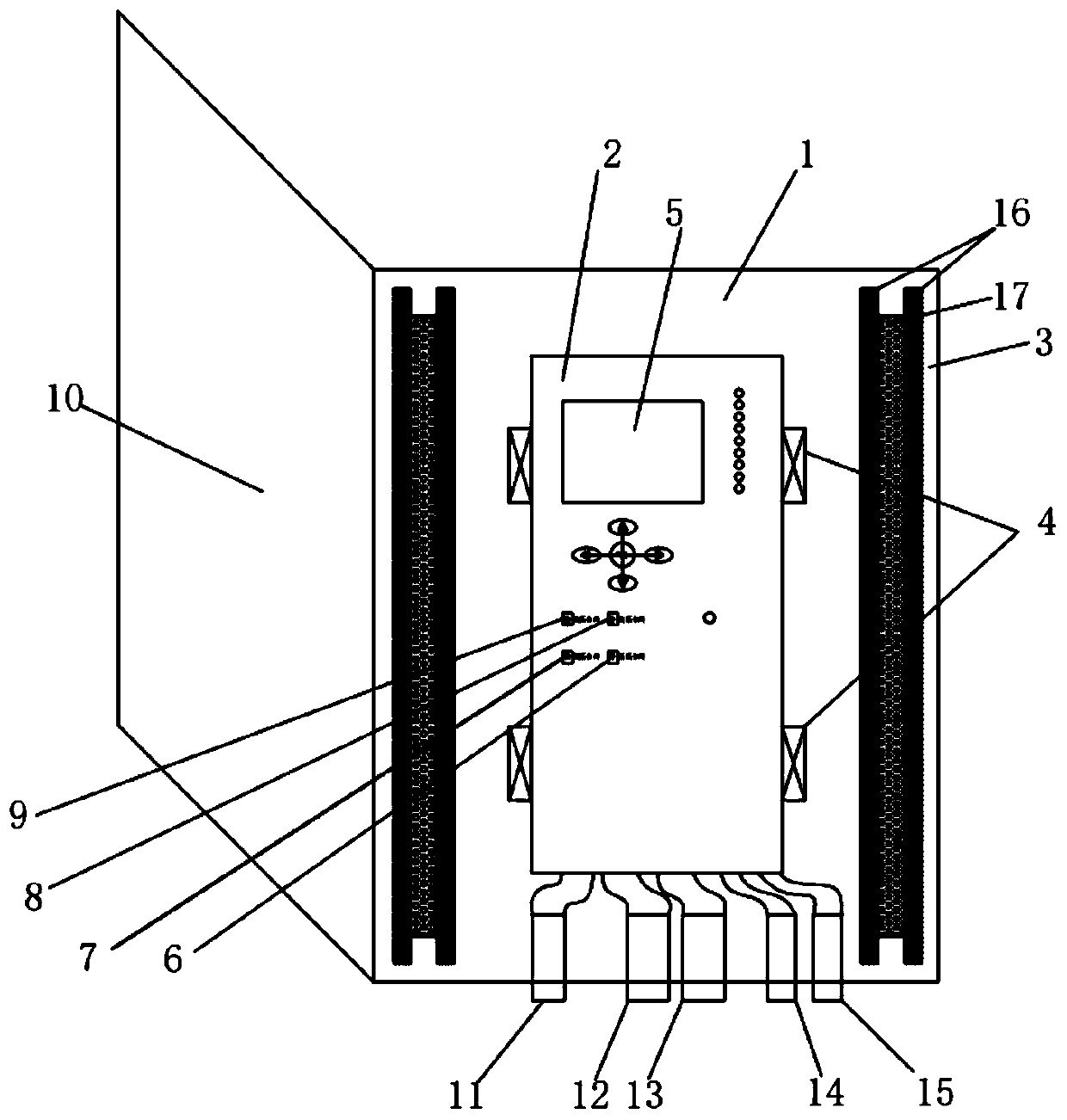
The invention discloses a short circuit detection and protection system based on DSP, which is composed of an analog channel processing unit, an A / D converter, a clock unit, a DSP central processing unit, a photoelectric isolation unit I, a photoelectric isolation unit II, a switching value input unit and a switching value output unit. The invention has the advantages that the short circuit detection and protection system overcomes the phenomenon that other fault current waveforms are easy to affect a short circuit current signal when the short circuit current signal is processed, thus improving the detection accuracy of the system; the short circuit detection and protection system takes DSP as a central processing chip, so that the system has great data processing amount, high instantaneity and precision, simple system structure and high cost performance, and the system rapidity is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
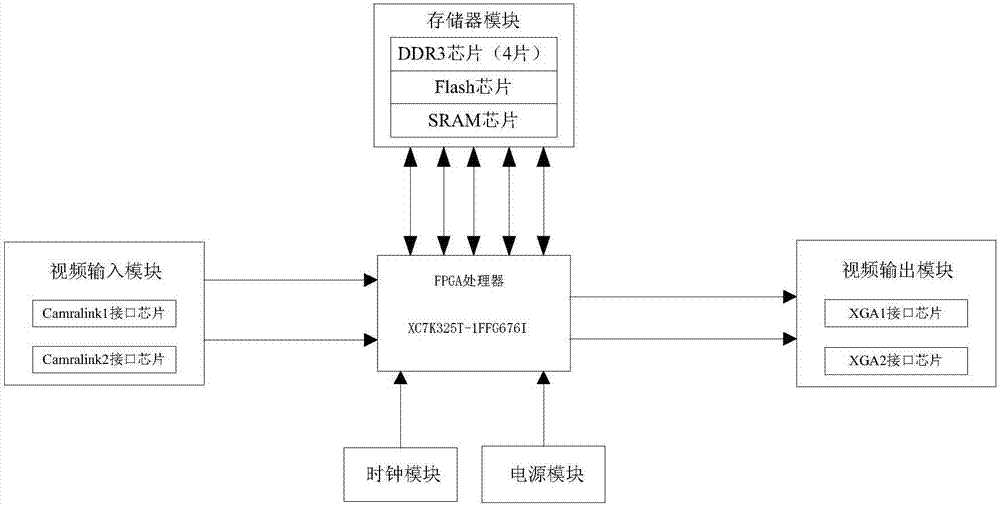
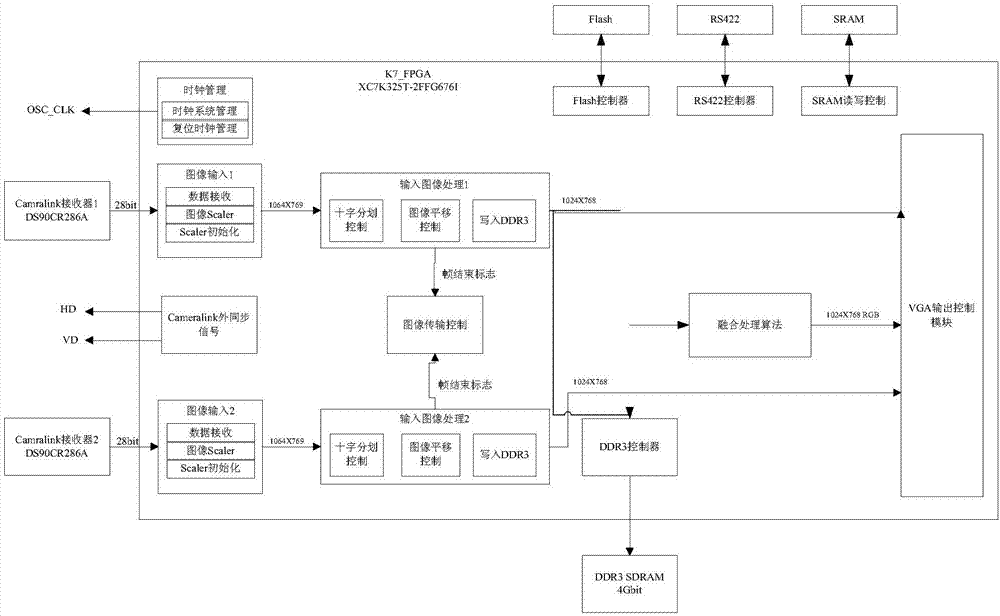
Fusion processing circuit of high-definition image
InactiveCN107169950AAchieve integrationHigh resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisHigh resolution imageVideo image
The invention relates to a fusion processing of a high-definition image. The circuit comprises a core processor, and a video input module, a video output module, a power supply module, a clock module and a memory module which are connected with the core processor. The video input module comprises two paths of Camralink port chips and is used for decoding Camralink data and transmitting decoded data to the core processor. The core processor is used for achieving receiving, image scaling, character superposition, image translation, image storage and an image fusion algorithm for real-time video image data, and achieving real-time video image data. The video output module is used for carrying out VGA output for the real-time video image data generated by the core processor. According to the invention, fusion of high-resolution real-time digital images is achieved; the processing speed is quicker and the data processing quantity is bigger than a simulation video image fusion processing circuit; and the resolution of the fused image is high.
Owner:江苏北方湖光光电有限公司
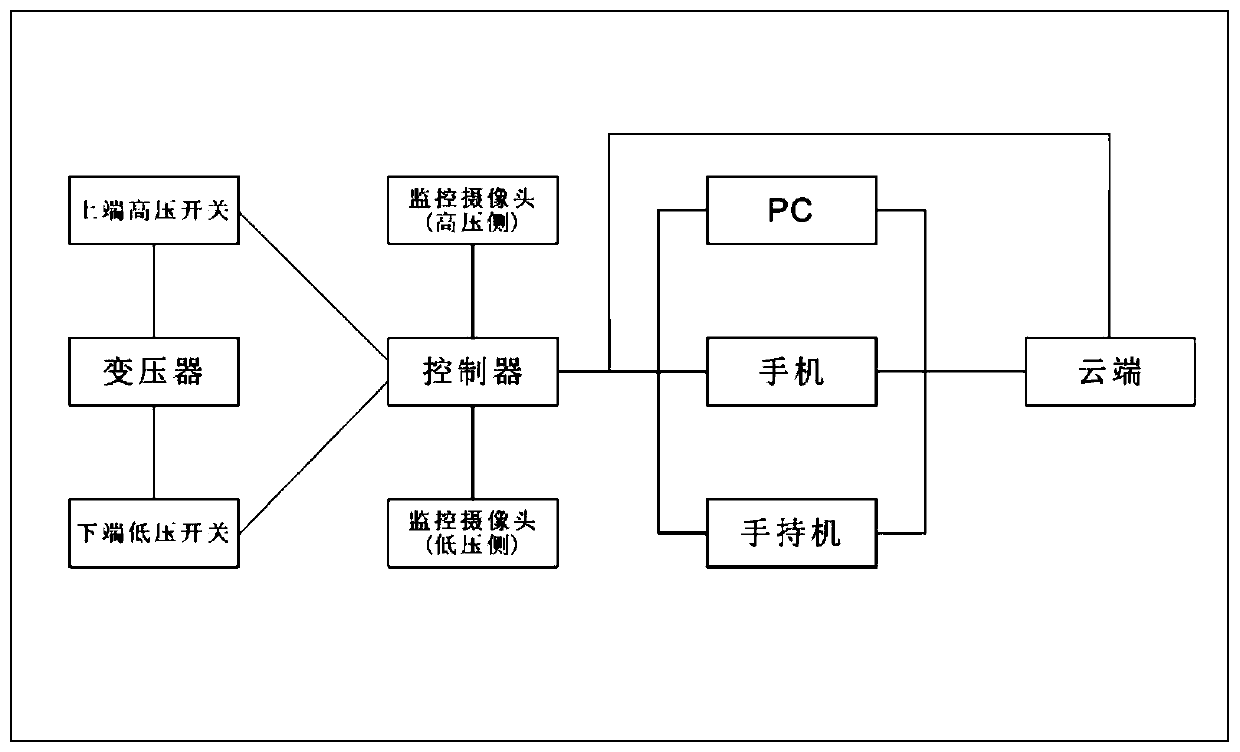
High-/low-voltage switch intelligent control system, controller and control method
InactiveCN110336376AGuaranteed accuracyLarge amount of data processingCircuit arrangementsElectricityReal-time data
A high- / low-voltage switch intelligent control system, a controller and a control method are provided. The high- / low-voltage switch intelligent control system includes a controller, a low-voltage switch measuring device and a high-voltage switch measuring device. The controller includes a main control module, a communication module, a timing module, a storage module and a power supply module. Thelow-voltage switch measuring device is installed at a low-voltage switch to be controlled and electrically connected with the controller, and is used for measuring the current and voltage signals of the low-voltage side and the opening / closing state signal of the low-voltage switch. The high-voltage switch measuring device is installed at a high-voltage switch to be controlled and electrically connected with the controller, and is used for measuring the current and voltage signals of the high-voltage side and the opening / closing state signal of the high-voltage switch. The main control moduleprocesses the received current and voltage signals of each phase at the low-voltage side / high-voltage side and the opening / closing state signals of the low-voltage switch / high-voltage switch to get fault information. The communication module sends the real-time data of the equipment, the opening / closing state information of the low-voltage switch / high-voltage switch and the fault information to the background, and receives operation instructions from the background.
Owner:陈儒丹
Test analysis method for automatic driving system
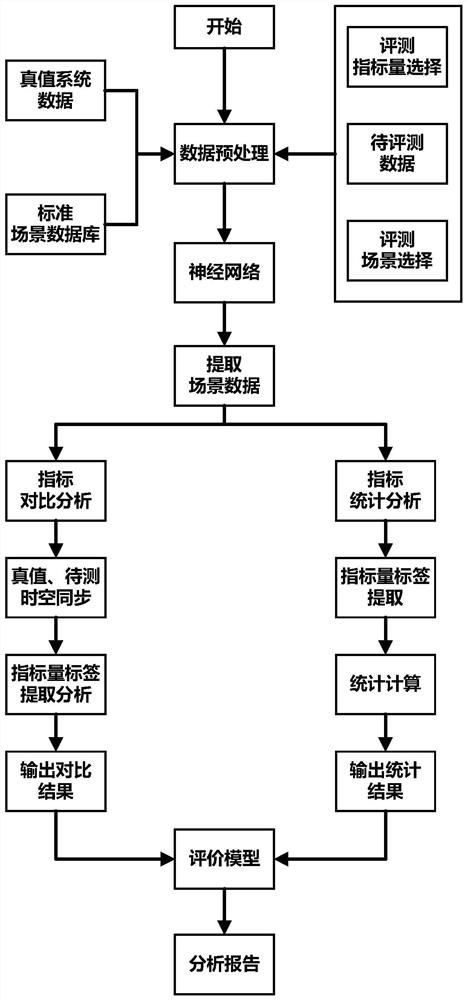
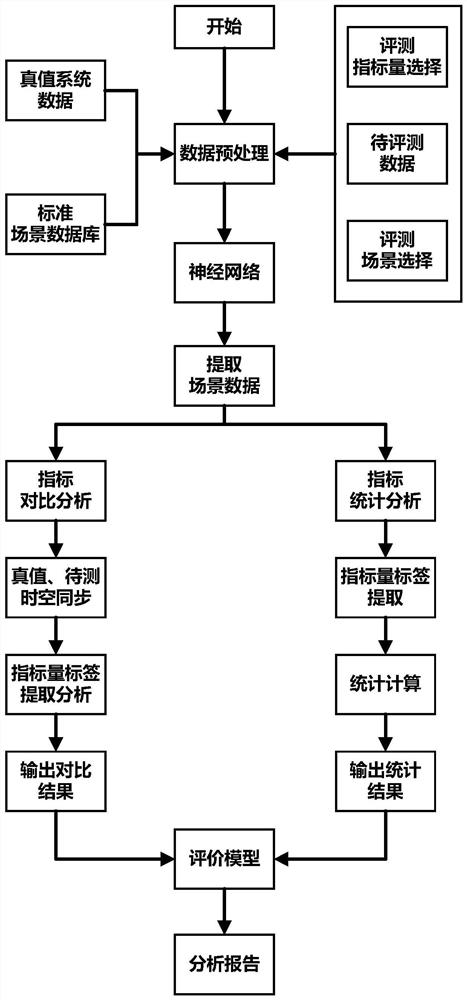
ActiveCN113074959AImprove efficiencyLarge amount of data processingVehicle testingNeural architecturesEvaluation resultAlgorithm
The invention discloses a test analysis method for an automatic driving system, and the method comprises the steps: loading to-be-evaluated data, and appointing an evaluation index and an evaluation scene which need to be evaluated; loading standard scene data as truth value data according to the evaluation scene; obtaining the characteristic quantity of the to-be-evaluated data; pairing the to-be-evaluated data with the truth value data according to the characteristic quantity consistency and / or the position consistency to form a data pair, wherein the position consistency refers to the consistency of positioning data in the to-be-evaluated data, the characteristic quantity consistency means that a characteristic quantity error is smaller than a threshold value; determining the matching degree of the data pair matching the evaluation scene and the evaluation index, and taking the data pair of which the matching degree exceeds a threshold value as an analysis object; and carrying out evaluation index analysis on the analysis object to obtain an evaluation result. The method can automatically process and analyze massive automatic driving data, and has the advantages of high efficiency, large data processing amount and accurate statistical indexes.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Video similarity detection method and device, terminal equipment and storage medium
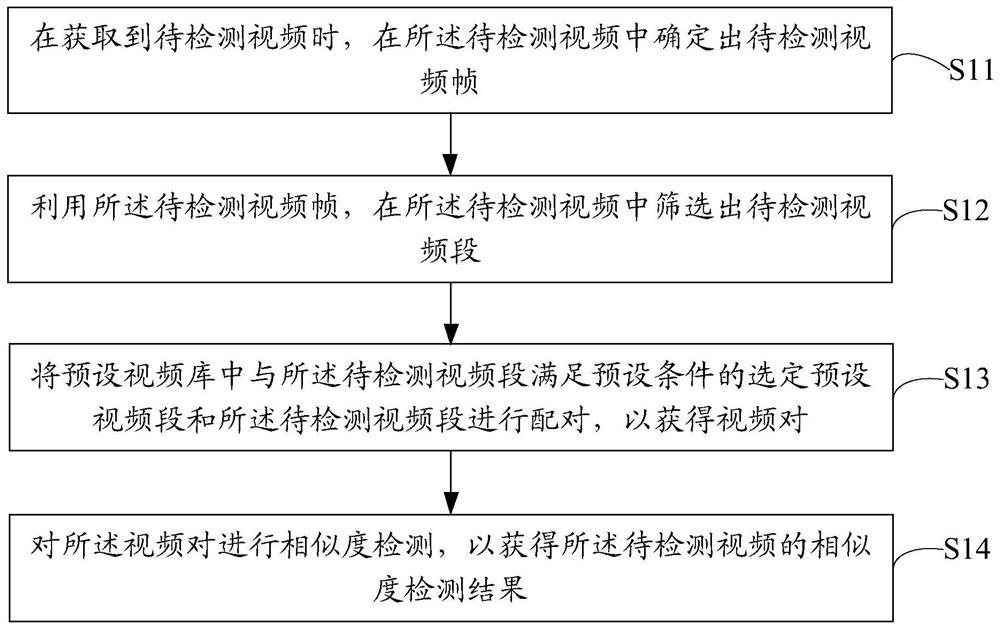
PendingCN112861717ALarge amount of data processingMore computing timeCharacter and pattern recognitionTerminal equipmentComputer vision
The invention discloses a video similarity detection method, and the method comprises the following steps: determining a to-be-detected video frame in a to-be-detected video when the to-be-detected video is obtained; screening out a to-be-detected video segment from the to-be-detected video by using the to-be-detected video frame; matching a selected preset video segment meeting a preset condition with the to-be-detected video segment in a preset video library with the to-be-detected video segment to obtain a video pair; and performing similarity detection on the video pair to obtain a similarity detection result of the to-be-detected video. The invention further discloses a video similarity detection device, terminal equipment and a computer readable storage medium. By using the video similarity detection method provided by the invention, the video similarity detection efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INVENO TECH
Intelligent gas field system and method for self-adaption and intelligent analysis and decision making
ActiveCN111963116AIncrease operating frequencyReduce operating frequencyFluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsControl engineeringComputer science
The invention relates to an intelligent gas field system and method for self-adaption and intelligent analysis and decision making. According to the system, an intelligent service module generates decision information for adjusting operating parameters of a gas production device on the basis of the operating parameters and / or gas well production parameters in combination with a machine learning algorithm model under a condition that a working condition recognition result and / or a prediction result of a working condition recognition and prediction module correspond / corresponds to a normal working condition, and feeds back the decision information to a production parameter adjustment module so as to optimize and adjust the production parameter adjustment module, or under a condition that theworking condition recognition result and / or the prediction result of the working condition recognition and prediction module correspond / corresponds to an abnormal working condition, the working condition recognition and prediction module generates emergency information and feeds the emergency information back to the production parameter adjustment module so as to carry out emergency adjustment ongas extraction parameters of the gas production device.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING) +1
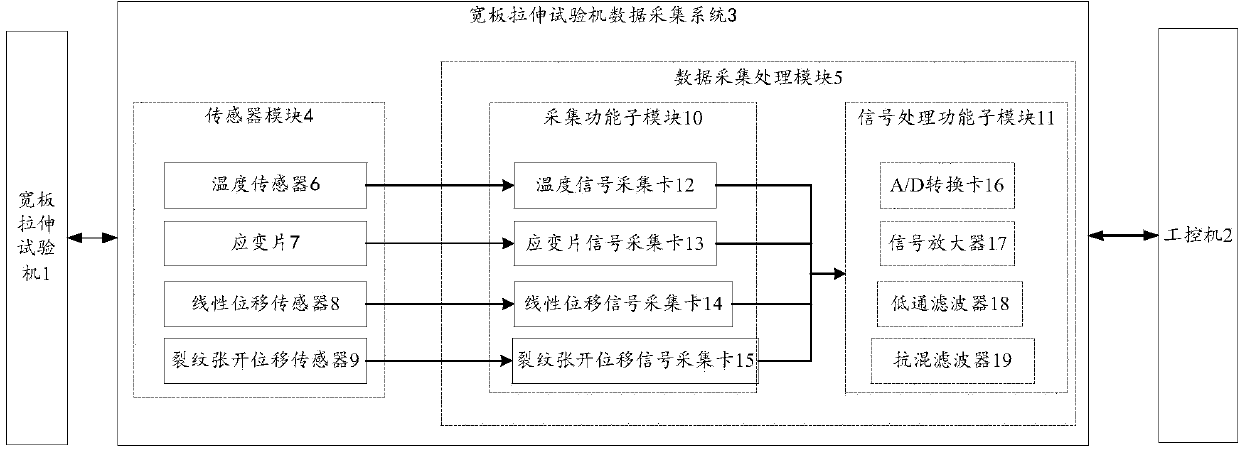
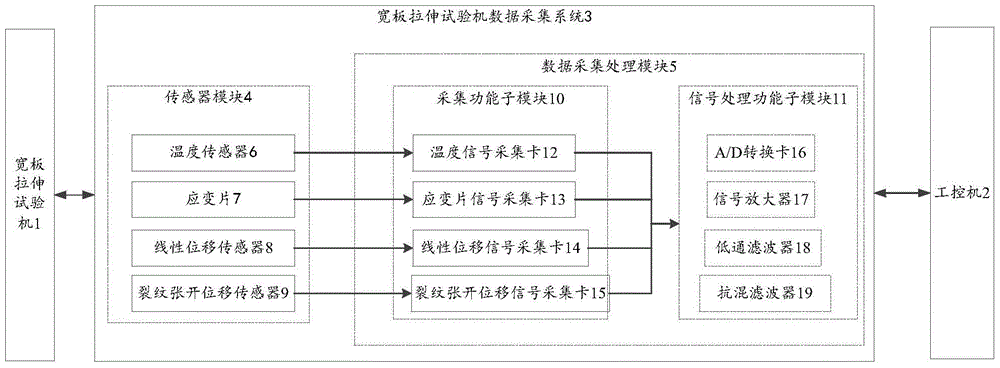
Data acquisition system of wide plate tension test machine
ActiveCN104198281AFast responseLarge amount of data processingStrength propertiesReal time acquisitionControl parameters
The invention discloses a data acquisition system of a wide plate tension test machine. The data acquisition system comprises a sensor module and a data acquiring-processing module, and is capable of acquiring and processing a crack opening displacement signal, a point strain signal, an area strain signal, a mechanics signal, a displacement signal and a temperature signal in a wide plate tension test; the data acquisition system has high reacting speed, achieves large data processing capacity and is capable of avoiding mutual interference among various types of data. Meanwhile, the crack opening displacement signal, the area strain signal, the mechanics signal and the displacement signal, which are acquired in the test process can be fed back in time, and test signals are fed back to an industrial personal computer to serve as main control parameters in the test process for controlling the test process. The data acquisition system is high in reacting frequency, strong in interference resisting capability, and high in real-time performance and reliability of data acquisition.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
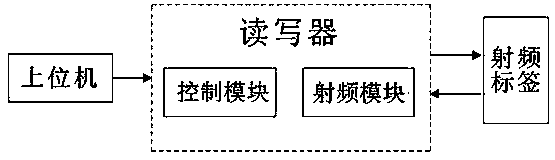
Automatic information management system
InactiveCN103678251AImprove work efficiencyLarge amount of data processingResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsData transmissionRF module
The invention discloses an automatic information management system which comprises a reader-writer, an upper computer and a radio frequency tag. The reader-writer comprises a control module and a radio frequency module, data can be transmitted between the control module and the radio frequency module via a data line, the upper computer is communicated with the control module via a serial interface, and the radio frequency module is in wireless radio frequency communication with the radio frequency tag. The automatic information management system has the advantage that information can be efficiently, quickly and effectively managed by the automatic information management system.
Owner:成都天志大行信息科技有限公司
Fan-out type packaging structure and packaging method
PendingCN114188227AEasy to integrateHighly integratedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipEngineering
The invention provides a fan-out packaging structure and a packaging method. The fan-out packaging structure comprises a first rewiring layer, a second rewiring layer, a metal connecting column, a semiconductor chip, a first filling layer, a first packaging layer, a stacked chip packaging body, a passive element, a second filling layer, a second packaging layer and a metal bump. According to the fan-out packaging structure, various chips with different functions can be integrated in one packaging structure, so that the integration of the fan-out packaging structure can be improved; through the first rewiring layer, the second rewiring layer and the metal connecting columns, three-dimensional vertical stacking packaging is achieved, the integration level of the packaging structure can be effectively improved, the conduction path can be effectively shortened, power consumption is reduced, the transmission speed is increased, and the data processing amount is increased.
Owner:SJ SEMICON JIANGYIN CORP
Signal-processing apparatus including a second processor that, after receiving an instruction from a first processor, independantly controls a second data processing unit without further instrcuction from the first processor
ActiveUS10230991B2High-performance and high-efficiencyLarge amount of data processingTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionImage compressionProcessing element
A signal-processing apparatus includes an instruction-parallel processor, a first data-parallel processor, a second data-parallel processor, and a motion detection unit, a de-blocking filtering unit and a variable-length coding / decoding unit which are dedicated hardware. With this structure, during signal processing of an image compression and decompression algorithm needing a large amount of processing, the load is distributed between software and hardware, so that the signal-processing apparatus can realize high processing capability and flexibility.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
FPGA-based multichannel cyclic data compressor and decompressor and method
ActiveCN104967453AReduce power consumptionReduce volumeCode conversionDesign technologyPower consumption
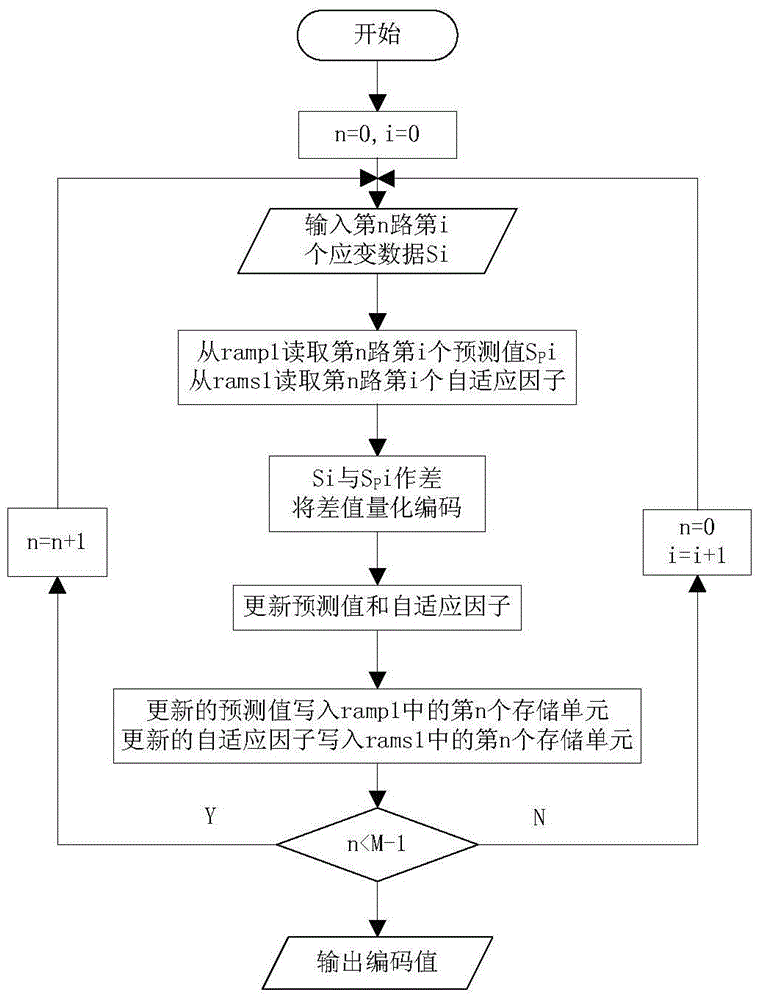
The invention relates to an FPGA-based multichannel cyclic data compressor and a decompressor and a method. An FPGA-based ASIC design technology is adopted, and performance requirements of low power consumption, small size, light weight, high integration, large data processing amount per unit time, good scalability and the like by a rotor strain data processing system can be met; the strain quantization level is selected to be 16bit, multi-rotor strain data acquisition precision is improved, and quantization precision is ensured and real-time processing is also realized; the data reduction error is between 10<-3> to 10<-2> magnitude, and precision demands can be met; and abnormal strain values can be reduced timely.
Owner:西安广角智创电子科技有限公司
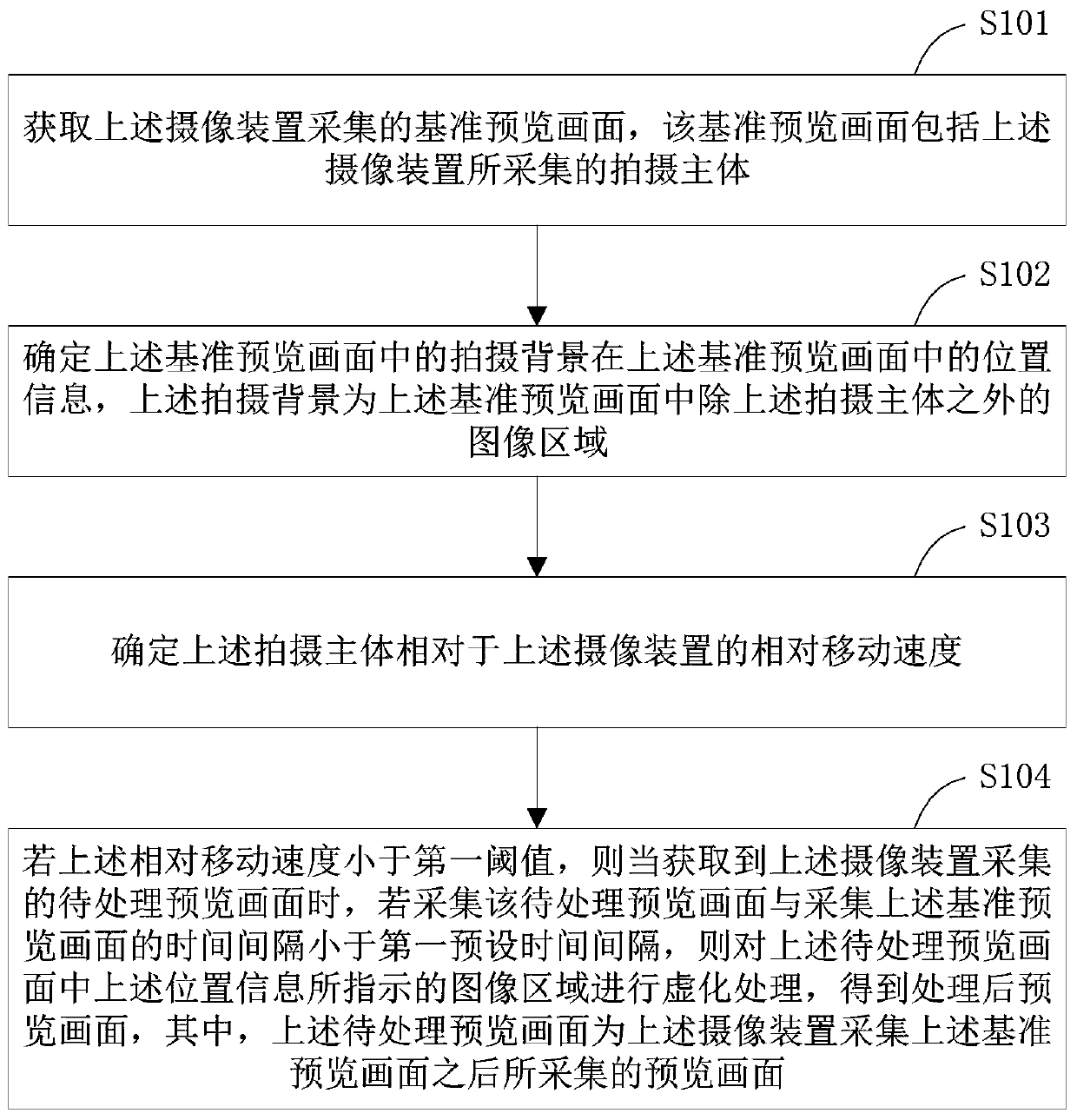
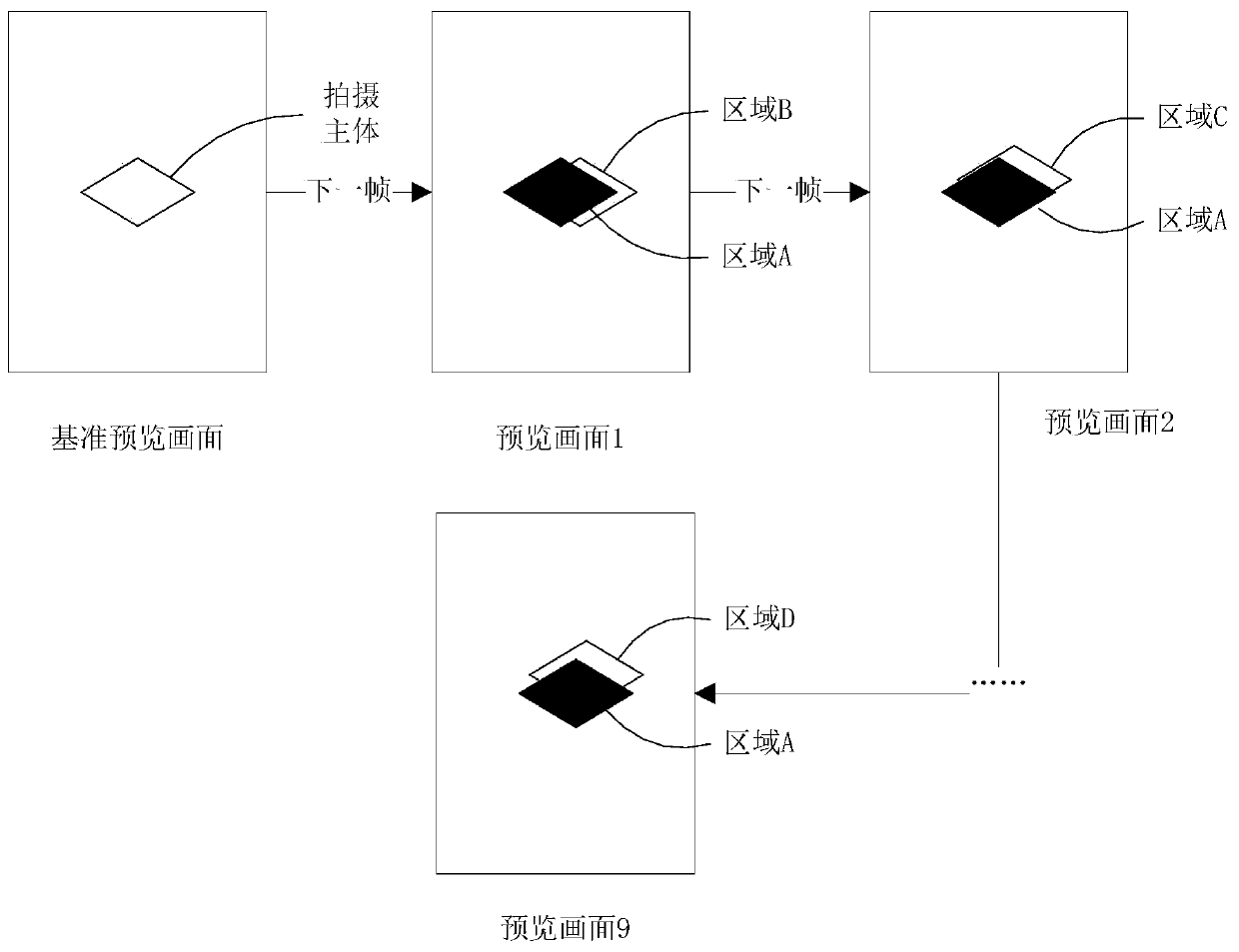
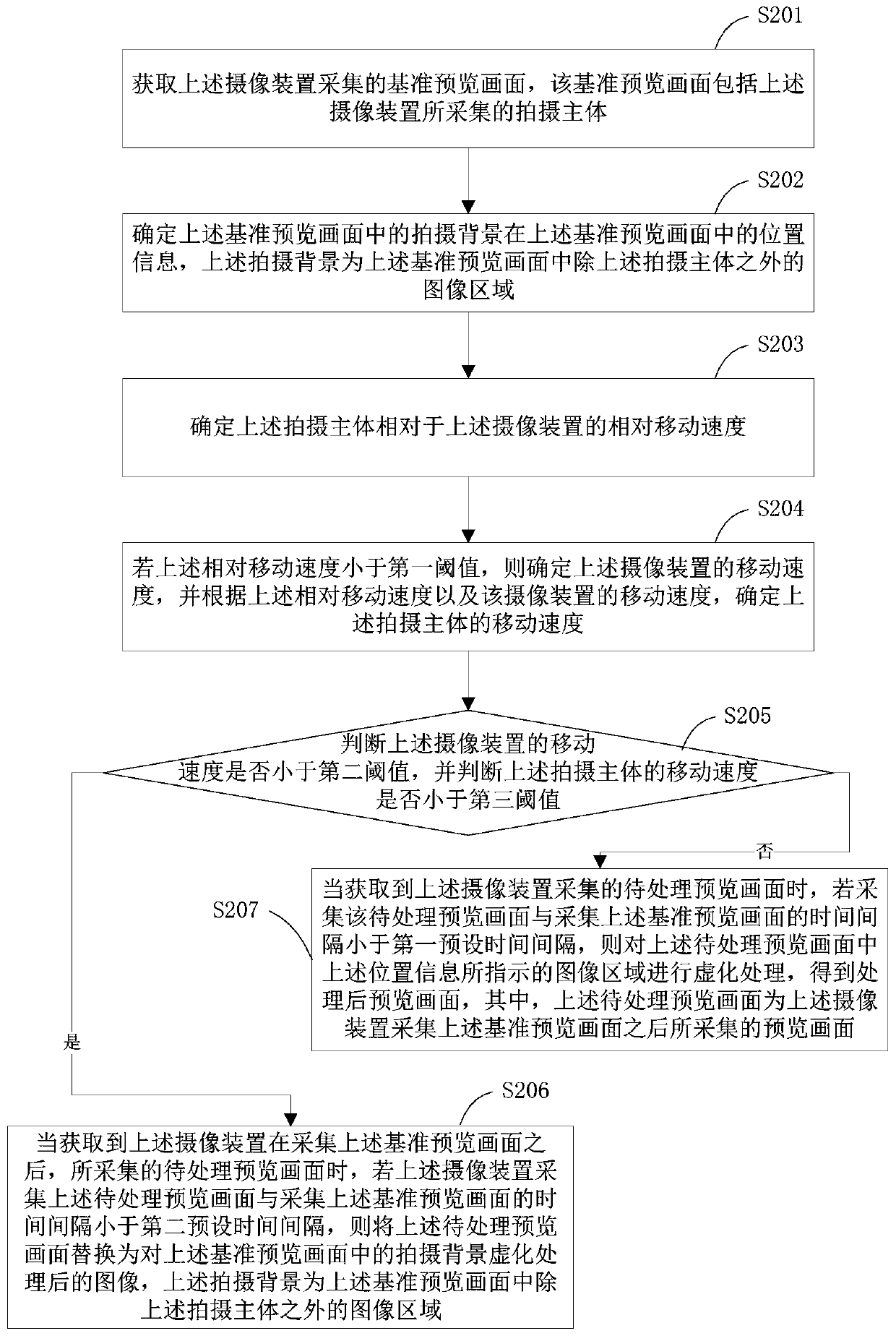
Preview image processing method, processing device, image pickup device and readable storage medium
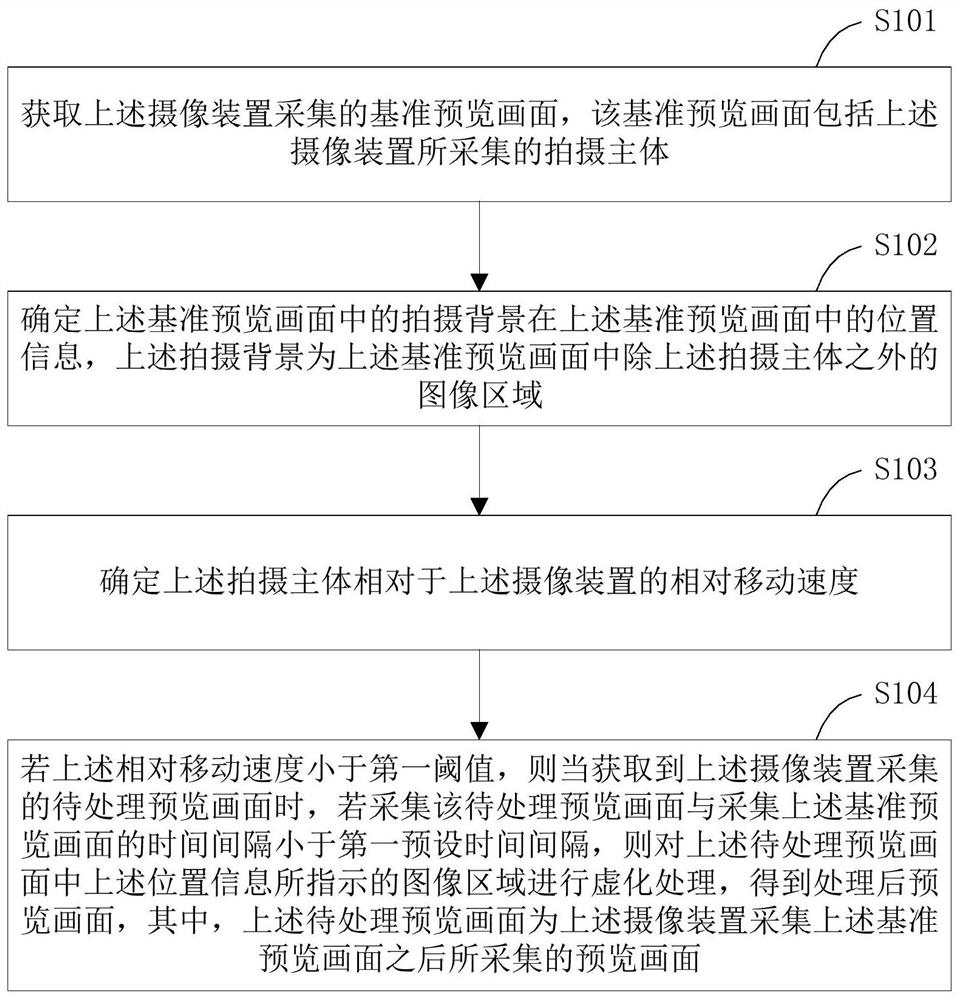
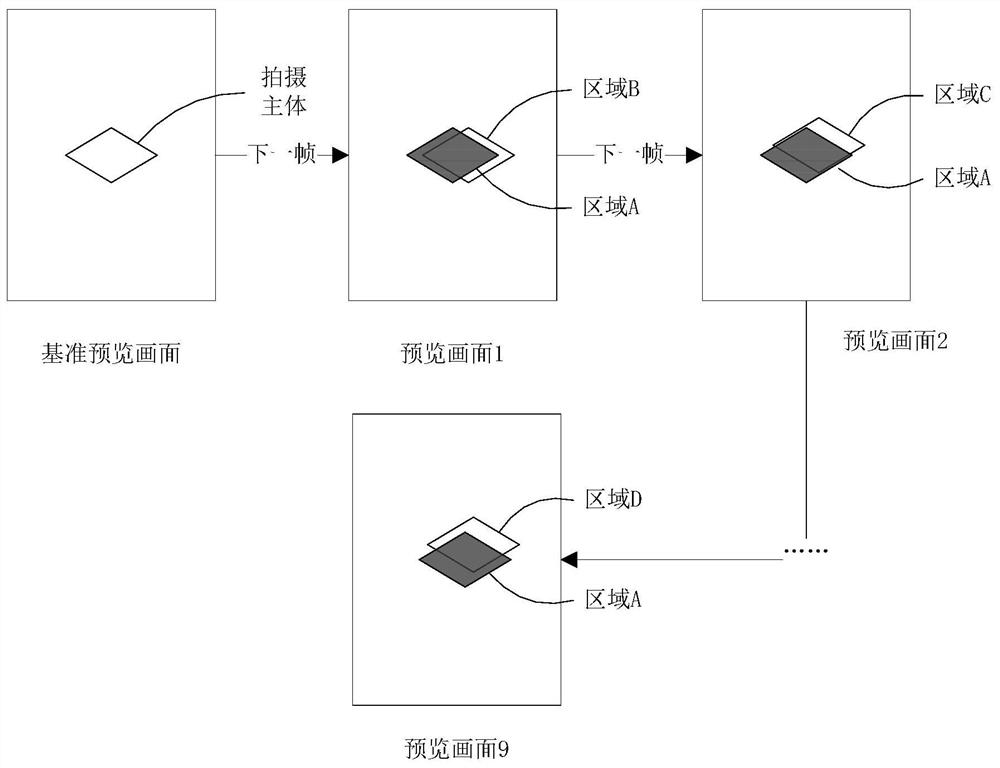
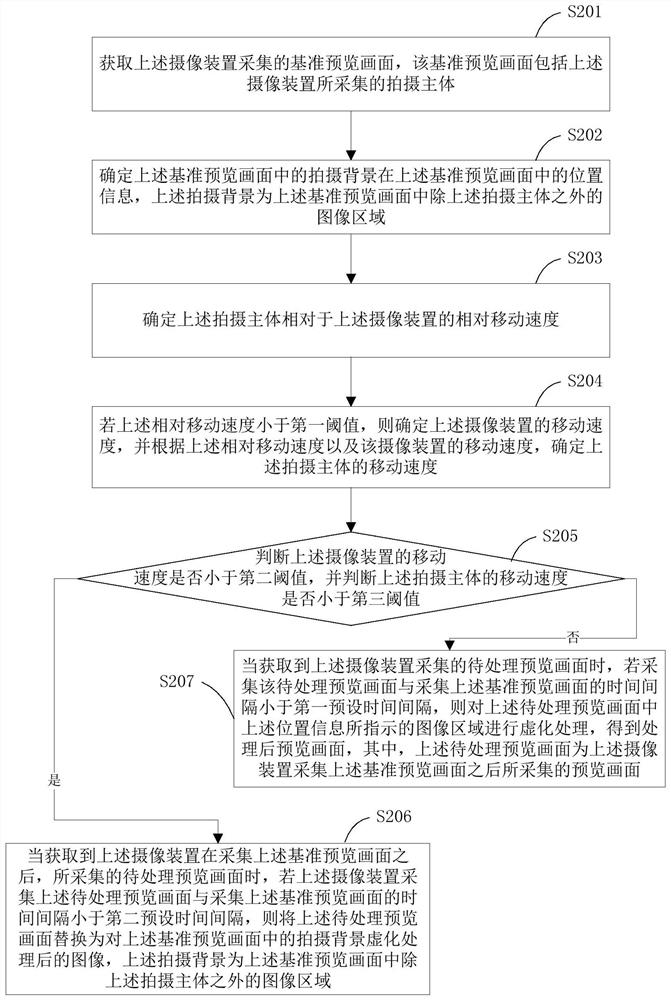
ActiveCN110266960ALarge amount of data processingImplementation of virtualizationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingImage area
The invention provides a preview image processing method and device, a camera device and a readable storage medium. The method is applied to the camera device and comprises the steps that a reference preview image collected by the camera device is obtained, and the reference preview image comprises a shooting body; determining position information of a shooting background in the reference preview image in the reference preview image; determining the relative movement speed of the shooting main body relative to the camera device; if the relative movement speed is smaller than a first threshold value, and if the time interval between the acquisition of the preview image to be processed and the acquisition of the reference preview image is smaller than a first preset time interval, performing blurring processing on an image area indicated by the position information in the preview image to be processed when the preview image to be processed acquired by the camera device subsequently is acquired. According to the invention, the blurring processing of the preview image can be realized on the premise that the data processing amount of the camera device is prevented from being too large.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
A method for testing and analyzing an automatic driving system
ActiveCN113074959BImprove efficiencyLarge amount of data processingVehicle testingNeural architecturesEvaluation resultTest analysis
The invention discloses a method for testing and analyzing an automatic driving system, which includes loading data to be evaluated, specifying evaluation indicators and evaluation scenarios required for evaluation; loading standard scene data as true value data according to the evaluation scene; obtaining feature quantities of the data to be evaluated; Feature quantity consistency and / or position consistency pair the data to be evaluated with the real value data to form a data pair; the position consistency refers to the consistency of positioning data in the data to be evaluated; the feature quantity consistency refers to The characteristic quantity error is smaller than the threshold; determine the matching degree of the data pair matching evaluation scene and the evaluation index, and use the data pair whose matching degree exceeds the threshold as the analysis object; analyze the evaluation index for the analysis object, and obtain the evaluation result. The invention can automatically process and analyze a large amount of automatic driving data, and has the advantages of high efficiency, large amount of data processing and accurate statistical indicators.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Preview image processing method, processing device, camera device and readable storage medium
ActiveCN110266960BLarge amount of data processingImplementation of virtualizationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
The present application provides a preview image processing method, a processing device, a camera device and a readable storage medium. The method is applied to an imaging device, and includes: obtaining a reference preview image collected by the imaging device, the reference preview image including the subject; determining the position information of the shooting background in the reference preview image in the reference preview image; determining The relative moving speed of the shooting subject relative to the camera device; if the relative moving speed is less than the first threshold, when the preview image to be processed subsequently collected by the camera device is acquired, if the preview image to be processed is acquired If the time interval between the image and the acquisition of the reference preview image is less than a first preset time interval, blurring is performed on the image area indicated by the position information in the preview image to be processed. In the present application, the blurring process of the preview image can be realized on the premise of avoiding an excessive data processing amount of the camera device.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
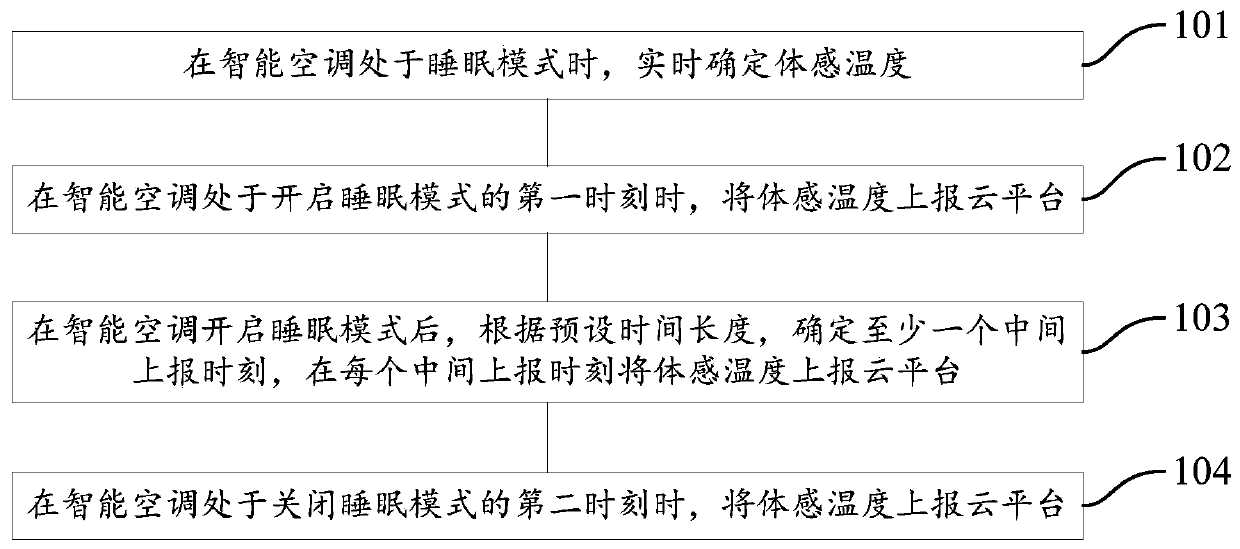
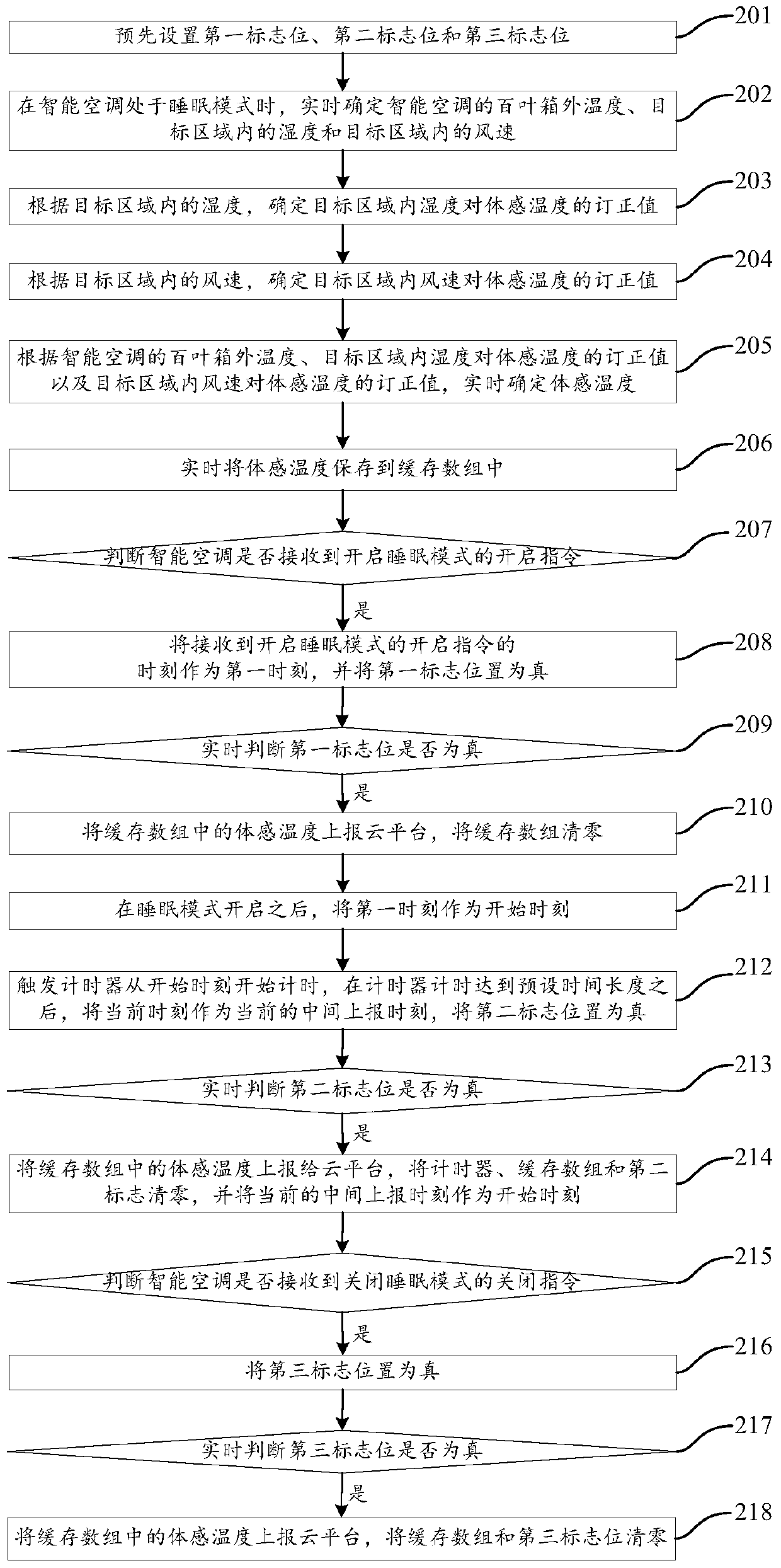
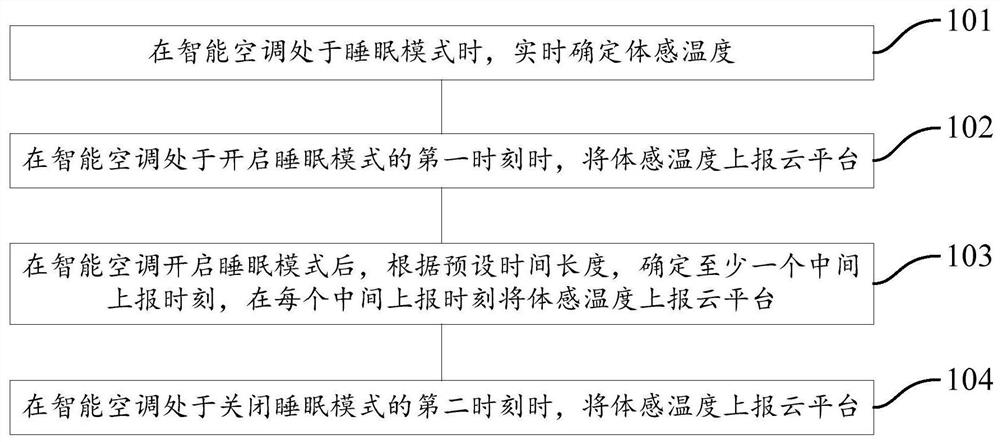
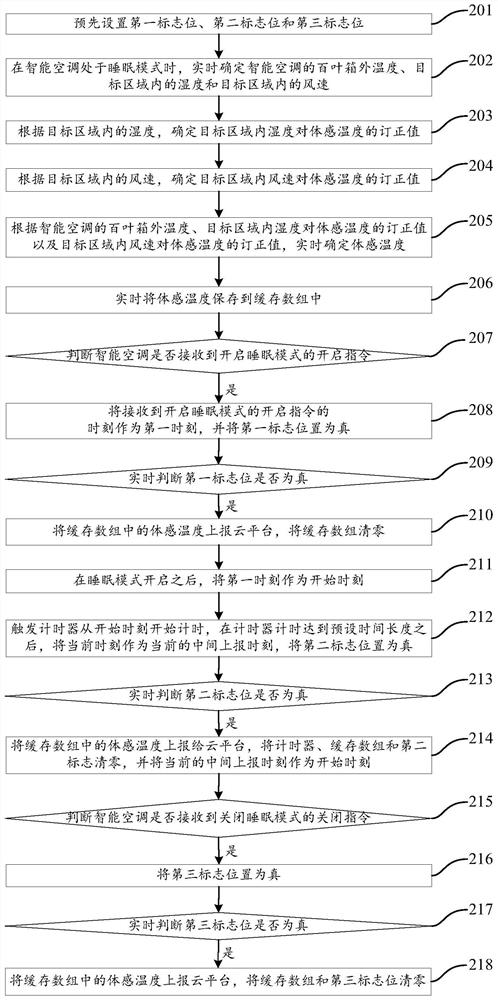
Sensible temperature reporting method and system and intelligent air-conditioner
ActiveCN111380190ALarge amount of data processingMechanical apparatusLighting and heating apparatusThermodynamicsEngineering
The invention provides a sensible temperature reporting method and system and an intelligent air-conditioner. The method includes the following steps that the sensible temperature is determined in real time when the intelligent air-conditioner is in a sleep mode; the sensible temperature is reported to a cloud platform at the first moment the intelligent air-conditioner starts the sleep mode; at least one middle reporting moment is determined according to the preset time duration after the intelligent air-conditioner starts the sleep mode, and the sensible temperature is reported to the cloudplatform at every middle reporting moment; and when the intelligent air-conditioner is at the second moment in a sleep shutdown mode, the sensible temperature is reported to the cloud platform. By adoption of the scheme, the sensible temperature can be reported.
Owner:SICHUAN HONGMEI INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
A Data Acquisition System for Wide Plate Tensile Testing Machine
ActiveCN104198281BQuick responseLarge amount of data processingStrength propertiesEngineeringTensile testing
The invention discloses a data acquisition system for a wide plate tensile testing machine, comprising: a sensor module, a data acquisition and processing module; capable of collecting and processing crack opening displacement signals, point strain signals, and regional strains during the wide plate tensile test process signal, mechanical signal, displacement signal and temperature signal, the acquisition system has a fast response speed, a large amount of data processing, and can prevent mutual interference between various signals. At the same time, the crack opening displacement signal, regional strain signal, mechanical signal and displacement signal collected in real time during the test can also be fed back in time, and the test signal can be fed back to the industrial computer as the main control parameter of the test process. Take control. Therefore, the wide-plate tensile test data acquisition system has high response frequency, strong anti-interference ability, high real-time data acquisition and high reliability.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Multi-machine cooperative control system based on UR robot
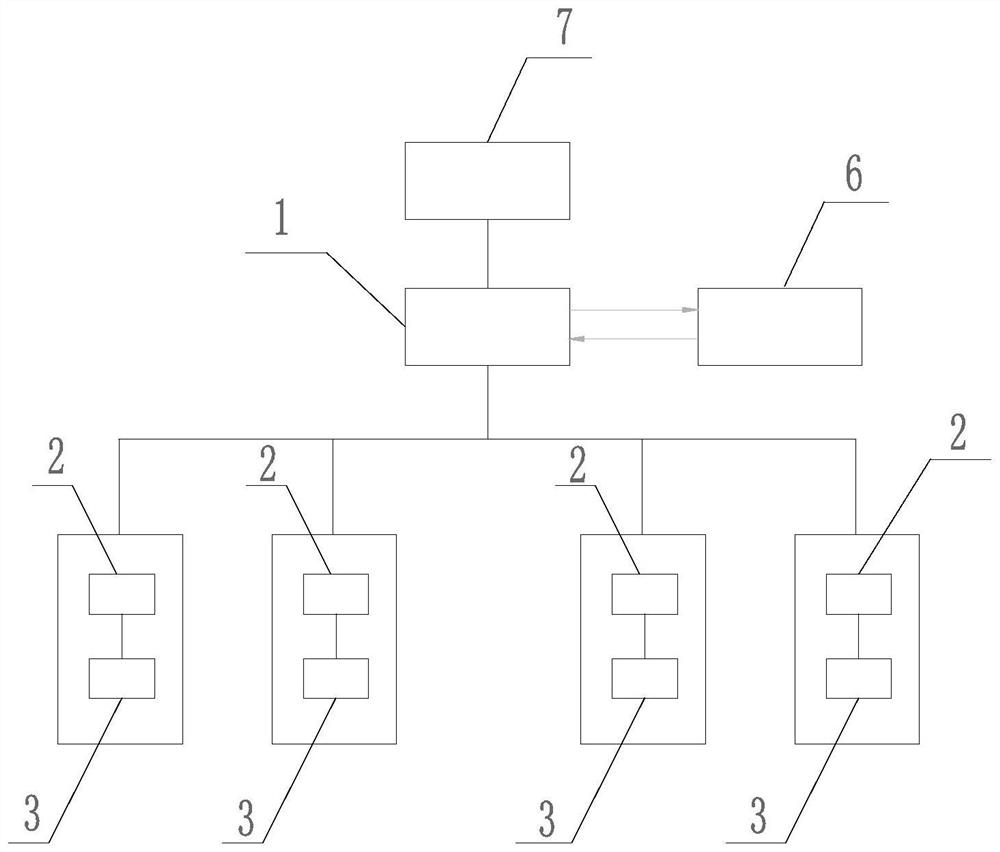
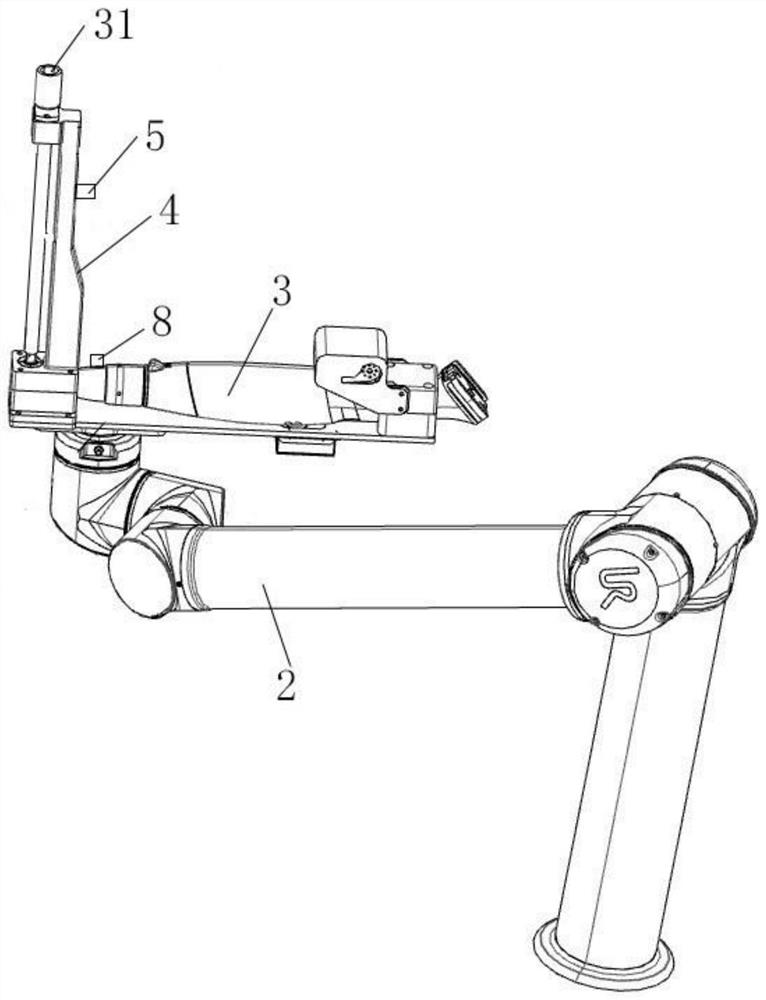
PendingCN114347073ANo location conflictReduce cost inputManipulatorControl systemControl engineering
The invention discloses a multi-machine cooperation control system based on a UR robot, the system comprises a plurality of tightening modules and an industrial personal computer, each tightening module comprises a UR robot, a clamp, a charging gun and a color sensor, the UR robot is connected with the clamp, the charging gun is installed on the clamp, the charging gun is used for tightening a bolt, and the industrial personal computer is connected with the industrial personal computer. Each charging gun is provided with a warning lamp, the warning lamps are used for representing the tightening result, the color sensor is used for sensing the lighting condition of the warning lamps, and the industrial personal computer is electrically connected with the color sensor, the UR robots and the charging guns. According to the multi-machine cooperative control system based on the UR robots, the industrial personal computer and the multiple tightening modules are arranged, the multiple tightening modules receive a unified instruction of the industrial personal computer, the robots are in mutual linkage, and position conflicts cannot be generated.
Owner:昆山青眼自动化技术有限公司
Method and system for reporting body temperature, intelligent air conditioner
ActiveCN111380190BLarge amount of data processingMechanical apparatusLighting and heating apparatusSimulationAir conditioning
The invention provides a method and system for reporting body-sensed temperature, and an intelligent air conditioner. The method includes the following steps: when the intelligent air-conditioner is in sleep mode, determine the body-sensed temperature in real time; Report to the cloud platform; after the smart air conditioner turns on the sleep mode, determine at least one intermediate reporting time according to the preset time length, and report the somatosensory temperature to the cloud platform at each intermediate reporting time; , and report the body temperature to the cloud platform. This solution can report the body temperature.
Owner:SICHUAN HONGMEI INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
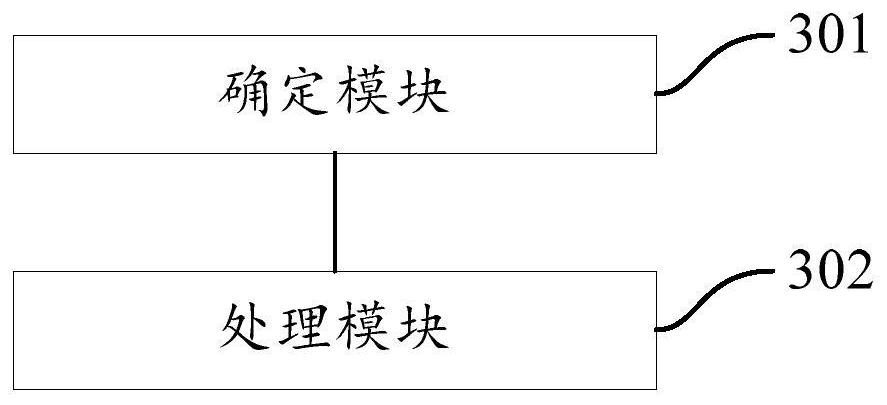
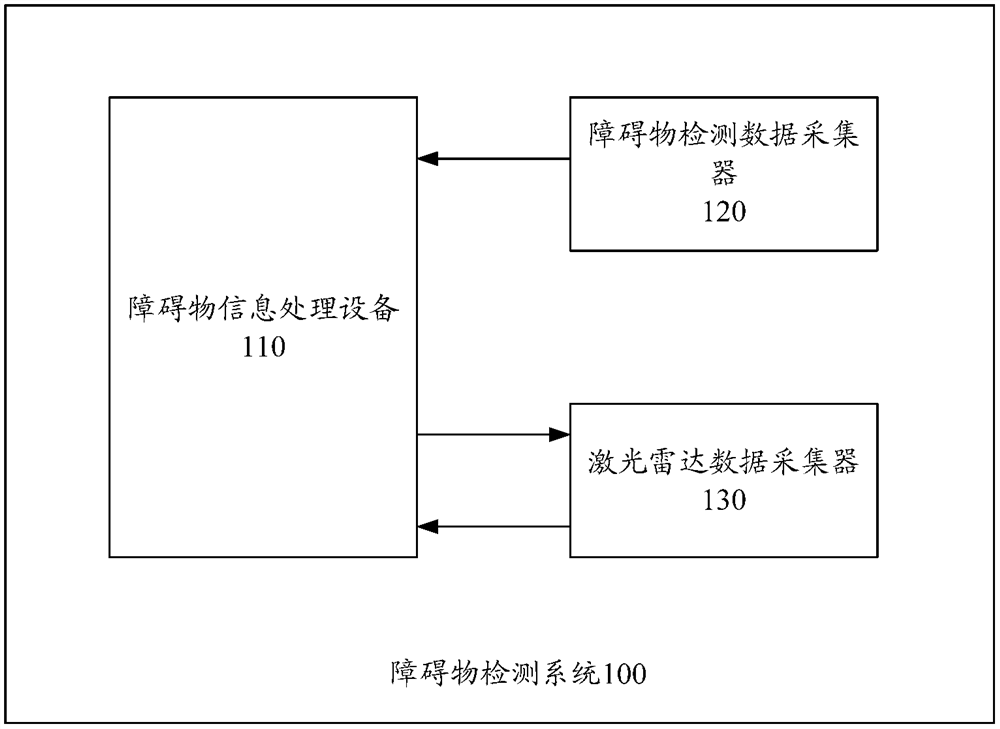
An obstacle detection method and device
ActiveCN110691990BGuaranteed recognition accuracyLarge amount of data processingScene recognitionElectromagnetic wave reradiationPattern recognitionInformation processing
An obstacle detection method and system (100), used to improve the accuracy of obstacle recognition while avoiding a large amount of data processing, the method includes: an obstacle information processing device (110) receiving an obstacle detection data collector (120) For the description information of n obstacles collected by the target vehicle, update the obstacle information list according to the description information of the n obstacles, and obtain the updated obstacle information list; the obstacle information processing device (110) according to the updated obstacle information object information list to obtain target area information and non-target area information, and send the target area information and non-target area information to the laser radar data collector (130); the obstacle information processing device (110) receives the laser radar data collector (130) ) collection of sampling points; finally, the obstacle information processing device (110) obtains an obstacle detection result according to the sampling point set and the updated obstacle information list. Therefore, a large amount of data processing is avoided, and at the same time, the accuracy of obstacle recognition is guaranteed.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
A Frequency Domain Analysis Method of Bridge Fatigue Life Based on Dynamic Weighing System
ActiveCN105005694BPrevent deviationThe calculation result is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsCurve fittingEngineering
The invention relates to a bridge fatigue life frequency domain analysis method based on a dynamic weighing system, comprising: collecting vehicle weight, vehicle speed, and wheelbase data of each vehicle passing the bridge; counting the collected data, and performing curve fitting; Based on the probability density curve of the vehicle, the cellular automaton simulation model of the vehicle is established to generate random traffic flow; the load time history under different traffic density conditions is simulated, and the load time history is loaded on the bridge influence line to obtain the stress time history Data; perform fast Fourier transform FFT on the stress time history, and obtain the stress power spectral density PSD, and calculate related parameters; use the Dirlik method to establish the empirical form of the stress probability density function PDF; calculate the remaining life. The invention results in a significant reduction in computing time.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
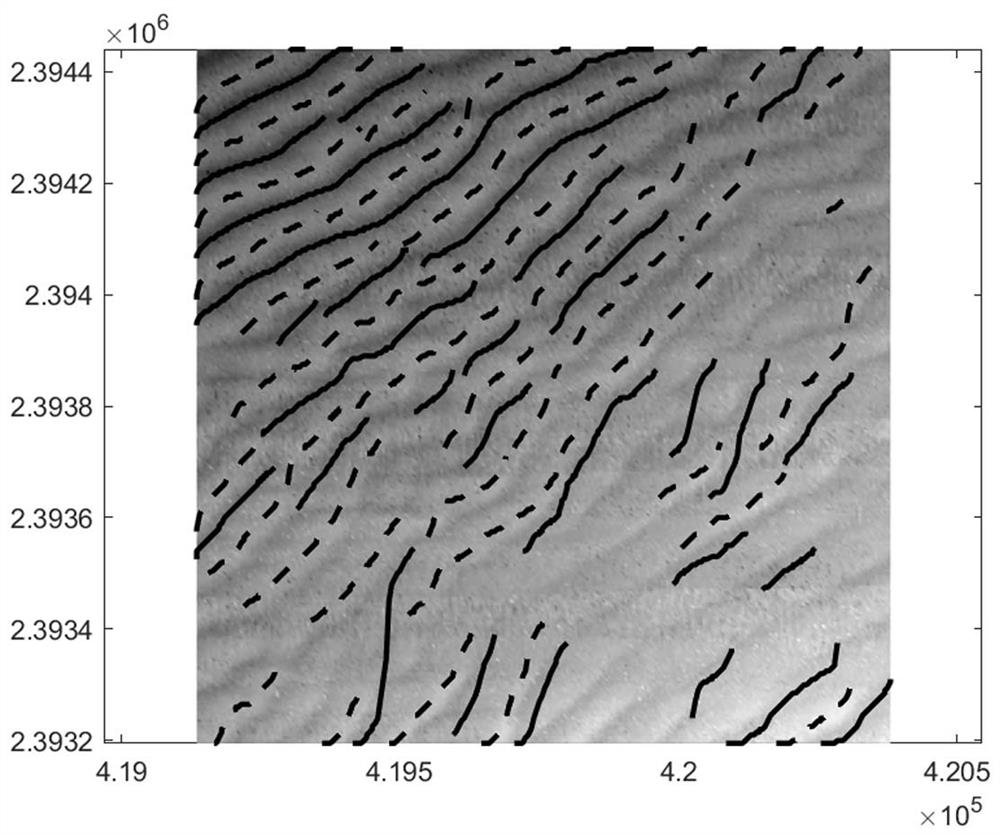
Seabed sand wave feature identification method
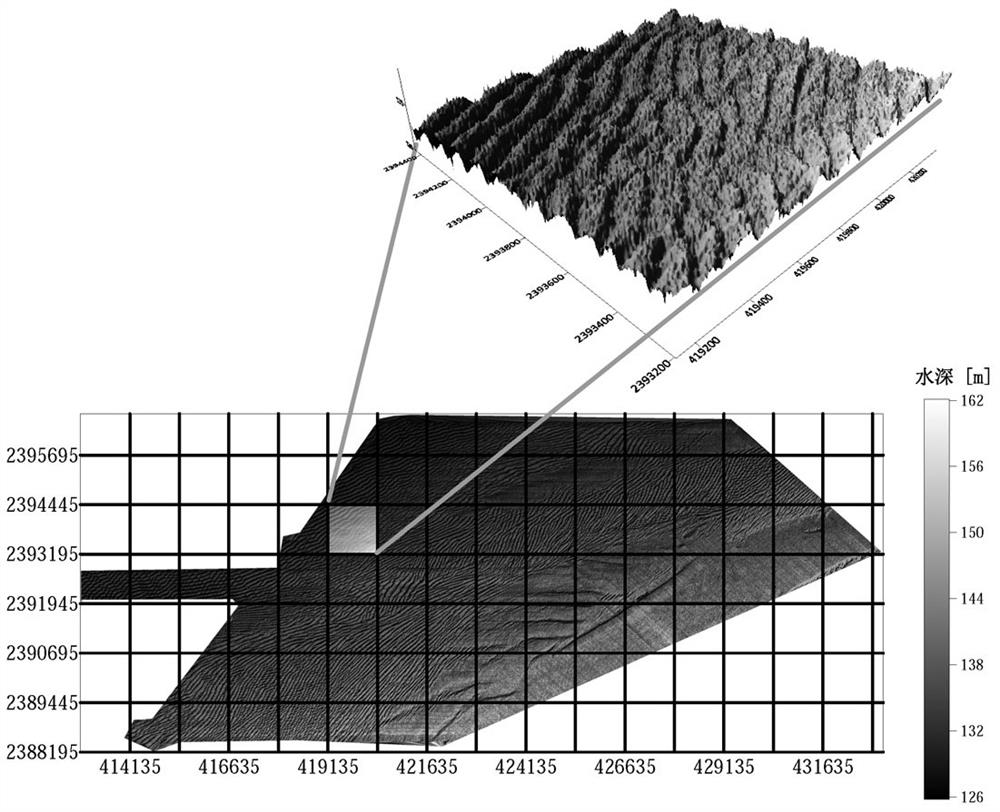
ActiveCN113283437ADosa wave feature samplesShorten the timeCharacter and pattern recognitionSand waveWave height
The invention discloses a seabed sand wave feature identification method, and relates to the technical field of offshore ocean engineering dynamic geologic and geomorphic environments. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring wave crest lines and wave trough lines of sand waves by utilizing actually measured water depth data and adopting an image identification method, grouping the wave crest lines and the wave trough lines of the sand waves through linear fitting and coordinate transformation, and further automatically acquiring characteristic information of the wave length, the wave height and the like of the sand waves in a large area by utilizing information of the wave crest lines and the wave trough lines of the sand waves. According to the method, the wave crest line and the wave trough line of the large-area seabed sand wave can be automatically identified, classified statistics can be automatically carried out on the wave crest line and the wave trough line of the sand wave, a large amount of sand wave characteristic data is further obtained, basic data is provided for further analyzing the relation among the wave length, the wave height, the water depth, the hydrodynamic force and the like of the sand wave, time and cost are saved, and efficiency is improved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
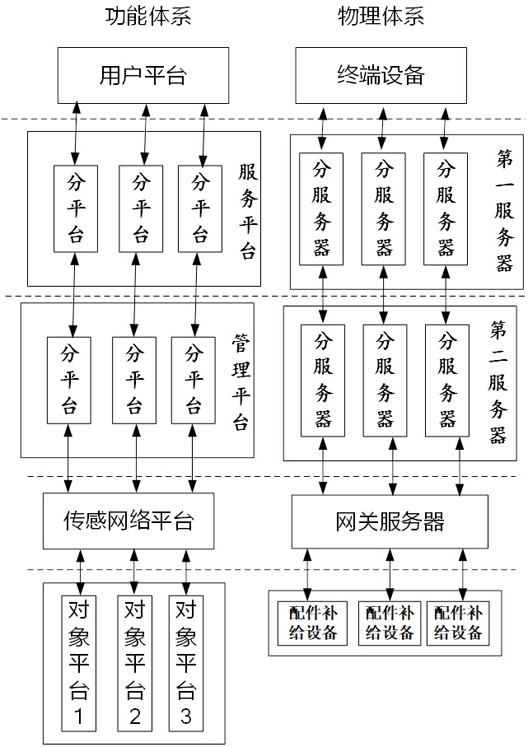
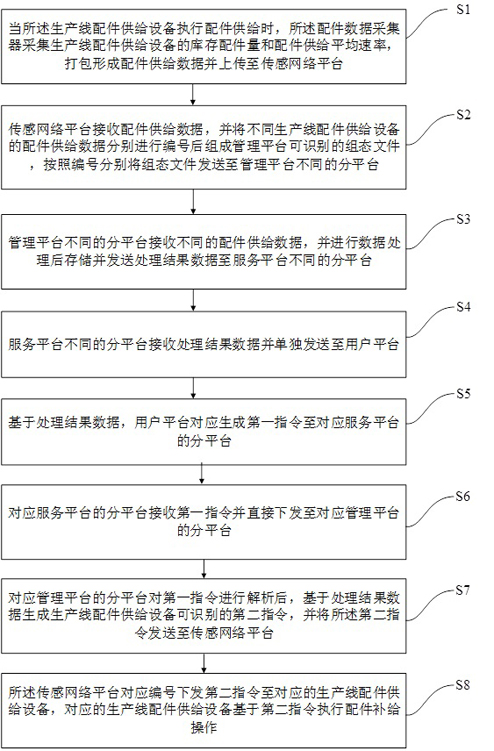
Industrial Internet of Things for regulating and controlling accessory inventory and control method thereof
ActiveCN114723375AEasy to handleReduce transfer volumeProgramme controlLogisticsProduction lineData acquisition
The invention discloses an industrial Internet of Things for regulating and controlling the inventory of accessories and a control method thereof. The industrial Internet of Things for regulating and controlling the inventory of accessories comprises a user platform, a service platform, a management platform, a sensing network platform and an object platform which are sequentially interacted with one another, the service platform and the management platform are arranged independently, and the sensing network platform is arranged in a centralized manner; the object platforms are configured as different production line accessory supply devices, and the production line accessory supply devices are each provided with an accessory data collector. The accessory storage and consumption conditions of the corresponding production line accessory supply equipment are obtained, the collected data are uploaded in real time, and data processing and transmission are separately and independently carried out through the independent service platform and the management platform, so that different data processing parameters can be set for different production line accessory supply equipment; therefore, the accessory inventory of different production line accessory supply devices is regulated and controlled, and an Internet of Things mode of unified data receiving and sending, classified processing and transmission is realized.
Owner:CHENGDU QINCHUAN IOT TECH CO LTD
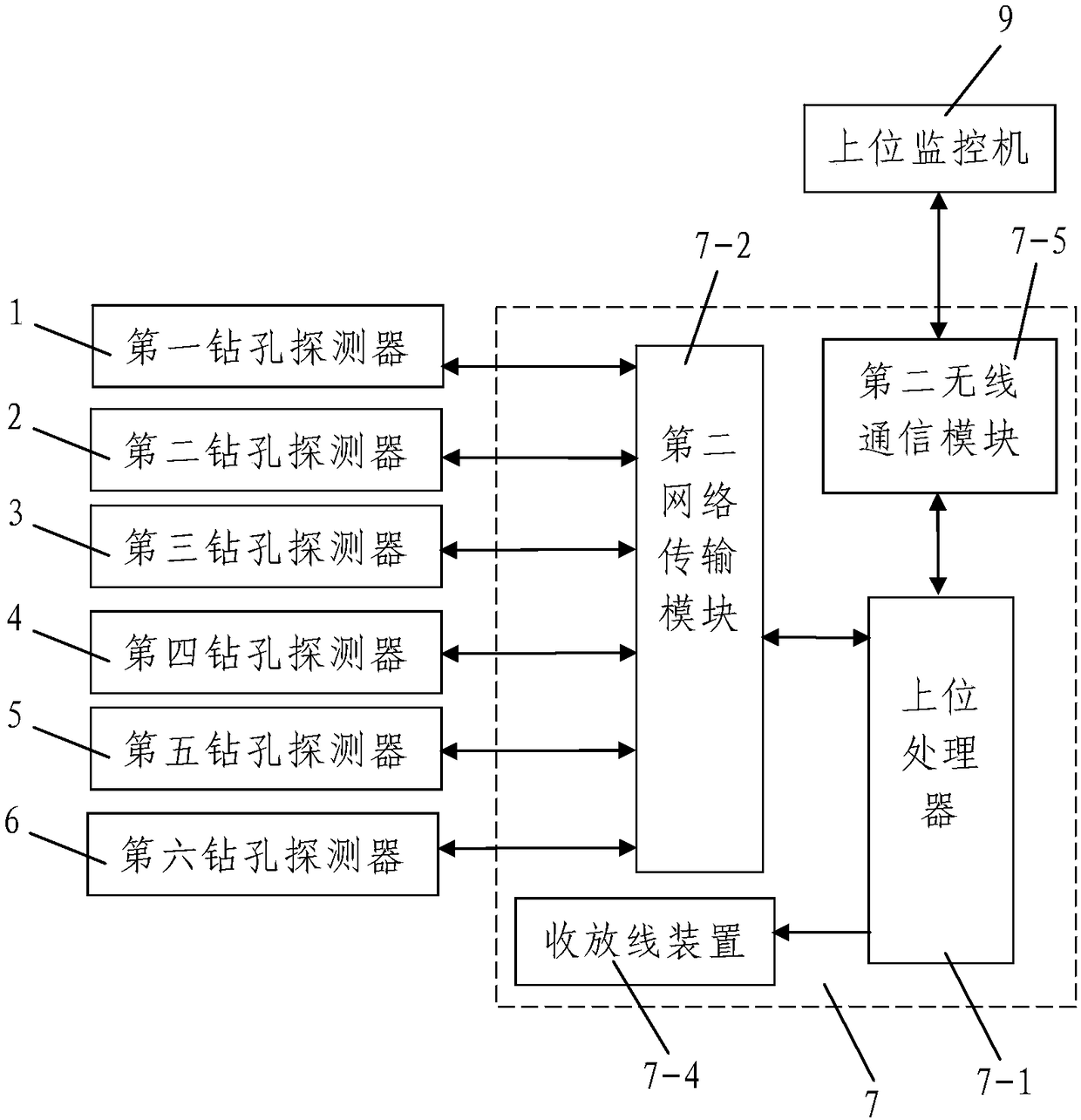
Multi-information life detection system and detection method for mine drilling rescue
ActiveCN106223999BSimple structureEasy wiringClosed circuit television systemsSafety equipmentsIntrinsic safetyLife detection
The invention discloses a mine drilling rescue diversified-information-based life detecting system and a detecting method. The mine drilling rescue diversified-information-based life detecting system comprises a drilled hole internal detecting device and a ground monitoring device. The drilled hole internal detecting device comprises six drilled hole detectors which can descend into drilled holes from bottom to top, and the six drilled hole detectors are connected with the ground monitoring device by data transmission lines; the six drilled hole detectors comprise detector shells and electronic circuit boards, the electronic circuit boards are arranged in the detector shells, and controllers, first network transmission modules and intrinsic safety power sources are arranged on the electronic circuit boards. The detecting method includes steps of firstly, drilling the holes in locations with drilling rescue requirements by the aid of drilling equipment; secondly, detecting lives by the aid of drilled hole detector combinations via the drilled holes. The mine drilling rescue diversified-information-based life detecting system and the detecting method have the advantages that the mine drilling rescue diversified-information-based life detecting system is reasonable in design, easy and convenient to use and flexible in usage modes, good use effects can be realized, internal information of the drilled holes can be easily, conveniently, quickly and comprehensively acquired and can be diversified, and accordingly reliable evidence can be provided for mine drilling rescue.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
FPGA-based multiplex loop data compressor and decompressor and method
ActiveCN104967453BReduce power consumptionReduce volumeCode conversionData processing systemPartition of unity
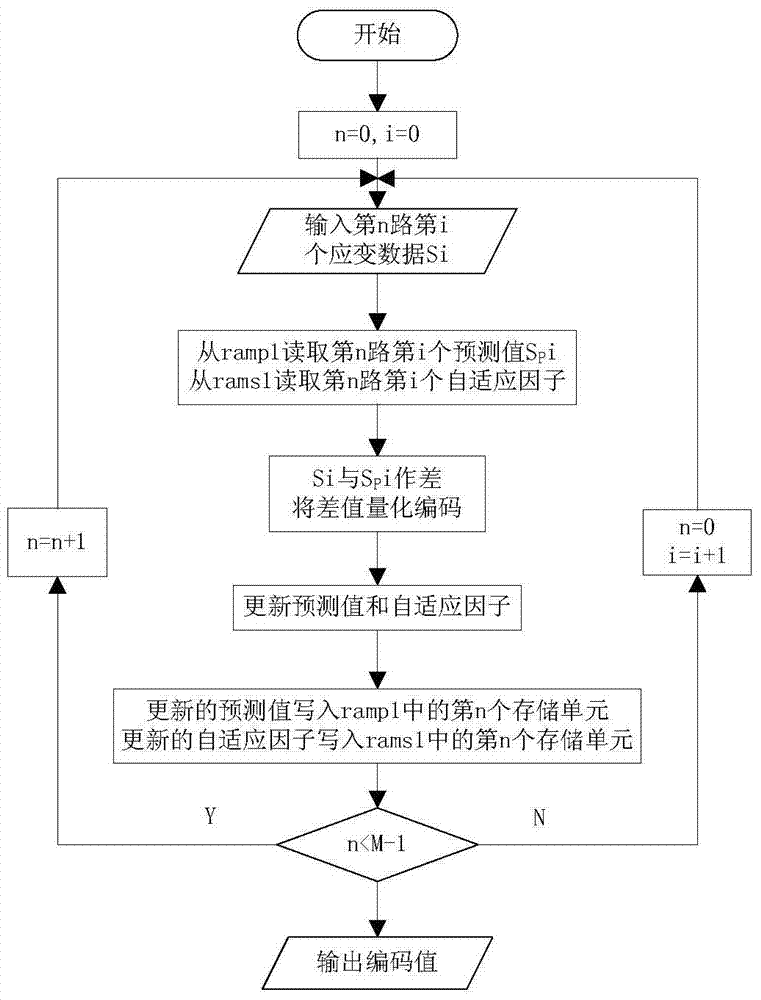
The invention relates to an FPGA-based multi-channel cyclic data compressor, decompressor and method, which adopts the FPGA-based ASIC design technology to meet the low power consumption, small volume, light weight, high integration, and unit time requirements of the rotor strain data processing system. Large amount of internal data processing, good scalability and other performance requirements; the quantization level of the strain variable is selected as 16bit, which improves the accuracy of the multi-rotor strain acquisition data, and realizes real-time processing while ensuring the quantification accuracy; the data restoration error is 10‑3 ~10‑2 order of magnitude, which meets the accuracy requirements; the abnormal strain value is restored in time.
Owner:西安广角智创电子科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com