Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44results about How to "Feature retention" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
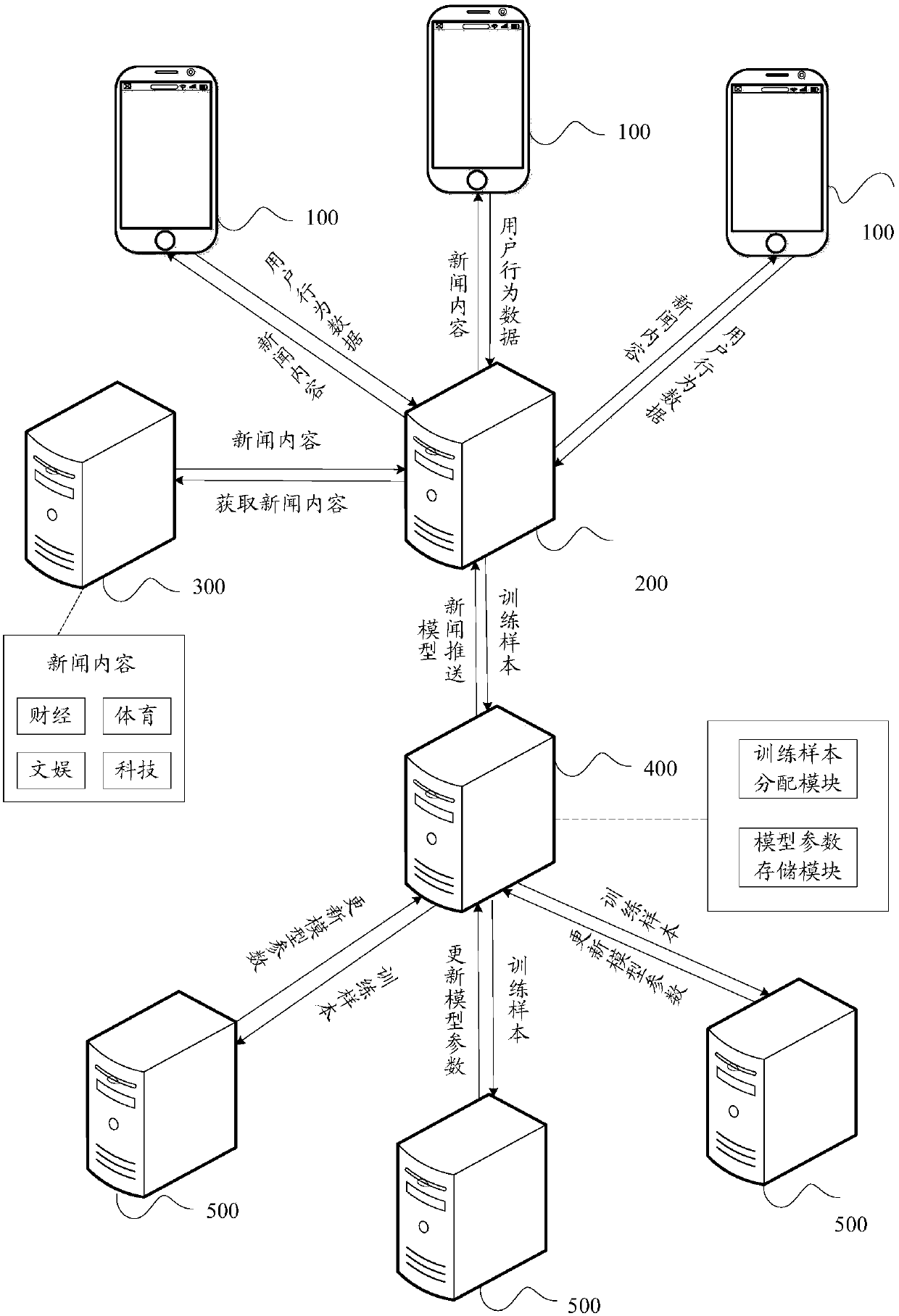
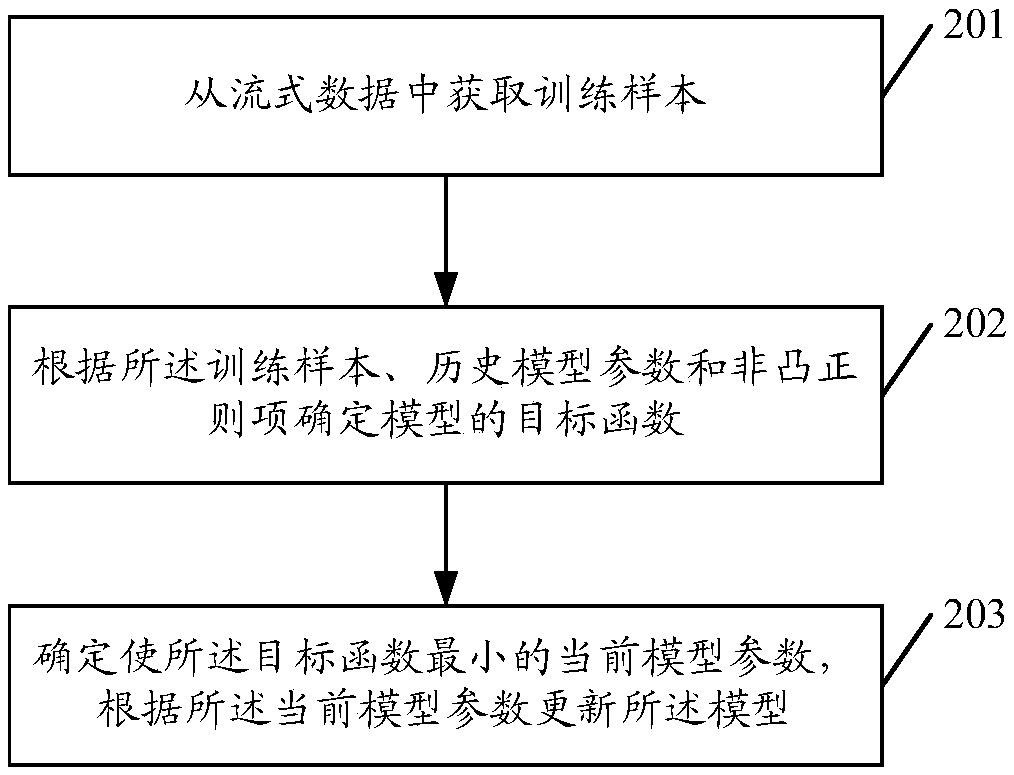
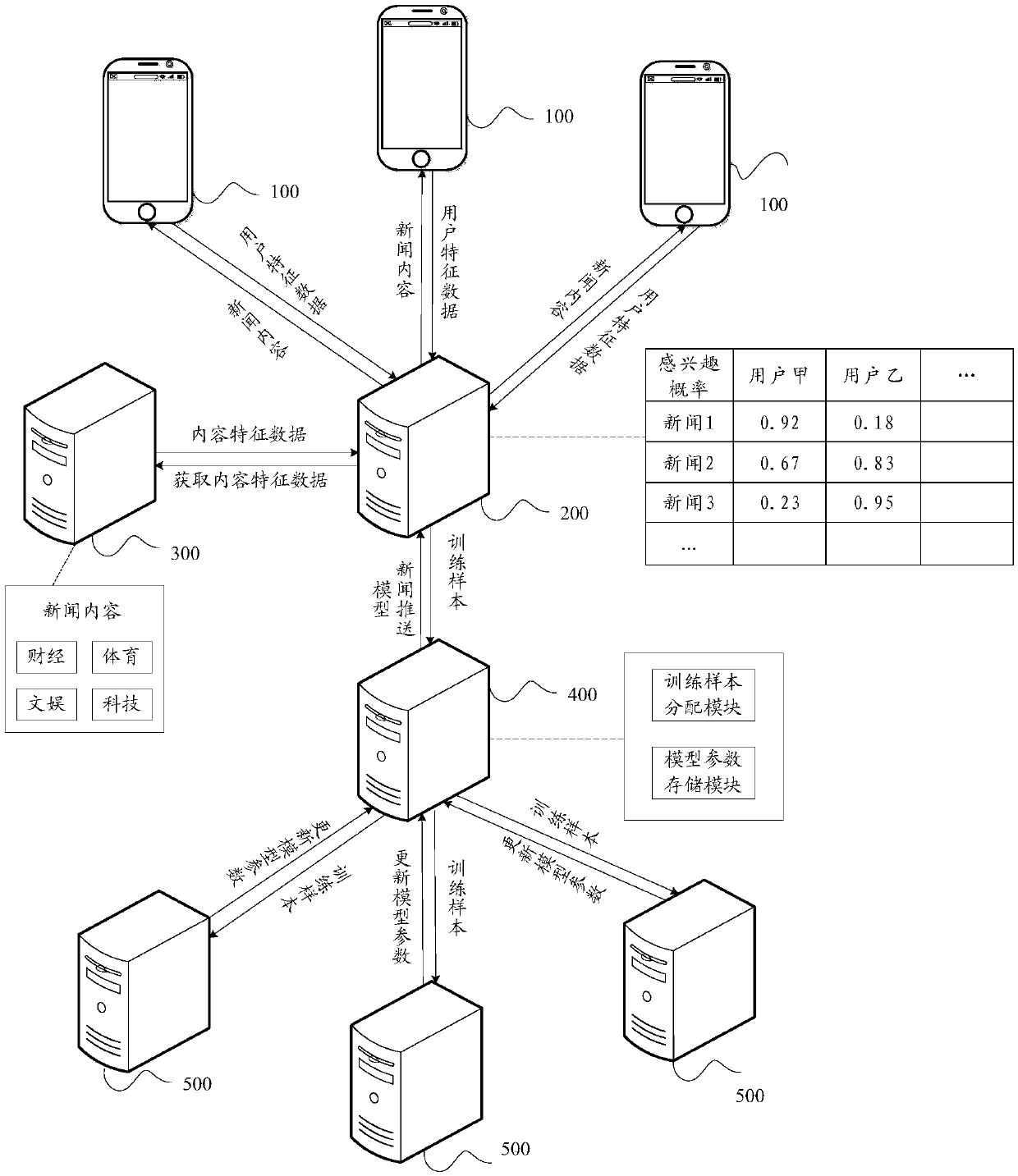
Online model training method, pushing method, device and equipment
ActiveCN110321422AImprove sparsityImprove forecast accuracyDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionHistorical modelStreaming data
The embodiment of the invention discloses an online model training method. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a training sample from streaming data, determining an objective function of the model according to the training sample, historical model parameters and non-convex regular terms, determining current model parameters enabling the objective function to be minimum, and updating the model according to the current model parameters. In the online training process, since the non-convex regular term is adopted to replace the L1 regular term for feature screening, the penalty deviationcan be reduced, effective features can be screened out, the sparsity is guaranteed, and the generalization performance of the model is improved. The invention further provides an information pushing method. The method comprises: obtaining user feature data and content feature data, based on the pushing model obtained by the online training model method, determining the probability that a target user is interested in target information according to the user feature data, the content feature data and the pushing model, and determining whether pushing is conducted or not according to the probability that the target user is interested in. The invention further provides an online model training device and an information pushing device.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
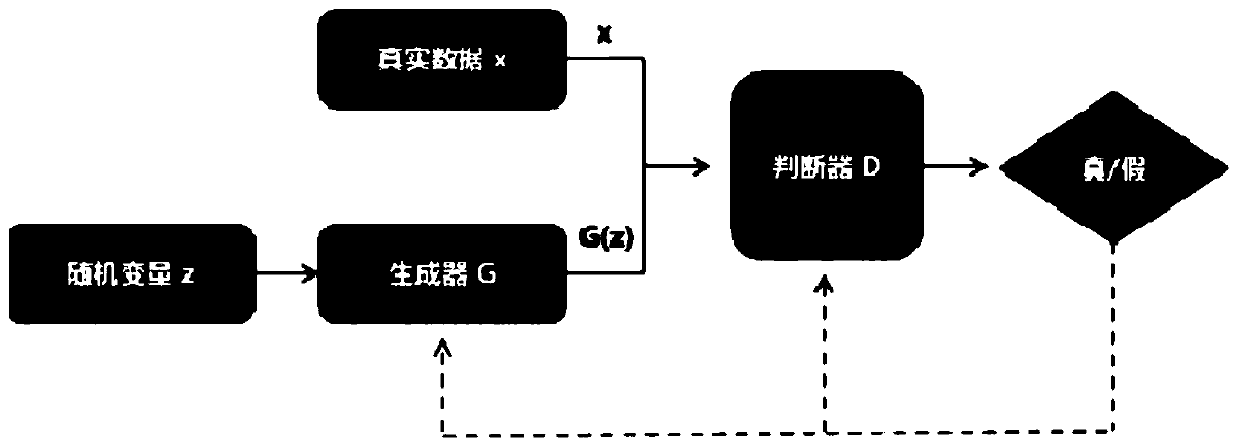
Electric power image data augmentation method based on generative adversarial network
InactiveCN110414362AQuality improvementImprove efficiencyChecking time patrolsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionSynthesis methods
The invention discloses an electric power image data augmentation method based on a generative adversarial network. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining an original image during electric power system inspection; performing image processing on the original image, eliminating interference and influence of noise and the like in the original image, and obtaining a high-quality target image; performing feature enhancement on the target image, and extracting image features; and performing game synthesis of the target image and the background image through a generative adversarial network method to generate new image data. According to the scheme, data augmentation is carried out on the power image through the generative adversarial network method, image annotation does not need tobe carried out on the synthesized image, manpower and material resource cost is saved, and meanwhile the synthesis method is scientific, reasonable, high in augmentation result quality, high in efficiency and high in scheme feasibility.
Owner:ANHUI JIYUAN SOFTWARE CO LTD +3
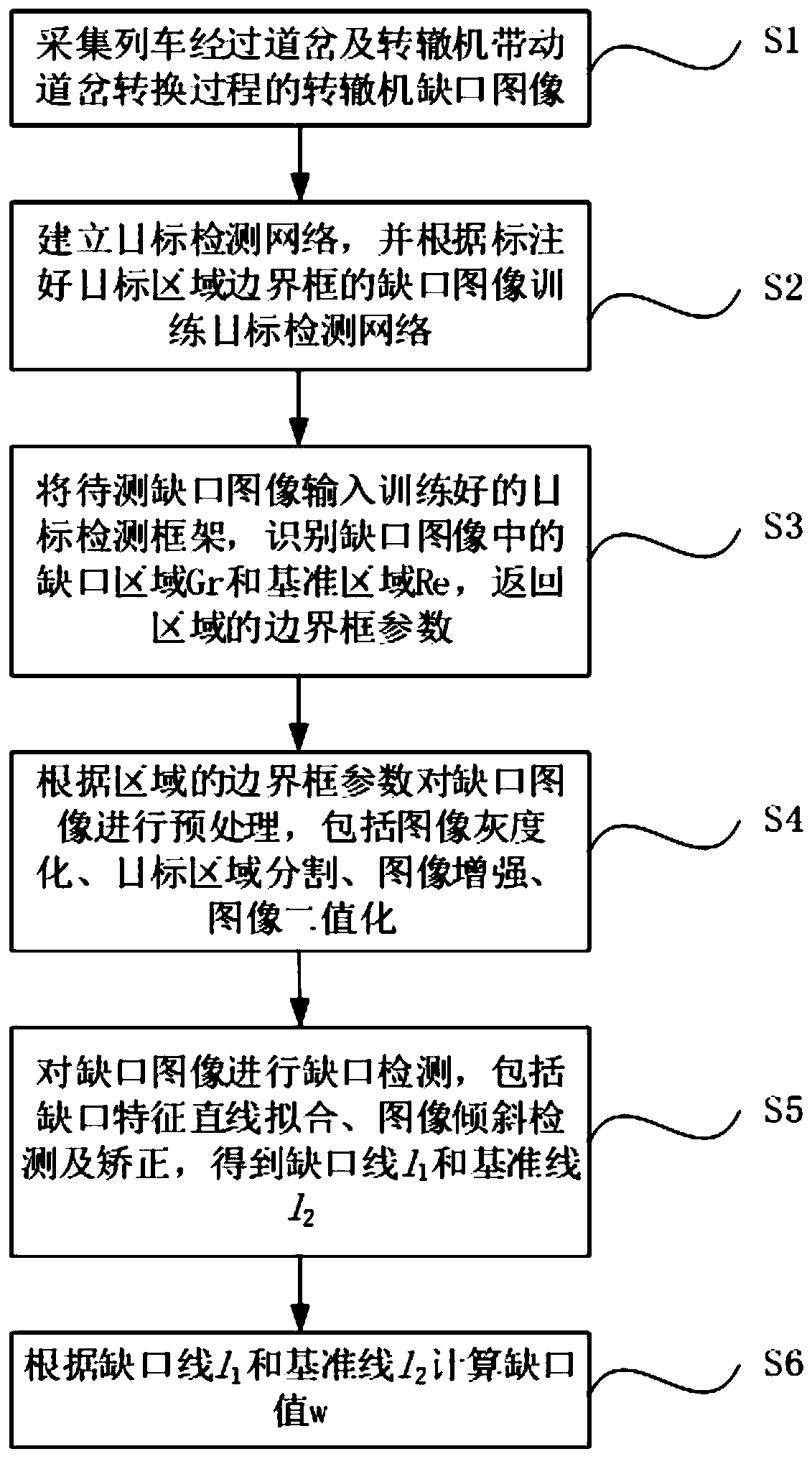
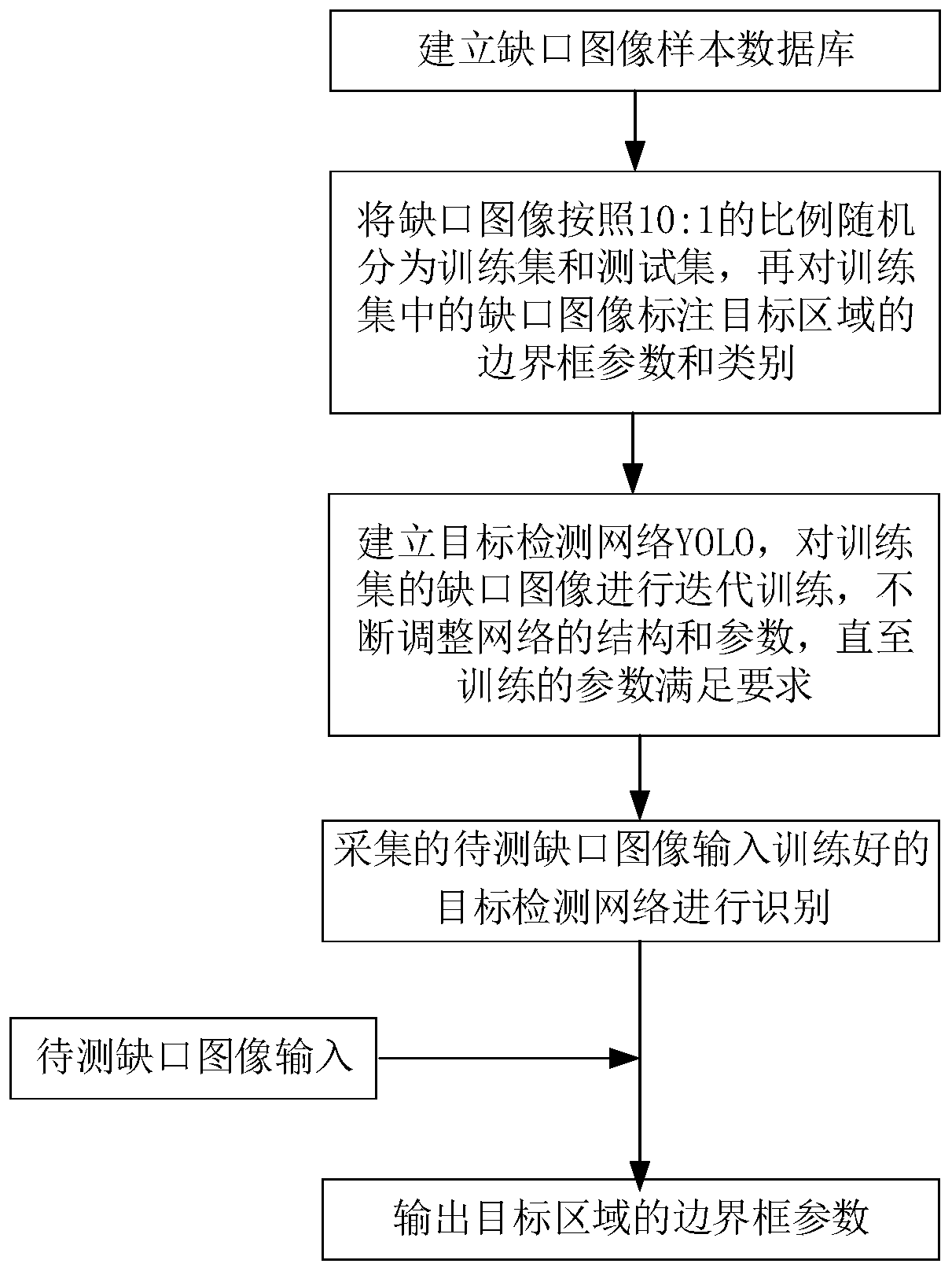
Point switch notch detection method based on target detection and image processing
ActiveCN110310255AReduce complexityGuaranteed uptimeImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
The invention provides a point switch notch detection method based on target detection and image processing. The point switch notch detection method comprises the steps: collecting a point switch notch image in the process that a train passes through a turnout and the turnout is driven by the point switch to be converted; establishing a target detection network and training; inputting the notch image to be detected into the trained target detection network, identifying a target area in the notch image, and obtaining a boundary frame parameter of the area; preprocessing the gap image accordingto the boundary frame parameters of the area; carrying out notch detection on the notch image, including notch feature straight line fitting and image inclination detection and correction; and calculating a gap value w according to the gap characteristic straight line. The point switch notch detection method can be directly applied to various types of switch machines, does not need to set different image preprocessing parameters for the different types of switch machines, is suitable for complex and severe operation conditions such as local overexposure of the notch image and inclination of the notch image, and can further improve the accuracy, robustness and universality of a notch detection system.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
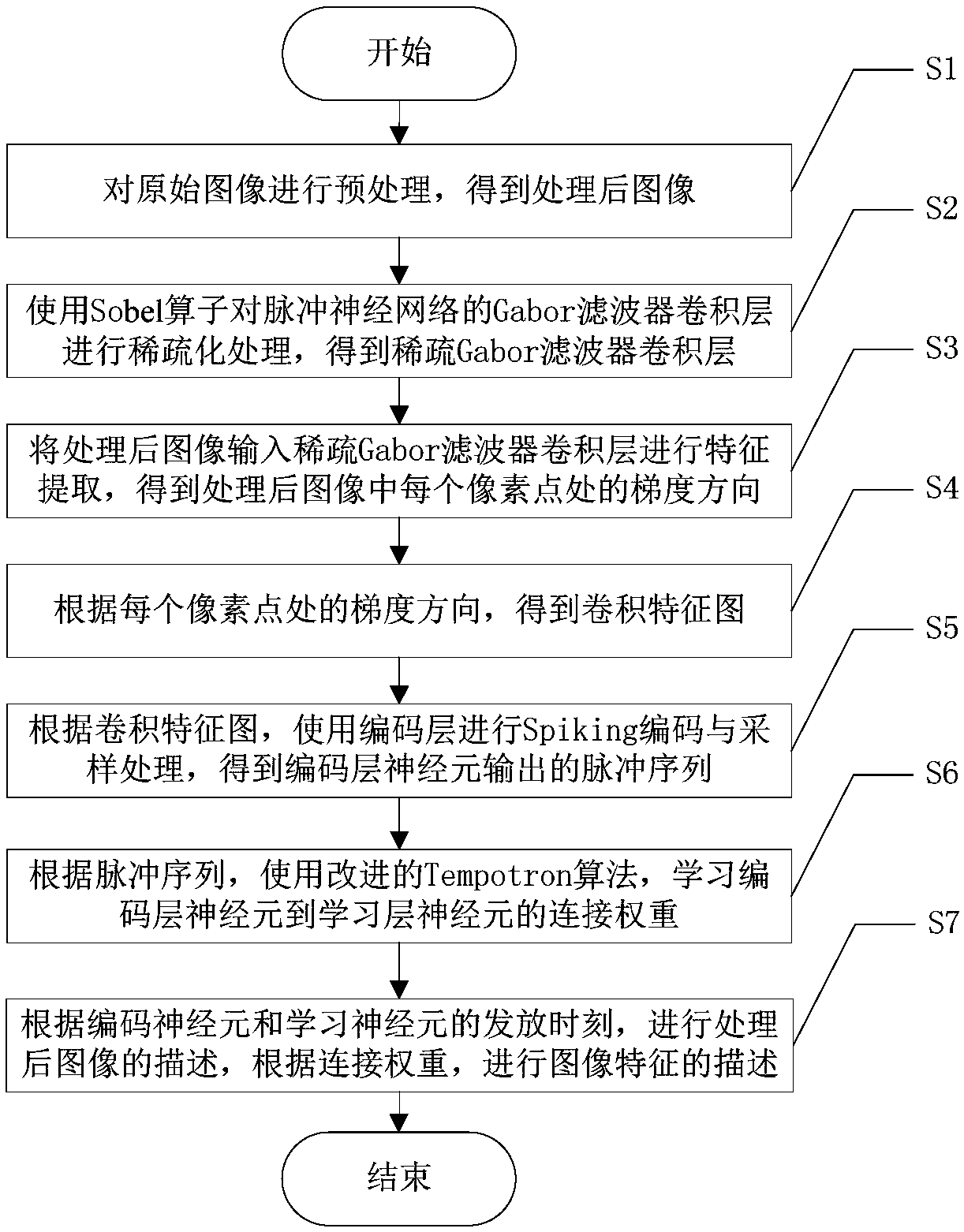
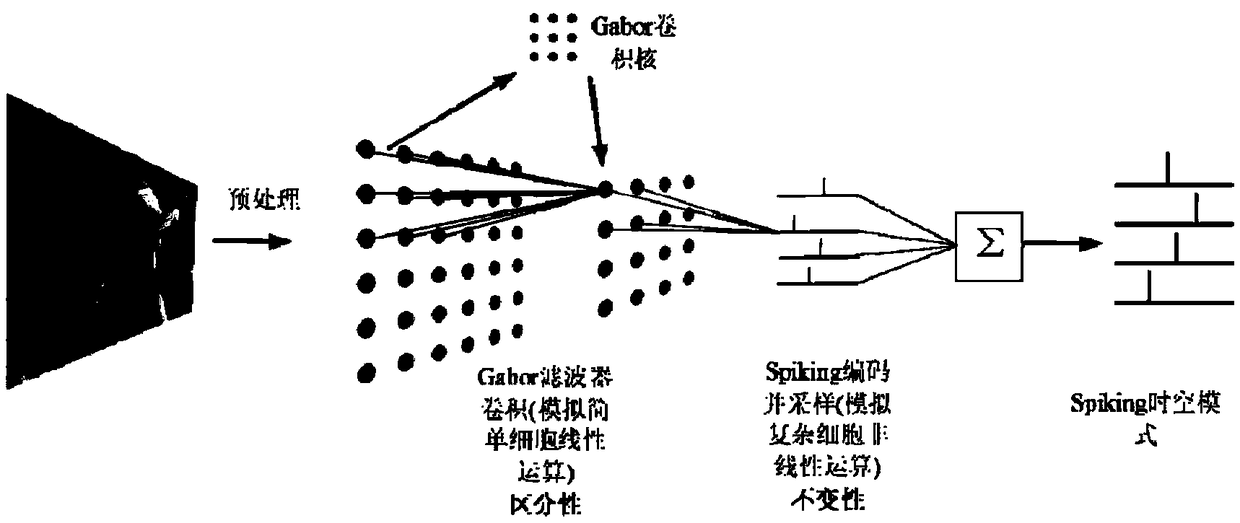
An image feature description method based on impulse neural network
InactiveCN109214395AImprove practicalityImprove the ability to distinguishCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesImaging FeaturePulse sequence
The invention discloses an image feature description method based on pulse neural network, which comprises the following steps: S1, preprocessing the original image; S2, the convolution layer of the Gabor filter of the impulse neural network is thinned by using the Sobel operator; 3, inputting the processed image into a sparse Gabor filt convolution layer for feature extraction; S4, realizing feature extraction; S5, spiking encoding and sampling processing are carried out by using the encoding layer; S6, according to the pulse sequence, using the improved Tempotron algorithm to learn the connection weights from the coding layer neurons to the learning layer neurons; S7, describing the processed image and describing the image features. The invention solves the problems existing in the priorart that the feature selection and extraction are tedious, the calculation is complex, the extracted feature is weak in distinguishing the object, the important feature is easy to lose and change, and the image can not be completely restored according to the memory.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
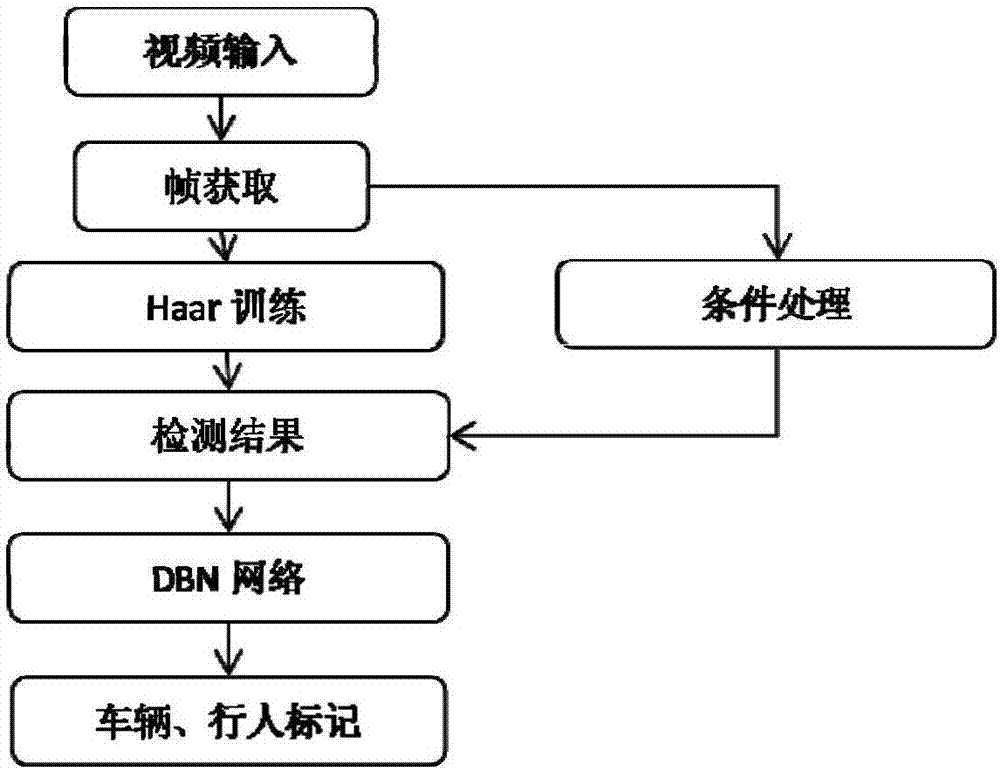
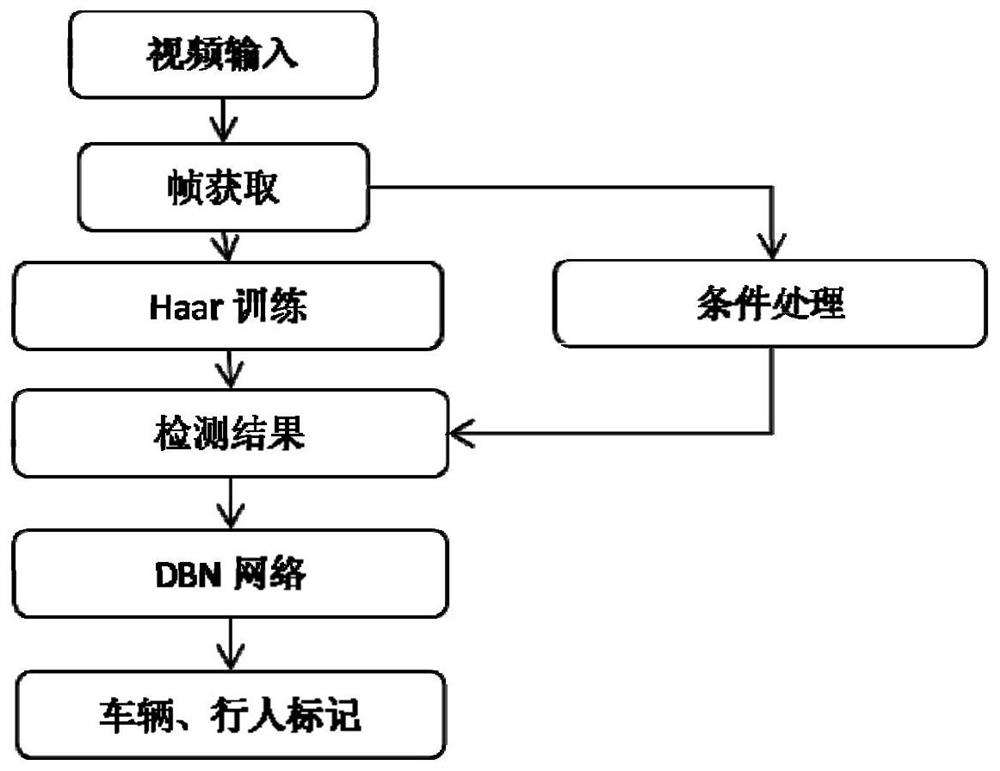
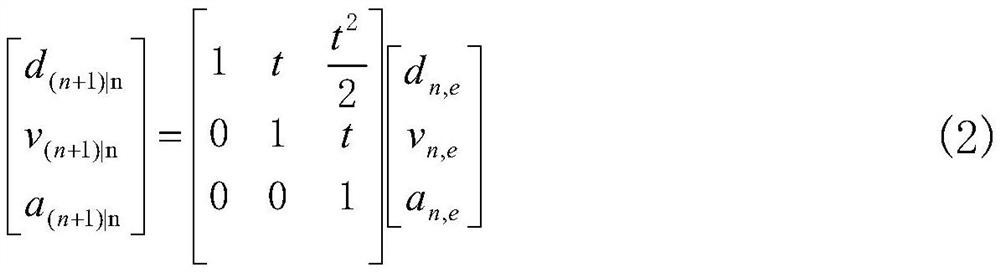
Visual perception-based automobile front-vision vehicle and pedestrian anti-collision warning system and method
ActiveCN107886043AFeature retentionEasy to identifyScene recognitionNeural architecturesKaiman filterCascading classifiers
The invention discloses a visual perception-based automobile front-vision vehicle and pedestrian anti-collision warning system and method. According to the visual perception-based automobile front-view vehicle and pedestrian anti-collision warning system and method of the invention, a video acquired by a front-vision camera of a vehicle is read frame by frame; a trained cascade classifier is adopted to recognize vehicles and pedestrians in the video frames; recognition results are filtered by means of straight line detection, so that non-vehicle and non-pedestrian parts can be removed; a deepDBN network is adopted complete the determination of vehicle and pedestrian information in front of the vehicle; after the positions of the vehicles and the pedestrians in front of the vehicle are confirmed, image coordinates are converted into vehicle body coordinates, so that relative distances and relative angles between the vehicle and the vehicles in front of the automobile, and between the vehicle and the pedestrians in front of the vehicle are obtained; a safety time-distance is calculated; a Kalman filter is adopted to predict the positions of the vehicles or pedestrians; and if the distances of the vehicles or pedestrians are smaller than the safety time-distance, an alarm is issued. With the visual perception-based automobile front-view vehicle and pedestrian anti-collision warning system and method of the invention adopted, the vehicles and pedestrians can be recognized more effectively and accurately, and therefore, anti-collision warning can be performed more accurately.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
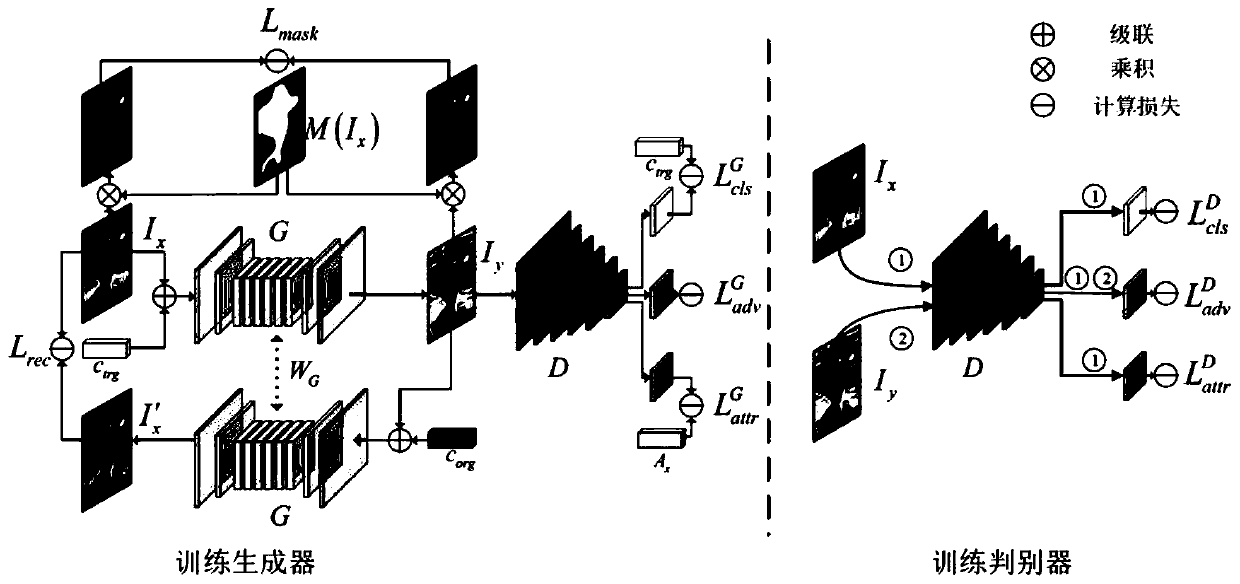
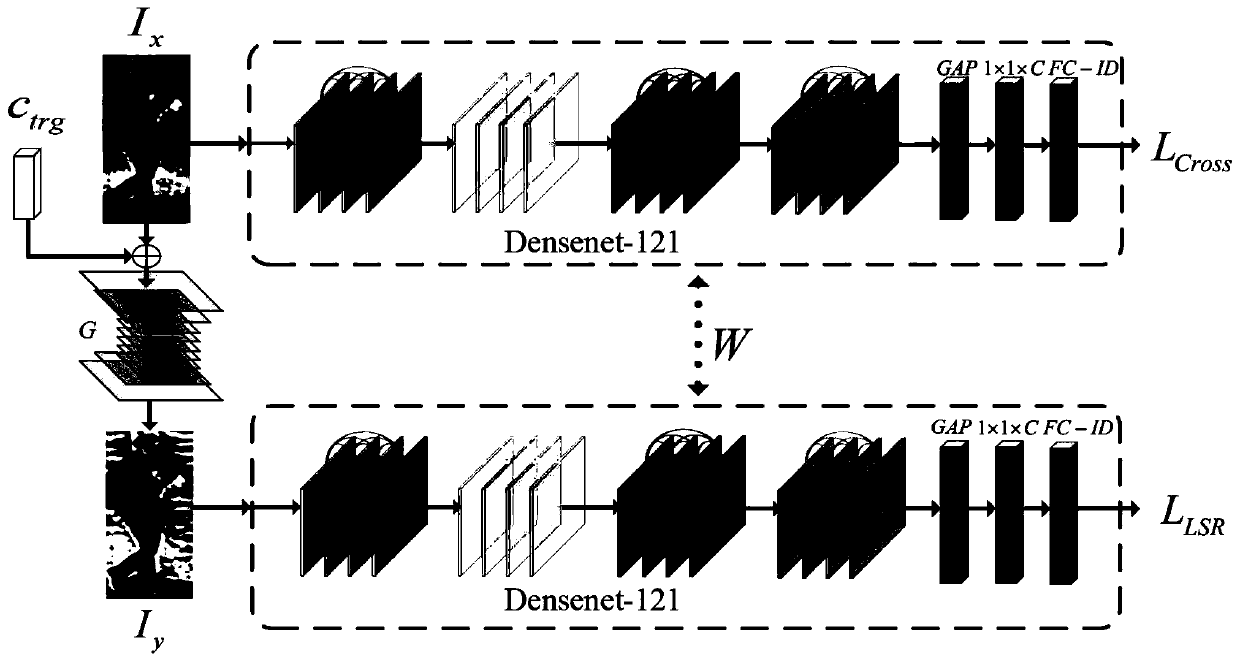
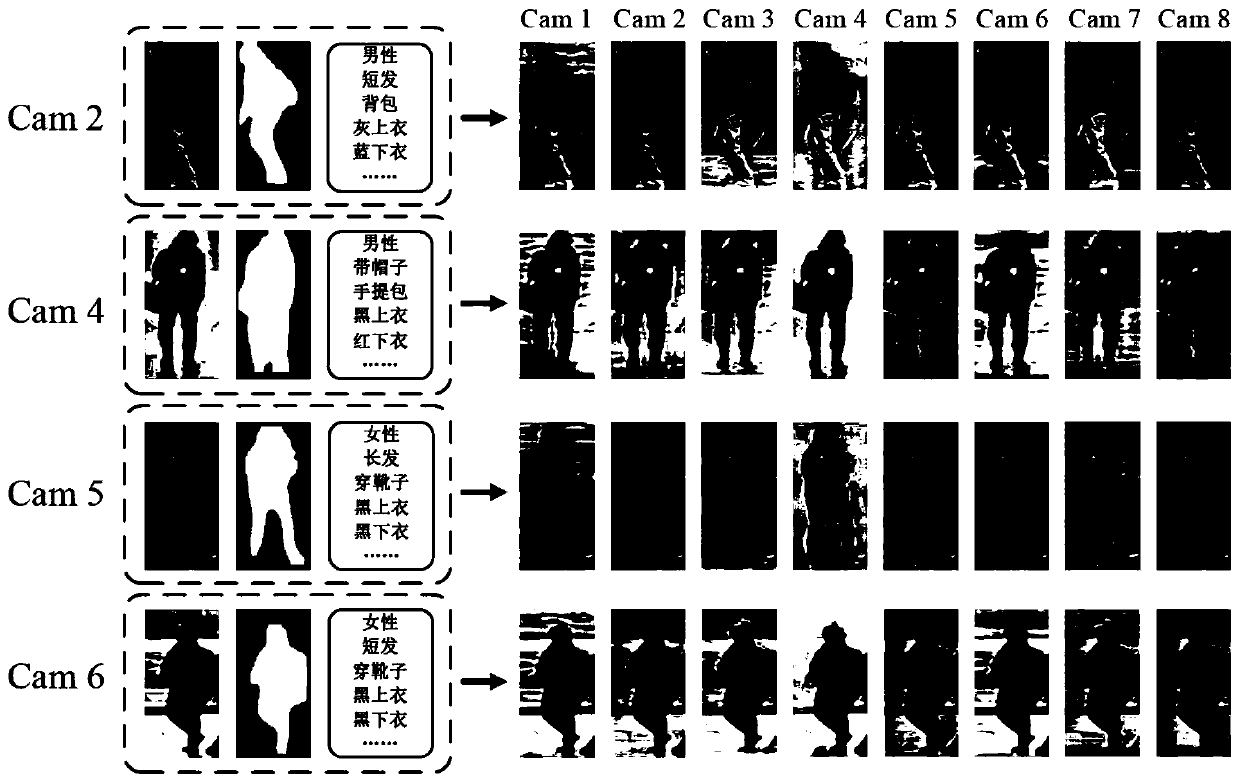
Data enhancement pedestrian re-identification method based on generative adversarial network model
InactiveCN110188835AStrong feature representationEliminate background distractionsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage segmentation algorithmGenerative adversarial network
The invention relates to a data enhancement pedestrian re-identification method based on a generative adversarial network model. The method comprises the following steps: segmenting a mask image of apedestrian in an image by using a Mask-RCNN image segmentation algorithm; training an end-to-end improved star-shaped generative adversarial network in combination with the mask image and the manuallylabeled pedestrian attributes, and generating false training images under any number of cameras from the real pedestrian image under one camera; generating false training images of all camera domainscorresponding to all real images by using the trained improved star generative adversarial network; and sending the real image and the false training image into a pedestrian re-identification model,calculating the distance between the pedestrian images, and completing a pedestrian re-identification function.using Mask-to perform pedestrian re-identification; segmenting a mask image of a pedestrian in the image by using an RCNN image segmentation algorithm; training an end-to-end improved star-shaped generative adversarial network in combination with the mask image and manually labeled pedestrian attributes, and generating false training images under any number of cameras from a real pedestrian image under one camera; using the trained improved star-shaped generative adversarial network to generate false training images of all camera domains corresponding to all real images; and sending the real image and the false training image into a pedestrian re-identification model, calculatingthe distance between the pedestrian images, and completing the pedestrian re-identification function. The method is reasonable in design, more training samples are generated through the generative adversarial network, meanwhile, the generated image background can effectively represent the real scene under the corresponding camera, the robustness and the judgment capability of the pedestrian re-identification model are effectively improved, and the accuracy of pedestrian re-identification is effectively improved.
Owner:ACADEMY OF BROADCASTING SCI STATE ADMINISTATION OF PRESS PUBLICATION RADIO FILM & TELEVISION +1
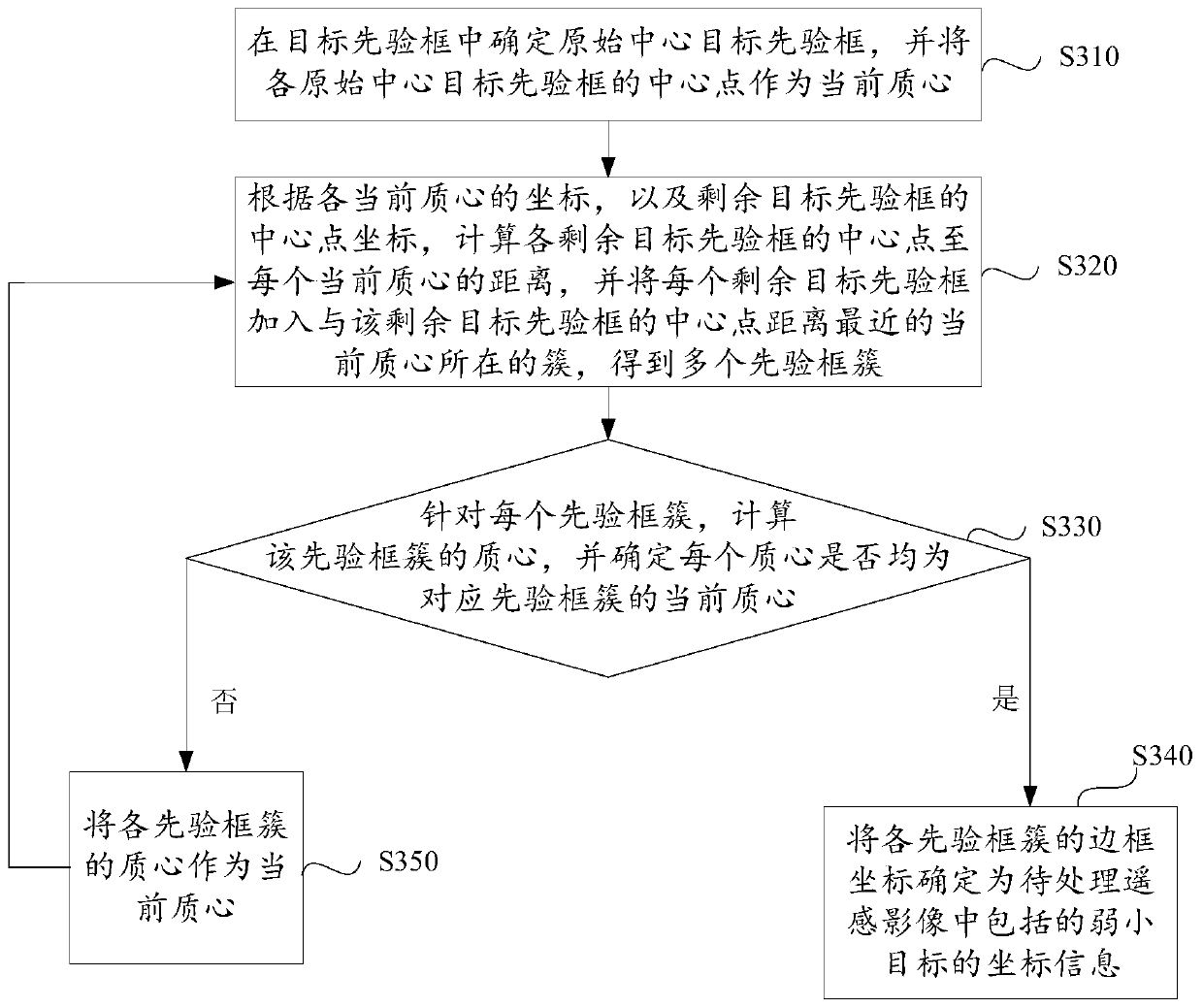
High-resolution remote sensing image weak and small target detection method based on deep learning
The embodiment of the invention discloses a high-resolution remote sensing image weak and small target detection method and device based on deep learning. The method comprises the steps of obtaining ato-be-processed remote sensing image; inputting the remote sensing image to be processed into a pre-trained convolutional neural network, carrying out 4-time downsampling, 8-time downsampling and 16-time downsampling respectively on the remote sensing image to be processed through the convolutional neural network; obtaining the priori boxes of different sizes corresponding to the to-be-processedremote sensing image, identifying the target priori boxes of which the target category confidence is greater than a preset threshold, and determining the coordinate information of a target included inthe to-be-processed remote sensing image through a preset clustering algorithm according to the coordinate information of each target priori box, wherein the first layer of the convolutional neural network comprises a residual component, the second layer, the third layer and the fourth layer of the convolutional neural network each comprise four residual components, and each residual component comprises two convolutional layers and a fast link. By applying the scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, the weak and small target detection precision can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE TITAN TECH CO LTD
Phase-coherent accumulation noise elimination-based radio frequency fingerprint feature extraction and recognition method
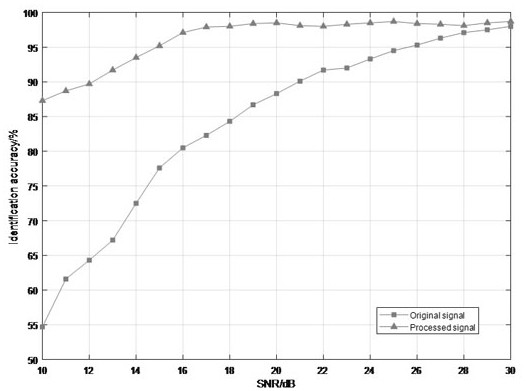
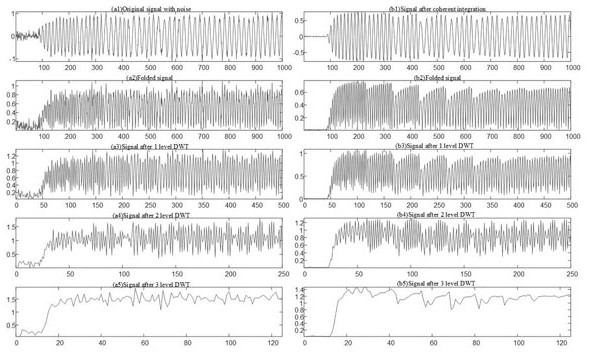
ActiveCN107392123AImprove recognition rateImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionTransmission monitoringRadio frequencySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
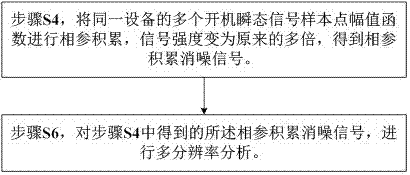
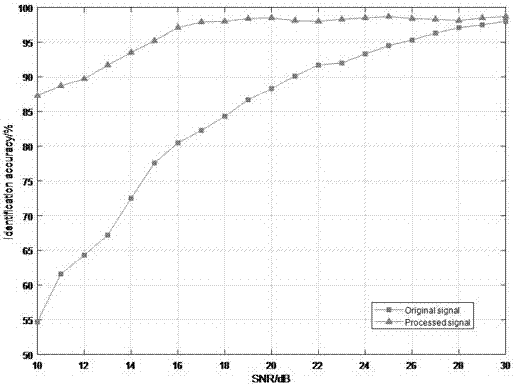
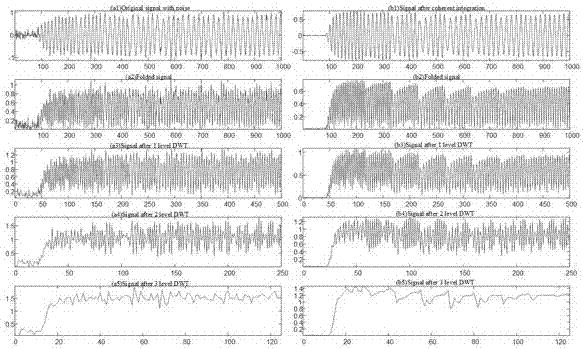
The invention discloses a phase-coherent accumulation noise elimination-based radio frequency fingerprint feature extraction and recognition method. The method comprises a phase-coherent accumulation noise elimination step S4 which is used for a radio frequency fingerprint identification technology and a step S6 which is used for performing multi-resolution analysis on waveforms in the radio frequency fingerprint identification technology. According to the S4, phase-coherent accumulation is performed on a plurality of power-on instantaneous signal sample point amplitude value functions of the same device, so that signal strength can be multiple times of original signal strength, and phase-coherent accumulation noise elimination signals are obtained. According to the S6, multi-resolution analysis is performed on the phase-coherent accumulation noise elimination signals obtained in the step A. According to the phase-coherent accumulation noise elimination-based radio frequency fingerprint feature extraction and recognition method of the invention, the phase-coherent accumulation method is adopted in the radio frequency fingerprint identification technology; the signal-to-noise ratio of the waveforms is improved, so that the accuracy of radio frequency identification can be improved; and on the basis of improving the accuracy of the radio frequency identification based on the phase-coherent accumulation, the multi-resolution analysis is utilized, and therefore, the computational complexity of the support vector machine-based radio frequency fingerprint identification technology is reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Modeling method based on multi-scale decomposition of wind power fluctuation
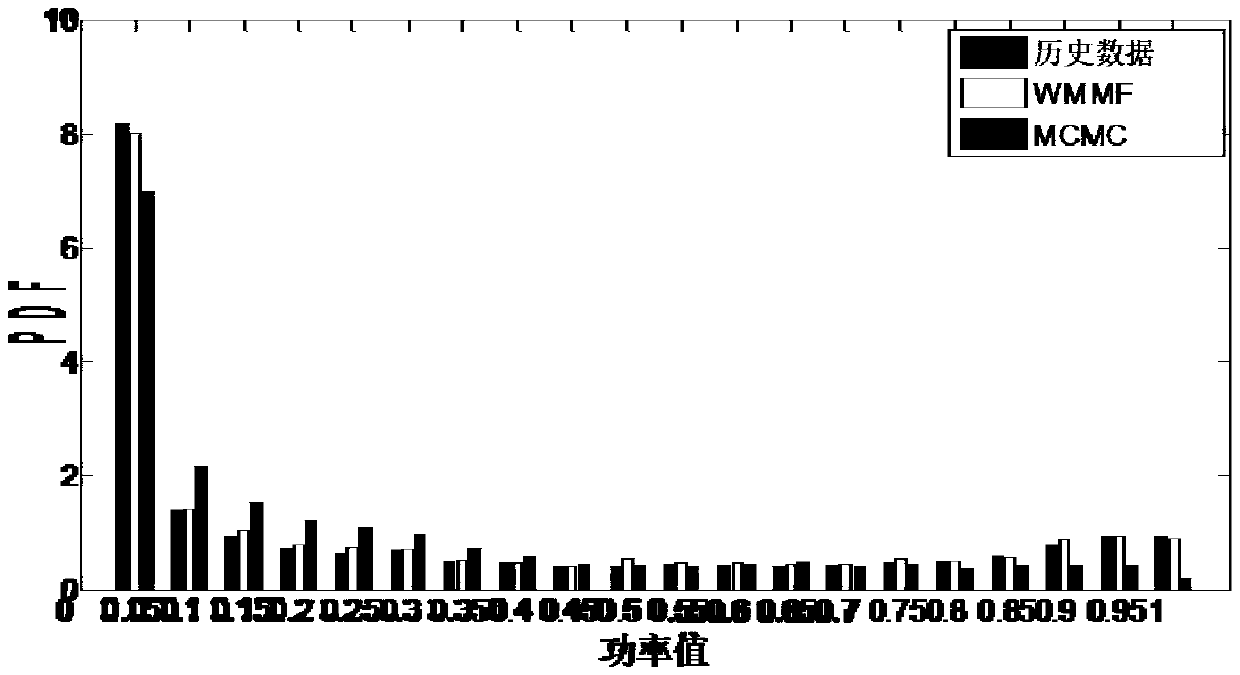
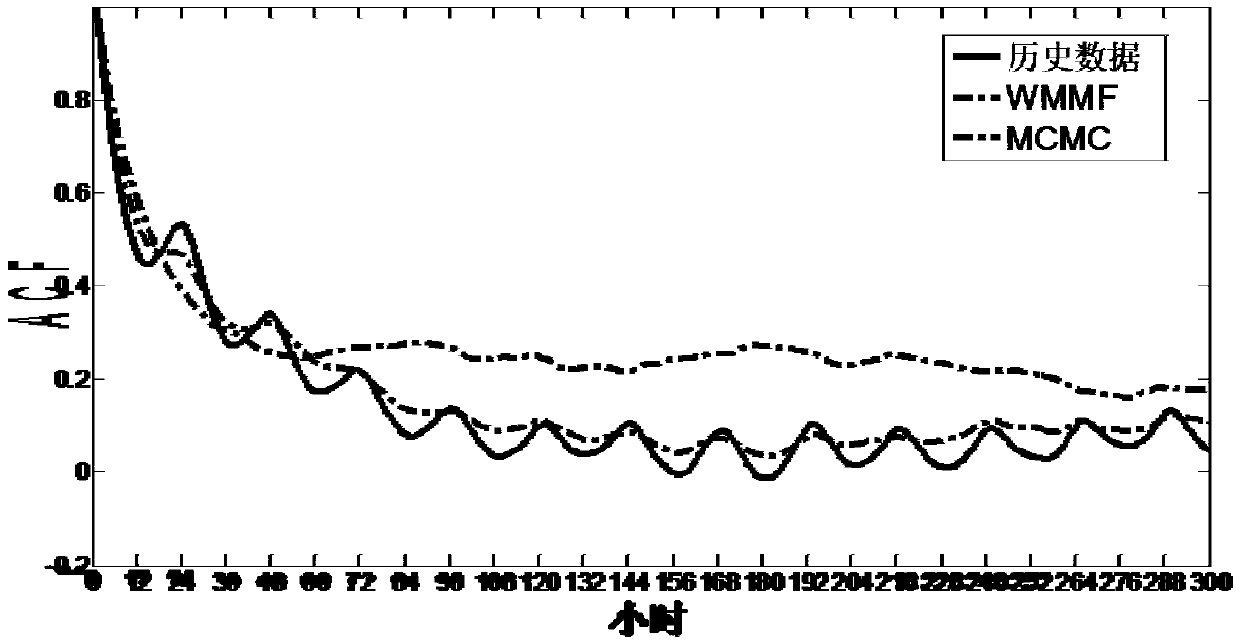
ActiveCN109038675AFeature reservedFeature retentionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationDecompositionHigh frequency
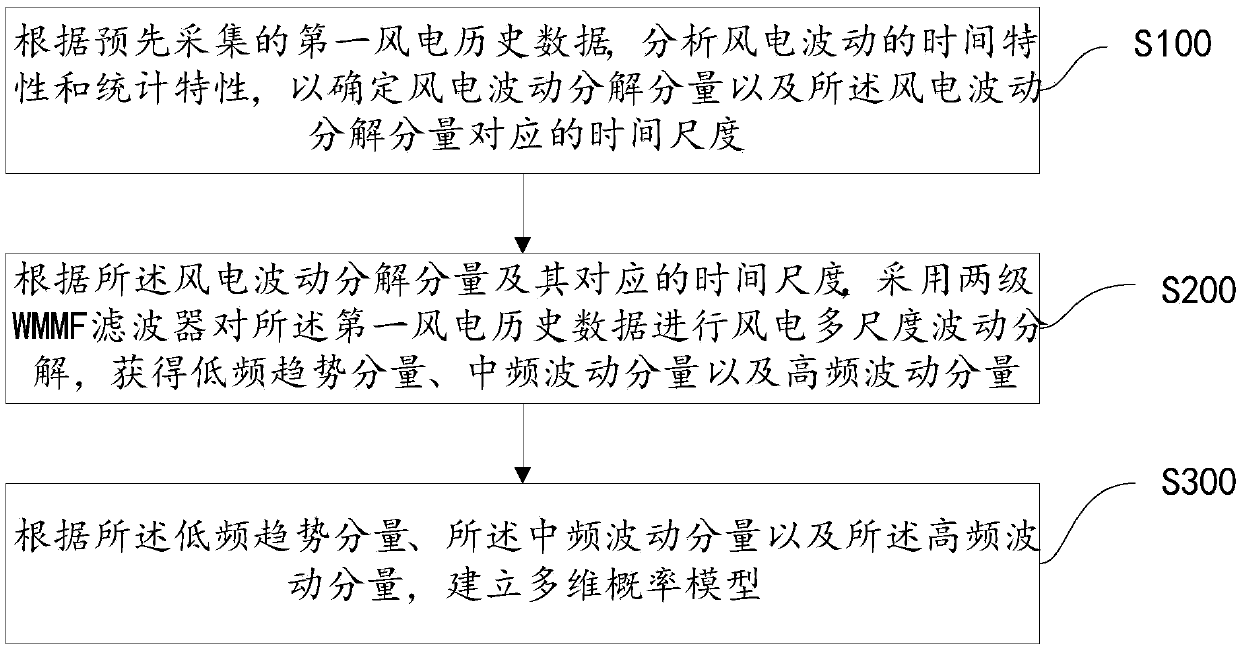
The invention provides a modeling method based on wind power fluctuation multi-scale decomposition, comprising: according to the first wind power historical data collected in advance, analyzing the time characteristic and statistical characteristic of wind power fluctuation, so as to determine the wind power fluctuation decomposition component and the time scale corresponding to the wind power fluctuation decomposition component; According to the wind power fluctuation decomposition component and its corresponding time scale, a two-stage WMMF filter is used to decompose the wind power multi-scale fluctuation of the first wind power historical data to obtain a low-frequency trend component, an intermediate-frequency fluctuation component and a high-frequency fluctuation component. Accordingto the low frequency trend component, the intermediate frequency fluctuation component and the high frequency fluctuation component, a multi-dimensional probability model is established. Through theabove method, the multi-dimensional probability model can be established according to the fluctuation characteristics and correlation of wind power fluctuation of the original wind power time series,thus retaining the characteristics of the complete wind power fluctuation process and simulating the wind power output characteristics to the maximum extent.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
A long data compression processing method suitable for small drawing interface
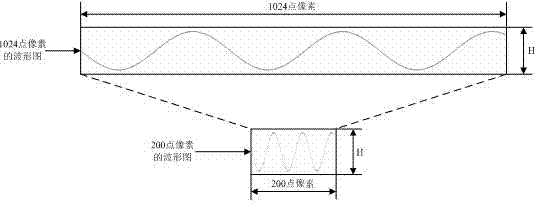
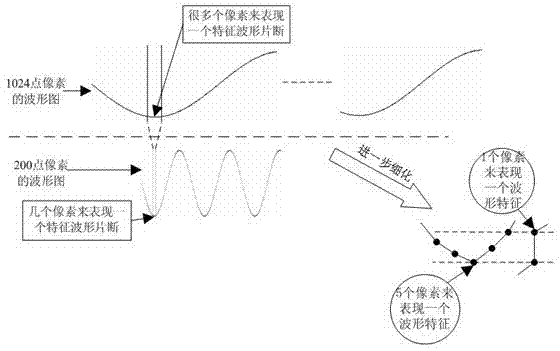
InactiveCN102263559AFeature retentionPreserve original waveform dataCode conversionData compressionDatasheet
The invention provides a processing method for drawing longer data on a low-resolution screen, and belongs to the technical field of data collection. Extract the maximum and minimum feature quantities of the data in sections from a large amount of data, and then draw only these feature quantities on the small screen, so as to achieve the purpose of showing the overall characteristics of the data. The curve displayed after compression by this method can well represent the waveform characteristics of the original data. The principle is simple and clear, and the algorithm is simple and efficient. It is especially suitable for long data representation in embedded state monitoring systems.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Electrocardio and heart sound signal combined analysis based coronary heart disease non-invasive screening system
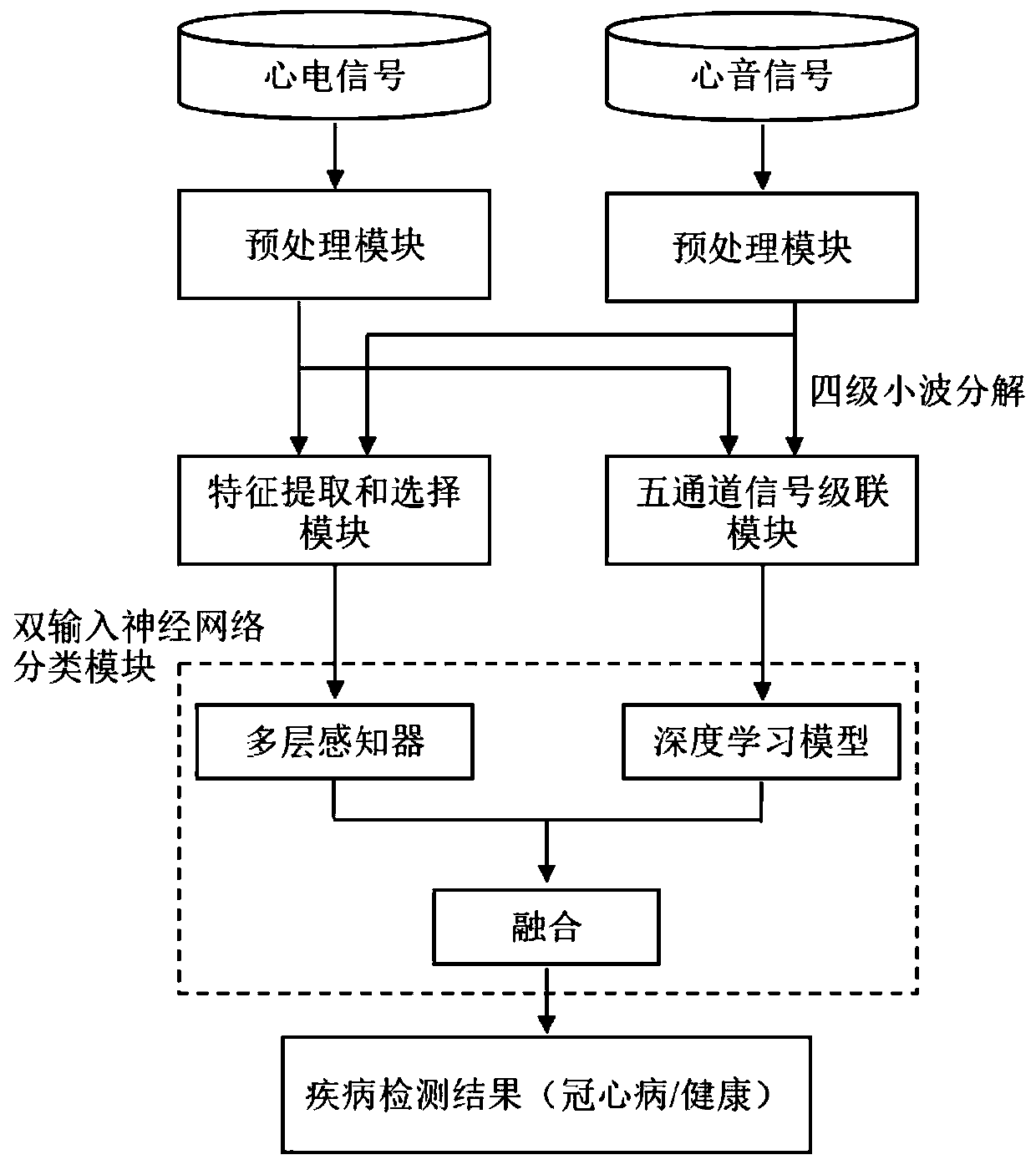
ActiveCN110537910AOvercome limitationsFeature retentionMedical imagingStethoscopeEcg signalCoronary artery disease
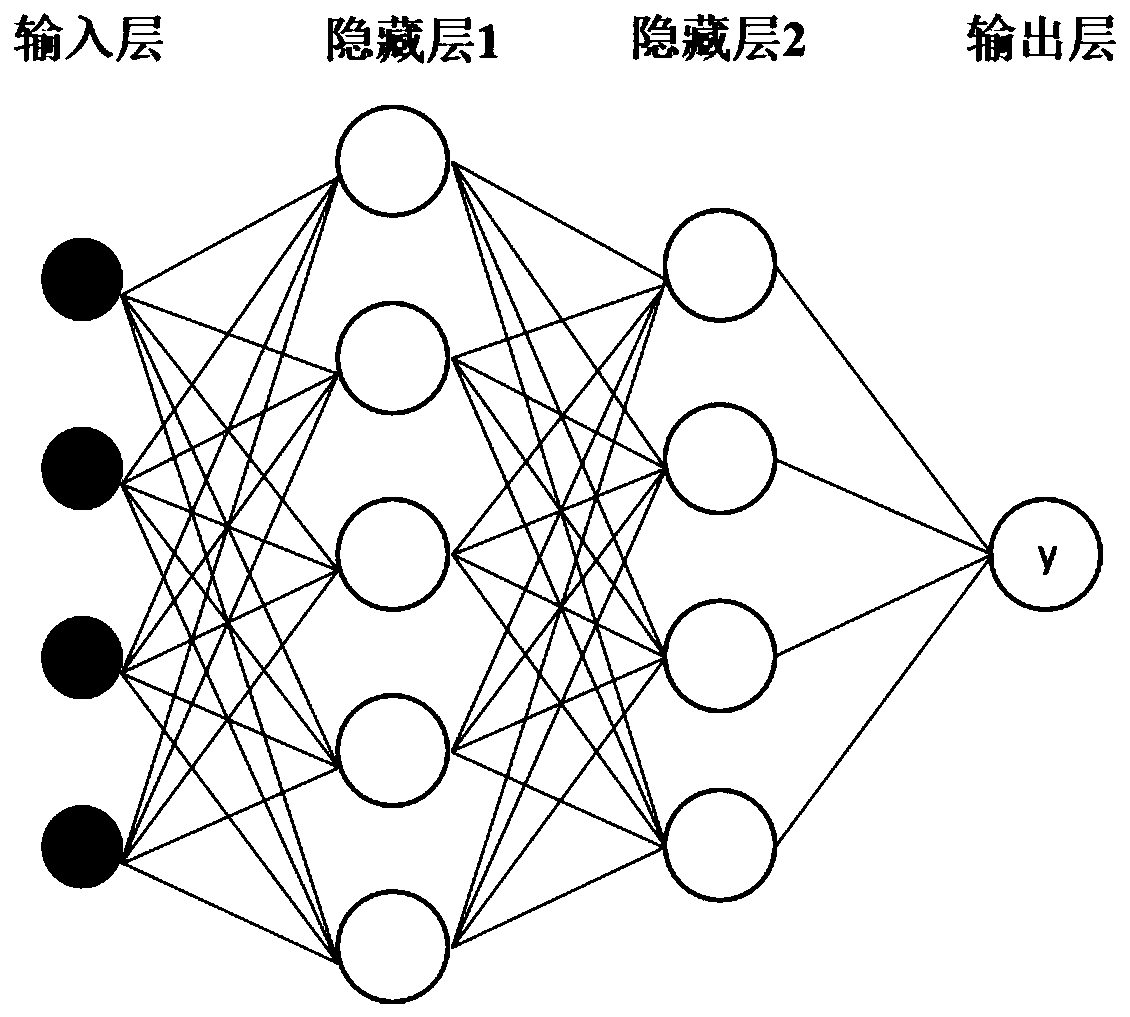
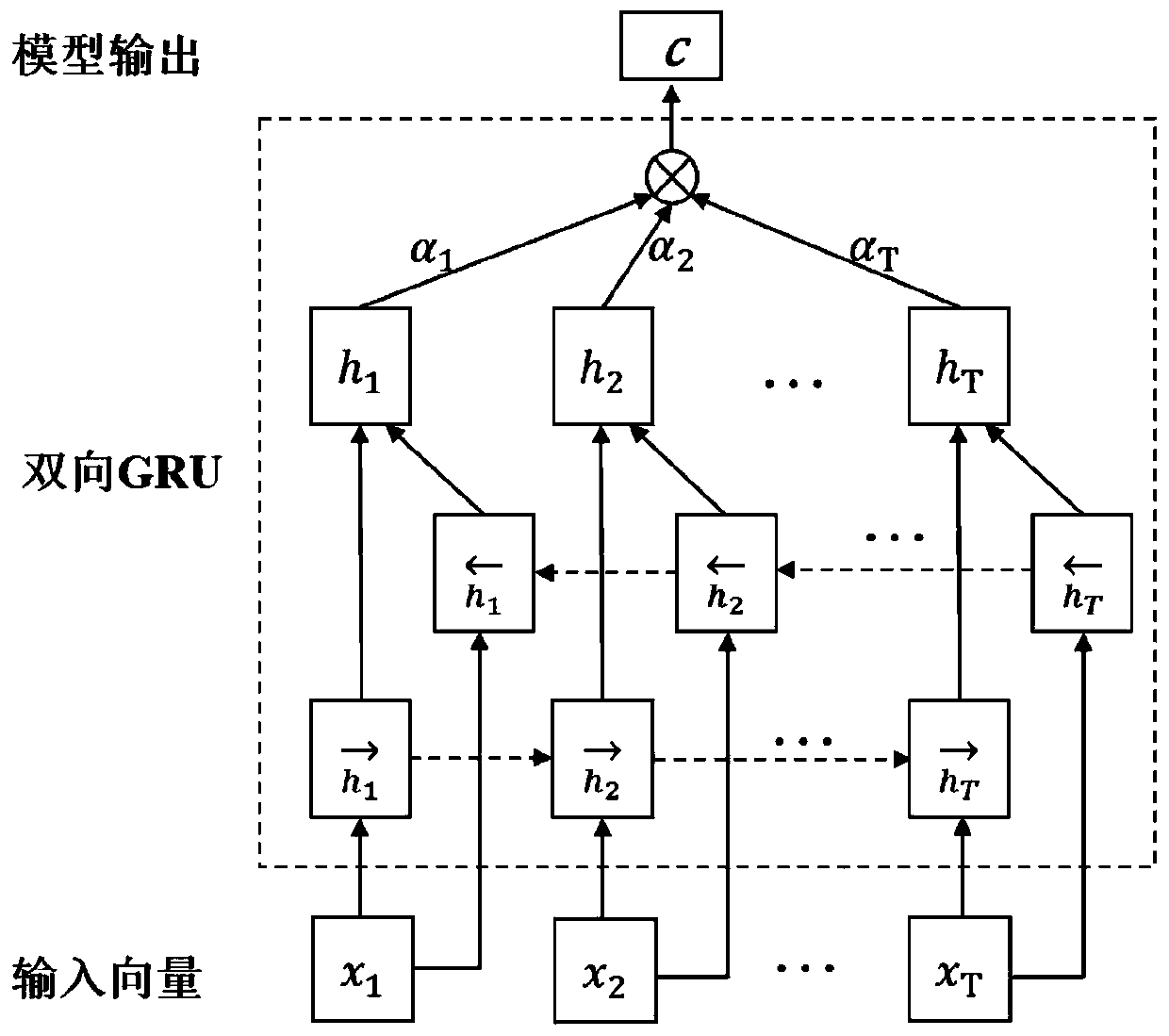
The invention discloses an electrocardio and heart sound signal combined analysis based coronary heart disease non-invasive screening system. The system comprises an electrocardiosignal preprocessingmodule used for filtering, denoising and normalizing an original electrocardiosignal, a heart sound signal preprocessing module used for filtering, denoising and normalizing an original heart sound signal, a characteristic extraction and selection module used for extracting and selecting multi-domain characteristics of the processed electrocardiosignal and heart sound signal, a five-channel cascade module used for performing wavelet transformation and reconstruction on the heart sound signal and connecting the reconstructed four-frequency-band heart sound signal and the electrocardiosignal into a five-channel group signal, and a double-input neural network classification module composed of a multi-layer perceptron, a deep learning model and an activation model and used for processing and analyzing electromechanical eigenvectors and the five-channel group signal. Therefore, the coronary heart diseases can be screened more accurately and non-invasively.
Owner:济南汇医融工科技有限公司
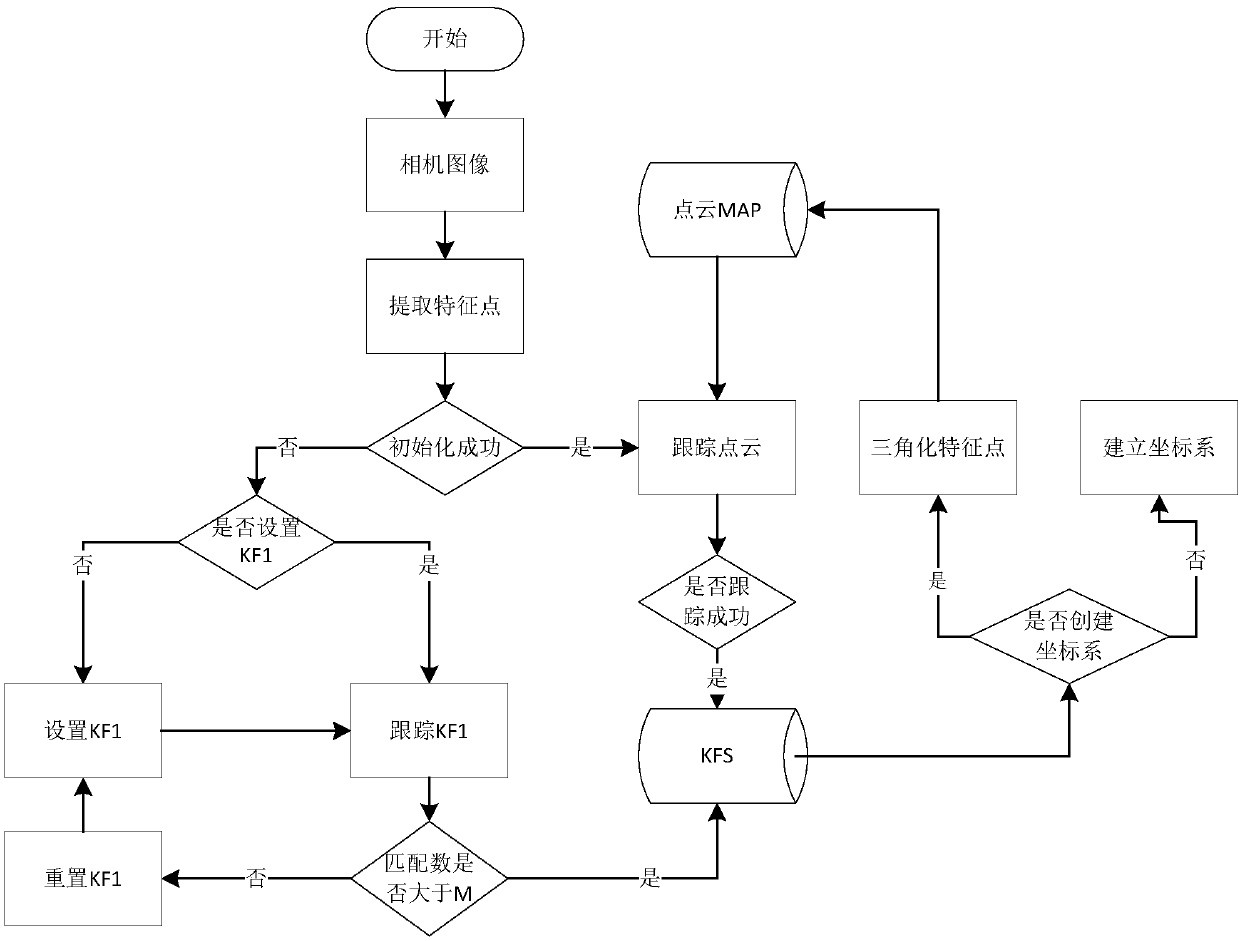
Real-time construction method based on sparse-slam
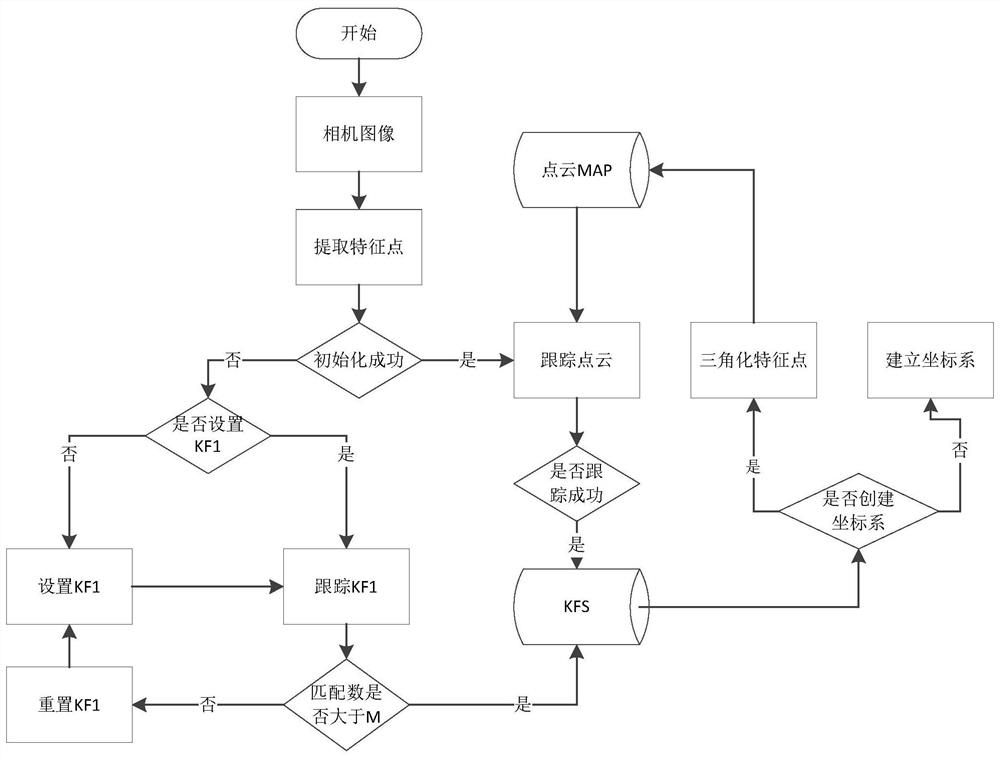
ActiveCN107767450AFeature retentionGuaranteed efficient and real-timeImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPoint cloudKey frame
The present invention provides a real-time graphing method based on the sparse-slam. The method comprises the following two threads running in parallel: thread 1, tracking and extracting key frames; and thread 2, creating and inserting the point cloud MAP. The real-time construction method of the present invention uses two parallel threads, so that the real-time performance of the two threads canbe ensured, the time is saved, features of the images are reserved as many as possible, and more scene information is retained on the premise that the algorithm is guaranteed to be highly efficient and real-time.
Owner:NANJING WEIJING SHIKONG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Geographic space multi-dimensional data visual analysis method based on parallel coordinate axis arrangement
ActiveCN109753547ASolve the problem of difficult integration of geospatial objectsResolve identifiabilityVisual data miningStructured data browsingVolumetric Mass DensityMulti dimensional data
The invention discloses a geographic space multi-dimensional data visual analysis method based on parallel coordinate axis arrangement. The method comprises: carrying out the clustering analysis of geographic space objects, carrying out the visual display of the clustering analysis result of the geographic space objects on a map, and obtaining a view of geographic space clustering; displaying themulti-dimensional attribute information by using parallel coordinates, and performing clustering analysis on the multi-dimensional attribute information by using kernel density clustering to obtain anattribute category; the correlation between the clustering analysis result of the geographic space object and the attribute category is measured by using mutual information; embedding a parallel coordinate system into a view of geographic space clustering, determining the arrangement sequence of parallel coordinate axes in the parallel coordinate system by utilizing the correlation, and rearranging the parallel coordinate axes in the parallel coordinate system according to the arrangement sequence. The problems that geographic space objects are difficult to integrate in a parallel coordinatesystem and multi-dimensional attribute information association features are difficult to identify and present can be effectively solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF FINANCE & ECONOMICS
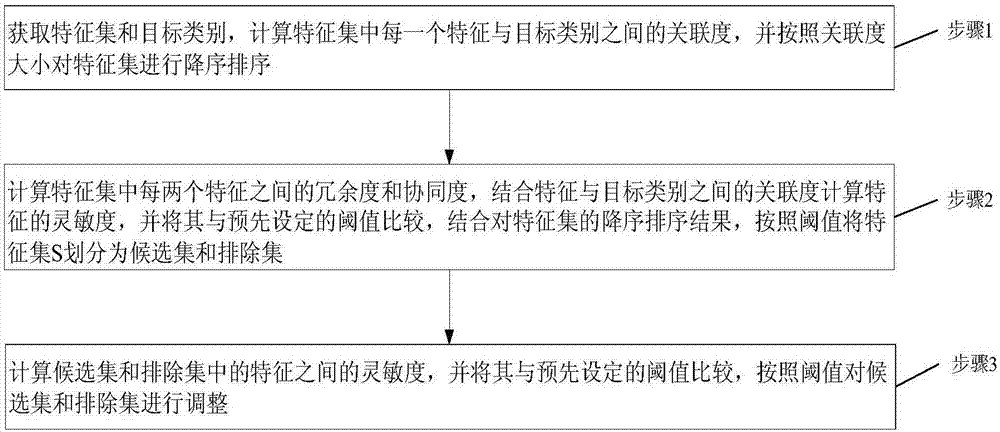
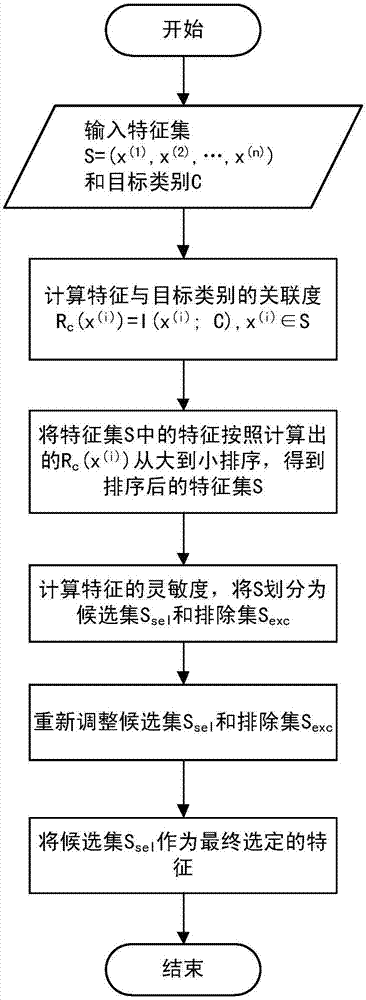
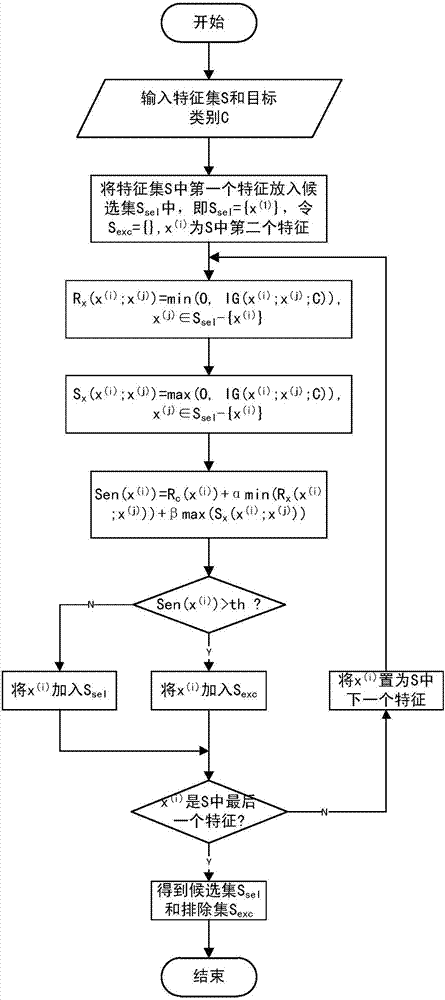
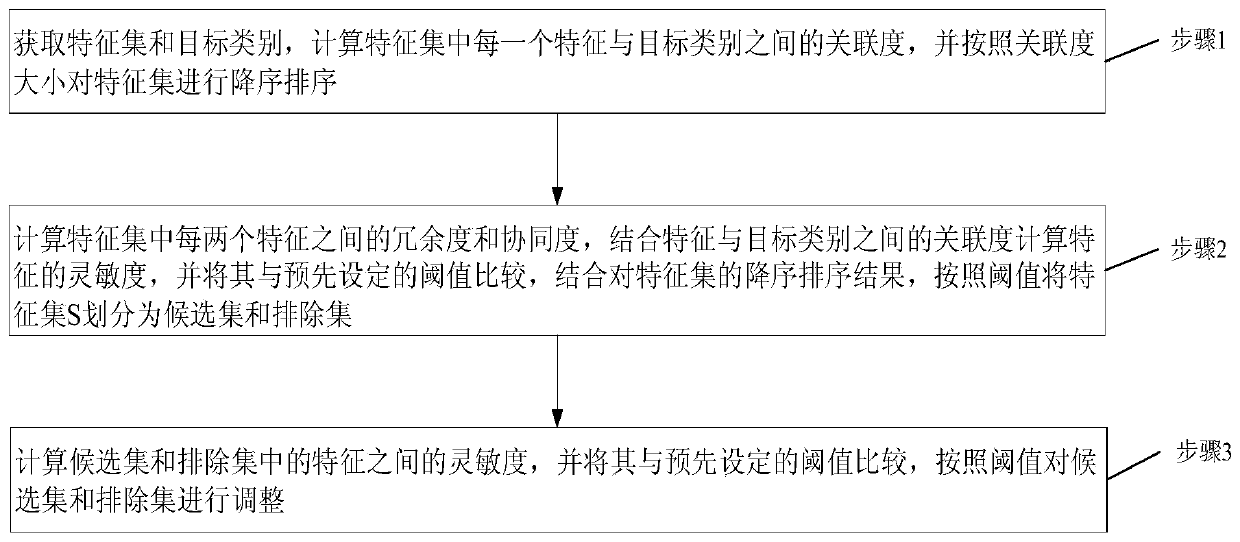
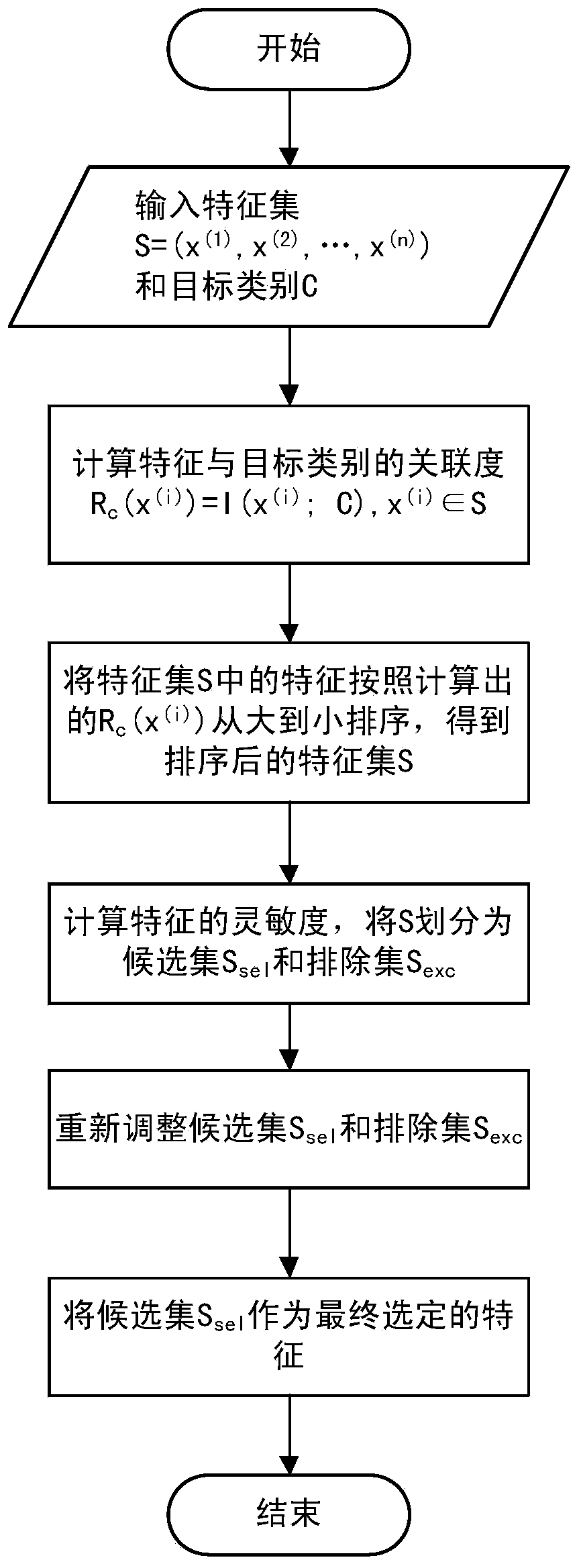
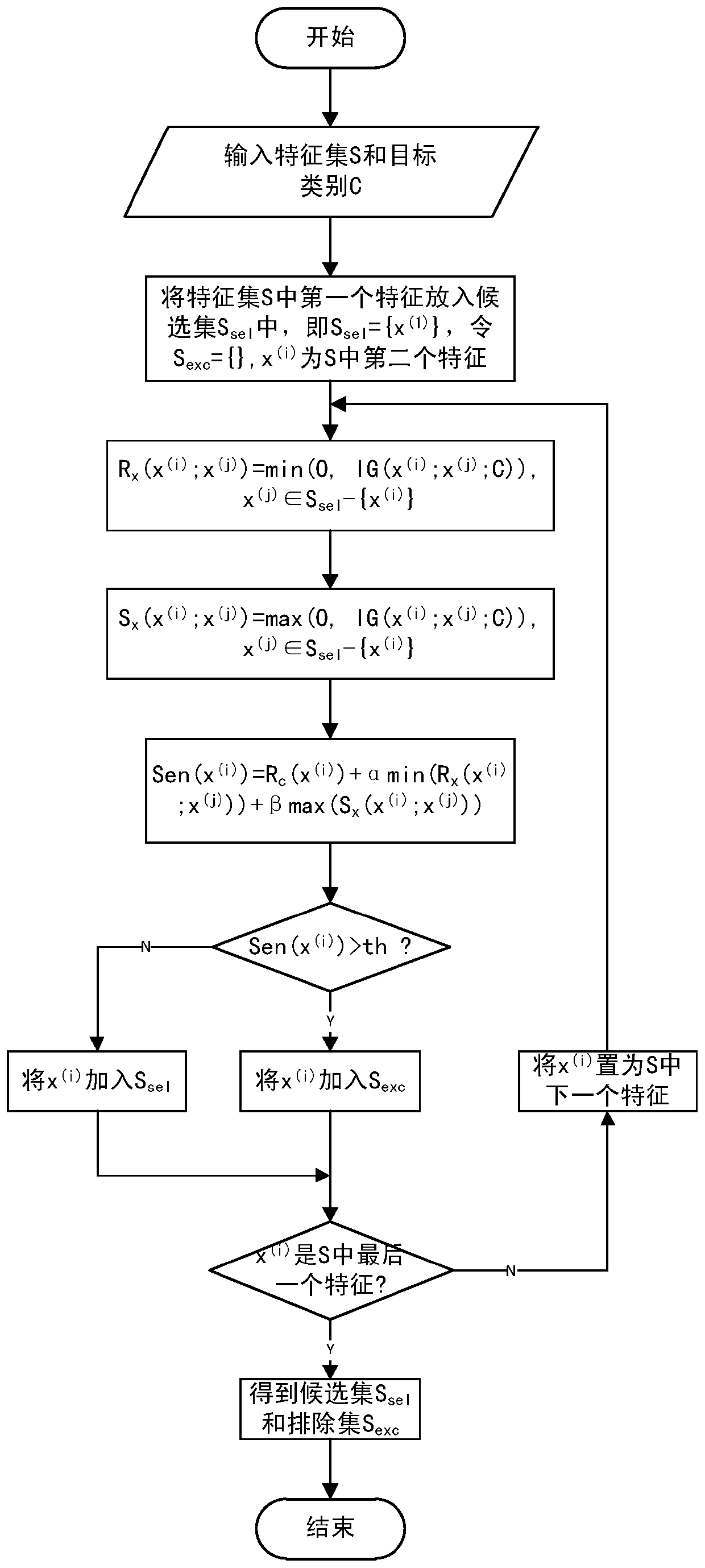
Text classification feature selecting method
ActiveCN107016073AFeature retentionReduced characteristicsSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionFeature set
The invention provides a text classification feature selecting method capable of reducing the characteristic dimension and the classification complexity and improving the classification accuracy. The method comprises the following steps that a feature set S and a target class C are obtained, the relevancy Rc(x(i)) between each feature x(i) in the feature set S and the target class C is calculated, and sort descending is conducted on the feature set S according to the size of the relevancy Rc(x(i)); the redundancy Rx and the synergy degree Sx between every two features in the feature set S are calculated, and the sensitivity Sen of each feature is calculated with the combination of the relevancy Rc(x(i)) between each feature and the target class, the sensitivities Sen are compared with a preset threshold th, and the feature set S is divided into a candidate set Ssel and an excluding set Sexc with the combination of the sort descending result of the feature set S according to the threshold th; the sensitivities Sen between the features in the candidate set Ssel and the features in the excluding set Sexc are calculated, the sensitivities Sen are compared with the preset threshold th, and the candidate set Ssel and the excluding set Sexc are adjusted according to the threshold th. The text classification feature selecting method is suitable for the field of machine learning text classification.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
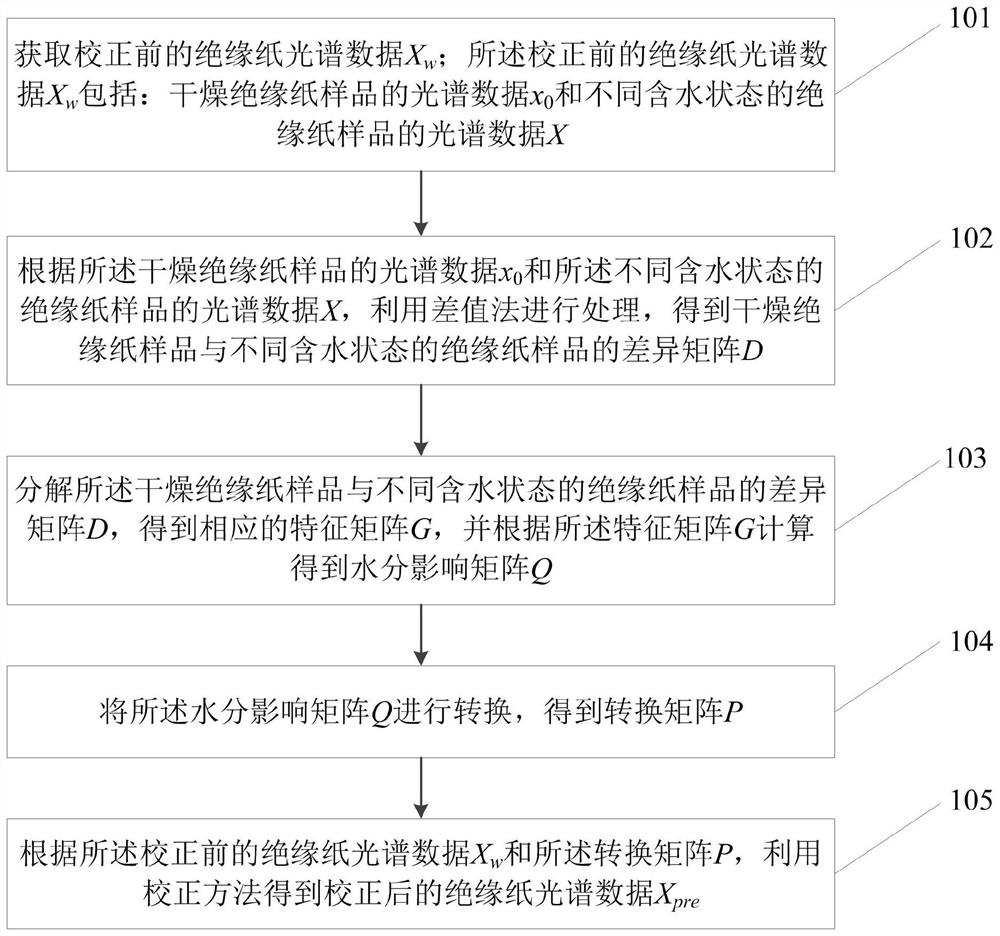
Moisture influence factor correction method and system for insulation paper spectrum
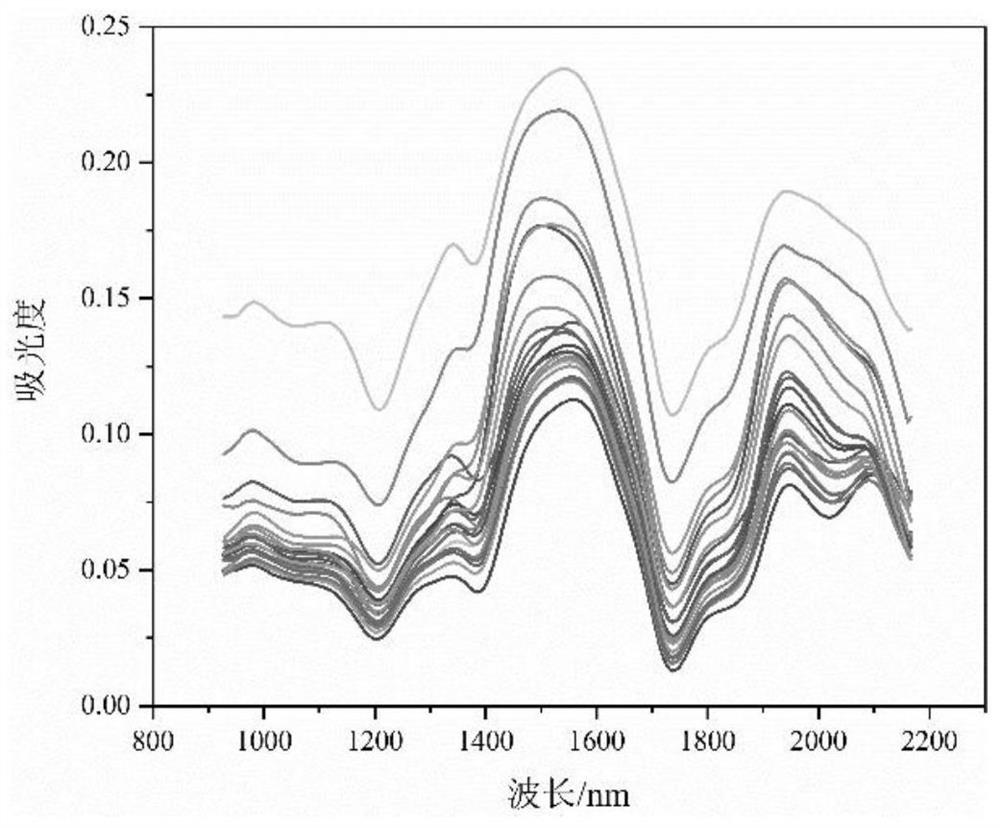
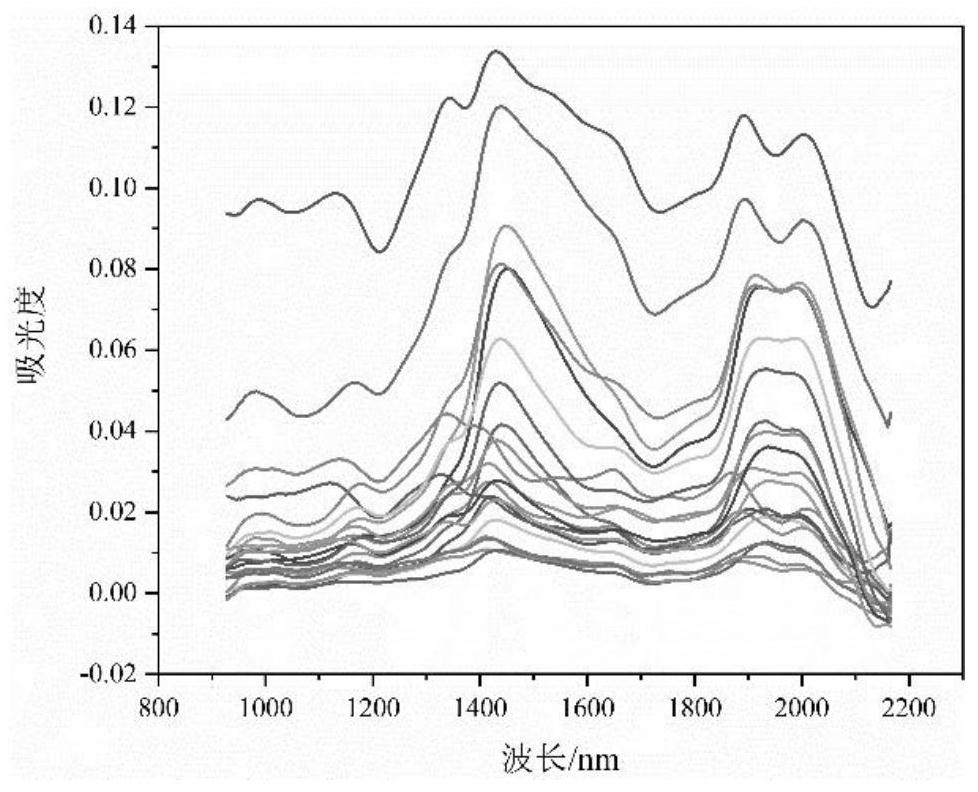
PendingCN113447452AImprove forecast accuracyReduce dimensionalityColor/spectral properties measurementsDesign optimisation/simulationPhysical chemistryMoisture
The invention relates to a moisture influence factor correction method and system for an insulation paper spectrum, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining insulation paper spectrum data Xw before correction, carrying out the processing through a difference method, obtaining a difference matrix D of a dry insulation paper sample and an insulation paper sample in different water-containing states, carrying out the principal component decomposition of the difference matrix D, and obtaining a matrix G; obtaining a moisture influence matrix Q; processing the moisture influence matrix Q to obtain a conversion matrix P; and finally, obtaining corrected insulation paper spectrum data Xpre by using a correction method. According to the method, the influence of the water content state difference between different samples on the prediction precision is considered, the part influenced by the water content in the sample spectrum is corrected, and the original spectrum data is mapped to the space orthogonal to the spectrum influenced by the water content, so that the spectrum change caused by the fluctuation of the water content factor is removed, and the prediction precision of the polymerization degree of the insulation paper is effectively improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Partial discharge denoising method
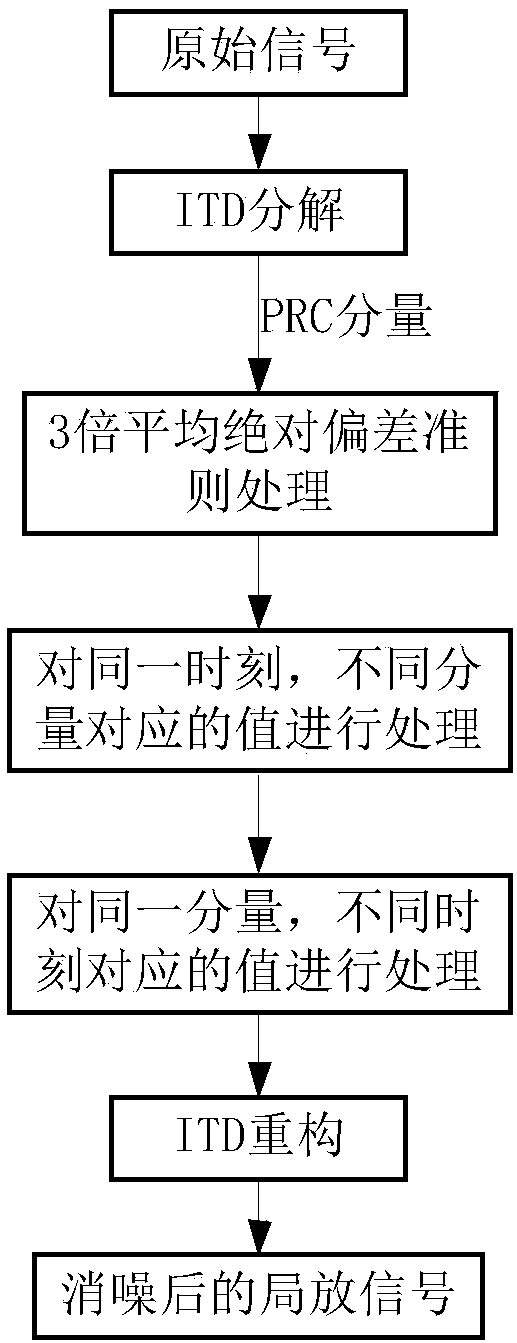
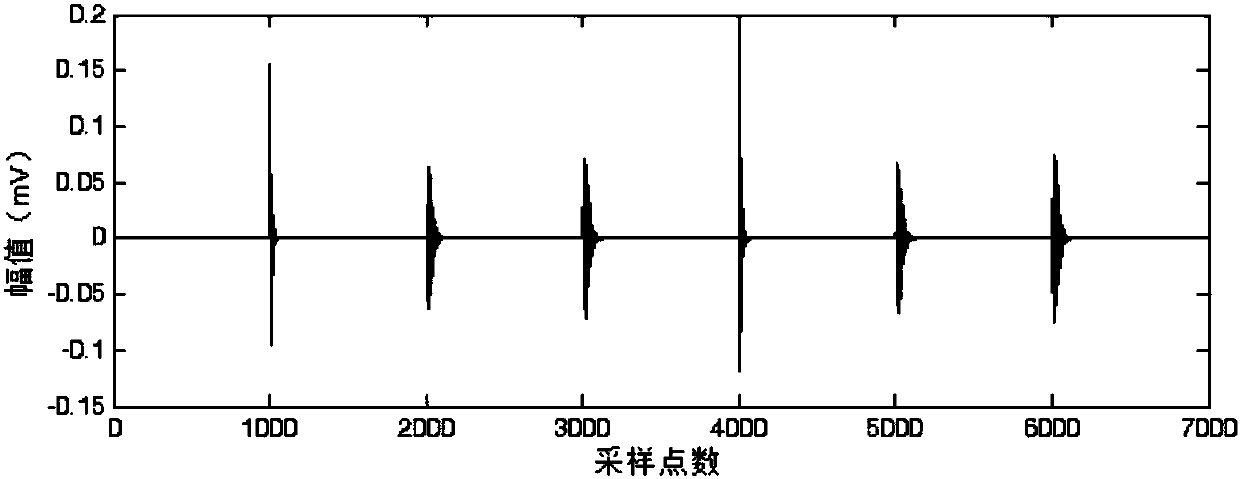
InactiveCN108020761AImprove signal-to-noise ratioNoise Cancellation ImplementationTesting dielectric strengthPattern recognitionDecomposition
The present invention relates to a partial discharge denoising method. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) employing an ITD decomposition method to perform adaptive decomposition of original partial discharge signals including noise, and obtaining a plurality of proper rotation components (PRC) including noise; 2) determining the denoising threshold of each PRC, performing processing of each PRC according to the obtained denoising thresholds, and obtaining the preliminary denoising result of each PRC; 3) performing processing of each PRC after the preliminary denoising according tothe energy of each PRC, removing burrs at singular points after preliminary denoising, and obtaining each processed PRC; and 4) performing ITD reconstruction of each PRC obtained in the step 3), andobtaining partial discharge signals after denoising. The method has adaptivity, a good denoising performance and a fast calculation speed, can greatly remove a lot of background noise included in thepartial discharge signals, and can be widely applied in the online monitoring field of insulation of electric devices.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
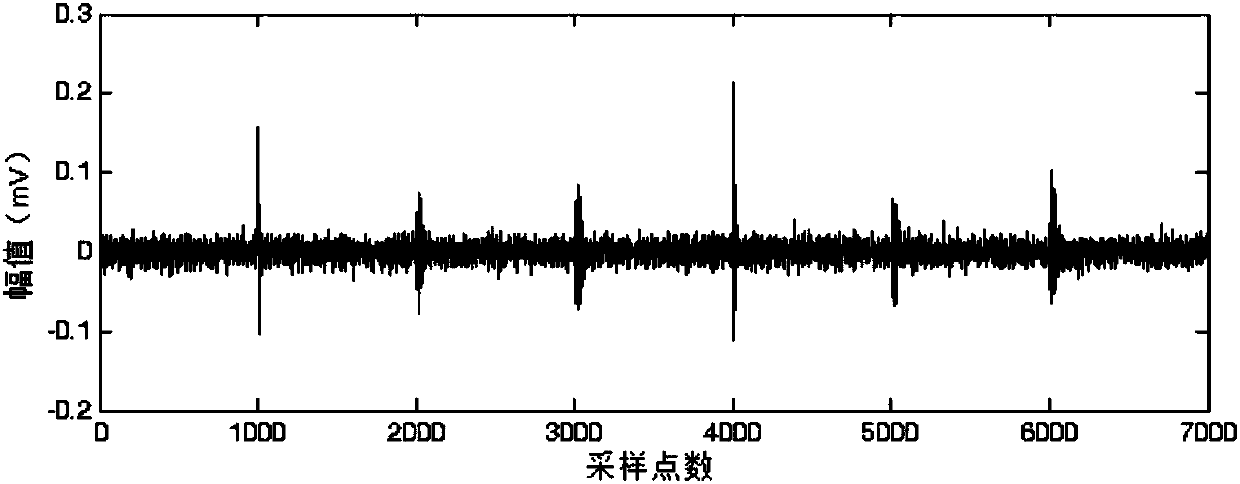
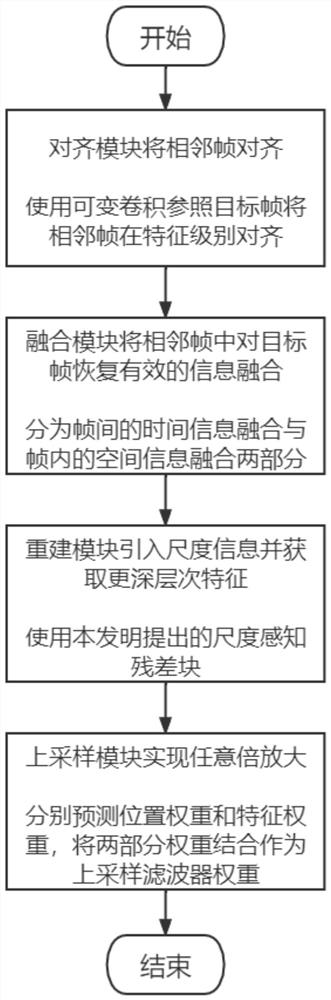
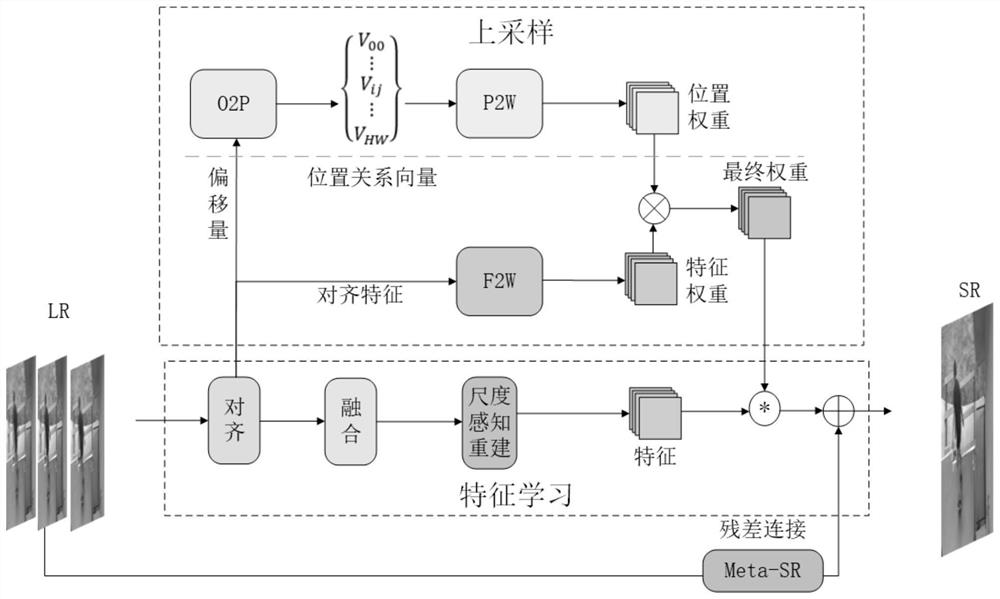
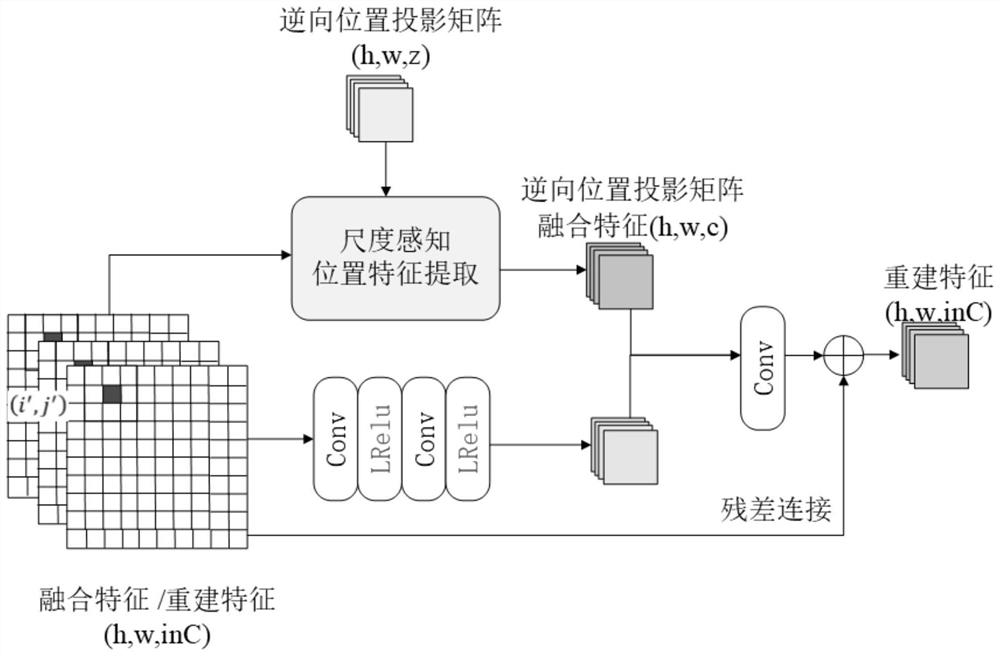
Arbitrary-multiple video super-resolution method introducing scale information
PendingCN113902623AFeature retentionGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Algorithm
The invention belongs to the field of super-resolution of computer vision, and aims to solve the problem of random magnification of super-resolution of a video and realize decimal magnification. According to the arbitrary-multiple video super-resolution method introducing scale information, firstly, adjacent frames are aligned at a feature level by using variable convolution; the method also includes fusing the features extracted by each element vector in the reverse position projection matrix by using a class attention mechanism; and finally, inputting the offset representing the movement of the pixel points between the continuous adjacent frames and the target frame into a position weight prediction module to obtain a position weight, and inputting the alignment features output by the alignment module into a feature weight prediction module to obtain a feature weight; and finally, correspondingly multiplying the two weights to obtain an up-sampling filtering kernel weight, and respectively multiplying the fusion feature by the up-sampling filtering kernel weight to realize amplification of any times. The invention is mainly applied to video super-resolution arbitrary-time amplification occasions.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
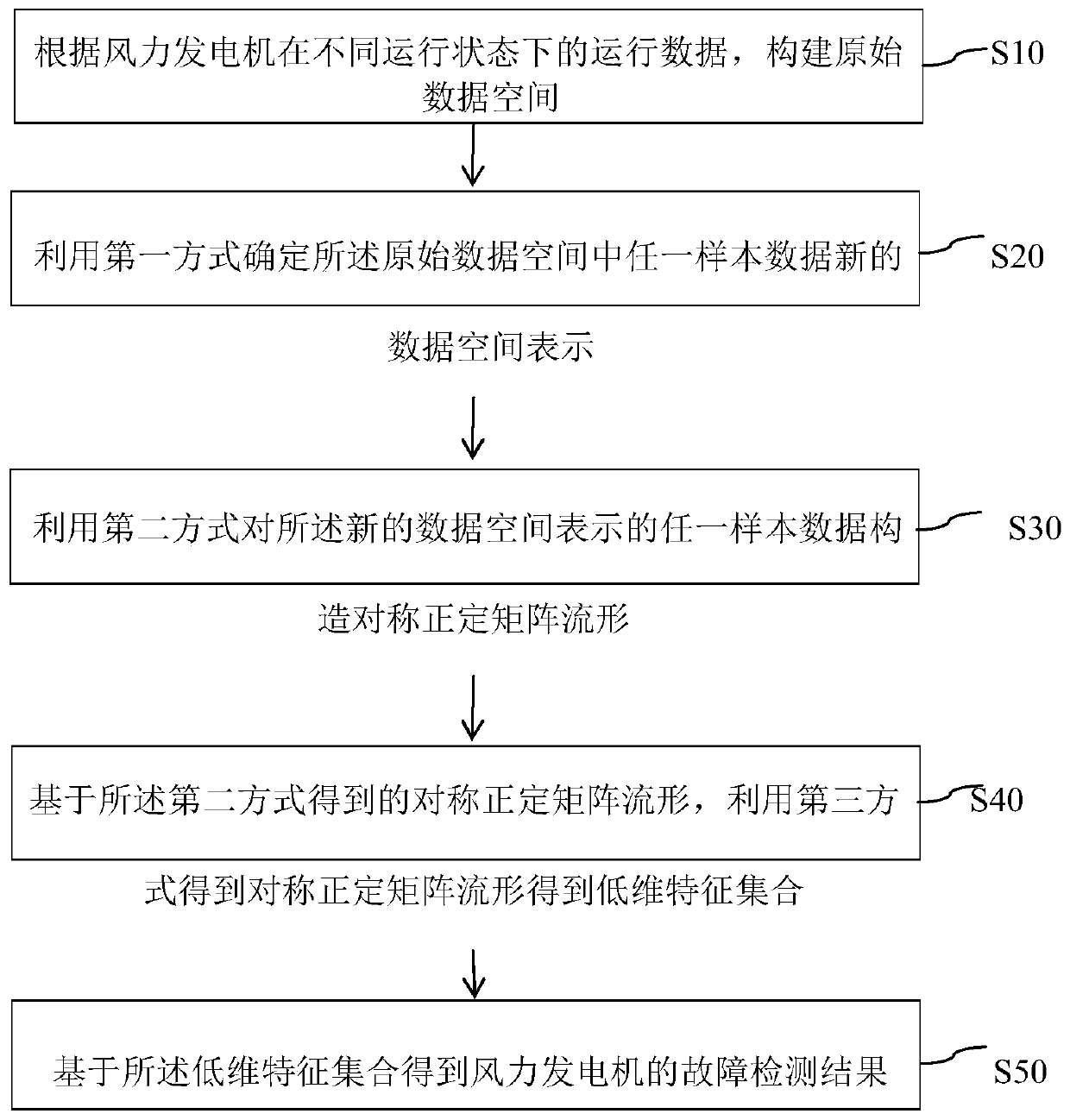
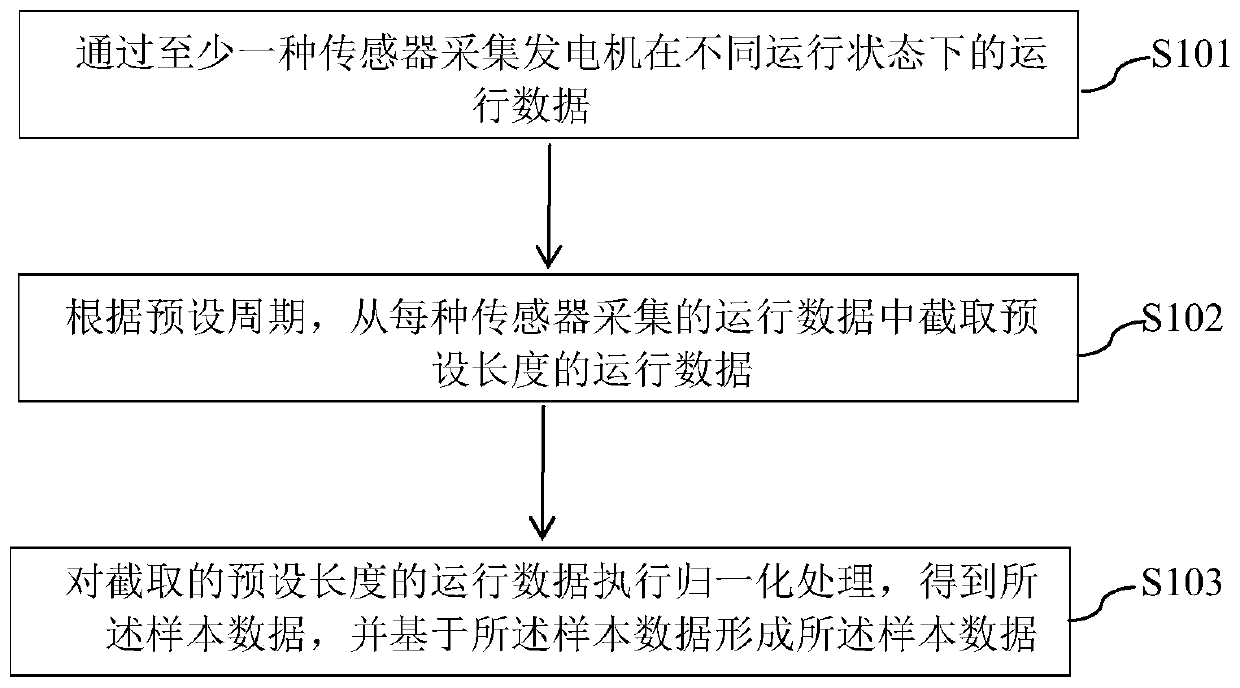
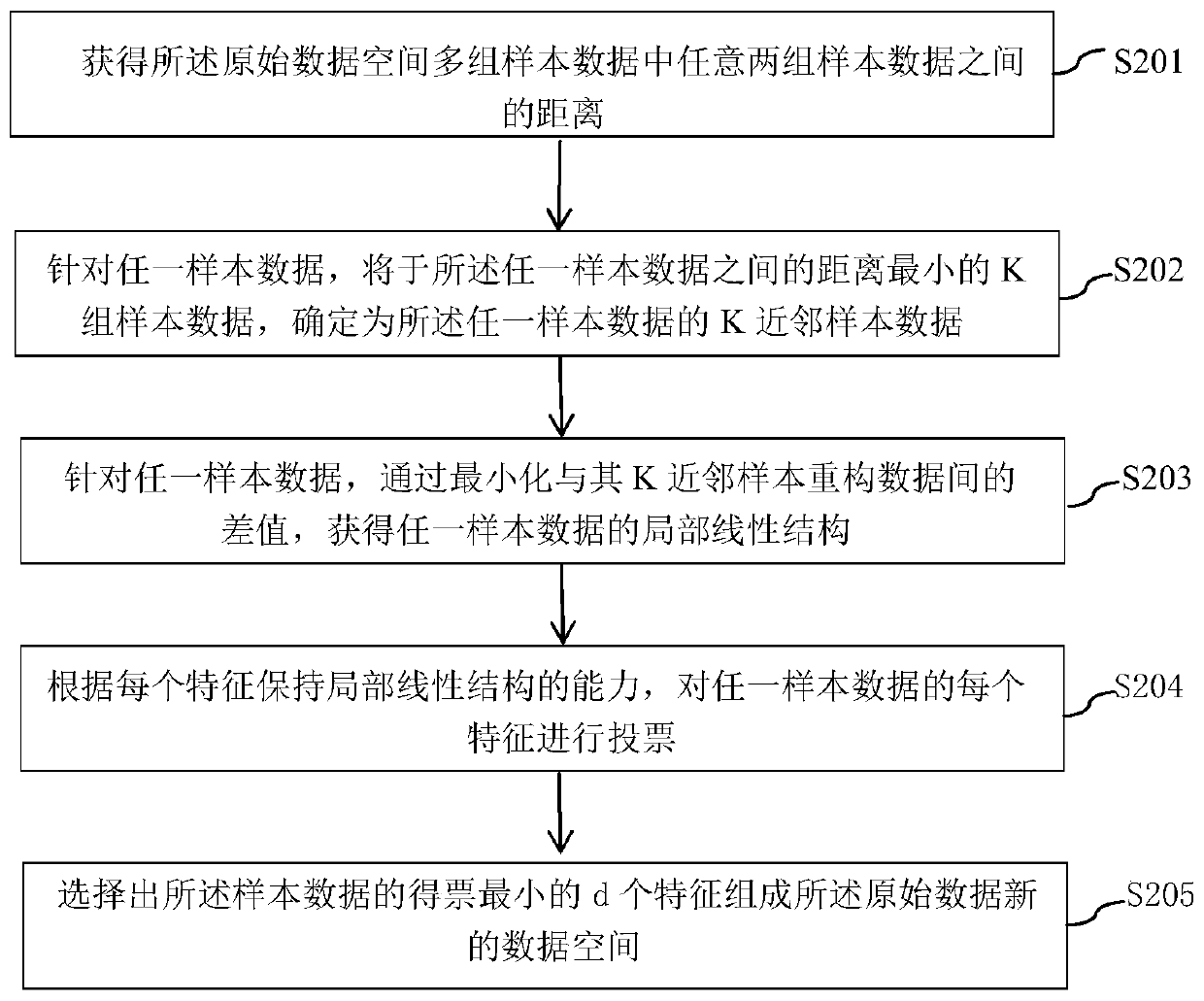
Method and device for diagnosing faults of wind driven generator in dimension reduction mode
ActiveCN111062447AReduce dimensionalityFeature retentionData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature setAlgorithm
The invention relates to a method and device for carrying out wind driven generator fault diagnosis in a dimension reduction mode. The method comprises the steps of constructing an original data spaceaccording to operation data of the wind driven generator in different operation states; performing feature selection on the sample data in the original data space by using a first mode to obtain a new data space; constructing a corresponding symmetric positive definite matrix manifold for any sample data in the new data space obtained based on the first mode by using a second mode; performing feature extraction on the symmetric positive definite matrix manifold of the sample data in a third mode to obtain a low-dimensional feature set of the sample data in the symmetric positive definite matrix manifold; and inputting the obtained low-dimensional feature set into a support vector machine, and detecting the fault of the wind driven generator according to the output information of the support vector machine. The fault detection precision of the wind driven generator can be improved.
Owner:NORTHEAST GASOLINEEUM UNIV
Soybean plant rapid three-dimensional reconstruction method based on phenotypic-oriented accurate identification
PendingCN112509142ASave money on purchasesSave time and costImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudAlgorithm
The invention discloses a soybean plant rapid three-dimensional reconstruction method based on phenotype-oriented accurate identification, and the method comprises the steps of enabling a user to useKinect to scan a soybean plant, i.e., a soybean plant, at intervals of a set angle, and obtaining a plurality of frames of point cloud scenes where the soybean plant is placed on an automatic rotatingdisc; after removing a point cloud background through straight-through filtering, calculating a rough registration matrix by using a Rodrigs formula according to a rotation angle provided by a user,performing fine registration by using an ICP algorithm, performing hierarchical clustering on plant point clouds to obtain skeleton points, setting each point to be adjacent to nearest K points for the skeleton points to obtain a plurality of connected components, performing trunk Dijkstra path growth, branch growth point selection and branch communication component Dijkstra path growth on trunk communication components where root nodes are located, and finally performing three-dimensional visualization of a plant skeleton through a pyvista visualization library. According to the invention, the plant point cloud does not need to be processed in advance through software to obtain the parameters, the purchase expenditure of modeling software and the learning and using time cost of the modeling software are saved, and the invention is more efficient.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
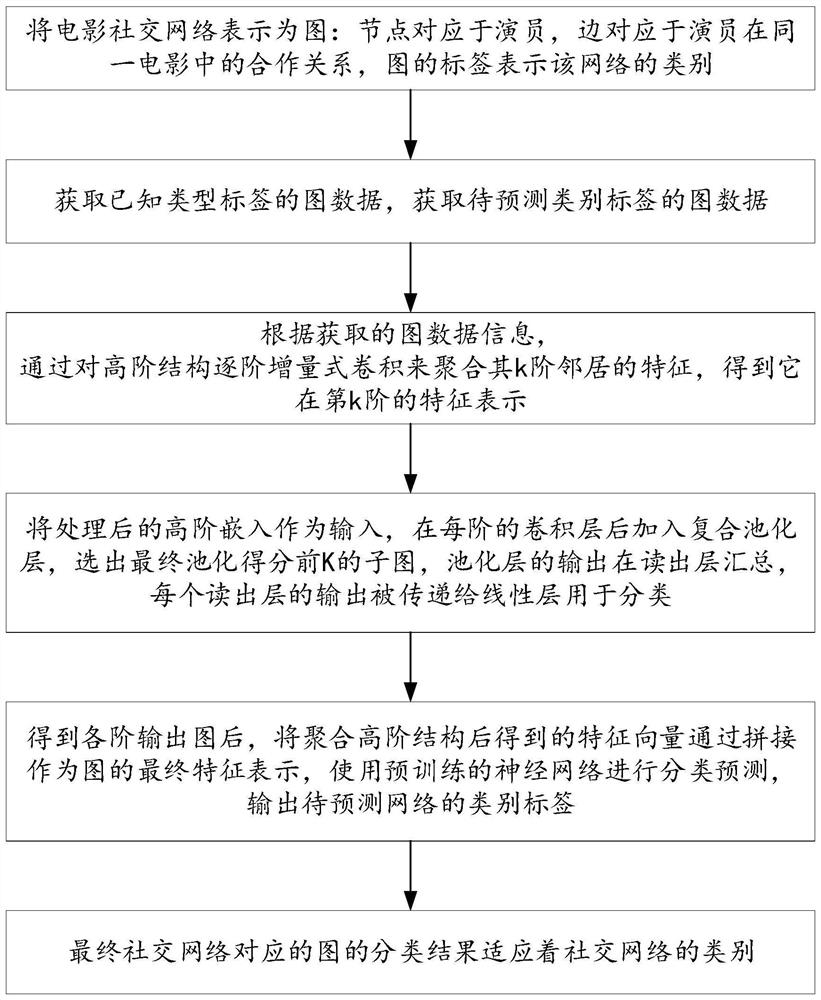
Graph classification method and system fusing high-order structure embedding and composite pooling
PendingCN114792384AFeature retentionEfficient use ofNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsGraph classificationMachine learning
The invention belongs to the technical field of artificial intelligence graph classification, and provides a graph classification method and system fusing high-order structure embedding and composite pooling, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a to-be-classified graph; inputting a to-be-classified graph into the graph neural network to obtain a category to which the graph belongs; wherein for each sub-graph set of the graph, each convolutional layer calculates the feature of each sub-graph based on the sub-graph set output by the previous neural network layer, each composite pooling layer updates the sub-graph set based on the feature of each sub-graph output by the convolutional layer, and meanwhile, for each sub-graph in the updated sub-graph set, the feature of each composite pooling layer is calculated based on the feature of each sub-graph output by the convolutional layer. The features of the sub-graphs in the local neighborhood are fused through an attention mechanism, and the features of the sub-graphs are updated; and obtaining a graph representation vector by the reading layer, and inputting the graph representation vector into the classifier to obtain a category to which the graph belongs. A high-order structure is utilized, messages are directly transmitted among the sub-graphs, structural information invisible in node level is captured, and the classification precision of the graphs is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
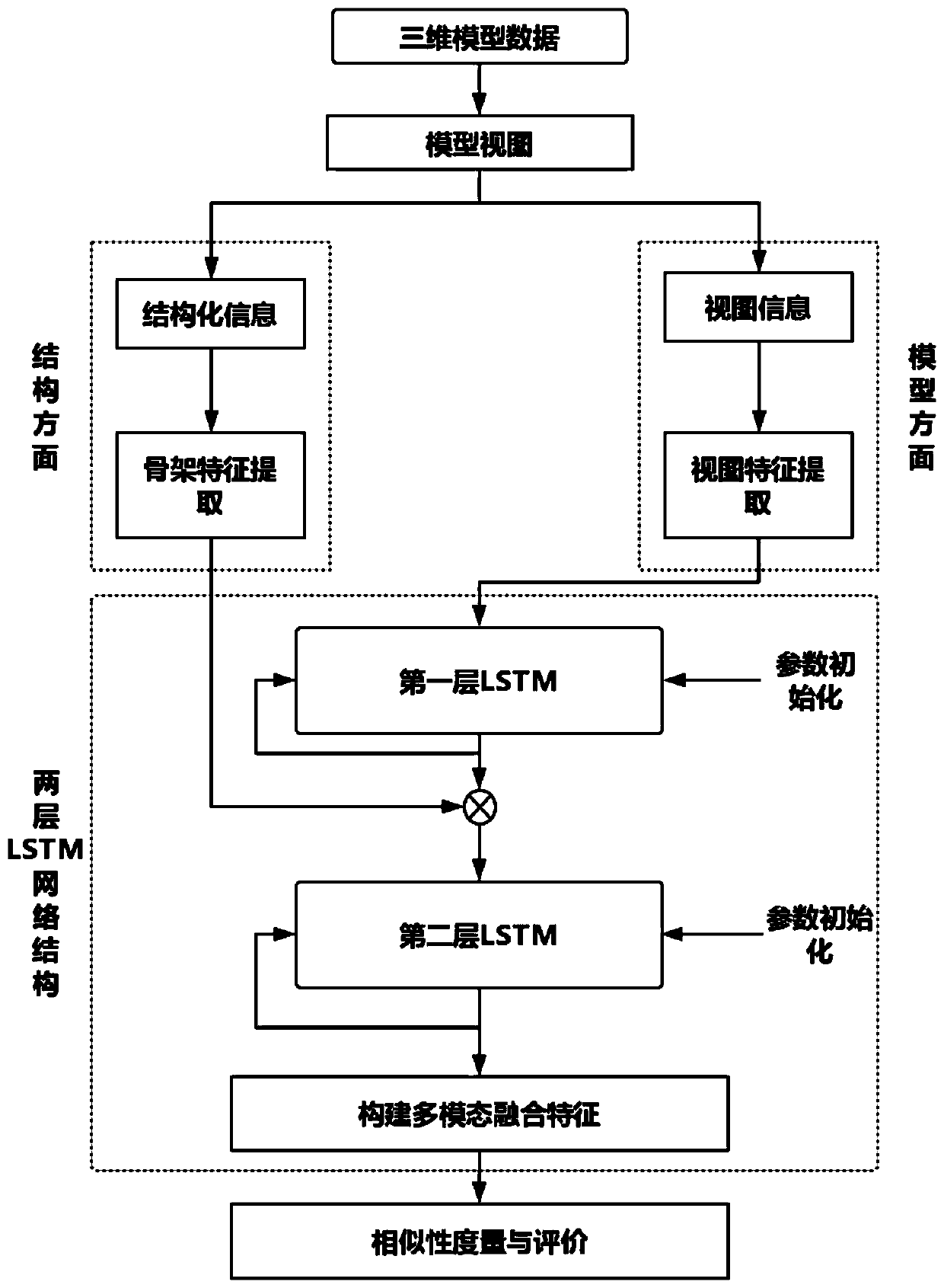
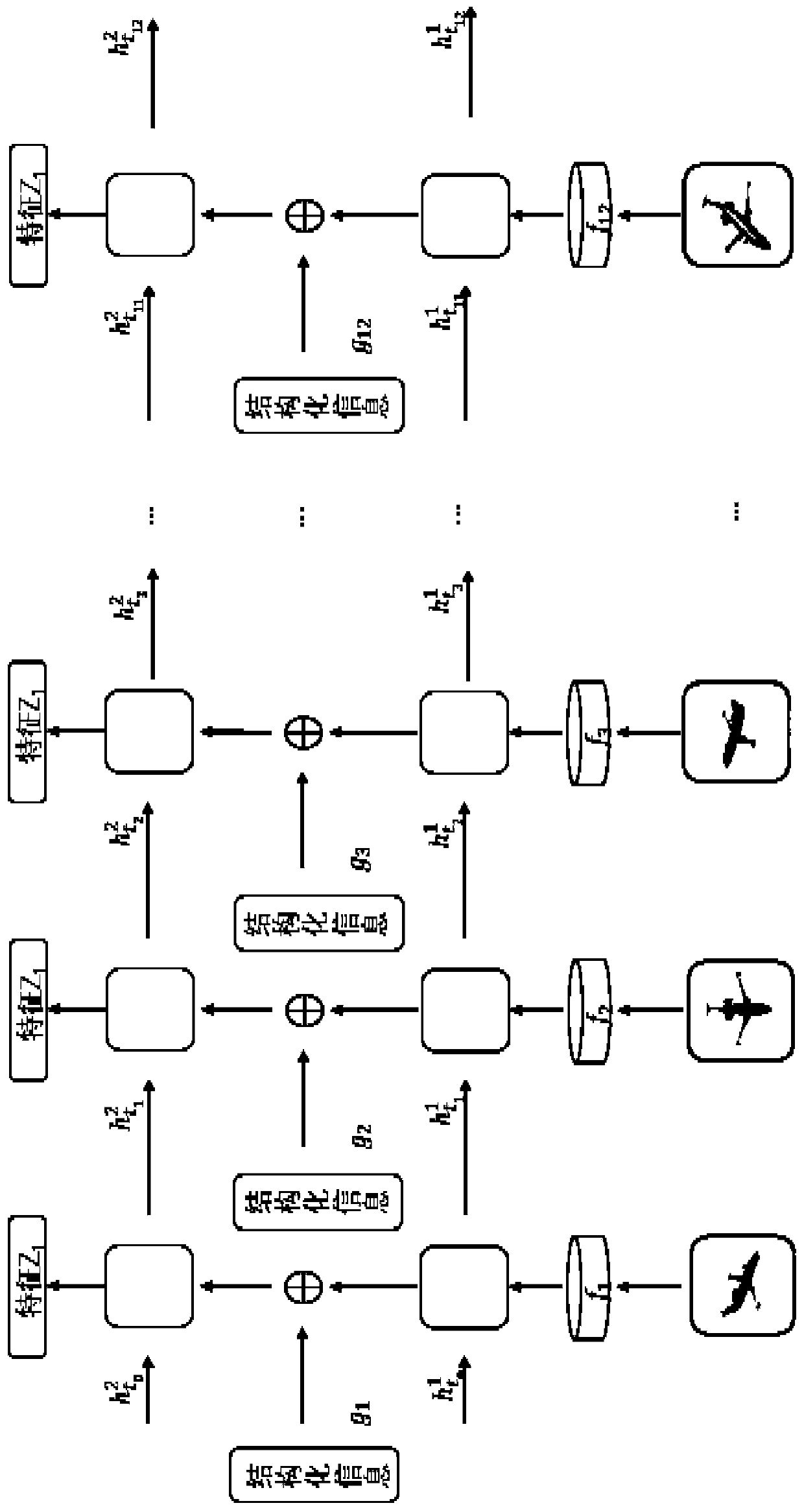
Three-dimensional model retrieval method based on LSTM network multi-modal information fusion
PendingCN110163091AComprehensive descriptionThe search result is accurateDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsThree dimensional modelDimensional modeling
The invention discloses a three-dimensional model retrieval method based on LSTM network multi-modal information fusion, and the method comprises the steps: for a given three-dimensional model, extracting a plurality of views of the three-dimensional model arranged according to a rotation angle sequence; extracting skeleton characteristics of a plurality of views in a multi-task and multi-angle manner, and obtaining structured information of the three-dimensional model according to the skeleton characteristics; extracting view feature vectors of a plurality of views, and inputting the view feature vectors into a layer of LSTM network structure; checking whether other feature vectors need to be extracted continuously or not; connecting the skeleton feature vector with the view feature vector subjected to one layer of LSTM to form a new feature vector, and inputting the new feature vector into a second layer of LSTM network structure for fusion; checking whether other to-be-fused featurevectors exist or not, if yes, forming a new feature vector again and inputting the new feature vector into the next layer of LSTM network structure for fusion; and taking the output of the last fusion as the final feature vector Q of the three-dimensional model, and finishing the final detection process of the three-dimensional model in combination with a similarity measurement method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
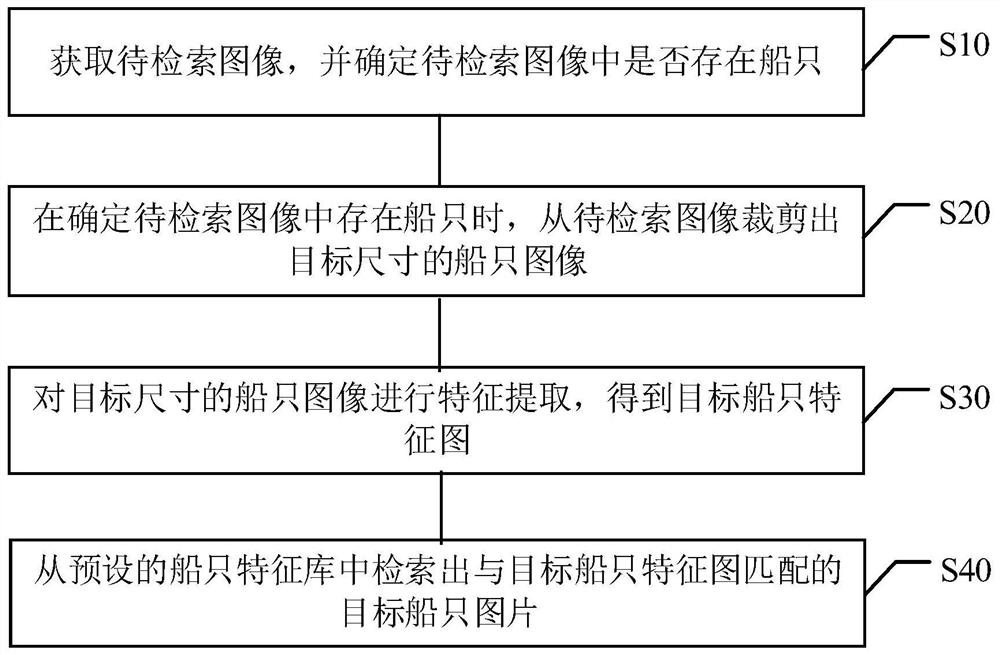
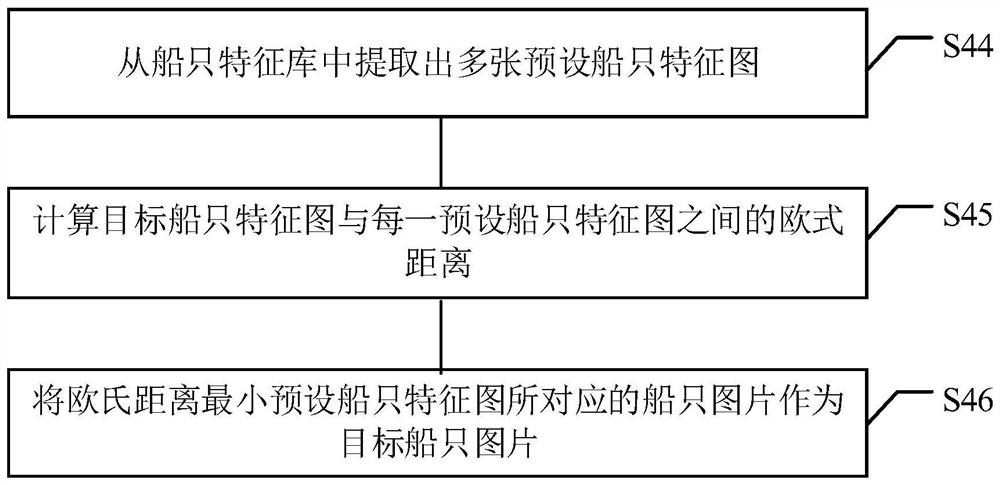
Ship retrieval method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
PendingCN112232291AFeature retentionFeatures retain moreScene recognitionFeature extractionMarine engineering
The invention discloses a ship retrieval method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a to-be-retrieved image, and determining whether a ship exists in the to-be-retrieved image or not; when determining that there is a ship in the to-be-retrieved image, cutting a ship image of a target size from the to-be-retrieved image; performing feature extraction on the ship image of the target size to obtain a target ship feature map; and retrieving a target ship picture matching the target ship feature map from a preset ship feature library. According to the ship retrieval method, the ship retrieval difficulty is reduced.
Owner:ZHUHAI DAHENGQIN TECH DEV CO LTD
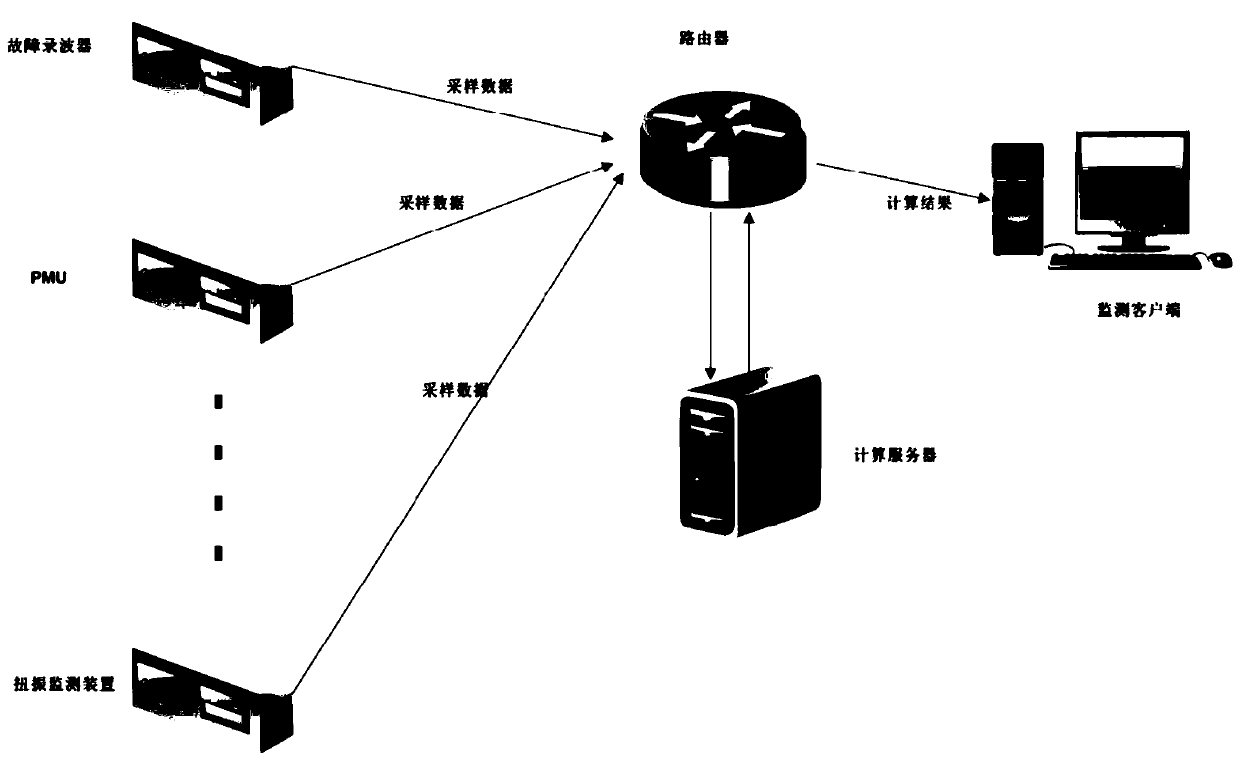
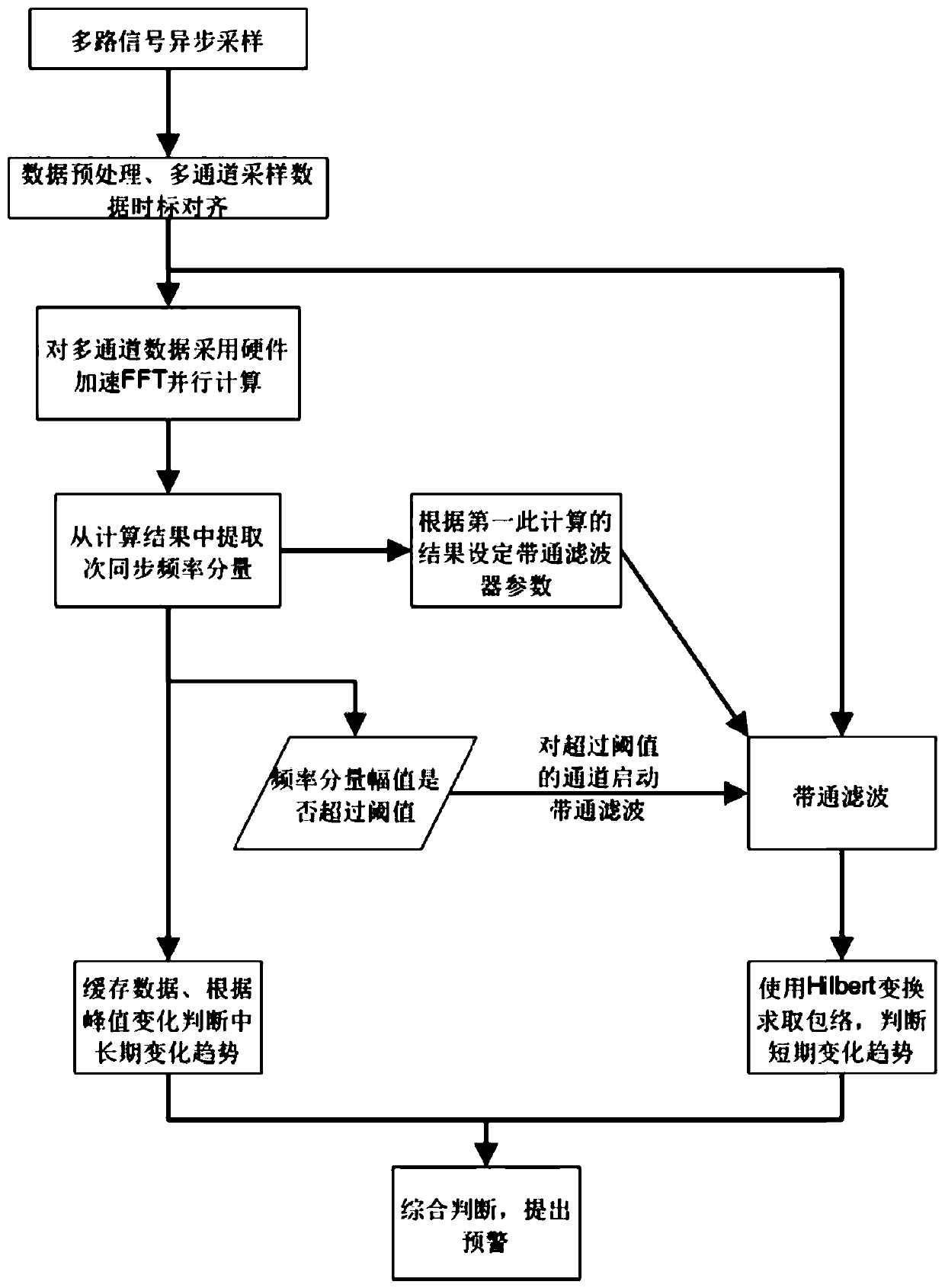
Real-time monitoring and early warning method for subsynchronous oscillation
ActiveCN111413578AGuaranteed real-timeOvercome limitationsFault locationComplex mathematical operationsSimulationPower grid
The invention aims to provide a real-time monitoring and early warning method for subsynchronous oscillation in a regional power grid, which performs real-time measurement and parallel calculation ona plurality of measuring points in the regional power grid, performs centralized monitoring on subsynchronous oscillation on equipment in the power grid at the same time, and provides risk early warning according to the subsynchronous oscillation mode change trend and severity.
Owner:NORTH CHINA POWER ENG +1
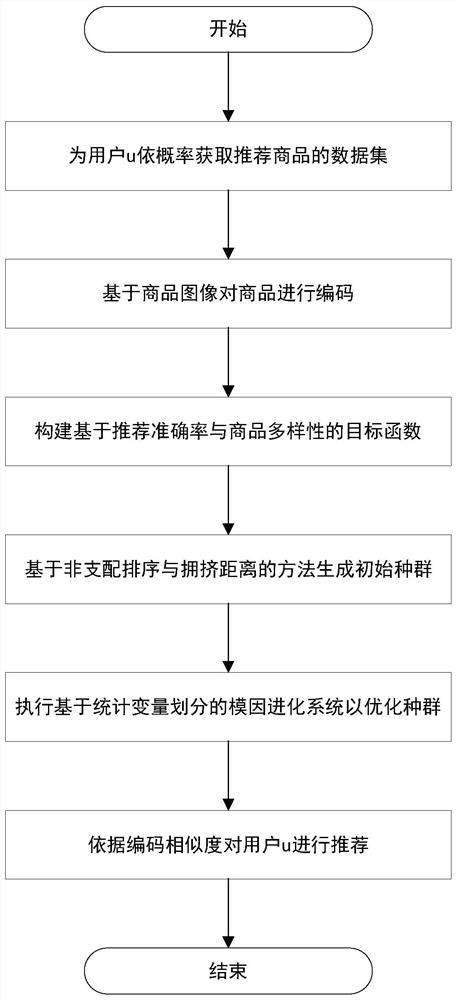
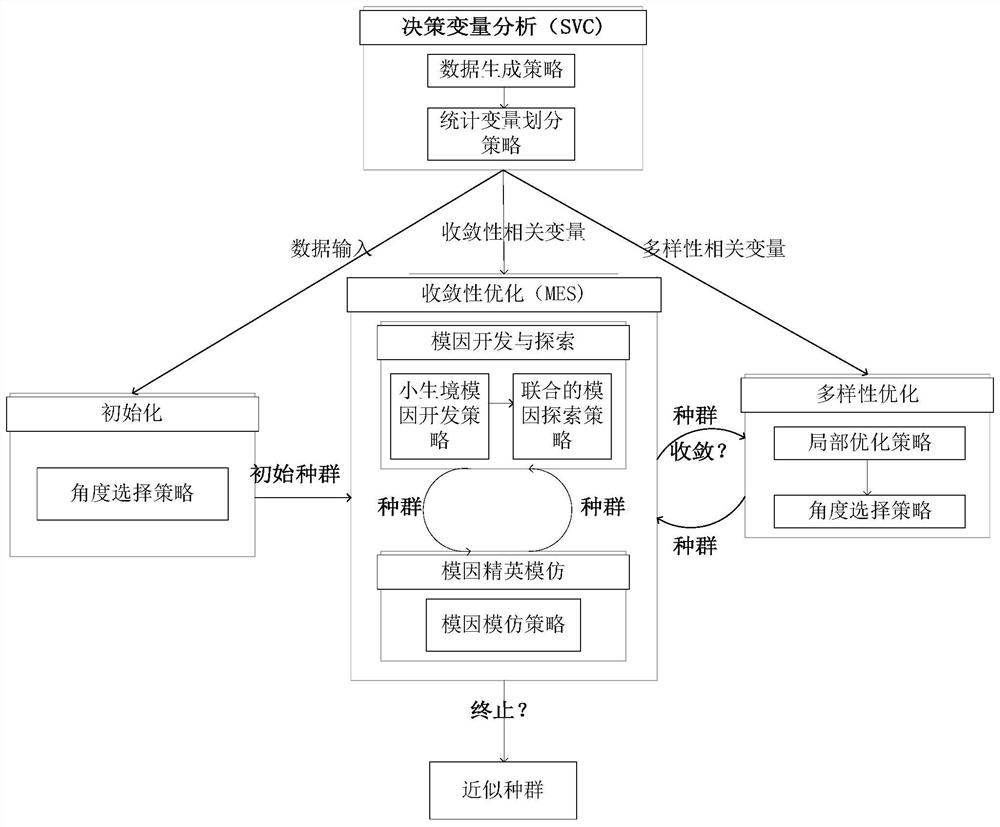
Large-scale multi-objective optimization commodity recommendation method based on image coding
PendingCN113269617ARich diversityIncrease coverageArtificial lifeBuying/selling/leasing transactionsMulti objective optimization algorithmData set
The invention belongs to the technical field of commodity recommendation, and discloses a large-scale multi-objective optimization commodity recommendation method based on image coding. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, obtaining a data set of recommended commodities for a user according to probability, then coding the commodities based on commodity images, then constructing a target function based on recommendation accuracy and commodity diversity, then generating an initial population based on a non-dominated sorting and crowding distance method, and executing a memetic evolution system based on variable statistical division to optimize the population, and finally recommending the user according to the coding similarity. According to the method, a large-scale multi-objective optimization algorithm based on image feature modeling is adopted for optimization, and articles with similar features are selected from recommended commodities according to an optimization result for recommendation, so that the recommendation accuracy of diversified commodities can be improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Vehicle and pedestrian anti-collision warning system and method based on visual perception
ActiveCN107886043BFeature retentionEasy to identifyScene recognitionNeural architecturesKaiman filterSimulation
Owner:JILIN UNIV
A Feature Selection Method for Text Classification
ActiveCN107016073BFeature retentionReduced characteristicsSpecial data processing applicationsText database clustering/classificationFeature setAlgorithm
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
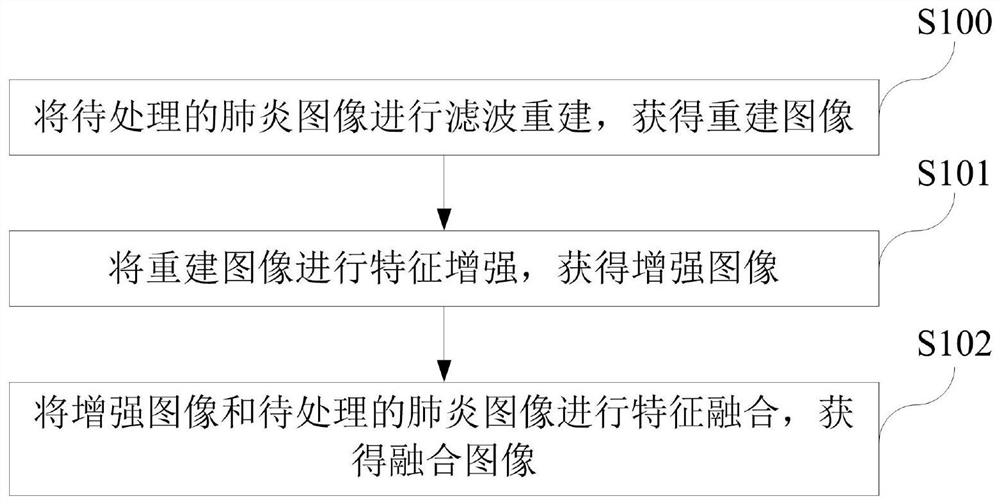
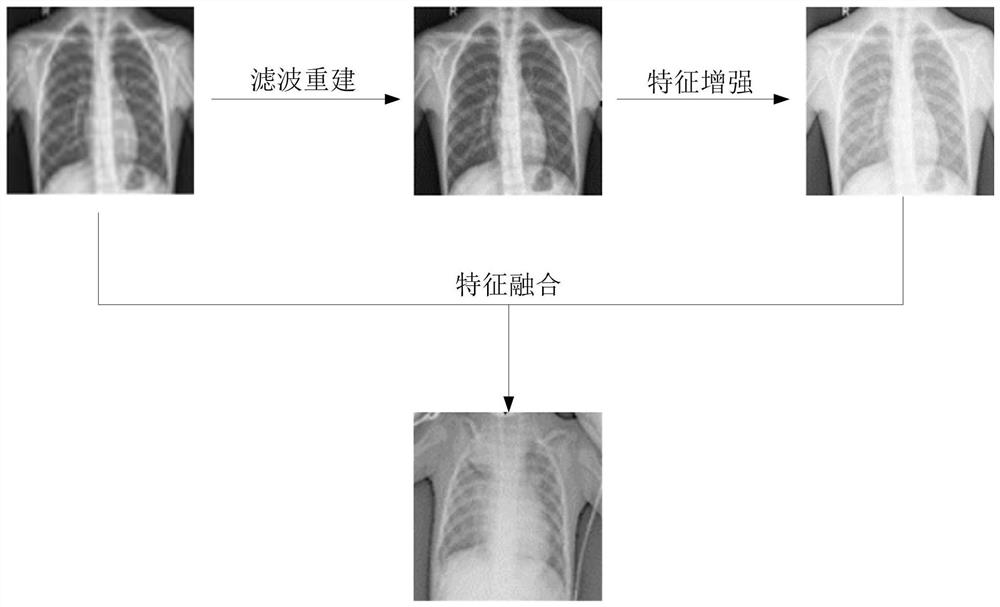
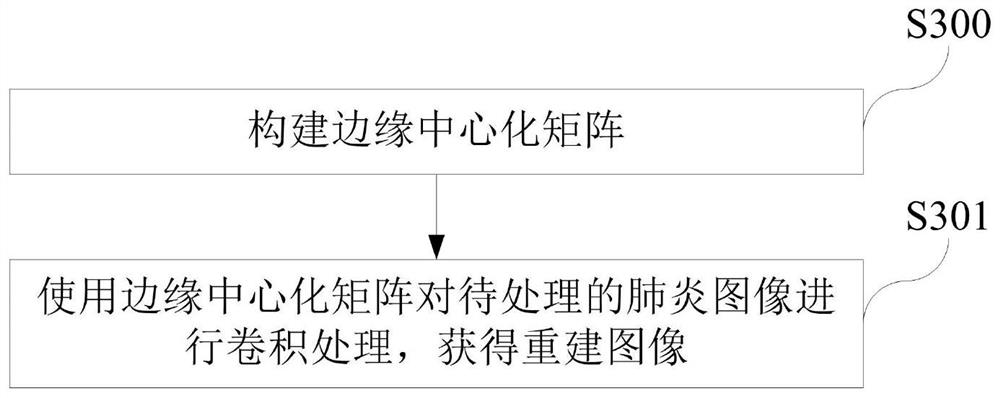
Pneumonia image processing method and system and storage medium
PendingCN113139925AGood for neural network learningFeature retentionImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionRetinex algorithmNeutral network
The invention discloses a pneumonia image processing method and system and a storage medium; the method comprises the steps: carrying out the filtering reconstruction and feature enhancement of a to-be-processed pneumonia image, and carrying out the fusion of the to-be-processed pneumonia image with an original pneumonia image, and maintaining the features of the original pneumonia image and the feature-enhanced image, thereby facilitating the subsequent neural network learning. Through verification of an InceptionV3 network, the pneumonia image is processed by adopting the method disclosed by the invention, and compared with an unprocessed pneumonia image and a pneumonia image which is processed only by using a Retinex algorithm, the obtained pneumonia image is improved in both accuracy and specificity.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
A Support Vector Machine Recognition Optimization Method Based on Multi-resolution Analysis
ActiveCN107341519BImprove accuracyReduce in quantityCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionMulti resolution analysis
The invention discloses a support vector machine recognition and optimization method based on multi-resolution analysis. It includes a step S6 of performing multi-resolution analysis on the waveform in the radio frequency fingerprint identification technology. The step S6 is to perform multi-resolution analysis on the coherent accumulation denoising signal obtained in step A. The present invention can improve the accuracy of radio frequency fingerprint identification by using support vector machine, reduce the computational complexity of support vector machine learning with a large number of sample signals, adopt the method of multi-resolution analysis to extract the feature points in signal samples, and ensure the accuracy of radio frequency fingerprint On the premise of features, the number of sample points for support vector machine learning is reduced, thereby reducing the computational complexity.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A real-time mapping method based on sparse-slam
ActiveCN107767450BFeature retentionGuaranteed efficient and real-timeImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPoint cloudEngineering
The present invention provides a sparse-slam-based real-time mapping method, including the following two threads running in parallel: thread 1, tracking and extracting key frames; thread 2, creating and inserting point cloud MAP. The real-time mapping method of the present invention adopts two parallel threads, which can ensure the real-time performance of the two threads, which not only saves time, but also preserves the characteristics of the image as much as possible. On the premise of ensuring efficient and real-time algorithm, more scene information.
Owner:NANJING WEIJING SHIKONG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Image feature recognition method
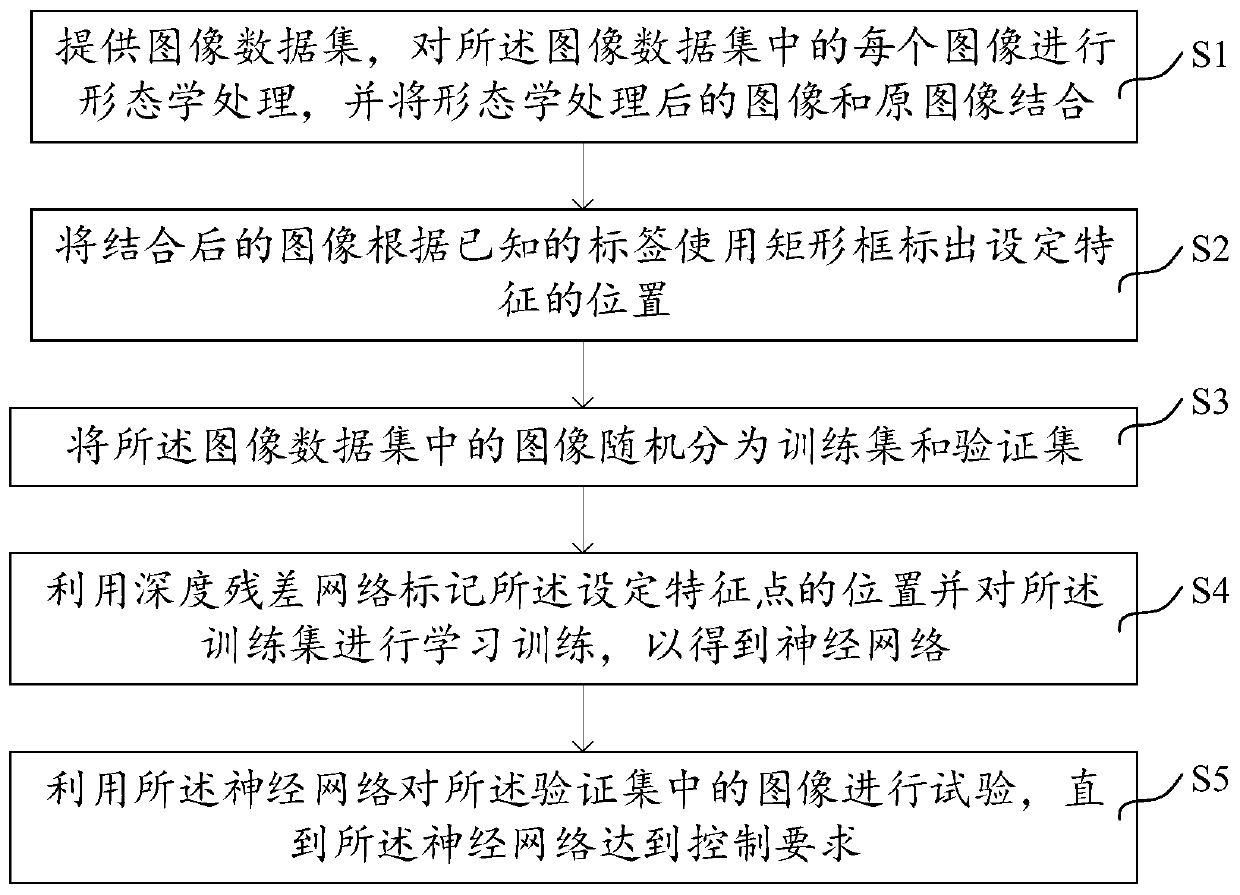
ActiveCN110705570AFeature retentionImprove accuracyImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionData setRadiology
The invention provides an image feature recognition method, comprising the steps: providing an image data set, carrying out the morphological processing of each image in the image data set, and combining the image after morphological processing with an original image; marking the position of a set feature of the combined image by using a rectangular frame according to a known label; images in theimage data set are randomly divided into a training set and a verification set; marking the positions of the set feature points by using a deep residual network and performing learning training on thetraining set to obtain a neural network; and testing the image in the verification set by using the neural network until the neural network meets the control requirement. According to the image feature recognition method, the residual network is used to effectively improve the identification accuracy of the set feature position in the image, and the contour of the image is not segmented, so thatall features in the image can be effectively retained, and a good experiment result is obtained.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com