Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34results about How to "Fairness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
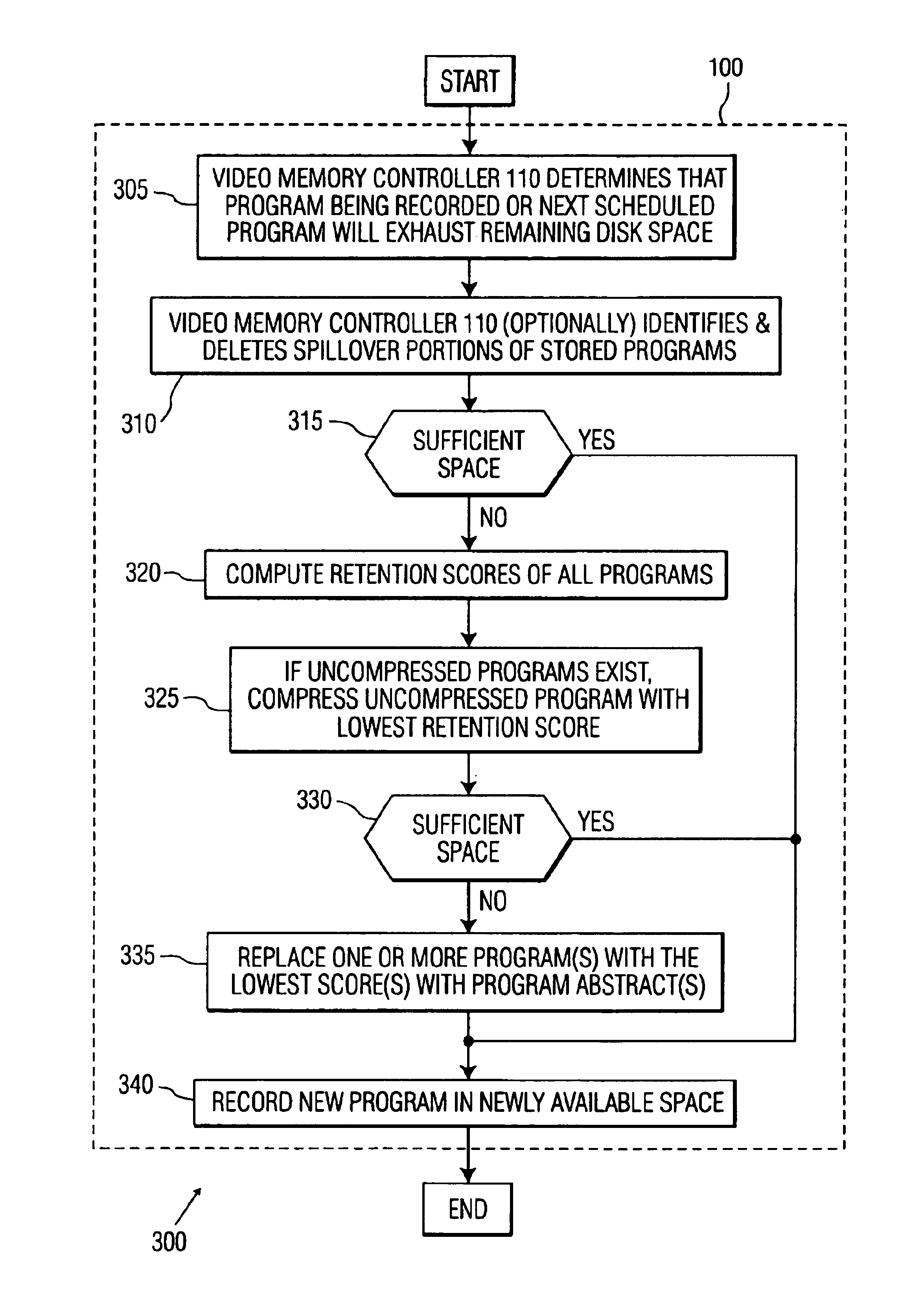
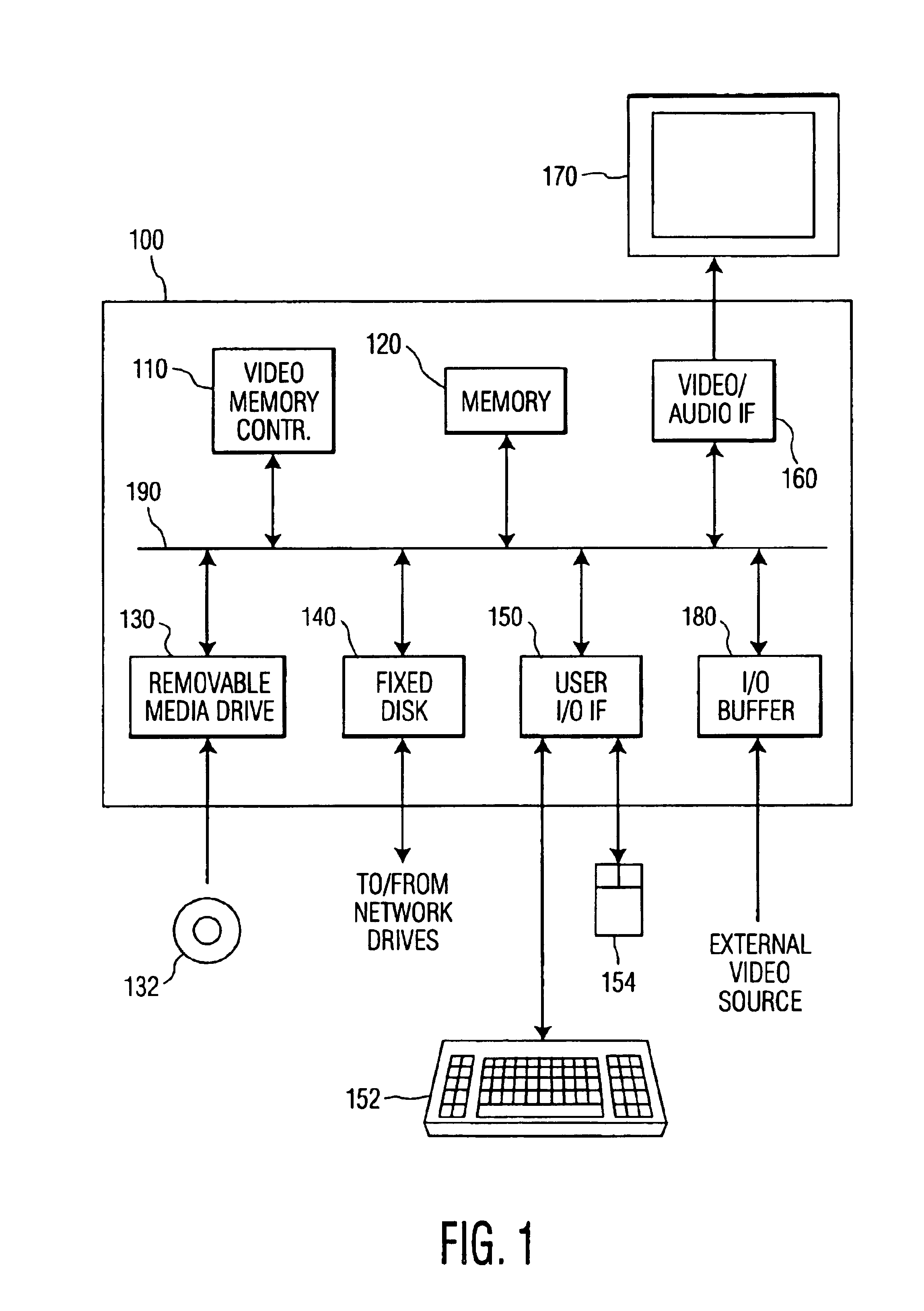
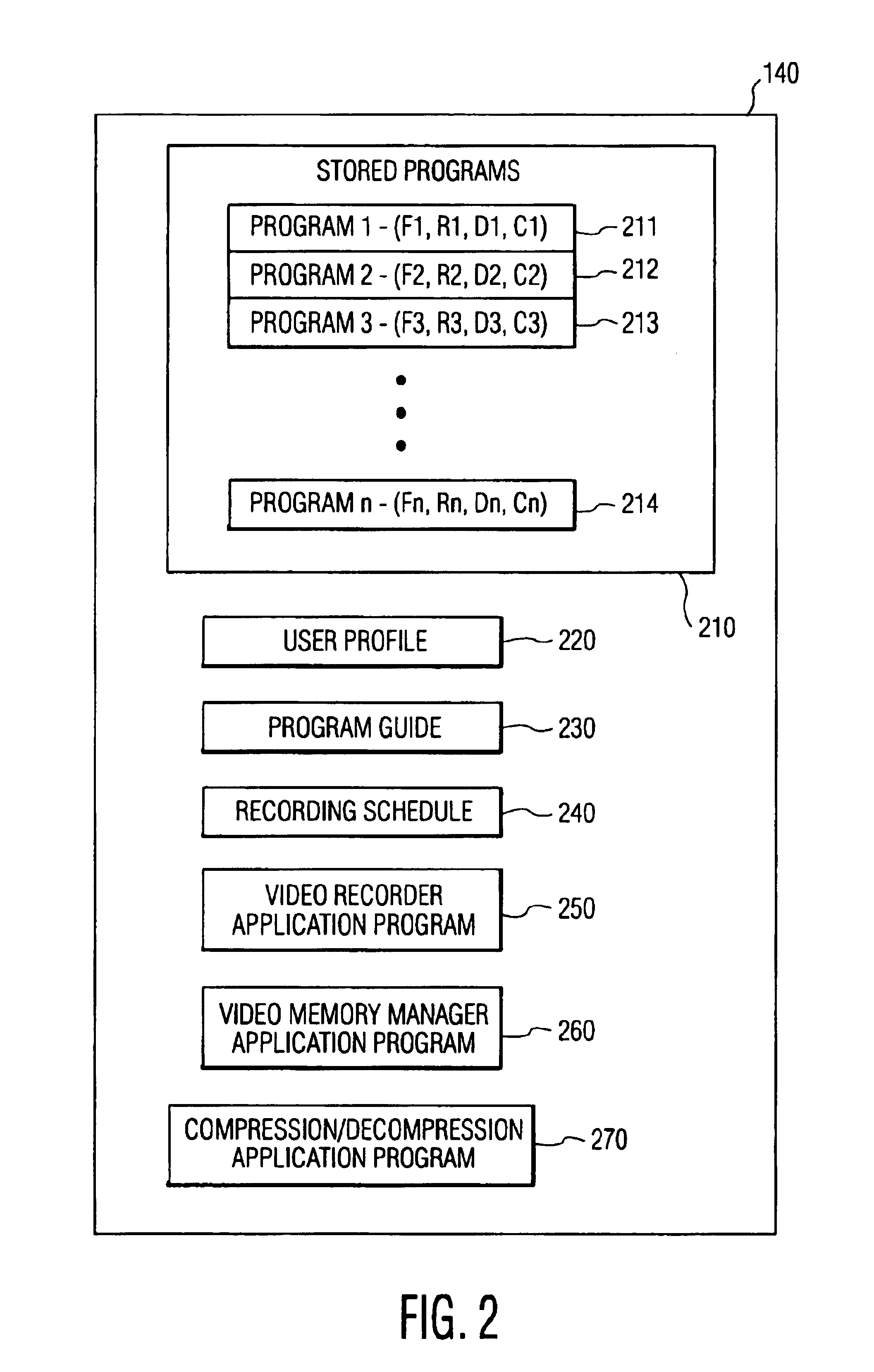
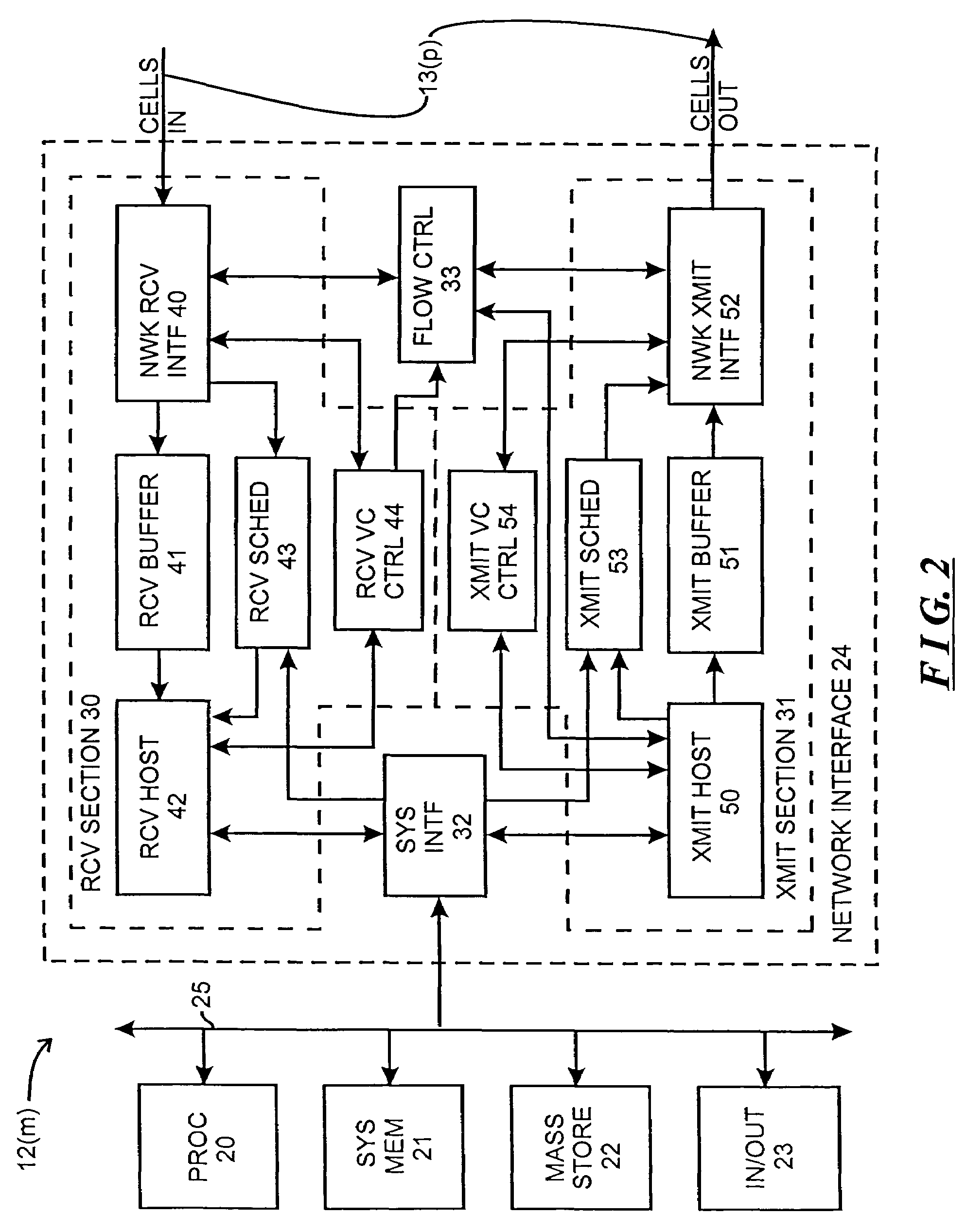
Video memory manager for use in a video recorder and method of operation
InactiveUS6920281B1FairnessTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsVideo memoryVideo storage
There is disclosed a video memory manager for use in a video recording device that stores of video programs on a disk drive. The video memory manager comprises a video memory controller for detecting that the disk drive does not contain sufficient storage space to store a next-to-be-recorded program. The video memory controller, in response to the detection, determines a first retention score associated with a first video program and a second retention score associated with a second video program. The first and second retention scores indicate a desirability of retaining the first and second video programs respectively. The video memory controller deletes a least desirable one of the first and second video programs.
Owner:HEPING GROUP
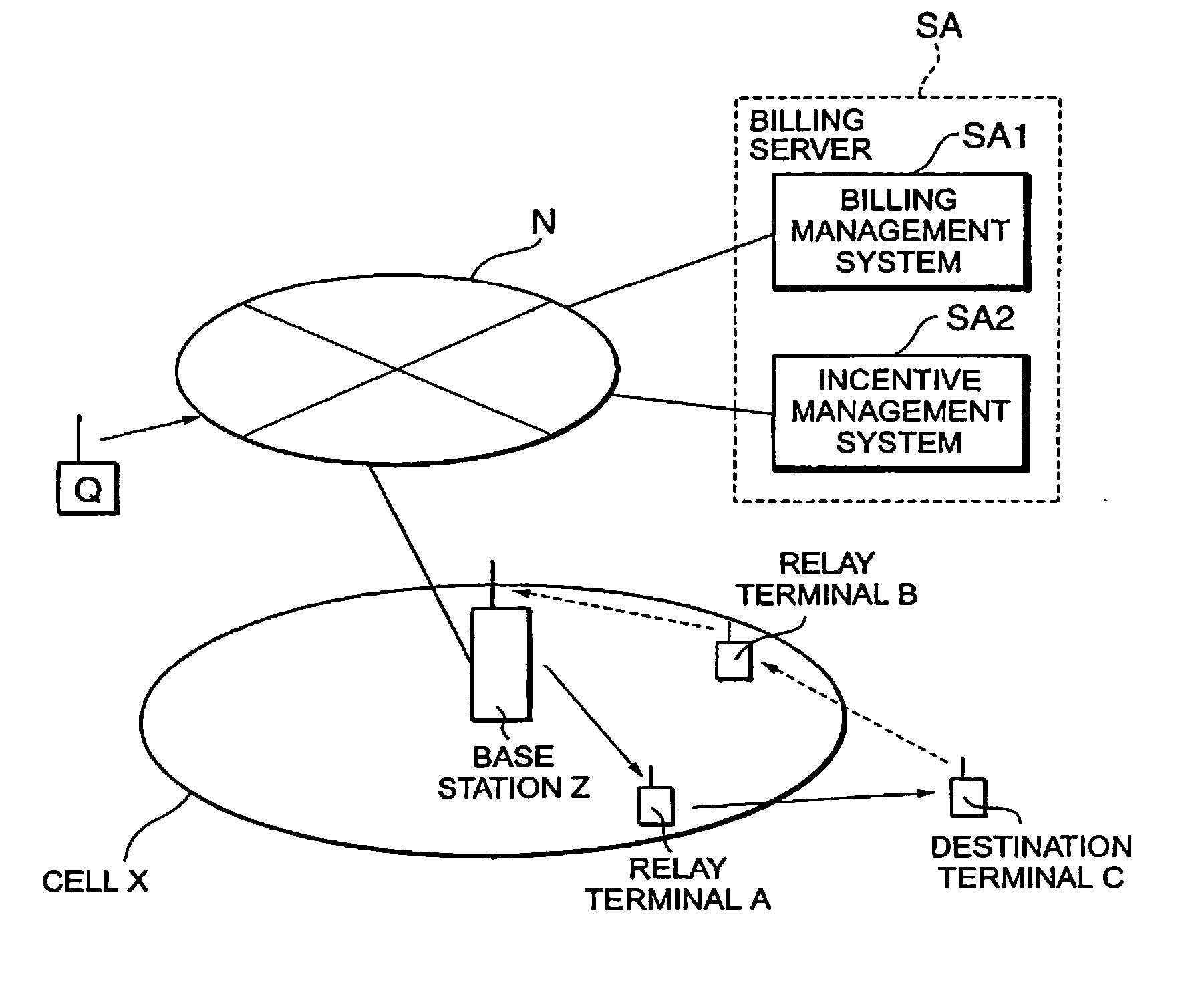
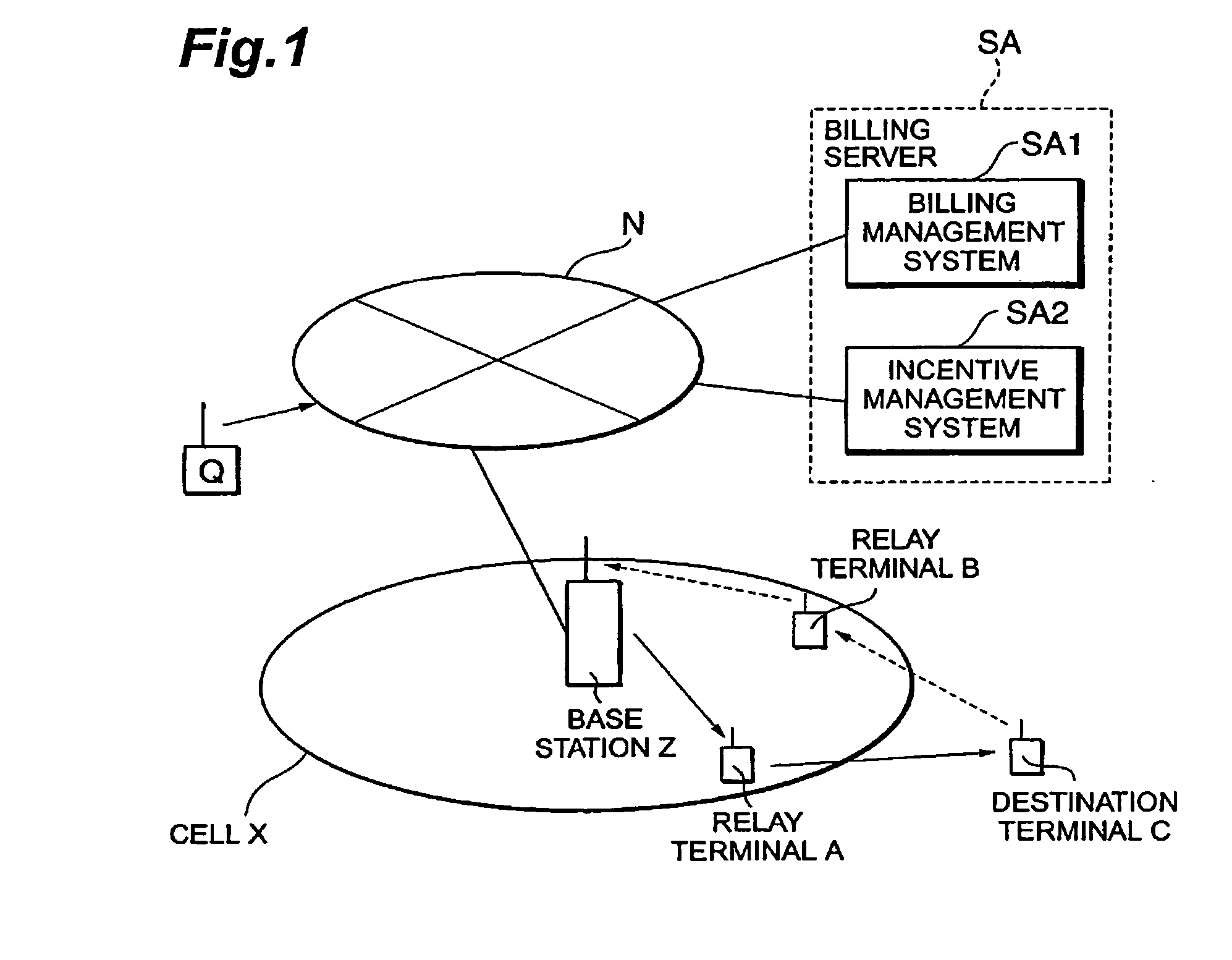
Relay terminal, base station, charging server, communication system, charging method, program computer data signal, and storage medium
InactiveUS20050222948A1FairnessEnsure fairnessNear-field transmissionMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsPacket communicationCommunications system
In a relay terminal A for relaying packet communication between a destination terminal C located outside a service area of a base station Z, and the base station Z, a contribution to relaying is measured and the measurement result is transmitted to a billing server SA configured to store an information communication charge of the relay terminal A, whereby it becomes feasible to give the relay terminal an incentive.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Device and method for multicast in wireless local access network
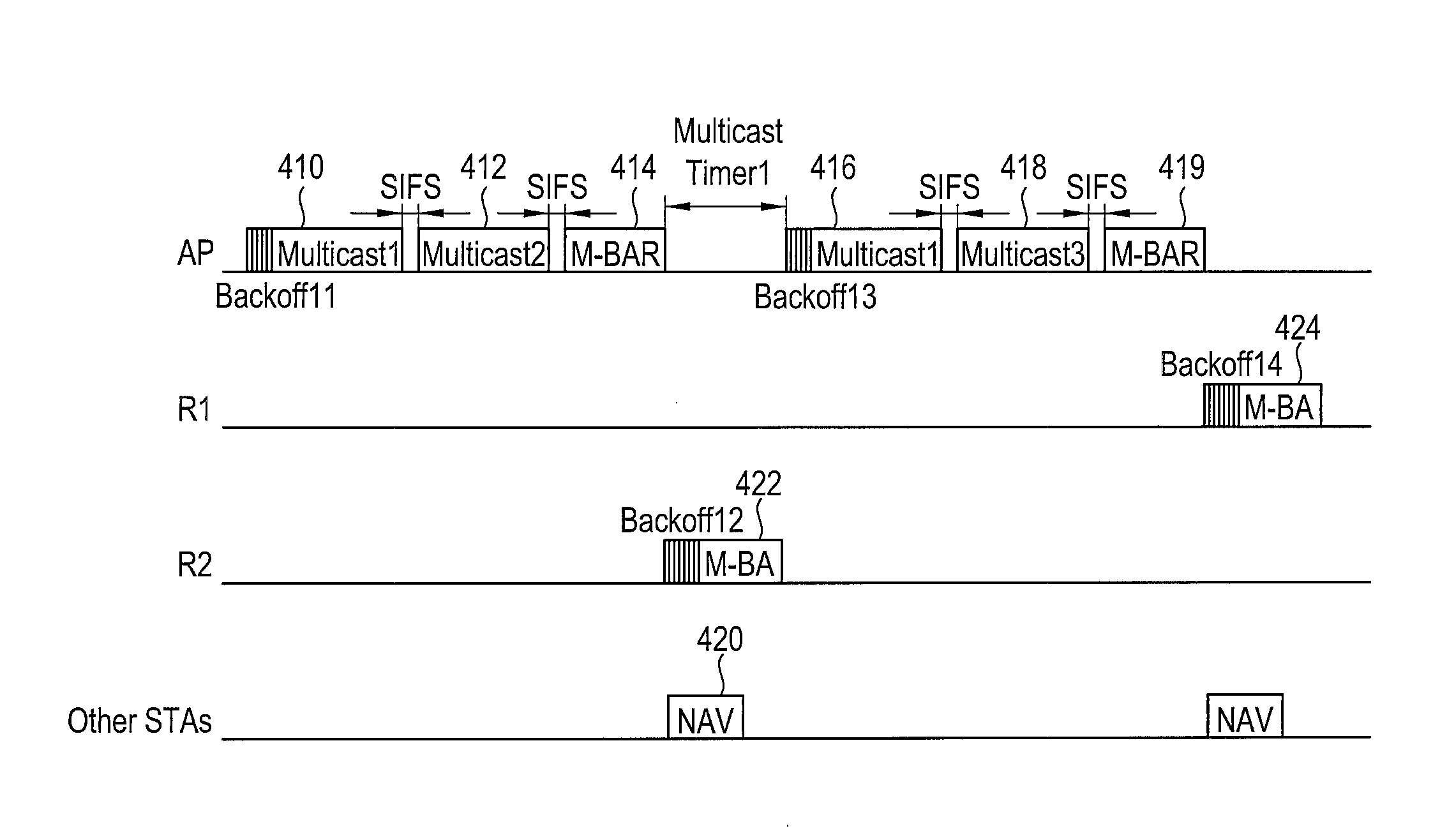
ActiveUS20090279470A1Improve transmission reliabilityFairness of transmission throughputNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesAccess networkWireless lan
A device and method for multicasting data in a wireless network. The method includes receiving multicast data at a specific node of the wireless network, the multicast data including a multicast acknowledgement request; and determining by the specific node whether or not the specific node is requested to send an acknowledgement to the multicast acknowledgement request. Also, a device and method for multicasting data in a wireless network. The method includes transmitting multicast data, the multicast data including a multicast acknowledgement request, the multicast acknowledgement request including information configured to enable a specific node of the wireless network to determine whether or not the specific node is requested to send an acknowledgement to the multicast acknowledgement request.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
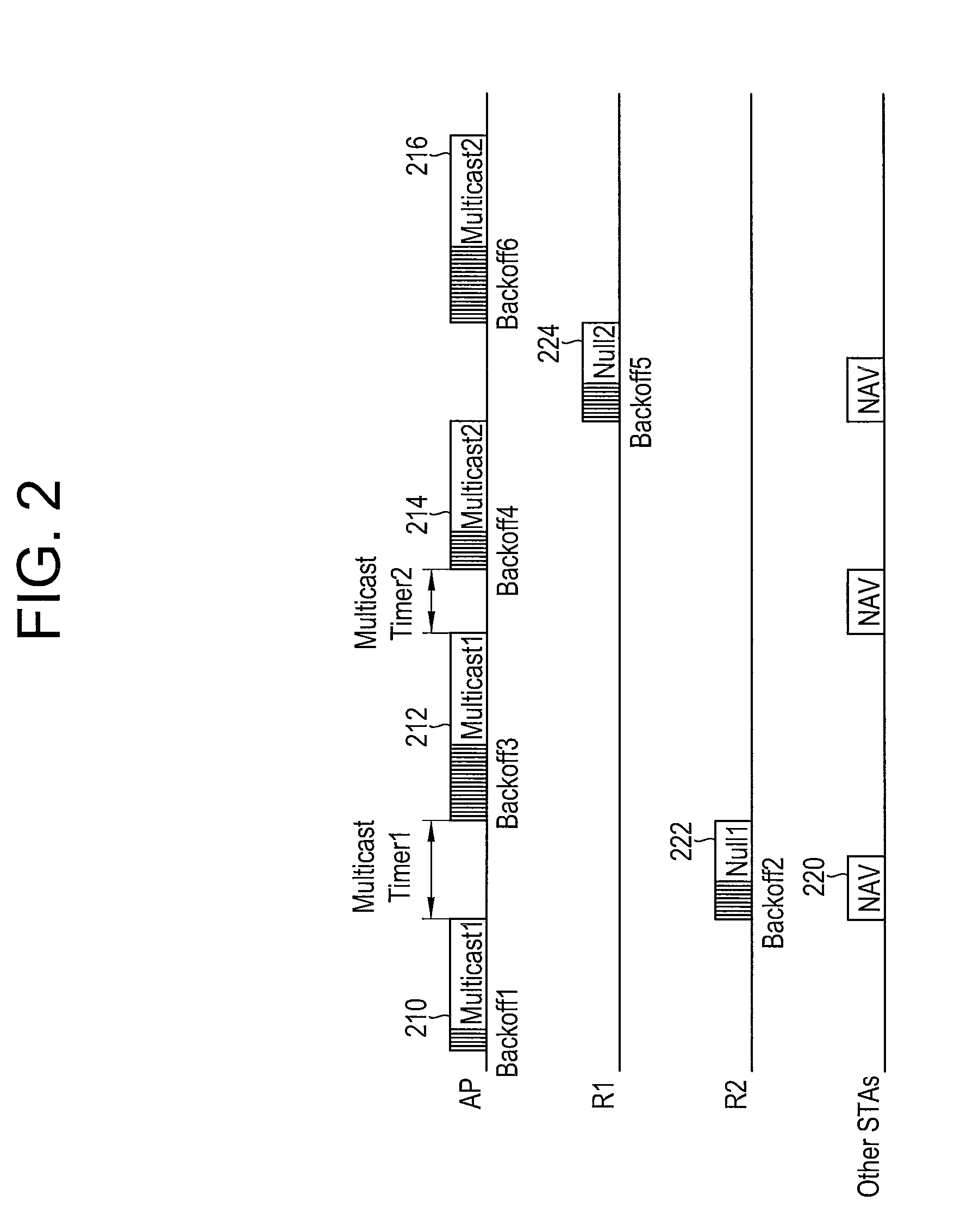
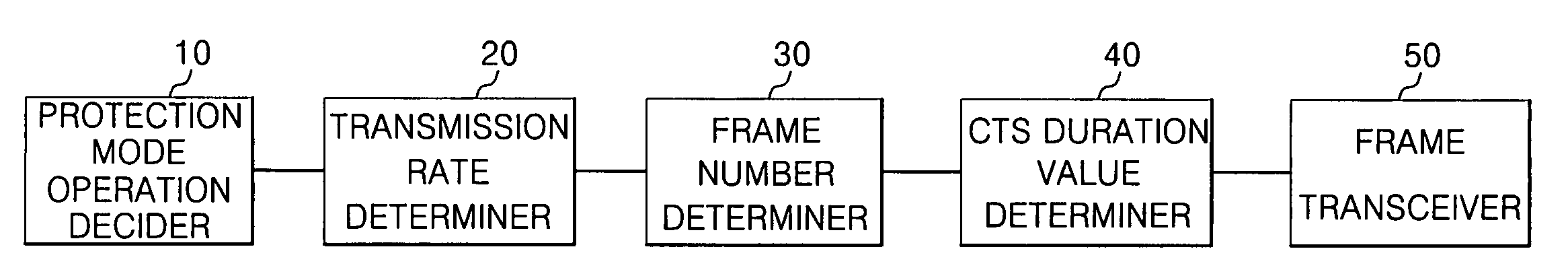
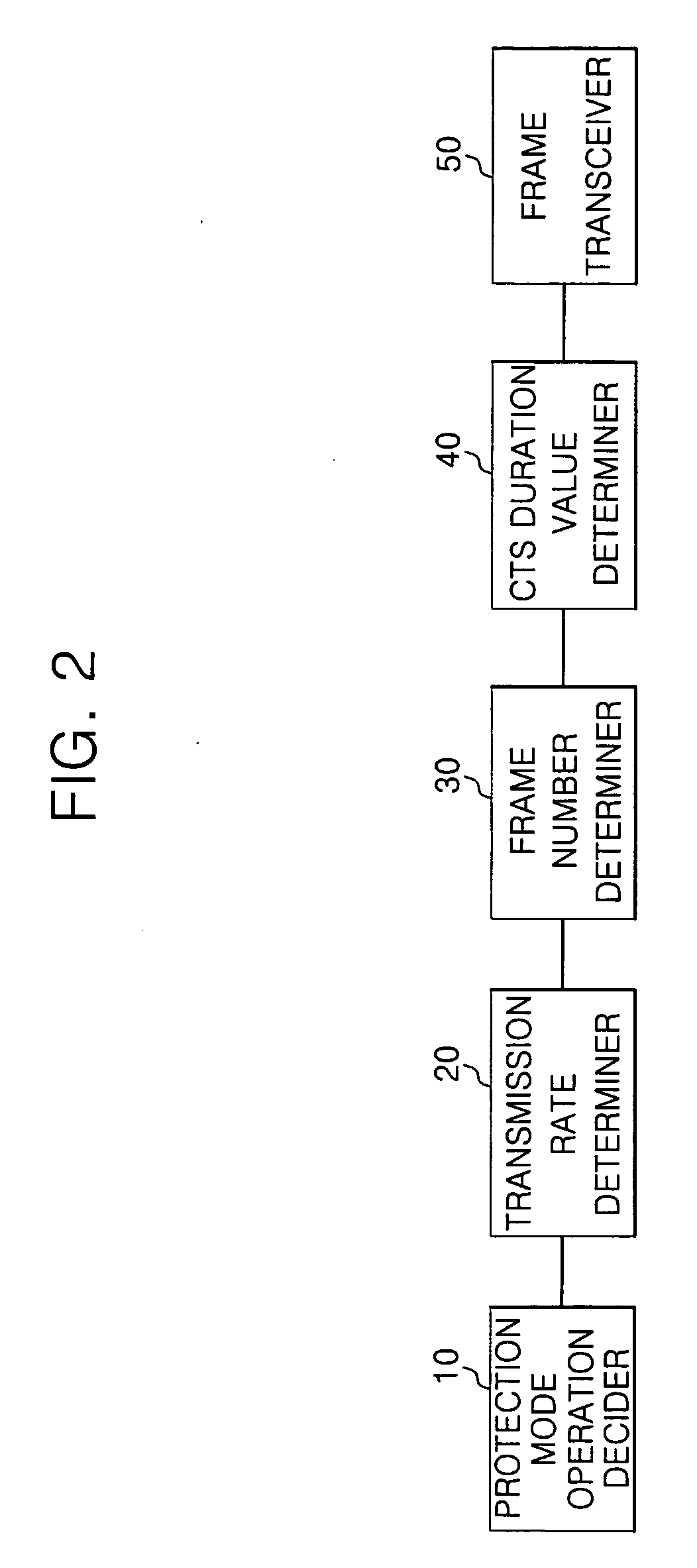
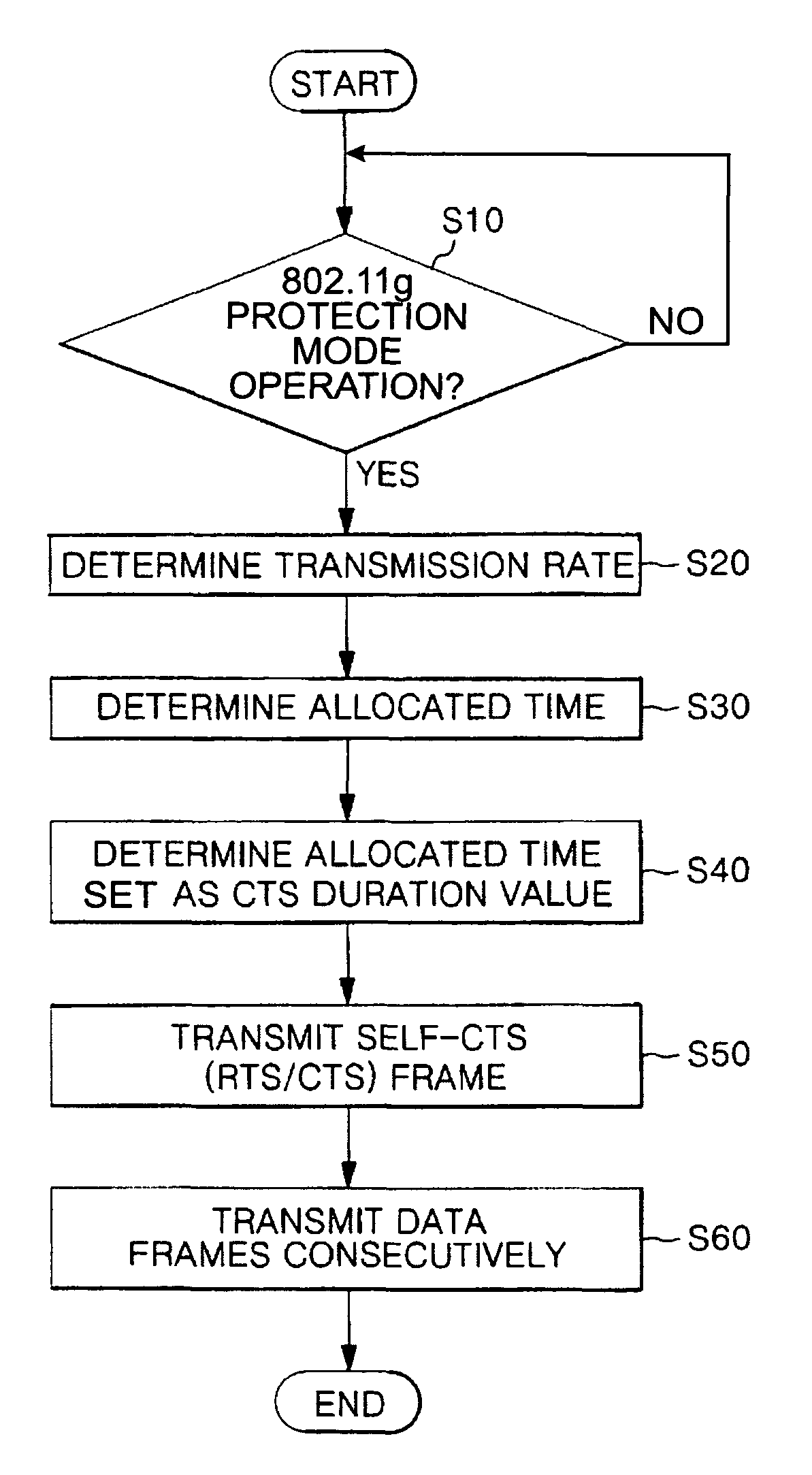
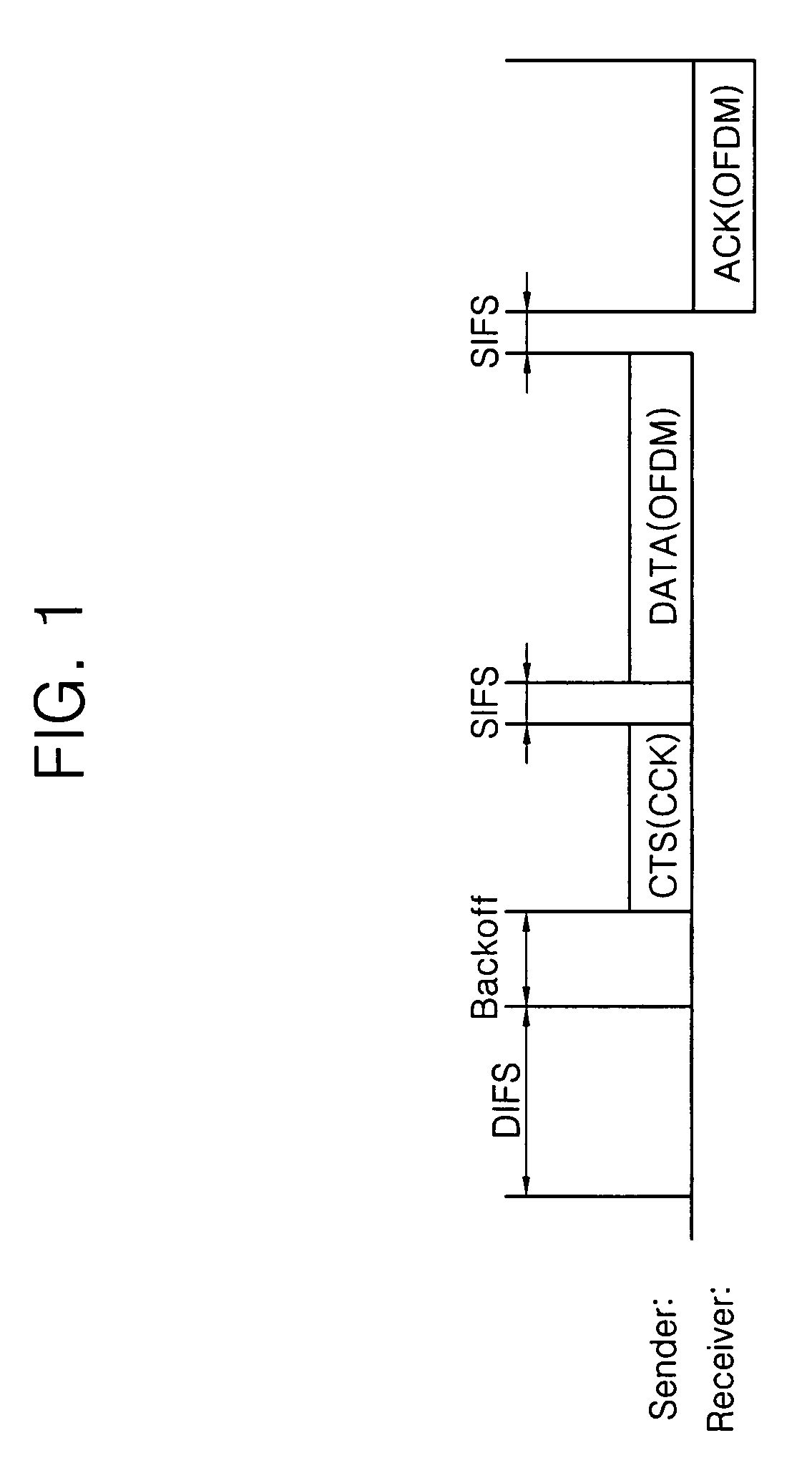
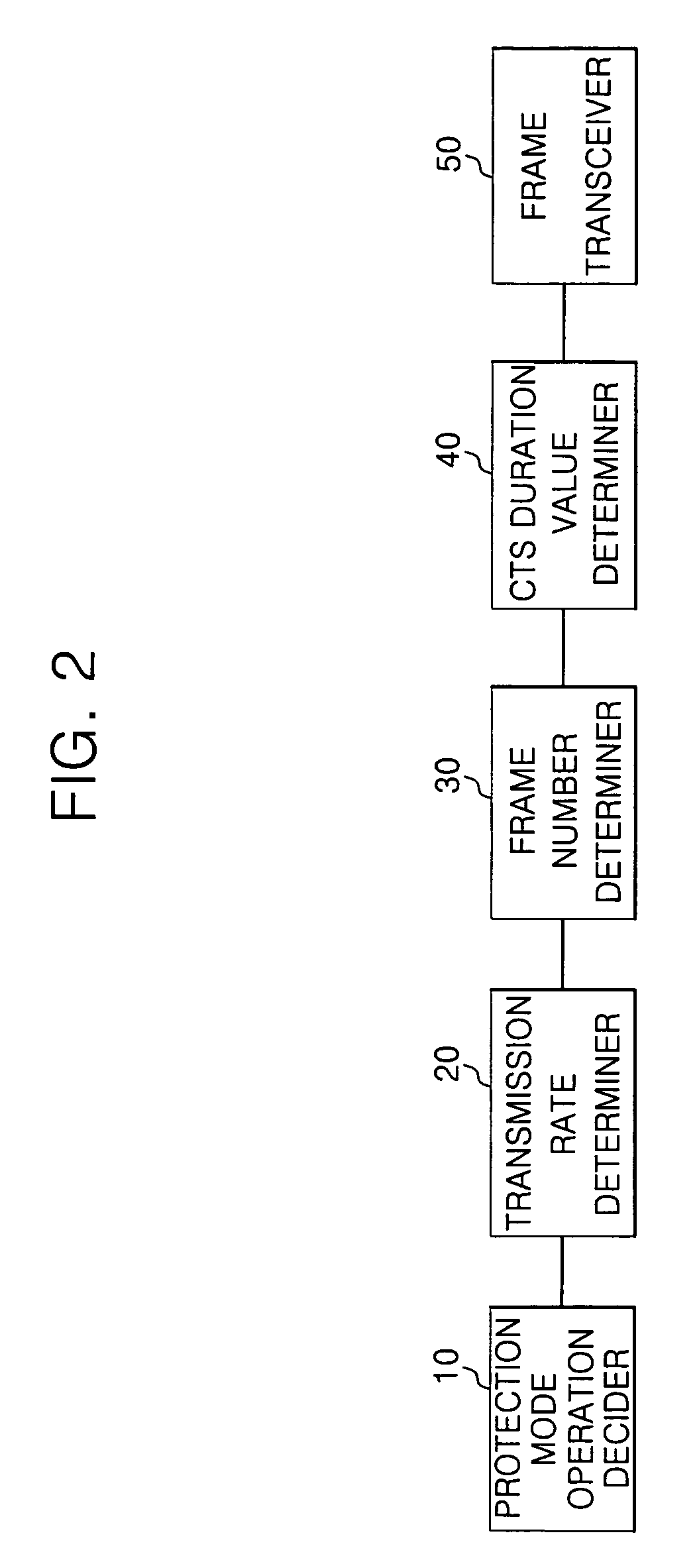
Apparatus and method for transmitting data frame in WLAN terminal
ActiveUS20070183443A1Reduce degradationTransmission fairnessNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionBeacon frameWireless lan
A system and method for transmitting data in a wireless local area network (WLAN) are provided. The data transmission system in the WLAN includes: an access point for periodically transmitting beacon frame information; and a wireless terminal for determining the number of data frames depending on a transmission rate of a current data frame, producing a setting frame containing duration information determined depending on the number of data frames, transmitting the setting frame, and then consecutively transmitting as many data frames as the determined number during a duration time when it is determined that a communication environment is an overlapping legacy BSS condition (OLBC) environment based on the beacon frame information received from the access point.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Allocating bandwidth using resilient packet ring (RPR) fairness mechanism
In allocating bandwidth using a Resilient Packet Ring (RPR) fairness mechanism in a node connected to an RPR network, when congestion occurs, an amount of traffic that the node has transmitted to a ring during one aging interval is recorded together with its own identifier in a fairness message as a fairness transmission rate to be advertised to its own upstream nodes and to be stored. The amount of traffic transmitted from the upstream node during the aging interval is measured and stored. When the congestion has been solved, an available bandwidth is calculated with reference to the fairness transmission rate which was recently advertised and the amount of traffic which has been transmitted from the upstream nodes, and the fairness transmission rate is calculated in order to fairly allocate the available bandwidth to the upstream nodes effectively so that the fairness transmission rate is transmitted to the upstream nodes. The upstream nodes transmit traffic in accordance with the fairness transmission rate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
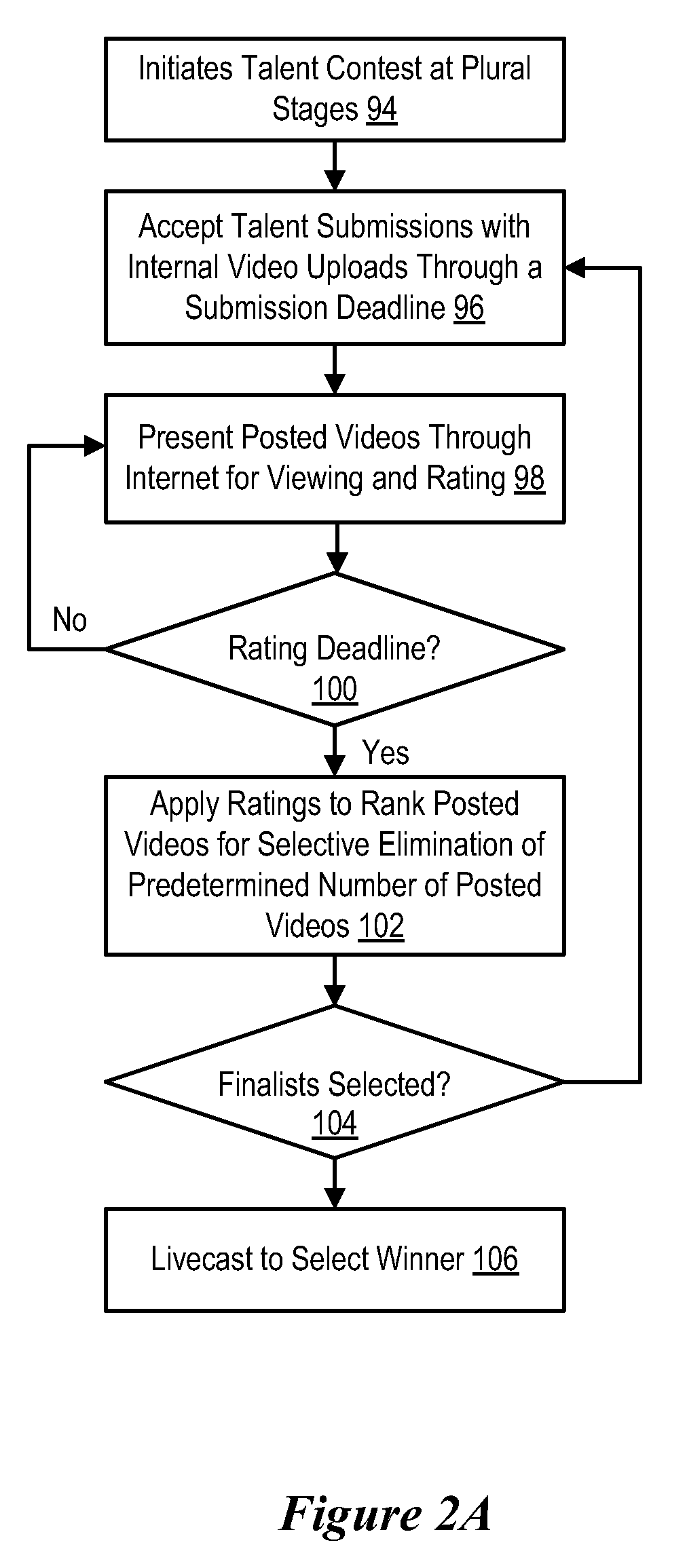
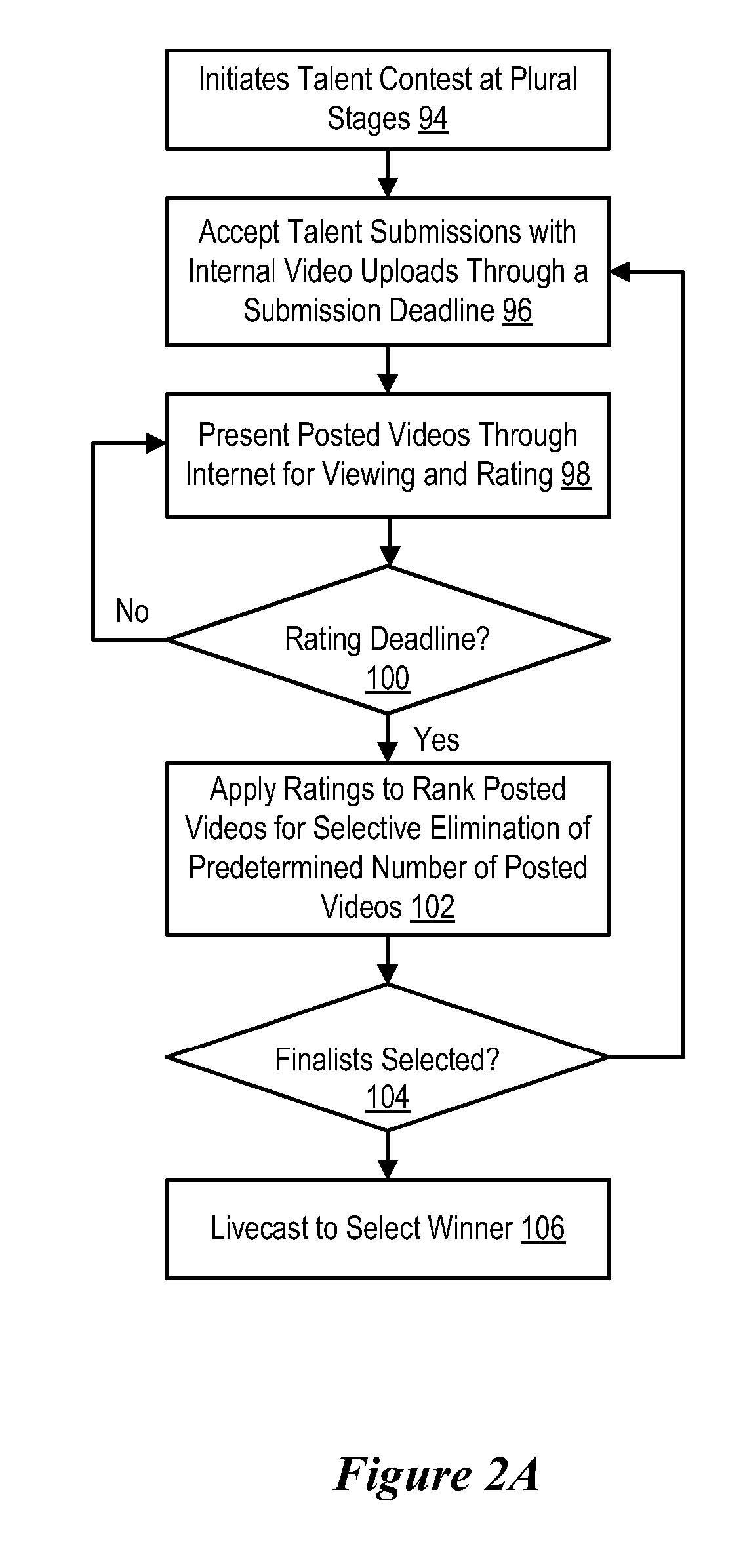
System and method for network-based talent contest
InactiveUS20080126197A1Fairness of anonymous voting through the InternetMaintain fairnessCommerceThe InternetComputer science
A talent contest management platform provides an interface for artists to submit video presentations and fans to view the video presentations through the Internet to allow fans to vote to select artist talent contest winners from plural contest stages, each stage having an associated content genre. A voting system accepts fan votes over predetermined time periods, such as through plural contest rounds, until finalists picked by voting perform for a final vote round, such as by a live webcast. The voting system ensures a fair and fraud-free contest winner selection by tracking fan registrations, monitoring fan votes and analyzing voting results to detect and address voting fraud.
Owner:SQUARE 1 BANK
System and method for network-based talent contest
InactiveUS20080000970A1Maintain fairnessFairness of anonymous voting through the InternetVoting apparatusError detection/correctionThe InternetComputer science
A talent contest management platform provides an interface for artists to submit video presentations and fans to view the video presentations through the Internet to allow fans to vote to select artist talent contest winners from plural contest stages, each stage having an associated content genre. A voting system accepts fan votes over predetermined time periods, such as through plural contest rounds, until finalists picked by voting perform for a final vote round, such as by a live webcast. The voting system ensures a fair and fraud-free contest winner selection by tracking fan registrations, monitoring fan votes and analyzing voting results to detect and address voting fraud.
Owner:SQUARE 1 BANK
Allocating bandwidth using resilient packet ring (RPR) fairness mechanism
InactiveUS7397813B2Increase usageEvenly distributedLoop networksBus networksResilient Packet RingFair distribution
In allocating bandwidth using a Resilient Packet Ring (RPR) fairness mechanism in a node connected to an RPR network, when congestion occurs, an amount of traffic that the node has transmitted to a ring during one aging interval is stored together with its own identifier in a fairness message as a fairness transmission rate to be advertised to its own upstream nodes. The amount of traffic transmitted from the upstream node during the aging interval is measured and stored. When the congestion has been solved, an available bandwidth is calculated with reference to the fairness transmission rate and the amount of traffic transmitted from the upstream nodes, and the fairness transmission rate is calculated to fairly allocate the available bandwidth to the upstream nodes so that the fairness transmission rate is transmitted to the upstream nodes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
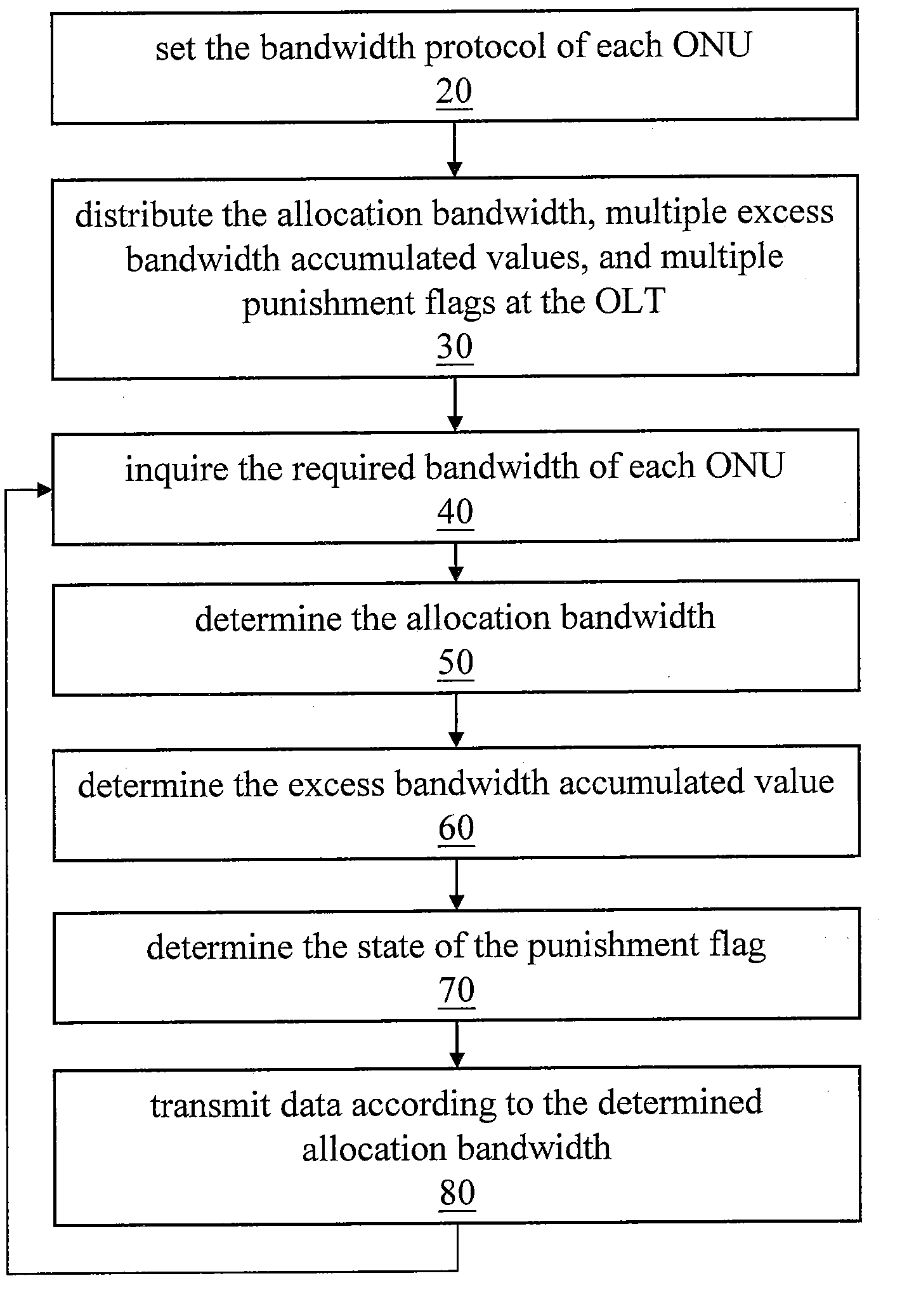
Dynamic bandwidth allocation method with punishment mechanism in passive optical network
InactiveUS20070147834A1Reduce transmission delayImprove throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexBandwidth allocationDynamic bandwidth allocation
A dynamic bandwidth allocation method with a punishment mechanism applicable in an Ethernet passive optical network (EPON) is provided. The method utilizes GATE message, report message format, and different data types of a multipoint control protocol (MPCP) to order various queues to make the queues have priority and transmit them sequentially in transmission. Meanwhile, the method can fairly allocate the bandwidth and reduce the delay time of queue according to an appropriately designed punishment mechanism and bandwidth allocation principle, so as to fulfill the requirements of Quality of Service (QoS).
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
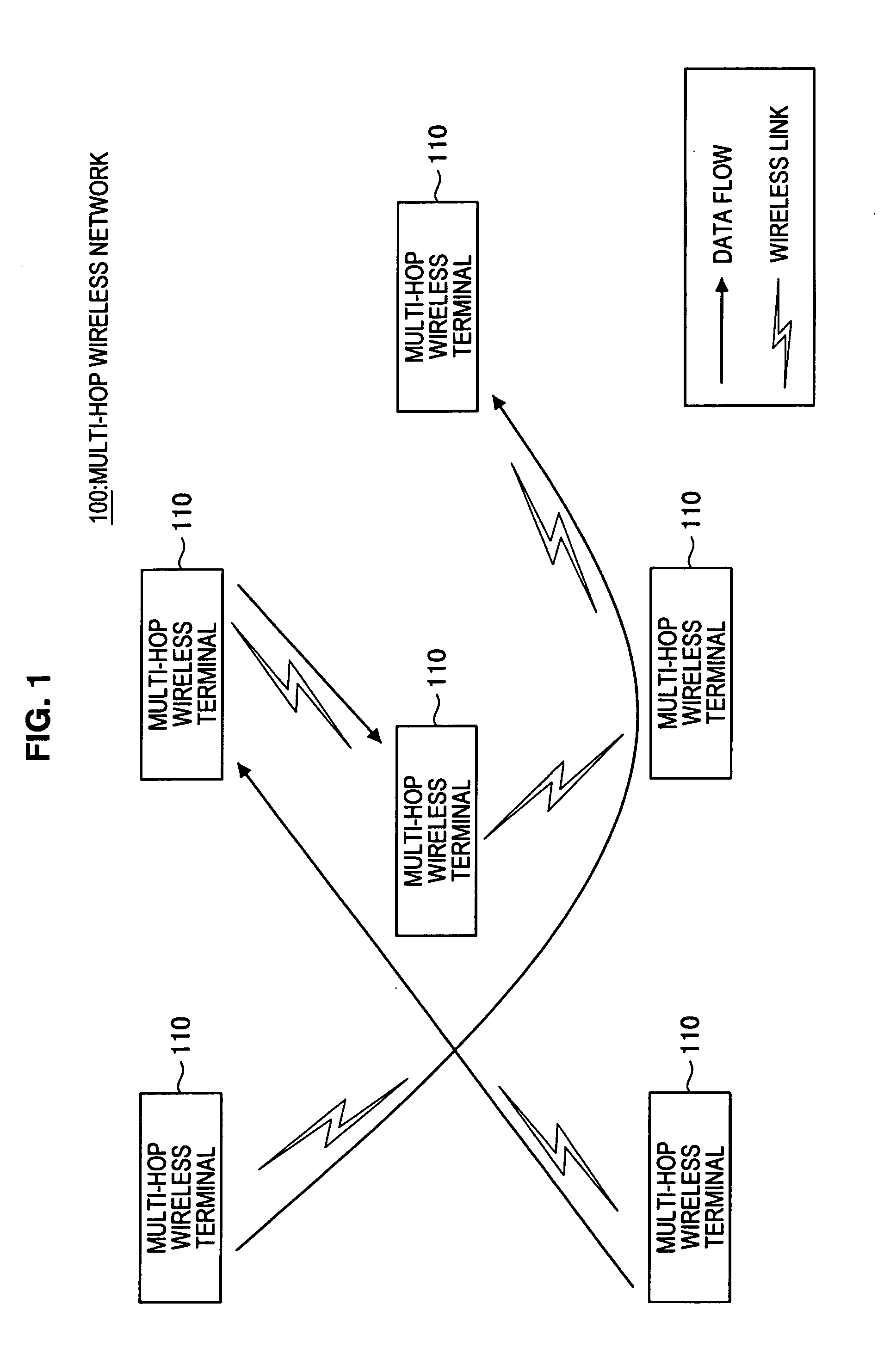
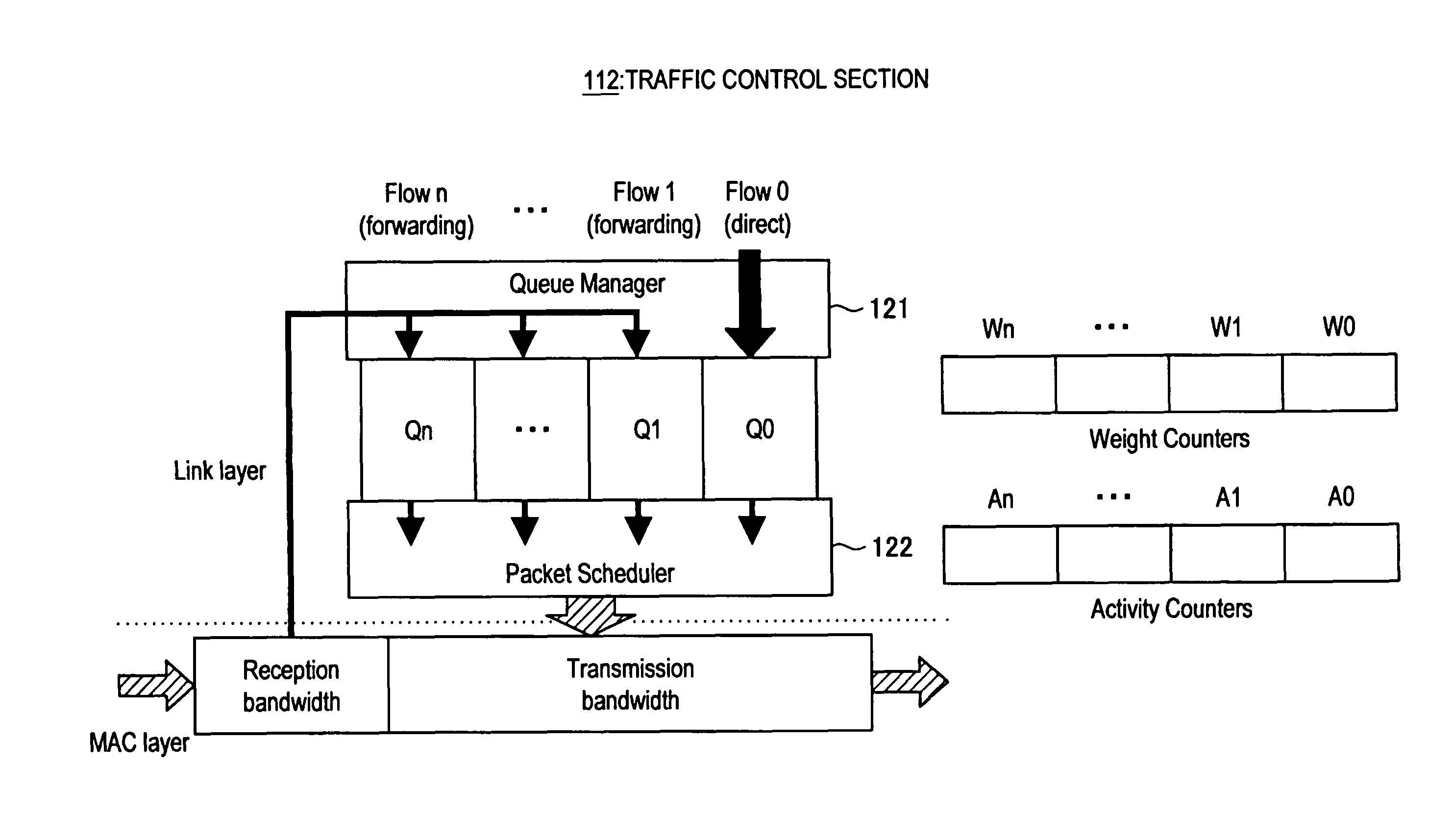
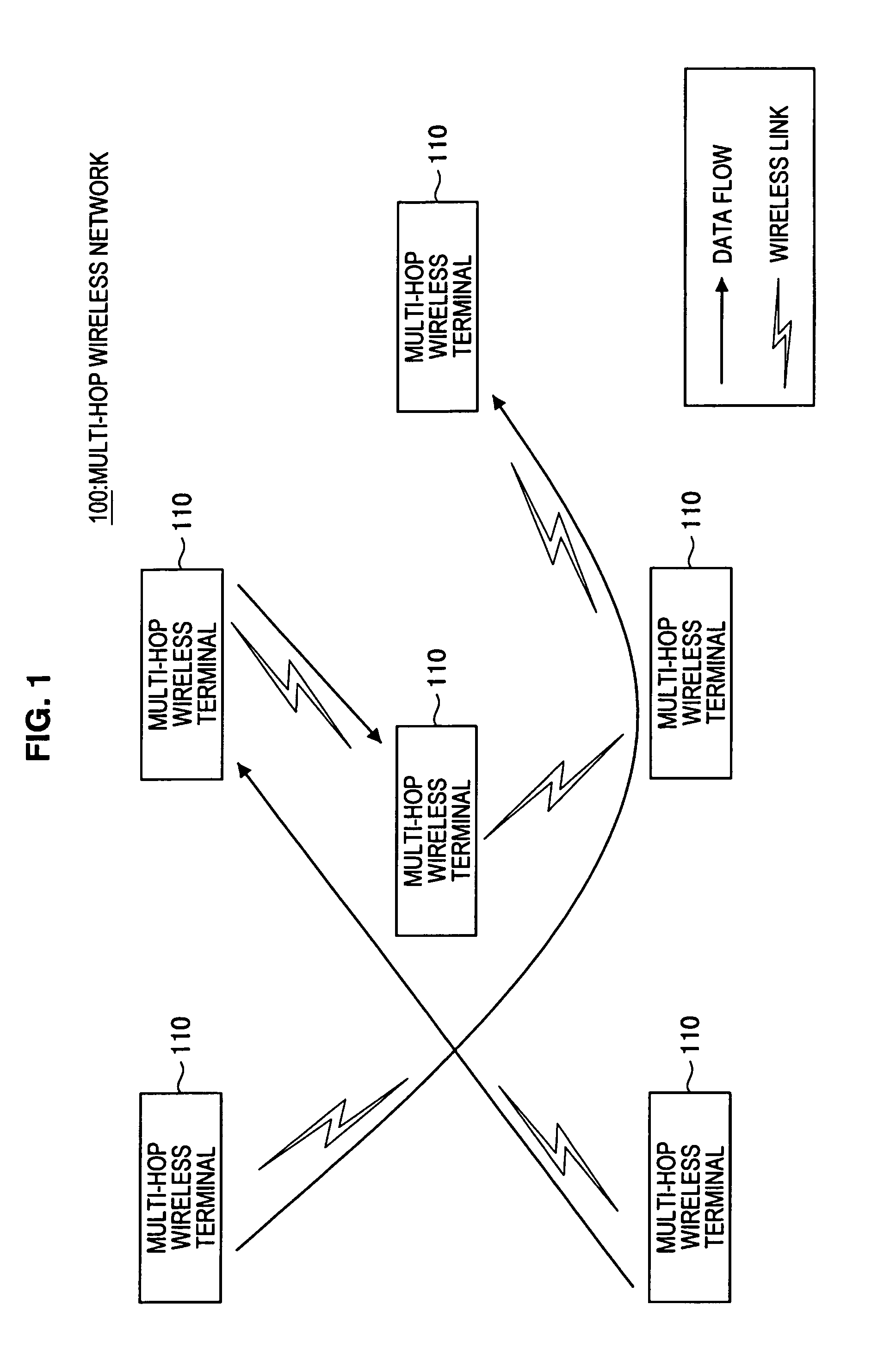
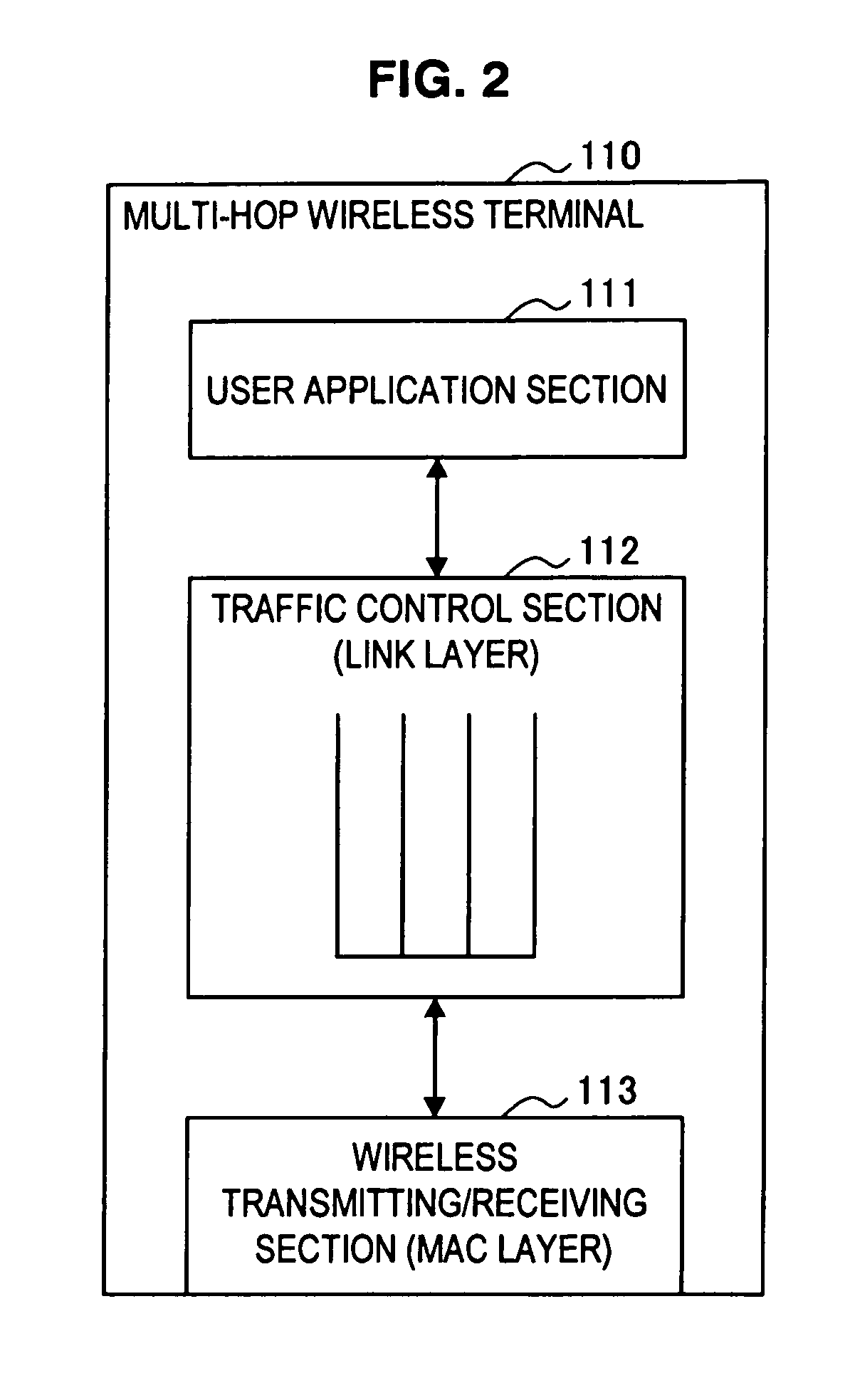
Multi-hop wireless terminal and traffic control method thereof
InactiveUS20110044170A1Transmission rate can be preventedLow transmission rateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityPacket scheduling
A multi-hop wireless terminal having a user application section, a traffic control section and a wireless transmitting / receiving section, the traffic control section enqueuing a packet of a transmission flow from the user application section and a packet of a forward flow from the wireless transmitting / receiving section in queues different for each flow and performing traffic control, where the traffic control section includes a queue manager for sorting a packet of each input flow into a corresponding queue and enqueuing the packet, and a packet scheduler for dequeuing a packet from each queue and outputting the packet, and where the packet scheduler selects from the queues a queue from which a packet is to be dequeued and output, based on transmission information of each of the flows.
Owner:SONY CORP
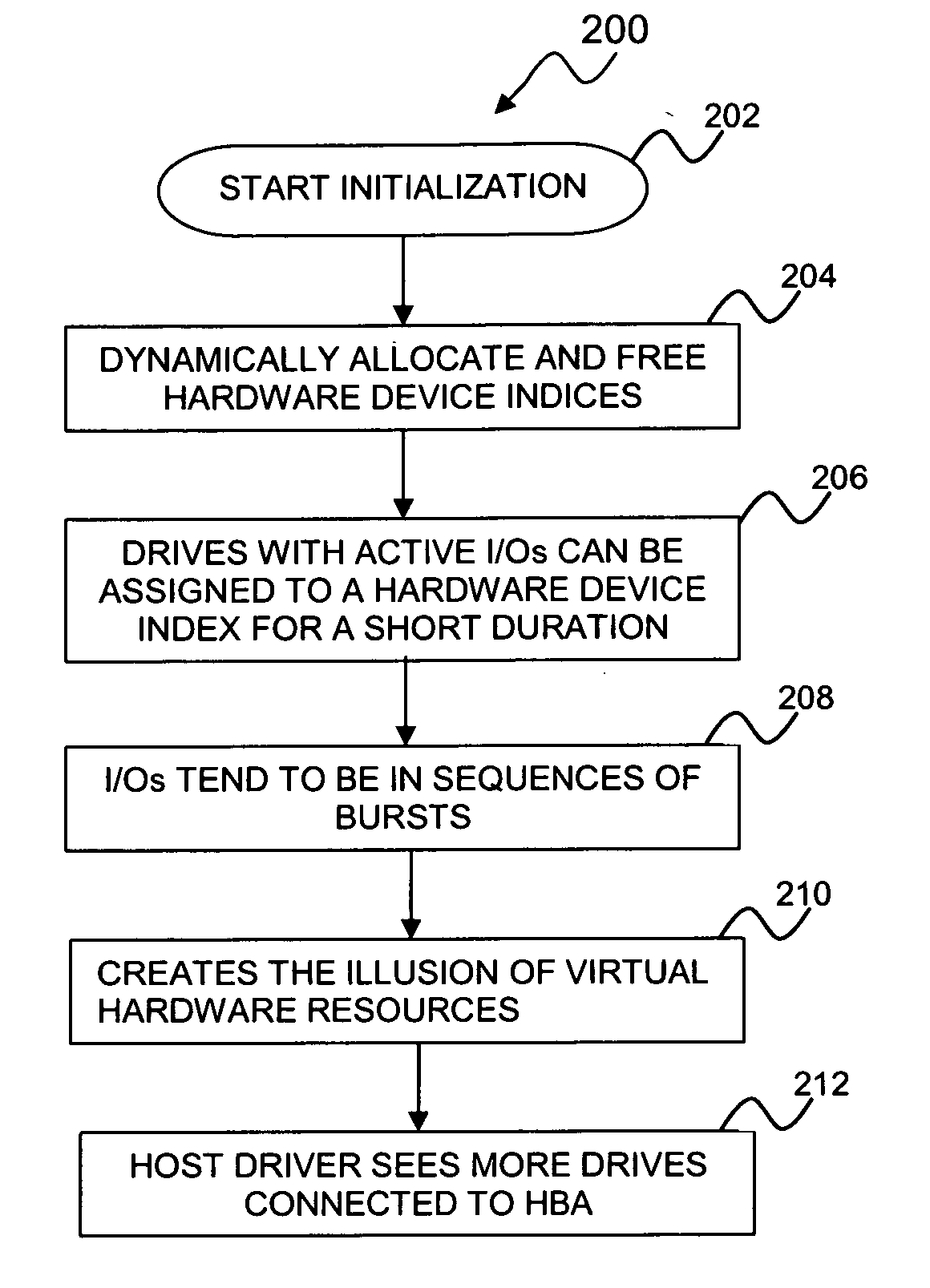
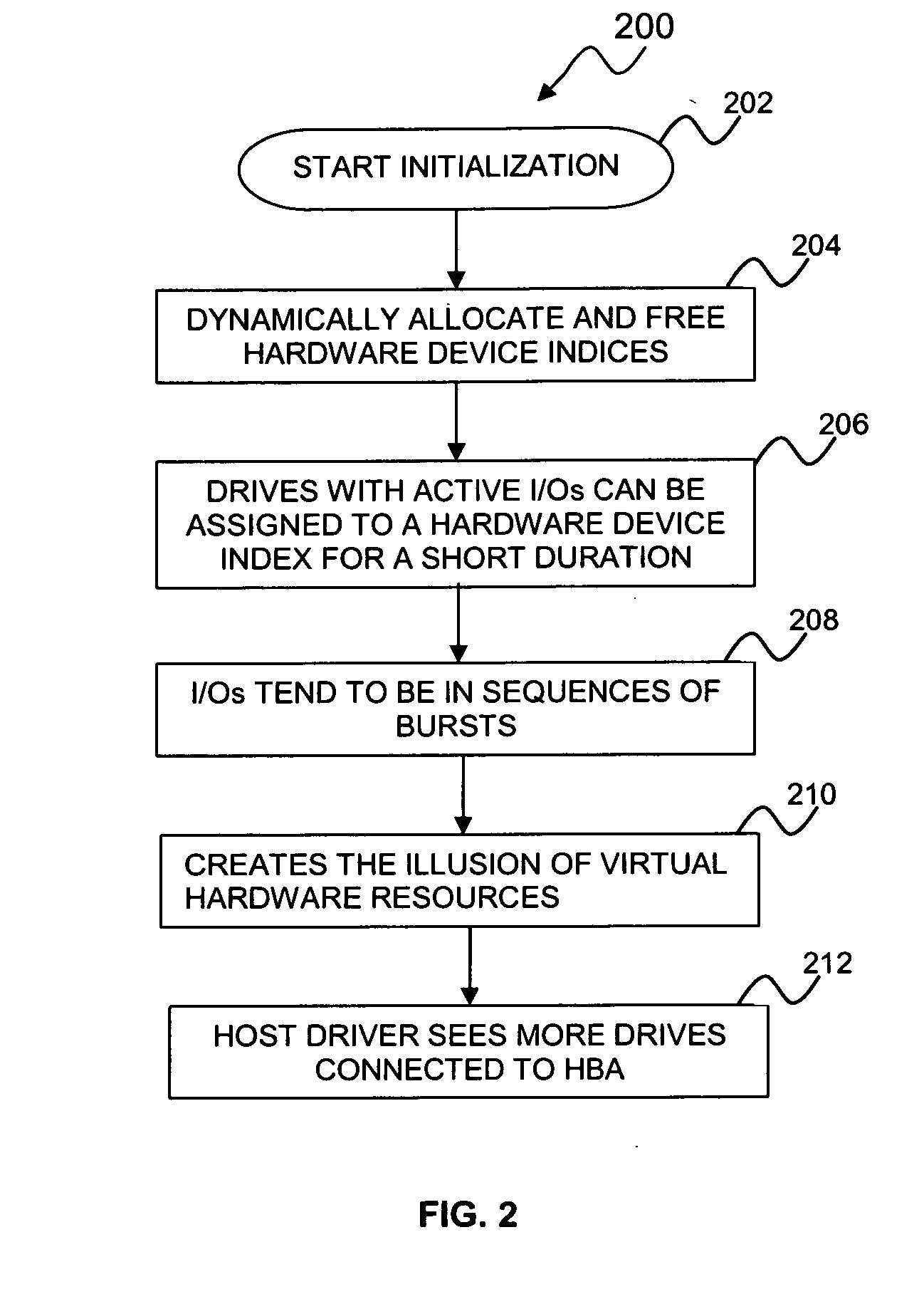
Method and system for creating and utilizing virtual hardware resources
ActiveUS20080040721A1FairnessMaintain fairnessMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsVirtual hardwareData processing
A data-processing method and system generally comprises identifying a plurality of hardware resources associated with a data-processing apparatus, time-slicing the plurality of hardware resources. Thereafter the plurality of active hardware resources can be allocated among a plurality of active hardware resources associated with the data-processing apparatus, thereby allowing a limited number of hardware resources to service a larger number of physical devices associated with the data-processing apparatus. An appropriate hardware resource can be selected from among the plurality of active hardware resources utilizing one or more swapping algorithms.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
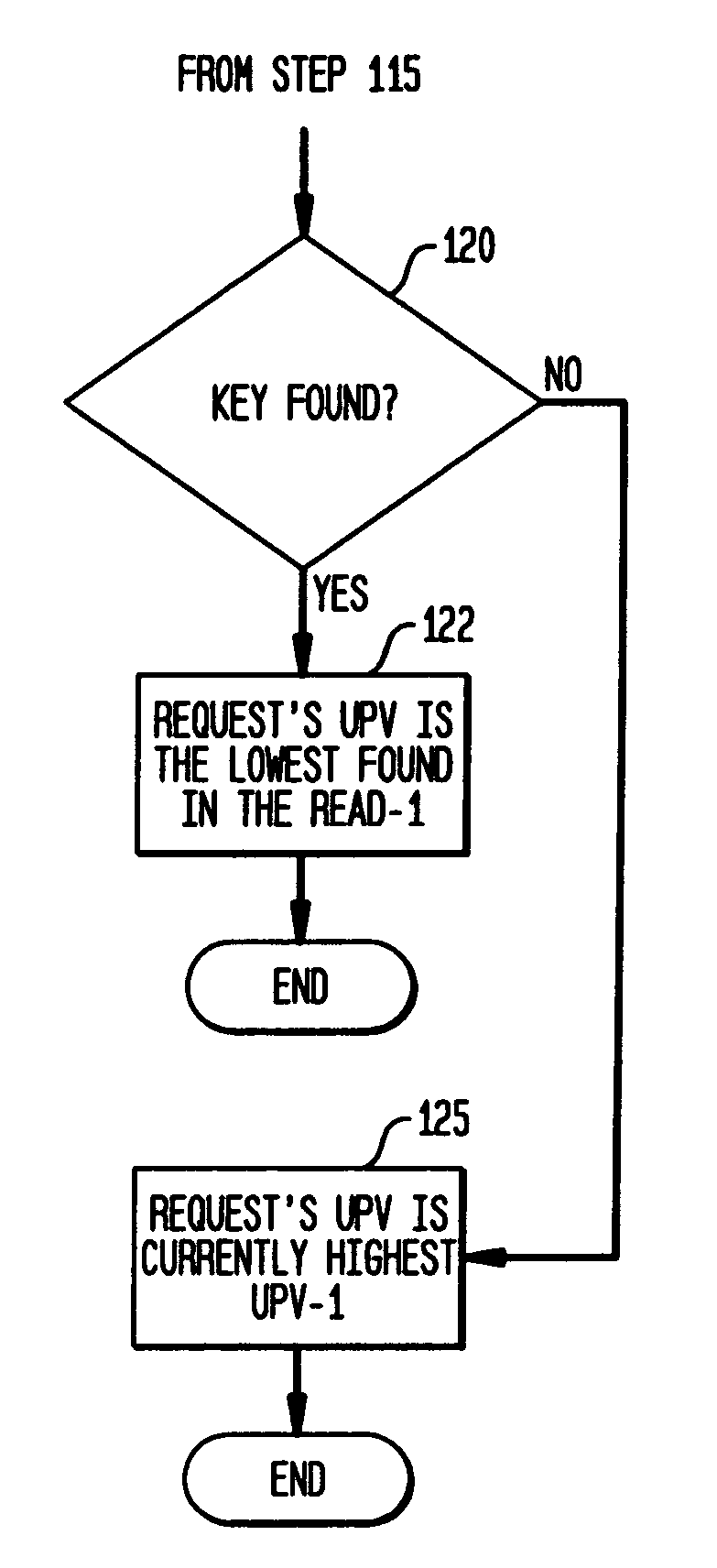
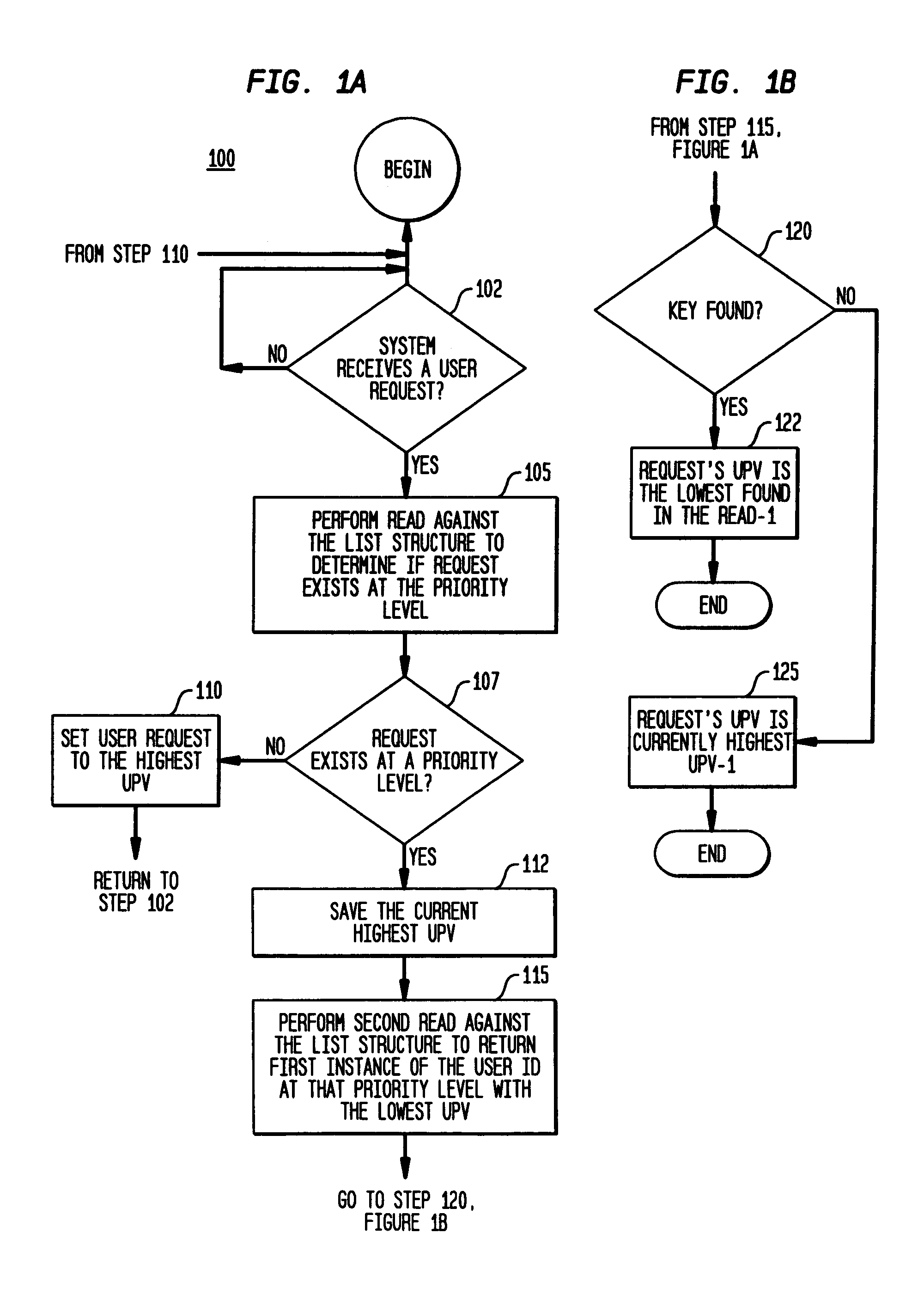
System and method for processing multiple work flow requests from multiple users in a queuing system
InactiveUS7114156B2Advanced technologyAchieve fairnessResource allocationDigital computer detailsUser identifierWork flow
A system and method for generating a key list structure forming a queue of users' work flow requests in a queuing system such that many requests from a single user will not prevent processing of requests from other users in the queuing system. The key list structure comprises keys associated with users' work flow requests, each key indicating a priority level associated with a request, a user identification (User ID) associated with a requestor, and, an assigned user priority value (UPV). The method assigns UPVs to user requests in a manner such that user request entries become interleaved in the key list structure to prevent a single user from dominating the request processing.
Owner:IBM CORP
Transmission control protocol (TCP) host with TCP convergence module
InactiveUS20070127493A1Less congestionLess operationData switching by path configurationNetwork segmentTransmission Control Protocol
A sending transmission control protocol (TCP) host is used in a first network node (106) to transmit TCP flows over a network segment to a receiving TCP host in a second network node (104). The sending TCP host comprises a TCP convergence module for aggregating all TCP flows through the network segment between the first network node (106) and the second network node (104) into an aggregate TCP flow (112). The receiving TCP host comprises a TCP convergence module for disaggregating the TCP flows from the aggregate TCP flow (112).
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Dynamic bandwidth allocation method with punishment mechanism in passive optical network
InactiveUS7843965B2Improve throughputAllocate bandwidthMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexDynamic bandwidth allocationRTP Control Protocol
A dynamic bandwidth allocation method with a punishment mechanism applicable in an Ethernet passive optical network (EPON) is provided. The method utilizes GATE message, report message format, and different data types of a multipoint control protocol (MPCP) to order various queues to make the queues have priority and transmit them sequentially in transmission. Meanwhile, the method can fairly allocate the bandwidth and reduce the delay time of queue according to an appropriately designed punishment mechanism and bandwidth allocation principle, so as to fulfill the requirements of Quality of Service (QoS).
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
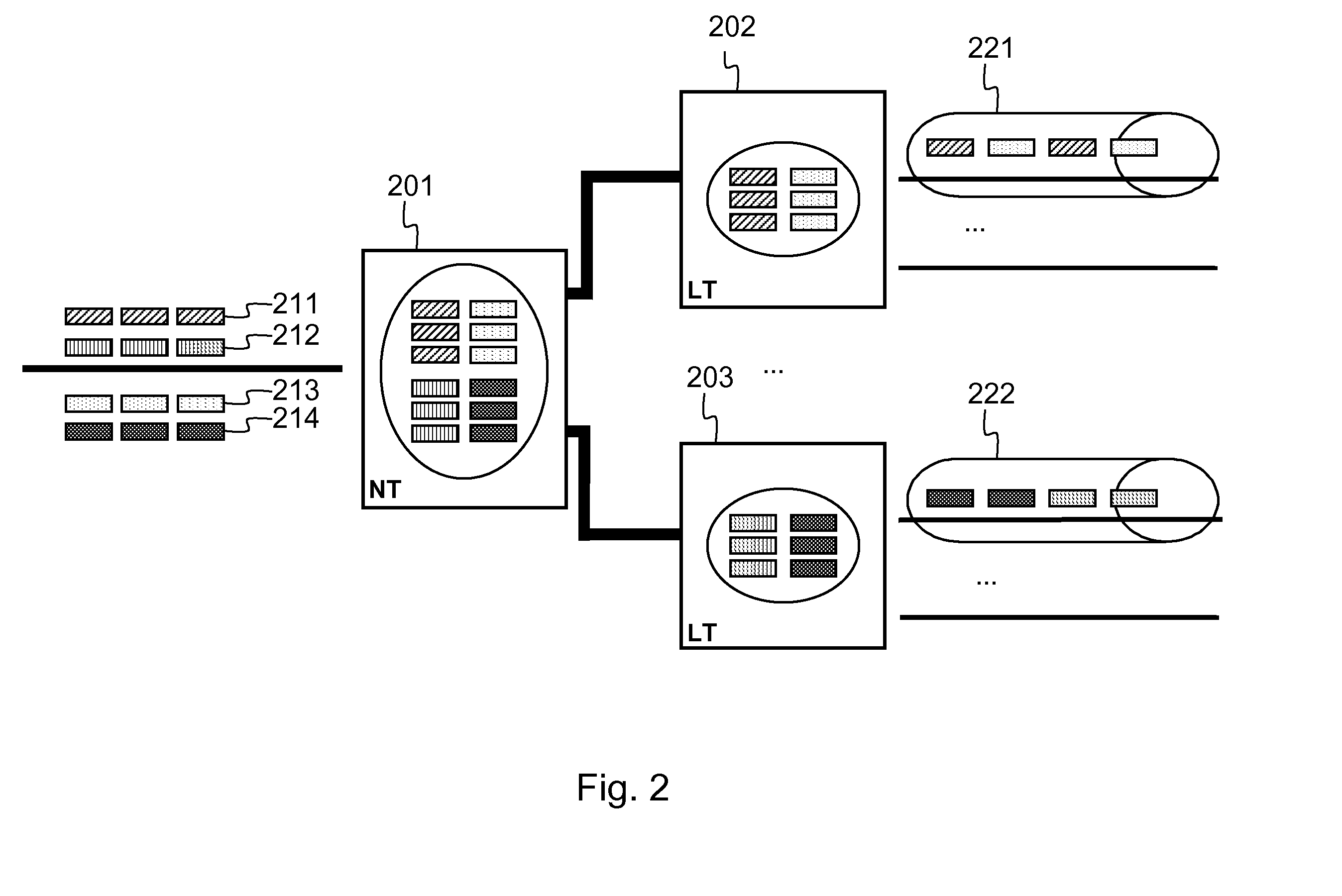
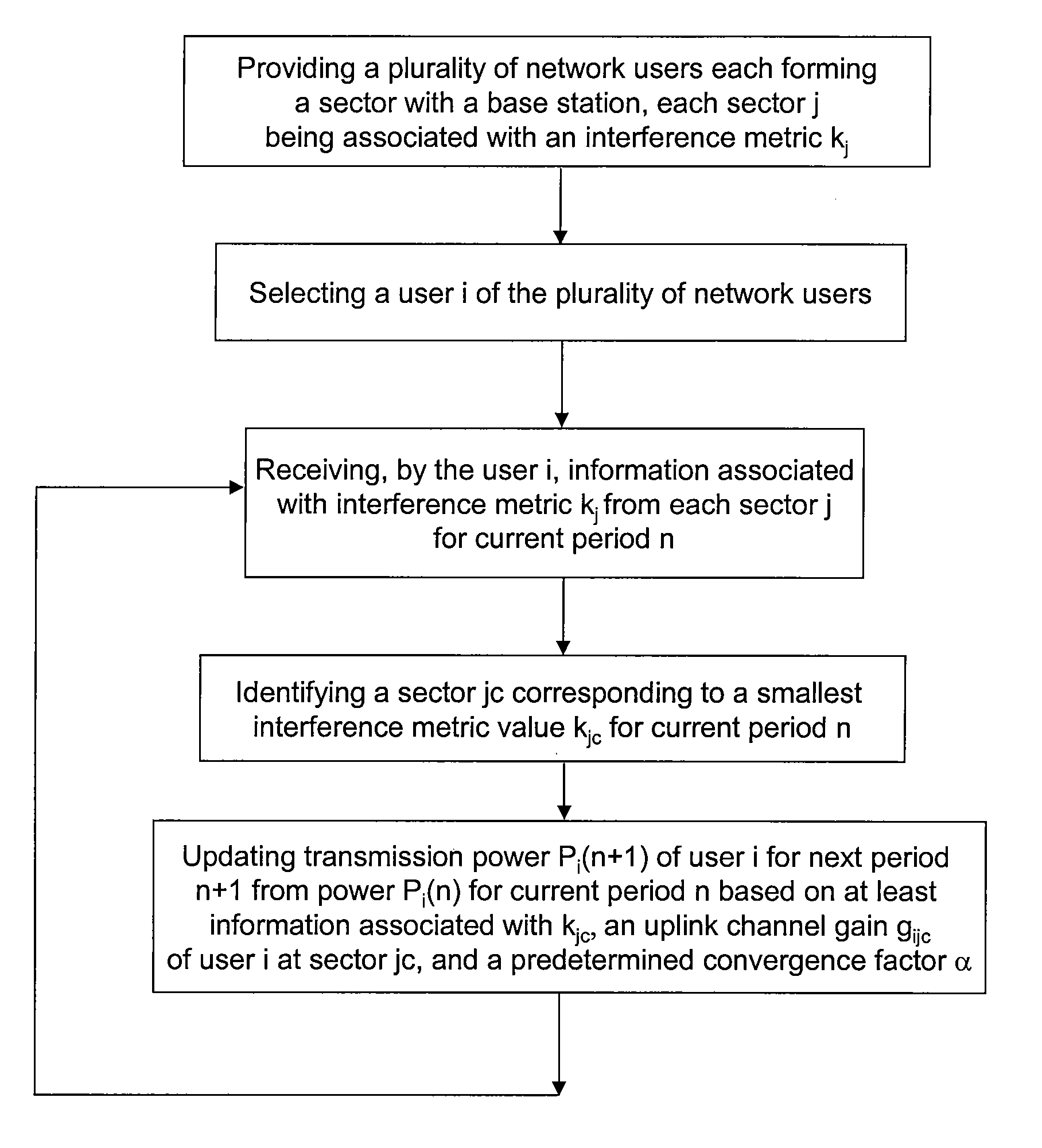
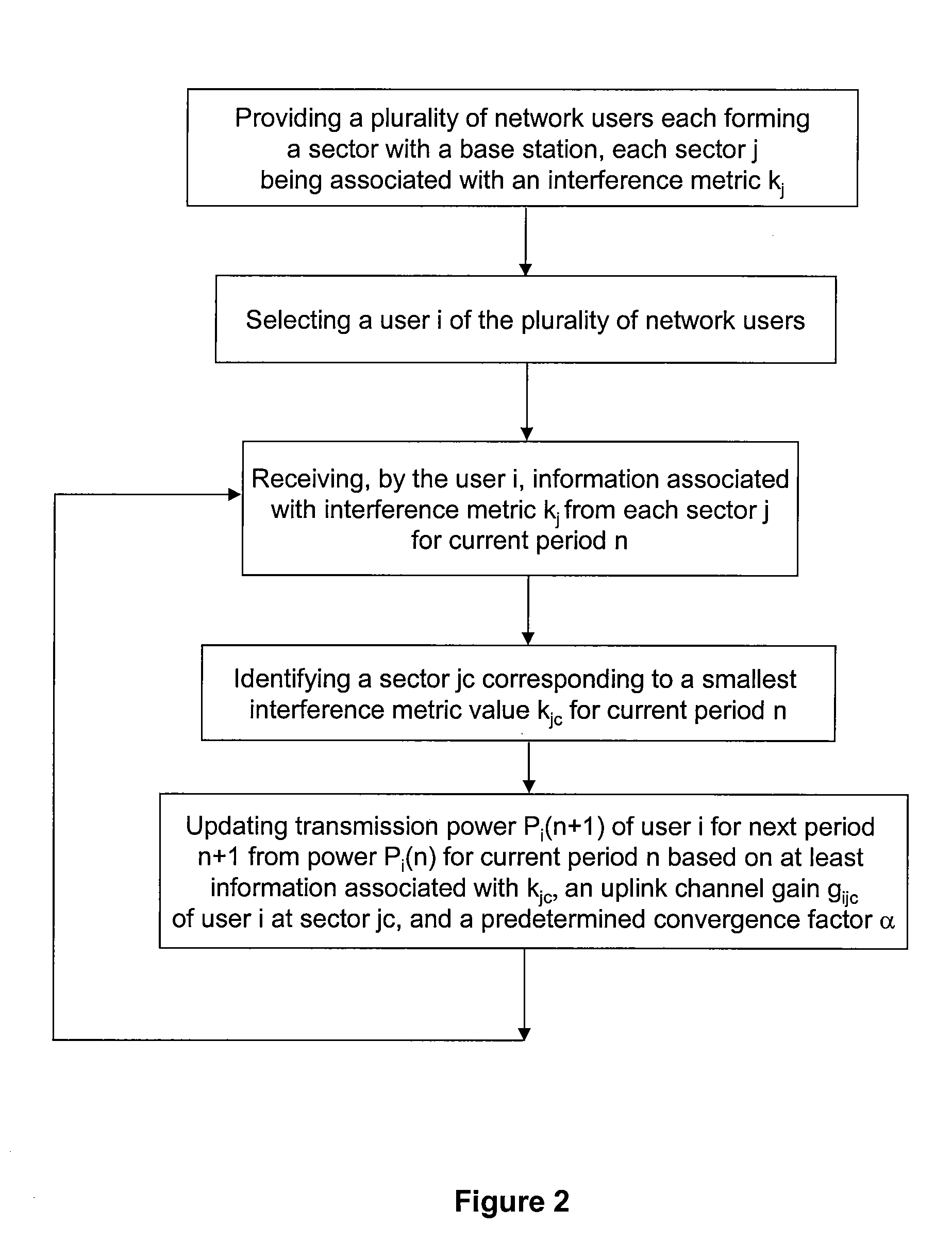
Method and system for optimal allocation of uplink transmission power in communication networks
InactiveUS8046019B2OptimizationImprove performancePower managementRadio transmissionUplink transmissionAssignment methods
A method for determining transmission power for a user in a network. The method includes receiving a plurality of interference indicators by a user which is associated with a sector. The plurality of interference indicators corresponds to a plurality of sectors respectively each associated with one of a plurality of users and a base station. The method further includes processing at least information associated with the plurality of interference indicators and selecting an interference indicator based on at least information associated with the plurality of interference indicators. The selected interference indictor corresponds to one of the plurality of sectors. Additionally, the method includes determining a gain indicator corresponding to both the user and the one of the plurality of sectors, and processing information associated with the gain indicator. Moreover, the method includes determining a transmission power of the user based on at least information associated with the gain indicator and the selected interference indictor.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
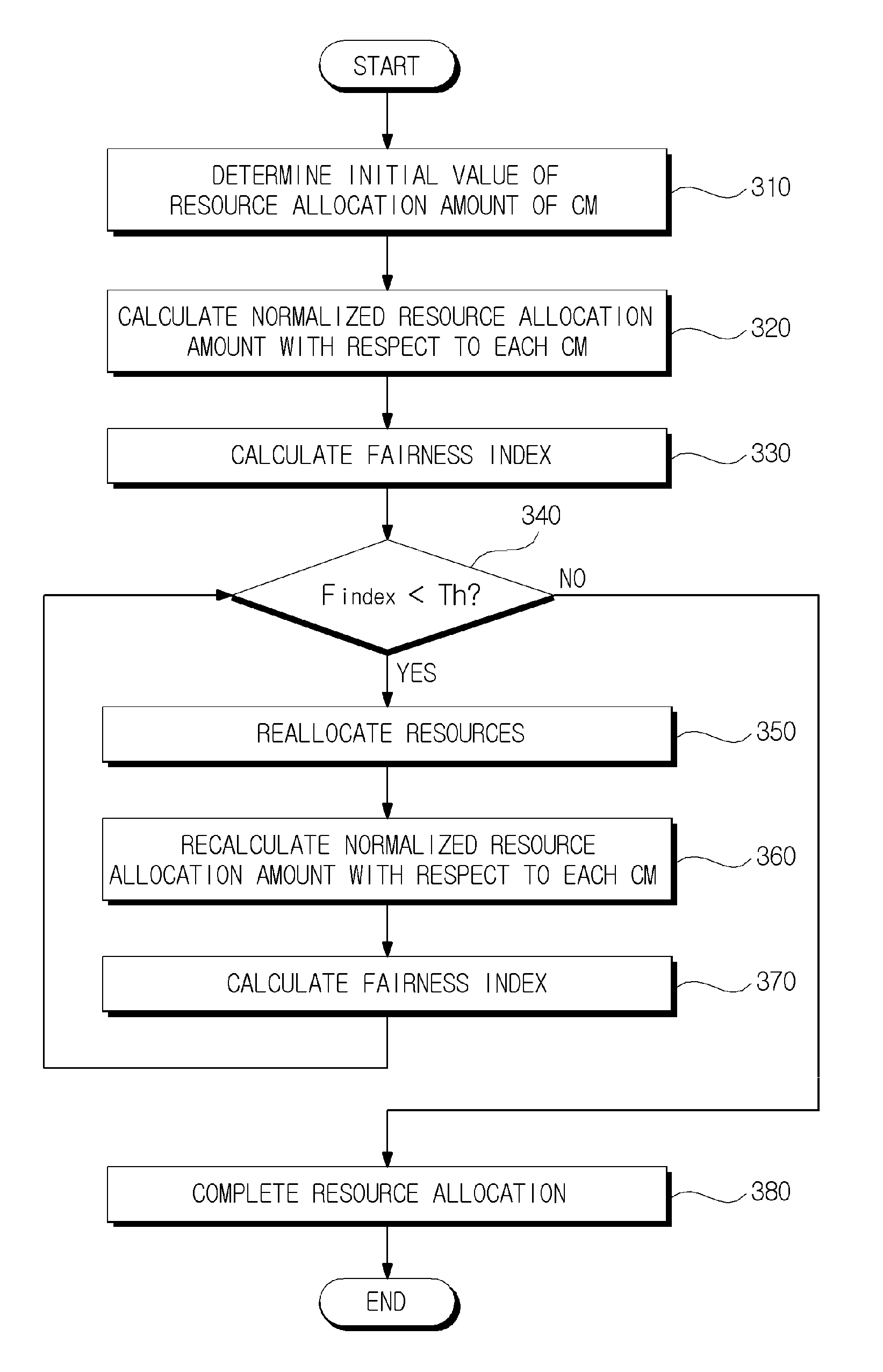
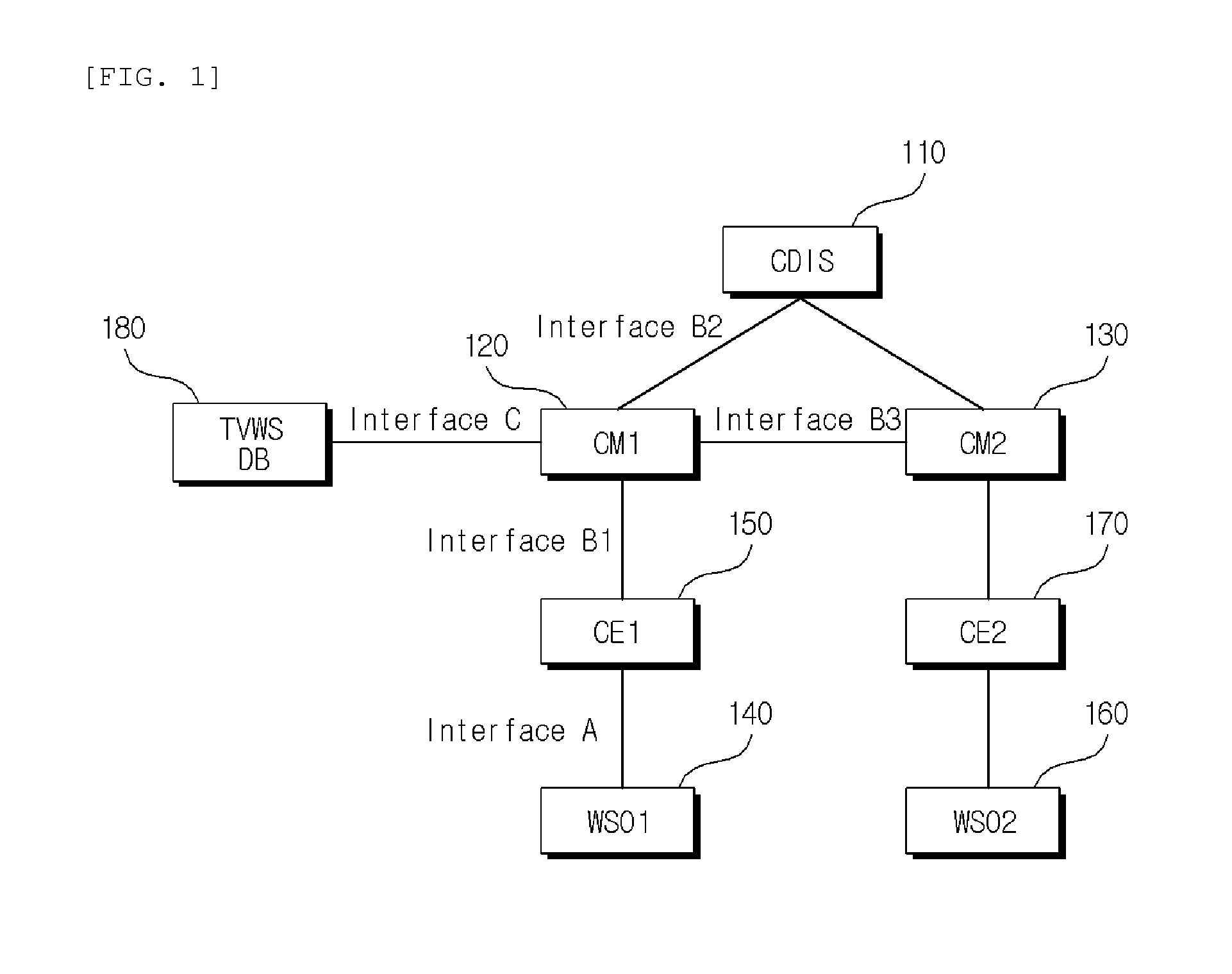
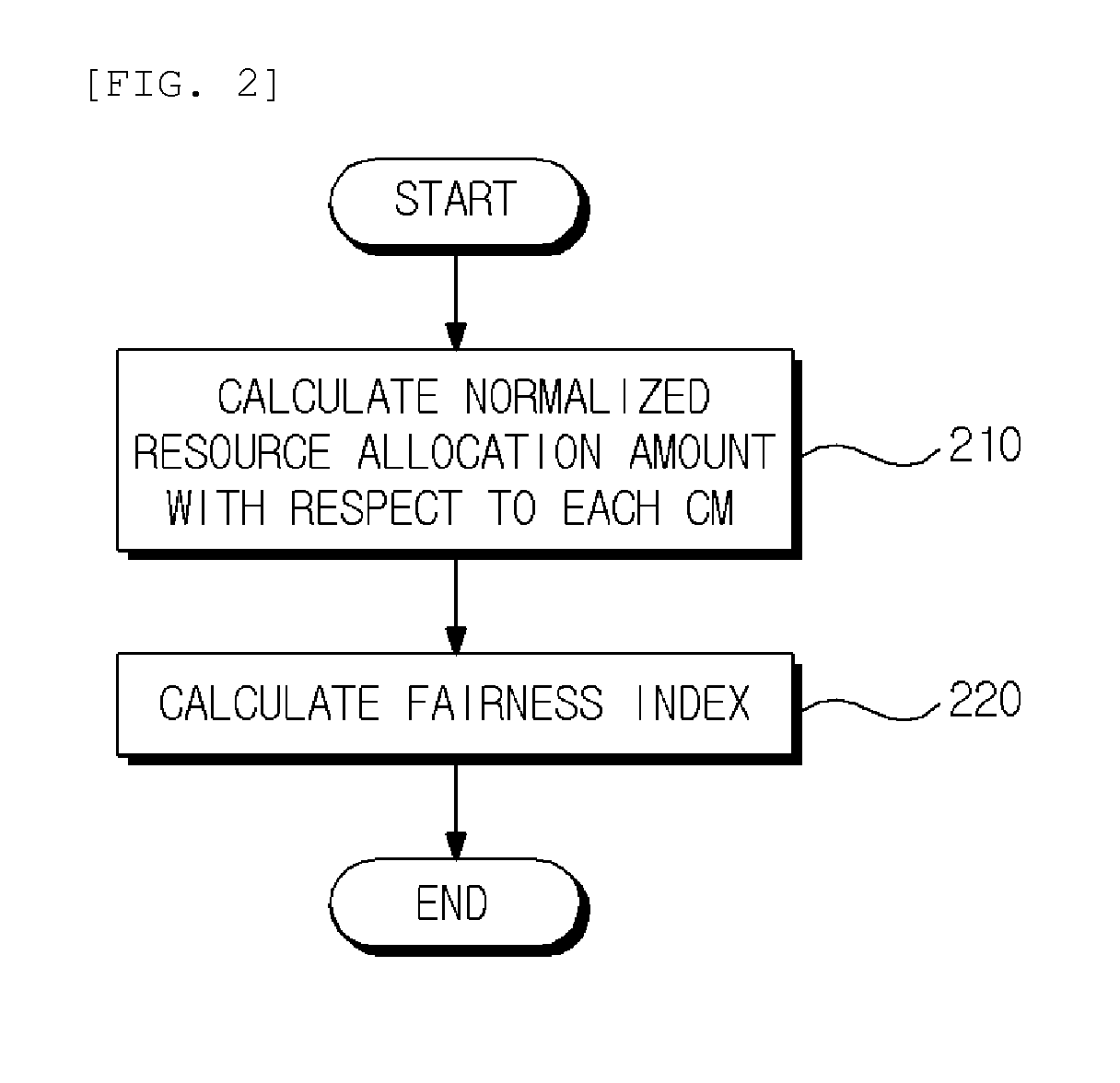
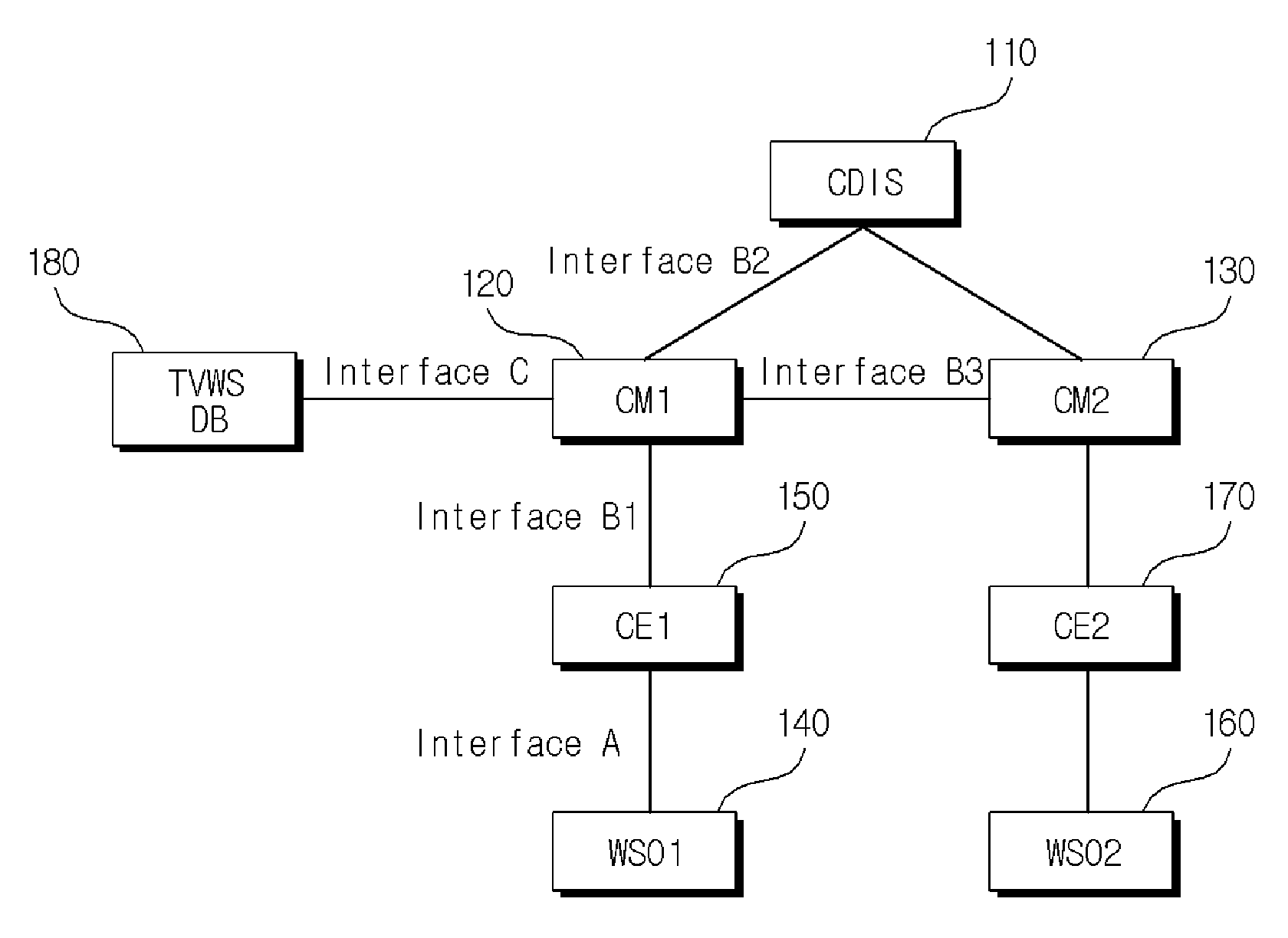
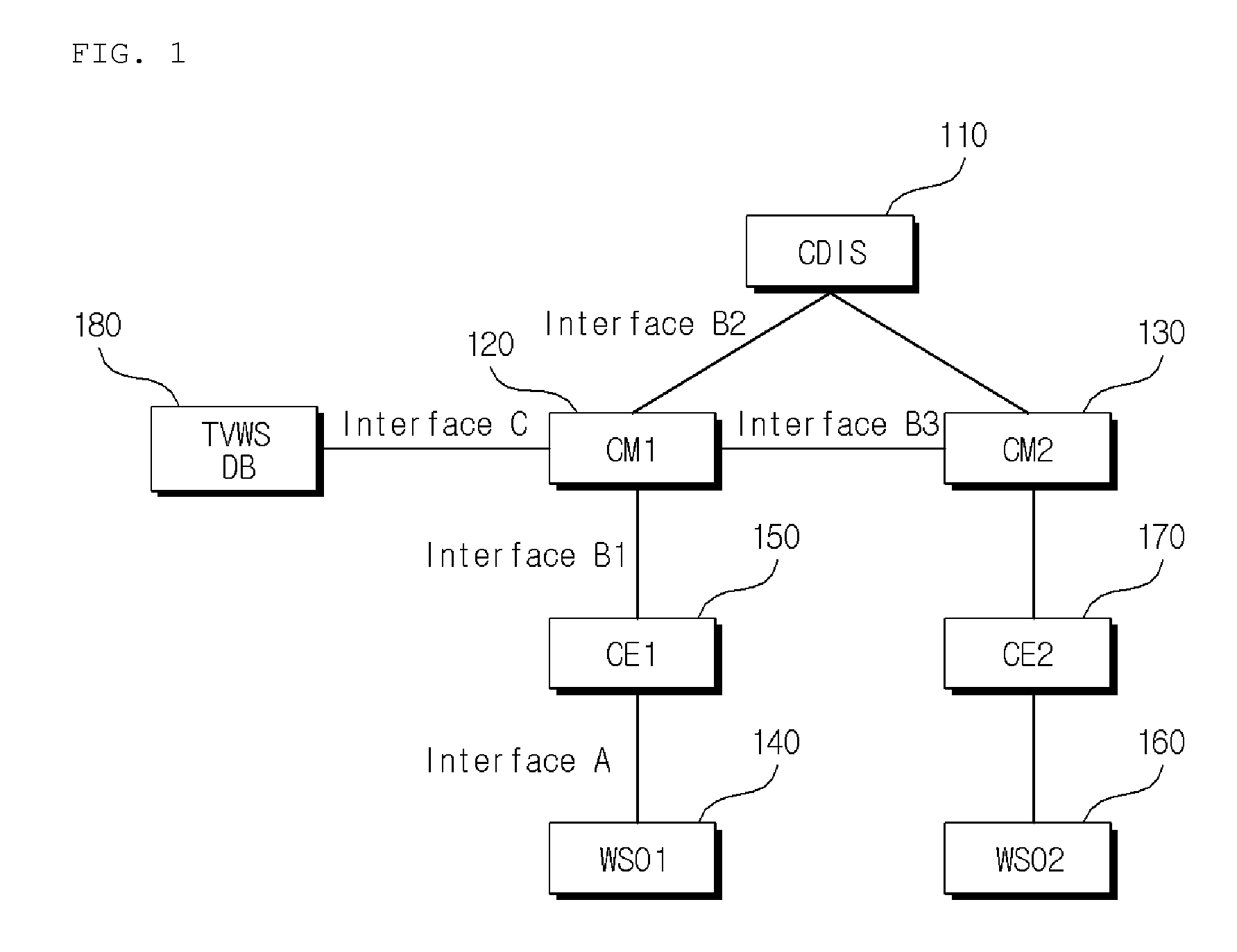
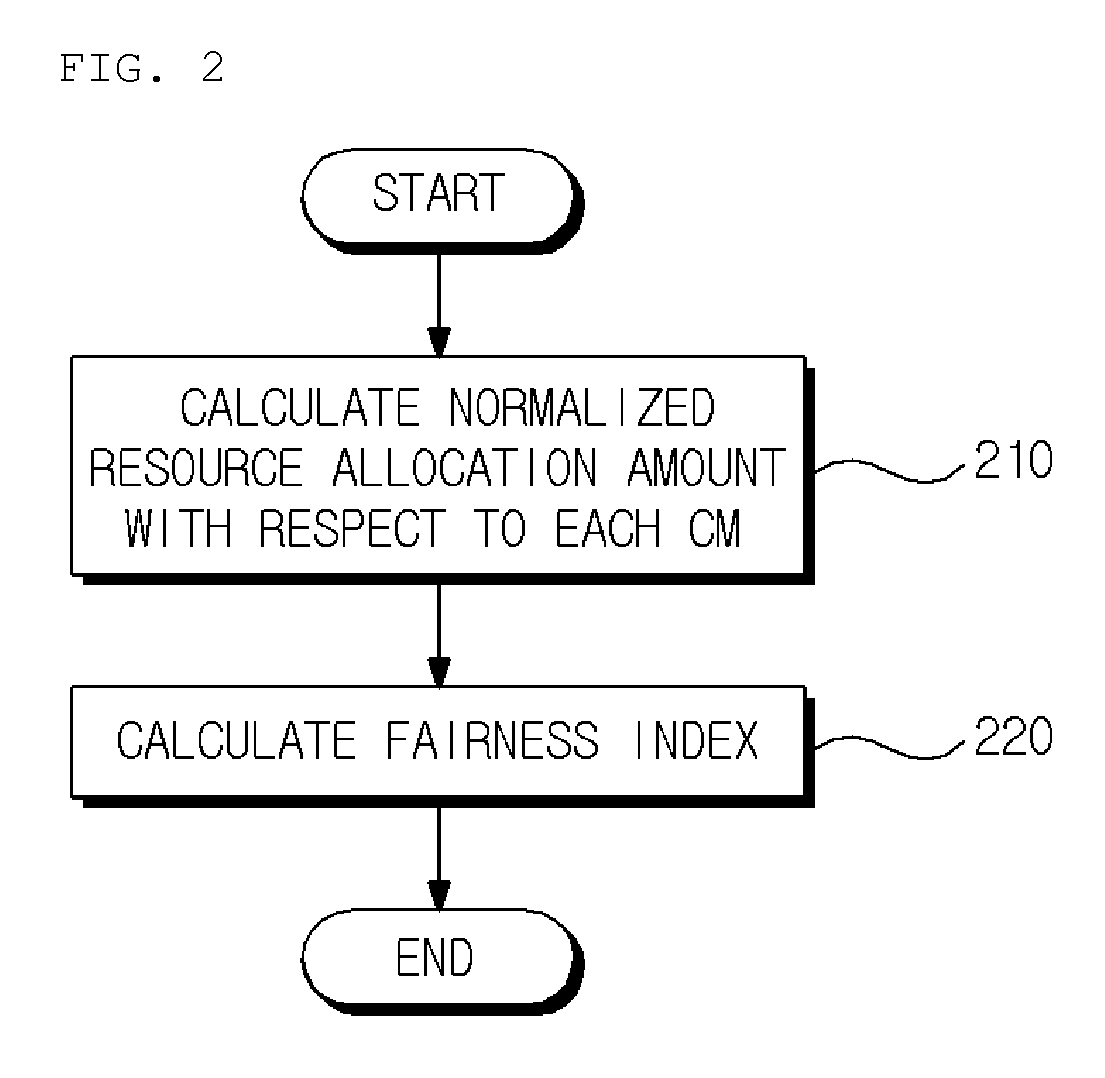
Method for calculating fairness index and method for allocating resources based on the fairness index in coexistence management system
Provided is a method of calculating a fairness index that is a criterion indicating fairness of resource allocation between coexistence managers in a coexistence management system, the method including: calculating a normalized resource allocation amount by normalizing an amount of resources allocated to a corresponding coexistence manager to an amount of resources required by the corresponding coexistence manager with respect to each of the coexistence managers; and calculating the fairness index using the normalized resource allocation amounts calculated with respect to the respective coexistence managers.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Device and method for multicast in wireless local access network
ActiveUS9577838B2Improve transmission reliabilityFairness of transmission throughputSpecial service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelAccess networkWireless network
A device and method for multicasting data in a wireless network. The method includes receiving multicast data at a specific node of the wireless network, the multicast data including a multicast acknowledgement request; and determining by the specific node whether or not the specific node is requested to send an acknowledgement to the multicast acknowledgement request. Also, a device and method for multicasting data in a wireless network. The method includes transmitting multicast data, the multicast data including a multicast acknowledgement request, the multicast acknowledgement request including information configured to enable a specific node of the wireless network to determine whether or not the specific node is requested to send an acknowledgement to the multicast acknowledgement request.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
System and method for scheduling message transmission and processing in a digital data network
InactiveUS7295557B2FairnessFairness in message processingData switching by path configurationDigital dataLink flow
A system includes a plurality of computers interconnected by a network including one or more switching nodes. The computers transfer messages over virtual circuits established thereamong. A computer, as a source computer for one or more virtual circuit(s), schedules transmission of messages on a round-robin basis as among the virtual circuits for which it is source computer. Each switching node which forms part of a path for respective virtual circuits also forwards messages for virtual circuits in a round-robin manner, and, a computer, as a destination computer for one or more virtual circuit(s), schedules processing of received messages in a round-robin manner. Round-robin transmission, forwarding and processing at the destination provides a degree of fairness in message transmission as among the virtual circuits established over the network. In addition, messages are transmitted in one or more cells, with the round-robin transmission being on a cell basis, so as to reduce delays which may occur for short messages if a long messages were transmitted in full for one virtual circuit before beginning transmission of a short message for another virtual circuit. For each virtual circuit, the destination computer and each switching node along the path for the virtual circuit can generate a virtual circuit flow control message for transmission to the source computer to temporarily limit transmission over the virtual circuit if the amount of resources being taken up by messages for the virtual circuit exceeds predetermined thresholds, further providing fairness as among the virtual circuits. In addition, each switching node or computer can generate link flow control messages for transmission to neighboring devices in the network to temporarily limit transmission thereto if the amount of resources taken up by all virtual circuits exceeds predetermined thresholds, so as to reduce the likelihood of message loss.
Owner:GIGANET
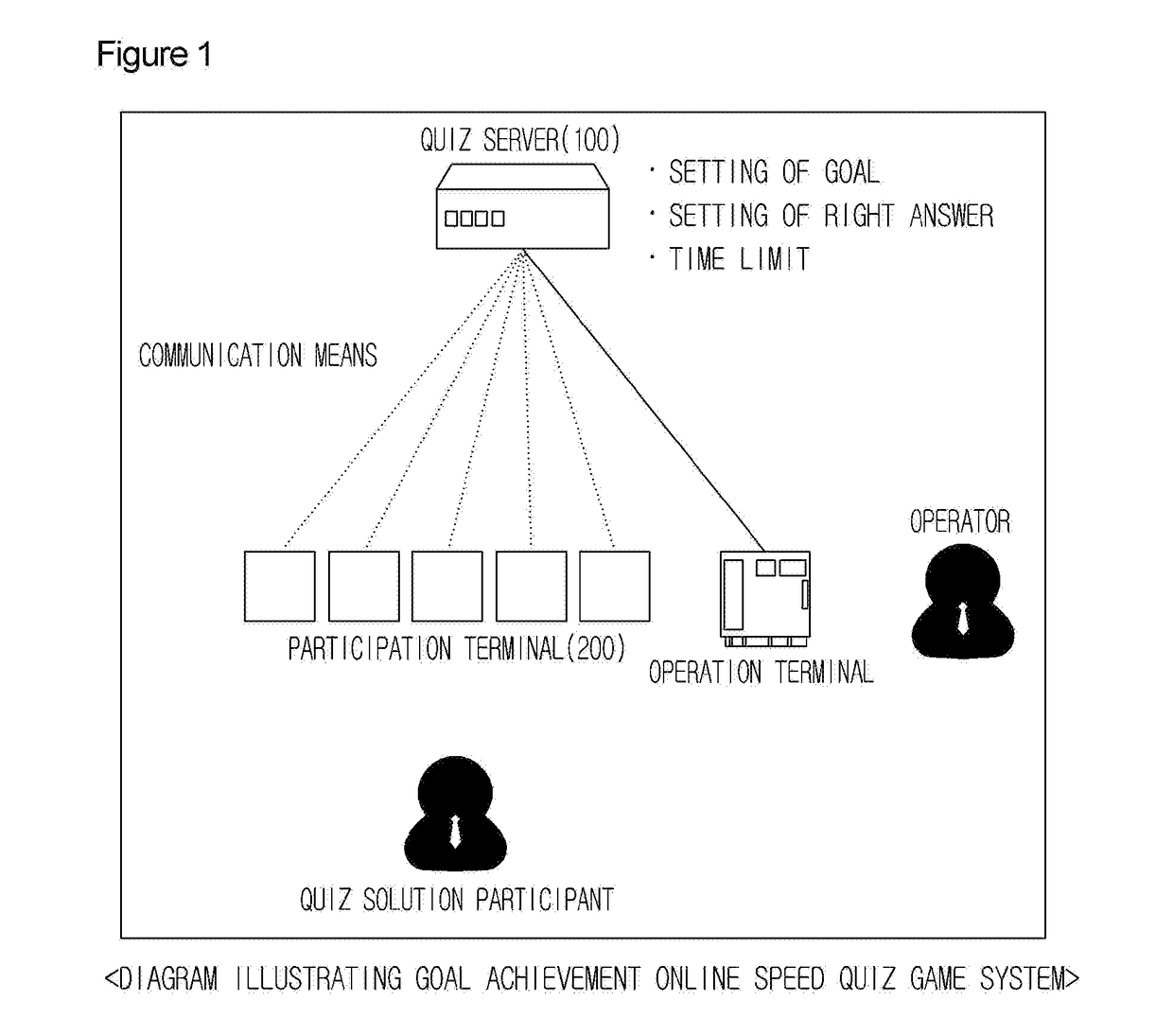
Goal achievement online speed quiz game providing method and system
InactiveUS20170182411A1Easy to operateEasy transferVideo gamesTransmissionComputer scienceTarget reaching
Owner:KSEEK CO LTD
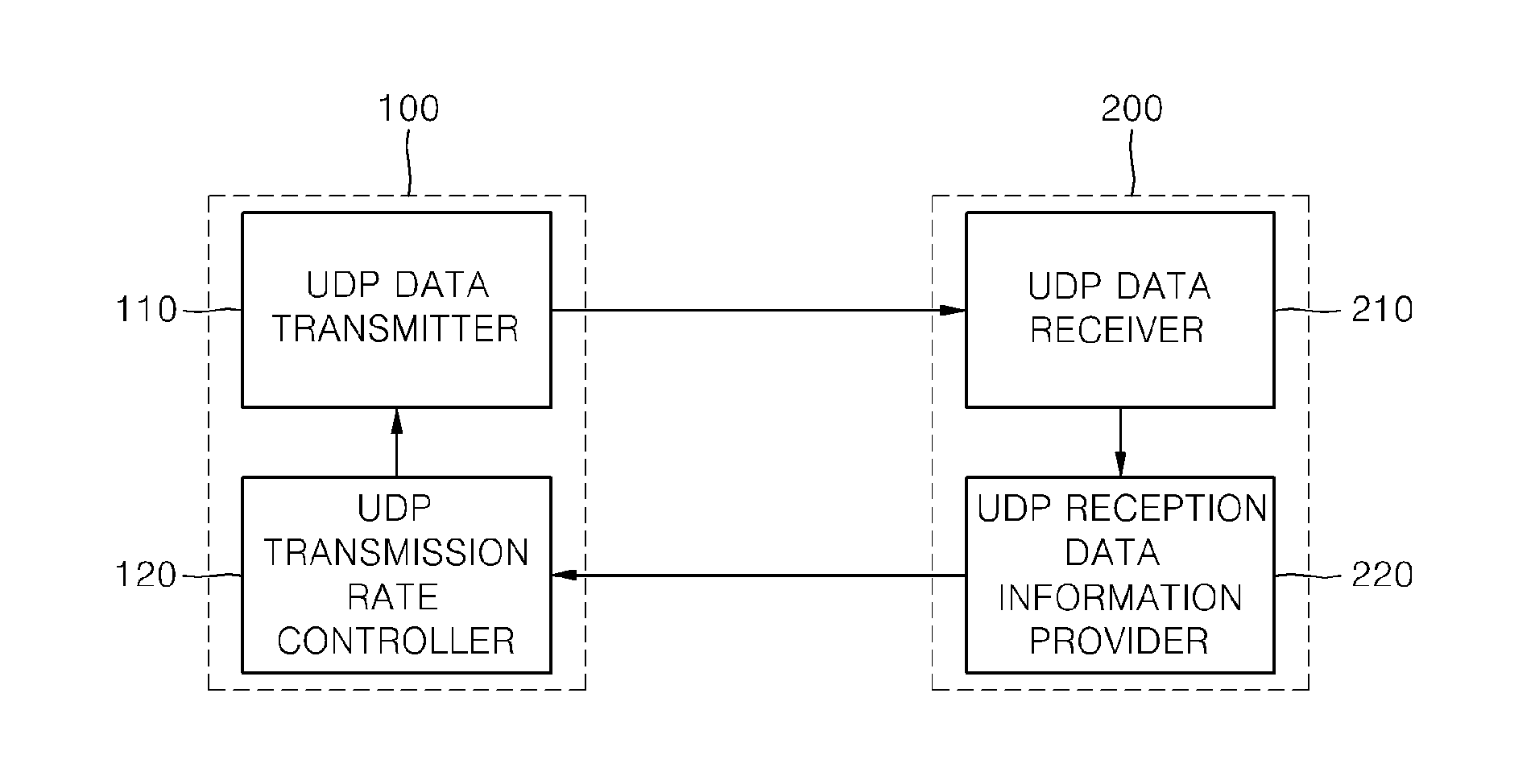
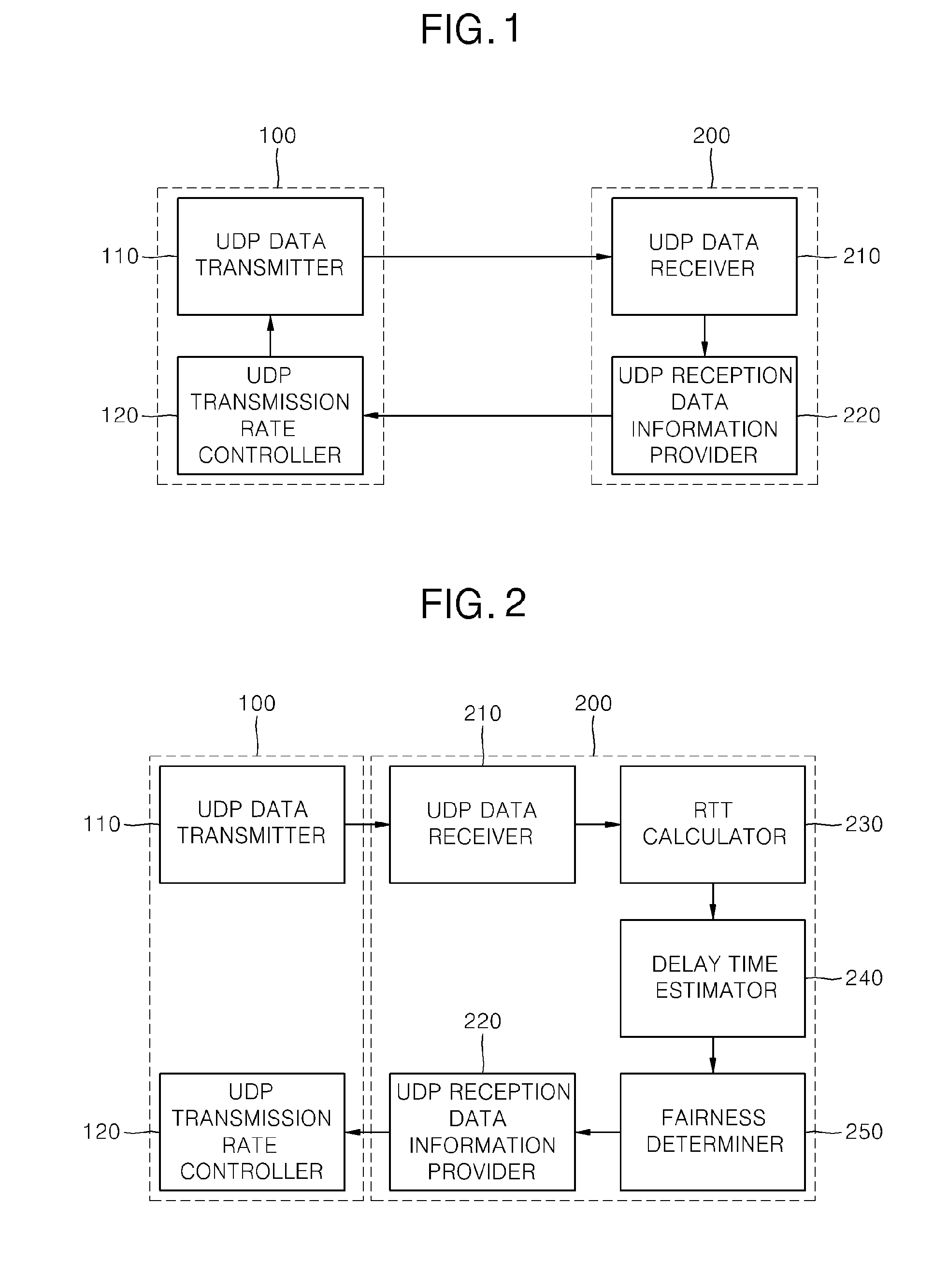
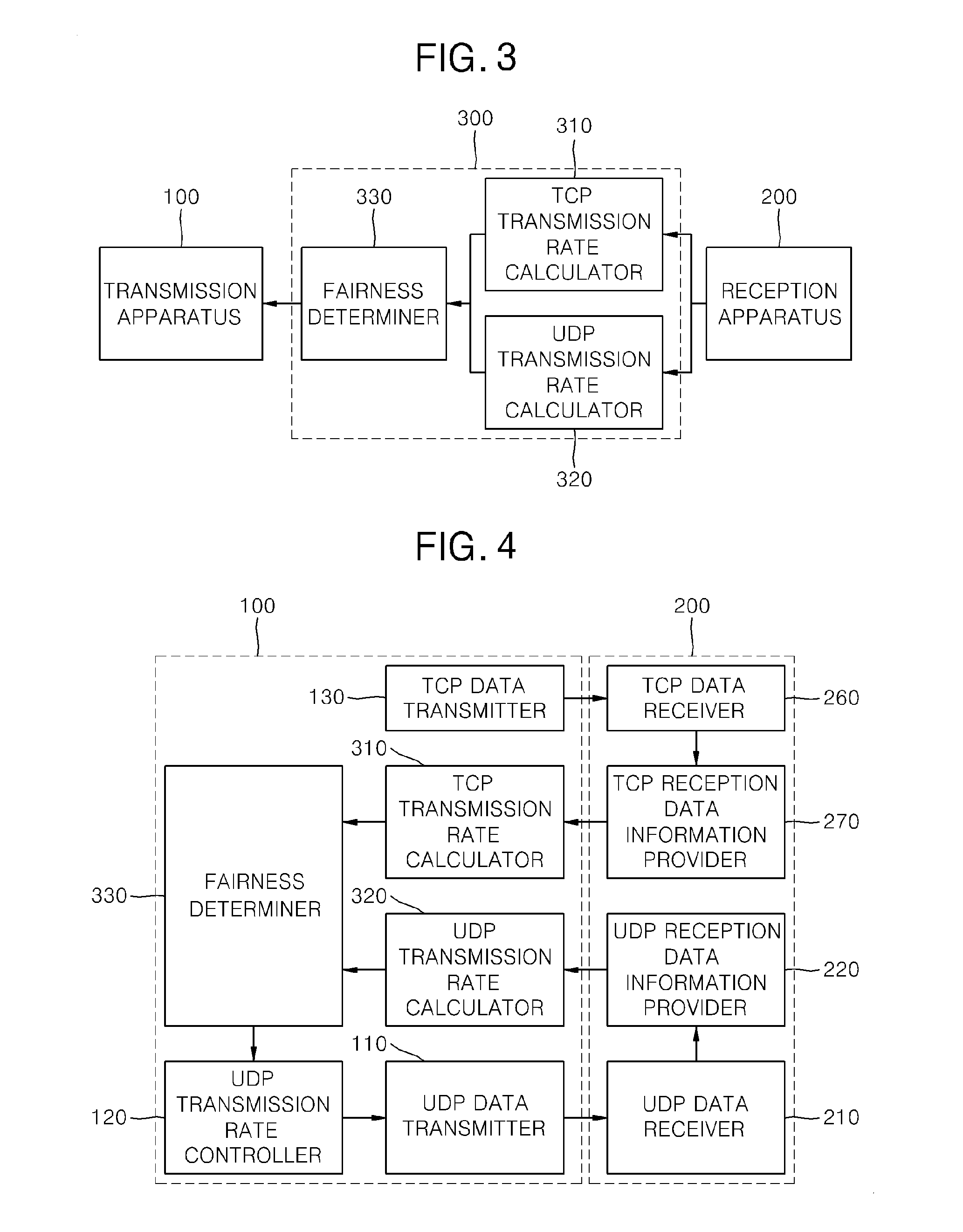
Apparatus and method for ensuring fairness of UDP data transmission in ethernet environment
ActiveUS20120110205A1Ensure fairnessFairnessMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksData streamProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
Provided are an apparatus and method for ensuring fairness of user datagram protocol (UDP) data transmission in an Ethernet environment. Transmission control protocol (TCP) transmission rate calculator calculates a current TCP transmission rate based on amount of a TCP data stream transmitted in real time from a transmission apparatus and received by a reception apparatus. TCP transmission rate calculator calculates the optimum transmission rate on the basis of the received amount of a TCP data stream transmitted to the reception apparatus before UDP data transmission of the transmission apparatus is started. When UDP data is transmitted from a transmission apparatus to a reception apparatus, a TCP data stream for determining fairness is transmitted together, so that the apparatus and method can be simplified by adding only the TCP stream without an additional module for estimating a queuing delay time on the basis of a round-trip time (RTT) and so on.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDS CO LTD
Method for calculating fairness index and method for allocating resources based on the fairness index in coexistence management system
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Control Device and Method for Power Supplying of Communications Network
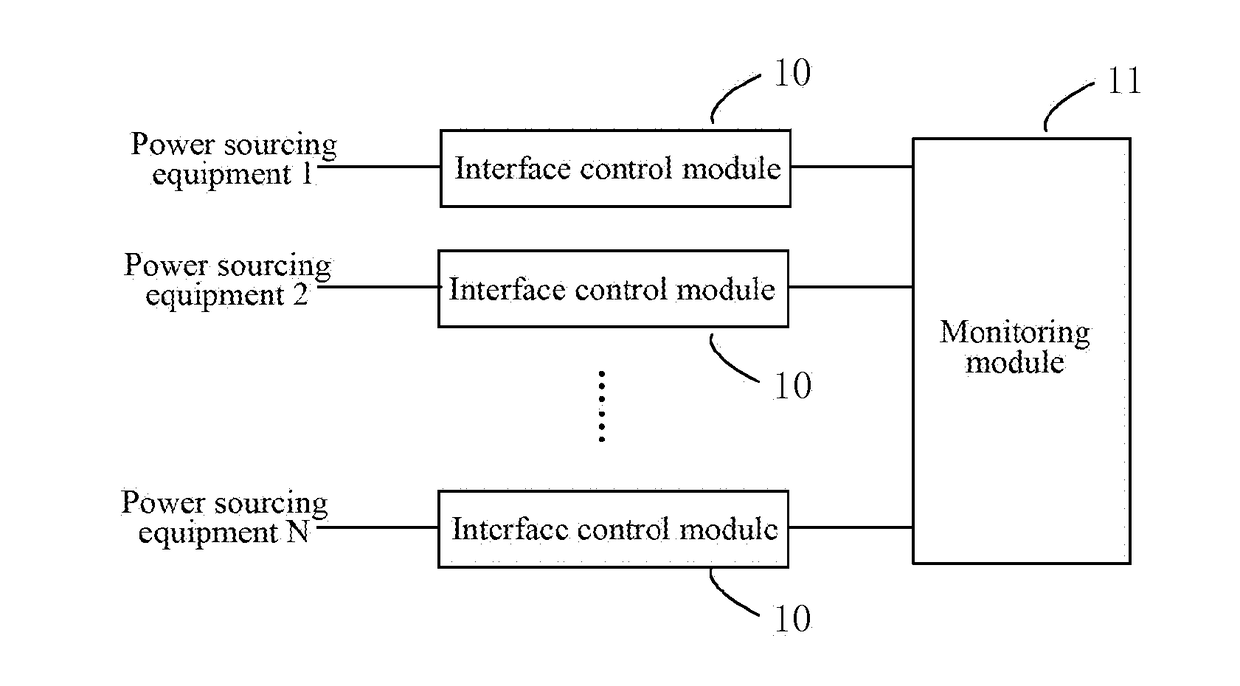
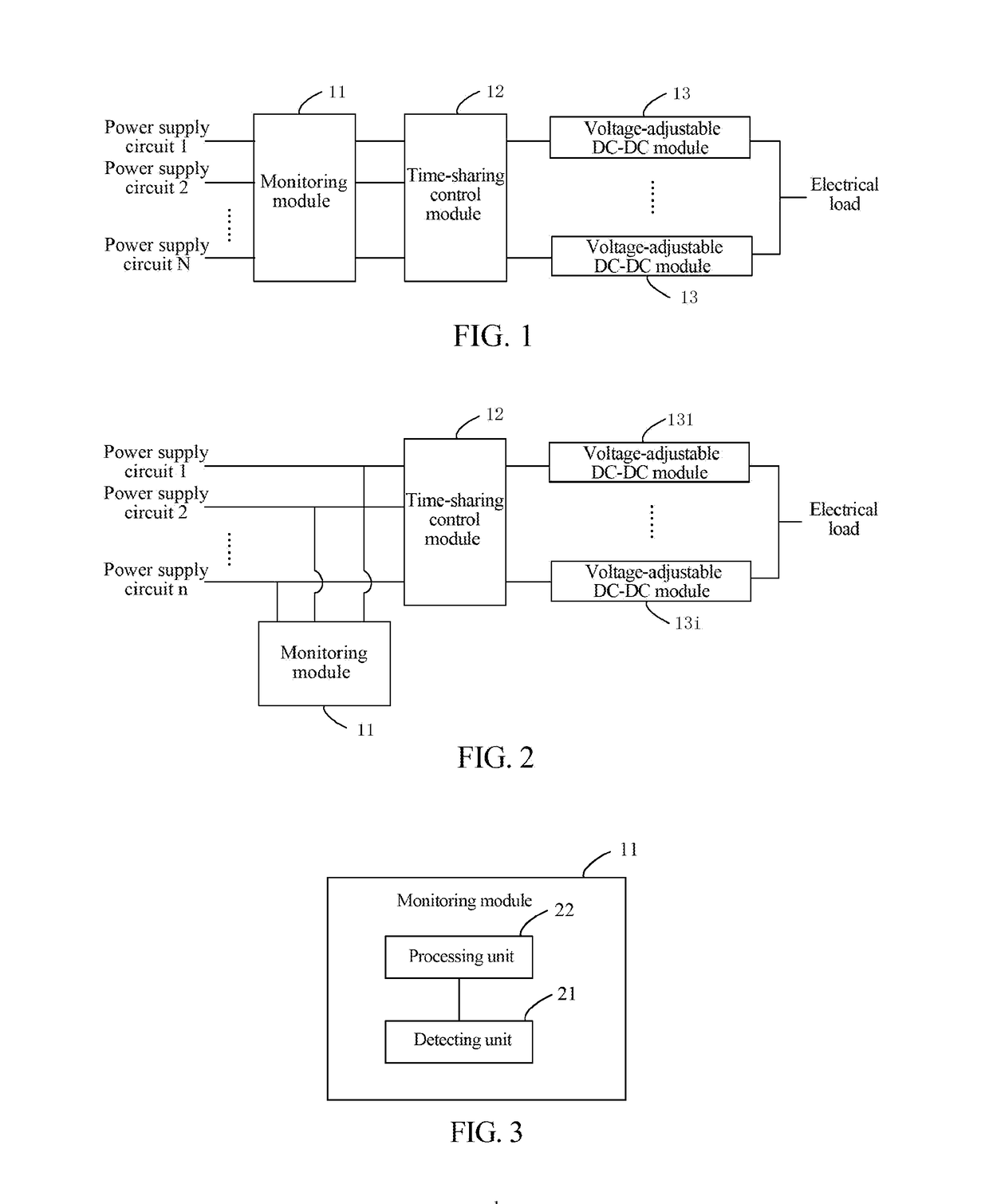
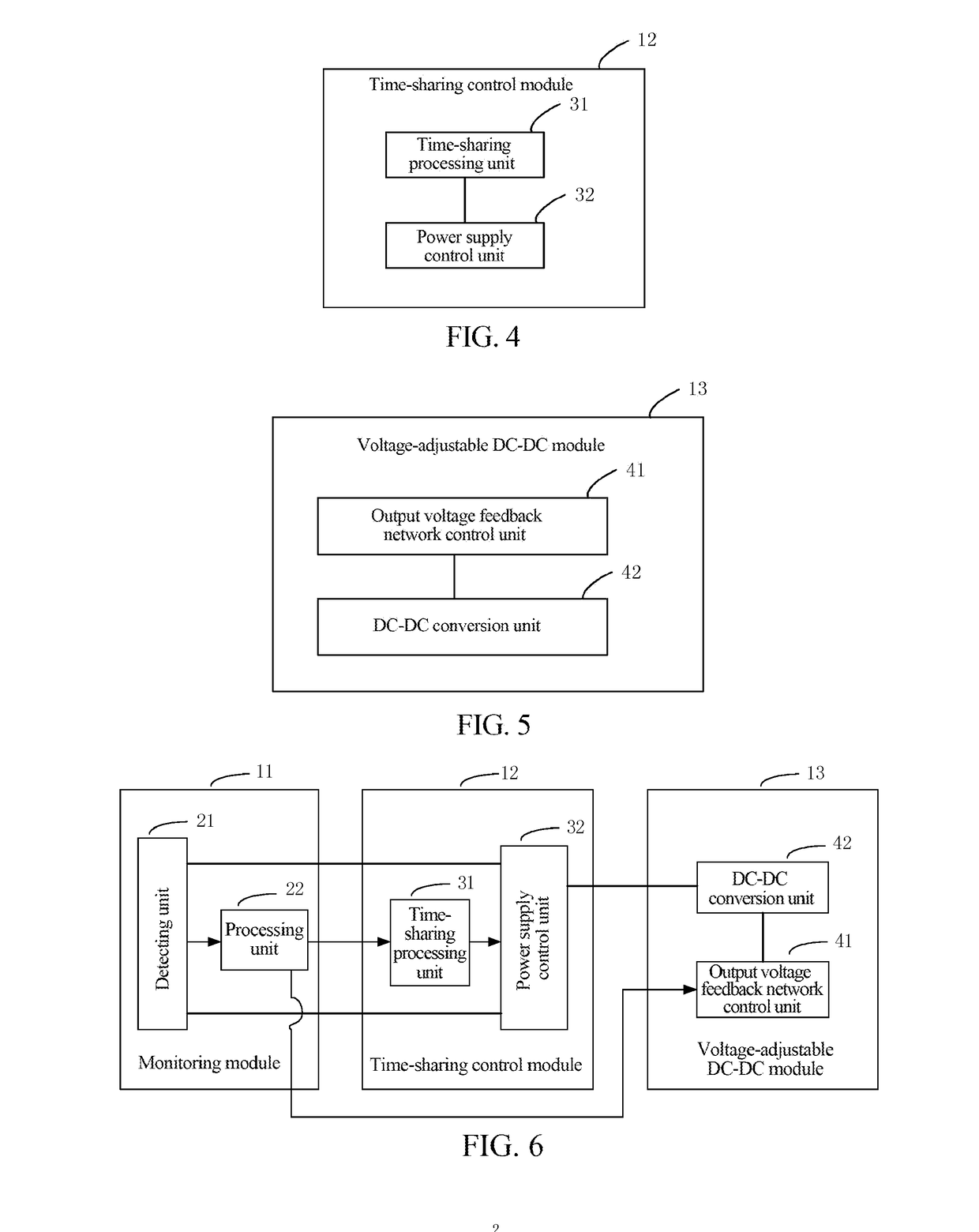
ActiveUS20170353321A1FairnessPower managementData switching current supplyPower circuitsControl equipment
A control apparatus and control method for power supply of a communication network are provided. The method includes: detecting circuit data of each power supply circuit, comparing the circuit data of the each power supply circuit to get an average value, and analyzing output circuit data that the each power supply circuit should have; adjusting an output voltage of each power supply circuit according to the output circuit data that each power supply circuit should have; and connecting output voltages of all the power supply circuits in parallel and supplying power to a next stage electrical load.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Multi-hop wireless terminal and traffic control method thereof
InactiveUS8644155B2FairnessWithout requiring complicated processError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDistributed computingQueue manager
A multi-hop wireless terminal having a user application section, a traffic control section and a wireless transmitting / receiving section, the traffic control section enqueuing a packet of a transmission flow from the user application section and a packet of a forward flow from the wireless transmitting / receiving section in queues different for each flow and performing traffic control, where the traffic control section includes a queue manager for sorting a packet of each input flow into a corresponding queue and enqueuing the packet, and a packet scheduler for dequeuing a packet from each queue and outputting the packet, and where the packet scheduler selects from the queues a queue from which a packet is to be dequeued and output, based on transmission information of each of the flows.
Owner:SONY CORP
Apparatus and method for transmitting data frame in WLAN terminal
ActiveUS8054812B2Reduce degradationTransmission fairnessNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionBeacon frameData transmission systems
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
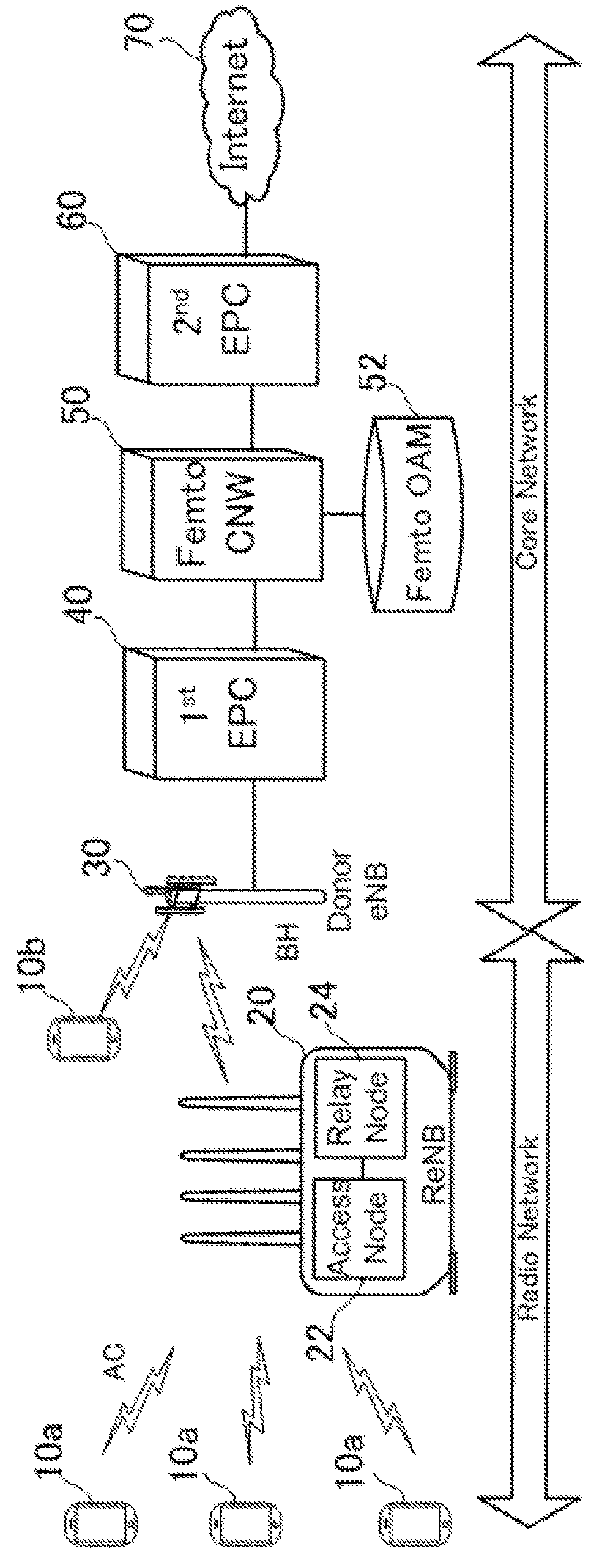
Relay apparatus and relay method
InactiveUS20180279205A1FairnessMaintain fairnessAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesTerminal equipmentComputer terminal
The fairness of radio communication between a donor base station and terminal devices is maintained. A relay apparatus 20 for relaying radio communication between one or more terminal devices 10 and a donor base station 30, wherein when the relay apparatus 20 receives a cell restriction instruction from the donor base station 30 to restrict a quantity of terminals capable of existing in a service area of a cell formed by the donor base station 30, the relay apparatus 20 executes processing for avoiding cell restriction operation on itself and transfers the cell restriction instruction received from the donor base station 30 to the terminal devices 10 existing in a service area of a cell formed by the relay apparatus itself.
Owner:SOFTBANK CORP
Inter-ring fairness control method and rpr node device
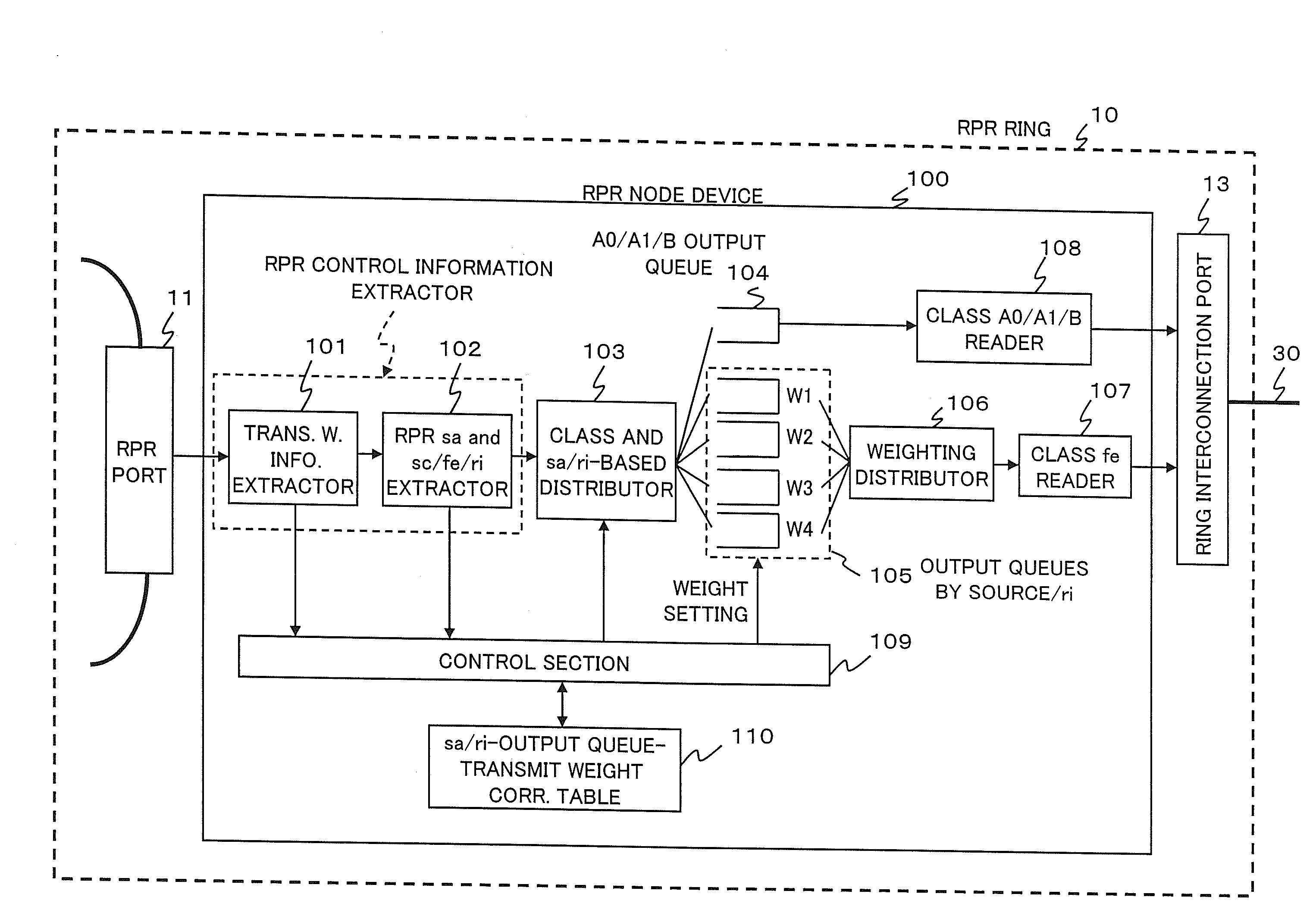
InactiveUS20080240007A1FairnessEnsure fairnessRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsLoop networksTorus interconnectTraffic capacity
The fairness of communication traffic guaranteed within an RPR ring is guaranteed also at a ring interconnection. Transmit weight information used for fairness control is extracted from RPR control information in an arrival packet. In addition to this transmit weight information, a source address, a service class, a fairness bit, and a ring transmit direction are also extracted. If the packet has a fairness bit of “0,” the packet is temporarily stored in an output queue by service class. If the packet has a fairness bit of “1,” the packet is weighted by source and ring transmit direction, based on the transmit weight information, and is temporarily stored in an output queue by source and ring transmit direction. Reading of packets from the output queue by service class is performed prior to reading of packets from the output queue by source and ring transmit direction.
Owner:NEC CORP
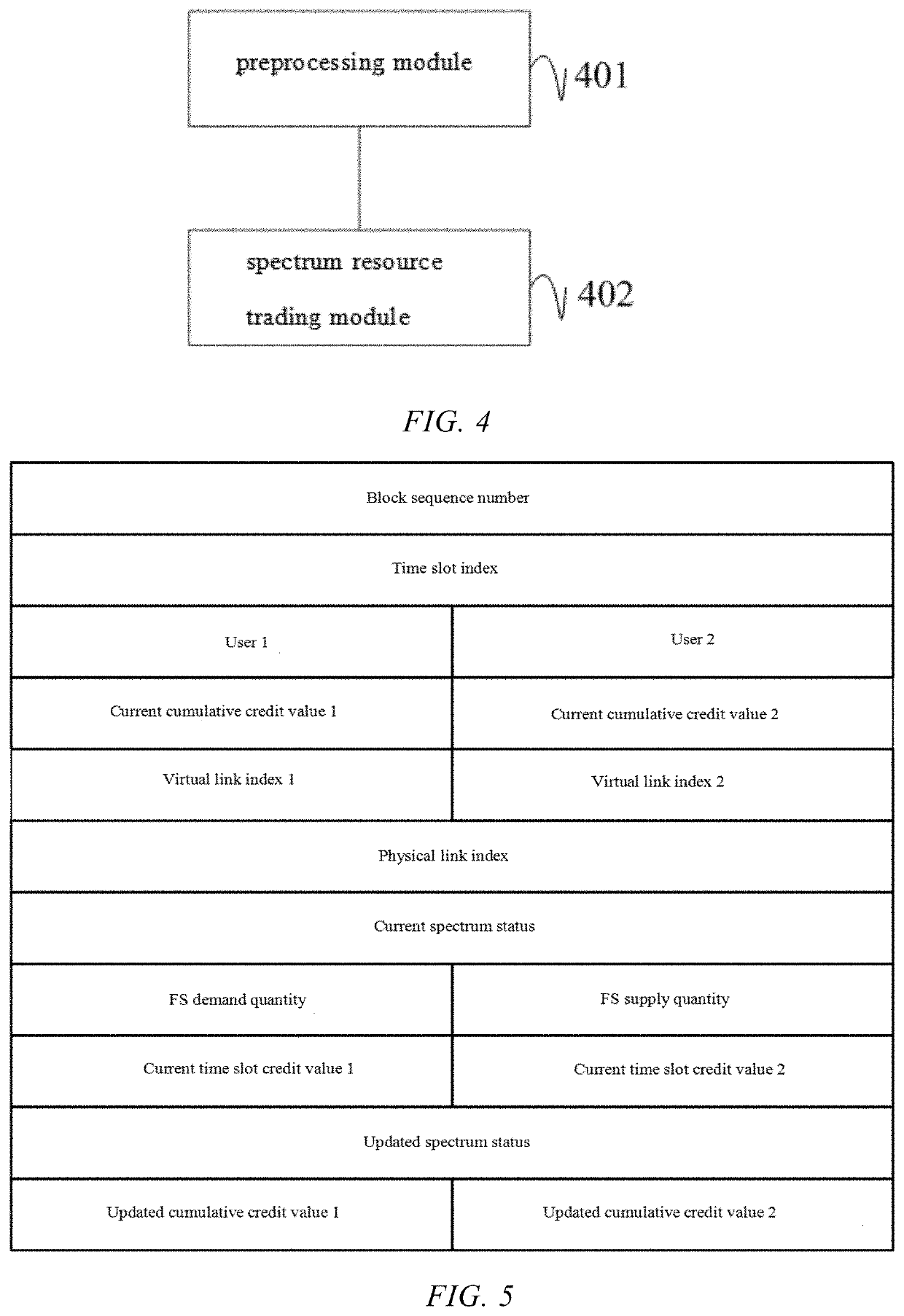
Virtual optical network-oriented spectrum resource trading method and system
ActiveUS11451890B2Improve spectrum utilizationIncrease profitMultiplex system selection arrangementsTransmissionEngineeringVirtual optical network
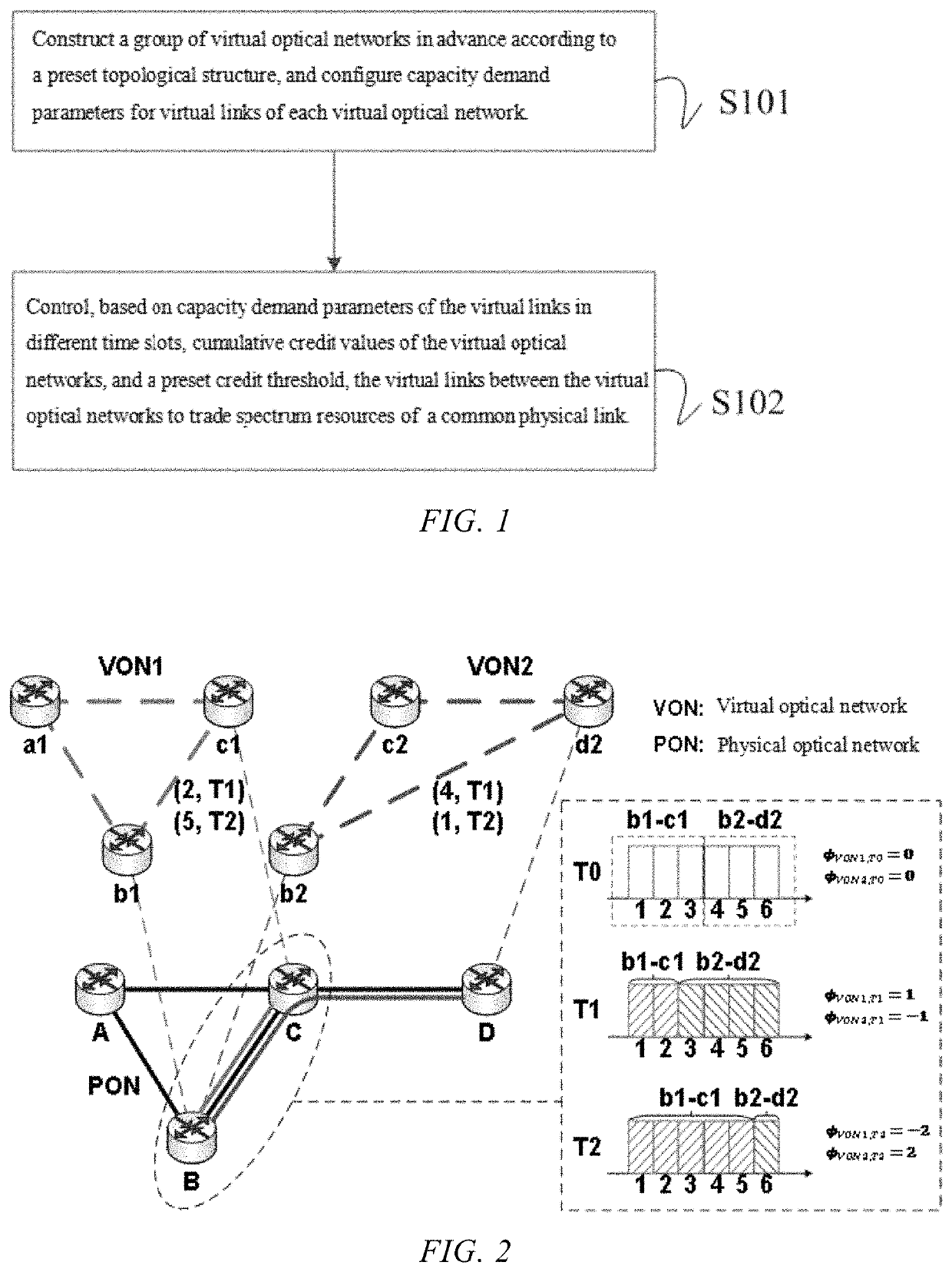
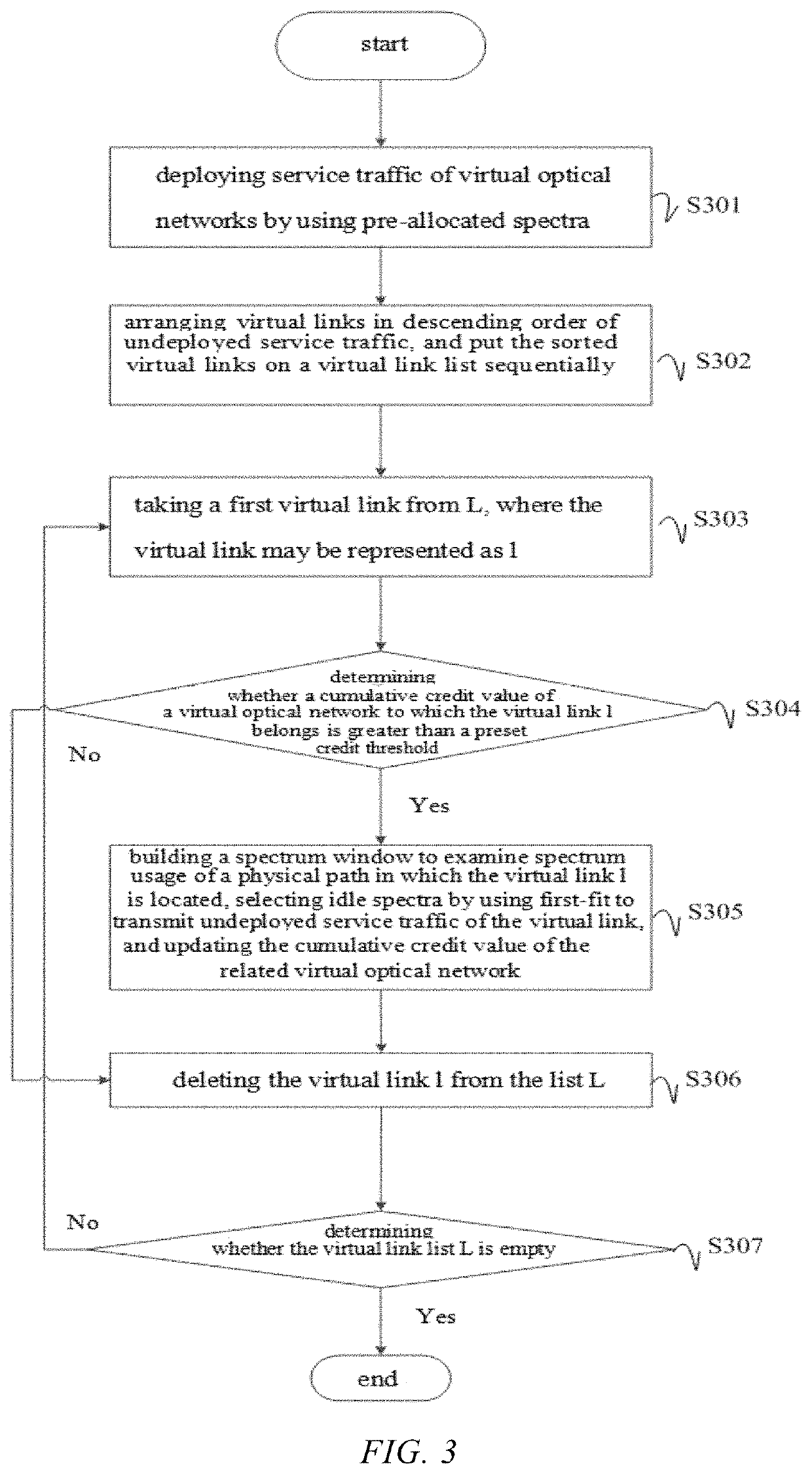
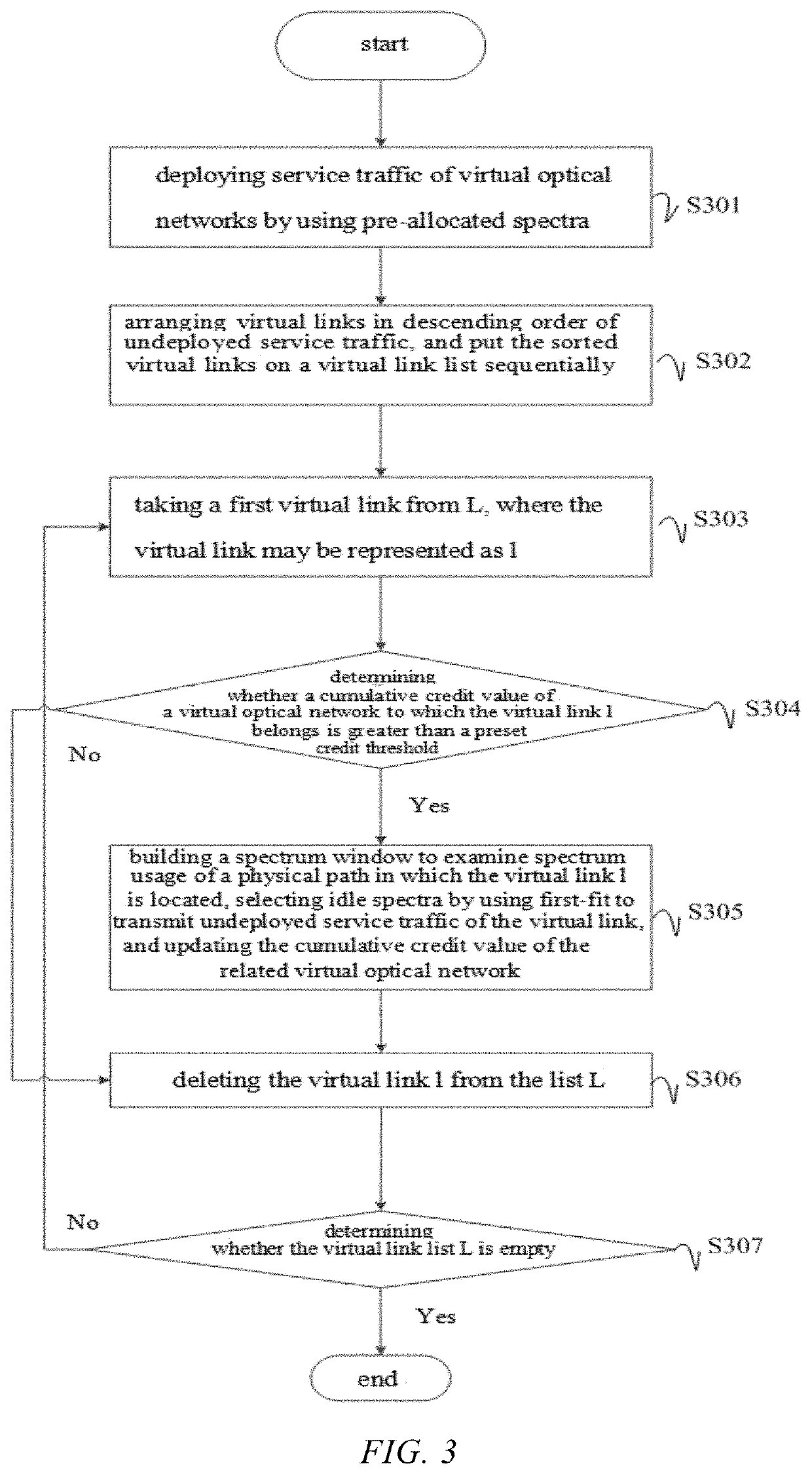
The invention provides a virtual optical network-oriented spectrum resource trading method and system. The method includes: after virtual optical networks are constructed according to a preset topological structure, in different time slots, controlling, based on capacity demand information of virtual links of the virtual networks, cumulative credit values of the virtual optical networks, and a preset credit threshold, the virtual links between the virtual optical networks to trade spectrum resources of a common physical link, to implement that the virtual optical networks trade spectrum resources according to a real-time capacity demand. A virtual link with idle spectrum resources can supply spectrum resources to a virtual link with insufficient capacity, and a virtual optical network with insufficient spectra can perform spectrum trading to use idle spectra of other virtual optical networks to transmit undeployed service traffic of the virtual optical network, thereby effectively improving the utilization of network spectrum resources.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Virtual optical network-oriented spectrum resource trading method and system
ActiveUS20220086539A1Improve spectrum utilizationIncrease profitMultiplex system selection arrangementsTransmissionEngineeringVirtual optical network
The invention provides a virtual optical network-oriented spectrum resource trading method and system. The method includes: after virtual optical networks are constructed according to a preset topological structure, in different time slots, controlling, based on capacity demand information of virtual links of the virtual networks, cumulative credit values of the virtual optical networks, and a preset credit threshold, the virtual links between the virtual optical networks to trade spectrum resources of a common physical link, to implement that the virtual optical networks trade spectrum resources according to a real-time capacity demand. A virtual link with idle spectrum resources can supply spectrum resources to a virtual link with insufficient capacity, and a virtual optical network with insufficient spectra can perform spectrum trading to use idle spectra of other virtual optical networks to transmit undeployed service traffic of the virtual optical network, thereby effectively improving the utilization of network spectrum resources.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
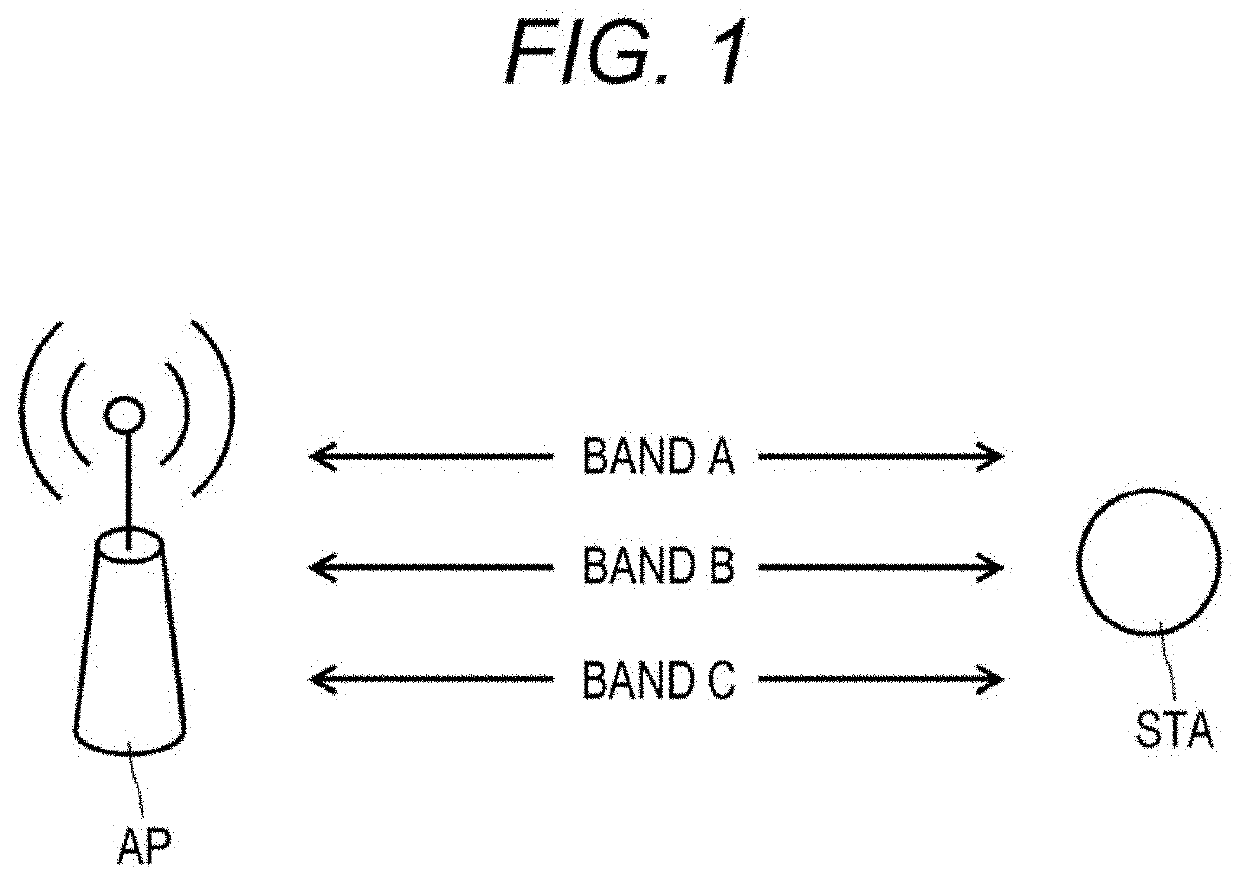
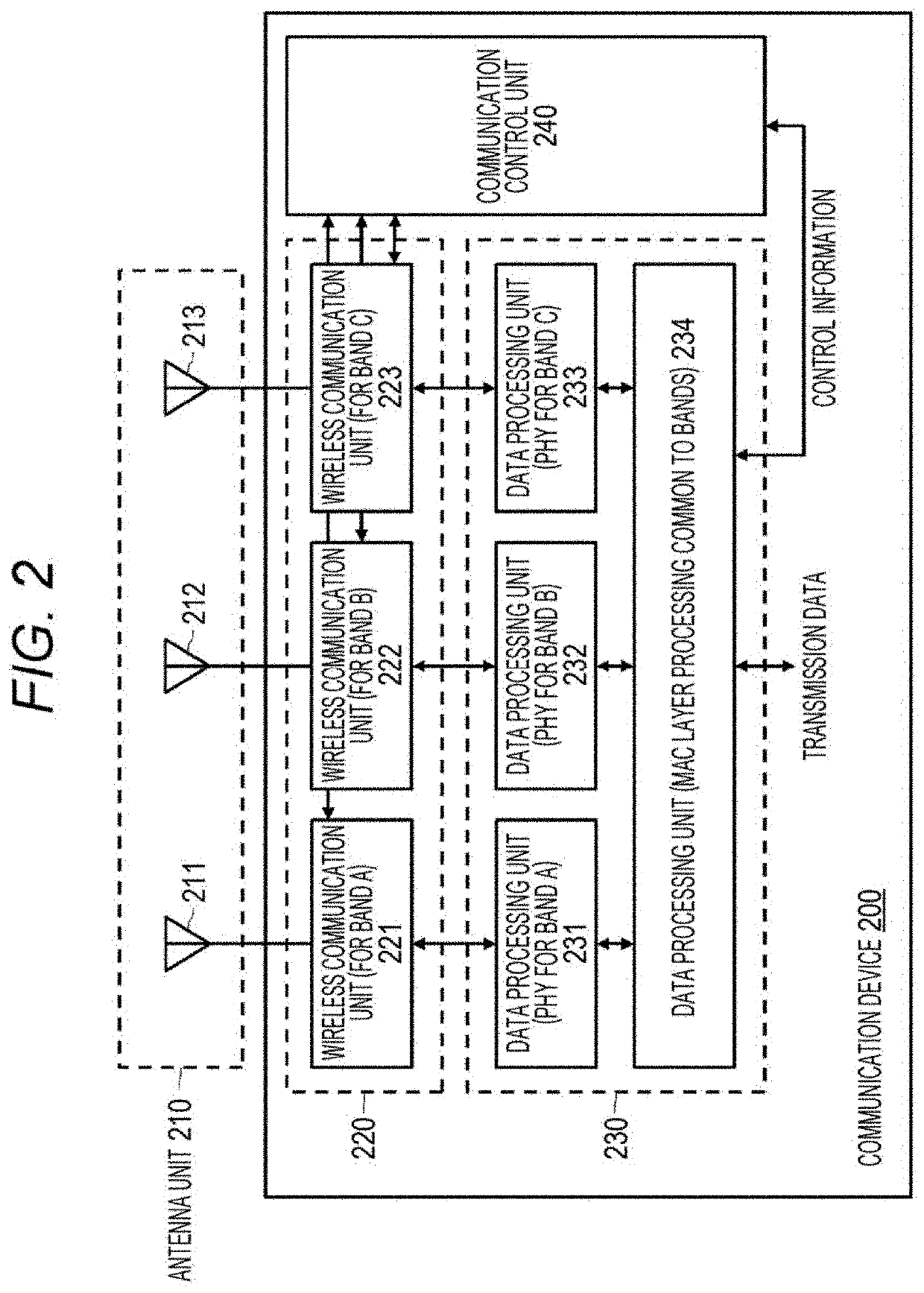
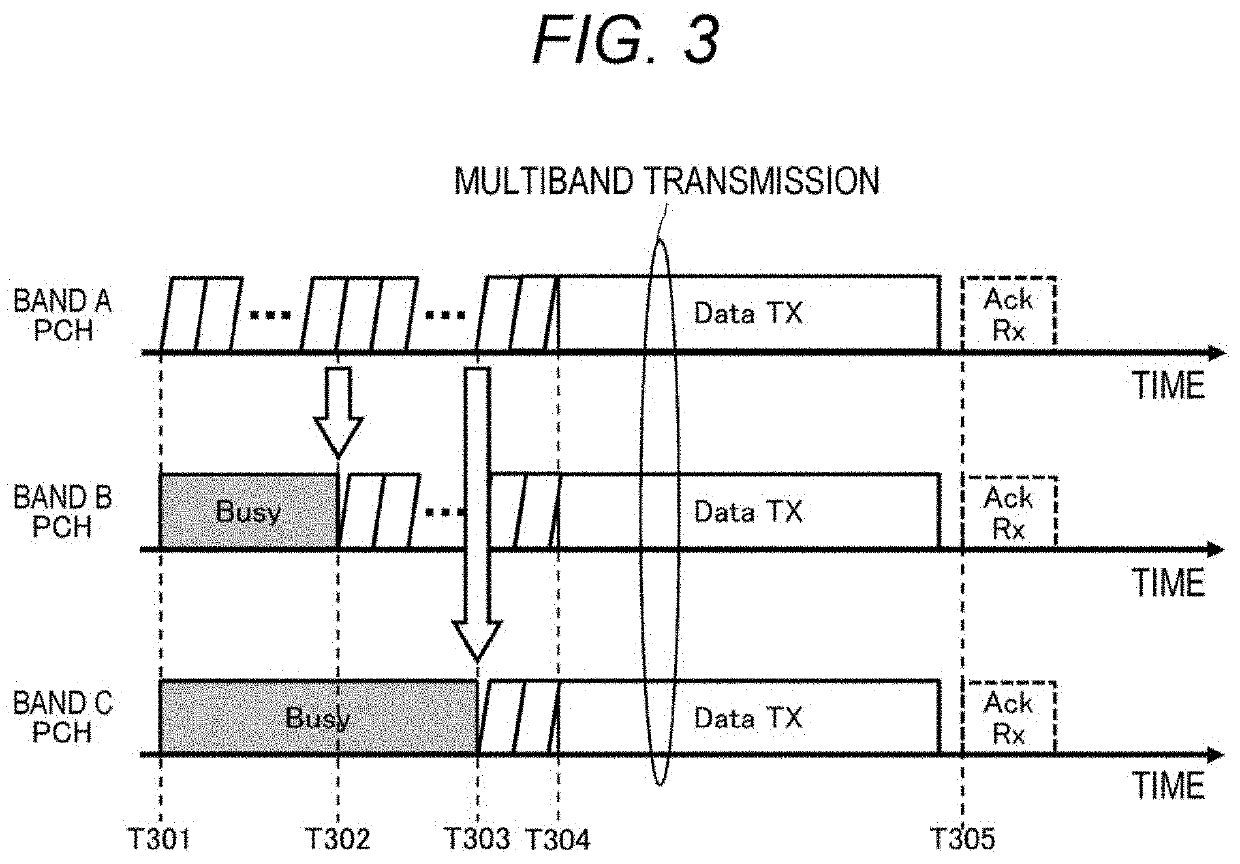
Communication device and communication method
PendingUS20220167411A1Achieve fairnessFairnessNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsCommunication unit
A communication device that determines a backoff time of multiband transmission is provided.A communication device includes: a communication unit that transmits and receives wireless signals in a plurality of bands; and a control unit that controls an operation in the communication unit. The control unit sets, for each band, a first random standby time for performing transmission in each of the plurality of bands, sets a second random standby time for performing simultaneous transmission of data in two or more of the plurality of bands, and controls countdown of the second random standby time or the first random standby time of each band on the basis of a comparison between the first random standby time of each band and the second random standby time.
Owner:SONY CORP
Resource management method and apparatus in user-centric wireless network
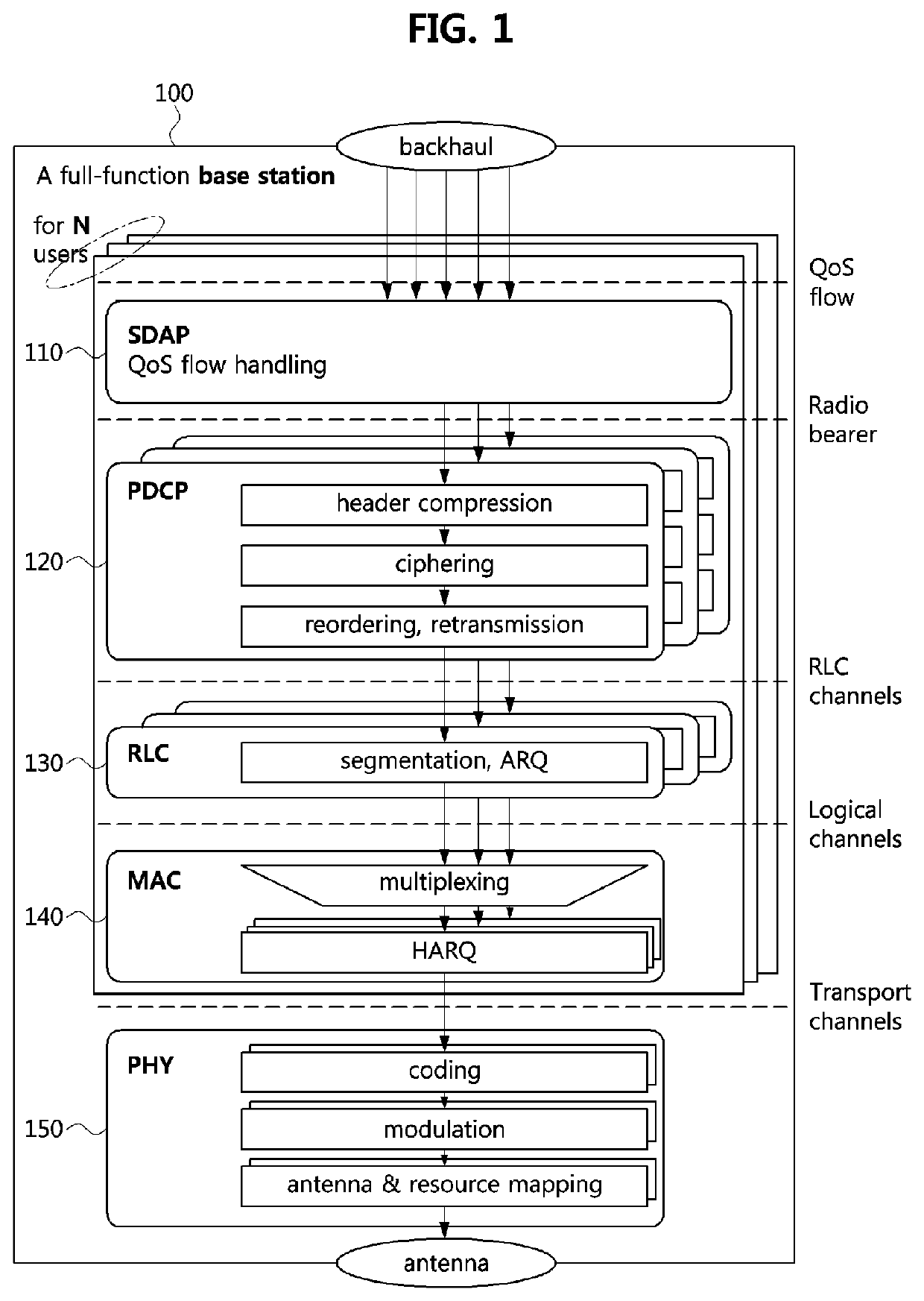
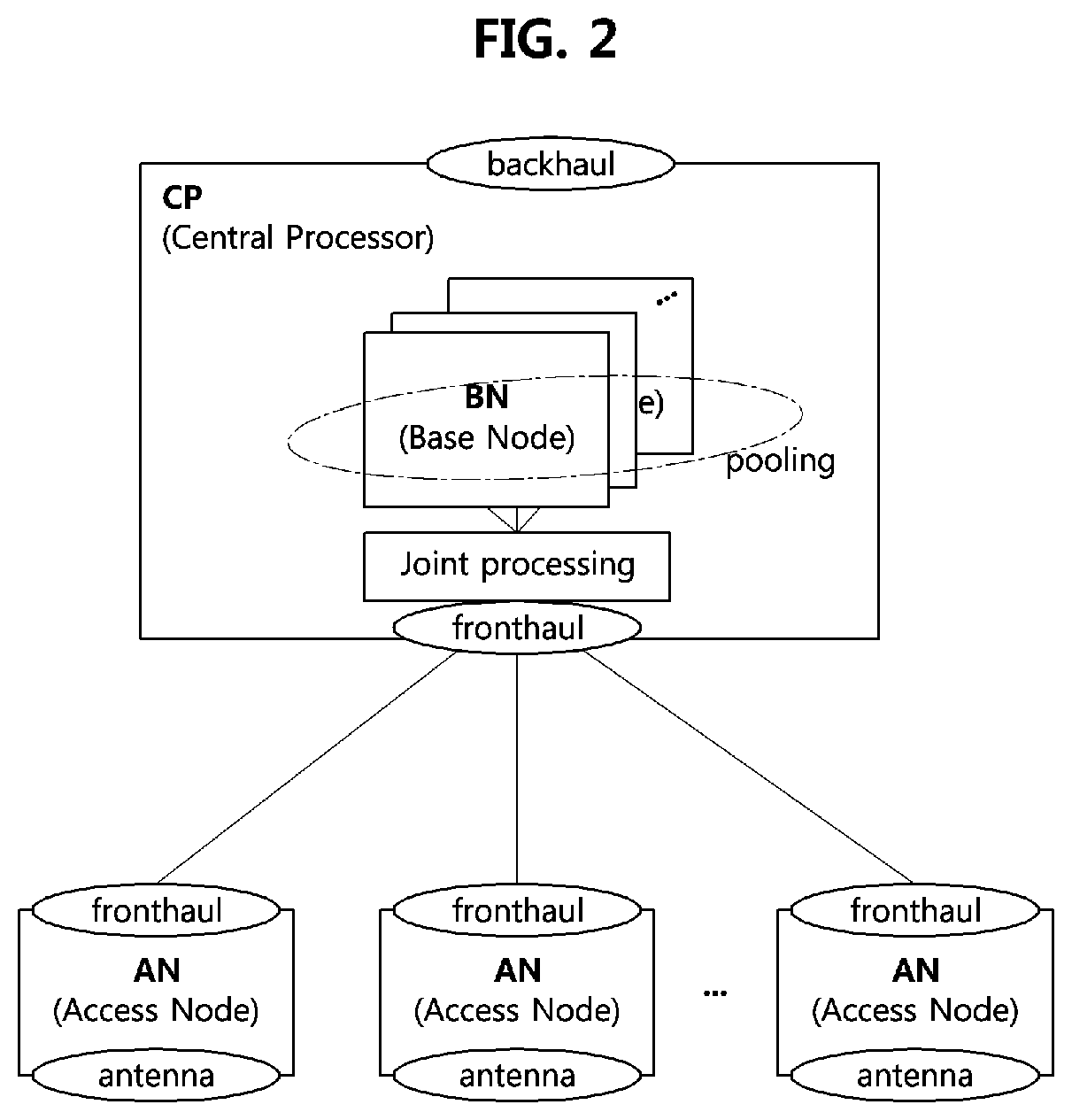
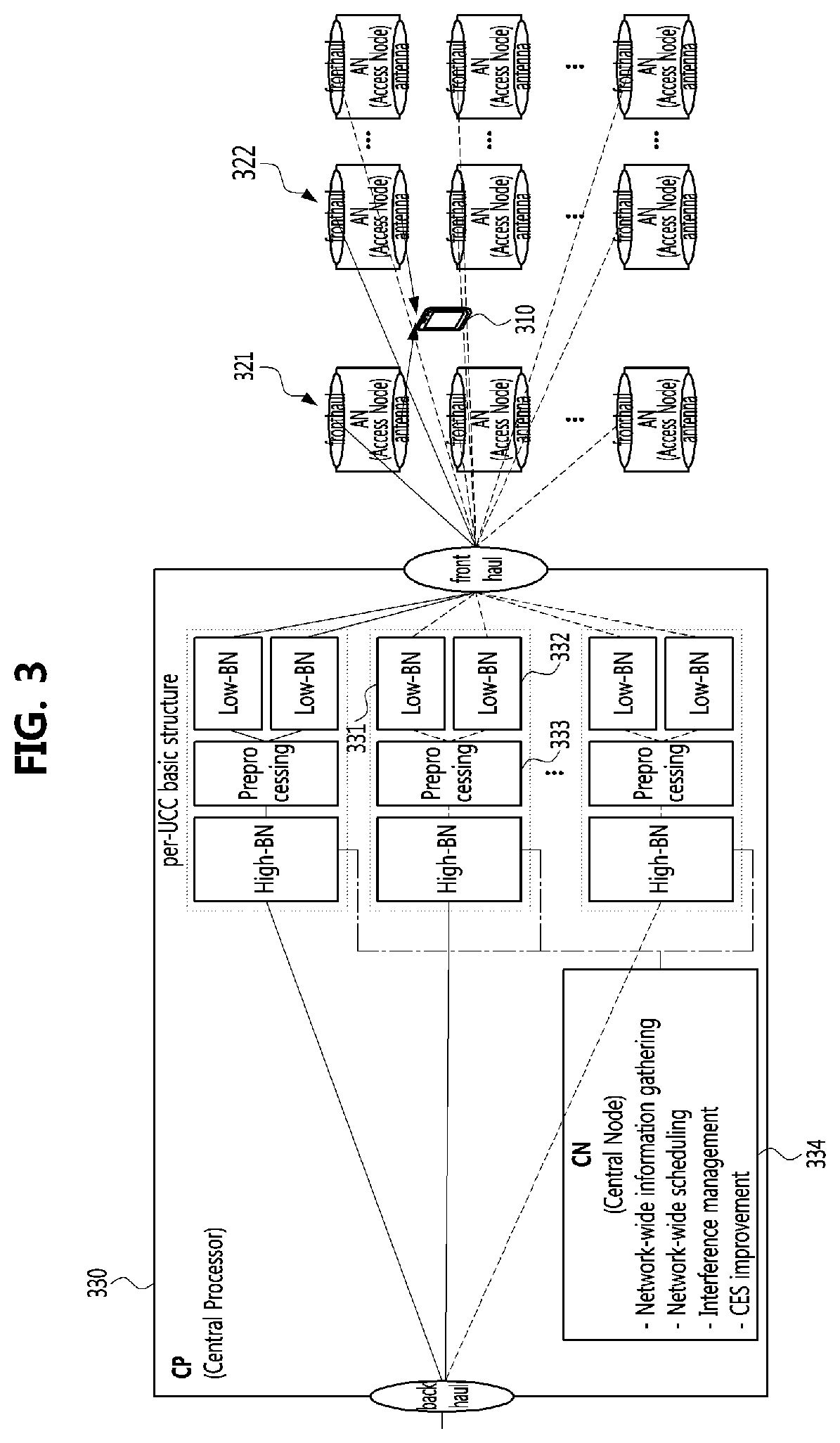
ActiveUS11510182B2Lower performance requirementsImprove performanceNetwork traffic/resource managementMulti-frequency code systemsComputer networkResource management
A resource management method performed by a CP in C-RAN system includes configuring M user-centric cells for M terminals with a plurality of ANs, and determining a number K of orthogonal resource sharing groups sharing a same orthogonal resource; selecting K user-centric cells as group headers for the K orthogonal resource sharing groups, and adding the selected K user-centric cells as group headers to the K orthogonal resource sharing groups; configuring the K orthogonal resource sharing groups by sequentially adding ungrouped user-centric cells to the K orthogonal resource sharing groups; and dividing total system resources into K orthogonal resources, and mapping the divided K orthogonal resources to the K orthogonal resource sharing groups, respectively.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com