Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
52results about How to "Decrease in amount" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
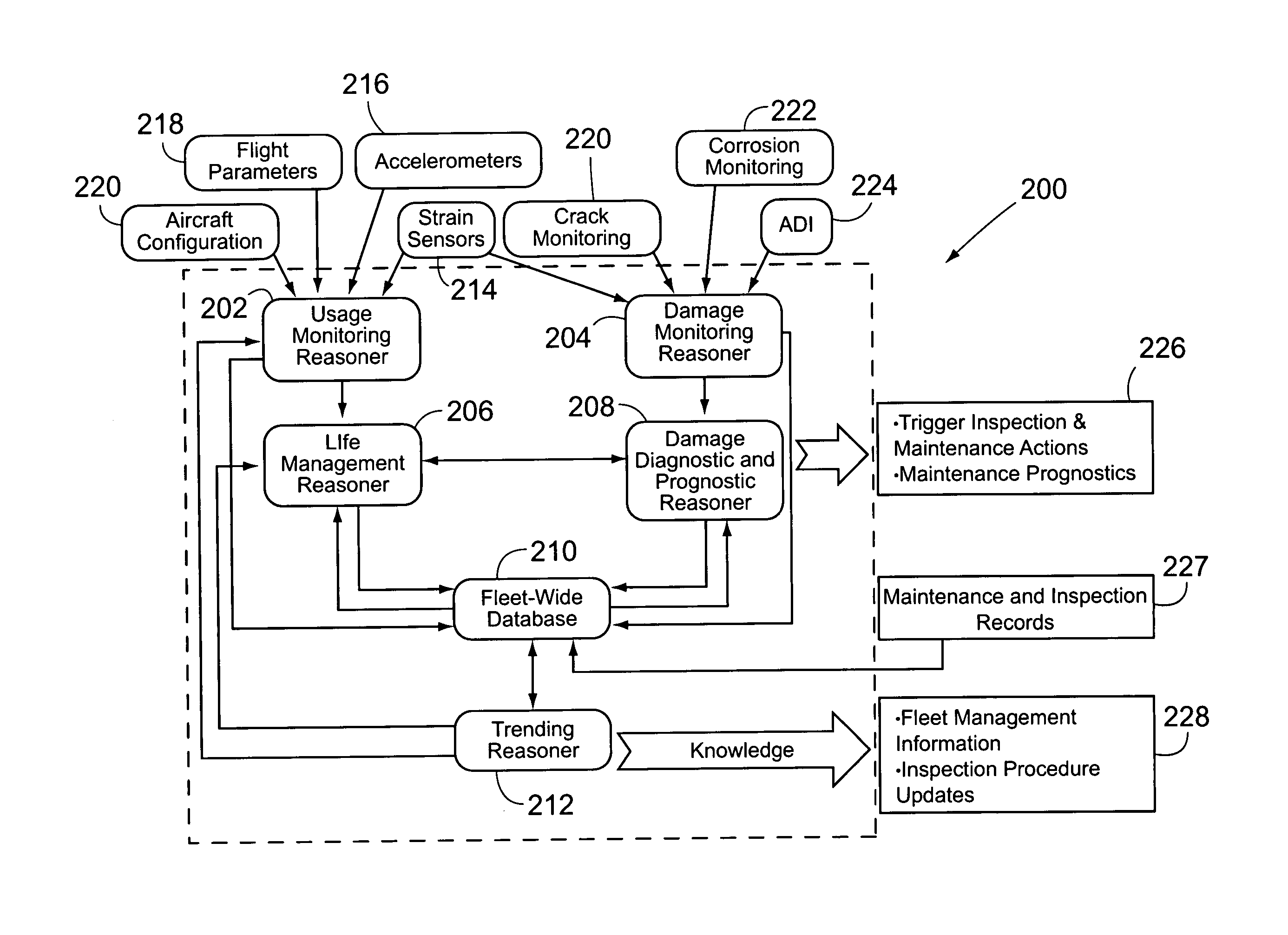
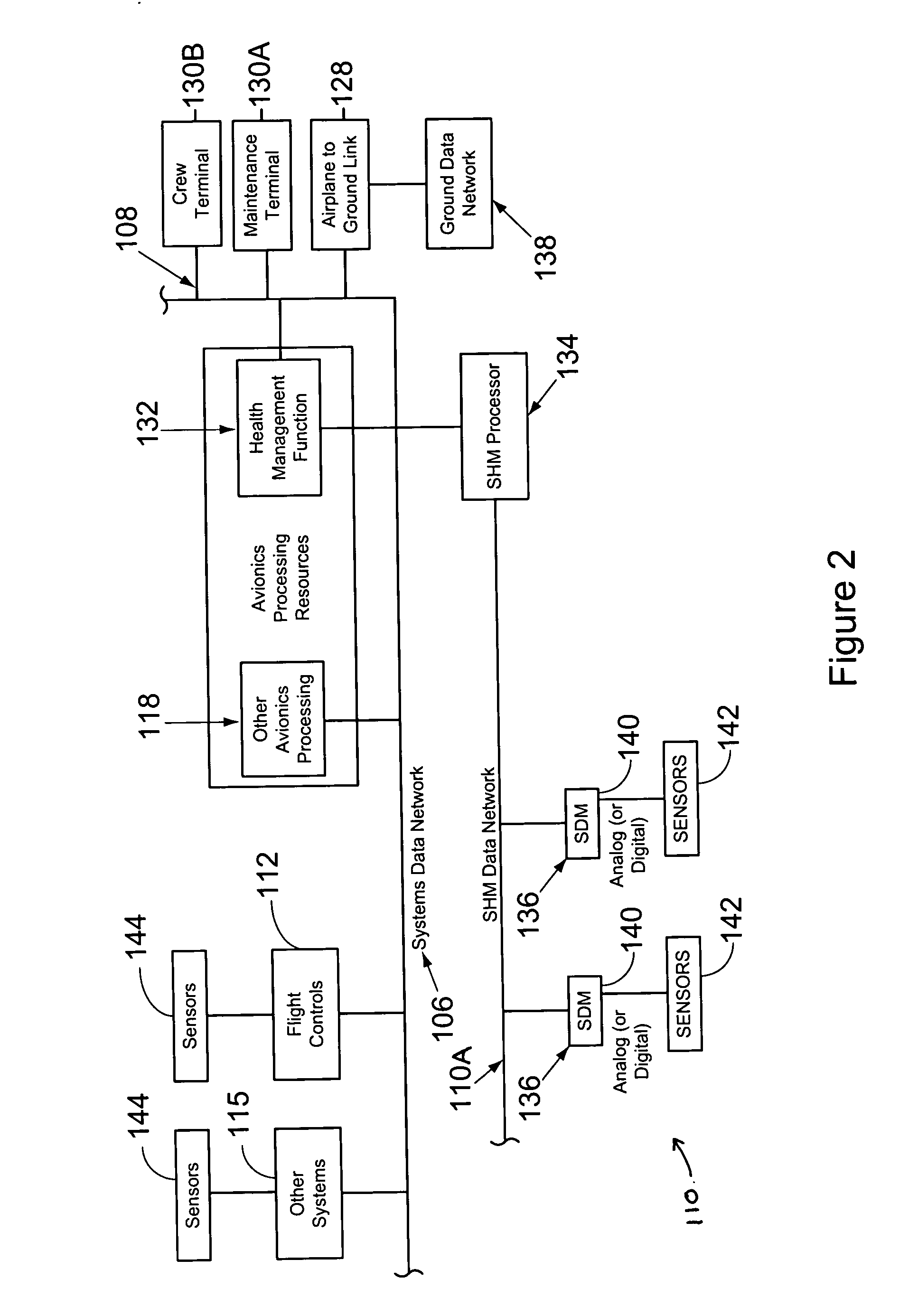
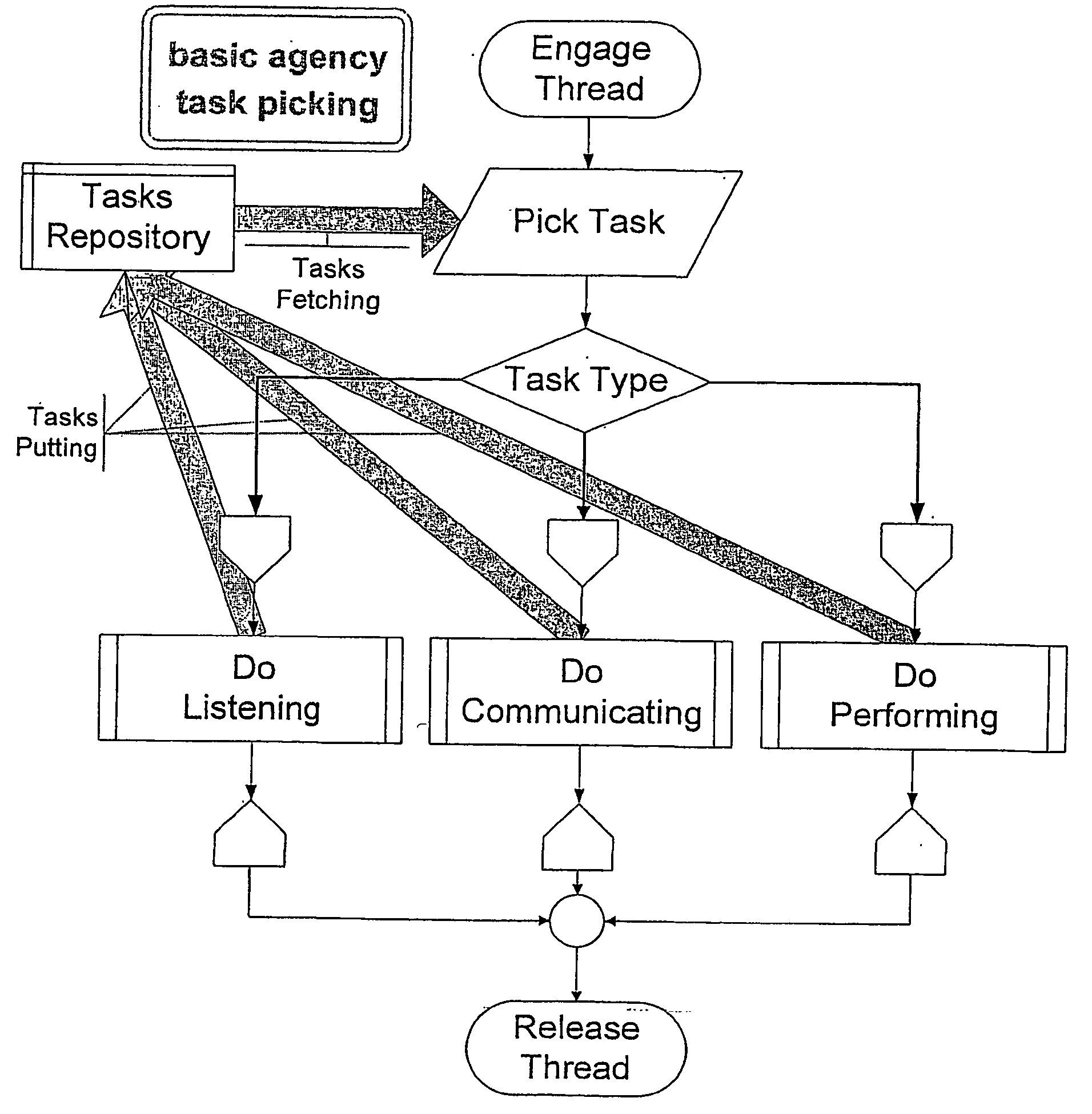
Structural health management architecture using sensor technology
InactiveUS20060004499A1Decrease in amountReduce amountVehicle testingAircraft health monitoring devicesEmbedded systemInformation system
A mobile platform comprising at least one mobile platform system that includes a processor, a structure, and an SHM system. The SHM system also includes a processor as well as a structural sensor. The SHM processor is separate from the mobile platform system processor. In other preferred embodiments, the mobile platform includes a flight control system, a maintenance information system, and an IVHM system. The SHM system may receive parameters from the flight control system and calculate loads therefrom. Alternatively, the sensor may be a structural load sensor, which the SHM processor uses along with the parameters, to calculate other structural loads. In still another preferred embodiment, a method is provided that includes separating SHM functions from a processor of a mobile platform system. The method also includes dedicating an SHM system to perform SHM functions and establishing communications between the SHM system and the mobile platform system.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Polyurethane molded article and production method thereof
InactiveUS20060141236A1Decrease in amountReduce the amount requiredThin material handlingMetal layered productsScavengerAldehyde
The amount of aldehyde emitted from a polyurethane and molded articles made of a polyurethane is reduced. The reduction of aldehyde emissions from polyurethanes is achieved by including a hydrazine compound as an aldehyde-scavenger in the polyol component of the polyurethane-forming reaction mixture. The hydrazine compound is used in an amount of 0.05 to 3.0 parts by weight, based on 100 parts by weight of the polyol mixture. Aldehyde emissions from molded polyurethane articles are reduced by including a hydrazine compound in the mold coating material in an amount of from 0.1 g / m2 to 10 g / m2.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
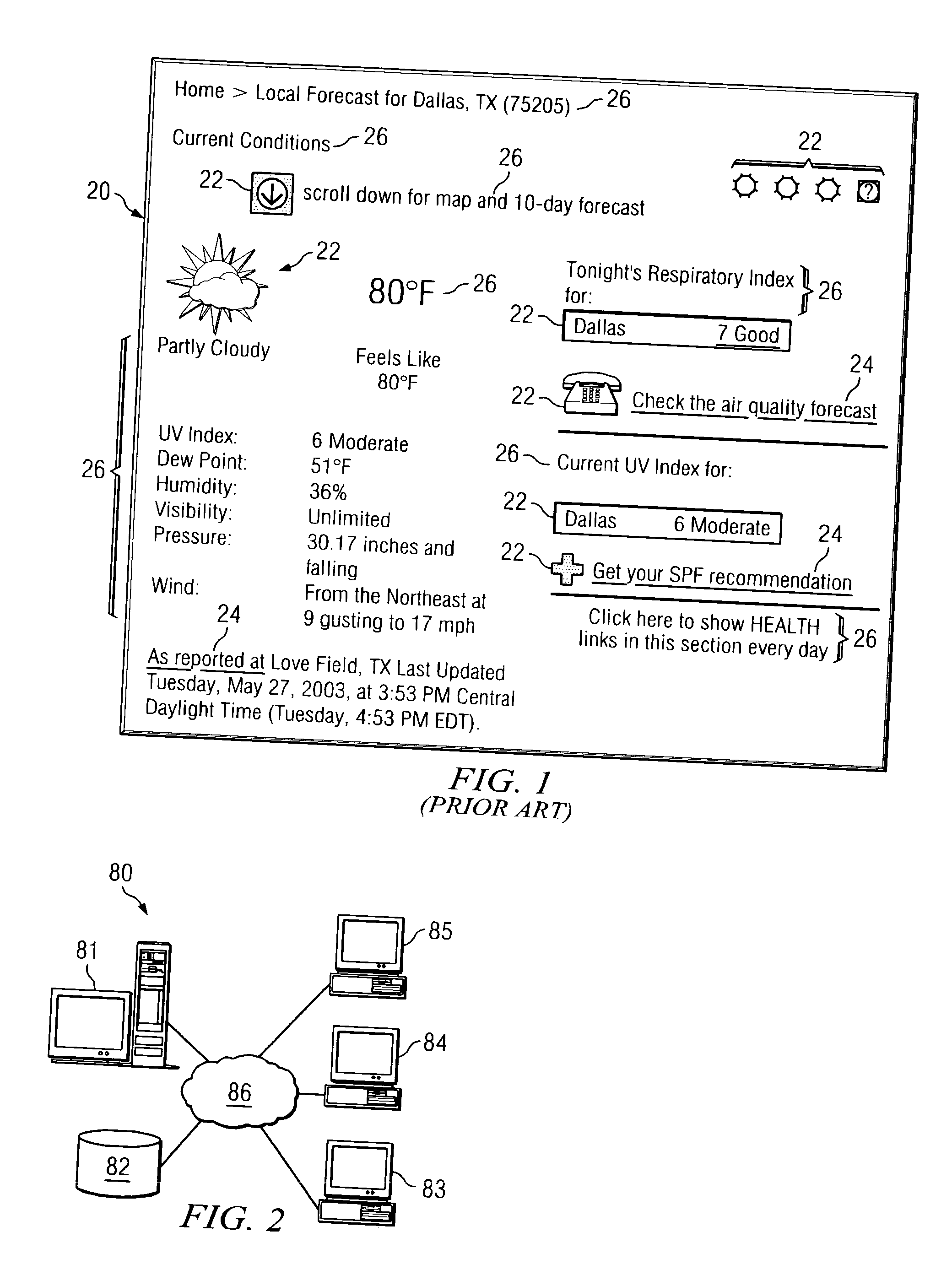
Apparatus and method for distributing portions of large web pages to fit smaller constrained viewing areas
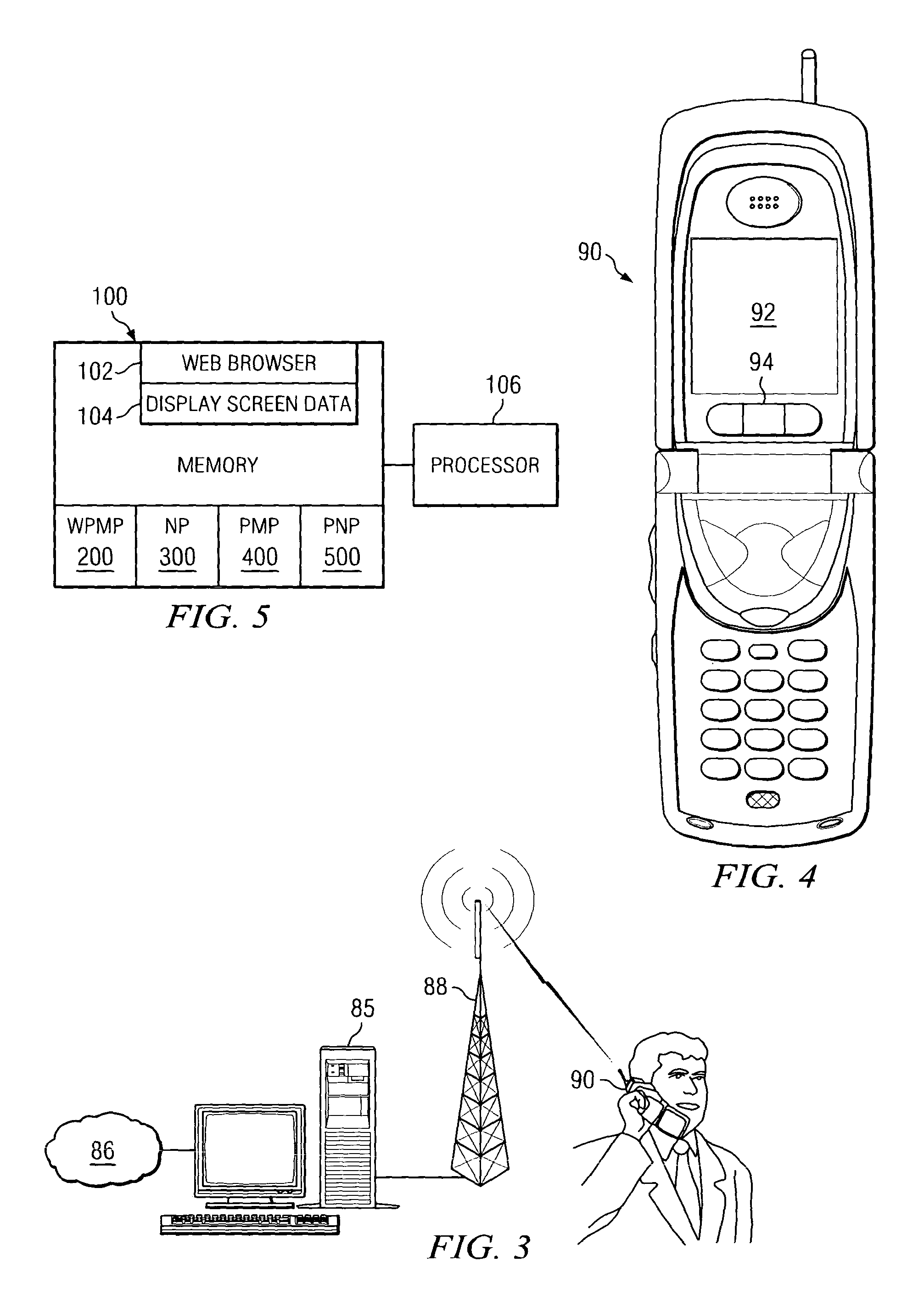
InactiveUS20050041858A1Decrease in amountReduce the amount requiredDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionHyperlink
The present invention is a methodology for displaying a web page on a hand held display device (HHDD). The invention comprises a Web Page Modification Program (WPMP) and a Navigation Program (NP). The WPMP creates a bitmap image of the web page. The WPMP records the location of the web page hyperlinks and creates an illusion of a working hyperlink by creating a segmented image on the image map where the hyperlink would be. The WPMP then displays a fragment of the image on the HHDD at the resolution intended by the web page designer. Thus the present invention allows the user to view a fragment of the web page at the intended resolution without having to load the entire web page onto the HHDD. The NP of the present invention allows the user to move from one fragment to another. An alternative embodiment utilizing a proxy is also disclosed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Treatment of conditions relating to hormone deficiencies by administration of progestins
InactiveUS7427609B2Constant amountDecrease in amountOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHigh dosesDose reduction
Owner:BARR LAB
Methods and compositions for dysferlin exon-skipping
InactiveUS20120270930A1Decrease in amountOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationExon skippingImproved method
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
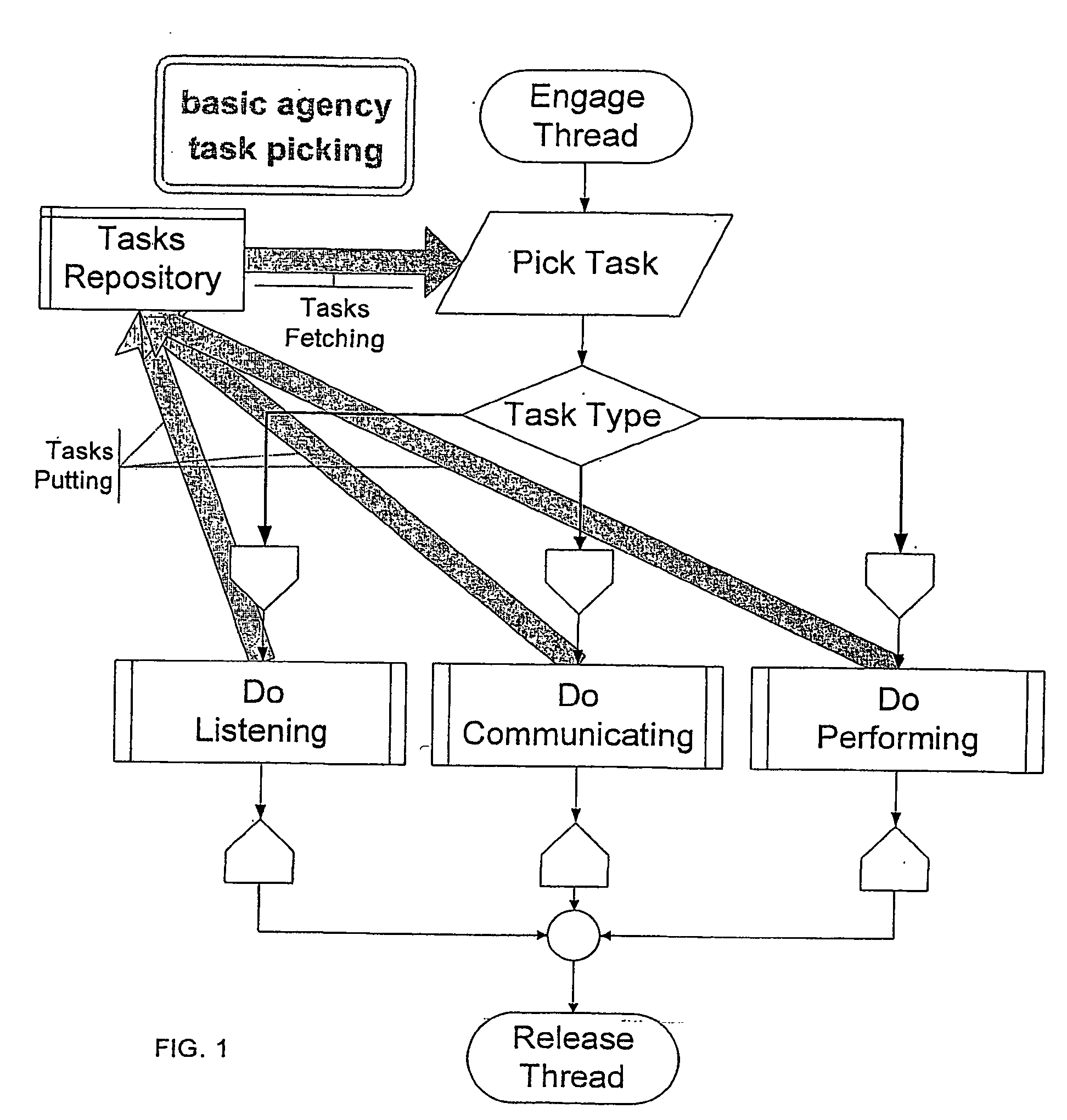
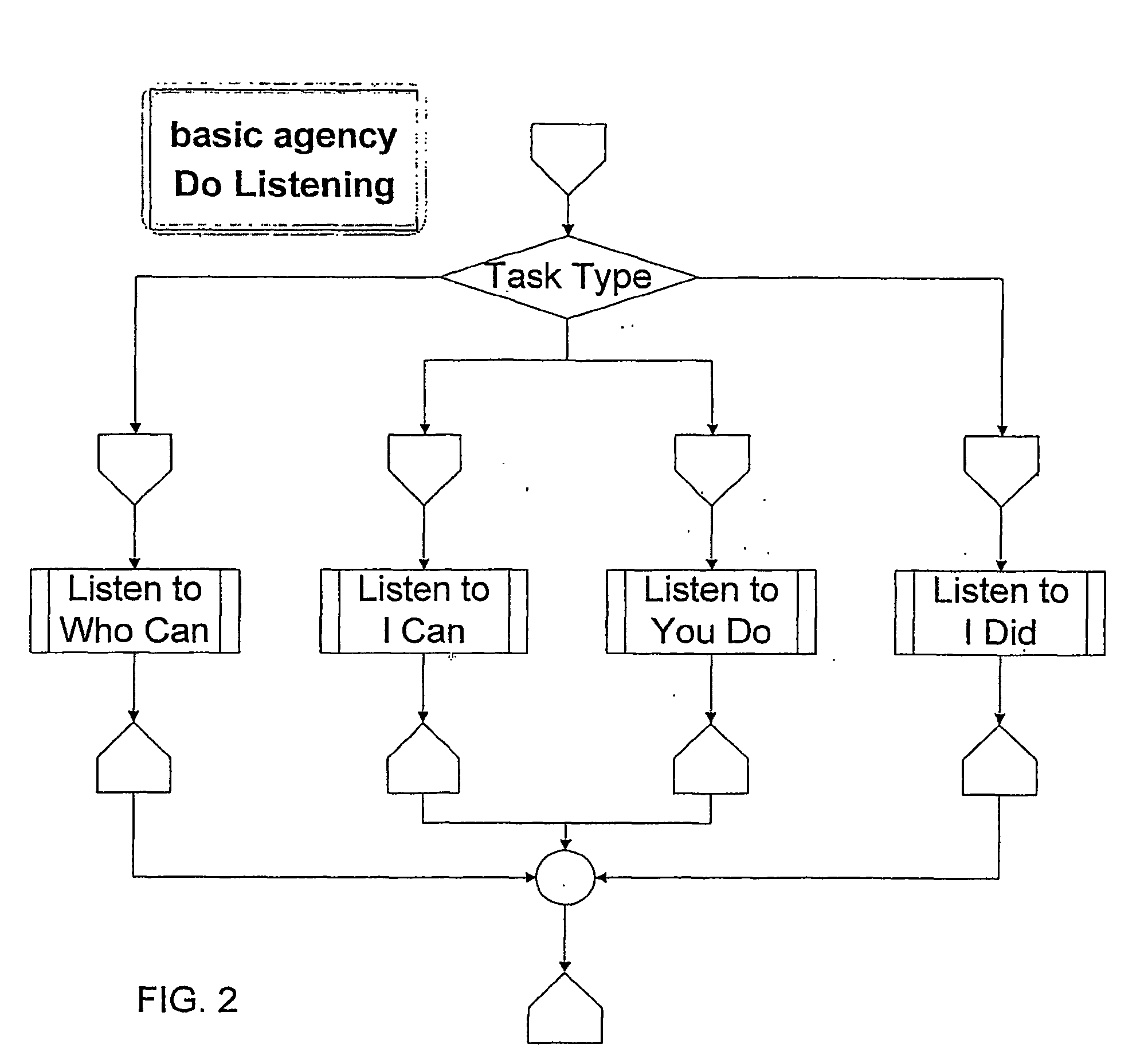
Non-hierarchical collaborative computing platform
InactiveUS20040068729A1Decrease in amountDecrease gapMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer processingMultimedia
A system for non-hierarchical collaborative computing, comprising at least two basic nodes, wherein each of the basic nodes has at least one agency, each of the agencies having incorporated therein a collaborative protocol, wherein the collaborative protocol enables a non-hierarchical collaborative computer processing to occur within said system.
Owner:COLLACOMP
Method of allocating resource for hierarchical cellular system and transmission frame for performing the method
ActiveUS20100291938A1Decrease in amountIncrease in amountNetwork topologiesDistributed computingShared resource
Described herein is a resource allocation method for a hierarchical cellular system, and a transmission frame for performing the method. A macrocell dedicated resource and a shared resource are respectively controlled based on a usage rate of the macrocell dedicated resource and a usage rate of the shared resource. The macrocell reports a usage plan of the shared resource that the macrocell uses to a small cell, and the small cell may allocate the shared resource to terminals based on the usage plan of the shared resource. A control message related to the usage plan may be transmitted / received via the transmission frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
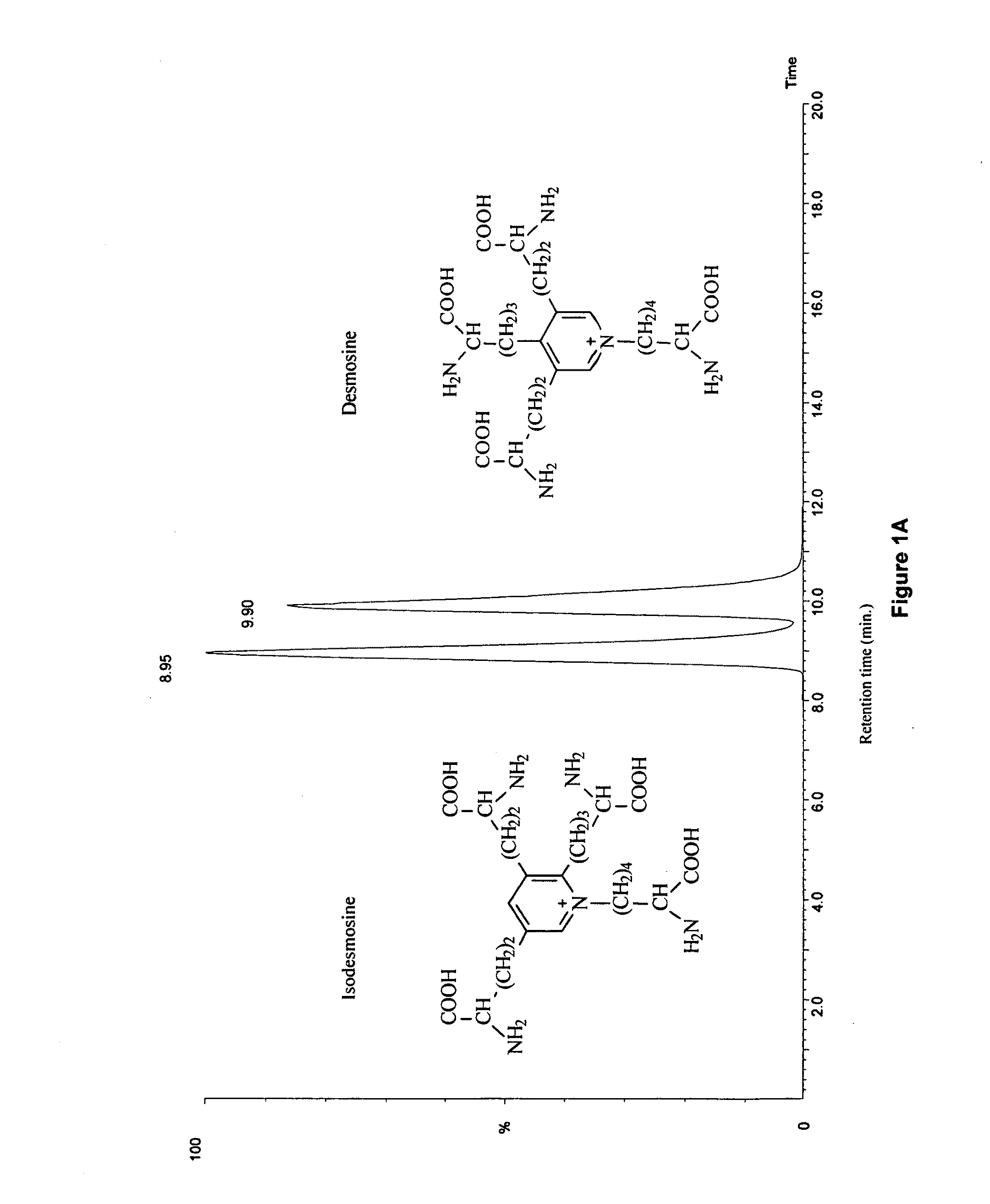
Methods and compositions for diagnosing musculoskeletal, arthritic and joint disorders by biomarker dating
InactiveUS20050124071A1EffectiveDecrease in amountPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsD aspartateChemistry
The present invention provides a method of determining, in a sample, the proportion of a total amount of a molecule that is derived from catabolism due to the presence of age-related molecular alterations on the molecule, comprising: a) determining the total amount of the molecule in the sample; b) determining the amount of the molecule in the sample that contains D-aspartate; and c) calculating the proportion of the amount of the molecule of step (b) relative to the total amount of the molecule as determined in step (a), thereby determining the proportion of the total amount of the molecule that is derived from catabolism due to the presence of age-related molecular alterations in the molecule. Further provided is a method of diagnosing a musculoskeletal, arthritic or joint disorder in a subject and / or identifying a subject at risk for developing such a disorder, comprising: a) measuring an amount of D-aspartate and / or an advanced glycation end product in a sample of the subject; and b) comparing the amount of D-aspartate and / or advanced glycation end product in the sample of (a) with an amount of D-aspartate and / or advanced glycation end product in a sample of a control subject, whereby an increased amount of D-aspartate and / or advanced glycation end product in the sample of the subject as compared to the amount of D-aspartate and / or advanced glycation end product in the sample of the control subject is diagnostic of a musculoskeletal, arthritic or joint disorder in the subject and / or identifies a subject at risk of developing such a disorder.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
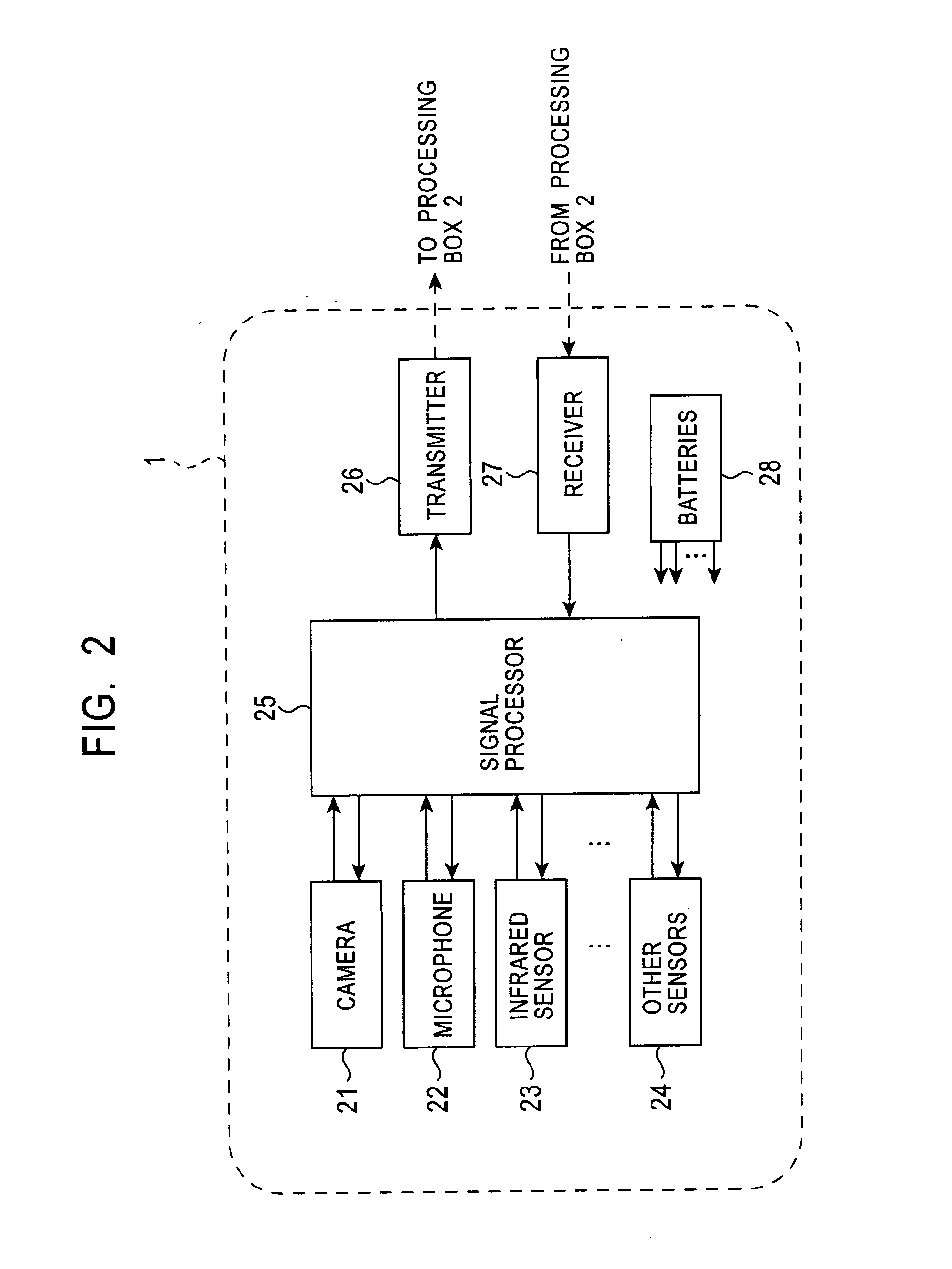
Information processing system and method, information processing apparatus, image-capturing device and method, recording medium, and program
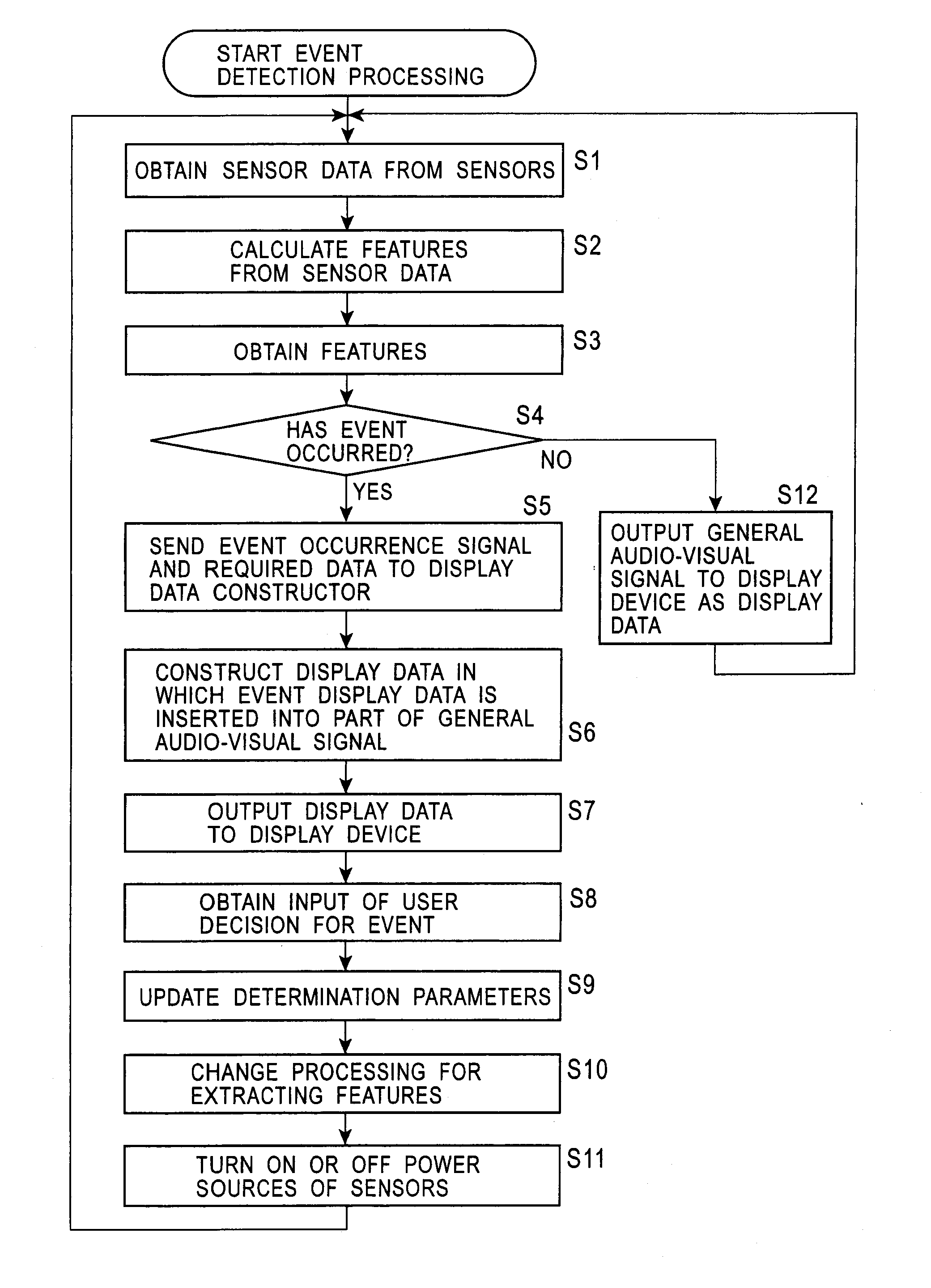
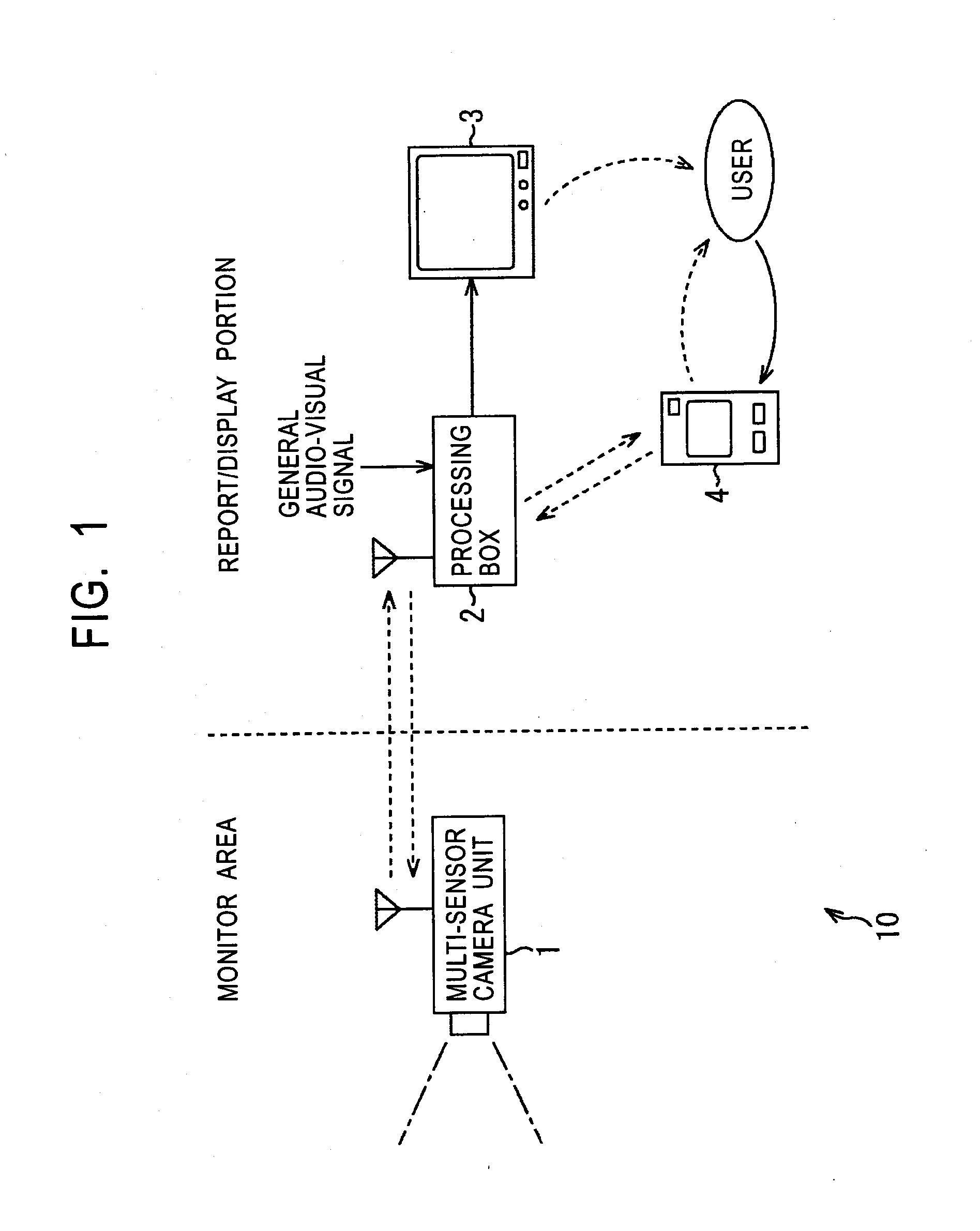
ActiveUS20070236497A1Inhibit power consumptionDecrease in amountDrawing from basic elementsComputer controlImaging SignalCommunication unit
A feature extracting unit obtains sensor data from a plurality of sensors to calculate each feature. When an event determining unit determines the occurrence of an event based on each feature, a display data constructor generates remote-controller display data for displaying the event, and controls a remote-controller display device to display the remote-controller display data. When a user decision is input from a user input if based on this display, a control unit controls the sensors to be turned ON or OFF. When an infrared sensor detects an abnormality, a microwave sensor whose power consumption is small after the infrared sensor is turned ON. When the microwave sensor detects an abnormality, a video camera and a microphone are turned ON, and the microwave sensor is turned OFF. A communication unit wirelessly transmits an image signal captured by the video camera and an audio signal processed by the microphone. Then, if the infrared sensor does not detect an abnormality, the video camera and the microphone are turned OFF. With this arrangement, power consumption can be suppressed. The present invention is applied to, for example, a security system, for example, for monitoring outside a vehicle by a video camera disposed in the vehicle when the vehicle is parked.
Owner:SONY CORP
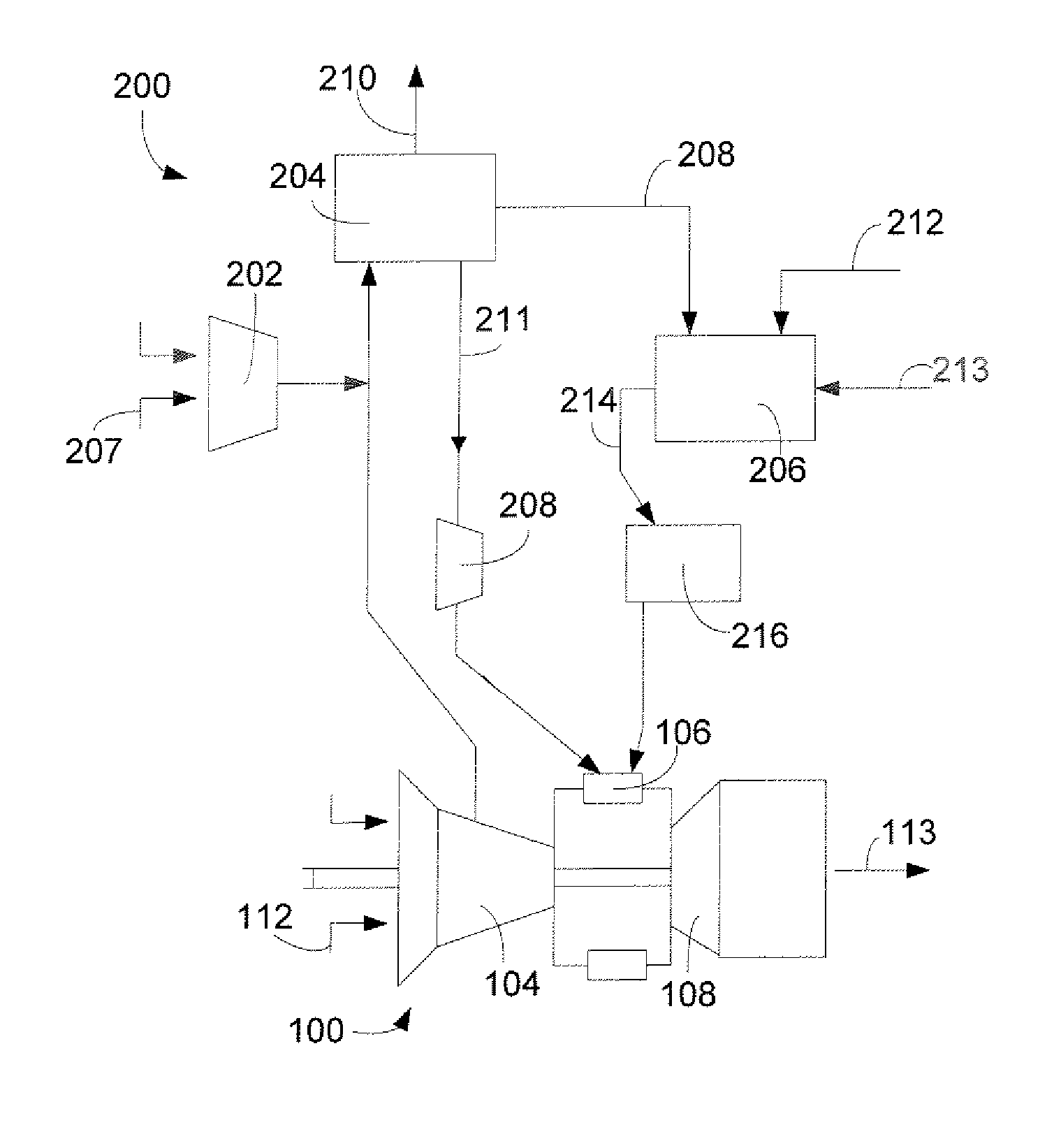
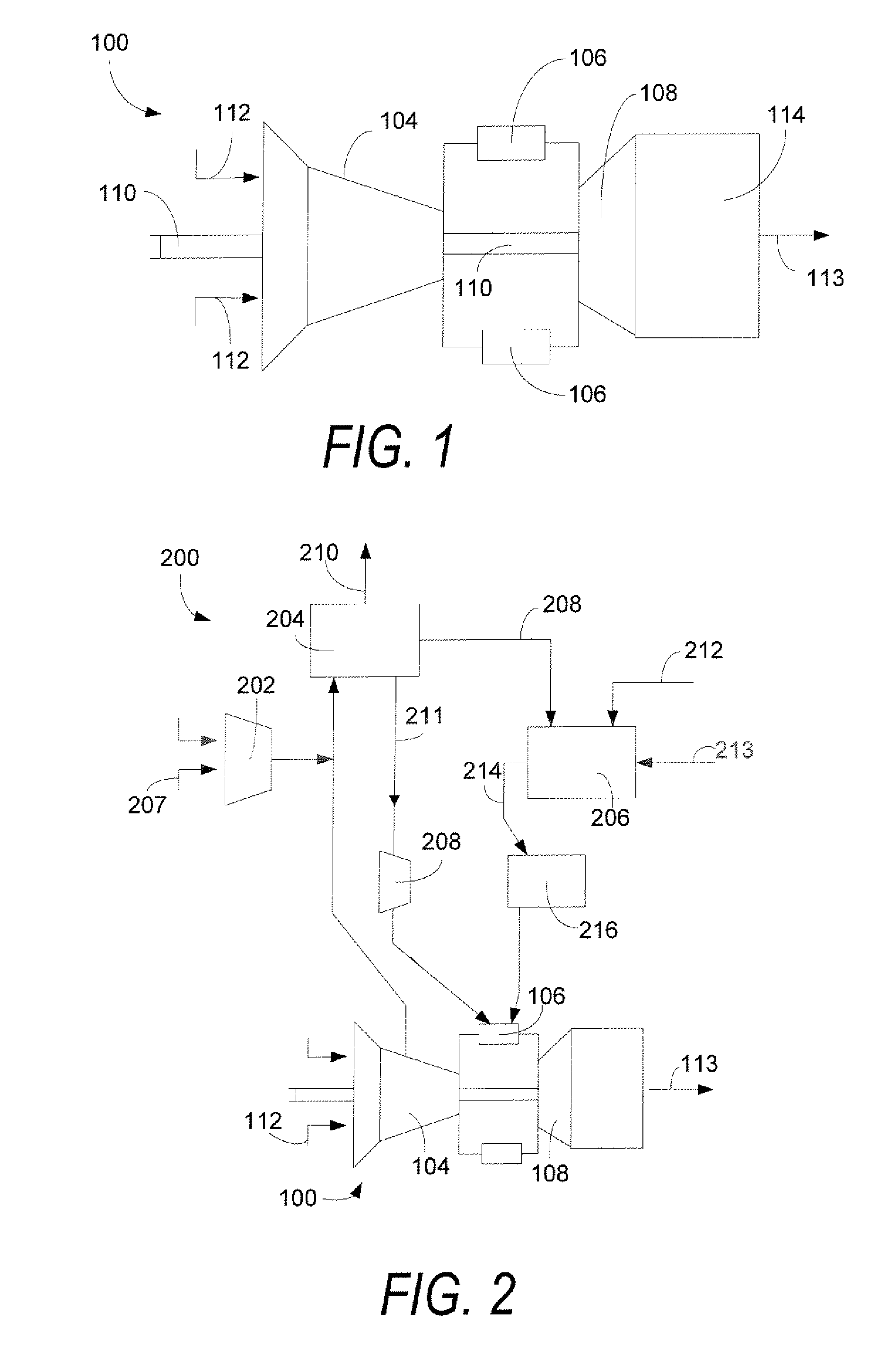
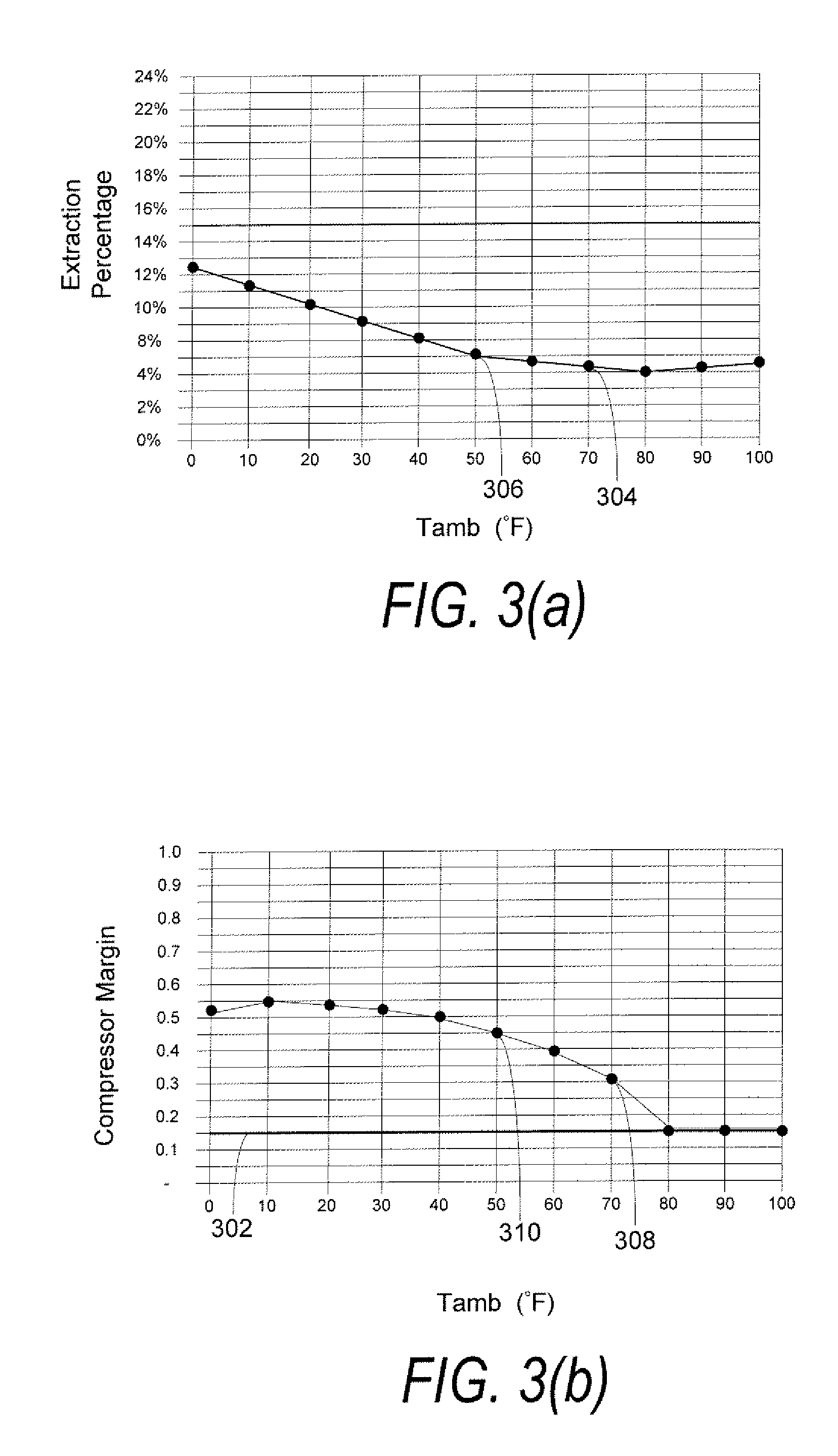
Methods and systems of variable extraction for compressor protection
InactiveUS20070204625A1Decrease in amountGas turbine plantsCombined combustion mitigationAir separationGas turbines
A method of protecting a turbine compressor of a gas turbine engine that is part of an integrated gasification combined-cycle power generation system that includes an air separation unit that may include the steps of: (1) extracting an amount of compressed air that is compressed by the turbine compressor; (2) supplying the extracted amount of compressed air to the air separation unit; and (3) varying the amount of compressed air extracted from the turbine compressor based upon a desired compressor pressure ratio across the turbine compressor. The method further may include the step of supplying the air separation unit with a supply of compressed air from a main air compressor. The amount of compressed air supplied to the air separation unit by the main air compressor may be varied based upon the amount of compressed air extracted from the turbine compressor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and device for multi-capped paste dispenser
InactiveUS6253958B1Decrease in amountInexpensive to manufactureOpening closed containersBottle/container closureBiomedical engineeringToothpaste
A dispensing device for viscous pastes, for multiple users, which deploys a plurality of color coded caps for their personal identification and use. The device is screwed onto a squeezable tube of paste (for example, toothpaste), and, as the tube is squeezed, the paste flows through the device, past caps in a "closed" position, and out of a desired number of caps in an "open" position, in order to dispense paste. The caps' conduits are of a predetermined circumference for dispensing the desired amount of the paste. A smaller circumference is more economical, as less paste would flow out of such a conduit. This would be especially useful when the users are children. Threaded or friction-fitting cap tops may be attached to the device. If attached by friction-fitting, the cap tops form orbital lips to ensure a tight frictional fit to the cap necks. Connecting bands link the dispensing cap tops to the device, so that the tops won't be lost. The device can be attached to various sized squeezable tubes by a threaded connector cap. The diameter and thread gauge of the connector cap is of a predetermined diameter and gauge, for matching diameters and thread gauges of squeezable tubes. The device is preferably composed of plastic material, which is easily cleanable, sanitary, as well as inexpensive to manufacture.
Owner:COLETTI THEODORE R
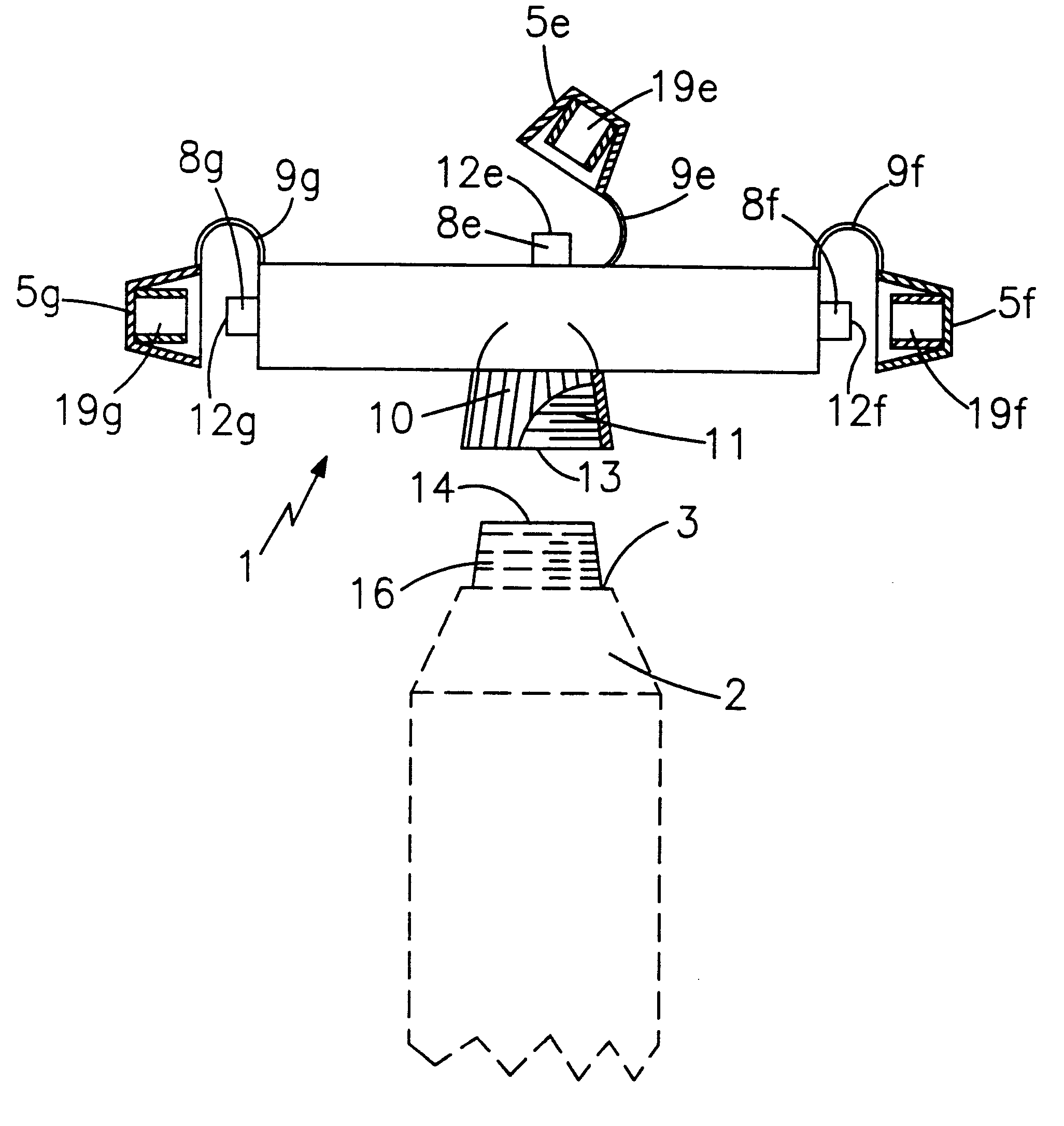
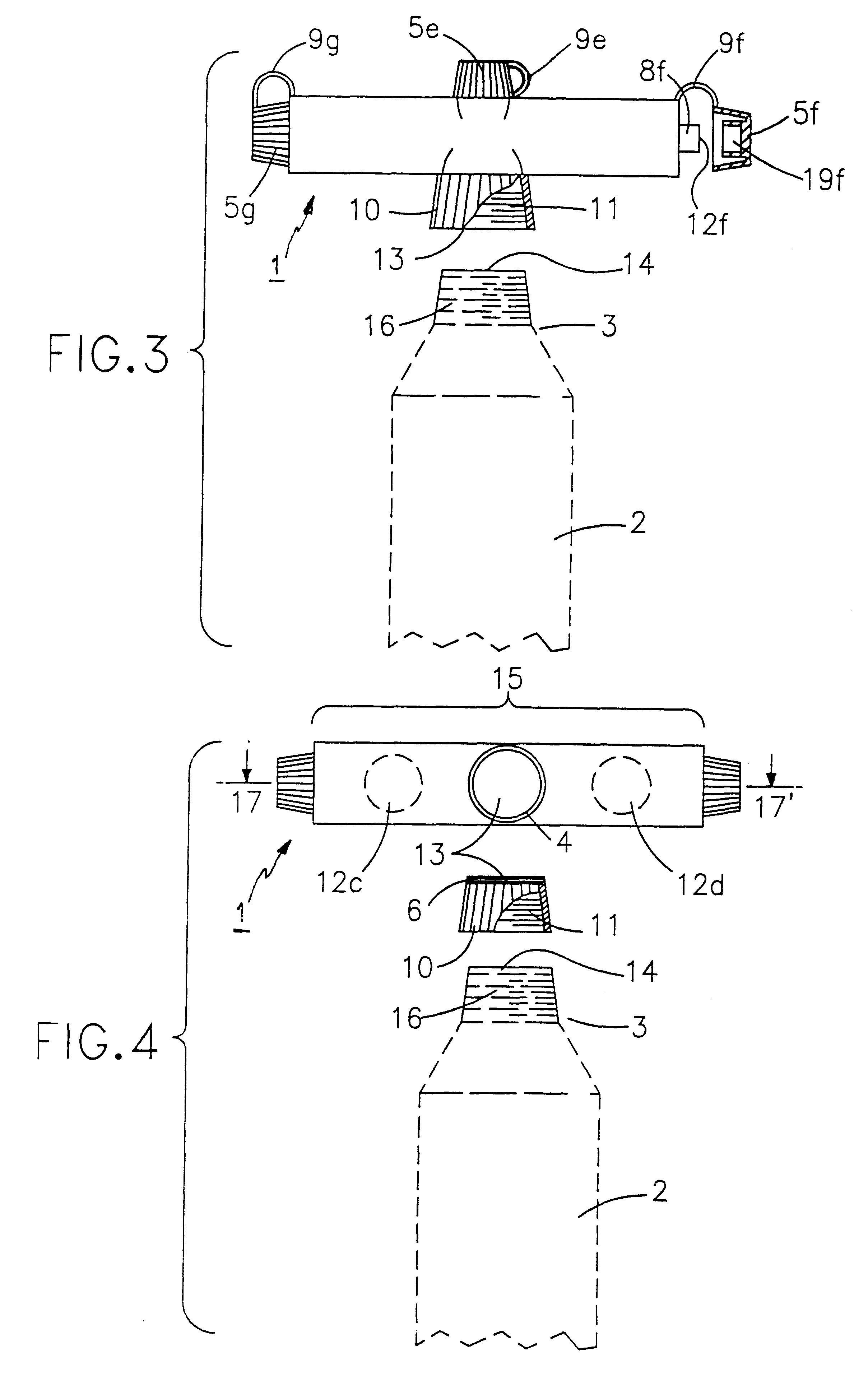
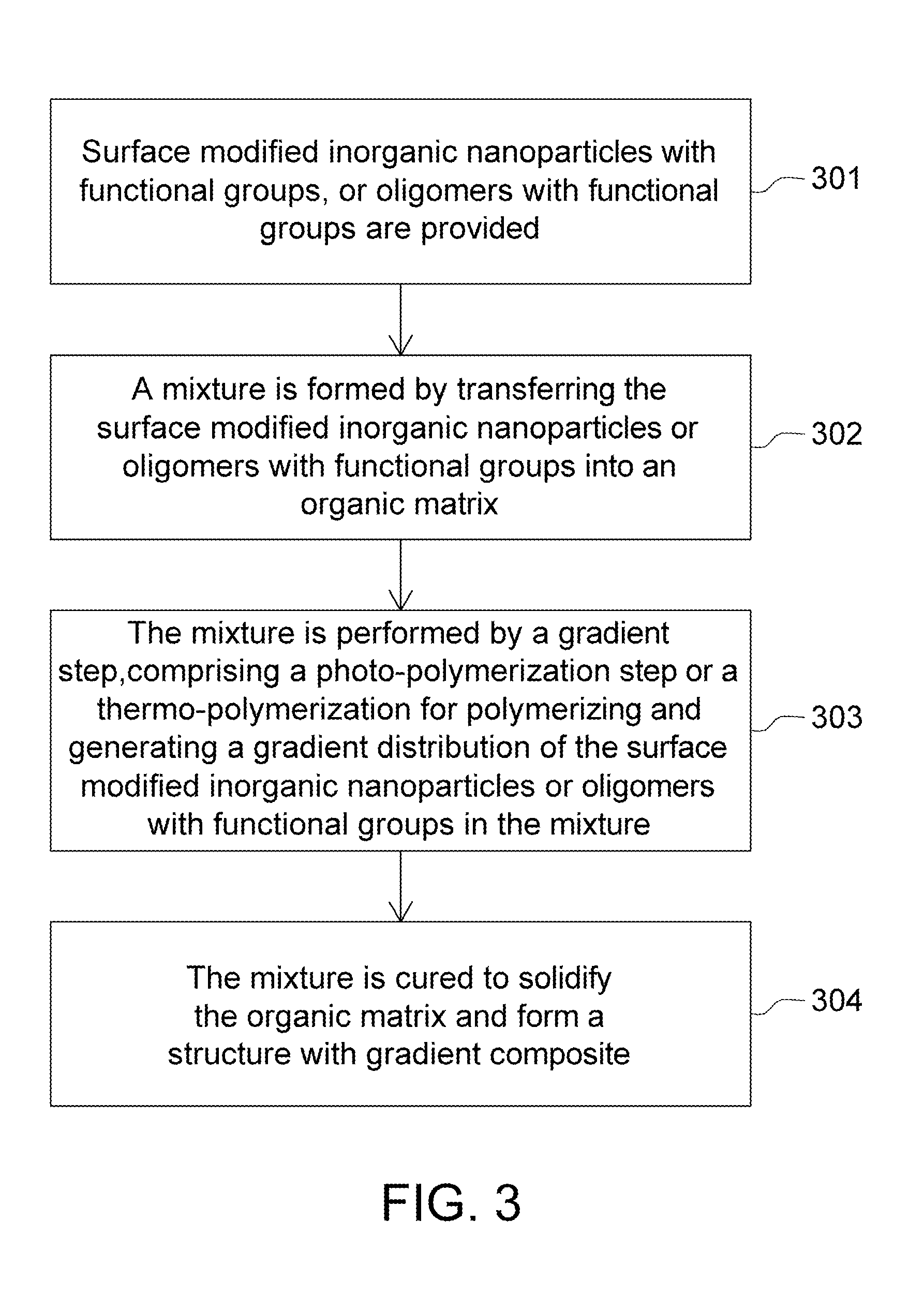
Gradient Composite Material and Method of Manufacturing the Same
ActiveUS20120112219A1Improved physical propertyDecrease in amountMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic chemistryNanometreOligomer
Method of manufacturing gradient composite material comprises steps of providing plural surface modified inorganic nanoparticles with functional groups or oligomers with functional groups; transferring the surface modified inorganic nanoparticles or oligomers with functional groups into an organic matrix to form a mixture; performing a photo polymerization step or a thermo-polymerization step for polymerizing and generating a gradient distribution of the surface modified inorganic nanoparticles or oligomers with functional groups in the mixture; and curing the mixture to solidify the organic matrix and form a structure with gradient composite, wherein the organic matrix is transferred into an organic polymer after curing.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
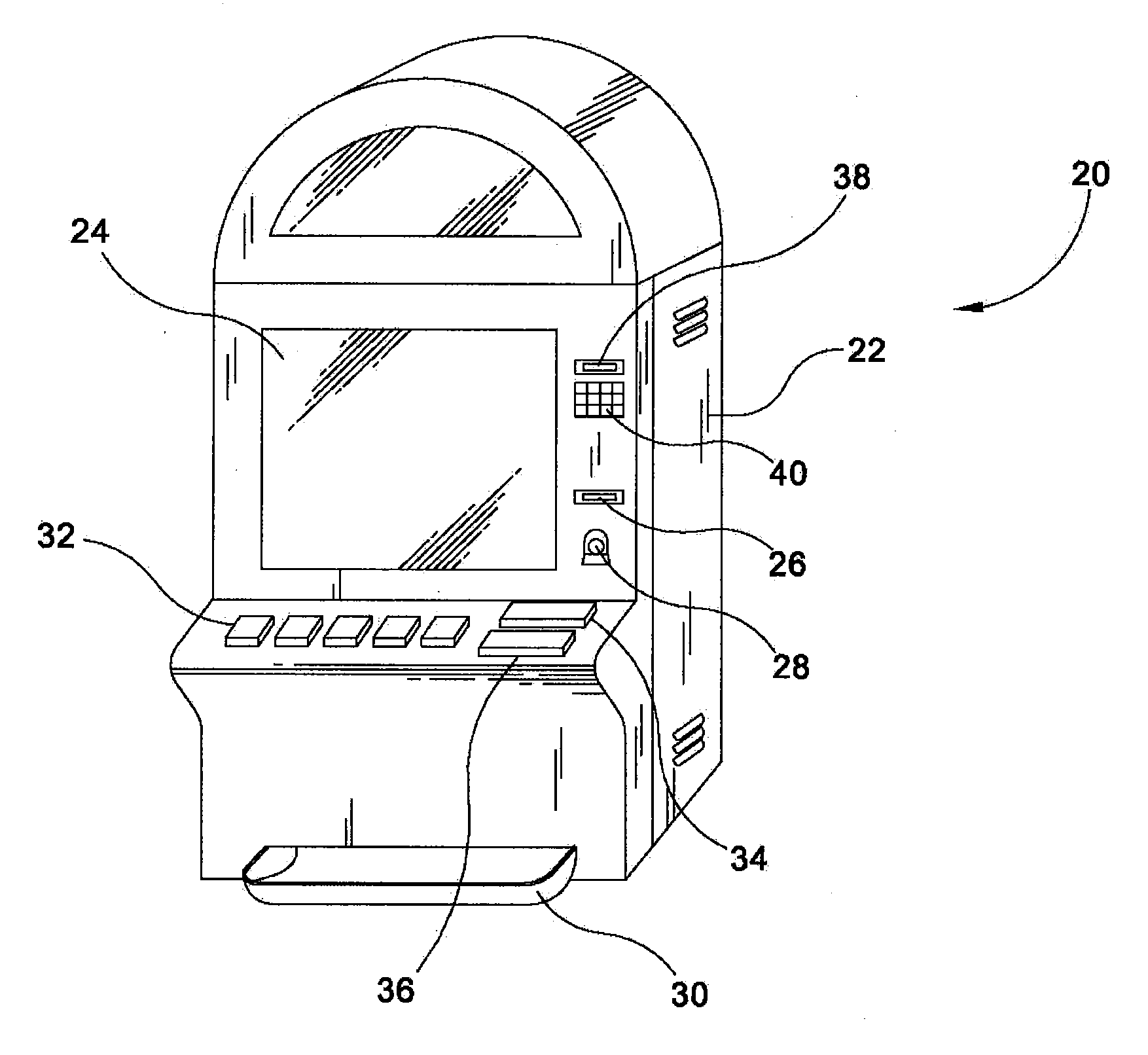
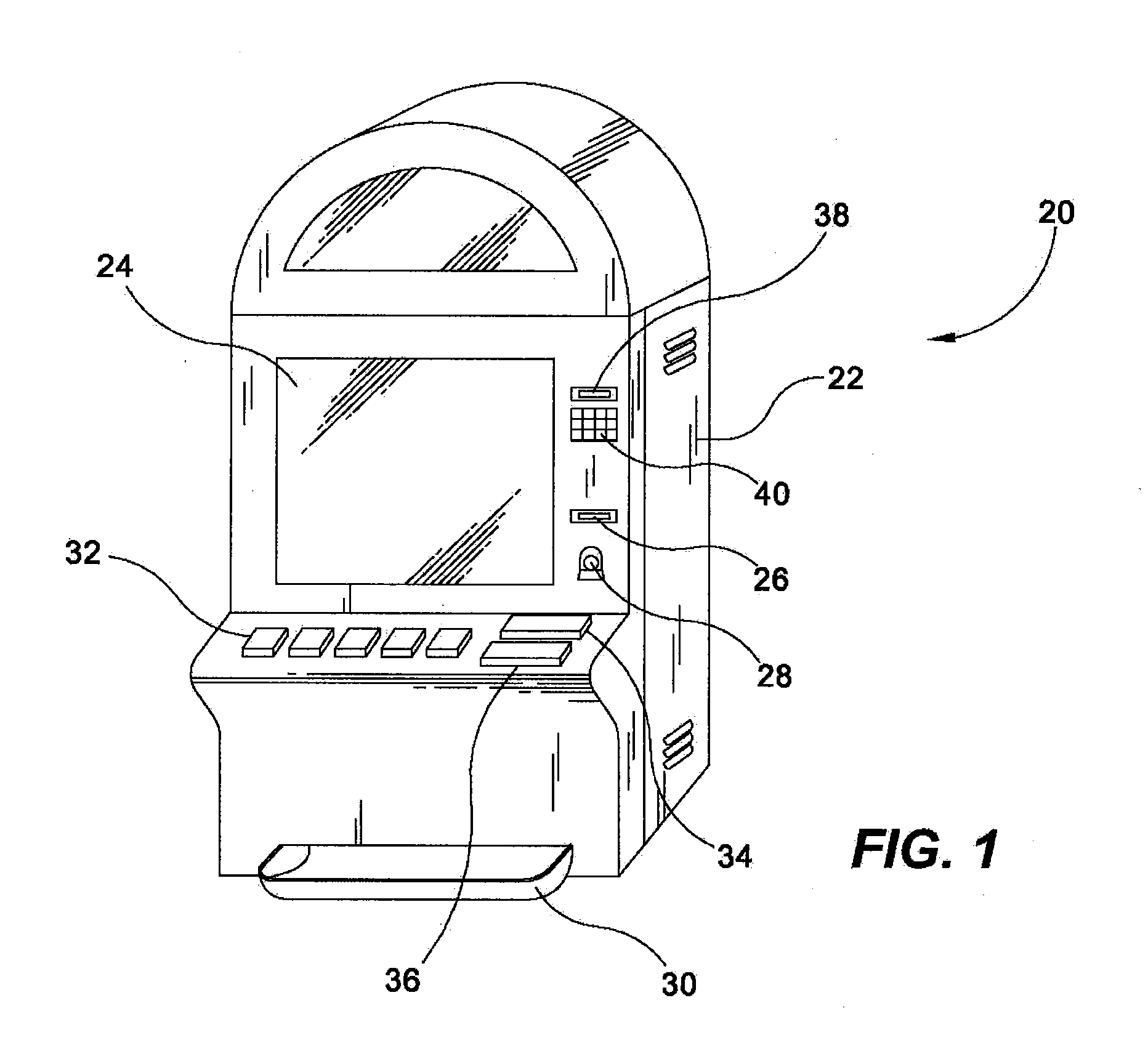
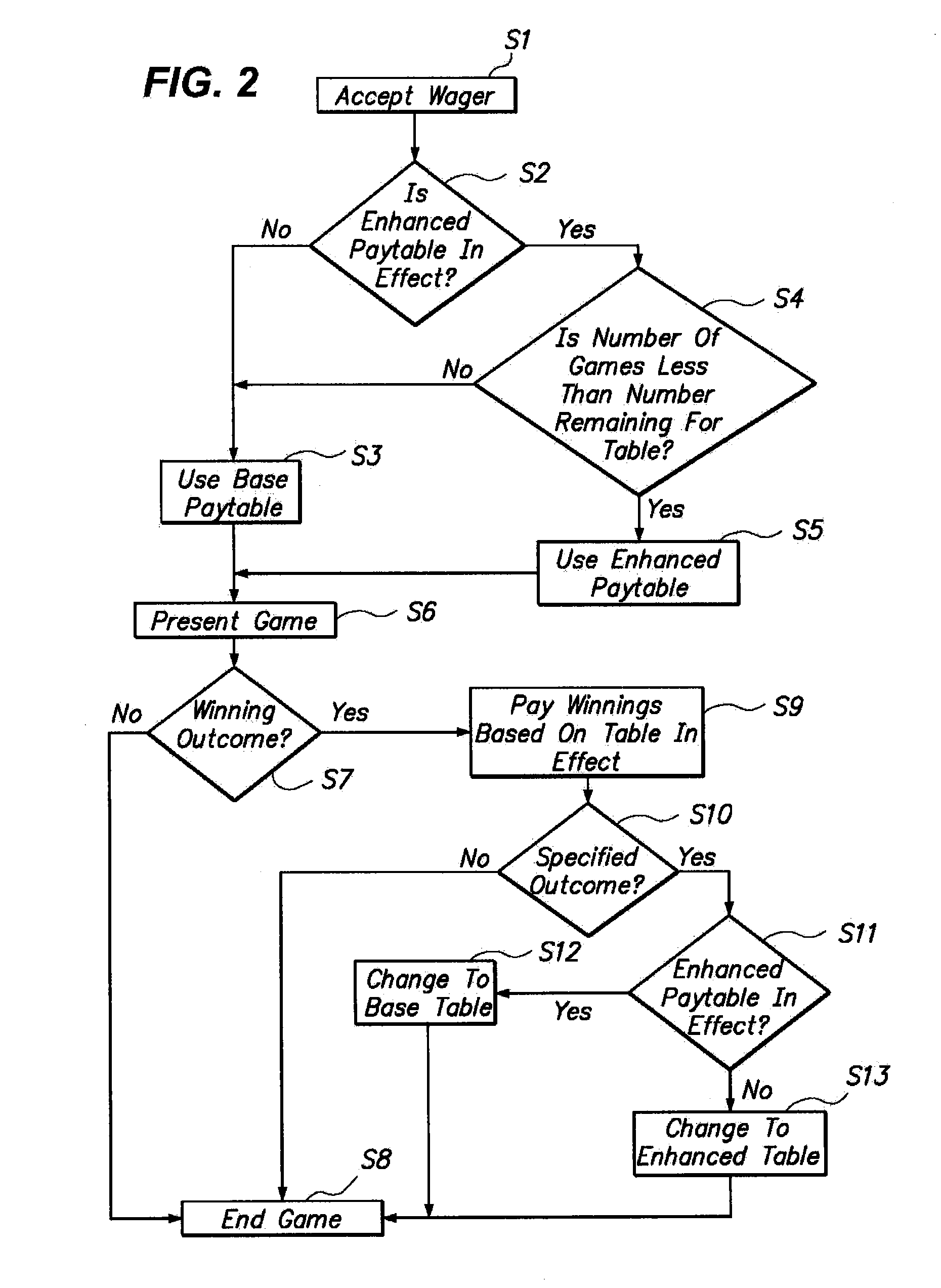
Method of presenting and playing a repeat outcome game
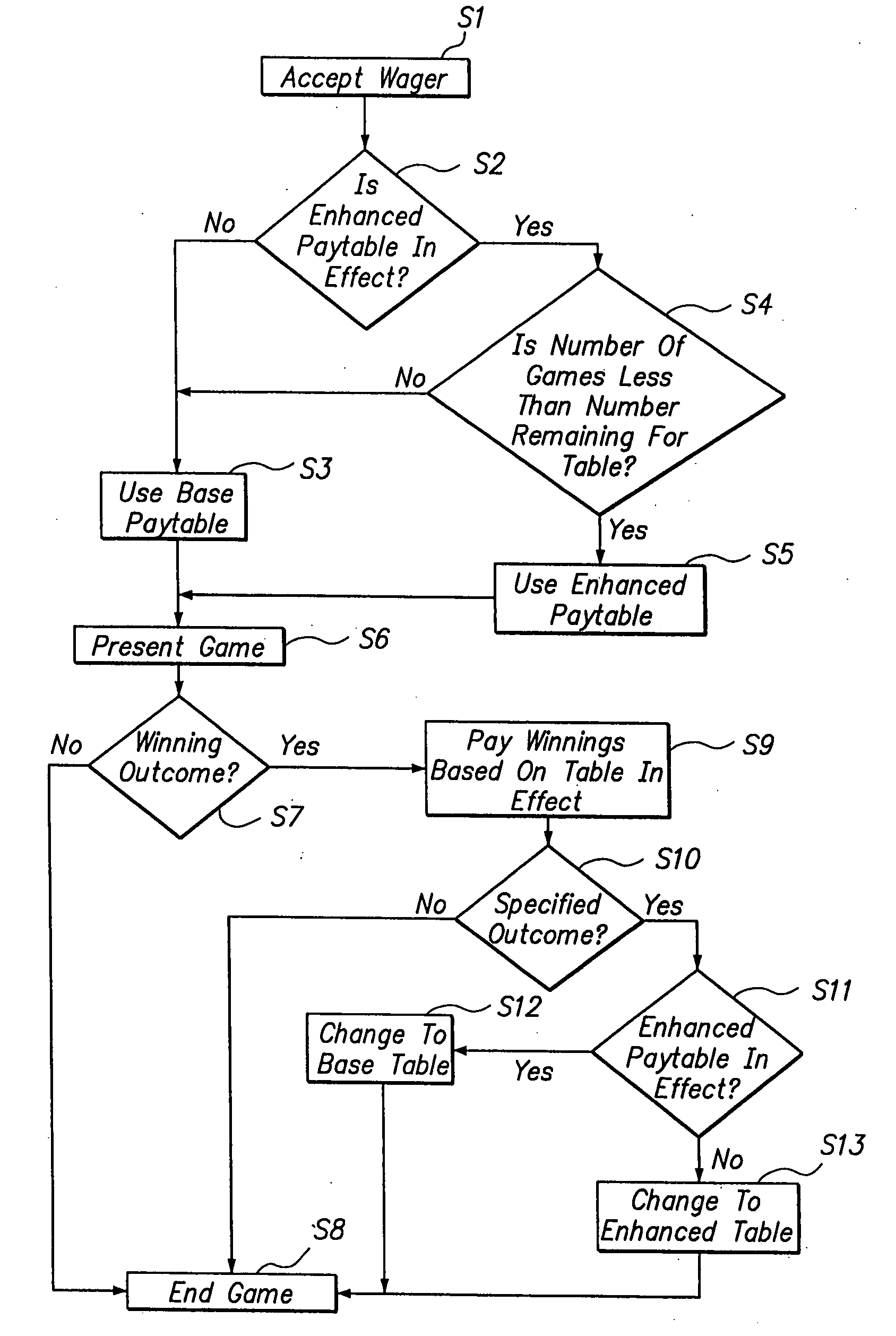
InactiveUS20110059791A1Decrease in amountApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesFIRST AwardHuman–computer interaction
In a method of presenting or playing a wagering game, if a winning outcome is received in the play of a first game, a first award is awarded and one or more awards associated with one or more winning outcomes for the game are then enhanced for potential award in a subsequent game or games. In one embodiment, a base paytable or award structure is modified or enhanced, such as by adjusting awards or associating multipliers or bonus values such as progressive awards, to create an enhanced paytable or award structure. The enhanced paytable or award structure may remain in effect for one subsequent game, a set or random number of games or a time, or until the same or another winning outcome is received in a subsequent game. The game which is presented may vary, such as being a wagering game of video poker, video slots or even a table game. In embodiment, the game offers a player an enhanced award if a winning outcome received in a first game is repeated in a defined number of subsequent games.
Owner:AGS CORP
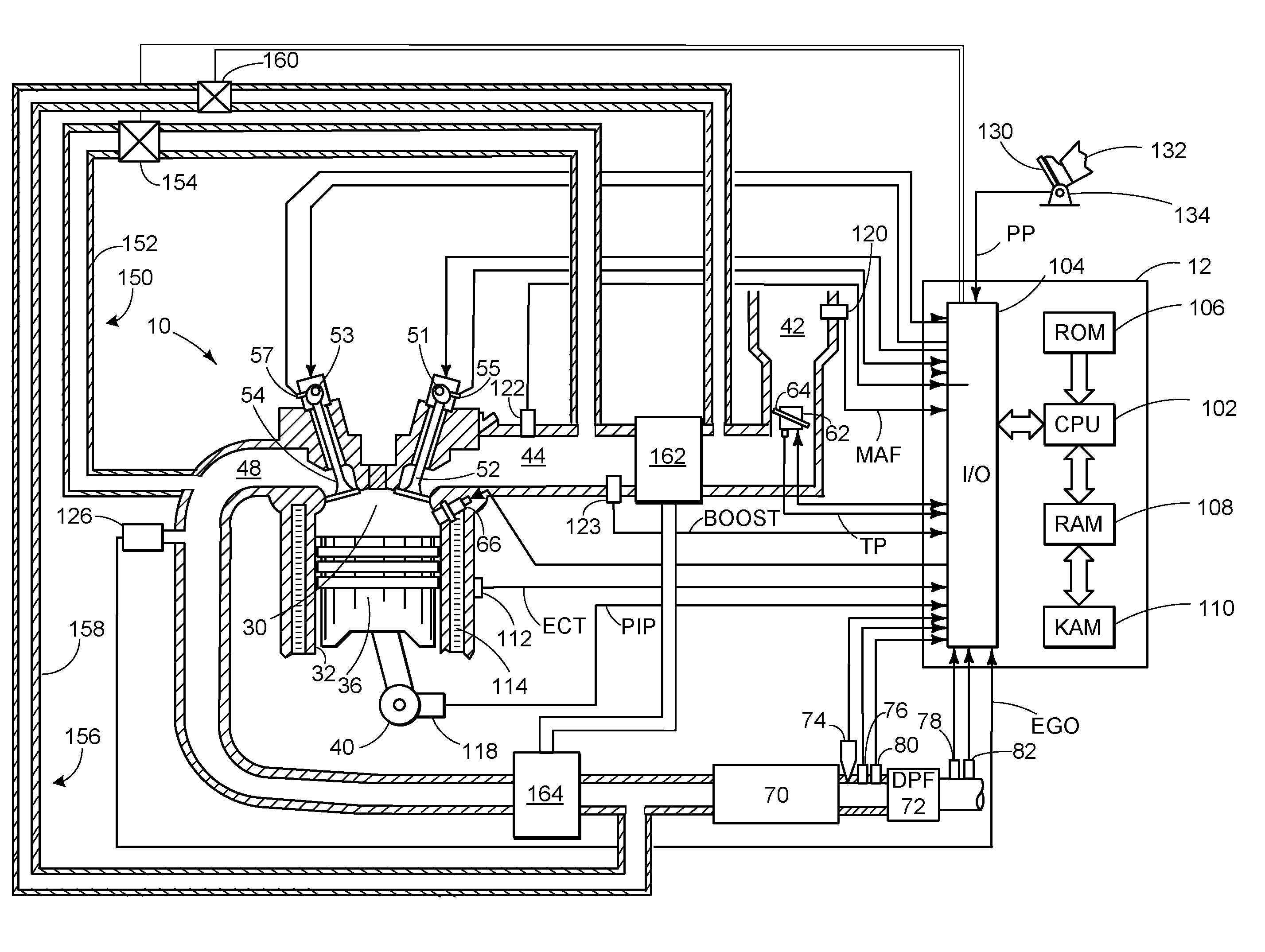
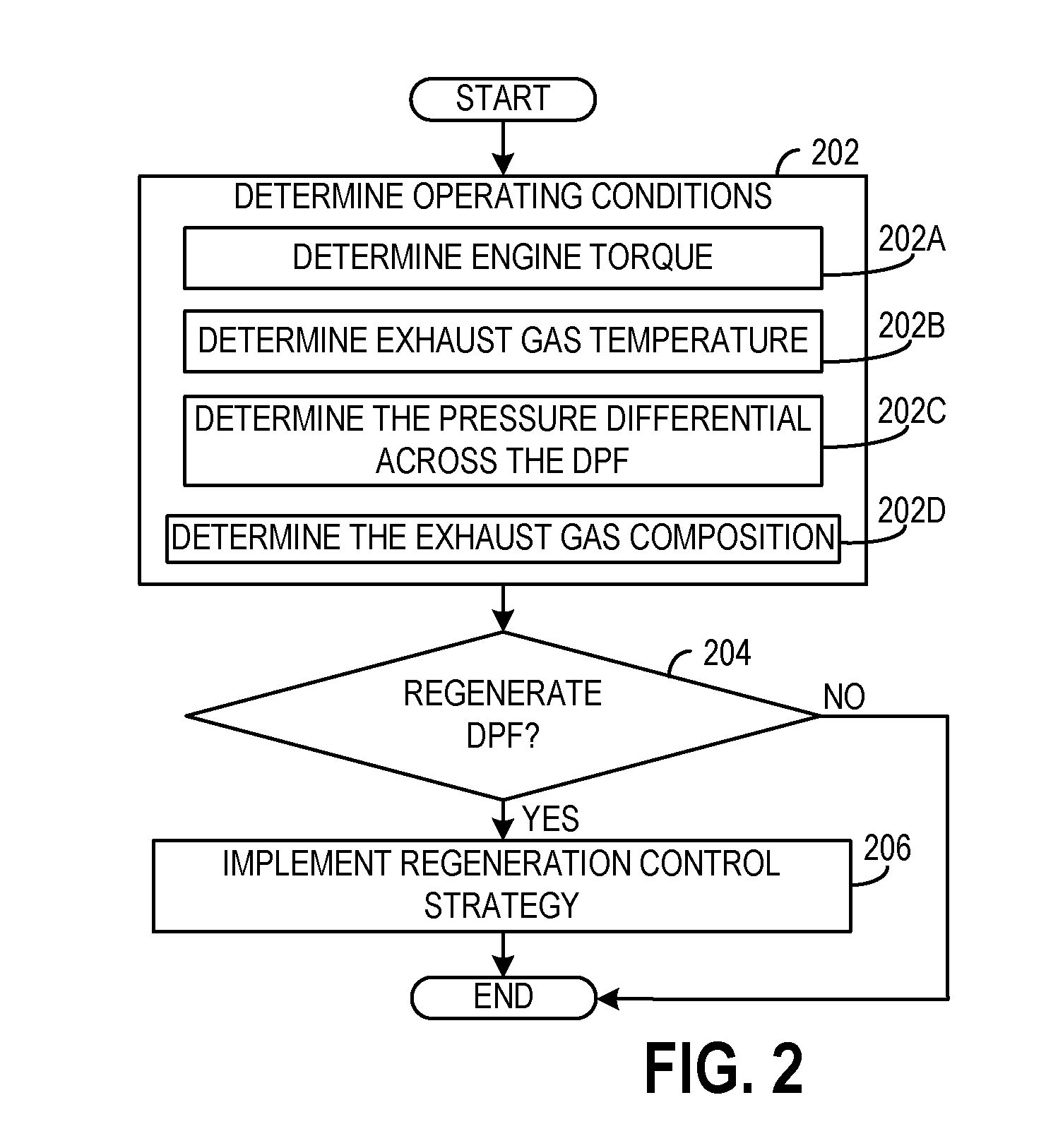
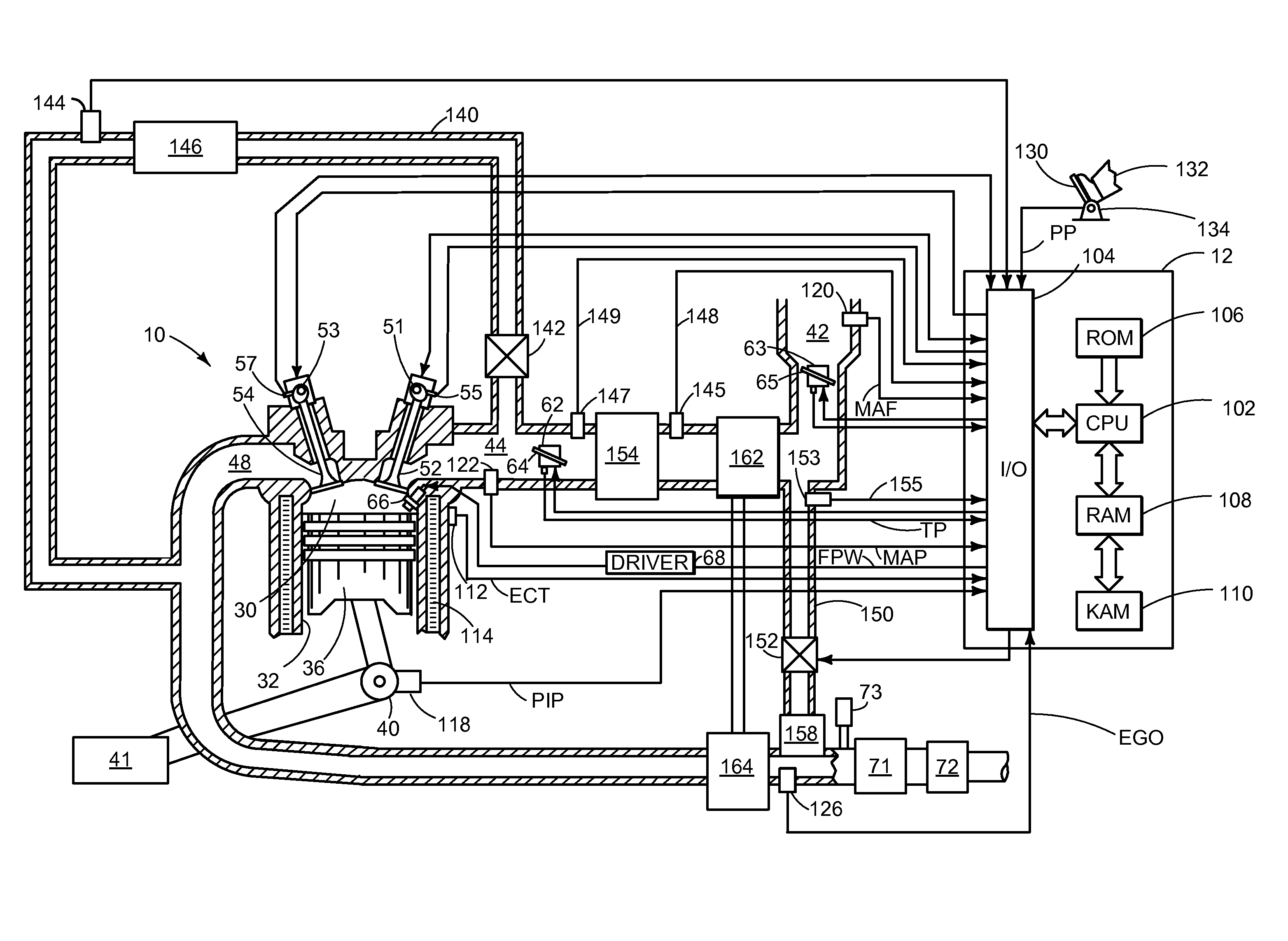
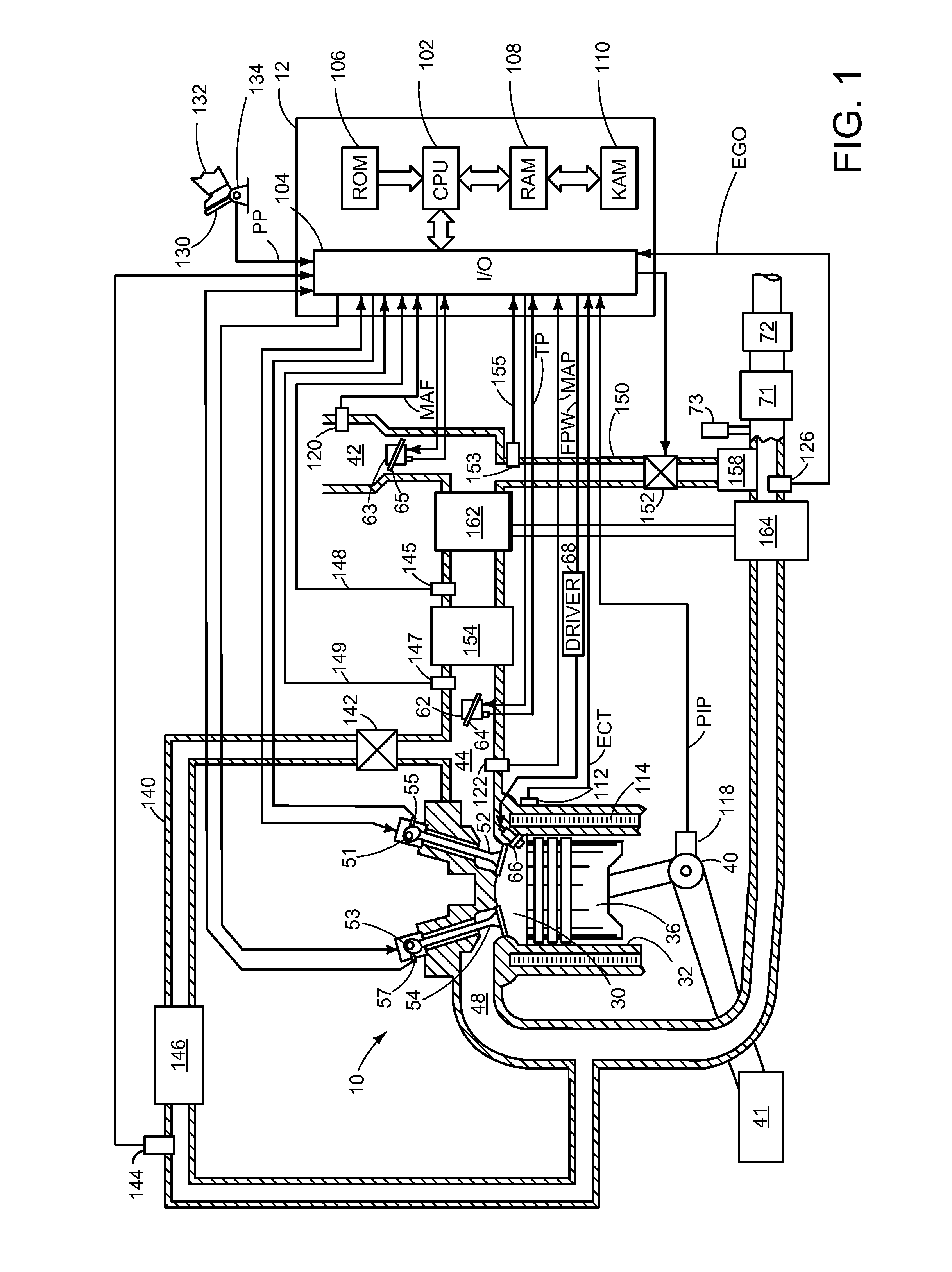
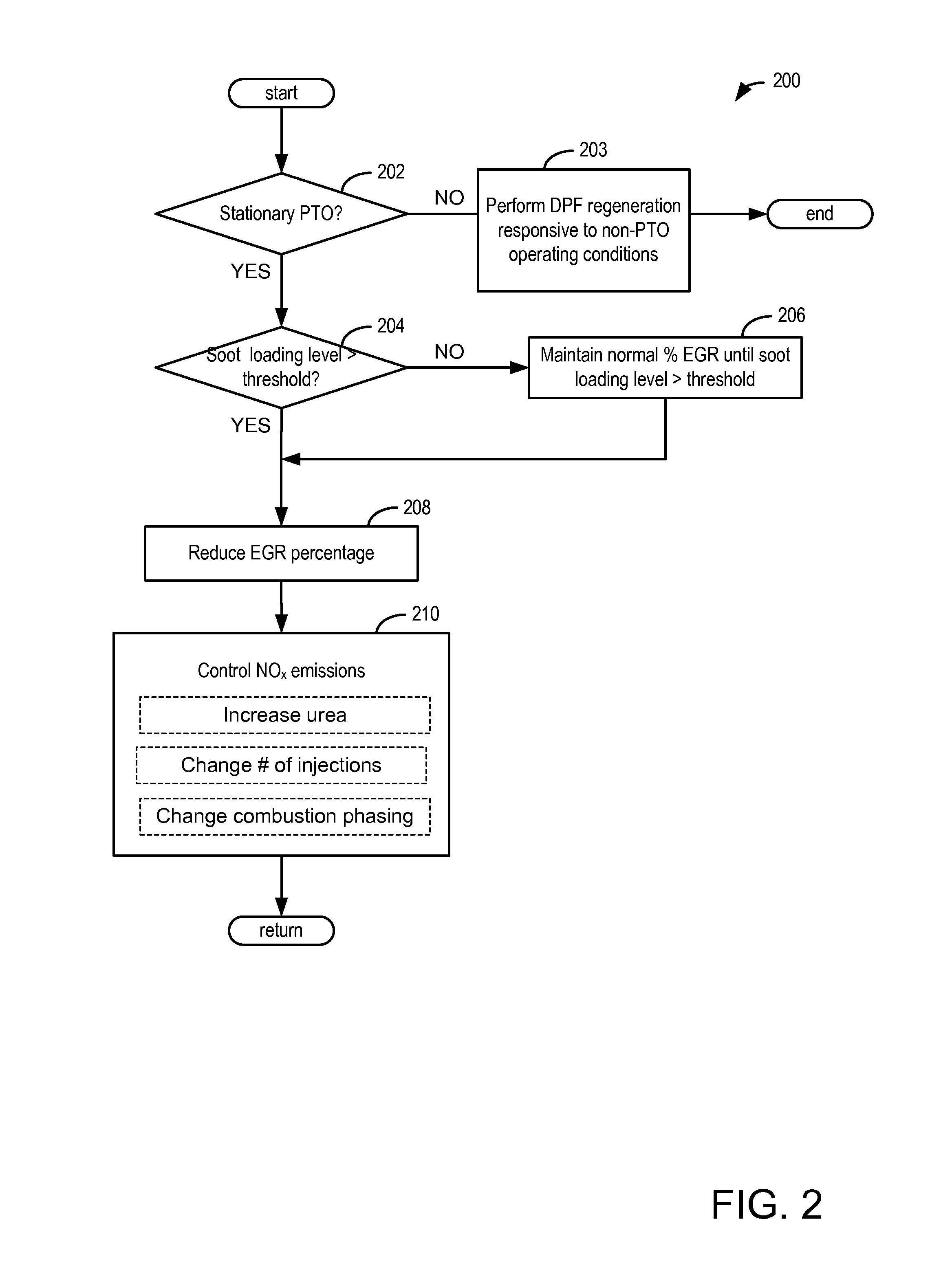
Control of diesel particulate filter regeneration duration
ActiveUS20110047982A1Reduce amountDecrease in amountInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusAutomotive engineeringDiesel particulate filter
Termination of regeneration of a particulate filter may be based on a variable percent threshold of stored particulate, where the percent threshold of stored particulate depends on a current soot burn rate. In one example approach, a method for controlling regeneration of a diesel particulate filter comprises: terminating regeneration based on a particulate burning rate; wherein the particulate burning rate is based on operating conditions of the diesel particulate filter; the operating conditions including an amount of stored particulate in the diesel particulate filter and a temperature of the diesel particulate filter.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
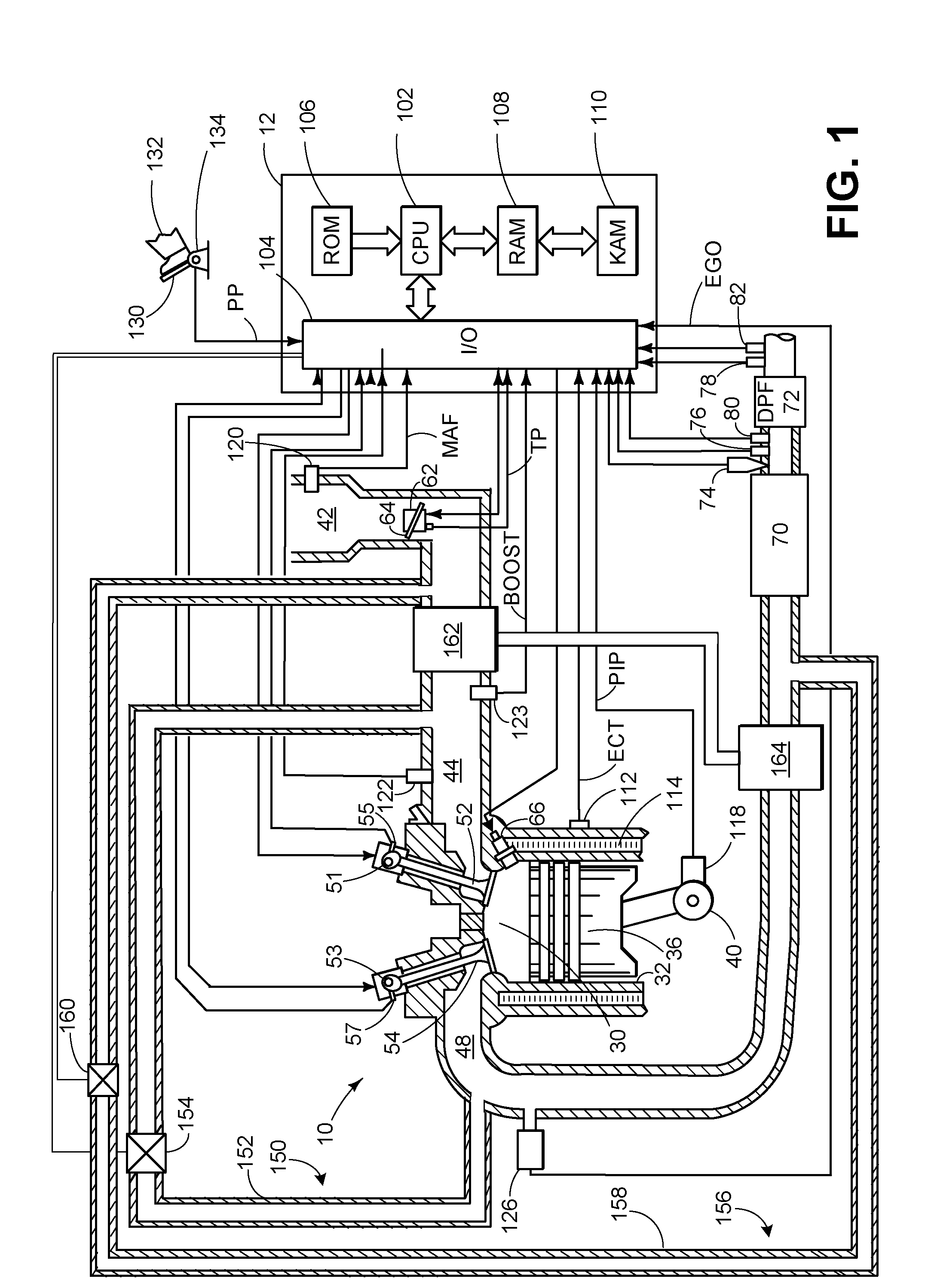
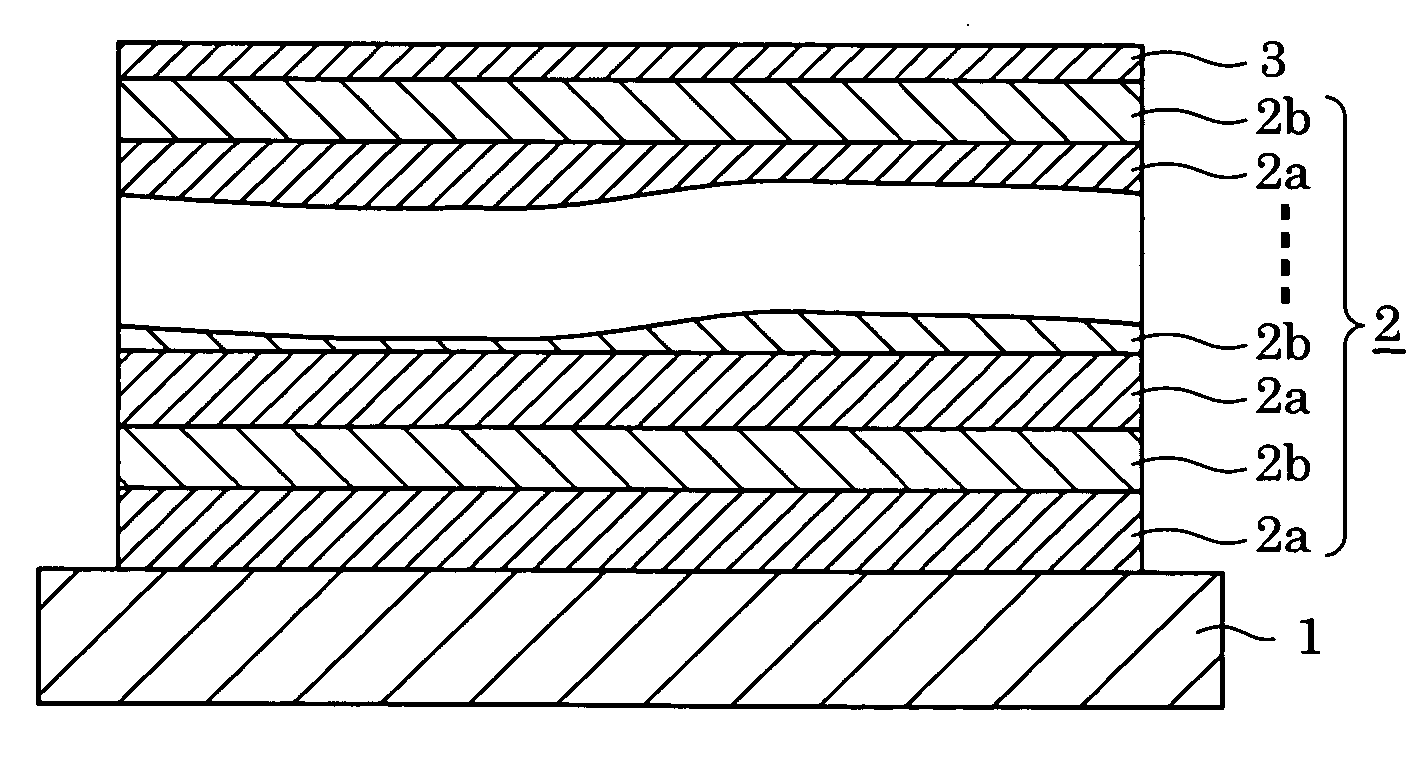
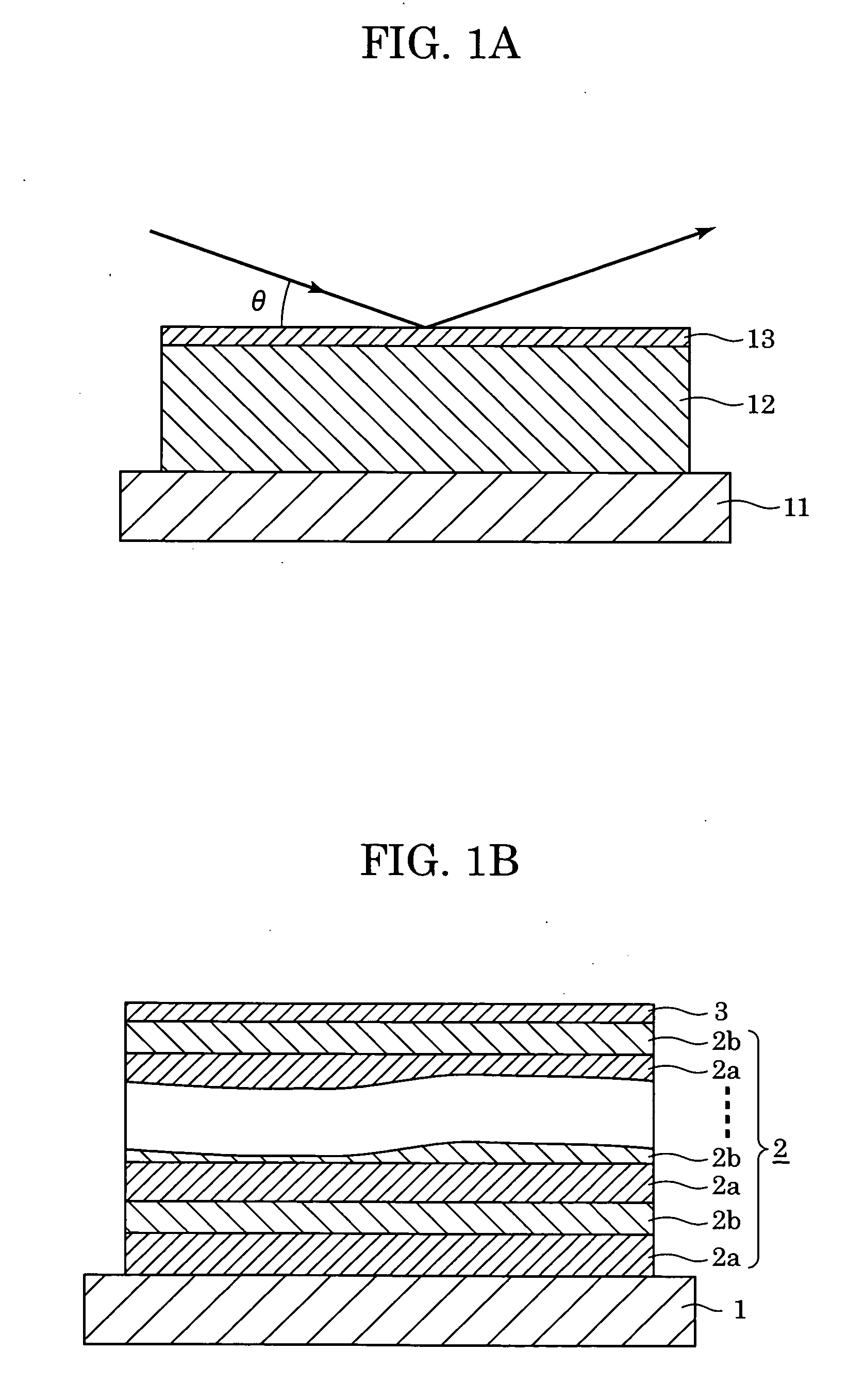
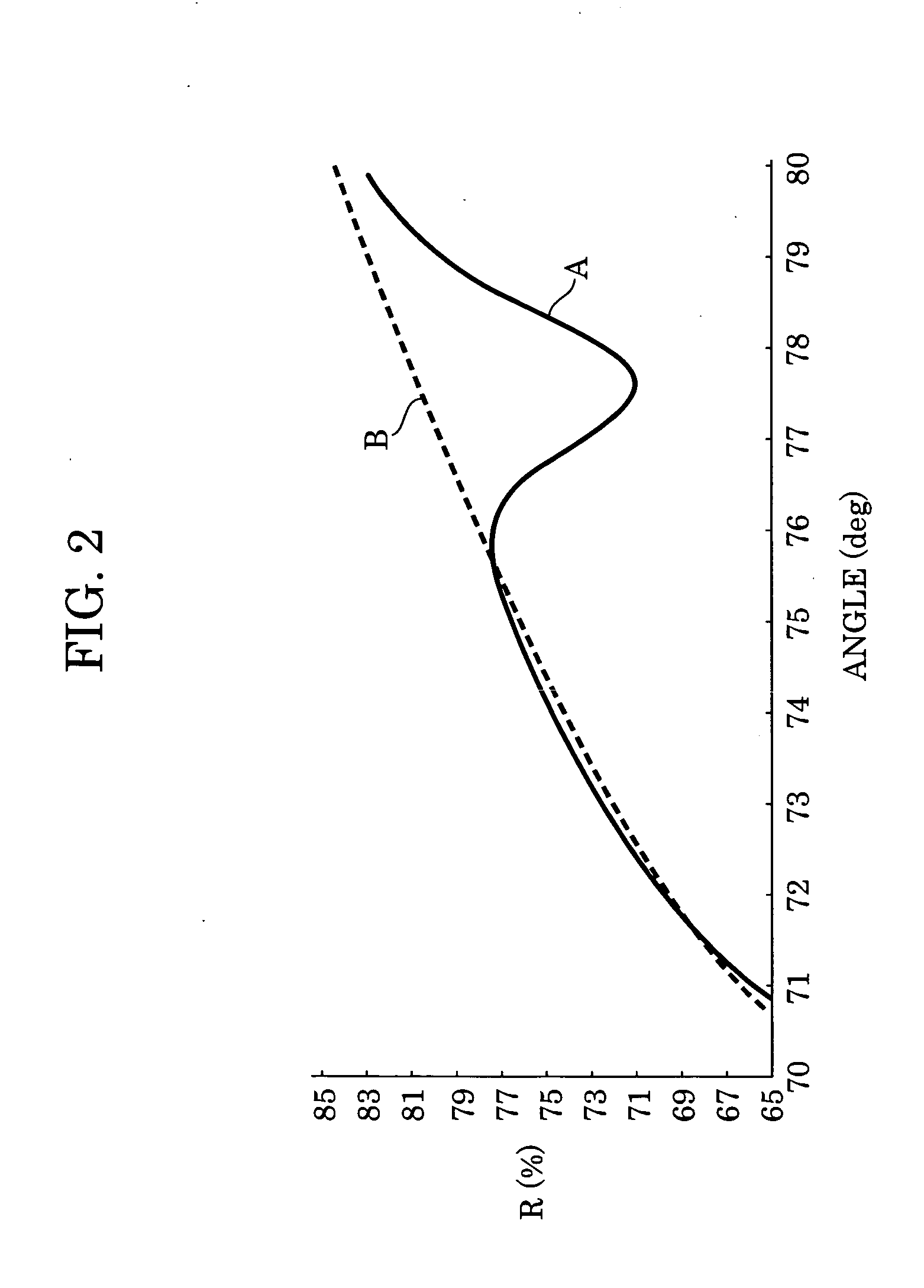
X-ray total reflection mirror and X-ray exposure apparatus
InactiveUS20050117233A1Decrease in amountDecrease density of filmMirrorsNanoinformaticsSecondary layerReflectivity
Multilayer film structure composed of at least one pair of layers including a first layer and a second layer, which are formed from different materials, and a protective layer provided thereon is formed so that the structure is optimized to have the same theoretical reflectance as that of a single-layer film structure at the same incident angle θ. Since the absorption of each layer is not significant, the actual reflectance of the X-ray total reflection mirror having the multilayer film structure is closer to the theoretical value as compared to that of the X-ray total reflection mirror having the single-layer film structure.
Owner:CANON KK
Catalyst And System For Reducing Exhaust Of Diesel Engines
InactiveUS20080141660A1Effectively removeDecrease in amountGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesDiesel particulate filterExhaust fumes
Owner:END SOLUTIONS
Diesel particulate filter passive regeneration during stationary power take-off
ActiveUS20140331643A1Decrease in amountReduce amountElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelDiesel particulate filterEngineering
The systems and method described above in the present disclosure allow for regeneration of a diesel particulate filter while a vehicle is in stationary power take-off mode. Described is a method of: during select power take-off conditions, reducing an EGR rate responsive to an indication to regenerate a diesel particulate filter.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
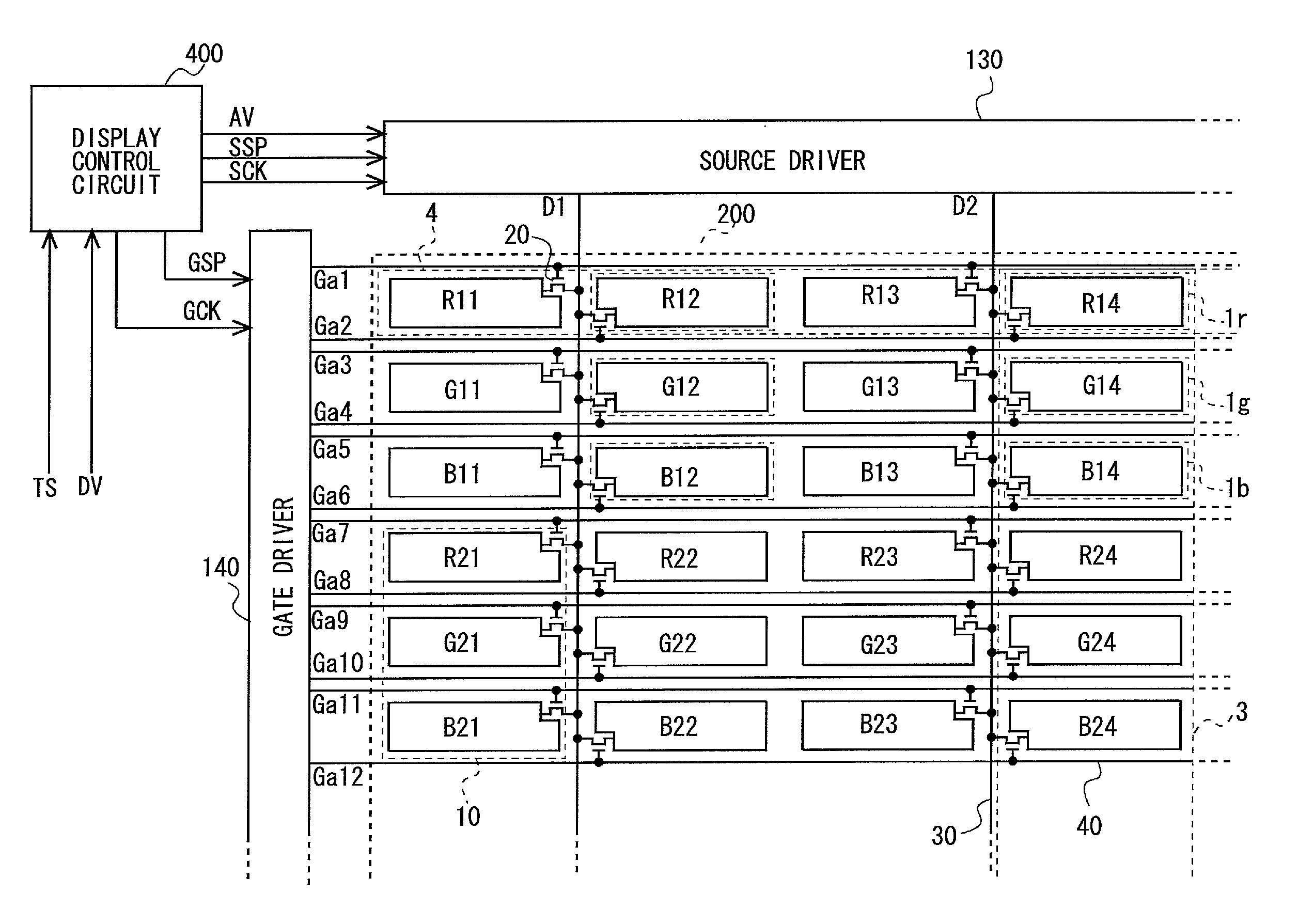
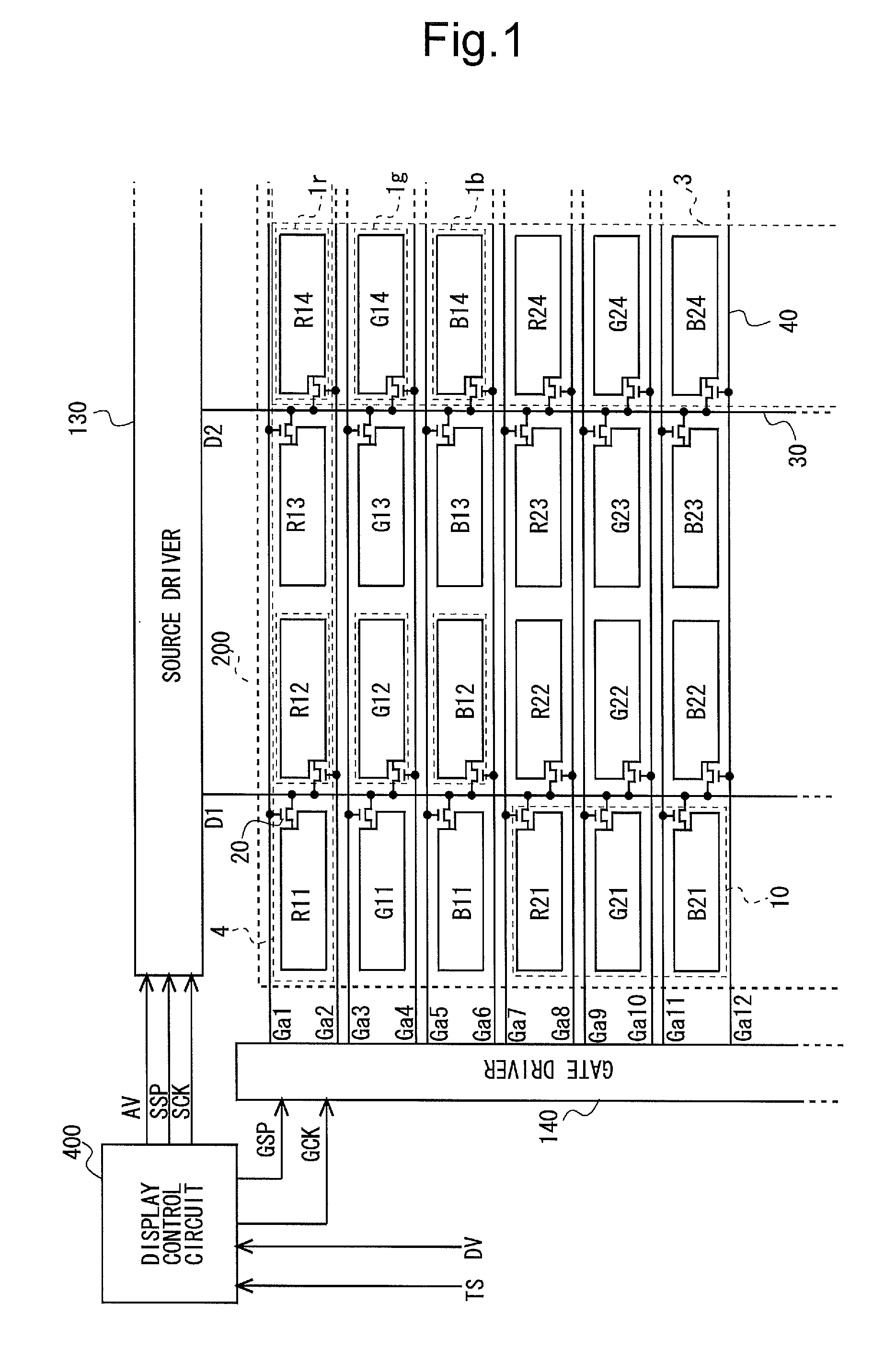
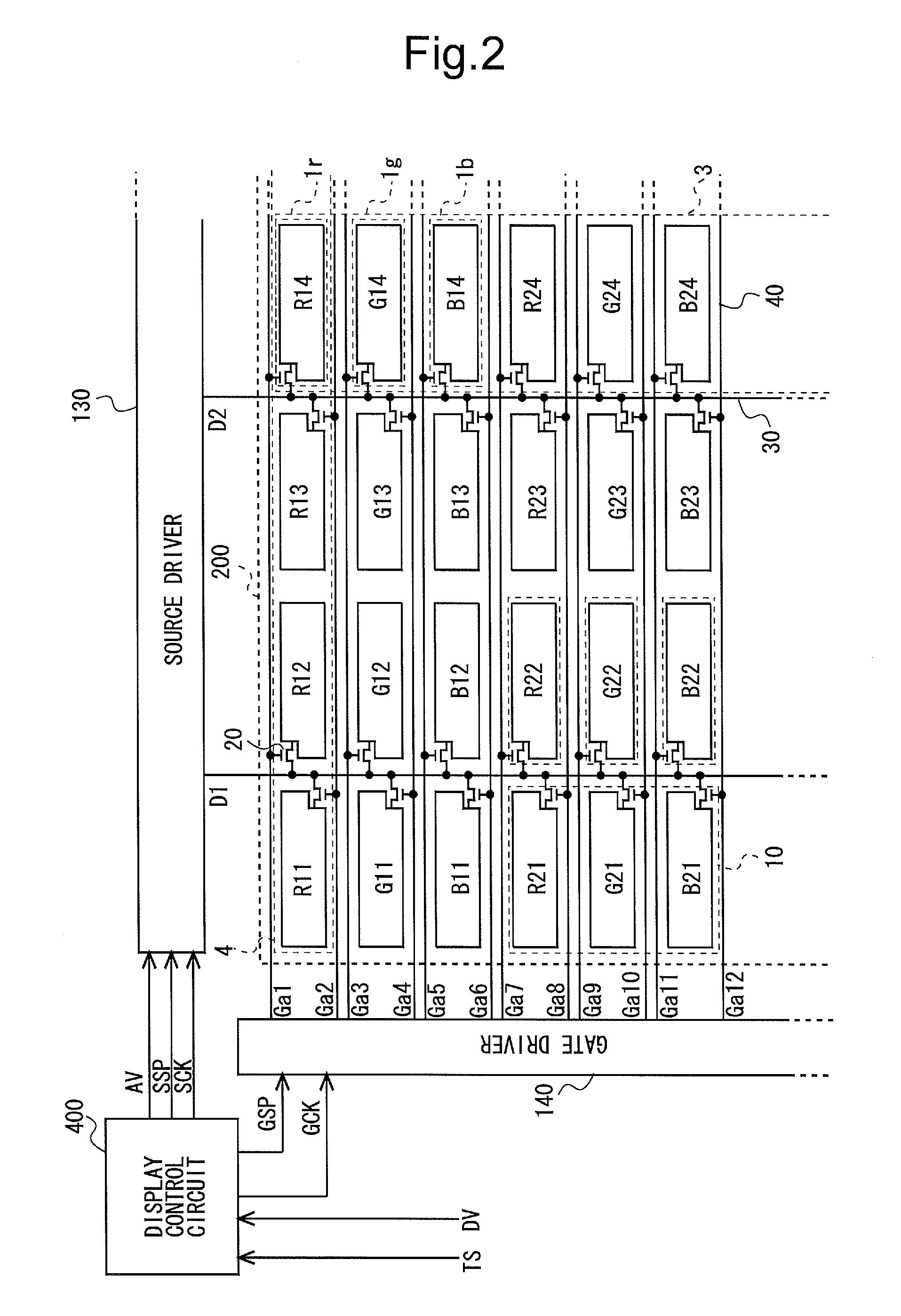
Display panel, display device, and method of driving the same
InactiveUS20130057598A1Decrease in amountCost and current consumption of be decreaseCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsSignal linesPower flow
The present invention provides a display panel having decreased cost and current consumption by decreasing the number of data signal lines from the conventional number, a display device including the display panel, and a method of driving the display device.Each pixel formation portion (10) included in a display unit (200) of a display device is configured to arrange three sub-pixel formation portions (1r, 1g, 1b) for forming sub-pixels of mutually different color components in a data signal line extension direction. Each one data signal line (30) is arranged between a sub-pixel formation portion vertical string (3) in an odd-order from a front of a scanning signal line extension direction and a sub-pixel formation portion vertical string (3) adjacent to the sub-pixel formation portion vertical string (3) at the back of the scanning signal line extension direction. Sub-pixel formation portion vertical strings (3, 3) positioned at both sides of each data signal line (30) are connected to the data signal line. Each one scanning signal line (40) is arranged at both sides of a sub-pixel formation portion in a data signal line extension direction. Mutually adjacent sub-pixel formation portion vertical strings (3, 3) are connected to mutually different scanning signal line (40).
Owner:SHARP KK
Steering wheel
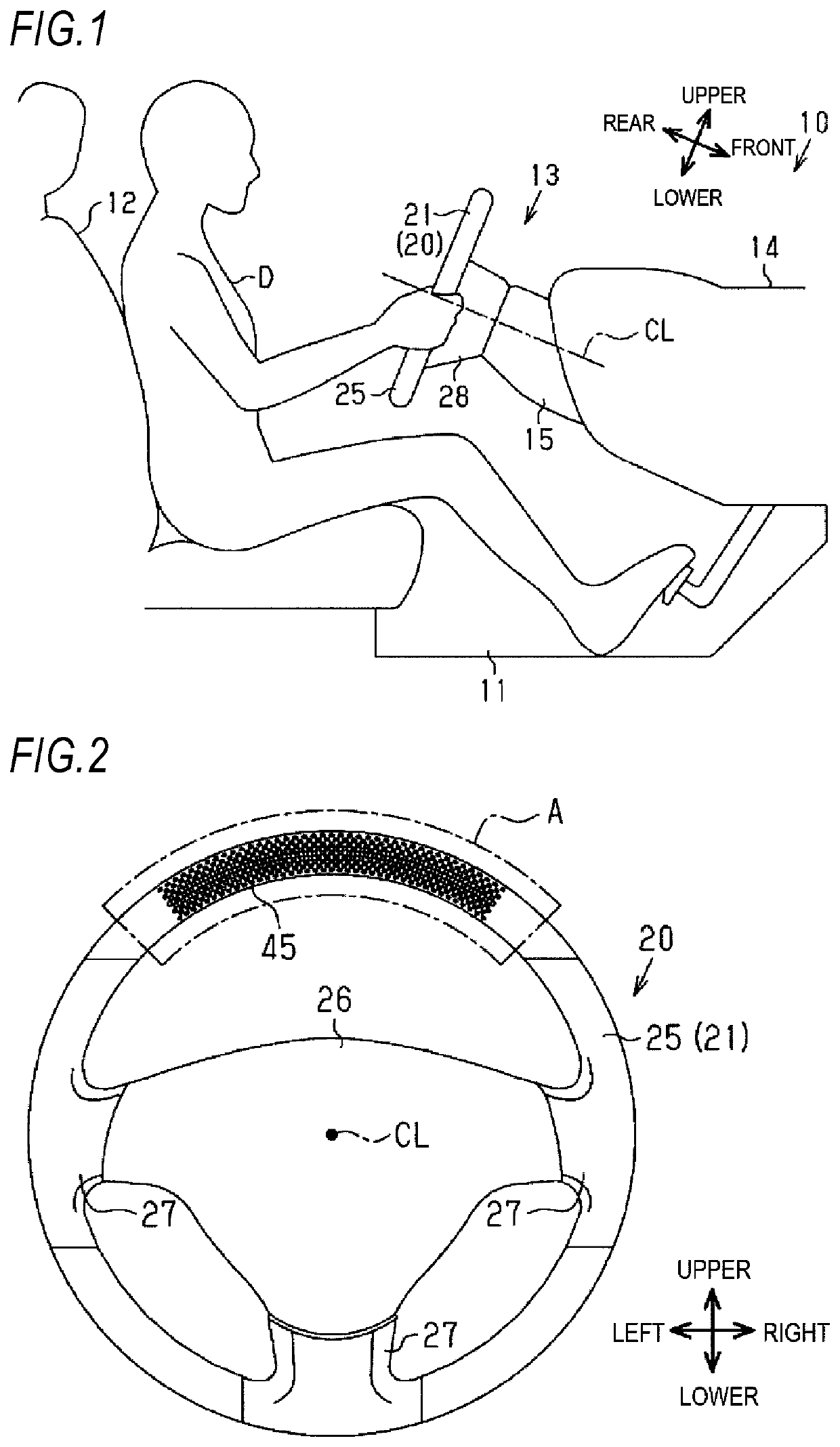
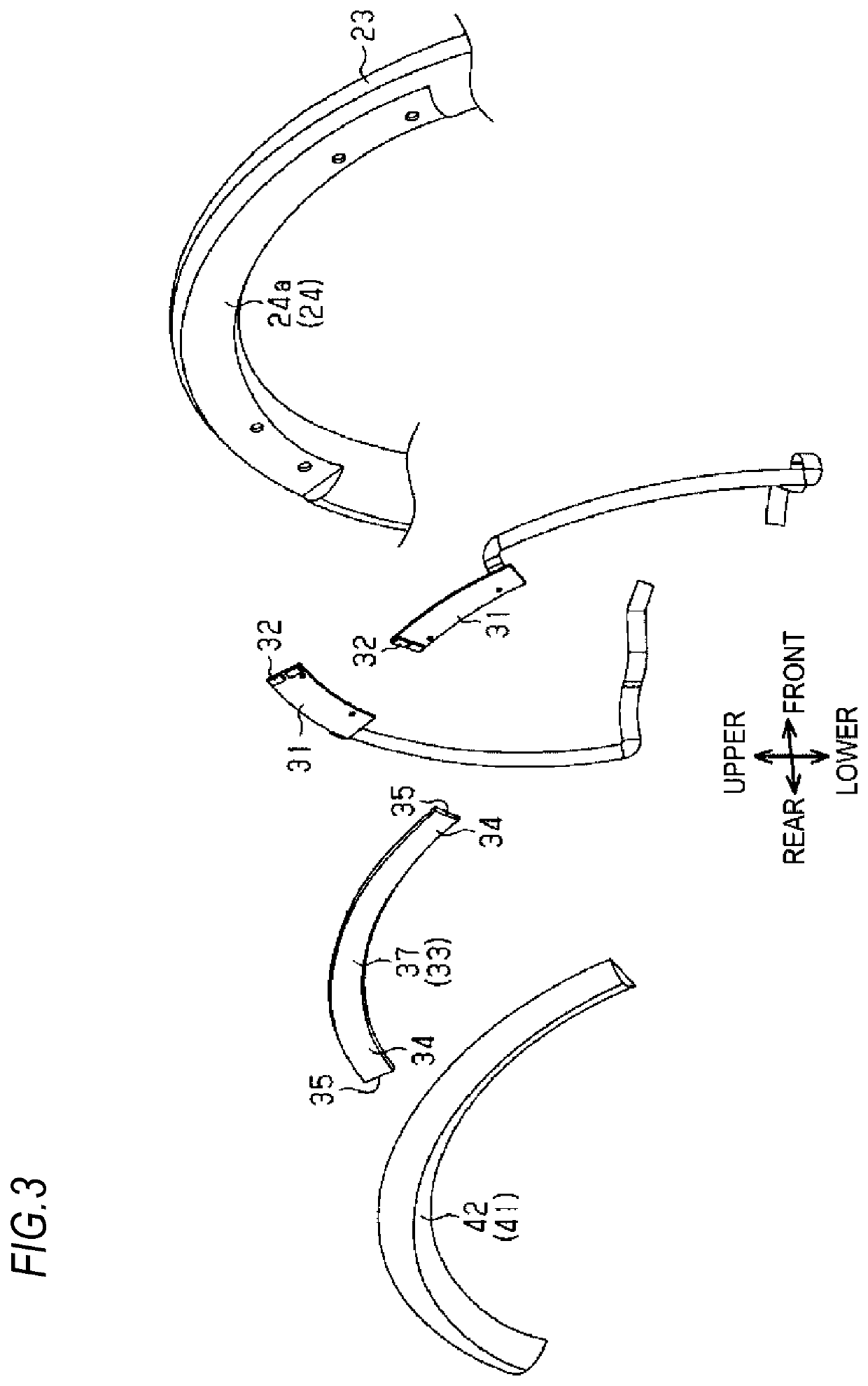
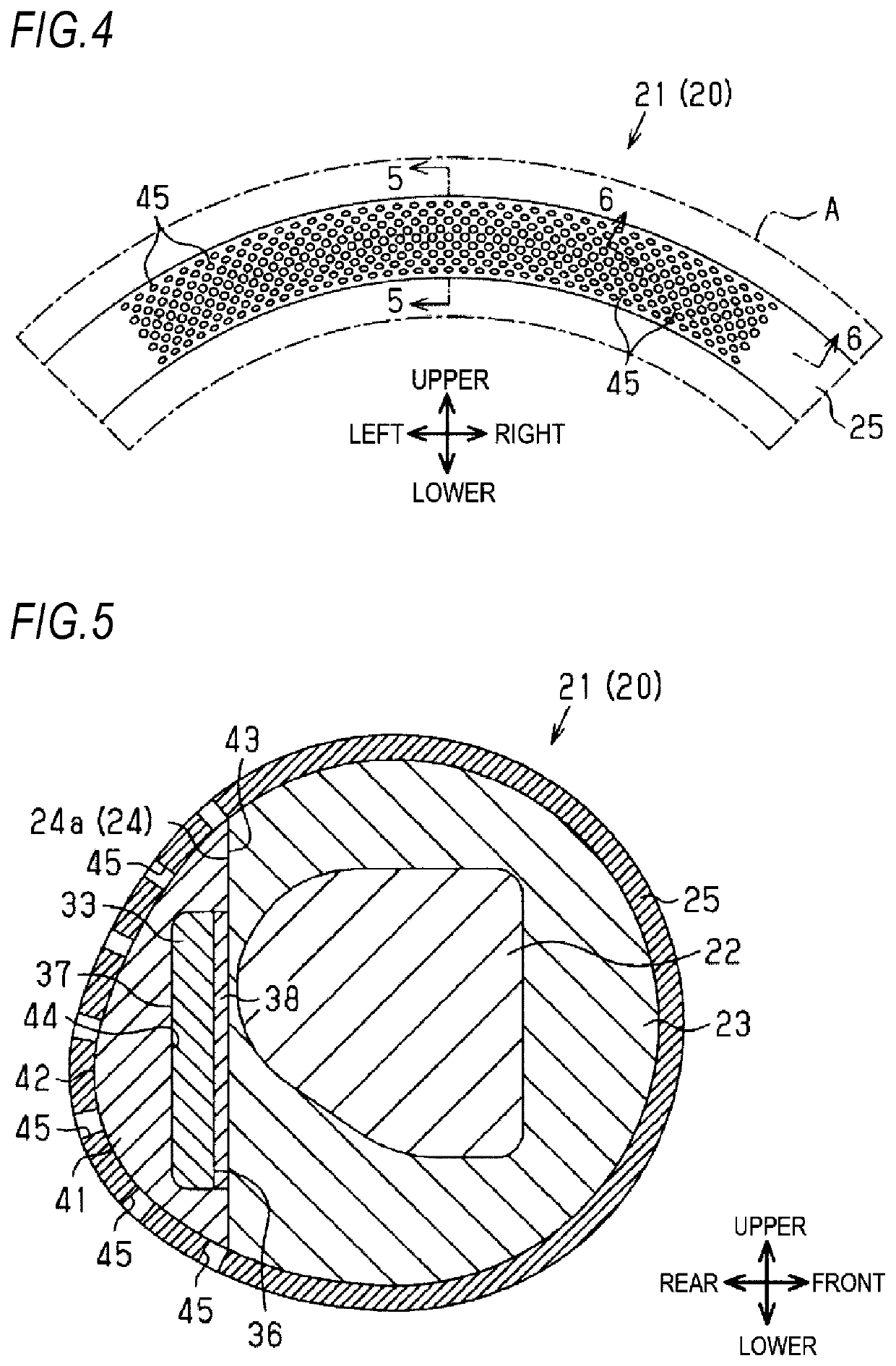
ActiveUS20200001782A1Decrease in amountTouch feeling and appearance of be improveMechanical apparatusPassenger/driving compartment lightingsPhysicsExit surface
A steering wheel includes a gripping portion that is gripped by a driver when a conveyance is steered, a light source that is disposed inside the gripping portion and is configured to emit light, a light guide body that is disposed inside the gripping portion such that an end portion of the light guide body faces the light source, the light guide body including an emission surface that is configured to emit light from the light source and incident on the end portion and that is formed on a surface on a driver side, and a covering portion that surrounds the light guide body and forms an outer layer portion of at least a part of the gripping portion around the light guide body. The covering portion is formed with a hole, through which light emitted from the emission surface passes.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
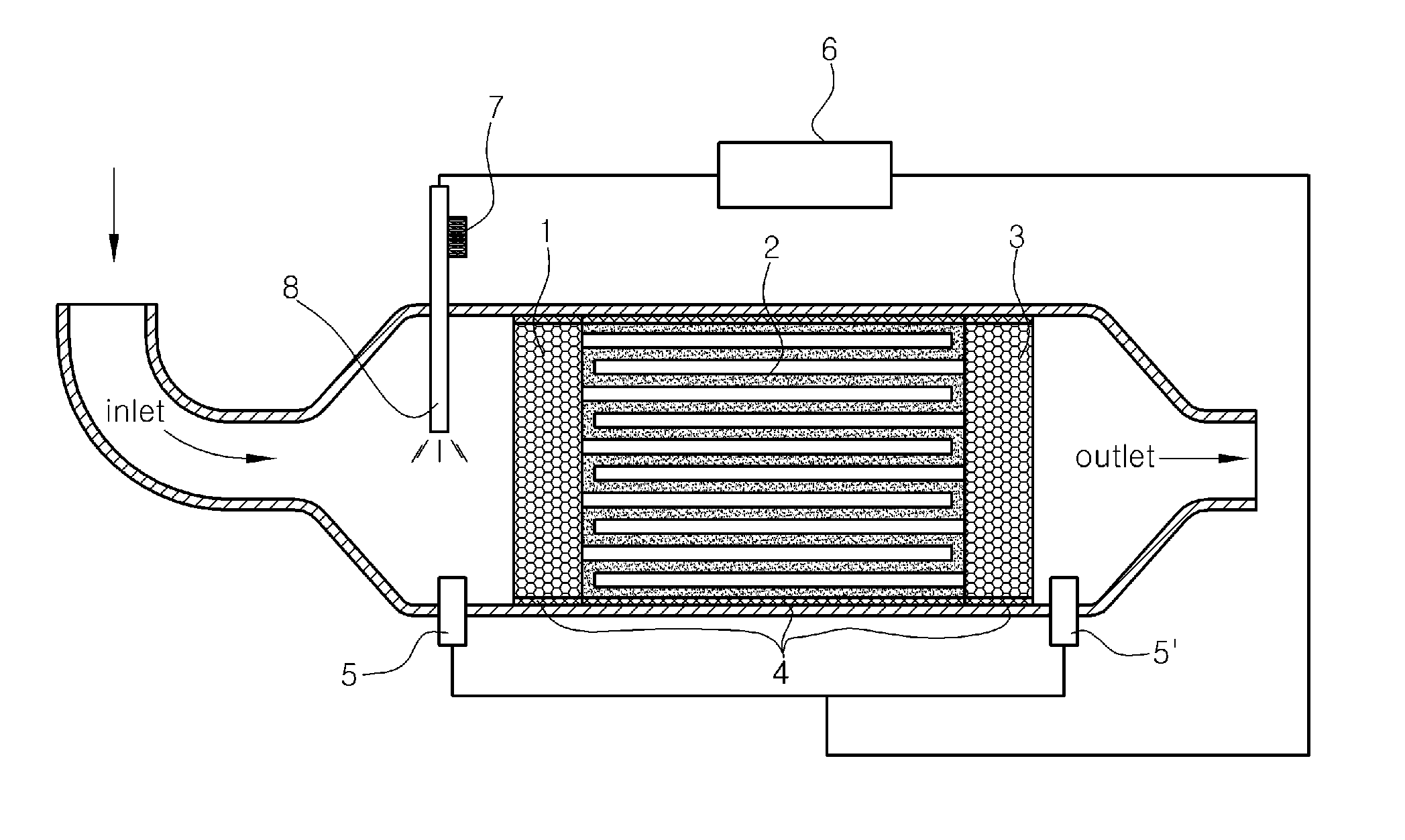
Method for treating exhaust gas and apparatus for treating exhaust gas
InactiveUS20070160512A1Reduce pressure lossDecrease in amountPressurized chemical processUsing liquid separation agentPlasma treatmentOxidative degradation
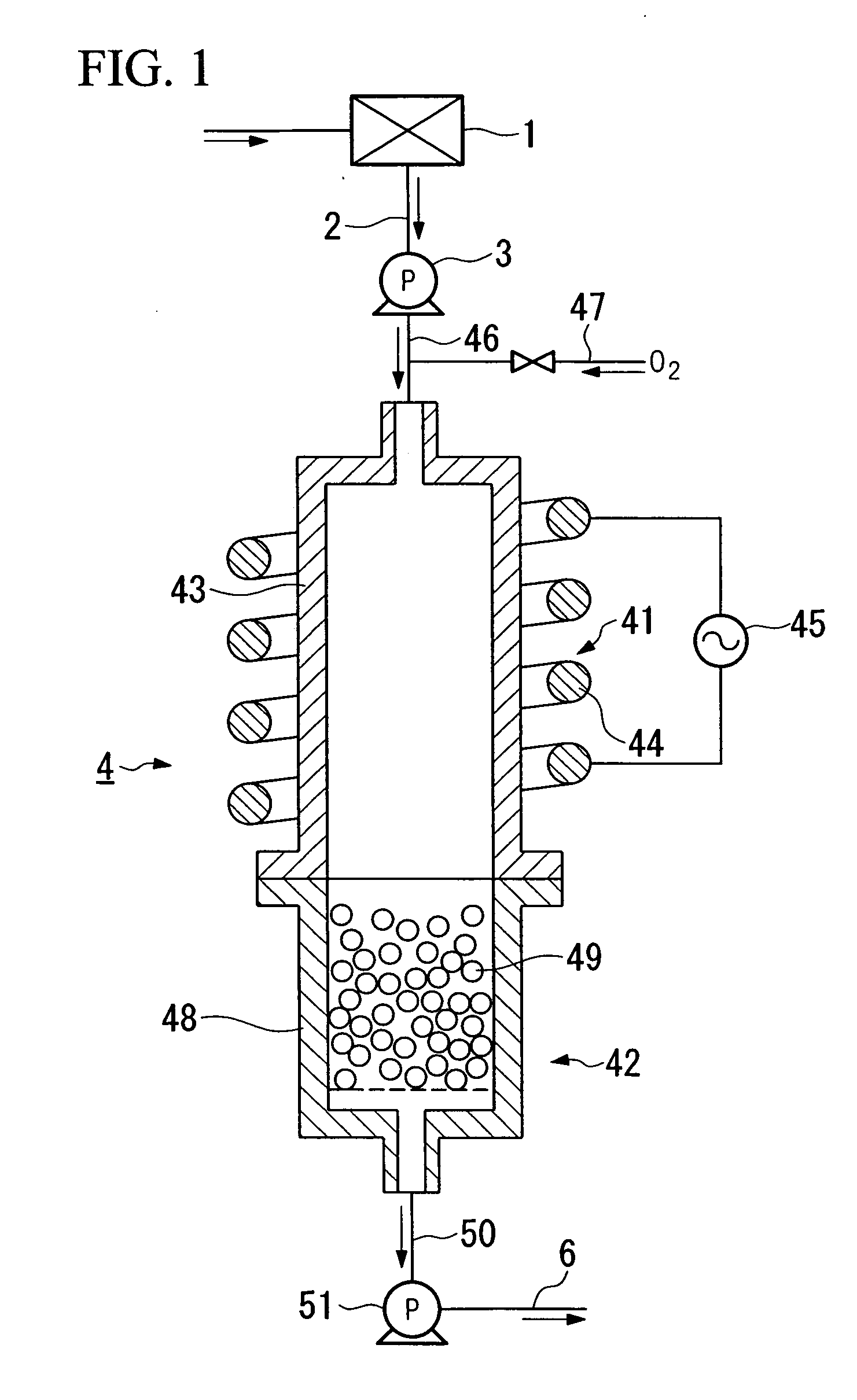
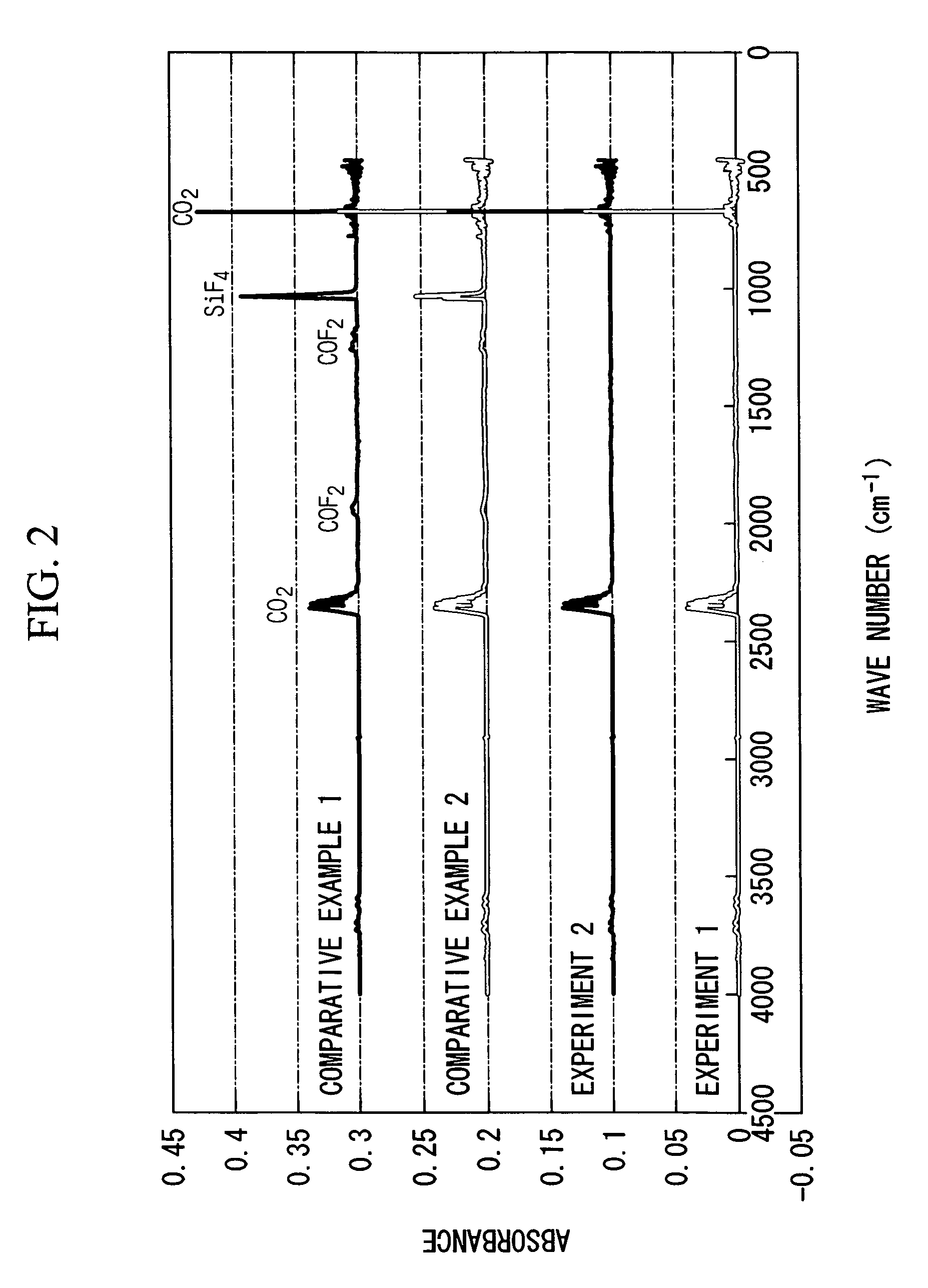
In the exhaust gas treatment method of the present invention, exhaust gas in an excited state in semiconductor device production equipment is introduced into a plasma treatment unit of a treatment unit under reduced pressure, introduced into a reactor of a reaction removal unit while maintained in an excited state by plasma generated in the plasma treatment unit, and is reacted with a reaction remover composed of particulate calcium oxide filled into the reactor to remove harmful gas components in the exhaust gas. Exhaust gas may also be reacted with the reaction remover after having degraded the harmful gas components by oxidative degradation in the presence of plasma by supplying oxygen to the plasma treatment unit.
Owner:TAIYO NIPPON SANSO CORP +1
Method for surface treatment of magnesium or magnesium alloy by anodization
InactiveUS20110114497A1Decrease in amountGood characteristicAnodisationSuperimposed coating processAnodic oxidationPre treatment
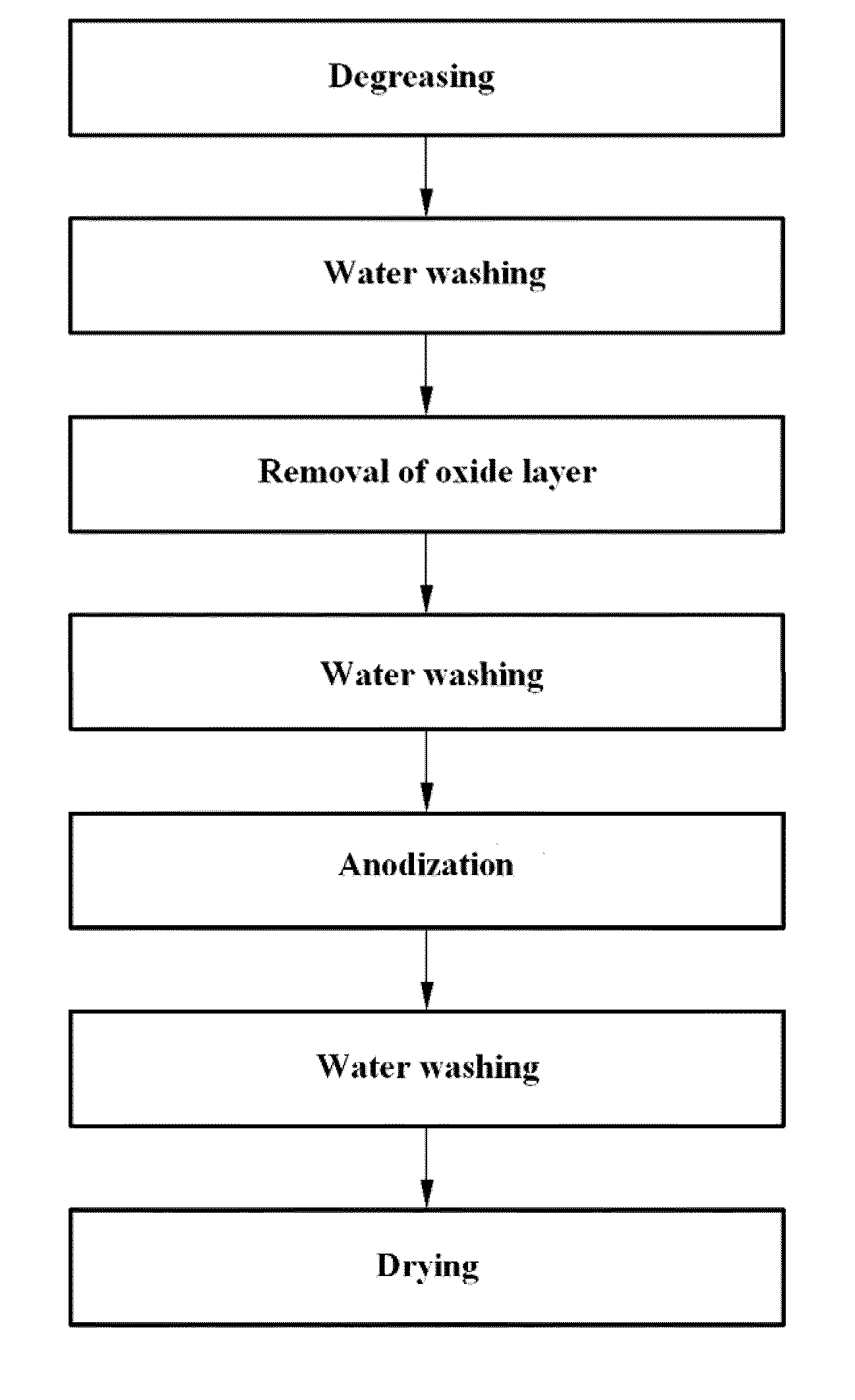
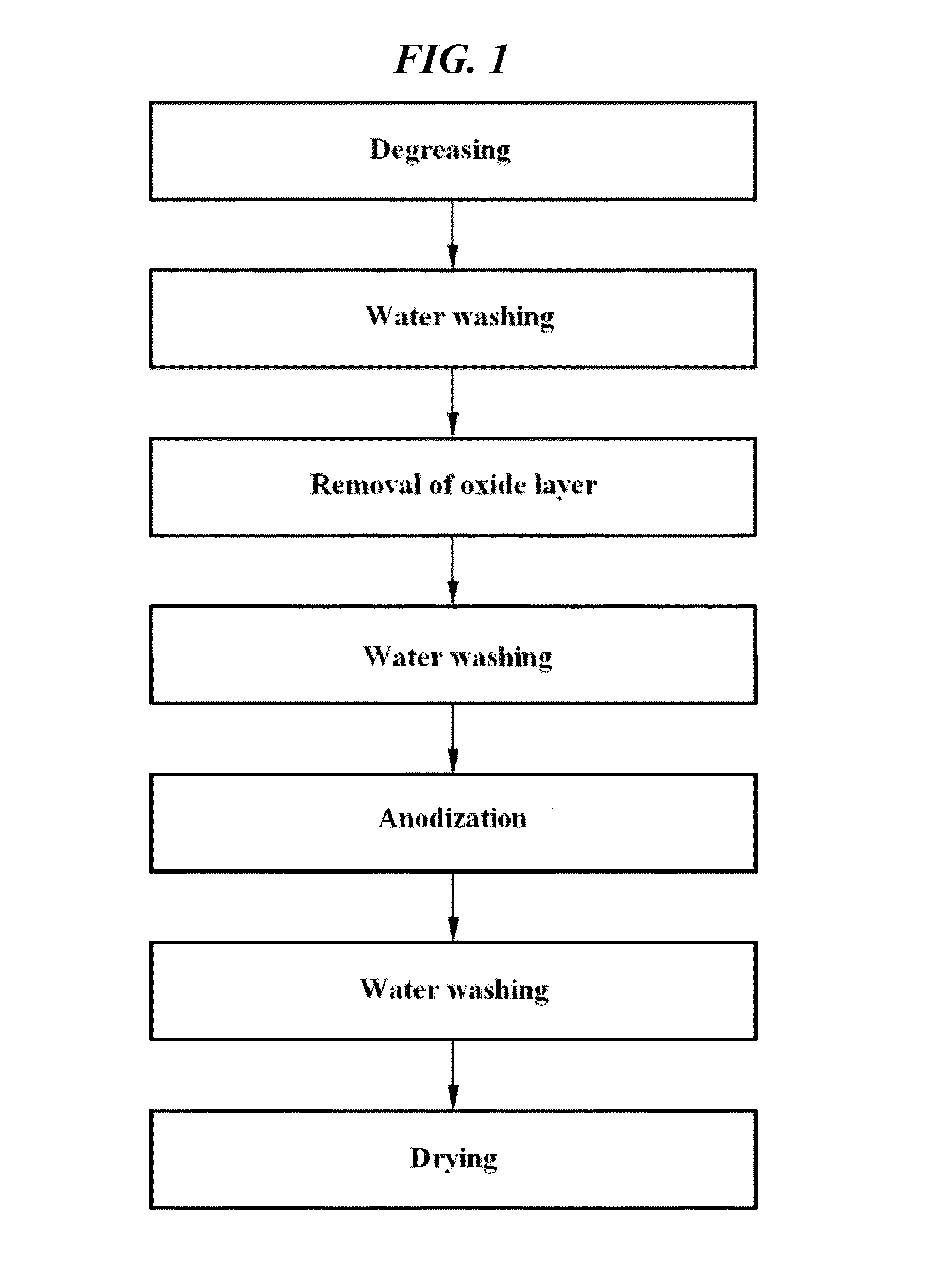
Disclosed herein is a method for the surface treatment of magnesium or a magnesium alloy by anodization to form an anodized oxide coating on the magnesium or magnesium alloy. The method comprises: removing impurities and an oxide layer present on the surface of magnesium or a magnesium alloy using a strongly alkaline aqueous solution (pretreatment); and immersing the pretreated magnesium or magnesium alloy in an alkaline electrolyte and applying a direct current having a current density of 3 A / dm2 or less to the electrolyte to form a magnesium oxide coating (microarc plasma anodization).
Owner:KCCHEM +1
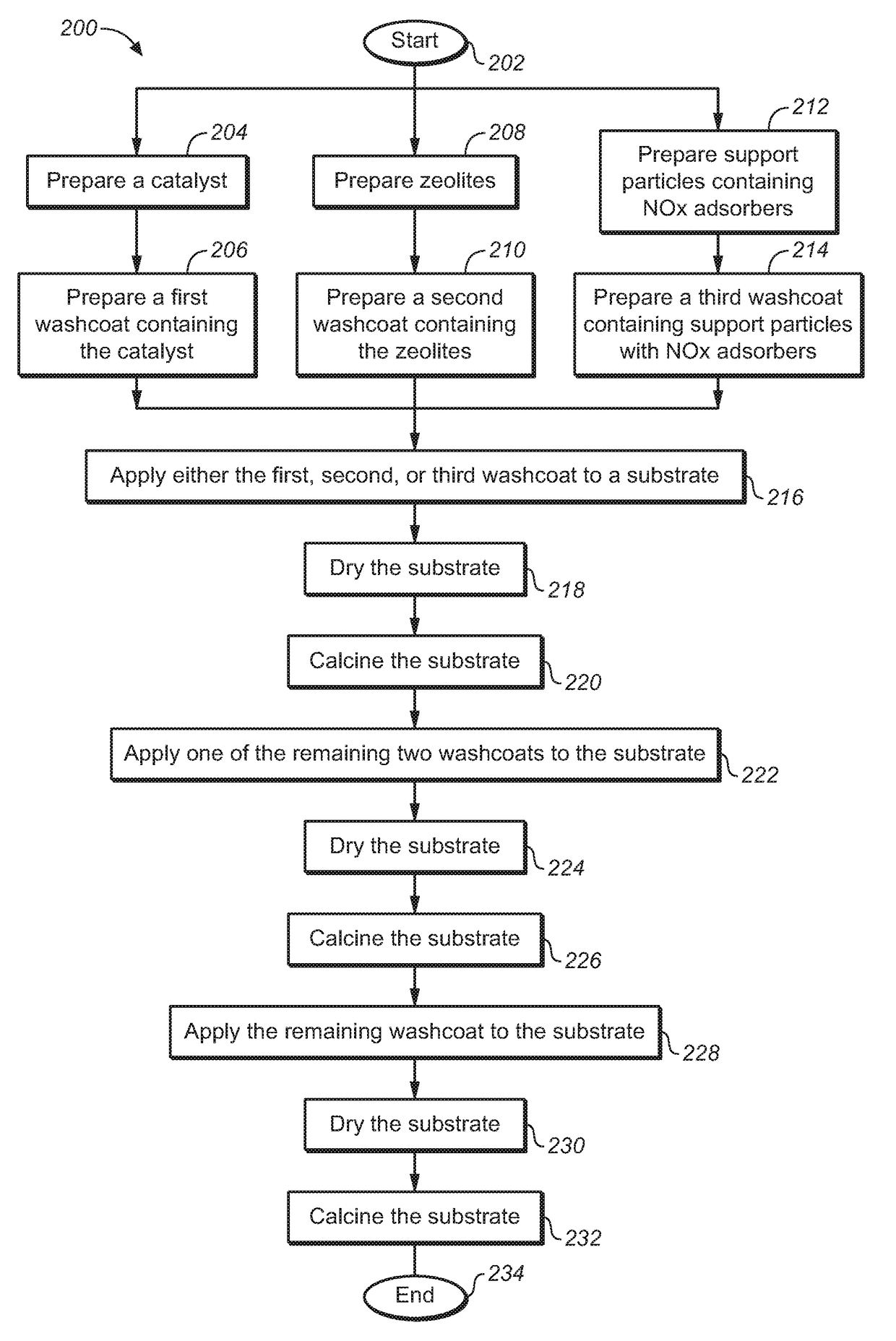
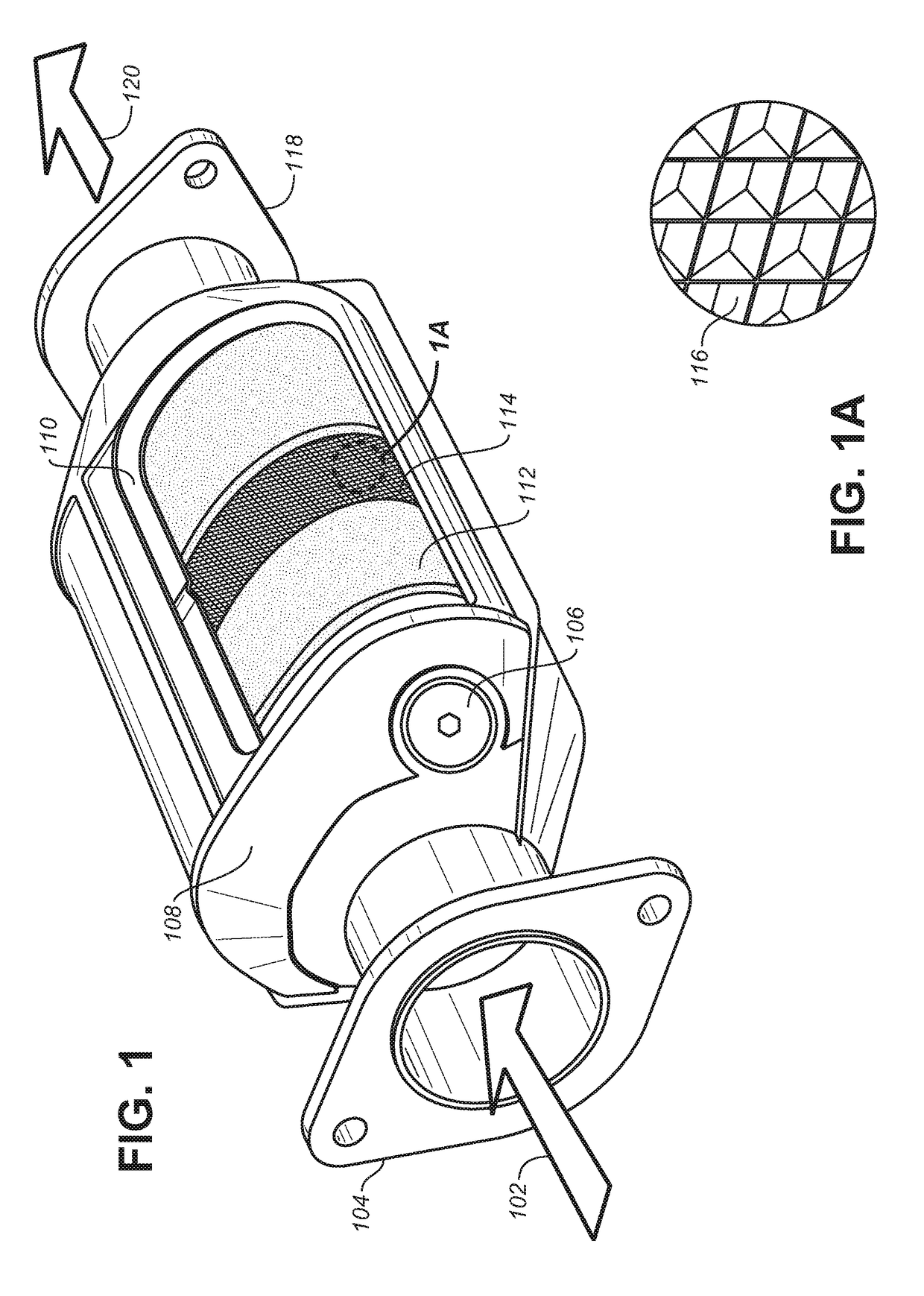
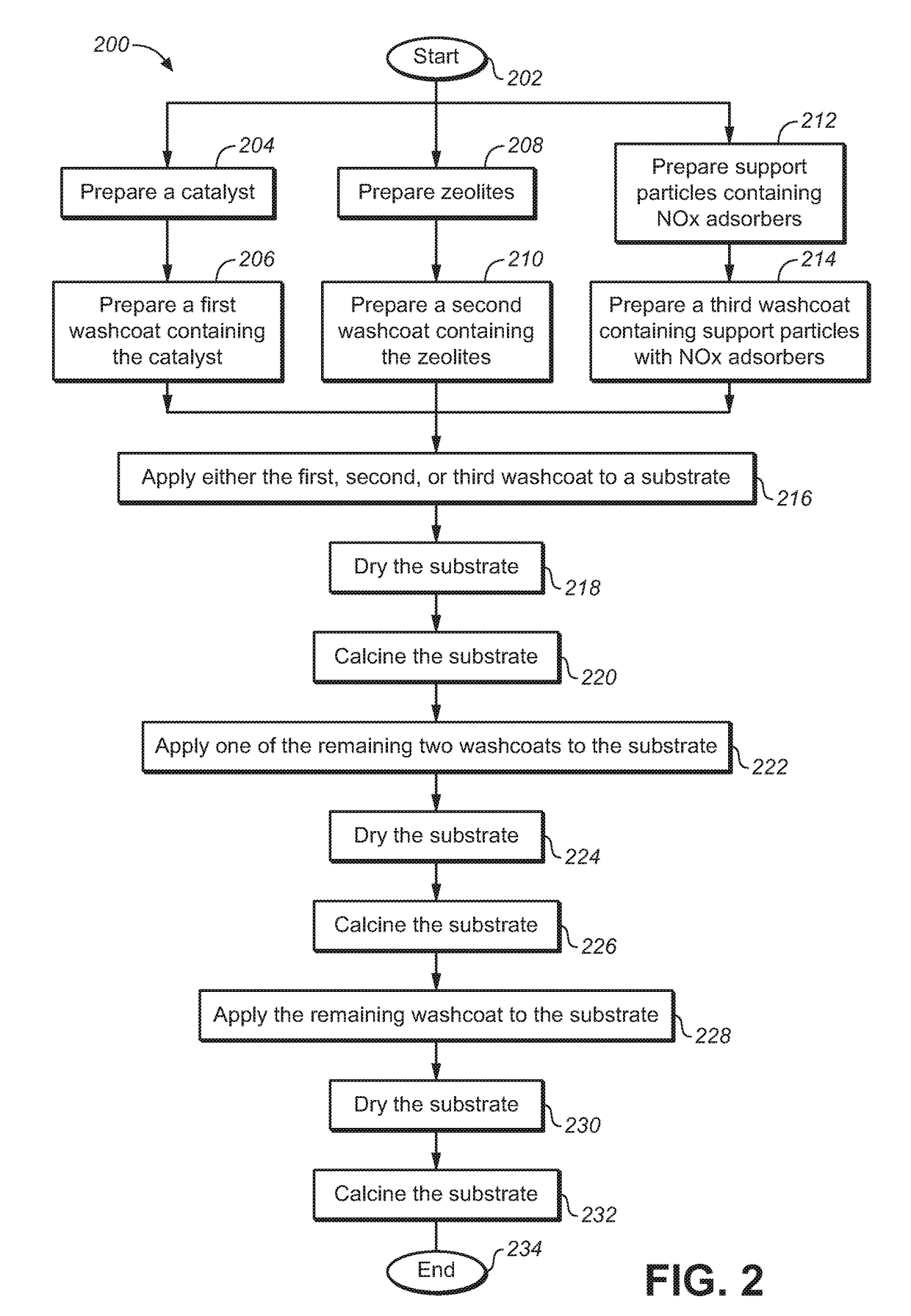
Compositions for Passive NOx Adsorption PNA Systems and Methods of Making and Using Same
InactiveUS20180318763A1Reduce amountDecrease in amountOther chemical processesExhaust apparatusLight dutyTreatment system
The present disclosure relates to a substrate containing passive NOx adsorption (PNA) materials for treatment of gases, and washcoats for use in preparing such a substrate. Also provided are methods of preparation of the PNA materials, as well as methods of preparation of the substrate containing the PNA materials. More specifically, the present disclosure relates to a coated substrate containing PNA materials for PNA systems, useful in the treatment of exhaust gases. Also disclosed are exhaust treatment systems, and vehicles, such as diesel or gasoline vehicles, particularly light-duty diesel or gasoline vehicles, using catalytic converters and exhaust treatment systems using the coated substrates.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
Optical compensatory sheet comprising cellulose acylate film
InactiveUS20050095373A1Low their retardationDecrease in amountLiquid crystal compositionsPolarising elementsChemistryCellulose
An optical compensatory sheet comprises a cellulose acylate film. The optical compensatory sheet can also comprises a transparent support and an optically anisotropic layer formed from a liquid crystal compound. The optical compensatory sheet is characterized in that the retardation value in plane measured at the temperature of 20° C. under the relative humidity of 20% is in the range of 97 to 103% based on the retardation value in plane measured at the temperature of 10° C. under the relative humidity of 20%.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP
Mass spectrometric measurement of b-lactamase resistances
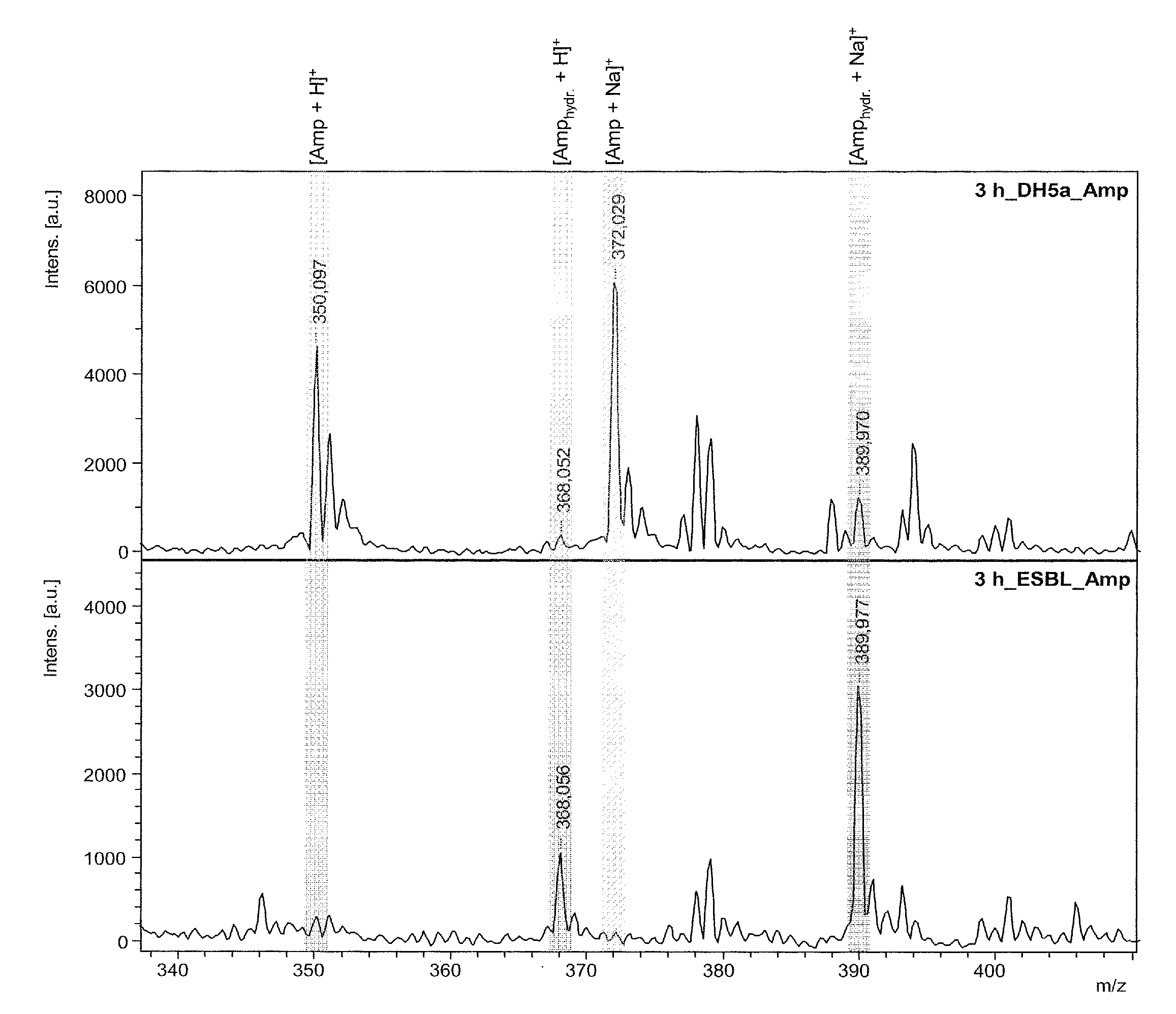
PendingUS20130095511A1Quickly and easily measureDecrease in amountMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisChemistryMass spectrometry
The invention relates to the determination of resistances of microorganisms which produce β-lactamases, in particular “extended spectrum β-lactamases” (ESBL). The invention provides a method whereby the microbial resistance can be measured very simply and quickly by means of the catalytic effect of the microbially produced β-lactamases on β-lactam antibiotics, which consists in a hydrolytic cleavage of the β-lactam ring. The method determines the resistance of the bacteria a few hours after a suitable substrate, either a β-lactam antibiotic or a customized β-lactam derivative, has been added to a suspension of the microbes, by direct mass spectrometric measurement of the substrate breakdown caused by the β-lactamases.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Method for monitoring early treatment response
InactiveUS20060222591A1Decrease in amountPositive responseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic chemistryTreatment responseMagnetic resonance spectroscopic
Disclosed is a method for monitoring early treatment response of a cancer treatment comprising measuring by magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), for example, proton MRS, the amount of Choline present in the endomembranes of the cancerous tissue before and after treatment; the treatment comprises administration of a cytotoxic therapy, whereby a decrease in the amount of Choline after treatment is indicative of a positive response. The decrease in the amount of Choline represents the decrease in the internal cell membrane as a result of down regulation of the organelles and their secretory granules and their transport vesicles. Disclosed also is a method for determining effectiveness of a cytotoxic treatment of cancer. In addition, a method for monitoring protein translation related to the cytotoxic treatment of cancer is disclosed.
Owner:RECEPTOMON LLC
Method of presenting and playing game where winning outcome triggers enhanced award opportunity in subsequent game
InactiveUS20070249419A1Decrease in amountApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesFIRST AwardGame play
In a method of presenting or playing a wagering game, if a winning outcome is received, a first award is awarded and one or more awards associated with one or more winnings outcomes for the game are then enhanced for potential award in a subsequent game or games. In one embodiment, a base paytable or award structure is modified or enhanced, such as by adjusting awards or associating multipliers or bonus values such as progressive awards, to create an enhanced paytable or award structure. The enhanced paytable or award structure may remain in effect for one subsequent game, a set number of games or a time, or until the same or another winning outcome is received in a subsequent game. The game which is presented may vary, such as being a wagering game of video poker, video slots or even a table game.
Owner:AGS CORP
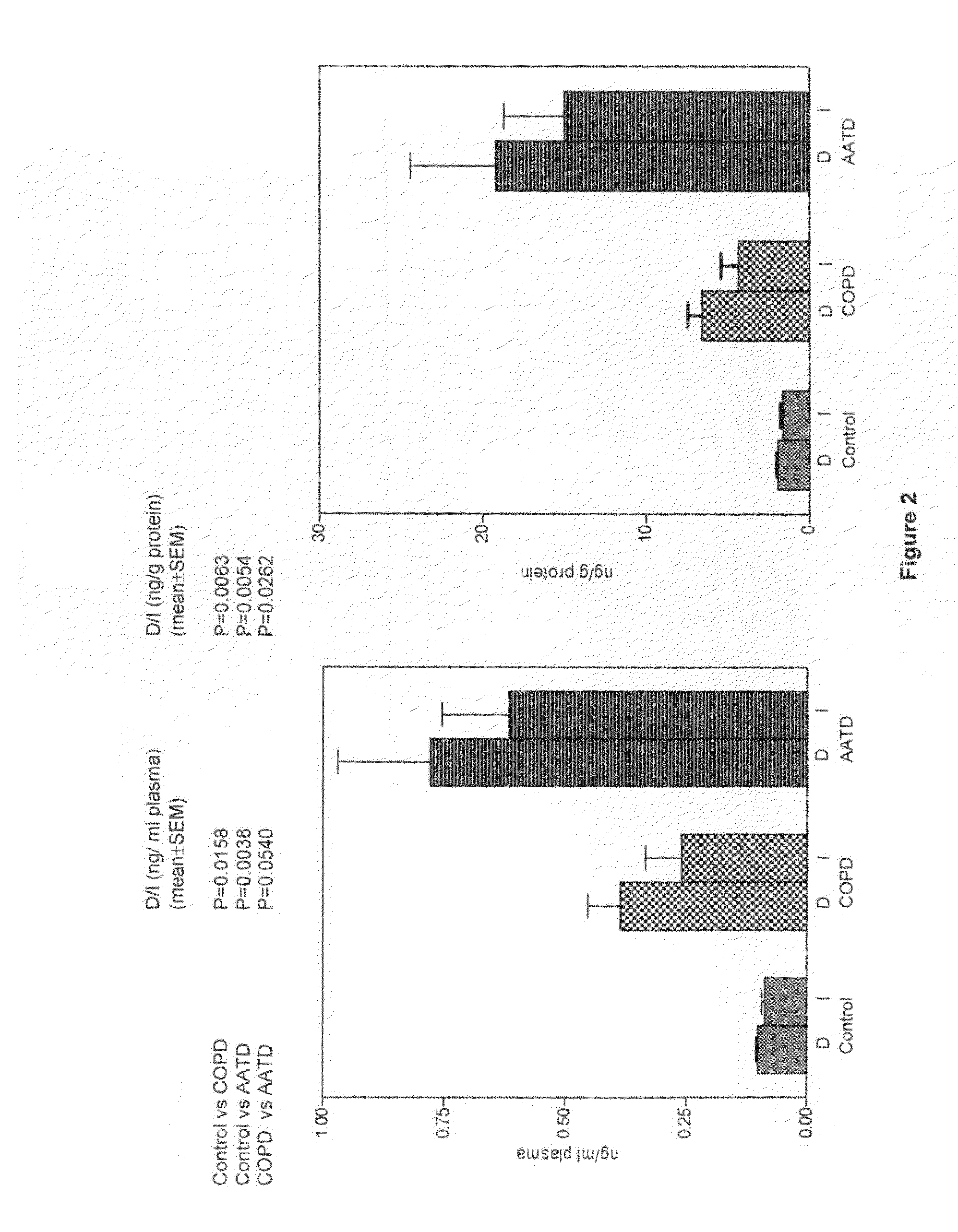
Methods of validating candidate compounds for use in treating COPD and other diseases
InactiveUS20100196885A1Decrease in amountPrevent and ameliorate effectParticle separator tubesMicrobiological testing/measurementElastin fiberElastic fiber
The present invention relates to methods of diagnosing and treating elastin fiber injuries. In additional preferred embodiments, the present invention relates to methods of validating candidate compounds for use in treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), chronic bronchitis, emphysema, refractory asthma, and other related diseases. Examples of such methods include determining if the candidate compound decreases the degradation of elastic fiber in a patient administered the candidate compound by measuring, using mass spectrometry, a marker of elastic fiber degradation in a sample of a body fluid or a tissue of the patient. The invention provides that a decrease in the presence of the marker compared to a control validates that the candidate compound is effective to treat, prevent, or ameliorate the disease.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Channel emulating device
InactiveUS20070136046A1Decrease in amountSimplify system complexityComputation using non-denominational number representationTransmission monitoringSignal productionComputer science
A channel emulating device includes a first choosing module, a first signal integrating module, a first parameter adjusting module, a second choosing module, a second signal integrating module, a second parameter adjusting module and a third choosing module. The first signal integrating module generates at least one first integrated signal in accordance with a first input signal and at least one second input signal. The first and the second parameter adjusting modules respectively generate at least one first parameter signal and at least one second parameter signal. The second signal integrating module generates a plurality of second integrated signals in accordance with the first parameter signal and the second parameter signal. One of the second integrated signals acts as a first output signal. The third choosing module receives the second parameter signal and outputs the second parameter signal through a fifth channel or receives the rest of the second integrated signals and outputs the rest of the second integrated signals through a sixth channel to act as at least one second output signal.
Owner:ACCTON TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Web splicing method and web splicing apparatus
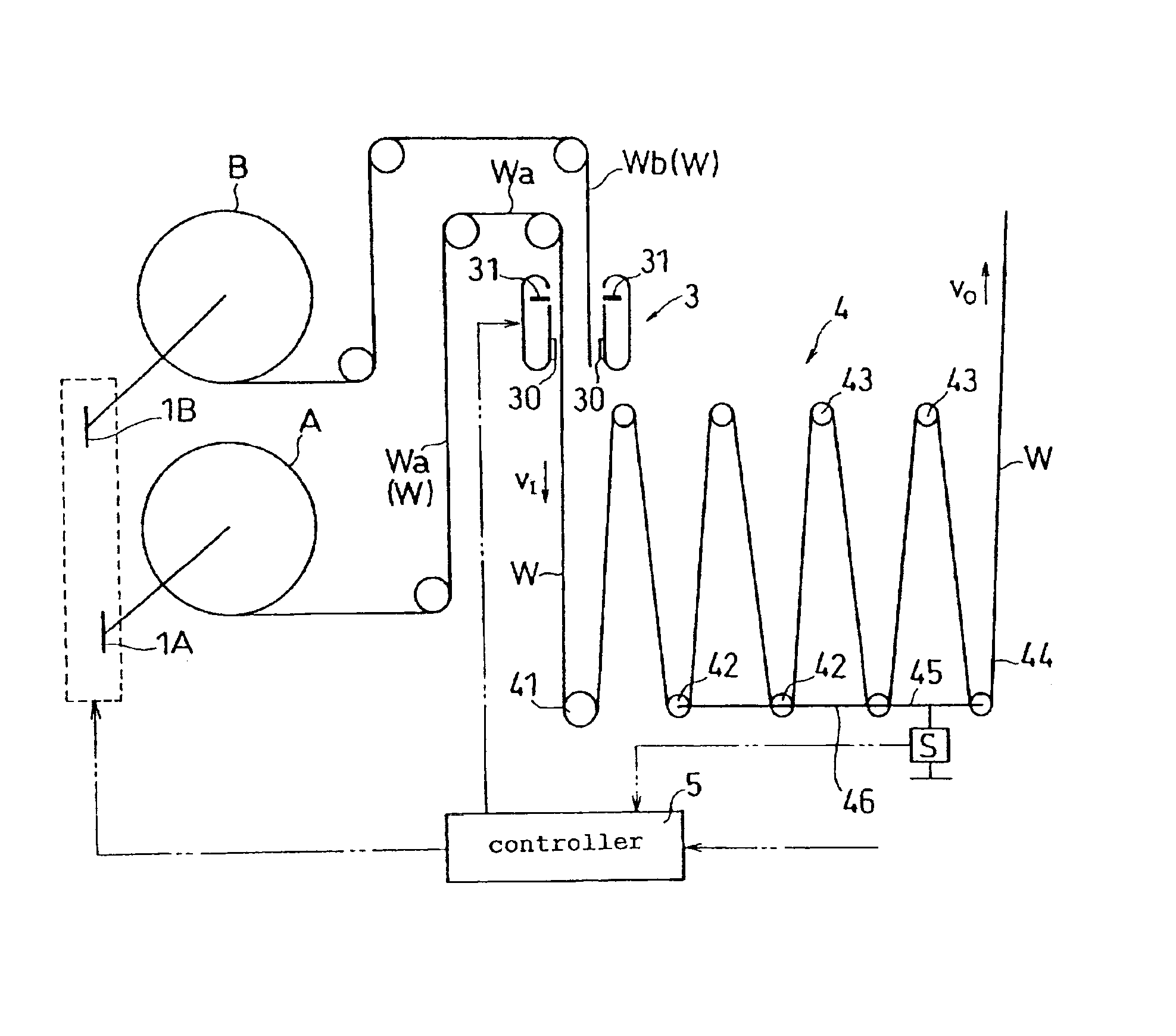
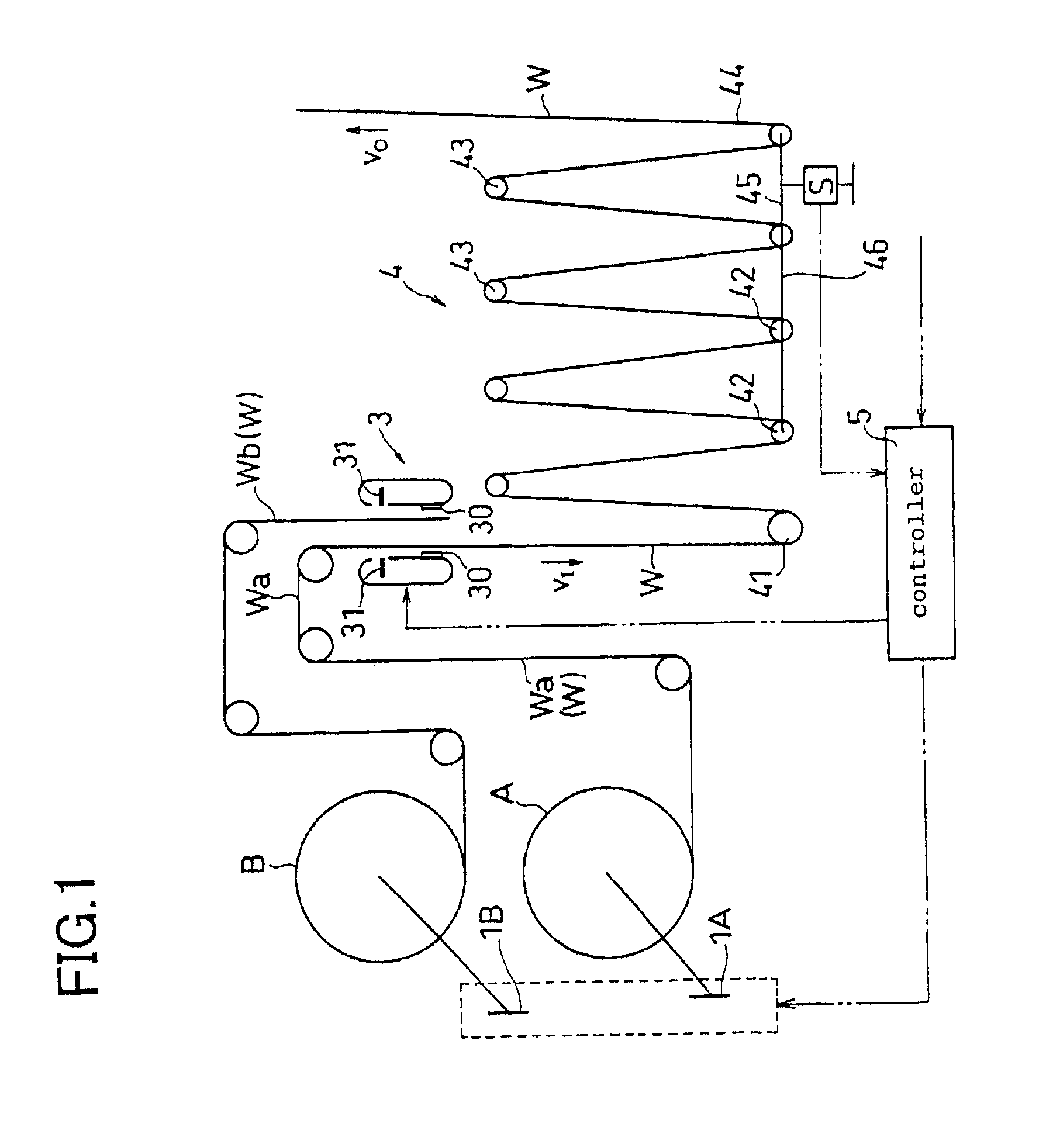
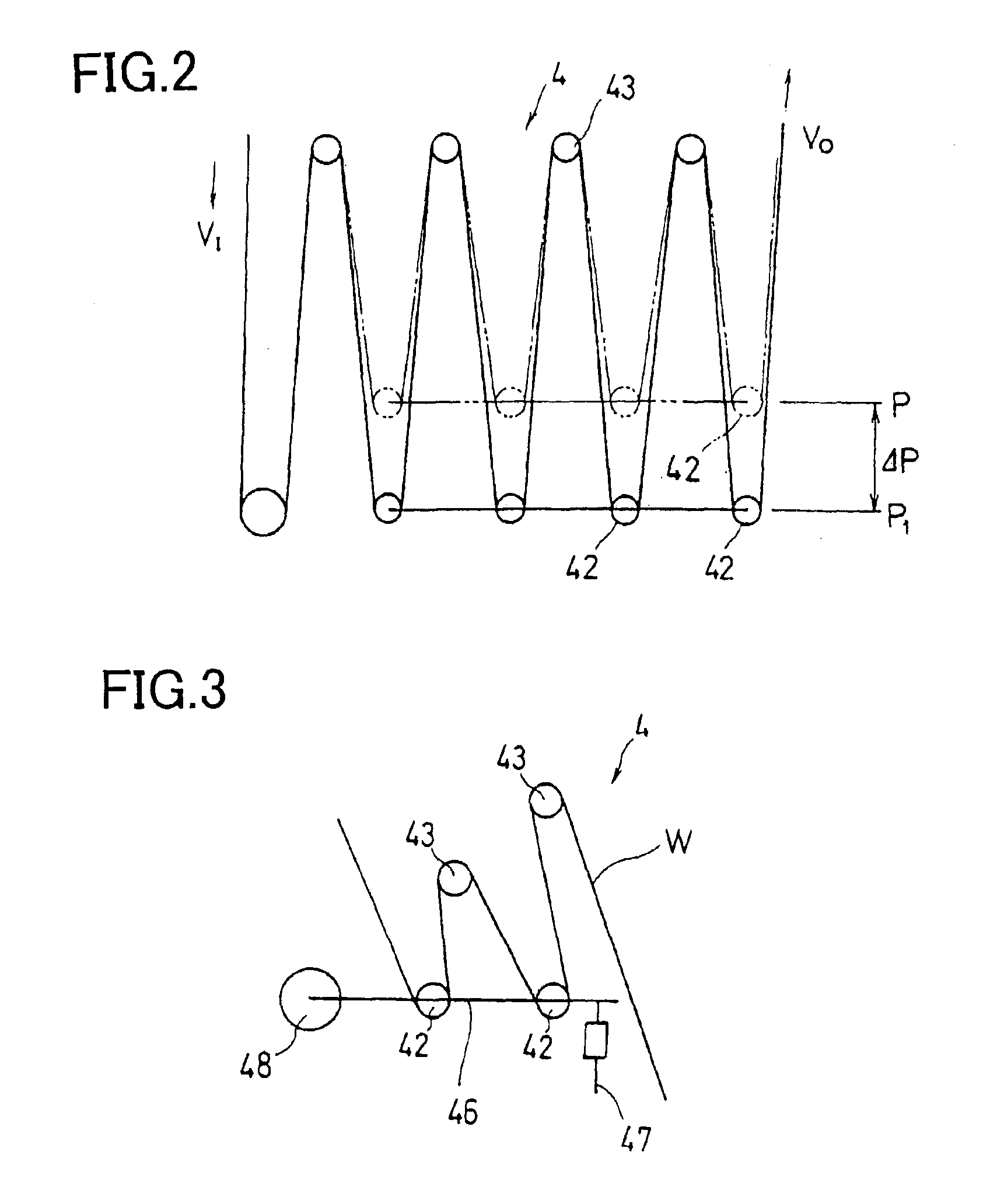
InactiveUS6886772B2Increase in amountDecrease in amountFilament handlingFunction indicatorsEngineeringDiameter control
The present invention provides a web splicing method and a web splicing apparatus with which a line velocity on an output side of the splicing apparatus does not fluctuate through a web splicing operation. The method and apparatus are further operable to maintain a line velocity at a predetermined velocity after the web splicing operation. The method of the present invention includes the steps of: connecting a second web Wb fed out from a second roll B to a first web Wa; cutting off the first web Wa at a position between a point at which the second web Wb is connected to the first web Wa and a first roll A; spinning the second roll B to feed out the second web Wb; obtaining a value of a diameter of the second roll B based on a state of an accumulator 4; and controlling a circumferential velocity of the second roll B based on the obtained diameter.
Owner:ZUIKO CORP
Perpendicular magnetic recording write head with enhancement capacitor on slider body for write current overshoot at write current switching
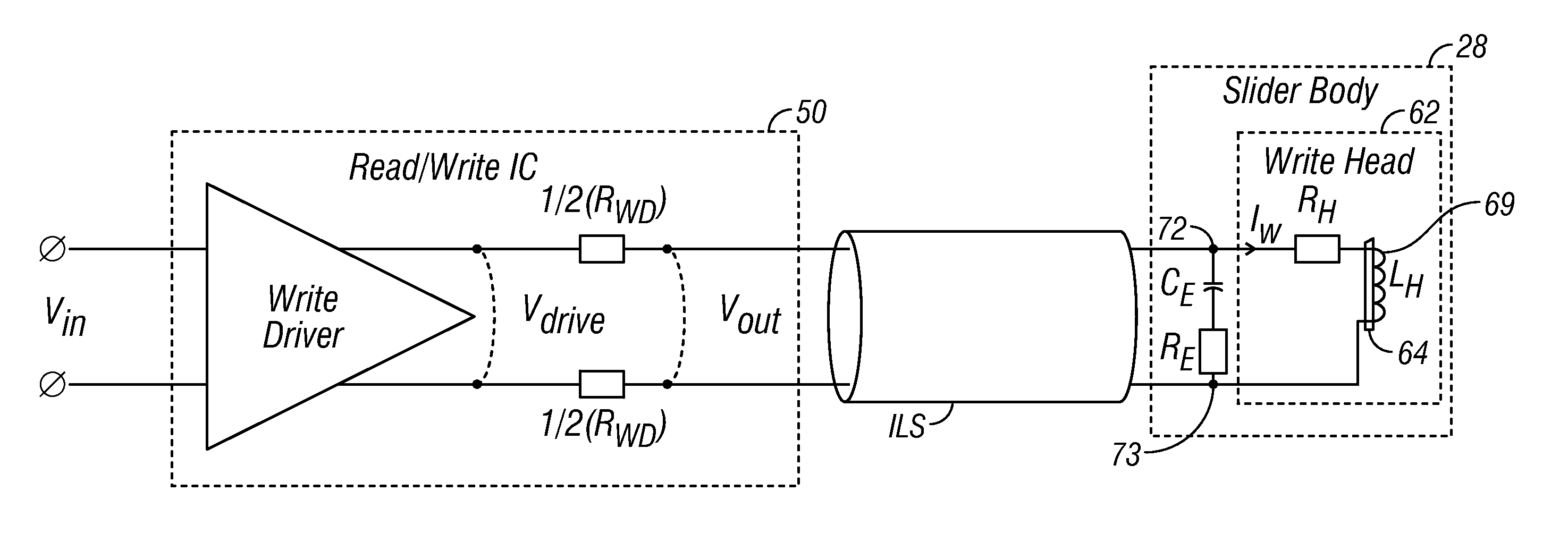
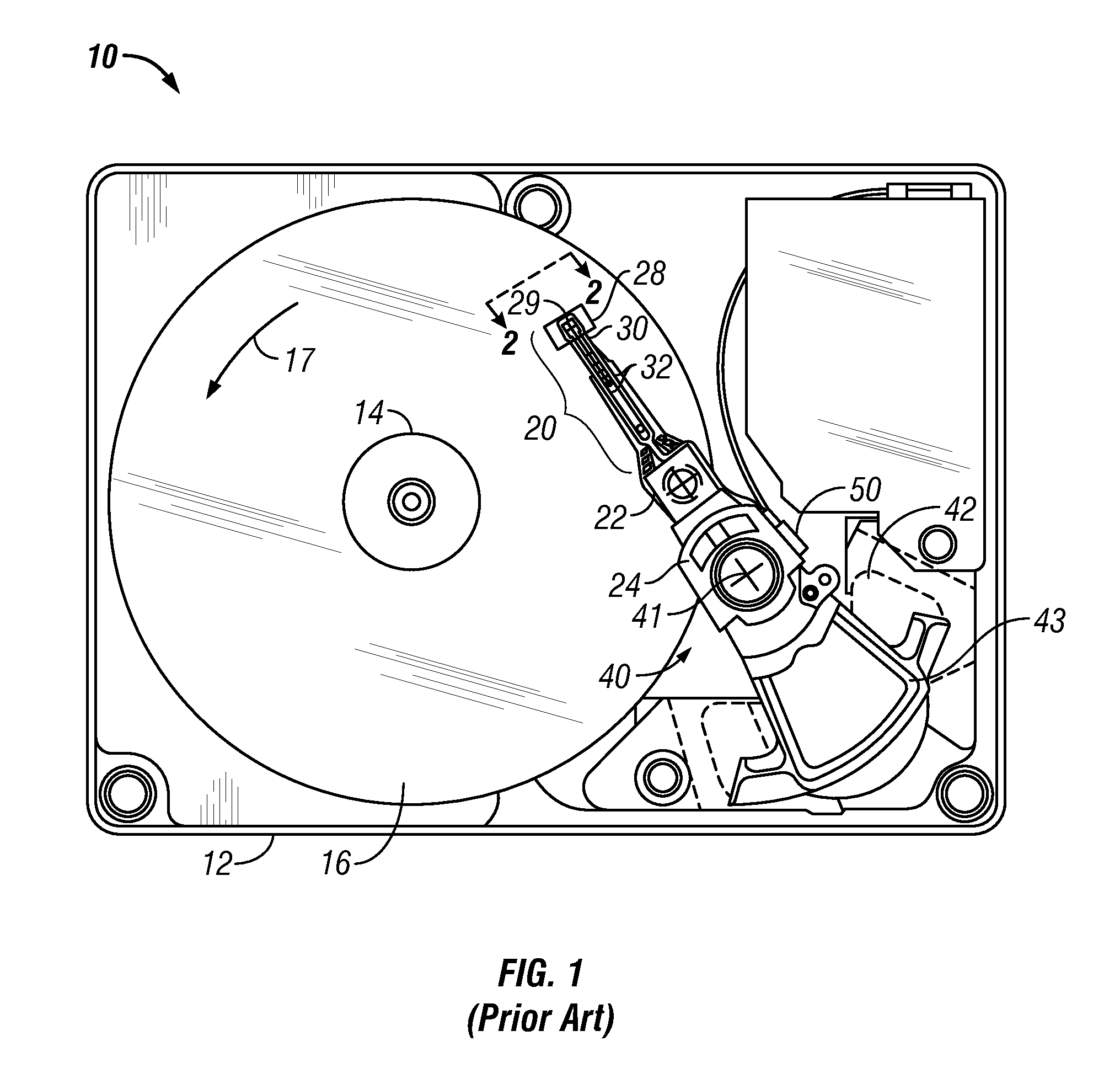
ActiveUS20110109993A1Decrease in amountIncrease resistanceConstruction of head windingsRecord information storageElectrically conductiveWrite current
Write enhancement circuitry on the head carrier of a magnetic recording disk drive provides additional write current overshoot beyond that provided by the write driver circuitry. An enhancement capacitor is formed with a dielectric layer between two layers of electrically-conductive magnetically-permeable shield material that serve as the capacitor plates. The write enhancement circuitry may also include an enhancement resistor. The enhancement capacitor and resistor are connected between the two terminals on the head carrier that connect to the write head coil. The capacitor and resistor are fabricated on the head carrier at the same time and in the same process as the read head. The first and second capacitor plates are generally coplanar with and formed of the same electrically-conductive magnetically-permeable material that forms the first and second magnetic shields for the read head. The enhancement resistor is a stack of layers that is coplanar with and formed of the same materials as the stack of layers that form the sensor portion of the read head between the two magnetic shields.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com