Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
160results about How to "Aberration suppression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
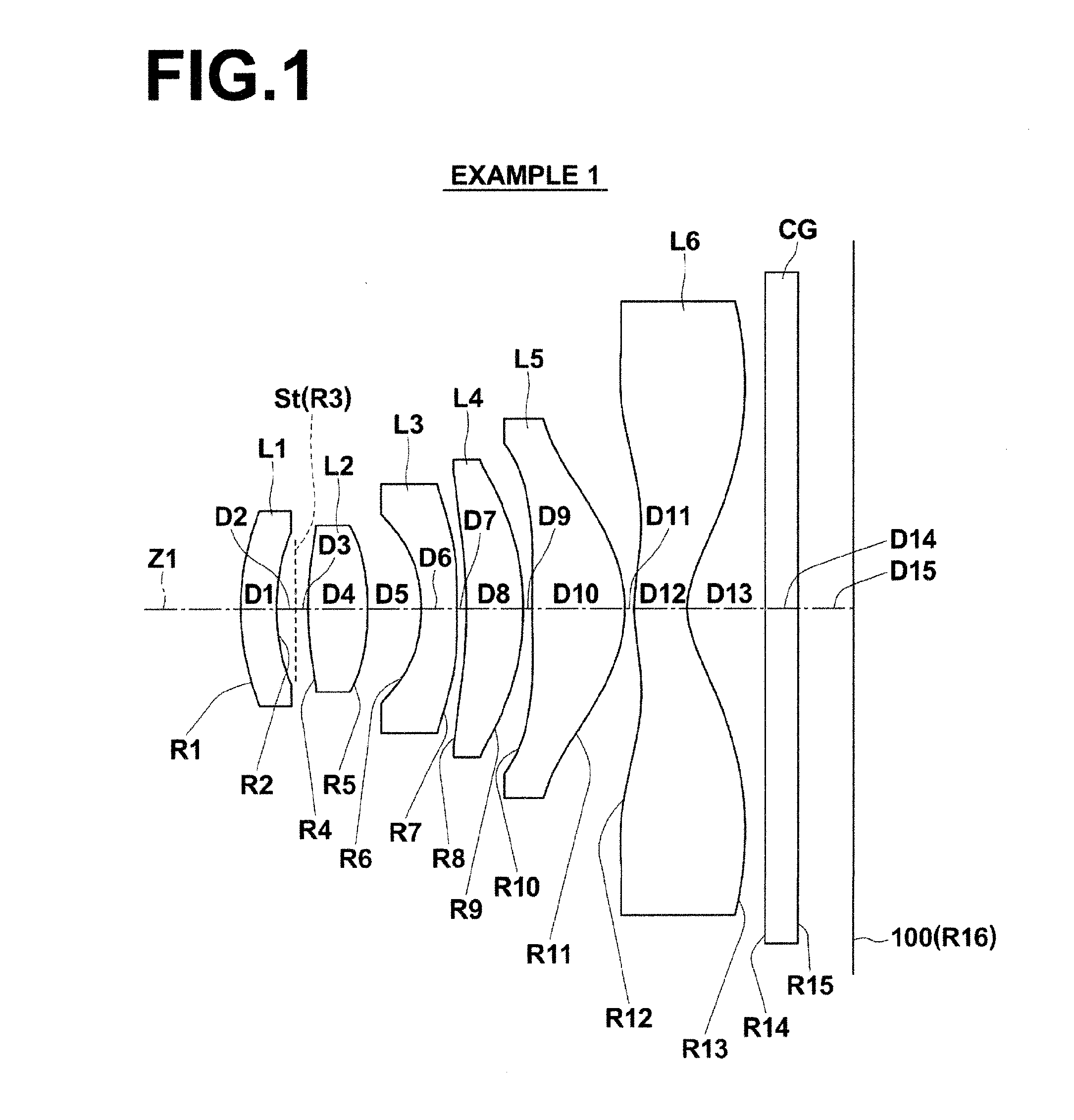
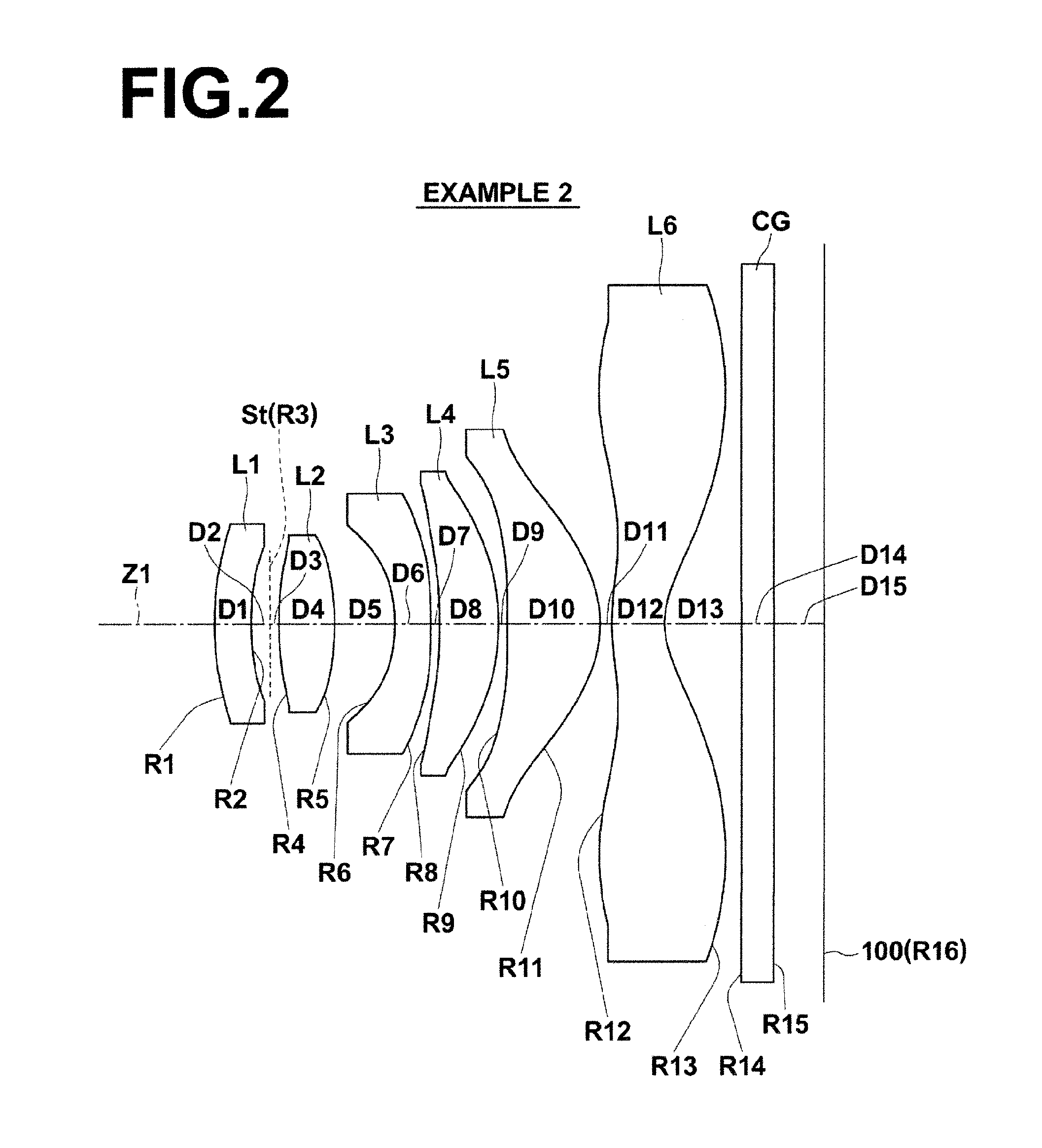
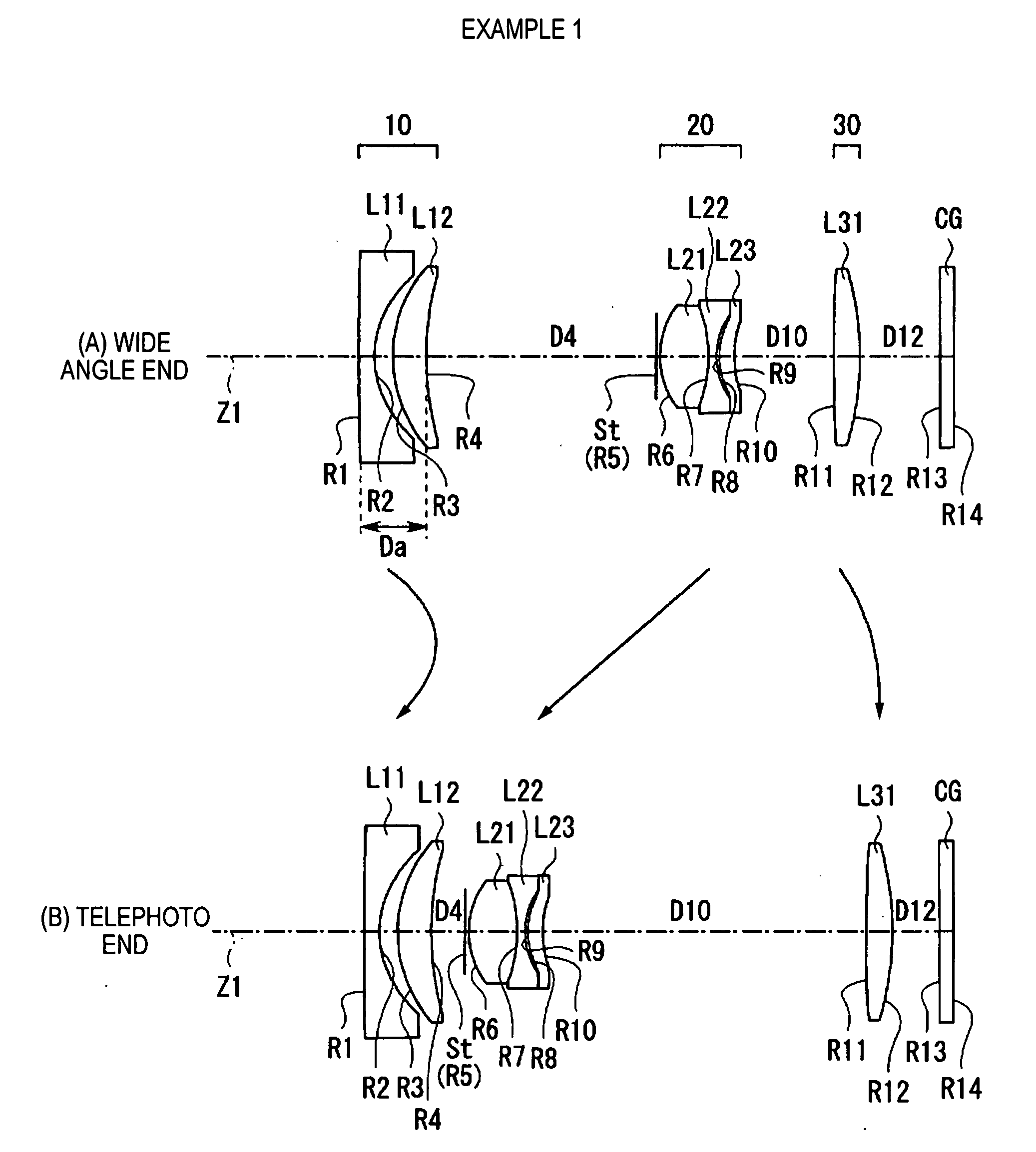
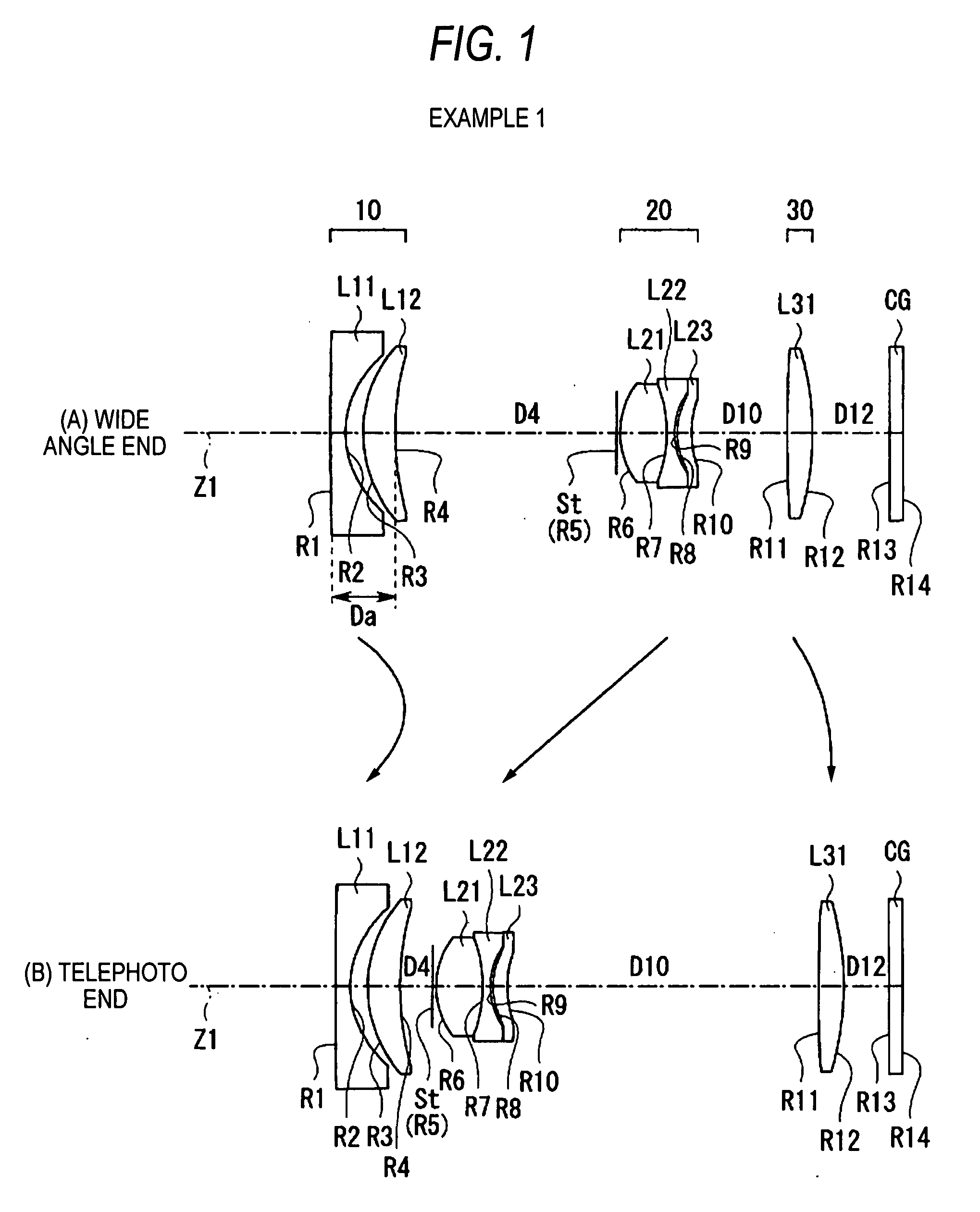
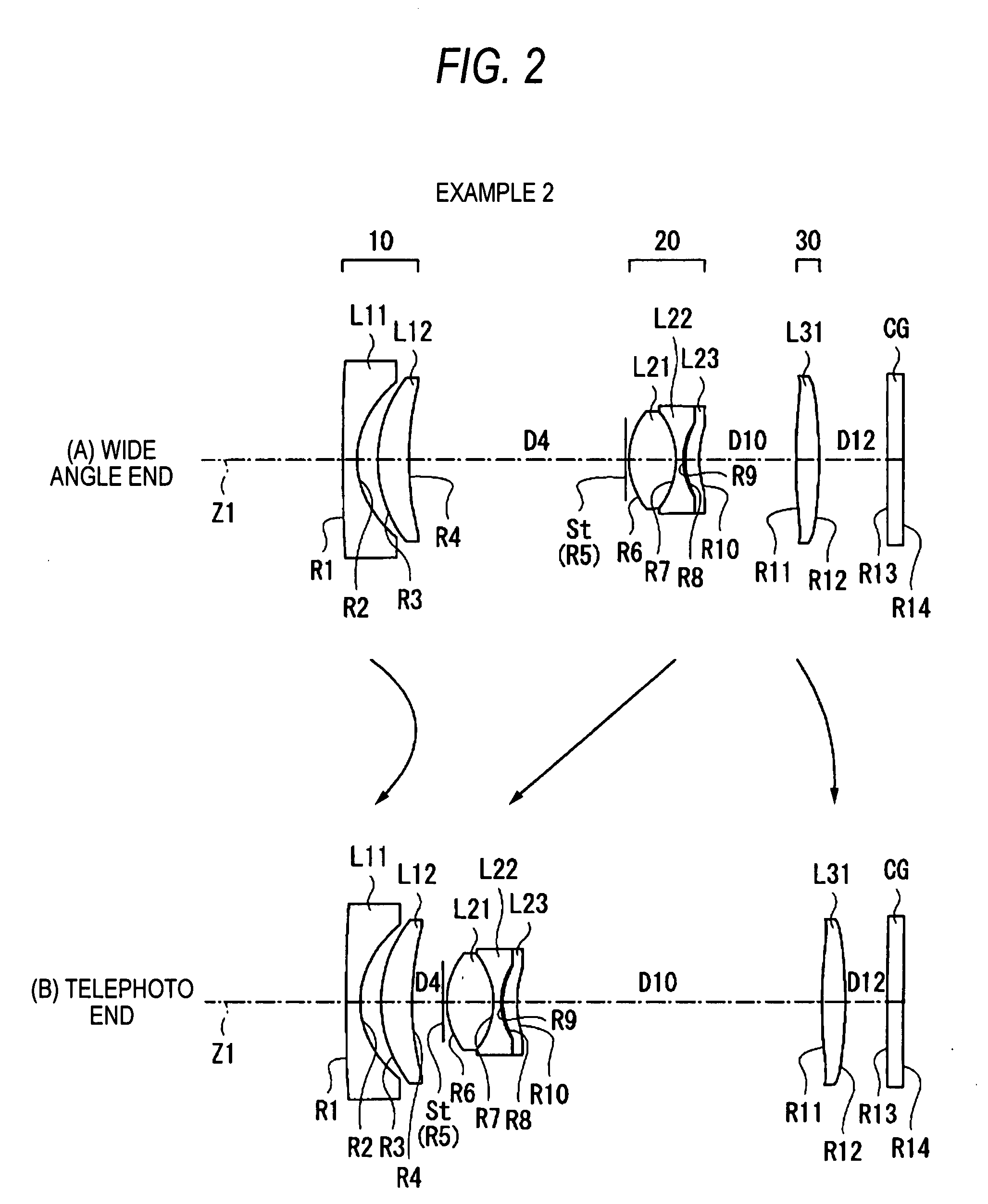
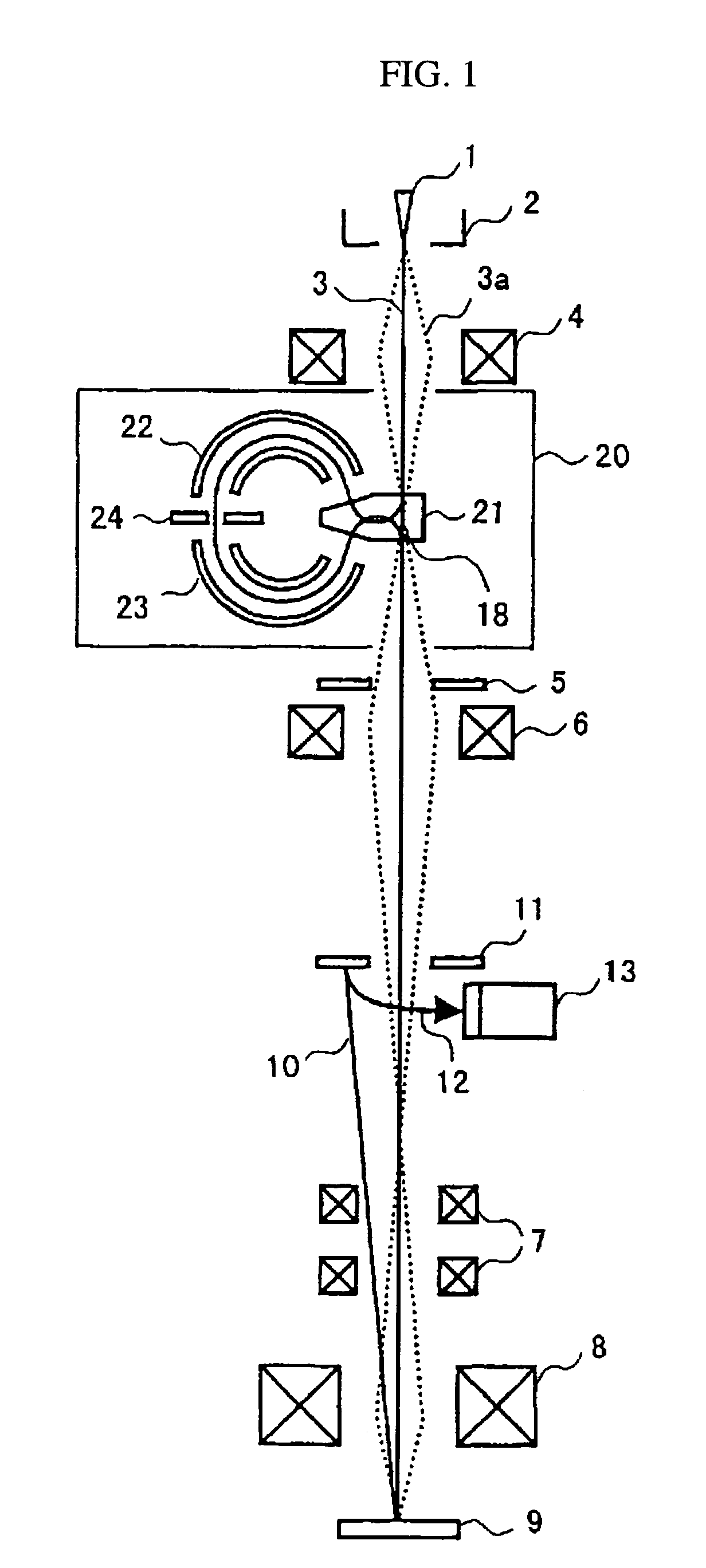
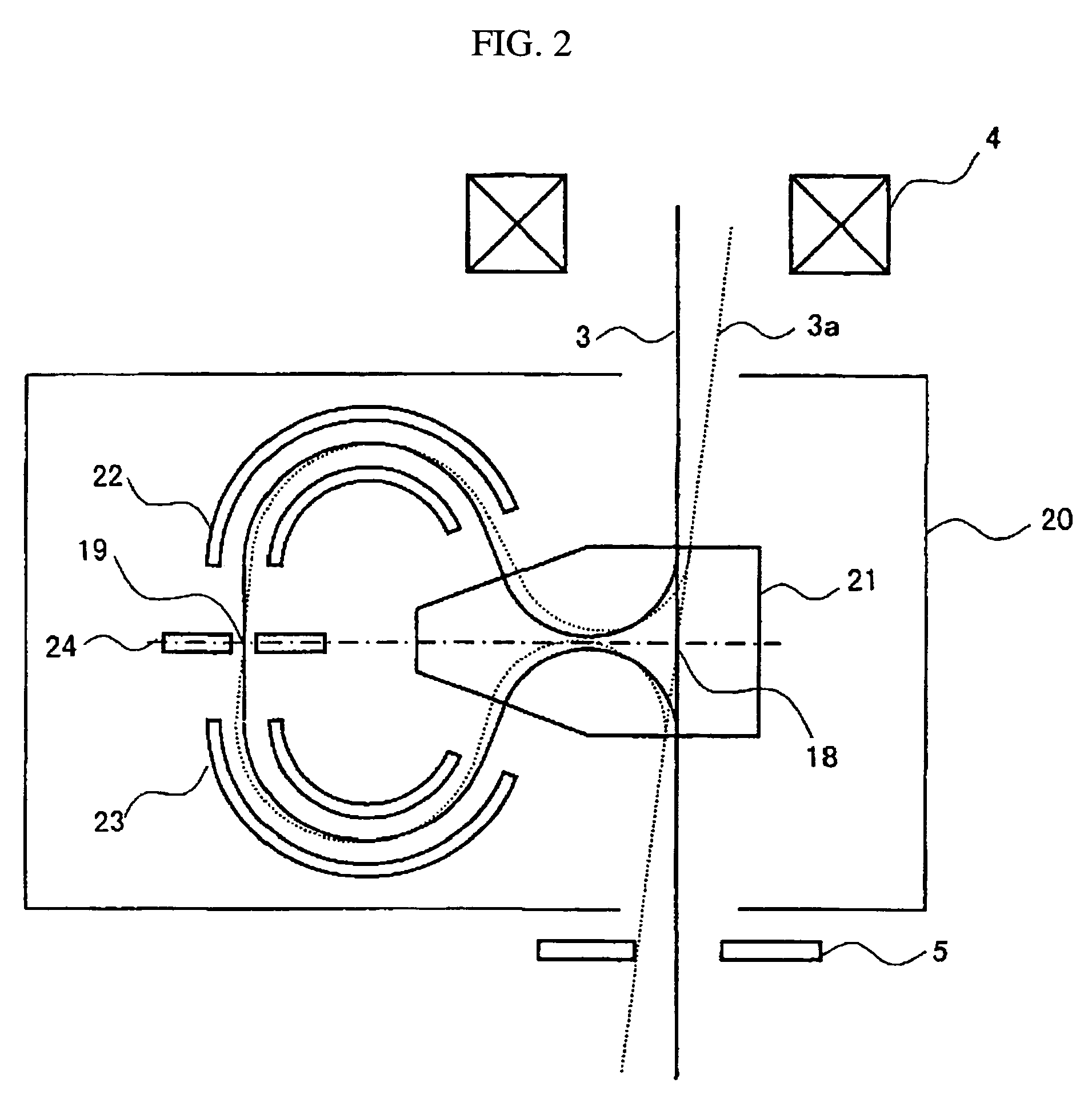
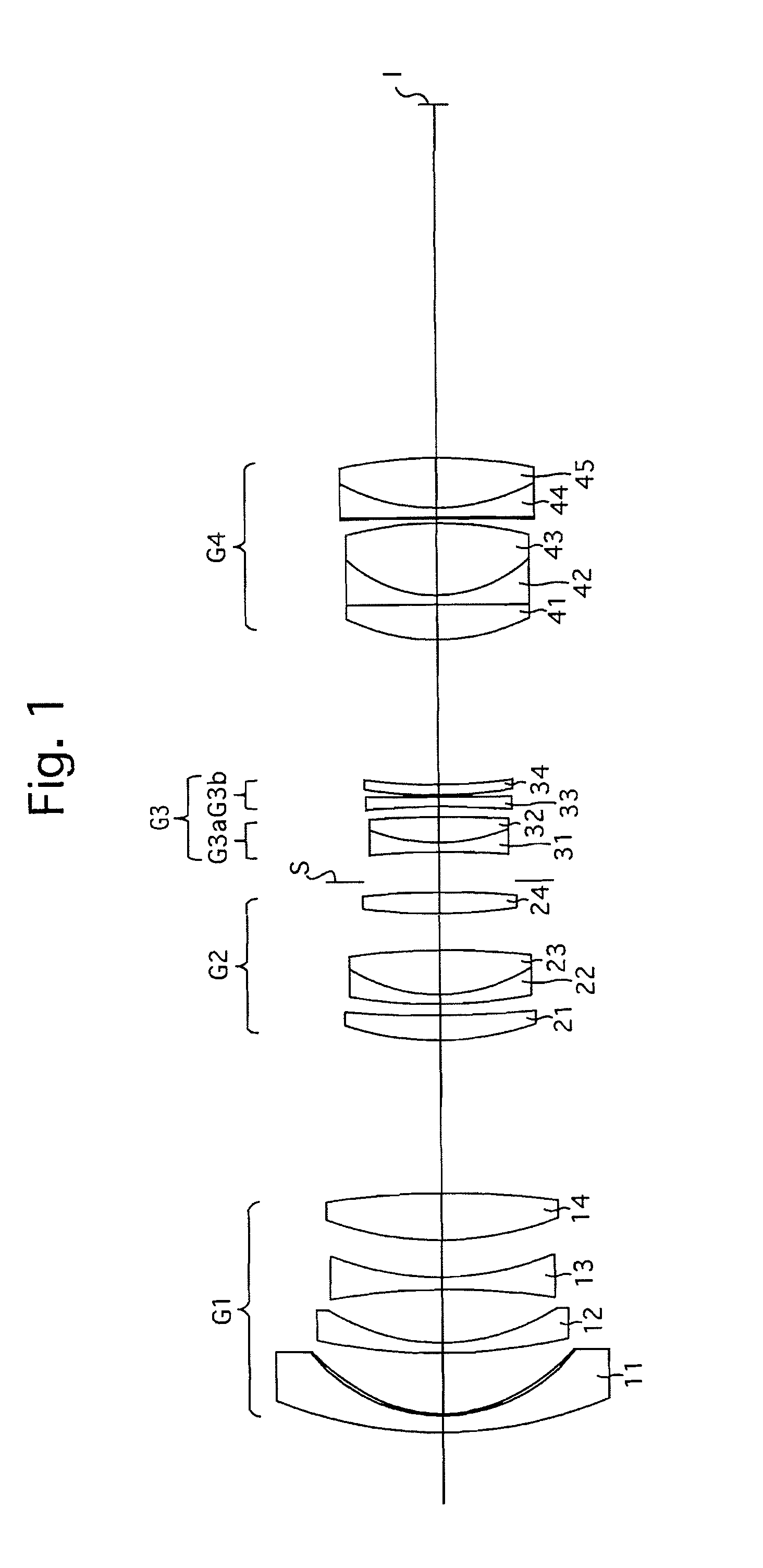
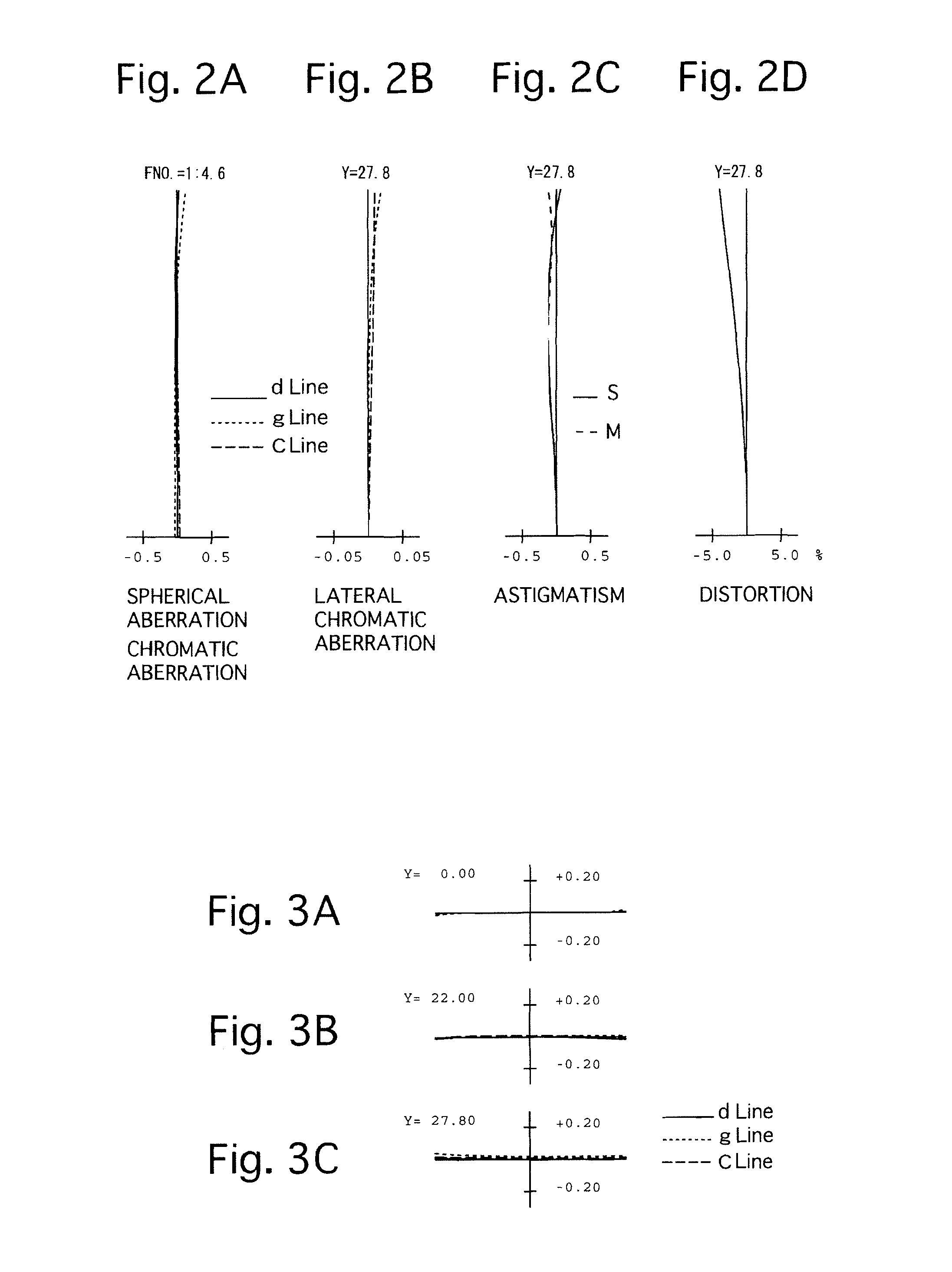
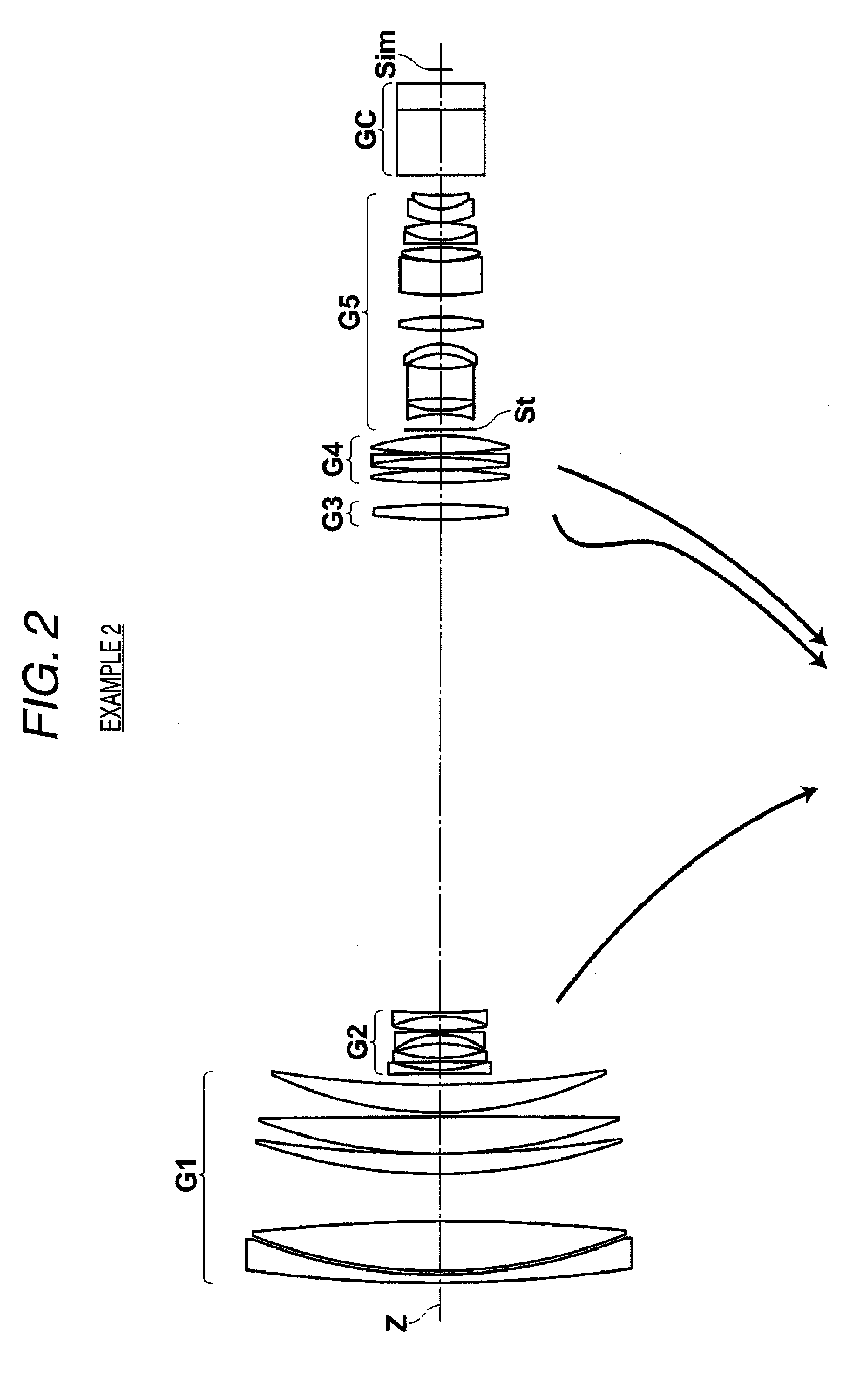
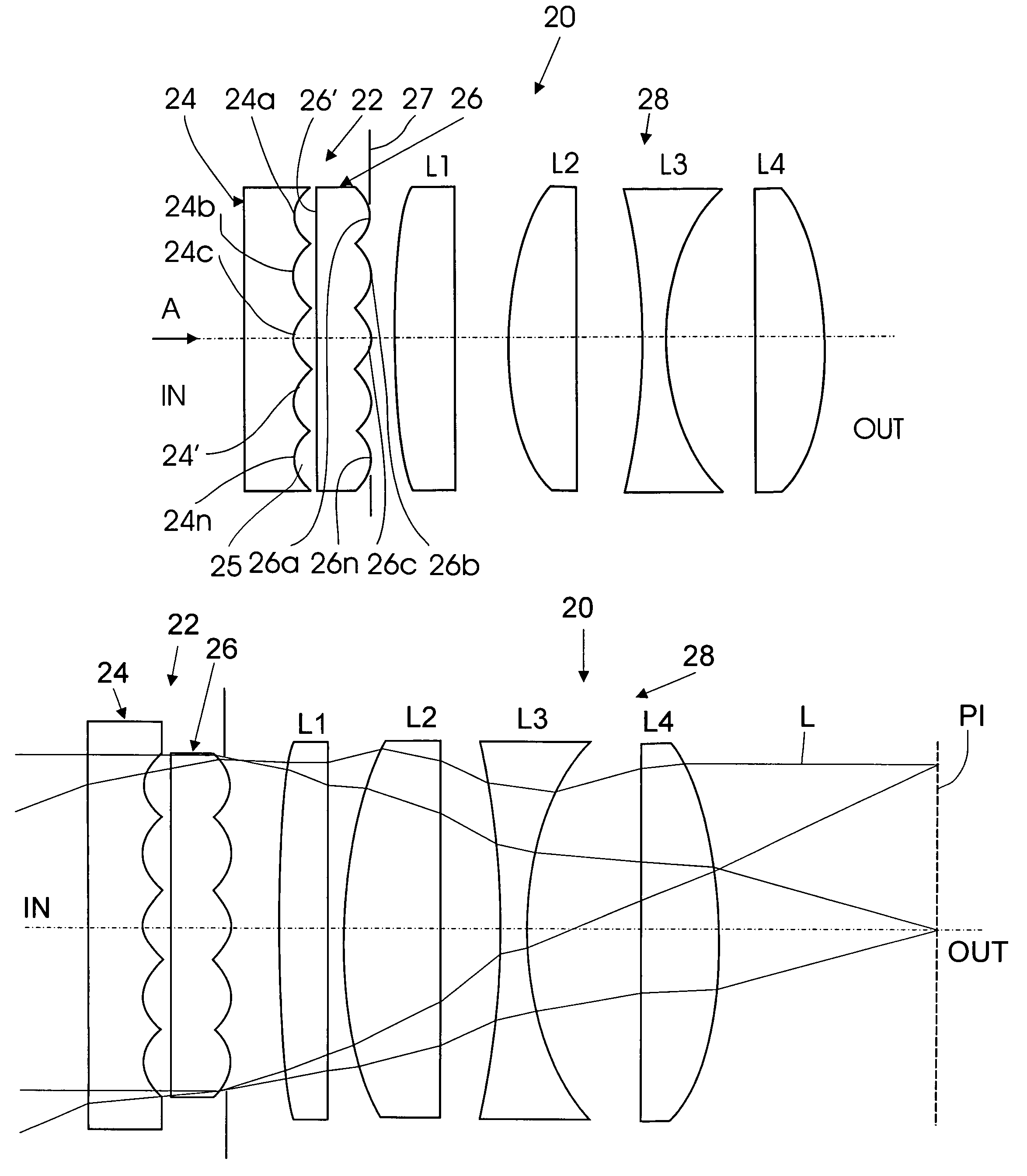
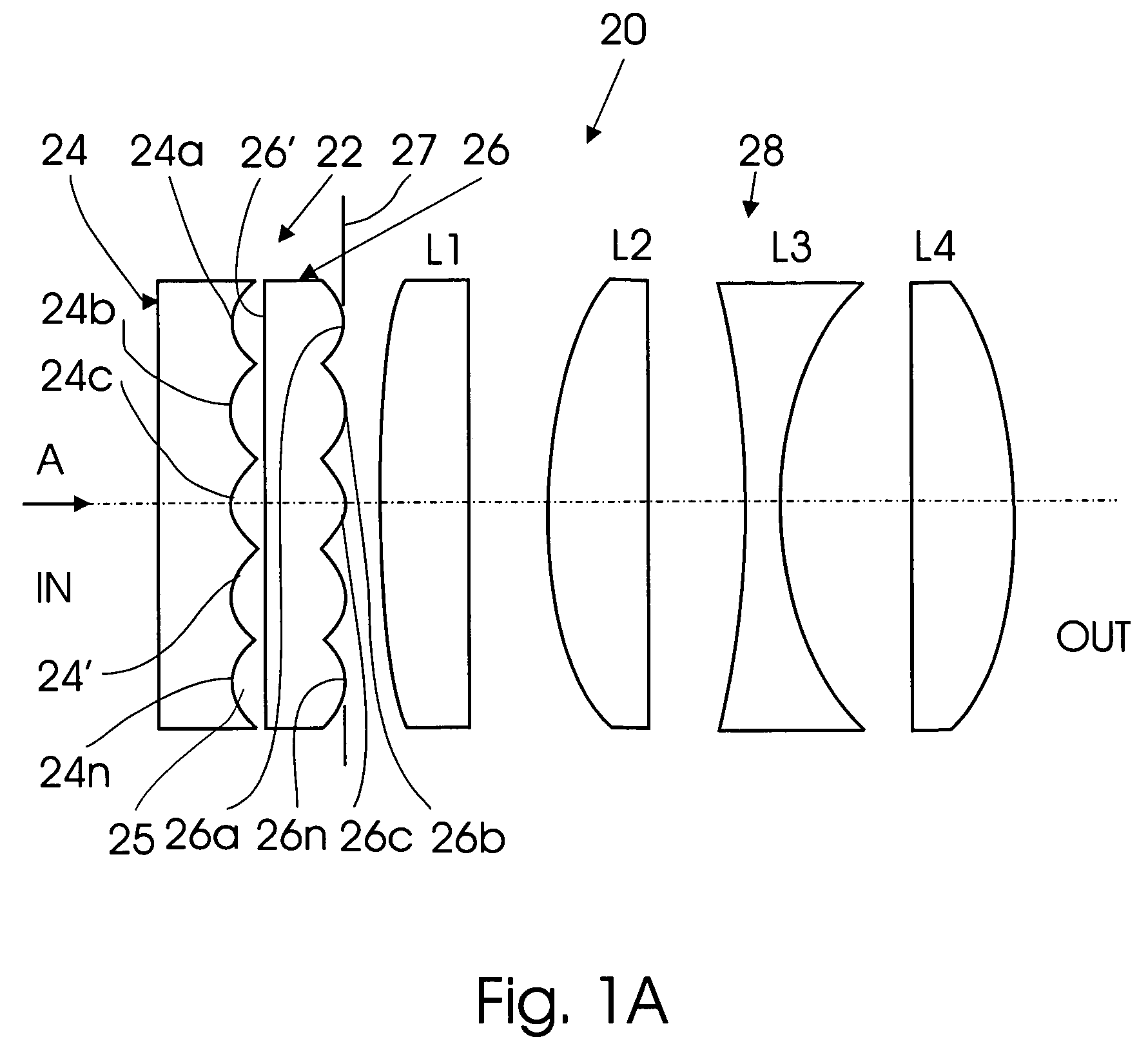
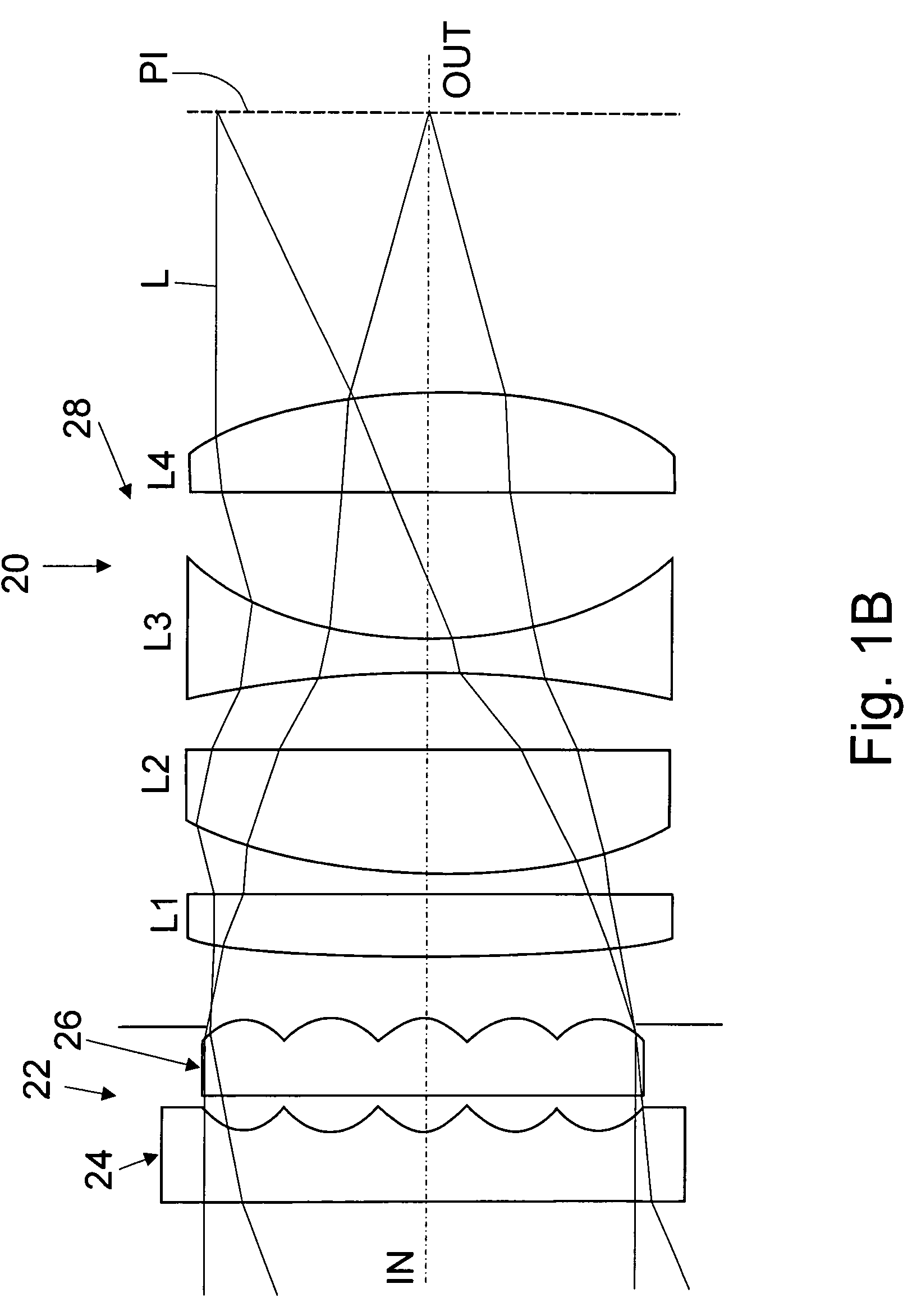
Flat wide-angle lens system
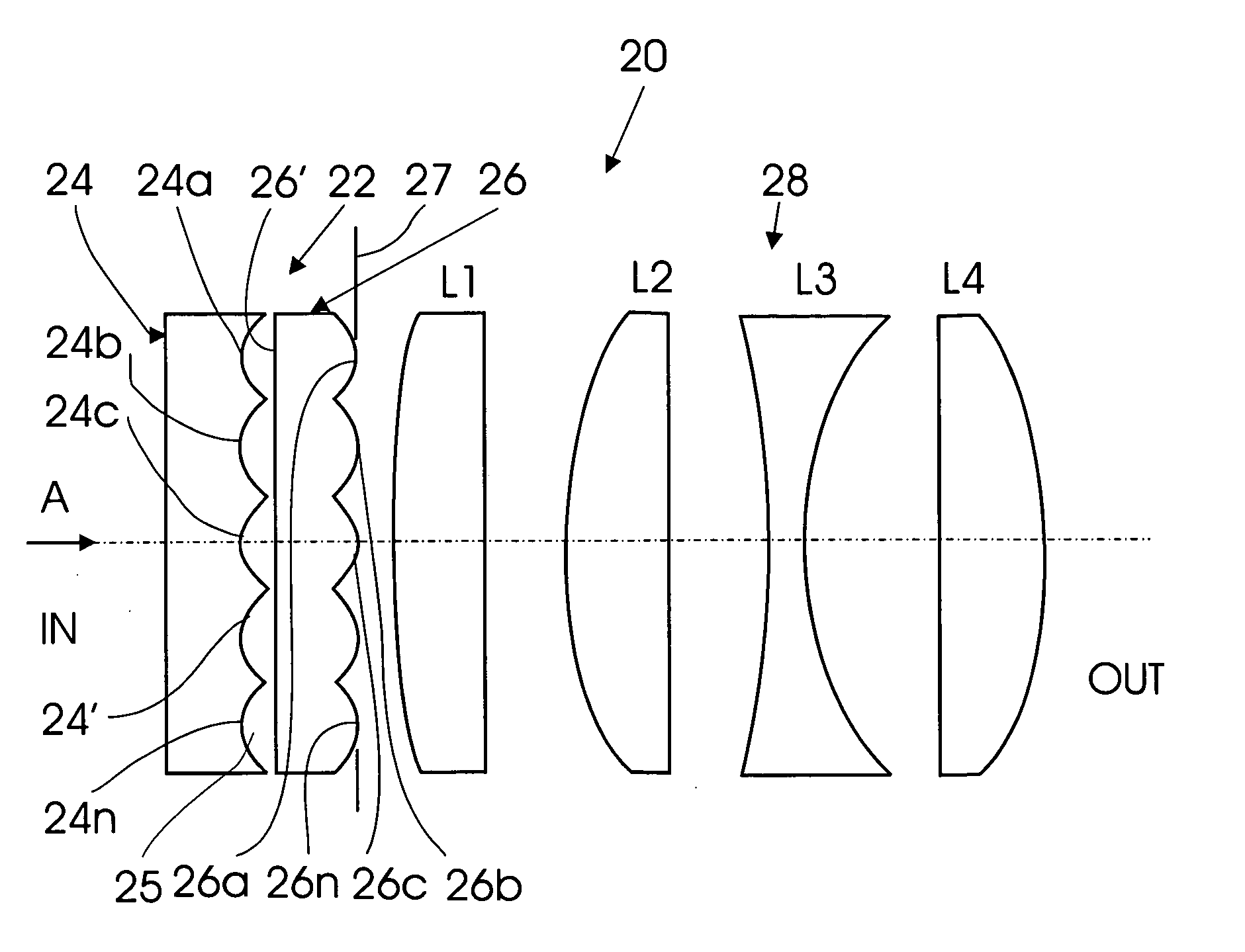
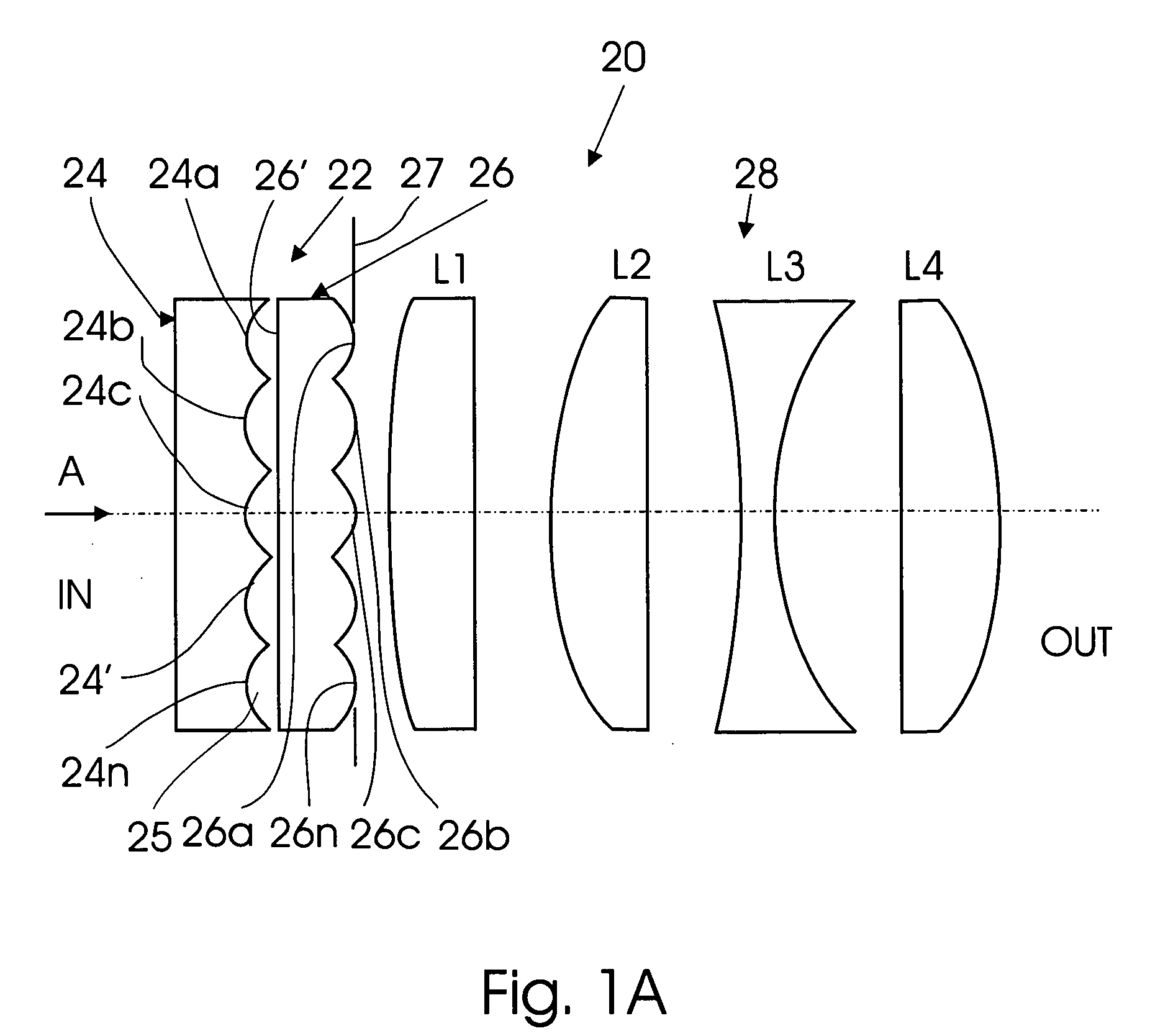
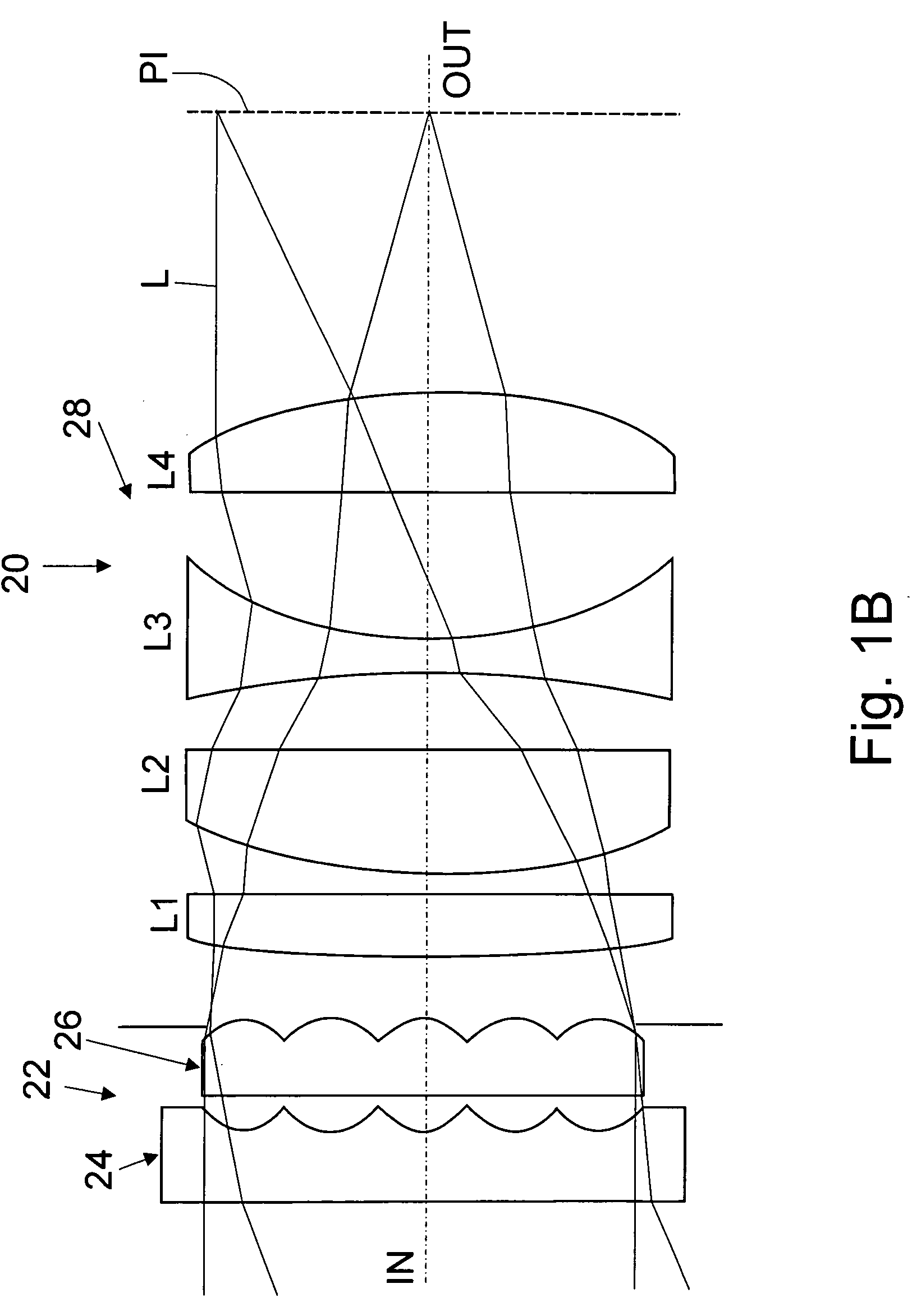
A flat wide-angle lens system of the invention has a reduced axial length and is intended for creating images with extremely wide angle of observation. The system consists of the first component which is intended for reduction of the field angle of light incidence onto the objective and comprises an assembly of at least two microlens arrays with the same pitch between the adjacent microlenses and arranged with respect to each other so as to provide afocality, and a second component that comprises an assembly of conventional spherical or aspherical microlenses that create an image on an image receiver. Each two coaxial microlenses of the microlens arrays of the first component form an inverted microtelescope of Galileo. The outlet aperture of a single microtelescope is made so that spherical aberration can be minimized almost to 0, while field aberrations can be corrected by design parameters of the microlenses.
Owner:MICROALIGN TECH
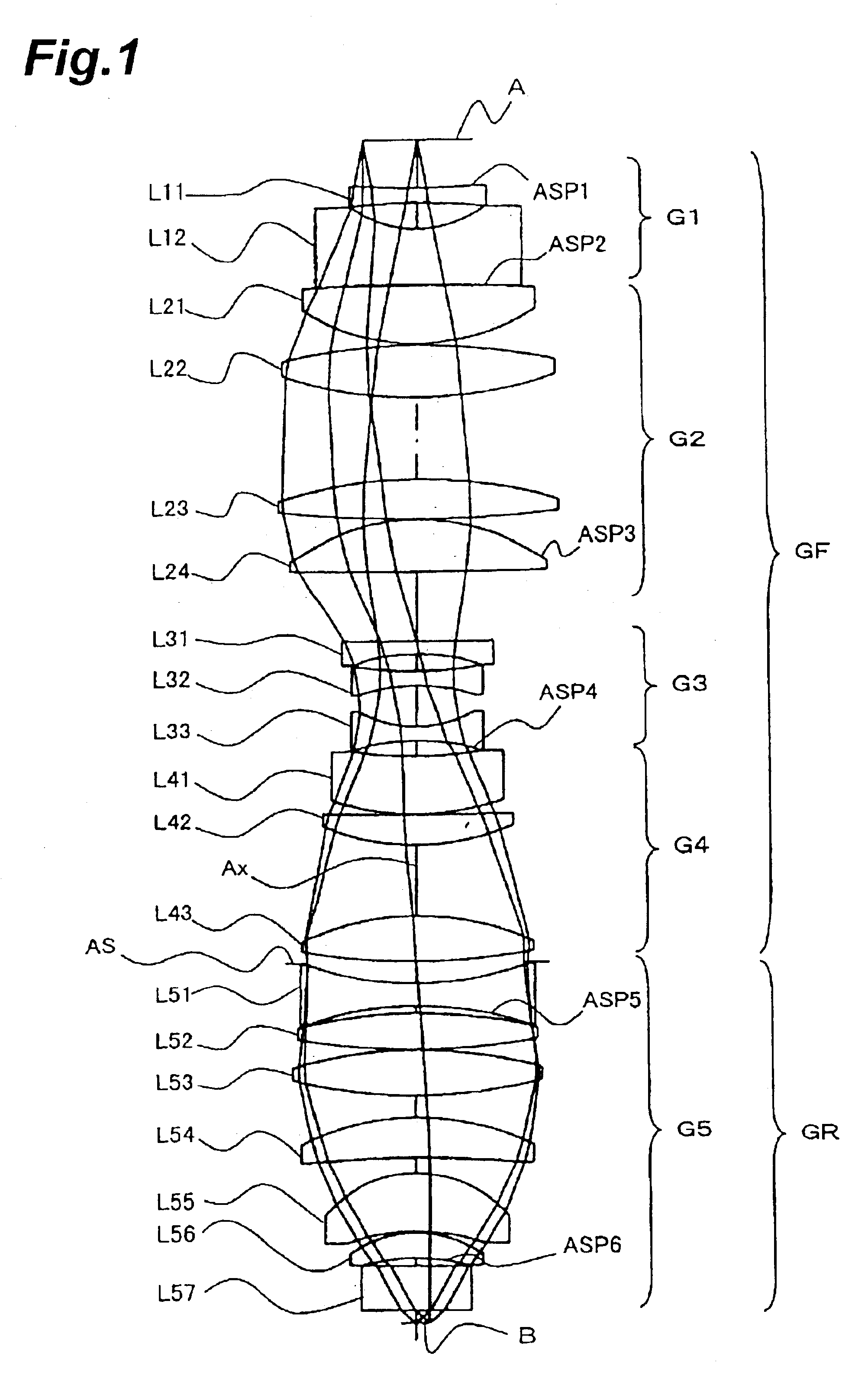
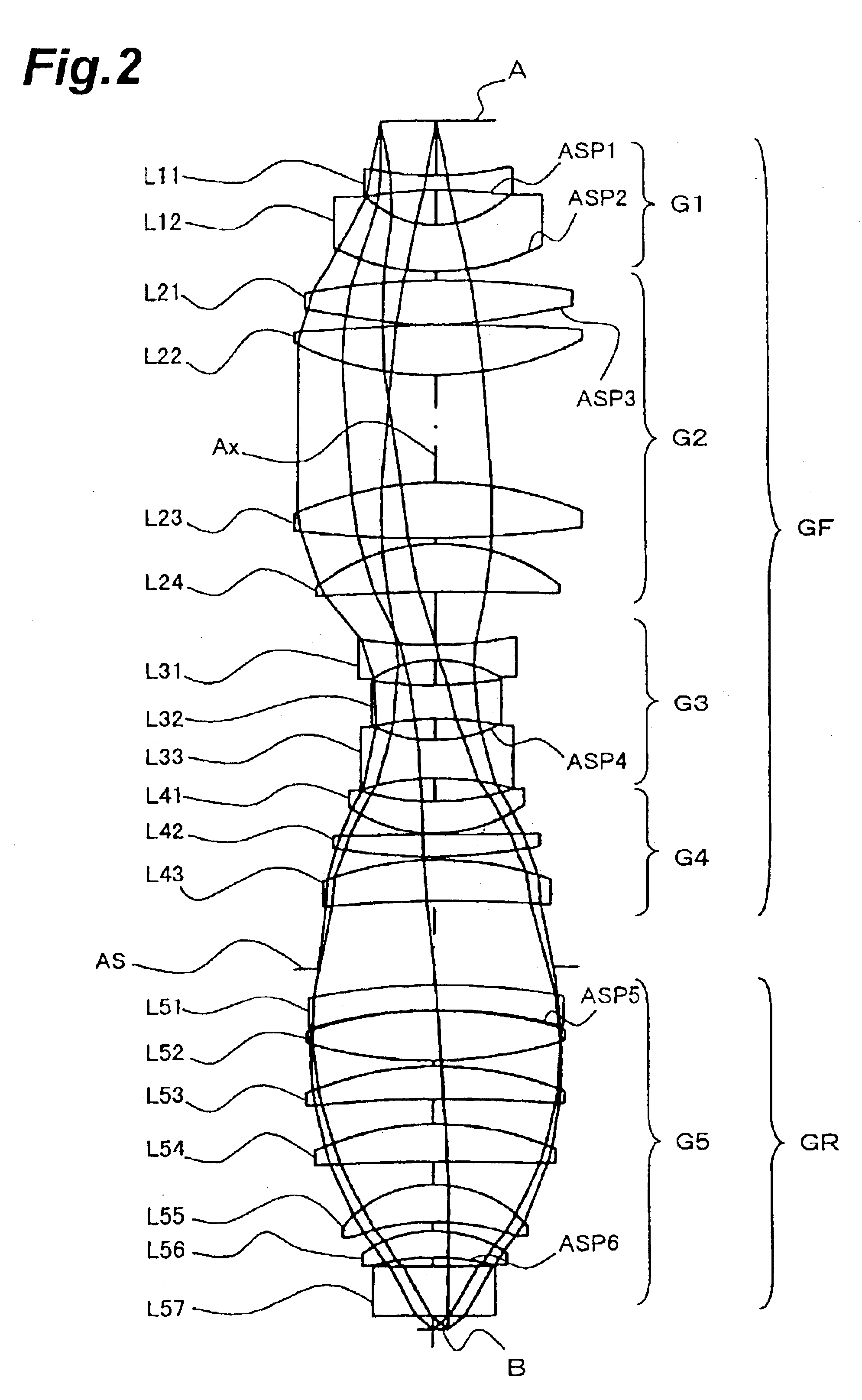
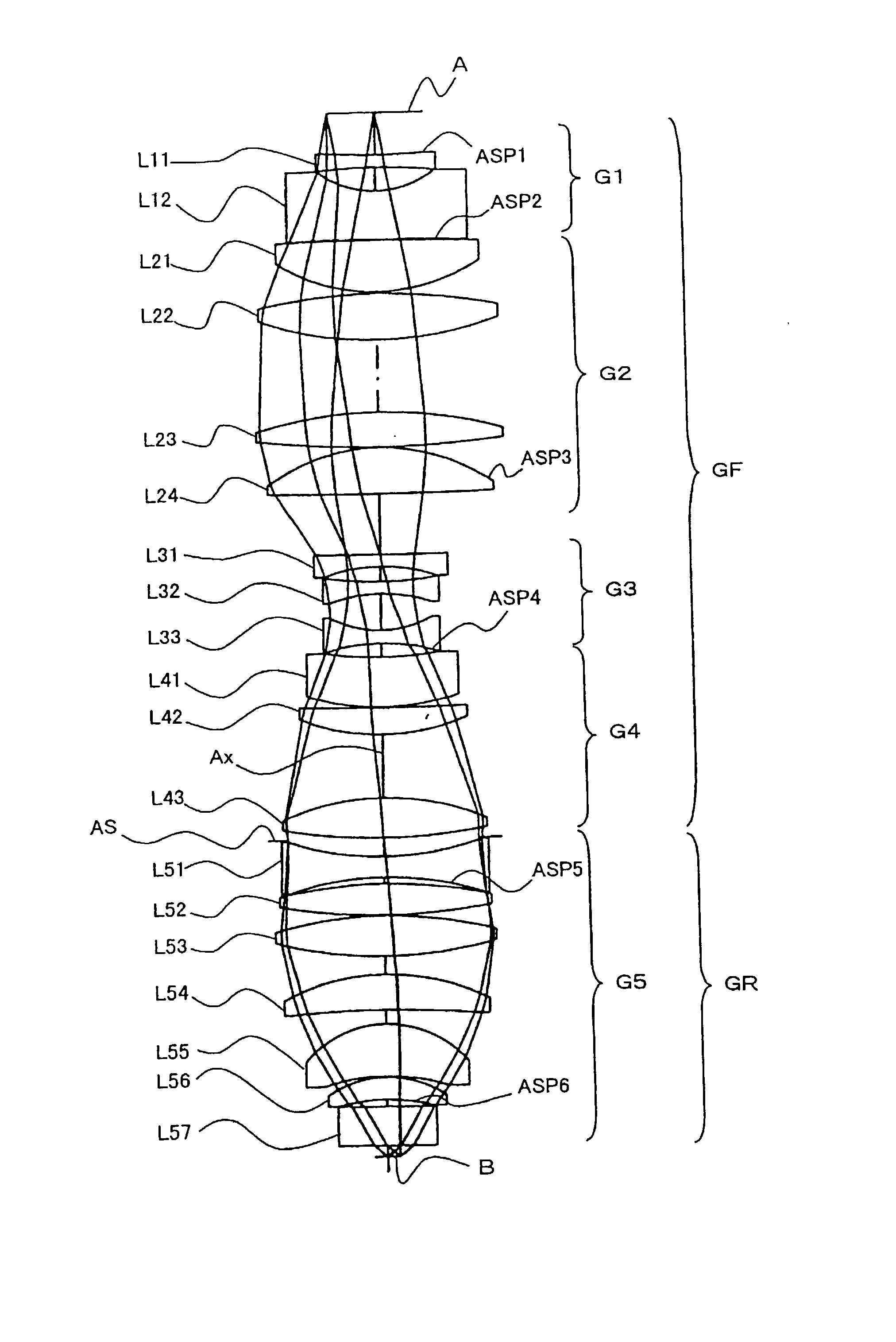
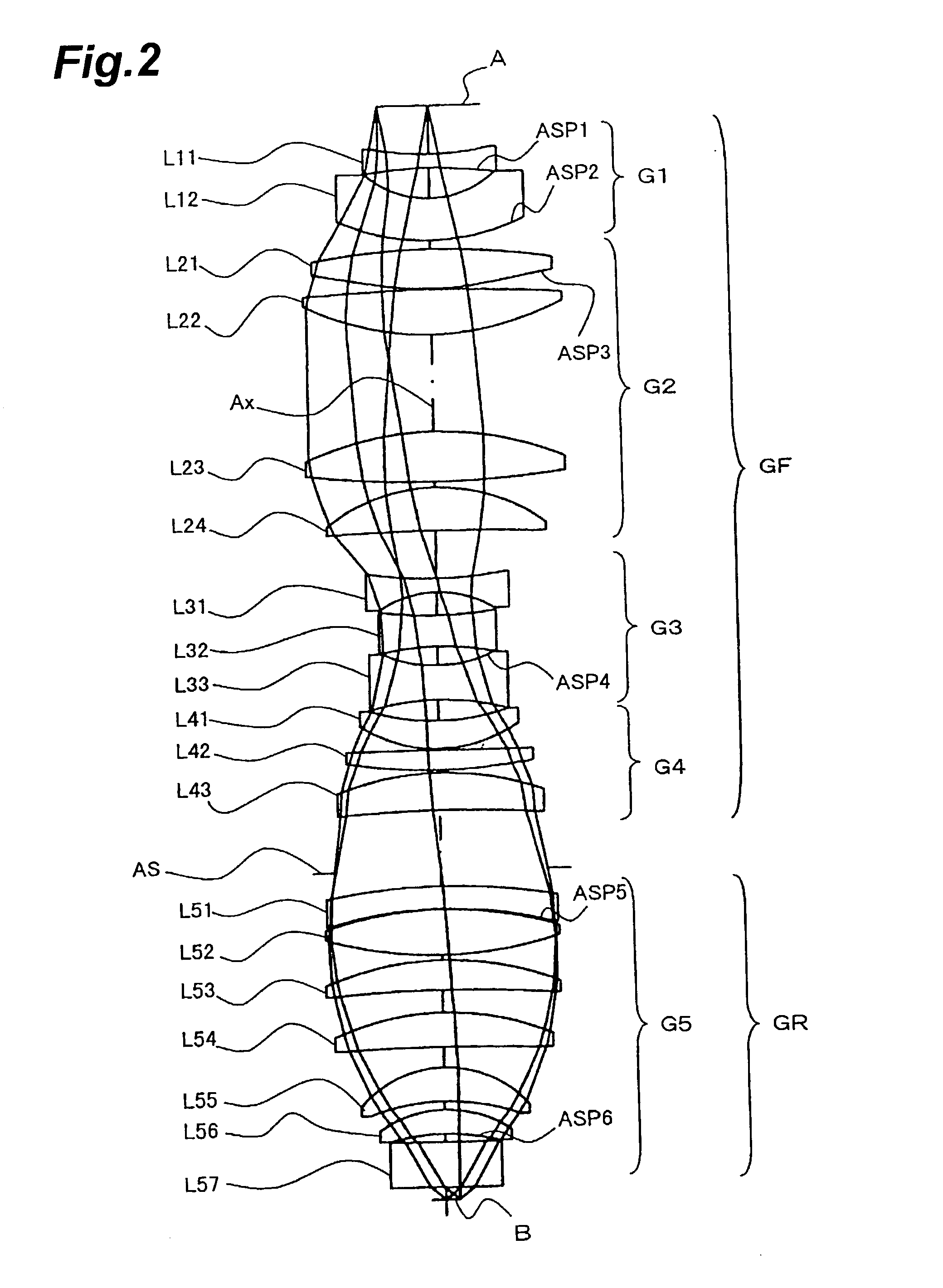
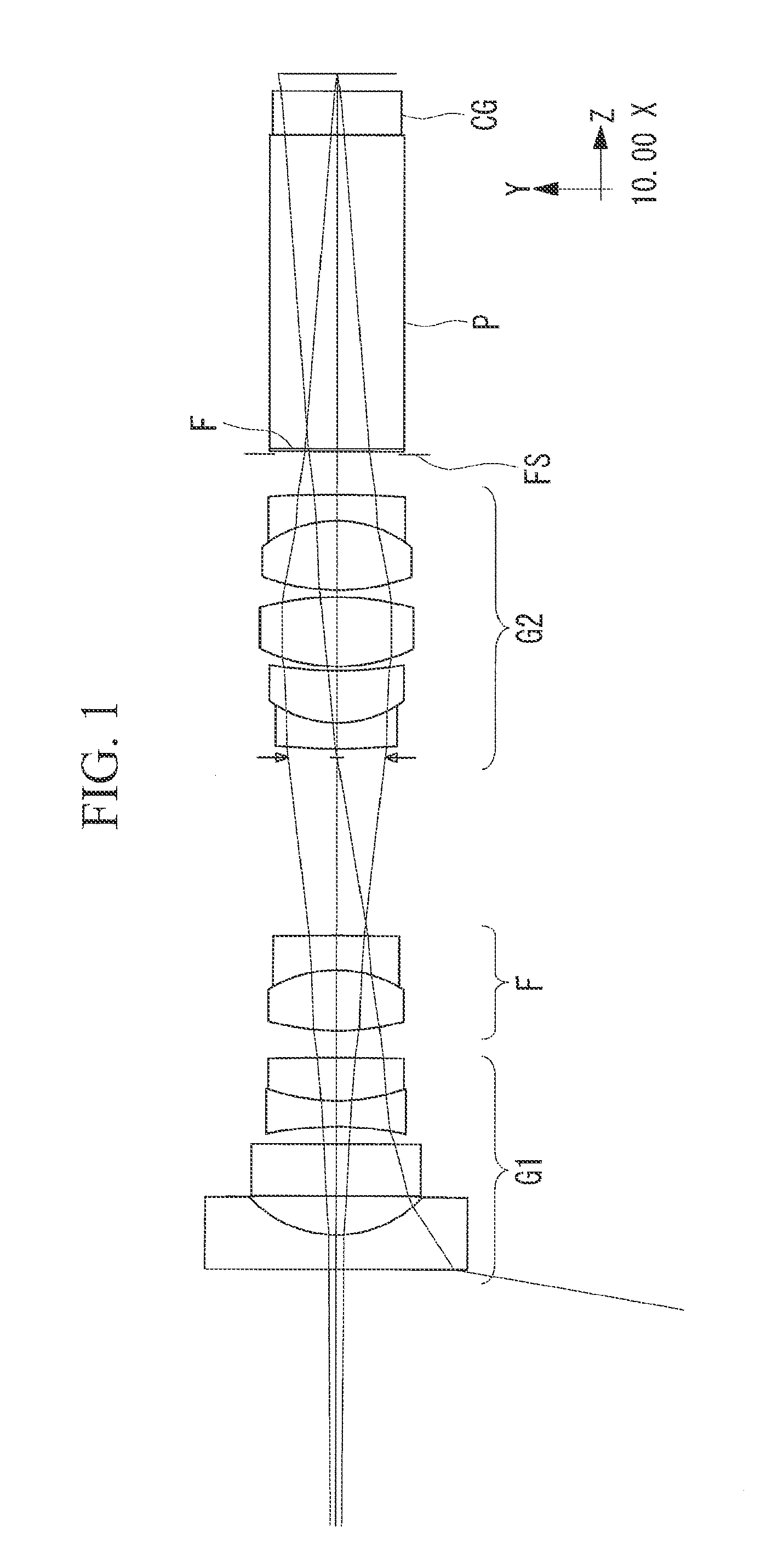
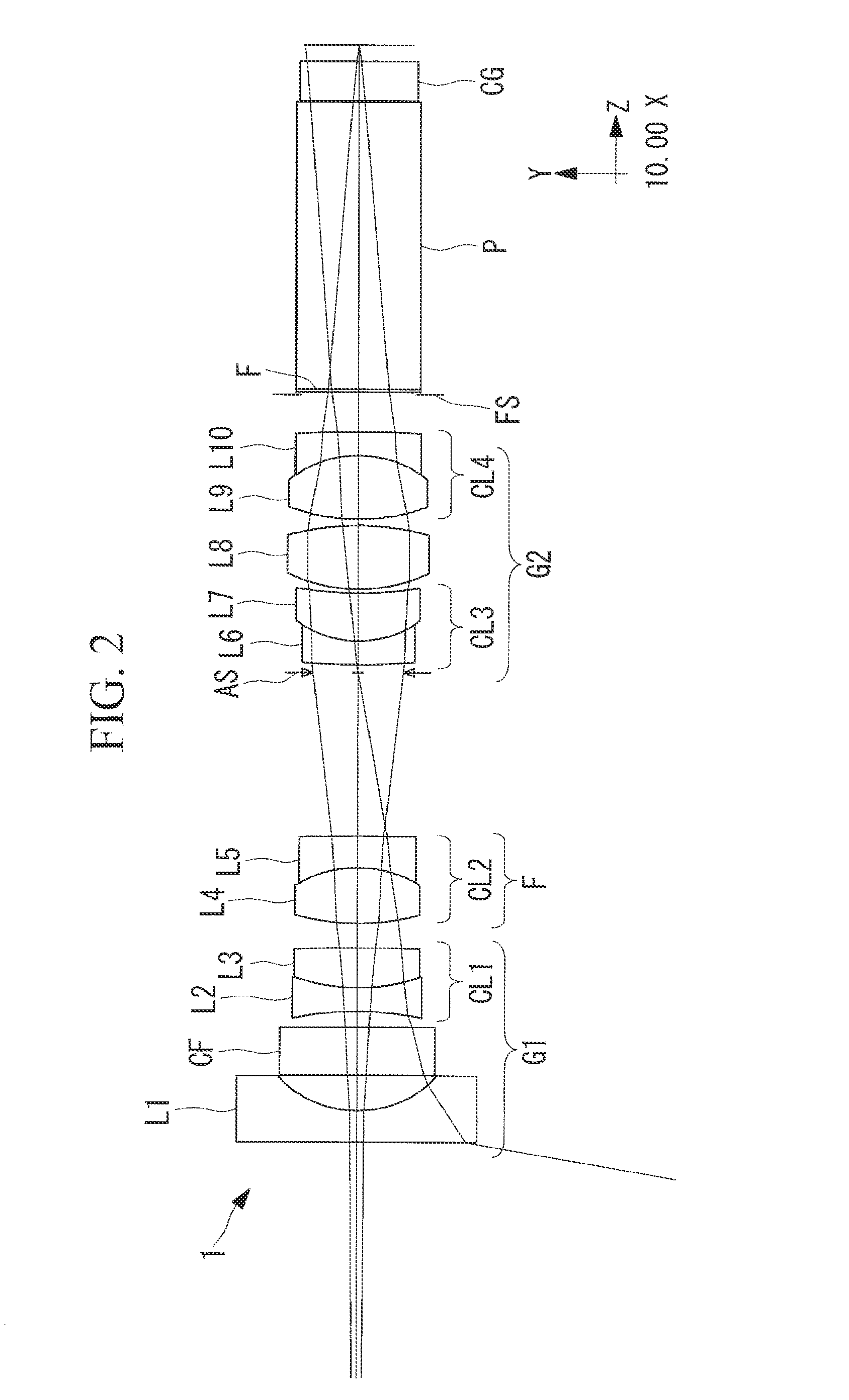
Projection exposure methods and apparatus, and projection optical systems
InactiveUS6864961B2Increase demandIncrease the number ofSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLithographic artistOptic system
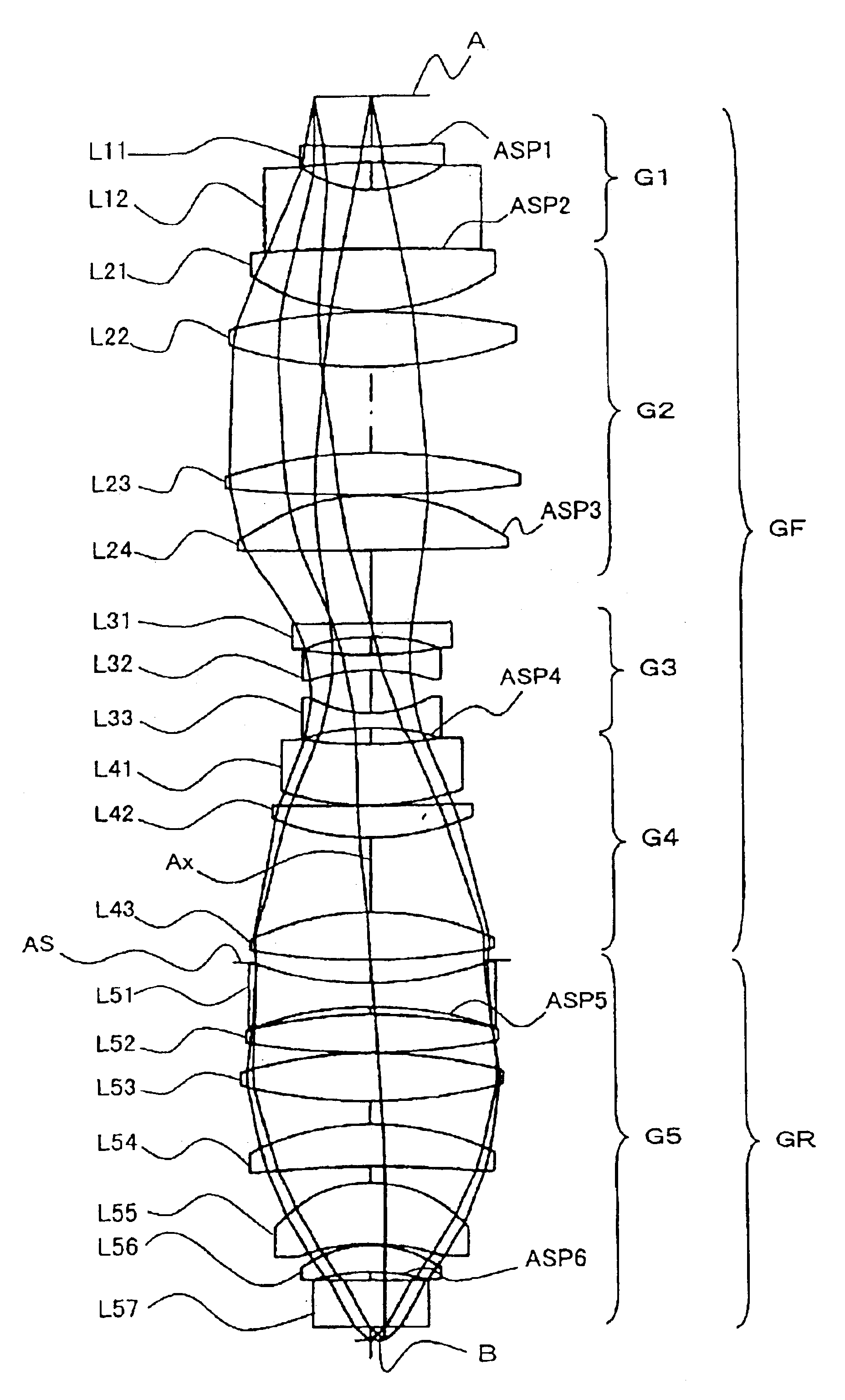
Provided is a dioptric projection optical system favorably applicable to projection exposure apparatus used in the lithography step in fabrication of microdevices such as semiconductor devices. This projection optical system includes a positive, front lens unit (GF), an aperture stop (AS), and a positive, rear lens unit (GR) and is a bitelecentric optical system. The optical system satisfies the following condition:0.065<f2 / L<0.125,where f2 is a focal length of the rear lens unit (GR) and L is a distance between an object and an image.The projection optical system includes at least one aspheric surface (ASP 1 to ASP 6).
Owner:NIKON CORP
Projection exposure methods and apparatus, and projection optical systems
InactiveUS20030147061A1Increase demandIncrease the number ofSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOptic systemRadiation
A dioptric projection optical system for imaging a reduced image of a pattern on a first surface onto a second surface using radiation-transmitting refractors. The projection optical system has a front lens unit of a positive refracting power and a rear lens unit of a positive refracting power. An aperture stop is located in the vicinity of a rear focal point of the front lens unit.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Imaging lens and imaging apparatus equipped with the imaging lens
ActiveUS20150022905A1Field curvature can be sufficiently correctedField curvature being excessively corrected can be suppressedAdaptive controlOptical elementsImaging lensImaging equipment
An imaging lens substantially includes six lenses, constituted by: a first lens having a negative refractive power, which is of a meniscus shape having a concave surface toward an image side; a second lens; a third lens; a fourth lens; a fifth lens having a positive refractive power; and a sixth lens having a negative refractive power, a concave surface toward the image side, and at least one inflection point in the surface toward the image side; provided in this order from an object side. The imaging lens satisfies a predetermined conditional formula.
Owner:JIANGXI OFILM OPTICAL CO LTD
Laser irradiation apparatus and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050111105A1Minimize regionImaging optical system can be miniaturizedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCondensersSemiconductorLens array
When a rectangular image having homogeneous intensity distribution is transferred by an imaging optical system, aberration adversely affects the homogeneity of the intensity distribution. The present invention provides a laser irradiation apparatus that can suppress the aberration due to the imaging optical system typified by a cylindrical lens, that can enlarge the square measure of the beam spot in which the intensity distribution is homogenous, and that can anneal the irradiated surface homogeneously efficiently. Moreover, the present invention provides a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device with the use of the laser irradiation apparatus. In the present invention, the divergence of the laser beam is suppressed and the size of the imaging optical system is miniaturized by using an off-axis lens array such as an off-axis cylindrical lens array. By the miniaturization, it is possible to reduce the cost, to facilitate the maintenance, and to suppress the aberration. By suppressing the aberration, the homogeneity of the intensity distribution of the beam spot can be improved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Zoom Lens And Image Pickup Device
ActiveUS20150109485A1Enhanced inhibitory effectSmall sizeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsConditional expressionRefractive index
A first lens group includes a plano-concave and negative first lens, a catoptric element having a flat object side surface and a flat image side surface, and a first cemented lens, for example. Here, the first cemented lens includes a negative second lens and a positive third lens in order from an object side. A second lens group includes an aperture stop and a positive second cemented lens, for example. The second cemented lens includes a positive fourth lens, a negative fifth lens, and a positive sixth lens in order from the object side. A zoom lens satisfies a conditional expression 1.59<n21<2.20, assuming that a value n21 indicates refractive index of the fourth lens on a side closest to an object in the second lens group.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
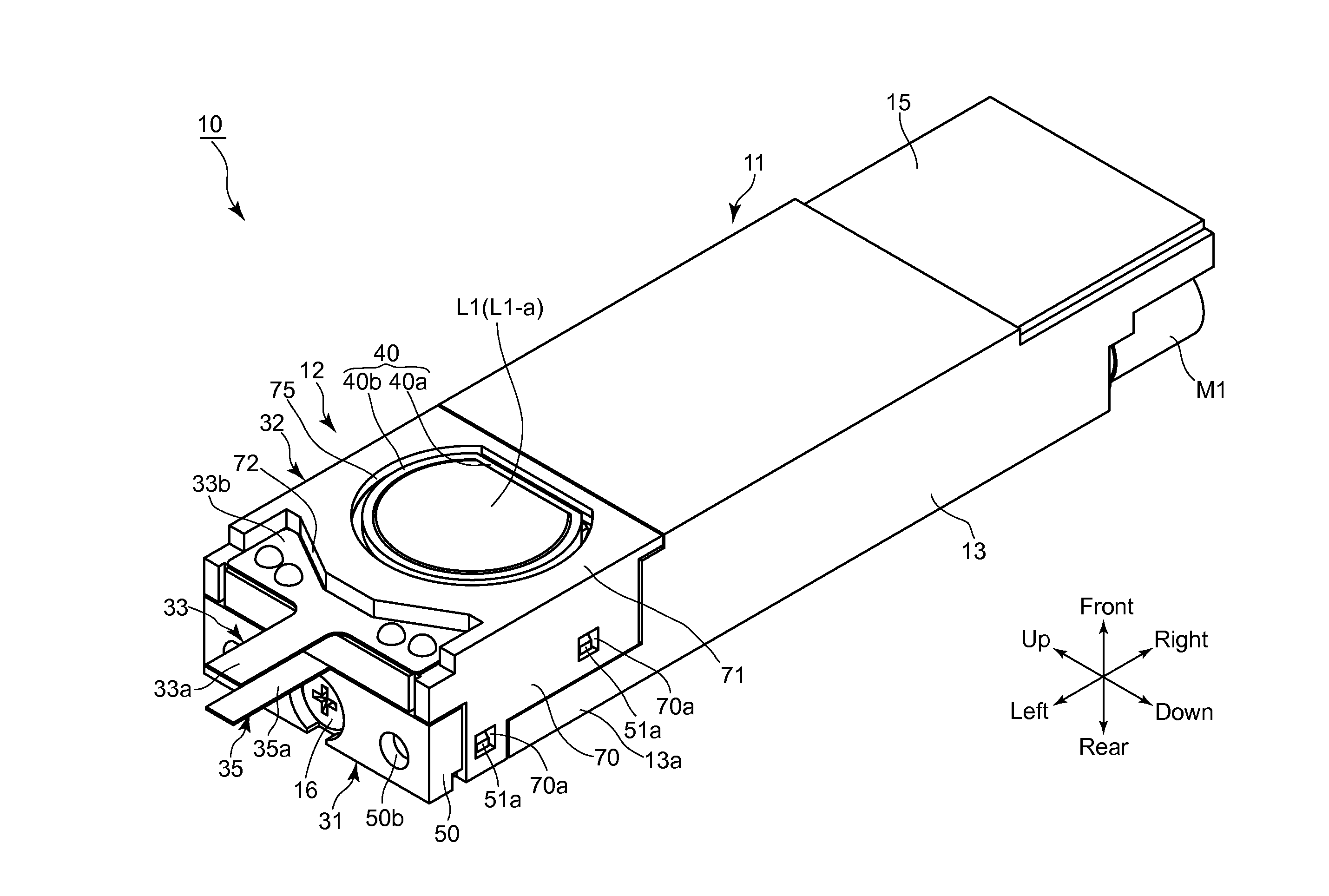
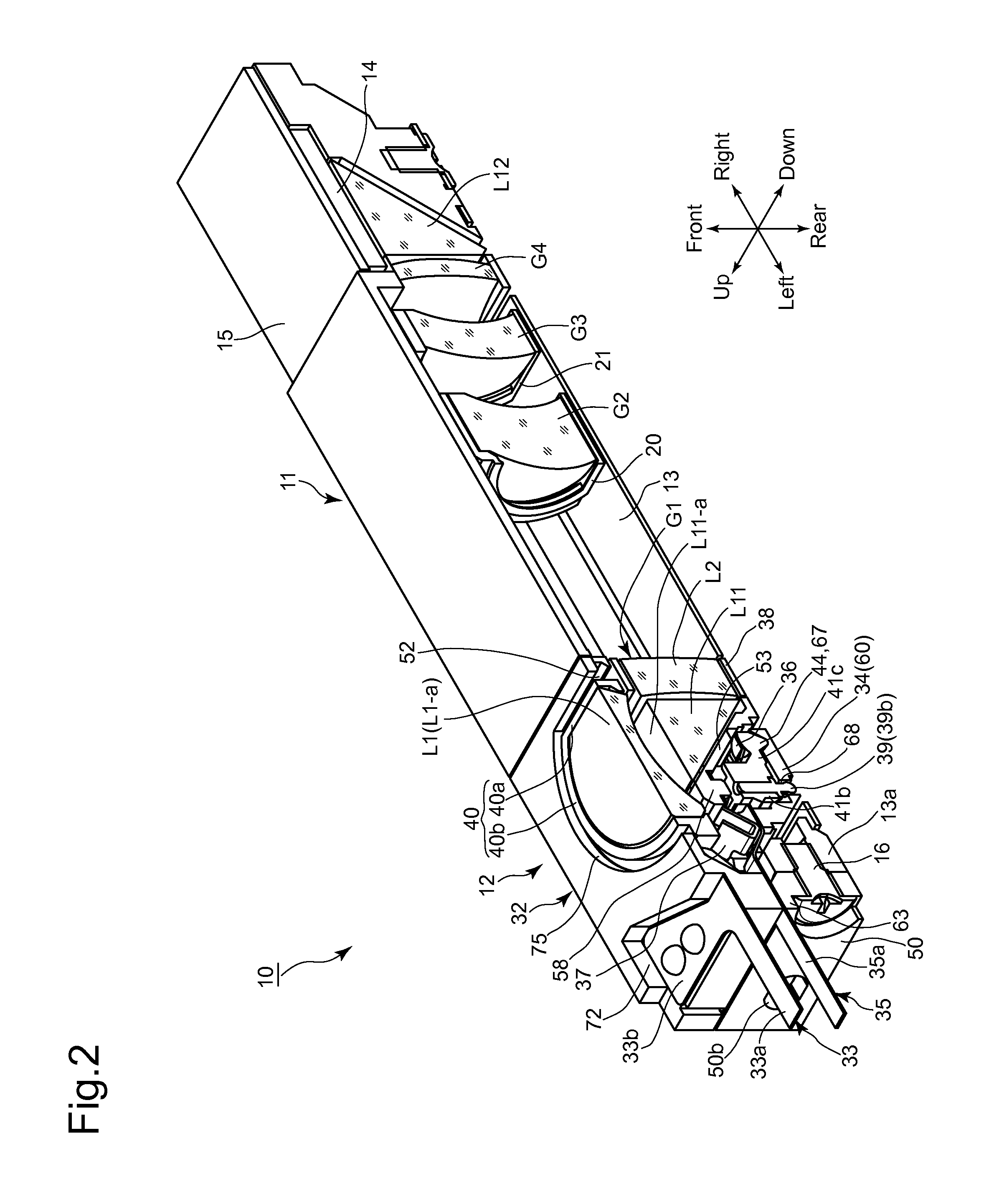
Imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20150215541A1Small sizeSuperior in image-stabilizing capabilityTelevision system detailsPrintersOptical axisOptoelectronics
An imaging apparatus includes a front lens group having a front lens element and a reflector, in that order from an object side. The reflector includes a reflection surface which reflects light rays, from the front lens element, toward a different direction; a rear lens group positioned closer to an image plane than the front lens group, the imaging apparatus performs an image-stabilizing operation by driving the front lens element, a movable frame holding the front lens element; a support member supporting the reflector and is immovable relative to an optical axis of the front lens element, in a reference state; and a support mechanism which supports the movable frame to spherically swing about a spherical-swinging center, positioned on an extension of the optical axis of the front lens element extending behind an underside of the reflection surface of the reflector.
Owner:HOYA CORP
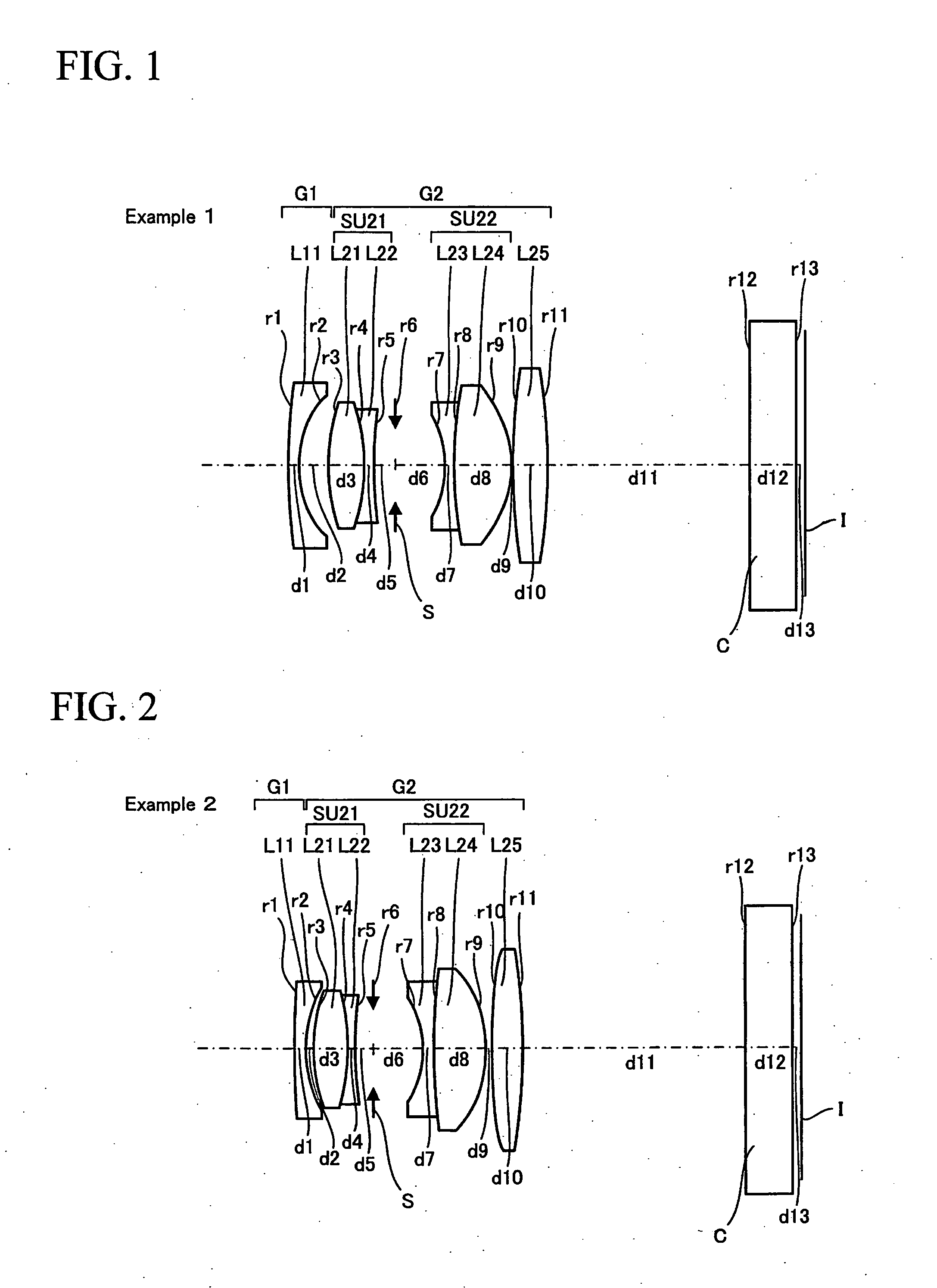
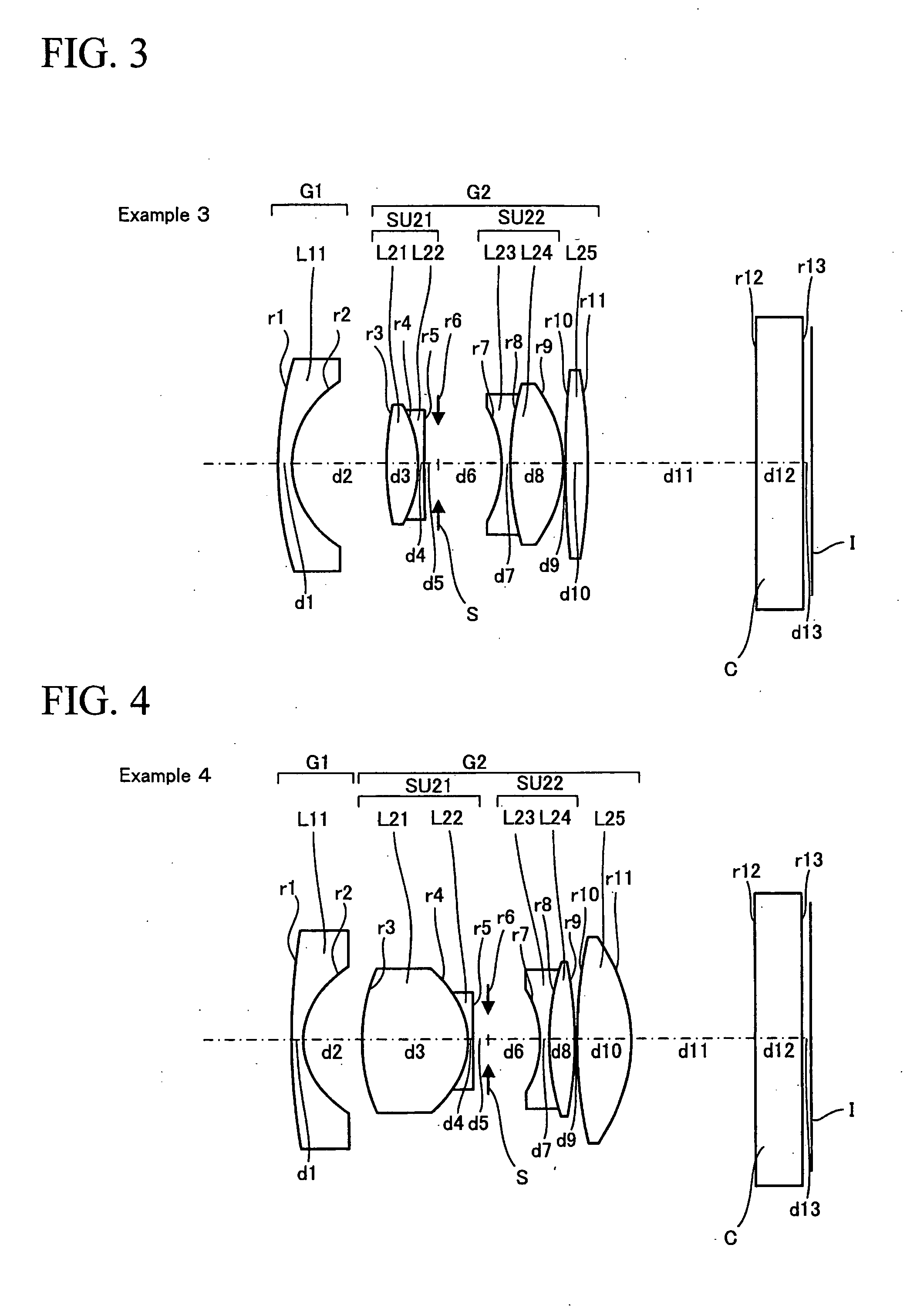
Wide angle optical system and image pickup apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20100201782A1Easy to correctHigh optical performanceTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementCamera lensLenticular lens
A wide angle optical system includes:a first lens group of negative refractive power; anda second lens group of positive refractive power;the first lens group and the second lens group being arranged in the above-mentioned order from the object side;the second lens group including:a cemented doublet SU21; an aperture diaphragm;a lens SU22; anda biconvex lens L25; the cemented doublet, the aperture diaphragm, the lens and the biconvex lens being arranged in the above-mentioned order from the object side;the largest ones of the air spaces on the axis being the front and rear spaces of the aperture diaphragm except the back focal length;the wide angle optical system being divided into the first lens group and the second lens group at the second largest air space operating as a boundary.
Owner:OM DIGITAL SOLUTIONS CORP
Photographing optical lens assembly, image capturing unit and electronic device
ActiveUS20160103299A1Shorten the lengthFavorable moldability and homogeneityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensPhysics
A photographing optical lens assembly includes, in order from an object side to an image side, a first lens element, a second lens element, a third lens element, a fourth lens element, a fifth lens element and a sixth lens element. The first lens element with positive refractive power has an object-side surface being convex in a paraxial region. The second lens element has refractive power. The third lens element has positive refractive power. The fourth lens element has refractive power. The fifth lens element with positive refractive power has an object-side surface being convex in a paraxial region and an image-side surface being convex in a paraxial region. The sixth lens element with positive refractive power has an object-side surface being convex in a paraxial region and an image-side surface being concave in a paraxial region, and the image-side surface thereof has at least one inflection point.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Zoom lens, image magnification projection system and video projector using the zoom lens and rear projector and multi-vision system using the video projector
ActiveUS7173766B2Back focal lengthAberration suppressionProjectorsDiffraction gratingsOphthalmologyRefractive index
The present invention provides a zoom lens that suppresses the generation of unnecessary light and is suitable for a projection lens. The zoom lens is used as a projection lens of a projector in which a prism is located between the projection lens and a spatial optical modulating element B. A lens closest to the spatial optical modulating element B is a meniscus positive lens whose convex surface faces a screen. A refractive index of the meniscus positive lens is 1.75 or more.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
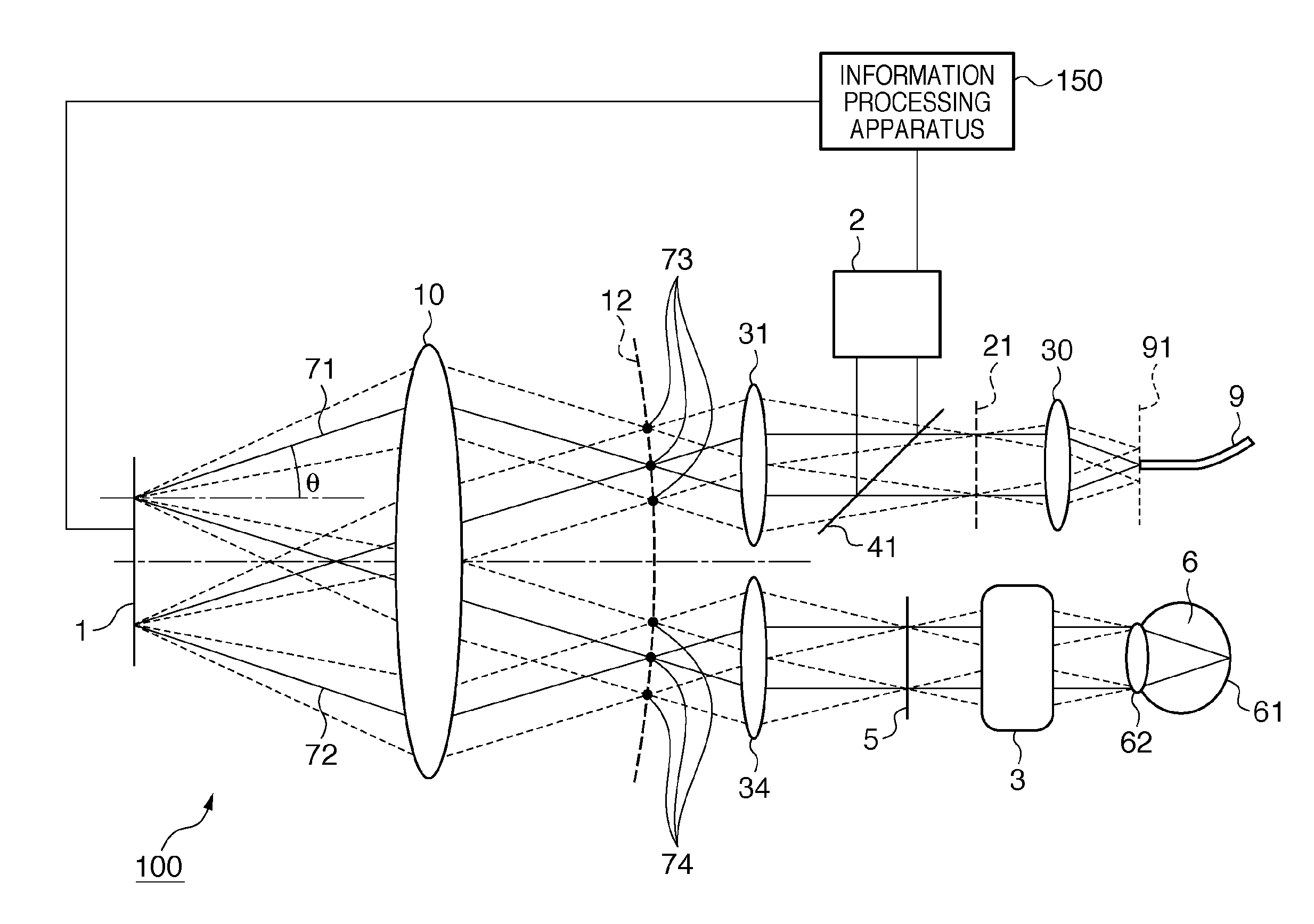
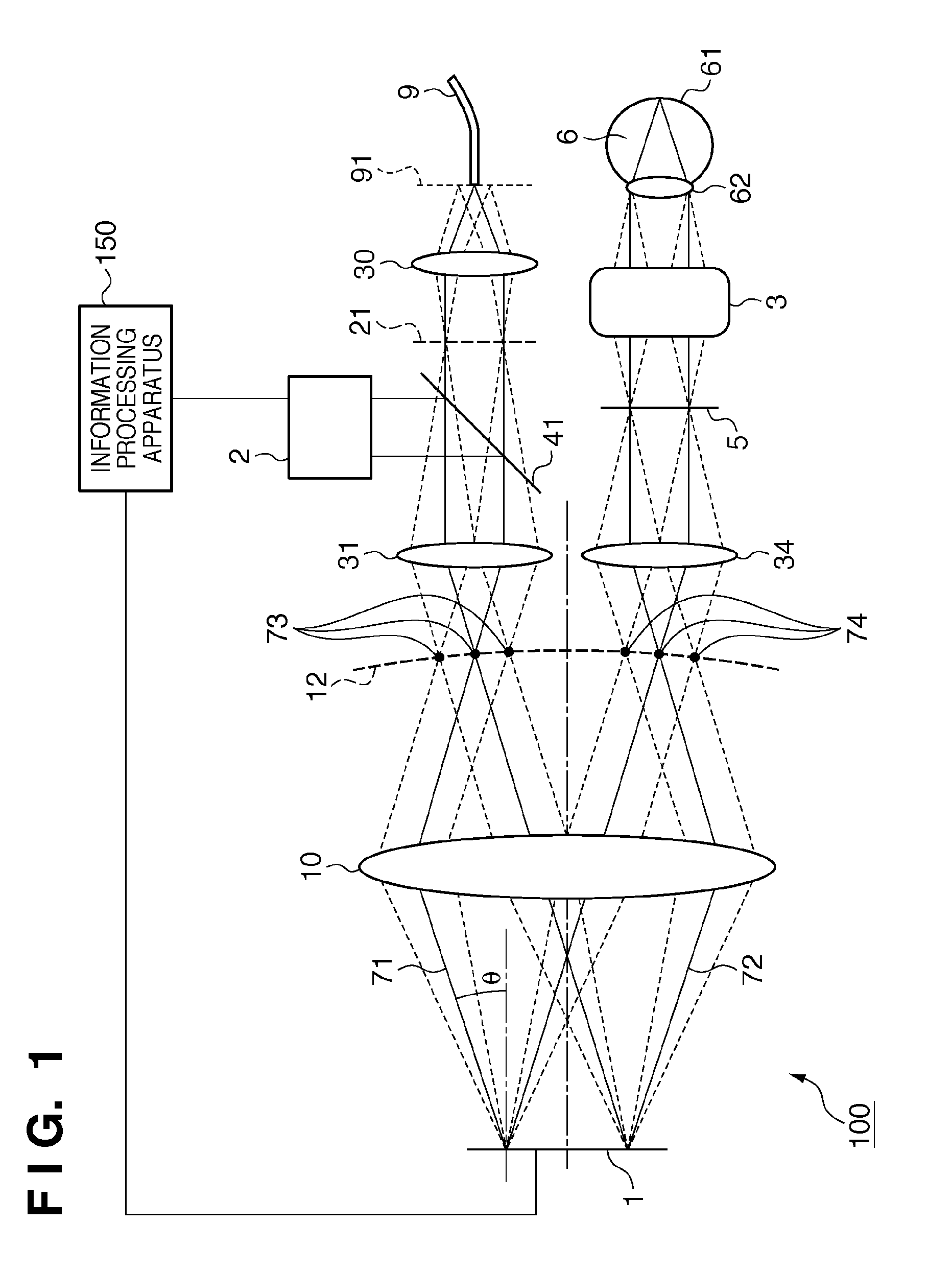
Ophthalmic apparatus, adaptive optical system, and image generating apparatus
ActiveUS20110279778A1Small sizeAberration suppressionPhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansOphthalmological deviceOptical aberration
An ophthalmic apparatus includes an aberration correction unit which corrects aberration occurring in light irradiating an eye to be examined; and a common optical system which is commonly provided for an optical path of irradiated light on the aberration correction unit and an optical path of reflected light from the aberration correction unit. The common optical system includes at least one optical element, and areas through which the irradiated light and the reflected light respectively pass overlap each other on the optical element.
Owner:CANON KK
Endoscopic Objective Optical System and Imaging Apparatus
ActiveUS20150042773A1Short work distanceBack focal lengthEndoscopesColor television detailsConditional expressionEngineering
To allow placement of optical members by providing a long back focus, make aberrations less subject to manufacturing errors, and reduce variations in aberrations during focusing. An endoscopic objective optical system includes, in order from an object side, a front group with negative refractive power, a focusing lens, and a rear group with positive refractive power, wherein: the endoscopic objective optical system satisfies conditional expressions (1) to (4) below:4<FB / FL (1)FL / |Fc|<0.1 (2)−3<F—F / FL<−0.9 (3)2.5<F—R / FL<5 (4)where FB is back focus of the entire system, FL is a focal length of the entire system, fc is a focal length of the focusing lens, |fc| is an absolute value of fc, F_F is a focal length of the front group, and F_R is a focal length of the rear group.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
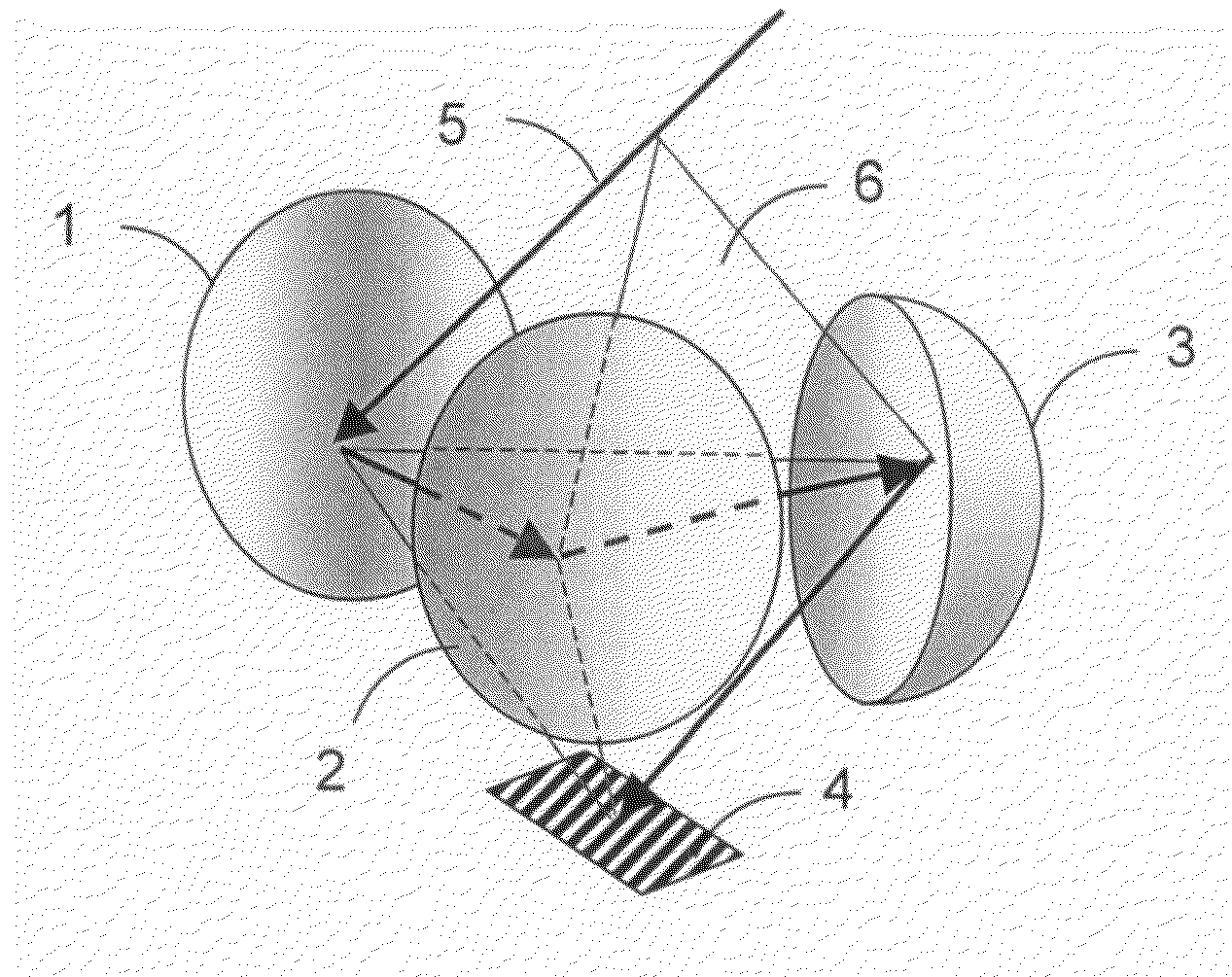
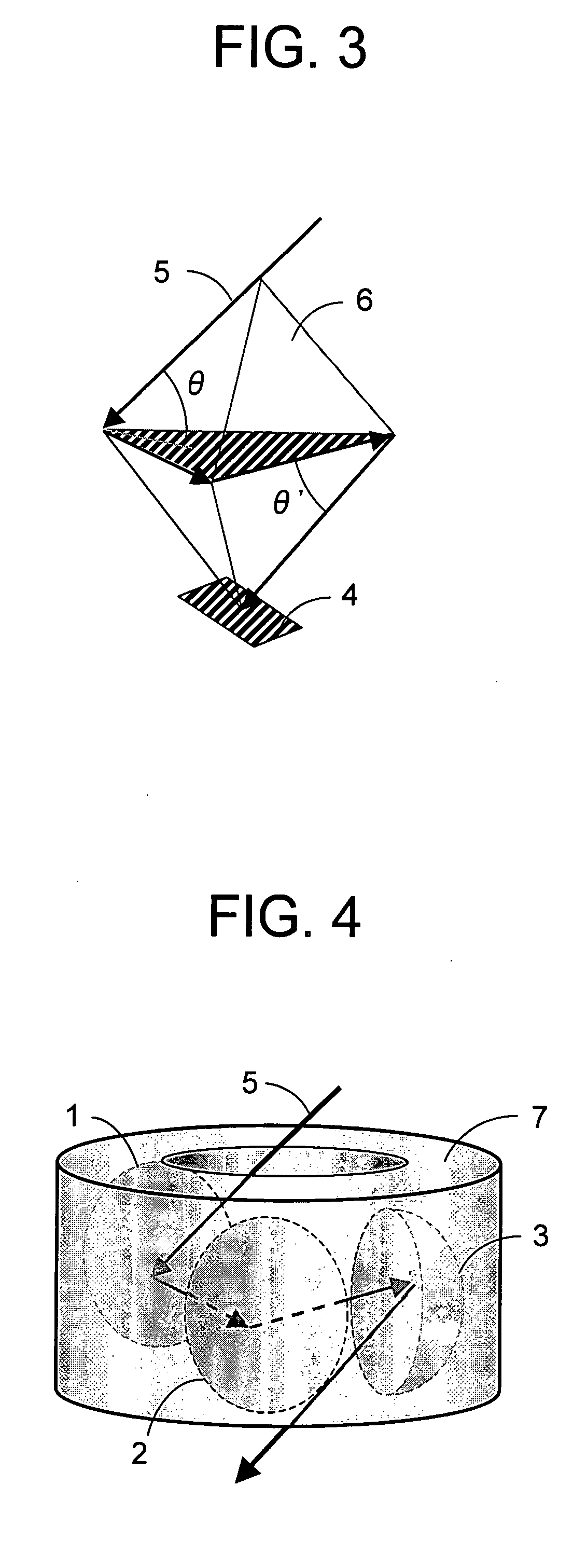
Imaging Optical System
InactiveUS20080123205A1Small sizeAberration suppressionMirrorsMicroscopesOptical pathImage-forming optical system
Provided is a compact and bright imaging optical system having a high resolution. The imaging optical system includes three reflectors composed of a first reflector (1), a second reflector (2), and a third reflector (3) that are arranged in this order on an optical path of incident ray so as not to block the incident light. In the imaging optical system, in which light beams reflected by the three reflectors form an image plane (4), a convex mirror is used for any one of the first reflector (1) and the third reflector (3) and a concave mirror is used for the other thereof, and vertexes of a triangular dipyramid (6) are defined in terms of a central chief ray (5) by an appropriate point on the central chief ray (5) that is incident to the first reflection surface, a reflection point of each central chief ray on the first to third reflection surfaces, and an image forming point of the central chief ray. A plane containing three reflection points of the central chief ray on the first to third reflection surfaces coincides with a bonding plane between two triangular pyramids forming the triangular dipyramid (6).
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
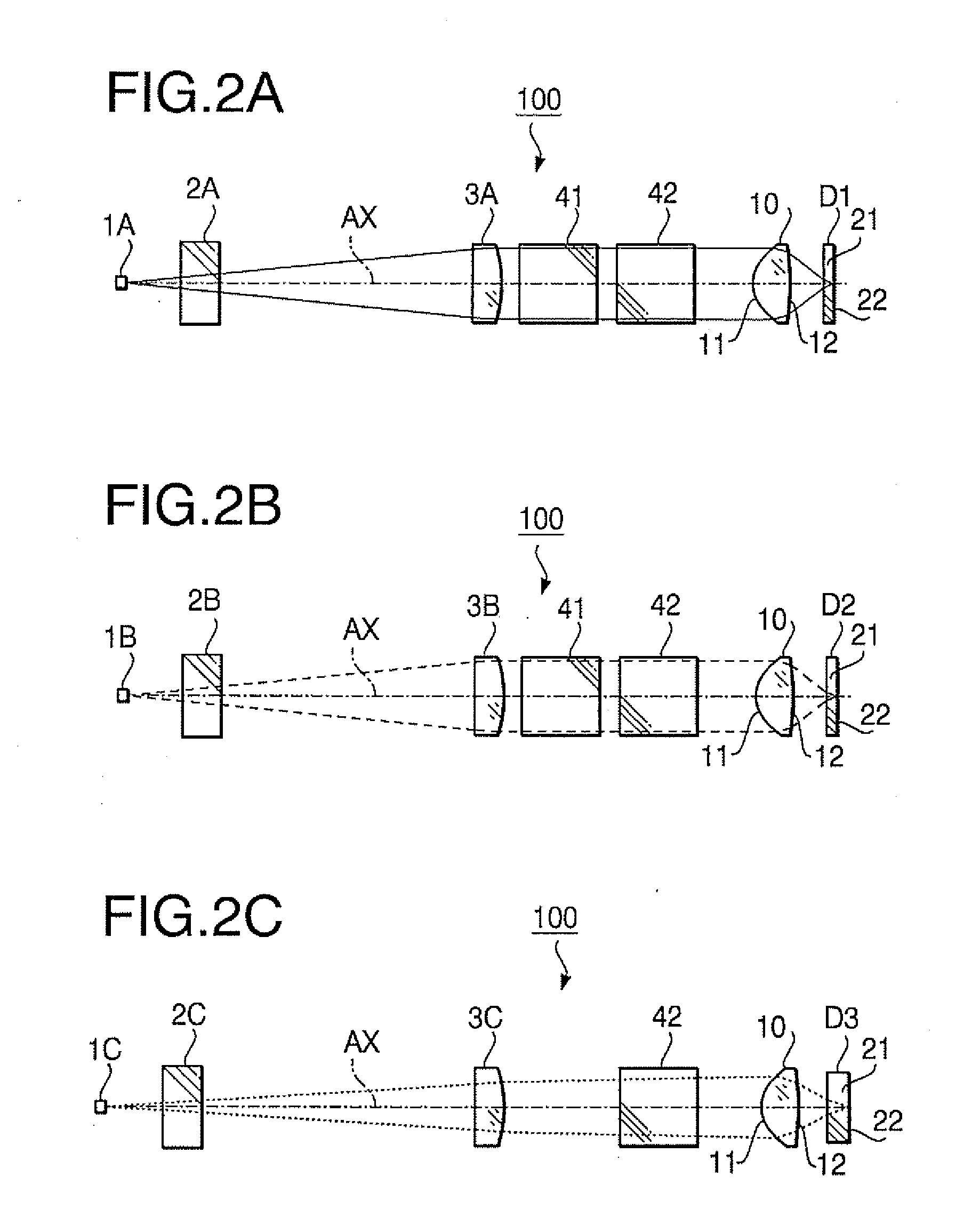
Objective lens for optical pick-up
InactiveUS20050281173A1Sufficiently suppress aberrationAberration suppressionOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageEffective radiusOptical axis
An objective lens for an optical pick-up which is used to record data to and / or to reproduce data from at least three types of optical discs by selectively using one of at least three light beams having different wavelengths is provided. When thicknesses of a first, second and optical discs are represented by t1, t2 and t3, respectively, a relationship t1≦t2<t3 is satisfied. When numerical apertures required for the first, second and third optical discs are represented by NA1, NA2 and NA3, respectively, a relationship NA1≧NA2>NA3 is satisfied. The first, second and third light beams are incident on the objective lens as substantially collimated light beams, respectively. In this configuration, at least one of surfaces of the objective lens includes a first area for attaining the numerical aperture required for recording data to and / or reproducing data from the third optical disc, and a second area located outside the first area. The first area includes an inner area including an optical axis of the objective lens, and an outer area located outside the inner area. The outer area is configured to converge the third light beam on a data recording layer of the third optical disc with an amount of an aberration being substantially zero. The objective lens satisfies a condition: 0.75<h1a / h1<0.87 . . . (1), where h1 represents an effective radius of the first area, and h1a represents an effective radius of the inner area.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Infrared sensor
ActiveUS20140291527A1InhibitionAberration suppressionPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansOptics
An infrared sensor includes: an infrared detecting device; a lens disposed above the infrared detecting device; an member that is disposed at a side of an upper surface of the lens and includes an opening; and a gap that intervenes between the member and the lens and has a wider range than the opening.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
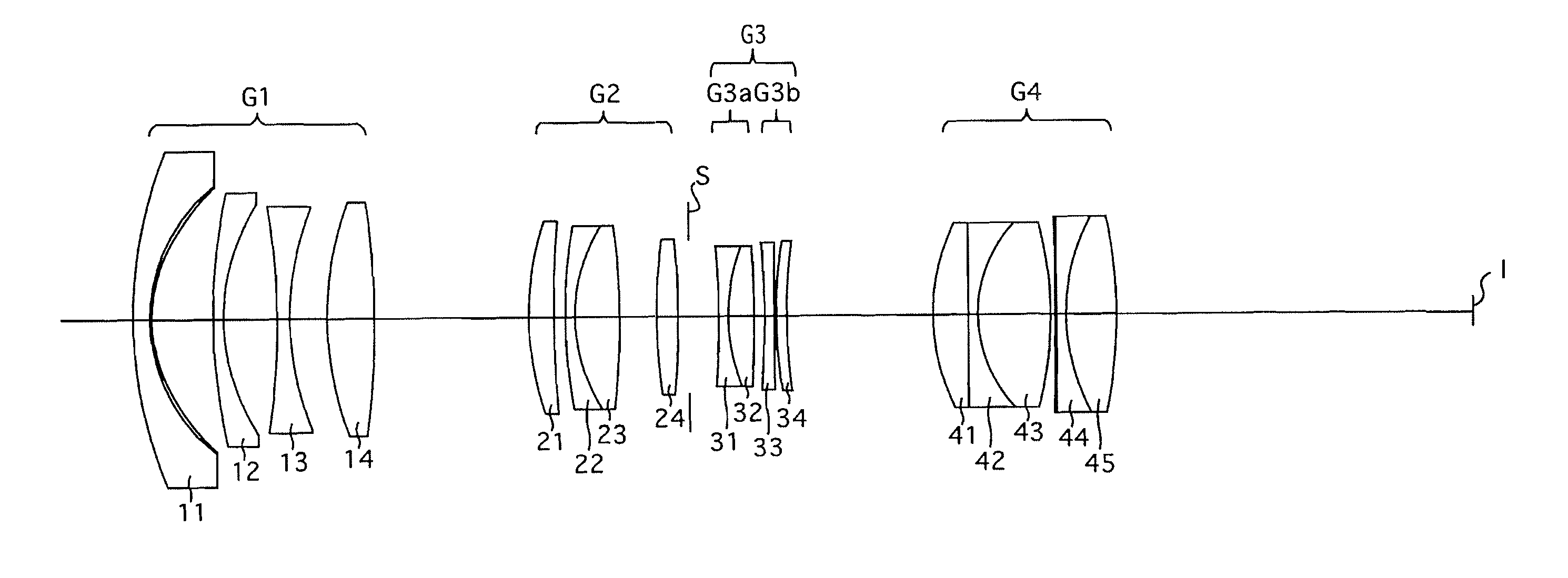
Taking lens system and image capturing apparatus
InactiveUS20060140606A1High zoom ratioSmall sizeCamera body detailsOptical elementsOptical powerImage capture
A taking lens system is provided with, from the side of the object to be photographed, a first lens unit (G1) having positive optical power, a second lens unit (G2) having negative optical power, a third lens unit (G3) having positive optical power and a fourth lens unit (G4) having positive optical power. Zooming is performed by moving the first to fourth lens units (G1) to (G4), and focusing is performed by moving the fourth lens unit (G4). When the distance from the most object-to-be-photographed side surface (r1) of the first lens unit (G1) to the imaging surface at the wide angle end is TLw, the overall focal length of the taking lens system at the telephoto end is ft, the overall focal length of the taking lens system at the wide angle end is fw, and the focal length of the first lens unit (G5) is fl, relationships 0.5≦TLw / ft≦1.0 and 6.0≦fl / fw≦20.0 are satisfied.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA PHOTO IMAGING
Zoom lens and imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20080043341A1Quality improvementAberration correctionOptical elementsCamera lensConditional expression
A zoom lens is provided and includes: in order from an object side thereof, a first lens group having a negative refractive power, a stop; a second lens group having a positive refractive power; and a third lens group having a positive refractive power. The magnification of the zoom lens is varied from a wide angle end to a telephoto end by changing a space between the first lens group and the second lens group and a space between the second lens group and the third lens group. The first lens group includes: in order from an object side thereof, a negative lens having at least one aspherical surface and having a concave surface on an image side thereof; and a positive meniscus lens having a convex surface on the object side thereof. The zoom lens satisfies conditional expressions specified in the specification.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
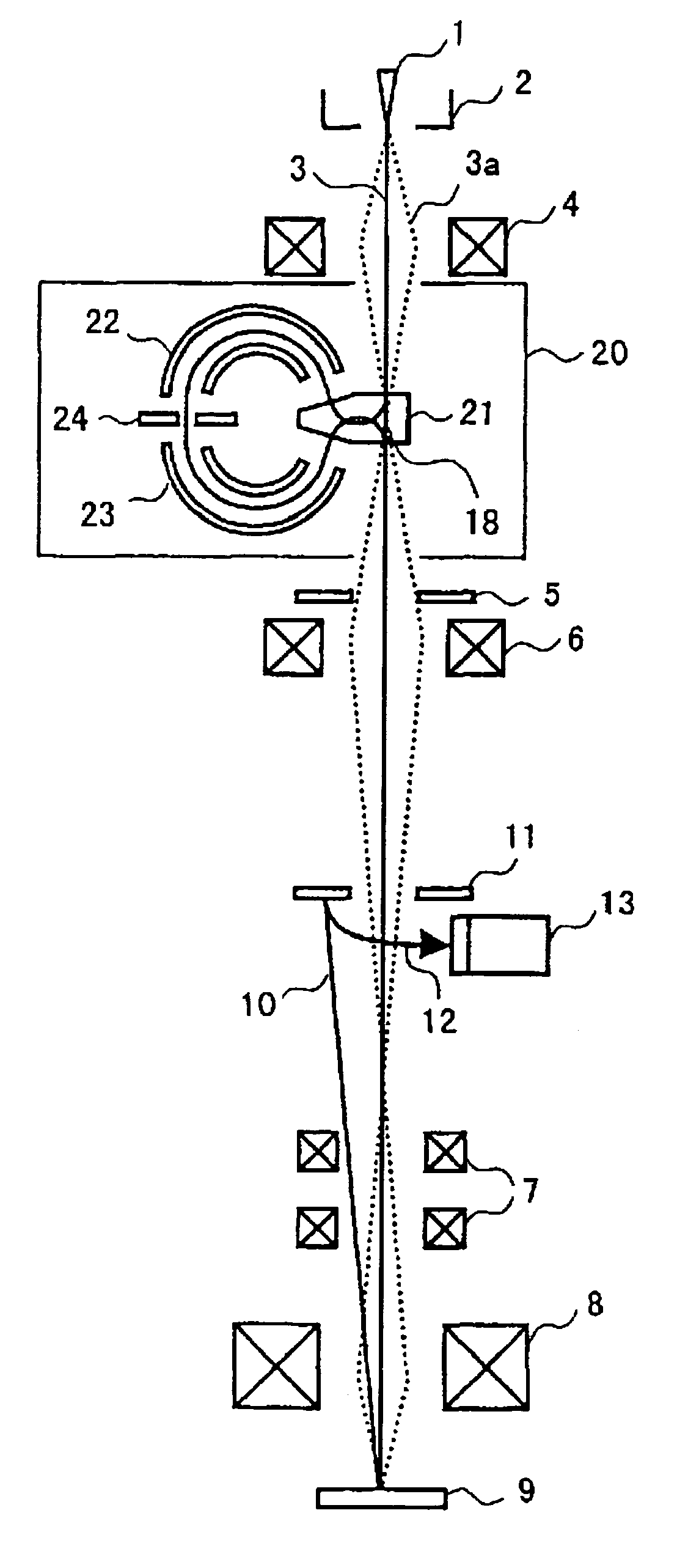
Monochromator and scanning electron microscope using the same
InactiveUS7022983B2High resolutionAberration suppressionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionMirror plane
An invention providing a scanning electron microscope composed of a monochromator capable of high resolution, monochromatizing the energy and reducing chromatic aberrations without significantly lowering the electrical current strength of the primary electron beam. A scanning electron microscope is installed with a pair of sectorial magnetic and electrical fields having opposite deflection directions to focus the electron beam and then limit the energy width by means of slits, and another pair of sectorial magnetic and electrical fields of the same shape is installed at a position forming a symmetrical mirror versus the surface containing the slits. This structure acts to cancel out energy dispersion at the object point and symmetrical mirror positions, and by spatially contracting the point-converged spot beam with a converging lens system, improves the image resolution of the scanning electron microscope.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Optical imaging lens
ActiveUS20170269329A1Good optical performanceShorten lens lengthOptical elementsCamera lensOptical axis
An optical imaging lens includes first, second, third, and fourth lens elements arranged in order from an object side to an image side along an optical axis. Each lens element has an object-side surface and an image-side surface. The first lens element has positive refracting power. The object-side surface of the first lens element has a convex portion in a vicinity of the optical axis and a convex portion in a vicinity of a periphery. The second lens element has negative refracting power. The object-side surface of the third lens element has a concave portion in a vicinity of a periphery. The image-side surface of the fourth lens element has a convex portion in a vicinity of a periphery.
Owner:GENIUS ELECTRONICS OPTICAL XIAMEN
Ophthalmic apparatus, adaptive optical system, and image generating apparatus
ActiveUS8506082B2Small sizeAberration suppressionPhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansOphthalmological deviceOptical aberration
An ophthalmic apparatus includes an aberration correction unit which corrects aberration occurring in light irradiating an eye to be examined; and a common optical system which is commonly provided for an optical path of irradiated light on the aberration correction unit and an optical path of reflected light from the aberration correction unit. The common optical system includes at least one optical element, and areas through which the irradiated light and the reflected light respectively pass overlap each other on the optical element.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical disc drive and objective lens for the same
InactiveUS20070014211A1Inhibit deteriorationImprove recording densityRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansLight beamLength wave
There is provided an objective lens used for three types of optical discs including by selectively using one of three types of light beams. At least one of surfaces of the objective lens is provided with a first region converging the third light beam on a recoding surface of the third optical disc. The first region has a step structure configured to have concentric refractive surface zones and to give an optical path length difference to an incident beam at each step formed between adjacent refractive surface zones. The step structure is configured such that the optical path length difference given by each step is substantially equal to an odd multiple of a wavelength of a first light beam, and a value of differentiation of an optical path difference function defining the step structure crosses zero in a height ranging from 30% to 70% of an effective diameter of the first region.
Owner:HOYA CORP
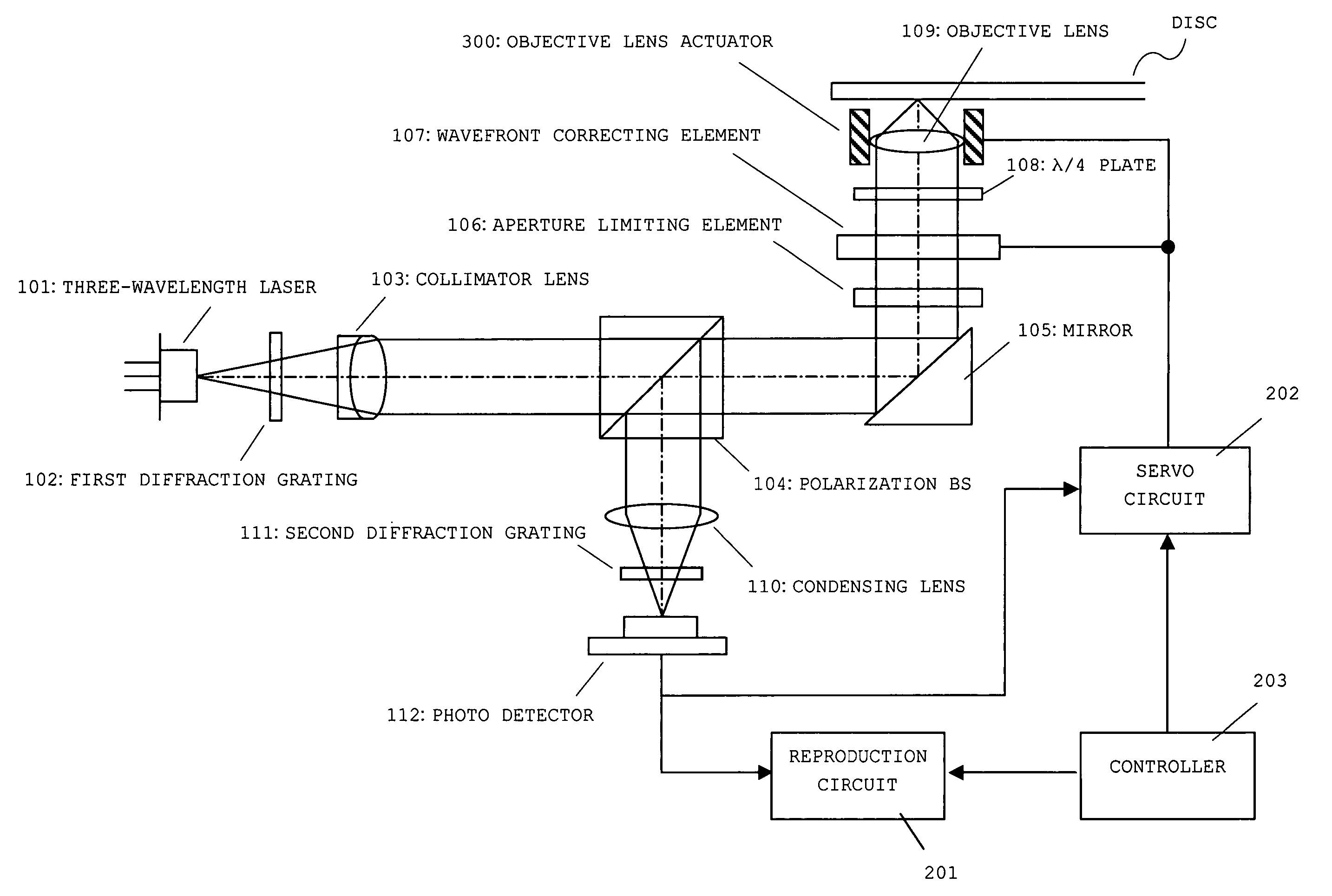
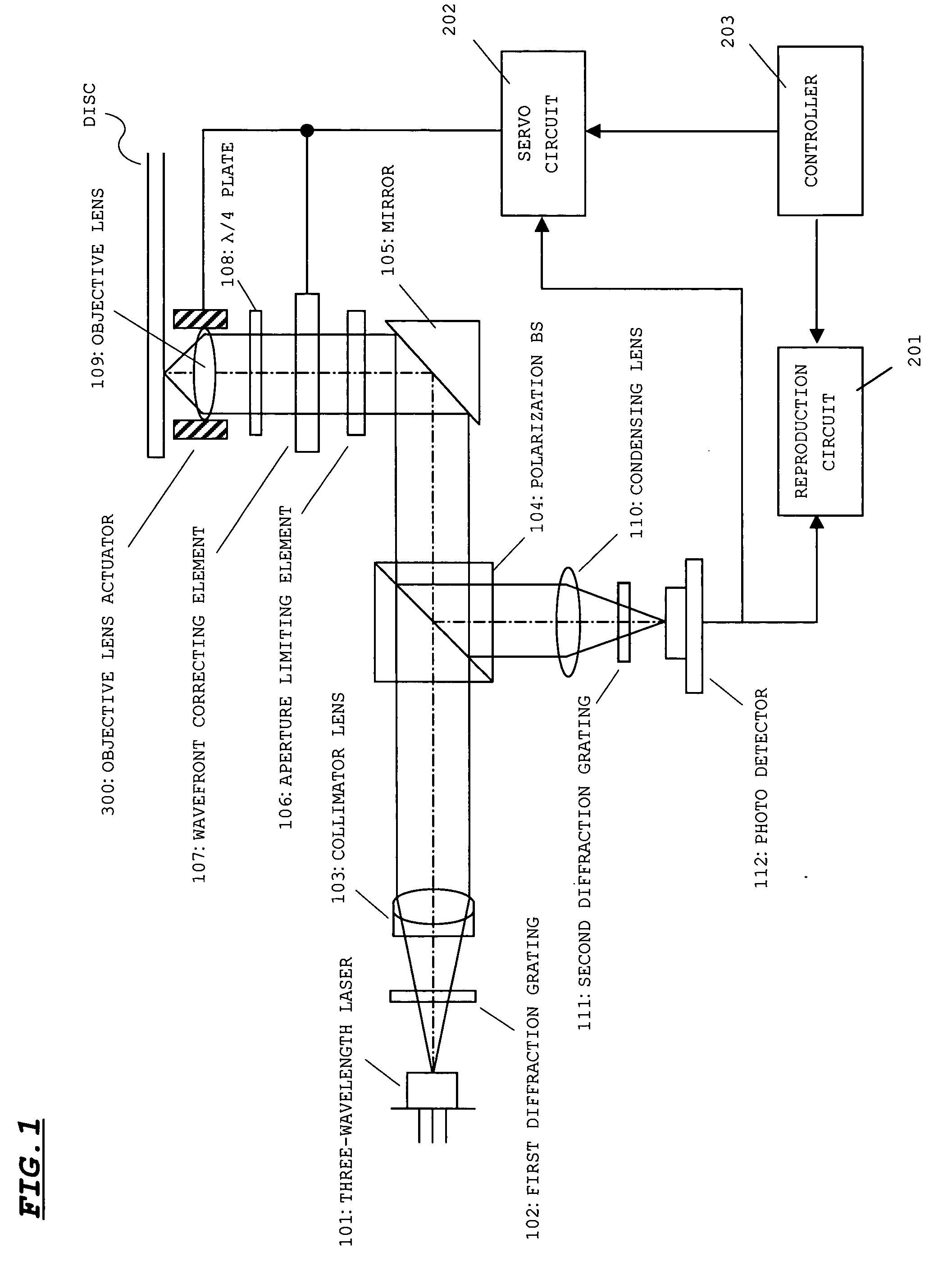
Optical pickup device
InactiveUS20050254391A1Process stabilityLow costOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageOptical pickupLaser light
An optical pickup device includes: a semiconductor laser that has three laser elements for emitting a laser light beam for DVD (wavelength: 655 nm), a laser light beam for CD (wavelength: 780 nm), and a laser light beam for next-generation DVD (wavelength: 408 nm), respectively, which are housed in the same case; and first and second diffraction gratings that substantially align optical axes of the laser light beams emitted from the laser elements with one another by diffracting action. The first diffraction grating aligns the optical axis of the laser light beam for DVD with the optical axis of the laser light beam for next-generation DVD, serving as a reference optical axis by diffracting action. The second diffraction grating aligns the optical axis of the laser light beam for CD with the optical axis of the laser light beam for next-generation DVD, serving as the reference optical axis by diffracting action. Even when a light emitting point gap between the laser elements varies, optical axis adjustment of the laser light beam can be adequately performed by fine adjustment of a corresponding diffraction grating in a reference optical axis direction.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Zoom lens system
InactiveUS20150124322A1Improve optical qualityAberration correctionOptical elementsOptical axisZoom lens
A zoom lens system includes a negative first lens group, a positive second lens group, a negative third lens group and a positive fourth lens group, in that order from the object side. Upon zooming from the short to long focal length extremities, at least the first lens group, the second lens group and the fourth lens group are moved in the optical axis direction. The third lens group includes a negative first sub-lens group and a negative second sub-lens group, in that order from the object side. The second sub-lens group is provided with a negative single lens element and a positive single lens element, wherein an air lens is formed between the negative single lens element and the positive single lens element.
Owner:RICOH IMAGING COMPANY
High power zoom lens system and image pickup apparatus
A high power zoom lens system includes, in order from the object side: a first lens group having a positive refractive power and remaining stationary during zooming; a second lens group having a negative refractive power and moving during zooming; a third lens group and a fourth lens group having a positive refractive power and being movable relative to each other to correct image plane variation accompanied by zooming; and a fifth lens group having a positive refractive power and including an aperture diaphragm, the fifth lens group being used for forming an image. The second lens group and a composite lens group formed by combining the third lens group and the fourth lens group pass simultaneously through −1×magnification points of the groups during zooming from a wide-angle end to a telephoto end. The fourth lens group has at least one aspheric surface.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Projection zoom lens and projection-type display apparatus
ActiveUS20100309562A1Decrease negative powerSuppress fluctuation in aberrationProjectorsLensCamera lensOptoelectronics
A projection zoom lens projects an optical image of rays, which are irradiated from a light source onto a light valve and are modulated by a predetermined image displayed on the light valve, onto a screen. The projection zoom lens includes a plurality of lens groups that is formed as a telecentric system on the reduction side thereof and includes at least two movable lens groups which are movable during zooming. In the projection zoom lens, the plurality of lens groups is arranged to include, in order from a magnification side, at least a first lens group and a second lens group. The first lens group has a negative refractive power, remains stationary during zooming, and performs focusing. The second lens group has a negative refractive power and remains stationary during zooming and focusing.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Electron Microscope
ActiveUS20100224781A1Easy to correctAberration suppressionElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationOptical axisElectron microscope
An electron microscope is offered which facilitates aberration correction even during high-magnification imaging. The microscope has a spherical aberration corrector, a transfer lens system mounted between the corrector and an objective lens, an aperture stop mounted in a stage preceding the corrector so as to be movable relative to the optical axis, and an angular aperture stop mounted at or near the principal plane of the transfer lens system movably relative to the optical axis to adjust the angular aperture of the electron beam.
Owner:JEOL LTD
Flat wide-angle lens system
A flat wide-angle lens system of the invention has a reduced axial length and is intended for creating images with extremely wide angle of observation. The system consists of the first component which is intended for reduction of the field angle of light incidence onto the objective and comprises an assembly of at least two microlens arrays with the same pitch between the adjacent microlenses and arranged with respect to each other so as to provide afocality, and a second component that comprises an assembly of conventional spherical or aspherical microlenses that create an image on an image receiver. Each two coaxial microlenses of the microlens arrays of the first component form an inverted microtelescope of Galileo. The outlet aperture of a single microtelescope is made so that spherical aberration can be minimized almost to 0, while field aberrations can be corrected by design parameters of the microlenses.
Owner:MICROALIGN TECH
Optical pick-up
InactiveUS20080074976A1Short timeSuppress generationCombination recordingRecord information storageOptoelectronicsOptical aberration
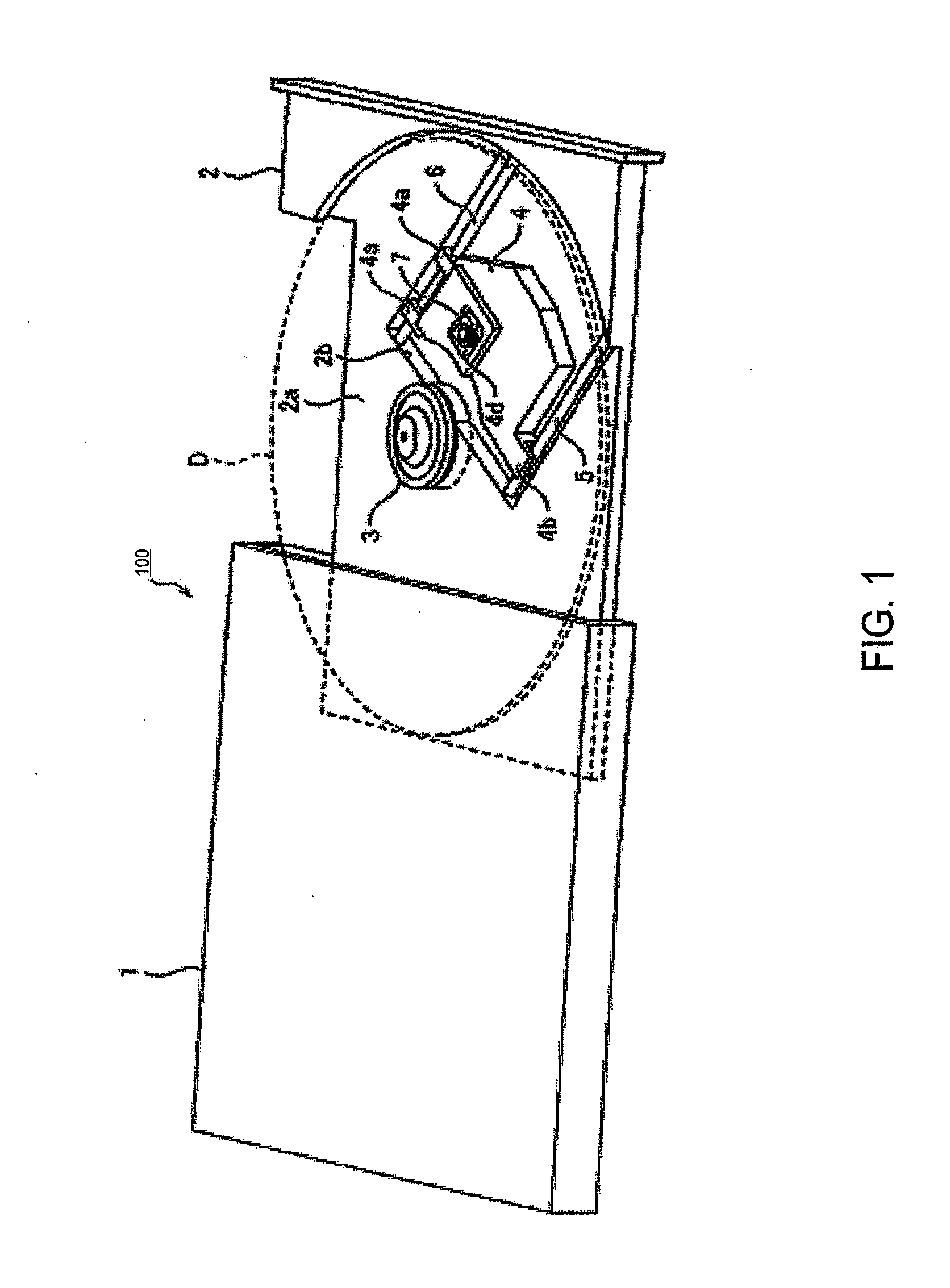
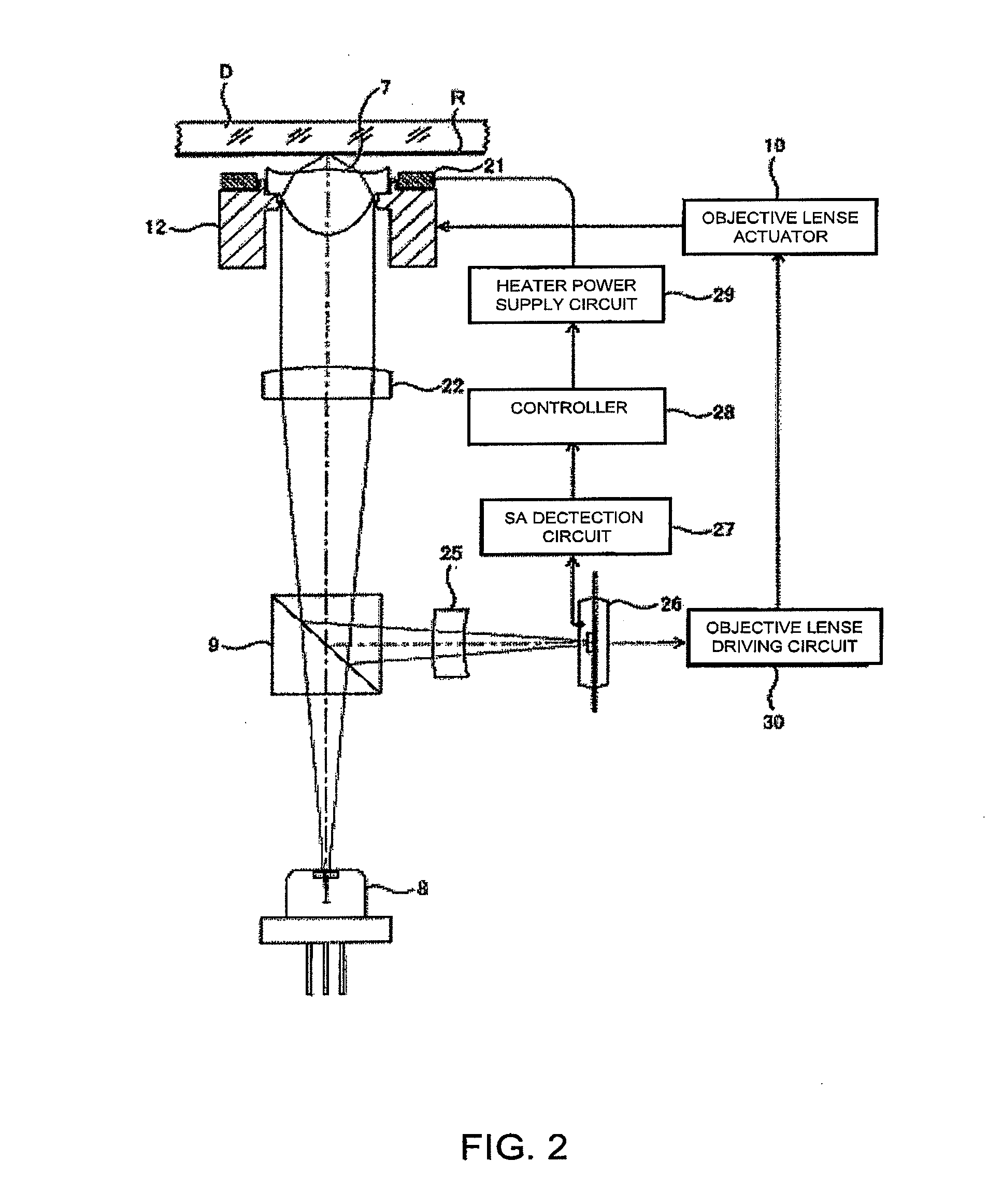
According to an aspect of the invention, there is provided an optical pick-up for an optical disc drive, which is provided with an objective lens configured to converge a laser beam emitted from a laser source on a recording surface of an optical disc, spherical aberration caused by the objective lens being compensated at a predetermined setting temperature of the objective lens, a heating unit configured to be driven to heat the objective lens, a spherical aberration detection unit which detects amount of spherical aberration caused by the objective lens, and a driving unit that drives the heating unit in accordance with the amount of the spherical aberration detected by the spherical aberration detection unit, the driving unit driving the heating unit when the spherical aberration detected by the spherical aberration detection unit is positive, the driving unit stopping driving the heating unit when the spherical aberration is zero or negative.
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK
Zoom lens, and electronic apparatus using the same
InactiveUS7061687B2Increase the diameterReduce exerciseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisDiagonal
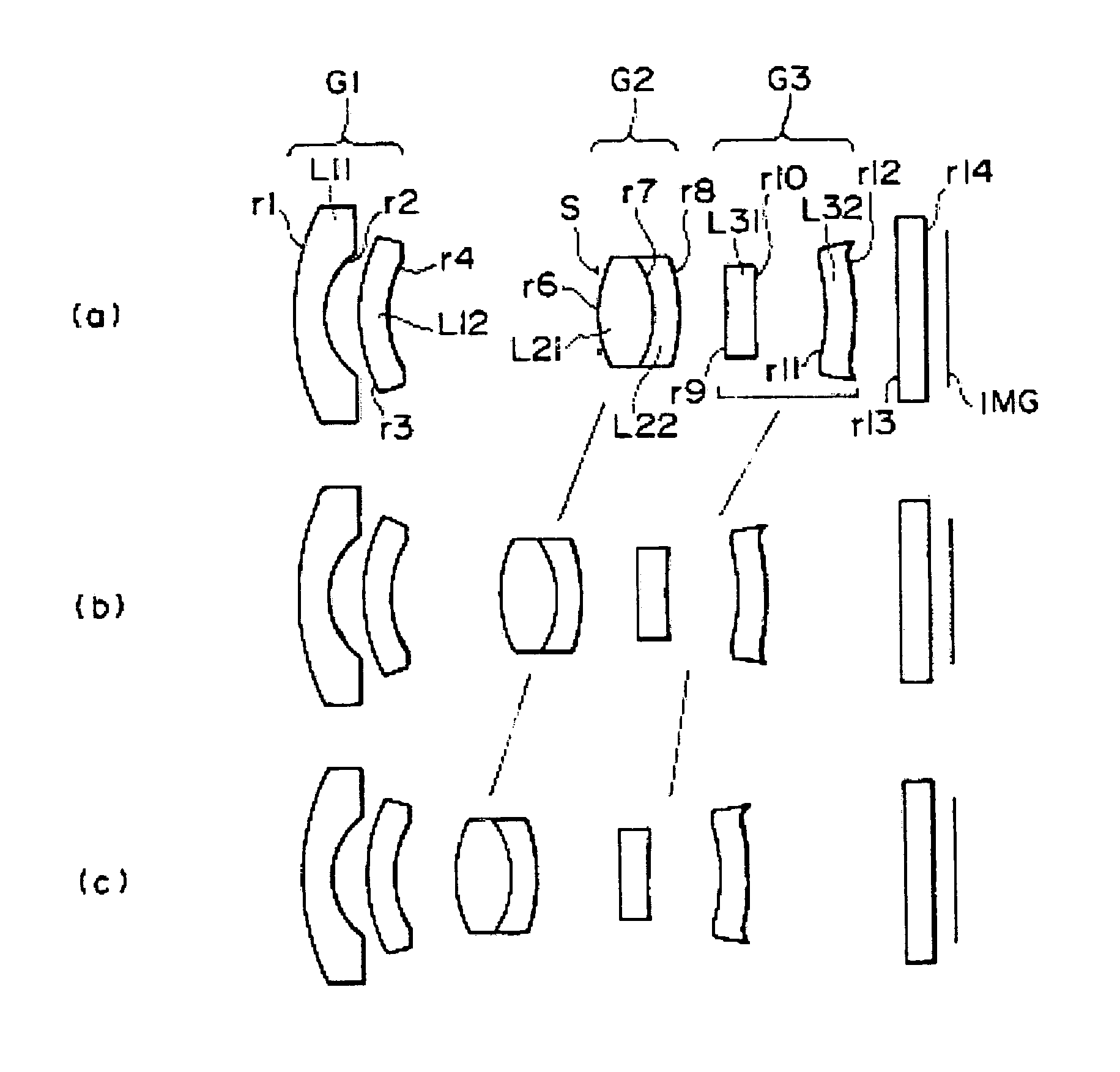
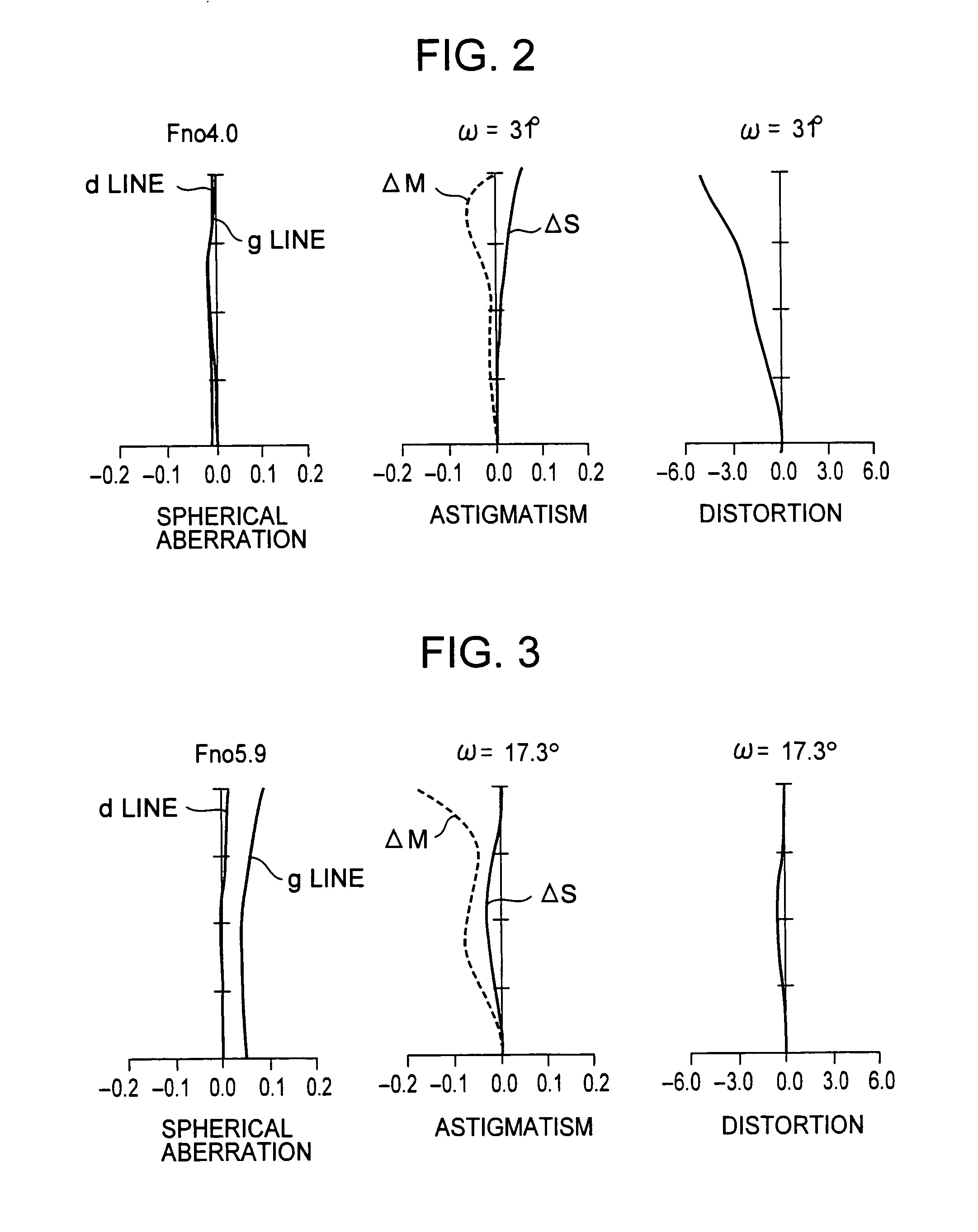
A zoom lens includes a negative first lens group G1 fixed during power variations, a positive second lens group G2 moving from an image side toward the object side from the wide-angle end toward the telescopic end during power variations, and a negative third lens group G3 moving on the optical axis during power variations in this order from an object side. The third lens group G3 is provided with a lens L31 serving as a front group, and a lens L32 arranged as a rear group with an air space interposed between this lens L31 and the lens L32. When f1 denotes the focal length of the first lens group G1, f2 denotes the focal length of the second lens group G2, and y denotes the diagonal length of an image pickup plane, Formulas 1.3<|f1 / y|<3.6, and 1.1<f2 / y<2.0 are satisfied.
Owner:SONY CORP
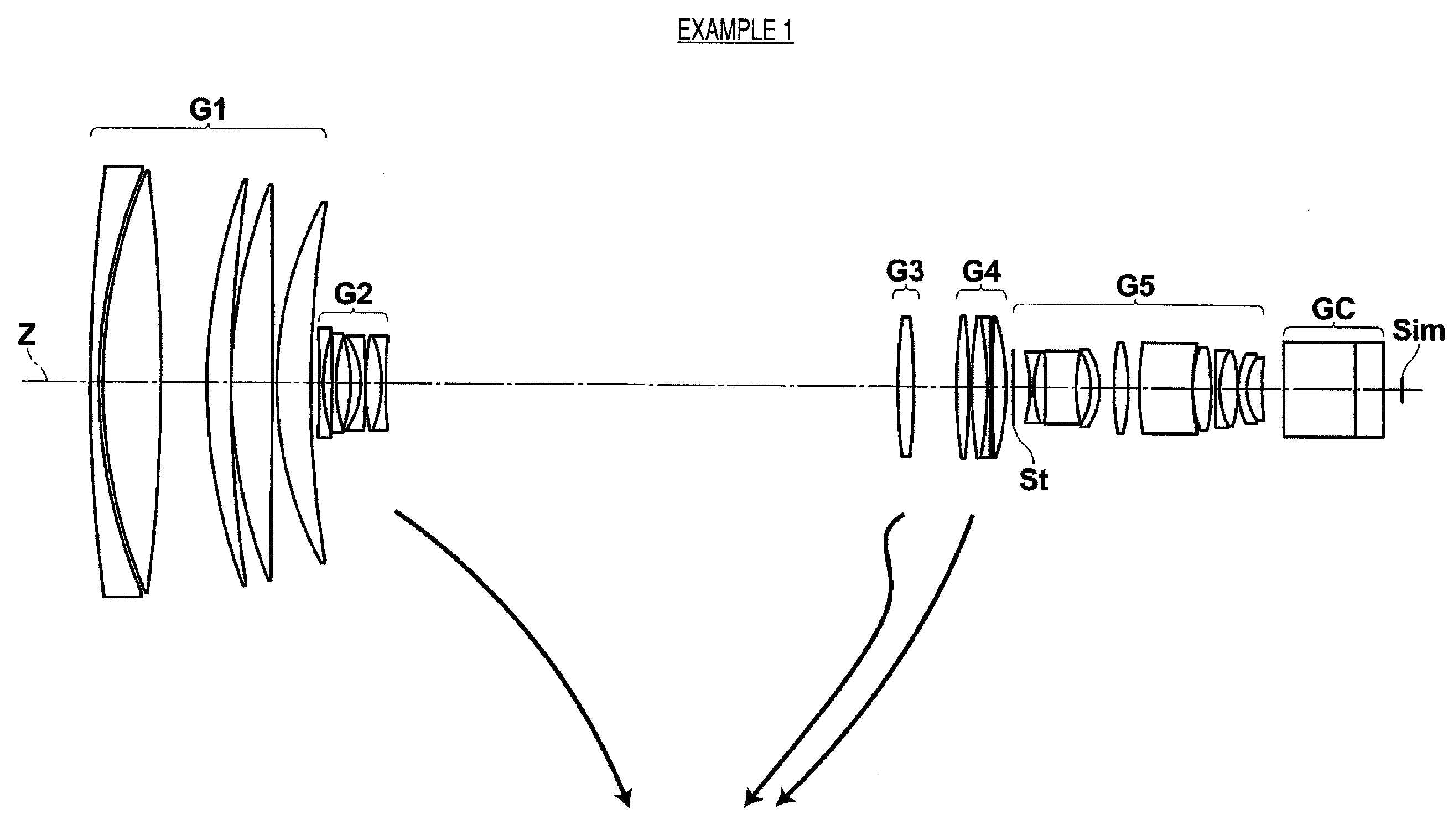
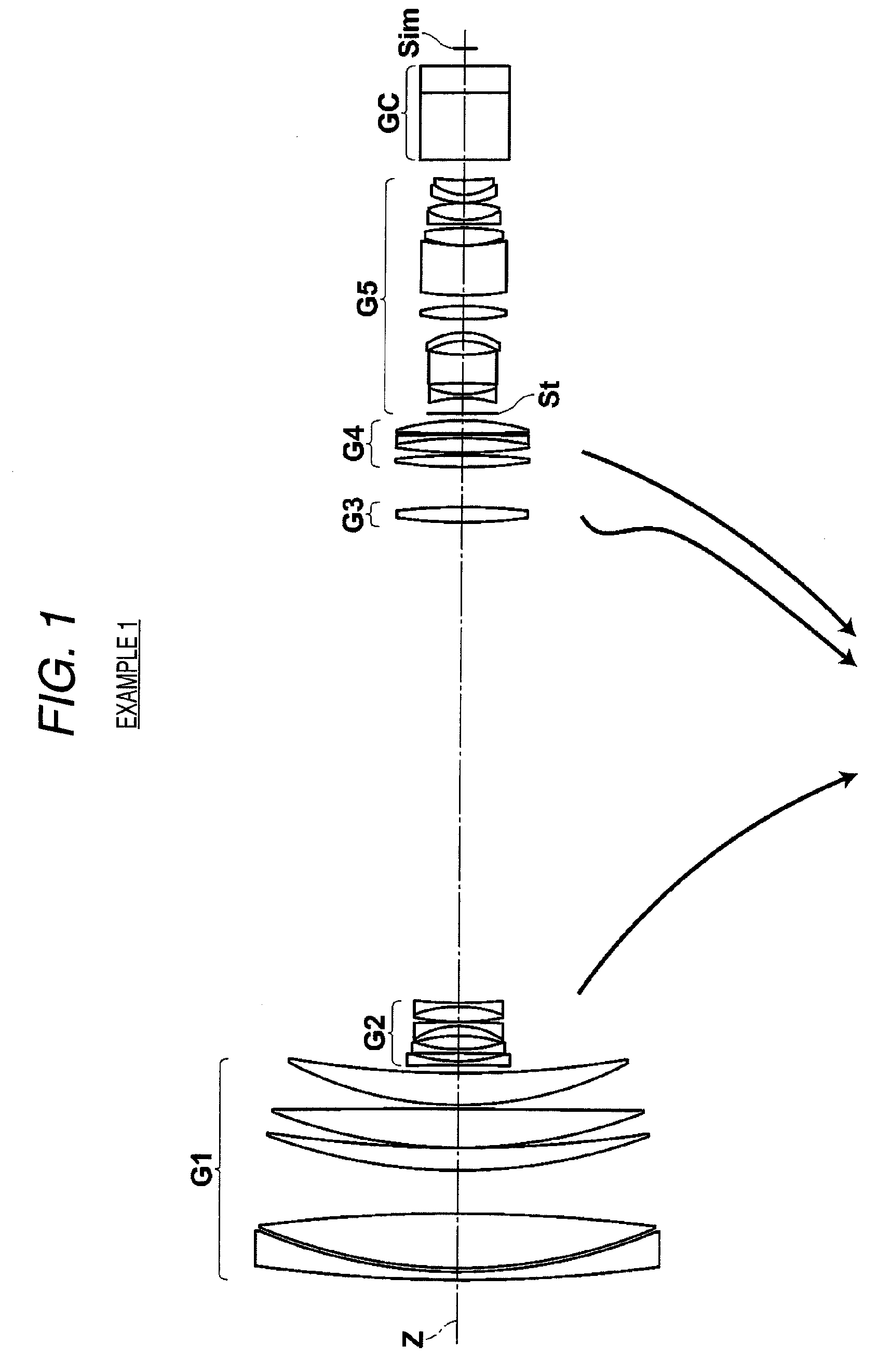
Super wide angle lens and imaging apparatus
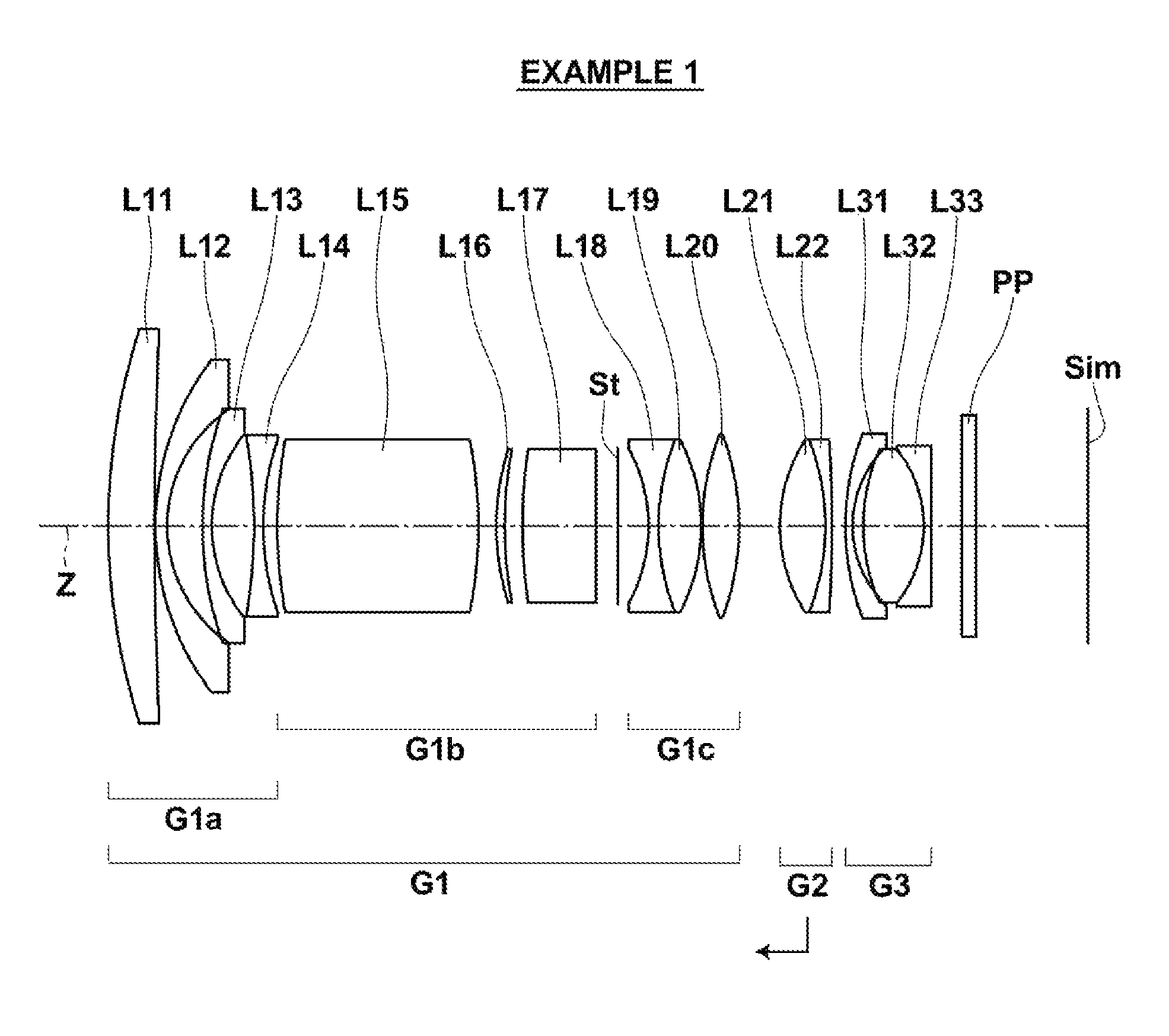
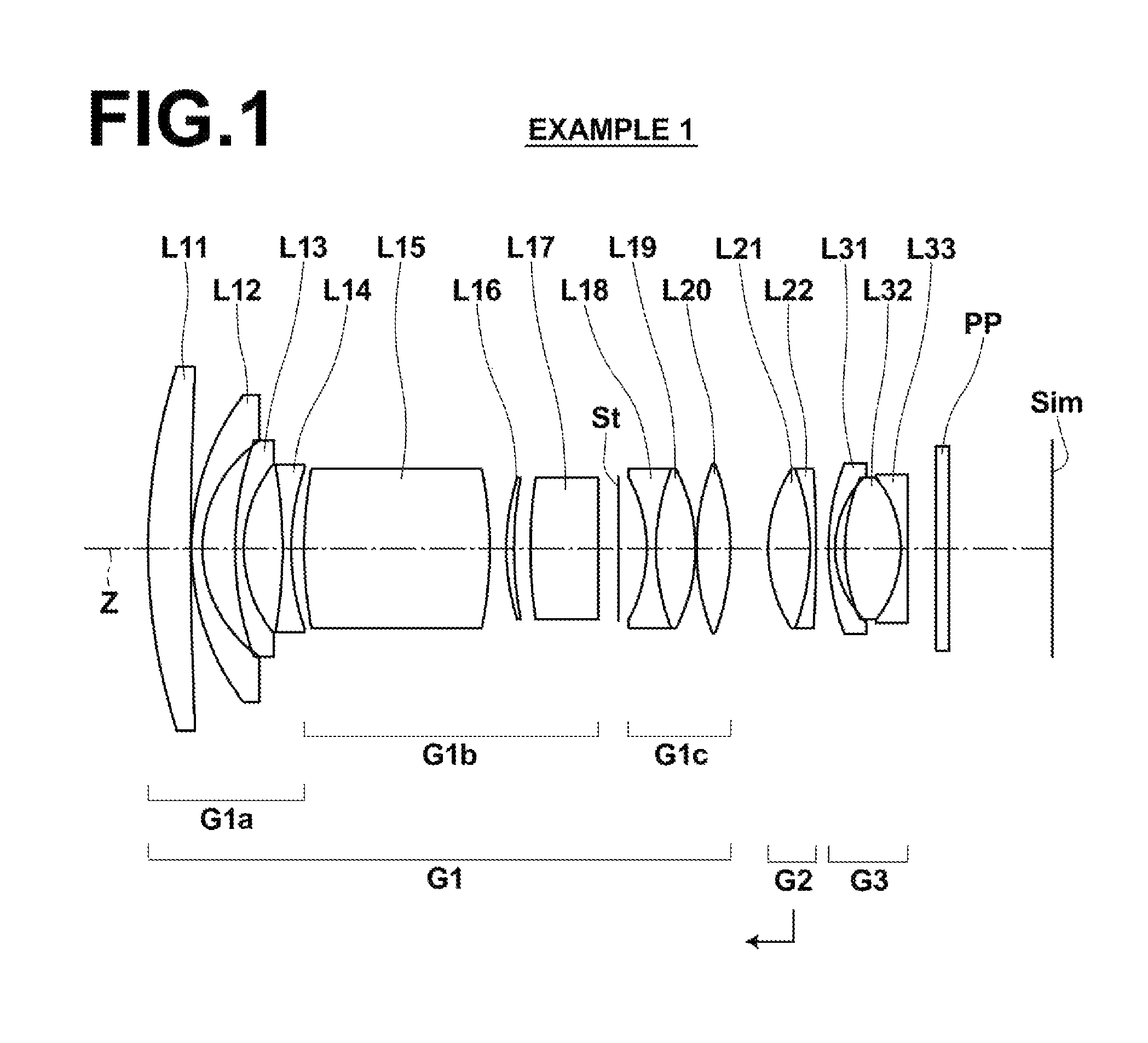
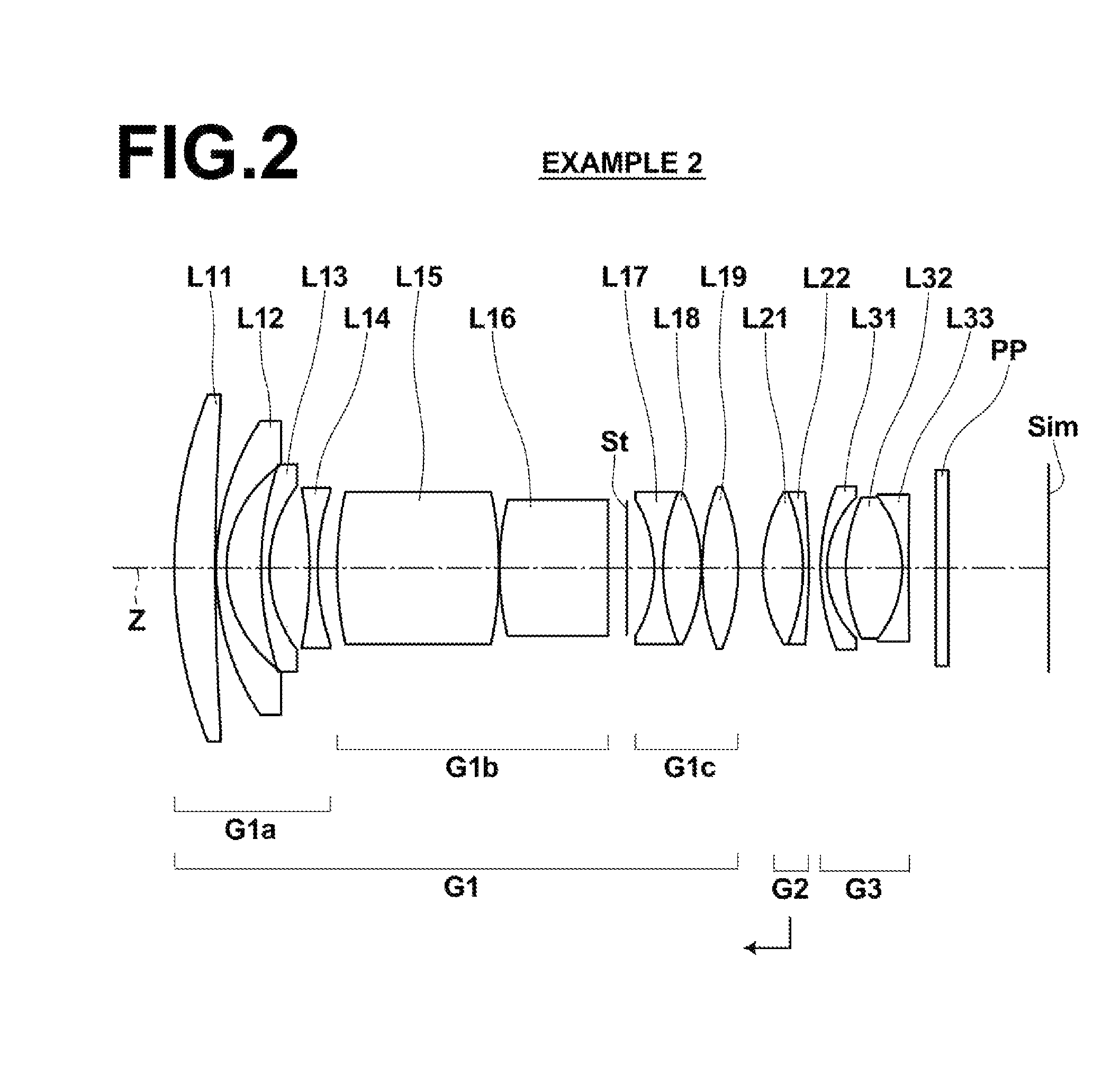
ActiveUS9164261B2Reduce weightGood optical performanceOptical elementsConditional expressionImaging equipment
This super-wide lens substantially consists of a positive first lens group, a positive second lens group, and a negative third lens group, in this order from the object side. The first lens group and the third lens group are fixed and the second lens group moves toward the object side while focusing from an object at infinity to an object at the closest distance. The first lens group substantially consists of a negative first sub lens group, a positive second sub lens group, an aperture stop, and a positive third sub lens group in this order from the object side. Conditional expressions (1) and (2) are satisfied:0.15<f1 / f2<0.60 (1)2.5<f2 / f<7.0 (2), wheref1: the focal length of the first lens group,f2: the focal length of the second lens group, andf: the focal length of the entire system when focusing on an object at infinity.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com