Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
654results about "Poultry incubation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Animal breeding system and utilization of the system
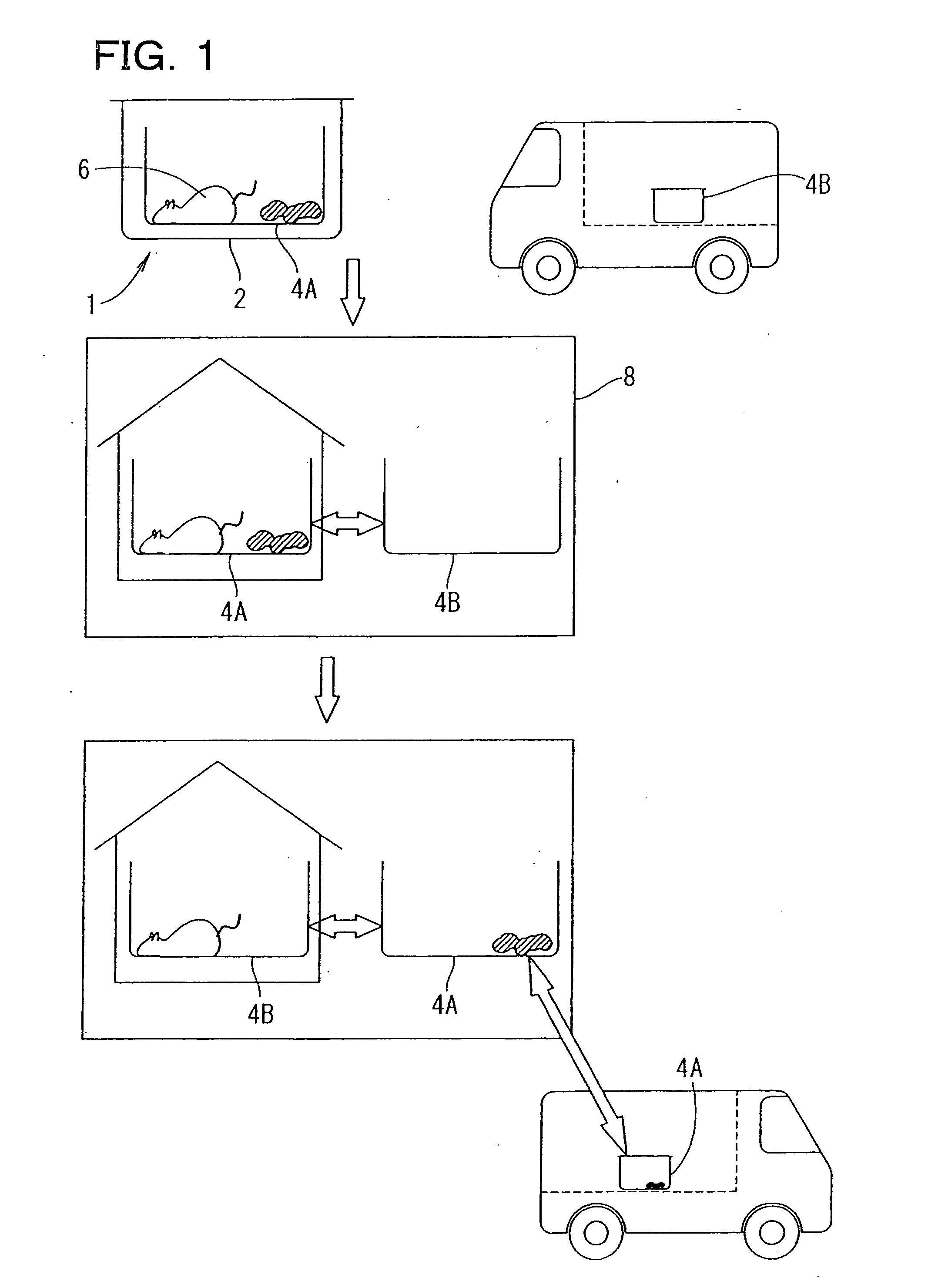
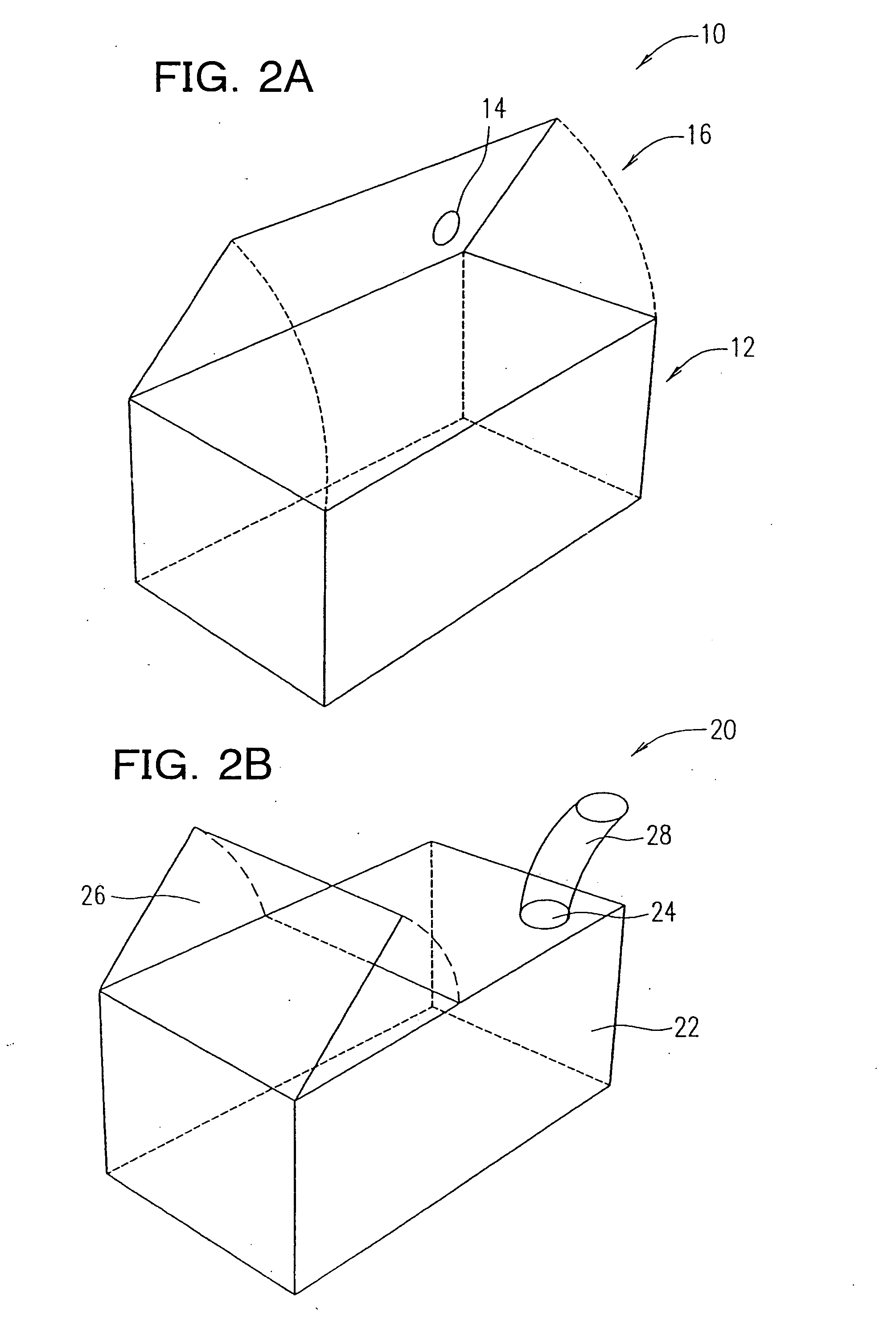
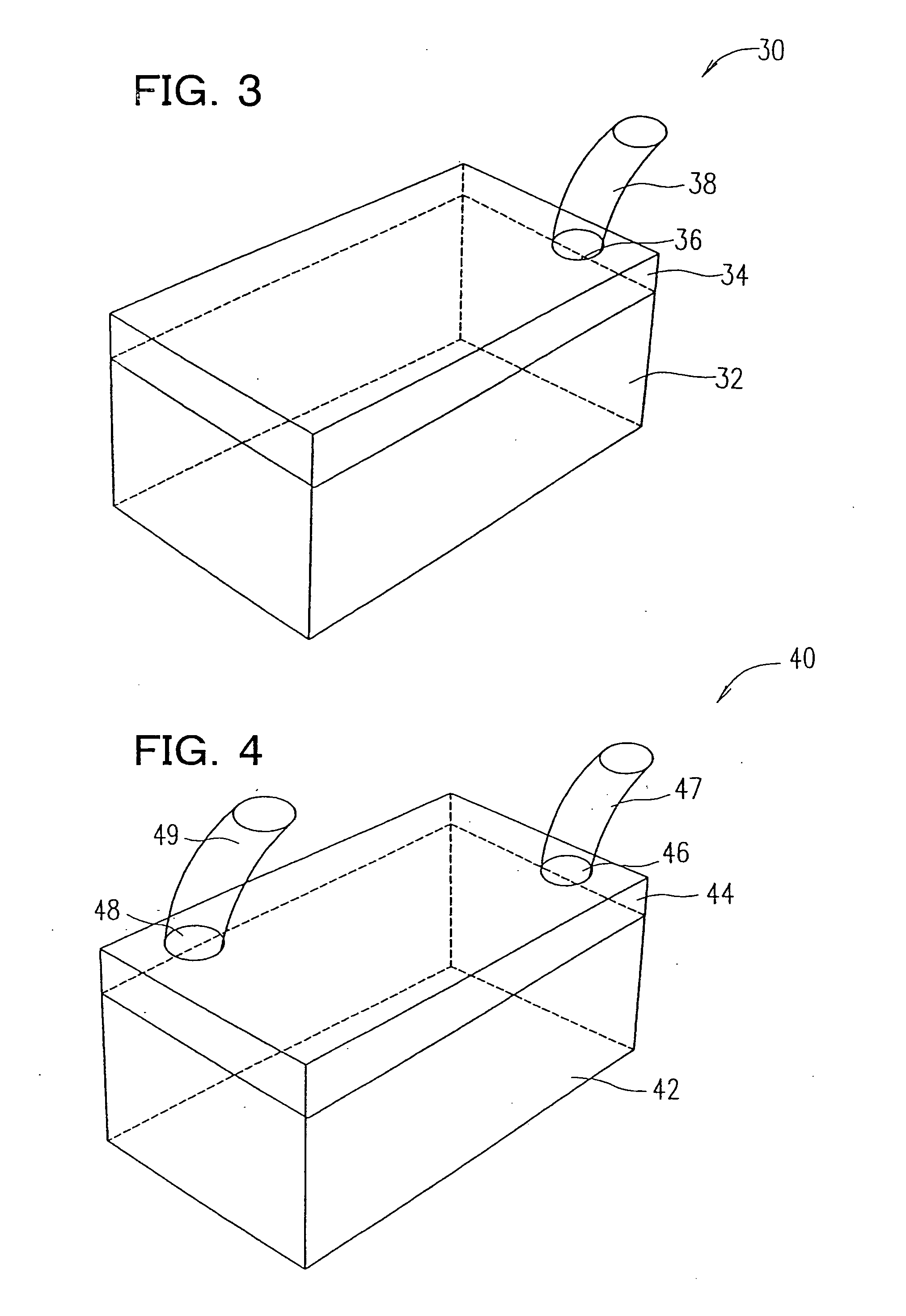
The present invention has objectives of providing a low-cost, easy-to-handle individual isolation animal breeding unit and a system for using the same, significantly reducing costs of facilities and maintenance for animal experiments and saving on labor, and providing a new animal transportation form (breeding cage having a transportation function). For achieving the objectives, the present invention provides a system for maintaining an animal breeding environment, comprising A) an animal breeding unit capable of comprising an internal tray having a sufficient space for breeding an animal of interest, comprising an external tray capable of accommodating the internal tray, and capable of keeping a predetermined cleanliness degree; B) means for providing the internal tray having the predetermined cleanliness degree; C) an internal tray exchange unit capable of accommodating the animal breeding unit and exchanging the internal tray while keeping the predetermined cleanliness degree; and D) means for recovering the exchanged internal tray.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
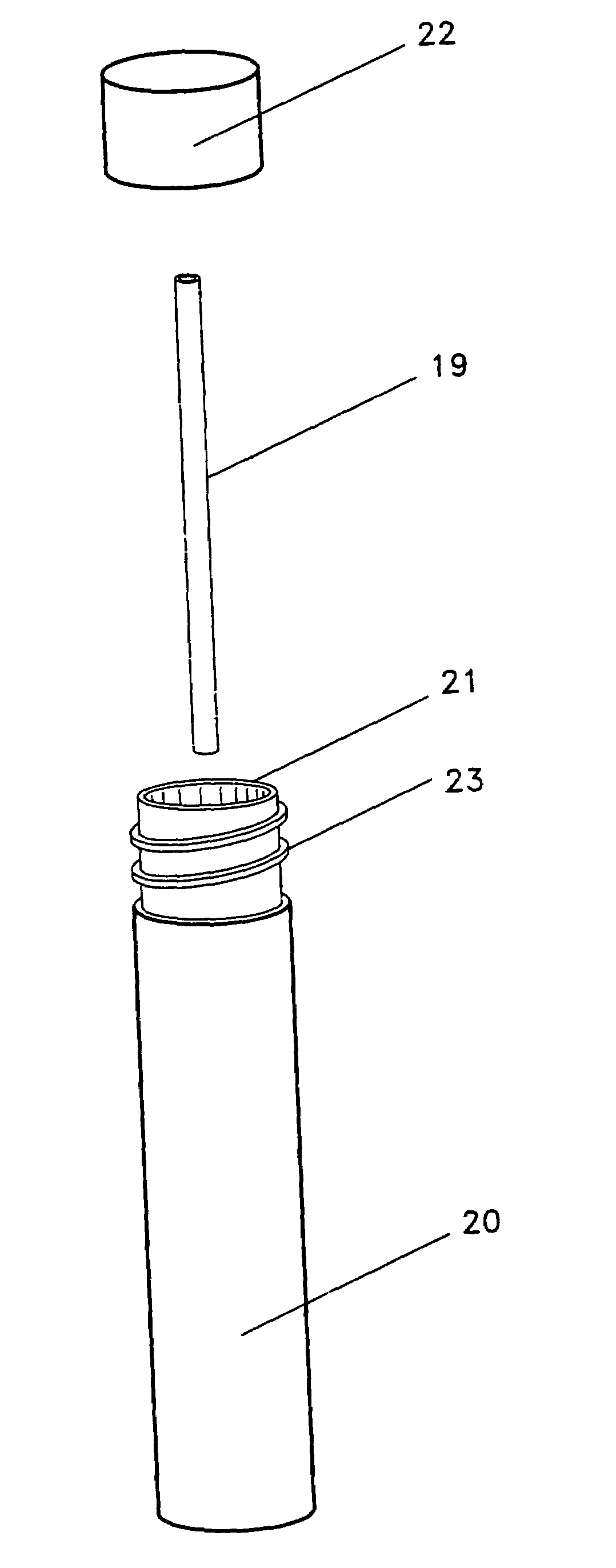
System for in-vitro fertilization with spermatozoa separated into X-chromosome and Y-chromosome bearing populations
InactiveUS7094527B2Promote divisionQuality improvementAnimal reproductionDead animal preservationX chromosomeBiology
An IVF system for successfully utilizing spermatozoa separated into X-chromosome bearing and into Y-chromosome bearing population for insemination. The IVF system includes fertilization medium that can shorten the time from insemination to cleavage and a portable incubator for the transportation of maturing oocytes and inseminated oocytes comrprising a straw (19) and an incubation element (20) that can be sealed with a cap (22).
Owner:XY
Production of a transgenic avian by cytoplasmic injection
InactiveUS20030126629A1Promote absorptionImprove efficiencyVirusesNucleic acid vectorEmbryoTransgene
This invention provides methods for the stable introduction of heterologous coding sequences into the genome of a bird and expressing the coding sequences to produce desired proteins or to alter the phenotype of the bird. The present invention provides preferred methods for introducing a transgene into the cytoplasm of avian embryonic cells by cytoplasmic microinjection. The embryo then develops into a transgenic adult capable of expressing a heterologous protein and / or capable of generating a line of transgenic birds through breeding. Synthetic vectors and gene promoters useful in the methods are also provided by the present invention, as are transgenic birds that express heterologous protein and avian eggs containing heterologous protein.
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
Method and apparatus for effecting rapid thermal cycling of samples in microtiter plate size
InactiveUS6482615B2Heating fastUniform heating and/or cooling of the samplesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrotiter plateClosed loop
A method and apparatus for effecting rapid thermal cycling of samples, by producing a high-velocity air flow through a closed loop flow path, and energizing an electrical heater within the closed loop flow path to heat the air flowing therethrough to a desired temperature. A sample holder is introduced into the closed loop flow path for exposing the sample holder to the high-velocity heated air flowing therethrough for rapidly heating the sample. The sample is rapidly cooled to a desired temperature by de-energizing the electrical heater, and opening an air outlet from the closed loop flow path, while continuing to produce the high-velocity air flow therethrough.
Owner:INTEGRATED GENETIC DEVICES
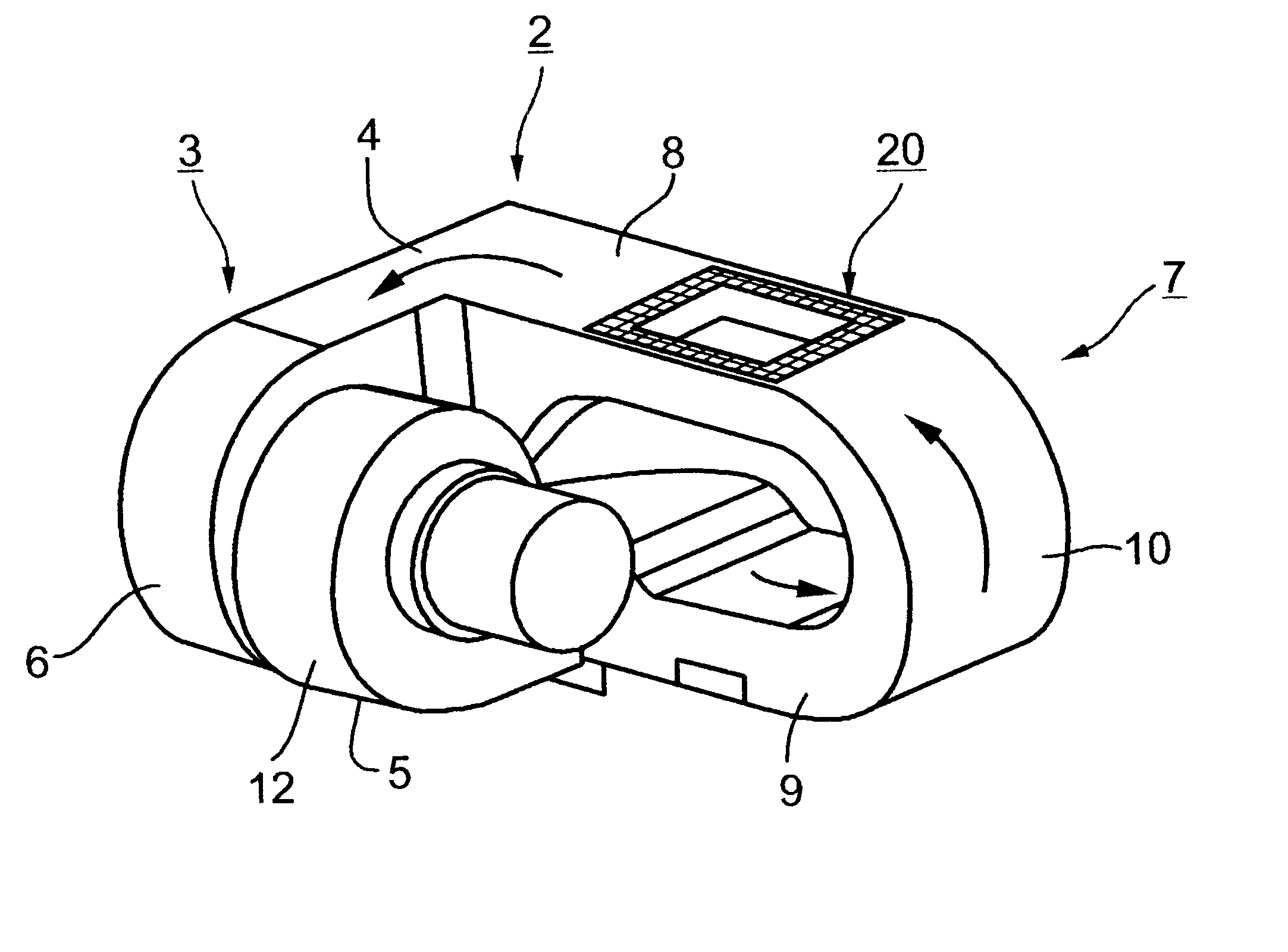
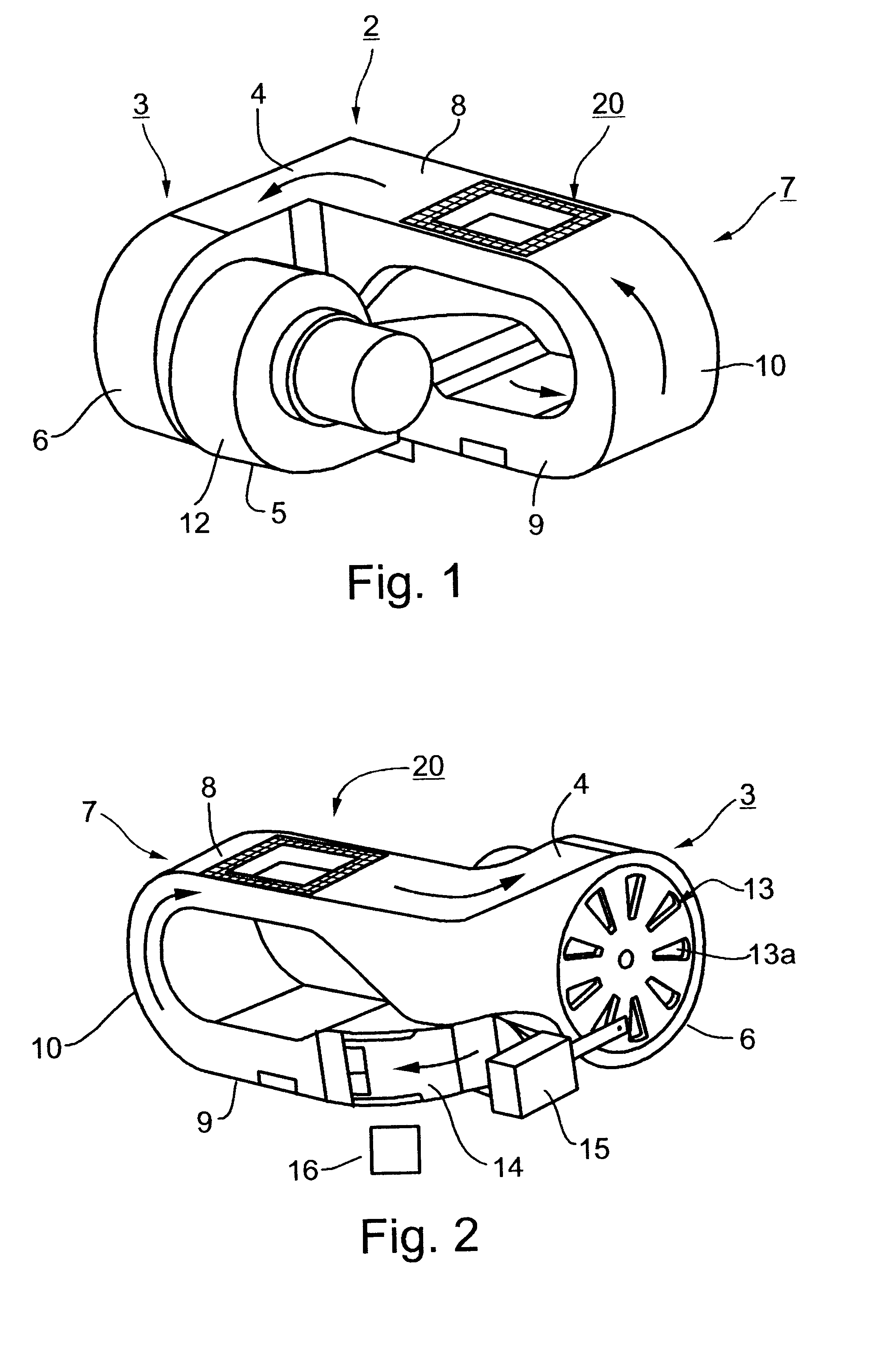
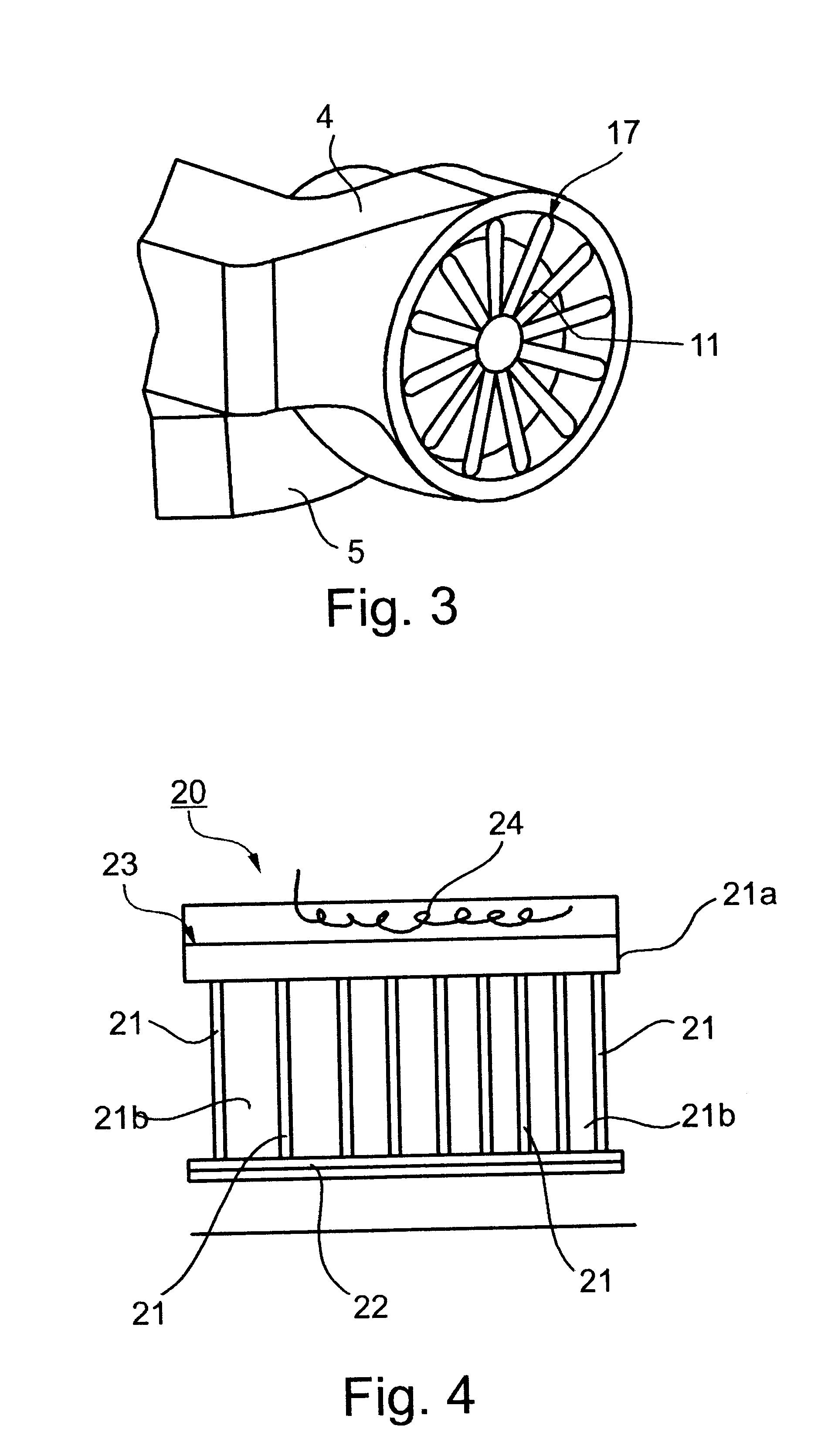
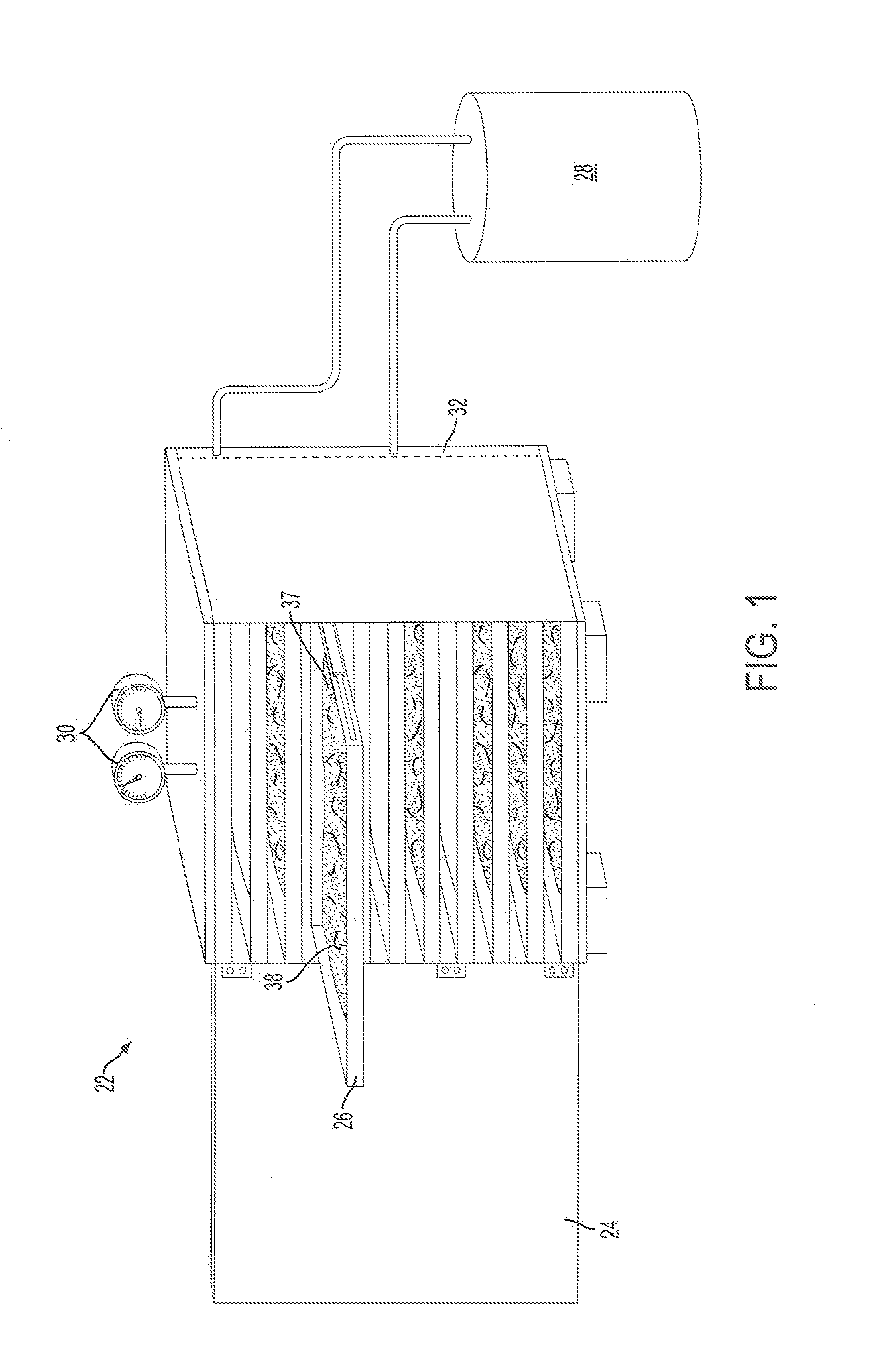
Livestock incubator
InactiveUS6425347B1Easy to cleanDomestic stoves or rangesElectrical heating fuelAnimal scienceDraft animals
A portable livestock incubating device is provided formed of a rectangular container having and incubating volume forming an incubating chamber defined by the zone within the incubating volume. Each each end wall further includes an access door hingedly attached to an upper portion above a clean out door for providing ingress and egress of livestock. Each access door has an exhaust vent located at an upper portion whereby heated air, generated via an electric heater within said the incubating chamber exhausts therethrough. A base with wheels mounted thereon for facilitating transportation of the portable livestock incubating device.
Owner:BOGNER DANIEL G +1
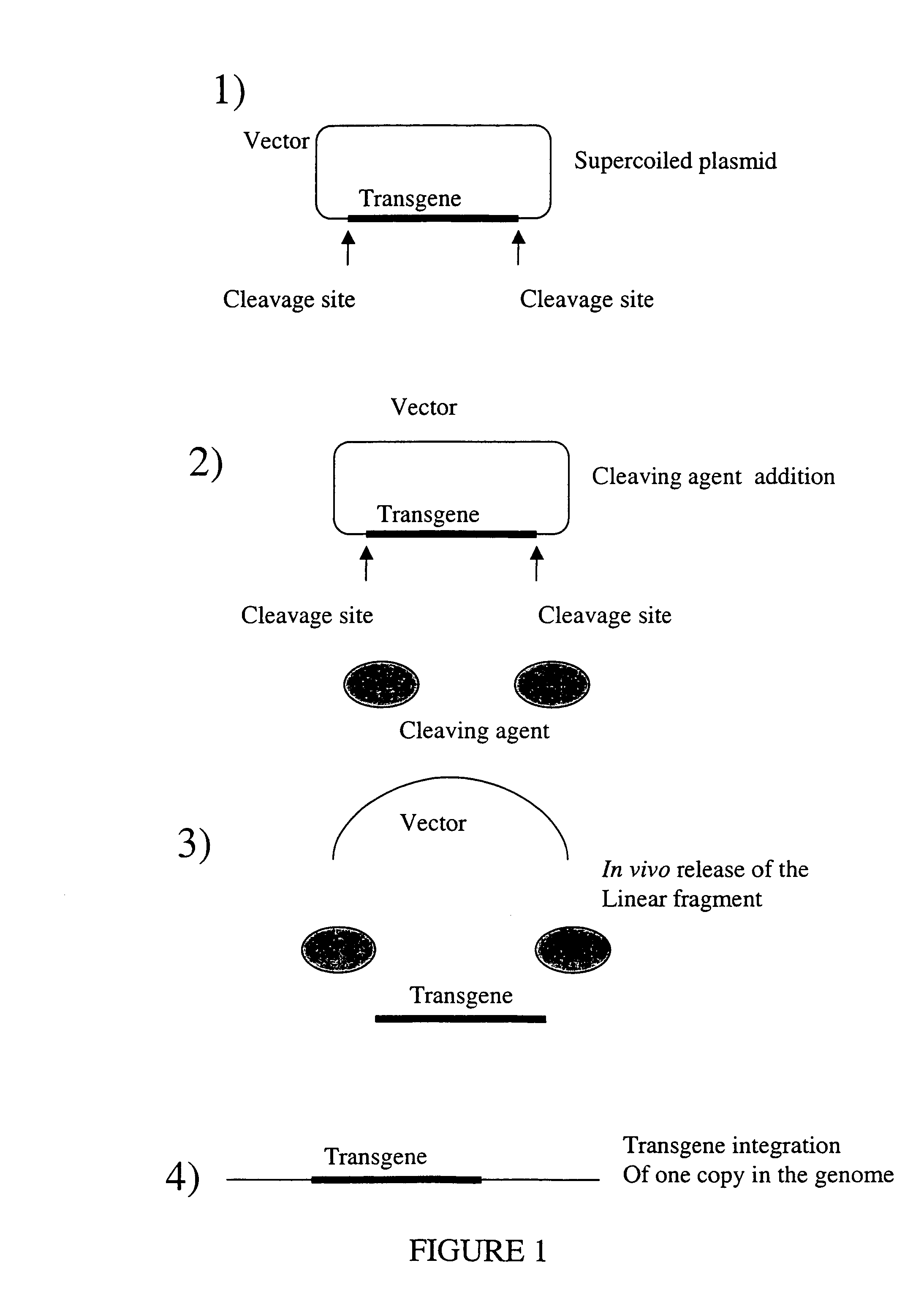
Random integration of a polynucleotide by in vivo linearization
ActiveUS7098031B2Improve efficiencyControl of integrityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideIn vivo
The present invention concerns a method for in vivo generation of a linear polynucleotide with 5′ and 3′ free ends from a vector having no free end, said linear polynucleotide being integrated into the host cell genome. The vector having no free end according to the present invention comprise the polynucleotide to be linearized or excised flanked by a cleavage site, said cleavage site being preferably not found in the host cell genome. The present invention also relates to the resulting cells and their uses, for example for production of proteins or other genes, biomolecules, biomaterials, transgenic plants, vaccines, transgenic animals or for treatment or prophylaxis of a condition or disorder in an individual.
Owner:COLLECTIS SA
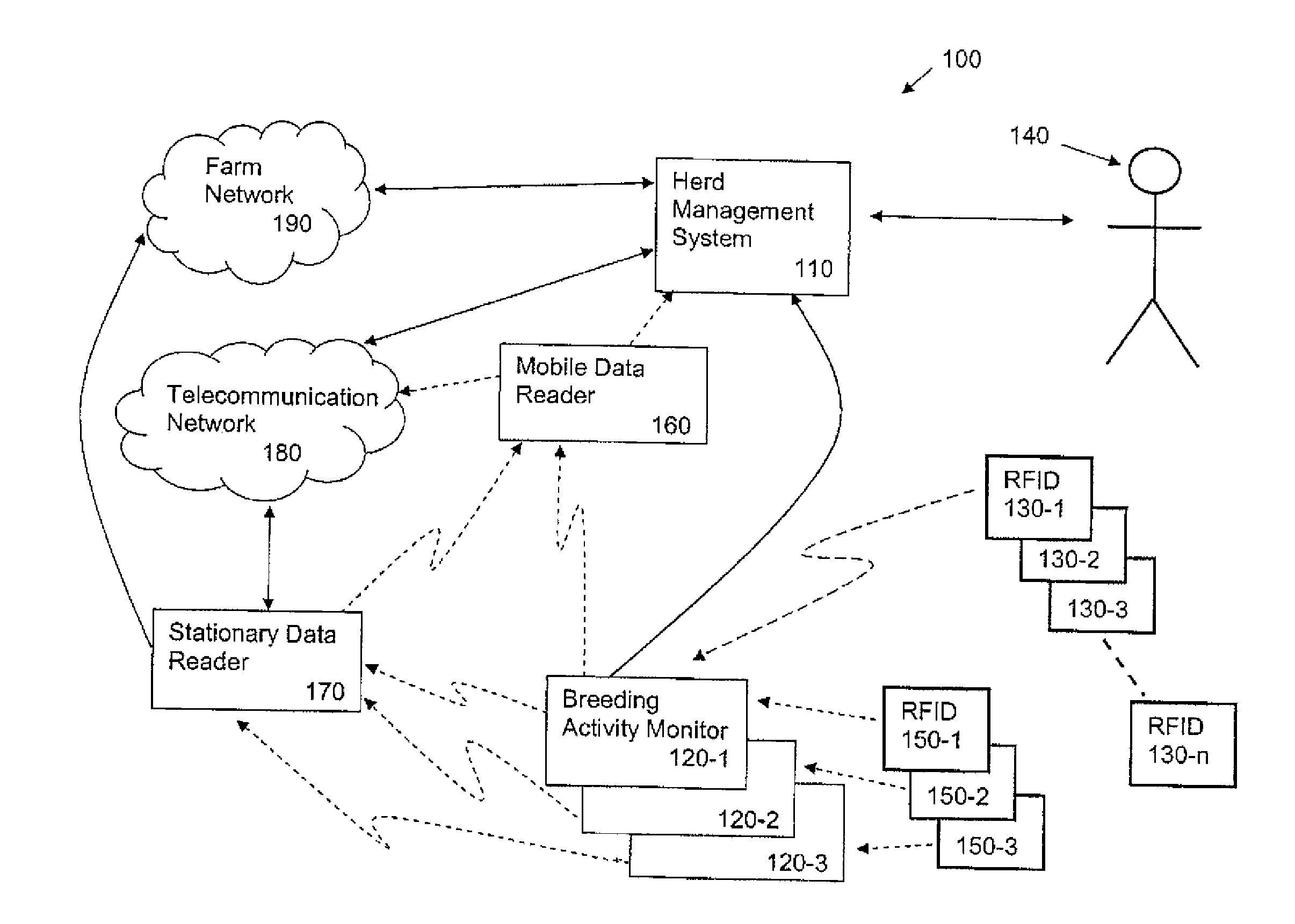
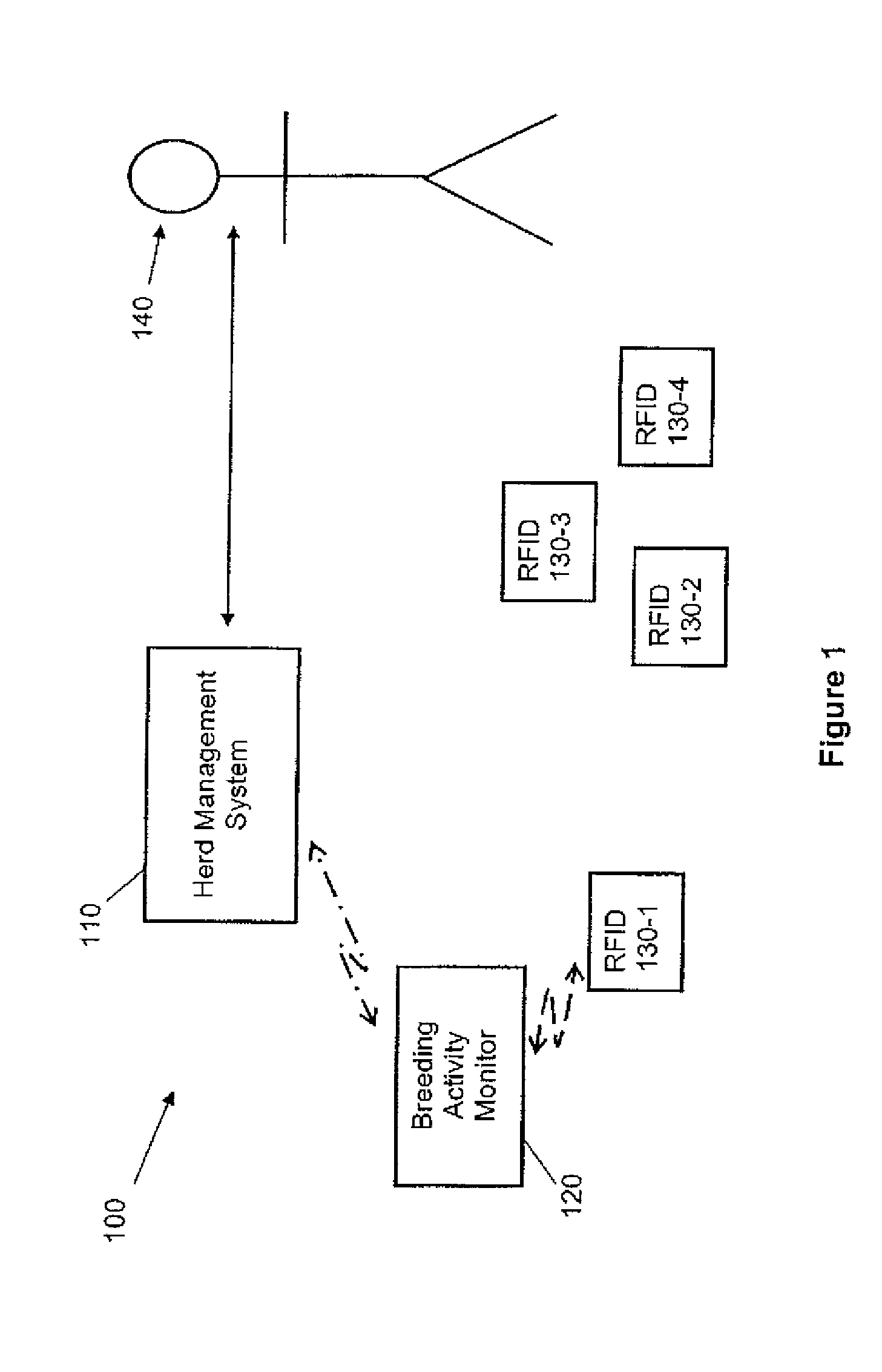
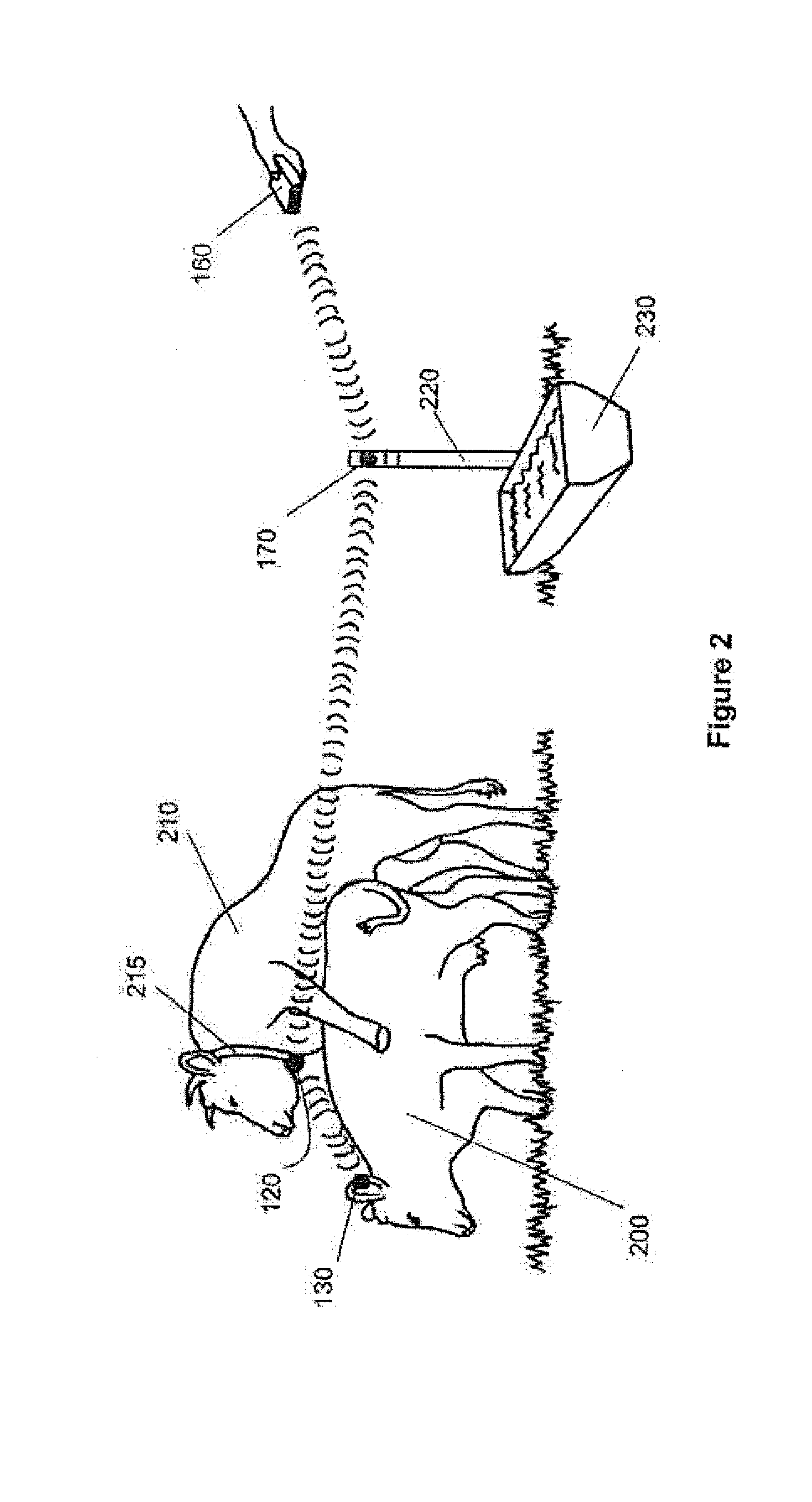
Livestock breeding and management system
A method and system for livestock breeding and management for use with a herd where each female animal carries a radio frequency identification (RFID) tag. The system comprises a herd management system and one or more breeding activity monitors to be carried by each male animal. Each breeding activity monitor is adapted to detect when the male animal is mounting a female animal based on the body position of the male animal, read identification data from the RFID tag carried by the mounted female animal, and generate breeding activity data including the identification data of the mounted female animal, mounting male animal and timing data for each mounting for output to the herd management system. The herd management system is adapted to process breeding activity data output from the breeding activity monitors to generate herd management data.
Owner:BREEDCARE
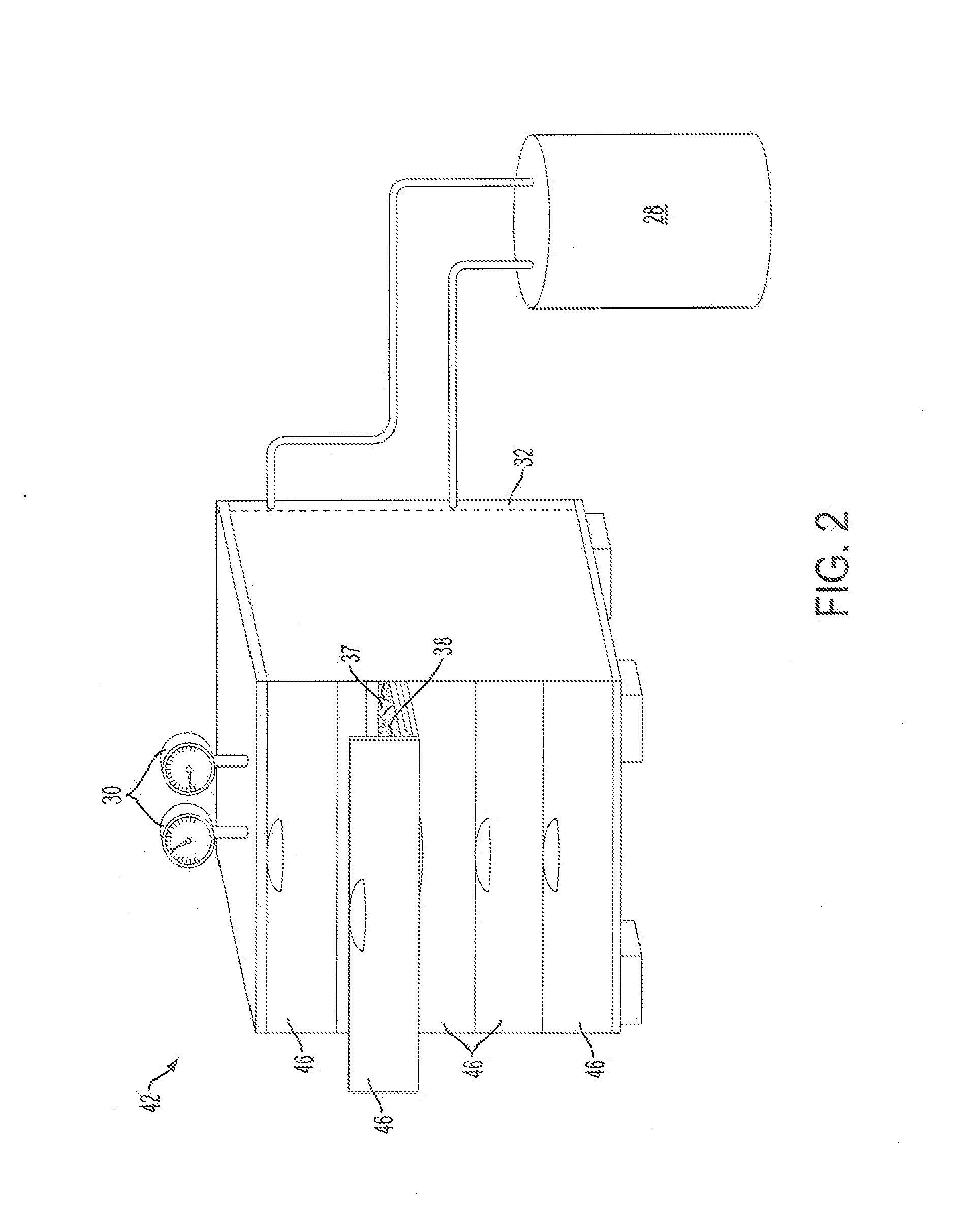
Temperature-Controlled Incubator Having A Receptacle Mixing Mechanism
InactiveUS20080063573A1Efficient and high through-put operationEfficient space utilizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusIsolation proceduresTemperature control
An automated analyzer for performing multiple diagnostic assays simultaneously includes multiple stations, or modules, in which discrete aspects of the assay are performed on fluid samples contained in reaction receptacles. The analyzer includes stations for automatically preparing a specimen sample, incubating the sample at prescribed temperatures for prescribed periods, performing an analyte isolation procedure, and ascertaining the presence of a target analyte. An automated receptacle transporting system moves the reaction receptacles from one station to the next. The analyzer further includes devices for carrying a plurality of specimen tubes and disposable pipette tips in a machine-accessible manner, a device for agitating containers of target capture reagents comprising suspensions of solid support material and for presenting the containers for machine access thereto, and a device for holding containers of reagents in a temperature controlled environment and presenting the containers for machine access thereto. A method for performing an automated diagnostic assay includes an automated process for isolating and amplifying a target analyte. The process is performed by automatically moving each of a plurality of reaction receptacles containing a solid support material and a fluid sample between stations for incubating the contents of the reaction receptacle and for separating the target analyte bound to the solid support from the fluid sample. An amplification reagent is added to the separated analyte after the analyte separation step and before a final incubation step.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Swiftlets farming for production of edible bird's nests
InactiveUS20080178819A1Keep properlyWithout harming wildlifeAnimal feeding devicesLivestock managementSwiftletHelminths
Owner:SIA YIK HEI
Depletion of endogenous primordial germ cells in avian species
InactiveUS20060095980A1Decrease in primordial germ cell numberIncrease in primordial germ cell numberVertebrate antigen ingredientsFermentationAntigenHigh concentration
Methods for modulating primordial germ cell (PGC) numbers and / or development in avians are provided. In one embodiment, the presently disclosed subject matter provides a method for modulating primordial germ cells numbers in an avian embryo comprising immunizing a female bird with an antigen associated with primordial germ cells, whereby an egg produced by the female bird comprises a sufficiently high concentration of antibodies specific for the antigen to modulate numbers of endogenous PGCs in an avian embryo present within in the egg. Also provided are methods for producing chimeric avians, methods for increasing the proportion of male birds in a plurality of eggs, methods of producing avian gametes, and methods for enhancing germ line transmission of nucleic acids in birds.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
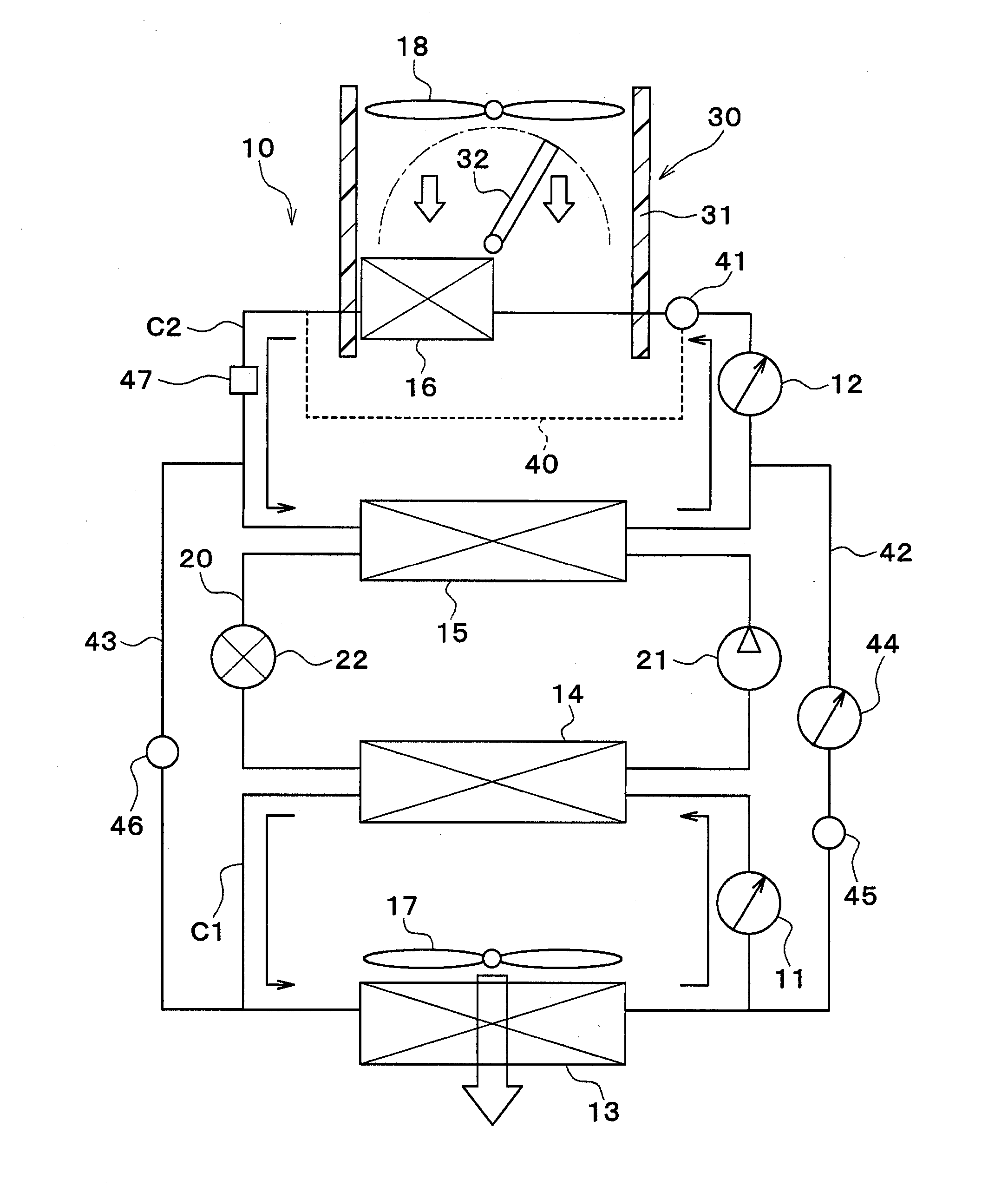
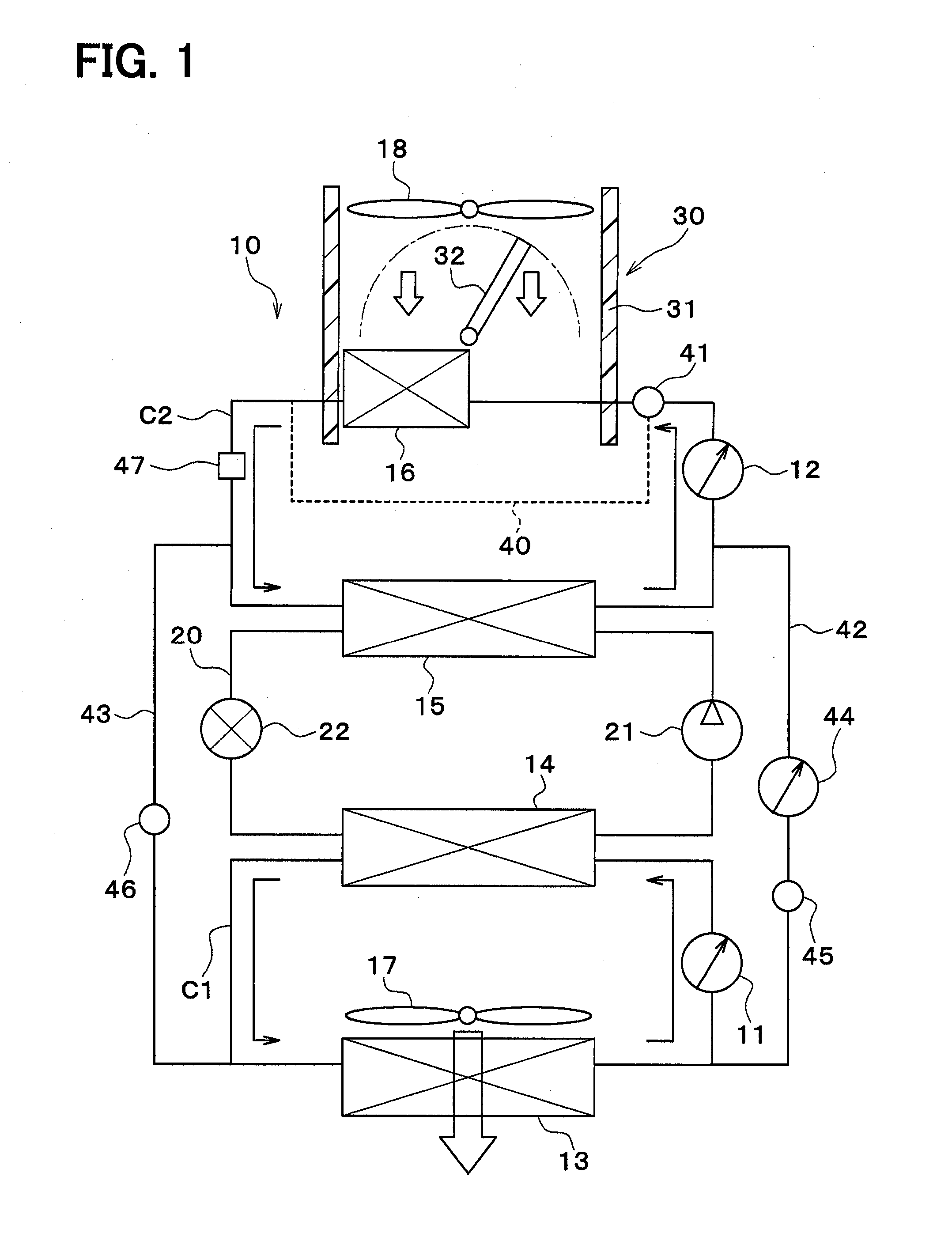
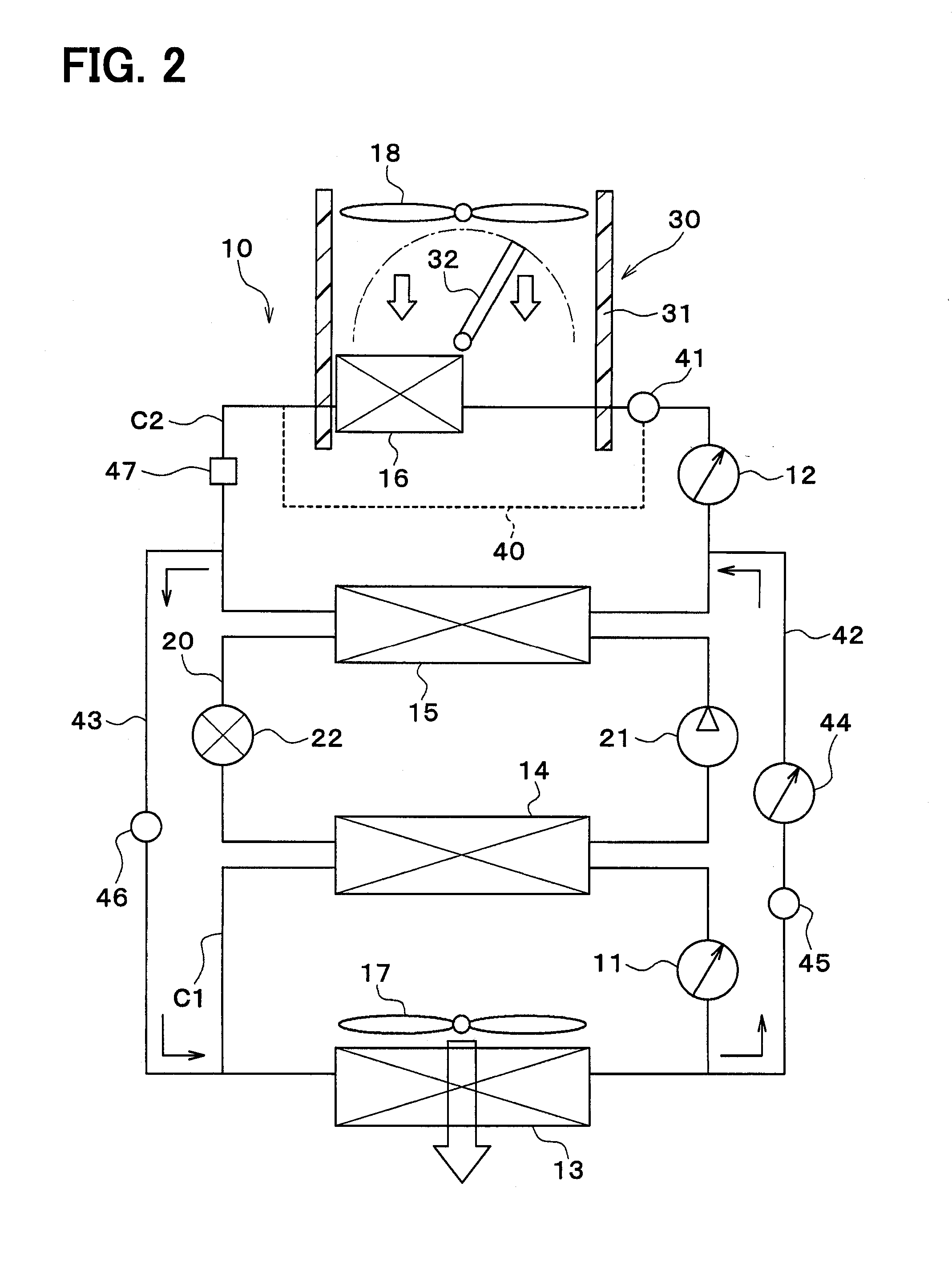
Vehicular heat management system
ActiveUS20160101666A1Inhibition releaseIncrease temperatureAir-treating devicesRailway heating/coolingHeat managementThermal management system
A vehicular heat management system includes: a refrigerant circuit; a first heat medium circuit in which a heat medium circulates and exchanges heat with a low-pressure side refrigerant of the refrigerant circuit; a second heat medium circuit in which a heat medium circulates and exchanges heat with a high-pressure side refrigerant of the refrigerant circuit; and a switching device configured to switch a mode between a communicating mode in which the first heat medium circuit and the second heat medium circuit are coupled and a non-communicating mode in which the first heat medium circuit and the second heat medium circuit are not coupled on the basis of a temperature of the heat medium in the first heat medium circuit.
Owner:DENSO CORP
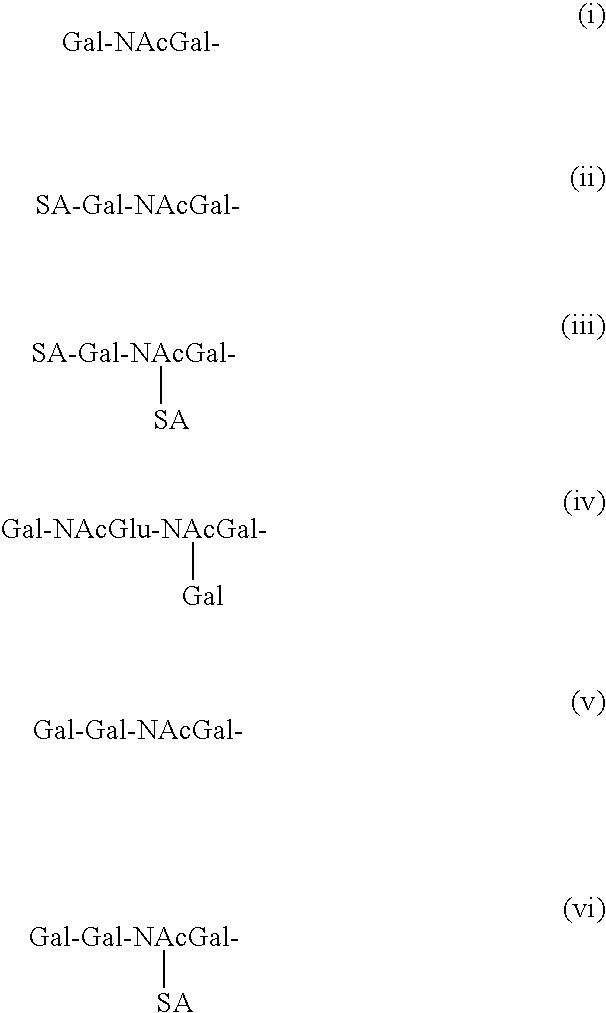
Tissue specific expression of exogenous proteins in transgenic chickens
InactiveUS20030172387A1Improve concentrationEasy to collectEgg immunoglobulinsVectorsGerm layerExogenous DNA
Transgenes encoding exogenous proteins are stably integrated into embryonic stem cells and are present in the somatic tissue of transgenic or chimeric birds. The transgenes encode exogenous proteins and are expressed in any of endodermal, ectodermal, mesodermal, or extra embryonic tissue. Tissue specificity is provided by selecting the content of the transgene accordingly. Transgenic birds whose genome is comprised of trangene derived exogenous DNA express exogenous proteins with tissue specificity, and specifically express exogenous proteins in the tubular gland cells of the oviduct to concentrate exogenous proteins in egg white..
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
Method for producing transgenic birds and fish
The present invention relates to methods for producing transgenic animals, particularly transgenic birds and fish, using retroviral constructs engineered to carry the transgene(s) of interest.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
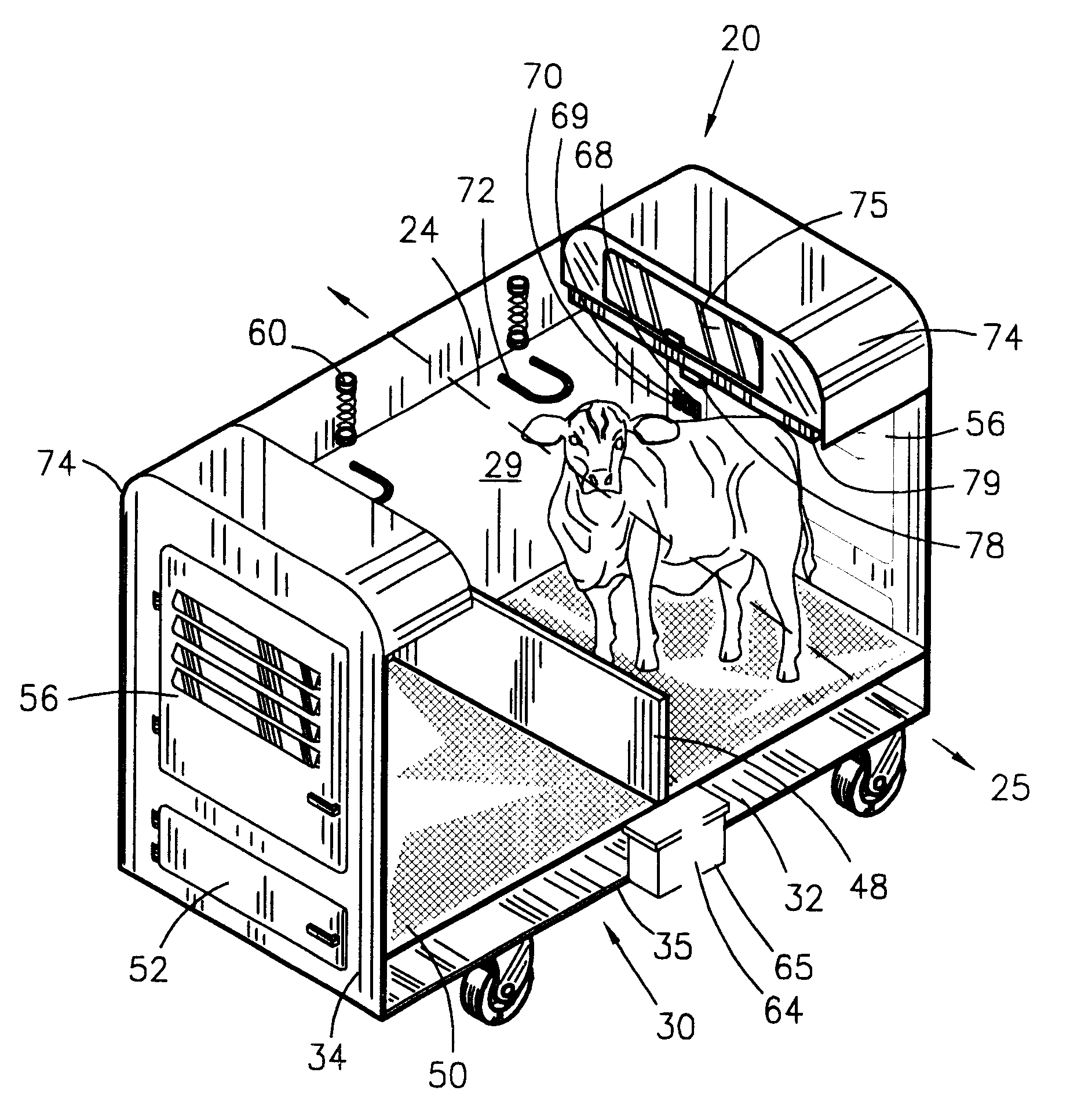
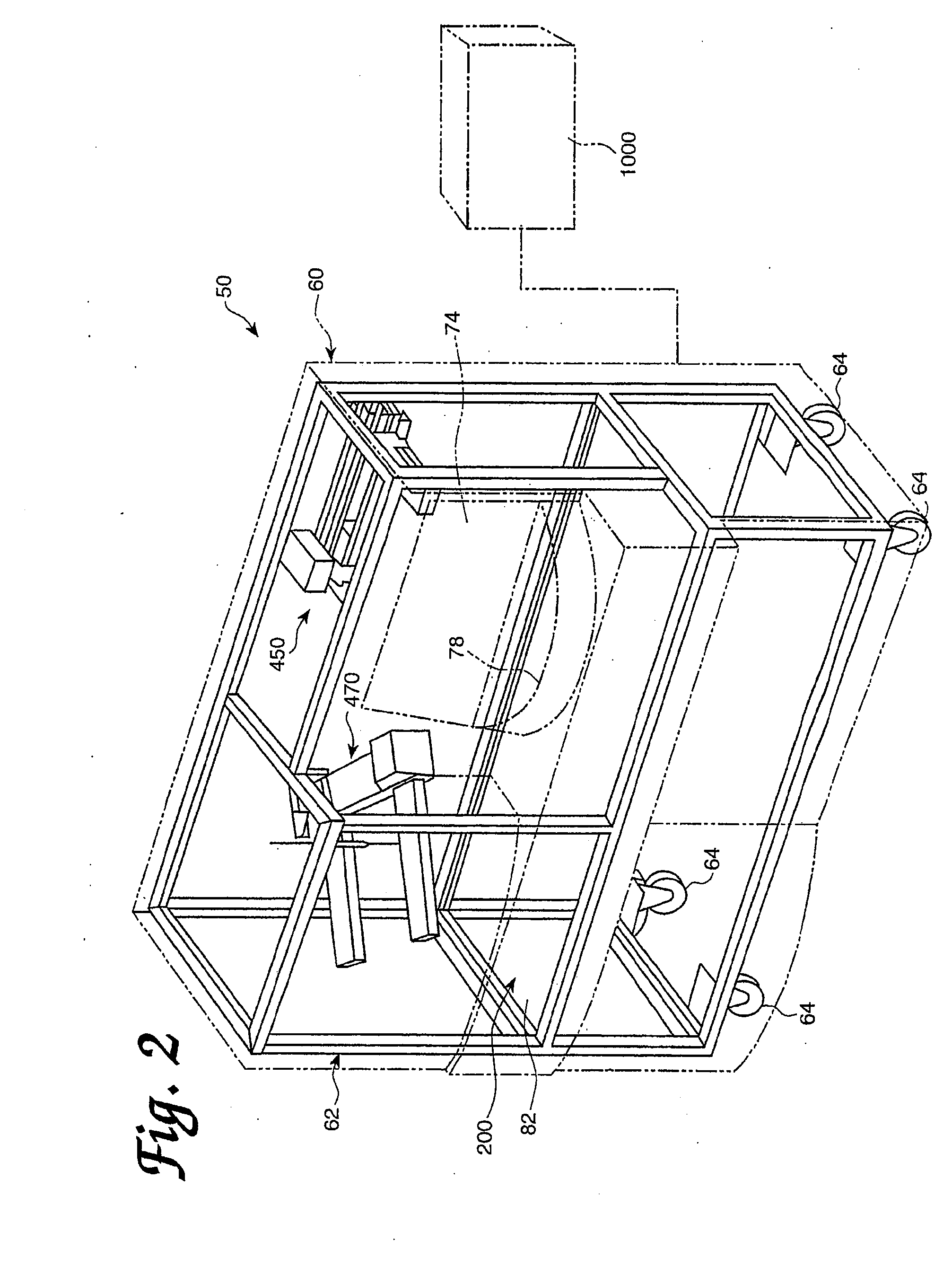
Methods and apparatus for supporting eggs during in ovo injection
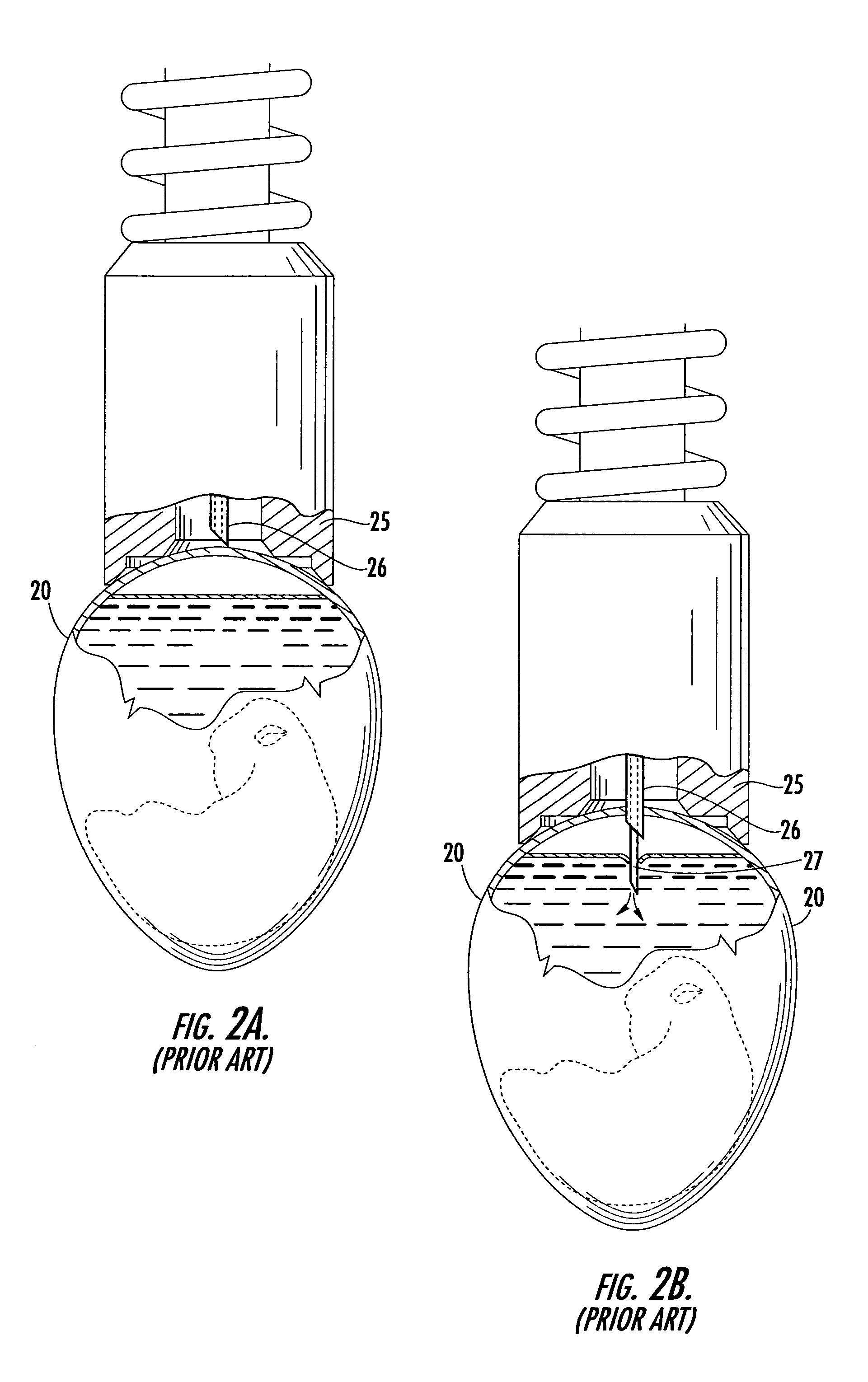
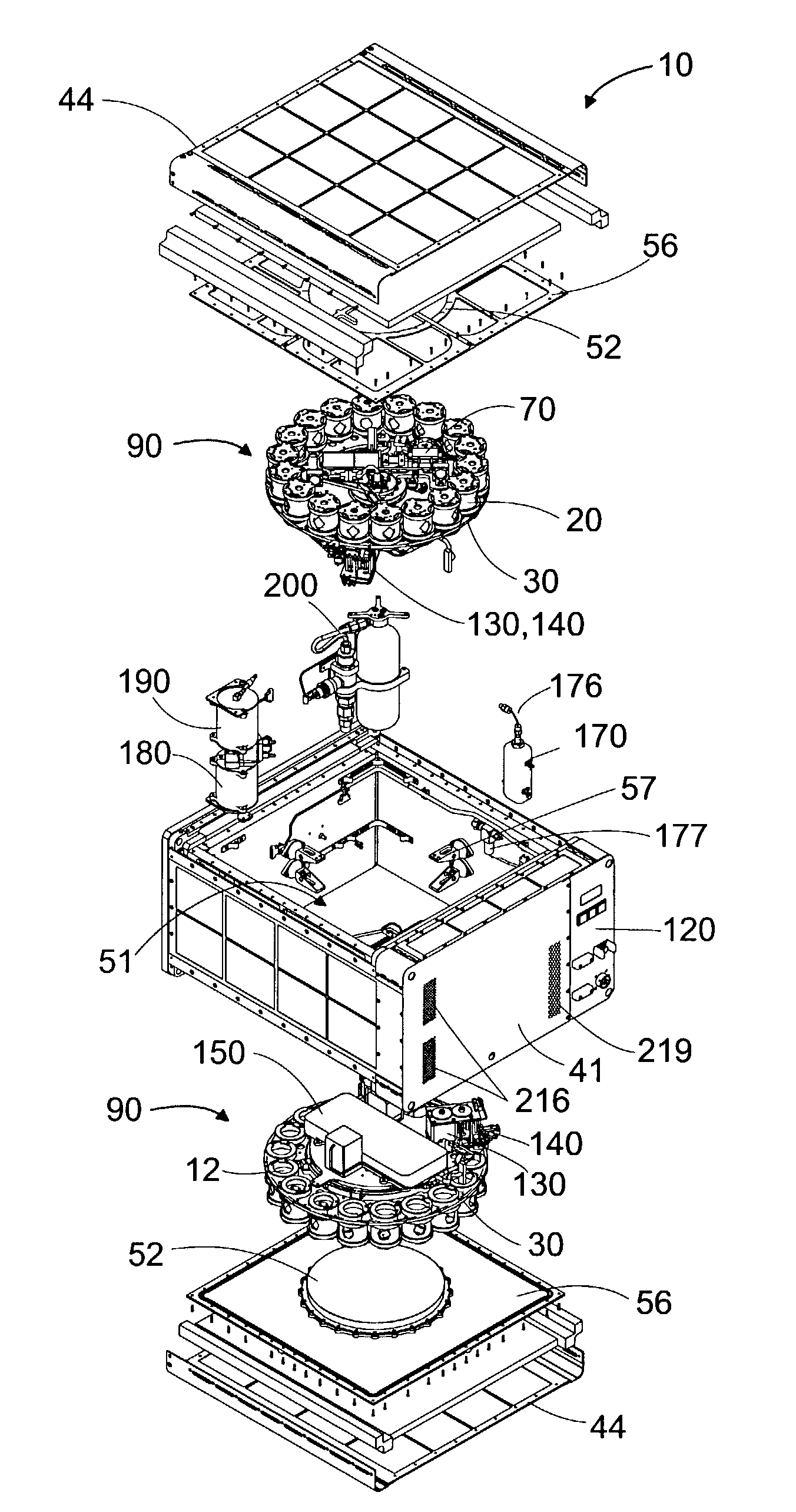
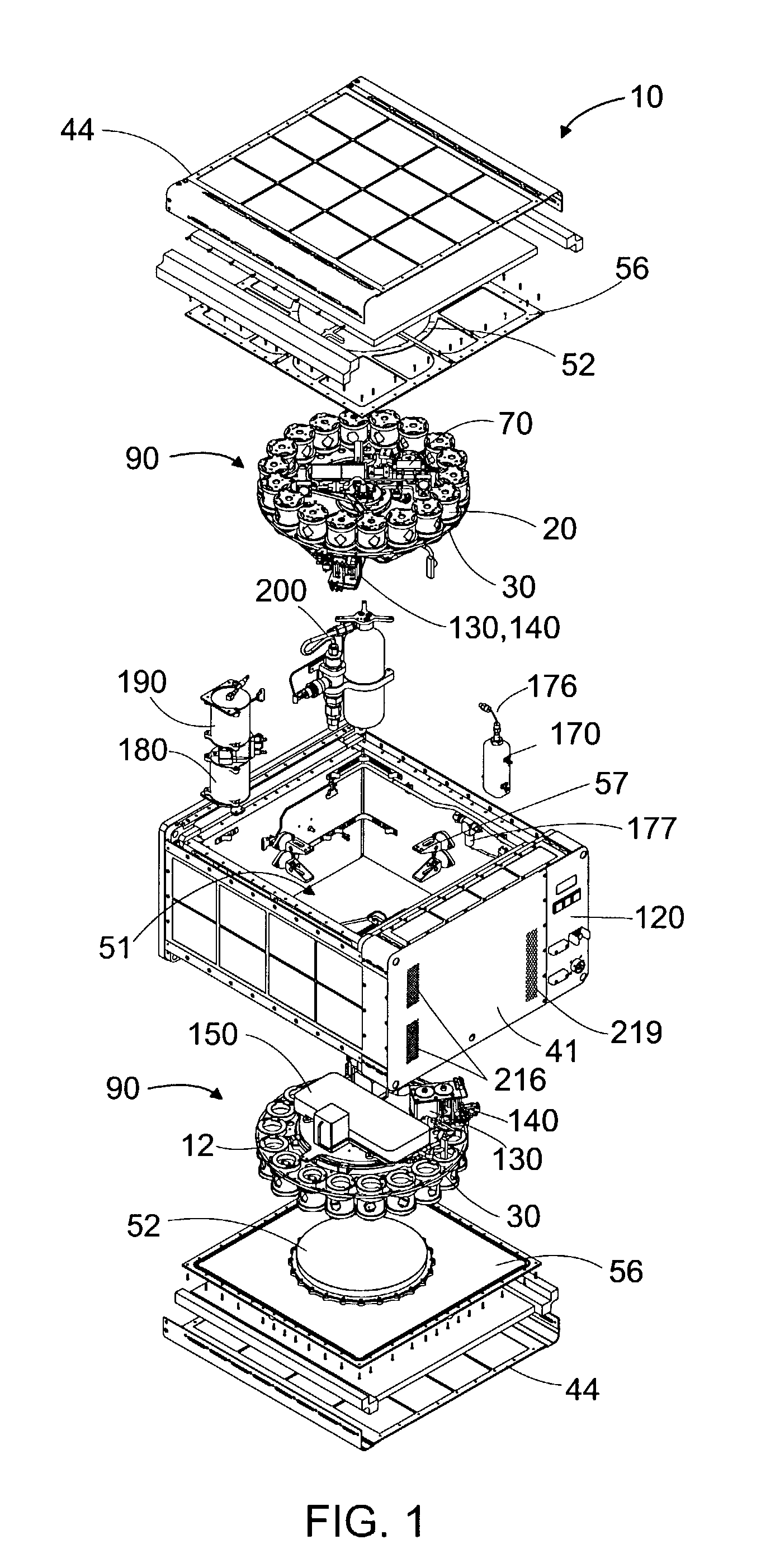
In ovo injection apparatus include an egg carrier configured to hold a plurality of eggs and to provide external access to the eggs, a plurality of injection devices positioned above the carrier, and an egg support assembly positioned beneath the carrier that is configured to support each egg in the carrier during contact therewith by a respective injection device. The egg support assembly includes a frame, a plate having an array of openings attached to the frame, and a plurality of pedestals removably secured within a respective one of the openings. The egg support assembly is operatively associated with the plurality of injection devices such that each pedestal moves upwardly through a respective opening in the carrier to support an egg as a respective injection device makes contact with the egg.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Methods for controlling sex of oviparous embryos using light sources
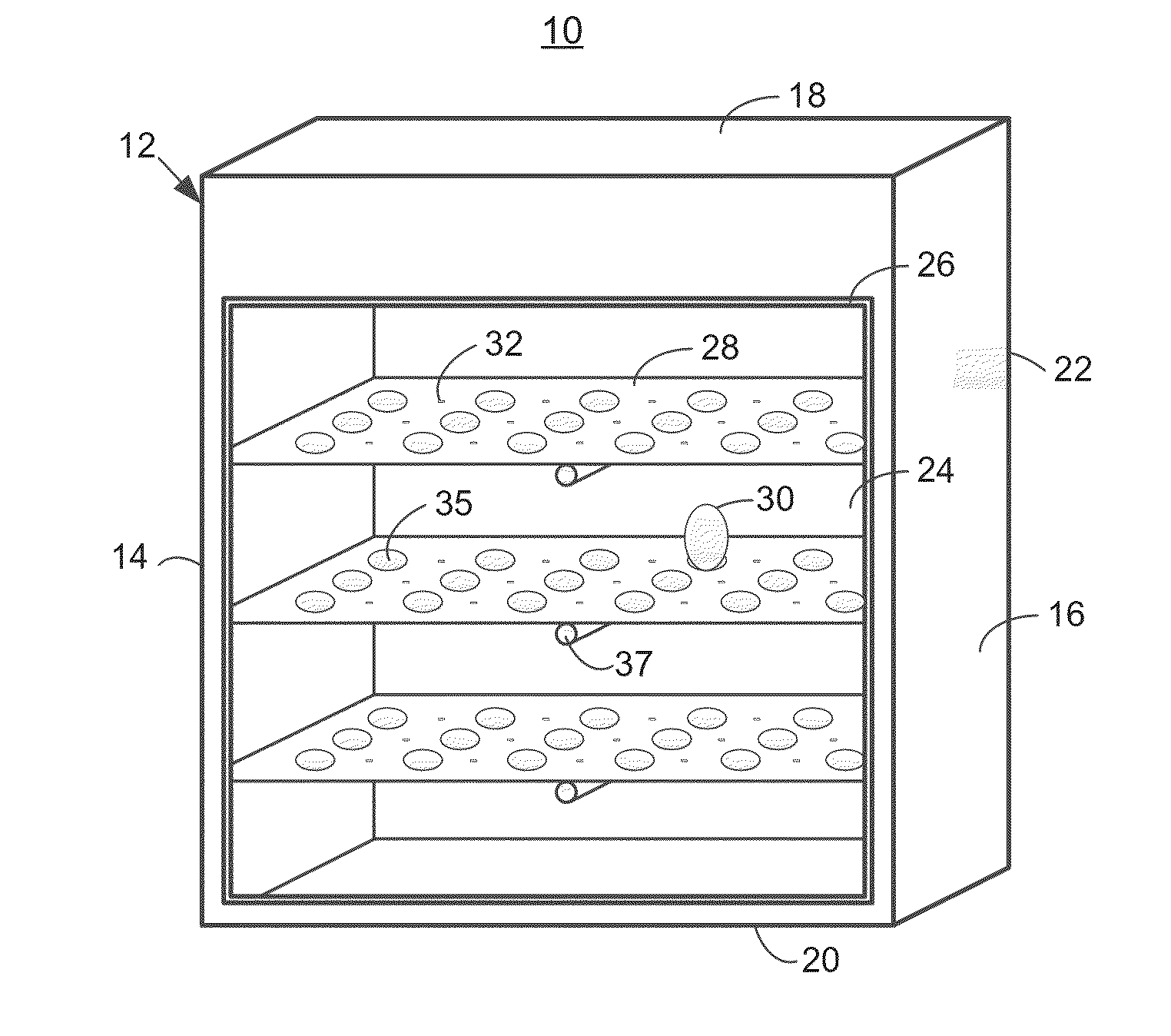
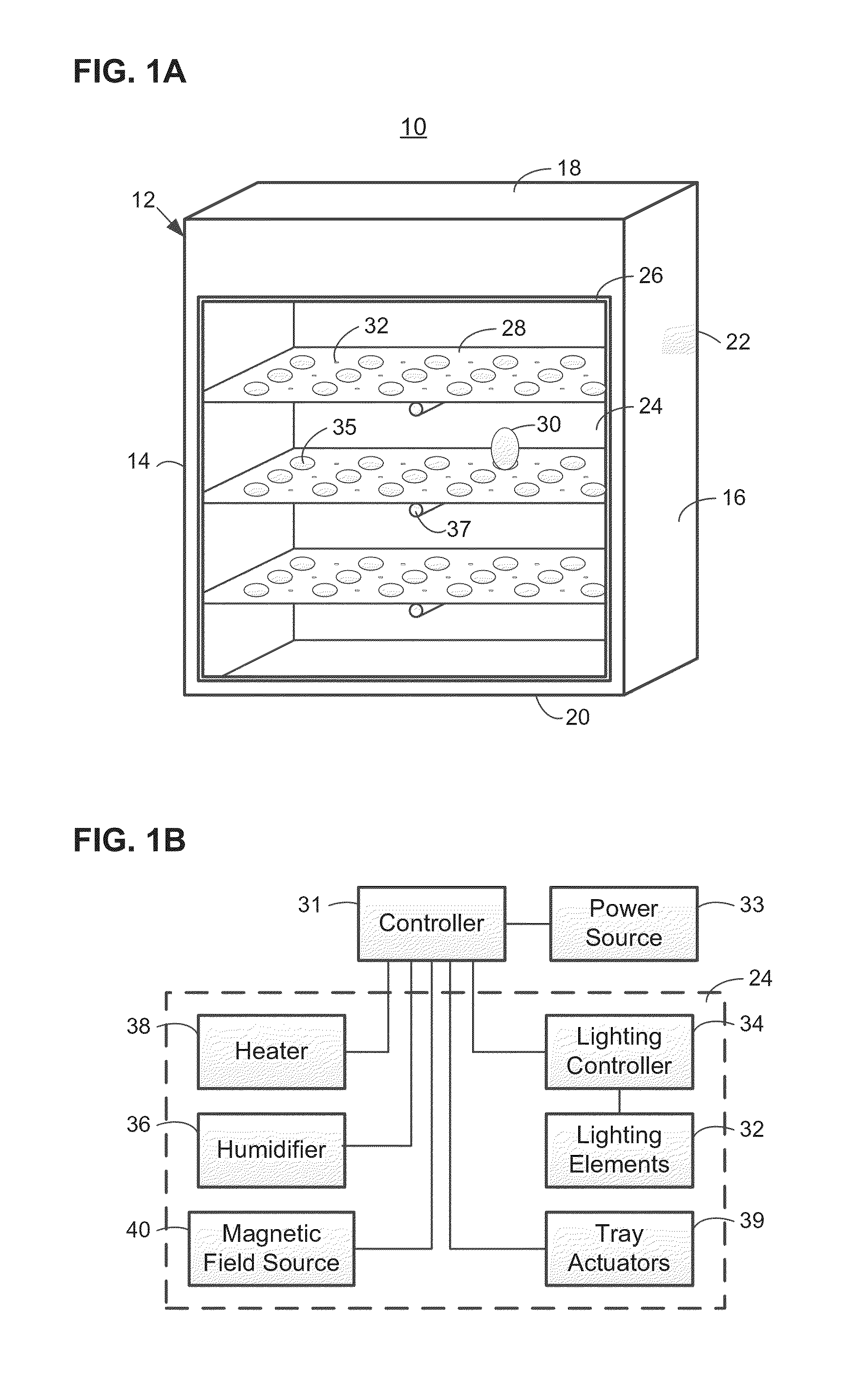
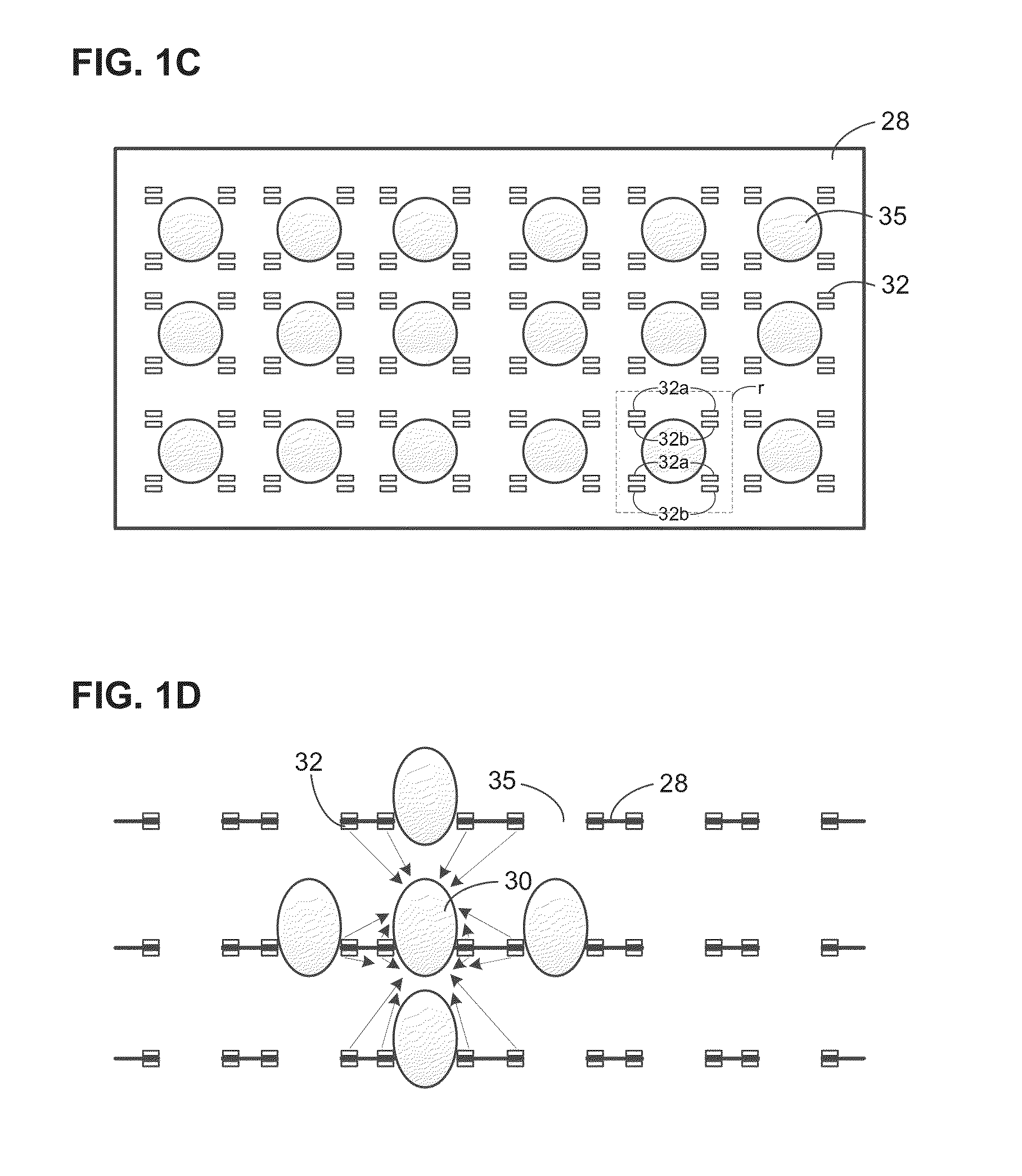
The sex of embryos in eggs is influenced or controlled through the application of light having selected wavelengths in order to promote the development of embryos of a selected sex. An incubating device is provided having an interior cavity that can be sealed from an outside, and having a plurality of lighting elements disposed on each of a plurality of trays disposed in the interior cavity. Eggs are disposed on the trays, and pre-determined environmental conditions are applied to the interior cavity to promote hatching of the eggs. Concurrently with the application of the environmental conditions, the eggs are irradiated according to pre-determined lighting conditions. The lighting conditions include applying light having wavelengths substantially concentrated in selected ranges, such as light wavelengths within the 390-419 nm, 410-450 nm, 420-450 nm, 450-495 nm, or other narrow range.
Owner:SIGNIFY NORTH AMERICA CORP
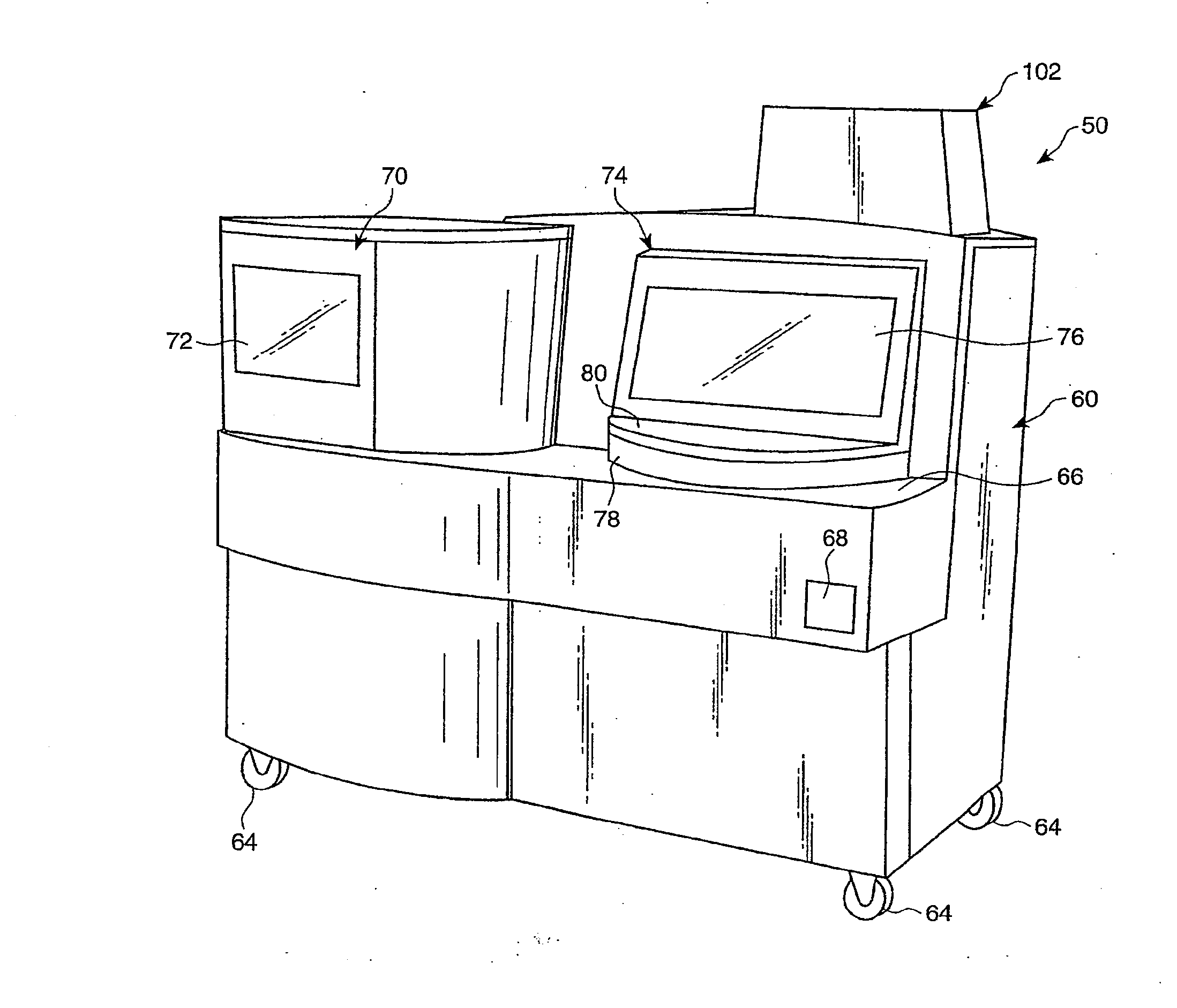
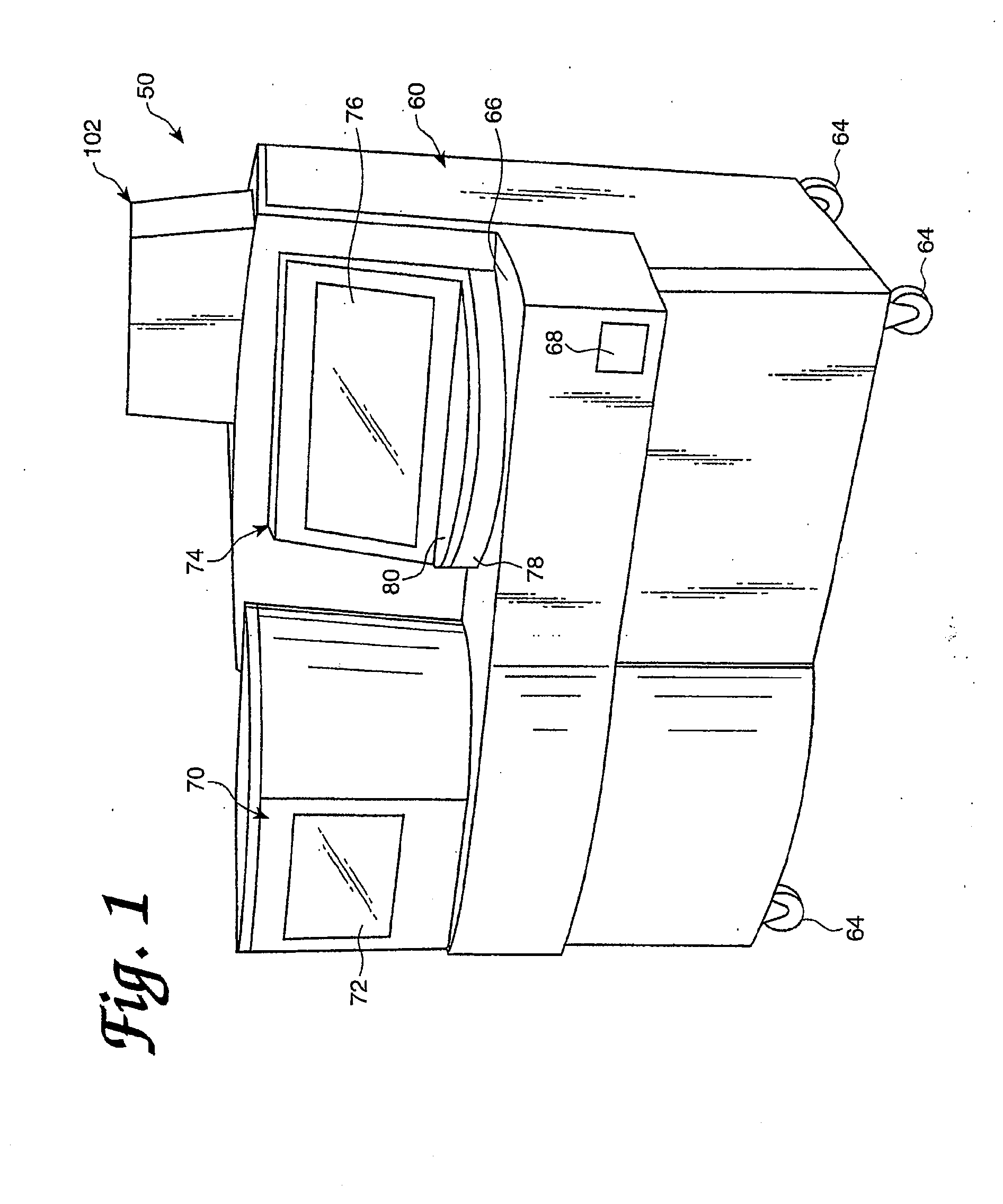
Apparatus and method for centrifugation and robotic manipulation of samples
A device for centrifugation and robotic manipulation of specimen samples, including incubating eggs, and uses thereof are provided. The device may advantageously be used for the incubation of avian, reptilian or any type of vertebrate eggs. The apparatus comprises a mechanism for holding samples individually, rotating them individually, rotating them on a centrifuge collectively, injecting them individually with a fixative or other chemical reagent, and maintaining them at controlled temperature, relative humidity and atmospheric composition. The device is applicable to experiments involving entities other than eggs, such as invertebrate specimens, plants, microorganisms and molecular systems.
Owner:TECHSHOT INC
Recombinant promoters in avian cells
InactiveUS7199279B2Reducing chromosomal positional effectReduce position changesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationHeterologousLysobacter enzymogenes
The invention provides for cells containing nucleic acids which include lysozyme gene expression controlling region nucleotide sequences which typically are linked to a polynucleotide encoding a heterologous polypeptide.
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
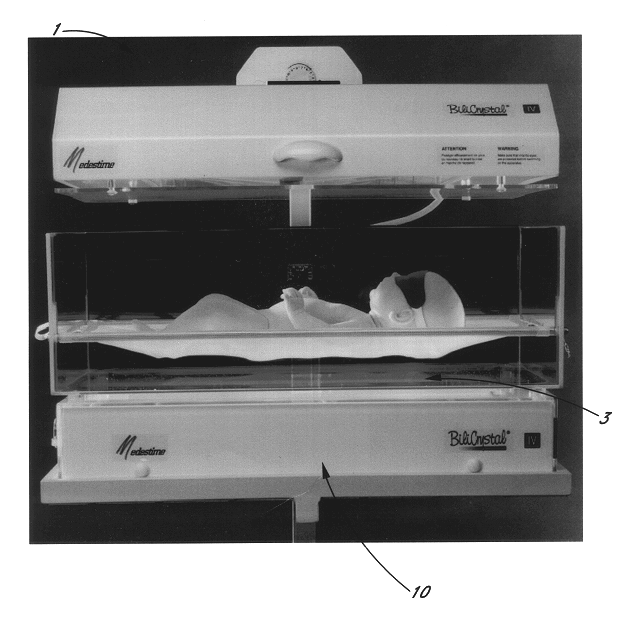
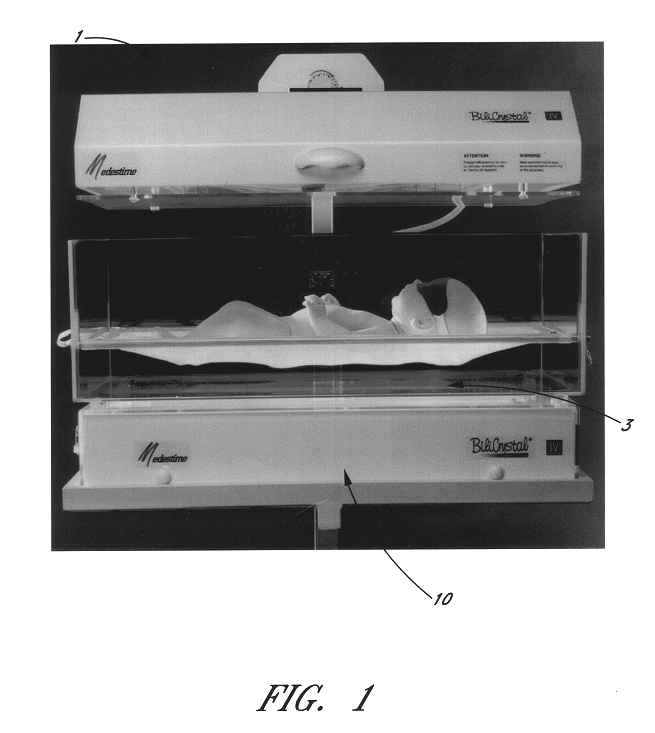
Intensive multidirectional phototherapy device
InactiveUS6464715B1Treatment safetyReduce the temperatureBaby-incubatorsElectric switchesLight treatmentEngineering
Disclosed is a phototherapy device for treating icterus in new-born patients, comprising a light box with at least one light source arranged in the box for illuminating the patient and a support for the patient to be placed upon which is at least partially transparent or tinted as to allow the light from the light box to expose the patient from below with respect to its direction of gravity, making it possible to expose areas having a high bilirubin concentration which tend to follow the direction of gravity.
Owner:MEDESTIME
Method for cultivating and producing dwarf green shell edge chicken
ActiveCN1748484AReduce consumptionImprove conversion efficiencyPoultry incubationF1 generationZoology
The medicine for cultivating and producing dwarf green shell egg layer includes the following steps: mating cock or hem with dwarf gene with hem or cock of green shell egg chicken to generate the F1 generation; selecting hems or cocks with dwarf gene characteristic from the F1 generation; re-selecting hems or cocks with dwarf gene characteristic to generate the F2 generation; selecting and leaving hems and cocks individuals with dwarf gene characteristic from the F2 generation; and genealogy selecting and breeding, individual selection, test crossing and detection. The present invention introduces dwarf gene into green shell egg chicken variety, and can utilize dwarf gene fully and protect green shell egg chicken variety resource.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
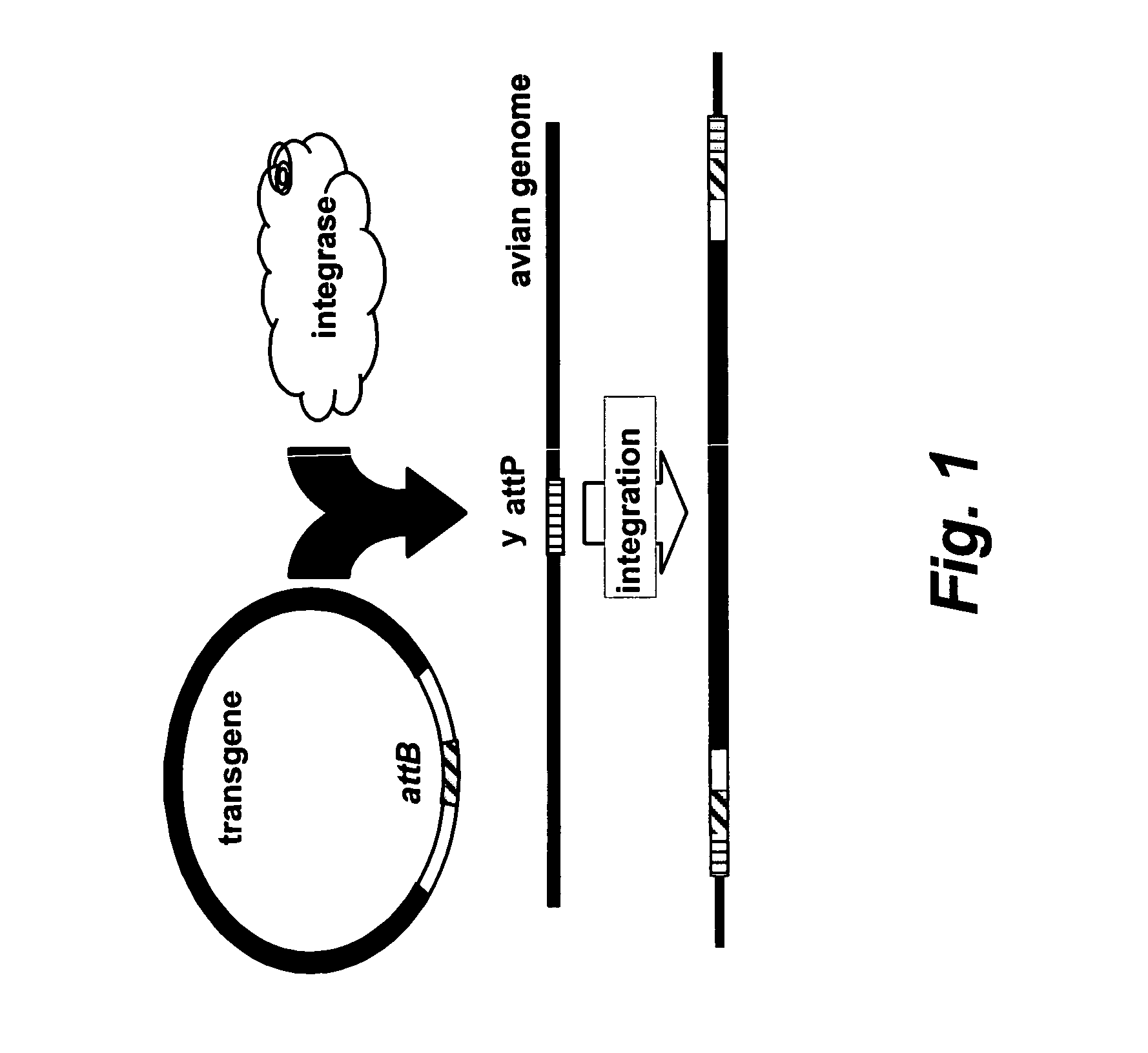
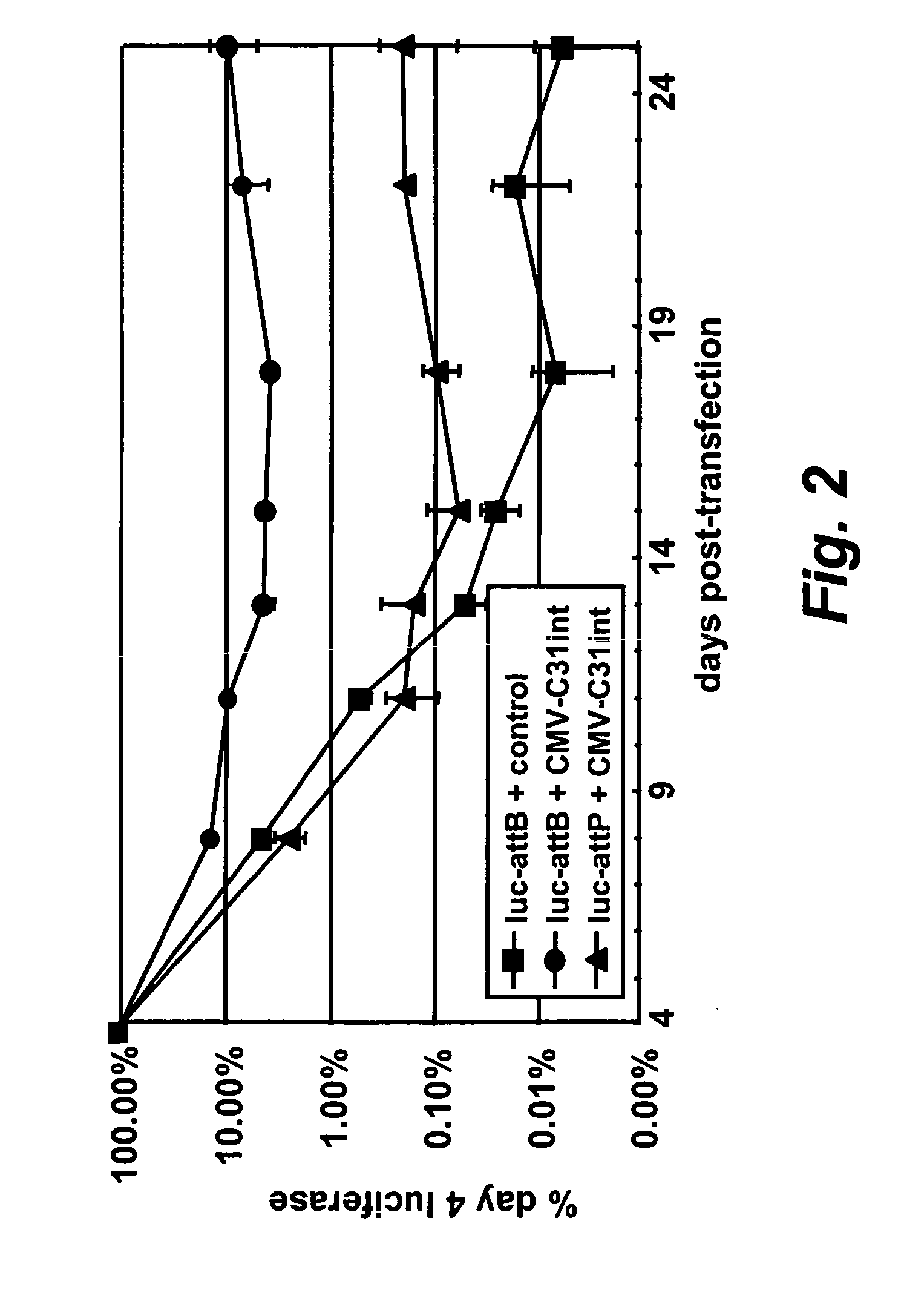
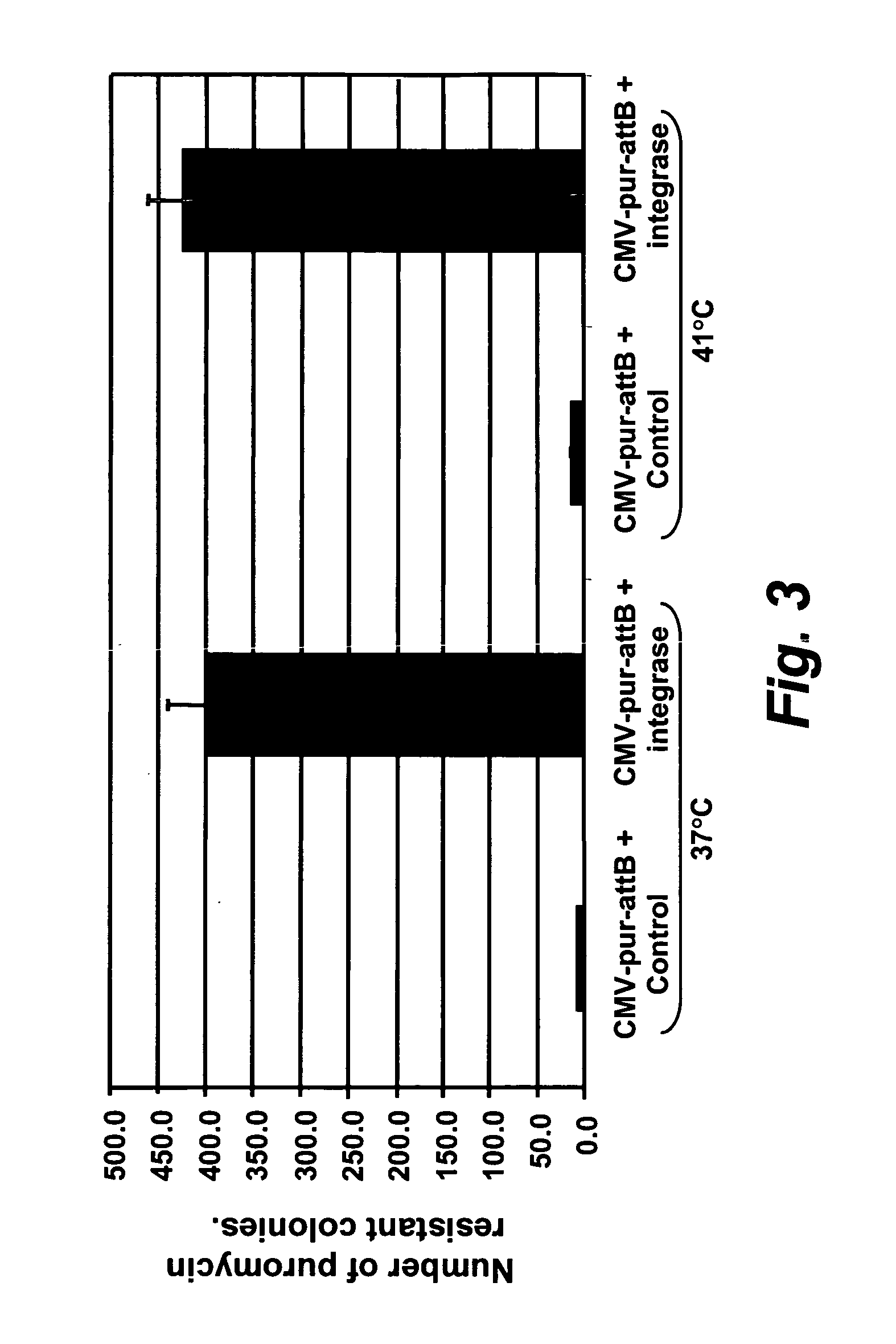
Site specific nucleic acid integration
InactiveUS20050034186A1Improve predictabilityStable introduction of DNANucleic acid vectorNucleotide sequencingGenome
The invention includes transgenic vertebrate animals and vertebrate animal cells and methods for site specifically introducing nucleotide sequences into the genome of vertebrate animals and vertebrate animal cells.
Owner:AVIGENICS
Production of heterologous proteins in avians
InactiveUS20060015960A1Altered phenotypeEfficient expressionVectorsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyHeterologous
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP +1
System and Method for Production of Predatory Mites
The insect inoculation system and method optimizes the conditions wherein host insect cadavers are infected by a selected parasite. Host insect cadavers are exposed to the selected parasite within the inoculation chamber. The inoculation chamber is configured to optimize the parasite infection and reproduction process. The insect parasites produce multiple offspring which remain in the infected insect cadavers. At the end of the inoculation process, the infected cadavers are removed from the chamber and the insect parasites are harvested and used in bio-pest control processes.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
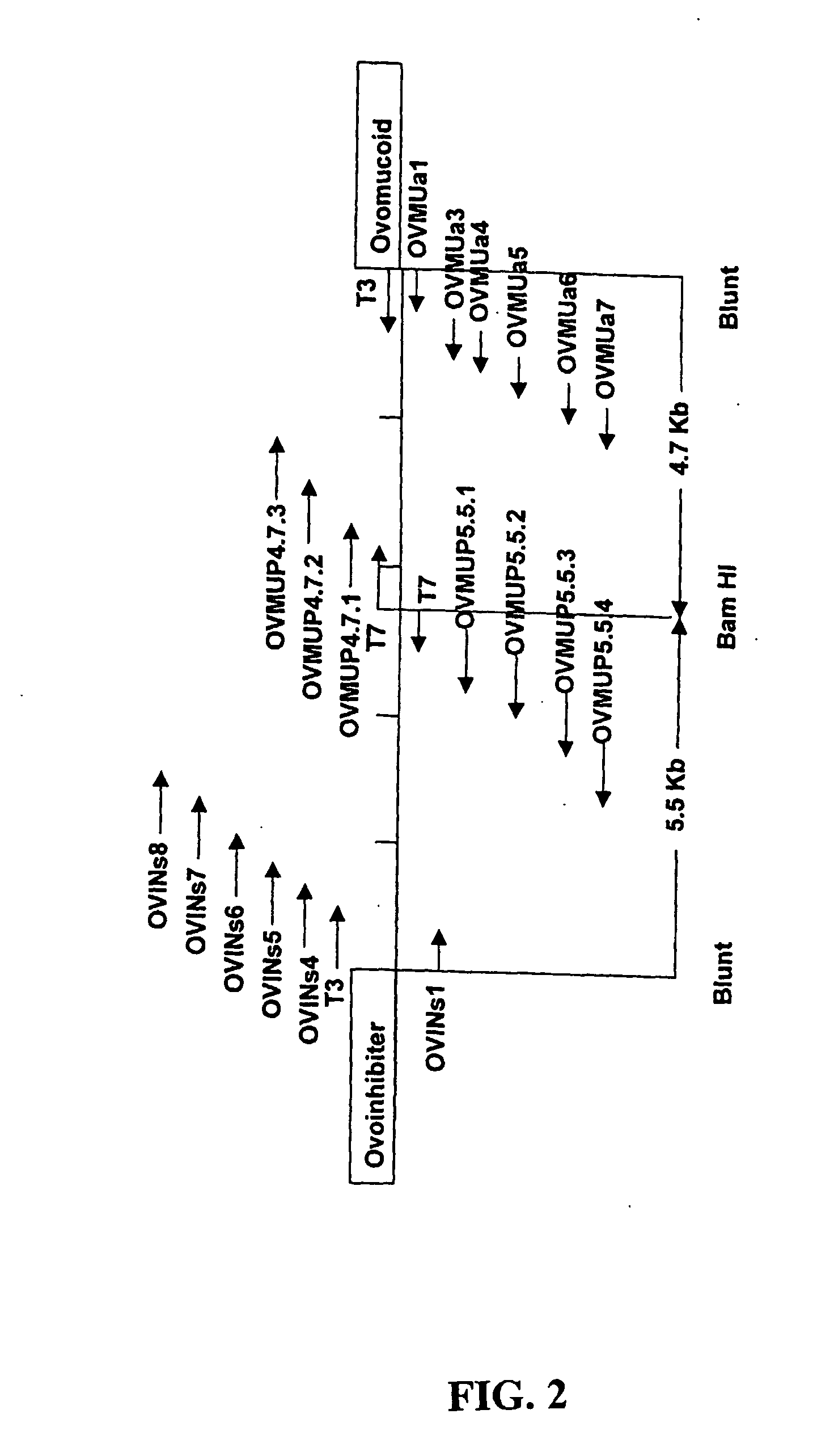
Ovomucoid promoters and methods of use
The present invention provides novel isolated nucleic acids that comprise an avian nucleic acid sequence comprising a ovomucoid gene expression control region. The ovomucoid promoter region of the present invention will allow expression of an operably linked heterologous nucleic acid insert in a transfected avian cell such as, for example, an oviduct cell. The isolated avian ovomucoid of the present invention may be operably linked with a selected nucleic acid insert, wherein the nucleic acid insert encodes a polypeptide desired to be expressed in a transfected cell. The recombinant DNA of the present invention may further comprise a polyadenylation signal sequence. The present invention further includes expression vectors comprising an isolated avian ovomucoid gene expression control region of the present invention, and transfected cells and transgenic avians comprising the expression vectors.
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
Method for breeding snowy region jungle fowl
The invention relates to a method for breeding snowy region jungle fowl. The method comprises the steps of: selecting healthy and high-yielding eggs of snowy region jungle fowl, adopting chameleon solution to fumigate the selected eggs and placing the eggs on egg plates under certain temperature and humidity conditions; placing the eggs in a breeding room, arranging egg plates and carrying out breeding after natural pre-heating; respectively controlling space temperature and humidity of breeding machines according to different breeding periods; ensuring regular egg-turning and plate-adjusting to lead all the parts of embryo to be heated equally; selecting shell less eggs and dead eggs during two-time of egg-illumination so as to ensure that the live and healthy embryonated eggs can obtain hatchability from the 20th day of the breeding period, and placing the embryonated eggs to rearing rooms or boxes for nursing. The method comprises the processes of selection, sterilization, humidification, heating, egg-turning, illumination and the like to breed the snowy region jungle fowl meeting green and organic standards, and the hatchability reaches 87 to 91 percent.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
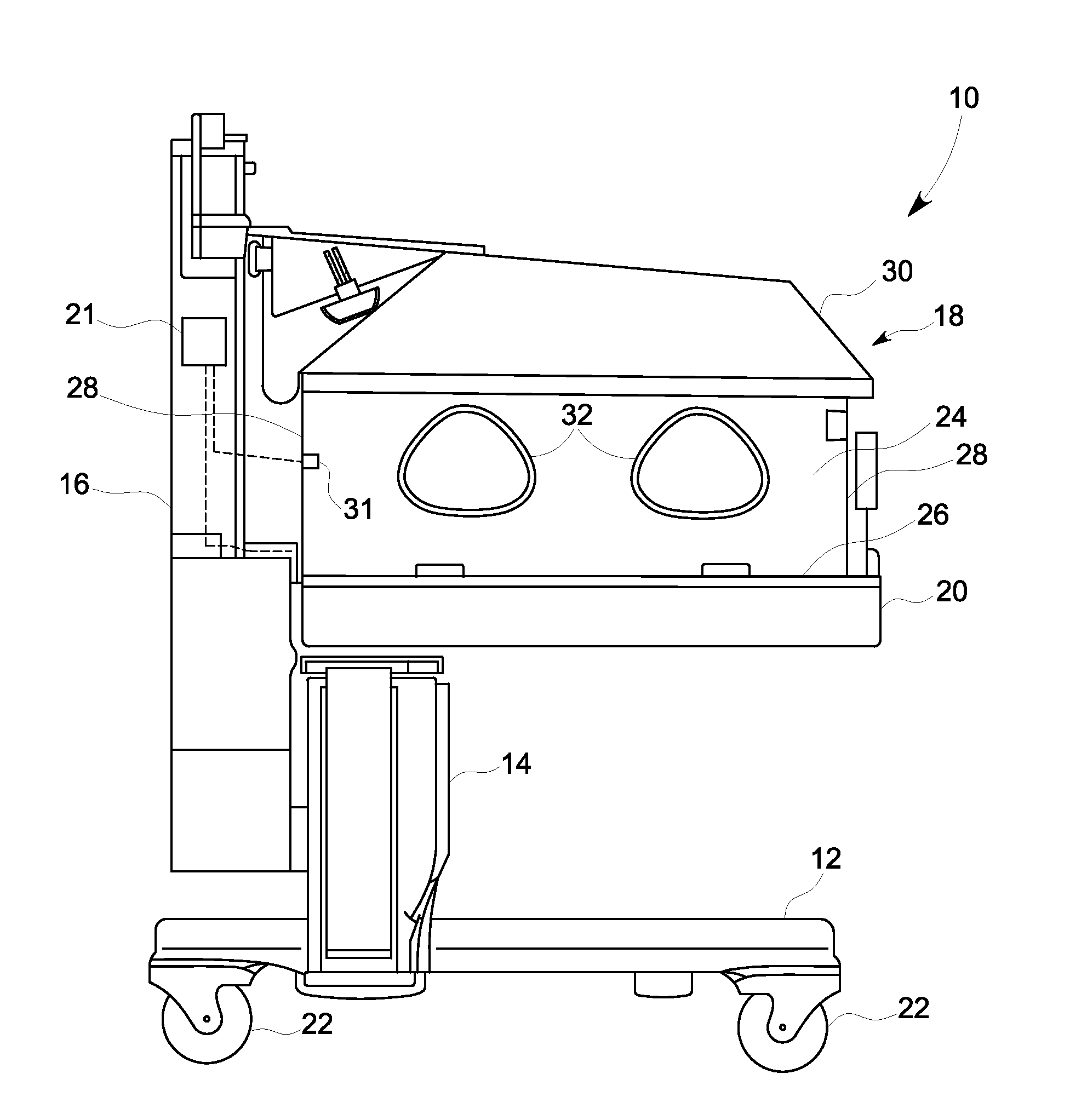
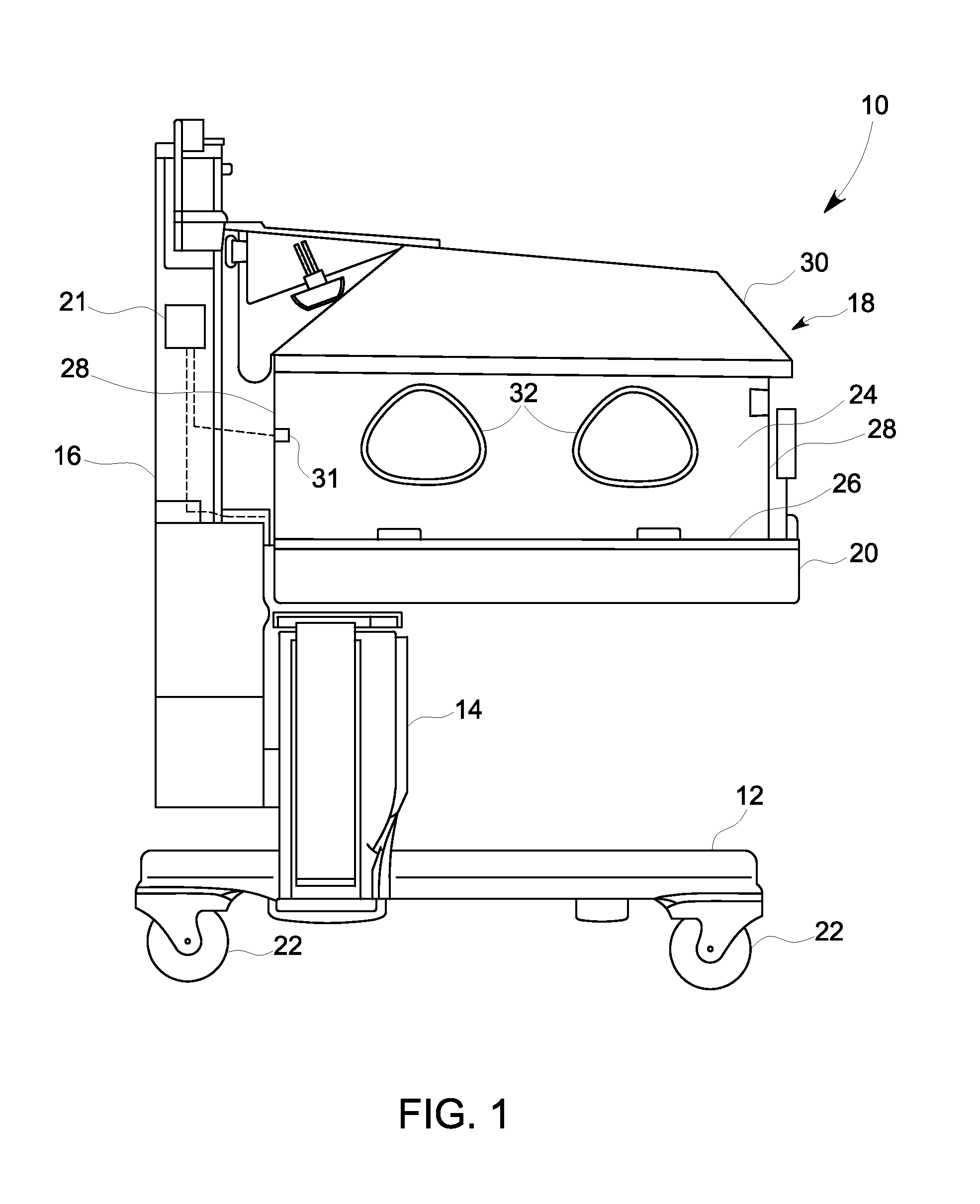
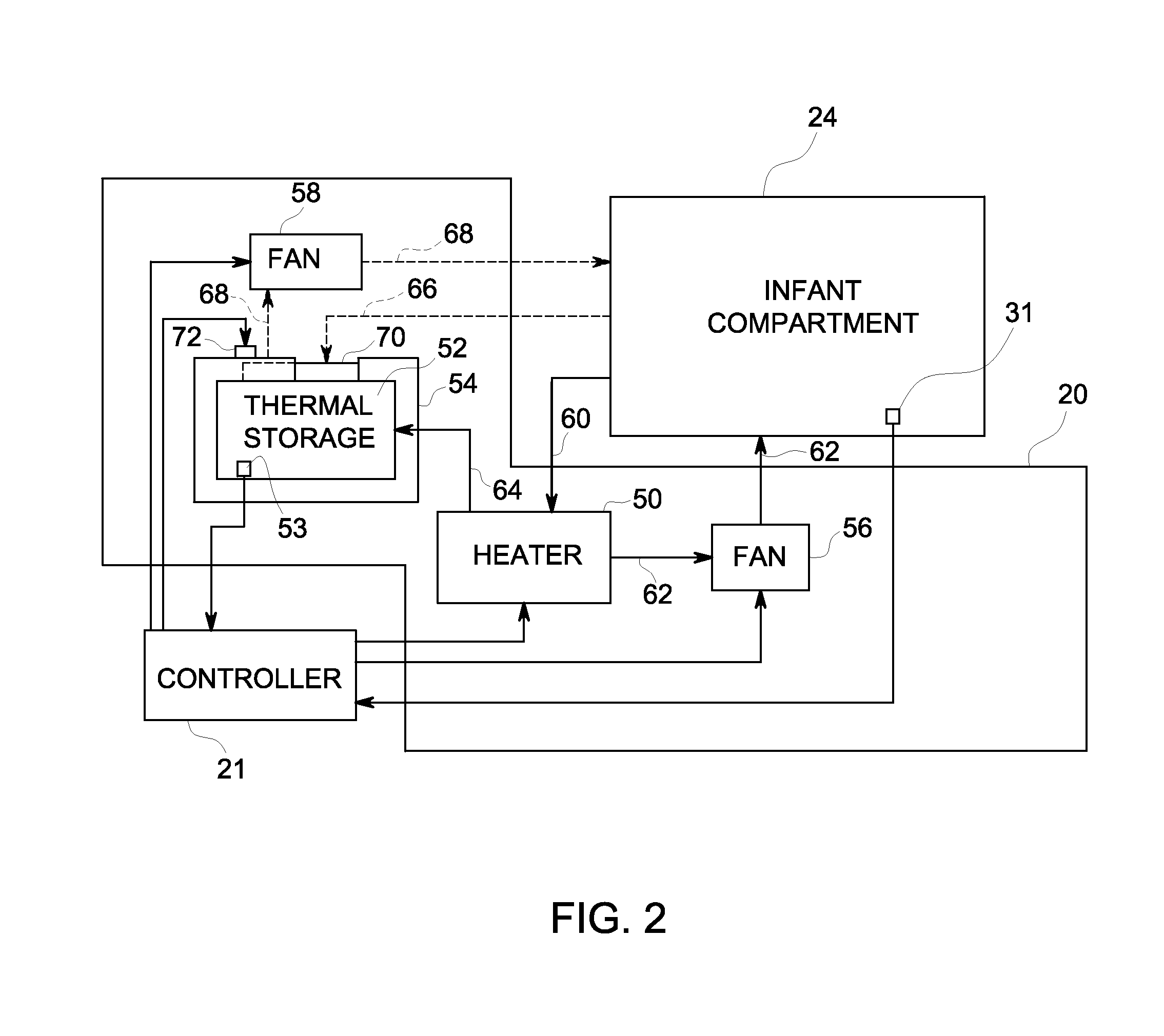
Infant warmer
ActiveUS20120078034A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHeat transmissionEngineering
An infant warmer includes an infant enclosure defining an infant compartment, and a heating system pneumatically coupled with the infant compartment. The heating system includes a heater configured to selectively transfer heat to the infant compartment, and a thermal storage device configured to store heat from the heater and to selectively transfer said stored heat to the infant compartment. The infant warmer also includes a controller operatively connected to the heating system. The controller is configured to regulate the transfer of heat from the thermal storage device such that a target temperature is maintained within the infant compartment.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Movable egg car hatcher
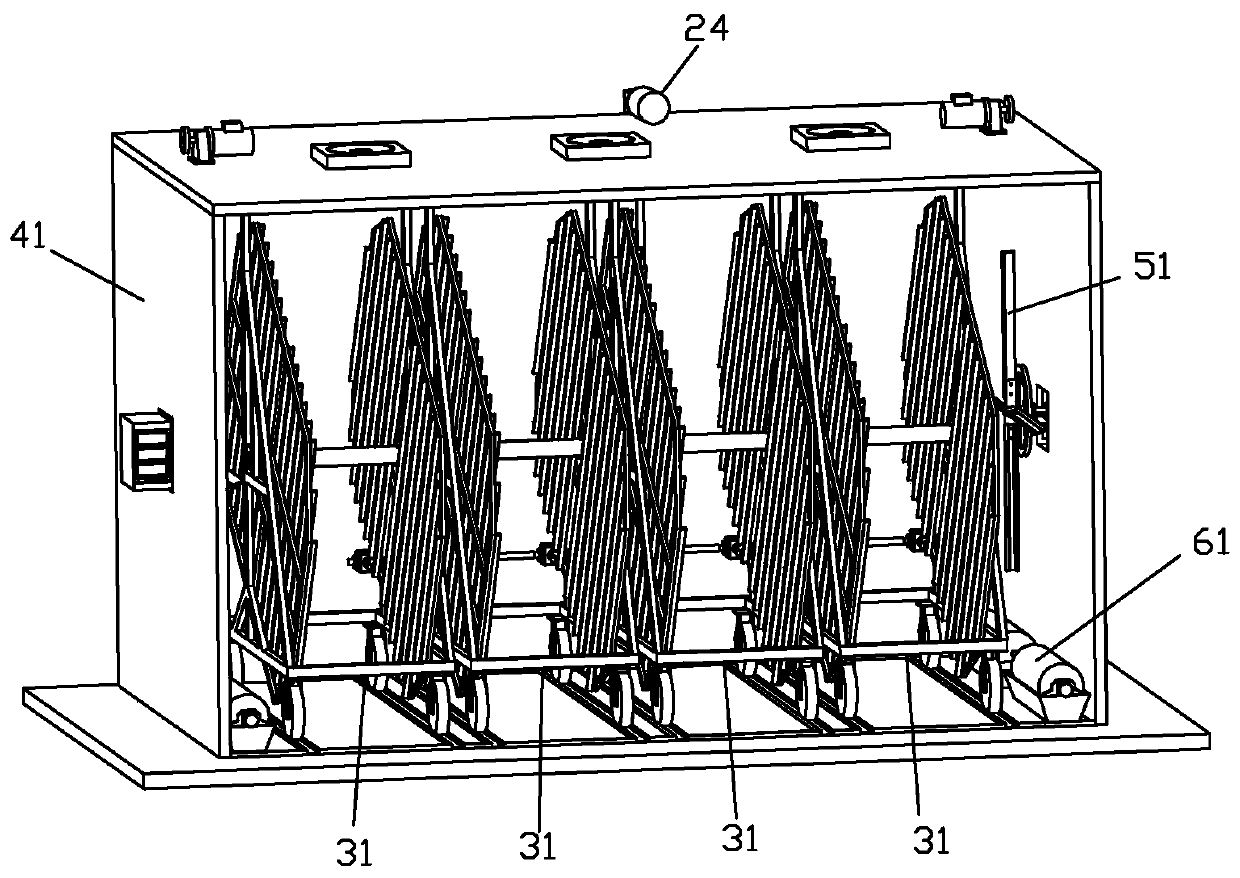
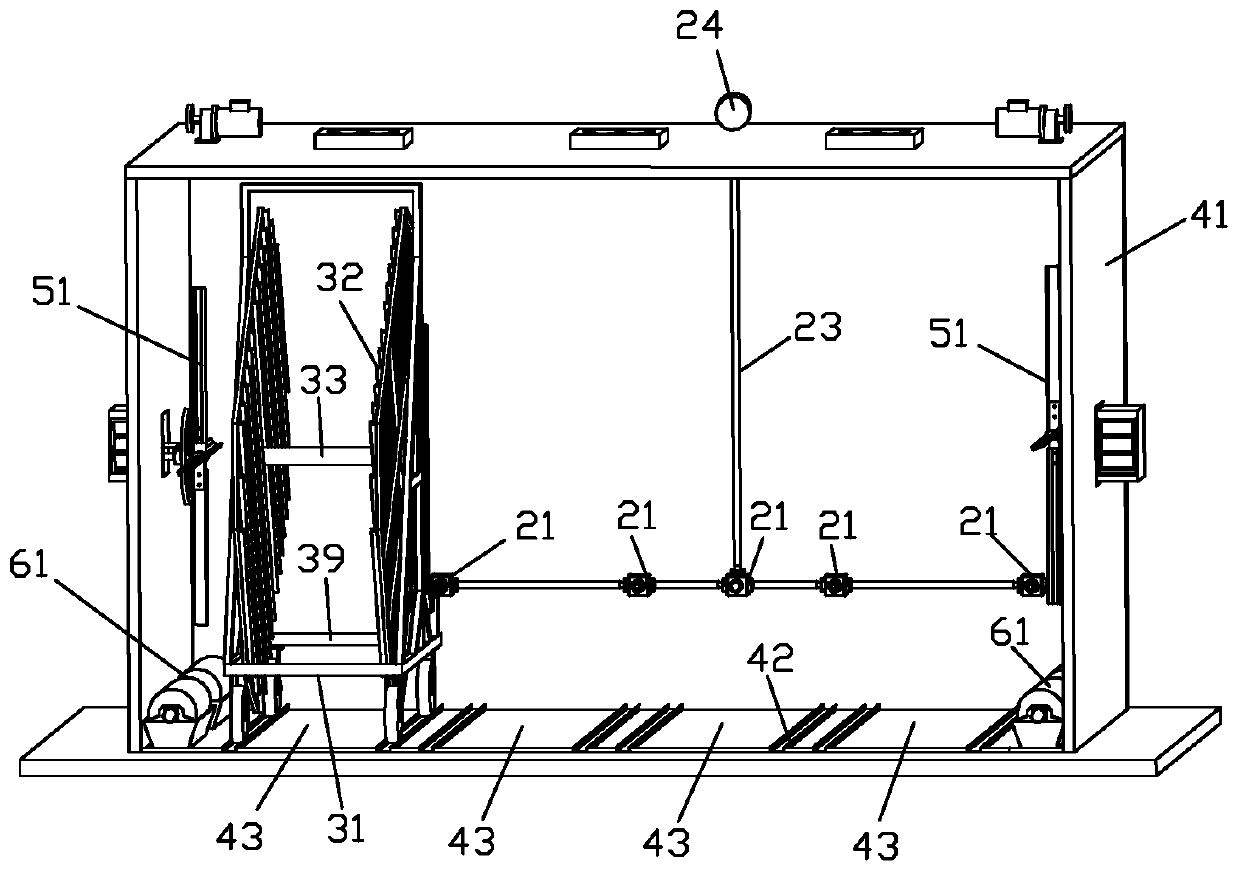
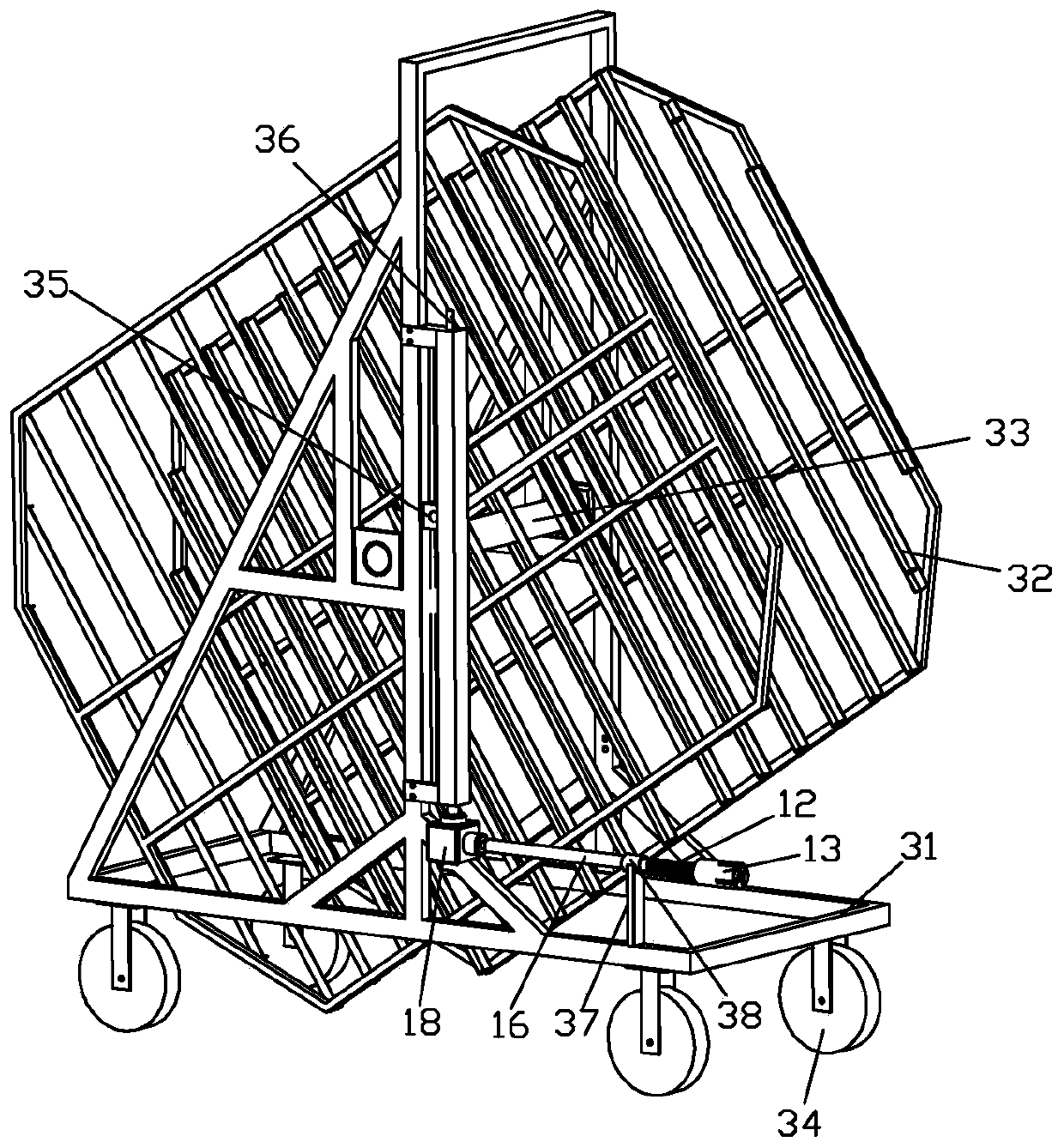
The invention discloses a movable egg car hatcher which comprises an incubator, a hatching adjustment system, at least one egg rack, at least one movable egg car, a power source and a transmission shaft component. The egg racks are erected on the corresponding movable egg cars in a suspended manner through rotating spindles, transmission mechanisms are arranged on the movable egg cars, parking spaces corresponding to the movable egg cars are arranged in the incubator, both the transmission shaft component and the power source are fixedly mounted on the incubator, the power source is connectedwith an input shaft of the transmission shaft component, the transmission shaft component is provided with output shafts corresponding to the parking spaces, a fixed butt joint part is arranged at theend of each output shaft, a butt joint shaft connected with the transmission mechanism of each movable egg car is arranged on each movable egg car, and a movable butt joint part is arranged at the end of each butt joint shaft. The movable egg car hatcher is reasonable in structure and simple to operate.
Owner:佛山市任氏机械科技有限公司
Systems and methods for promoting biological responses in incubated eggs
InactiveUS20170074464A1Small sizePromote biological responseProgramme controlPlanar light sourcesLength waveOrganism
A system and method to promote biological responses within incubated eggs using lighting devices within an incubation chamber. A light supporting device is installed within the incubation chamber in spaced relation to an incubation device housing a plurality of eggs. The light supporting device is positioned to direct light at pre-determined wavelengths into the interior cavity of the incubation device to irradiate the plurality of eggs to promote a. biological response within the eggs.
Owner:SIGNIFY NORTH AMERICA CORP
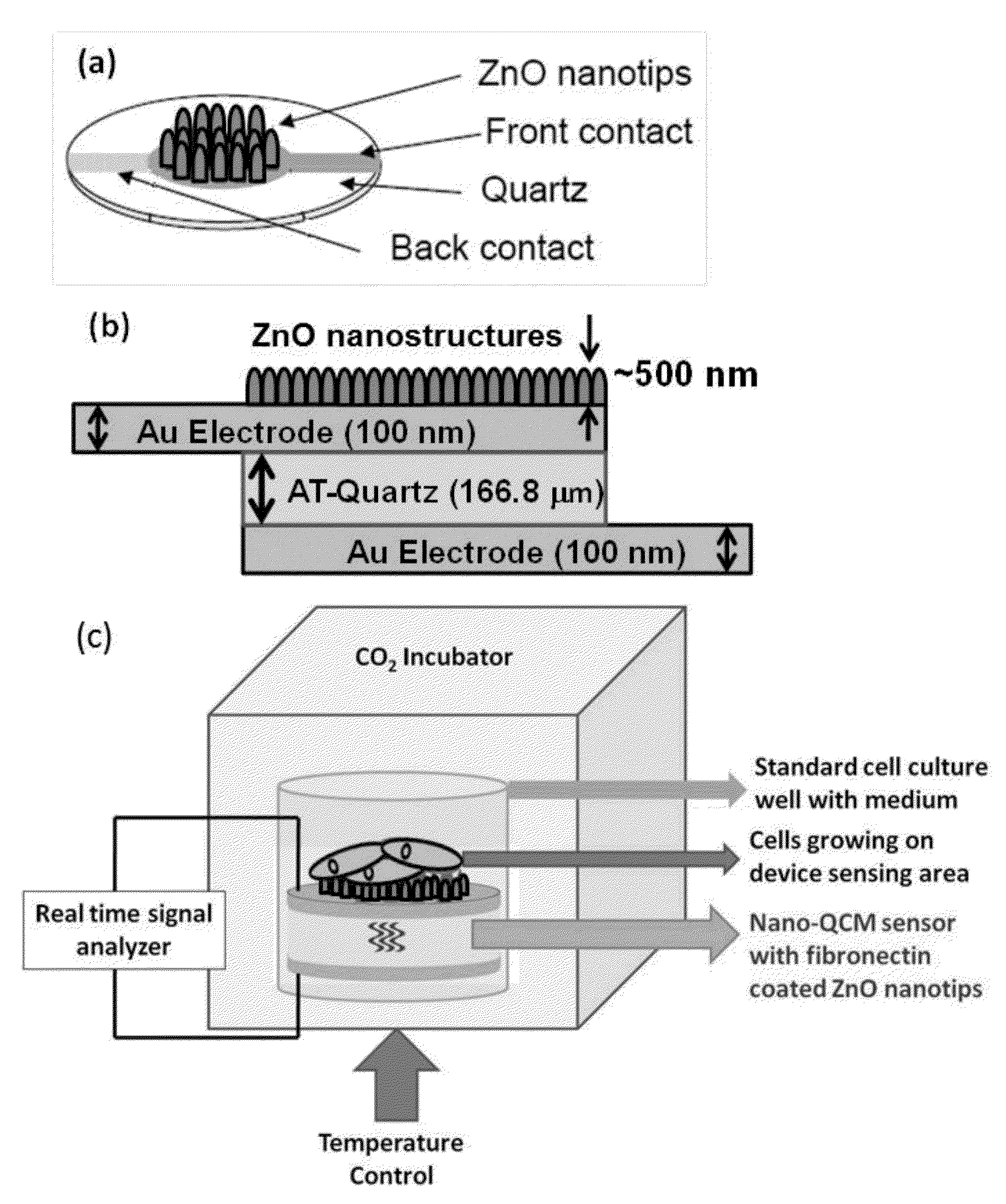
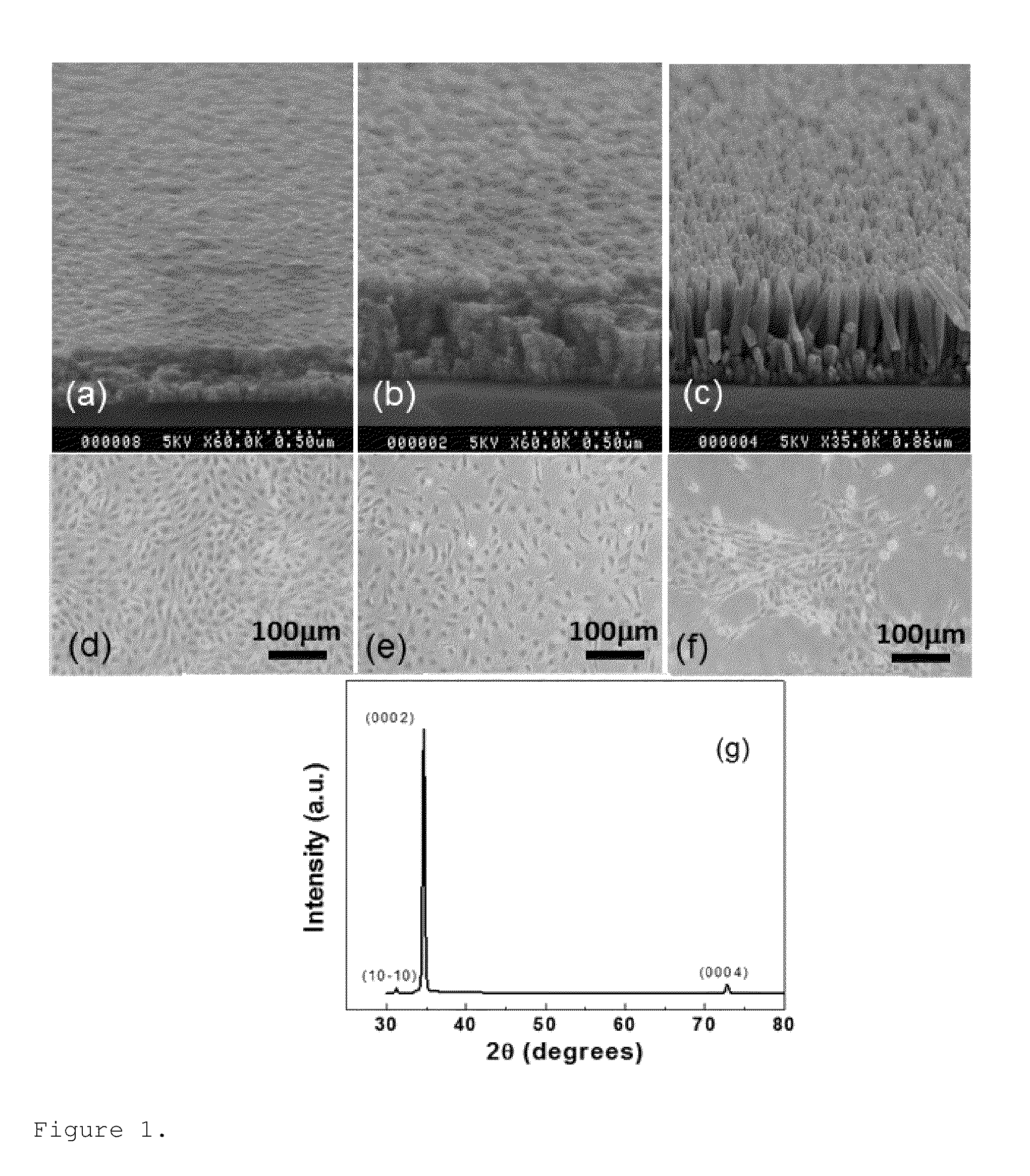
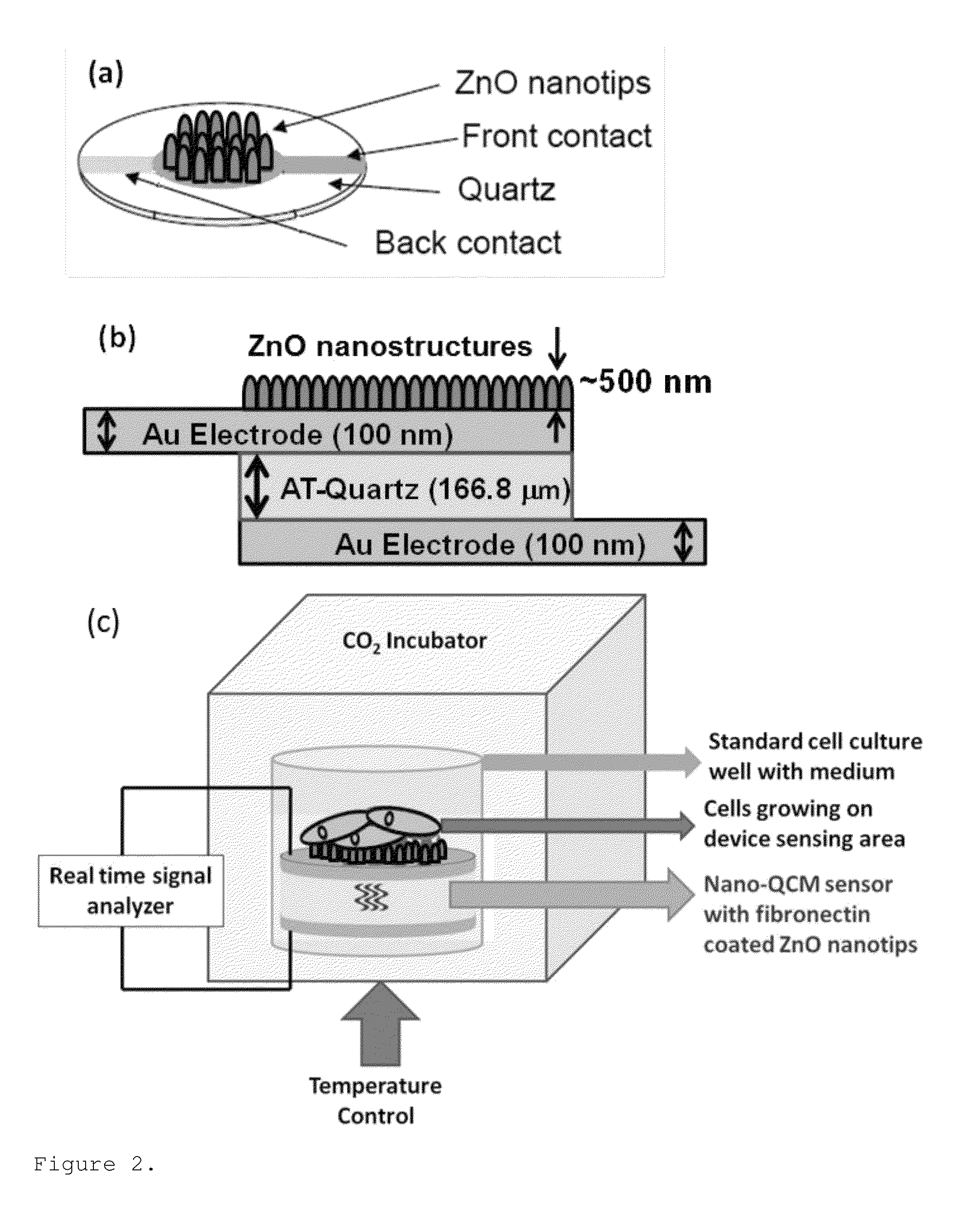
Zinc oxide-based nanostructure modified QCM for dynamic monitoring of cell adhesion and proliferation
InactiveUS8377683B2Reduce consumptionHigh sensitivityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological cellCell adhesion
A dynamic and noninvasive method of monitoring the adhesion and proliferation of biological cells through multimode operation (acoustic and optical) using a ZnO nanostructure-modified quartz crystal microbalance (ZnOnano-QCM) biosensor is disclosed.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
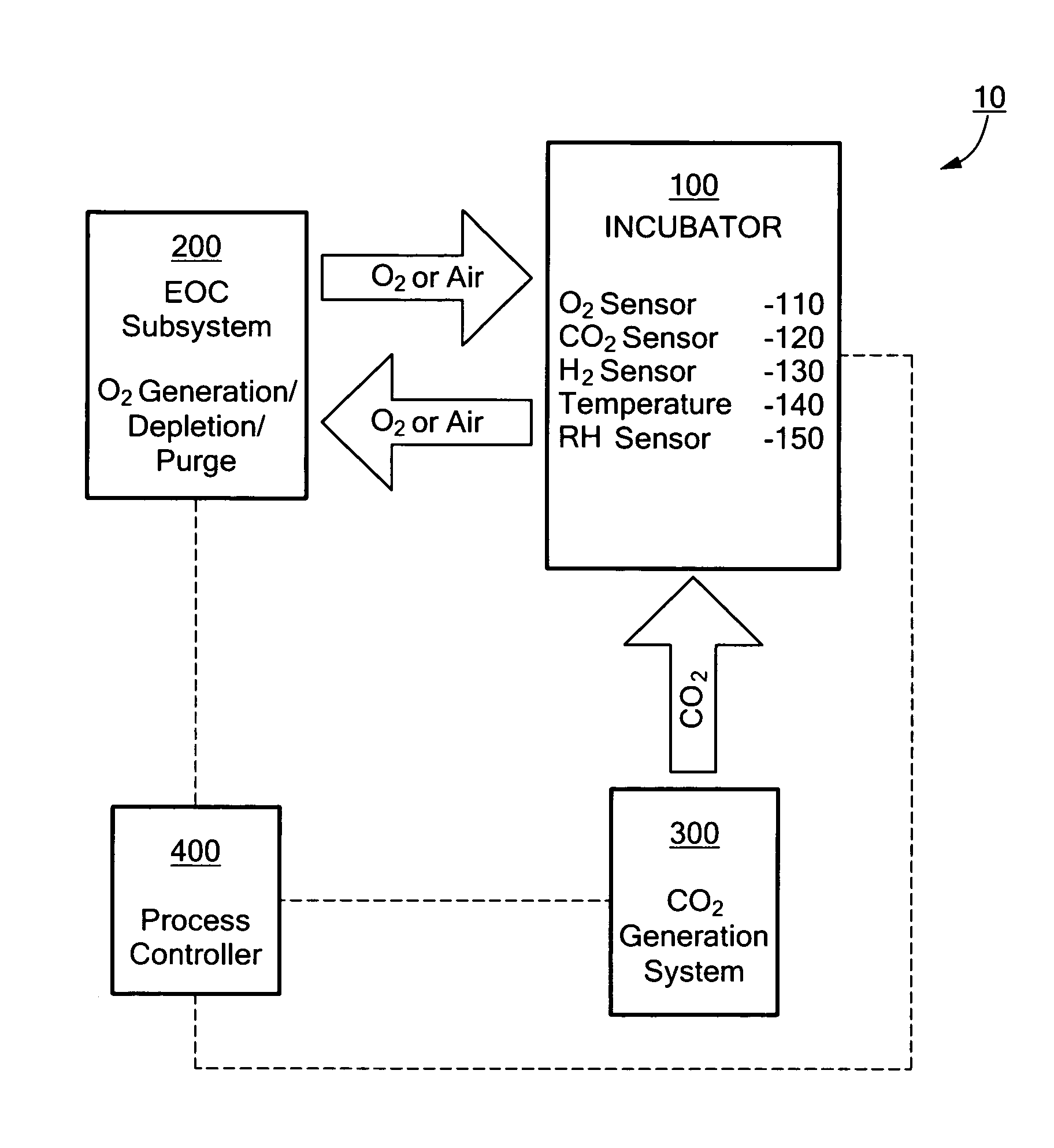
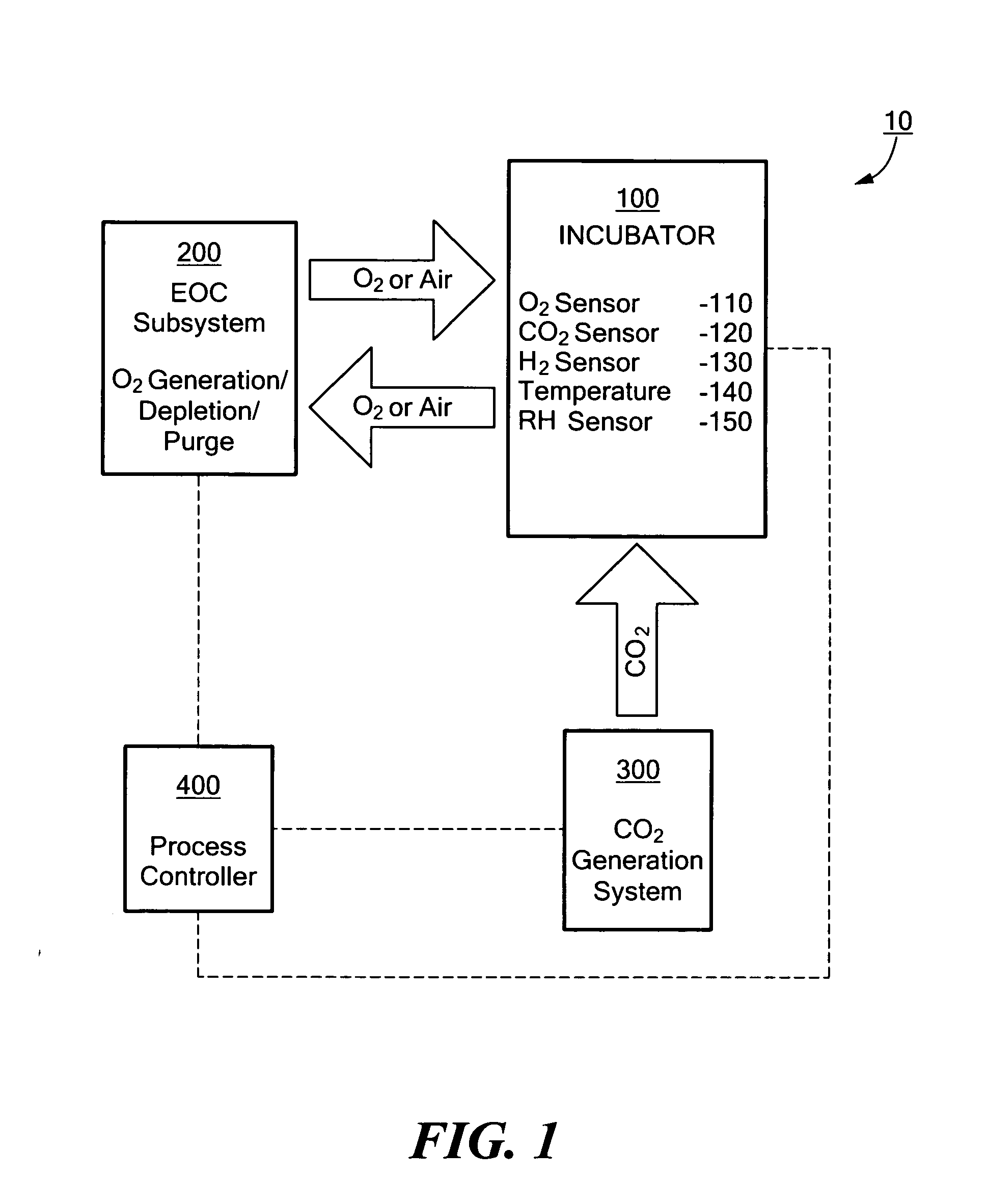
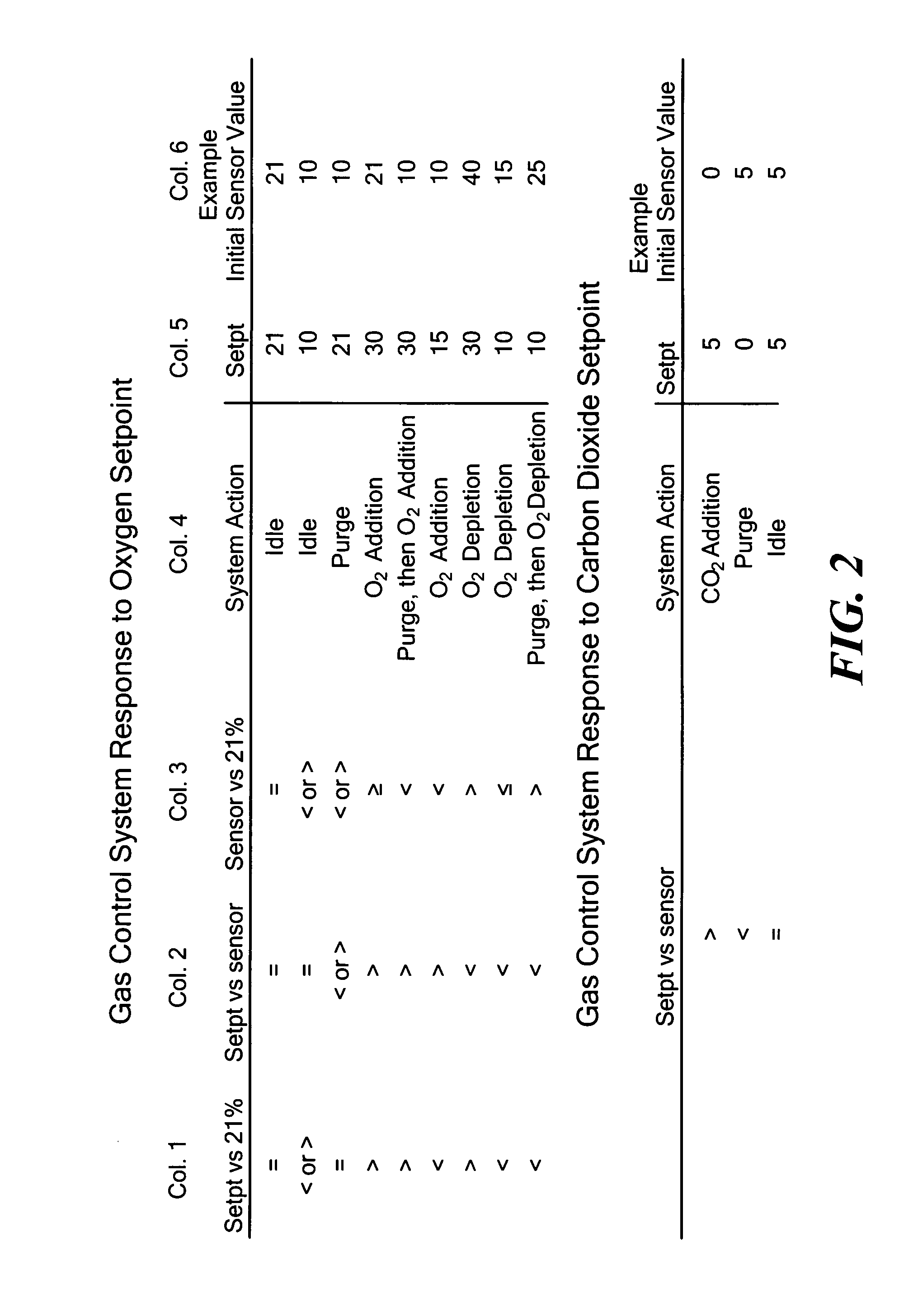
System for modifying the atmosphere within an enclosed space and incubator system including the same
ActiveUS20080282653A1Increase and to decrease oxygen concentrationIncrease carbon dioxide concentrationCombination devicesSludge treatmentChemical compositionGas cylinder
System for modifying the chemical composition of atmosphere within an enclosed space and incubator system including such a system. The concentration of oxygen within the enclosed space may be either increased or decreased using an electrochemical device. The concentration of carbon dioxide within the enclosed space may be increased using an electrochemical or chemical device. As necessary, purging of the system with ambient air can be a part of the process of controlling the chemical composition of the atmosphere. The present invention obviates the need to use pressurized gas cylinders to supply atmospheric gases to the enclosed space.
Owner:GINER INC
Method for improving laying hen hatching rate
The invention relates to a method for improving laying hen hatching rate and provides a method for improving the hatching rate of hatching eggs of laying hens in the hatching process. Suitable temperature, humidity and ventilation conditions and a correct egg turning method are provided. The method has the advantages that on the premise that health high-yield breeder flocks are bred, the quality of the hatching eggs is improved, the sterilization of the hatching eggs is reinforced, and the like, by providing suitable temperature and humidity and by adopting scientific ventilation, egg turning and egg cooling methods, the laying hen hatching rate and the quality of chickens can be improved and good economic benefits can be obtained.
Owner:黄治东
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com