Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
63 results about "In ovo" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In ovo is Latin for in the egg. In medical usage it refers to the growth of live virus in chicken egg embryos for vaccine development for human use, as well as an effective method for vaccination of poultry against various Avian influenza and coronaviruses. During the incubation period, the virus replicates in the cells that make up the chorioallantoic membrane.
In ovo delivery of an immunogen containing implant
InactiveUS20070098733A1Relieve pressureReduces vaccine reactionSnake antigen ingredientsGranular deliveryIn ovoPrimary immune response
The disclosure provides a method for administering an agent to an avian species by in ovo delivery of an implant releasably containing the agent. In one embodiment, the method is particularly advantageous for stimulating an immune response in a bird by in ovo administration of a biocompatible implant releasably containing an immunogen. The implant can provide for sustained or delayed release of the immunogen or both. The amount of immunogen that is released from the implant into the bird is preferably sufficient to effectively stimulate a primary immune response to the immunogen. Other agents which can be administered according to the method of the invention are disclosed.
Owner:EPITOPIX LLC
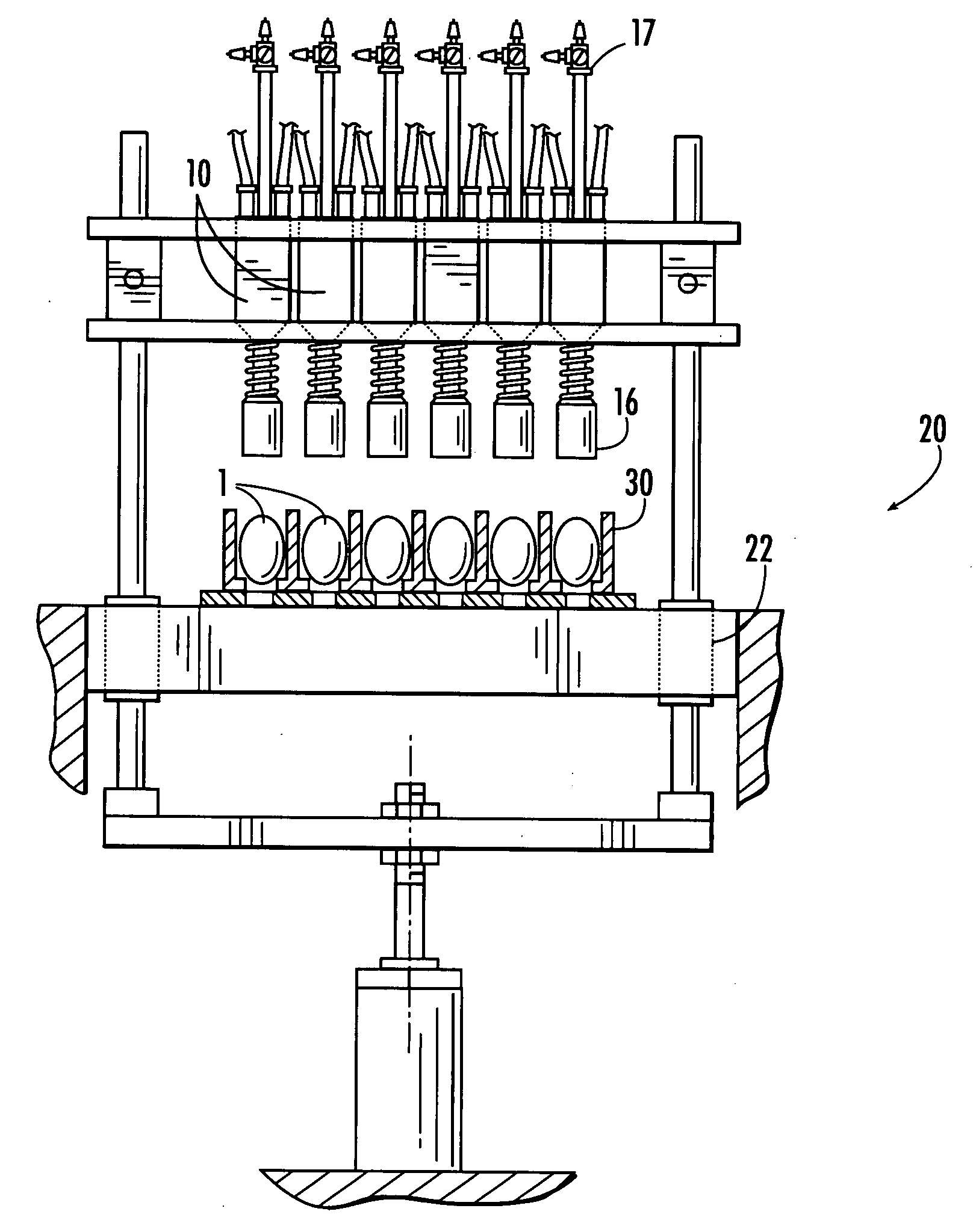
Methods and apparatus for supporting eggs during in ovo injection
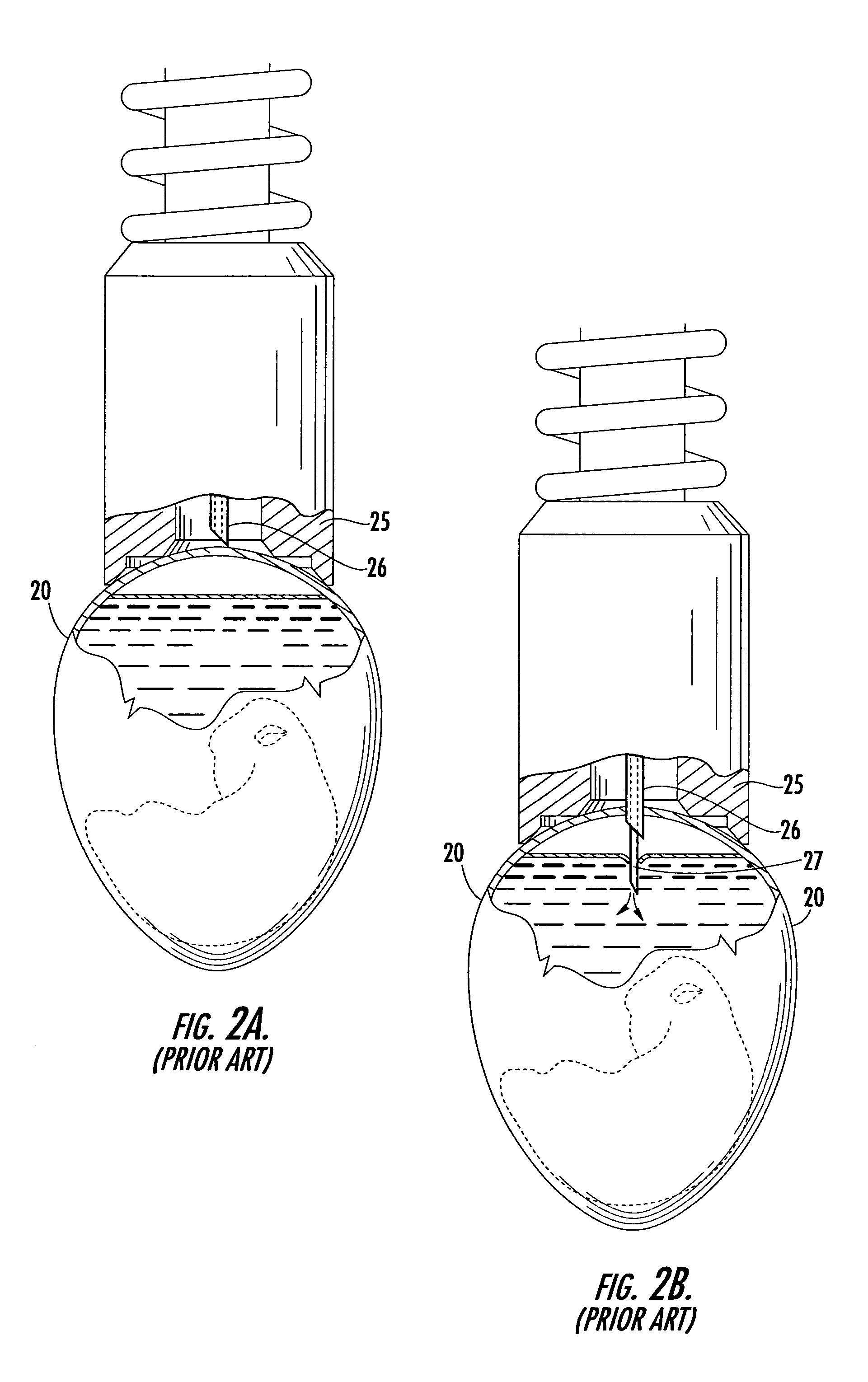
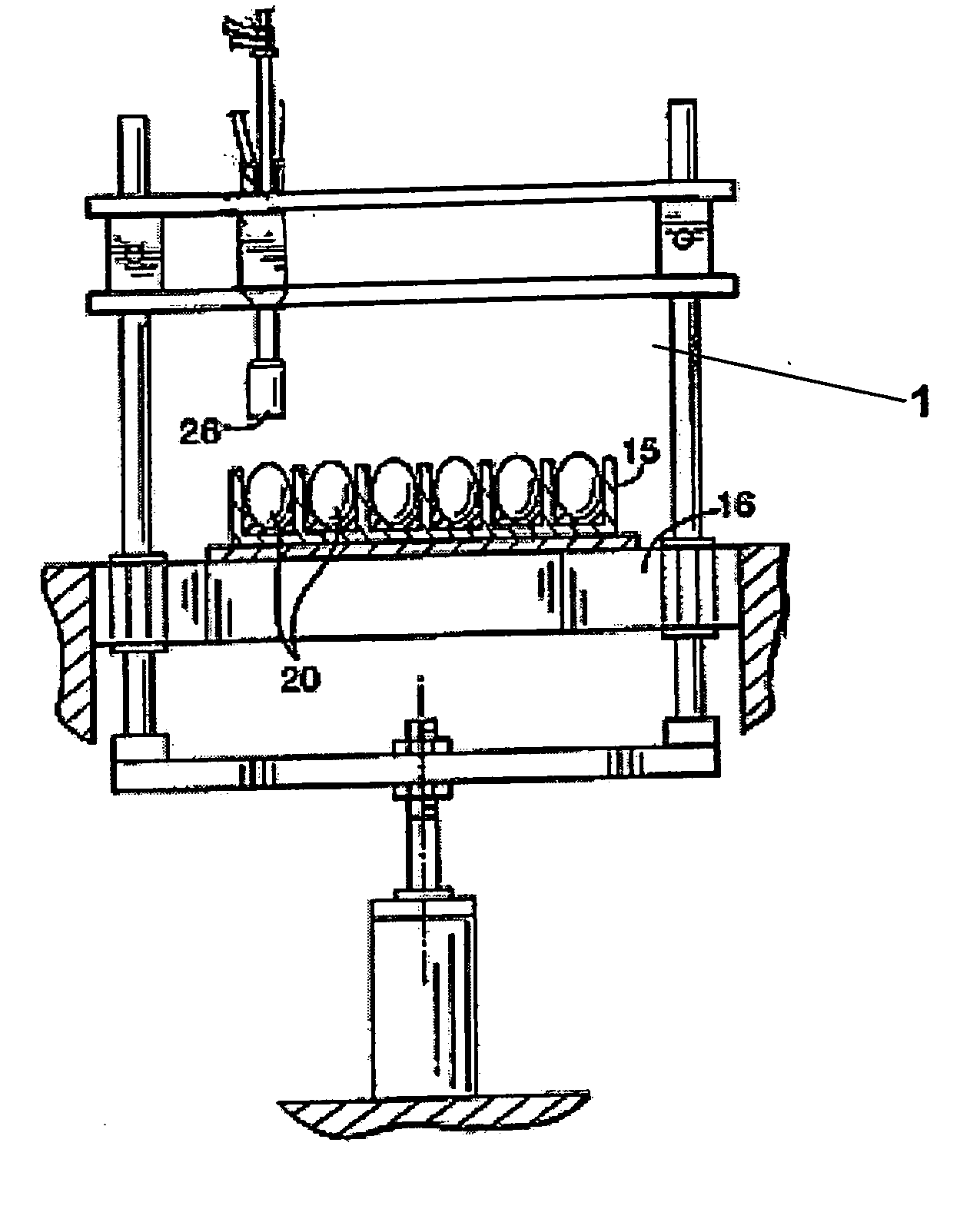
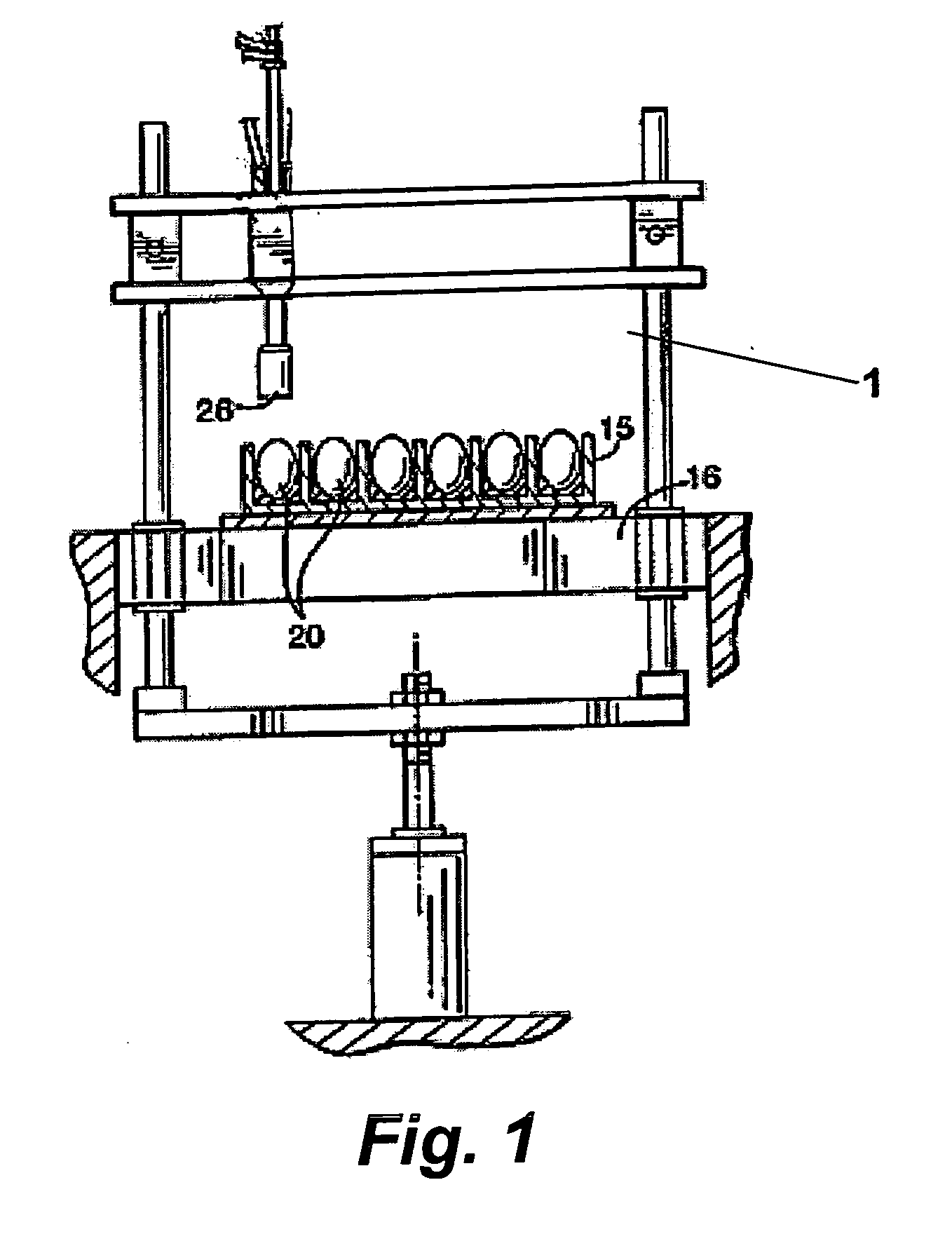
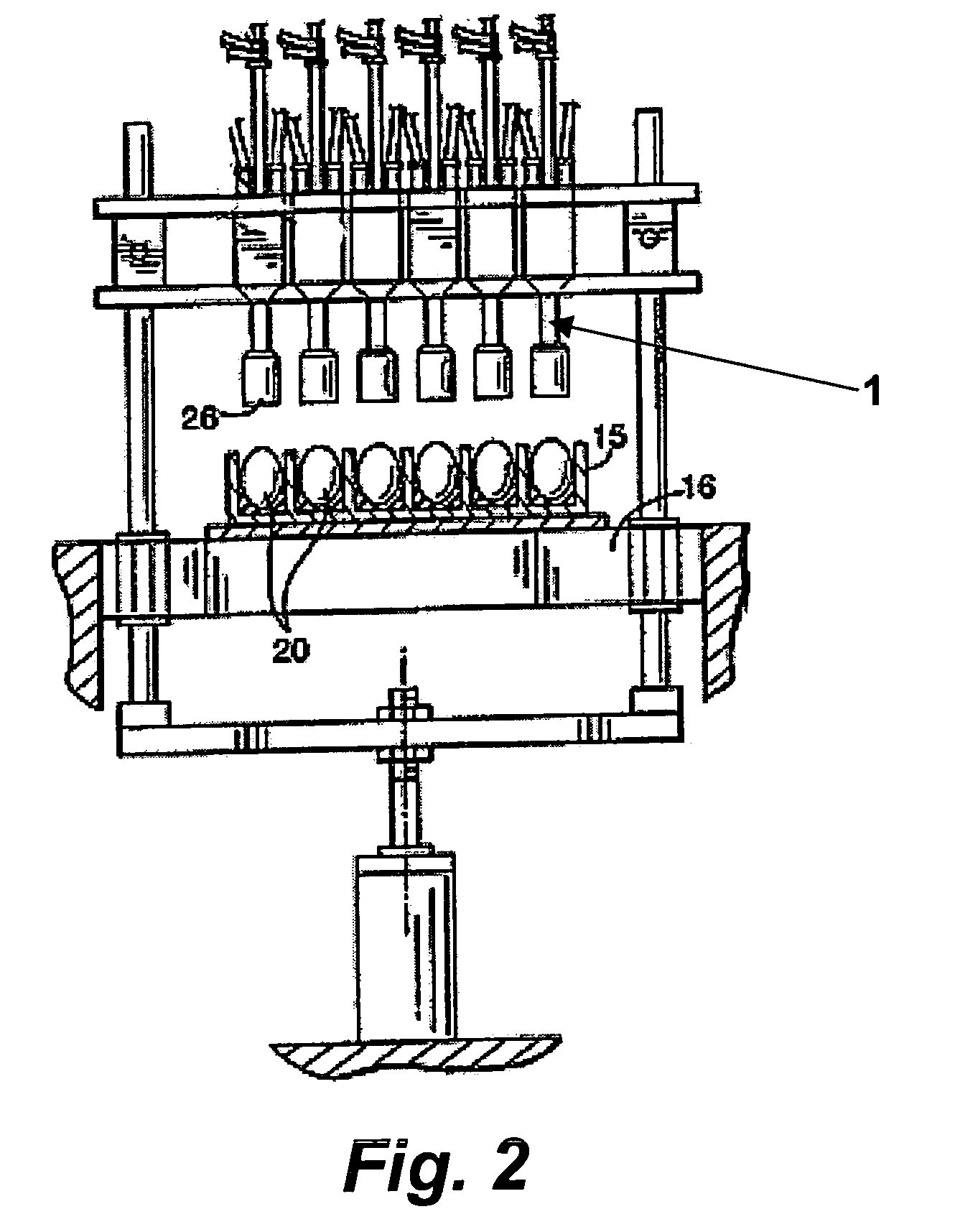
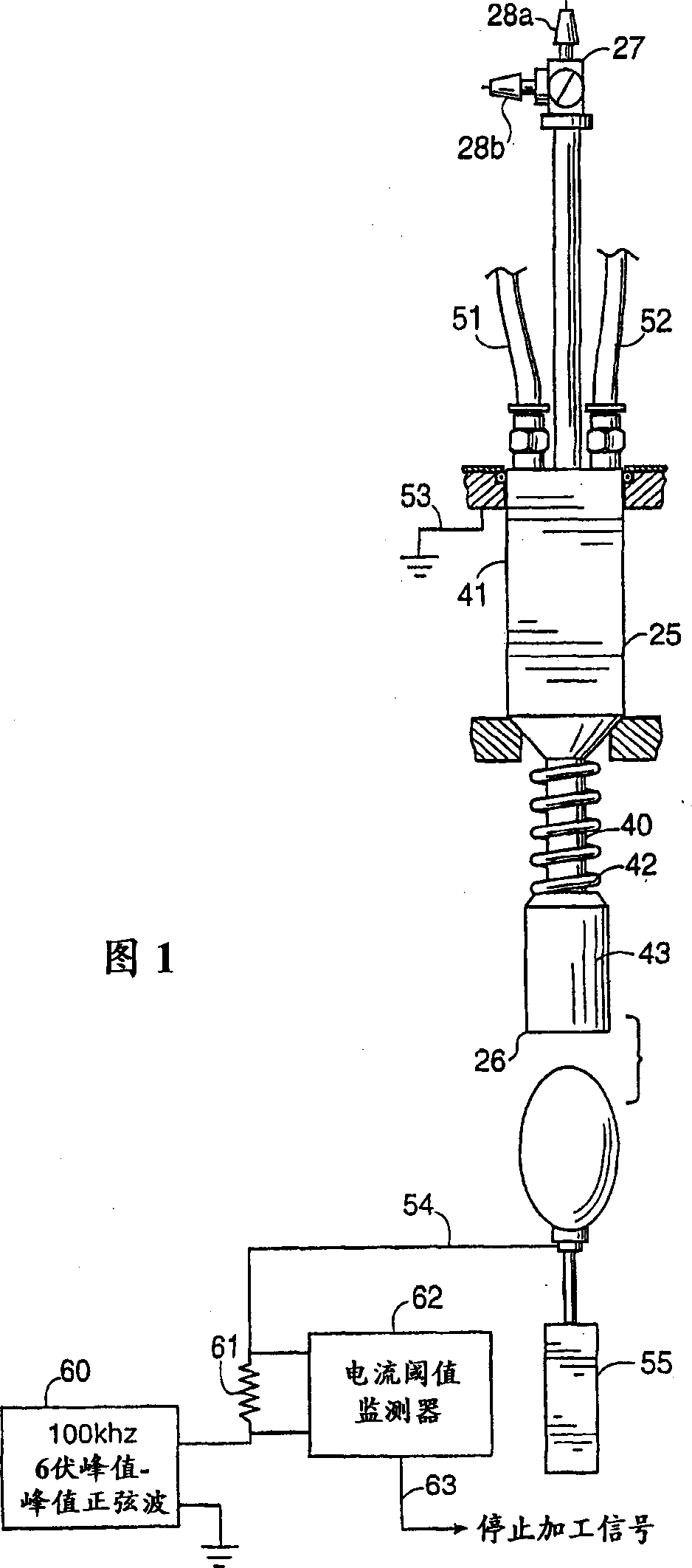
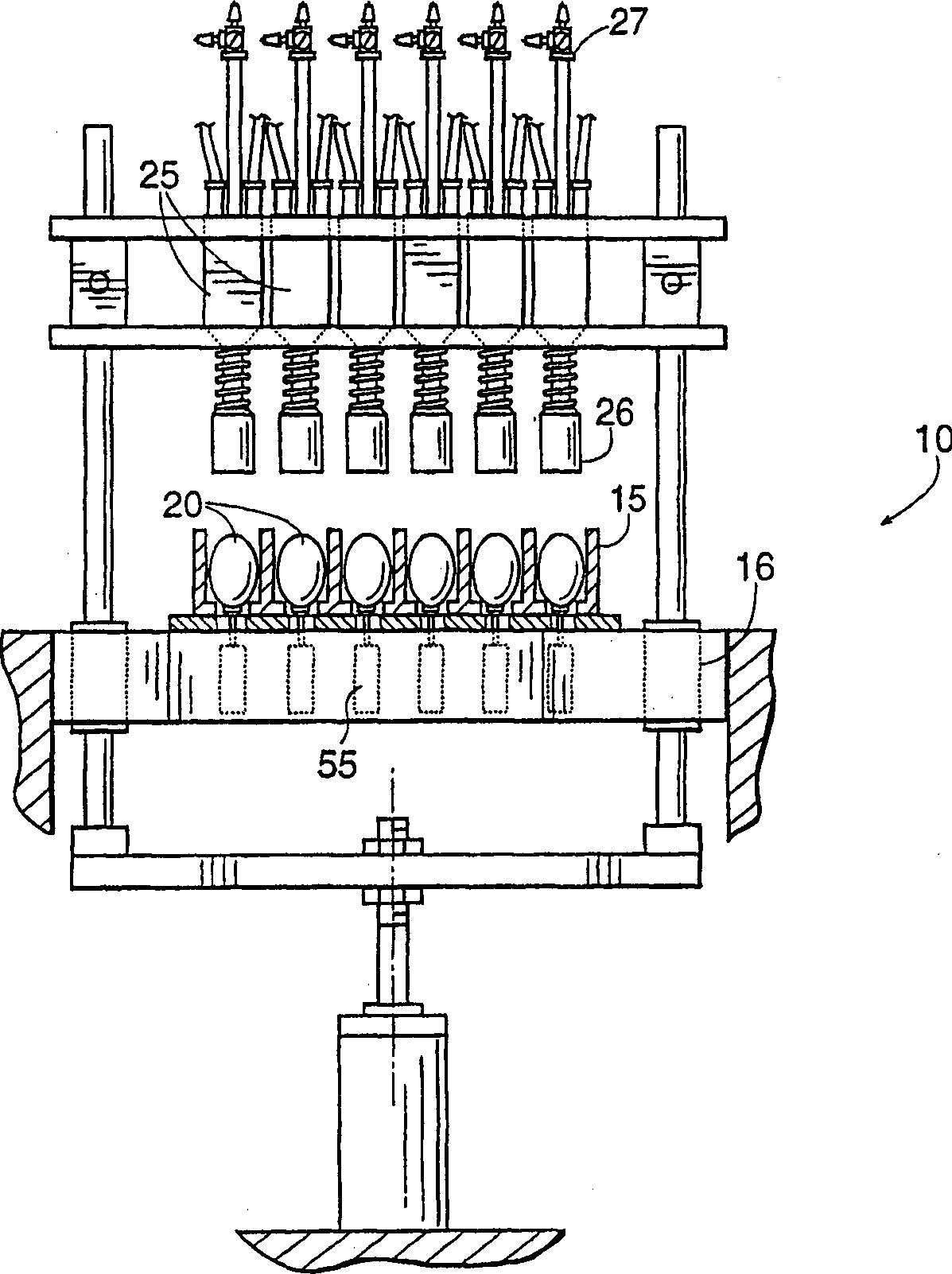
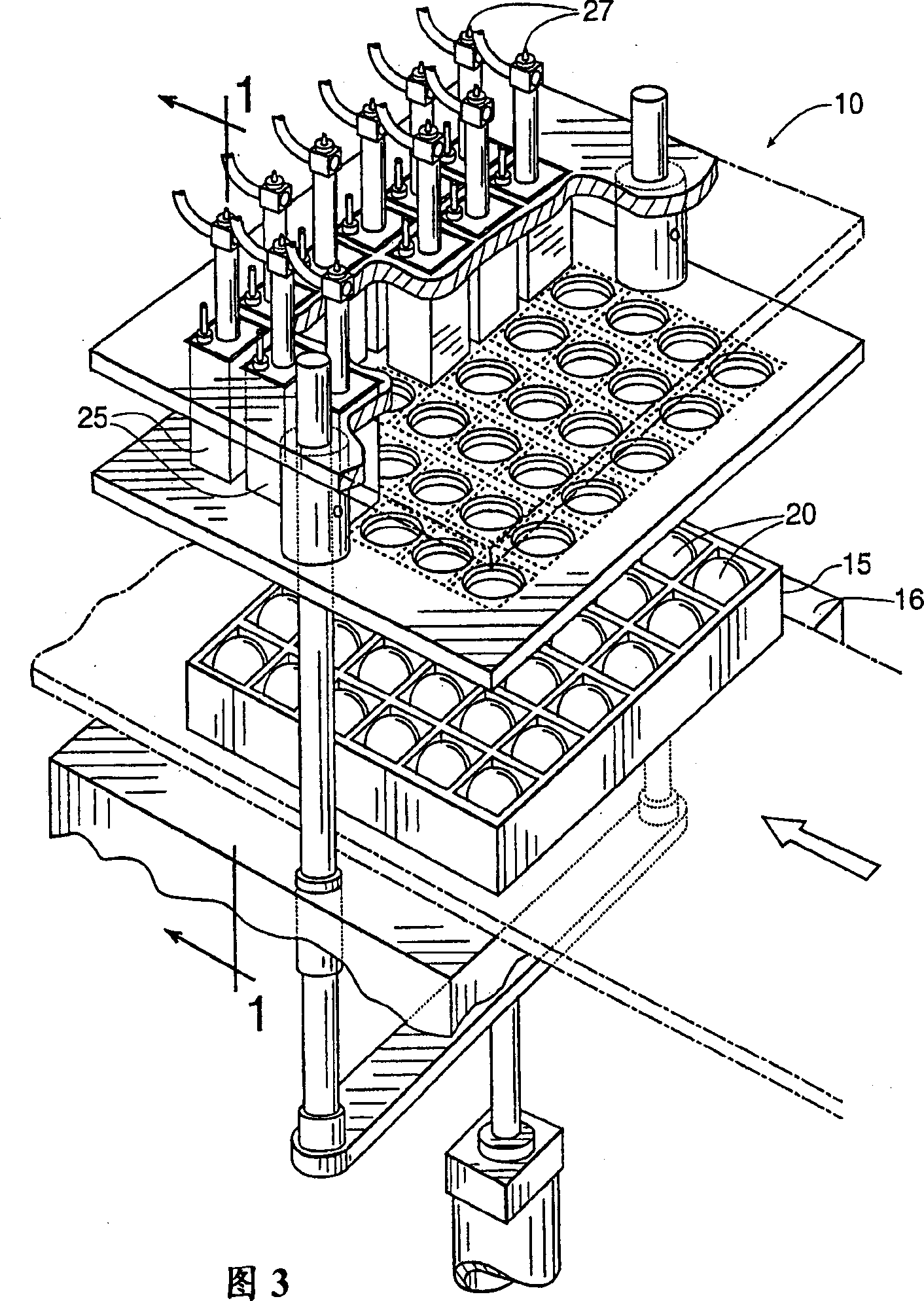
In ovo injection apparatus include an egg carrier configured to hold a plurality of eggs and to provide external access to the eggs, a plurality of injection devices positioned above the carrier, and an egg support assembly positioned beneath the carrier that is configured to support each egg in the carrier during contact therewith by a respective injection device. The egg support assembly includes a frame, a plate having an array of openings attached to the frame, and a plurality of pedestals removably secured within a respective one of the openings. The egg support assembly is operatively associated with the plurality of injection devices such that each pedestal moves upwardly through a respective opening in the carrier to support an egg as a respective injection device makes contact with the egg.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Immunostimulation methods for providing disease protection in poultry
InactiveUS6019985ACause painCause stressBacterial antigen ingredientsProtozoa antigen ingredientsIn ovoCoccidiosis
Methods are provided for improved immunization against coccidiosis and other bacterial, viral, or parasitic diseases in poultry. One method includes administering a solution of Propionibacterium acnes suspended in normal saline to a chick at age day one, following hatching. An anticoccidial vaccine and / or other vaccine is then administered to the chick such as by oral administration. Alternatively the method includes the steps of aseptically injecting Propionibacterium acnes in ovo at about day 18 in development, followed by post-hatching vaccination with an anticoccidial vaccine and / or other vaccine. Alternatively, either method can be utilized without the subsequent vaccination step for stimulating non-specific cell-mediated immune responses in poultry.
Owner:NEOGEN CORP
Methods and apparatus for automatic jet injection of bird eggs
An in ovo jet injection apparatus and related methods for treating live eggs. The jet injection apparatus includes one or more jet injection delivery devices configured to deliver one or more treatment substances to predetermined areas of eggs using a high pressure stream of the treatment substance(s). Multiple treatment substances can be delivered so that they are spatially and / or temporally separate. The devices and methods of the invention enable the effective use of a plurality of treatment substances, including those that are effective when used alone but can be noxious if mixed. The methods and apparatus for the jet injection of substances into embryonic chicks reduce the risk of mechanical injury to the developing birds that would be caused by injection needles. The methods and apparatus of the invention can also reduce the introduction of an infection into the chicks.
Owner:MERIAL INC
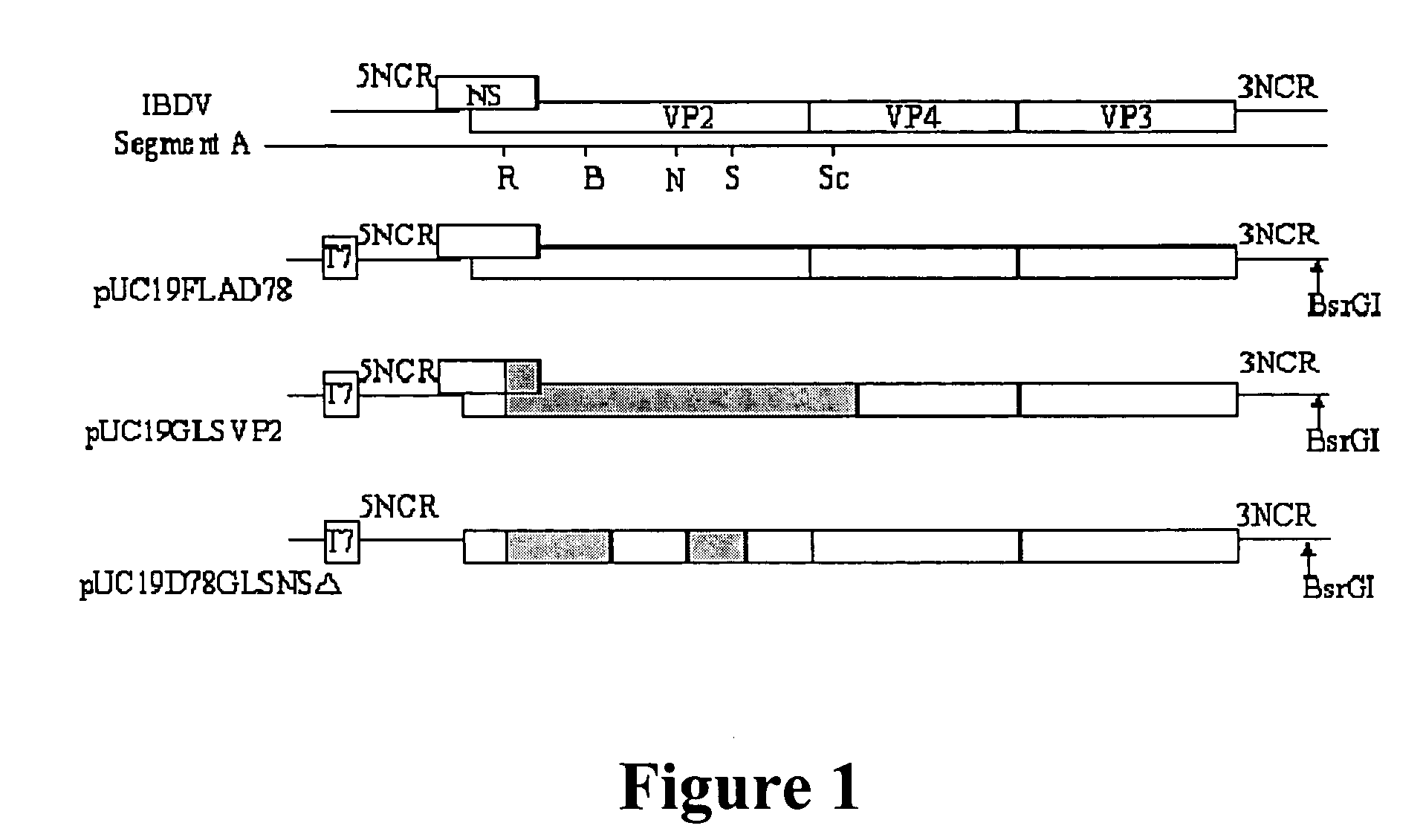
In Ovo vaccine against infectious bursal disease
The present invention relates to a non pathogenic vaccine comprising a recombinant Infectious Bursal Disease virus that includes a recombinant Segment A, designated as rD78GLSNSΔ, that includes sequences from D78 and GLS strains and wherein the NS protein is not expressed.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BIOTECH INST
Methods and apparatus for delivering multiple substances in ovo
In ovo injection methods and apparatus are provided wherein multiple substances, particularly incompatible substances such as oil-based and aqueous-based substances, can be injected without reducing efficacy of the substances and without requiring complex mechanical injection devices. Injection of multiple substances may occur simultaneously or sequentially.
Owner:EMBREX INC
Modulating production traits in avians
InactiveUS20100306869A1Modify phenotypeDecrease in levelAnimal cellsSpecial deliveryBiotechnologyIn ovo
The present invention relates to methods of modulating traits, particularly production traits, in avians such as chickens. In particular, the invention relates to the in ovo delivery of a dsRNA molecule, especially siRNAs, to modify production traits in commercially important birds.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
Concurrent in ovo injection and detection method and apparatus
A method of injecting a plurality of bird eggs comprises: (a) orienting a plurality of avian eggs in a predetermined position; (b) forming an opening in the shell of each of the eggs; (c) extending an elongate delivery device through each of the openings and into the eggs, each of the delivery devices comprising a detector and an injection needle, with the injection needle having a lumen formed therein; (d) detecting with the detector information from the interior of each of the plurality of eggs; and (e) injecting a substance into each of the plurality of eggs through the lumen of said injection needle. The detected information can be used for a variety of purposes, including adjusting the depth of penetration of the injection needle to more precisely control the location of the injection, identifying the gender of the eggs for subsequent sorting of the eggs, distinguishing viable from non-viable eggs, etc. When used for controlling depth penetration, the method positions the needle tip for any purpose, including withdrawing biological material as well as injecting substances. Apparatus, particularly high-speed apparatus, for carrying out the method is also disclosed.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Gender, viability and/or developmental stage determination of avian embryos in ovo
InactiveUS20150260704A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisIn ovoDevelopmental stage
The present invention relates to a process for the non-destructive determination of gender, developmental stage and / or viability of an avian embryo in an egg, comprising (a) detecting at least a first developmental marker compound selected from sugars and / or amino acids, precursors and metabolites thereof in an egg at a time period of from the beginning of the incubation of the egg until the hatching; (b) measuring the amount of the at least first detected developmental marker compound, and (c) comparing the amount to a base line established for male and female, developmental stage of the embryo, and / or alive and deceased or non-developed embryo, to determine whether the embryo is viable, male and / or female, and / or the developmental stage of the embryo.
Owner:IN OVO BV
Process of manufacturing viral vaccines in suspension avian embryonic derived stem cell lines
Owner:ВАЛЬНЕВА
Method for injecting leptin in egg white
The invention discloses a method for injecting leptin into egg white, and belongs to the technical field of animal growth regulation. The method comprises: before incubation, disinfecting the small end of a hatching egg; drilling a hole lightly on the disinfected part by a toad marrow puncture needle; injecting leptin injection reagent into the egg white through the hole by a micro injector; and sealing the hole by paraffin. After the leptin with certain concentration is injected into the egg white, the leptin is observed to inhibit the development of embryo of table poultry and reduce body weight of newly hatched offspring, but promote early growing development of the table poultry after hatch, and the leptin can be taken as semiochemicals to mediate the routinization effect on the early growing development of filial generations of the table poultry.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
System and method for in ovo sexing of avian embryos
A system for determining the gender and / or fertility status of avian eggs including a sampling apparatus and an electromagnetic radiation transmitter and detector. In certain embodiments, the transmitter operates in the terahertz range. The sampling apparatus can be coupled to an avian egg. The sampling apparatus includes a vacuum source, a gas collection device, and a membrane that can be positioned in the passageway coupling the vacuum source to the gas collection device. The membrane is capable of capturing volatile organic compounds. The sampling apparatus applies a vacuum from the vacuum source to the gas proximate to the avian egg and directs the gas captured from the vicinity of the egg toward the membrane. Subsequently, the membrane is positioned within the electromagnetic radiation emitted by the transmitter, generating a spectrum which can be analyzed to determine whether the egg is fertile or infertile, and if fertile, whether the egg is male or female. In an embodiment, the captured volatile organic compounds are transferred to a sample chamber where the captured gas is analyzed.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD +2
Method for the purification, recovery, and sporulation of cysts and oocysts
A vaccine for in ovo vaccination against avian coccidiosis produced by a method including obtaining the coccidial oocysts from a fecal suspension, homogenizing the fecal suspension, separating the oocysts from the fecal debris by either salt flotation using sodium sulfate or gas flotation using air, sporulating the oocysts using hydrogen peroxide and air sparging, bleaching the sporulated oocysts, washing the bleached oocysts, concentrating the sterile washed oocysts and combining the concentrates of various species of coccidial oocysts, and producing a vaccine. The method in whole or in part can be applied to other kinds of encysted protozoa to produce vaccines for various types of animals.
Owner:HUVEPHARMA EOOD
In ovo vaccination against coccidiosis
The invention relates to a method of vaccinating a domesticated bird against coccidiosis comprising administering in ovo an effective immnunizing dose of live Eimeria sporozoites or merozoites, or a mixture thereof. In a preferred embodiment, the domesticated bird that is vaccinated is a chicken or turkey.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Method and Device for Conditional in ovo Injection
InactiveUS20150327521A1Easily and cost-effectively adaptedEasy to adaptCannulasIntravenous devicesNeedle penetrationMedicine
The present invention provides in ovo injection devices, including a novel vaccine / substance conservation valve (VCV), a needle depth adjuster (NDA), and methods for selectively delivering vaccines and other substances to eggs in the context of poultry hatcheries. The valve of the present invention allows for the conditional dispensing of vaccines and other substances dependent upon the presence or absence of an egg. When an egg is present, the valve becomes activated, allowing vaccines or other substances to be injected. When an egg is absent, the valve is not activated, thus vaccines and other valuable substances are conserved. The NDA allows embryonated eggs to be more safely injected by reducing the depth of needle penetration, particularly in smaller eggs.
Owner:MERIAL INC
In ovo activation of an egg in the shell
The present invention relates to the field of avian reproduction. In particular, the present invention provides a method of activating an egg in a shell. The invention also provides a method of activating an egg in a shell, whereby a live chick is hatched.
Owner:CANTRELL TIM +1
Method and apparatus for targeting localized electroporation
InactiveUS6977172B2Minimizing invasivenessEliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyForeign matterIn ovo
The invention comprises an apparatus and a method of effecting localized electroporation in a relatively small target area and for introducing foreign matter into cellular material in which the target area is located. The cellular material may be in vitro, in ovo or in vivo.
Owner:INNOVATION & DEV CORP
Vaccines containing viruses involved in avian malabsorption syndrome and methods of administration therefor
Owner:WYETH LLC
Attenuated mutant newcastle disease virus strains for in ovo vaccination, method for preparing and their use
InactiveUS7252984B2Reduce pathogenicityReduce strainSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsIn ovoDisease
The present invention relates to new attenuated mutant New Castle's disease La SotaNewcastle disease virus strains suitable for in ovo vaccination of avian species comprising a mutation in the gene sequences encoding the HN and / or F glycoproteins of said virus. Furthermore, the invention relates to a vaccine composition comprising said attenuated mutant Newcastle's disease La Sota virus strain, and to the use thereof for the preparation of a vaccine for in ovo vaccination of avian species against Newcastle's disease.
Owner:CENT VOOR ONDERZOEK & DIERGENEESKUNDE & AGROCHEM
Vaccine for in ovo inoculation
InactiveCN101374547ABroad protective immunityReduce pathogenicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsIn ovoViral disease
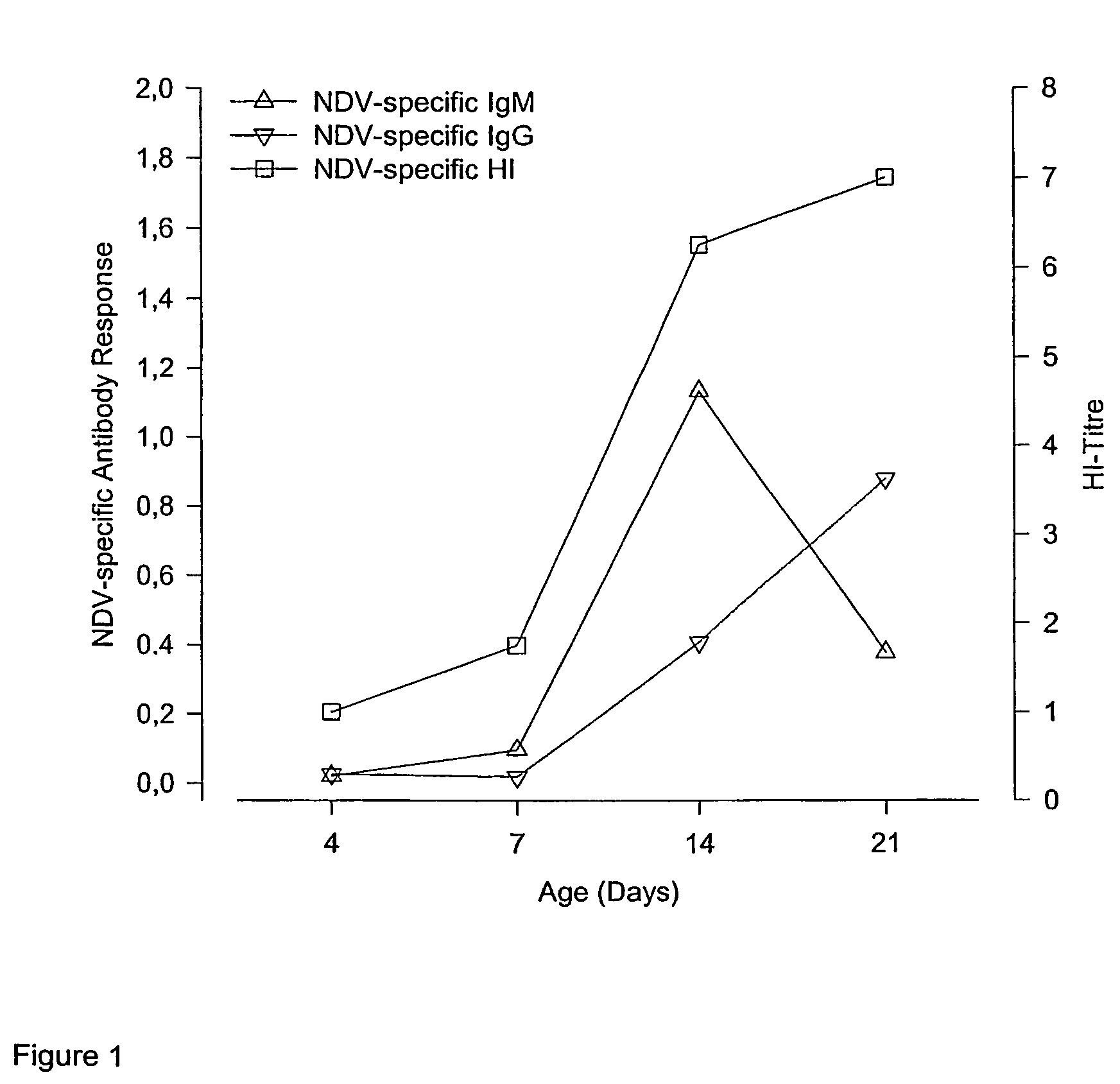
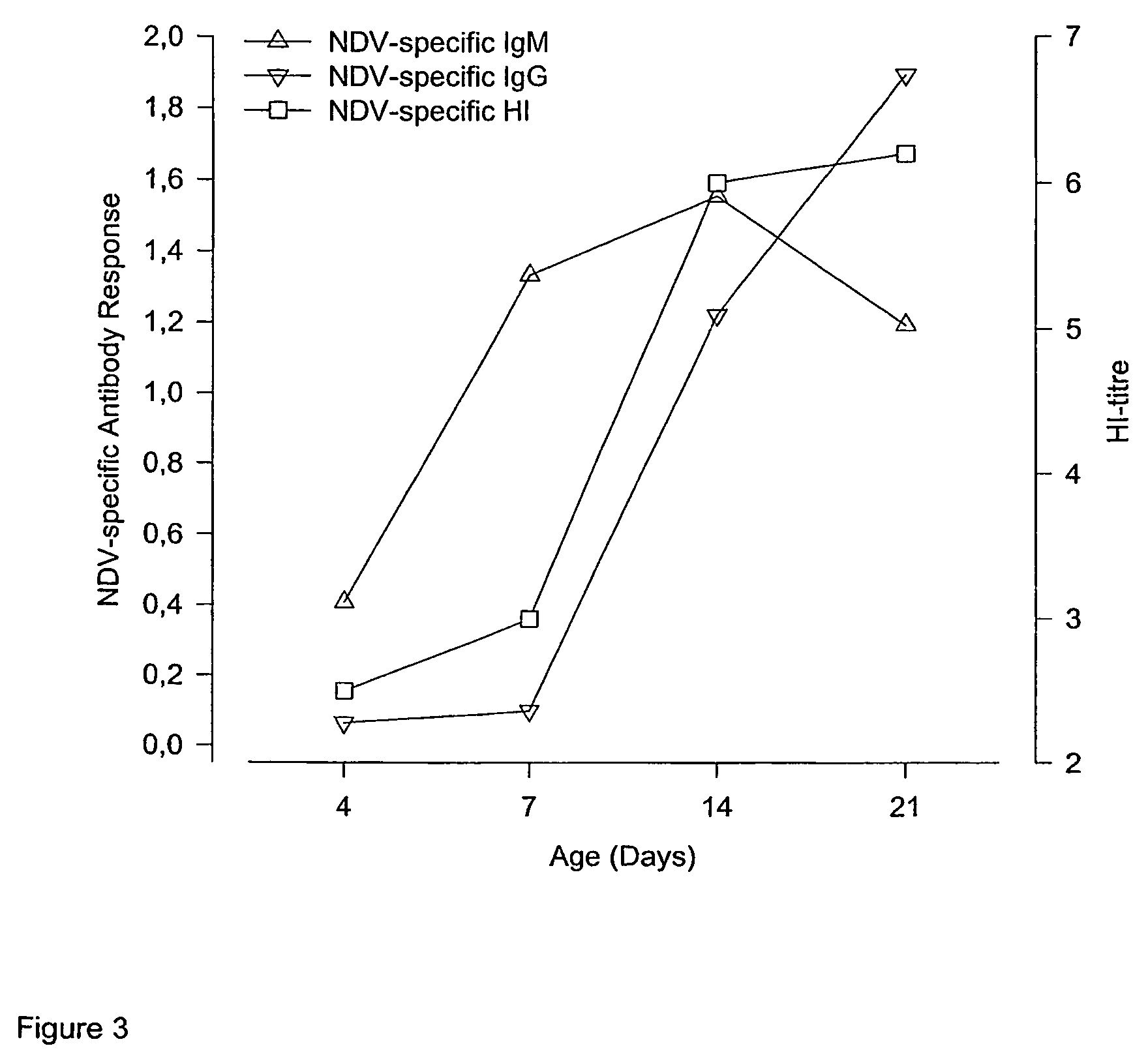
It is intended to provide a vaccine for in ovo inoculation which is effective in the prevention of all poultry viral diseases. It is a poultry vaccine for in ovo inoculation with high effectiveness also from a safety aspect in which the pathogenicity of a virus whose practical application as a vaccine for in ovo inoculation was difficult in the past against embryo is reduced by adsorbing and retaining the virus onto an virus adsorbing agent thereby to make the virus growth in ovo after inoculation slow and the improvement in a decrease in the hatching rate and the alleviation of severe clinical symptoms after hatching can be realized. As the virus adsorbing agent, an aluminum compound such as an aluminum hydroxide gel or aluminum potassium sulfate is used.
Owner:JURIDICAL FOUND THE CHEMO SERO THERAPEUTIC RES INST
Method and system for the non-destructive in ovo determination of fowl gender
ActiveUS20200116730A1Quality improvementAnalysis can be performedTesting eggsComponent separationIn ovoFowl
The present invention relates to a method for non-destructively identifying a characteristic of a Gallus Gallus domesticus embryo in ovo, the method comprising: (a) obtaining a sample of material associated with an egg comprising the embryo, and (b) measuring a score value for the presence of, and concentration of at least a first biomarker in the sample indicative of the characteristic of the embryo, and (c) applying a threshold to the score value and concentration obtained in (b) to identify the characteristic for the embryo associated with the presence and concentration of the biomarker, wherein an at least first biomarker comprises an amino compound having a molecular weight in the range of from 140 to 190 g / mole, wherein step (c) further comprises: (i) correlating each relevant biomarker signal with a reference biomarker by matching the spectrum of each correlating signal with the expected spectrum of the correlating reference biomarker using a similarity measure, to define at least one positively correlating signal; (ii) measuring the intensity of each positively correlating signal and scoring its absolute and / or relative signal intensity; and (iii) applying a threshold to the score value obtained from a similarity function to determine the correlated embryo characteristic.
Owner:IN OVO HLDG BV
Methods for producing oocysts
The present invention provides improved methods and compositions for producing oocysts. The oocysts produced according to the invention find use in the manufacture of vaccines. In preferred embodiments, the present invention provides methods and compositions for the production of Eimeria oocysts. Vaccines containing Eimeria oocysts, sporocysts and / or sporozoites produced according to the present invention may be used to immunize birds against coccidiosis either in ovo or post hatch.
Owner:HUVEPHARMA EOOD
Ovo immunization against infectious bronchitis
The present invention is directed to processes and compositions for protecting host animals (e.g., chickens) from exposure to virulent infectious bronchitis virus. In ovo administration of live, avirulent strains of IB at appropriate dosage levels on a per egg basis provides an effective and efficient vaccination having acceptable safety and efficacy features.
Owner:WYETH
Systems and methods for sanitizing egg processing equipment
InactiveUS20070215050A1Extended durationIncrease frequencyAvicultureComputer scienceImproved sanitation
Systems and methods for processing sets of eggs with improved sanitation treatment are provided. A method includes obtaining information about a set of eggs to be processed in ovo, and / or determining the number of non-live eggs in the set, selecting a sanitizing treatment for in ovo processing equipment to be used in processing the set of eggs, wherein the selected sanitizing treatment is based on the obtained information and / or number of non-live eggs in the set, processing the set of eggs via the in ovo processing equipment (e.g., injecting a substance into the eggs, and / or removing material from the eggs), and sanitizing the in ovo processing equipment according to the selected sanitizing treatment. A selected sanitizing treatment may include increased frequency and / or duration, increased concentration of sanitizing fluid, applying sanitizing fluid to the shell of the eggs, and / or adding / increasing an antibiotic to a substance injected into the eggs.
Owner:EMBREX INC
Multiple and multivalent DNA vaccines in ovo
The present invention provides a muliple DNA vaccine and / or a multivalent DNA vaccine for use in aquiring embroyonic immunity in fowl eggs. The multiple DNA vaccine contains two or more DNA constructs, each containing a DNA molecule encoding an avian viral protein or a fragment thereof capable of inducing a protective immune response against the avian viral disease in fowl. The multivalent DNA vaccine contains one DNA construct which contains two or more DNA molecules, each representing an avian viral gene or a fragment thereof. The multivalent DNA vaccine is capable of expressing two or more viral antigens and inducing protective immune responses against the avian viral diseases in fowl. Both the multiple DNA vaccine and the multivalent DNA vaccine are preferred to be injected into the amniotic fluid of the fowl egg after being fertilized for about 18 days.
Owner:SCHWEITZER CHEM
Methods for Injecting Avian Eggs
InactiveUS20080022931A1Reduce traumaLow level of morbidity and mortalityAvicultureVector-based foreign material introductionIn ovoAvian embryo
Owner:EMBREX INC
In ovo vaccine against infectious bursal disease
The present invention relates to a non pathogenic vaccine comprising a recombinant Infectious Bursal Disease virus that includes a recombinant Segment A, designated as rD78GLSNSΔ, that includes sequences from D78 and GLS strains and wherein the NS protein is not expressed.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BIOTECH INST
In ovo activation of an egg in the shell
The present invention relates to the field of avian reproduction. In particular, the present invention provides a method of activating an egg in a shell. The invention also provides a method of activating an egg in a shell, whereby a live chick is hatched.
Owner:CANTRELL TIM +1
Methods for producing oocysts
The present invention provides improved methods and compositions for producing oocysts. The oocysts produced according to the invention find use in the manufacture of vaccines. In preferred embodiments, the present invention provides methods and compositions for the production of Eimeria oocysts. Vaccines containing Eimeria oocysts, sporocysts and / or sporozoites produced according to the present invention may be used to immunize birds against coccidiosis either in ovo or post hatch.
Owner:HUVEPHARMA EOOD
Methods for gamete production in birds
A method for the production and collection of avian sperm comprises the steps of: providing primordial germ cells from a donor avian species; administering the primordial germ cells to a recipient avian species in ovo; incubating the recipient avian species to hatch; and then collecting sperm of the donor avian species from the recipient avian species. For example, the donor avian species may be a whooping crane, and the recipient avian species may be a sand hill crane. In another example, the donor avian species may be a turkey, and the recipient avian species may be a chicken.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com