Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
131results about "Mechanically effected encryption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
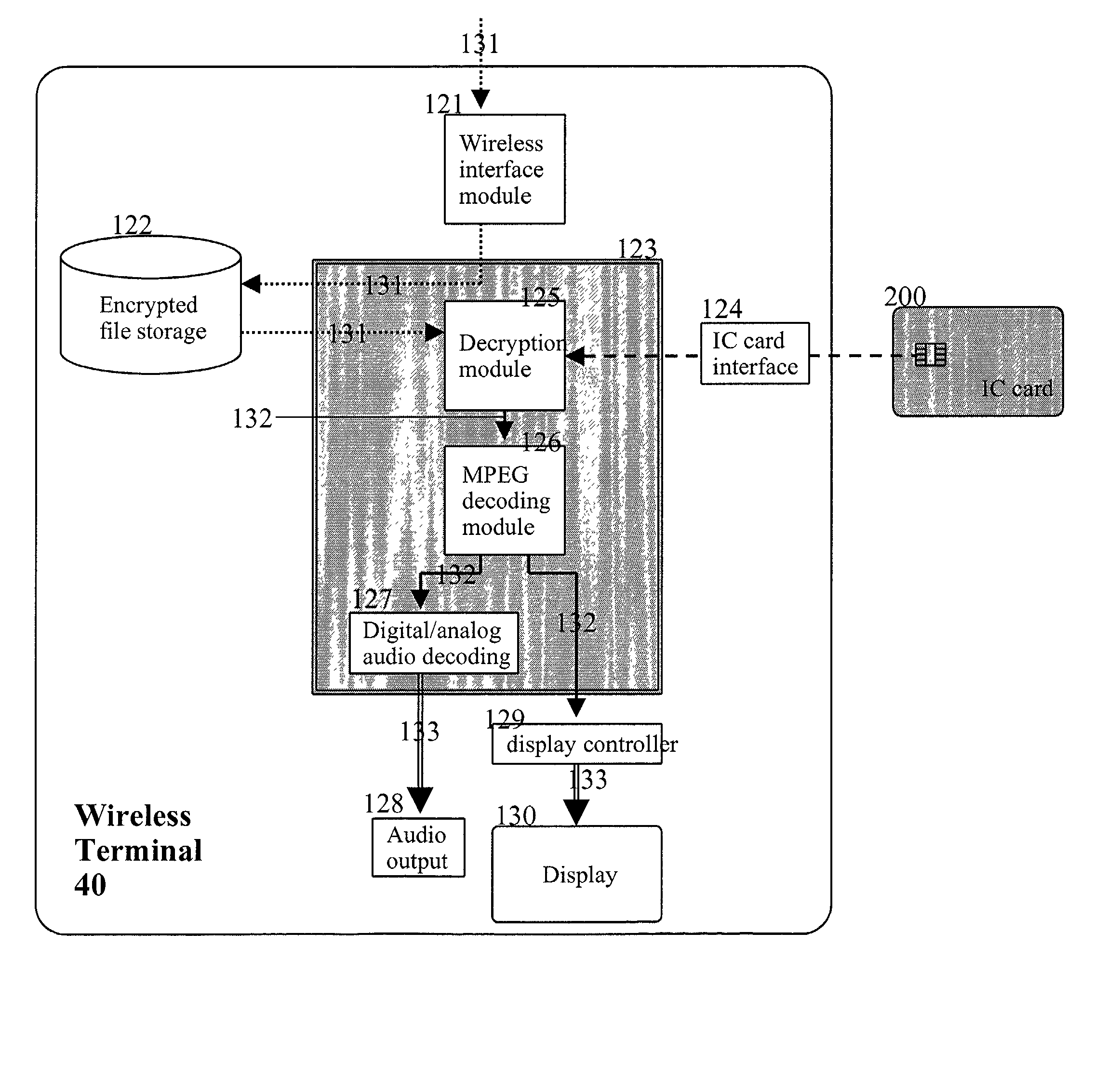
Method for providing multimedia files and terminal therefor
InactiveUS20020076051A1Easy accessMechanically effected encryptionPayment architectureComputer hardwareData file
A method of and a system for securely distributing data files to a user. A first key is encrypted using a second key. The encrypted first key is stored on an integrated circuit card that is associated with the user. The integrated circuit card is provided to the user. Data files are encrypted using the first key to get an encrypted data file at a first party. The encryption parameters are exchanged between the first party and integrated circuit card.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Network arrangement for communication
InactiveUS20020049902A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsDigital data processing detailsSecure communicationComputer science
A method for secure communication between a first end terminal located in a first secure network and a second end terminal located in a second secure network, said first and second networks being separated by a relatively insecure intermediate network, wherein the method including the steps of: selectively routing a communication from the first end terminal to the second end terminal over said relatively insecure intermediate network by means of one or more network elements triggerable to selectively route said communication; and encrypting said selectively routed communication by means of an encryption engine before it traverses said intermediate network, wherein said one or more network elements and said encryption engine are located substantially within said firs secure network.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
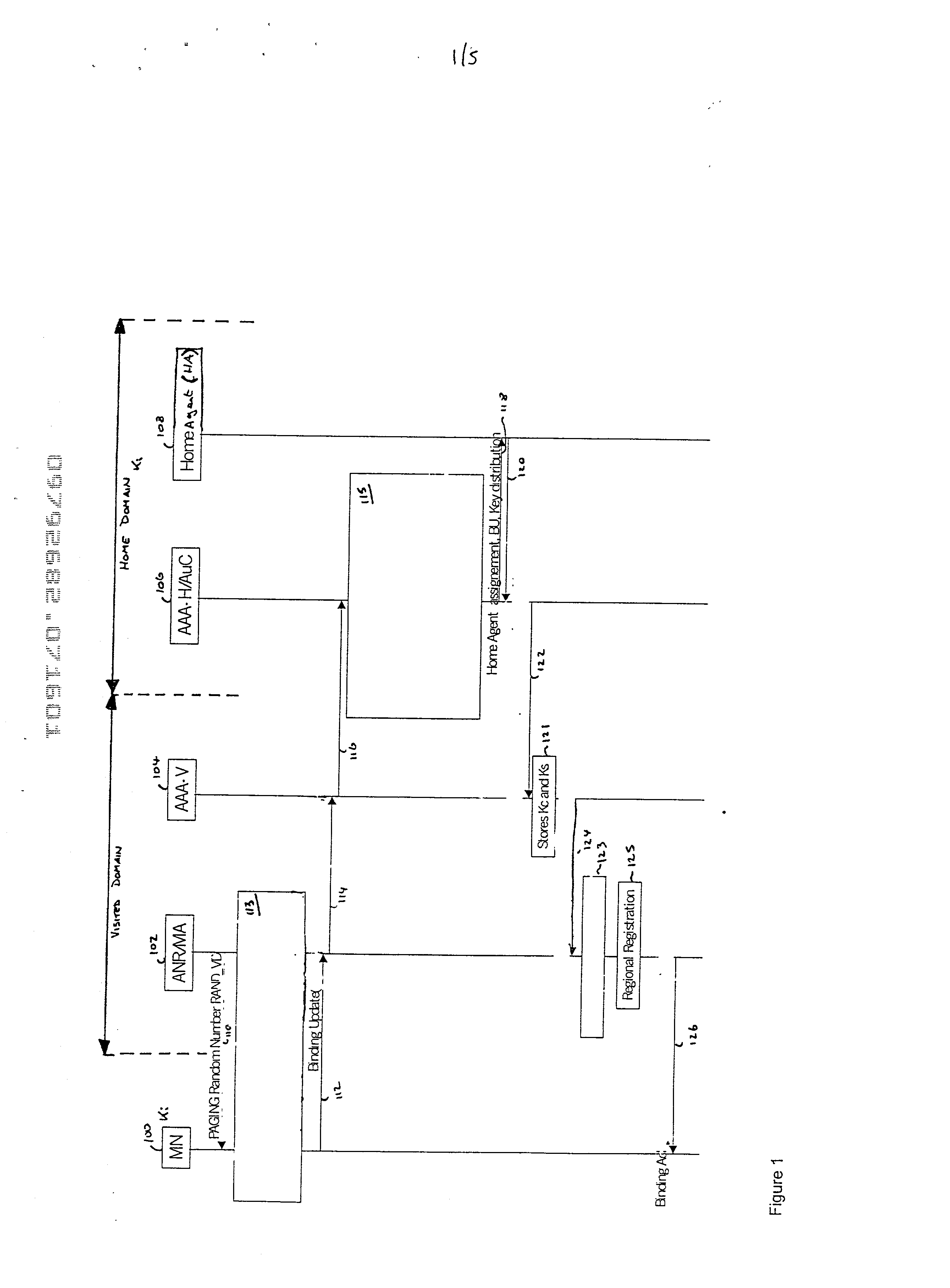
Authentication and distribution of keys in mobile IP network
InactiveUS20020120844A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationTelecommunicationsSecurity association
There is disclosed a method of establishing a connection between a mobile station and a serving domain, in which a first security association exists between the mobile node and an associated home domain, and a second security association exists between the serving domain and the home domain, the method comprising: transmitting a first message from the mobile node to the serving domain, the first message being encrypted in accordance with the first security association; transmitting the first message from the serving domain to the home domain; decrypting the first message in the home domain in accordance with the first security association; transmitting a second message from the home domain to the serving domain, the second message being encrypted according to the first security association; transmitting the second message from the serving domain to the mobile node; decrypting the second message in the mobile node in accordance with the first security association.
Owner:NOKIA NETWORKS OY
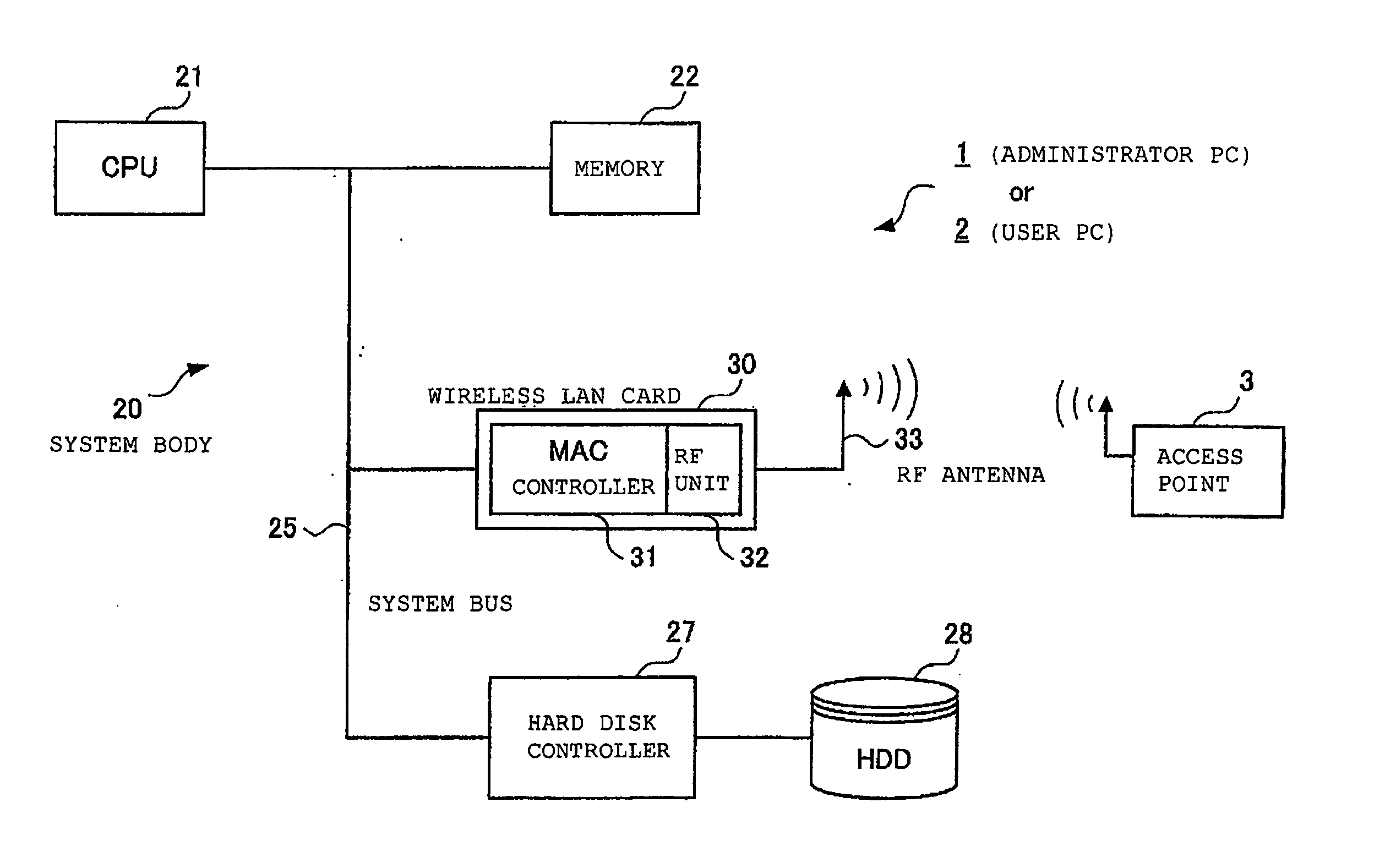
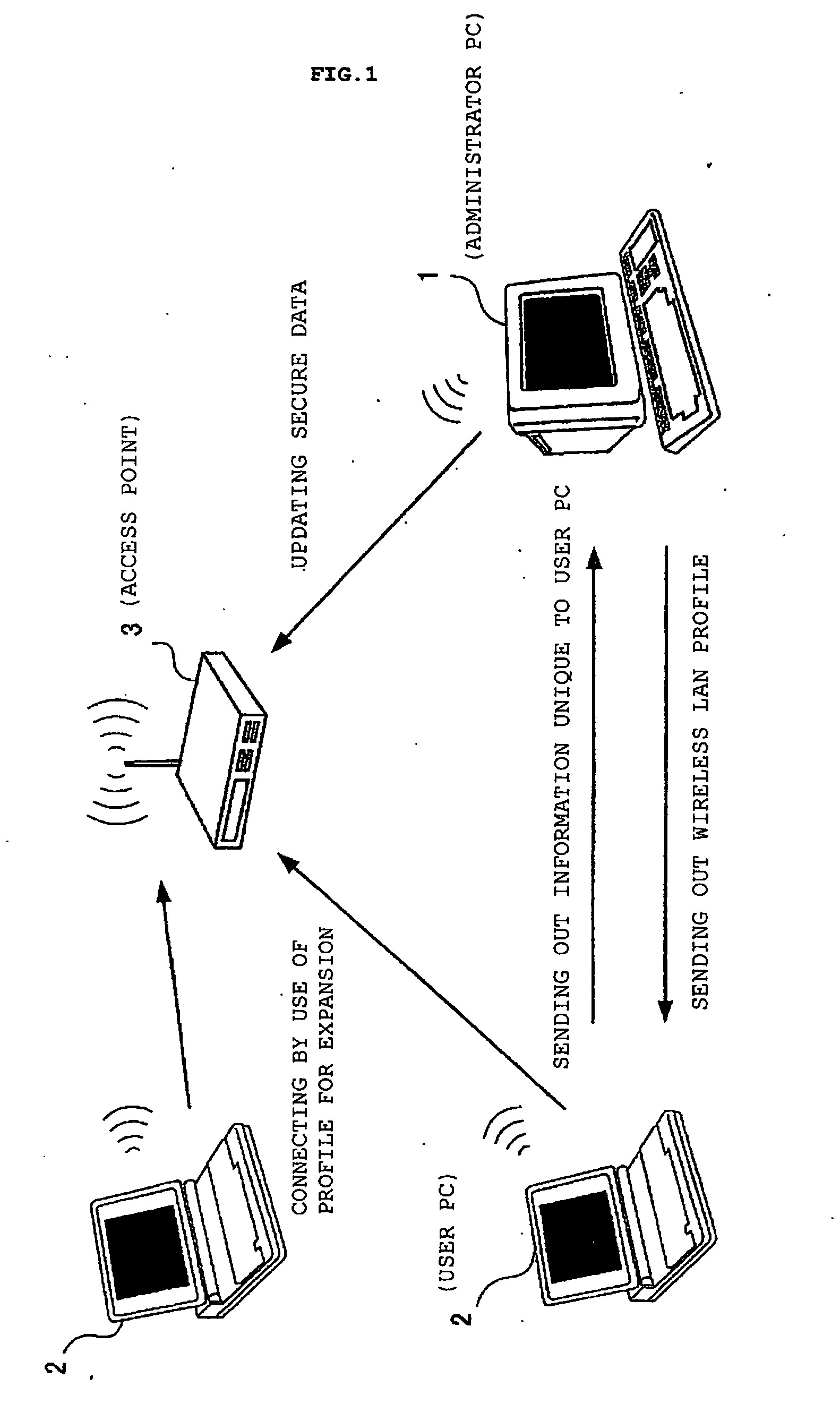
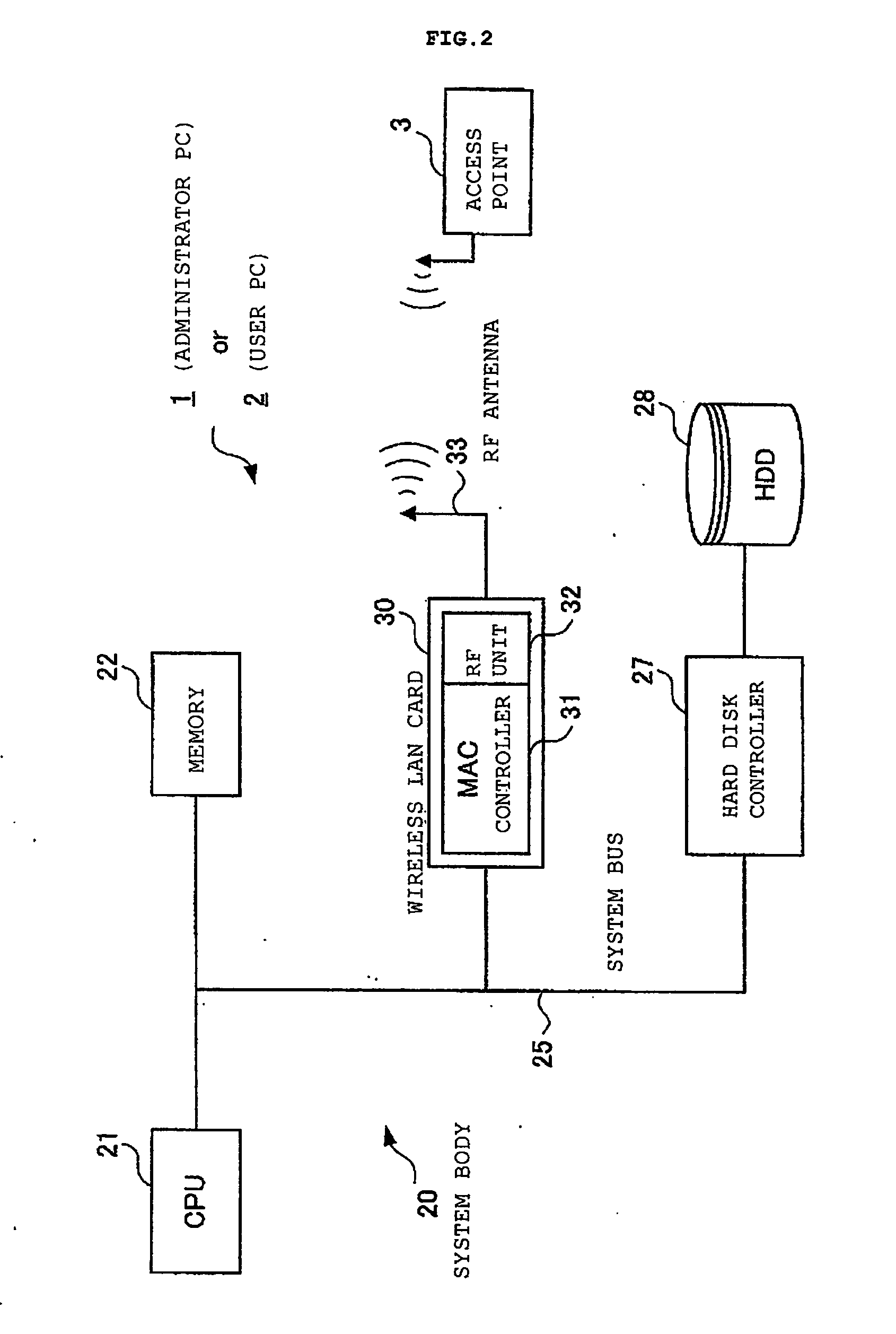
Profiled access to wireless LANs
InactiveUS20050050318A1Work lessImprove securityAssess restrictionDigital data processing detailsTelecommunicationsWireless lan
A user PC reads security information regarding itself, and acquires a profile including security information in a profile acquisition / output unit, the profile being created in an administrator's PC administering the setting of an access point. The security information included in the profile and the read information are compared with each other, and when both coincide, a setting of wireless communications is performed by a communication setting unit by use of the profile. Furthermore, status of a validity period and the like, when the wireless communications are set by use of the profile, are monitored by a status monitoring processing unit. When it is judged necessary to update the profile based on the monitored status, a profile including an update request is created by a data update processing unit, and the created profile is sent out to the administrator's PC.
Owner:LENOVO (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
Dynamic password update for wireless encryption system
ActiveUS20040083393A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsCommunications systemPassword
A method and system for dynamically changing password-keys in a secured wireless communication system includes initiating a password key change, generating a new password key, embedding the new password key and a password key indicator in a first message, encrypting the first message using an old password key, storing the new password key, sending the formatted encrypted first message over a wireless communication system, receiving a subsequent second message, and decrypting the subsequent second message using the new password key.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
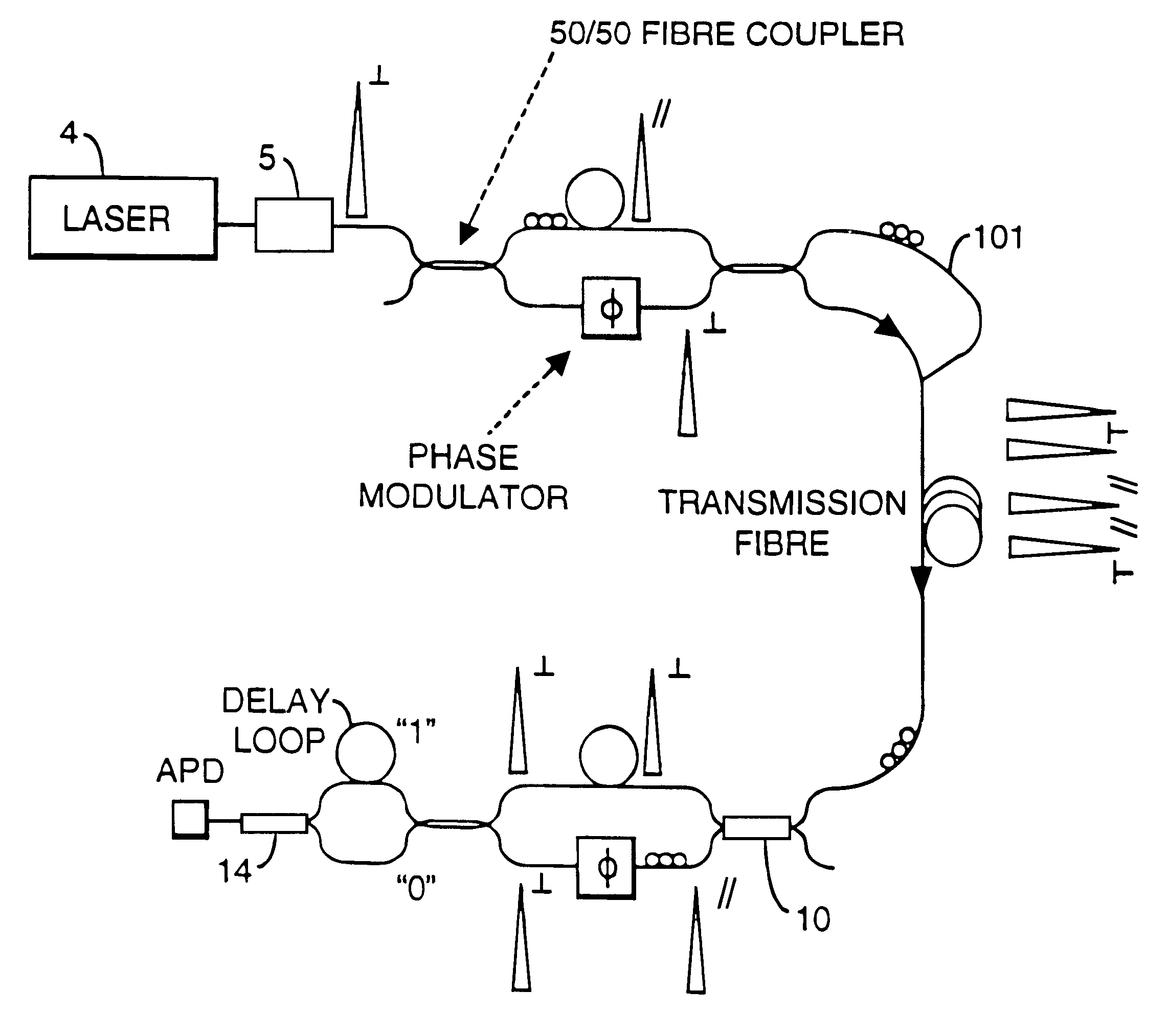
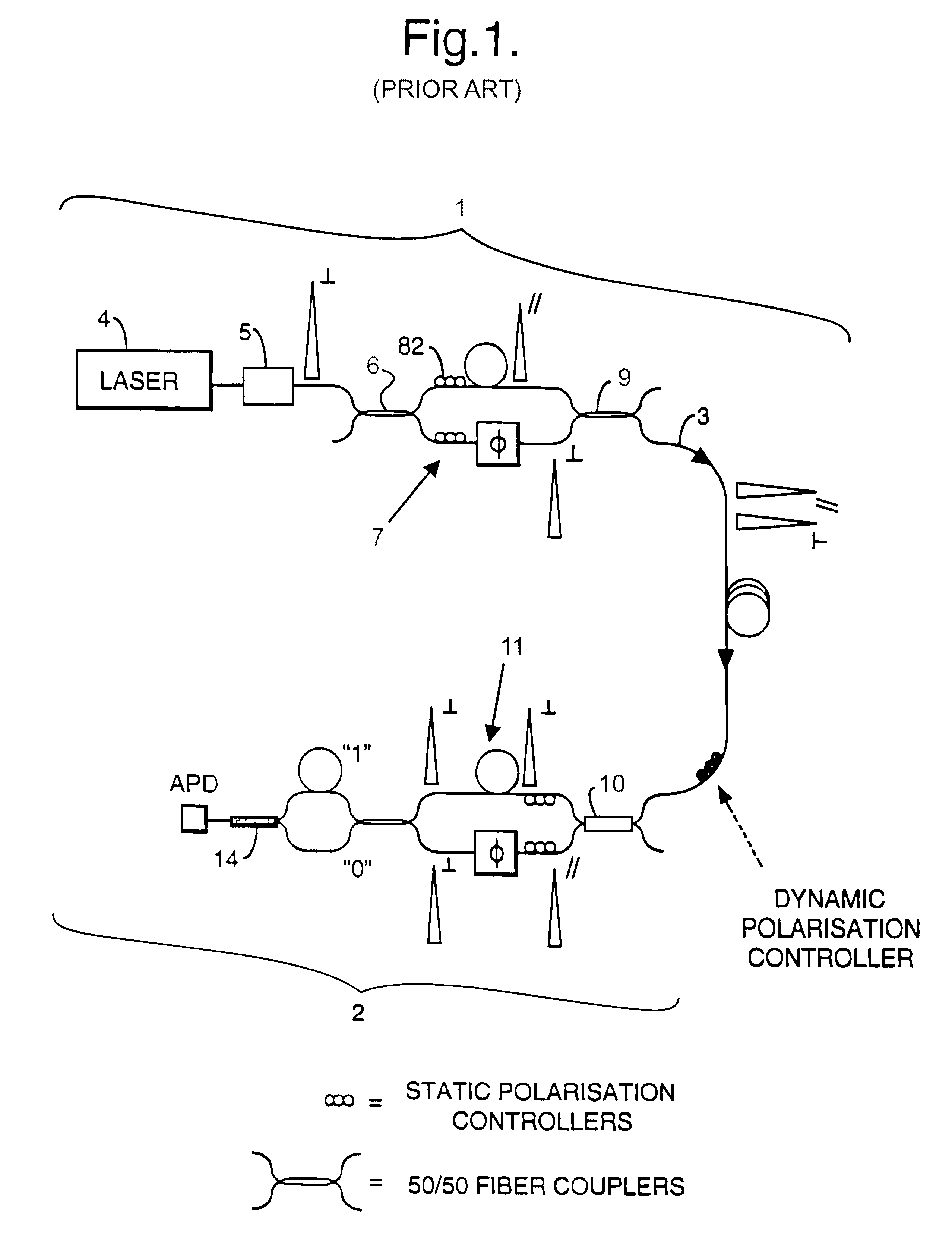
Method and apparatus for polarization-insensitive quantum cryptography
InactiveUS6529601B1Key distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesCommunications systemSingle polarization
A communication system uses quantum cryptography for the secure distribution of a key. A single-photon signal is phase-modulated and transmitted over a pair of time-multiplexed transmission paths. With each original single-photon signal in a given one of the transmission paths, a duplicate signal is transmitted. The duplicate is identically modulated and orthogonally polarized. At the receiver, the outputs of the two paths are combined interferometrically. A single polarization-insensitive measurement is derived from the combined contributions of the orthogonally polarized signals.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Multi-featured power meter with feature key
InactiveUS7249265B2Easy to reconfigureMaintaining price structureSubstation/switching arrangement detailsSpecial tariff metersComputer moduleIntelligent electronic device
An intelligent electronic device (“IED”) includes at least one function module that performs a specified function or feature. The function module operates to perform a power management function in conjunction with IED. The IED operates with a one key code corresponding to the power management function. The key code operates to enable or disable the power management function.
Owner:POWER MEASUREMENT LTD
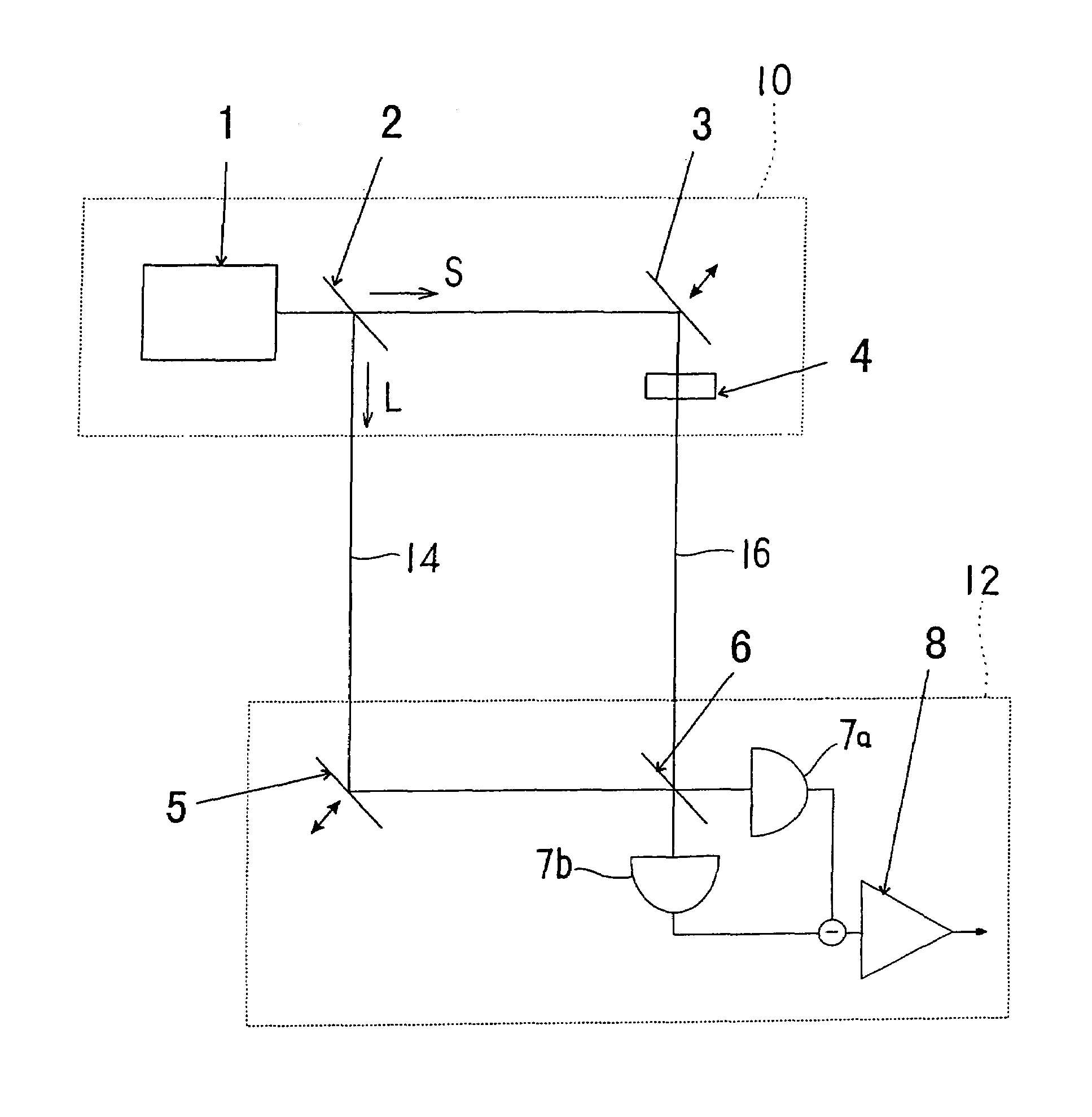
Cryptographic receiver
InactiveUS6028935AKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesFiber couplerPhoton detector
PCT No. PCT / GB94 / 02067 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 10, 1996 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 10, 1996 PCT Filed Sep. 23, 1994 PCT Pub. No. WO95 / 10907 PCT Pub. Date Apr. 20, 1995A cryptographic receiver (10) includes photon detectors (52, 54, 56, 58) arranged to detect photons arriving from filters (22) and (24). A fiber coupler (14) randomly distributes each received photon (16) from an optical fiber toone of two photon channels (18, 20). The filters (22, 24) are each unbalanced Mach-Zehner interferometers with a phase modulator (34, 44) in one arm (28, 38). The filters (22, 24) impose non-orthogonal measurement bases on photons within the respective channels (18, 20). A signal processor (60) derives a cryptographic key-code by analysis of signals received from the photon detectors (52, 54, 46, 58).
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
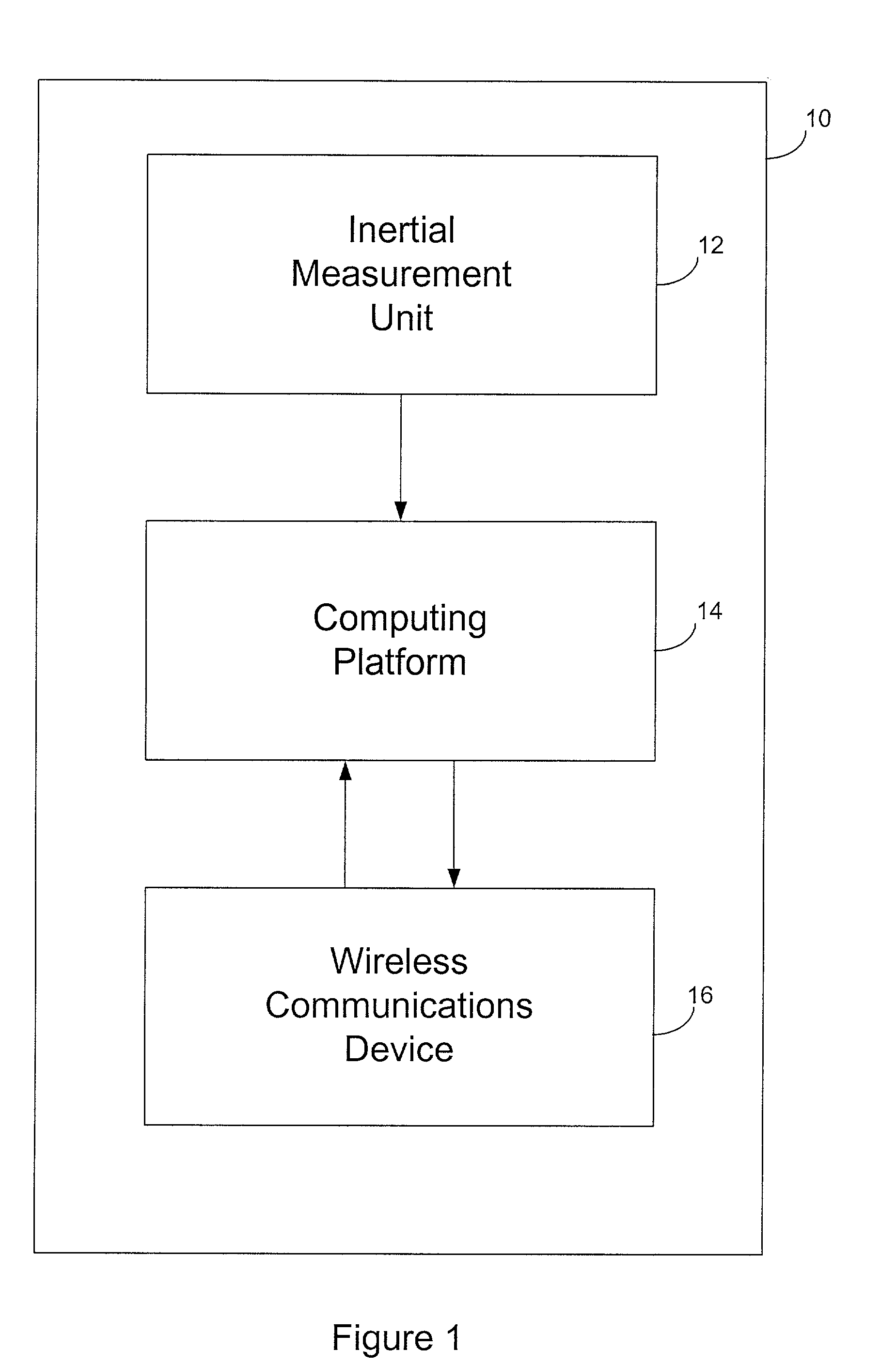
Entropy sources for encryption key generation
InactiveUS20020131592A1Maintain securityNecessary computer processing powerMechanically effected encryptionSecret communicationCryptographic key generationNumber generator
Inertial measurement units are subject to drift and noise characteristics that are normally distributed. While that drift and noise is problematic for inertial navigation, it is ideal for encryption key generation. The measurement values from an inertial measurement unit are random on several levels and can be used to effectively seed a pseudo random number generator for encryption key generation.
Owner:AIRBIQUITY INC
Data recording/reproducing method, data recording/reproducing system, recording apparatus
InactiveUS7239709B1Television system detailsKey distribution for secure communicationDigital dataData recording
A data recording / reproducing method wherein encrypted digital data obtained by subjecting digital data to first encrypting by using a contents key and encrypted contents key obtained by subjecting the contents key to second encrypting are recorded on a recording medium, the encrypted digital data and the encrypted contents key, having been recorded, are reproduced, and the encrypted digital data is decrypted by using the contents key obtained by decrypting the encrypted contents key, thereby to obtain the digital data.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Advanced stream format (ASF) data stream header object protection
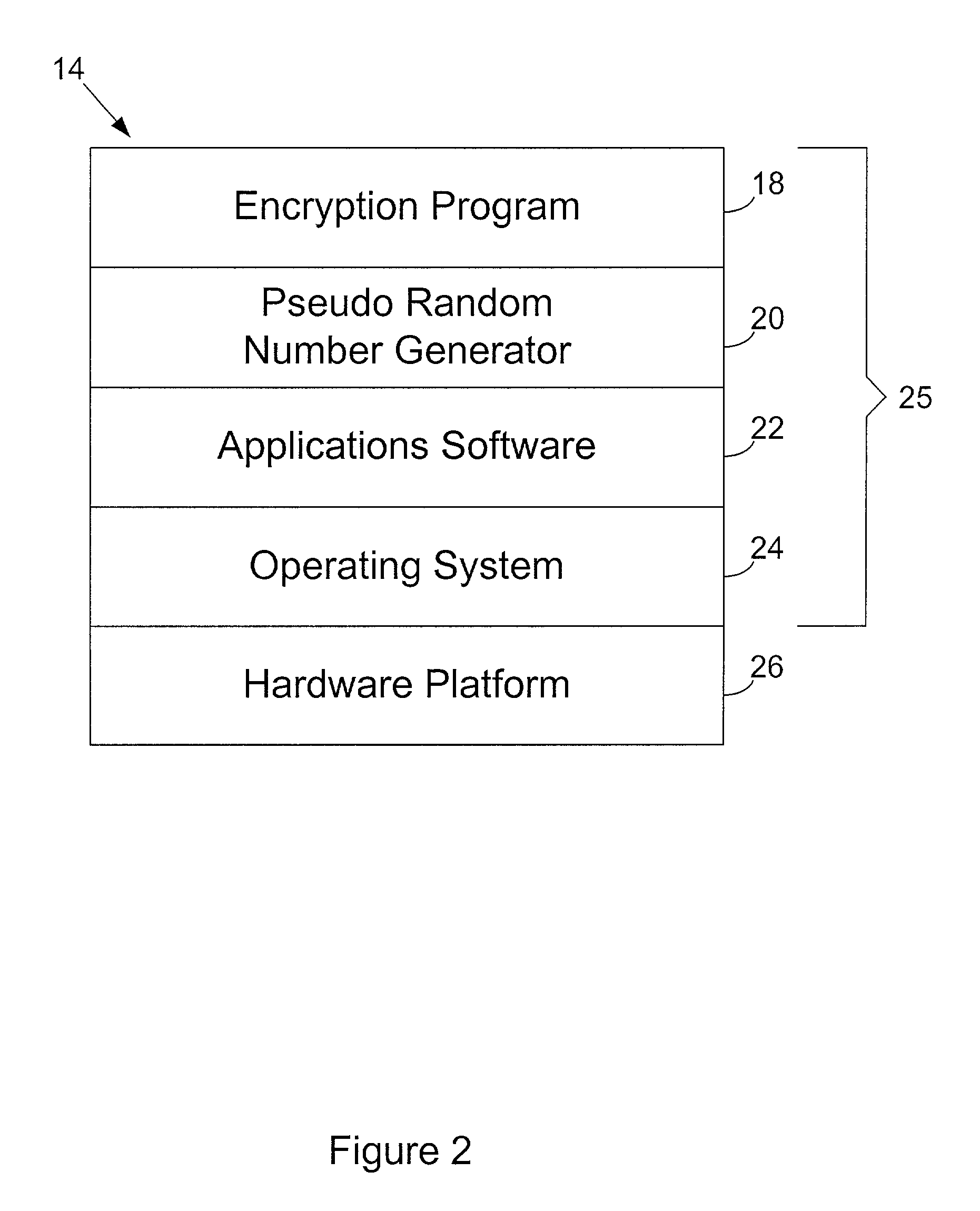
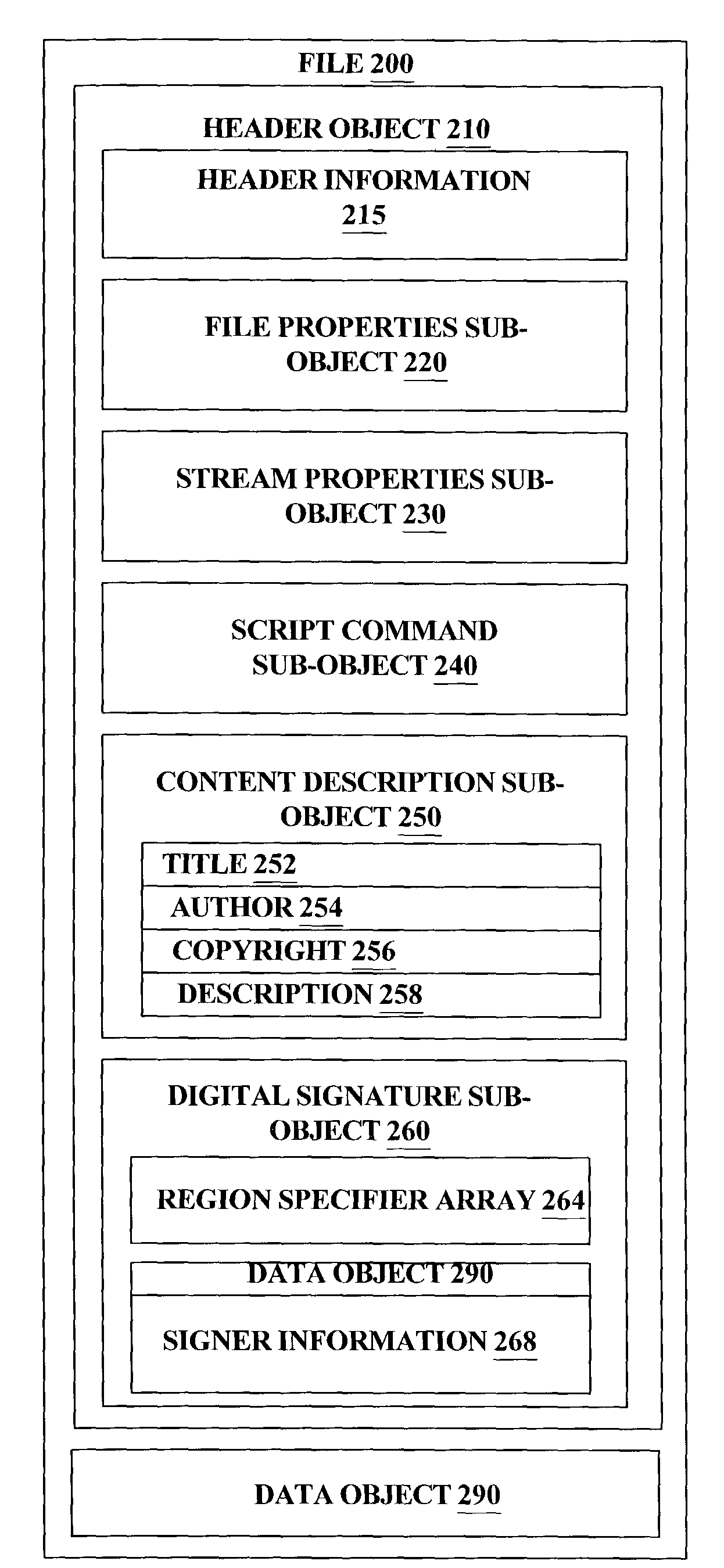
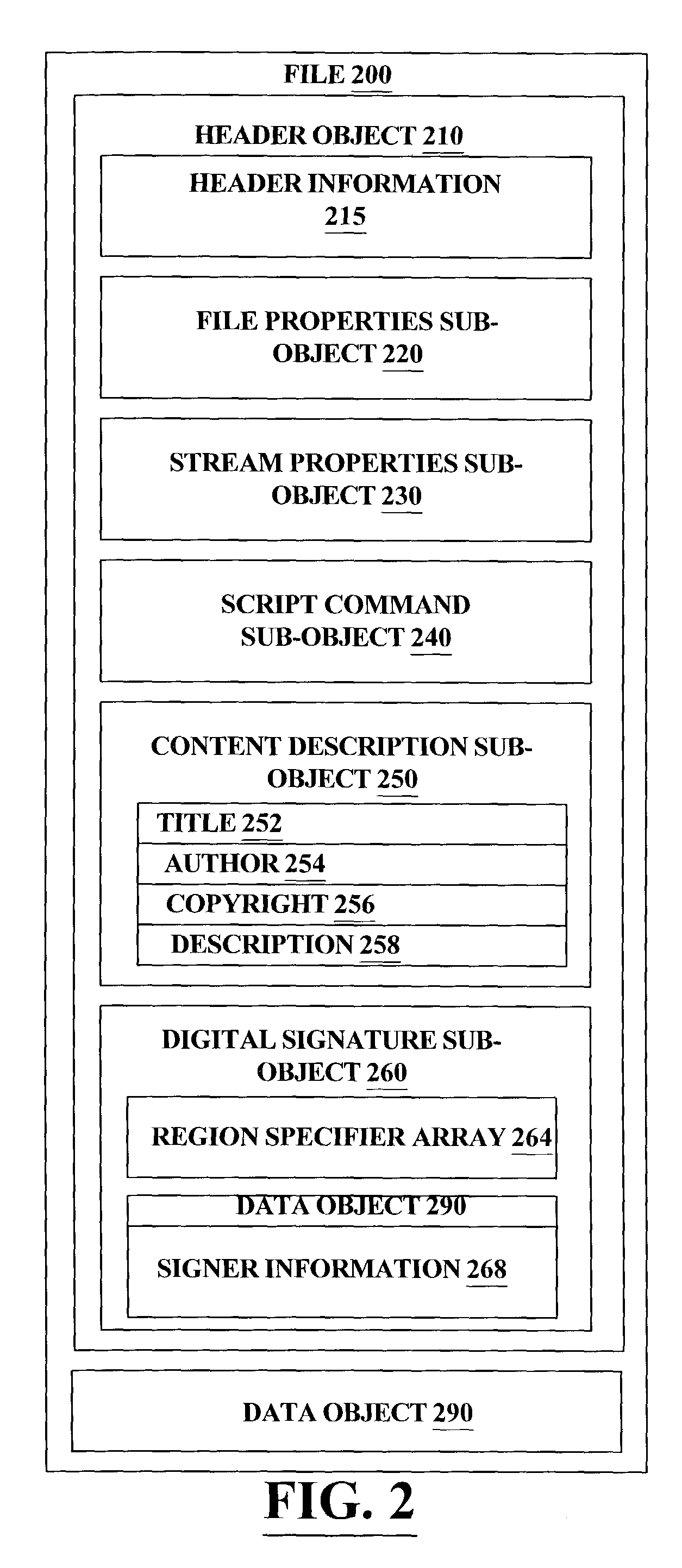
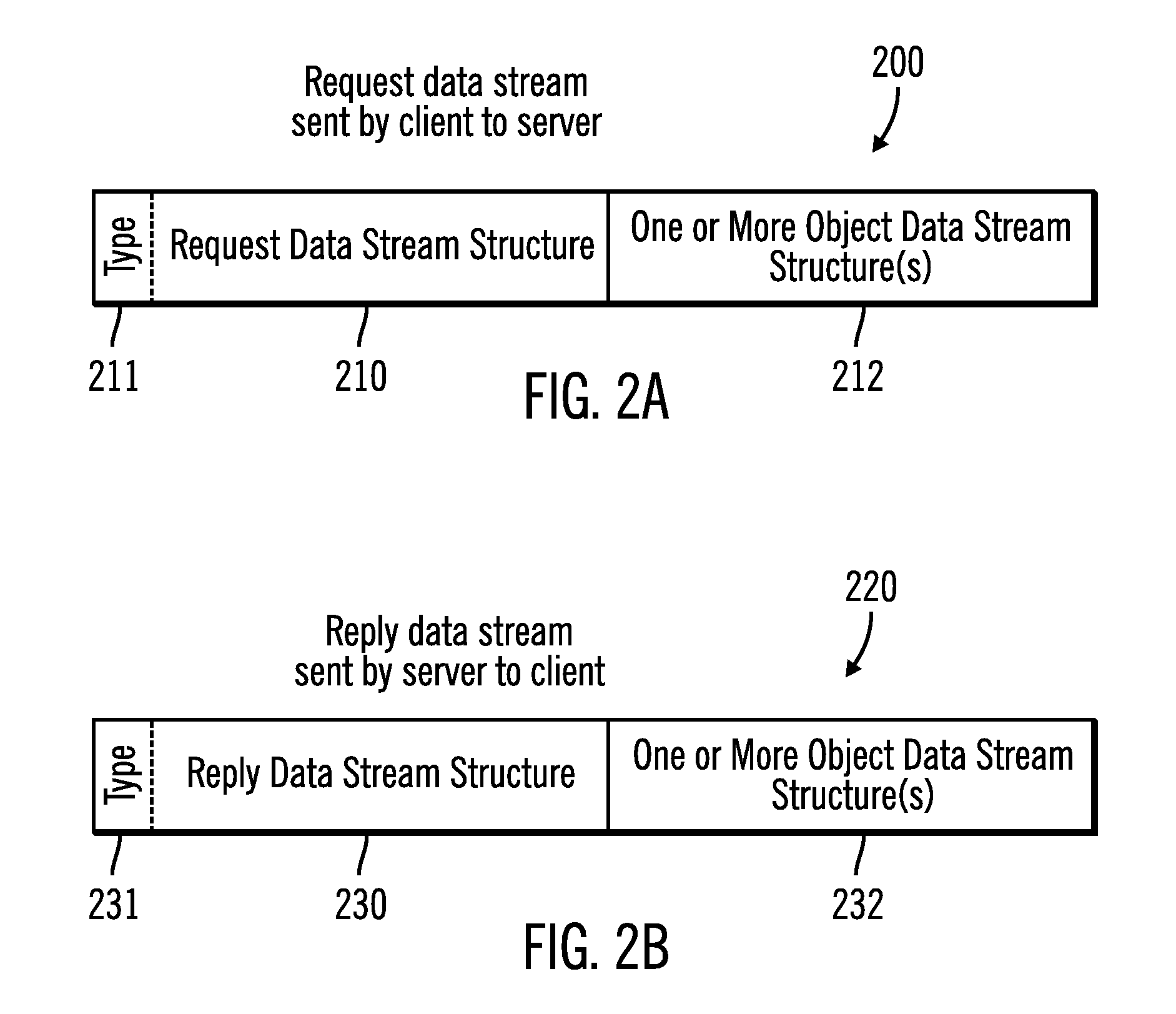
InactiveUS7401221B2Program control using stored programsDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwareObject composition
A header object for a data file is comprised of sub-objects which specify properties of the data stream and contains information needed to properly verify and interpret the information within the data object. In order to allow the protection of any set of sub-objects without requiring that the sub-objects follow any specific ordering, a new sub-object is introduced which includes region specifiers identifying regions within sub-objects and verification information for those regions. This new sub-object in the header object allows the modification of non-protected regions and reorganization of sub-objects in a header without invalidating verification information.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system for managing the presentation of information
InactiveUS20030037243A1Mechanically effected encryptionInternal/peripheral component protectionComputer science
A method (and system) includes receiving a request to present information selected from a plurality of examples of information, reading an identification token of at least one user, and determining whether the at least one user is authorized to be presented the information.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for performing permutations using permutation instructions based on modified omega and flip stages
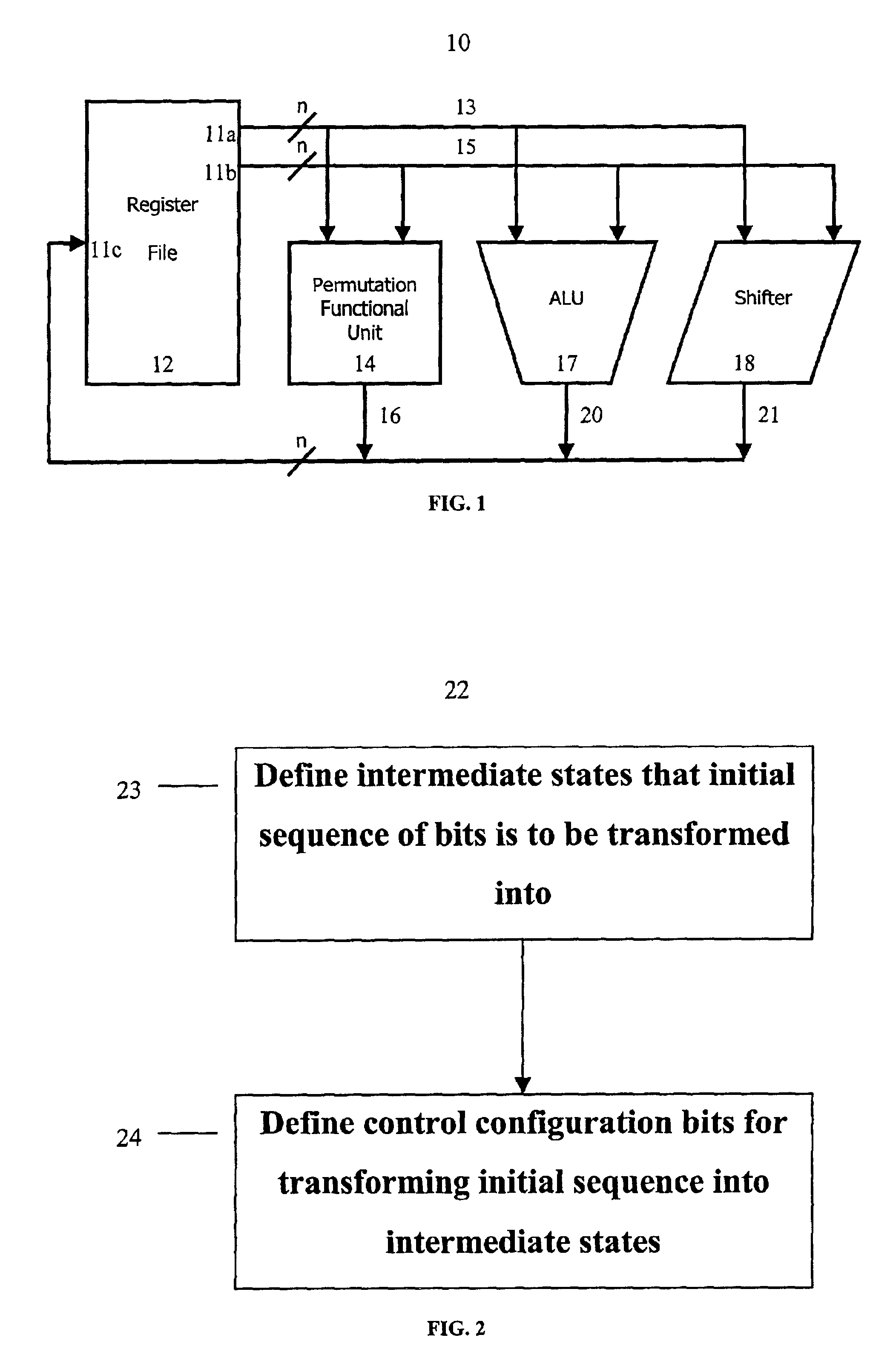
InactiveUS6952478B2Digital computer detailsHandling data according to predetermined rulesComputer architectureOmega network
The present invention provides permutation instructions which can be used in software executed in a programmable processor for solving permutation problems in cryptography, multimedia and other applications. The permute instructions are based on an omega-flip network comprising at least two stages in which each stage can perform the function of either an omega network stage or a flip network stage. Intermediate sequences of bits are defined that an initial sequence of bits from a source register are transformed into. Each intermediate sequence of bits is used as input to a subsequent permutation instruction. Permutation instructions are determined for permuting the initial source sequence of bits into one or more intermediate sequence of bits until a desired sequence is obtained. The intermediate sequences of bits are determined by configuration bits. The permutation instructions form a permutation instruction sequence, of at least one instruction. At most 21 gr / m permutation instructions are used in the permutation instruction sequence, where r is the number of k-bit subwords to be permuted, and m is the number of network stages executed in one instruction. The permutation instructions can be used to permute k-bit subwords packed into an n-bit word, where k can be 1, 2, . . . , or n bits, and k*r=n.
Owner:TELEPUTERS
Cloud key escrow system
ActiveUS8891772B2Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsThird partyData access
Embodiments are directed to allowing a user to store encrypted, third-party-accessible data in a data store and to providing third party data access to a user's encrypted data according to a predefined policy. A data storage system receives encrypted data from a user at a data storage system. The data is encrypted using the user's private key. The data storage system stores the received encrypted data according to a predefined policy. The encryption prevents the storage system from gaining access to the encrypted data, while the policy allows the encrypted data to be released upon receiving a threshold number of requests from verified third parties. The data storage system implements a verifiable secret sharing scheme to verify that the encrypted data can be reconstituted without the data storage system accessing the encrypted data. The data storage system synchronously acknowledges that the received encrypted data has been verified and successfully stored.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method And System For Computational Transformation
InactiveUS20070195952A1Unauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringComputer hardwareRandom number generation
The invention generally relates to computational transformation process, which has applications in cryptography, random number generation, hash code generation etc. The computational transformation module uses a keyset, which is designed using a two dimensional array. Since the process of forward transformation used in the invention is a symmetric encryption process and if used to send data securely over a communications network, the same keyset needs to be present at the sending computer to encrypt the data and the receiving computer to go through a reverse transformation and decrypt the data. When the first ‘n’ bit block of input-data is transformed into the first ‘m’ bit block of output-data, the keyset is transformed into a different keyset based on a nonlinear or one-way transformation on the keyset. The next input block is encrypted using a transformed keyset, hence satisfying Shanons theory of perfect secrecy. It uses the same logic with additional parameters and operations to create random numbers and unique hash codes. The computational transformation process is a one-way process which is based on a principle where given the input value ‘x’, it is easy to transform ‘x’ to ‘y’ using a function ‘F’ i.e. F(x)=y. However, given ‘y’ in the range of F, it is hard to find an x such that F(x)=y. In this system, the same transformation function and same keyset is used for both encryption as well as decryption with only a change in the constant value.
Owner:SINGANAMALA PRAHLAD P
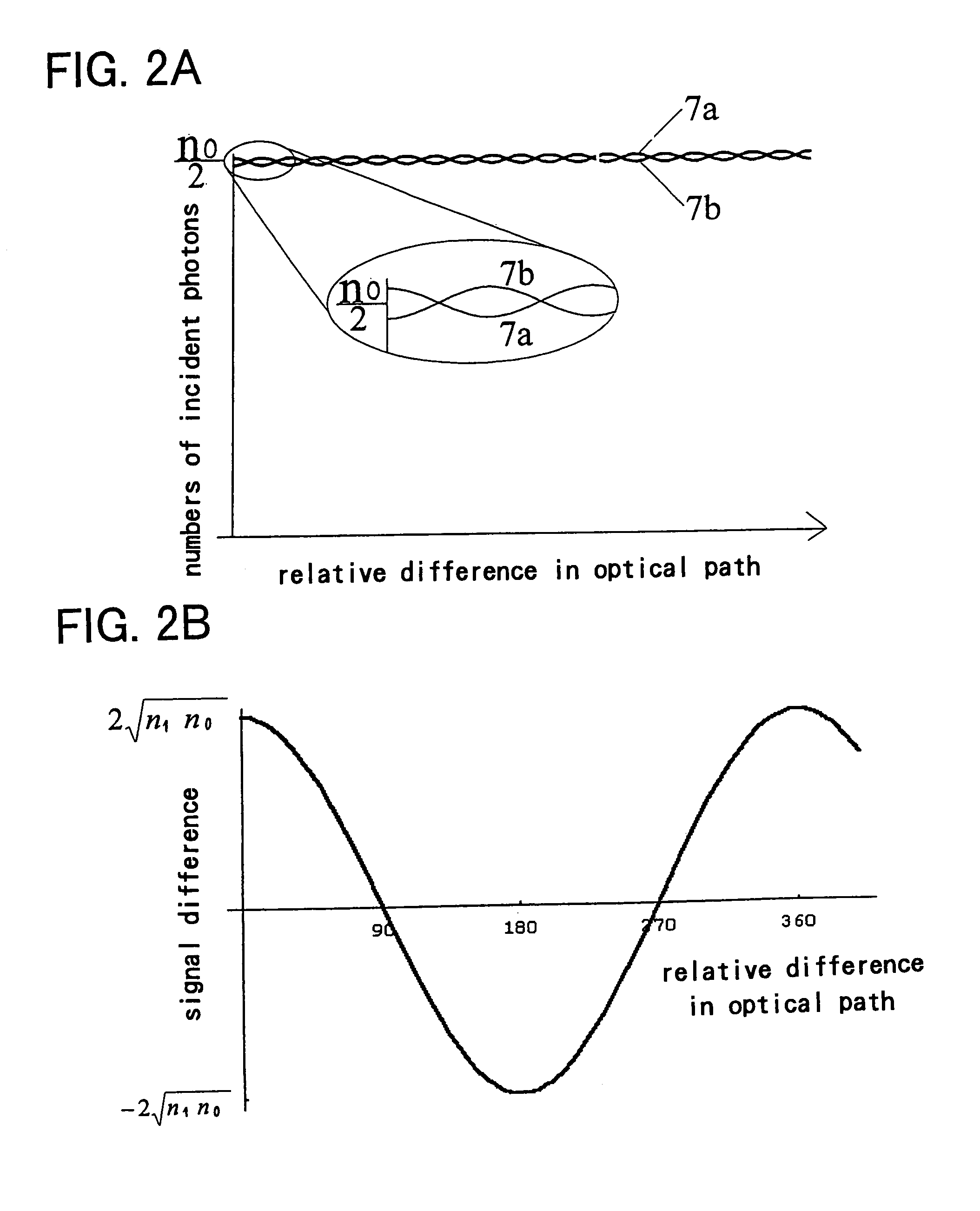
Quantum cipher communication system
InactiveUS7305091B1Improve quantum efficiencyImprove signal-to-noise ratioKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesBeam splittingLaser beams
A quantum cipher communication system includes a sender's apparatus, a recipient's apparatus and a transmission path. The sender's apparatus includes a beam splitting for splitting a laser beam into a weak signal light and an intense reference light, a phase modulation unit for imparting a phase change on either the weak signal light or the intense reference light. The recipient's apparatus includes a phase modulation unit for imparting a phase change on either the weak signal light or the intense reference light, a superimposing unit for superimposing the weak signal light and the intense reference light, a pair of photoconductive diodes for converting two output lights from the superimposing unit into electric signals, and an amplifying unit for amplifying a difference signal between the electric signals, wherein the recipient assigns bit values by comparing the difference signal with threshold values.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Method for performing short-range wireless transactions between an hybrid wireless terminal and a service terminal over an interface for short-range wireless access and corresponding service terminal
InactiveUS20020126845A1Data taking preventionMechanically effected encryptionComputer terminalUser authentication
The invention relates notably to a method for performing a short-range wireless transaction between an hybrid wireless terminal and a service terminal. The hybrid terminal is able to communicate over a first interface with a radio communication network and over a second interface for short-range wireless access with a service terminal, the hybrid wireless terminal comprises a user authentication information for authenticating a user in the radio communication network. According to the invention, the method comprises the steps of: transmitting over the second interface for short-range wireless a message to the service terminal comprising at least the user authentication information; authenticating the user at the service terminal by checking the received user authentication information against an authentication database; enabling the transaction if the user authentication has been successful.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method for secure communication in multiple access systems
InactiveUS20010038695A1Key distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwareSecure communication
A key agreement method for secure communication in a multiple access system is provided. A key agreement method for secure communication in a multiple access system, the key agreement method includes the steps of (a) a first user, modulating signals from a source by a bit sequence and transmitting the modulated signal, (b) a second user, a legitimate counterpart of the first user, decoding, making decision for each bit of the signal with a detector affected by noise and recording the measured values, (c) the second user, deciding a threshold value of measurement with consideration of other factors such as a transmission rate, tolerable error rates, and a degree of security, (d) the second user adopting as a key string only bits having values beyond the threshold value and ignoring bits falling the erroneous region below the threshold, (e) the second user informing the first user that the n-th bit is adopted, not telling the value of the bit, and (f) the users, the first user and the second user, taking as a key string the values of the n-th bits adopted in (e), and discarding the values of the other bits.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
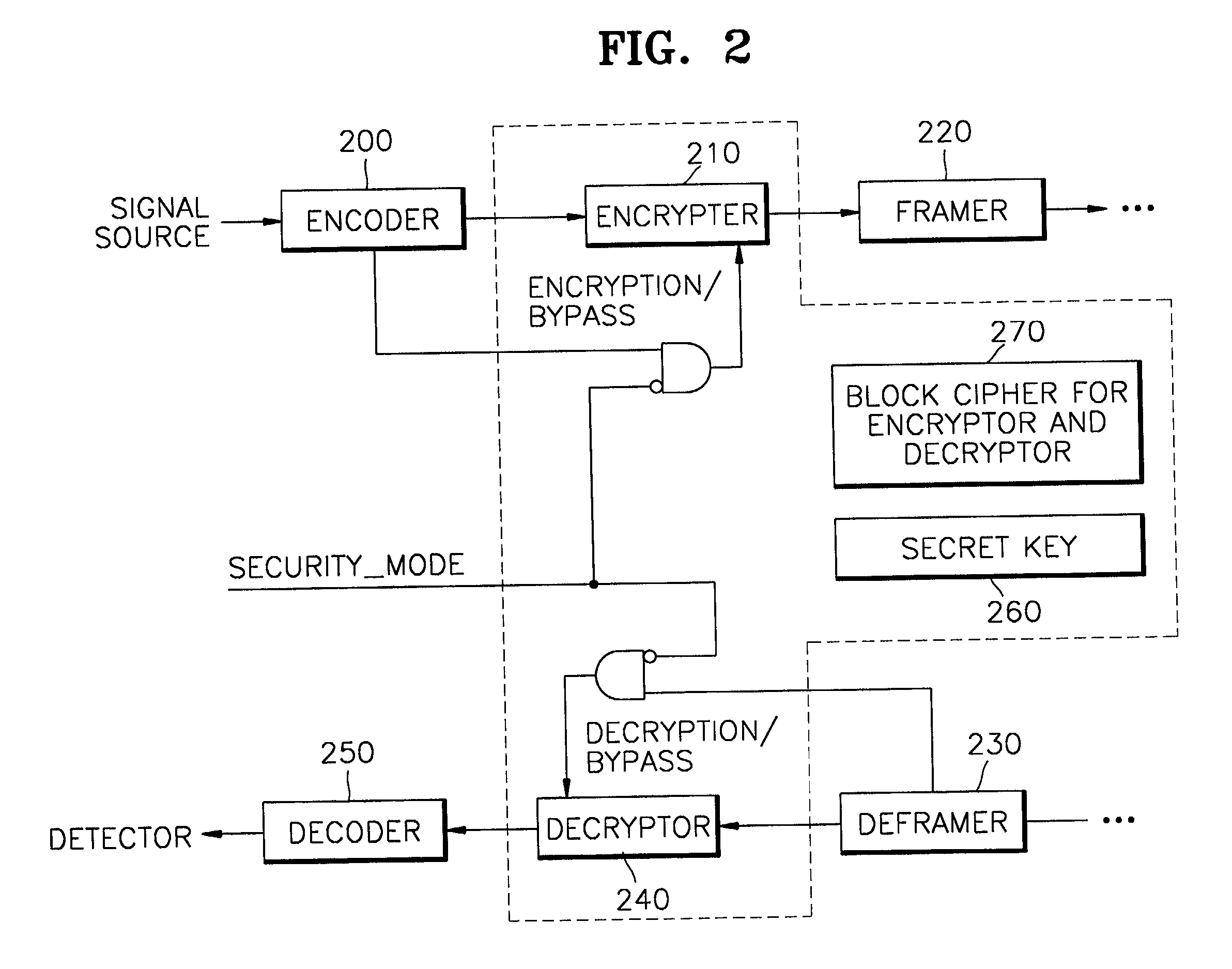
Secure presentation of media streams in response to encrypted digital content
Secure presentation of media streams includes encoding the media streams into digital content, encrypting a portion of that digital content, the portion being required for presentation, in which the encrypted version is substantially unchanged in formatting parameters from the clear version of the digital content. Selecting those portions for encryption so there is no change in distribution of the media stream: packetization of the digital data, or synchronization of audio with video portions of the media stream. When encoding the media stream into MPEG-2, refraining from encrypting information by which the video block data is described, packet formatting information, and encrypting the video block data using a block-substitution cipher. A block-substitution cipher can be used to encrypt each sequence of 16 bytes of video data in each packet, possibly leaving as many as 15 bytes of video data in each packet in the clear.
Owner:KALEIDESCAPE
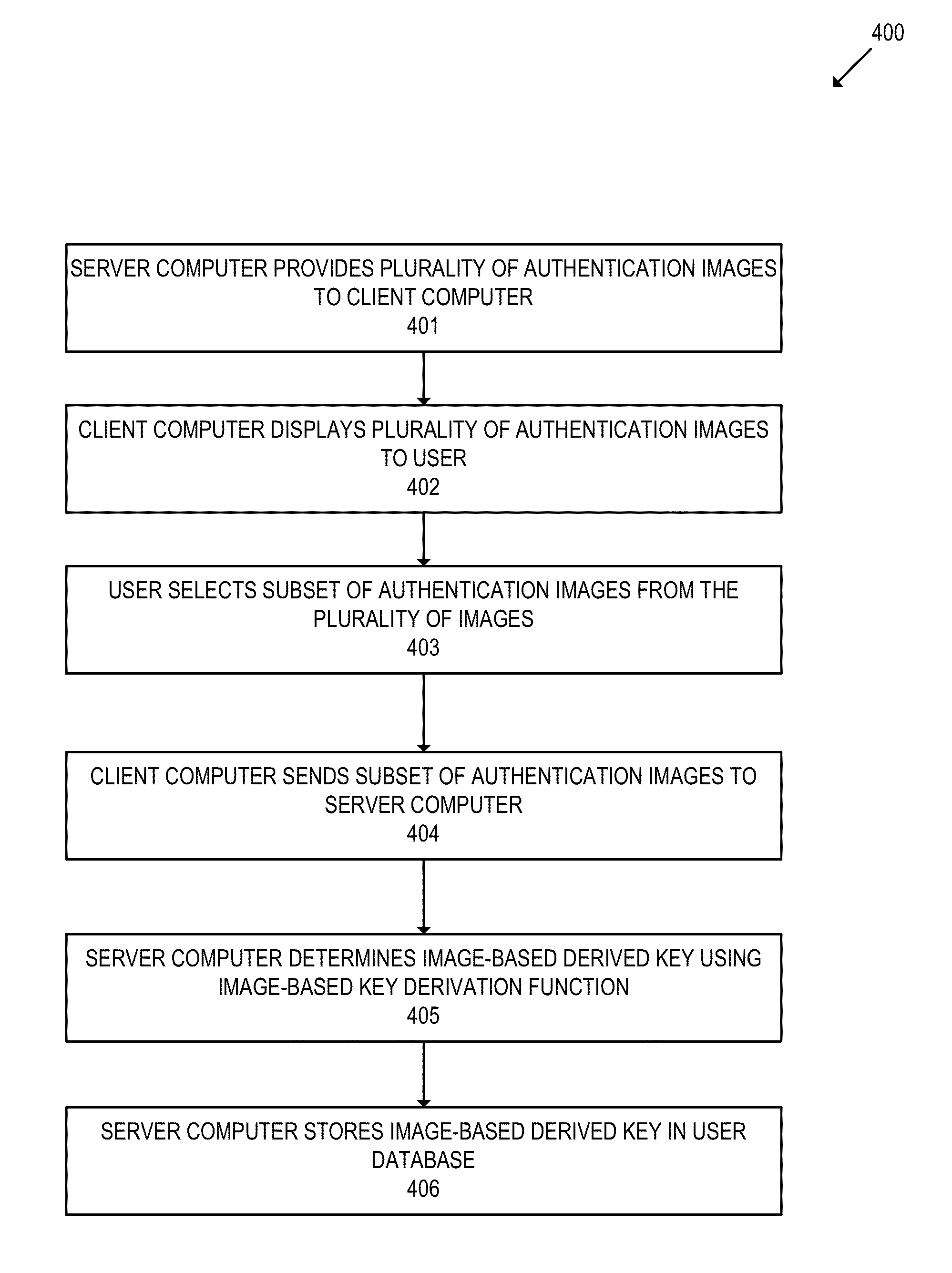
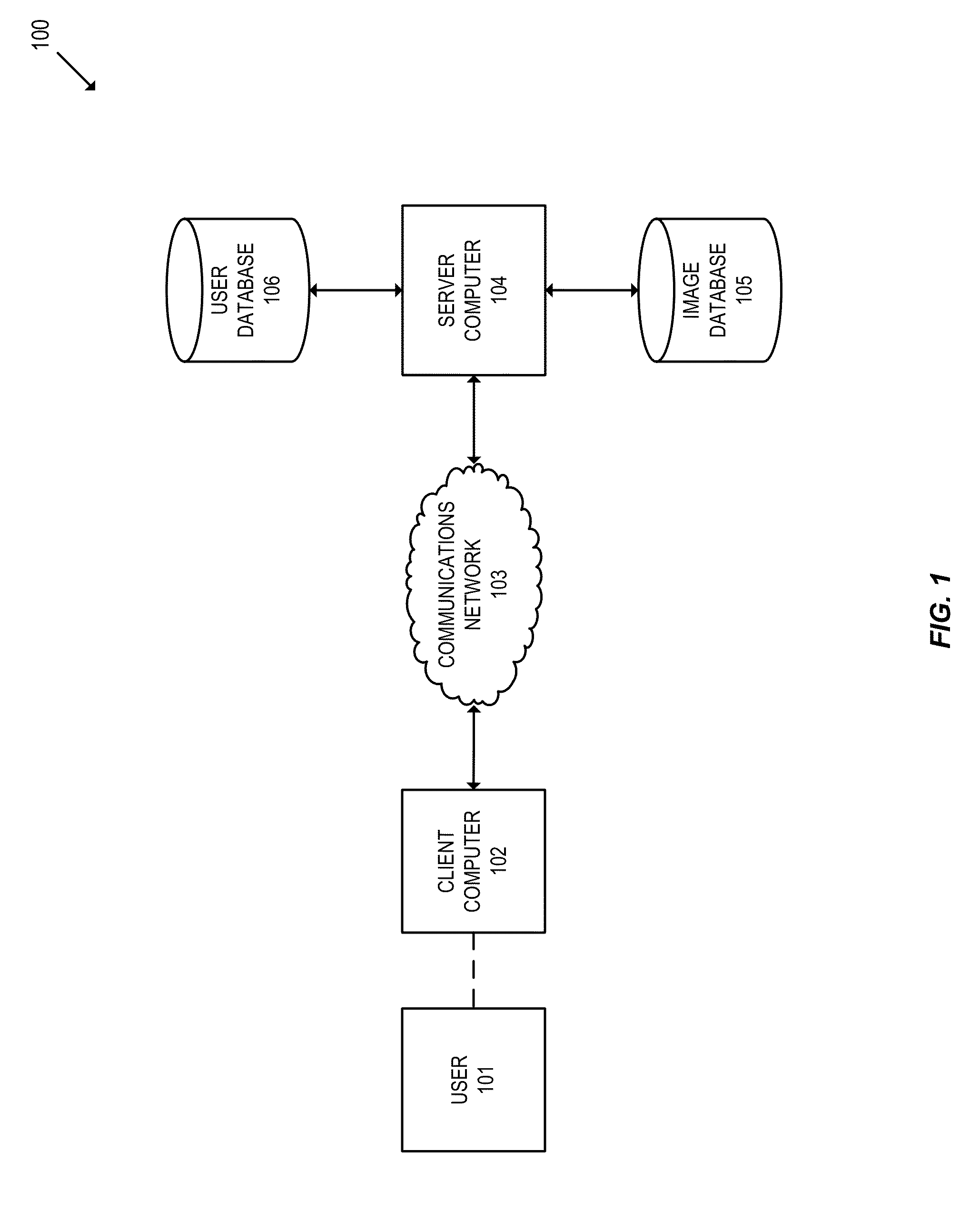
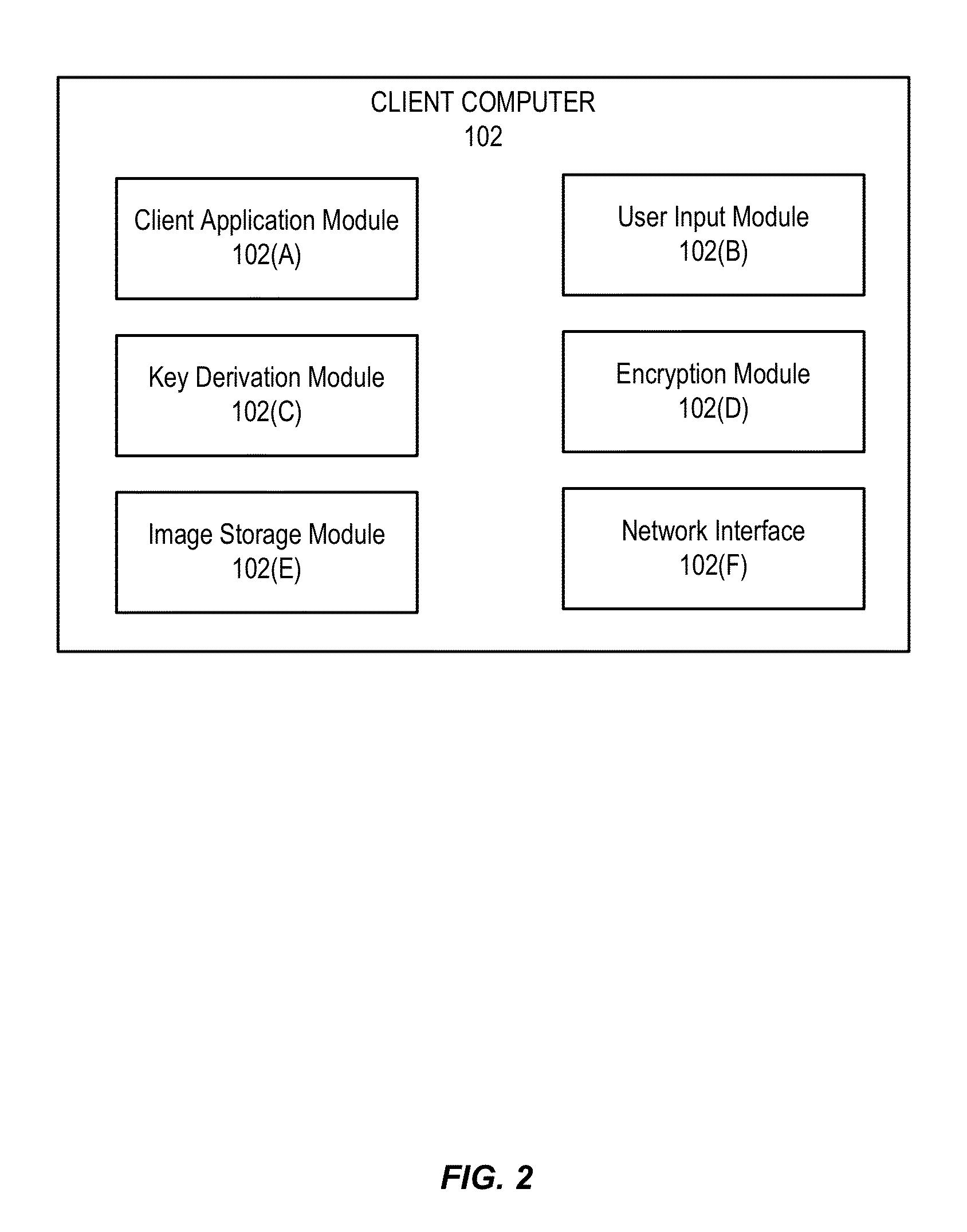
Image based key derivation function
ActiveUS20140372754A1Easy authenticationFacilitate data encryptionUser identity/authority verificationMechanically effected encryptionKey derivation functionUser authentication
Embodiments of the invention relate to methods of generating and using an image-based derived key. In various embodiments, the image-based derived key may be used to facilitate user authentication and data encryption. For some embodiments, a method is disclosed comprising determining an image-based derived key, wherein the image-based derived key is generated from a selection of authentication images chosen by a user, encrypting data using the image-based derived key, and transmitting the encrypted data.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
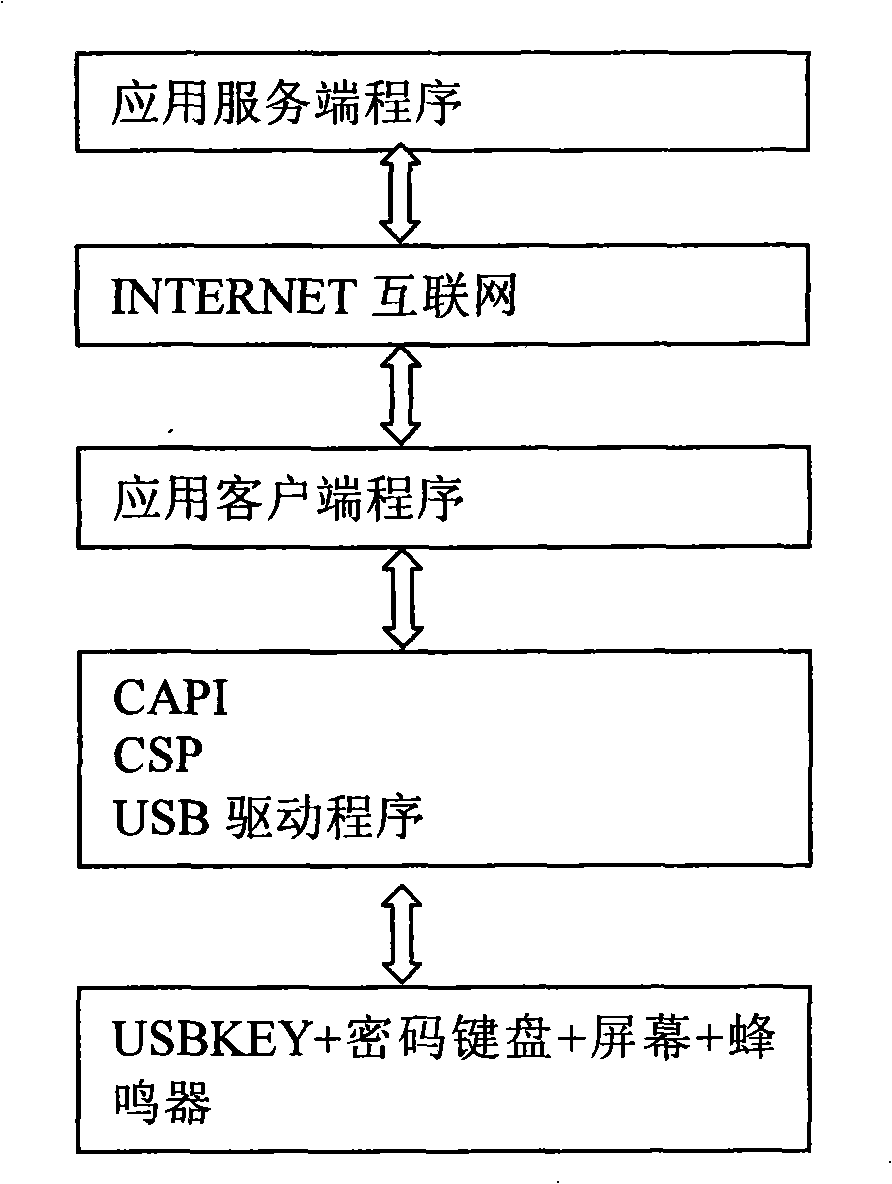
Cipher keyboard apparatus and implementing method thereof
InactiveCN101340294AImprove securityUser identity/authority verificationMechanically effected encryptionPasswordSmart card
The invention discloses a password keyboard device and a realization method thereof; the device comprises an interface connected with a computer end, and a hardware chip used for data communication with the application layer software of the computer end by the interface. In the software of the equipment, a smart card layer is arranged above the interface, wherein, the smart card layer comprises an encryption algorithm database and an information input module; the encryption algorithm database comprises a plurality of existing algorithms; the software of the equipment is used for the encryption of the information of the information input module according to the appointed algorithm and sending the encrypted information to the application layer of the computer end. In the password keyboard device of the invention and the realization method thereof improve the safety of the data in a way that the functions of USBKEY, a keyboard, a screen, and the like, are integrated and arranged on hardware equipment, certain encryption methods are used for the data encryption of the data input from the USBKEY password keyboard and the encrypted data is transmitted.
Owner:SHENZHEN ZIJIN FULCRUM TECH
Common key block encryption device, common key block encryption method, and program
ActiveUS20110211691A1More processing timeSatisfies requirementEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwareVariable length
A common key block encryption device includes a first hash unit applying locked key permutation to a variable-length s-bit plaintext, and outputting a fixed-length n-bit first block and a second (s-n)-bit block; a first encryption processing unit outputting a third block encrypted by element of n-bit block tweakable block cipher using tweak, inputting the first block; a second encryption processing unit generating a random number (s-n)-bit block with a result of group computation of the third block and the first block as input by using an arbitrary cipher having theoretical security at least against a known-plaintext attack; and a second hash unit applying the locked key permutation to the result of the group computation of the random number block and the second block, and to the third block to output a fifth n-bit block and a sixth (s-n)-bit block. The fifth and sixth blocks are concatenated into an s-bit encryption.
Owner:NEC CORP
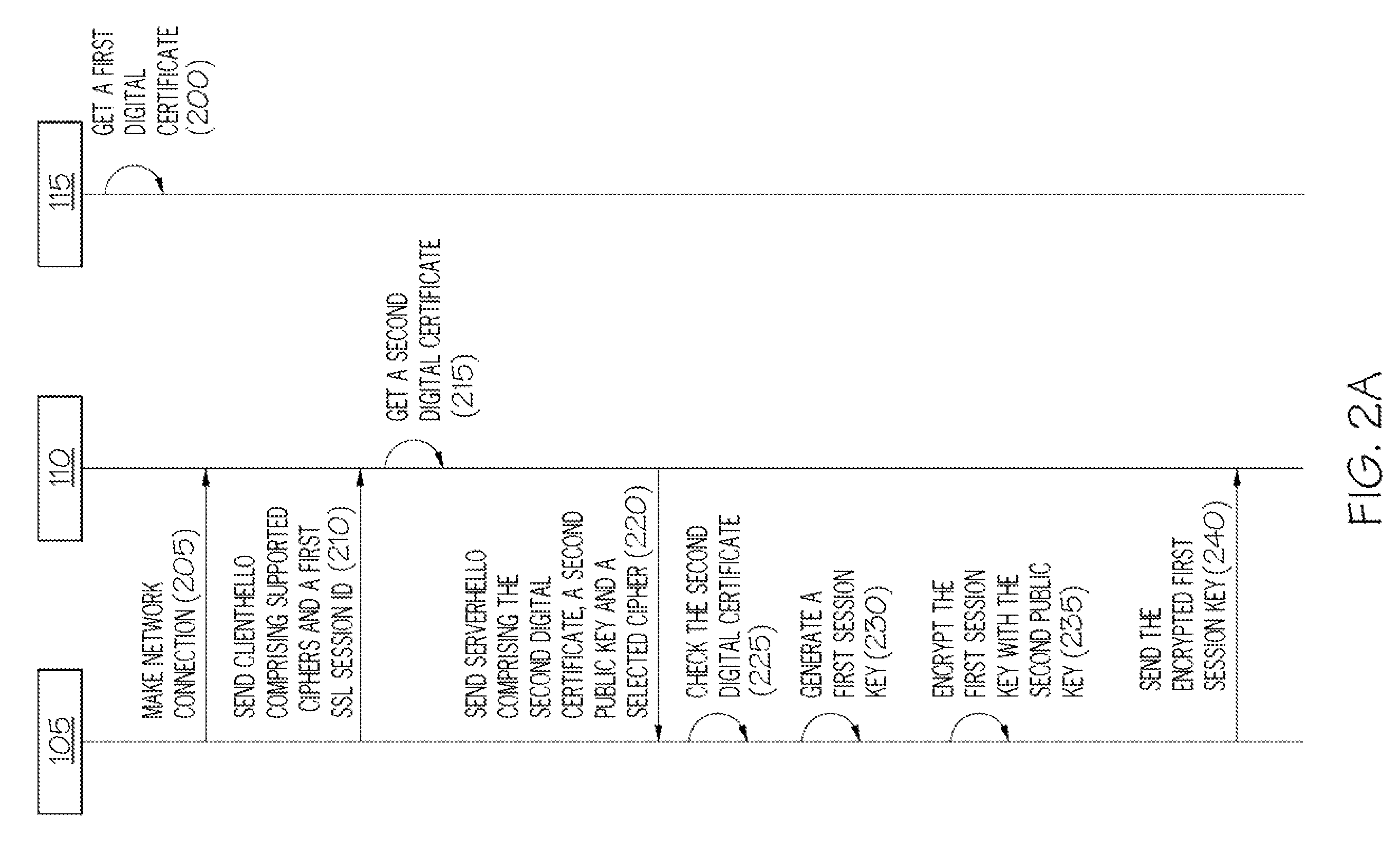
Securing a communications exchange between computers
InactiveUS7945779B2Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsClient-sideClient machine
For use in a distributed system where a client computer is operable to communicate with a server computer and to receive a digital certificate associated with a remote external component, apparatus for securing a communications exchange between computers includes a hasher, responsive to the client computer receiving a digital certificate, for hashing data associated with the client computer and the server computer with data associated with the digital certificate to create a first message digest, and a first transmitter for transmitting the first message digest to the remote external component.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Homomorphic evaluation including key switching, modulus switching, and dynamic noise management
InactiveUS9281941B2Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageCiphertextDynamic noise
Homomorphic evaluations of functions are performed. The functions include operation(s). Variants of key switching and modulus switching are described and are performed prior to or after the operation(s). A key switching transformation converts a ciphertext with respect to a first secret key and a first modulus to a ciphertext with respect to a second secret key and a second modulus. A key switching transformation converts a first version of a ciphertext with respect to a first secret key and with some number r bits of precision to a second version of the selected ciphertext with respect to a second keys and with some other number r′ bits of precision. The ciphertexts may be operated on as polynomials represented using evaluation representation, which has benefits for multiplication and automorphism. Further, ciphertexts are associated with an estimate of noise, which is used to determine when to perform modulus switching on the ciphertexts.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP +1
Microprocessor apparatus and method for performing block cipher cryptographic functions
ActiveUS7844053B2Good techniqueEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesDigital data processing detailsBlock cipherMicroprocessor
A microprocessor apparatus is provided, for performing a cryptographic operation. The microprocessor apparatus includes an x86-compatible microprocessor that has fetch logic, a cryptography unit, and an integer unit. The fetch logic is configured to fetch an application program from memory for execution by the x86-compatible microprocessor. The application program includes an atomic instruction that directs the x86-compatible microprocessor to perform the cryptographic operation. The atomic instruction has and opcode field and a repeat prefix field. The opcode field prescribes that the device accomplish the cryptographic operation as further specified within a control word stored in a memory. The repeat prefix field is coupled to the opcode field. The repeat prefix field indicates that the cryptographic operation prescribed by the atomic instruction is to be accomplished on a plurality of blocks of input data.
Owner:IP FIRST
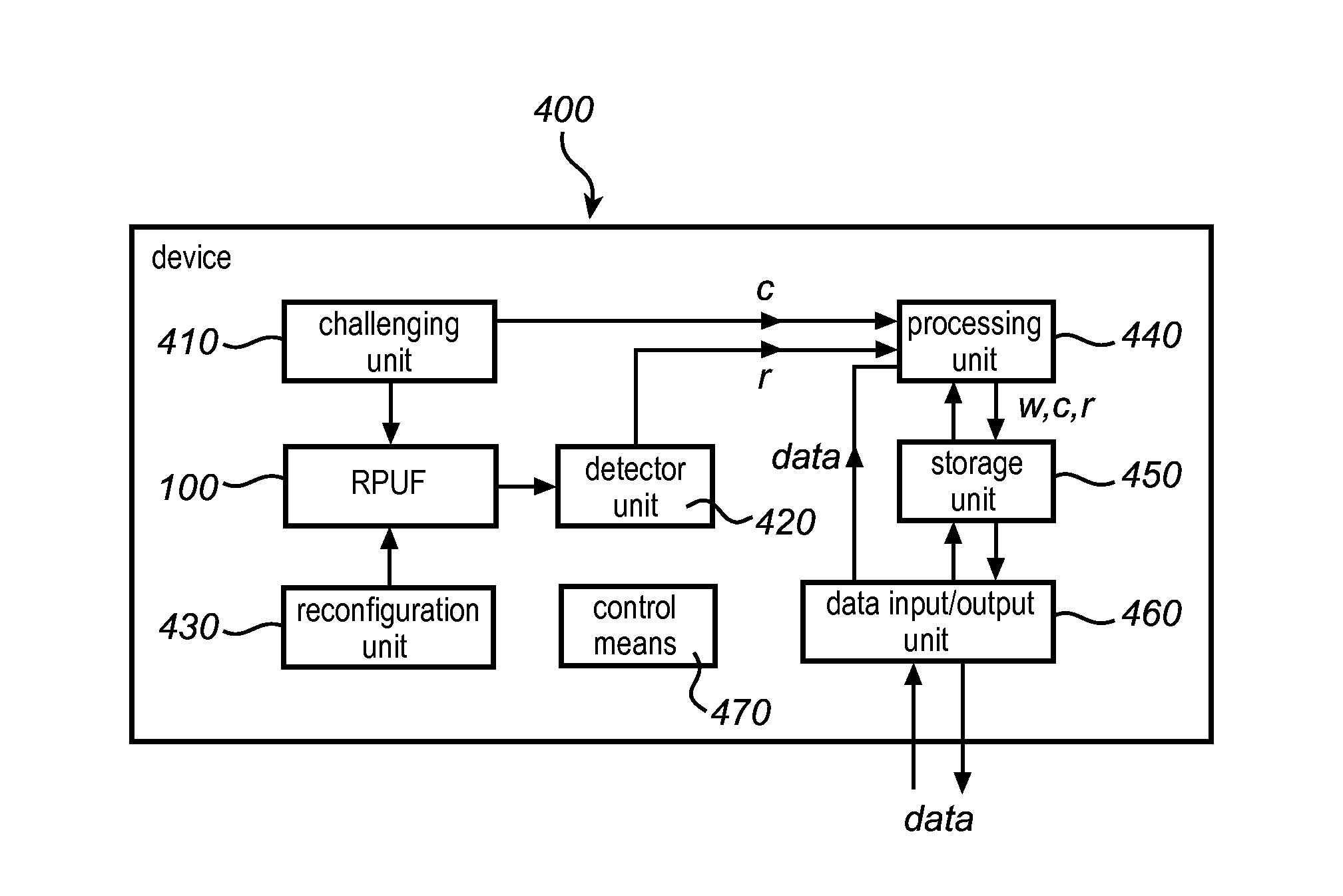
Method and device for providing digital security
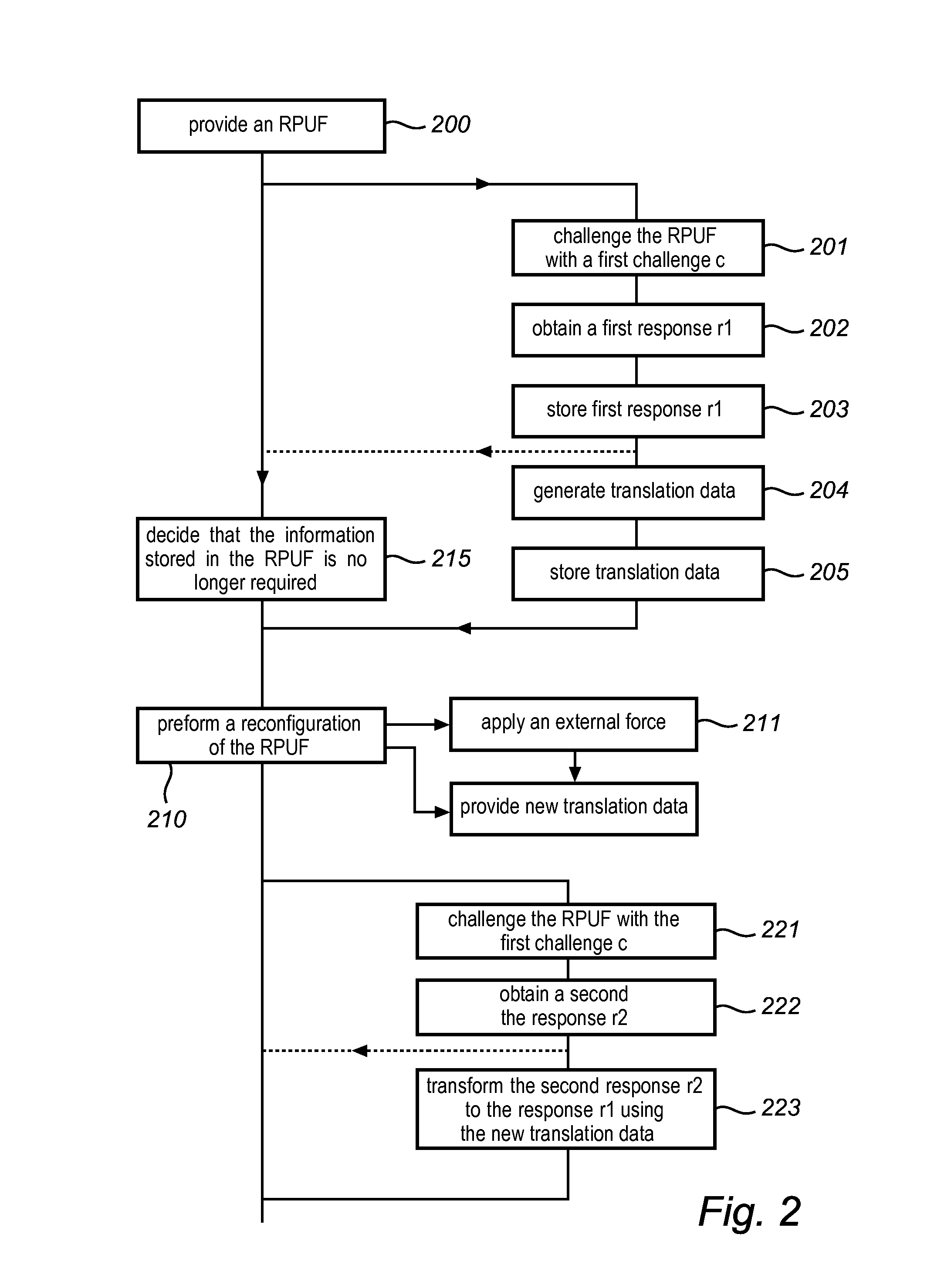
ActiveUS8446250B2Mitigate such drawbackEfficient use ofElectric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usagePhysical systemDigital security
This invention relates to a method and system for providing digital security by means of a reconfigurable physical uncloneable function, RPUF. The RPUF comprises a physical system constituted by distributed components arranged to generate a first response when receiving a first challenge at a point of the physical system. The physical reconfiguring of the RPUF comprises redistributing the components such that they generate a second response, which differs from said first response, when again applying the first challenge at the point. The reconfiguration step is further utilized in providing secure storage for digital items. The digital item is data of any kind, including data that needs to be accessed and updated, i.e. which is dynamic in nature. The method is exemplified by implementations such as secure storage of a key, a secure counter and a seed generator.
Owner:INTRINSIC ID
Data Encryption and Input System
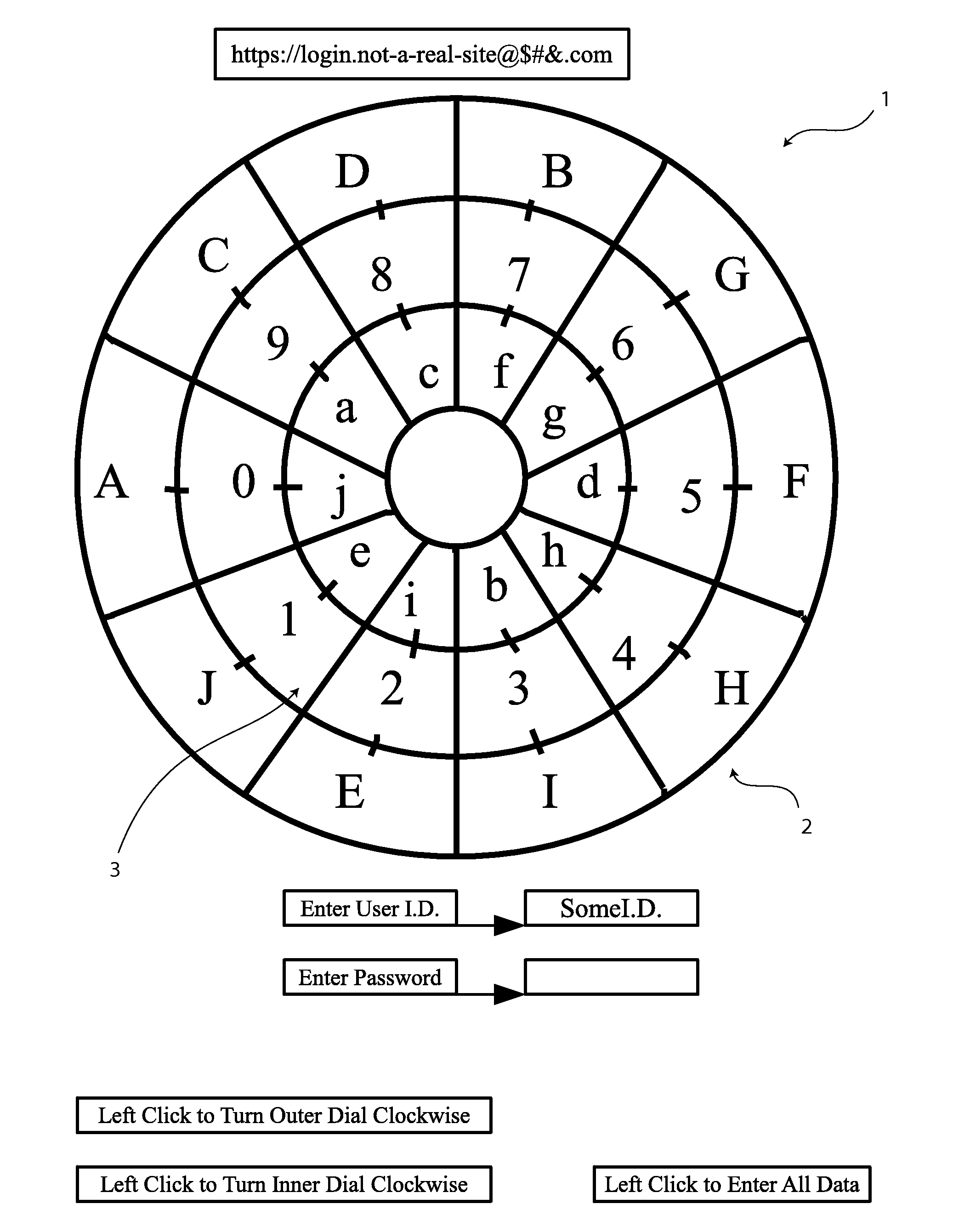
InactiveUS20120082306A1Easily be configured into gameReduce the possibilityAcutation objectsUser identity/authority verificationDigital dataData value
A method of encrypting and inputting data by creating a relationship between a predetermined indicator key and the data to be passed on is presented. In the preferred embodiment, one or more data encryption dials are presented, each with a compartmentalized ring containing numerical data values. At least one compartmentalized ring containing indicator keys is also positioned on the encryption dial which can be rotated into apposition with the numerical data values. When data values are entered, the interface uses the data value that is in apposition with the predetermined indicator key as the data value to be passed on to a data receiving system. Upon submission of the first data value, the positions of the indicator keys and numerical data values change randomly before allowing the user to use the encryption dials to submit the second data value.
Owner:HULSE ANDREW WILLIAM
Information Processing System And Information Processing Method For Use Therewith, Information Processing Apparatus And Information Processing Method For Use Therewith, And Program
InactiveUS20070223697A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionMultiple keys/algorithms usageInformation processingImage resolution
The present invention relates to an information processing system and a method for use therewith, an information processing apparatus and a method for use therewith, and a program which are capable of decrypting desired portions of encrypted data. Of packets 211 through 216 constituting a bit stream of layered-encoded image data 201 according to JPEG 2000, the packets 211 through 213 are each encrypted independently of the packets 214 through 216 which are also encrypted each. This produces encrypted split data 262 with the resolution at level zero (corresponding to R0) and encrypted split data 263 with the resolution at level one (corresponding to R1). The header (ranging from SOC to SOD) of layered-encoded image data 201 is appropriated for a header 261, followed by encrypted split data 262 and 263 and an EOC 264, in that order, the whole data array constituting data 251 that is output as the definitive encrypted data. This invention is particularly applicable to image delivery apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
Encryption of security-sensitive data by re-using a connection
InactiveUS20110055563A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationData sourceSecurity properties
Techniques are provided for processing data. Connections having different security properties are stored, wherein each of the connections allows applications at the client computer to access data sources at a server computer. A request is received from an application to access a data source, wherein the request has associated security properties. In response to the client computer requesting establishment of a connection on behalf of the application, it is determined whether there is a stored connection that used a same set of security properties as are associated with the request from the application and that connected to the data source that the application requests access to. In response to determining that there is a stored connection that used the same set of security properties and that connected to the data source, the connection and an associated client encryption seed, client encryption token, server encryption seed, and server encryption token are re-used. In response to determining that there is not a connection that used the same set of security properties and that connected to the data source, a new client connection key, client encryption seed, client encryption token, sever connection key, server encryption seed, and server encryption token are generated.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for distributing key
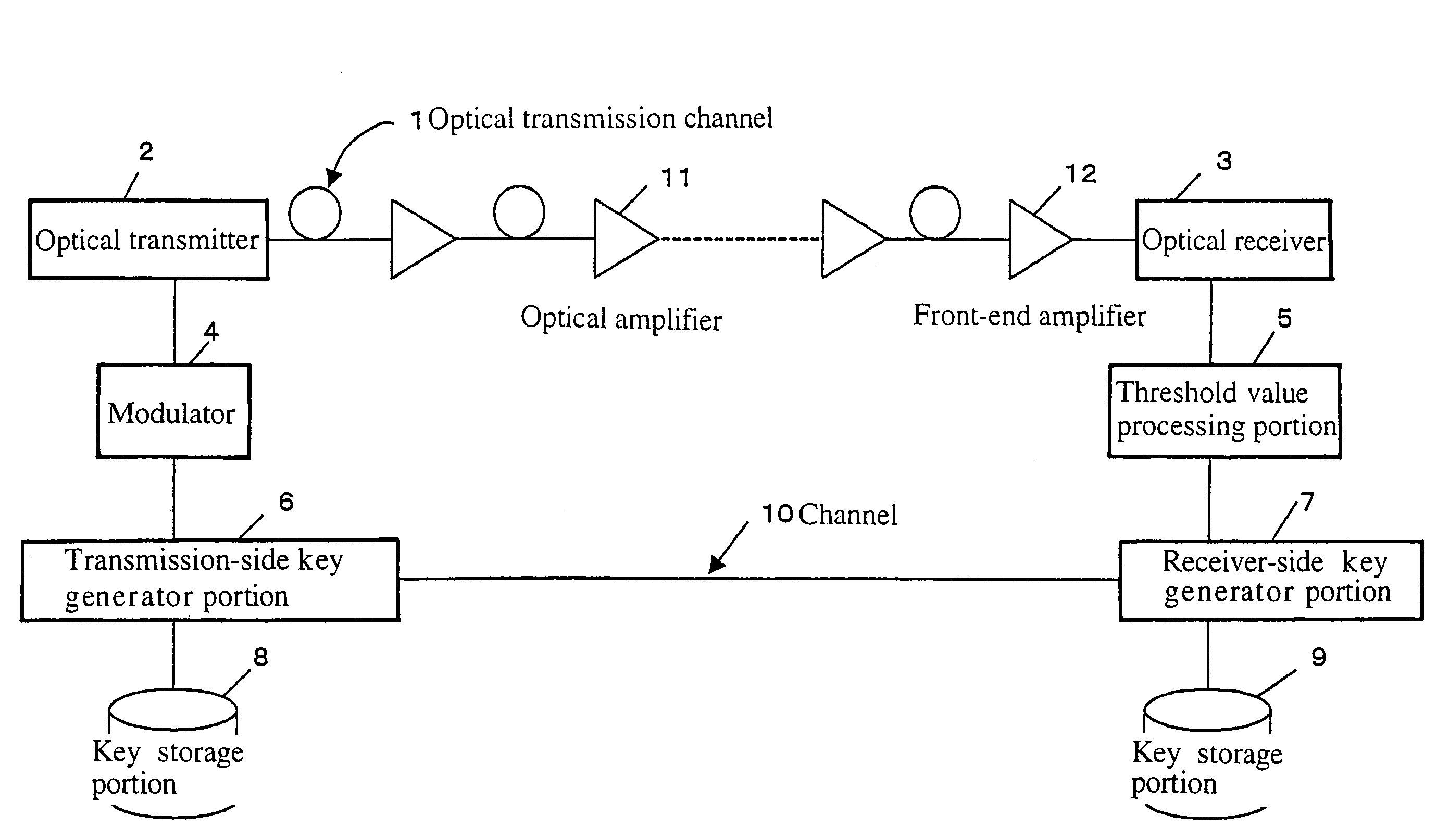
ActiveUS7245722B2Effective attenuationLong to transmitKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesSecurity MeasureEavesdropping
A method and system for distributing a key is provided which make use of effects of noise caused at the time of transmitting or receiving a signal to send a key. A transmission signal is amplified at a plurality of stages while the relationship between the transmission signal and noise is being maintained at a level enough to satisfy predetermined criteria for security measures against eavesdropping activities, and the key is sent over a long distance. The aforementioned operation makes it possible to transmit or distribute a key over a long distance while maintaining the relationship between the transmission signal and noise at a level enough to satisfy the criteria for security measures against eavesdropping activities.
Owner:HIROTA OSAMU +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com