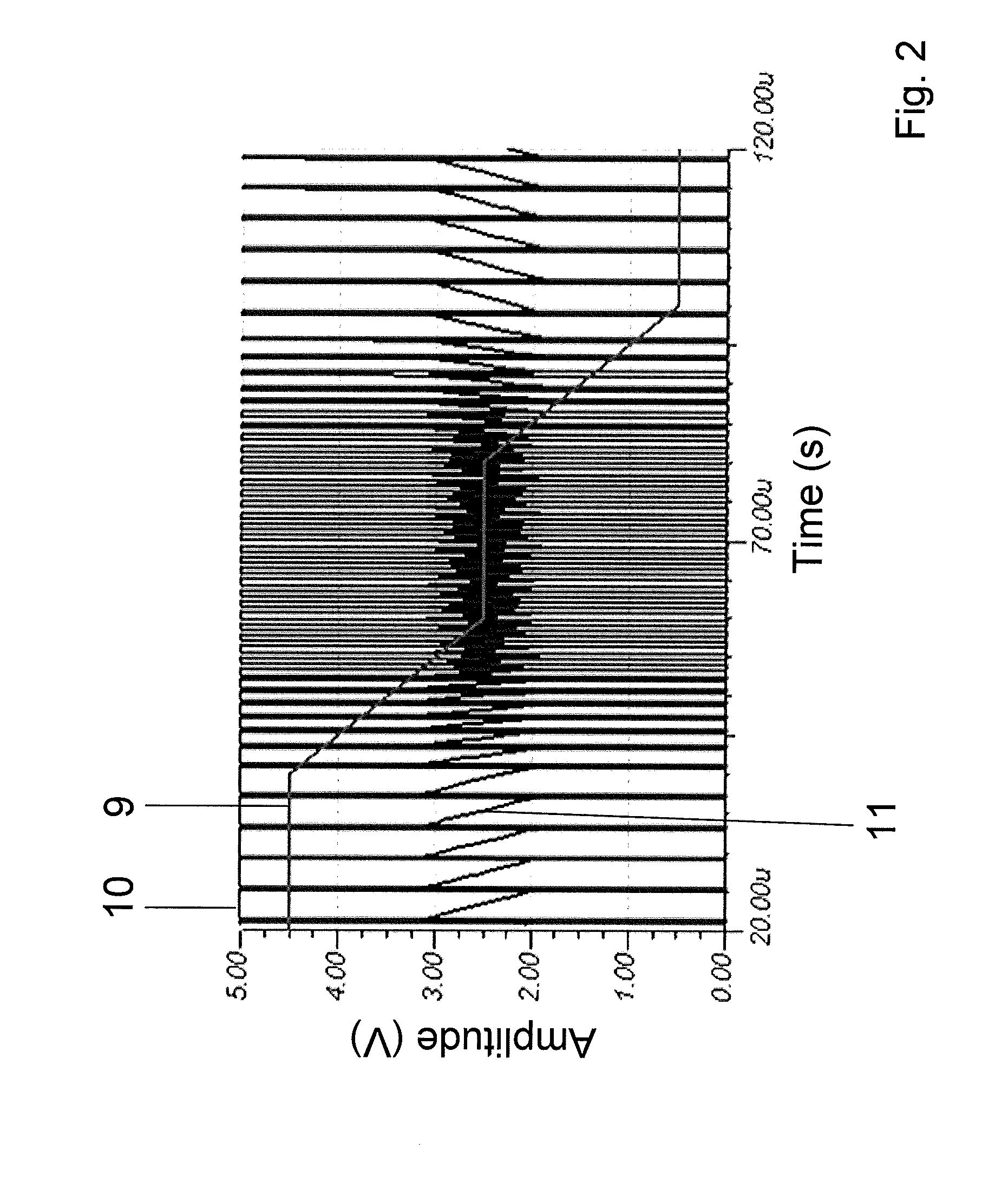
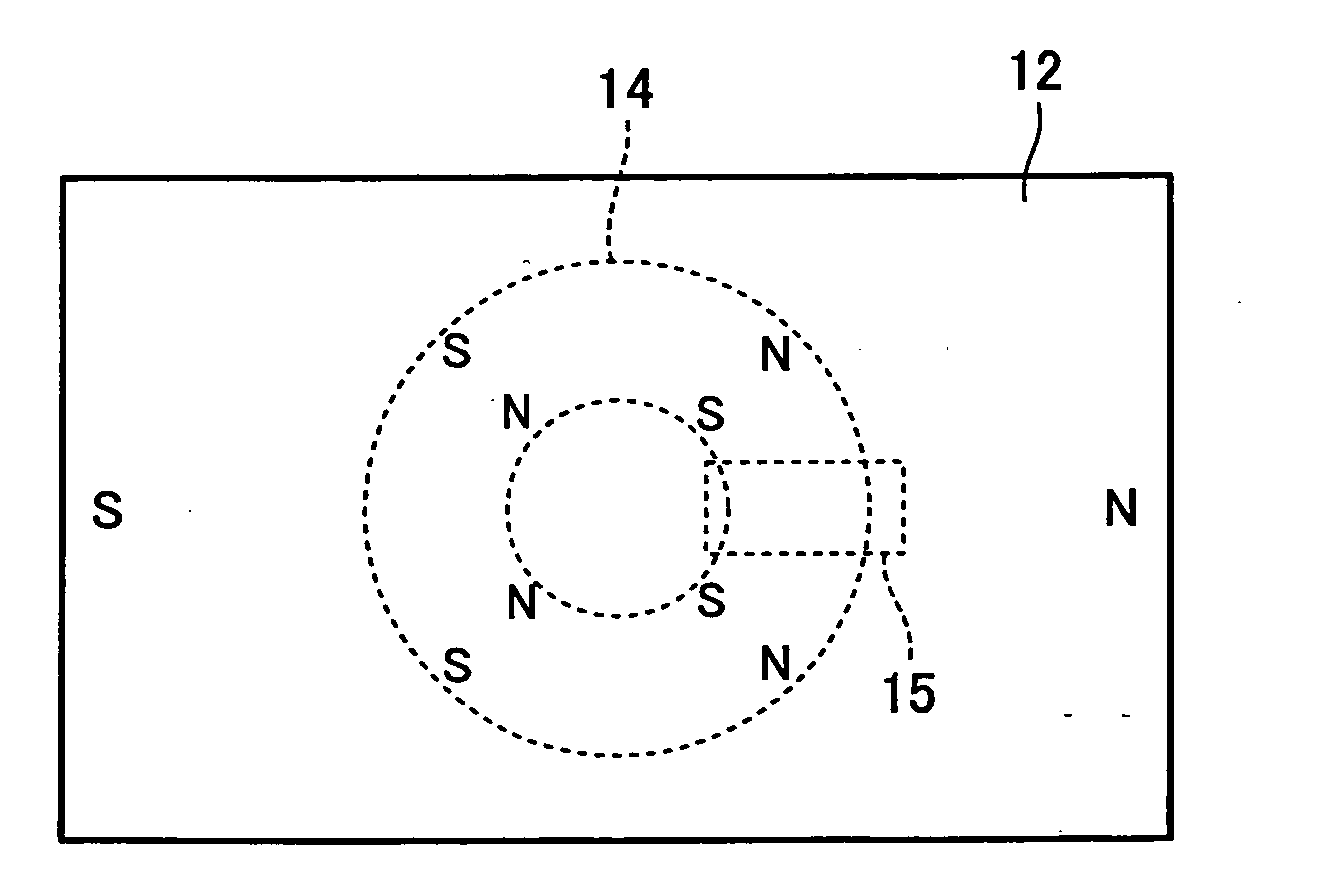
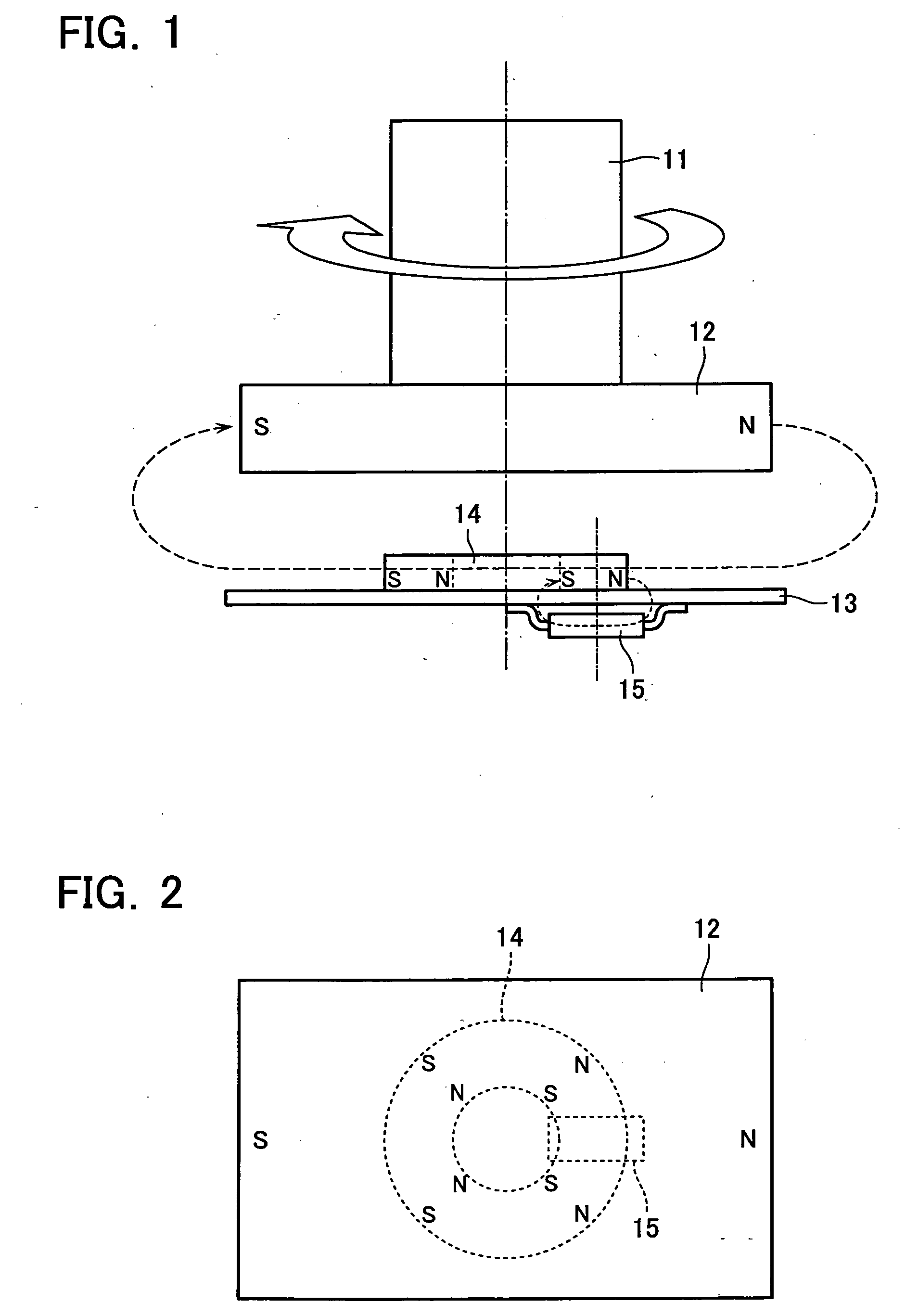
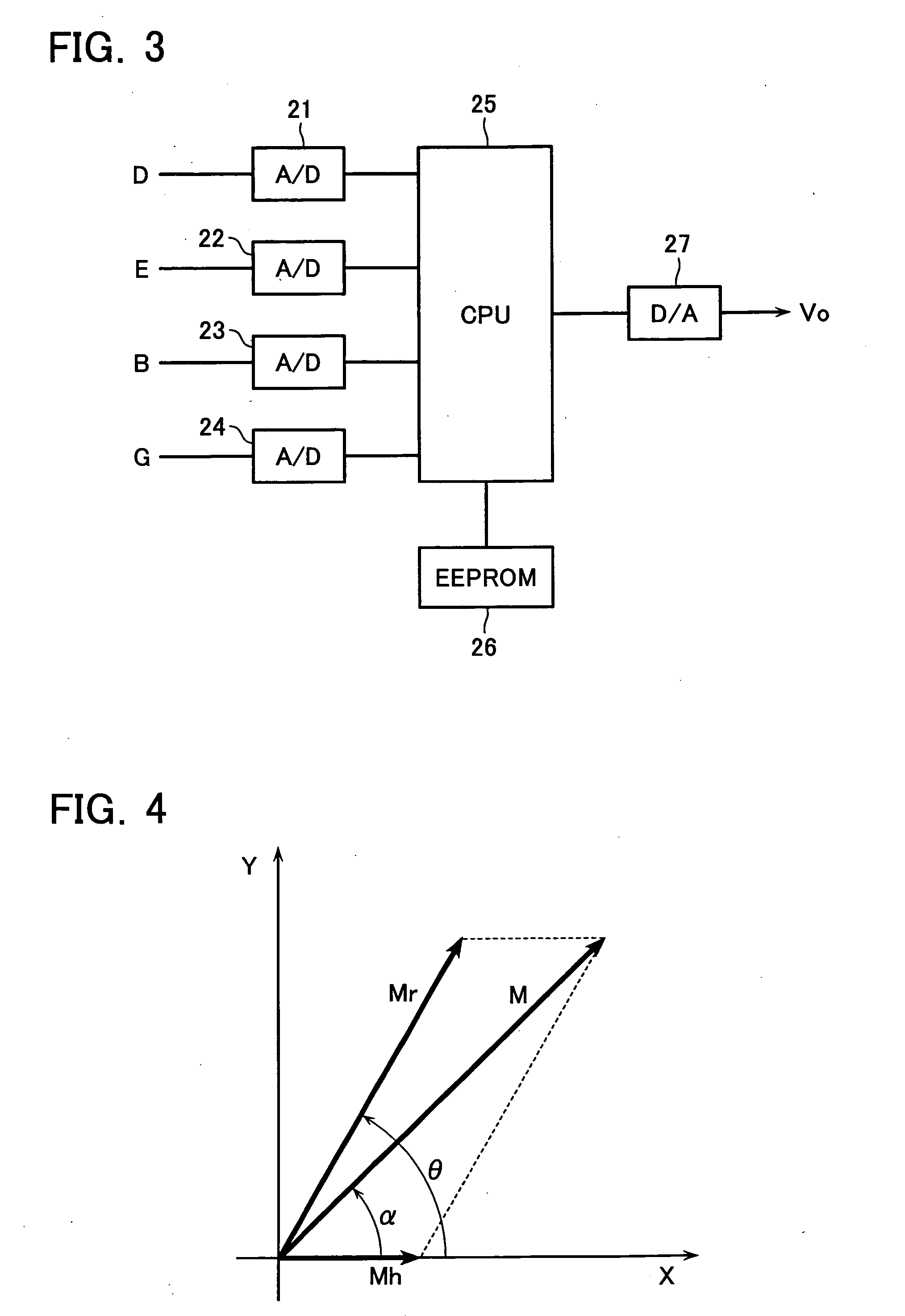
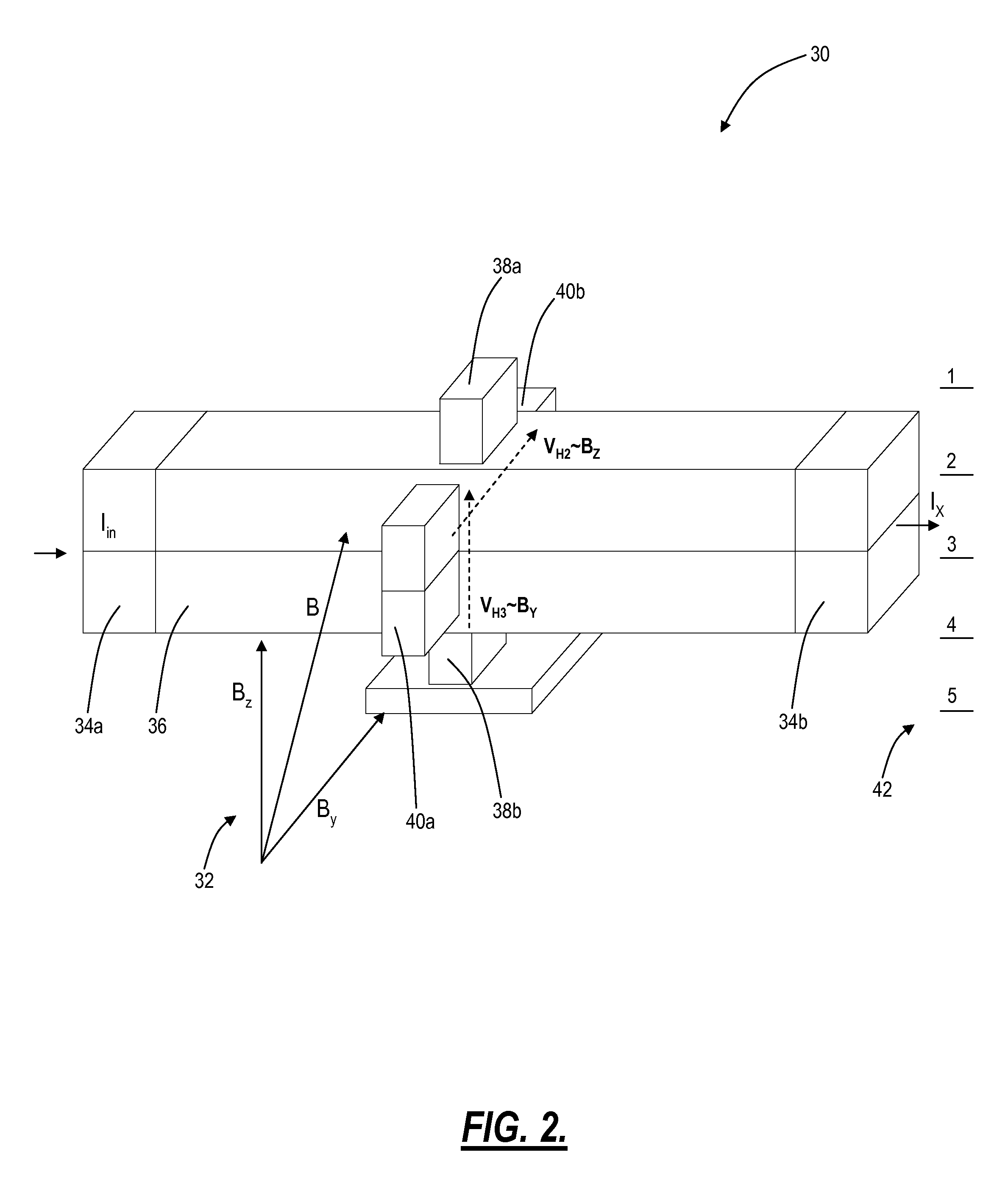Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
393results about "Magnetic sensor geometrical arrangements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
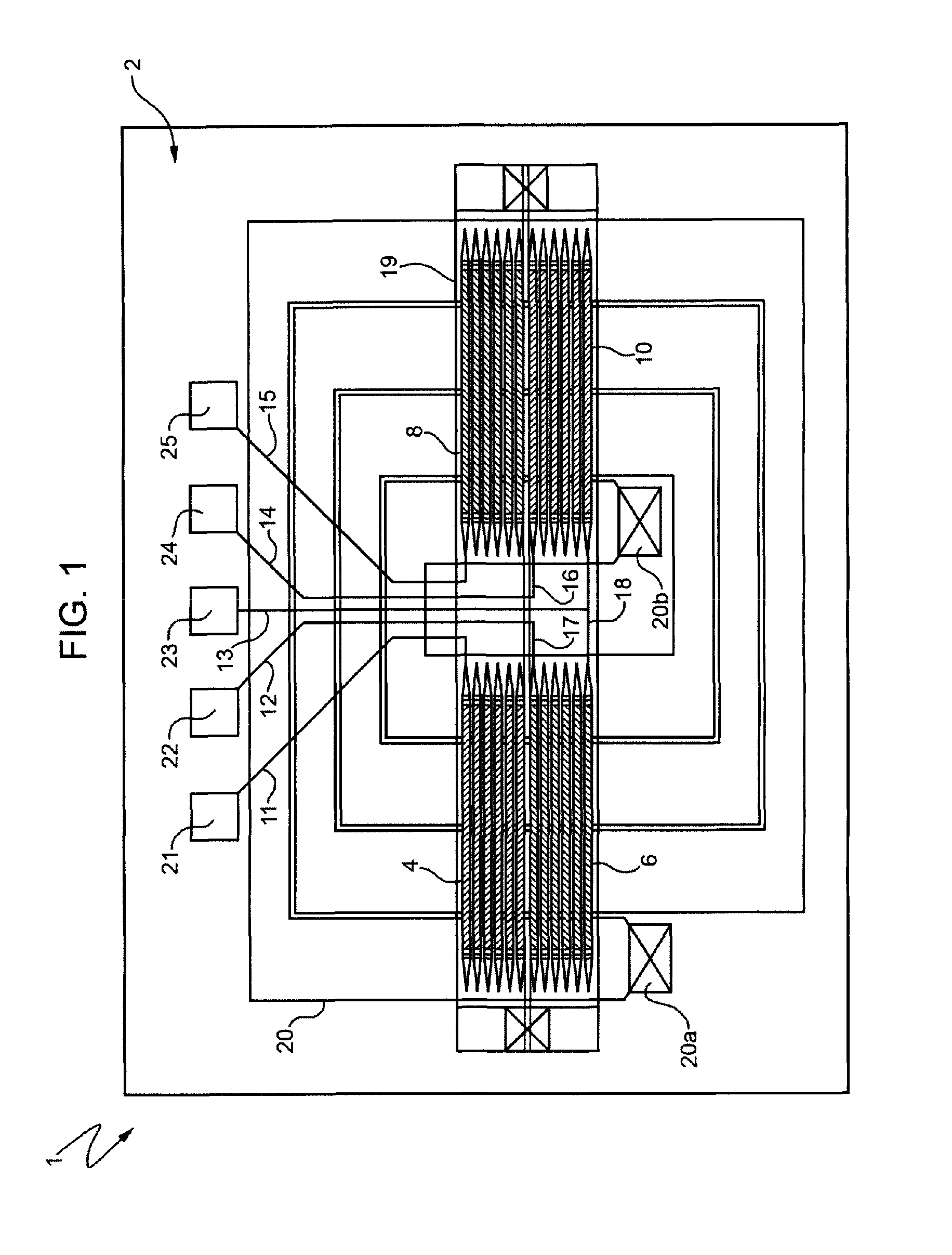
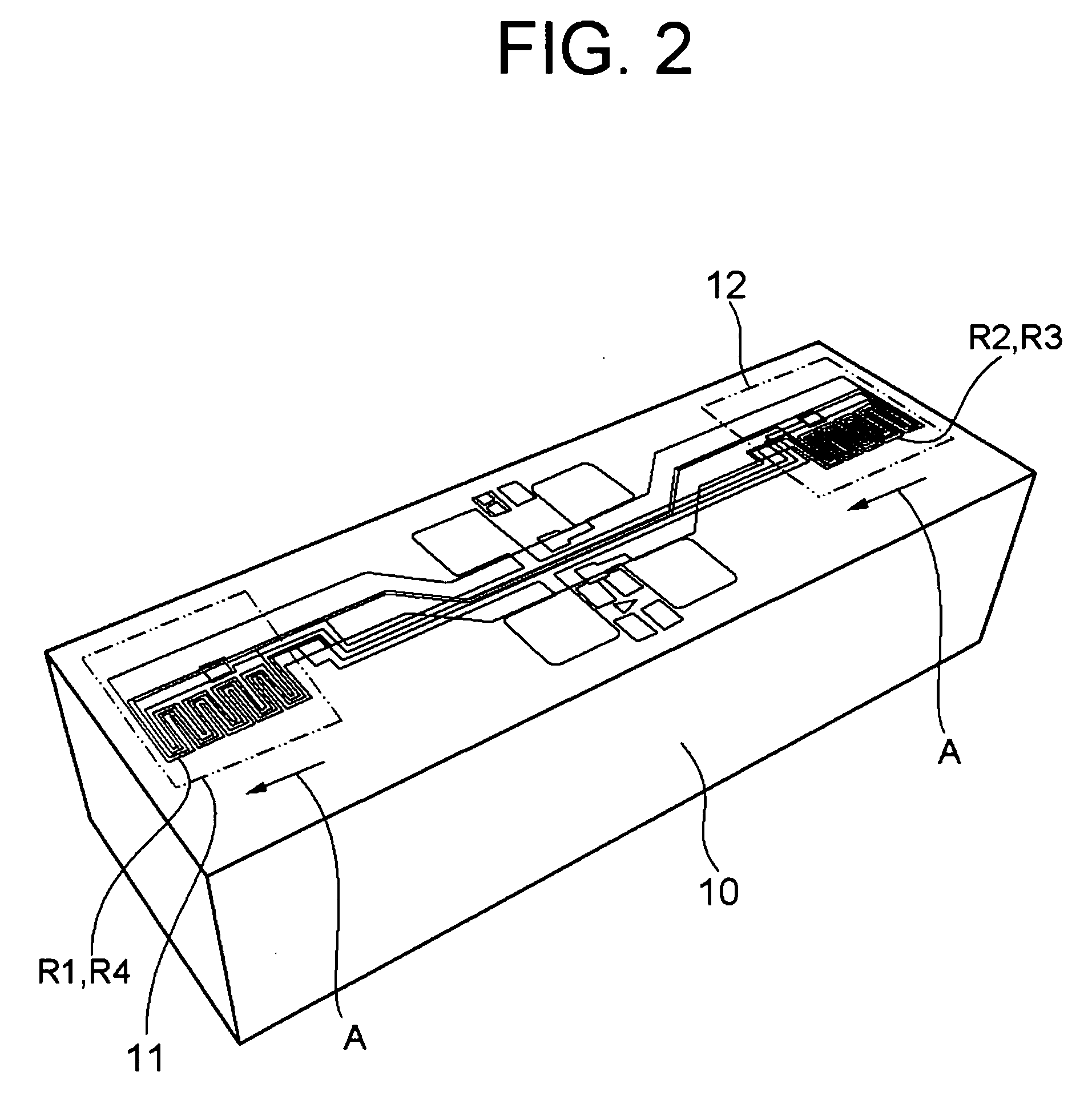
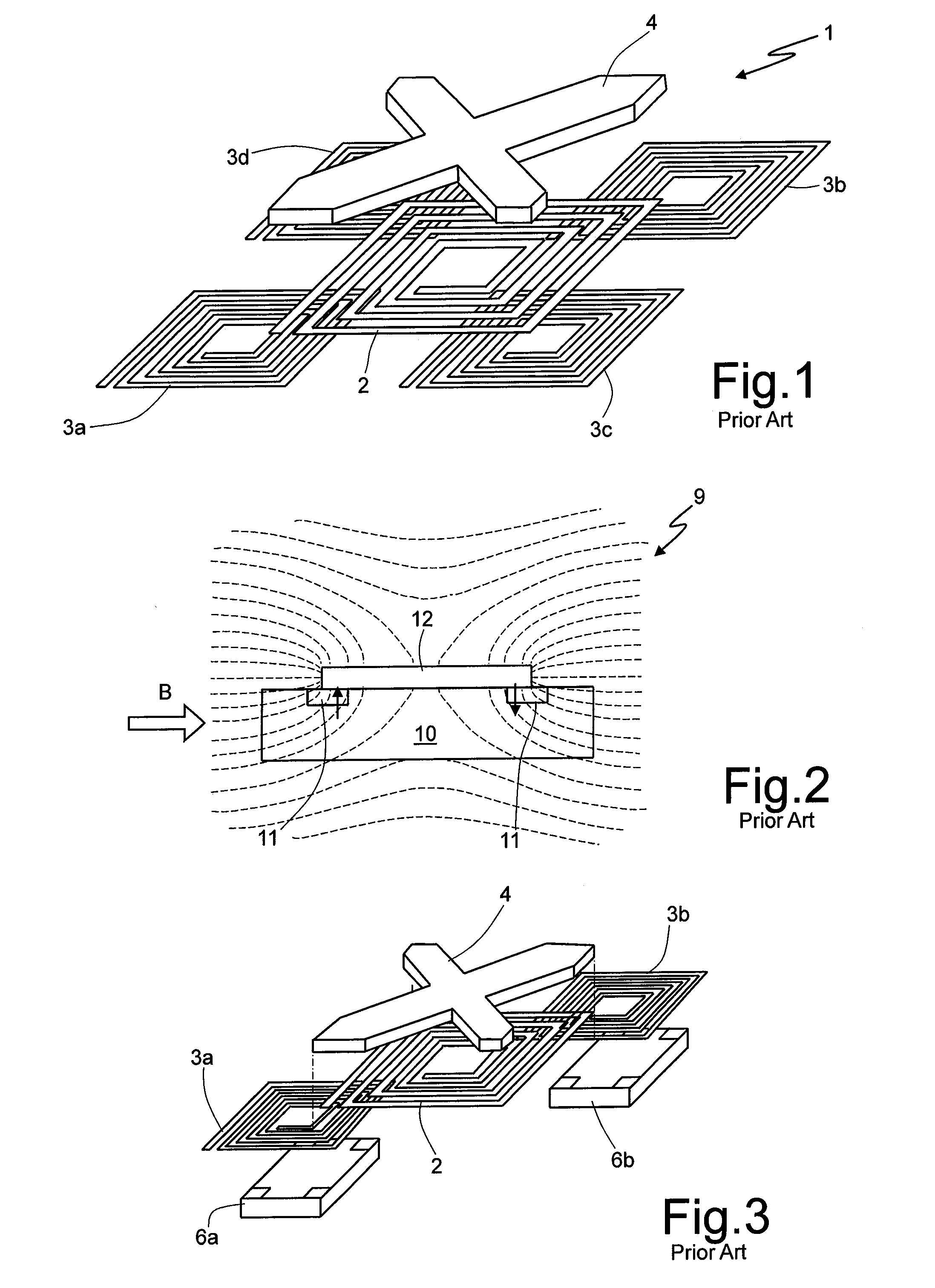
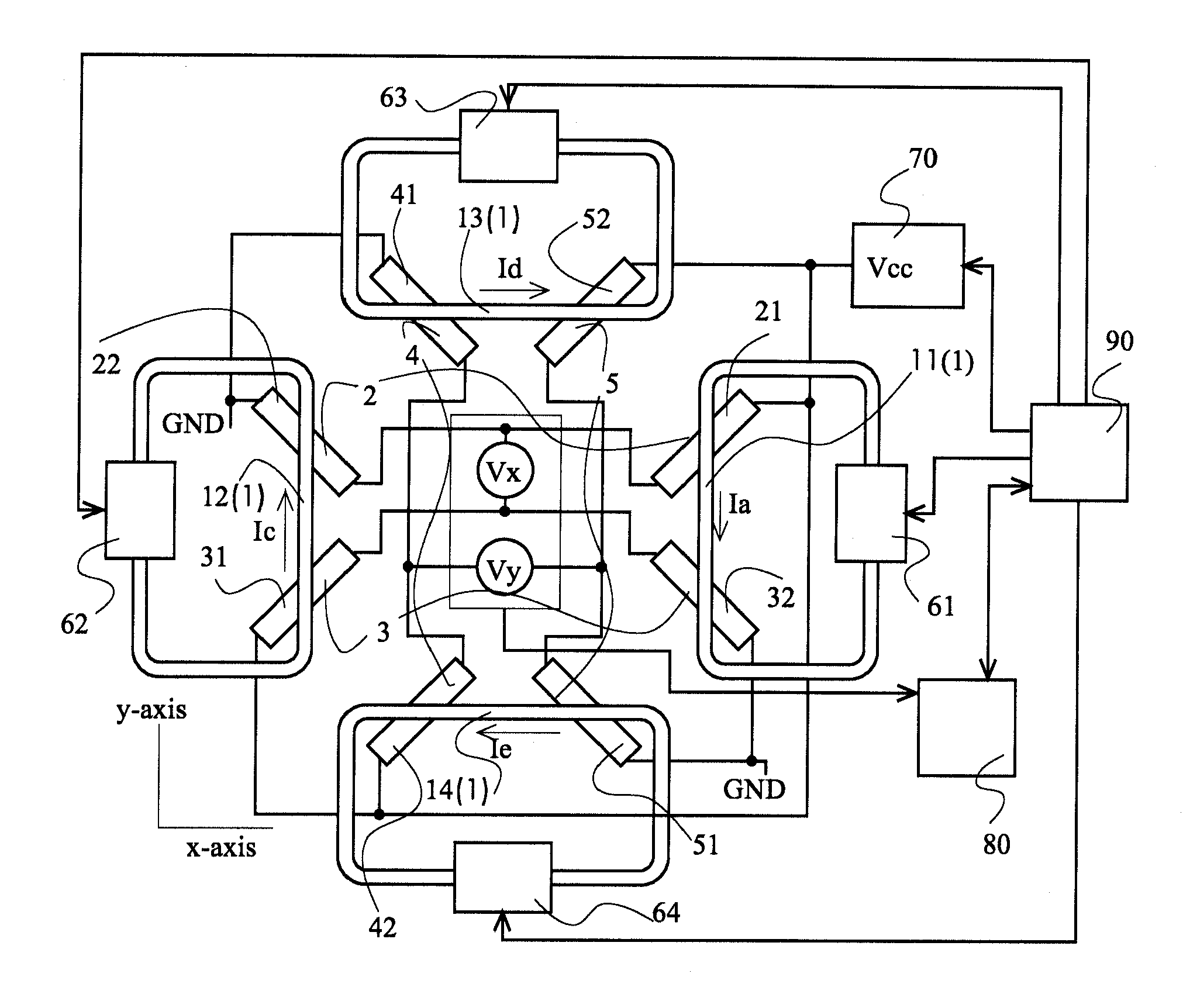
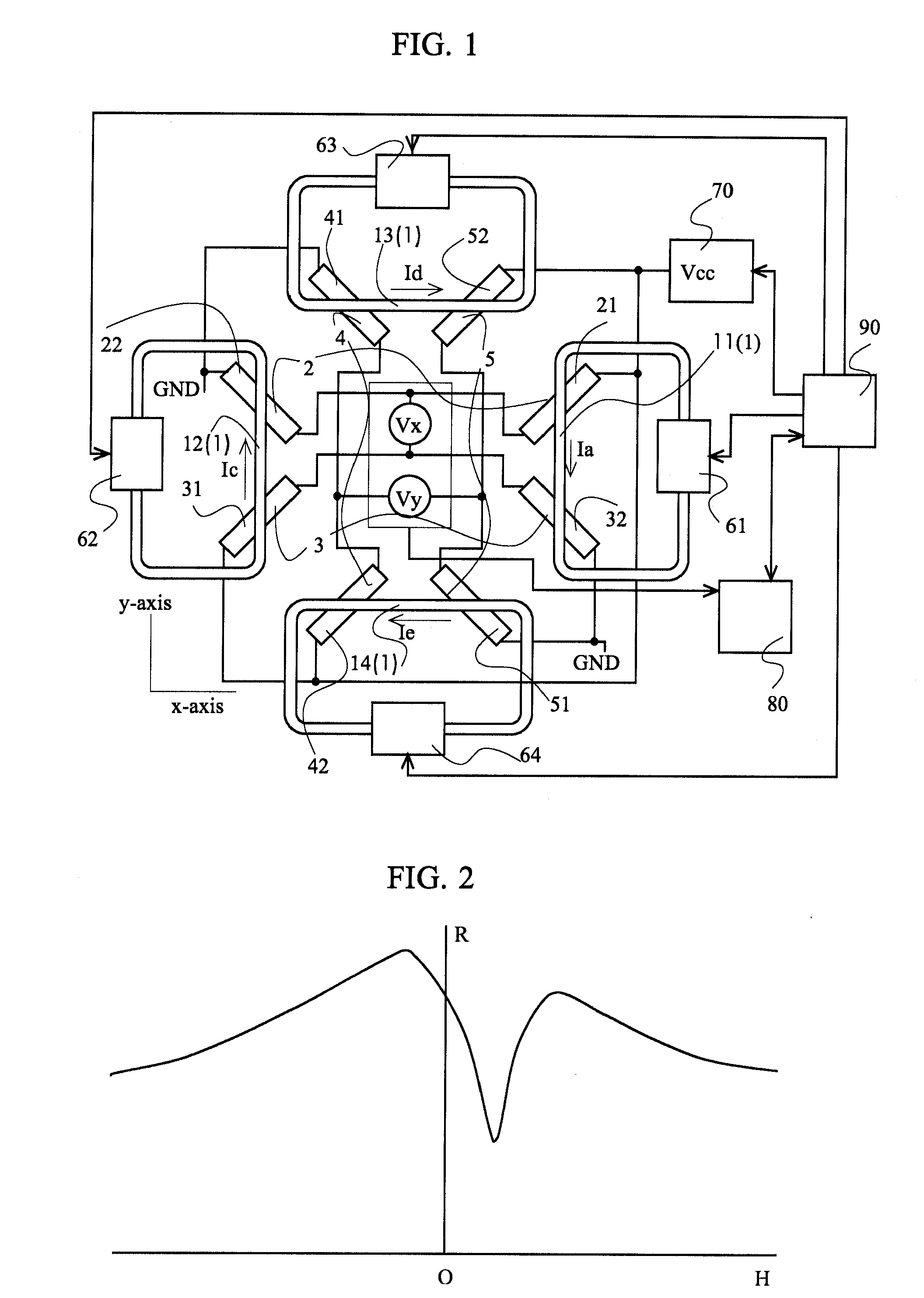
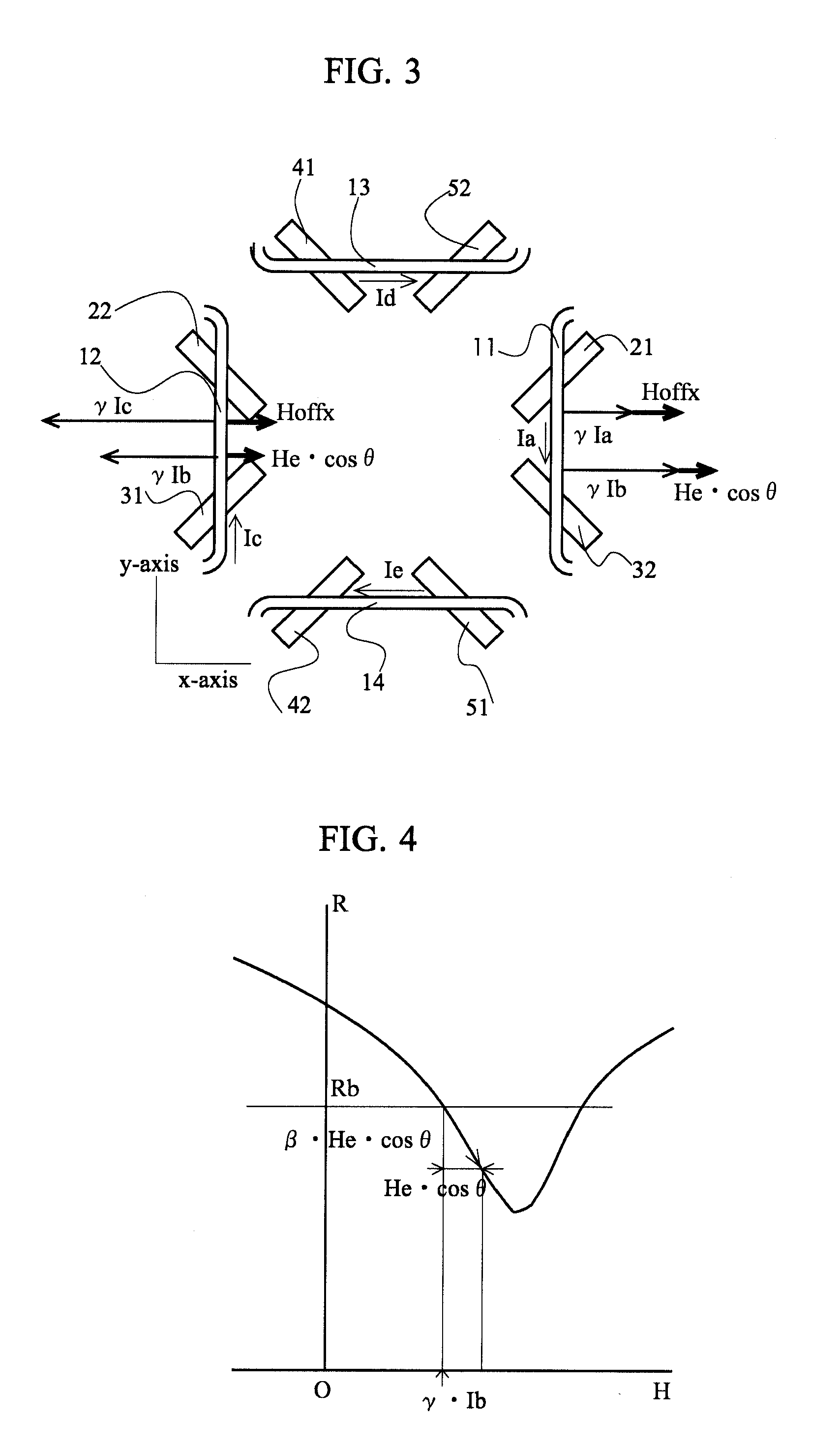
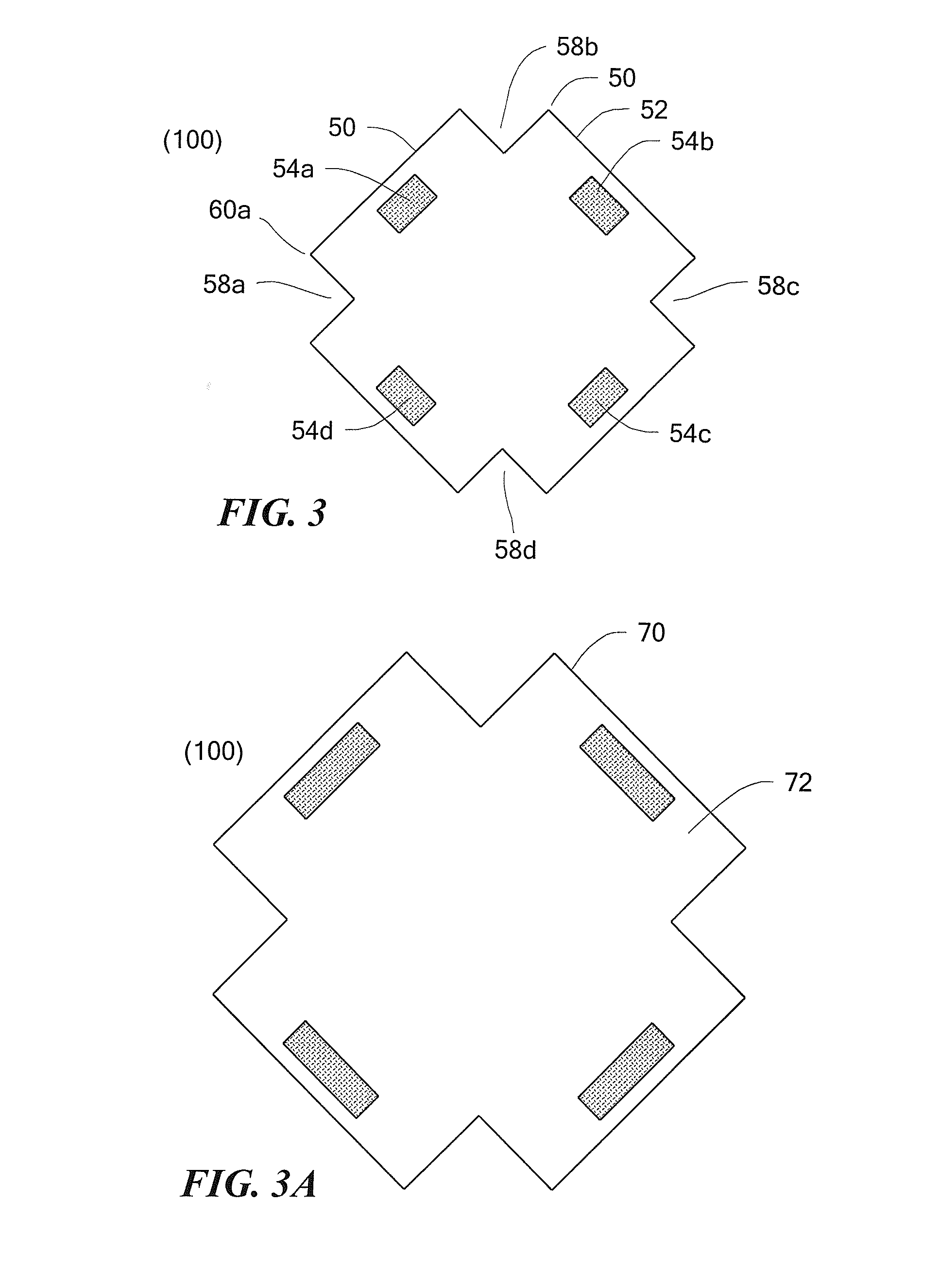
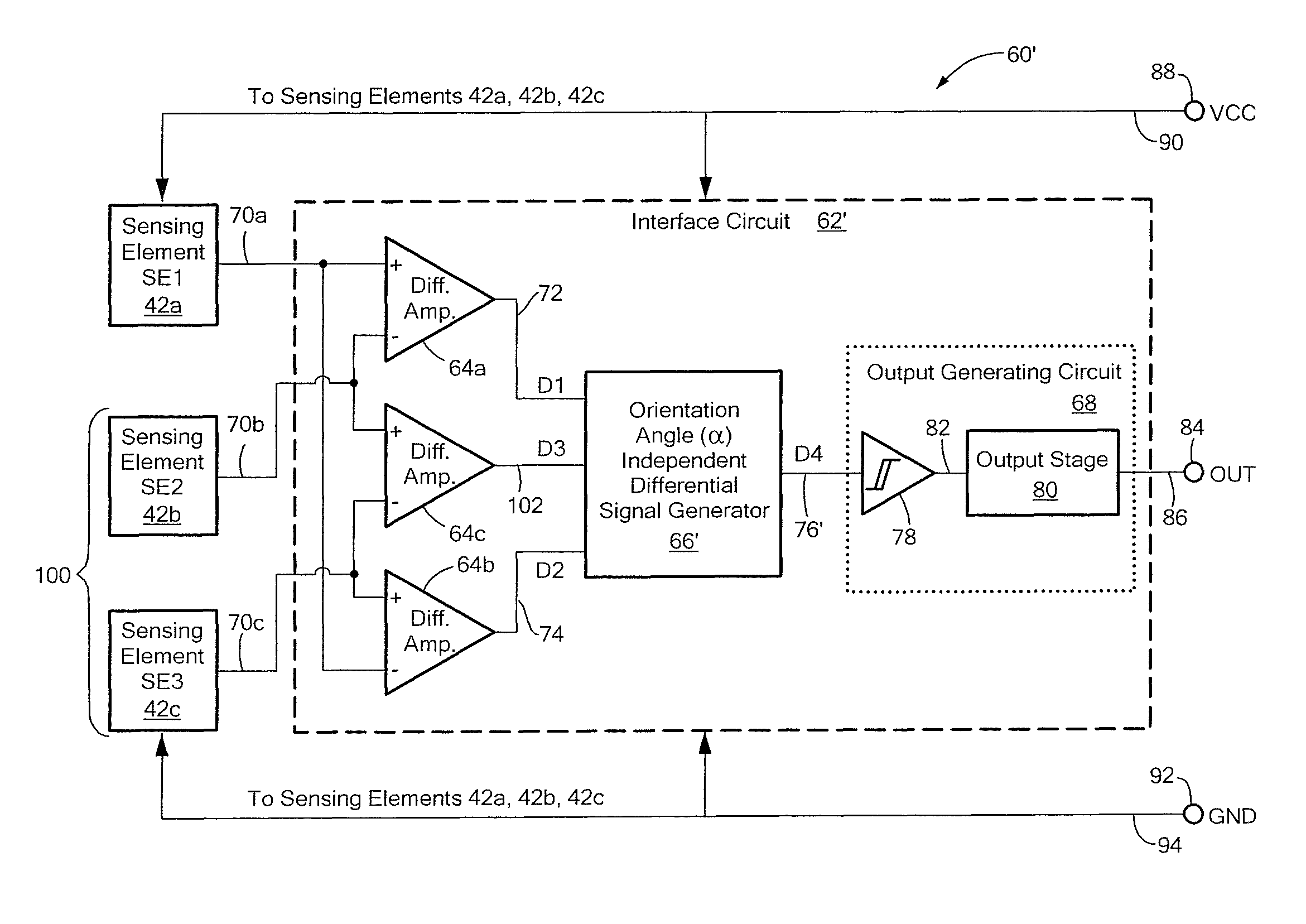
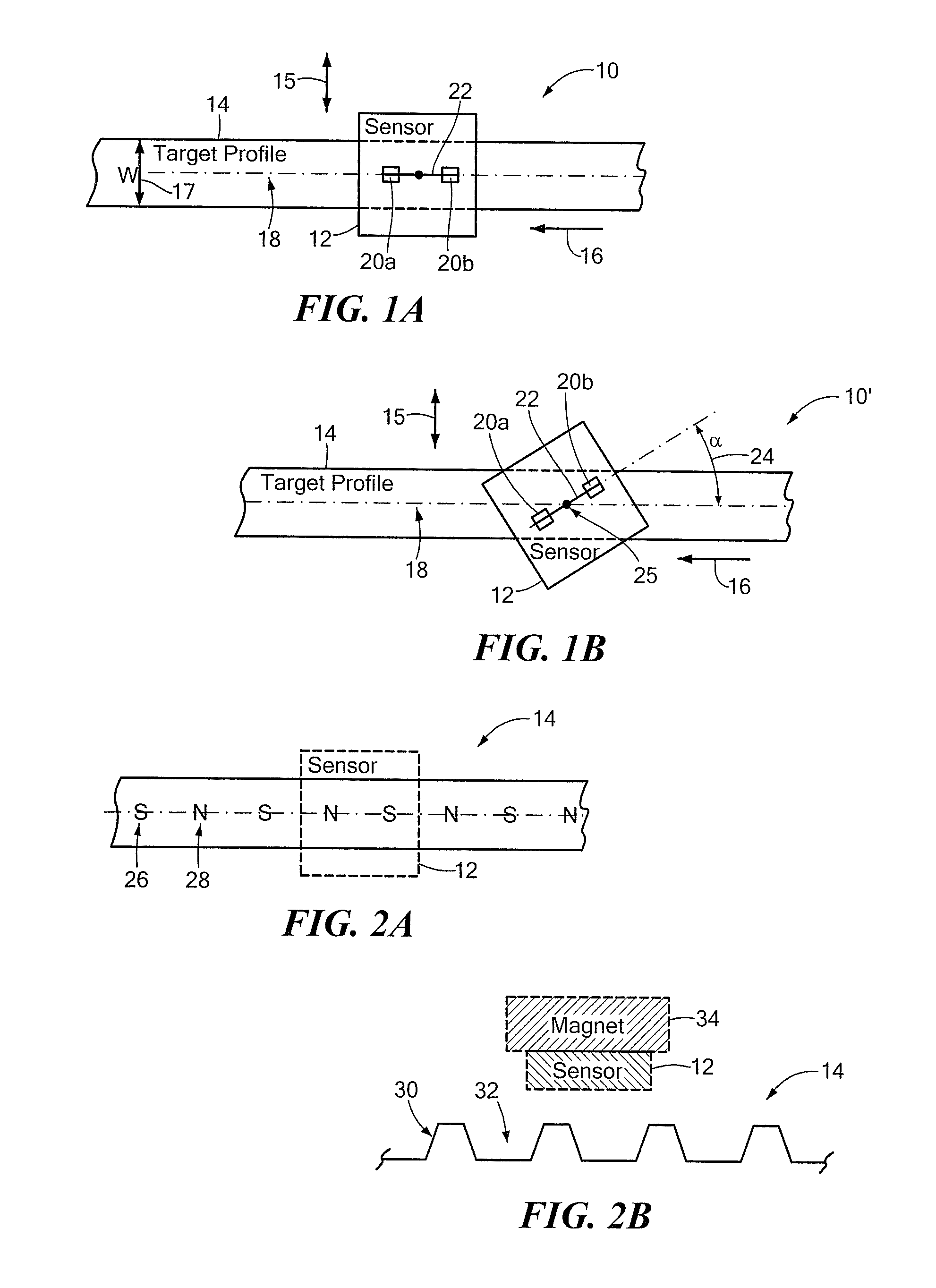
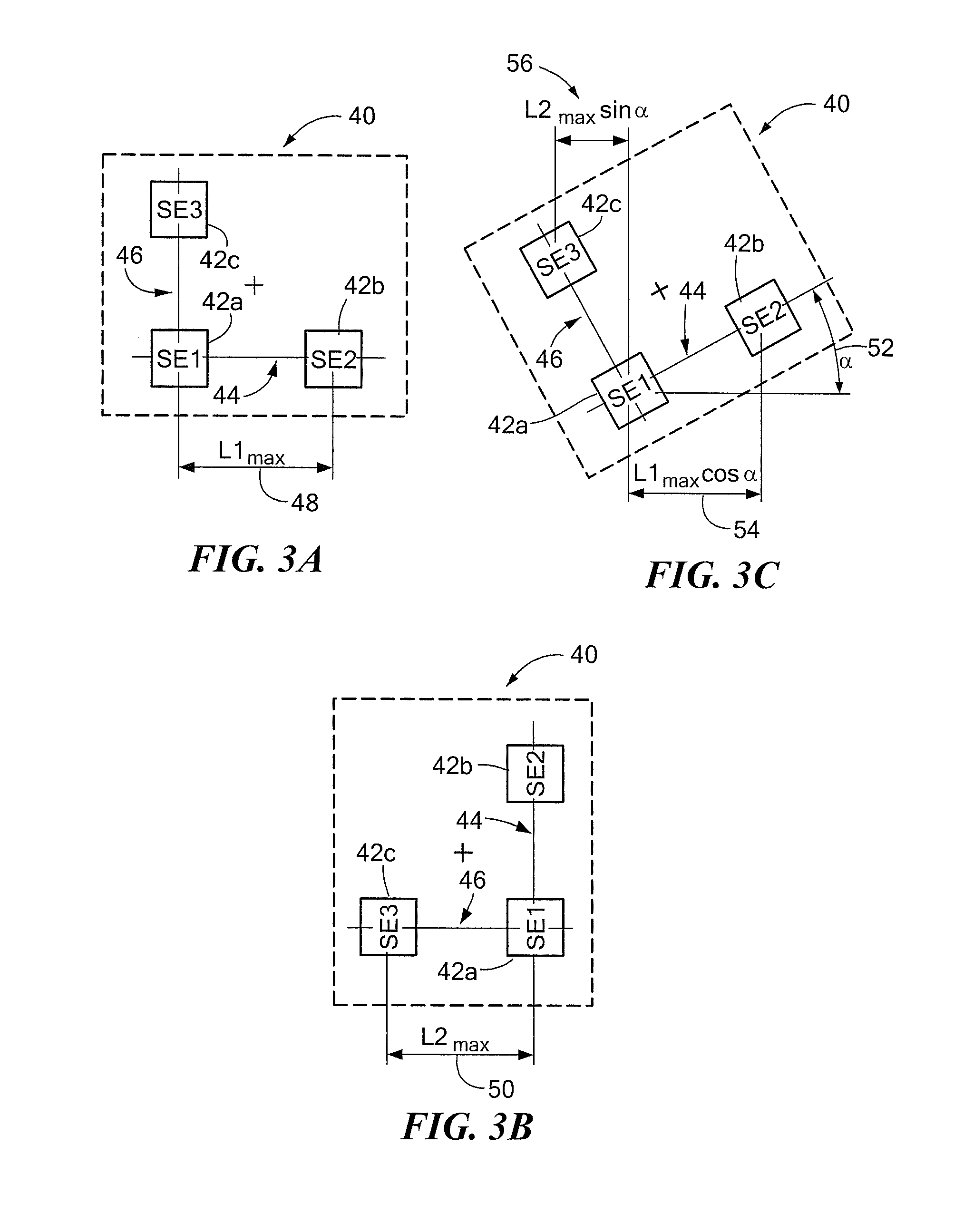
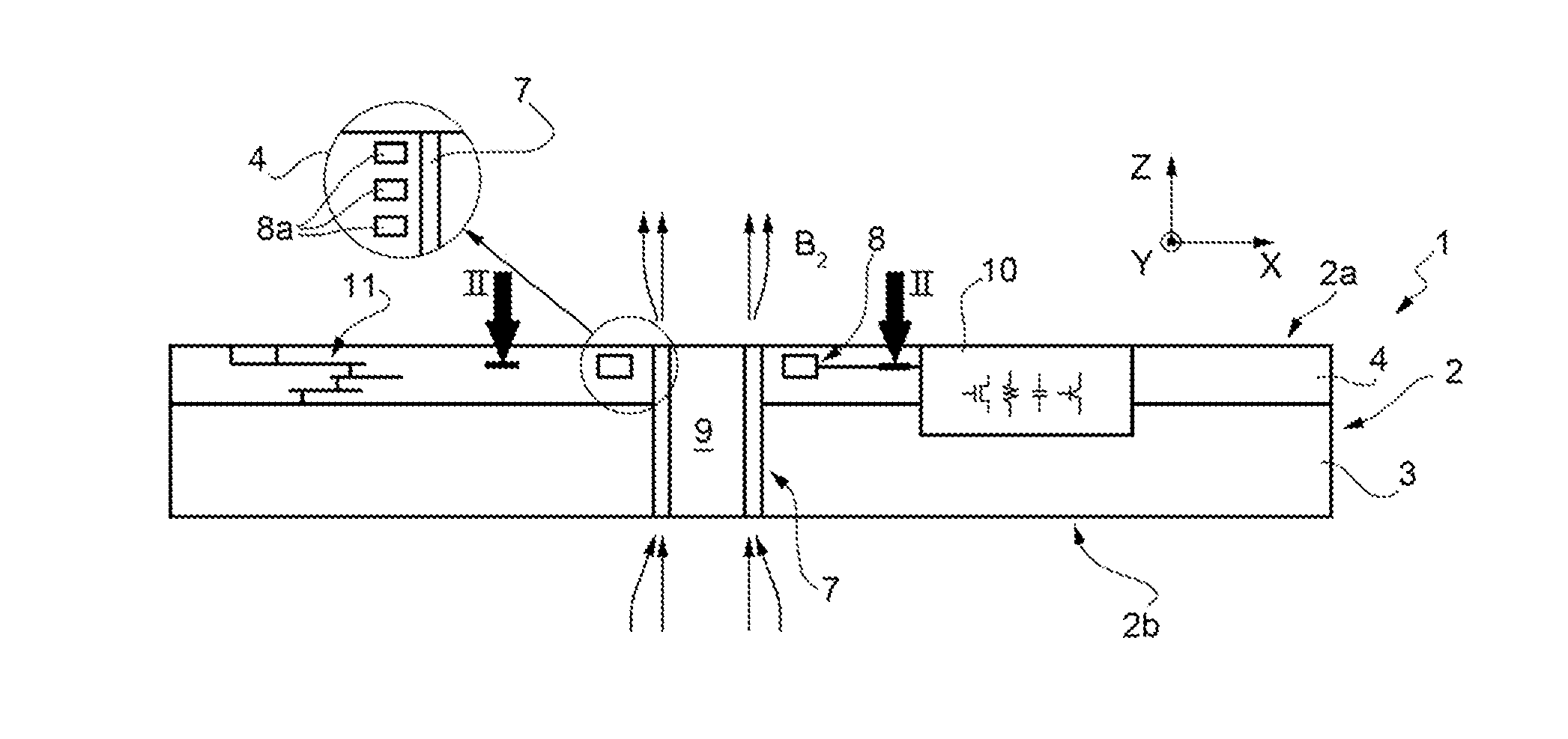
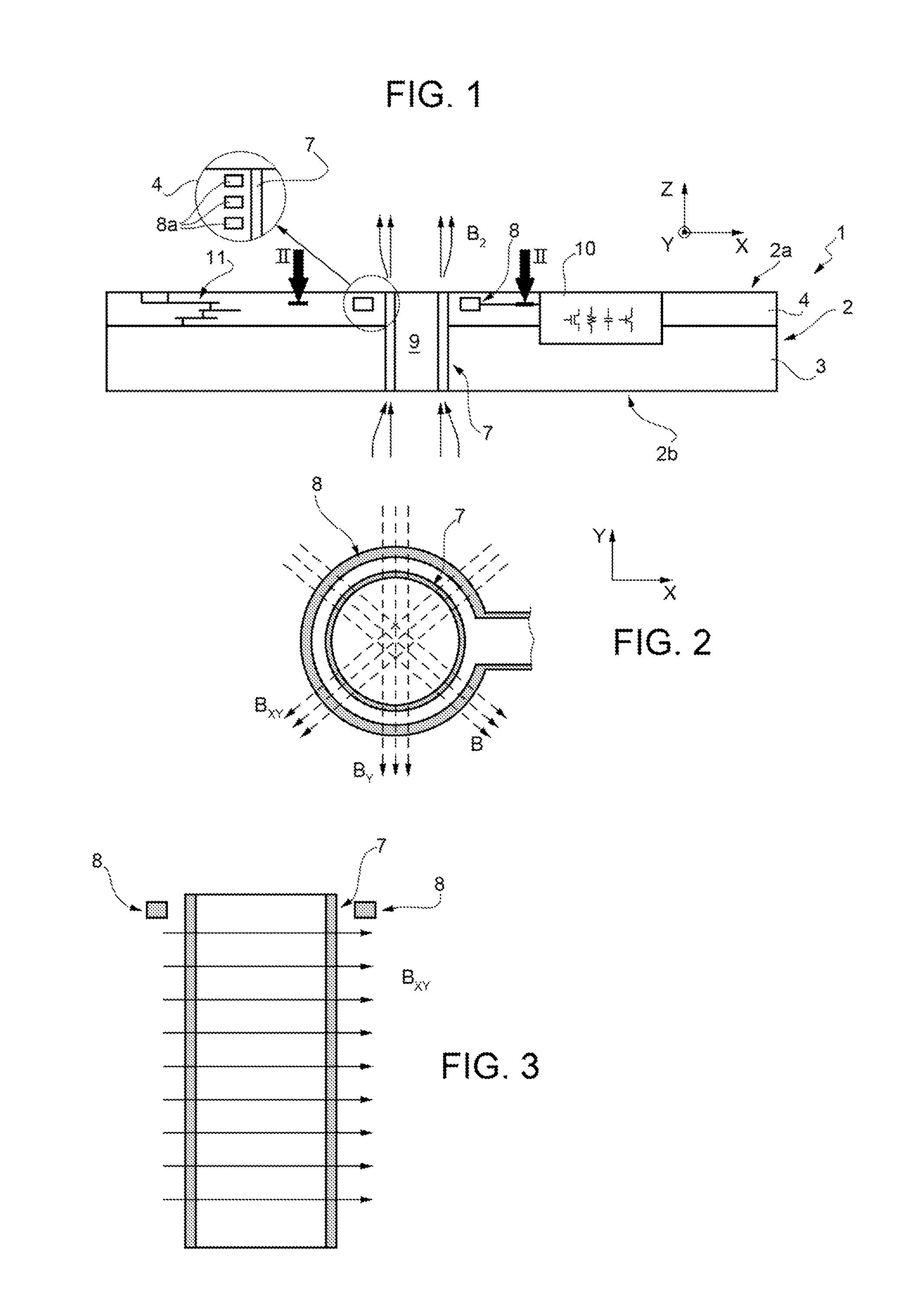
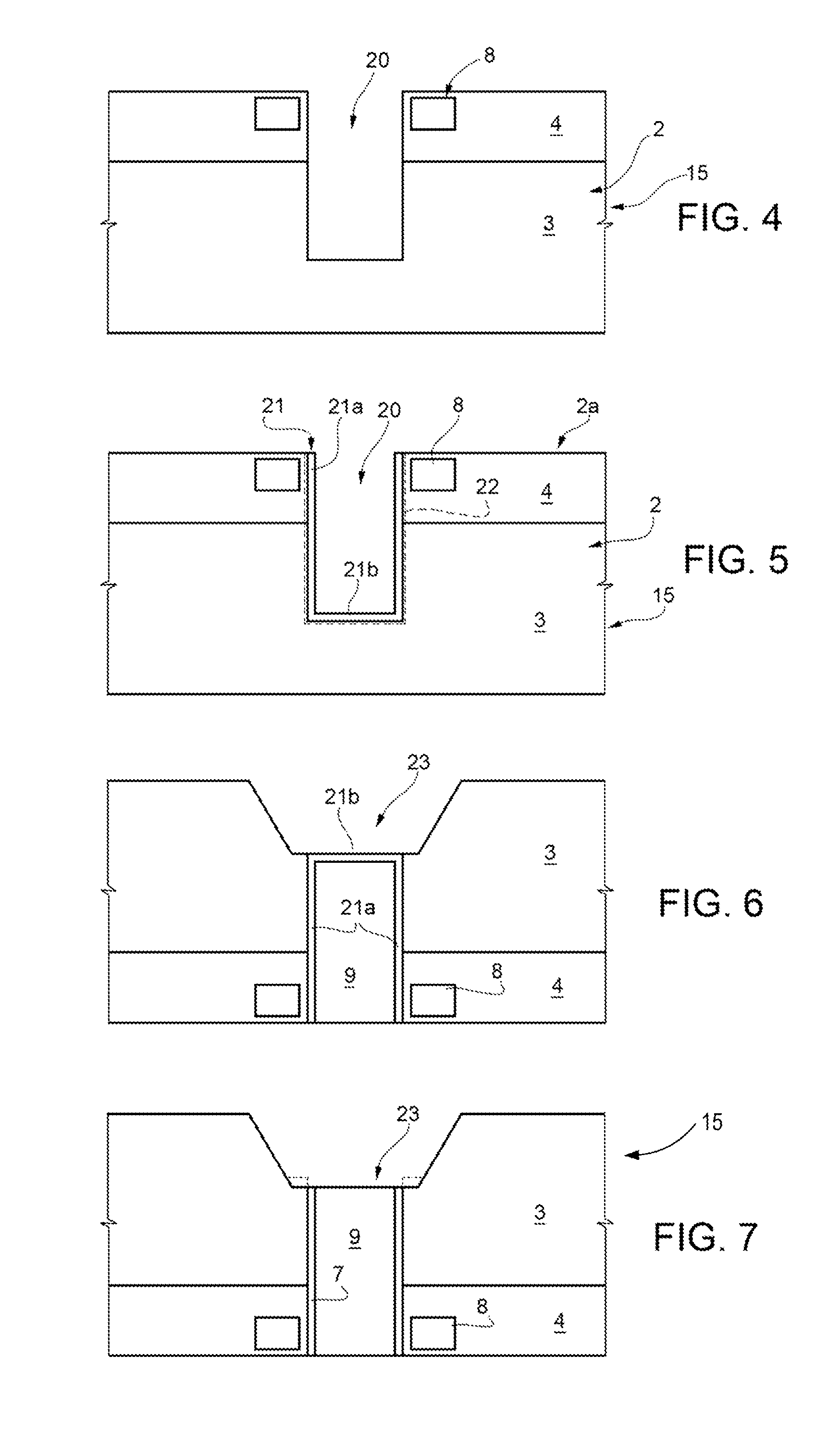
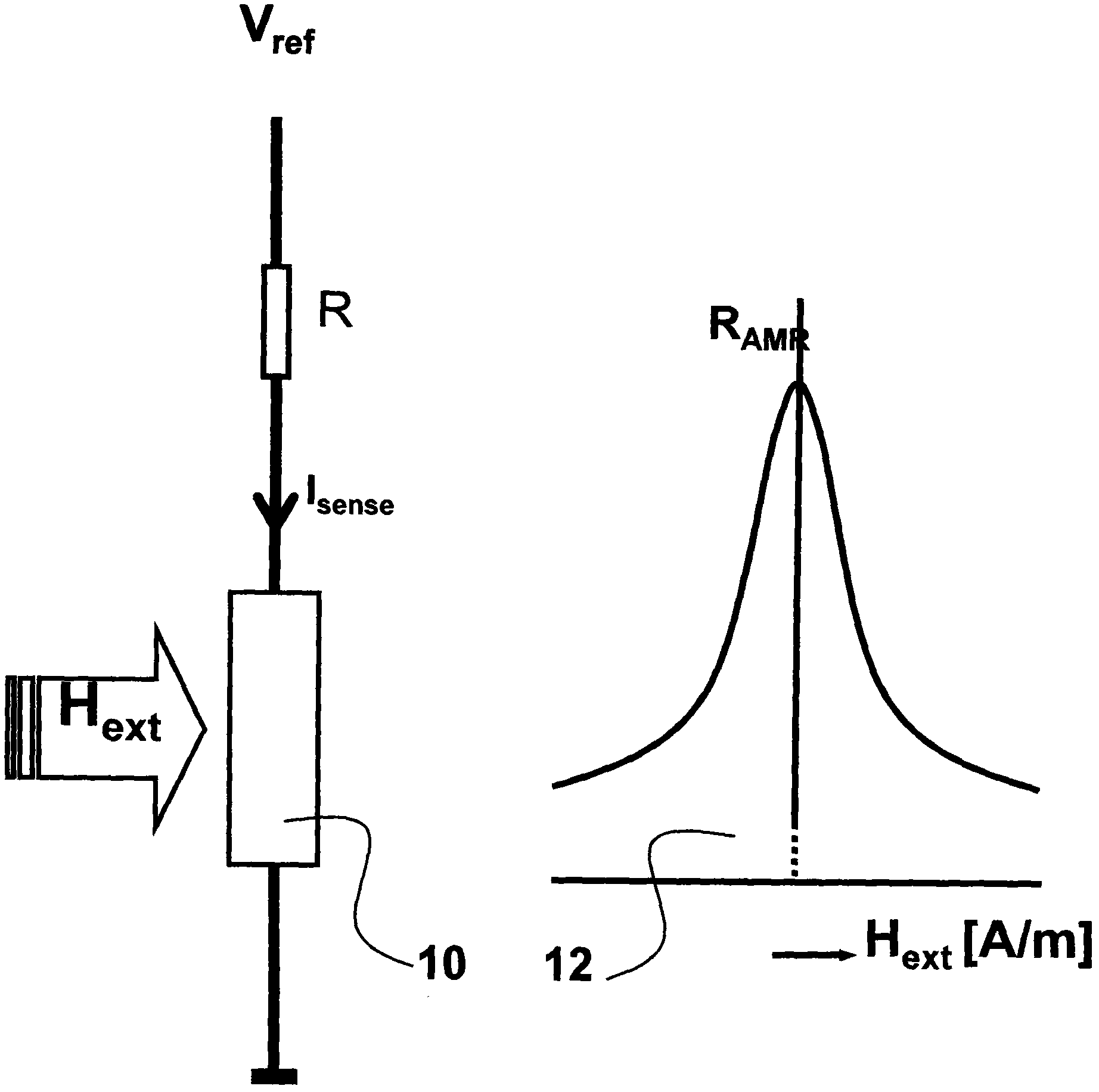
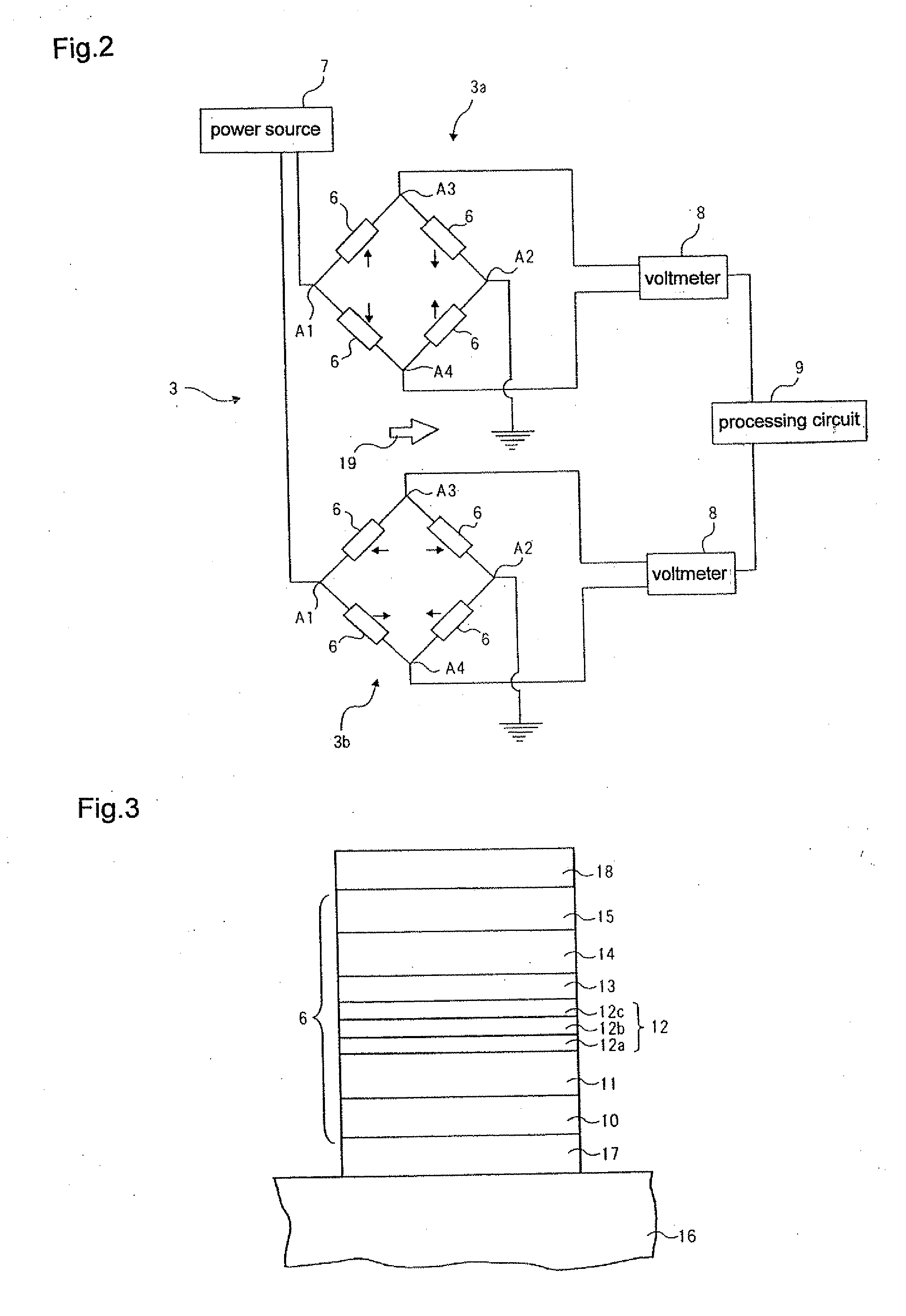
Differential magnetic field sensor structure for orientation independent measurement
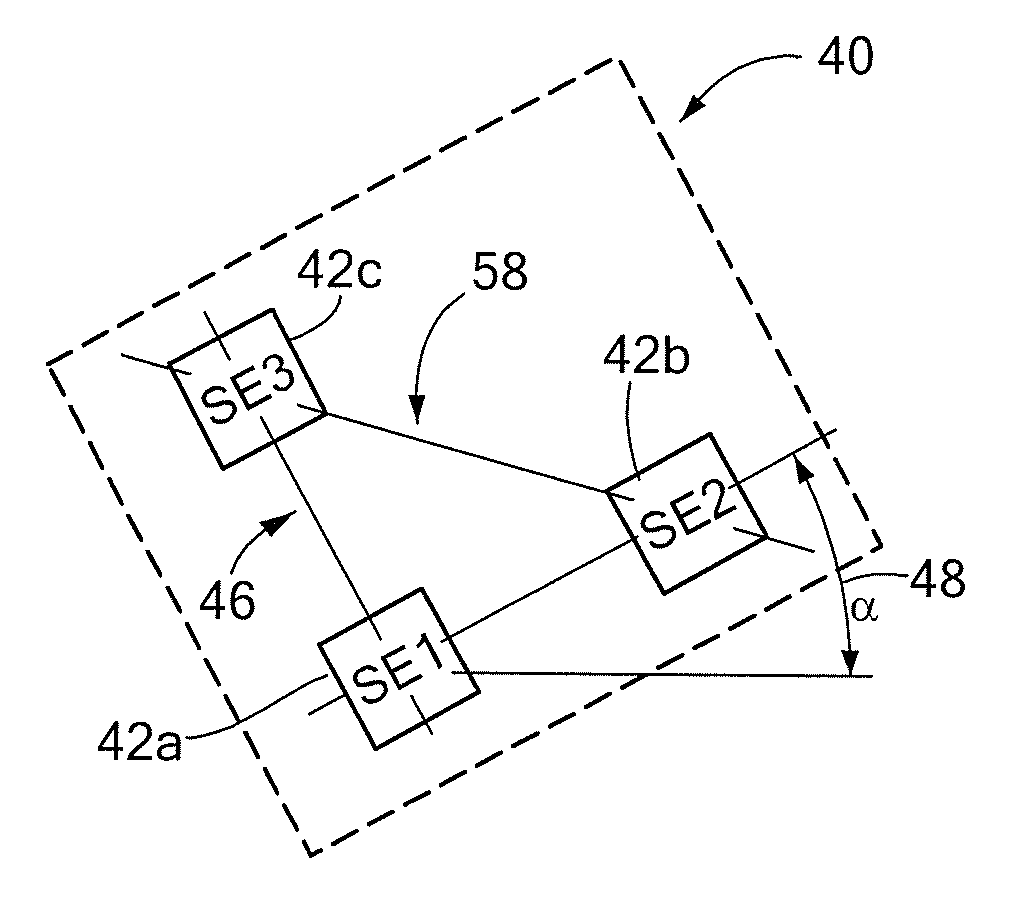
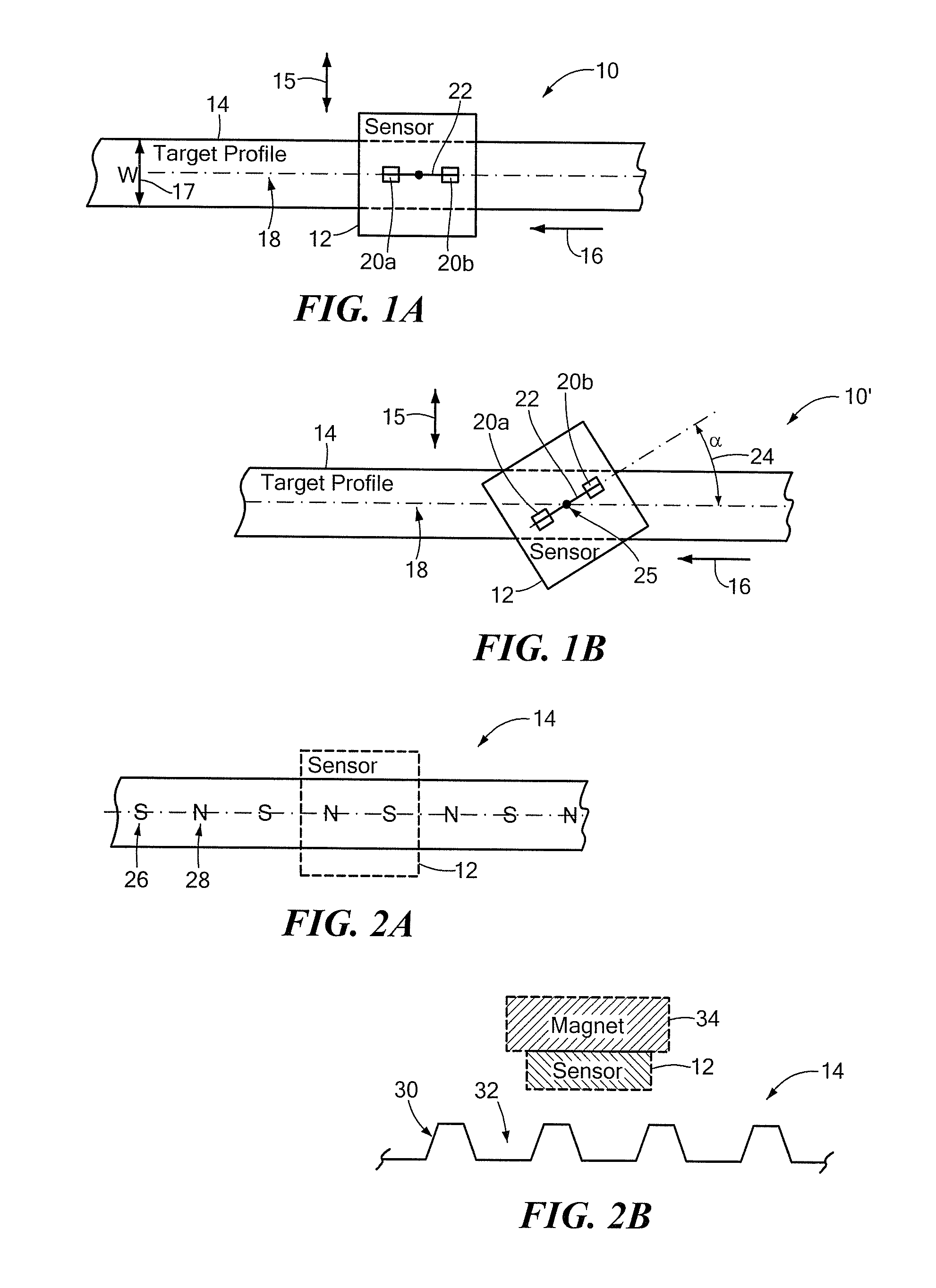
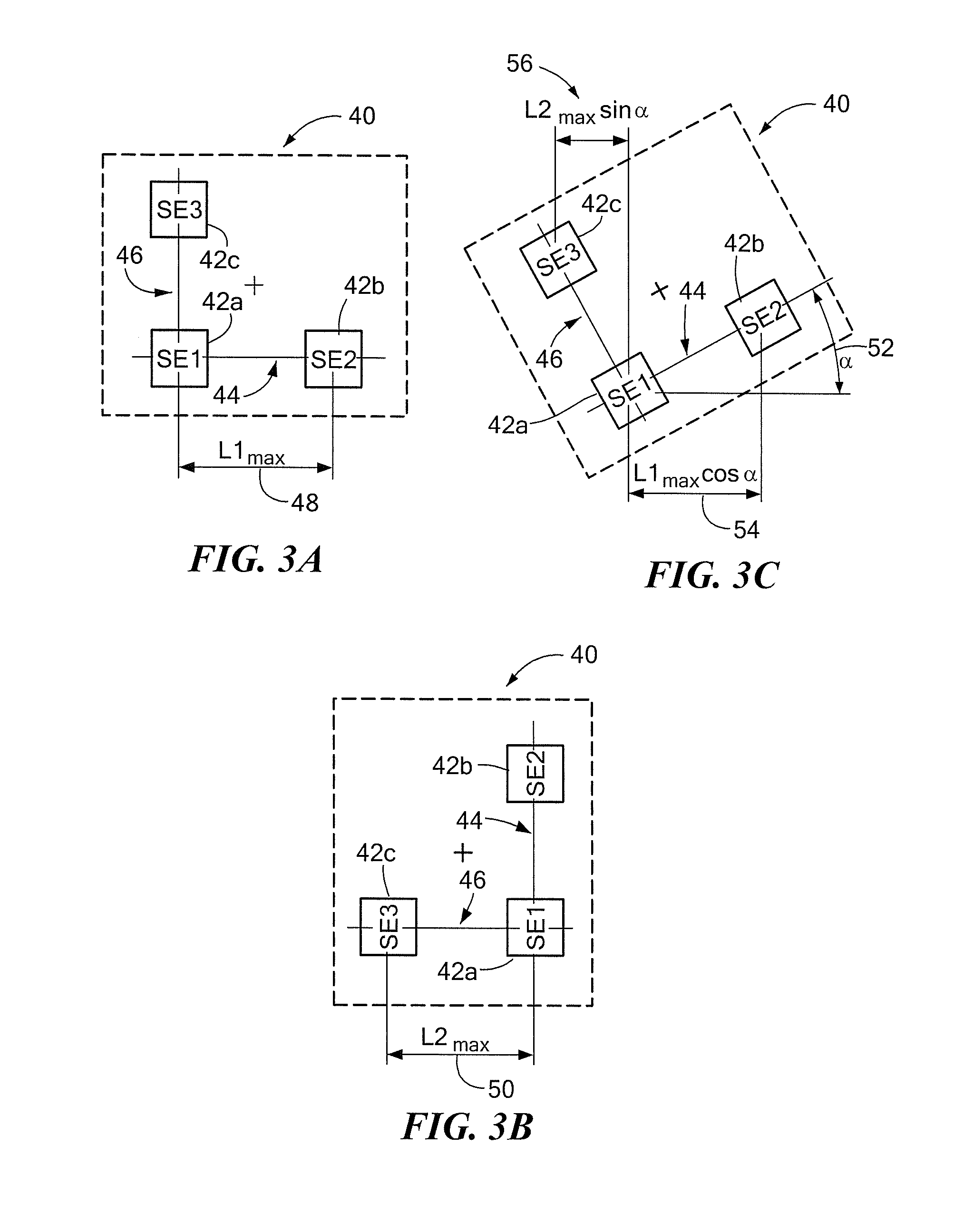
ActiveUS20120249133A1Magnetic sensor geometrical arrangementsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsChannel correlationCondensed matter physics
A differential magnetic field sensor that enables operation that is independent of sensor-to-target orientation is presented. The differential magnetic field sensor is provided with at least two differential channels. Each differential channel includes a pair of magnetic field sensing elements and has a respective sensing axis defined by those magnetic field sensing elements. The sensing axes are not aligned with respect to each other. One sensing axis is positioned relative to a reference axis of a target profile to define an orientation angle between the sensing axis and the reference axis. The differential magnetic field sensor includes circuitry to produce differential signals associated with the differential channels and use those differential signals to produce a single differential signal having an amplitude that is independent of the orientation angle.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Magnetoresistive sensor with reduced parasitic capacitance, and method
ActiveUS20120161759A1NanomagnetismMagnetic sensor geometrical arrangementsElectronic circuitElectricity
A magnetic-field sensor adapted to detect an external magnetic field, comprising: a first chip, including a first magnetoresistive structure for detection of the external magnetic field, the first magnetoresistive detection structure including an electrical-contact pad and magnetoresistive means; and a second chip housing an integrated electronic circuit and a magnetic-field generator, the first and second chips being mutually arranged in such a way that the integrated electronic circuit can be electrically coupled to the electrical-contact pad of the magnetoresistive structure and in such a way that the magnetic-field generator can be magnetically coupled to the magnetoresistive structure.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
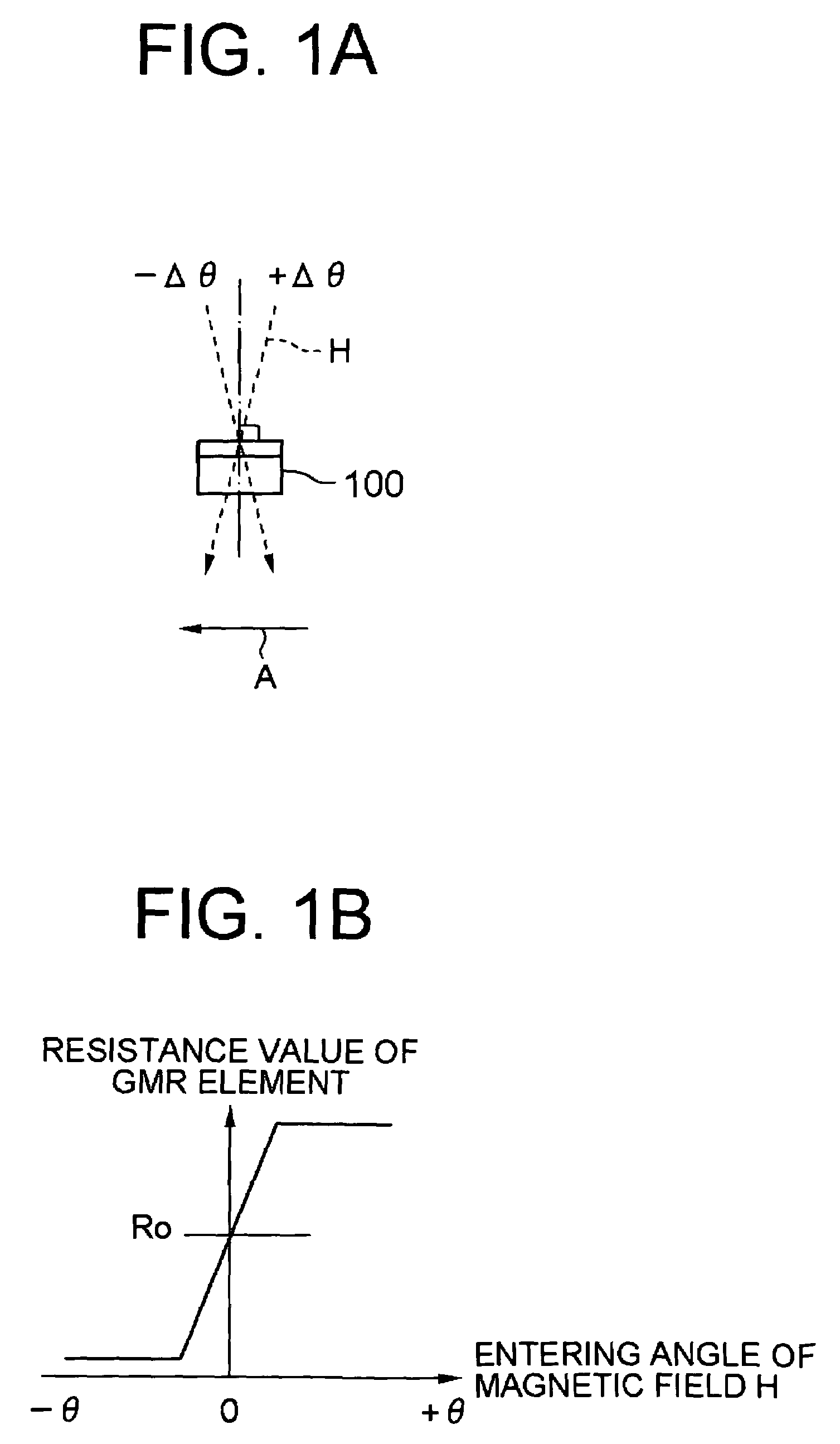
Magnetic sensor
ActiveUS20090284254A1Improve detection accuracyLow costMeasurement using dc-ac conversionWave amplification devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetization
A magnetic sensor capable of detecting a magnetic field with high sensitivity is provided. The magnetic sensor includes a bridge circuit having a plurality of magneto resistive effect elements connected with each other, and is capable of detecting a differential voltage between predetermined connecting points. The magneto resistive effect elements output resistance values which vary in accordance with a direction of a magnetic field to be input, and are arranged such that fixed magnetization directions of all magneto resistive effect elements are in the same direction. Further, a magnetic body which changes the direction of the magnetic field to be input to the magneto resistive effect elements is also provided in the vicinity of the bridge circuit.
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
Single-chip push-pull bridge-type magnetic field sensor
ActiveUS20140035570A1Cryptography processingMagnetic sensor geometrical arrangementsBridge typeMagnetic reluctance
The present invention discloses a design of a single-chip push-pull bridge sensor, composed of magnetoresistive elements, utilizing on-chip permanent magnets. The permanent magnets are oriented to preset magnetization directions of free layers of adjacent sensor bridge arms so that they point to different directions with respect the same sensing direction, enabling push-pull operation. The push-pull bridge sensor of the present invention is integrated on a single chip. Additionally, an on-chip coil is disclosed to reset or calibrate the magnetization directions of the free layers of the magnetoresistive elements.
Owner:MULTIDIMENSION TECH CO LTD
Integrated magnetic sensor for detecting horizontal magnetic fields and manufacturing process thereof
ActiveUS20110210722A1High sensitivityMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleMagnetic sensor packagingSemiconductor materialsConcentrator
The integrated magnetic sensor for detecting an external magnetic field, is formed by a body of semiconductor material having a surface; an insulating layer covering the body of semiconductor material; a magnetically sensitive region, for example a Hall cell, extending inside the body; and a concentrator of ferromagnetic material, extending on the Hall cell and having a planar portion extending parallel to the surface of the substrate on the insulating layer. The concentrator terminates with a tip protruding peripherally from, and transversely to, the planar portion toward the Hall cell. When the magnetically sensitive region is a sensing coil of a fluxgate sensor, it is formed on the substrate, embedded in the insulating layer, and the tip of the concentrator can reach as far as the sensing coil.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Magnetic field sensing apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20140266185A1Improve directionalityHigh sensitivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesCouplingCondensed matter physics
Magnetic field sensor designs that provide both increased directionality and proximate coupling desirable for improved directionality and sensitivity and methods for fabricating them.
Owner:PLURES TECH
System and method for magnetic occult lesion localization and imaging
Systems and methods for marking the location and extent of an anatomical region-of-interest, such as a tumor, using magnetic seeds whose position and orientation are measured or otherwise detected using a detection device that includes two or more magnetic sensors are described. One or more magnetic seeds are implanted to mark and define the center and extent of an anatomical region-of-interest and a magnetic sensor-based detector system is used to accurately identify the location of the magnetic seeds.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK RES INST
Triaxial magnetic field sensor
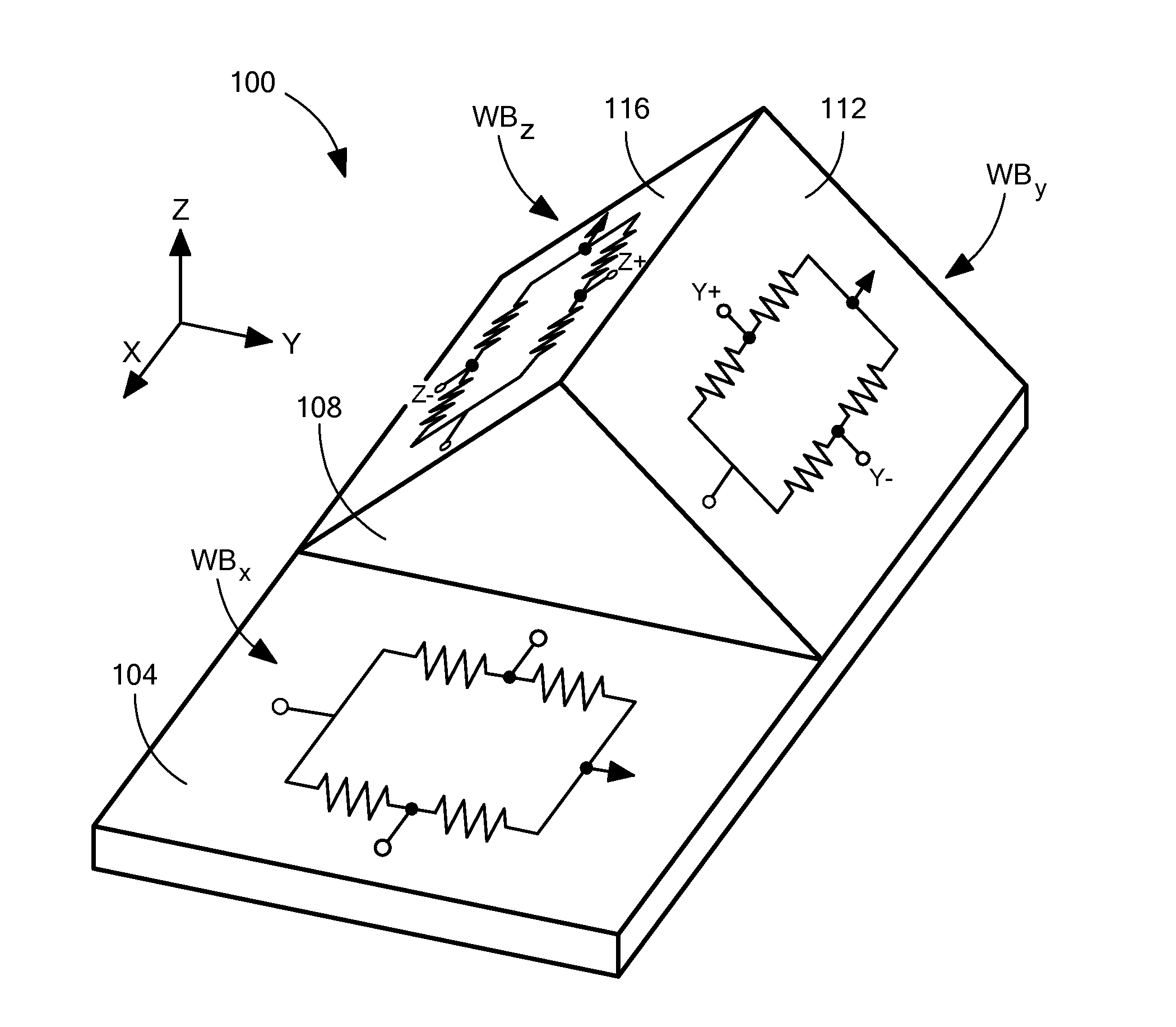
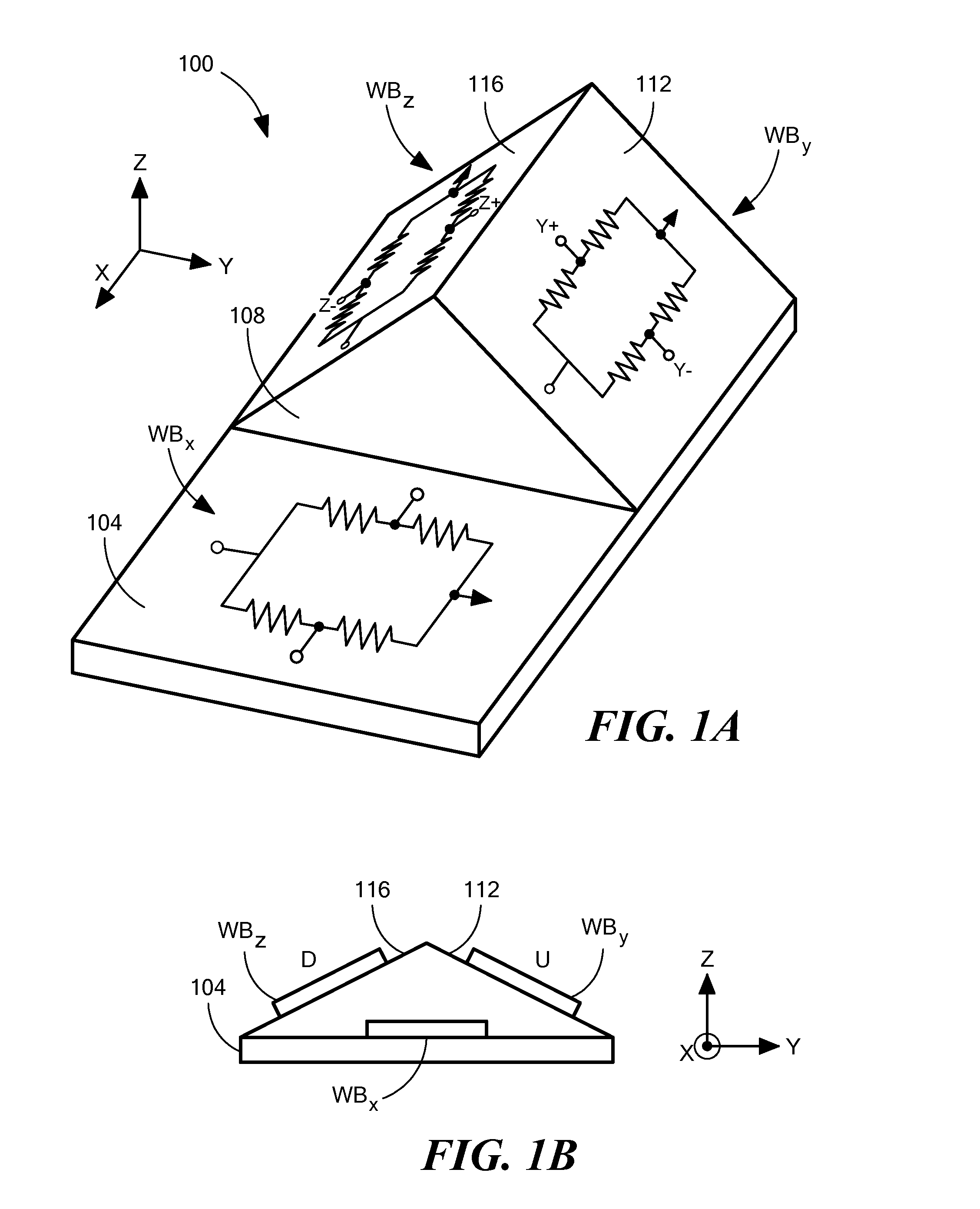
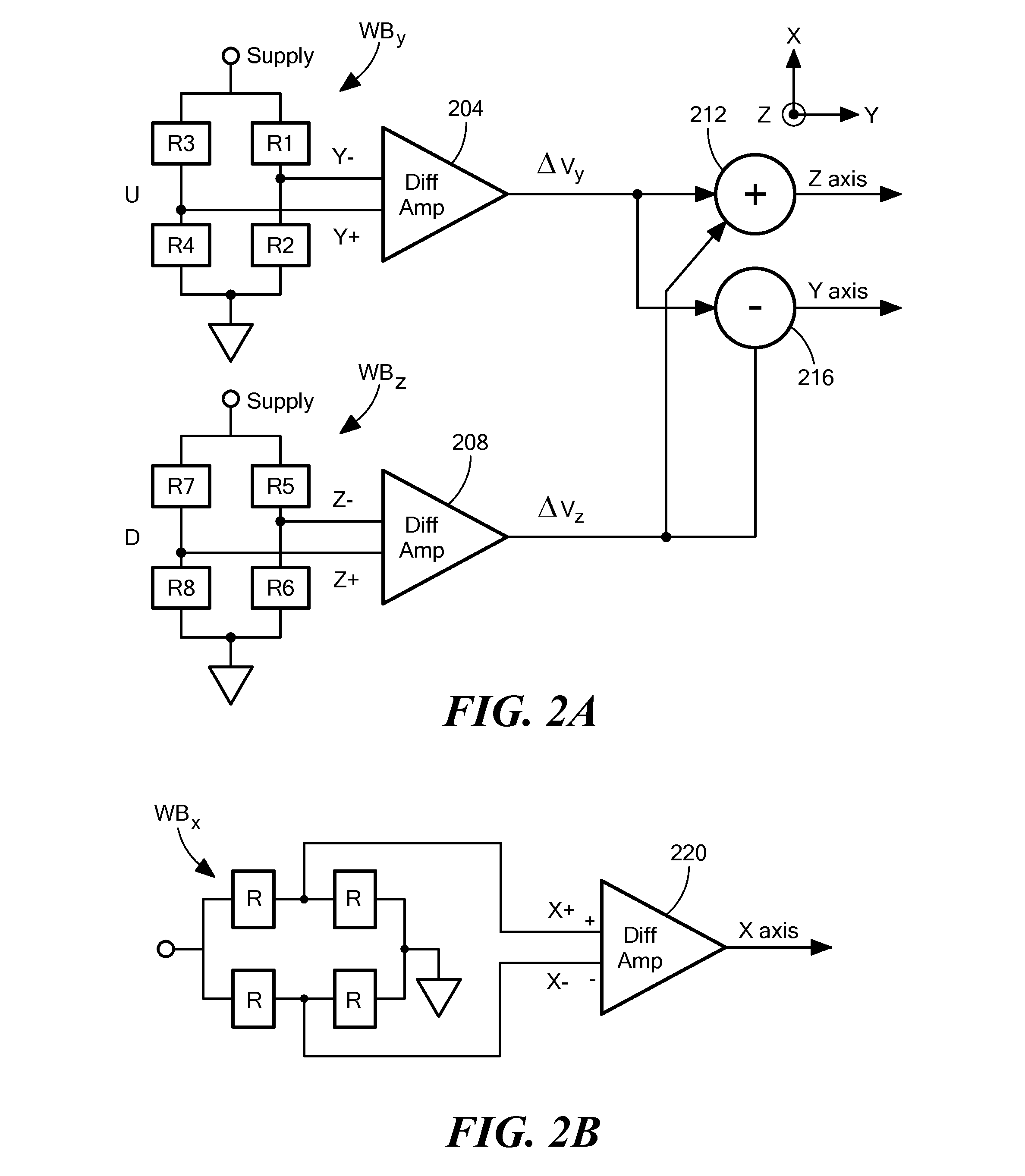
ActiveUS20140247042A1Easy to integrateReduce magnetic noiseMagnetic sensor geometrical arrangementsElectrodynamic magnetometersThermal stabilitySingle chip
The present invention discloses a triaxial magnetoresistive sensor. It comprises a substrate integrated with a biaxial magnetic field sensor, a Z-axis sensor that has a sensing direction along Z-axis perpendicular to the two axes of the biaxial magnetic field sensor, and an ASIC. The biaxial magnetic field sensor comprises an X-axis bridge sensor and a Y-axis bridge sensor. The Z-axis sensor and the two-axis sensor are electrically interconnected with the ASIC. A single-chip implementation of the triaxial magnetic field sensor comprises a substrate, onto which a triaxial magnetic field sensor and an ASIC are stacked. The triaxial magnetic field sensor comprises an X-axis bridge sensor, a Y-axis bridge sensor, and a Z-axis bridge sensor. The above design provides a highly integrated sensor with high sensitivity, low power consumption, good linearity, wide dynamic range, excellent thermal stability, and low magnetic noise.
Owner:MULTIDIMENSION TECH CO LTD
Magnetic Field Sensor and Method For Sensing Relative Location of the Magnetic Field Sensor and a Target Object Along a Movement Line
ActiveUS20150176962A1Magnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesUsing electrical meansMagnetMagnetic field
A magnetic field sensor with a magnet is disposed proximate to a ferromagnetic target object having at least one ferromagnetic surface. The magnetic field sensor is operable to sense a relative location between the magnetic field sensor and the ferromagnetic target object along a movement line. In some embodiments, the target object is also spinning about a rotation axis parallel to the movement line. A corresponding method is described.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
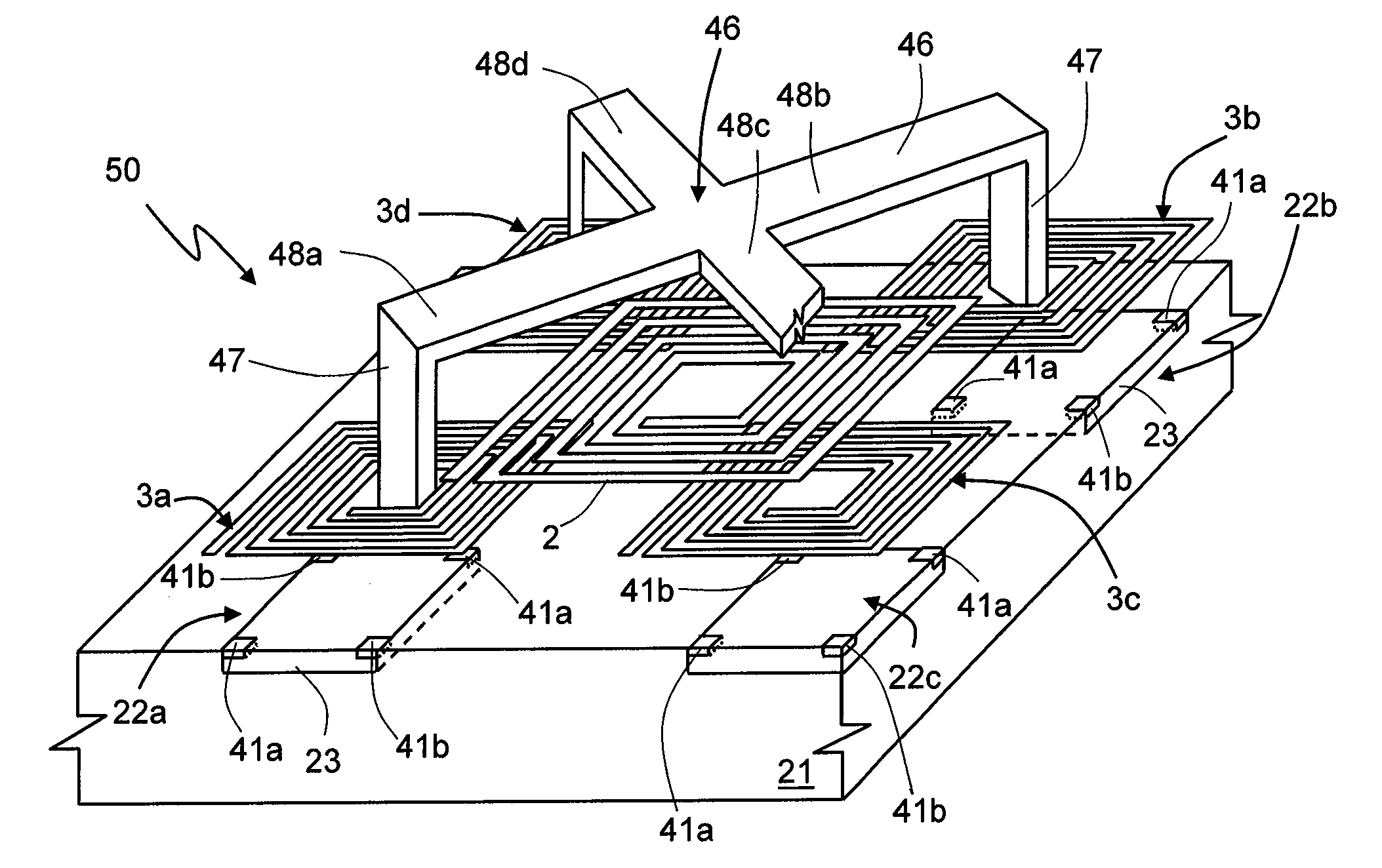
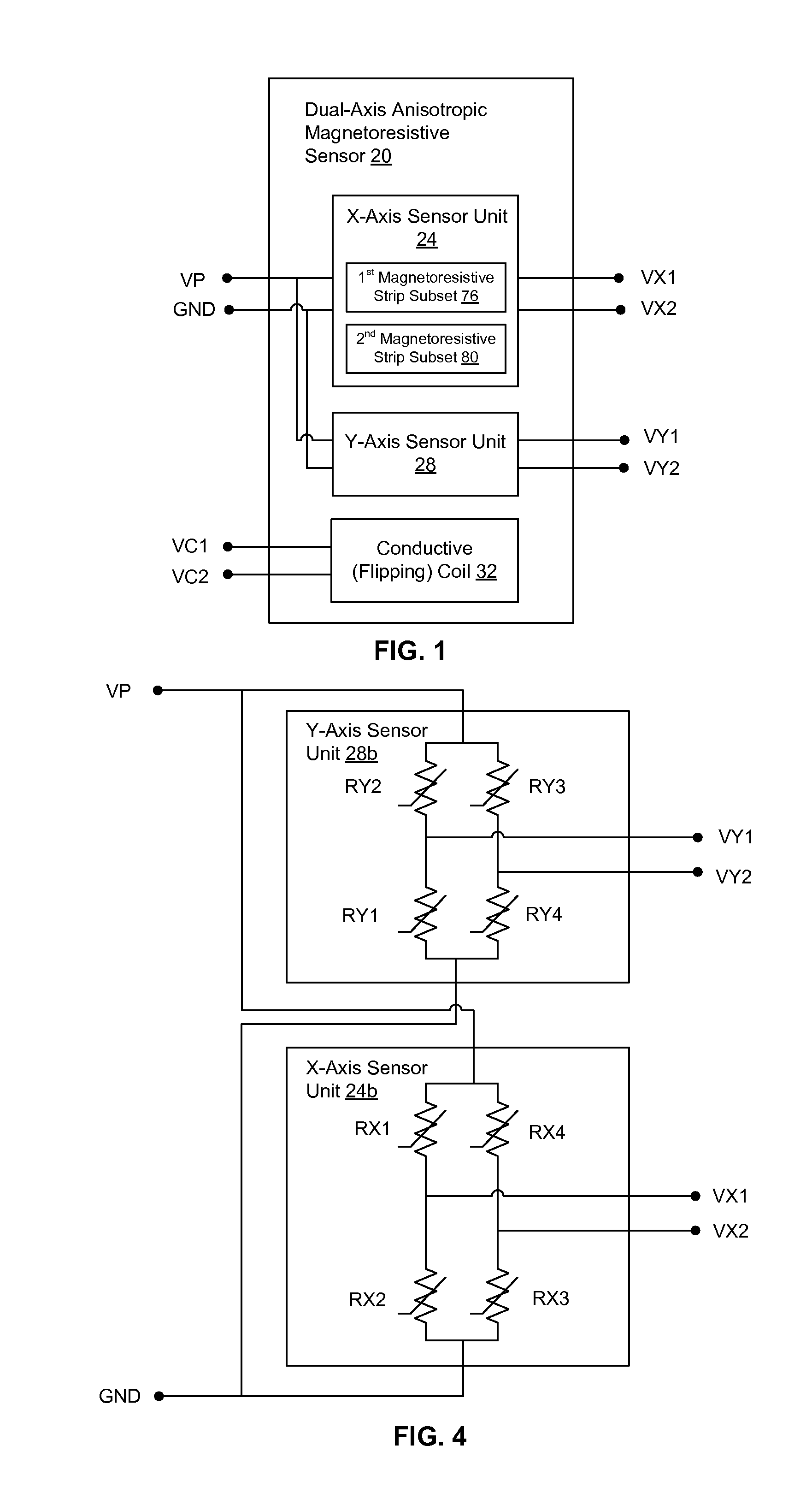
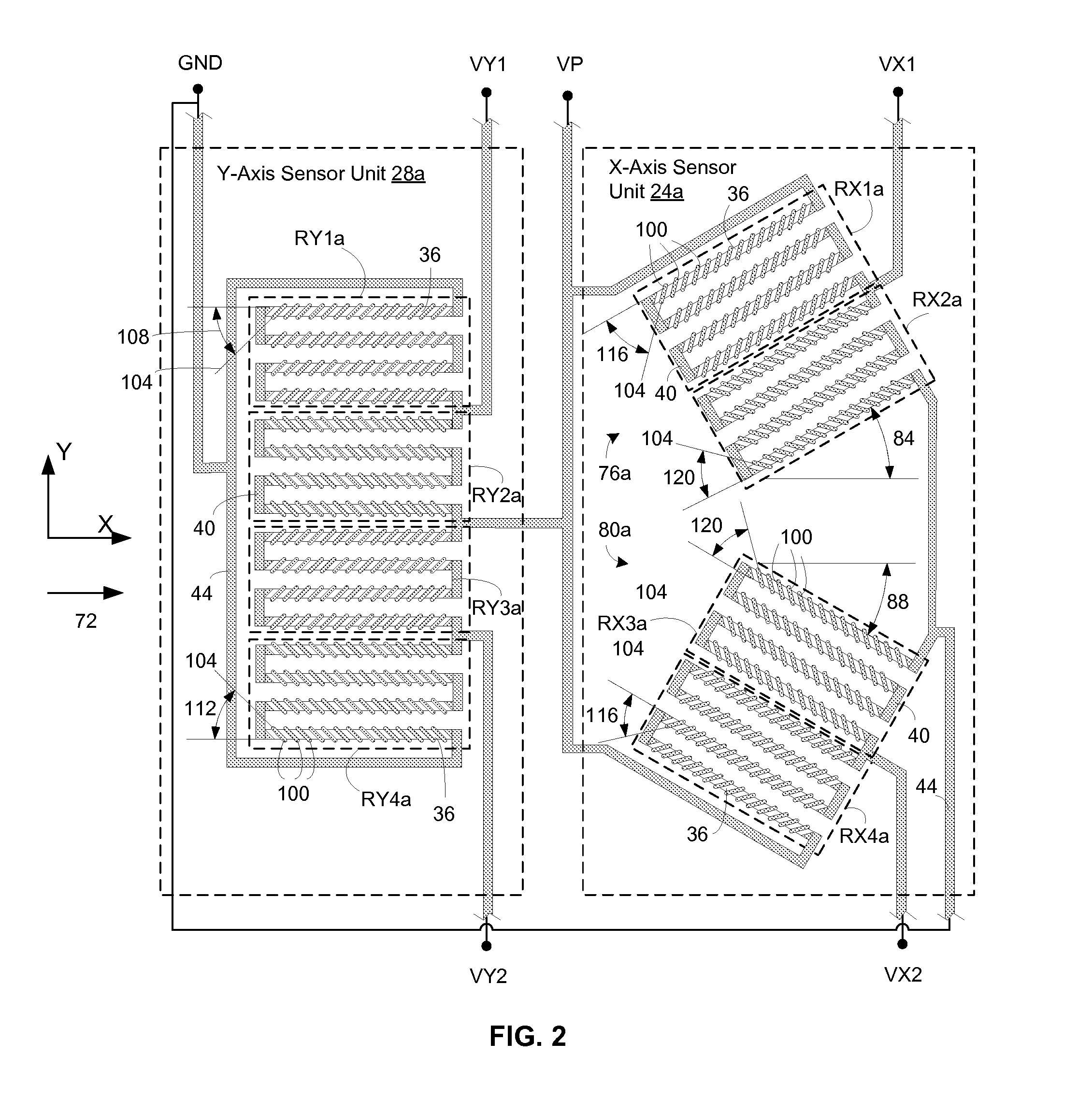
Dual-axis anisotropic magnetoresistive sensors
ActiveUS20130099783A1Magnetic sensor geometrical arrangementsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsMagnetic reluctanceEngineering
An integrated dual-axis anisotropic magnetoresistive sensor can include first and second sensor units. A resistor bridge of the first sensor unit can include a plurality of magnetoresistors, each having at least one strip of anisotropic magnetoresistive material with a longitudinal axis substantially parallel to the technological anisotropy axis of the material. A resistor bridge of the second sensor unit can include a plurality of magnetoresistors having a plurality of strips of the anisotropic magnetoresistive material, the plurality of strips including a first subset having longitudinal axes aligned at a first angle to the technological anisotropy axis and a second subset having longitudinal axes aligned at a second angle to the technological anisotropy axis. The second angle can have the same magnitude as the first, but be rotated in an opposite direction from the technological anisotropy axis.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE CORK NAT UNIV OF IRELAND CORK
Two-axis magnetic field sensor
InactiveUS20090108841A1Small and simple structureLow priceMagnetic sensor geometrical arrangementsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical conductor
Disclosed is a small-sized two-axis magnetic field sensor having a function to cause a magnetic field canceling an external offset magnetic field. The two-axis magnetic field sensor contains a plane coil disposed on a plane and four sets of magneto-resistance element pairs on a plane parallel to the plane coil. The plane coil includes at least two pairs of parallel conductors, and two magneto-resistance elements cross only a single conductor of the coil. A current for canceling the external offset magnetic field is determined in advance, and while a DC current that causes total magnetic fields of biasing magnetic fields plus a magnetic field for canceling the external offset magnetic field flows through the coil, intermediate potential outputs from the magneto-resistance element pairs are detected to measure a magnetic field direction, such as geo-magnetism.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Magnetic sensor and magnetic sensor module
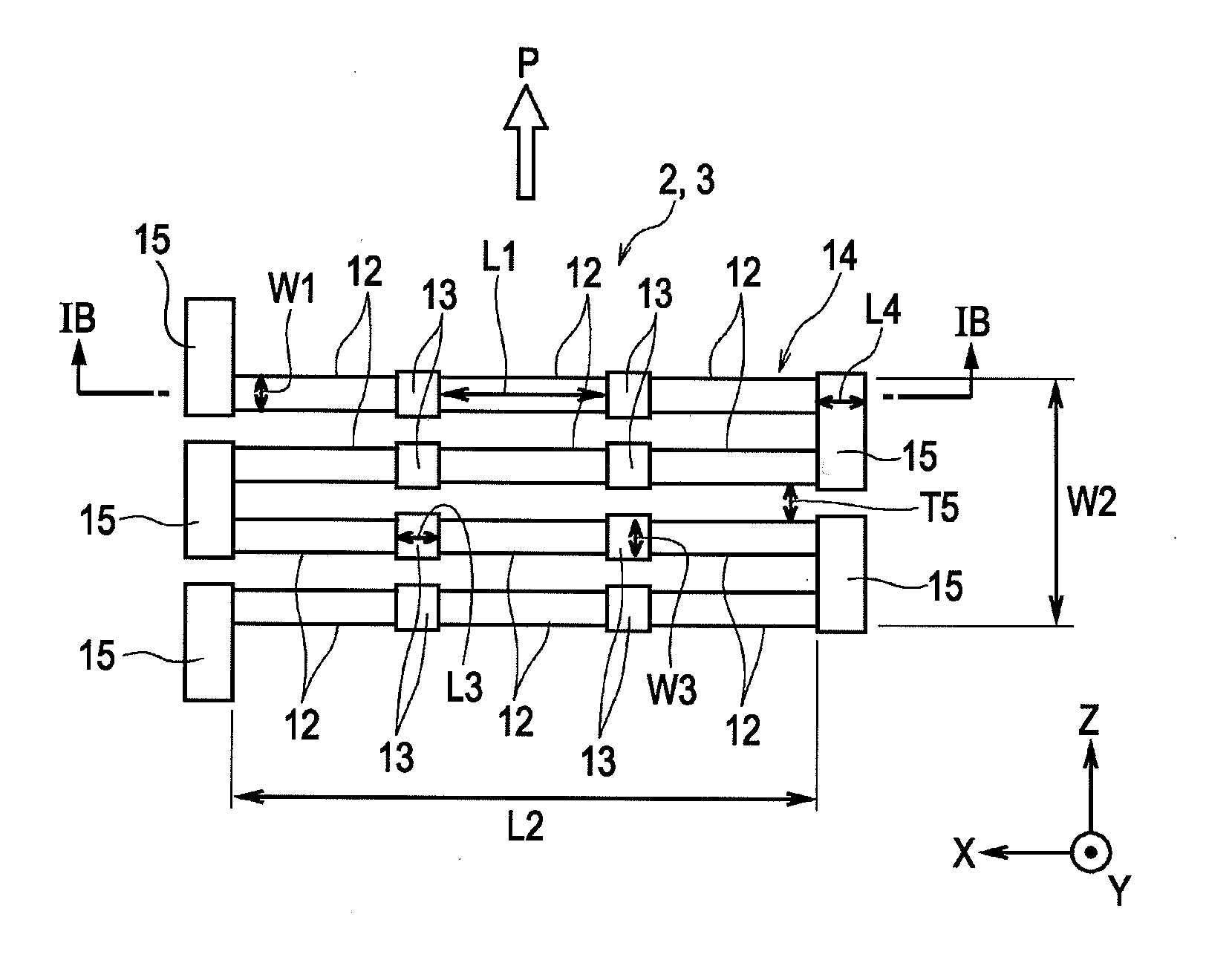
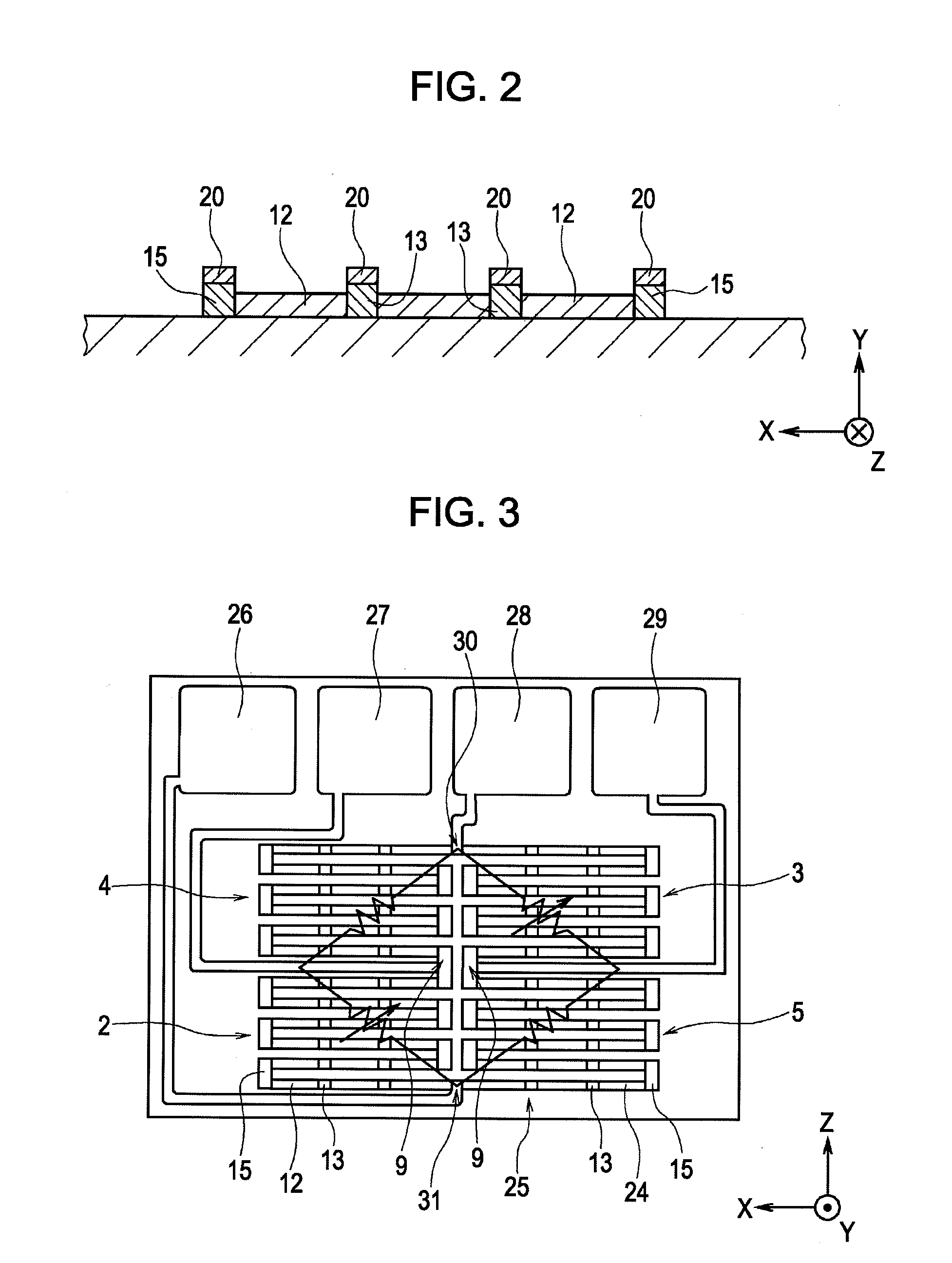
ActiveUS20100253330A1Efficient arrangementDownsizeNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnet
A magnetic sensor including a magnetoresistive effect element has the following structure. Element units each having an element width W1 and an element length L1 perpendicular to the element width W1 and producing a magnetoresistive effect in which electrical resistance changes in response to an external magnetic field are arranged in an element-length direction with a space therebetween. An intermediate permanent magnet layer is disposed in the space, and the element units are connected to each other with the intermediate permanent magnet layer therebetween to form a connected-element body. A plurality of the connected-element bodies are arranged so as to be adjacent to one another in an element-width direction with a space therebetween, the ends of the connected-element bodies are connected to each other with an outer permanent magnet layer therebetween to form a magnetoresistive effect element having a meandering shape.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
MEMS 2d and 3D magnetic field sensors and associated manufacturing method
ActiveUS20100097059A1Galvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesMicroelectromechanical systemsAbsolute measurement
The disclosure provides Hall effect device configurations capable of measuring magnetic fields in two dimensions (2D) and three dimensions (3D) along with associated microelectromechanical system (MEMS) manufacturing methods. The present invention includes various geometric layout configurations for 2D and 3D Hall effect devices with multidimensional magnetic field sensing elements. Advantageously, the present invention can provide, simultaneously and independently, absolute measurement of each of the components (i.e., x-, y-, and z-components) of a magnetic field. Additionally, the geometric layout configurations enable the Hall effect devices to be constructed with MEMS fabrication techniques.
Owner:JUNIVERSITI OF NORT KAROLINA EHT SHARLOTT
Nanowire magnetic sensor
InactiveUS20100223797A1High precisionImprove resolutionElectric/magnetic position measurementsManufacture of electrical instrumentsNanowireCondensed matter physics
A nanowire magnetic sensor includes an array of magneto-resistive (MR) nanosensors with each MR nanosensor including a set of MR nanowires that are all aligned in the same position for one direction. The substrate can be a flexible substrate bent into a circular configuration for compass applications. A plurality of individual nanosensors can be connected into resistive Wheatstone bridge configurations by metallization.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Inductively interrogated passive sensor apparatus
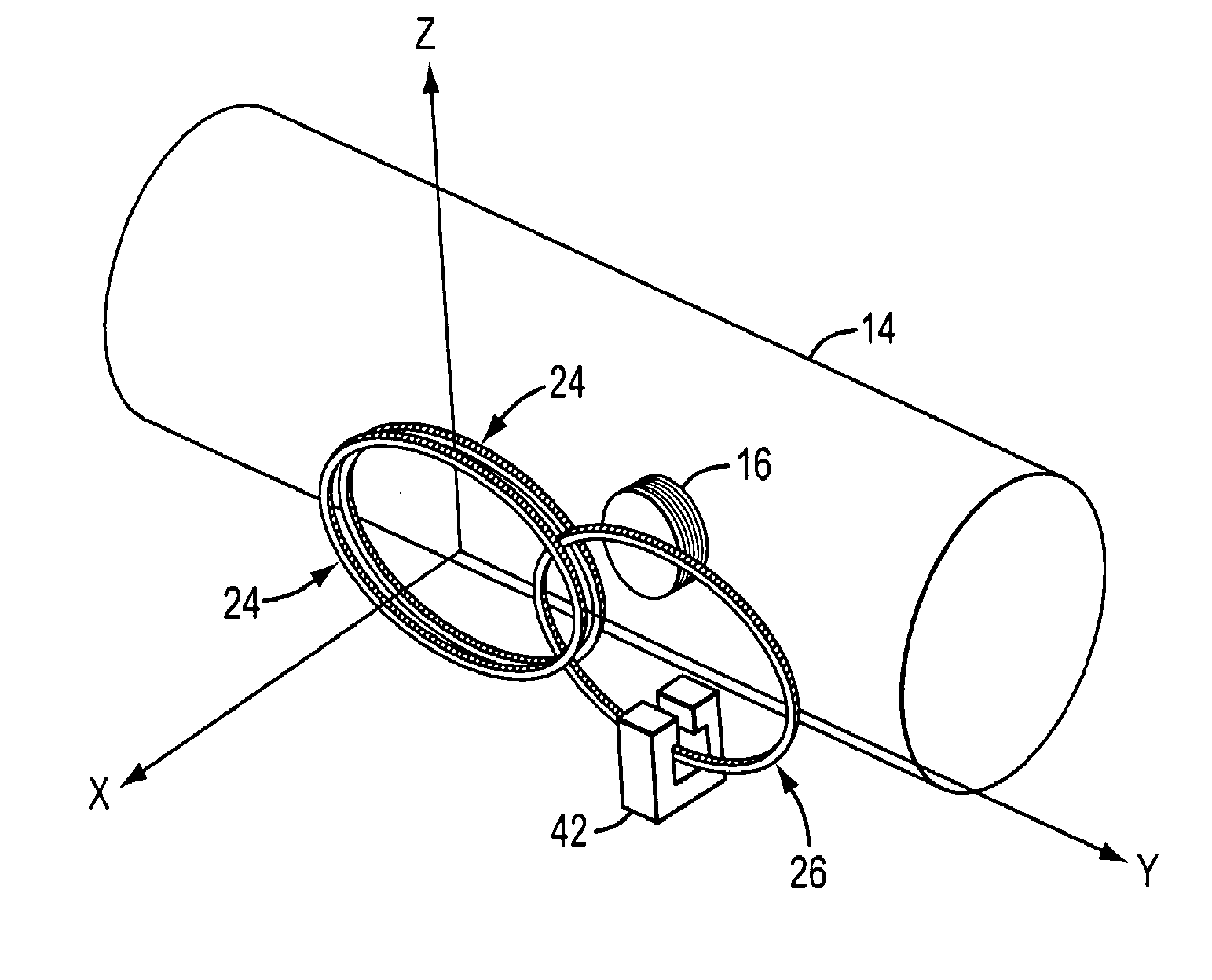
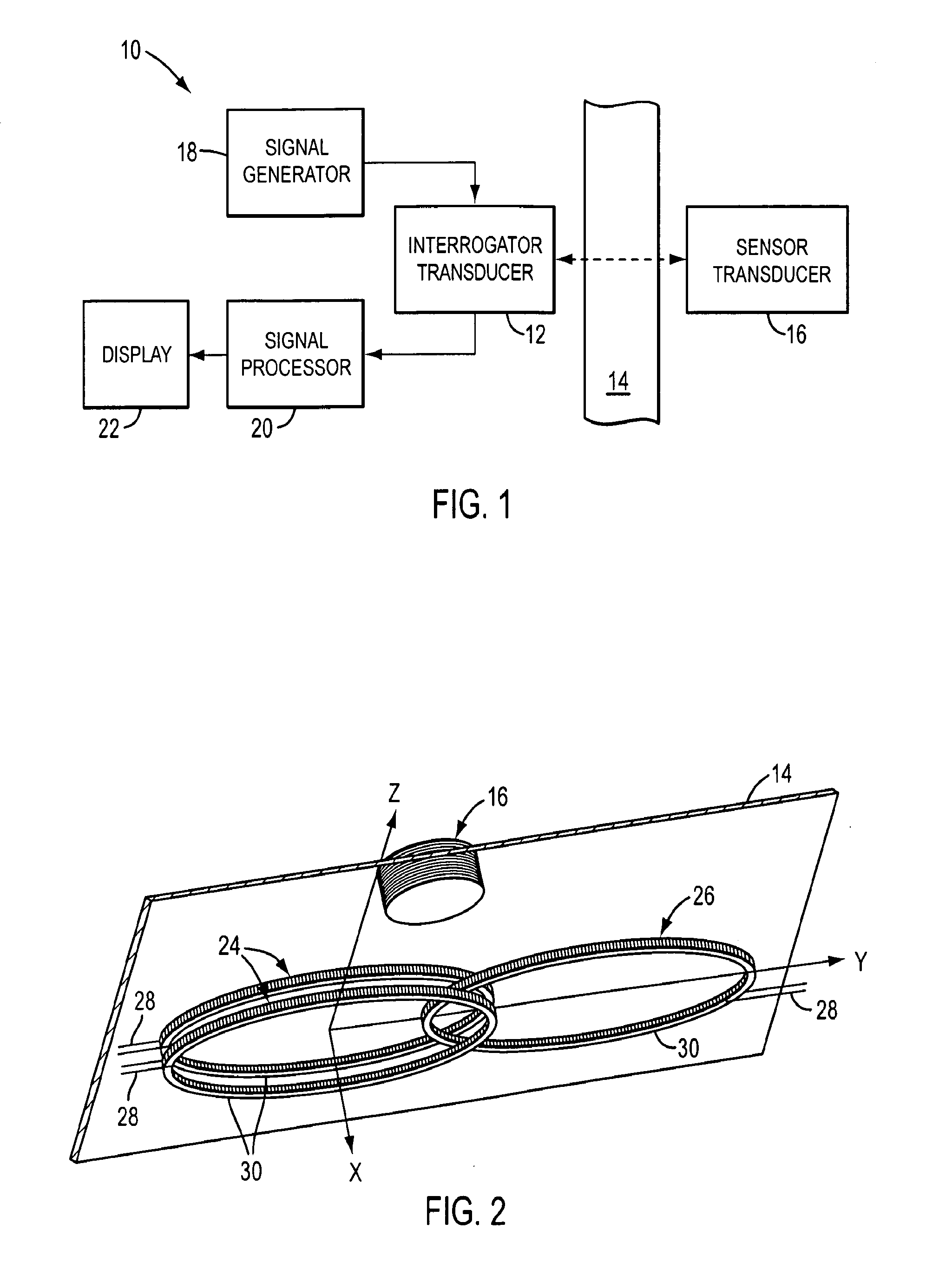
ActiveUS20130147470A1Effectively nulls out the eddy current-generated magnetic fieldMagnetic field offset compensationMagnetic property measurementsElectricityMagnetic transducers
A sensor apparatus comprises a first magnetic transducer which in use is positioned on a first side of a barrier and a second magnetic transducer which in use is positioned on a second side of the barrier opposite the first side. The second transducer comprises a magnetic or electrical property which is dependent upon a sensible condition on the second side of the barrier, such as the pressure or temperature on the second side of the barrier. In operation, the first transducer generates a first magnetic field which induces the second transducer to generate a second magnetic field that is dependent upon the magnetic or electrical property of the second transducer. The first transducer detects the second magnetic field and generates a signal which is representative of the sensible condition on the second side of the barrier.
Owner:FMC TECH INC
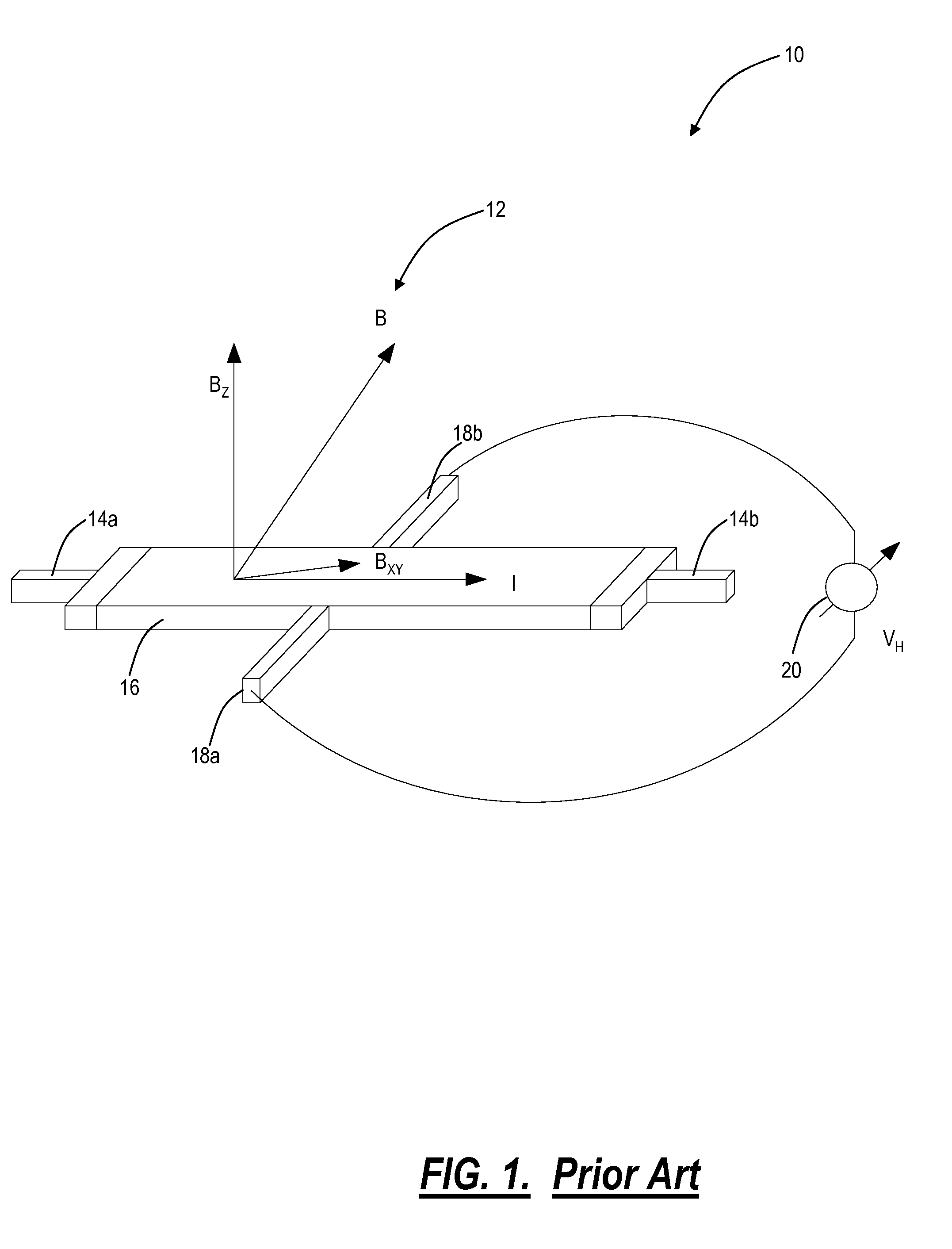
Hall effect element having a wide cross shape with dimensions selected to result in improved performance characteristics
A Hall effect element includes a Hall plate having geometric features selected to result in a highest ratio of a sensitivity divided by a plate resistance. The resulting shape is a so-called “wide-cross” shape.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
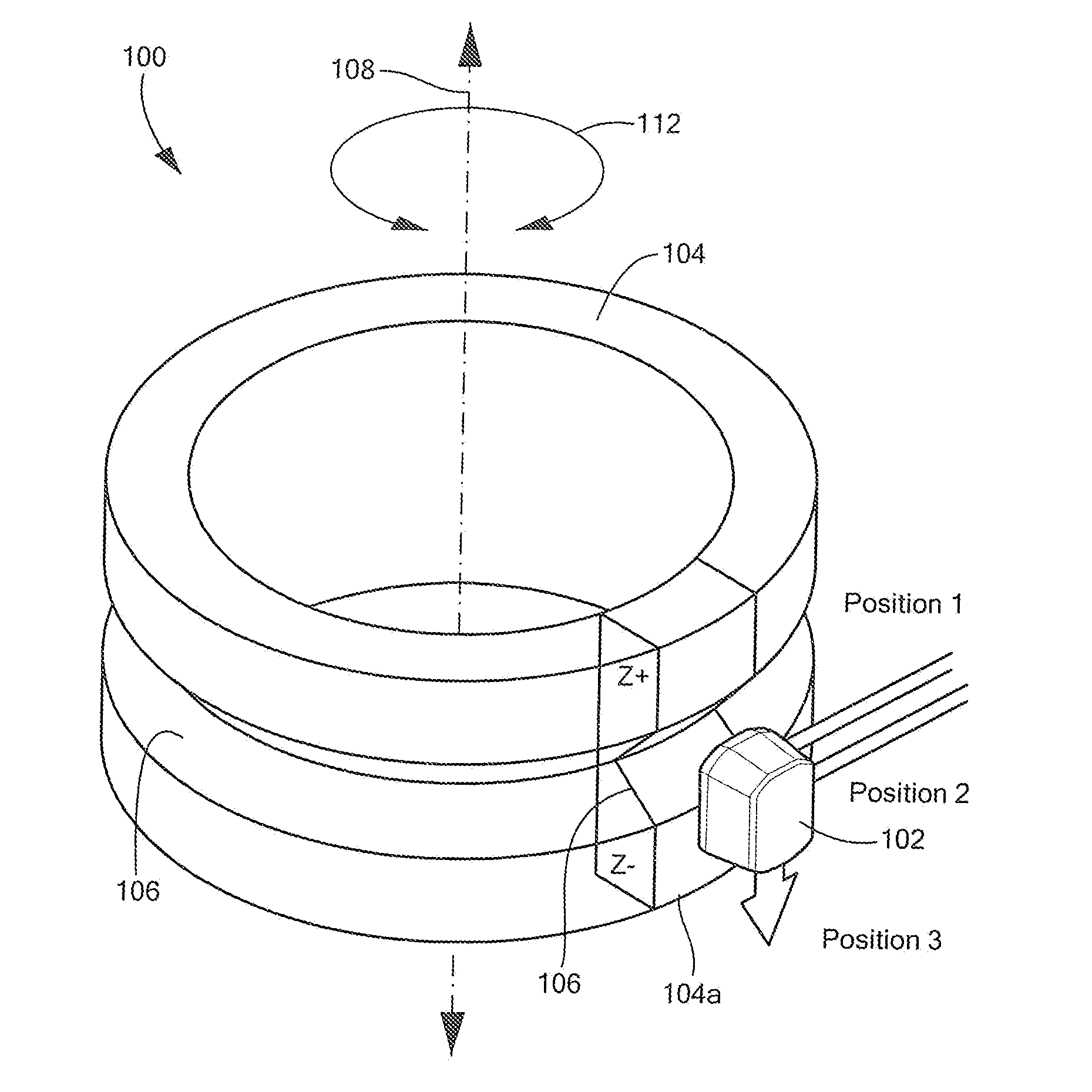
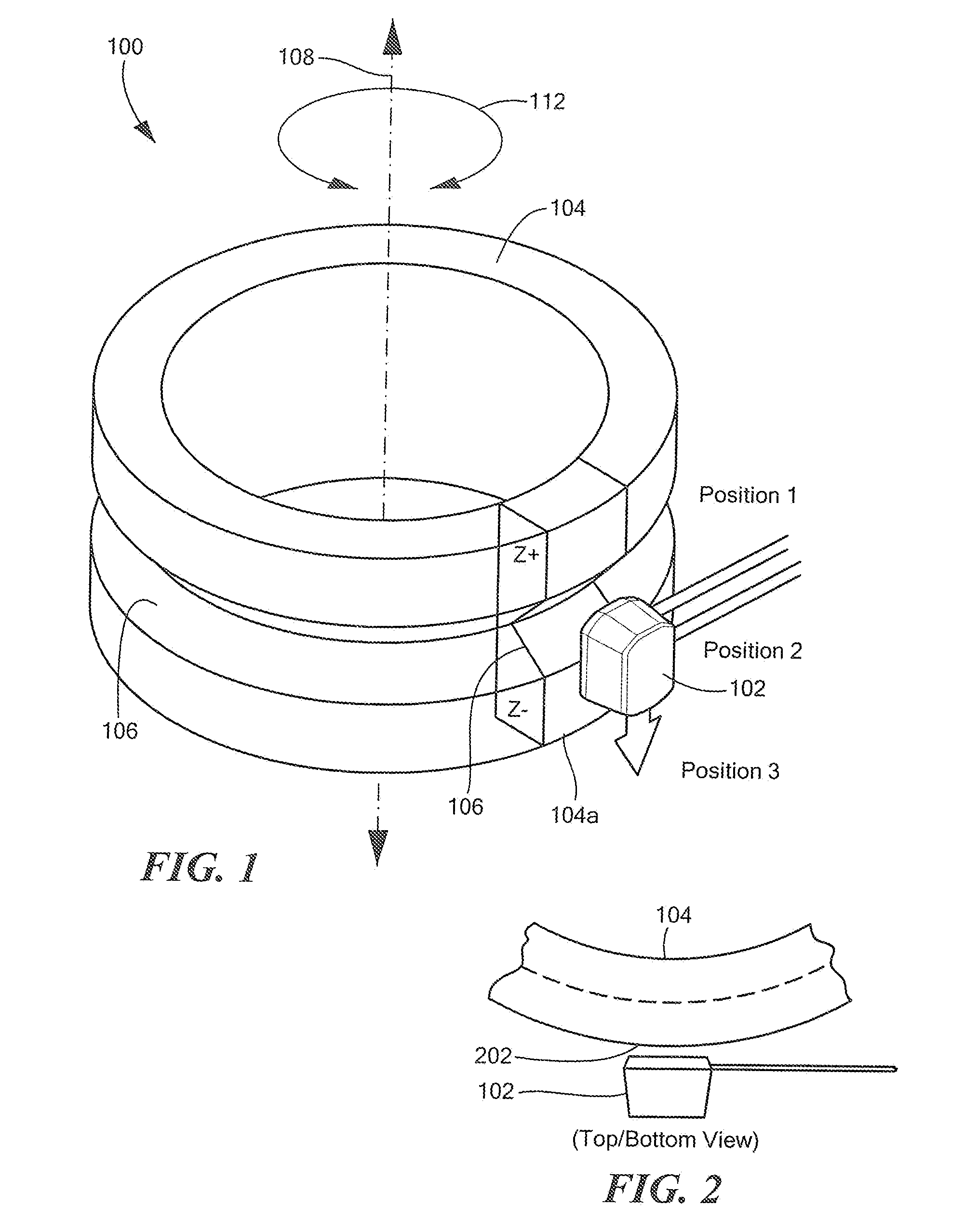
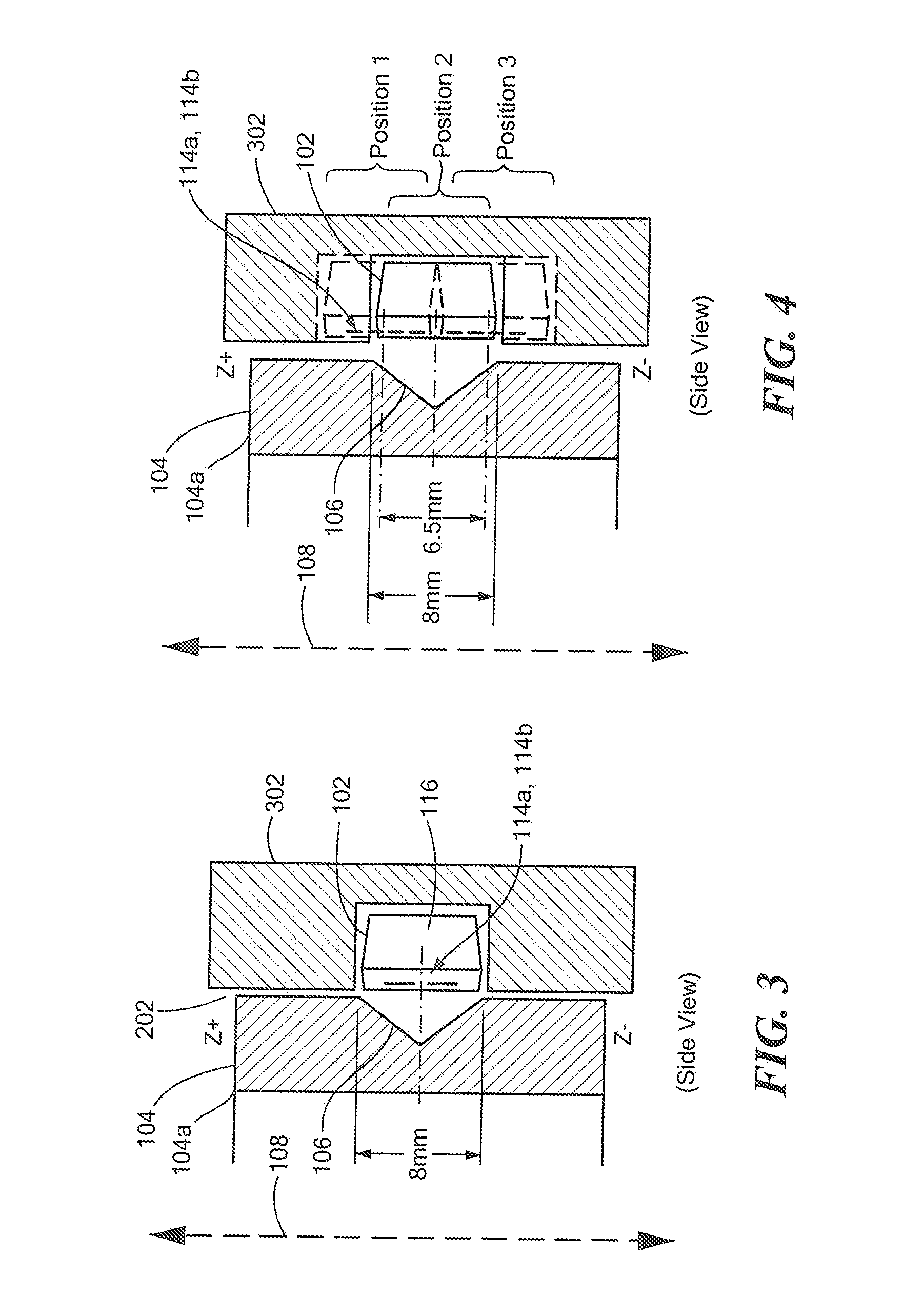
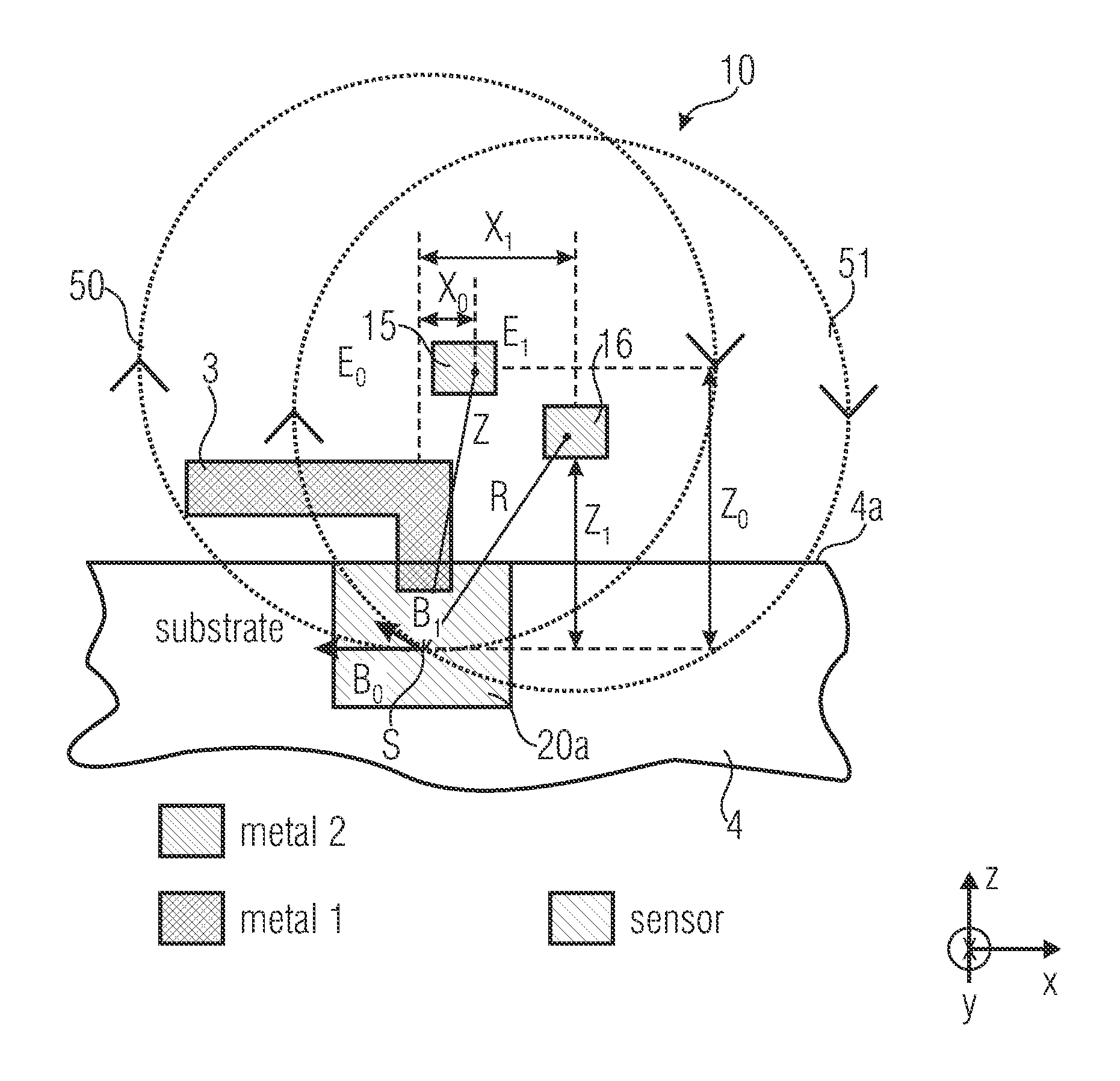
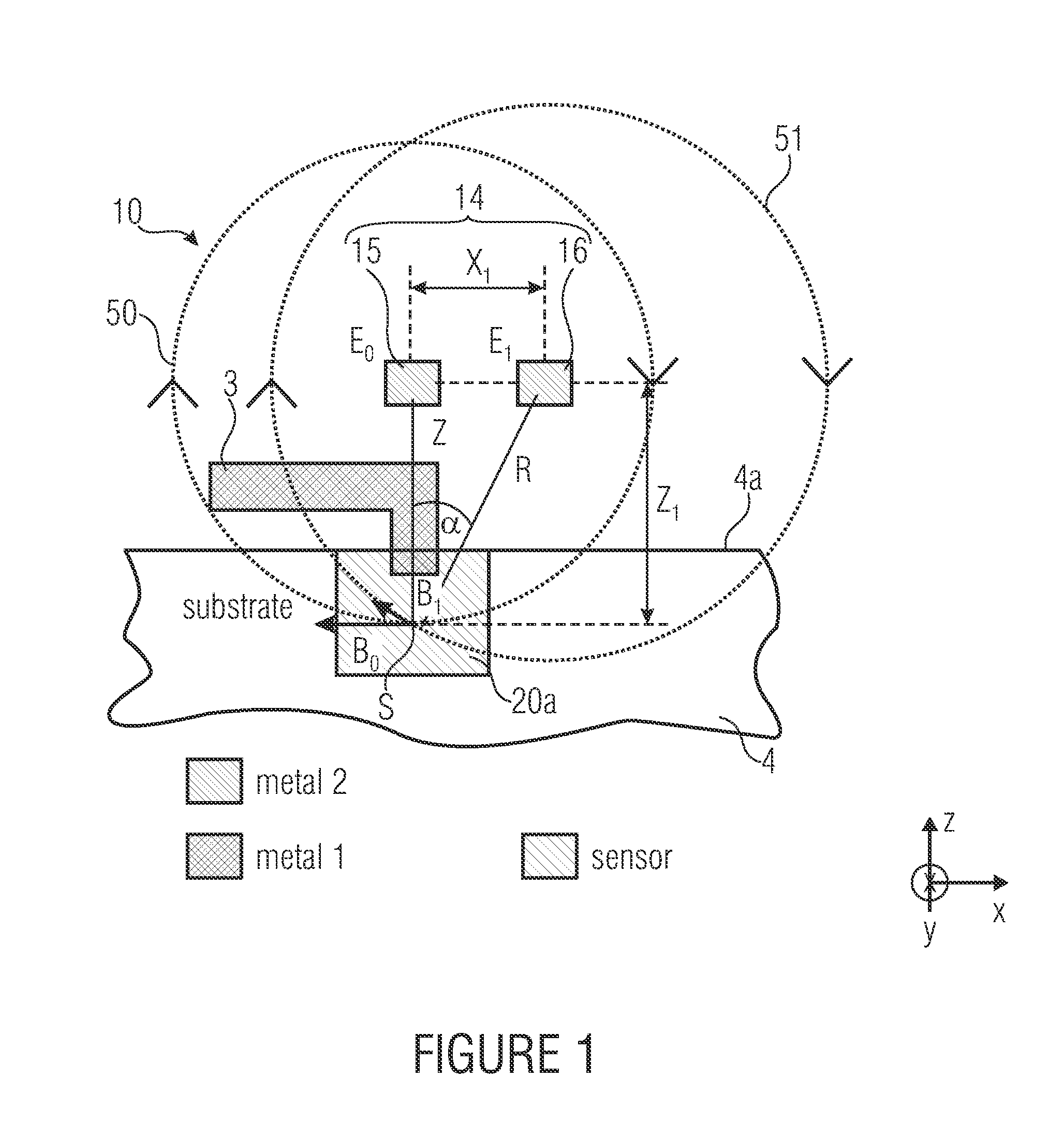
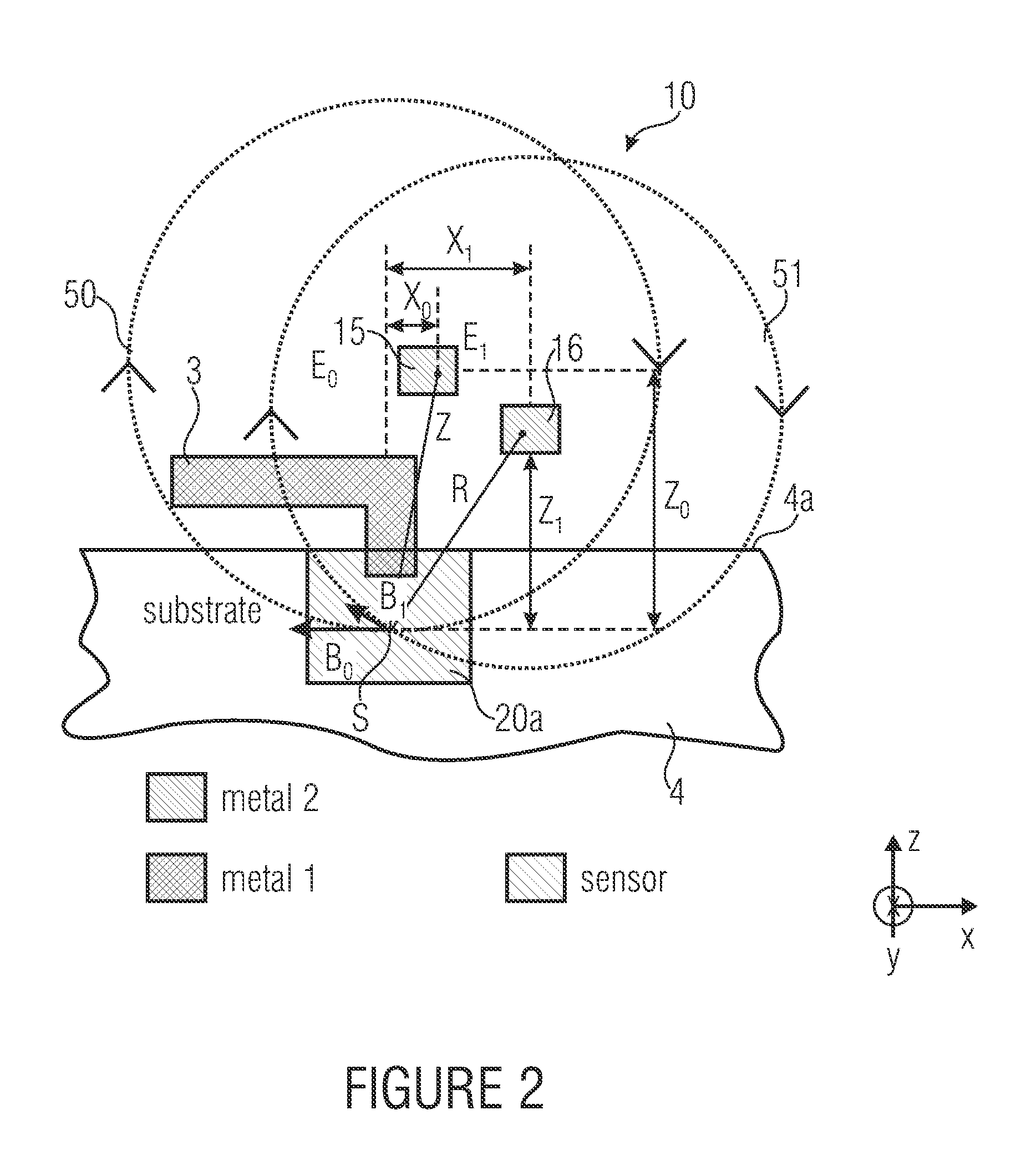
Differential magnetic field sensor structure for orientation independent measurement
ActiveUS8729892B2Magnetic sensor geometrical arrangementsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsDifferential signalingCondensed matter physics
A differential magnetic field sensor that enables operation that is independent of sensor-to-target orientation is presented. The differential magnetic field sensor is provided with at least two differential channels. Each differential channel includes a pair of magnetic field sensing elements and has a respective sensing axis defined by those magnetic field sensing elements. The sensing axes are not aligned with respect to each other. One sensing axis is positioned relative to a reference axis of a target profile to define an orientation angle between the sensing axis and the reference axis. The differential magnetic field sensor includes circuitry to produce differential signals associated with the differential channels and use those differential signals to produce a single differential signal having an amplitude that is independent of the orientation angle.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
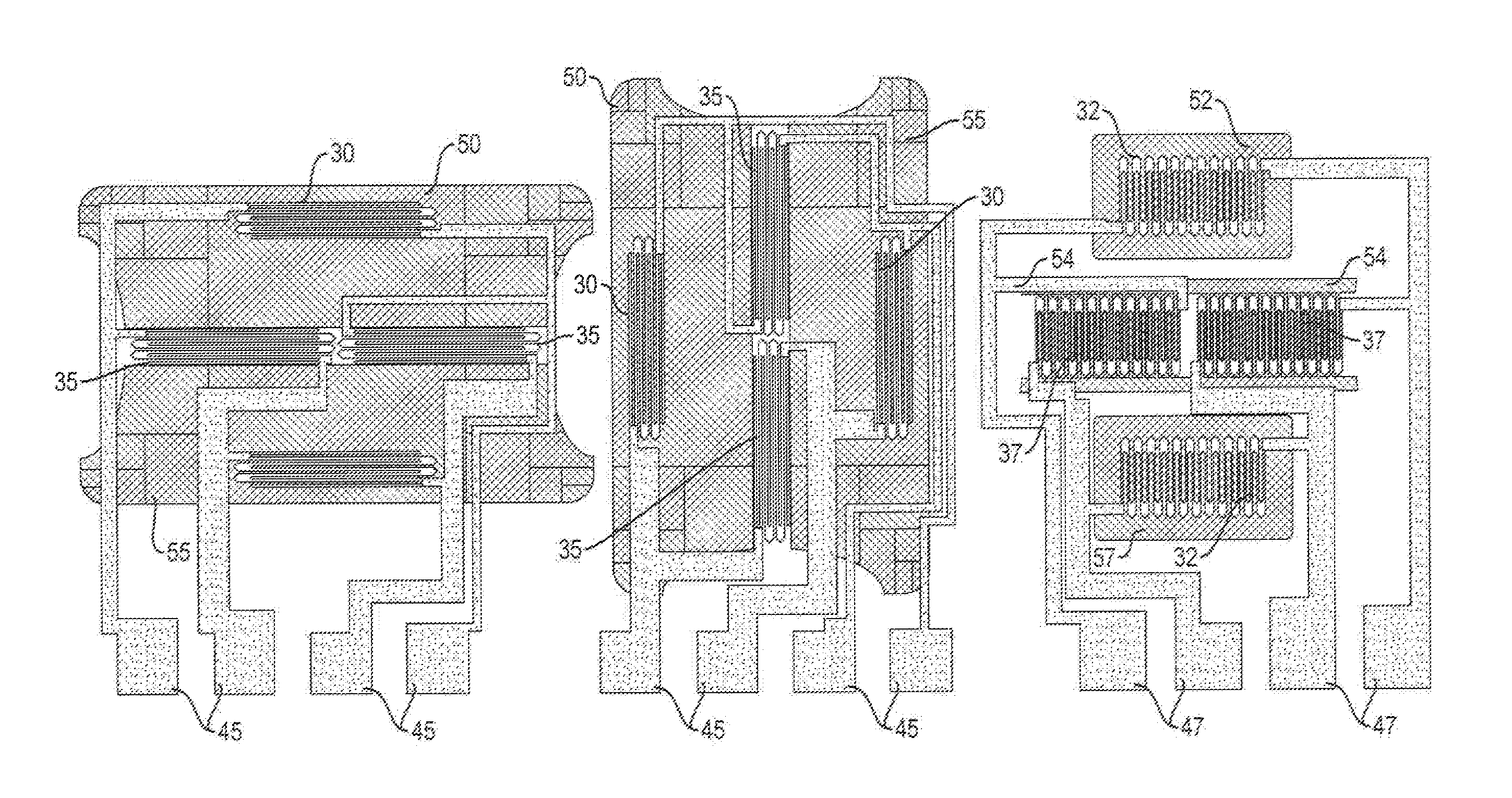
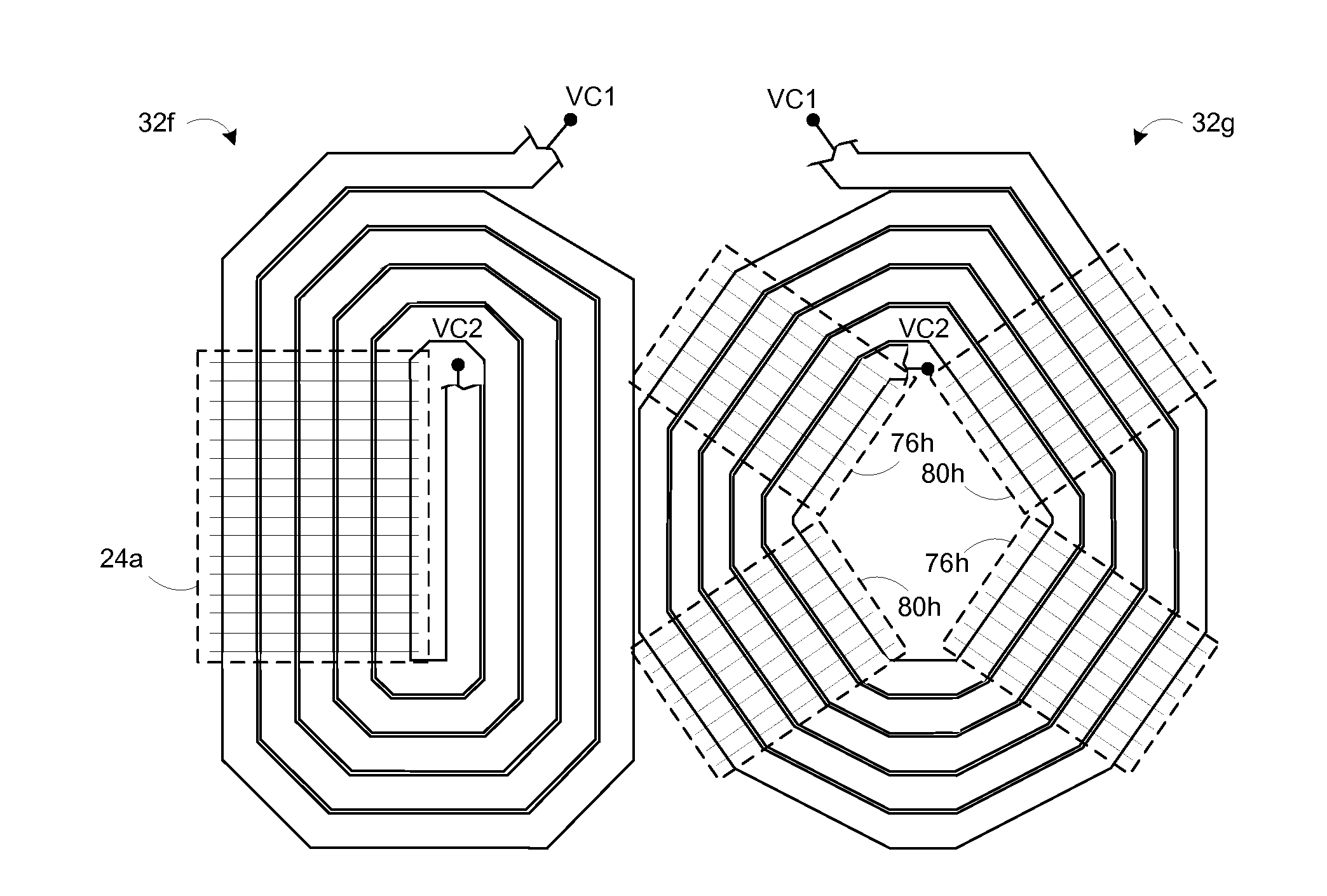
Monolithic three-axis magnetic field sensor
ActiveUS20150285873A1Magnetic sensor geometrical arrangementsThree-component magnetometersOptoelectronicsMagnetometer
A three-axis magnetic sensor or magnetometer is provided. Two magnetic sensor Wheatstone bridges using barber pole AMR structures are fabricated on opposite sides of a bump structure formed on a substrate to provide surfaces that are at a pre-determined angle with respect to the flat surface of the substrate. The bridge assembly is oriented along the Y axis and the bridges are interconnected such that Y and Z channel signals can be produced by processing of the bridge signals. The X channel signals are provided by an X axis sensor provided on the level surface of the substrate.
Owner:MEMSIC
Magnetoresistance element with increased operational range
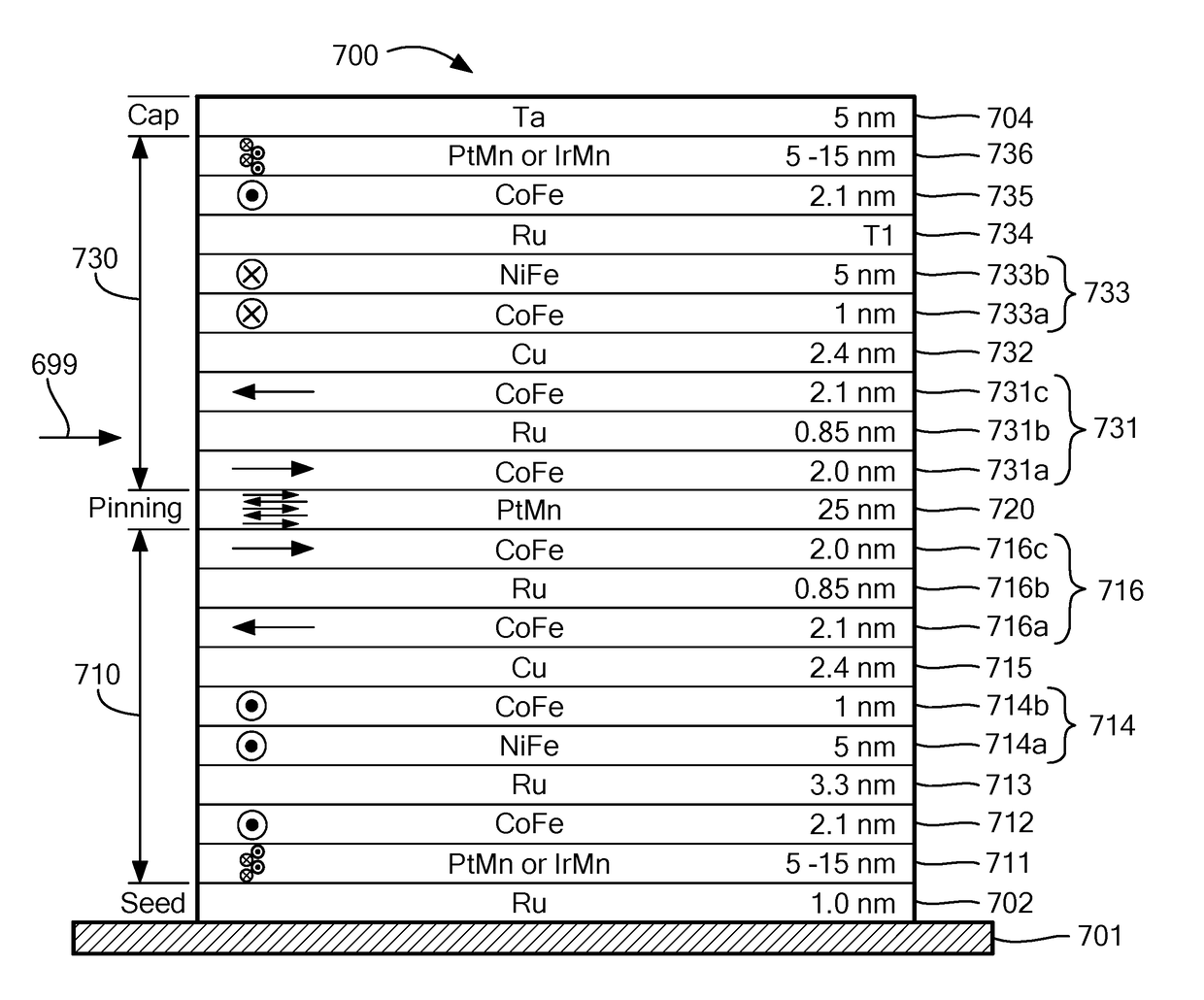
ActiveUS20180335484A1Expand the scope of operationGreat offset drift tolerationMagnetic sensor geometrical arrangementsCondensed matter physicsMaterials science
A magnetoresistance element deposited upon a substrate includes a first stack portion having opposing first and second surfaces and including a first plurality of layers. The first stack portion has a first substantially linear response corresponding to an applied magnetic field over a first magnetic field strength range. The magnetoresistance element also includes a second stack portion having opposing first and second surfaces and including a second plurality of layers. The first surface of the second stack portion is disposed over the second surface of the first stack portion and the second stack portion has a second substantially linear response that is different than the first substantially linear response. The second substantially linear response corresponds to the applied magnetic field over a second magnetic field strength range.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Magnetic signal measurement apparatus
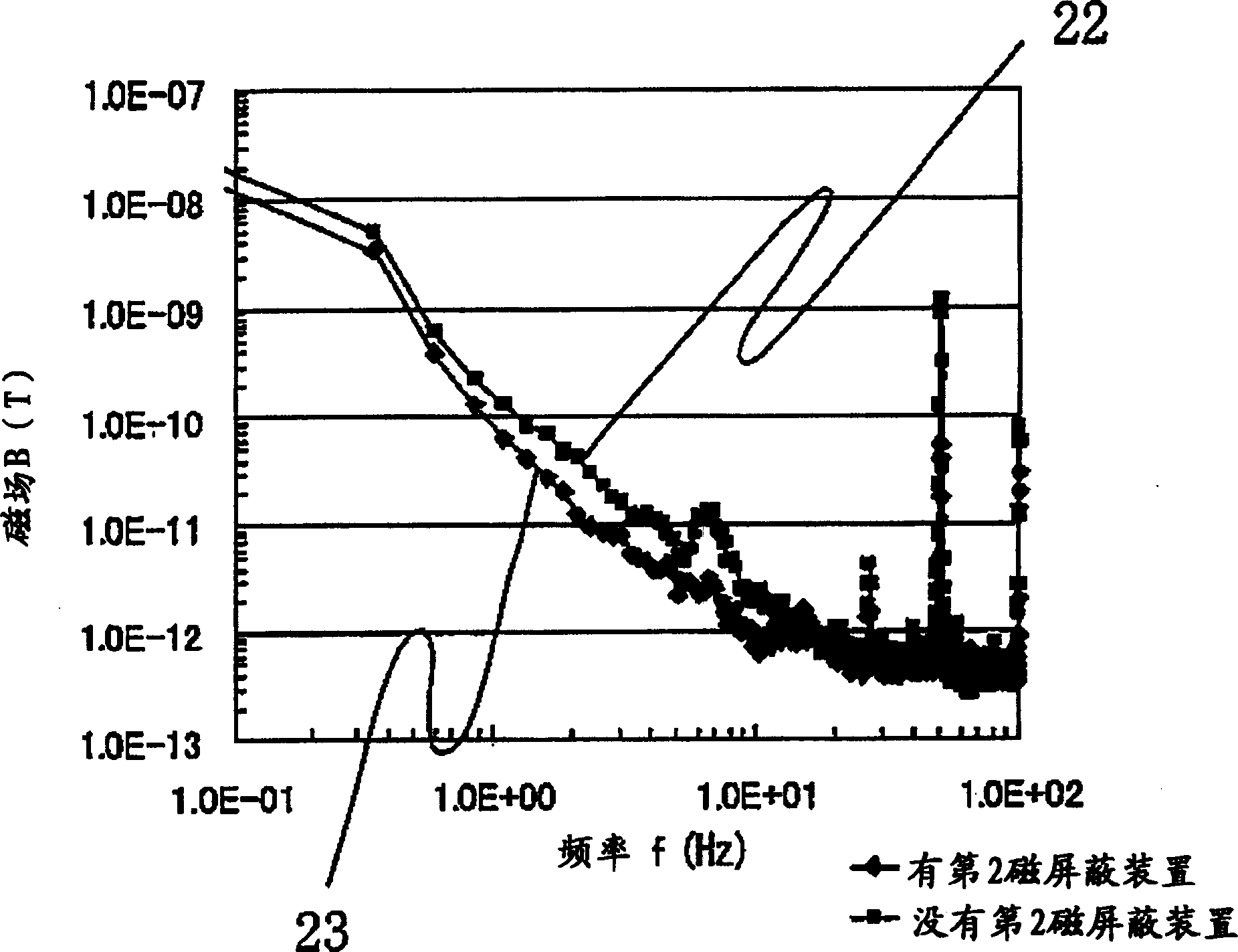
InactiveCN1877354AShorten the lengthReduce deformation effectsMagnetic/electric field screeningMagnetic sensor packagingMagnetic measurementsScreening effect
If the length of cylinder of magnetic screening arrangement is shorter, the magnetic screening effect is reduced. At the two ends of magnetic-measurement, there is the second magnetic screening arrangement, which is in the first magnetic screening arrangement. The second magnetic screening arrangement can shield the magnetic-field component which the first magnetic screening arrangement can't shield.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Method for determining an exciter conductor spacing from a magnetic field sensor, method for calibrating the magnetic field sensor as well as calibratable magnetic field sensor and usage of an exciter conductor structure for determining an exciter conductor spacing
ActiveUS20130057256A1Using electrical meansMagnetic sensor geometrical arrangementsElectrical conductorPhysics
In determining an exciter conductor spacing of an exciter conductor of an exciter conductor structure from a sensor element of a calibratable magnetic field sensor, first and second electric currents are impressed into the first and second exciter conductors of the exciter conductor structure to generate first and second magnetic field components in the sensor element of the magnetic field sensor, and a quantity is determined depending on the first and second magnetic field components by means of the sensor element. Further, the exciter conductor spacing of the exciter conductor from the sensor element of the magnetic field sensor is established in dependence on an exciter conductor intermediate spacing between the first exciter conductor and the spaced-apart second exciter conductor and the quantities depending on the first and second magnetic field components.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Near-field magnetic object tracking
InactiveUS20150285611A1Magnetic sensor geometrical arrangementsPoint coordinate measurementsSensor clusterSensor grid
An object tracking system includes a sensor grid having a plurality of sensor clusters configured to sense the presence of a magnetic field of an object. Each sensor cluster includes three or more single-axis magnetic sensors. The sensors in a cluster may be arranged with their axes parallel to one another. The sensor grid may account for ambient magnetic noise by measuring the magnetic field in a zone a distance away from the object to update the ambient magnetic field noise measurement. The sensor grid or a portion thereof may include a plurality of sensors printed on a common sheet. The sensor grid may comprise one or more sheets overlapped or interconnected. The system may track an object and determine up to three degrees of positioning and three degrees of orientation by using a geometric solution of the intercepts of magnetic field strengths obtained from information collected by the magnetic sensors.
Owner:LOWERY ANDREW D +2
Integrated triaxial magnetometer of semiconductor material manufactured in MEMS technology
ActiveUS20110140693A1Low costSmall dimensionMagnetic field measurement using permanent magnetsMagnetic sensor geometrical arrangementsSemiconductor materialsClassical mechanics
Two suspended masses are configured so as to be flowed by respective currents flowing in the magnetometer plane in mutually transversal directions and are capacitively coupled to lower electrodes. Mobile sensing electrodes are carried by the first suspended mass and are capacitively coupled to respective fixed sensing electrodes. The first suspended mass is configured so as to be mobile in a direction transversal to the plane in presence of a magnetic field having a component in a first horizontal direction. The second suspended mass is configured so as to be mobile in a direction transversal to the plane in presence of a magnetic field having a component in a second horizontal direction, and the first suspended mass is configured so as to be mobile in a direction parallel to the plane and transversal to the current flowing in the first suspended mass in presence of a magnetic field having a component in a vertical direction.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Magnetic sensor
ActiveUS8193805B2Improving accuracy in detecting magnetic fieldReduce variationWave amplification devicesMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetoHemt circuits
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
Current sensor operating in accordance with the principle of compensation
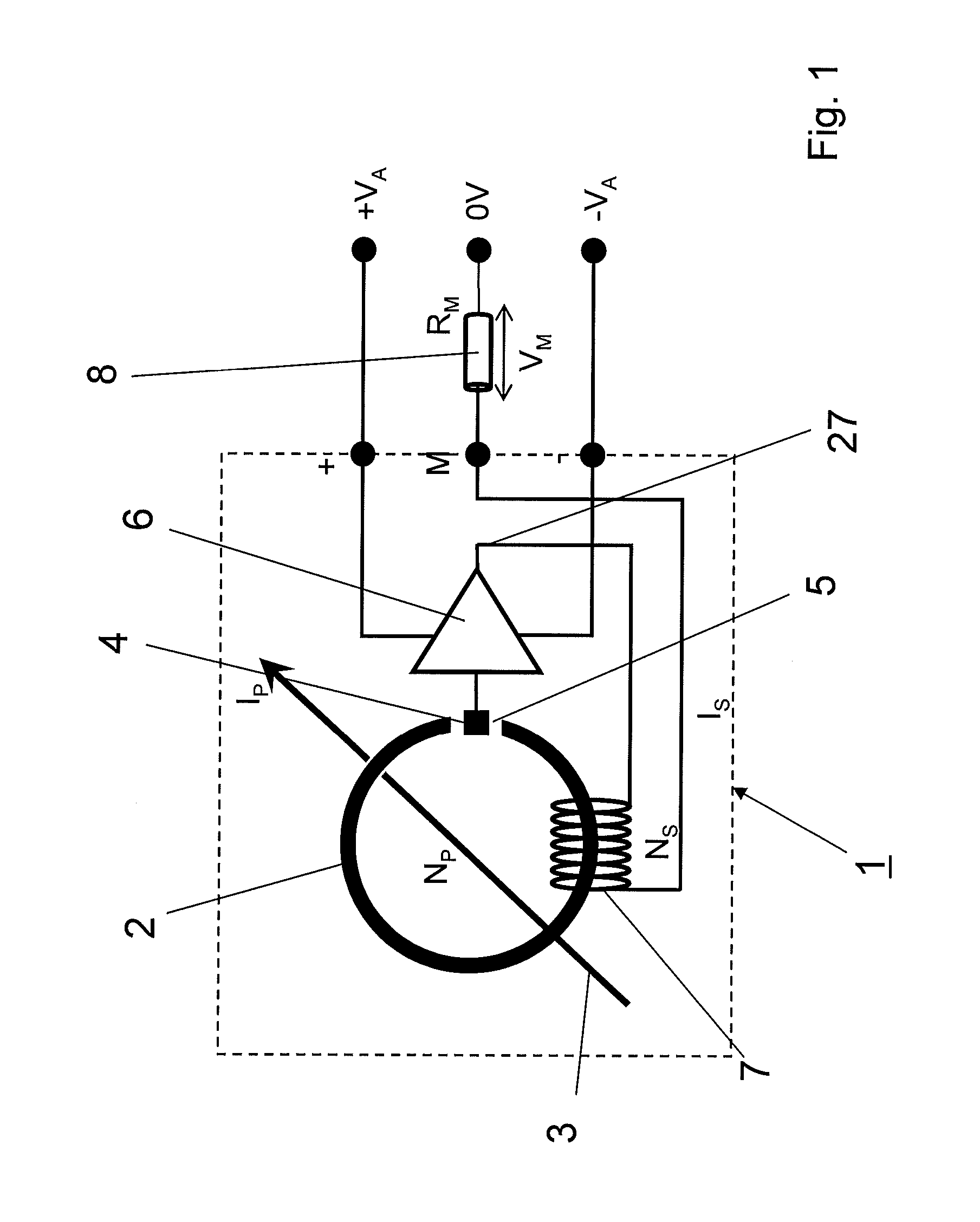
ActiveUS20120268108A1Low maximum lossesLow costMagnetic sensor geometrical arrangementsElectrical measurementsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
An exemplary current sensor operating in accordance with the principle of compensation includes a primary winding creating a magnetic field based on a current to be measured, a secondary winding generating a magnetic field compensating the primary winding based on a compensation current. The current sensor also includes a magnetic core, a terminating resistor connected in series to the secondary winding, and sensor means. A booster circuit is connected downstream of the sensor means and feeds the compensation current to the secondary winding via the terminating resistor. The booster circuit includes a switched mode amplifier with a pulse width and density modulator that operates based on pulse width and density modulation, turning the compensation current into a pulse width and density modulated current. The switched mode amplifier having a switching frequency that is high at when the compensation current is small and low when the compensation current is high.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Rotational Angle Detection Device
InactiveUS20090033321A1Without any changeMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesAtomic physicsMagnet
Owner:TOMEN ELECTRONICS CORP
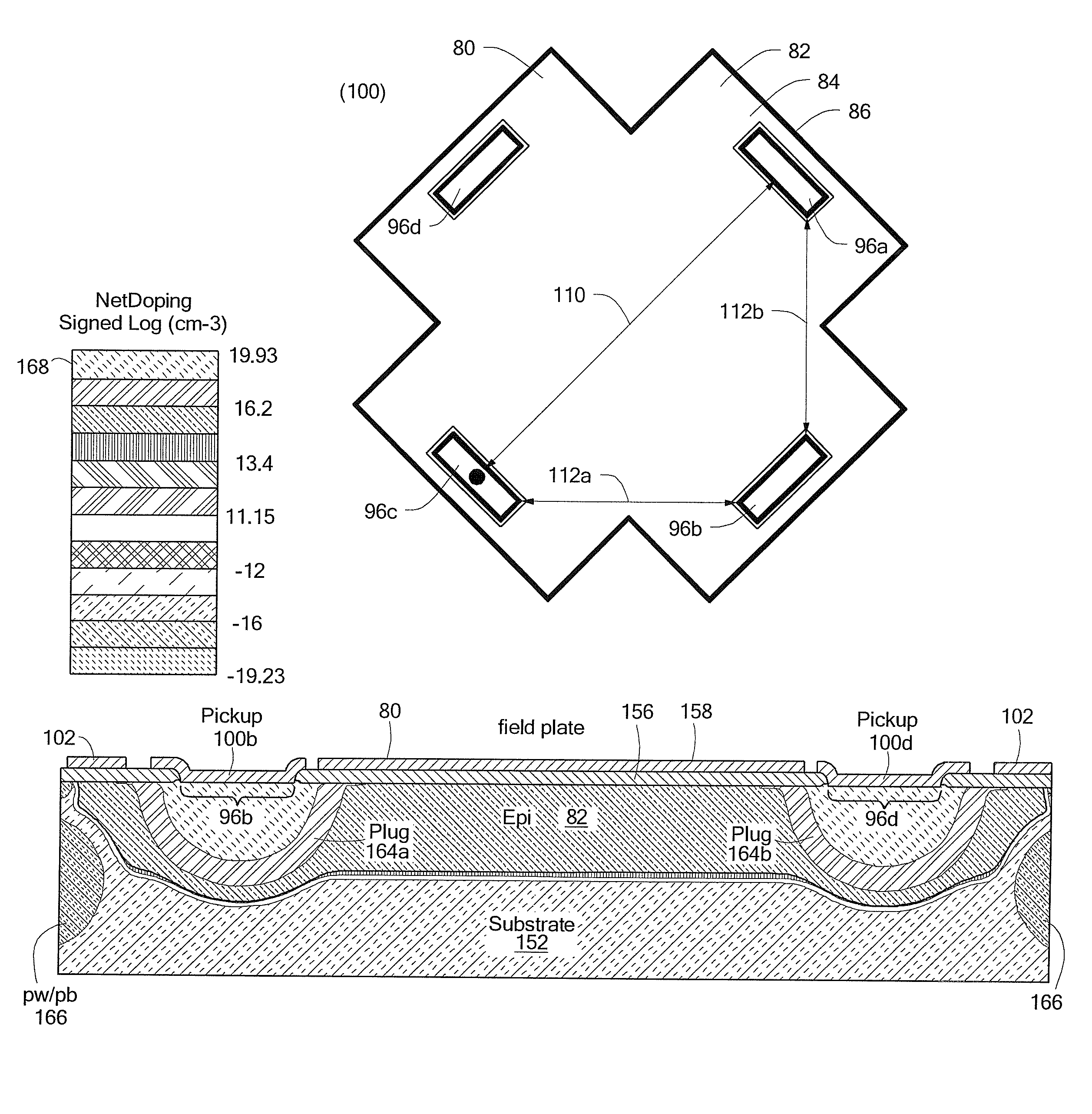
Magnetic sensor integrated in a chip for detecting magnetic fields perpendicular to the chip and manufacturing process thereof
ActiveUS20140217533A1Magnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipPhysics
An integrated magnetic sensor formed by a semiconductor chip having a surface and accommodating a magnetic via and a sensing coil. The magnetic via is formed by a cylindrical layer of ferromagnetic material that extends perpendicular to the surface of the first chip and has in cross-section an annular shape of a circular or elliptical or curvilinear type. The sensing coil surrounds the magnetic via at a distance and is connected to an electronic circuit.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Magnetic field sensor
An MR sensor arrangement is integrated with an IC. A metal layer of the IC structure (e.g. CMOS) is patterned to define at least first and second contact regions. Metal connecting plugs are provided below the first and second contact regions of the metal layer for making contact to terminals of the integrated circuit. A magnetoresistive material layer is above the metal layer and separated by a dielectric layer. Second metal connecting plugs extend up from the metal layer to an MR sensor layer. The sensor layer is thus formed over the top of the layers of the IC structure.
Owner:NXP BV
Magneto-resistance effect element and sensor
ActiveUS20110025322A1Improve sensing accuracyWeakening rangeMagnetic sensor geometrical arrangementsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsMagnetizationMagneto resistance
A magneto-resistance effect element for a sensor to sense a variation in externally applied magnetism includes a pinned layer having a fixed magnetization direction, a free layer having a magnetization direction which varies in response to an external magnetic field, and an intermediate layer provided between the pinned layer and the free layer. The pinned layer has a planar shape which is long in the fixed magnetization direction and which is short in a direction orthogonal to the fixed magnetization direction. Moreover, the pinned layer preferably has a planar shape in which the pinned layer is divided into a plurality of sections.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Three-dimensional hall sensor for detecting a spatial magnetic field
ActiveCN104181475AFirmly connectedMagnetic sensor geometrical arrangementsThree-component magnetometersPower flowElectrode pair
A three-dimensional Hall sensor can be used for detecting a spatial magnetic field. A method for measuring a spatial magnetic field can be performed using this Hall sensor. The Hall sensor comprises an electrically conducting base body and at least three electrode pairs, wherein each electrode pair has a first terminal and a second terminal, which are arranged such on the base body, that a current can flow from the first terminal to the second terminal through the base body. At least three first terminals are arranged on a first surface of the base body and at least three second terminals are arranged on the second surface, different from the first surface of the base body, wherein the first and the second surfaces oppose each other.
Owner:TDK MICRONAS 有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com