Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
147results about "Heads relative to rotating disc" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
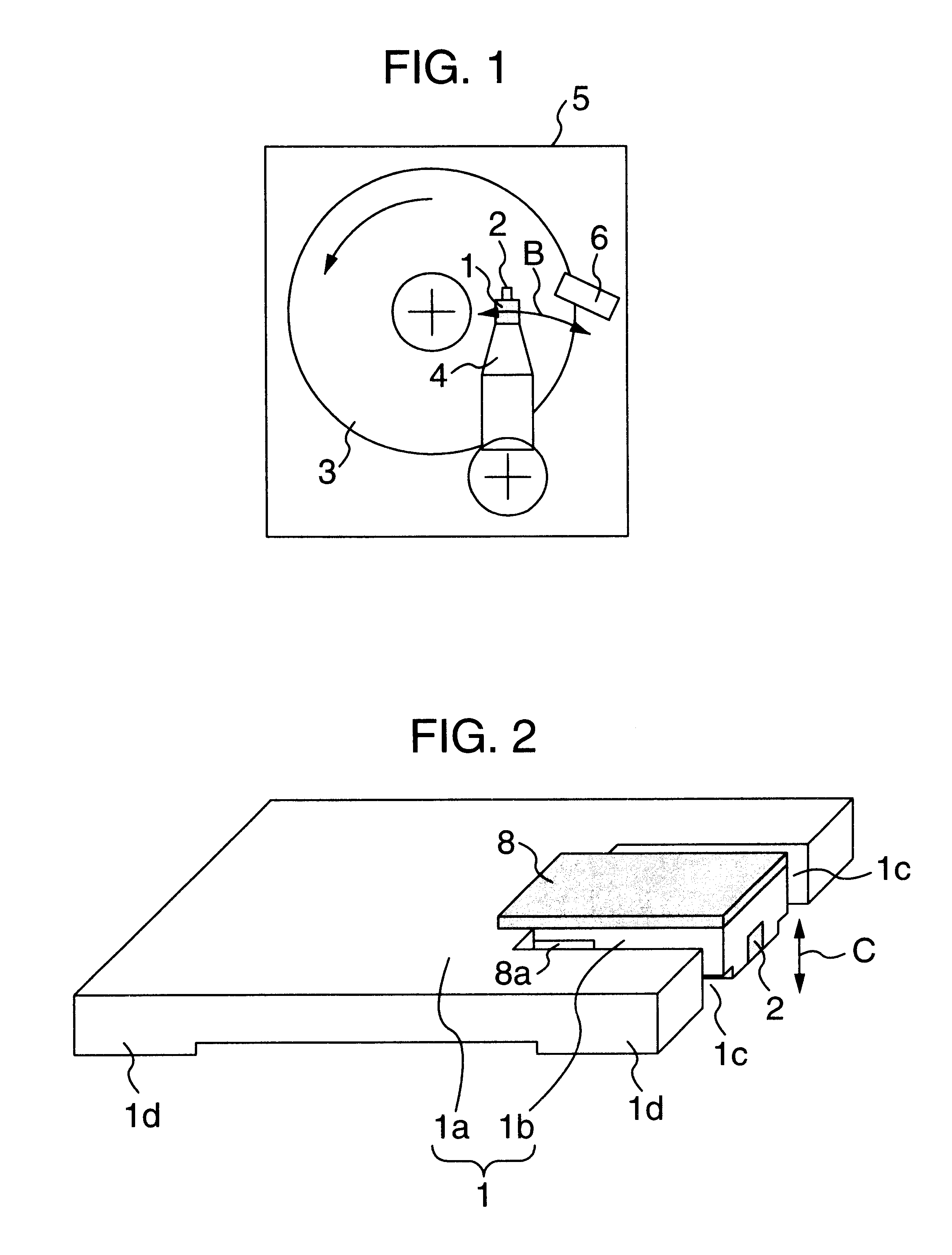
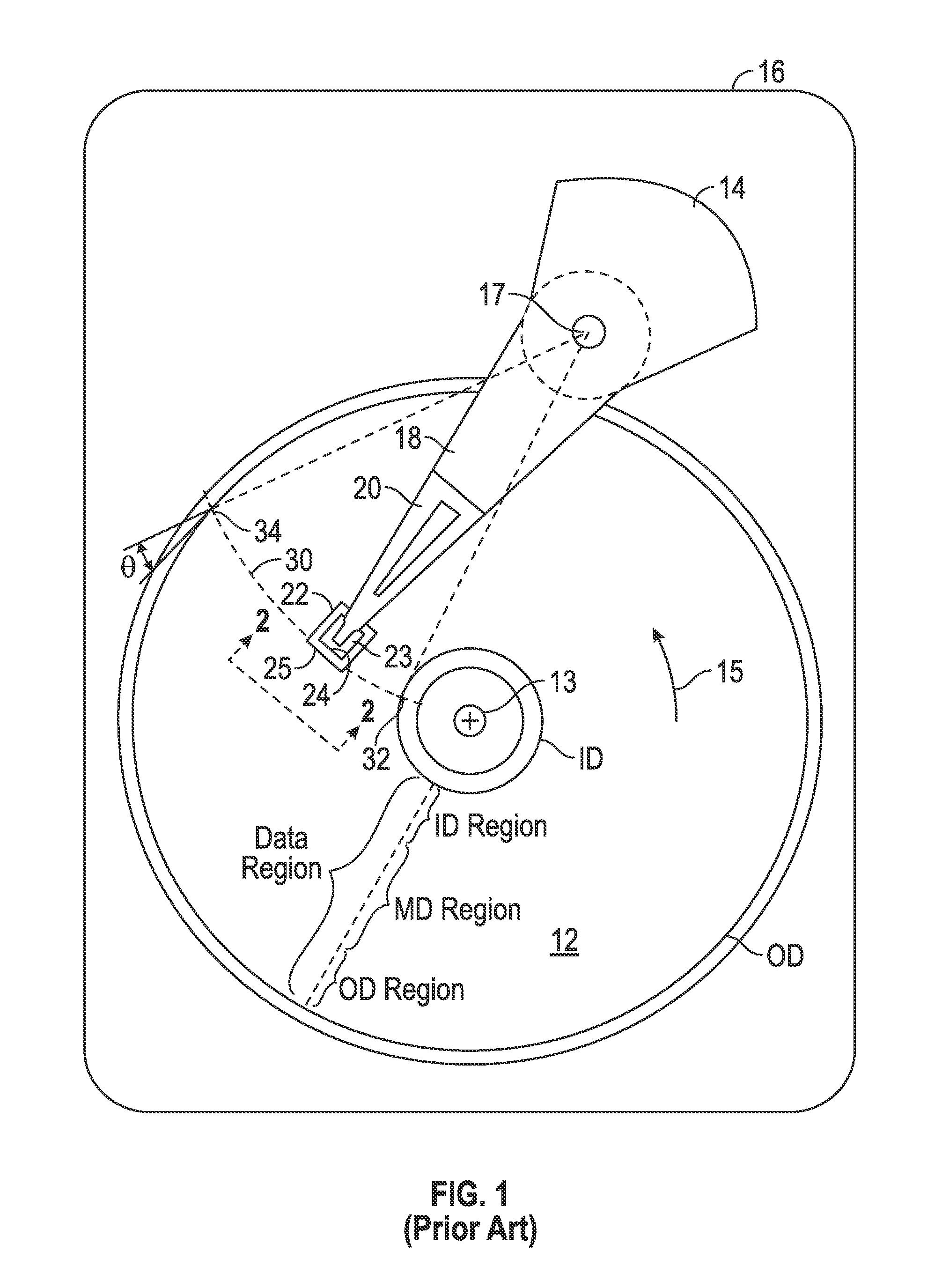
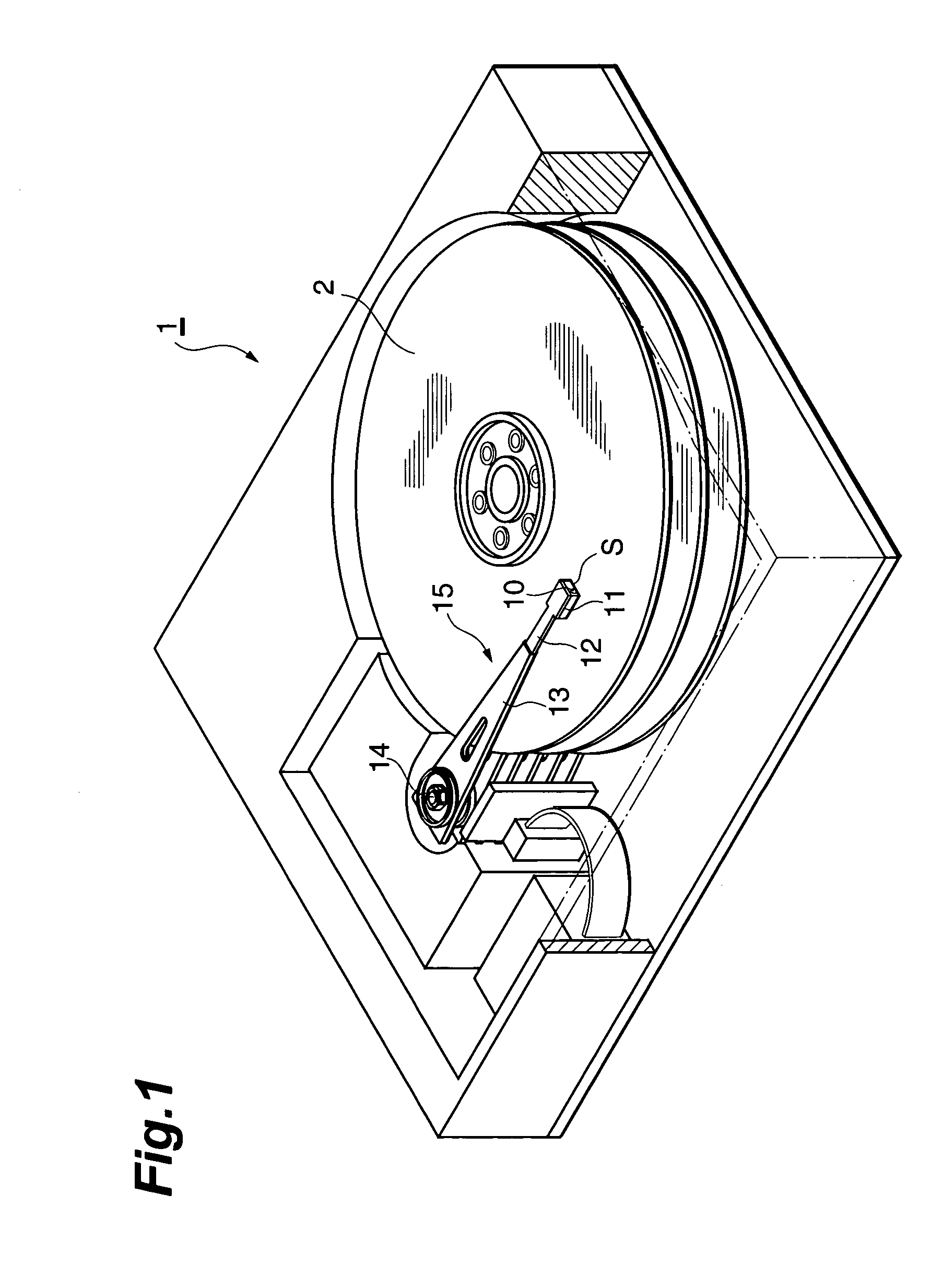
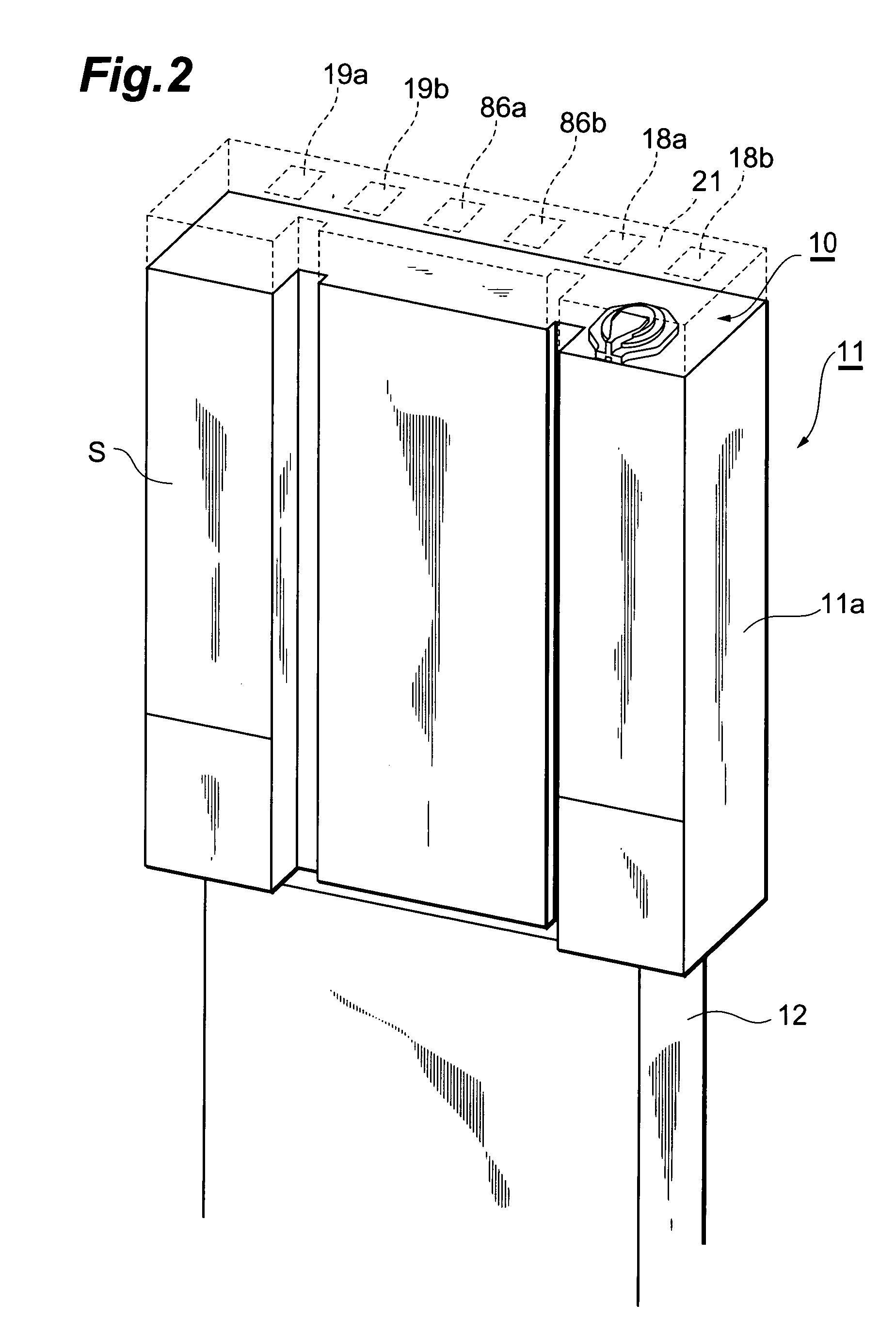
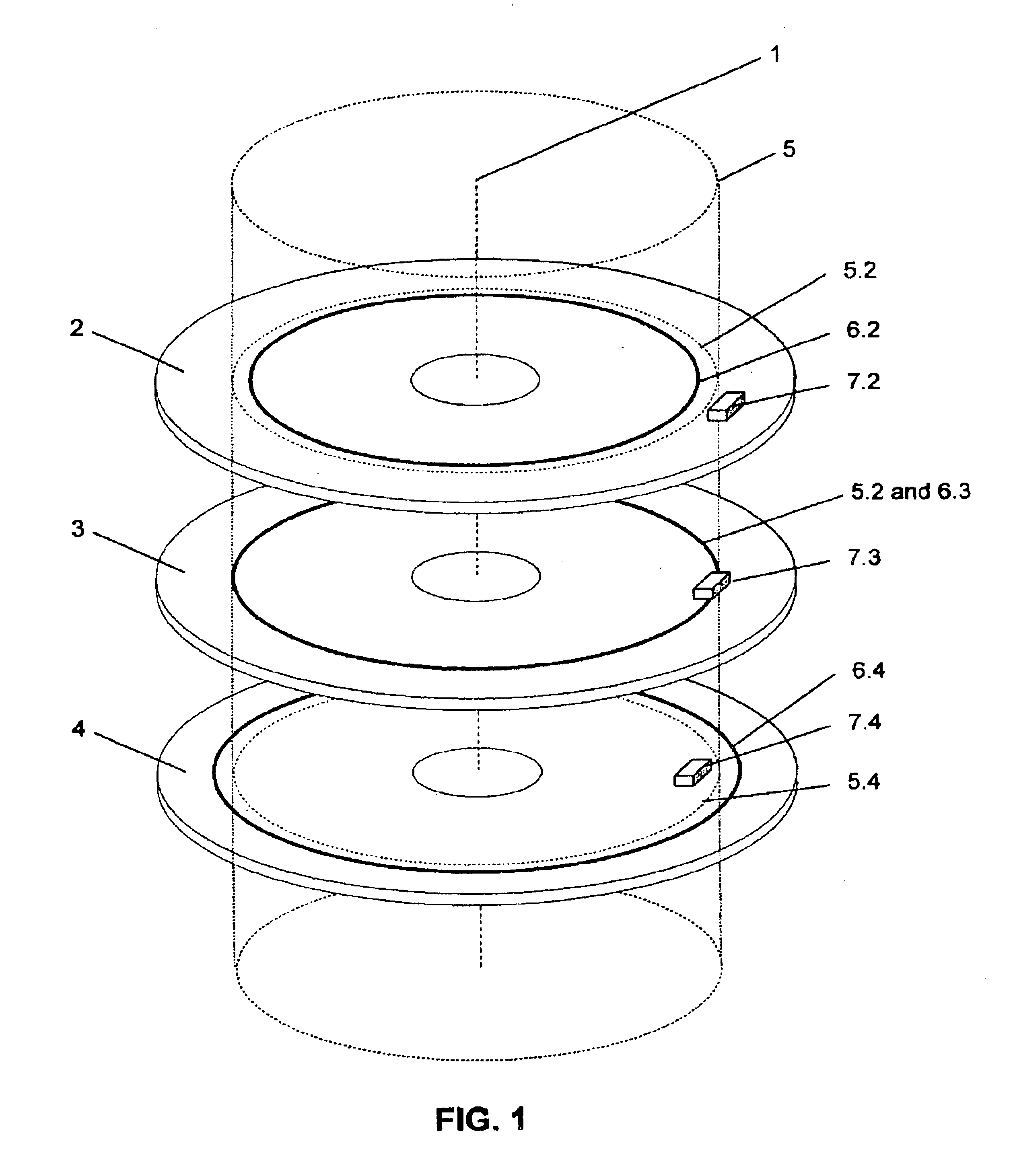
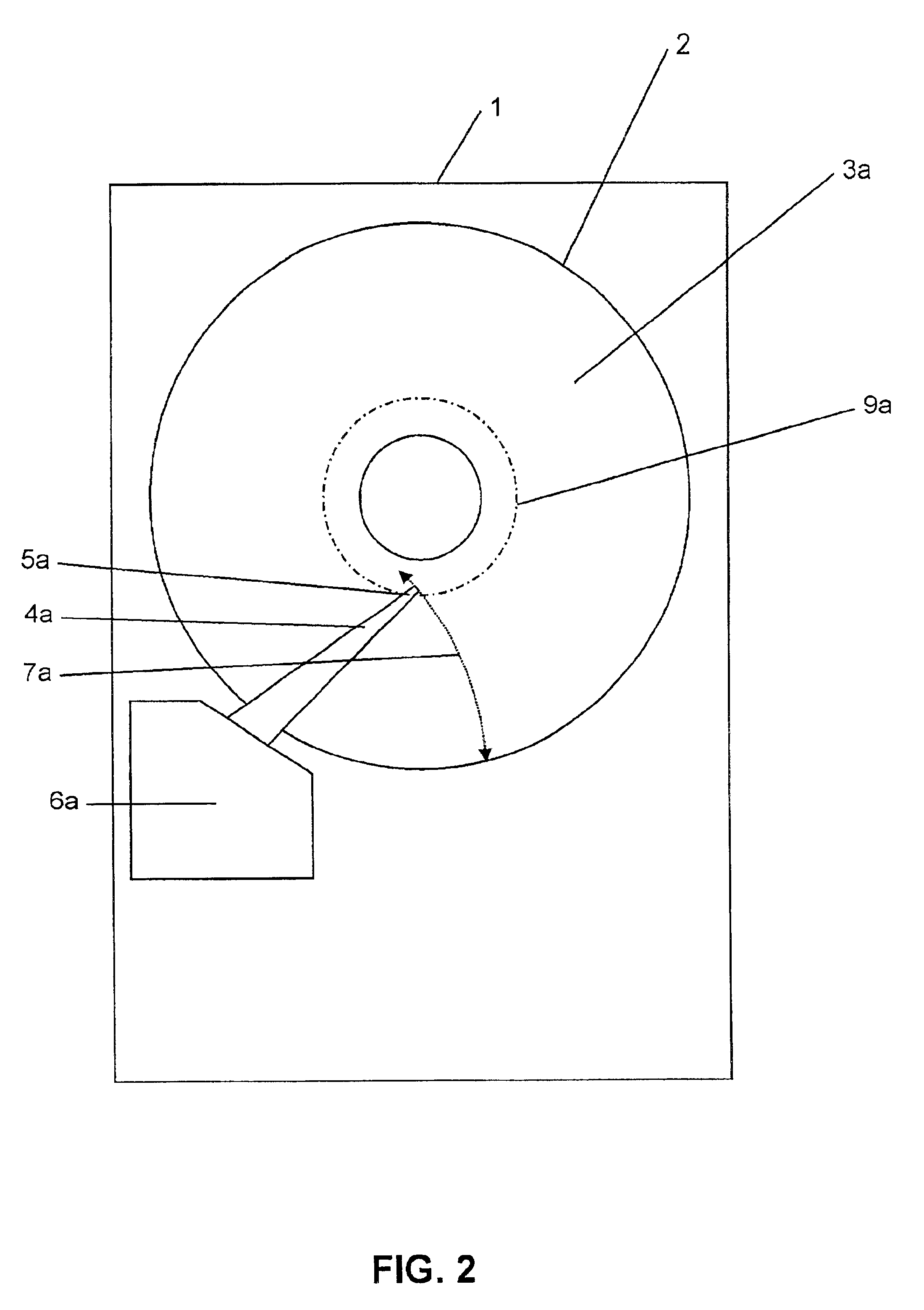
Magnetic data storage fixed hard disk drive using stationary microhead array chips in place of flying-heads and rotary voice-coil actuators
InactiveUS6249824B1Input/output to record carriersApparatus modification to store record carriersHard disc driveTransducer
A magnetic data storage fixed hard disk drive using stationary Microhead Array Chips in place of conventional Flying-Heads and Rotary Voice-Coil Actuators or other Servo-Tracking mechanisms. Every Microhead Array Chip has a minimum of one thousand or maximum of four billion individual and addressable microhead read and write data-transducers built into it. The hard disk drive unit assembly that uses the Microhead Array Chip approach will have within its assembly as few as two or as many as twenty-eight installed Microhead Array Chips. The Microhead Array Chip hard disk drive unit assemblies will have at least one storage disk-platter with two disk-platter data-surfaces containing a multiplicity of concentric data-tracks that rotates at a substantially constant angular velocity. While Microhead Array Chips are made stationary by specially designed circuit boards, that positions a Microhead Array Chip over each of two data-surfaces of every disk-platter within the hard disk drive assembly. The total number of microheads within a stationary positioned Microhead Array Chip's Microhead Array is what determines the total number of available tracks on and across a data-platter's data-surface (i.e., 65,000 microheads would equal 65,000 cylinder / tracks).
Owner:OPTICAL STORAGE DEVICES
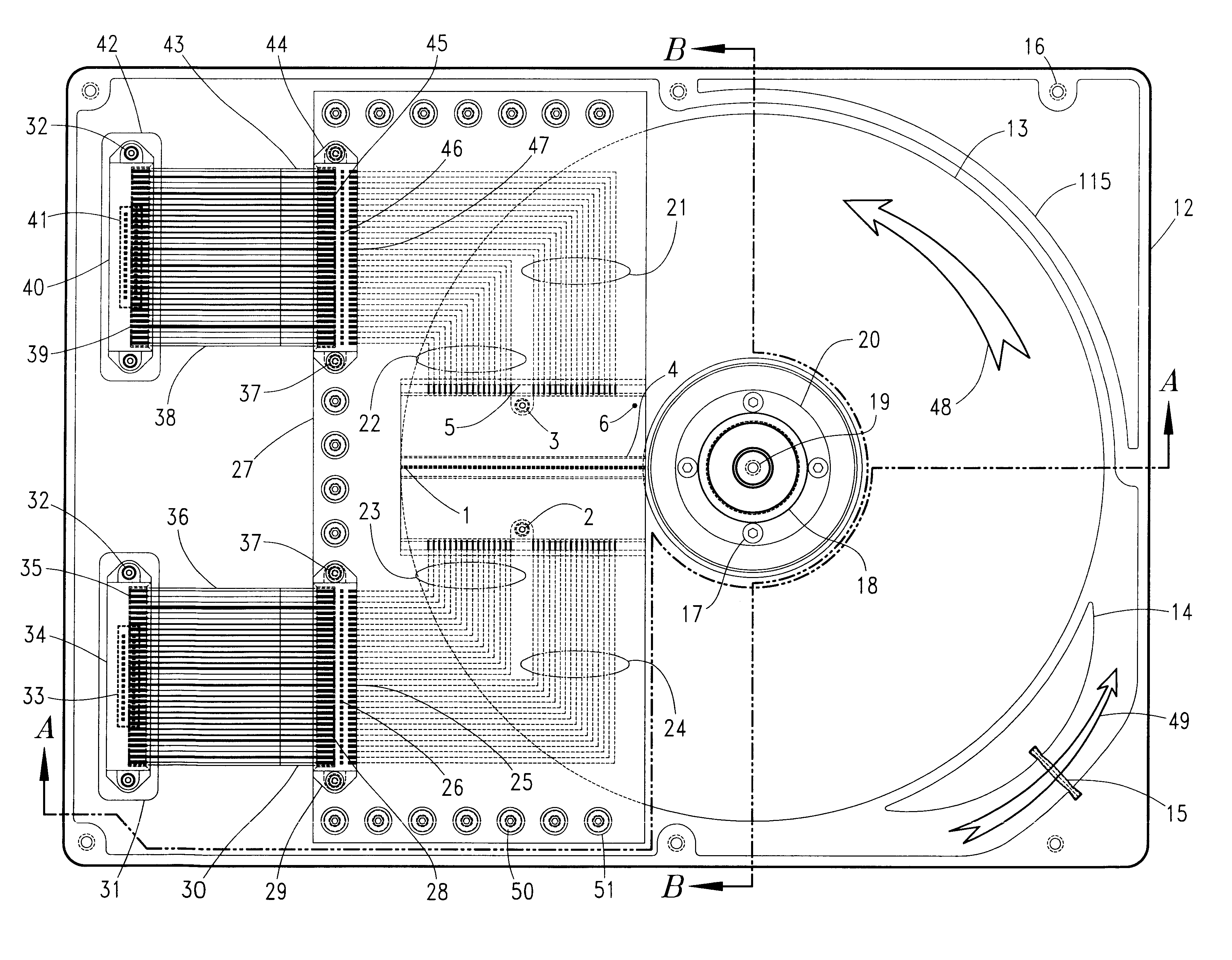
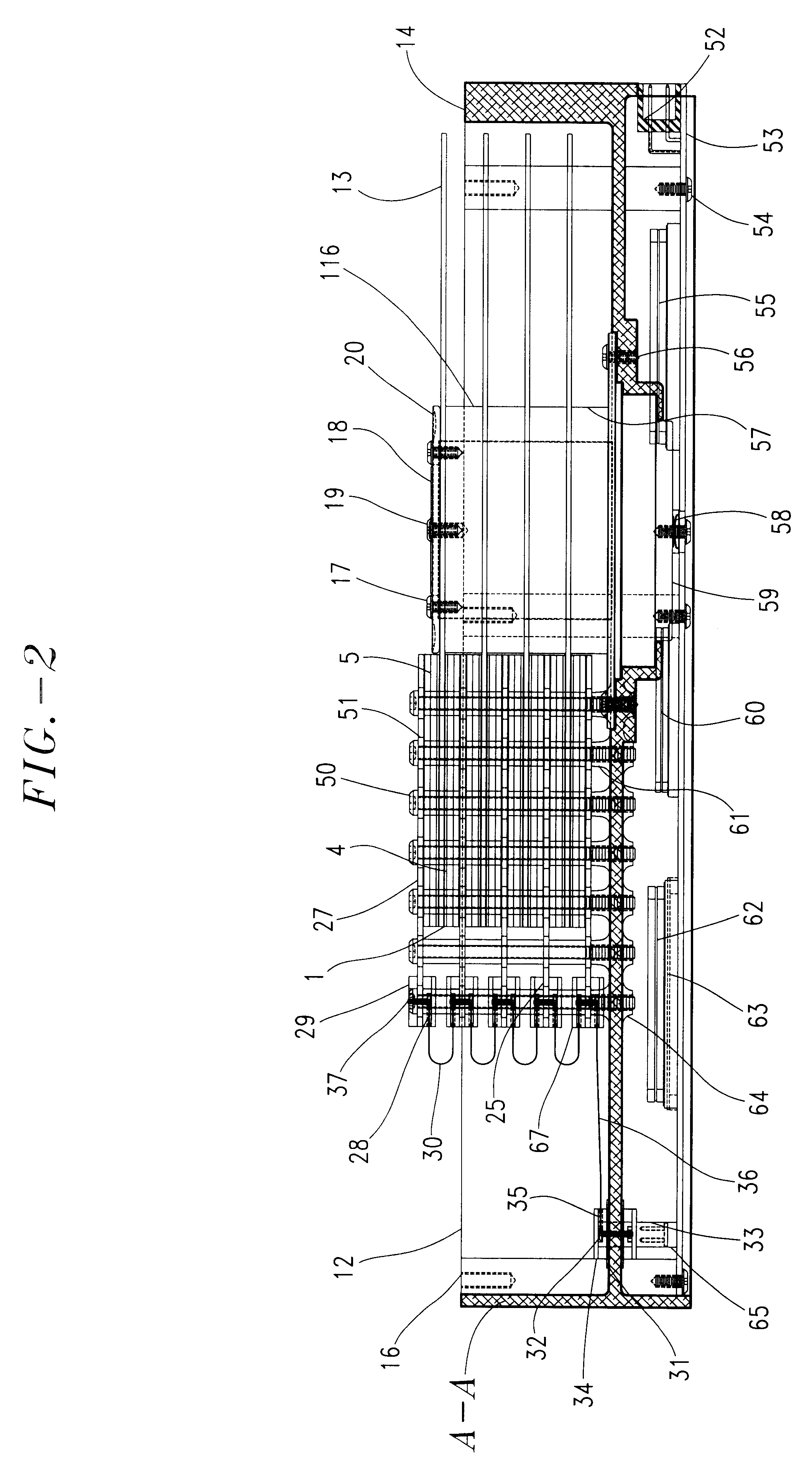
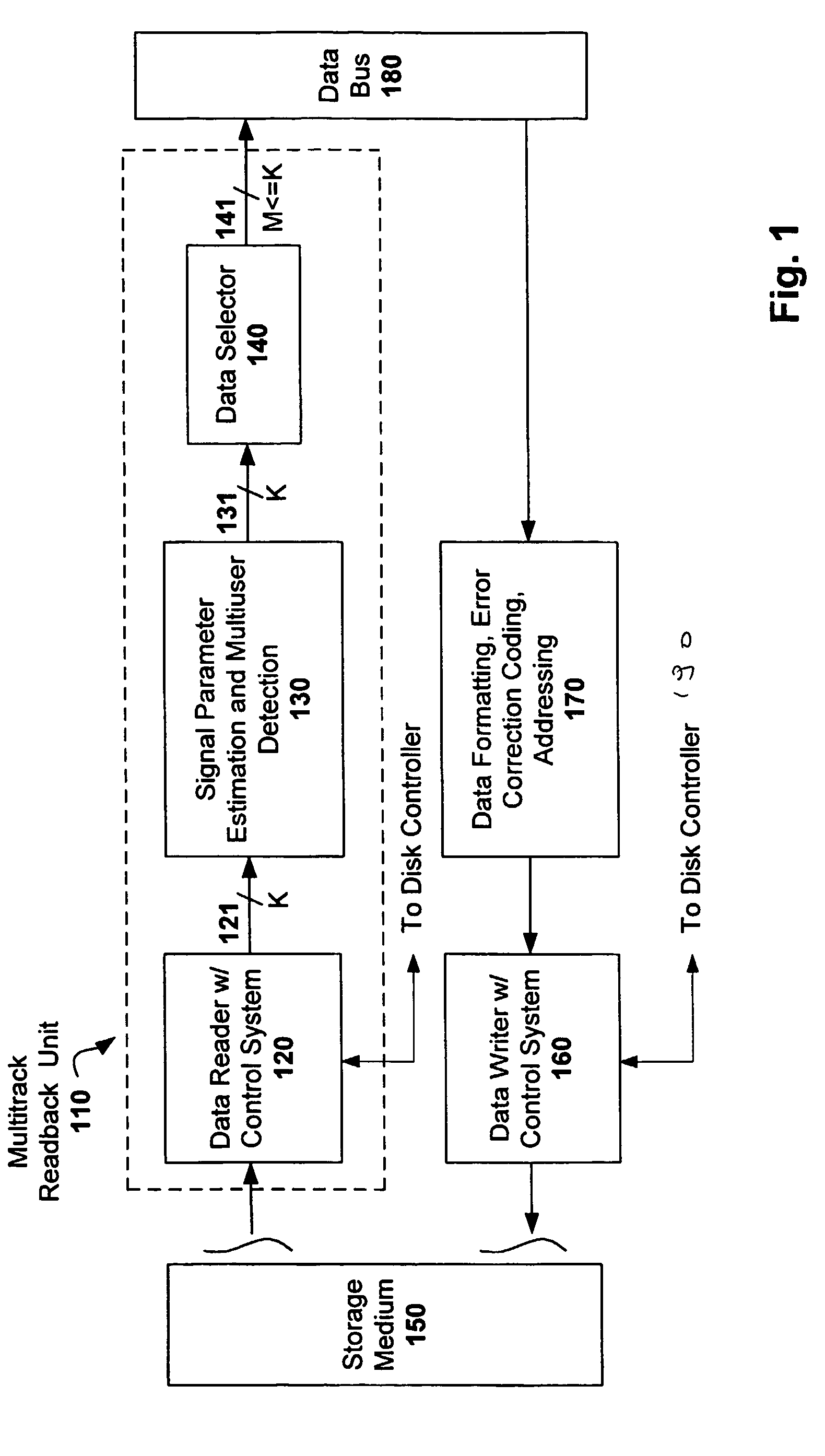
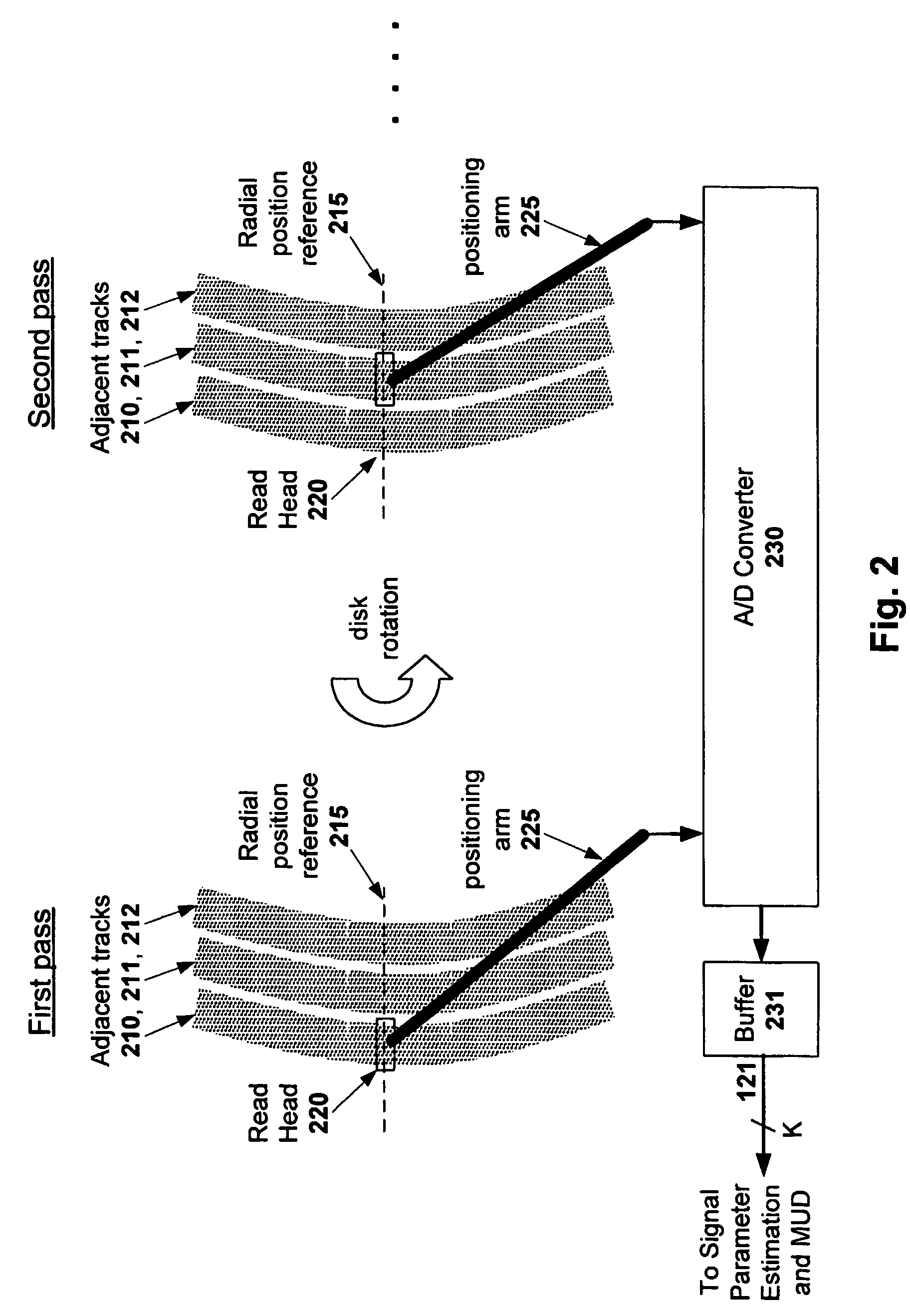
Multitrack readback and multiuser detection for disk drives
Techniques for reading data from a storage medium (150) having a high track density prone to adjacent track interference are disclosed. One or more sensing elements (120) are used to extract data stored on adjacent tracks. Multiuser detection (130) is then used to detect / decode a single track that is closely spaced to its neighboring tracks, resolve interference from adjacent tracks, or to simultaneously detect / decode multiple adjacent closely packed tracks.
Owner:COLLISION COMM INC
Roll-biased head suspension for reduced track misregistration
InactiveUS6088192ADecreased TMRReduce TMR otherwiseCarrier indicating/warning arrangementsRecord information storageHard disc driveOut of plane motion
Owner:MAXTOR
Magnetic disk apparatus and method of controlling the same
InactiveUS6798605B2Increase storage capacityHigh densityDriving/moving recording headsFluid-dynamic spacing of headsEngineeringControl unit
A magnetic disk apparatus includes a rotation mechanism for driving a magnetic disk, a magnetic head slider being floated in close proximity to a surface of the magnetic disk, a recording / reproduction element for performing recording and playback of information, a drive unit for causing a distance between the record / reproduction element and the magnetic disk to change, and means for performing position determination of the magnetic head slider, wherein the apparatus has a detection unit for permitting the drive unit to gradually reduce the distance between the record / reproduction element and the magnetic disk and for detecting occurrence of contact therebetween, and a control unit for controlling the drive unit in such a way as to cause, the record / reproduction element to shift in position by a fixed amount to thereby let the distance between this element and magnetic disk increase accordingly.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD
Data recording and reproducing device, data recording and reproducing method, and recording medium
InactiveUS20060182004A1Improve recording densityImprove reading resolutionNanoinformaticsRecord information storageData recordingCantilever
A position control area (76A) is partly formed in the recording area (75) of a recording medium (70) and position information is recorded only in the position control area (76A). To record data in the recording medium (70) by a head (60) having a plurality of cantilevers (62A), (62B), . . . , the position information is read by the cantilever (62E) corresponding to the position control area (76A) and, based on the position information, the positioning control or moving control of all the other cantilevers is performed.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
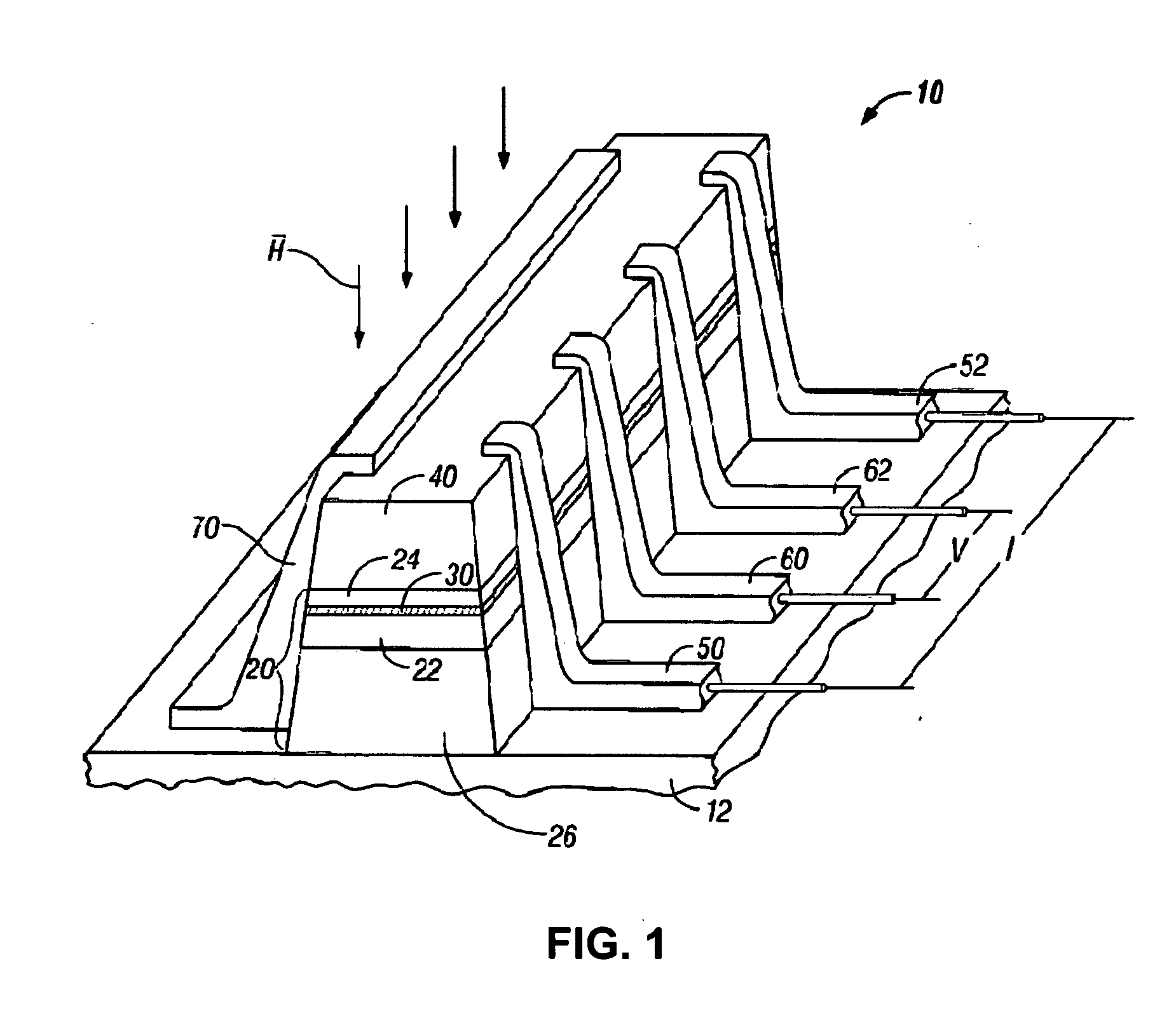
Current-perpendicular-to-the-plane (CPP) magnetoresistive (MR) sensor structure with stacked sensors for minimization of the effect of head skew
ActiveUS9099125B1Manufacturing heads with multiple gapsRecord information storageRadial positionSkew angle
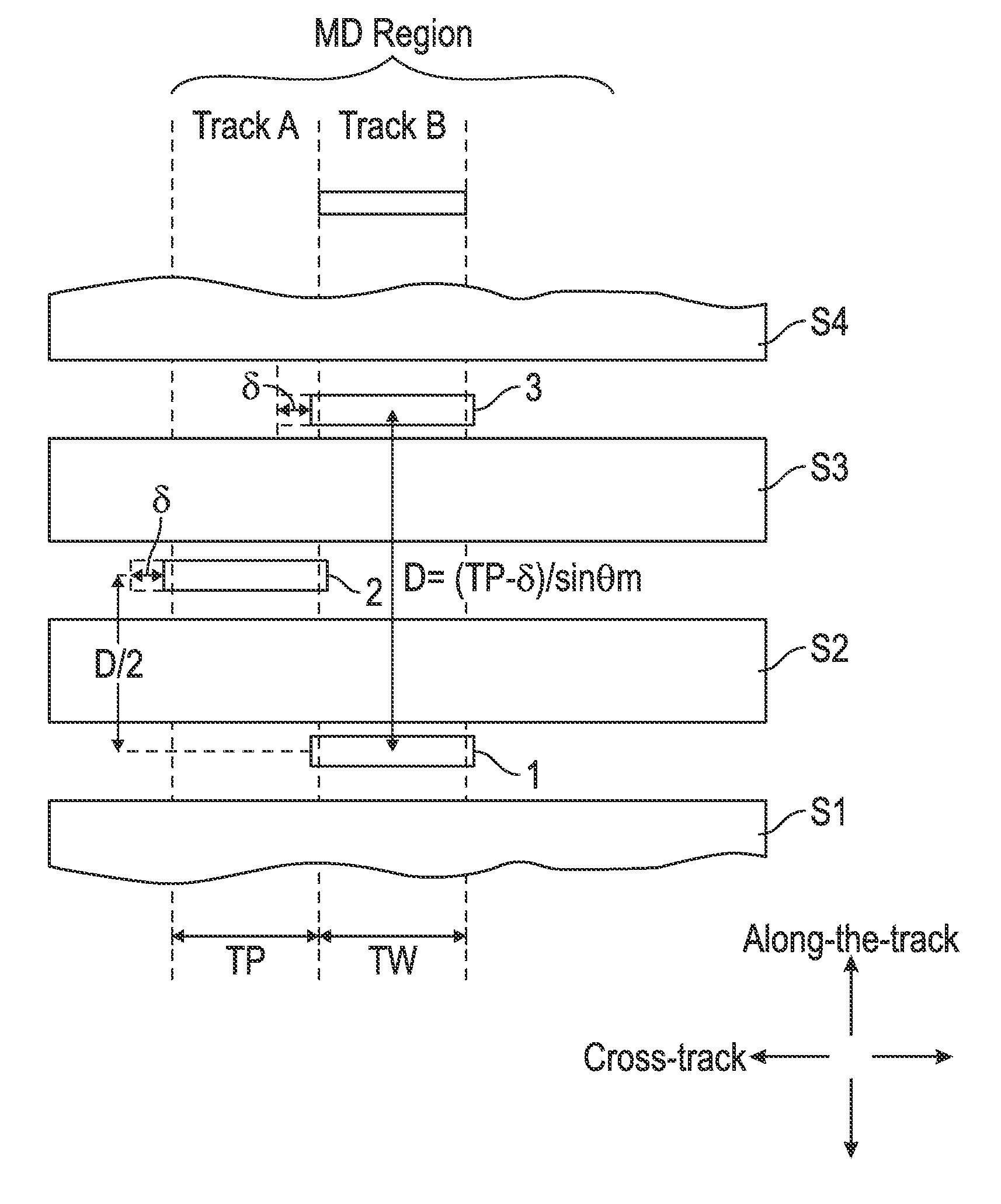
A two-dimensional magnetic recording (TDMR) multi-sensor read head has three stacked sensors separated by magnetic shields. The lower sensor is the primary sensor that is always aligned with the target track. The middle sensor is spaced laterally from the lower sensor a distance substantially equal to the track pitch (TP). The upper sensor is aligned with the lower sensor. The spacing D between the lower and upper sensors is selected to be related to TP and a maximum skew angle, where the skew angle is the angle between a line orthogonal to the sensor and the data track that varies with radial position of the head. The read head is connected to circuitry that selects two of the three sensors to be the active sensors depending on the radial position of the head and thus the skew angle of the head.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Thin-film merged magnetic head having a heat-generating layer
ActiveUS6920020B2High reproductive outputGood thermal expansionHeads using thin filmsRecord information storageMagnetic reluctanceTransducer
In the thin-film magnetic head of the present invention, the distance to a heat-generating layer is shorter from the end part on the side facing, a recording medium in a magnetoresistive device than from the end part on the side facing the recording medium in an electromagnetic transducer. Therefore, even when the thin-film magnetic head tilts so that its electromagnetic transducer side approaches the recording medium when floating up from the recording medium, the amount of thermal expansion caused by the heat from the heat-generating layer is greater in the magnetoresistive device than in the electromagnetic transducer. This reduces the gap between the magnetoresistive device and the recording medium, whereby a high reproducing output can be obtained.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Patterned media having offset tracks
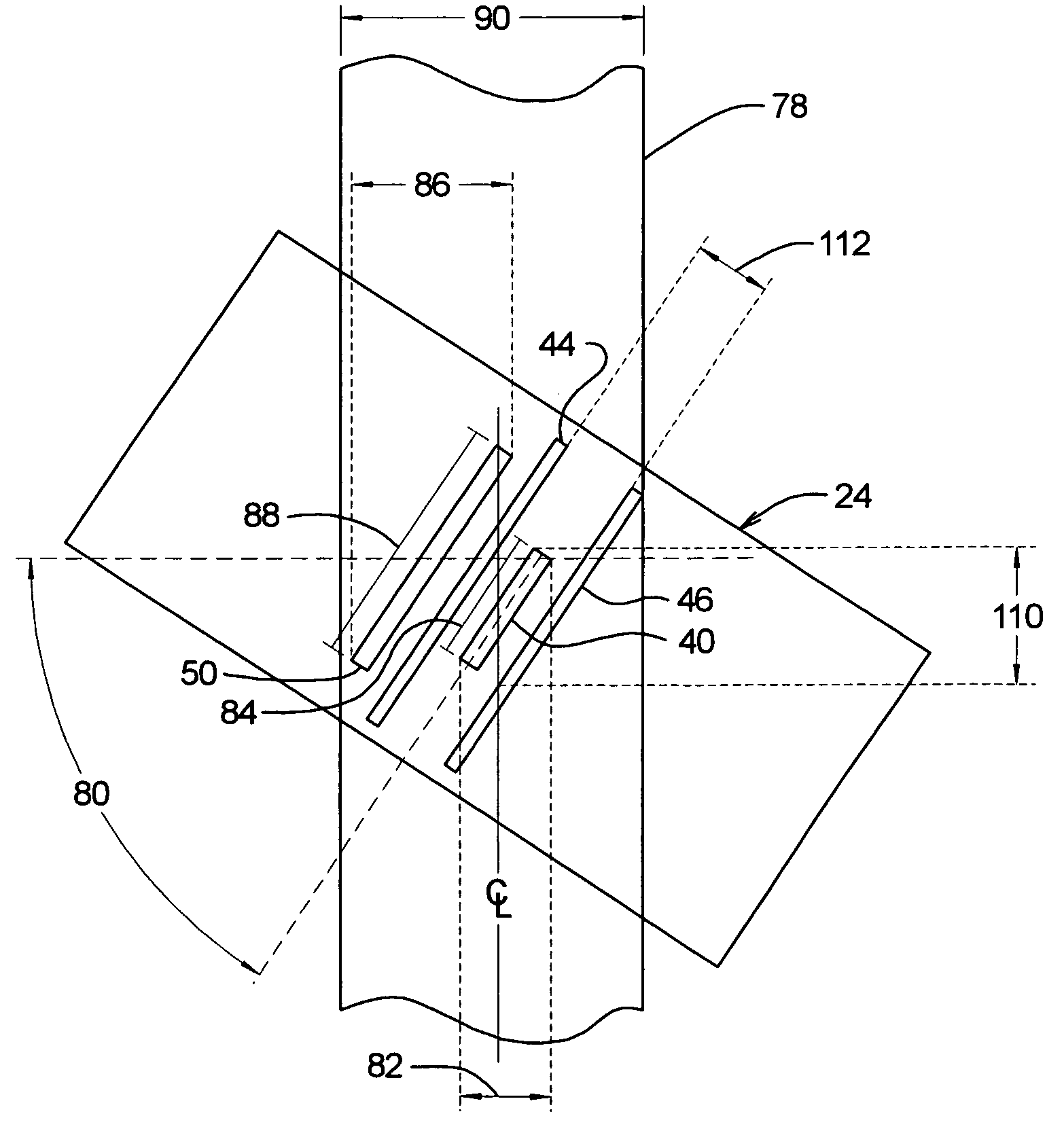
InactiveUS6937421B2Improve performanceNanoinformaticsRecord information storagePatterned mediaOptical medium
An information recording system includes a storage medium, such as a magnetic or an optical medium, that is formed to have a plurality of adjacent tracks. Each track includes a plurality of storage elements that are arranged substantially along the track in a regular manner. A head disposed in proximity to the storage medium and has a width that spans at least two adjacent tracks. The storage elements are further arranged substantially along first and second axes, such that the first and second axes are substantially perpendicular to each other and are each substantially oriented 45° from an along-track direction associated with a track. The head reads and / or writes information from at least two adjacent tracks spanned by the head.
Owner:IBM CORP
Magnetic recording medium, magnetic recording apparatus using the same, and method and apparatus for manufacturing the magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20040106009A1Without adversely affecting the thermal stabilityIncrease areal densityRecord information storageDigital recordingImage resolutionMagnetization
A magnetic recording apparatus provides improved resolution and S / N without adversely affecting thermal stability. An angle formed by the direction of easy magnetization of a recording layer and the direction normal to a magnetic recording medium is in the range between 5° and 55°, the easy magnetization direction is from a back surface of the recording layer toward a front surface thereof, and when a recording track direction is from the upstream of the direction of transportation of the medium toward the downstream thereof, an angle formed by the direction of a projection of the easy magnetization direction on the medium plane and the recording track direction is in the range between 0° and 70°.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD
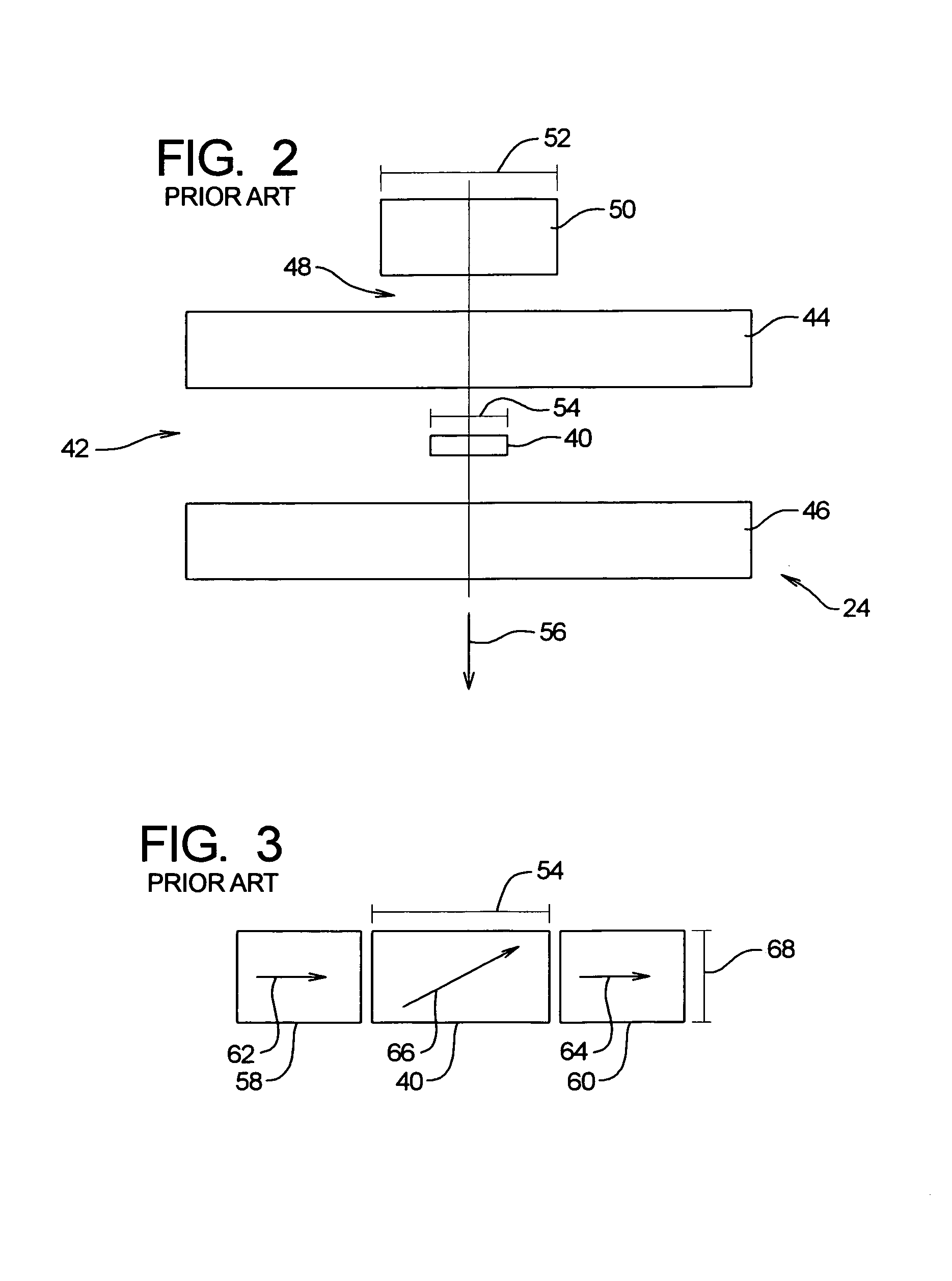
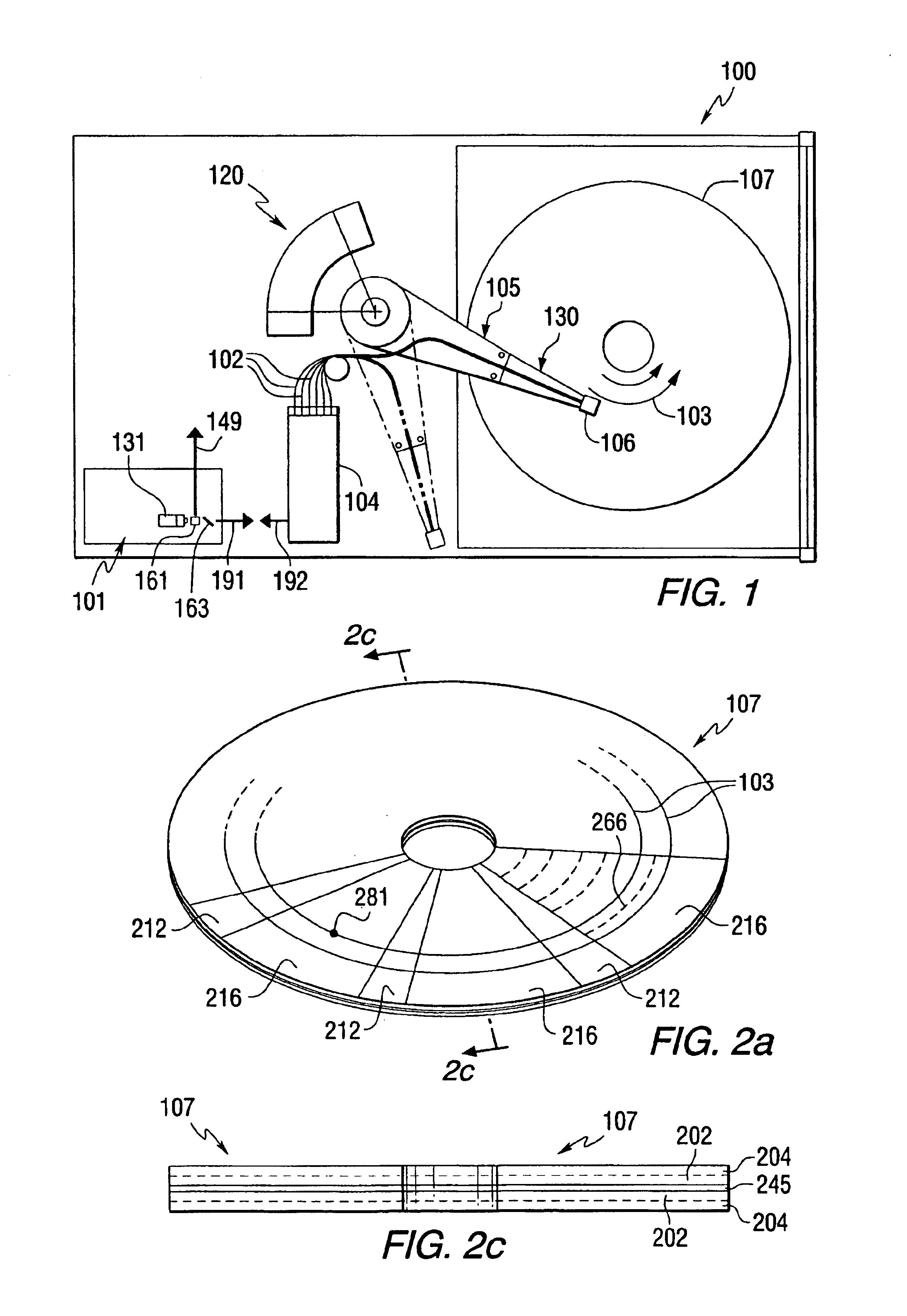
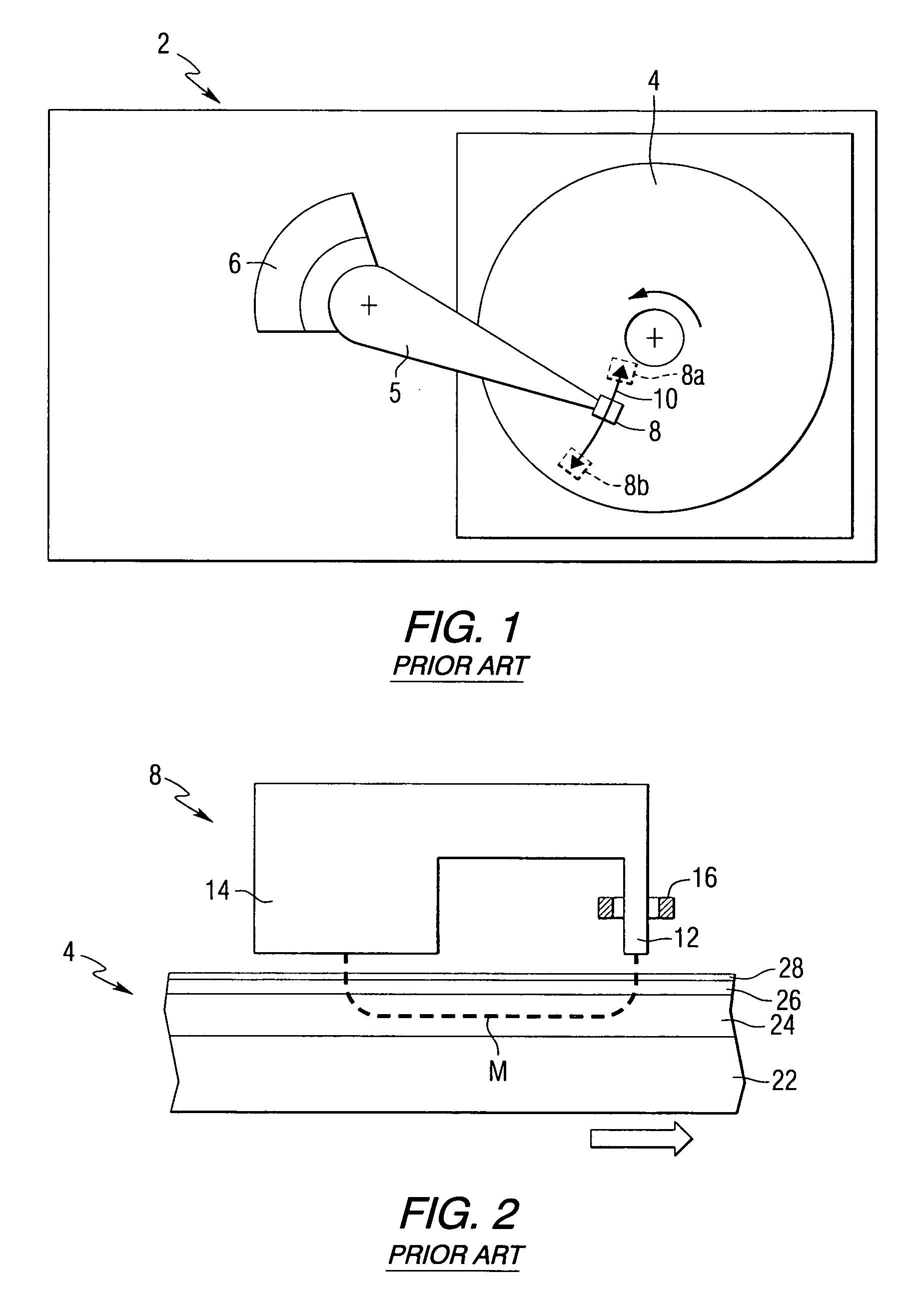
High reliability-parallel data transfer hard disk drive
InactiveUS7199981B2Avoid constraintsOvercomes shortcomingHeads using thin filmsRecord information storageData streamAccess time
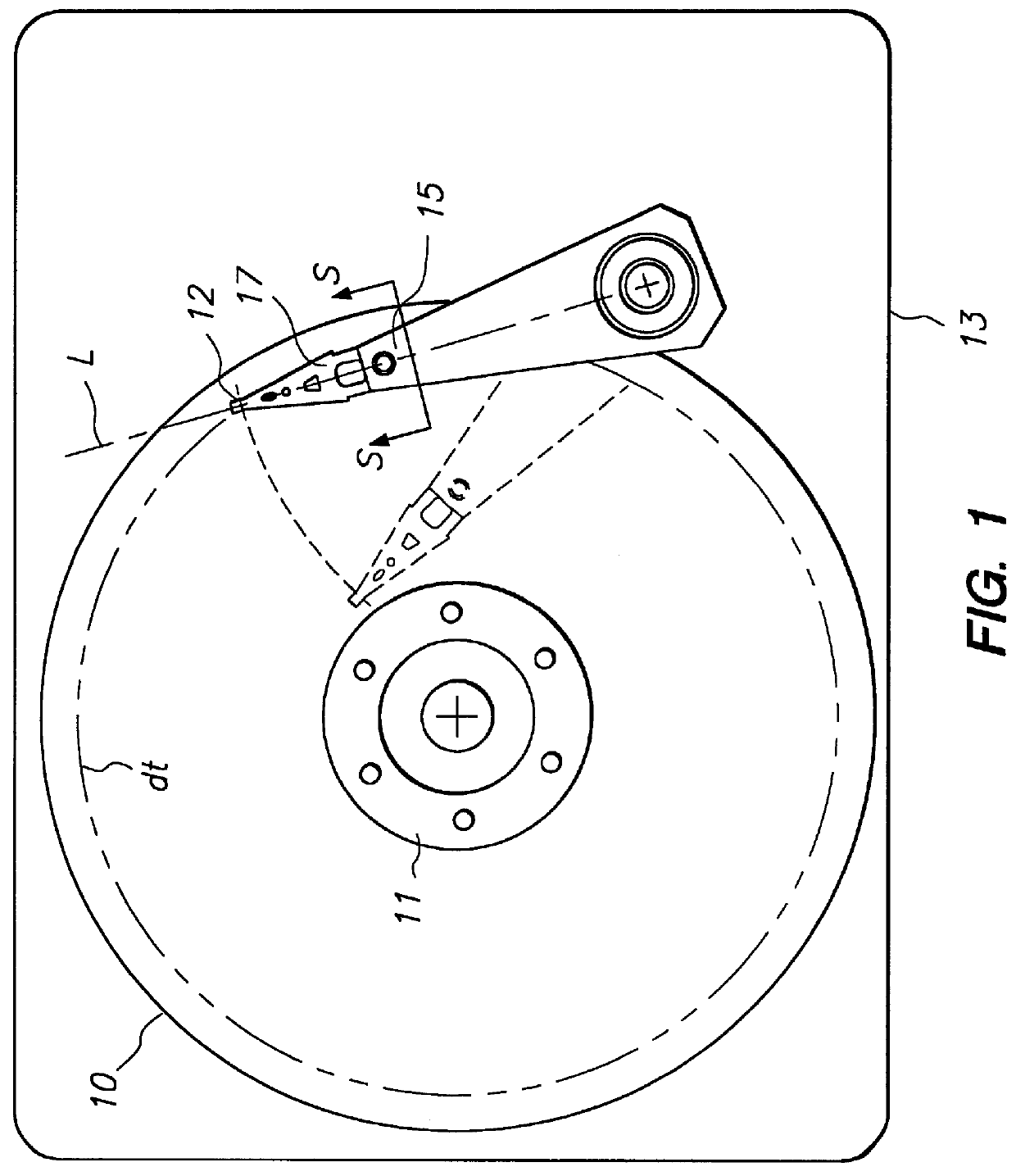
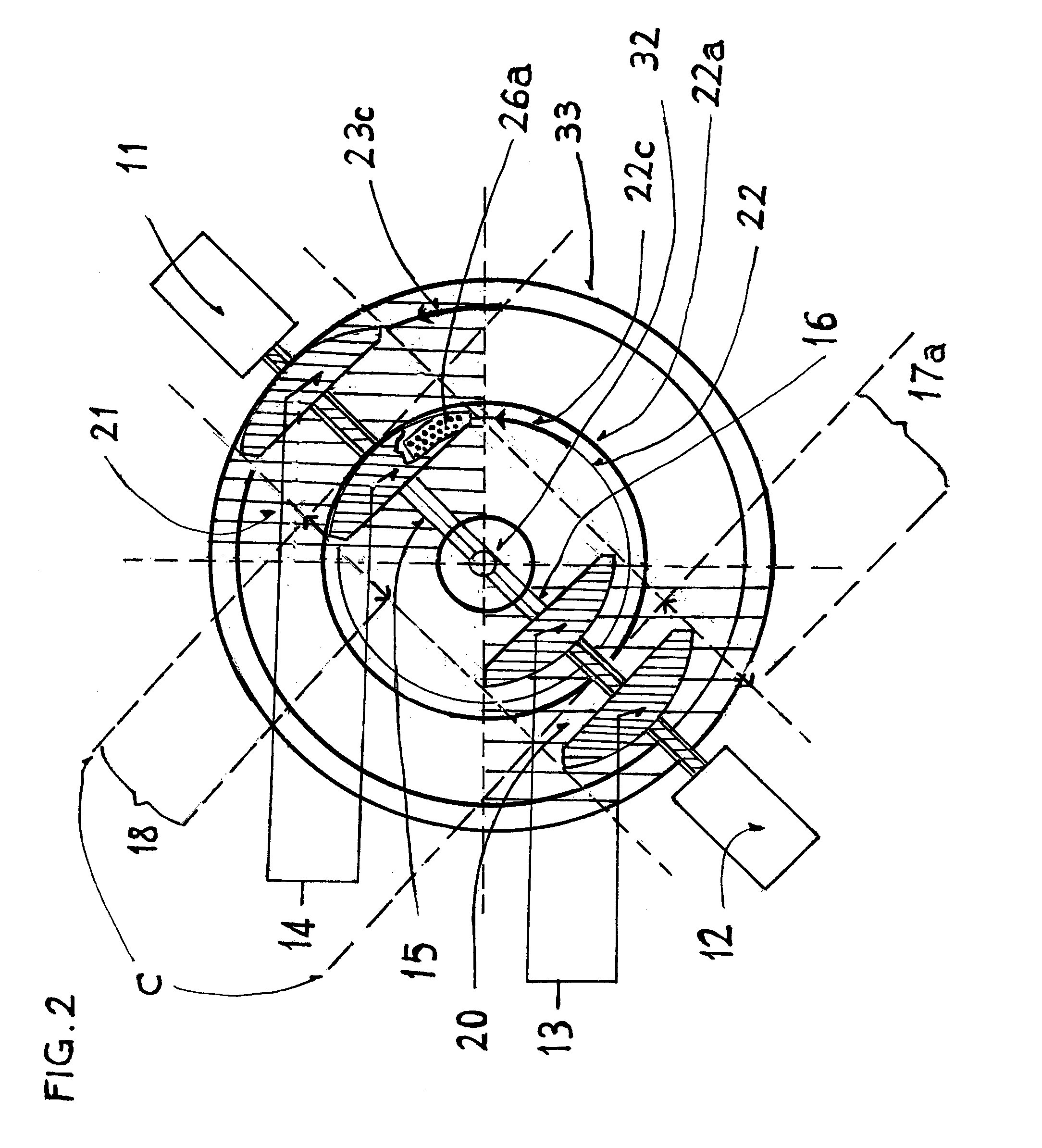
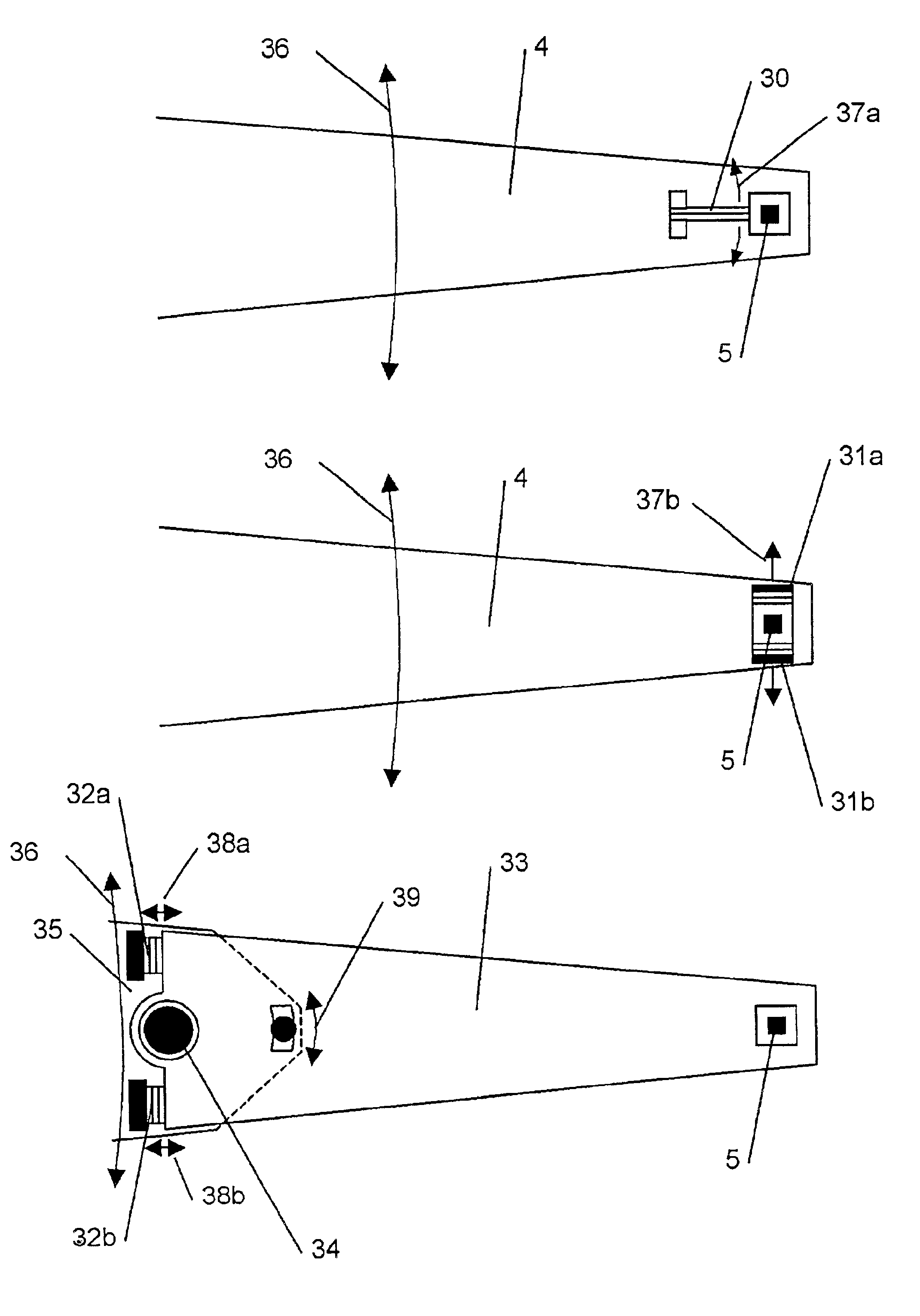
A dual actuator arm assembly system that uses two pairs of actuator-carriage arms that linearly move over a stationary micro-rail independently. The geometric shape of the two pairs of actuator carriage arms conform to the arcs of the data tracks at an acute angle. System enables micro-actuation that is integrated to actuator arm and is a function of its geometry. Uninterrupted data stream and sector coverage and thus parallel data transfer scheme is made possible. Each actuator move only within a limited range of disk area, thus precision is increased, vibration is minimized and external transfer rate is speeded up and overall access time is shortened. Instant access to two quarters of the disk with two pairs of actuators and to park these without landing the heads—by positioning and constant fly height during idle mode, or when system is turned off, are introduced as what are new in the art.
Owner:ZABTCIOGLU FIKRET M
Magnetic recording head for perpendicular recording and including a portion protruding toward a mail pole and magnetic disc storage apparatus mounting the magnetic head
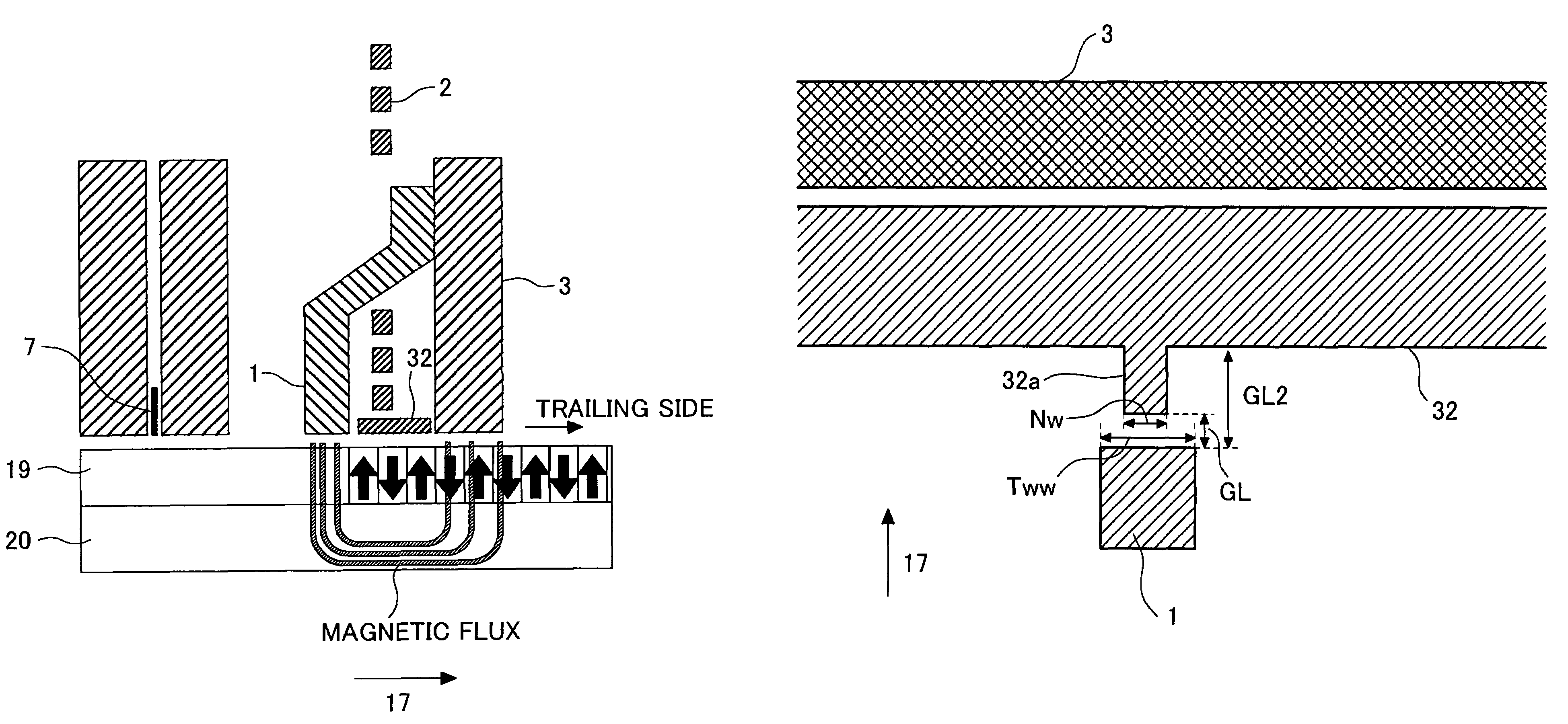
InactiveUS7054105B2Improve recording densityReduce widthManufacture head surfaceHeads using thin filmsMagnetic transitionsEngineering
A magnetic field distribution of a recording head is made linear so that a curvature of the magnetic-transition pattern in recording bit cells can be corrected. In a SPT head having a main pole 1 and an auxiliary pole 3, a magnetic layer 32 is disposed on a trailing side of the main pole. The magnetic layer is provided with a protruding portion 32a protruding towards the main pole. A width Nw of a side of the protruding portion opposite the main pole of the protruding portion is made smaller than a width Tww of the main pole on the trailing side.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC +1
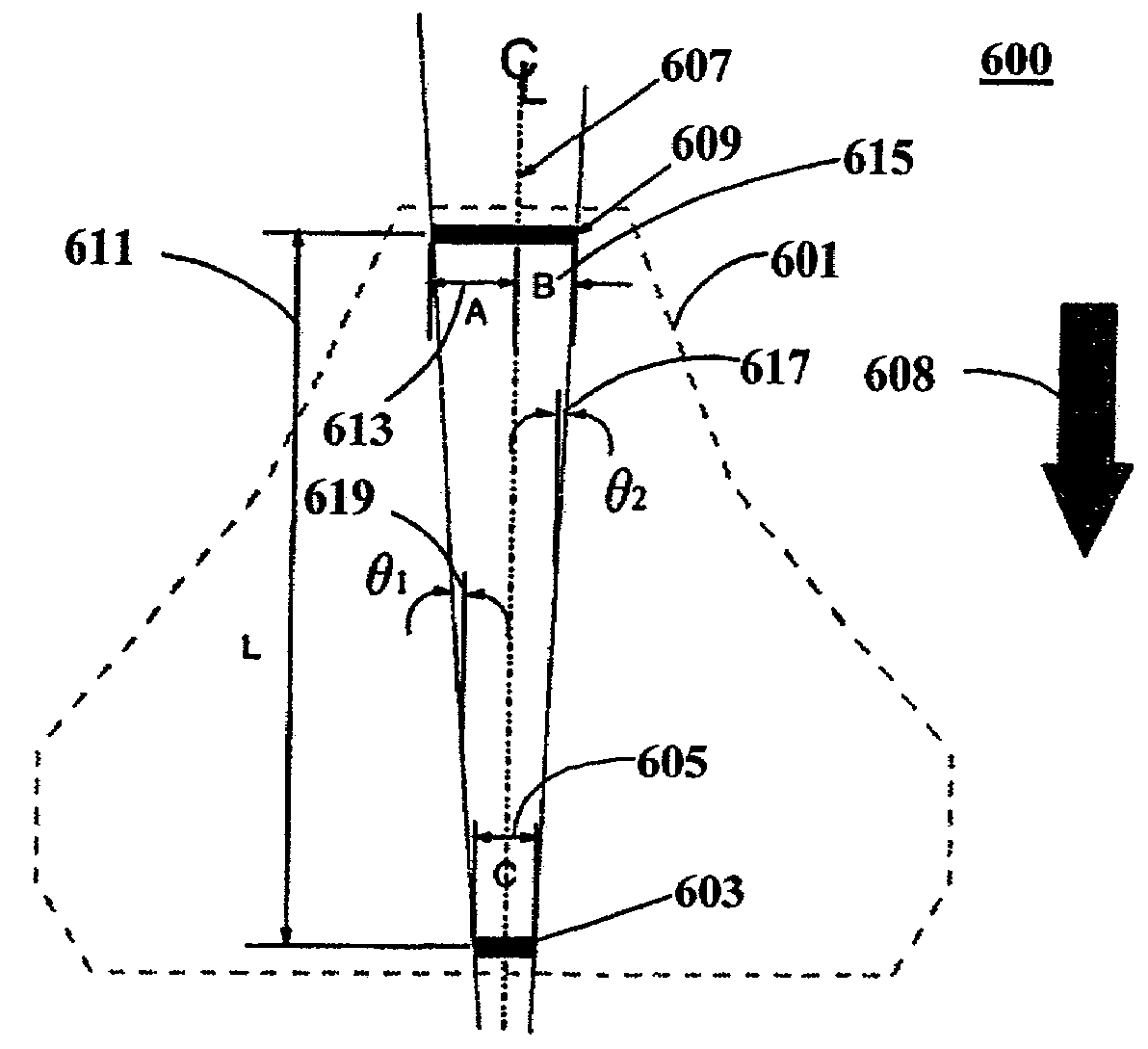
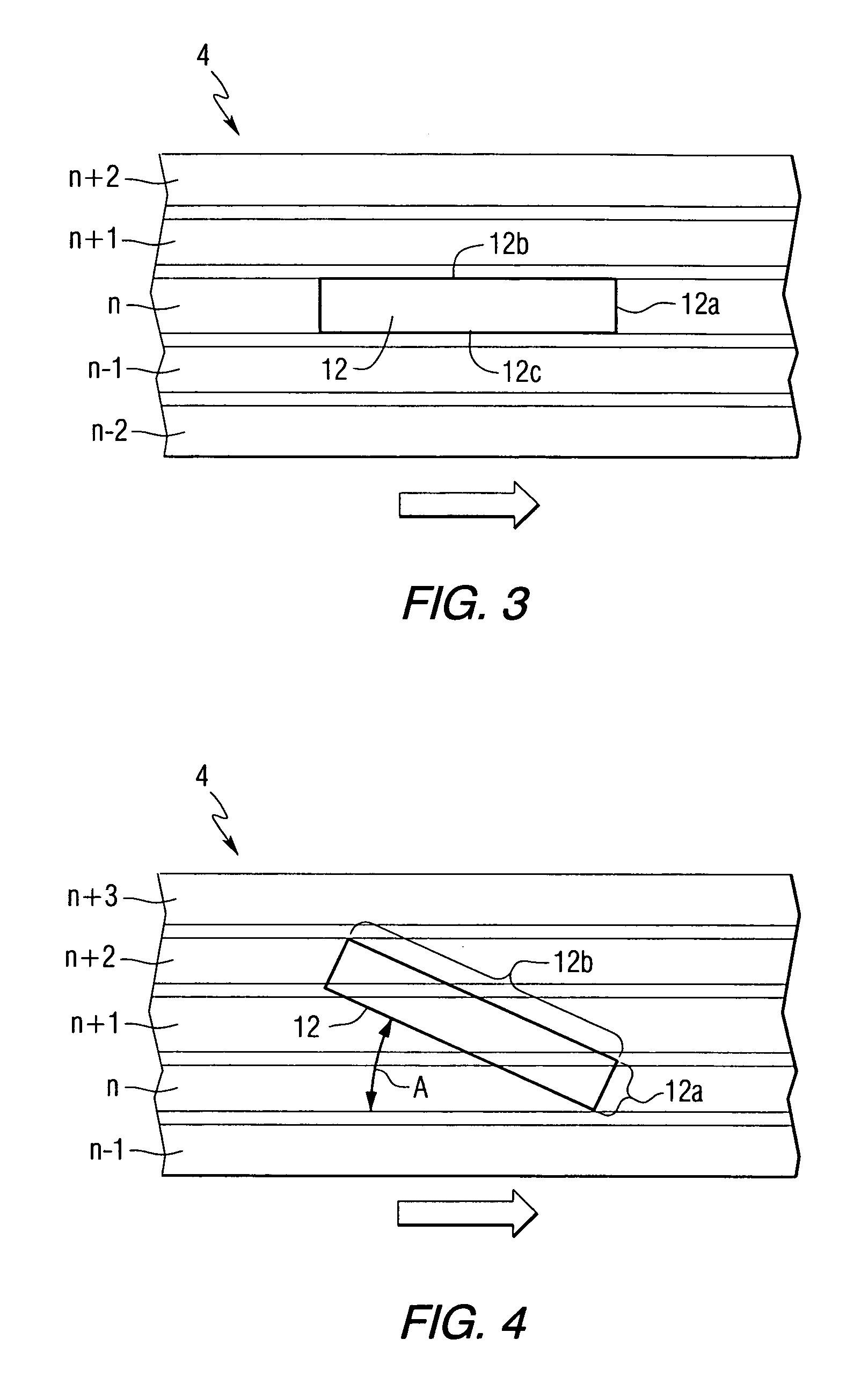
Method and apparatus for reducing effective track width through highly skewed head angles
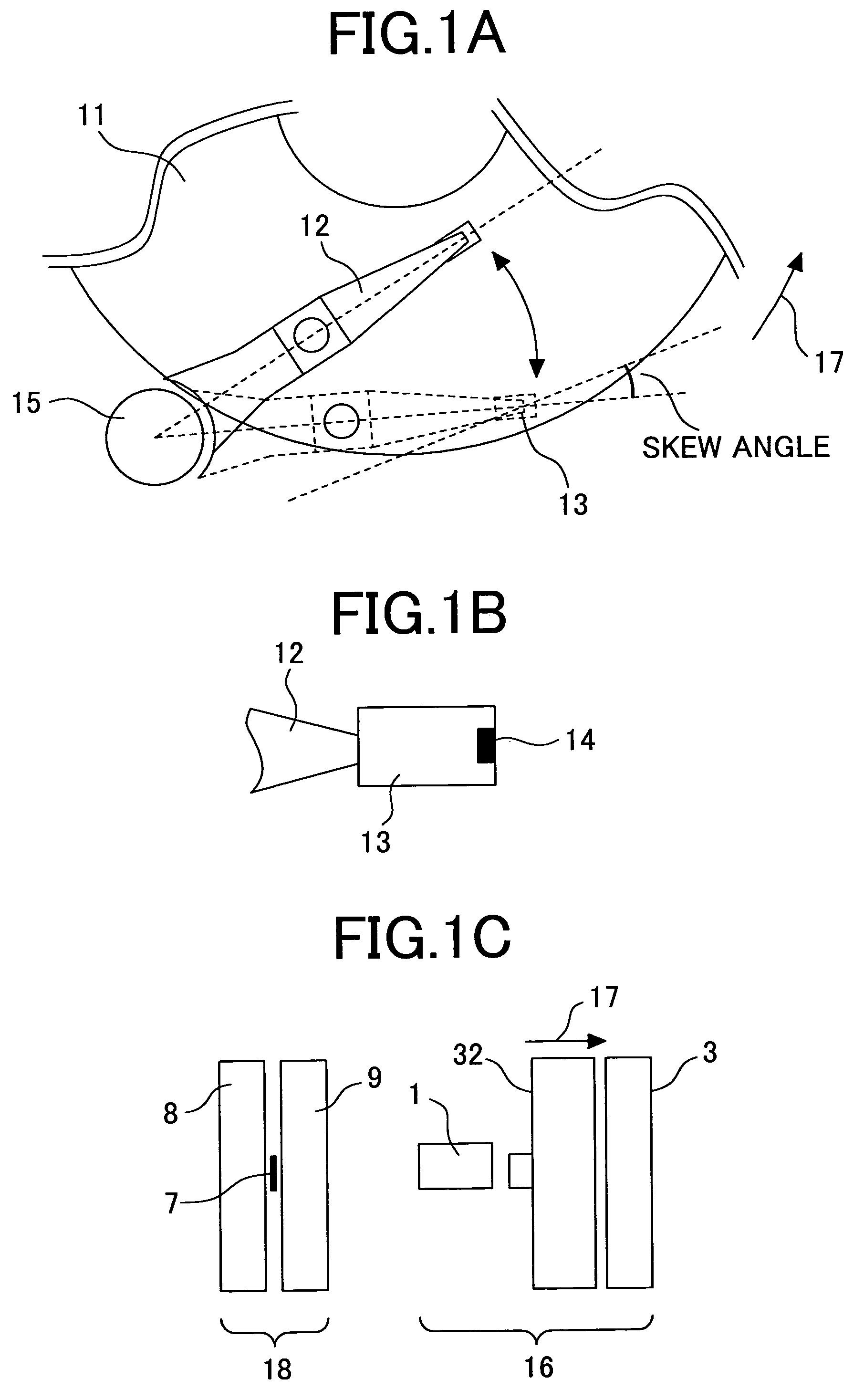
InactiveUS7193807B1Shorten the lengthOptimization rangeRecord information storageAlignment for track following on disksComputer hardwareSkew angle
A disk drive provides increased read and write element widths and tolerances, and also provides reduced track widths. The head with the read and write elements has a large skew angle relative to the tracks on the disk. The skew angle reduces the effective width of the read and write elements. Based on this reduction in effective width, the physical width of the read and write elements may be increased. Furthermore, the width of the tracks may be reduced instead of, or in addition to, the increased read and write element width.
Owner:MAXTOR
Apparatus for look-ahead thermal sensing in a data storage device
InactiveUS7027263B2Addressing slow performanceDisc-shaped record carriersRecord information storageLeading edgeEngineering
A slider having leading and trailing edges is configured to fly on an airbearing above a data storage disk rotating from the leading edge to the trailing edge. Read and write heads are mounted on the slider proximate the trailing edge. An auxiliary thermal sensor is mounted on the slider, but preferably nearer the leading edge. Forward placement of the sensor allows it to sense mechanical defects before they reach the heads, thereby permitting a write inhibit operation, for example. The sensor may also be used to detect airbearing modulation. Appropriate action may be taken when unacceptable airbearing modulation is detected, such as notifying the user and / or scrubbing the slider. The sensor is preferably wider than the heads. This allows, for example, an in-situ glide test to be performed faster using the sensor. An arm electronics module is preferably configured to permit concurrent operation of the sensor and heads.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
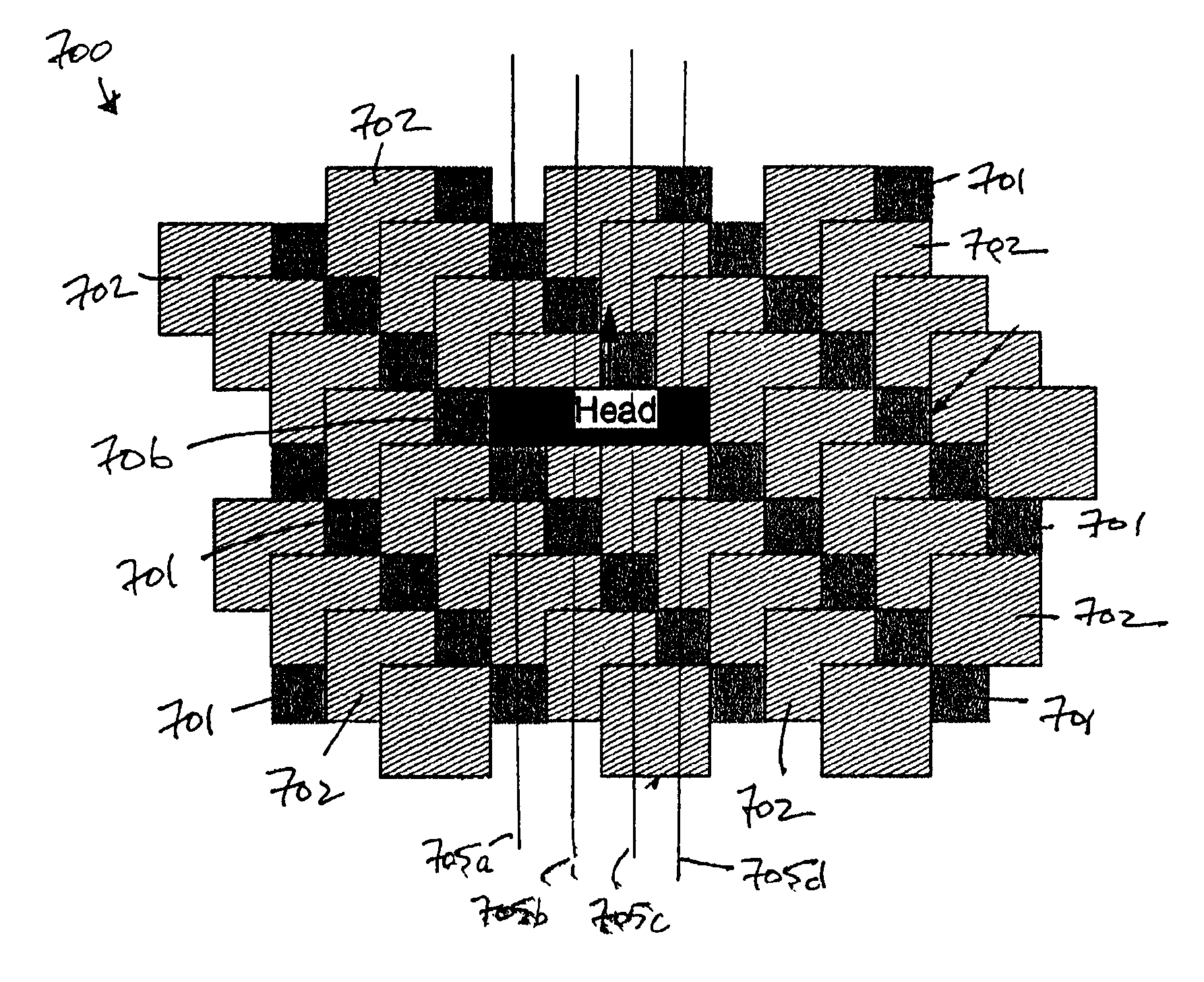
Positioning of a magnetic head in a magnetic data recording device using a multiple sensor array
InactiveUS7502193B2Saves valuable media real estateHigher magnetoresistive responseDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageSensor arrayMultiple sensor
A system method and apparatus for determining a position error signal (PES) for servo tracking in a data recording system using a data track. The PES is determined using a sensor array that includes a plurality of sensors offset from one another by certain predetermined distances in a direction perpendicular to the track direction. Correlation functions can be determined for pairs of sensors in the sensor array based on the signals read by the sensors. The results of these correlation functions can then be used to determine a PES by using a look up table or computational processor.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Laser assisted track width definition and radial control with magnetic recording
InactiveUS6775100B1Increase data capacityReduce the total massTrack finding/aligningNanomagnetismComputer architectureLaser assisted
The present invention provides for the enhancement of the storage capacity of a data disk drive while reducing optical path optics, electronics and / or the mass and complexity of associated read / write heads. The system utilizes light transmitted by optical elements to servo track a data disk and to heat the data disk during reading and writing of data, and magnetic elements for actual reading and writing.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Positioning of a magnetic head in a magnetic data recording device using a multiple sensor array
InactiveUS20070201160A1Higher magnetoresistive responseImprove spatial resolutionDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageSensor arrayCorrelation function
A system method and apparatus for determining a position error signal (PES) for servo tracking in a data recording system using a data track. The PES is determined using a sensor array that includes a plurality of sensors offset from one another by certain predetermined distances in a direction perpendicular to the track direction. Correlation functions can be determined for pairs of sensors in the sensor array based on the signals read by the sensors. The results of these correlation functions can then be used to determine a PES by using a look up table or computational processor.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Systems and methods for calibrating read and write operations in two dimensional magnetic recording
ActiveUS9311937B2Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksControl circuitComputer science
Systems and methods are provided for calibrating signals retrieved from a storage device using a first reader and a second reader. The systems and methods further include reading a first signal using the first reader and a second signal using the second reader. Control circuitry computes a calibration metric associated with the first reader and the second reader based on the combination of the first signal and the second signal. At least one of the first signal and the second signal is subsequently decoded based in part on the computed calibration metric.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
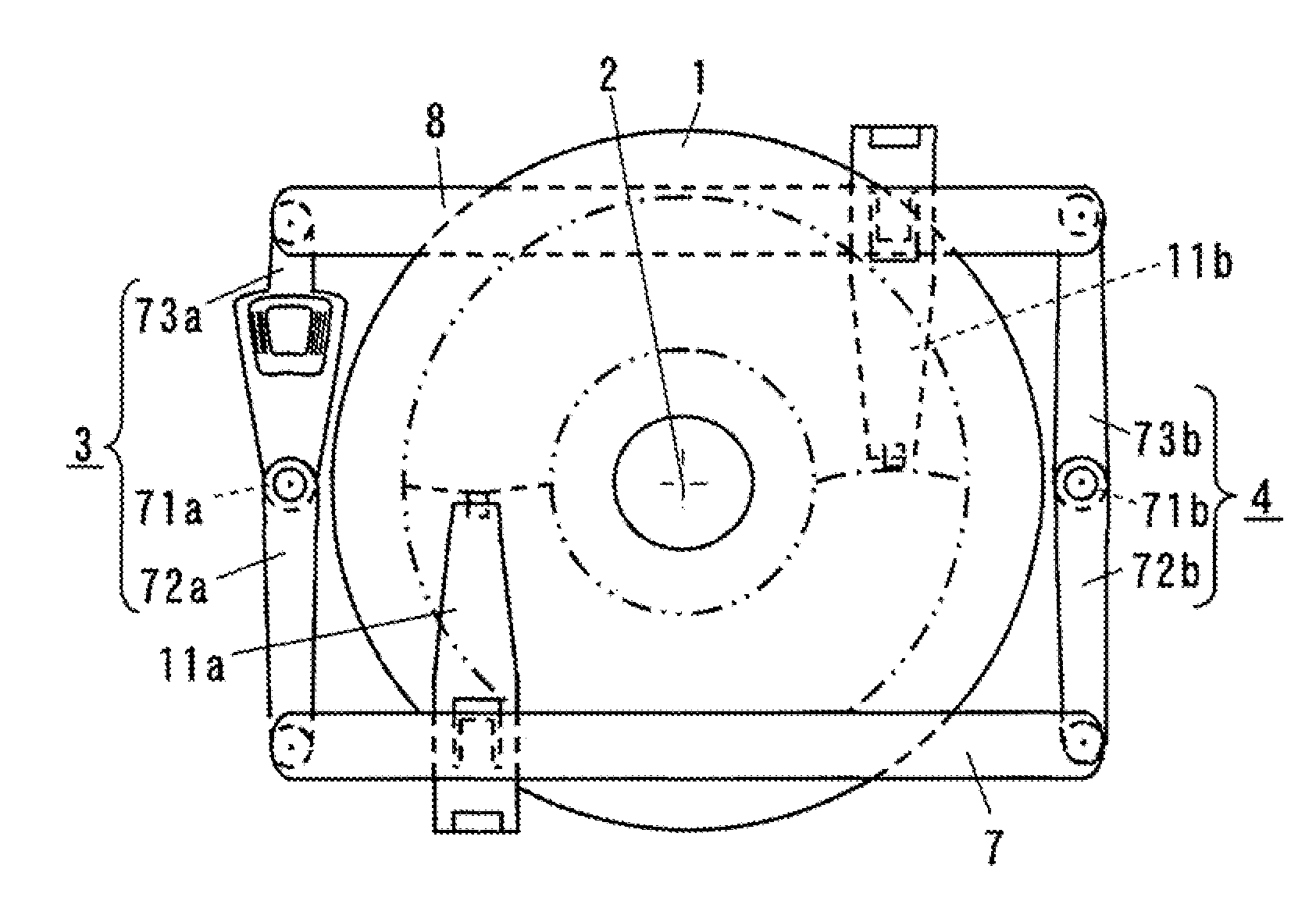
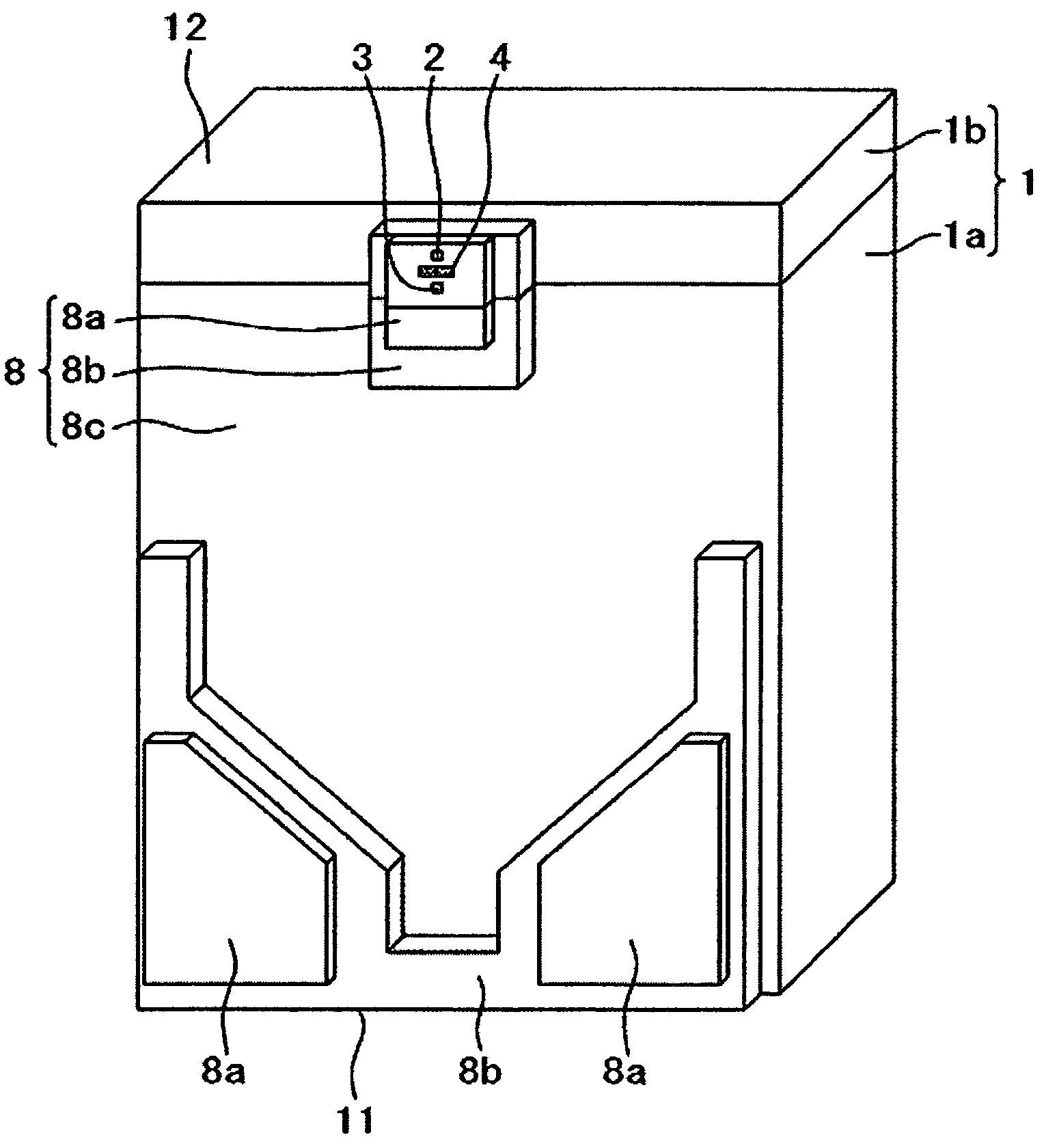
Head support device and it's driving method, and drive disk using same
InactiveUS7146623B2Reduce distanceAccurate and fast positioningRecord information storageRecord carrier guidanceEngineeringRecording media
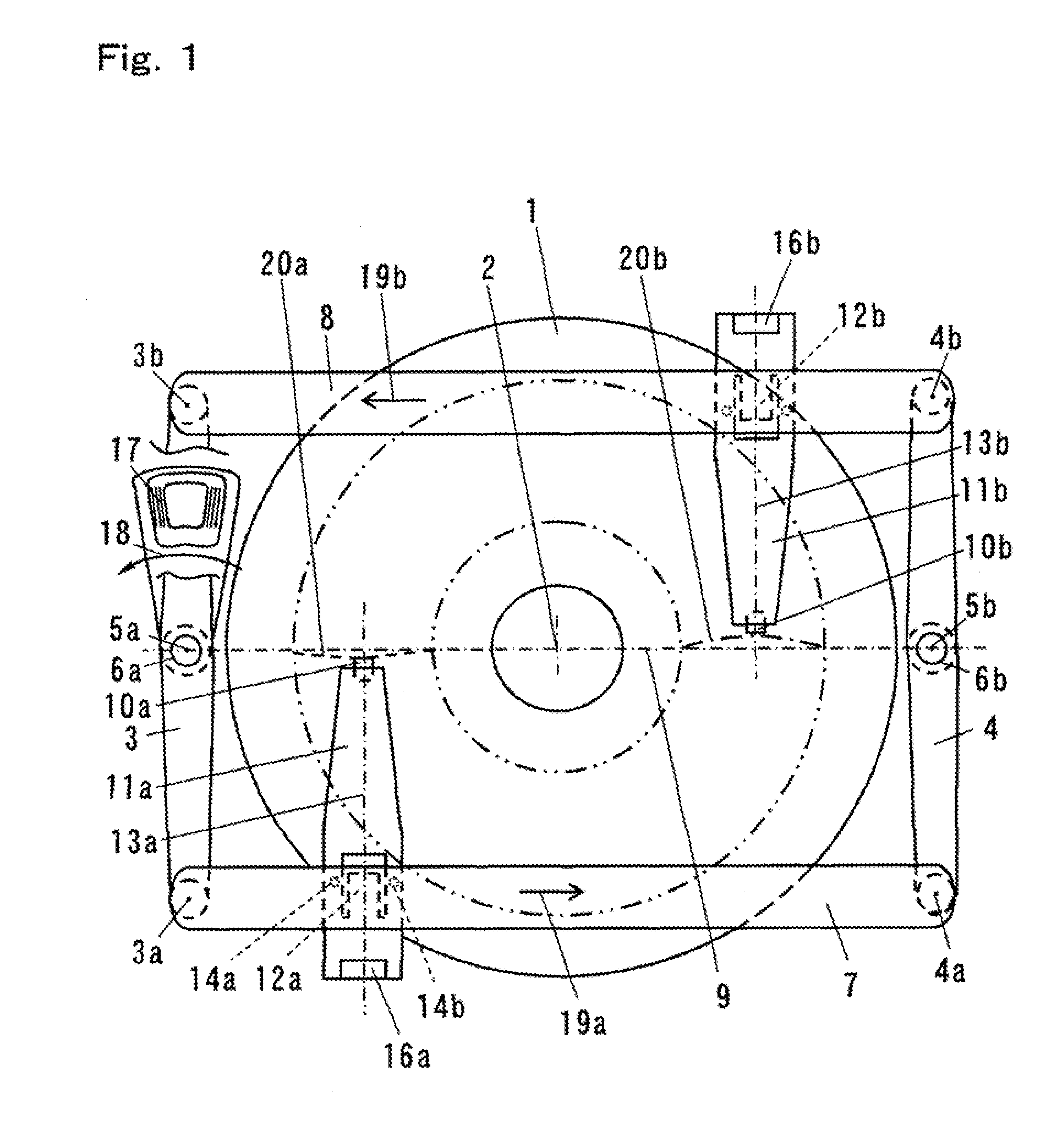
The present invention provides a head support mechanism wherein the position can be accurately corrected at a high speed when the mode is shifted from reproducing to recording, and also, the deflection of recording magnetic field from the direction of initialized magnetic orientation is little and it is possible to suppress the deterioration of the recording characteristics and to make the skew very small. The first link 3 and the second link 4 respectively rotate about the first rotational center 5a and the second rotational center 5b, to which the third link 7 and the fourth link 8 are rotatably connected. The lengths of the first link 3 and the second link 4 are nearly equal to each other, and the lengths of the third link 7 and the fourth link 8 are set to a length nearly equal to the distance between the first rotational center 5a and the second rotational center 5b. As the first link 3 rotates, the third link 7 and the fourth link 8 reciprocate while keeping a state of being parallel to the diametric line 9 of the recording medium that connects the first rotational center 5a to the second rotational center 5b, and then the sliders 10 mounted with magnetic heads of the suspension 11a and 11b fixed thereon reciprocate.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
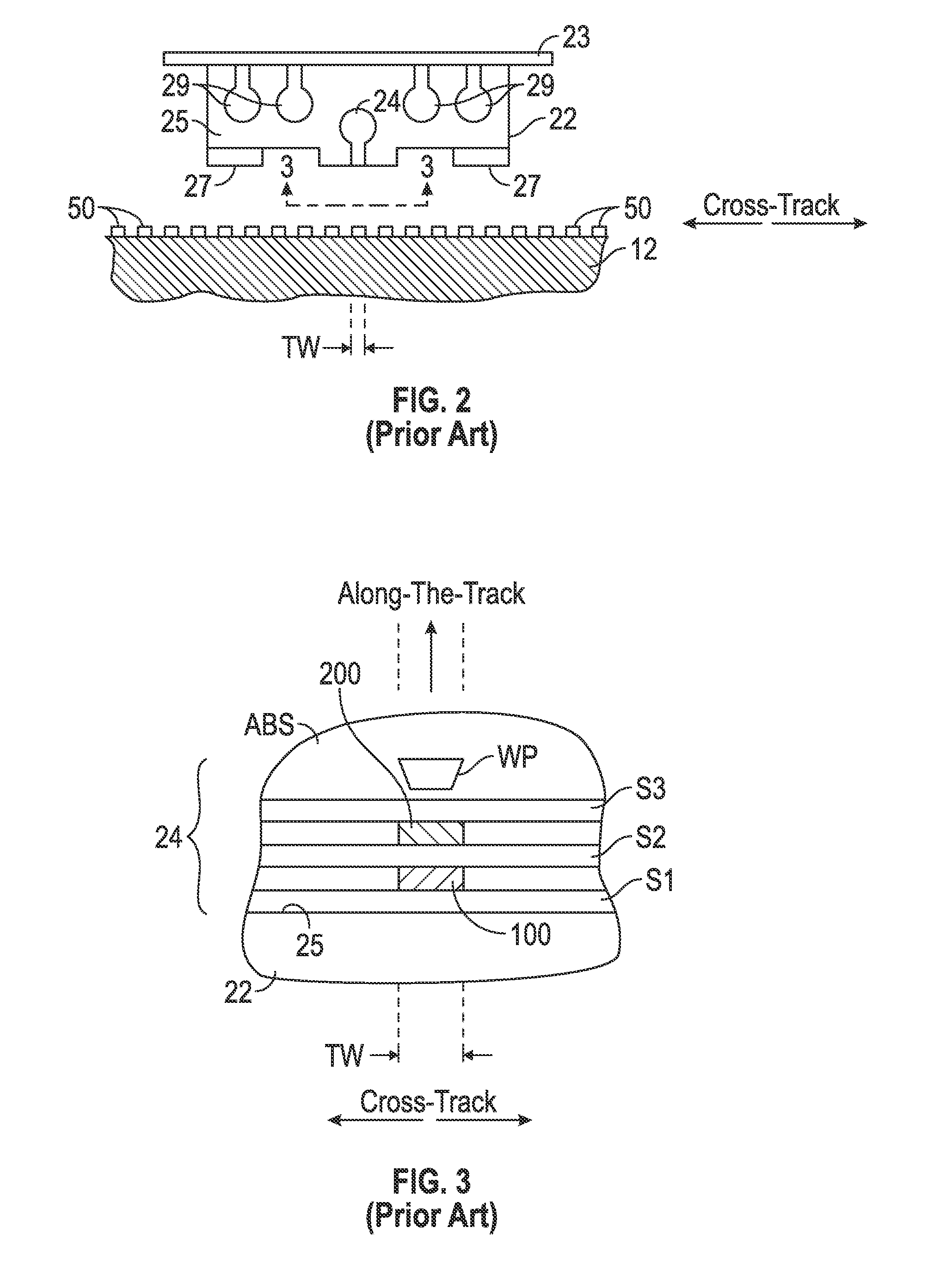
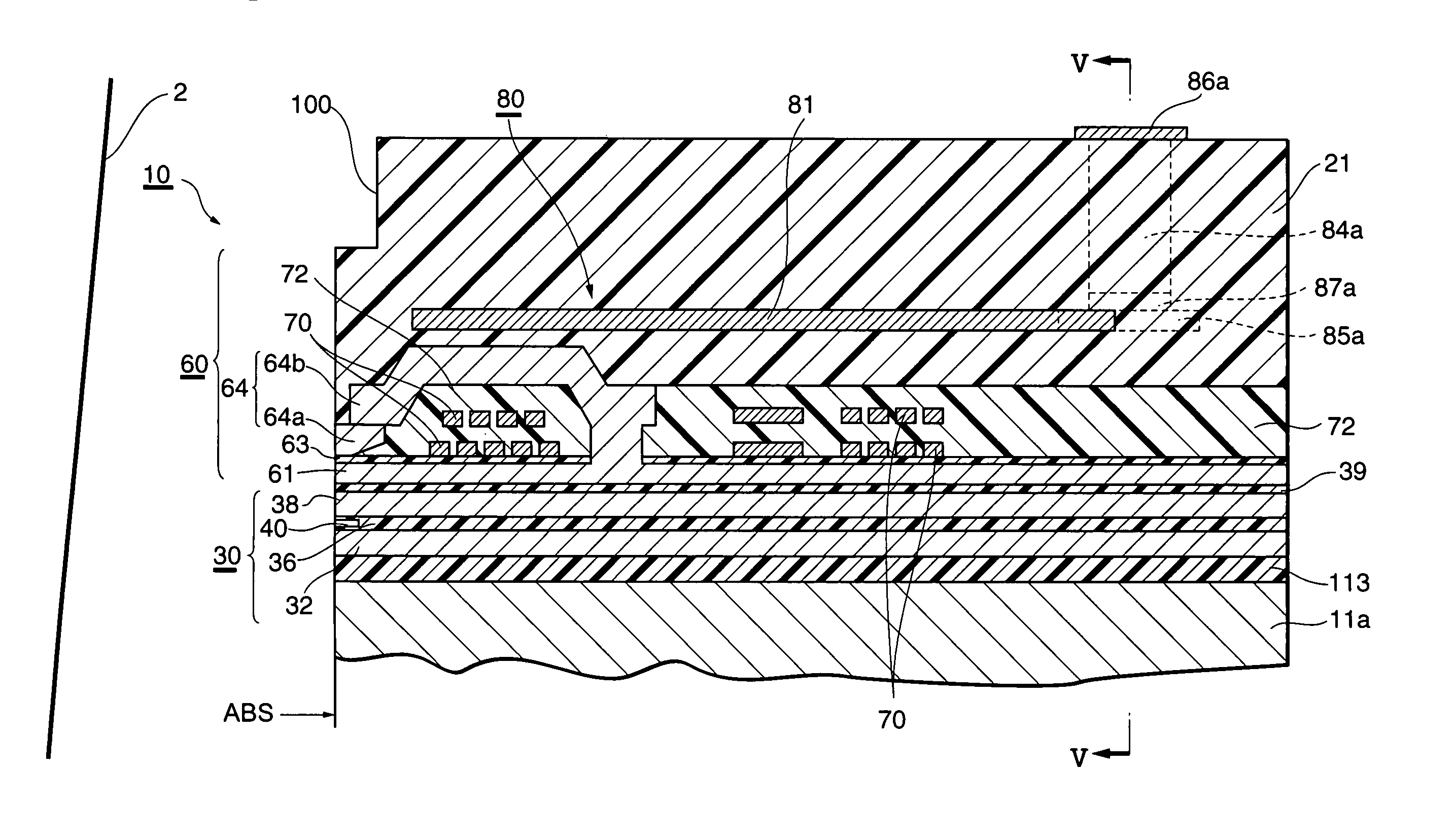
Composite magnetic head arranged so the reproducing elements do not overlap a pole of a recording element
A conventional magnetic head has a structure, in which a MR element and a recording element are stacked. The influence of a recording magnetic field on the magnetically sensitive portion of a reproduction element is lessened and the performance of the MR element is stabilized. Also, the reliability of the magnetic disk drive using a MR element is enhanced. The magnetic disk drive uses a composite magnet head, which has a plurality of reproduction elements arranged such that the magnetically sensitive layer of a reproduction element of the composite magnetic head does not overlap with the normal direction projection of the recording element, and which lessens the influence of a recording magnetic field on the magnetically sensitive portion of each reproduction element.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD
Thin-film magnetic head, head gimbal assembly, and hard disk drive incorporating a heater
ActiveUS7224553B2Reduce gapReduce distanceManufacture head surfaceHeads using thin filmsHard disc driveTransducer
A thin-film magnetic head comprises at least one of an electromagnetic transducer and a magnetoresistive device, and a heater member adapted to generate heat upon energization. The heater member contains NiCu or NiCr.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Magnetic recording system which eliminates skew angle effect
InactiveUS6987637B2Reduces and eliminates skew angle effectIncrease areal densityRecord information storageAlignment for track following on disksSkew angleComputer science
A perpendicular magnetic recording system is provided which eliminates unwanted side writing to adjacent recording tracks due to the skew angle effect. The system includes a perpendicular magnetic recording head with a write pole that is used to sequentially write to adjacent tracks of a magnetic recording disk. In one embodiment, the write pole is aligned at a compensation angle with respect to the recording tracks which remains greater than zero as the recording head travels in an arc across the disk. When the recording head moves radially inwardly or outwardly across the tracks of the disk, the compensation angle remains greater than zero. Any side writing by the write pole to adjacent tracks is eliminated as the write pole sequentially writes to the next adjacent track. By eliminating the skew angle effect, smaller spacings may be provided between adjacent tracks, thereby increasing data storage densities.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Systems and methods for calibrating read and write operations in two dimensional magnetic recording
Systems and methods are provided for calibrating signals retrieved from a storage device using a first reader and a second reader. The systems and methods further include reading a first signal using the first reader and a second signal using the second reader. Control circuitry computes a calibration metric associated with the first reader and the second reader based on the combination of the first signal and the second signal. At least one of the first signal and the second signal is subsequently decoded based in part on the computed calibration metric.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Dual writer head design
ActiveUS20160148629A1Well formedFilamentary/web carriers operation controlHeads using thin filmsComputer hardwareTransducer
A storage device includes a transducer head with multiple write elements having write poles of different sizes. For example, the transducer head may include two write poles of different width configured to write to a same surface of a storage medium. A controller of the storage device is configured to selectively engage one of the multiple write elements to write data to the storage medium.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Optical irradiation head and information recording/reproducing device
ActiveUS6930975B2Improve batch productivityGood reproducibilityNanoinformaticsRecord information storageEngineeringPrism
An optical irradiation head including a trapezoidal prism having a pair of trapezoidal principal surfaces parallel to each other, a rectangular bottom surface, a rectangular top surface parallel to the rectangular bottom surface, and a pair of oblique side surfaces connecting the top surface, the bottom surface, and the principal surfaces, and a cover member for covering the principal surfaces and the oblique side surfaces. The trapezoidal prism is formed of a first material, and the cover member is formed of a second material. Linearly polarized light having a polarization direction perpendicular to the principal surfaces is incident on the bottom surface. For example, the first material is a dielectric transparent to the incident light, and the second material is metal such as Al, Au, or Ag.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
High-speed disk drive system
InactiveUS6883062B2Improve data transfer rateHigh data reliabilityApparatus for flat record carriersRecord information storageData transmissionComputer science
A high-speed disk drive system that features significant performance improvements over previously available systems. By immediately fetching the data as soon as heads reach the destination cylinder, internally stripping the data across the surfaces and plurality of read / write heads on every surface the data transfer speeds many times depending on other characteristics of the system. By implementing plurality of read / write heads and internal parity surfaces or distributed parity blocks / zones the system achieves higher reliability (fault resistance) with head and surface fail-over fail-safing.
Owner:SUSNJAR ALEKSANDAR
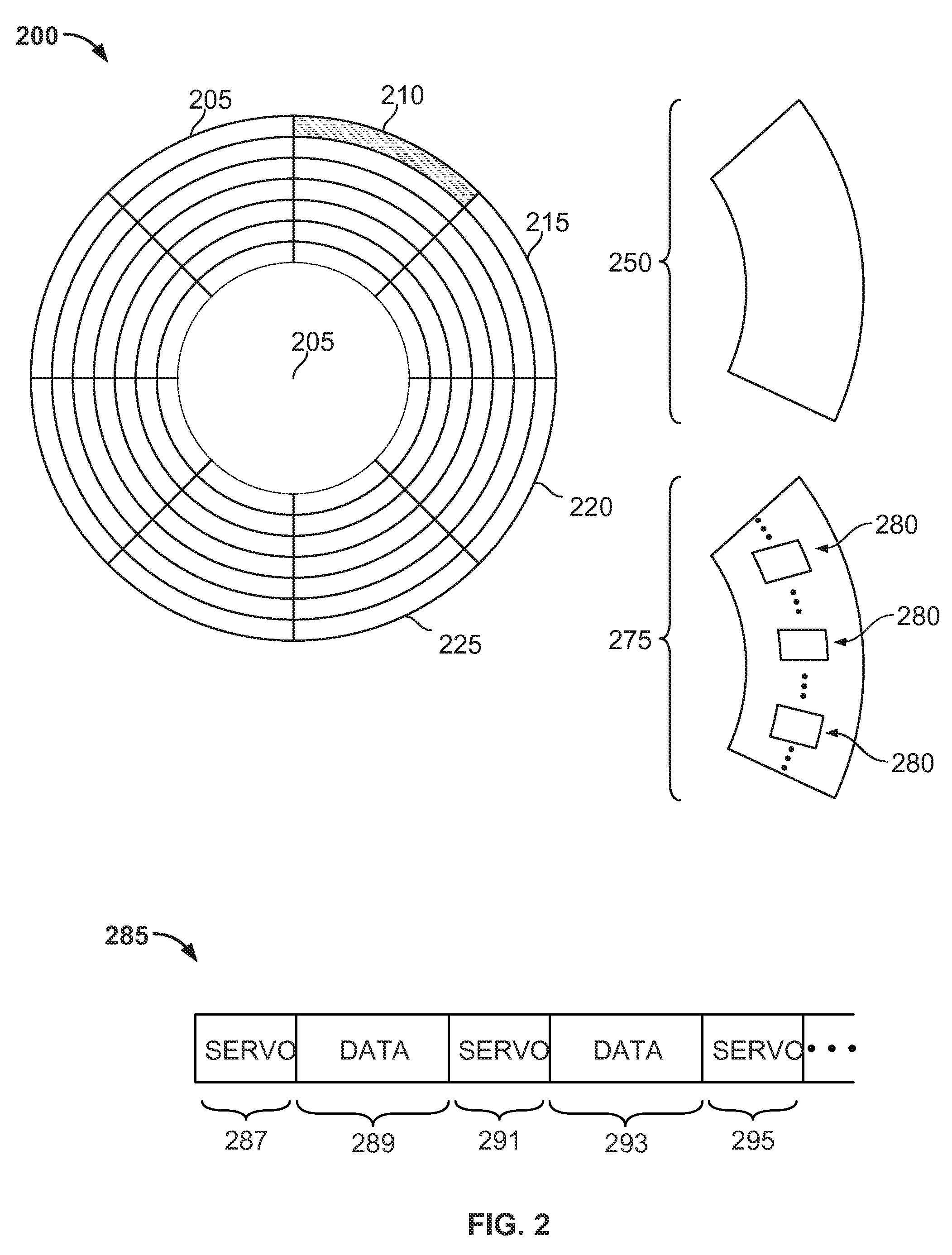
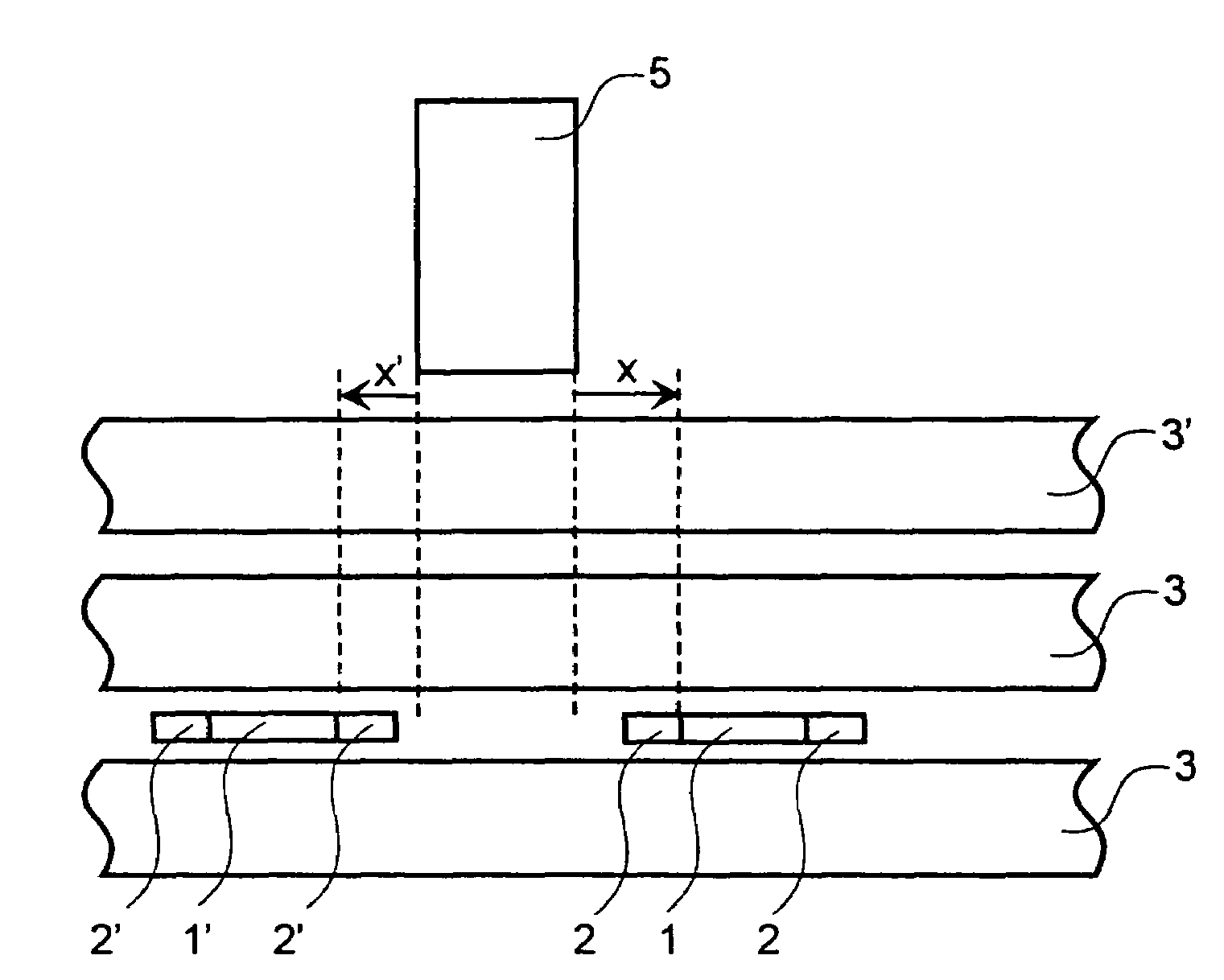
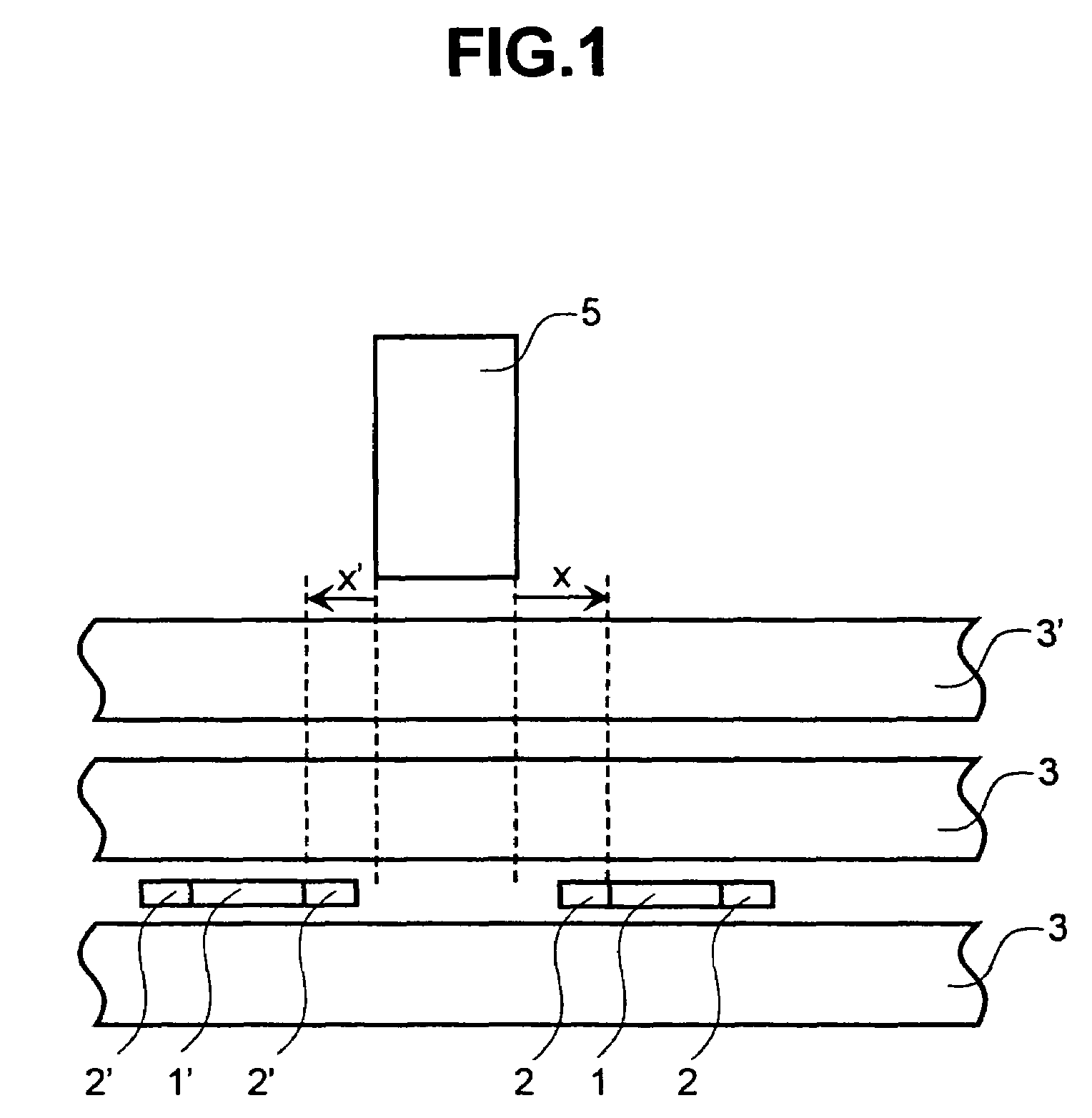
Magnetic storage medium, method for controlling track pitch thereof, and magnetic recorder for medium
InactiveUS6950256B2Improve efficiencyTrack finding/aligningManufacture unitary devices of plural headsMagnetic storageEngineering
A magnetic storage medium is configured to store data along tracks on a disk-shaped storage medium. A distance between the tracks adjacent to each other in a radius direction of the storage medium is different depending on each position in a radius direction of the storage medium.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Thermal assist head slider
InactiveUS7525765B2Reduce in quantityLow powerRecord information storageFluid-dynamic spacing of headsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingEngineering
In a magnetic disk apparatus, mounting of plural heating elements to a magnetic head slider is permitted. Thermally assisted magnetic recording from inner to outer surface is permitted at a small amount of power consumption. In one embodiment, the magnetic disk apparatus has a magnetic disk on which magnetic information is recorded, a magnetic head slider having an air bearing surface for floating from the magnetic disk in proximity thereto, and a rotary actuator moving over the disk arcuately while supporting the magnetic head slider by a suspension. A recording element acting to record magnetic information on the magnetic disk, a playback element acting to play back the magnetic information recorded on the magnetic disk, and plural heating elements acting to locally heat the magnetic disk are carried on the magnetic head slider. A circuit for switching energization to the plural heating elements and according to information about the direction of a DC power supply VH, frequency contained in an AC power supply, or the like is formed.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Thermal assist head slider
InactiveUS20060119971A1Small amount of power consumptionReduce in quantityFluid-dynamic spacing of headsRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingEngineering
In a magnetic disk apparatus, mounting of plural heating elements to a magnetic head slider is permitted. Thermally assisted magnetic recording from inner to outer surface is permitted at a small amount of power consumption. In one embodiment, the magnetic disk apparatus has a magnetic disk on which magnetic information is recorded, a magnetic head slider having an air bearing surface for floating from the magnetic disk in proximity thereto, and a rotary actuator moving over the disk arcuately while supporting the magnetic head slider by a suspension. A recording element acting to record magnetic information on the magnetic disk, a playback element acting to play back the magnetic information recorded on the magnetic disk, and plural heating elements acting to locally heat the magnetic disk are carried on the magnetic head slider. A circuit for switching energization to the plural heating elements and according to information about the direction of a DC power supply VH, frequency contained in an AC power supply, or the like is formed.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic data recording system with mirror image asymmetric magnetic write elements
ActiveUS8848317B2Improves speed and performanceFacilitate the shingled magnetic recordingManufacture head surfaceRecord information storageMagnetic mediaData recording
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic recording medium, magnetic recording apparatus using the same, and method and apparatus for manufacturing the magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS6894856B2Increase areal densityHigh resolutionRecord information storageDigital recordingImage resolutionMagnetization
A magnetic recording apparatus provides improved resolution and S / N without adversely affecting thermal stability. An angle formed by the direction of easy magnetization of a recording layer and the direction normal to a magnetic recording medium is in the range between 5° and 55°, the easy magnetization direction is from a back surface of the recording layer toward a front surface thereof, and when a recording track direction is from the upstream of the direction of transportation of the medium toward the downstream thereof, an angle formed by the direction of a projection of the easy magnetization direction on the medium plane and the recording track direction is in the range between 0° and 70°.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD
Popular searches
Undesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorption Casings/cabinets/drawers details Hermetically-sealed casings Track selection/addressing details Recording on magnetic disks Heads relative to rotating disc Digital signal formatting Record carrier types Digital signal error detection/correction Optical recording/reproducing
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com