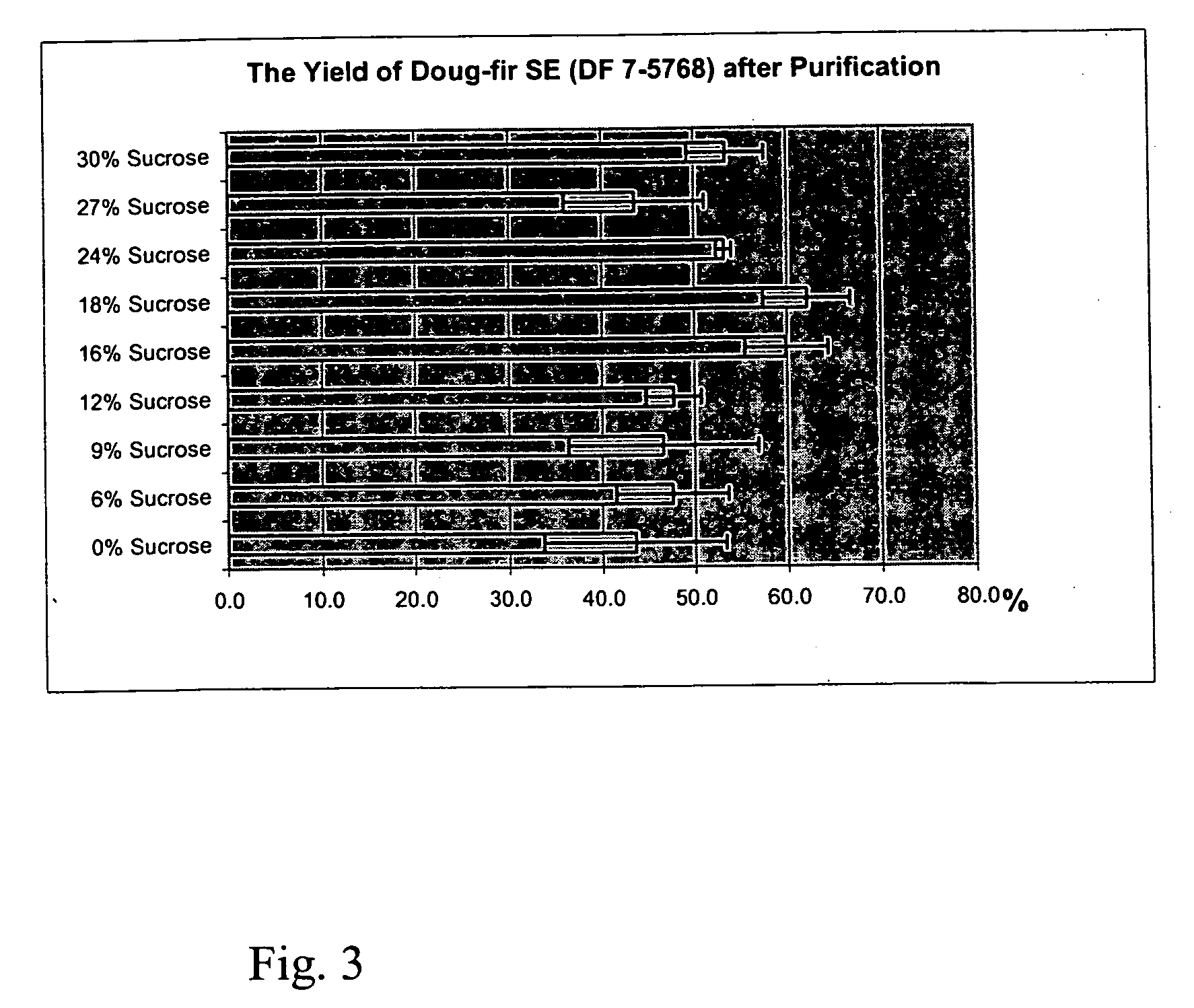
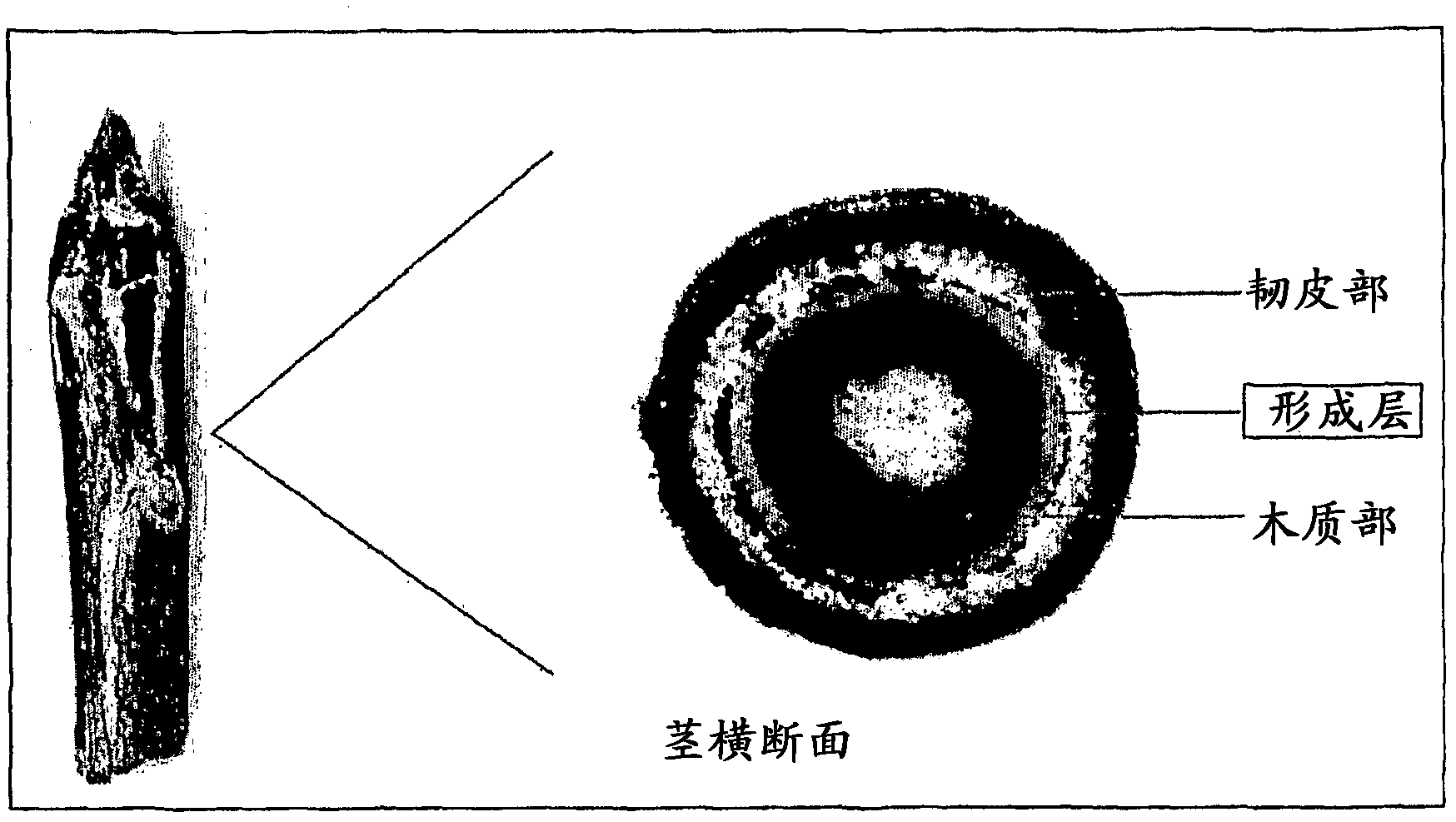
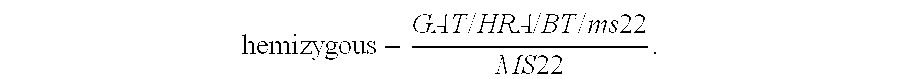Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
114results about "Gymnosperms" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method to enhance yield and purity of hybrid crops
ActiveUS20090165166A1Improve satisfactionExpensive to developBiocideSugar derivativesHybrid seedHybrid species
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
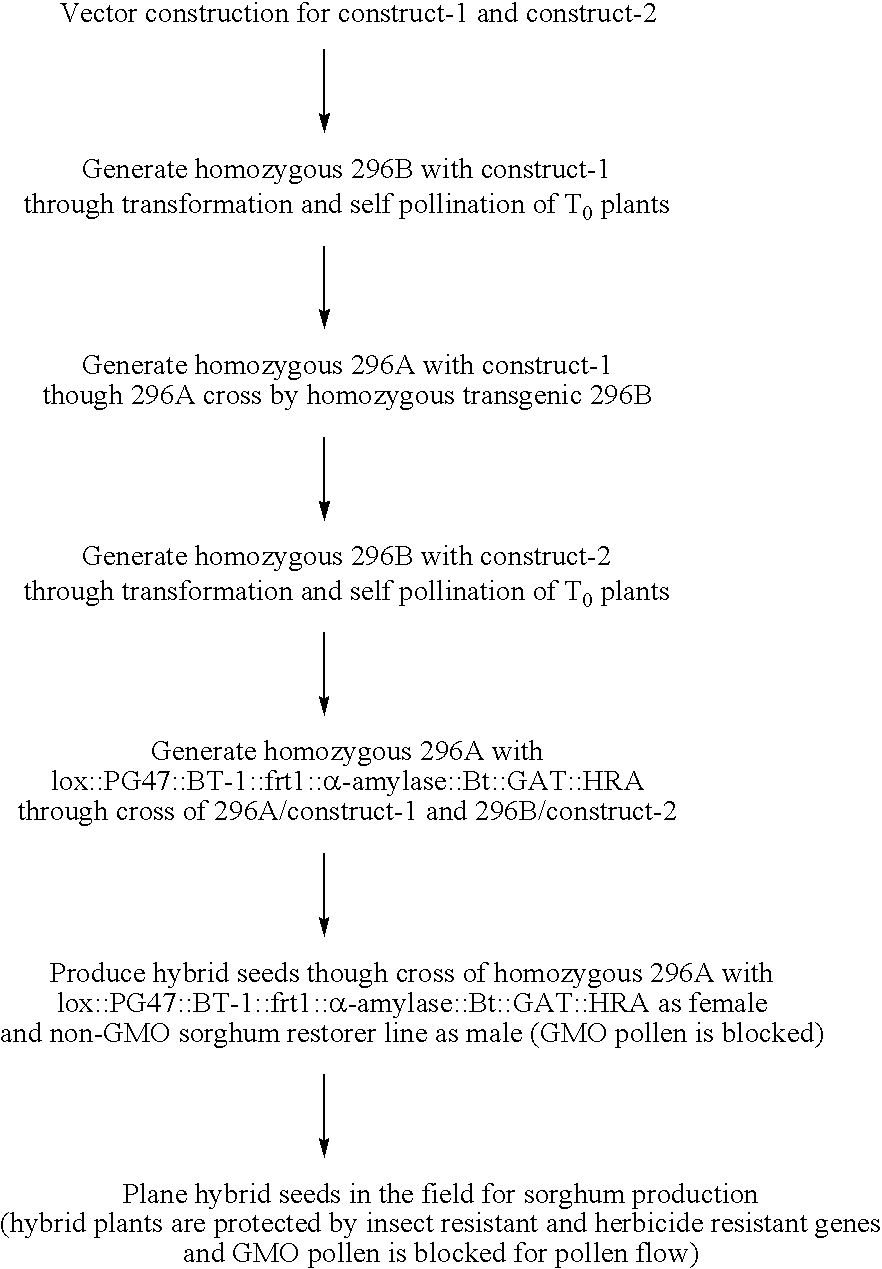
Methods and compositions for pollination disruption
Pollination process is disrupted by use of a pollination-disruption polynucleotide that renders the pollen unable to fertilize a sexually compatible ovule. The non-lethal nature of the pollen disruption polynucleotide is advantageous, particularly when operably linked to a transgenic polynucleotide of interest and prevents transmission of the polynucleotide through pollen. non-lethal markers are employed in an embodiment in which transgenic and non-transgenic seed can be sorted. A recombinase excision system is employed in an embodiment to activate the pollen disruption polynucleotide.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
Endophyte enhanced seedlings with increased pest tolerance
ActiveUS8455395B2Improve toleranceInoculation is highBiocideFungiIncreased toleranceFungal endophyte
The invention provides methods for preparing a conifer seedling with increased tolerance to a pest. A conifer seedling is inoculated with an isolated endophyte when the conifer seedling is susceptible to colonization by the endophyte.
Owner:J D IRVING
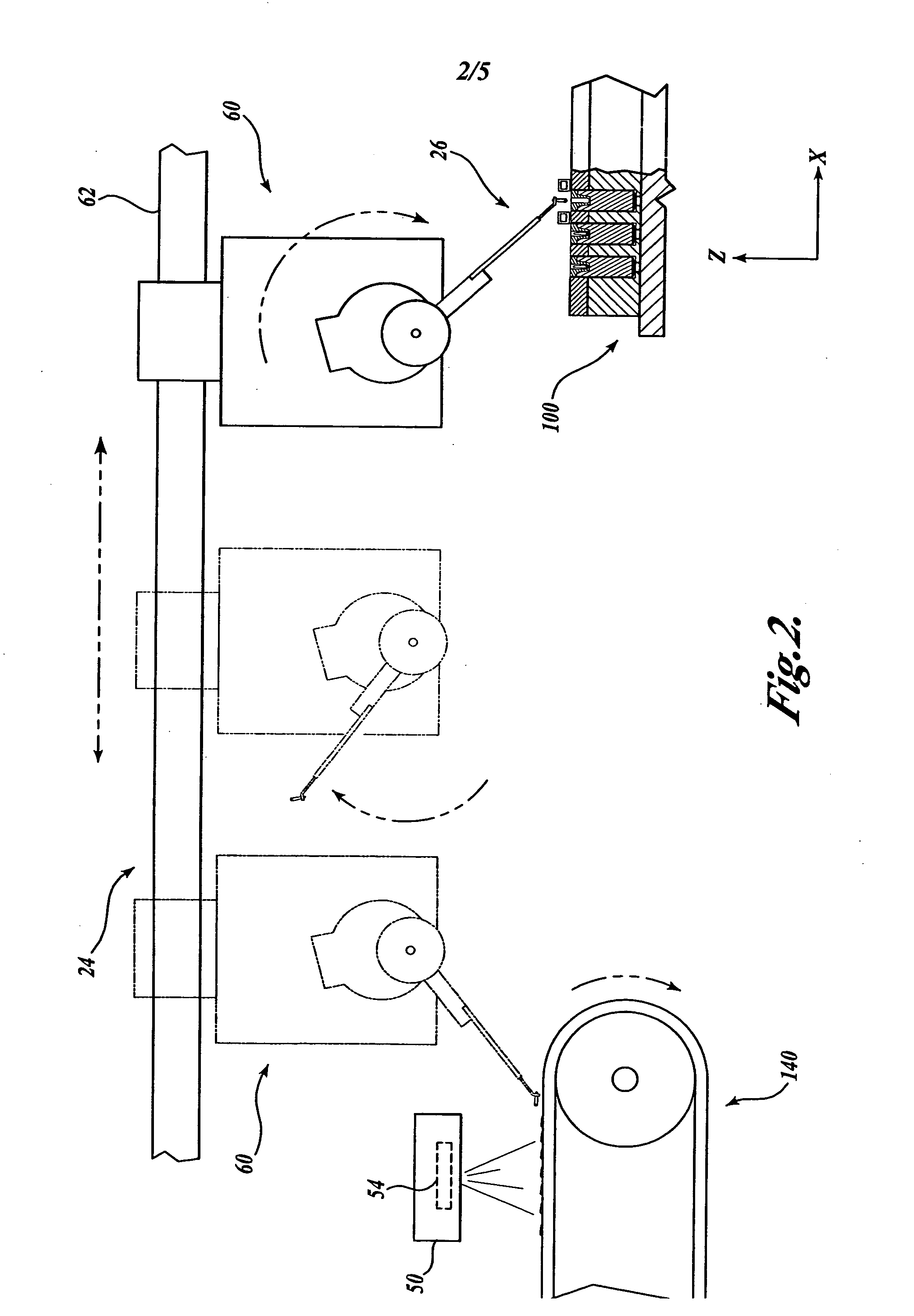
System and method of embryo delivery for manufactured seeds
InactiveUS20050114918A1Improved embryo release capabilityReduce surface tensionSeed and root treatmentCharacter and pattern recognitionBiotechnologyControl system
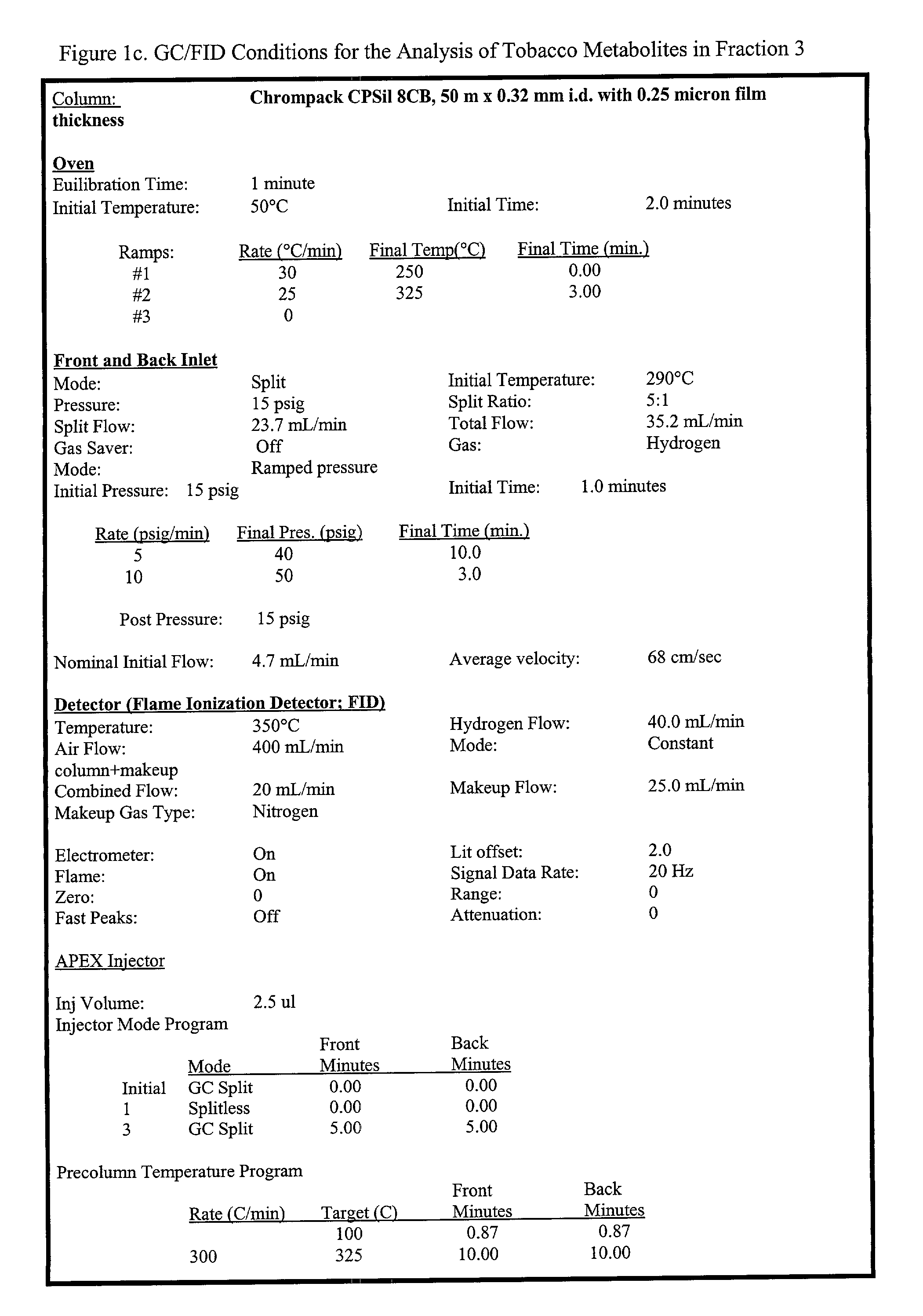
A embryo delivery system 20 is composed of an embryo orientation assembly 22, a transfer assembly 24, and an embryo reception assembly 26. In operation, the embryo delivery system 20 retrieves plant embryos one at a time from a position on the manufactured seed production line with microtweezers and places each embryo into a separate growing medium, such as a seed coat. The embryo delivery system 20 further includes a control system 28 having a computer 56 or other general computing device for automating the embryo delivery process.
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER CO
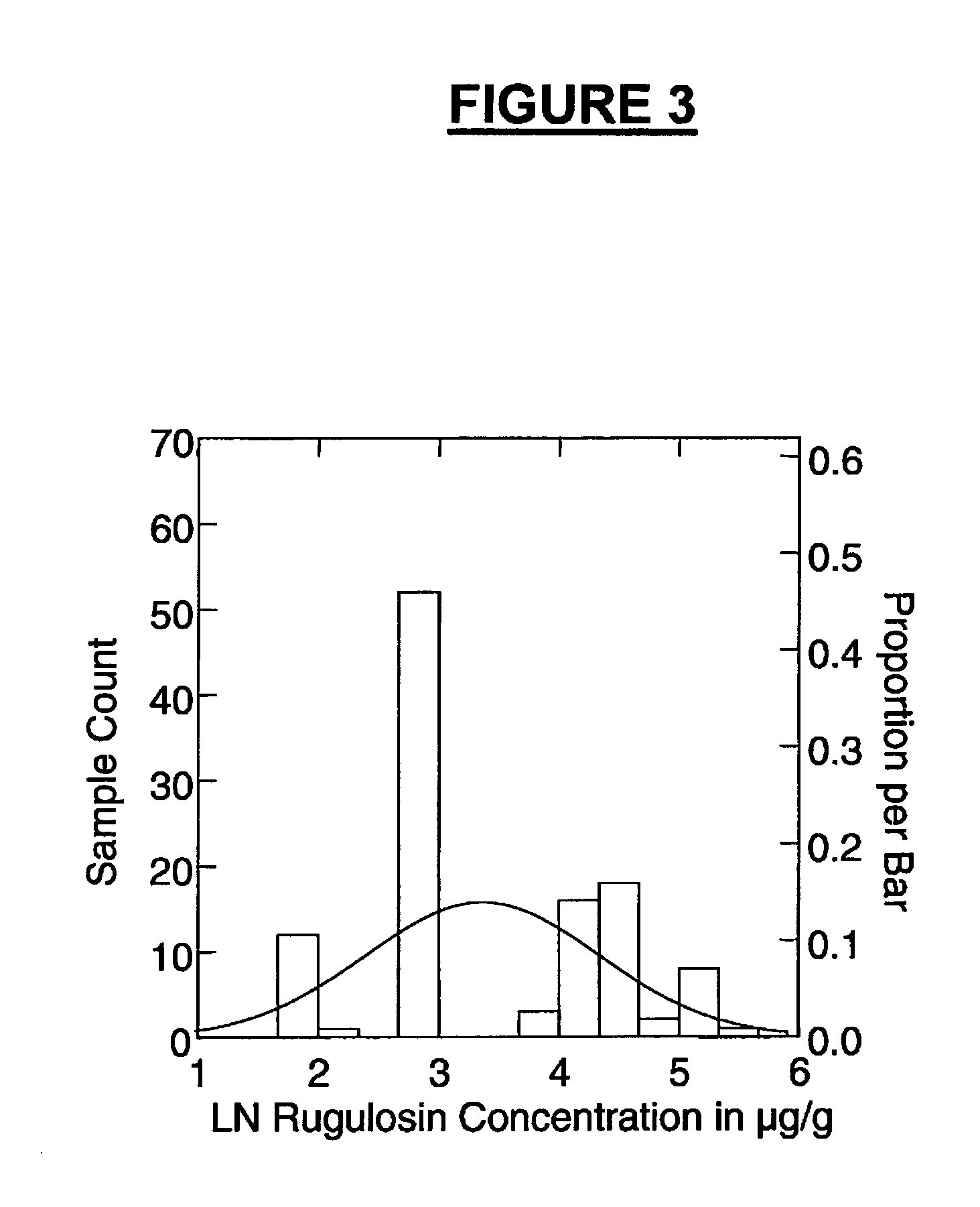
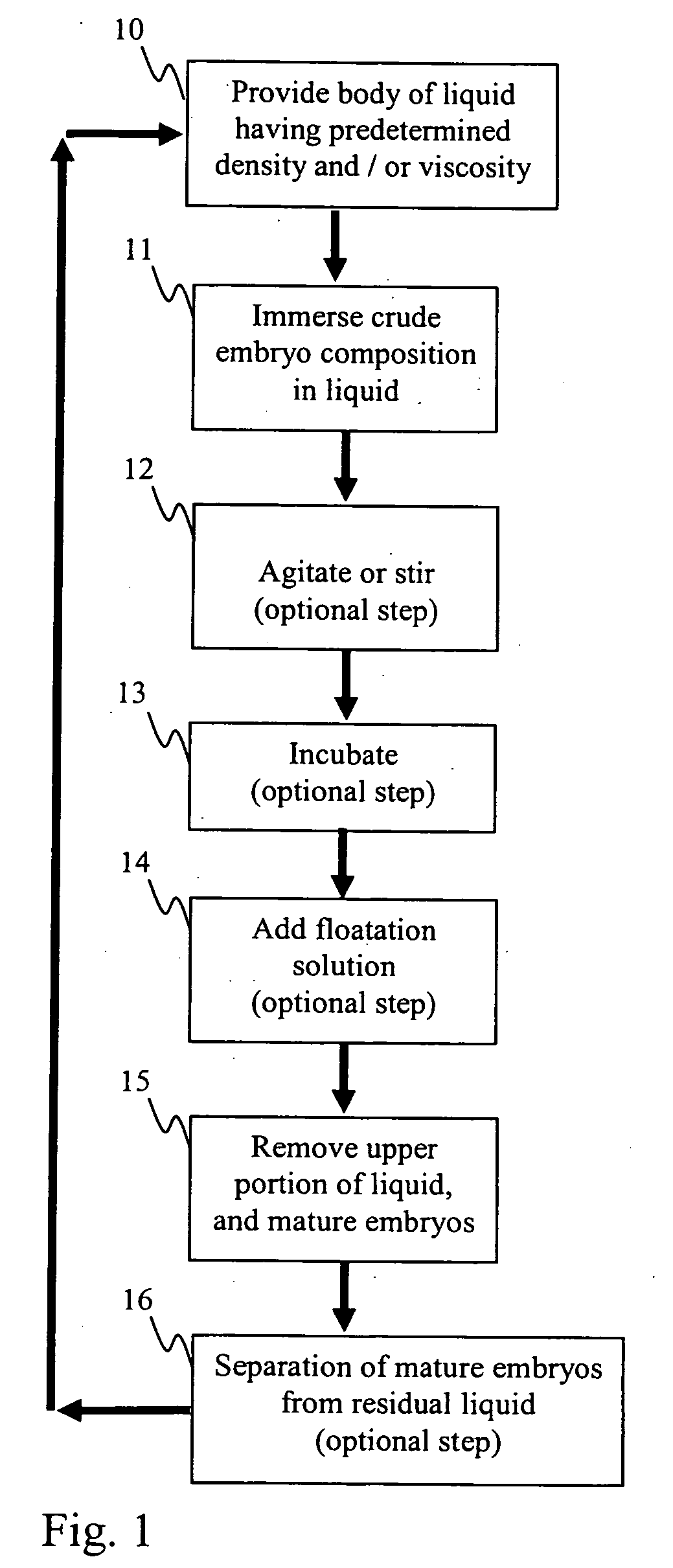
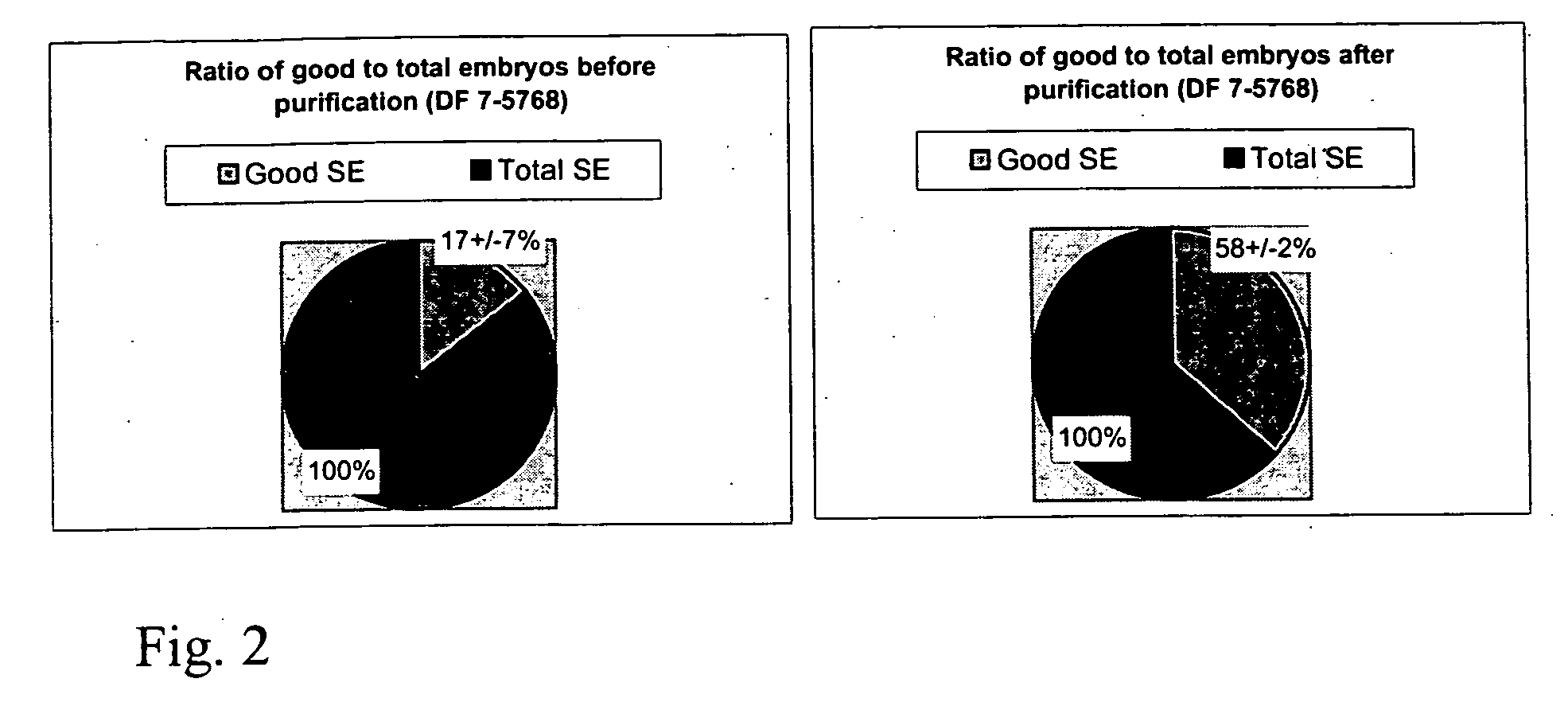
Bulk sorting of conifer somatic embryos
InactiveUS20050246802A1Quality improvementImprove isolationHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureHigh probabilitySomatic embryogenesis
The selection and isolation of mature somatic conifer embryos has previously involved chemical based or labour intensive techniques. Disclosed are simple yet highly effective methods to sort somatic embryos according to maturity to generate a population of quality somatic embryos that exhibit a high probability of successful conversion and germination. The methods include liquid sorting of somatic embryos using an aqueous liquid having a specific solute concentration and / or a viscosity. In this way, embryos that have attained a degree of maturity (and preferably desiccation tolerance) can be separated both from embryos that are comparatively immature and importantly from significant quantities of proliferation material and other organic matter generated during embryo propagation.
Owner:CELLFOR
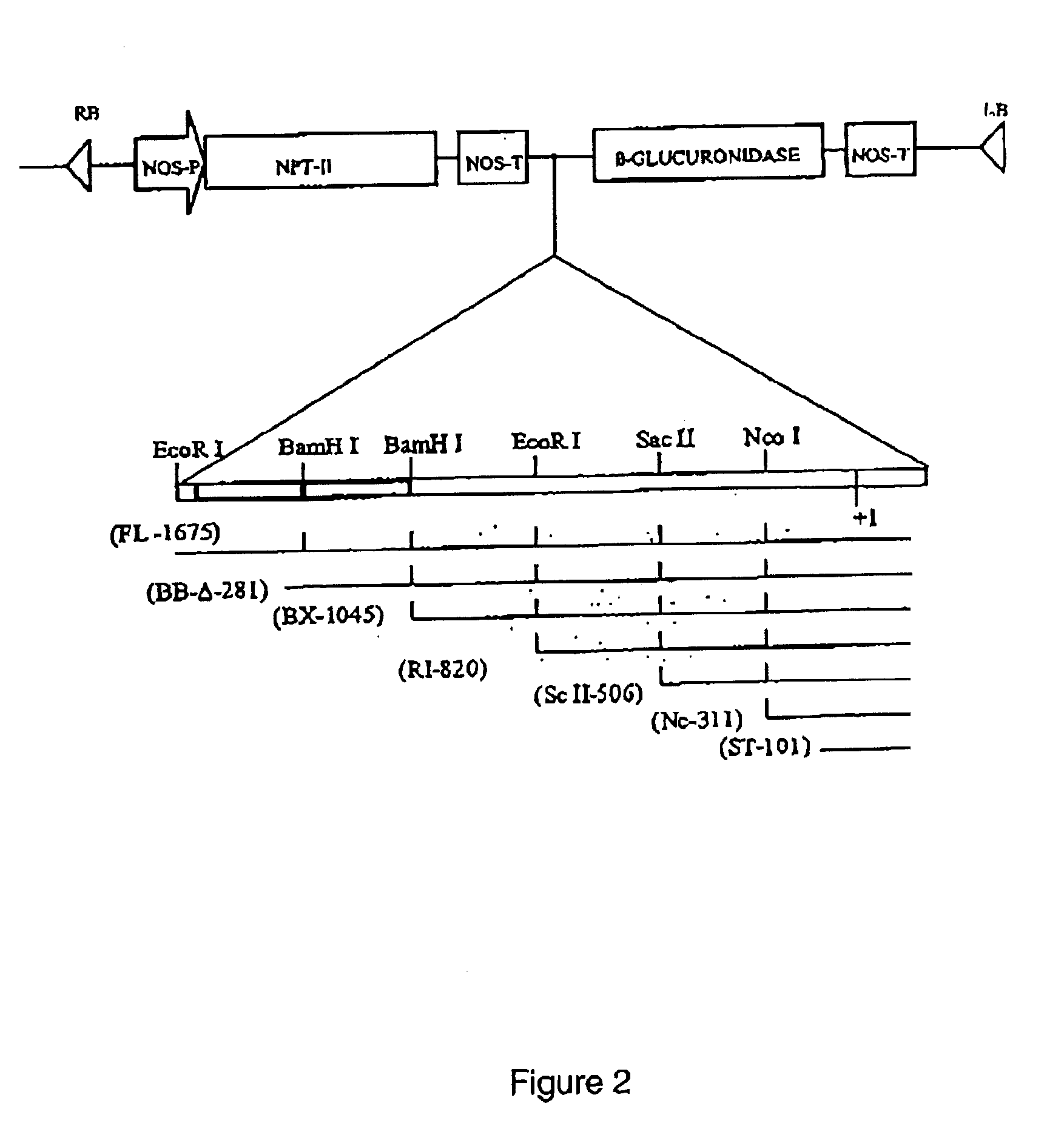
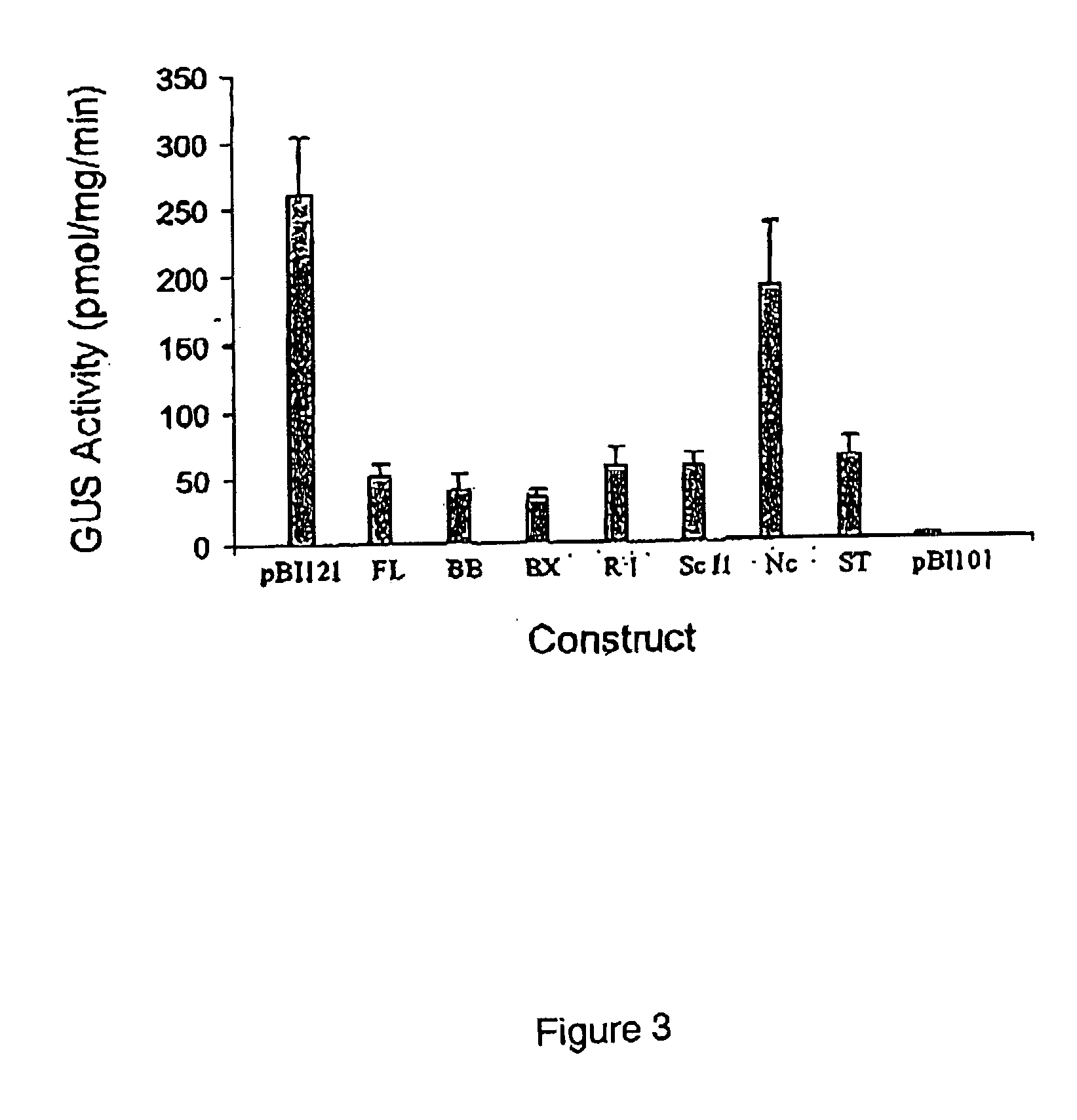
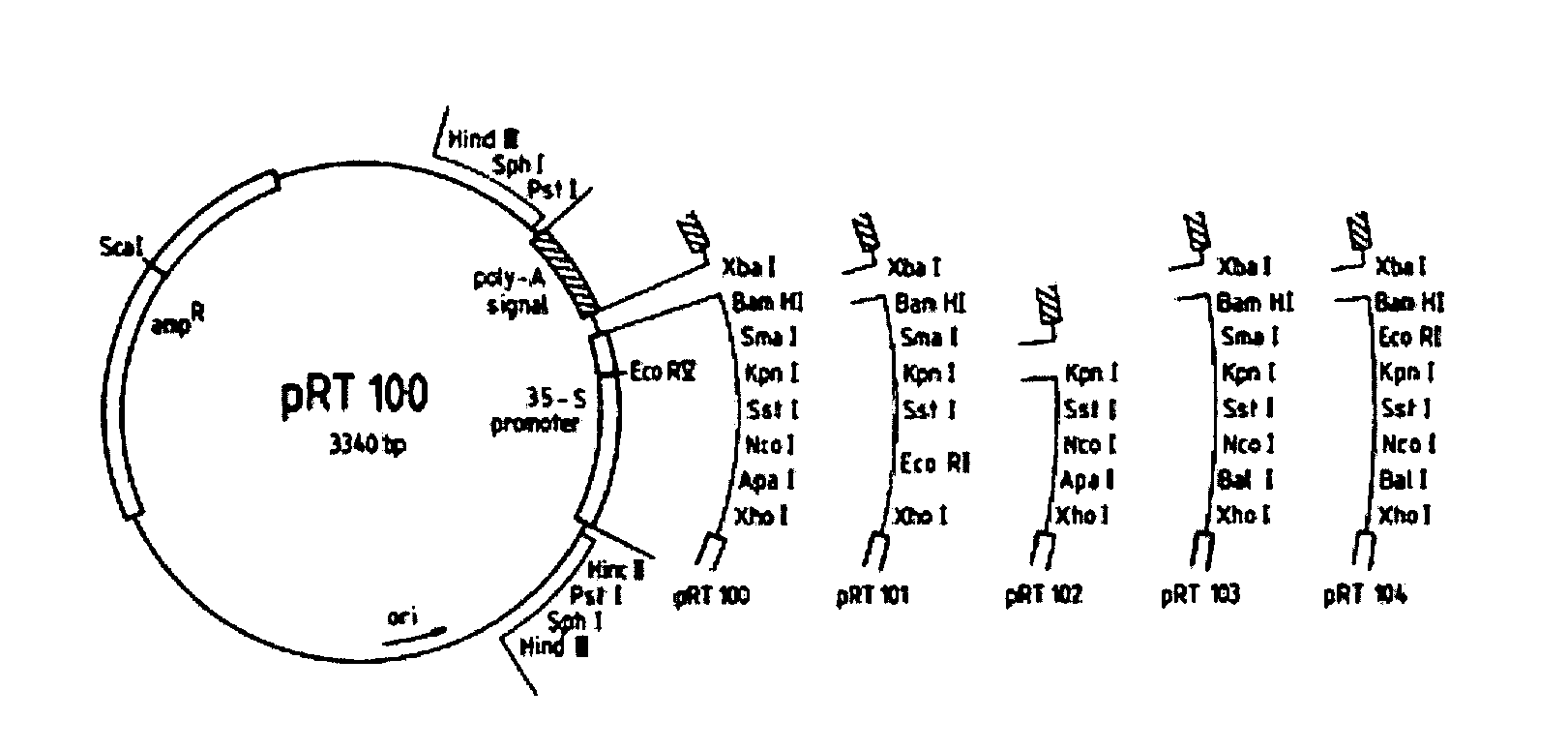
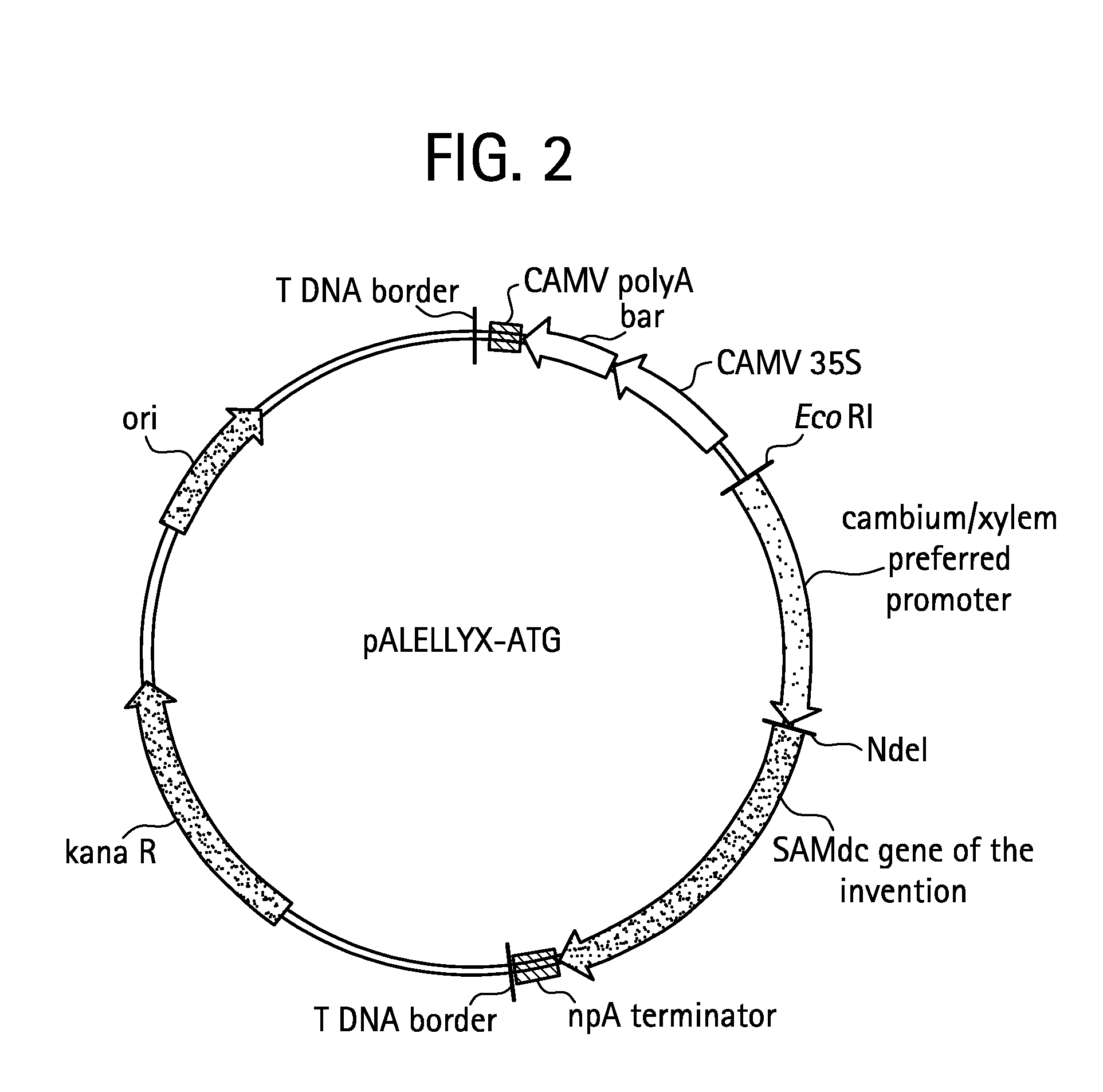
Tissue specific promoters
Tissue specific promoters (SEQ. ID. No. 1-5) are disclosed, these being preferentially expressed in the xylem tissue of woody plants. These promoters are used e.g. to specifically regulate gene expression in xylem tissue and alter xylem properties in plants. Transgenic plants, exhibiting modified xylem properties can be produced using these promoters.
Owner:SWETREE TECHOLOGIES AB
Plant stem cell derived from cambium of family gingkoaceae and method for isolation thereof
The present invention relates to a stem cell derived from cambium of family Gingkoaceae and to method for the isolated culturing thereof. The stem cell derived from cambium of family Gingkoaceae according to the present invention is advantageous as it is isolated at a non-differentiated state without passing through a dedifferentiation process and stably maintained without causing a variation in the cellular growth rate and growth pattern even during a long-term culture, thereby enabling a mass culture. In addition, the stem cell derived from cambium of family Gingkoaceae according to the present invention showed an antioxidant effect similar to or higher than that of existing synthetic antioxidants when the radical-scavenging activity for scavenging radicals generated by the treatment of an oxidant is measured, and thus can be valuably used as an excellent anti-inflammatory composition.
Owner:深圳露泉实业有限公司
Modification of plant development and morphology
ActiveUS20090249518A1Outgrowth of lateral shoots may be enhancedPrevent and reduce delaySugar derivativesClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyGene product
A method of modifying morphology in a plant by introducing into a plant at least one chimaeric gene having a promoter sequence operably associated with a nucleic acid sequence, the promoter sequence being operable to direct expression in specific cells of the plant and the nucleic acid sequence encoding at least one gene product capable of altering the metabolism of or causing death of the specific cells and / or nearby cells. In particular, the promoter sequence is operable to direct expression in lateral bud or lateral shoot and the nucleic acid encoding at least one gene product capable of disrupting the metabolism of or causing the death of the lateral bud or lateral shoot or nearby cells. Preferably the promoter sequence has the sequence shown as SEQ ID No. 1 or SEQ ID No. 7 or SEQ ID No. 4, or a part thereof capable of regulating expression of a gene, or a sequence having at least 60%, preferably at least 75%, homology to SEQ ID No. 1 or SEQ ID No. 7 and being capable of regulating expression of a gene.
Owner:BRITISH AMERICAN TOBACCO (INVESTMENTS) LTD
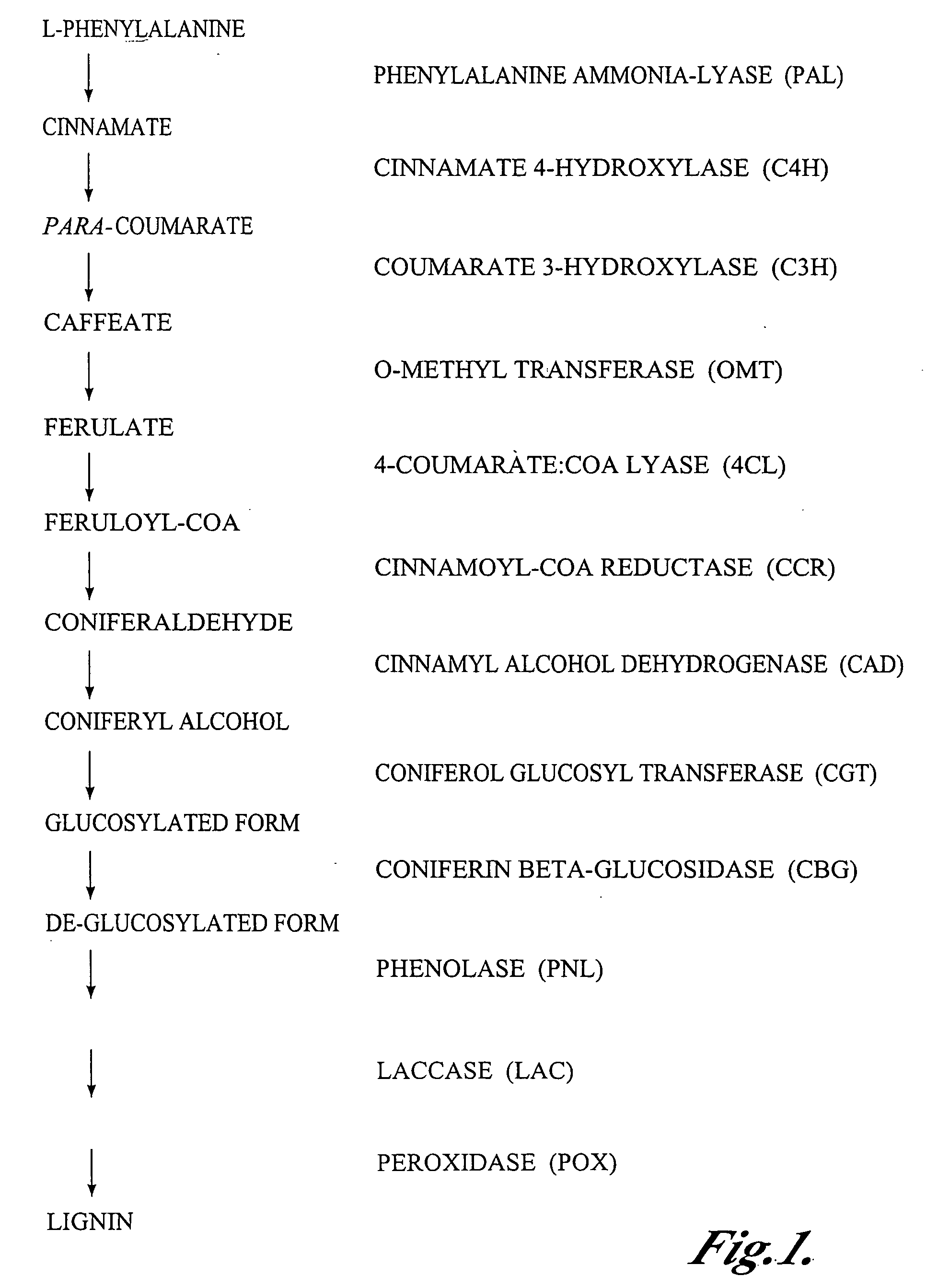
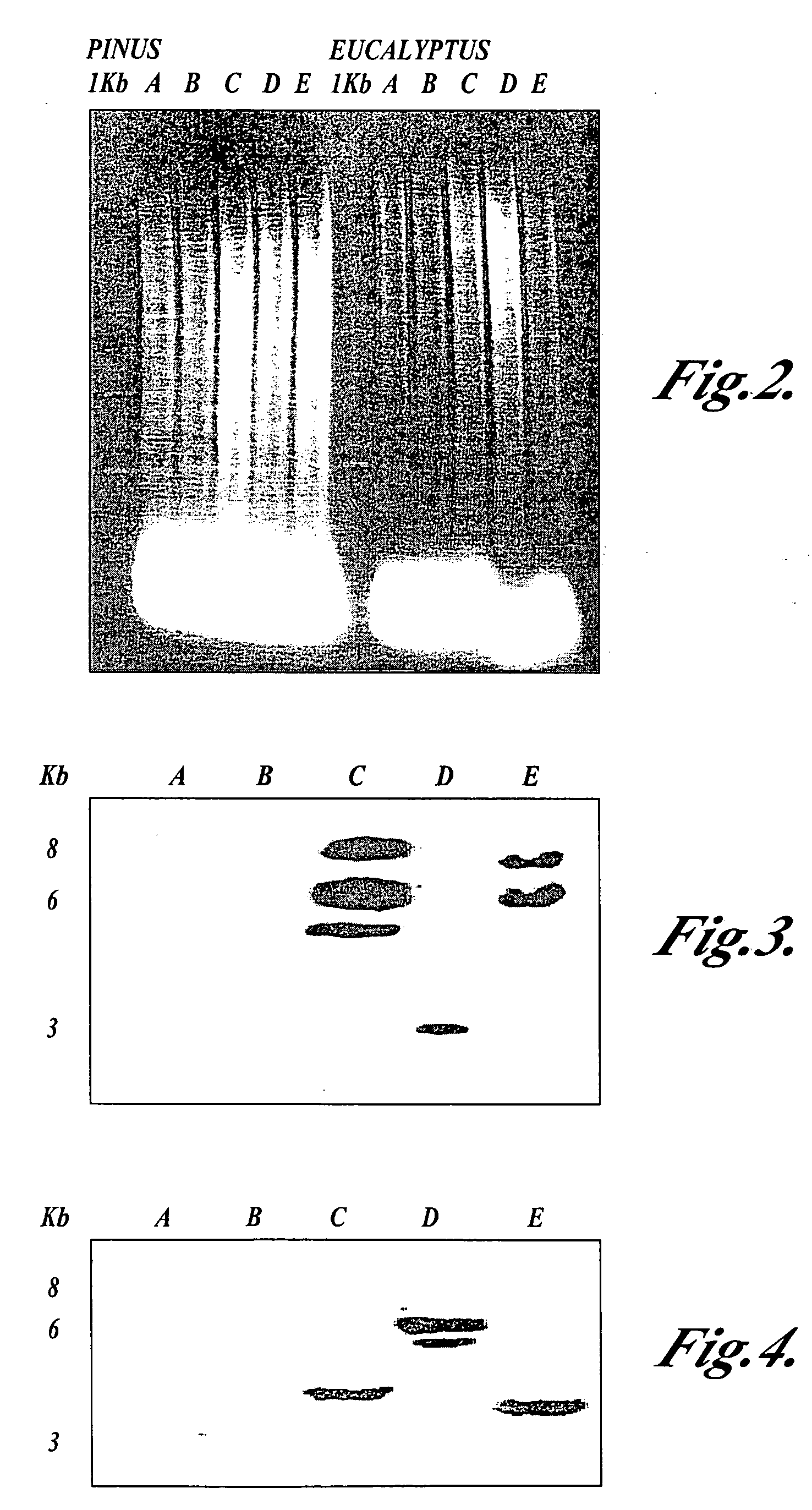
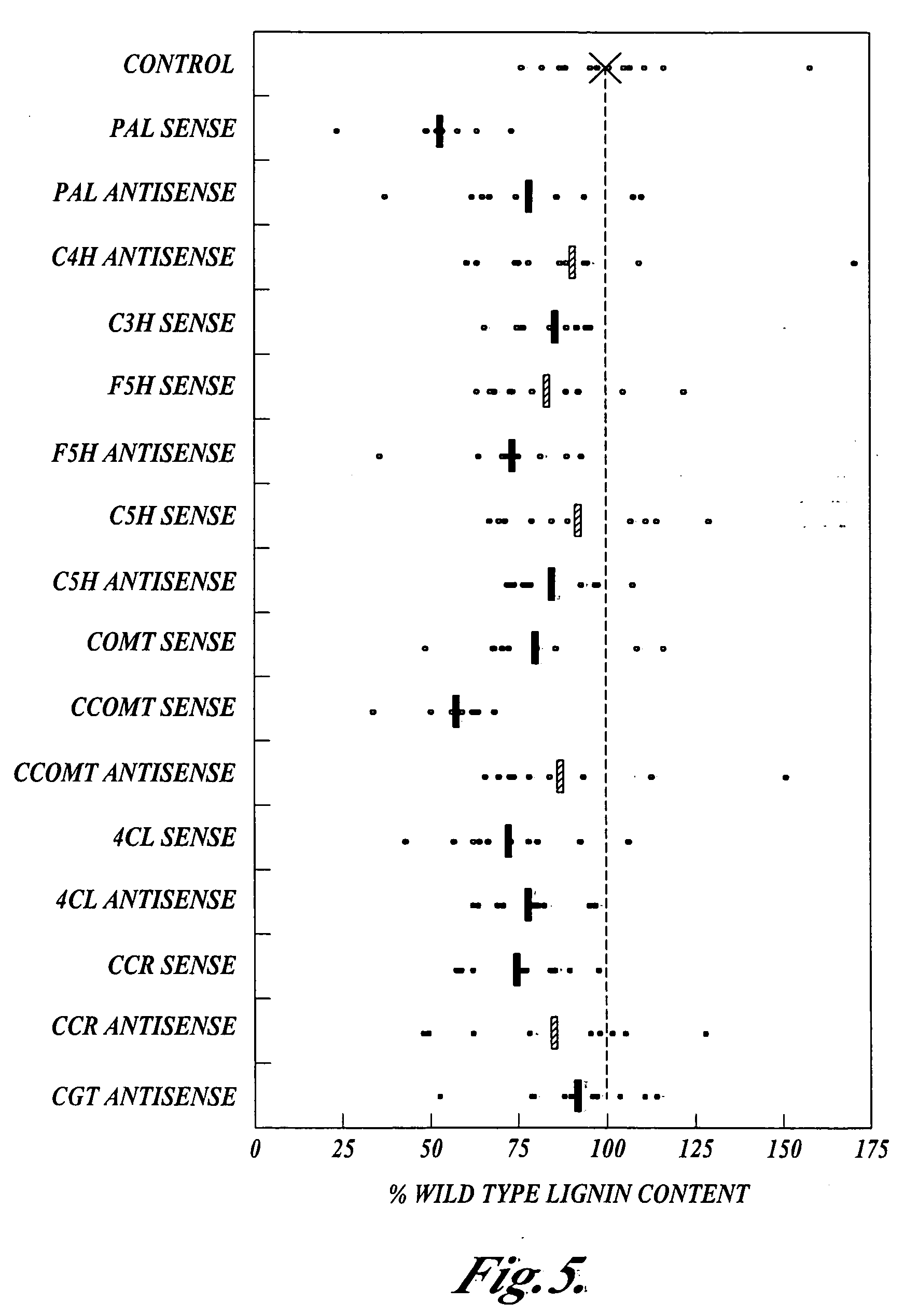
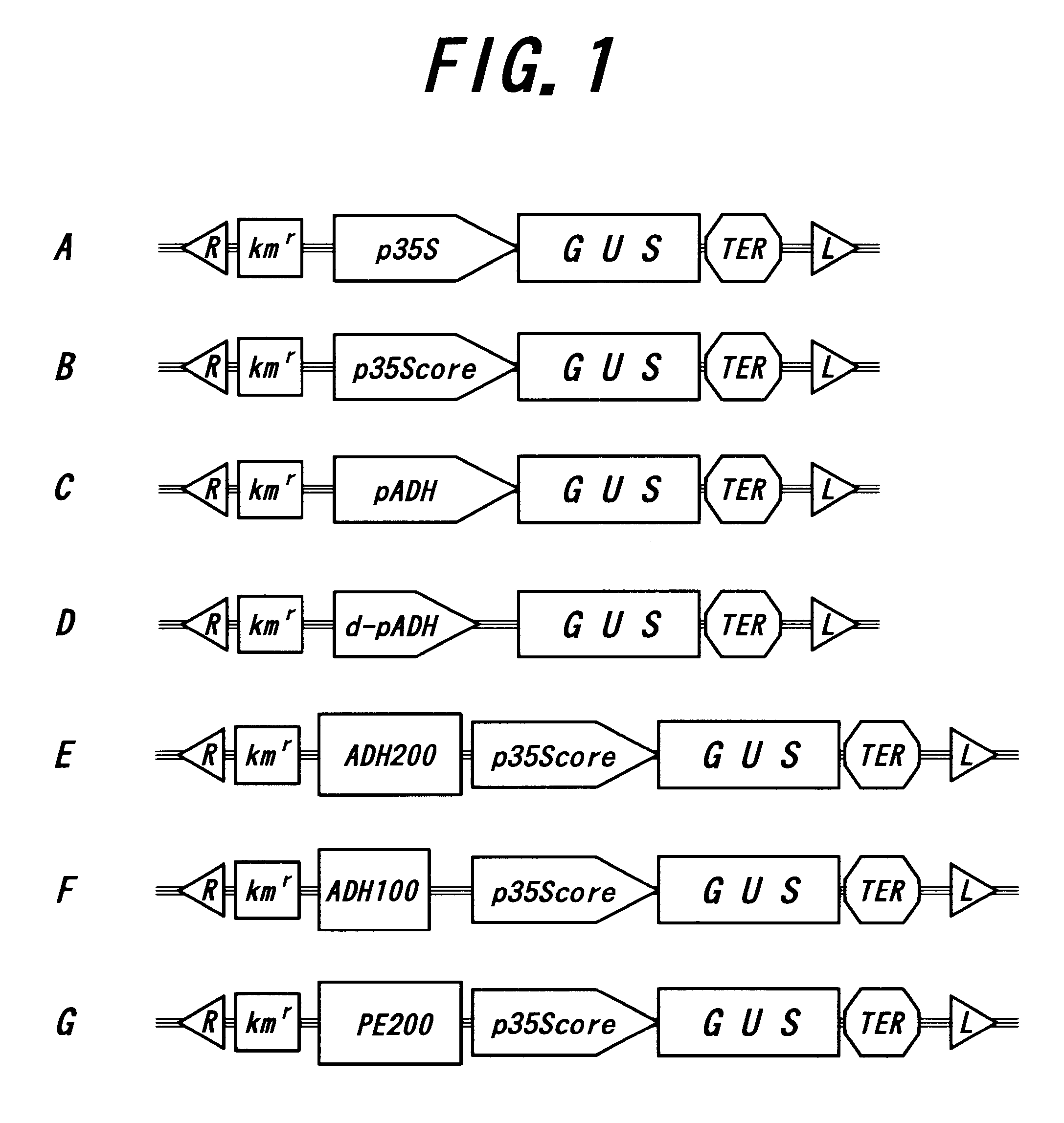
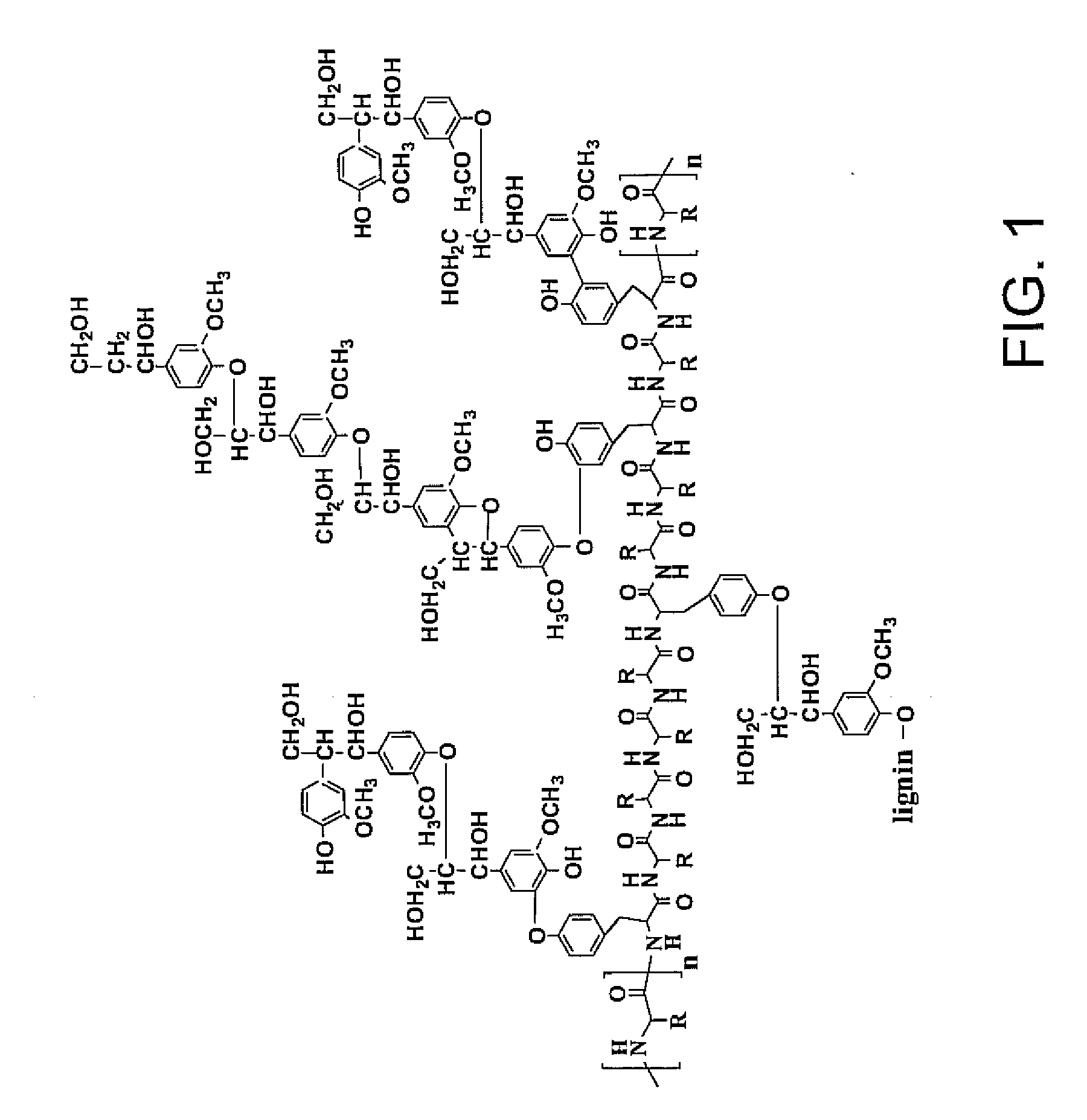
Materials and methods for the modification of plant lignin content
Novel isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides associated with the lignin biosynthetic pathway are provided, together with genetic constructs including such sequences. Methods for the modulation of lignin content, lignin structure and lignin composition in target organisms are also disclosed, the methods comprising incorporating one or more of the polynucleotides of the present invention into the genome of a target organism.
Owner:ARBORGEN
Enhanced transformation and regeneration of transformed embryogenic pine tissue
InactiveUS7157620B2Promote recoveryMinimal loss of cellsOther foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureSubgenusPinus cembroides
Owner:ARBORGEN
DNA fragment for stable expression of an exogenous gene in a plant
InactiveUS6573429B1Stable expressionHigh homologySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesDNA fragmentationGene
Owner:NARA INST OF SCI OF TECH
Methods of creating dwarf phenotypes in plants
InactiveUS20020194646A1Increase ratingsDesirable propertyClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesNicotiana tabacumTobacco product
The invention is directed to the application of gene sequences which cause a dwarf phenotype in plants to the fields of forestry plants, ornamental horticultural plants, medicinal plants, and Nicotiana plants which are used for purposes other than for traditional tobacco products. The invention provides cDNAs identified by the polynucleotide sequences SEQ ID NO: 1-122 that may be used to create transfected or transgenic plants exhibiting a dwarf phenotype. The invention also provides methods of creating a transfected or transgenic plant exhibiting a dwarf phenotype by expressing in the plant DNA or mRNA identified by the sequences SEQ ID NO:1-122.
Owner:LARGE SCALE BIOLOGY
Method of ex vitro sowing, germination, growth and conversion of plant somatic embryos or germinants, and nutrient medium used therefor
InactiveUS20050124065A1Buffer stressPromote absorptionCulture processCell culture mediaSolid componentNutrient solution
A method of sowing a somatic plant embryo or germinant of a conifer species to facilitate subsequent development of the embryo or germinant into an autotrophic seedling. The method involves the following steps carried out ex vitro in non-sterile conditions: providing a nutrient medium comprising particles of a solid component present within a flowable or semi-solid component containing water and a carbohydrate nutrient for the embryo or germinant, dispensing a quantity of the nutrient medium onto a surface of a porous solid growth substrate for the somatic plant embryo or germinant, and contacting the plant embryo or germinant with the nutrient medium. The nutrient medium has a fluidity such that at least some of the flowable or semi-solid component containing the carbohydrate nutrient remains in contact with the embryo or germinant at least until the embryo or germinant establishes vigorous growth under environmental conditions effective for such growth. The particles of the solid component are adapted to remain in contact with the embryo or germinant after of the flowable or semisolid material dissipates, thereby providing continuing physical support for the embryo or germinant after the dissipation. The invention also relates to seedlings produced in this way and to the nutrient solution.
Owner:ARBORGEN
Method of ex vitro sowing, germination, growth and conversion of plant somatic embryos or germinants, and nutrient medium used therefor
A method of sowing a somatic plant embryo or germinant of a conifer species to facilitate subsequent development of the embryo or germinant into an autotrophic seedling. The method involves the following steps carried out ex vitro in non-sterile conditions: providing a nutrient medium comprising particles of a solid component present within a flowable or semi-solid component containing water and a carbohydrate nutrient for the embryo or germinant, dispensing a quantity of the nutrient medium onto a surface of a porous solid growth substrate for the somatic plant embryo or germinant, and contacting the plant embryo or germinant with the nutrient medium. The nutrient medium has a fluidity such that at least some of the flowable or semi-solid component containing the carbohydrate nutrient remains in contact with the embryo or germinant at least until the embryo or germinant establishes vigorous growth under environmental conditions effective for such growth. The particles of the solid component are adapted to remain in contact with the embryo or germinant after of the flowable or semi-solid material dissipates, thereby providing continuing physical support for the embryo or germinant after the dissipation. The invention also relates to seedlings produced in this way and to the nutrient solution.
Owner:FAN SHIHE +4
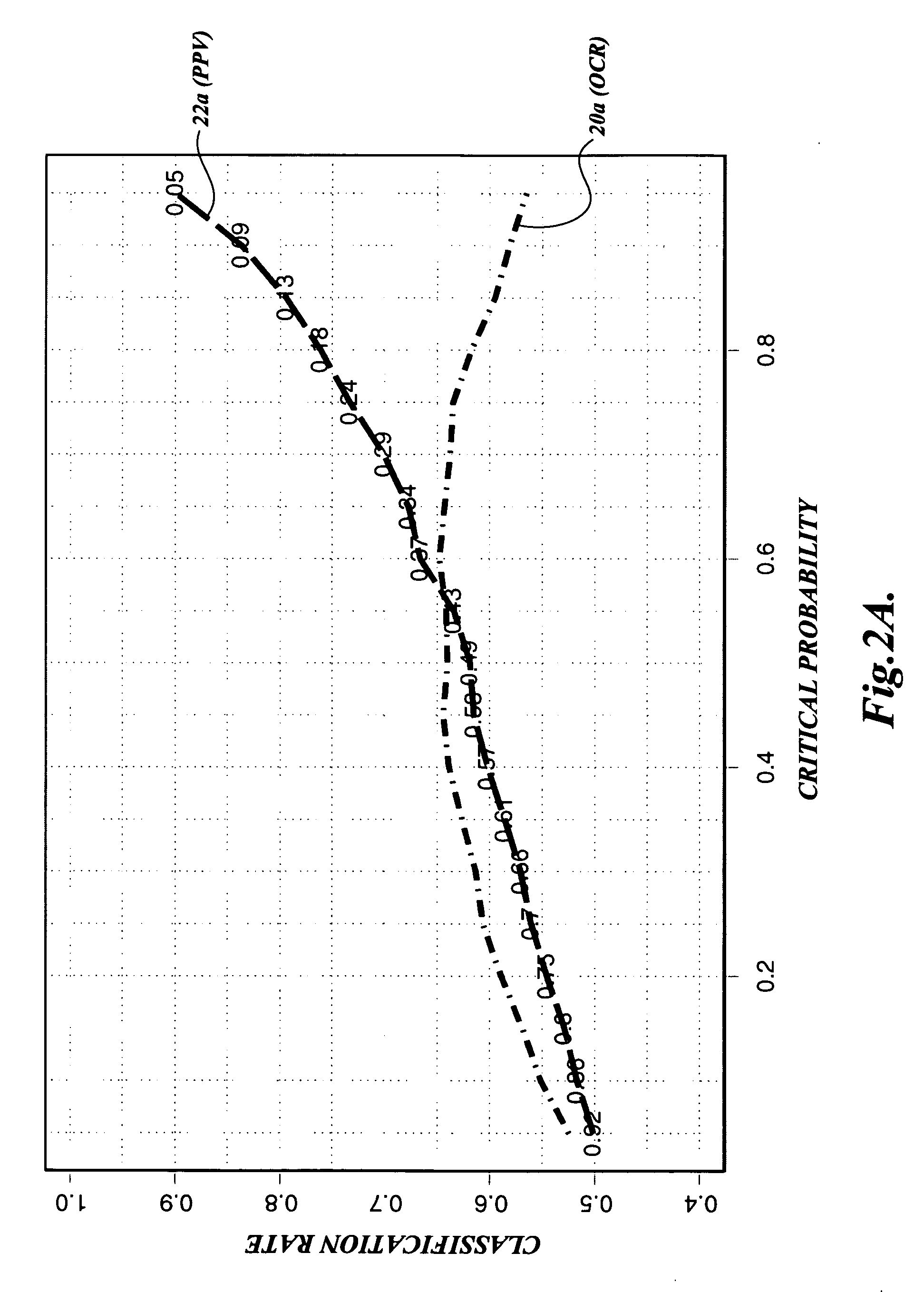
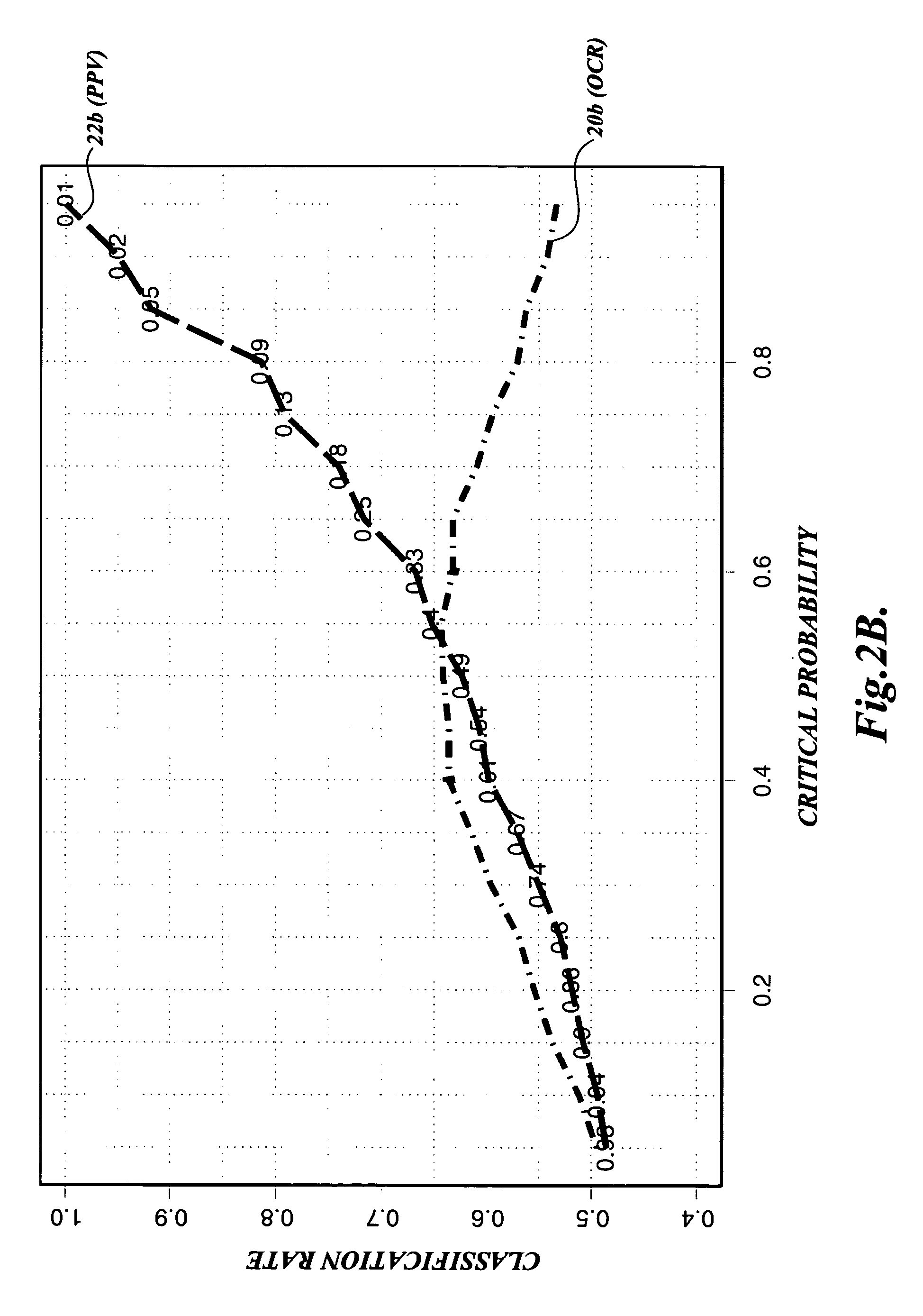
Method of classifying plant embryos using penalized logistic regression
ActiveUS20060068372A1Seed and root treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementPattern recognitionData set
A method is disclosed for classifying plant embryos according to their quality using a penalized logistic regression (PLR) model. First, sets of image or spectral data are acquired from plant embryos of known quality, respectively. Second, each of the acquired sets of image or spectral data is associated with one of multiple class labels according to the corresponding embryo's known quality. Third, sets of metrics are calculated based on the acquired sets of image or spectral data, respectively. Fourth, a penalized logistic regression (PLR) analysis is applied to the sets of metrics and their corresponding class labels to develop a PLR-based classification model. Fifth, image or spectral data are acquired from a plant embryo of unknown quality, and metrics are calculated based therefrom. Sixth, the PLR-based classification model is applied to the metrics calculated for the plant embryo of unknown quality to classify the same.
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
Root-specific conifer gene promoter and its use
There is provided an isolated polynucleotide sequence useful as a promoter in plant root tissue. The sequence is derived from the promoter for the Western white pine gene PR10. The sequence comprises at least 45 nucleotidcs, and has at least two Dof elements which individually may be in a forward or inverted orientation. Each Dof element has a sequence NNNWAAAGNNN, wherein N is A, T, G, or, C, and, W is A or T. The Dof elements are separated from each other by between 10 and 20 nucleotides. The sequence also has a TATA box located between 15 and 25 nucleotides in the 3′ direction of the closest Dof element. In some instances, the polynucleotide has one Dof element with the sequence NNNWAAAGNNN and another with the sequence NNNCTTTWNNN. In some instances the polynucleotide sequence is one where the 5′ Dof element sequence is CTCTCTTTAAT, and another Dof element (which may be the next Dof element) sequence is TTTTAAAGGTT and the TATA box sequence is TACAATAAATA or TATAWAWA, wherein W is A or T. Also provided are sequences useful in modulating gene expression in stem and leaf tissue.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF NATURAL RESOURCES
Process for ex vitro sowing and germination of plant somatic embryos
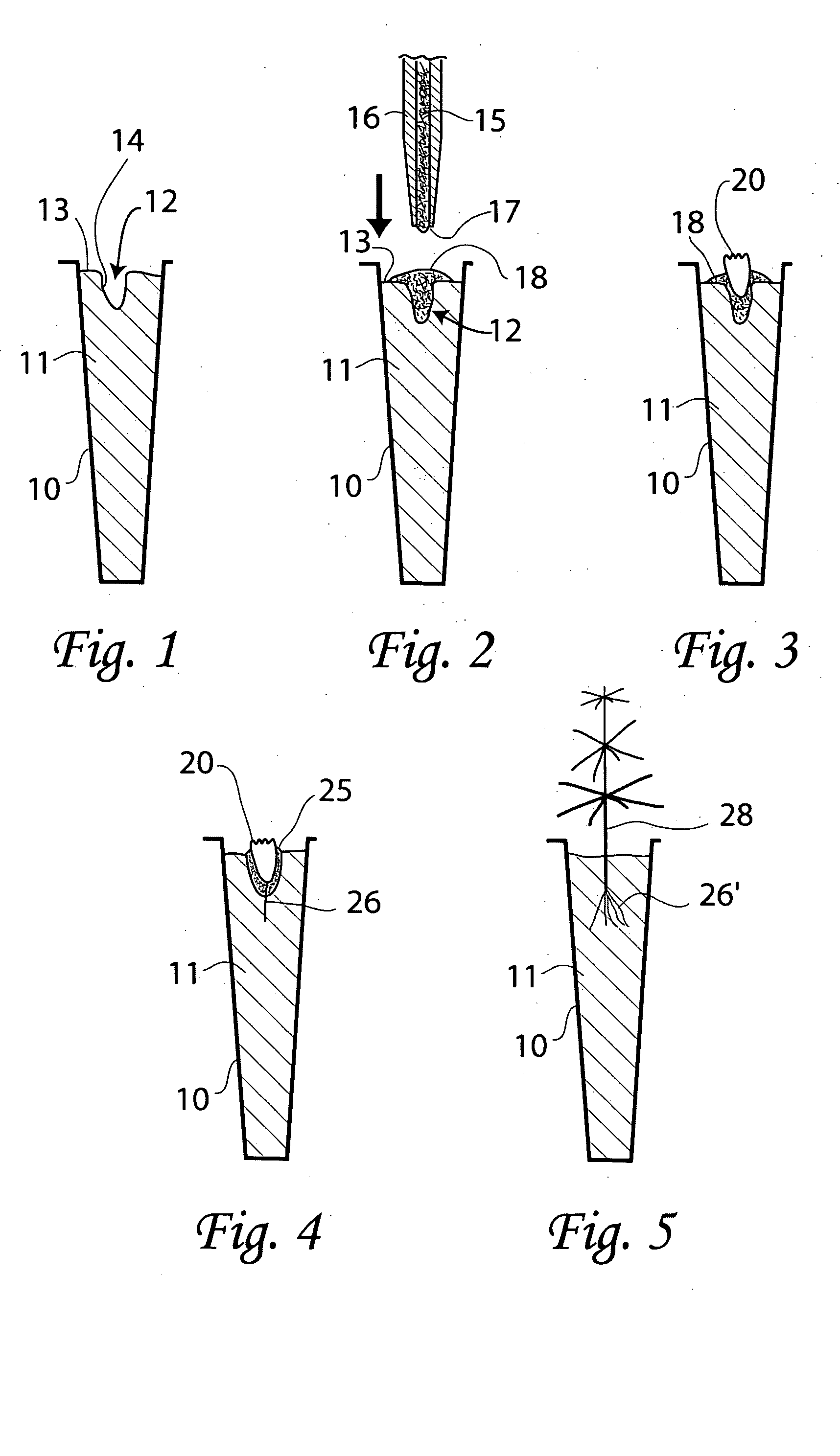
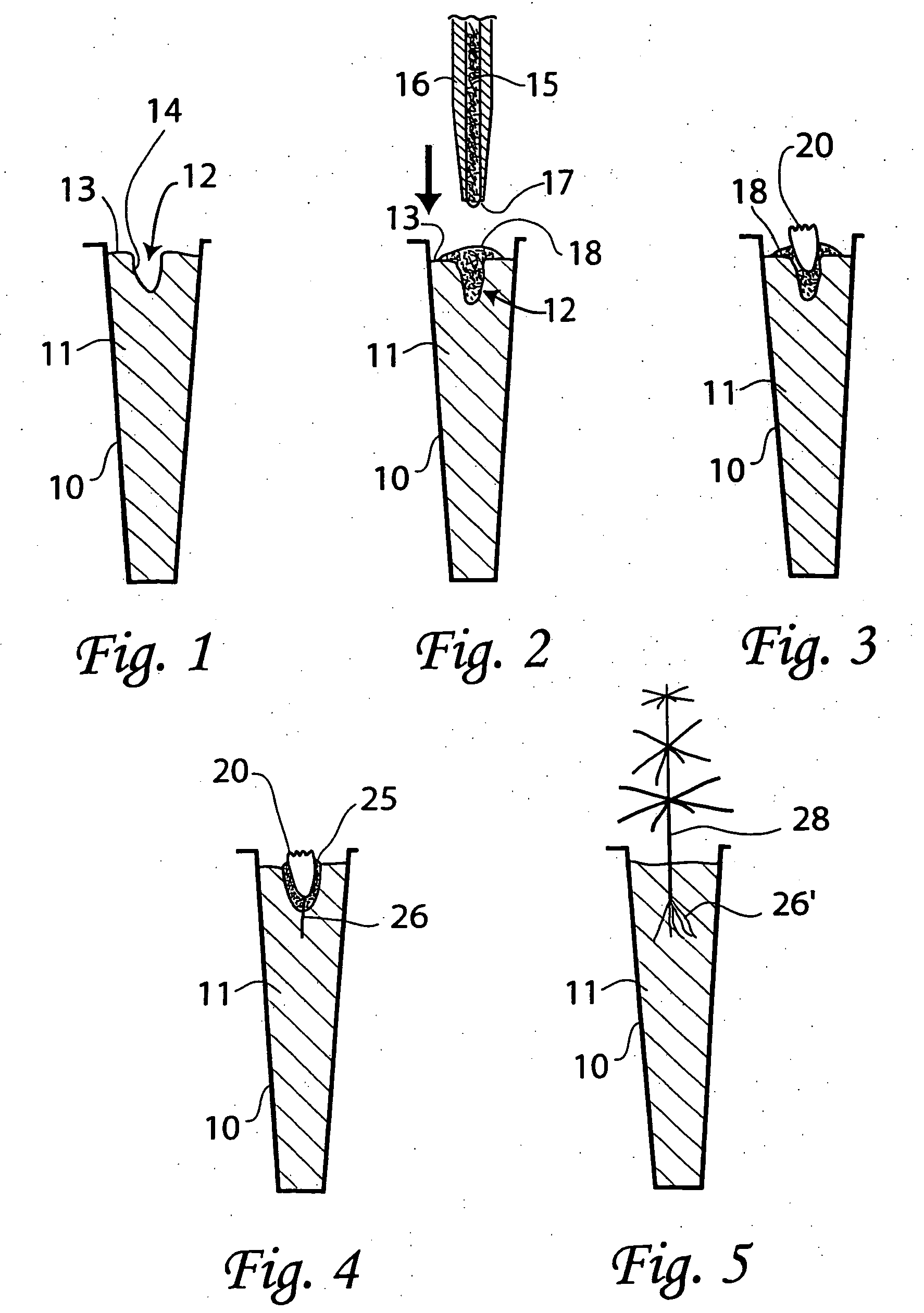
A multi-step process by which plant somatic embryos can be sown and germinated ex vitro using conventional seeding equipment, growing mixes, and plant propagation environments. The process most preferably comprises the steps of: placing a somatic embryo on or within a three-phase substrate, the phases comprising solid, liquid and gas phases, placing the substrate containing a somatic embryo into an environmentally-controlled plant-growing environment in which at least one environmental factor (i.e. moisture level within the three-phase substrate, atmospheric humidity, temperature, nutrients, ambient light intensity and diurnal photoperiod) may be controlled and manipulated, manipulating at least one of the environmental factors to enable and facilitate germination of the somatic embryo, and applying water and / or nutrient solutions at regular intervals, the intervals preferably ranging from 1 minute-24 hours, to the surface of the substrate in the form of microdroplets, preferably for a period of time ranging between 3 to eight weeks, such that somatic embryo imbibition, germination, growth and development occur. The process can be practiced in non-sterile conditions with “naked” fresh and / or HRHT-treated and / or desiccated embryos, i.e., non-encapsulated or otherwise uncoated embryos, and does not require the use of aseptic techniques or sterilized media or equipment.
Owner:ARBORGEN
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with transcription in plants and uses thereof for plant improvement
InactiveUS20150082481A1Climate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyPlant Sources
Polynucleotides useful for improvement of plants are provided. In particular, polynucleotide sequences are provided from plant sources. Polypeptides encoded by the polynucleotide sequences are also provided. The disclosed polynucleotides and polypeptides find use in production of transgenic plants to produce plants having improved properties.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Continuous culture of conifer embryogenic tissue
ActiveUS20050188436A1Easy to produceIncrease probabilityCell culture mediaOther foreign material introduction processesEmbryoBiology
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
Polynucleotide for identifying male and female ginkgo strains and application thereof
ActiveCN110195068AThe result is stable and accurateGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesPhysiologyNucleotide
The invention provides a polynucleotide for identifying male and female ginkgo strains. The polynucleotide comprises or consists of: 1) a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 5; or 2) a complement,degenerate or homologous sequence of the sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 5; or 3) a polynucleotide which hybridizes to the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 5 under stringent conditions or a complement thereof; 4) a coding sequence of any of the sequences 1) to 3); or 5) a nucleotide sequence identical to a nucleotide of 10 bp or more in any of the sequences of sequences 1) to 4). The polynucleotide provided by the present invention is unique among male ginkgo plants, uses the same to identify male and female plants of ginkgo, has the advantages of stable and accurate results, good reproducibility and rapid detection, and provides a basis for the identification of male and female ginkgo by molecular markers.
Owner:AGRI GENOMICS INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Method for maturation of conifer somatic embryos
InactiveUS6897065B1Promote maturityBulk materialHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGrowth plantCell mass
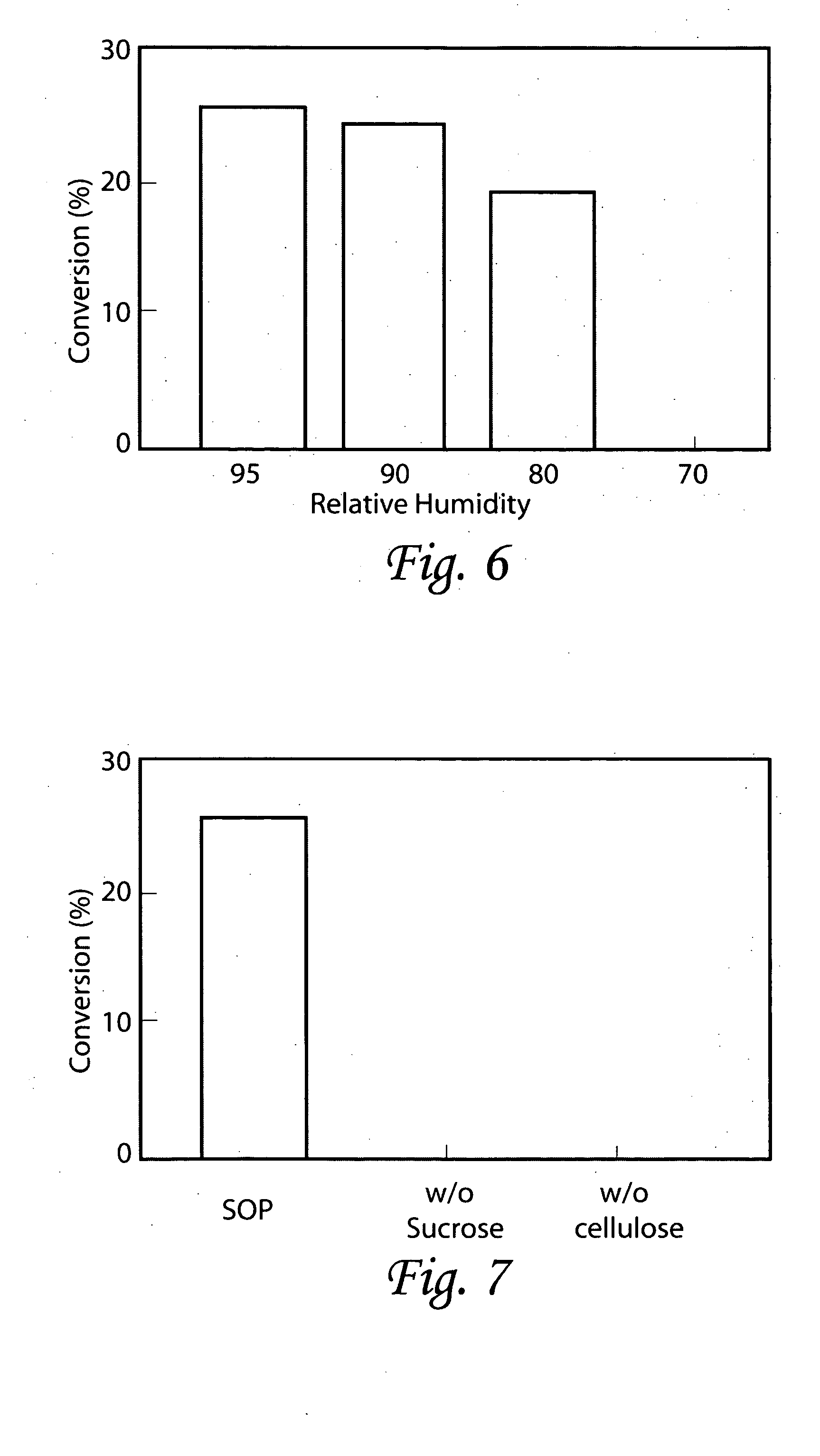
According to the invention an embryogenic cell mass is cultured with a culture medium comprising an anti-auxin resulting in an unexpected shift in physiology from proliferation to maturation. Proliferation is reduced so that the formation of new immature embryos ceases. Reduction of proliferation facilitates the transition from proliferation to maturation and maturation frequency is increased to a much larger extend than expected. Surprisingly, it has been discovered that the quality of the somatic embryos is not reduced, although the activity of the important endogenous plant growth regulator, auxin, is reduced. As a mater of fact, the overall quality of the mature embryos harvested at the end of maturation is actually increased over the prior art.
Owner:WOODY PLANT BIOTECH
A nucleic acid-based method for tree phenotype prediction
The present invention relates to a novel method for the prediction of fibre length and the rapid selection of superior trees for given pulp and paper product lines using a DNA probe. The method comprises the isolation of tree genomic DNA from a hybrid spruce live tissue source, hybridization of the spruce DNA probe to that genomic DNA and the densitometric assessment of the intensity of the hybridization pattern obtained. This determines the precise degree of genetic admixing (or introgression) of the two parent species within the hybrid population. Due to the linear relationship - in the hybrid spruce population examined - between degree of genetic introgression and fibre length (discovered in this method), the intensity of the DNA probe hybridization pattern can be used to directly, accurately and reproducibly predict the fibre length found (for a given tree age) within an individual hybrid spruce within the population.
Owner:PULP & PAPER RES INST OF CANADA
Use of porous membrane to support developing conifer somatic embryos
InactiveUS20070099293A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPorous membraneEmbryo
The present invention provides methods for developing conifer cotyledonary somatic embryos. In some embodiments, the methods of the invention include the step of culturing conifer pre-cotyledonary somatic embryos on a porous membrane, that is at least intermittently contacted with liquid development medium, for a period of time sufficient to produce conifer, cotyledonary, somatic embryos from the pre-cotyledonary somatic embryos.
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
Protection against herbivores
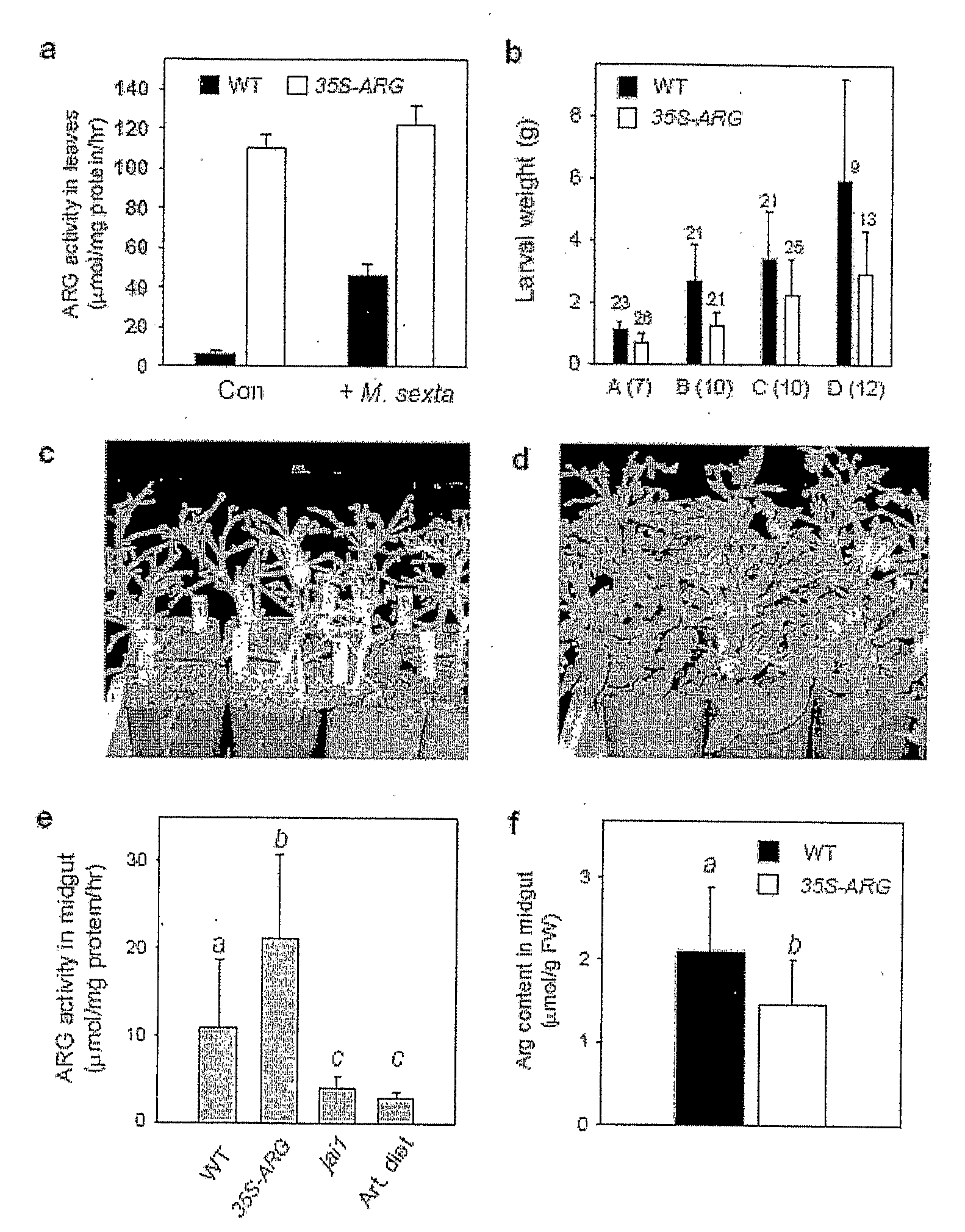
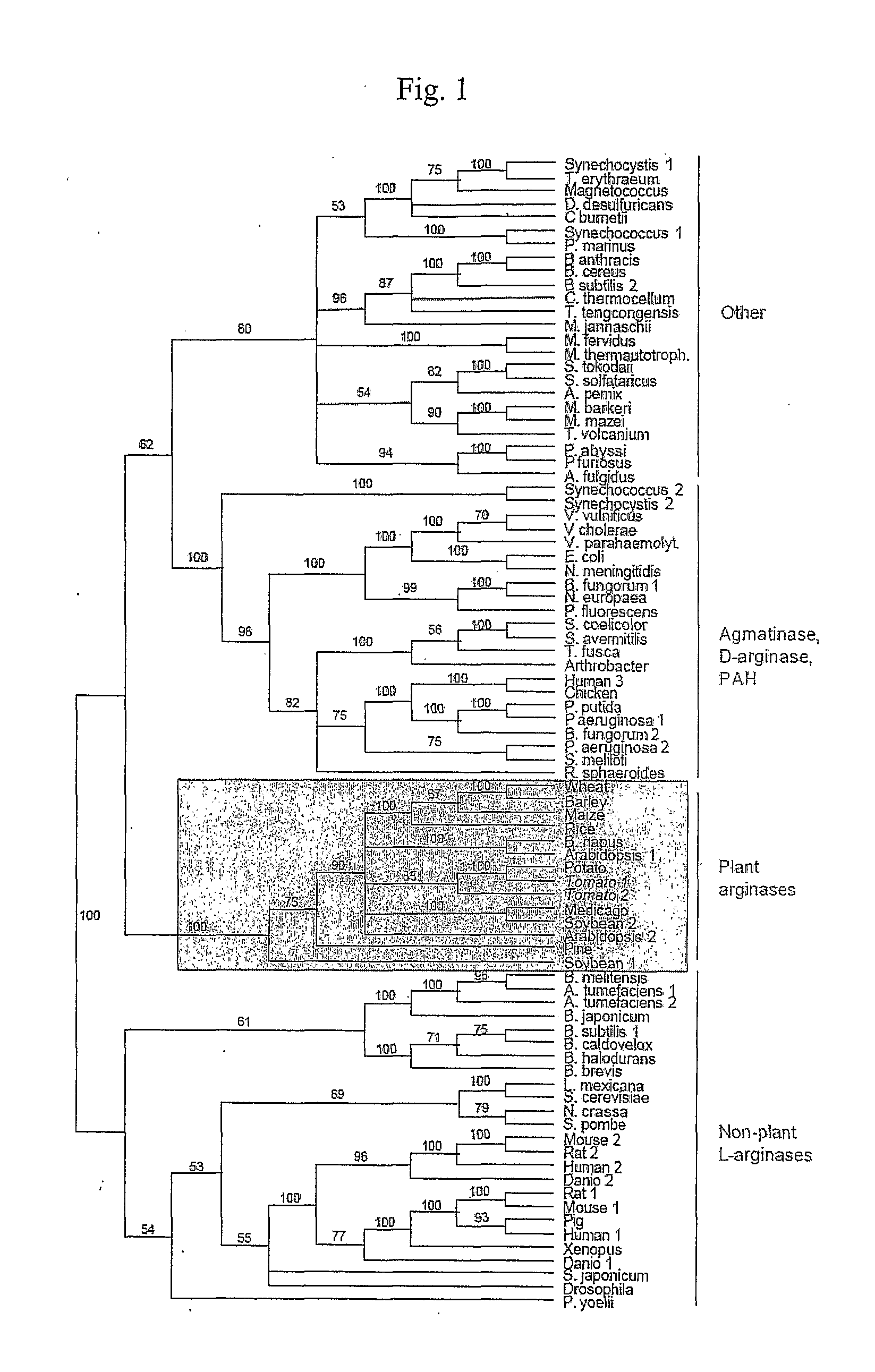
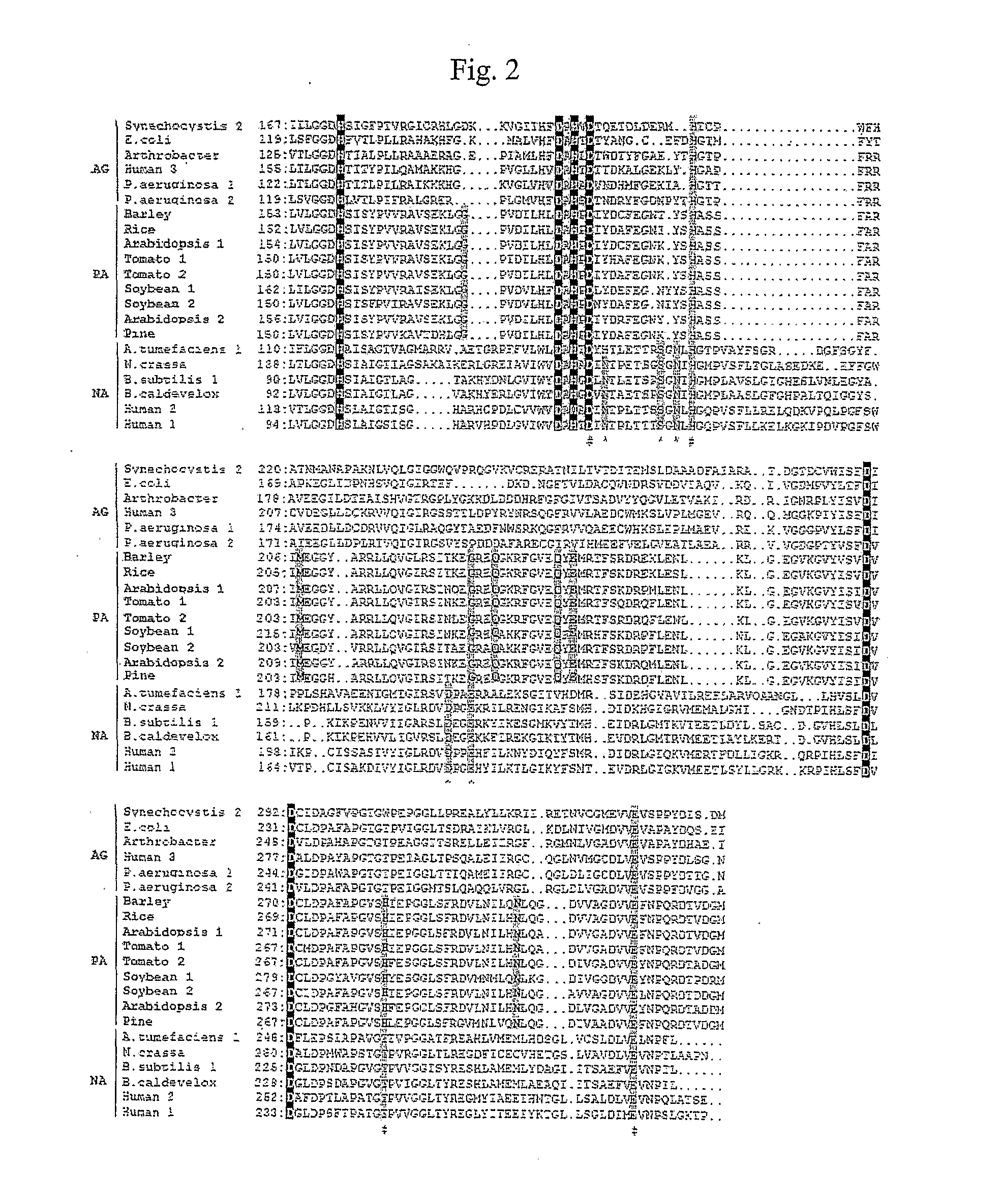
The present invention relates to genes, proteins and methods comprising molecules that alter amino acid levels. In one embodiment, the present invention relates to altering guanidino substrate hydrolysis activities in plants, arthropods and microorganisms using molecules within the arginase family and other molecules that alter an amino acid levels. In ones embodiment, the present invention relates to altering threonine substrate deamination and dehydration activities in plants, arthropods and microorganisms using molecules within the threonine deaminase family and other molecules that alter amino acid levels. In one embodiment, the present invention relates to using genes, proteins and methods comprising arginase or threonine deaminase for altering the pathophysiology of plants, arthropods and microorganisms. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention relates to altering guanidino substrate hydrolysis activity in plants, arthropods, and microorganisms using arginase. In another preferred embodiment, the invention relates to altering threonine substrated deamination and dehydration activity in plants, arthropods, and microorganisms using threonine deaminase. In some embodiments, the invention related to overexpression and increased activity of arginase, threonine deaminase and a proteinase inhibitor.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Novel plants
InactiveUS20090307801A1High expressionIncreased flowering capacitySeed and root treatmentClimate change adaptationGrowth retardantHeterologous
Disclosed are novel genetically modified plant cells wherein a SHI (short internodes) family gene is integrated into the nuclear genome. Also disclosed are plant cells where a SHI antisense gene is integrated or plants including heterologous expression control of autologous SHI genes. The plant cells confer novel phenotypes upon plants incorporating the SHI family gene. The invention also discloses transgenic plants and methods for plant production, where the plants are dwarfed, but exhibit normal or increased flower set after induction of flowering with GA. The plants of the invention are obtained without use of any growth retardants.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF COPENHAGEN
Compositions and methods relating to transgenic plants and cellulosic ethanol production
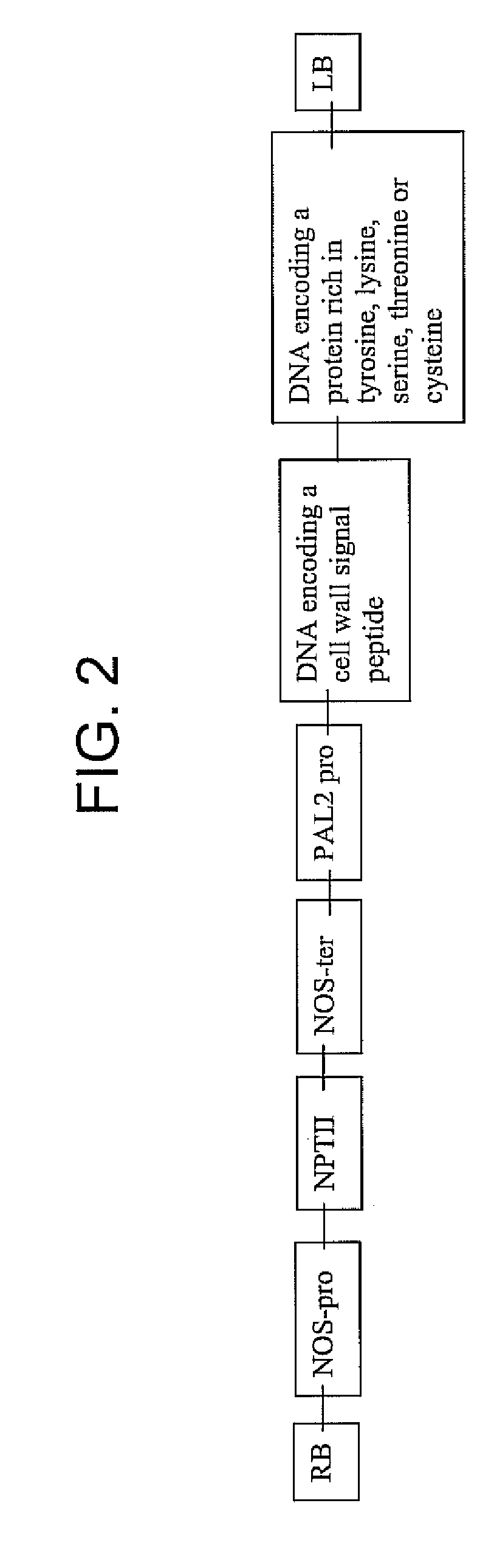
Transgenic lignocellulosic plants are provided according to embodiments of the present invention, the transgenic plants transformed with an expression cassette encoding a protein operably linked to a signal peptide which targets the protein to a cell wall of the transgenic plant, where at least 5% of the total amino acid residues of the protein are tyrosine, lysine, serine, threonine or cysteine. Methods of increasing lignin-protein bonds in a lignocellulosic plant are provided according to embodiments of the present invention which include expressing a recombinant nucleic acid in a lignocellulosic plant, the recombinant nucleic acid encoding a protein operably linked to a signal peptide which targets the protein to the cell wall of a plant, where at least 5% of the total amino acid residues of the protein are tyrosine, lysine, serine, threonine or cysteine.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Continuous culture of conifer embryogenic tissue
ActiveUS7625754B2Easy to produceIncrease probabilityCell culture mediaOther foreign material introduction processesEmbryogenesisBiology
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
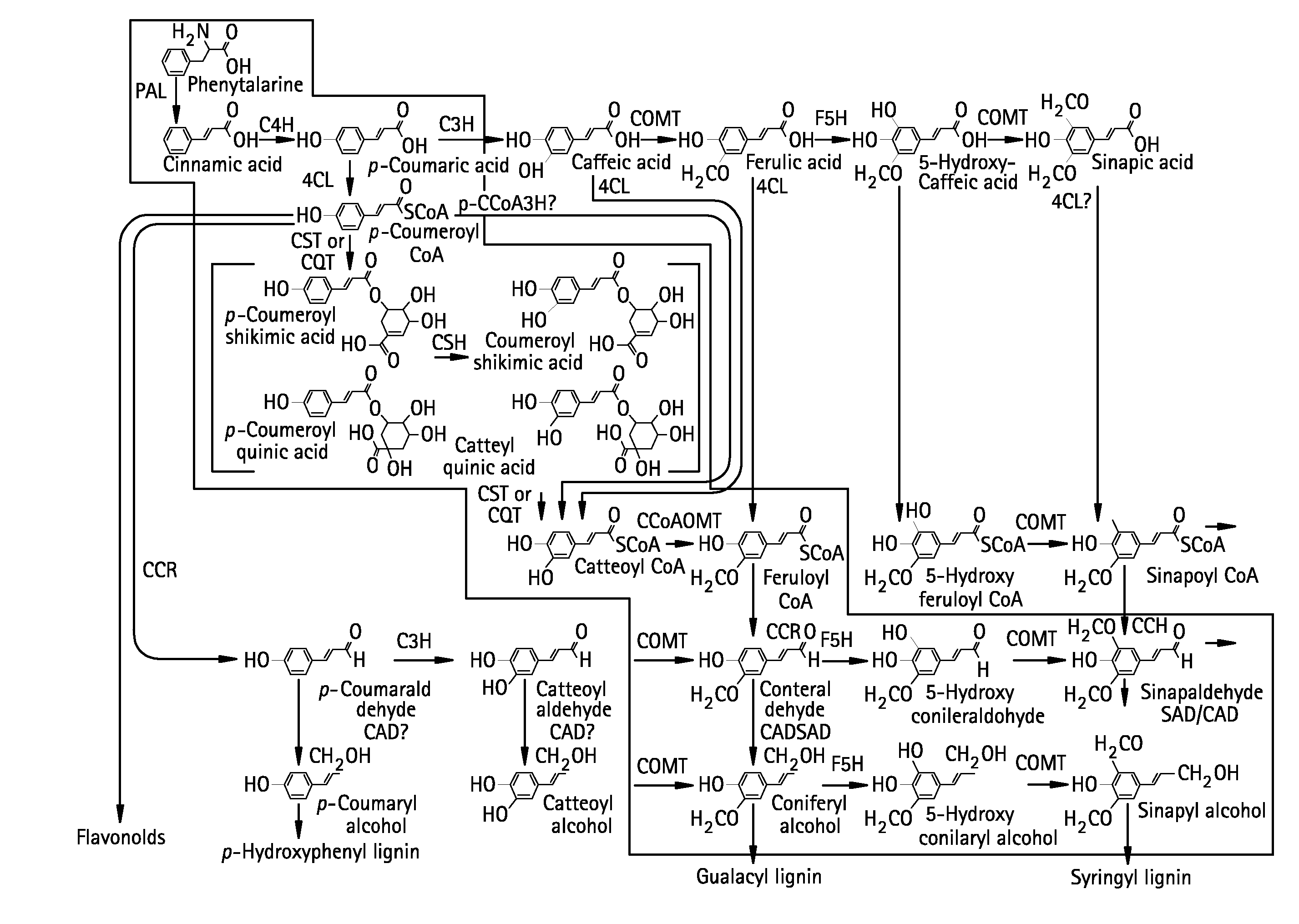
Altering lignin and wood density
ActiveUS20080058510A1Increasing wood densityLow lignin contentBryophytesSugar derivativesLignin degradationNucleotide sequencing
In angiosperm and gymnosperm plants, overexpressing a SAMdc nucleotide sequence can decrease lignin content and, for plants with woody tissue, increase wood density.
Owner:FIBRIA CELULOSE SA
Selective control of lignin biosythesis in transgenic plants
InactiveUS20030005481A1Enhancing lignificationLignification is enhancedBryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesLignin biosynthesisGene product
The present invention provides methods of selectively controlling lignin biosynthesis in plants such that lignification is reduced or enhanced, as desired. The invention provides, for example, a method of reducing lignification in a vascular plant by ectopically expressing a nucleic acid molecule encoding an AGL8-like gene product in the plant, whereby lignification is reduced due to ectopic expression of the nucleic acid molecule. An AGL8-like gene product useful in the invention can have, for example, substantially the amino acid sequence of an AGL8 ortholog such as Arabidopsis AGL8 (SEQ ID NO:2).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods for conditioning plant somatic embryos
InactiveUS20070087438A1Promote physiological maturationImprove germination rateSeed and root treatmentFermentationEmbryoSomatic cell
The present invention provides methods for conditioning plant somatic embryos. The methods include the step of exposing the somatic embryos to a gas stream having a selected moisture content for a period of time sufficient to change the moisture content of the somatic embryo to a desired moisture content, wherein the gas stream is produced using an ionomeric membrane.
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com