Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
331 results about "Somatic embryogenesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
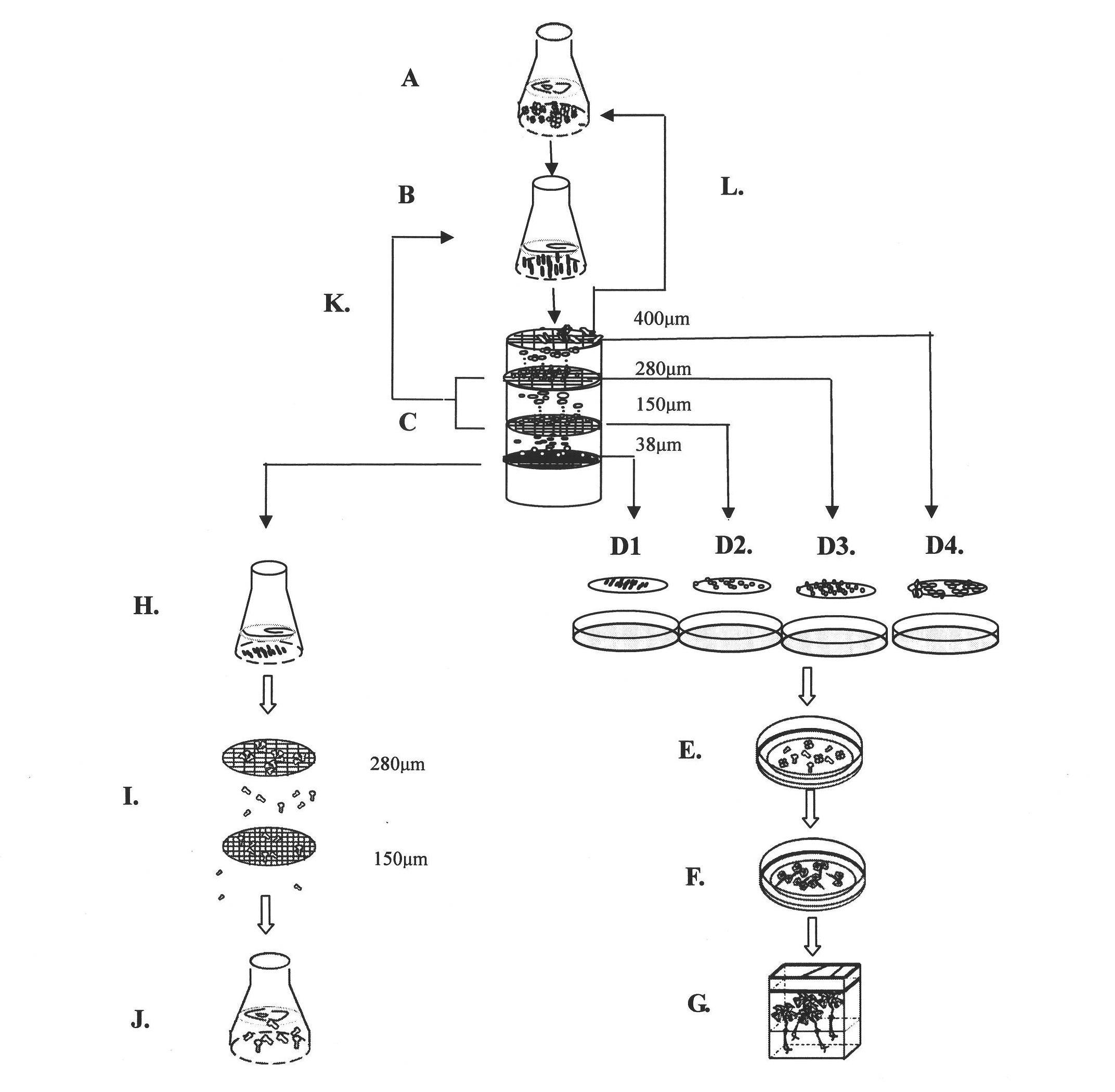
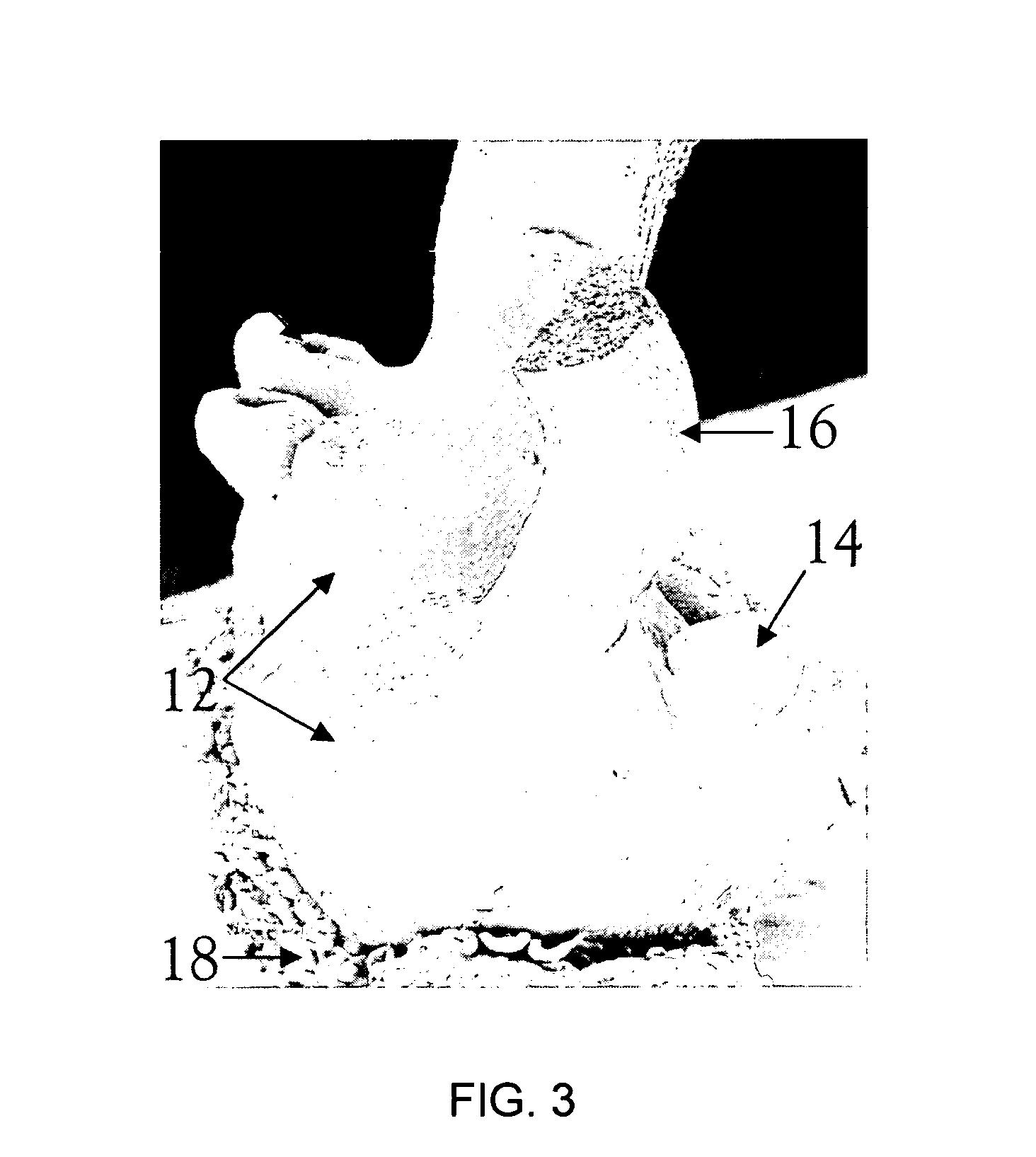
Somatic embryogenesis is an artificial process in which a plant or embryo is derived from a single somatic cell. Somatic embryos are formed from plant cells that are not normally involved in the development of embryos, i.e. ordinary plant tissue. No endosperm or seed coat is formed around a somatic embryo. Applications of this process include: clonal propagation of genetically uniform plant material; elimination of viruses; provision of source tissue for genetic transformation; generation of whole plants from single cells called protoplasts; development of synthetic seed technology. Cells derived from competent source tissue are cultured to form an undifferentiated mass of cells called a callus. Plant growth regulators in the tissue culture medium can be manipulated to induce callus formation and subsequently changed to induce embryos to form the callus. The ratio of different plant growth regulators required to induce callus or embryo formation varies with the type of plant. Somatic embryos are mainly produced in vitro and for laboratory purposes, using either solid or liquid nutrient media which contain plant growth regulators (PGR’s). The main PGRs used are auxins but can contain cytokinin in a smaller amount. Shoots and roots are monopolar while somatic embryos are bipolar, allowing them to form a whole plant without culturing on multiple media types. Somatic embryogenesis has served as a model to understand the physiological and biochemical events that occur during plant developmental processes as well as a component to biotechnological advancement. The first documentation of somatic embryogenesis was by Steward et al. in 1958 and Reinert in 1959 with carrot cell suspension cultures.
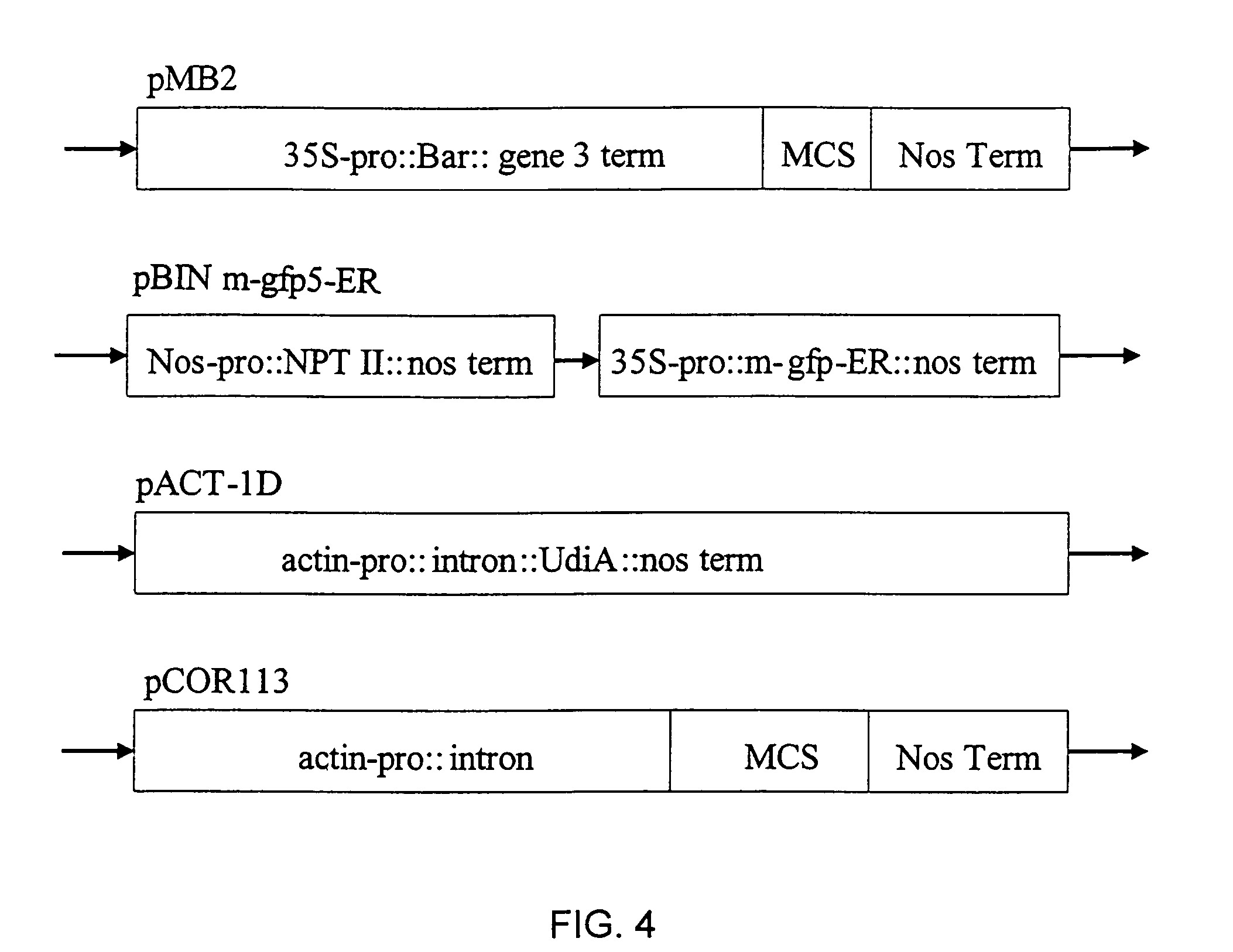
Promotion of somatic embryogenesis in plants by PGA37 gene expression
InactiveUS7148402B2Climate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesApomixisSomatic embryogenesis
The present invention relates to methods for promoting somatic embryogenesis from a plant cell, tissue, organ, callus or cell culture, by overexpressing a PGA37 gene in the tissue or organ. In one embodiment, such overexpression can be used as a silent selectable marker for transgenic plants. In another embodiment, such expression can be used to confer apomixis to a plant. In another embodiment, such overexpression can be used to create haploid plants, which can be used to produce dihaploid plants.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Process for cultivation of algae
The present invention provides a tissue culture method for cultivation of marine algae, said method comprising the steps of (i) establishing axenic viable algal material by sequential treatment thereof in sterile sea water supplemented with domestic liquid detergent, incubating the treated material, (ii) culturing the axenic explants on agarified medium for induction of callus; (iii) excising and subculturing the calli from the axenic explants on fresh agar plates to obtain differentiated densely pigmented oval or spherical shaped micro-propagules (iv) subculturing the pigmented calli in agarified medium to achieve enhanced somatic embryogenesis and micro-propagule formation in pigmented filamentous callus, (v) transferring the filamentous calli with somatic embryos for morphogenesis and development of young plantlets; and (vi) cultivating algal biomass on a large scale by growing the young plantlets in enclosed perforated polythene bags.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Preparation method of virus-free seedlings of sweet potato
ActiveCN104067821AEarly germinationEasy to stripPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBudSomatic cell
The invention provides a preparation method of virus-free seedlings of sweet potato. The method comprises the following steps: placing sweet potato blocks that are exposed under the sun and matured banana together for 3 to 5 days; planting the sweet potatoes in sandy soil to accelerate the germination in a culture box; setting relatively high temperature; picking 1-2cm top end of the seedling based on the length; cutting off the visual leaves; disinfecting the surface; rinsing with sterile water; picking off stem tip with 1 to 2 leaf primordium; inoculating to the corresponding culture medium to respectively induce differentiation of adventitious buds and generation of somatic embryogenesis; performing virus detection to a regeneration plant; performing subculture for the virus-free seedling; hardening-seedling; directly planting into a plastic greenhouse; performing flood irrigation with more water; preventing direct exposing under sun at noon in the first two weeks after transplanting; applying urea three weeks after transplanting; watering to obtain virus-free seedlings. According to the preparation method of the virus-free seedlings of sweet potato, the virus-free test-tube plantlets are acclimated and then directly planted into the plastic greenhouse, thus the survival rate is obviously raised, and the operation processes are decreased; the process of acclimating in an acclimating room is saved, and as a result, labor, materials and property are saved.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Spruce somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration method
ActiveCN101983556AImprove efficiencyEasy to storePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSomatic embryogenesisGenetic resources
The invention discloses a spruce somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration method, which comprises preparation of immature seed embryo of spruce, initial induction of embryonal suspensor mass (ESM), maintenance and proliferation of the ESM, prophase maturation culture of the somatic embryo, maturation culture of the somatic embryo and germination of the somatic. The spruce plant regeneration method has the advantages of high propagation coefficient and no limitation on the propagation season and provides an efficient means for the rapid propagation of the genetically improved materials of spruce, which not only is conducive to the storage of genetic resources of spruce, but also provides a large number of genetically improved plant materials for accelerating the cultivation of the improved materials of spruce, eases urgent requirements of the society on the genetically improved nursery stock of spruce, and provides a technology for producing an improved variety of nursery stock with short period, high efficiency and low cost.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
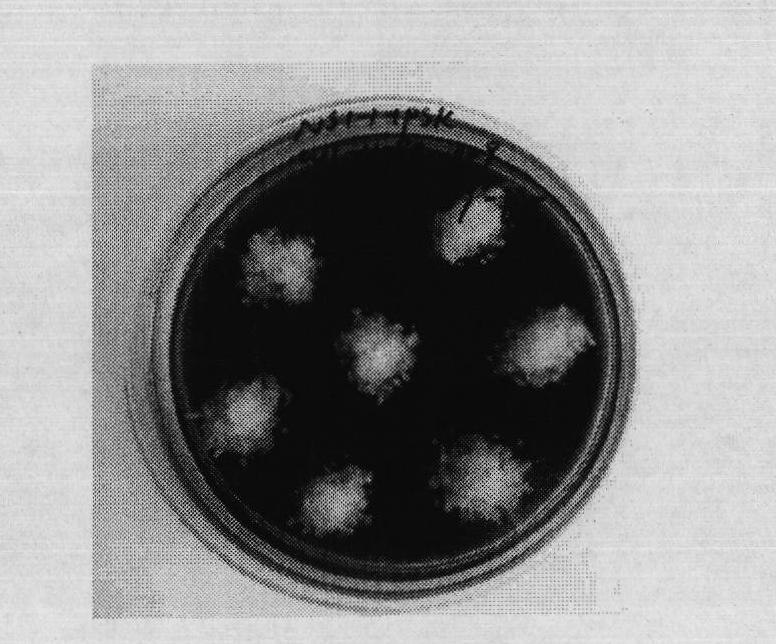
Bulk sorting of conifer somatic embryos
InactiveUS20050246802A1Quality improvementImprove isolationHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureHigh probabilitySomatic embryogenesis
The selection and isolation of mature somatic conifer embryos has previously involved chemical based or labour intensive techniques. Disclosed are simple yet highly effective methods to sort somatic embryos according to maturity to generate a population of quality somatic embryos that exhibit a high probability of successful conversion and germination. The methods include liquid sorting of somatic embryos using an aqueous liquid having a specific solute concentration and / or a viscosity. In this way, embryos that have attained a degree of maturity (and preferably desiccation tolerance) can be separated both from embryos that are comparatively immature and importantly from significant quantities of proliferation material and other organic matter generated during embryo propagation.
Owner:CELLFOR
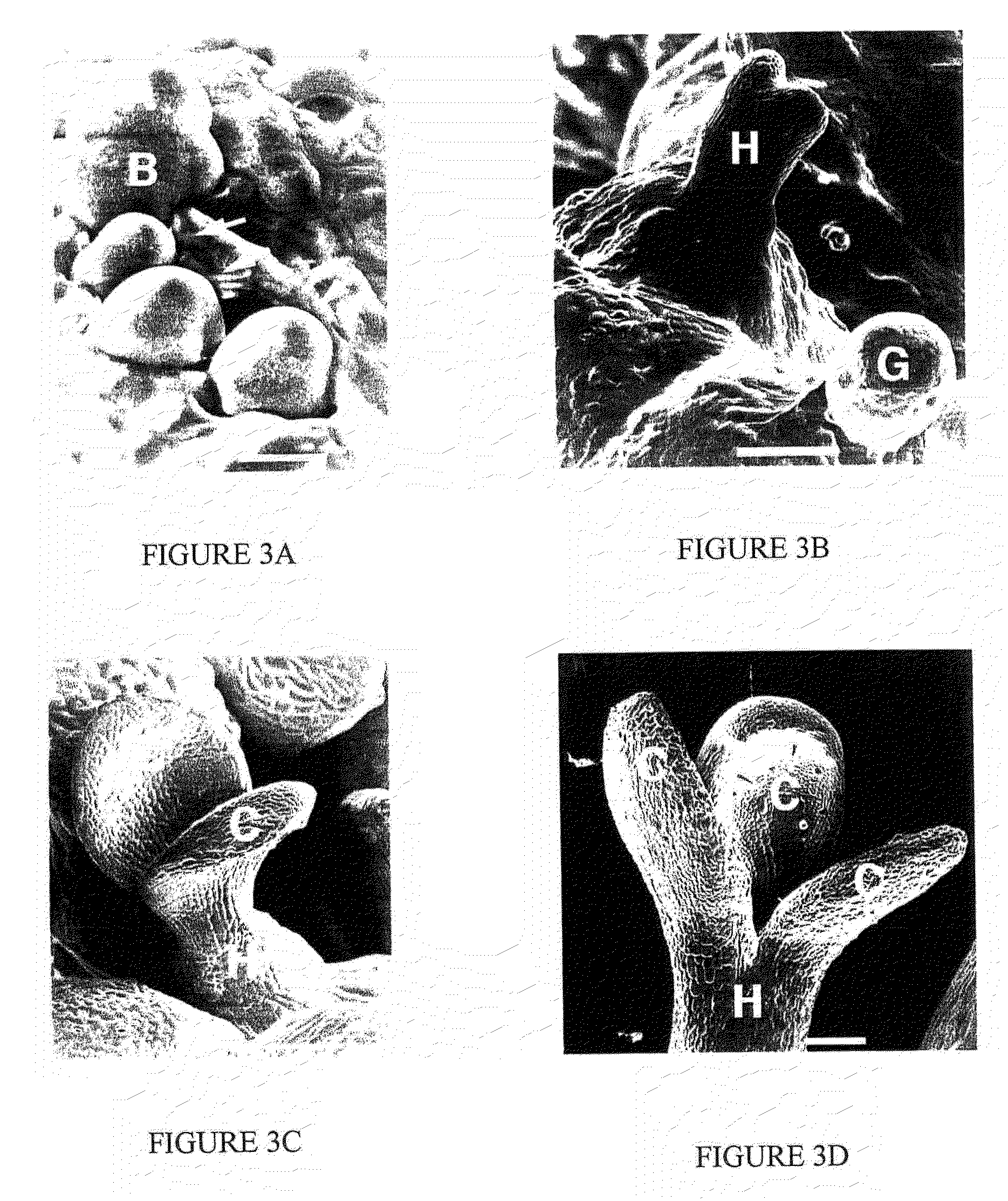
Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration technology for hybridized Chinese tuliptree
The invention is characterized by that on the basis of choice of parents of basswood generic cross and breeding of interspecfic hybridization, the immature embryo of limited quantities got respectively from normal, reciprocal an rotation cross is engaged in induction and cultivation of embryo somatric cell, produces large quantities of embryo of somatic cell in synchronizing development, and leads to cultivate embryo of somatic cell into whole tree characteristics.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method of somatic embryogenesis of cassava and rapid propagation of regenerated plant
The invention relates to a tissue culture propagating method of Manihot esculenta Crantz. As one of the global three-top tuber crops and the number one alimentarn crop in Africa, the Manihot esculenta Crantz is currently ranked as a vital biological energy crop in our country. Stem section vegetative cottage is commonly adopted for propagation, and the low propagation rate thereof is a restrictive factor for popularizing the new variety and shortening the breeding period. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: the Manihot esculenta Crantz stem section with stem apexes or lateral buds is taken as an explant, and the Manihot esculenta Crantz tissue culture plantlets are quickly obtained in virtue of the micro-propagation method; young leaves, stem apexes and axillary buds of the sterile plantlets obtained from micro-propagation are taken as explants, somatic embryo generation and plant regeneration are induced, thus the Manihot esculenta Crantz somatic cell regeneration system is established. By adopting the method, the Manihot esculenta Crantz has the advantages of high propagation rate, no genotype dependence, and the like; the method has high value on the quick propagation and large-scale production of the Manihot esculenta Crantz improved variety in a short term, and establishes a technical basis for the Manihot esculenta Crantz transgene and other breeding.
Owner:朱文丽 +4
Embryogenesis and plant strain regeneration method for hybrid somatic cell of slash pine and cuban pine
InactiveCN101218894ASolve the shortageClimate change adaptationAfforestationSomatic embryogenesisSomatic cell
A method for somatic cell embryo generation and plant regeneration of a hybrid of a slash pine and a Caribbean pine is characterized in that the invention relates to a method which adopts a immature zygotic embryos of the hybrid of the slash pine and the Caribbean pine to carry out somatic cell embryo generation and plant regeneration and uses liquid and slide improved P6 mediums to alternatively combine for adjustment and control culture during the process of the somatic cell embryo generation and plant regeneration for a plurality of times and is appended with proper auxin combination. The invention provides a packaged technology for fast breeding the hybrid seedlings of the slash pine and the Caribbean pine industrializedly and can solve the current problem of short supply of the seedlings during the hybrid afforestation of the slash pin and the Caribbean pine.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method for efficiently regenerating plant through Hedychium coccineum Buch.-Ham somatic embryogenesis
ActiveCN102845309AQuality improvementGood effectHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGeneration rateBud
The invention discloses a method for efficiently regenerating plant through Hedychium coccineum Buch.-Ham somatic embryogenesis. The method comprises the following steps of: inducing calluses by using immature filaments and anthers of Hedychium coccineum Buch.-Ham as explants, conducting optimization, screening and subculture to obtain high-quality embryonic calluses, conducting suspension culture to the embryonic calluses and establishing an embryonic cell suspension culture system of Hedychium coccineum Buch.-Ham. A great number of somatic embryos can be obtained by using embryonic cell suspension cultures for inducing somatic embryos, an optimum effect can be obtained by using SH inorganic salt and 150mug.L<-1> TDZ, and the somatic embryo generation rate can reach 4429 / ml SCV (settled cell volume); the obtained somatic embryos can germinate seedlings with buds and roots on somatic embryo germination culture medium; and when SH culture medium is used as basic culture medium and the concentration of 6-BA is 0.5-1.0mg.L<-1>, the germination rate of the somatic embryos can reach 100 percent. Due to the method, a foundation is laid for the in-vitro rapid propagation and the biotechnological breeding of Hedychium coccineum Buch.-Ham, the large-scale popularization and application are facilitated and the application prospect is better.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF EDUCATION
Promotion of somatic embryogenesis in plants by wuschel gene expression
InactiveUS7700829B2Climate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesApomixisPlant tissue
The present invention relates to methods for promoting somatic embryogenesis from a tissue or organ of a plant, by overexpressing a Wuschel gene in said tissue or organ. In one embodiment, such overexpression can be used as a silent selectable marker for transgenic plants. In another embodiment, such expression can be used to confer apomixis to a plant. In another embodiment, such overexpression can be used to create haploid plants, which can be used to produce dihaploid plants.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Pinus thunbergii cell embryogenesis and plant regeneration method
InactiveCN102577956AHigh reproductive rateImprove practicalityClimate change adaptationAfforestationPinus thunbergiiSomatic embryogenesis
The invention discloses a pinus thunbergii cell embryogenesis and plant regeneration method. Embryogenic calluses are induced from immature zygotic embryos; the embryogenic calluses are maintained, proliferated and matured to obtain somatic embryos; the somatic embryos are germinated to obtain regenerated plants; and finally the regenerated plants are transplanted. Due to the adoption of the pinus thunbergii cell embryogenesis and plant regeneration method, high reproduction rate of the pinus thunbergii plant is achived. After the embryogenic calluses are cultured for 70 days in a maturing culturing medium, 144-216 mature somatic embryos can be obtained in each culture utensil on average; the somatic embryo germination rate is 63.8%; and the plant transformation rate is 43.5%. Therefore, a large number of somatic embryo seedlings can be obtained every year, thus a foundation is laid for the pinus thunbergii cell embryogenesis and the regenerated plant bath production, and the current problem of afforestation seedling shortage is solved. The pinus thunbergii cell embryogenesis and plant regeneration method has very good practicality.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Somatic embryogenesis method of phyllostachys heterocycla var. pubescens
The invention discloses a somatic embryogenesis method of phyllostachys heterocycla var. pubescens, which includes the following steps that an explant of phyllostachys heterocycla var. pubescens is appropriately disinfected and then is induced on an inductive medium to produce a callus tissue; after being processed with multiplication culturing, the callus tissue firstly forms an embryoid on a differential medium and then the embryoid bourgeons and forms a regenerated plant on a germination medium; finally the regenerated plant is processed with the cultivations of seedling toughening up and seedling exercising and then is transplanted to survive. The invention solves the technical difficulty in somatic embryogenesis of phyllostachys heterocycla var. pubescens and provides a technology platform for the technical breeding of scattered bamboo plants.
Owner:袁金玲 +2
Promotion of somatic embryogenesis in plants by Wuschel gene expression
InactiveUS7816580B2Climate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyApomixis
The present invention relates to methods for promoting somatic embryogenesis from a tissue or organ of a plant, by overexpressing a Wuschel gene in said tissue or organ. In one embodiment, such overexpression can be used as a silent selectable marker for transgenic plants. In another embodiment, such expression can be used to confer apomixis to a plant. In another embodiment, such overexpression can be used to create haploid plants, which can be used to produce dihaploid plants.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Induction rapid-propagation culture method for Photinia fraseri in-vitro leaf somatic embryos
InactiveCN102124955ASolve the problem of germplasm degradationHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologySomatic embryogenesis
The invention provides an induction rapid-propagation culture method for Photinia fraseri in-vitro leaf somatic embryos, comprising the following steps: (1) building a regeneration system of a Photinia fraseri asepsis test tube seedling; (2) building a high-frequency rapid-propagation system induced by an in-vitro somatic embryo and an adventitious bud; and (3) rooting, acclimatizing and transplanting for the test tube seedling. The induction rapid-propagation culture method for Photinia fraseri in-vitro leaf somatic embryos is characterized in that coordinated sets of measures of selecting a proper explant, improving a basic culture medium and ingredients, regulating culture conditions and the like are adopted, and the Photinia fraseri of which the seed is difficult to breed is subjected to path rapid propagation by the somatic embryos; the plant transplantation survival rate is higher than 95%; the germchit grows strongly to solve the problem that an excellent germchit quality degenerates, and a great quantity of purified and rejuvenated detoxification nursery stock with good quality can be provided for production; and in addition, and ideal receptor system is provided for breeding new specimens for Photinia fraseri by genetic transformation or mutation breeding.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE OF AGRI & FORESTRY +1
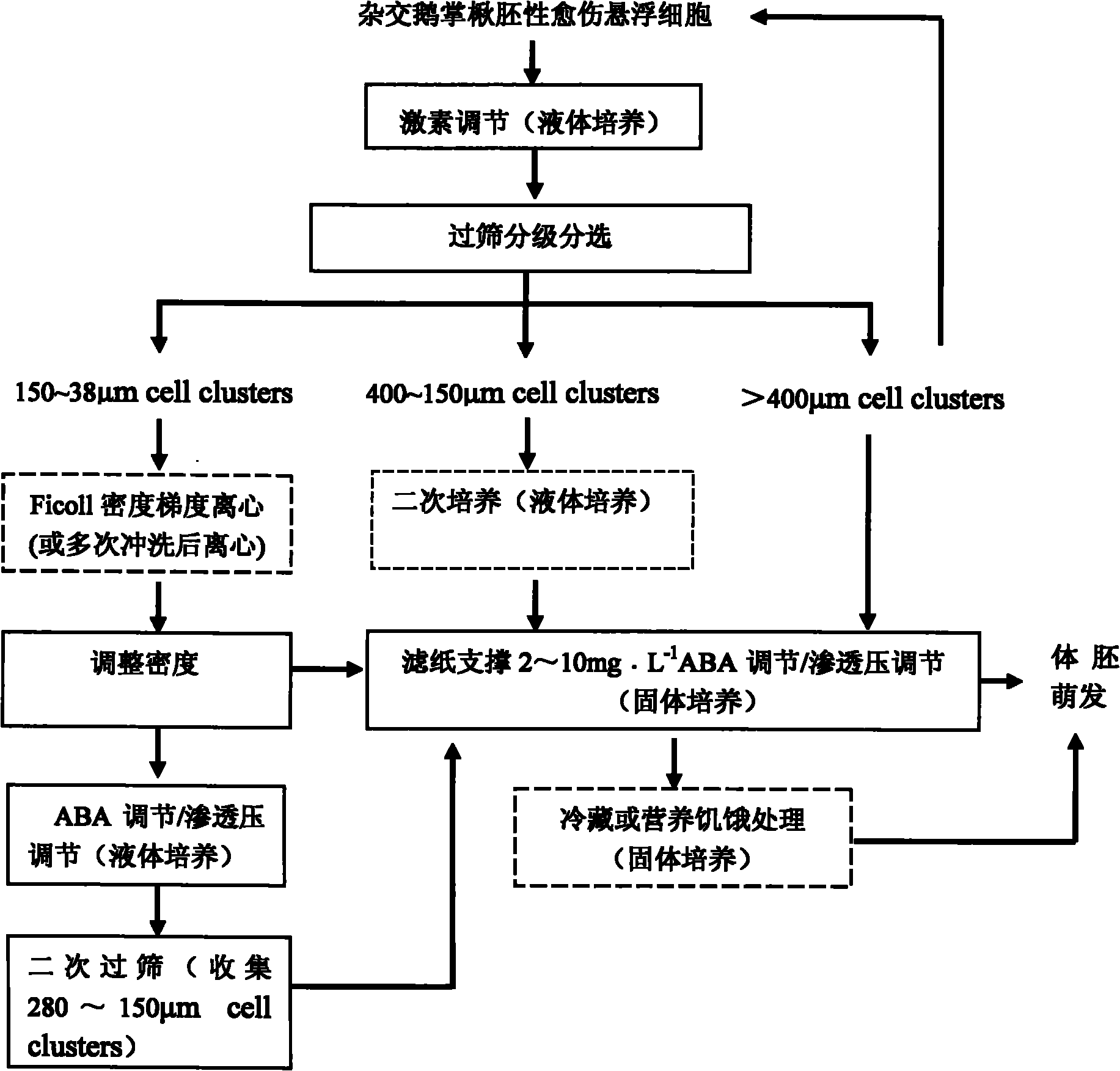
Hybrid liriodendron somatic embryogenesis synchronization control method
ActiveCN102037896AImprove conversion rateStimulus generationHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureLiriodendronSomatic embryogenesis
The invention discloses a hybrid liriodendron somatic embryogenesis synchronization control method. In the method, 2,4-D concentration is reduced gradually by utilizing a growth hormone regulating mechanism; kinetin (KT) with the dose of 0.5 mg.L<-1> is added to induce uniform embryonic cell masses; the embryonic cell masses are subjected to fractional culture by a mechanically sieving method; and different subsequent synchronization control methods are adopted according to different cell mass sizes and somatic embryogenesis modes. After the synchronization control, the somatic growth synchronization ratio of hybrid liriodendron subjected to classified screening at the stage of globular embryo reaches about 90 percent; the synchronization ratio of fractional treatment at the stages of heart-shaped embryo and torpedo-shaped embryo is about 40 percent; after a proper period of refrigeration, the synchronization ratio is increased to some extent; and the conversion rate of a mature embryo, which develops from a material at the stage of globular embryo, to a regeneration plant can reach 70 to 80 percent.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Micropropagation method of fraxinus rhynchophylla
InactiveCN102228001AImprove proliferation efficiencyRealize automated productionHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureFraxinusCotyledon plant
The invention discloses a micropropagation method of fraxinus rhynchophylla and relates to the micropropagation method. The problems of long reproductive cycle, low reproduction efficiency and poor offspring genetic stability in nursery stock propagation of fraxinus rhynchophylla are solved. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, sterilizing fraxinus rhynchophylla seeds, and culturing single cotyledons of zygotic embryos to obtain cotyledonal cell embryos; 2, performing maturation cultivation on the cotyledonal cell embryos; 3, performing sprouting cultivation on the cotyledonal cellembryos subjected to maturation cultivation to obtain regenerated plants; and 4, transplanting the regenerated plants into a culture medium to culture until new leaves are completely unfolded, and removing a covered plastic thin film. The micropropagation method has the advantages of short nursery stock reproductive cycle, high reproductive rate (culturing for 60 to 70 days) and high reproductionefficiency (each explant can generate 15 to 20 somatic embryos); the germination rate of the somatic embryos is up to 87 to 89.55 percent; the transplanting survival rate of the regenerated plants isup to 75 to 80 percent; and the regeneration plants with the same good characteristics as female parents can be generated in mass.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +2
Process for inducing direct somatic embryogenesis in immature scutella cells of pooideae, and rapidly regenerating fertile plants
InactiveUS6995016B2Lower levelTissue cultureOther foreign material introduction processesDevelopmental stagePooideae
A process is provided for inducing direct somatic embryogenesis in Pooideae and rapidly regenerating fertile plants by first culturing isolated immature scutella cells in culture medium comprising auxin, cytokinin and polyamine in amounts effective to cause direct formation of primary embryos without an intervening callus stage, at least until at least one primary embryo reaches the globular developmental stage, the auxin being present in greater proportion than cytokinin. A second step includes either a) culturing the primary embryos under conditions to regenerate plantlets, and culturing the primary embryos in regeneration medium; or b) culturing the primary embryos at the globular developmental stage and no longer than the coleoptilar stage in culture medium comprising auxin, cytokinin, and polyamine in amounts effective to cause induction of secondary embryo formation, at least until secondary embryogenesis is detected, the cytokinin being present in greater proportion than auxin, and culturing the secondary embryos under conditions to regenerate plantlets.
Owner:AGRI & AGRI FOOD
Somatic embryogenesis method for cunninghamia lanceolata
ActiveCN103070074APromote browningGuaranteed stabilityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureCell divisionSomatic embryogenesis
The invention discloses a somatic embryogenesis method for cunninghamia lanceolata, which comprises the steps of initial induction of an embryogenic suspensor cell mass, maintenance and multiplication of an ESM (embryogenic suspensor mass), and development and maturity of a somatic embryo, wherein the development and maturity of the somatic embryo can adopt an indirect somatic embryogenesis way or a direct somatic embryogenesis way. With the adoption of the somatic embryogenesis method for the cunninghamia lanceolata, browning in an establishment process of the conventional liquid suspension system can be effectively improved, cell division under a low density condition is started, and the stability of suspensor cells is maintained, so that a stable multiplication liquid suspension cell line is established. The somatic embryogenesis frequency of the cunninghamia lanceolata can be increased by about 20 times at most through the direct and indirect somatic embryogenesis ways, the problem of low somatic embryogenesis frequency caused by an incomplete somatic embryogenesis system of the cunninghamia lanceolata can be well solved, the cost is saved, conditions are prepared for factory production of the cunninghamia lanceolata, and a pace of industrial production of the cunninghamia lanceolata is accelerated.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method for inducing regeneration plant of tetraena mongolica by somatic cell embryo
The invention discloses a method for inducing a regeneration plant of tetraena mongolica by a somatic cell embryo. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) inducing the cut stem of the tetraena mongolica to form a callus; 2) inoculating the callus obtained in the step 1 into an embryonic callus induction medium to form an embryonic callus; 3) performing maturation and germination culture on the callus obtained in the step 2 to form a sprout; and 4) inoculating the sprout of the step 3 into an elongation and rooting medium to obtain a complete regeneration plant. The research induces the somatic cell embryo so as to form the regeneration plant by taking the callus of the tetraena mongolica as an explant, lays a foundation for establishing a high-efficiency and stable somatic embryogeny system, and has very import significance to the researches in the aspects such as rapid propagation, gene engineering, genetic transformation, genetic improvement and the like of the tetraena mongolica.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration of Lijiang spruce
InactiveCN102792888AReduce concentrationLow costPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSomatic embryogenesisSomatic cell
The invention relates to a method for somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration of Lijiang spruce, comprising the following steps that: open-pollinated clonal cones of Lijiang spruce are collected and mature zygotic embryo is separated out for somatic embryogenesis cultivation; the somatic embryogenesis cultivation is divided into the stages of embryonal callus induction, embryonal callus proliferation, somatic embryo maturity, and somatic embryo germination. Compared with the prior art, the method is beneficial for maintaining the embryonal capacity of embryonal callus and the risk of losing embryonal capacity is reduced and the differentiation rate and the germination rate are both increased. A method for large-scale vegetative propagation seedling raising of Lijiang spruce with short period, high reproductive rate and low cost is provided.
Owner:INST OF FORESTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Method for inducing plant regeneratation using somatic embryo of picea koraiensis nakai
InactiveCN101228848AShorten the breeding cycleRich breeding cycleHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSomatic embryogenesisPicea koraiensis
A plant regeneration method inducted by a somatic embryo of Korean spruce relates to a method for inducing the plant to regenerate with the somatic embryo of Korean spruce, which solves the problems that the conventional breeding of Korean spruce is of long period and low reproduction rate. The method is that: I. callus culture with zygotic embryo; II. Culturing the somatic embryo to be mature and drying the mature somatic embryo; III. Culturing the mature somatic embryo till the germination of the somatic embryo; IV. Continuing to culture until the root and stem forms, thus acquiring the regeneration plant of Korean spruce. The plant regeneration method inducted by the somatic embryo of Korean spruce of the invention uses the immature seed of Korean spruce as an explant induction somatic embryo to acquire the regeneration plant, thus shortening the breeding period of Korean spruce, the cycle is increased by 3 to 6 times compared with cottage grafting vegetative propagation, and the reproduction rate is high.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Methods for improving conifer embryogenesis
InactiveUS6893873B2High frequencyPromote cell differentiationTissue cultureHorticulture methodsOrganic acidSomatic embryogenesis
The present invention provides methods for initiating, capturing, maintaining and multiplying embryogenic cultures of coniferous plants. Methods include the use of novel media compositions containing Vitamin B12, Vitamin E, or organic acids including α-ketoglutaric acid, pyruvic acid, or p-aminobenzoic acid to improve the frequency of embryogenic tissue initiation, capture, maintenance and multiplication. The methods are well suited for initiating embryogenic cultures in recalcitrant conifer varieties. The method is also well suited for producing somatic embryos that can be further cultured to produce large numbers of plants. Further, the invention provides novel methods that may be used to enhance somatic embryogenesis in a broad range of species.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Method for detoxifying lily by means of somatic embryogenesis
ActiveCN103947554ATake off completelyLower requirementPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSomatic embryogenesisLilium
The invention discloses a method for detoxifying lily by means of somatic embryogenesis. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing embryonic callus induction, namely inducing embryonic calluses by taking lily scales, cultured under an aseptic condition, as explant; (2) performing selective subculture on embryonic calluses, namely selecting a new spherical somatic embryo, produced by the embryonic calluses, as a subculture material; and (3) performing subculture of the spherical somatic embryo, namely inoculating a solid proliferation culture medium or a liquid proliferation culture medium with the spherical somatic embryo for performing subculture till no virus is detected in the subcultured spherical somatic embryo. The operating method is simple, repeated subculture is performed on a to-be-detoxified material by an ordinary tester, and the requirements on test conditions and operating workers are low. Through rapid proliferation of the somatic embryo, complete detoxification can be realized, and a good detoxification effect is achieved.
Owner:CHONGQING LANDSCAPE & GARDENING RES INST +1
Efficient genetic transformation method of hybridized tulip tree
ActiveCN103088059AReduce generationEasy to importFermentationGenetic engineeringSomatic embryogenesisTulip Trees
The invention discloses an efficient genetic transformation method of a hybridized tulip tree. The efficient genetic transformation method comprises the following steps of: setting up a hybridized tulip tree transformation receptor, preparing agrobacterium, infecting, culturing without bacterium and culturing in a screening manner. According to the efficient genetic transformation method, unicell subjected to the suspension cultivation of the hybridized tulip tree serves as a genetic transformation acceptor system; the GUS gene is regarded as a report gene through a southern buddhism; and transient expression and long-term expression of the GUS gene are determined through a cytological method and efficient transformation of foreign gene is determined by detecting through a molecular biological method. As a somatic embryogenesis system generated by the unicell of the hybridized tulip tree is adopted, the efficient genetic transformation method of the hybridized tulip tree is good for leading in the foreign gene, and reduces generation of chimera.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Succeeding preservation method for embryogenic callus of China fir and subculture medium used therein
InactiveCN102369879AImprove training effectAbility to maintain embryonicityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSomatic embryogenesisOrganogenesis
The invention discloses a succeeding preservation method for embryogenic callus and a subculture medium used therein. The succeeding preservation method for embryogenic callus is to subculture embryogenic callus with the subculture medium. The succeeding preservation method for embryogenic callus and the subculture medium provided in the invention has a good culture effect on embryogenic callus of China fir, enable embryogenic competence of callus of China fir to be maintained for a long time, provide great convenience to subsequent research on somatic embryogenesis, organogenesis and the like of China fir and have a great practical application value.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for rapidly propagating aralia elata through somatic embryo and secondary somatic embryogenesis
InactiveCN101548646AEasy to operateImprove efficiencyCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue cultureAralia elataSucrose
The present invention provides a method for rapidly propagating aralia elata through somatic embryo and secondary somatic embryogenesis. The invention uses the leaf, petiole and root segment of young seedling of aralia elata as explants. The explants are dark-cultivated for 35 days in the SH cultivation with 3.0mg / L, 2.0mg / L and 0.3mg / L of IBA concentration respectively and 2% of sucrose. The somatic embryo inductivities of three explants can equally obtain 100%. Furthermore each explant generates more somatic embryos (8.6-11.3). The sucrose concentration and IBA can equally affect the generation of secondary somatic embryo. After the explants are dark-cultivated for 4 weeks in the cultivation condition of 3.0mg / L IBA+ 2% of sucrose+ SH culture medium, 100% of somatic embryos are generated with secondary somatic embryos. The obtained mature primary somatic embryos and secondary somatic embryos are transferred to a WPM culture medium with no hormone. The mature primary somatic embryos and secondary somatic embryos can quickly germinate and grow to seedling. The robust seedling with length about 5cm is transplanted into the soil, and the survival rate can obtain 89%. The method which is provided by the invention and has the advantages of simple culturing, short regenerate cycle and capability for continuously obtaining the regenerated plant can be used for the industrial production of aralia elata seedling.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +1
Fujian cypress somatic cell embryogenesis and plant regeneration technique
The somatic embryogenesis and cloned plant regeneration process for Fujian cypress includes the steps of inducing embryonic suspensor cell group with immature zygotic embryo, sustaining, proliferation, pre-maturation, maturation to obtain somatic embryo, and germinating culture to obtain regenerated plant. The minimal culture mediums for different stages are DCR minimal medium and improved DCR minimal medium with halved macro elements. The present invention makes it possible to obtain great amount of cloned regenerated plants with identical genetic base, and provides new technological process of providing great amount of Fujian cypress seedlings in short period, high efficiency and low cost.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method for inducing embryo callus of larch, and dedicated culture medium
InactiveCN1915002AImprove the induction effectConvenient inductionPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSaccharumSucrose
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-frequency somatic embryo regeneration culture method for overcoming alfalfa variety genotype limitation
InactiveCN101926285AOvercome different breedsOvercoming the genotype restriction problemHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureHypocotylSomatic embryogenesis
The invention discloses a high-frequency somatic embryo regeneration culture method for overcoming alfalfa variety genotype limitation, which comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting materials: selecting three explants of the epicotyl, the hypocotyl and the regenerated plant blade of an aseptic seedling after flushing, sterilizing and disinfecting as well as drying a mature alfalfa seed; (2) inoculating the selected explants onto a somatic embryogenesis induced culture medium for culture; (3) inoculating the explants subjected to somatic embryogenesis induced culture onto an embryo successive formation culture medium for culture; (4) inoculating the explants subjected to embryo successive formation culture onto an embryo maturation germination seeding-formation culture medium for culture to form a seedling; (5) carrying out seedling strengthening and rooting culture; and (6) transplanting a regenerated plant to survive. The invention can effectively overcome the problems of different varieties and genotype limitation in alfalfa high-frequency somatic embryo regeneration culture, greatly improves the somatic embryogenesis frequency and the plant regeneration frequency and improves the breeding efficiency.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE OF AGRI & FORESTRY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com