Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
170results about "Computing operations for addition/subtraction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
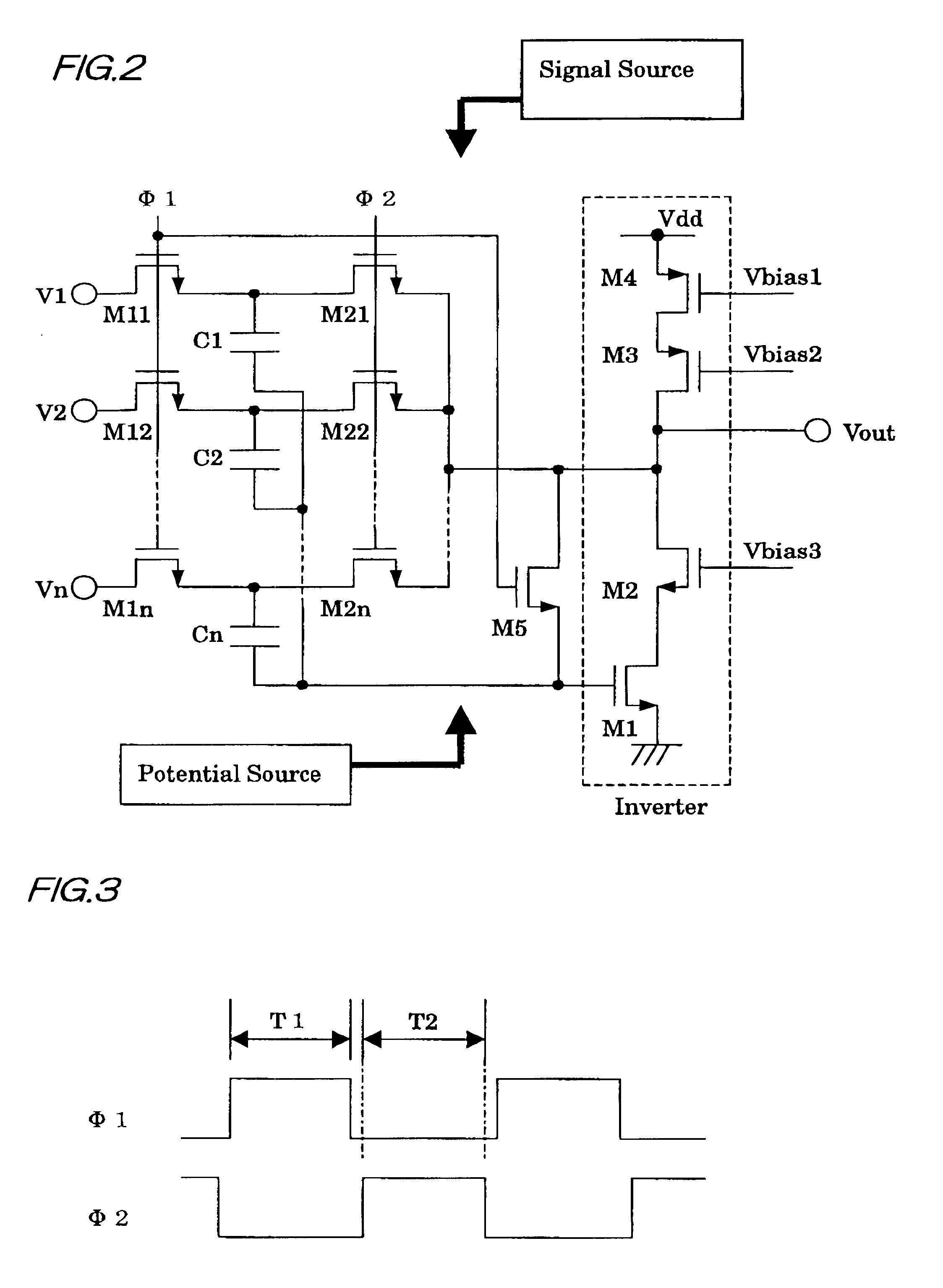
Digital to analog converter with a weighted capacitive circuit
InactiveUS6906653B2Reduce areaImprove accuracyElectric signal transmission systemsComputing operations for addition/subtractionDigital dataVoltage reference
D / A converter of this invention including n+1 capacitors in total consisting of one terminating capacitor (C0) and n binary-weighted capacitors (C1-4) that are subjected to binary weighting ratio of 1:2:4: . . . :2(n−1), and, an inverting amplifier (INV1), further comprising: a feedback switching means (SWR5) provided between the input and output of the inverting amplifier (INV1); a switching means for terminating operation (SWR0) supplies one of two main reference voltages (VB,VT) to the terminating capacitor (C0), and then, makes connection of the terminating capacitor (C0) to the output of the inverting amplifier (INV1); a plurality of switching means for input operation (SWD1-4,SWR1-4) makes selection of one of the two main reference voltages (VB,VT) to be provided for the n binary-weighted capacitors (C1-4) depending on digital data (D1-4), and then, makes connection of the second terminal side of the n binary-weighted capacitors (C1-4) to the output of the inverting amplifier (INV1).
Owner:LINEAR CELL DESIGN COJ
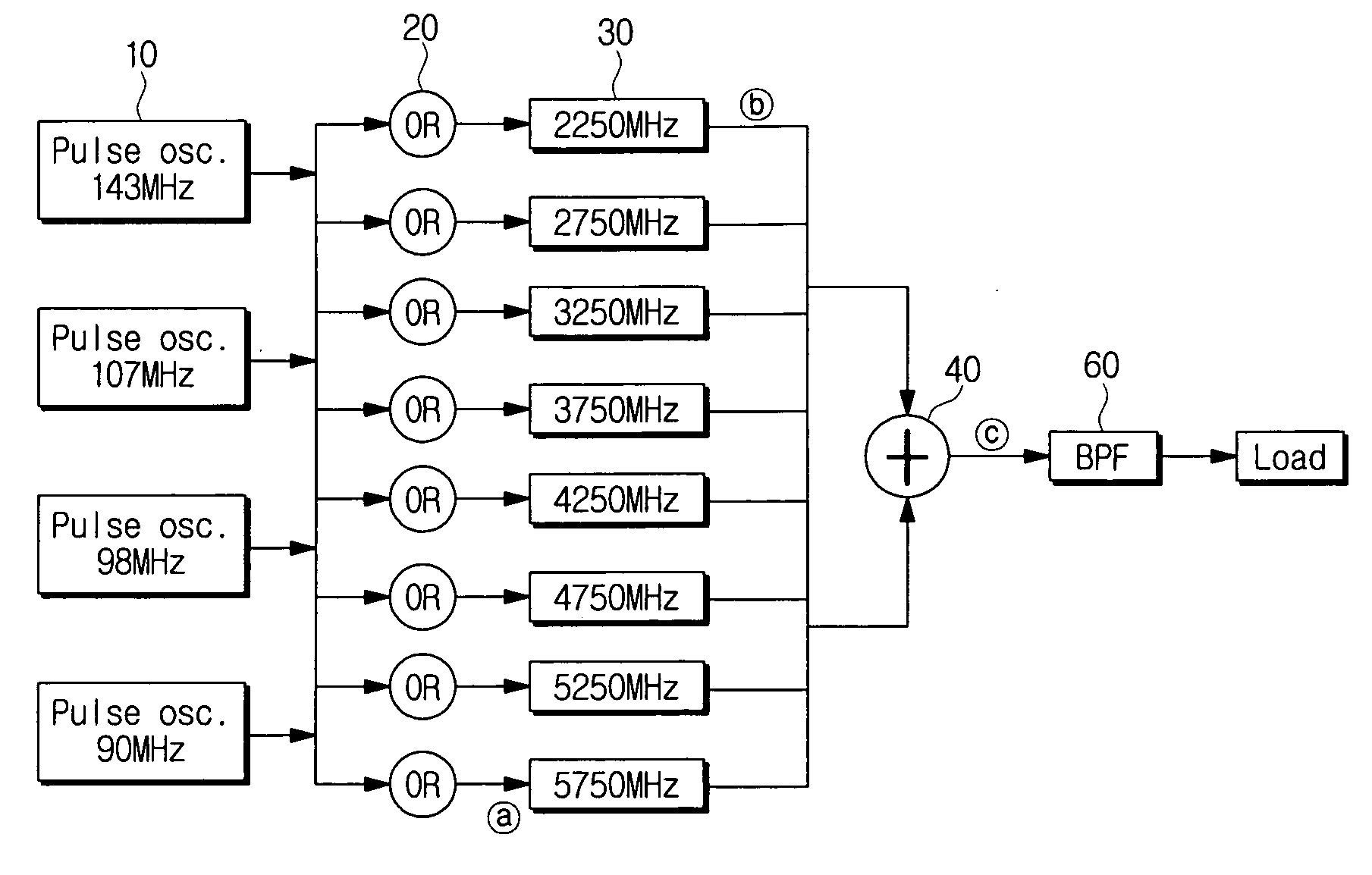
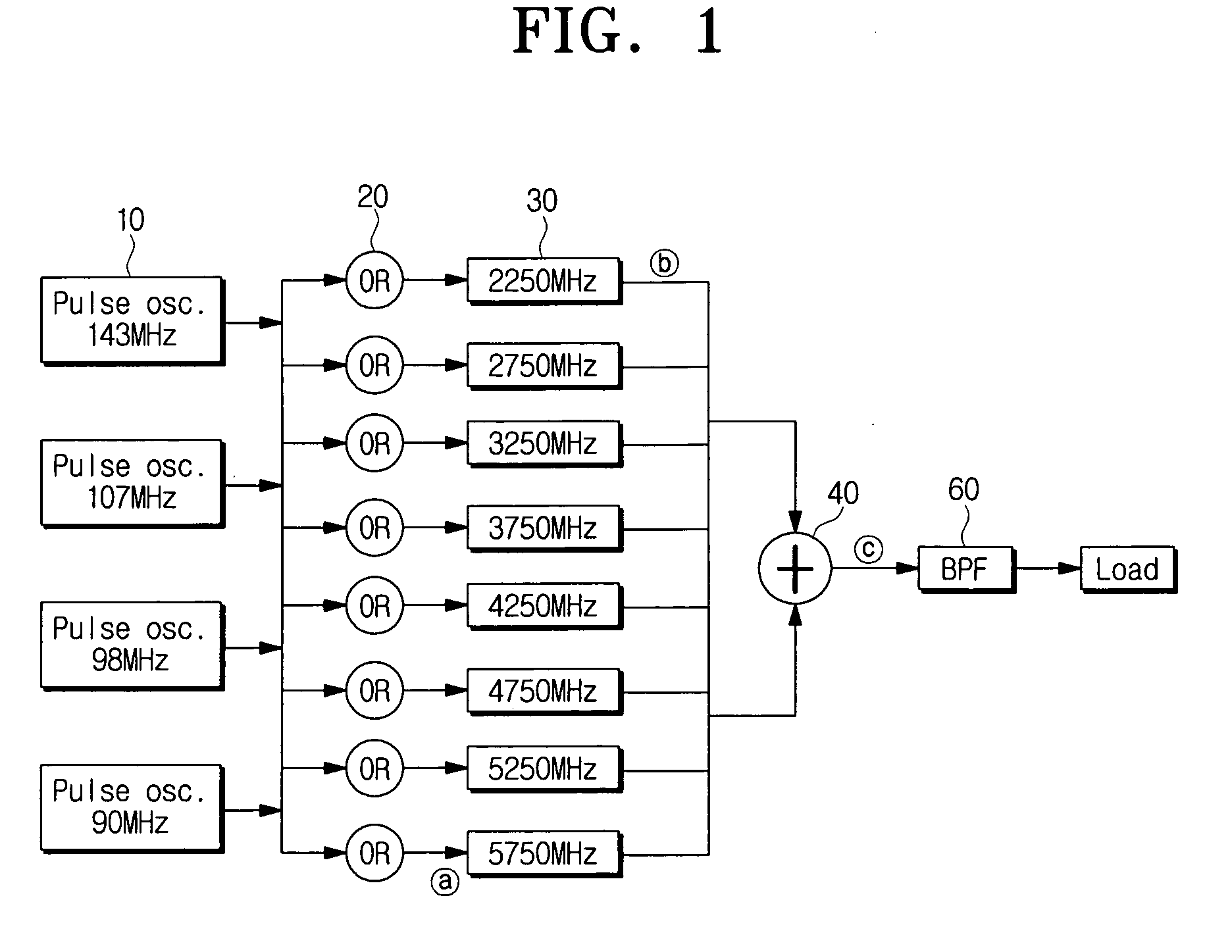
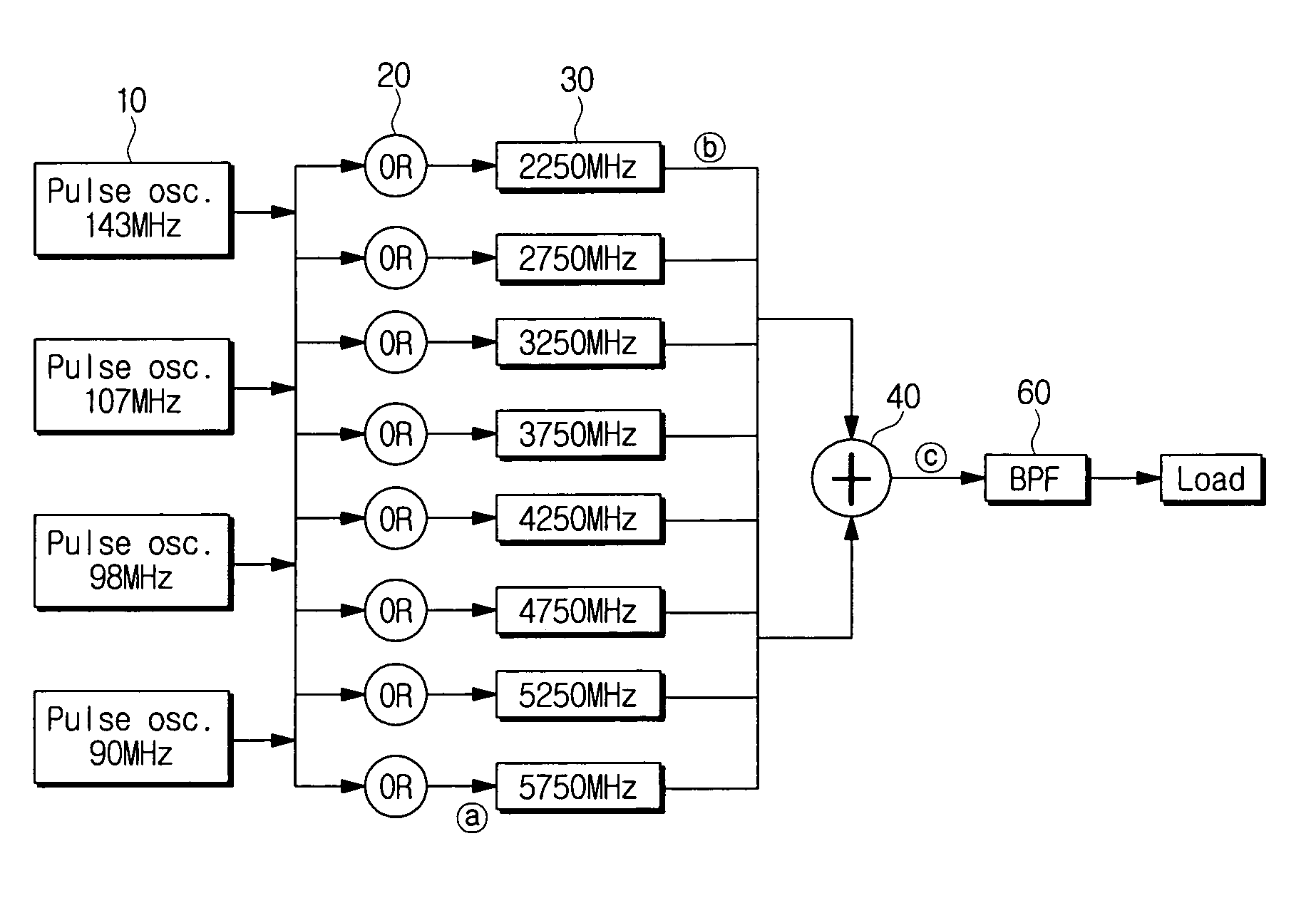
Adjustable chaotic signal generator using pulse modulation for ultra wideband (UWB) communications and chaotic signal generating method thereof
ActiveUS20070121945A1Computations using contact-making devicesModulated-carrier systemsUltra-widebandLocal oscillator
An adjustable chaotic signal generator using pulse modulation for UWB communications, and a chaotic signal generating method thereof are provided. The chaotic signal generator for UWB communications includes a plurality of pulse generators which generates pulses of different frequencies; at least one combiner which combines the pulses generated at the pulse generators; and a plurality of local oscillators which receives signals from the combiner, respectively, and generates a chaotic signal by increasing the received signals to different frequency bands. Accordingly, a plurality of users can conduct the radio communications in a specific wireless communication range at the same time by generating the chaotic signal that can be split to the multiple channels. Also, the chaotic signal generator is structured using devices integratable on an integrated circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Analog finite impulse response filter
ActiveUS20100271107A1Transversal filtersComputations using contact-making devicesParasitic capacitanceEngineering
According to one embodiment of the invention, a programmable finite impulse response (FIR) filter is implemented with differential isolation circuits to isolate parasitic capacitance from attenuating an output signal at both a first and second differential output terminals of the FIR filter. The FIR includes a summing circuit that provides operational advantages to the FIR filter.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
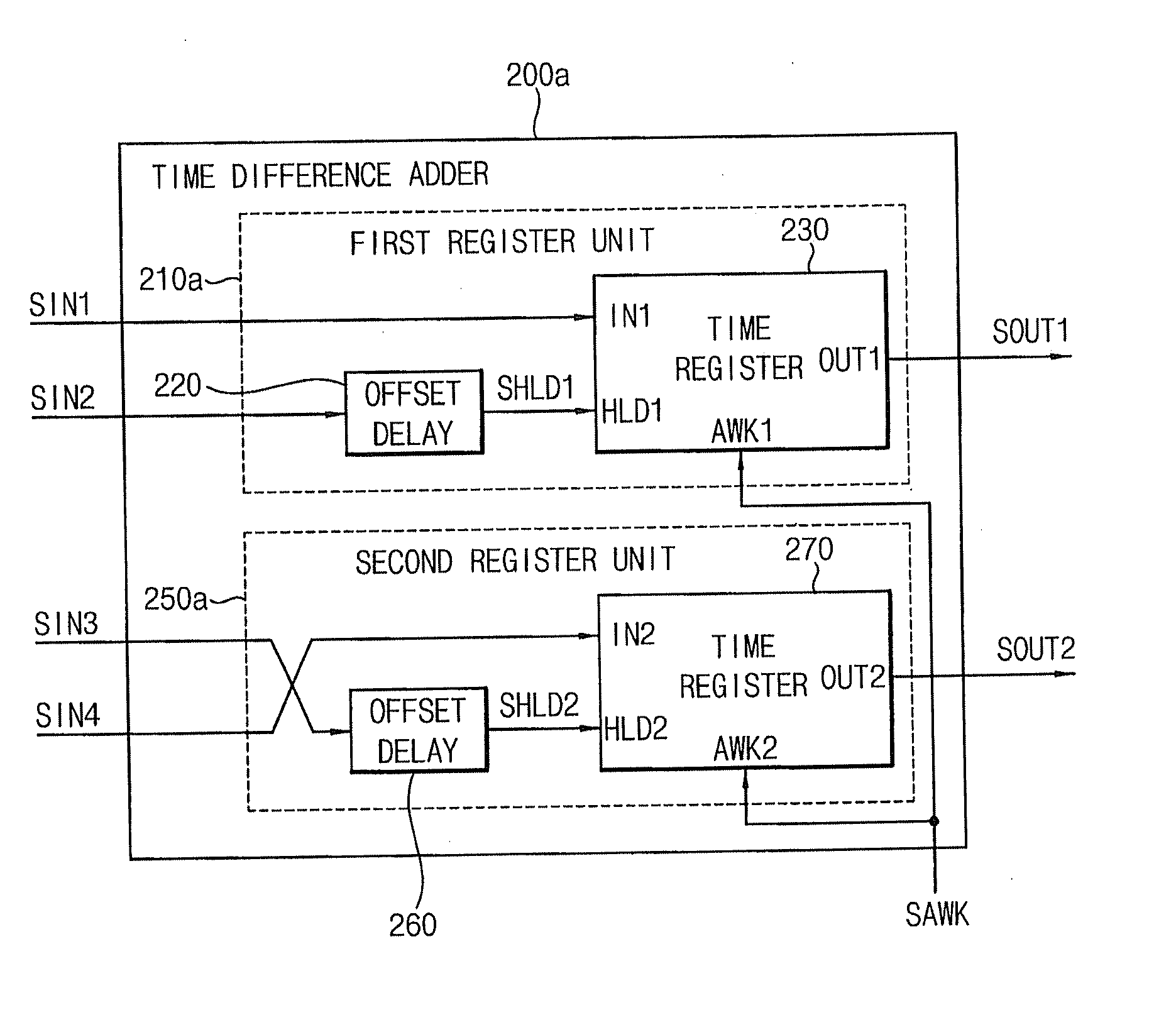
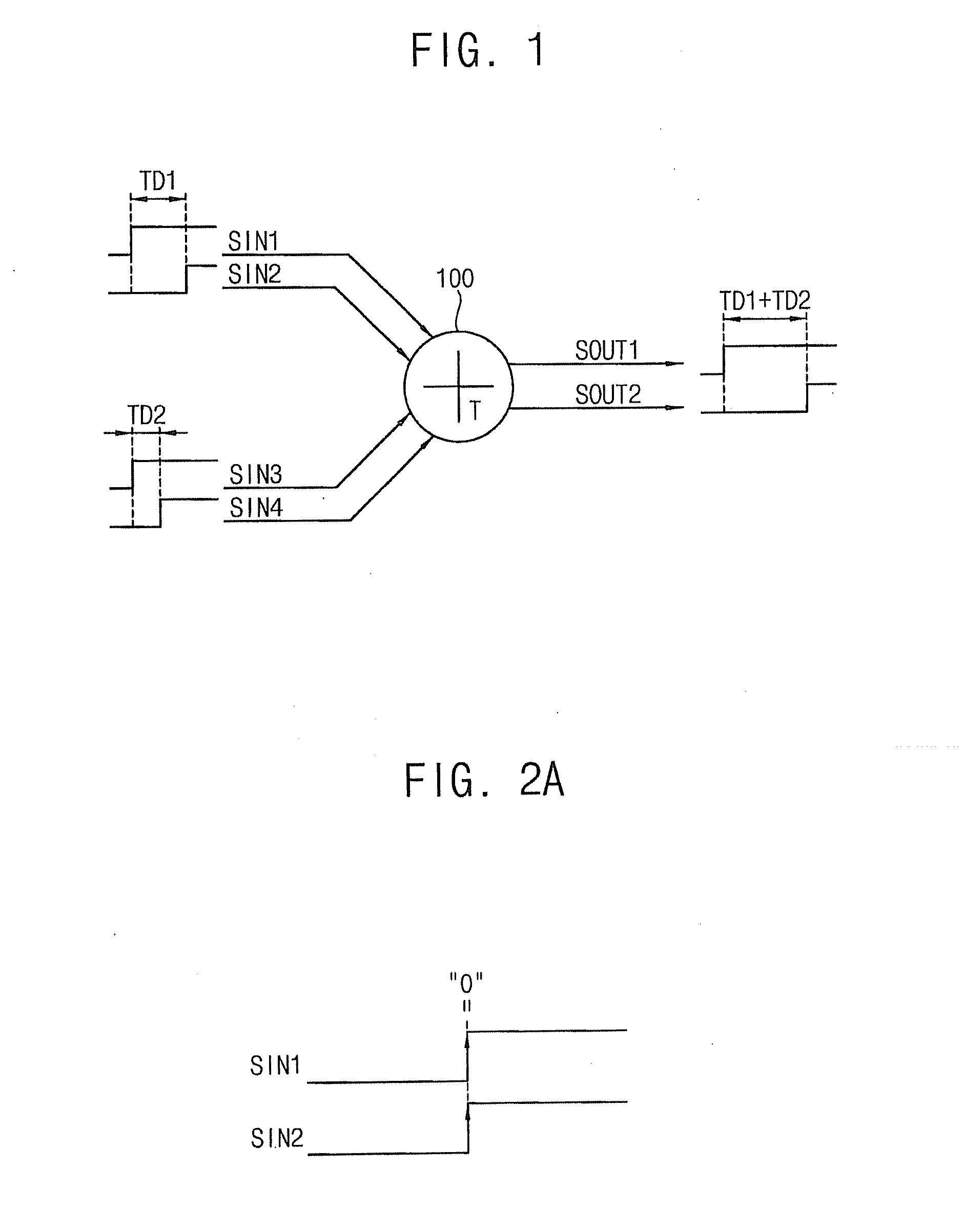
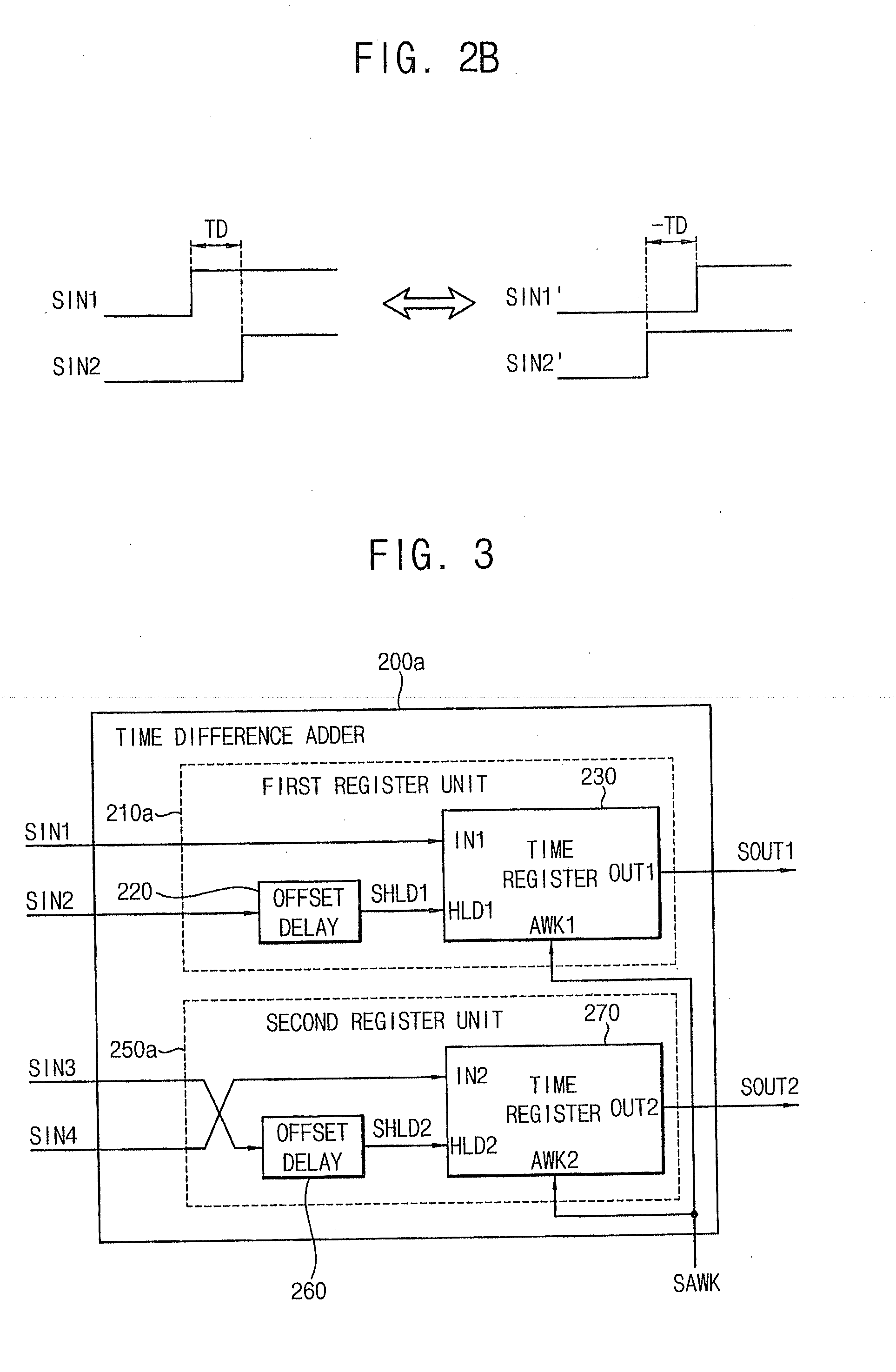
Time difference adders, time difference accumulators, sigma-delta time-to-digital converters, digital phase locked loops and temperature sensors
ActiveUS20120306553A1Computations using contact-making devicesPulse automatic controlDigital down converterProcessor register
A time difference adder included in a system-on-chip (SOC) includes a first register unit and a second register unit. The first register unit is configured to receive first and second input signals having a first time difference, and generate a first output signal in response to a first signal. The second register unit is configured to receive third and fourth input signals having a second time difference, and generate a second output signal having a third time difference with respect to the first output signal in response to the first signal. The third time difference corresponds to a sum of the first time difference and the second time difference.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
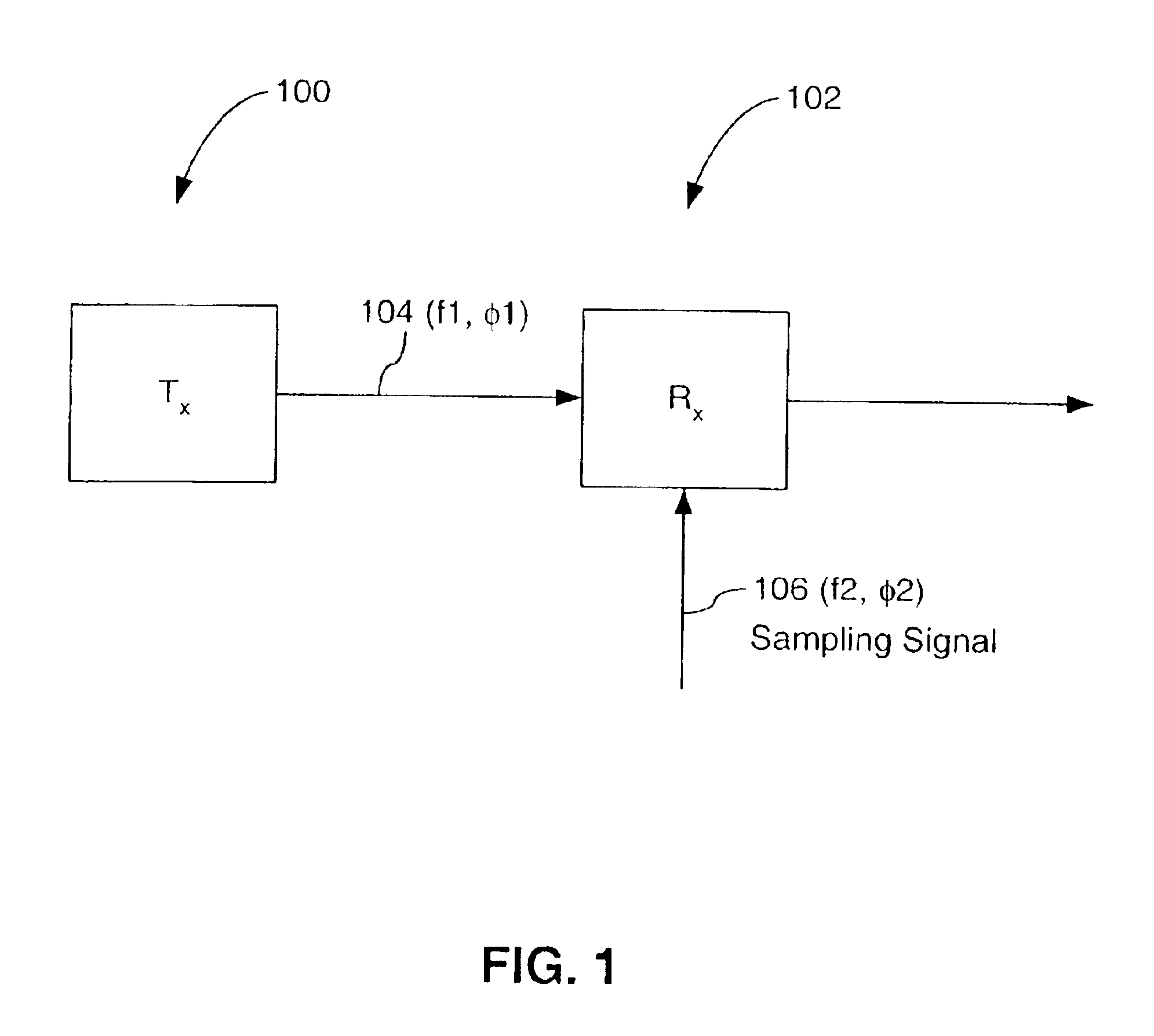
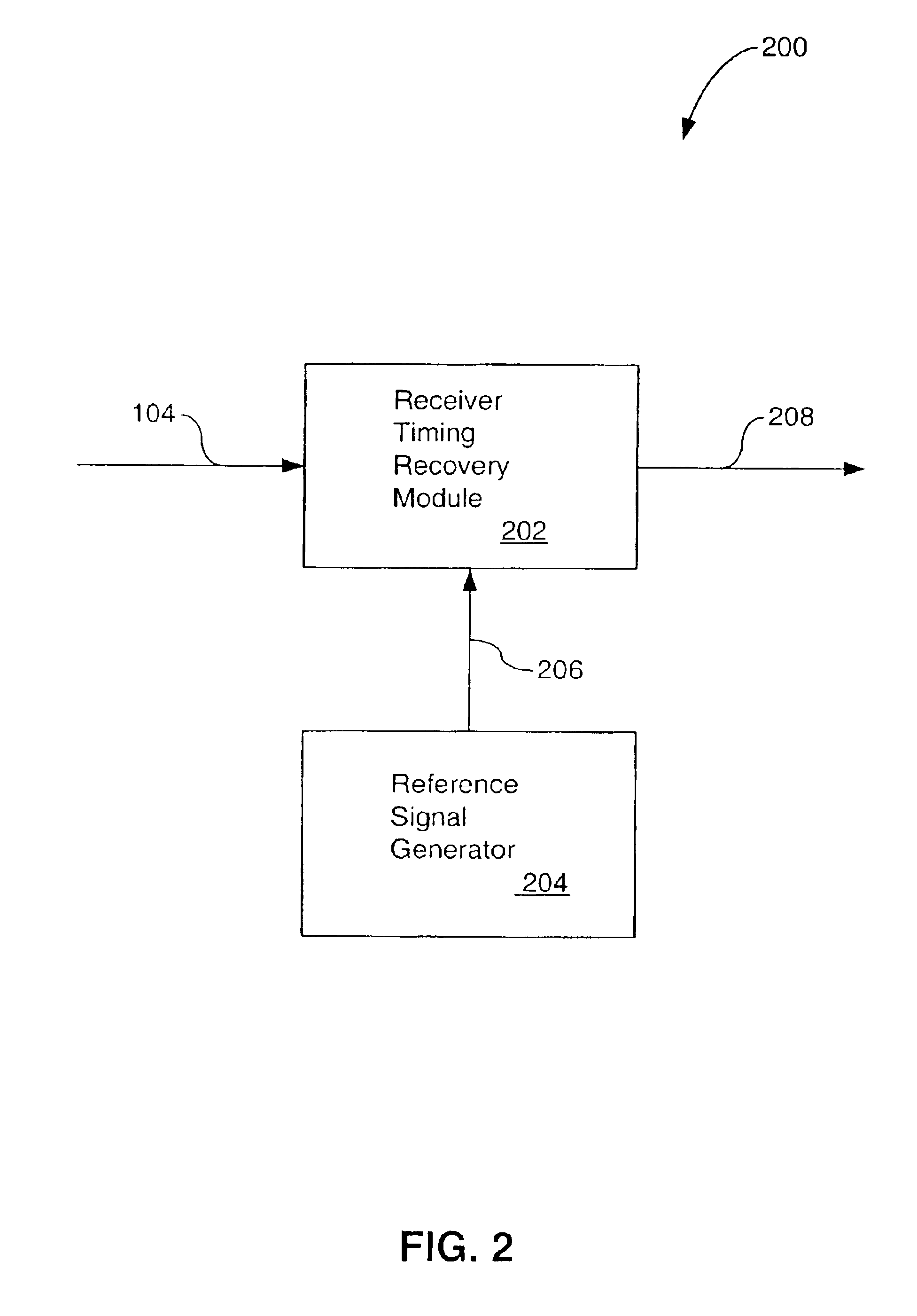
Phase interpolator device and method
InactiveUS6791388B2Reduce frequency offsetComputations using contact-making devicesPulse automatic controlTransceiverGigabit
A high-speed serial data transceiver includes multiple receivers and transmitters for receiving and transmitting multiple analog, serial data signals at multi-gigabit-per-second data rates. Each receiver includes a timing recovery system for tracking a phase and a frequency of the serial data signal associated with the receiver. The timing recovery system includes a phase interpolator responsive to phase control signals and a set of reference signals having different predetermined phases. The phase interpolator derives a sampling signal, having an interpolated phase, to sample the serial data signal. The timing recovery system in each receiver independently phase-aligns and frequency synchronizes the sampling signal to the serial data signal associated with the receiver. A receiver can include multiple paths for sampling a received, serial data signal in accordance with multiple time-staggered sampling signals, each having an interpolated phase.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Adjustable chaotic signal generator using pulse modulation for ultra wideband (UWB) communications and chaotic signal generating method thereof
ActiveUS7830214B2Computations using contact-making devicesModulated-carrier systemsUltra-widebandLocal oscillator
An adjustable chaotic signal generator using pulse modulation for UWB communications, and a chaotic signal generating method thereof are provided. The chaotic signal generator for UWB communications includes a plurality of pulse generators which generates pulses of different frequencies; at least one combiner which combines the pulses generated at the pulse generators; and a plurality of local oscillators which receives signals from the combiner, respectively, and generates a chaotic signal by increasing the received signals to different frequency bands. Accordingly, a plurality of users can conduct the radio communications in a specific wireless communication range at the same time by generating the chaotic signal that can be split to the multiple channels. Also, the chaotic signal generator is structured using devices integratable on an integrated circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
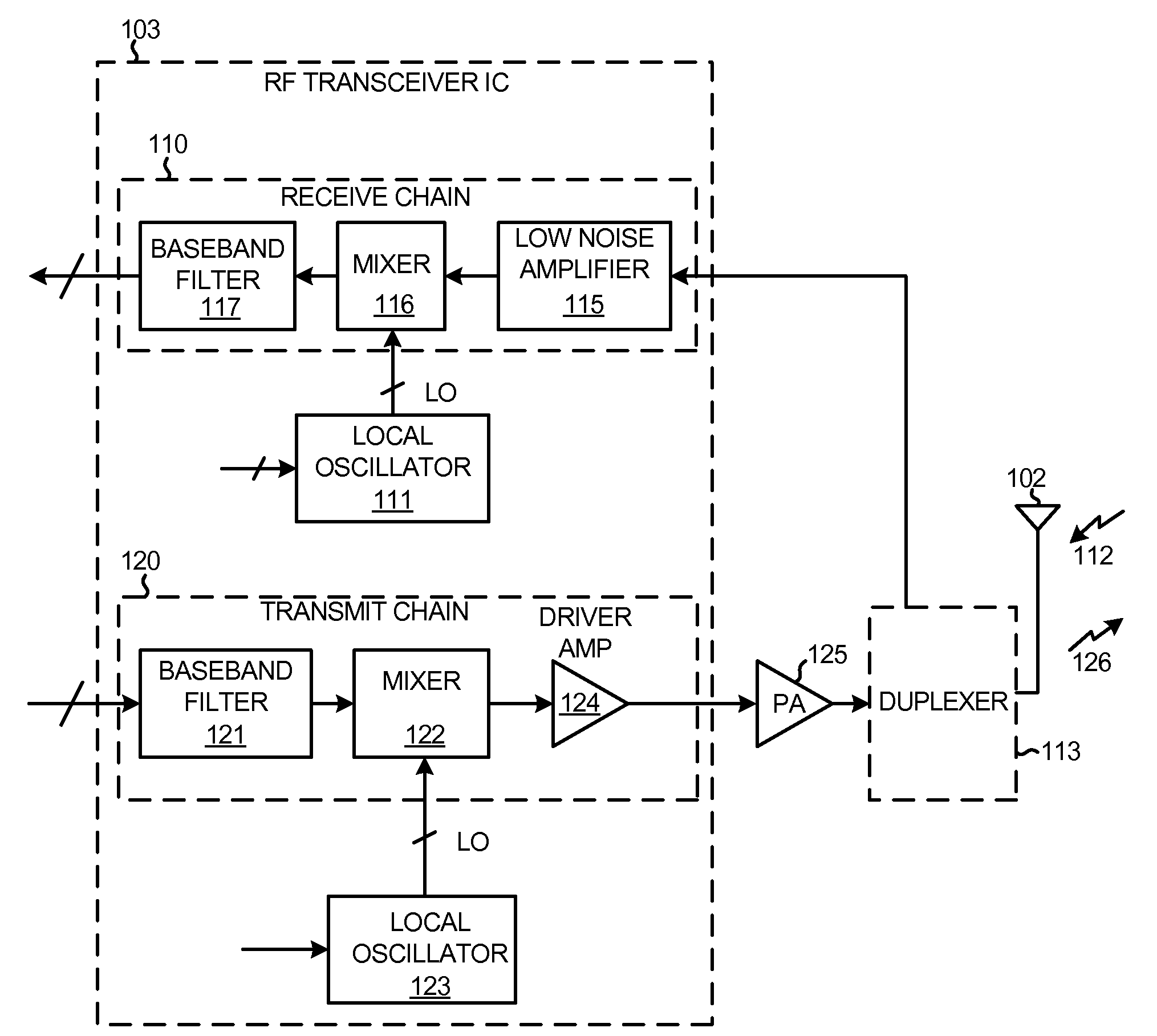
High q transformer disposed at least partly in a non-semiconductor substrate
ActiveUS20100026368A1High degree of couplingReduce parasitic capacitanceComputations using contact-making devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTransceiverTransformer
An assembly involves an integrated circuit die that is bonded, e.g., flip-chip bonded, to a non-semiconductor substrate by a plurality of low-resistance microbumps. In one novel aspect, at least a part of a novel high-frequency transformer is disposed in the non-semiconductor substrate where the non-semiconductor substrate is the substrate of a ball grid array (BGA) integrated circuit package. At least one of the low-resistance microbumps connects the part of the transformer in the substrate to a circuit in the integrated circuit die. At two gigahertz, the novel transformer has a coupling coefficient k of at least at least 0.4 and also has a transformer quality factor Q of at least ten. The novel transformer structure sees use in coupling differential outputs of a mixer to a single-ended input of a driver amplifier in a transmit chain of an RF transceiver within a cellular telephone.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Dual-mode mixer circuit and method
ActiveUS20100120377A1Eliminate the problemIncrease rangeResonant long antennasComputations using contact-making devicesLocal oscillator signalPhase shifted
The present invention relates to a mixer circuit and method of frequency transformation, wherein an input signal is switched in accordance with a first local oscillator signal and in accordance with at least one second local oscillator signal having a smaller duty cycle than said first local oscillator signal, or having a respective predetermined phase shift with respect to said first local oscillator signal. Output signals obtained by the switching in accordance with the first and at least one second local oscillator signals are summed and the polarity of one of said first local oscillator signal and said at least one second local oscillator signal is switched in response to a control input, to thereby switch between a harmonic-rejection mode and a sub-harmonic mixing mode.
Owner:NXP BV
Power supply voltage droop compensated clock modulation for microprocessors
InactiveUS20050022042A1Computations using contact-making devicesVolume/mass flow measurementClock rateEngineering
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Phase interpolator device and method
InactiveUS6995594B2Reduce frequency offsetComputations using contact-making devicesPulse automatic controlTransceiverData signal
A high-speed serial data transceiver includes multiple receivers and transmitters for receiving and transmitting multiple analog, serial data signals at multi-gigabit-per-second data rates. Each receiver includes a timing recovery system for tracking a phase and a frequency of the serial data signal associated with the receiver. The timing recovery system includes a phase interpolator responsive to phase control signals and a set of reference signals having different predetermined phases. The phase interpolator derives a sampling signal, having an interpolated phase, to sample the serial data signal. The timing recovery system in each receiver independently phase-aligns and frequency synchronizes the sampling signal to the serial data signal associated with the receiver. A receiver can include multiple paths for sampling a received, serial data signal in accordance with multiple time-staggered sampling signals, each having an interpolated phase.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Information processing apparatus, and signal transmission method
InactiveUS20110037759A1Efficient data transferExtended range of motionComputations using contact-making devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsInformation processingData signal
Provided is an information processing apparatus which includes a first module including a signal addition unit that generates an addition signal by adding a data signal to a clock, a signal subtraction unit that generates a subtraction signal by subtracting the data signal from the clock, a first signal transmission unit that transmits the addition signal through a first transmission line, and a second signal transmission unit that transmits the subtraction signal through a second transmission line, and a second module including a data component extraction unit that extracts a component of the data signal by subtracting the subtraction signal received through the second transmission line from the addition signal received through the first transmission line, and a clock component extraction unit that extracts a component of the clock by adding the subtraction signal received through the second transmission line to the addition signal received through the first transmission line.
Owner:SONY CORP
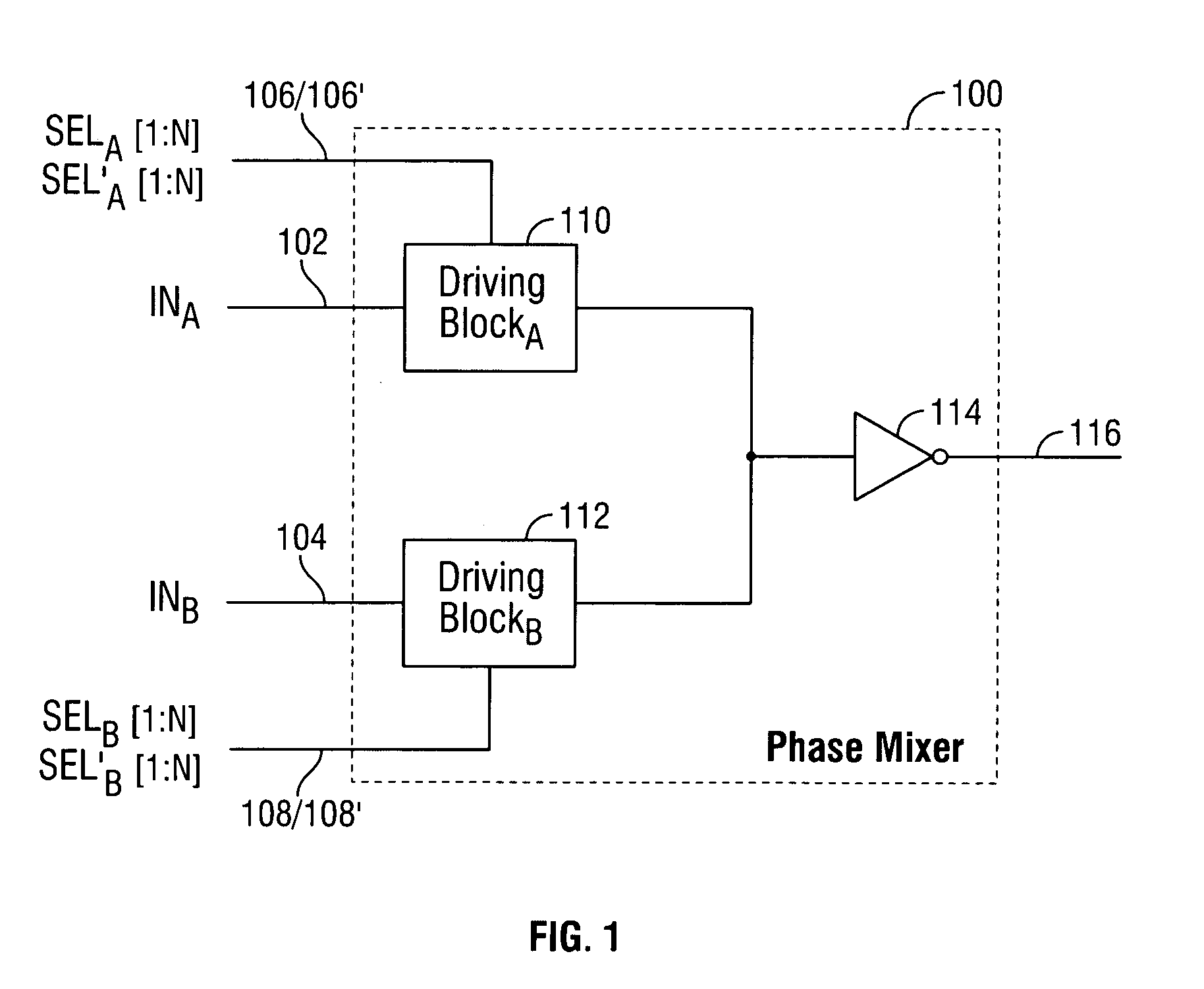
Digital delay-locked loop circuits with hierarchical delay adjustment
InactiveUS6982578B2Computations using contact-making devicesPulse automatic controlPhase differenceDigital delay locked loop
Fine tuned signal phase adjustments are provided by multiple cascaded phase mixers. Each phase mixer outputs a signal having a phase between the phases of its two input signals. With each subsequent stage of phase mixers, the signals generated by the phase mixers have a smaller phase difference, thereby providing finer delay adjustments. Multiple stages of phase mixers can be provided in digital delay-locked loop circuitry to provide additional hierarchical delay adjustment.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Direct current sum bandgap voltage comparator
InactiveUSRE39918E1Multiple input and output pulse circuitsComputations using contact-making devicesEngineeringVoltage variation
A direct current sum bandgap voltage comparator for detecting voltage changes in a power supply. The direct current sum bandgap voltage comparator includes a summing node, current sources connected to the summing node and the power supply, and an indicator circuit connected to the summing node. Each current source supplies a current to the summing node wherein the summing node voltage level is responsive to the currents supplied. The indicator circuit is responsive to changes in the summing node voltage level and generates at an output a logical signal at one state when the summing node voltage level is greater than a predetermined value and generates the logical signal at the output at another state when the summing node voltage level is less than the predetermined value, the predetermined value corresponding to a preselected power supply voltage.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
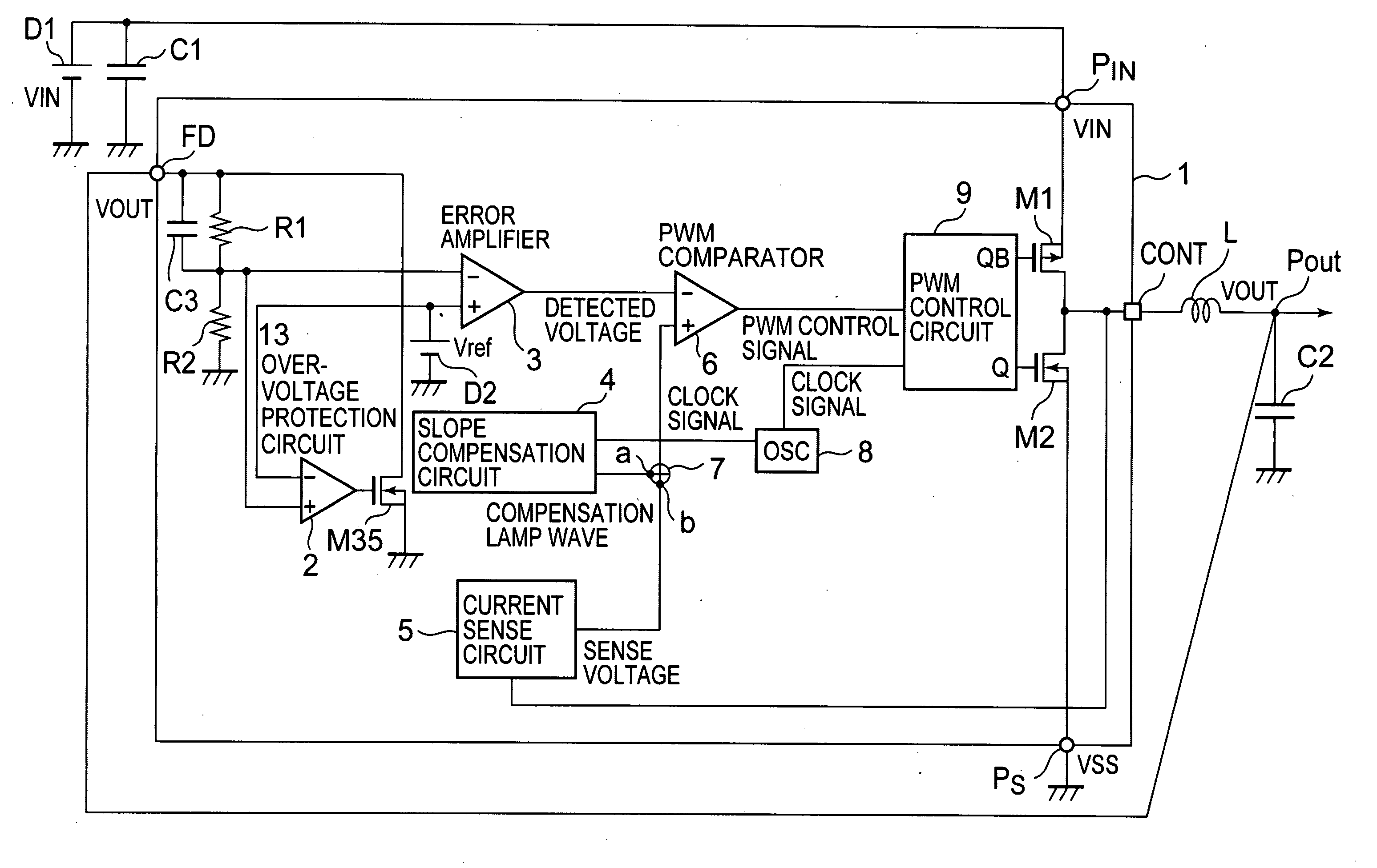
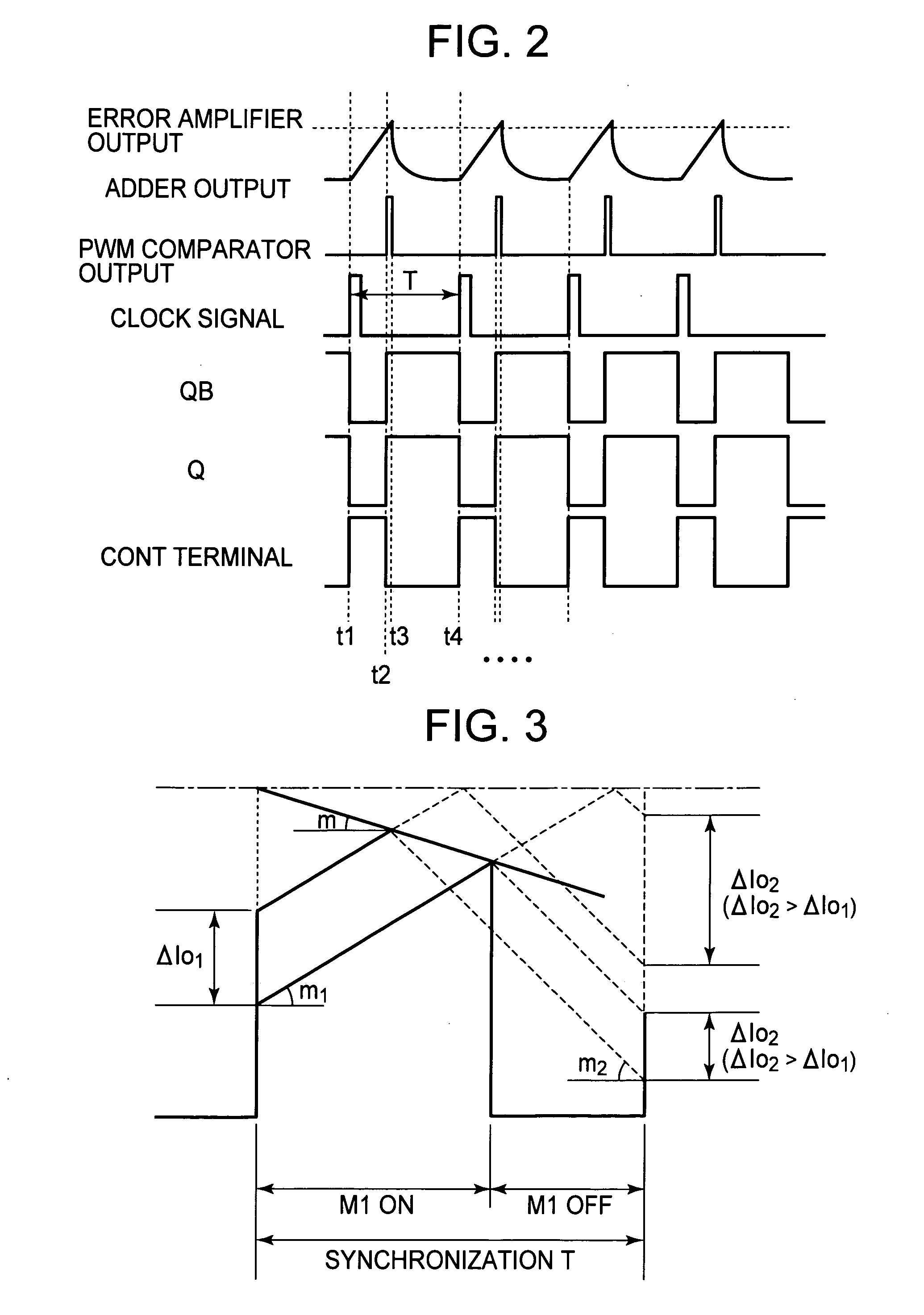
Adder and current mode switching regulator
InactiveUS7615973B2Suppress a variation caused by the threshold voltageSimple processComputations using contact-making devicesDc-dc conversionCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
Provided is an adder in which all of circuits can be constituted by CMOS transistors, a process is simplified, and a chip size can be reduced as compared with a conventional art. The adder according to the present invention includes: a first VI converter and a second VI converter that allow a current corresponding to an input voltage to flow therein; and a current addition resistor having one end commonly connected to output terminals of the first VI converter and the second VI converter and another end grounded, which is adjustable in a resistance value. Each of the first VI converter and the second VI converter includes: a prestage VI converter that generates a reference current; a poststage VI converter that generates a current corresponding to the input voltage; a first current mirror circuit whose first terminal on a reference side is connected with the prestage VI converter and whose first output terminal in which a current corresponding to the first terminal flows is connected with the poststage VI converter; and a second current mirror circuit whose second terminal on the reference side is connected to the first output terminal, and which can adjust a current ratio from a second output terminal in correspondence with the current that flows in the second terminal. A voltage at the one end of the current addition resistor is output as an addition voltage.
Owner:ABLIC INC
Self-calibrating wideband phase continuous synthesizer and associated methods
InactiveUS20050156781A1Reduce discontinuityComputations using contact-making devicesComputing operations for multiplication/divisionEngineeringWideband
The synthesizer and method provide a relatively wideband swept frequency signal and include generating a first swept frequency signal with a first generator, and successively switching between different frequency signals with a second generator. Such switching creates undesired phase discontinuities in the output swept frequency signal. The first swept frequency signal is combined with the successively switched different frequency signals to produce the relatively wideband swept frequency signal, and the second generator is calibrated to reduce the undesired phase discontinuities during switching based upon the output swept frequency signal.
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
Adder and current mode switching regulator
InactiveUS20080203988A1Simple processReduce chip sizeComputations using contact-making devicesDc-dc conversionCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
Provided is an adder in which all of circuits can be constituted by CMOS transistors, a process is simplified, and a chip size can be reduced as compared with a conventional art. The adder according to the present invention includes: a first VI converter and a second VI converter that allow a current corresponding to an input voltage to flow therein; and a current addition resistor having one end commonly connected to output terminals of the first VI converter and the second VI converter and another end grounded, which is adjustable in a resistance value. Each of the first VI converter and the second VI converter includes: a prestage VI converter that generates a reference current; a poststage VI converter that generates a current corresponding to the input voltage; a first current mirror circuit whose first terminal on a reference side is connected with the prestage VI converter and whose first output terminal in which a current corresponding to the first terminal flows is connected with the poststage VI converter; and a second current mirror circuit whose second terminal on the reference side is connected to the first output terminal, and which can adjust a current ratio from a second output terminal in correspondence with the current that flows in the second terminal. A voltage at the one end of the current addition resistor is output as an addition voltage.
Owner:ABLIC INC
Charge Domain Filter Circuit
InactiveUS20090134938A1Reconfigurable filter characteristicsReduce power consumptionMultiple-port networksTransversal filtersCapacitanceEngineering
A charge domain filter circuit includes a first signal output portion, at least one second signal output, portion, a third signal output portion, and an adder portion. The first signal output portion outputs a first signal that is sampled at a specified time interval. Each second signal, output portion outputs a second signal that is sampled after a specified delay after the first signal is sampled. Where a plurality of the second signal output portions is included, the second signals are sampled in succession. The third signal output portion outputs a third signal that is sampled after a specified delay after the last second signal is sampled. The adder portion adds the first, second, and third signals together and outputs the result. The capacitance ratio of the sampling capacitors in the first signal output portion and the second signal output portion is one of continuously or discretely varied.
Owner:SONY CORP
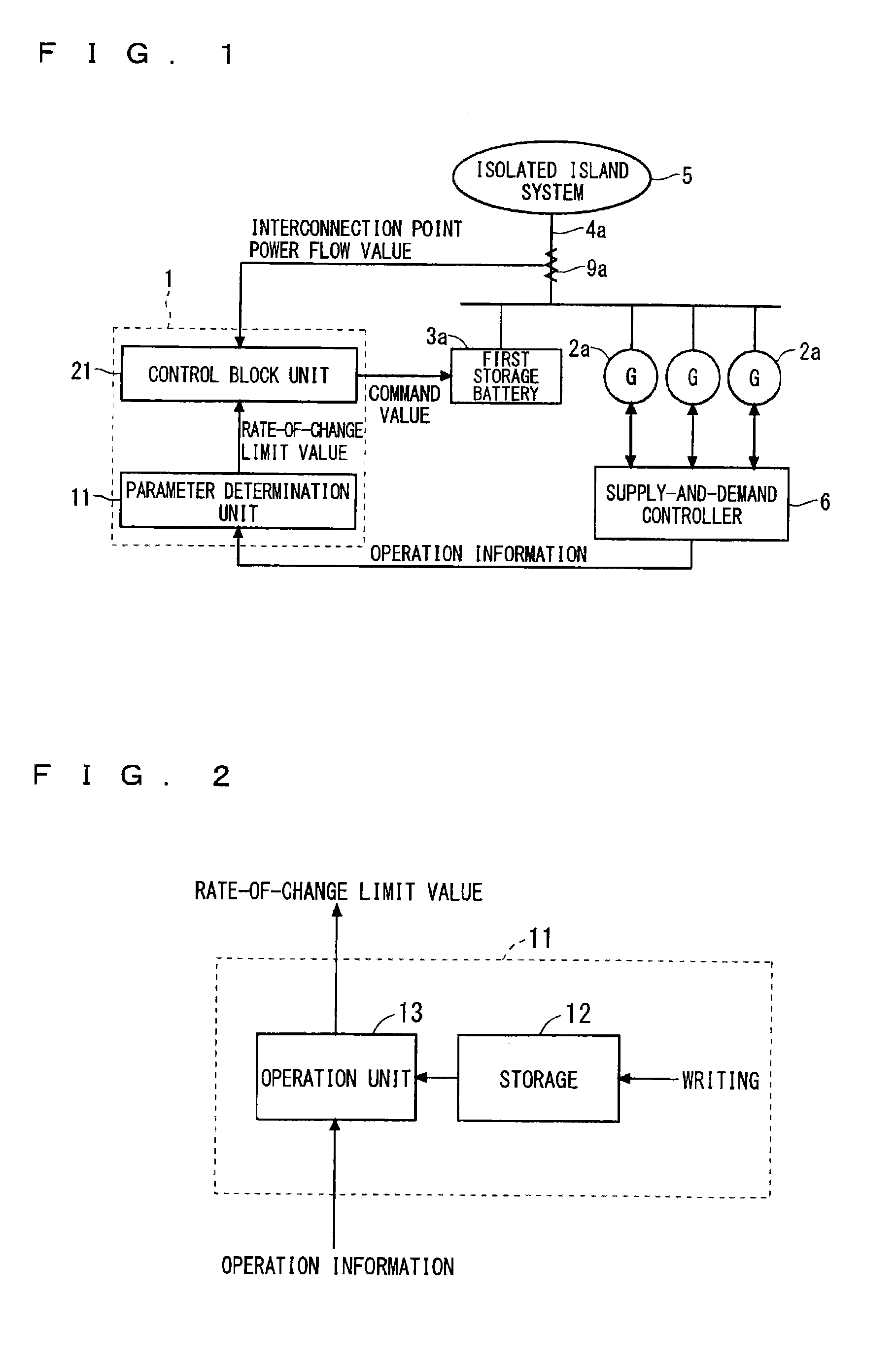
System stabilization device
ActiveUS20150001939A1Avoid changeNot affect power frequencyElectric signal transmission systemsBatteries circuit arrangementsPower flowEngineering
A technique with which a change in power frequency can be suppressed. A power system stabilizer issues a control command to a first storage battery among a plurality of first power generators and the first storage battery that are connected to an isolated island system via a first tie-line. The power system stabilizer includes a parameter determination unit and a control block unit. The parameter determination unit obtains, on the basis of operation information, a rate-of-change limit value that indicates a limit to be imposed on a total value of changes in the overall output of first power generators in operation. The control block unit generates a command value to be given to the first storage battery on the basis of an interconnection point power flow value measured on the first tie-line and the rate-of-change limit value obtained by the parameter determination unit.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Digital delay-locked loop circuits with hierarchical delay adjustment
InactiveUS20050110539A1Computations using contact-making devicesPulse automatic controlPhase differenceDigital delay locked loop
Fine tuned signal phase adjustments are provided by multiple cascaded phase mixers. Each phase mixer outputs a signal having a phase between the phases of its two input signals. With each subsequent stage of phase mixers, the signals generated by the phase mixers have a smaller phase difference, thereby providing finer delay adjustments. Multiple stages of phase mixers can be provided in digital delay-locked loop circuitry to provide additional hierarchical delay adjustment.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
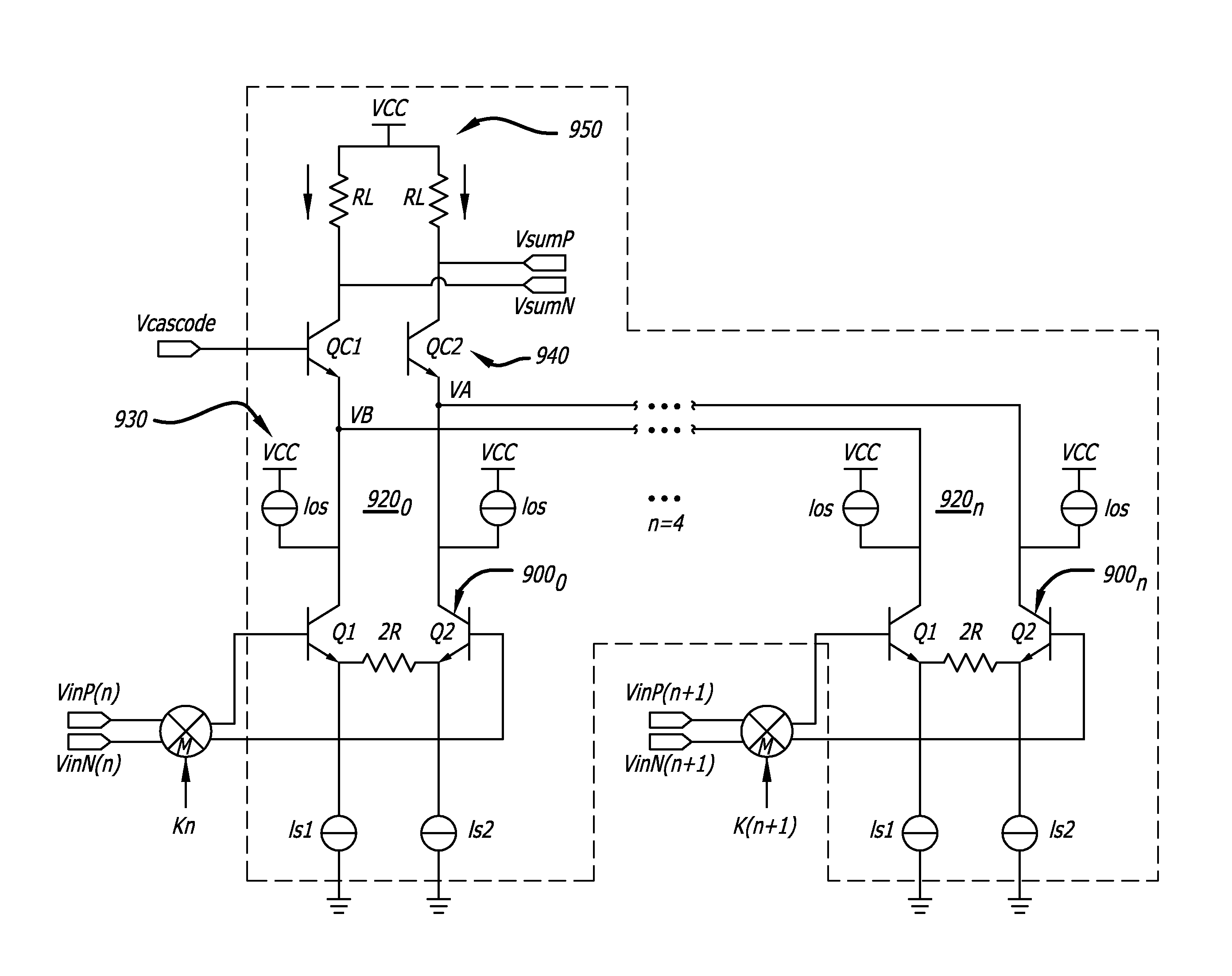
Dual Gilbert Cell Mixer with Offset Cancellation
InactiveUS20090149149A1Quality improvementWell mixedModulation transferenceComputations using contact-making devicesOffset cancellationSignal on
An electronic device includes a first mixer portion having a first stage and a second stage, and a second mixer portion having a first stage and a second stage. A first electrical path is coupled to the first mixer portion and the second mixer portion, and a second electrical path is coupled to the first mixer portion and the second mixer portion. The first mixer portion is adapted to receive a first input signal on the first stage and a second input signal on the second stage. The second mixer portion is adapted to receive the second input signal on the first stage and the first input signal on the second stage.
Owner:EPCOS AG
Passive harmonic-rejection mixer
ActiveUS8138817B2Reduce impactComputations using contact-making devicesComputing operations for addition/subtractionAudio power amplifierHarmonic
Owner:III HLDG 6
Passive harmonic-rejection mixer
ActiveUS20100253412A1Reduce the impactReduce impactComputations using contact-making devicesComputing operations for addition/subtractionAudio power amplifierControl signal
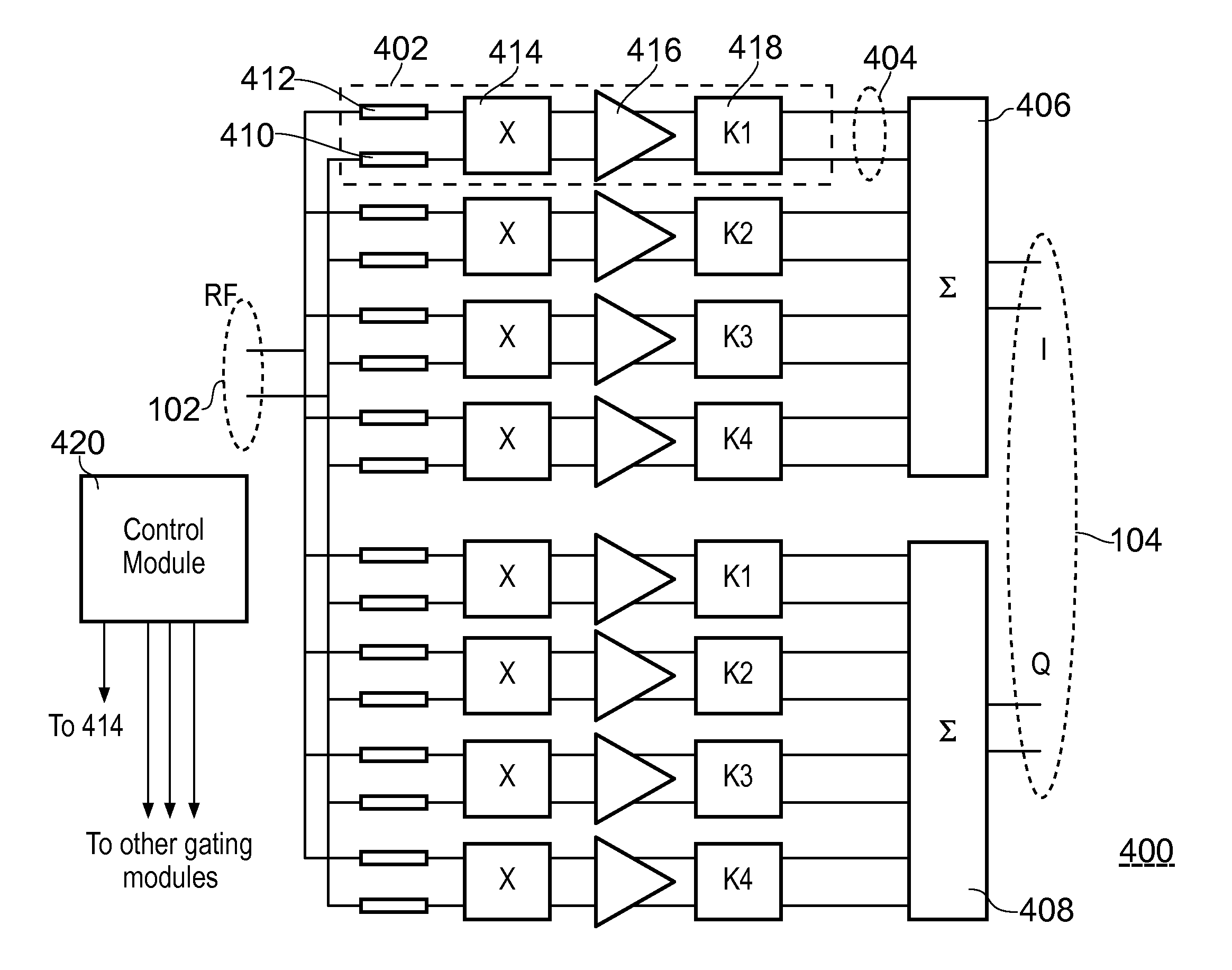
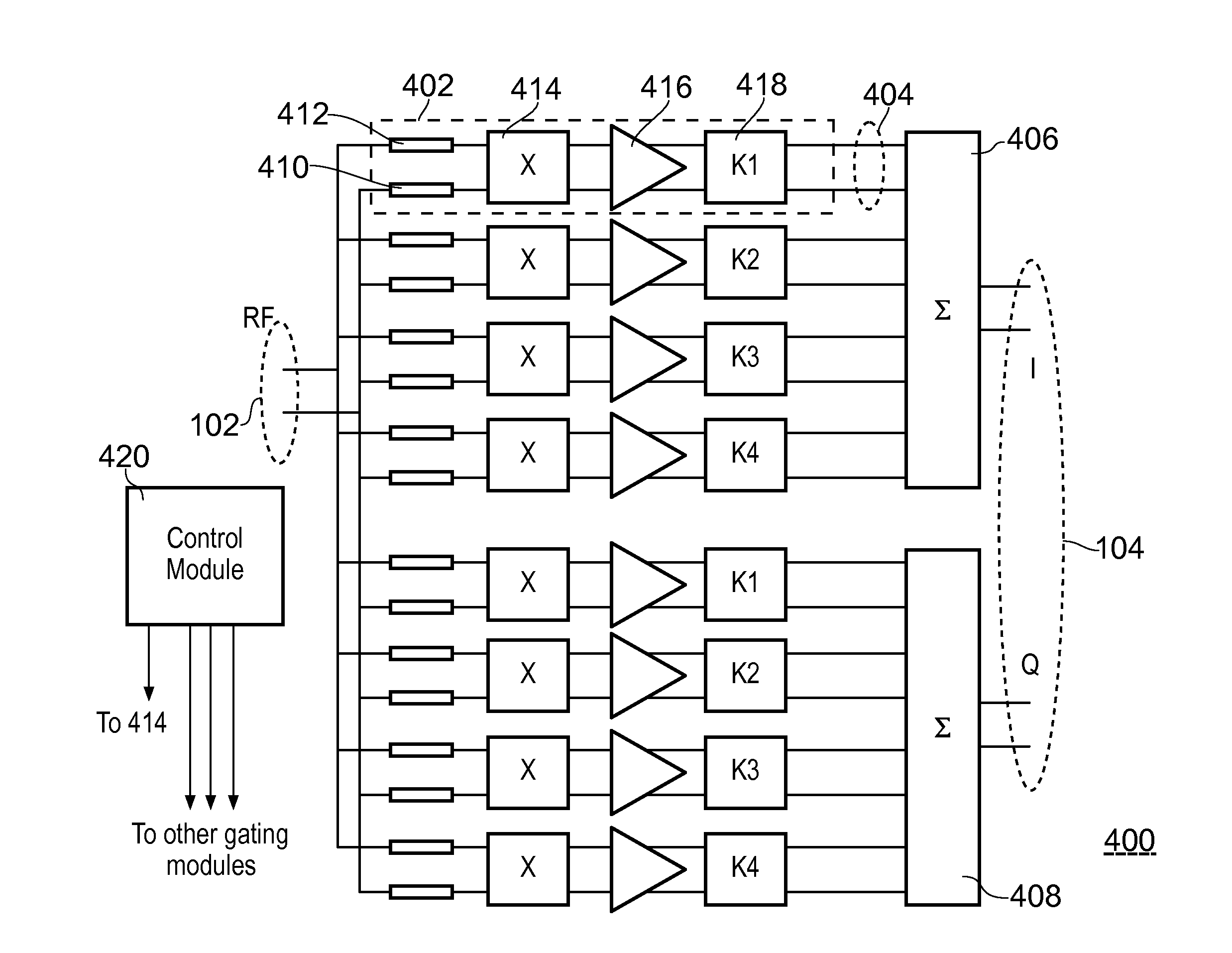
An electronic device comprising a passive harmonic-rejection mixer. The passive harmonic rejection mixer has an input connected to several sub-mixer stages, and the sub-mixer stages are connected to a summing module for generating the output. Each sub-mixing stage comprises a gating module and a respective amplifier, the gating module adapted to selectively pass the input signal or the input signal with inverted polarity under the control of control signals.
Owner:III HLDG 6
Weighted mean calculation circuit
InactiveUS6611164B2Reduce power consumptionSmall footprintAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsElectrical polarityEngineering
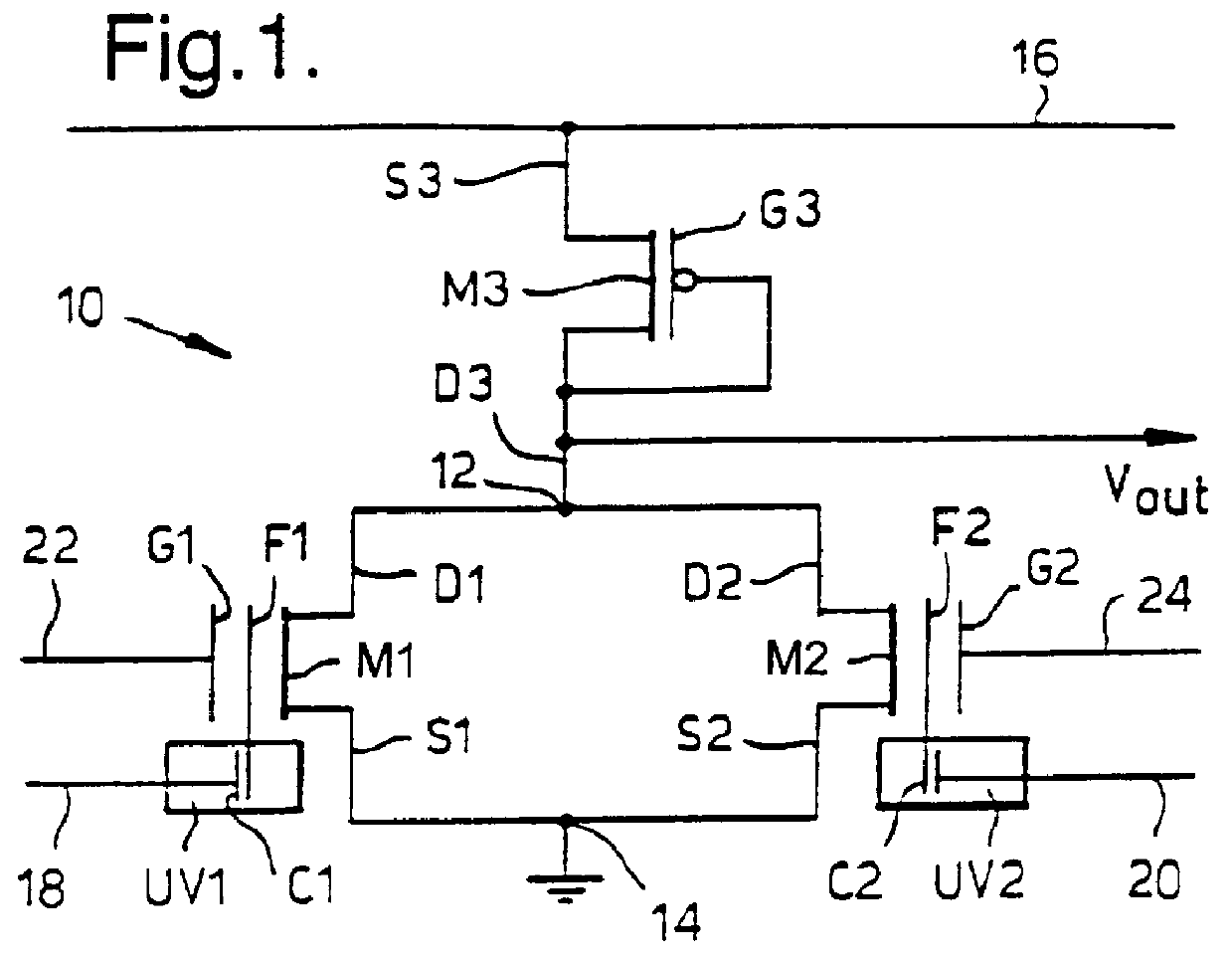
The present invention relates to a weighted mean calculation circuit that comprises an inverting amplifier; a plurality of capacitors C1 through Cn connected to the input terminal thereof; switches SW1 through SWn that connect the capacitors C1 through Cn to the input and output terminals of the inverting amplifier; and a switch SW0 that is provided between the input and output of the inverting amplifier. A signal voltage is applied to respective capacitors while making the SW0 conductive when inputting a signal, and the capacitors C1 through Cn are connected in parallel between the input and output of the inverting amplifier while making the SW0 non-conductive when outputting a signal, whereby an output signal Vout is read, and a weighted mean value output that does not include any offset and is normalized as a normal polarity output can be obtained.
Owner:LINEAR CELL DESIGN COJ
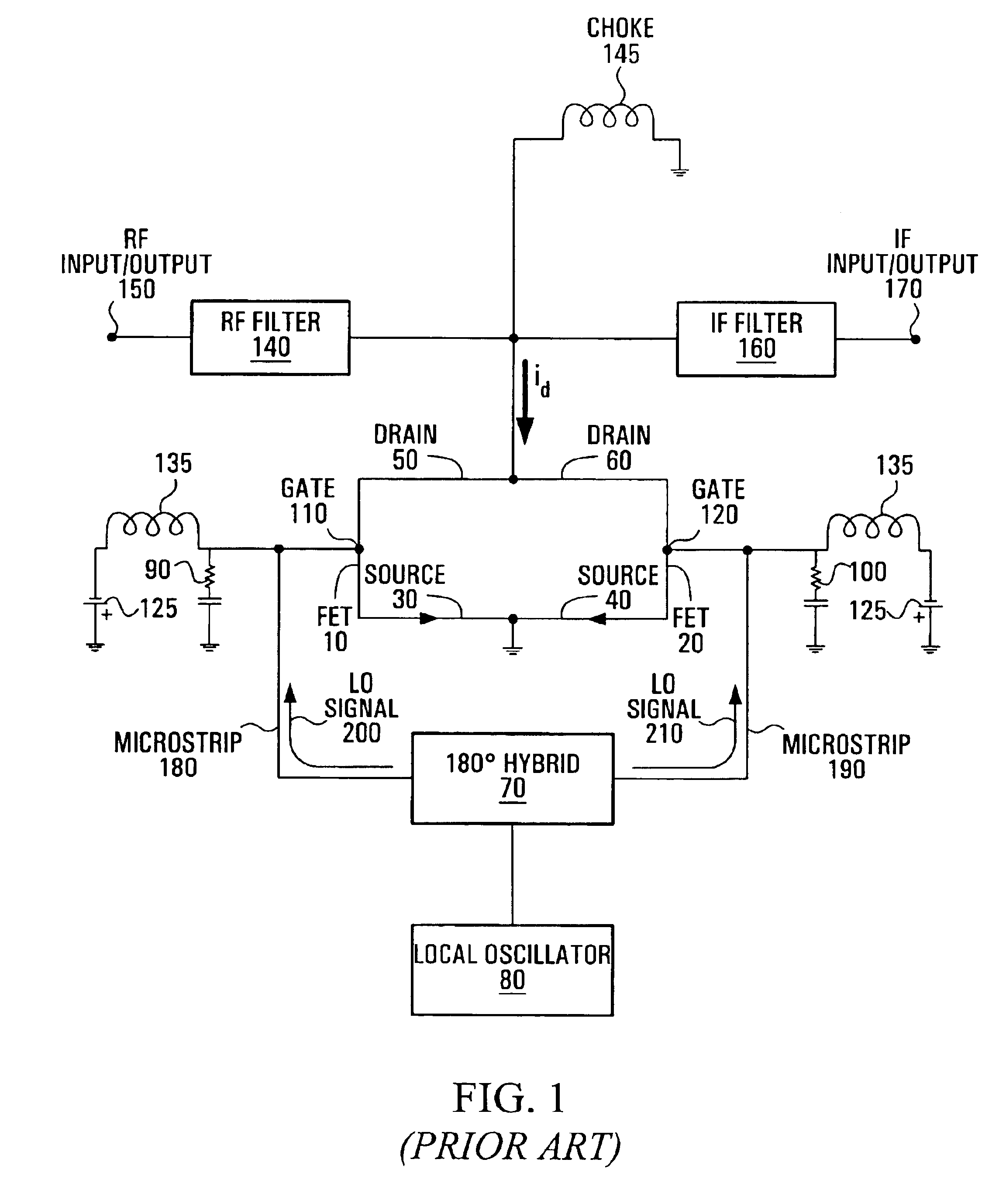
Sub-harmonic mixer
ActiveUS6861891B2Simplify the manufacturing processReduce area requirementsModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesComputations using contact-making devicesLocal oscillator signalFrequency mixer
A sub-harmonic mixer comprises two field effect transistors in which the sources of the transistors are connected together and the drains of the transistors are connected together. The mixer includes signal generating means for generating a local oscillator (LO) signal coupled to the gate of one of the FETs. Circuit means is provided for maintaining the potential of the gate of the other FET at a substantially constant value relative to the local oscillator signal applied to the gate of the driven FET, and the FET's are arranged to permit the local oscillator signal applied to gate of the driven FET to drive a voltage across the gate-source of both FET's. An input and output port is coupled to the drains for receiving input signals for the mixer and outputting output signals from the mixer.
Owner:COMS IP HLDG LLC
AC-coupled differential drive circuit for opto-electronic modulators
ActiveUS20080088354A1Increase available bandwidthEliminate needComputations using contact-making devicesComputing operations for addition/subtractionDriver circuitLow-pass filter
An AC-coupled differential drive circuit for an optical modulator is utilized, where a common “node” is defined between top (or bottom) plates of the modulator arms themselves (the “arms” of a modulator taking the form of MOS capacitors). A low pass filter is disposed between the differential driver output and the modulator's common node to provide the desired AC coupling by filtering out the DC bias voltage of the driver circuit itself without the need for a separate, external AC coupling capacitor. An independent, adjustable DC potential can then be applied to the common node, and will appear in a balanced manner across each arm of the modulator to provide the desired DC bias for the modulator independent of the DC bias of the driver circuit.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
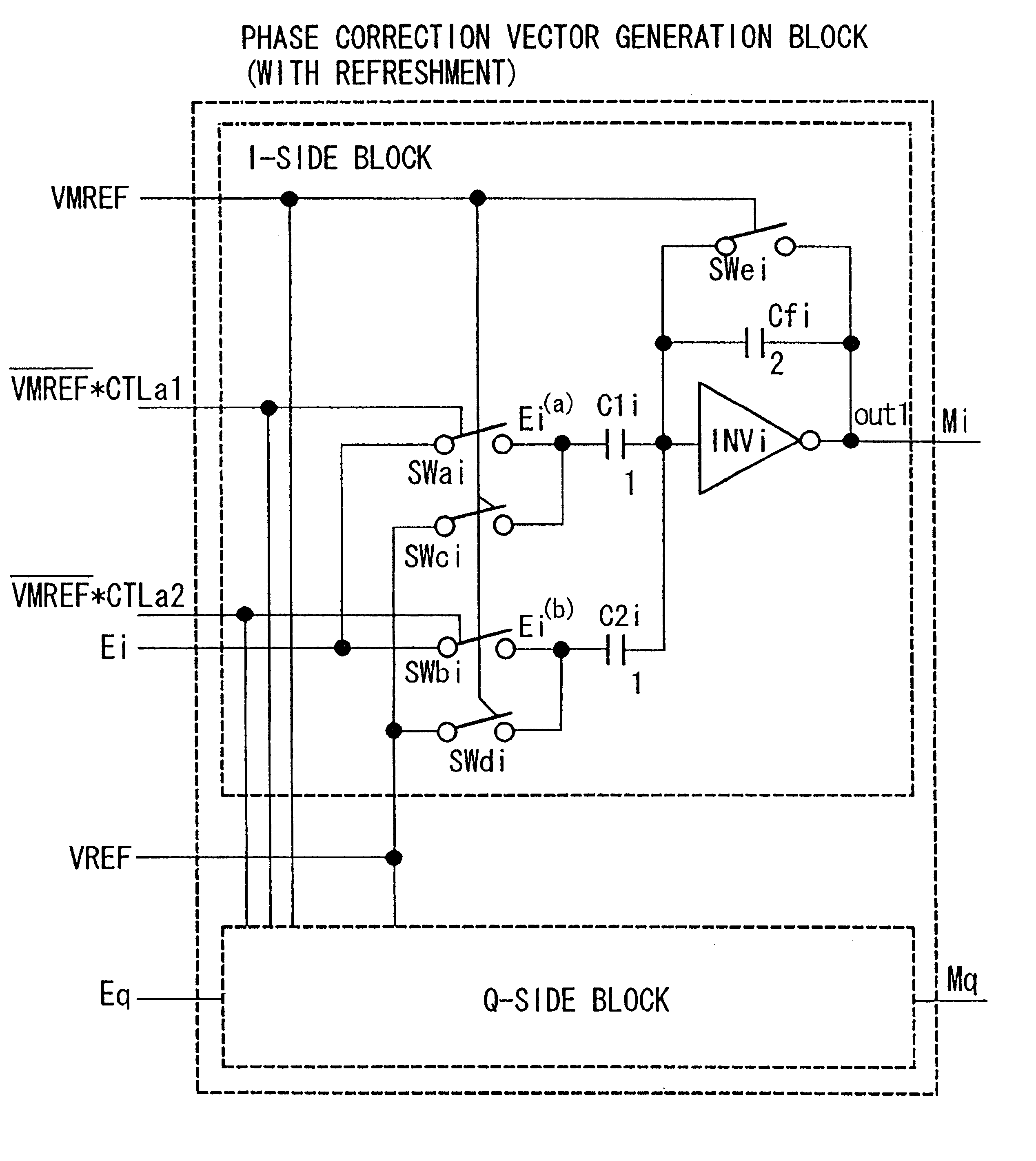
Receiver in a spread spectrum communication system having low power analog multipliers and adders
InactiveUS6278724B1Multiple input and output pulse circuitsComputations using contact-making devicesComplex typePhase correction
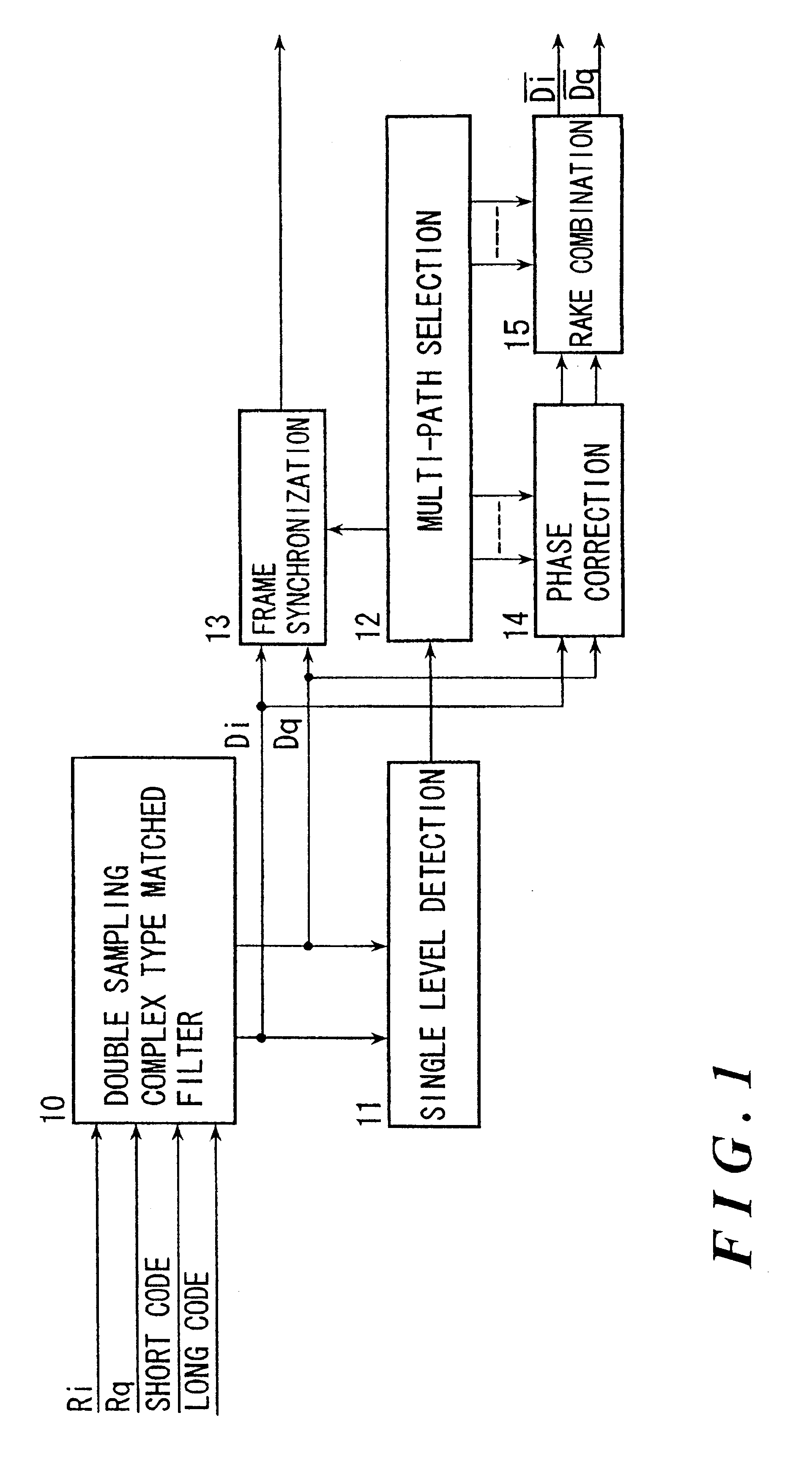
A signal reception apparatus in the spread spectrum communication system requires only a small amount of circuitry and consumes a small amount of electric power. A quadrature detector decomposes received signals into in-phase components and quadrature components, and supplies them to a complex-type matched filter. The complex-type matched filter de-spreads the in-phase components and the quadrature components and sends them to a multi-path selector. The multi-path selector selects, from among the received de-spread signals, multiple paths having high levels of signal electric powers and sends the received signals of the selected paths to multiple phase correction blocks. Analog operation circuits calculate phase errors of the received signals of two successive pilot symbol blocks for each path. An analog operation circuit corrects the phases of the received signals of the information symbol block that has been received between the two successive pilot symbol blocks. A rake combiner synchronously combines the phase-corrected de-spread received signals of each path.
Owner:YOZAN INC +1
Multiplication and accumulation circuit based on radix-4 coding and differential weight storage
ActiveCN110209375AIncrease power consumptionIncrease the areaDigital data processing detailsComputing operations for multiplication/divisionHigh energyComputer science
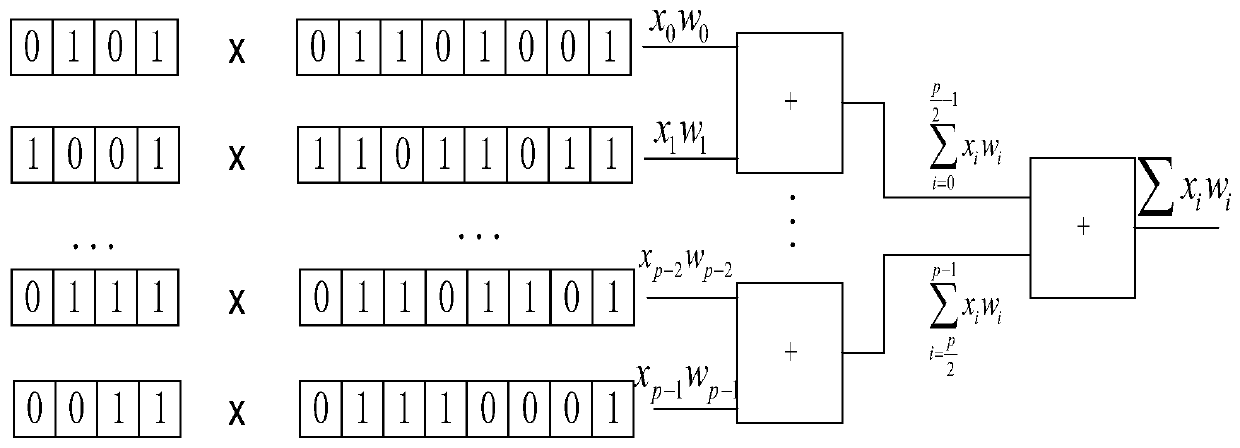
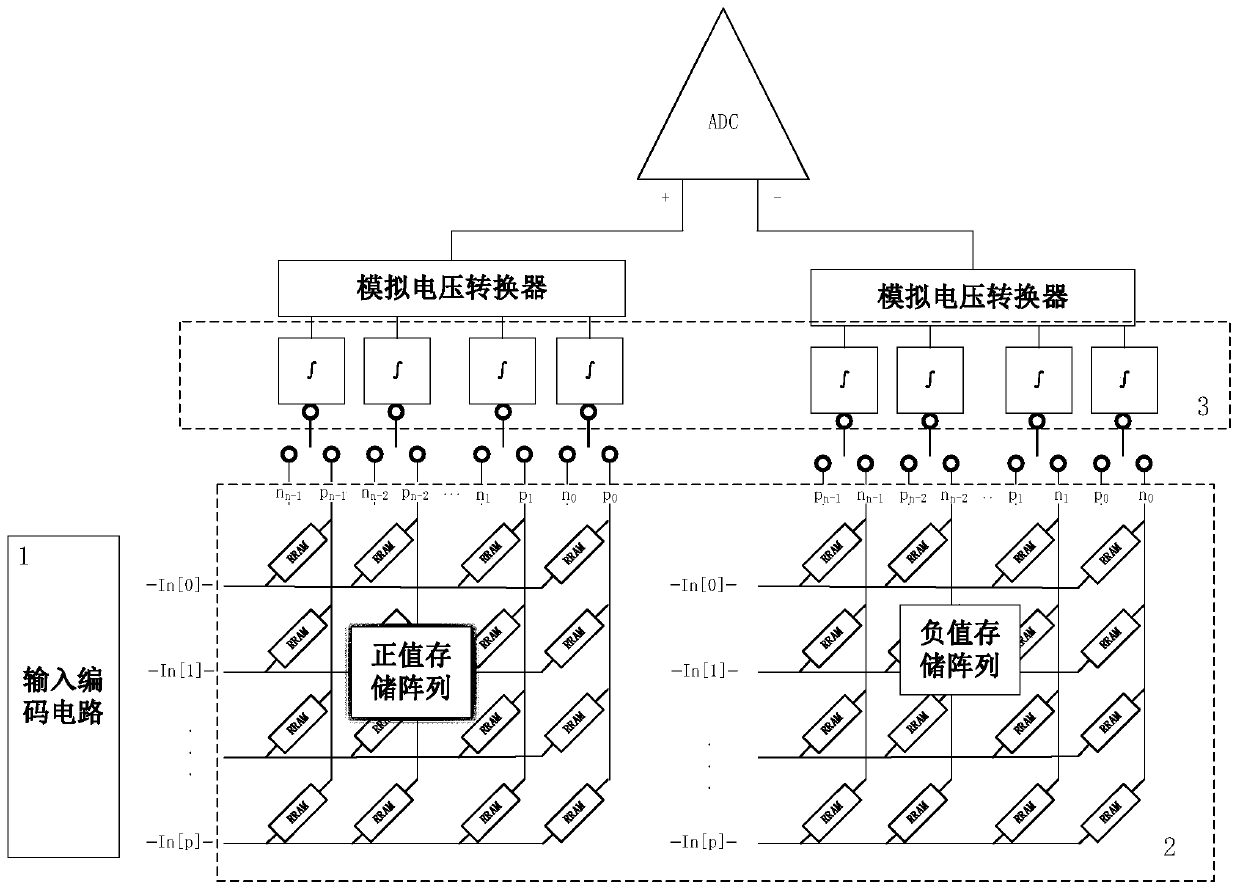
The invention discloses a multiplication and accumulation circuit based on radix-4 coding and differential weight storage. The circuit comprises an input data coding circuit, a differential weight storage circuit, an integral calculation circuit and a differential ADC circuit; the output end of the input data coding circuit is connected with the differential ADC circuit after sequentially passingthrough the differential weight storage circuit and the integral calculation circuit, and the differential ADC circuit outputs a multiplication and accumulation result; original input data is coded bythe input data coding circuit and then multiplied by a weight value stored in the differential weight storage circuit. The positive value and the negative value of each multiplication result are respectively accumulated through the integral calculation circuit, and then the difference of the positive value and the negative value is subjected to analog-to-digital conversion through the differenceADC circuit, so that the final multiplication and accumulation result is obtained. The multiplication and accumulation circuit has the advantages of being small in area, high in calculation speed, lowin power consumption and the like, can be used for neural form chips, and particularly can achieve large-scale parallel calculation in edge calculation equipment with high energy consumption requirements.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
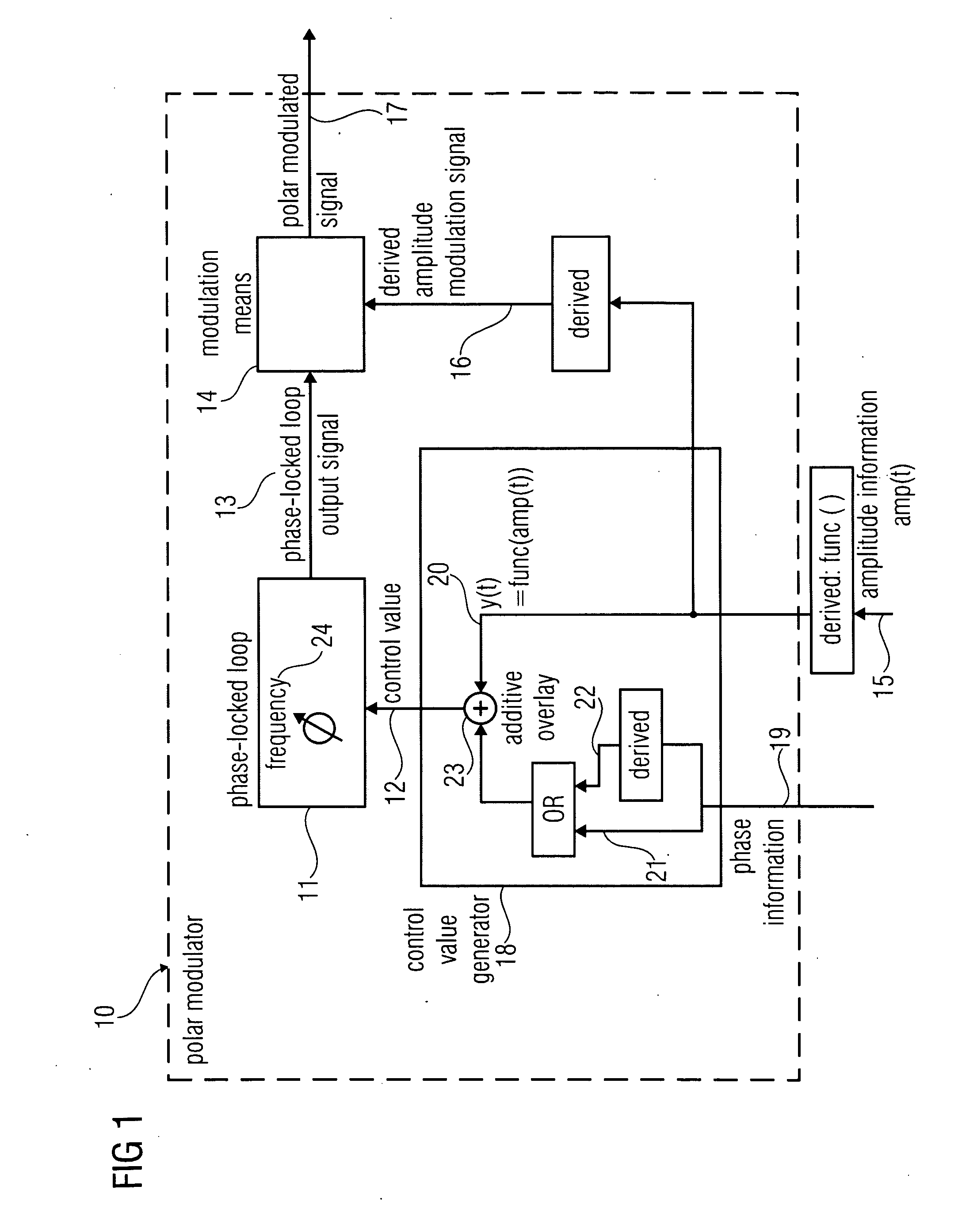
Polar Modulator and Method for Generating a Polar-Modulated Signal
ActiveUS20090275359A1Resonant long antennasComputations using contact-making devicesPolar modulationPhase-locked loop
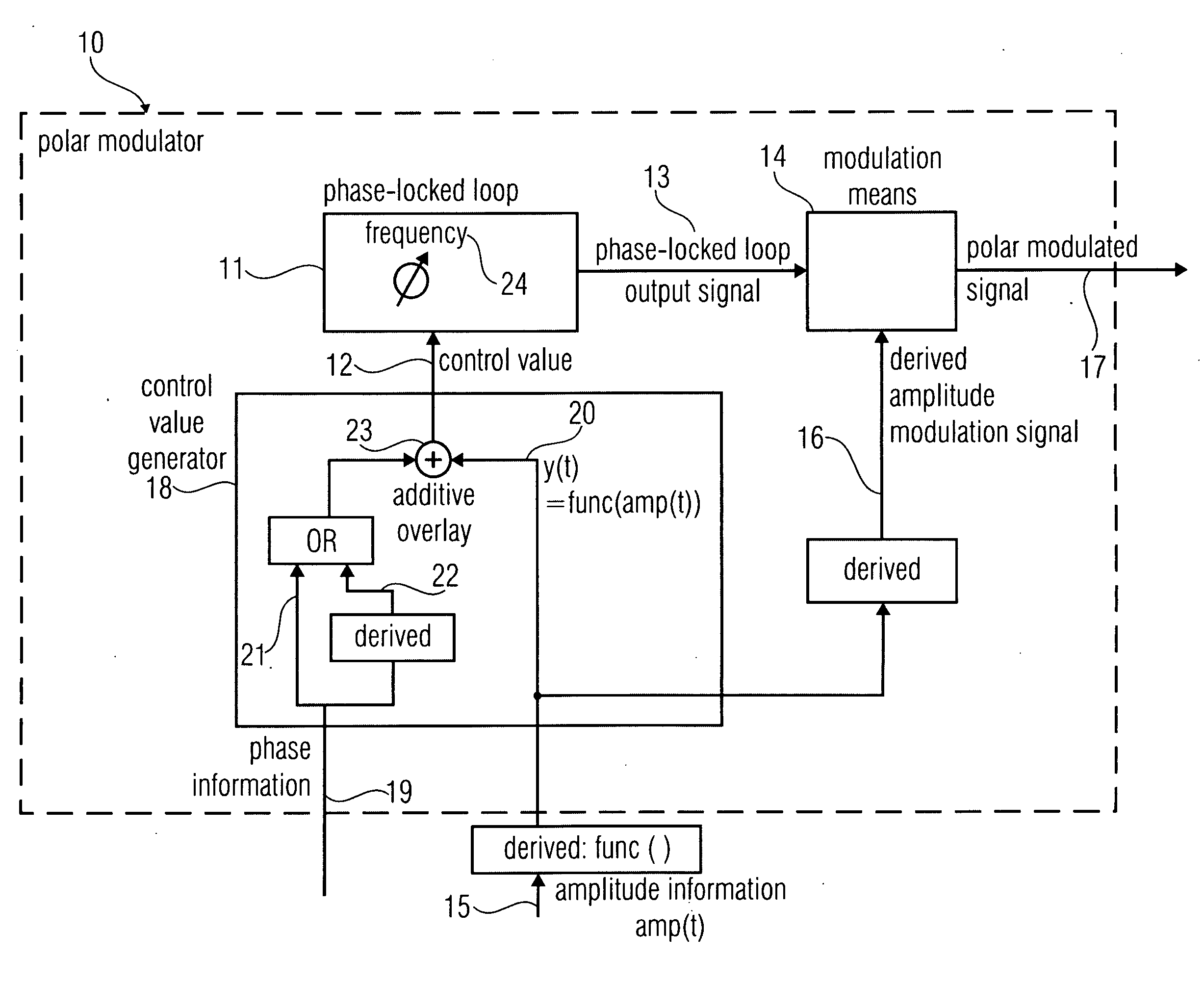
A polar modulator for generating a polar-modulated signal based on amplitude information and phase information includes a phase-locked loop which is implemented to enable a setting of a frequency depending on a control value to obtain a phase-locked loop output signal. The polar modulator further includes a modulation means which is implemented to combine an amplitude modulation signal derived from the amplitude information with the phase-locked loop output signal to generate the polar-modulated signal. The polar modulator further includes a control value generator which is implemented to high-pass filter an amplitude signal derived from the amplitude information, to obtain a high-pass filtered amplitude signal, wherein the control value generator is implemented to combine the high-pass filtered amplitude signal with a phase signal based on the phase information to generate the control value signal representing the control value.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Electronic circuit for determination of distances between reference and data points
InactiveUS6014685AReduced Power RequirementsIncrease speedComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for logarithmic/exponential functionsEngineeringEuclidean distance
PCT No. PCT / GB95 / 00741 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 12, 1996 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 12, 1996 PCT Filed Mar. 31, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO95 / 30963 PCT Pub. Date Nov. 16, 1995An electronic circuit for Euclidean distance determination includes two floating gate transistors (M1, M2) connected in parallel. Voltages representing a reference point and its complement are applied to input lines (22, 24) and corresponding charges become stored on the transistors' floating gates (F1, F2). Voltages representing a data point and its complement are input to control gates (G1, G2). The transistors (M1, M2) produce a combined output current which is a quadratic or exponential function of the distance between the data and reference points according to whether the transistors are above or below threshold. The circuit (10 ) includes a diode-connected load device (M3) for deriving the square root of the output current, which is proportional to Euclidean distance when the transistors are operated above threshold. Refresh means (M44, M45) may be provided for resetting reference points. An array of circuits of the invention is employed for determination of distances between vector quantities.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
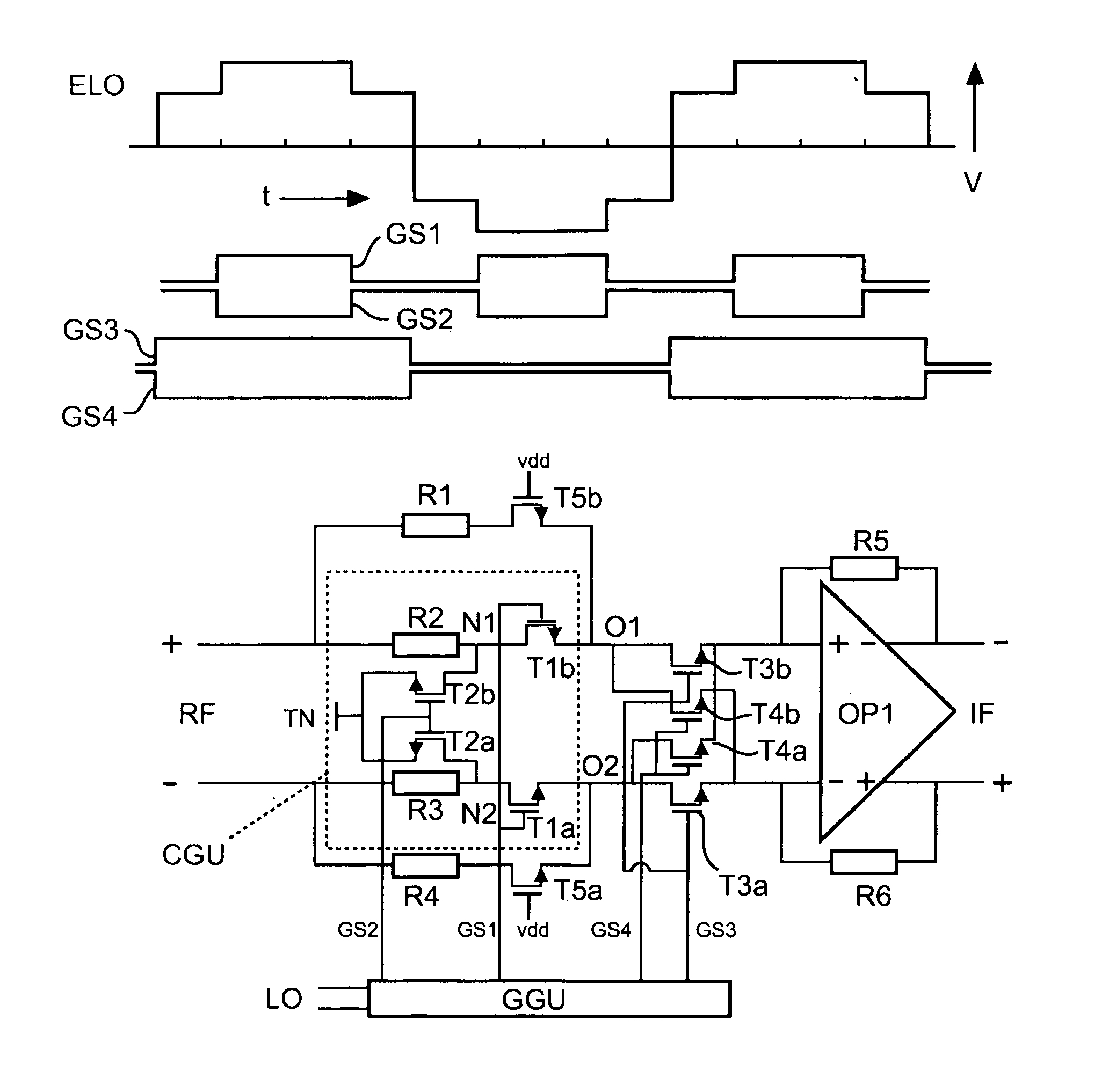
Harmonic rejection mixer unit and method for performing a harmonic rejection mixing
ActiveUS20100283526A1Computations using contact-making devicesComputing operations for addition/subtractionLocal oscillator signalControl signal
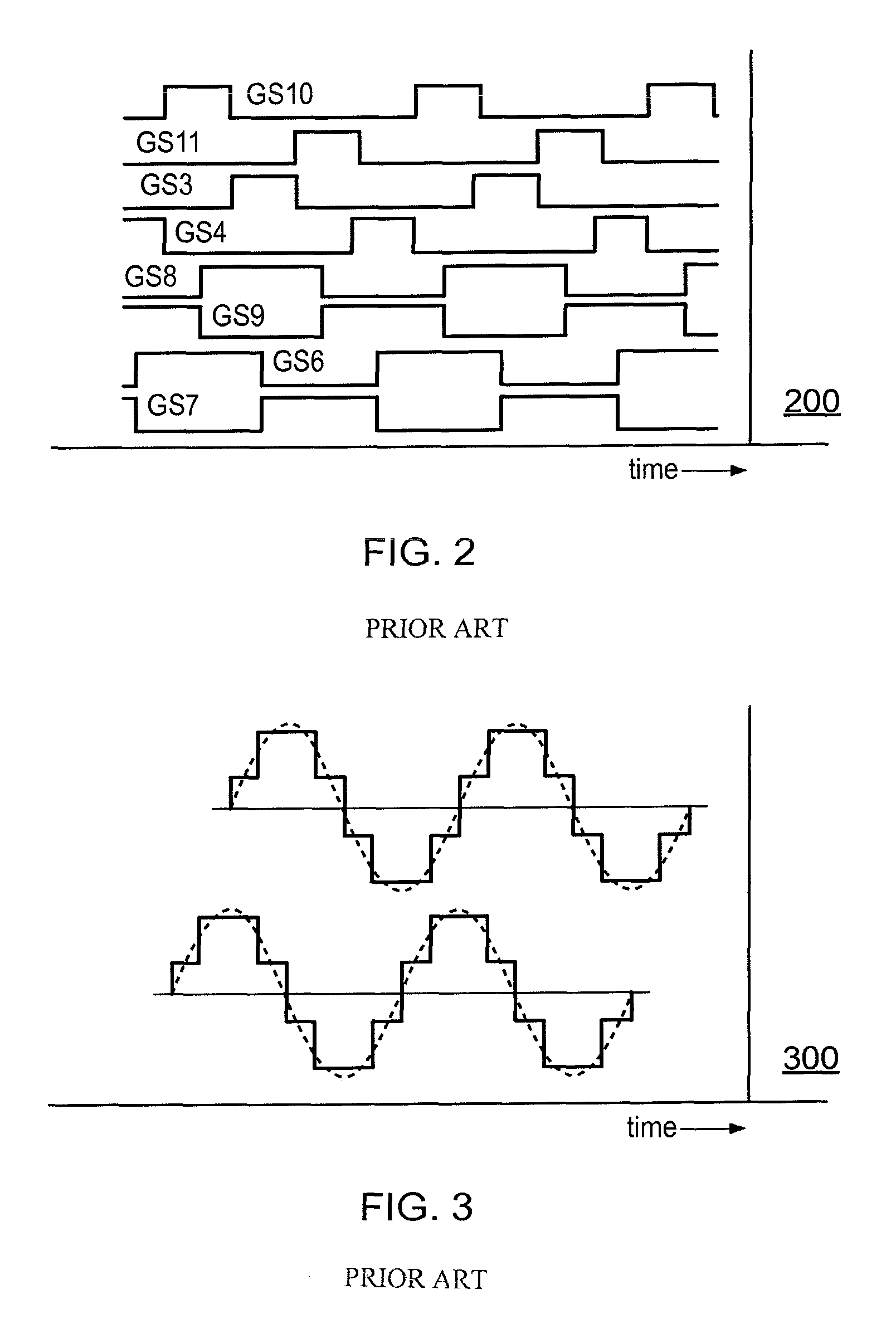
A harmonic rejection mixer unit is provided which comprises an input (RF), at least one harmonic rejection unit (HRU) with at least two transistor units (T3a, T3b; T4a, T4b) for multiplying an input signal from the input (RF) with a multiplication signal (ELO). The harmonic rejection mixer unit furthermore comprises a transistor control signal generating unit (GGU) for generating transistor control signals (GS1-GS4) for the at least two transistor units (T3a, T3b; T4a, T4b) of the at least one harmonic rejection unit (HRU) by deriving the transistor control signals (GS1-GS4) from a local oscillator signal (LO). The transistor control signals (GS3, GS4) for the at least two transistor units (T3a, T3b; T4a, T4b) are generated with a duty cycle of <50% and are generated such that the shape of the multiplication signal ELO) is achieved by a constructive summation of the output signals from the transistor units (T3a, T3b; T4a, T4b). The transistor control signals (GS1-GS4) are generated such that only a summation of output signals from the transistor units with the same sign or with zero is performed.
Owner:NXP BV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com