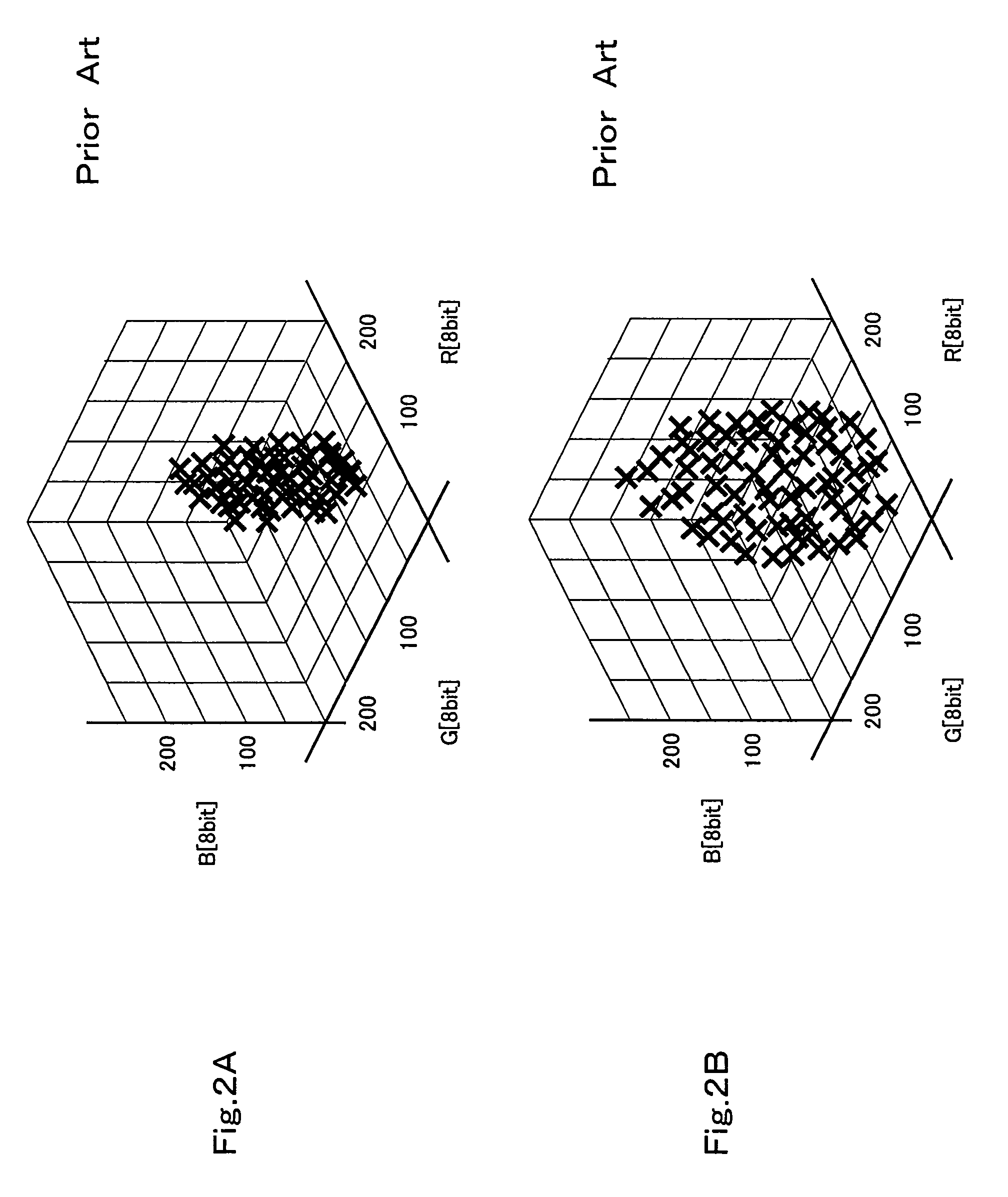
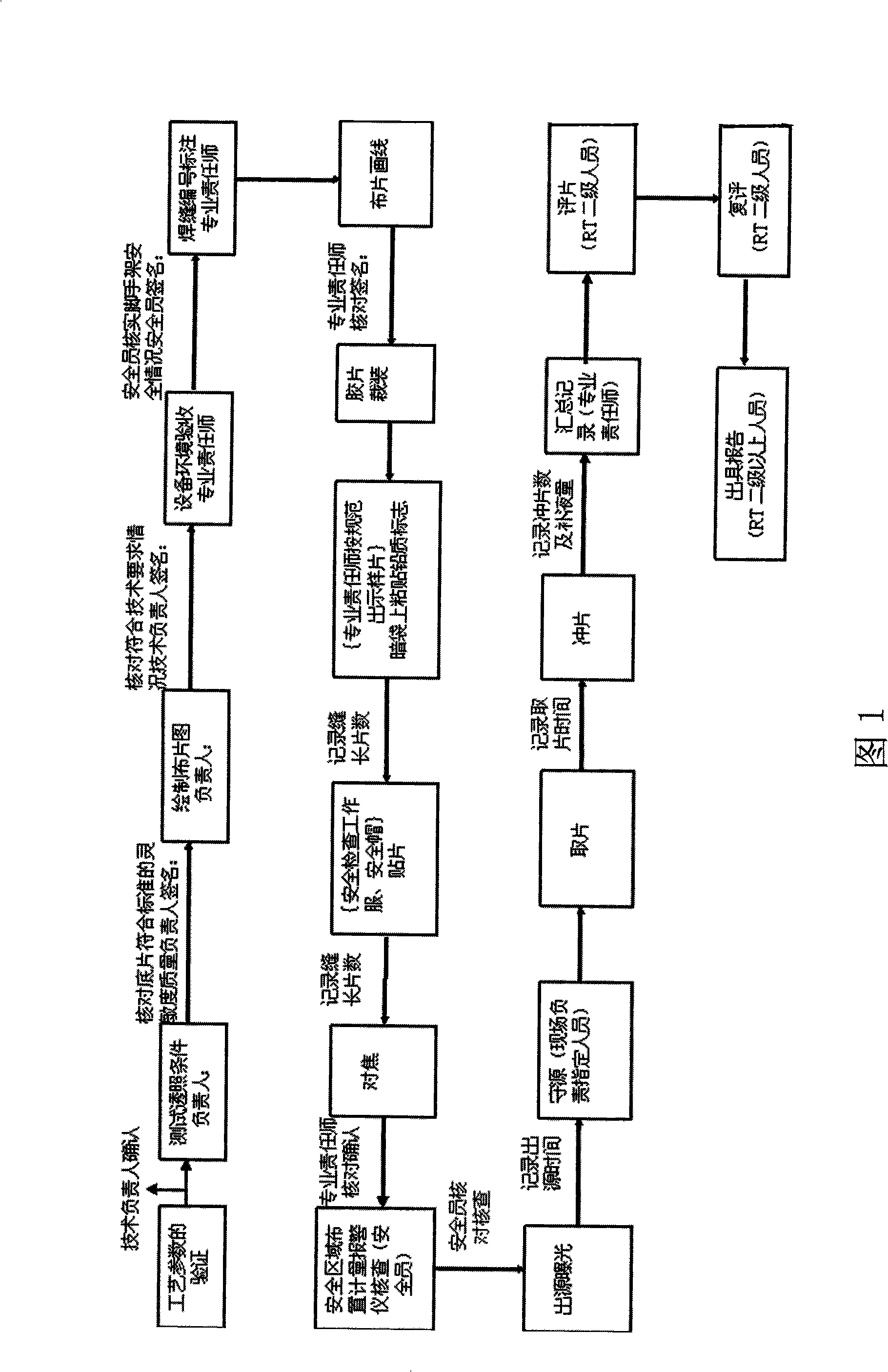
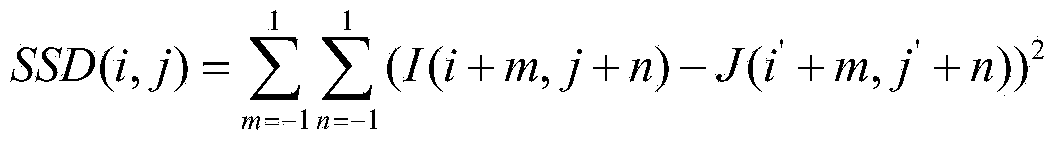Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58 results about "Unsharpness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
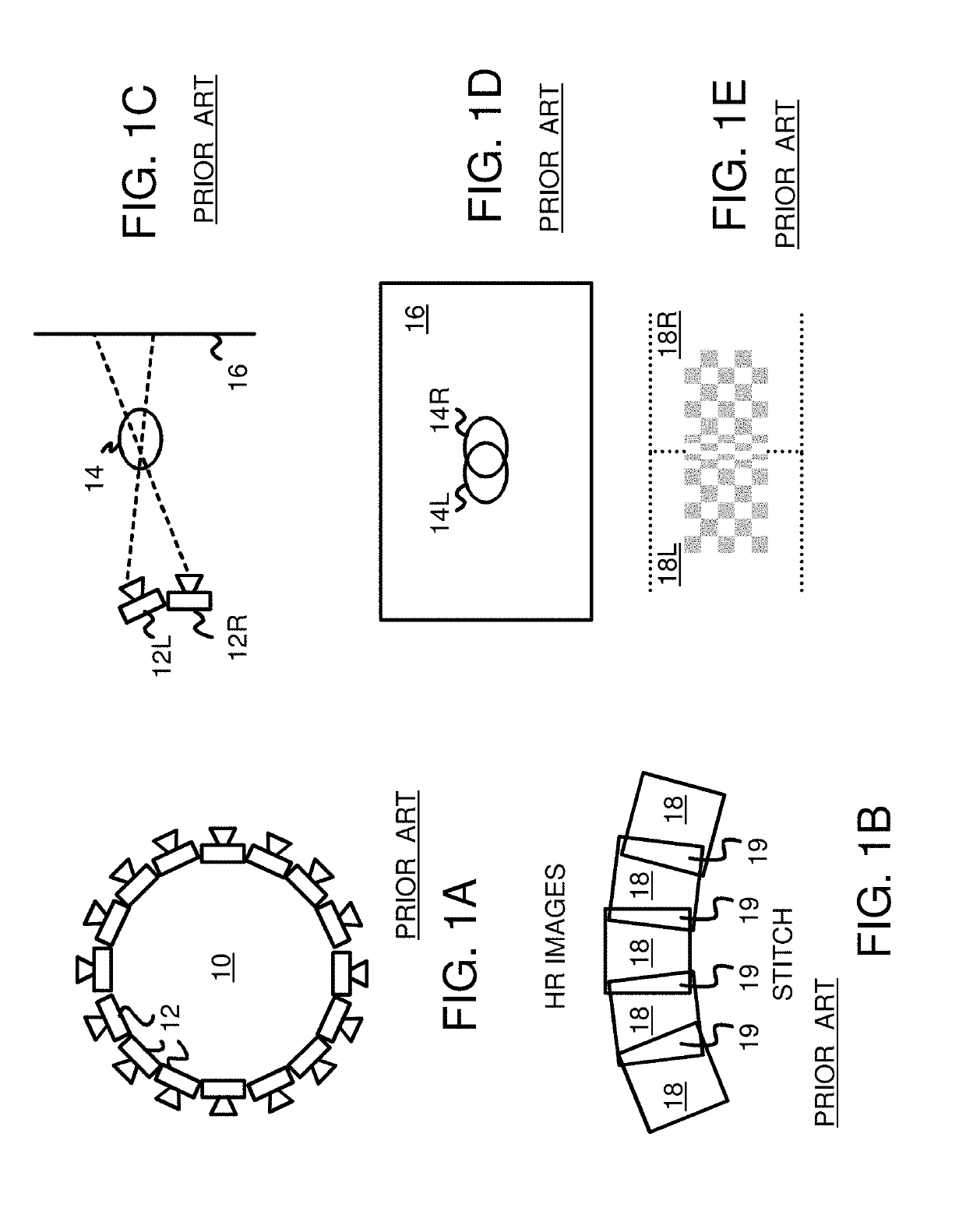
Unsharpness is the loss of spatial resolution in a radiographic image. There are generally considered to be three types of unsharpness: geometric unsharpness, motion unsharpness and photographic or system unsharpness.
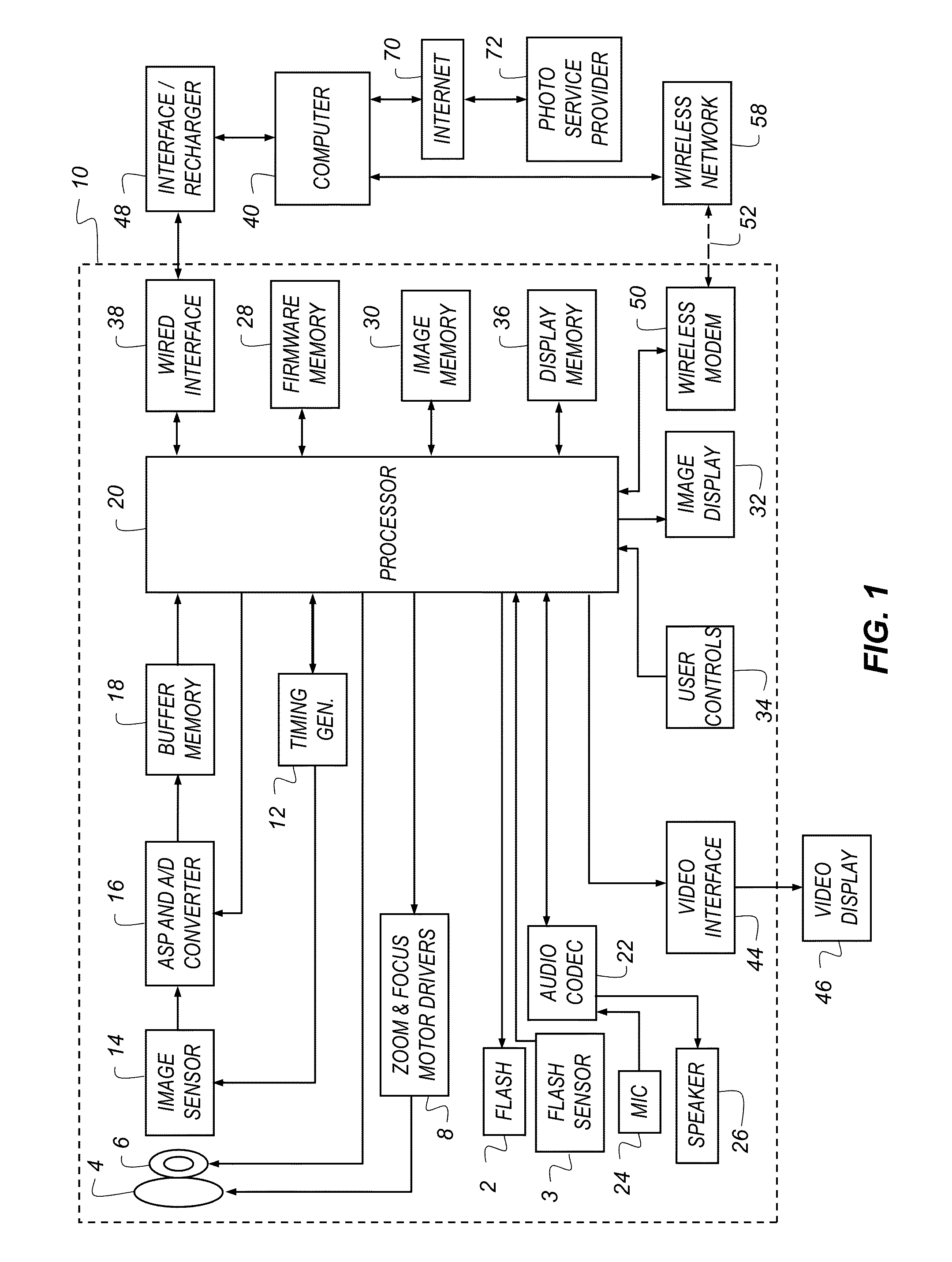
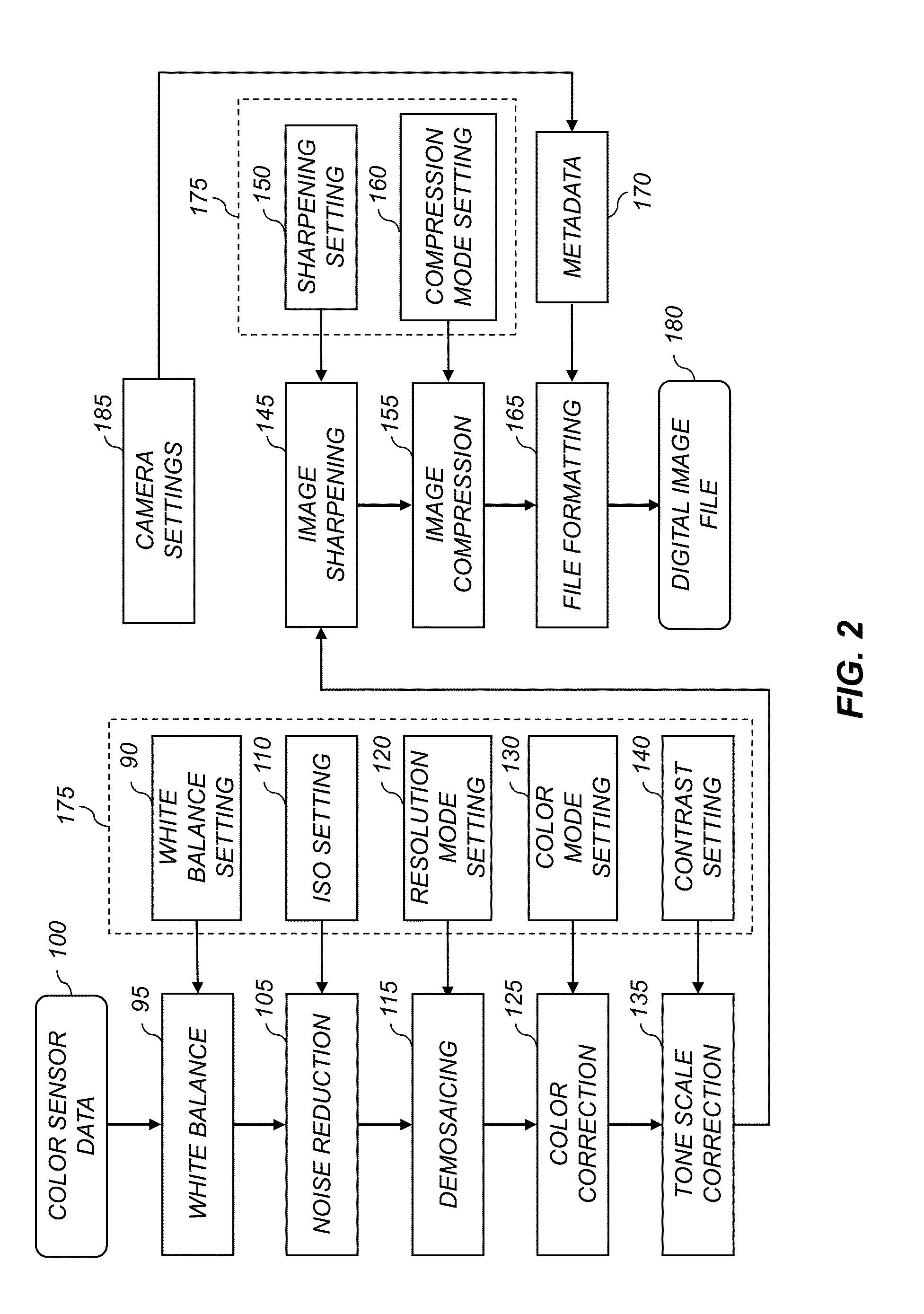
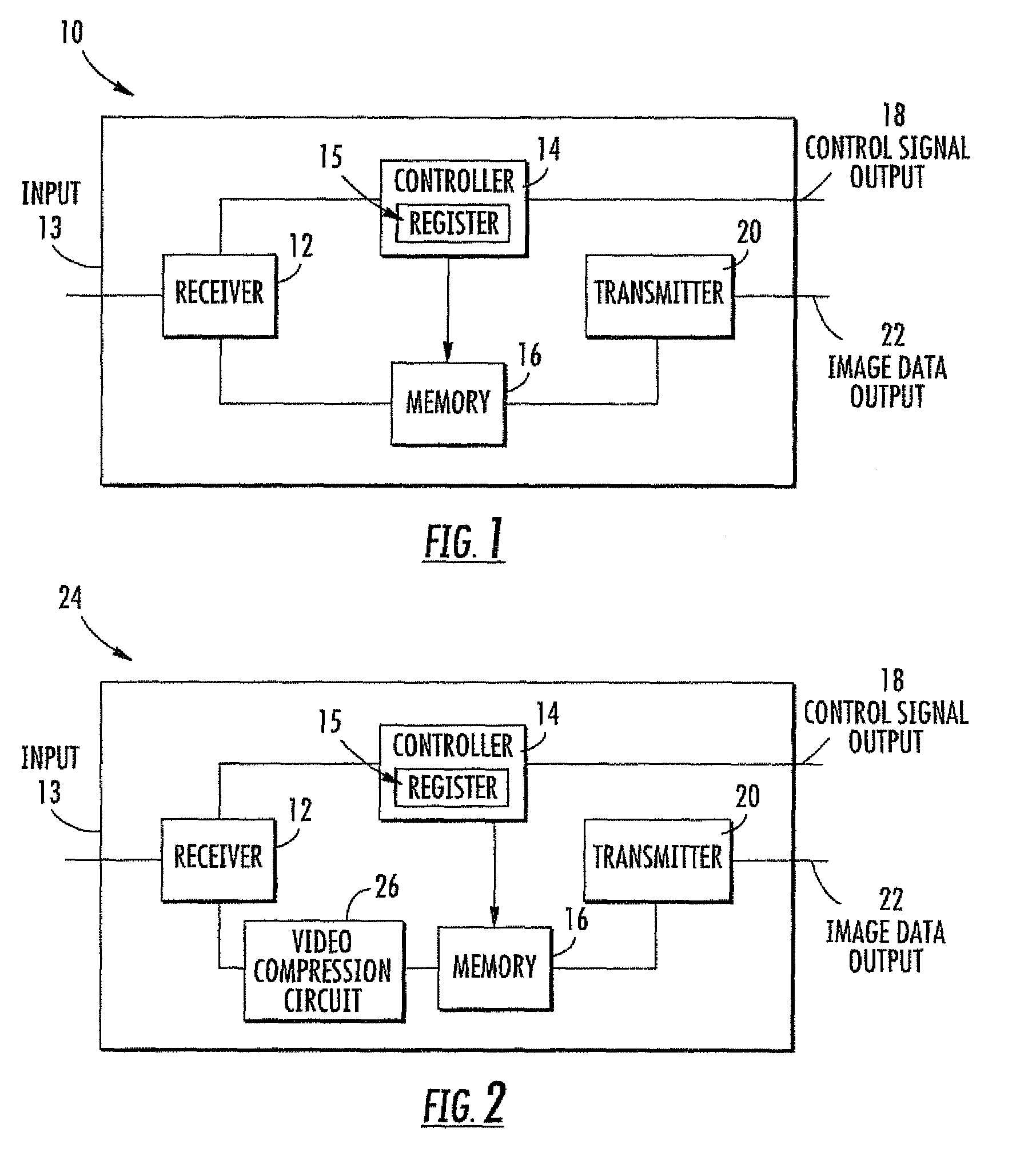
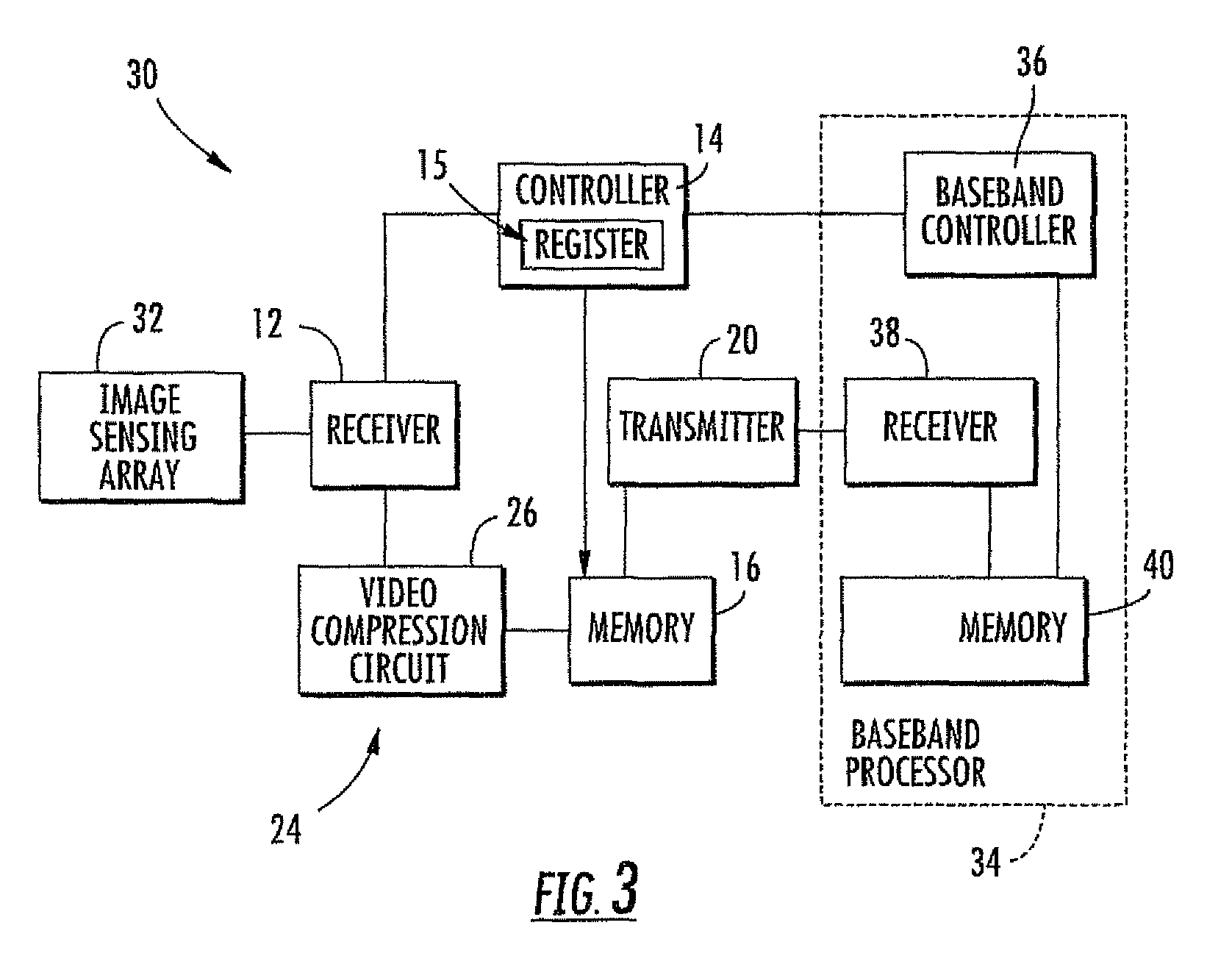
Adjusting the sharpness of a digital image
InactiveUS20140086486A1Enhance the imageAutomatic controlImage enhancementImage analysisTyping ClassificationImage segmentation
The sharpness of a digital image is adjusted according to defined aim subject and background sharpness levels. An image segmentation process is used to segment an input digital image into a subject region and a background region. The subject and background regions are analyzed to determine corresponding subject and background sharpness levels. An enhanced digital image is formed wherein the sharpness of the subject region is adjusted responsive to the subject sharpness level and the aim subject sharpness level, and the sharpness of the background region is adjusted responsive to the background sharpness level and the aim background sharpness level. In some embodiments, the input digital image is analyzed to determined a scene type classification and the aim subject and background sharpness levels are defined in accordance with the determined scene type classification.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
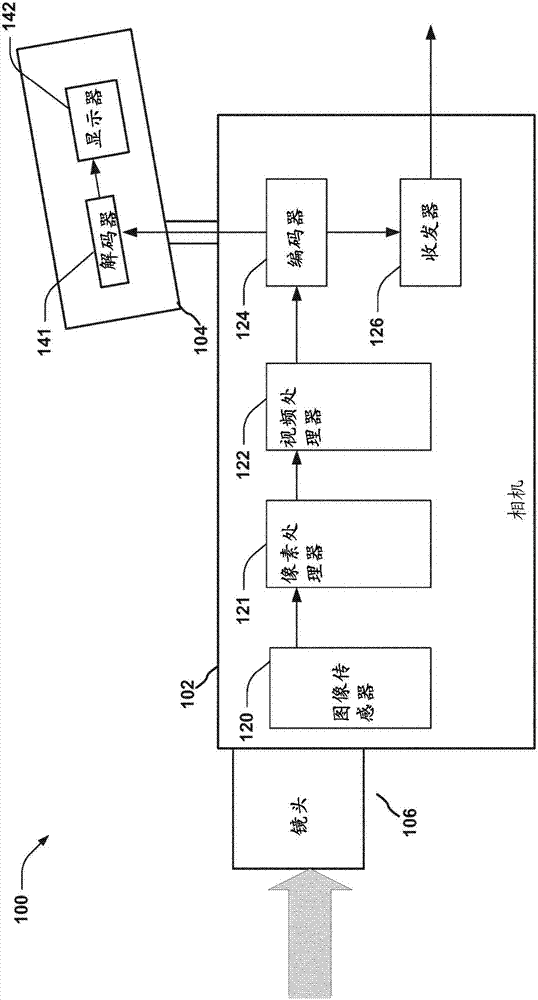
Image capture unit in a surgical instrument
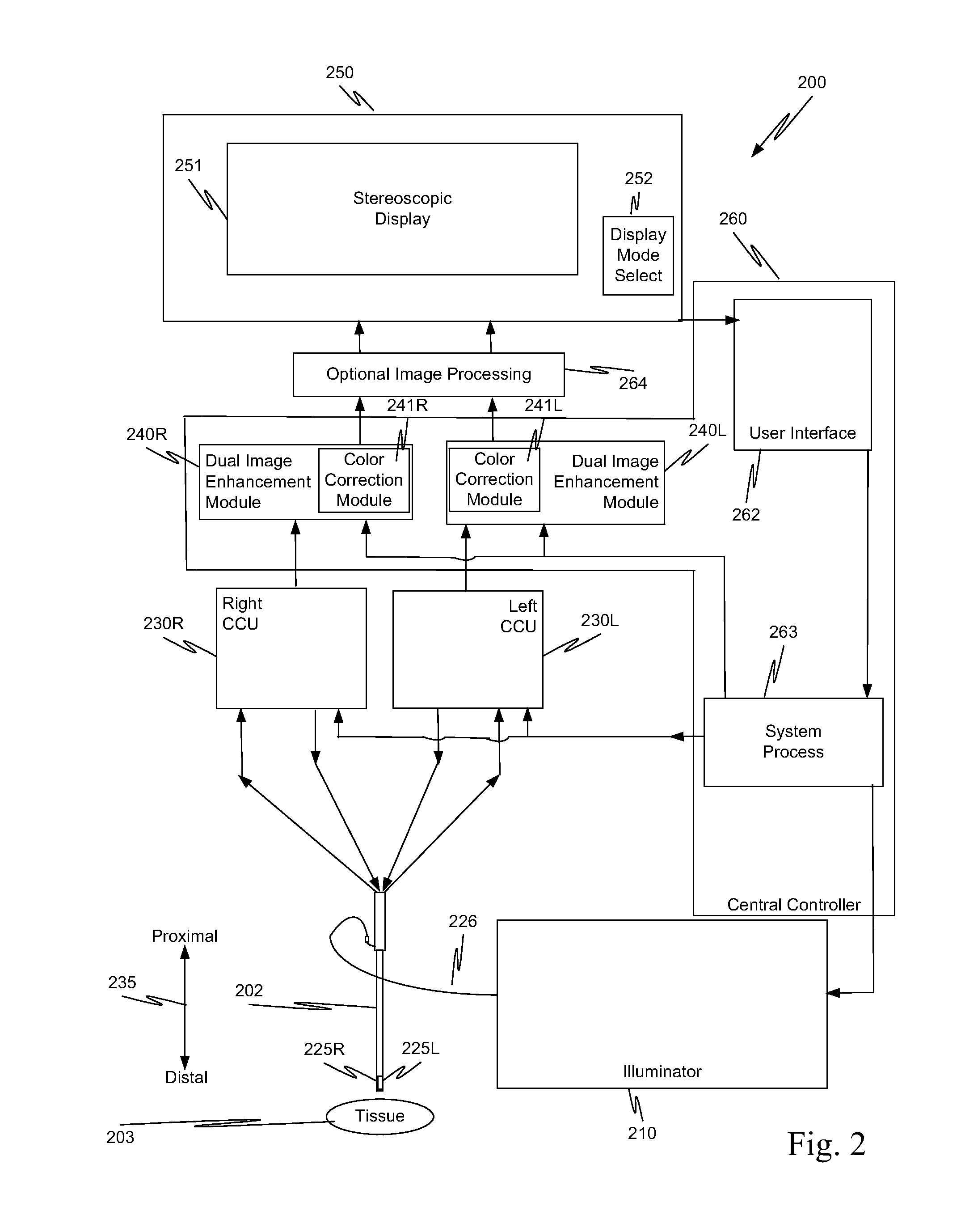
ActiveUS8672838B2Eliminates the need for calibration of lens artifactsOvercomes shortcomingSurgeryEndoscopesImage resolutionDepth of field
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
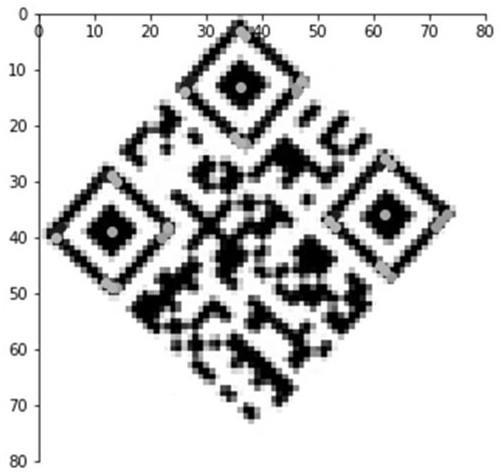
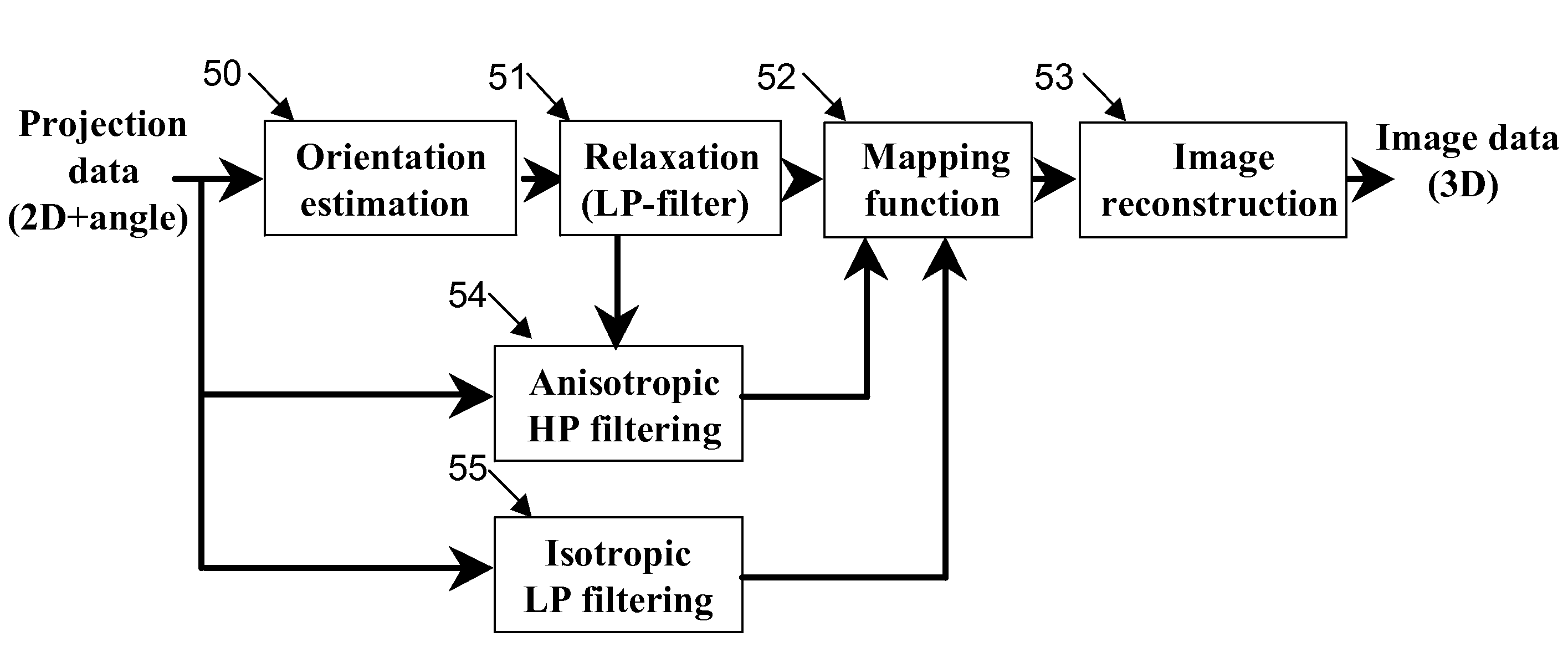
Adaptive anisotropic filtering of projection data for computed tomography
ActiveUS20080069294A1Reduce high frequency noiseReduce radiation doseImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionLow-pass filterImaging quality
CT imaging is enhanced by adaptively filtering x-ray attenuation data prior to image reconstruction. Detected x-ray projection data are adaptively and anisotropically filtered based on the locally estimated orientation of structures within the projection data from an object being imaged at a plurality of rotation positions. The detected x-ray data are uniformly low pass filtered to preserve the local mean values in the data, while the high pass filtering is controlled based on the estimated orientations. The resulting filtered data provide projection data with smoothing along the structures while maintaining sharpness along edges. Image noise and noise induced streak artifacts are reduced without increased blurring along edges in the reconstructed images. The enhanced image allows reduced x-ray dose while maintaining image quality.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
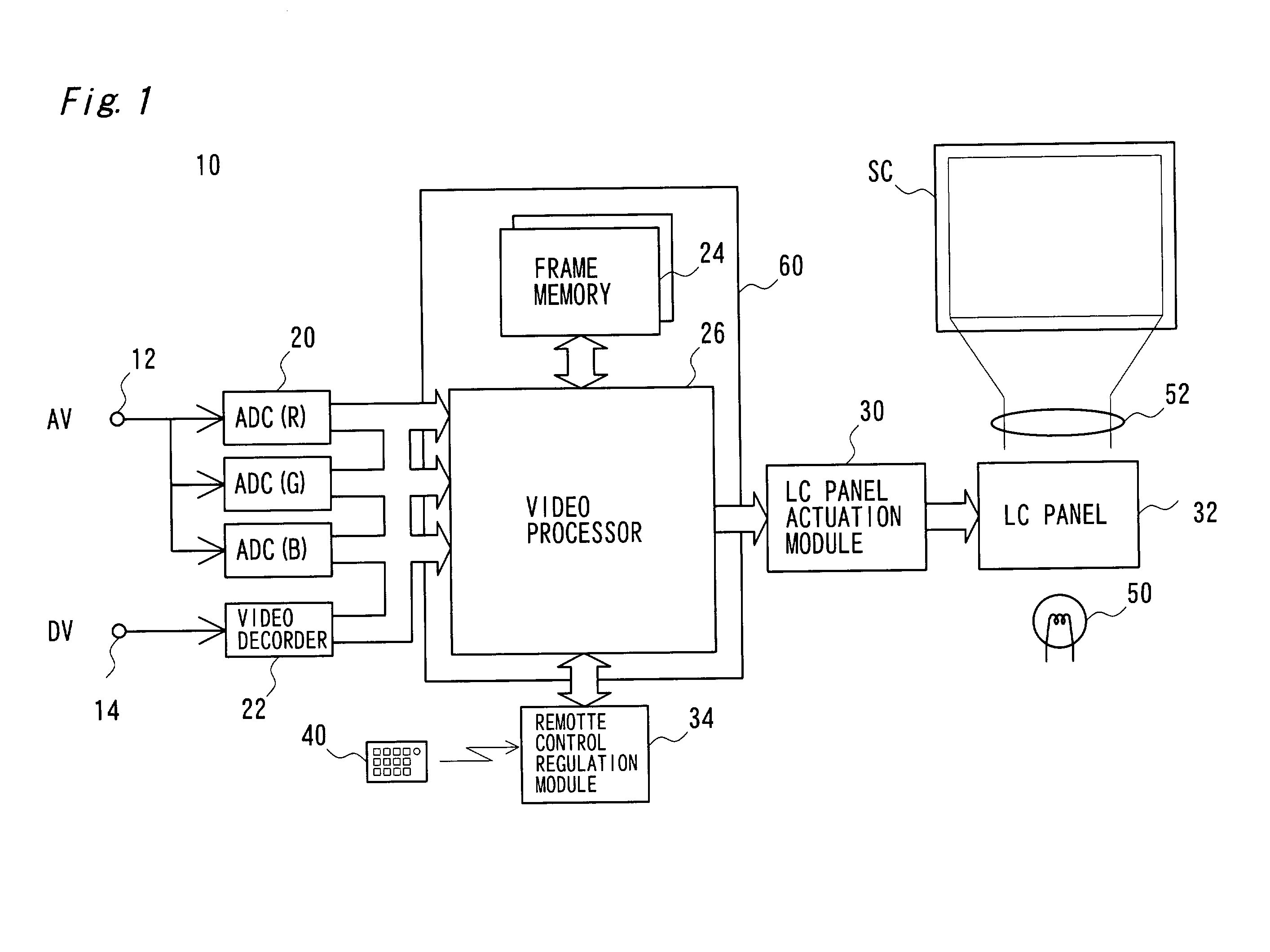
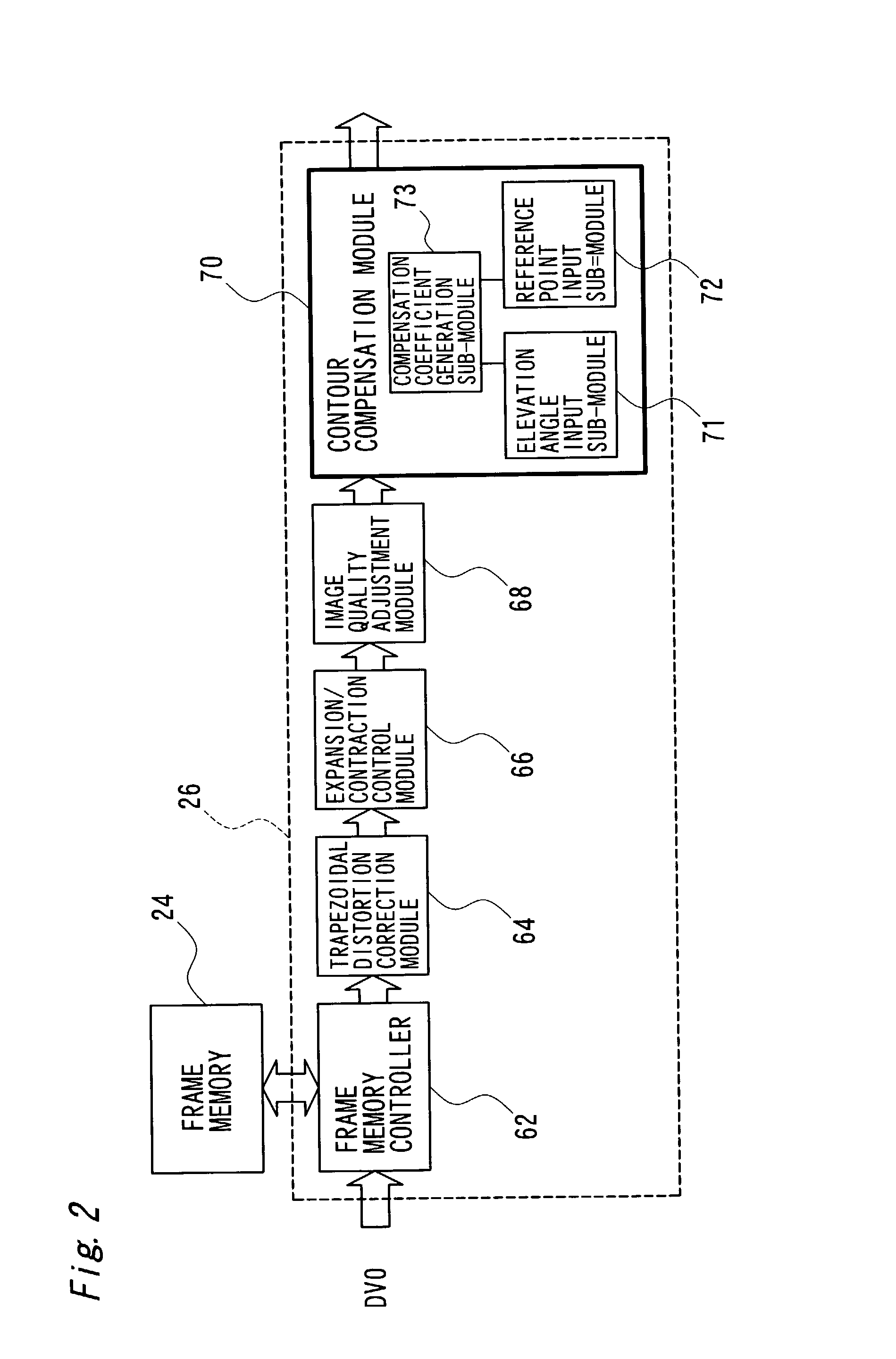
Image processing technique for images projected by projector
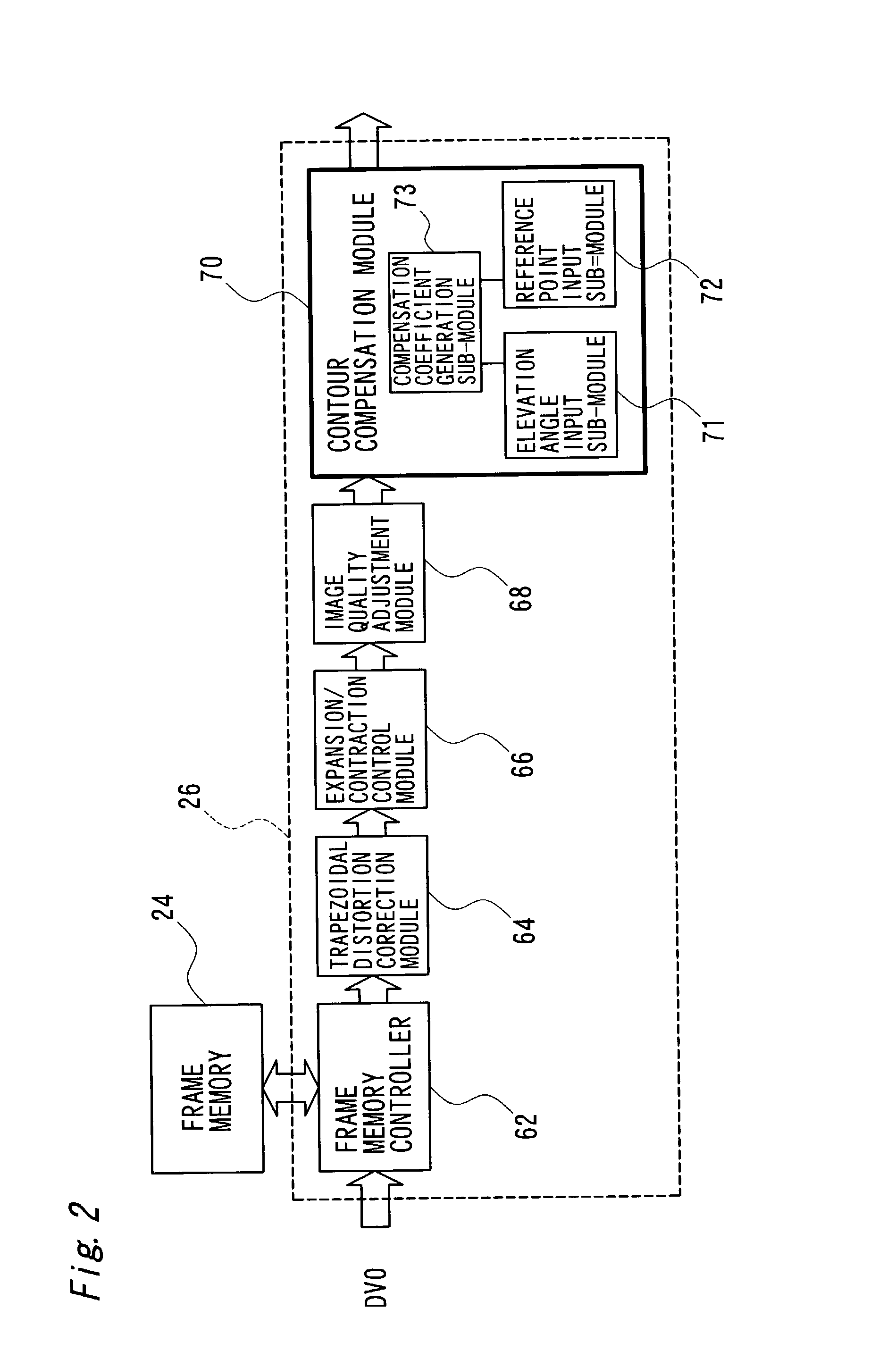
ActiveUS7003172B2Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationTelevision system detailsImage enhancementElevation angleImaging processing
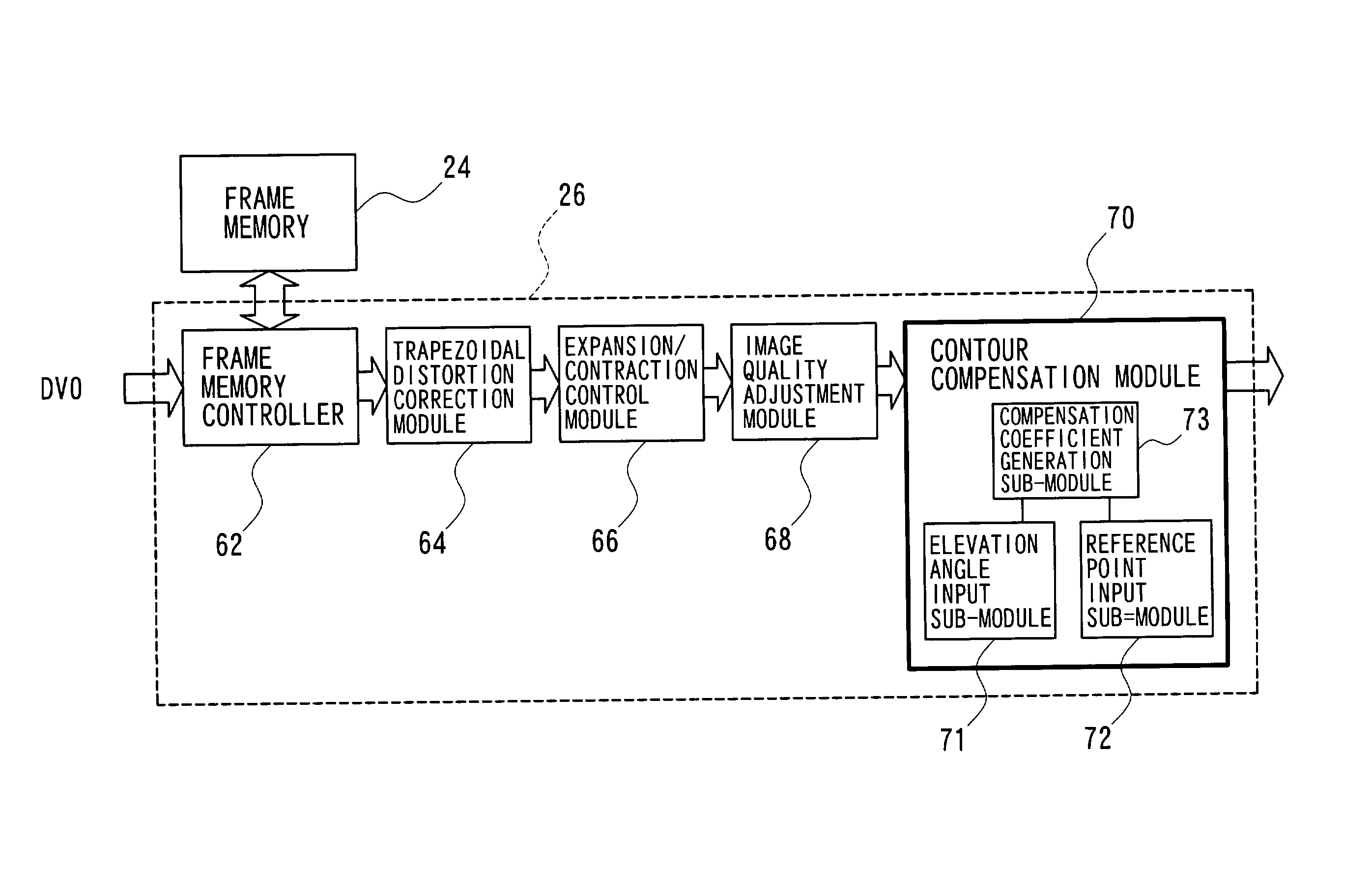
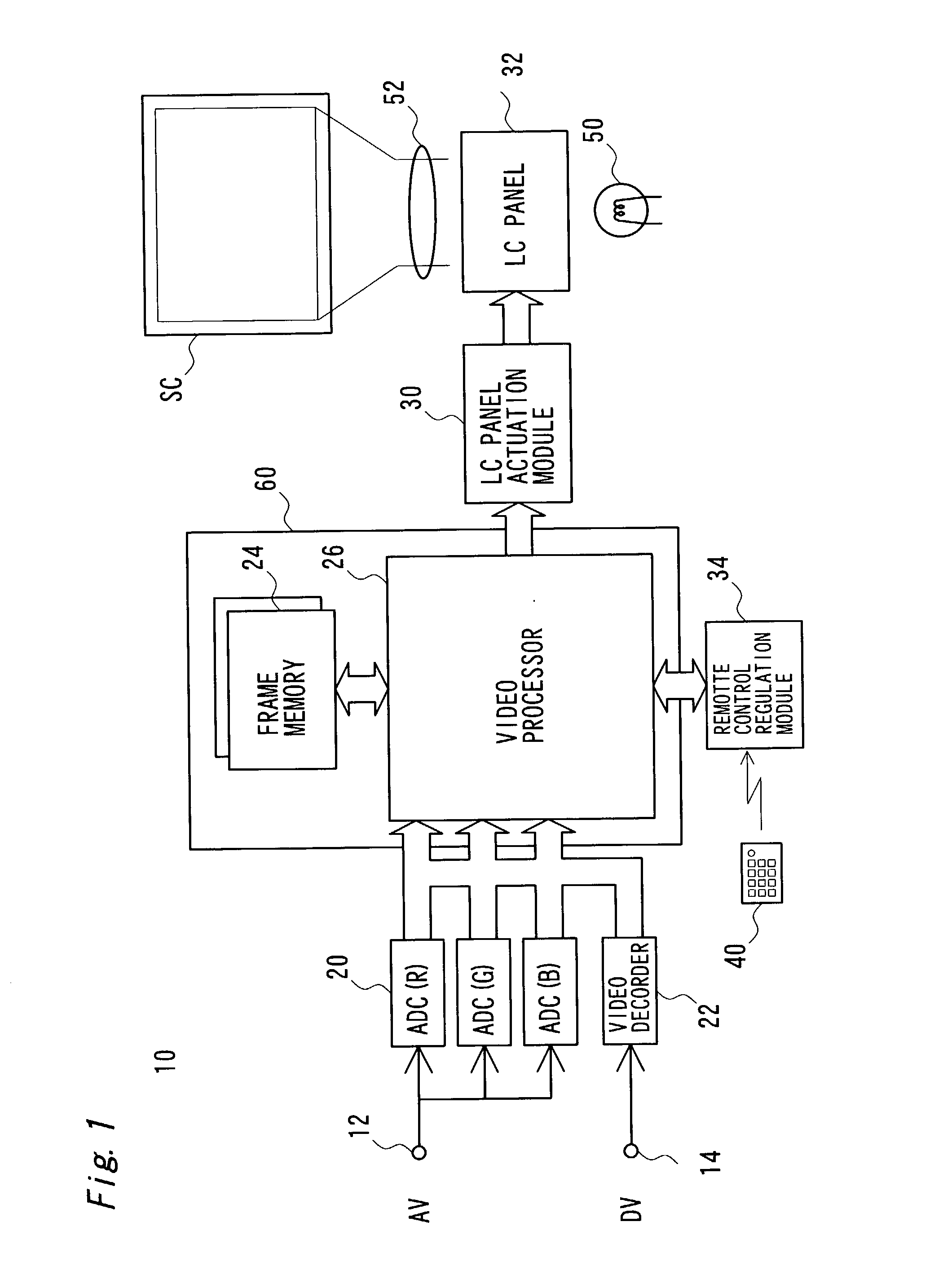
The technique of the present invention carries out specific image processing that emphasizes articulation of display with a varying degree of emphasis for respective sites of an image projected by a projector. A typical example of such image processing is sharpness adjustment. The degree of emphasis in sharpness adjustment at each site is specified, based on an elevation angle of the projector and a focalized position of the projected image. The technique of the invention thus readily prevents deterioration of the image quality due to out-of-focus state of the projected image.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD +1
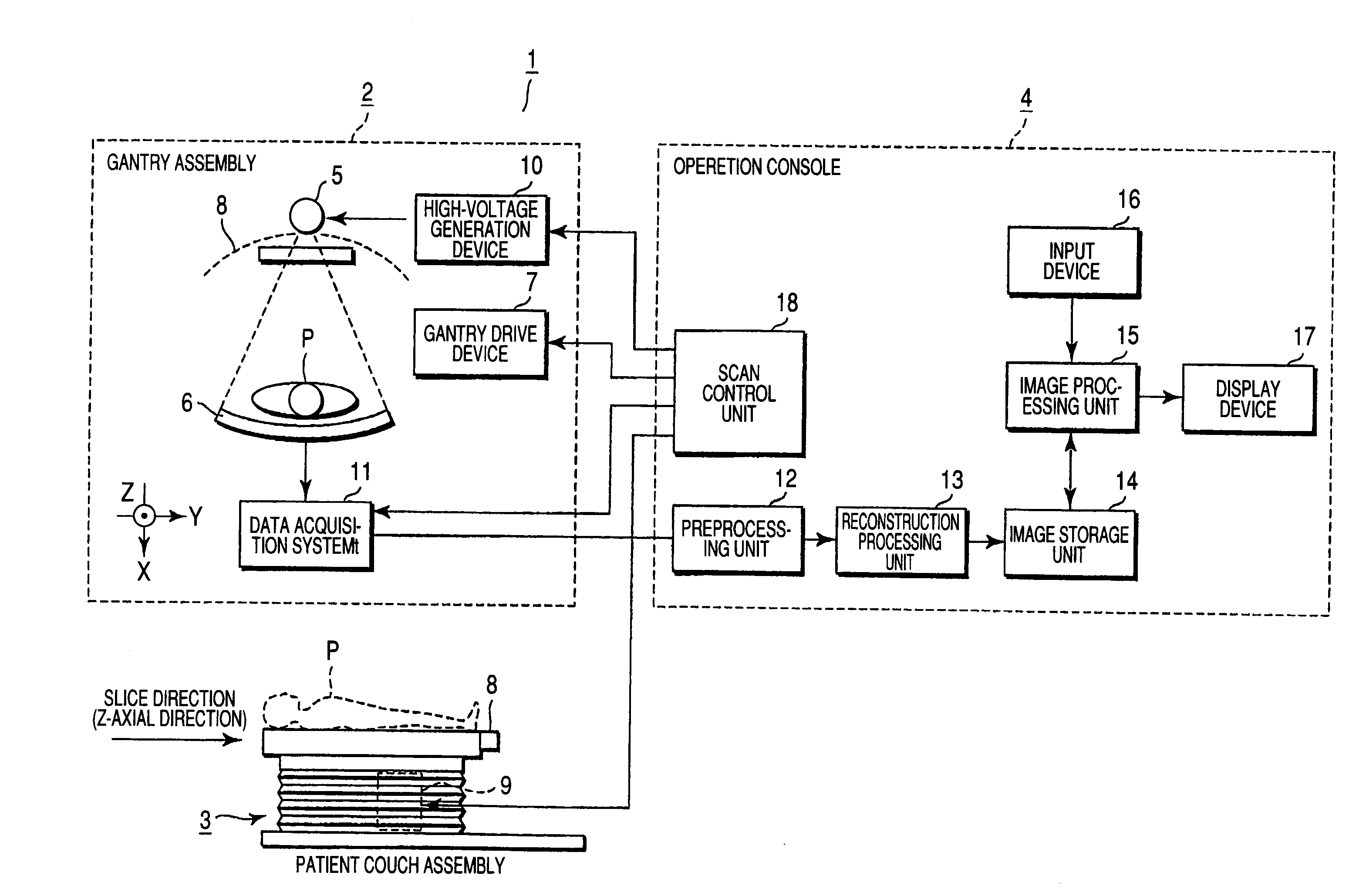
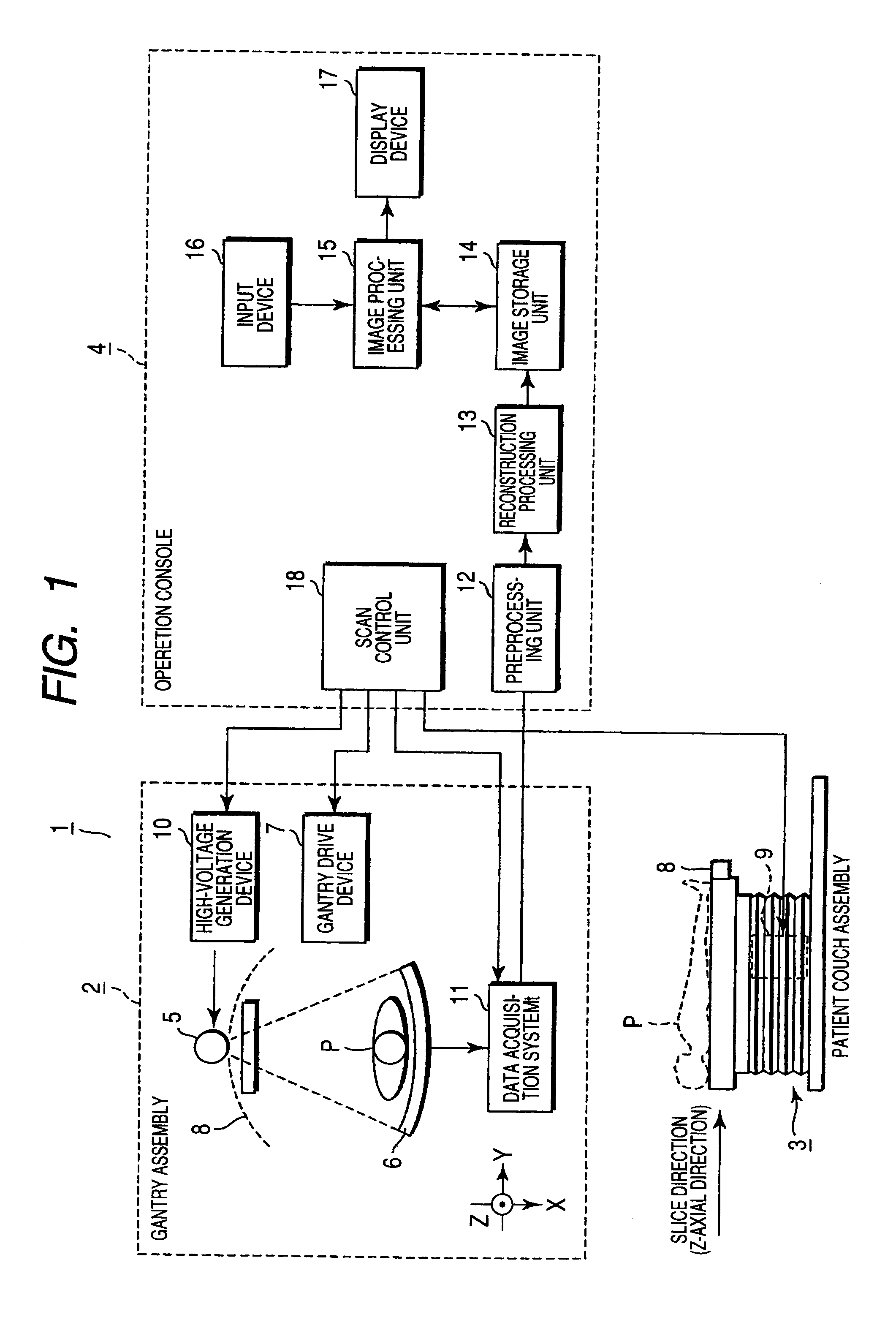
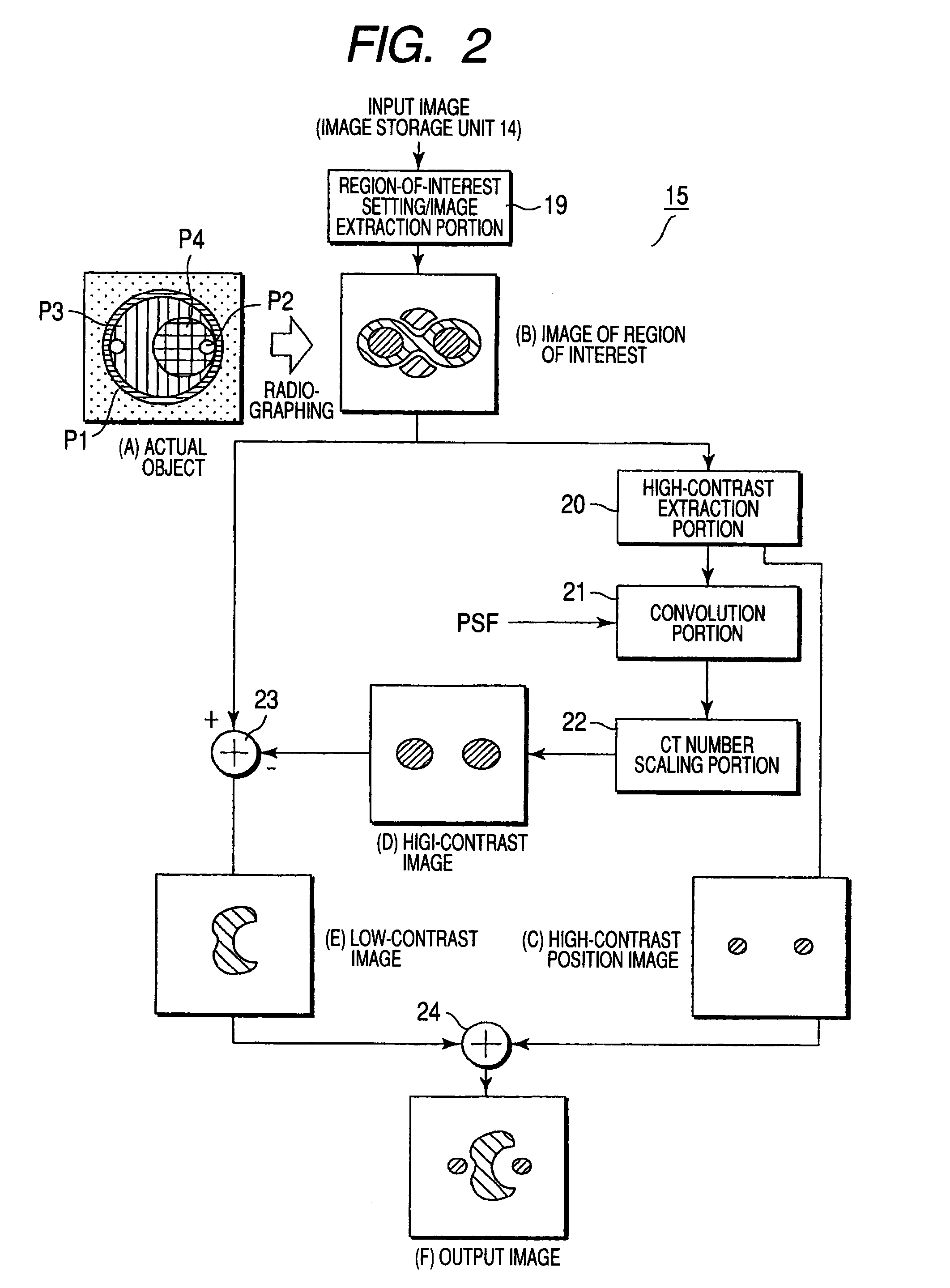
X-ray CT apparatus and image processing apparatus
InactiveUS20070230653A1Reduce unclearReduction factorImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionAttenuation coefficientImaging processing
An X-ray CT apparatus includes a unit which extracts a high-contrast region of comparatively high X-ray attenuation coefficient from an image, units which generate an unsharp image concerning the high-contrast region, on the basis of the position of the extracted high-contrast region and a point spread function peculiar to the apparatus, and a unit which subtracts the unsharp image from the original image in order to generate a low-contrast image concerning a low-contrast region of comparatively low X-ray attenuation coefficient.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
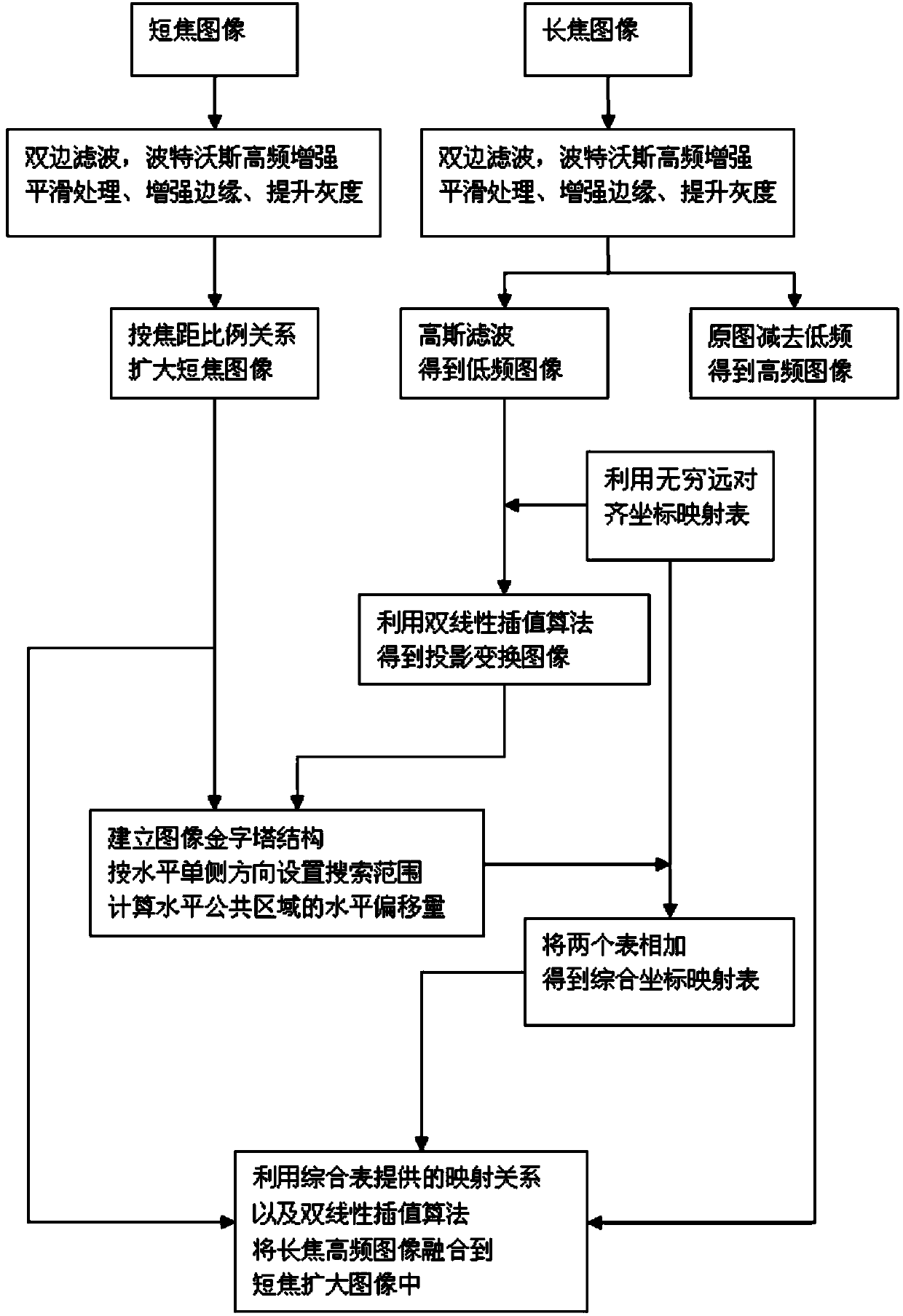
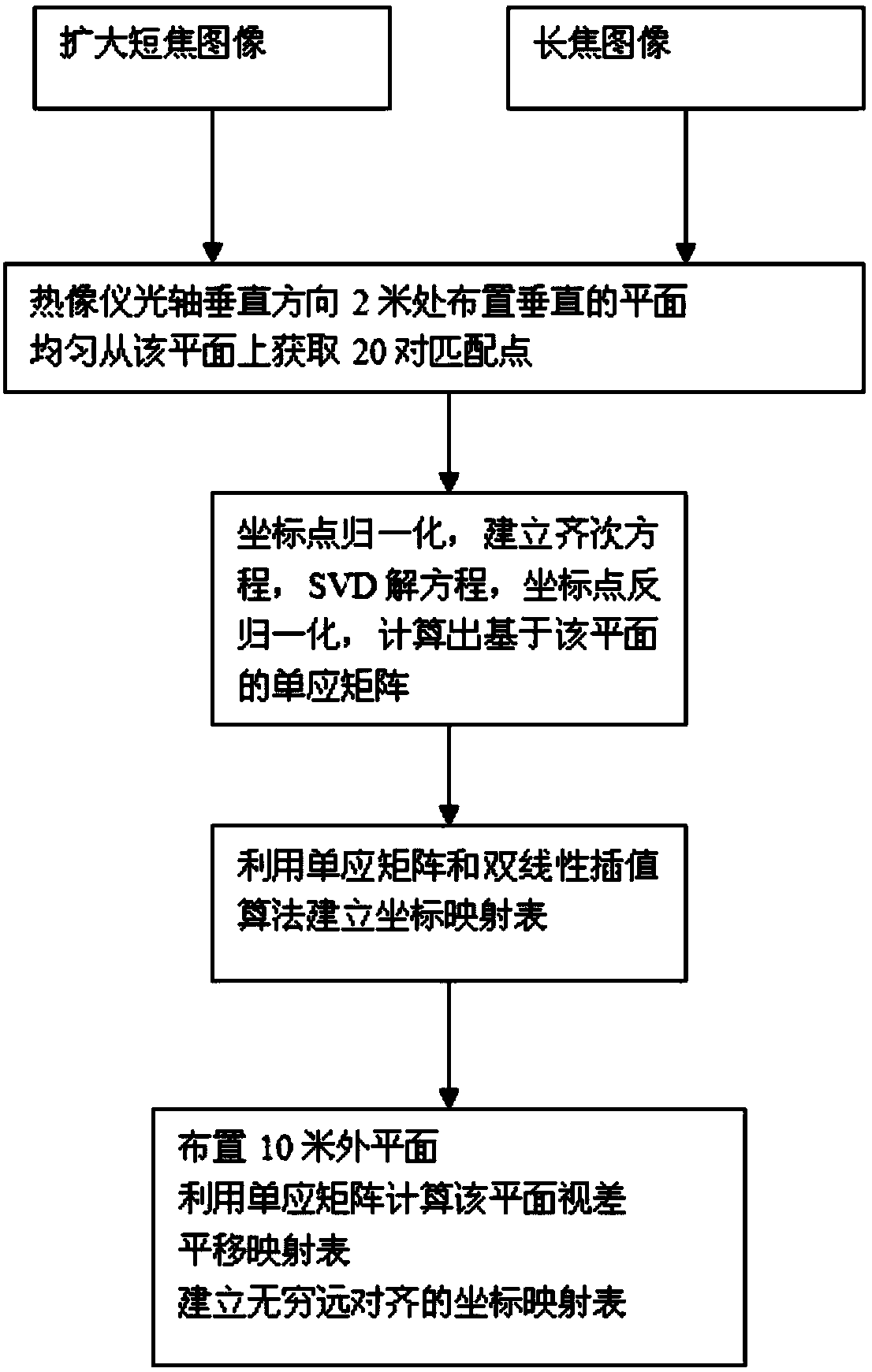
Infrared thermal image resolution enhancing method
The invention discloses an infrared thermal image resolution enhancing method, which comprises the following steps of: A, acquiring infrared thermal images and performing enhancing contrast ratio pre-treatment, wherein the infrared thermal image is obtained through two infrared thermal image instruments which are parallel with an optical axis structures and have different focal distances, and the infrared thermal images comprise short-focus images and long-focus images; B, enlarging the short-focus images, and dividing the long-focus images into low-frequency images and high-frequency images; C, establishing a mapping relationship of planes at infinity of the enlarged short-focus images and the original long-focus images by utilizing an DLT algorithm and a translation mapping table; D, establishing an image pyramid, and calculating an optical parallax among the images in the horizontal direction; E, partially fusing the high-frequency images of the long-focus image into the enlarged short-focus images, and partially fusing the high-frequency images into the enlarged short-focus images. In comparison with a high-resolution infrared thermal image instrument, the cost is reduced, a relatively big visual angle range is guaranteed, and the resolution of a local region is increased at the same time.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Image super-resolution and image quality enhancement method
InactiveCN103310427AImprove image qualityHigh resolutionImage enhancementImaging qualityHorizontal and vertical
The invention provides an image super-resolution and image quality enhancement method and relates to the technical field of digital image processing in a space remote sensing imaging system. The image super-resolution and image quality enhancement method solves the problems that optimization elements which can be utilized are less, the improvement space of the image quality is limited, and accordingly the image quality cannot be effectively improved in the existing Wiener filtering image restoration method. The image super-resolution and image quality enhancement method comprises utilizing a light beam splitter to collect in-focus images and out-of-focus images in two channels respectively and collect N staggered in-focus images which enable 1 / N pixels to be staggered in the horizontal and vertical direction relative to the in-focus images; performing PD (Phase Diversity) processing on the in-focus images and the out-of-focus images; utilizing a conjugate gradient algorithm to obtain an aberration coefficient; obtaining restored target images after the PD processing and calculating an objective function; performing Wiener filtering processing on the staggered in-focus images and the restored target images; and performing sub-pixel integration on the two restored images to obtain a restored image with ultrahigh resolution. The image super-resolution and image quality enhancement method achieves super-resolution and high definition of images and improves the resolution by 1.4 times.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for converting two-dimensional image into three-dimensional image, and three-dimensional imaging system
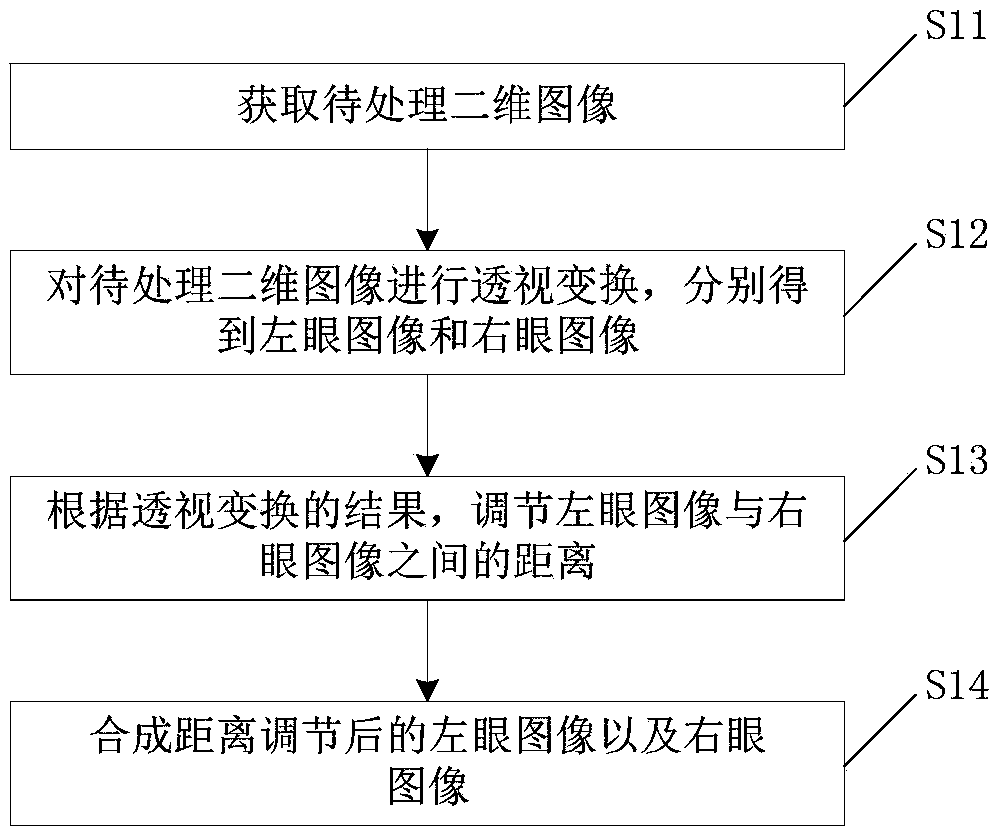
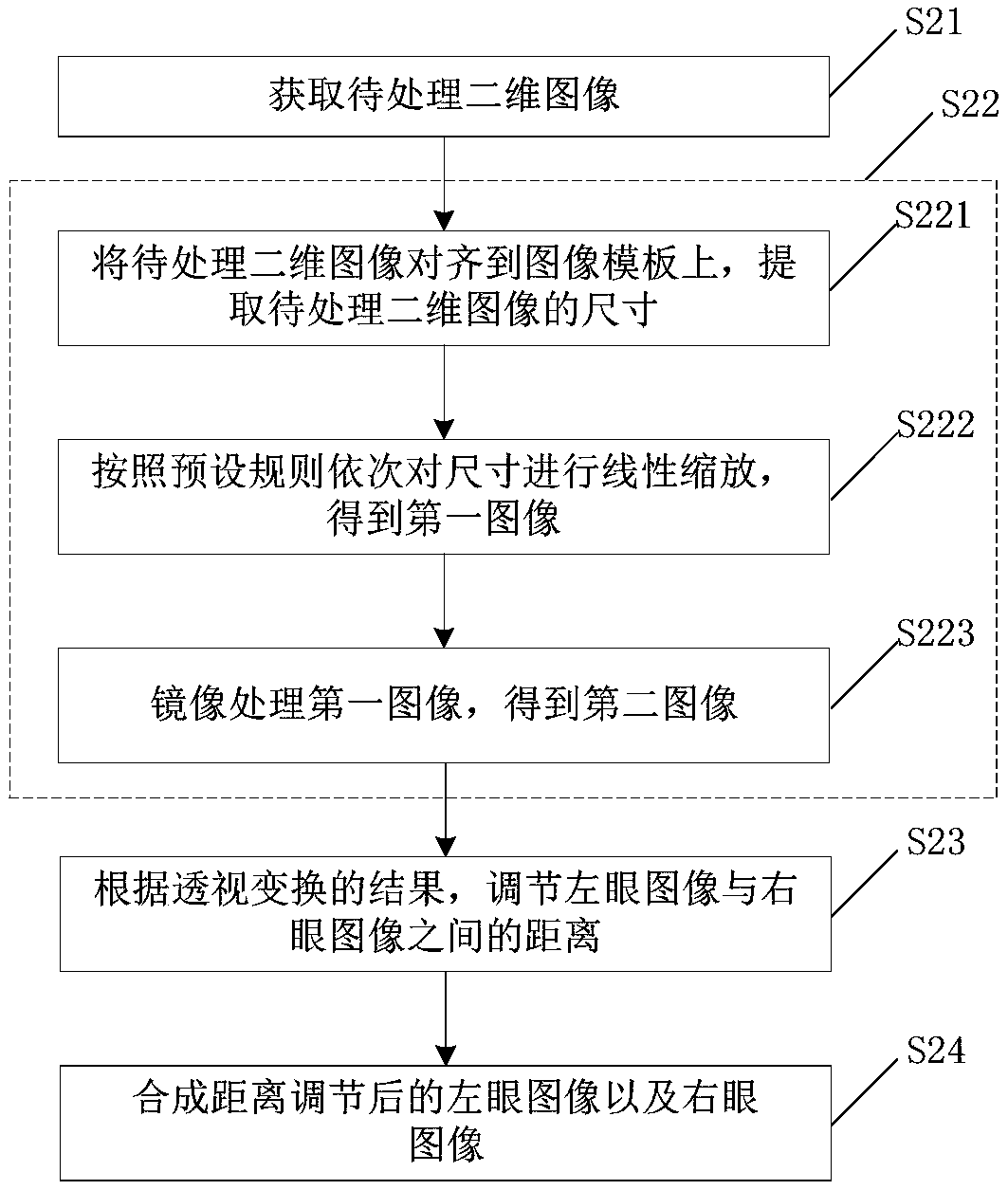
ActiveCN108712643AImprove conversion efficiencyAdjustable distanceTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationImaging qualityPerspective transformation
The invention discloses a method and device for converting a two-dimensional image into a three-dimensional image, and a three-dimensional imaging system. The method for converting the two-dimensionalimage into the three-dimensional image comprises the following steps: obtaining a two-dimensional image to be processed; performing perspective transformation on the two-dimensional image to be processed to obtain a left eye image and a right eye image separately; adjusting the distance between the left eye image and the right eye image according to the result of the perspective transformation; and synthesizing the left eye image and the right eye image after distance adjusting. According to the embodiment of the invention, a binocular parallax image is created through performing perspectivetransformation on the two-dimensional image to be processed; and the distance adjusting is performed on the left eye image and the right eye image after perspective transformation to form the binocular parallax and create a convergence angle, so that the image observed by naked eyes lies at different depths and different stereoscopic effects can be seen. The image transformation is performed through the two-dimensional image, which does not relate to the resolution and clarity of the image; therefore, the image quality of the image of 3D imaging is the same as that of the original two-dimensional image, and the effect of 3D imaging is not affected.
Owner:STSIVITA MEDIKAL TECH KO LTD
Image processing technique for images projected by projector
ActiveUS20030035590A1High-speed image processingInhibit deteriorationImage enhancementTelevision system detailsElevation angleImaging processing
The technique of the present invention carries out specific image processing that emphasizes articulation of display with a varying degree of emphasis for respective sites of an image projected by a projector. A typical example of such image processing is sharpness adjustment. The degree of emphasis in sharpness adjustment at each site is specified, based on an elevation angle of the projector and a focalized position of the projected image. The technique of the invention thus readily prevents deterioration of the image quality due to out-of-focus state of the projected image.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD +1
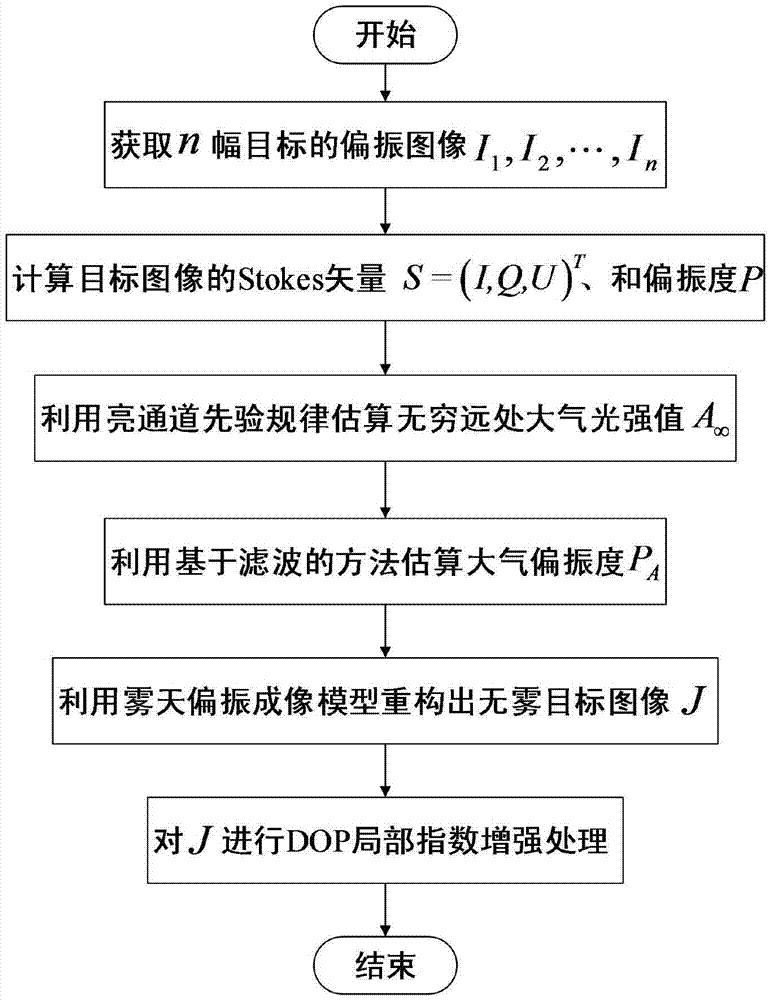
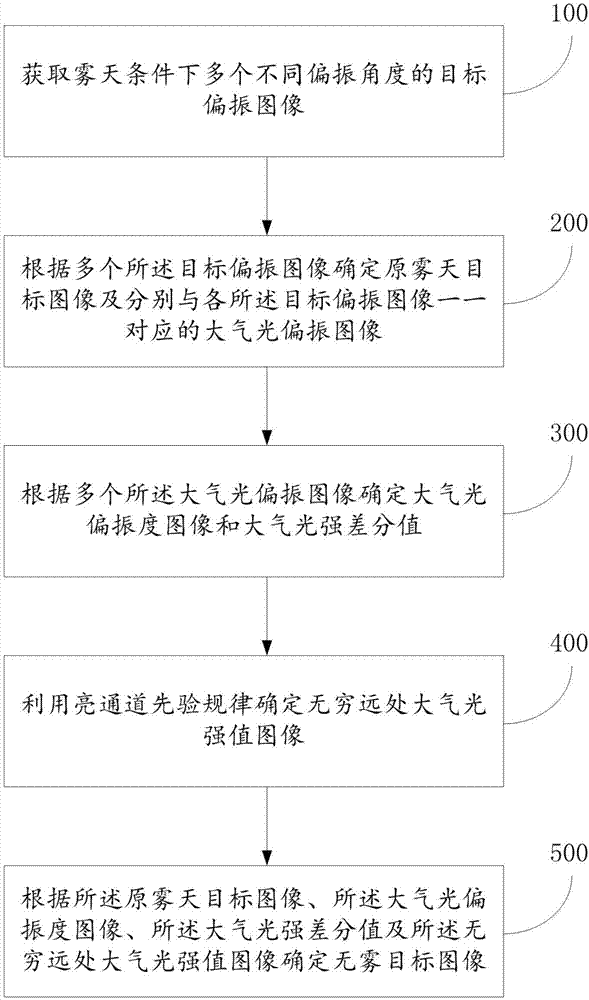
Foggy weather image reconstruction method based on polarization
InactiveCN105447833AImprove visual effectsQuality improvementImage enhancementImage analysisReconstruction methodAtmosphere
The invention discloses a foggy weather image reconstruction method based on polarization, comprising following steps: 1, obtaining the polarization images in different polarization angles; 2, calculating the Stokes vector value of an object image; 3, estimating the atmosphere light intensity value of the infinite distance by using light channel priori rules; 4, estimating the atmosphere light polarization degree by using a filtering method; 5, reconstructing a fogless scenery image; 6, carrying out DOP partial index enhancement to the fogless image. According to the invention, the fogless image from the foggy weather image can be reconstructed well; and the definition of the image is improved.
Owner:合肥视展光电科技有限公司
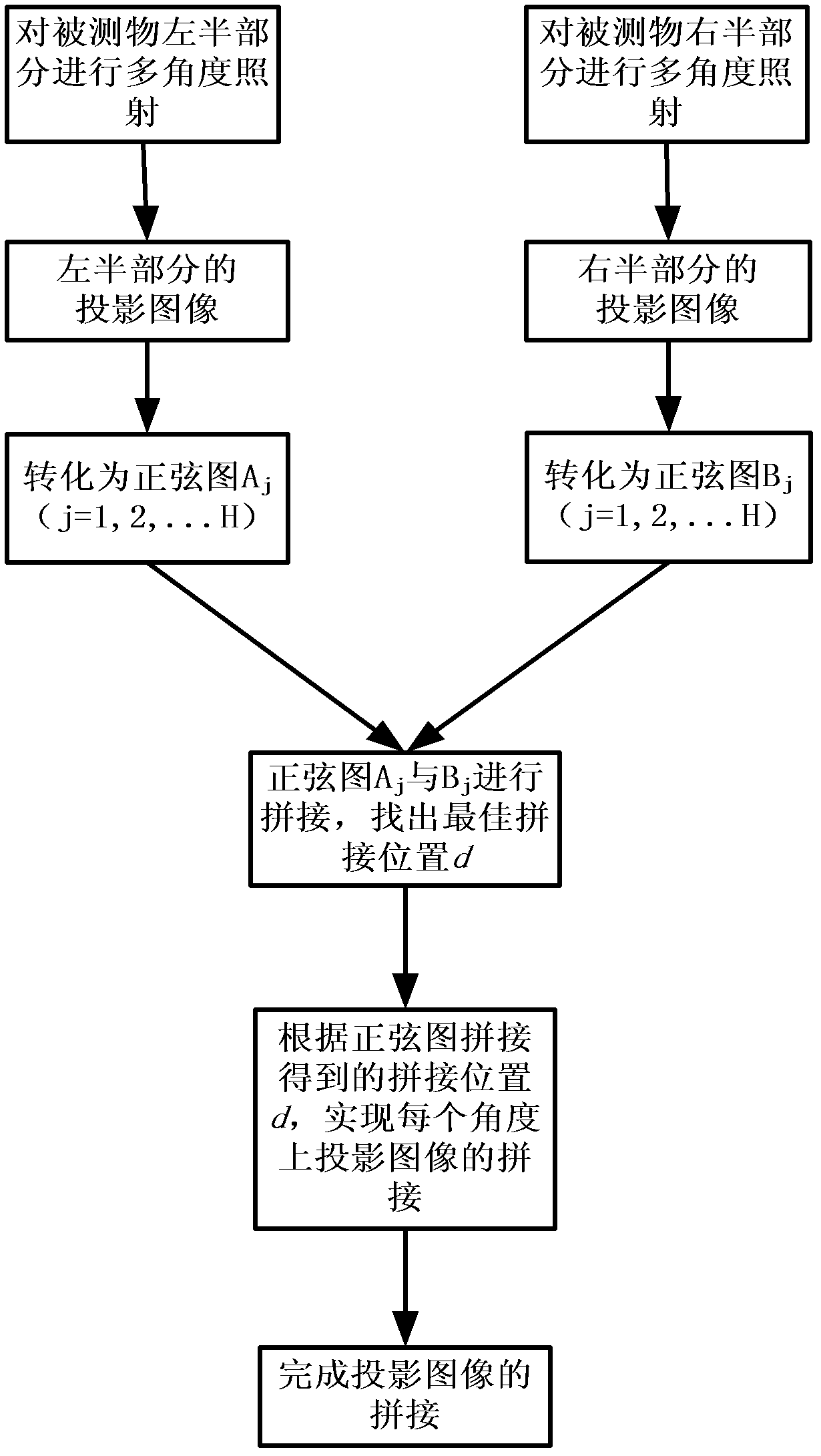
Measured object image splicing method based on optical projection tomographic imaging system
InactiveCN102324101AAvoid the obviousAvoid the disadvantage of image blurring in the stitching area2D-image generationMaterial analysis by optical meansLeft halfProjection image
The invention discloses a measured object image splicing method based on an optical projection tomographic imaging system, which mainly solves the problem of blurring spliced regional images or obvious splicing mark in splicing a measured object image based on the optical projection tomographic imaging system in the prior art is solved. The measured object image splicing method based on the optical projection tomographic imaging system is realized by the following steps of: (1) respectively irradiating the left half part and the right half part of a measured object, and collecting to obtain projection images of the left half part and the right half part of the measured object; (2) respectively converting the left half part and the right half part of the measured object into a sinogram with a clear textural feature; (3) splicing the sinograms and confirming the splicing distance between the projection images by utilizing the correlation of image overlapping regions; and (4) finishing the splicing the projection images in a ramp function weighting way. The measured object image splicing method based on the optical projection tomographic imaging system has the advantages of high definition of spliced regions, small splicing marks and small calculated amount and can be used for carrying out three-dimensional reconstruction on the measured object.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
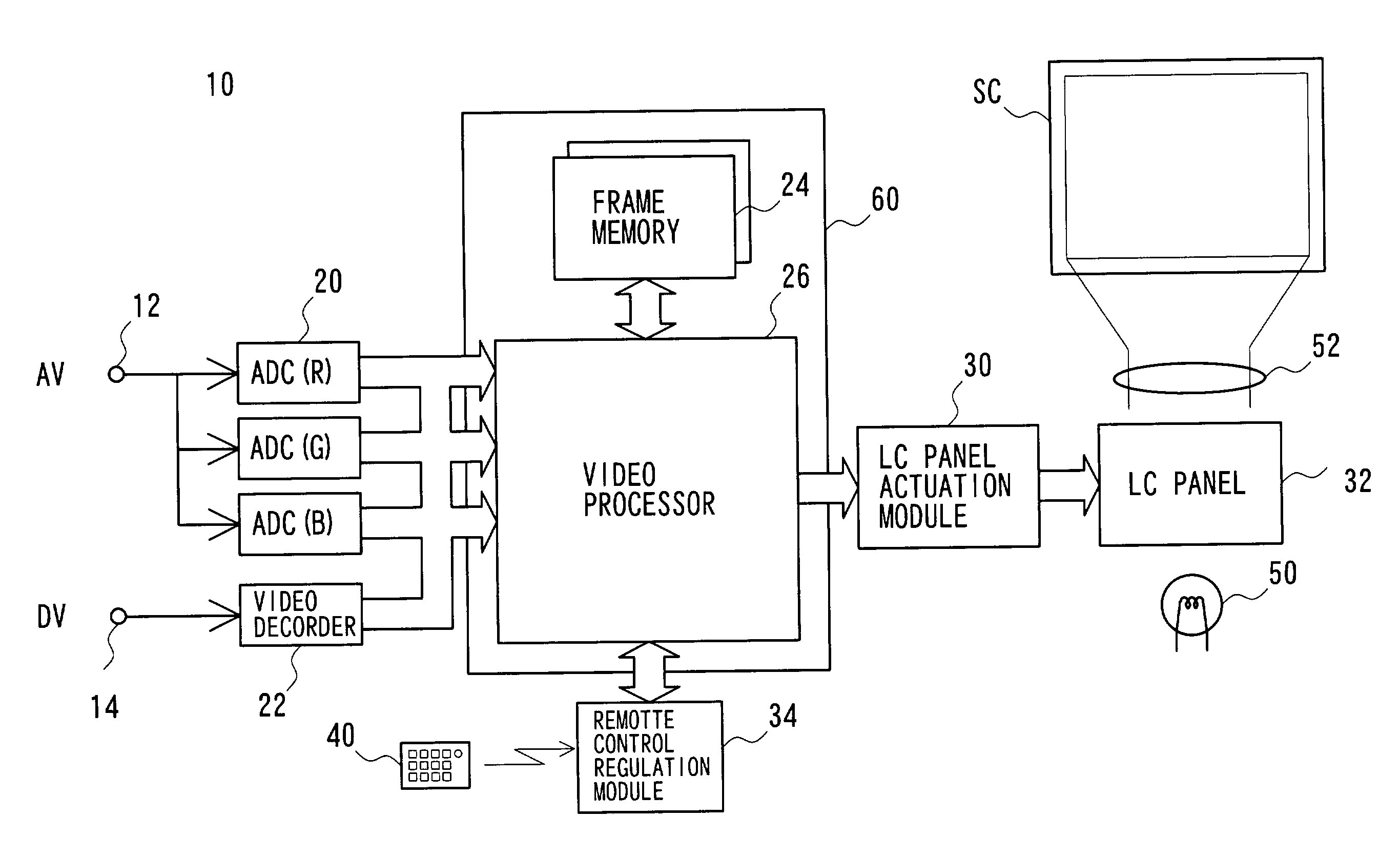
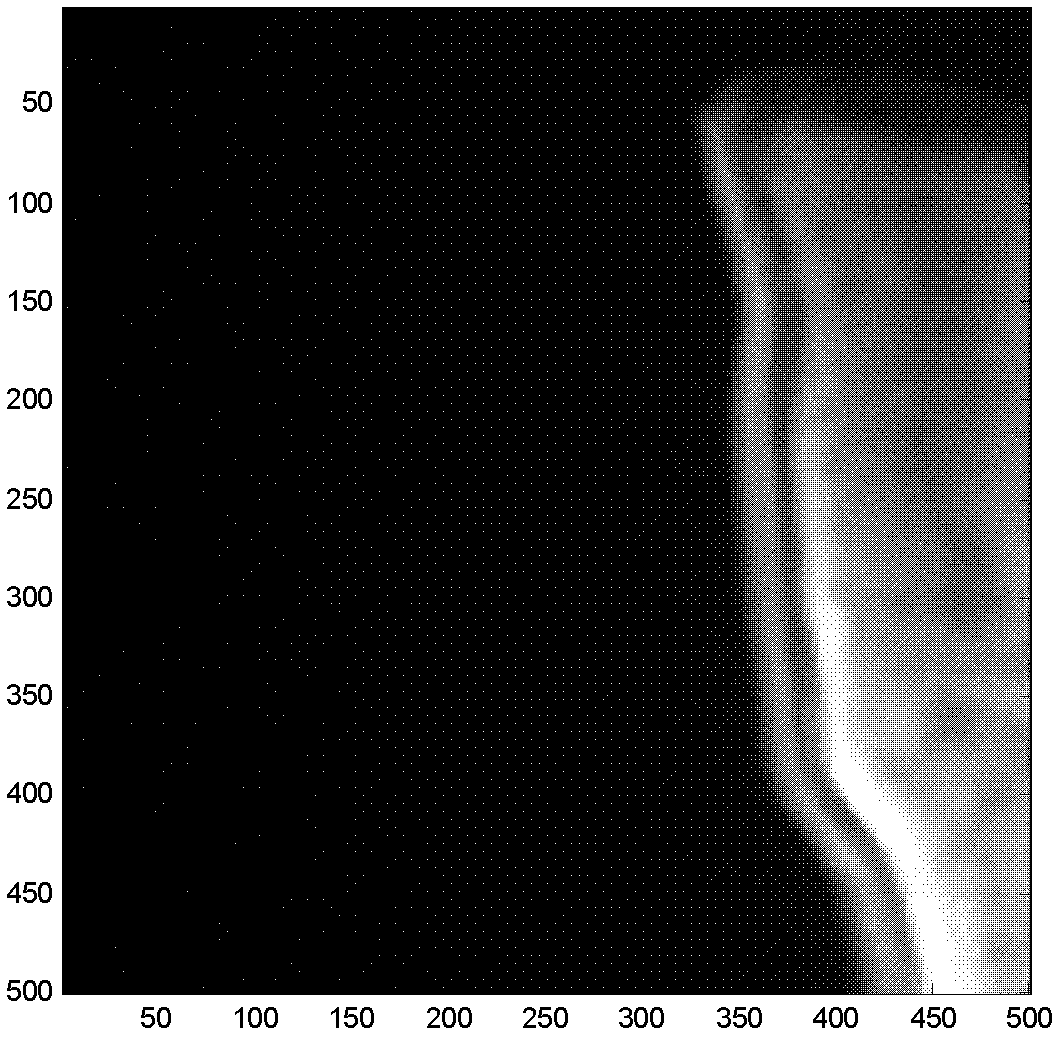
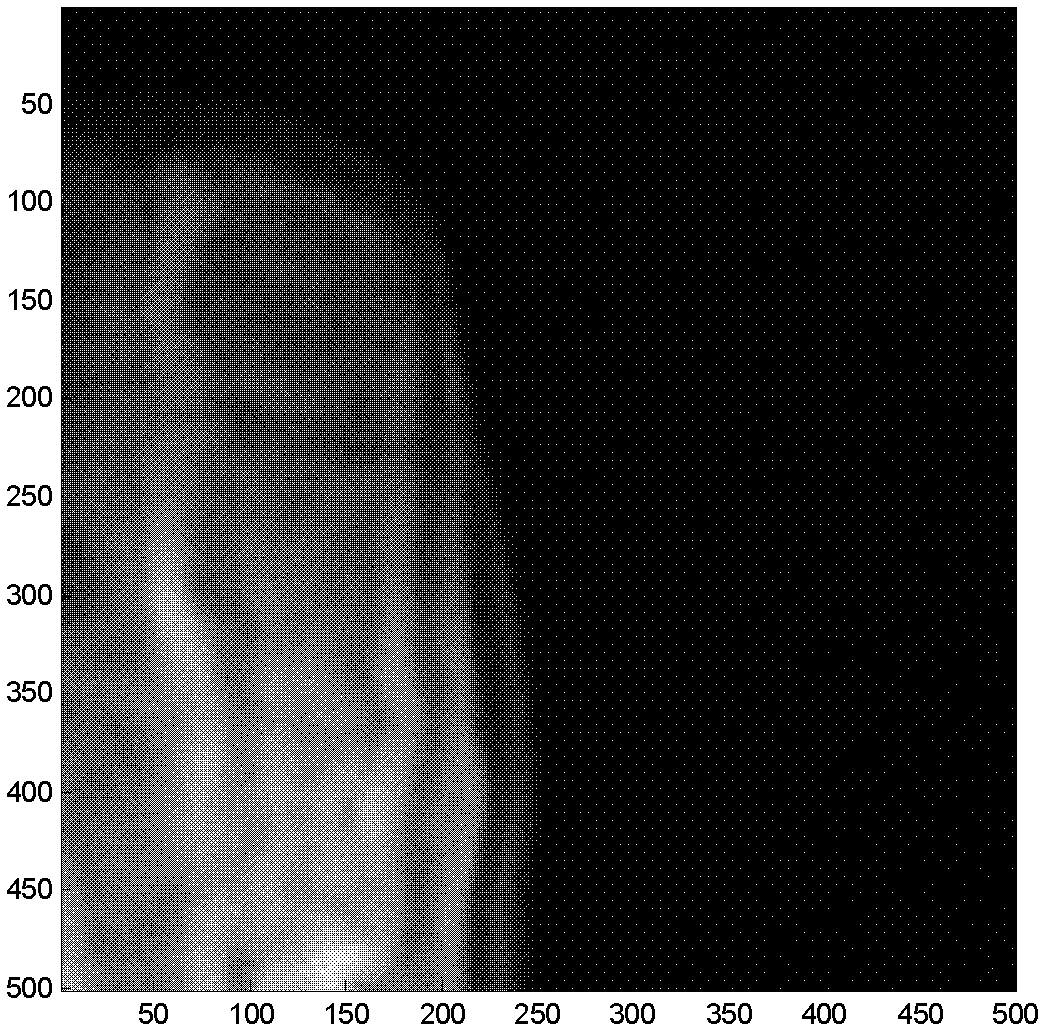
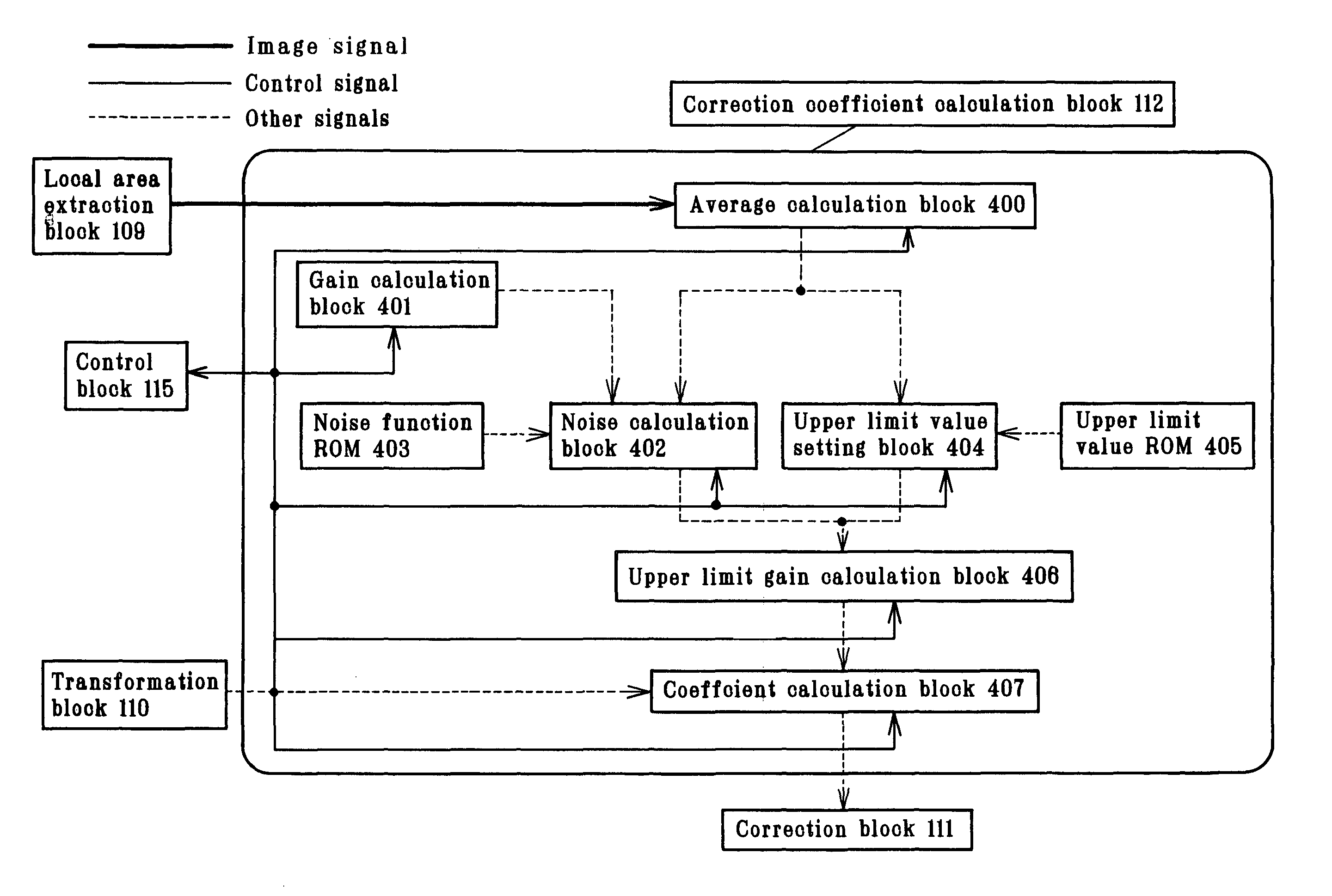
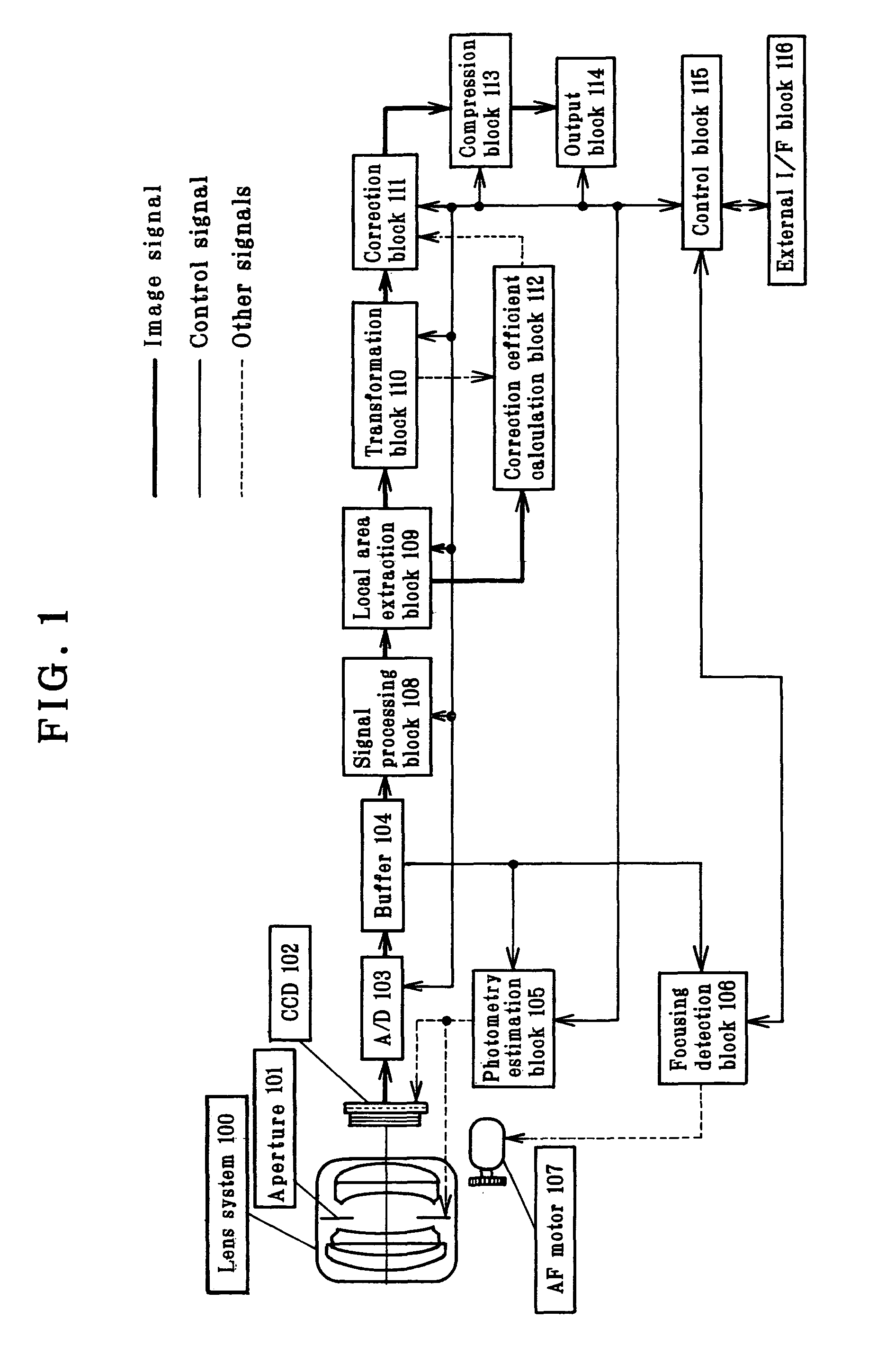
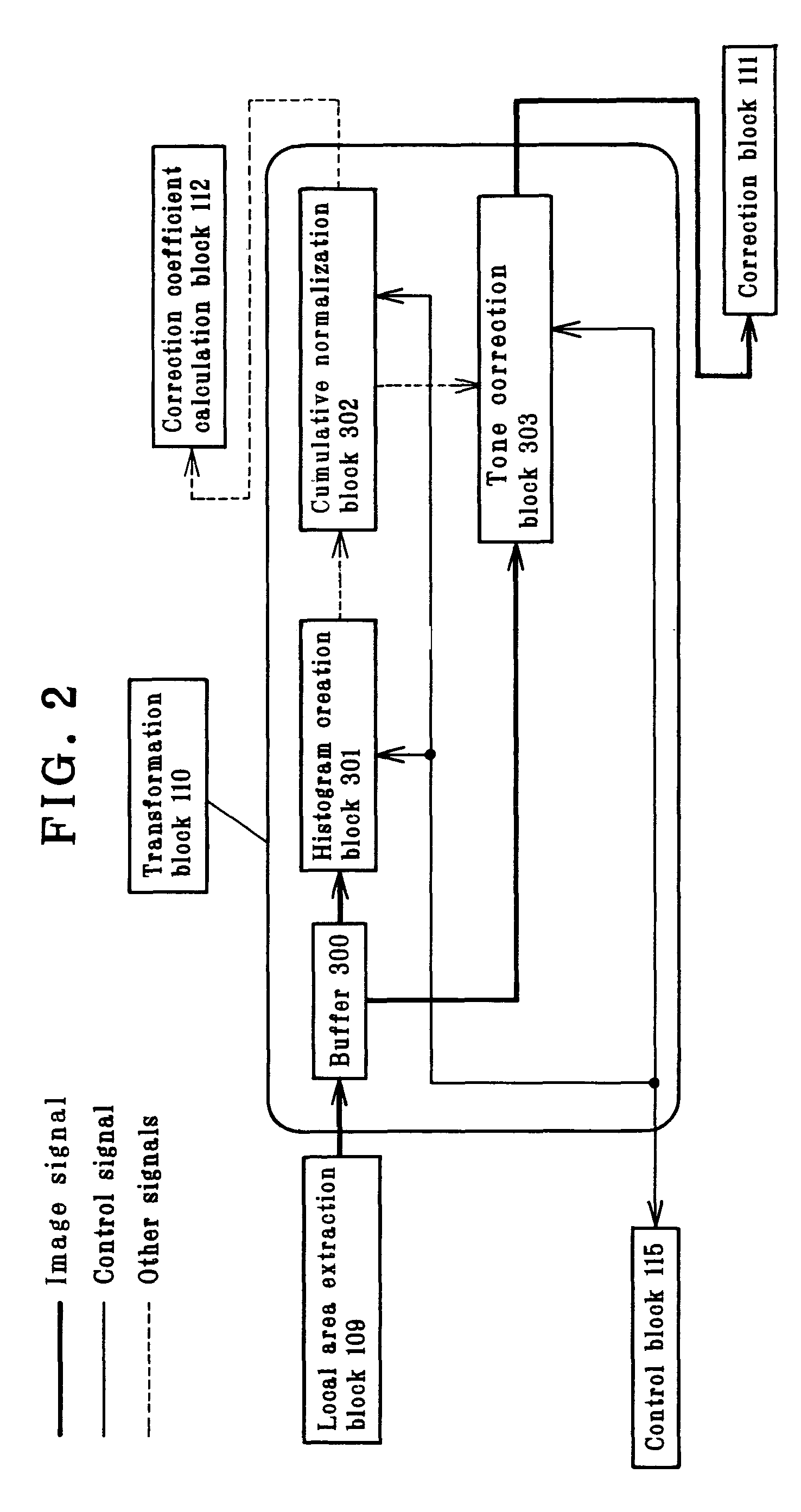
Image processing apparatus which calculates a correction coefficient with respect to a pixel of interest and uses the correction coefficient to apply tone correction to the pixel of interest
ActiveUS8035853B2Easy to buildAdditional componentTelevision system detailsDigitally marking record carriersImaging processingJPEG
The invention provides an image signal processing apparatus, an image signal processing program and an image signal recording medium, each capable of generating high-definition image signals with no or little artifacts. The image signal processing apparatus adapted to implement tone correction of an image signal comprises correction coefficient calculation block (112) for calculating a correction coefficient for a pixel of interest in that image signal and a neighborhood area, transformation block (110) for applying tone correction processing to that pixel of interest, and correction block (111) for using that correction coefficient to make correction of each pixel after that tone correction processing. An image signal of each pixel of interest from correction block (111) is forwarded to compression block (113), and at a time when all image signals are in order, compression processing such as known JPEG is applied to them for their forwarding to output block (114).
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
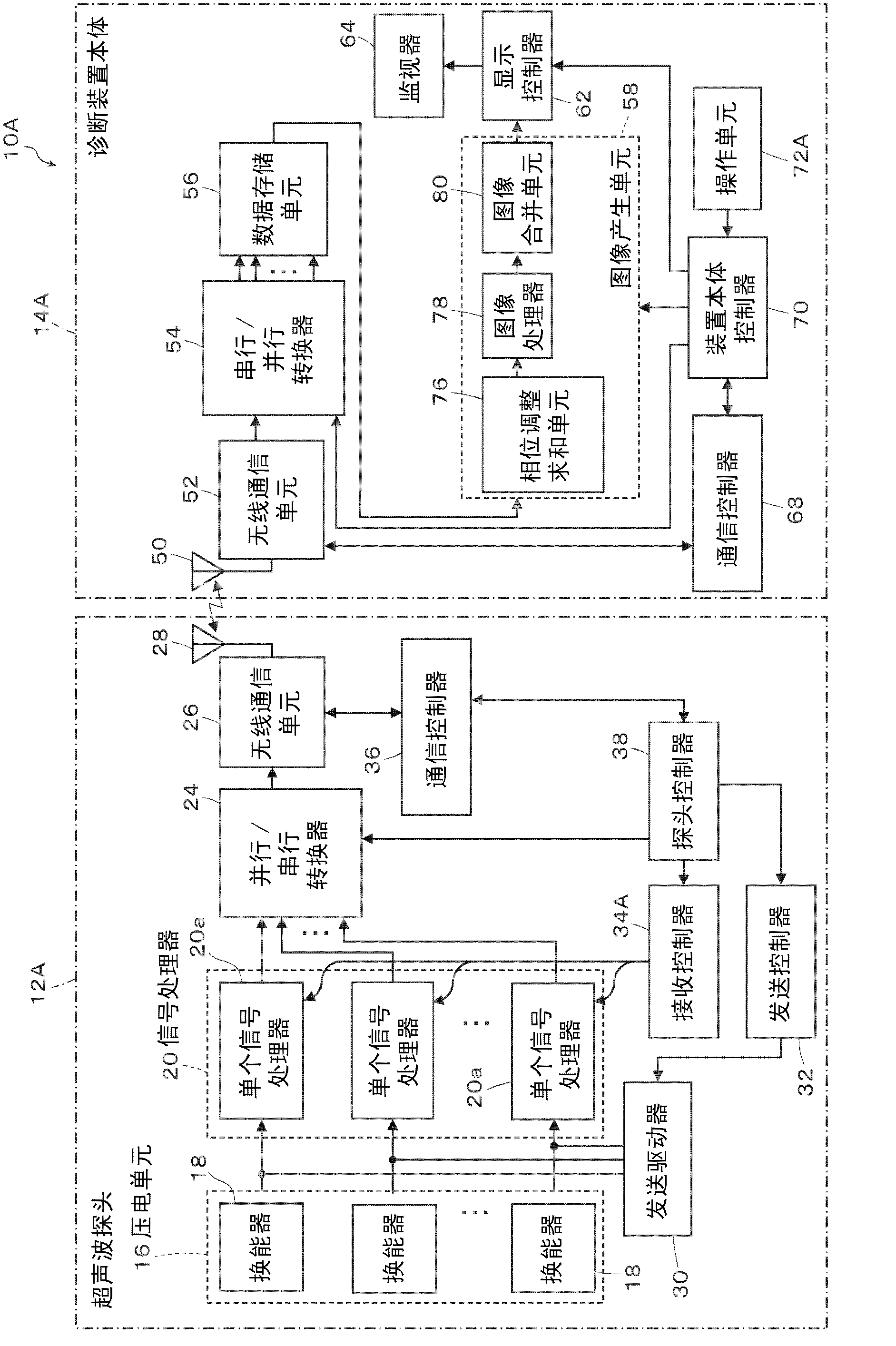
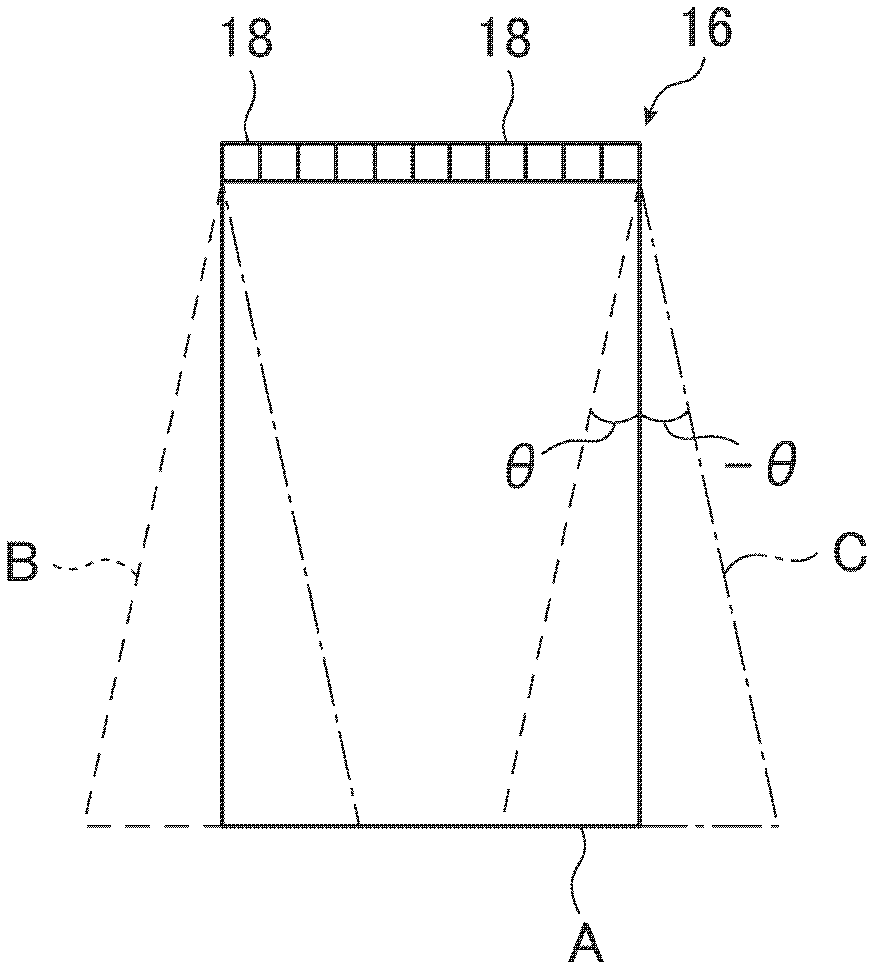
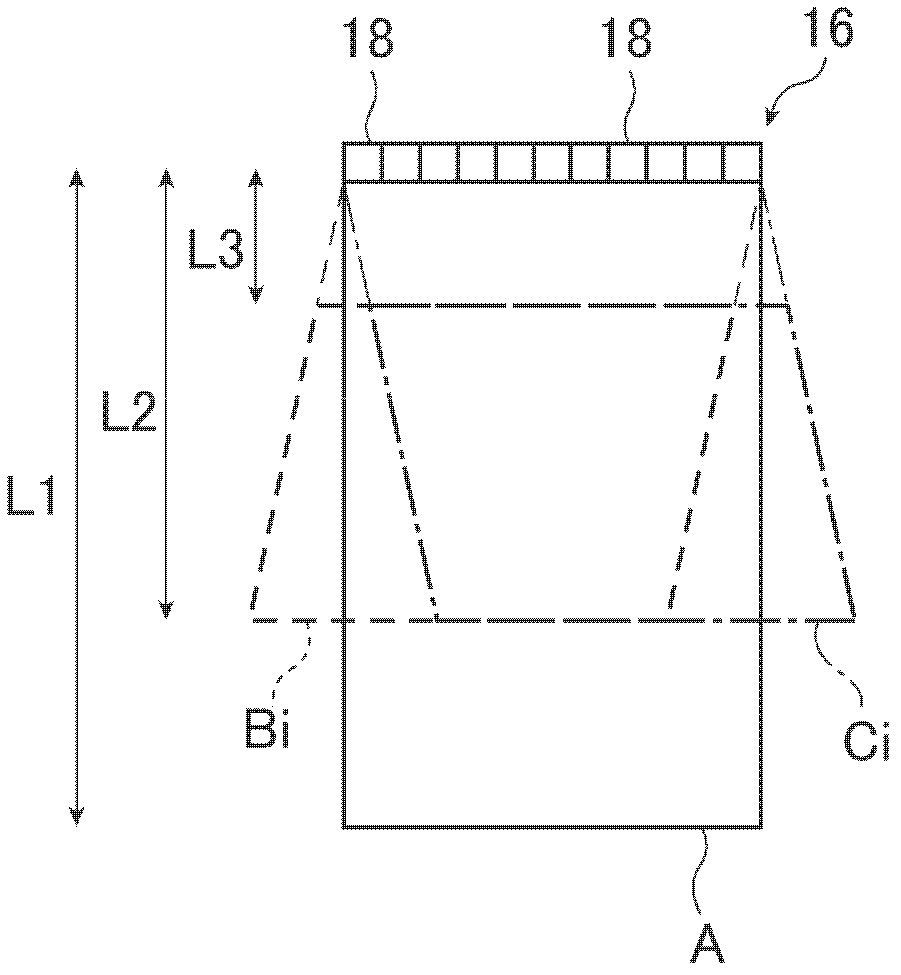
Ultrasound diagnostic apparatus
An ultrasound diagnostic apparatus is provided which includes an ultrasound probe performing ultrasound transmission and reception in different directions and a diagnostic apparatus body combining images different in the direction of transmission and reception to produce an ultrasound image. At least one of ultrasound images to be combined is changed depending on the set region of interest (ROI) to an image of the depth corresponding to the ROI. When an acoustic coupler is attached, the depth of at least one of ultrasound images to be combined is increased. The ultrasound diagnostic apparatus is capable of improving the image quality of the ROI and obtaining efficient high-definition ultrasound images reaching a predetermined depth when the acoustic coupler is attached.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
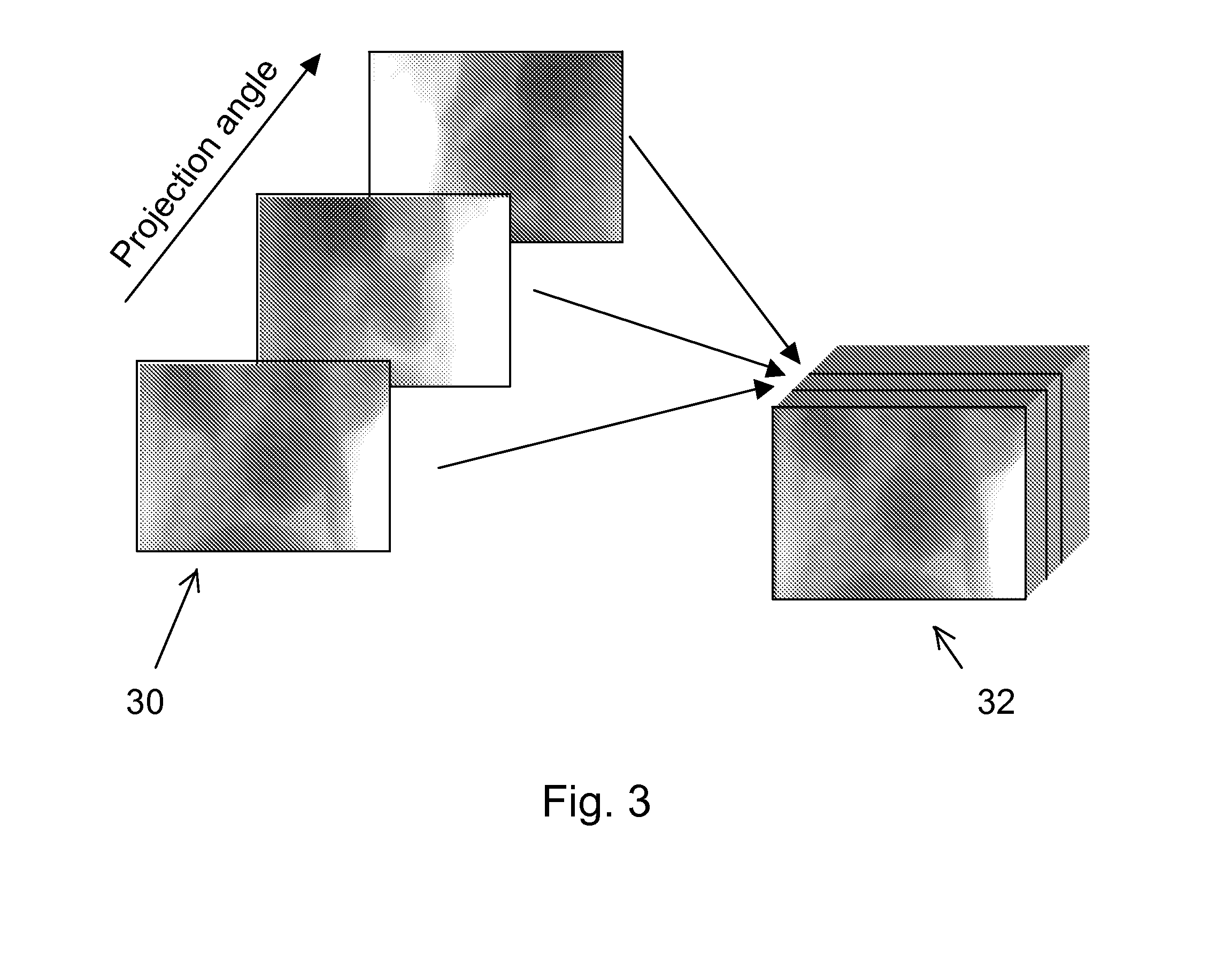
Method for High-Quality Panorama Generation with Color, Luminance, and Sharpness Balancing
Color, luminance, and sharpness balancing across images that are stitched together in a panorama compensates for exposure, alignment, and other differences between the images. Histograms counting occurrences of Y, U, and V values in overlapping regions between images are generated. The Y-value histograms are converted to Cumulative Density Functions (CDF's) and then to a Y color transfer curve which is averaged to generate a smoother averaged Y color transfer curve. Artifacts and loss of image detail caused by color transfer are suppressed by the averaging. For U and V color values the histogram bars are directly averaged using a moving average and then CDF's generated from the moving average of the histograms. Color transfer curves are generated for U and V from the CDF's for source and target images that overlap. All pixels in the source image are adjusted using the color transfer curves to perform color and luminance balancing.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
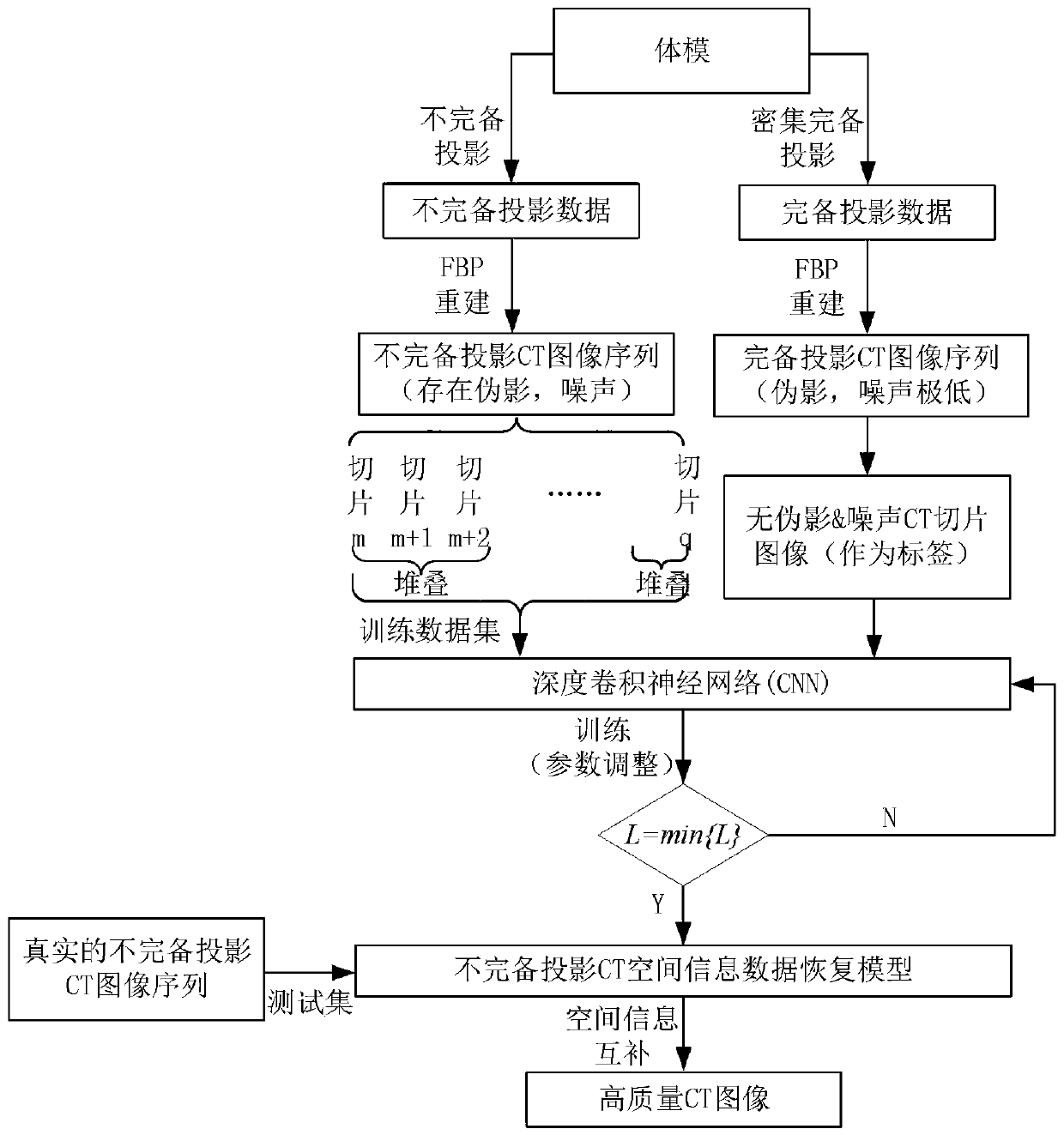
CT image reconstruction method under condition that CT projection paths are reduced
PendingCN110503699AIncrease contrastImprove clarityReconstruction from projectionNeural architecturesData setX-Ray Tube Current
The invention relates to a CT image reconstruction method under the condition that CT projection paths are reduced. The CT image reconstruction method comprises the following steps: obtaining a seriesof continuous incomplete projections through scanning in different incomplete projection modes, and obtaining a CT image sequence through reconstruction; performing CT image spatial information datarecovery and image reconstruction by using a deep convolutional neural network; in a network training process, firstly, utilizing a data set of incomplete projection for pre-training a network, then,utilizing a complete data set for carrying out large-scale iterative training on the network, and obtaining an incomplete projection CT spatial information data recovery model; and inputting the realincomplete projection CT image slice into a data recovery model to obtain a high-quality CT reconstructed image. The CT image reconstruction method is reasonable in design, can obtain the high-qualityCT reconstructed image with high contrast, high definition and good detail description, and can greatly improve the reconstruction quality of the incomplete projection CT image under the condition that the X-ray tube current is reduced and the projection path is reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
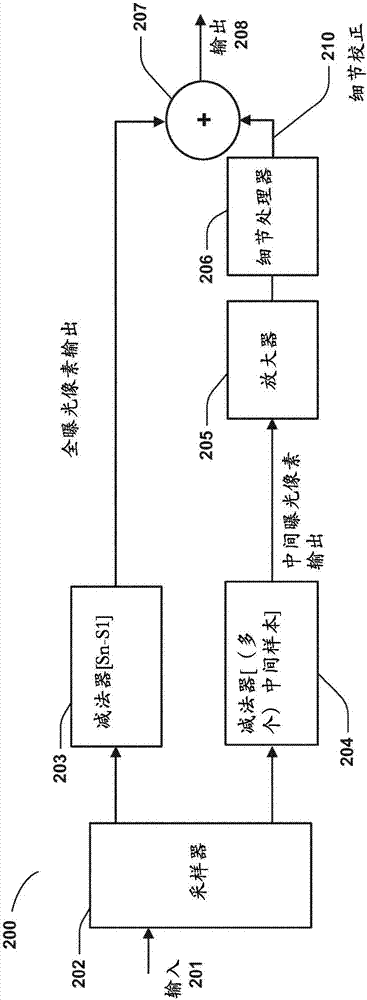
Image capture having improved temporal resolution and perceived image sharpness
ActiveCN107211092AReduce motion blurTelevision system detailsColor television detailsTemporal resolutionImage resolution
A camera for capturing video images in a series of frames includes an image sensor having an array of pixels. Each pixel receives an image and accumulates an electrical charge representative of the image during a frame. The camera also includes a pixel processor to sample a pixel output for each of the pixels of the image sensor during an intermediate portion of the frame to produce a signal representative of the image.
Owner:GVBB HLDG R L
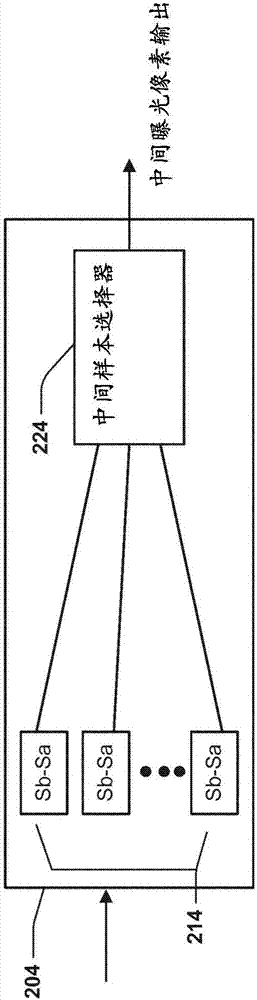
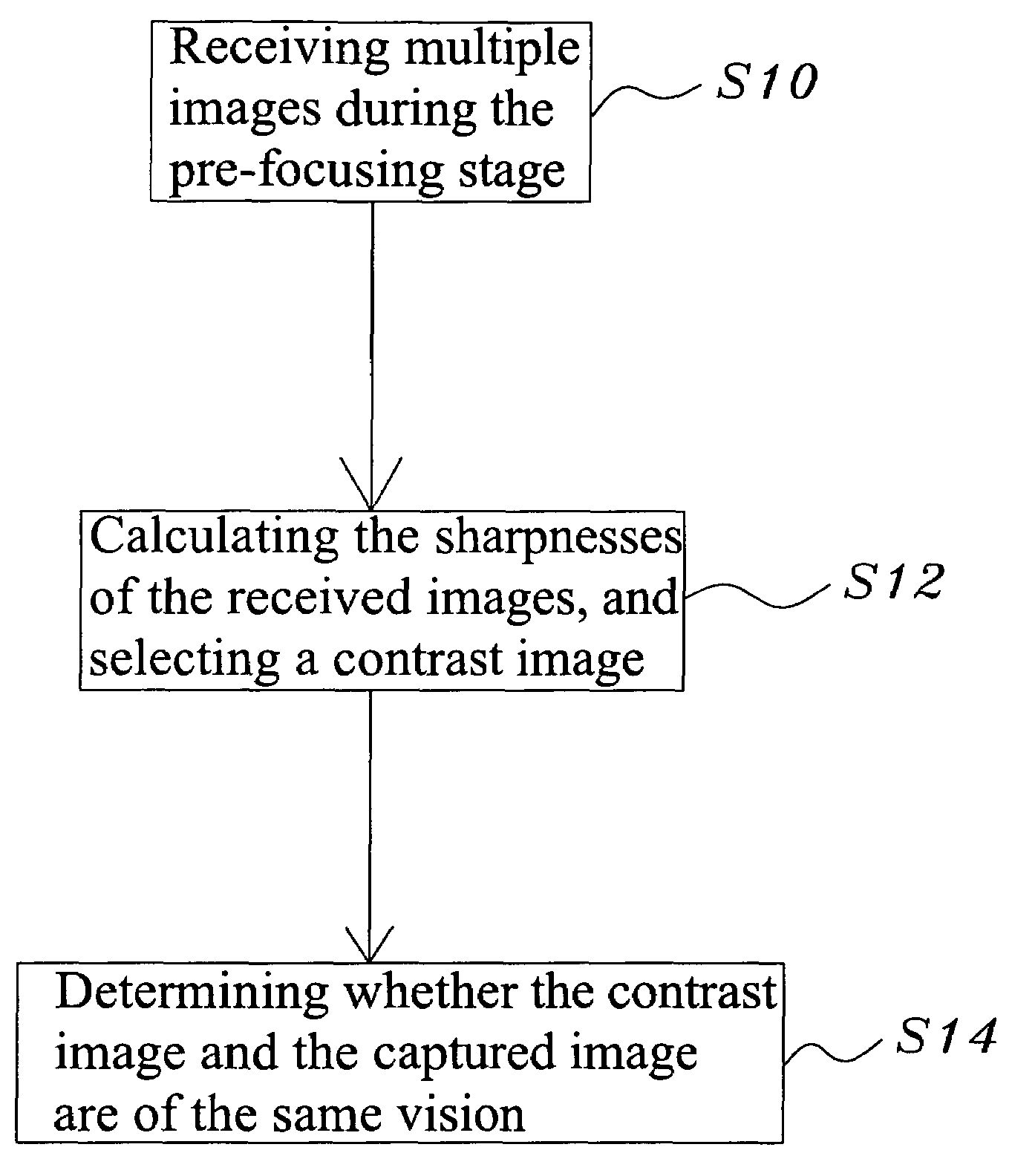
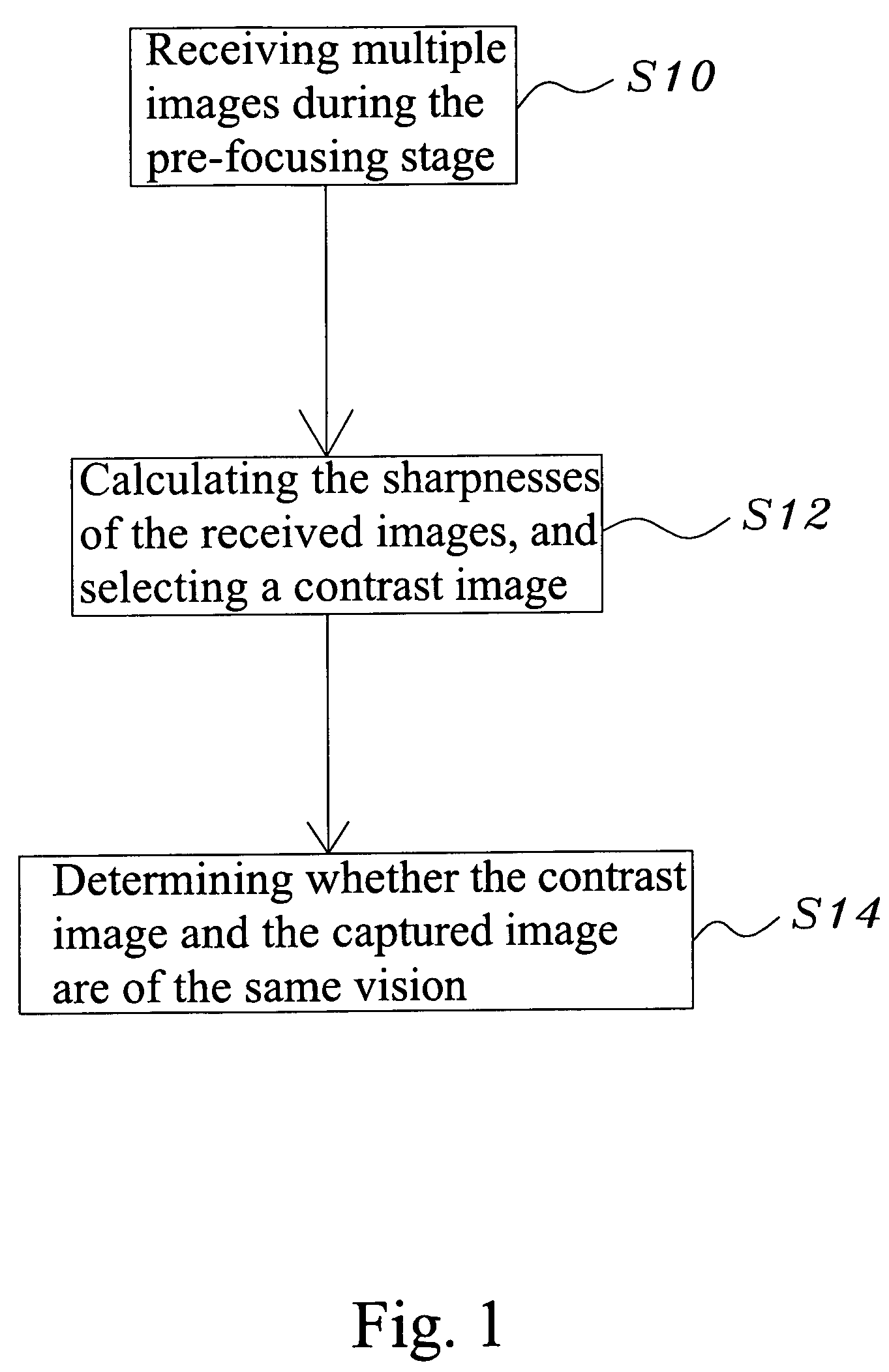
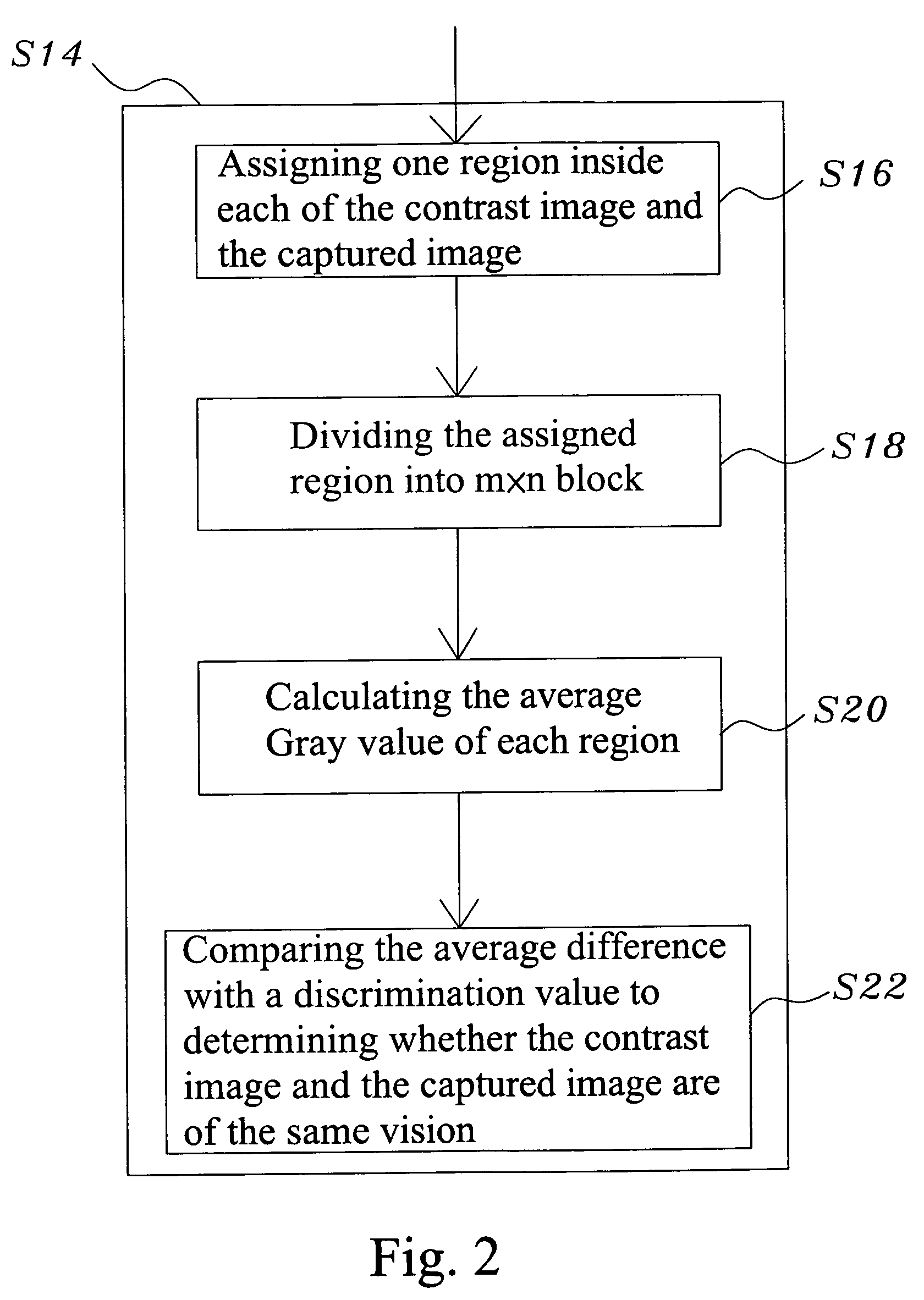
Image unsharpness test method for a camera device
ActiveUS7483054B2Sufficient sharpnessReduce errorsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer visionElectron
An image unsharpness test method for a camera device, wherein firstly, during the focusing stage of an electronic camera device, the image with the highest sharpness is selected to be a contrast image; next, the contrast image is compared with a captured image to obtain the sharpness difference is too great, the captured image is determined to unsharp; vice versa, if the difference is very small, the captured image is determined to be sharp. Thereby, the image unsharpness test method for a camera device of the present invention not only can determine whether a captured is sharp enough but also can reduce the photographic errors and promote photographic efficiency.
Owner:ALTEK (KUNSHAN) CO LTD
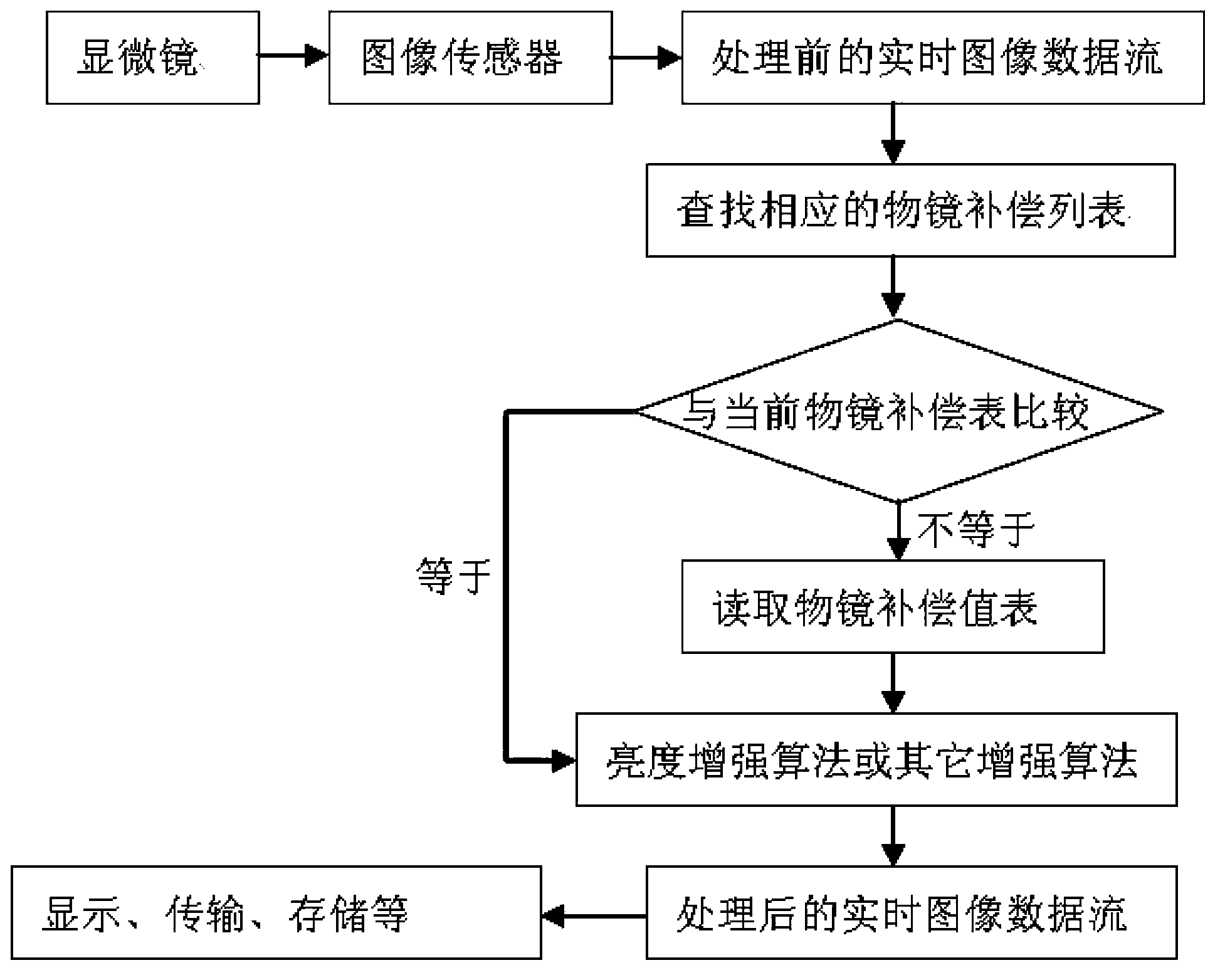
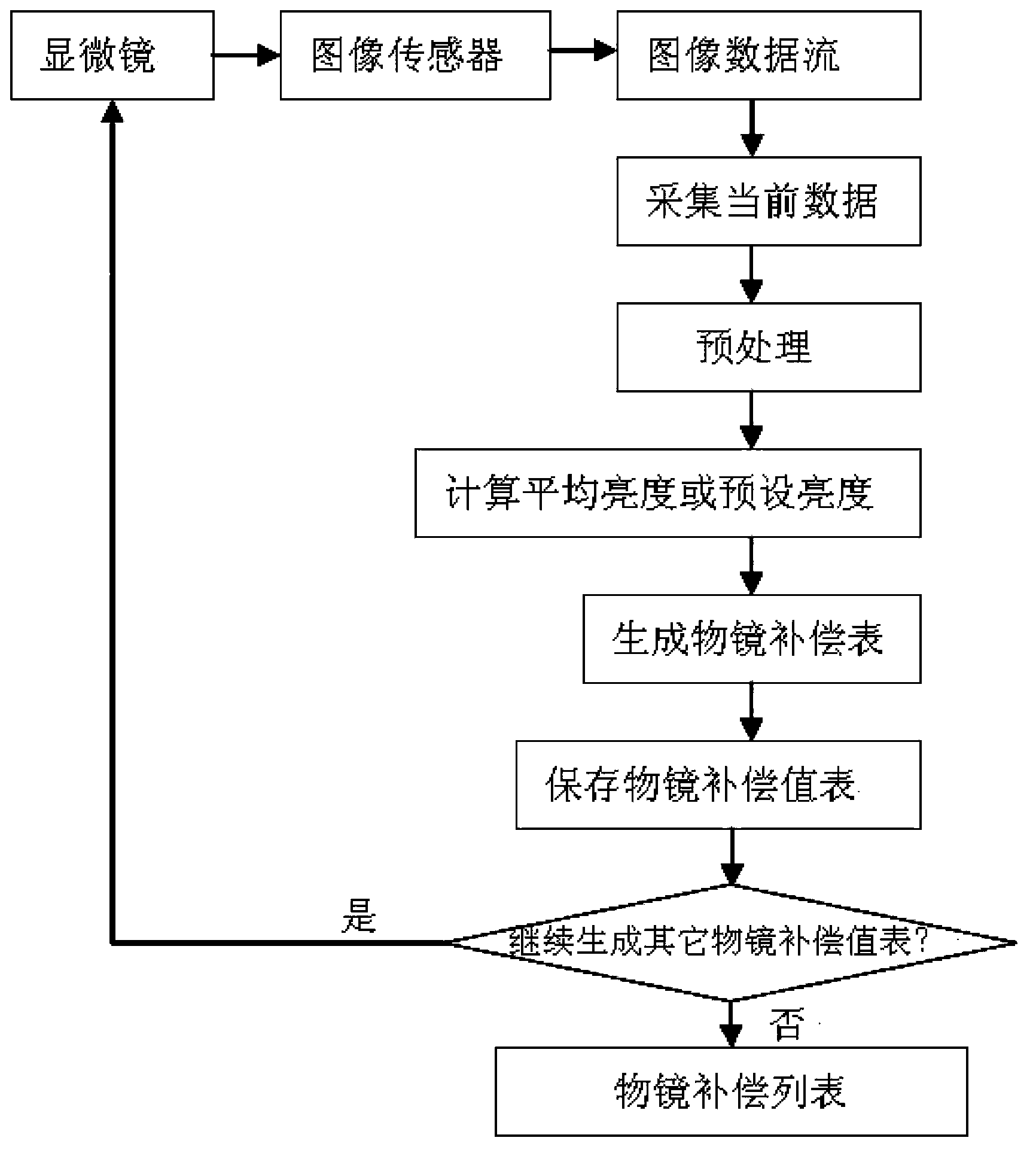
Microscopic video image objective lens compensation method
The invention provides a microscopic video image objective lens compensation method. An image sensor is connected with a microscope through an optical adapter. The image sensor outputs collected microscopic image data flow to a processor. The processor reads a preset objective lens compensation value table to compensate each pixel point in the image data flow. Follow-up microscopic video image operations can be carried out on the processed real-time image data flow. Through the microscopic video image objective lens compensation method, the illumination uniformity of microscopic video images can be greatly improved, and the integral sharpness of the images can be improved.
Owner:NINGBO SUNNY INSTR
Digital imaging system of X rays acquired from fluorescent screen images
InactiveCN101543410AEasy data managementEasy for network transmissionComputerised tomographsTomographyCamera lensMedical record
The invention discloses a digital imaging system of X rays acquired from fluorescent screen images, which is characterized in that the system consists of an X ray generator, a fluorescent screen, a lens, an imager, an image acquisition card and a computer, wherein the X ray generator presents body images projected by high-voltage X rays on a medical fluorescent screen, the lens, the imager and the image acquisition card acquire the images on the fluorescent screen to achieve the conversion between the X rays and visible light, then the acquired images are transmitted to the computer or an LCD display by a data wire or a Bluetooth wirelessly, and the computer of the LCD display restores or reinforces the images acquired by low dosage of the X rays for auxiliary diagnosis by a doctor. Compared with the prior art, the digital imaging system has the advantages of simple structure, convenient operation, high image definition and low production cost, is convenient for data management and network transmission of image case histories, creates a condition for remote diagnosis, and is particularly suitable to be popularized and applied in community and rural medical institutions.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
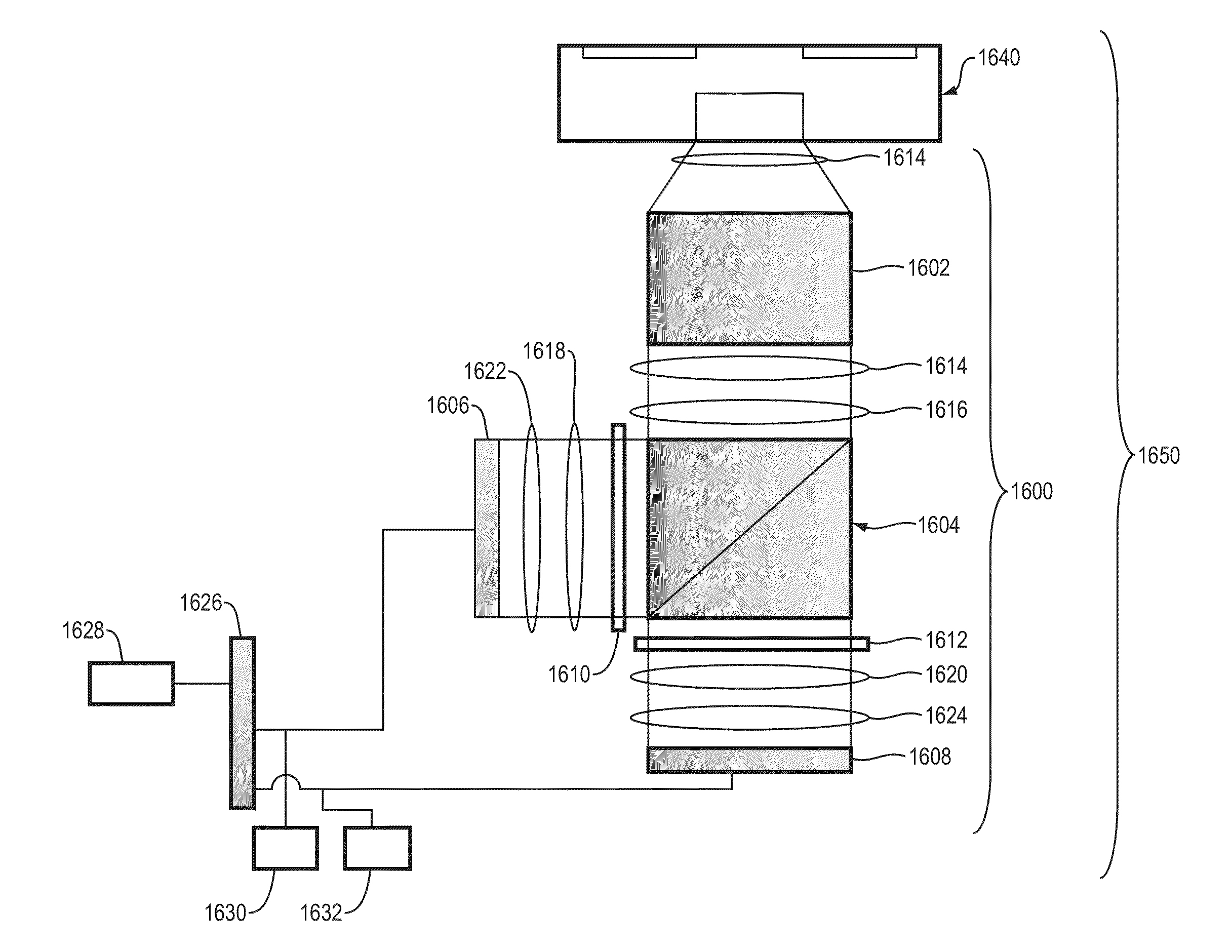
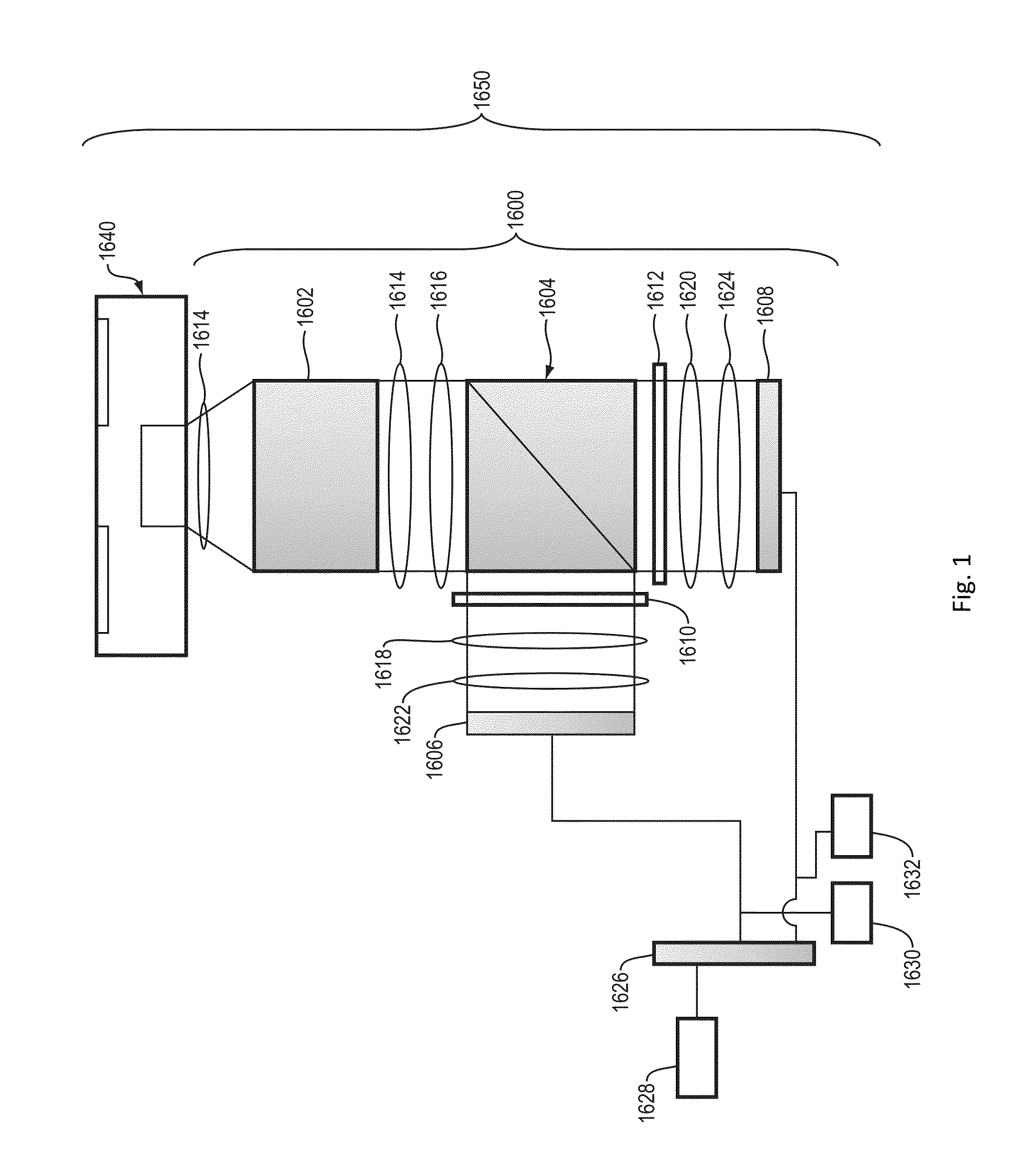
Image acquisition apparatus including adaptive optics
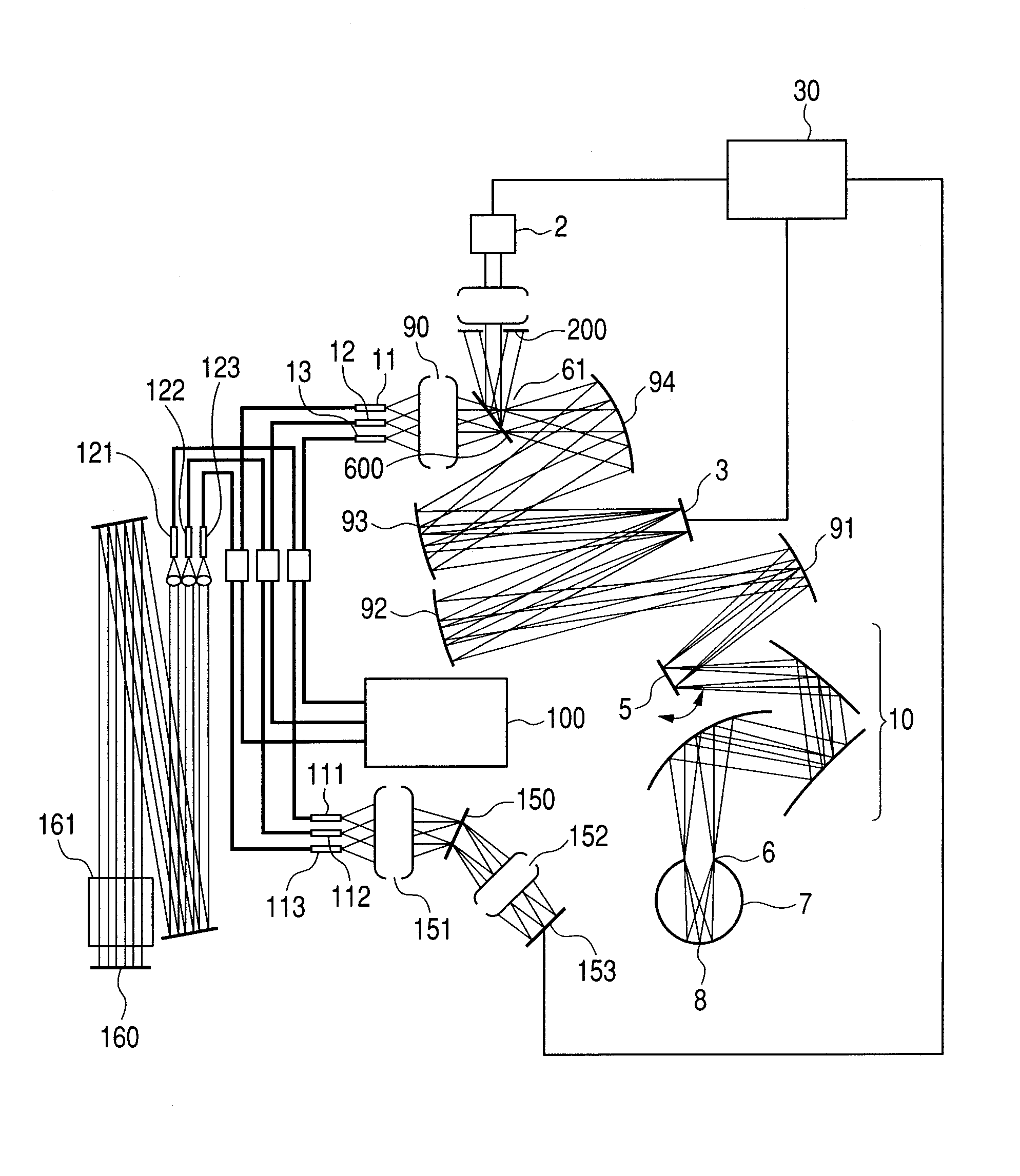
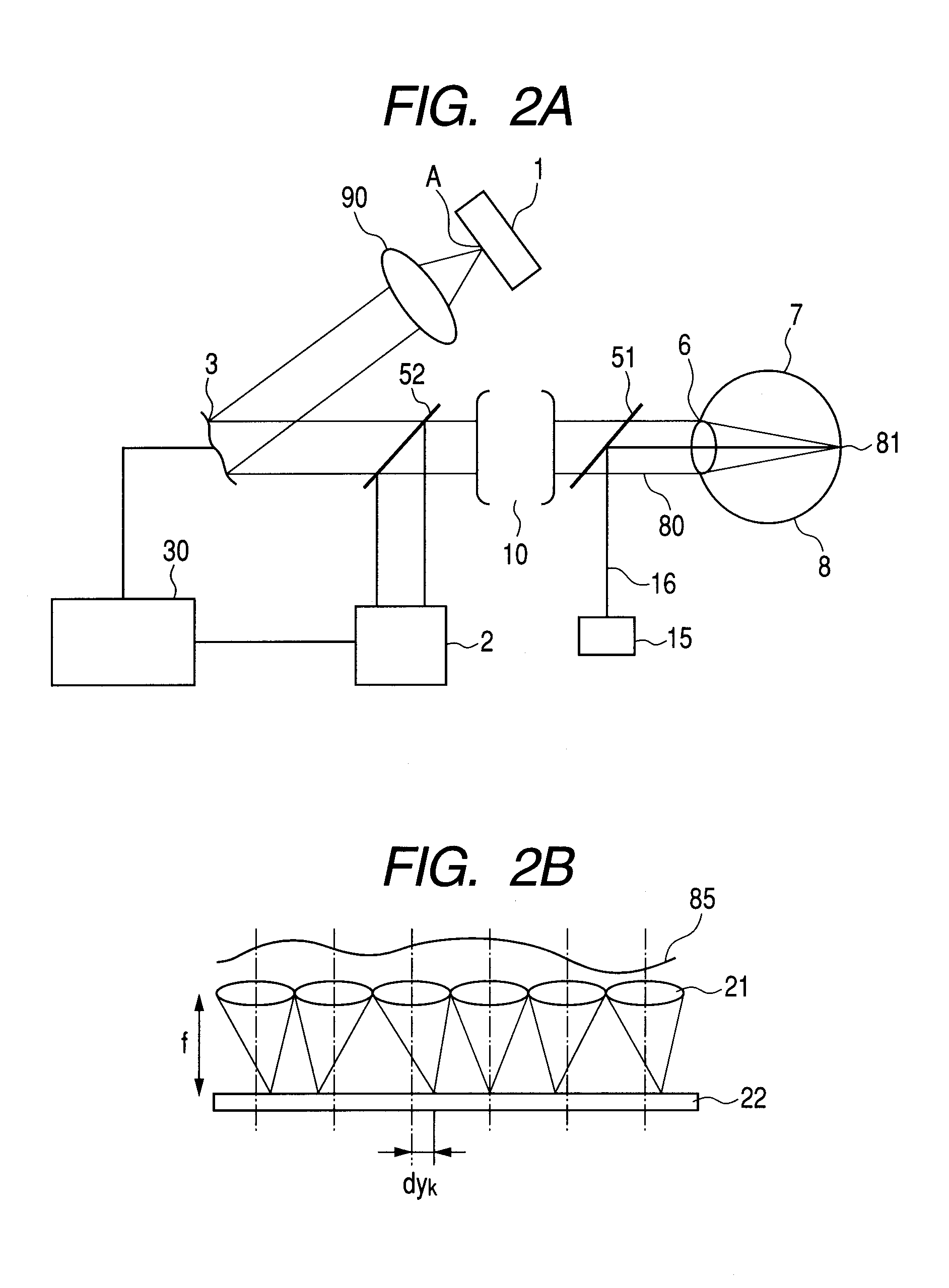
InactiveUS20120033221A1High image definitionHigh definitionOptical measurementsScattering properties measurementsImage formationLight beam
An image forming apparatus including an adaptive optics realizing a reduction in image acquisition time and high definition without significantly increasing a light amount of a beam for scanning is provided, the apparatus including an adaptive optics scanning a plurality of areas in an object with a deflector using a measuring beam including a plurality of beams and corrects reflected and / or scattered beam from the object to acquire an image of the object, including: one or more wavefront aberration detecting device detecting wavefront aberration in each of the plurality of beams caused by the object when scanned by the measuring beam including the plurality of beams; and a single wavefront aberration correcting device correcting the wavefront aberration of each of the plurality of beams according to the detected wavefront aberration, the single wavefront aberration correcting device arranged in a position optically conjugate with the deflector.
Owner:CANON KK
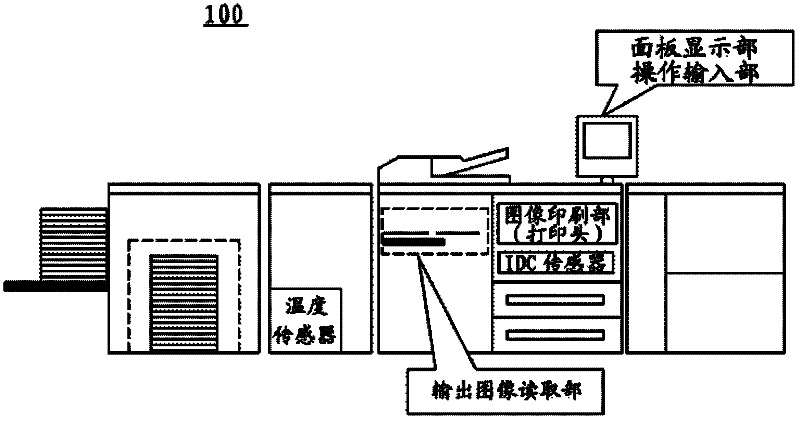
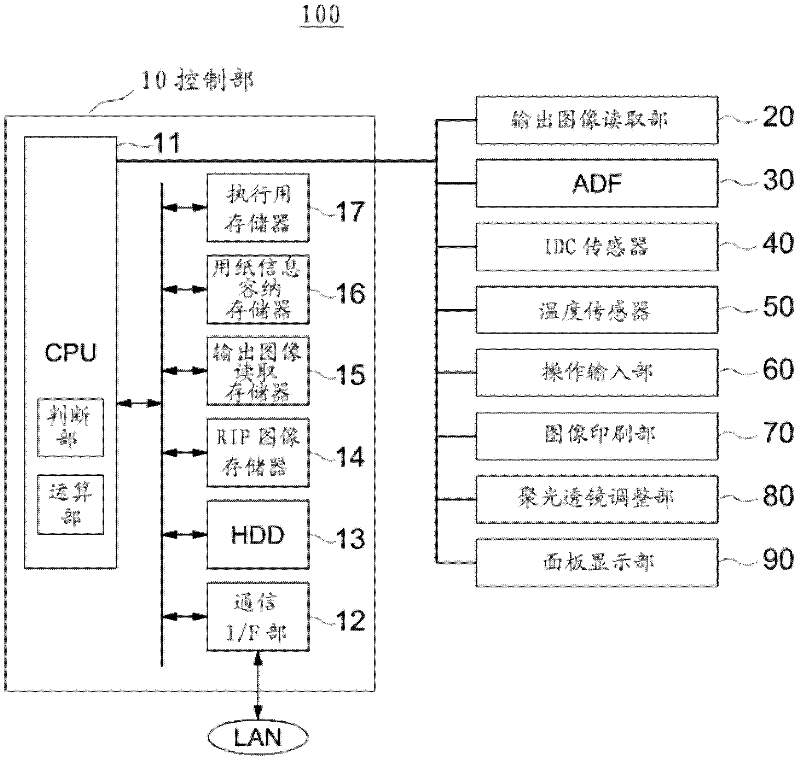
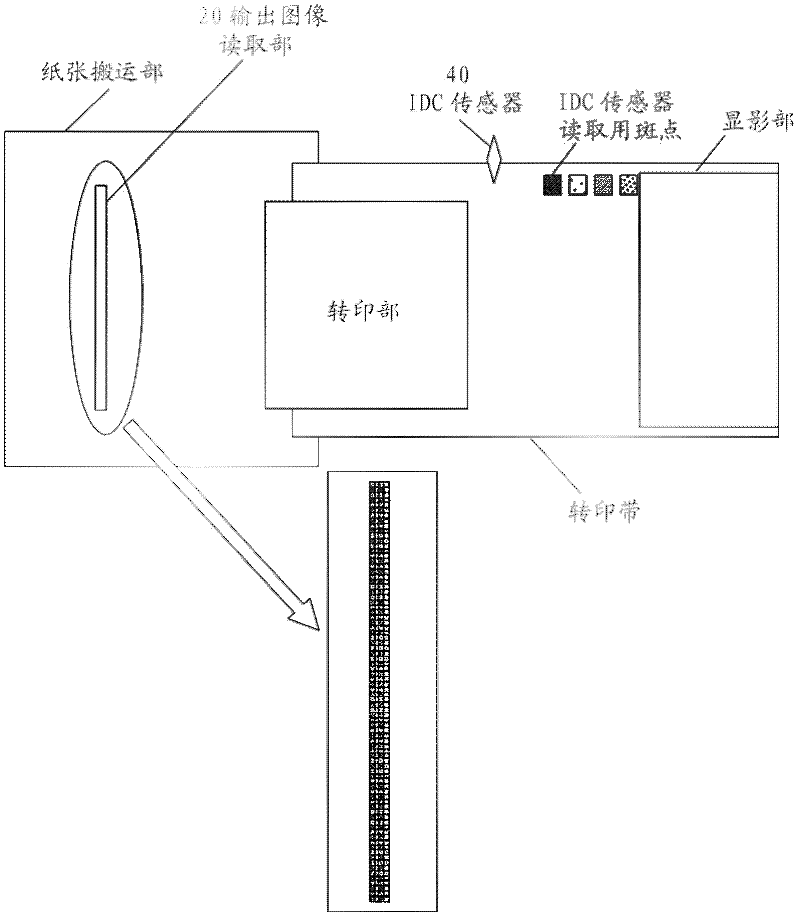
Image processing apparatus and image processing method
The present invention provides an image processing apparatus and an image processing method for inhibiting smallest-unit point or line type unsharpness and gap. The image processing apparatus comprises an image printing unit for printing an image on papers, an output image reading unit for scanning the papers and reading the image printed on the papers, and a control unit, wherein the control unit, on the basis of the information related with the papers and the information related with the image processing apparatus, according to a pre-stored table, determines whether the unsharpness and gap can be divided into one or two point units for printing, when it is determined that the unsharpness and gap can not be divided, according to the image read by the output image reading unit it is determined that the image printing unit can print the image using a point as a unit, and when it is determine that the image can not be printed using a point as a unit, one point of the work page image can be converted two points.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA BUSINESS TECH INC
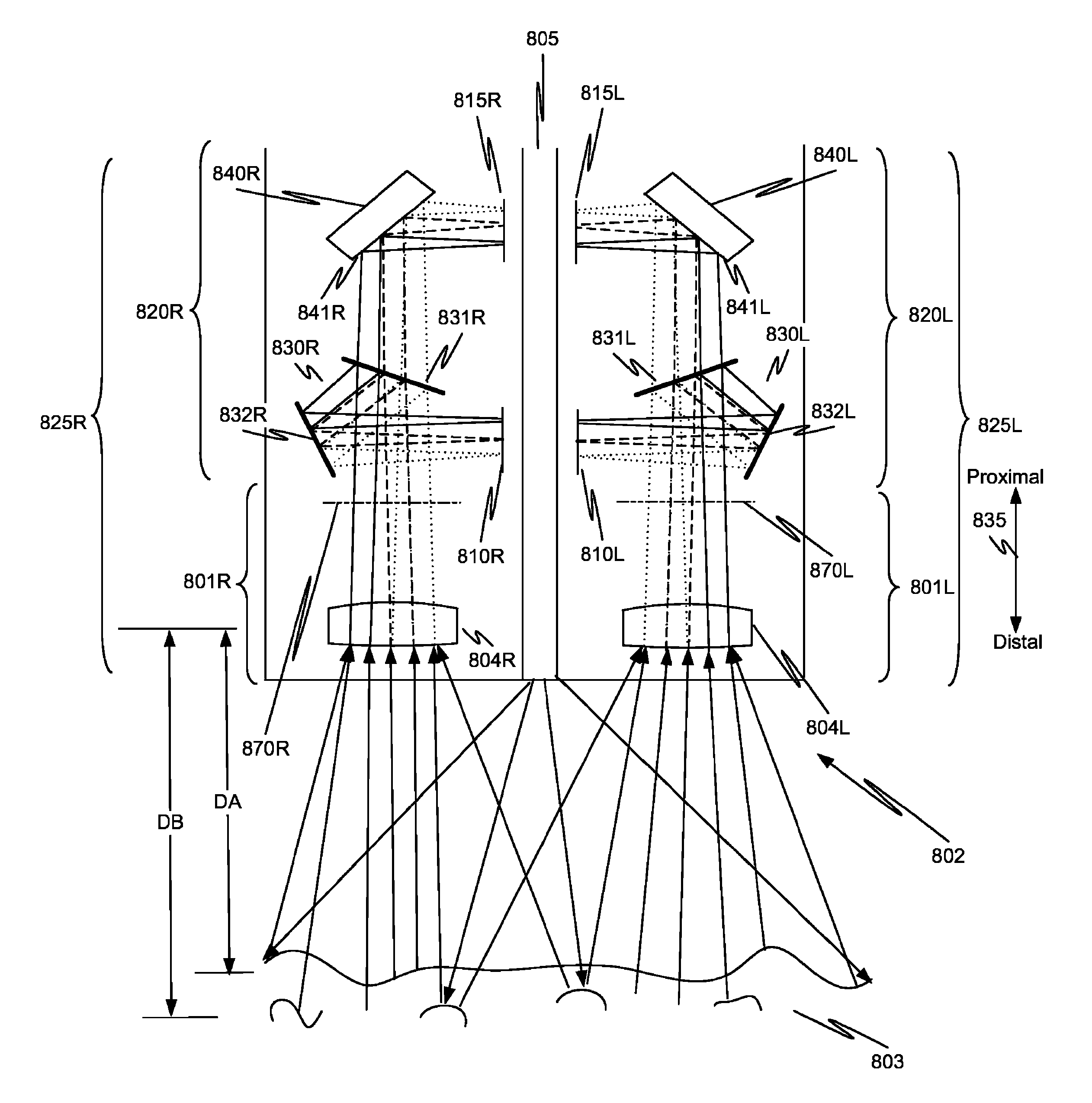
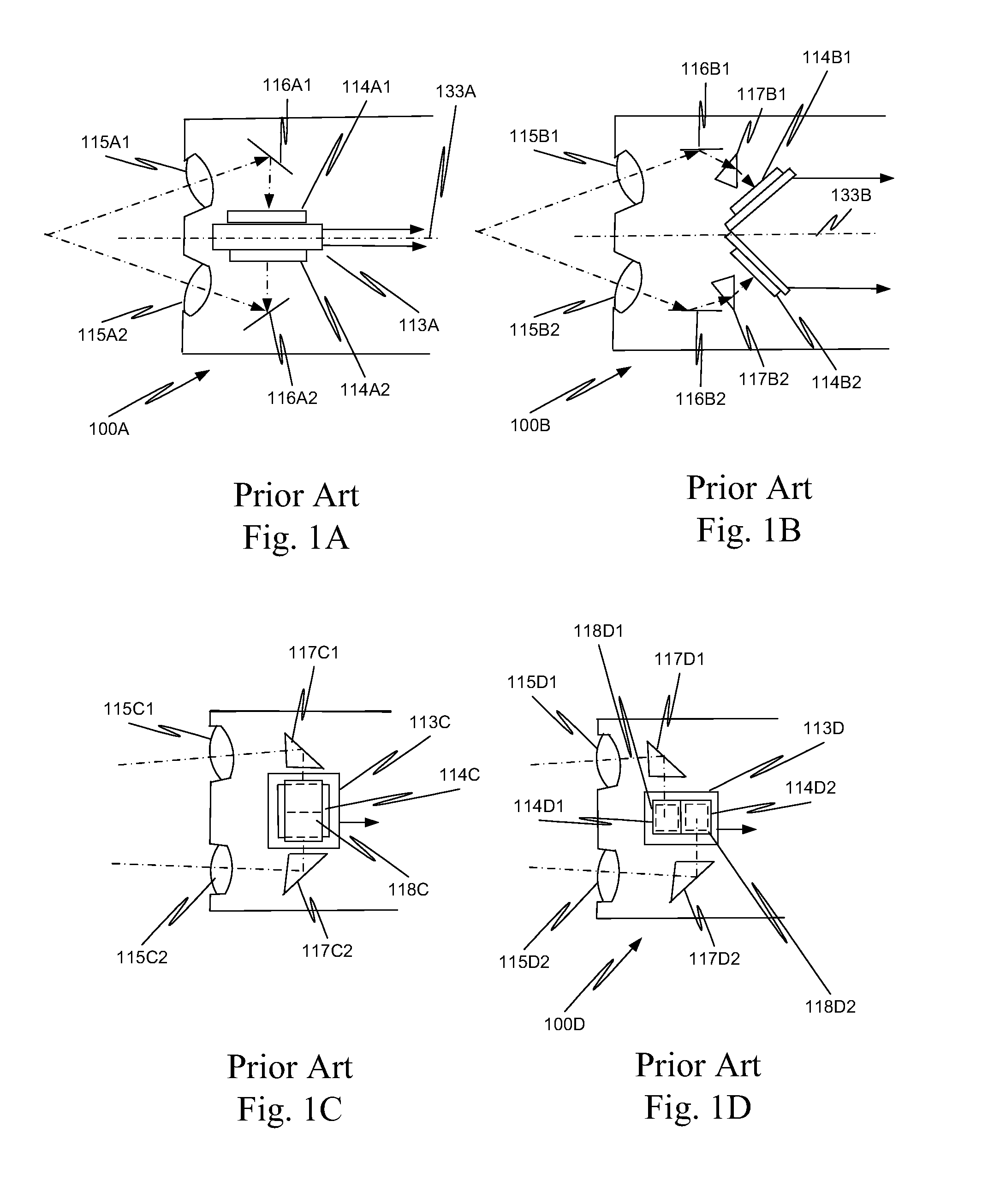
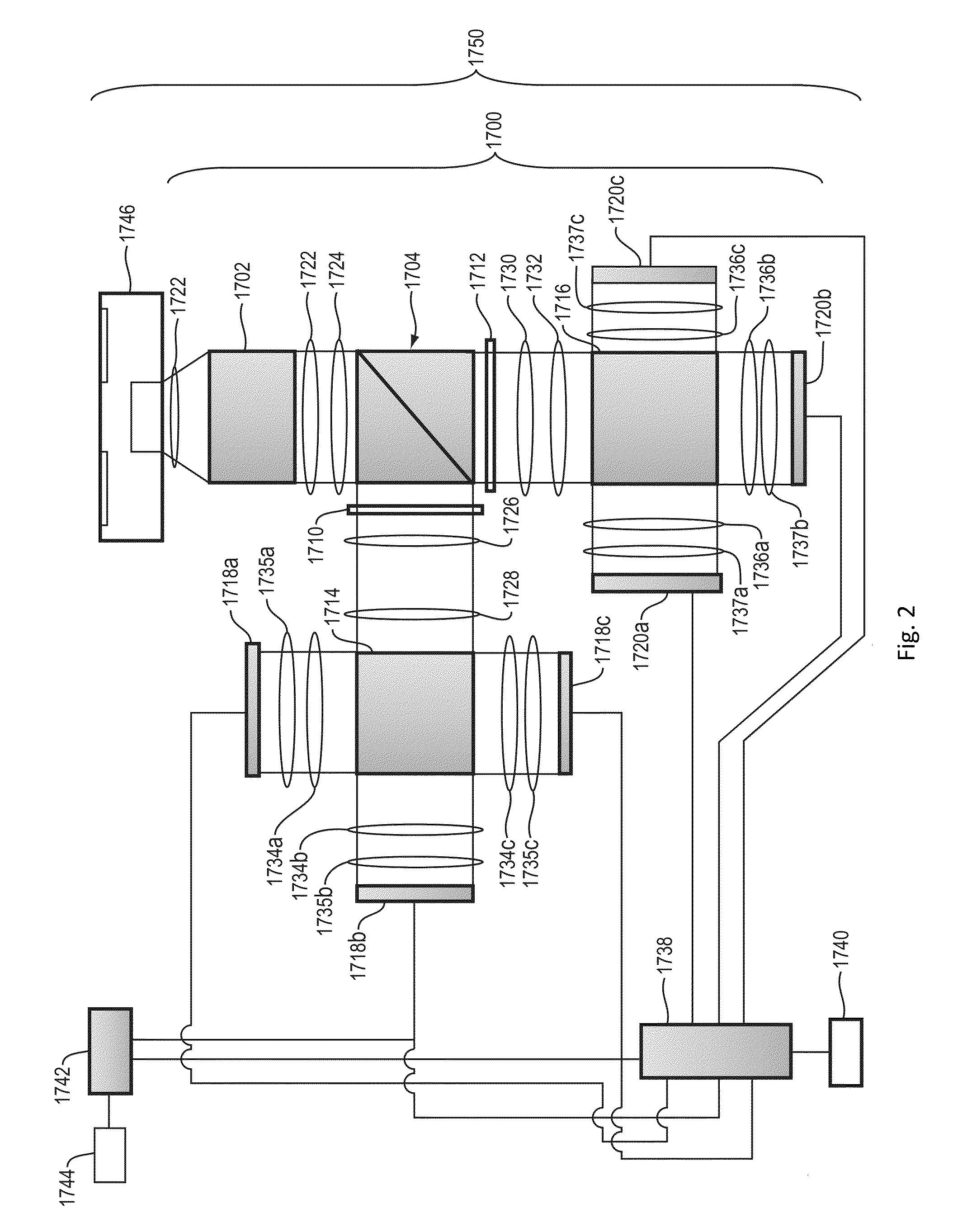
Method and apparatus for stereoscopic imaging
A device is disclosed that utilizes color or polarization to generate two separate images of the same object taken from the two perspectives that correspond to the left and right eyes of an observer. The two separate images are captured through a single camera objective (e.g., a single shutter camera), resulting in a single image with 3D information encoded in the color or polarization. Advantageously, the images are captured simultaneously, permitting obtaining stereoscopic images of both static and moving subjects, allowing 3D video capture. Examples include stereoscopic image acquisition devices that employ two or more image sensors, allowing for an acquisition of a high-definition image. For example, the device can include a trichroic prism and six image sensors, thus capturing left-eye and right-eye sets of color component images.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
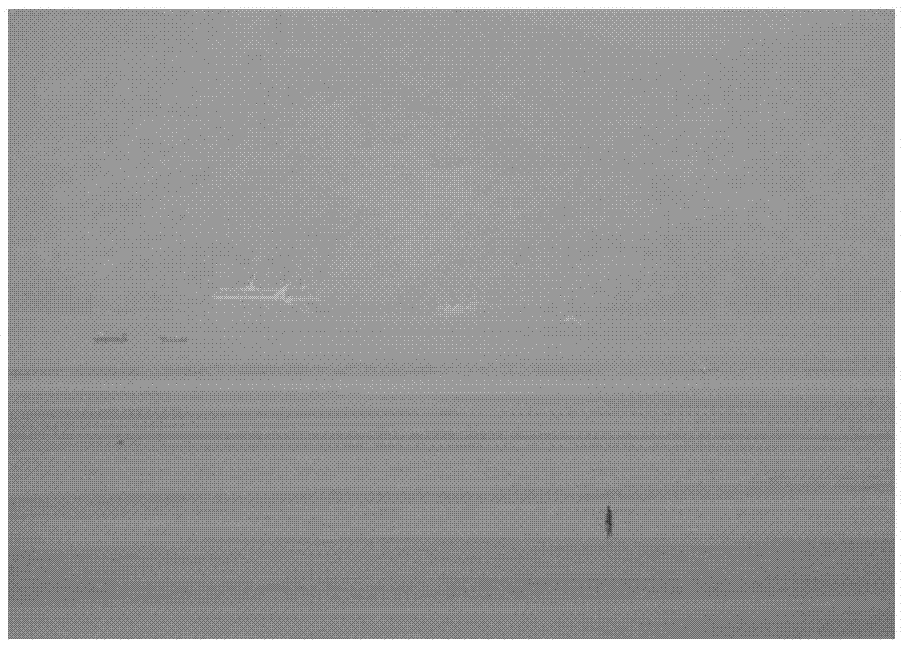
Foggy day image reconstruction method and system
InactiveCN107240080AImprove clarityAvoid cumbersomenessImage enhancementImage analysisReconstruction methodOptical polarization
The invention discloses a foggy day image reconstruction method and system; the method comprises the following steps: obtaining target polarization images of a plurality of different polarization angles under foggy day weather; determining the original foggy day target image and atmosphere light polarization images respectively corresponding to the target polarization images one by one according to the plurality of target polarization images; determining an atmosphere light polarization degree image and an atmosphere light intensity difference value according to the plurality of atmosphere light polarization images; determining an infinite distance atmosphere light intensity value image according to a bright channel prior rule; finally using the original foggy day target image, the atmosphere light polarization degree image, the atmosphere light intensity difference value and the infinite distance atmosphere light intensity value image to determine a fog-free target image. The method and system can solve the problems that a conventional method only consider the atmosphere light polarization characteristics, cannot consider the target light polarization characteristics, thus reducing the image sharpness.
Owner:合肥视展光电科技有限公司
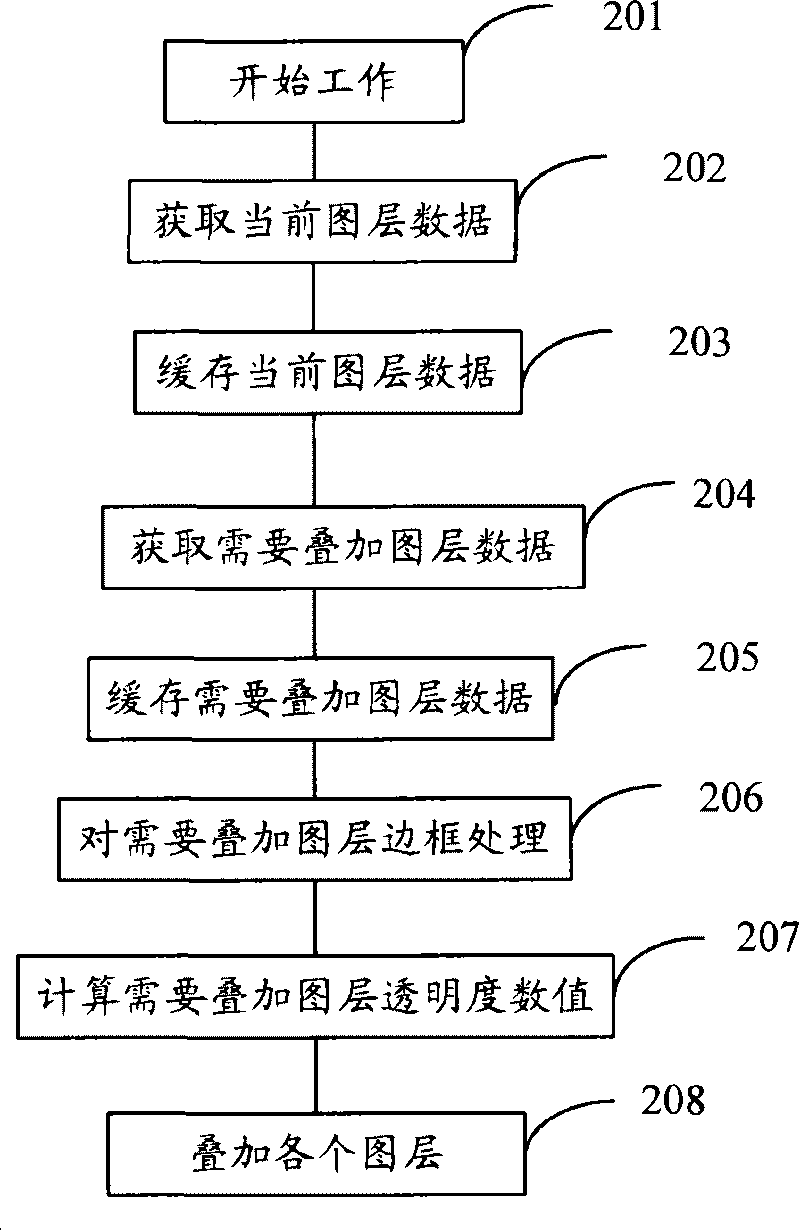
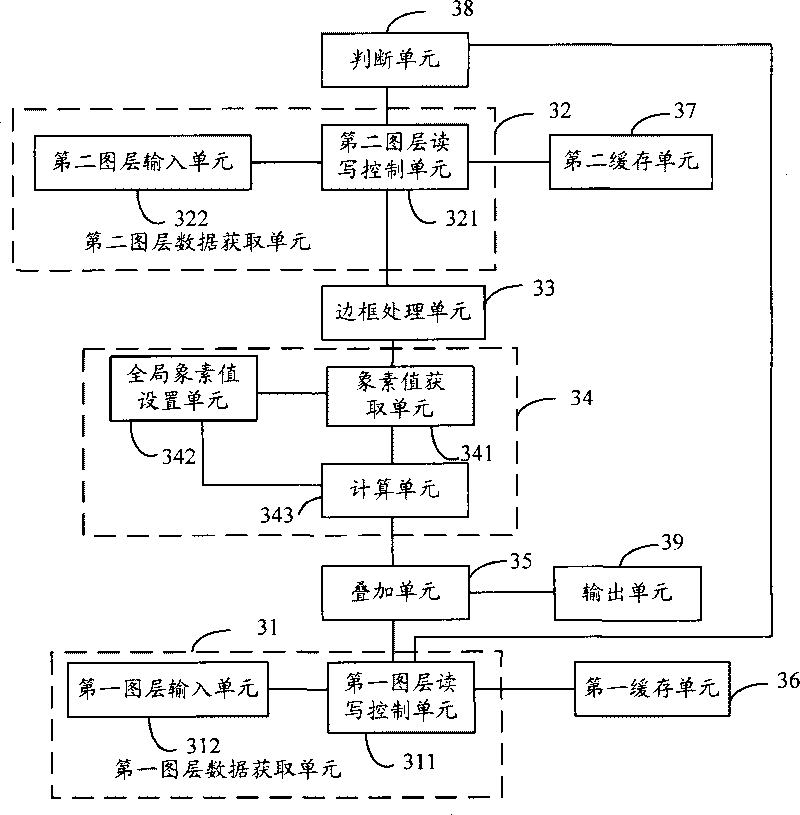
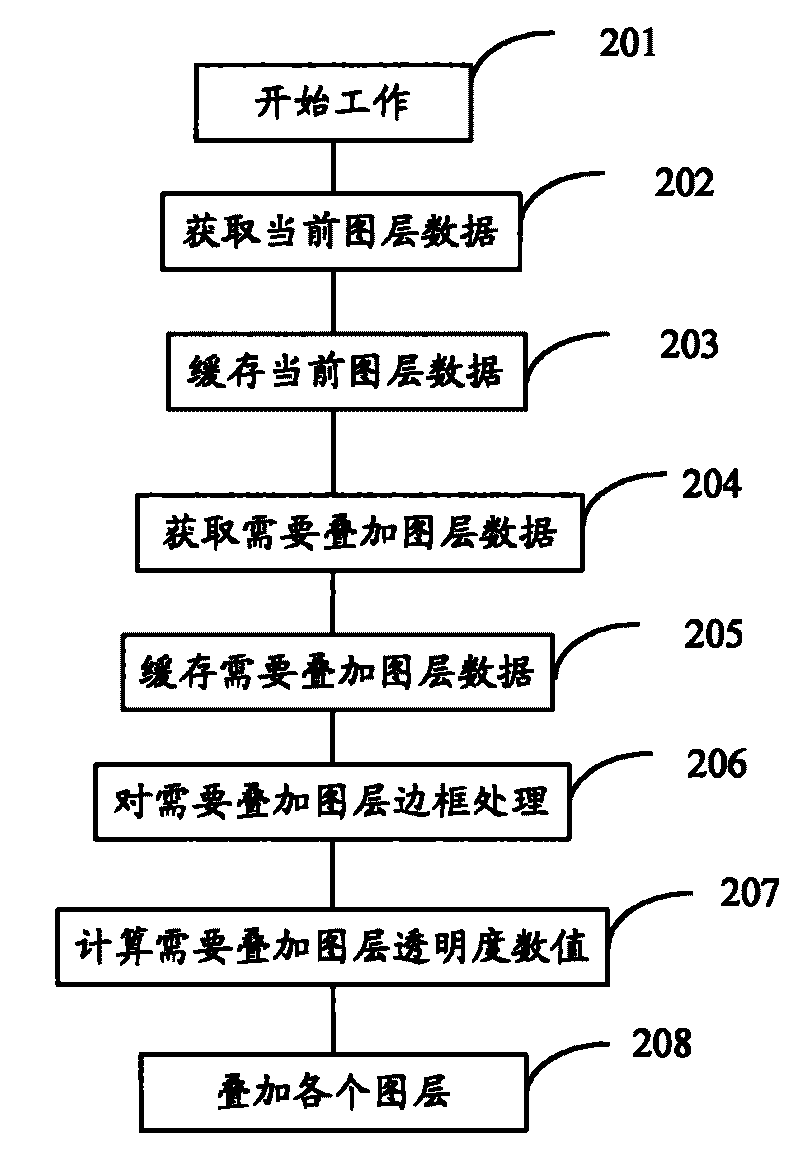
Method and device for multi-drawing layer stacking
ActiveCN101321240BAvoid unclearQuickly adjust transparencyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer hardwareUnsharpness
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and device of stacking multi layer. The method of stacking multi layer comprises: obtaining the data of the current layer and the data of the layer needed to be stacked; executing frame processing to the obtained data of the layer needed to be stacked; executing stack processing to the current layer and the layer needed to be stacked executed by framing processing to obtain the stacked image result. The technical proposal provided by the embodiment of the invention is able to realize to rapidly adjust the video or transparency of the image andsolve the problem of unclarity of the layer after stacking.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
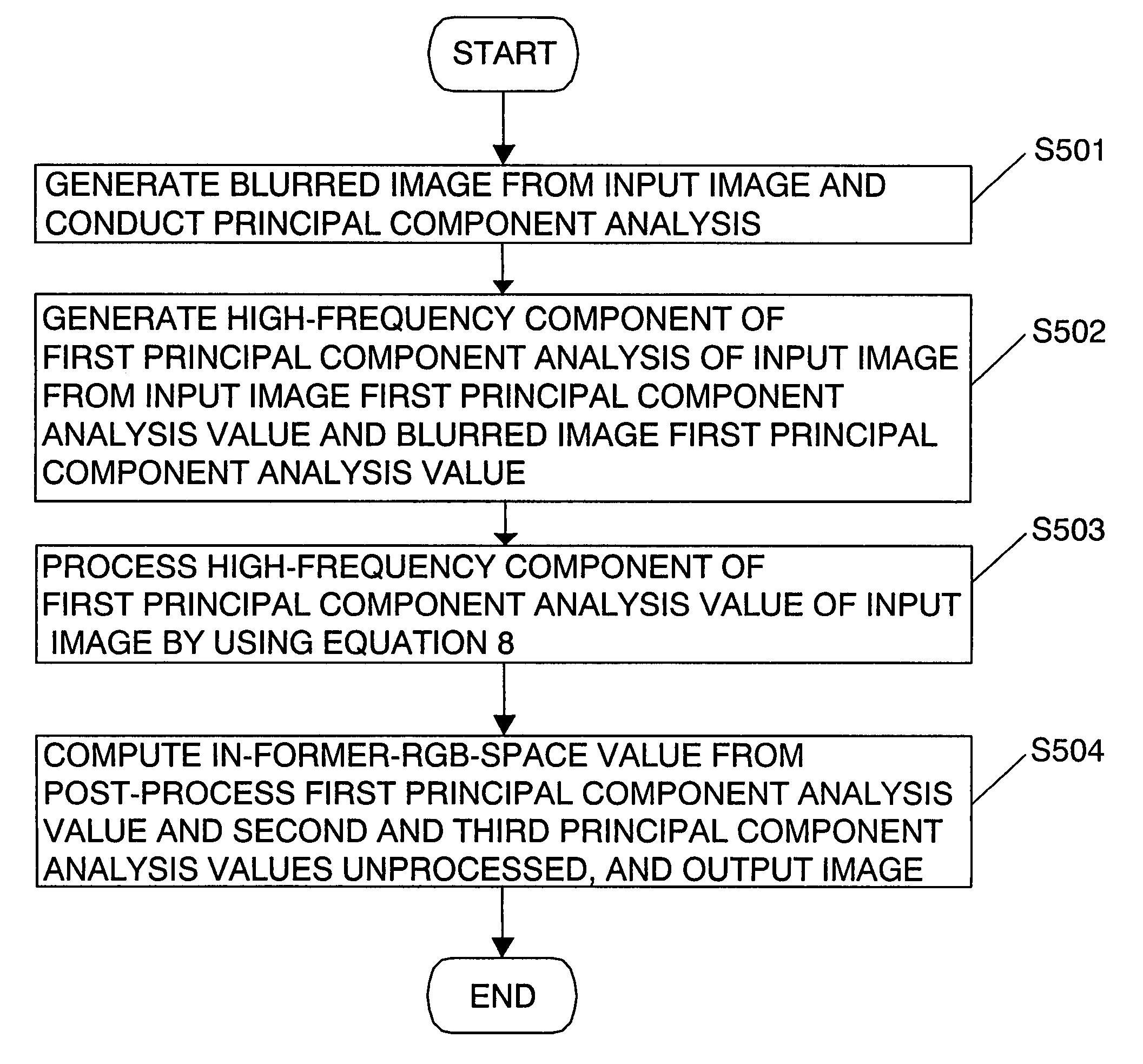
Image processor with sharpness enhancement
ActiveUS7324700B2Easy to viewImprove textureImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPrincipal component analysisDisplay device
When an image inputted is displayed on the display, determined is an enhancing degree as a parameter for enhancing the sharpness of the input image by using at least one of information about a subject included in the input image and information about the display for displaying the input image. By using the enhancing degree determined, color distribution is controlled on a first principal component analysis axis obtained by analysis based on a principal component analysis in a color space. Furthermore, the texture of the subject is magnified in size and again mapped onto the subject. Due to this, the input image can be enhancement-processed to a well texture feeling easy to view.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and device for enhancing image
InactiveCN104346774AEnhanced Velocity FalloffPrevent over-removalImage enhancementTelevision system detailsUser deviceUnsharpness
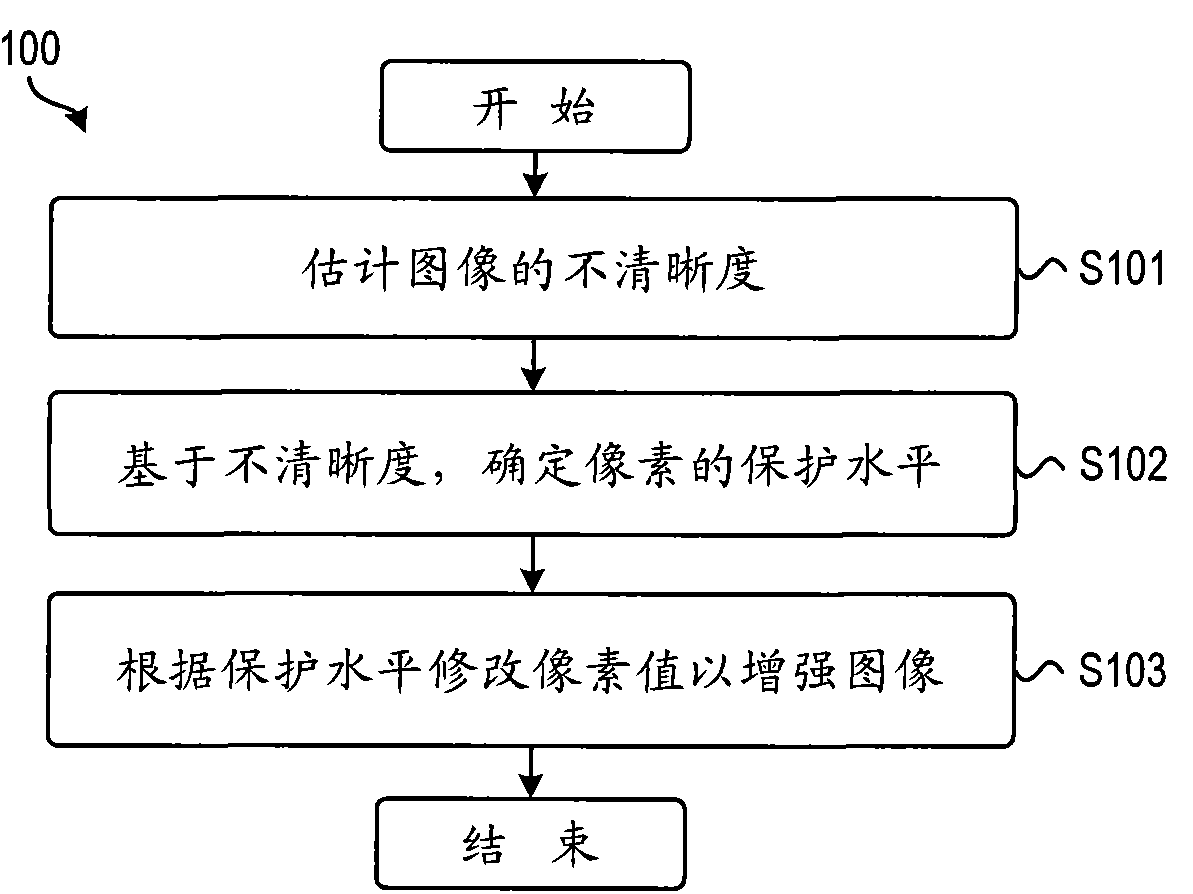
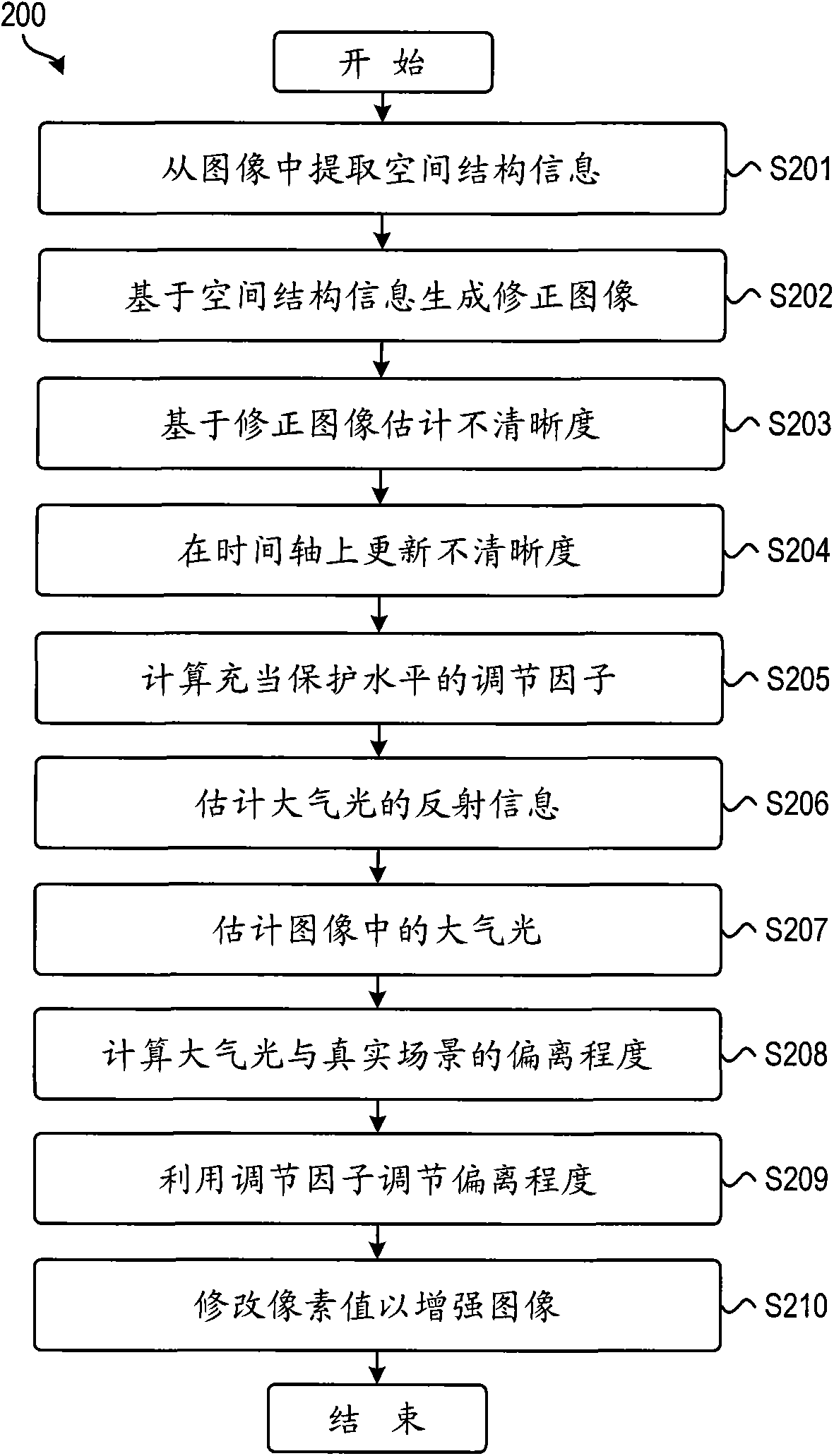
Embodiments of the present invention relate to a method and apparatus for image enhancement. In particular, there is provided a method for image enhancement, the method comprising: estimating unsharpness of the image (S201 -S204); determining a protection level of at least one pixel in the image based on the unsharpness (S205); and modifying a value of the at least one pixel to enhance the image, an amount of the modifying being determined at least in part based on the protection level (S206-S210). A corresponding apparatus and user device are disclosed. The invention may be applied to fog or haze removal from images or video without producing over-removal artifacts. In some embodiments, the invention may also be used to remove noise from low-light images.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
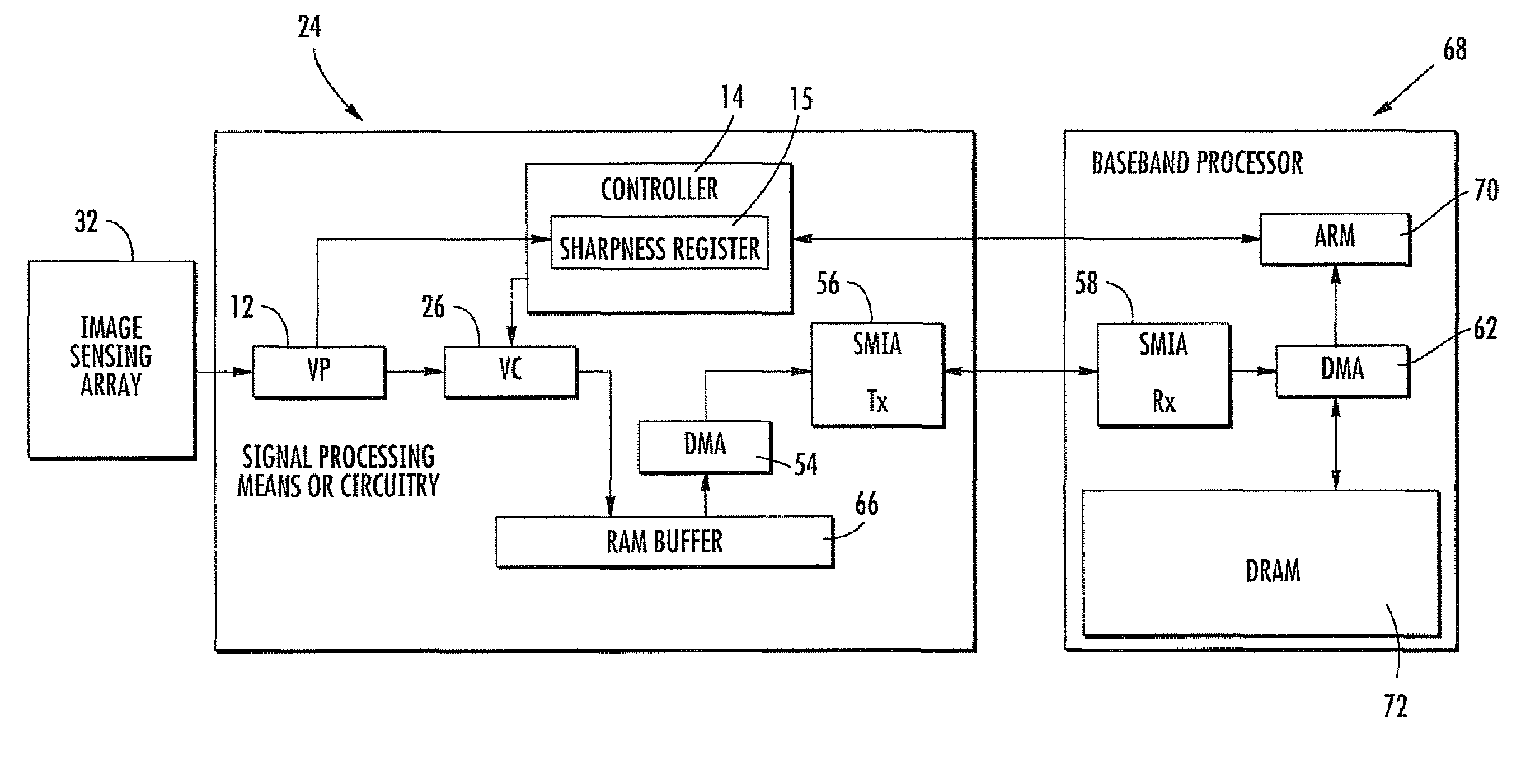
Image sensors for establishing an image sharpness value
A method of compensating for camera shake includes reading a sequential series of images from an image sensing array, establishing a sharpness value for each of the sequential series of images, and performing an image selection based upon each sharpness value. The sharpness value is calculated for each image of the sequential series thereof during the reading.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (RES & DEV) LTD
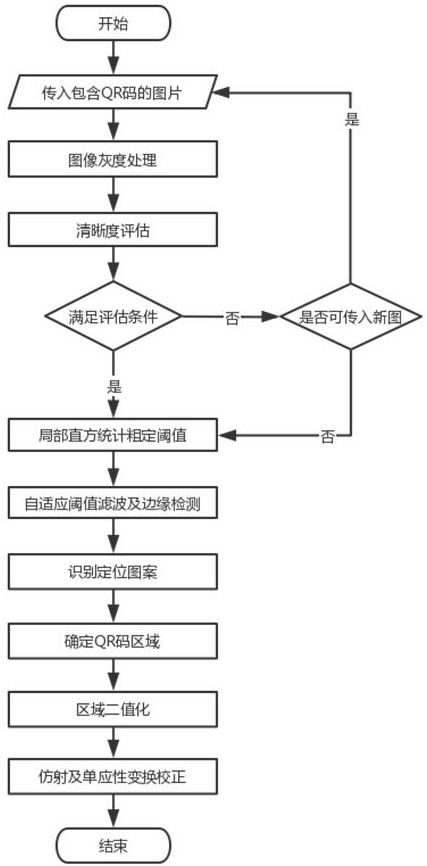
Method for quickly positioning damaged QR code according to image redundancy information
ActiveCN112560538AReduce the number of traversalsHigh speedImage enhancementImage analysisGradationEngineering
The invention discloses a method for quickly positioning a damaged QR code according to image redundancy information. The method comprises the following steps: performing gray processing on a picturecontaining the QR code; carrying out definition evaluation on the grayscale picture; performing filtering and edge detection on the grayscale picture; determining three positioning patterns of the QRcode according to the width ratio of the stripes; performing adaptive binarization on the QR code region in combination with the size of the positioning pattern; and searching four edges of the QR code through affine transformation, and finally performing positioning correction by using homography transformation. According to the method for quickly positioning the damaged QR code, redundant information in the image is fully utilized, the image traversal frequency is reduced as much as possible, and the algorithm speed is increased; self-adaptive threshold edge detection and self-adaptive threshold binaryzation are adopted, so that the edge detection and binaryzation effects are improved; unclear images are filtered, and excessive waste of computing resources can be avoided.
Owner:JIANGSU SEUIC TECH CO LTD
Adaptive anisotropic filtering of projection data for computed tomography
ActiveUS7656990B2Reduce high frequency noiseReduce radiation doseImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionLow-pass filterImaging quality
CT imaging is enhanced by adaptively filtering x-ray attenuation data prior to image reconstruction. Detected x-ray projection data are adaptively and anisotropically filtered based on the locally estimated orientation of structures within the projection data from an object being imaged at a plurality of rotation positions. The detected x-ray data are uniformly low pass filtered to preserve the local mean values in the data, while the high pass filtering is controlled based on the estimated orientations. The resulting filtered data provide projection data with smoothing along the structures while maintaining sharpness along edges. Image noise and noise induced streak artifacts are reduced without increased blurring along edges in the reconstructed images. The enhanced image allows reduced x-ray dose while maintaining image quality.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
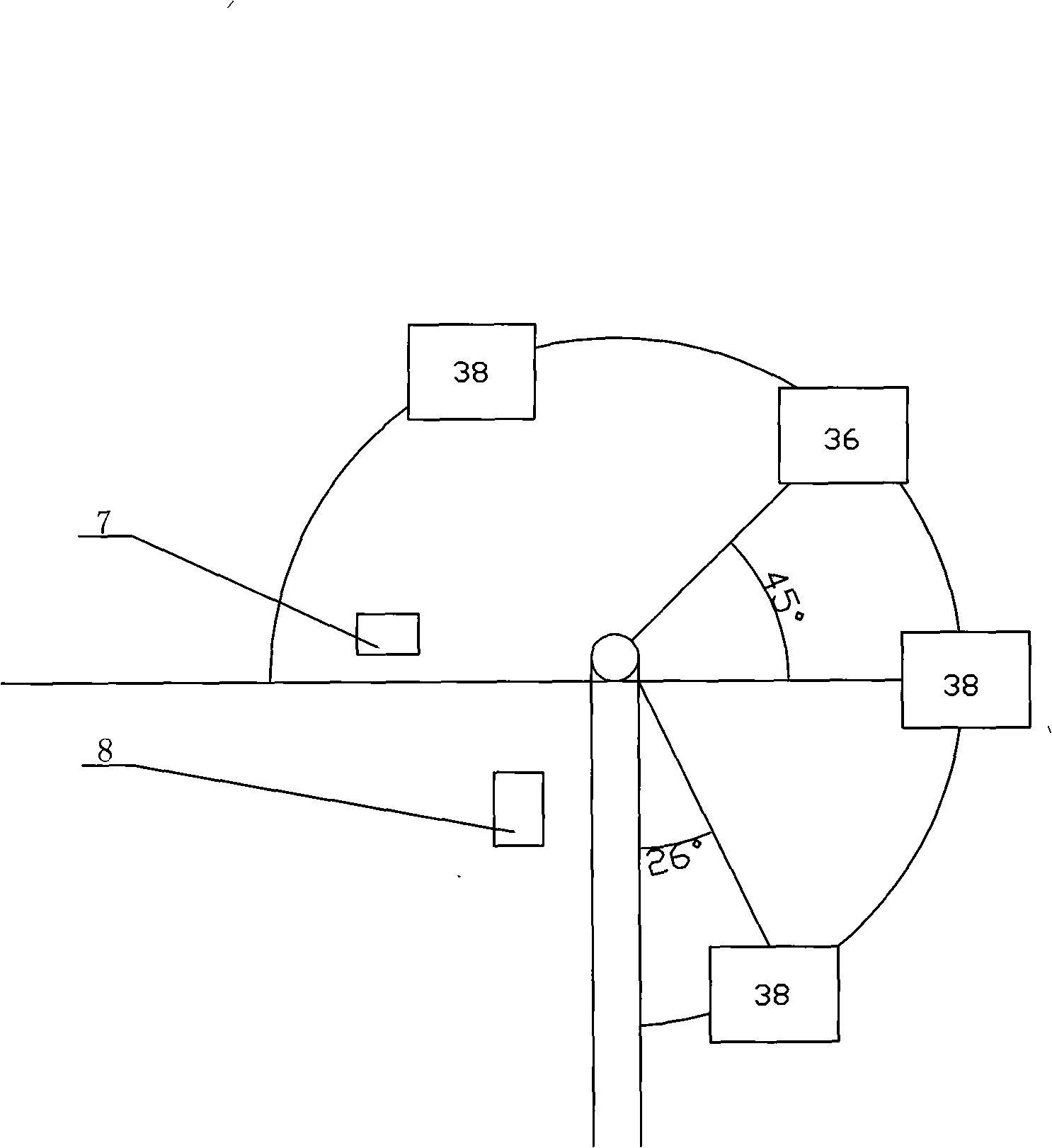
Gamma source three-source combined full view exposure method for macrotype spherical storage tank
InactiveCN101344496ASatisfied with the quality effectBasically uniform panoramic radiation fieldMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation fieldPhotographic plate
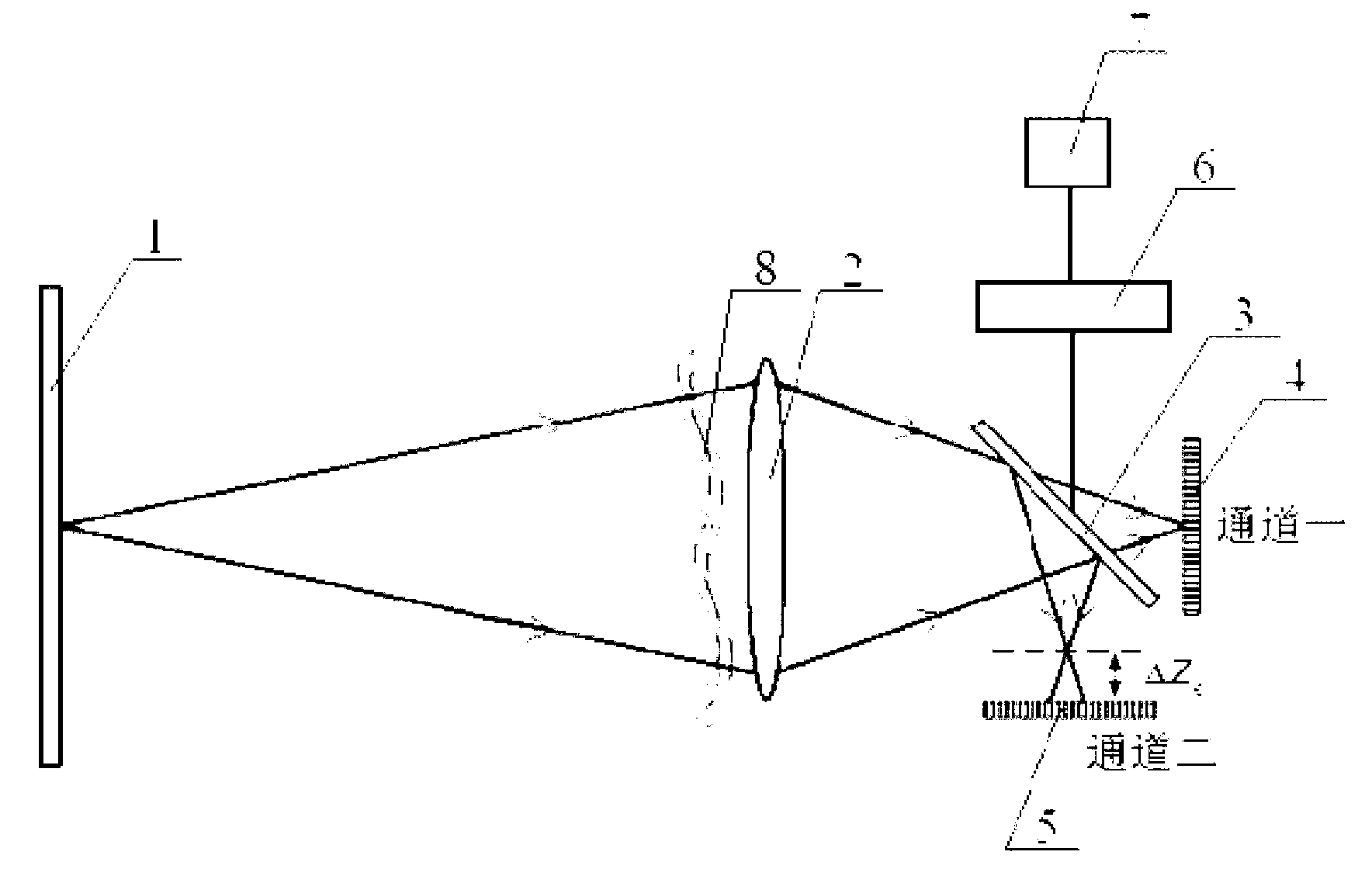
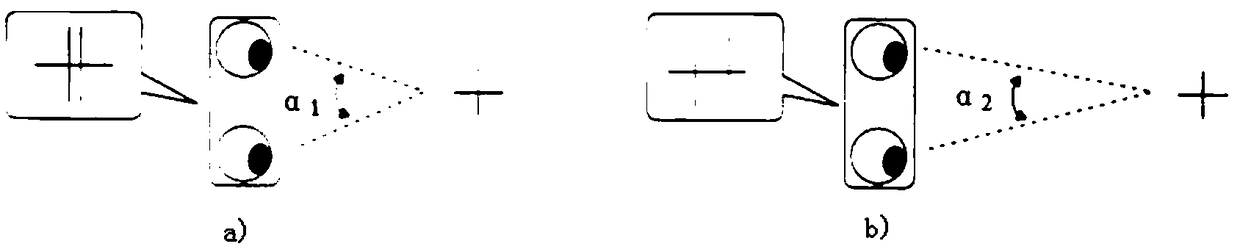
The invention relates to a panoramic exposure method with three-source Gamma source combination of a large-scale spherical storage tank, which adopts the irradiation with three-source bound combination, can obtain a basically even panoramic radiation field, completely satisfies the standard fog density and sensitivity requirements of photographic plates, has greatly shortened irradiation time and novel techniques, is simple, convenient, safe, reliable and environment-protective, and can improve the nondestructive examination quality. The panoramic exposure method comprises the following technical steps: a central point of the spherical storage tank is obtained by measurement, a Gamma source head is packed on a nylon belt and positioned at the central point of the spherical storage tank, and the nylon belt is fixed in centers of an upper inlet orifice and a lower inlet orifice and strung by an euphroe, thus avoiding swinging; a source tank is connected with a drive device, and source transmission pipes and a drive hose are straightly positioned with the bend radius no less than the least Phi 500; the three source transmission pipes are bound together, and under the precondition that the geometric unsharpness is ensured, three irradiation heads turn outward in a petal shape so as to reduce mutual influence, increase irradiation area and reduce fade zone.
Owner:陕西化建工程有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com