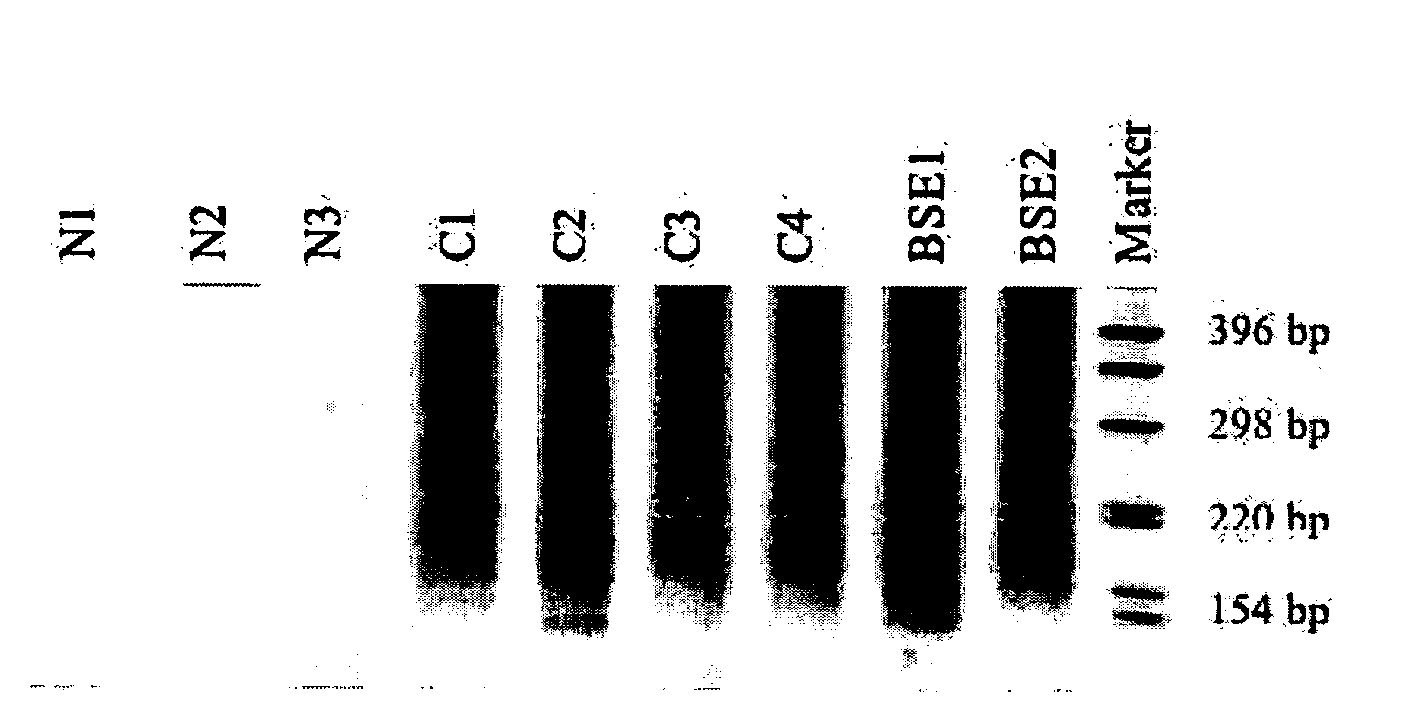Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
60 results about "Transmissible spongiform encephalopathy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
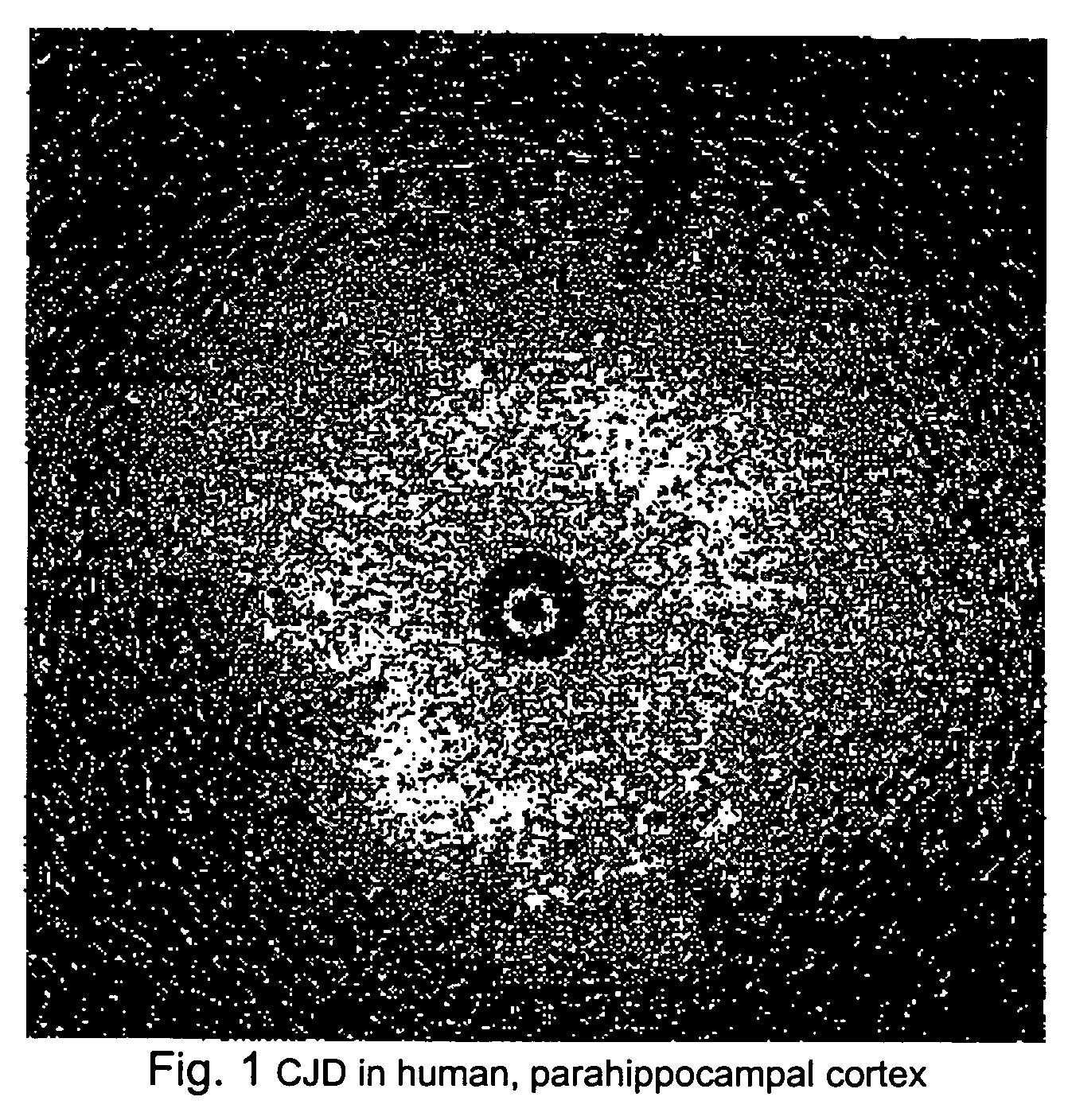
Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) are a group of progressive, invariably fatal, conditions that are associated with prions and affect the brain (encephalopathies) and nervous system of many animals, including humans, cattle, and sheep. According to the most widespread hypothesis, they are transmitted by prions, though some other data suggest an involvement of a Spiroplasma infection. Mental and physical abilities deteriorate and many tiny holes appear in the cortex causing it to appear like a sponge when brain tissue obtained at autopsy is examined under a microscope. The disorders cause impairment of brain function, including memory changes, personality changes and problems with movement that worsen chronically.
Methods for sterilizing biological materials
InactiveUS6946098B2Lowered residual solventReduce the temperatureOther blood circulation devicesFood preservationBiochemistryBiological materials
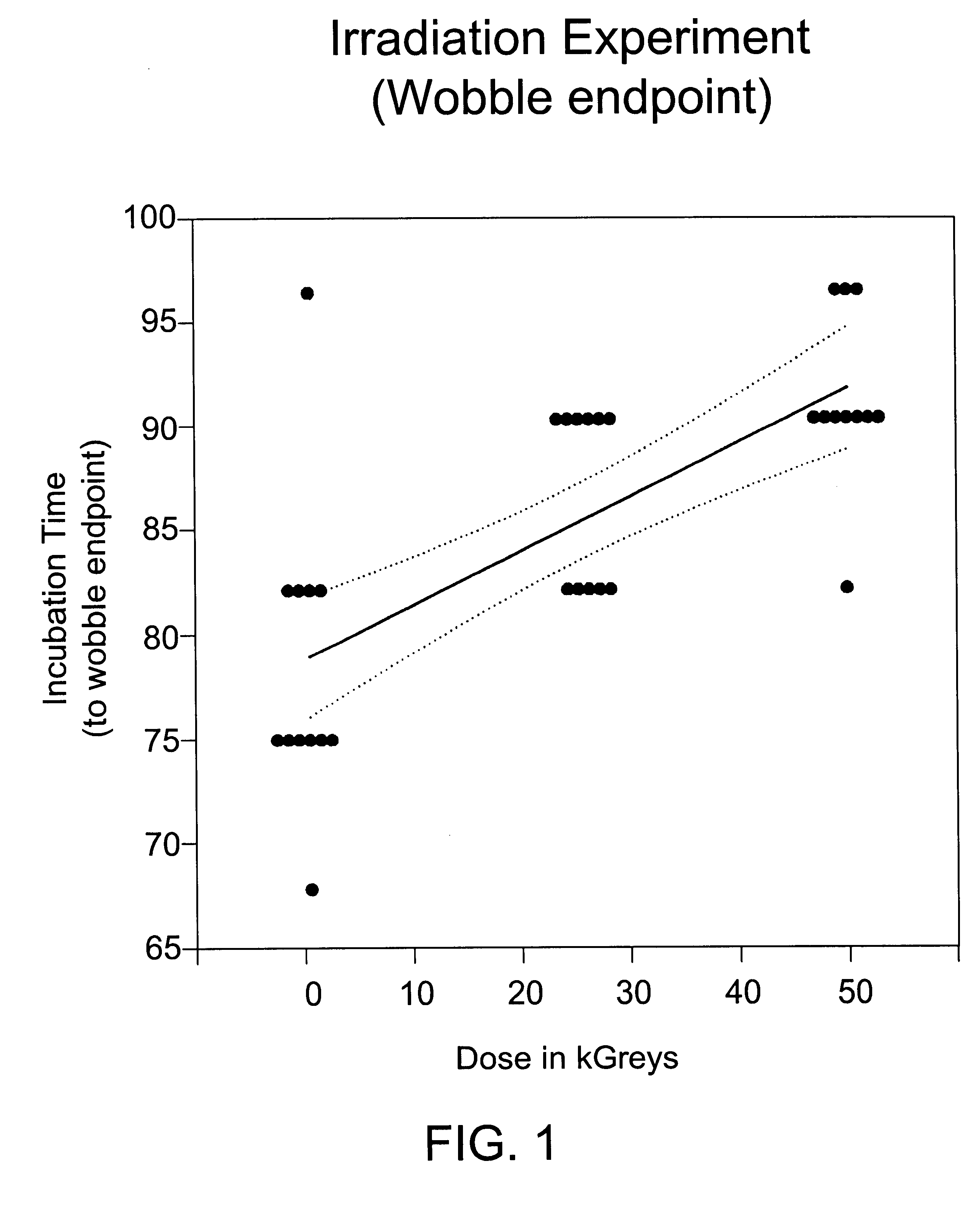
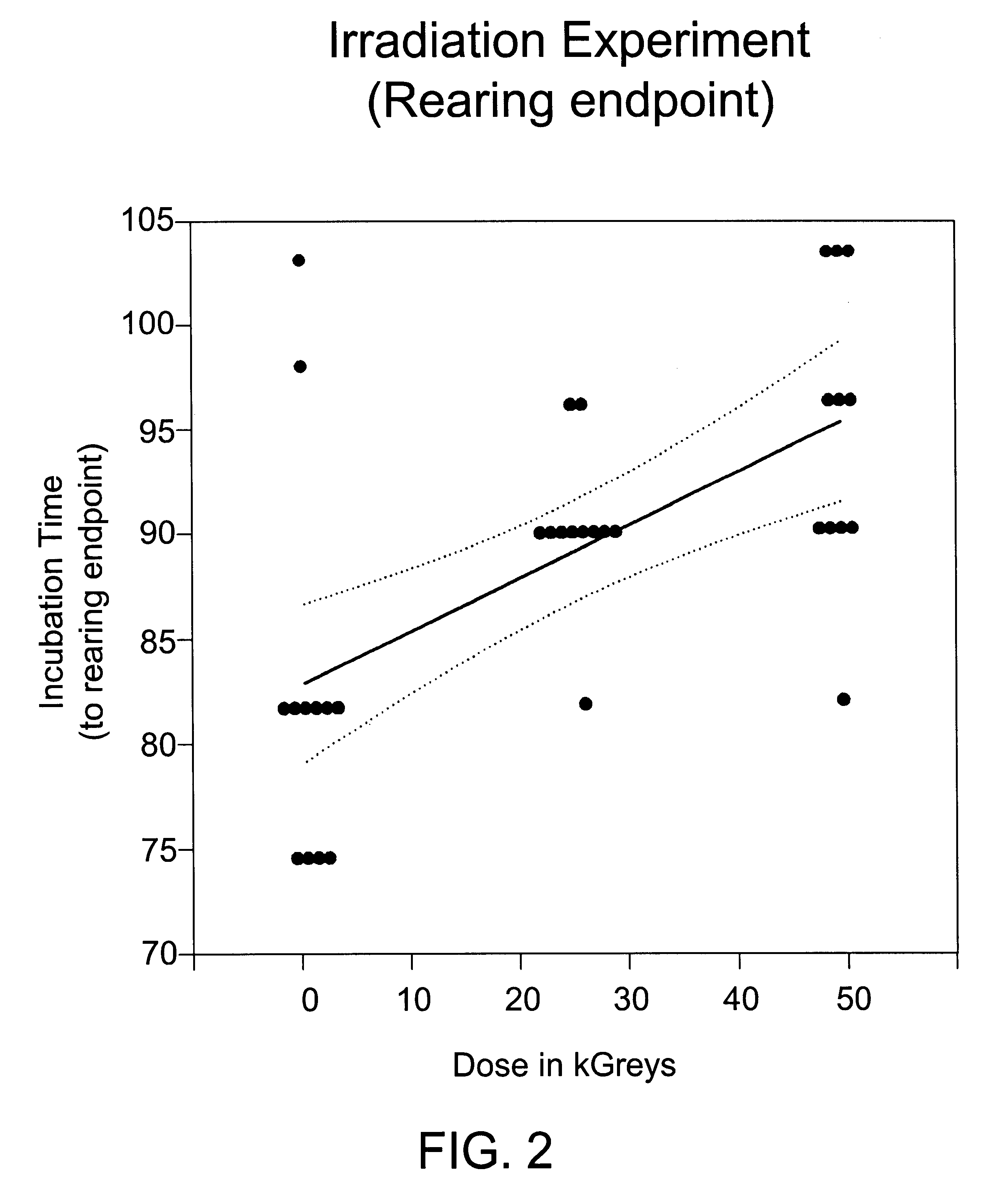
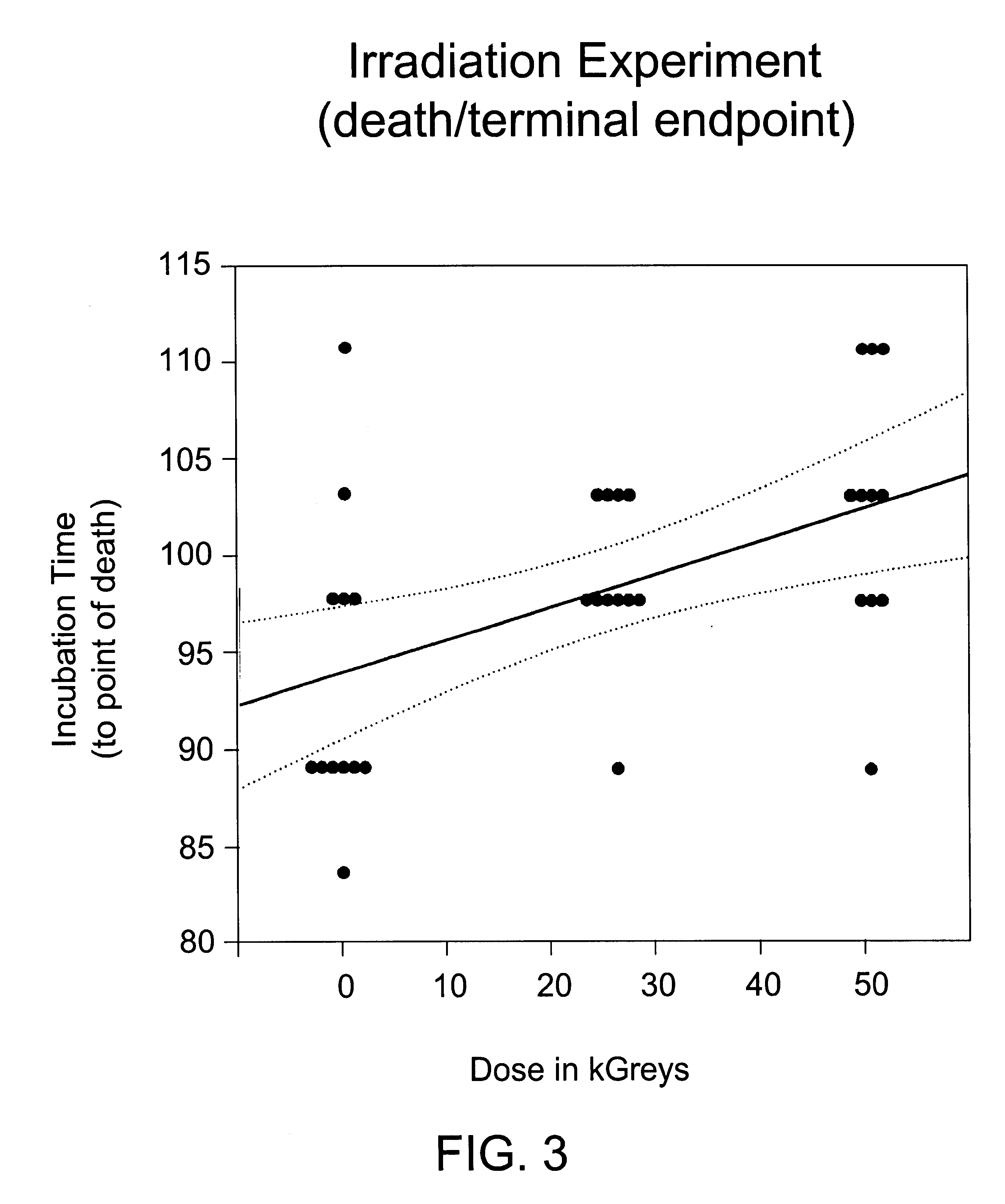
Methods are disclosed for sterilizing biological materials to reduce the level therein of one or more biological contaminants or pathogens, such as prions, responsible for the disease states known as transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) in mammals. These methods involve sterilizing biological materials with irradiation.
Owner:CLEARANT
Method and kit for extracting prion protein
InactiveUS6150172AMethod is fastThe testing process is simplePeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesIonic strengthSheep brain
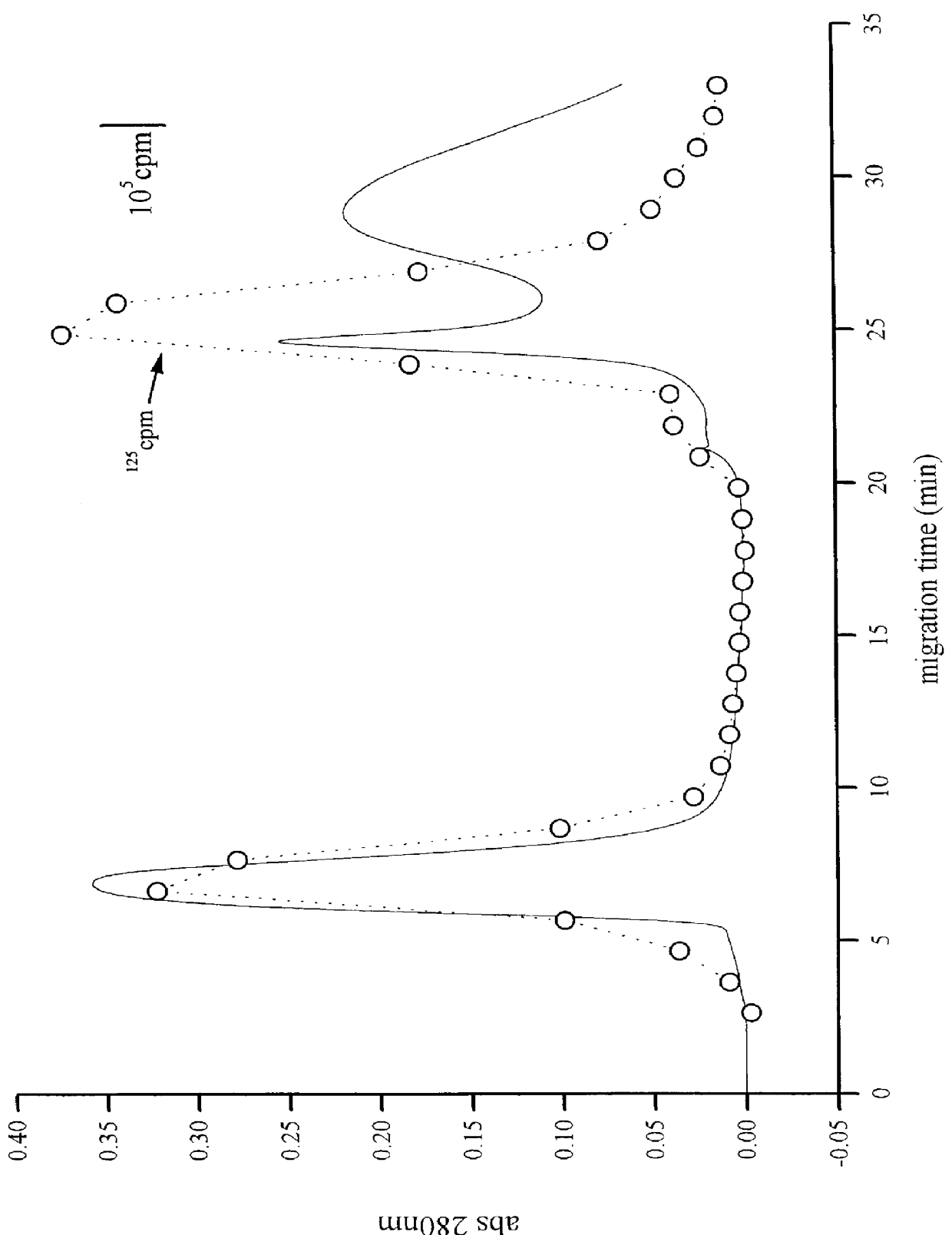
A method for extracting prion protein from a biological material, e.g., an animal tissue or product. In a specific example, abnormal prion protein is extracted from homogenized sheep brain with hexafluoro-2-propanol. The hexafluoro-2-propanol is separated from the aqueous brain preparation by increasing the ionic strength of the aqueous solution. Prion protein in the organic extract can be further purified, or the extract can be tested, e.g., by immunoassay, for the presence of prion protein, and more particularly abnormal prion protein. The extraction process permits testing for the presence of abnormal prior protein, e.g., for diagnosis of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSE).
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Methods for immunoglobulin purification
InactiveUS20050272917A1Serum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansImmunglobulin eBovine serum albumin
Disclosed herein are methods for purifying immunoglobulin G (IgG). The methods feature the use of particular buffers and reagents to isolate and purify human IgG or to remove host contaminating proteins, non-human or chimeric IgG, IgG dimers, IgG aggregates, bovine serum albumin, transmissible spongiform encephalopathy, DNA, viral DNA, or viral particles from a feedstock. IgG purified by the methods described herein can be used for research, diagnostic, or therapeutic purposes.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
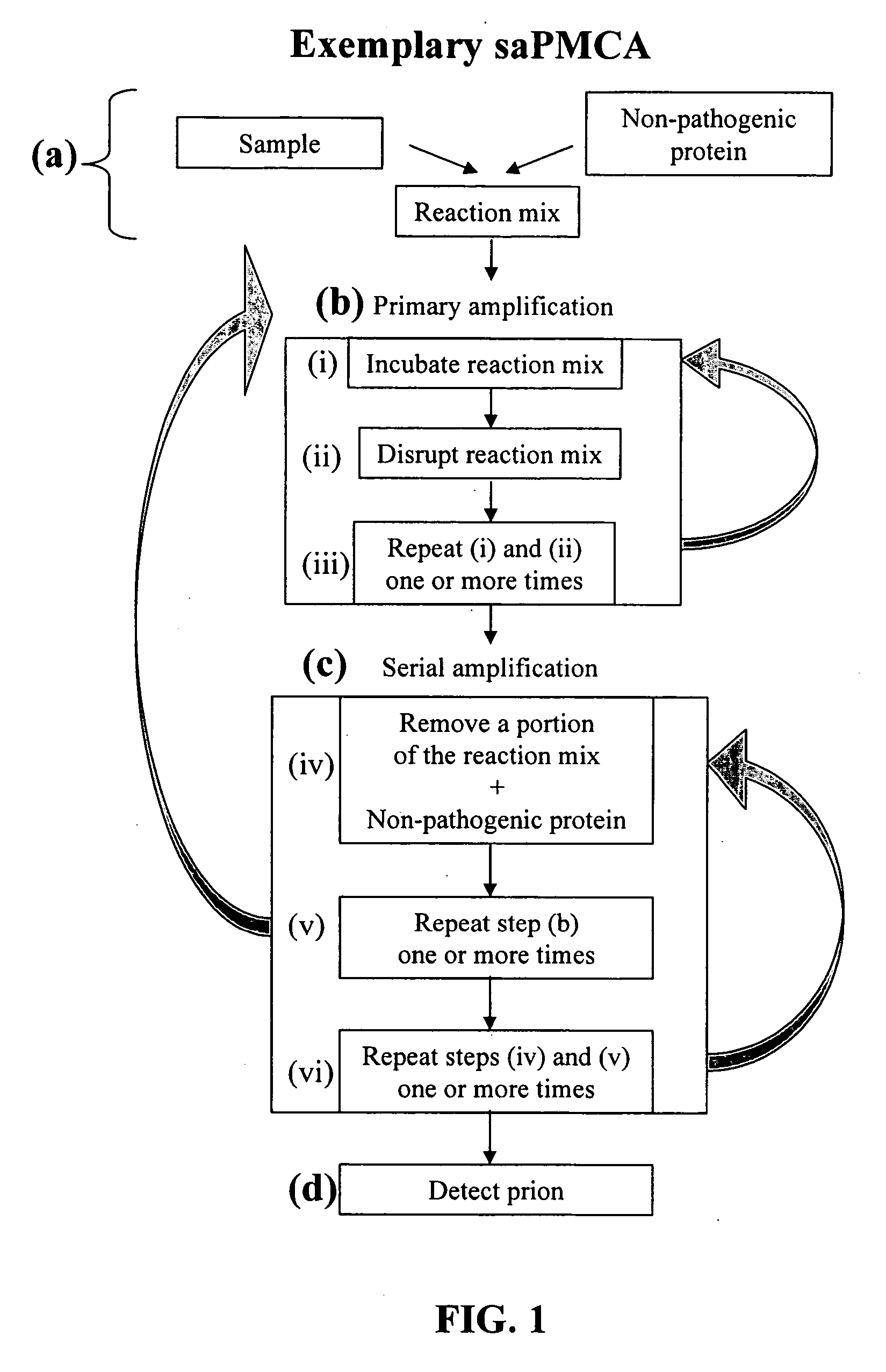
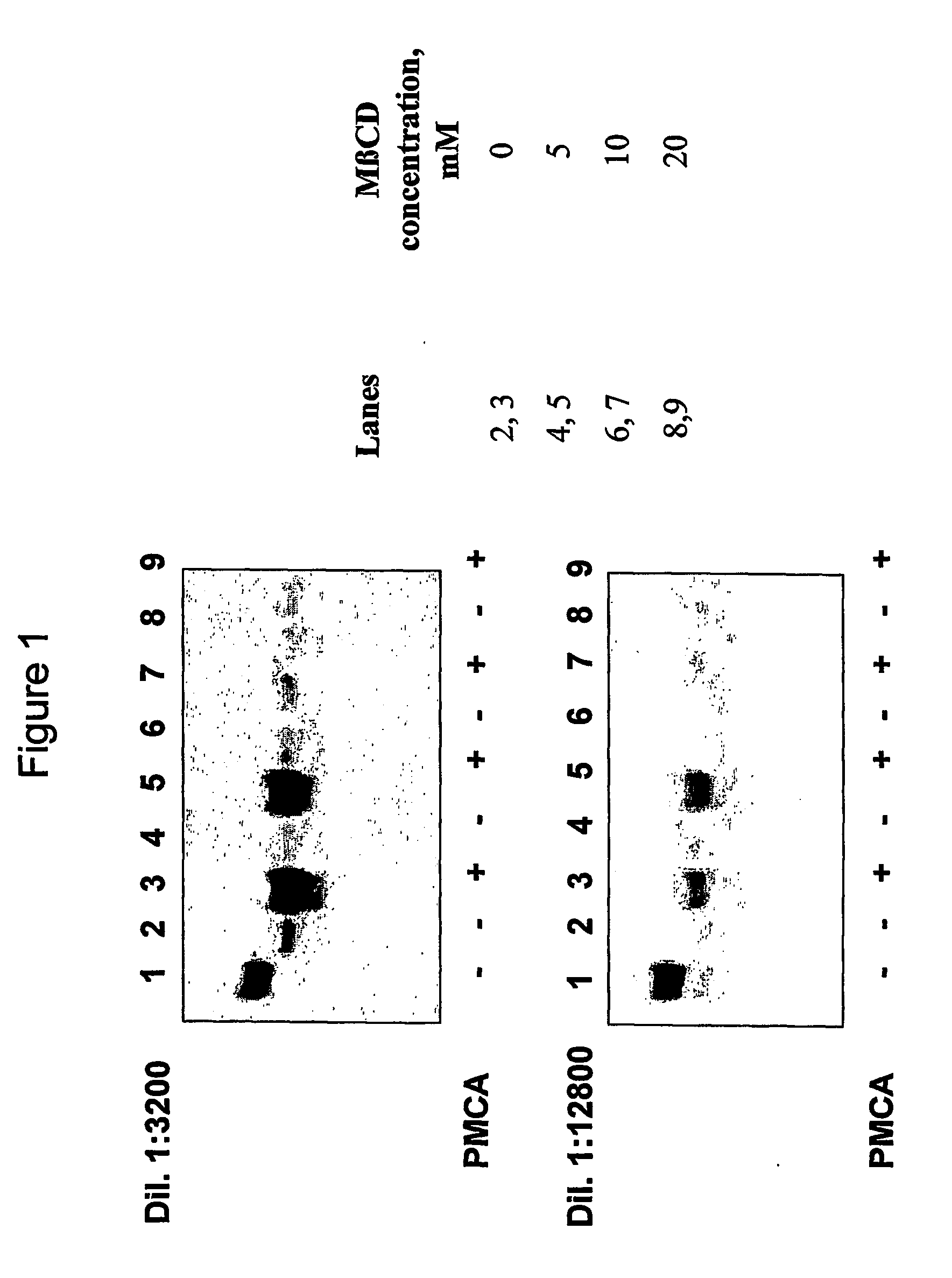
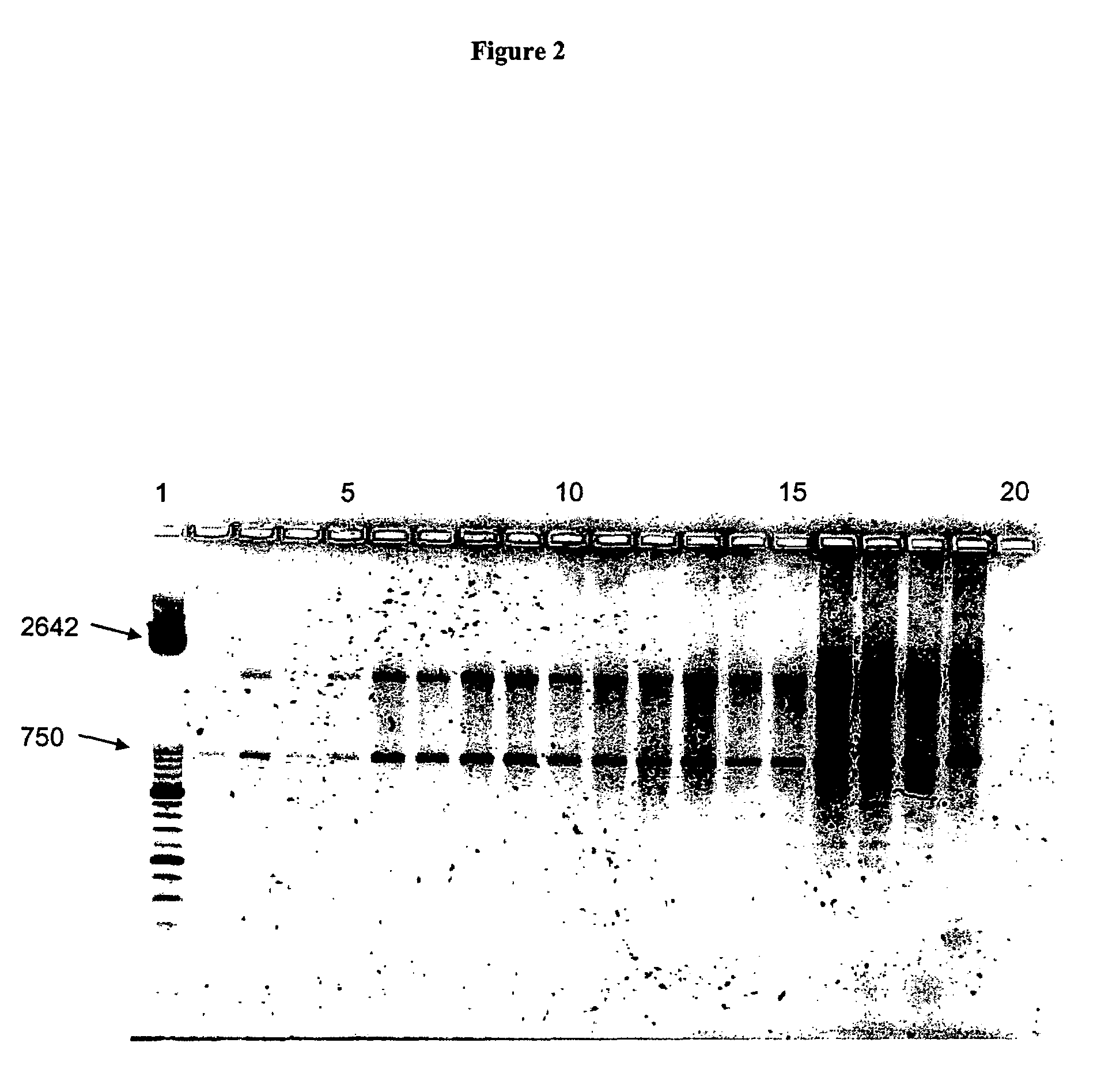
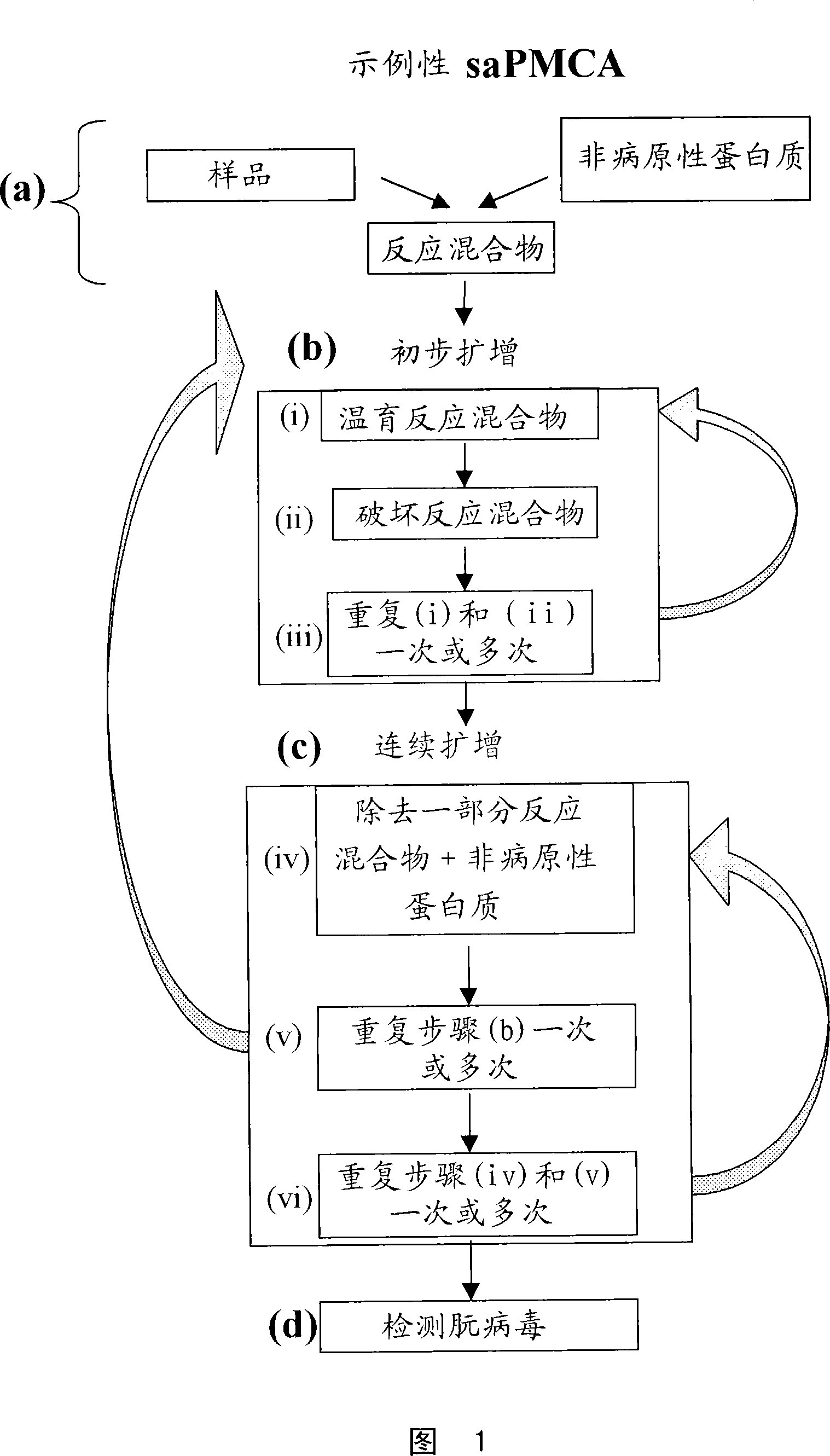
Ultrasensitive detection of prions by automated protein misfolding cyclic amplification
InactiveUS20060263767A1Easy to copyDegree of improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisChronic wasting diseaseScrapie Virus
A highly sensitive method is provided for the detection of prions in a sample. These methods may be used to diagnose prion mediated transmissible spongiform encephalopathies such as bovine spongiform encephalopathy, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie, or chronic wasting disease. In particular a method for serial automated cyclic amplification of prion is disclosed. The method is both rapid and highly sensitive making it ideal for high throughput testing.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF TEXAS SYST THE
Detection of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies
InactiveUS6033858ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSpiroplasmaTransmissible mink encephalopathy
Provided is a method of detecting transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. The method comprises: selecting a sample from a subject to determine whether the subject has a transmissible spongiform encephalopathy; and detecting spiroplasma-specific 16S rDNA indicative of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies in the sample. The spiroplasma-specific 16S rDNA is preferably detected by contacting the sample with a pair of oligonucleotide primers under polymerase chain reaction conditions and detecting the resulting polymerase chain reaction product, wherein each of the pair of the oligonucleotide primers is complementary to spiroplasma-specific 16S rDNA indicative of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Further provided is an oligonucleotide having a nucleotide sequence complementary to spiroplasma-specific 16S rDNA indicative of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies; as well as an oligonucleotide having a nucleotide sequence specific to spiroplasma-specific 16S rDNA indicative of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies.
Owner:BASTIAN FR O
Rapid prion-detection assay
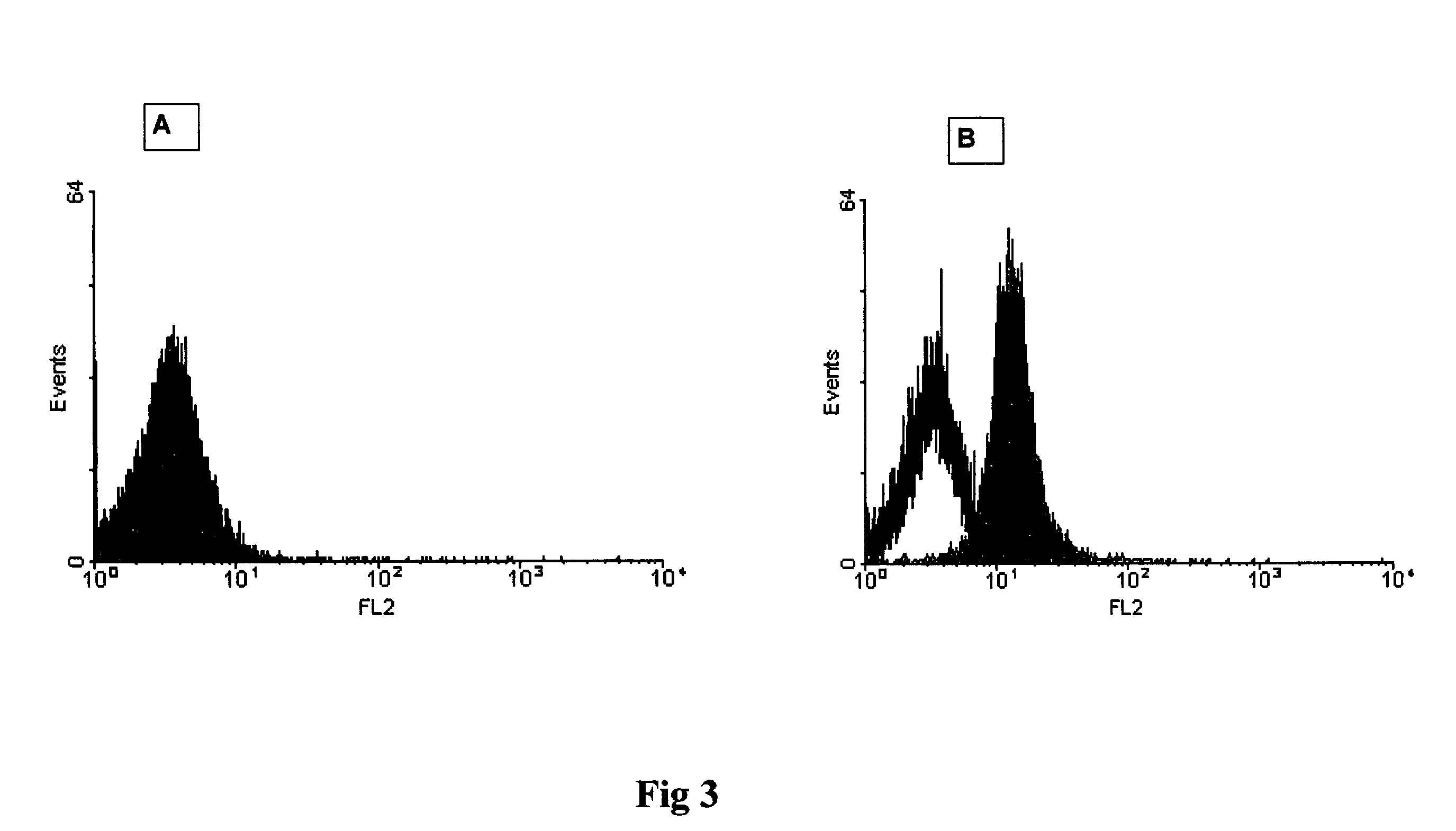
Assays are provided for rapid detection, with high specificity of the pathogenic form of prion protein responsible for neurodegenerative diseases affecting humans and animals, such as transmissible spongiform encephalopathy in bovine, sheep, and cats. Also provided are assays for testing animal feedstock, such as animal feed, for the presence or concentration of pathogenic prion protein. Results are available in from about 0.5 to about 20 minutes and preferably within from about 5 to about 10 minutes. The assays employ proteinase-K to remove normal prion protein from a biological sample, so that the sample may be analyzed by immunochromatography to determine the presence and concentration of pathogenic prion protein. Because the proteinase-K is immobilized on a solid support for in situ removal of interfering components, the present invention obviates the need for subsequent extraction of the desired analyte. All aspects of the present invention are suitable for quantifying the minimal detectable amount of pathogenic prion protein in a biological sample. Moreover, the simplicity of sample preparation makes the present invention suitable for use in the field.
Owner:PRION DEVAL LAB
Diagnostics And Therapeutics For Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy And Methods For The Manufacture Of Non-Infective Blood Products And Tissued Derived Products
InactiveUS20080063600A1Efficiently depletedOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderBiological bodyWhole blood product
B-cells have been identified as being the crucial carriers of infectivity in the spread of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy within an infected organism. In a second step, B-cells may infect further components_of the immune system, e.g. T-cells. Accordingly, the present invention provides B-cell and T-cell specific ligands for the use in diagnostics and therapeutics for transmissible spongiform encephalopathy and provides methods for the manufacture of non-infective blood products and tissue derived products. Thus, the present invention provides medicaments comprising B-cell and / or T-cell depletants, for the treatment of pathologies where the depletion of B-cells and / or T-cells, and more particularly of tse-infected B-cells and / or T-cells is therapeutically effective.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Rapid prion-detection assay
Owner:PRION DEVAL LAB
Prion inhibiting peptides and derivatives thereof
InactiveUS20050181998A1Nervous disorderTetrapeptide ingredientsTransmissible spongiform encephalopathyProteinaceous infectious particle
Short peptides and derivatives or analogs thereof for the treatment or prevention of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies, in particular CJD are herein described. These peptides and / or their derivatives have been designed to block the conformational changes that occur in the prion protein (PrP) and which are implicated in the pathogenesis of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies as well as to dissolve the fibrillar deposits already formed
Owner:LAB SERONO SA
Diagnostic assay for transmissible spongiform encephalopathies
InactiveUS7368247B2Microbiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesFatty acid bindingEnzyme immunoassays
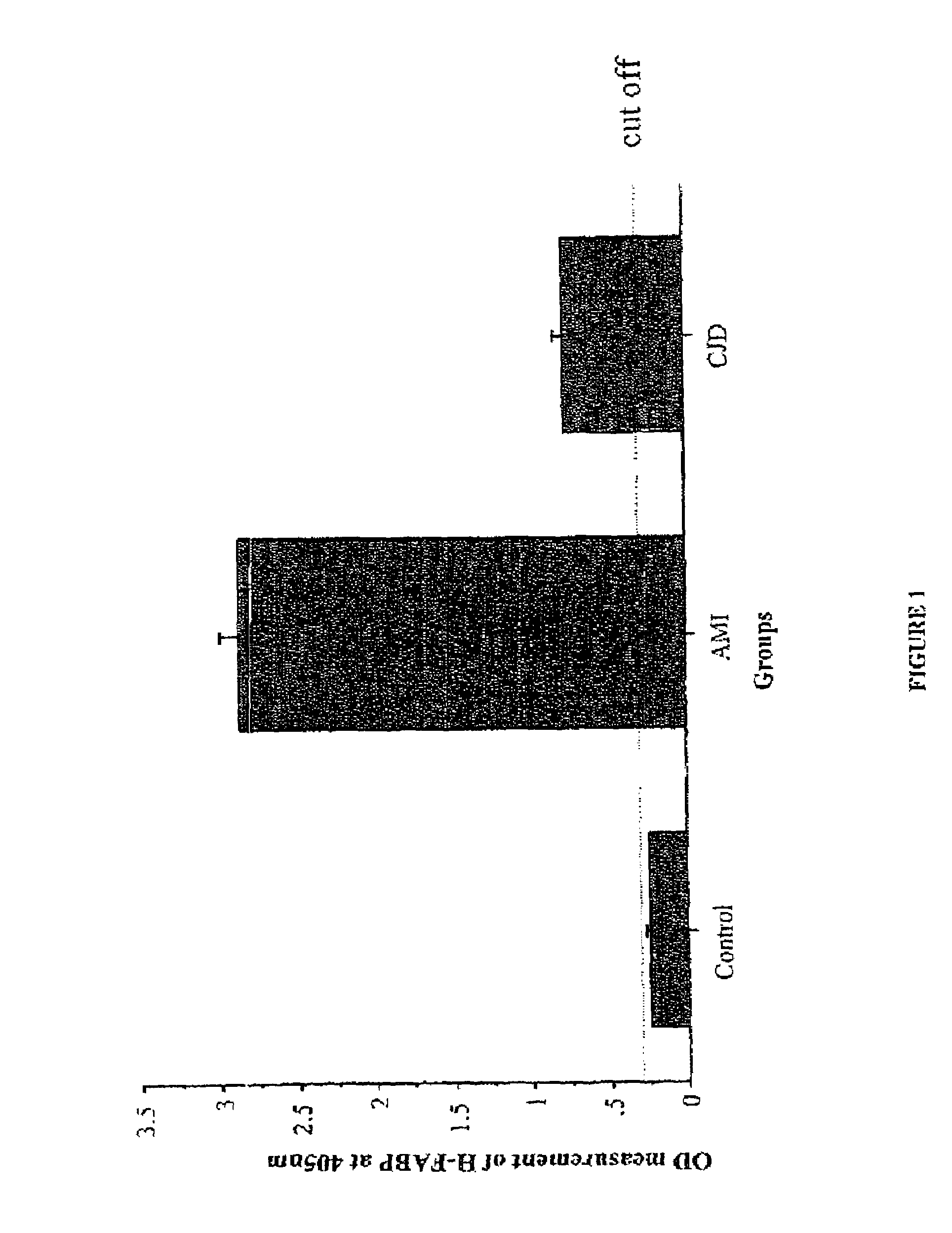
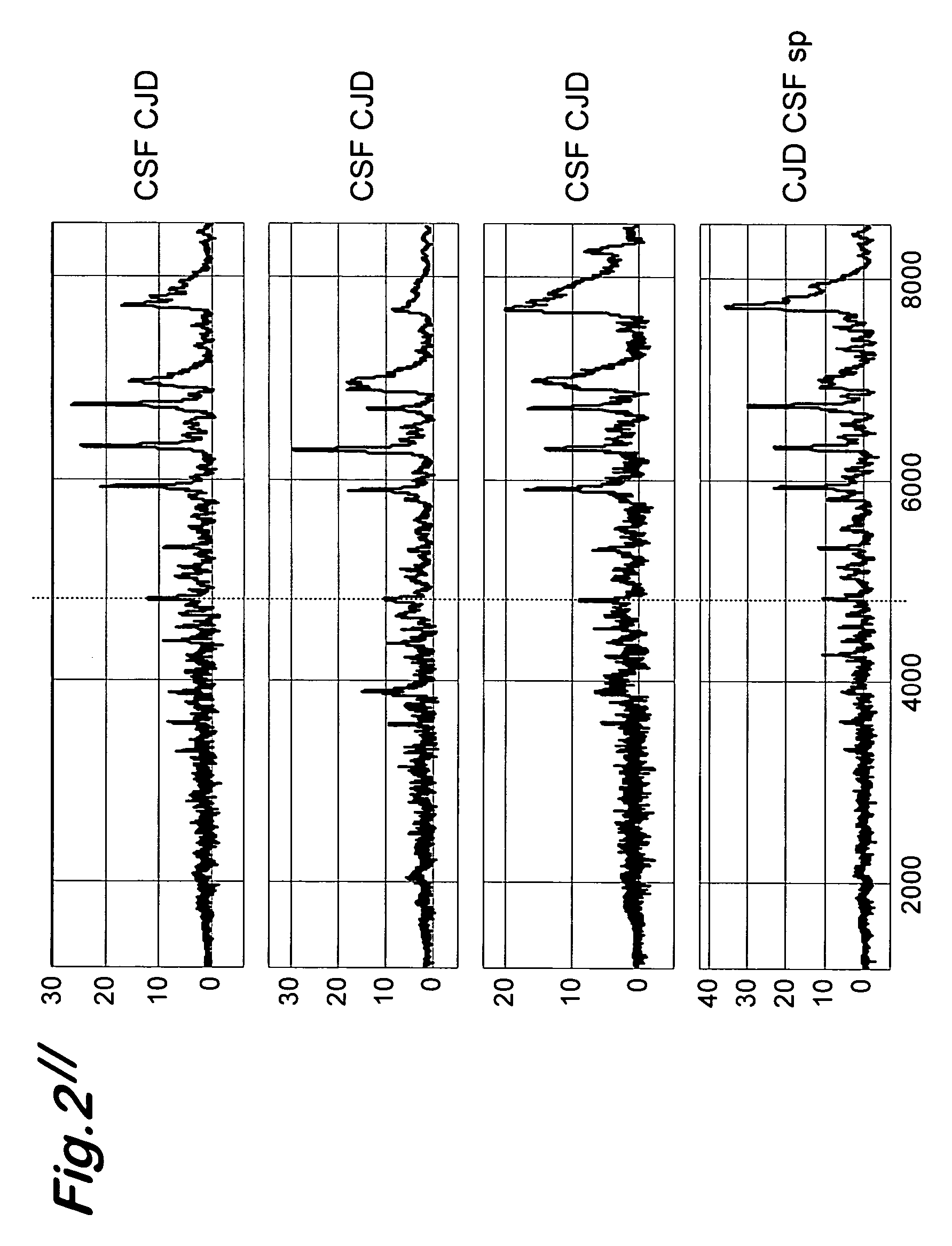
Heart and brain fatty acid binding proteins (H-FABP, B-FABP) are markers for TSEs, especially CJD. The invention provides a diagnostic assay for either of these markers, preferably by enzyme immunoassay using a specific antibody thereto. Since H-FABP is also a marker for acute myocardial infarction (AMI), to distinguish CJD from AMI requires an assay specific to AMI, e.g. using troponin-1 or CK-MB as a marker, also to be carried out.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA
Use of prion conversion modulating agents
The use of Apolipoprotein B, Apolipoprotein E, fragments and mimetics thereof is provided for diagnostic, detection, prognostic and therapeutic applications In prion diseases. More specifically, the invention provides the use of Apolipoprotein B or fragments thereof for modulating or identifying modulators of the prion protein replication which are implicated in the pathogenesis of transmissible spongiform encephalopathics and other prion diseases.
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA
Safe method for isolation of prion protein and diagnosis of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies
InactiveUS20050255525A1Easy to distinguishEffectively infectivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisWestern blotBiology
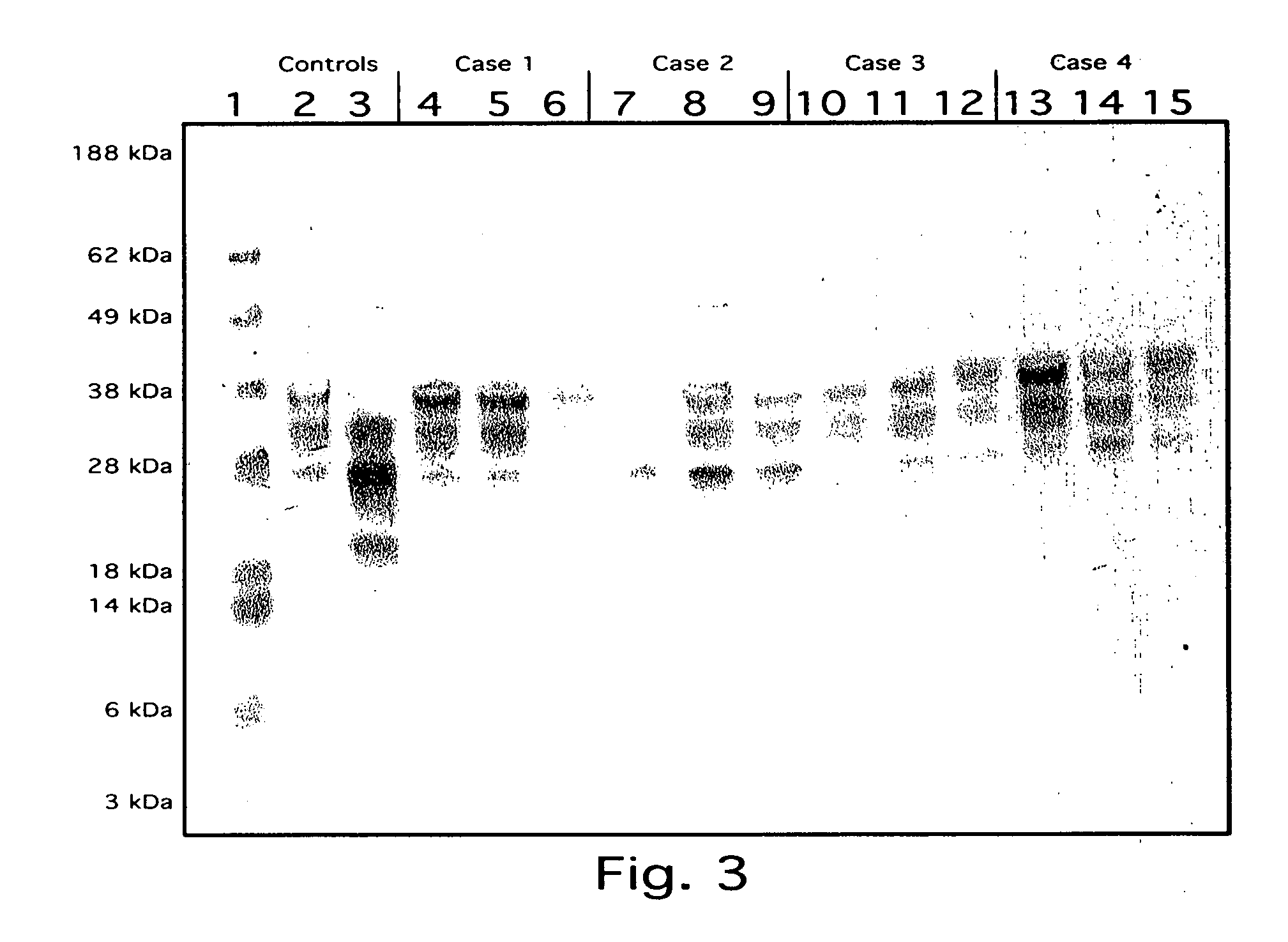
Provided is a safe novel method for detecting Transmissible Spongiform encephalopathies (TSE). The method comprises: selecting a sample from a subject to determine whether the subject has transmissible spongiform encephalopathy; and detecting abnormal prion protein (Prpes) in the sample. The method detects PrPres without Proteinase-K treatment by disrupting the sample in guanidine thiocyanate lysis solution followed by phenol purification of proteins, and demonstration of the abnormal prion isoform by Western blotting using monoclonal antibodies against prion protein structure. Guanidine salts effectively kill TSE infectivity providing a laboratory safe environment and stabilize biomolecules so TSE samples can be procured in the field and transported to the laboratory in guanidine lysis solution for processing at a later date. This method provides for rapid detection of the abnormal prion isoform diagnostic of TSE and results are easily interpretable based upon very different Western blot patterns for abnormal prion isoform versus the normal prion.
Owner:BASTIAN FRANK OWEN
Diagnostic method for transmissible spongiform encephalopathies
InactiveUS20040171026A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryBody fluid
Transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) is diagnosed in a subject by using mass spectrometry to observe a polypeptide in a sample of body fluid taken from the subject. The polypeptide is differentially contained in the body fluid of TSE-infected subjects and non-infected subjects, and has a molecular weight in the range of from 1000 to 100000.
Owner:PROTEOME SCINECES
Process for detecting PrP using a macrocyclic adjuvant ligand
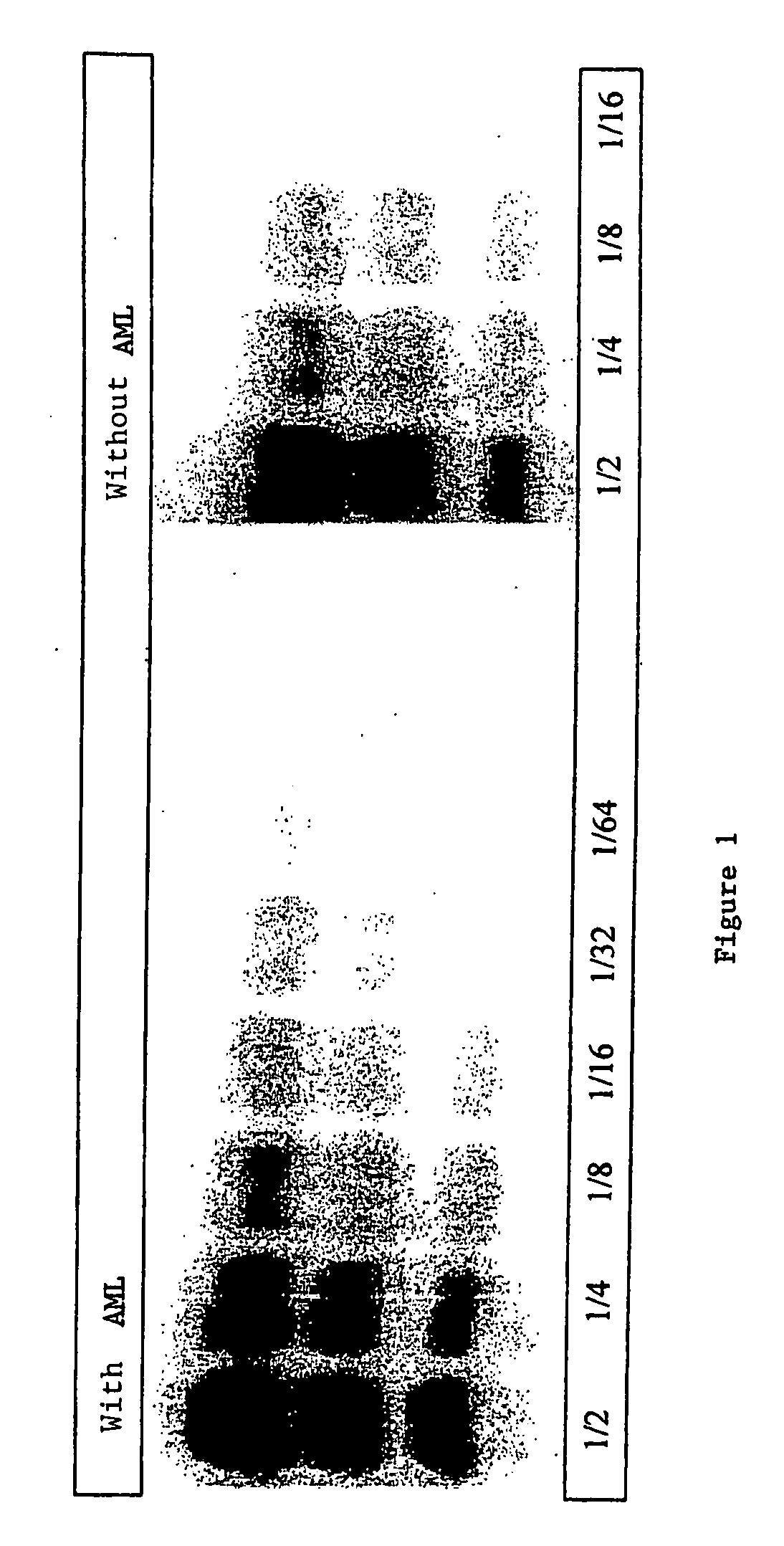
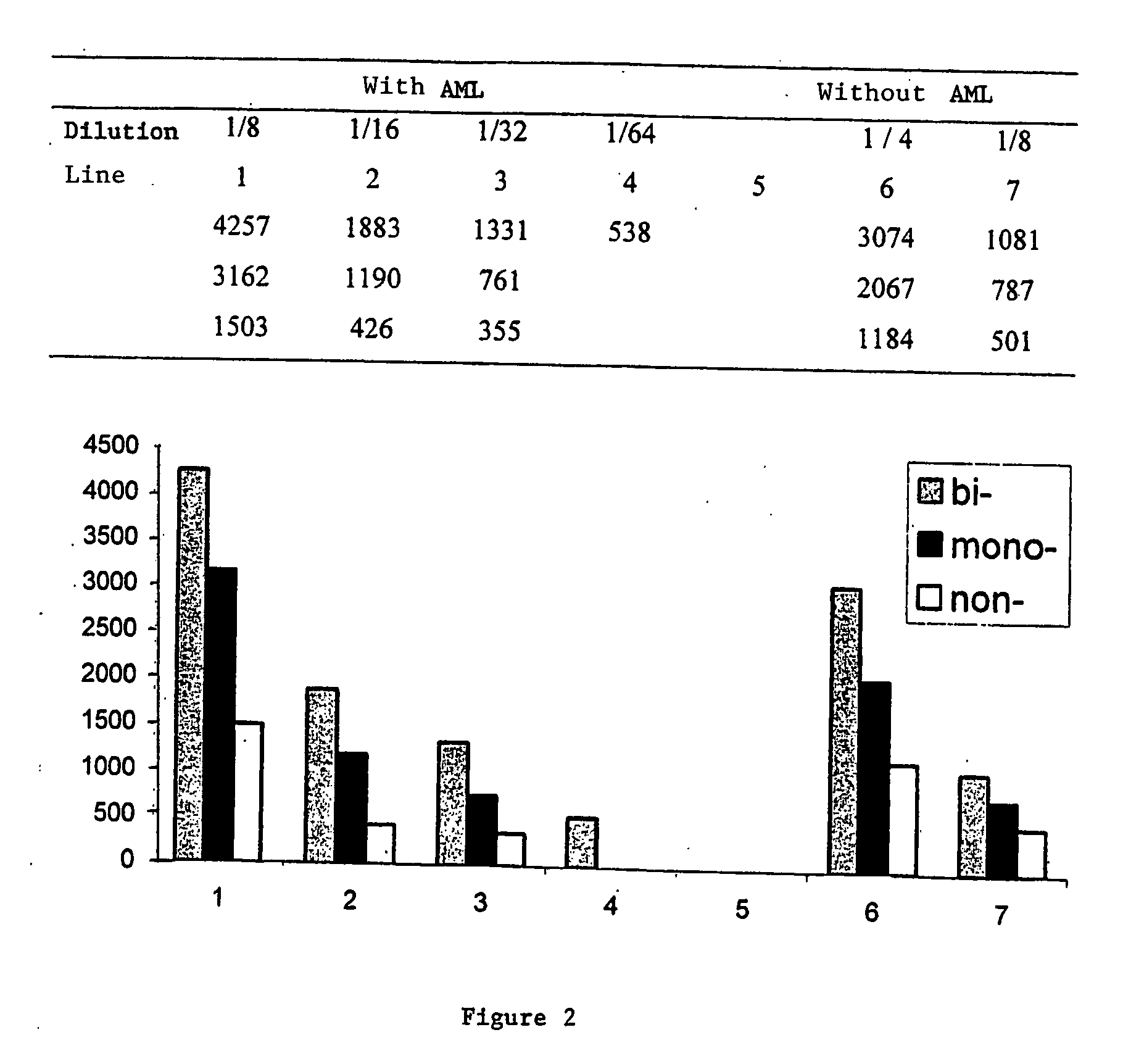
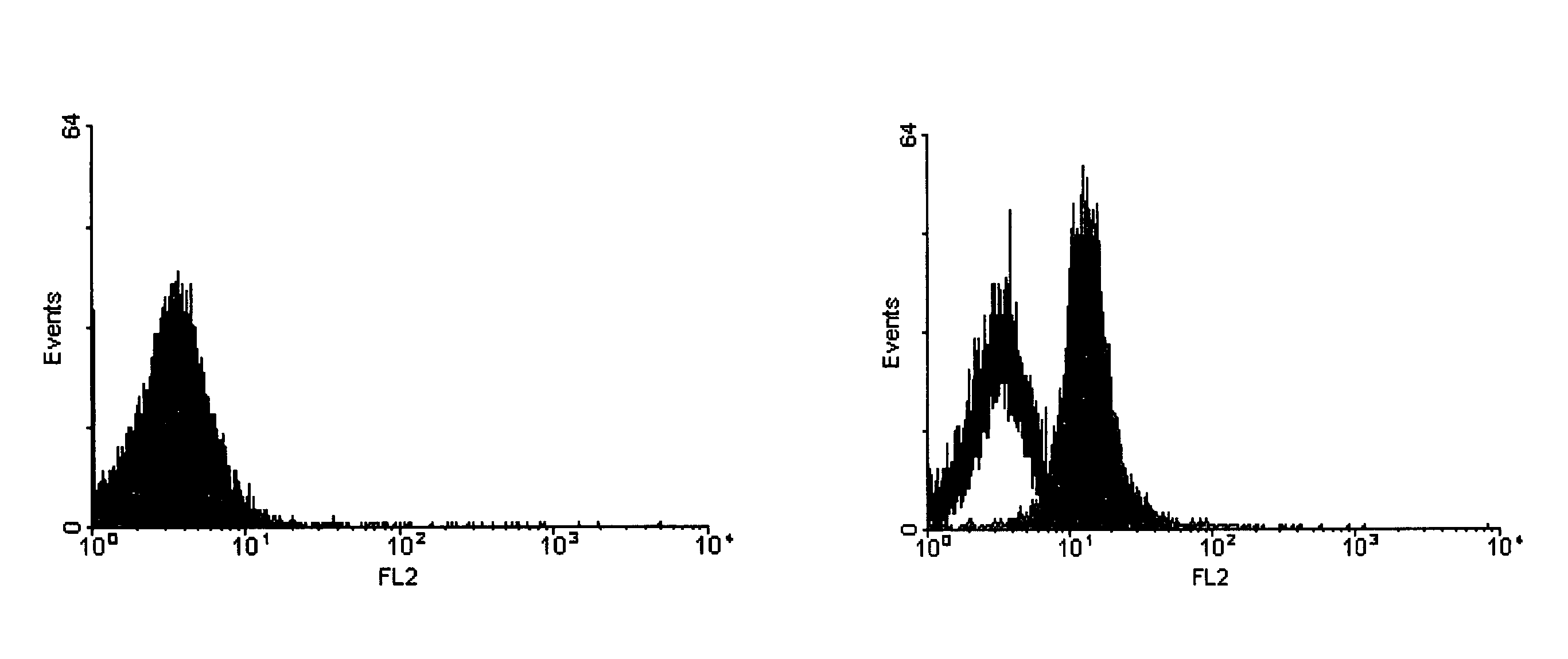
A process for detecting the forms of the prion pathogens responsible for subacute, transmissible, spongiform encephalopathies, including a macrocyclic adjuvant ligand (AML), free or bound to a support, that is added to a biological sample capable of containing PrPsc, the resulting suspension then being reacted with an anti-PrPsc antibody, and the presence of PrP is then detected.
Owner:AGENCE FRE DE SECURITE SANITAIRE DES ALIMENT +3
Method for the Detection of Disease-Related Prion
InactiveUS20080220447A1Disease diagnosisBiological testingBiologyTransmissible spongiform encephalopathy
Methods for the detection of the disease associated conformation of the prion protein as an indication of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs), including preclinical detection of infected live animals and humans, and post-mortem detection methods are disclosed. In one aspect, the tissue or body fluid sample of a test subject is contacted with an antibody that binds only the disease related conformation of the prion protein under non-denaturing conditions.
Owner:PRIONICS
Method for the detection of proteins of animal origin in complex mixtures
InactiveUS20050118720A1Avoid spreadingLow impurity contentNervous disorderComponent separationHigh concentrationLiquid chromatography mass spectroscopy
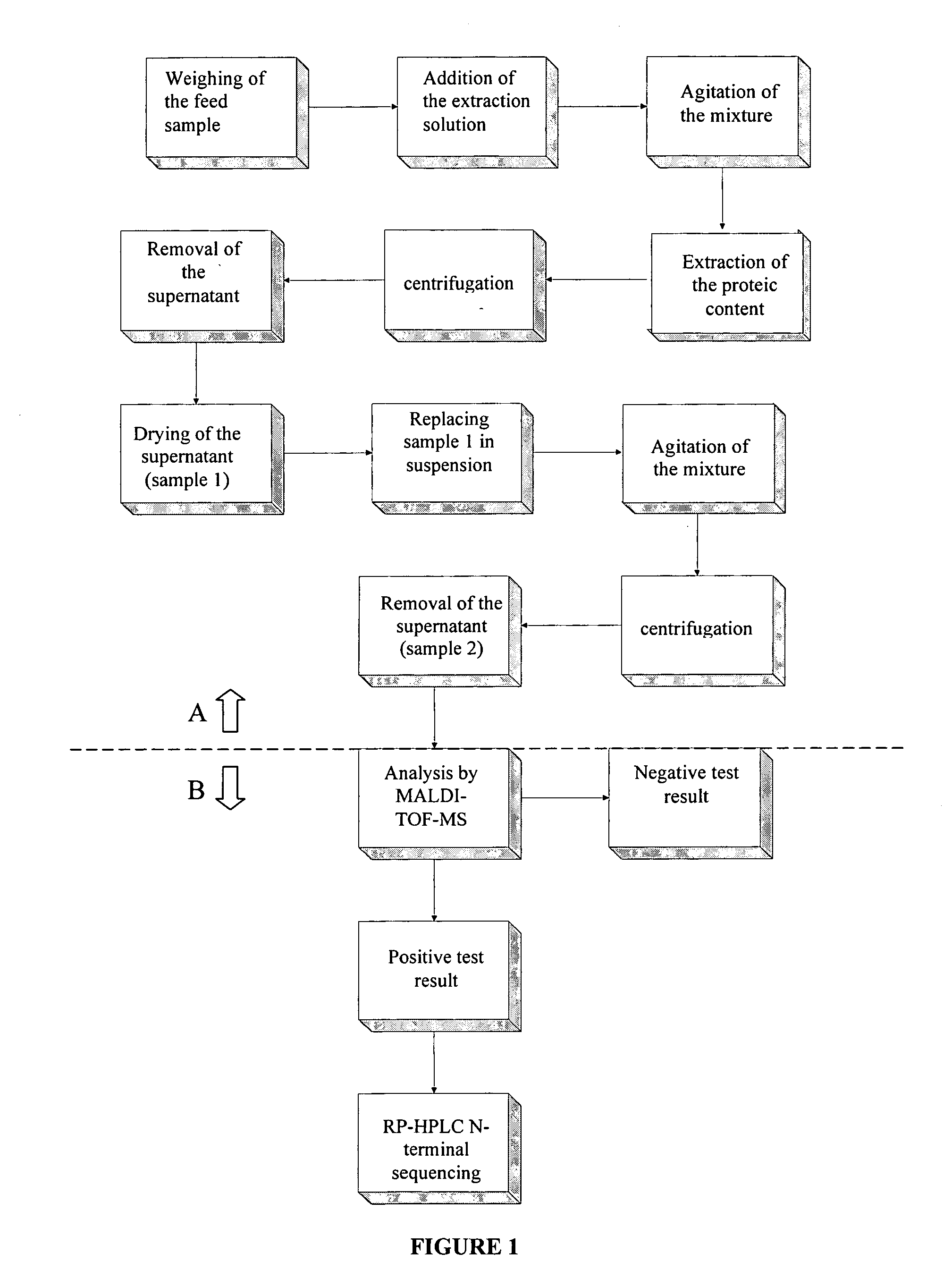
The purpose of the present invention is to evaluate the quality of feed for ruminants and consequently, avoid the transmission of TSEs through the detection of animal proteins in these foods. This purpose is embodied in the form of a method for detecting proteins of animal origin in complex mixtures comprising the stages of: (i) extraction of the proteic matter in high concentration from a sample of the initial complex mixture in a manner as to substantially remove all interferents; (ii) preparation of the matrix-analyte in a manner as to maintain low levels of impurities and an adequate matrix-analyte molar rate; (iii) analysis of the material obtained in the prior stage by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry; (iv) optionally, fractionation of the samples or isolation of the components by RP-HPLC and identification of the components by means of automatic sequencing of the N-terminal region and sequencing of its peptidic fragments by liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (LC / MS / MS). The present invention also contemplates the use of this method in the detection of proteins of animal origin in feed for ruminants, which permits the interruption of transmission of Transmittable Spongiform Encephalopathies, and more particularly Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathies (BSE).
Owner:EMPRESA BRASILEIRA DE PESQUISA AGROPECUARIA EMBRAPA
Methods of treating prion disease in mammals
The invention is related to the treatment of prion-related diseases such as the transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) in mammals by administering chaotropic agents to or inducing a hyperthermia state in the affected mammals.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Nucleotide sequence for assessing transmissible spongiform encephalopathies
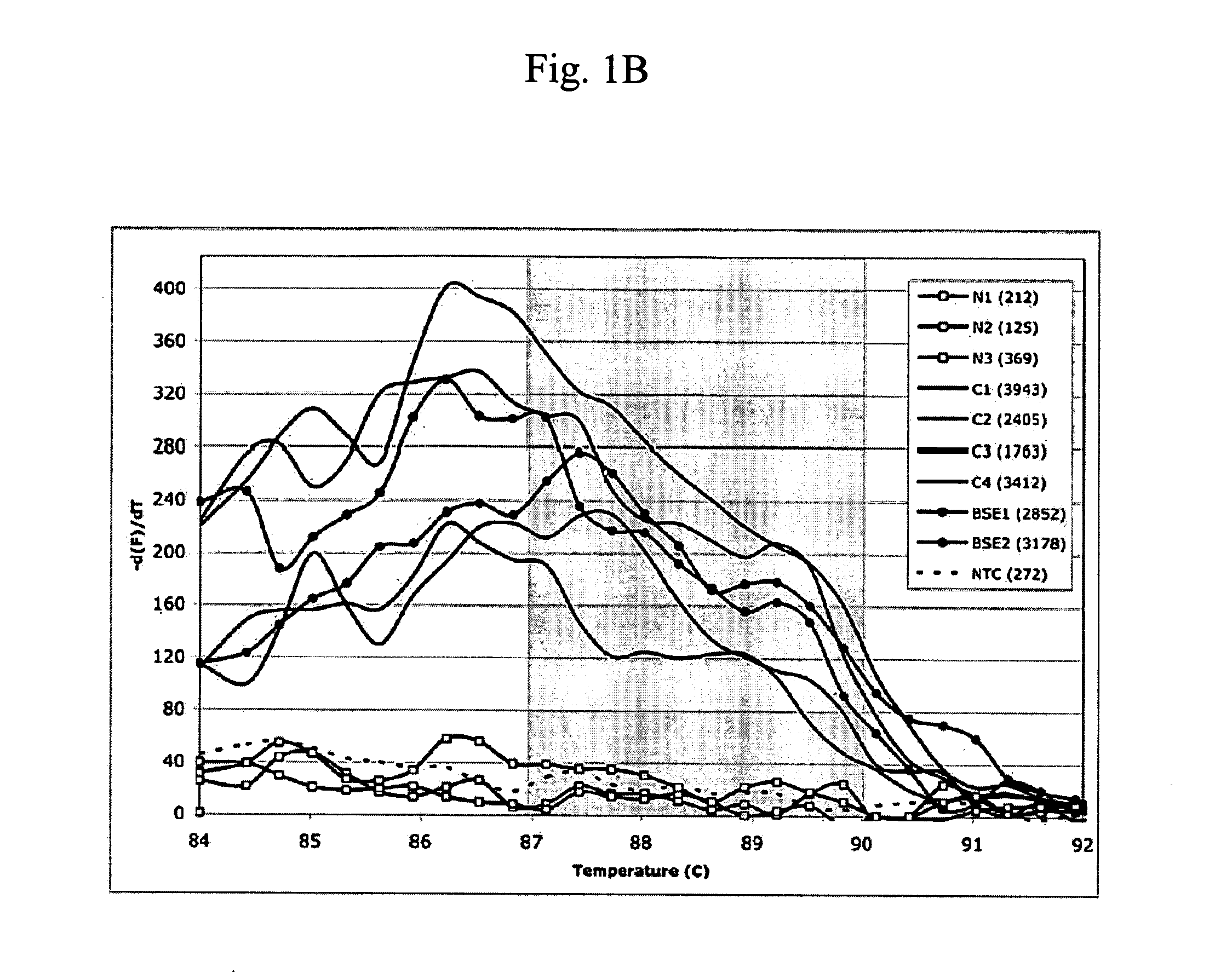
The present invention is directed to the assessment of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) using a sample from a living individual. The assessment is based on the use of an RNA marker molecule in a sample of whole blood. The RNA encodes a hypothetical cystein protease. The invention is further directed to the detection of the marker molecule by means of real-time PCR. The invention provides the use of the nucleotide sequence as a marker in the assessment of TSE, a method for assessing bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) in a bovine animal as well as kits to practice the invention.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Methods for rapid screening of mad cow disease and other transmissible spongiform encephalopathies
Methods for diagnosing altered neuropathology in an animal are disclosed, wherein said methods comprise imaging brain, spinal cord, or other neural tissue of the animal, analyzing the appearance of the tissue, and determining whether the appearance of the tissue is altered relative to corresponding unaltered tissue. Also disclosed are methods for diagnosing spongiform encephalopathies in an animal, wherein said methods comprise imaging brain, spinal cord, or other neural tissues of the animal, analyzing the appearance of vacuoles in the tissue, and determining whether the appearance of the vacuoles in the tissue is altered relative to corresponding spongiform encephalopathy-free tissue. Also disclosed are automated methods for diagnosing altered neuropathy and spongiform encephalopathies.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
Detection of nucleic acids to assess risk for bovine spongiform encephalopathy
ActiveUS20060068419A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyTransmissible spongiform encephalopathy
The present invention provides a method of detecting abnormal serum nucleic acid profiles to assess the risk of a transmissible spongiform encephalopathy, e.g., BSE.
Owner:CHRONIX BIOMEDICAL
Methods and compositions for treating diseases associated with pathogenic proteins
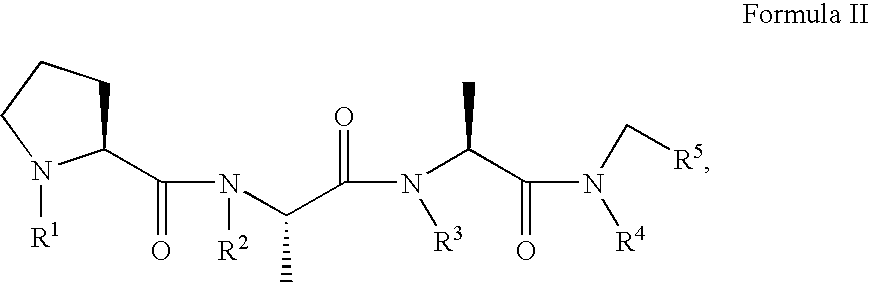
InactiveUS20070179123A1Preventing prion infectionAvoid infectionBiocideAnimal repellantsMedicineNeuro-degenerative disease
Methods and compositions are provided comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula I wherein R1-4, W, X, Y and Z are as defined in the specification, for inhibiting and treating diseases and disorders associated with pathogenic proteins causing neurodegenerative diseases and amyloid diseases, such as protease resistant prion proteins (PrPSc) and those associated with transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs), Alzheimer's Disease, amyloidosis, and the like.
Owner:CHIANG PETER K +4
Method to Detect Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies Via Electroretinogram
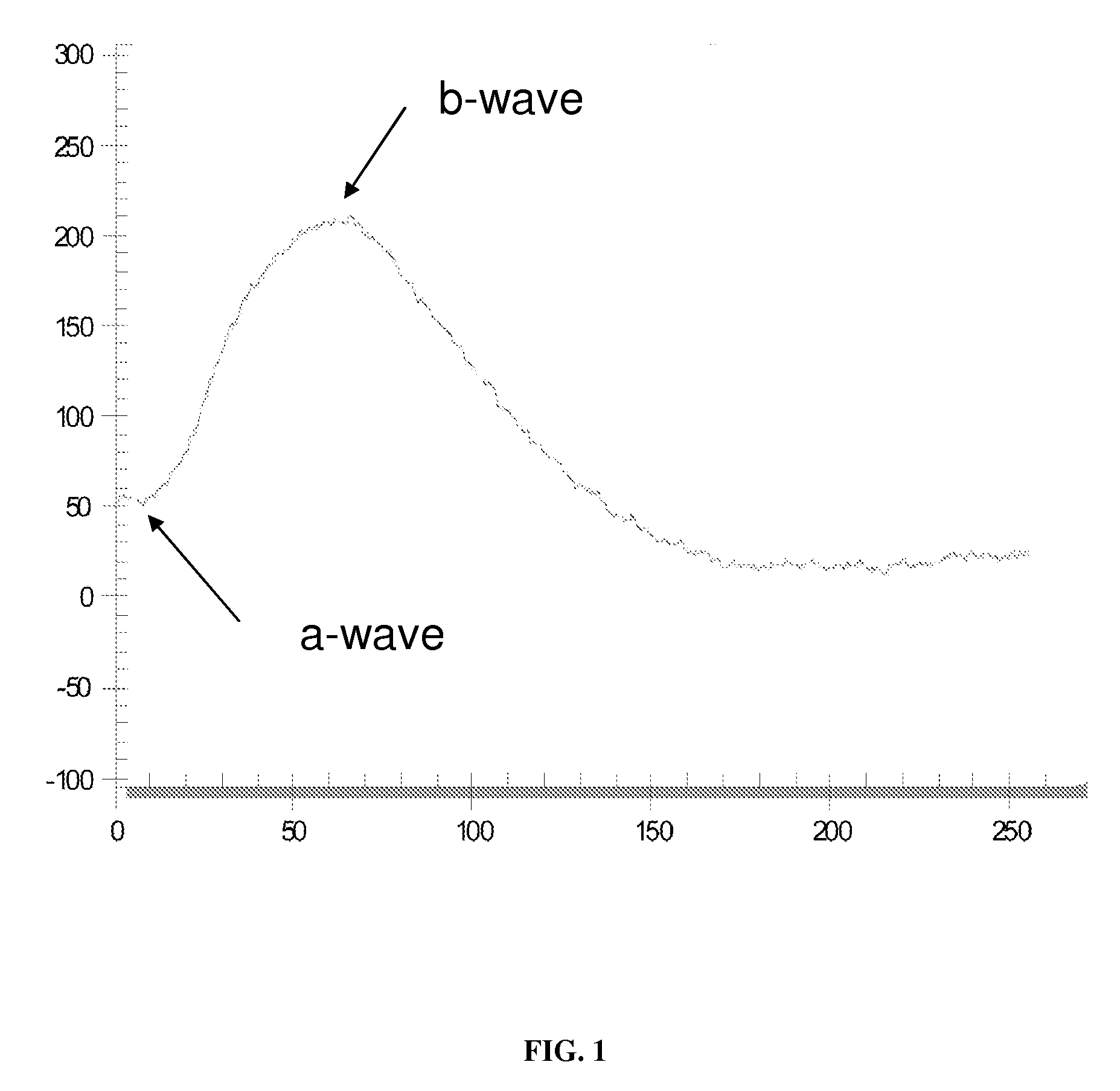
InactiveUS20090257023A1Increased b-waveExtension of timeElectro-oculographyEye diagnosticsB-wave implicit timeTransmissible spongiform encephalopathy
Disclosed is a method for identifying transmissible spongiform encephalopathy in livestock via an electroretinogram, the method comprises producing a biphasic electroretinogram waveform having an a-wave and b-wave from livestock retina in response to photic stimulus, measuring the amplitude of the b-wave, wherein the amplitude is measured from the trough of the a-wave to the peak of the b-wave, measuring the implicit time of the b-wave, wherein the implicit time is measured from onset of photic stimulus to b-wave peak; and comparing said produced waveform to a comparative waveform of livestock known not to have transmissible spongiform encephalopathy, wherein the produced waveform having a decrease b-wave amplitude and increased b-wave implicit time being indicative of livestock having transmissible spongiform encephalopathy.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
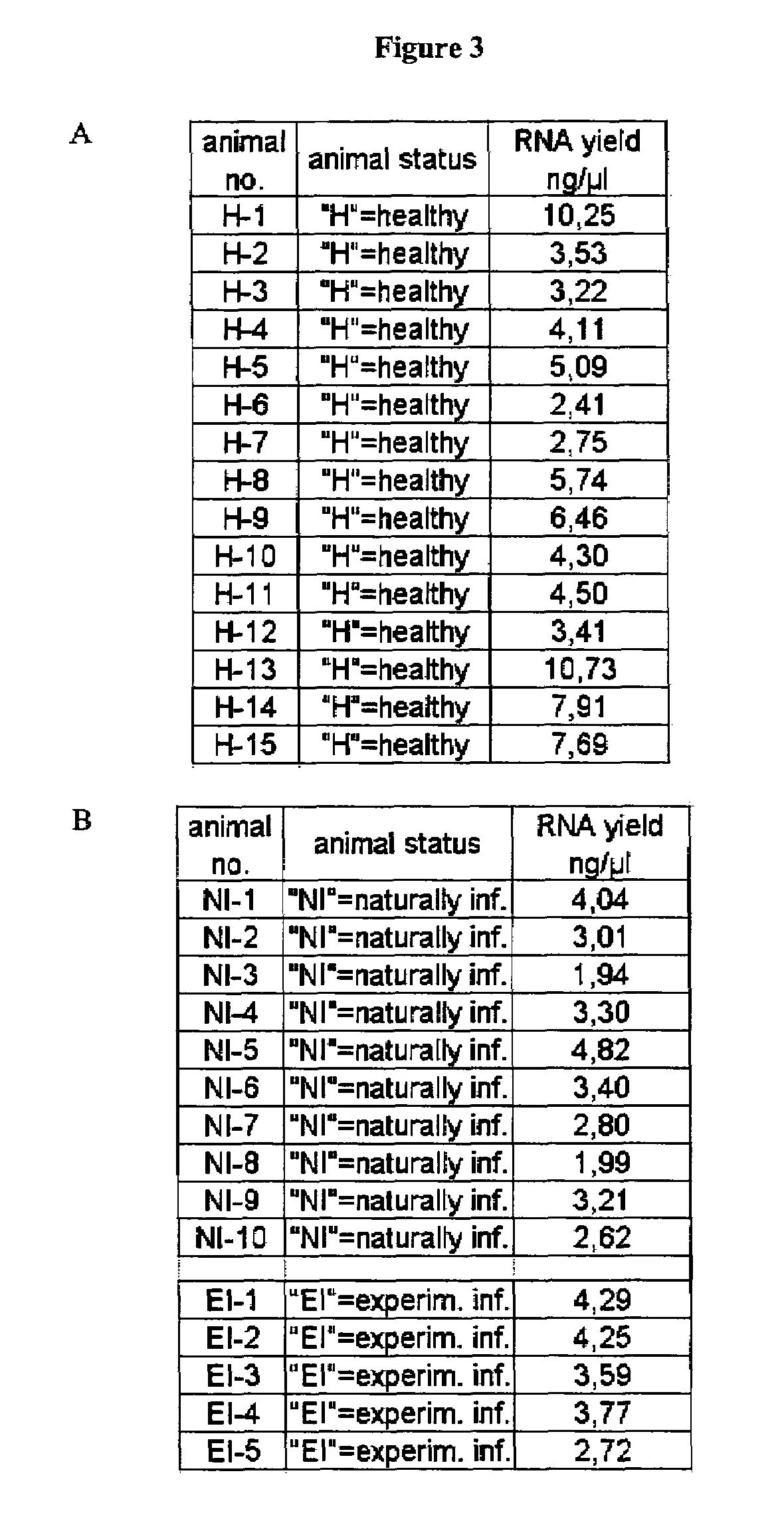
Nucleic acid preparation from whole blood for use in diagnosis of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy
The present invention deals with a method of preparing nucleic acids, particularly RNA, from a whole blood sample. The nucleic acids purified by the method of the invention are particularly suited for detection of nucleic acid marker molecules. Preferred are markers for the diagnosis of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE). Such diagnosis is based on the detection, by means of real-time PCR, of certain mRNAs of the TSE-infected organism. Said mRNAs specifically originate as splicing variants and are isolated from whole blood by the method of the invention.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Ultrasensitive detection of prions by automated protein misfolding cyclic amplification
A highly sensitive method for detecting prions in a sample is provided. These methods can be used to diagnose prion-mediated transmissible spongiform encephalopathy, such as bovine spongiform encephalopathy, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie or chronic wasting disease. In particular, methods for continuous automated cyclic expansion of prions are disclosed. The method is fast and highly sensitive, making it ideal for high-throughput testing.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
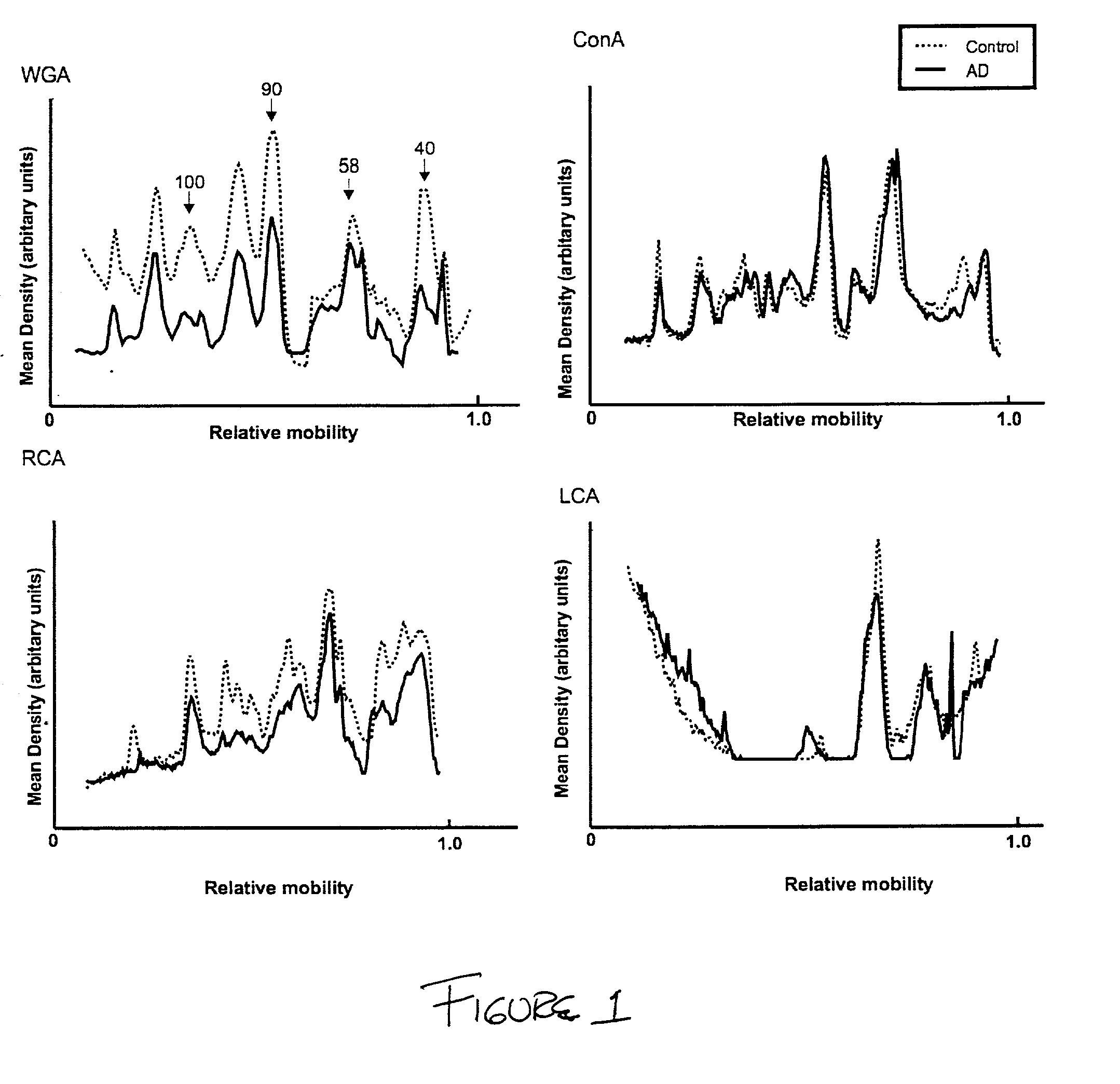
Method for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease and other prion related disorders
InactiveUS20020150878A1High sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisButyrylcholinesteraseAcetylhomocholine
The invention provides a method for the diagnosis of dementia and transmissible spongiform encephalopathies in a subject by detecting the levels of glycoproteins that bind wheat germ agglutinin. The invention also provides a method for diagnosis of dementia and transmissible spongiform encephalopathies in a subject by comparing the levels of glycoproteins that bind wheat germ agglutinin with the glycosylation patterns of biomarkers, acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase.
Owner:AXONYX INC +1
Rapid prion-detection device, system and test kit
InactiveUS20050130247A1Quick checkBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNeuro-degenerative diseaseOrganism
Test devices, systems, and test kits are provided for rapid detection with high specificity of the pathogenic form of prion protein responsible for neurodegenerative diseases affecting humans and animals, such as transmissible spongiform encephalopathy in bovine, sheep, and cats. The present invention is also useful for testing animal feedstock made from animal parts. Results are available in from about 0.5 to about 20 minutes and preferably from about 5 to about 10 minutes after the sample is introduced to the device and system. The devices, systems, and test kits employ proteinase-K to remove noninfectious prion protein from a biological sample, so that the sample may be analyzed by immunochromatography to determine the presence and concentration of pathogenic prion protein. Because the proteinase-K is immobilized on a solid support for in-situ removal of interfering components, the present invention obviates the need for subsequent extraction of the desired analyte. All aspects of the present invention are suitable for quantifying the minimal detectable amount of pathogenic prion protein in a biological sample. Moreover, the simplicity of sample preparation makes the present invention suitable for use in the field.
Owner:HAJIZADEH KIAMARS +1
Method of preparing cells susceptible to transmissible spongiform encephalopathy and the creation of TSE persistently infected cells
ActiveUS9359595B2Microbiological testing/measurementHybrid cell preparationPersistently infectedEtiology
Owner:ANIMAL PLANT & FISHERIES QUARANTINE & INSPECTION AGENCY
Antibodies for discrimination of prions
ActiveUS7399603B2Improve isolationMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTransmissible spongiform encephalopathyProteinaceous infectious particle
Owner:ORTHO-CLINICAL DIAGNOSTICS
Complexes comprising a prion protein and a peptidyl prolyl isomerase chaperone, and method for producing and using them
The present invention relates to the diagnosis of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs). It especially teaches the production of a soluble prion protein (PrP)-chaperone complex and the advantageous use of such chaperone-PrP complex, especially in the detection of PrP in an immunoassay, as well as its use as and immunogen.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Medium composition for preparing botulinum toxin
The present invention relates to a medium composition for production of botulinum toxin and, more particularly, to a medium composition for culture of Clostridium sp. capable of producing botulinum toxin. The medium composition of the present invention comprises at least one plant-derived peptone selected from the group consisting of a garden pea hydrolysate, a cotton seed hydrolysate and a wheat gluten hydrolysate. When the medium according to the present invention, which contains plant-derived peptones and minerals, is used for culture of Clostridium botulinum, the growth rate of the bacterium in the medium is about 1.5-2 times higher than that in the medium that is in current use. In addition, when botulinum toxin is produced by culturing the bacterium in the medium, infection with transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) or the like can be prevented by blocking introduction of animal-derived components.
Owner:DAEWOONG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com