Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
156 results about "Neural tissues" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
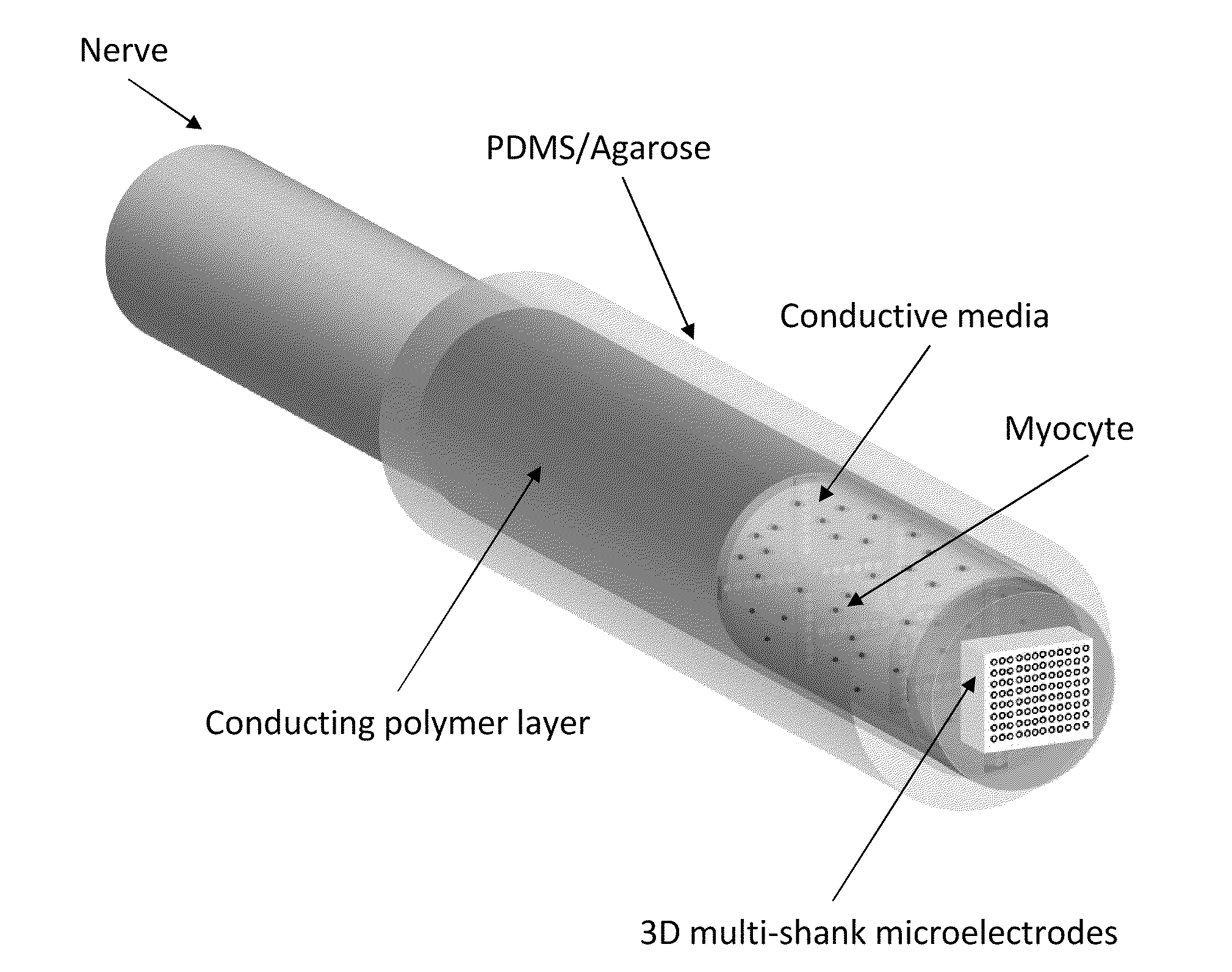
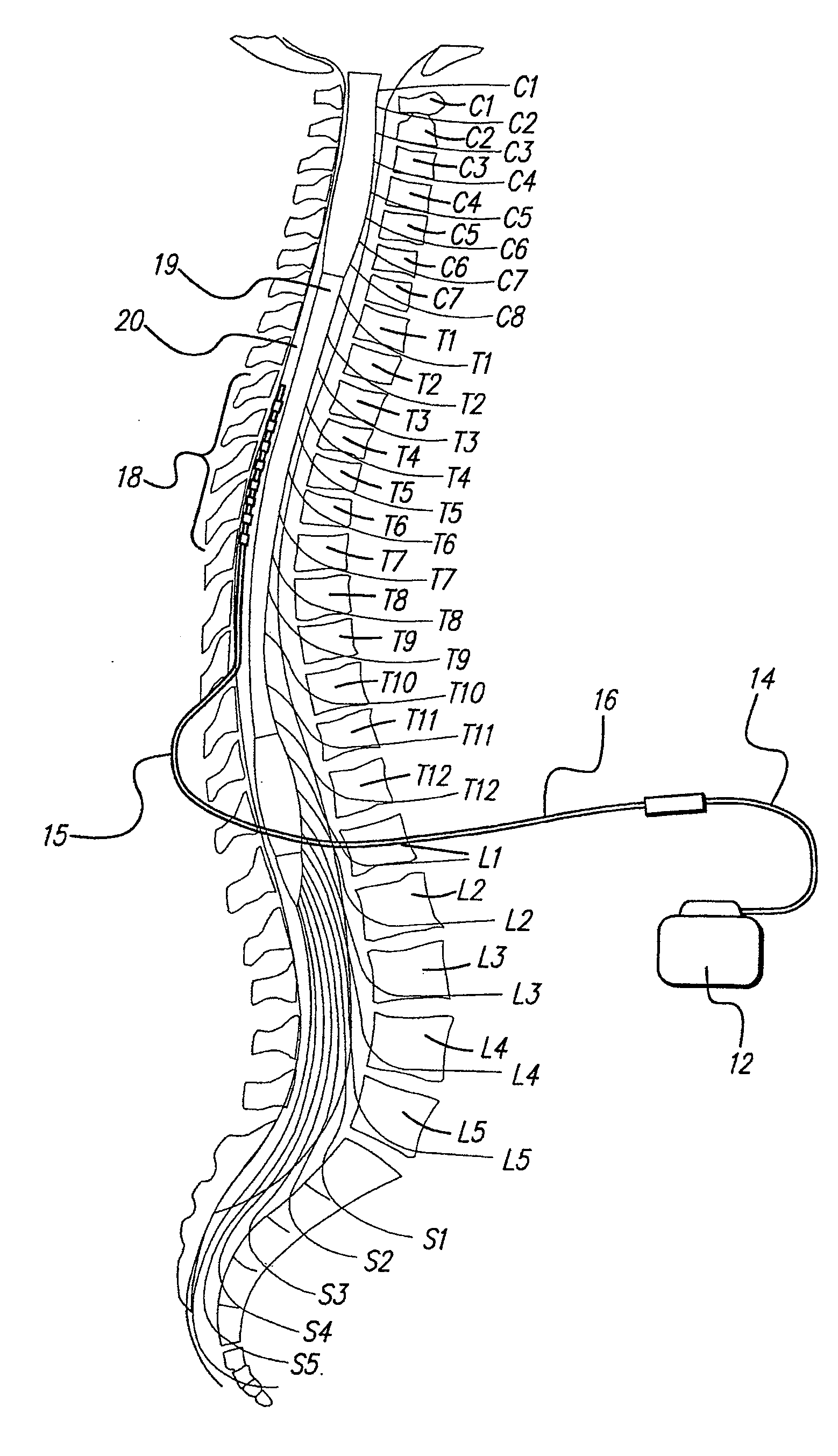
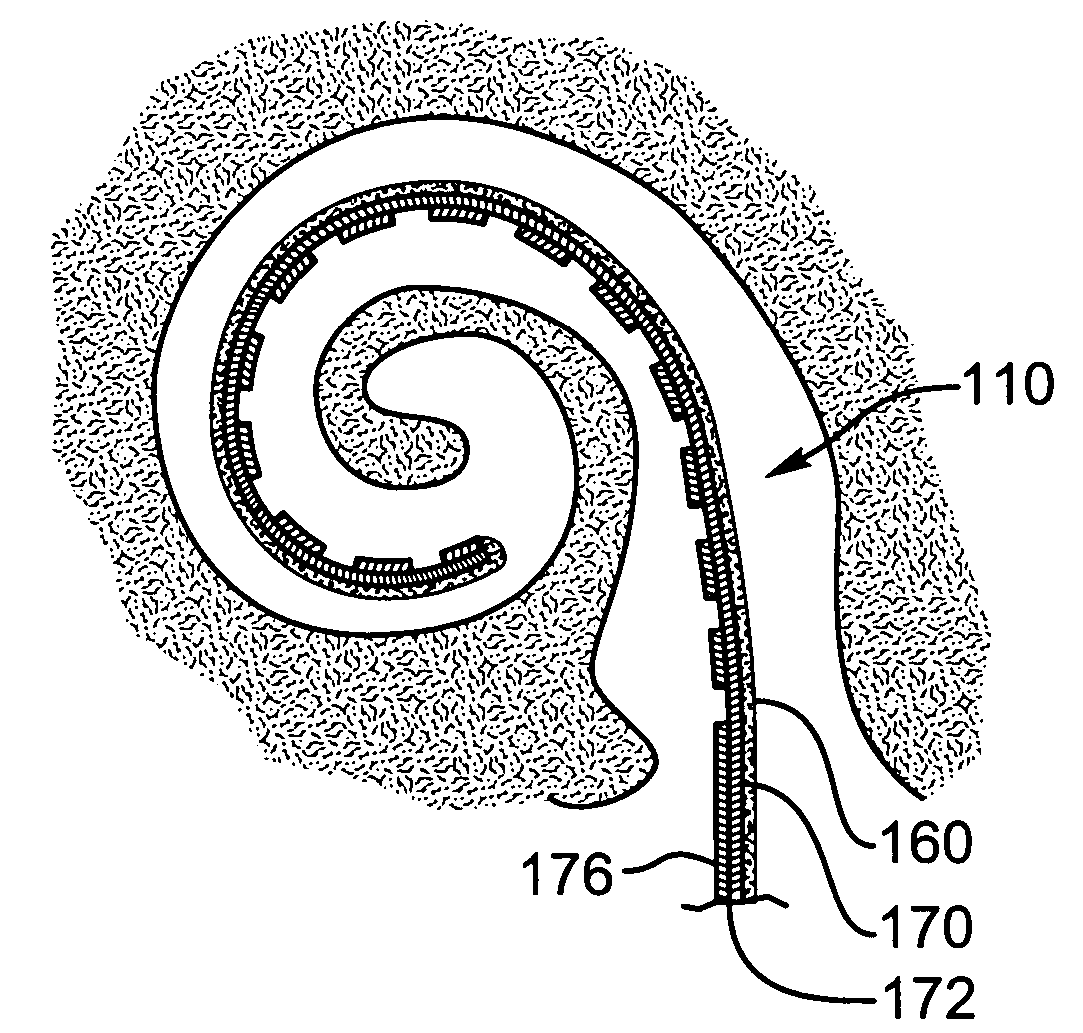
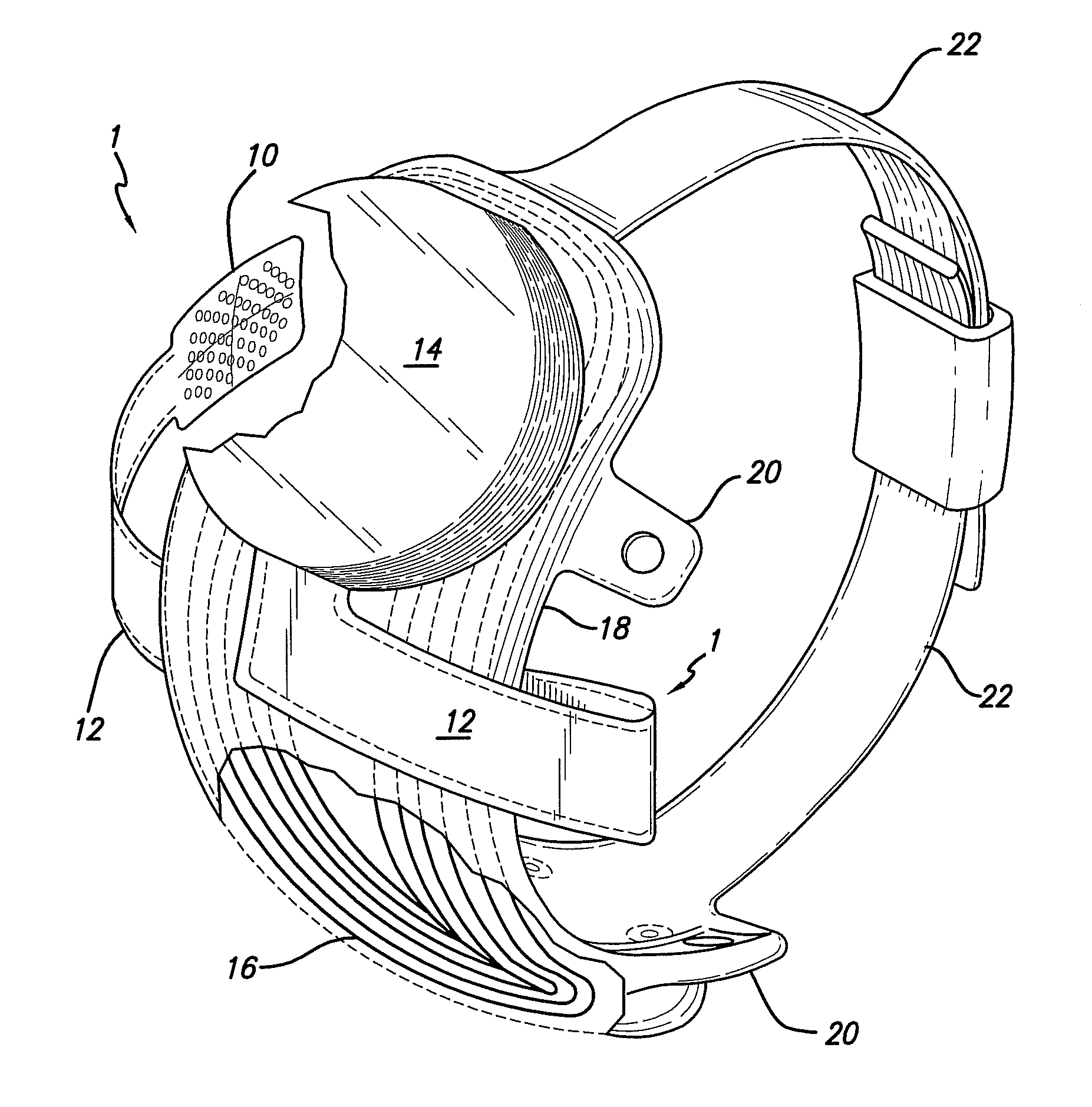
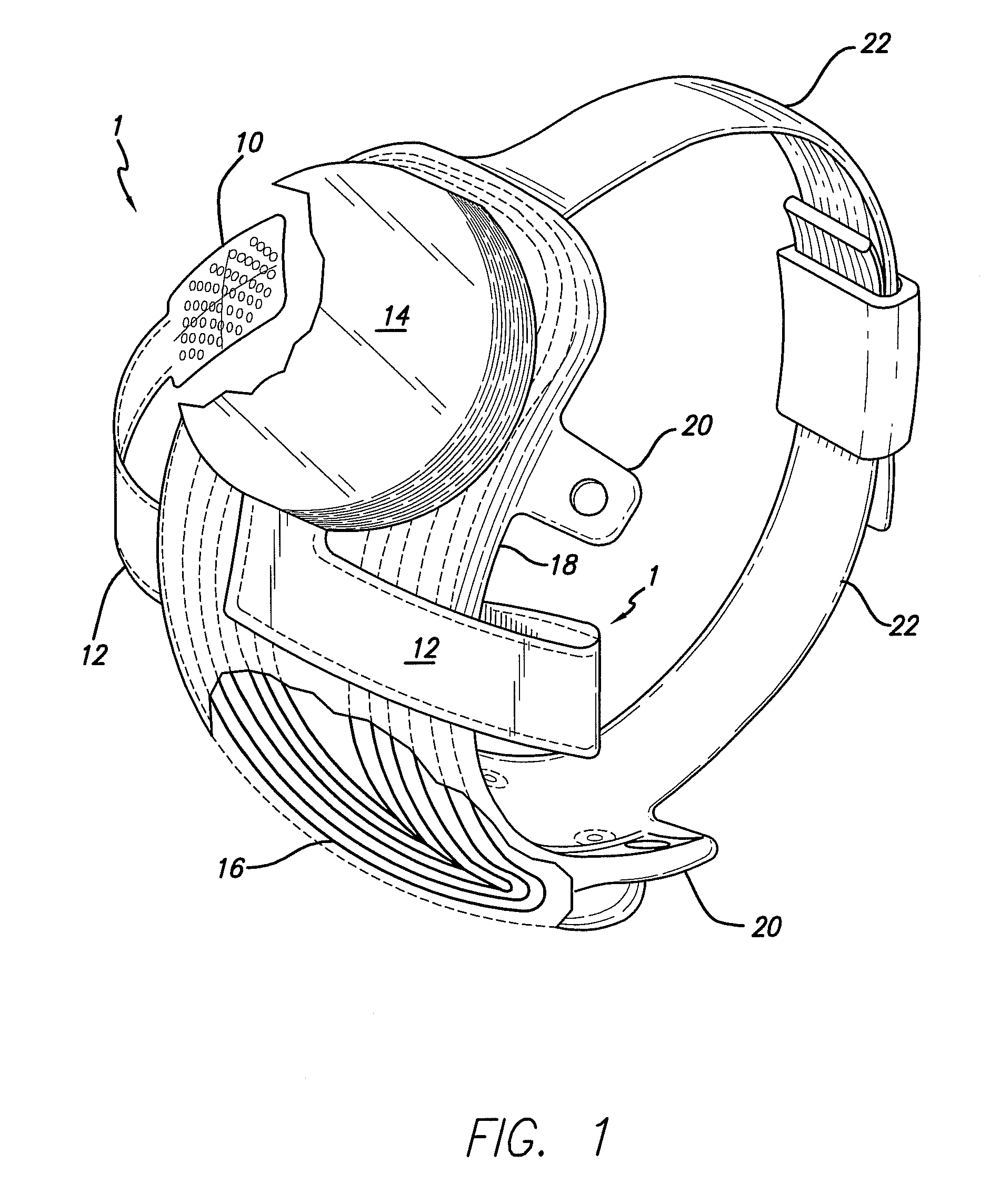
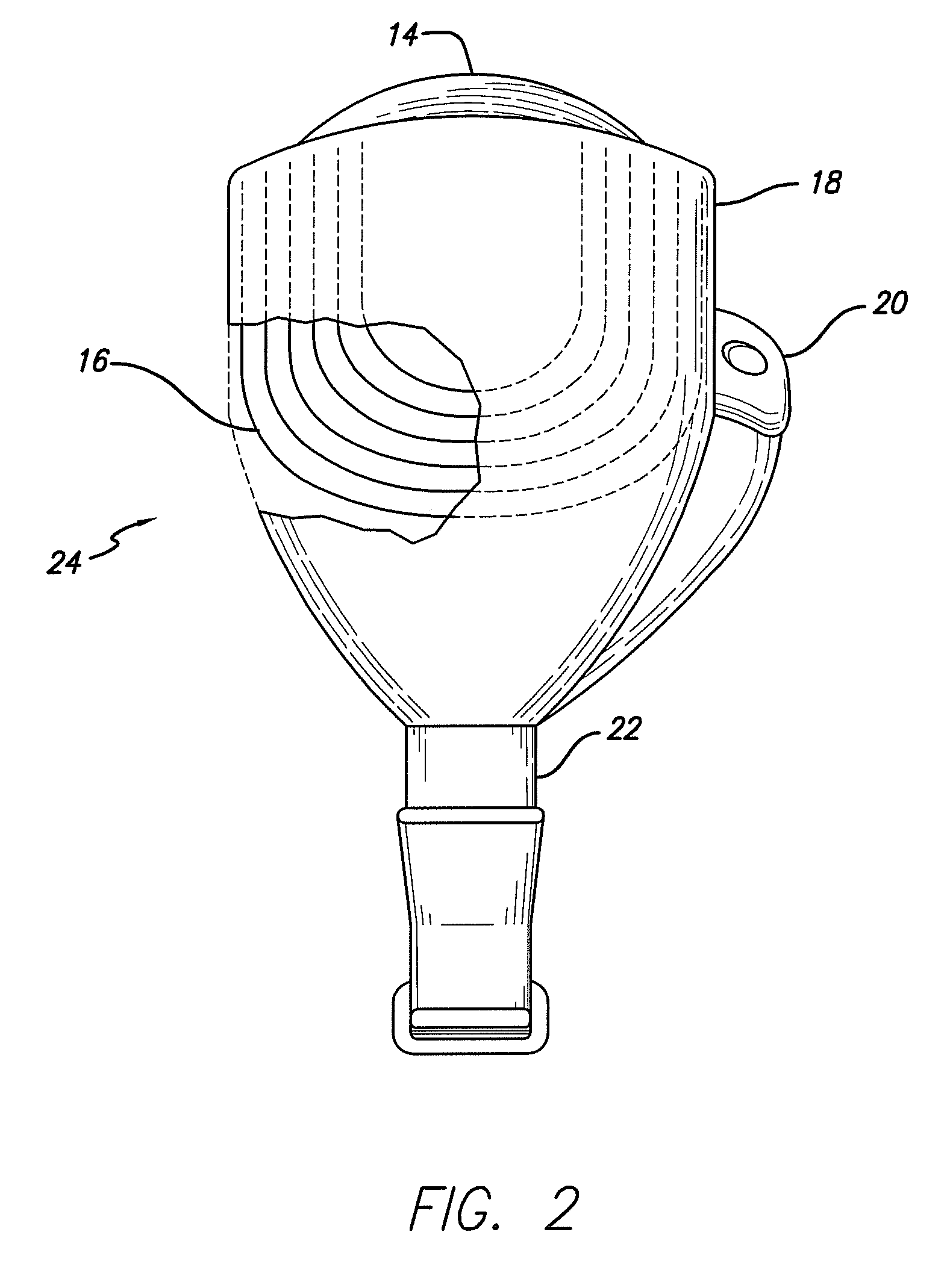
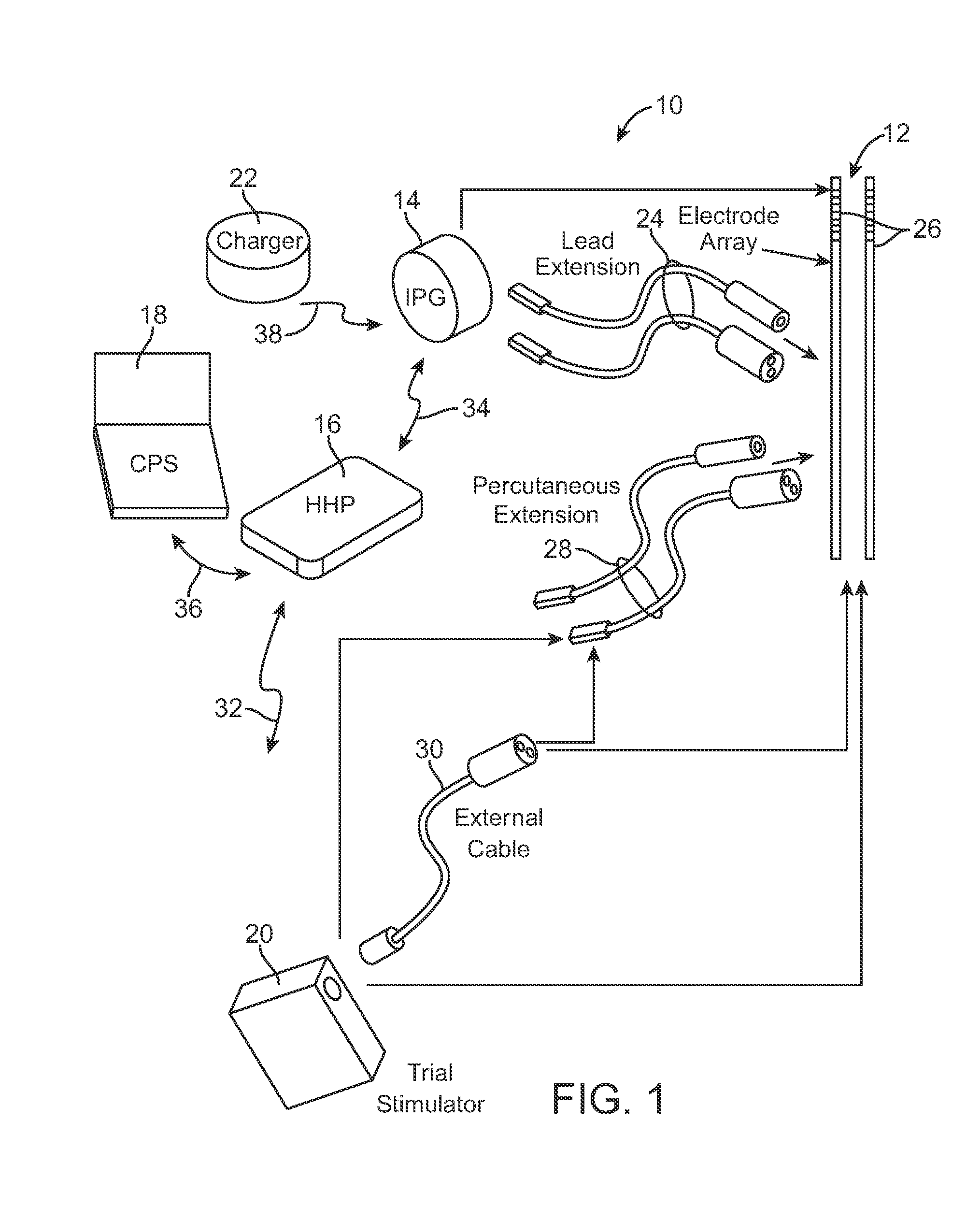
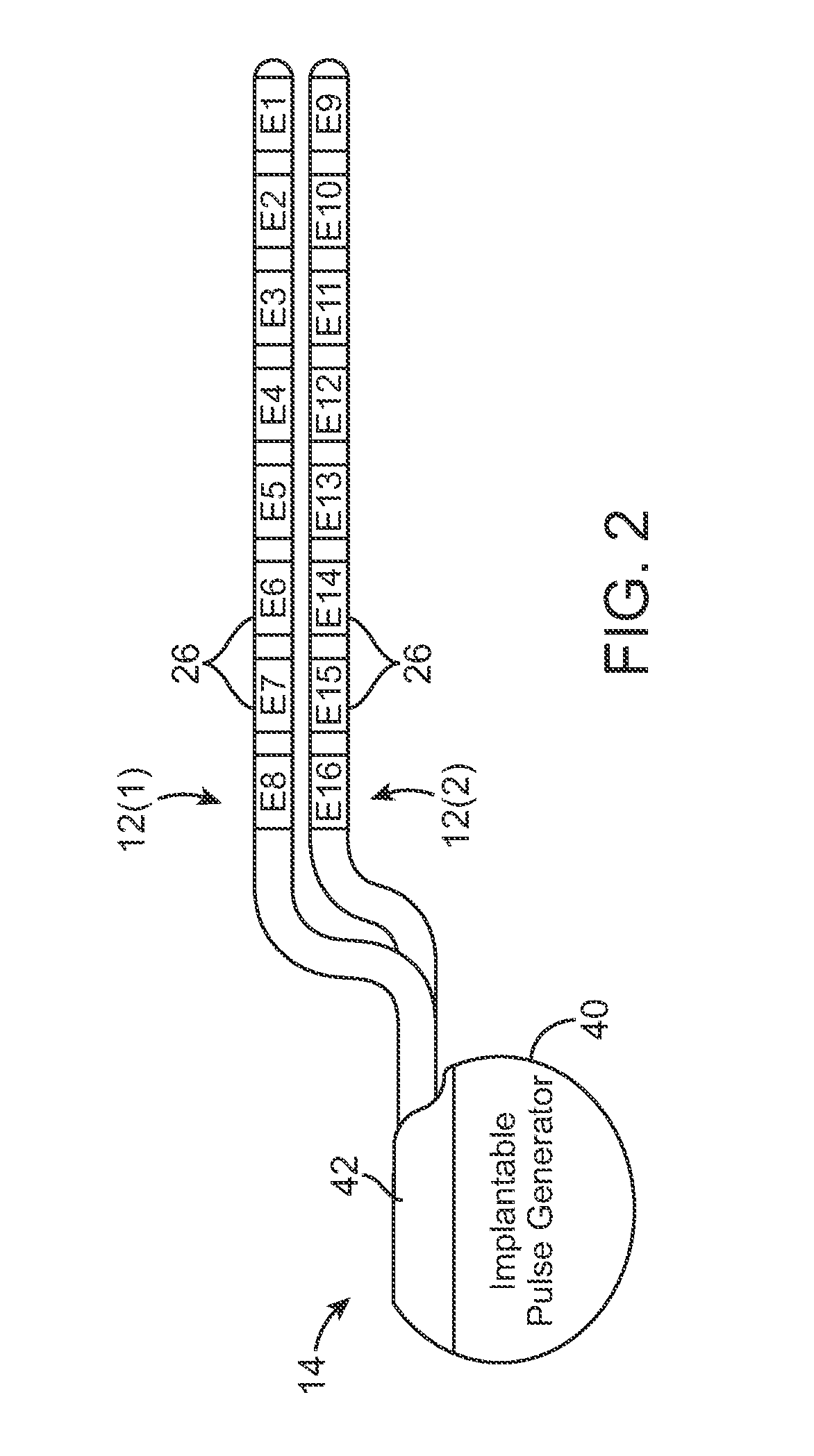
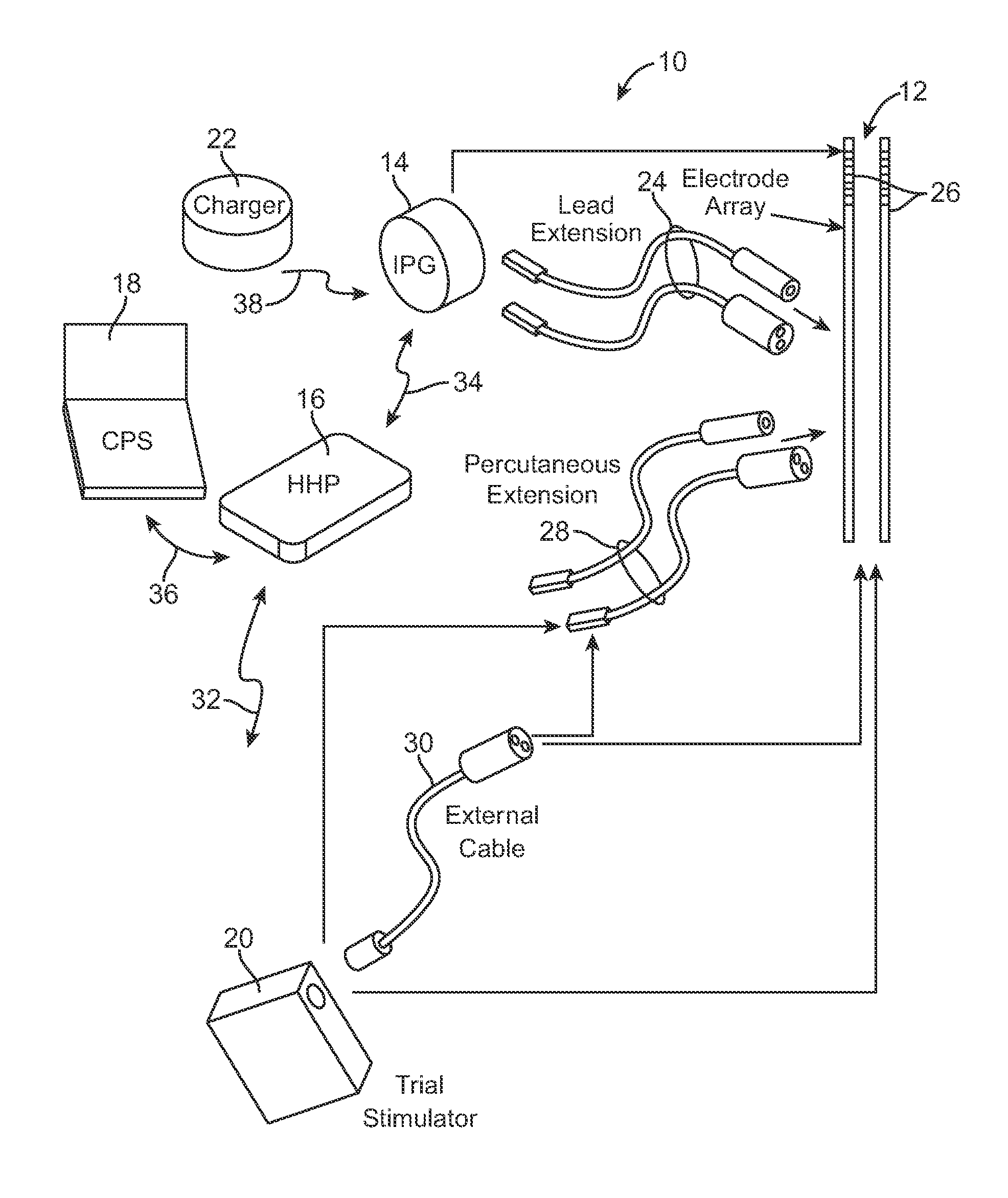
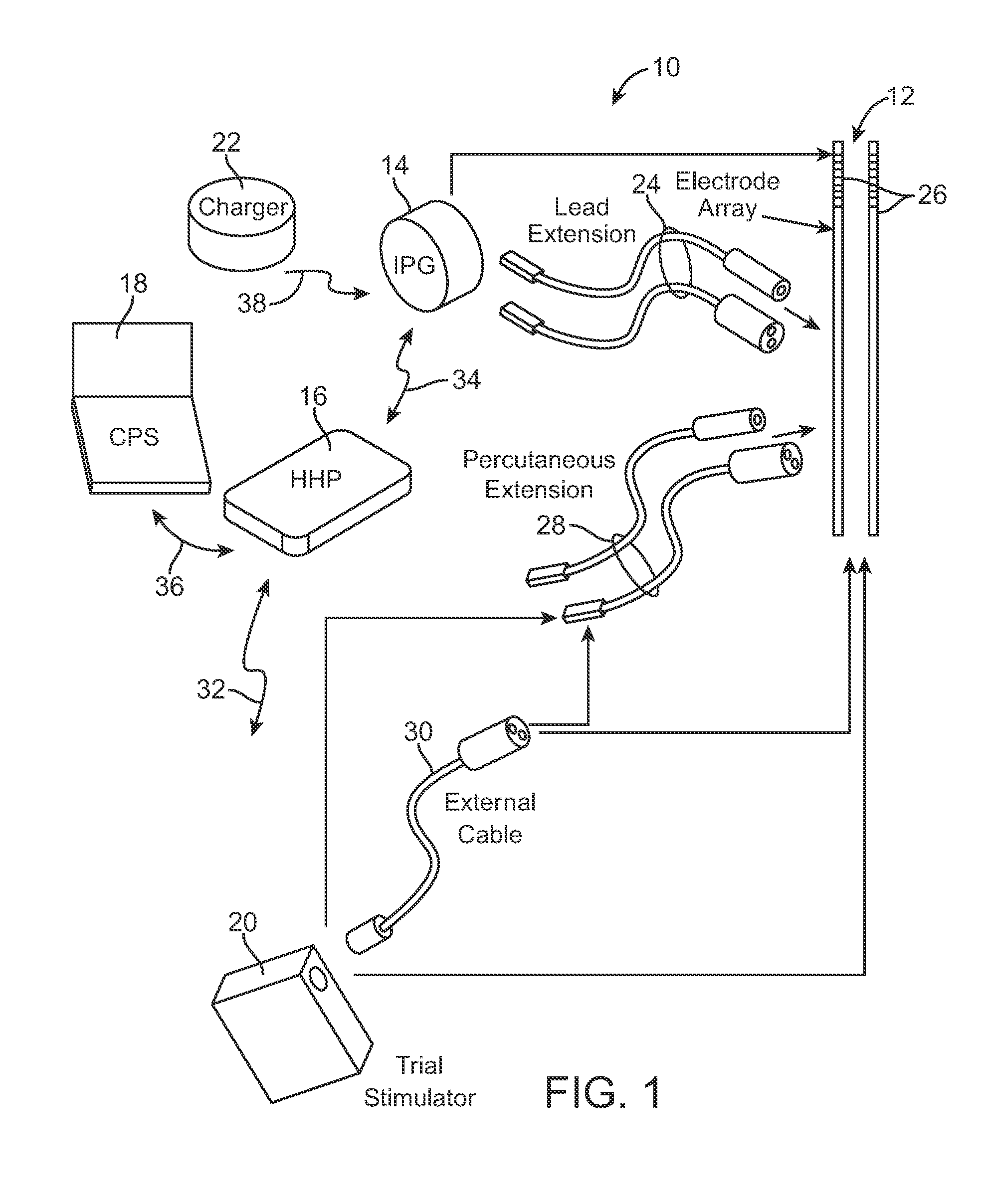
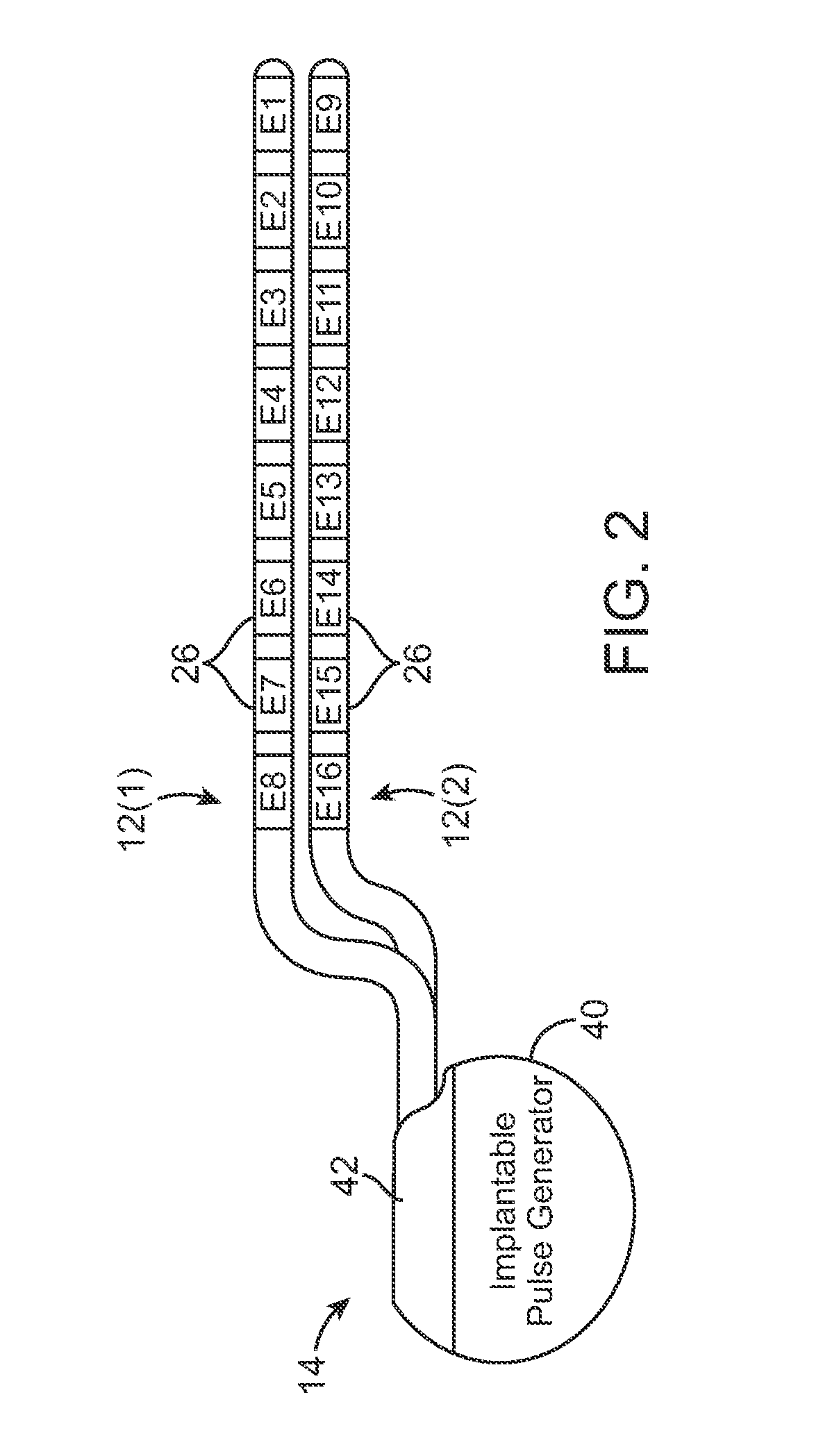
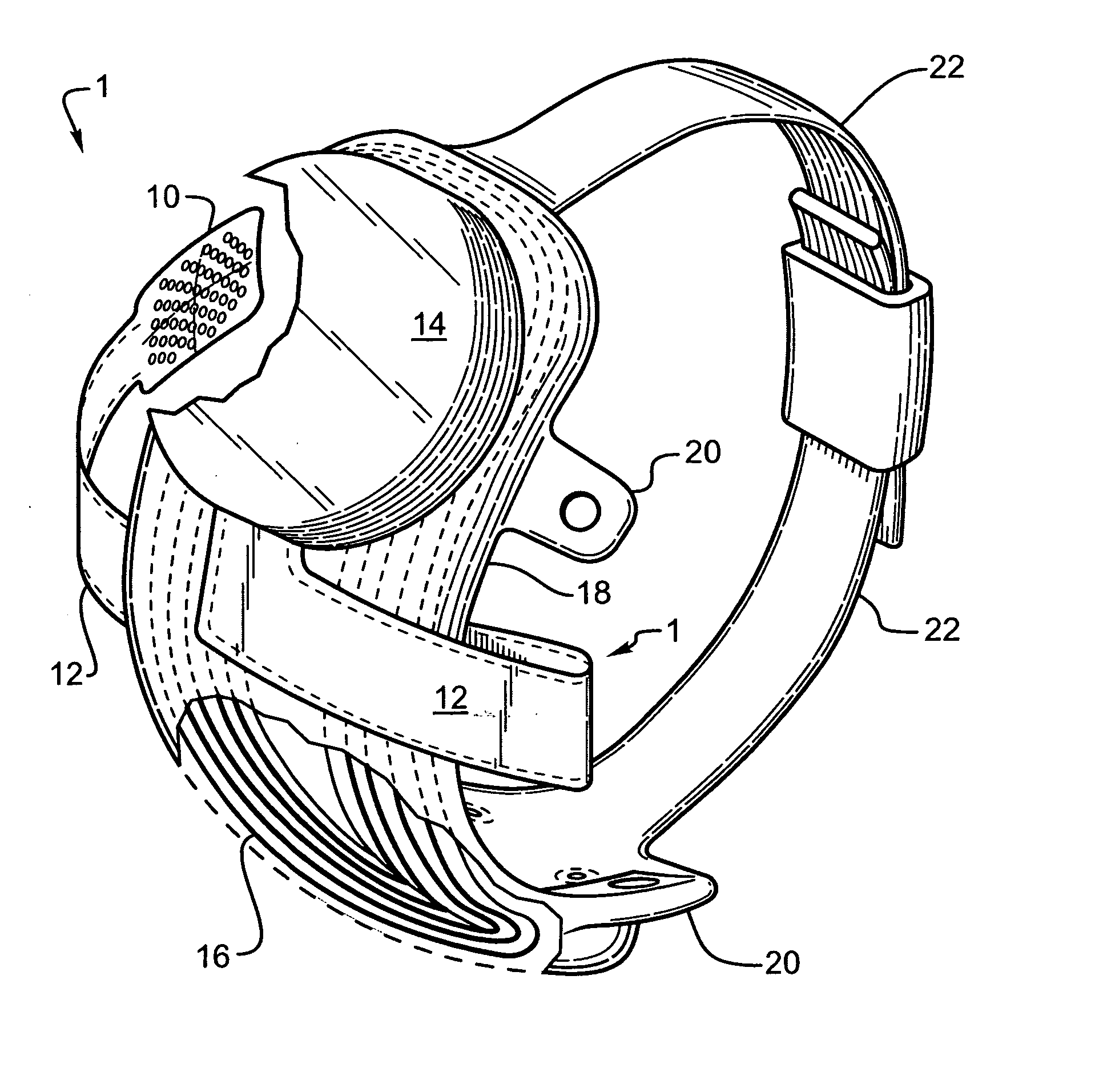
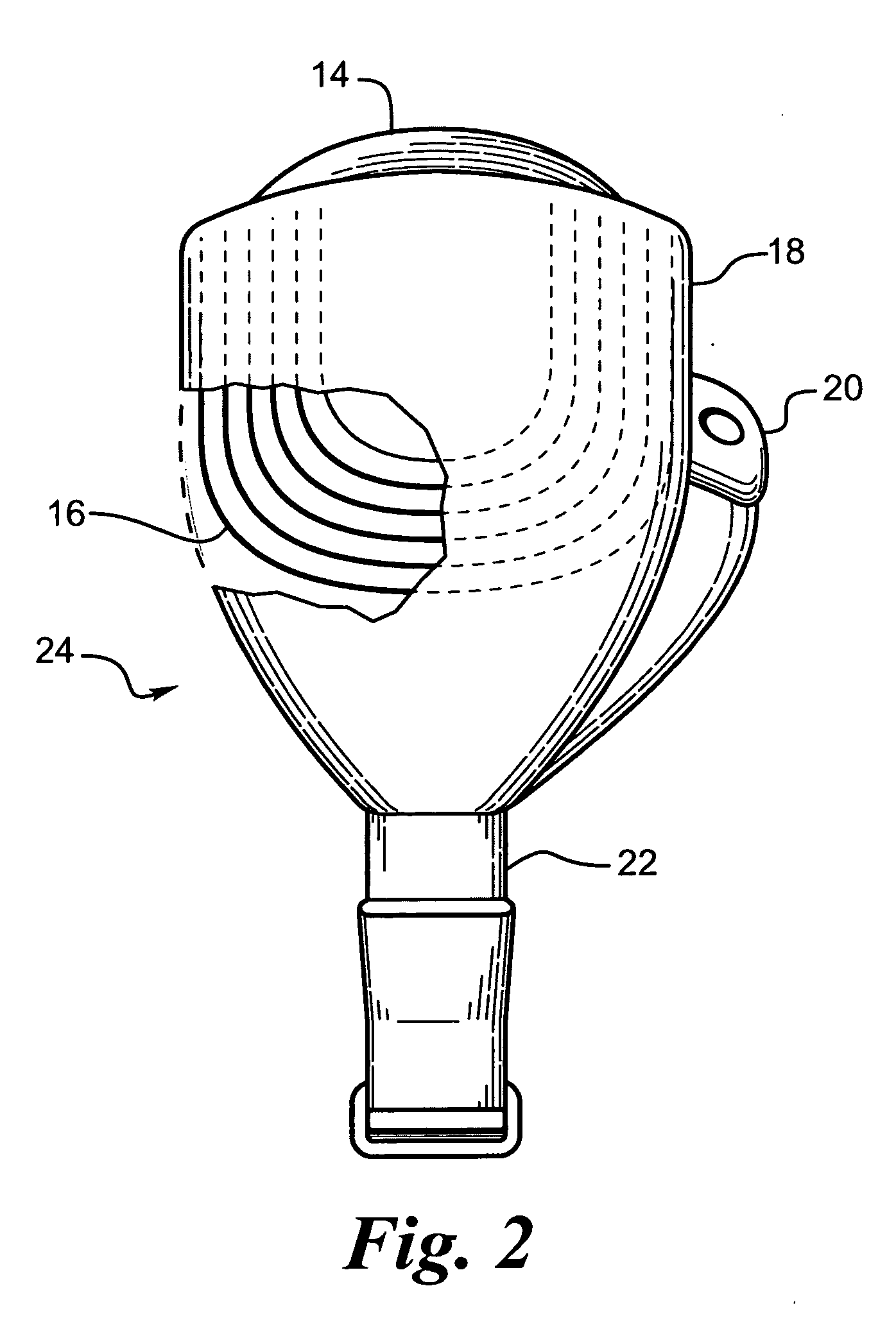
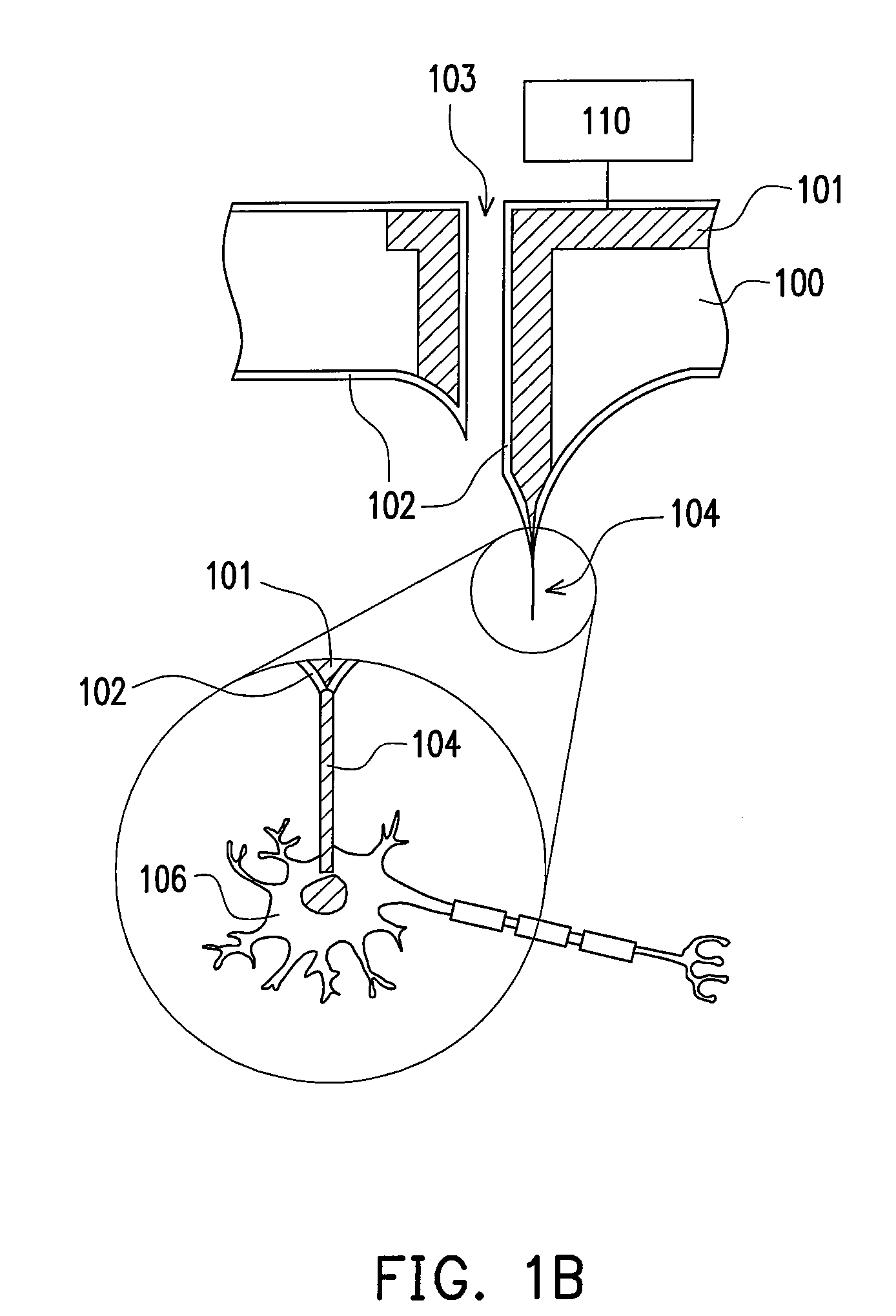
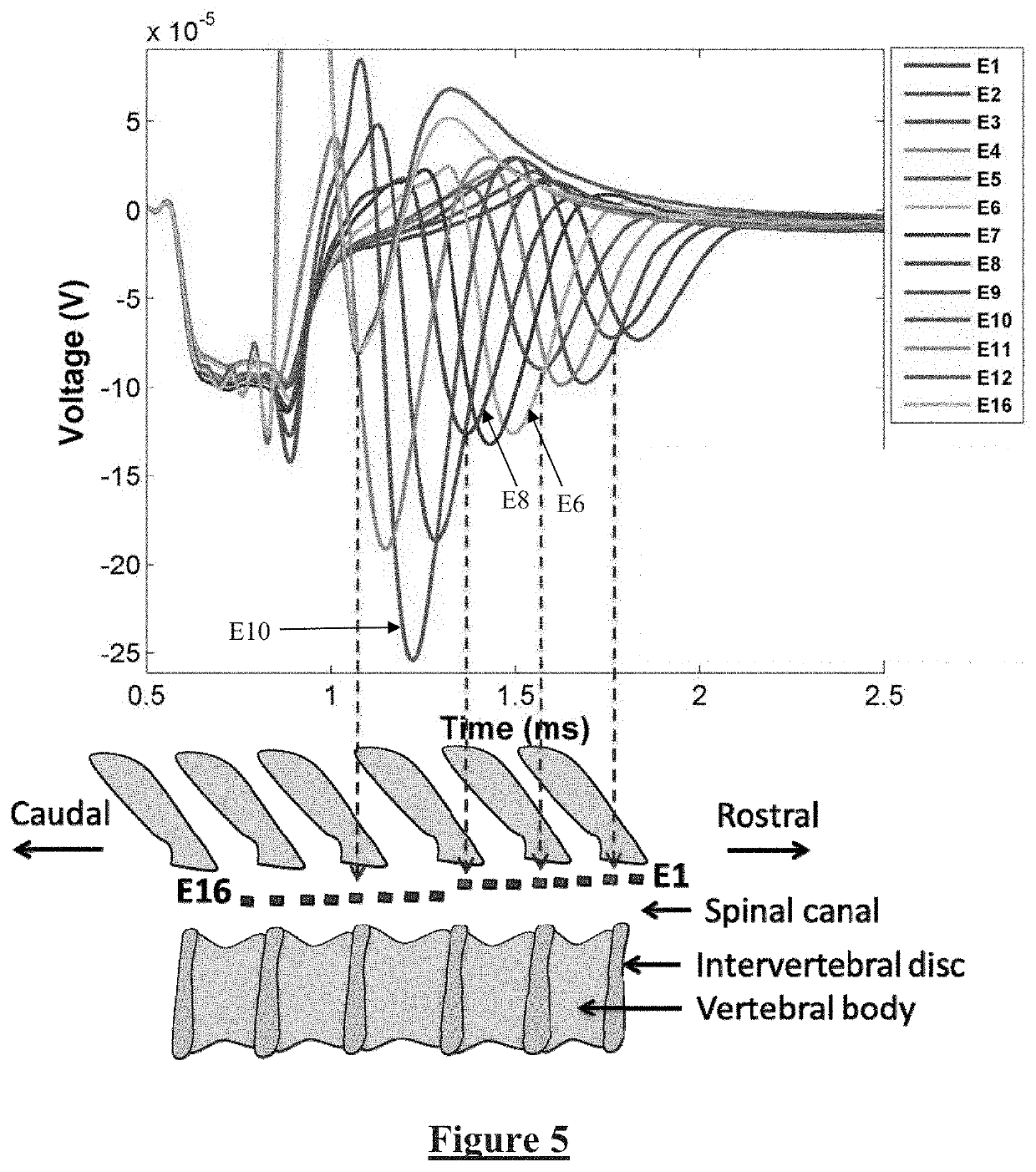
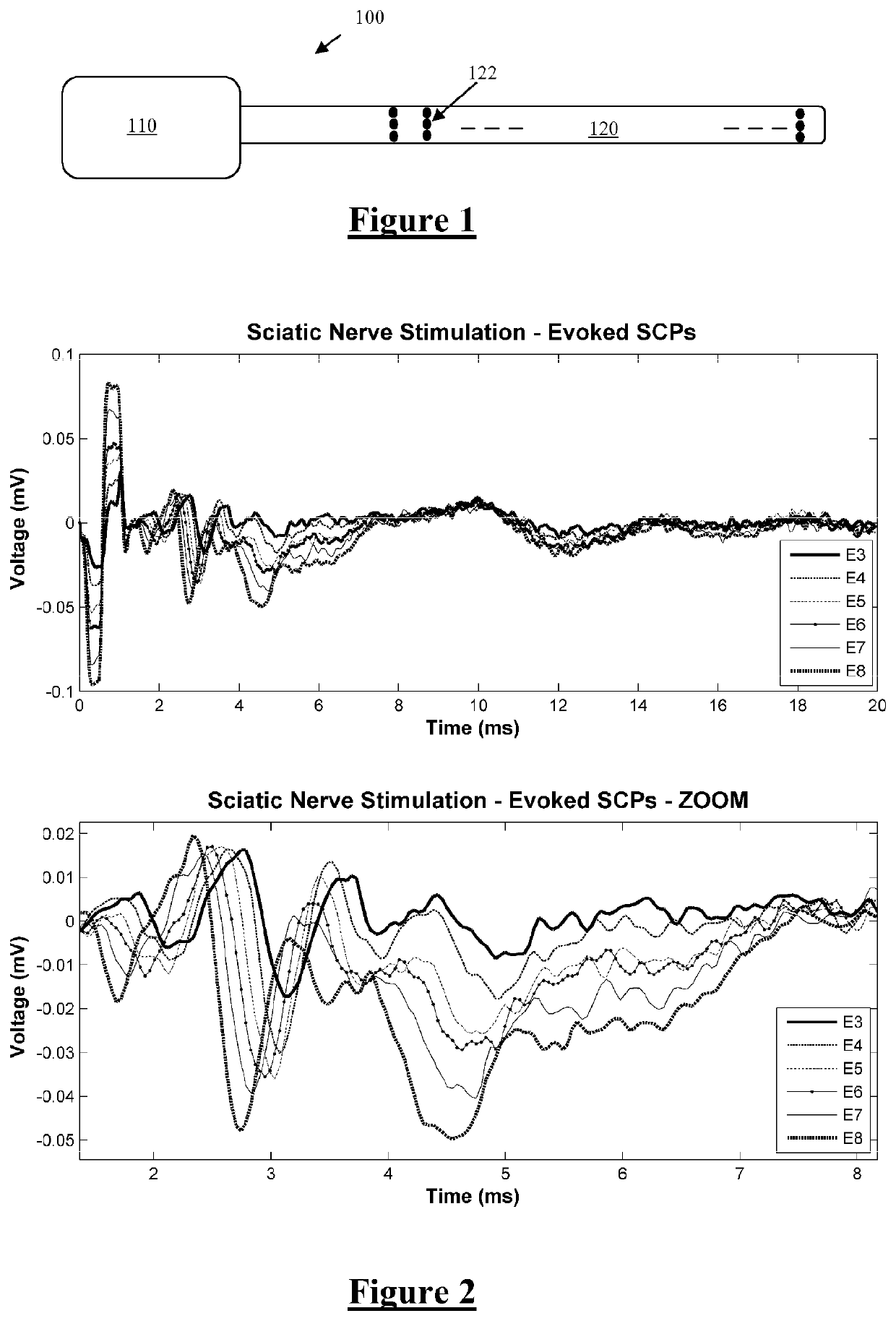
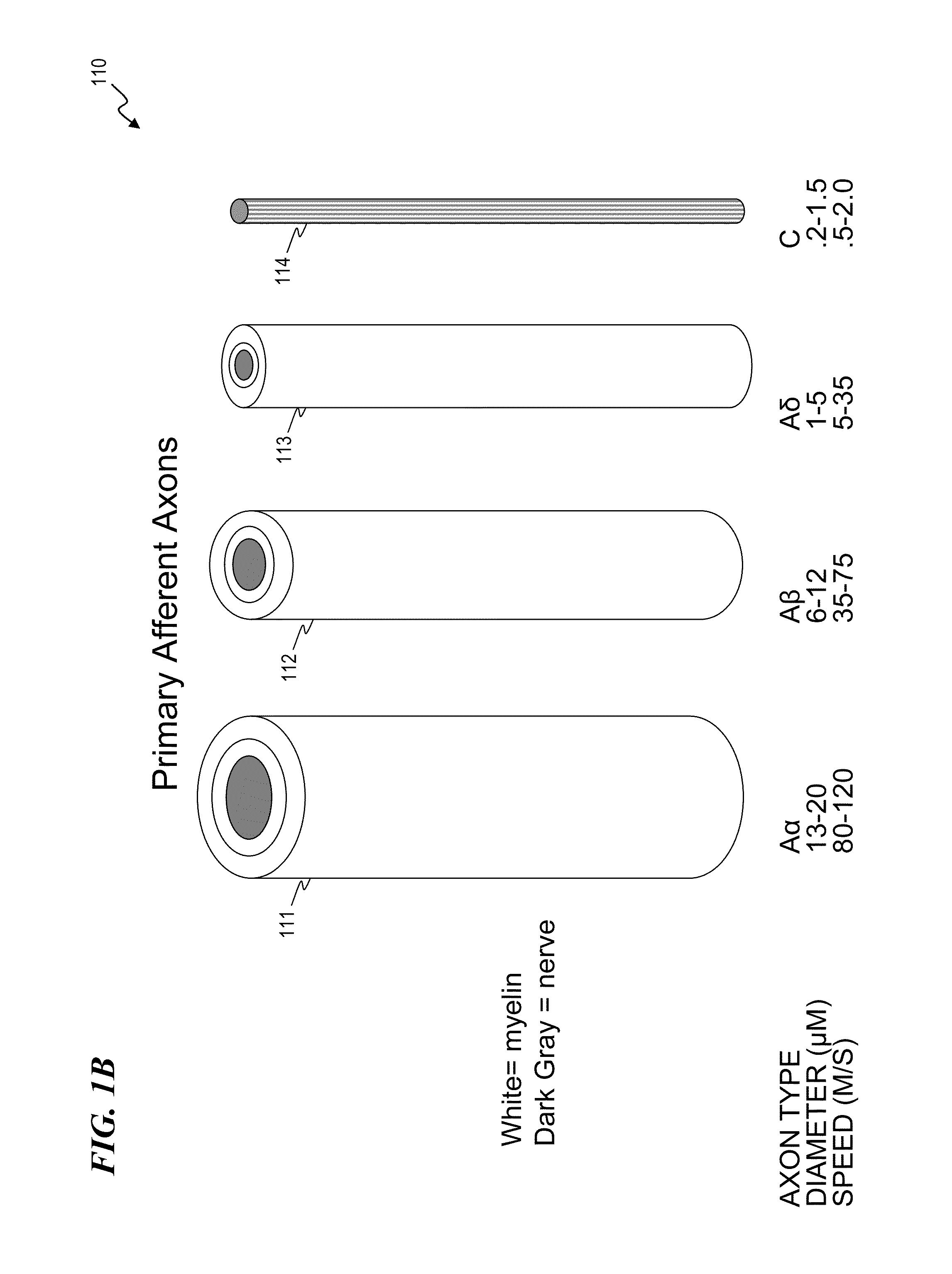
Methods and devices for optical stimulation of neural tissues
InactiveUS6921413B2Increasing electrical field sizeHighly specificElectrotherapySurgeryPHYSICAL MANIPULATIONSOptical stimulation
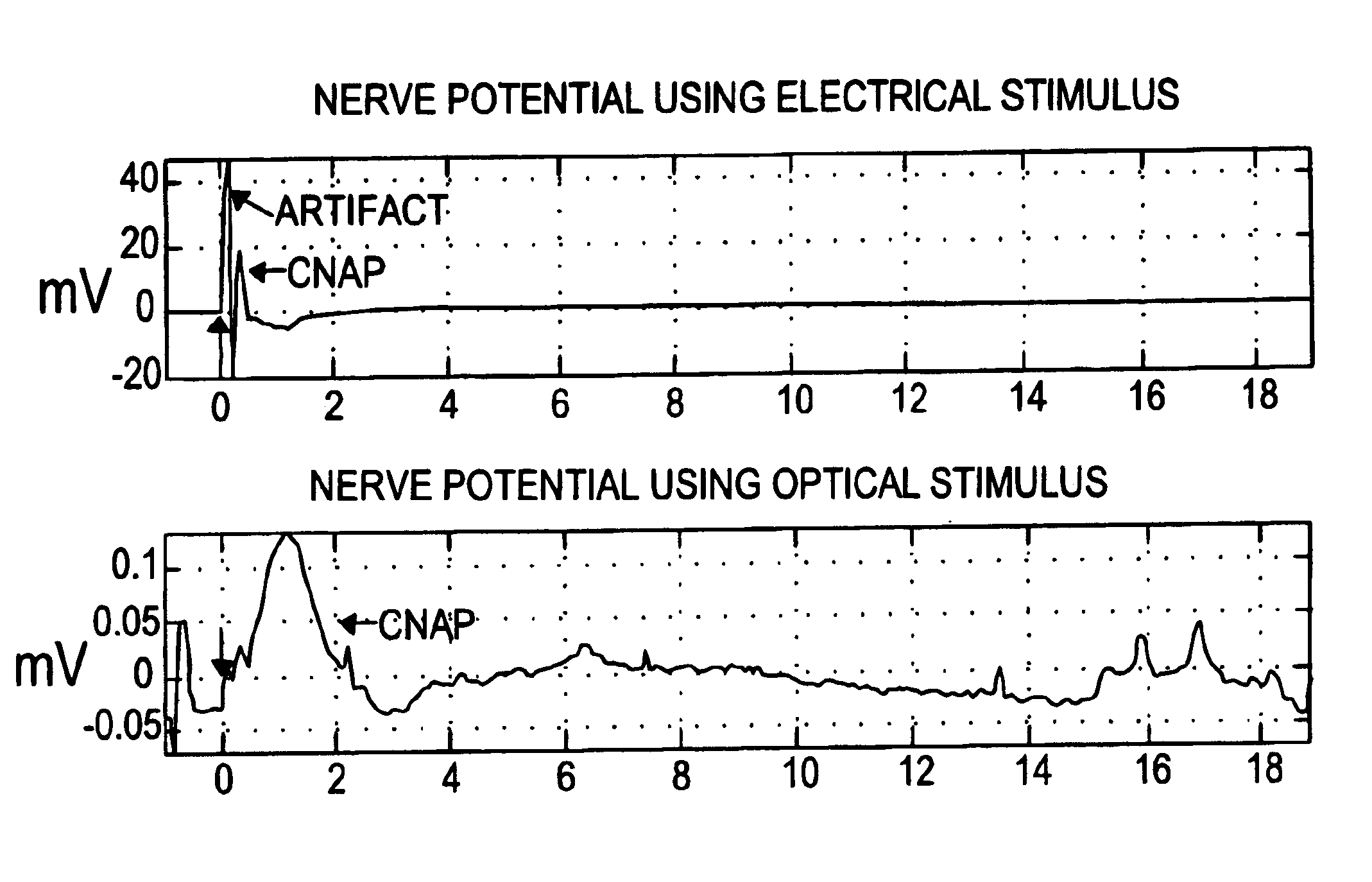
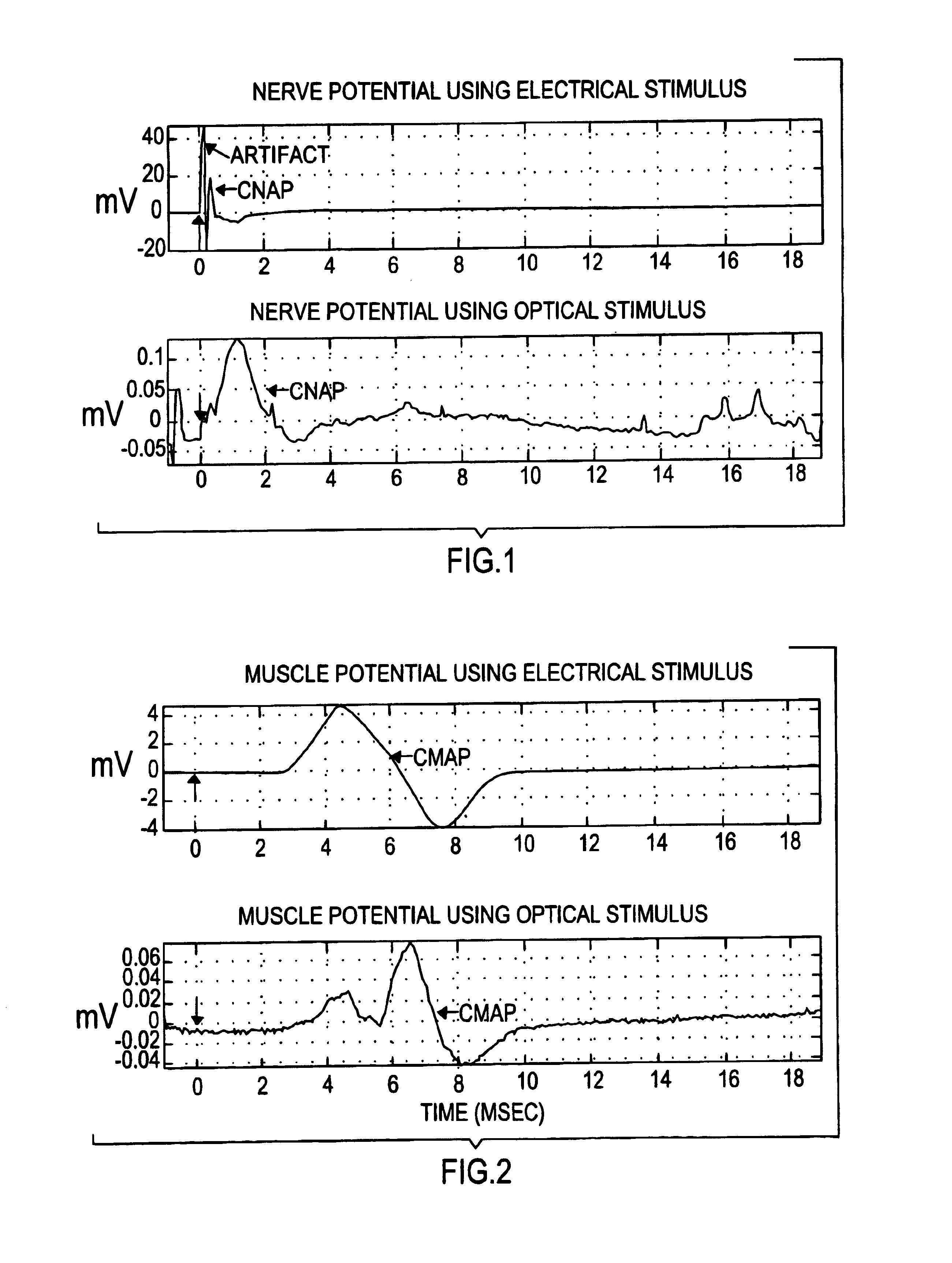
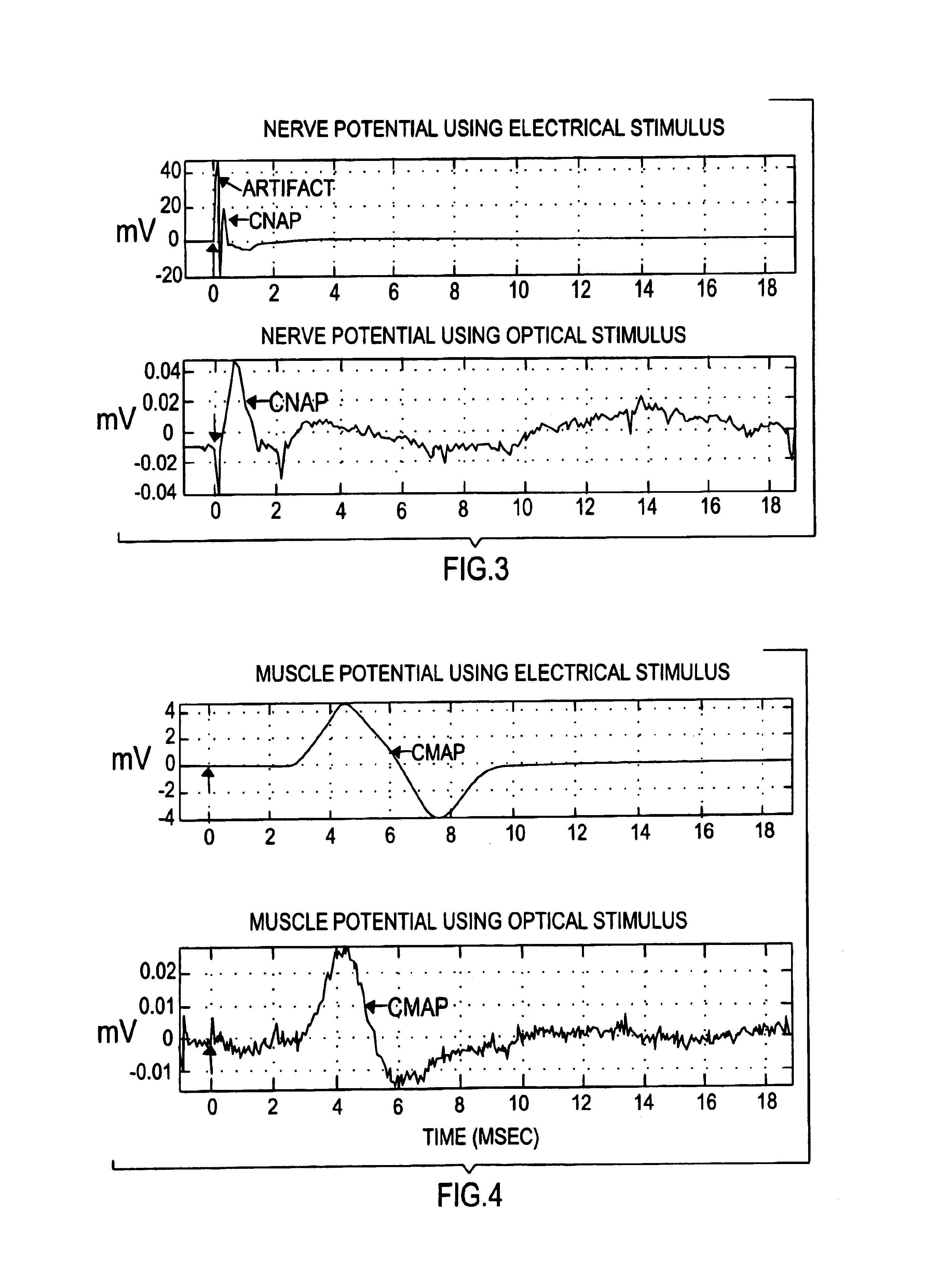
The present invention provides methods of directly stimulating neural tissue with optical energy. By stimulating neural tissue at wavelengths, laser pulses, and spot sizes disclosed herein, nerve stimulation may be used to uniquely stimulate neural tissue in way not afforded by other means of stimulation. It can allow basic scientists to study the properties of individual neurons or populations of neurons without piercing tissue with fragile microelectrodes. Furthermore, responses of neural tissue can be studied in a pure fashion without contamination by electrical artifact commonly seen with electrical stimulation. With respect to clinical uses, optical stimulation can be used to map function in subsections of peripheral nerves as an aid to operative repair. Finally, stimulation with optical energy does not require physical contact with the nerve which may be an advantage clinically when physical manipulation of neural tissue is not desired.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
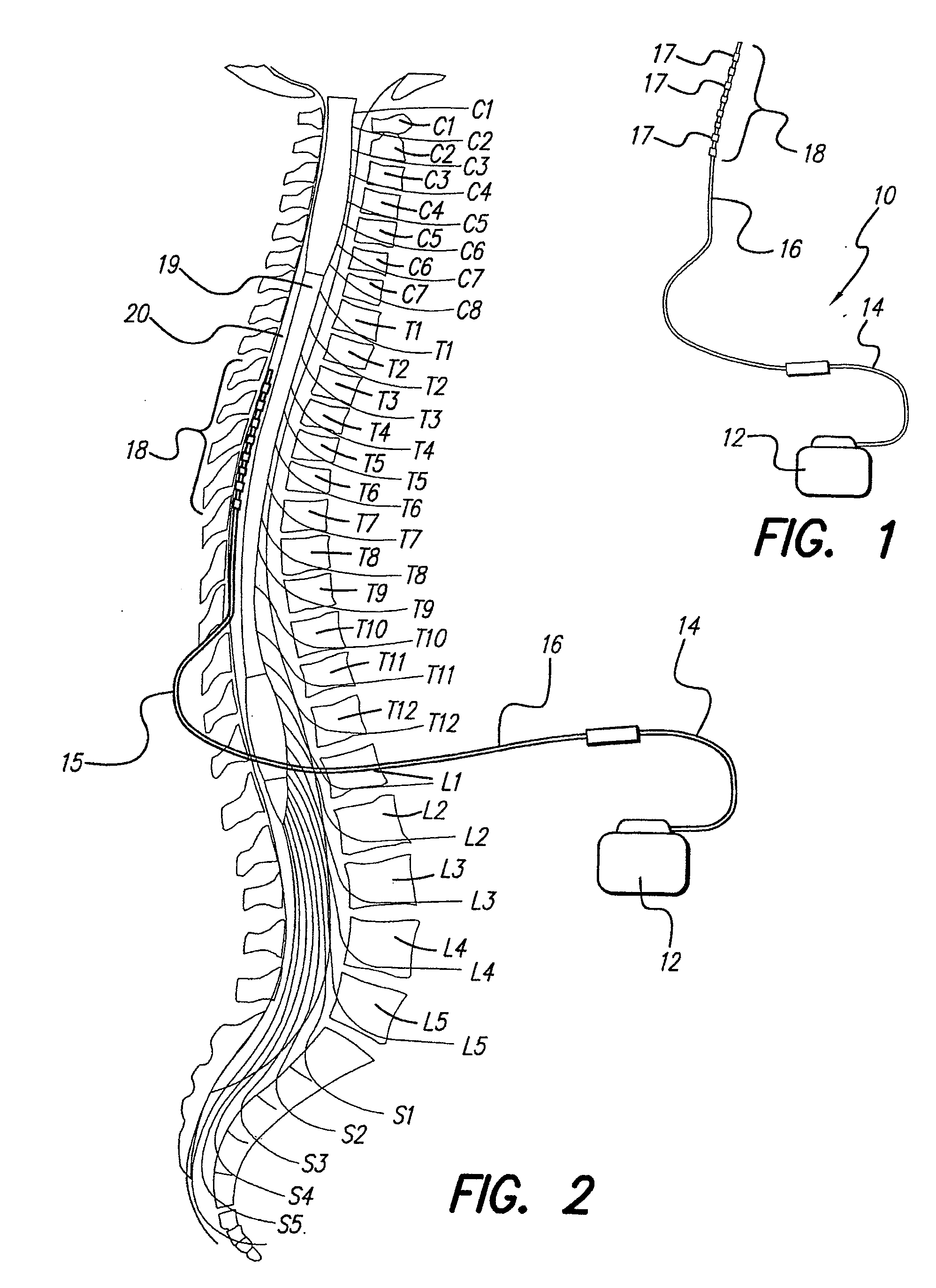
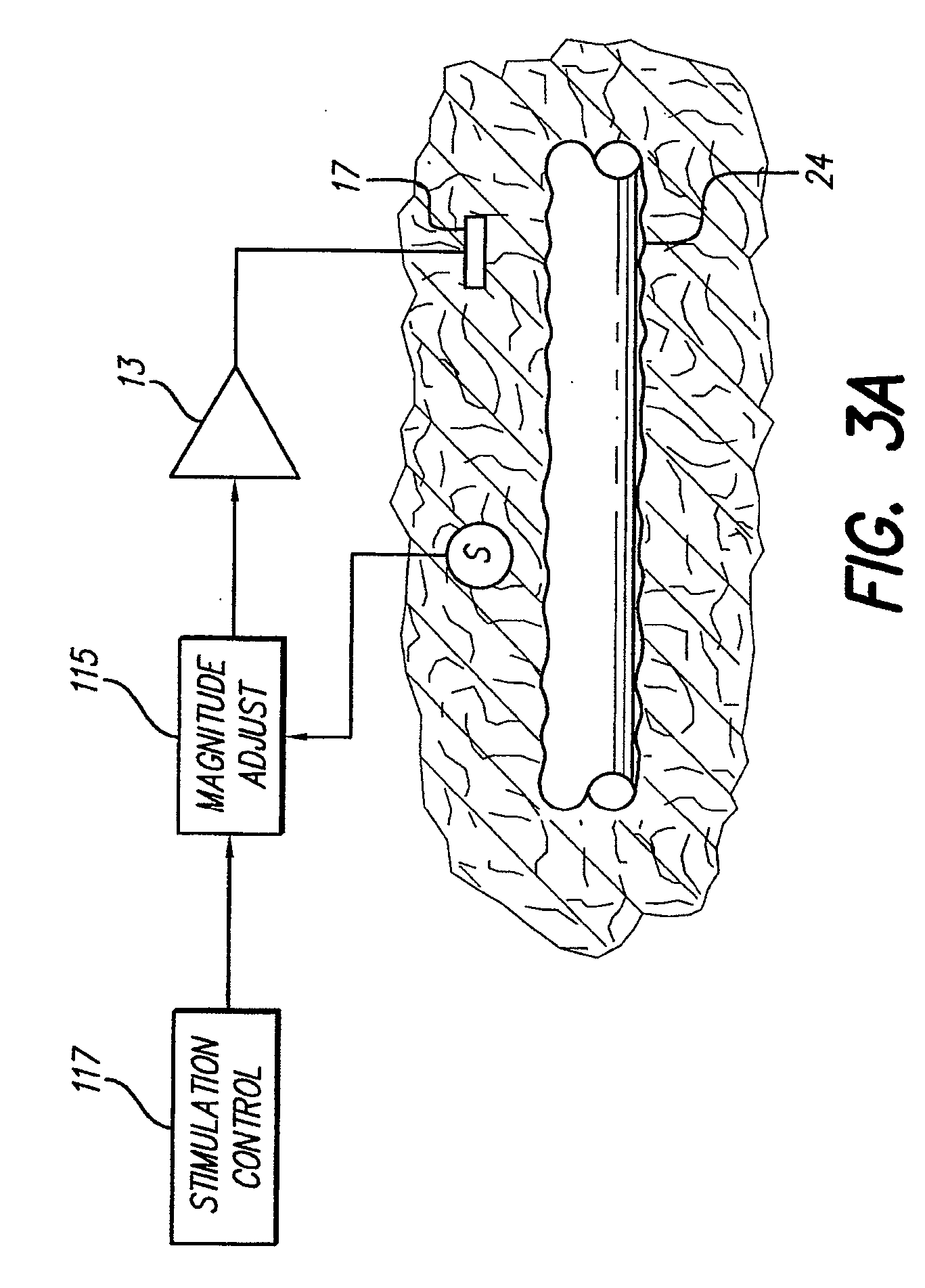
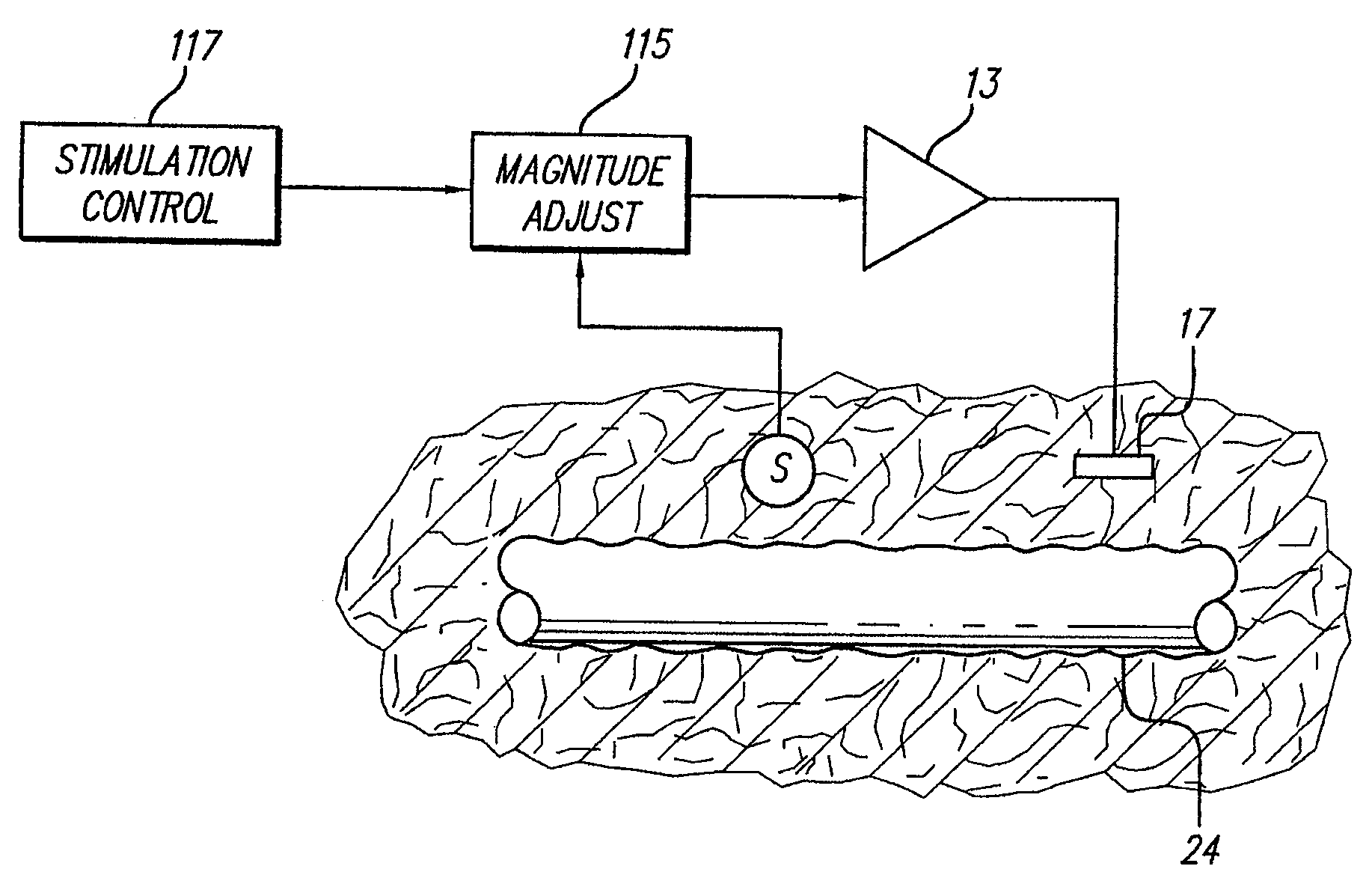
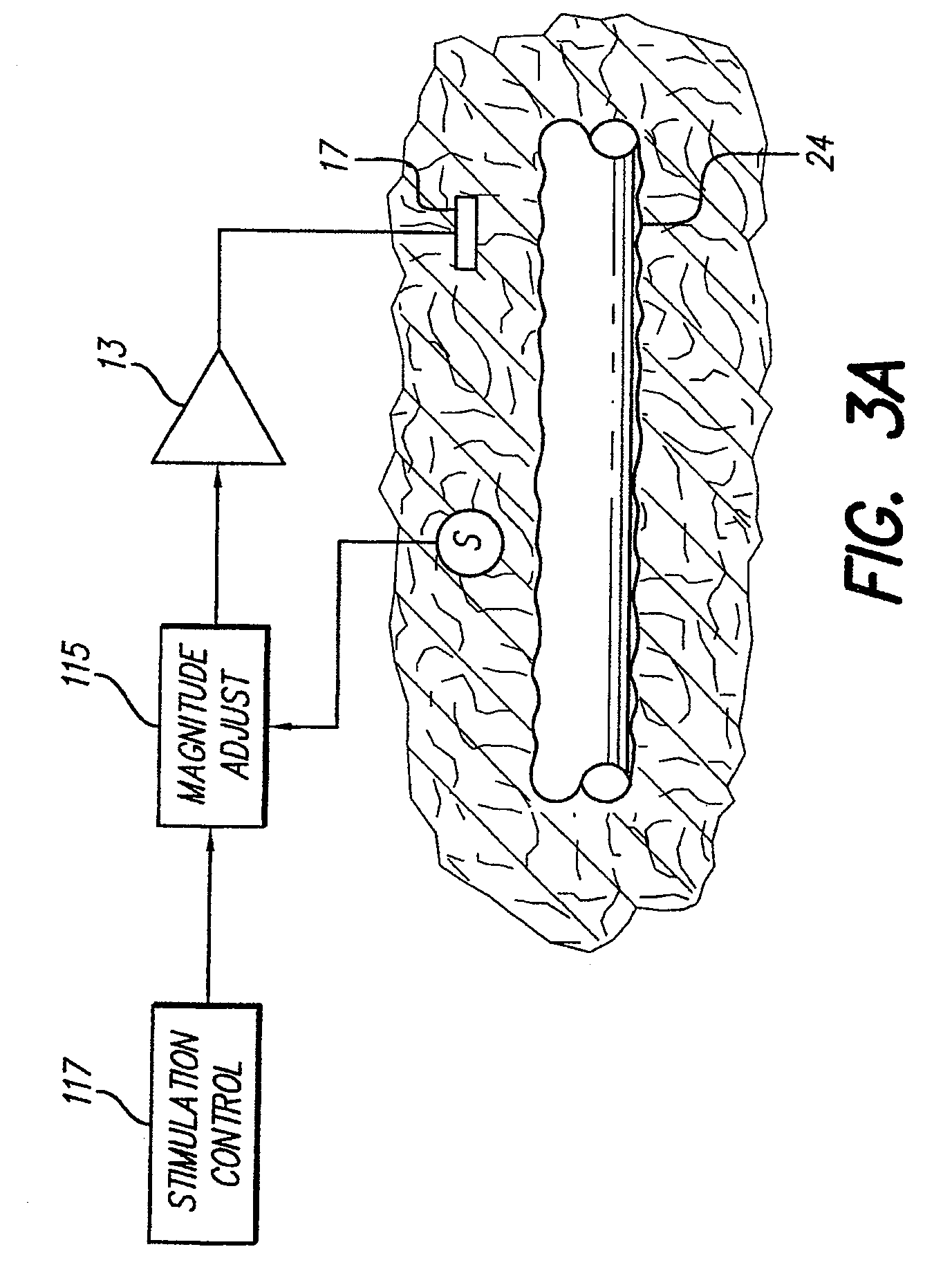
Neural stimulation system providing auto adjustment of stimulus output as a function of sensed impedance
InactiveUS20070208394A1Effectively auto correct output amplitudeMinimize occurrenceElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringNeural tissuesStimulus magnitude
A neural stimulation system automatically corrects or adjusts the stimulus magnitude (stimulation energy) in order to maintain a comfortable and effective stimulation therapy. Because the changes in impedance associated with the electrode-tissue interface can indicate obstruction of current flow and positional lead displacement, lead impedance can indicate the quantity of electrical stimulation energy that should be delivered to the target neural tissue to provide corrective adjustment. Hence, a change in impedance or morphology of an impedance curve may be used in a feedback loop to indicate that the stimulation energy needs to be adjusted and the system can effectively auto correct the magnitude of stimulation energy to maintain a desired therapeutic effect.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
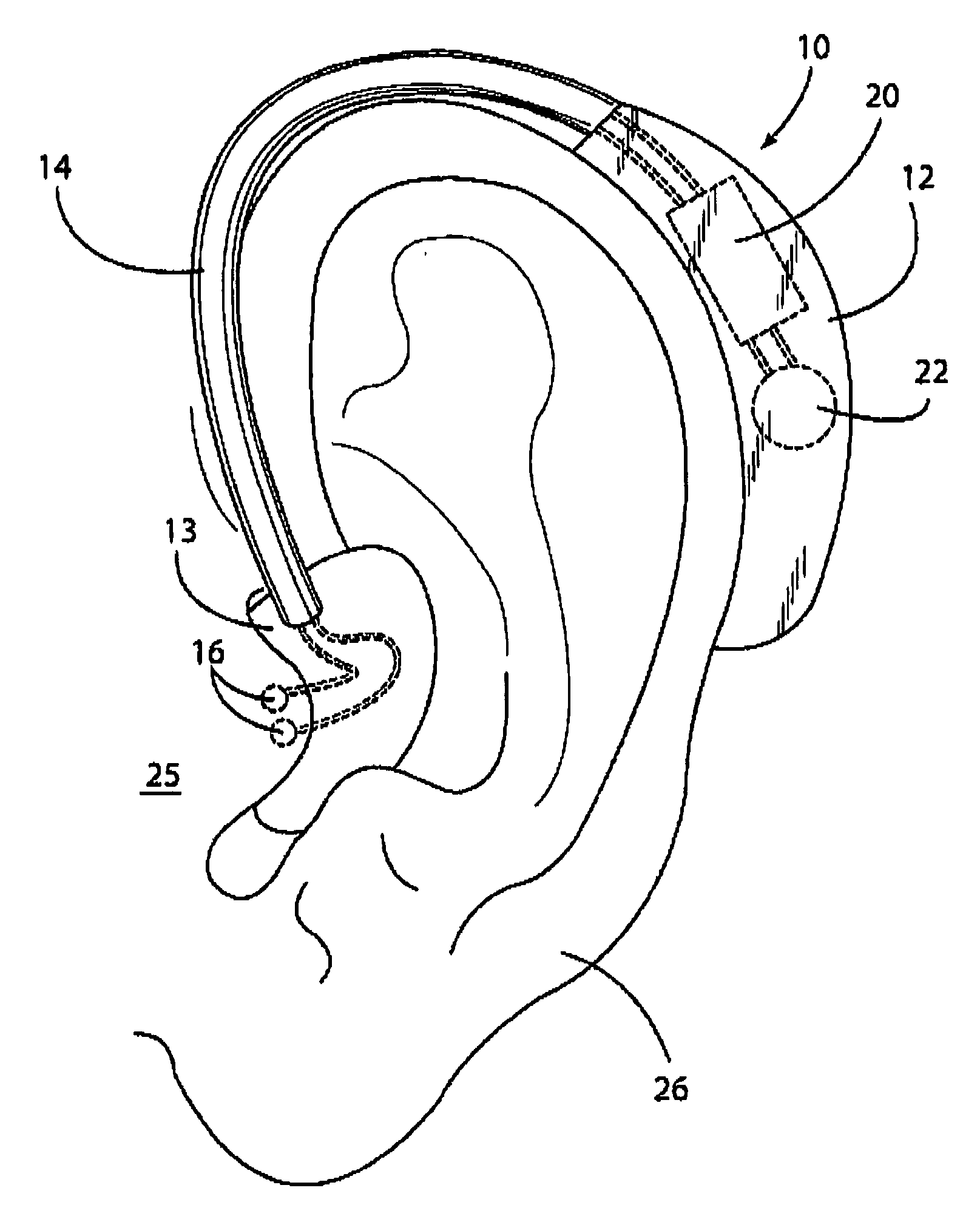
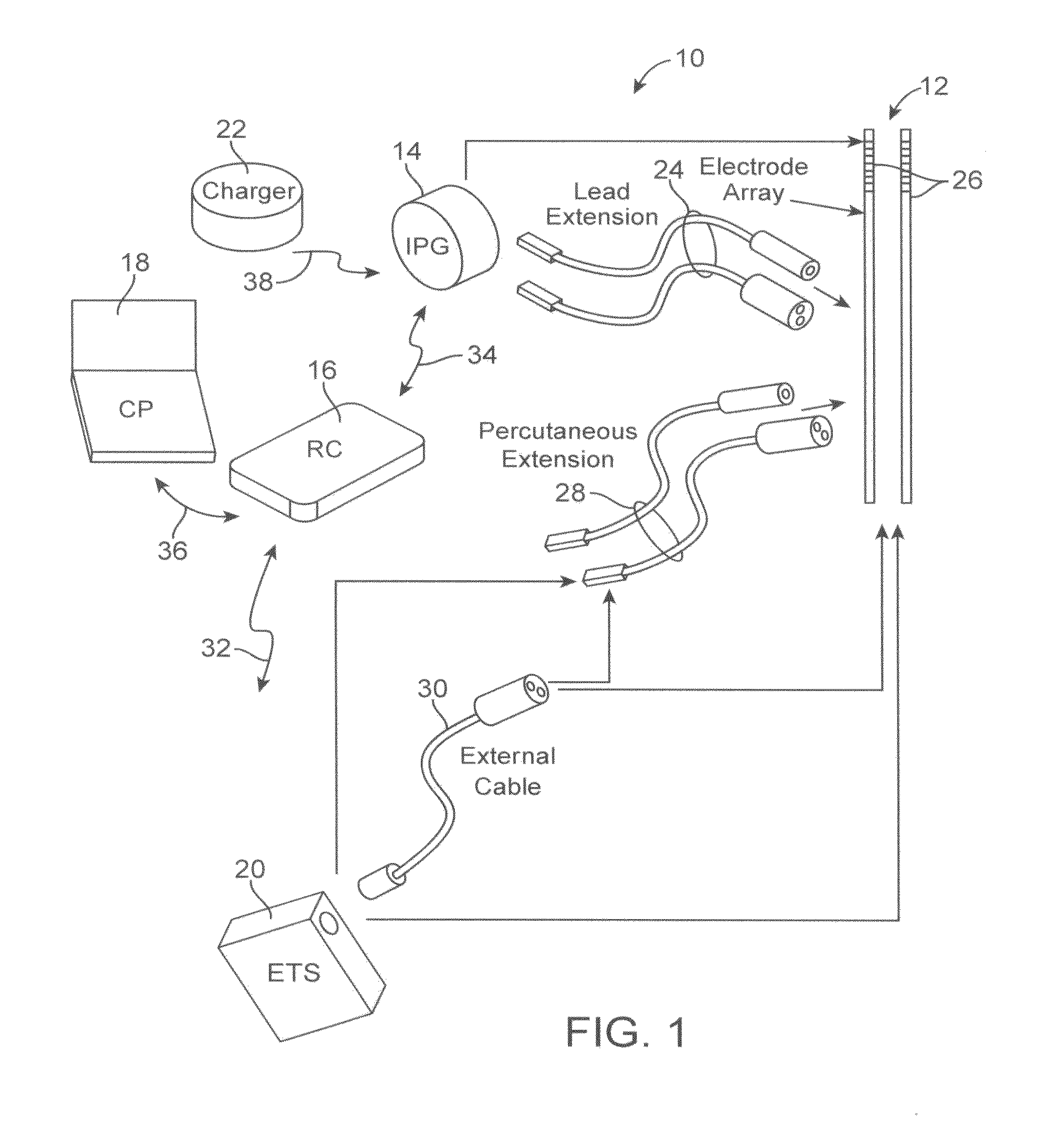
Non-invasive device and method for electrical stimulation of neural tissue
InactiveUS20070150027A1Quality improvementLow costHead electrodesSkin piercing electrodesElectricityHearing aid
A non-invasive device and method for stimulation of neural tissue of a patient comprises a power source and at least one pair of electrodes. The power source applies a voltage to the pair of electrodes, and the electrodes extend through a top layer of skin generally adjacent Arnold's nerve. The device can be formed in shape similar to a hearing aid. A second pair of electrodes may also be used, positioned on the skin generally adjacent the auriculotemporal nerve.
Owner:ROGERS LESCO L
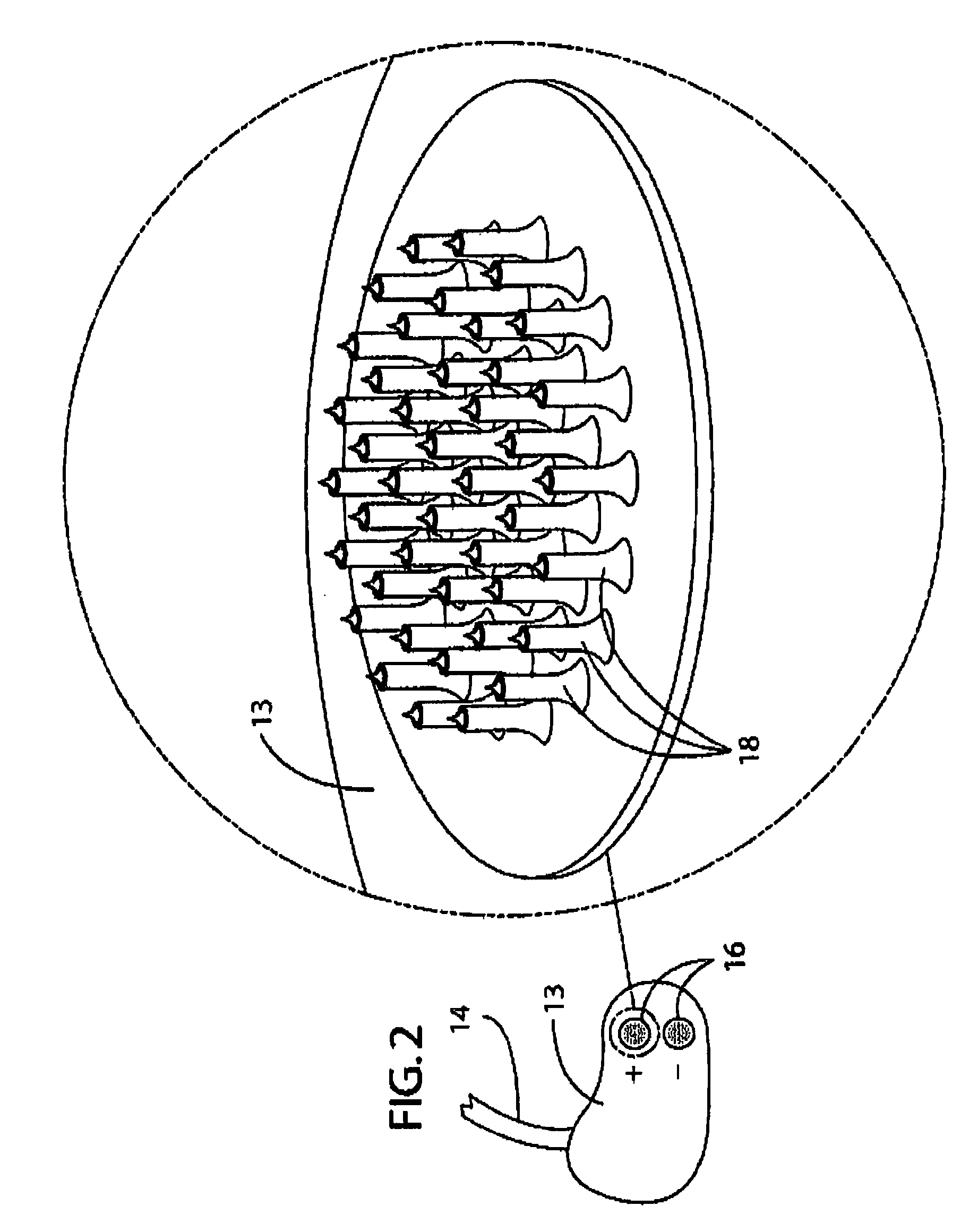
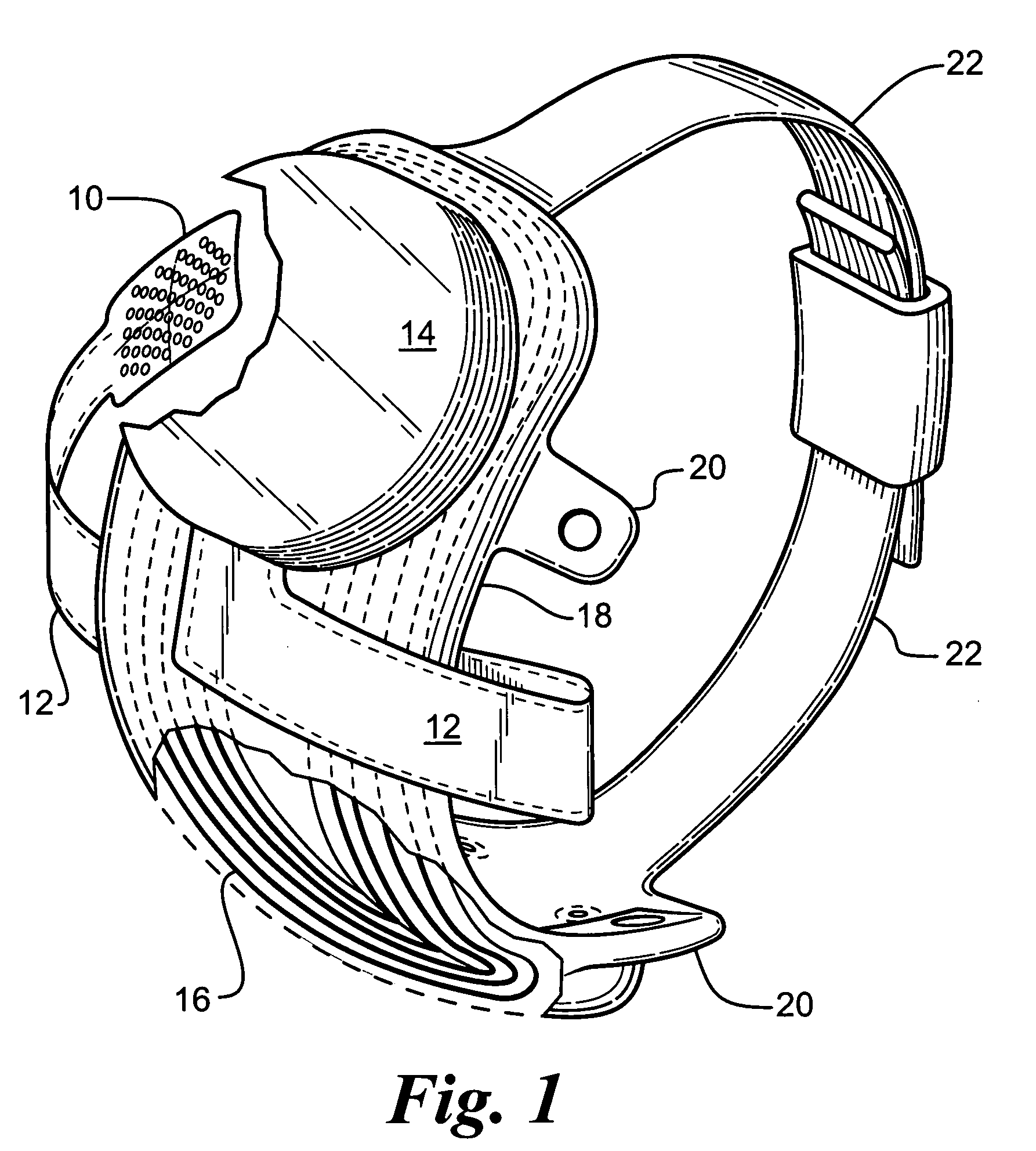
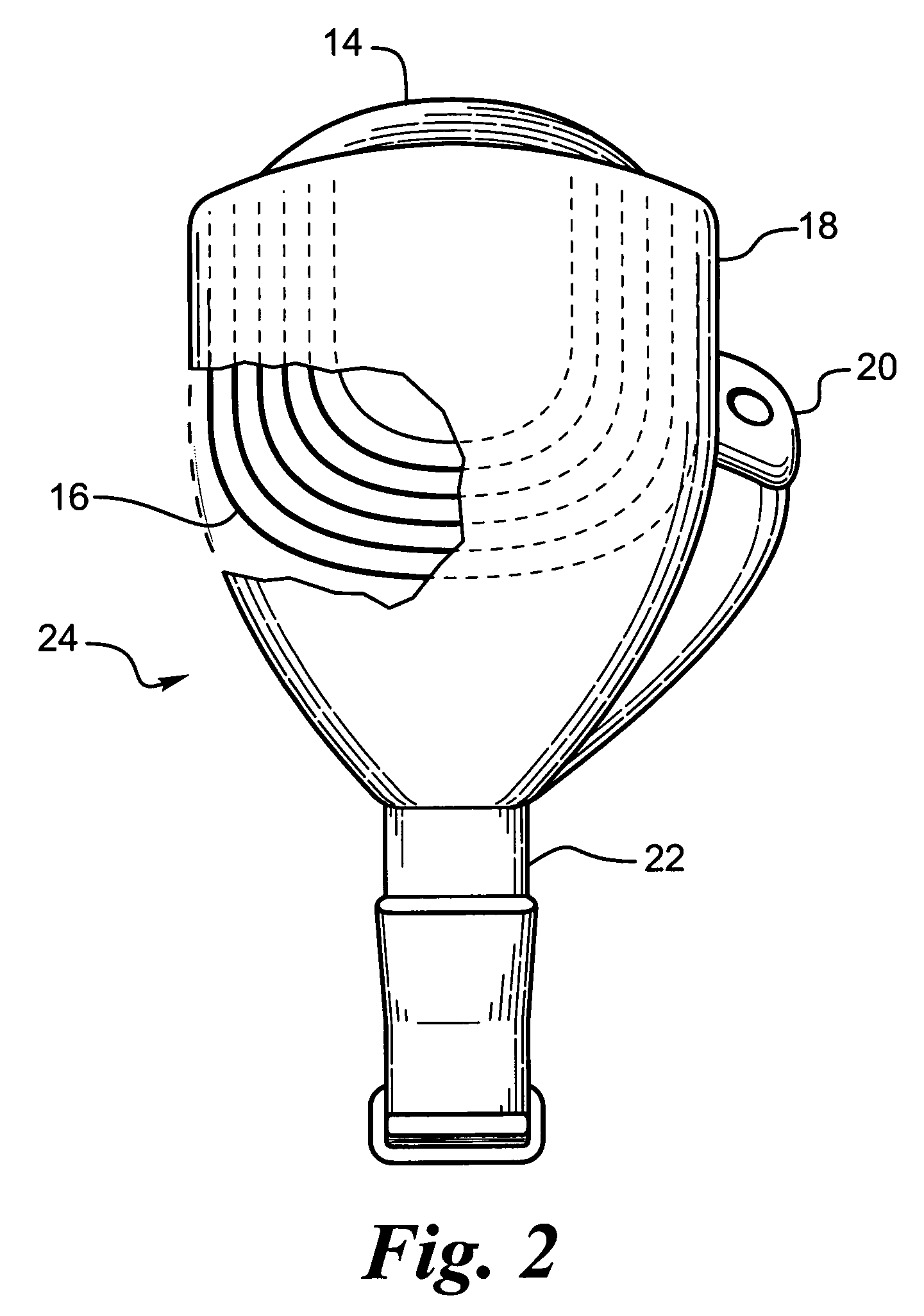
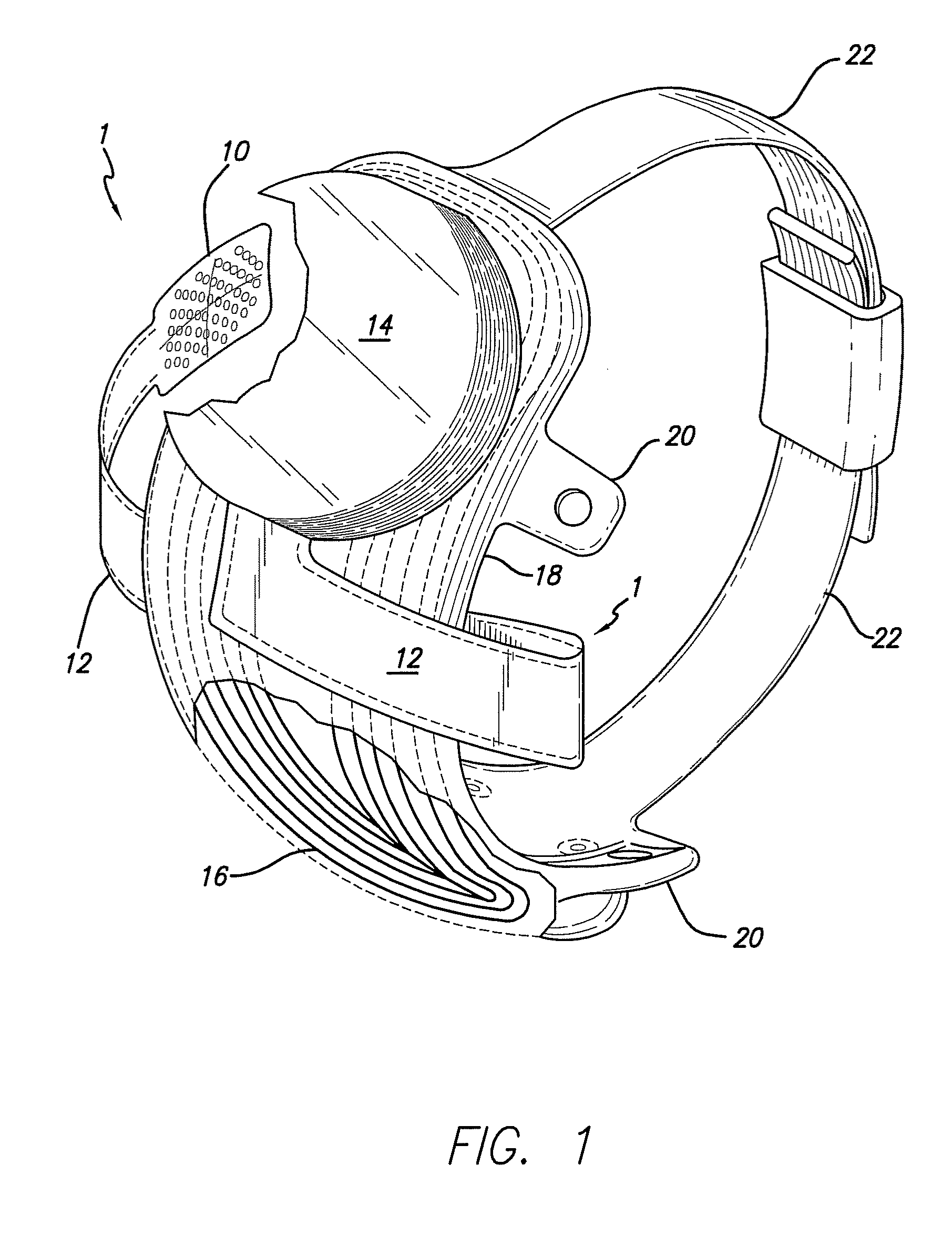
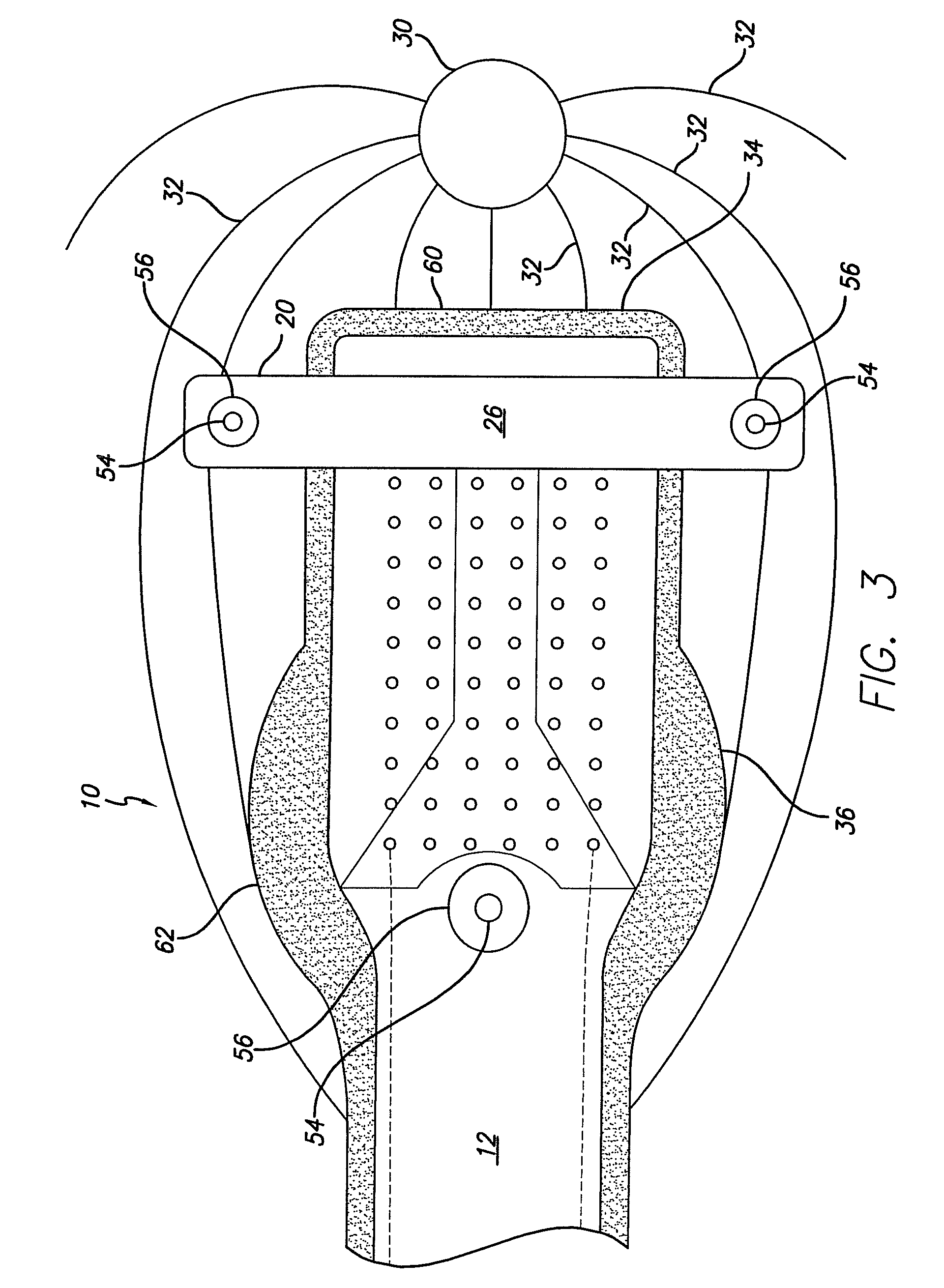
Flexible circuit electrode array
ActiveUS20060247754A1Improve the immunityCut the delicate retinal tissueHead electrodesPrinted circuit manufactureFlexible circuitsHearing perception
Polymer materials are useful as electrode array bodies for neural stimulation. They are particularly useful for retinal stimulation to create artificial vision, cochlear stimulation to create artificial hearing, or cortical stimulation many purposes. The pressure applied against the retina, or other neural tissue, by an electrode array is critical. Too little pressure causes increased electrical resistance, along with electric field dispersion. Too much pressure may block blood flow. Common flexible circuit fabrication techniques generally require that a flexible circuit electrode array be made flat. Since neural tissue is almost never flat, a flat array will necessarily apply uneven pressure. Further, the edges of a flexible circuit polymer array may be sharp and cut the delicate neural tissue. By applying the right amount of heat to a completed array, a curve can be induced. With a thermoplastic polymer it may be further advantageous to repeatedly heat the flexible circuit in multiple molds, each with a decreasing radius. Further, it is advantageous to add material along the edges. It is further advantageous to provide a fold or twist in the flexible circuit array. Additional material may be added inside and outside the fold to promote a good seal with tissue.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC +1
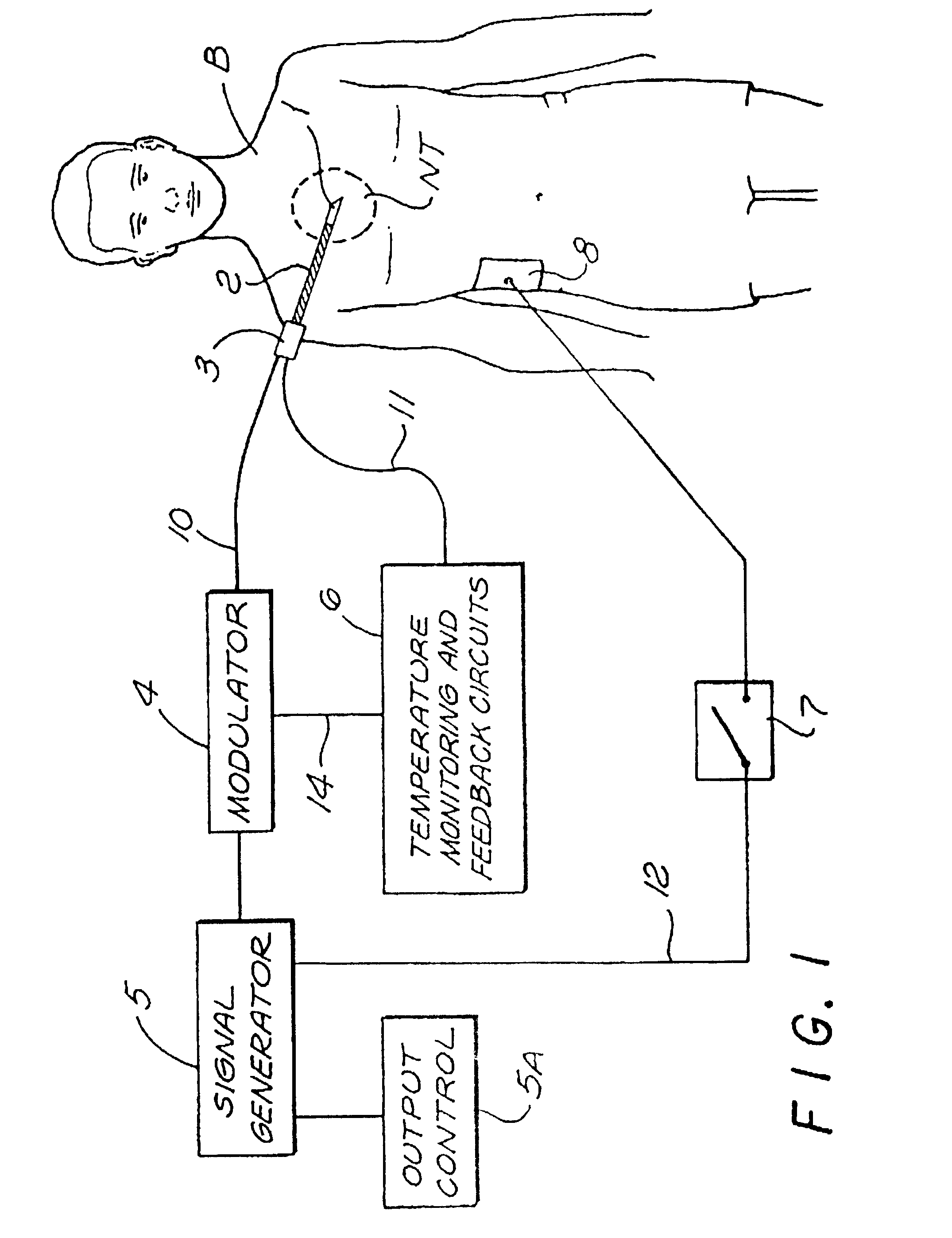
Method and system for neural tissue modification
InactiveUSRE40279E1Relief the painModifiesElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingMedicineTEMPERATURE ELEVATION
A method and apparatus for altering a function of neural tissue in a patient. An electromagnetic signal is applied to the neural tissue through an electrode. The electromagnetic signal has a frequency component above the physiological stimulation frequency range and an intensity sufficient to produce an alteration of the neural tissue, the alteration causing the patient to experience a reduction in pain, and a waveform that prevents lethal temperature elevation of the neural tissue during application of the electromagnetic signal to the neural tissue.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Flexible Circuit Electrode Array
ActiveUS20080288037A1Head electrodesPrinted circuit secondary treatmentFlexible circuitsElectrode array
A flexible circuit electrode array with more than one layer of metal traces comprising: a polymer base layer; more than one layer of metal traces, separated by polymer layers, deposited on said polymer base layer, including electrodes suitable to stimulate neural tissue; and a polymer top layer deposited on said polymer base layer and said metal traces. Polymer materials are useful as electrode array bodies for neural stimulation. They are particularly useful for retinal stimulation to create artificial vision, cochlear stimulation to create artificial hearing, or cortical stimulation many purposes. The pressure applied against the retina, or other neural tissue, by an electrode array is critical. Too little pressure causes increased electrical resistance, along with electric field dispersion. Too much pressure may block blood flow.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
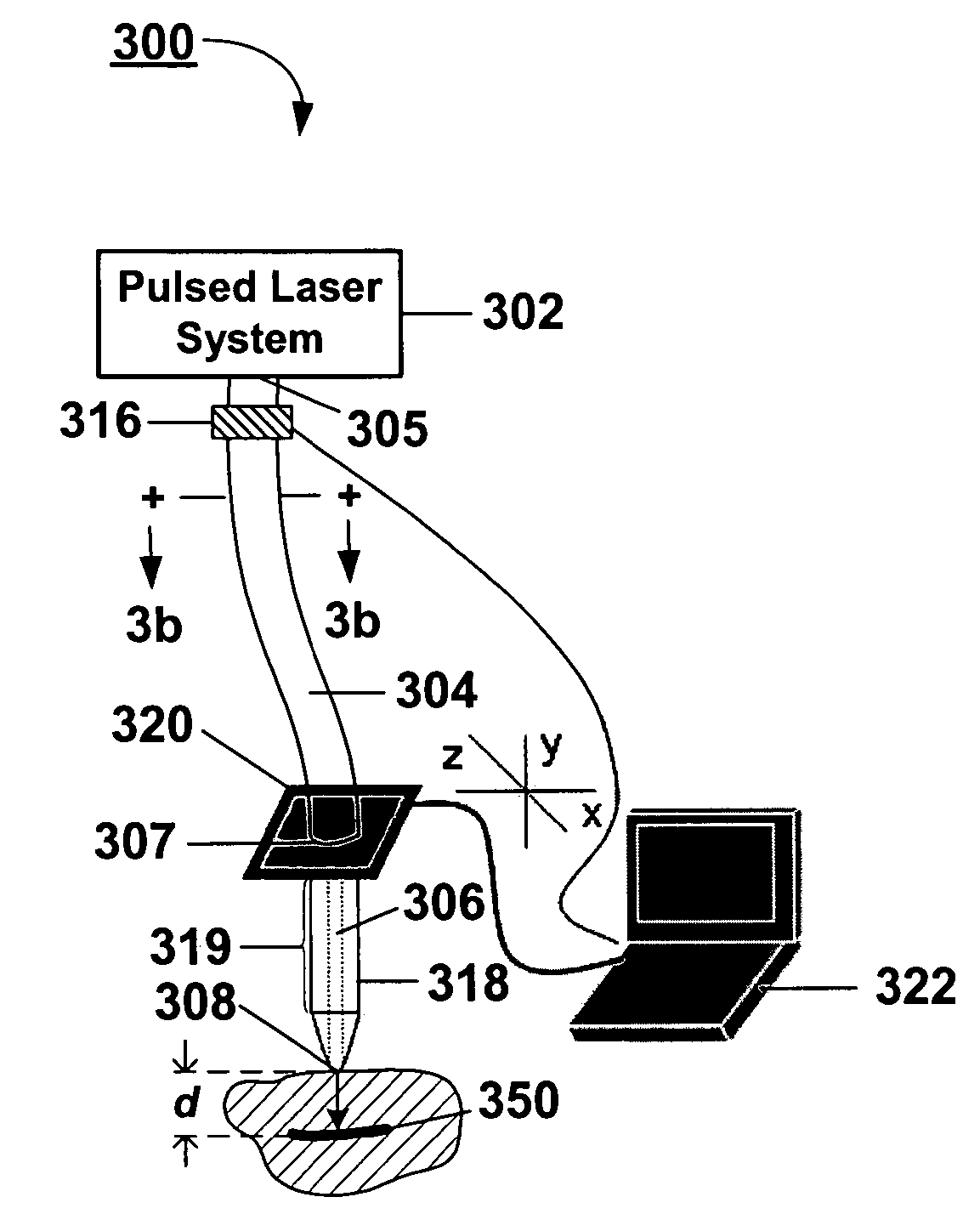
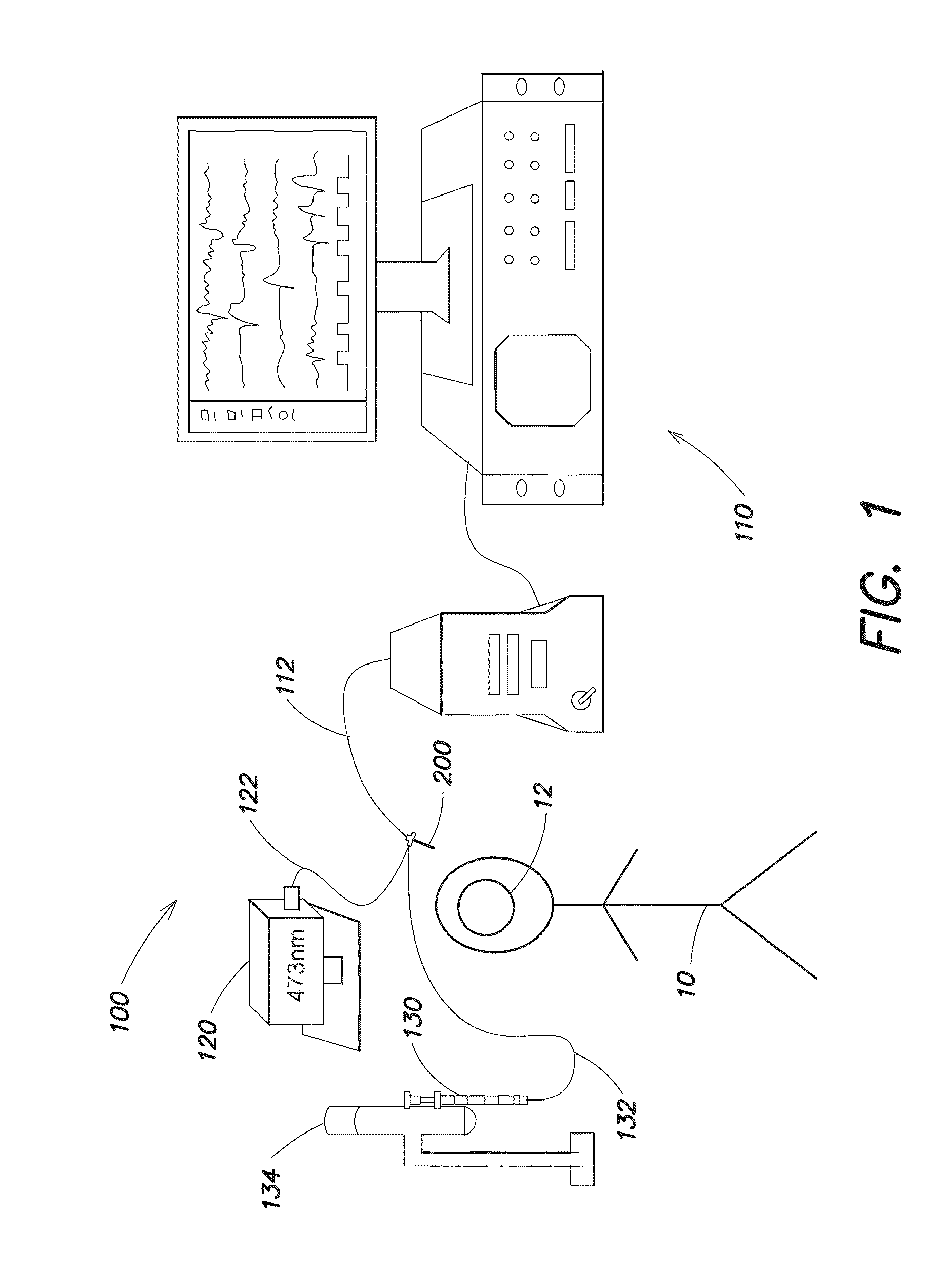
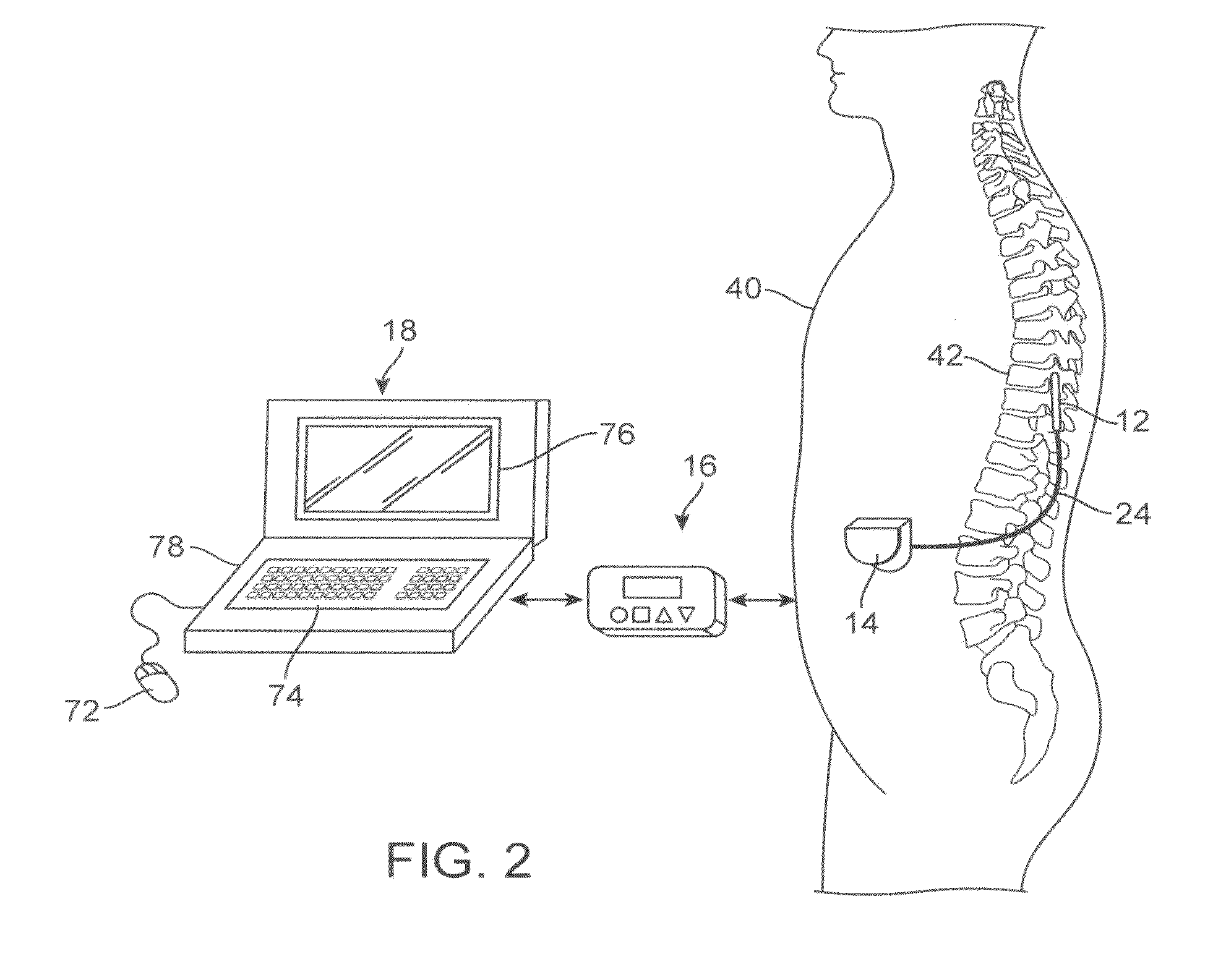
System and methods for optical stimulation of neural tissues
The present invention, in one aspect, relates to a system for stimulating neural tissue of a living subject. The system comprises an energy source capable of generating optical energy, a connector having a first end and a second end capable of transmitting optical energy, and a probe operably coupled to the second end of the connector and having an end portion for delivering optical energy to a target neural tissue. In one embodiment, the energy source comprises a tunable laser.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
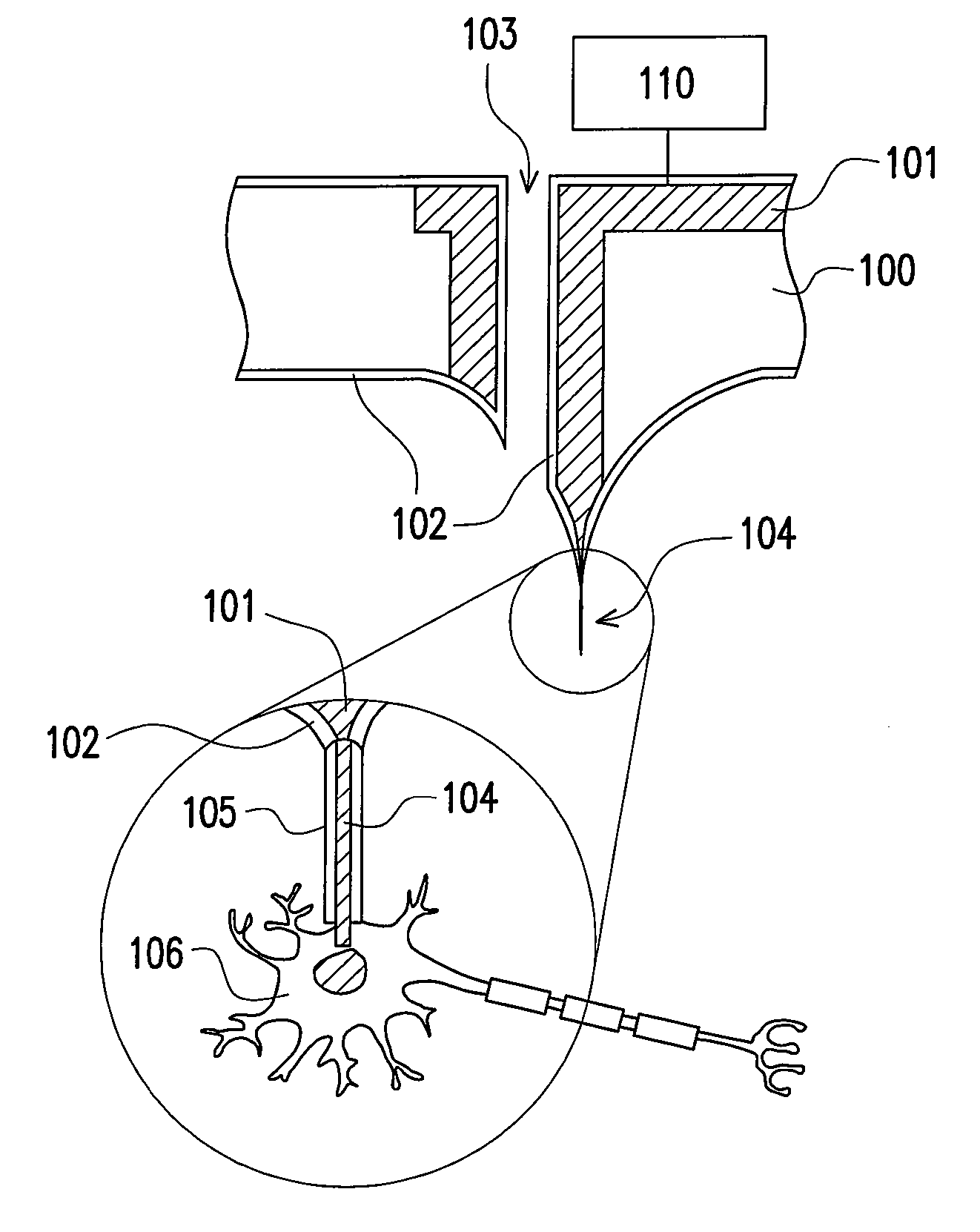
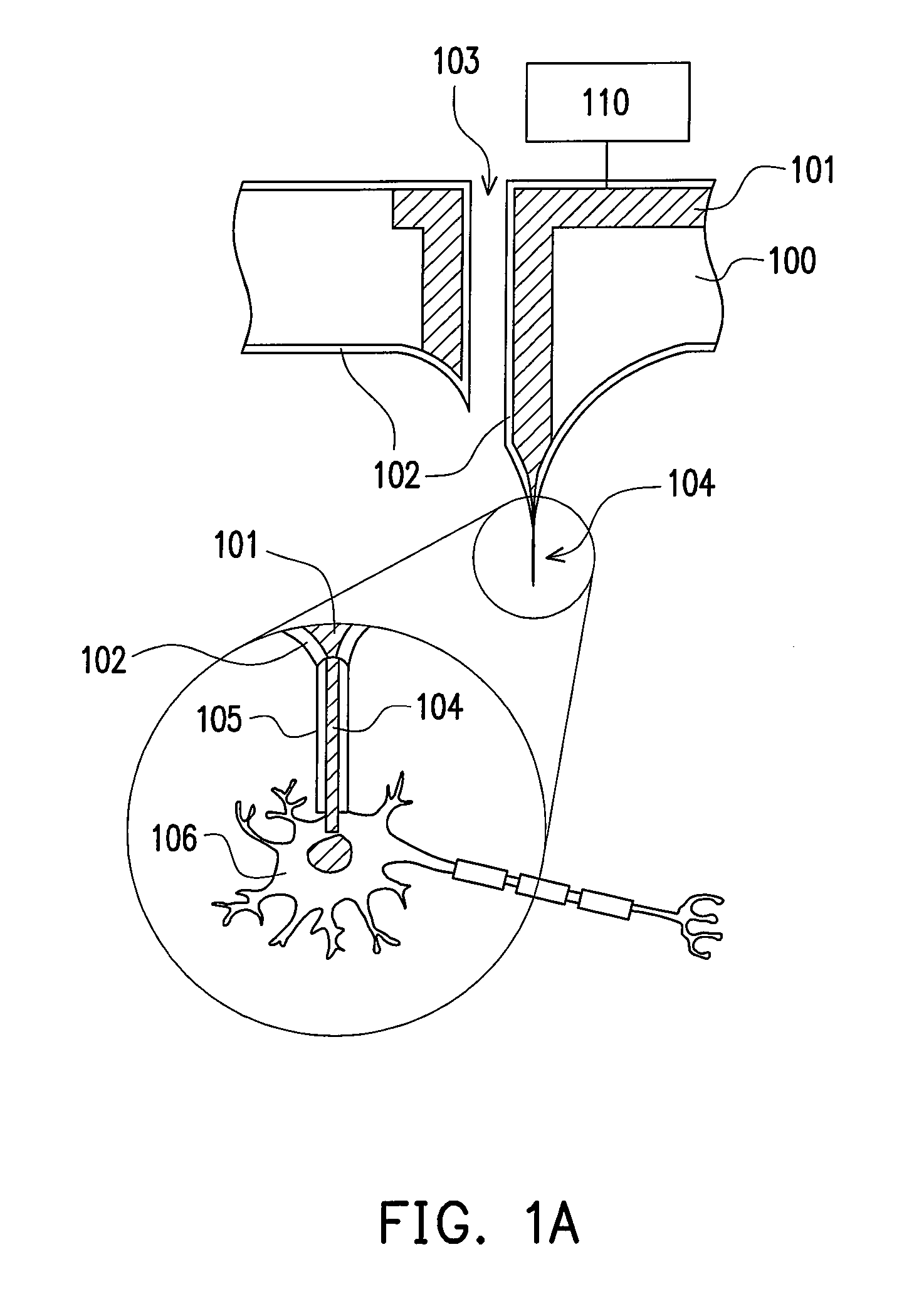
Method And Apparatus For The Detection Of Neural Tissue
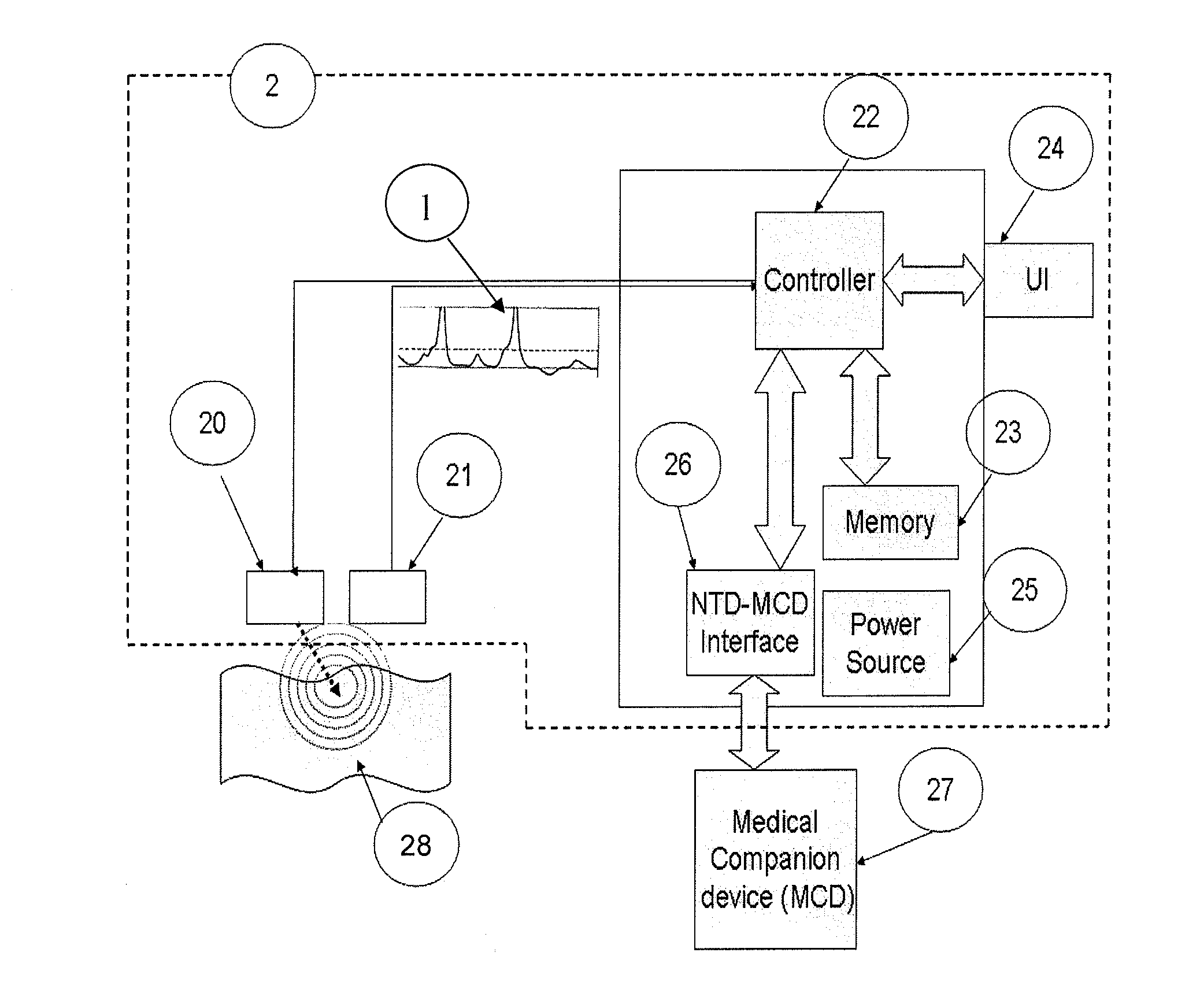
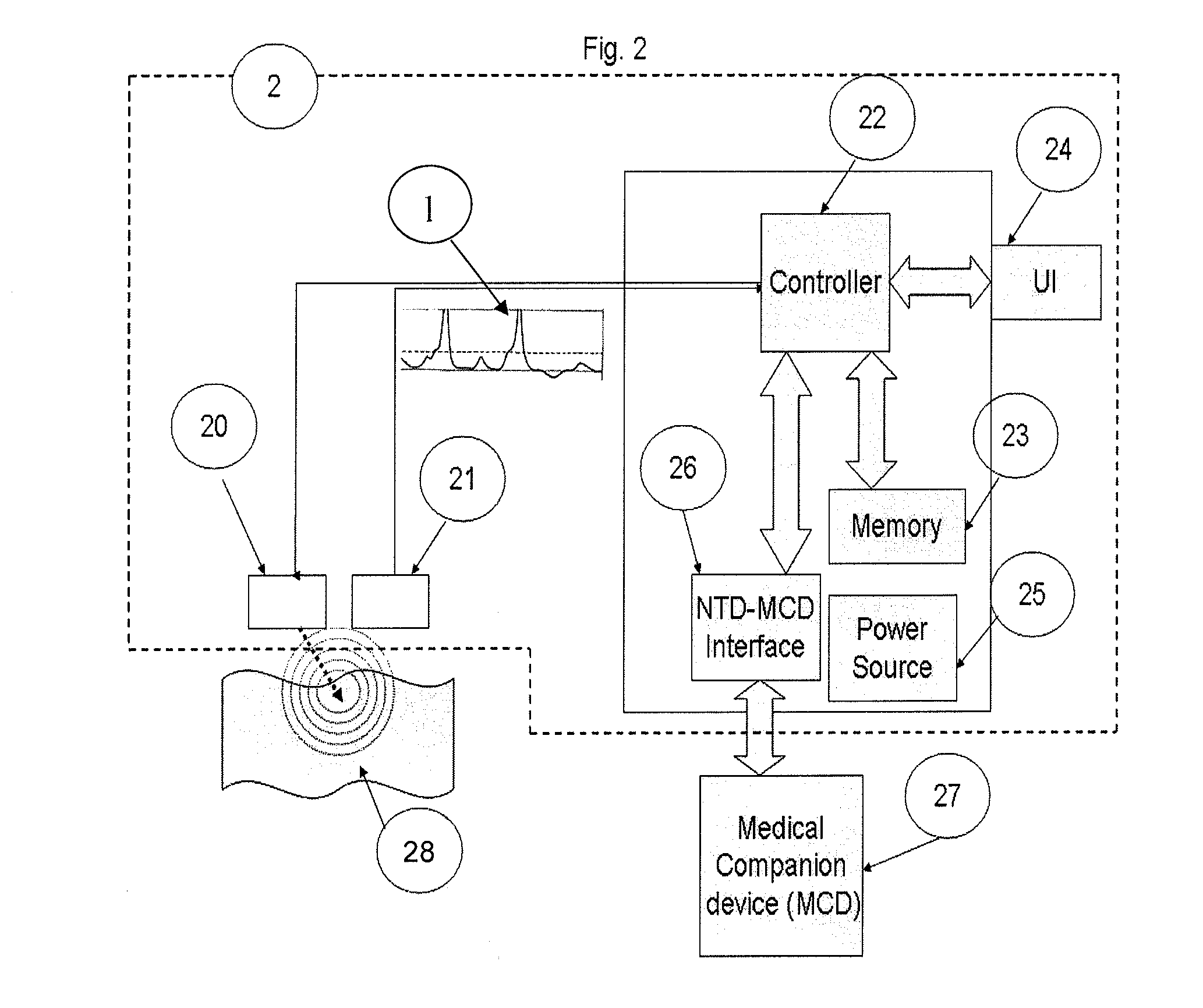
InactiveUS20150208934A1SensorsNeuroelectric signal measurementIntravascular catheterBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for neural tissue detection carried out using the Neural Tissue Detector (NTD), which is the apparatus that embodies the hardware aspect of the invention. The NTD enables neural tissue detection by stimulating a small tissue area and by measuring possible occurrences of induced response from neural tissue, if neural tissue is present in said small stimulated tissue area. The information gathered by the measurement provides a real-time assessment of the nature of the tissue which is targeted by the NTD. The invention is applicable to all types of neural tissues, including motor, and / or sensory and / or other types of neural tissues. The invention offers particular advantages in robot based surgical procedures or intravascular catheter based procedures but can also be used for manual surgery, according to different specific embodiments.
Owner:SZTRUBEL GENEVIEVE +1
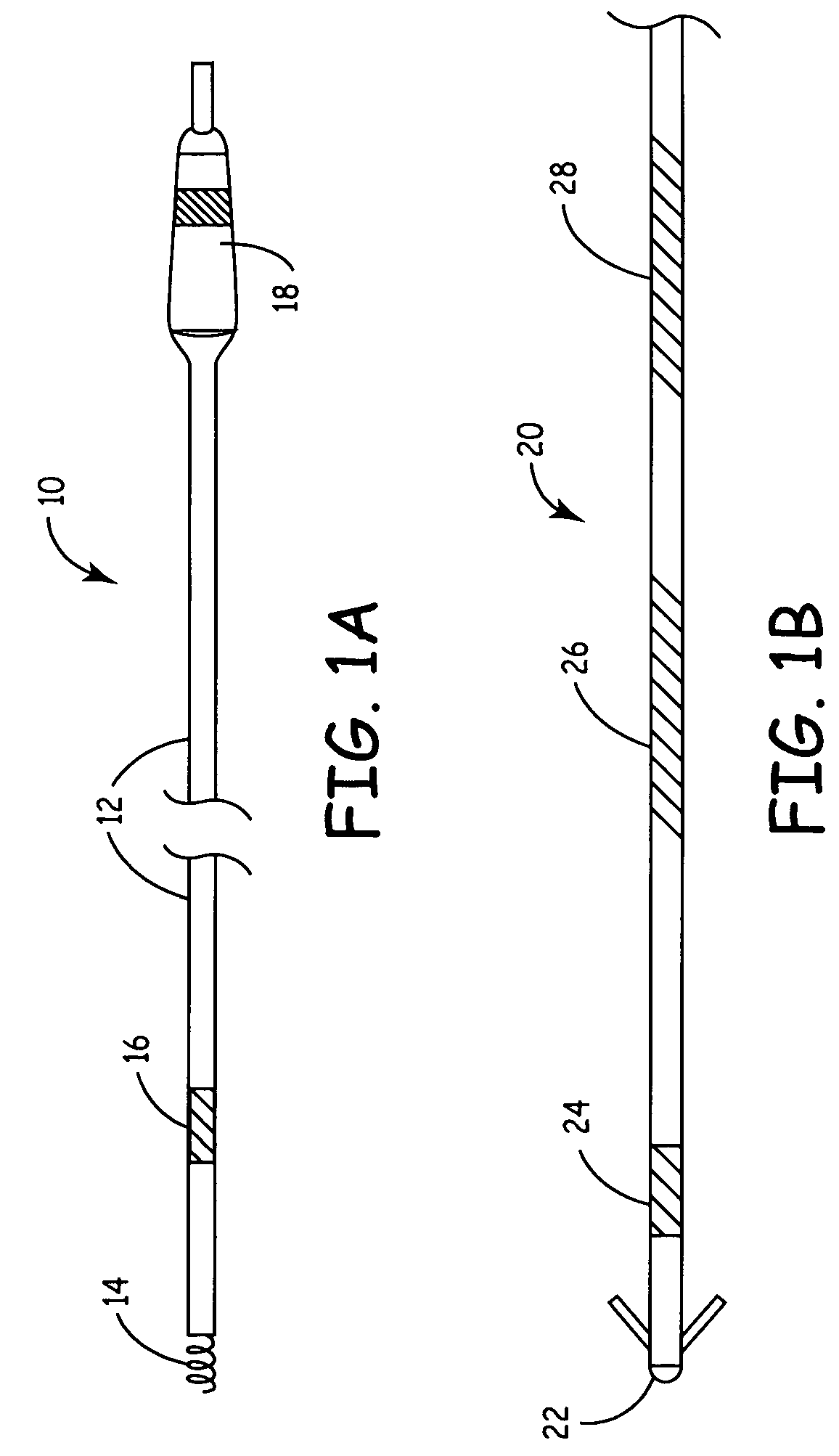
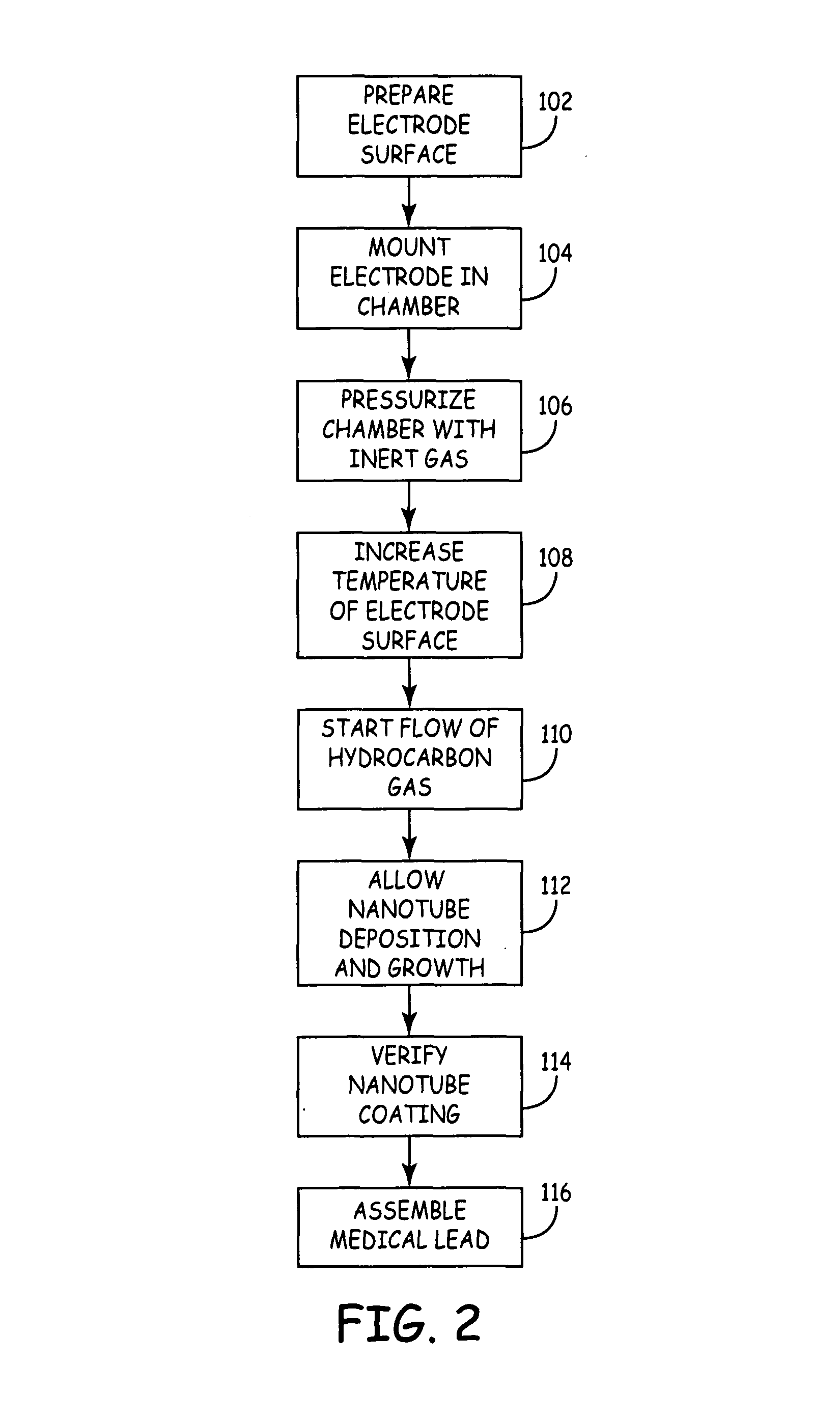
Medical devices incorporating carbon nanotube material and methods of fabricating same
InactiveUS7596415B2High strengthStable stateNanotechTransvascular endocardial electrodesMuscle tissueCarbon nanotube
The present invention relates generally to medical devices; in particular and without limitation, to unique electrodes and / or electrical lead assemblies for stimulating cardiac tissue, muscle tissue, neurological tissue, brain tissue and / or organ tissue; to electrophysiology mapping and ablation catheters for monitoring and selectively altering physiologic conduction pathways; and, wherein said electrodes, lead assemblies and catheters optionally include fluid irrigation conduit(s) for providing therapeutic and / or performance enhancing materials to adjacent biological tissue, and wherein each said device is coupled to or incorporates nanostructure or materials therein. The present invention also provides methods for fabricating, deploying, and operating such medical devices.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for measurement of neural response
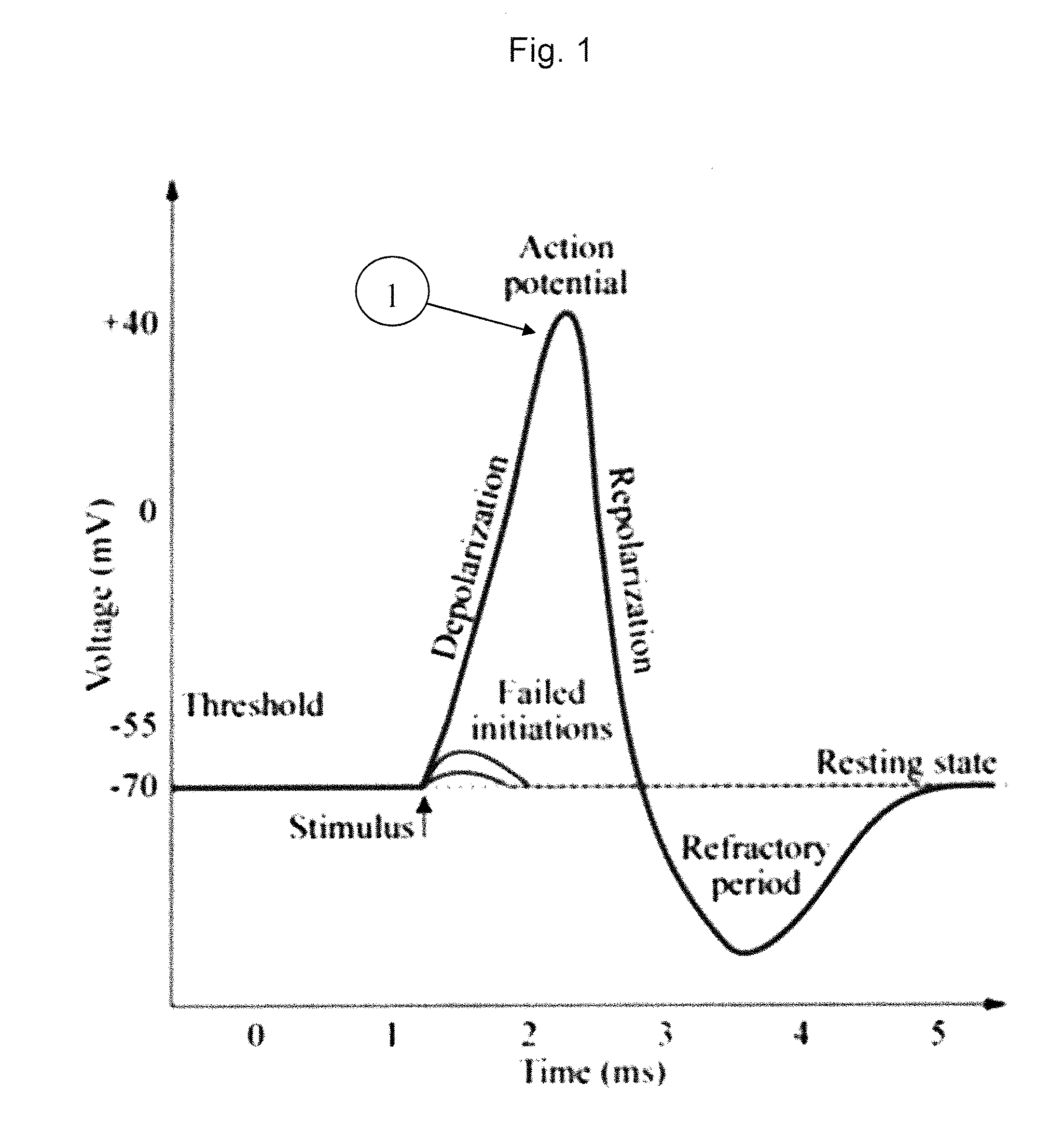
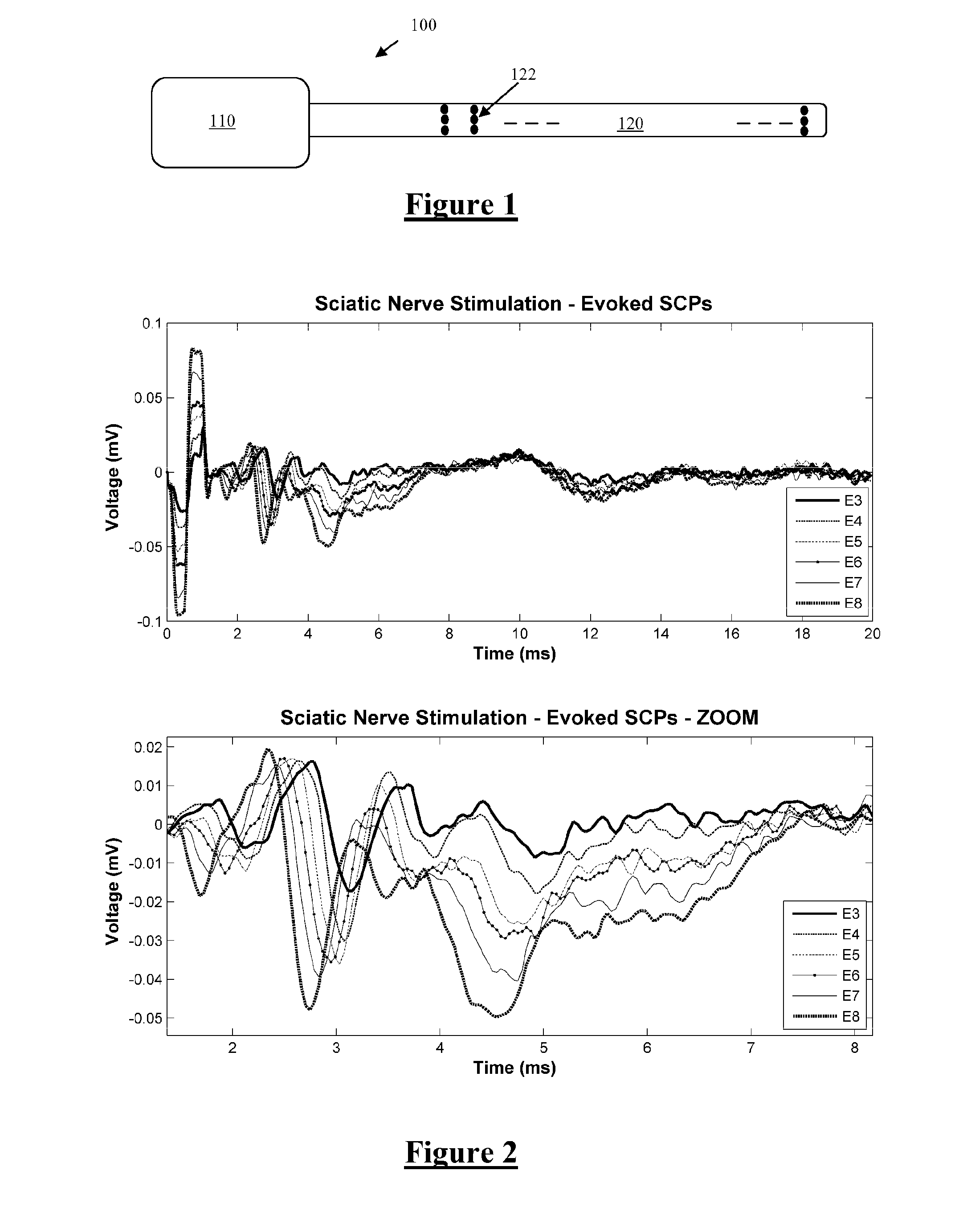
ActiveUS20140296737A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh sensitivitySpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsMedicineAxonal action potential
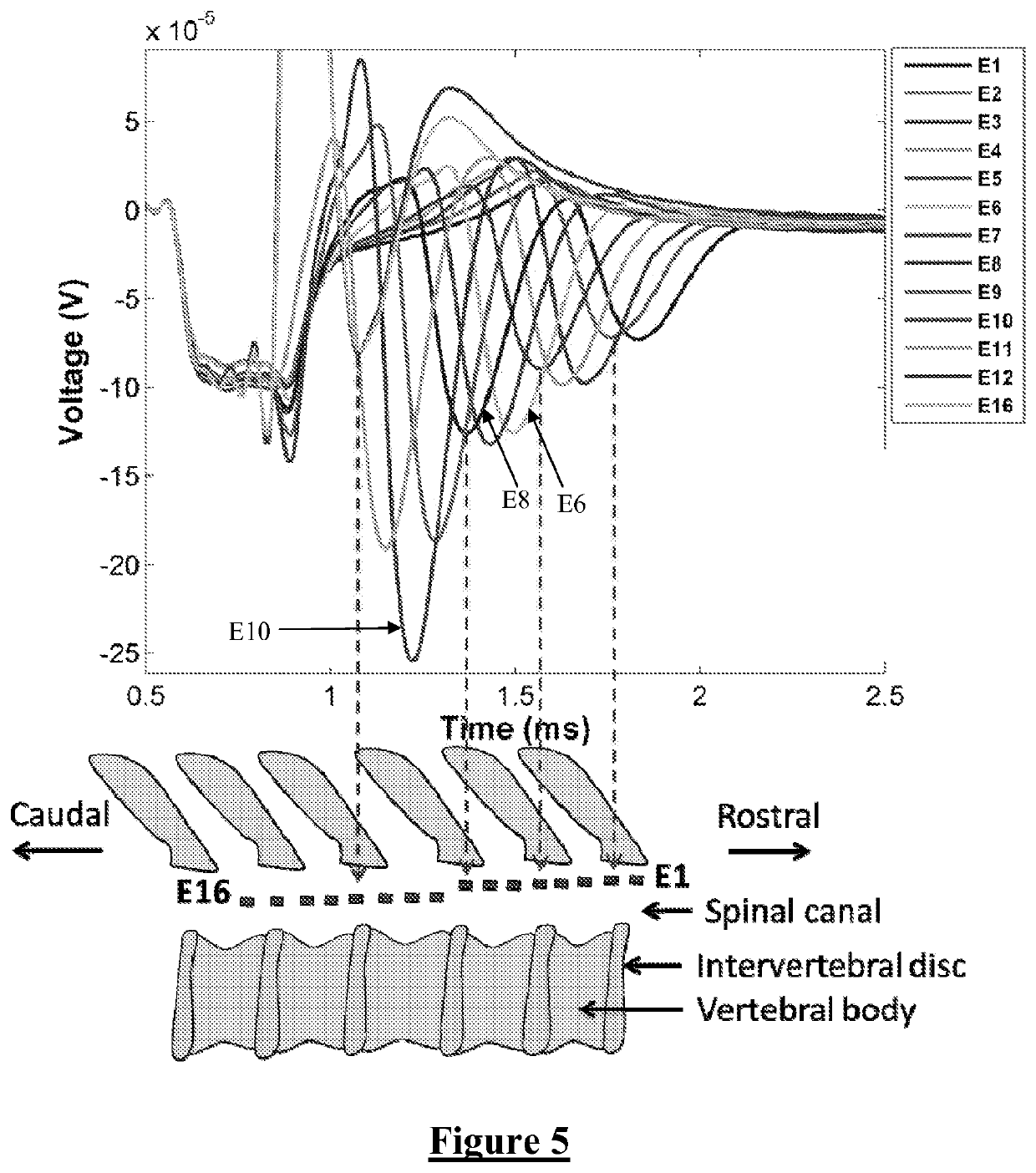
A method for determining a desired location at which to apply a neural therapy. An array of electrodes is positioned proximal to neural tissue. A stimulus is applied from the array which evokes a neural compound action potential response in the neural tissue proximal to the array. A plurality of electrodes of the array simultaneously obtain respective measurements of the neural compound action potential response. From the measurements of the neural compound action potential response a desired location for a neural therapy is determined.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
Hybrid bioelectrical interface device
InactiveUS20090292325A1Lack of directionalityGood handling characteristicsSpinal electrodesHead electrodesElectricityNervous system
A hybrid bioelectrical interface (HBI) device can be an implantable device comprising an abiotic component operable to transmit charge via electrons or ions; a biological component interfacing with the neural tissue, the biological component being sourced from biologic, biologically-derived, or bio-functionalized material; and a conjugated polymer component that together provide a means to chronically interface living neural tissue with electronic devices for extended durations (e.g. greater than 10 years). In some embodiments, conjugated polymers provide a functional electrical interface for charge transfer and signal transduction between the nervous system and an electronic device (e.g. robotic prosthetic limb, retinal implant, microchip).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Neural tissue stimulation, assessment, mapping, and therapy utilizing targeted acoustic mechanisms
InactiveUS20080033297A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectroencephalographyTherapeutic treatmentNeural tissues
A system is disclosed for the diagnostic or therapeutic treatment of a patient's neural tissues. The system includes at least a means to directly or indirectly acoustically expose or acoustically displace at least a first tissue portion. The system further includes a means to impose, directly or indirectly, an electromagnetic, electrical, magnetic or optical field on at least a second neural tissue portion. The combined or cooperative action of the acoustic exposure / displacement and the field, whether sequentially or simultaneously applied, causes at least one diagnostically or therapeutically useful mechanism. The two tissue portions may be the same portion or different portions.
Owner:I P FOUNDRY
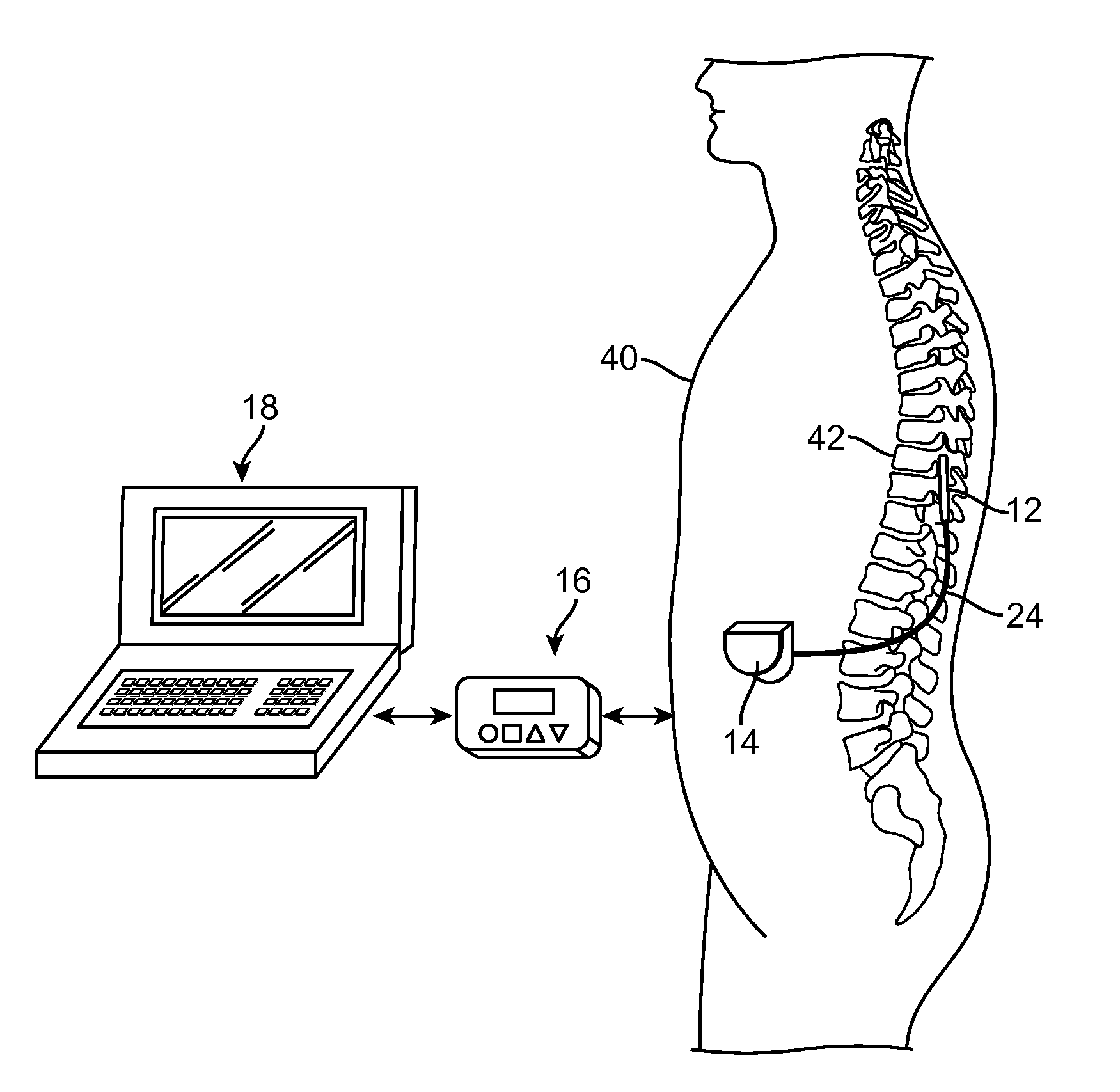
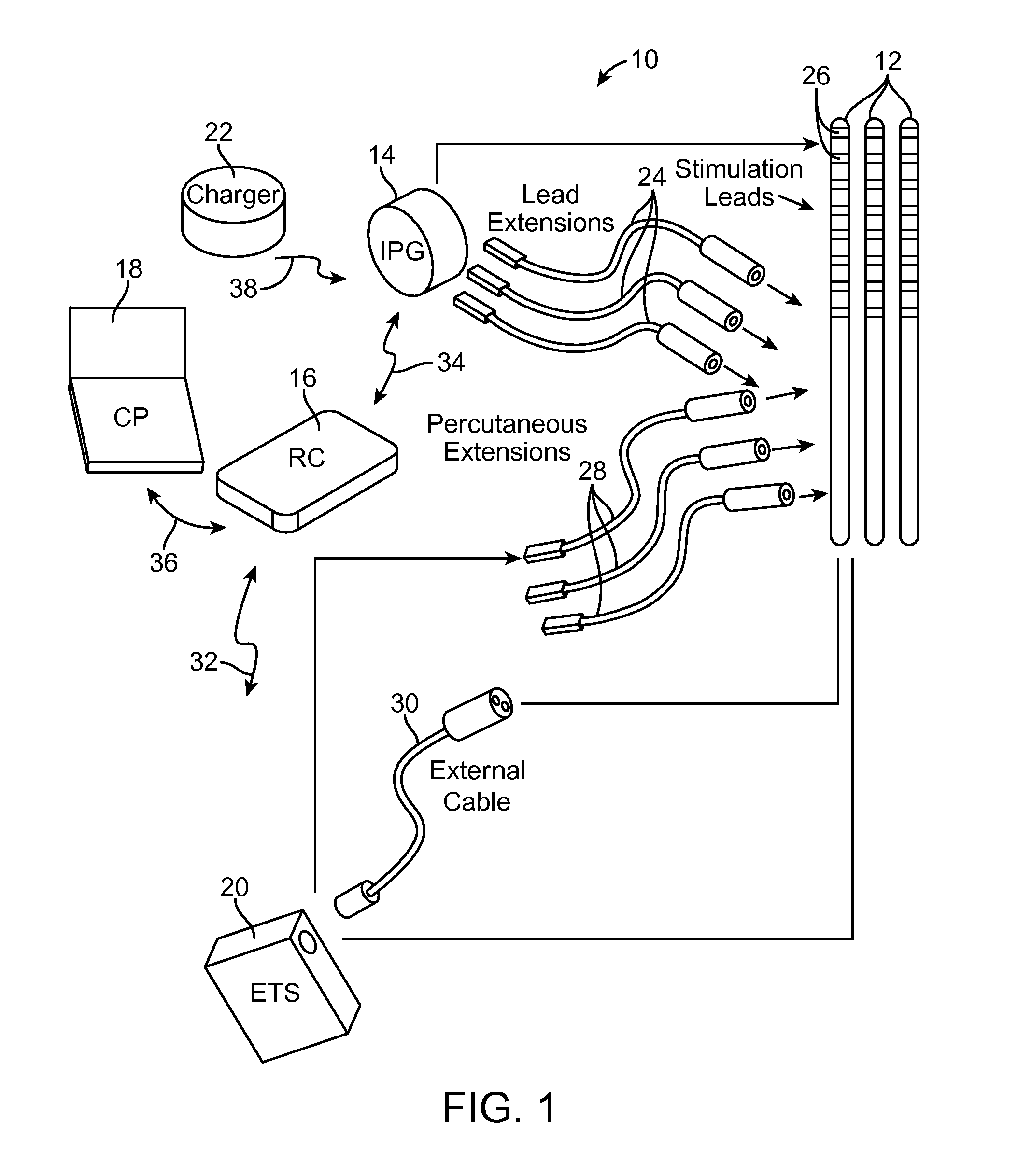
System and method for avoiding, reversing, and managing neurological accomodation to eletrical stimulation
A method and programmer for programming a neurostimulation device are provided. The method comprises varying a first stimulation parameter under user control, automatically varying a second stimulation parameter, generating a plurality of stimulation parameter sets from the varied first and second stimulation parameters, outputting a pulsed electrical waveform from the neurostimulation device between a plurality of electrodes in accordance with the stimulation parameter sets, such that neural tissue is stimulated without undergoing neurological accommodation that would otherwise occur if the second stimulation parameter were not varied, and programming the neurostimulation device with a new set of stimulation parameters based on a result of the neural tissue stimulation The programmer comprises a user interface capable of receiving an input from a user, a processor configured for performing the previous steps, and output circuitry configured for transmitting the stimulation parameter sets and the new stimulation parameter set to the neurostimulation device.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
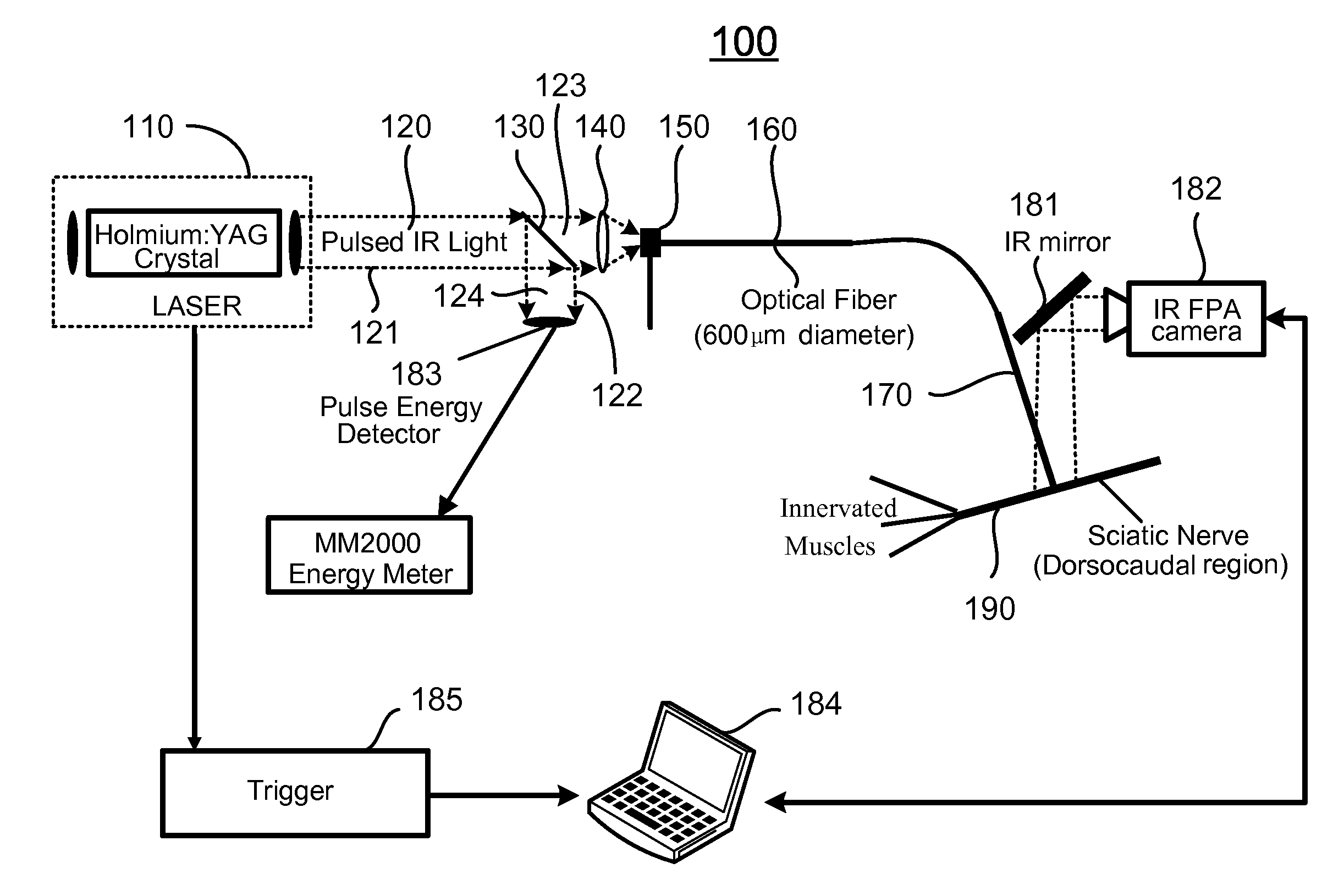
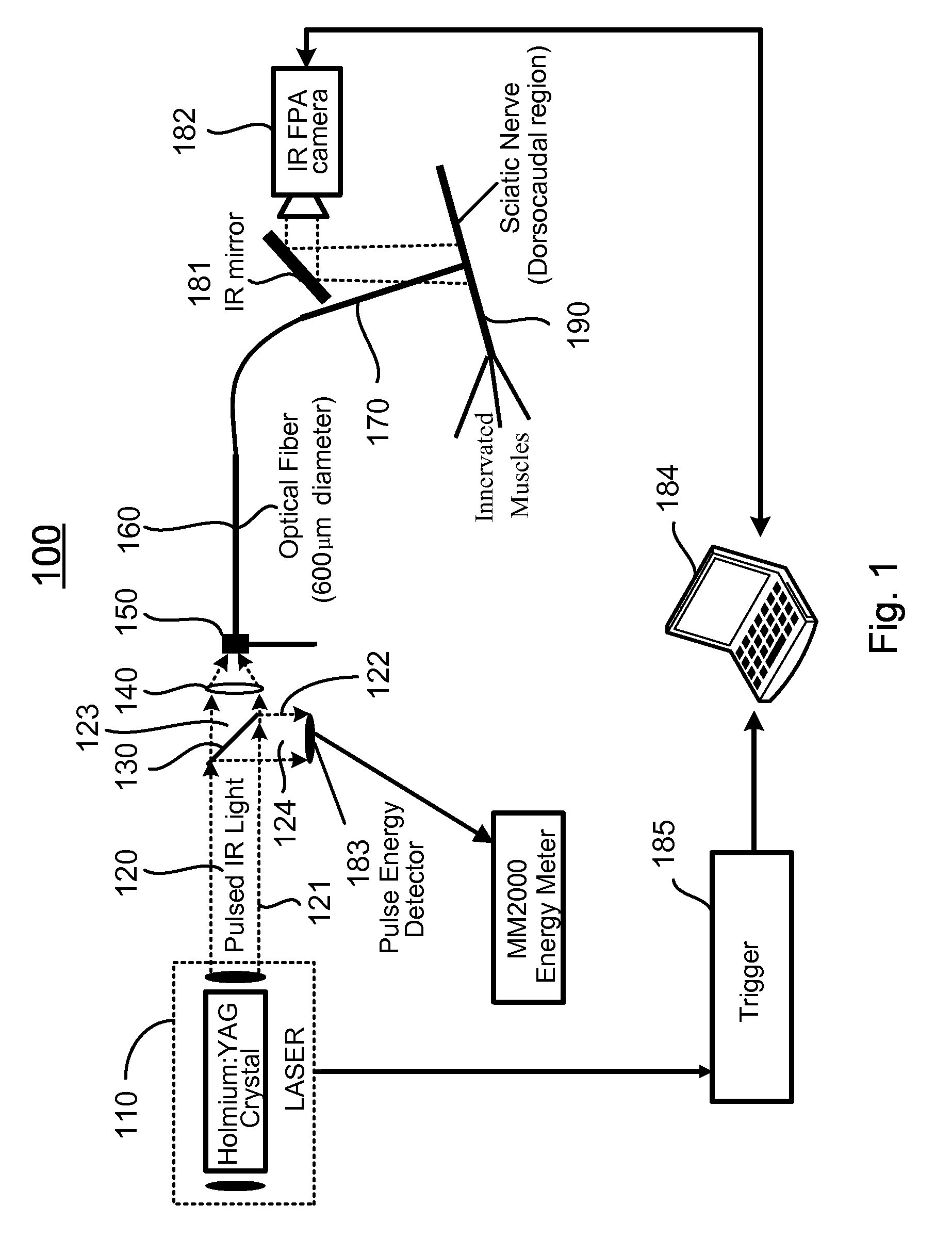
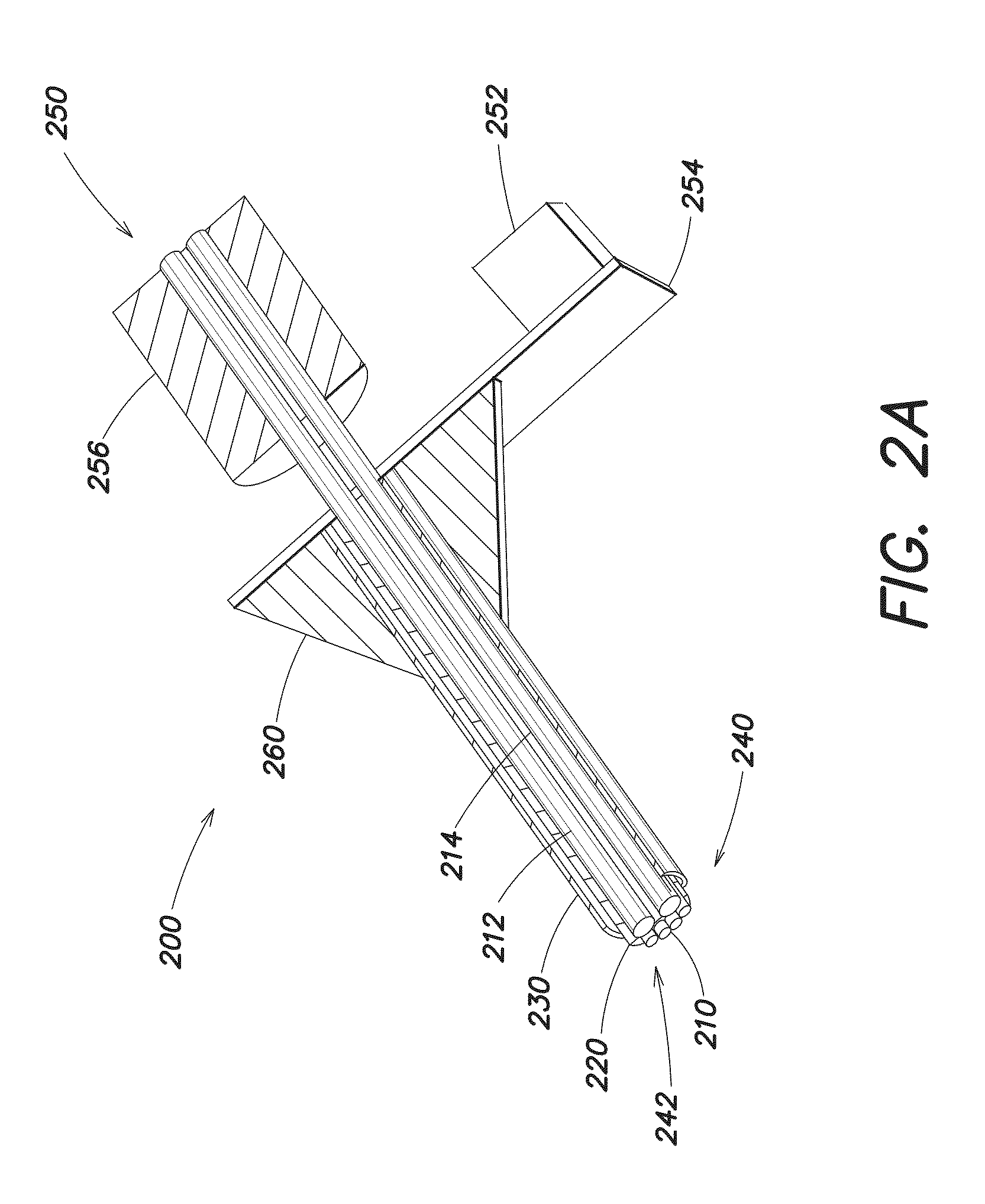
Apparatus and methods for optical stimulation of neural tissues
InactiveUS20090069871A1Minimal tissue damageSubstantial temperature increaseDiagnosticsSurgeryFluenceOptical stimulation
The present invention, in one aspect, relates to a method for stimulating neural tissue of a living subject. In one embodiment, the method has the steps of generating at least one beam of radiation; introducing at least one of one or more chromophores and one or more optical agents to a target neural tissue; and delivering the at least one beam of radiation to the target neural tissue, wherein the at least one beam of radiation is delivered with a radiant exposure that causes a thermal gradient in the target neural tissue, thereby stimulating the target neural tissue.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Method and apparatus for measurement of neural response
ActiveUS20150164354A1Reduced dynamic rangeSimple morphologyElectrotherapyMedical devicesEngineeringSteady state
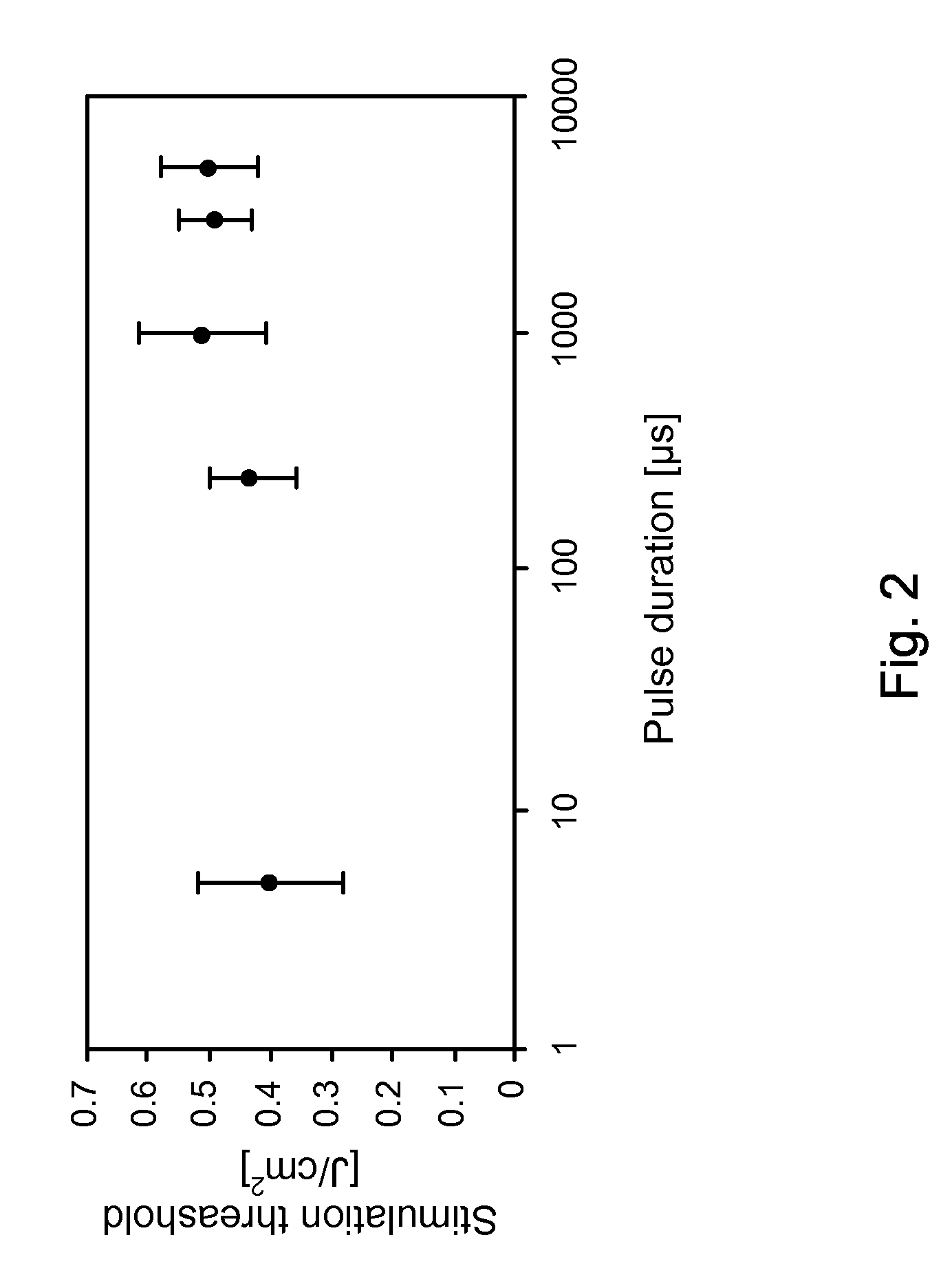
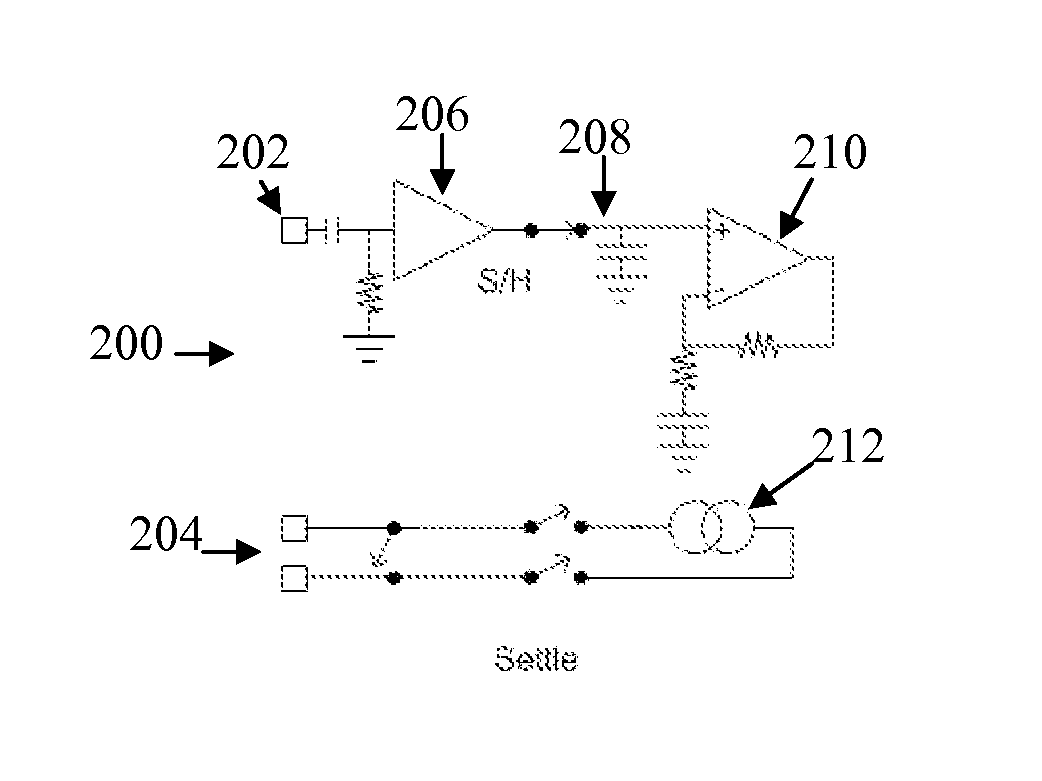
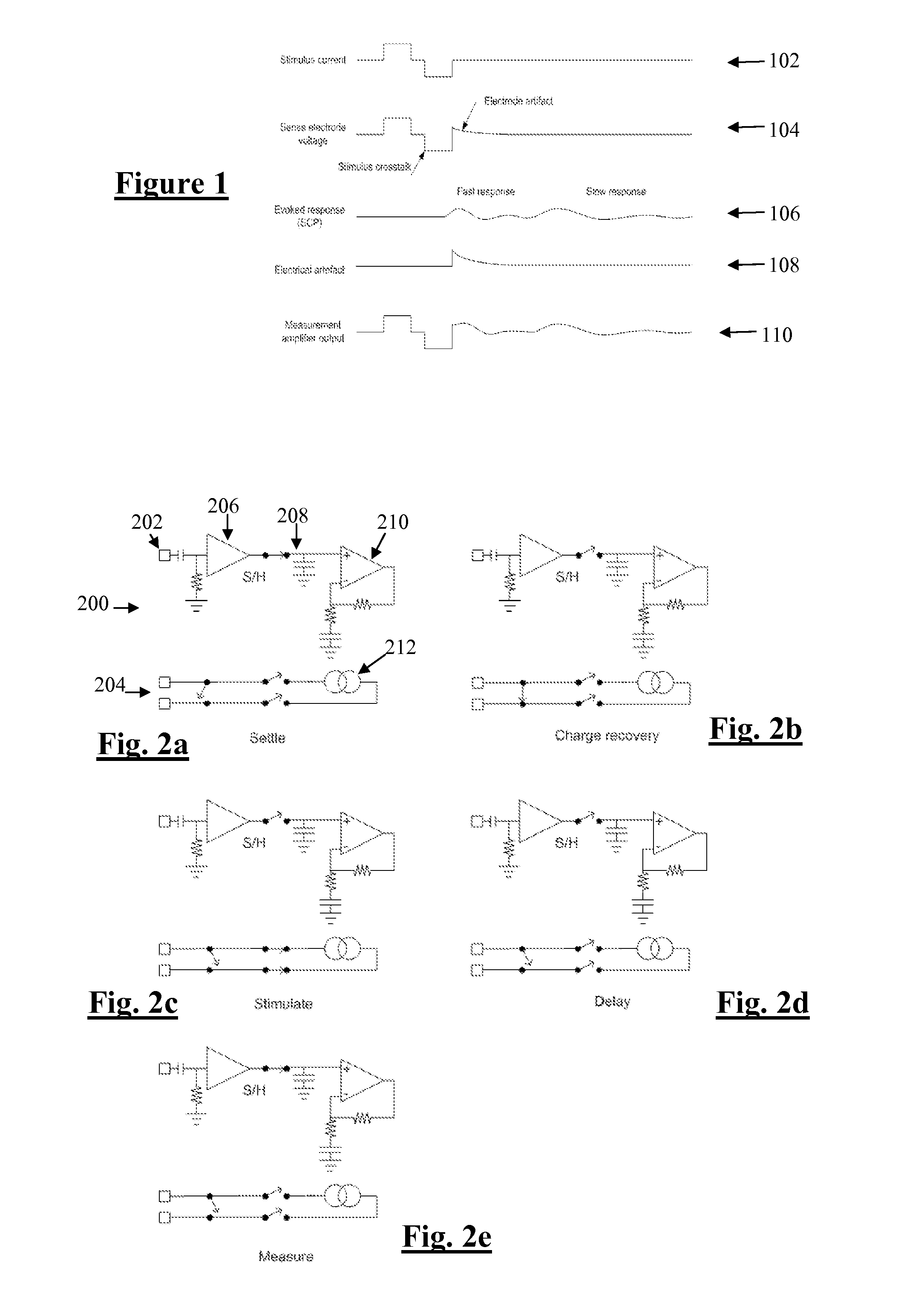
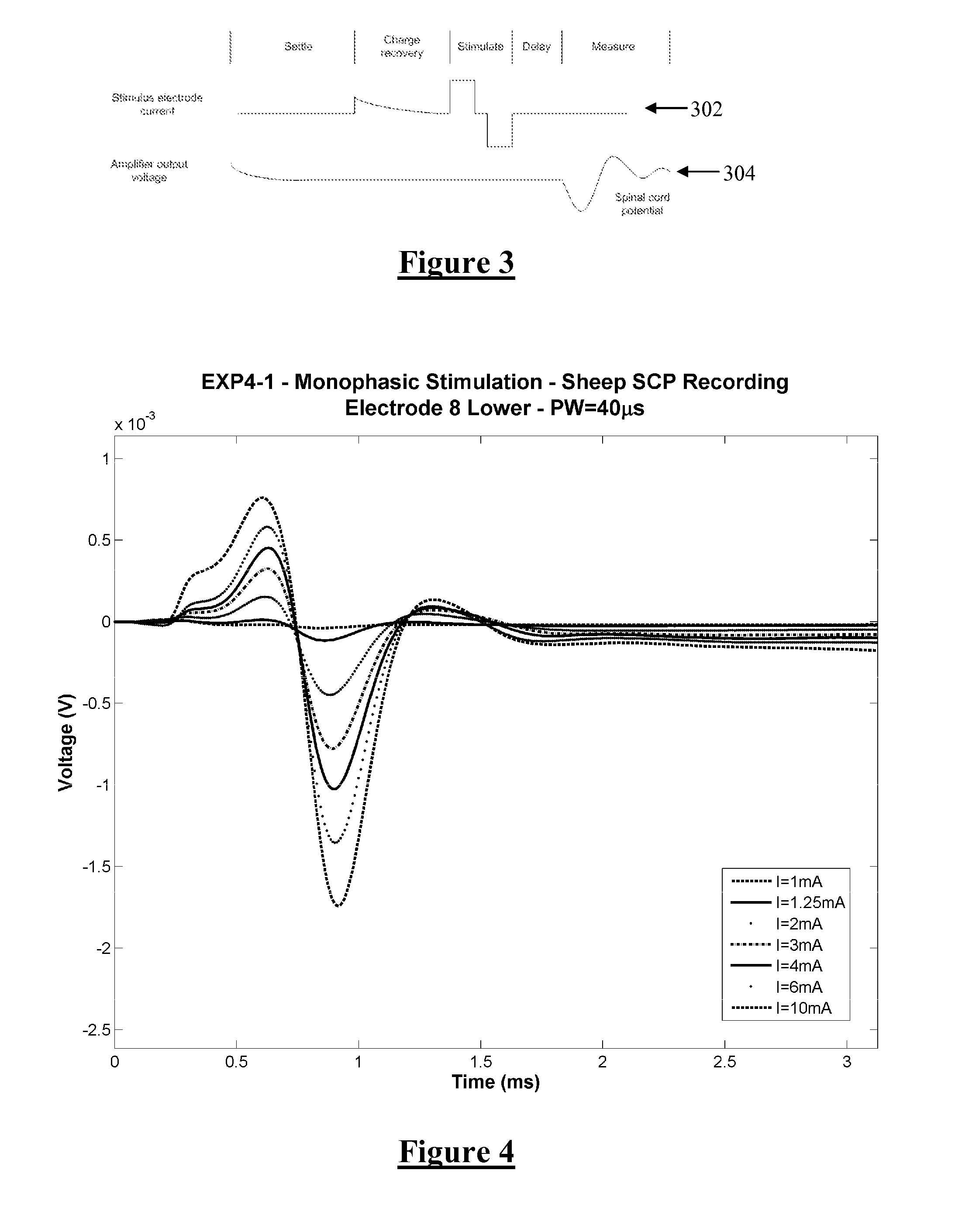
A method for measuring a neural response to a stimulus. Measurement circuitry is settled prior to a stimulus, by connecting a sense electrode to the measurement circuitry to allow the measurement circuitry to settle towards a bio-electrically defined steady state. Charge is recovered on stimulus electrodes by short circuiting the stimulus electrodes to each other. An electrical stimulus is then applied from the stimulus electrodes to neural tissue, while keeping the sense electrode disconnected from the measurement circuitry. After the stimulus, a delay is imposed during which the stimulus electrodes are open circuited and the sense electrode is disconnected from the measurement circuitry and from the stimulus electrodes. After the delay, a neural response signal present at the sense electrode is measured by connecting the sense electrode to the measurement circuitry.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
System and method for avoiding, reversing, and managing neurological accommodation to electrical stimulation
A method and programmer for programming a neurostimulation device are provided. The method comprises varying a first stimulation parameter under user control, automatically varying a second stimulation parameter, generating a plurality of stimulation parameter sets from the varied first and second stimulation parameters, outputting a pulsed electrical waveform from the neurostimulation device between a plurality of electrodes in accordance with the stimulation parameter sets, such that neural tissue is stimulated without undergoing neurological accommodation that would otherwise occur if the second stimulation parameter were not varied, and programming the neurostimulation device with a new set of stimulation parameters based on a result of the neural tissue stimulation The programmer comprises a user interface capable of receiving an input from a user, a processor configured for performing the previous steps, and output circuitry configured for transmitting the stimulation parameter sets and the new stimulation parameter set to the neurostimulation device.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Retinal Prosthesis with a New Configuration
ActiveUS20080275527A1Improve the immunityCut the delicate retinal tissueCircuit bendability/stretchabilityHead electrodesFlexible circuitsRetinal Prosthesis
Polymer materials are useful as electrode array bodies for neural stimulation. They are particularly useful for retinal stimulation to create artificial vision, cochlear stimulation to create artificial hearing, and cortical stimulation, and many related purposes. The pressure applied against the retina, or other neural tissue, by an electrode array is critical. Too little pressure causes increased electrical resistance, along with electric field dispersion. Too much pressure may block blood flow. Common flexible circuit fabrication techniques generally require that a flexible circuit electrode array be made flat. Since neural tissue is almost never flat, a flat array will necessarily apply uneven pressure. Further, the edges of a flexible circuit polymer array may be sharp and cut the delicate neural tissue. By applying the right amount of heat to a completed array, a curve can be induced. With a thermoplastic polymer it may be further advantageous to repeatedly heat the flexible circuit in multiple molds, each with a decreasing radius. Further, it is advantageous to add material along the edges. It is further advantageous to provide a fold or twist in the flexible circuit array. Additional material may be added inside and outside the fold to promote a good seal with tissue.
Owner:SECOND SIGHT MEDICAL PRODS +1
Flexible circuit electrode array
ActiveUS20060259112A1Improve the immunityCut the delicate retinal tissueHead electrodesPrinted circuit manufactureFlexible circuitsHearing perception
Owner:SECOND SIGHT MEDICAL PRODS +2
Multifunctional nano-probe interface structure for neural prostheses and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20080140195A1Accurately and regionally stimulateEasy to combineSpinal electrodesHead electrodesNeural cellIsolation layer
A novel multifunctional nano-probe interface is proposed for applications in neural stimulation and detecting. The nano-probe interface structure consists of a carbon nanotube coated with a thin isolation layer, a micro-electrode substrate array, and a controller IC for neural cell recording and stimulation. The micro-electrode substrate array contains wires connecting the carbon nanotube with the controller IC, as well as microfluidic channels for supplying neural tissues with essential nutrition and medicine. The carbon nanotube is disposed on the micro-electrode substrate array made by silicon, coated with a thin isolation layer around thereof, and employed as a nano-probe for neural recording and stimulation.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Field augmented current steering using voltage sources
A neurostimulation comprises a plurality of electrical terminals configured for being respectively coupled to an array of electrodes, at least three configurable sources respectively coupled to at least three of the electrical terminals, and control circuitry configured for programming each of the at least three configurable sources to be either a current source or a voltage source. A method of providing neurostimulation therapy to a patient using an array of electrodes implanted adjacent neural tissue of the patient, comprises conveying electrical stimulation energy between a first one the electrodes and a second one of the electrodes, thereby creating an electrical field potential within the neural tissue, regulating a first current flowing through the first electrode, and regulating a first voltage at a third different one of the electrodes, thereby modifying a shape of the electrical field potential within the neural tissue.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Methods and apparatuses for the automated production, collection, handling, and imaging of large numbers of serial tissue sections
ActiveUS7677289B2Create efficientlyLamination ancillary operationsElectric discharge tubesMagnetic tapeSoftware engineering
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Medical devices incorporating carbon nanotube material and methods of fabricating same
InactiveUS7844347B2High strengthStable stateSpinal electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesMuscle tissueNanotube
Unique electrodes and / or electrical lead assemblies are provided for stimulating cardiac tissue, muscle tissue, neurological tissue, brain tissue and / or organ tissue; to electrophysiology mapping and ablation catheters for monitoring and selectively altering physiologic conduction pathways. The electrodes, lead assemblies and catheters optionally include fluid irrigation conduit(s) for providing therapeutic and / or performance enhancing materials to adjacent biological tissue. Each device is coupled to or incorporates nanotube structures or materials therein. Methods for fabricating, deploying, and operating such medical devices are also provided.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Neural stimulation system providing auto adjustment of stimulus output as a function of sensed pressure changes
A neural stimulation system automatically corrects or adjusts the stimulus magnitude in order to maintain a comfortable and effective stimulation therapy. Auto correction of the stimulus magnitude is linked to the measurement of pressure in the vicinity of the electrode-tissue interface. Because the pressure near the electrode-tissue interface can provide a measure of the electrode contacts' proximity to the neural tissue, and hence quantity of electrical energy delivered to the neural tissue, a change in the measured pressure or pressure morphology indicates that the stimulation energy may need to be adjusted. Hence, changes in pressure provide a feedback mechanism that permit the system to effectively auto correct the stimulus amplitude in order to maintain a desired therapeutic effect.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Method and Apparatus for Measurement of Neural Response
ActiveUS20200129108A1Quick measurementImprove signal-to-noise ratioSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsPhysical therapyBiomedical engineering
A method for determining a desired location at which to apply a neural therapy. An array of electrodes is positioned proximal to neural tissue. A stimulus is applied from the array which evokes a neural compound action potential response in the neural tissue proximal to the array. A plurality of electrodes of the array simultaneously obtain respective measurements of the neural compound action potential response. From the measurements of the neural compound action potential response a desired location for a neural therapy is determined.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
Methods and apparatus for stimulating and recording neural activity
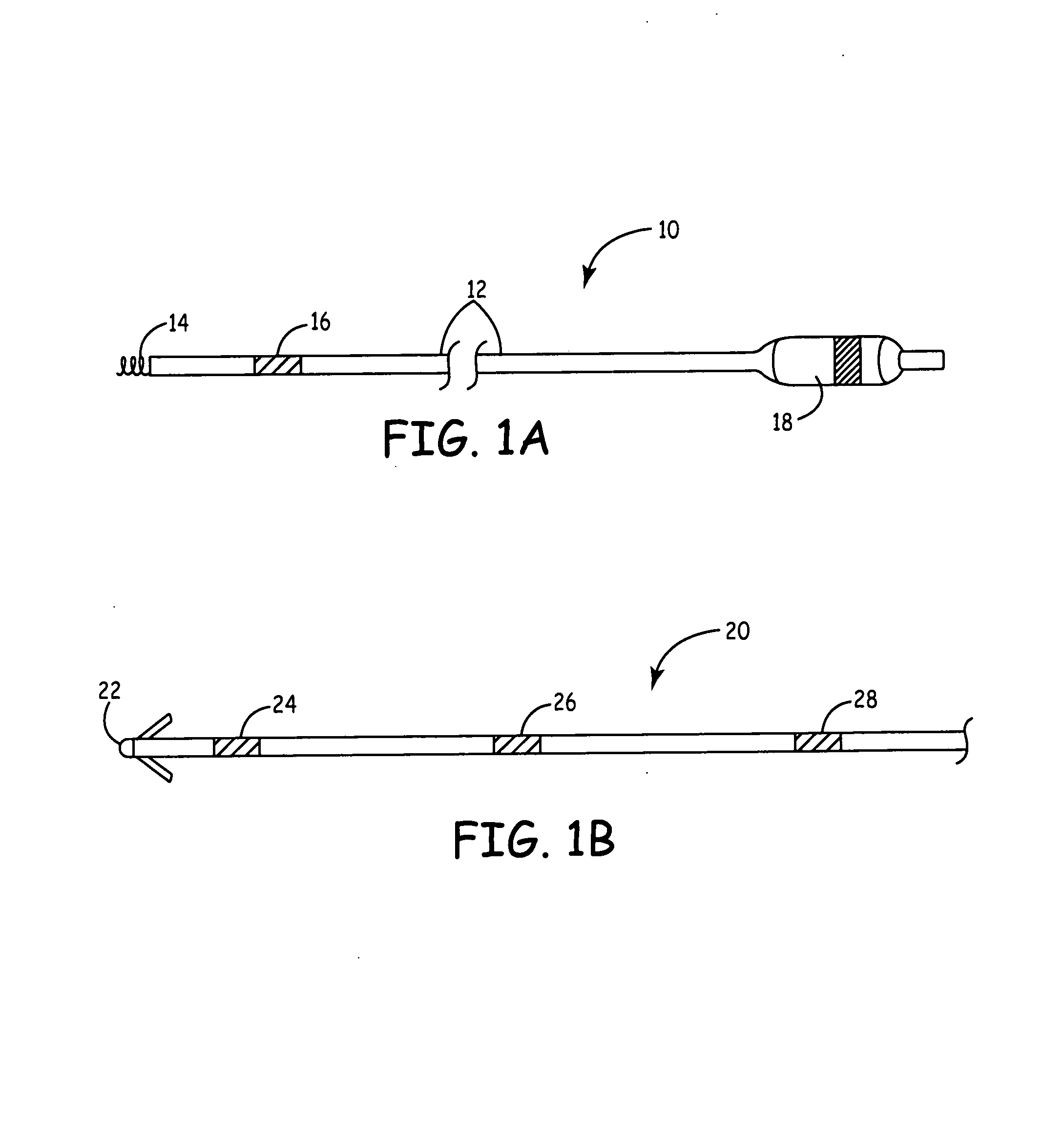
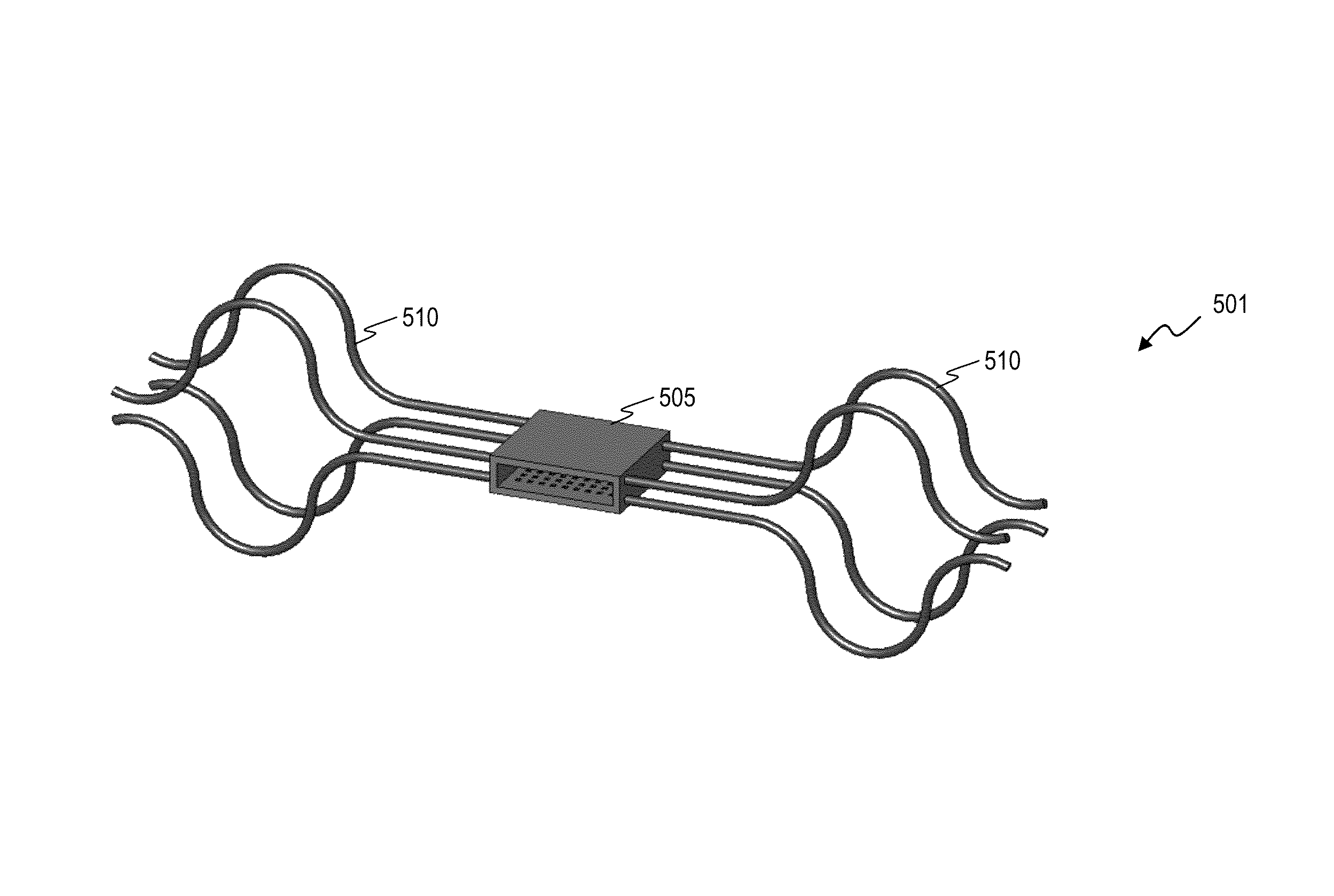
ActiveUS20140371564A1Quality improvementReduce signal to noise ratioSpinal electrodesHead electrodesFiberConductive polymer
Thermal drawing processes can be used to make multifunctional, high-resolution neural probes for neural recording and stimulation. An exemplary neural probe may include one or more conductive fibers or microelectrodes coated with two or more layers of insulating material, at least one of which is partially etched to expose a tip at the neural probe's distal end. The conductive fibers conduct electrical signals (e.g., neural spikes or electrical stimulation) between the tip and the neural probe's proximal end. Optional optical and fluidic waveguides may guide light and fluid, respectively, between the tip and the proximal end. A neural probe may be flexible enough for long-term (chronic) implantation in neural tissue (e.g., the brain) without excessive tissue damage, even during movement of the brain in the skull. The probe may be made from biocompatible materials, such as insulating and conductive polymers, that have negligible (insignificant) interaction with the surrounding tissue.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for measurement of neural response
ActiveUS10568559B2Quick measurementImprove signal-to-noise ratioSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsBiomedical engineeringBioinformatics
A method for determining a desired location at which to apply a neural therapy. An array of electrodes is positioned proximal to neural tissue. A stimulus is applied from the array which evokes a neural compound action potential response in the neural tissue proximal to the array. A plurality of electrodes of the array simultaneously obtain respective measurements of the neural compound action potential response. From the measurements of the neural compound action potential response a desired location for a neural therapy is determined.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
Display of region of activation in neurostimulation programming screen
A system for use with a neurostimulator coupled to one or more electrodes implanted adjacent neural tissue of a patient. The system comprises a user input device configured for allowing a user to select different nerve fiber diameters and to select a set of stimulation parameters. The system further comprises processing circuitry configured estimating regions of activation within the neural tissue of the patient based on the selected nerve fiber diameters and the selected stimulation parameter set. The system further comprises a display device configured for displaying the estimated regions of tissue activation. The user input device may further be configured for allowing the user to select different tissue regions of therapy, in which case, the display device may display the different tissue region on a human body map, and different indicia associating the displayed tissue regions for therapy to displayed estimated regions of tissue activation.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
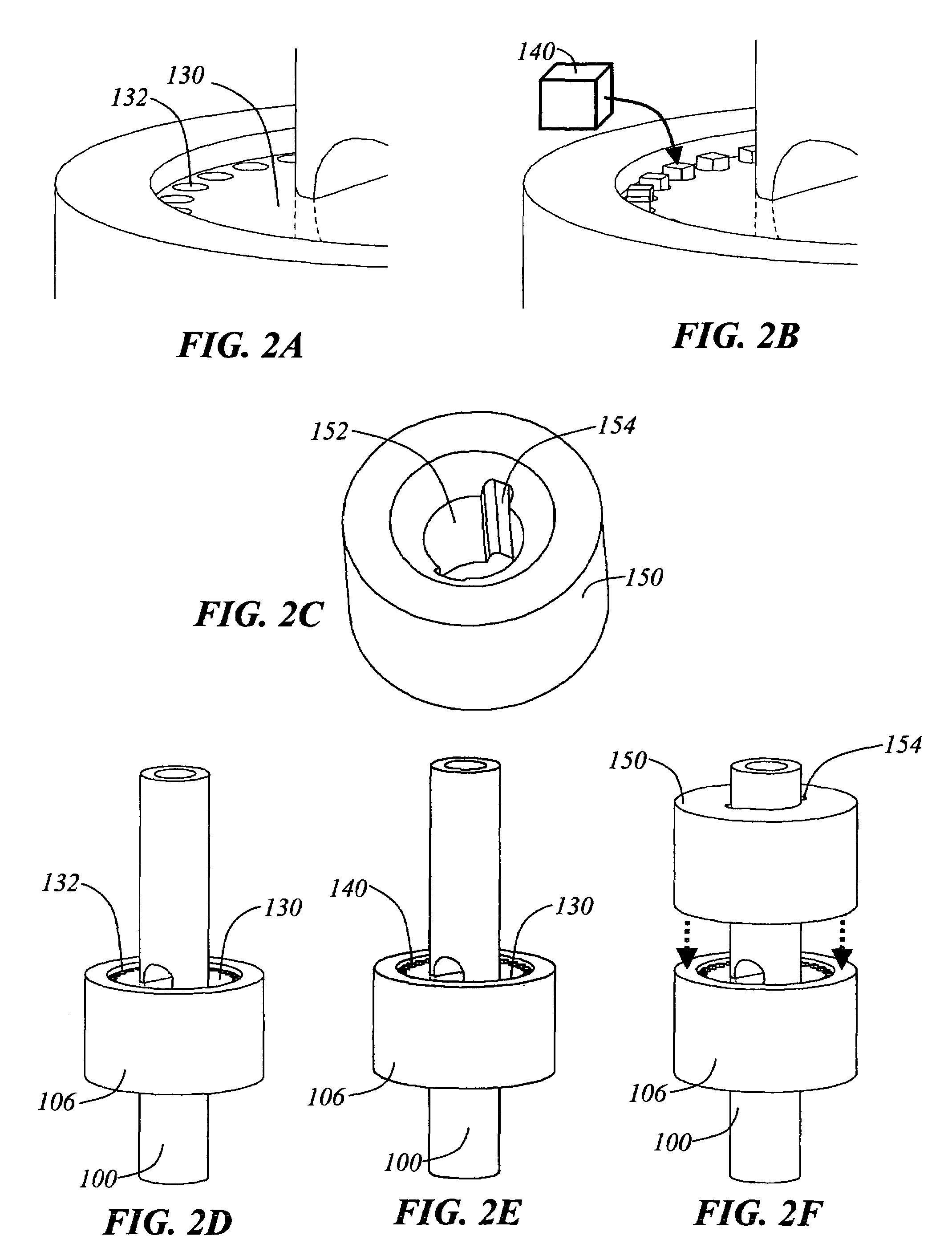
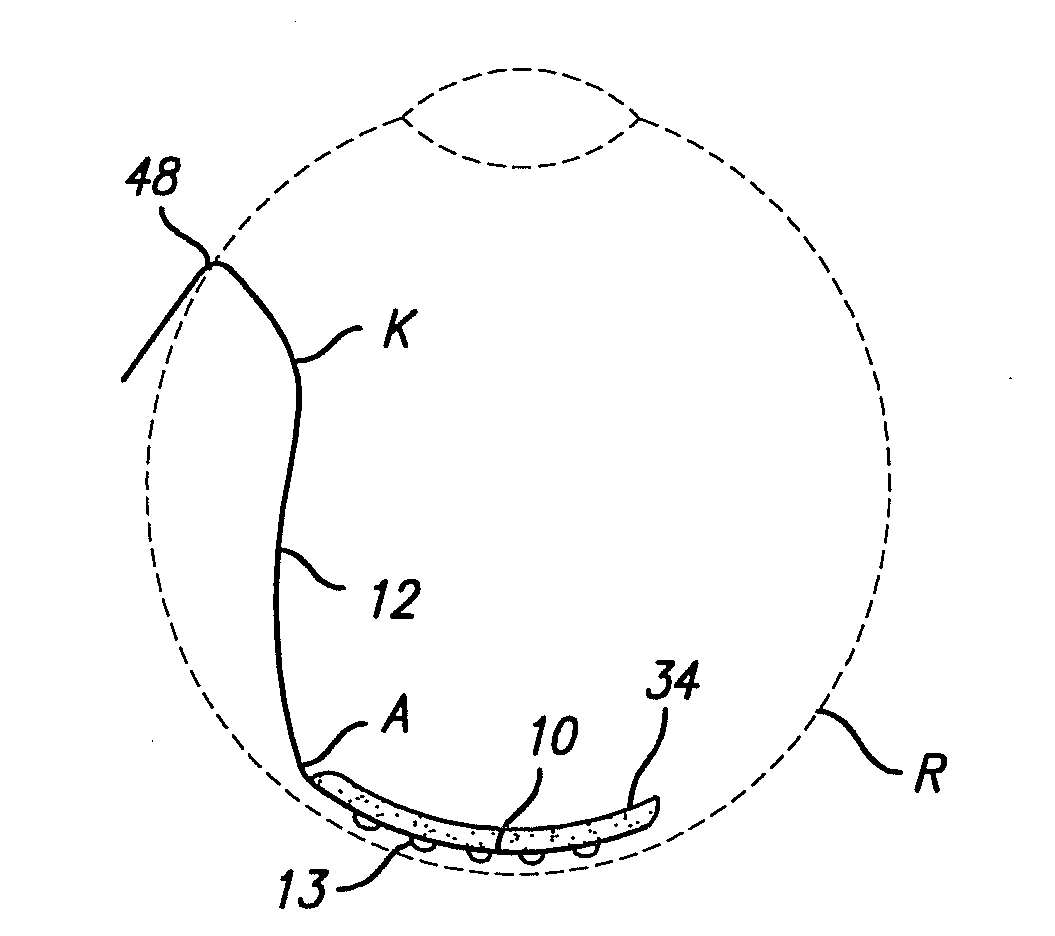
Electrode Array for Even Neural Pressure
An electrode array attached to neural tissue, such as the retina, necessarily has graded pressure exerted on the tissue, with higher pressure near the attachment point. Greater pressure improves contact between the electrodes and neural tissue while too much pressure may damage neural tissue. Hence it is advantageous to obtain equal pressure across the array field. In the present invention multiple and selective attachment points are provided on an electrode array allowing a surgeon to select the attachment points providing the best electrode tissue contact.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
Apparatus and method for managing chronic pain with infrared light sources and heat
Method and apparatus for infrared-light nerve stimulation-plus-therapeutic-heat (INS-plus-TH) that includes providing a plurality of light sources; providing a plurality of thermally conductive extensions configured to transfer heat generated by the plurality of light sources away from the plurality of light sources; emitting a plurality of infrared-light nerve-stimulation signals toward neural tissue of an animal from the plurality of light sources, wherein the emitted infrared-light nerve-stimulation signals are configured to generate action potentials in the neural tissue, and wherein the emitting of the plurality of infrared-light nerve-stimulation signals includes generating heat; controlling the emitting of the plurality of infrared-light nerve-stimulation signals to generate action potentials in the neural tissue; and transferring the heat generated by the plurality of light sources during the emitting of the plurality of infrared-light nerve-stimulation signals away from the plurality of light sources and into surrounding tissue of the animal using the plurality of thermally conductive extensions.
Owner:NERVESENSE LTD
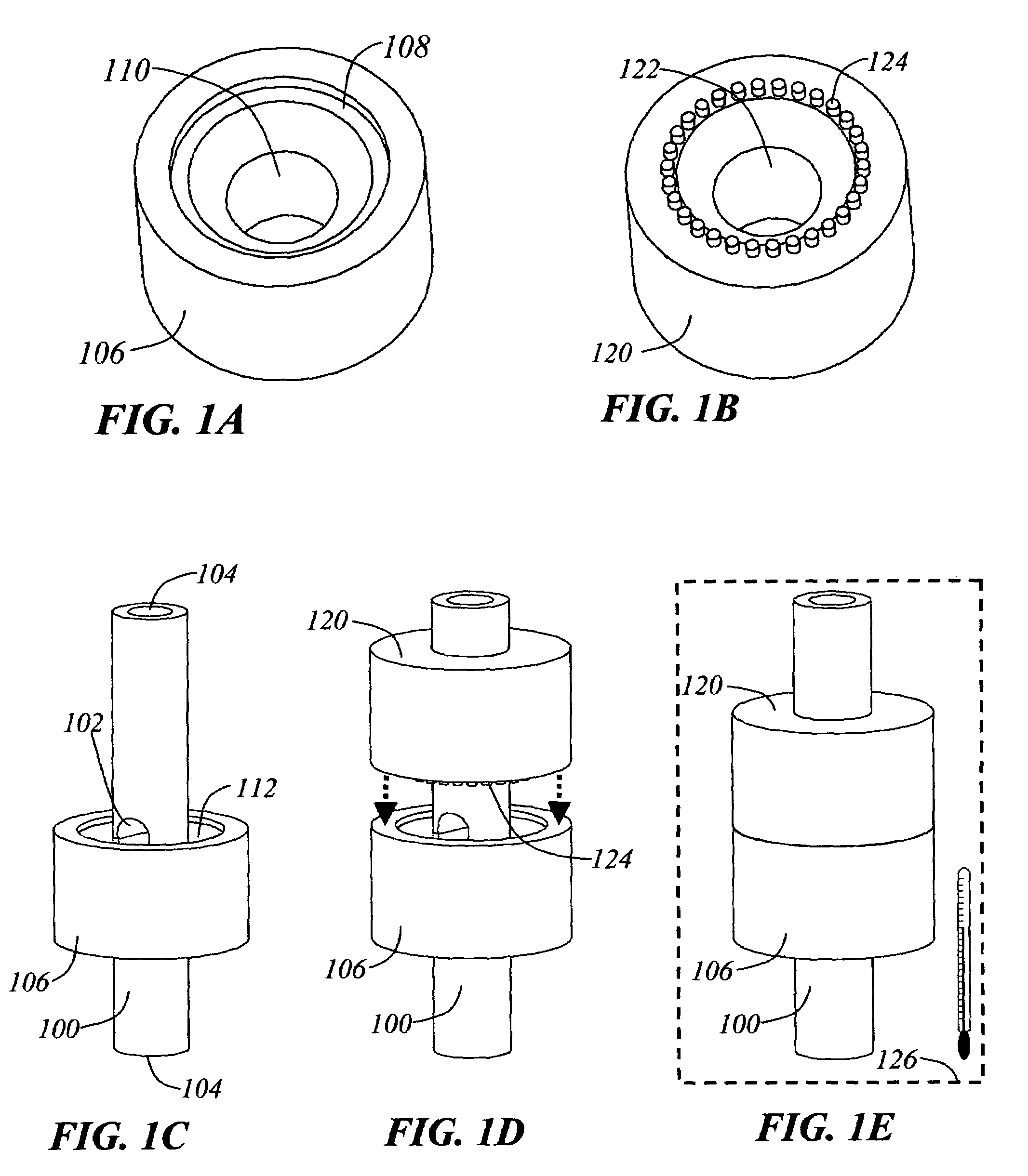
Device and Method for Manipulating and Inserting Electrode Arrays into Neural Tissues
ActiveUS20080221589A1Improve insertion speedMinimize timeSpinal electrodesHead electrodesVacuum pressurePositive pressure
An insertion device for inserting a therapeutic device into organic tissue is disclosed and described. The device is particularly suited to insertion of such as nerve stimulating electrode arrays. The insertion device has at least one controllable positive pressure source (greater than atomospheric), two vacuum sources and a dual vacuum pressure control system. The positive pressure and the dual vacuum pressure control systems are manipulated to allow the manipulation and insertion or retrieval of a therapeutic device. The insertion device can be spatially manipulated by hand, without requiring other equipment for positioning the insertion device.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com