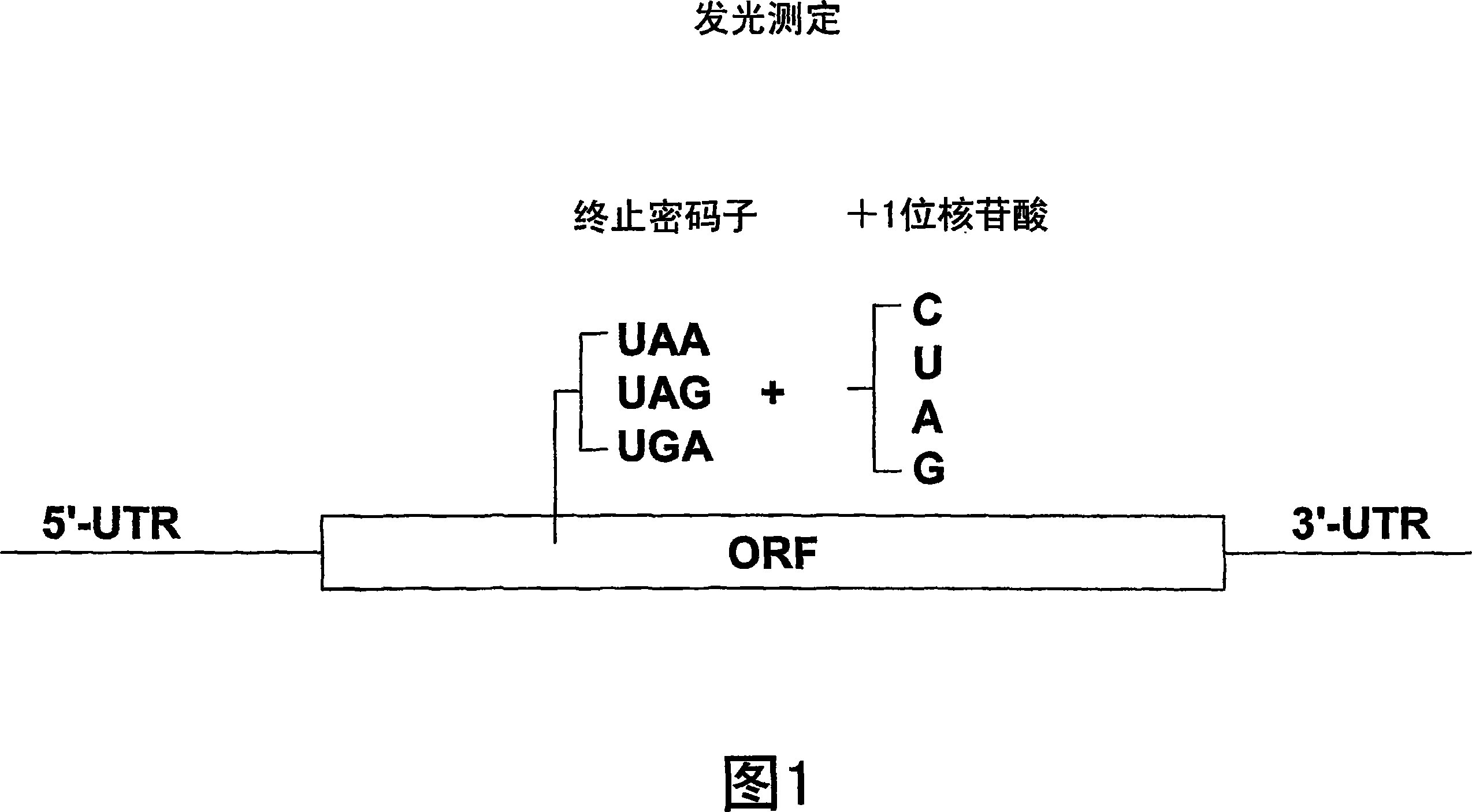
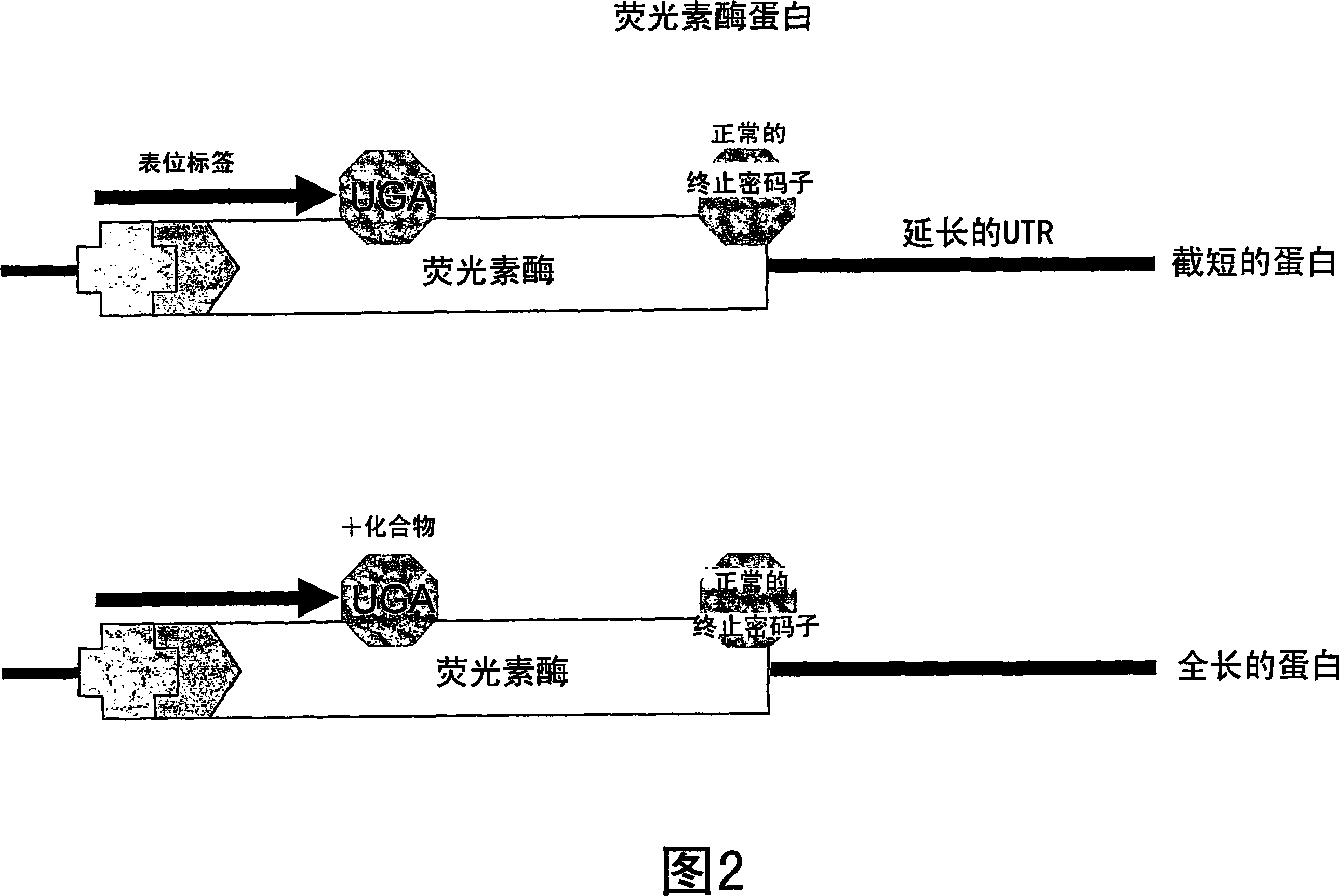
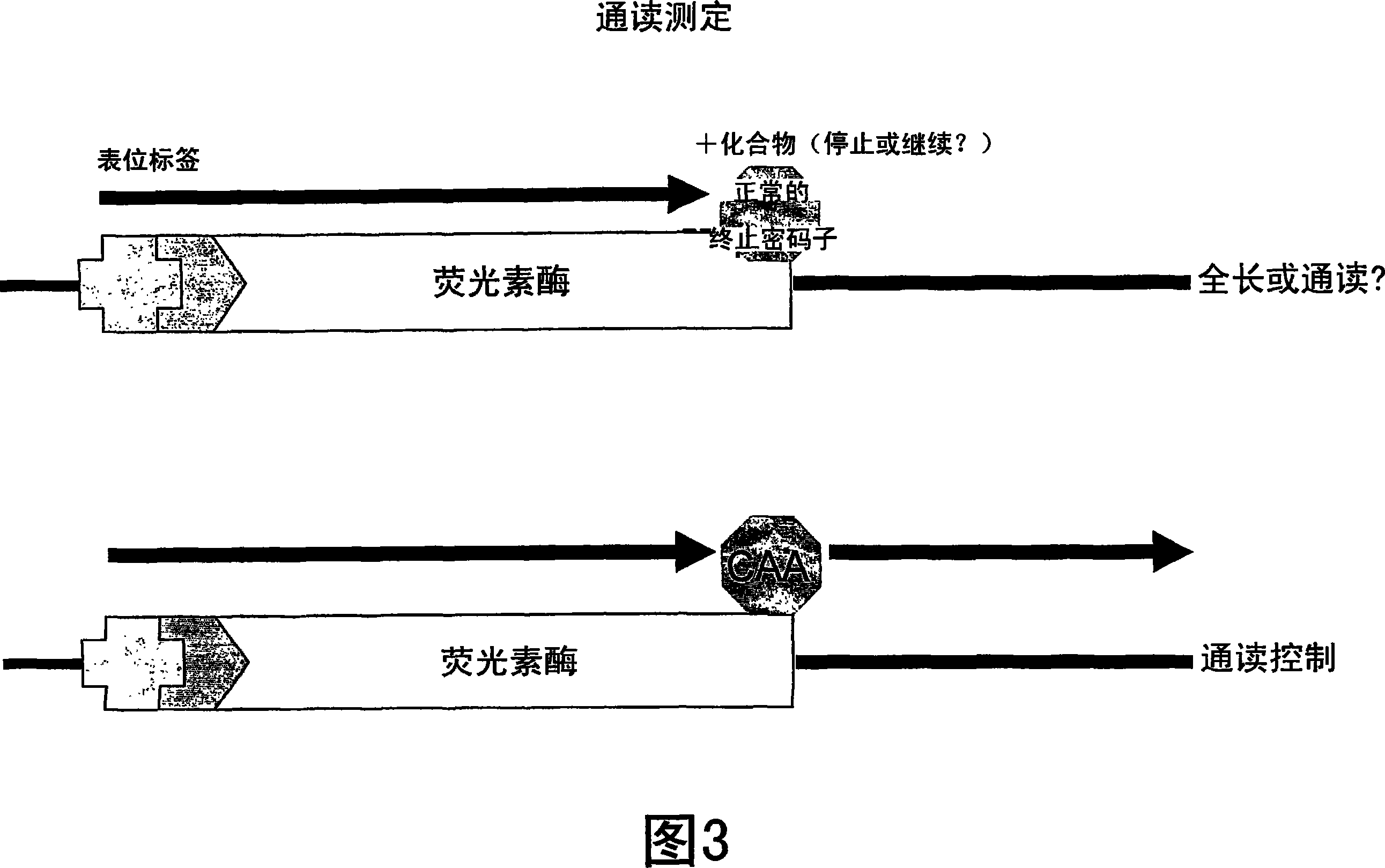
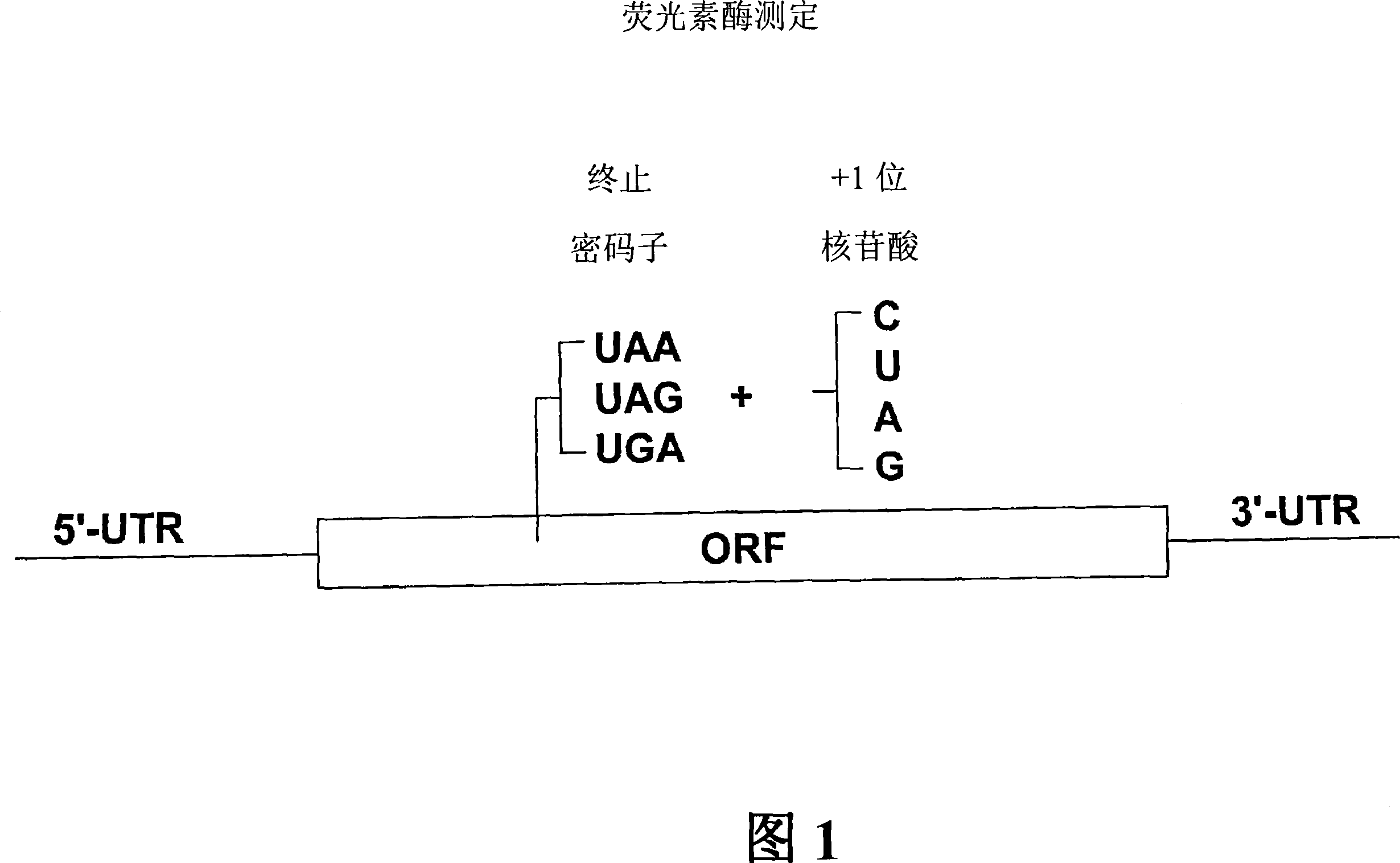
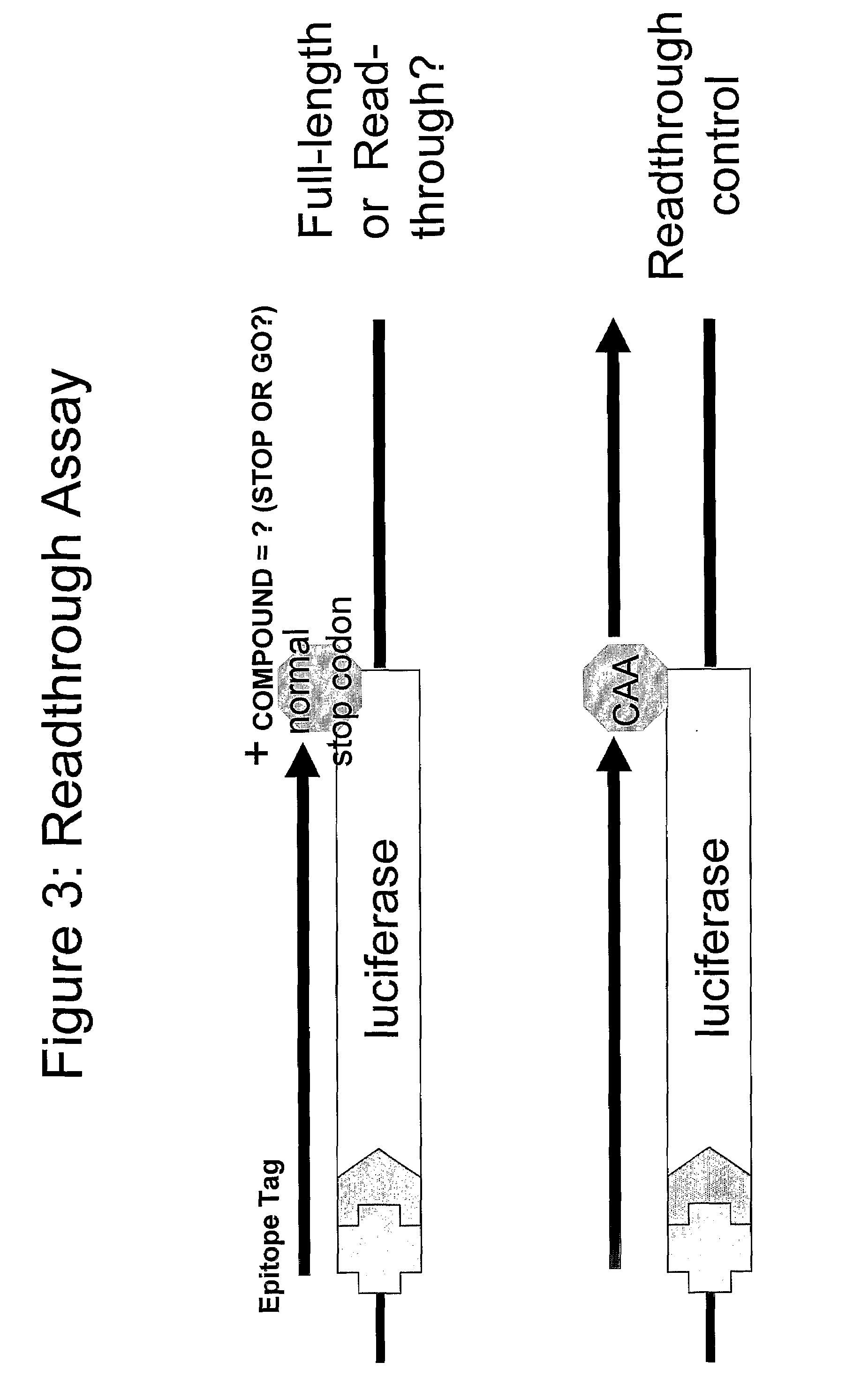
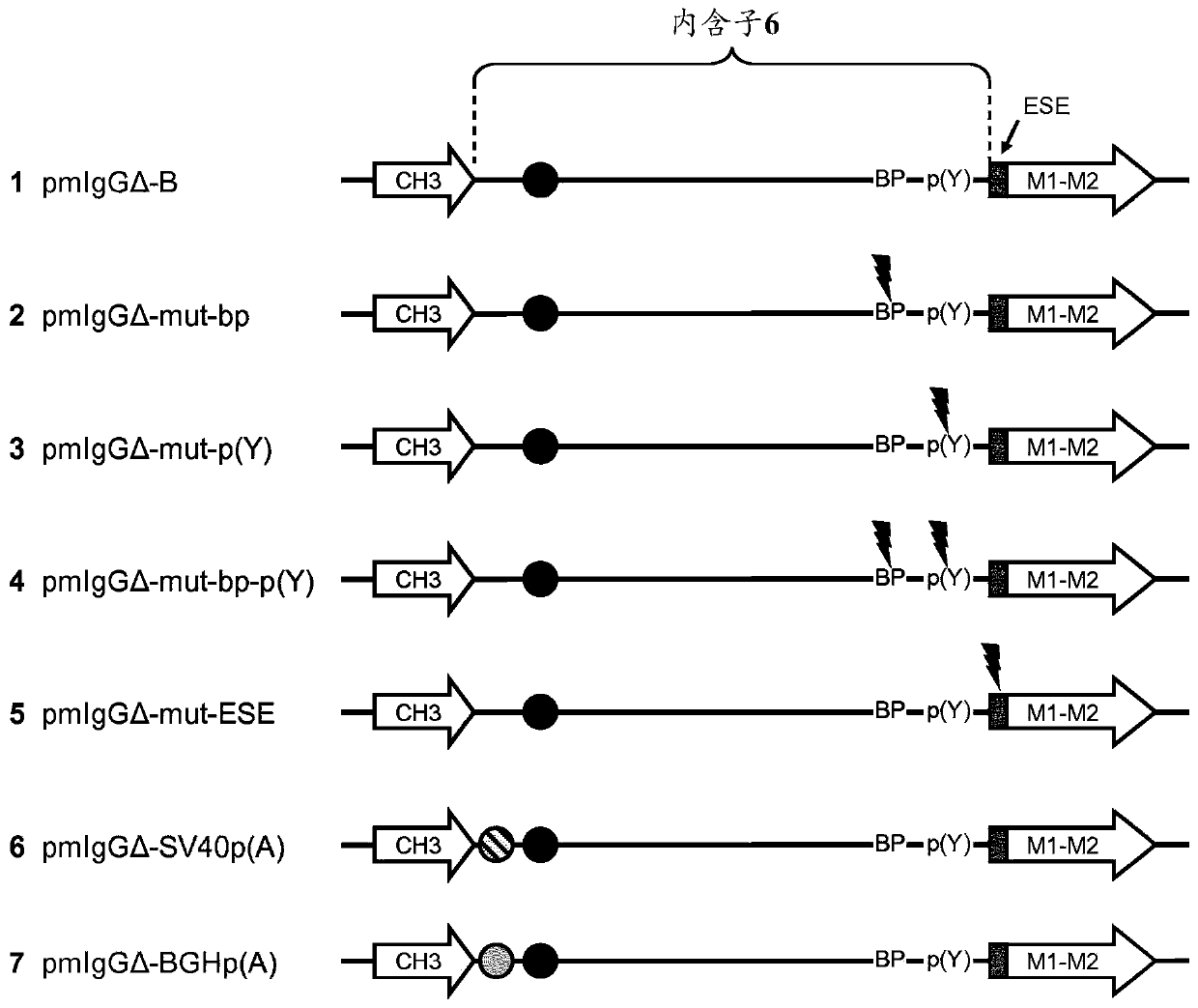
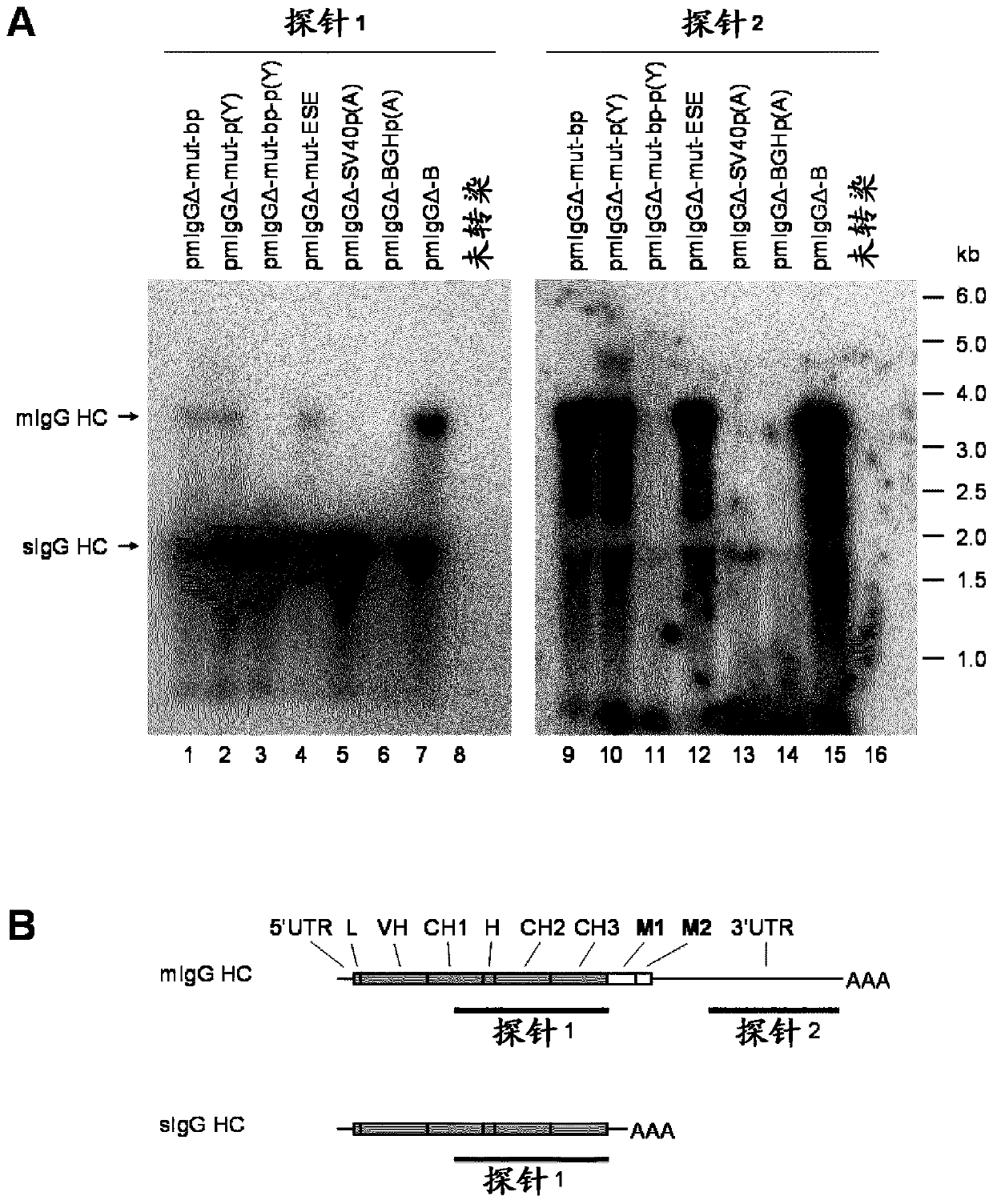
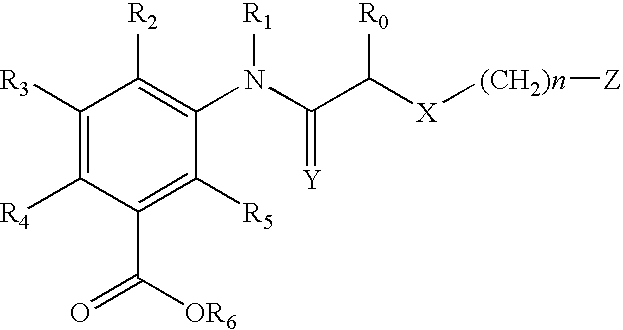
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Translation termination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
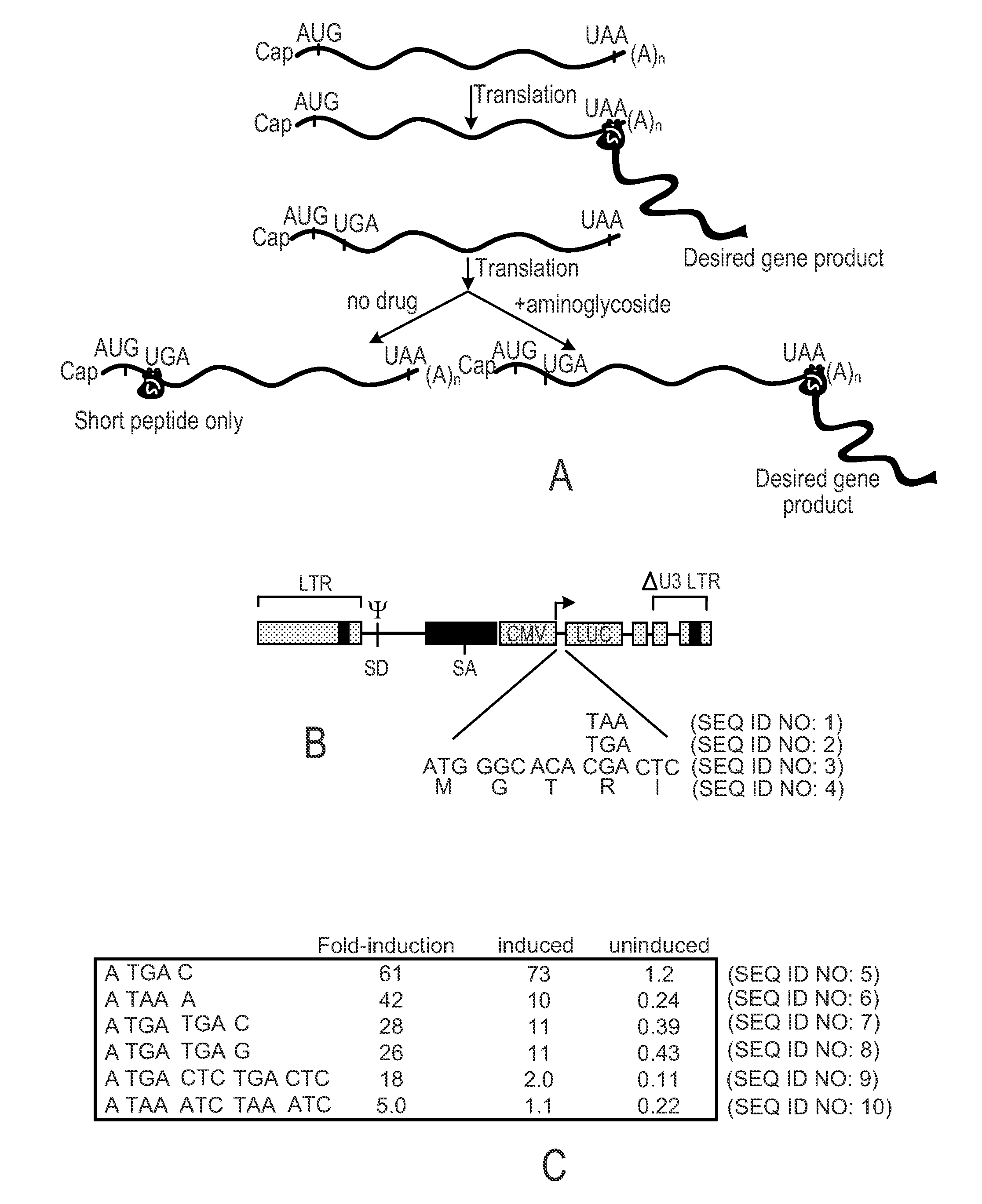
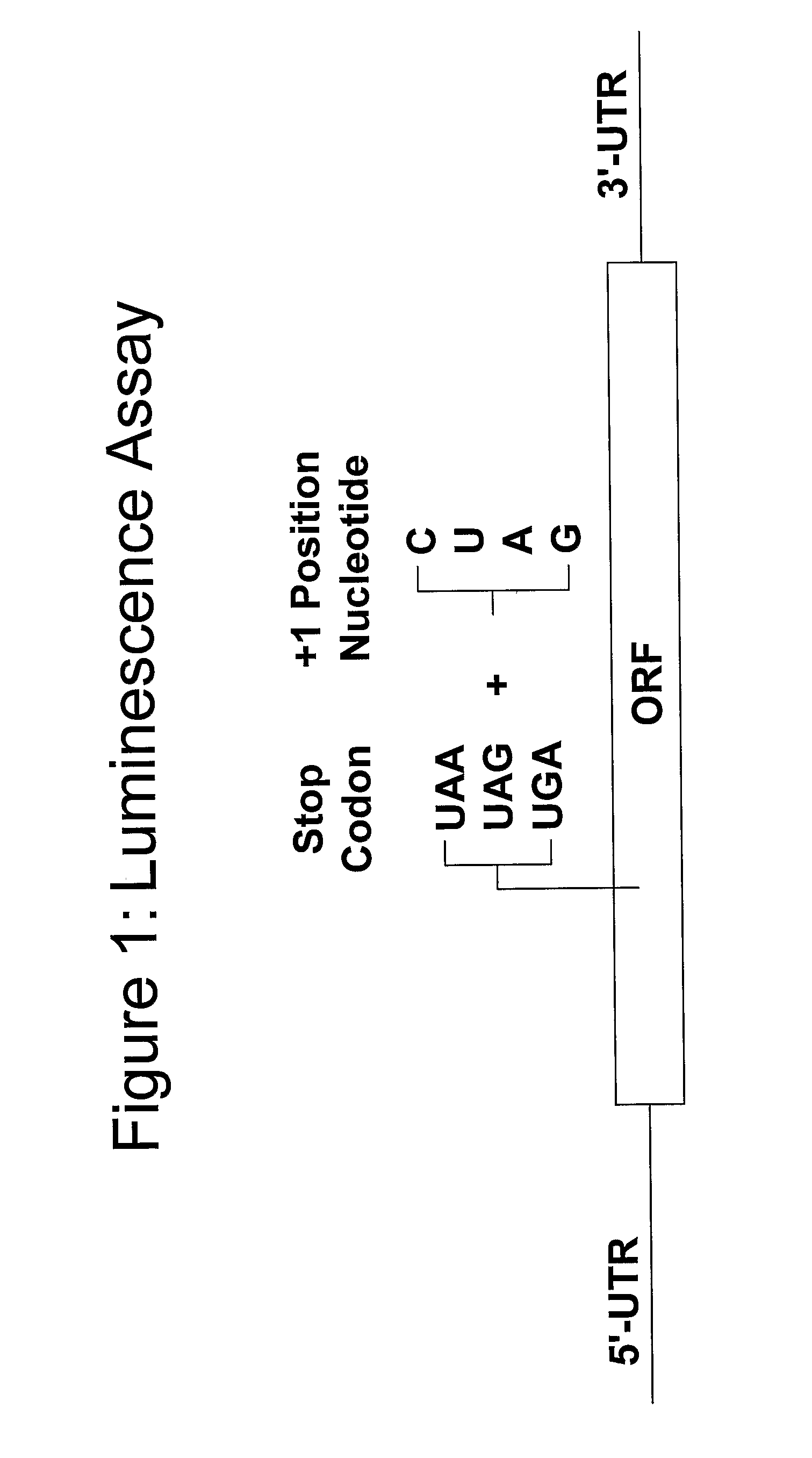
Termination of translation occurs when the ribosome encounters a stop codon. There are slighty different views as to what happens; some textbooks state that there is a release factor bound to the stop codon, that displaces the ribosome when it reaches that point.
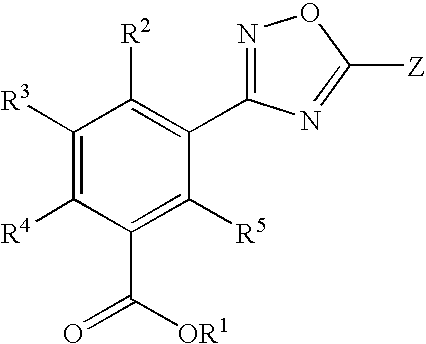
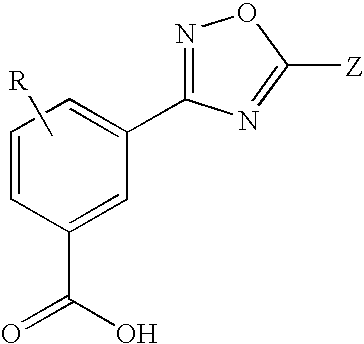
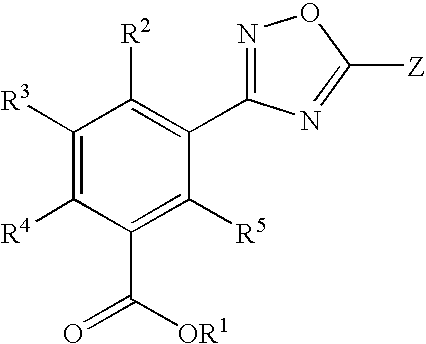
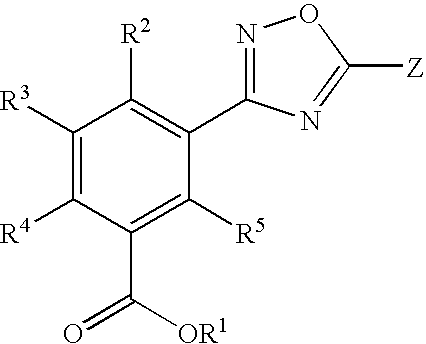
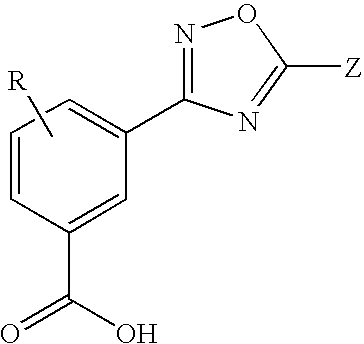
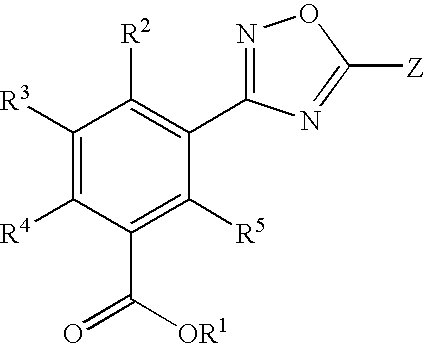
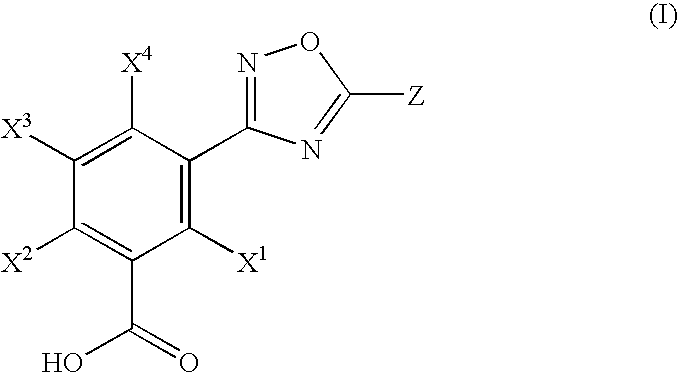
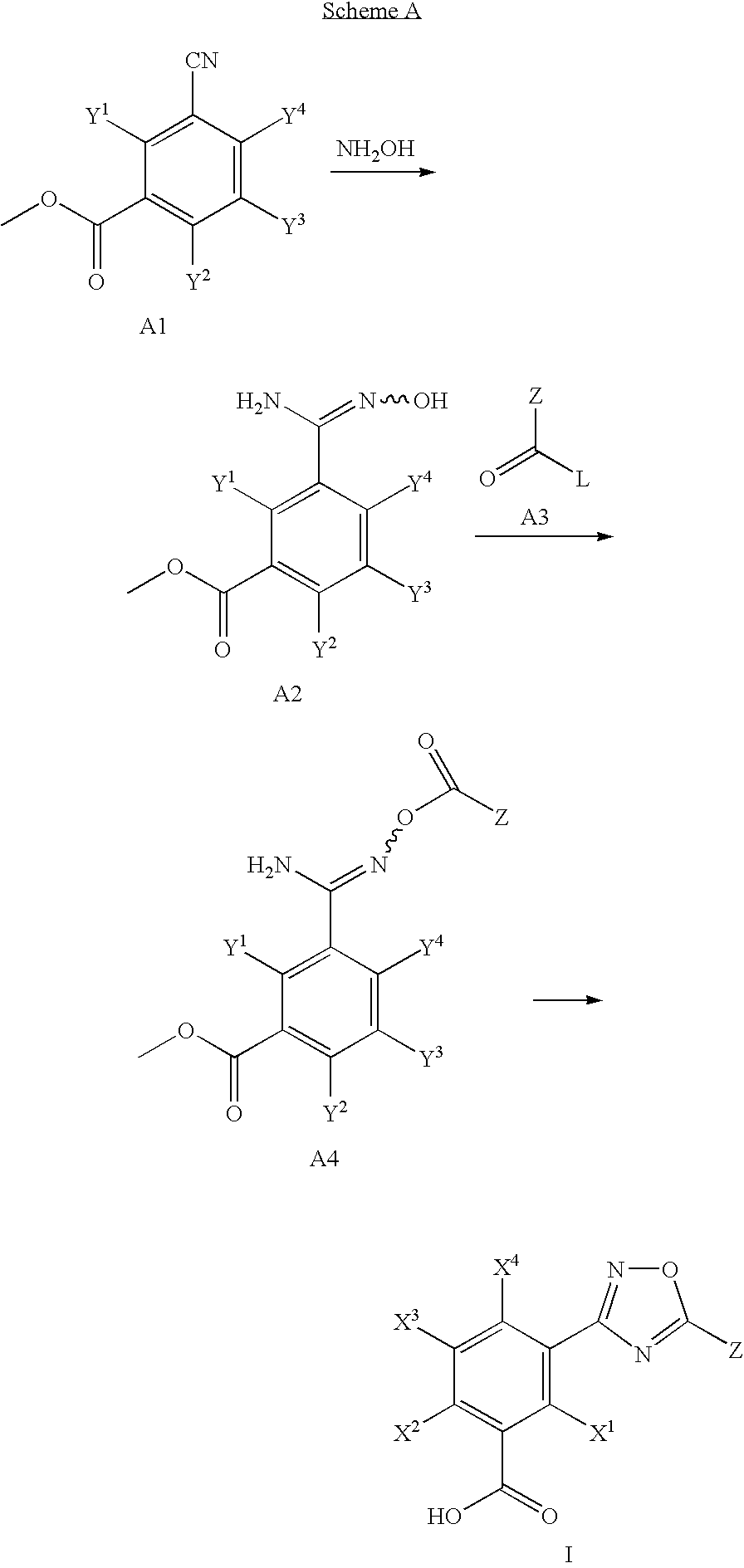
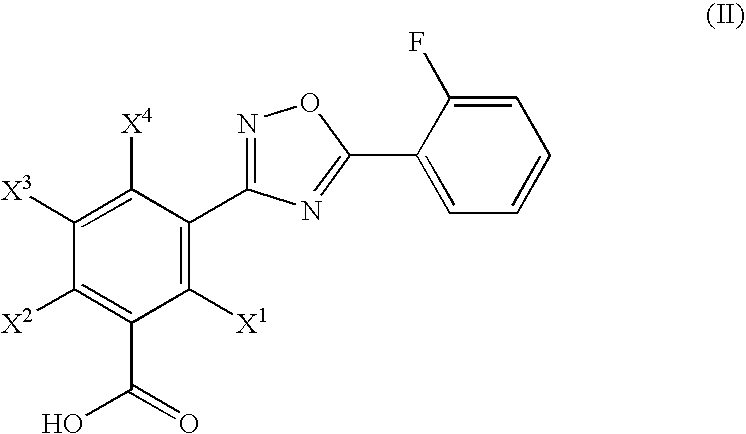
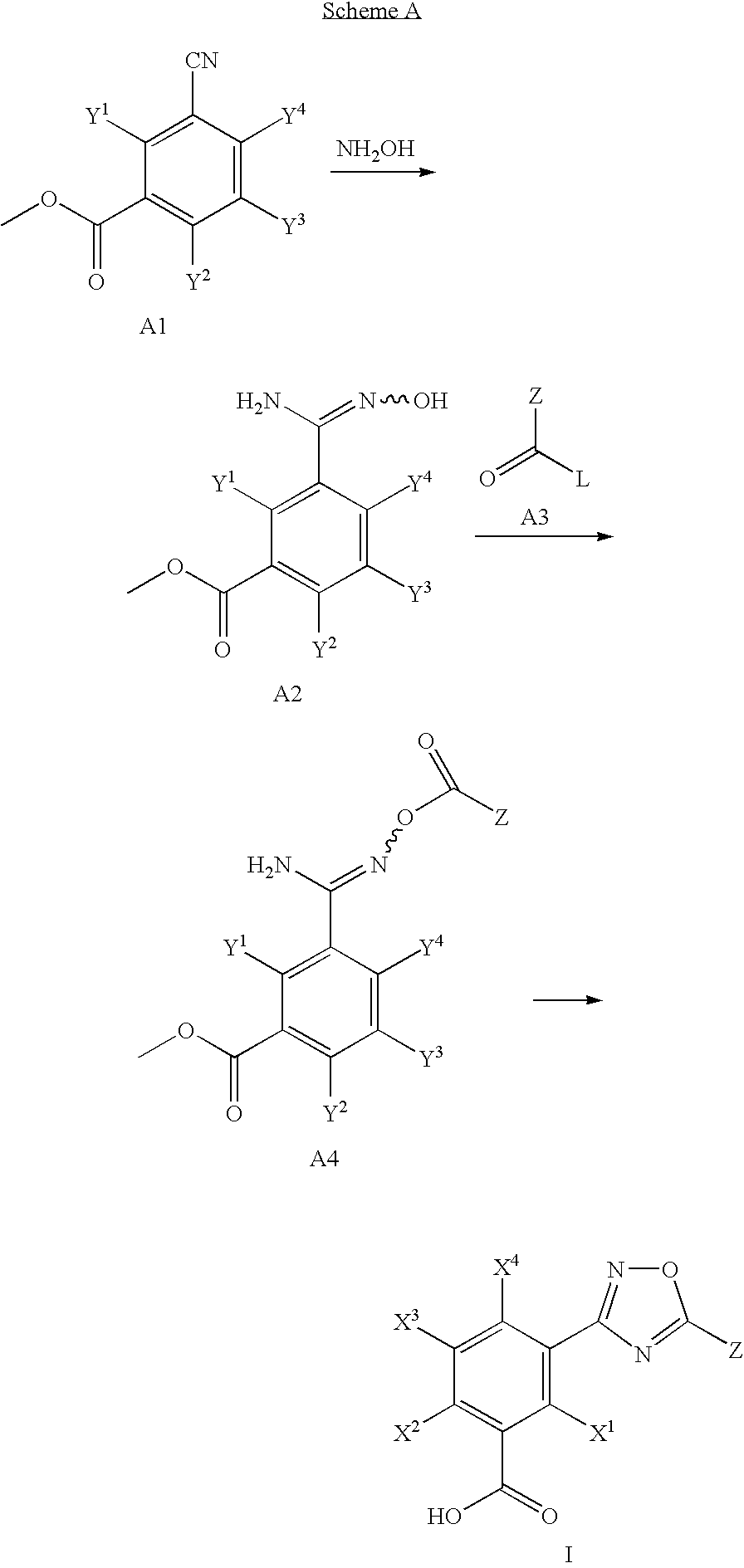
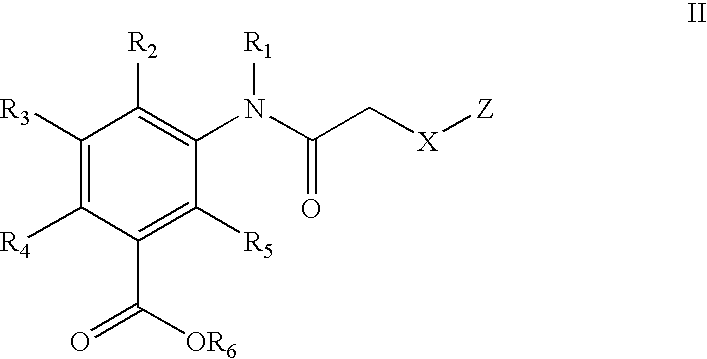
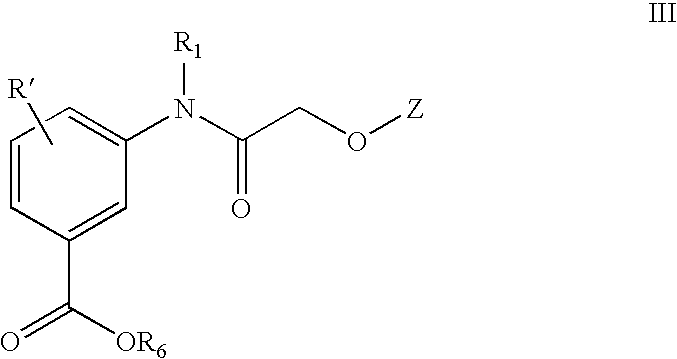
1,2,4-Oxadiazole benzoic acid compounds and their use for nonsense suppression and the treatment of disease
ActiveUS20050164973A1Promote readthroughDecreased amount of producedBiocideSenses disorderBenzoic acidMRNA Decay
Novel 1,2,4-oxadiazole benzoic acid compounds, methods of using and pharmaceutical compositions comprising an 1,2,4-oxadiazole benzoic acid derivative are disclosed. The methods include methods of treating or preventing a disease ameliorated by modulation of premature translation termination or nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated therewith.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
1,2,4-oxadiazole benzoic acid compounds and their use for nonsense suppression and the treatment of disease
ActiveUS20040204461A1Eradication ameliorationMinimizing spreadBiocideSenses disorderBenzoic acidMRNA Decay
Novel 1,2,4-oxadiazole benzoic acid compounds, methods of using and pharmaceutical compositions comprising an 1,2,4-oxadiazole benzoic acid derivative are disclosed. The methods include methods of treating or preventing a disease ameliorated by modulation of premature translation termination or nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated therewith.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
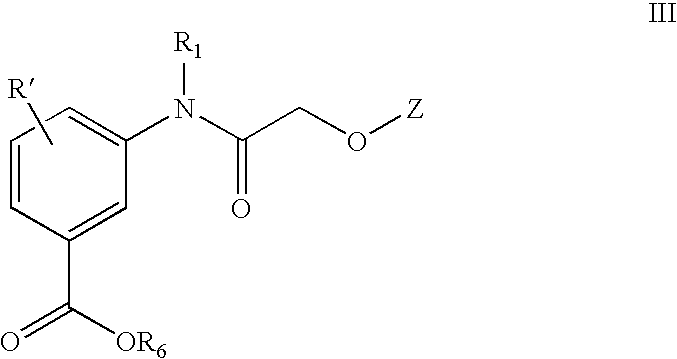
Acetylamino benzoic acid compounds and their use for nonsense suppression and the treatment of disease
ActiveUS20060167263A1Minimizing spreadMinimizing worseningOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationBenzoic acidMRNA Decay
Novel acetylamino benzoic acid compounds, methods of using and pharmaceutical compositions comprising an acetylamino benzoic acid derivative are disclosed. The methods include methods of treating or preventing a disease ameliorated by modulation of premature translation termination or nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated therewith.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Method and materials for producing deletion derivatives of polypeptides
The present invention describes an in vitro transposition-based methodology for generation of deletion derivatives of polypeptides. An artificial transposon containing at least partly within its transposon ends a modification with translation stop codons in three reading frames is provided. In the method, transposition complexes are assembled using the modified transposon and essentially random integrations into the target plasmid, containing a polypeptide coding nucleic acid of interest, are recovered as a plasmid pool. Subsequent manipulation steps including restriction enzyme digestions and ligation result in pools of mutant clones from which deletion derivatives of a polypeptide coding nucleic acid of interest and its respective deletion polypeptides could be produced.
Owner:FINNZYMES
Pyrazole or triazole compounds and their use for the manufacture of a medicament for treating somatic mutation-related diseases
The present invention relates to methods, compounds, and compositions for treating or preventing diseases associated with nonsense mutations in an mRNA by administering the compounds or compositions of the present invention. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods, compounds, and compositions for suppressing premature translation termination associated with a nonsense mutation in an mRNA.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Compounds and their use for treating somatic mutation-related diseases
The present invention relates to methods, compounds, and compositions for treating or preventing diseases associated with nonsense mutations in an mRNA by administering the compounds or compositions of the present invention. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods, compounds, and compositions for suppressing premature translation termination associated with a nonsense mutation in an mRNA.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
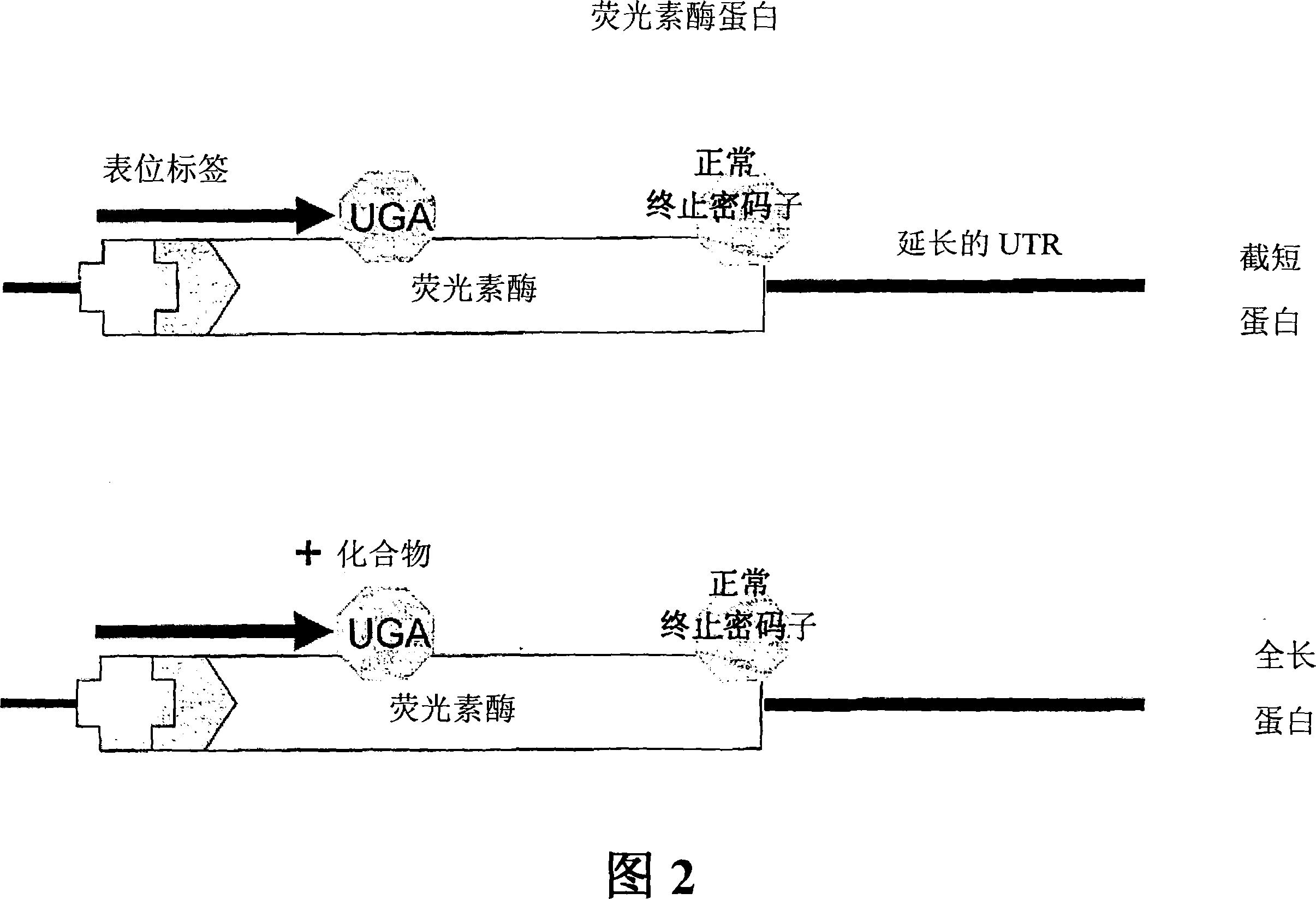
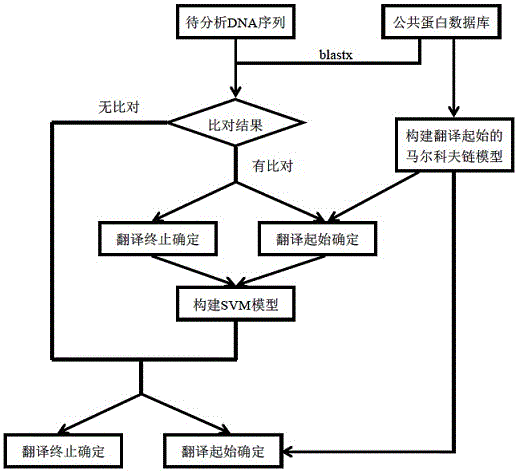
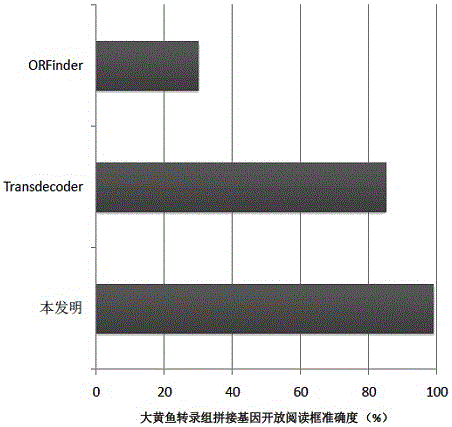
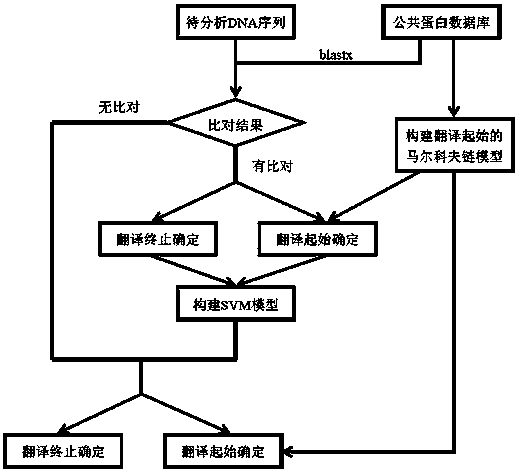
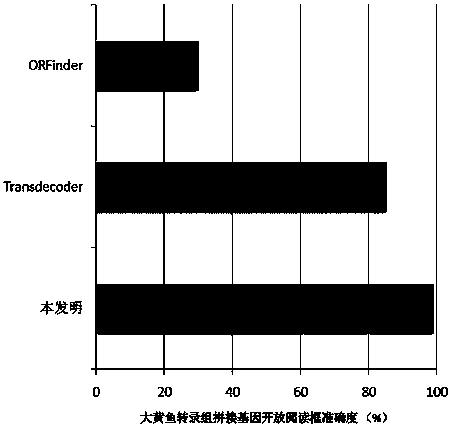
Method for analyzing structure of transcriptome gene sequence of non-model organism
ActiveCN106202998AEnrich the connotation of annotationsDefine biological functionBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsStructural analysisNucleic acid sequence
The invention discloses a method for analyzing a structure of a transcriptome gene sequence of a non-model organism. The method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining an optimal comparison result; (2) determining a protein coding mode and determining a translation termination position; (3) determining a coding starting position of the gene sequence; (4) classifying by utilizing a gene mode; (5) determining a nucleic acid sequence of a coding manner by utilizing a transcriptome sequence and training a nucleic acid sequence mode of a coding protein by utilizing a Markov chain; (6) determining a coding manner of a protein coding sequence of a gene which is not compared. The method disclosed by the invention is used for carrying out high-throughput structural analysis on a lot of gene sequences obtained by transcriptome sequencing of any non-model organism and function annotation of the transcriptome sequence is automatically finished in an analysis process; a Markov model and a support vector machine model are constructed by utilizing a compared high-reliability protein coding nucleic acid sequence, and a gene sequence which is not compared is analyzed, so that the credibility of the structural analysis of the sequence is higher.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Hydroxylated 1,2,4-oxadiazole benzoic acid compounds and compositions thereof
Novel hydroxylated 1,2,4-oxadiazole benzoic acid compounds, methods of using and pharmaceutical compositions comprising a hydroxylated 1,2,4-oxadiazole benzoic acid derivative are disclosed. The methods include methods of treating or preventing a disease ameliorated by modulation of premature translation termination or nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated therewith.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
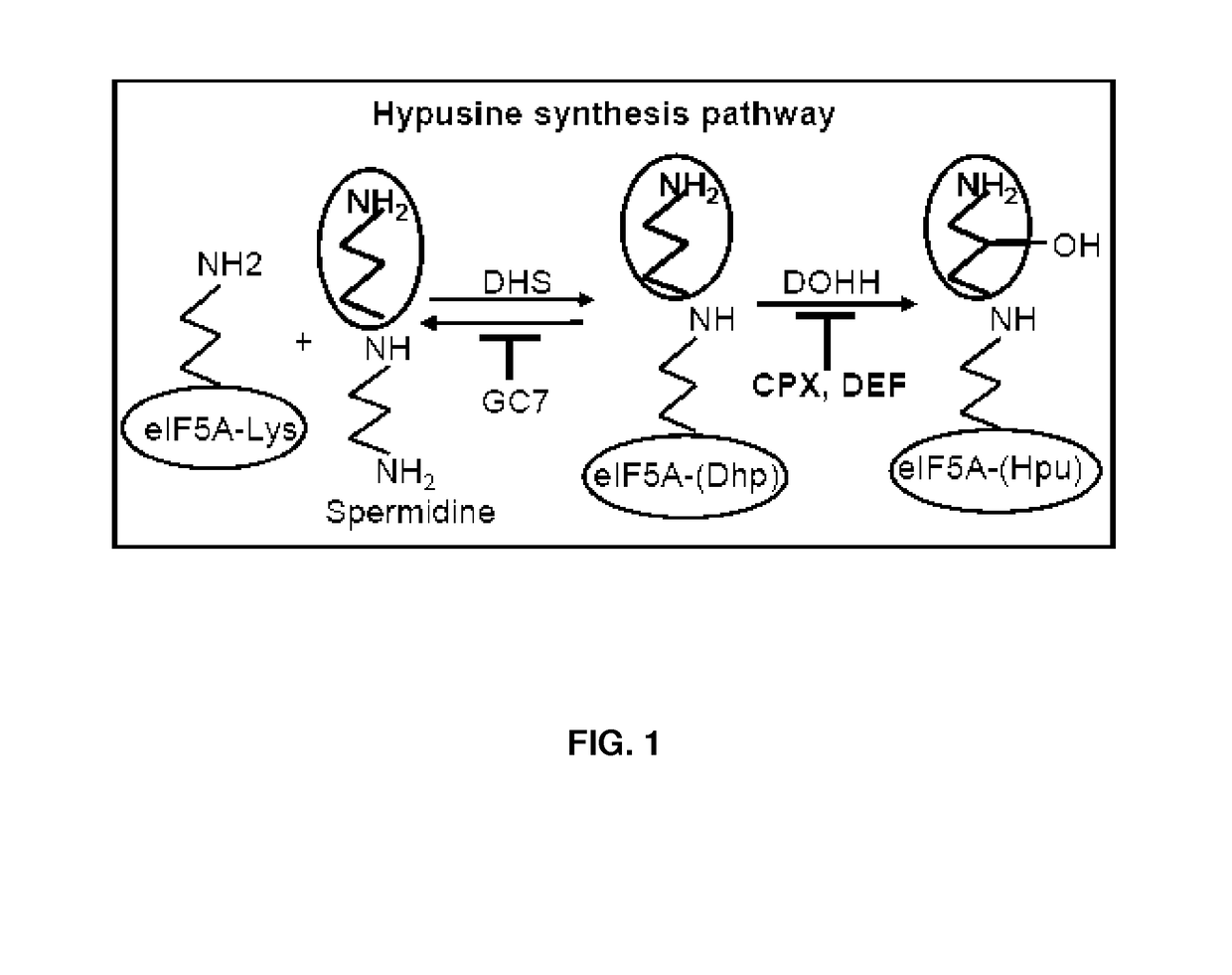
Inhibition of Nonsense Mediated mRNA Decay by Drugs that Prevent Hypusination of Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 5A
ActiveUS20140206637A1Reduce degradationInhibition can be terminatedBiocideGenetic material ingredientsEukaryotic initiation factorMRNA Decay
Provided are methods for treating a NAD comprising administering to a patient suffering from a NAD an inhibitor of NMD and a nonsense suppressor, whereby degradation of NMD susceptible mRNA is decreased and translation termination at a misplaced nonsense codon is blocked.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Hydroxylated 1,2,4-oxadiazole benzoic acid compounds, composistions thereof and the use for nonsense suppression
InactiveUS20080139632A1Minimizing spreadMinimizing worseningBiocideNervous disorderBenzoic acidDisease
Novel hydroxylated 1,2,4-oxadiazole benzoic acid compounds, methods of using and pharmaceutical compositions comprising a hydroxylated 1,2,4-oxadiazole benzoic acid derivative are disclosed. The methods include methods of treating or preventing a disease ameliorated by modulation of premature translation termination or nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated therewith.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Compounds and their use for treating somatic mutation-related diseases
The present invention relates to methods, compounds, and compositions for treating or preventing diseases associated with nonsense mutations in an mRNA by administering the compounds or compositions of the present invention. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods, compounds, and compositions for suppressing premature translation termination associated with a nonsense mutation in an mRNA.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Novel SMG-1
InactiveUS20040137592A1Alleviate gene mutationNew typeCompound screeningFungiDiseasePhosphatidyl inositol
A novel polypeptide and a novel polynucleotide encoding the same are disclosed. The polypeptide is SMG-1, a protein included in the phosphatidyl inositol kinase related kinase family, and is useful in constructing a screening system for agents of treating and / or preventing a disease caused by a premature translation termination codon generated by a nonsense mutation.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Use of an aminoglycoside for nonsense mutation suppression and the treatment of disease
ActiveUS20180147228A1Minimizing spreadMinimizing worseningOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesPremature Stop CodonPyran
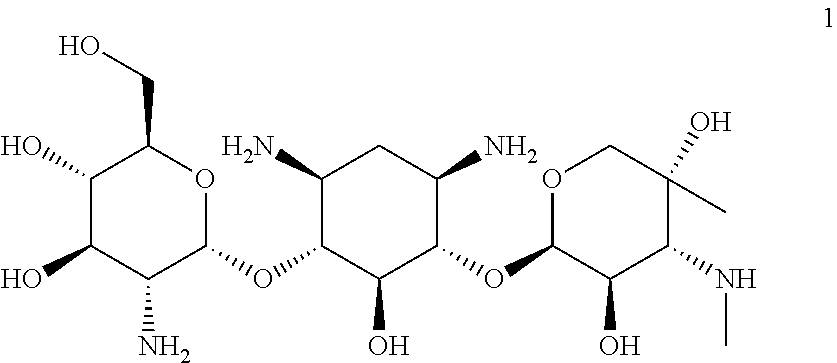
Methods of using and pharmaceutical compositions comprising (2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-5-amino-6-(((1R,2S,3S,4R,6S)-4,6-diamino-3-(((2R,3R,4R,5R)-3,5-dihydroxy-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)-2-hydroxycyclohexyl)oxy)- 2-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4-diol are disclosed, including methods of treating or preventing a nonsense mutation mediated disease associated with premature translation termination or a premature stop codon resulting from a germline or somatic nonsense mutation.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Modified FBXW7 circular RNA and application thereof in tumor drugs and new crown vaccines
ActiveCN112574997AAdaptableImprove expression vitalitySsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsIn vivoTGE VACCINE
The present invention relates to a circular RNA modified body obtained by modifying a large number of artificial sequences on the basis of a natural FBXW7 circular RNA, the modified body having excellent translation and translation termination effects, and being capable of expressing the protein in vivo after an appropriate protein-encoding RNA sequence is inserted into the insertion site of the modified body. Different proteins can have different effects, so that the modified FBXW7 circular RNA can be used for preparing tumor treatment medicines and new crown vaccines.
Owner:楷拓生物科技(苏州)有限公司 +2
Methods And Compositions For Regulating Gene Expression
In certain embodiments, the disclosure relates to compositions and methods relating to a translation-based gene regulation system that functions in mammalian cells. In certain specific embodiments, the disclosure relates to methods of regulating gene expression via modulating translation termination.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
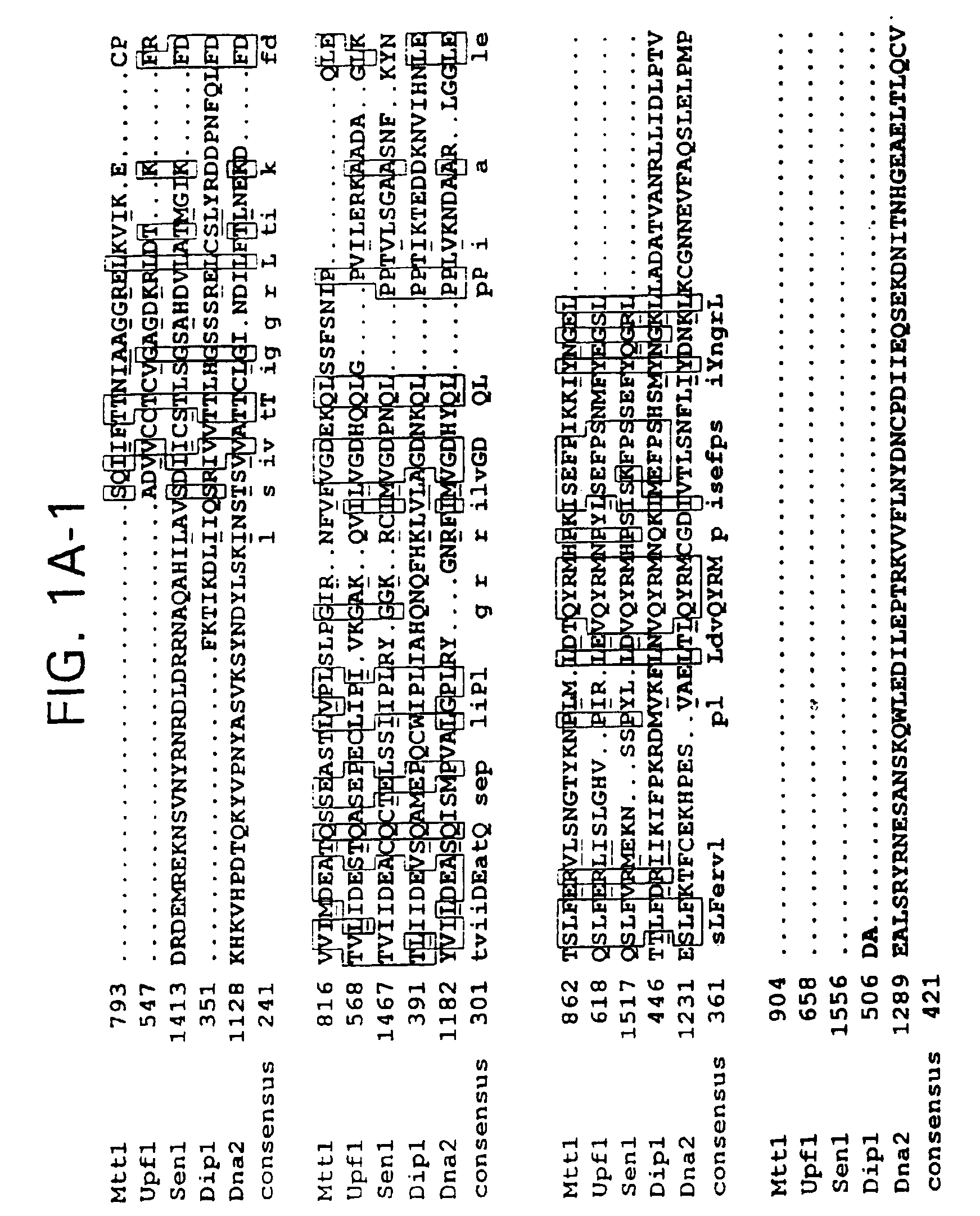
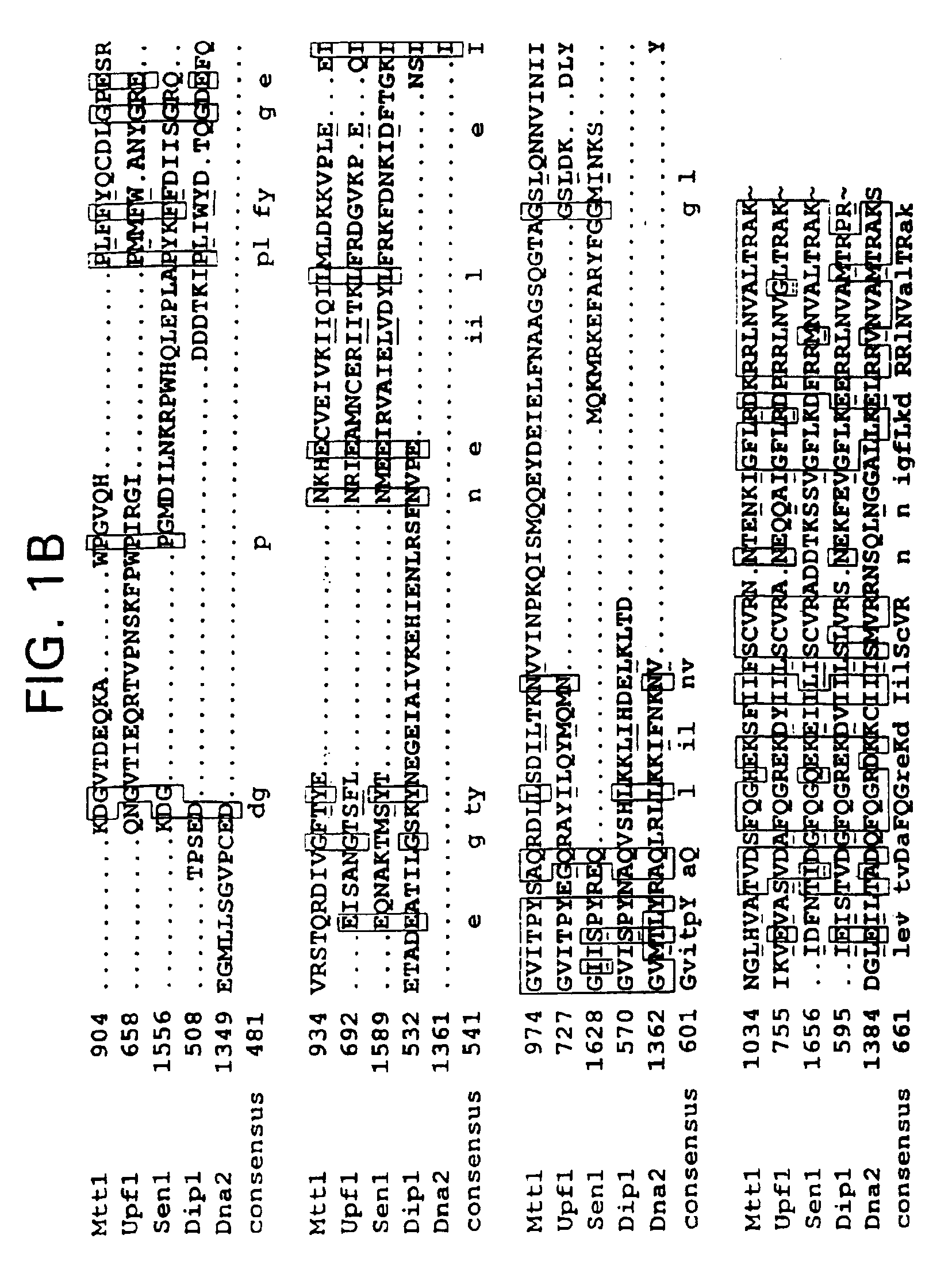
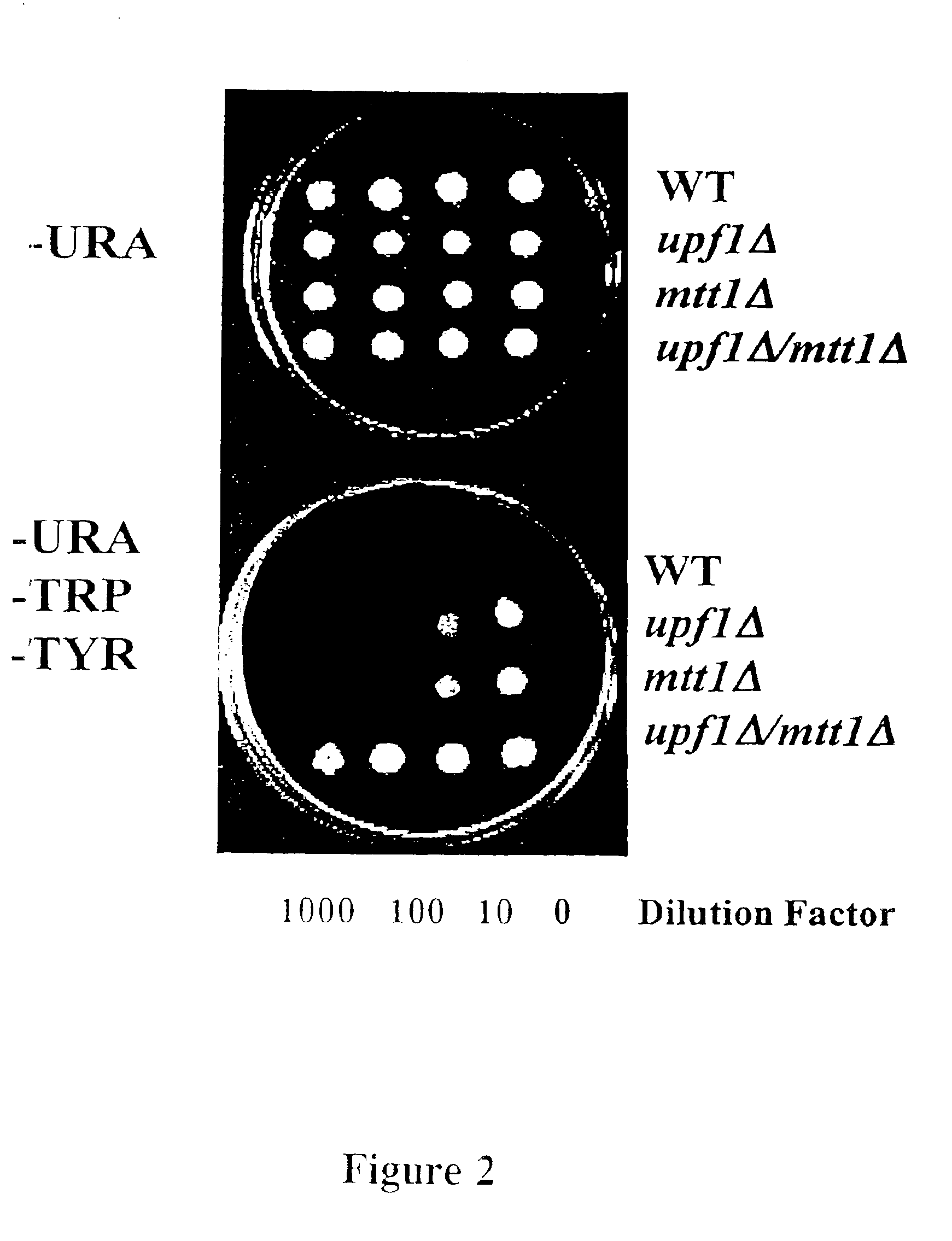
Subfamily of RNA helicases which are modulators of the fidelity of translation termination and uses thereof
InactiveUS6989256B2Inhibit bindingImprove bindingCompound screeningApoptosis detectionMultiprotein complexPeptidyl transferase
An isolated multiprotein complex of S. cerevisiae components is provided that is effective to modulate peptidyl transferase activity during translation. This complex includes a Modulator of Translation Termination protein (Mtt1p, also referred to as helicase B), a Upf1 protein, a peptidyl eukaryotic release factor 1 (eRF1) and a peptidyl eukaryotic release factor 3 (eRF3).
Owner:UNIV OF MEDICINE & DENTISTRY OF NEW JERSEY
Oligonucleotide for inhibiting blood-mediated inflammatory reaction in pancreatic islet transplantation
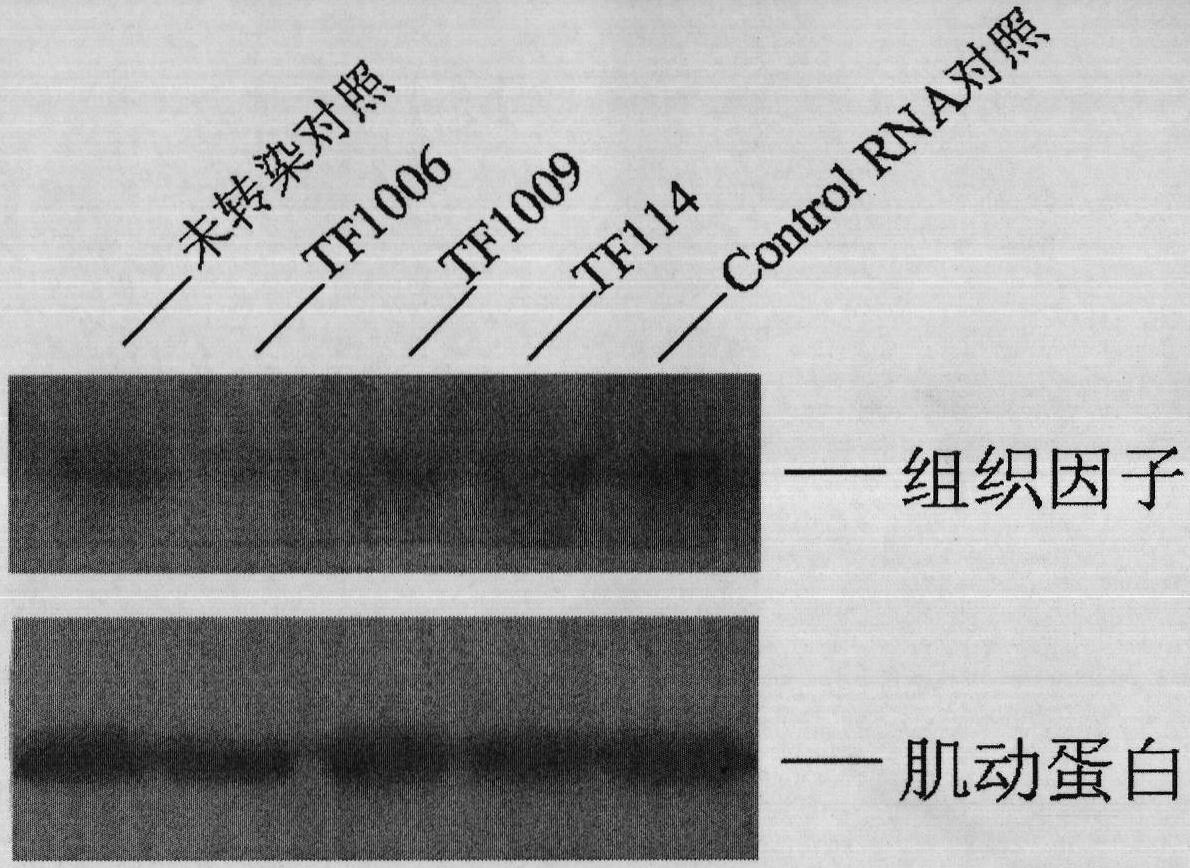
The invention discloses an oligonucleotide for inhibiting a blood-mediated inflammatory reaction in pancreatic islet transplantation. The oligonucleotide comprises 7 to 75 nucleotides, at least comprises 3 three continuous achiral 5' to 3' nucleoside-triphosphate bonds, comprises a 5'-end untranslated region, a translation initiation region, a 3'-end untranslated region and / or a translation termination region which are complemented for a TF gene, and has the melting temperature of between 75 DEG C and 115 DEG C under the concentration of 1mmol. The oligonucleotide can be a ribose oligonucleotide or a deoxyribose oligonucleotide, can be modified chemically and can be used for preparing medicinal compositions for resisting the blood-mediated inflammatory reaction in the islet transplantation.
Owner:王维 +2
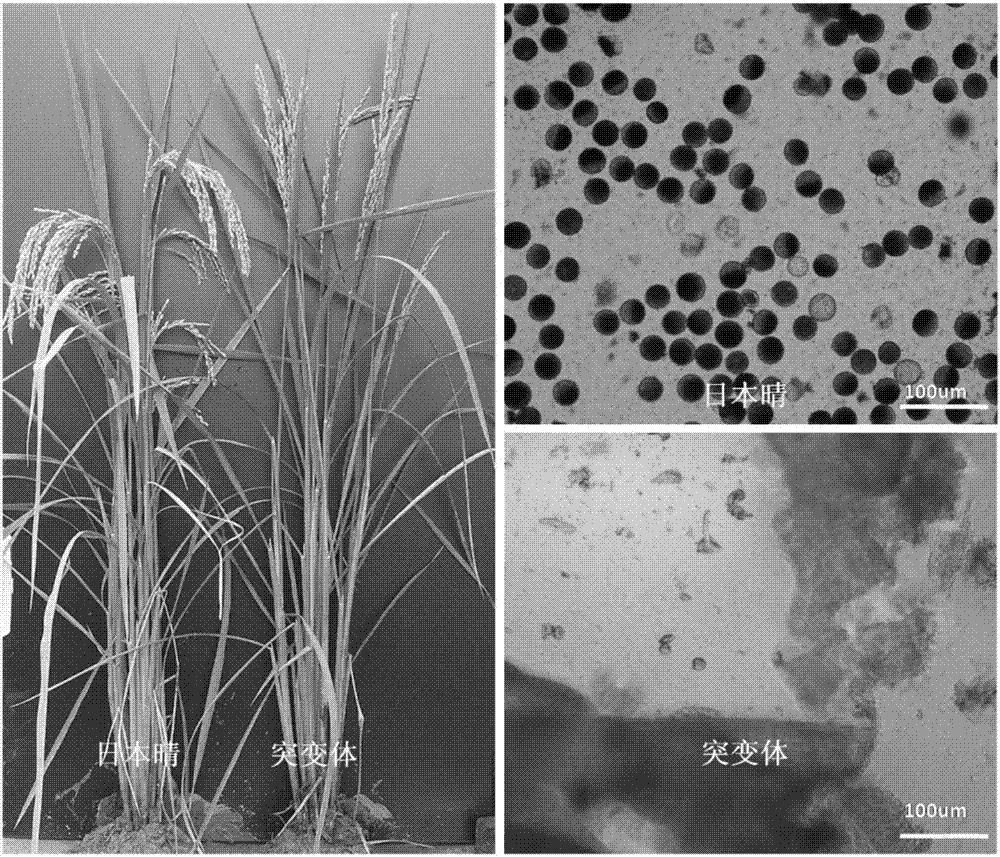
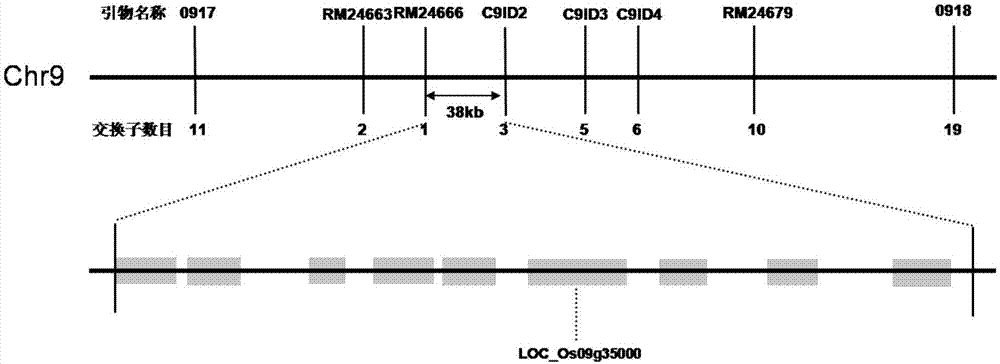
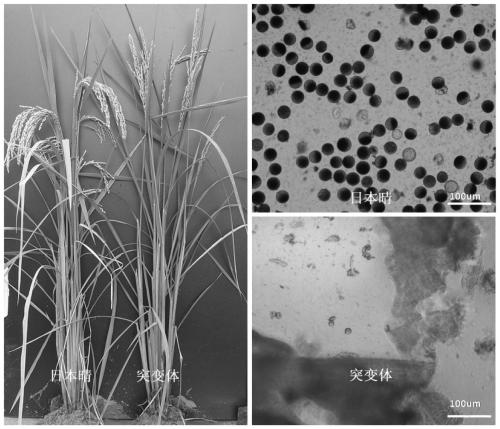
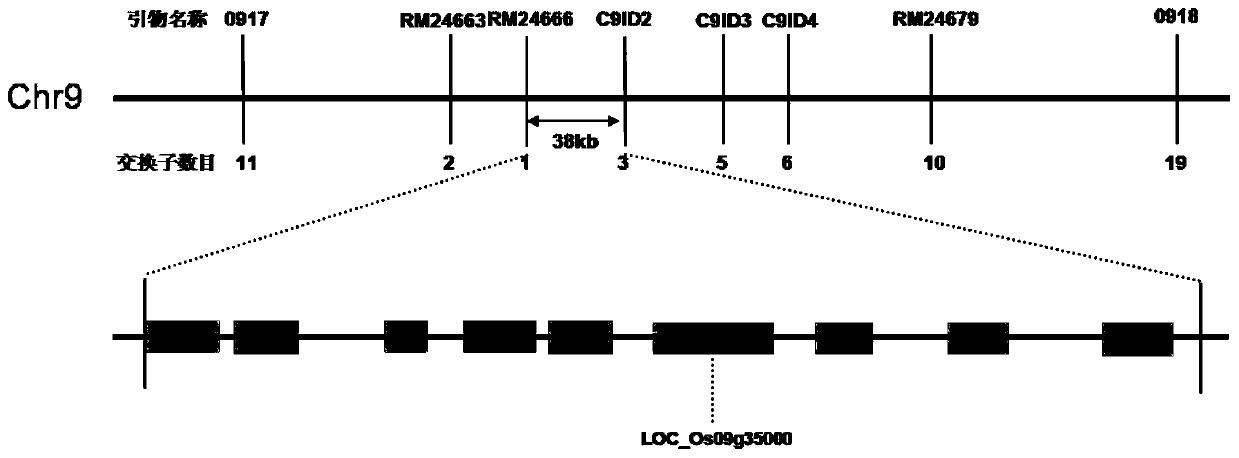
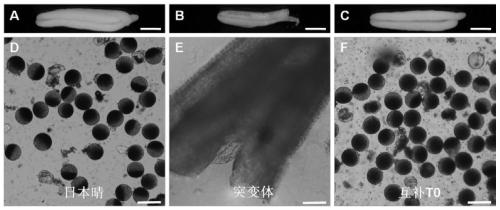
Mutant gene of rice nuclease gene OsGEN-L and application thereof
The invention relates to a mutant of a rice nuclease gene OsGEN-L and application thereof, which belong to the technical field of genetic engineering. In the mutant provided by the invention, the nuclease gene OsGEN-L is mutated into osgen-l, a nucleotide sequence of the normal OsGEN-L gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, and a nucleotide sequence of the mutant gene osgen-l of the OsGEN-L is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 4. The mutation is concretely characterized in that the first A base deletion after the 1053th bases of the OsGEN-L gene causes premature translation termination, and the mutation finally causes pollen sterility of the mutant, can be used for preparing recessive male sterile line, and plays an important role on genetic improvement, variety breeding and seed production of rice.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Compounds for Nonsense Suppression, Use of These Compounds for the Manufacture of a Medicament for Treating Somatic Mutation-Related Diseases
The present invention relates to methods, compounds, and compositions for treating or preventing diseases associated with nonsense mutations in an mRNA by administering the compounds or compositions of the present invention. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods, compounds, and compositions for suppressing premature translation termination associated with a nonsense mutation in an mRNA.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Use of system in improving insertion efficiency of non-natural amino acid
PendingCN113322267AProduces a translation termination mechanismIncrease insertion efficiencyVectorsFermentationEscherichia coliProtein target
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, in particular to use of a system in improving insertion efficiency of a non-natural amino acid. The system can degrade termination factors (RF1, RF2, ArfB and Pth) in an escherichia coli translation system and generates a codon-independent translation termination mechanism. The system can degrade the termination factors in the escherichia coli translation system and can improve insertion efficiency of simultaneously inserting a plurality of non-natural amino acids into a target protein. On a protein level, the system can completely degrade the termination factors in the escherichia coli translation system. After the termination factors in the escherichia coli translation system are degraded, non-natural amino acids can be inserted into TAG, TGA and TAA codons, and insertion of the non-natural amino acids of the three termination codons is realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Inhibition of nonsense mediated mRNA decay by drugs that prevent hypusination of eukaryotic initiation factor 5a
ActiveUS20170319612A9Inhibition is effectiveReduce concentrationOrganic active ingredientsEukaryotic initiation factorMRNA Decay
Provided are methods for treating a NAD comprising administering to a patient suffering from a NAD an inhibitor of NMD and a nonsense suppressor, whereby degradation of NMD susceptible mRNA is decreased and translation termination at a misplaced nonsense codon is blocked.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
A method for analyzing the gene sequence structure of non-model organism transcriptome
ActiveCN106202998BEnrich the connotation of annotationsDefine biological functionBiostatisticsSequence analysisStructural analysisOrganism
The invention discloses a method for analyzing a structure of a transcriptome gene sequence of a non-model organism. The method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining an optimal comparison result; (2) determining a protein coding mode and determining a translation termination position; (3) determining a coding starting position of the gene sequence; (4) classifying by utilizing a gene mode; (5) determining a nucleic acid sequence of a coding manner by utilizing a transcriptome sequence and training a nucleic acid sequence mode of a coding protein by utilizing a Markov chain; (6) determining a coding manner of a protein coding sequence of a gene which is not compared. The method disclosed by the invention is used for carrying out high-throughput structural analysis on a lot of gene sequences obtained by transcriptome sequencing of any non-model organism and function annotation of the transcriptome sequence is automatically finished in an analysis process; a Markov model and a support vector machine model are constructed by utilizing a compared high-reliability protein coding nucleic acid sequence, and a gene sequence which is not compared is analyzed, so that the credibility of the structural analysis of the sequence is higher.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Method for selecting polypeptide producing cells
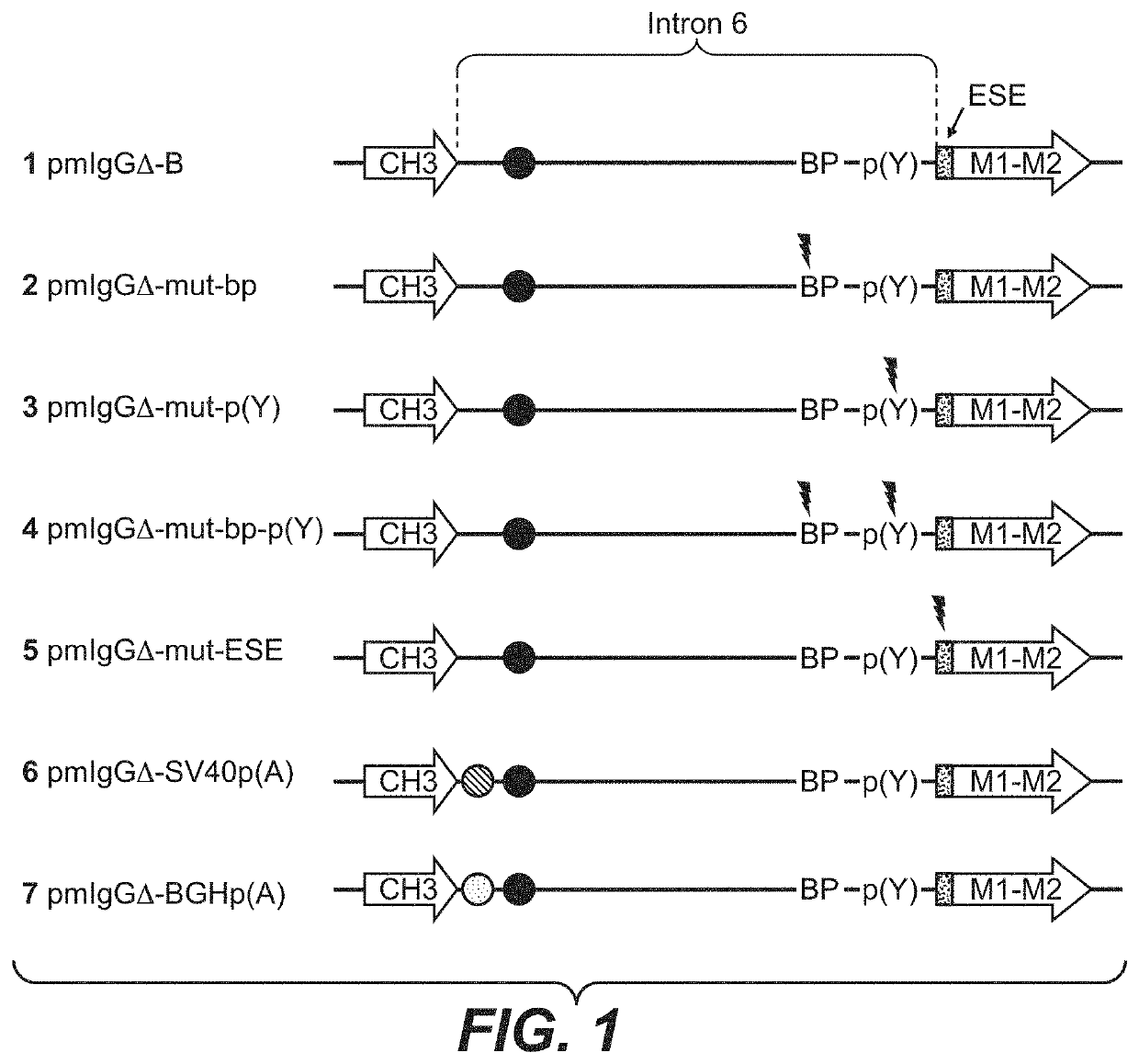
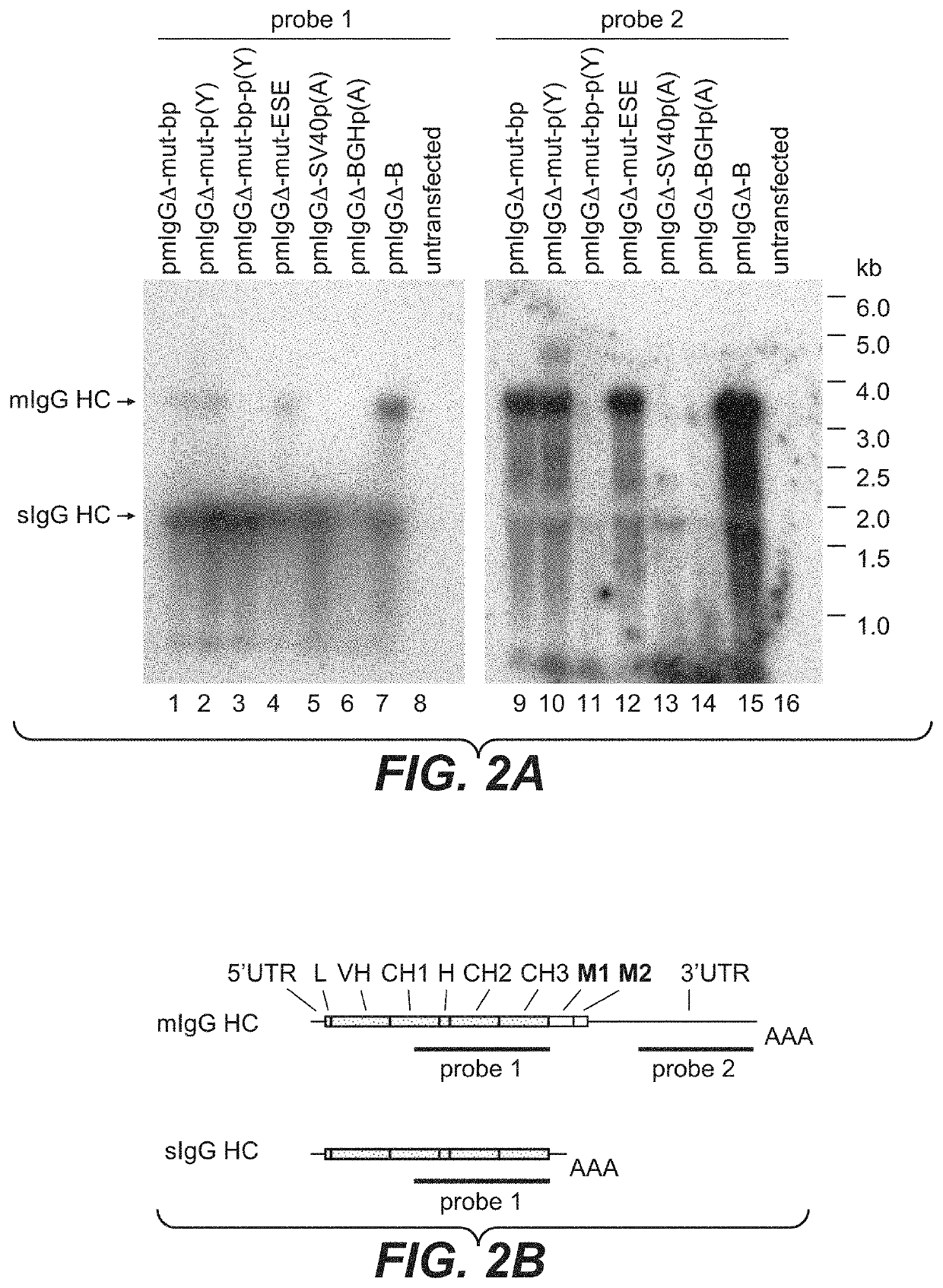
ActiveUS20200157189A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifVectorsImmunoglobulin heavy chainNucleotide
Herein is reported a nucleic acid comprising in 5′ to 3′ direction i) a first nucleic acid fragment encoding a polypeptide of interest without an in frame translational stop codon, ii) a second nucleic acid fragment operably linked to said first nucleic acid fragment which is beginning with the 5′ splice donor site of an immunoglobulin heavy chain CH3 or CH4 domain and which is terminated by the 3′ splice acceptor site of the succeeding immunoglobulin heavy chain transmembrane domain exon M1 and which comprises in frame translational stop codon and a polyadenylation signal, and iii) a third nucleic acid fragment operably linked to said second nucleic acid encoding at least a fragment of a transmembrane domain, wherein the second nucleic acid fragment has at its 3′ terminus the nucleotide sequence CTACCACCCCCTTCCTGTCCAG (SEQ ID NO: 29) or TGACCACGCCAATCGTGTCCAG (SEQ ID NO: 14) or CTACCACGCCAATCGTGTCCAG (SEQ ID NO: 31).
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
A mutant gene of rice nuclease gene osgen-1 and its application
The invention relates to a mutant of a rice nuclease gene OsGEN-L and application thereof, which belong to the technical field of genetic engineering. In the mutant provided by the invention, the nuclease gene OsGEN-L is mutated into osgen-l, a nucleotide sequence of the normal OsGEN-L gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, and a nucleotide sequence of the mutant gene osgen-l of the OsGEN-L is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 4. The mutation is concretely characterized in that the first A base deletion after the 1053th bases of the OsGEN-L gene causes premature translation termination, and the mutation finally causes pollen sterility of the mutant, can be used for preparing recessive male sterile line, and plays an important role on genetic improvement, variety breeding and seed production of rice.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
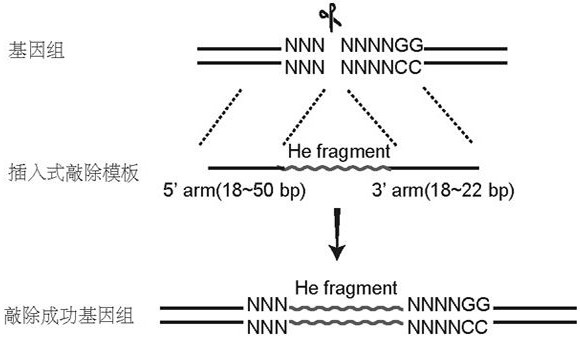
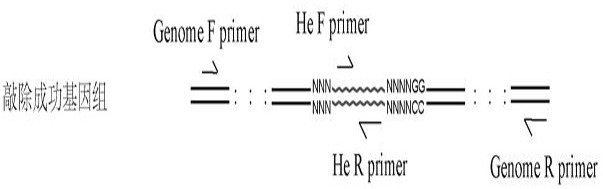
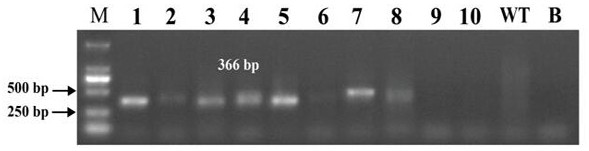
Method for realizing fixed-point insertion type knockout and identification in zebra fish genome
PendingCN112921037AImprove controllabilityImprove certaintyHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGuide RNA
The invention provides a method for realizing fixed-point insertion type knockout and identification in a zebra fish genome. Cas9 proteins are utilized, a genome targets specific guide RNA, and a universal type translation termination sequence with short homologous arms at two ends, the middle inserted in the zebra fish genome and without similar sequences is used for assistance, so that efficient, accurate, fixed-point and directional zebrafish genome insertion type knockout is realized. Besides, a specific primer for detecting the insert fragment is provided, so that the rapid detection of gene knockout is helped to be realized. According to the method, the problems of low efficiency, mutation randomness, difficulty in positive identification and the like of an existing random knockout method are solved.
Owner:福州百维斯生物科技有限公司
Method of designing multifunctional base sequence
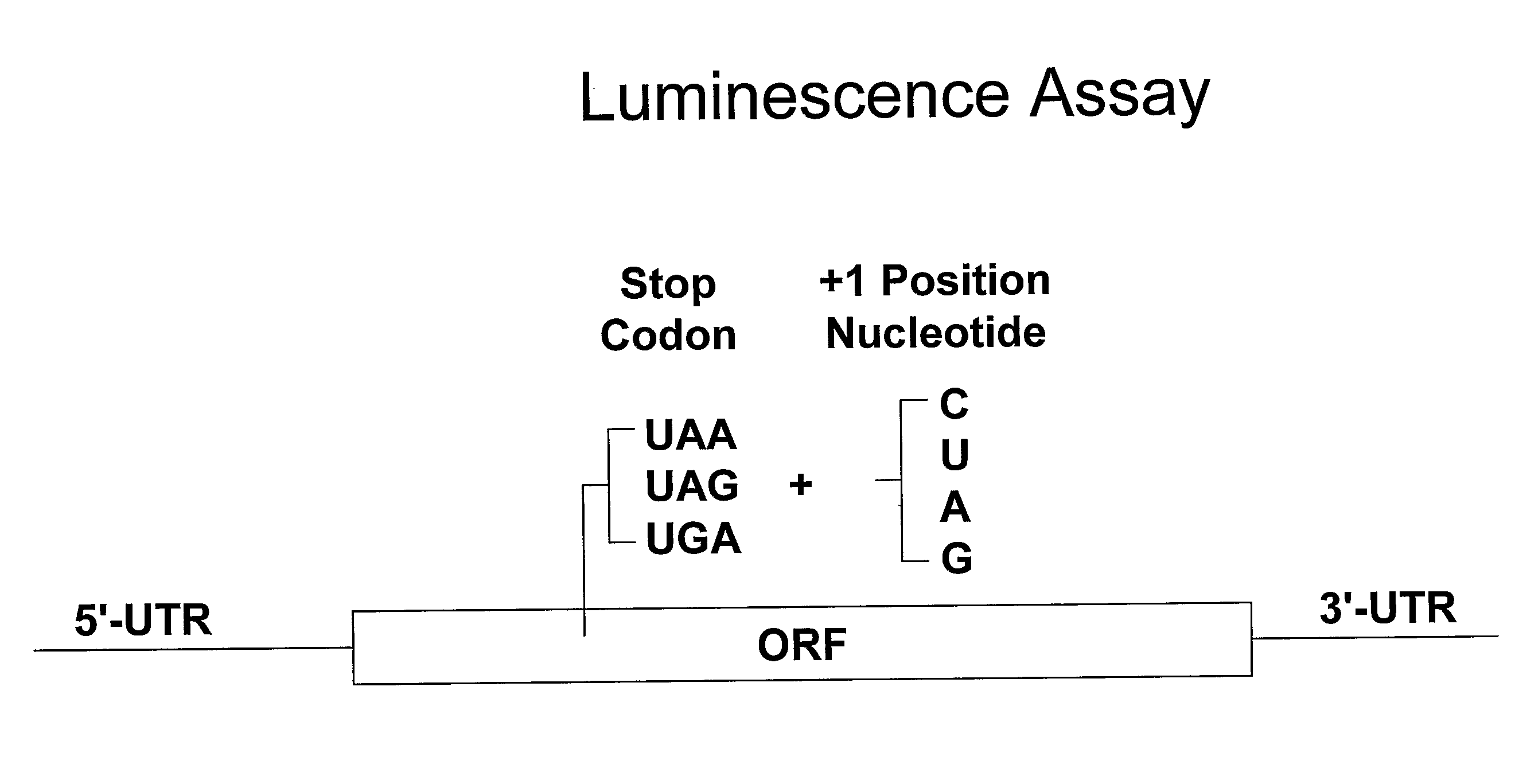
A multifunctional base sequence method largely shortens the calculation time and reduces the volume of memory consumption of a processor by carrying out calculation with the advance exclusion of base sequences in which translation termination codons emerge in the second and third reading frames, which are to be excluded in the end. Focusing on the fact that a dipeptide sequence already contains information about the translation products of the second and third reading frames, proteins are analyzed and calculated as duplicated connective products of dipeptide sequences, and are not analyzed as connective products of 20 kinds of amino acids.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD +1
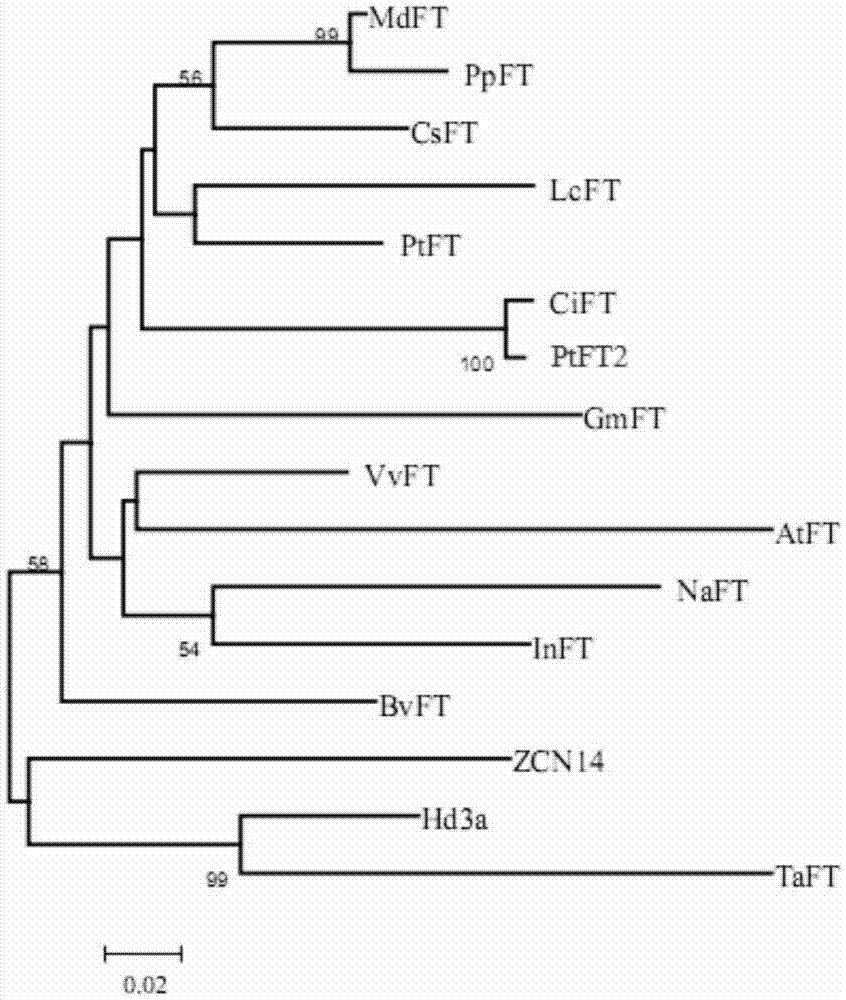
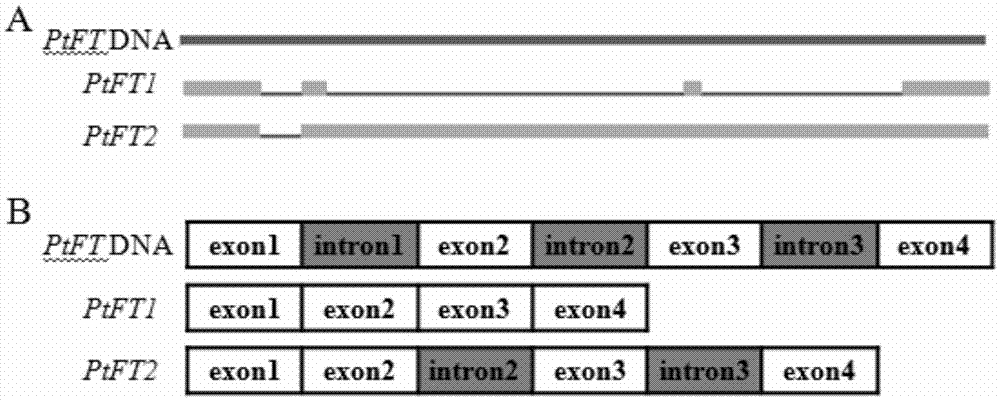
Precocious trifoliate orange flowering gene spliced variant PtFT2 and application of precocious trifoliate orange flowering gene spliced variant PtFT2 to regulating flowering of plants
InactiveCN107201369AShorten flowering timeShort childhoodPlant peptidesFermentationNicotiana tabacumNucleotide
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and in particular relates to the flowering gene PtFT2 of trifoliate trifoliate fruit and its application in regulating plant flowering. The present invention newly discovered a flowering regulatory gene PtFT2 from Trifoliate Fructus Trifoliate Fructus. Through gene isolation, structural analysis, cloning and functional verification, the PtFT2 gene was obtained from the RNA level for the first time. The gene PtFT2 is the spliced version of the PtFT1 gene. Compared with the genome, the excised version lacks the first intron in gene structure, and its translation terminates early after the second exon. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. Transforming tobacco with PtFT2 gene can obviously promote the flowering time of tobacco earlier, and the gene is expected to play an important role in shortening childhood and earlier flowering of perennial woody fruit trees.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Compounds for Nonsense Suppression, and Methods for Their Use
The present invention relates to methods, compounds, and compositions for treating or preventing diseases associated with nonsense mutations in an mRNA by administering the compounds or compositions of the present invention. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods, compounds, and compositions for suppressing premature translation termination associated with a nonsense mutation in an mRNA.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Improved method for selecting polypeptide producing cells
ActiveCN109790214APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifVectorsImmunoglobulin heavy chainNucleotide
Herein is reported a nucleic acid comprising in 5' to 3' direction i) a first nucleic acid fragment encoding a polypeptide of interest without an in frame translational stop codon, ii) a second nucleic acid fragment operably linked to said first nucleic acid fragment which is beginning with the 5' splice donor site of an 5 immunoglobulin heavy chain CH3 or CH4 domain and which is terminated by the3' splice acceptor site of the succeeding immunoglobulin heavy chain transmembrane domain exon M1 and which comprises in frame translational stop codon and a polyadenylation signal, and iii) a thirdnucleic acid fragment operably linked to said second nucleic acid encoding at least a fragment of a transmembrane 10 domain, wherein the second nucleic acid fragment has at its 3' terminus the nucleotide sequence CTACCACCCCCTTCCTGTCCAG (SEQ ID NO: 29) or TGACCACGCCAATCGTGTCCAG (SEQ ID NO: 14) or CTACCACGCCAATCGTGTCCAG (SEQ ID NO: 31).
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Acetylamino benzoic acid compounds and their use for nonsense suppression and the treatment of disease
ActiveUS7247741B2Promote readthroughDecreased amount of producedOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationDiseaseBenzoic acid
Novel acetylamino benzoic acid compounds, methods of using and pharmaceutical compositions comprising an acetylamino benzoic acid derivative are disclosed. The methods include methods of treating or preventing a disease ameliorated by modulation of premature translation termination or nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated therewith.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com