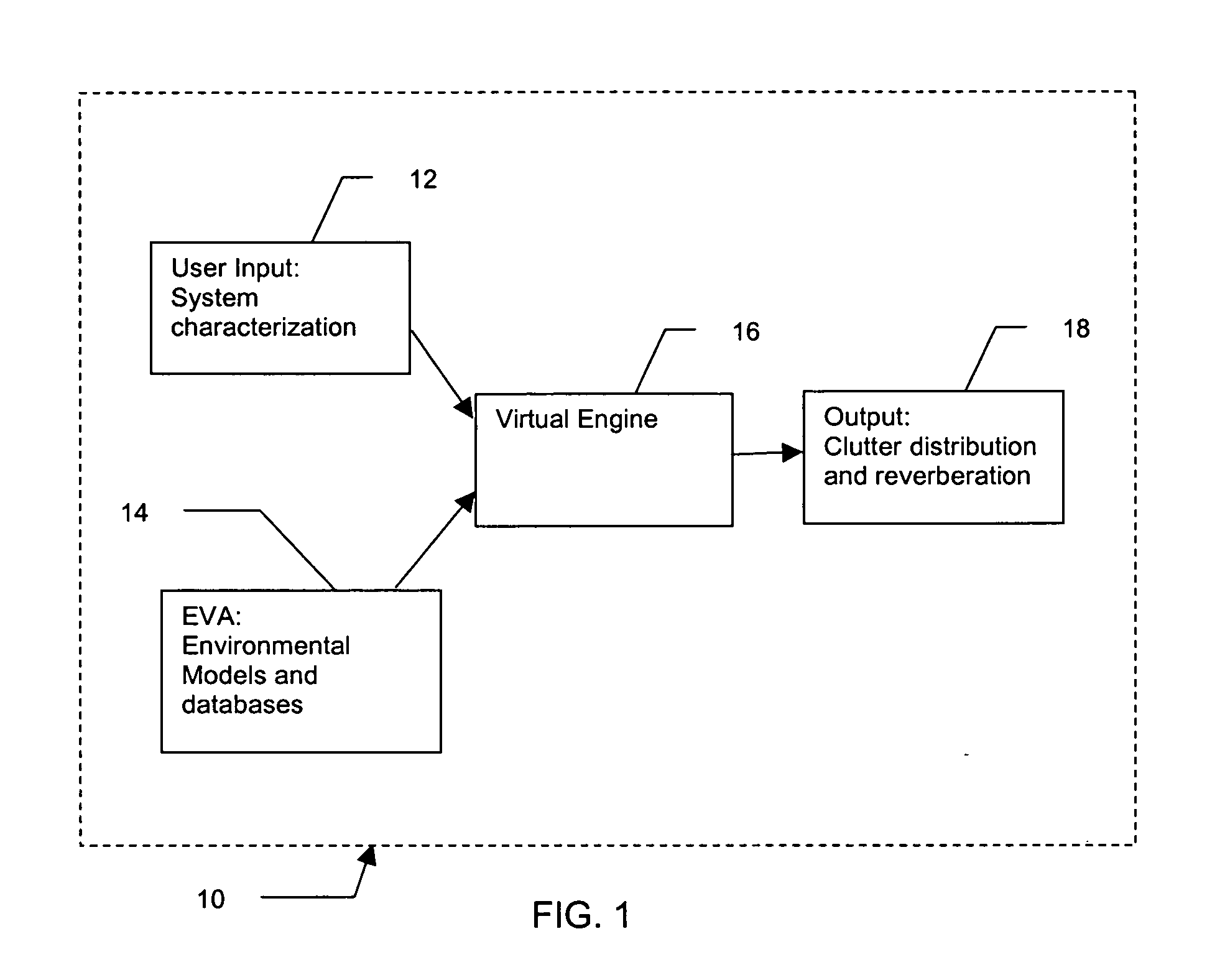
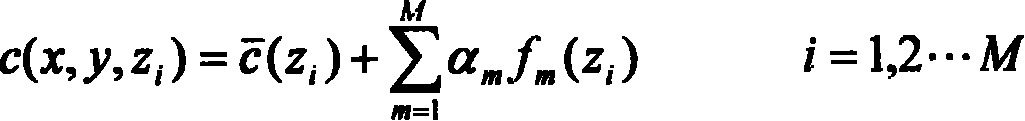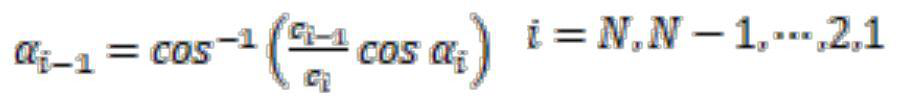Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
83 results about "Sound speed profile" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
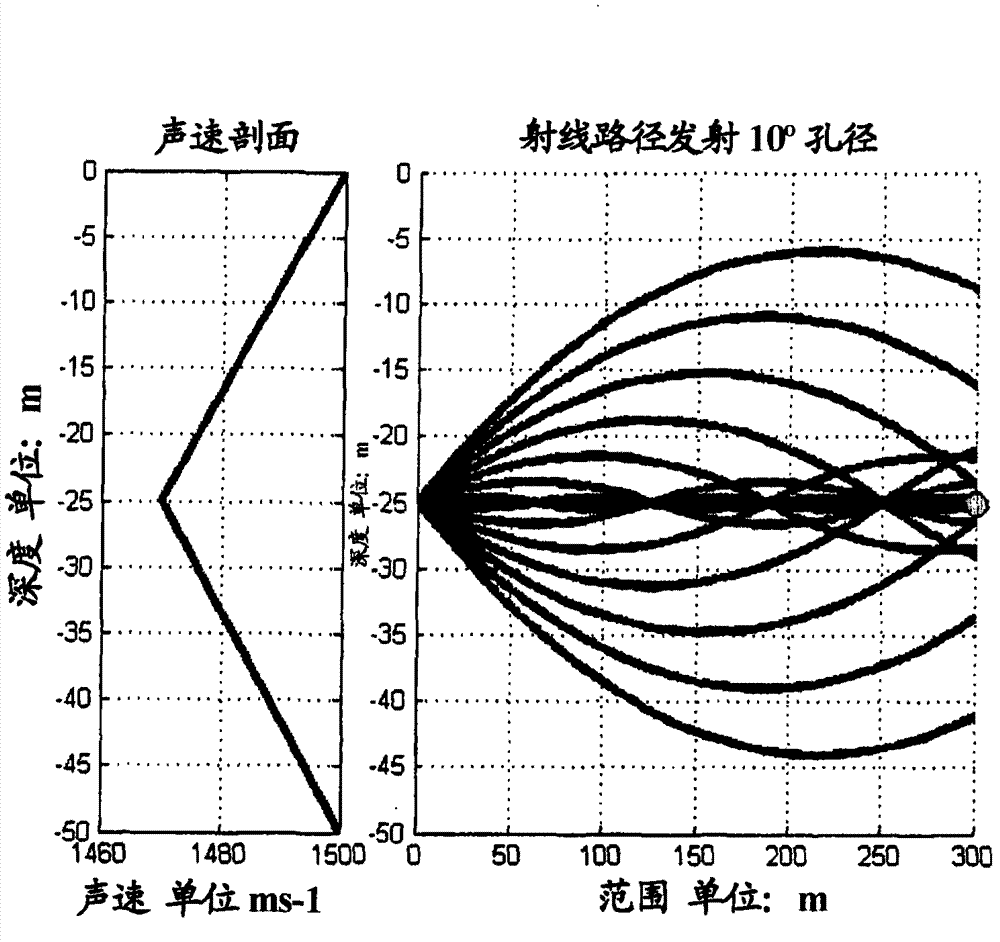
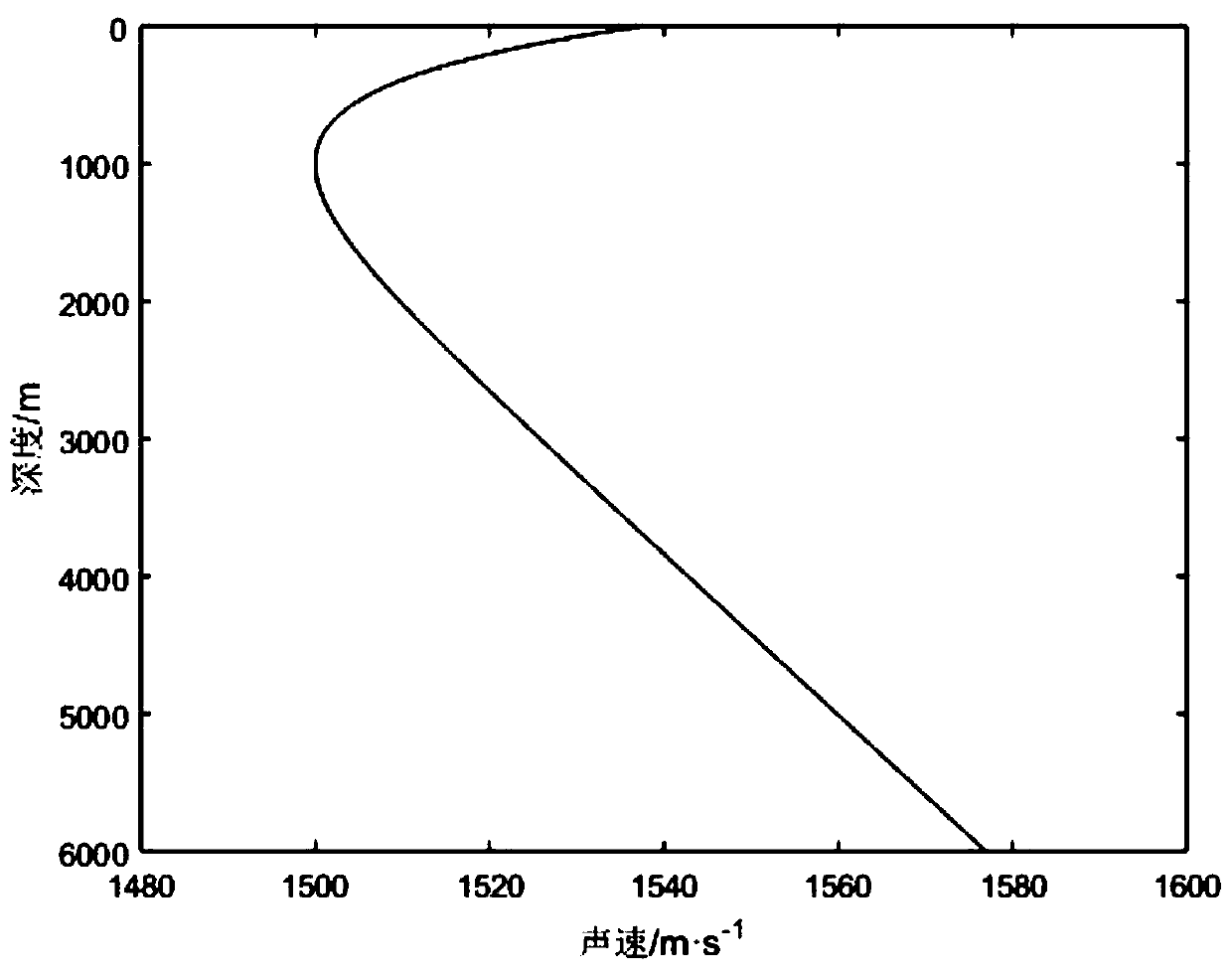
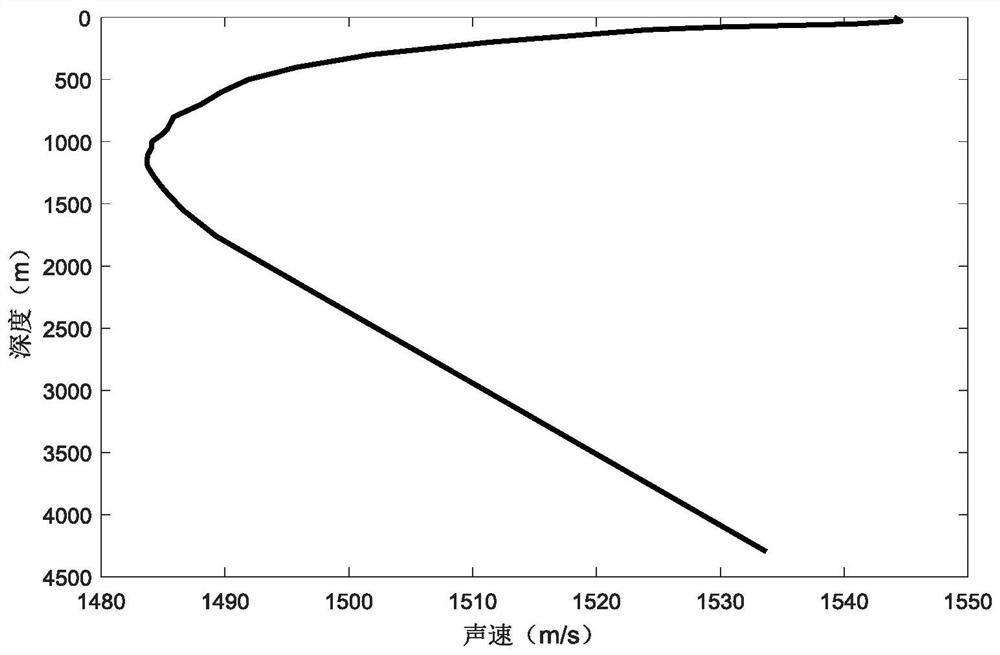
A sound speed profile shows the speed of sound in water at different vertical levels. Table 1 shows an example of the first representation; figure 1 shows the same information using the second representation.
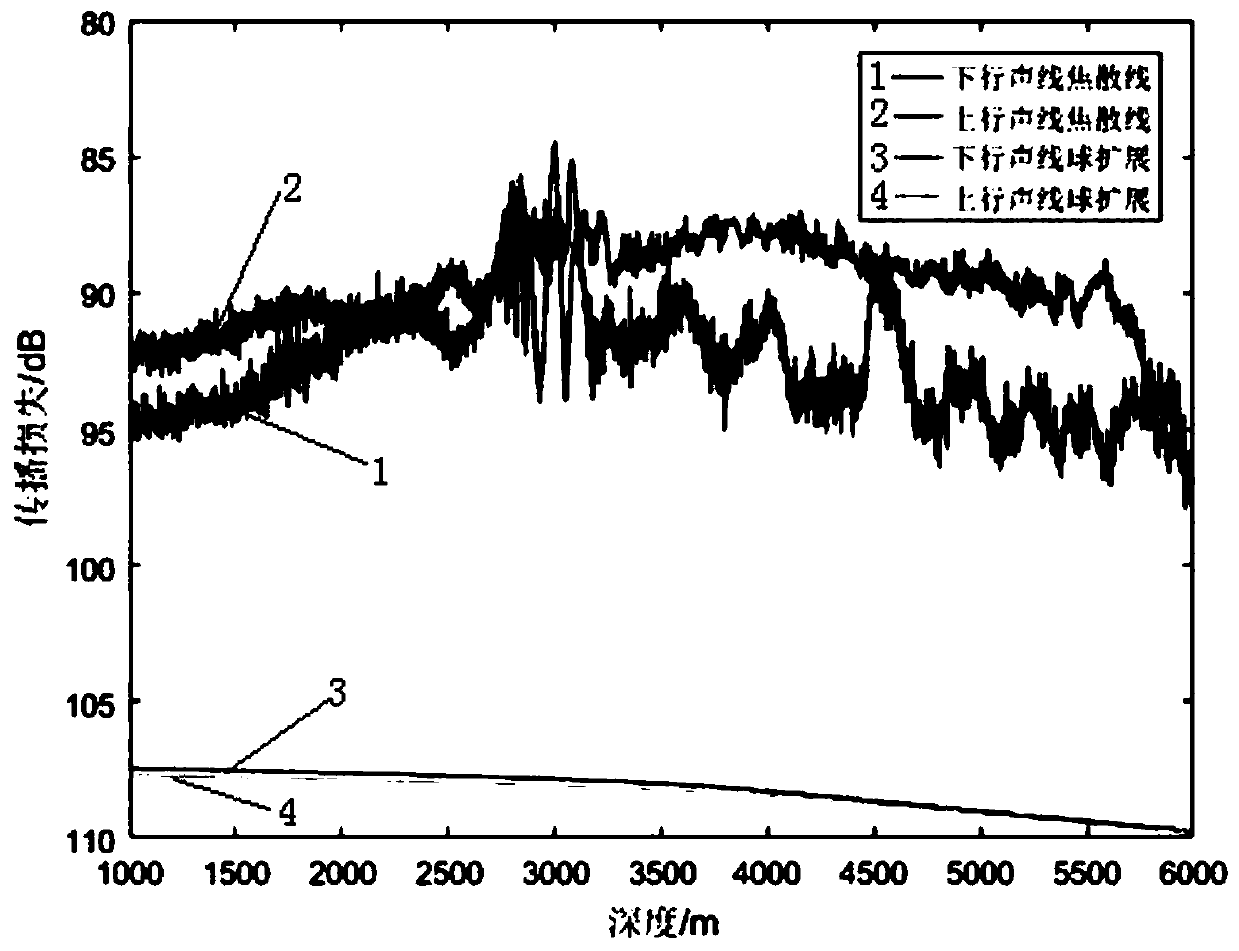
Deep sea multibeam sound ray accurate tracking method
InactiveCN106886024AHigh precisionHigh resolutionAcoustic wave reradiationSound speed profileTracking model
The invention discloses a deep sea multibeam sound ray accurate tracking method. The method mainly comprises the steps of (1) establishing a spatial and temporal variation ocean temperature and salinity field model on the basis of the comprehensive analysis of influence factors of sea surface temperature and salinity and with the integration of marine satellites and Argo buoy multiple-source marine physical hydrological observation data, (2) calculating each beam initial incident angle through analyzing the influence of a ship instantaneous attitude on a beam initial incident angle and considering a ship attitude, (3) calculating a sound speed and an inversion sound speed based on an empirical orthogonal function through the spatial and temporal temperature and salinity field at a sound speed profile no-measured area, obtaining the average value of sound speeds obtained by two methods at a corresponding point as the sound speed of the point, and thus calculating a three-dimensional sound speed profile model, (4) constructing an efficient constant gradient sound ray accurate tracking model, and (5) providing a sound ray tracking precision evaluation method. According to the method, the influence of the ship attitude on the beam initial incident angle is considered, the precision of beam footprint coordinates can be greatly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
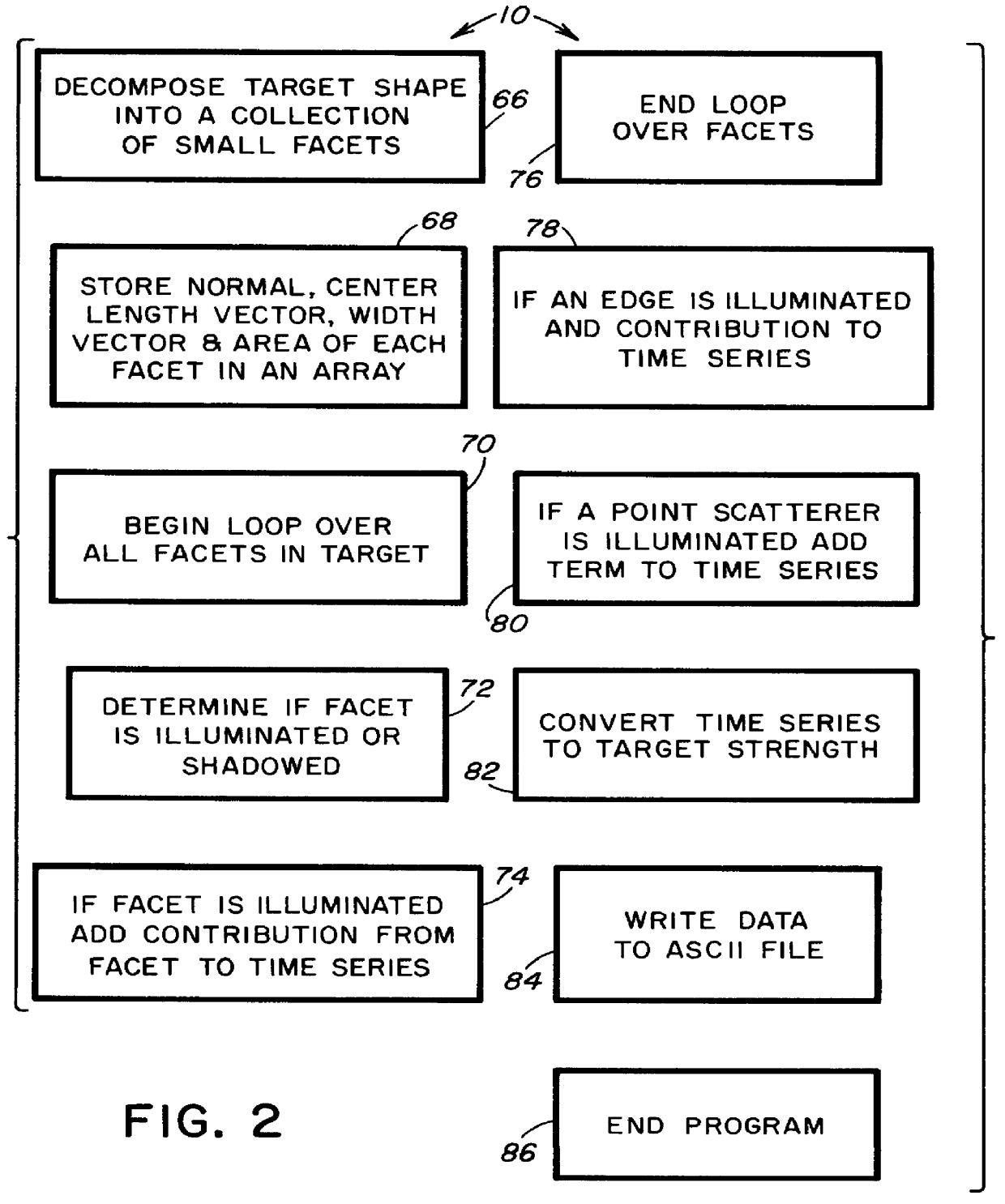
Computer-readable software and computer-implemented method for performing an integrated sonar simulation
InactiveUS6096085AWave based measurement systemsComputation using non-denominational number representationSonarBeam pattern
A computer-readable software stored on a storage medium and executed on a computer to perform an integrated sonar simulation, includes a parameter definition code for defining a plurality of parameters of a sonar, target and sonar environment, and a SNR computation code for computing a SNR of the sonar as a function of range to target, based upon the parameters defined by the parameter definition code. The parameters defined by the parameter definition code include ambient noise, volume scattering strength of the sonar environment, sound velocity profile of the sonar, beam patterns of both projector and receiver of the sonar, type of sonar, range resolution of the sonar, number of eigenrays striking the surface and bottom of the sonar environment, number of eigenrays striking the target, ray trajectories to the target, and surface and bottom scattering strength as a function of angle. The software also includes a target strength model generating code for computing scattering from a selected complex target of a stored set of complex target selections, to thereby generate a target strength model for the selected complex target.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
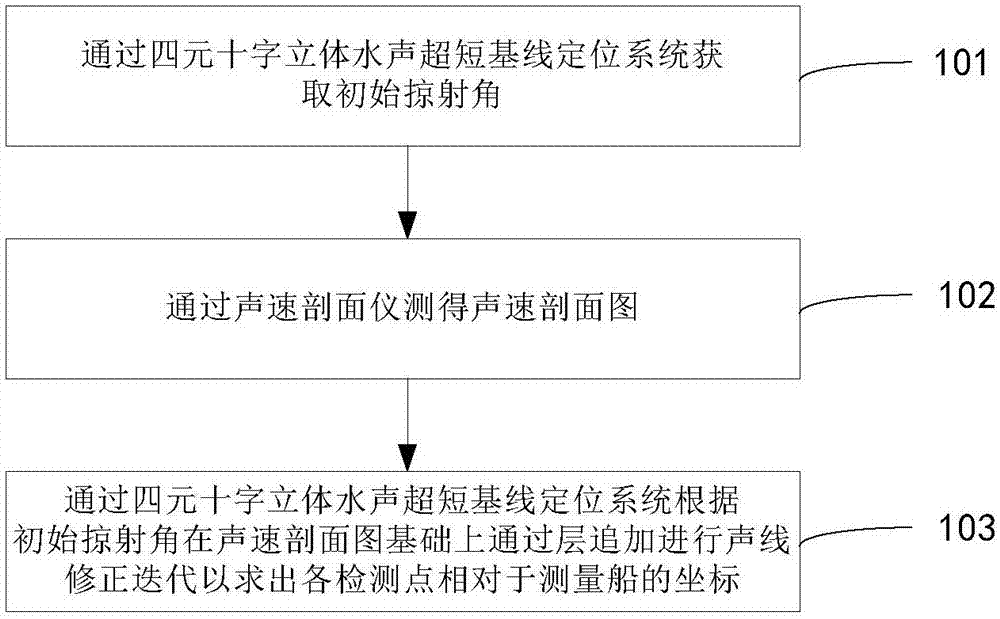
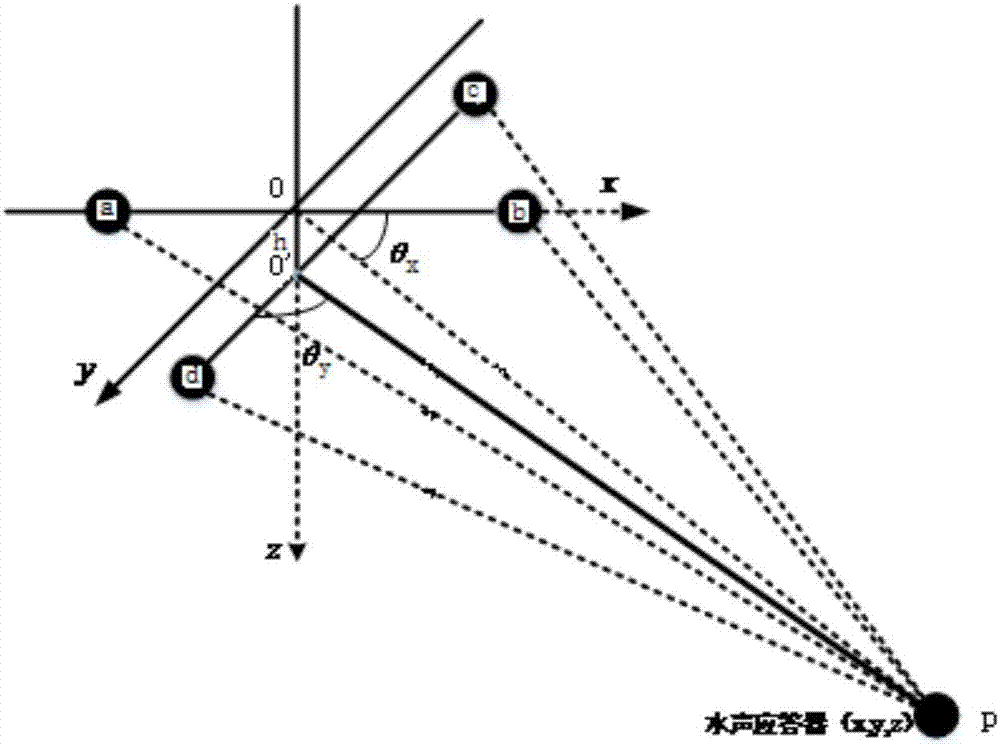
Sound ray correction method and system based on water sound ultrashort baseline positioning system
ActiveCN107132520AWide pointing opening angleThe positioning result is accurateWave based measurement systemsPhase differenceSelf adaptive
The invention provides a sound ray correction method based on a water sound ultrashort baseline positioning system. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining an initial glancing angle theta0 through a quaternary cross-shaped stereoscopic water sound ultrashort baseline positioning system; measuring the sound velocity profile through a sound velocity profiler; carrying out the sound ray correction iteration on the basis of the sound velocity profile in a mode of layer adding according to the initial glancing angle theta0 through the quaternary cross-shaped stereoscopic water sound ultrashort baseline positioning system, so as to solve the coordinates of each detection point relative to a measurement ship. According to the invention, the method obtains a phase difference estimation value according to a quaternary stereoscopic water sound ultrashort baseline array, and the iteration is carried out through employing an adaptive layered adding method, thereby solving the coordinates of each detection point relative to the measurement ship. Compared with a conventional mean sound velocity algorithm, the method greatly improves the range finding precision, effectively corrects a curved propagation path of sound rays in an underwater complex environment, and improves the underwater range finding and positioning precision of the water sound ultrashort baseline positioning system.
Owner:江苏中海达海洋信息技术有限公司
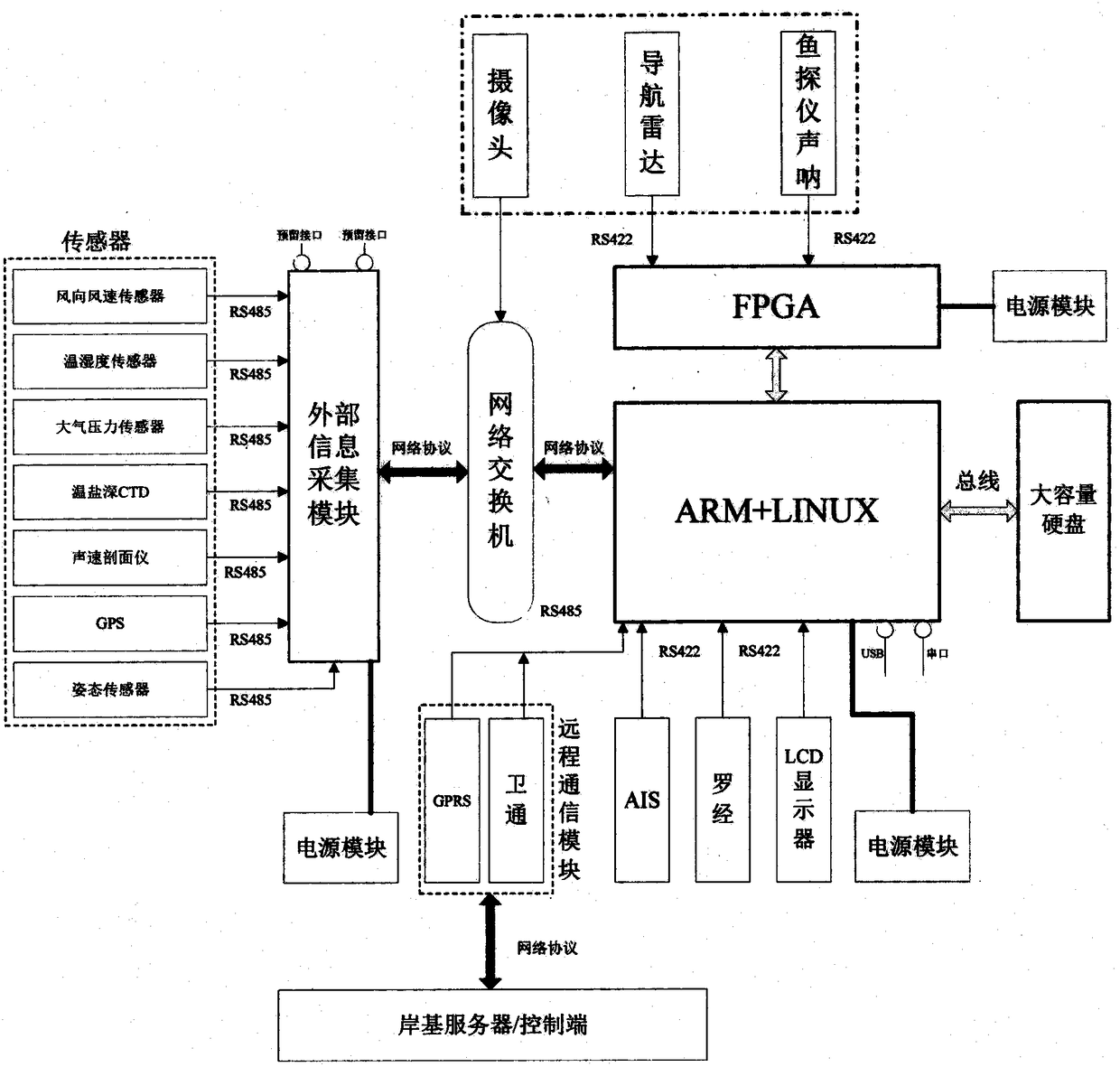
Onboard multivariate ocean information collection system
ActiveCN108540775AIncrease job securityImprove navigation safetyMeasurement devicesClosed circuit television systemsVideo monitoringCollection system
The invention discloses an onboard multivariate ocean information collection system, comprising two parts: a software part and a hardware part. The hardware part comprises an FPGA radar collection module, a fish detection sonar collection module, an AIS collection module, a system storage module, a display terminal, an external information collection module, satellite communication, a GPRS wireless module, a navigation radar, a single-beam (multibeam) fish detector, video monitoring, AIS, an aerovane, a temperature and humidity instrument, an atmospheric pressure sensor, a temperature and salinity profiler, a sound velocity profiler, a DGPS and an attitude sensor. The system has the beneficial effects that the fishing boat marine operation, sailing safety and fishery supervision capacity and efficiency are improved, the necessary manpower for ocean environment collection, landform investigation and ocean monitoring is greatly reduced, a practical engineering demand for maritime measurement and control can be satisfied, a technical gap is filled up, and the relatively high social benefits and economic benefits are produced.
Owner:宁波世纪海洋信息科技有限公司
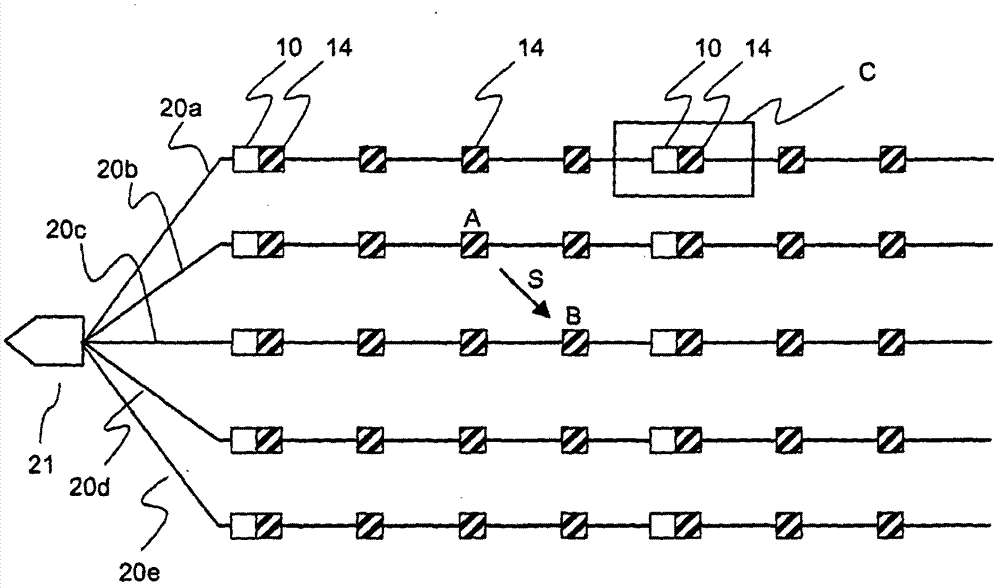
Method and device for estimating an inter-node distance between nodes arranged along towed acoustic linear antennas
InactiveCN103176210ABeacon systems using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesUsing reradiationSound speed profileComputer science
It is proposed a method for estimating an inter-node distance between a sender node (A) and a receiver node (B) belonging to a network comprising a plurality of nodes arranged along towed acoustic linear antennas (20a-20e), an acoustic signal being transmitted from the sender node to the receiver node through an underwater acoustic channel. The method comprises a step of estimating the inter-node distance as a function of an estimate of a sound speed profile of the underwater acoustic channel, said sound speed profile depending on depth.
Owner:SERCEL INC
Water column sound speed profiling system
InactiveUS6577557B1Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesVelocity propogationFree fallingSound sources
A system and method for determining a sound speed profile of a water column. A free falling sound source is deployed in the water at a known location and time. The sound source transmits acoustic pulses omnidirectionally therefrom at predetermined times after deployment. An acoustic receiver located at a known location detects each acoustic pulse. The time differential between each predetermined time and a time of arrival for each subsequent acoustic pulse is determined. Speed of sound for each portion of the water column is then determined as a function of the time differential, the known locations of sound source deployment and the acoustic receiver, and the known rate of descent of the sound source. The sound source can be constructed from a hydrodynamic body housing a power source, timing electronics, and spark gap electrodes. A bubble, generated by the spark gap electrodes, implodes to create the acoustic pulse.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Method and apparatus for active sonar performance prediction
InactiveUS20050286345A1Wave based measurement systemsSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionMathematical modelSound speed profile
A system and method for predicting active, low-frequency sonar array performance in shallow, littoral waters using a physics-based modeling of acoustic reverberation. An operator characterizes the active sonar's acoustic transmitter and receiver, the environment it is operating in and the targets to be detected. The operator selects appropriate bathymetry, bottom composition and sound-speed profile. The spatial resolution of the bathymetry database is enhanced using fractal interpolation and a bottom-loss-and-scattering corrected-for-slope is calculated. A semi-empirical scattering strength is derived from a wind-speed data base and a stochastic biologic realization is derived from a biologic population database. These are then used to calculate a deterministic component of bottom, surface and volume reverberation using a normal mode mathematical model of acoustic wave propagation. A stochastic realization of clutter is calculated using a Generalized Gamma distribution database, and combined with the deterministic components of reverberation.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Sound velocity profile inversion method based on empirical orthogonal function method
PendingCN113218493AImprove performanceImprove relevanceVibration measurement in fluidVelocity propogationSound detectionSound speed profile
The invention provides a novel method for inverting a sound velocity profile of a whole sea area by using sea surface height data, sea surface temperature data and feedback temperature data based on an empirical orthogonal function. The method comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring an Argo sound velocity profile and sea surface remote sensing data; s2, reconstructing the sound velocity profile based on an empirical orthogonal function; and s3, performing sound velocity profile inversion based on the sea surface parameters; the invention further provides a method for optimizing the regression relation by using the seawater layer temperature data with the poor inversion effect and application of the method. Compared with a previous inversion method based on EOF decomposition of a first mode, the method considers more modes, optimizes a sound velocity profile inversion method, improves the correlation between the sea surface data and each order of mode of the sound velocity profile, and improves the performance of the inversion method in each sea area. And a powerful basis is provided for applying inversion sound velocity profile data to the fields of underwater sound detection, marine environment monitoring, sonar performance evaluation and the like in the future.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Ocean sound velocity profile acquisition method based on self-organizing competitive neural network
PendingCN112598113AHigh precisionFully subdividedCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesSound speed profileAcoustics
The invention discloses an ocean sound velocity profile acquisition method based on a self-organizing competitive neural network, and relates to the field of ocean sound velocity profiles, which comprises the following steps: firstly, expressing a sample profile of a historical sound velocity profile as a form that average value is added to the orthogonal empirical function vector and then multiplied by the corresponding coefficient An of each order; processing the historical sea surface parameter Xn; forming a sample training vector by the An in the S1 and the historical sea surface parameterXn in the S2; training the sample set by adopting a self-organizing competitive neural network algorithm to form an artificial neuron topological structure; acquiring real-time sea surface parameters, inputting the real-time sea surface parameters into the neuron topological structure, and acquiring An corresponding to the real-time sea surface parameters; and finally, in combination with the historical average sound velocity profile, the EOF vector and the real-time EOF coefficient, expressing the sample profile as an An form to obtain a real-time ocean sound velocity profile. According to the method, the relation between the sound velocity profile contained in the sample data and the sea surface remote sensing parameters is mined through the artificial neural network, and the precisionof the obtained sound velocity profile can be improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
Sound velocity profile inversion method based on buoyage
InactiveCN1995932ASimple structureEasy to usePosition fixationVelocity propogationHydrophoneSound sources
The sound speed profile inversion method comprises using several buoys as signal receiving system each composed of a receiving matrix, floating cloth on the sea, receiving matrix connected below the buoy, receiving sound signal of the sound source through the receiving hydrophone, collecting and recording signal data, proceeding inversion method through the duration of the sound source transmitting to receiving matrix, optimizing the calculation through heritage method. It can get the sound speed profile quickly through inversion, with simple structures of the buoys.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Propagation time measurement method for direct signals based on autonomous underwater vehicles
ActiveCN109724684AReduce approximation errorVelocity propogationSound speed profileMeasurement point
The invention provides a propagation time measurement method for direct signals based on autonomous underwater vehicles. The invention comprises the steps of: determining a set of measurement time ofdirect signal propagation point in a known task area with to be measured sound speed; placing a sending underwater autonomous vehicle and a receiving underwater autonomous vehicle at the known task area with to be measured sound speed to measure propagation time of direct sound signals through a single-input-multiple-output double direction interaction communication mode; according to the propagation time of direct sound signals, acquiring a sound speed profile by adopting a sound speed profile inversion algorithm which based on a matched field processing technology; and carrying out measurement and sound speed profile inversion on each latitude and longitude coordinate point to construct a sound speed profile set according to the sound speed profile inversion algorithm which based on thematched field processing technology. The method has the advantages that influence of boundary parameter mismatch is reduced, and an approximate error of representing sound speed distribution of the whole area is avoided.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for quickly simplifying and automatically optimizing sound velocity profile based on maximum offset of sound velocity
ActiveCN103591942AWith artificial intelligenceComply with multi-beam detection accuracy requirementsSeismologyOpen water surveySound speed profileEngineering
The invention discloses a method for quickly simplifying and automatically optimizing sound velocity profile based on maximum offset of sound velocity (MOV), and provides detailed comprehensive technical process so as to solve the problem that the work efficiency of multi-beam detection and data processing is seriously influenced because the original sound velocity profile has large data quantity. An MOV method is provided and is used for deleting the redundant points of automatically and quickly and evaluating the influence of the simplified sound velocity profile on precision of multi-beam depth sounding through ray tracing and error analysis. According to actual tests, the simplification rate of the processed sound velocity profile reaches 90%, and the multi-beam footprint calculation requirement can be met by evaluating the precision of the sound velocity profile. By the method, multi-beam surveying and data processing time can be greatly reduced, and multi-beam work efficiency can be effectively improved by more than three times. The method has an important actual application value in the aspects of hydrographic surveying and charting, multi-beam surveying, a marine geographic information system, computer graphics, submarine science research and the like, and can be popularized and used.
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR
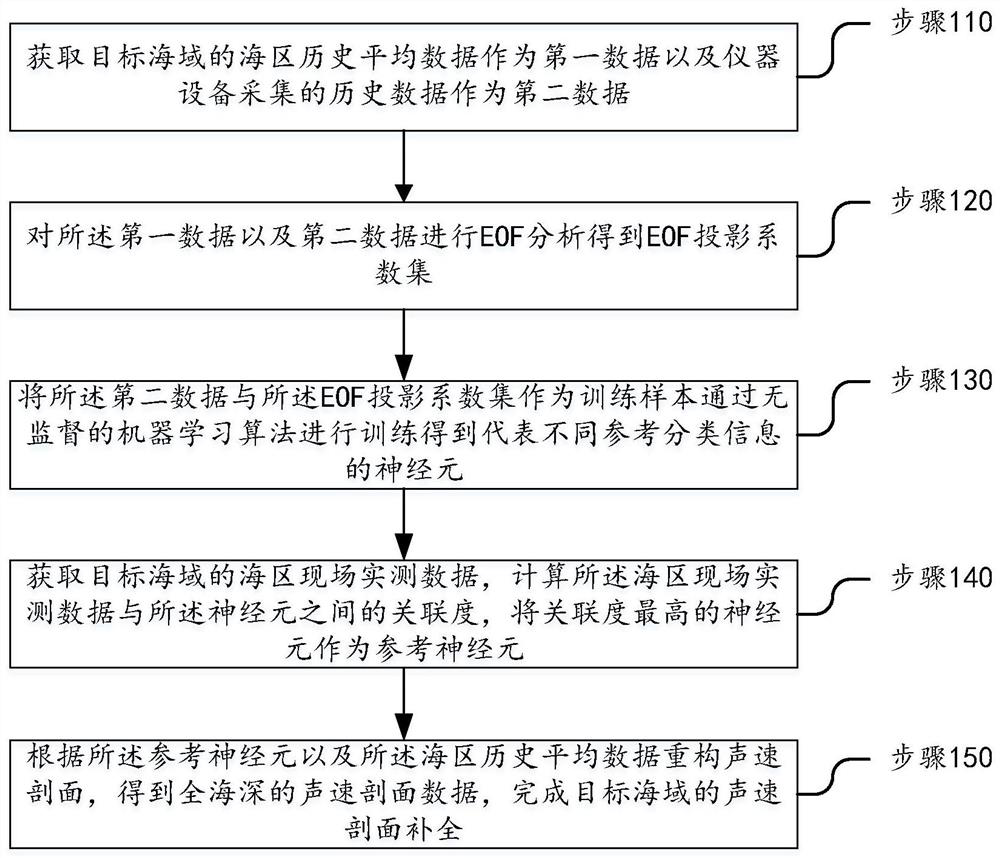
Sound velocity profile completion method and device based on historical data and machine learning
ActiveCN113486574AAccording to the law of disturbanceDesign optimisation/simulationNeural architecturesSound speed profileAcoustics
The invention relates to a sound velocity profile completion method based on historical data and machine learning. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining sea area historical average data of a target sea area as first data and historical data collected by instrument equipment as second data; performing EOF analysis on the first data and the second data to obtain an EOF projection coefficient set; taking the second data and the EOF projection coefficient set as training samples for training to obtain neurons representing different reference classification information; obtaining sea area field measured data of a target sea area, and calculating and obtaining a reference neuron with the highest correlation degree with the sea area field measured data; and reconstructing a sound velocity profile according to the reference neurons and the sea area historical average data, and completing sound velocity profile completion of the target sea area. The sound velocity profile reconstruction result established through the method conforms to the disturbance law, the reconstruction result not conforming to the reality is avoided, the characteristics of the small-time-scale sound velocity profile fine structure of the target sea area are included, and the complex disturbance state in the practical situation can be reflected.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
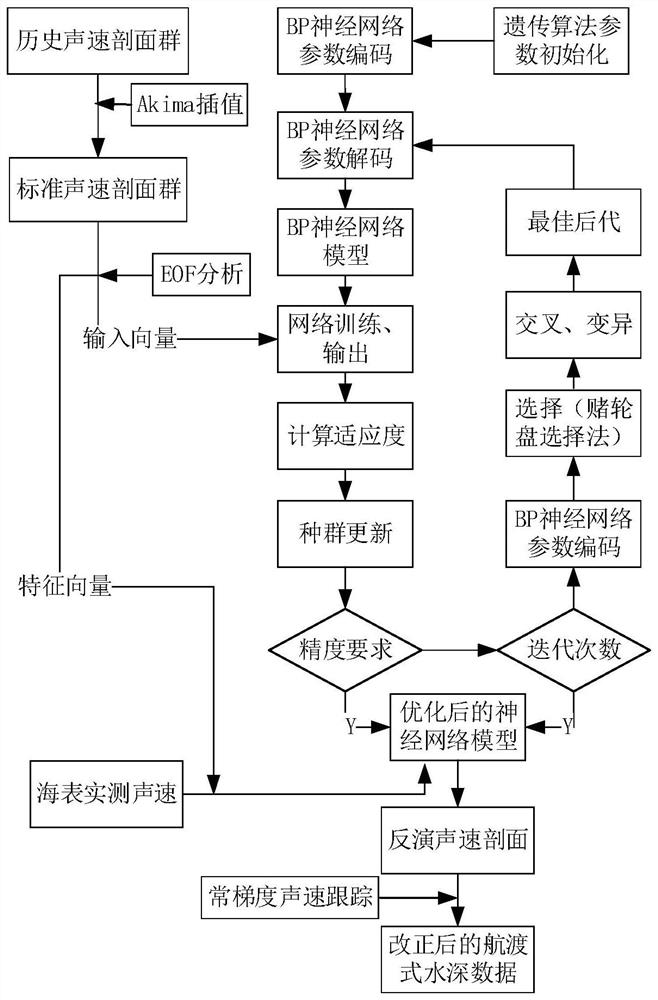
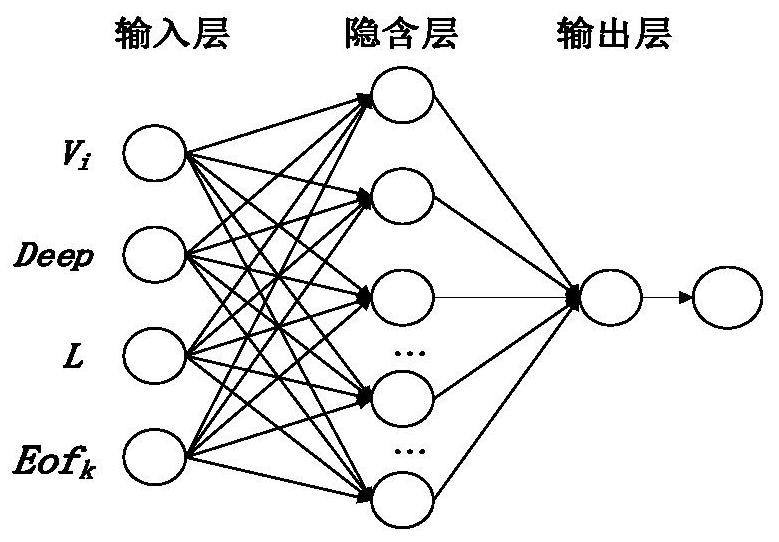
Flight-crossing type sounding data profile sound velocity correction method combining historical profile sound velocity and actually measured surface sound velocity
ActiveCN113191087AHigh precisionReduce the effect of sound velocity errorDesign optimisation/simulationNeural architecturesSound speed profileNetwork model
The invention provides a flight-crossing type sounding data profile sound velocity correction method combining historical profile sound velocity and actually measured surface sound velocity, and belongs to the technical field of marine surveying and mapping. The method comprises the steps: inputting historical water temperature, salinity and pressure data of a flight-crossing type deep sea measurement area, and calculating sound velocity profile data; carrying out vertical layering of the standardized sound velocity profile; carrying out EOF analysis on a standardized historical sound velocity profile group to obtain a reconstruction coefficient range and a feature vector; constructing a genetic algorithm to optimize a neural network model, and selecting a fitness function; inputting historical sound velocity profile data, and training the model; inputting the actually measured surface sound velocity, the position information, the depth and the feature vector into the trained model, and inverting a sound velocity profile; and carrying out sound velocity correction on the flight-crossing sounding data by adopting constant gradient sound ray tracking. According to the method, the defect that a high-precision sound velocity profile for sound velocity correction is lacked in the post-processing stage of the current flight-crossing type water depth data is overcome, the influence of sound velocity errors is weakened, and the precision of the flight-crossing type sounding data is improved.
Owner:PLA DALIAN NAVAL ACADEMY
Gain calculation method for caustic convergence region under deep sea complete sound channel based on ray normal mode theory
ActiveCN110968830AGain is efficiently obtained byComplex mathematical operationsICT adaptationSound speed profileNormal mode
The invention provides a gain calculation method for a caustic convergence region under a deep sea complete sound channel based on a ray normal mode theory. The gain calculation method is characterized in that under the deep sea complete sound channel condition, a typical deep sea Munk sound velocity profile situation is analyzed by using a ray normal mode theory, and then an expression of the sound pressure is obtained; the sound intensity is calculated according to the expression of the sound pressure; the average sound intensity value of the energy is calculated in the bandwidth of the 1 / 3octave of the central frequency; the average propagation loss value of the energy is calculated; the spherical wave propagation loss value at the caustics of the convergence region is calculated; andthe energy average propagation loss value is compared with the spherical wave propagation loss value, so that the gain value at the caustic convergence region is solved, and the result proves that thegain calculation method provided by the invention has a very good effect.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method and apparatus for active sonar performance prediction
InactiveUS7002877B2Wave based measurement systemsSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionWater useMathematical model
A system and method for predicting active, low-frequency sonar array performance in shallow, littoral waters using a physics-based modeling of acoustic reverberation. An operator characterizes the active sonar's acoustic transmitter and receiver, the environment it is operating in and the targets to be detected. The operator selects appropriate bathymetry, bottom composition and sound-speed profile. The spatial resolution of the bathymetry database is enhanced using fractal interpolation and a bottom-loss-and-scattering corrected-for-slope is calculated. A semi-empirical scattering strength is derived from a wind-speed data base and a stochastic biologic realization is derived from a biologic population database. These are then used to calculate a deterministic component of bottom, surface and volume reverberation using a normal mode mathematical model of acoustic wave propagation. A stochastic realization of clutter is calculated using a Generalized Gamma distribution database, and combined with the deterministic components of reverberation.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Underwater pulse acoustic positioning system based on multi-acoustic wave glider and water surface unmanned boat
ActiveCN110703202AEasy and smooth communicationImprove communication efficiencyPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingMarine engineeringUnderwater
The invention provides an underwater pulse acoustic positioning system based on a multi-acoustic wave glider and a water surface unmanned boat, and relates to the technical field of underwater positioning. In order to solve the problem of communication difficulty in the underwater pulse acoustic positioning based on the multi-acoustic wave glider in the prior art, the underwater pulse acoustic positioning system provided by the invention implements local positioning networking of the multi-acoustic wave glider, determines the number of AWGs and designs an optimal formation of AWGs and USV according to a sea depth, a sound velocity profile and a positioning area required for a task, and monitors and controls the formation of the AWGs through the USV, meanwhile maintains the USV at the central positions of the AWGs to ensure easy and smooth communication, and furthermore, the communication efficiency is high.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Application of sound ray correction algorithm based on spatial scale in long baseline underwater acoustic positioning system
PendingCN112540348AReduce calculation iterationsFast operationPosition fixationAlgorithmSound speed profile
The invention relates to a sound ray correction method, in particular to application of a sound ray correction algorithm based on a spatial scale to a long baseline underwater acoustic positioning system. By knowing the depths of a transponder and an underwater target, according to the vertical distance simplification principle, the sound velocity profile is simplified, redundant repeated data which can generate interference are abandoned, data which are obvious in change and have calculation value are reserved, calculation iteration of sound ray correction is greatly reduced, rapid simplification operation is achieved, and the data processing efficiency of sound ray tracking is obviously improved. The simplified sound velocity profile is layered on the spatial scale, and the non-uniform spatial distribution of seawater is further considered, so that the method is more in line with the actual scene.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Sound velocity profile inversion method based on over-complete dictionary
ActiveCN110837791AHigh precisionFlexible training dataCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsSound sourcesAlgorithm
The invention discloses a sound velocity profile inversion method based on an over-complete dictionary, and the method comprises the steps: 1), constructing a non-orthogonal and over-complete dictionary D of a sound velocity profile based on a K-SVD algorithm according to historical data; 2) linearizing the nonlinear response of the forward model by using a first-order Taylor expansion, and creating a measurement matrix Q; 3) laying a single sound source and a vertical array in a sea area to be measured, and transmitting and receiving signals; 4) based on an OMP algorithm, inverting a sparse coefficient vector X of the over-complete dictionary atoms; and 5) calculating the sound velocity profile according to the time-varying non-orthogonal dictionary atomic coefficient obtained by inversion. Compared with a method based on an empirical orthogonal function, the method is based on an over-complete dictionary, the intrinsic characteristics of the sound velocity profile can be better captured through redundancy characteristics, and the inversion precision of the sound velocity profile is greatly improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
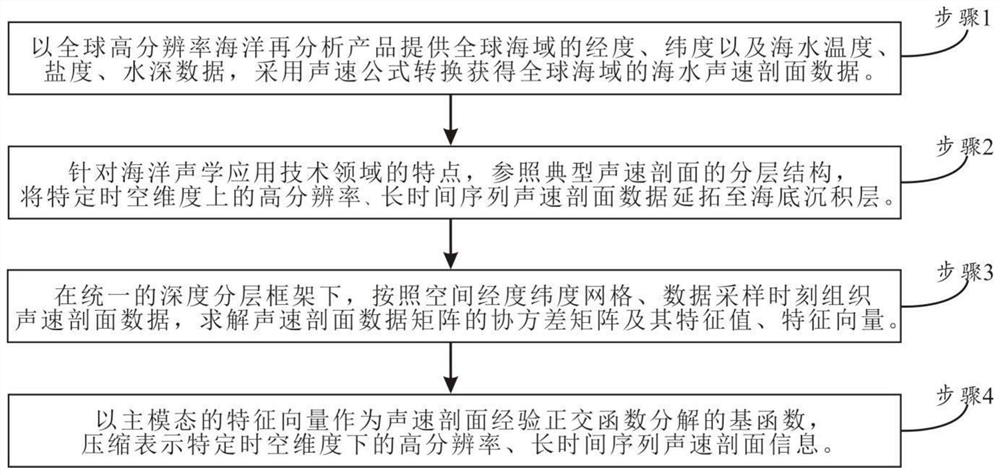
High-resolution sound velocity profile data compression method based on empirical orthogonal function decomposition
ActiveCN113051260AHigh resolutionEasy to implement electronicallyRelational databasesGeographical information databasesData compressionSound speed profile
The invention belongs to the technical field of marine acoustics application of three-dimensional temperature-salinity-depth data, and particularly relates to a high-resolution sound velocity profile data compression method based on empirical orthogonal function decomposition. The method specifically comprises the following steps of providing data by using a high-resolution marine reanalysis product, and converting by using a sound velocity formula to obtain the seawater sound velocity profile data; according to the characteristics of the technical field of marine acoustics application, extending the high-resolution and long-time sequence sound velocity profile data under a certain space-time dimension to a seabed sedimentary layer; using a feature vector of a main mode as a primary function of the sound velocity profile empirical orthogonal function decomposition, and compressing and expressing the high-resolution and long-time sequence sound velocity profile information under the certain space-time dimension. According to the invention, the technical scheme of obtaining sound velocity profile data compression from a high-resolution ocean reanalysis product is realized; the effective compression of the sound velocity profile data under the certain time-space dimension is realized, and the beneficial effect that the compression rate of the high resolution and long-time sequence sound velocity profile data is more than 90%, is obtained.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Marine sound velocity profile classification method and device based on machine learning
PendingCN114782745AImplement classificationPrevent deviationCharacter and pattern recognitionMachine learningPrincipal component analysisOriginal data
The invention relates to an ocean sound velocity profile classification method based on machine learning, and the method comprises the following steps: obtaining sound velocity original data of a target classification region, carrying out the preprocessing of the sound velocity original data, interpolating the sound velocity data to a standard depth point, and obtaining a to-be-classified sample set; converting the to-be-classified sample set into a sound velocity anomaly matrix; performing principal component analysis on the sound velocity anomaly matrix to obtain a projection coefficient set; and performing sound velocity profile classification on the target classification region according to the projection coefficient set. According to the method, space grids do not need to be preset in classification, and standard deep processing grids are adopted in the vertical direction, so that deviation of a classification result due to artificial grid setting is avoided; the amplitude of the disturbance mode of the whole section is taken as an input vector to reflect the disturbance characteristics of the whole section, and the amplitude value of the mode is taken as the characteristic quantity to be extracted more simply; according to the invention, the classification of the ocean sound velocity profile of the target classification area can be rapidly and effectively realized.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
Ocean front reconstruction method based on K-means algorithm iterative hierarchical clustering of sound velocity profiles
ActiveCN114004300AImplement refactoringImplement accuracy verificationCharacter and pattern recognitionICT adaptationCluster algorithmSound speed profile
The invention belongs to the fields of physical ocean, ocean technology, underwater acoustic engineering and the like, and particularly relates to an ocean front reconstruction method based on K-means algorithm iterative hierarchical clustering of sound velocity profiles, and the method uses the K-means algorithm to perform hierarchical clustering on the sound velocity profiles of an ocean front sea area according to a hierarchical principle. Compared with other clustering algorithms, the method is simple in thought, high in convergence speed, good in clustering effect and capable of meeting the clustering requirement when a large number of sound velocity profiles exist in the ocean front sea area. And the accuracy of the clustering result can be verified through the calculation of the sound propagation loss, and the iterative optimization is provided for the hierarchy according to the error threshold until all the hierarchical clustering results meet an allowable error threshold, and finally the ocean front reconstruction based on K-means algorithm iterative hierarchical clustering of sound velocity profiles is realized.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
OBS precise positioning method based on acoustic ranging and multi-beam terrain
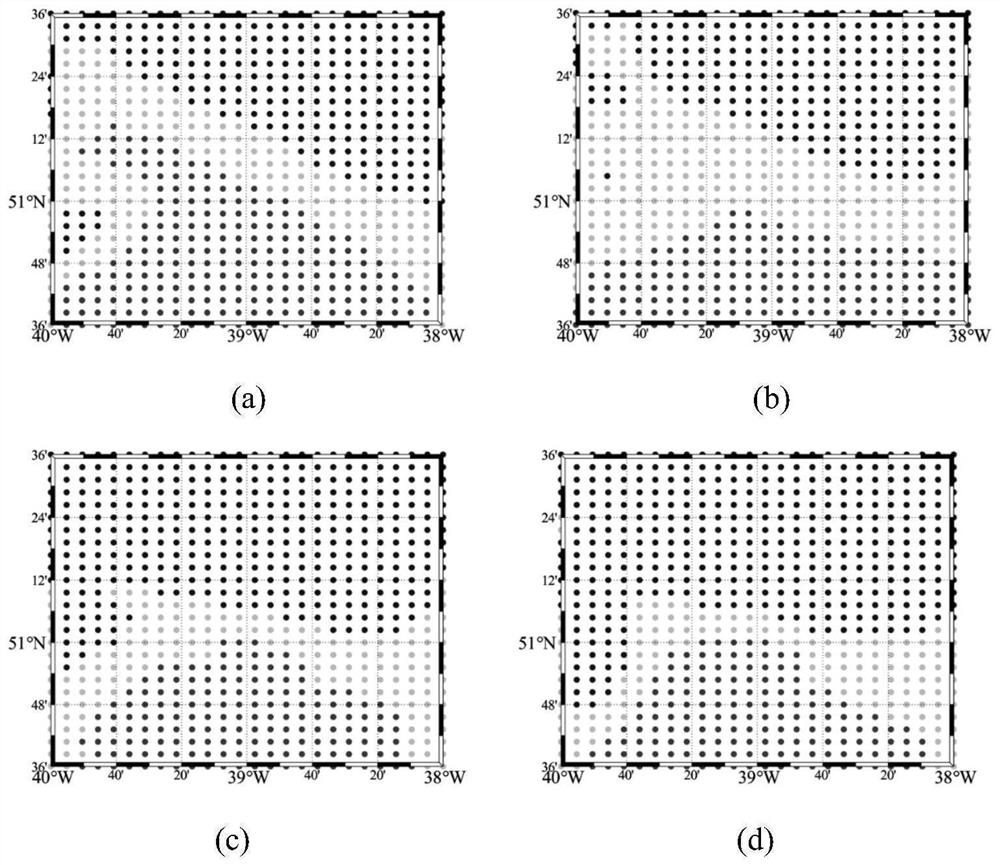
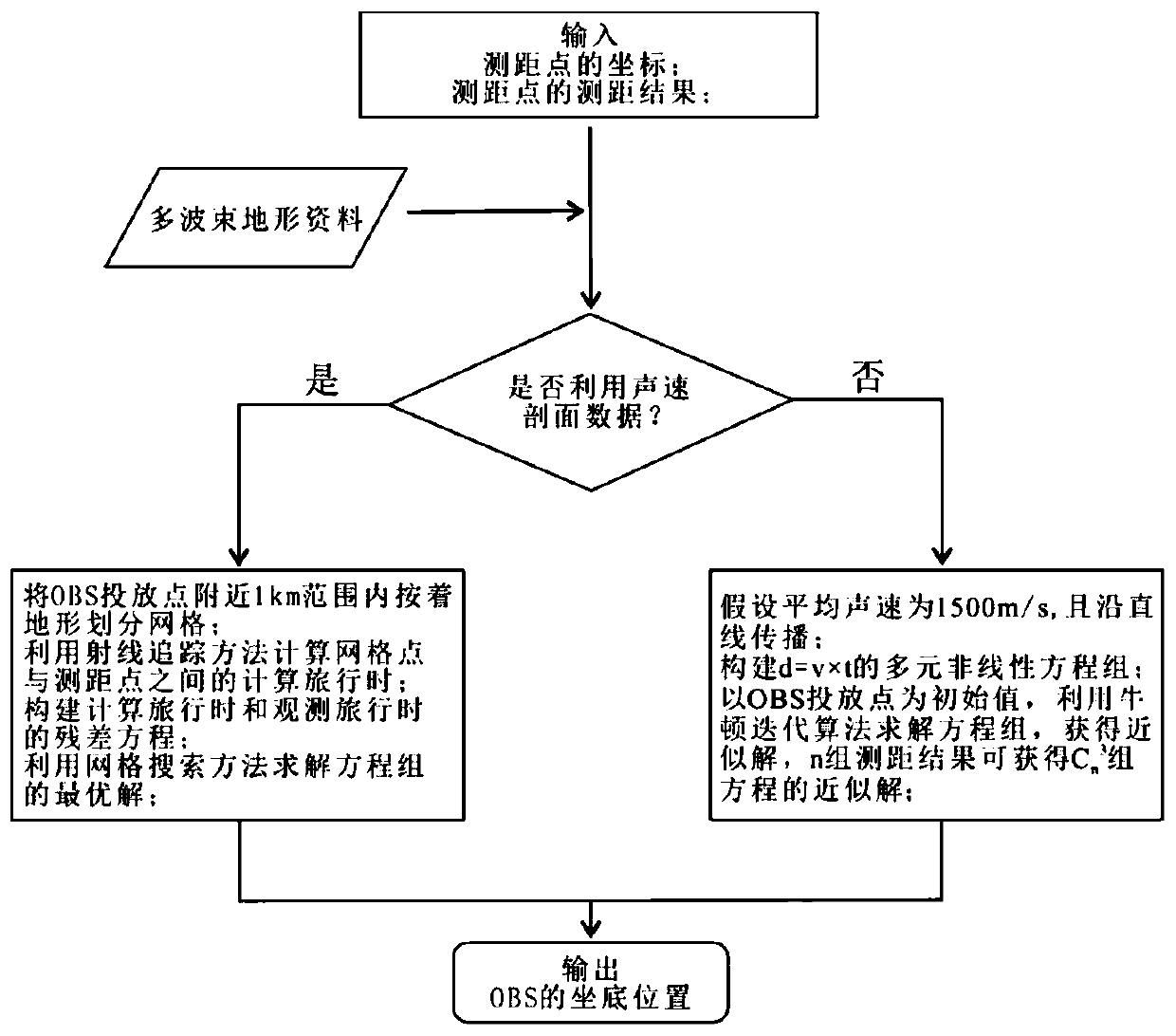
ActiveCN110824551APrecise positioningTroubleshoot calibration issuesSeismic signal receiversTerrainSound speed profile
The invention discloses an OBS precise positioning method based on underwater acoustic ranging and multi-beam terrain. Firstly, an acoustic communication machine is used to measure the distance of theOBS within the effective range of the OBS delivery point; when the sound velocity profile is not considered, the nonlinear equations are constructed by the relationship between the slant distance from the OBS to the ranging point and the travel time, and the bottom position of the OBS is obtained by solving the equations with Newton iterative algorithm; when the sound velocity profile is considered, the multi-beam seabed terrain near the OBS delivery point is gridded, according to the sound velocity profile, the calculated travel time between each grid point and the ranging point is calculated by using the ray tracing method, and the residual equations for calculated travel time and observed travel time between OBS and each ranging point are constructed; the grid search method is used tosolve the optimal solution of the residual equations, that is, the bottom position of the OBS. The method of the invention has the characteristics of simple operation, time-saving and accurate calculation, and realizes the accurate positioning of the OBS seabed for free falling body dropping.
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR
Target detection method in deep sea incomplete sound channel
PendingCN112526589ATarget detection facilitatesAcoustic presence detectionHydrophoneSound speed profile
The invention provides a target detection method in a deep sea incomplete sound channel, and relates to the technical field of submarine incomplete sound channel underwater acoustic detection, and themethod comprises the steps: obtaining the relation between the sound ray horizontal distance and depth under a specific sound velocity profile based on a ray simple positive wave, and enabling a marine environment to be an incomplete sound channel, i.e., the submarine sound velocity is smaller than the sea surface sound velocity; according to the determined relationship between the sound ray horizontal distance and the depth, obtaining a point of a sound ray minimum value position, and determining the position of a lower reversal point convergence area; selecting a plurality of hydrophones toform a multi-element vertical receiving array, arranging the multi-element vertical receiving array in a lower reversal point convergence area, and detecting a long-distance target to obtain a detection signal; and determining whether the detection target exists or not according to a detection signal obtained by detecting the long-distance target. According to the invention, large-depth arrayingis carried out in an incomplete sound channel by using the lower inversion point convergence region, so that the detection of a target is realized.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Sound Velocity Profile Streamlining and Optimization Method Based on Maximum Offset of Velocity
InactiveUS20150124561A1Reduce computing timeImprove work efficiencySeismic signal processingSound speed profileComputer graphics
The invention discloses a sound velocity profile (SVP) streamlining and optimization method based on maximum offset of velocity, and provides detailed comprehensive technical process so as to solve the problem that the work efficiency of multi-beam detection and data processing are seriously influenced because the original sound velocity profile has a large data quantity. An MOV method is provided and is used for deleting the redundant points automatically and quickly, and for evaluating the influence of the streamlined sound velocity profile on precision of multi-beam sounding through ray tracing and error analysis. The method has an important actual application value in the aspects of marine surveying and charting, multi-beam surveying, a marine geographic information system, computer graphics, submarine science research and the like, and can be popularized.
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR
Method for carrying out EOF analysis by using improved Argo buoy data
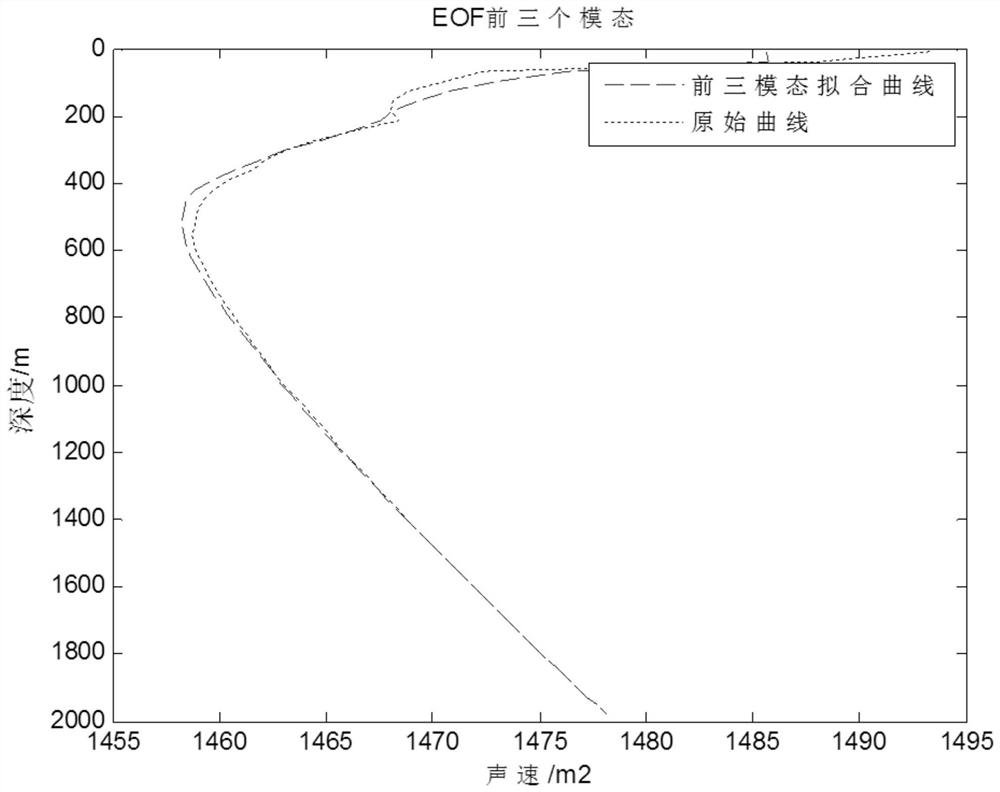
The invention relates to the technical field of ocean underwater acoustic modeling, in particular to a method for performing EOF analysis by using improved Argo buoy data, which comprises the following steps: decomposing a certain number of acoustic velocity profile sample sequences into orthogonal space vectors and time vectors by using an EOF analysis method; and generally, any section in the sequence can be reconstructed more accurately only by using the first few modes, so that the parameters required for describing the vertical structure of the sound velocity section are greatly reduced by the processing method. In the research in recent years, many scholars prove the effectiveness and feasibility of the method to a certain extent, and propose that the EOF function is the most effective function for describing the sound velocity profile.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Rock breaking construction method of underwater deep foundation trench
InactiveCN112227296AAdaptableStrong implementation precisionSoil-shifting machines/dredgersStream regulationDetonatorSound speed profile
The invention relates to a rock breaking construction method of an underwater deep foundation trench. The method comprises the following steps that the depth and sound velocity profile information ofa dredging construction area is determined; a construction ship accurately positions the dredging construction area through a positioning system; the construction ship excavates the soil covering layer of the dredging construction area; the rock distribution condition of the dredging construction area is determined through secondary measurement; rock drilling points and the number of times of rockdrilling are set, and rock breaking construction is conducted through a rock breaking hammer; broken rock is removed; and the dredging construction area is measured, and if the measurement result meets the acceptance standard, construction of the dredging construction area is finished. According to the method, rock breaking treatment can be conducted on rock of an underwater deep trench foundation bed, the adaptability is high, the method can be applied to treatment construction of rock strata with various strengths and large water depth, the implementation precision is high, the implementation process does not relate to use of detonators and explosives, the influence on the surrounding environment is small, environmental protection is achieved, the operation process is safe and reliable,and the popularization value is extremely high.
Owner:CCCC GUANGZHOU DREDGING
Seabed sonar reference beacon positioning method and device and seabed positioning system
PendingCN112946574AHigh precisionReduce the impact of errorsPosition fixationSonarSound speed profile
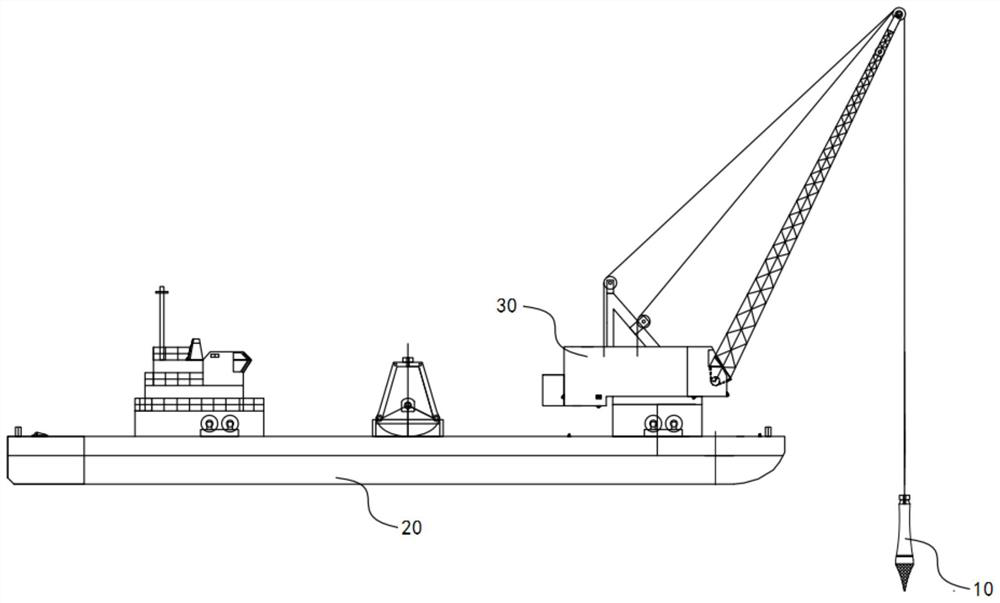
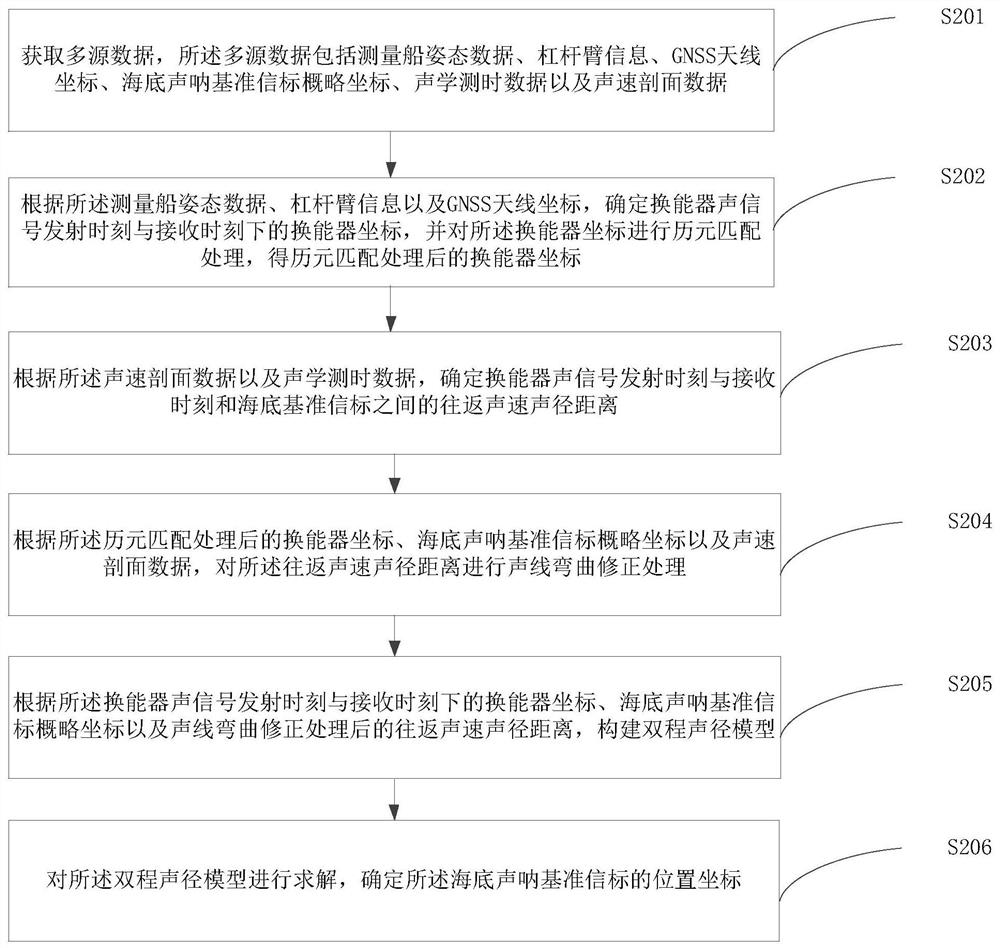
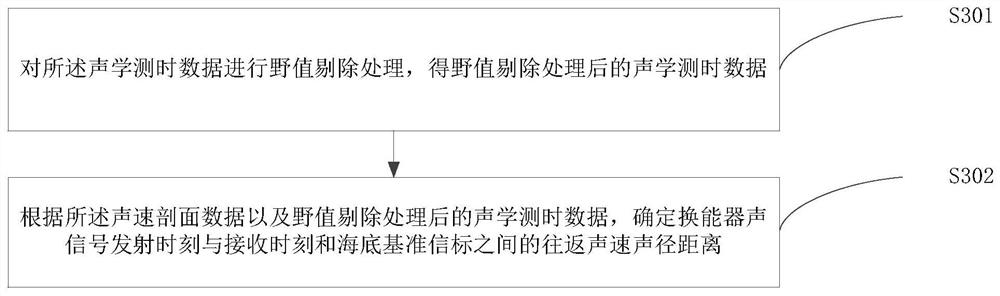
The invention is applicable to the technical field of sonar, and provides a seabed sonar reference beacon positioning method and device and a seabed positioning system, and the method comprises the steps: determining the coordinates of a transducer according to the attitude data of a measurement ship, the information of a lever arm and the coordinates of a GNSS antenna, and carrying out the epoch matching processing; according to the sound velocity profile data and the acoustic time measurement data, determining a back-and-forth sound velocity sound path distance between a transducer sound signal transmitting moment and a transducer sound signal receiving moment and the seabed reference beacon; according to the coordinates of the transducer, the approximate coordinates of the seabed sonar reference beacon and the sound velocity profile data, carrying out sound ray bending correction processing on the back-and-forth sound velocity sound path distance; and constructing a two-way sound path model to position the seabed sonar reference beacon according to the coordinates of the transducer, the approximate coordinates of the seabed sonar reference beacon and the back-and-forth sound velocity sound path distance. According to the method, the data quality is controlled by preprocessing the multi-source data, the change of the position of the transducer in the acoustic signal propagation process is considered, acoustic ray bending correction is carried out through acoustic ray tracking, the error influence is weakened, and the positioning precision is improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Underwater control point positioning method considering surface acoustic velocity and coordinate prior information
ActiveCN112526454ASave ship timeImprove work efficiencyPosition fixationMeasuring open water depthSound speed profileClassical mechanics
The invention provides an underwater control point positioning method considering surface acoustic velocity and the coordinate prior information and belongs to the technical field of underwater positioning. According to the method, surface acoustic velocity and coordinate prior information are considered, acoustic velocity errors of a circular sailing method and acquisition of control point planecoordinate prior information are analyzed, control point coordinates and a water depth value measured by a pressure sensor are regarded as random quantities, and a water depth observation value is endowed with a first empirical variance which is 0.1% of the water depth according to experience; and finally, coordinates of the control points are solved by adopting a generalized least square principle. Simulation of 50m and 1500m water depth positioning experiments proves that under the condition of not using a sound velocity profile, only surface sound velocity and coordinate prior information are considered, a high-precision positioning result can also be obtained, the ship hour can be effectively saved, and operation efficiency is improved. The method is high in practicability, stable andreliable in result and high in efficiency, and is mainly used for transmitting the absolute coordinate reference of the underwater control network.
Owner:THE FIRST INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY SOA
Underwater acoustic sensor network deep sea target positioning method based on glancing angle sound ray correction
PendingCN113671443AHigh positioning accuracyExact horizontal distancePosition fixationDirection/deviation determination systemsSound speed profileSensor node
The invention provides an underwater acoustic sensor network deep sea target positioning method based on glancing angle sound ray correction; under the condition that the sound velocity profile and the glancing angle of a node receiving end are known, the accurate horizontal distance between the node and the target can be obtained, and then the target positioning accuracy is improved. According to the method, the technical problem that a time-based distance measurement method and a traditional sound ray correction method cannot be used under the condition that a sensor node and a target clock are asynchronous is solved, the influence of sound ray bending on distance measurement and target positioning is corrected, and the target positioning precision is obviously improved; the glancing-angle-based sound ray correction method can be used for deep-sea target positioning of an underwater acoustic sensor network and can also be used for deep-sea target positioning of other underwater acoustic positioning systems.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com