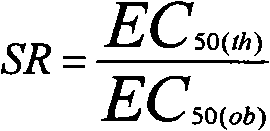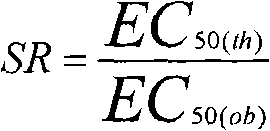Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Sitobion avenae" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The English Grain Aphid (Sitobion avenae) is an aphid in the superfamily Aphidoidea in the order Hemiptera. It is a true bug and sucks sap from plants. It lives on grasses, sedge and rushes and can be a significant pest of cereals.
dsRNA (double-strand ribonucleic acid) and application of combination thereof to control aphid damage
ActiveCN103571844AImprove aphid resistanceBiocideAnimal repellantsBiotechnologyComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
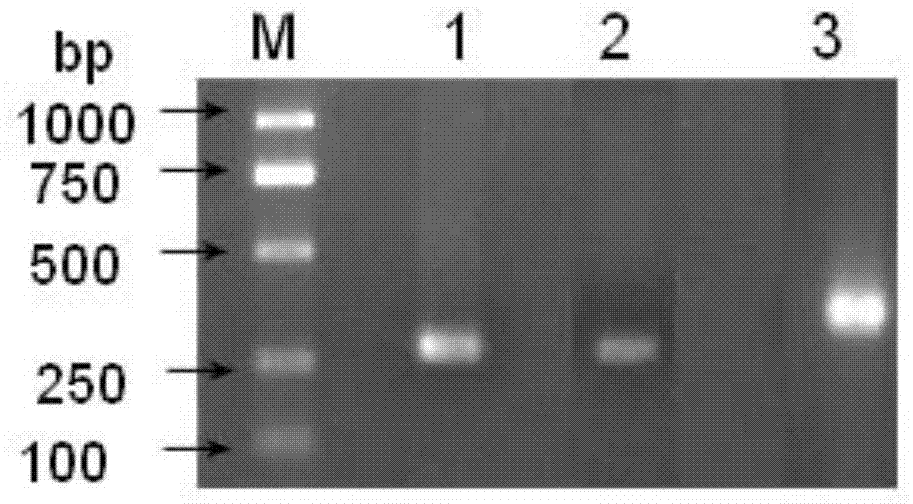
The invention discloses a dsRNA (double-strand ribonucleic acid) and an application of combinations thereof to control aphid damage. The dsRNA consists of (1) a nucleotide shown as a sequence 4 in a sequence table and a nucleotide shown as a reversely complementary sequence of the sequence 4; (2) a nucleotide shown in a sequence 5 in the sequence table and a nucleotide shown as a reversely complementary sequence of the sequence 5; or (3) a dsRNA shown by (1) and a dsRNA shown by (2). Experiments show that effects of inhibiting the growth and development of sitobion avenae and causing the death of the sitobion avenae are achieved by feeding the dsRNA for growth and development related genes 8273 and 22544 cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) of the sitobion avenae in vitro and silencing the growth and development related genes 8273 and 22544 of the sitobion avenae by utilizing an RNAi (RNA interference) technology.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Aphid biological control method with barley and Sitobion avenae as storage carriers
ActiveCN104938262AEfficient biological controlEasy to operatePlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsHordeum vulgareMoisture
The invention discloses an aphid biological control method with barley and Sitobion avenae as storage carriers. The method comprises the steps that A. barley reproduction is carried out, wherein after barley seeds are subjected to sterilization and deinsectization, a culturing medium is used for barley reproduction; B. Sitobion avenae reproduction is carried out, wherein Sitobion avenae is collected and sent into barley for culturing reproduction; C. aphidiidae inoculation is carried out, the aphidiidae is collected and put into barley where aphid breeding is completed for culturing; D. field releasing is carried out, wherein barley with aphidiidae are placed between lines of crops; and E. carrier plant maintaining and replacing are carried out, wherein timing moisture supplementing and in-due-time barley replacing are carried out. The aphid biological control method with the barley and the Sitobion avenae as the storage carriers is easy to operate, low in cost and obvious in effect.
Owner:NINGBO ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Bacteria and pest killing compound agent for wheat
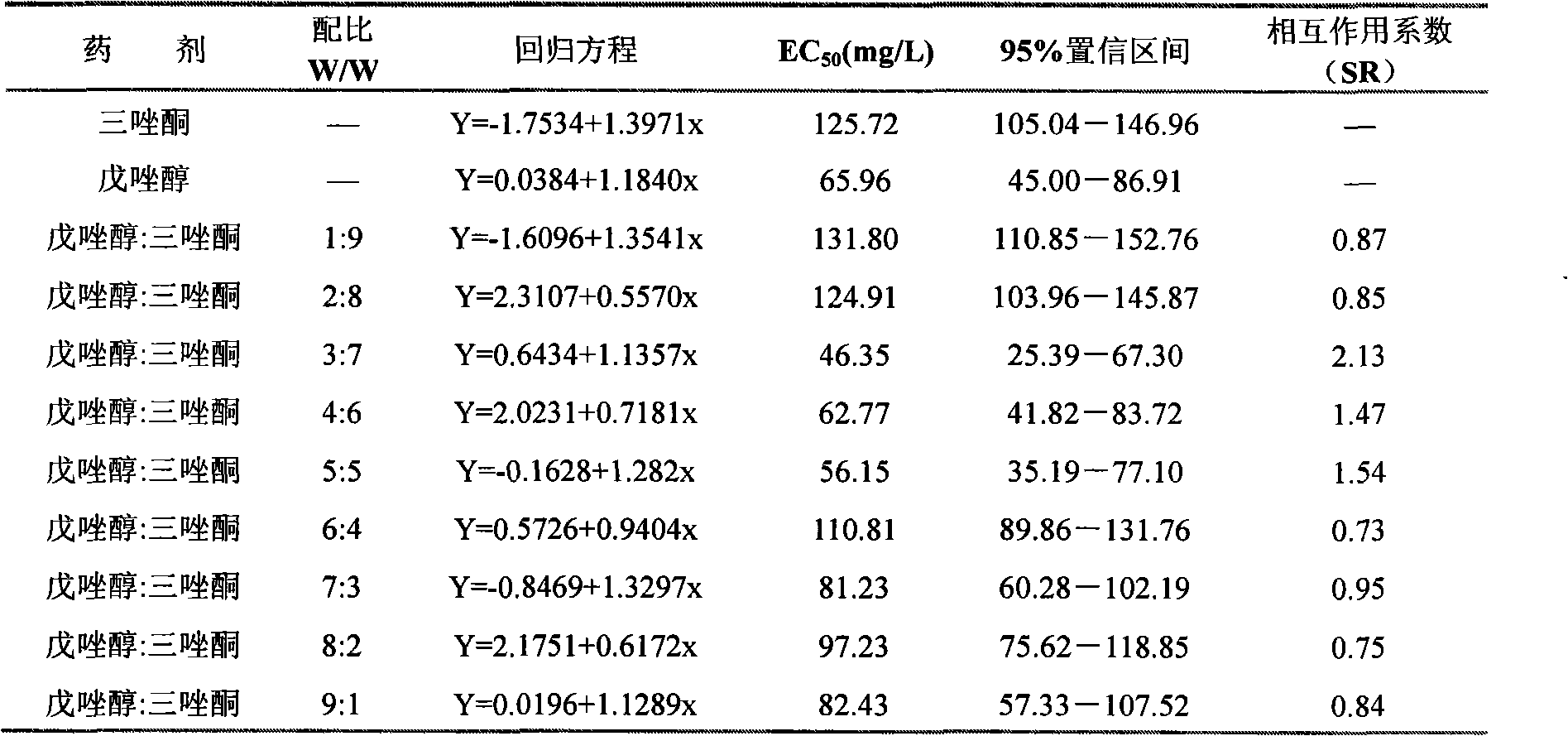
The invention relates to the development and application of a bacteria and pest killing compound agent for wheat. The compound agent mainly consists of tebuconazole, triazolone and imidacloprid and can be prepared into missible oil, missible oil, wettable powder and the like. Demonstrated by biological test, the compound agent has obvious synergistic function for wheat stripe rust and erysiphe graminis and can also prevent and kill aphid. According to field experiments, the compound agent can achieve 90 percent of effect in preventing wheat leaf diseases, more than 90 percent of effect in preventing the erysiphe graminis, no less than 98 percent of effect in preventing and controlling wheat sitobion avenae. The compound agent has the functions of killing bacteria and pests, is conveniently used, saves work time, reduces cost and environment pollution, and actively responds to the national policy of energy conservation and emission reduction. Meanwhile, the compound agent has simple process, is easy to produce, can be directly transformed into a production capability and can obtain economic and social benefits as soon as possible.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Bactericidal and pesticidal compound agent for wheat
The invention relates to research and application of a bactericidal and pesticidal compound agent for wheat. The compound agent for wheat is mainly prepared from diniconazole, triadimefon and imidacloprid and can be prepared into emulsifiable oil, microemulsion, wettable powder and the other formulations. The biological tests show that the compound agent for wheat has obvious synergism on wheat rust and wheat powdery mildew and also has a favorable curative effect on wheat aphids. The field tests show that the compound agent for wheat achieves the wheat rust prevention effect of 90 percent, the wheat powdery mildew prevention effect of over 90 percent and the sitobion avenae prevention and control effect of no less than 98 percent. The compound agent for wheat has bactericidal and pesticidal effects, is convenient to use, time-saving and labor-saving, ensures that the cost is lowered and the environmental pollution is reduced, and actively cooperates with the energy saving and emission reducing state policy. In addition, the compound agent for wheat is simple in preparation process, is easy to prepare and can be directly converted into productive force to gain economic and social benefits as soon as possible.
Owner:CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI LANGFANG PESTICIDE PILOT PLANT
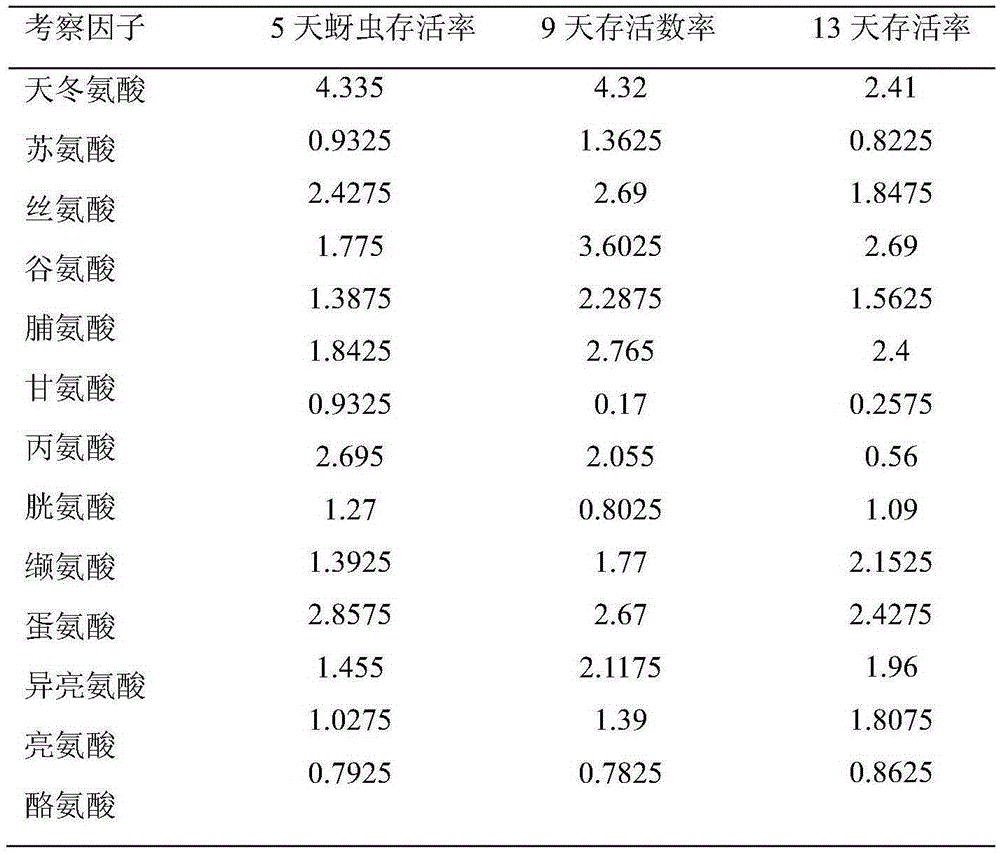
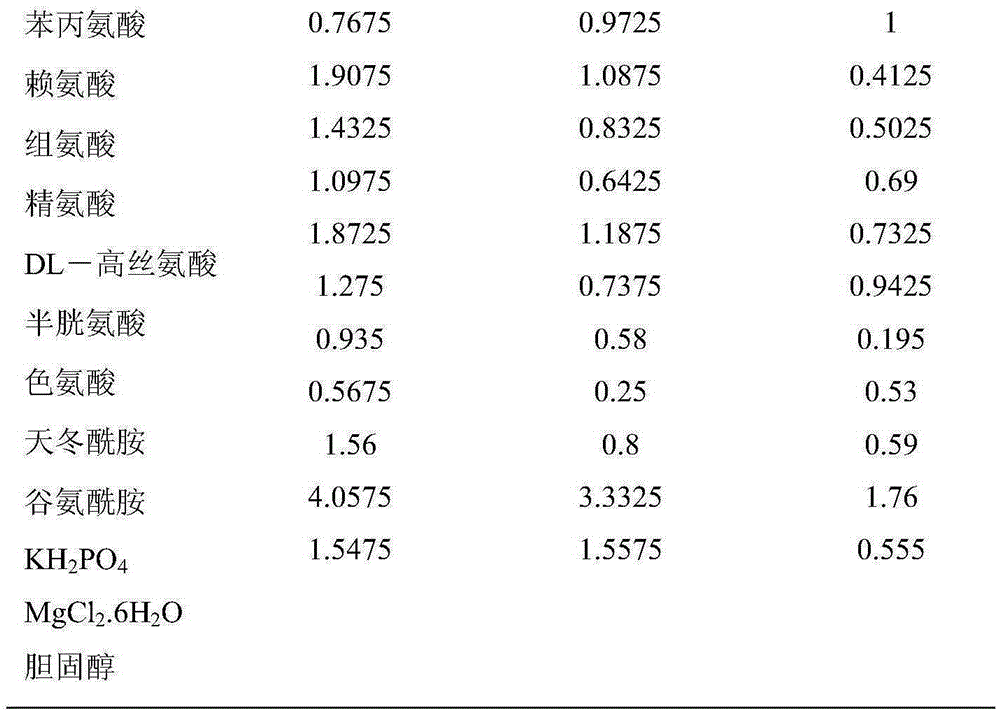
Chemically-defined diet and artificial mass rearing method for wheat aphids
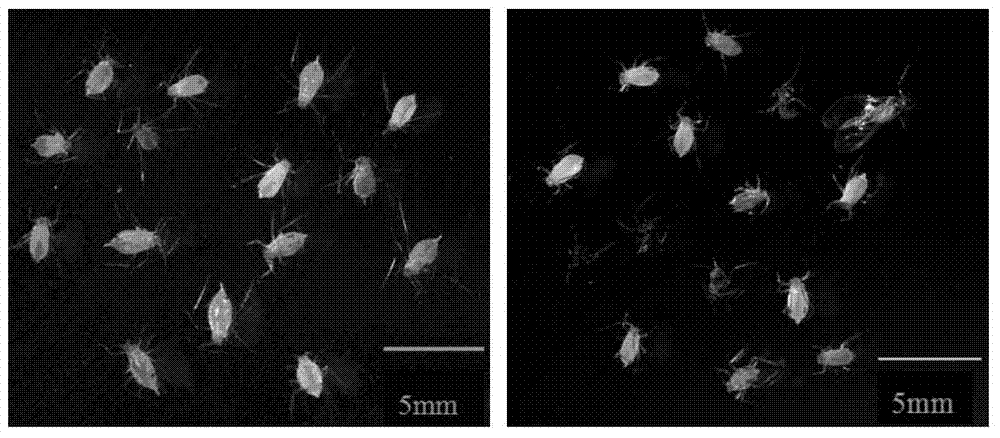
The invention relates to a chemically-defined diet and artificial mass rearing method for wheat aphids. The chemically-defined diet for the wheat aphids comprises an artificial diet applicable to the growth and development of Sitobion avenae and an artificial diet applicable to the proliferation of Sitobion avenae, is an optimized formula of the two kinds of diets and can enable Sitobion avenae to survive normally, grow, develop and reproduce offspring, thereby having a broad application prospect. The rearing method for Sitobion avenae, provided by the invention, is characterized in that the growth and development diet is adopted at a young aphid stage of Sitobion avenae; and the proliferation and development diet is adopted at an adult aphid stage of Sitobion avenae. According to the chemically-defined diet and the artificial mass rearing method, the adult ratio and birth ratio of the aphids are increased, the mass rearing method is established, and a reliable and important evaluation means for providing test aphids with uniform nutrition background and implementing researches on aphid nutrition physiology, wheat insect-resisting substances and transgenic insect-resisting protein activity is provided.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
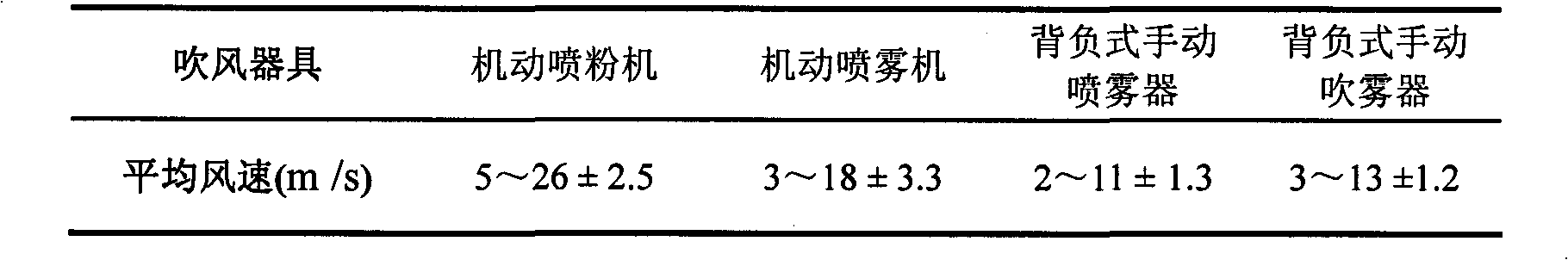
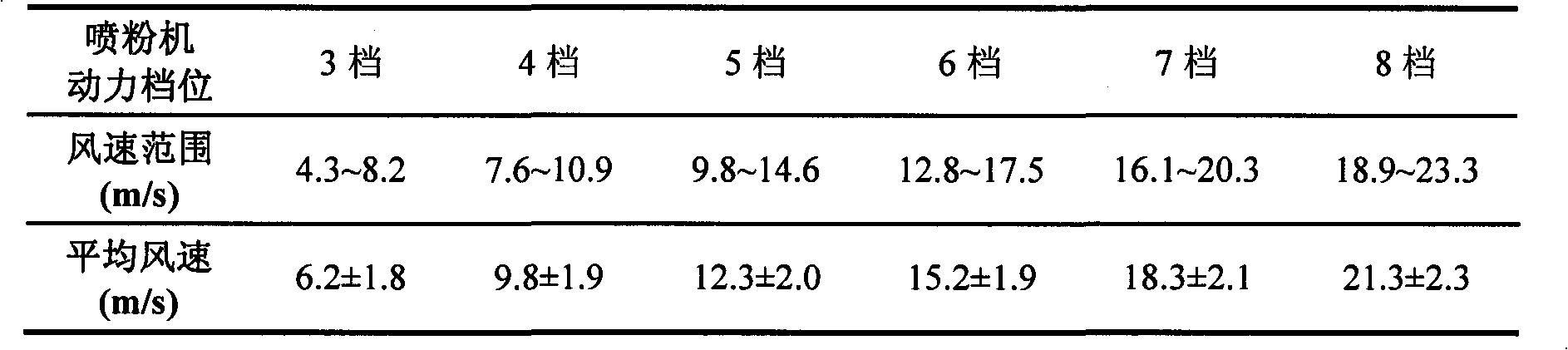
Green energy-saving wheat aphid prevention and control technology
InactiveCN102067802AReduce in quantityReduce direct insecticideRenewable energy machinesPlant protectionSocial benefitsPesticide pollution
The invention relates to a using technology for controlling wheat aphid damages by utilizing a blowing measure. In the invention, wind power generated by a motorized duster is used for carrying out physical interference on wheat aphids to cause direct impact harms to the wheat aphid without using any chemical pesticide or chemical substances, biological drugs and water so as to reduce the aphid density on wheat plants, increase the predator to prey ratio (i.e. the quantity ratio of natural enemies to the wheat aphids) and achieve the purpose of controlling the damages of the wheat aphids to the wheat. Proved by field measurement, the prevention and control effect of the technology on sitobion avenae can reach higher than 85 percent, and compared with a chemical prevention and control technology frequently used in production at present, the technology has the advantages of cost saving (drugs or water is not used) and no pesticide pollution and can sufficiently play a role of controlling the aphids by utilizing the natural enemies in the field; and meanwhile, the technology also has the advantages of convenience for use, working hour saving, easiness of popularization and application, direct conversion to productivity and obvious economic, ecological and social benefits.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
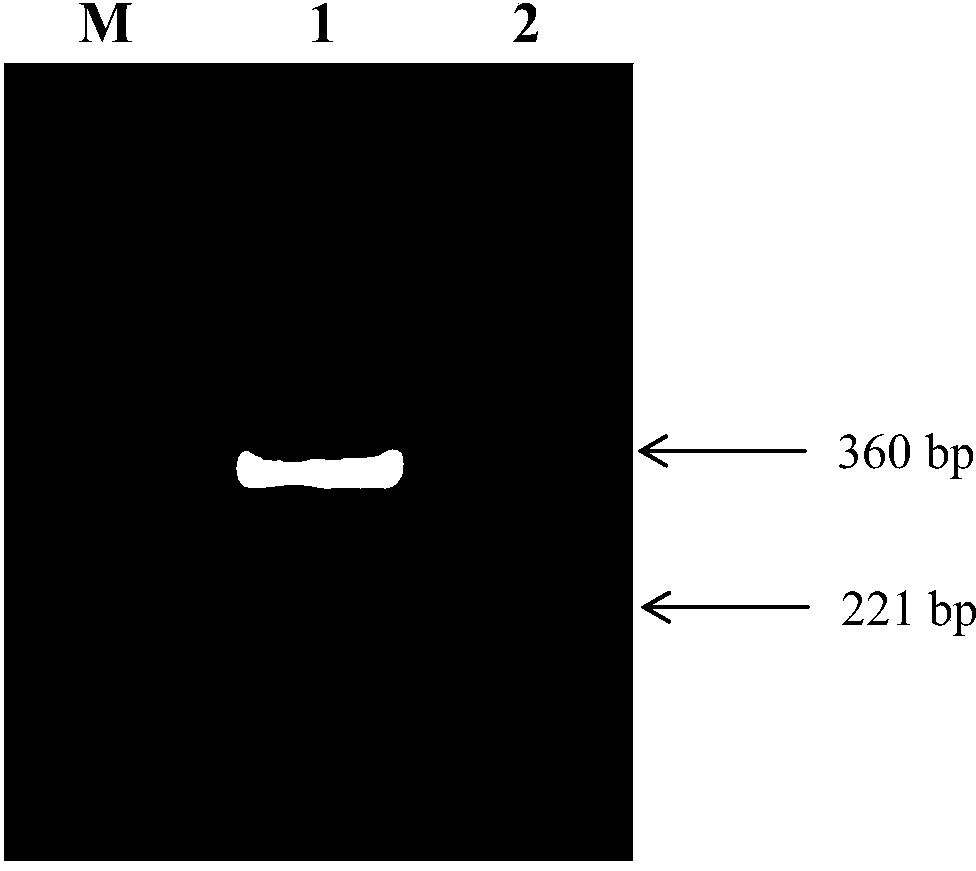
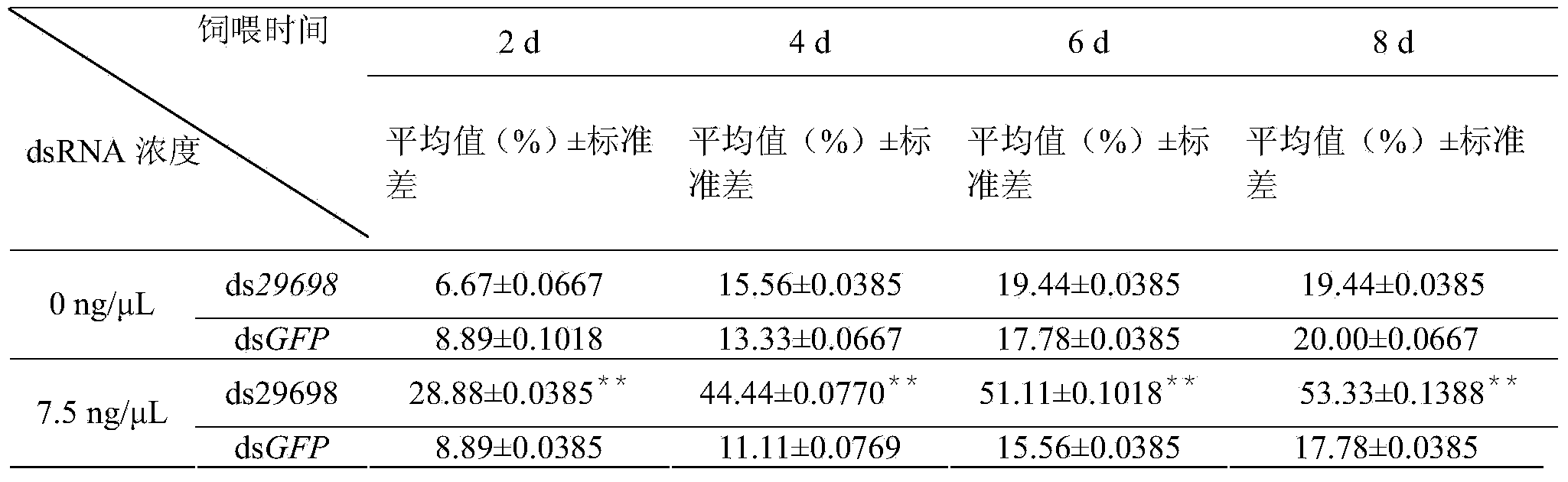
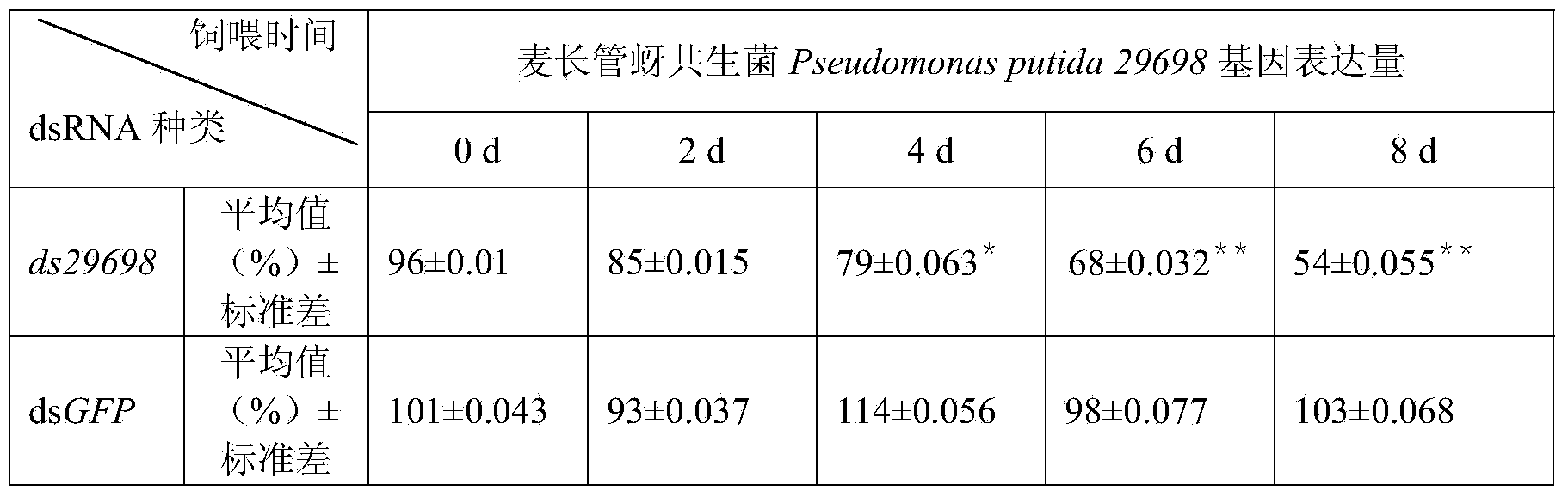
dsRNA (double-stranded ribonucleic acid) of sitobion avenae symbiotic bacteria gene and application thereof in reducing sitobion avenae survival rate
InactiveCN104263731AImprove aphid resistanceBiocideAnimal repellantsConserved sequenceSymbiotic bacteria
The invention discloses a dsRNA (Double-stranded Ribonucleic Acid) of a sitobion avenae symbiotic bacteria gene and application thereof in reducing the sitobion avenae survival rate. The dsRNA provided by the invention is a double-stranded RNA consisting of the nucleotide shown as a sequence 1 in a sequence list and the nucleotide shown as a reverse complementary sequence. According to the dsRNA provided by the invention, the Pseudomonas putida 29698 gene of the symbiotic bacteria in a sitobion avenae body is silenced by an in-vitro dsRNA feeding method through the utilization of a RNAi (RNA interfere) technology, lethal effect is produced on the sitobion avenae, and the dead rate of the sitobion avenae is gradually increased with the prolongation of the feeding time. The real-time fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction study of the Pseudomonas putida 29698 gene of the symbiotic bacteria in the fed avenae body shows that the expression of the 29698 gene is obviously inhibited and that a conservative sequence of the Pseudomonas putida 29698 gene of the symbiotic bacteria in the avenae body can be applied in a study improving the wheat avenae resistance through a plant mediating RNAi technology.
Owner:NANYANG NORMAL UNIV
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule for expressing hairpin type RNA (ribonucleic acid) for suppressing sitobion avenae carboxylesterase and application of DNA molecule
InactiveCN103589728AReduce expressionReduce enzyme activityBiocideAnimal repellantsBiotechnologyA-DNA
The invention discloses a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule for expressing a hairpin type RNA (ribonucleic acid) for suppressing sitobion avenae carboxylesterase and application of the DNA molecule. The structure of the DNA molecule disclosed by the invention is SEQ (forward)-X-SEQ (reverse); the sequence of the SEQ (forward) is from a locus 1 to a locus 345 of a sequence 1; the sequence of the SEQ (reverse) is reversely complementary to that of the SEQ (forward); the X is an interval sequence between the SEQ (forward) and the SEQ (reverse); according to the sequence, the X is not complementary to the SEQ (forward) and the SEQ (reverse). An experiment shows that the DNA molecule is converted into an immature embryo callus of wheat to obtain a transgenic line; the transgenic line is subjected to an aphid feeding test; after sitobion avenae is fed on transgenic leaves, the carboxylesterase gene expression quantity and the enzymatic activity are obviously alleviated, and the rate of reproduction is reduced; furthermore, the tolerance of the sitobion avenae to a phoxim solvent is reduced by 20-30 percent. Therefore, the DNA molecule has a great significance for prevention and treatment of insects of agricultural production.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
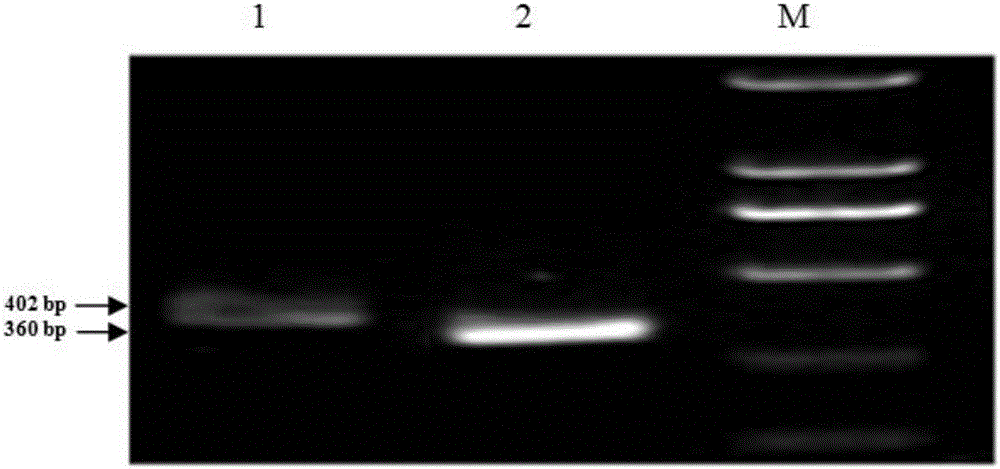
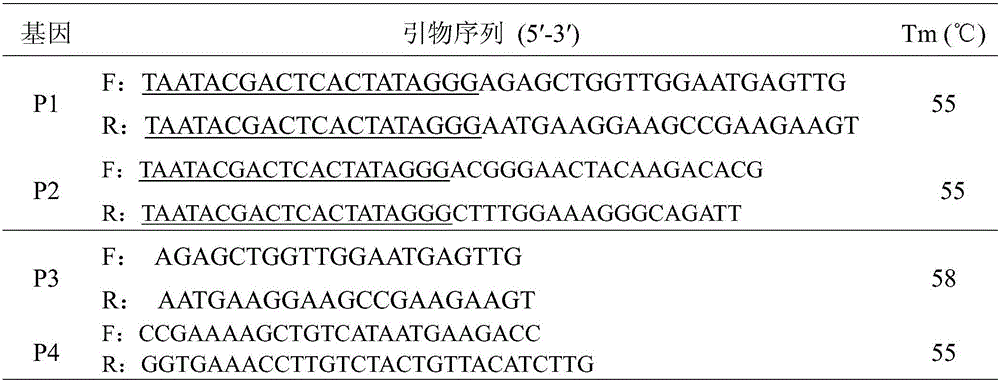
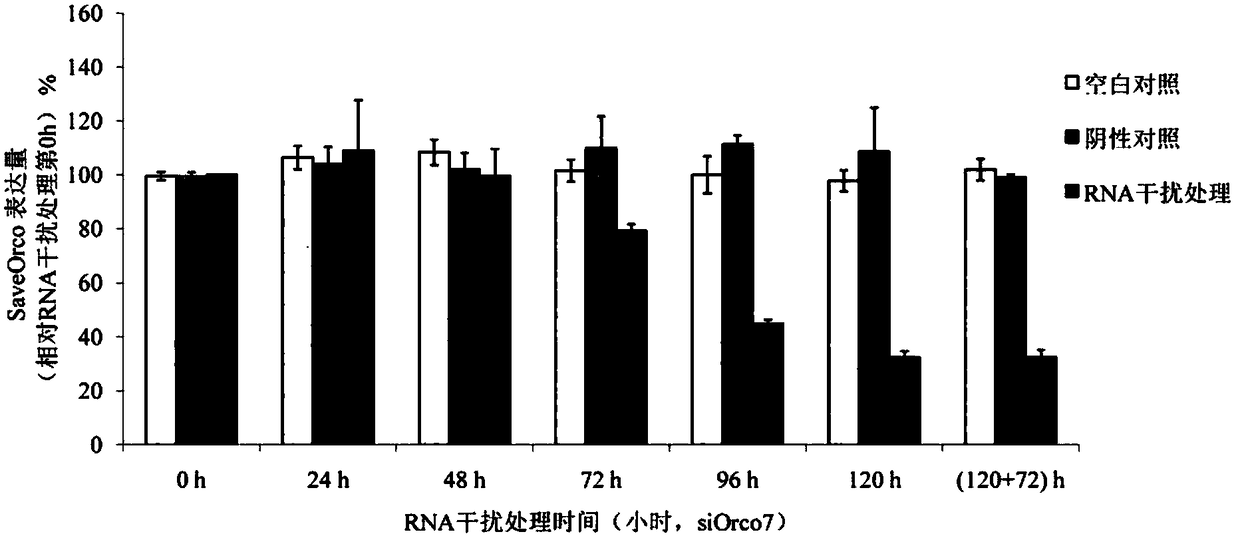
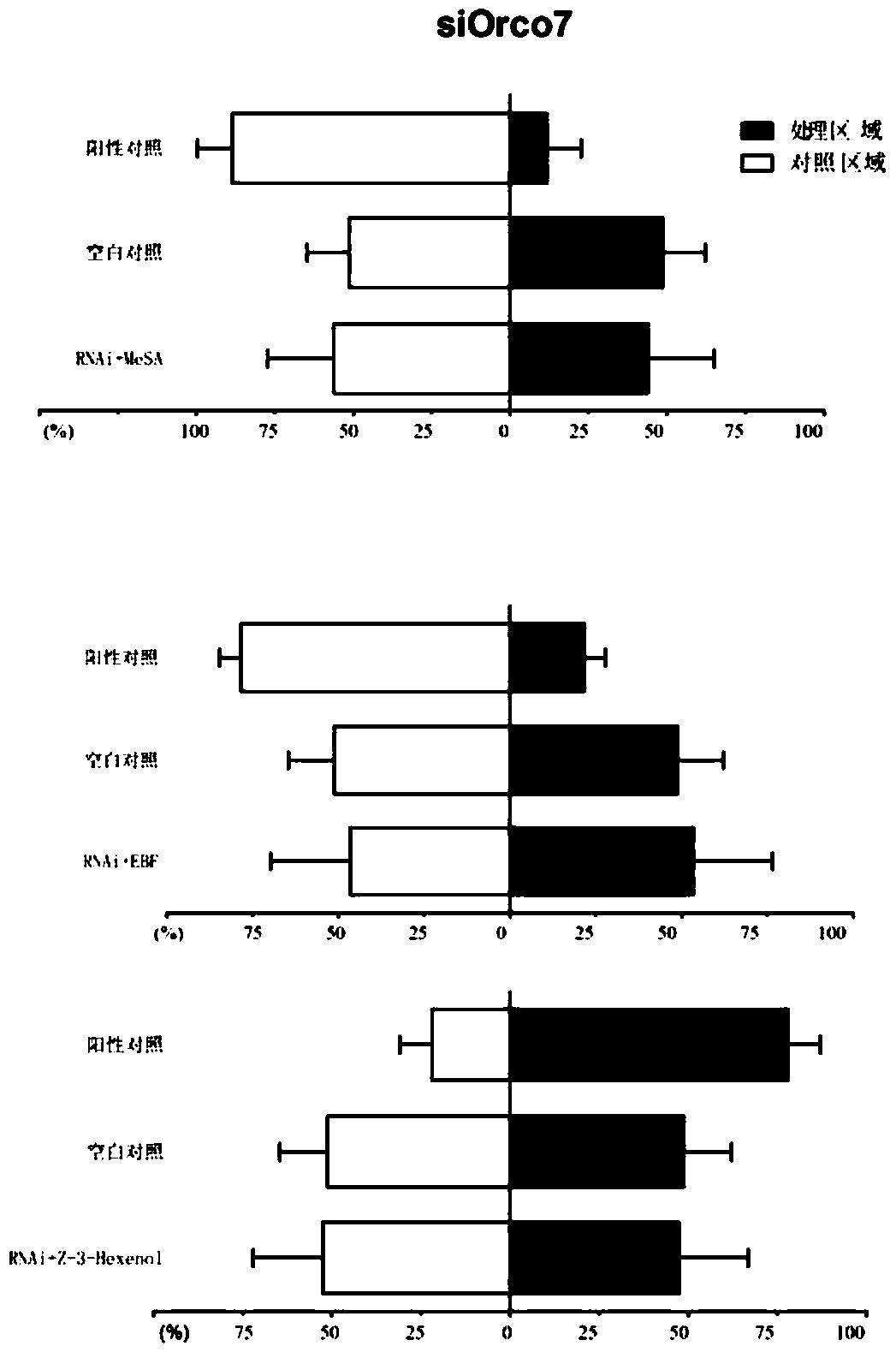
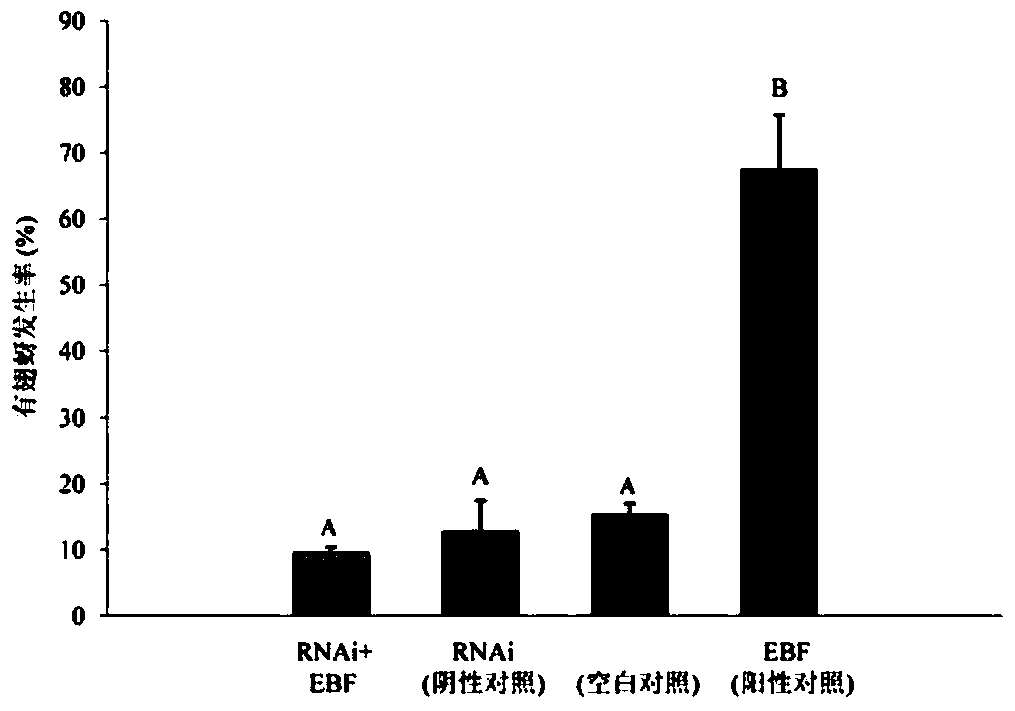
SiRNA based on Sitobion avenae SaveOrco gene design and application thereof
ActiveCN105755003AHigh sequence identityAchieve targetedBiocideAnimal repellantsConserved sequenceMethyl salicylate
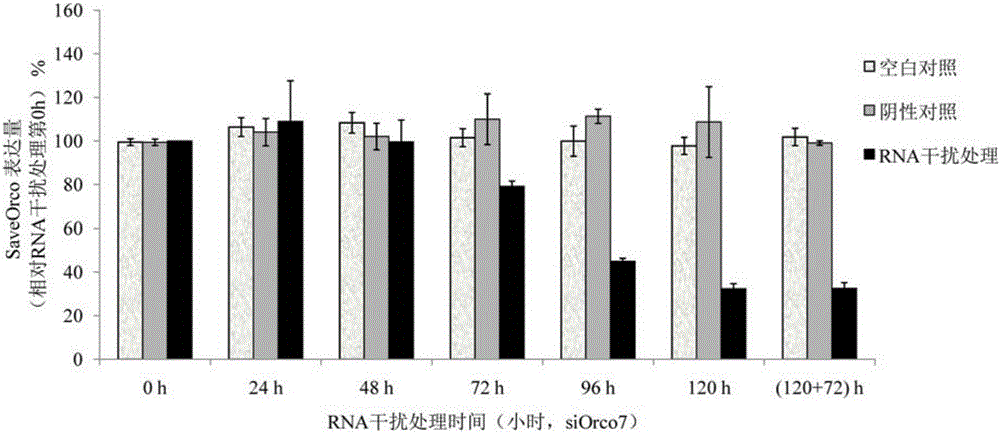
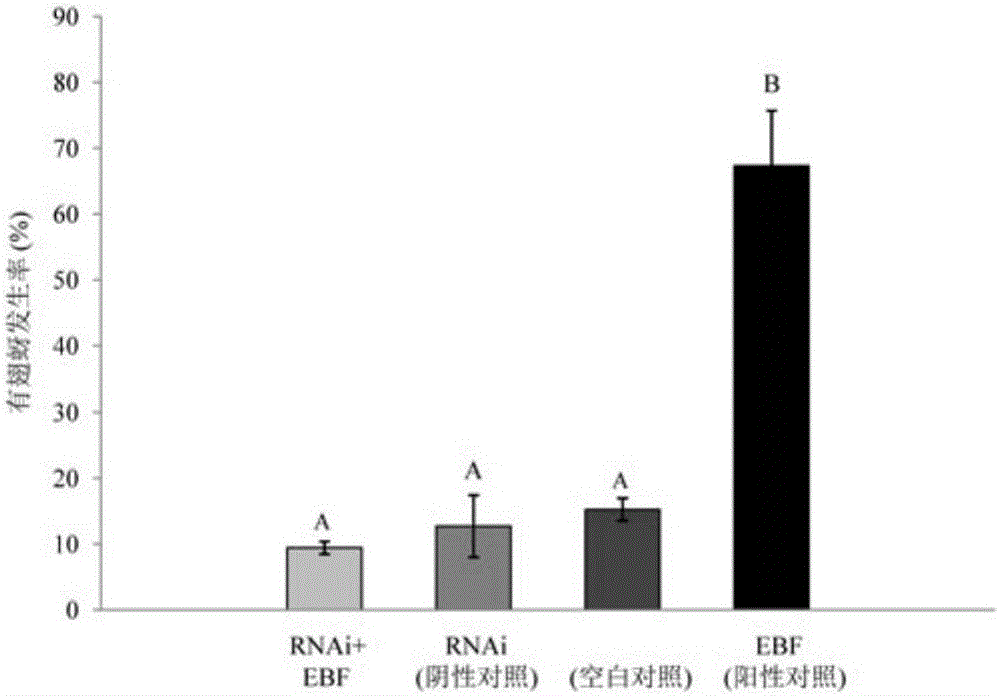
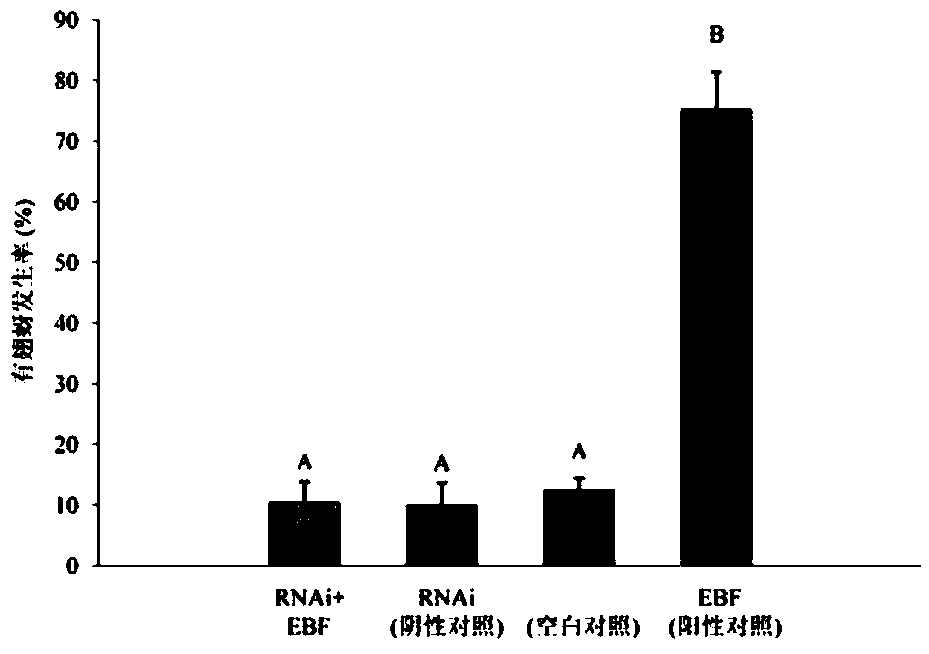
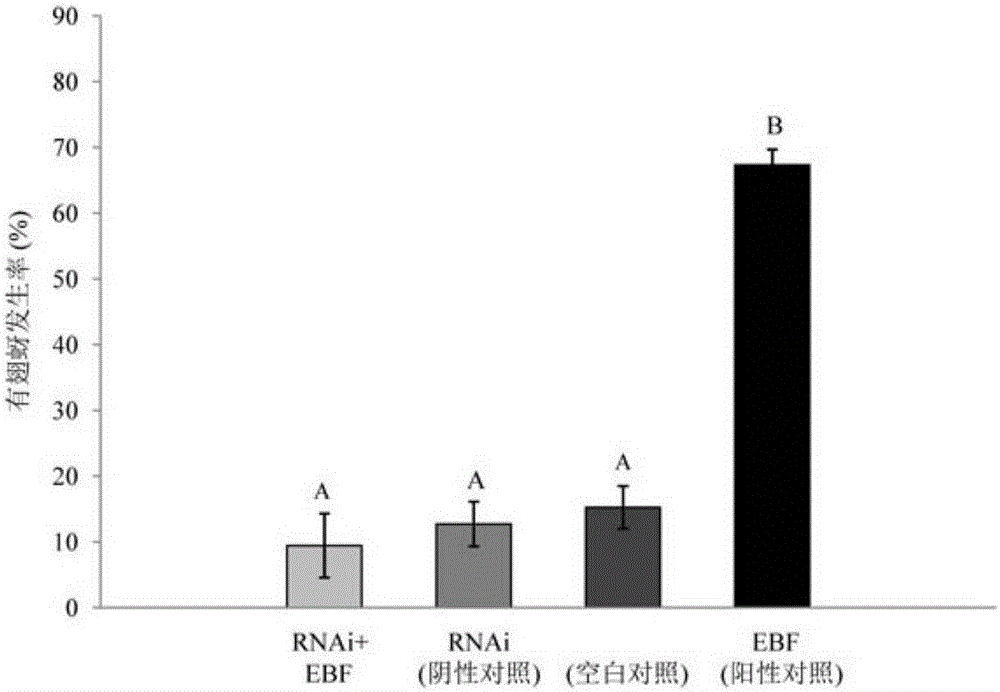
The invention relates to siRNA based on Sitobion avenae SaveOrco gene design and application thereof.Transcription of a SaveOrco gene is interfered through feeding of siOrco7.Real-time fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) research shows that the expression of the SaveOrco gene is obviously restrained.Olfactory behavior reaction detection results show that the responding rates of silenced aphids to z-3-hexenol, methyl salicylate and EBF are obviously reduced under SaveOroco expression.An EBF inducing experiment for sitobion avenae winged morph differentiation is developed, siRNA processed aphids stop inducing of EBF, normal chemical communication of the aphids is interfered, and stress inducible wing bud generation is also stopped.In this way, a conserved sequence of the Orco gene can be applied to an RNAi technology mediated by siRNA, and the aphids can be effectively restrained from rapidly diffusing to be harmful and are prevented and treated.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
DsRNA of ecdysone receptor (EcR) gene and application thereof to control of damage caused by aphids
ActiveCN104109672AIncreased mortalityImprove aphid resistanceBiocideAnimal repellantsBiologyNucleotide composition
The invention discloses an application of dsRNA of an ecdysone receptor (EcR) related gene to control of damage caused by aphids. DsRNA provided by the invention is double-stranded RNA formed by a nucleotide shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table and a nucleotide shown in an inverse complementary sequence of the sequence 2. Experiments prove that dsRNA of cDNA of the EcR related gene of sitobion avenae is obtained; expression of the EcR gene in sitobion avenae can be inhibited, impaired growth and development of wheat aphids can be caused and lethal effects can be generated by adopting the method of feeding dsRNA in vitro.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Carboxylesterase gene dsRNA and applications thereof in prevention and treatment of sitobion avenae
The invention discloses a carboxylesterase gene dsRNA and applications thereof in prevention and treatment of sitobion avenae. The dsRNA is a double-chain RNA consisting of nucleotide shown in a sequence 1 in a sequence table and nucleotide shown in a reverse complementary sequence of the sequence 1. Experiments proves that carboxylesterase genes in sitobion avenae are reduced to different degrees after the sitobion avenae is fed with carboxylesterase gene dsRNA, which means that dsRNA taken in by a lancet enters the cells of the sitobion avenae to generate RNAi cascade reaction and the expression of a target gene is interfered. In a morphological view, the growth state of the sitobion avenae is changed, and the ecdysis index of the sitobion avenae fed with the carboxylesterase gene dsRNA is significantly reduced in comparison with a control. Therefore, carboxylesterase gene dsRNA can be used in prevention and control of sitobion avenae. The invention lays a foundation for construction of new germplasm of wheat by using plant-mediated RNAi technology in the future.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
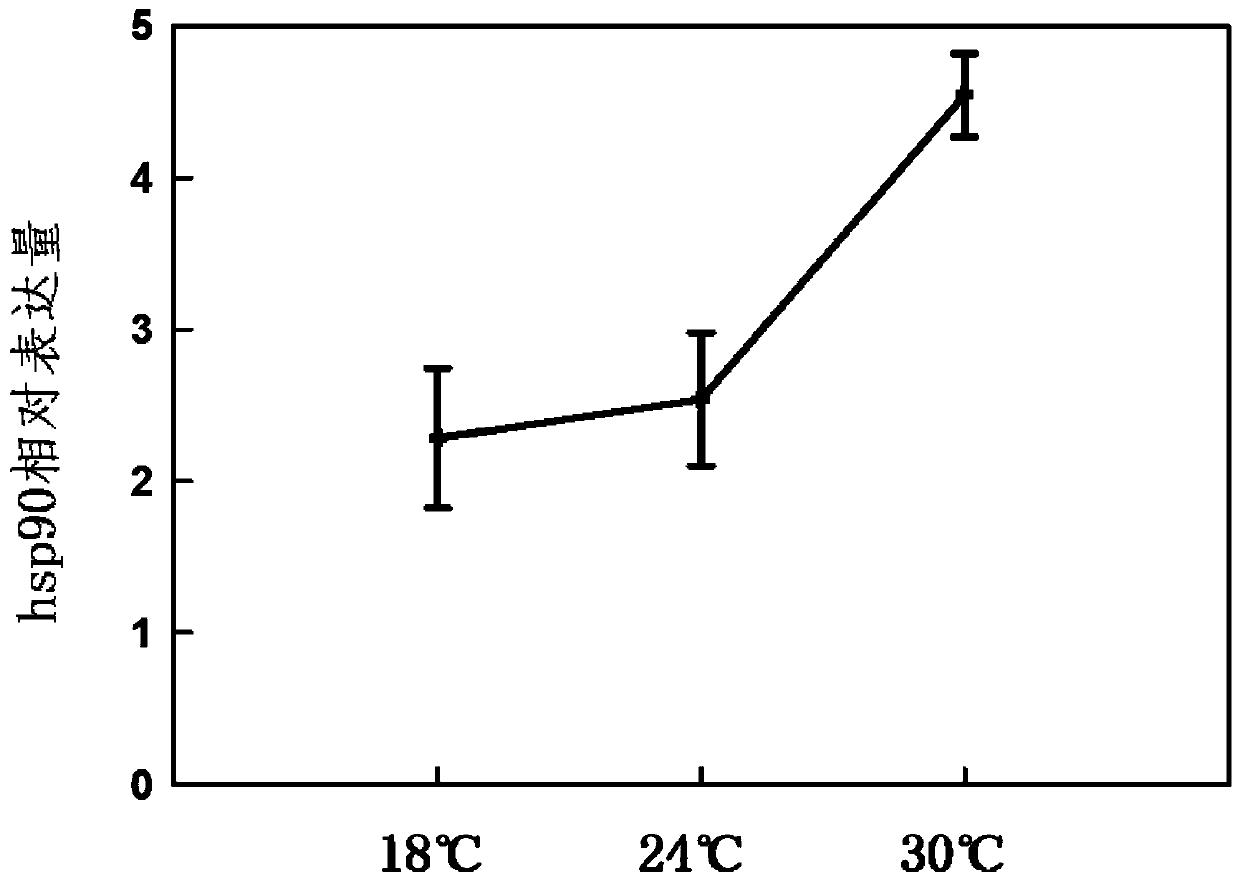
Screening method of reference genes in stable expression in sitobion avenae fabricius at different temperatures and application
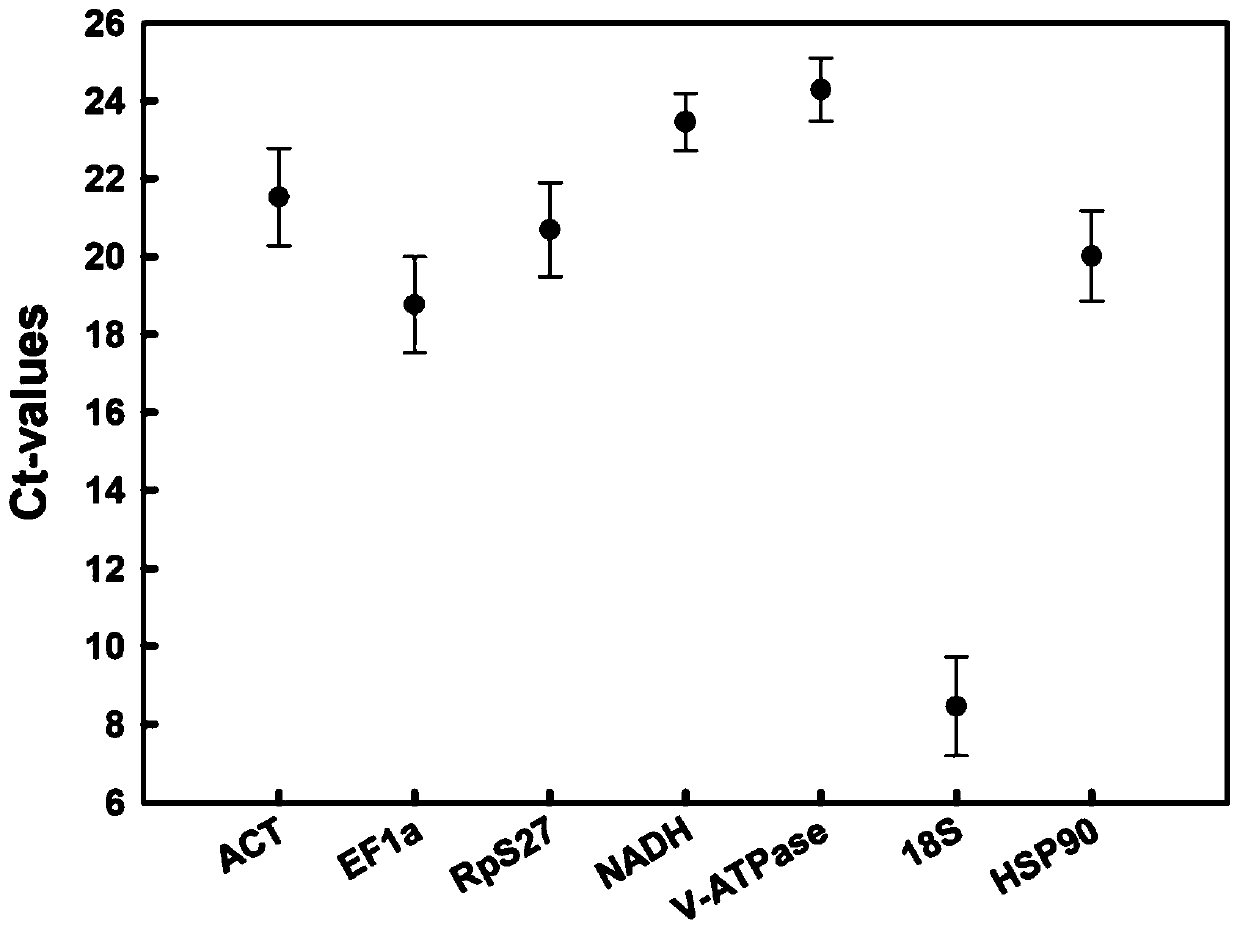
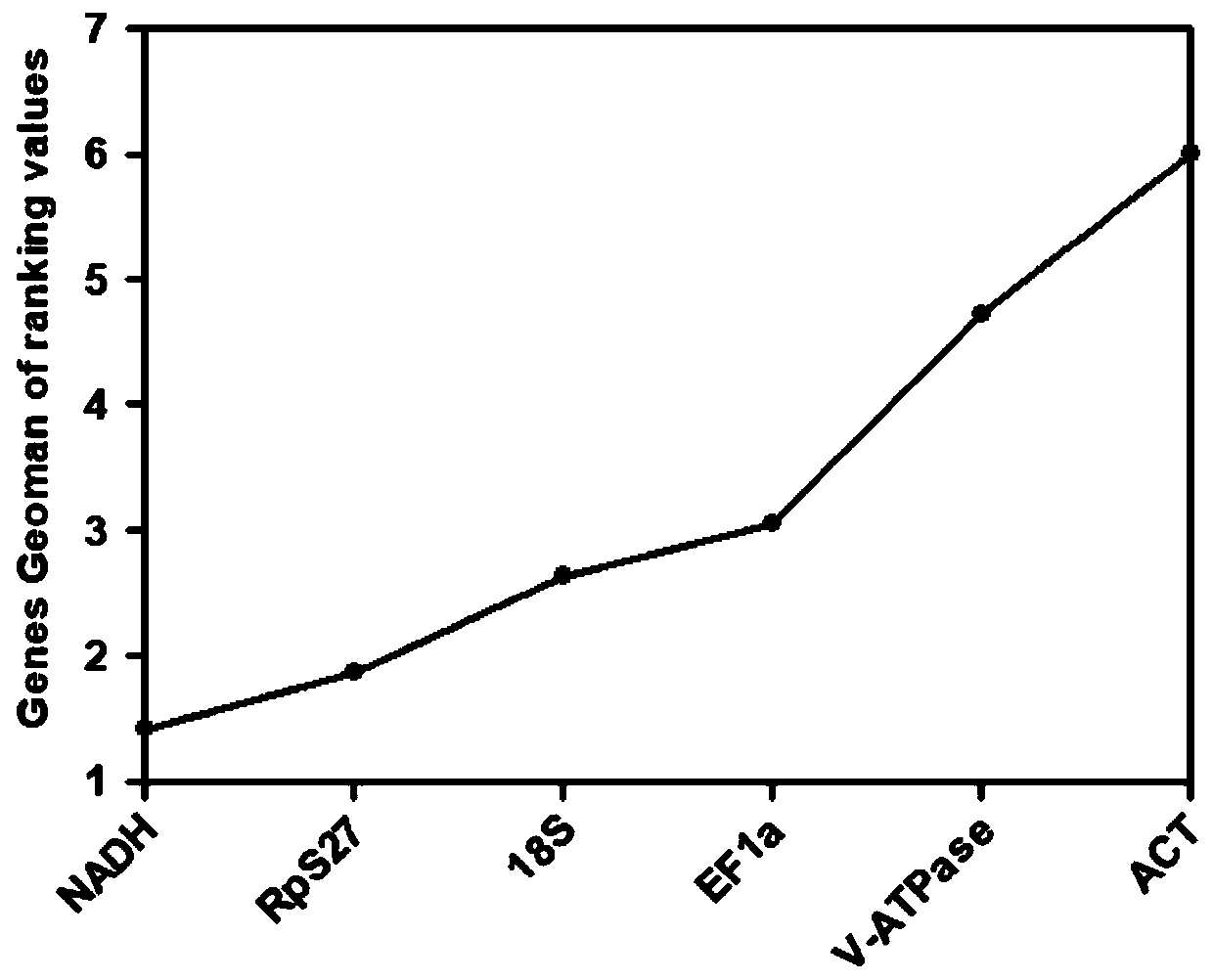
InactiveCN110734959ASpecificOptimizing the Amplification ProgramMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesHeat shock protein
The invention discloses a screening method of reference genes in stable expression in sitobion avenae fabricius at different temperatures and application and belongs to the field of molecular biology.According to the screening method, sitobion avenae fabricius treated at different temperatures is adopted as an experimental material to conduct fluorescence quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) research, quantitative PCR data of each candidate reference gene is input into RefFinder for reference gene stability analysis, and thus reference gene-NADH (reduced form of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotid) which is most suitable and stably expressed in the sitobion avenae fabricius in treatment at different temperatures can be screened. On the basis, the inventor takes the sitobion avenae fabricius after high temperature stress as a sample, takes a sitobion avenae fabricius heat shock protein hsp90 as a target gene, screen NADH genes as the reference genes, and studies expression rules of the sitobion avenae fabricius hsp90 genes at high temperature stress.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
DsRNA of ecdysone receptor (EcR) gene USP and application thereof to control of damage caused by aphids
ActiveCN104109673AIncreased mortalityImprove aphid resistanceBiocideAnimal repellantsNucleotide compositionBiology
The invention discloses an application of dsRNA of an ecdysone receptor (EcR) related gene USP to control of damage caused by aphids. DsRNA provided by the invention is double-stranded RNA formed by a nucleotide shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table and a nucleotide shown in an inverse complementary sequence of the sequence 2. Experiments prove that dsRNA of cDNA of the EcR related gene of sitobion avenae is obtained; expression of the gene USP in sitobion avenae can be inhibited, impaired growth and development of wheat aphids can be caused and lethal effects can be generated by adopting the method of feeding dsRNA in vitro.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
DNA molecule for expressing hairpin RNA for inhibiting macrosiphum avenae lipoprotein lipase and applications thereof
InactiveCN103667294BReduce reproductive rateInhibit expressionBiocideAnimal repellantsEnzyme GeneA lipoprotein
The invention discloses a DNA molecule for expressing hairpin RNA for inhibiting a macrosiphum avenae lipoprotein lipase and applications thereof. The structure of the DNA molecule provided by the invention is SEQ positive direction and -X-SEQ reverse direction, and the sequence of the SEQ positive direction is 21st-563rd position of a sequence 1 in a sequence table; the sequence if the SEQ reverse direction is reversely complemented to the sequence of the SEQ positive direction; and X is an interval sequence between the SEQ positive direction and the SEQ reverse direction, and in the sequence, X does not complement to the SEQ positive direction and the SEQ reverse direction. Proved by an experiment, the DNA molecule is converted to be wheat, to obtain transgene lines for carrying out a aphid feeding test, and after a macrosiphum avenae eats transgene leaves, a lipoprotein lipase gene expression level and reproductive rate decrease. Thus, the DNA molecule provided by the invention has an important meaning for controlling insects in agricultural production.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
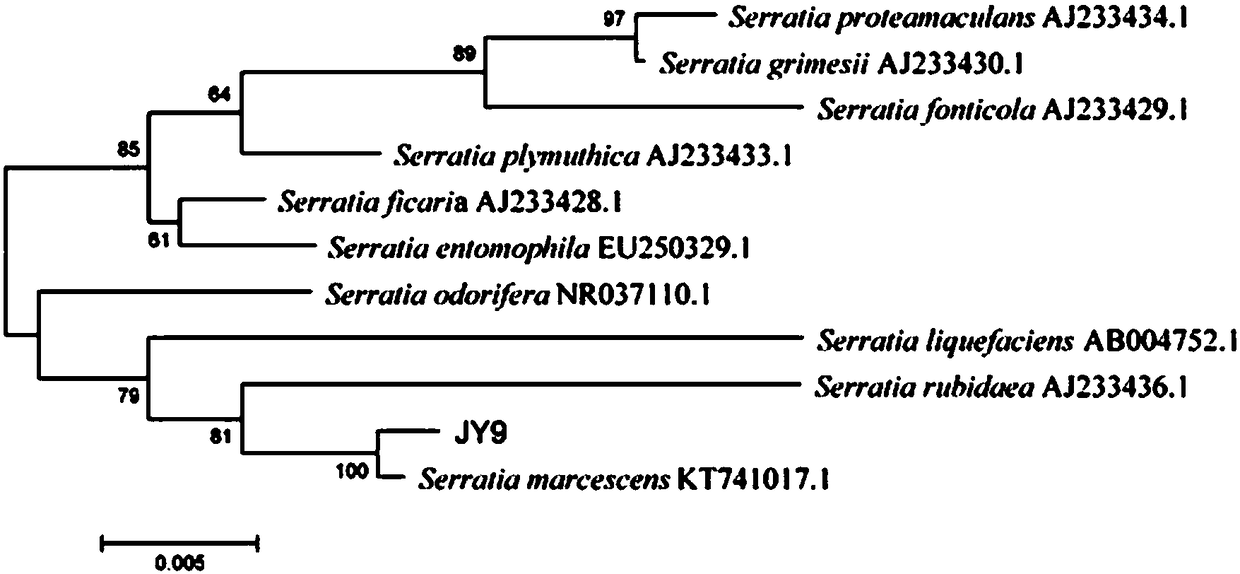
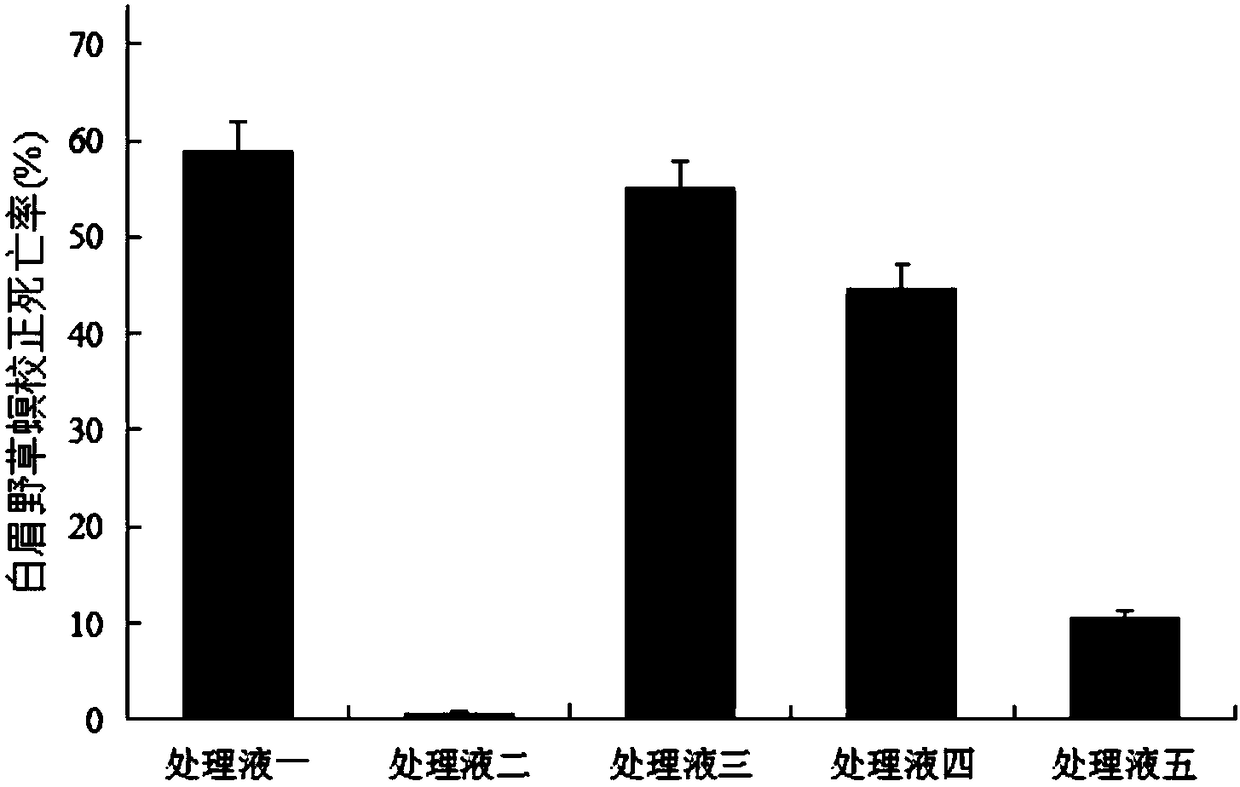
Serratia marcescens derived from agriphilaaeneociliella diseased insect bodies and application thereof
ActiveCN108179123AImprove the effect of prevention and controlReduce usageBiocideBacteriaCulture mediumsMicrobiological culture
The invention discloses serratia marcescens JY9 derived from agriphilaaeneociliella diseased insect bodies. The strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on December 5, 2017 and the biological preservation number is CGMCC NO. 15020. The serratia marcescens JY9 strain provided by the invention is fermented and cultured to obtain a fermentation solution,bacterium suspension and supernatant which can be applied to prevention and control of agriphilaaeneociliella and sitobion avenae; when the bacterium concentration of the fermentation solution which is cultured in an LB culture medium for 16h is 6*10<8>cfu / ml, the fatality rate on mature larvae of the agriphilaaeneociliella can reach 55 percent or more; the fermented supernatant is directly sprayed and applied to wheat seedlings and the wheat seedlings are treated for 4d; the prevention effect on the sitobion avenae can reach 50 percent or more.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
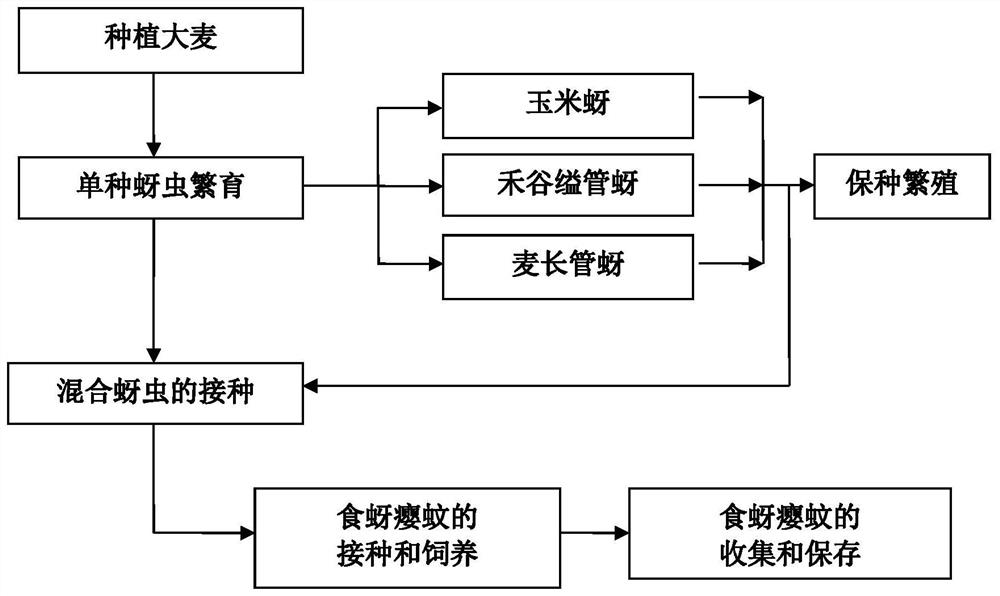
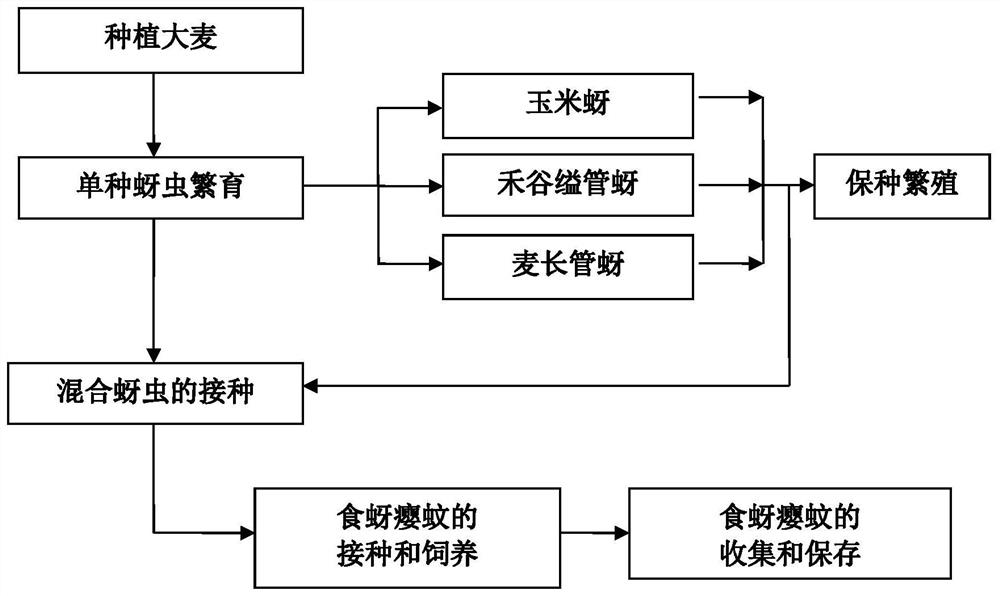
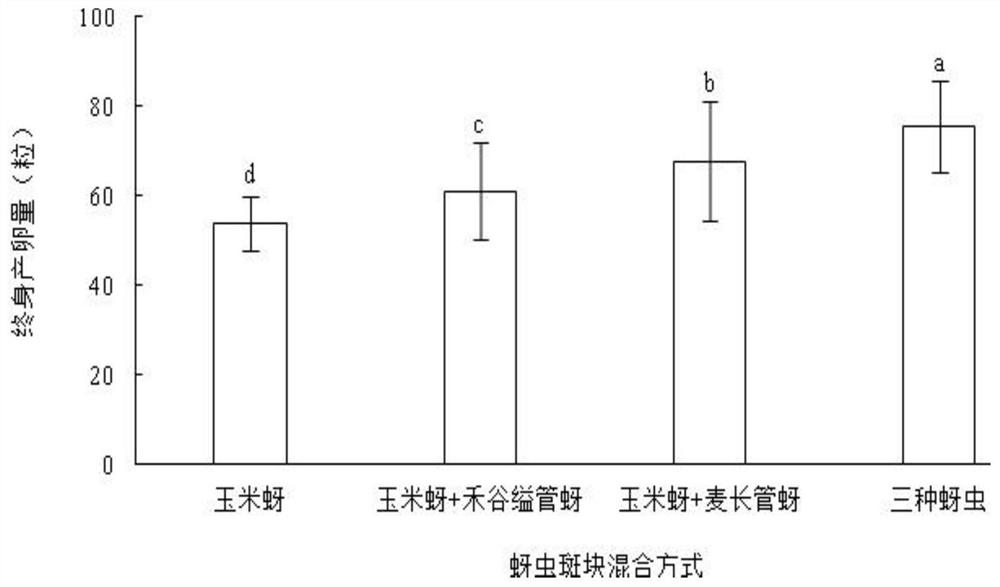
Method for feeding aphidoletes aphidimyza by utilizing mixed population of various aphids on barley
ActiveCN111802332AShort breeding cycleIncrease planting densityAnimal feeding stuffCereal cultivationBiotechnologyAphidoletes aphidimyza
The invention relates to a method for feeding aphidoletes aphidimyza by utilizing a mixed population of various aphids on barley. According to the method, barley seedlings are selected as host plants,a mixed population of three aphids including corn aphids, rhopalosiphum padi and macrosiphum avenae is taken as an intermediate host, aphid-carrying barley seedlings of the three-aphid mixed population are used for breeding aphidoletes aphidimyza, and the large-scale breeding efficiency of the aphidoletes aphidimyza is improved. Barley is used as a host plant, and the method has the advantages ofbeing short in seedling raising period, high in planting density, large in aphid carrying capacity and the like. Meanwhile, the invention further discloses the method for feeding the aphidoletes aphidimyza by adopting the mixed population of three different aphids (corn aphid, rhopalosiphum padi and macrosiphum avenae), so that the large-scale propagation efficiency is further improved. Under thecondition that the prey aphid bearing capacity on a host plant has an upper limit, the egg laying amount of the aphidoletes aphidimyza is increased by increasing the aphid variety, and a new way forimproving the large-scale propagation efficiency is opened up.
Owner:DRY LAND FARMING INST OF HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
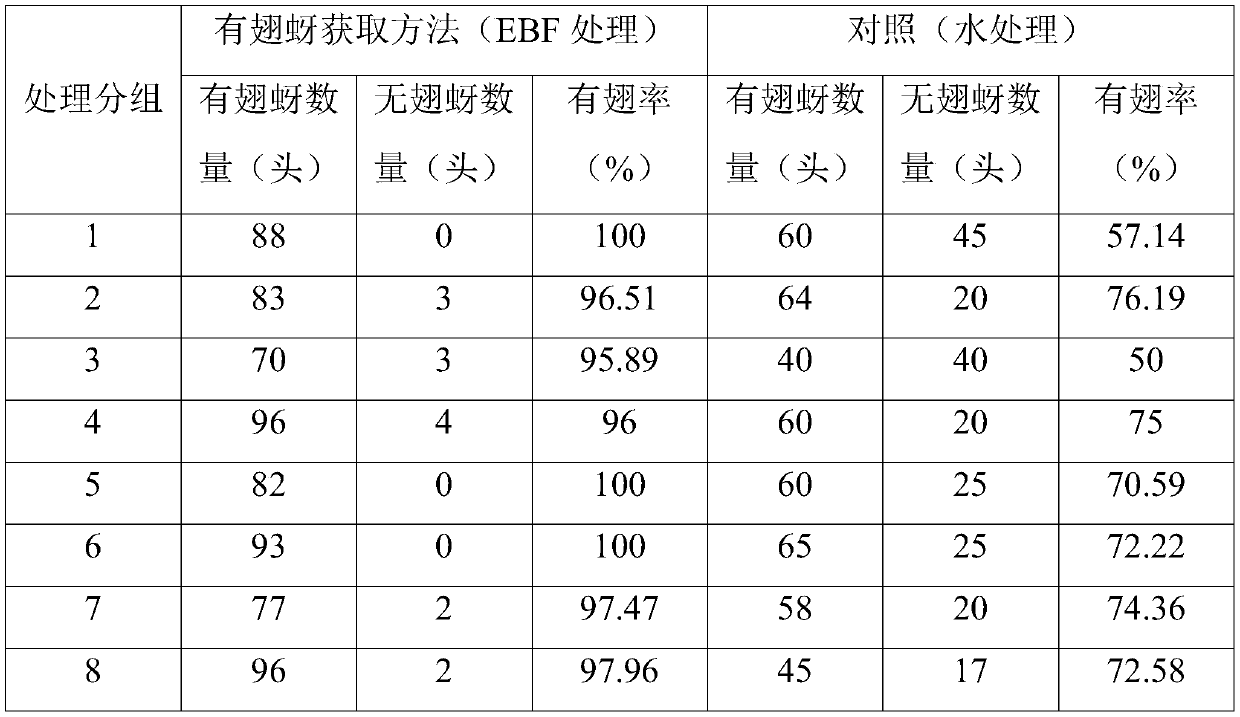
A method for rapid and directional acquisition of young nymphs
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
ds RNA inhabiting expression of chloride channel gene of aphid and application thereof
InactiveCN105255893AIncreased mortalityImprove aphid resistanceBiocideAnimal repellantsBiotechnologyIonic Channels
The invention relates to a ds RNA inhabiting expression of chloride channel gene of aphid and an application thereof. Particularly, the ds RNA inhabiting expression of chloride channel gene of aphid is a double-stranded RNA composed of nucleotide of sequences represented by SEQ ID No:1 and the nucleotide of reverse complementary sequences. The application is that the ds RNA is introduced into aphid so as to prevent and control aphid, reduce aphid survival rate or inhabit expression of chloride channel gene of aphid. The invention uses the method of in vitro ds RNA feeding, and adopts the RNA i technology to silence expression of chloride channel gene of sitobion avenae to produce lethal effect on sitobion avenae. According to real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR study on chloride channel gene of aphid after feeding, expression of chloride channel gene is remarkably inhabited. The invention shows that sequences of chloride channel gene of aphid can be applied to research on increasing wheat resistance to aphids through plant mediating RNA i technology.
Owner:NANYANG NORMAL UNIV
siRNA designed based on the conserved olfactory receptor Orco gene of sitobion avenae and its application
ActiveCN105695467BHigh sequence identityAchieve targetedBiocideAnimal repellantsConserved sequenceResponsivity
The invention relates to siRNA designed based on the conservative olfactory receptor Orco gene of sitobion avenae and an application thereof. In the invention, siOrco8 is fed to interfere with the transcription of the SaveOrco gene. Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR study indicates that the expression of the SaveOrco gene is obviously inhibited. The olfactory behavior reaction detection result shows that the responsivity of aphids with expression loss of SaveOrco to cis-3-hexenol, methyl salicylate and EBF is remarkably reduced. In an experiment of EBF inducing wing dimorphism of sitobion avenae, the aphids treated with siRNA stop induction of EBF, normal chemical communication of the aphids is disturbed, and the stress-inducible wing bud generation is also stopped. Therefore, the conservative sequence of the Orco gene can be used for effectively preventing aphids from quickly spreading and doing harm through the siRNA-mediated RNAi technology so as to control aphids.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
siRNA designed based on conservative sequence of olfactory receptor SaveOrco of sitobion avenae and application thereof
ActiveCN105695468AHigh sequence identityAchieve targetedBiocideAnimal repellantsConserved sequenceResponsivity
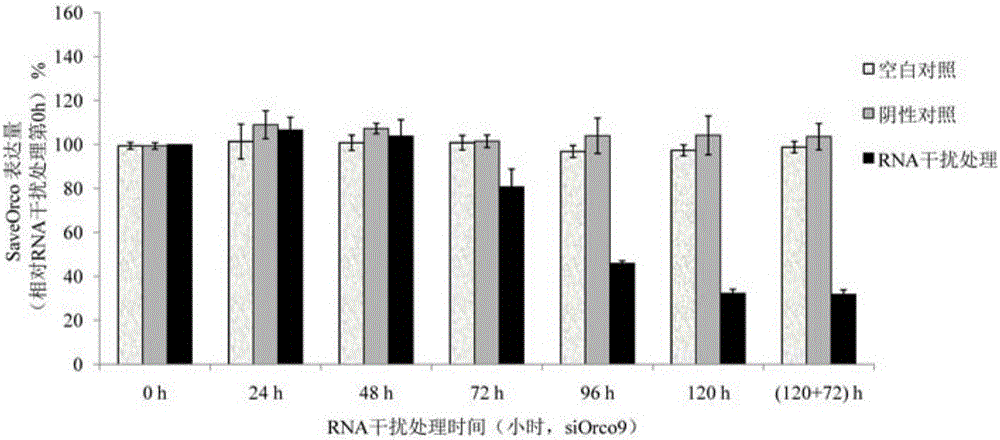
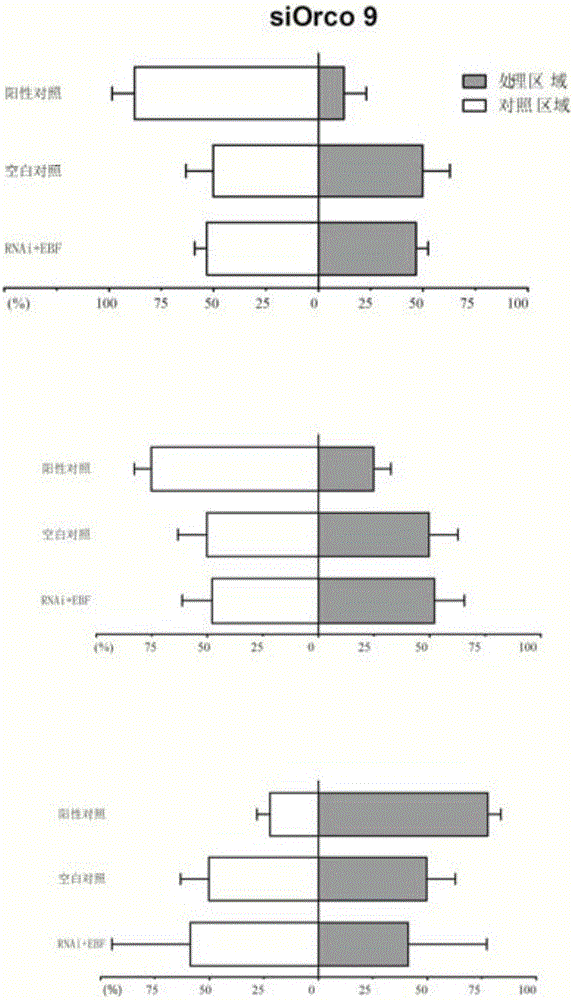
The invention relates to siRNA designed based on the conservative sequence of an olfactory receptor SaveOrco of sitobion avenae and an application thereof. In the invention, siOrco9 is fed to interfere with the transcription of the SaveOrco gene. Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR study indicates that the expression of the SaveOrco gene is obviously inhibited. The olfactory behavior reaction detection result shows that the responsivity of aphids with expression loss of SaveOrco to cis-3-hexenol, methyl salicylate and EBF is remarkably reduced. In an experiment of EBF inducing wing dimorphism of sitobion avenae, the aphids treated with siRNA stop induction of EBF, normal chemical communication of the aphids is disturbed, and the stress-inducible wing bud generation is also stopped. Therefore, the conservative sequence of the Orco gene can be used for effectively preventing aphids from quickly spreading and doing harm through the siRNA-mediated RNAi technology so as to control aphids.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A kind of aphid biological control method using wheat seedlings and straw aphid as storage carriers
ActiveCN104938262BEfficient biological controlEasy to operateCereal cultivationCultivating equipmentsOrganismSeedling
The invention discloses an aphid biological control method with barley and Sitobion avenae as storage carriers. The method comprises the steps that A. barley reproduction is carried out, wherein after barley seeds are subjected to sterilization and deinsectization, a culturing medium is used for barley reproduction; B. Sitobion avenae reproduction is carried out, wherein Sitobion avenae is collected and sent into barley for culturing reproduction; C. aphidiidae inoculation is carried out, the aphidiidae is collected and put into barley where aphid breeding is completed for culturing; D. field releasing is carried out, wherein barley with aphidiidae are placed between lines of crops; and E. carrier plant maintaining and replacing are carried out, wherein timing moisture supplementing and in-due-time barley replacing are carried out. The aphid biological control method with the barley and the Sitobion avenae as the storage carriers is easy to operate, low in cost and obvious in effect.
Owner:NINGBO ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A kind of ecdysone receptor gene usp dsRNA and its application in controlling aphid damage
ActiveCN104109673BIncreased mortalityImprove aphid resistanceBiocideAnimal repellantsAgricultural scienceNucleotide composition
The invention discloses an application of dsRNA of an ecdysone receptor (EcR) related gene USP to control of damage caused by aphids. DsRNA provided by the invention is double-stranded RNA formed by a nucleotide shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table and a nucleotide shown in an inverse complementary sequence of the sequence 2. Experiments prove that dsRNA of cDNA of the EcR related gene of sitobion avenae is obtained; expression of the gene USP in sitobion avenae can be inhibited, impaired growth and development of wheat aphids can be caused and lethal effects can be generated by adopting the method of feeding dsRNA in vitro.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A kind of carboxylesterase gene dsrna and its application in the prevention and treatment of the wheat aphid
The invention discloses a carboxylesterase gene dsRNA and applications thereof in prevention and treatment of sitobion avenae. The dsRNA is a double-chain RNA consisting of nucleotide shown in a sequence 1 in a sequence table and nucleotide shown in a reverse complementary sequence of the sequence 1. Experiments proves that carboxylesterase genes in sitobion avenae are reduced to different degrees after the sitobion avenae is fed with carboxylesterase gene dsRNA, which means that dsRNA taken in by a lancet enters the cells of the sitobion avenae to generate RNAi cascade reaction and the expression of a target gene is interfered. In a morphological view, the growth state of the sitobion avenae is changed, and the ecdysis index of the sitobion avenae fed with the carboxylesterase gene dsRNA is significantly reduced in comparison with a control. Therefore, carboxylesterase gene dsRNA can be used in prevention and control of sitobion avenae. The invention lays a foundation for construction of new germplasm of wheat by using plant-mediated RNAi technology in the future.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for obtaining young winged aphids of macrosiphum avenae in rapid and directional mode
The invention relates to a method for obtaining young winged aphids of macrosiphum avenae in a rapid and directional mode. The method comprises the steps that S1, adult wingless aphids of macrosiphum avenae are raised in a single mode, and propagation of three generation is carried out; S2, aphids of the fourth generation are raised to third instar in a single mode, and a plurality of raised aphids of the fourth generation are put into a same culture device; S3, E-beta-farnesene solutions are added into the culture device repeatedly, and after the E-beta-farnesene solutions are added, young winged pseudo embryos and / or aphids of macrosiphum avenae are collected. According to the method for obtaining the young winged aphids of macrosiphum avenae in a directional mode, pseudo embryos which can develop winged macrosiphum avenae, first instar aphids and second instar aphids which can develop winged macrosiphum avenae, third instar aphids of winged macrosiphum avenae, fourth instar aphids of winged macrosiphum avenae and adult aphids of winged macrosiphum avenae are obtained in a directional mode, and the basis of the aphid gene expression study of the pseudo embryo period, first instar period and second instar period is provided; the method is convenient, simple and easy to operate, and wide in application prospect.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
siRNA designed based on the olfactory receptor SaveOrco gene of the wheat aphid sitobion avenae and its application
ActiveCN105755003BHigh sequence identityAchieve targetedBiocideAnimal repellantsBiotechnologyConserved sequence
The invention relates to siRNA based on Sitobion avenae SaveOrco gene design and application thereof.Transcription of a SaveOrco gene is interfered through feeding of siOrco7.Real-time fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) research shows that the expression of the SaveOrco gene is obviously restrained.Olfactory behavior reaction detection results show that the responding rates of silenced aphids to z-3-hexenol, methyl salicylate and EBF are obviously reduced under SaveOroco expression.An EBF inducing experiment for sitobion avenae winged morph differentiation is developed, siRNA processed aphids stop inducing of EBF, normal chemical communication of the aphids is interfered, and stress inducible wing bud generation is also stopped.In this way, a conserved sequence of the Orco gene can be applied to an RNAi technology mediated by siRNA, and the aphids can be effectively restrained from rapidly diffusing to be harmful and are prevented and treated.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A method of raising aphid-eating gall midges by using a mixed population of various aphids on barley
ActiveCN111802332BShort breeding cycleIncrease planting densityAnimal feeding stuffCereal cultivationAphidoletes aphidimyzaHordeum vulgare
Owner:DRY LAND FARMING INST OF HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
An ecdysone receptor gene ecr dsRNA and its application in controlling aphid damage
ActiveCN104109672BIncreased mortalityImprove aphid resistanceBiocideAnimal repellantsBiotechnologyAphis
The invention discloses an application of dsRNA of an ecdysone receptor (EcR) related gene to control of damage caused by aphids. DsRNA provided by the invention is double-stranded RNA formed by a nucleotide shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table and a nucleotide shown in an inverse complementary sequence of the sequence 2. Experiments prove that dsRNA of cDNA of the EcR related gene of sitobion avenae is obtained; expression of the EcR gene in sitobion avenae can be inhibited, impaired growth and development of wheat aphids can be caused and lethal effects can be generated by adopting the method of feeding dsRNA in vitro.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
DNA molecule for expressive inhibition of hairpin RNA of Sitobion avenae chitin synthetase 1 gene and application thereof
InactiveCN106011138AReduce usageControl quantityAngiosperms/flowering plantsDNA/RNA fragmentationA-DNAInsect
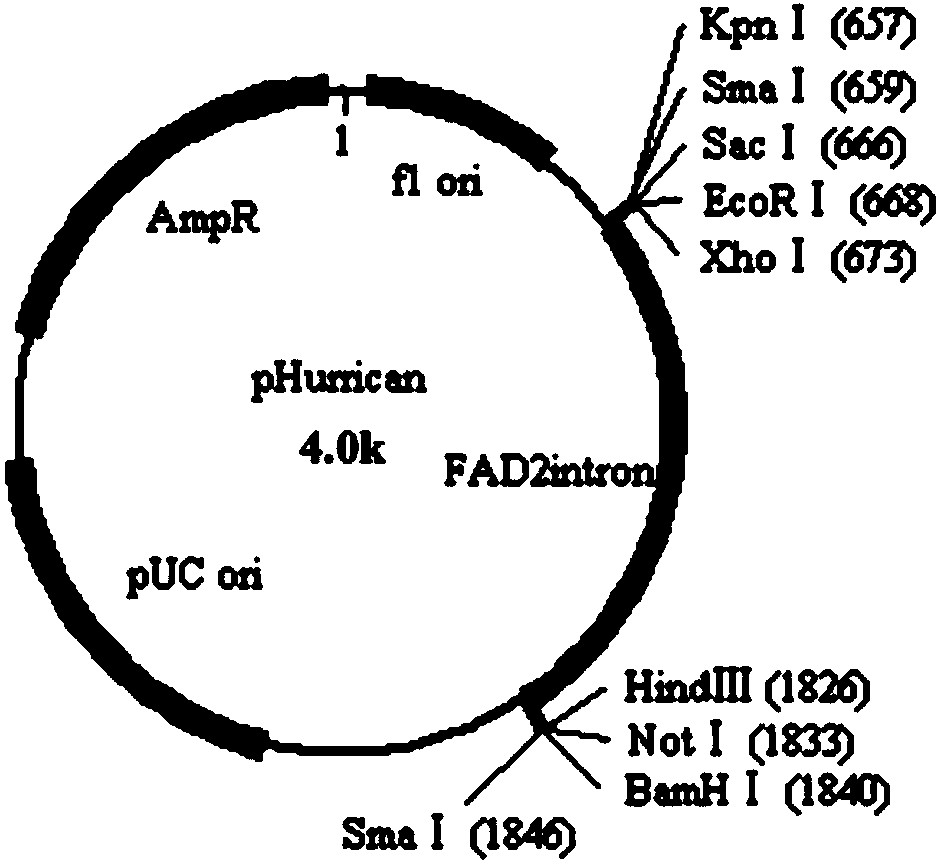
The invention discloses DNA molecule for expressive inhibition of hairpin RNA of Sitobion avenae chitin synthetase 1 gene and an application thereof. A DNA molecular structure for expressive inhibition of hairpin RNA of Sitobion avenae chitin synthetase 1 gene is shown as a formula (I) in the specification: SEQ forward sequence-X-SEQ reverse sequence (I); the SEQ forward sequence is 31 th-637th bit in the sequence 1; and the SEQ reverse sequence is reversely complemented with the SEQ forward sequence; X is a spacer sequence between the SEQ forward sequence and the SEQ reverse sequence, and X is neither complemented with the SEQ forward sequence nor complemented with the SEQ reverse sequence; a X sequence is the sequence containing FAD2 Intron1, and the FAD2 Intron1 sequence is the 664th-1793th bit of the sequence 1. The experiment proves that the transgenic lines through conversion of the DNA molecule to wheat can inhibiting breeding and ecdysis of Sitobion avenae, and the prevention and treatment on insects from agriculture production can be achieved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Bacteria and pest killing compound agent for wheat
The invention relates to the development and application of a bacteria and pest killing compound agent for wheat. The compound agent mainly consists of tebuconazole, triazolone and imidacloprid and can be prepared into missible oil, missible oil, wettable powder and the like. Demonstrated by biological test, the compound agent has obvious synergistic function for wheat stripe rust and erysiphe graminis and can also prevent and kill aphid. According to field experiments, the compound agent can achieve 90 percent of effect in preventing wheat leaf diseases, more than 90 percent of effect in preventing the erysiphe graminis, no less than 98 percent of effect in preventing and controlling wheat sitobion avenae. The compound agent has the functions of killing bacteria and pests, is conveniently used, saves work time, reduces cost and environment pollution, and actively responds to the national policy of energy conservation and emission reduction. Meanwhile, the compound agent has simple process, is easy to produce, can be directly transformed into a production capability and can obtain economic and social benefits as soon as possible.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
The Partial Sequence, Cloning Method and Application of Internal Reference Gene of Aphid argentina
ActiveCN110734912BSpecificOptimizing the Amplification ProgramMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesBiotechnologyReference genes
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com