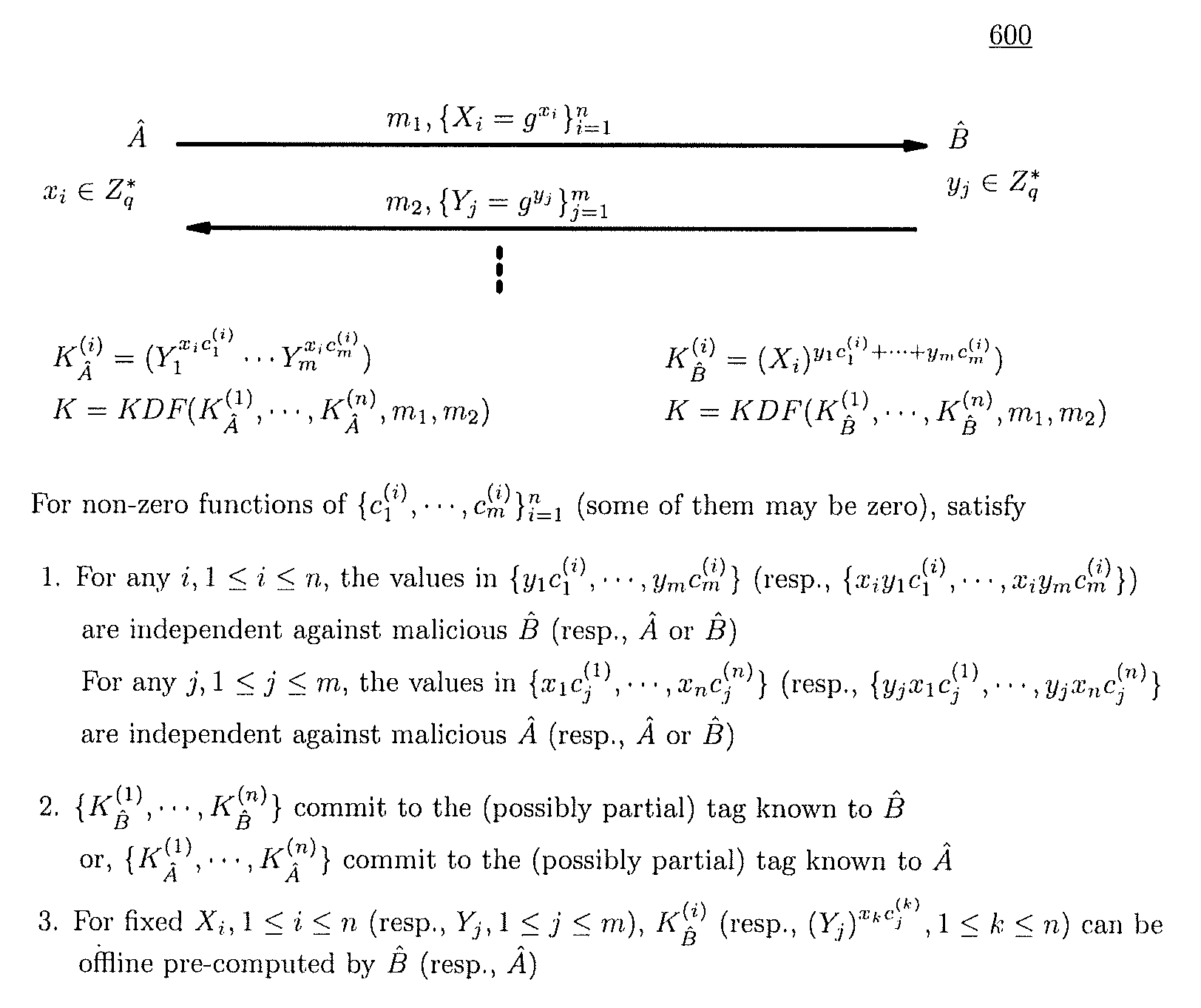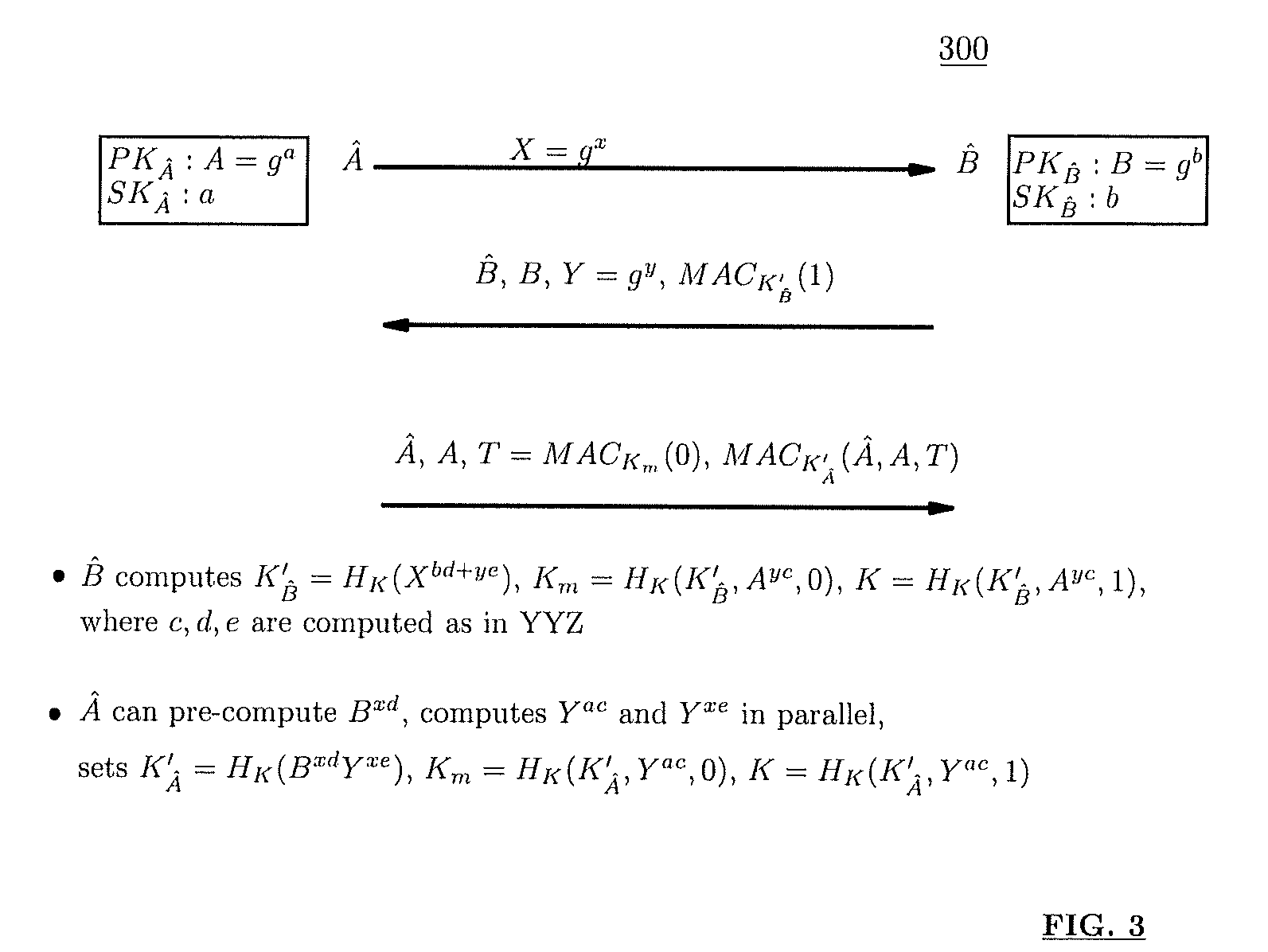Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
99 results about "Prove it" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
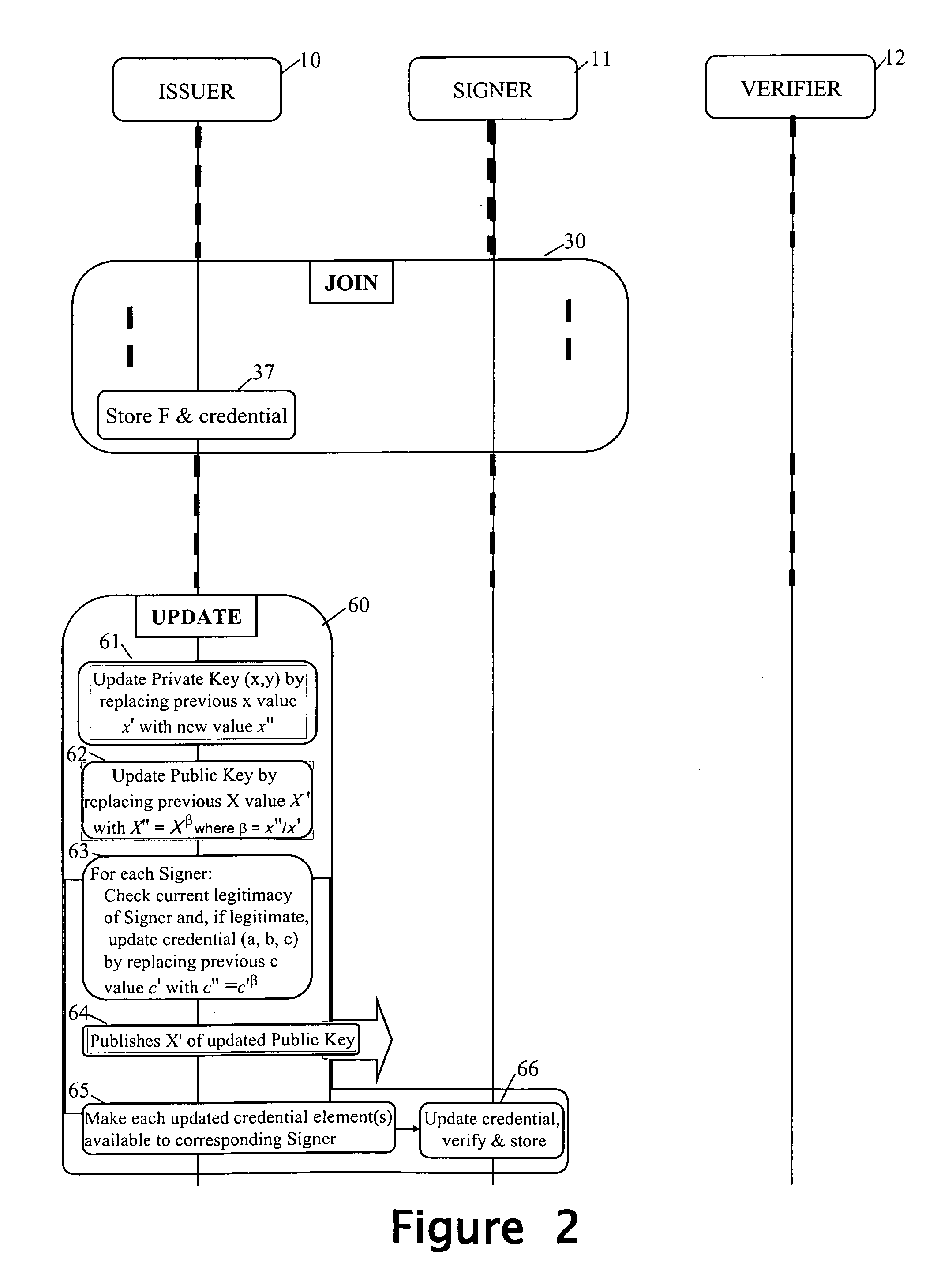
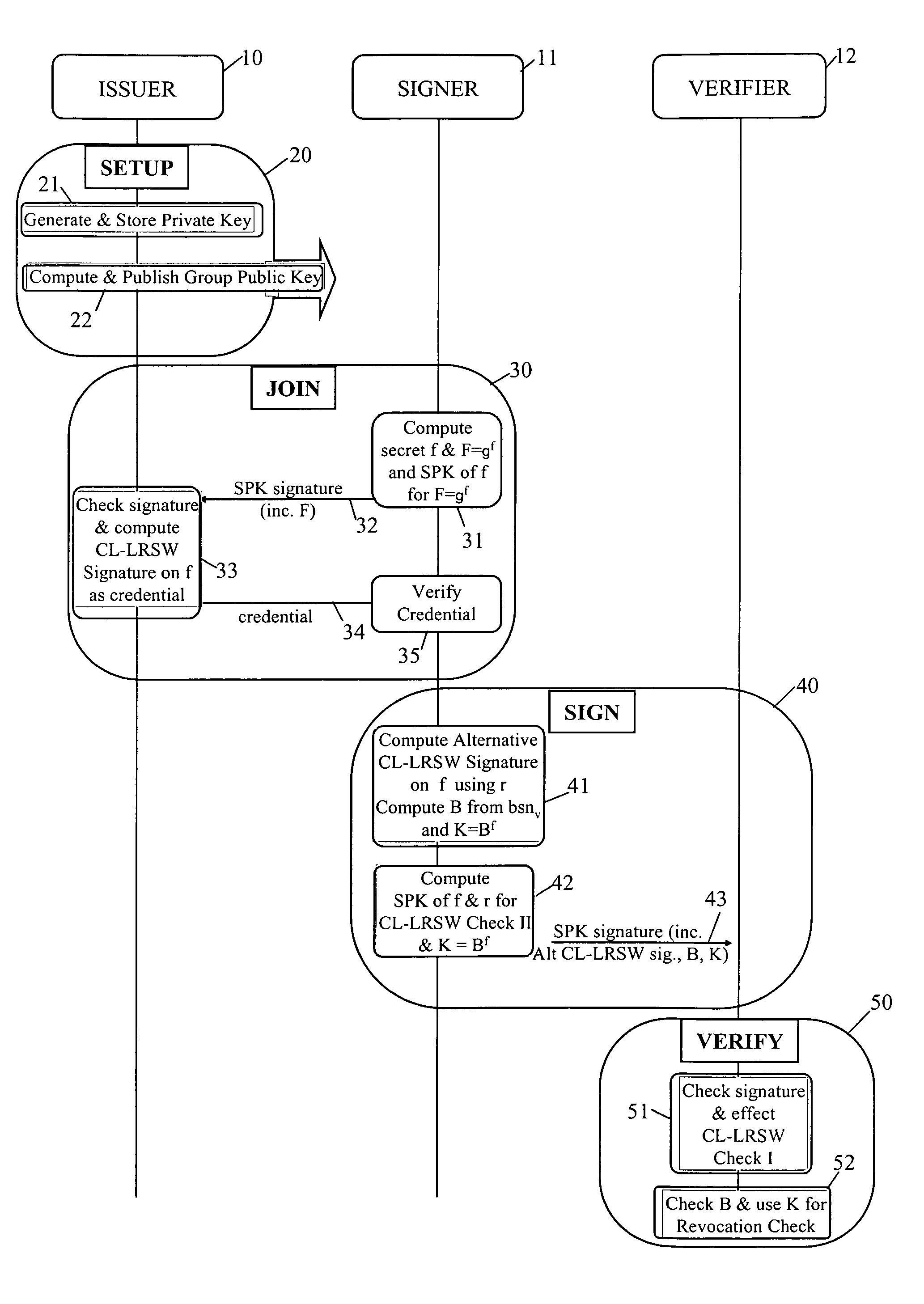
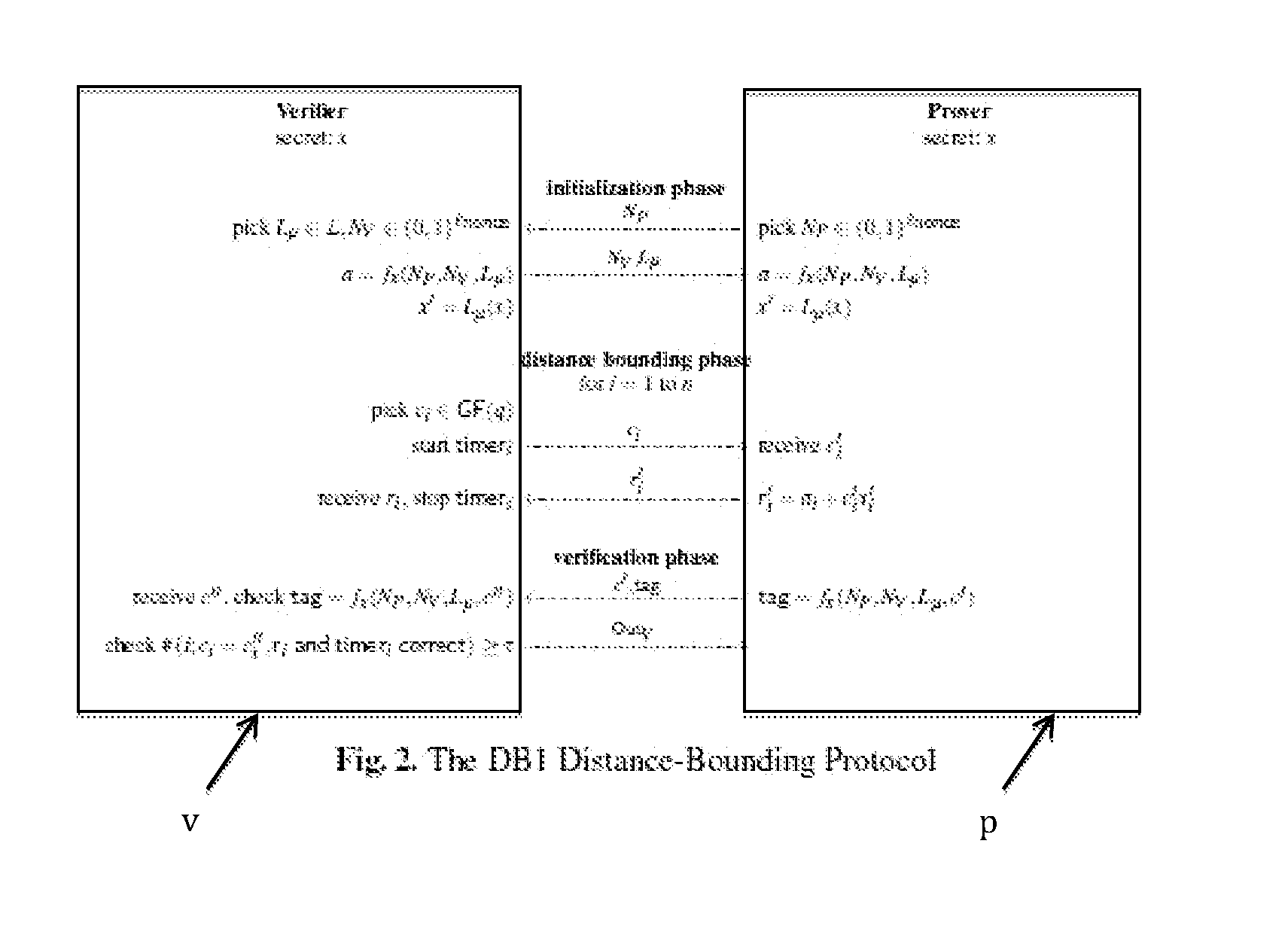
Revocation for direct anonymous attestation
ActiveUS20090210705A1Multiple keys/algorithms usagePublic key for secure communicationProve itDirect Anonymous Attestation
Direct Anonymous Attestation involves a Signer using a credential supplied by an Issuer to anonymously prove to a Verifier, on the basis of a public key of the Issuer, the Issuer's attestation to the Signer's membership of a particular group. To facilitate membership revocation, the Issuer updates the public key at intervals, and also effects a complementary updating to the Signer's credential unless the Signer has ceased to be a legitimate group member. A non-updated credential is inadequate to enable the Signer to prove its Issuer attested group membership to a Verifier on the basis of the updated Issuer public key.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
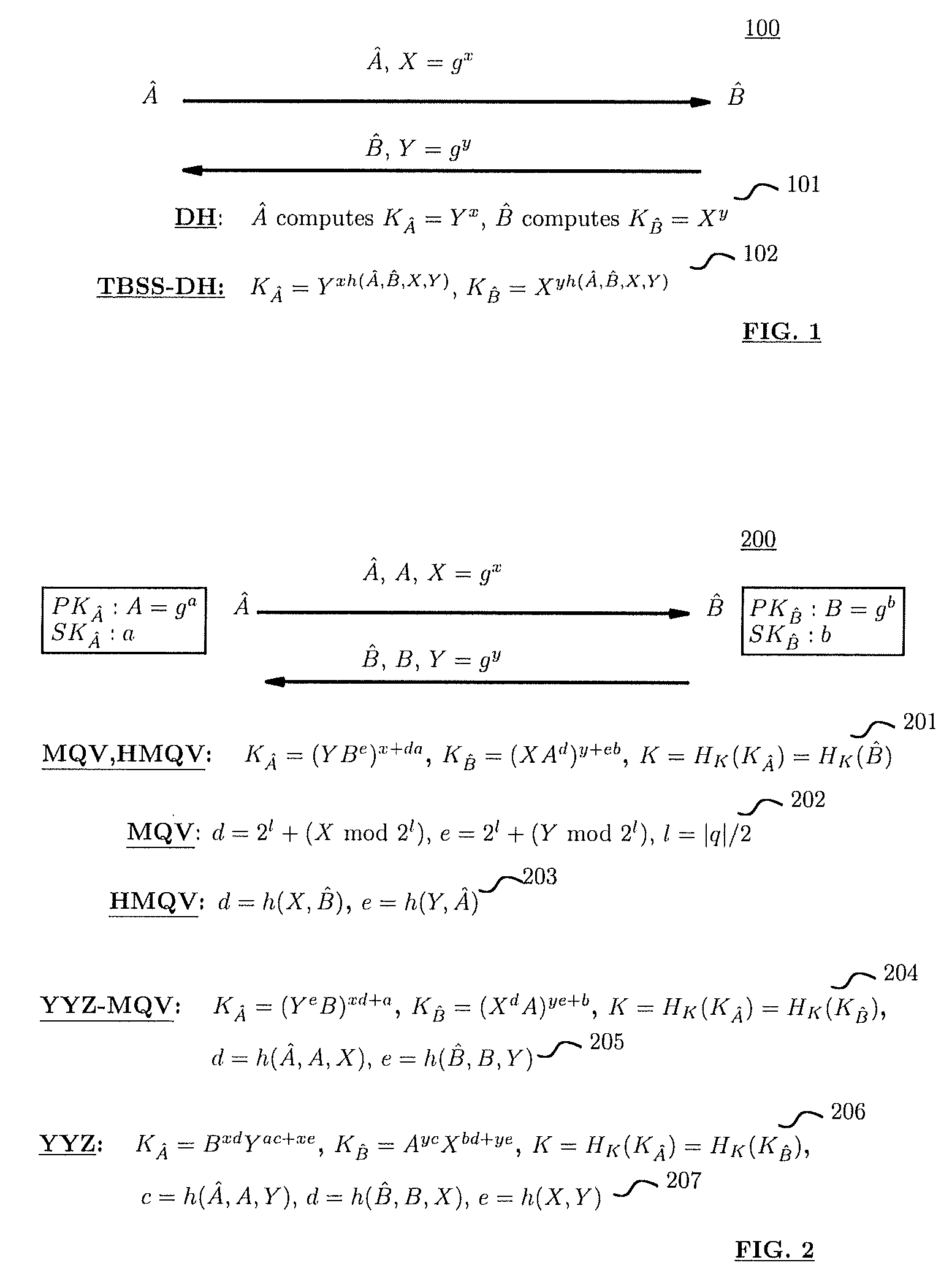
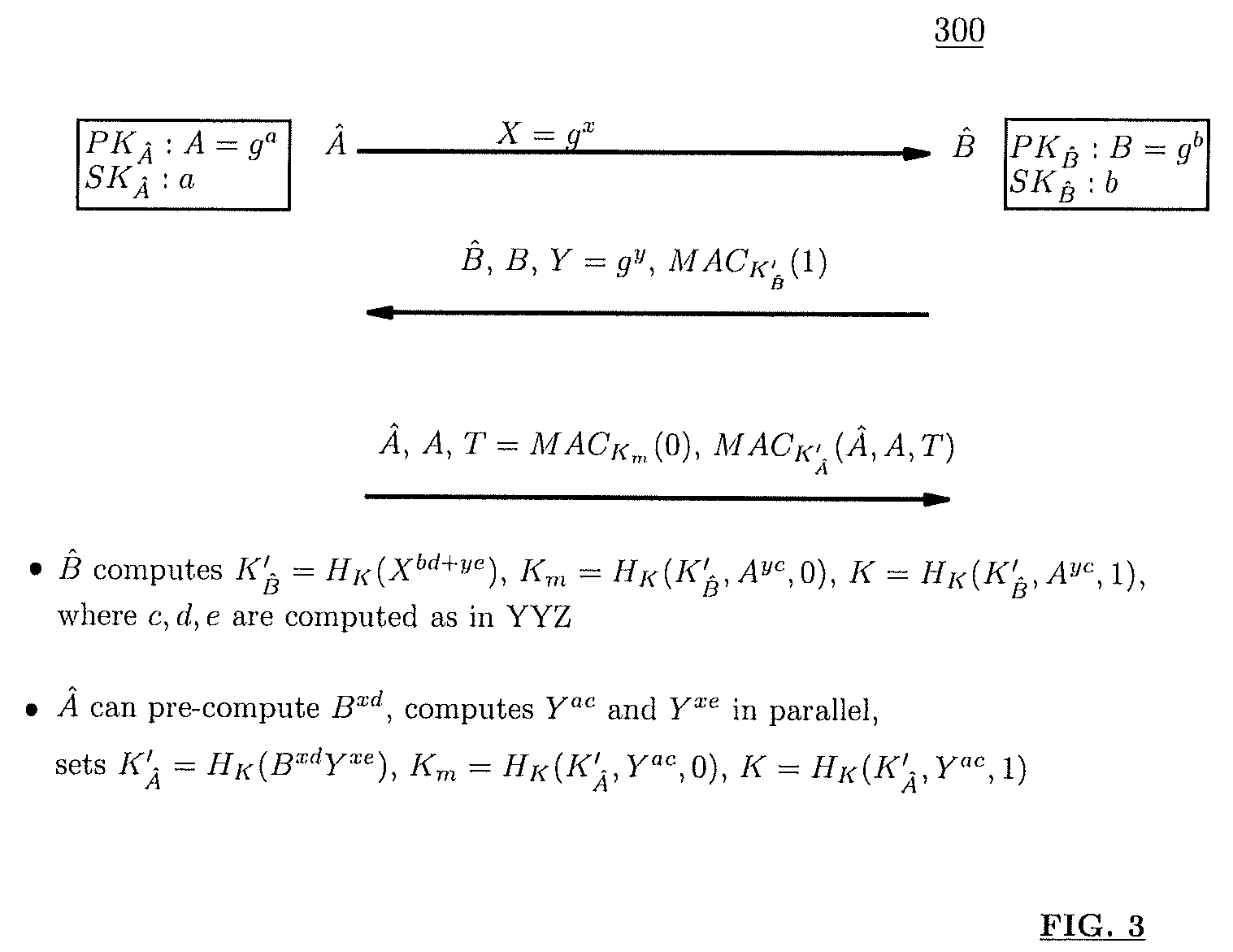
Method and structure for self-sealed joint proof-of-knowledge and diffie-hellman key-exchange protocols
InactiveUS20100205443A1Robust resistance against malicious disclosureImproving security and privacy and efficiencyUser identity/authority verificationSecret communicationDiffie–Hellman key exchangeCryptographic protocol
A method (and structure) for a party (the prover) to prove its knowledge, jointly and non-malleably, of multiple secret (fixed and / or ephemeral) Diffie-Hellman exponents (DH-exponents), corresponding to its public (fixed and / or ephemeral) DH-components and with respect to the public (fixed and / or ephemeral) challenging DH-components from another party (the verifier). The joint proof-of-knowledge (JPOK) consists of secrets made by multiplying multiple DH-secrets, which can be generated and verified by each party by its own secret DH-exponents and the public DH-components of both parties. To ensure the non-malleability of the JPOK, the method invented herein makes all these multiplied DH-secrets to be independent, and makes the session-tag committed to the multiplied DH-secrets. To preserve players' privacy and / or to improve protocol efficiency, the invented method makes the DH-secrets to be multiplied to further satisfy at least one of the following (besides above independence and commitments properties): (1) Deniability: all the DH-secrets to be multiplied can be computed out merely from the ephemeral secret DH-exponents and the public DH-components of both parties; (2) Pre-computability: a DH-secret involving a fixed DH-component of a party can be offline pre-computed by its peer; (3) Post-ID computability: a DH-secret involving an ephemeral DH-component of a party can be computed by its peer without knowing that party's identity and / or fixed DH-components. The secrets made by multiplying multiple DH-secrets can then be used to derive session-keys and to generate and verify authenticators between the parties. The invented method can also be used in parallel or subsequently by the parties, possibly with reserved player roles in different runs of the method, for mutual identifications, key confirmations, and for achieving more advanced cryptographic protocols in various settings.
Owner:ANDREW C YAO
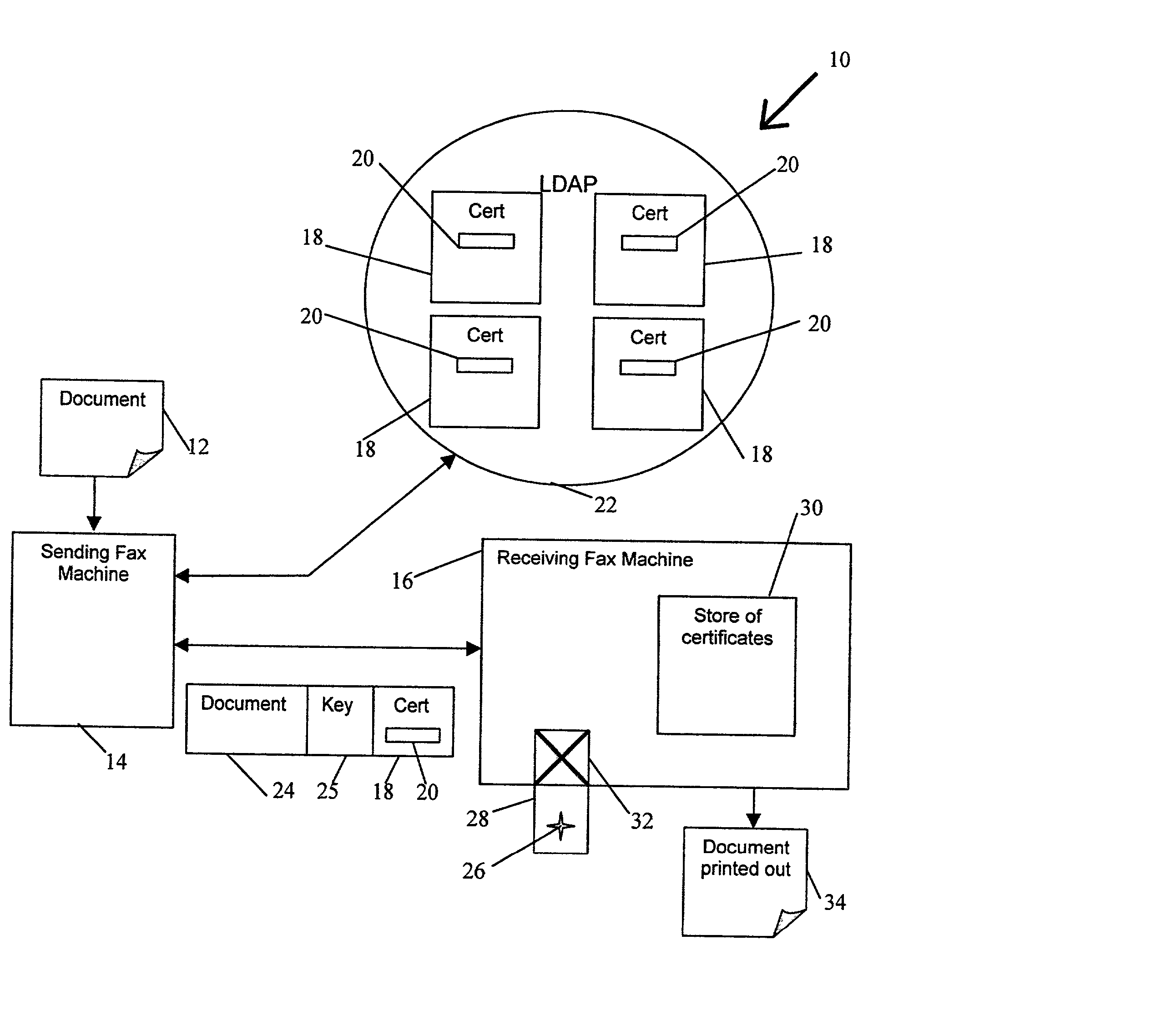
Document transmission Techniques I
InactiveUS20020054334A1None of methods is secureConfidenceUser identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsFile transmissionSmart card
A method of delivering a digital document to an intended recipient at a printout station, such as a fax machine. The method comprises receiving and securely retaining a transmitted document and a transmitted independently verifiable data record such as a digital certificate of the intended recipient at the printout station. A first token, such as a public key, of the intended recipient is obtained, usually from the transmitted information. The method includes requesting proof of the intended recipient's identity at the receiving fax machine using data in the digital certificate of the intended recipient and releasing the document when the intended recipient has proved their identity by use of a second token, such as a private key, that is uniquely related to the first token. The private key may be provided on a portable smart card. Also envelope data encryption techniques may be used to add security to the transmission of the document.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Anonymous Preservation of a Relationship and Its Application in Account System Management
InactiveUS20110078779A1Improve security levelDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsHash functionInternet privacy
Disclosed is a system or method of using hash functions to preserve a relationship. A relationship is anonymously preserved by storing the hash result of a relationship token that comprises a finite set of values of a plurality of objects. Specifically, an account anonymous identifier of an account can be produced by hashing a relationship token that comprises identity information of an owner of said account. A party that has enough knowledge of an account owner can independently produces said account anonymous identifier and therefore, securely communicates with a specific account without prior communication or a password. An account owner can further prove his / her ownership of an account by submitting related documents and a relationship token that comprises his / her identity information to an account system.
Owner:LIU SONG +1
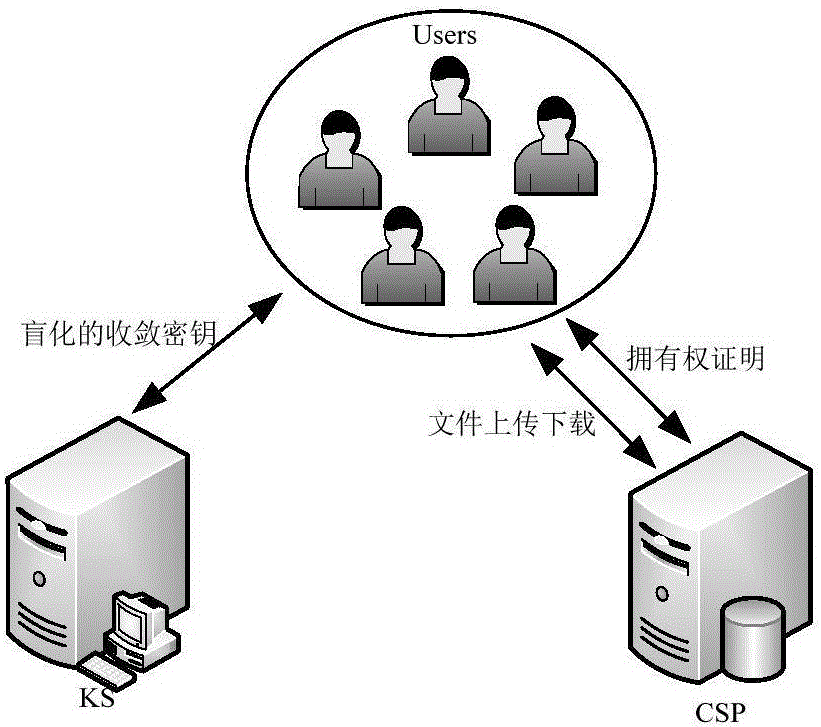
Client secure deduplication method of ciphertext data in cloud storage
ActiveCN105939191AProtection securityAvoid attackKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCiphertextBlind signature
The invention discloses a client secure deduplication method of ciphertext data in cloud storage. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) key generation; (2) file initialization; (3) data block initialization; (4) data block verification; (5) file storage; (6) challenge generation; (7) proof generation; (8) proof verification; and (9) file decryption. According to the method of the invention, a secure key generation protocol is constructed based on blind signature, and therefore, secondary encryption of convergence keys is realized, and the security of the keys can be ensured; and a signature-based ownership proving method is put forward based on the above encryption, and with the method adopted, it can be ensured that a user can prove his or her ownership of a certain file in the could storage to a could server in a safer and more efficient way, and file-level and block-level deduplication of a ciphertext file can be realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Client software attestation
ActiveUS20180114000A1Lower quality of serviceReduce server loadEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareClient-side
A server computing device can determine if a software application executing on a client computing device has not been tampered. Software executes on the server device and communicates either directly or indirectly with an attestation service; a client software application running on the client computing device communicates with the same attestation service. A client software application that is able to calculate a cryptographic hash fingerprint of its executing code image communicates to the attestation service to prove it is untampered with. The attestation service then generates a pass or fail attestation result. The attestation result is communicated between the attestation service and the server computing device. The behaviour of the server computing device is controlled in a way that is conditional on whether a prior attestation of the client software was a pass or fail attestation result.
Owner:CRITICAL BLUE
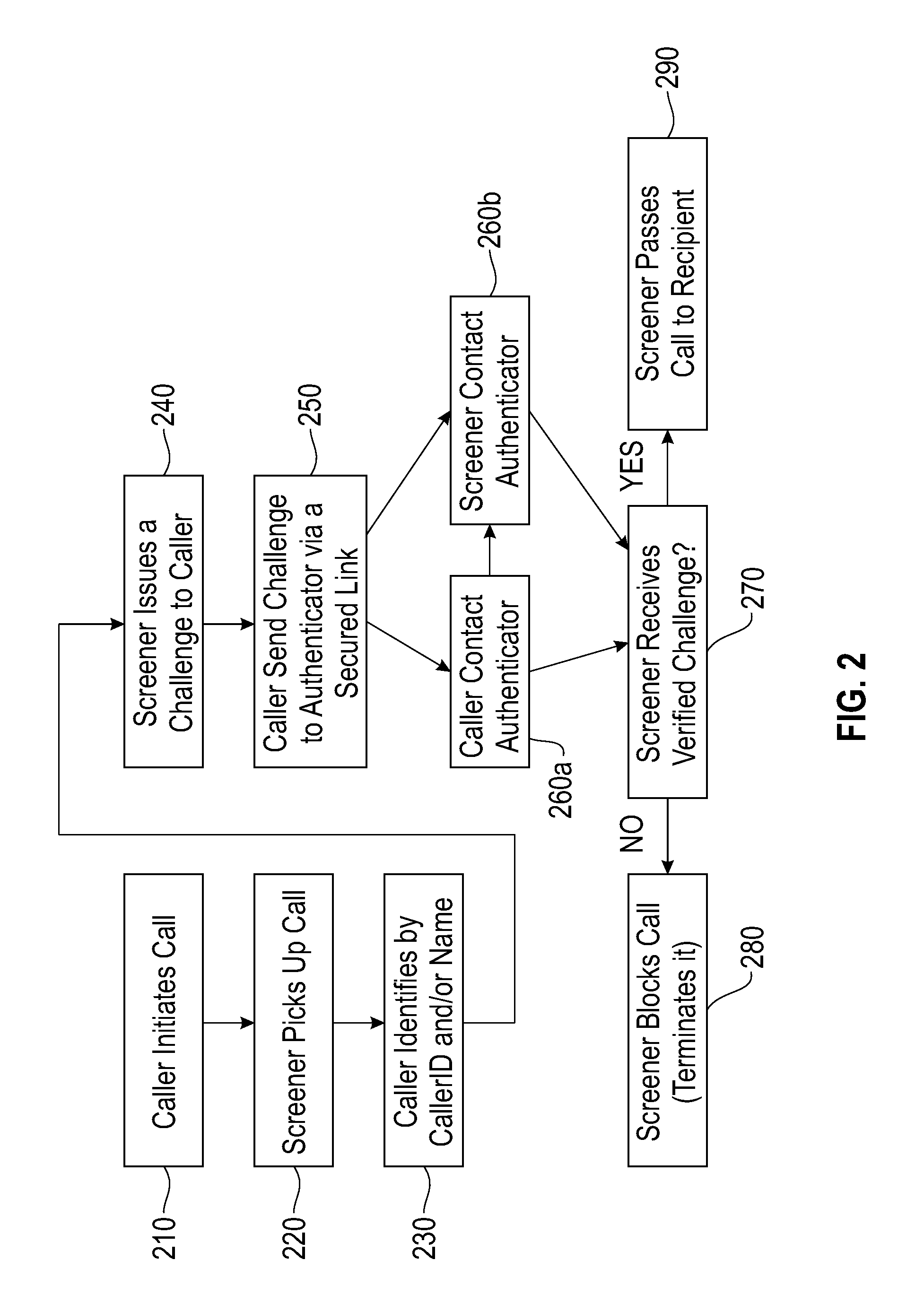
Method and system for authenticating telephone callers and avoiding unwanted calls
ActiveUS20110026699A1Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingCalled number recording/indicationProve itAuthentication
A service that handles incoming telephone calls without bothering the telephone subscriber is disclosed. The service permits a call to go through to a subscriber if the service determines that the call is not unwanted and the caller has been unauthenticated. The authentication is based on challenging the caller to prove its identity rather than relying on caller ID displays. Prospective callers pre-register with the service providing caller account information. When a caller is issued a challenge, the caller may prove its authenticity by supplying the challenge back to the service along with its registered information.
Owner:IBM CORP
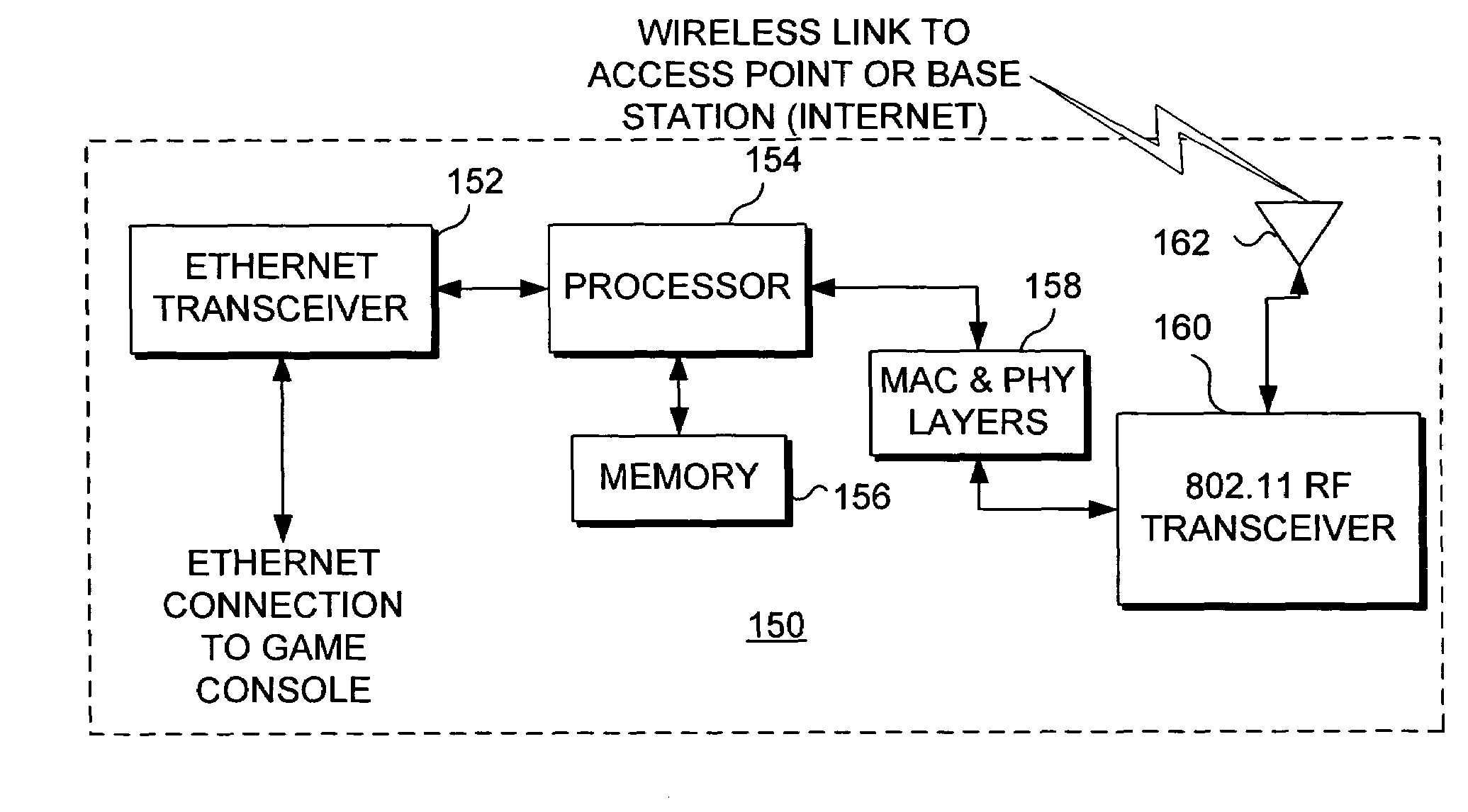
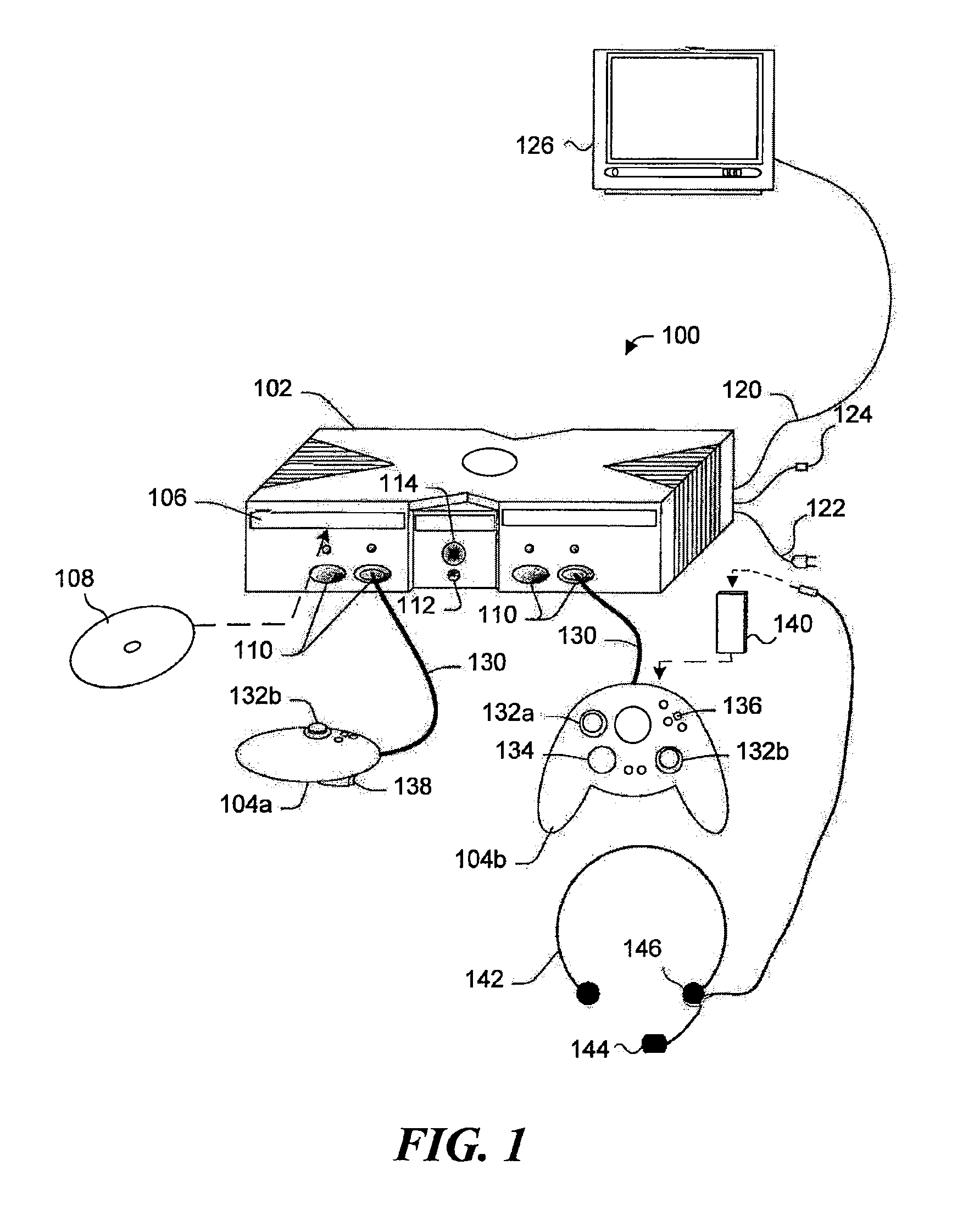
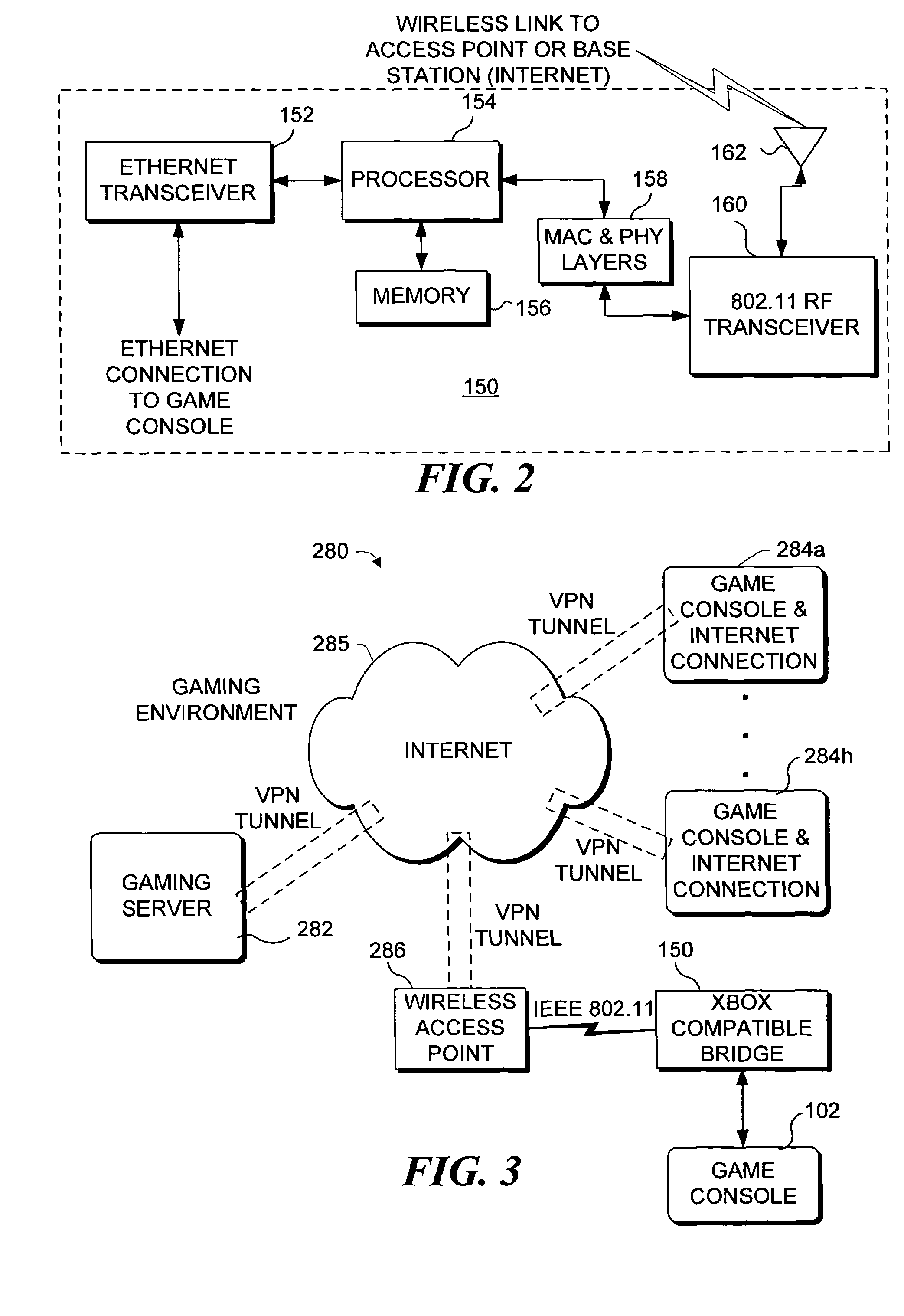
Bridging a gaming console with a wireless network
InactiveUS7412542B1Multiple digital computer combinationsApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingWireless mesh networkWeb browser
Apparatus and system for configuring a wireless bridge for a computing device such as a game console. The wireless bridge must include a key (not known to the public) employed in producing a digest. The digest is passed to the game console to authenticate that the wireless bridge is compatible and can thus be configured by the game console. Once the wireless bridge proves its compatibility, a configuration procedure included in an operating system on the game console configures the wireless bridge to connect to a wireless network so that the game console can communicate through the wireless bridge with a gaming site that is accessed over the Internet. The configuration is done without using a web browser program or a configuration program that is specific to a particular model and manufacturer of the wireless bridge.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
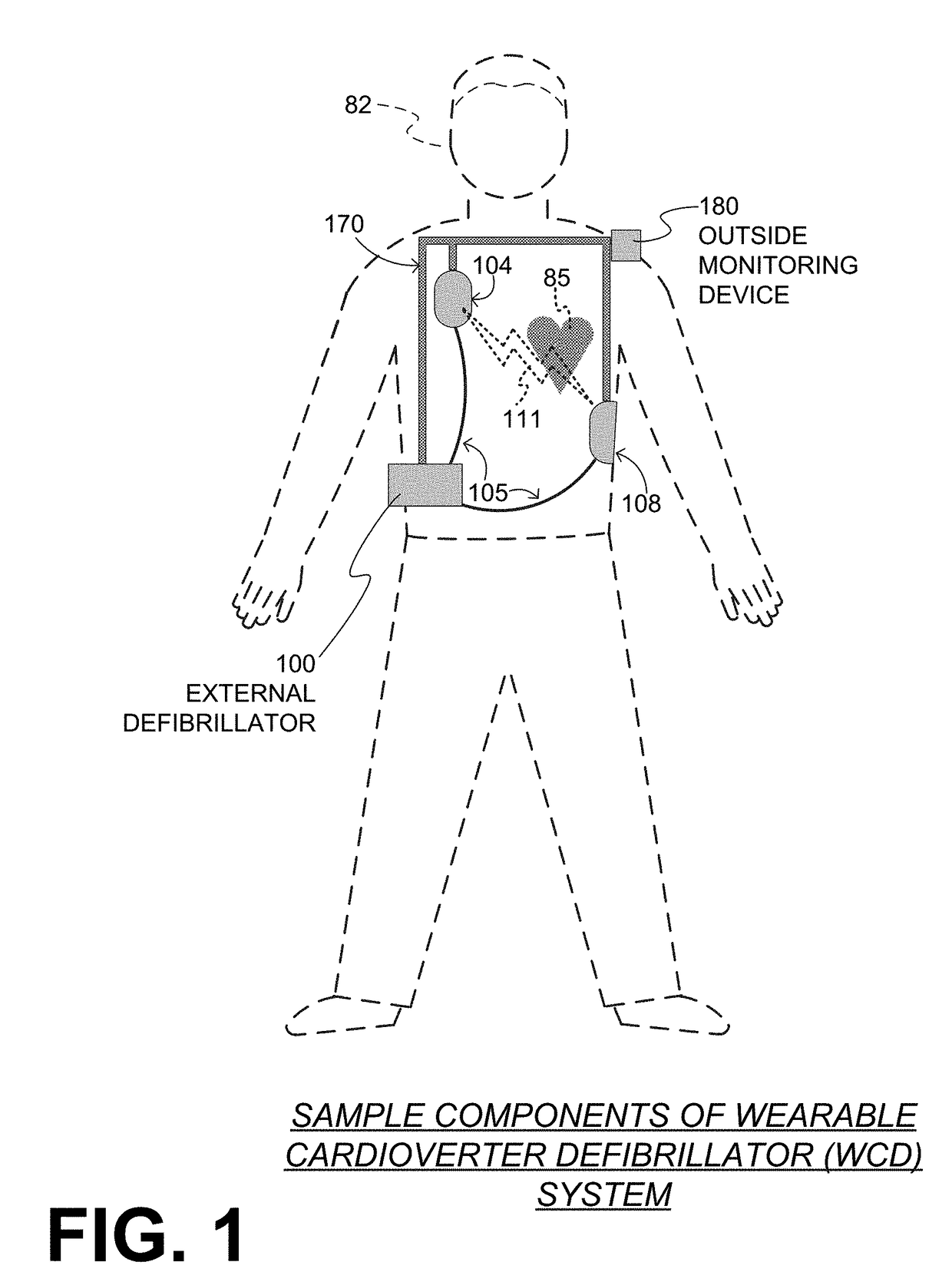
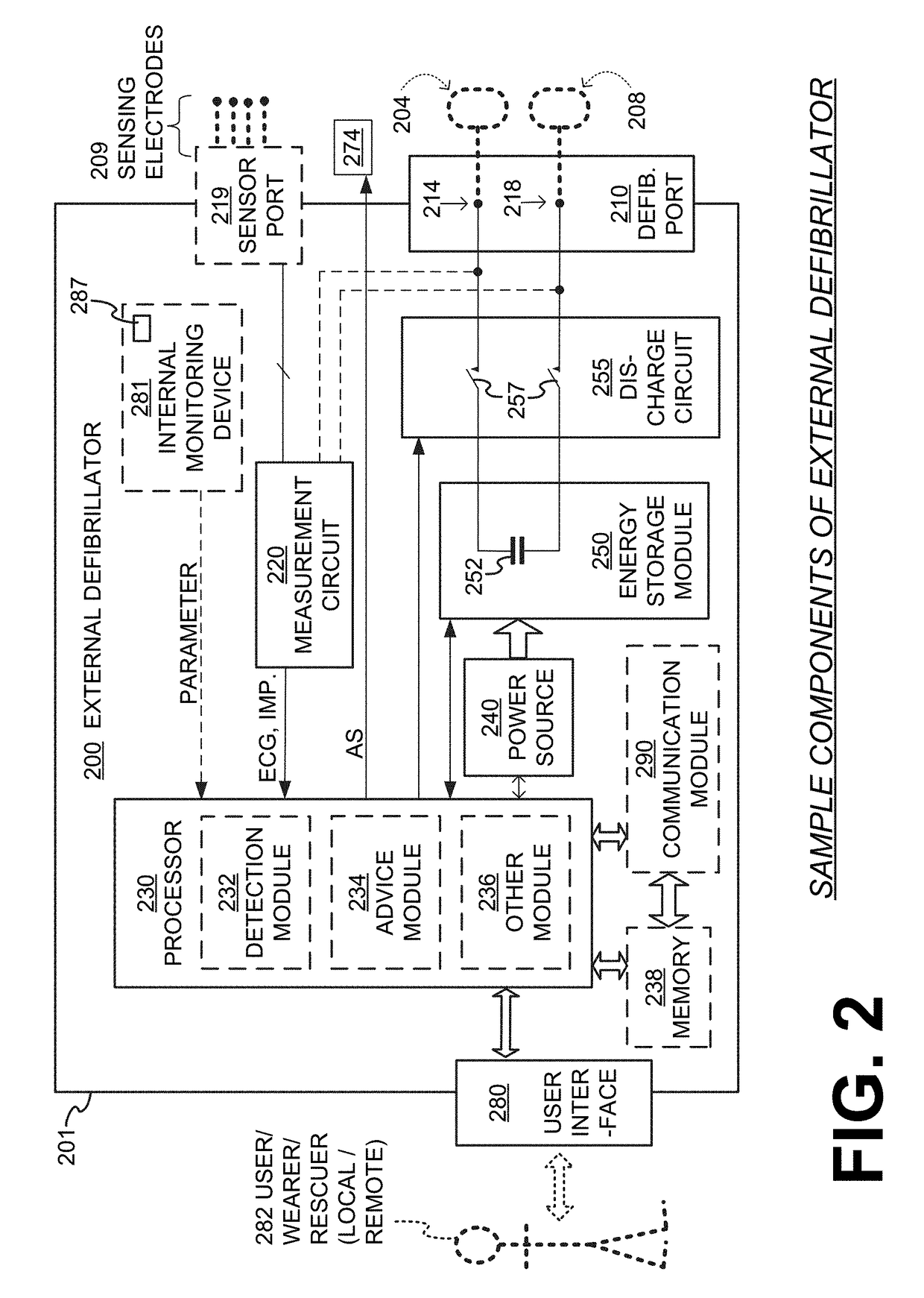
Wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) system reacting to high-amplitude ECG noise
ActiveUS20190030352A1Reduce noiseMore compliantElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsEcg signalWearable cardioverter defibrillator
In embodiments a WCD system is worn and / or carried by an ambulatory patient. The WCD system analyzes an ECG signal of the patient, to determine whether or not the patient should be given an electric shock to restart their heart. If so, then the WCD system first gives a preliminary alarm to the patient, asking them to prove they are alive if they are. The WCD system further determines whether the ECG signal contains too much High Amplitude (H-A) noise, which can distort the analysis of the ECG signal. If too much H-A noise is detected for a long time, the WCD system may eventually alert the patient about their activity, so that the ECG noise may be abated. The WCD system may even pause the analysis of the ECG signal, so that there will be no preliminary alarms that could be false until the ECG noise is abated.
Owner:STRYKER CORP +1
Method and device for reading authentication means and adapted identification means
InactiveUS7380128B2Read intuitivelyFast imagingStampsUser identity/authority verificationAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
Owner:NOVATEC SA
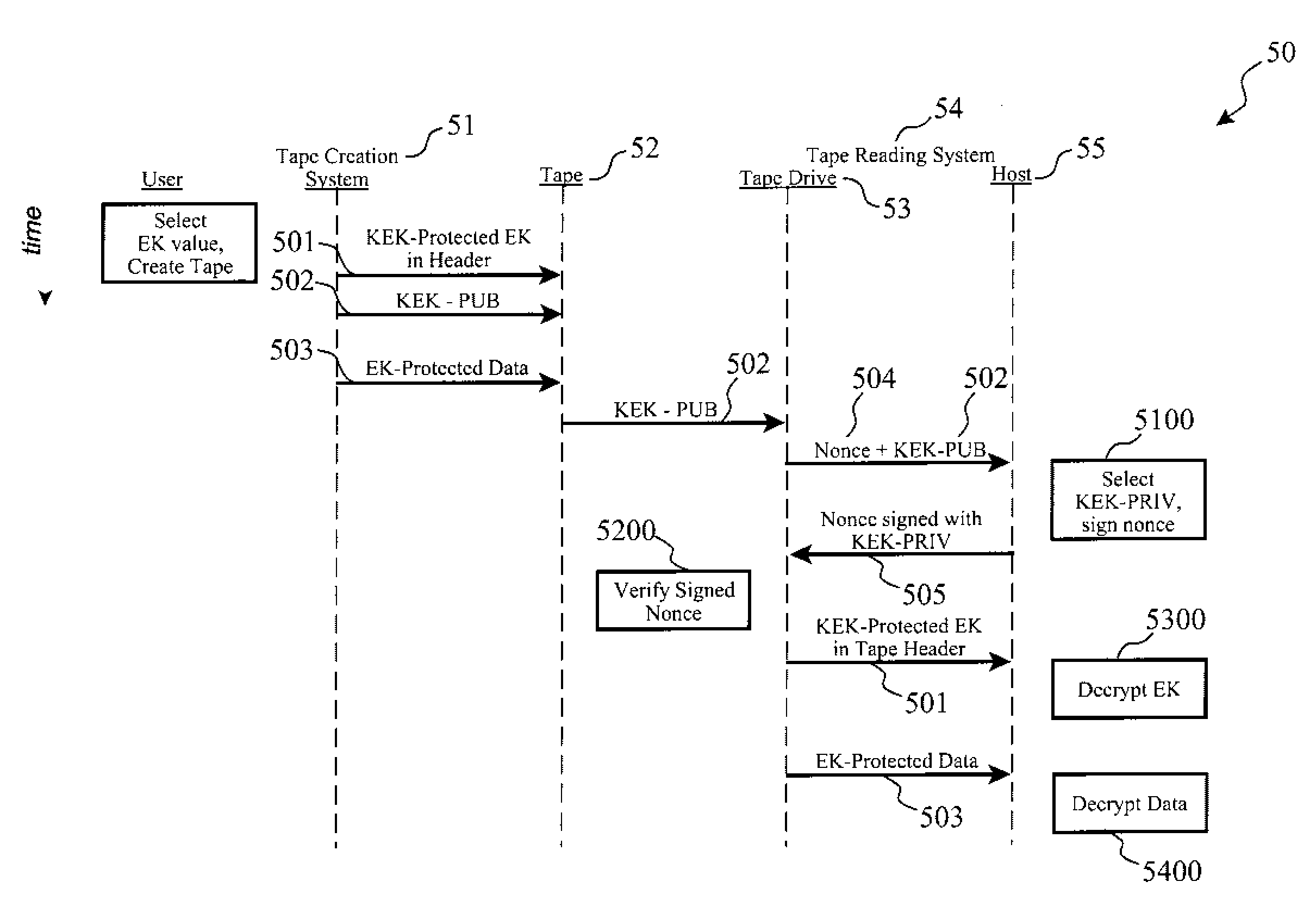
Encrypted Tape Access Control via Challenge-Response Protocol
InactiveUS20080123863A1Easy to useDifficult to automateKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationMagnetic tapeKey Wrap
Access to encrypted data on a removable computer media such as a computer tape is controlled via a uniquely-structured header on the medium having a symmetrical key wrapped by asymmetrical encryption plus a public key associated with the asymmetrical encryption. The data on the medium is encrypted using the symmetrical key. Prior to automated reading of the data by a reader, a challenge is issued to a host system including the public key and preferably a nonce value. The host responds by signing the nonce using a private key associated with the public key in order to prove it has rights to decrypt the data. The symmetrical key is unwrapped using the private key, and finally the unwrapped symmetrical key is used to decrypt the data on the medium, thereby allowing automated reading of the tape data without the need or risk of two administrators sharing a symmetrical key value.
Owner:IBM CORP
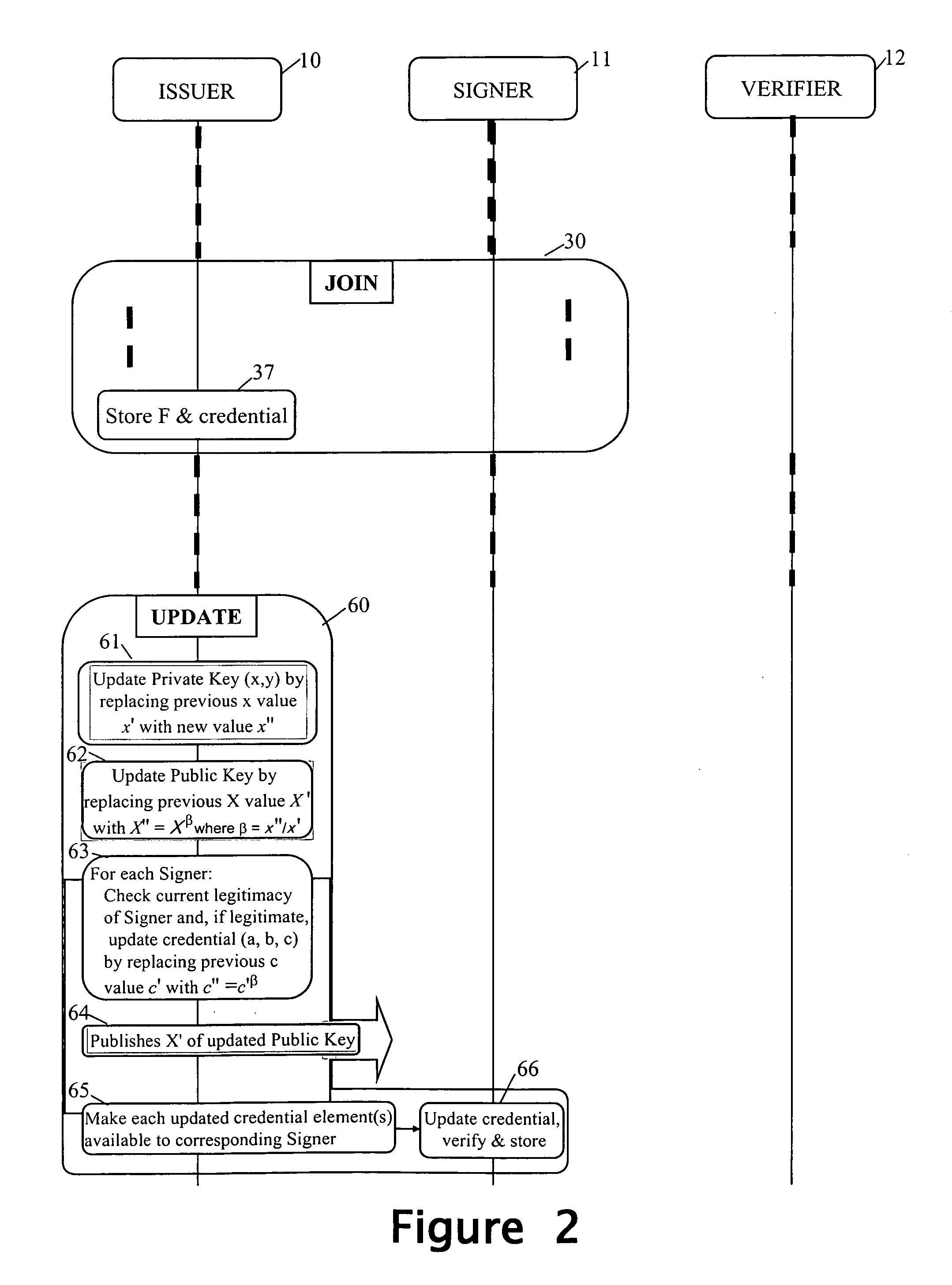
Revocation for direct anonymous attestation
Direct Anonymous Attestation involves a Signer using a credential supplied by an Issuer to anonymously prove to a Verifier, on the basis of a public key of the Issuer, the Issuer's attestation to the Signer's membership of a particular group. To facilitate membership revocation, the Issuer updates the public key at intervals, and also effects a complementary updating to the Signer's credential unless the Signer has ceased to be a legitimate group member. A non-updated credential is inadequate to enable the Signer to prove its Issuer attested group membership to a Verifier on the basis of the updated Issuer public key.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
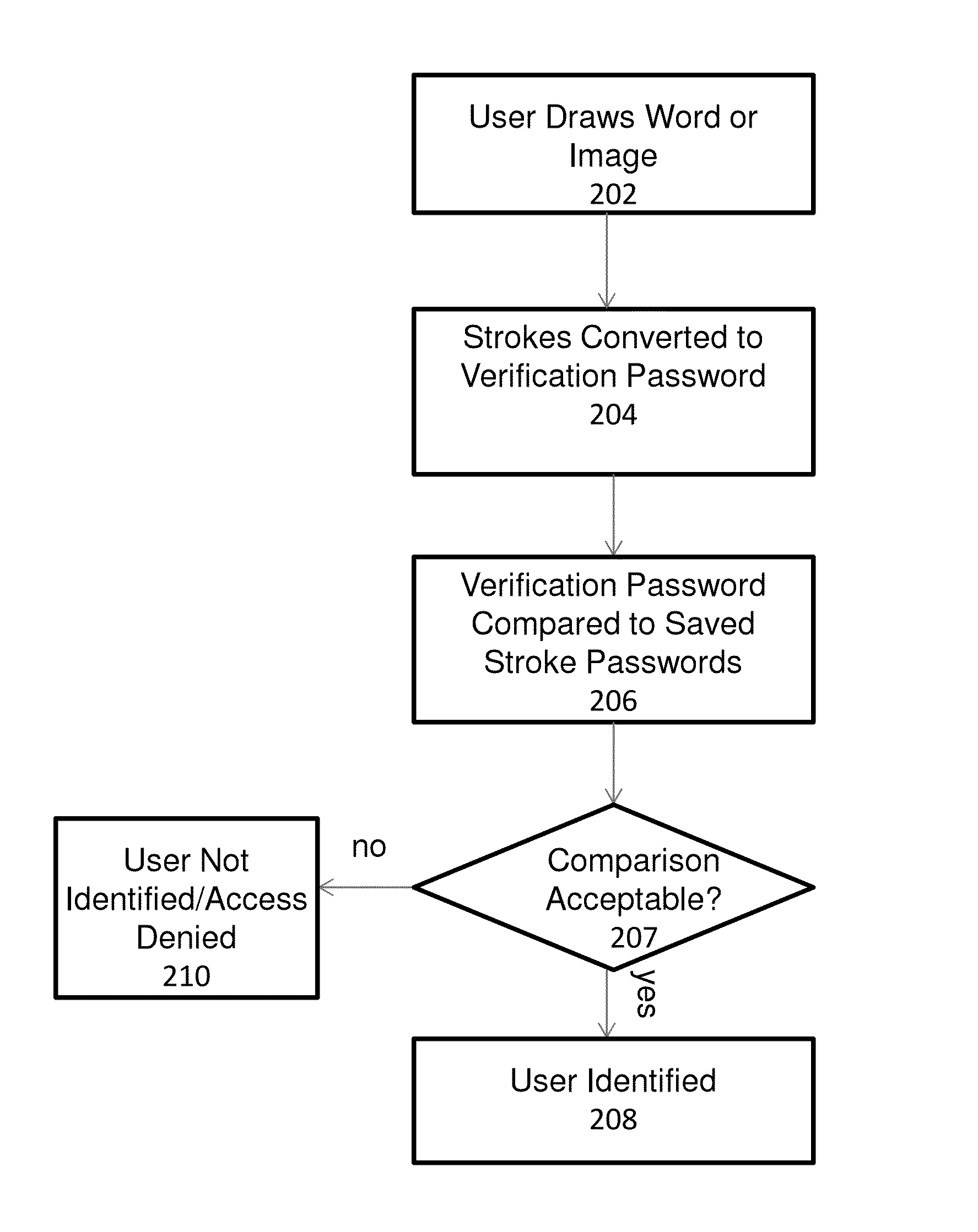
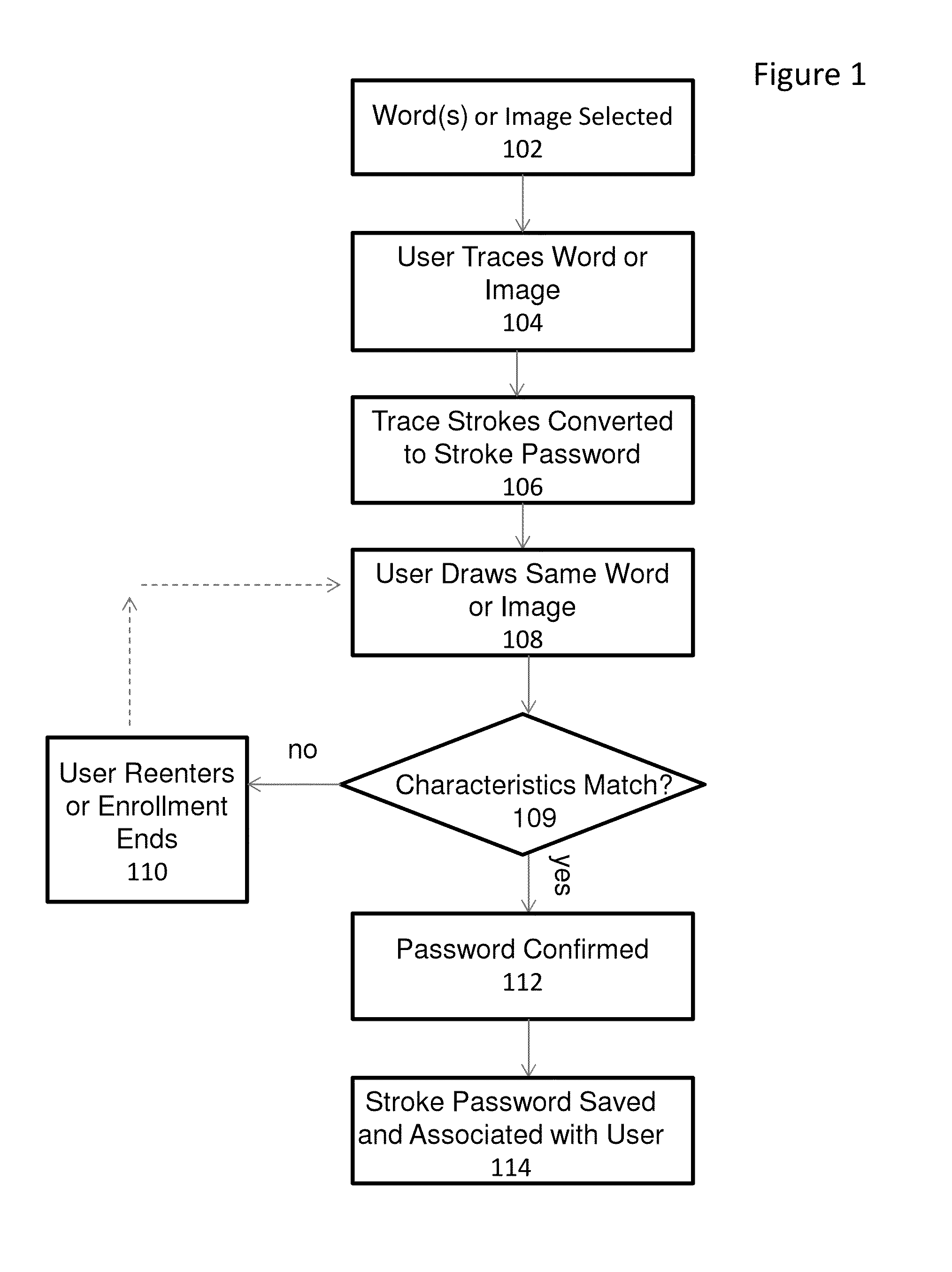
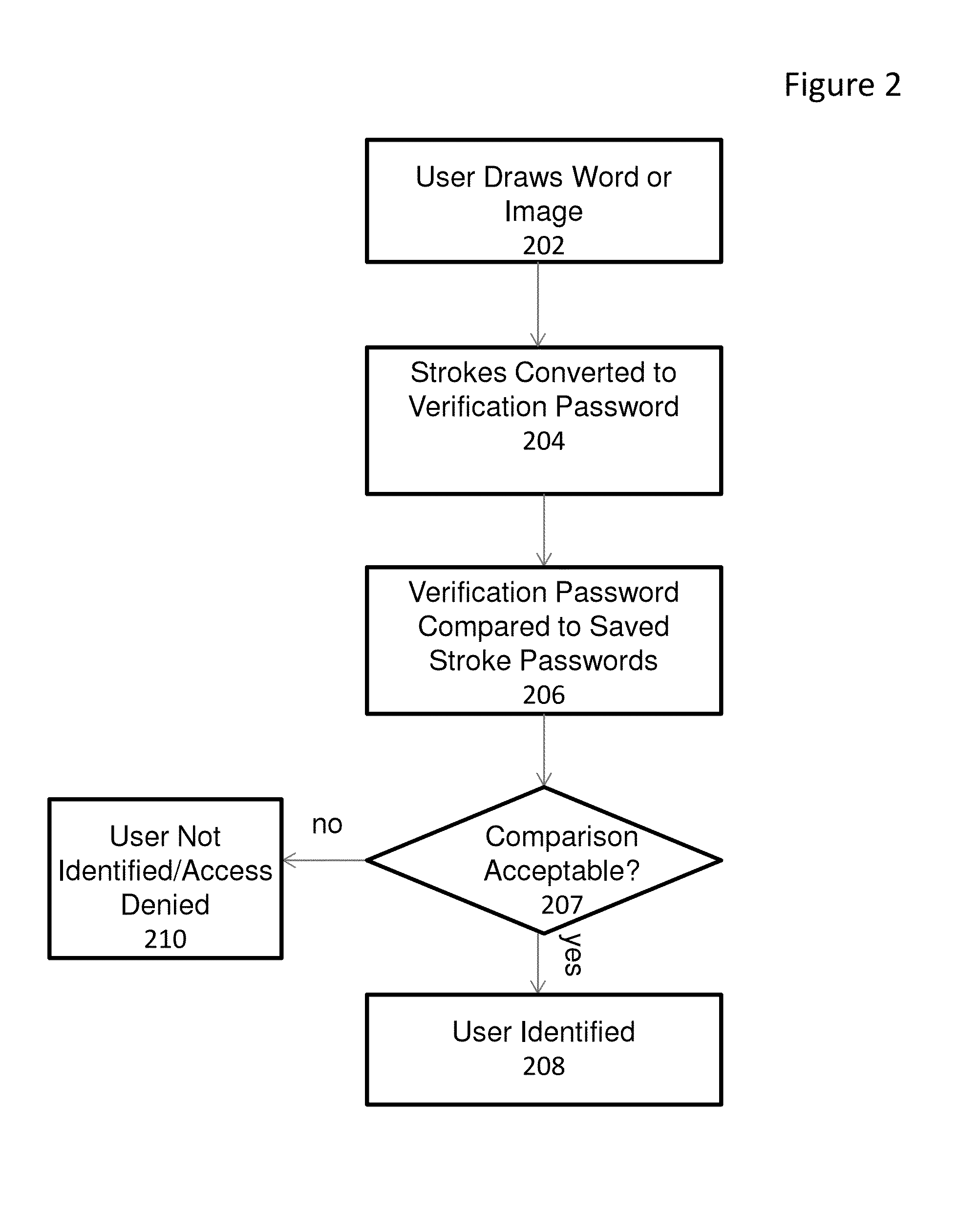
System and method for providing gesture-based user identification
ActiveUS20140075549A1Small sizeLimited codingDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionGraphicsHuman–computer interaction
A mechanism for allowing a user to prove their identity on touch-based devices employing the use of a touch surface in firmware-controlled environments is discussed. The user may prove his or her identity by entering a series of strokes on the touch-based device to form a word or image. Characteristics of the entered strokes such as stroke order and stroke direction are compared to stored stroke characteristics that were gathered from a drawing of the same word or image during a user enrollment process. If the stroke characteristics comparison is acceptable, the user identity is verified.
Owner:INSYDE SOFTWARE
Dyslexia glasses that remove the problems associated with visual dyslexia
Owner:HAYES JOHN ATLEY
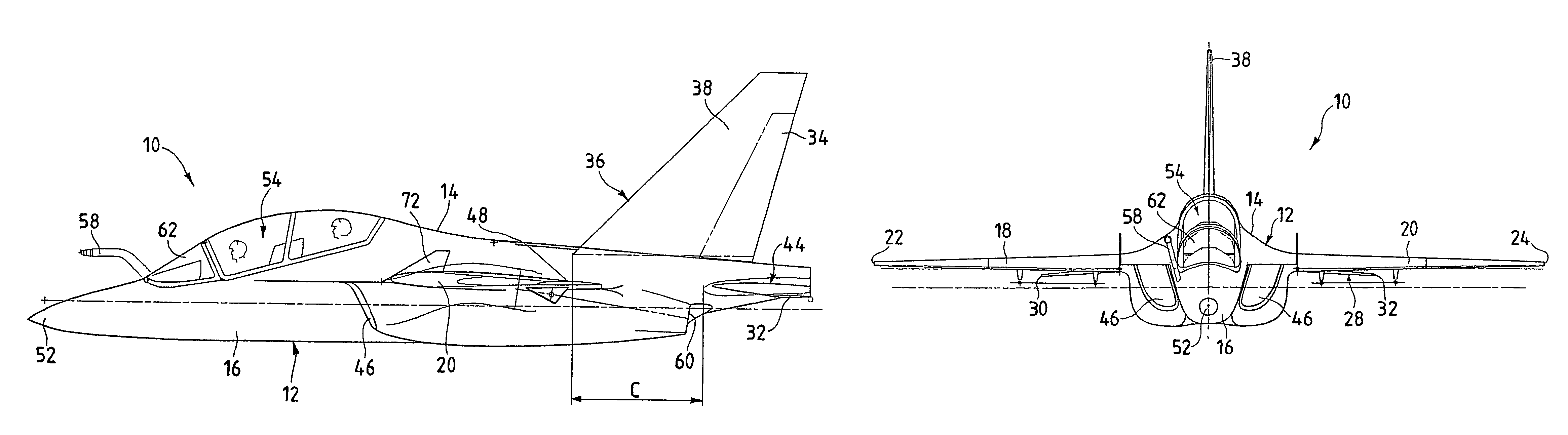
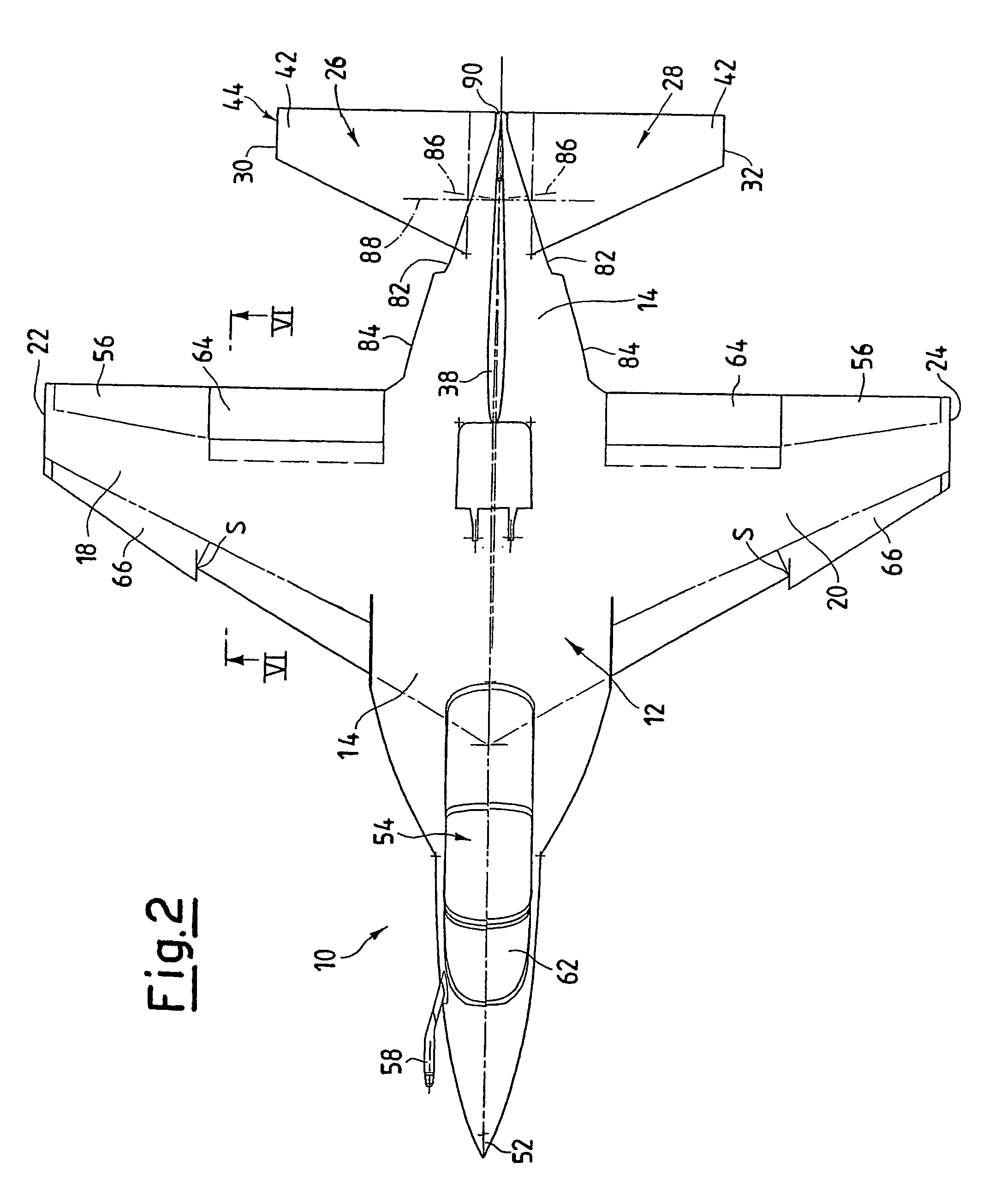
Aircraft configuration with improved aerodynamic performance
InactiveUS7520470B2Reduce air resistanceOptimize aircraft spin behaviorInfluencers by generating vorticesWingsProve itAirplane
An aircraft (10), in particular a trainer aircraft with improved aerodynamic performance, having a configuration able to keep a directional stability and a very good aerodynamic behaviour even at very high angles of attack, where, traditional configurations prove themselves inefficient. In particular, this configuration foresees a forebody (52) with variable section, optimised for high angle of attack flights, a LEX vortex control device (72) at least one diverterless air intake (46), and a wing profile (18, 20) optimised in order to reduce the buffet effects typical of low aspect ratio wings with thin profile and variable camber. The aircraft (10) presents, finally, staggered tails (44 and 38), to optimise the aerodynamic performance.
Owner:ALENIA AERMACCHI
System providing medical personnel with immediate critical data for emergency treatments
An RFID transponder on a person or animal provides the health care or security personnel with the critical information when the personnel employs a reader terminal capable of reading the RFID transponder. The transponder, after being interrogated by the reader, supplies the critical data such as name, blood type, allergies, directives, medicines, and emergency contact numbers. The reader immediately displays such critical information on its screen. The RFID tag can substantiate that it belongs to its owner. This identification process can involve biometric analysis. The reader terminal downloads additional data from a server and the additional data is presented on a reader terminal's screen. The server queries the wireless carrier for reader terminal's location data, correlates the reader location data with hospital location data, and sends the critical information to the nearby hospitals. Additionally, the server sends alert information to other firms or individuals contained in the transponder wearer's data record. The RFID tag is the healthcare record. It relates and integrates into a larger database and network. It proves its owner and through wireless technology identifies location and other data characteristics of its owner.
Owner:MIDAMERICAN HEALTHCARE
Method for accessing goods or services following an action performed by a viewer of broadcast program content
ActiveUS20110314491A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsBroadcast services for monitoring/identification/recognitionGraphicsApplication software
Owner:NAGRAVISION SA
Method and system for authenticating telephone callers and avoiding unwanted calls
ActiveUS8467512B2Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingCalled number recording/indicationProve itAuthentication
A service that handles incoming telephone calls without bothering the telephone subscriber is disclosed. The service permits a call to go through to a subscriber if the service determines that the call is not unwanted and the caller has been unauthenticated. The authentication is based on challenging the caller to prove its identity rather than relying on caller ID displays. Prospective callers pre-register with the service providing caller account information. When a caller is issued a challenge, the caller may prove its authenticity by supplying the challenge back to the service along with its registered information.
Owner:IBM CORP
Health preserving liver protection tea and its preparing method
ActiveCN1820618ARich in nutrientsHas an adjuvant therapeutic effectDigestive systemTea substituesFatty liverSide effect
The present invention relates to health preserving and liver protecting tea and its preparation process. The health preserving and liver protecting tea is prepared with nine kinds of Chinese medicinal materials, including gynostemma pentaphylla, haw, wolfberry fruit, red sage, fleeceflower root, etc in certain weight proportion, and through water decoction or alcohol extraction, mixing, drying, frying, bagging, Co-60 irradiation and other steps. The medicinal tea contains rich nutrients, and animal experiment and practical application proves its functions of preventing and treating chemical liver damage, raising body's immunity and helping treatment of fatty liver and no toxic side effect.
Owner:王晓
Method and device for proving his identity
ActiveUS20150264570A1Less roundedLess dataDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer hardwareProve it
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Method and structure for self-sealed joint proof-of-knowledge and diffie-hellman key-exchange protocols
InactiveUS8464060B2Robust resistance against malicious disclosureImproving security and privacy and efficiencyUser identity/authority verificationSecret communicationDiffie–Hellman key exchangeComputer science
A method (and structure) for a party (the prover) to prove its knowledge, jointly and non-malleably, of multiple secret (fixed and / or ephemeral) Diffie-Hellman exponents (DH-exponents), corresponding to its public (fixed and / or ephemeral) DH-components and with respect to the public (fixed and / or ephemeral) challenging DH-components from another party (the verifier). The joint proof-of-knowledge (JPOK) consists of secrets made by multiplying multiple DH-secrets, which can be generated and verified by each party by its own secret DH-exponents and the public DH-components of both parties. To ensure the non-malleability of the JPOK, the method makes all these multiplied DH-secrets to be independent, and makes the session-tag committed to the multiplied DH-secrets. In addition, the invented method makes the DH-secrets to be multiplied to further satisfy at least one of the following: (1) deniability; (2) pre-computability; and (3) post-ID computability.
Owner:ANDREW C YAO
Chinese medicine preparation for treating fatty liver and its preparation method
InactiveCN1524540ARaw materials are easy to getRaw materials are easily obtained through exquisite processing technologyDigestive systemUnknown materialsSalvia miltiorrhizaFatty liver
The invention relates to a traditional Chinese preparation for treating fatty liver and process for preparation, characterized by that, the constituent percentage by weight of the raw material are, alisol 12-30%, radix salvia miltiorrhiza 10-25%, haw 12-30%, cassia seed 10-25%, prepared fleece-flower root 5-20%, bupleurum root 5-20%. And the making process comprises the steps of, (1) extracting by ethanol backflow, (2) combination of extract, filtering, depression reclaiming, condensation into clear plaster, (3) watering and immersing, vacuum drying, (4) filling starch into plaster powder, blending, then filling ethanol to obtain the finished product. Clinical application of the invention has proved its substantial curative effect and no side effect.
Owner:唐山市福乐药业有限公司
Communication within a communication network
The entirety of a web page, including clickthroughs, is cached at a location within a network intermediate a client requesting the page and the host web site for the page. Activation of a clickthrough, whether held in session cache on the client machine, or in the network cache causes a javascript program to generate an activation identifier giving the IP address of the machine activating the clickthrough and the time. This ID, together with an ID giving the IP address from which the web page originally hosting the clickthrough was retrieved is sent to the host web site, enabling them to prove their role in the establishment of communication between the client and the site targeted by the clickthrough. The generation of such identifiers also has applicability in the field of text messages, e.g. sent out by a publicity agent, and actuable to connect to a telephone number held by an enterprise within the telephone network. Activation of such a text message results in the return of suitable identifiers to the publicity agent to enable them to seek remuneration from the enterprise.
Owner:KNAPP INVESTMENT
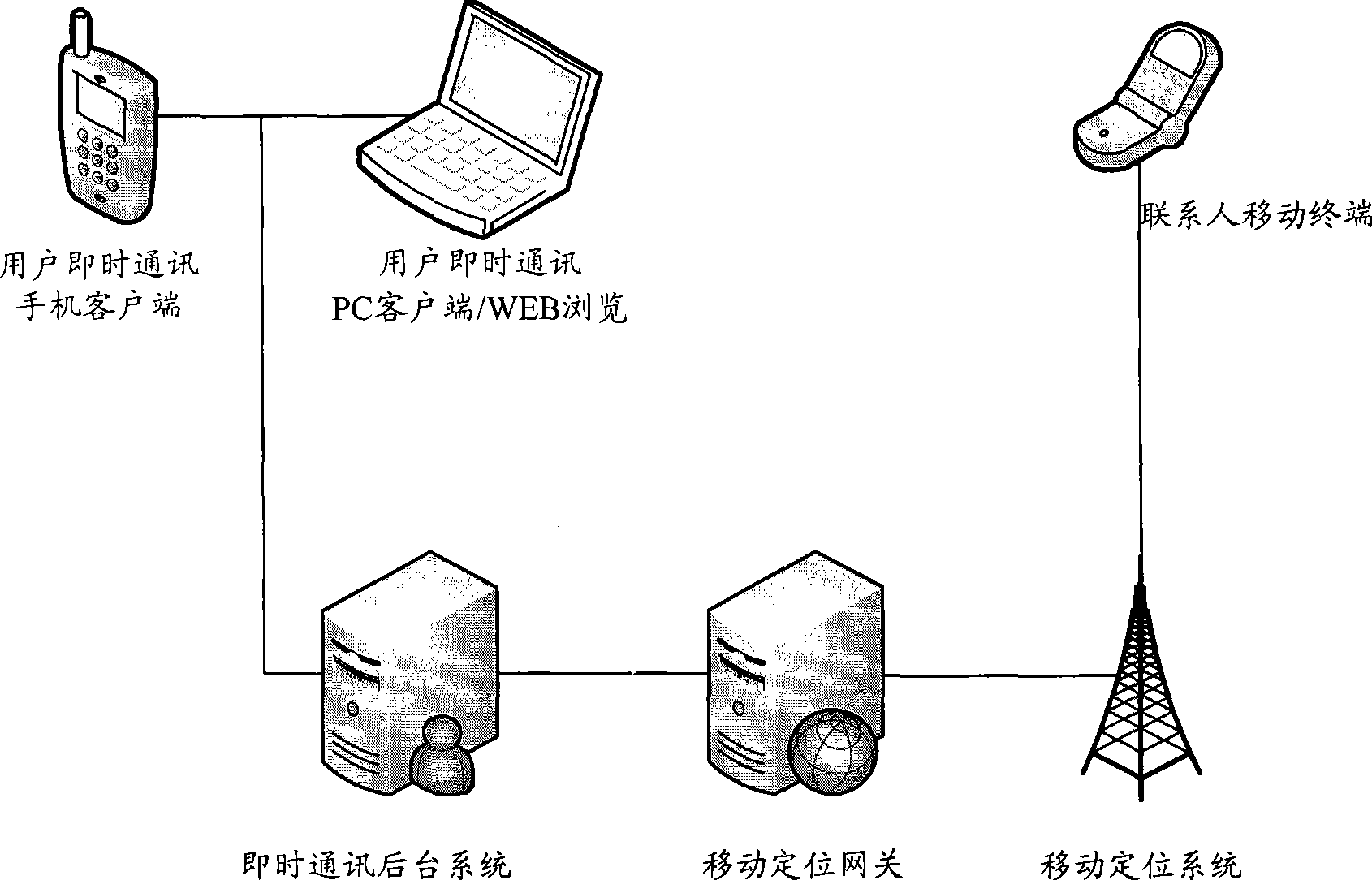
Method and system for acquiring position information of contact
ActiveCN101388860AHigh precisionImprove accuracyPosition fixationData switching networksCommunications systemComputer terminal
The invention discloses a method and system to acquiring contact man position information for solving the problem of low precision and accuracy of the acquired contact man position in group in the communication system. The method comprises: the instant communication background system receives the contact man position information request, judges whether the contact man position information is in the buffer memory; while the contact man position information is in the buffer memory, the information is sent to the user terminal; while the contact man position information is not in the buffer memory, the instant communication background system sends the contact man position information acquiring request to the positioning system; the communication background system receives the contact man position information from the positioning system and proving it to the user terminal. The scheme provided in the invention improves the precision and accuracy of the acquired contact man position information in the communication system.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GRP BEIJING
Chinese medicine compound preparation for curing pancreatic cancer
The present invention belongs to the field of Chinese medicine and especially a kind of compound Chinese medicine preparation for treating pancreatic cancer. Based on the traditional Chinese medicinal principle of clearing away pancreas heat and dispelling mass, the Chinese medicinal materials including Sheliugu, oldenlandia, sun plant, gynostemma pentaphylla and while amomum fruit are prepared into the oral preparation in granule, medicine powder, capsule, tablet, syrup or other form. The animal experiment proves its inhibiting effect on S180 cancer cell and pancreatic cancer, and the medicine has obvious treating effect on mid and later stage pancreatic cancer.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV SHANGHAI CANCER CENT
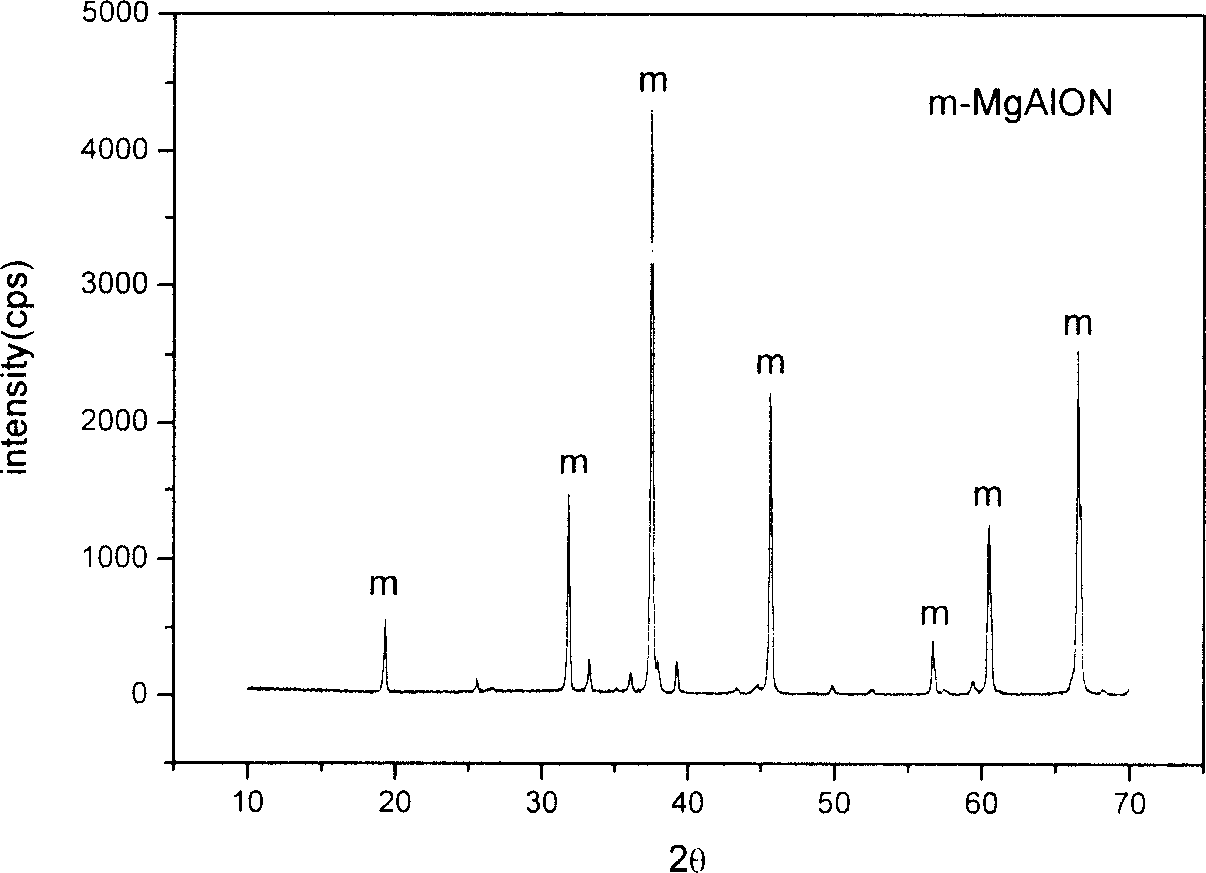
Process of preparing magnesia Allen ceramic material with waste magnesia carbon brick and magnesia alumina carbon brick
The present invention is process of preparing magnesia Allen ceramic material with waste magnesia carbon brick and magnesia alumina carbon brick, and belongs to the field of waste refractory material recovery and reuse, and the preparation process is low in cost and easy application in industrial production. Waste magnesia carbon brick in 10-60 wt% and magnesia alumina carbon brick in 40-90 wt% as materials are crushed, mixed, dried, pressure formed and sintered to form magnesia Allen ceramic material. X ray diffraction result shows that the magnesia Allen ceramic material has MgAlON content up to 95 % and the excellent performance similar that that of conventional magnesia Allen ceramic material, and the SEM pictures proves its excellent mechanical performance.
Owner:山西昊业新材料开发有限公司 +1
User authentication systems for remote computers, internet applications and online services
InactiveUS20140282979A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsGraphicsRemote system
A system for authenticating users to a remote computers, networks and applications is provided whereby a user provides a remote system with basic identification, the remote system contacts an authentication server, the authentication system provides the user with one or more graphical challenge interfaces that require a user to select specific locations in one or more graphics to prove his identity, where the user has previously chosen the graphics and specific locations, the graphics and specific locations are stored securely in the authentication server, and successful identification of the preselected locations authenticates the user to the remote computer, networks and / or application.
Owner:ANDON CHARLES A
Sulfonated changium root polysaccharides and preparing method and use thereof
InactiveCN1844160ANovel preparation processLow costOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsChangiumSulfated polysaccharides
In this invention, we extract raw polysaccharides from changium root named A B C respectively, and purify to get 6 polysaccharides I,II,III,IV,V,VI. After sulfation, we get sulfated polysaccharides A1, B1,C1. A1 has two sulfate groups on each monosaccharide at the average while B1 and C1 have three. The sulfated polysaccharides' molecular weight is more than 2 million D. The glycoside link is alpha type. The whole procedure of changium root sulfated polysaccharides is as followings: extract raw polysaccharides from changium root, and then get the polysaccharides sulfated. It is advantageous in simplied-manipulation and low cost. The pharmacological experiments prove its obvious suppression on rat transplanting tumor(S-180) and the reduction of platelet aggregation ratio and whole blood viscosity. It also reduces coagulant time.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Compound Chinese medicine prepn for treating muscular atrophy and amyasthenia and its prepn process
InactiveCN1526440AAbundant resourcesMature production processMuscular disorderUnknown materialsCentipedeGastrodia
The present invention is compound Chinese medicine preparation for treating muscular atrophy and amyasthenia and its preparation process. The compound Chinese medicine preparation is prepared with gastrodia tuber, scorpion, centipede, earthworm, achyranthes root, teasel root and eucommia bark charcoal, and through the process of washing with drinking water, stoving at 50 deg.c, milling into fine powder of 100-300 mesh, mixing through stirring and capsulizing 0.25 g each. Clinical application proves its high effective rate.
Owner:夏玉卿 +2
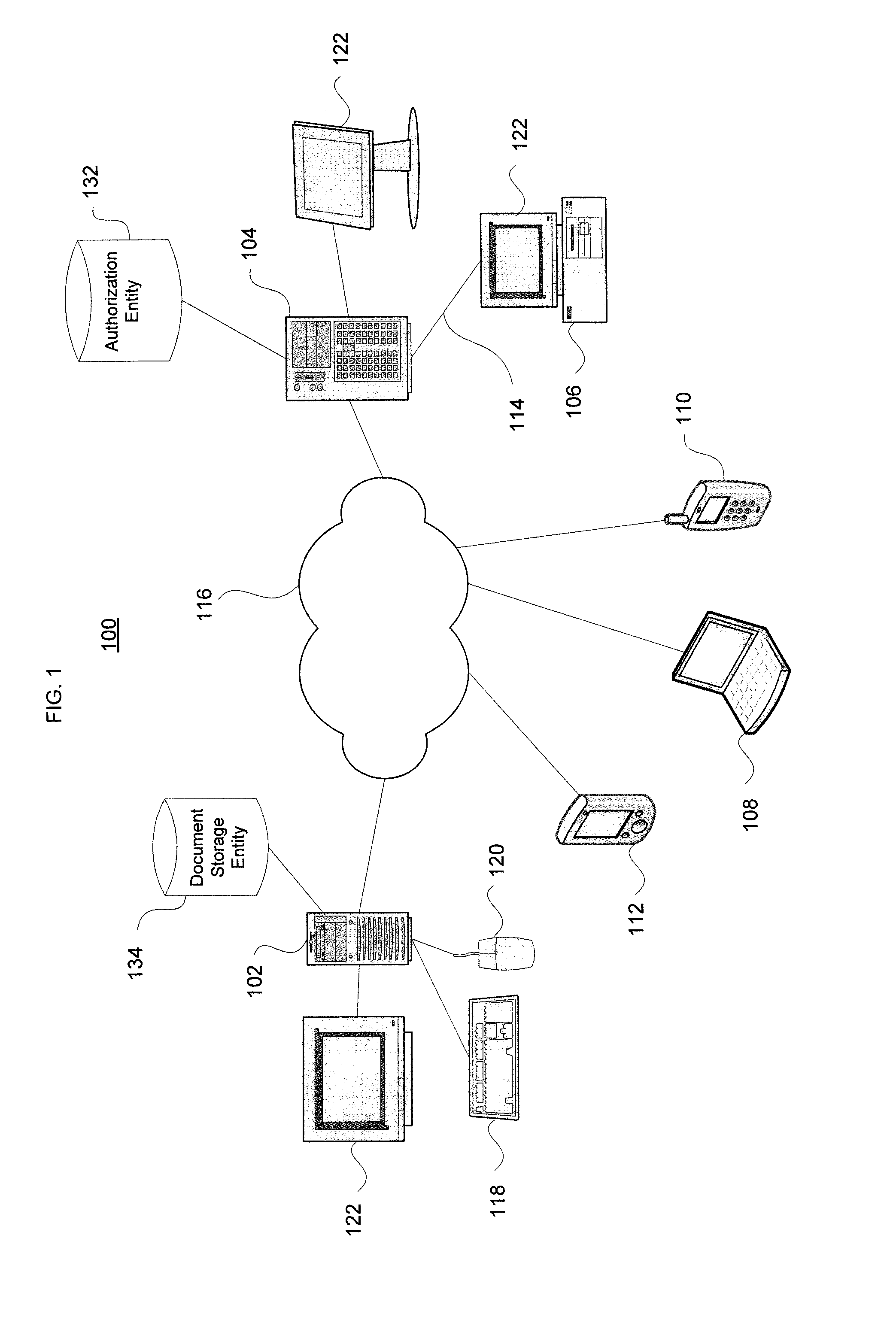
Systems and methods for verifying an electronic documents provenance date
InactiveUS8677133B1Safe storageUser identity/authority verificationPayments involving neutral partyElectronic documentThird party
The present invention validates provenance dates of electronic documents. A document version date may be determined by creating a unique checksum for the document and having the document's owner digitally sign it with a private key. The checksum and digital signature are securely stored by an authorization entity along with a timestamp fixing the date / time. A unique resource identifier is returned to the user. Subsequently, if the document's date needs to be proved to a third party, a verification program is applied to the original document to create a new checksum. The unique resource identifier is used to retrieve the signed checksum from the authorization entity. Upon verification of matching checksums, the timestamp provided by the authorization entity proves the date / time the document existed. In addition, the public key provided by the document owner proves that the checksum was signed by the owner's private key, proving their ownership.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com