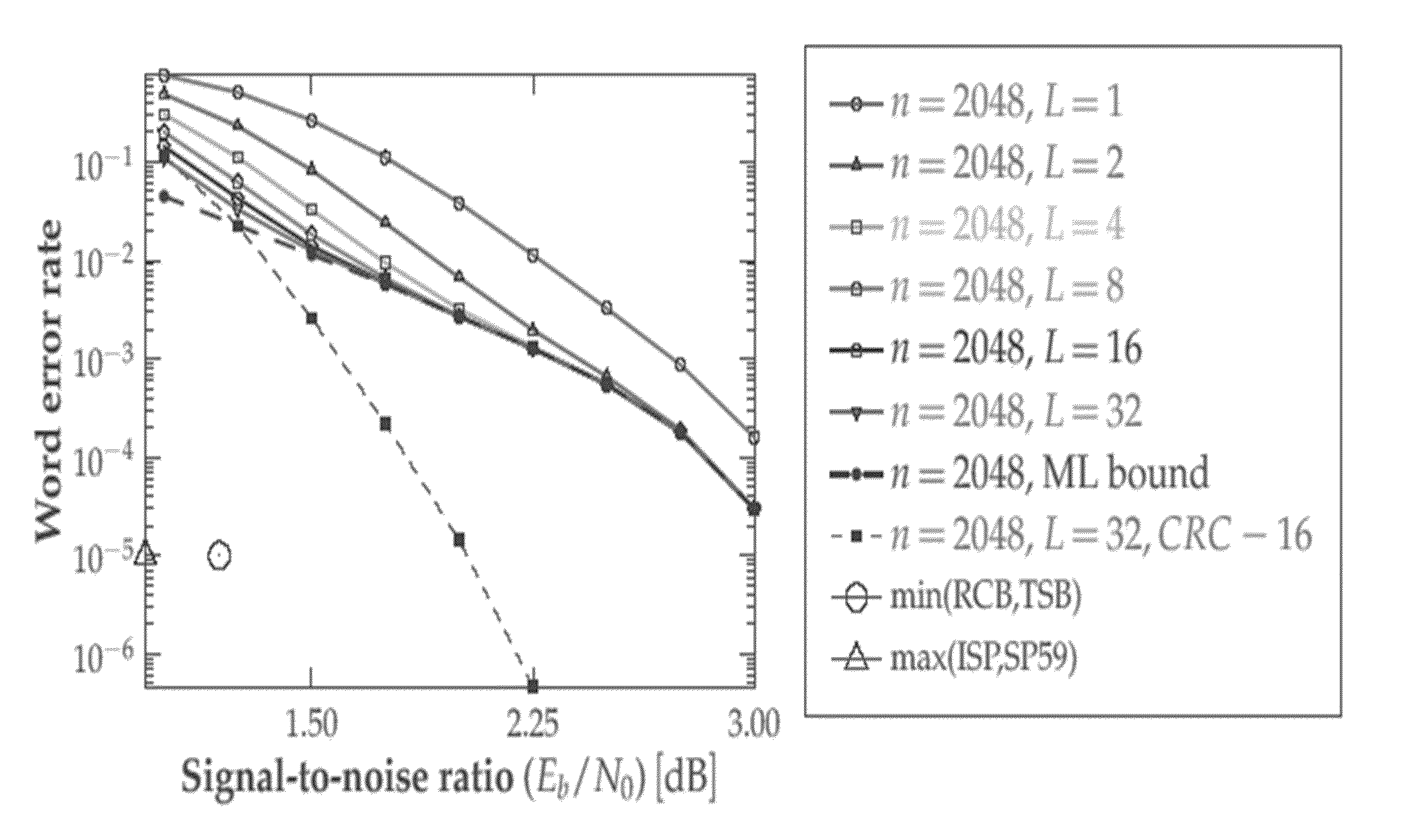
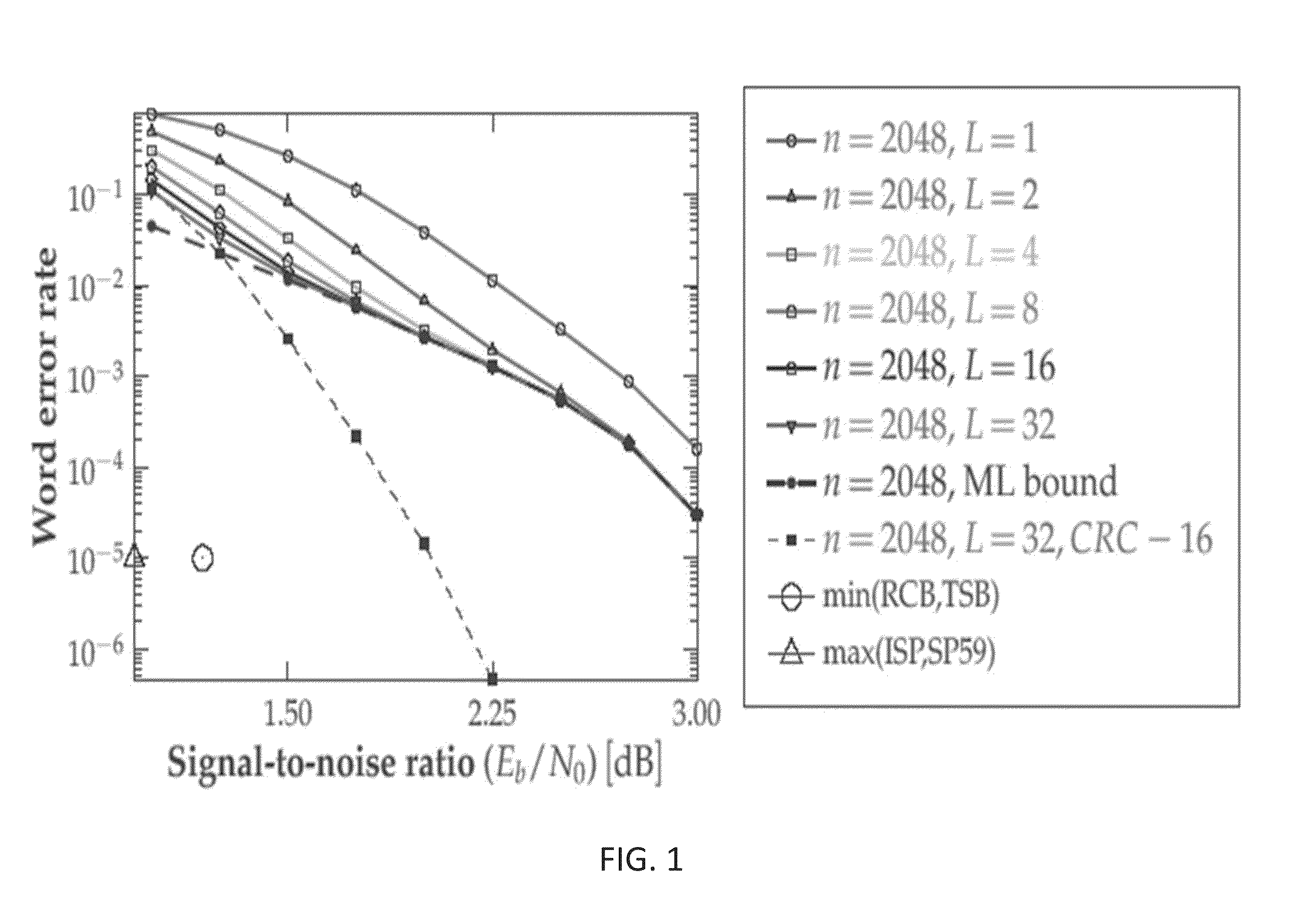
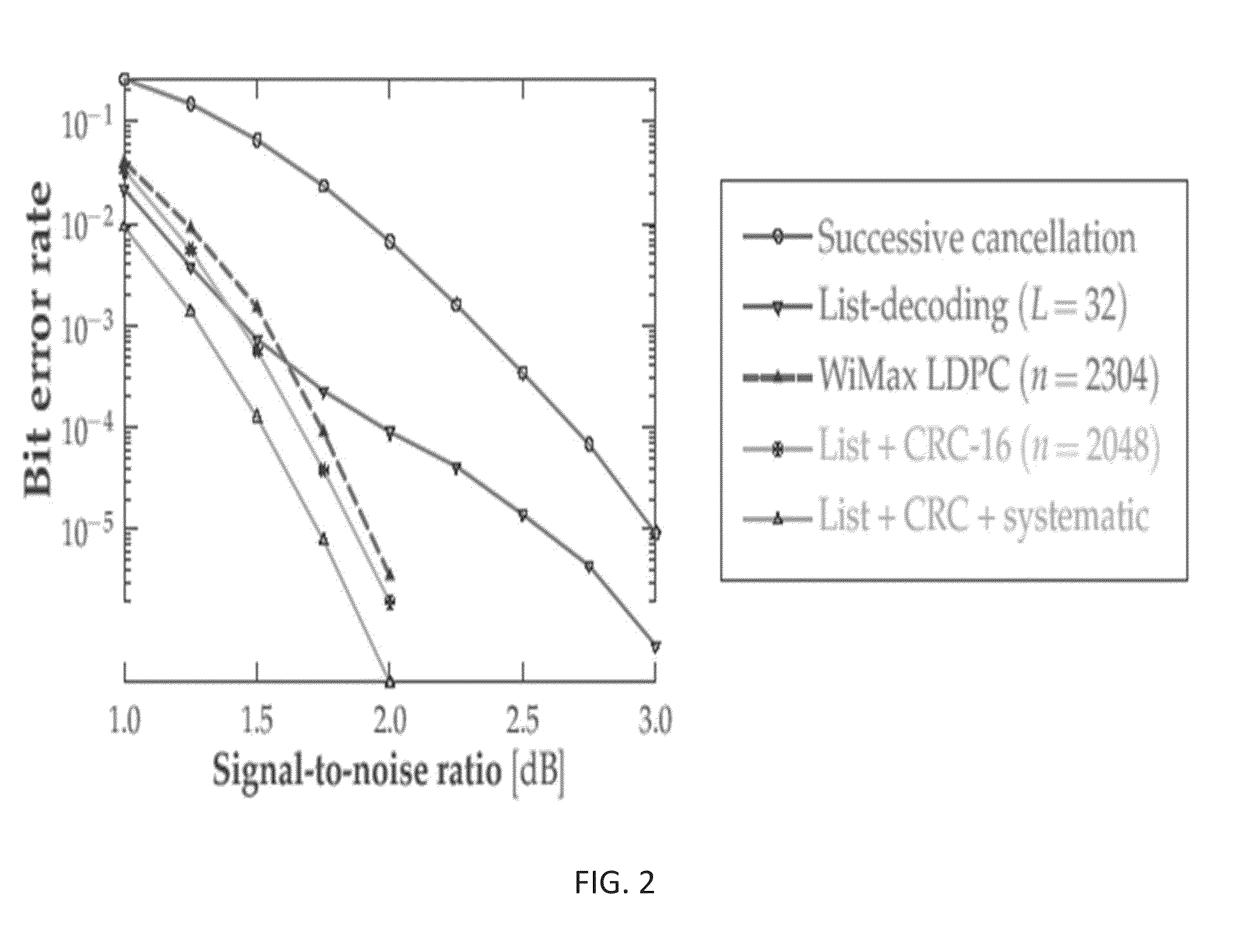
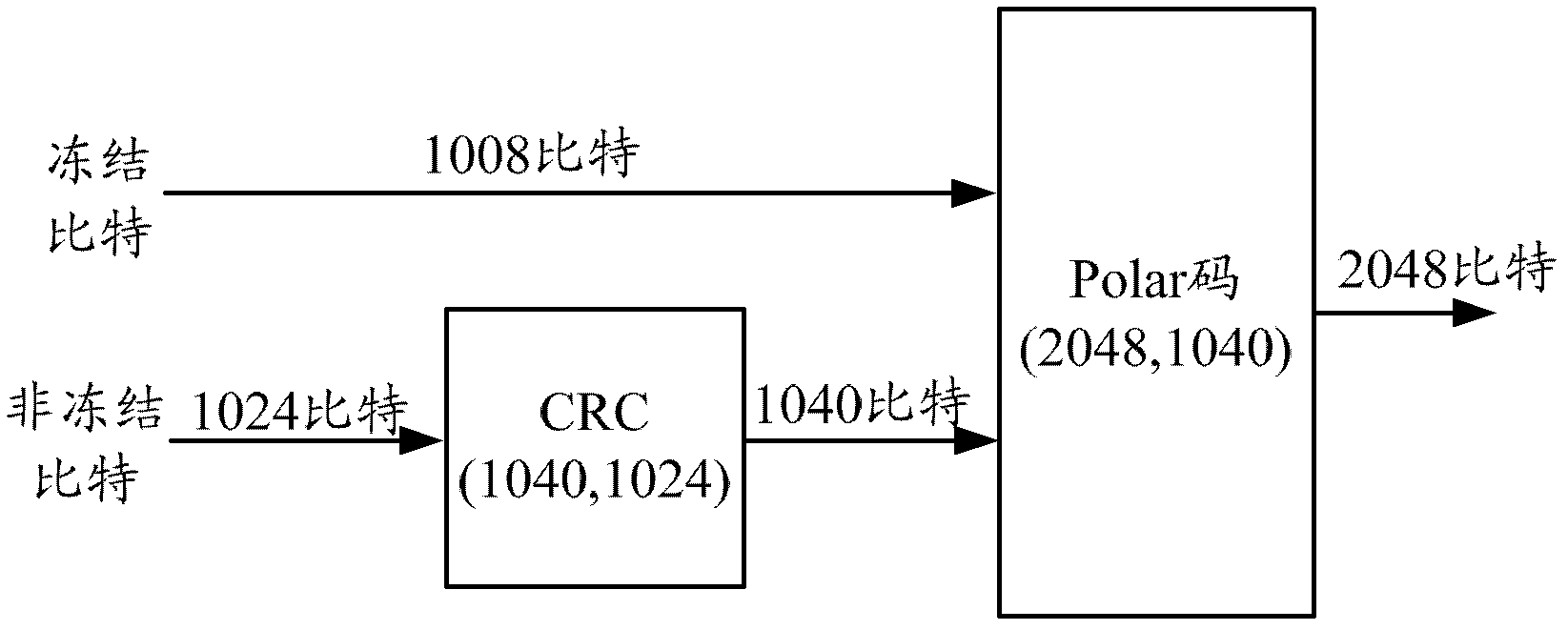
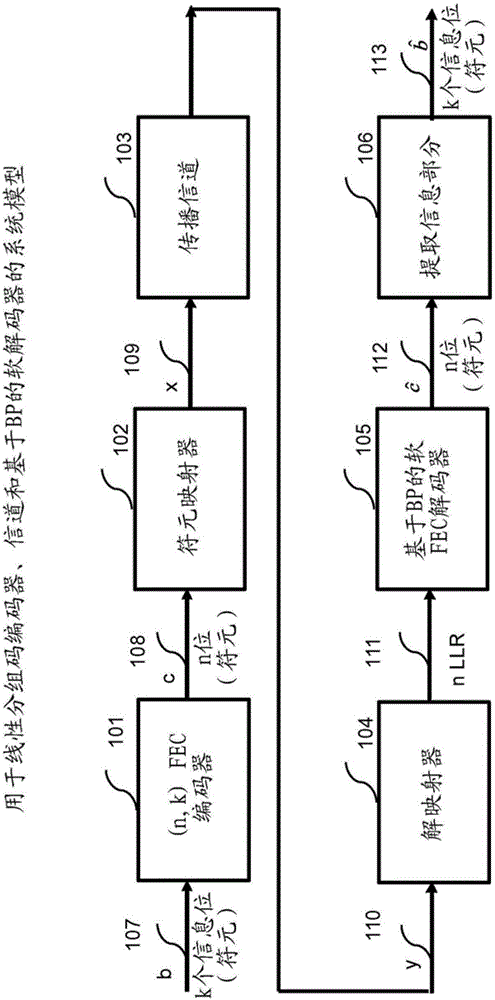
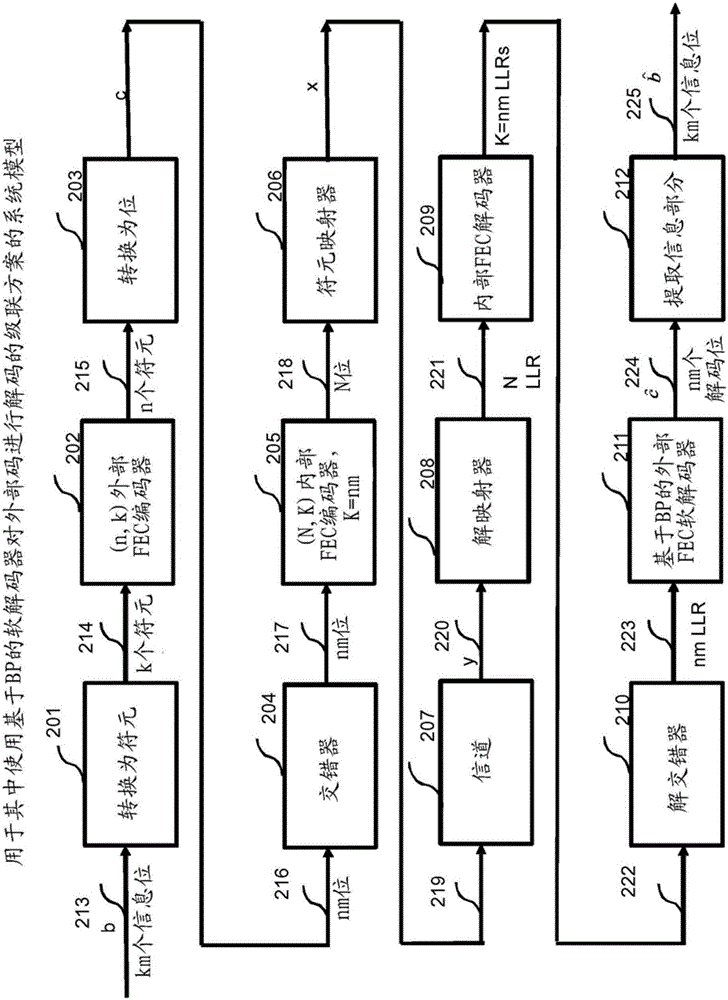
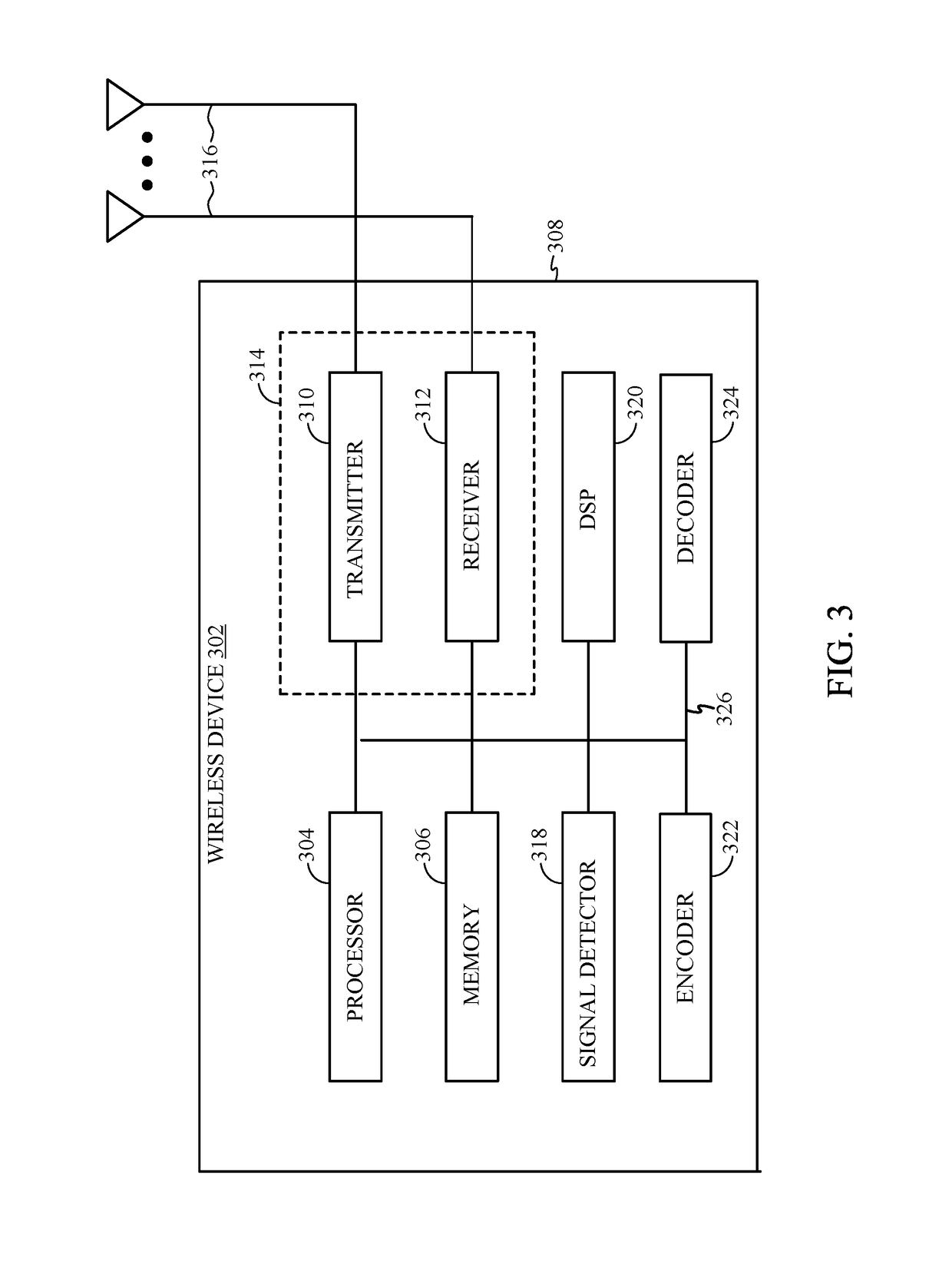
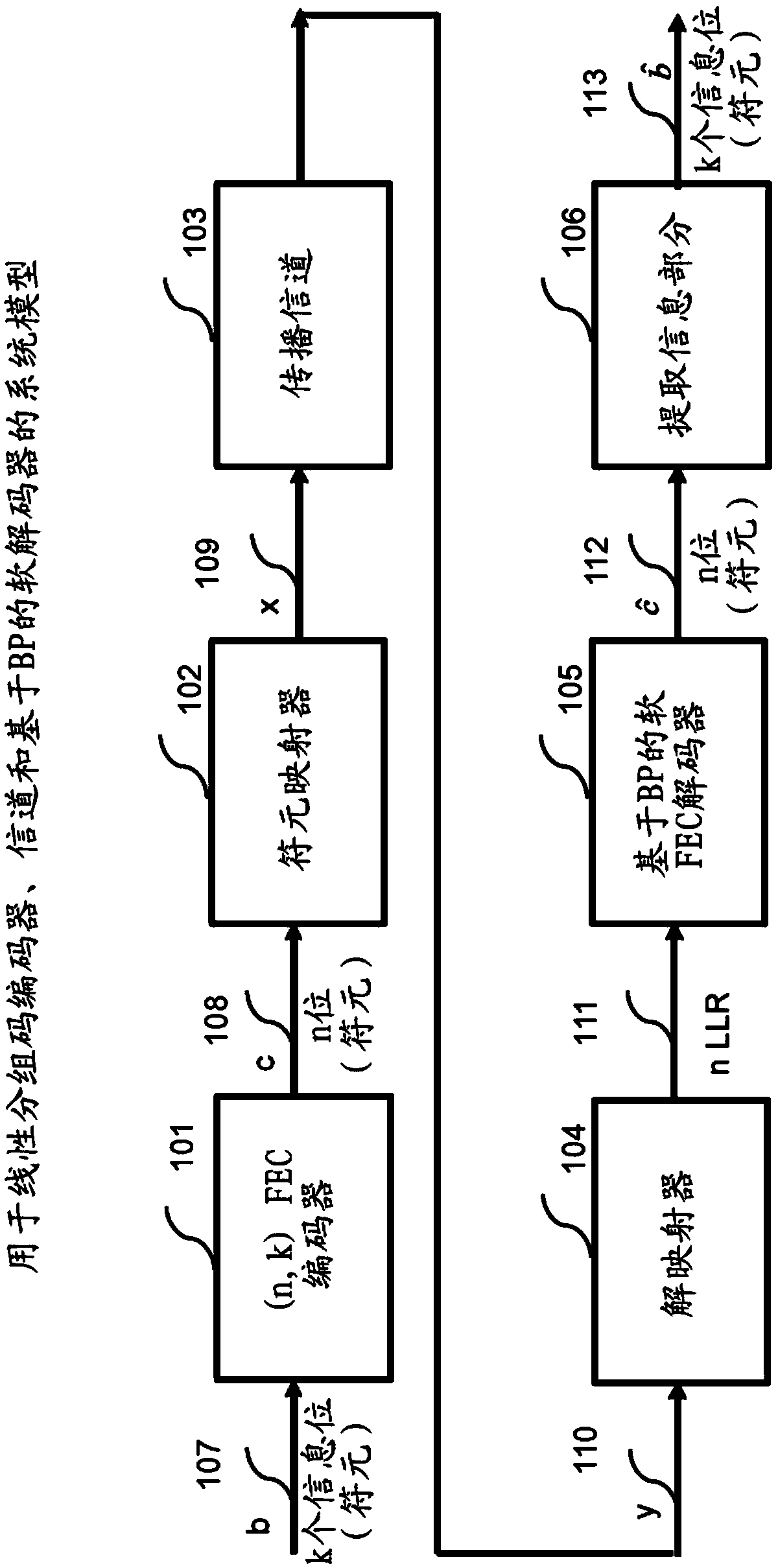
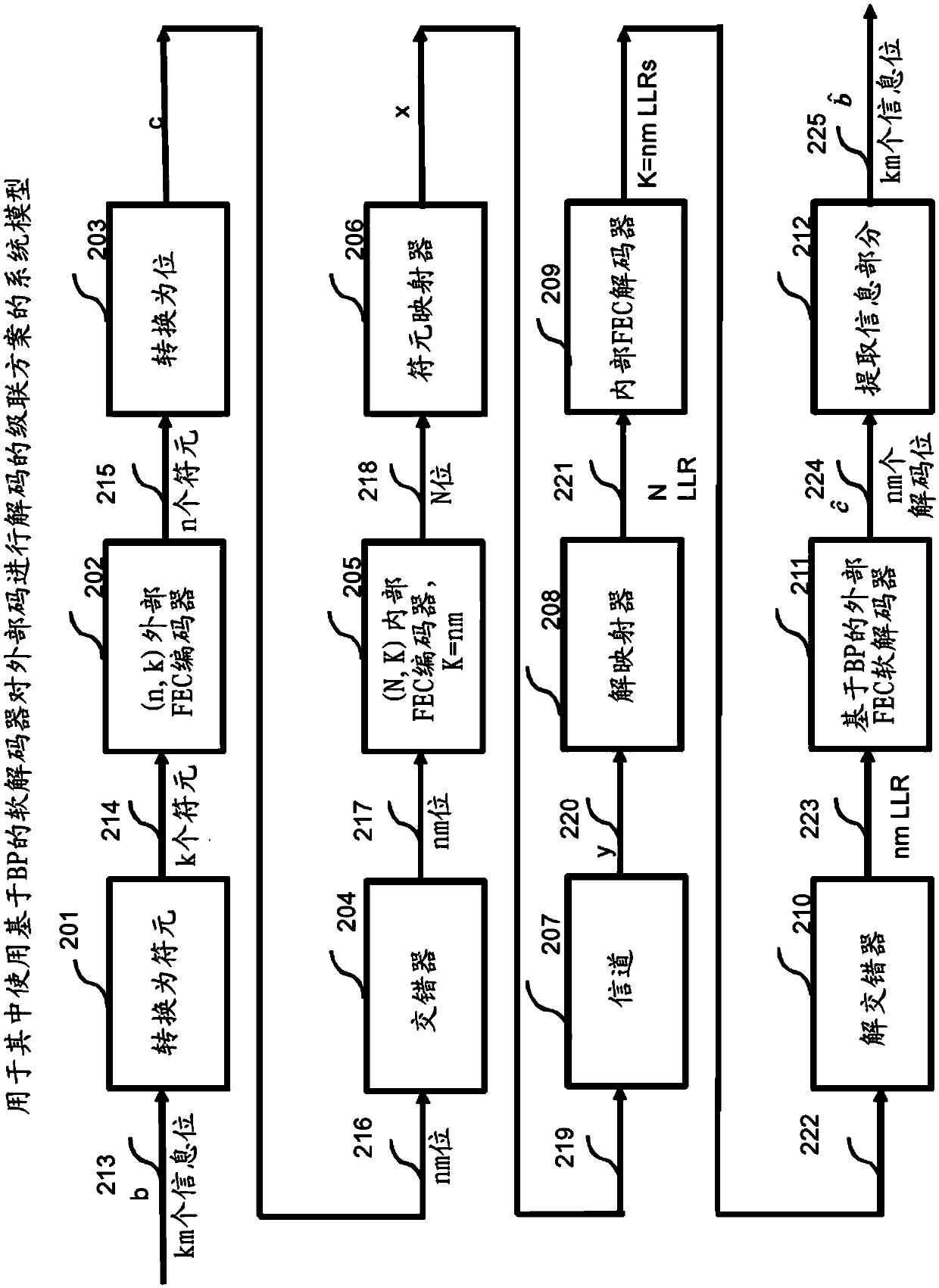
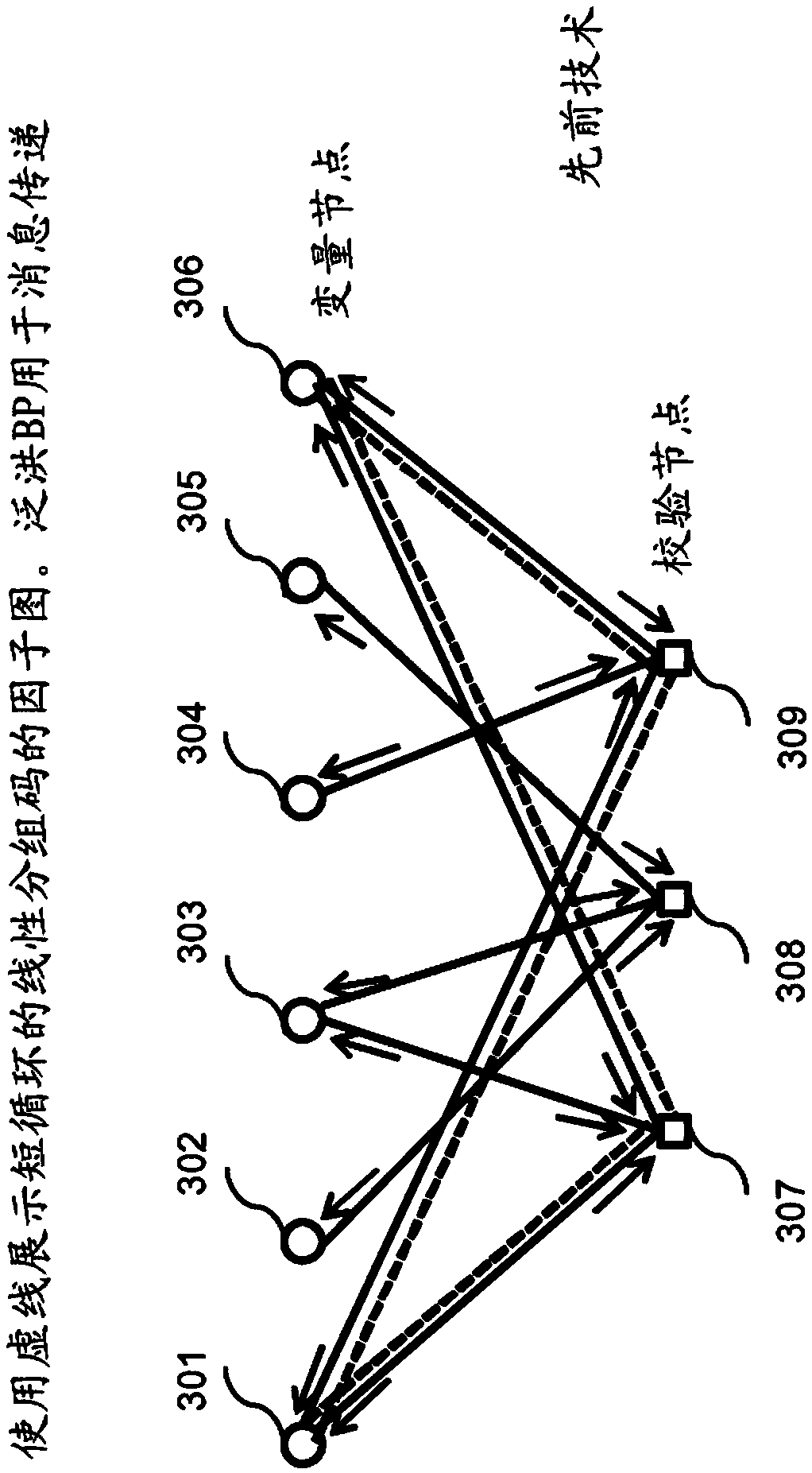
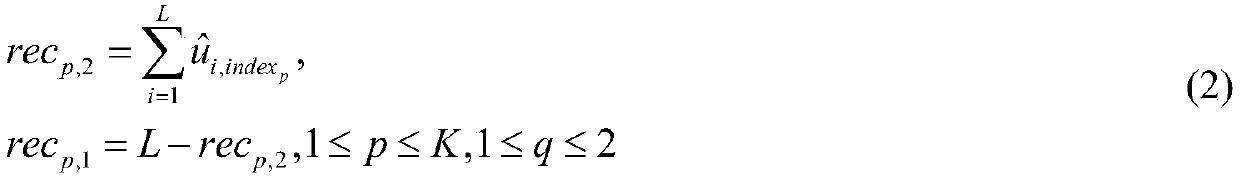Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
86 results about "List decoding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In coding theory, list decoding is an alternative to unique decoding of error-correcting codes for large error rates. The notion was proposed by Elias in the 1950s. The main idea behind list decoding is that the decoding algorithm instead of outputting a single possible message outputs a list of possibilities one of which is correct. This allows for handling a greater number of errors than that allowed by unique decoding.
Ecc polar coding and list decoding methods and codecs
A method of decoding data encoded with a polar code and devices that encode data with a polar code. A received word of polar encoded data is decoded following several distinct decoding paths to generate a list of codeword candidates. The decoding paths are successively duplicated and selectively pruned to generate a list of potential decoding paths. A single decoding path among the list of potential decoding paths is selected as the output and a single candidate codeword is thereby identified. In another preferred embodiment, the polar encoded data includes redundancy values in its unfrozen bits. The redundancy values aid the selection of the single decoding path. A preferred device of the invention is a cellular network device, (e.g., a handset) that conducts decoding in accordance with the methods of the invention.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
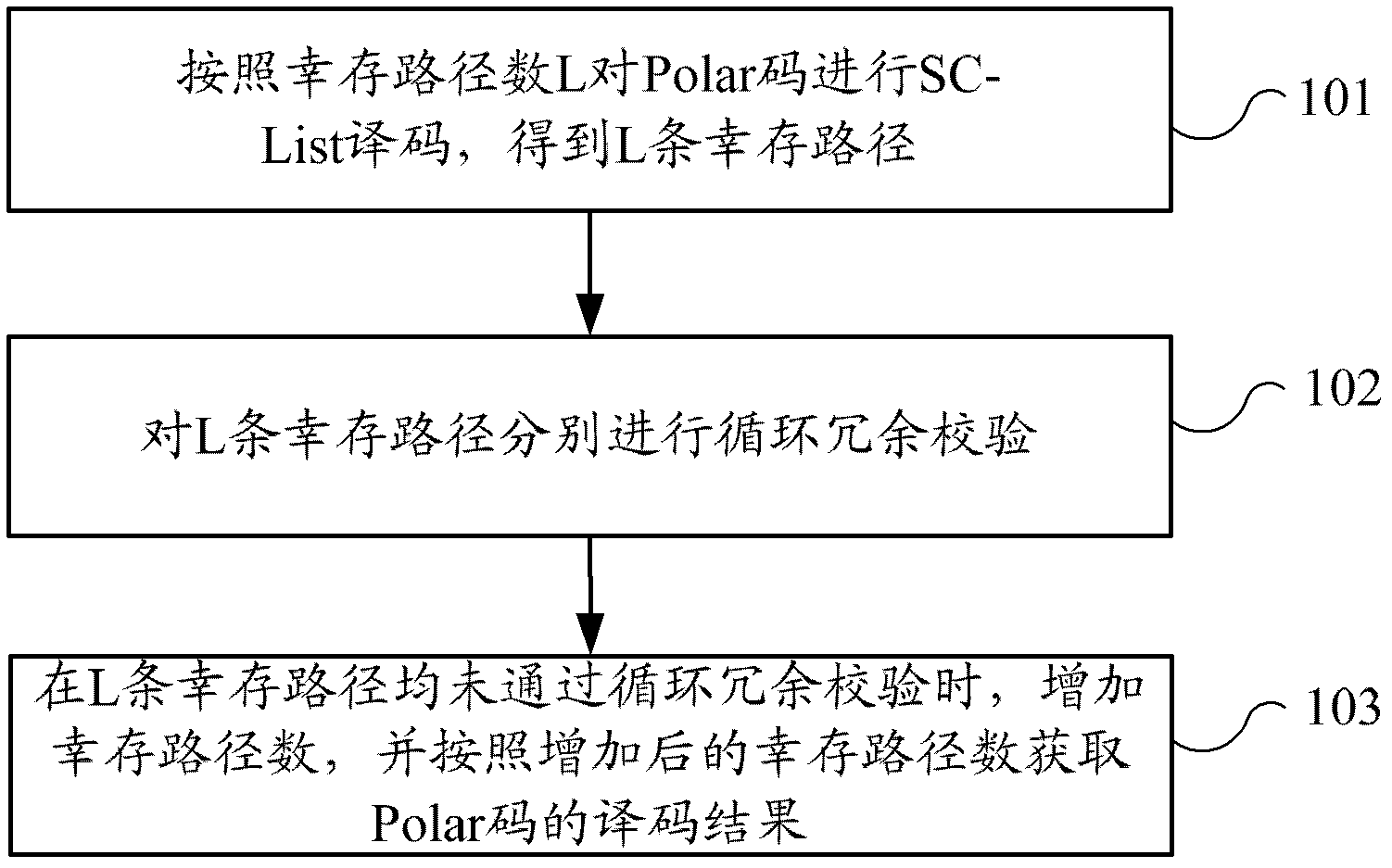
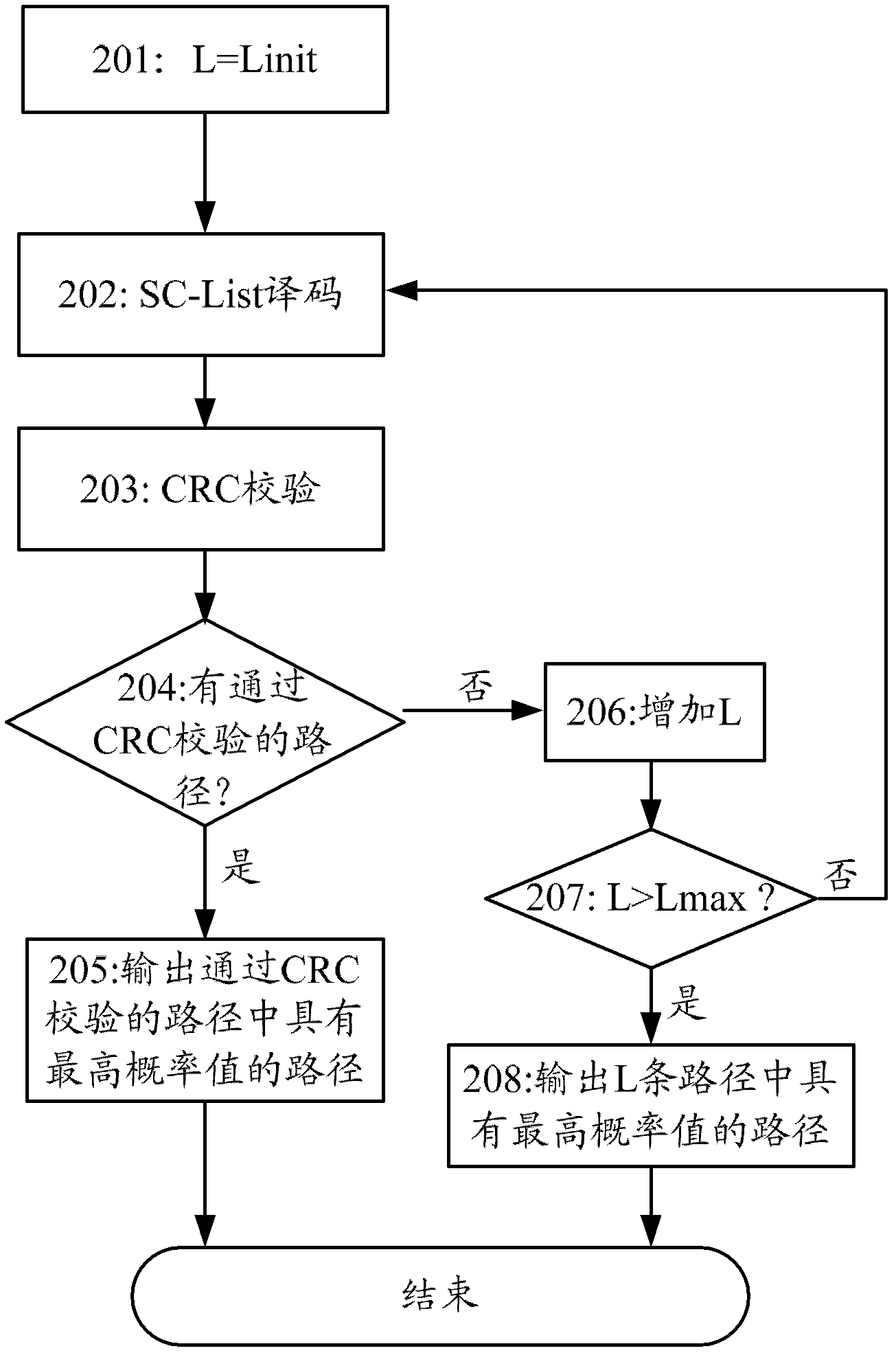
Decoding method and decoding device for polar codes concatenated with cyclic redundancy checks (CRC)
ActiveCN103220001AImprove decoding performanceError preventionCode conversionDecoding methodsPath number
The invention provides a decoding method and a decoding device for polar codes concatenated with a cyclic redundancy check (CRC). The decoding method includes the following steps: SC-list decoding is carried out on the polar codes according to the number, which is L, of survival paths to obtain the L survival paths, wherein the L is a positive integer; each of the L survival paths is subjected to the CRC; and when none of the L survival paths passes the CRC, the number of the survival paths is increased, and decoding results of the polar codes are obtained according to the number, which is increased, of the survival paths. According to the decoding method and the decoding device for the polar codes concatenated with the CRC, the path number of the survival paths is adjusted according to the result of the CRC, and therefore the paths which can pass the CRC can be output as far as possible, and the decoding performance is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
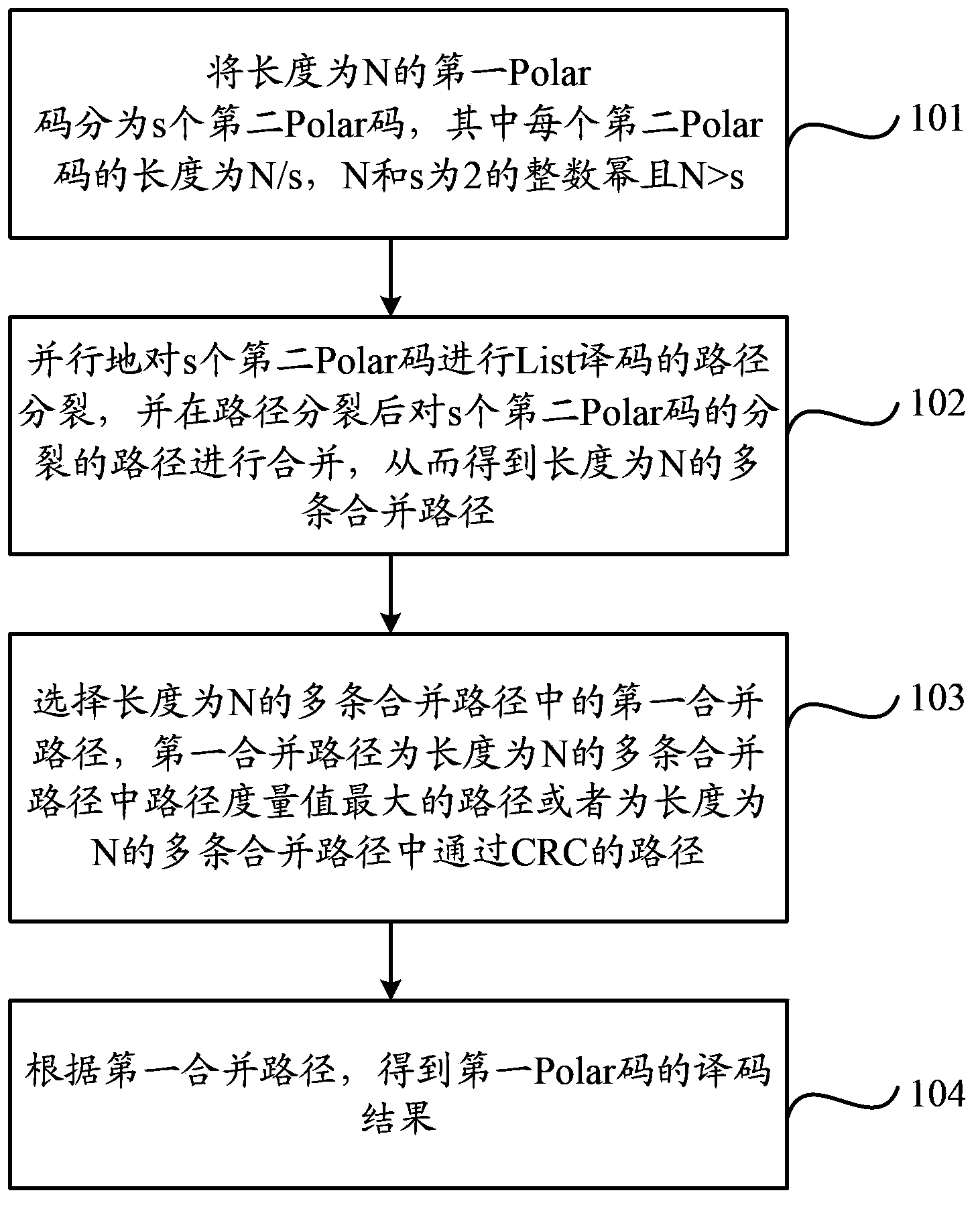
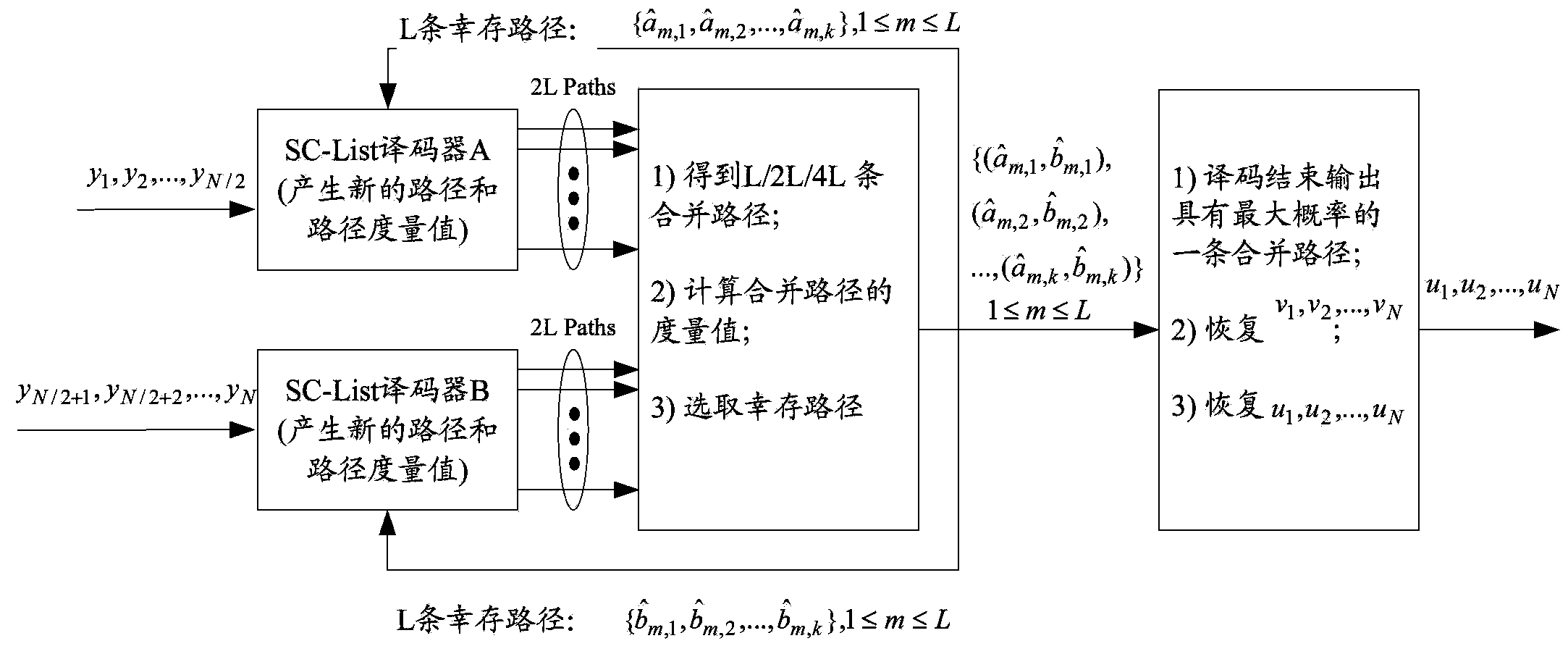
Polar code decoding method and decoding device
ActiveCN104124979AImprove decoding throughputReduce Decoding LatencyError preventionError correction/detection using linear codesDecoding methodsComputer science
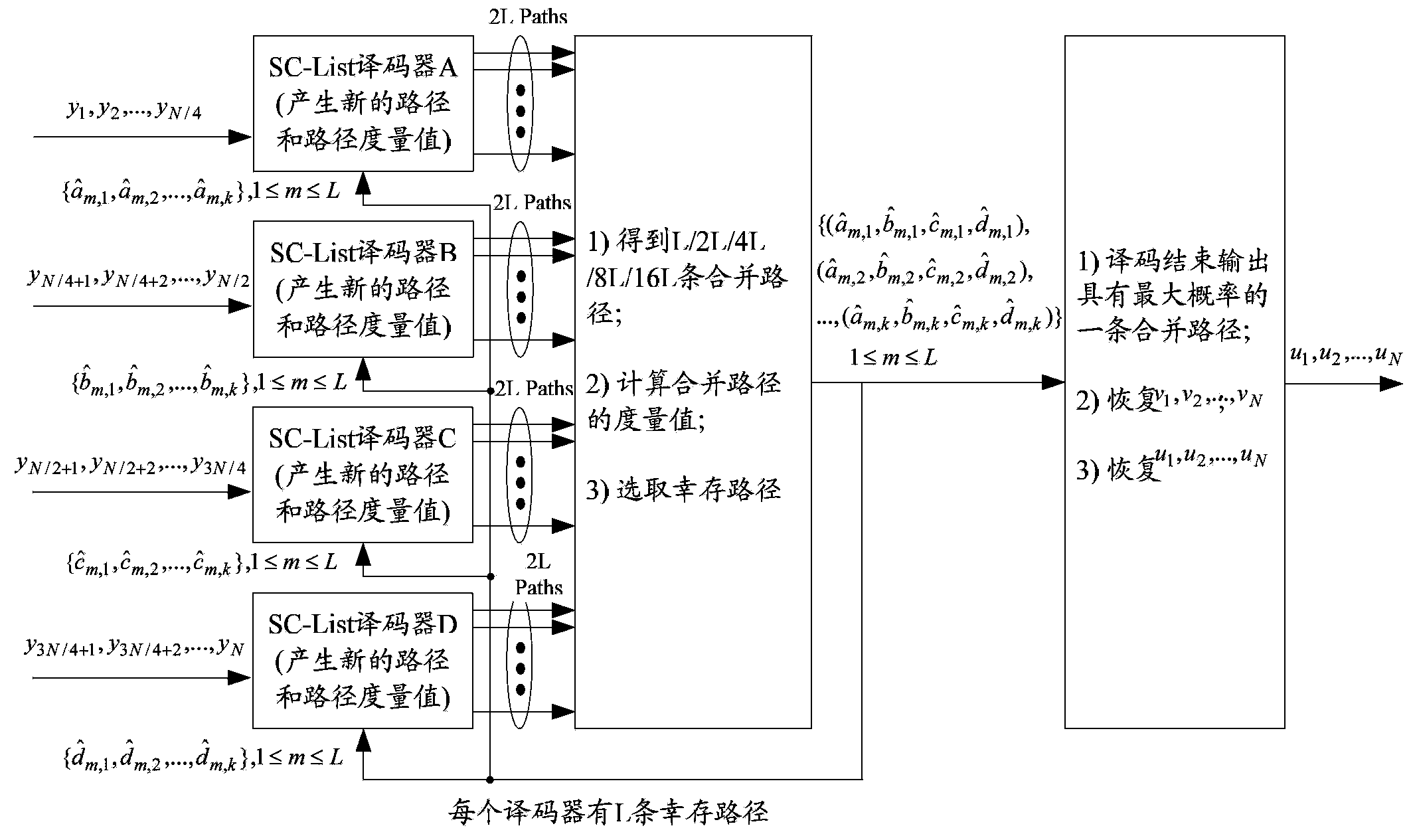
Embodiments of the present invention provide a decoding method and a decoding apparatus for a polar code. The method comprises: grouping a first polar code having a length of N into s second polar codes, a length of each second polar code being N / s, N and s being integer powers of 2, and N>s; performing path splitting of list decoding on s second polar codes concurrently, and combining split paths of s second polar codes after path splitting, so as to obtain multiple combined paths having a length of N; choosing a first combined path from multiple combined paths having a length of N bits, the first combined path being a path having the greatest path metric value among the multiple combined paths having a length of N bits, or a path passing cyclic redundancy check (CRC) among the multiple combined paths having a length of N bits; and obtaining a decoding result of the first polar code according to the first combined path. In this case, a decoding throughput of the polar code can be improved, and a decoding delay can be decreased.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Memory Management and Path Sort Techniques in a Polar Code Successive Cancellation List Decoder
ActiveUS20170149531A1Easy to operateGreat numerical stabilityError preventionOther decoding techniquesMemory managementList decoding
Various embodiments are described of a system and method for improved SCL decoder operation. In particular, various embodiments are described which improve the efficiency of the buffer management based on updated path metric statistics. In some embodiments, the SCL decoder may perform selective replacement to limit the extent of LLR updates per row only to the statistics that have changed since the previous update cycle. In some embodiments, the SCL decoder may perform deferred updates, which may involves in-place calculation of both ûφ=0 and ûφ=1 bit estimate (LLR) updates based on the row from which the updated row will be derived.
Owner:COHERENT LOGIX
ECC polar coding and list decoding methods and codecs
A method of decoding data encoded with a polar code and devices that encode data with a polar code. A received word of polar encoded data is decoded following several distinct decoding paths to generate a list of codeword candidates. The decoding paths are successively duplicated and selectively pruned to generate a list of potential decoding paths. A single decoding path among the list of potential decoding paths is selected as the output and a single candidate codeword is thereby identified. In another preferred embodiment, the polar encoded data includes redundancy values in its unfrozen bits. The redundancy values aid the selection of the single decoding path. A preferred device of the invention is a cellular network device, (e.g., a handset) that conducts decoding in accordance with the methods of the invention.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Architecture and control of reed-solomon error-correction decoding
ActiveUS7444582B1Joint error correctionOther decoding techniquesComputer architectureBerlekamp–Massey algorithm
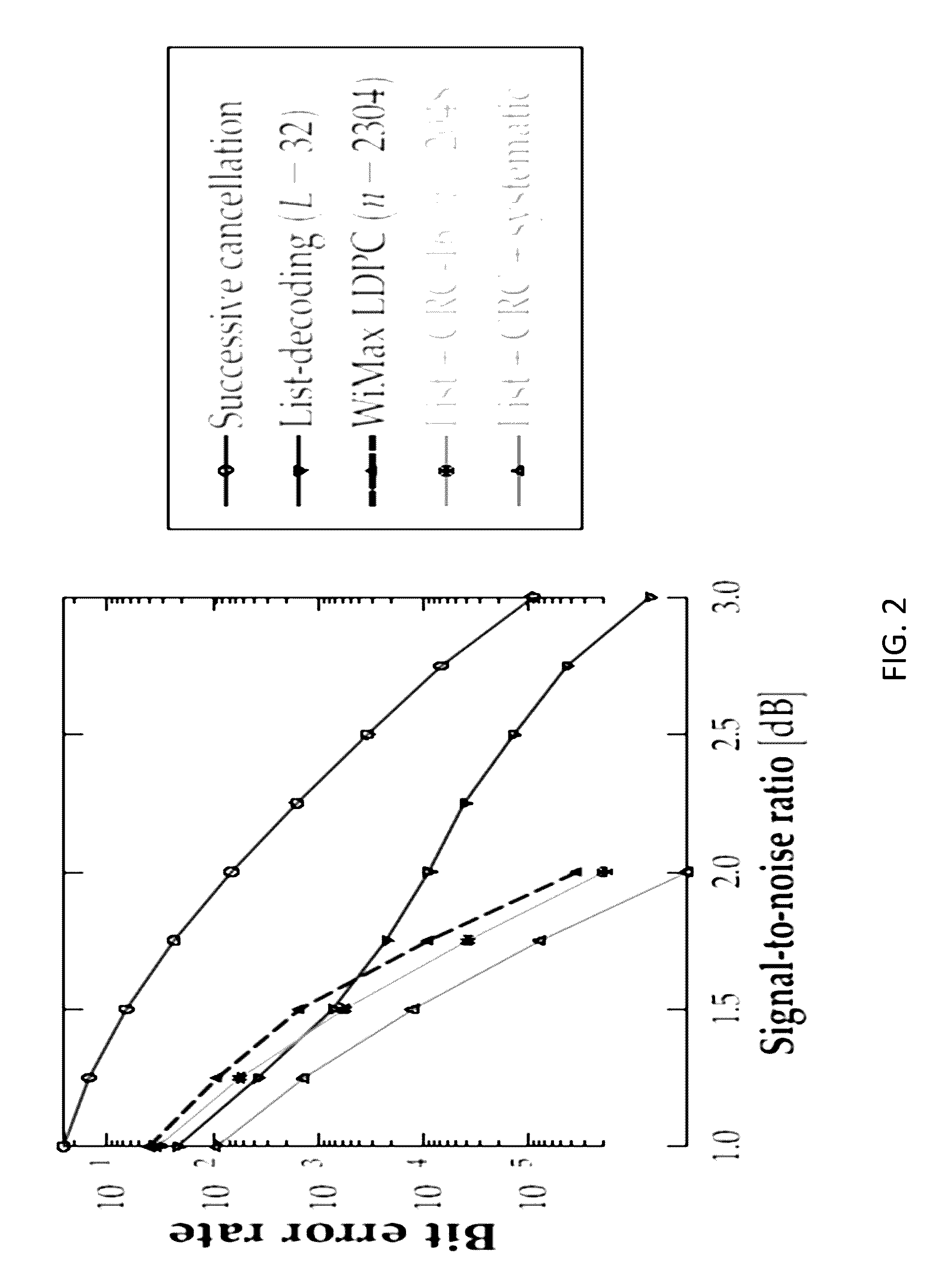
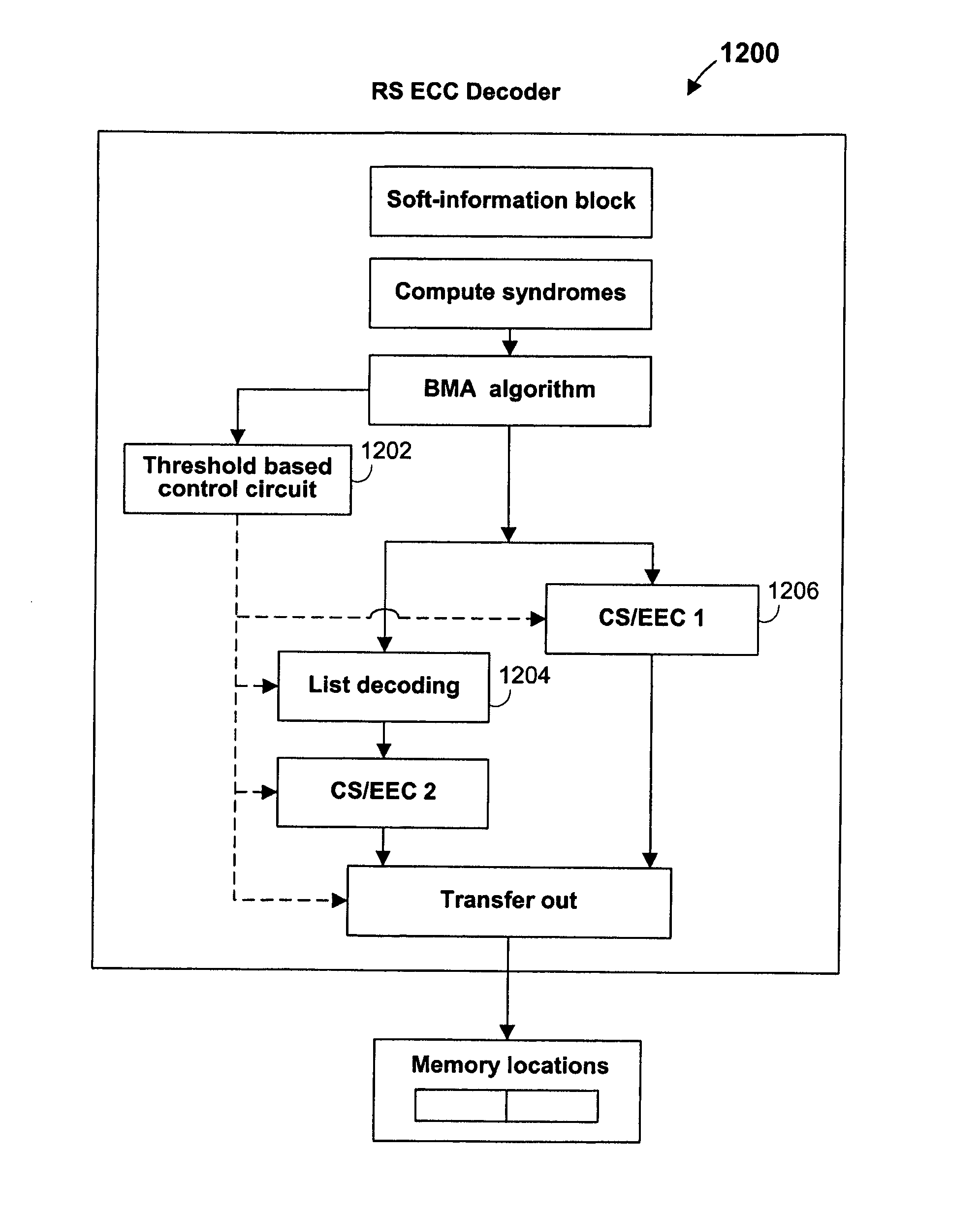
Systems and methods are provided for implementing various aspects of a Reed-Solomon (RS) error-correction system. A detector can provide a decision-codeword from a channel and can also provide soft-information for the decision-codeword. If the decision-codeword corresponds to an inner code and an RS code is the outer code, a soft-information map can process the soft-information for the decision-codeword to produce soft-information for a RS decision-codeword. A RS decoder can employ the Berlekamp-Massey algorithm (BMA), list decoding, and a Chien search, and can include a pipelined architecture. A threshold-based control circuit can be used to predict whether list decoding will be needed and can suspend the list decoding operation if it predicts that list decoding is not needed.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
List-viterbi hard iterative decoder for multilevel codes
InactiveUS20110044399A1Data representation error detection/correctionError preventionAlgorithmList decoding
Two decoding algorithms are introduced for the decoding of multi-level coded modulation and other types of coded modulation involving component codes and interleaving operations. An improved hard iterative decoding (IHID) algorithm is presented that improves upon a hard iteration decoding technique by adding a stopping criterion. Also, a list Viterbi hard iteration decoding (LV-IHID) algorithm is presented that employs list decoding in conjunction with the IHID algorithm. Both of these decoding algorithms improve upon conventional multi-stage decoding by reducing the effective error multiplicity that is observed at the lowest coding level. It is demonstrated that the LV-IHID algorithm performs close to soft iterative decoding. The computational and delay complexity of the proposed decoding algorithms compare favorably with soft iterative decoding strategies. Also, a novel labeling strategy for MLC design is presented.
Owner:TRELLIS PHASE COMM LP
Polarization code decoding method based on bit fliping serial elimination list algorithm
ActiveCN108282264AImprove error correction performanceRemove complexityError preventionCode conversionCoding decodingTime complexity
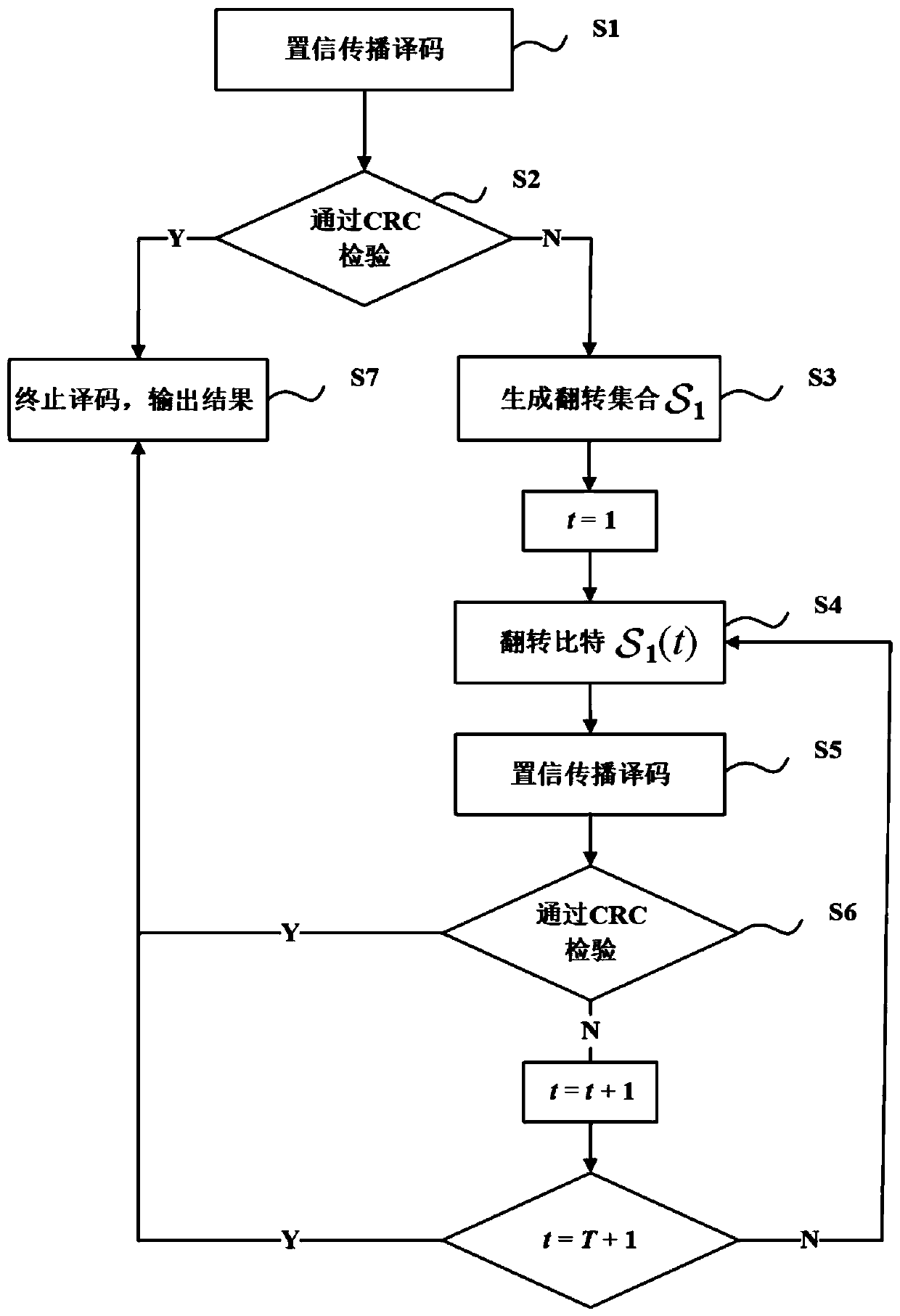
The invention discloses a polarization code decoding method based on a bit flipping serial elimination list algorithm, and solves the problem that an existing SCL (Successive Cancellation List) algorithm has higher time complexity. The method comprises the following steps: step (1), receiving a sequence to be decoded by a communication terminal; step (2), performing SC (Successive Cancellation) decoding on the received sequence to be decoded; step (3), judging whether an SC decoded sequence passes CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check); step (4), initializing the list width and the number of bit flipping; step (5), selecting a judgment error position set; step (6), selecting one element from the judgment error position set; step (7), decoding by using the bit flipping serial elimination list algorithm; step (8), judging whether elements in the judgment error position set are all selected or not; step (9), the decoding is successful; and step (10), the decoding fails. According to the polarization code decoding method based on the bit flipping serial elimination list algorithm provided by the invention, the SC decoding is carried out firstly, and when the decoding fails, bit flipping and list decoding are combined for re-decoding, thus the decoding performance is improved, and the time complexity of a decoding algorithm is reduced.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Systems and methods for advanced iterative decoding and channel estimation of concatenated coding systems
InactiveCN105144598AError correction/detection using convolutional codesModulated-carrier systemsHD RadioAlgorithm
Systems and methods for decoding block and concatenated codes are provided. These include advanced iterative decoding techniques based on belief propagation algorithms, with particular advantages when applied to codes having higher density parity check matrices. Improvements are also provided for performing channel state information estimation including the use of optimum filter lengths based on channel selectivity and adaptive decision-directed channel estimation. These improvements enhance the performance of various communication systems and consumer electronics. Particular improvements are also provided for decoding HD Radio signals, including enhanced decoding of reference subcarriers based on soft-diversity combining, joint enhanced channel state information estimation, as well as iterative soft-input soft-output and list decoding of convolutional codes and Reed-Solomon codes. These and other improvements enhance the decoding of different logical channels in HD Radio systems.
Owner:LN2 DB LLC
Polarization code belief propagation list decoding method based on bit flipping
ActiveCN110278002AImprove frame error rate performanceImproved frame error rate performanceCode conversionCyclic codesBelief propagationLog likelihood
The invention discloses a polarization code belief propagation list decoding method based on bit flipping. Code words used in the method are cascade codes formed by CRC codes and polarization codes. According to the method provided by the invention, under the condition that the BPL decoding result does not pass the CRC check, a decoding result in a BPL decoding method is analyzed, a Flip Bits Set (FBS) is constructed, and information bits, located in the FBS, of the polarization codes are flipped (bit flipping is achieved by setting the prior log-likelihood ratio of flipped bits to be infinite). Errors in part of BPL decoders can be corrected, and then the bit error rate and the frame error rate performance of the BPL decoding method are improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Architecture and control of reed-solomon list decoding
ActiveUS7454690B1Reduce the amount of memoryReduce the amount requiredJoint error correctionOther decoding techniquesTheoretical computer scienceSoft information
Systems and methods are provided for implementing list decoding in a Reed-Solomon (RS) error-correction system. A detector can provide a decision-codeword from a channel and can also provide soft-information for the decision-codeword. The soft-information can be organized into an order of combinations of error events for list decoding. An RS decoder can employ a list decoder that uses a pipelined list decoder architecture. The list decoder can include one or more syndrome modification circuits that can compute syndromes in parallel. A long division circuit can include multiple units that operate to compute multiple quotient polynomial coefficients in parallel. The list decoder can employ iterative decoding and a validity test to generate error indicators. The iterative decoding and validity test can use the lower syndromes.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
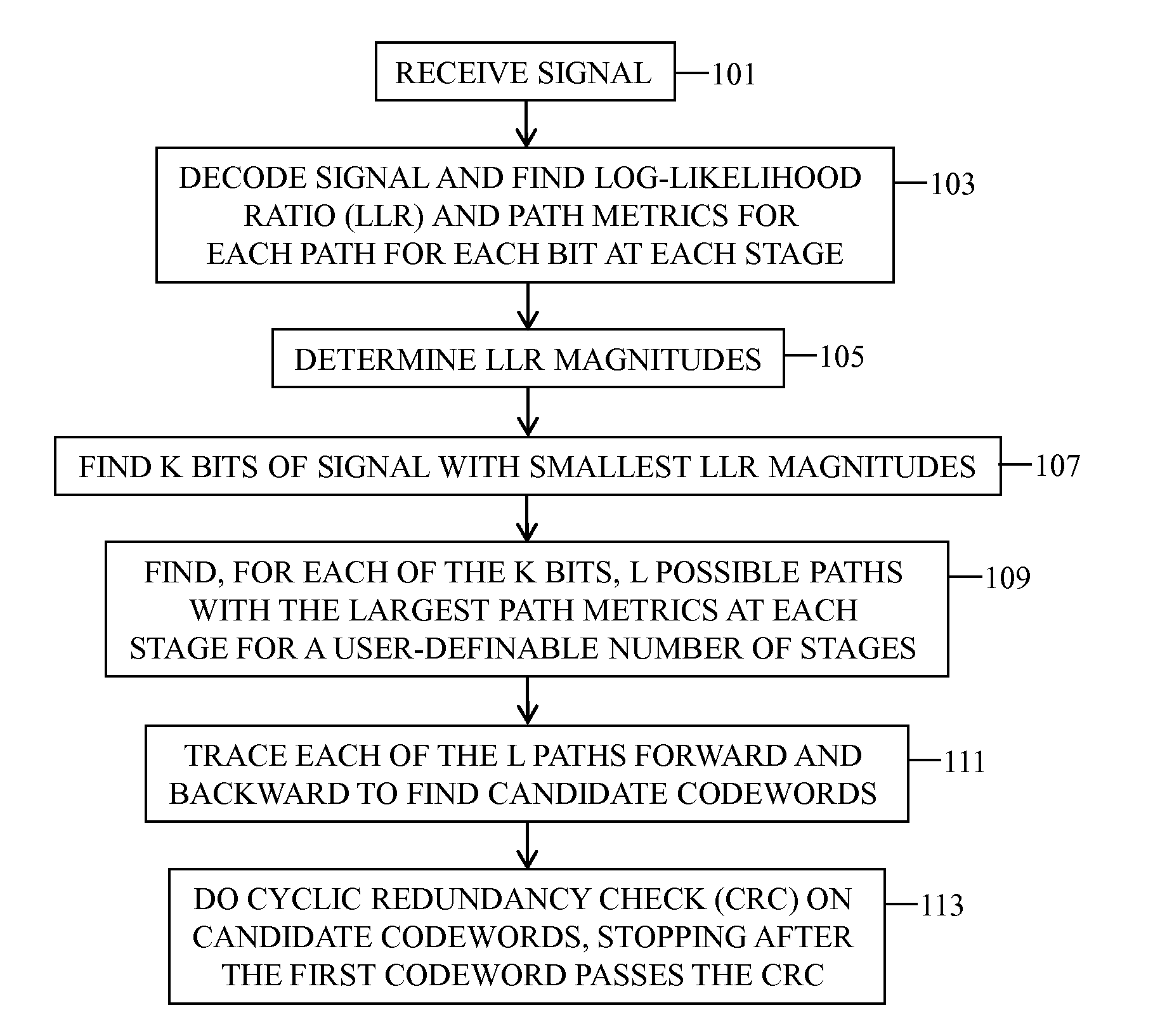
System and methods for low complexity list decoding of turbo codes and convolutional codes
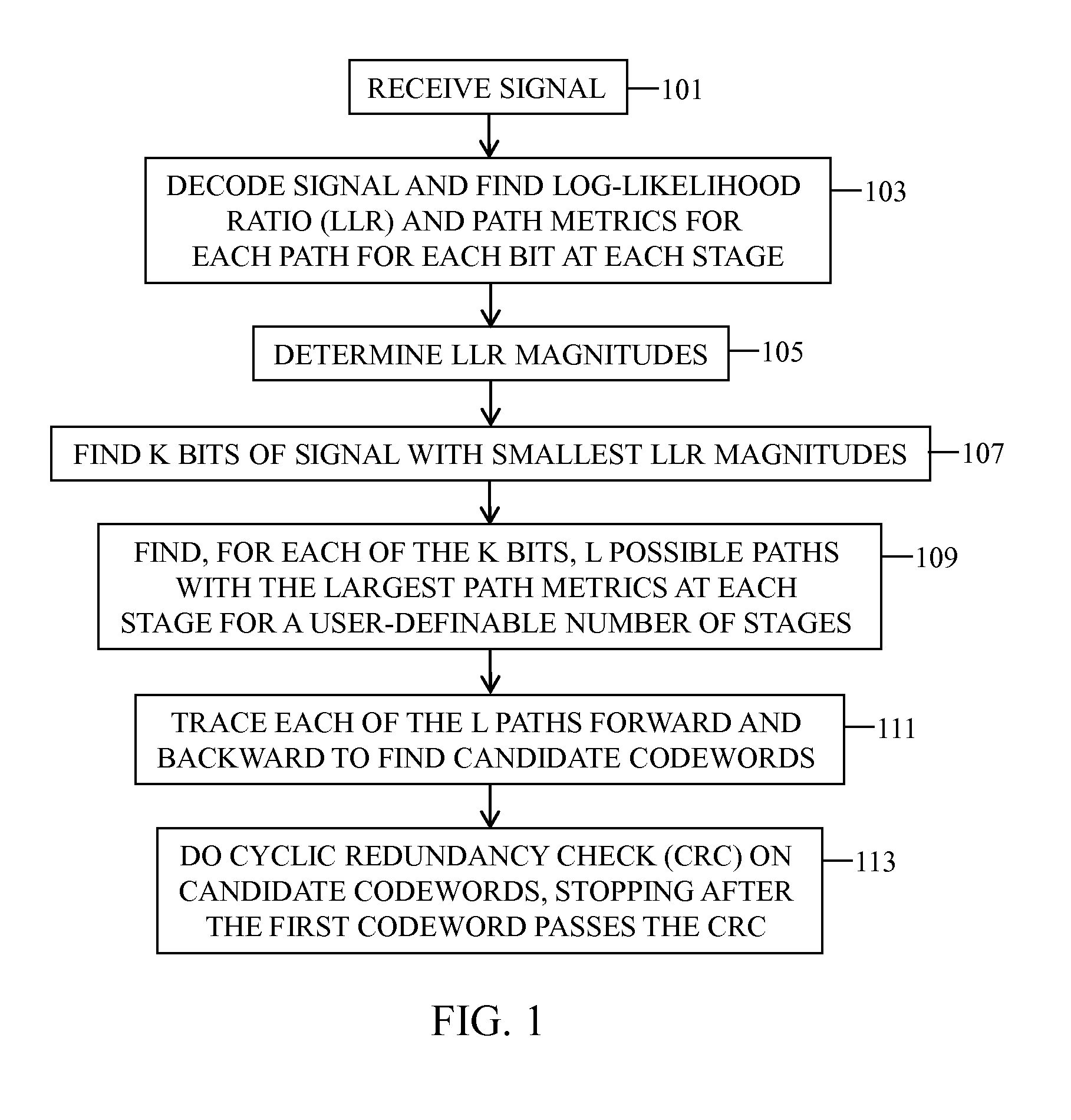
A method and system for decoding a signal are provided. The method includes receiving a signal, where the signal includes at least one symbol; decoding the signal in stages, where each at least one symbol is decoded into at least one bit per stage, wherein a Log-Likelihood Ratio (LLR) and a path metric are determined for each possible path for each at least one bit at each stage; determining the magnitudes of the LLRs; identifying K bits of the signal with the smallest corresponding LLR magnitudes; identifying, for each of the K bits, L possible paths with the largest path metrics at each decoder stage for a user-definable number of decoder stages; performing forward and backward traces, for each of the L possible paths, to determine candidate codewords; performing a Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) on the candidate codewords, and stopping after a first candidate codeword passes the CRC.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Continuous elimination list decoding method of software polarization code
ActiveCN106253911AReduce in quantityThe acceleration effect is obviousError correction/detection using linear codesDecoding methodsComputer science
The invention discloses a continuous elimination list decoding method of a software polarization code. Through establishment of a reference matrix and combination with the position of a current decoding bit, an upper bound and a lower bound of a phase needing to be copied are positioned; and the upper bound and the lower bound are mapped to a memory, only values between the two bounds are copied, and thus the quantity of copy operation is reduced. Compared to a conventional decoding technology, the method has the following advantages: under the condition that the decoding performance is not affected, the same data is prevented from being copied when a path is updated, the path updating time delay is substantially reduced, and the decoding throughput is improved; after the current bit is decoded, the reference matrix is updated; and the decoding method provided by the invention has universality and can be applied to different polarization code lengths, code rates and path numbers.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Sliding window list decoder for error correcting codes
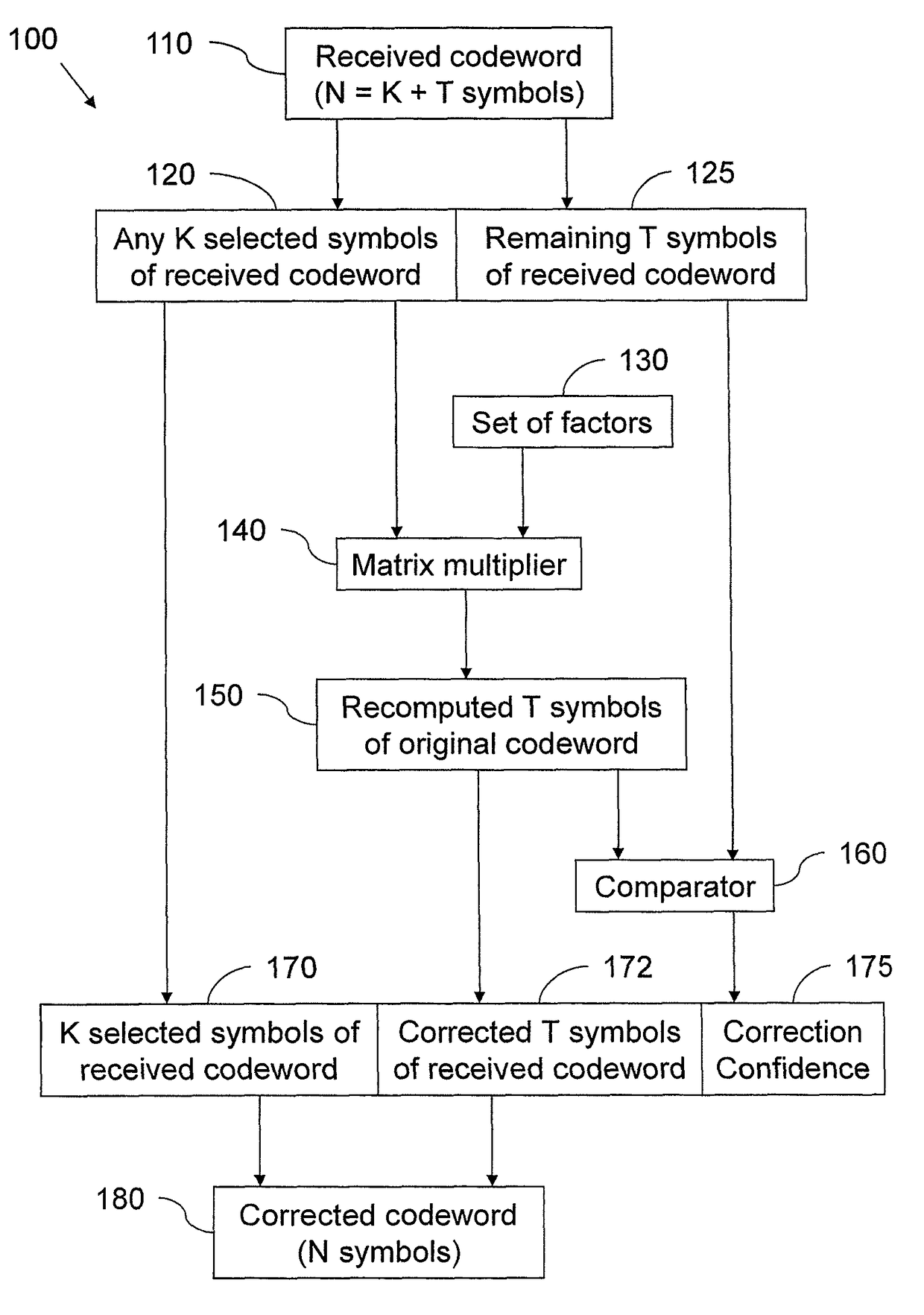
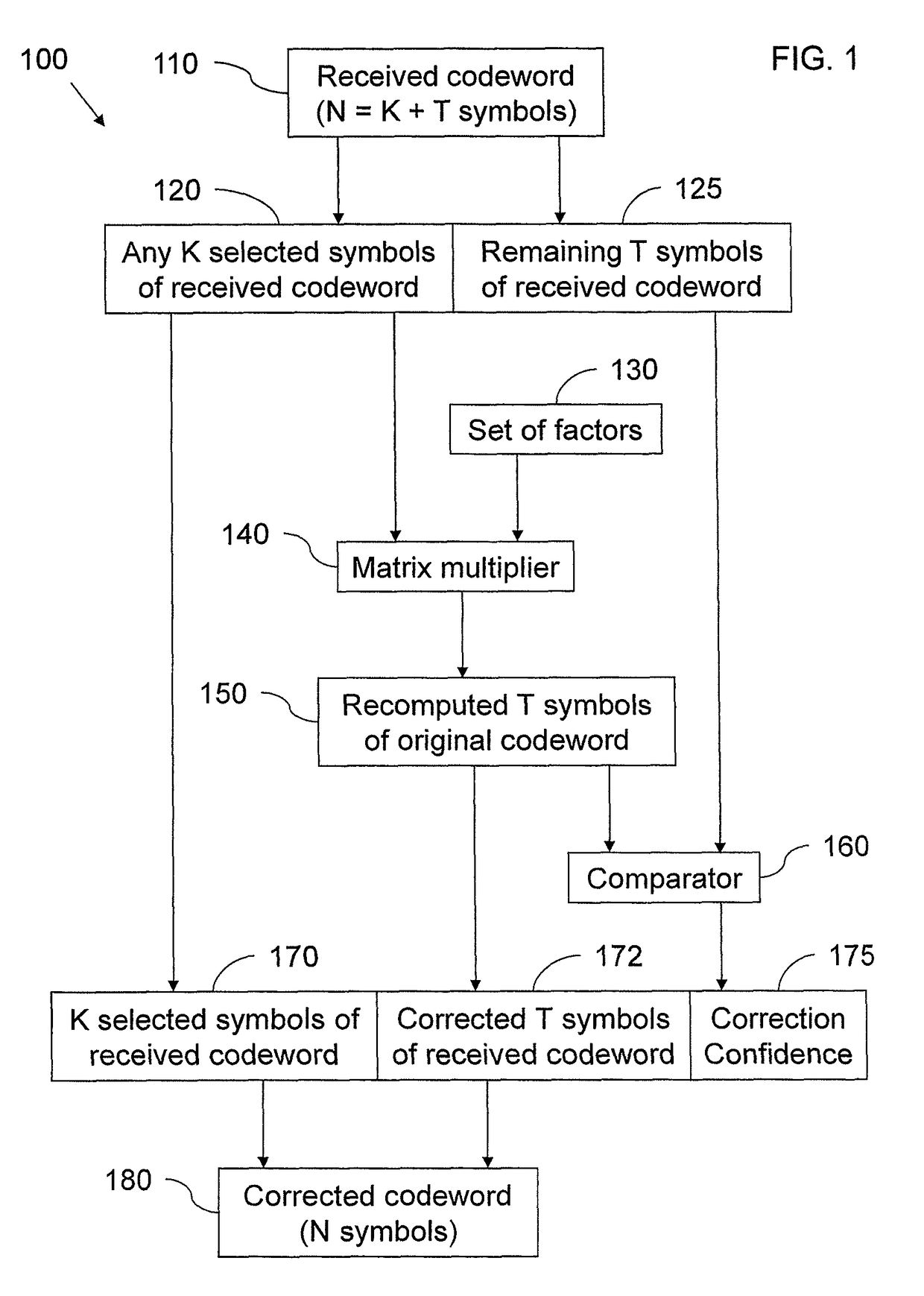
ActiveUS9722632B2Process can be speededEliminating many caseCode conversionCyclic codesSlide windowError correcting
A system for hardware error-correcting code (ECC) detection or correction of a received codeword from an original codeword includes an error-detecting circuit configured to process a selection of symbols of the received codeword using a set of factors, the original codeword being recomputable from a corresponding said selection of symbols of the original codeword using the set of factors. The error-detecting circuit includes a hardware multiplier and accumulator configured to use the set of factors and the selection of symbols of the received codeword to recompute remaining symbols of the original codeword, and a hardware comparator configured to compare the recomputed remaining symbols of the original codeword with corresponding said remaining symbols of the received codeword and to output first results of this comparison.
Owner:STREAMSCALE
Rapid optimization method for polarization code decoding parameters
InactiveCN108777584AGuaranteed performanceQuick classificationError preventionCharacter and pattern recognitionRadial basis function neuralFast optimization
The invention provides a rapid optimization method for polarization code decoding parameters. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, starting from collection and sorting of sample data;then carrying out modeling according to the characteristics and the size of the sample data, and adopting a supervised learning and random gradient optimization method for training a network; then inputting the likelihood ratio obtained by calculation of the received signal into a radial basis function neural network model which completes the training and outputting M; and finally, initializing Lto M and executing a serial offset list decoding algorithm. According to the method, a radial basis function neural network technology and a polarization code decoding technology are combined, so thatunnecessary calculation operation is avoided, and therefore the coding complexity of polarization codes is greatly lowered.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Hard iterative decoder for multilevel codes
Two decoding algorithms are introduced for the decoding of multi-level coded modulation and other types of coded modulation involving component codes and interleaving operations. An improved hard iterative decoding (IHID) algorithm is presented that improves upon a hard iteration decoding technique by adding a stopping criterion. Also, a list Viterbi hard iteration decoding (LV-IHID) algorithm is presented that employs list decoding in conjunction with the IHID algorithm. Both of these decoding algorithms improve upon conventional multi-stage decoding by reducing the effective error multiplicity that is observed at the lowest coding level. It is demonstrated that the LV-IHID algorithm performs close to soft iterative decoding. The computational and delay complexity of the proposed decoding algorithms compare favorably with soft iterative decoding strategies. Also, a novel labeling strategy for MLC design is presented.
Owner:TRELLIS PHASE COMM LP
Efficient list decoding of LDPC codes
ActiveUS20180131391A1Facilitate communicationError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionLow-density parity-check codeTheoretical computer science
Certain aspects of the present disclosure generally relate to methods and apparatus for decoding low density parity check (LDPC) codes, and more particularly to an efficient list decoder for list decoding low density parity check (LDPC) codes.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
An adaptive fusion serial cancellation list polarization code decoding method and system
ActiveCN109921804AJudgment valueAverage complexity neutralCyclic codesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Coding decoding
The invention discloses a self-adaptive fusion serial cancellation list polarization code decoding method and a self-adaptive fusion serial cancellation list polarization code decoding system. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining bits in a to-be-decoded sequence; screening out information bits in the sequence to be decoded; judging whether the log-likelihood ratio of each information bit meets a positive threshold judgment condition which is greater than 0 and greater than a positive threshold or a negative threshold judgment condition which is less than 0 and less than a negative threshold one by one according to the arrangement sequence of the coded bit sequence to obtain a first judgment result; when the first judgment result is negative information bits, the informationbits of which the arrangement sequence is before the information bits of which the first judgment result is negative are decoded one by one by adopting a serial offset decoding method; and decoding the information bits with the first judgment result being no and all the bits behind the information bits one by one by adopting a cyclic redundancy auxiliary serial offset list decoding method. According to the invention, the average complexity of the adaptive serial cancellation list decoding method under a low signal-to-noise ratio can be reduced, and the low average complexity under a high signal-to-noise ratio can be maintained.
Owner:COMMUNICATION UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
Systems and methods for advanced iterative decoding and channel estimation of concatenated coding systems
InactiveCN105122655AError correction/detection using convolutional codesModulated-carrier systemsHD RadioAlgorithm
Systems and methods for decoding block and concatenated codes are provided. These include advanced iterative decoding techniques based on belief propagation algorithms, with particular advantages when applied to codes having higher density parity check matrices. Improvements are also provided for performing channel state information estimation including the use of optimum filter lengths based on channel selectivity and adaptive decision-directed channel estimation. These improvements enhance the performance of various communication systems and consumer electronics. Particular improvements are also provided for decoding HD Radio signals, including enhanced decoding of reference subcarriers based on soft-diversity combining, joint enhanced channel state information estimation, as well as iterative soft-input soft-output and list decoding of convolutional codes and Reed-Solomon codes. These and other improvements enhance the decoding of different logical channels in HD Radio systems.
Owner:LN2 DB LLC
Reinforced list decoding
Certain aspects of the present disclosure relate to techniques and apparatus for increasing decoding performance and / or reducing decoding complexity. A transmitter may divide data of a codeword into two or more sections and then calculate redundancy check information (e.g., a cyclic redundancy check or a parity check) for each section and attach the redundancy check information to the codeword. A decoder of a receiver may decode each section of the codeword and check the decoding against the corresponding redundancy check information. If decoding of a section fails, the decoder may use information regarding section(s) that the decoder successfully decoded in re-attempting to decode the section(s) that failed decoding. In addition, the decoder may use a different technique to decode the section(s) that failed decoding. If the decoder is still unsuccessful in decoding the section(s), then the receiver may request retransmission of the failed section(s) or of the entire codeword.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Joint decoding method and apparatus based on continuous elimination list decoding and list sphere decoding
The invention discloses a joint decoding method and apparatus based on continuous elimination list decoding and list sphere decoding. According to the joint decoding method and apparatus disclosed bythe invention, the continuous elimination list decoding and the list sphere decoding are combined, decoding is performed from the first bit to the Mth bit by using a continuous elimination list decoding mode, and decoding is performed from the last bit to the (M+1)th bit by using a list sphere decoding mode; and in a matching phase, a path i in a list of the continuous elimination list decoding and a path j in a list of the list sphere decoding are respectively selected, an Euclidean distance between a synthetic code word and a receiving code word is calculated and matched, and the code word having the minimum Euclidean distance is selected as the output of the decoding method. The joint decoding method and apparatus disclosed by the invention have the advantages of lower delay and higherefficiency.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method of list decoding and relative decoder for LDPC codes
A method is for generating, for each check node related to a parity check equation of a LDPC code, signals representing a first output table of corrected values of symbols of a word received through a communication channel and transmitted according to the LDPC code, and signals representing a second output table of the logarithm of the ratio between the respective probability of correctness of the values of same coordinates in the first output table and their corresponding maximum probability of correctness. The method is implemented by processing the components of a first input table of values of a Galois Field of symbols that may have been transmitted and of a second input table of corresponding probability of correctness of each value.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Apparatus and method for parallelized successive cancellation decoding and successive cancellation list decoding of polar codes
ActiveUS20180083655A1Error preventionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementTheoretical computer scienceLog likelihood
An apparatus and a method. The apparatus includes a receiver to receive a polar codeword of length mj; a processor configured to determine a decoding node tree structure with mj leaf nodes for the received codeword, and receive i indicating a level at which parallelism of order m is applied to the decoding node tree structure, wherein i indicates levels of the decoding node tree structure, and wherein the mj leaf nodes are at level j; and m successive cancellation list decoders (SCLDs) applied to each child node of each node in the decoding node tree structure at level i−1, wherein each of the m SCLDs executes in parallel to determine log likelihood ratios (LLRs) for a codeword of length mj−i, and wherein each of the m SCLDs uses LLRs of an associated parent node without using a hard decision or a soft reliability estimate of any other node of the other m SCLDs.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
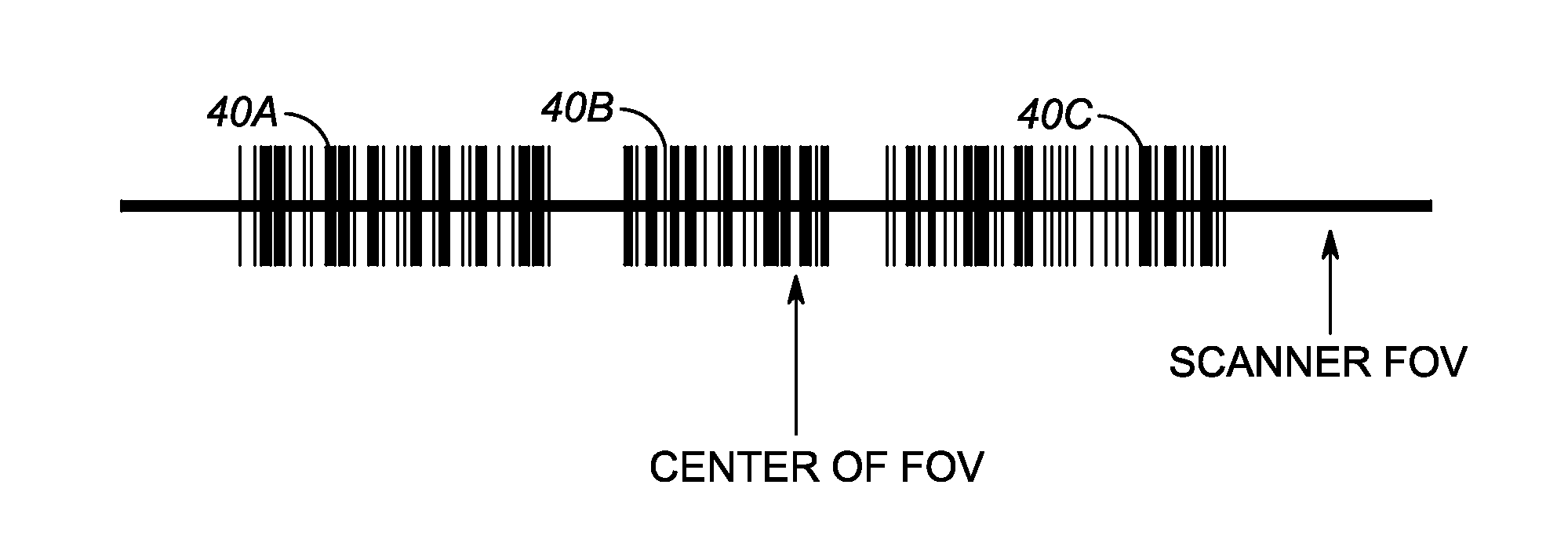
Decoding barcode using smart linear picklist
ActiveUS20150310246A1Character and pattern recognitionVerifying markings correctnessPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
A method of decoding a barcode includes determining number of barcode candidates in the image captured and processing the image captured in accordance with the number of barcode candidates found. If the number of barcode candidates is one, the image captured is processed to decode the only one barcode candidate in the image captured. If the number of barcode candidates is larger than one, the image captured is processed to find a barcode candidate that overlays with an aiming location between a first location and a second location on a scan line and to decode the barcode candidate that is found that overlays with the aiming location.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
Adaptive belief propagation list decoding method for polar codes
ActiveCN110233628AImprove bit error rateImproved frame error rate performanceError detection onlyError correction/detection using linear codesBelief propagationComputer science
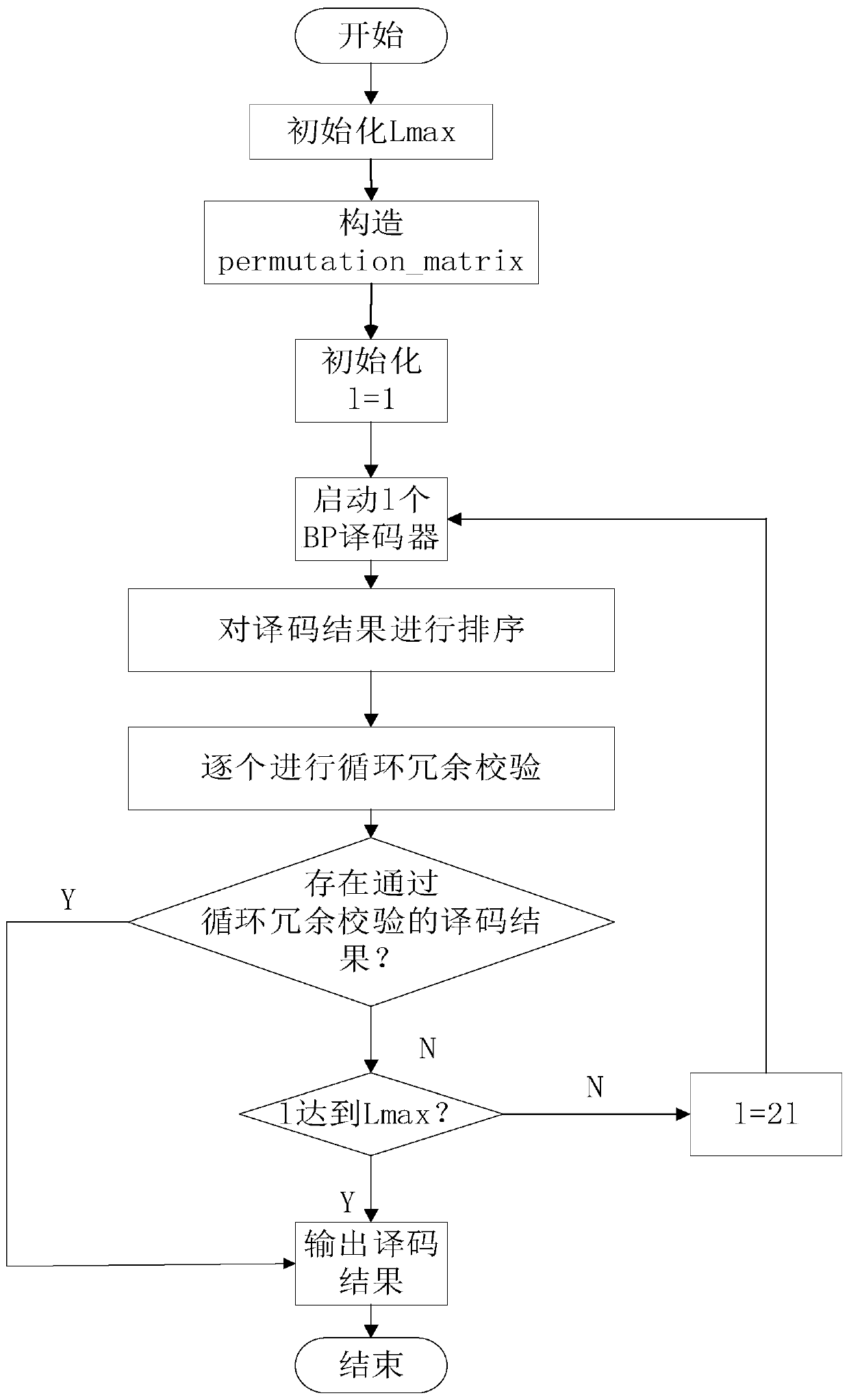
The invention discloses an adaptive belief propagation list decoding method for polar codes. The method comprises: firstly, determining the number of BP decoders owned by a receiving end; determiningthe maximum list number of the method; obtaining a BP decoding factor graph capable of achieving a good decoding effect through calculation by a Gaussian approximation method; then, selecting different BP decoding factor graphs for decoding from the BP decoders recorded in the list; and sequencing the decoding results, then carrying out cyclic redundancy check, if a result passing through the cyclic redundancy check exists, determining that the decoding is successful and stopping the decoding, otherwise, automatically adjusting the size of the list, expanding the number of the list by two times of the original number, and continuing to use the BP decoder in the list to decode.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Bm-based fast chase decoding of binary bch codes through degenerate list decoding
ActiveUS20180205398A1Other decoding techniquesCode conversionAlgorithmApplication-specific integrated circuit
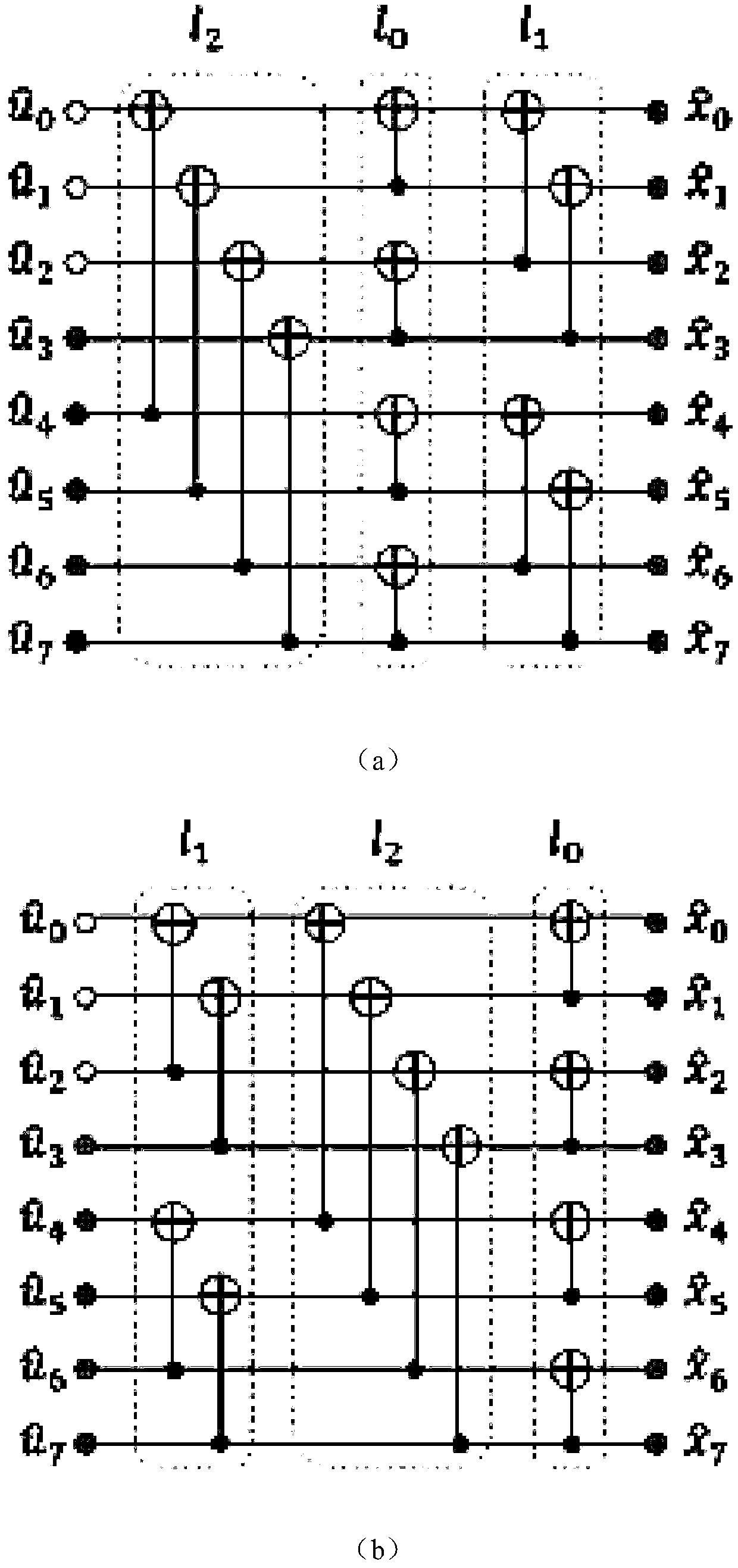
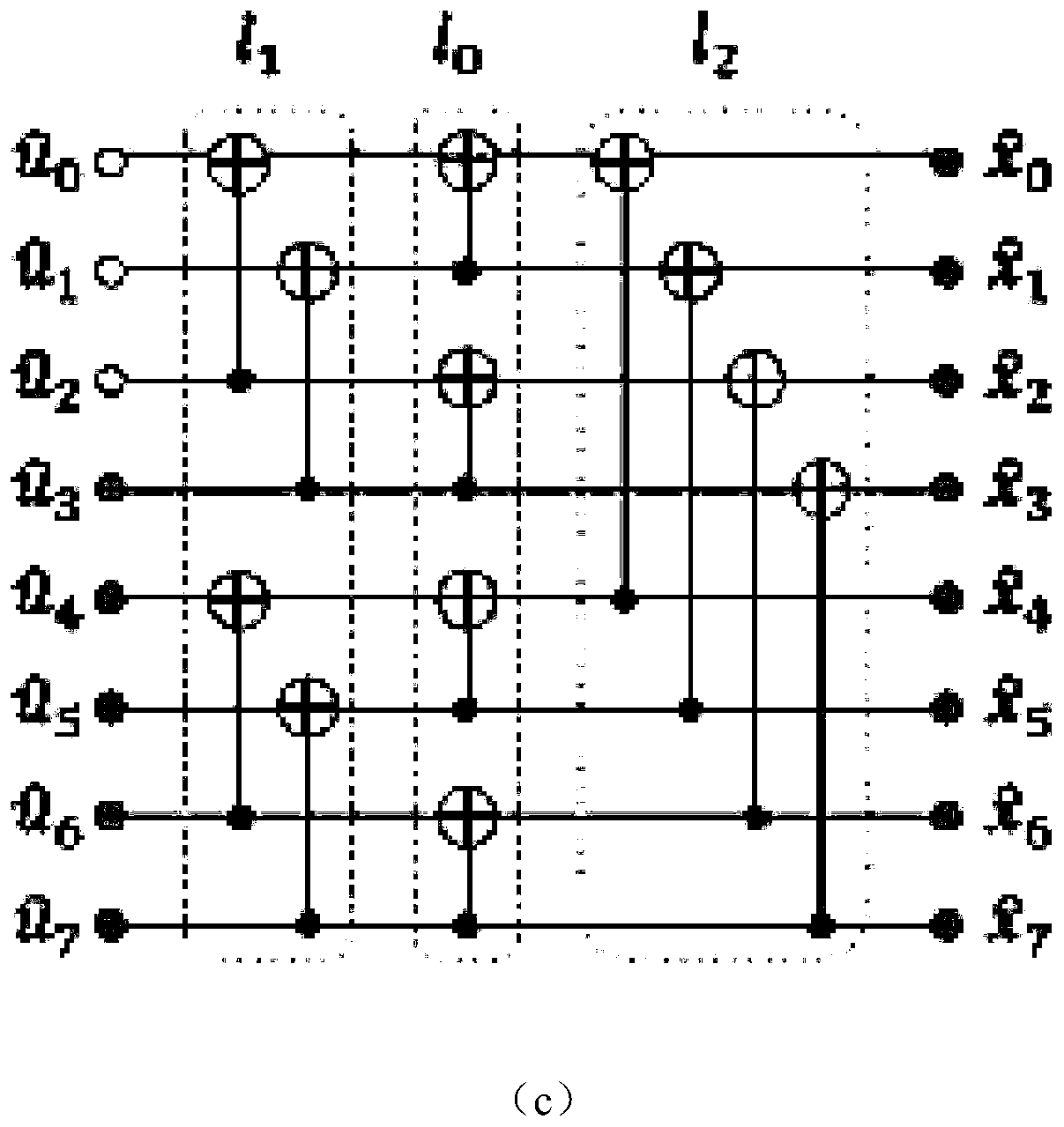
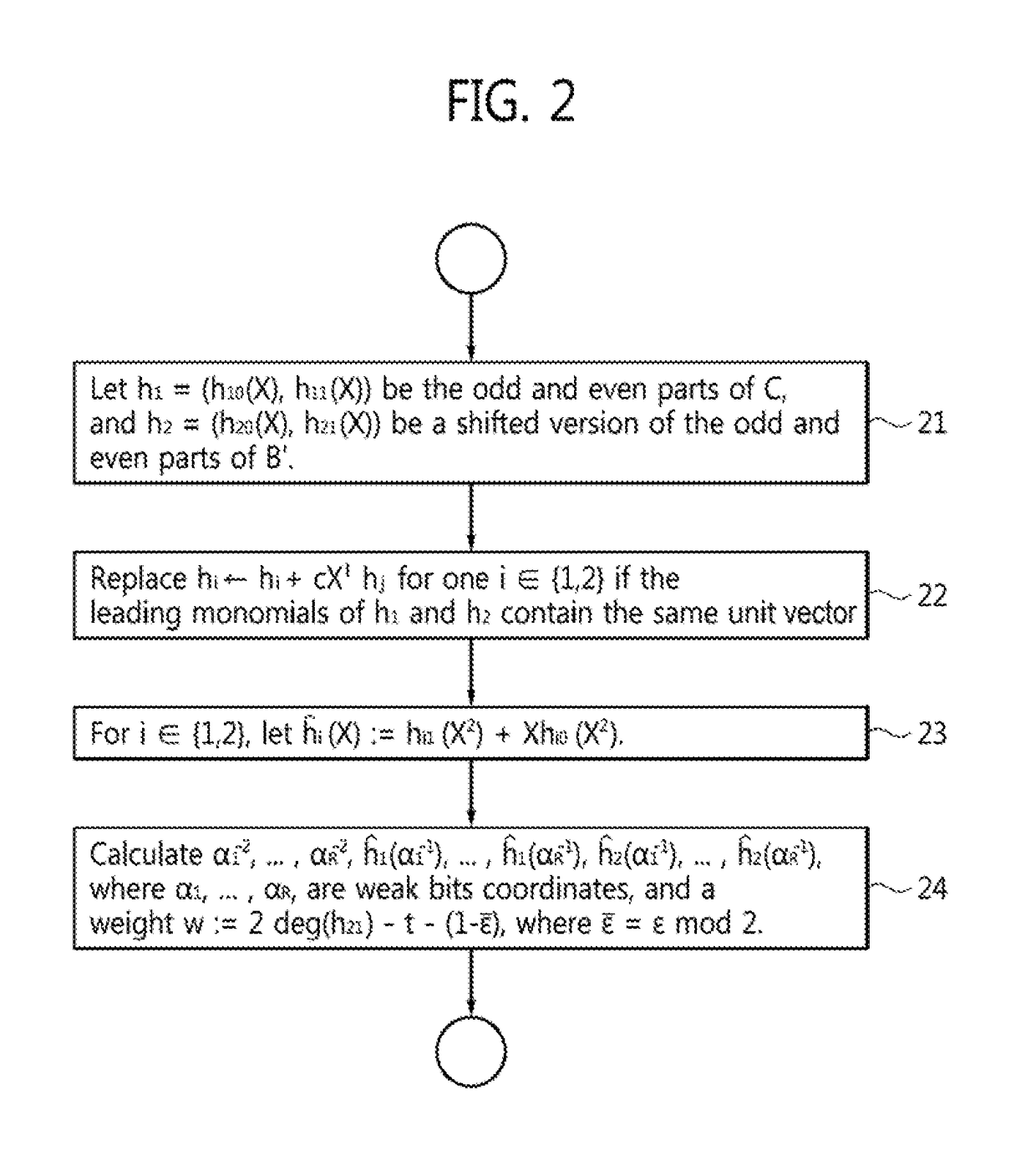
An application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) tangibly encodes a method for fast polynomial updates in fast Chase decoding of binary Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquenghem (BCH) codes. The method includes the steps of using outputs of a syndrome-based hard-decision (HD) algorithm to find a Groebner basis for a solution module of a modified key equation, upon failure of HD decoding of a BCH codeword received by the ASIC from a communication channel; evaluating polynomials obtained from said Groebner basis at inverses of specified weak-bit locations; and transforming a Groebner basis for a set of flipped weak-bit locations (α1, . . . , αr−1) to a Groebner basis for (α1, . . . , αr), wherein αr is a next weak-bit location, wherein r is a difference between a number of errors and a HD correction radius of the BCH codeword.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Hard iterative decoder for multilevel codes
Owner:TRELLIS PHASE COMM LP
Polarization code belief propagation decoding method and device and storage medium
ActiveCN111416624AAchieve throughputAchieve error correction performance indicatorsError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionParallel computingEngineering
The invention discloses a polarization code belief propagation decoding method and device, and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out belief propagation decoding on information received by a decoder; judging whether a decoding result of the belief propagation decoding meets a judgment condition or not, if so, stopping executing the belief propagation decoding, andotherwise, generating an overturning set based on the decoding result; performing flip-based decoding according to the flip set. According to the method disclosed in the invention, the error correction performance of the list decoding method and equipment can be continuously eliminated while the high decoding throughput rate is achieved, and soft information can be iteratively output; thus co-architecture design of joint detection decoding, LDPC and polarization codes becomes possible.
Owner:PURPLE MOUNTAIN LAB
Polarization code serial cancellation list decoding method based on simplified third-order critical set
ActiveCN109525252AReduce latencyReduced number of splitsError correction/detection using linear codesNODALTime delays
The invention discloses a polarization code serial cancellation list decoding method based on a simplified third-order critical set, and belongs to the technical field of channel coding in wireless communication. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, constructing a third-order critical set TCS, wherein the TCS is composed of the first 3 bits in all R1 nodes in the polarization code, and the R1 nodes refer to the nodes in a polarization code decoding binary tree where all leaf nodes represent information bits; step 2, constructing a simplified third-order critical set STCS; and step3, classifying decoding paths by the simplified third-order critical set STCS according to the decoding index, and performing separate decoding. By defining the simplified third-order critical set, the method only performs path splitting on information bits located in the STCS, and does not perform path splitting on information bits not located in the STCS, so as to reduce the number of splittingof the decoding paths, thereby reducing the number of path management in the CA-SCL decoder and reducing the time delay of the CA-SCL decoding method.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Improved polar code BP List decoding method
ActiveCN111010196ALower latencyMeet the needs of engineering applicationsError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionTime delaysTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses an improved polar code BP List decoding method which comprises the following steps: 1, selecting a factor graph set according to a factor graph error probability method; 2, selecting one factor graph from the factor graph set Z in sequence to perform BP decoding; 3, if the decoding is correct, ending the decoding; otherwise, executing the step 4; 4, if the factor graph is the last factor graph, determining that the decoding fails, and ending the decoding; otherwise, executing the step 5; 5, selecting two positions with the lowest reliability in the x end according to adecoding result in the current factor graph, namely selecting an unreliable position; 6, selecting an unreliable position symbol; and 7, updating the channel initial information, and then turning to the step 2 for execution. According to the method, the performance of BP decoding is close to the performance of CASCL8, the requirement of engineering application is met, meanwhile, the time delay ofthe algorithm can be effectively reduced through parallelization, and the time delay requirement is met.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com