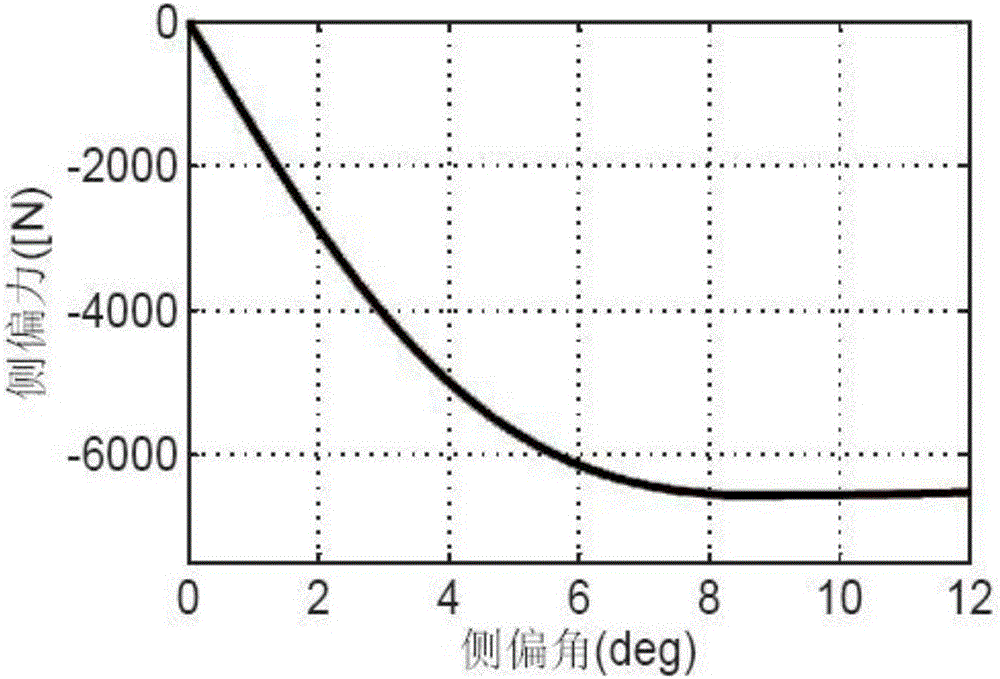
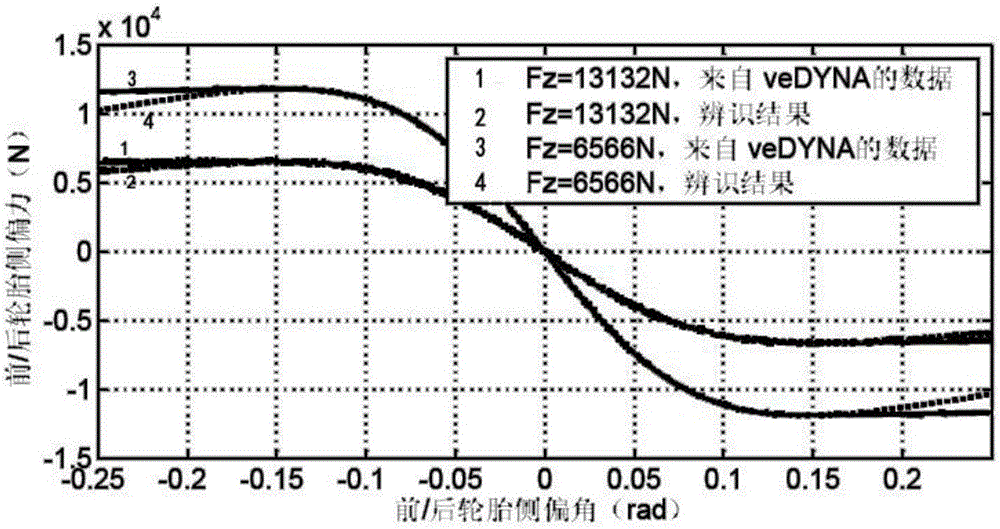
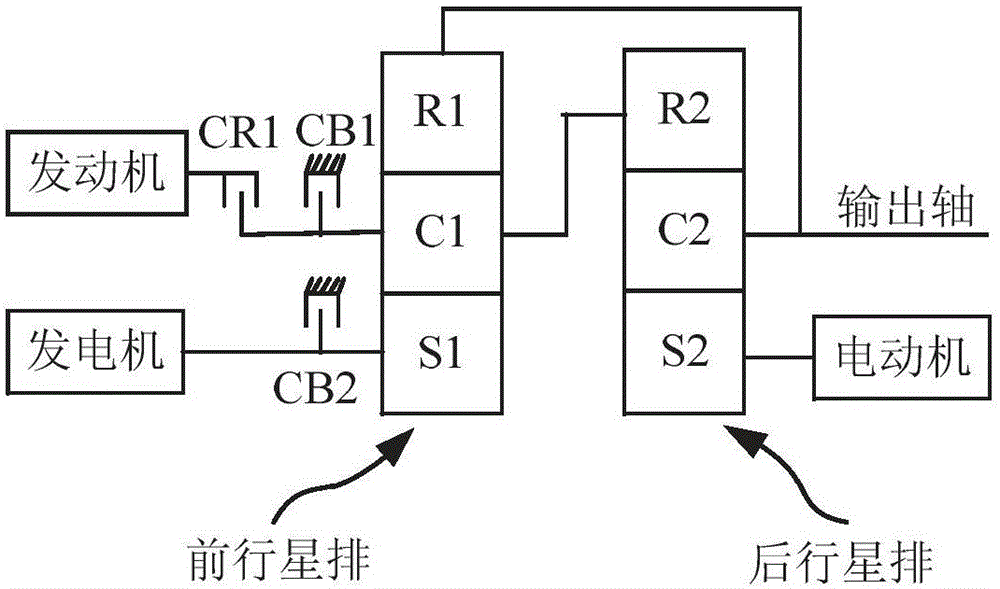
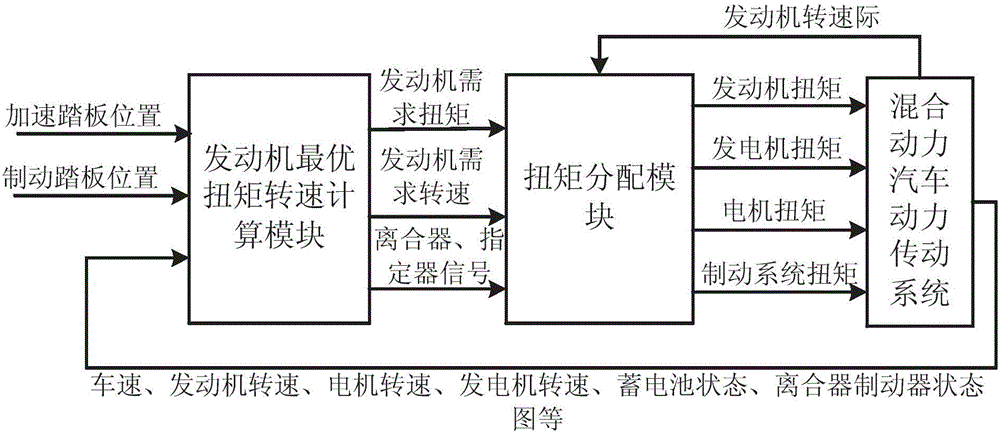
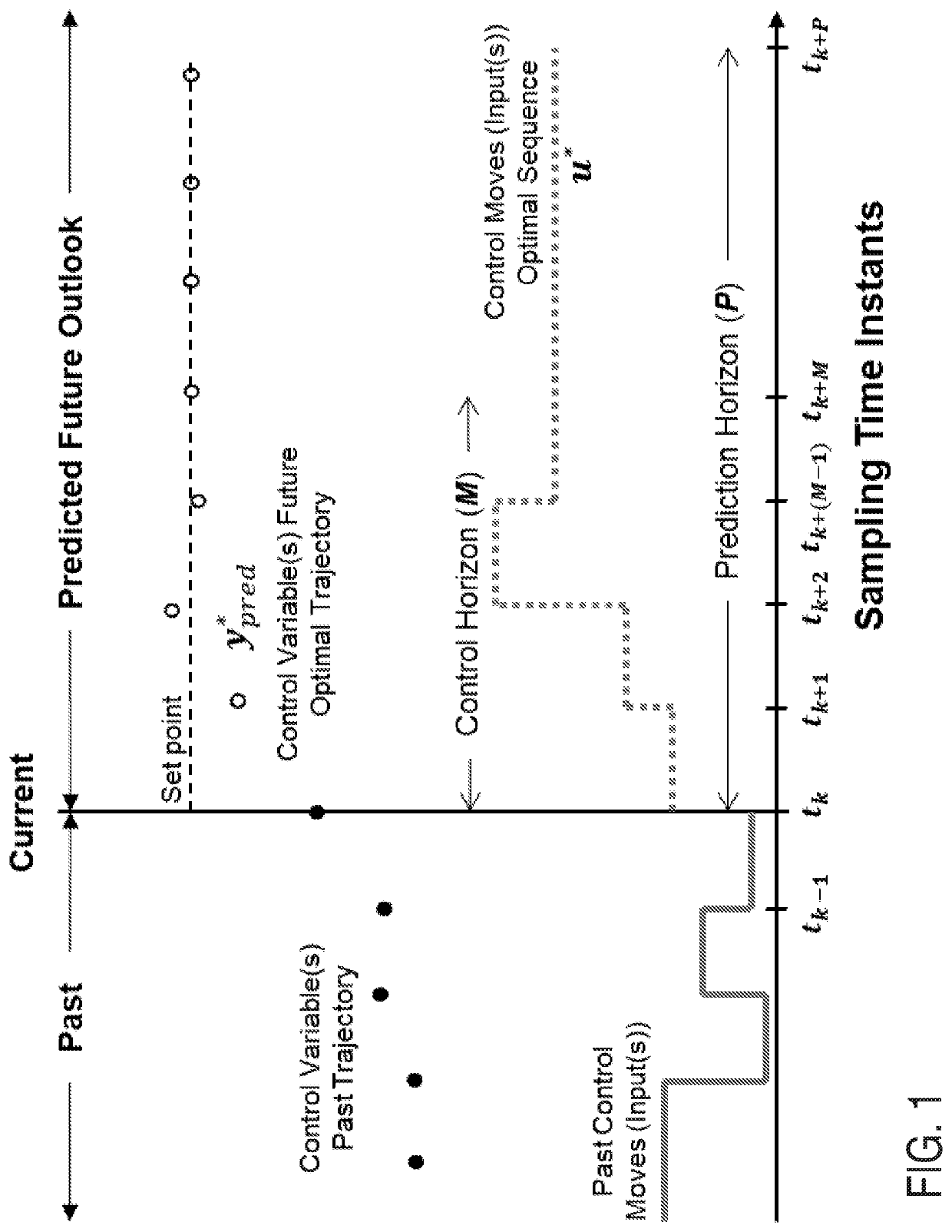
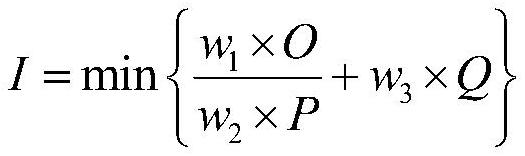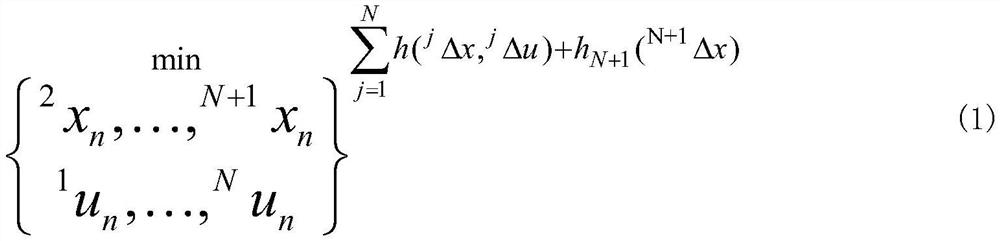Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Linear model predictive control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
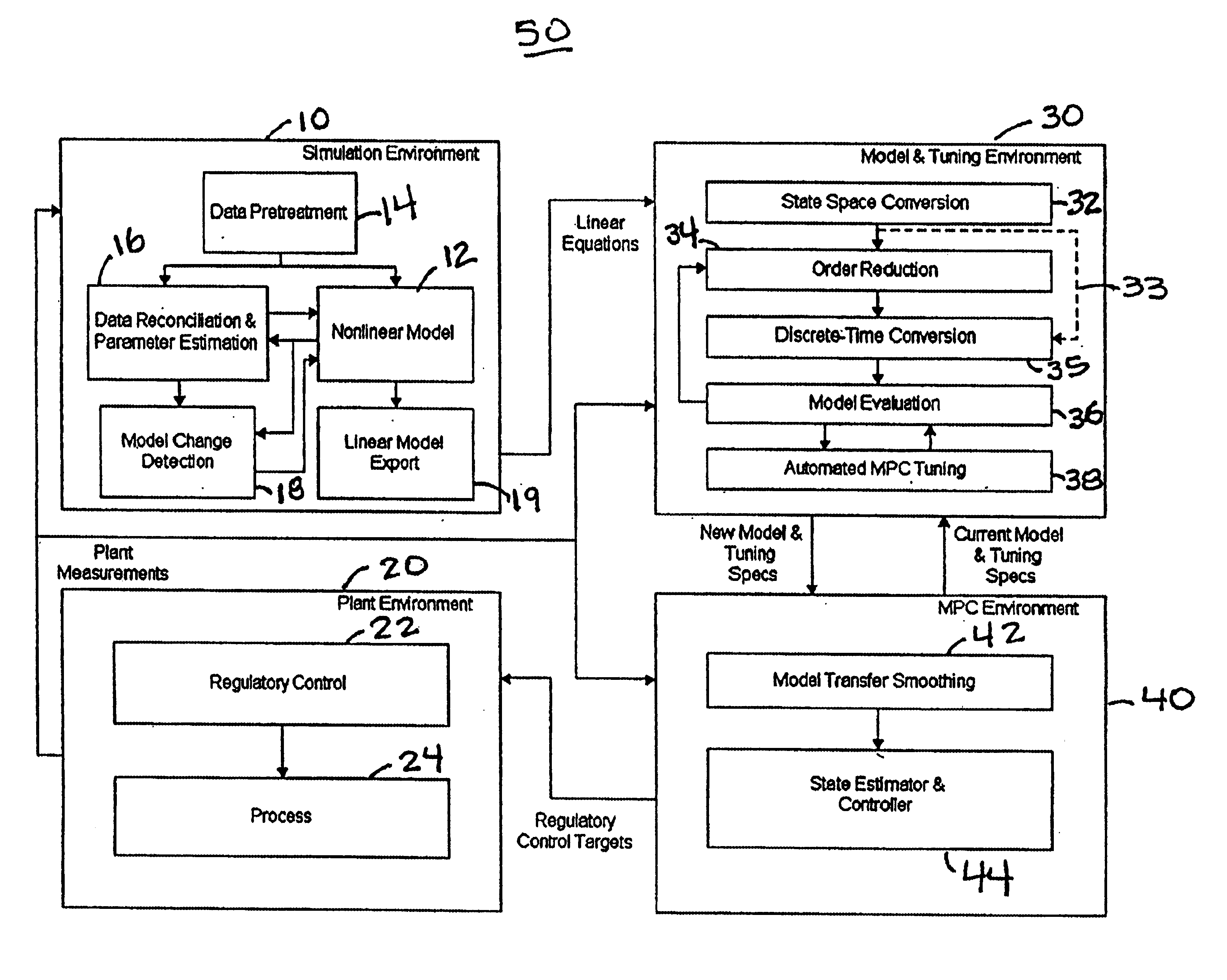
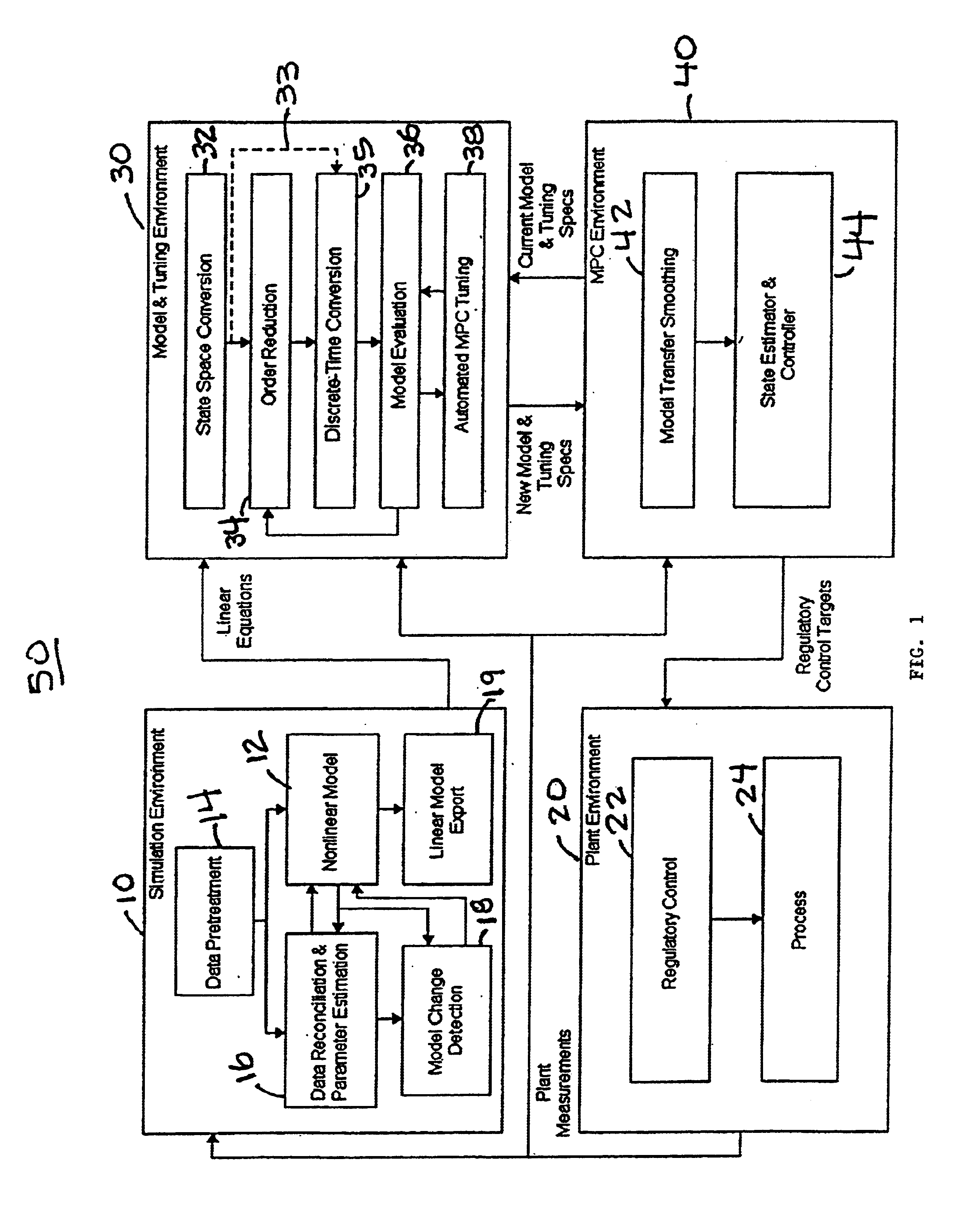
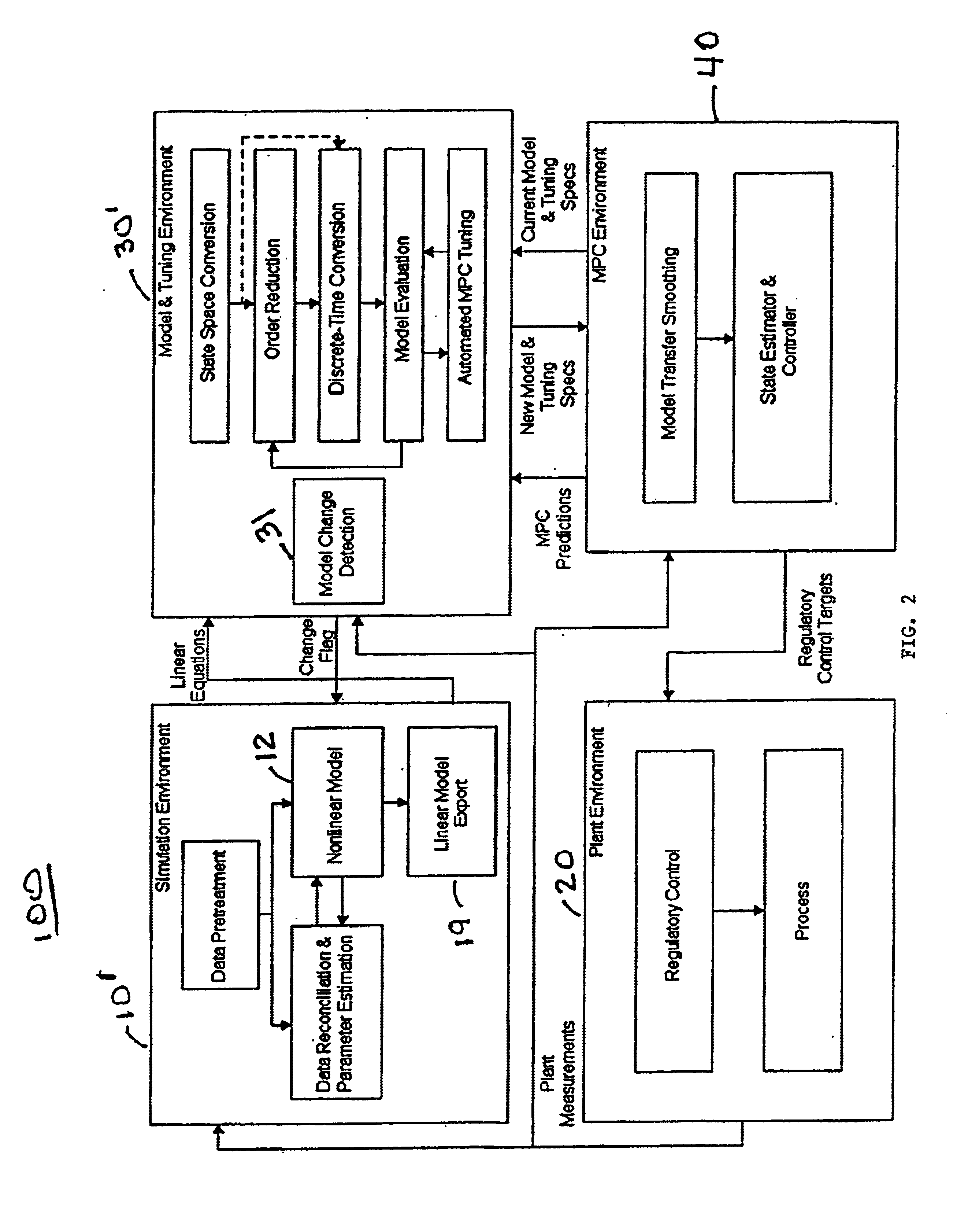
System and methodology and adaptive, linear model predictive control based on rigorous, nonlinear process model
InactiveUS6826521B1Analogue computers for chemical processesAdaptive controlSoftware systemPredictive controller
A methodology for process modeling and control and the software system implementation of this methodology, which includes a rigorous, nonlinear process simulation model, the generation of appropriate linear models derived from the rigorous model, and an adaptive, linear model predictive controller (MPC) that utilizes the derived linear models. A state space, multivariable, model predictive controller (MPC) is the preferred choice for the MPC since the nonlinear simulation model is analytically translated into a set of linear state equations and thus simplifies the translation of the linearized simulation equations to the modeling format required by the controller. Various other MPC modeling forms such as transfer functions, impulse response coefficients, and step response coefficients may also be used. The methodology is very general in that any model predictive controller using one of the above modeling forms can be used as the controller. The methodology also includes various modules that improve reliability and performance. For example, there is a data pretreatment module used to pre-process the plant measurements for gross error detection. A data reconciliation and parameter estimation module is then used to correct for instrumentation errors and to adjust model parameters based on current operating conditions. The full-order state space model can be reduced by the order reduction module to obtain fewer states for the controller model. Automated MPC tuning is also provided to improve control performance.
Owner:ABB AUTOMATION INC
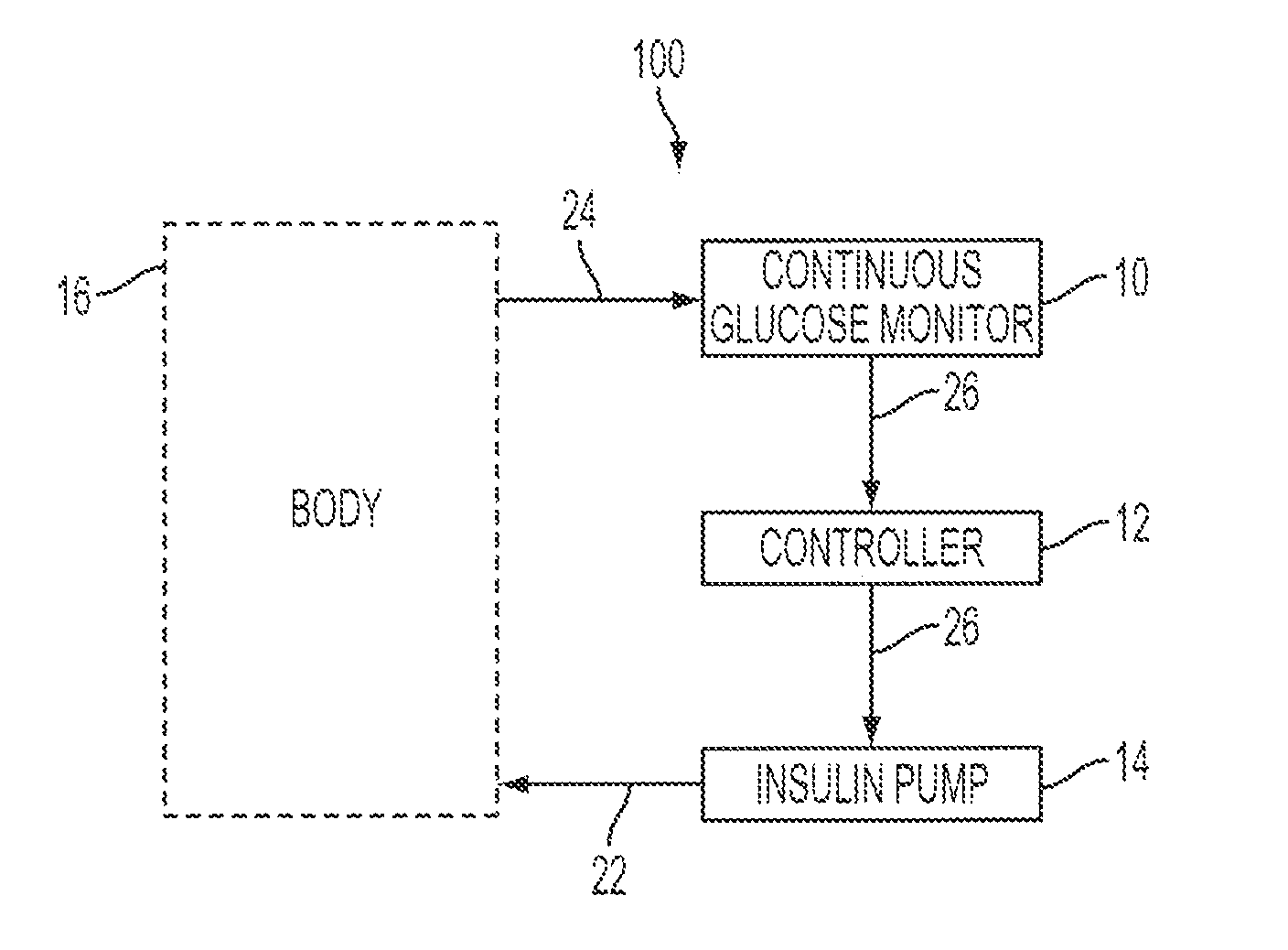
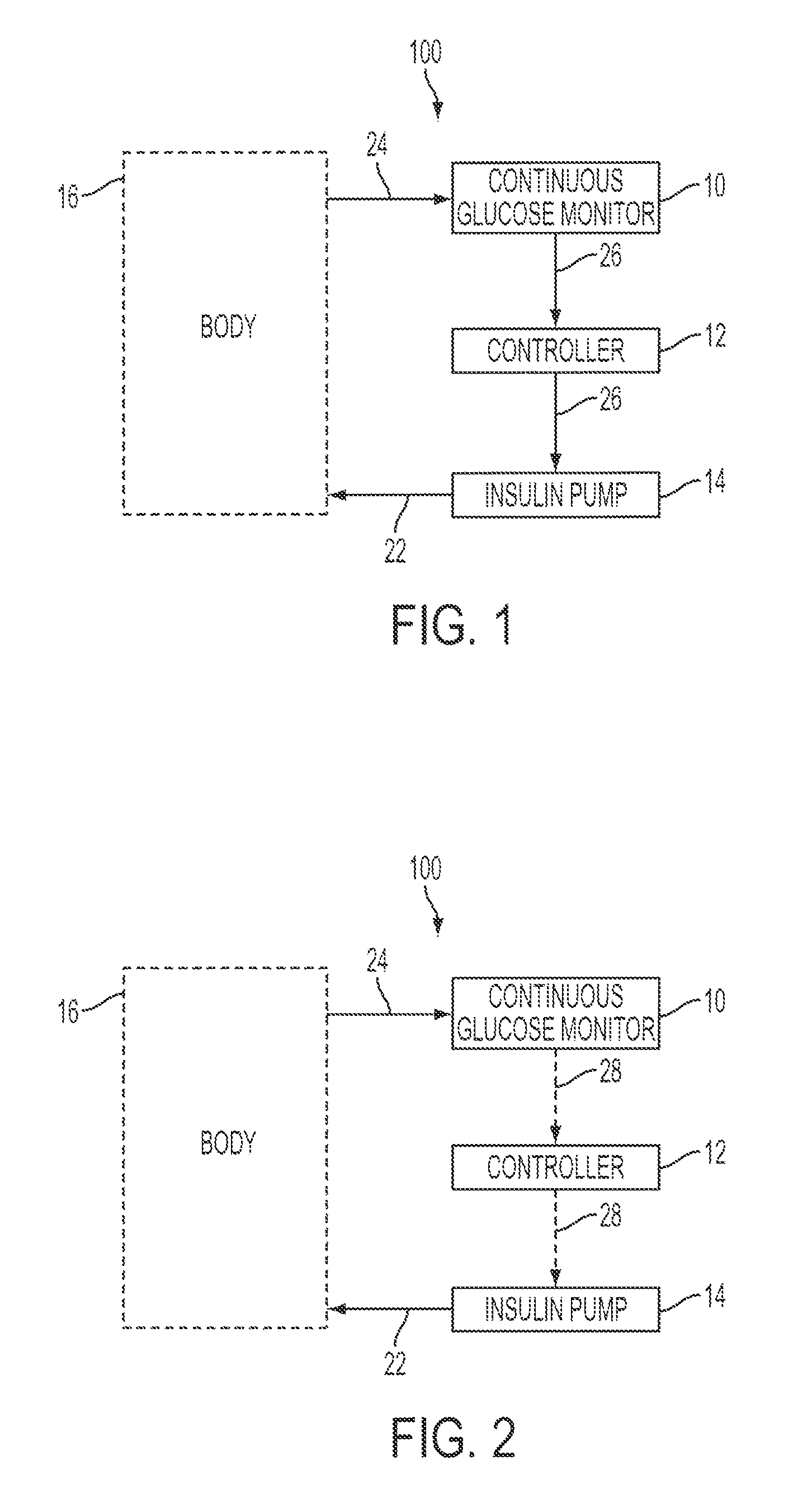
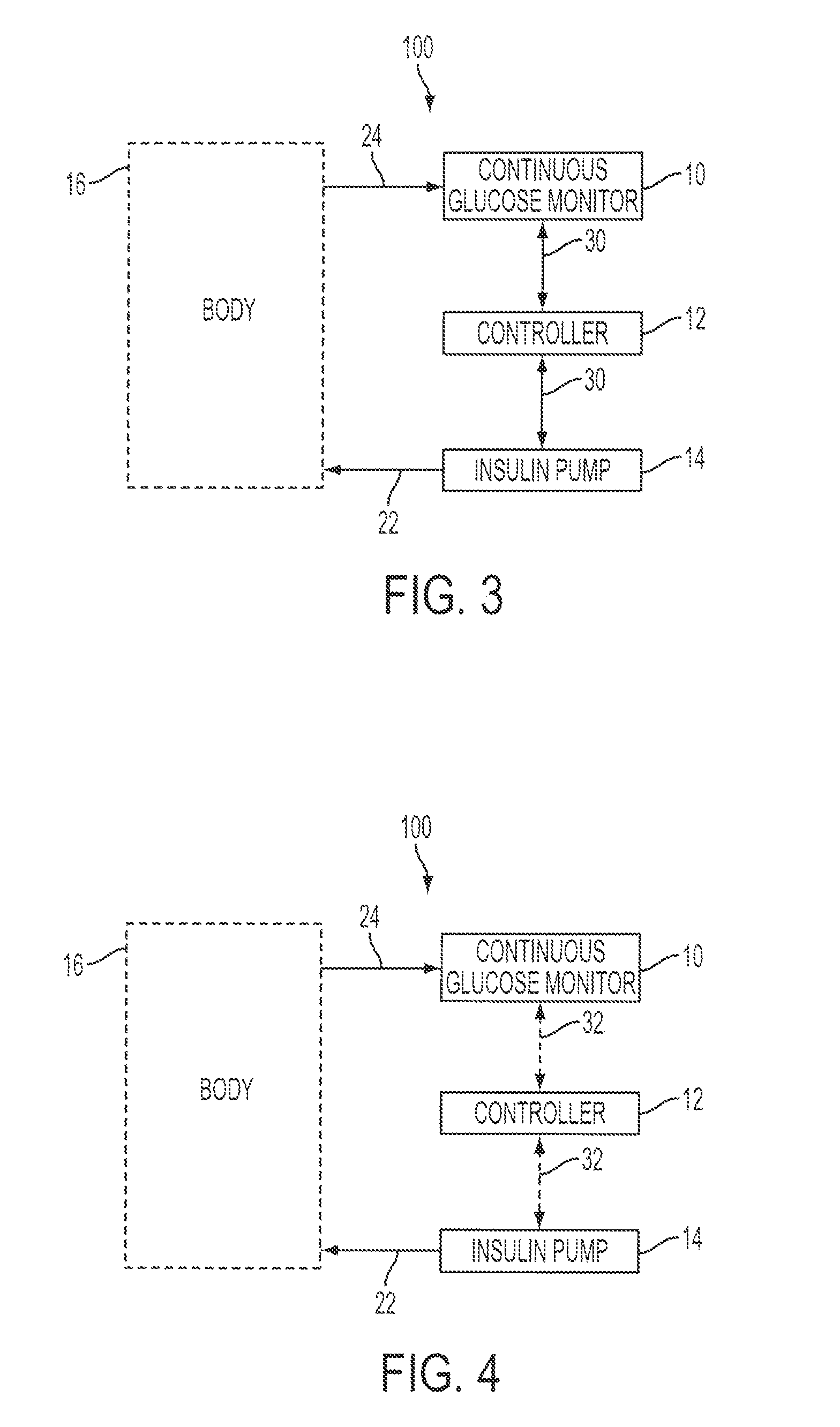
Predictive control based system and method for control of insulin delivery in diabetes using glucose sensing
A system and method for providing optimal insulin injections to a subject, using a controller, a continuous glucose monitor, and an insulin delivery unit is disclosed. The controller possesses a discrete-time, linear model predictive control law, means for sending information to the insulin delivery unit, and means for receiving information from the CGM. The control law implemented is derived from a discrete-time model of glucose insulin dynamics and an aggressiveness parameter. The result is that using only glucose measurements obtained from sensor readings and, prior values of external insulin infusion and meal and exercise announcement the optimal insulin injection necessary to safely regulate blood glucose can be calculated.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
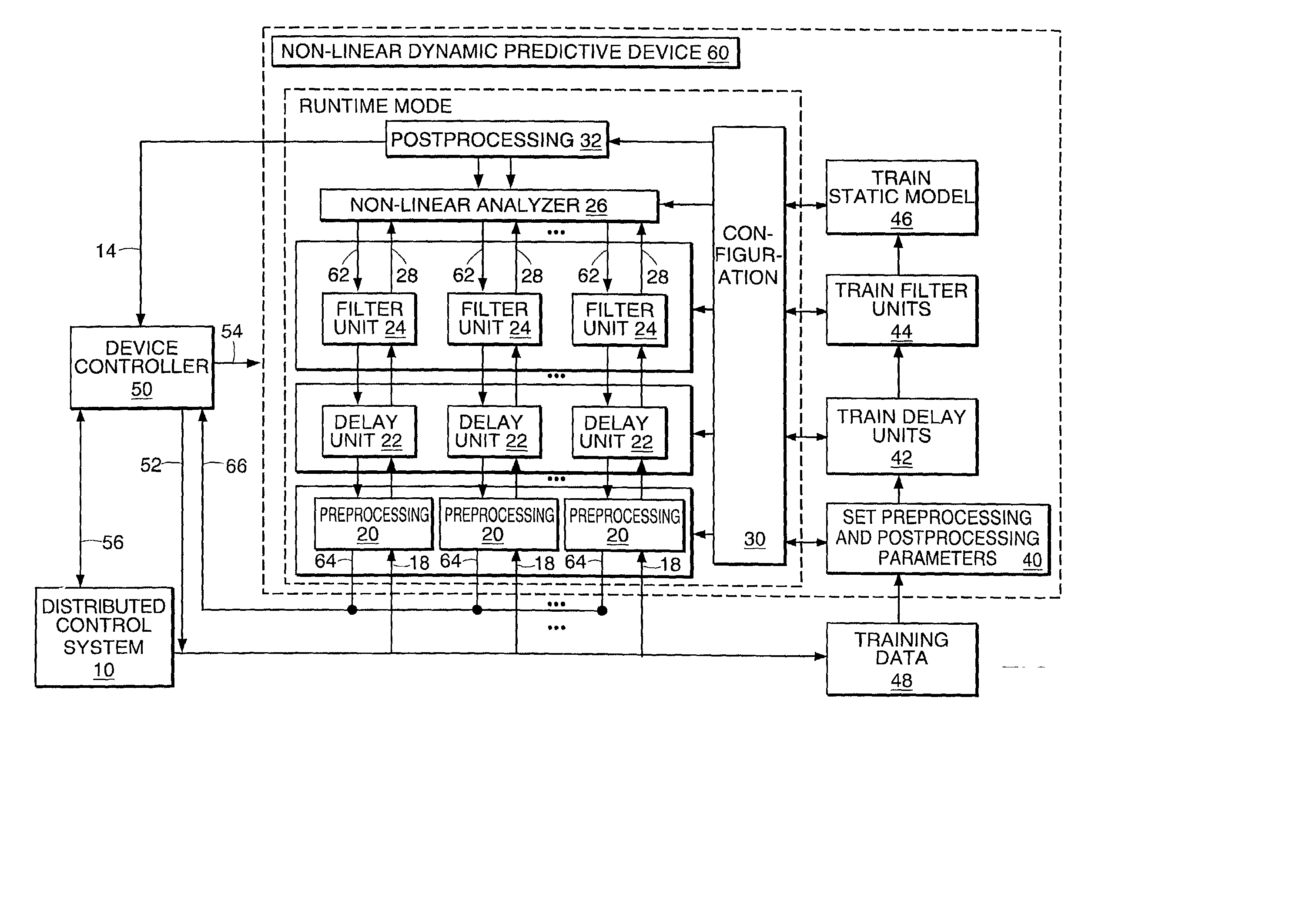
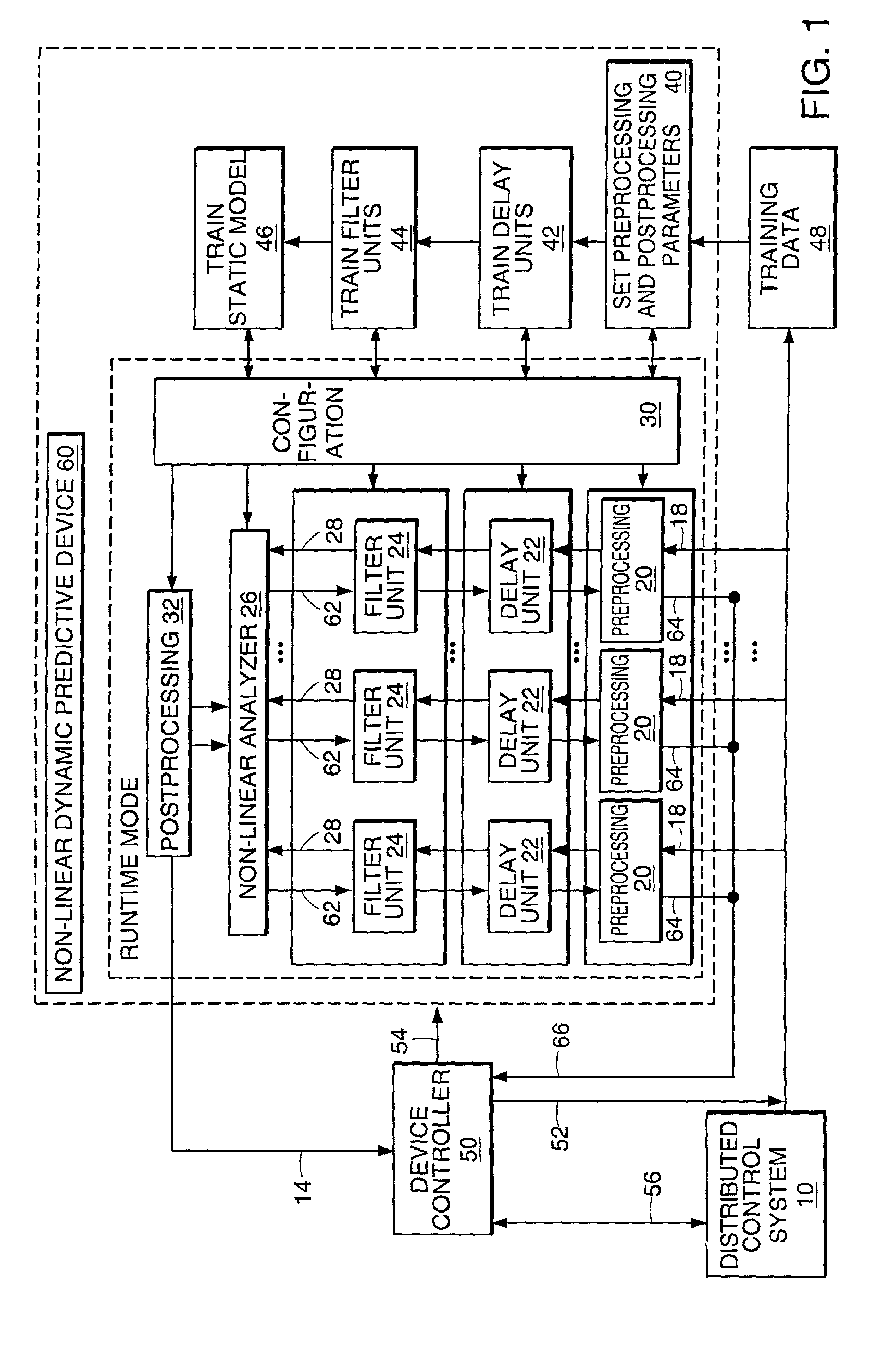
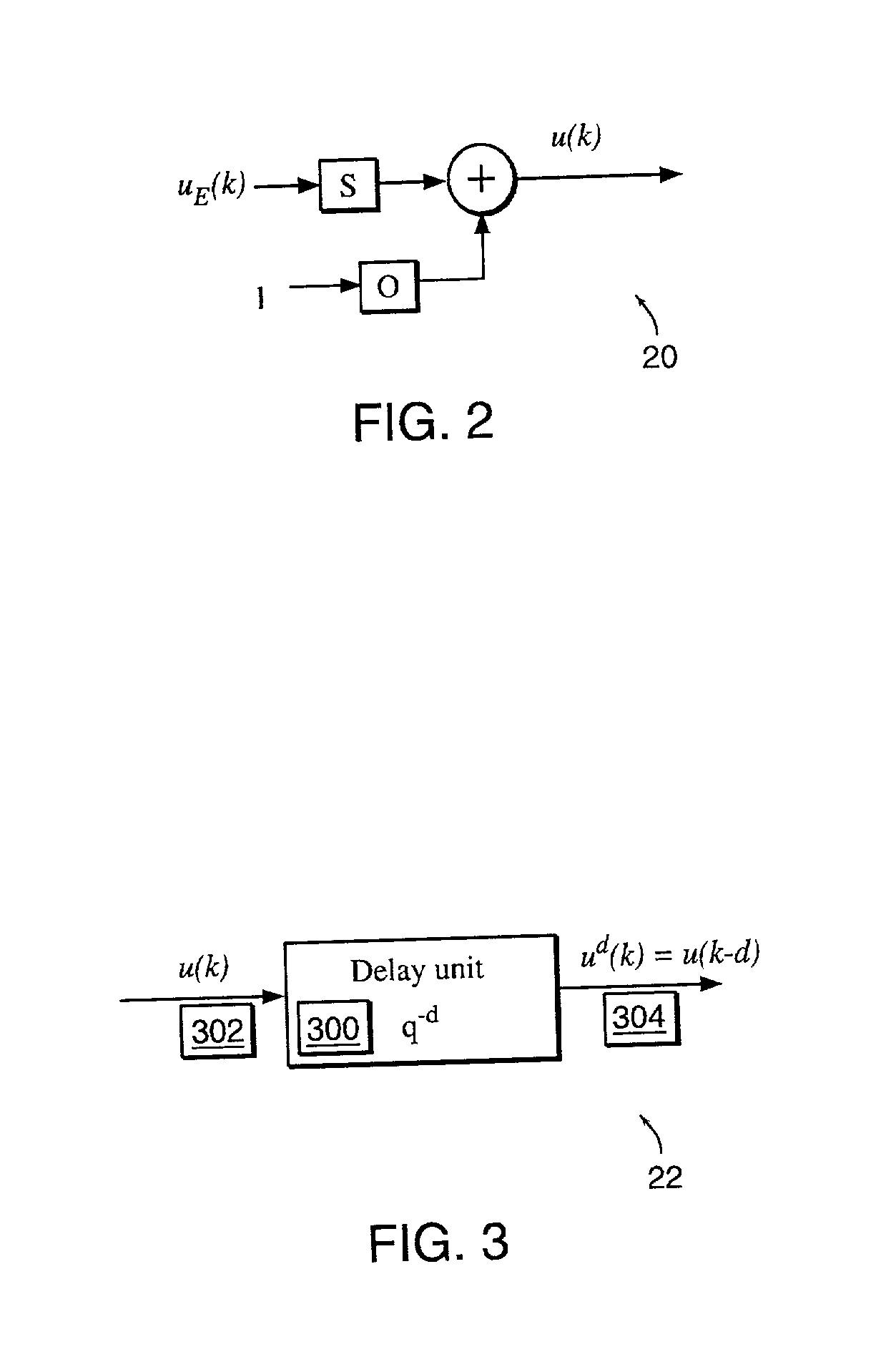
Non-linear dynamic predictive device
InactiveUS20020178133A1Fast computerImprove accuracySimulator controlElectric testing/monitoringNonlinear approximationDead time
A non-linear dynamic predictive device (60) is disclosed which operates either in a configuration mode or in one of three runtime modes: prediction mode, horizon mode, or reverse horizon mode. An external device controller (50) sets the mode and determines the data source and the frequency of data. In the forward modes (prediction and horizon), the data are passed to a series of preprocessing units (20) which convert each input variable (18) from engineering units to normalized units. Each preprocessing unit feeds a delay unit (22) that time-aligns the input to take into account dead time effects. The output of each delay unit is passed to a dynamic filter unit (24). Each dynamic filter unit internally utilizes one or more feedback paths that provide representations of the dynamic information in the process. The outputs (28) of the dynamic filter units are passed to a non-linear approximator (26) which outputs a value in normalized units. The output of the approximator is passed to a post-processing unit (32) that converts the output to engineering units. This output represents a prediction of the output of the modeled process. In reverse horizon mode, data is passed through the device in a reverse flow to produce a set of outputs (64) at the input of the predictive device. These are returned to the device controller through path (66). The purpose of the reverse horizon mode is to provide information for process control and optimization. The predictive device approximates a large class of non-linear dynamic processes. The structure of the predictive device allows it to be incorporated into a practical multivariable non-linear Model Predictive Control scheme, or used to estimate process properties.
Owner:ASPENTECH CORP
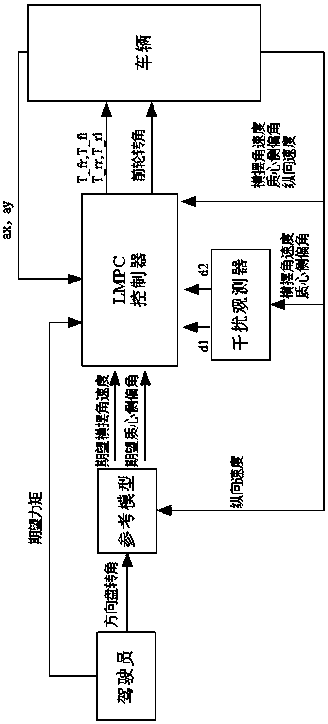
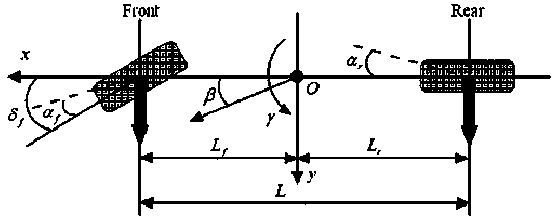
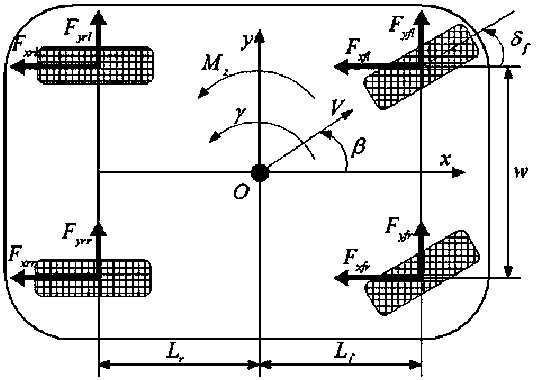
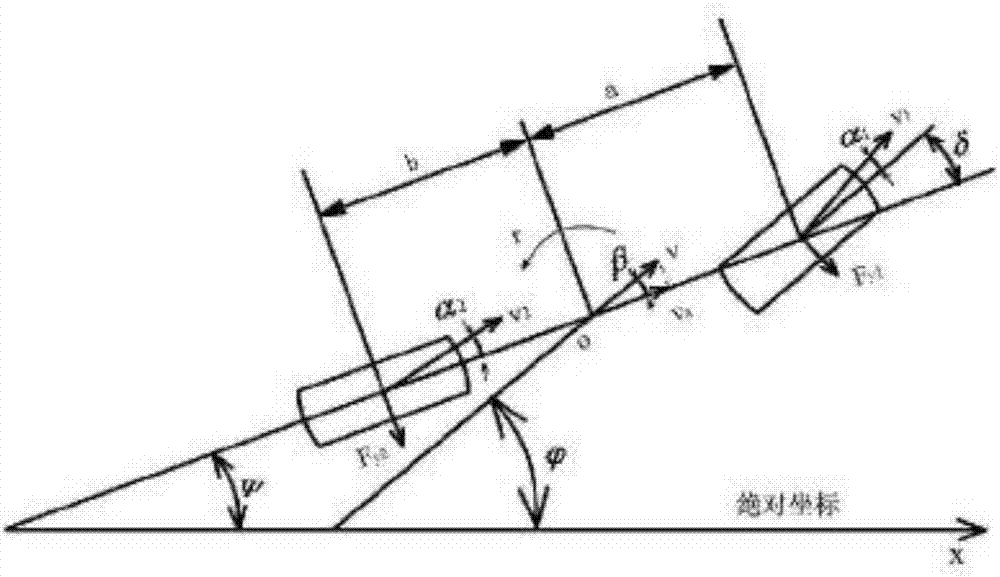
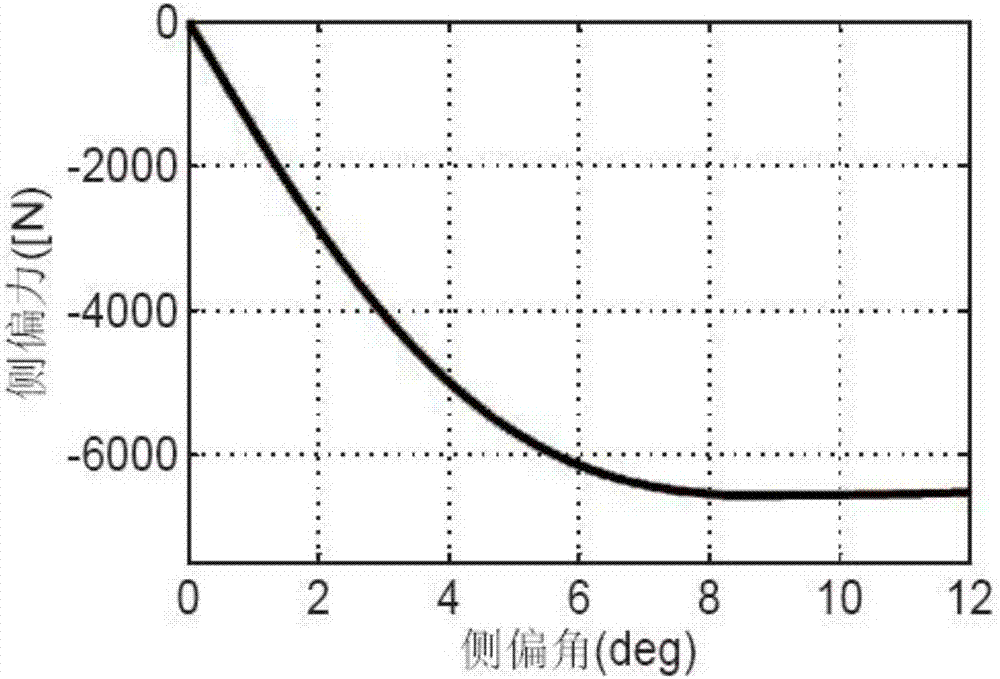
Vehicle yaw stability predicting model control method
ActiveCN108482363AMeet the needs of time controlLighten the computational burdenReference modelNonlinear model
The invention relates to a vehicle yaw stability predicting model control method and belongs to the technical field of a vehicle control. The disturbance-observer-based vehicle yaw stability predicting model control method uses a model predicting control method to design a linear model predicting controller, considers constraint conditions and can reduce computation time, track an expected value as much as possible and keep vehicle stability. The method includes: designing a reference model; performing linearization on a vehicle two-freedom-degree nonlinear model to obtain a linear model withmodel error disturbance terms; designing error terms in a disturbance observer pair model according to the linear model; using a model predicting control algorithm to build a target function, and solving an optimal problem corresponding to a cost function to obtain control input acting to a system to allow the vehicle system to track the expected value as much as possible so as to guaranteed vehicle stability. By the method, model complexity can be lowered effectively, control precision requirements are satisfied, and the constraint of driving torque is considered.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Adaptive nonlinear model predictive control using a neural network and input sampling
InactiveUS20170017212A1Reduce tracking errorOutput constraint satisfactionProgramme controlMachine learningNerve networkNonlinear model
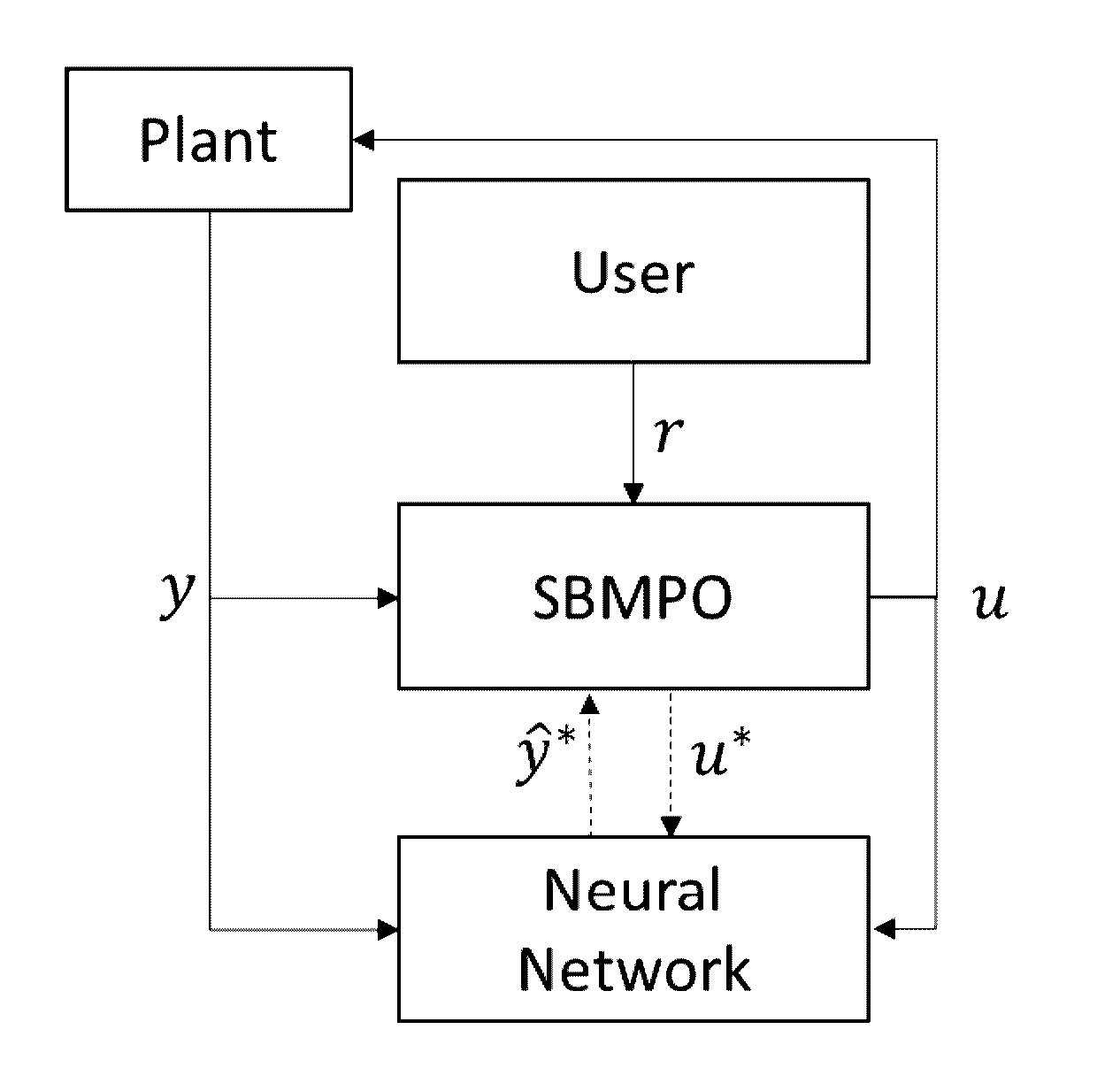
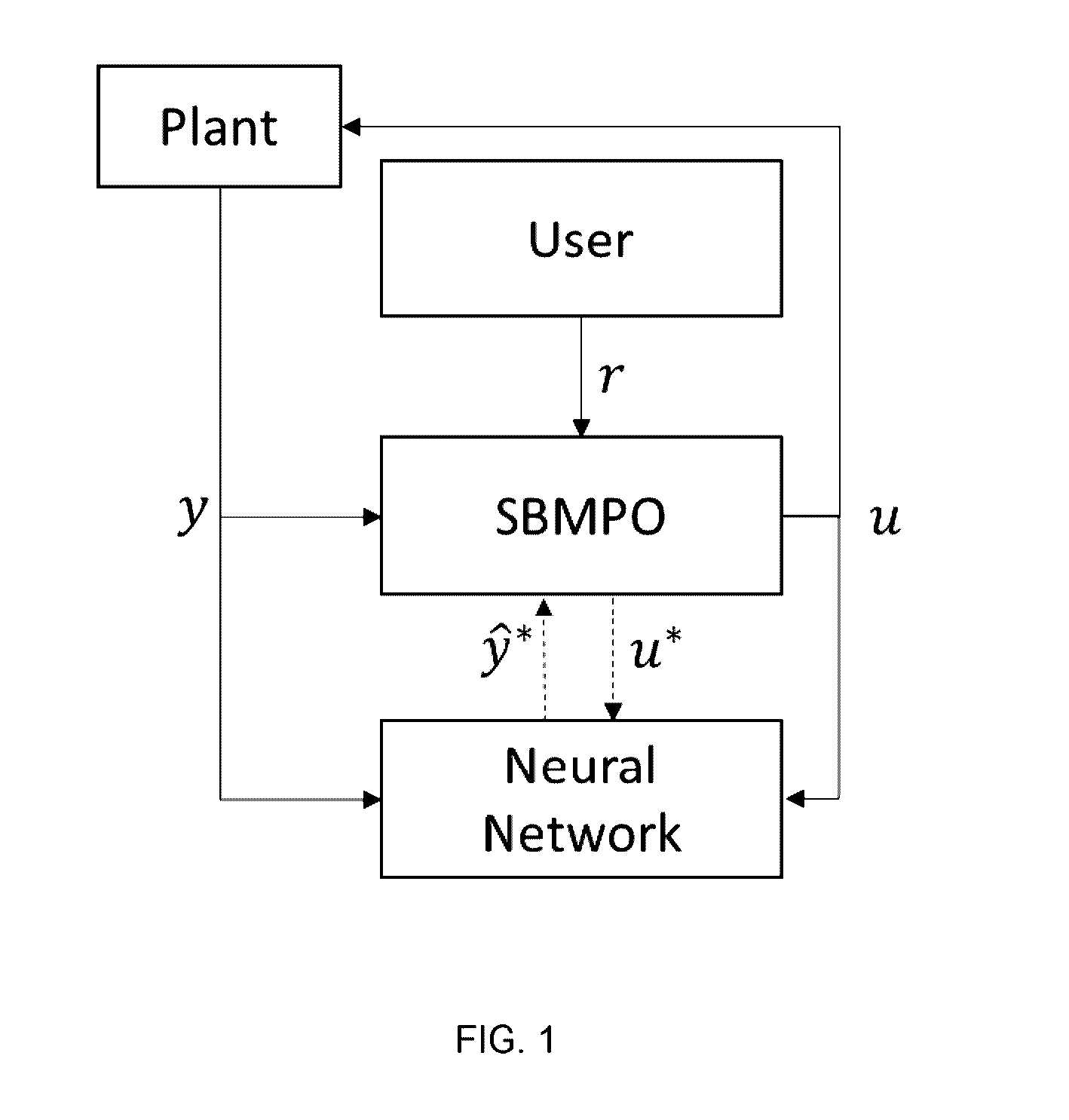
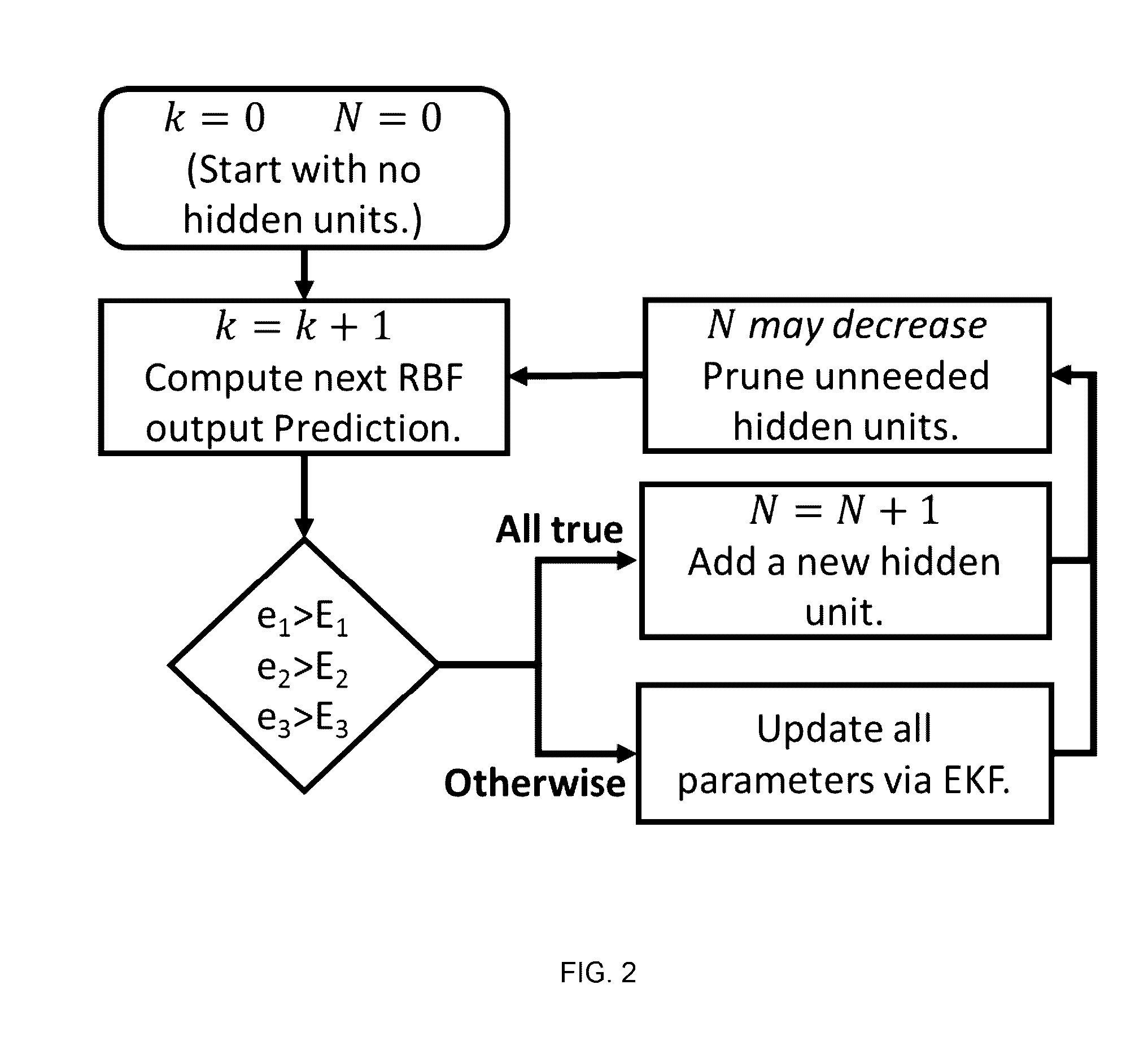
A novel method for adaptive Nonlinear Model Predictive Control (NMPC) of multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) systems, called Sampling Based Model Predictive Control (SBMPC) that has the ability to enforce hard constraints on the system inputs and states. However, unlike other NMPC methods, it does not rely on linearizing the system or gradient based optimization. Instead, it discretizes the input space to the model via pseudo-random sampling and feeds the sampled inputs through the nonlinear plant, hence producing a graph for which an optimal path can be found using an efficient graph search method.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Vehicle lateral stability nonlinear integration control method
ActiveCN105045102ASave resourcesImprove online computing performanceAdaptive controlVehicle dynamicsActive safety
The invention relates to a vehicle active safety control method, and particularly relates to a vehicle lateral stability nonlinear integration control method. Firstly, a simplified vehicle dynamics model is built; then, design of a nonlinear model predictive controller is carried out, expected yaw angle velocity information is inputted to the nonlinear controller module, according to the value of the expected yaw angle velocity and sideslip angle velocities of a front wheel and a rear wheel of the vehicle and the yaw angle velocity fed back in real time, a model predicative control method is used for predicting future dynamic performance of the system, optimization is carried out at the same time, an additional yaw moment and the optimized steering wheel angle information are decided and outputted to an execution mechanism corresponding to the vehicle, and the vehicle is kept in a yaw stability state. The method of the invention is successfully realized by the controller through FPGA full hardware, the FPGA uses a parallel hardware calculation method for acquiring the optimized control sequence in a limited sampling time domain, requirements of high real-time performance and miniaturization on the vehicle-mounted nonlinear model predictive controller can be met, and the calculation performance of the control system is improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Non-linear model prediction control method for double planetary gear row type hybrid electric vehicle
ActiveCN106080585AEfficient managementAvoid heavy computationHybrid vehiclesGas pressure propulsion mountingPower couplingOptimal control
The invention provides a non-linear model prediction control method for a double planetary gear row type hybrid electric vehicle. According to the method, based on the predicted rotation speed of the finished vehicle and the torque requirement, optimization solution is conducted on an objective function during the prediction time interval through a non-linear optimization algorithm, the optimal control sequence of controlled quantities is obtained, and the required torques of a power system engine, a motor, a power generator and a brake system are determined by combining the first controlled quantity of the control sequence with kinetic equations of the double planetary gear row type hybrid electric vehicle in various modes. According to the characteristic that the number of working modes of the double planetary gear row type hybrid electric vehicle is large, control prediction and optimization are achieved through a non-linear model, the combination and disconnection states of all clutches and braking force in a power coupling mechanism can be effectively controlled, optimization of the different working modes and optimal energy distribution among different power components are achieved, and the advantage that the number of the working modes of the double planetary gear row type hybrid electric vehicle is large is brought into full play.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
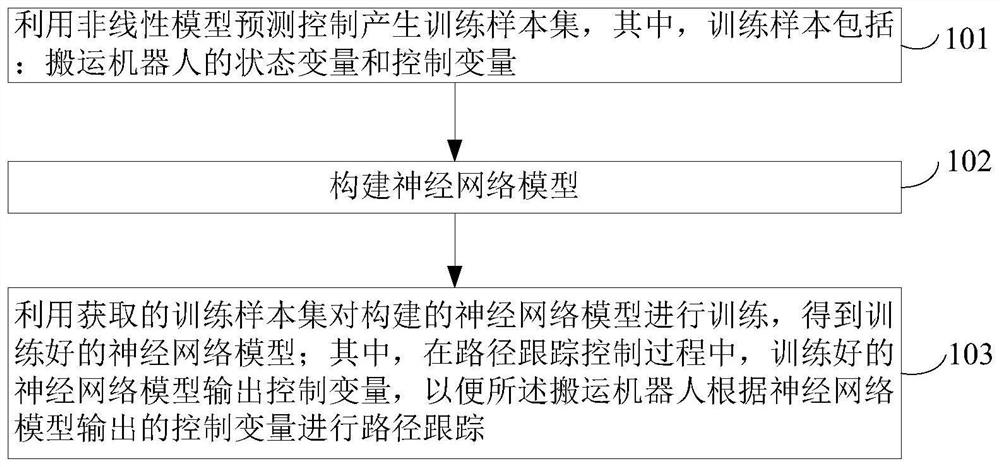
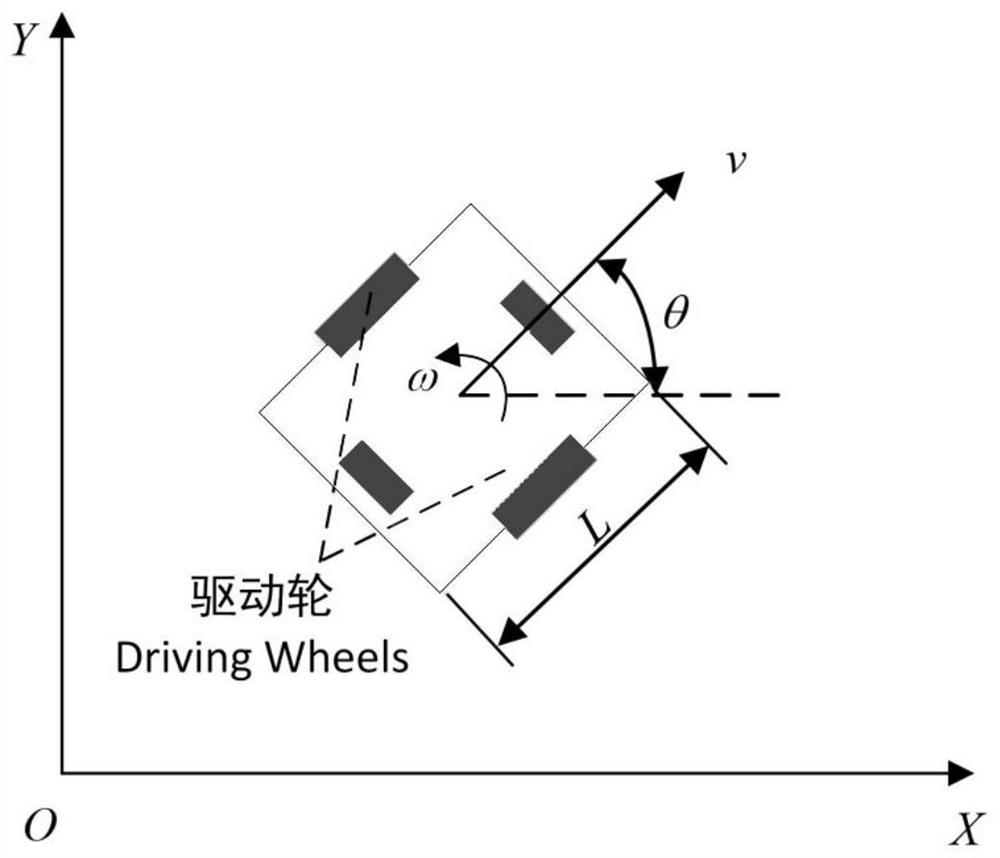
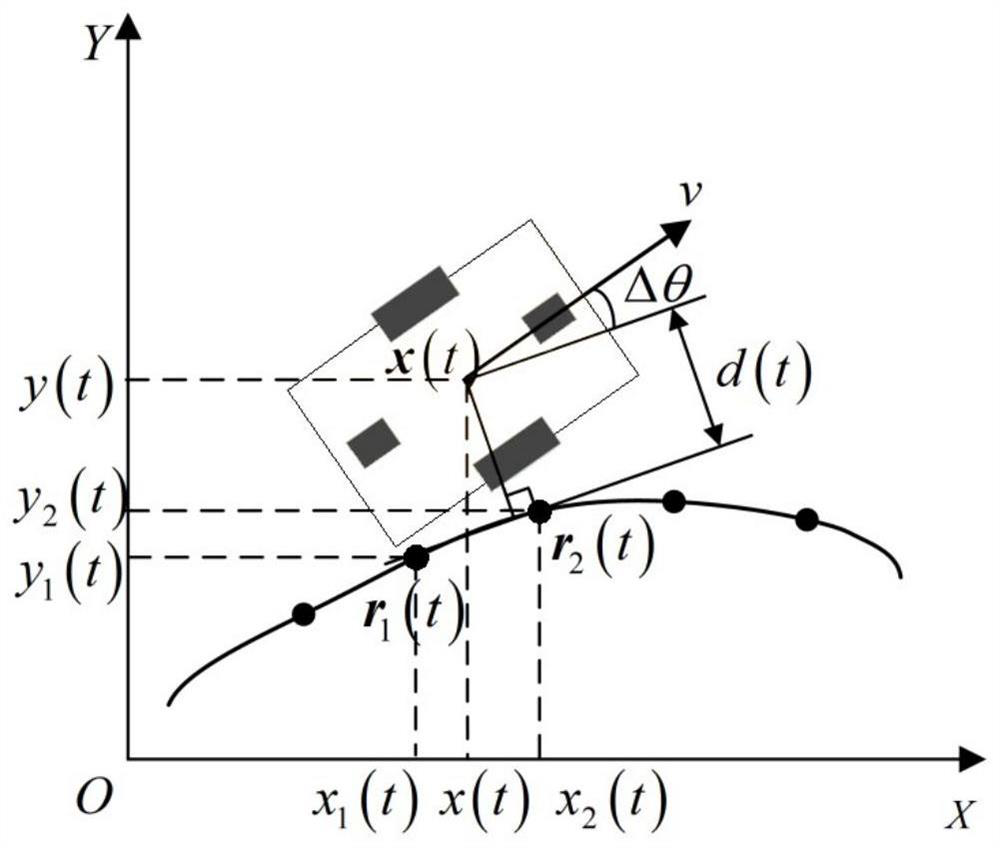
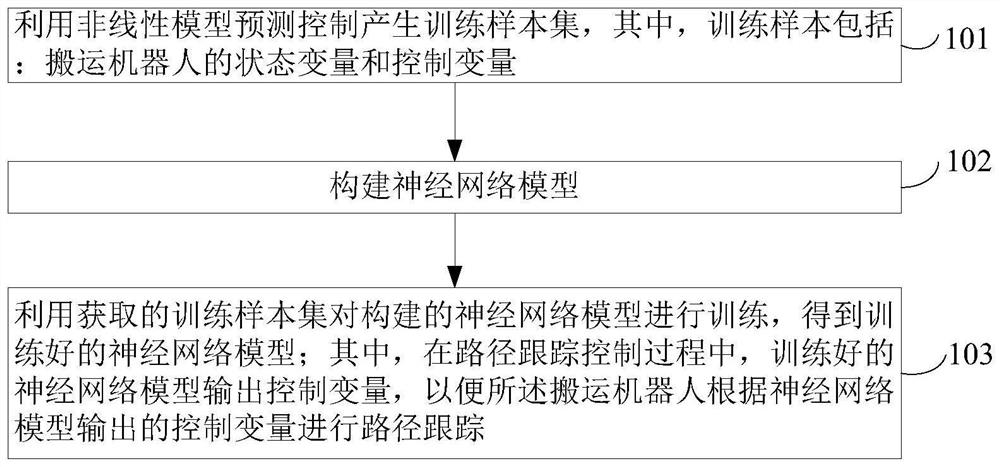
Path tracking control method of transfer robot based on neural network
ActiveCN111624992AOvercoming the problem of poor real-time performance of predictive controlGood real-time controlNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsState variableSimulation
The invention provides a path tracking control method of a transfer robot based on a neural network. The method can improve the real-time performance of nonlinear model prediction control. The methodcomprises the steps: generating a training sample set through nonlinear model predictive control, wherein the training samples comprise state variables and control variables of the transfer robot; constructing a neural network model; and training the constructed neural network model by using the obtained training sample set to obtain a trained neural network model, wherein in the path tracking control process, the trained neural network model outputs a control variable, so that the transfer robot performs path tracking according to the control variable output by the neural network model. The invention relates to the field of mobile robot autonomous driving control.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
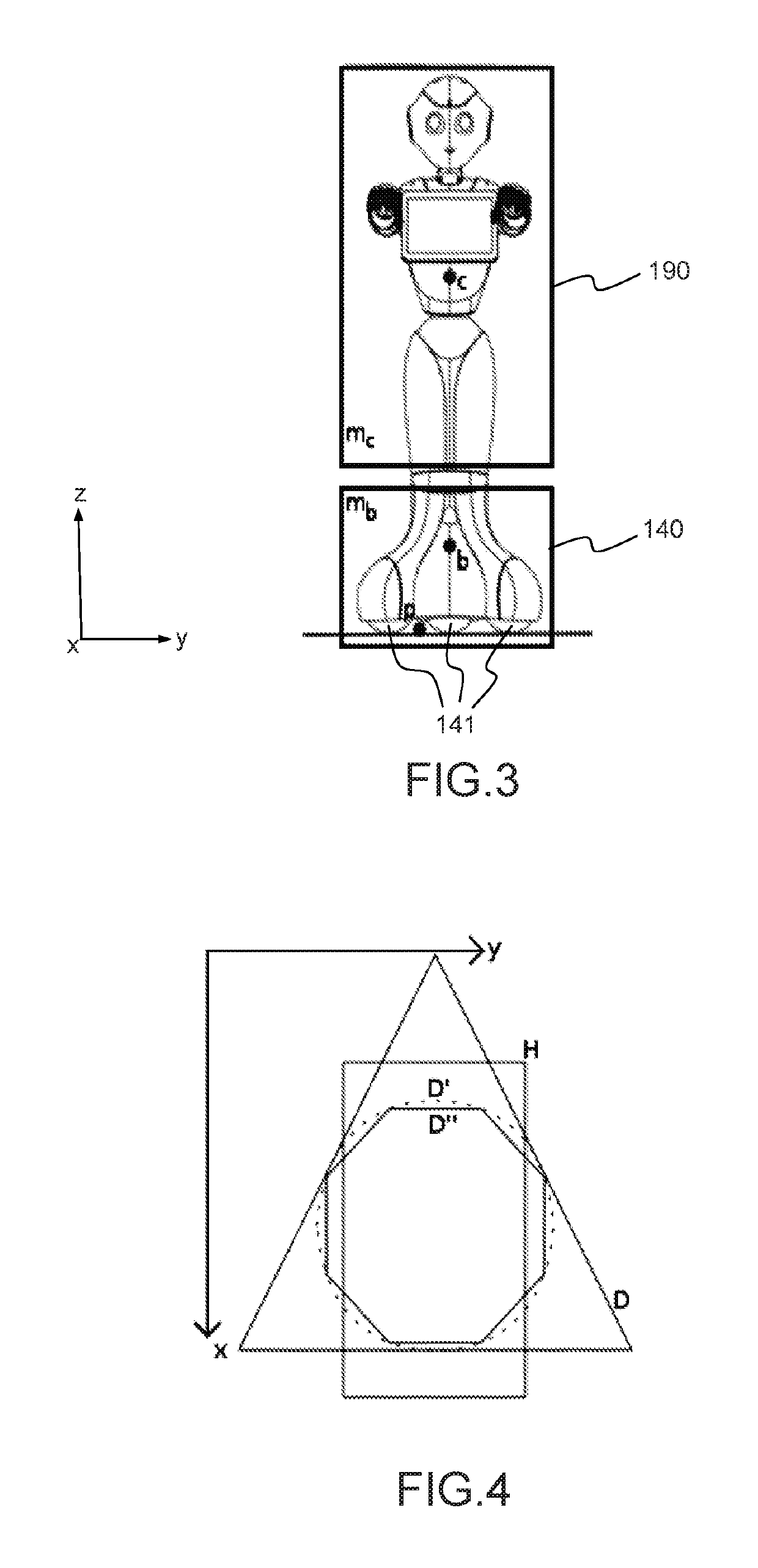
Omnidirectional wheeled humanoid robot based on a linear predictive position and velocity controller
ActiveCN106573370ALarge dynamic bandwidth and shortShort dynamic bandwidthProgramme-controlled manipulatorAttitude controlHumanoid robot naoAngular velocity
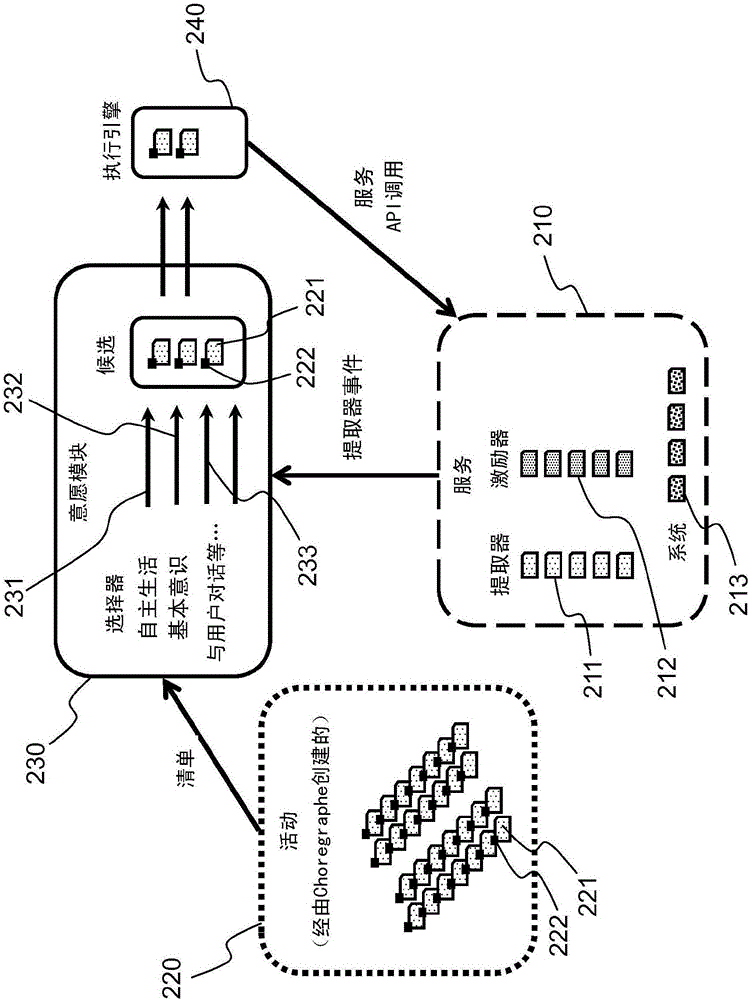
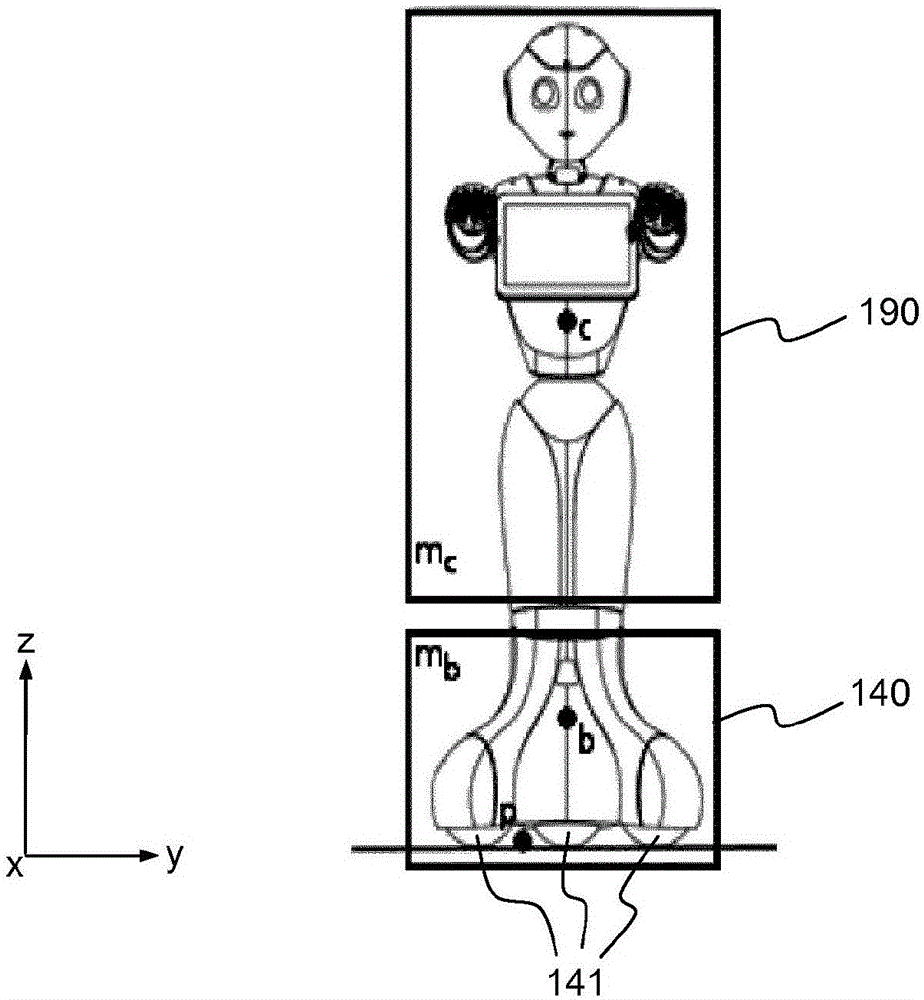
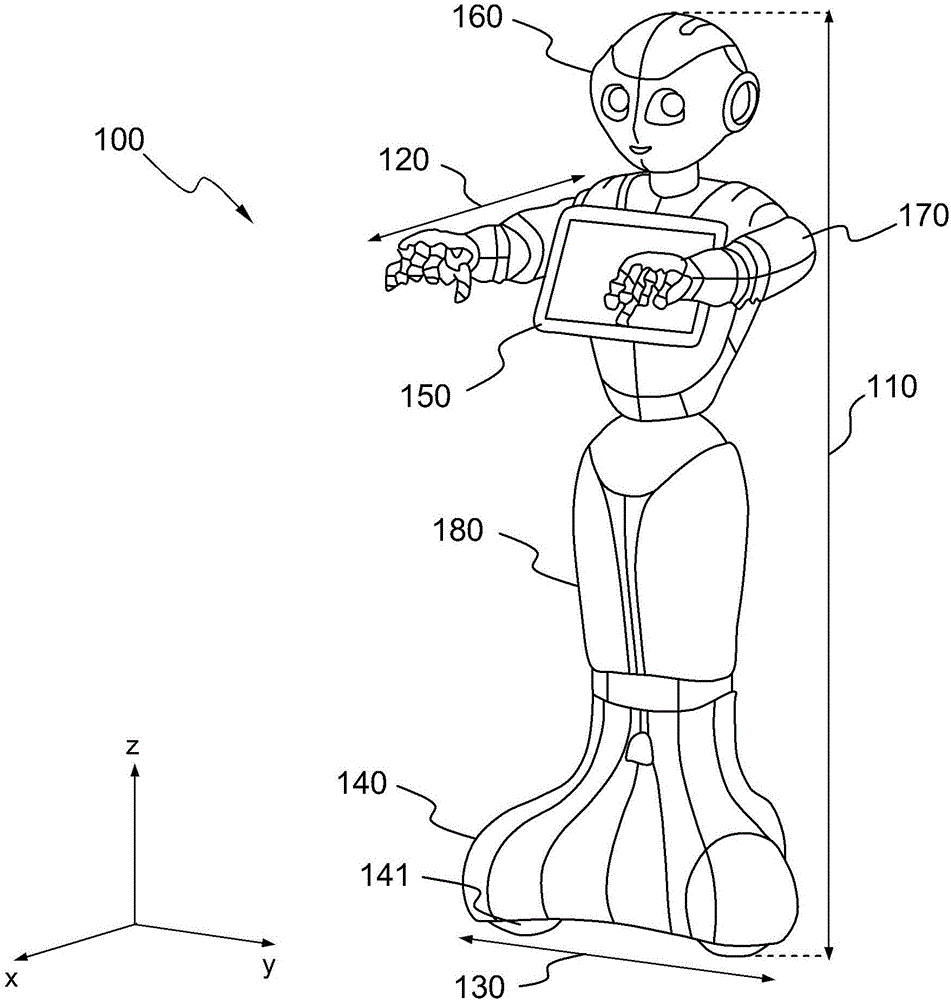
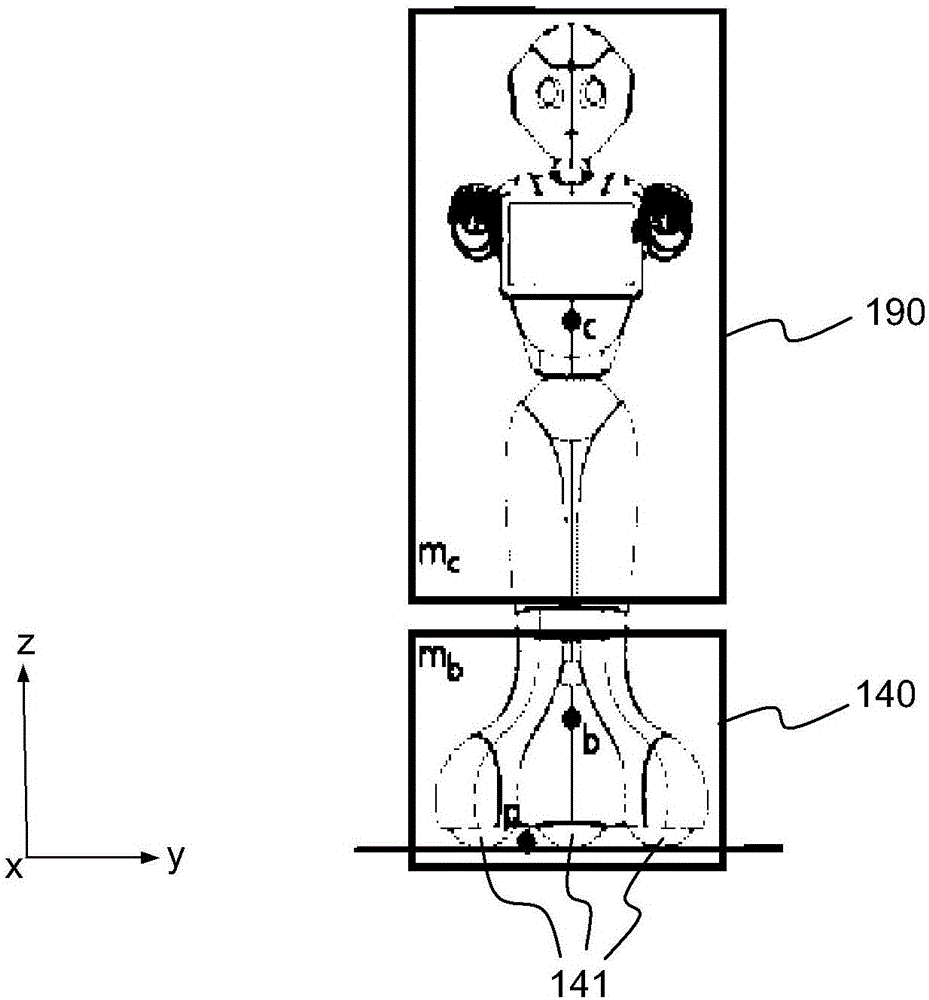
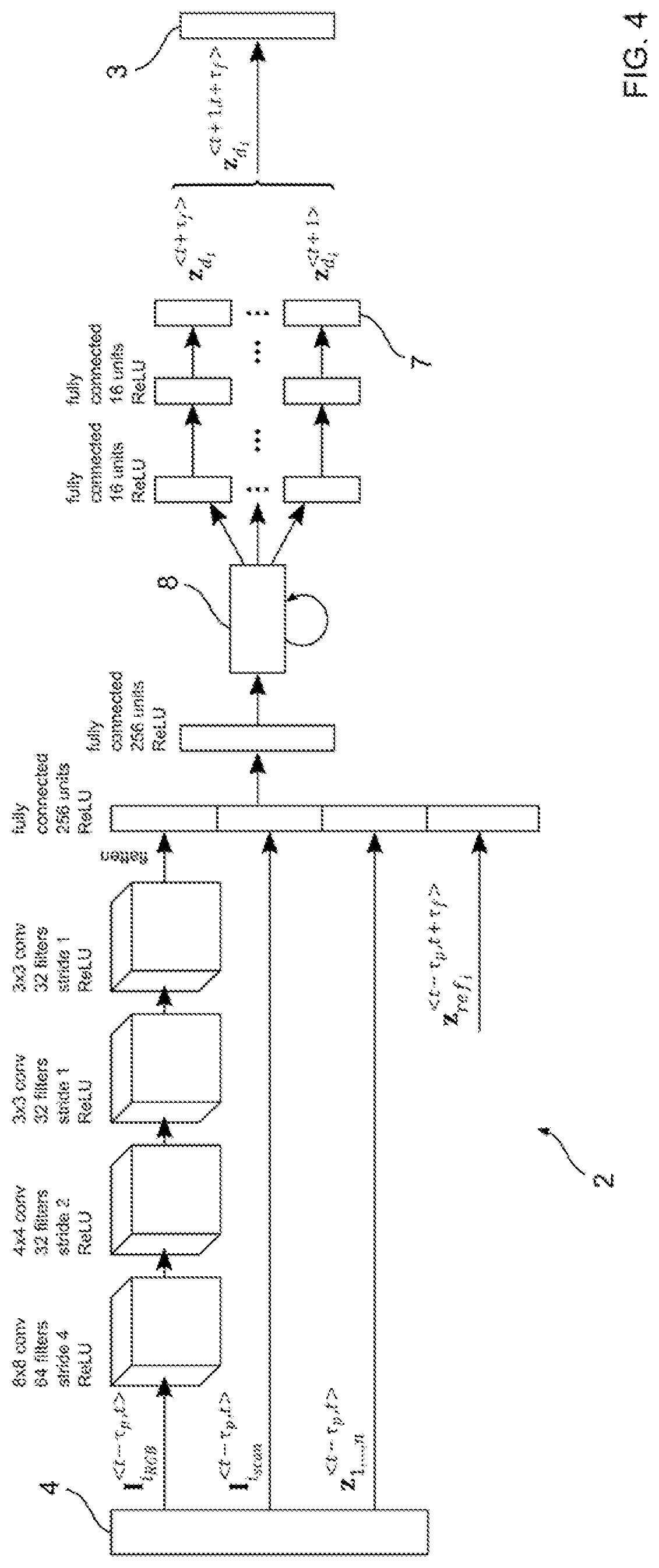
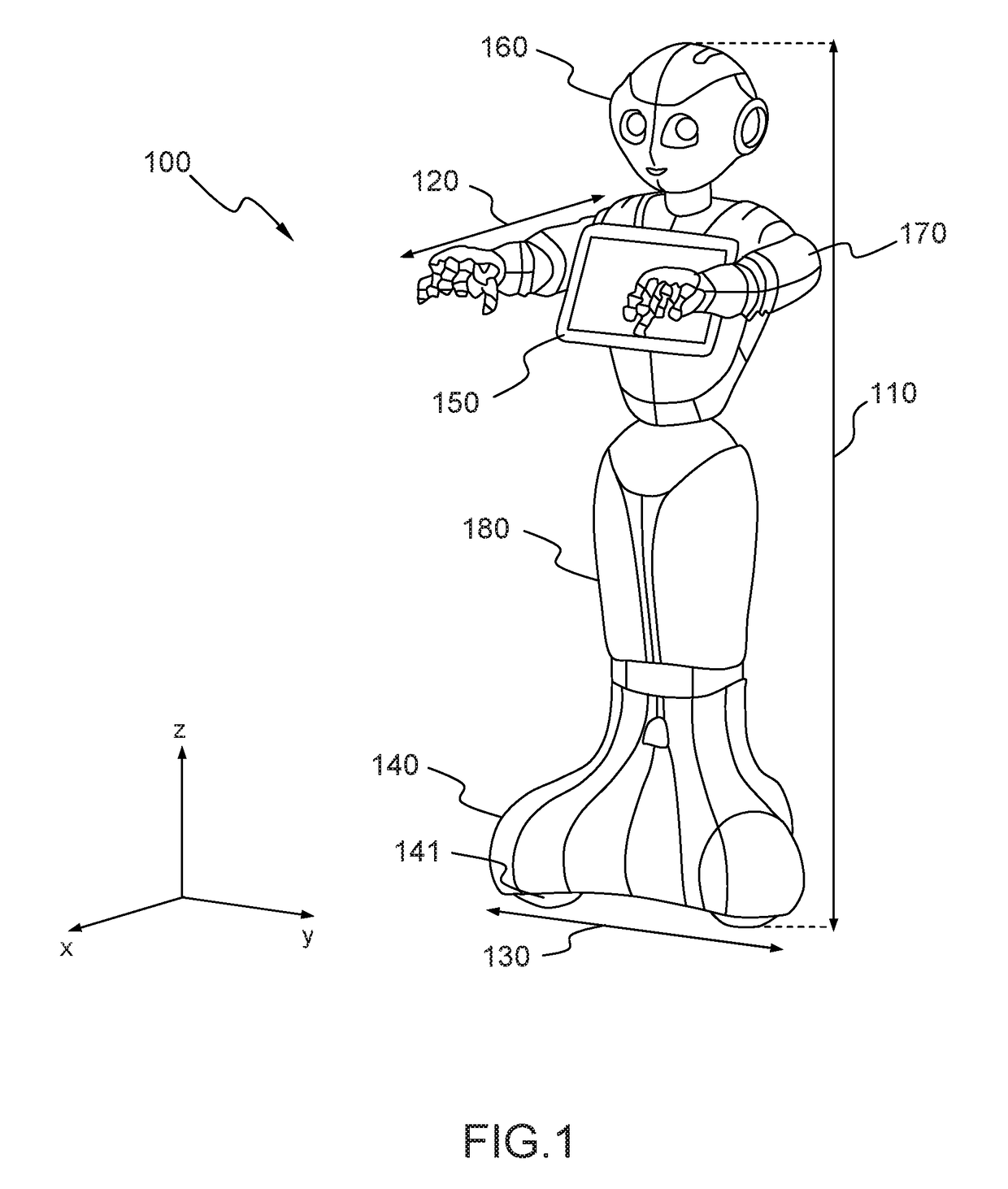
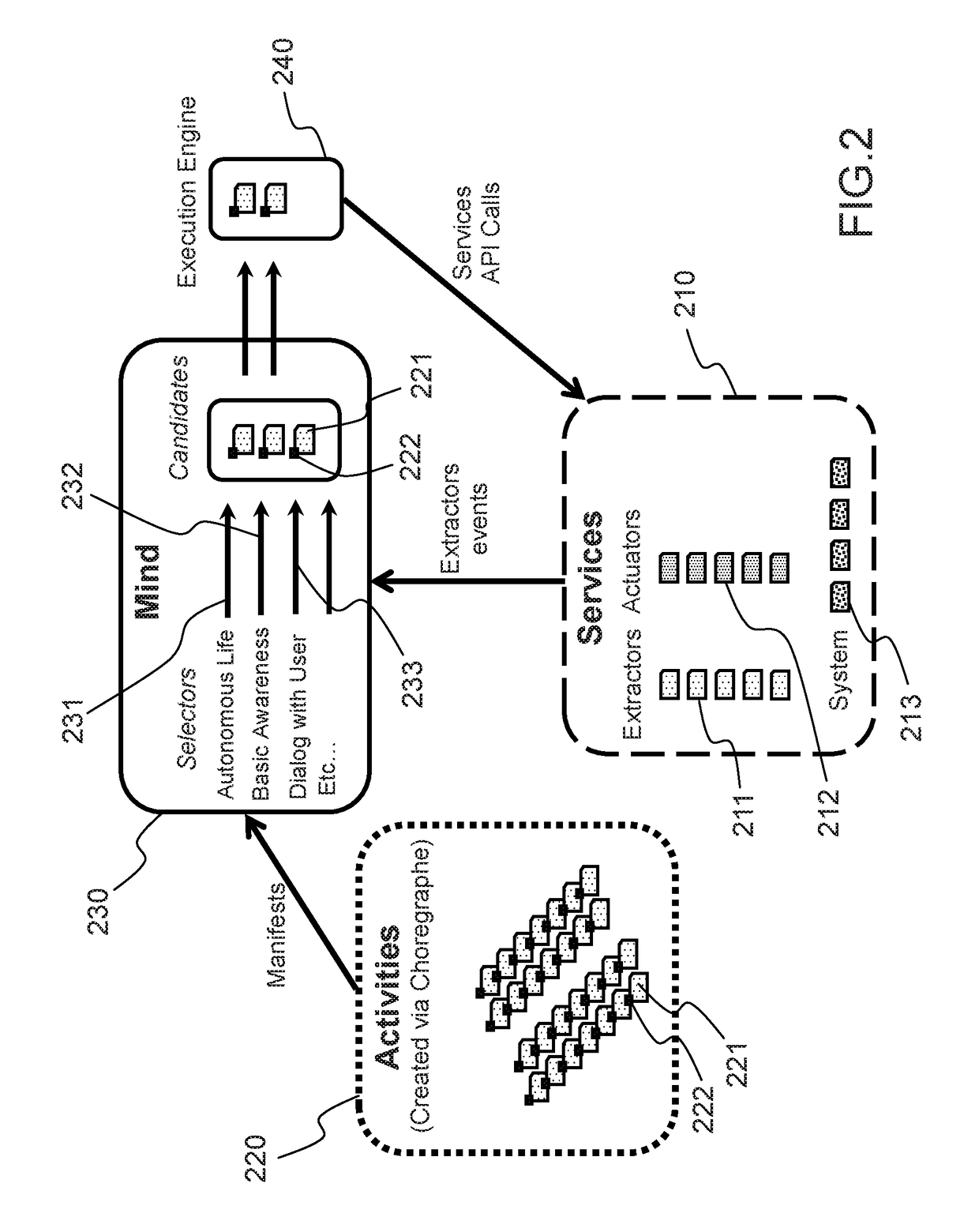
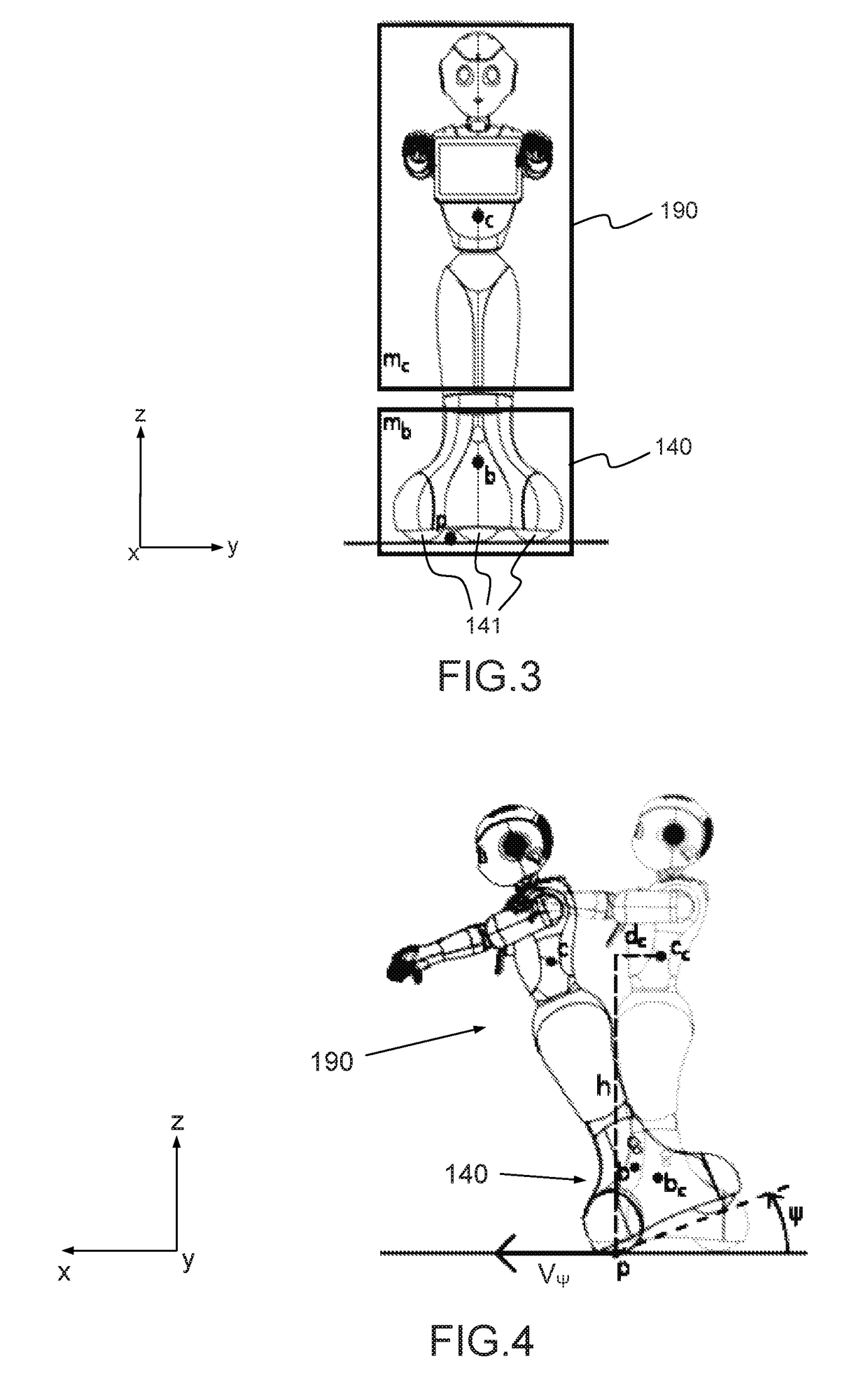
The object of the invention is a humanoid robot (100) with a body (190) joined to an omnidirectional mobile ground base (140), equipped with : - a body position sensor, a base position sensor and an angular velocity sensor to provide measures, - actuators (212) comprising at least 3 wheels located in the omnidirectional mobile base, - extractors (211) for converting sensored measures into useful data, - a supervisor (500) to calculate position, velocity and acceleration commands from the useful data, - means for converting commands into instructions for the actuators, characterized in that the supervisor comprises: - a no-tilt state controller (501), a tilt state controller (502) and a landing state controller (503), each controller comprising means for calculating, position, velocity and acceleration commands based on a double point-mass robot model with tilt motion and on a linear model predictive control law, expressed as a quadratic optimization formulation with a weighted sum of objectives, and a set of predefined linear constraints.
Owner:SOFTBANK ROBOTICS EURO +1
Intelligent trolley 2.5-dimensional visual servo control method based on nonlinear model prediction
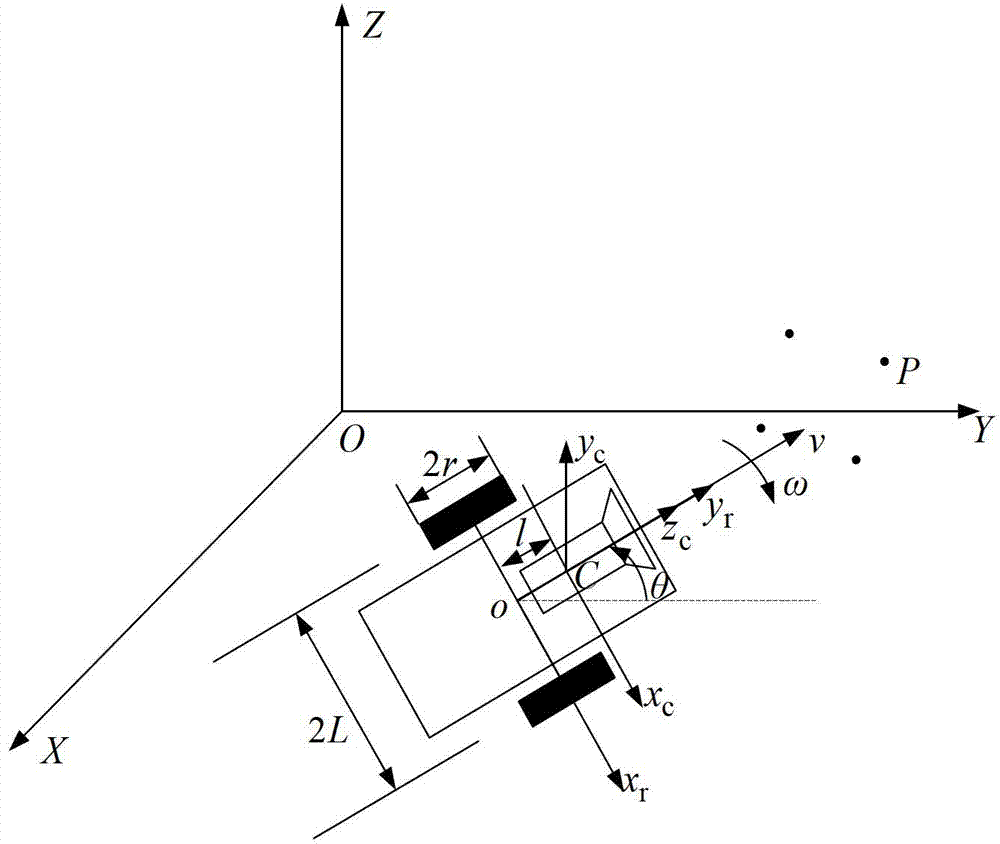
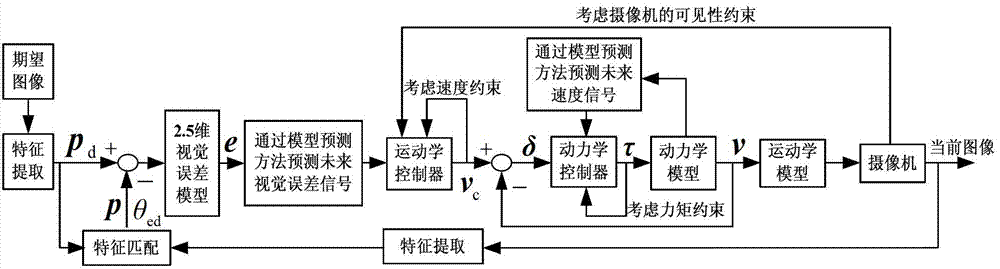
InactiveCN102880062AImprove reliabilityImprove securitySimulator controlPosition/course control in two dimensionsVisual servoing systemNon linear model predictive control
The invention discloses an intelligent trolley 2.5-dimensional visual servo control method based on nonlinear model prediction. The intelligent trolley 2.5-dimensional visual servo control method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, obtaining a current image and an expected image of a reference target respectively through a video camera at a current pose and an expected pose; secondly, extracting the characteristic points of the reference target and the pose information of the trolley, organically combining a two-dimensional image signal with a three-dimensional pose signal through coordinate conversion, and building a 2.5-dimensional visual error model; and lastly, aiming at the 2.5-dimensional visual error model, designing a multilevel visual predication controller by utilizing a nonlinear model prediction control method. According to the intelligent trolley 2.5-dimensional visual servo control method, the problem that velocity and torque constraint of a motion performing system and visibility constraint of the video camera cannot be processed by the conventional 2.5-dimensional visual servo control method is solved, the reference target can be guaranteed to remain visible all the time in the servo process, and the reliability and the safety of a visual servo system are greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Trajectory planner
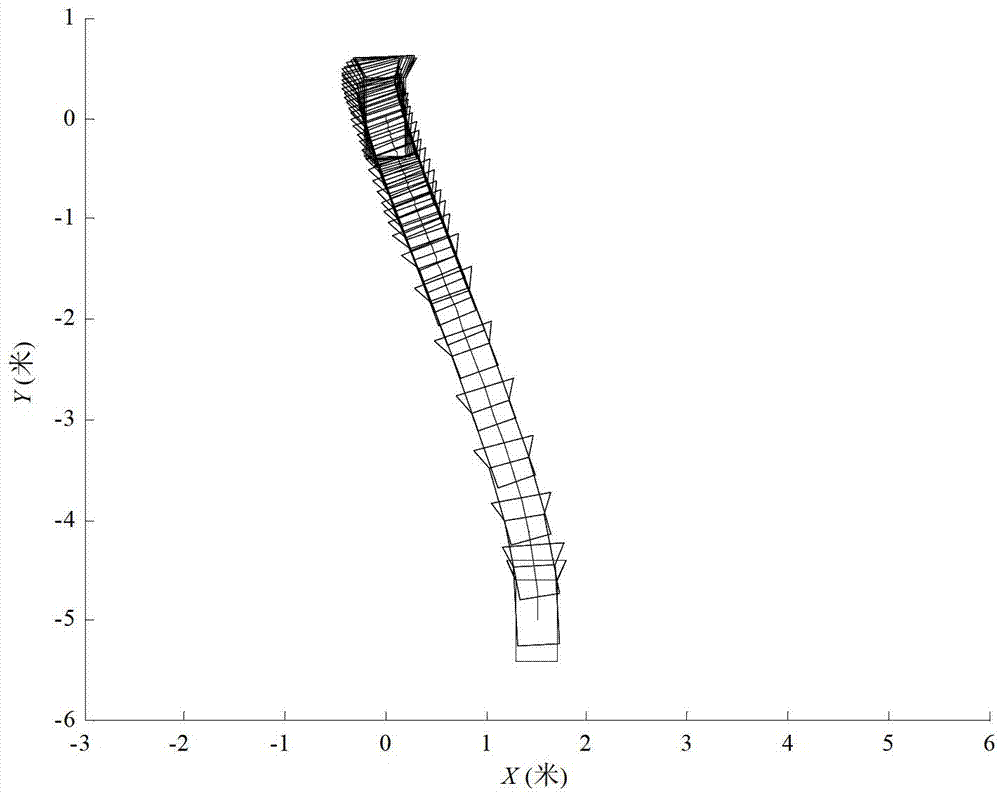
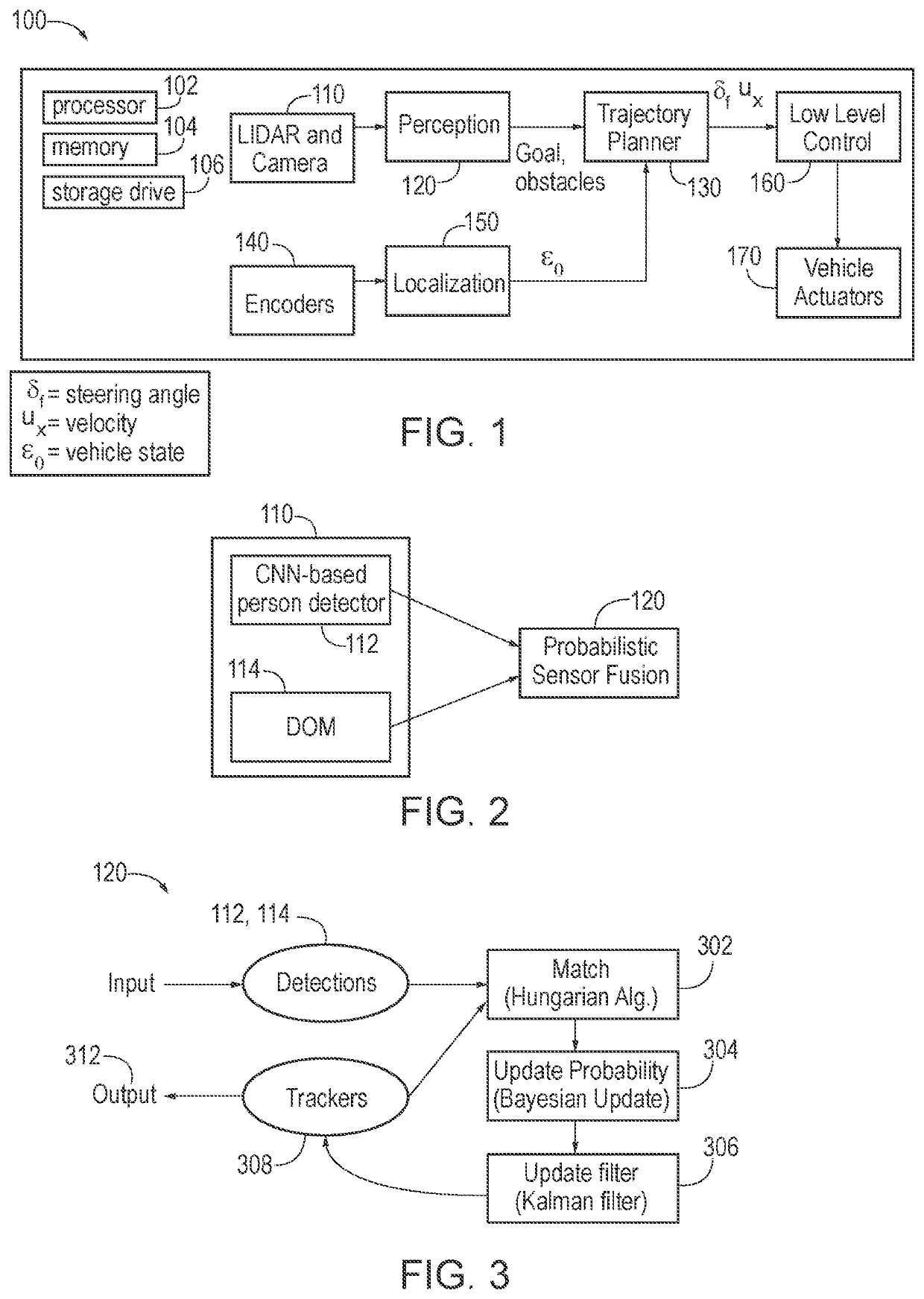
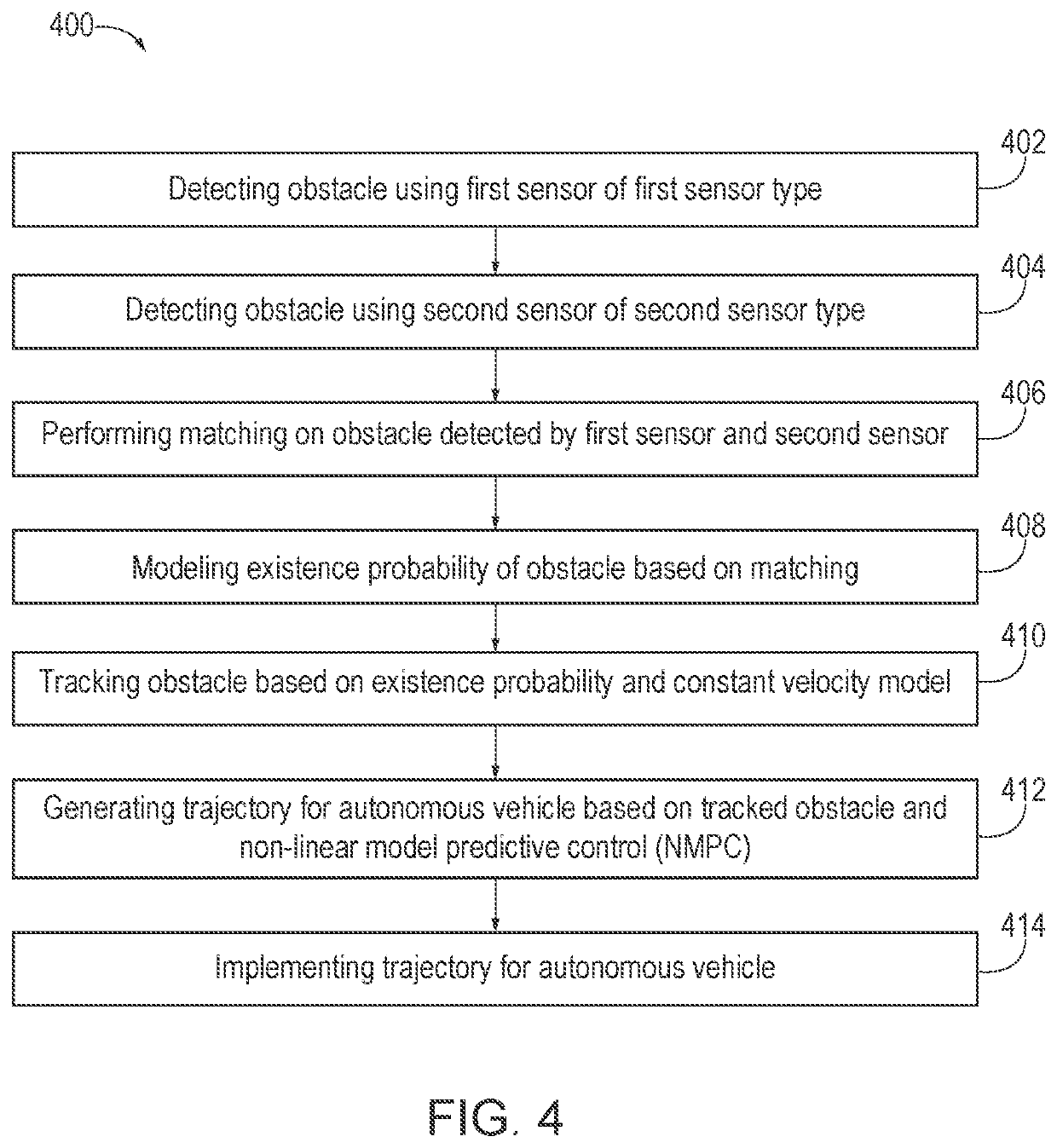
An autonomous vehicle capable of trajectory prediction may include a first sensor, a second sensor, a processor, a trajectory planner, a low-level controller, and vehicle actuators. The first sensor may be of a first sensor type and may detect an obstacle and a goal. The second sensor may be of a second sensor type and may detect the obstacle and the goal. The processor may perform matching on the obstacle detected by the first sensor and the obstacle detected by the second sensor, model an existence probability of the obstacle based on the matching, and track the obstacle based on the existence probability and a constant velocity model. The trajectory planner may generate a trajectory for the autonomous vehicle based on the tracked obstacle, the goal, and a non-linear model predictive control (NMPC). The low-level controller may implement the trajectory for the autonomous vehicle by driving vehicle actuators.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Omnidirectional wheeled humanoid robot based on a linear predictive position and velocity controller
ActiveCN106794576AProtect mechanical partsPrioritize robustnessProgramme-controlled manipulatorAttitude controlEngineeringBody positions
Owner:SOFTBANK ROBOTICS EURO +1
Deep learning based motion control of a group of autonomous vehicles
PendingUS20210171024A1Easy to solveTechnique is limitedRoad vehicles traffic controlCharacter and pattern recognitionPredictive controllerEngineering
A controller for an agent of a group of agents, in particular for a group of autonomous or semi-autonomous vehicles, and to a computer program implementing such a controller. A temporal deep network for such a controller and to a method, a computer program and an apparatus for training the temporal deep network. The controller includes a temporal deep network designed to calculate a desired trajectory for the agent, a nonlinear model predictive controller designed to calculate commands for the agent based on the desired trajectory and desired trajectories of the other agents of the group of agents, and an augmented memory designed to integrate historic system states of the group of agents for the temporal deep network.
Owner:ELEKTROBIT AUTOMOTIVE
Omnidirectional wheeled humanoid robot based on a linear predictive position and velocity controller
ActiveUS10232508B2Minimize impactHigh bandwidthProgramme-controlled manipulatorAttitude controlHumanoid robot naoAngular velocity
A humanoid robot with a body joined to an omnidirectional mobile ground base, equipped with: a body position sensor, a base position sensor and an angular velocity sensor to provide measures, actuators comprising at least 3 wheels located in the omnidirectional mobile base, extractors for converting sensored measures into useful data, a supervisor to calculate position, velocity and acceleration commands from the useful data, means for converting commands into instructions for the actuators, wherein the supervisor comprises: a no-tilt state controller, a tilt state controller and a landing state controller, each controller comprising means for calculating, position, velocity and acceleration commands based on a double point-mass robot model with tilt motion and on a linear model predictive control law, expressed as a quadratic optimization formulation with a weighted sum of objectives, and a set of predefined linear constraints.
Owner:SOFTBANK ROBOTICS EURO +1
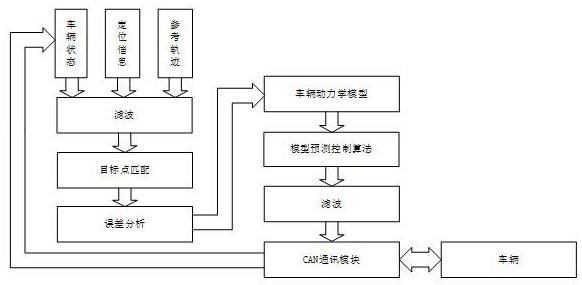
Vehicle trajectory tracking control method based on linear model predictive control algorithm
PendingCN112394734AImprove trajectory tracking performanceGuaranteed stabilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehicle dynamicsSteering wheel
The invention discloses a vehicle trajectory tracking control method based on a linear model predictive control algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: S1, collecting vehicle state information, vehicle positioning information and a reference trajectory; S2, conducting filtering processing on the collected items; S3, acquiring a real-time target point of the vehicle; S4, obtaining a vehicle transverse error and a vehicle course angle error; S5, establishing a linear vehicle dynamics model; S6, obtaining a vehicle steering wheel rotation angle and a vehicle steering wheel rotation speed; S7, respectively carrying out amplitude limiting filtering on the vehicle steering wheel angle and the vehicle steering wheel rotating speed; and S8, sending a result to a controlled vehicle torealize trajectory tracking control. On the basis of the linear vehicle dynamics model, a linear model prediction control algorithm is used, and the real-time performance of control is improved. Meanwhile, the dynamic characteristics of the vehicle and the abrupt change of the vehicle control quantity are fully considered, the vehicle trajectory tracking capability is improved, and the stability of the controlled vehicle during medium-speed and high-speed running is ensured.
Owner:SUZHOU GST INFOMATION TECH CO LTD
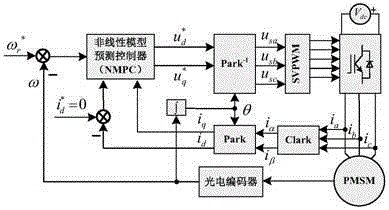
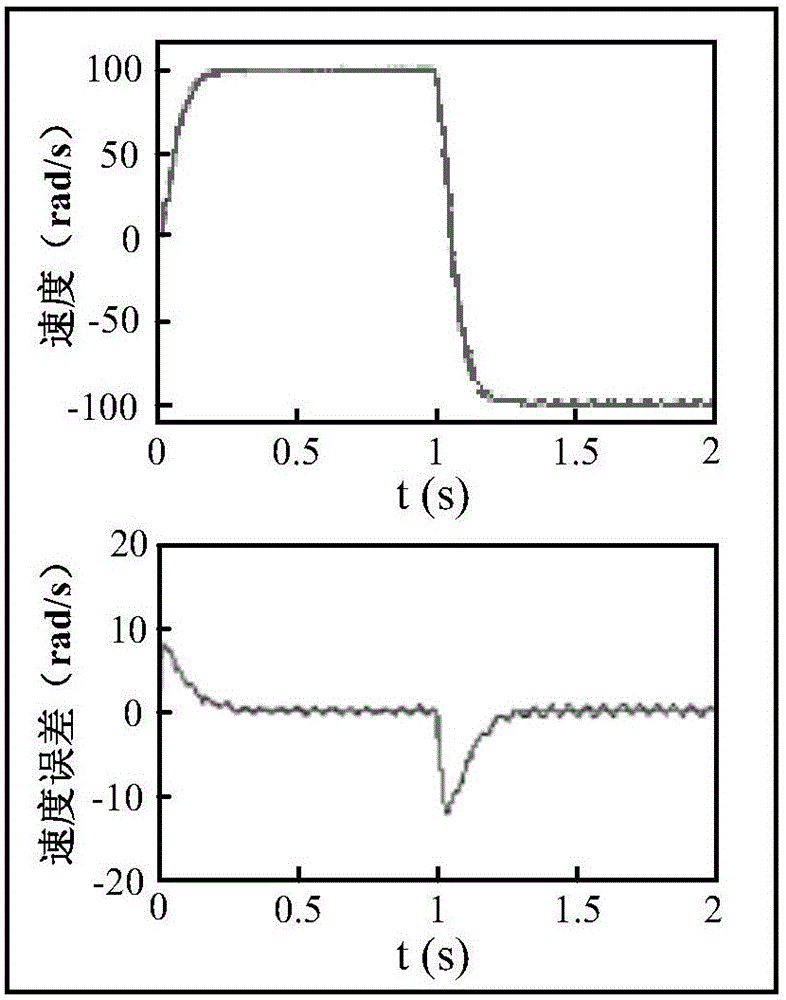
Minimum variance-based nonlinear model prediction controller design method for permanent magnet servo system
InactiveCN105871277AAvoid Solving Nonlinearly Constrained ProblemsElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsHorizonNonlinear model
The invention discloses a minimum variance-based nonlinear model prediction controller (NMPC) design for a permanent magnet servo system, and belongs to the technical field of high-performance servo control systems. The method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, a nonlinear mathematic model of a PMSM is built under a dq coordinate system; secondly, a cost function of the prediction control rate of the PMSM is selected on the basis of the model according to the minimum variance prediction control theory; and the selected cost function is minimized to search for the optimal control rate in a receding horizon, so that output of the system within prediction time can track a given reference value to reach the prediction control target. Through a receding horizon control strategy of model prediction control (MPC), adverse effects caused by various system model parameter changes and uncertain random disturbance can be processed online by the control system; and the disturbance resistance of the control system is strengthened. Through an experiment, high-rotating speed tracking performance and good robustness of the method in an actual control system are verified.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
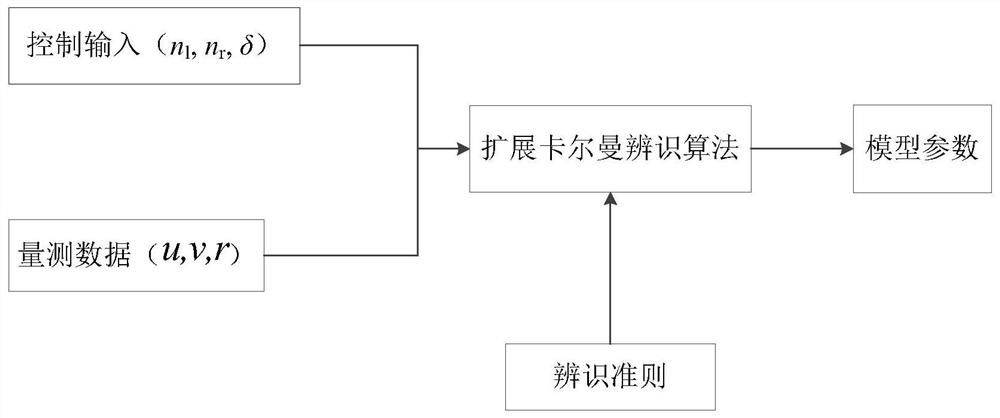
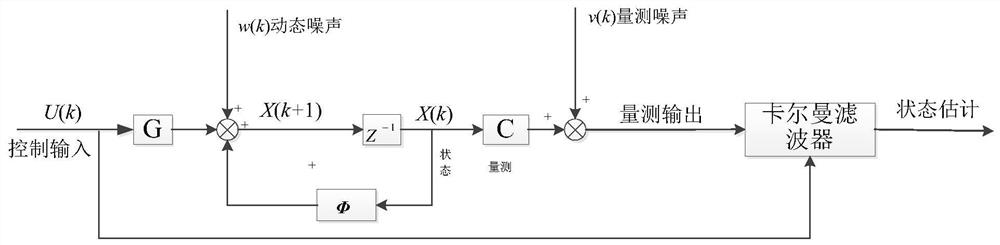
Control method applied to autonomous berthing of under-actuated double-propeller double-rudder ship
ActiveCN113110468AImplement Adaptive CorrectionOvercoming the shortcomings of control instructionsPosition/course control in two dimensionsNonlinear motionNon linear model predictive control
The invention discloses a control method applied to autonomous berthing of an under-actuated double-propeller double-rudder ship, and the method comprises the steps: a ship motion model parameter identification step: based on an extended Kalman filtering method, considering the factors, such as frequent staggering and back-up, occurring in the actual berthing process in an identified motion model structure, self-adaptive correction of ship motion model parameters in the berthing navigation process is achieved; and a model prediction control step and a PID control step, wherein path planning and tracking control of the berthing process are realized by using nonlinear model prediction control and PID control technologies. A nonlinear model is utilized to predict, control and plan a route, the influence of ship nonlinear motion characteristics and actual environment and obstacle factors is considered, and the limitation that nonlinear model predictive control is low in solving speed and long in solving period is solved through PID control; the defect that control instructions are generated by a nonlinear model prediction control method due to changes of factors such as model parameter changes and environment interference in a nonlinear model prediction period is overcome.
Owner:中国船舶集团有限公司第七零七研究所九江分部
Non-linear model predictive control of process
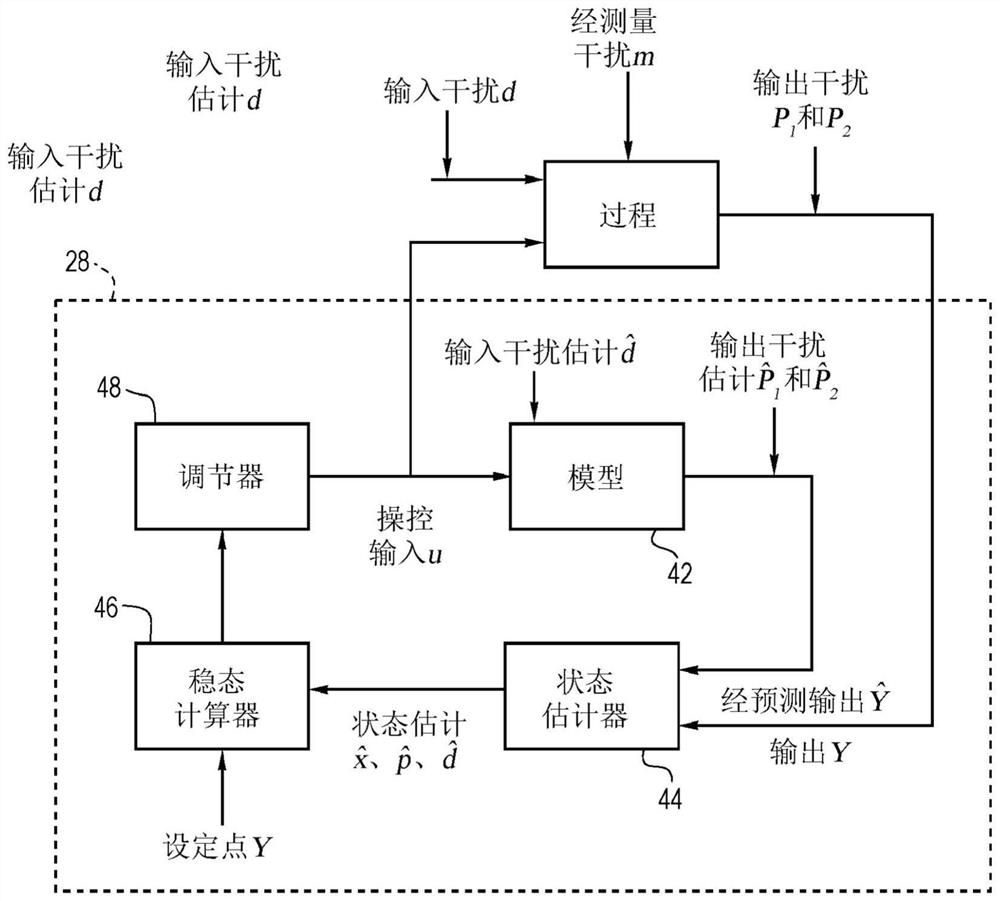
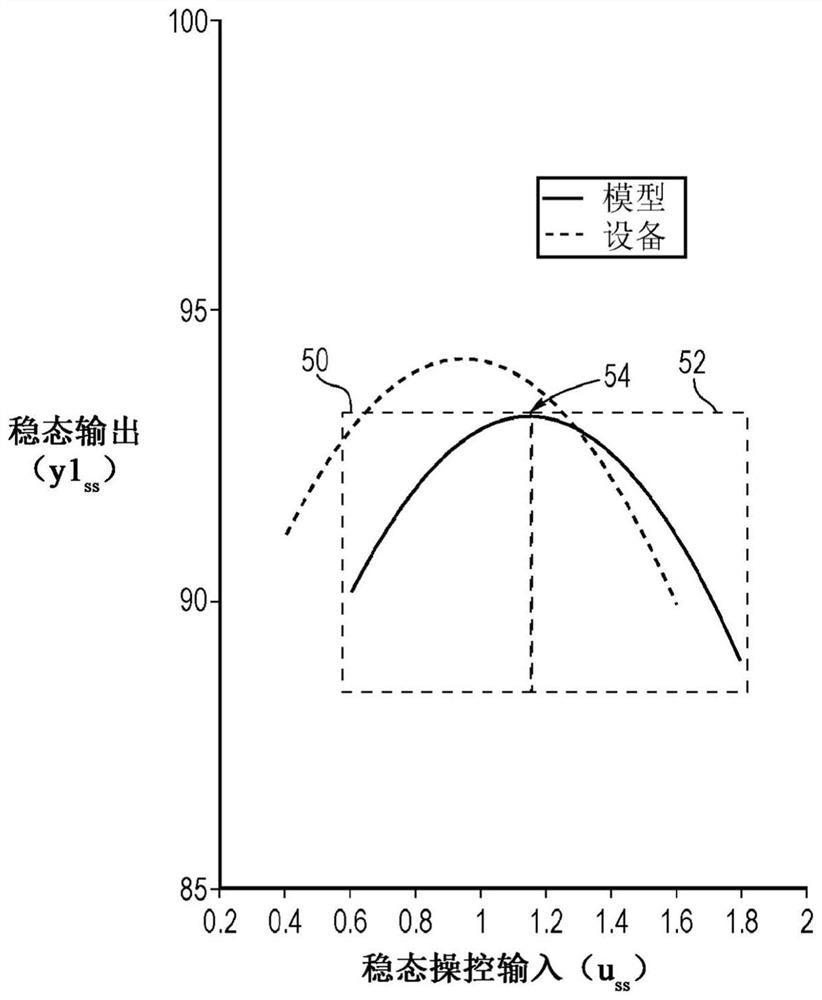
Provided herein is a chemical system for exhibiting operation of steady state gain reversal, and the chemical system comprises: a reactor configured to receive a feed stream and generate an outlet stream to form a process; and a control device configured to control the process. The control device receives an input indicative of an operating parameter and receives an output variable, and provides a steady-state manipulation input configured to control or optimize the process in response to the input and the output variable. The control device includes an input disturbance model, a state estimator, a non-linear steady-state target calculator, and a regulator configured to provide a signal for regulating one or more inputs based on the steady-state manipulation input and associated output variables.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
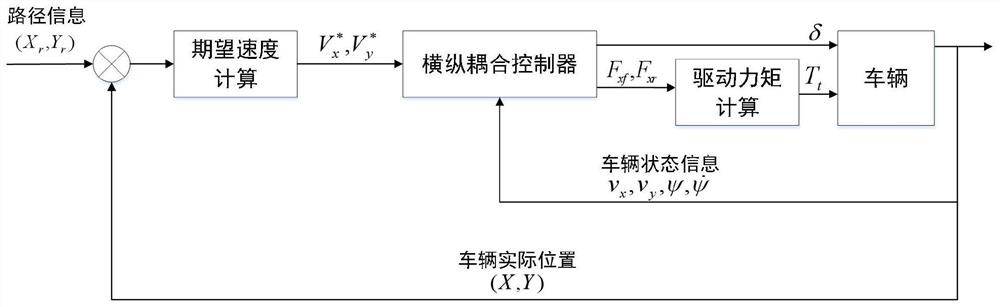
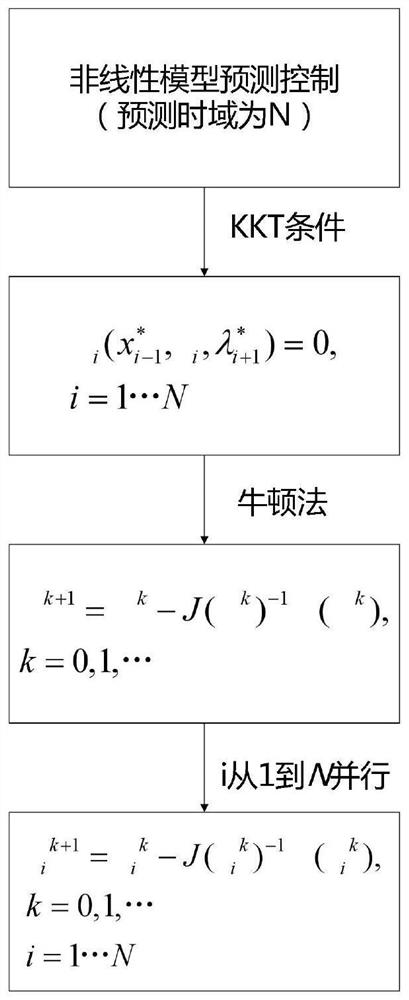
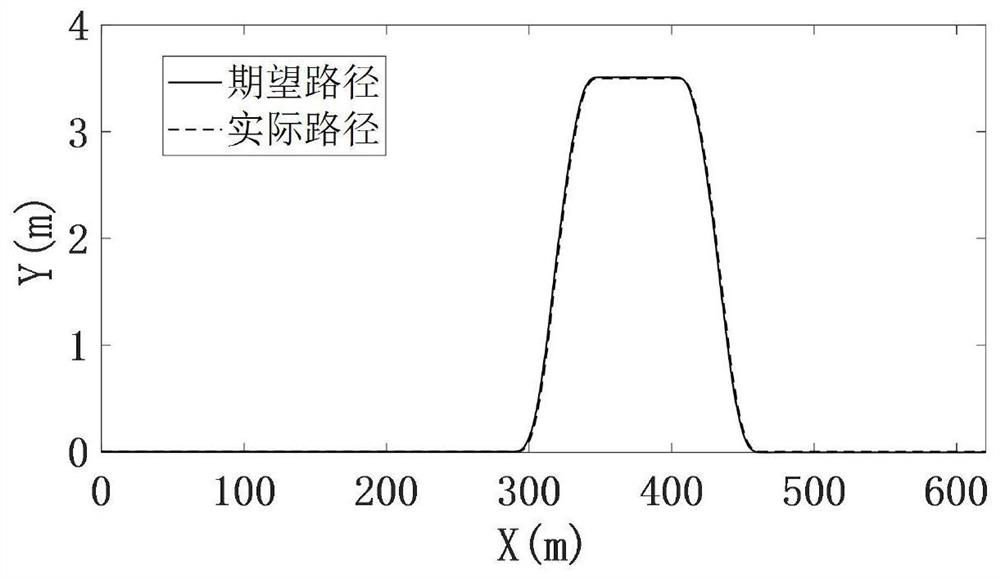
Vehicle transverse and longitudinal coupling nonlinear model prediction controller based on parallel Newton solution
ActiveCN112462612AGuaranteed accuracyNon-linear preservationAdaptive controlVehicle dynamicsNon linear model predictive control
The invention discloses a vehicle transverse and longitudinal coupling nonlinear model prediction controller based on parallel Newton solution, which obtains a transverse and longitudinal coupling nonlinear control model through a vehicle three-degree-of-freedom kinetic model, and by adopting a front wheel steering angle and front and rear wheel driving force as control variables, according to a model prediction control algorithm, vehicle physical constraints are considered and a cost function is constructed. Aiming at the vehicle path tracking control problem, a transverse and longitudinal coupling control model is obtained by using vehicle dynamics, a nonlinear model prediction controller is designed by using the model, and rapid solution of the nonlinear controller is realized by usinga parallel Newton method. The vehicle transverse and longitudinal coupling path tracking nonlinear model prediction controller is derived through a vehicle three-degree-of-freedom kinetic model, the mutual influence between the transverse direction and the longitudinal direction is considered, the nonlinear prediction controller is designed according to the model, the nonlinearity of a vehicle system is reserved, and the model precision is ensured.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
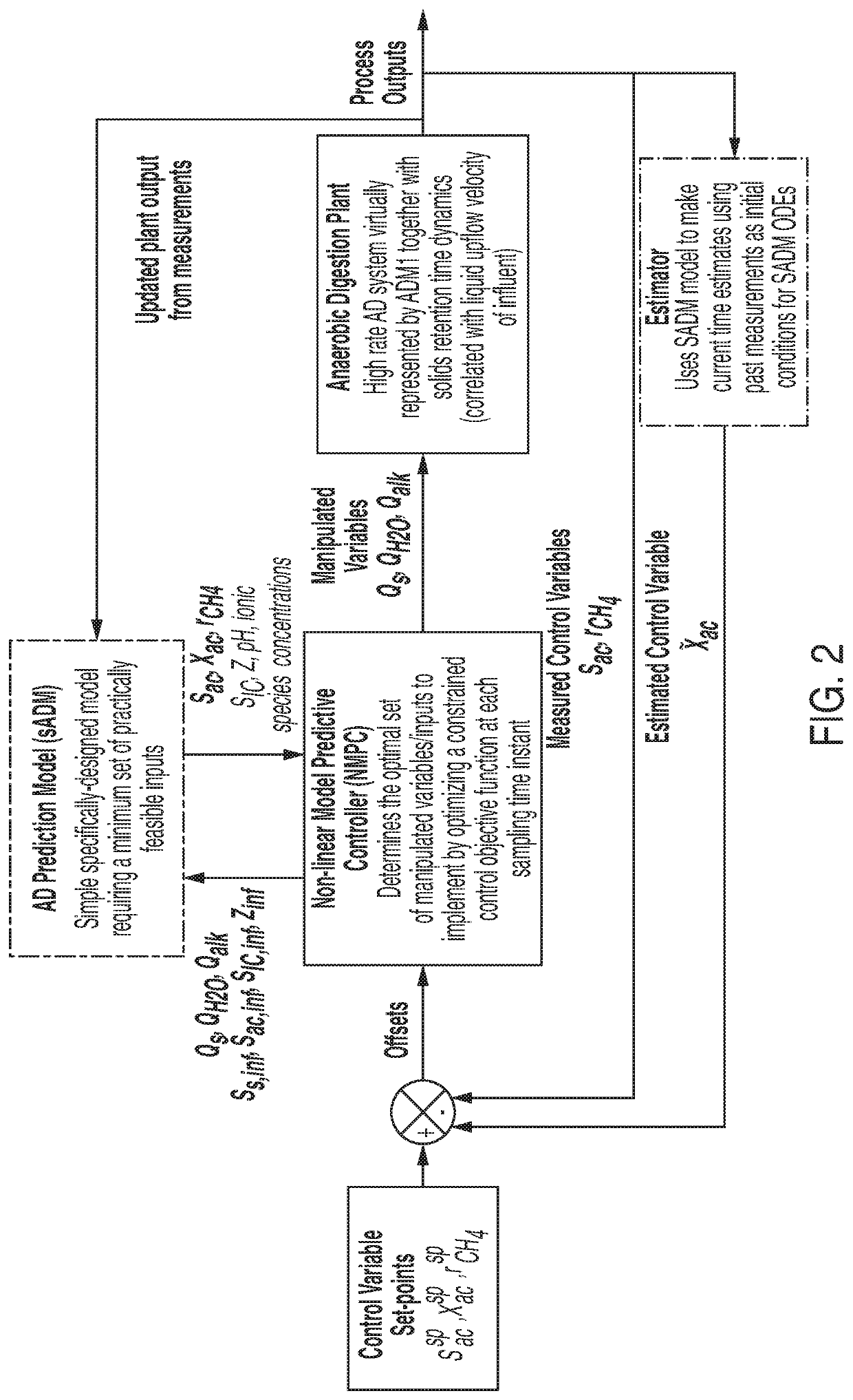
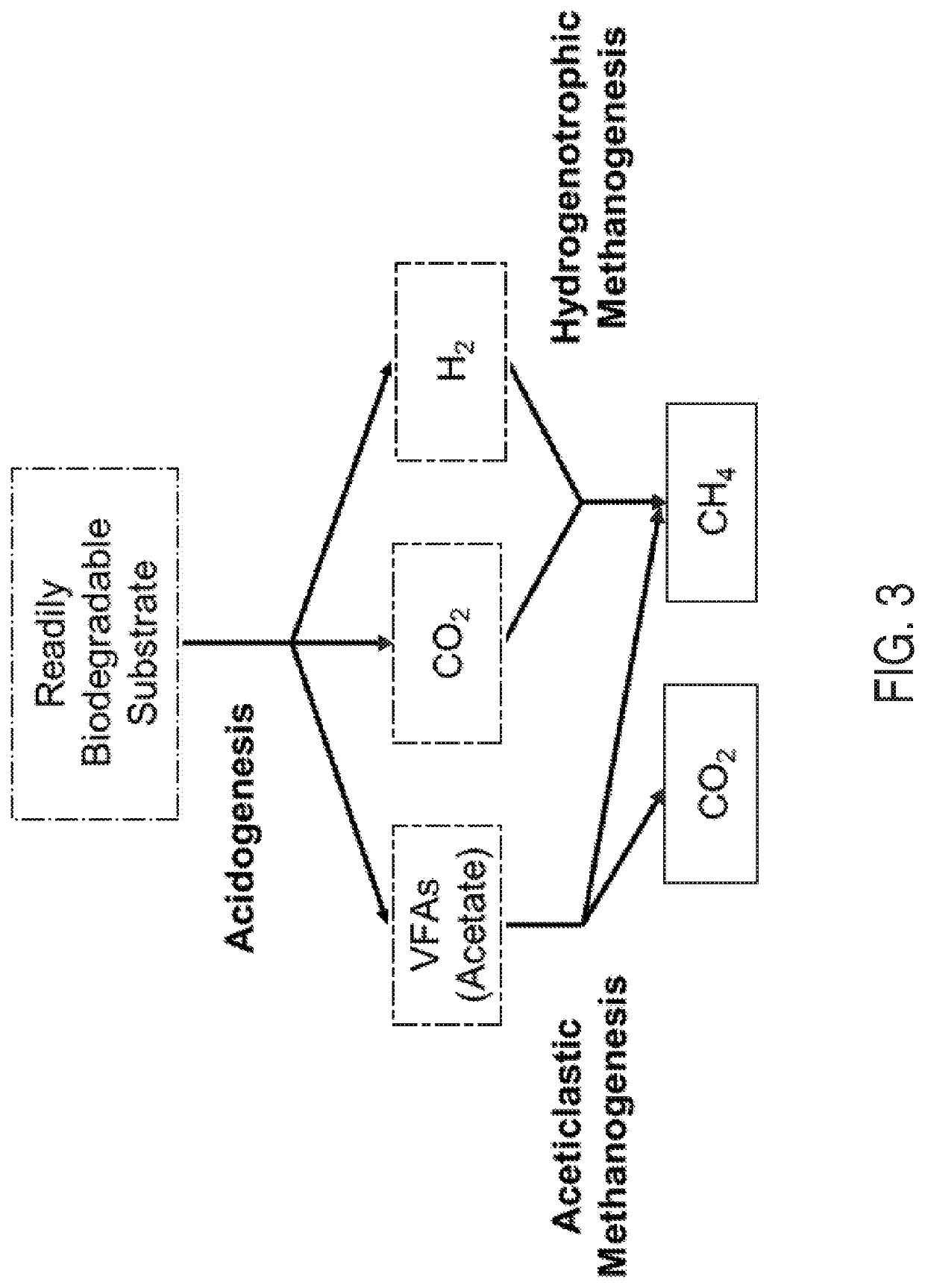
Automatic start-up of anaerobic digestion reactors using model predictive control and practically feasible sets of measurements
PendingUS20220228174A1Reduce in quantityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProcess engineeringNon linear model predictive control
Provided is a non-linear model predictive control (NMPC) system for automatic and optimum start-up of an anaerobic digestion (AD) system. The NMPC provides an optimum set of values of manipulated variables for controlling some of the key AD process variables during start-up. The NMPC based automatic start-up system was evaluated against a virtual AD process plant scenario involving a high rate AD reactor treating a readily biodegradable carbohydrate based substrate.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
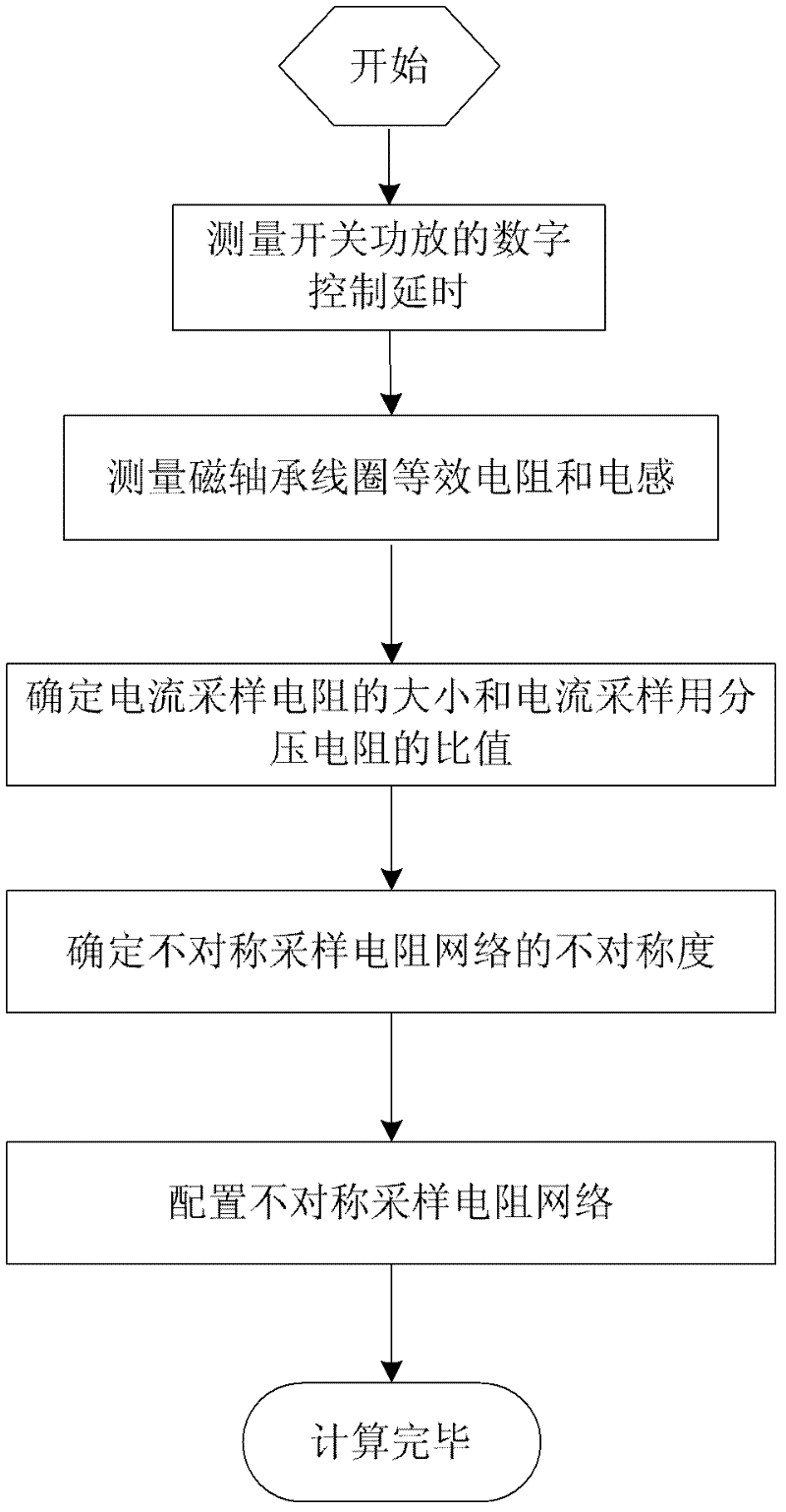
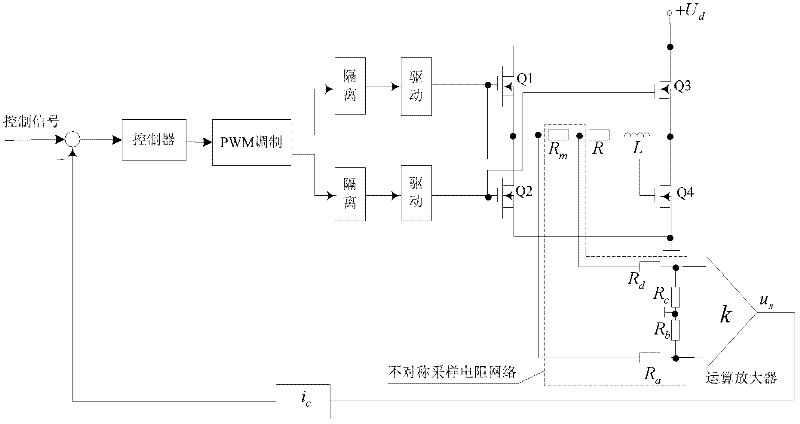
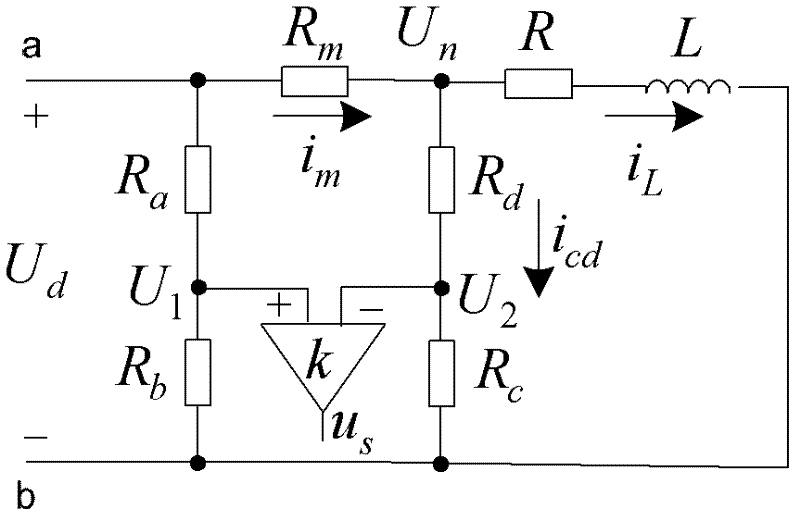
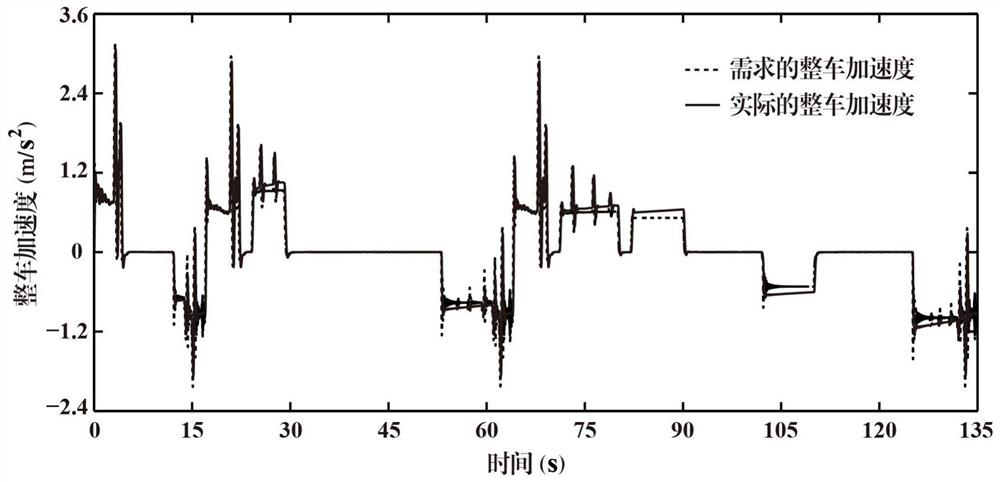
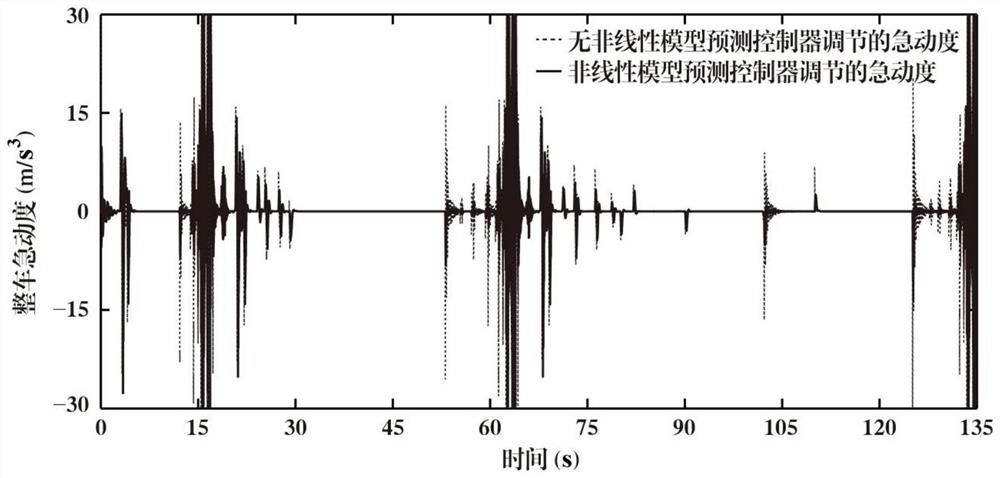
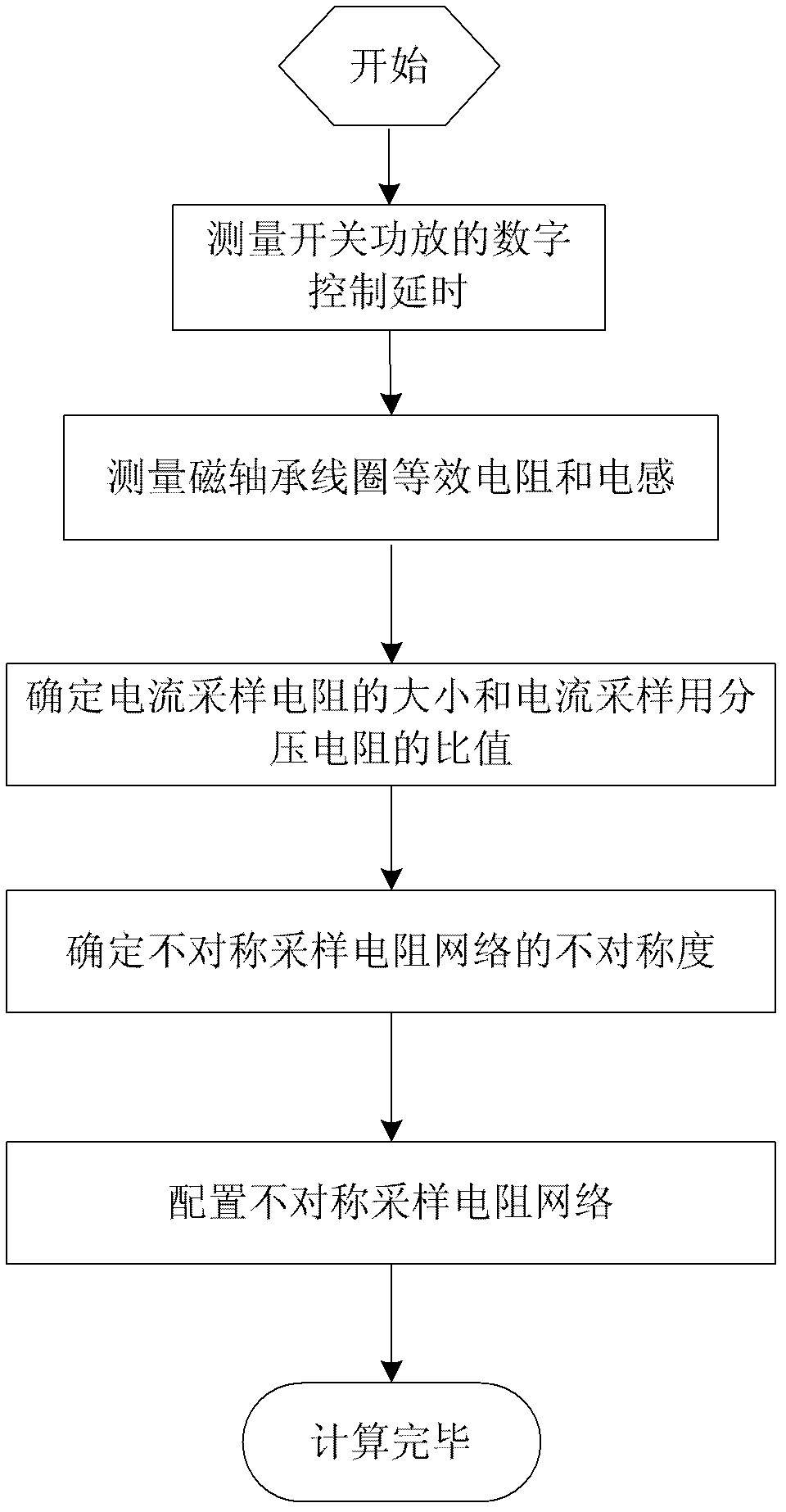
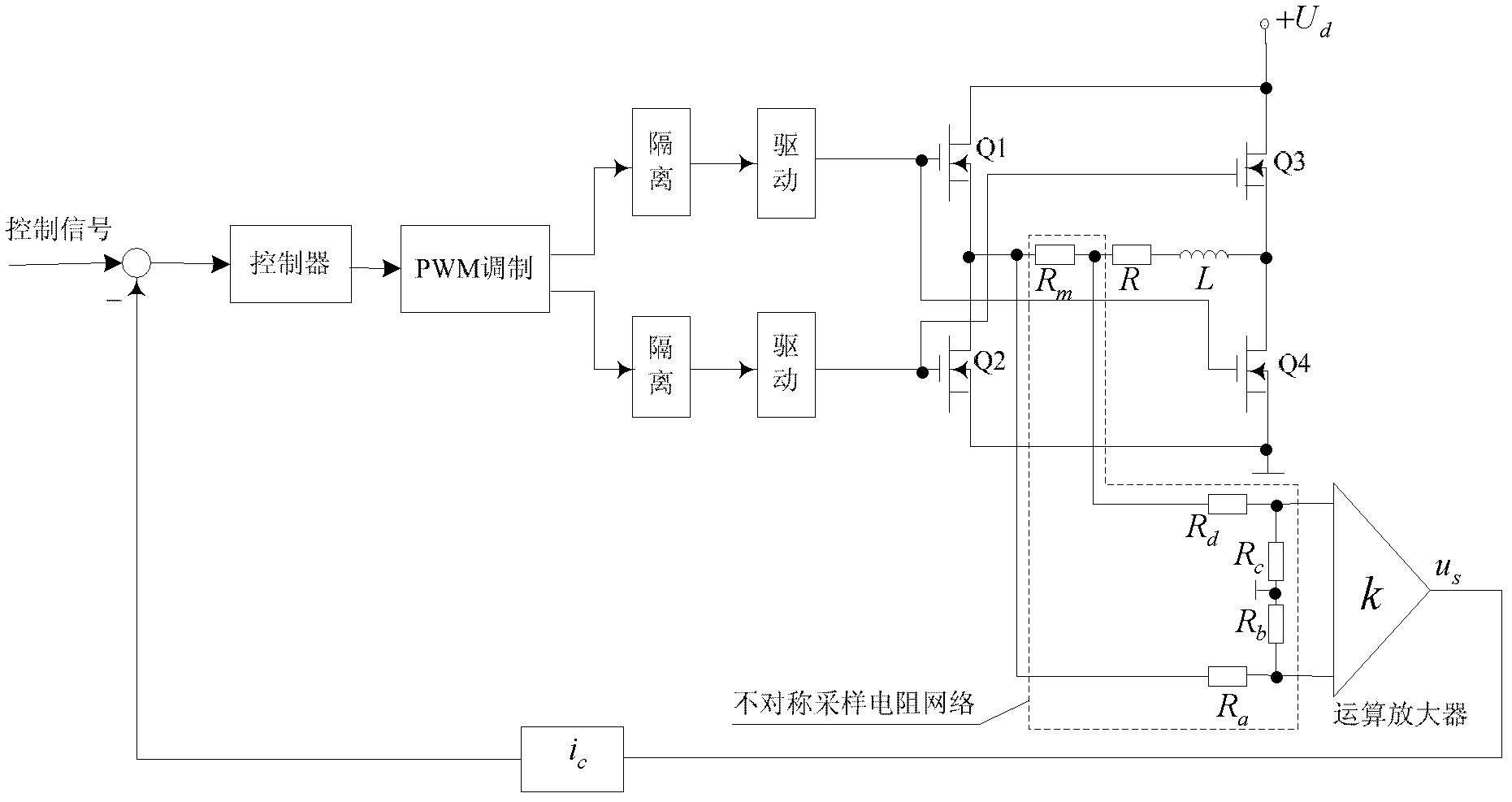
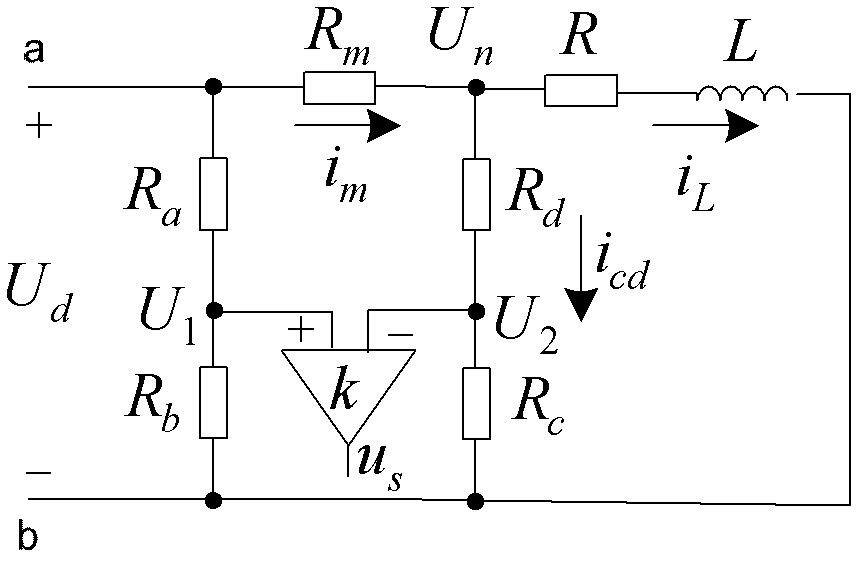
Method for compensating digital control delay of magnetic bearing switch power amplifier
ActiveCN102508433AImprove tracking accuracyAvoid calculation delaysAdaptive controlElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetic bearing
The invention discloses a method for compensating digital control delay of a magnetic bearing switch power amplifier, which is a method capable of compensating the digital control delay of a magnetic bearing switch power amplifier. The method comprises the steps of setting asymmetric factors of asymmetric sampling resistor networks according to a linear model predictive control theory on the basis of measuring the digital control delay of a switch power amplifier system and equivalent inductance and resistance of a magnetic bearing winding, and finally setting the asymmetric sampling resistance networks according to the asymmetric factors. The method for compensating the digital control delay of the magnetic bearing switch power amplifier belongs to the technical field of magnetic bearing control and can be applied to the fast response and high-stable control of a high-speed magnetic suspension rotor system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A Neural Network-Based Path Tracking Control Method for Handling Robot
ActiveCN111624992BOvercoming the problem of poor real-time performance of predictive controlGood real-time controlNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsPathPingState variable
The invention provides a path tracking control method of a handling robot based on a neural network, which can improve the real-time performance of nonlinear model predictive control. The method includes: using nonlinear model predictive control to generate a training sample set, wherein the training sample includes: state variables and control variables of the handling robot; constructing a neural network model; using the obtained training sample set to train the constructed neural network model , to obtain a trained neural network model; wherein, in the path tracking control process, the trained neural network model outputs control variables, so that the handling robot performs path tracking according to the control variables output by the neural network model. The invention relates to the field of autonomous driving control of mobile robots.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Control method for regenerative braking system of electric vehicle
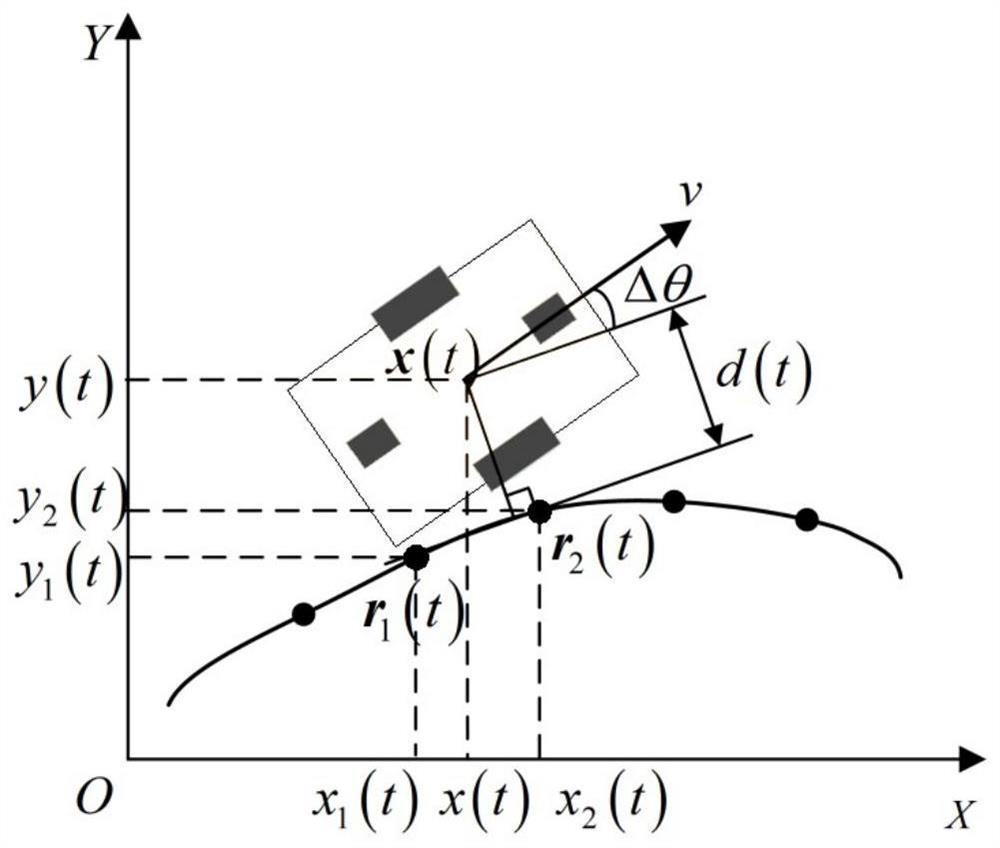
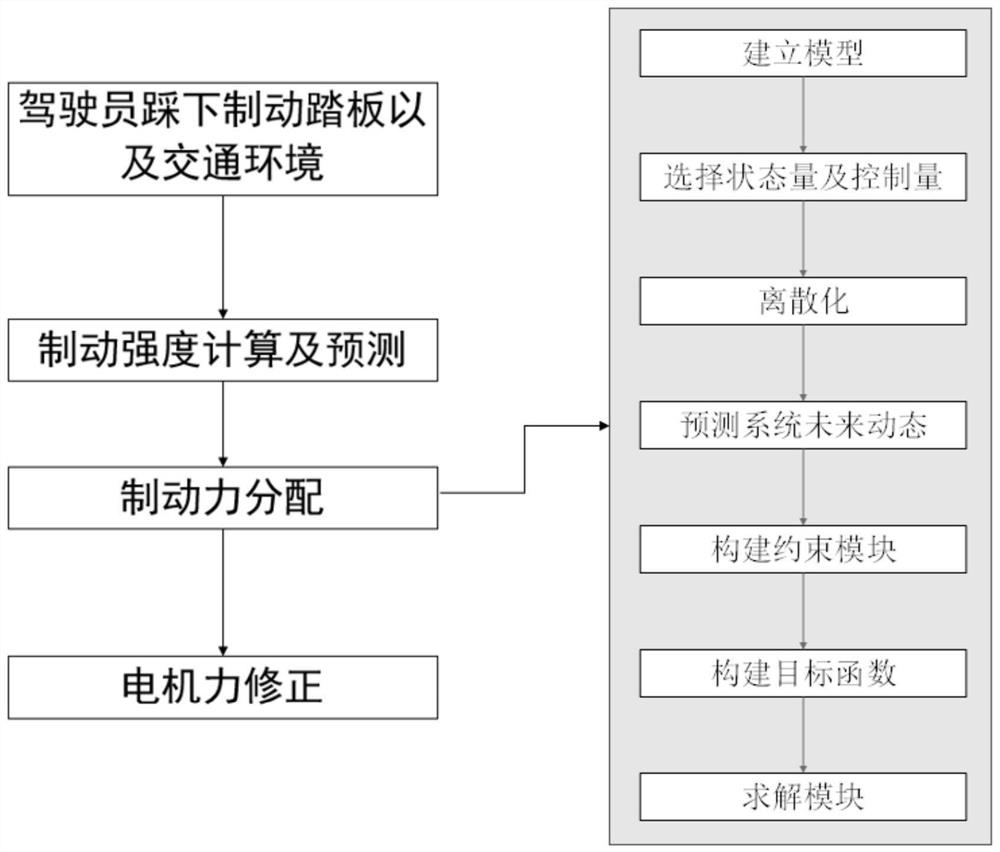
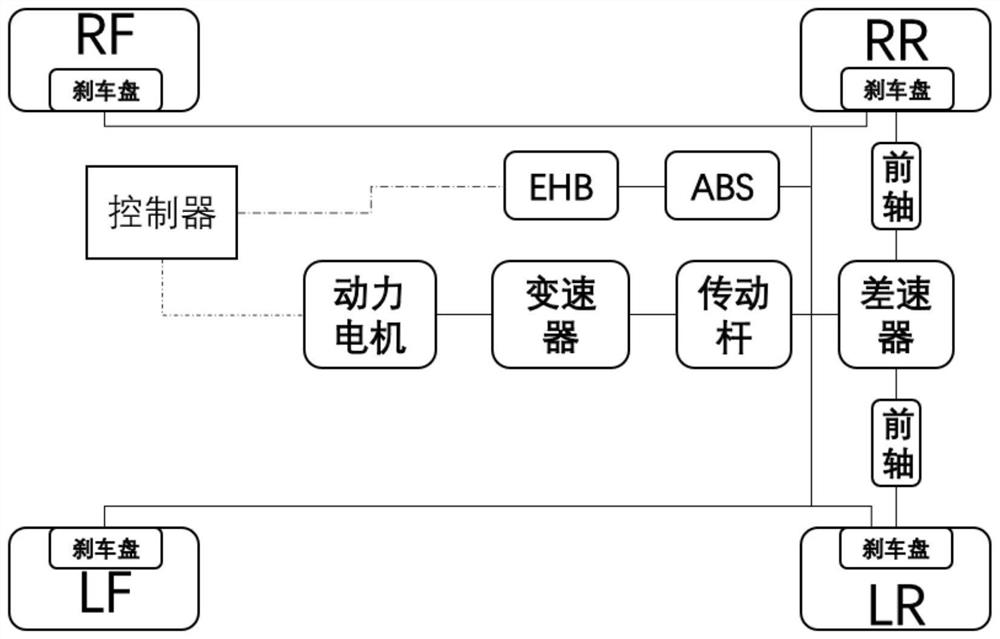
PendingCN112776610AEnsure braking comfortGood pedal feelSpeed controllerElectrodynamic brake systemsDriver/operatorElectric vehicle
The invention discloses a control method for a regenerative braking system of an electric automobile, and relates to the field of automobile braking control. The control method comprises the steps of braking strength prediction, optimal braking force distribution and motor torque compensation, wherein the braking strength prediction is to predict the braking demand change of a driver by adopting an autoregression model or a Markov probability transfer model according to the vehicle state and the traffic environment in combination with the current braking demand of the driver. According to the current braking demand of the driver and the predicted braking demand change of the driver, a regenerative braking torque and a friction braking torque are distributed in combination with a nonlinear model prediction control method, and factors such as the braking energy recovery rate, the driver pedal feeling and the braking comfort are considered, thereby designing a constrained nonlinear model prediction controller considering the braking behavior of the driver; and finally, the difference value between the target friction braking torque and the actual friction braking torque of the electric power-assisted braking system is directly compensated through the regenerative braking torque of the power motor, and the situation that the response speed of the hydraulic braking system is low is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
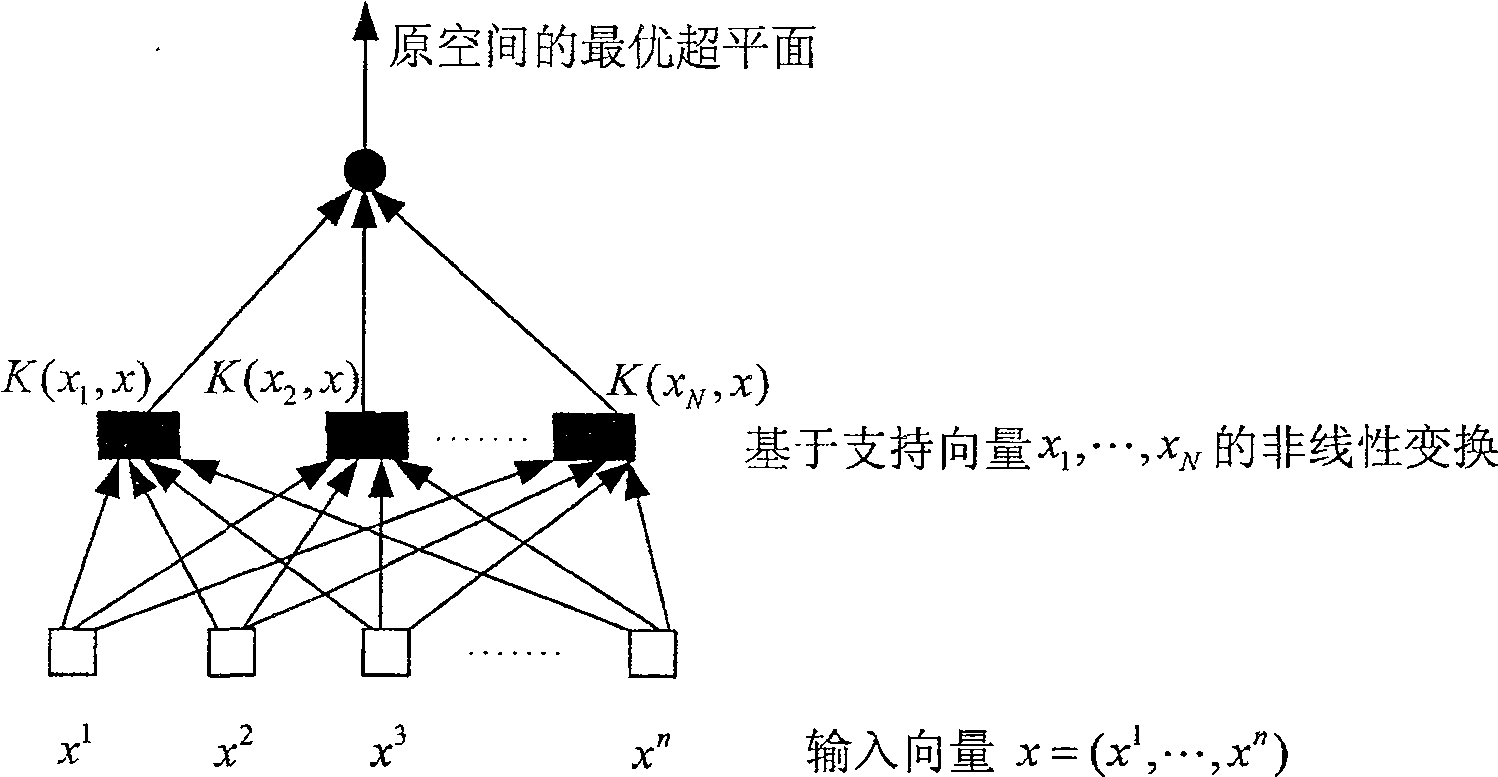
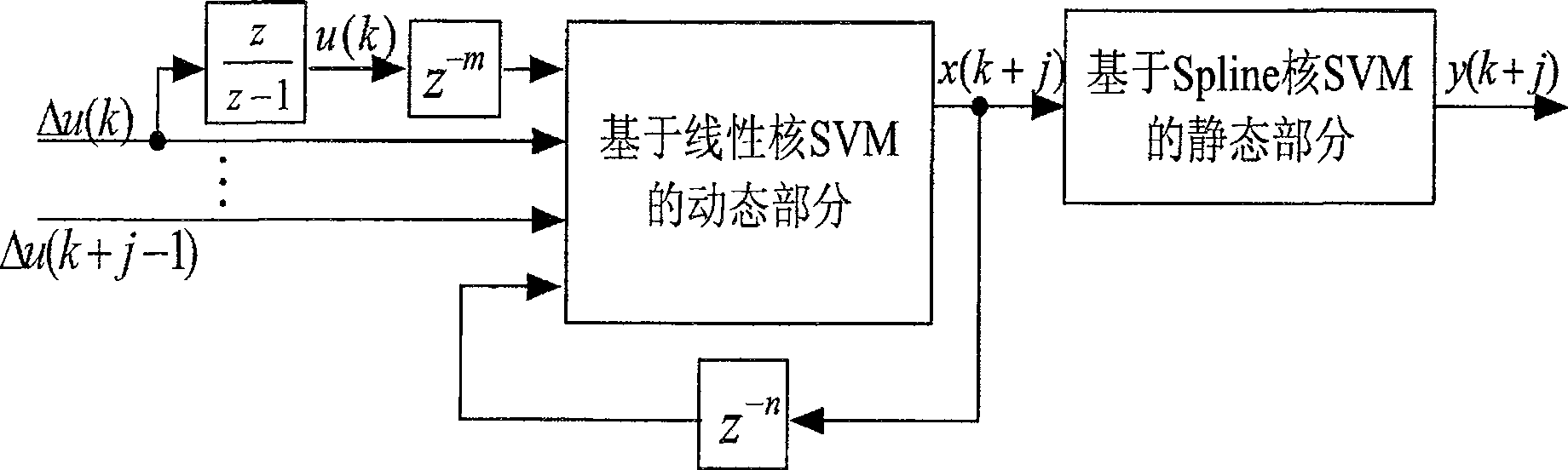
Groove type reactor non-linear predication control method based on multi-kernel support vector machine
InactiveCN100511042CFew adjustable parametersEasy to identifyAdaptive controlAutomatic controlOptimal control
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A Nonlinear Integrated Control Method for Vehicle Lateral Stability
ActiveCN105045102BImprove computing powerOptimal control sequenceAdaptive controlVehicle dynamicsActive safety
The invention relates to a vehicle active safety control method, and particularly relates to a vehicle lateral stability nonlinear integration control method. Firstly, a simplified vehicle dynamics model is built; then, design of a nonlinear model predictive controller is carried out, expected yaw angle velocity information is inputted to the nonlinear controller module, according to the value of the expected yaw angle velocity and sideslip angle velocities of a front wheel and a rear wheel of the vehicle and the yaw angle velocity fed back in real time, a model predicative control method is used for predicting future dynamic performance of the system, optimization is carried out at the same time, an additional yaw moment and the optimized steering wheel angle information are decided and outputted to an execution mechanism corresponding to the vehicle, and the vehicle is kept in a yaw stability state. The method of the invention is successfully realized by the controller through FPGA full hardware, the FPGA uses a parallel hardware calculation method for acquiring the optimized control sequence in a limited sampling time domain, requirements of high real-time performance and miniaturization on the vehicle-mounted nonlinear model predictive controller can be met, and the calculation performance of the control system is improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Global balance control method and device for foot-type robot and foot-type robot
The embodiment of the invention provides a global balance control method and device for a foot type robot and the foot type robot. The method comprises the steps that the motion state of the foot type robot at the current moment is obtained; obtaining a system state equation of the foot type robot at the current moment according to the motion state at the current moment and a kinetic equation of a flywheel inverted pendulum simplified model corresponding to the foot type robot; according to the system state equation at the current moment, through nonlinear model predictive control, obtaining a control input quantity required for global balance control at the current moment; and performing motion control on the foot type robot according to the control input quantity. According to the method, model simplification is carried out based on a flywheel inverted pendulum model, balance optimization control is carried out by using a nonlinear model prediction control technology, and balance control of the whole system of the foot type robot can be realized.
Owner:UBTECH ROBOTICS CORP LTD
Non-linear model predictive control method for single pedal of pure electric vehicle
ActiveCN113386768AExact demand torqueSatisfy the motivationSpeed controllerElectric energy managementDriver/operatorPredictive controller
The invention discloses a nonlinear model predictive control method for a single pedal of a pure electric vehicle. The nonlinear model predictive control method comprises the following steps: 1, acquiring the opening degree of the pedal; 2, establishing a single-pedal dynamics model by using the pedal opening and the pedal rotation angular velocity; 3, designing a sliding-mode observer to obtain a pedal torque acting on a pedal by a driver; 4, performing driving / braking driving mode recognition according to the pedal torque; 5, establishing a single-pedal control system model in combination with the whole vehicle state; and 6, constructing a nonlinear model predictive controller, and obtaining an optimal motor driving / braking torque by using a direct mapping relation between a pedal torque and a motor torque and by taking optimization of energy consumption, comfort and safety as targets so as to realize motor torque control. The integration degree of the driving function and the motor braking function in the single pedal mode is deepened, and the single pedal in the true sense is achieved. Meanwhile, the method can meet the dynamic property requirement of a driver, the driving safety and the energy utilization rate are improved, and the riding comfort is improved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for compensating digital control delay of magnetic bearing switch power amplifier
ActiveCN102508433BImprove tracking accuracyAvoid calculation delaysAdaptive controlElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetic bearing
The invention discloses a method for compensating digital control delay of a magnetic bearing switch power amplifier, which is a method capable of compensating the digital control delay of a magnetic bearing switch power amplifier. The method comprises the steps of setting asymmetric factors of asymmetric sampling resistor networks according to a linear model predictive control theory on the basis of measuring the digital control delay of a switch power amplifier system and equivalent inductance and resistance of a magnetic bearing winding, and finally setting the asymmetric sampling resistance networks according to the asymmetric factors. The method for compensating the digital control delay of the magnetic bearing switch power amplifier belongs to the technical field of magnetic bearing control and can be applied to the fast response and high-stable control of a high-speed magnetic suspension rotor system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
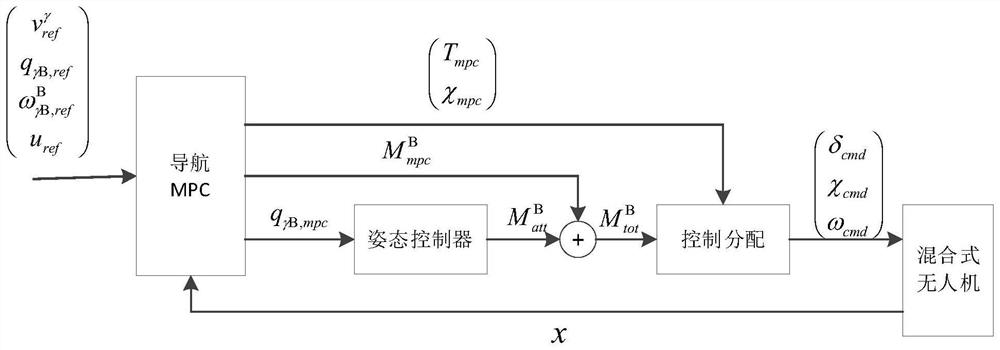
Rotor wing-tilt hybrid unmanned aerial vehicle nonlinear model predictive control method
ActiveCN114488816AAny flight angleRealize automatic mutual conversionInternal combustion piston enginesAdaptive controlNonlinear algorithmsClassical mechanics
The invention relates to a nonlinear model predictive control method for a rotor-tilt hybrid unmanned aerial vehicle. The method comprises the following steps: defining important parameters of the unmanned aerial vehicle; designing a nonlinear model based on a navigation MPC algorithm; designing a control distribution algorithm; and designing an unmanned aerial vehicle flight experiment. The method has the beneficial effects that an MPC (Model Predictive Control) method is designed and is applied to the rotor wing-tilt hybrid unmanned aerial vehicle, the nonlinear model of the unmanned aerial vehicle is deduced and established, and a multi-stage control distribution algorithm is designed; according to the method, nonlinear dynamic characteristics of the unmanned aerial vehicle are considered, a nonlinear MPC algorithm equation is established, a navigation MPC module calculates three types of control input variables including optimal driving force, an inclination angle and torque according to a reference speed, and automatic mutual conversion between an RW mode and an FW mode is achieved; the unmanned aerial vehicle applied by the invention can realize any flight angle on a mechanical structure.
Owner:浙江蓝盒子航空科技有限公司
Omnidirectional wheeled humanoid robot based on a linear predictive position and velocity controller
ActiveUS10293486B2High motionVelocity increasesProgramme-controlled manipulatorAttitude controlHumanoid robot naoBody positions
A humanoid robot with a body joined to an omnidirectional mobile ground base, and equipped with: a body position sensor and a base position sensor to provide measures, actuators comprising at least 3 wheels located in the omnidirectional mobile base, extractors for converting the measures into useful data, a controller to calculate position, velocity and acceleration commands from the useful data using a robot model and pre-ordered position and velocity references, means for converting the commands into instructions for the actuators, wherein the robot model is a double point-mass model, and wherein the commands are based on a linear model predictive control law with a discretized time according to a sampling time period and a number of predicted samples, and expressed as a quadratic optimization formulation with: a weighted sum of objectives and a set of predefined linear constraints.
Owner:SOFTBANK ROBOTICS EURO +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com