Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1293 results about "Linear compressor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
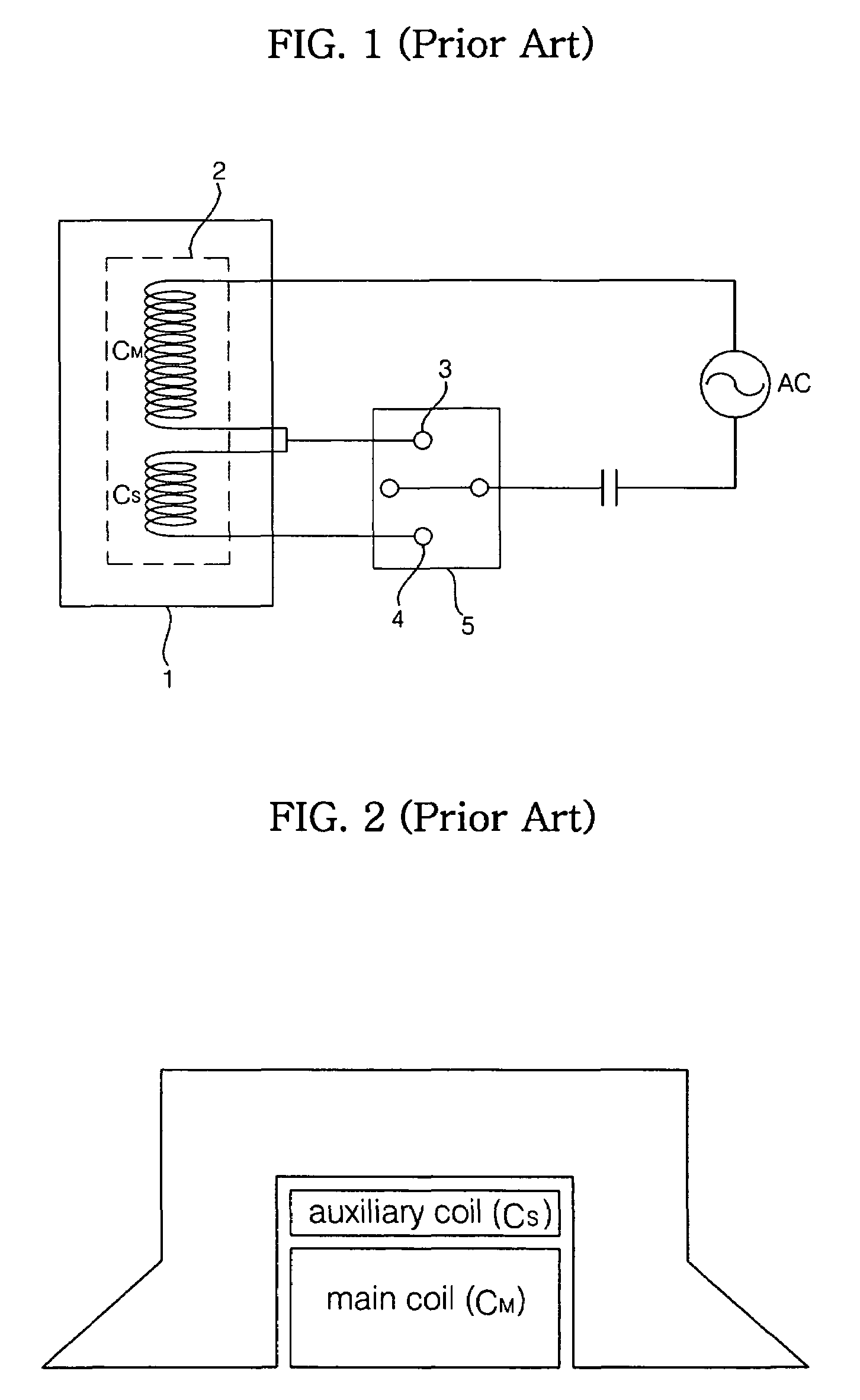
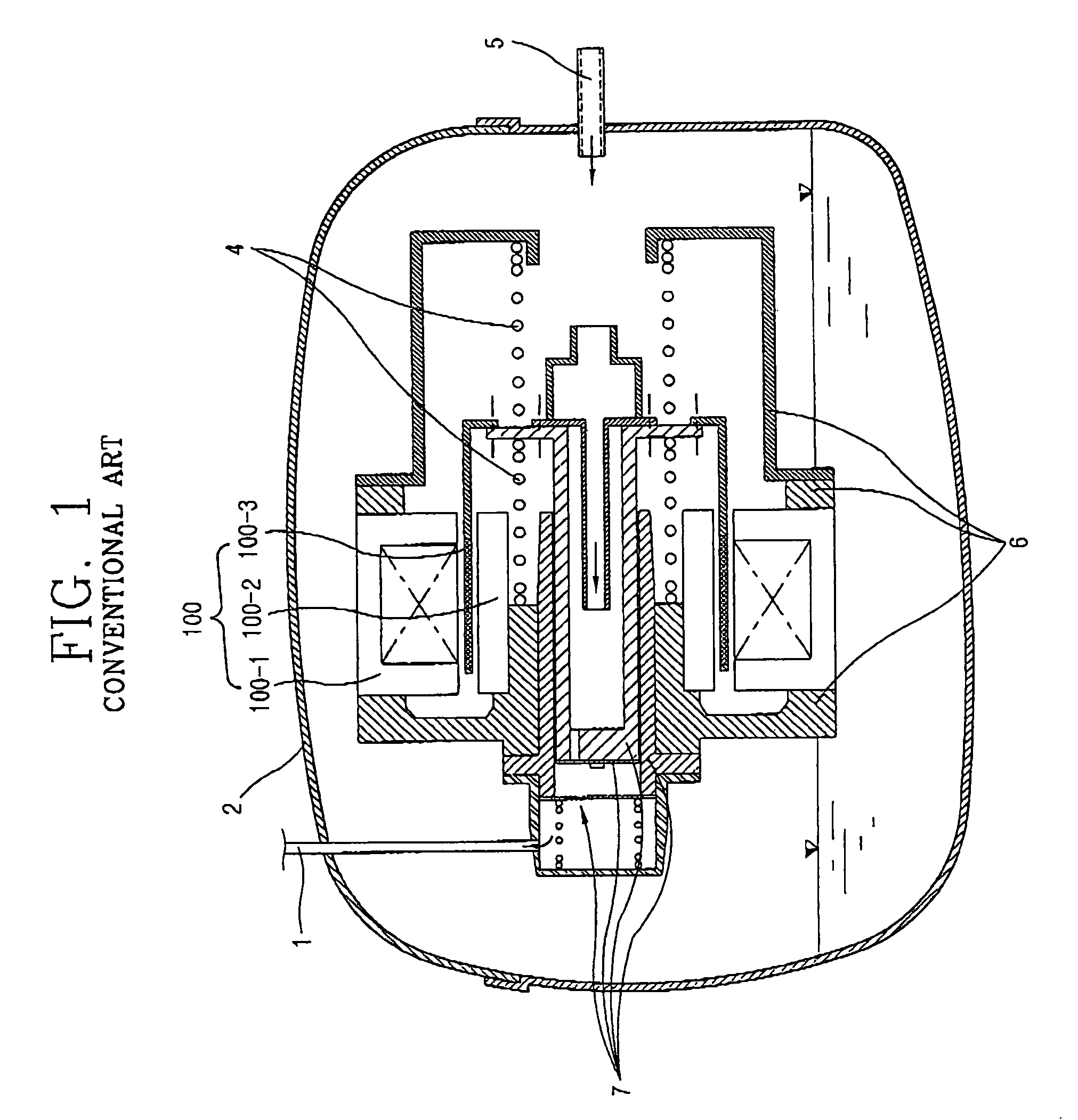
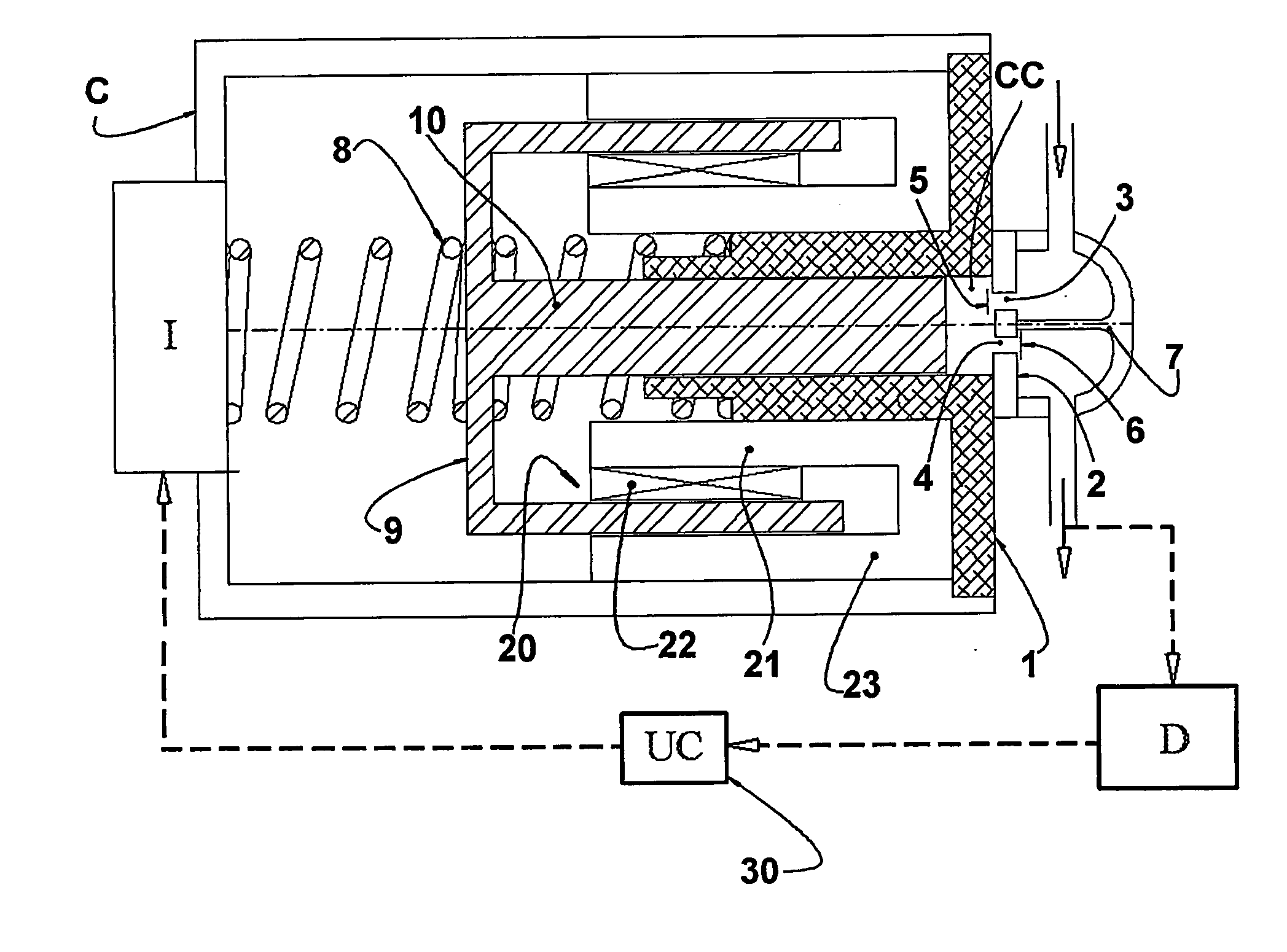
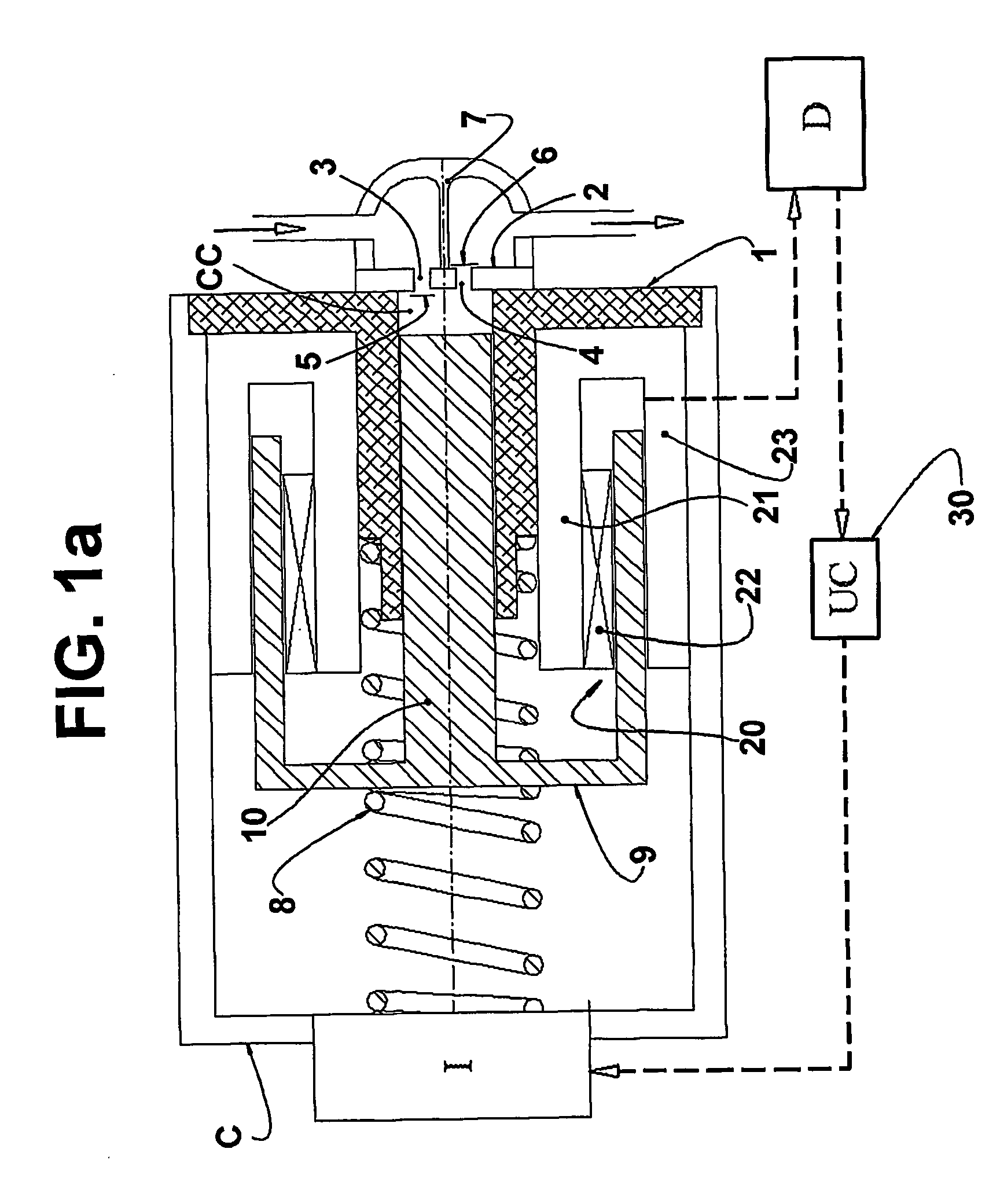
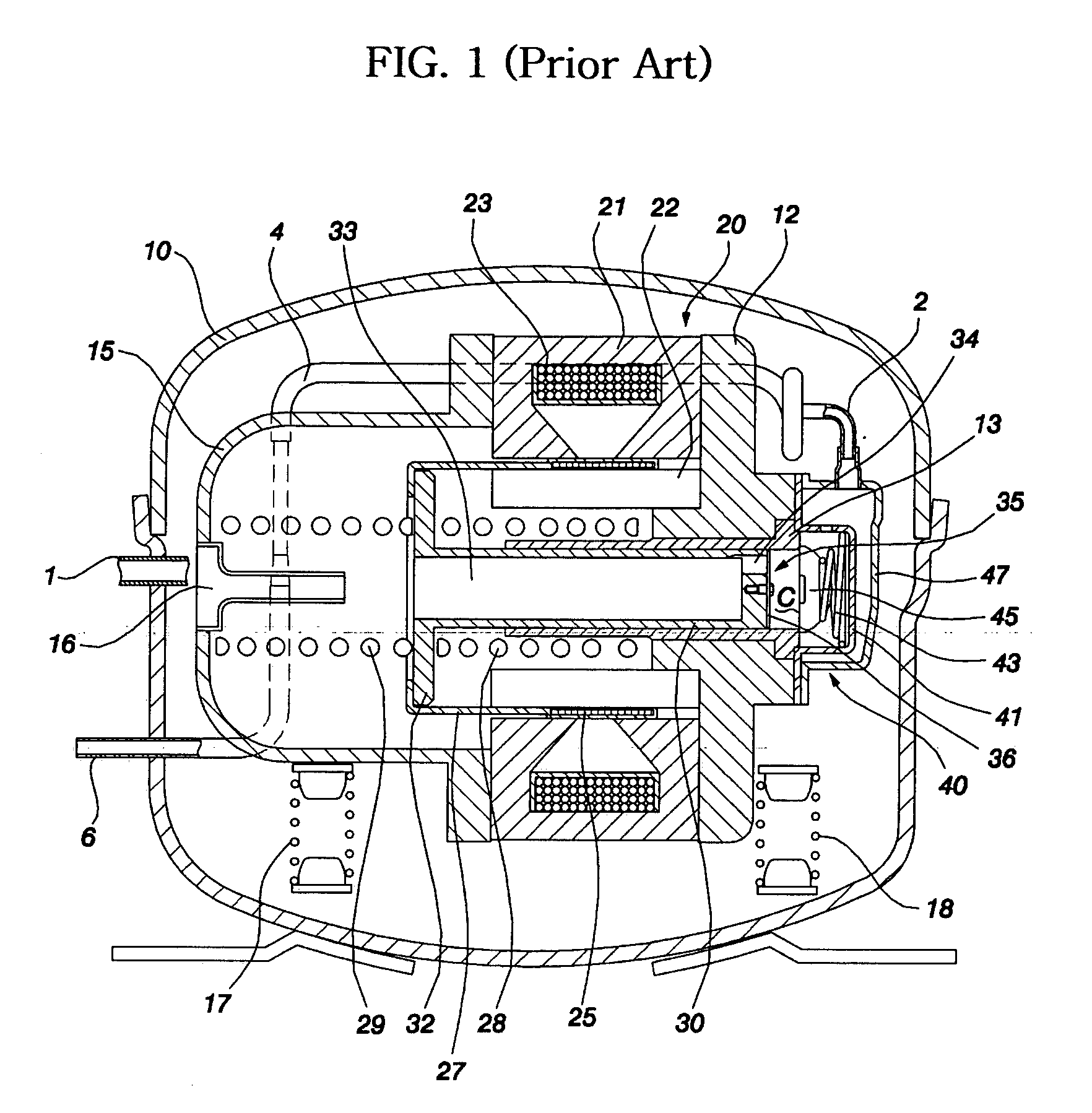
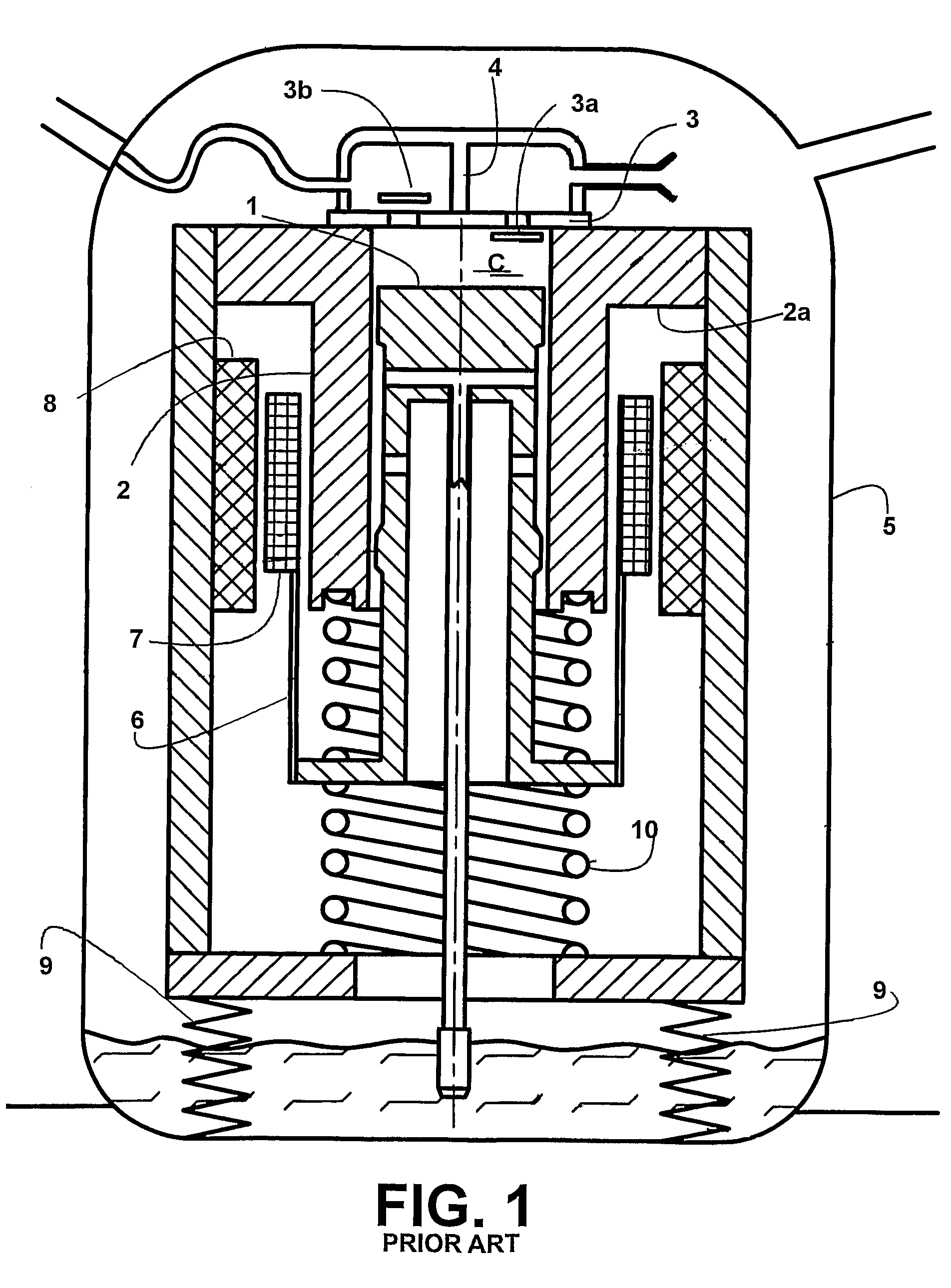
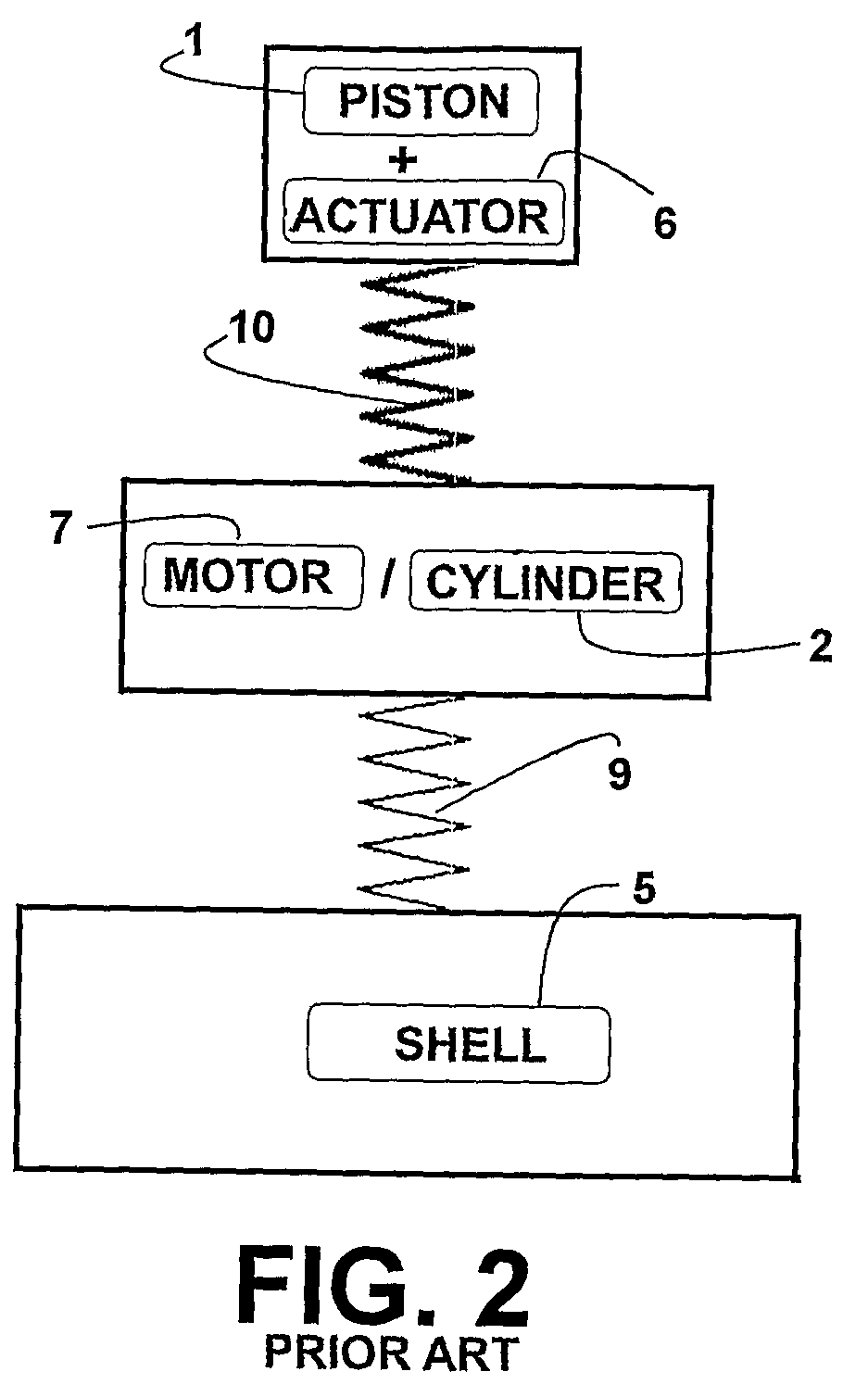
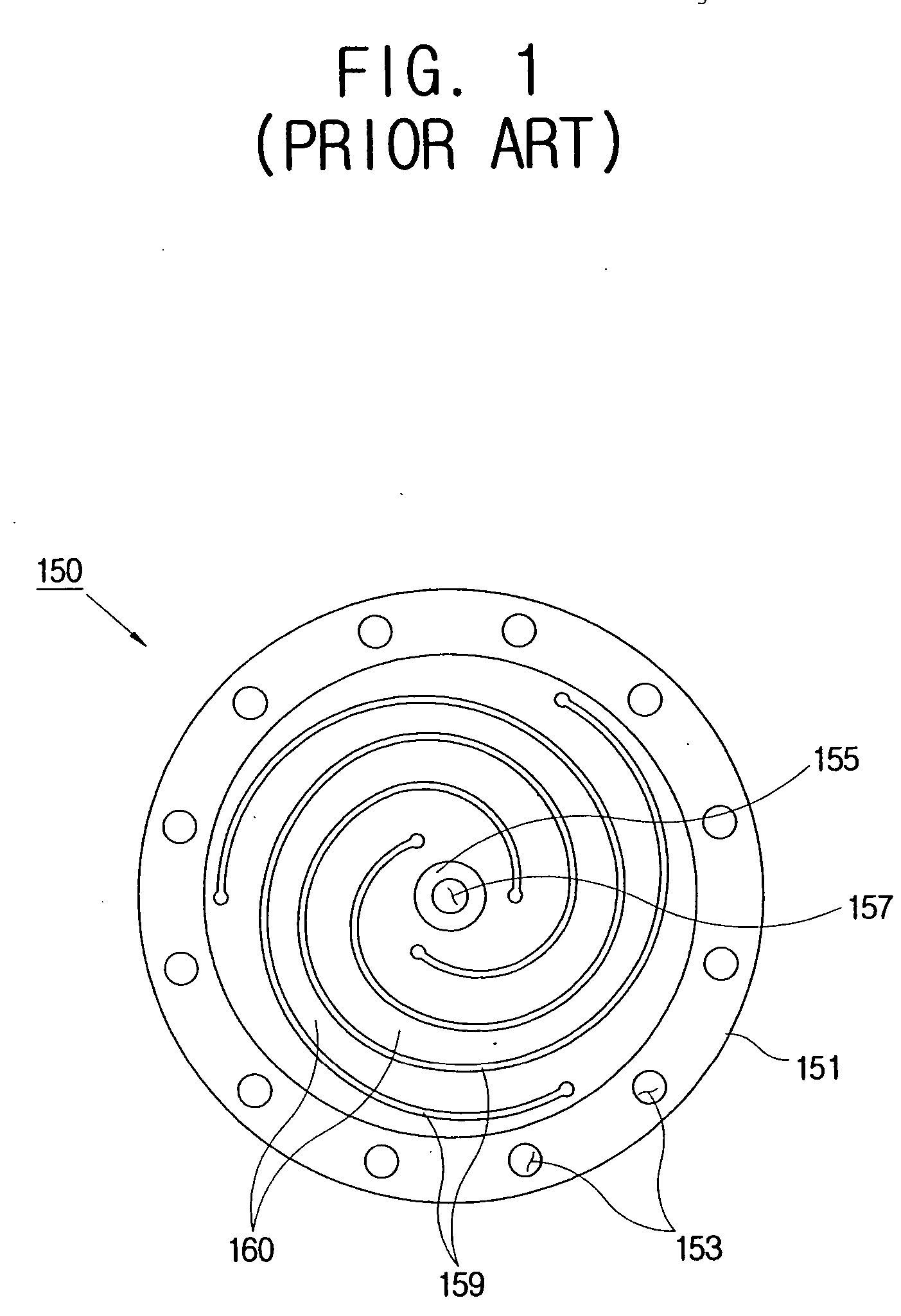
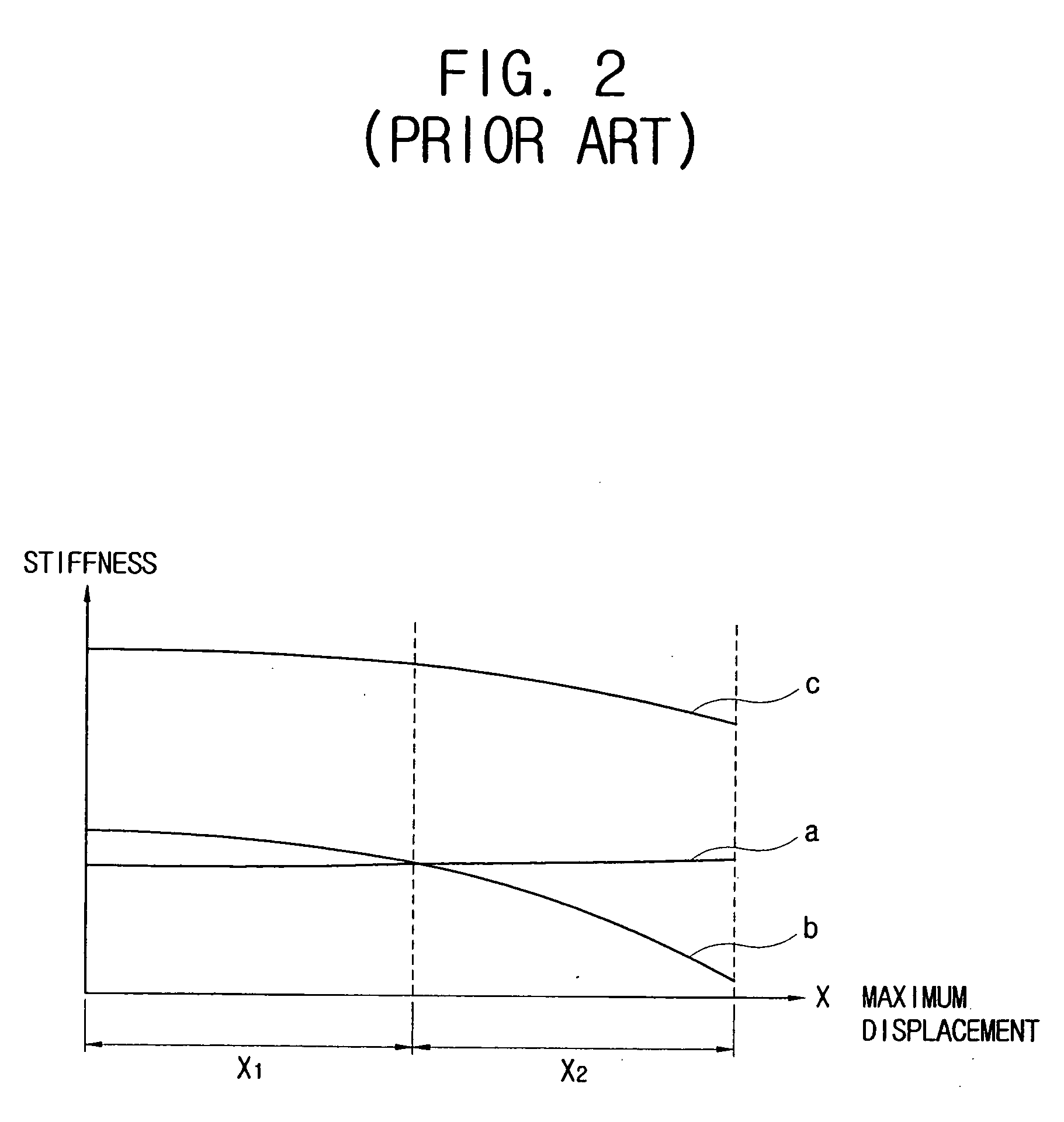
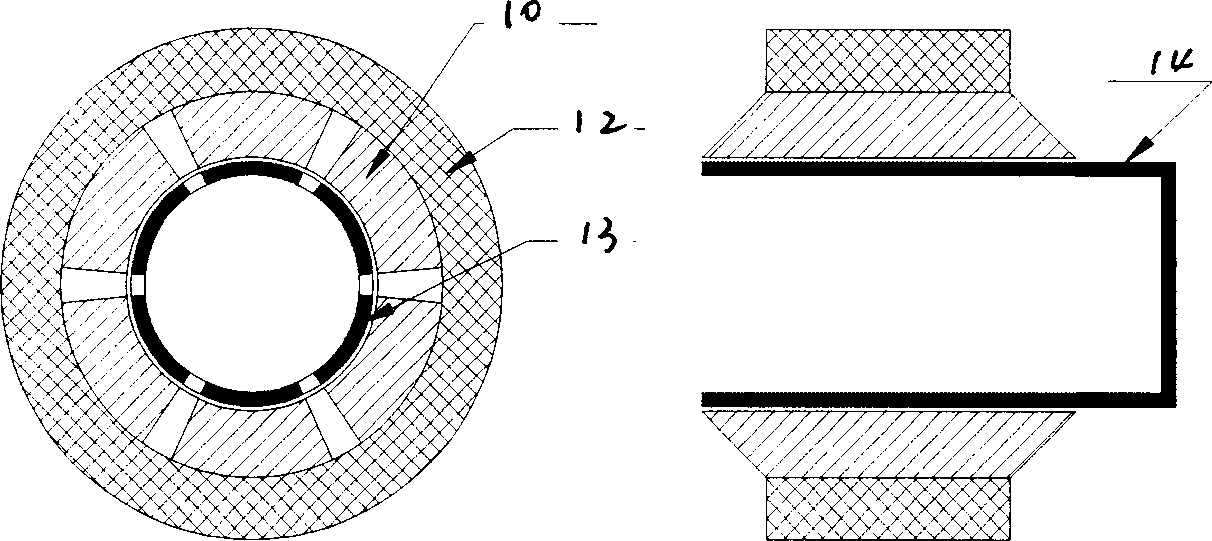
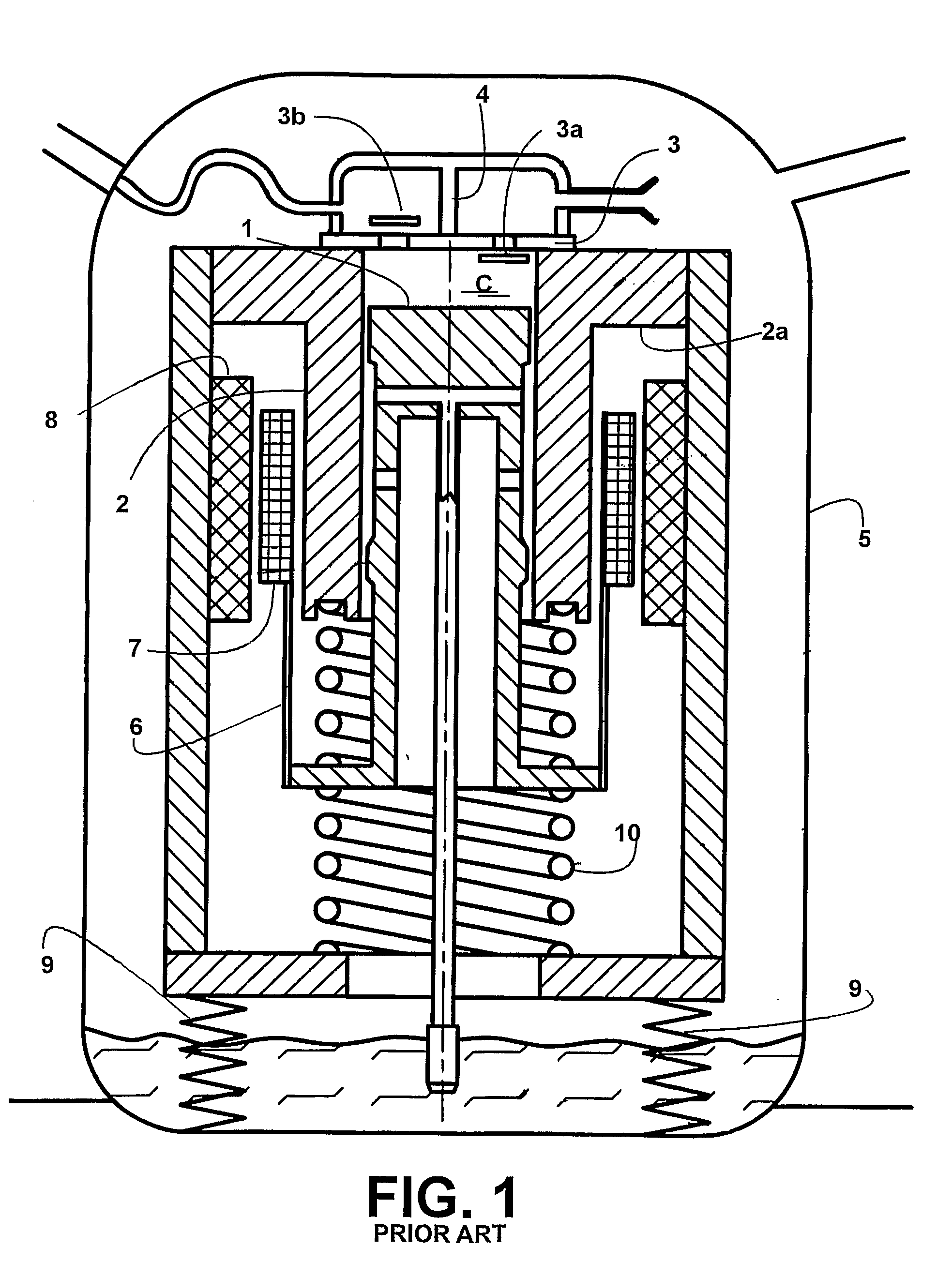
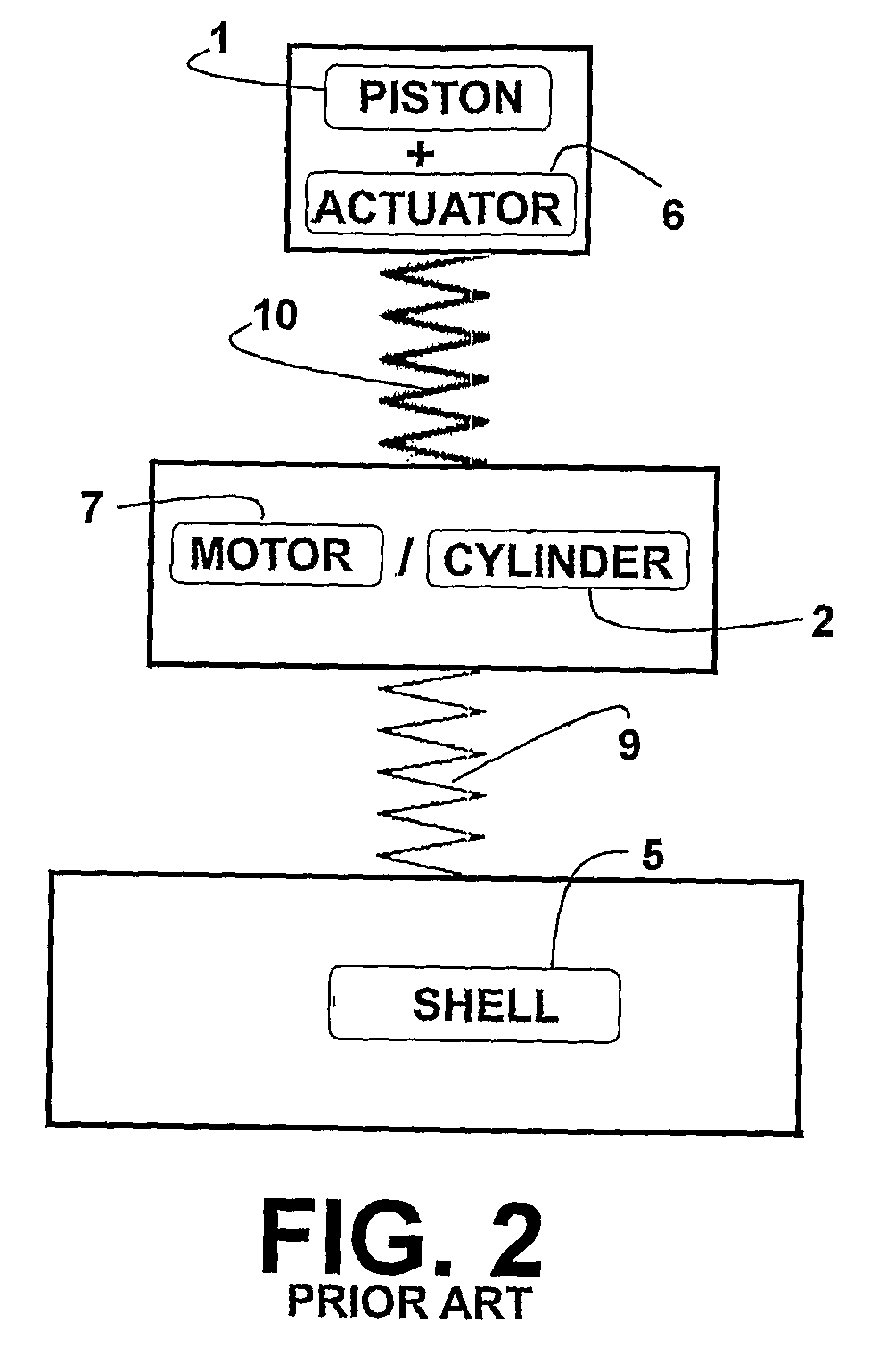
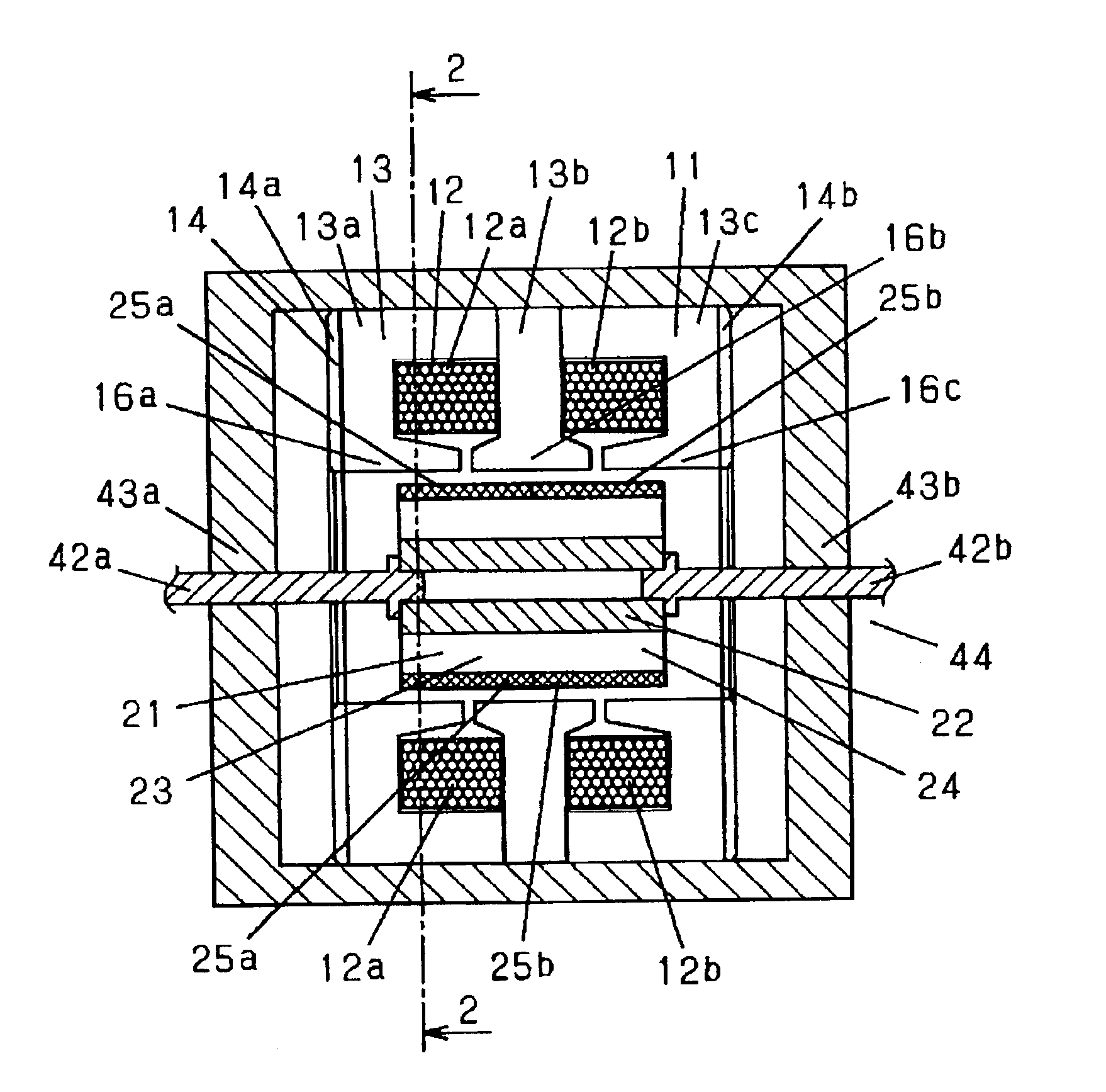
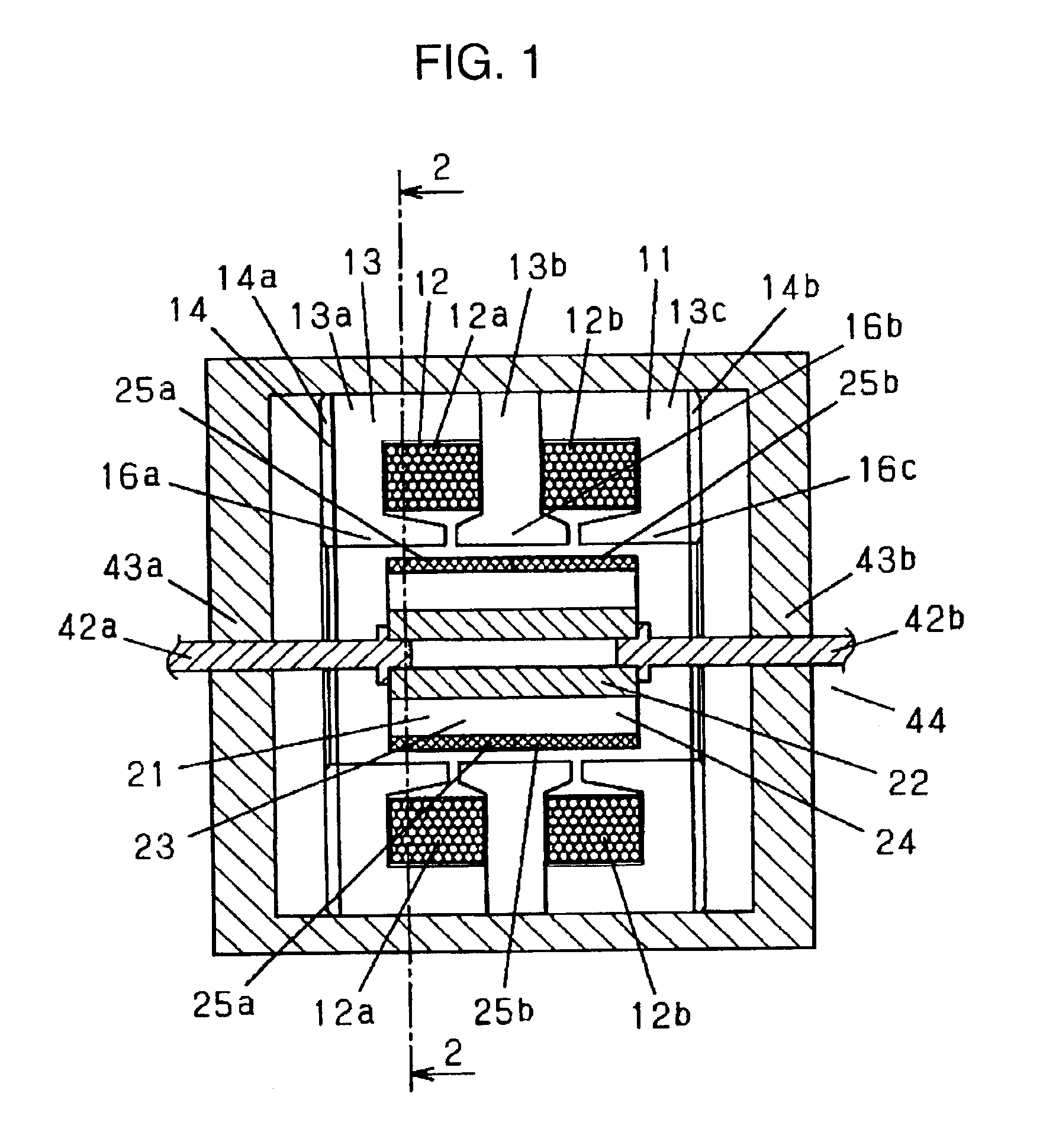
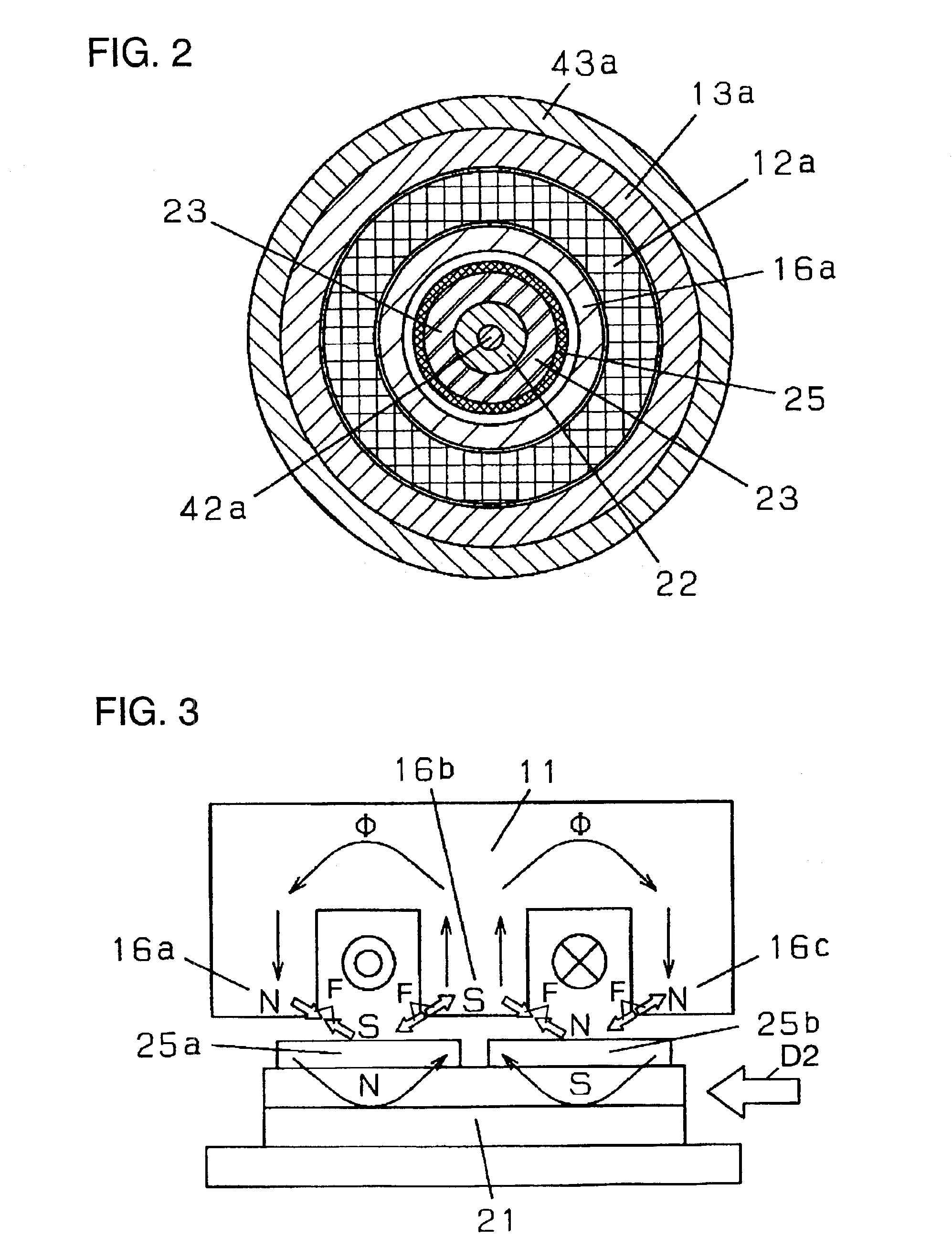
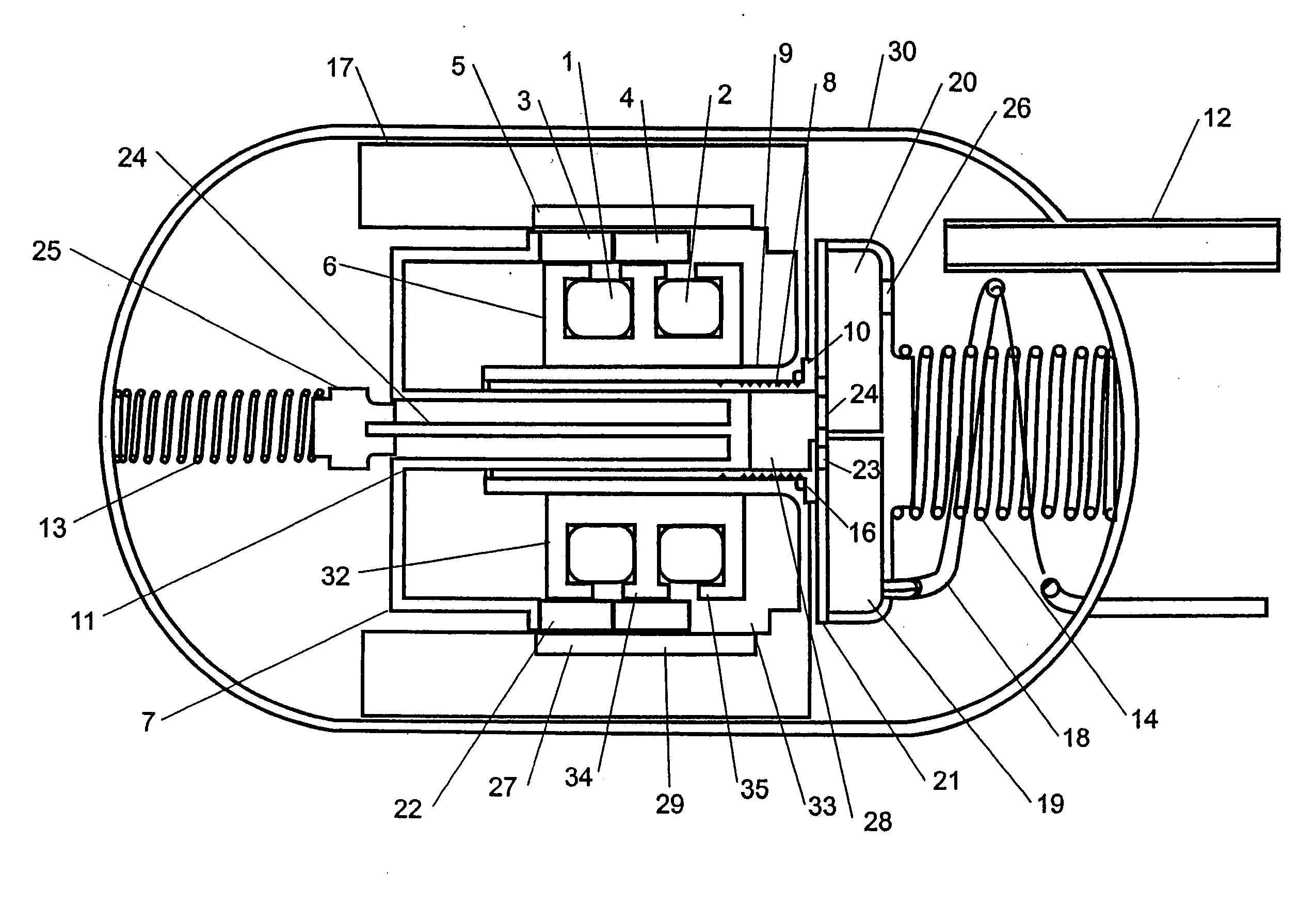
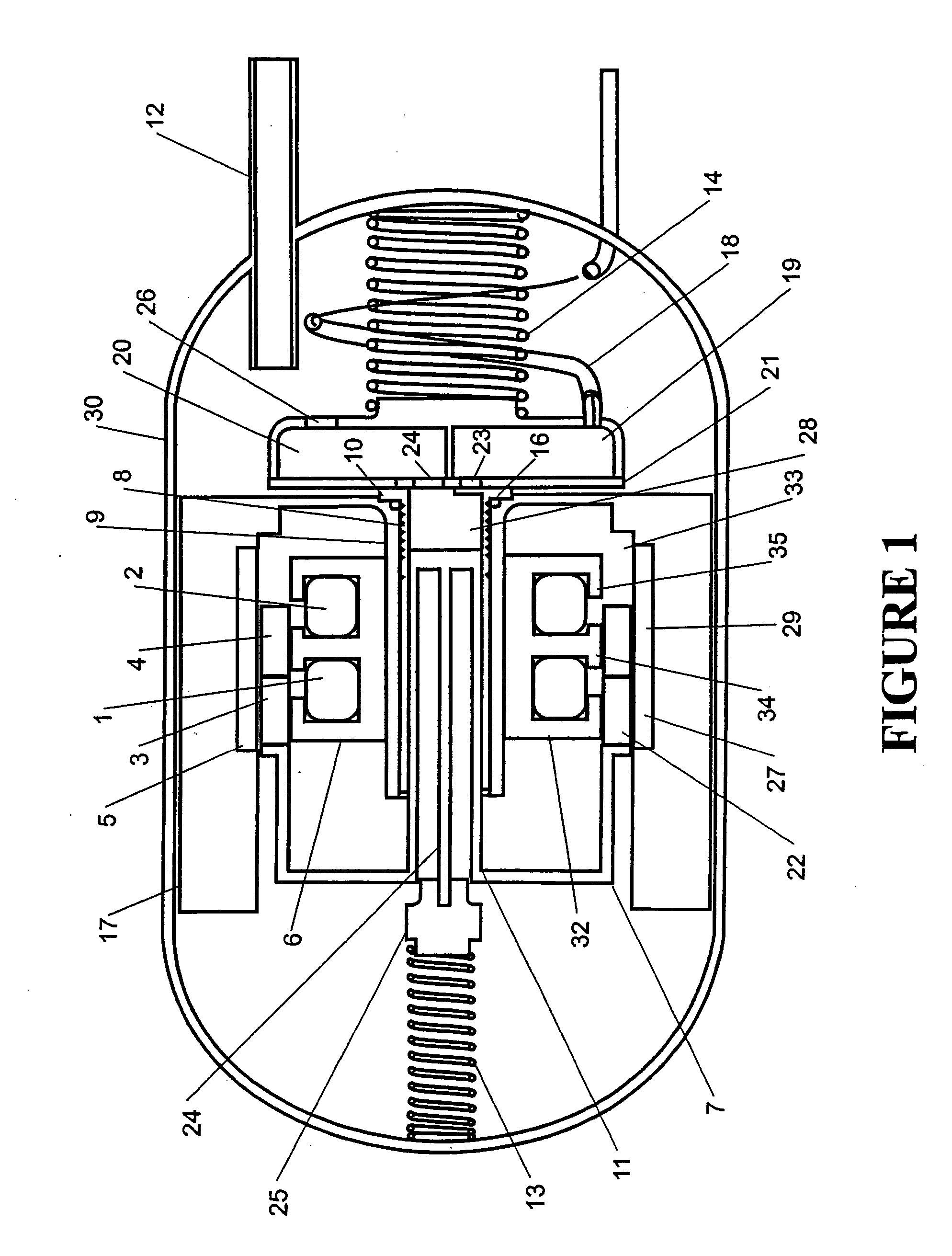
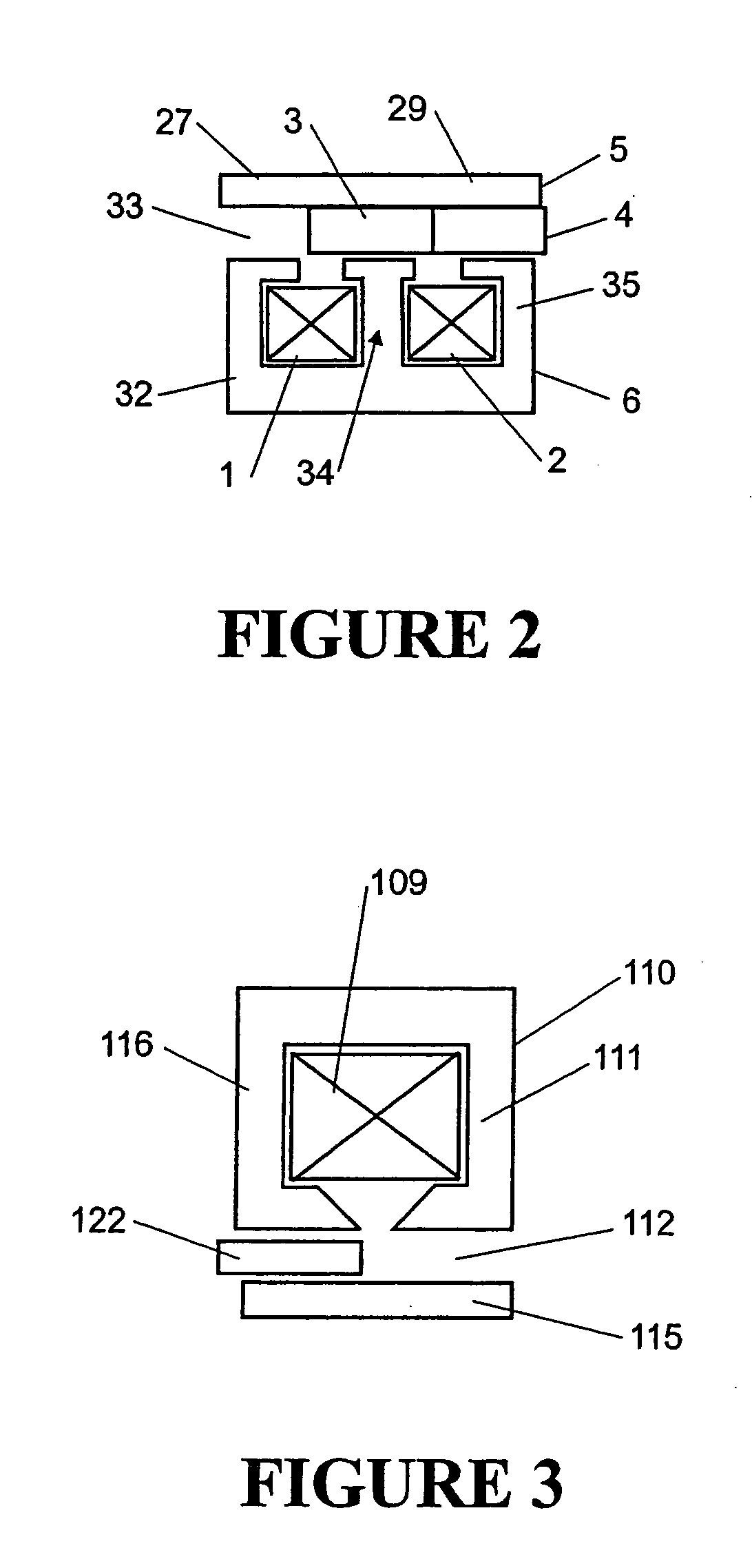
A linear compressor is a gas compressor where the piston moves along a linear track to minimize friction and reduce energy loss during conversion of motion. This technology has been successfully used in cryogenic applications which must be oilless. Suspension spring can be flexure type or coil type. Oil-free valved linear compressor allows the use of compact heat exchangers.
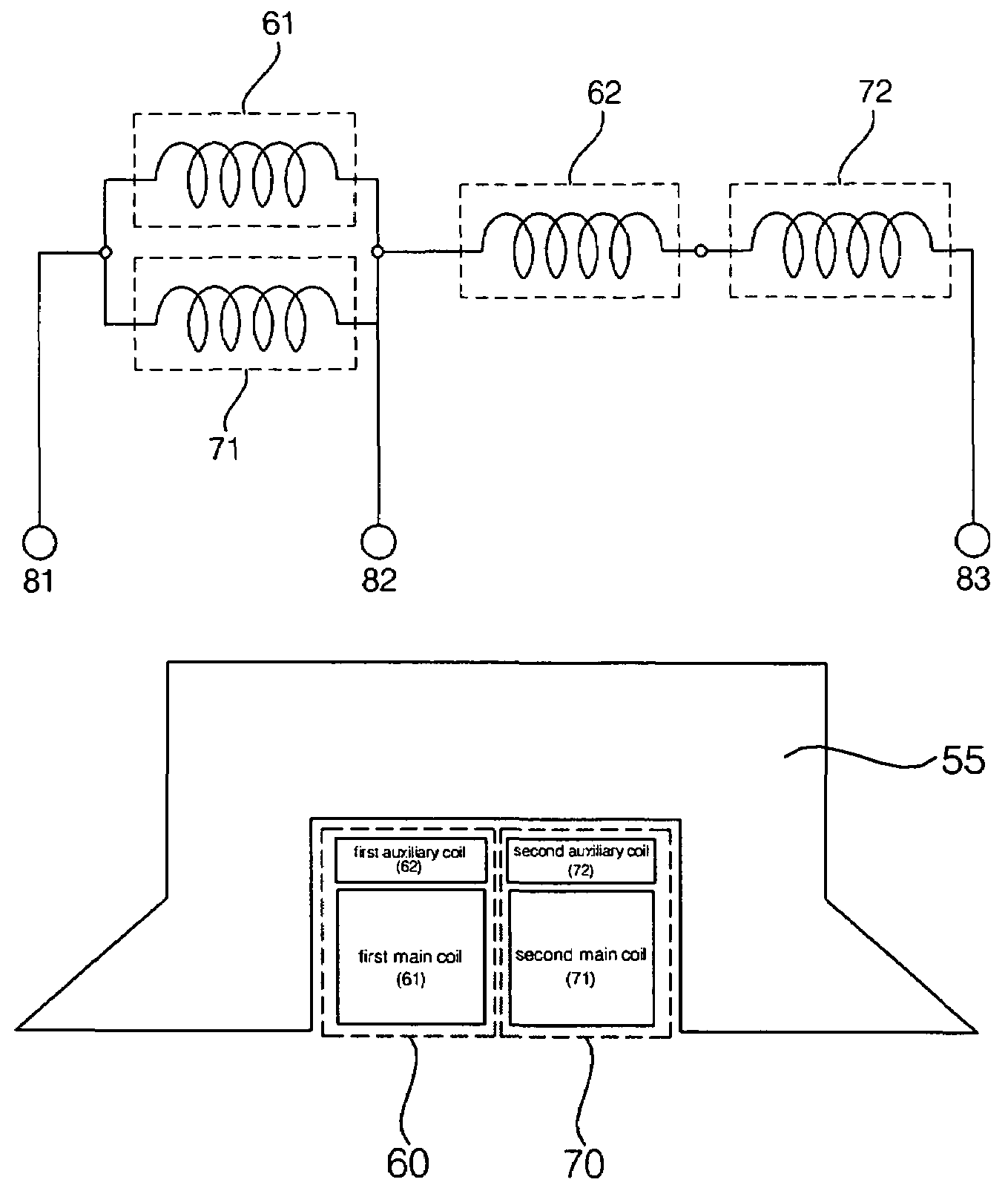
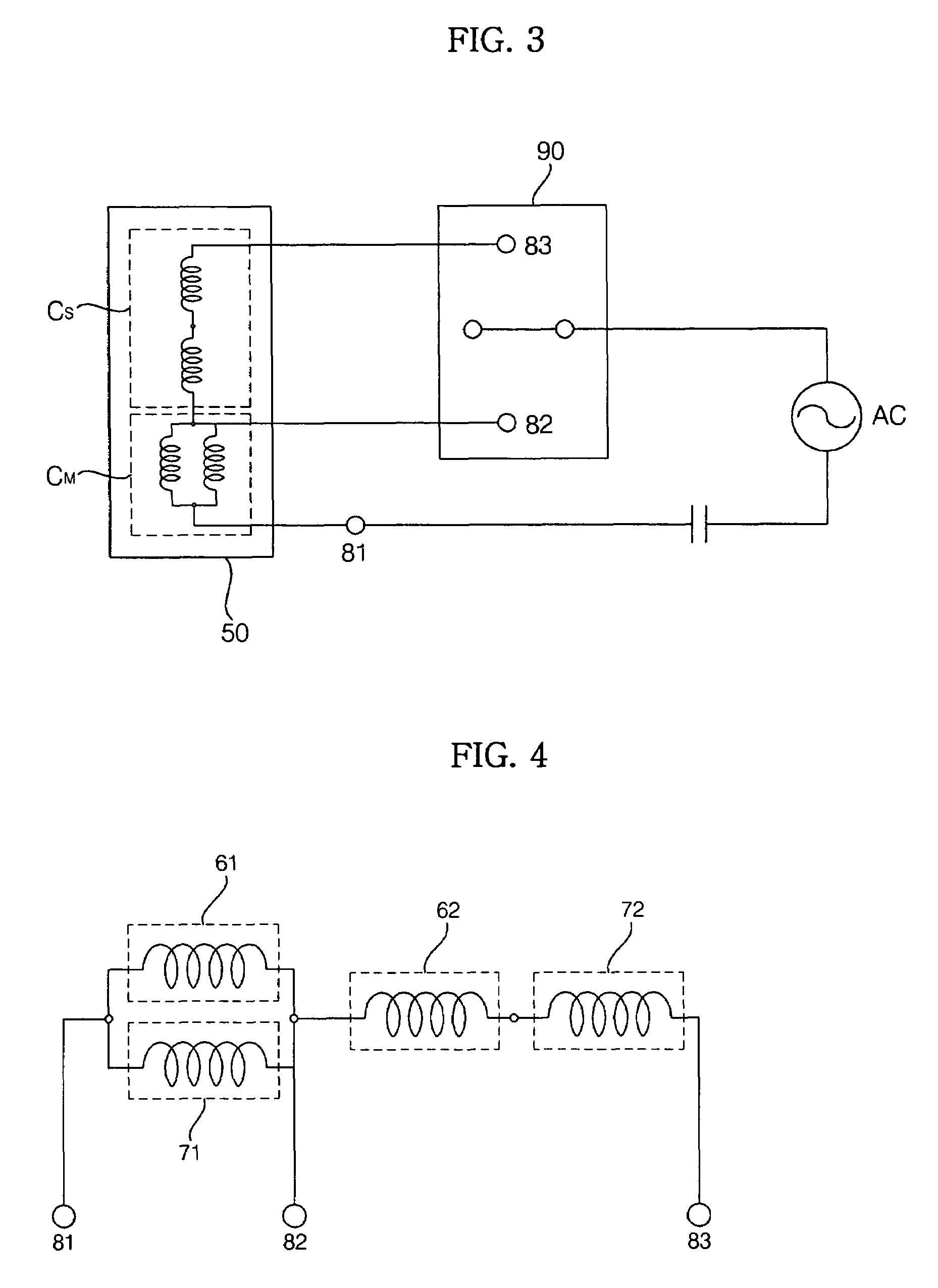
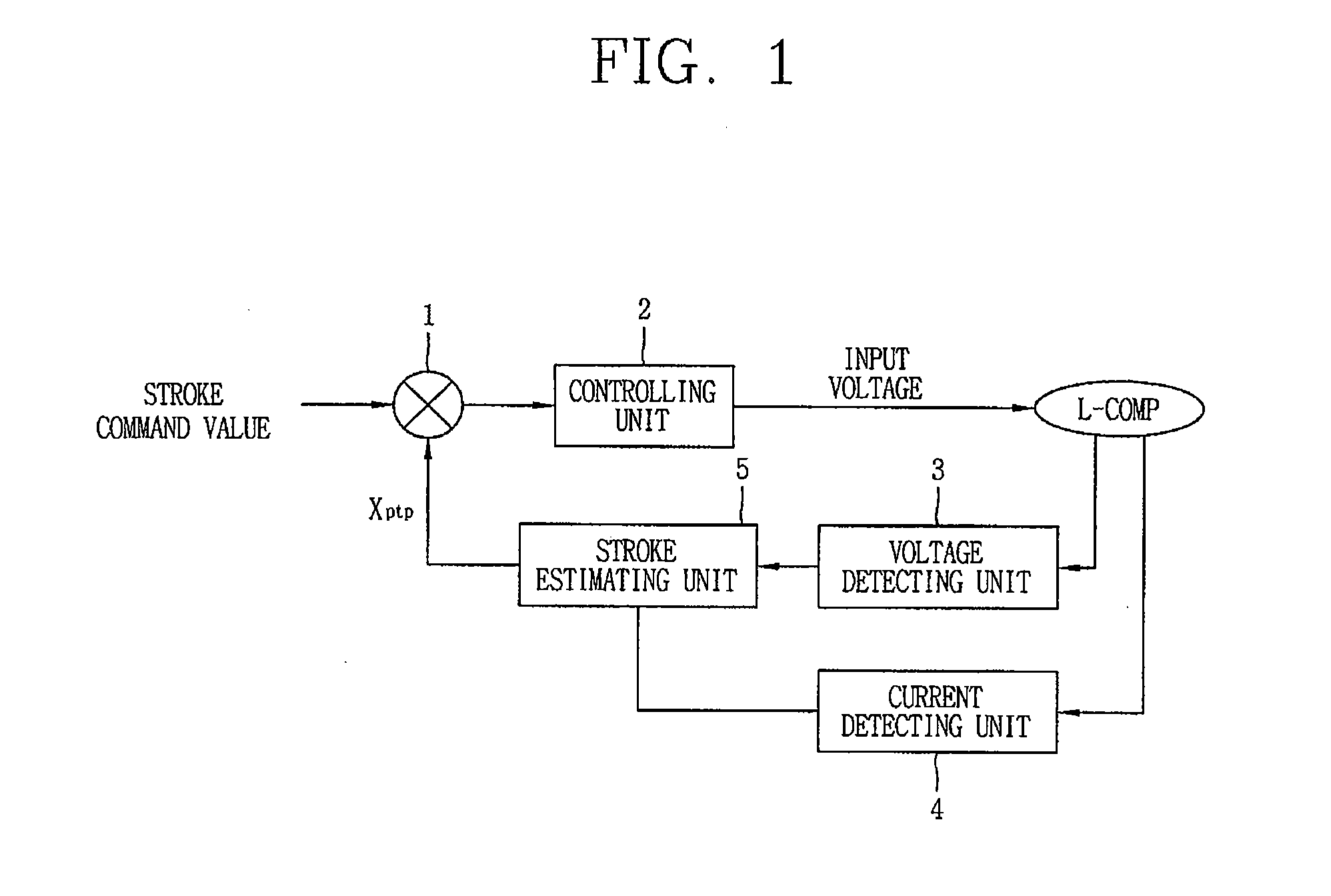
Linear motor and linear compressor using the same
ActiveUS7489055B2Improve efficiencySmall sizeAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlBobbinElectrical conductor
Disclosed herein is a linear motor in which a plurality of coil groups are connected in series or in parallel and driving power is applied to part or all of the coil groups according to load applied to the linear motor, thereby achieving improved motor efficiency with a reduced motor size. The linear motor includes a bobbin, the plurality of coil groups wound on the bobbin, the plurality of coil groups being connected in series or in parallel to allow the driving power to be applied to part or all of the coil groups, and a magnet adapted to be linearly reciprocated by a magnetic field produced by the coil groups depending on load current flowing through the coil groups. As a result of connecting the plurality of coil groups, which are formed of a plurality of coil conductors, in series or in parallel, the capacity of the coil groups is variable depending on the load of the motor, resulting in improved motor efficiency. Also, using the coil conductors having a small cross sectional area enables reduction in the size of the motor.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
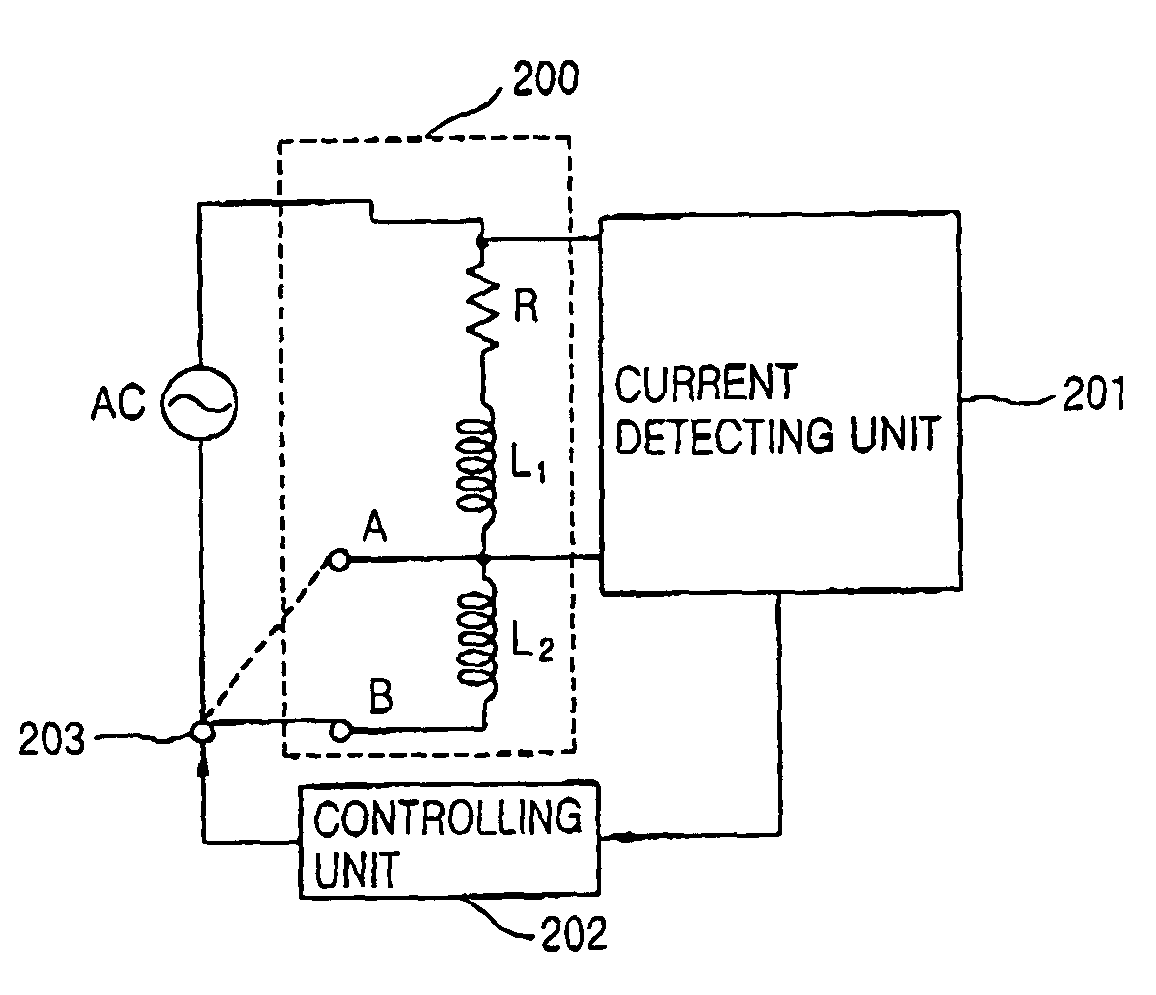
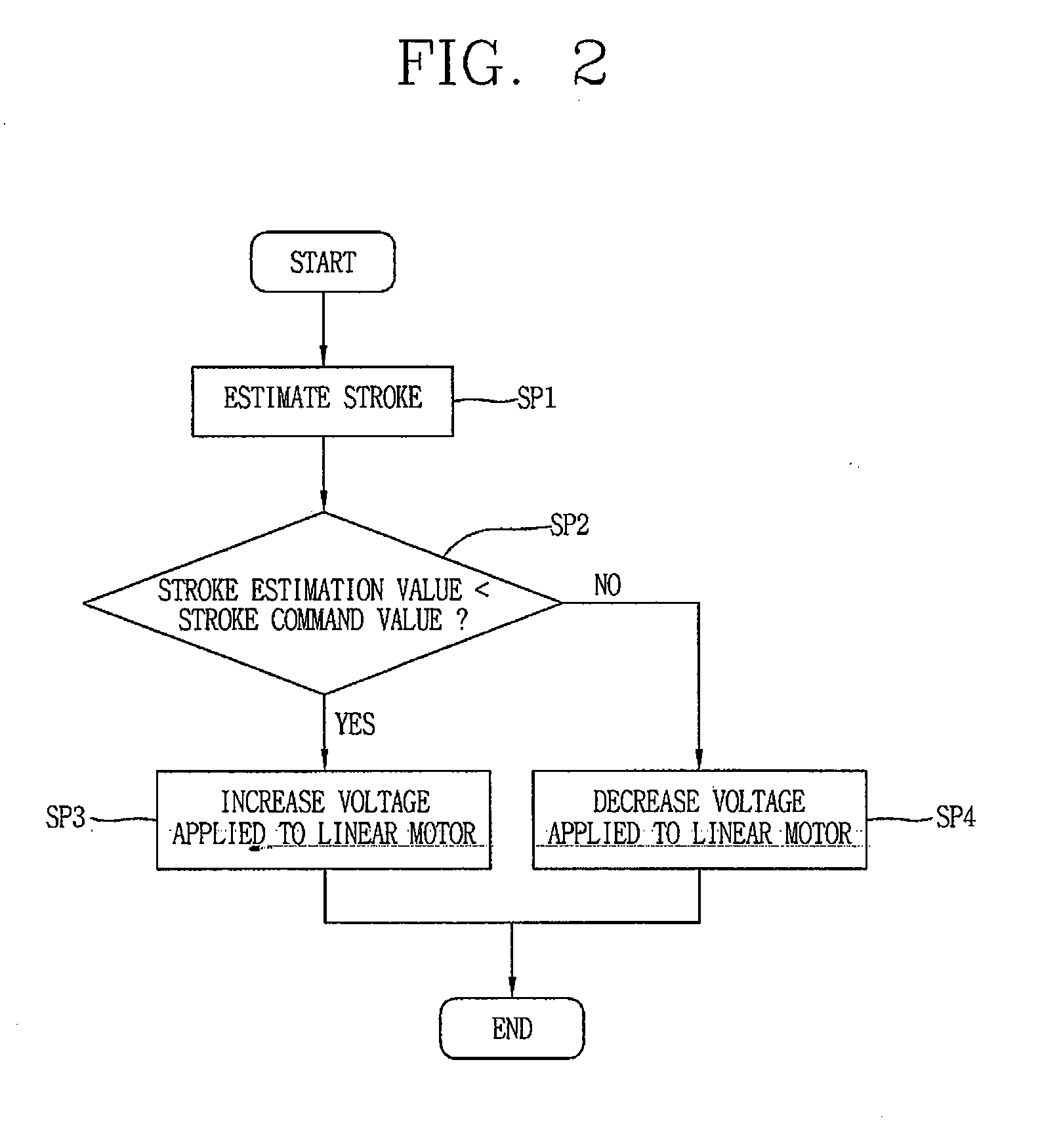
Apparatus and method for controlling driving of linear motor
InactiveUS6998736B2Increase efficiency of linearMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlControl signalLinear compressor
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Driving controlling apparatus for linear compressor and method thereof
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Linear compressor and apparatus to control the same
InactiveUS20050031470A1Most efficientDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlDriving currentResonance
A linear compressor and apparatus to control the linear compressor are provided which allows a frequency of a drive current supplied to a drive motor to synchronize with a resonance frequency varying according to a load fluctuation, in real time, thus obtaining a maximum efficiency of the linear compressor. The linear compressor includes a drive motor, a piston reciprocating by the drive motor and a control unit generating a reference current having a phase difference of 90° with respect to a displacement waveform of the piston and a frequency equal to the displacement waveform of the piston, and controls a drive current supplied to the drive motor to synchronize with a resonance frequency of the piston by synchronizing the drive current with the reference current.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System for adjusting resonance frequencies in a linear compressor
InactiveUS20060110259A1Low costIncreased energy lossFluid parameterPositive displacement pump componentsReciprocating motionLinear compressor
A system for adjusting resonant frequencies in a linear compressor comprising, in the interior of a shell: a linear motor: a cylinder; a piston reciprocating inside the cylinder; and an actuating means operatively coupling the piston to the linear motor, said system comprising: a detecting means to detect a load imposed to the linear motor, in an operational condition of the latter related to the gas pressure in the discharge thereof; and a frequency adjusting means operatively associated with the detecting means and with the resonant assembly, in order to define, as a function of said operational condition, a frequency adjustment, by varying at least one of the values related to the mass of the resonant assembly and to the average stroke of the piston, to a value of the mechanical resonance frequency corresponding to the electrical supply frequency.
Owner:EMPRESA BRASILEIRA DE COMPRESSORES SA (EMBRACO)
Linear motor, and linear compressor using the same
A linear motor of the present invention has: a stator having a stationary iron core and a magnet wire; a mover having a moving iron core and a magnet; and a plate-shaped elastic member for supporting the mover in a manner to rock in the rocking directions. This construction eliminates a sliding portion for supporting the mover so that it can reduce the loss, which might otherwise accompany the reciprocation of the mover. Moreover, a linear compressor using this linear motor is high in efficiency and reliability.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Sensor-less control method for linear compressors
ActiveUS20070196214A1Optimal control methodAllow optimizationDC motor speed/torque controlElectric motor speed/torque regulationTemperature controlPower flow
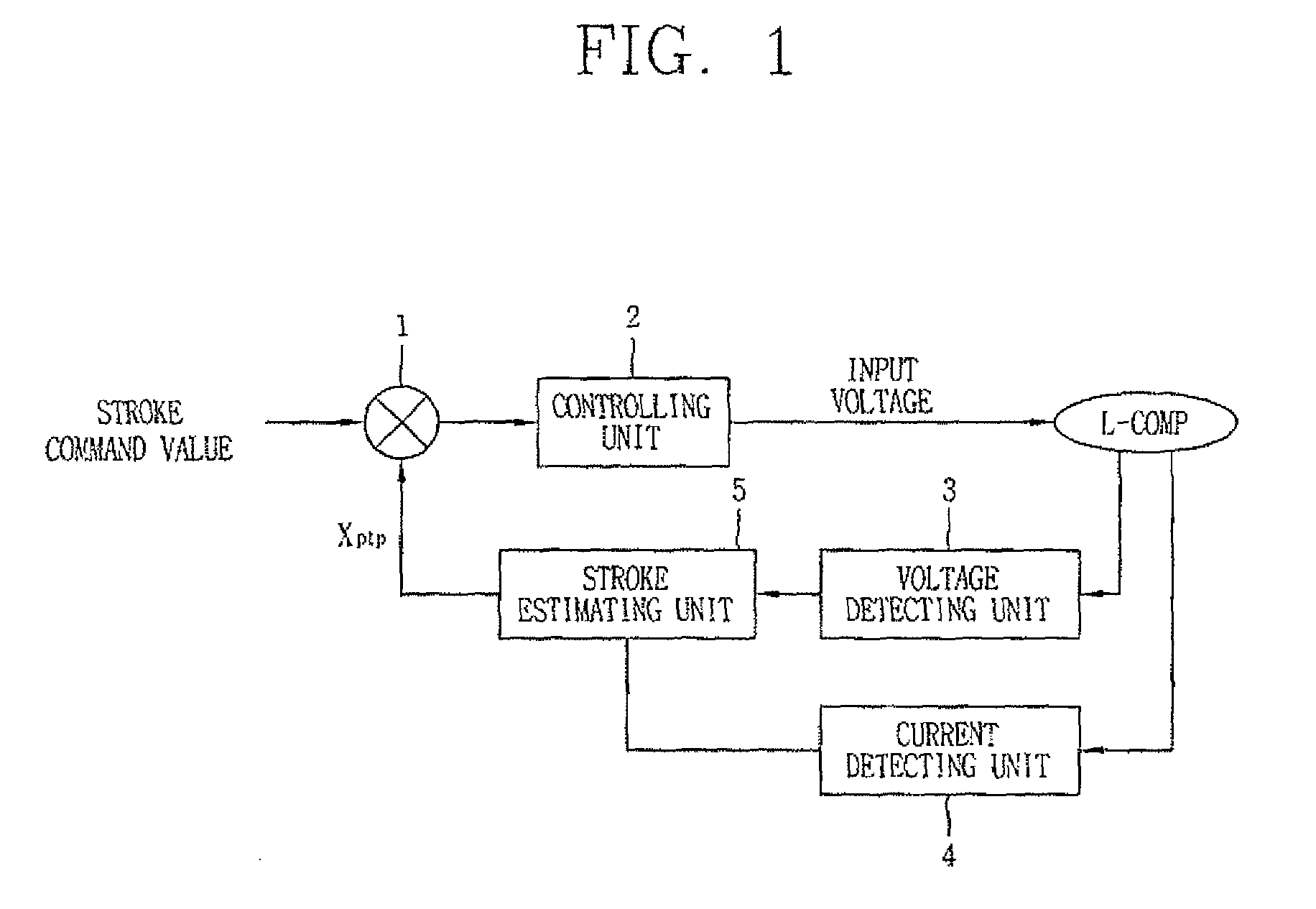
A method of protecting a cylinder of a compressor comprising a piston, a linear permanent magnet (PM) having a coil and a magnet, and a sensor-less control of the PM for moving the piston in and out of the cylinder. The method including the steps of receiving a reference position of the piston from a temperature control loop; deriving a compensation voltage and a load spring effect information from a current through the coil; providing a model input voltage to a model of a mechanical structure of the compressor for predicting position of the piston, the model input voltage comprising a first voltage derived from the reference position; a compressor input voltage comprising the first voltage and the compensation voltage; and using a position control loop to recognize when the maximum compression ratio is desired and controlling the piston to achieve maximum compression ratio without causing damage to the discharge valve.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
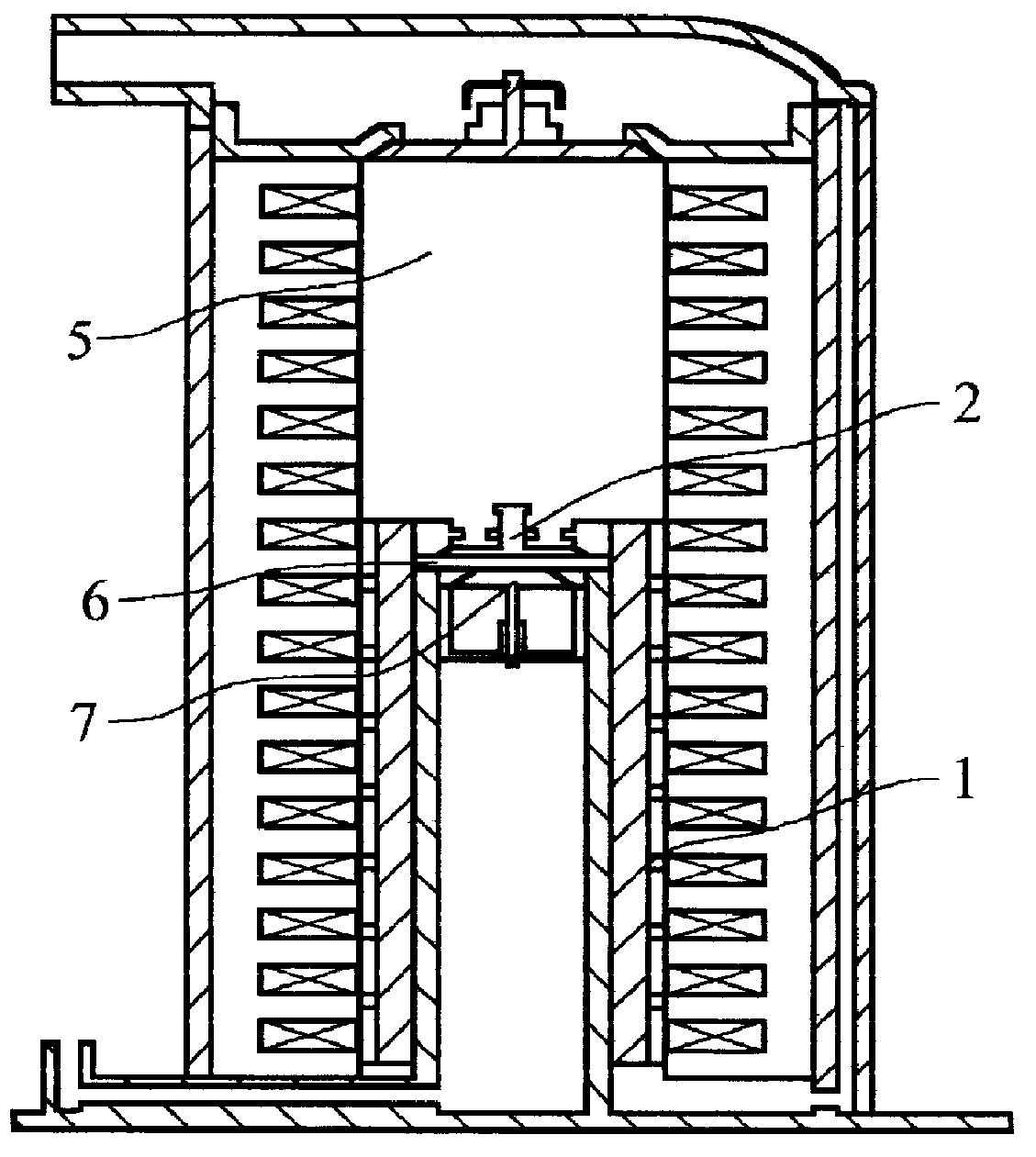
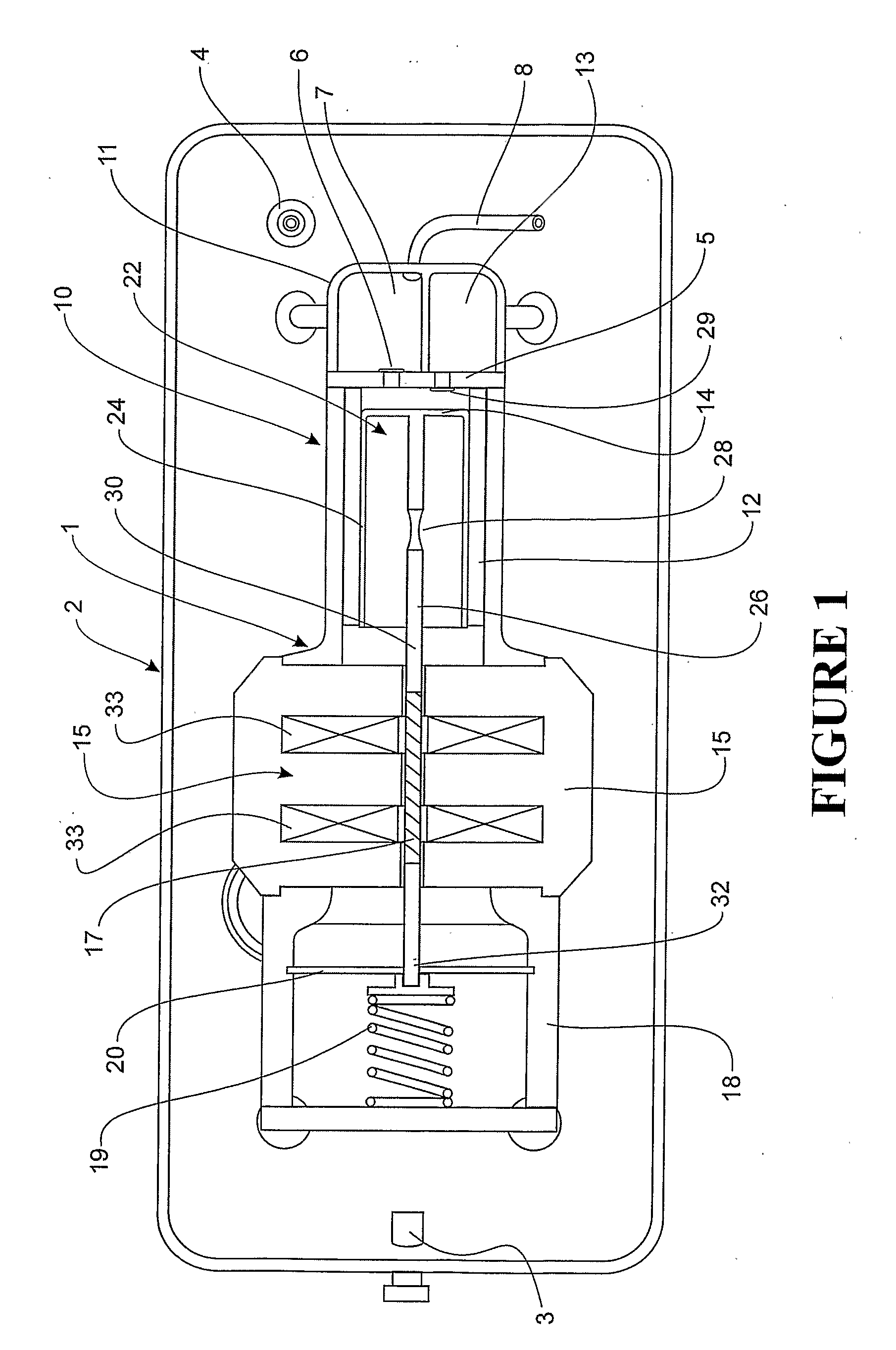
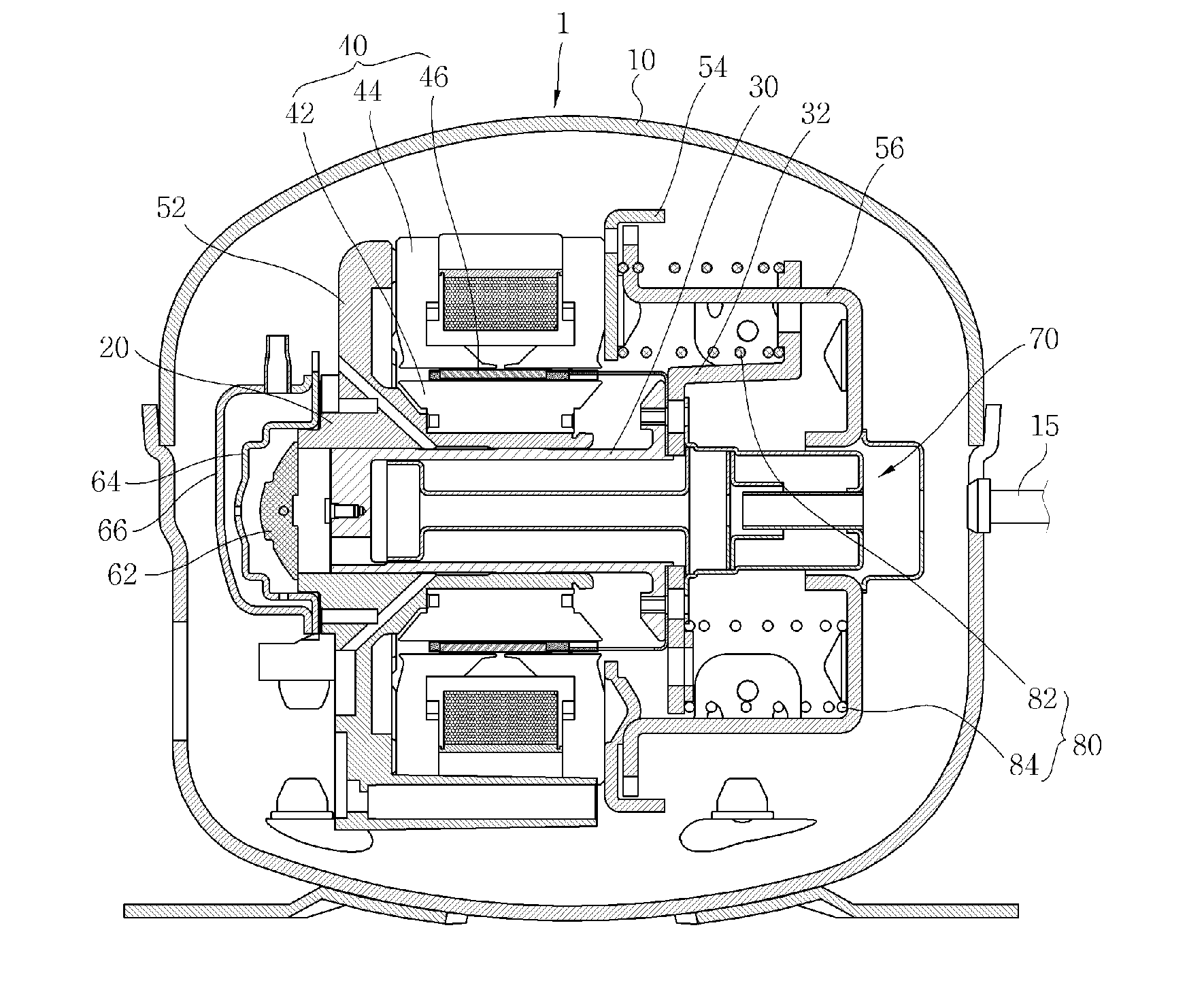
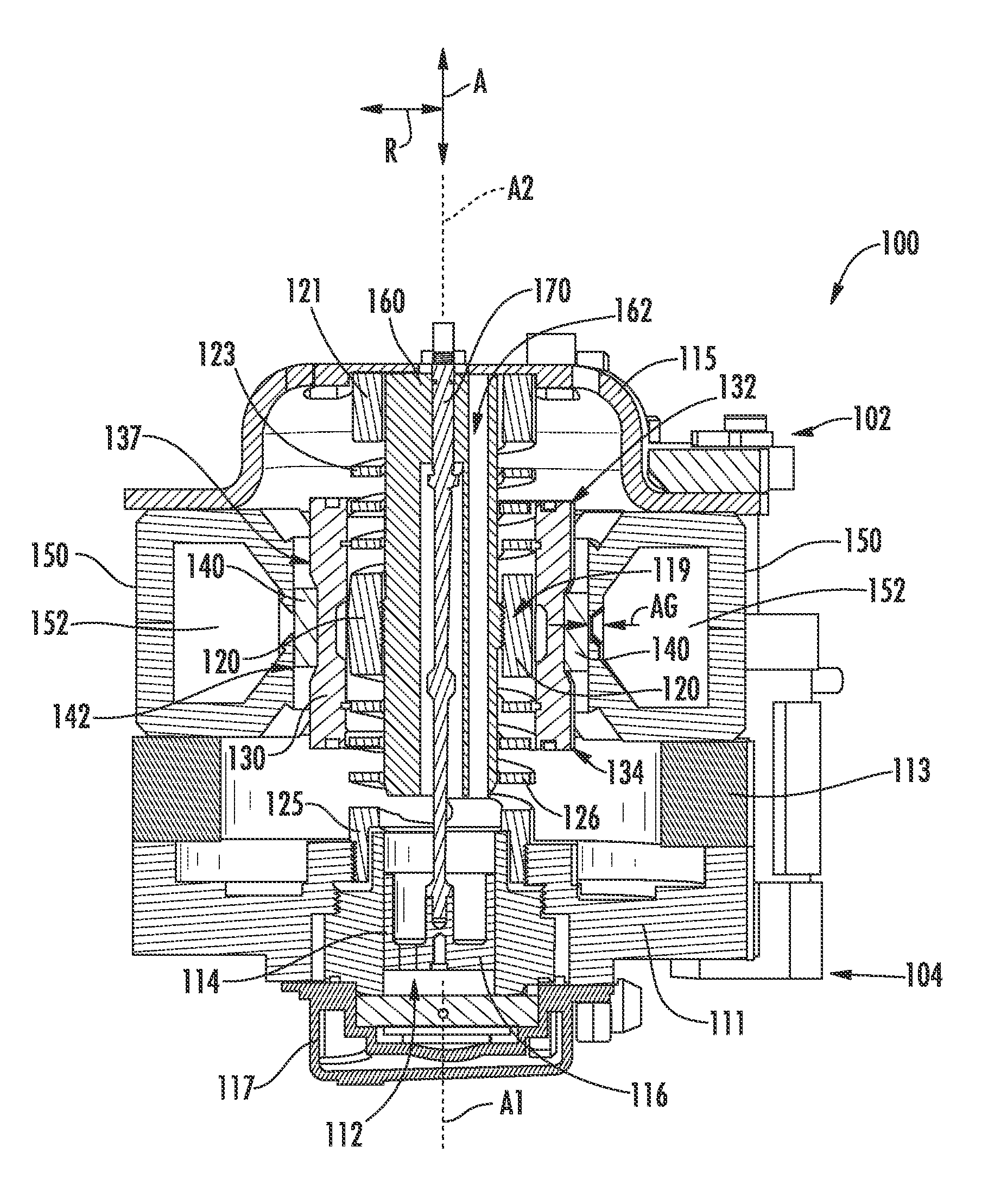
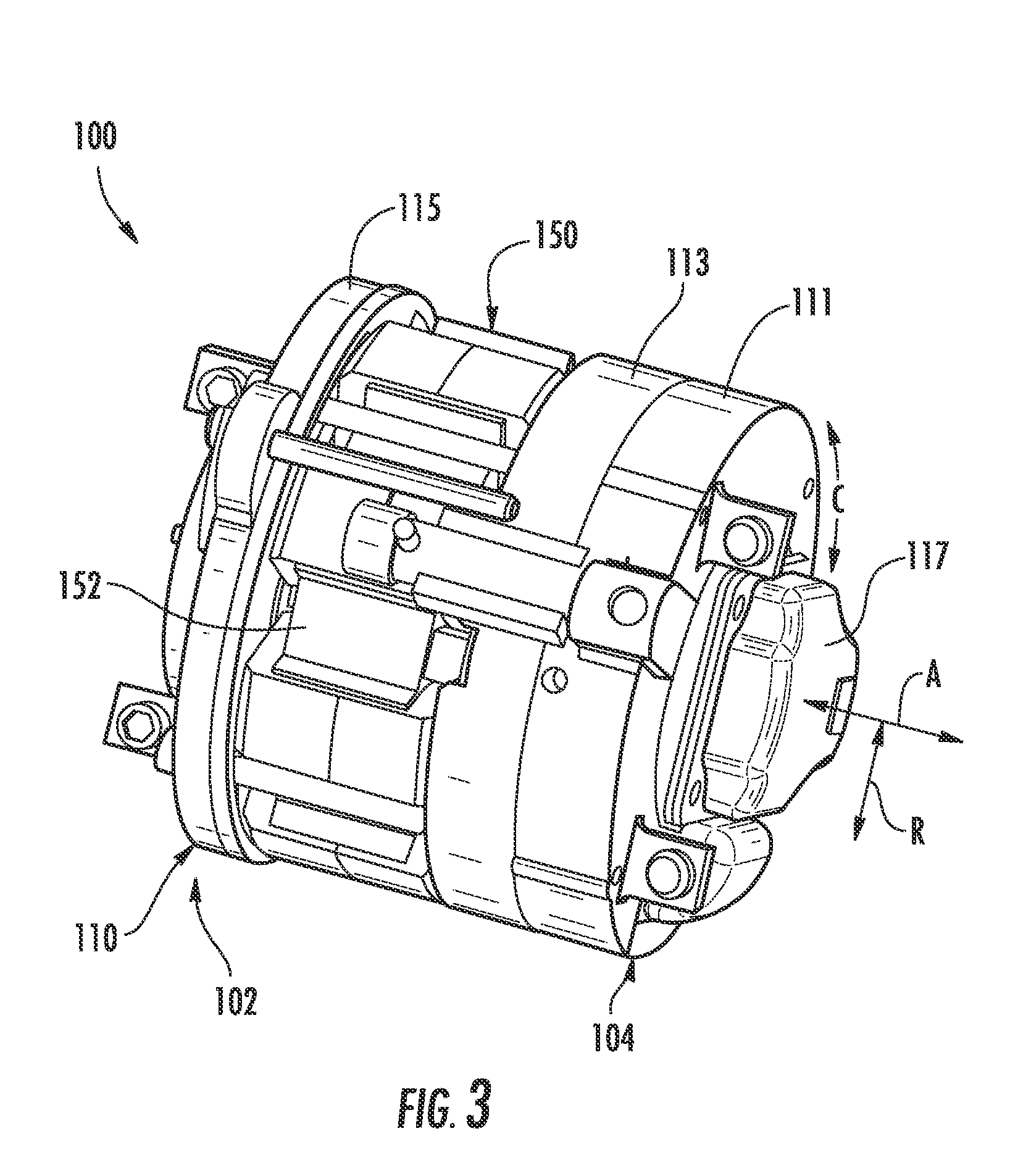
Linear compressor
InactiveUS20050175473A1Small sizeEffective absorptionEngine sealsPositive displacement pump componentsLinear compressorReciprocating motion
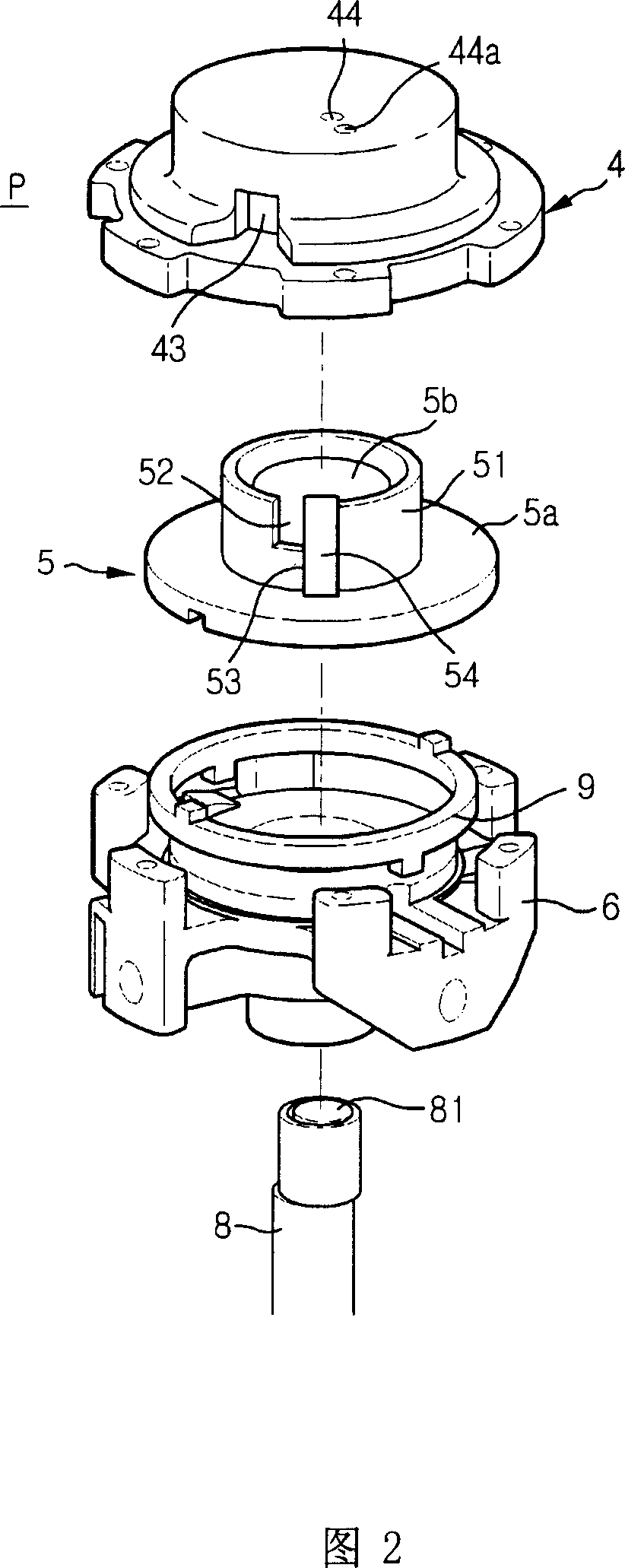
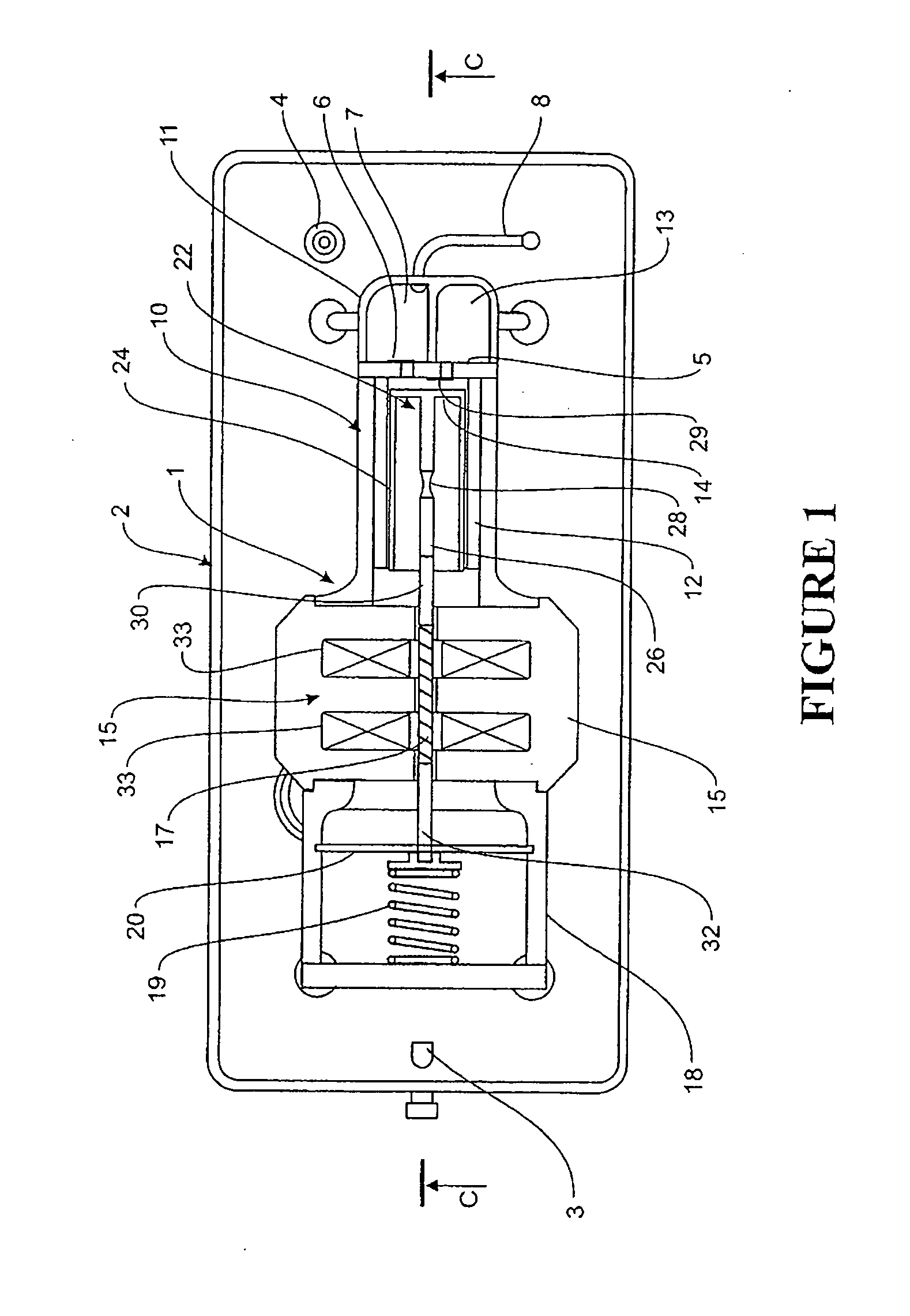
Disclosed herein is a linear compressor. The linear compressor comprises a hermetically sealed container having an inlet port and an outlet port formed at both ends thereof. In the hermetically sealed container is mounted a compression unit to compress and discharge a fluid. The compression unit comprises a linear motor, a cylinder, and a piston disposed in the cylinder such that the piston is linearly reciprocated in the cylinder by means of the linear motor. The linear compressor further comprises a discharging unit assembly disposed in front of the outlet port at the outside of the hermetically sealed container such that a fluid compressed in the cylinder is discharged through the discharging unit assembly, a container-supporting stand to support the hermetically sealed container at the outside of the hermetically sealed container, and shock-absorbing springs disposed between the container-supporting stand and the hermetically sealed container for performing shock-absorbing operations. According to the present invention, the size of the hermetically sealed container is reduced, whereby the linear compressor is miniaturized, and thus the linear compressor is designed without limits.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Linear compressor
ActiveUS8241015B2Reduced dimensionPositive displacement pump componentsFlexible member pumpsReciprocating motionLinear compressor
Owner:EMBRACO IND DE COMPRESSORES E SOLUCOES EM REFRIGERACAO LTDA
Linear compressor or pump with integral motor
InactiveUS6015270AEasy to operateFew moving partsPositive displacement pump componentsPiston pumpsLinear compressorWorking fluid
A two stage compressor or pump with integral electronically controlled multiphase linear motor incorporates a cup shaped moving piston as a stator. The linear motor body has an intake head with valve fitted at the end adjacent to the closed end of the cup shaped piston. A discharge head with a central discharge tube extending into the hollow center of the cup shaped moving piston is fitted to the opposite end of the motor body. As the piston reciprocates it draws the working fluid in through the intake valve, compresses and transfers it through an interstage valve in the closed end of the moving piston into a second variable volume chamber formed by the inside of the cup shaped piston and the discharge tube which acts as a fixed piston, and then further compresses and transfers it out through a valve in the discharge tube. While the design is particularly well suited for use as a compressor in air conditioning and refrigeration systems, it can also be used as a pump.
Owner:AIR CONDITIONING TECH
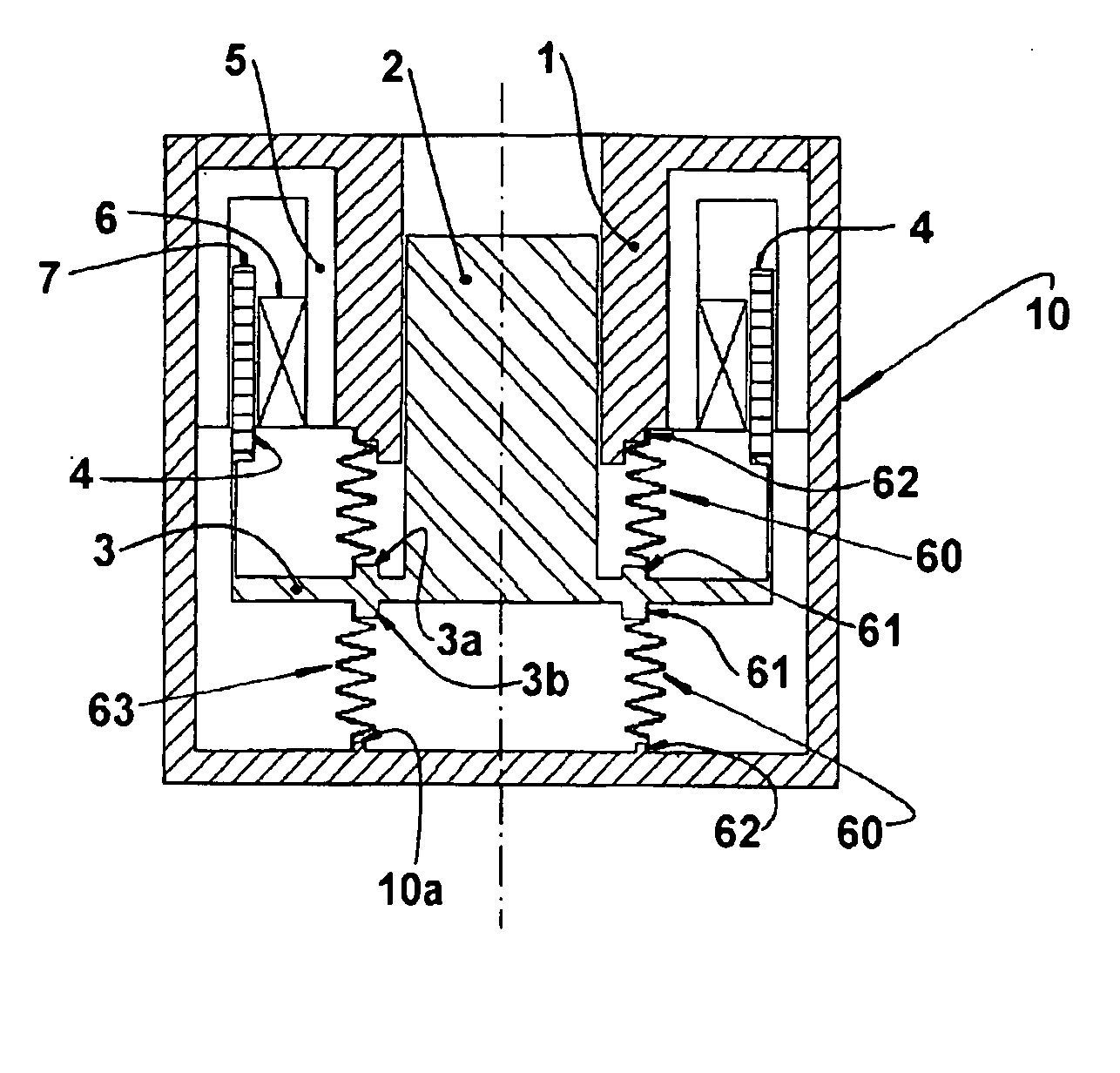
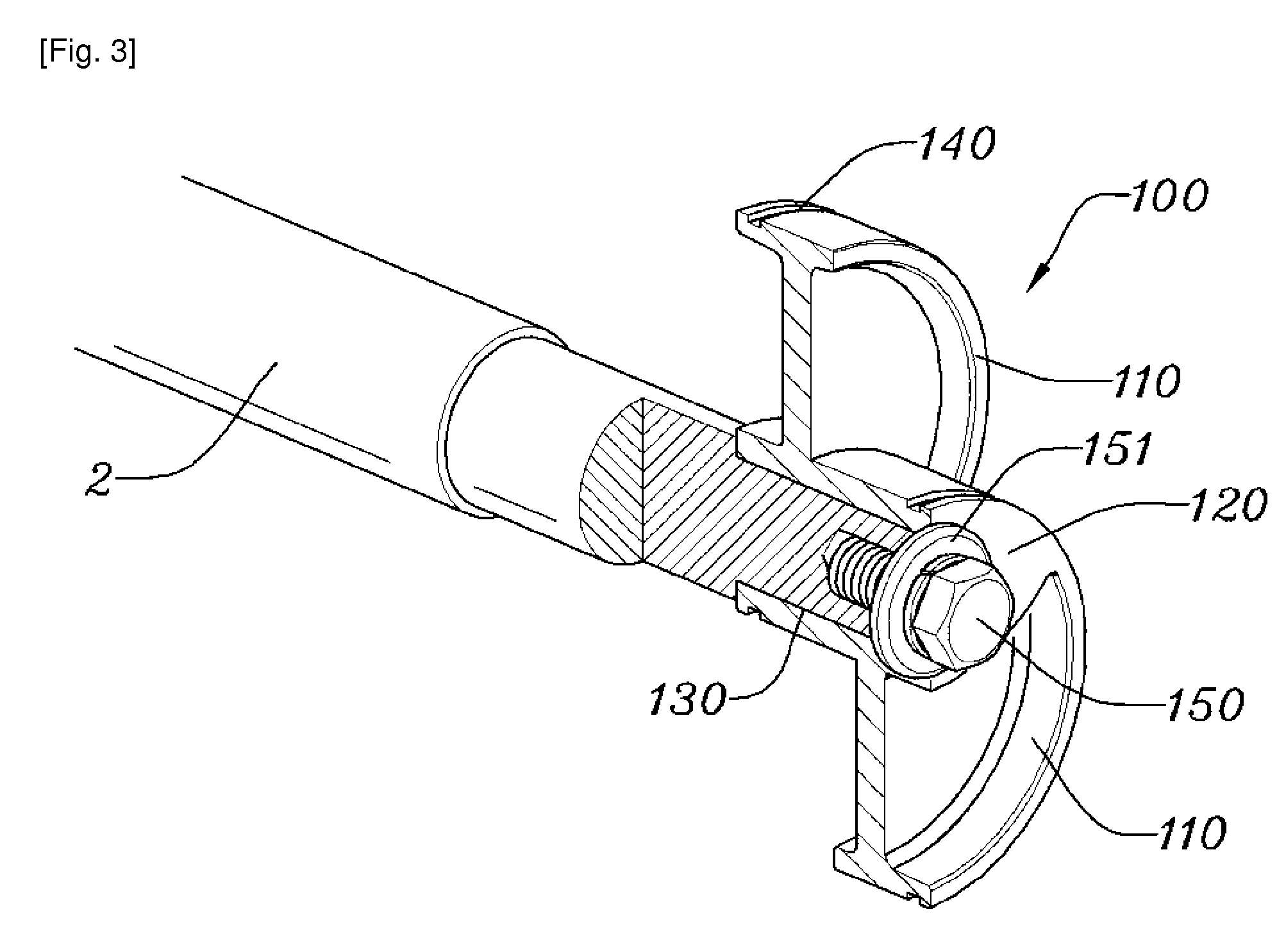
Resonant arrangement for a linear compressor
InactiveUS20050163635A1Simple and reliable processLow costPositive displacement pump componentsPiston pumpsReciprocating motionLinear compressor
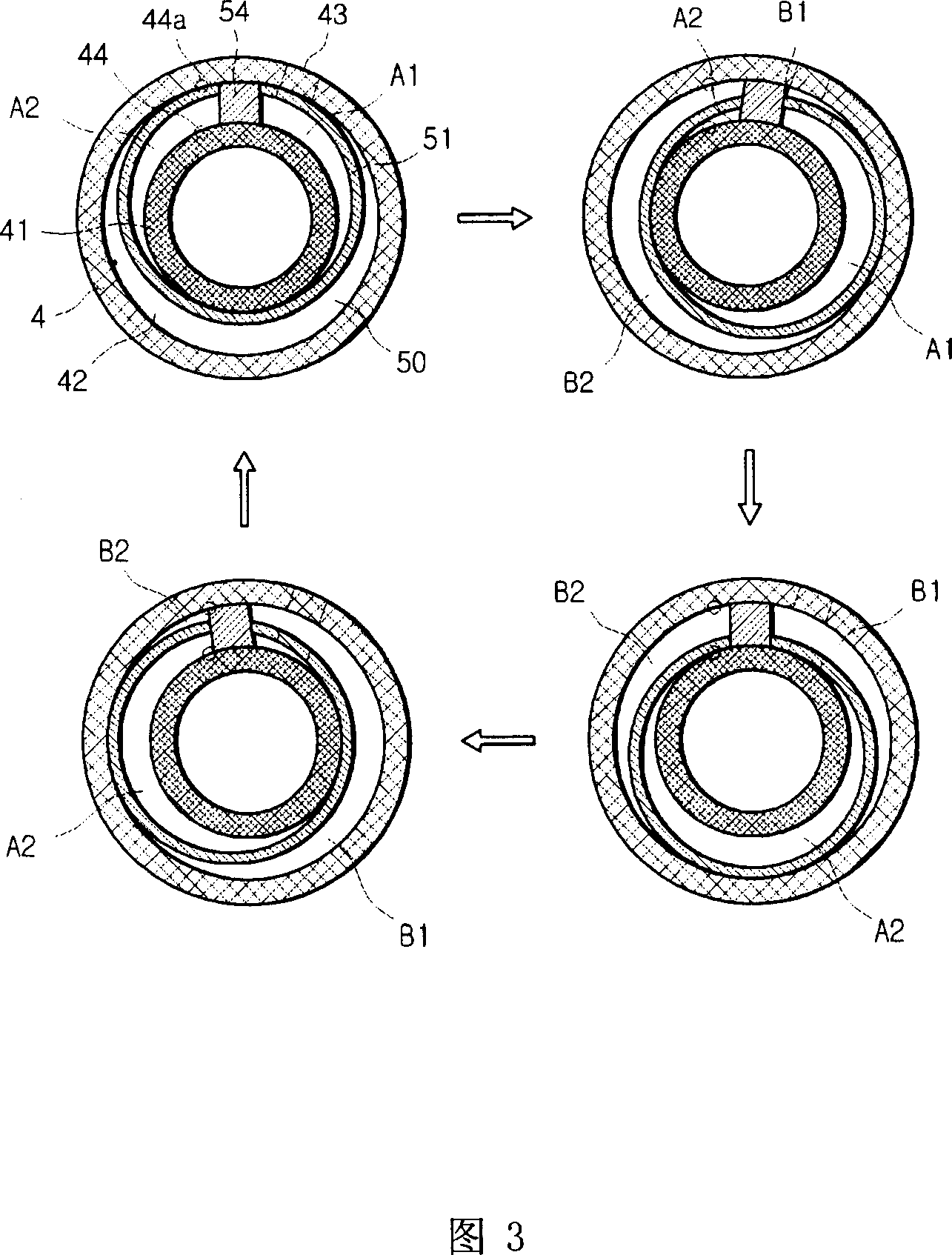
A resonant arrangement for a linear compressor, comprising a non-resonant assembly formed by a motor and a cylinder (1); a resonant assembly formed by a piston (2) reciprocating inside the cylinder (1); an actuating means (3) operatively coupling the piston (2) to the motor, and at least one spring means presenting an elongated tubular body (50) which is coaxial to the axis of the piston (2) and is operatively coupled to the actuating means (3) and to the non-resonant assembly, said tubular body (50) having at least part of the extension therof folded in circumferential sectors (53), each circumferential sector (53) being elastically deformed in the axial direction upon displacement of the piston (2).
Owner:EMPRESA BRASILEIRA DE COMPRESSORES SA (EMBRACO)
Linear compressor
InactiveUS20050135946A1Reduce stiffnessPositive displacement pump componentsPiston pumpsReciprocating motionLinear compressor
A linear compressor includes: a cylinder block forming a compressing chamber; a piston reciprocatably provided in the compressing chamber; a reciprocating member connected to the piston to reciprocate with the piston as a single body; a driver driving the reciprocating member to reciprocate; and a resonance spring including a first connecting part formed with a plurality of first connecting holes to permit connection to the cylinder block, and a second connecting part that is provided inside of the first connecting part and formed with a second connecting hole to permit connection to the reciprocating member to reciprocate with the reciprocating member. A plurality of arms spaced apart from one another are disposed between the first connecting part and the second connecting part, each of the arms including a first end connected to the first connecting part to be positioned between the plurality of first connecting holes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
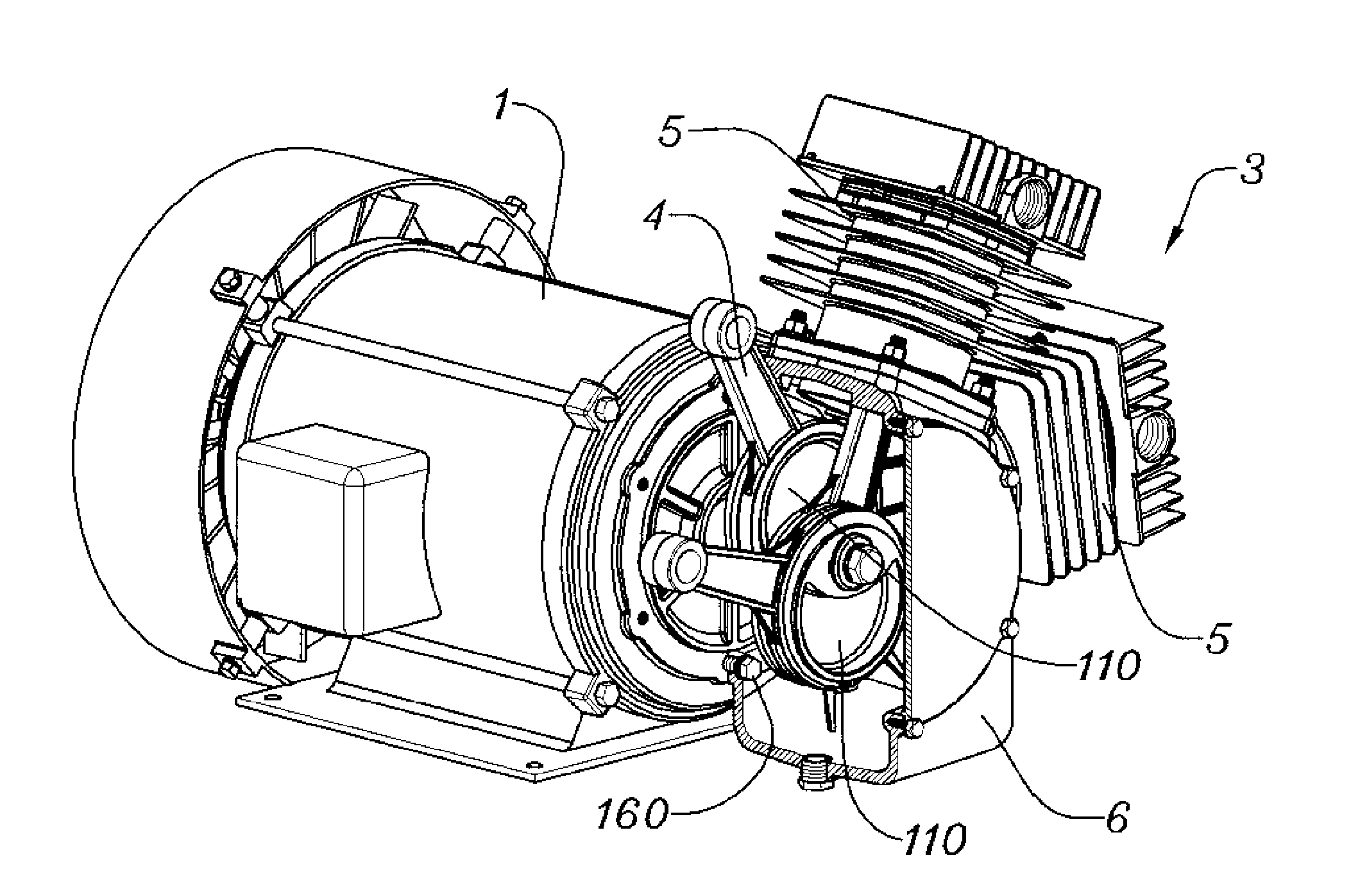
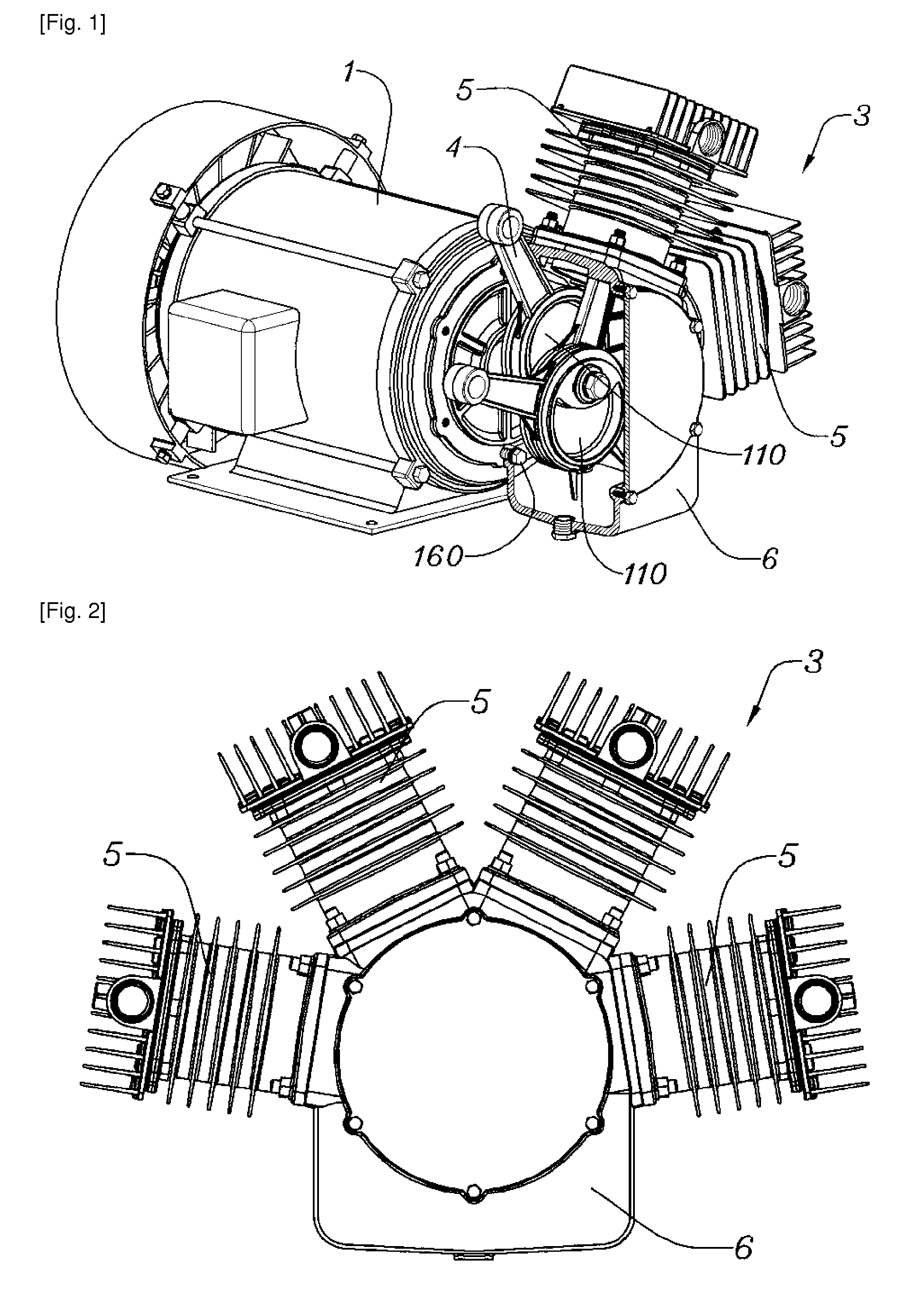
Direct crankshaft of air compressor
InactiveUS8388317B2Configured more compactlyCompact configurationPositive displacement pump componentsPortable liftingCompression PumpEngineering
There is provided a direct crankshaft of an air compressor for producing compressed air in which a crankshaft is implemented by two crank plates integrally overlapped with each other so that compression cylinders can be arranged in the radial direction to exhibit an excellent air cooling performance, top dead centers and bottom dead centers of the compression cylinders are symmetrically arranged so that the cancellation between pressurizing and vacuuming phenomena and the running of a motor can be smoothly performed, and the motor is integrated with a compression pump so that various driving components such as belts, pulleys, covers, and the like are eliminated and manufacturing costs are remarkably reduced. The direct crankshaft includes crank plates integrated with each other to form an overlapping unit. The overlapping unit has a shaft coupling hole through which a motor shaft penetrates such that the direct crankshaft is directly coupled with a motor.
Owner:KOHANDS CO LTD
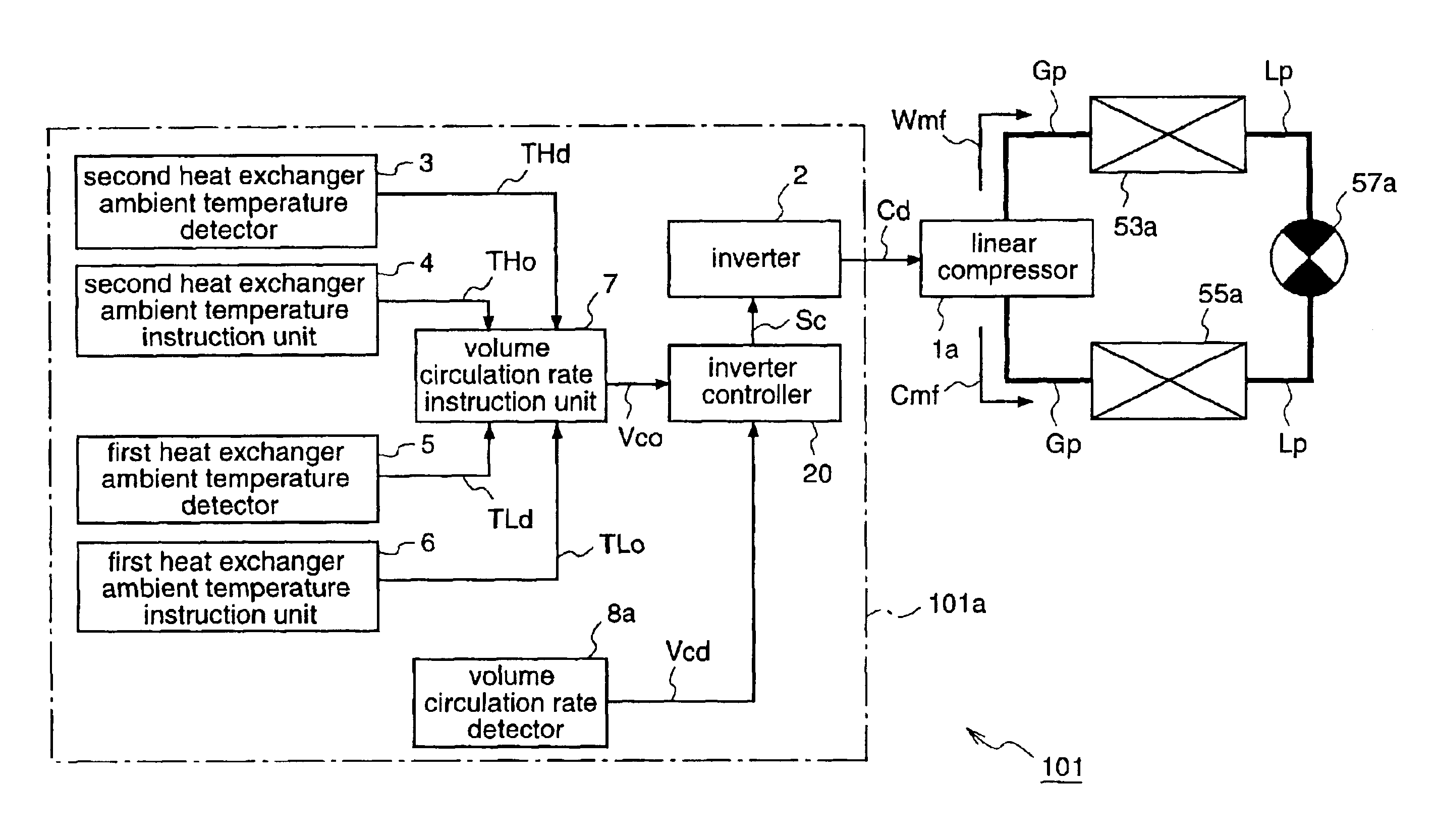
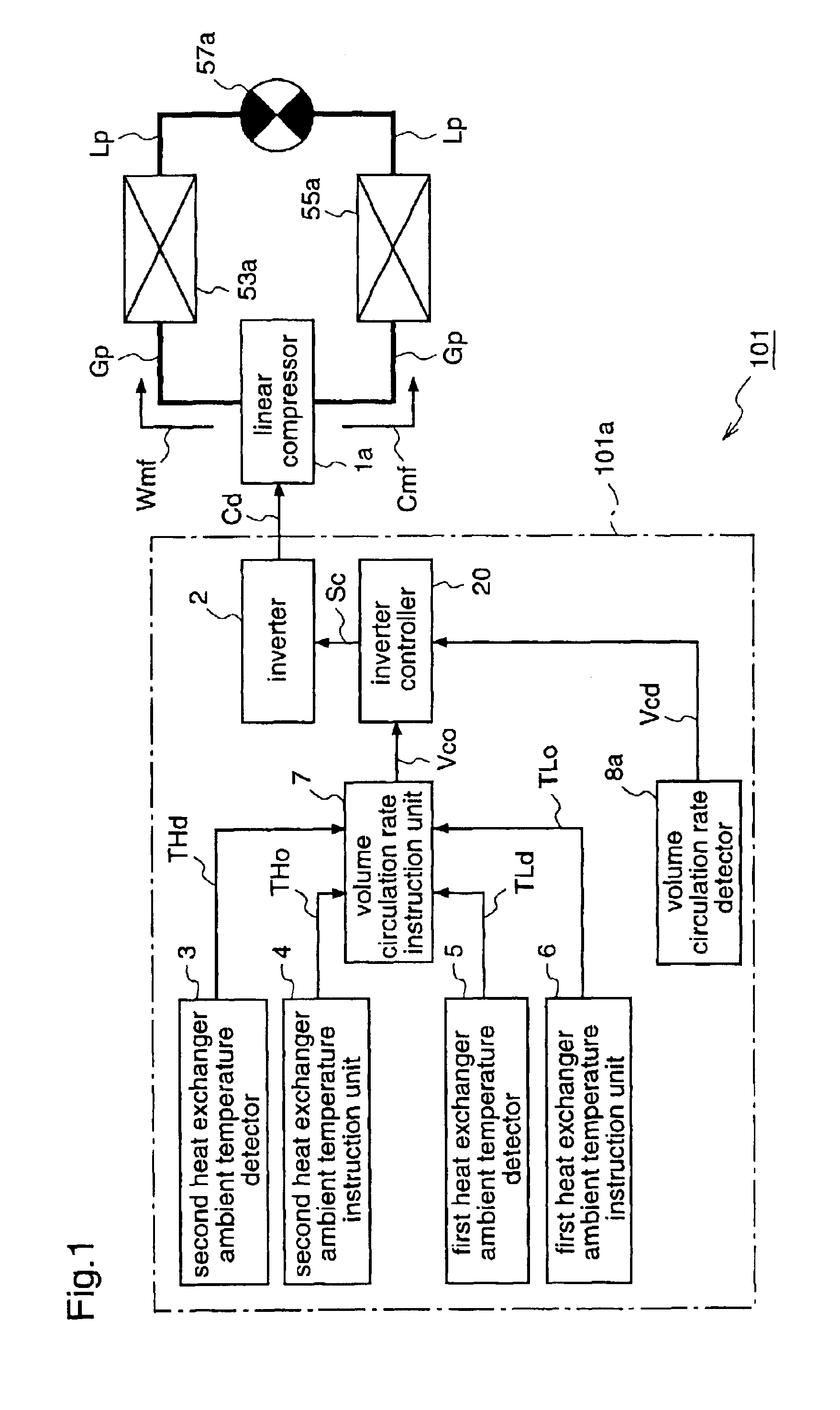
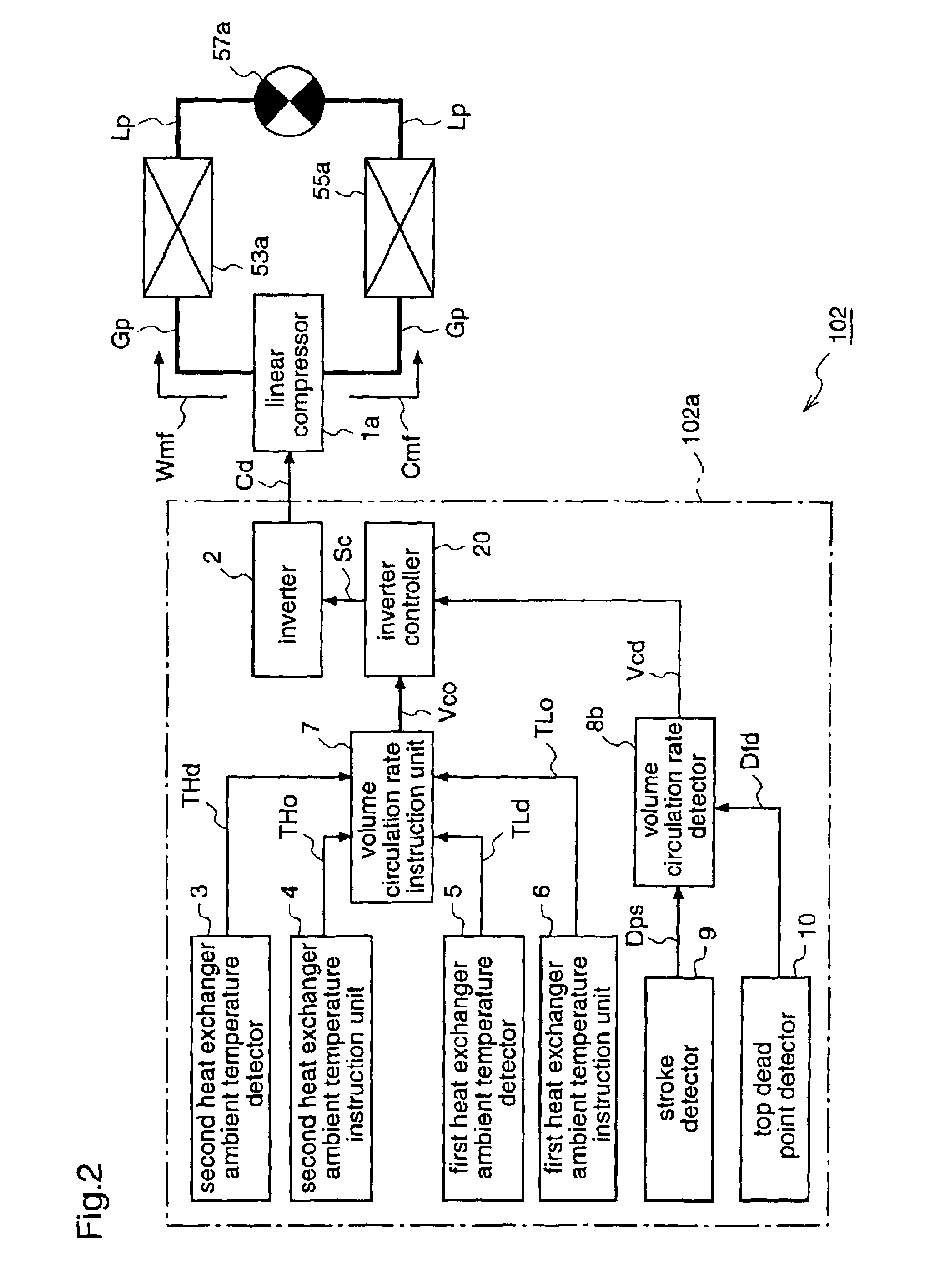
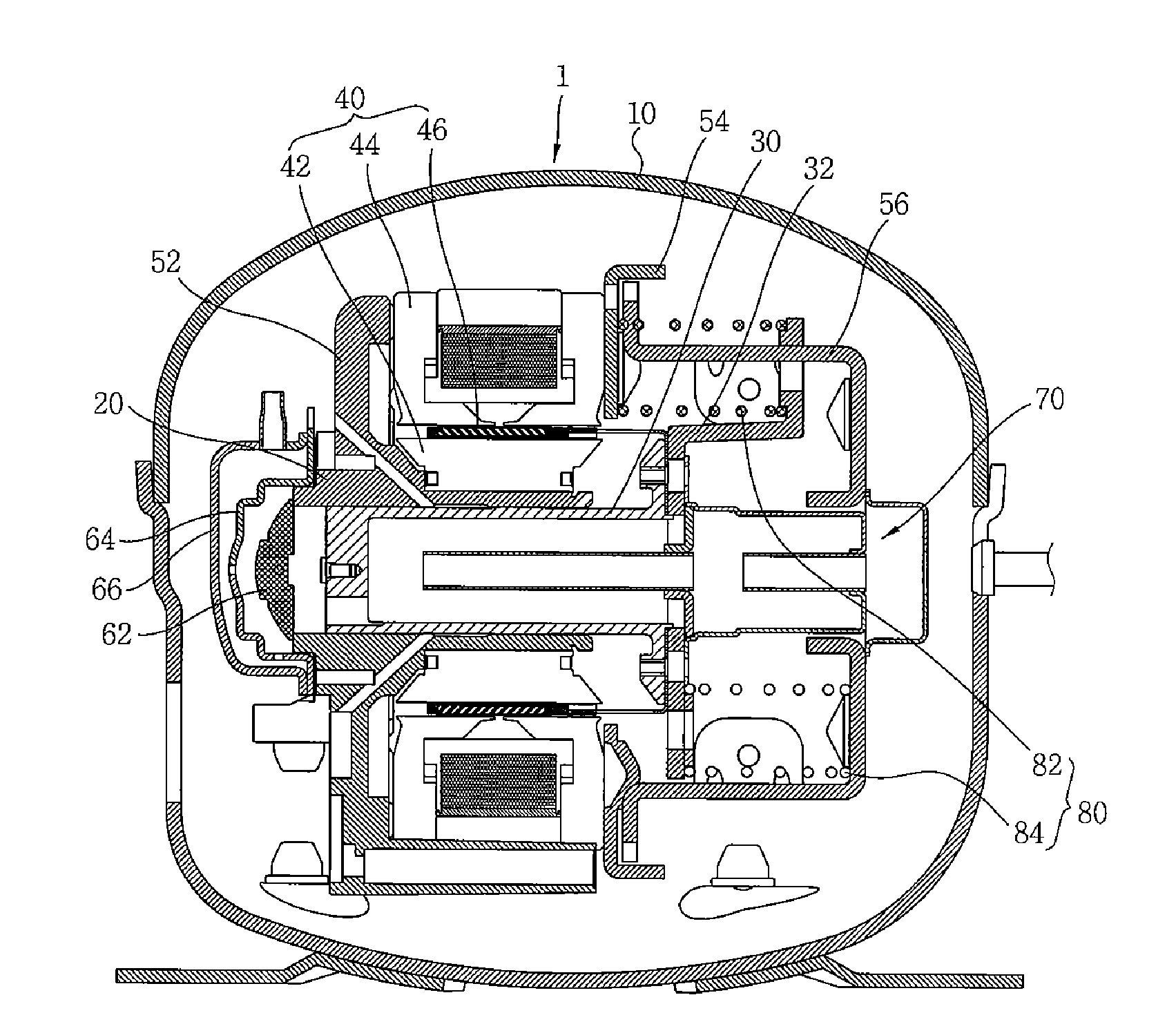
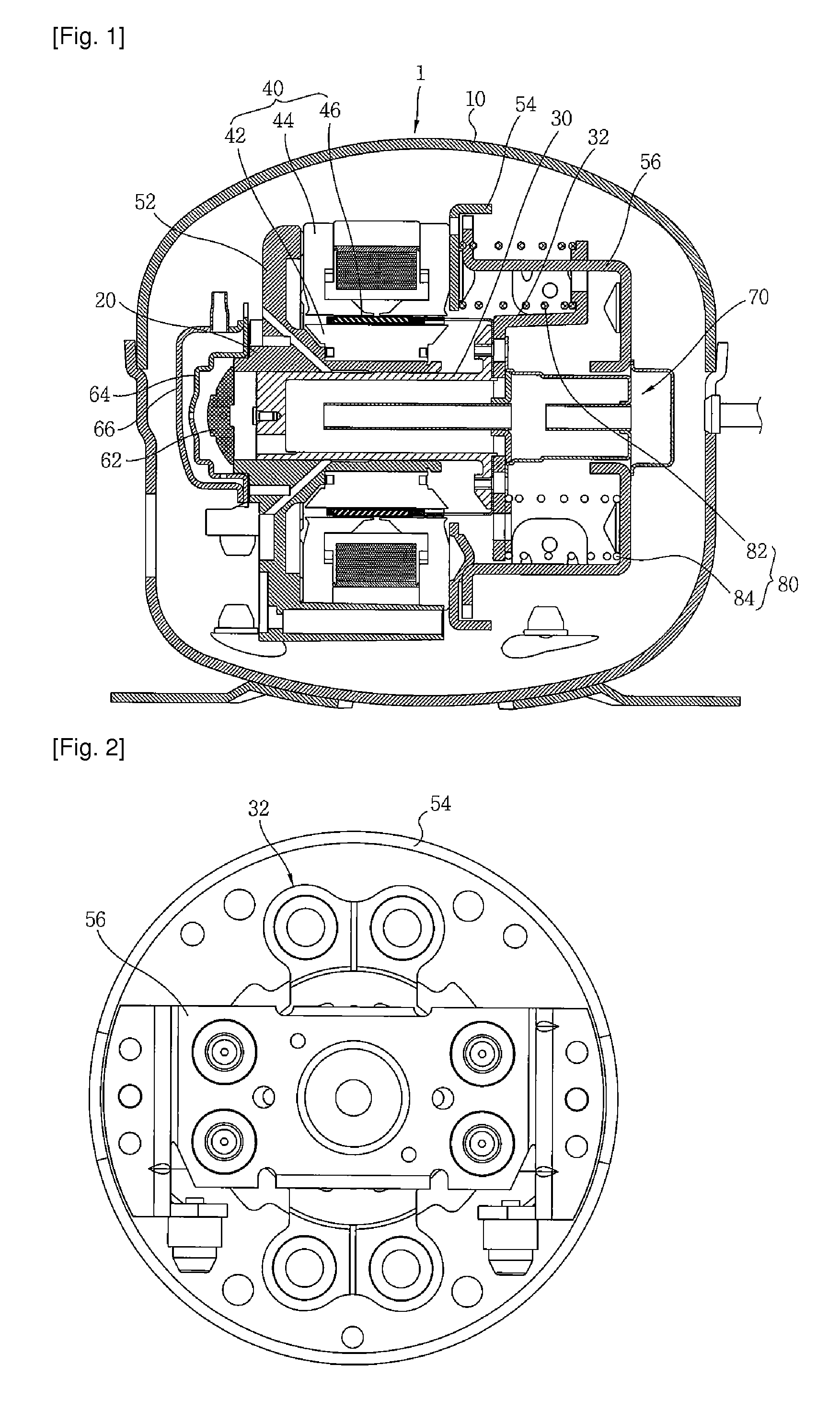
Refrigeration cycle apparatus
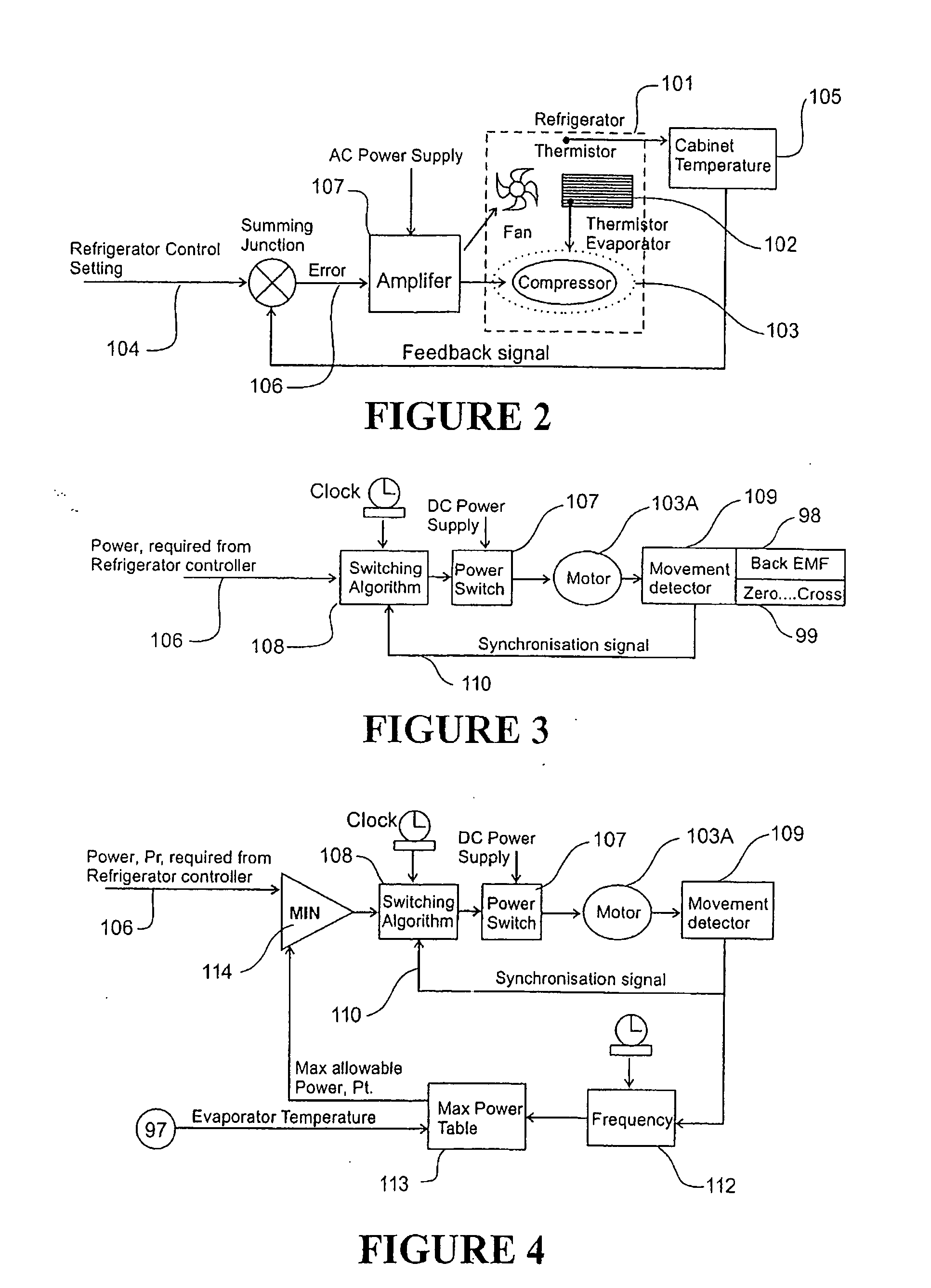
InactiveUS6868686B2Improve efficiencyShort timeHeat pumpsCompression machines with non-reversible cycleCycle rateInstruction unit
A refrigeration cycle apparatus having a linear compressor is provided with a volume circulation rate instruction unit for obtaining a volume circulation rate Vco of a refrigerant in accordance with refrigerating capacity required of the refrigeration cycle apparatus, on the basis of an ambient temperature of an indoor heat exchanger (evaporator), a target temperature set on the evaporator by the user, and an ambient temperature of an outdoor heat exchanger (condenser). A volume circulation rate detector is provided for detecting a volume circulation rate Vcd of the refrigerant that actually circulates in a refrigerant circulation path of the refrigeration cycle apparatus; and an inverter is provided for generating an AC current for driving the linear compressor. The inverter is controlled so as to decrease a difference between the volume circulation rate Vco and the volume circulation rate Vcd.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
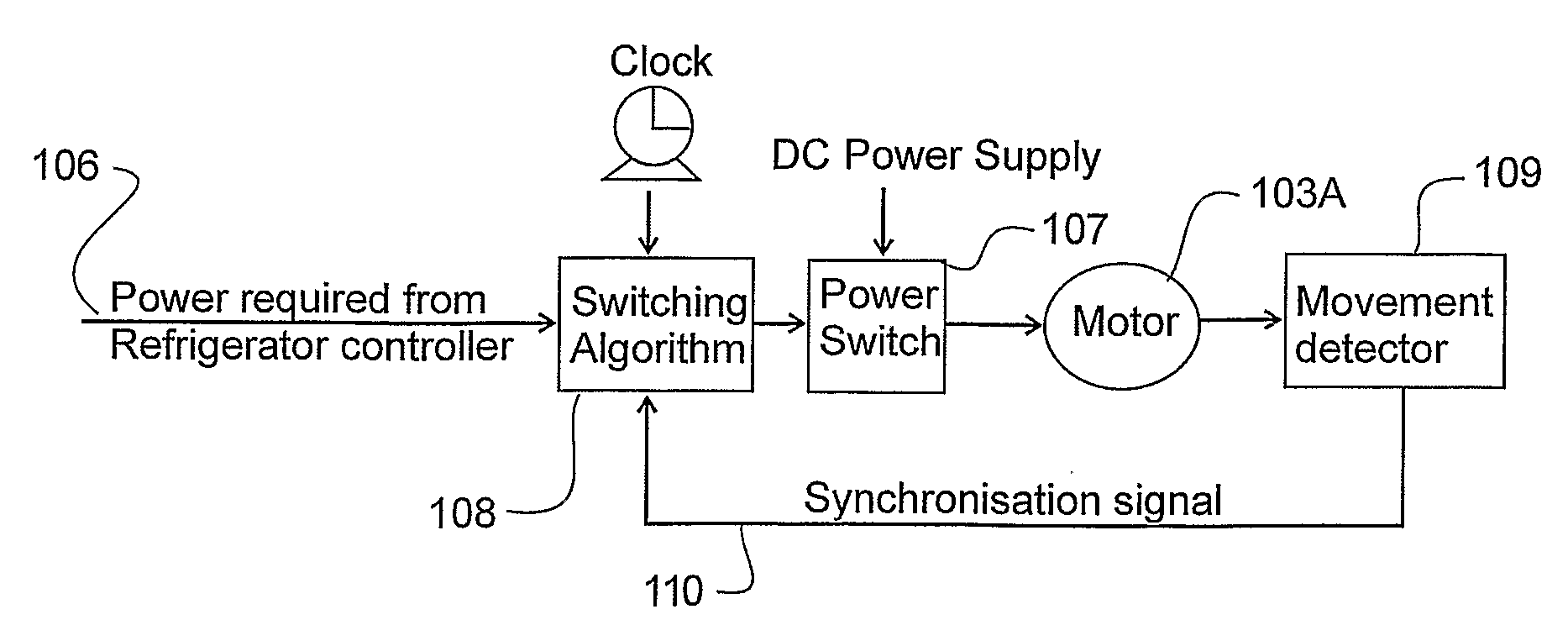
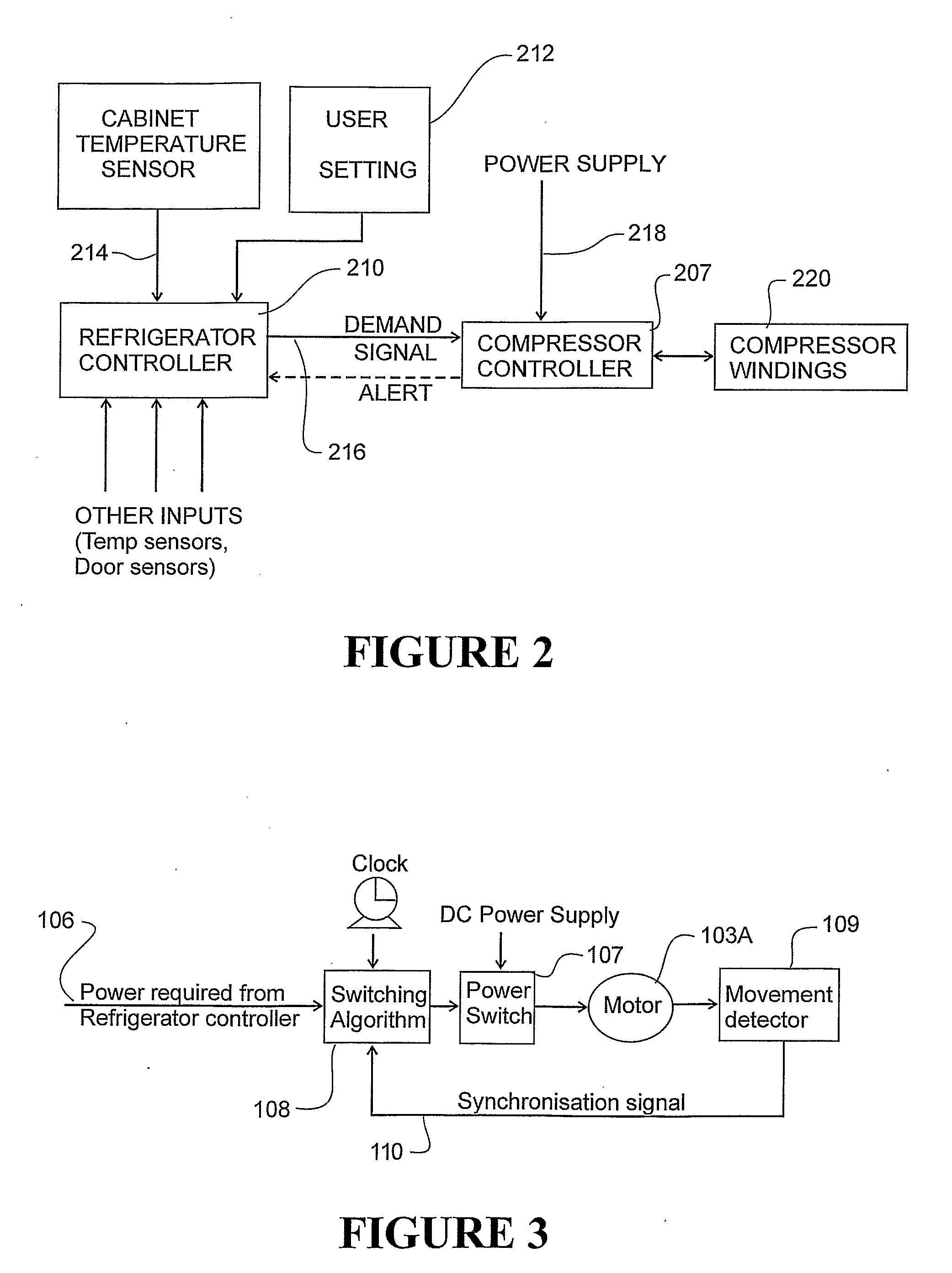
Linear compressor controller
ActiveUS20090081049A1Reduce stepsReduce total powerExternal parameterFluid-pressure actuatorsLower limitLinear compressor
A control for a linear compressor energises the linear motor in harmony with the present natural frequency of the compressor. The controller monitors the present operating frequency and compares the frequency with one or more outer limit thresholds. The control may remove power from the linear motor if the running frequency drops below a lower threshold. The control may reduce power to the linear motor if the running frequency rises above an upper threshold. The control uses compressor running frequency to operate the comperssor within safe operating limits.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL APPLIANCES LTD
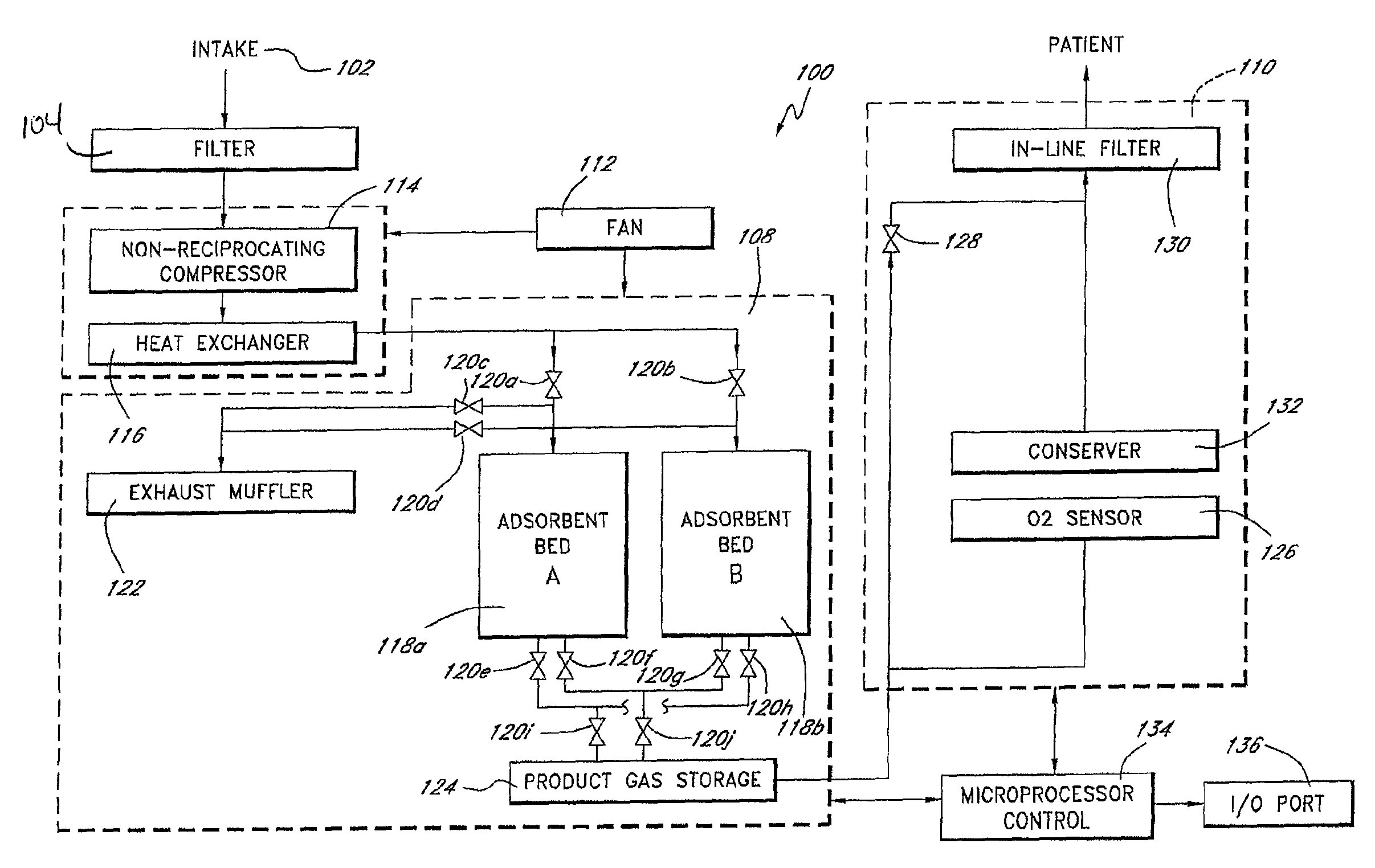
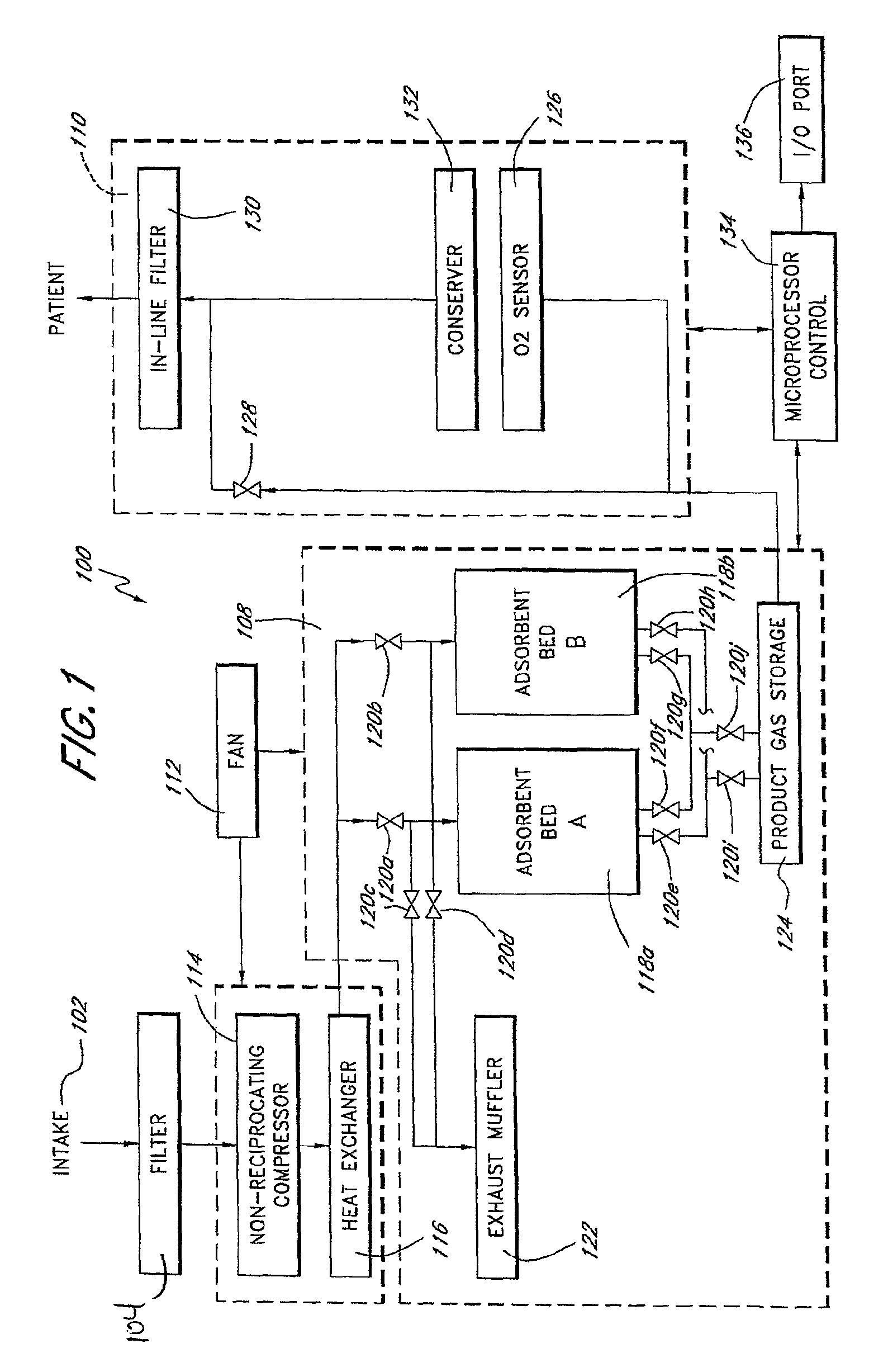
Portable gas fractionalization system
InactiveUS7922789B1Reduce heat loadReduce noiseCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentLow noiseLinear compressor
A portable gas fractionalization apparatus that provides oxygen rich air to patients is provided. The apparatus is compact, lightweight, and low-noise. The components are assembled in a housing that is divided into two compartments. One compartment is maintained at a lower temperature than the other compartment. The lower temperature compartment is configured for mounting components that can be damaged by heat. The higher temperature compartment is configured for mounting heat generating components. An air stream is directed to flow from an ambient air inlet to an air outlet constantly so that there is always a fresh source of cooling air. The apparatus utilizes a PSA unit to produce an oxygen enriched product. The PSA unit incorporates a novel compressor system which includes the use of free piston linear compressors so as to reduce power consumption, noise and vibration reduction.
Owner:INOGEN INC
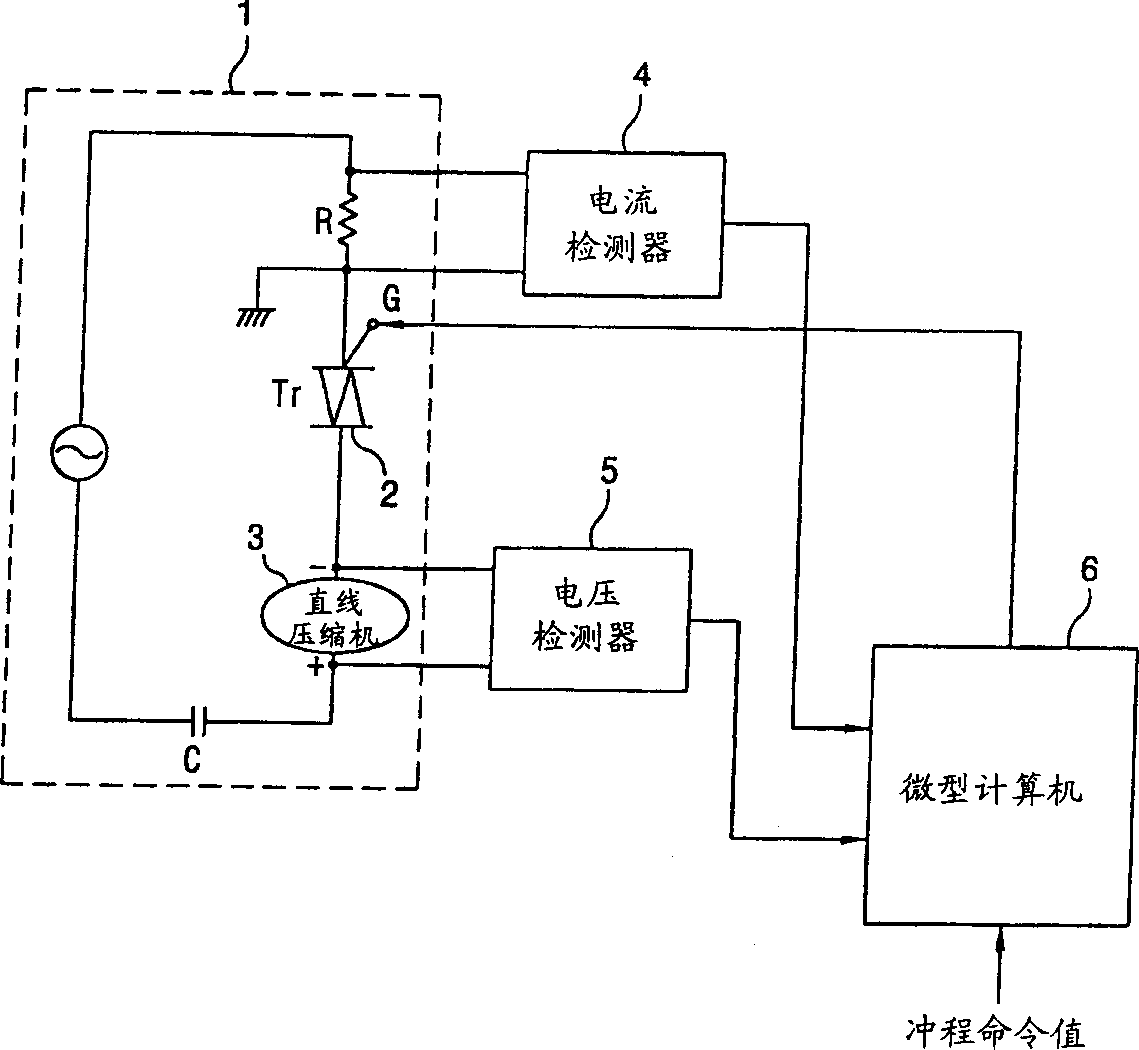
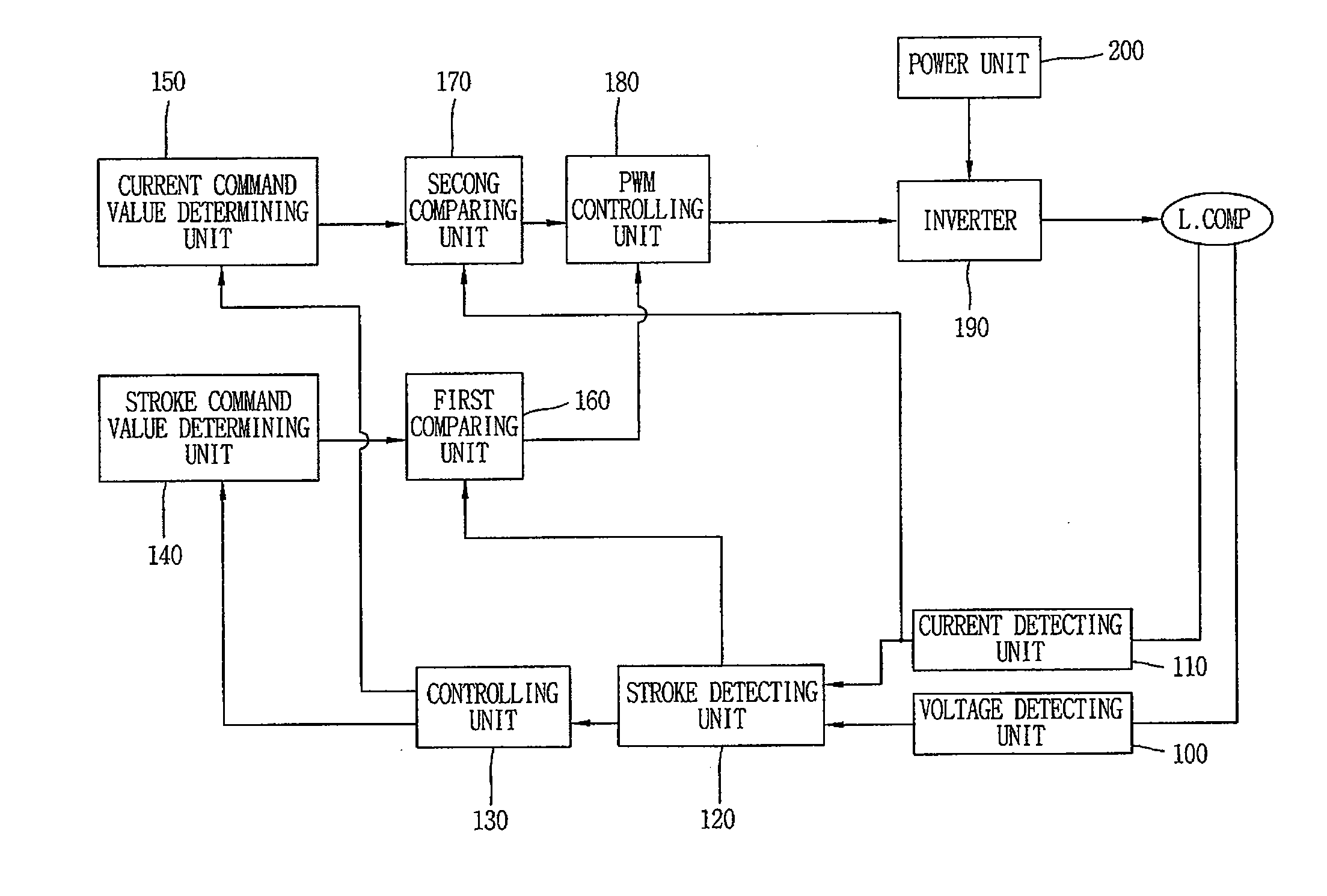
Equipment and method for controlling operation of linear compressor
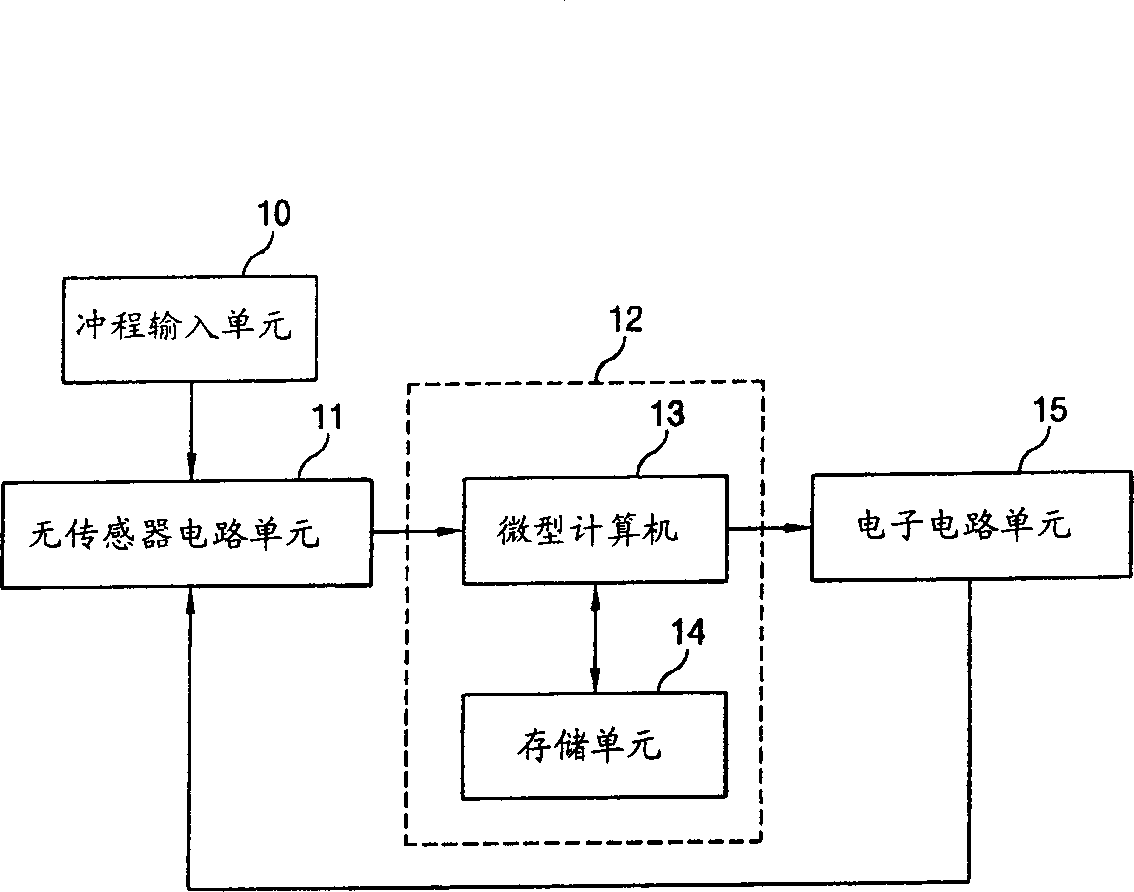
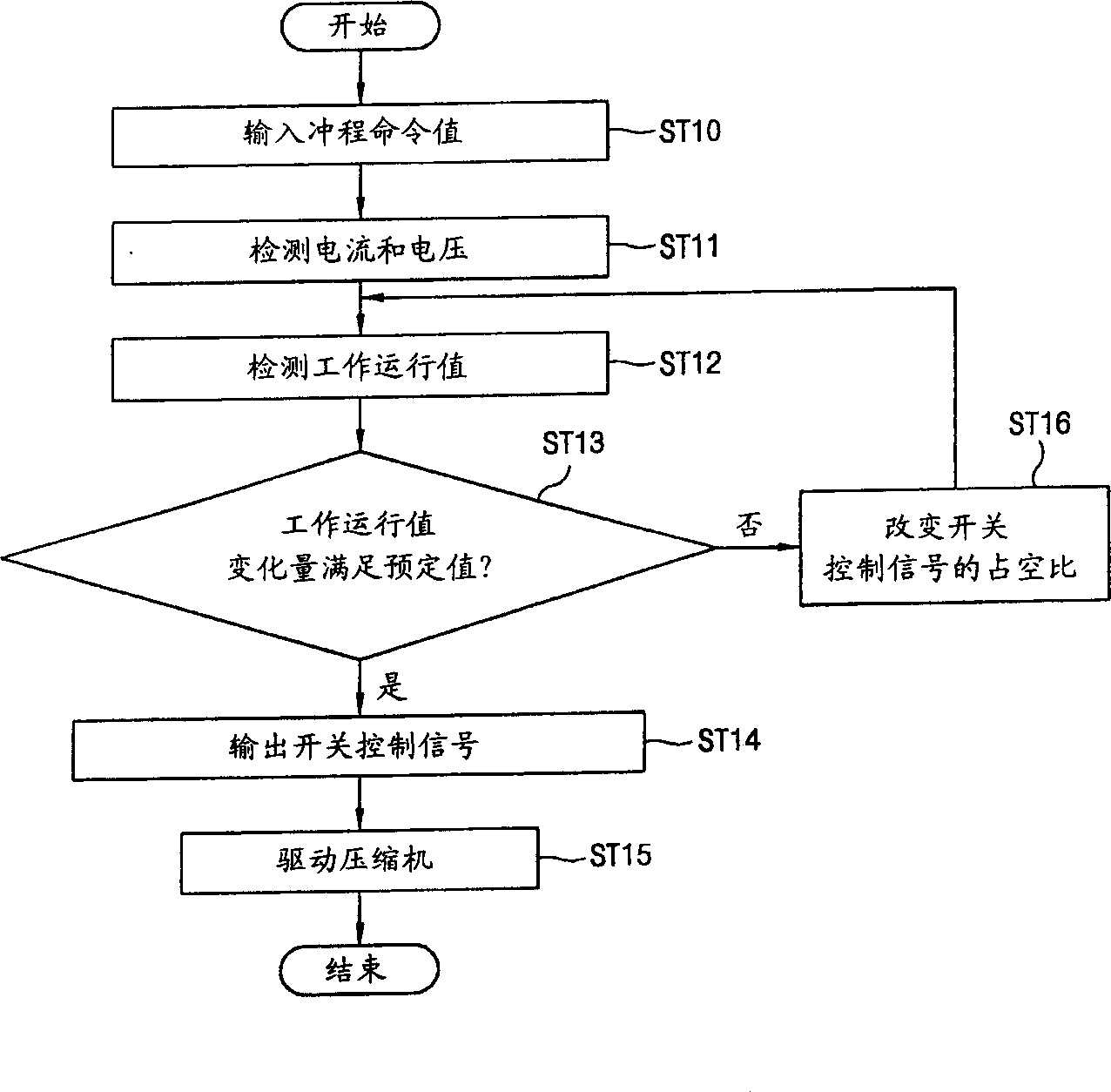
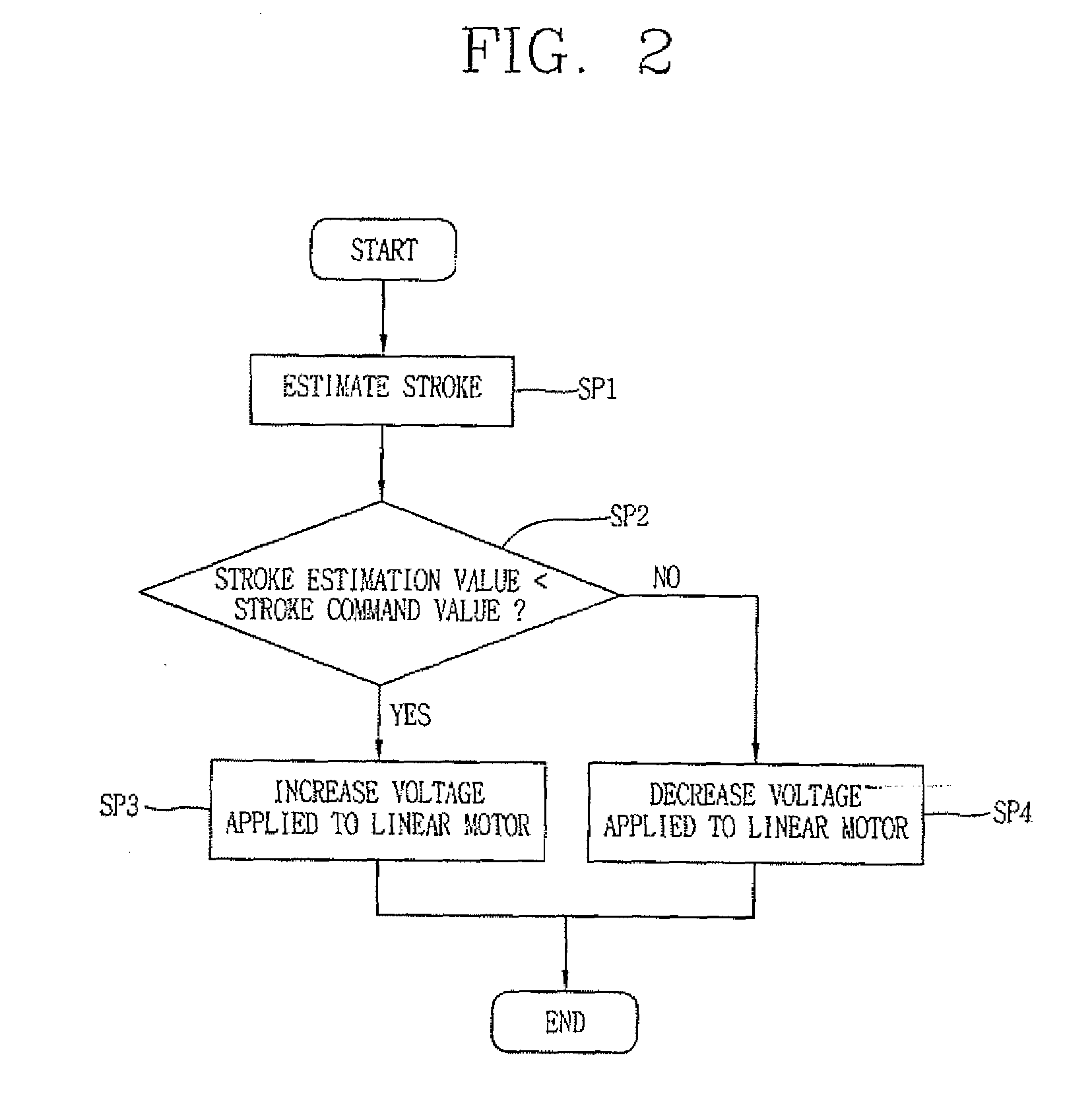
InactiveCN1356472AImprove operational efficiencyCompression machines with non-reversible cycleMotor parameterLinear compressorControl signal
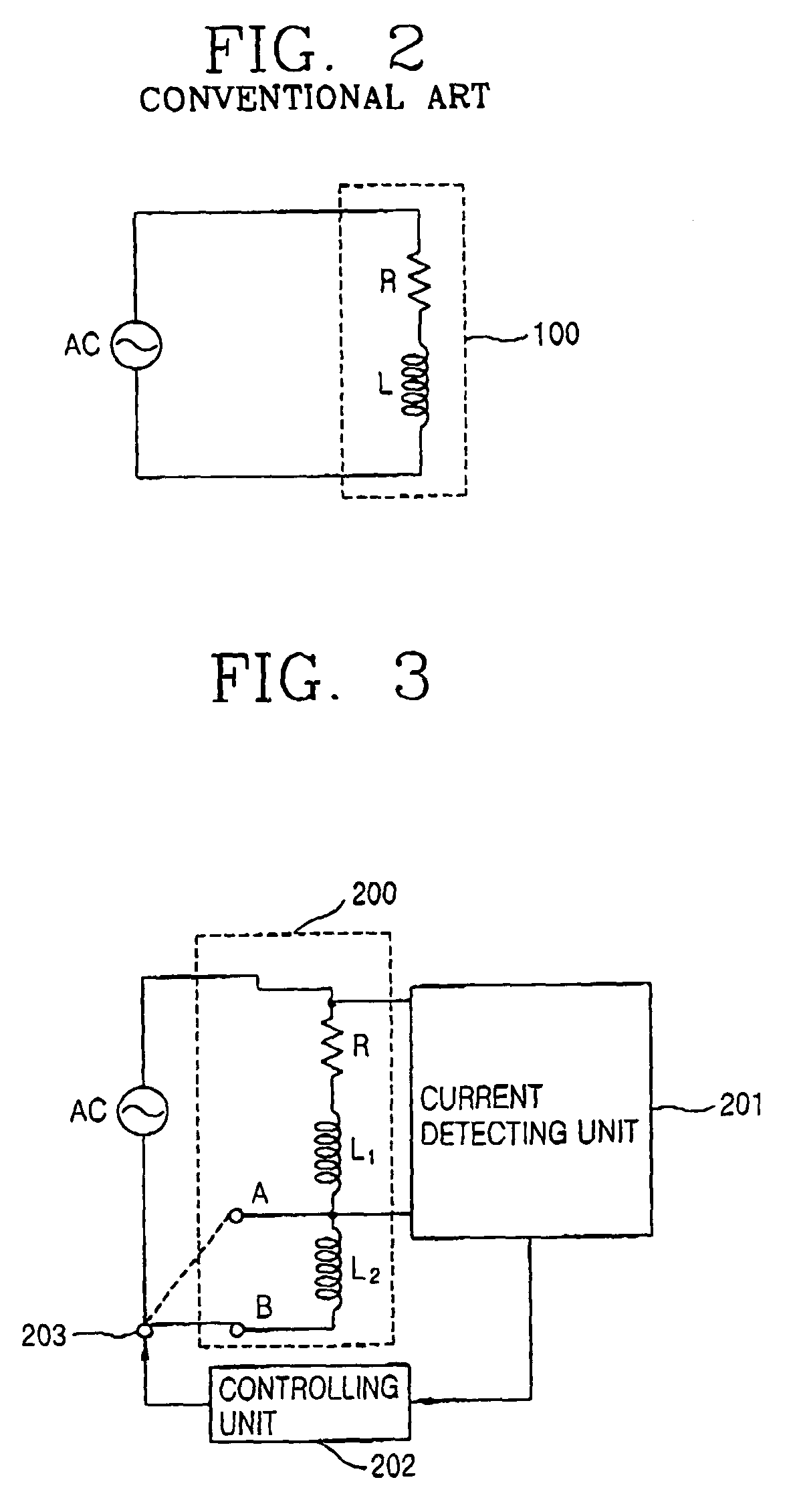
An apparatus for controlling an operation of a linear compressor includes: a sensorless circuit unit for detecting a current and a voltage applied to a linear compressor and outputting a work operation value corresponding to them; a stroke controller for receiving the work operation value and outputting a switching control signal corresponding to a variation amount of the work operation value; and an electric circuit unit for receiving the switching control signal from the stroke controller and outputting a certain voltage to the linear compressor, accordingly, a TDC of the piston in consideration of an error due to the nonlinear characteristic can be controlled, and thus, an operation efficiency of the linear compressor can be improved.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Driving controlling apparatus for linear compressor and method thereof
InactiveUS20070241698A1Stable changeDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlPhase differenceLinear compressor
A driving controlling apparatus for a linear compressor, comprises: a storing unit for storing a reference phase difference to judge an overload state; and a controlling unit for judging an overload state based on a comparison result between the reference phase difference and a phase difference between a current and a stroke, and controlling a voltage or a current applied to a linear motor based on the judgement result.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Compressor intercooler unloader arrangement
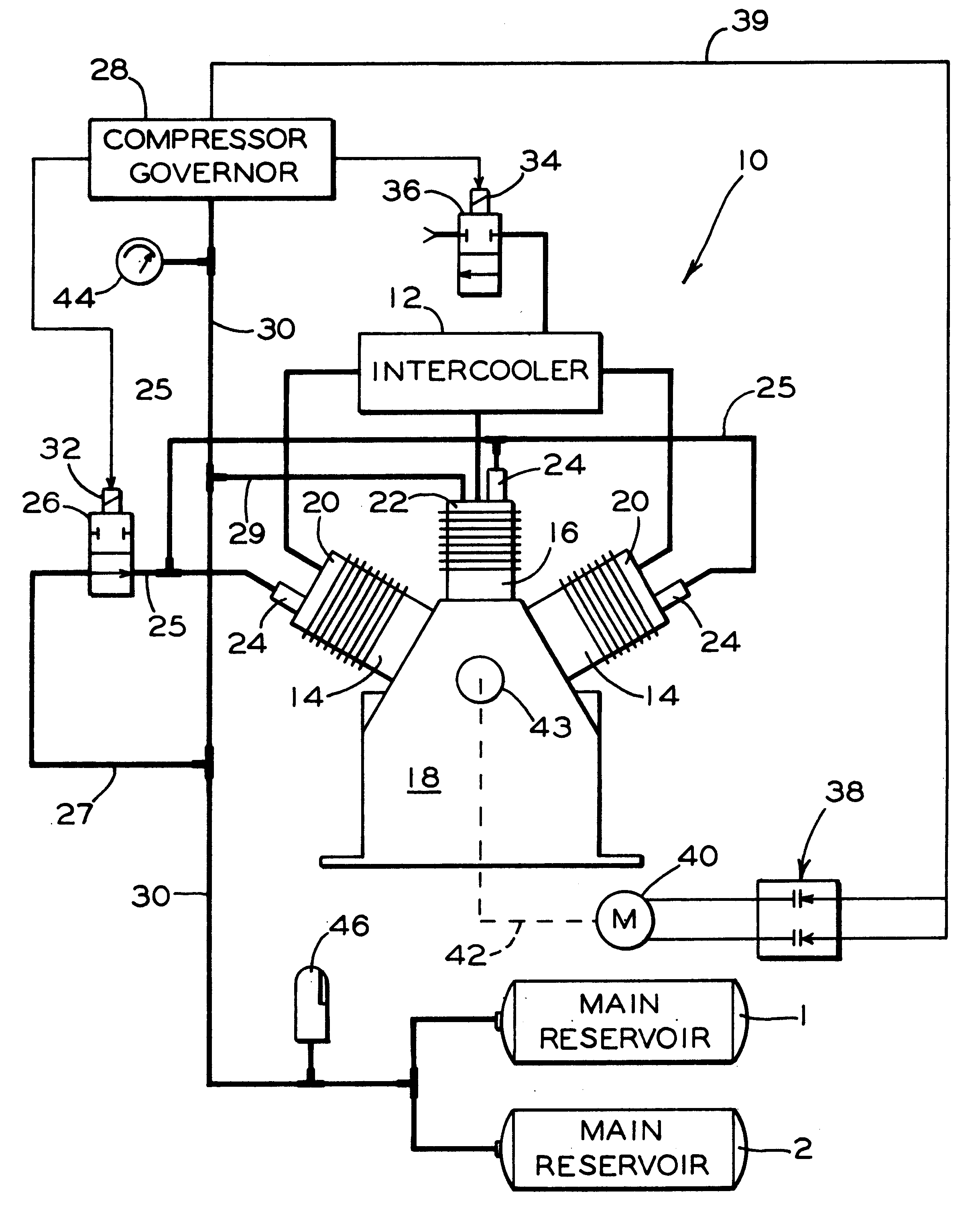
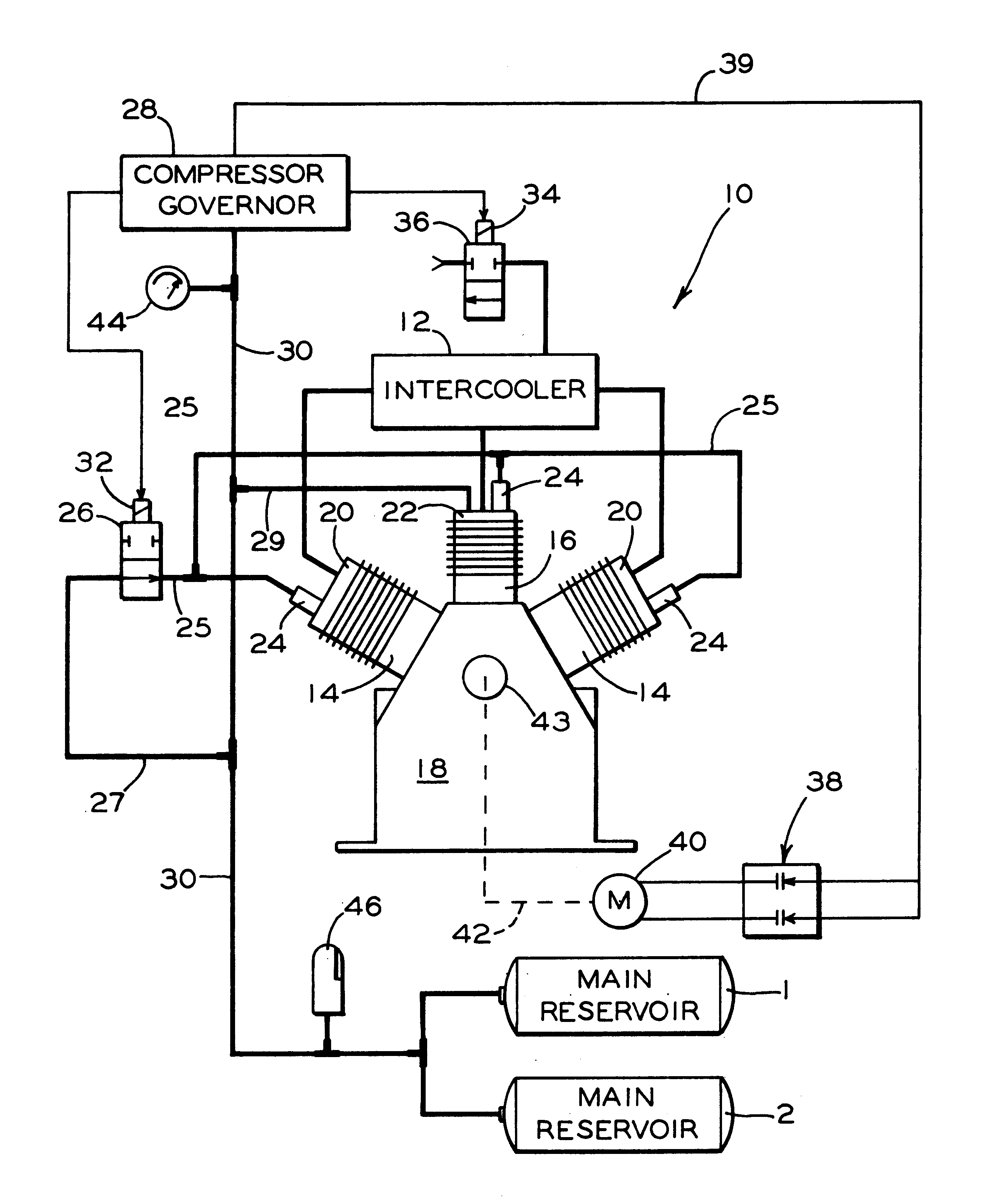
InactiveUS6203285B1Eliminate compressor motor heat buildupProlong lifePositive displacement pump componentsFlexible member pumpsElectricityLinear compressor
Apparatus for rapidly unloading air pressure in an intercooler to atmosphere when a compressor pneumatically connected to the intercooler is unloaded. The apparatus includes a governor pneumatically connected to a reservoir, that, in turn, is connected to receive pressurized air from the air compressor. The governor has a pressure sensing device operable to order unloading of the compressor when air pressure level in the reservoir tank reaches a preset level. An electrically operated valve is pneumatically connected to the intercooler and connected electrically to the pressure sensing device of the governor, with the electrically operated valve being effective to exhaust air pressure in the intercooler when the valve receives an unload signal from the pressure sensing device. The compressor is driven, by an electrical motor having one or more speed configurations, with transition occurring between one configuration and another when the compressor is unloaded. The electrically operated valve is effective to unload the intercooler at the time of speed configuration transition to reduce undue motor and electrical contactor heat and thus increase life expectancy of the motor and contactors.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE AIR BRAKE CO
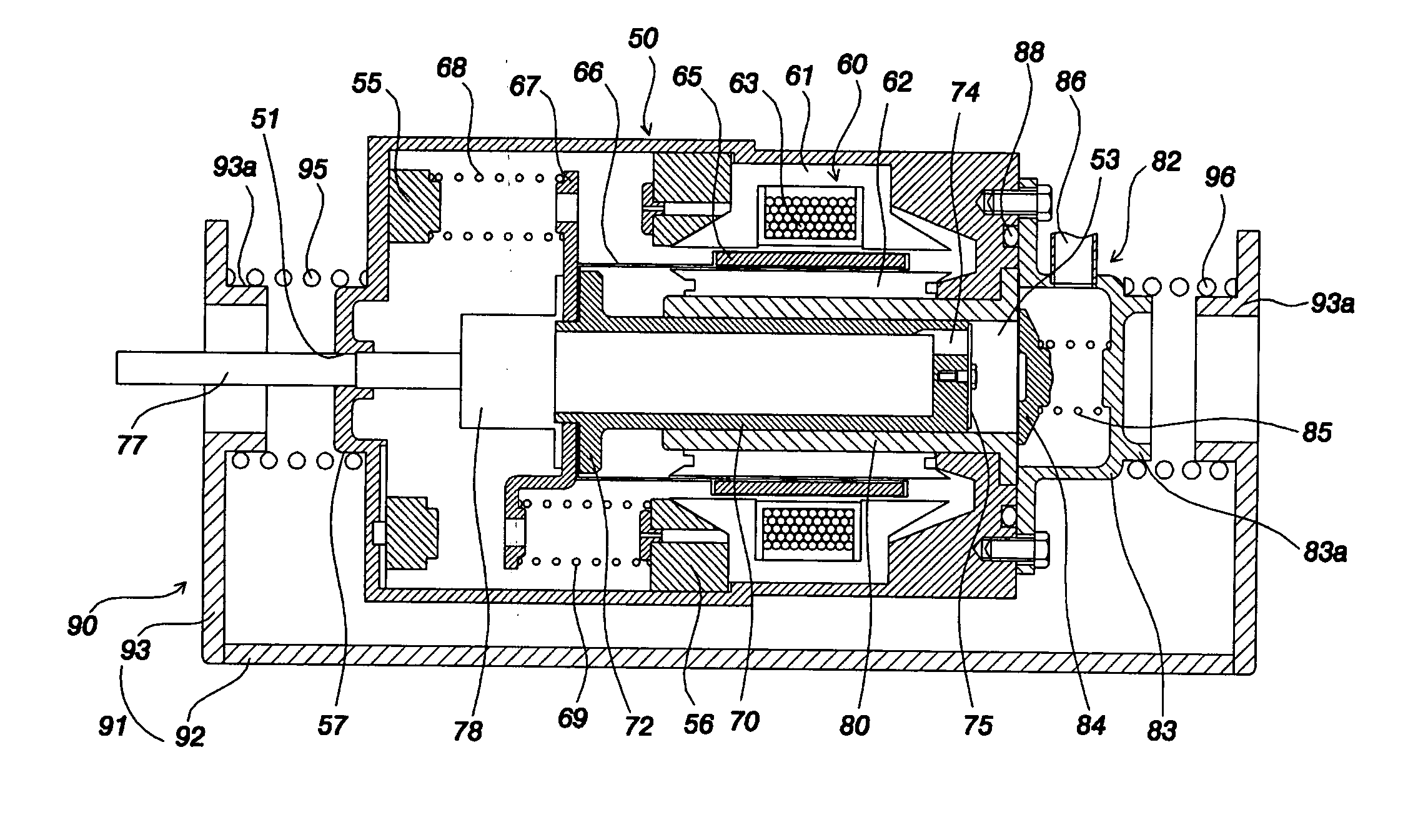
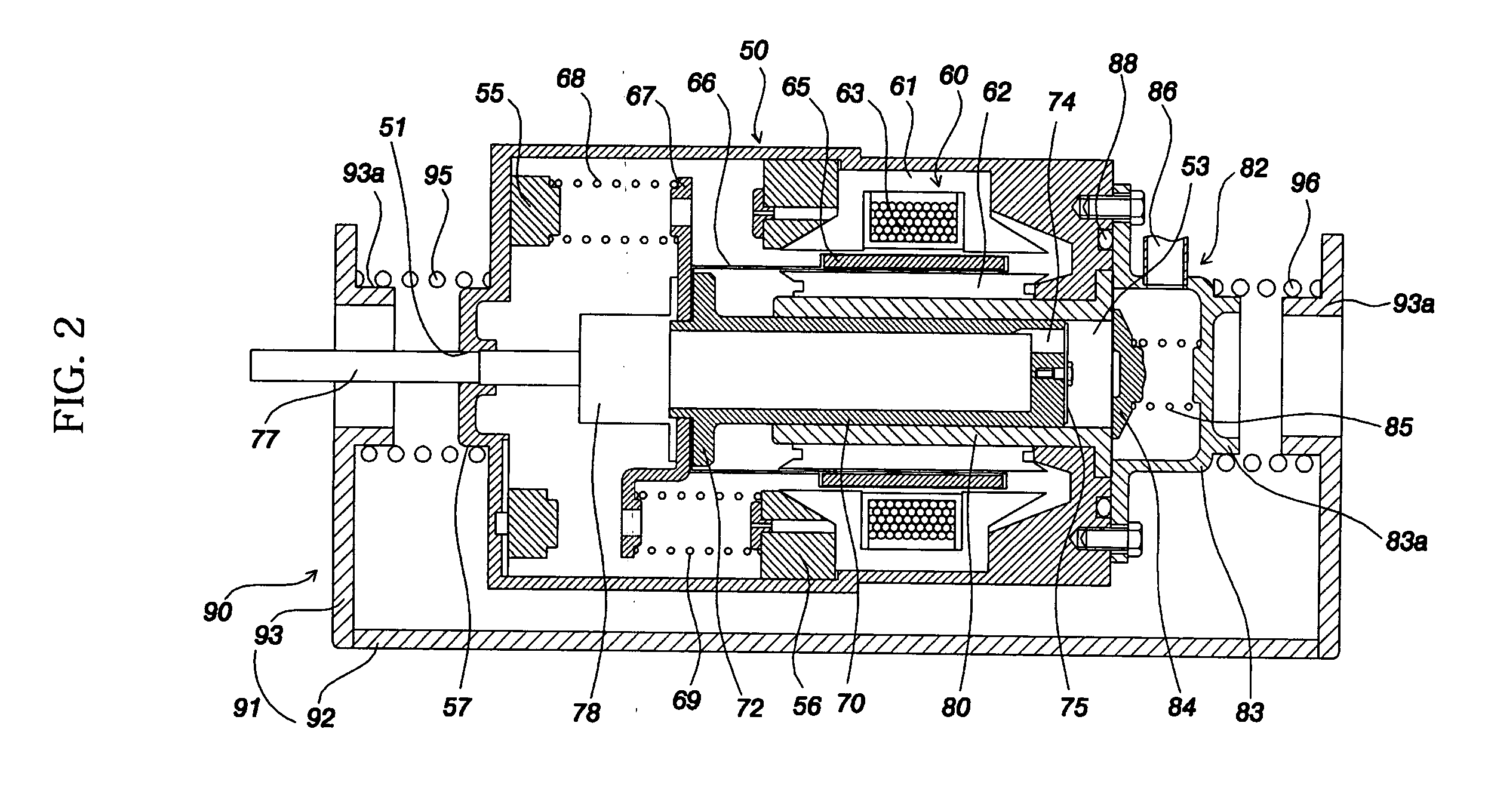
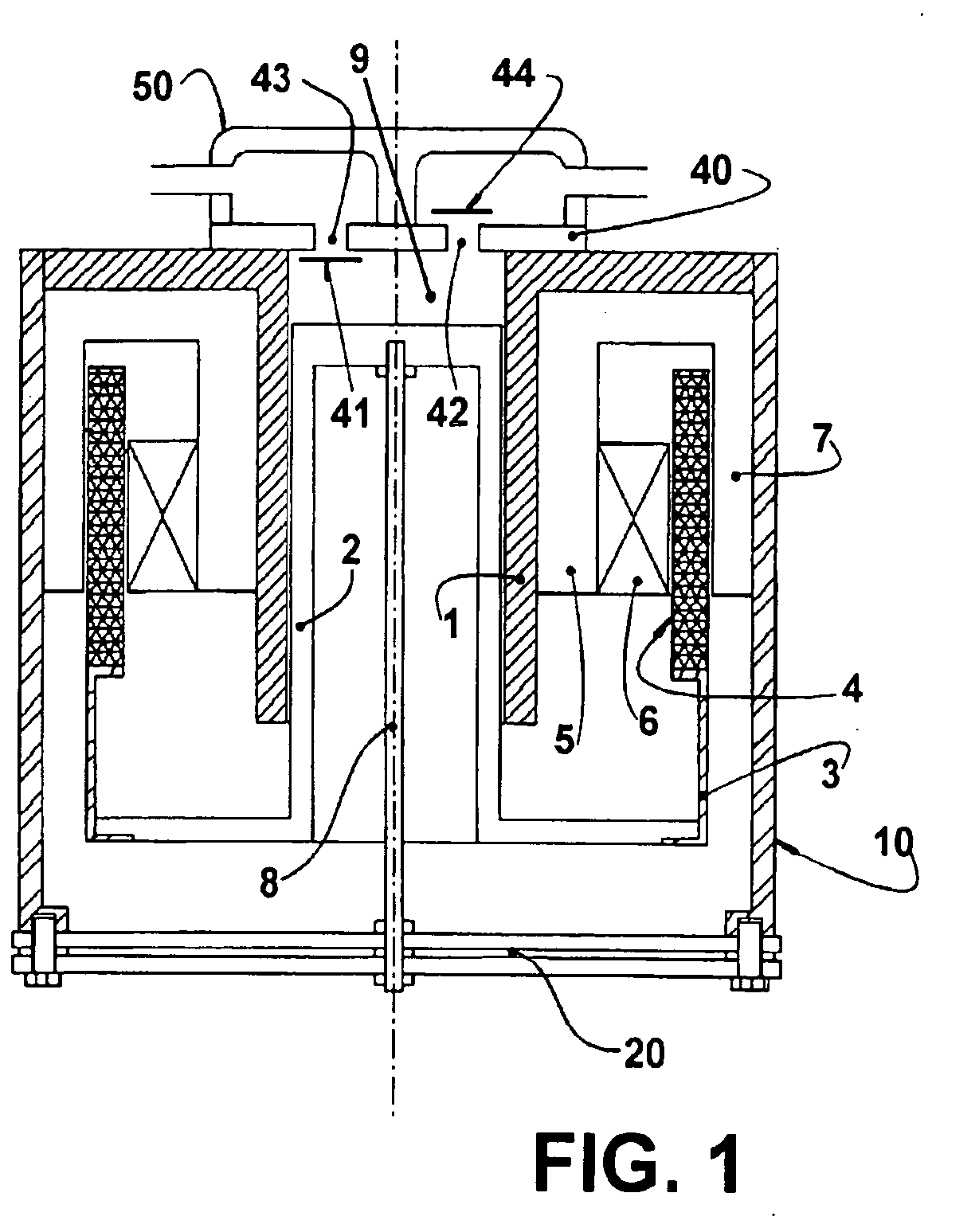
Linear compressor
InactiveUS20100098566A1Reduce noiseReduce vibrationPositive displacement pump componentsNon-rotating vibration suppressionElastomerReciprocating motion
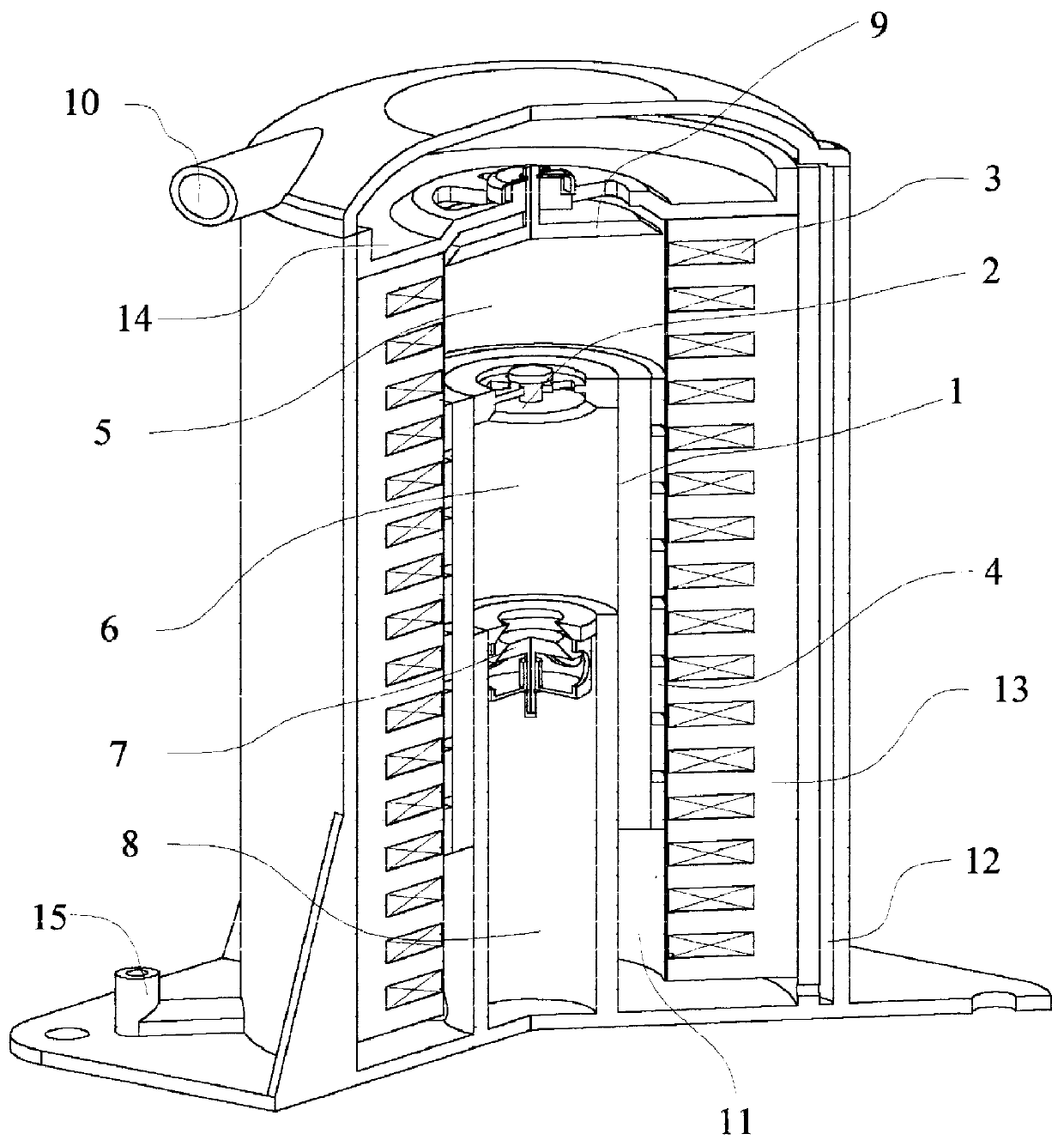
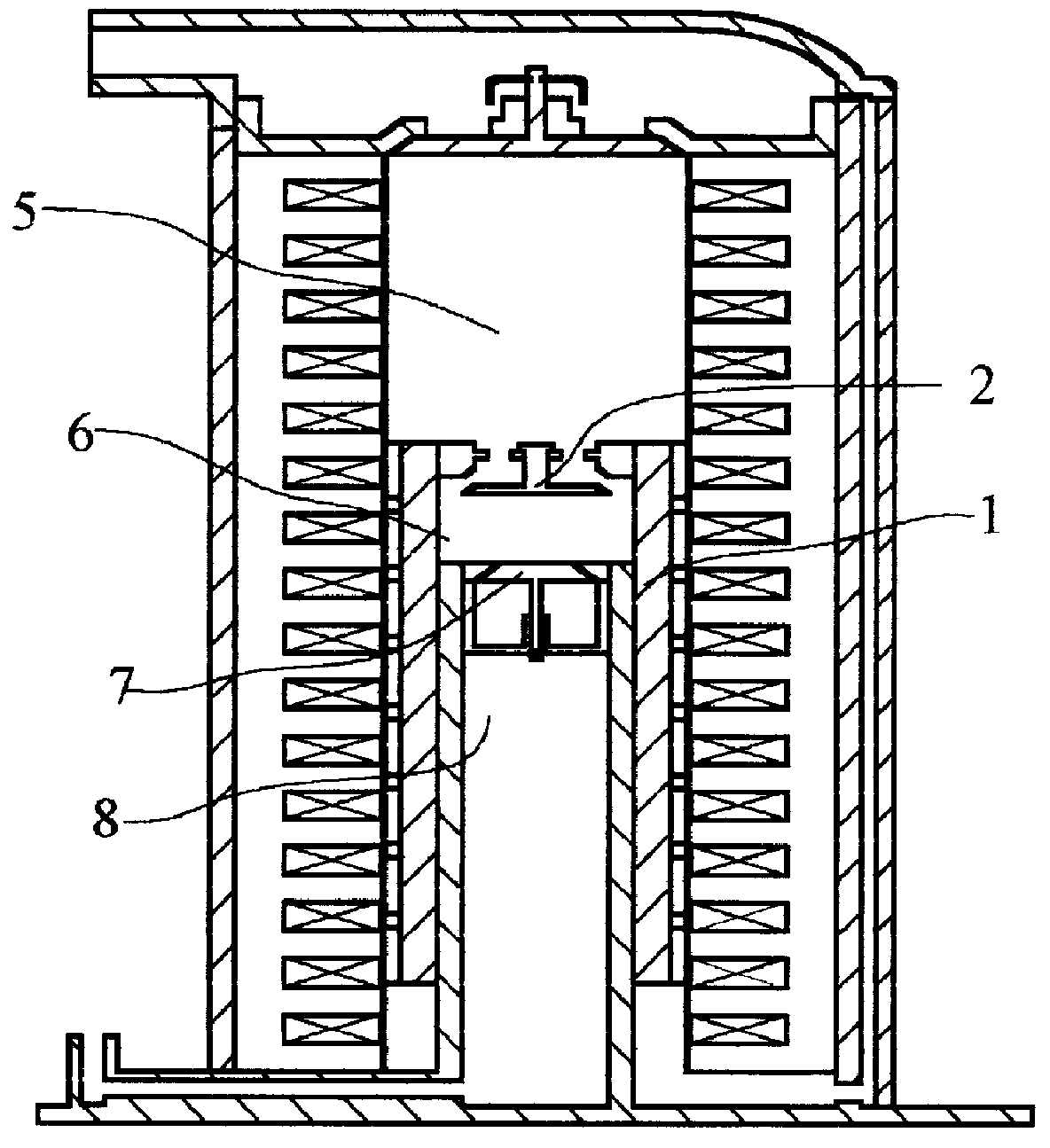
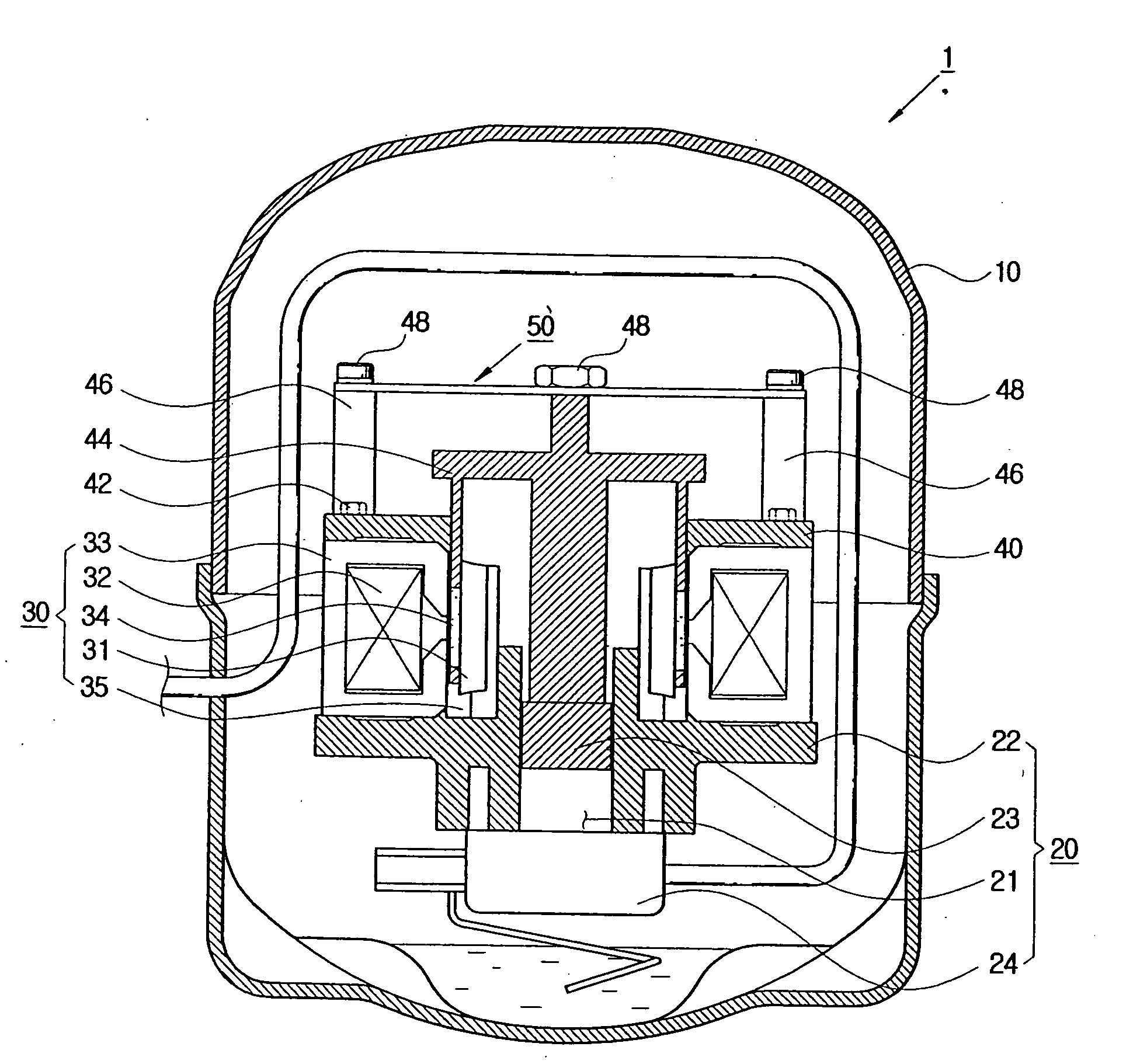
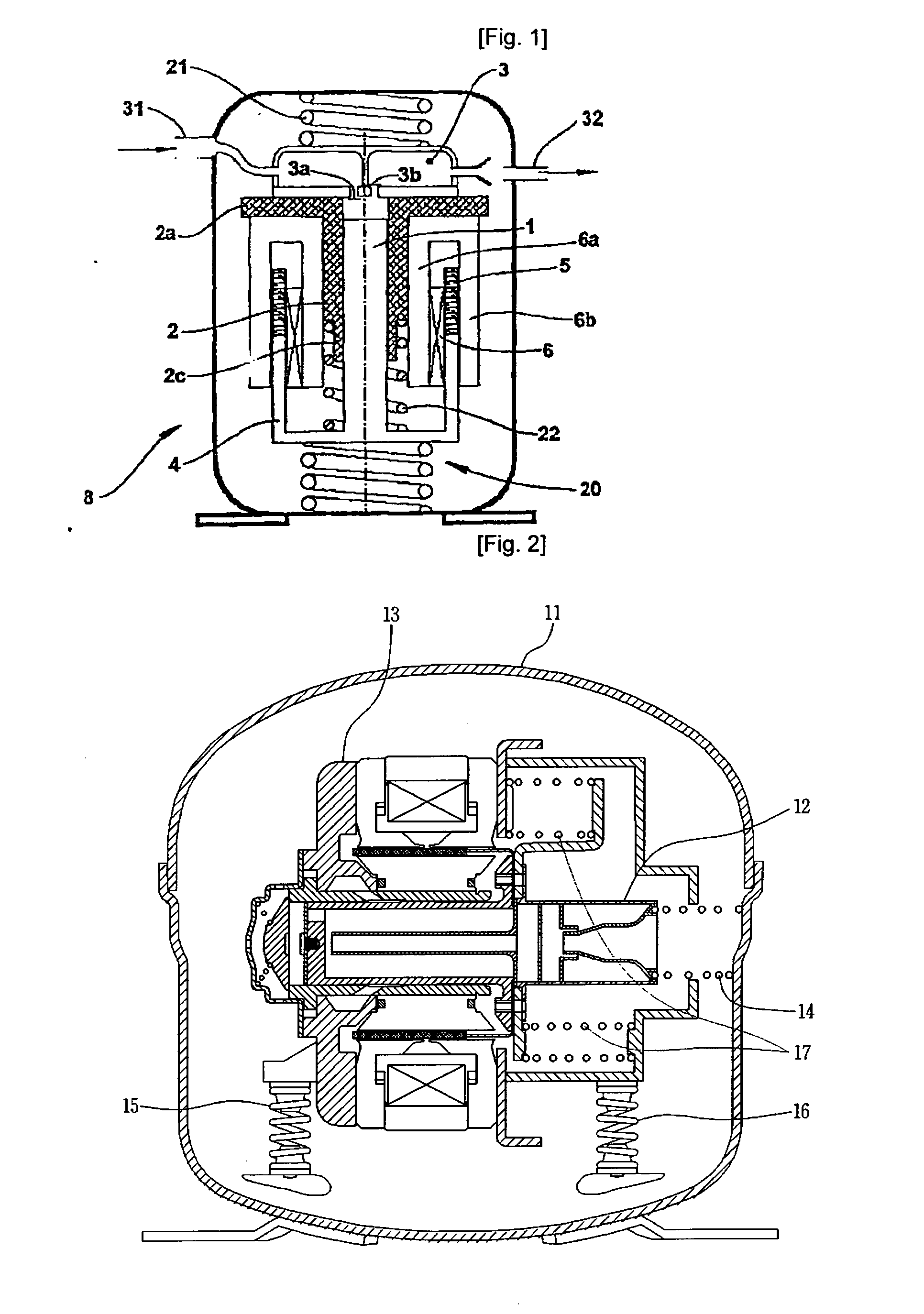
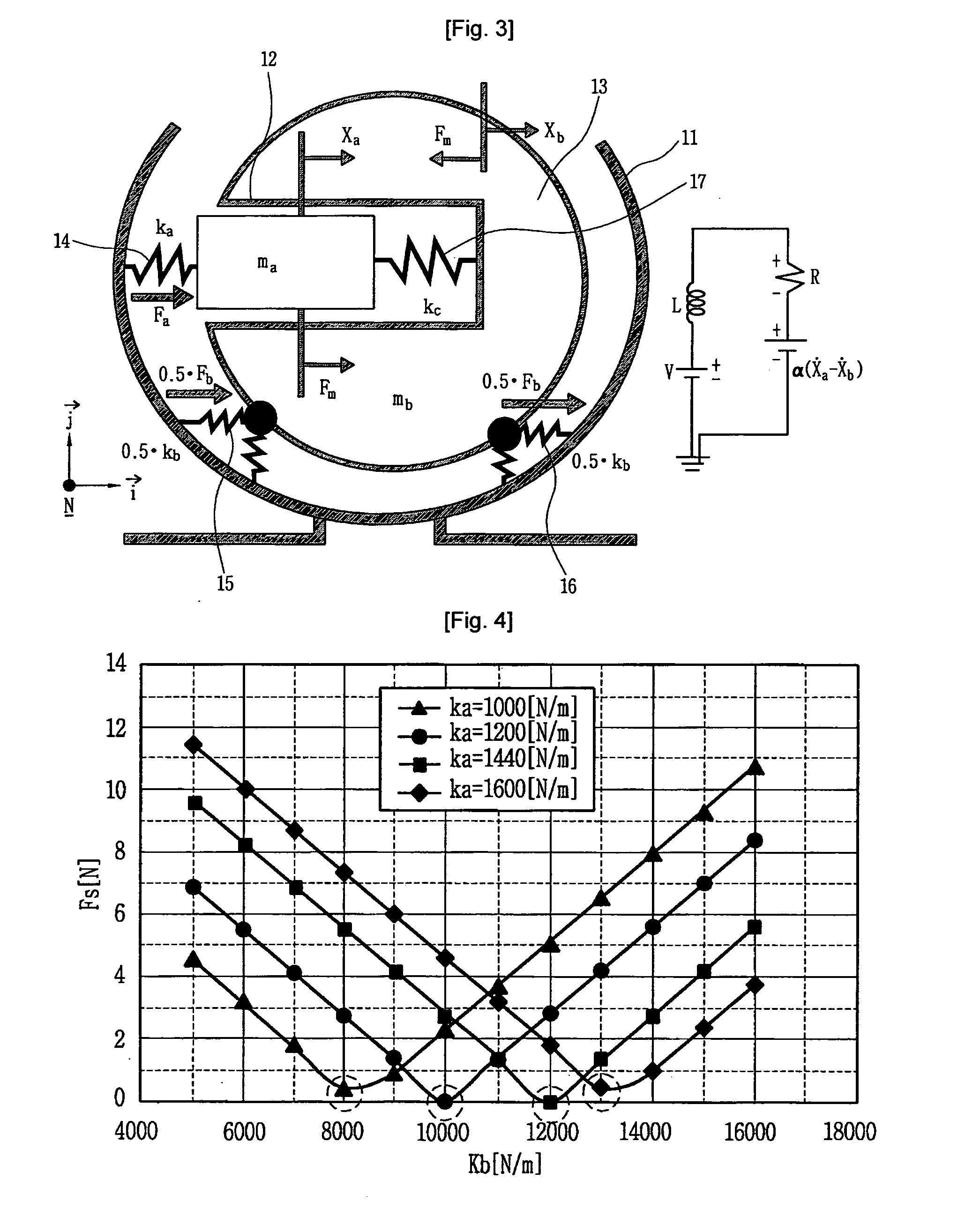
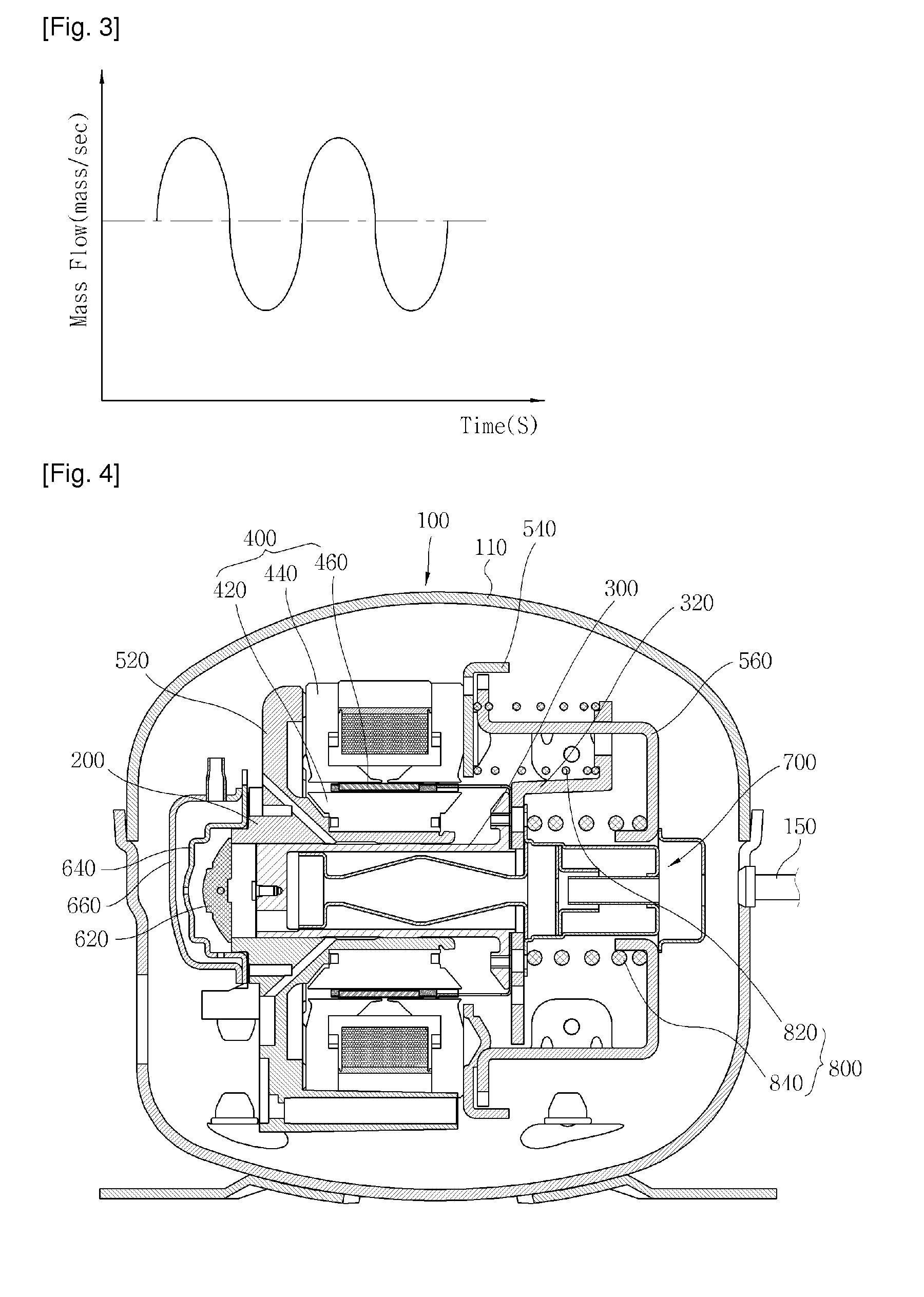
The present invention provides a linear compressor having an elastic body capable of reducing vibration transferred to a shell due to a motion of a moving part. The linear compressor includes a shell defining a hermetic space, a stationary part installed in the shell and having a mass of Mb, a moving part reciprocating linearly inside the stationary part at a frequency of ω to compress a fluid, and having a mass of Ma, a first elastic body having both ends supported on the moving part and the shell respectively, and having an spring constant of ka, a second elastic body having both ends supported on the shell and the stationary part respectively, and having an spring constant of kb, and a third elastic body having both ends supported on the stationary part and the moving part respectively, and having an spring constant of k. The frequency ω satisfies ω2>(ka / Ma). In the above configuration, the spring constant kc of the third elastic body is always a positive number, so that the third elastic body can be implemented with a mechanical elastic body more easily designed and controlled than a gas elastic body.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Moving-magnetic linear compressor
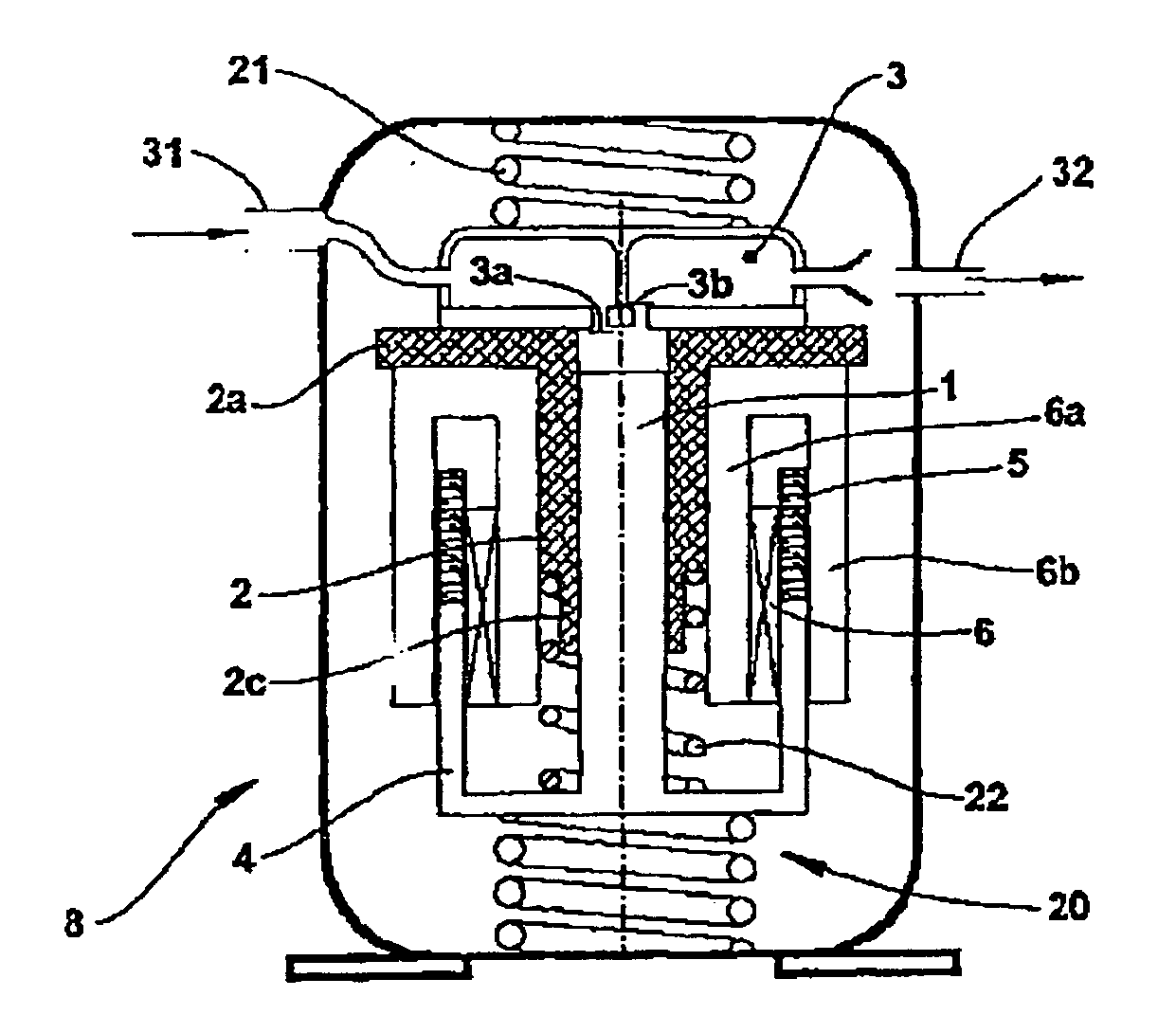
InactiveCN1773112AReduced risk of demagnetizationReduce frictionPiston pumpsPositive-displacement liquid enginesMagnetic tension forceExhaust valve
The present invention relates to a moving-magnet straight-line compressor. It includes a linear motor component, it mainly has inner and outer magnetic yokes with concentric combined structure, moving-magnet coil, permanent magnet and motor runner bracket, the permanent magnet is positioned on the motor rotor bracket and placed in the magnetic field formed from inner and outer magnetic yokes; a compressor component, it mainly has machine seat, cylinder, exhaust valve and suction valve which are positioned on the machine seat and piston connected with motor runner; and a machine shell which is seal-connected with machine seat. It is characterized by that it also includes a suspension component, it mainly has a spring support frame, flexible springs, inner and outer washers and collision-prevention mechanism, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
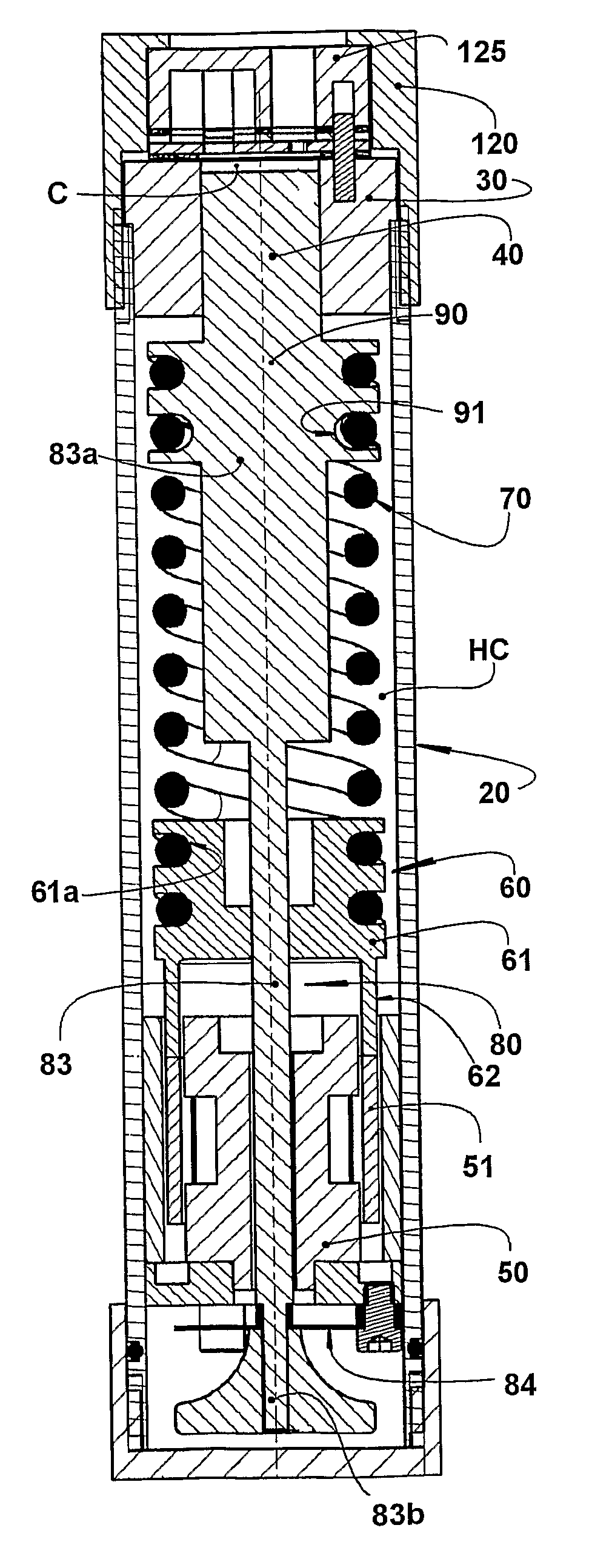
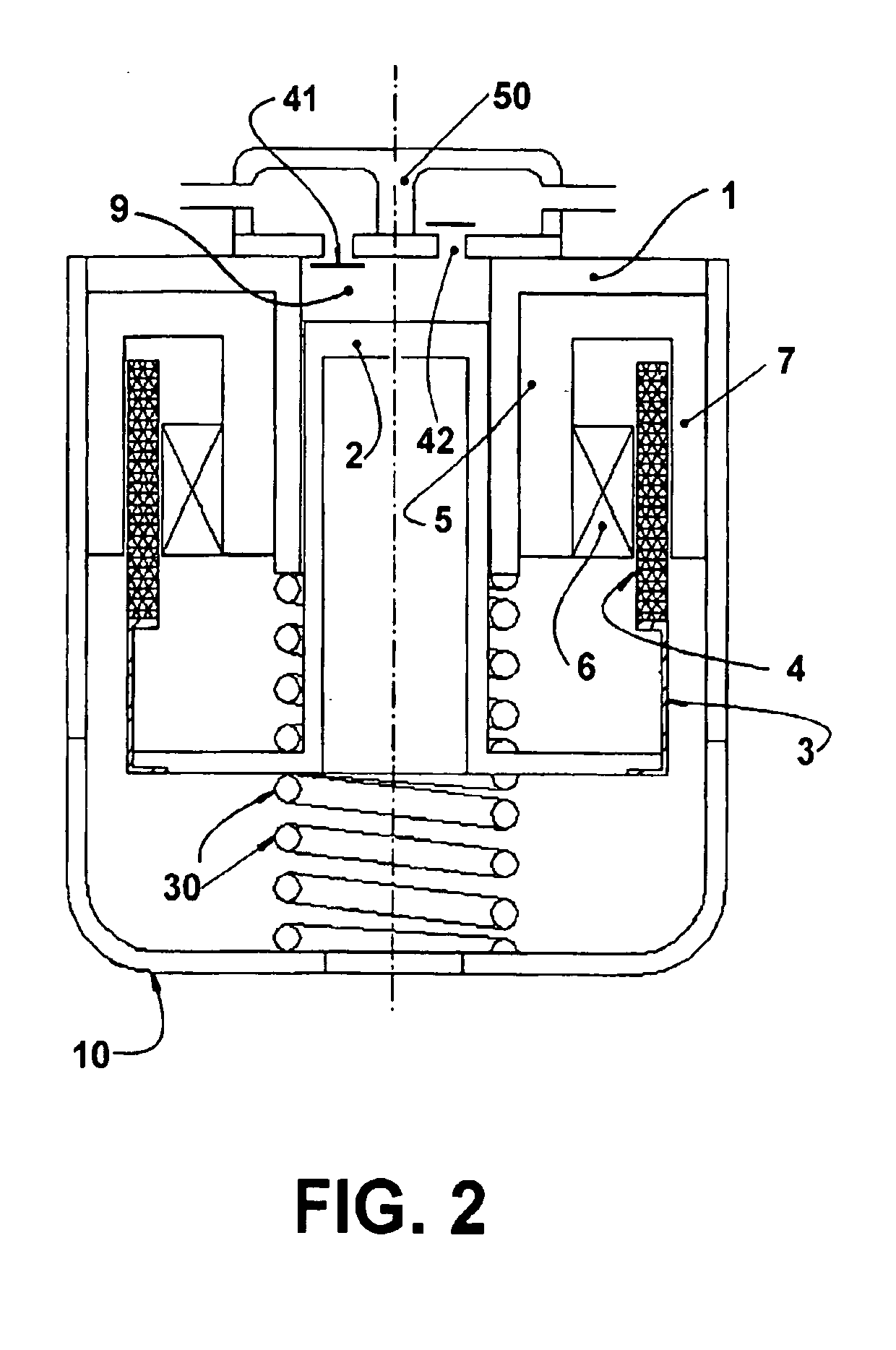
Linear compressor
ActiveUS20090280015A1Reduced dimensionPositive displacement pump componentsFlexible member pumpsLinear compressorReciprocating motion
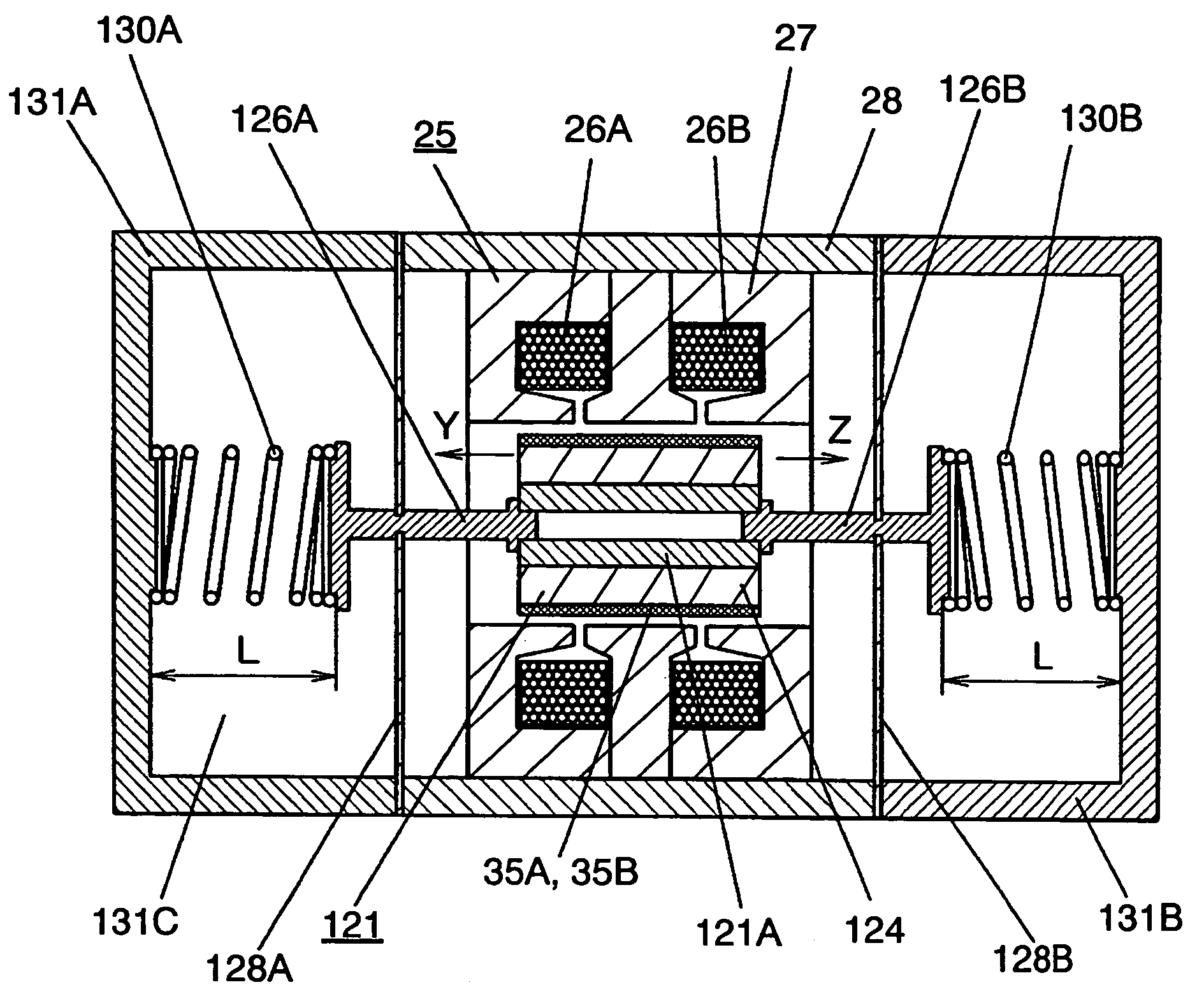
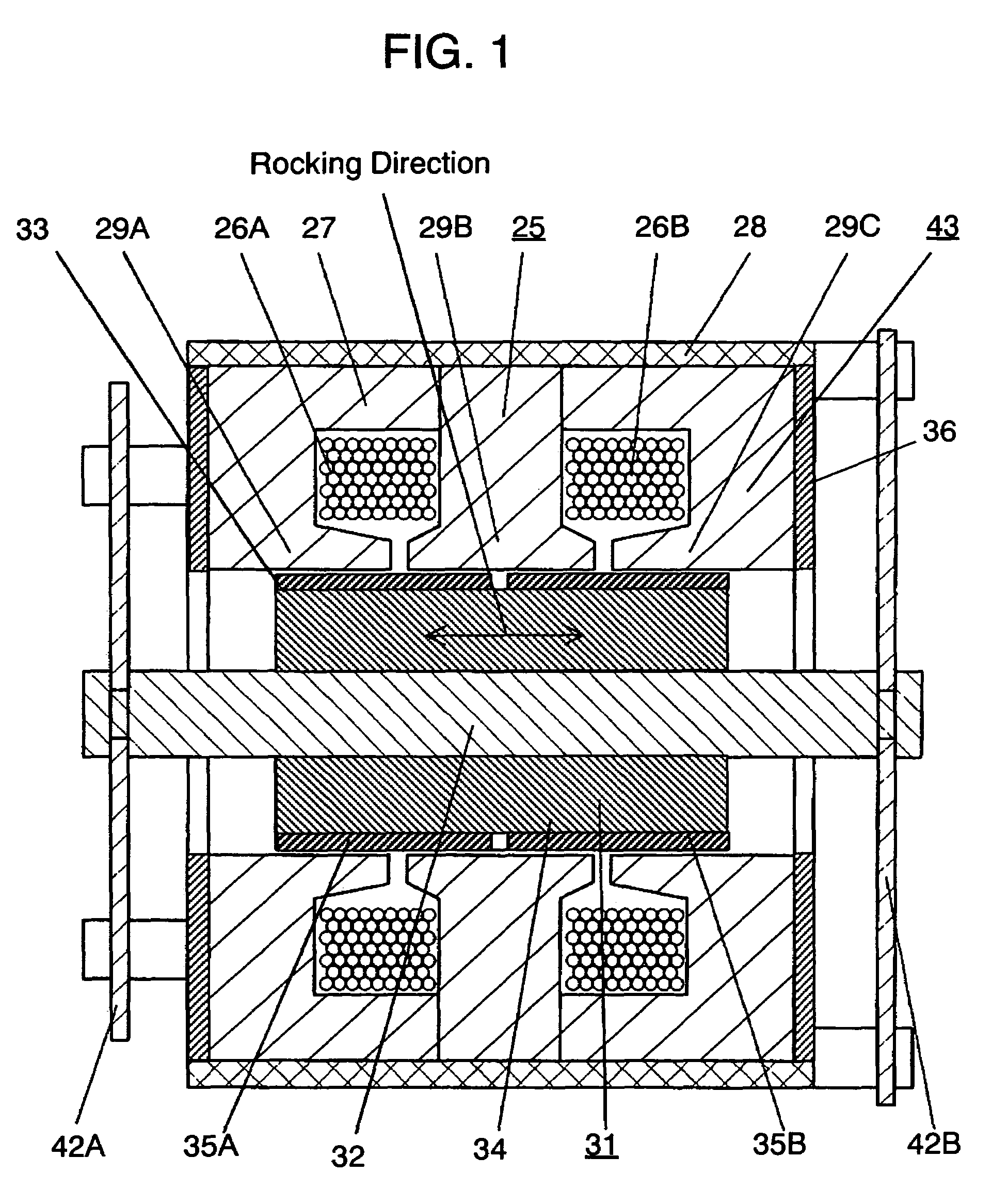
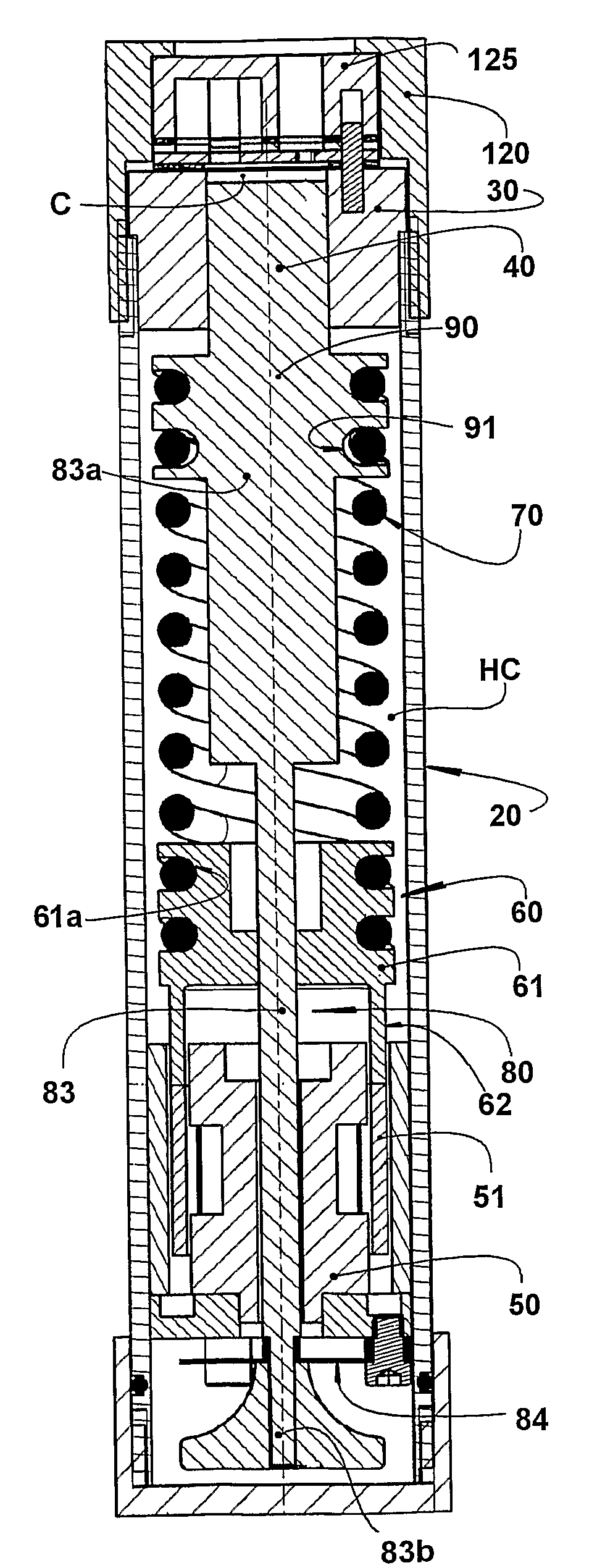
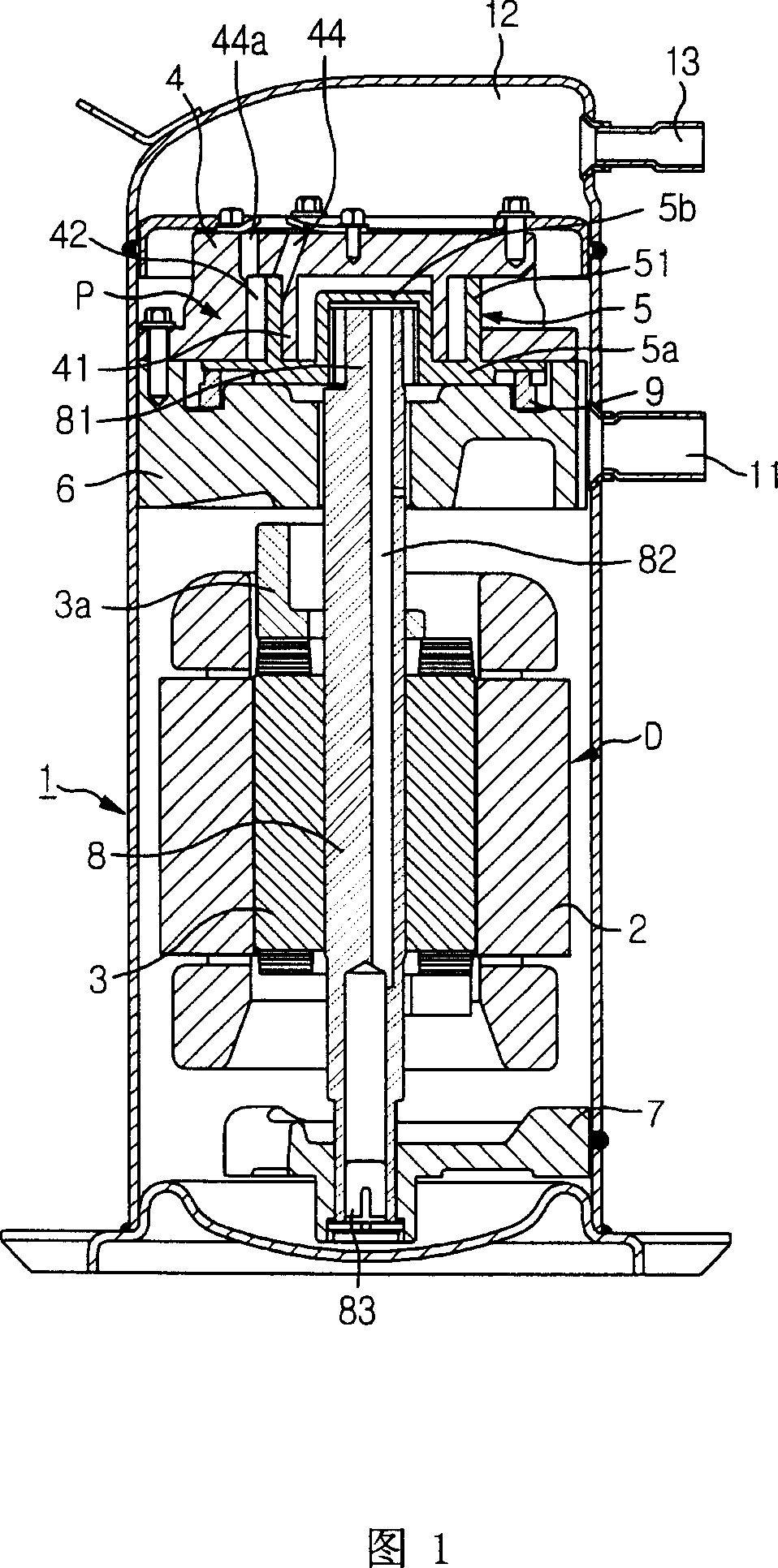
The invention refers to a linear compressor, comprising: a shell (20); a cylinder (30) affixed to the shell (20) and defining a compression chamber (C); a piston (40) to be displaced in reciprocating movement in the interior of the compression chamber (C) during the operation of the compressor; a linear electric motor (50) mounted to the shell (20); and an actuating means (60) operatively coupling the piston (40) to the linear electric motor (50), in order to make the latter displace the piston (40) in a reciprocating movement in the interior of the compression chamber (C), the actuating means (60) being coupled to the piston (40) by an elastic means (70), so that the actuating means (60) and the piston (40) be displaced in phase opposition during the operation of the compressor.
Owner:EMBRACO IND DE COMPRESSORES E SOLUCOES EM REFRIGERACAO LTDA
Linear motor and linear compressor
InactiveUS6946754B2Reduce the total massOperation efficiency can be improvedMagnetic circuit stationary partsPiston pumpsLinear compressorMagnetic poles
A linear motor includes a stator including a stator core for forming plural magnetic poles and a magnetic wire mounted on the stator core, and a mover provided at the interior of the stator and including a mover core and a magnet mounted on the outer side of the mover core. The linear motor has the magnet have a reduced mass, thus having a small size, a low overall cost, and a high operating efficiency.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Linear compressor
ActiveUS20100260629A1High efficiency cooling forceReduce manufacturing costPositive displacement pump componentsPiston pumpsReciprocating motionLinear compressor
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Volume varying device for rotating blade type compressor
InactiveCN1963214AChange capacityEnsure economical useRotary piston pumpsRotary piston liquid enginesGas compressorReciprocating motion
The volume changeable device of a circling vane compressor comprises the compressing section, driving section, round vanes with circling vanes of the compressing section, compressing chamber formed by the ring space and outside of the cylinder interior and the said round vane having a linear slider in straight reciprocating movement along the cylinder's sliding guide face, and a pair of side through channel symmetrically set on both sides of the broken part with whose middle as the center on the sliding contact surface one side of the linear slider. Opposite to the linear slider, inside the said cylinder, a sliding valve is set to move forward, set back, contact or open the broken part driven by the driving part. With circling vanes circling in the cylinder with simple valve operation, it can realize compression model change both in the inside compressing chamber or the outside compressing chamber, and change the volume of the compressor, not only ensuring the using economy of the compressor, but also preventing the abrasion for relevant components and supply waste while turning on or off the compressor.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS (TIANJIN) APPLIANCES CO LTD
Linear compressor controller
InactiveUS20070095073A1High power operationHigh operating requirementsEngine fuctionsCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEnergy collisionLinear compressor
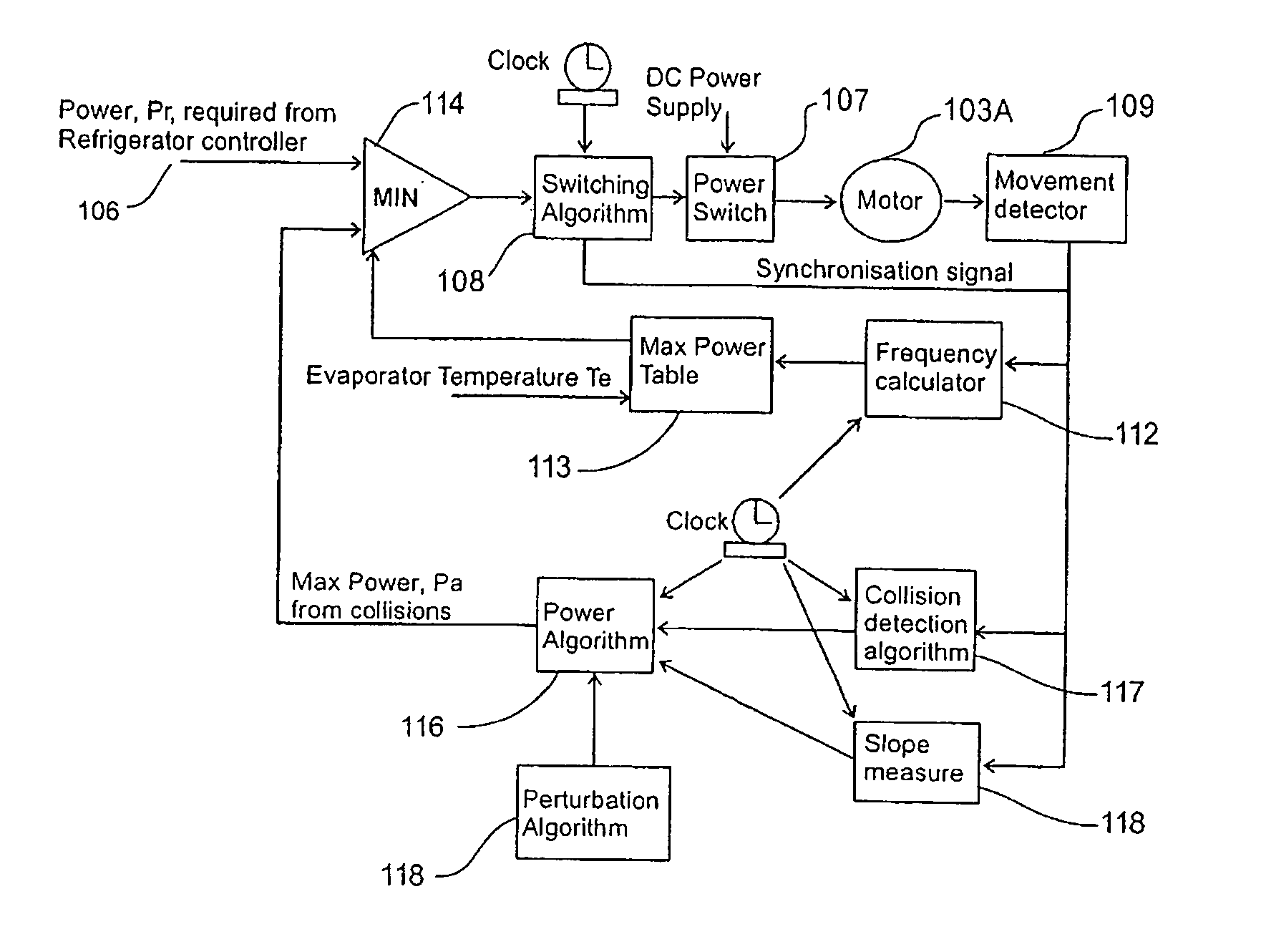
A free-piston linear compressor (1) controlled to achieve high volumetric efficiency by a controller including an algorithm (116) for ramping up input power until piston-cylinder head collisions are detected using a detection algorithm (117 / 118) which then decrements power input whereupon input power is again ramped up by algorithm (116). Non-damaging low energy collisions are achieved by the controller including a perturbation algorithm (119) which perturbates the input power ramp with periodic transient pulses of power to ensure piston collisions are provoked during the transient power pulses.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL APPLIANCES LTD
Linear motor controller
ActiveUS20050168179A1Decline in power responseAvoid Compressor DamageWorking fluid for enginesElectric motor speed/torque regulationLinear compressorGas compressor
A sensorless method of detecting piston collisions in a reciprocating free piston linear compressor driven by an electronically commutated linear motor having at least one excitation winding is provided. A free piston gas compressor is also provided.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL APPLIANCES LTD
Driving controlling apparatus for linear compressor and method thereof
ActiveUS20070241697A1Short strokeIncrease currentMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlPhase differenceLinear compressor
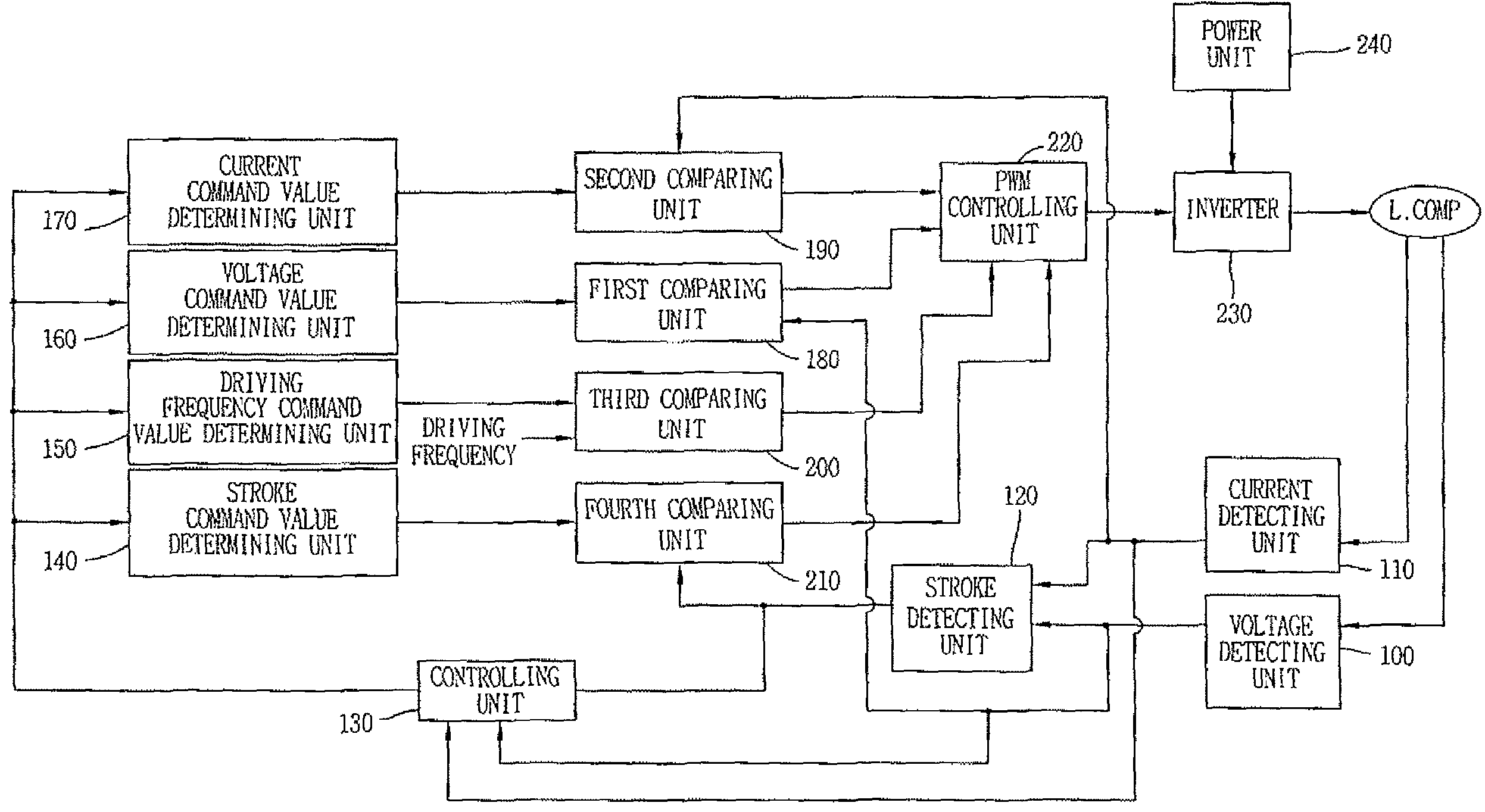
A driving controlling apparatus for a linear compressor, comprises a controlling unit for detecting a TDC by a phase difference inflection point between a stoke and a current with increasing the stroke by controlling the current applied to a linear motor, and for varying the current applied to the linear motor based on the detected TDC.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
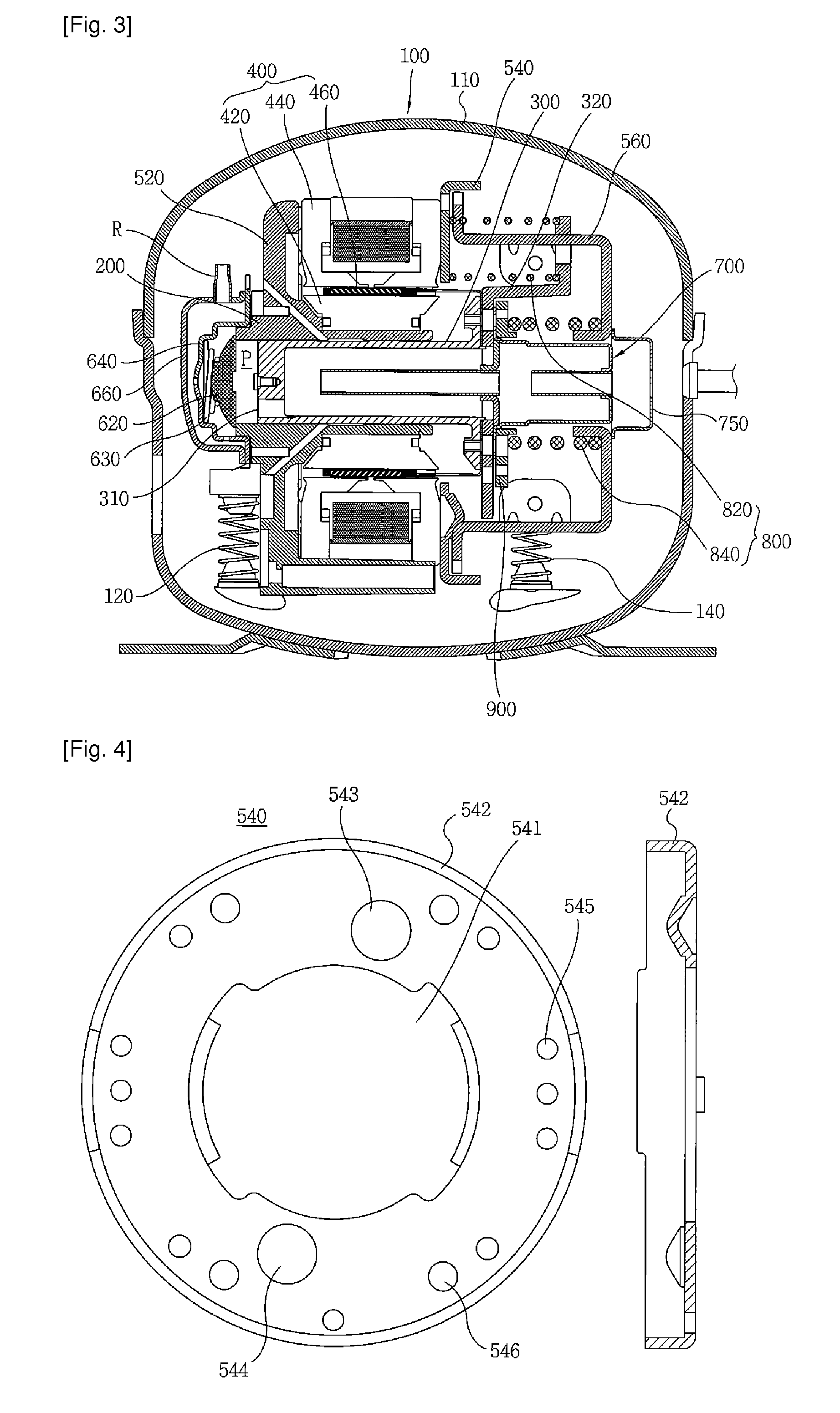
Linear compressor
A linear compressor is provided. The linear compressor includes a piston. The piston includes a piston cylinder having a head plate. The head plate defines a passage that extends through the head plate. A reed valve is mounted to the head plate and positioned over the passage of the head plate. A valve seat is positioned at and extends about the passage of the head plate.
Owner:HAIER US APPLIANCE SOLUTIONS INC
Linear compressor
ActiveUS20110194957A1Reduce part production costReduce in quantityPositive displacement pump componentsNon-rotating vibration suppressionResonanceReciprocating motion
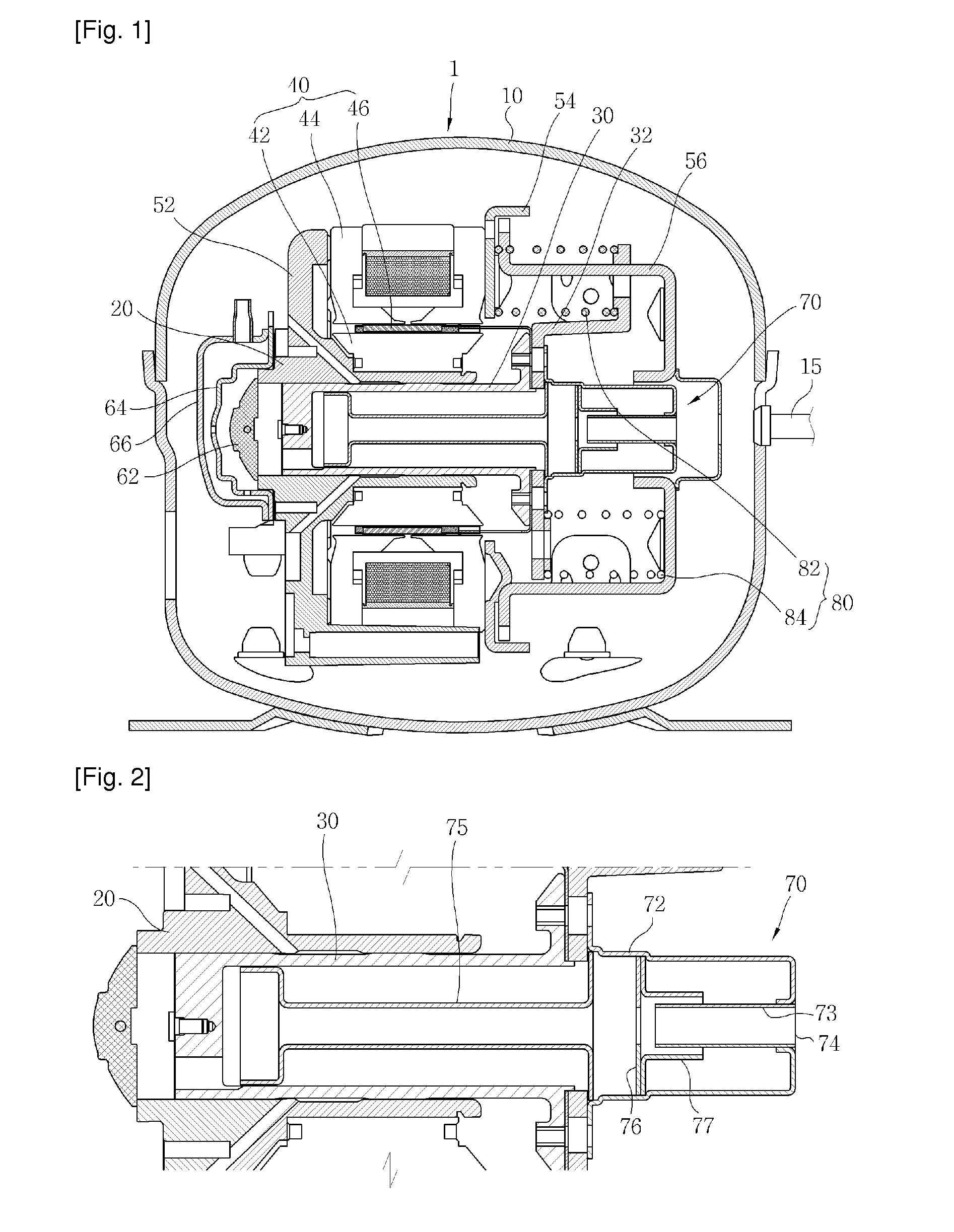
There is provided a linear compressor (100), which has a reduced number of front main springs (820) located at the front among springs continuously transmitting a force so that a piston (300) can move in a resonance condition. The linear compressor (100) comprises: a hermetic container (110) to be filled with a refrigerant; a linear motor including an inner stator; an outer stator, and a permanent magnet; a piston linearly reciprocating by the linear motor; a cylinder (200) for providing a space for compressing the refrigerant upon linear reciprocation of the piston (300); a supporter piston (300) having a connecting portion connected to one end of the piston (300) and contacting with the piston (300), a support portion extended from the connecting portion and an additional mass member (350) fixing portion extended from the connecting portion; a plurality of front main springs (820) mounted at positions symmetrical with respect to the center of the piston (300) and the supporter piston (320), one ends of which being supported by one surface of the supporter piston (320); and one rear main spring (840), one end of which being supported by the other surface of the supporter piston (320).
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com