Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
477 results about "Light scan" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High-speed scanning and overall imaging three-dimensional (3D) measurement method
InactiveCN102589476AFast measurementLittle effect on reflectivityUsing optical meansThree dimensional measurementPrism
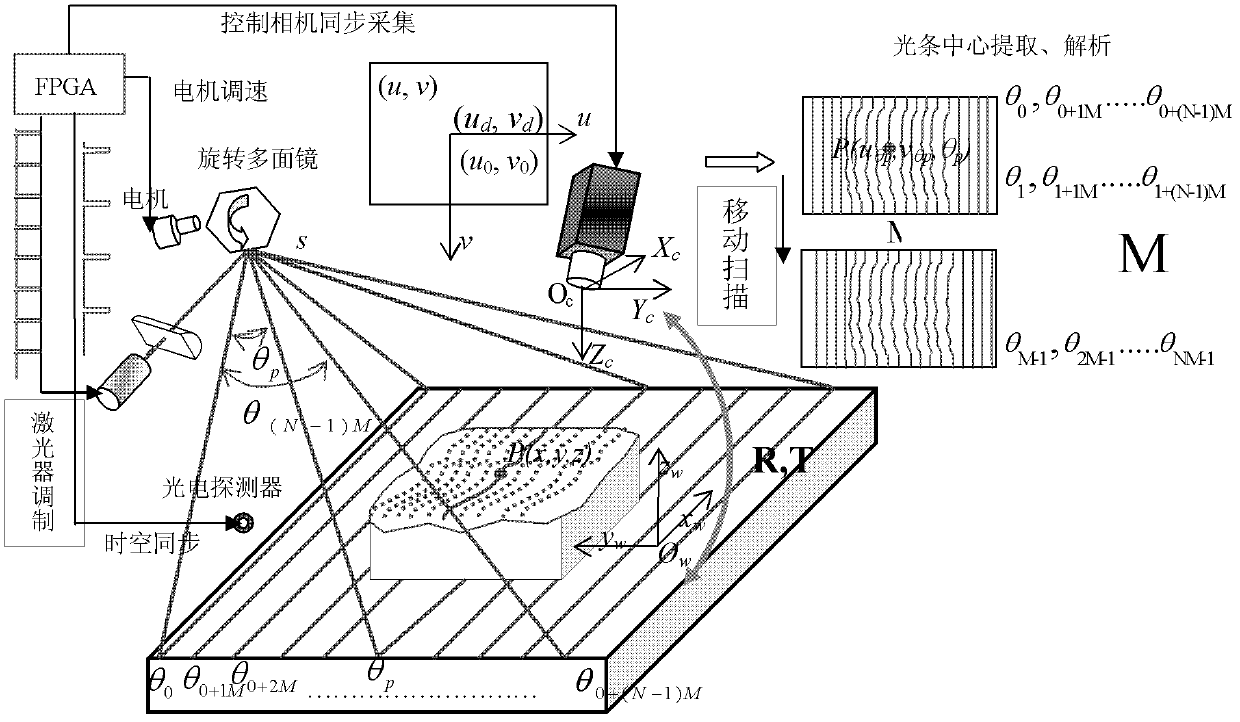
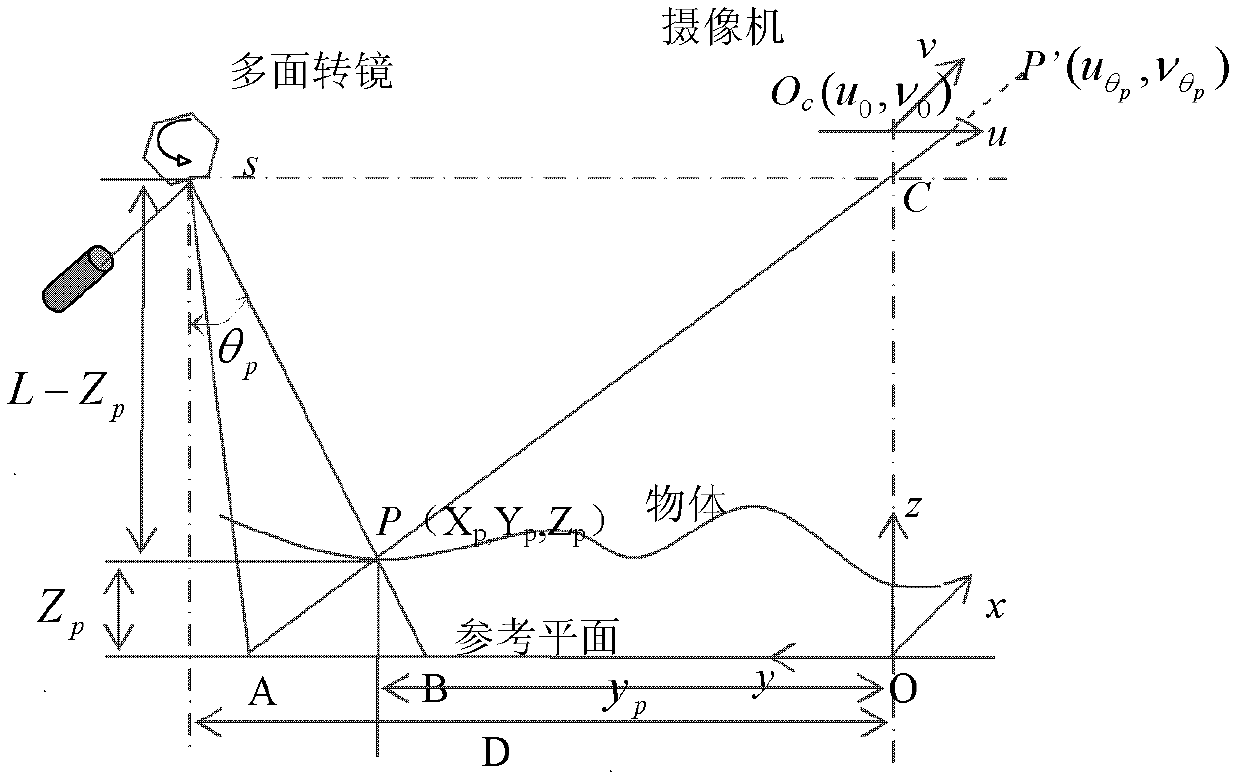
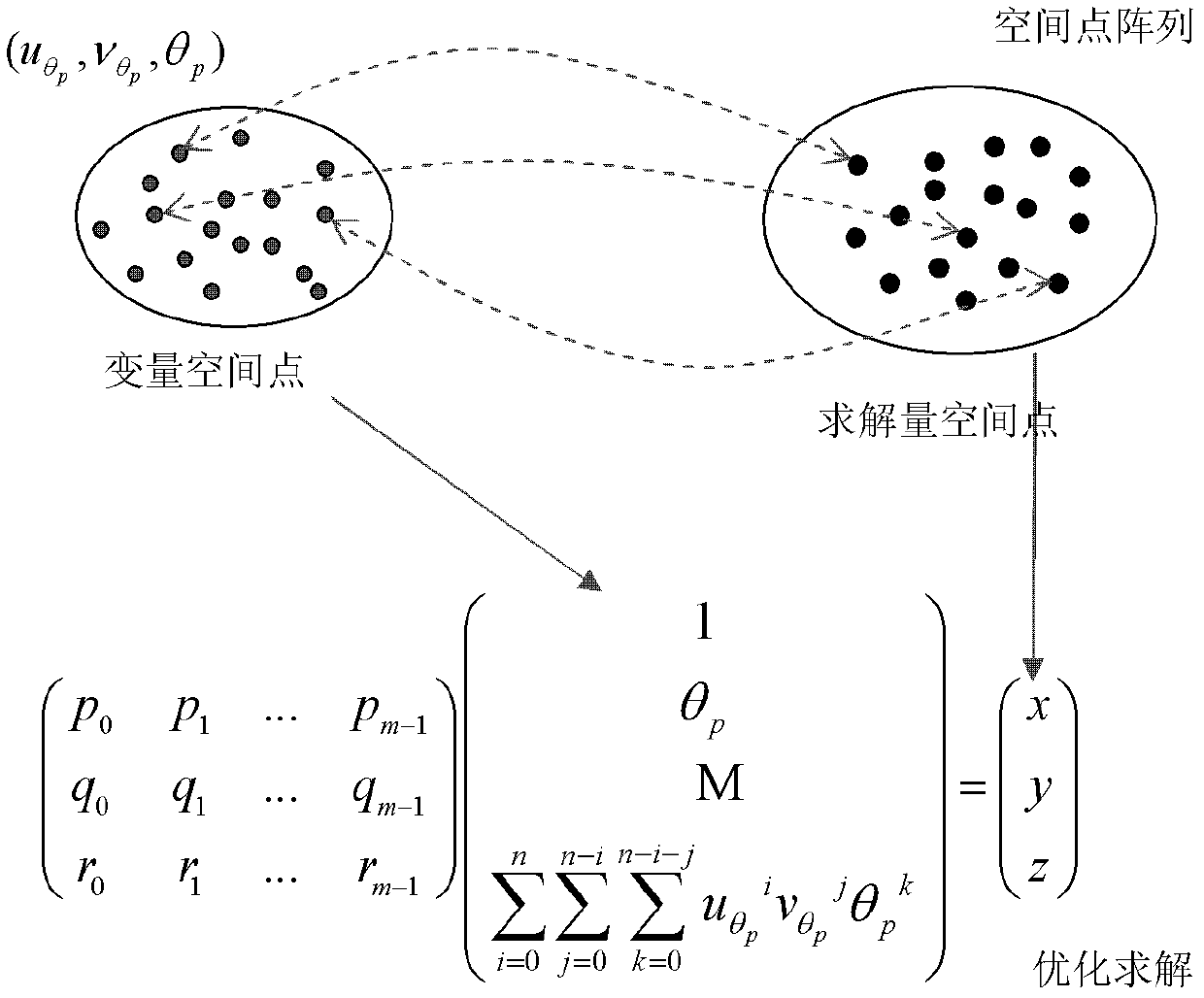
The invention relates to a visual inspection technology. In order to meet the requirements of fast and high-accurate surface three-dimensional (3D) topography online measurement and the detection requirements of a production line on intelligence, fastness, high accuracy and low cost, the invention adopts the technical scheme that: a high-speed scanning and overall imaging 3D measurement method comprises the following steps of: carrying out external modulation on a driving power supply by using a laser so as to control the output of a word line laser; rotating a multifaceted prism under the drive of a high-speed motor, wherein line-structured light outputted by the laser is reflected and projected to the surface of a measured object by the multifaceted prism; and placing a photoelectric detector at a position which is the limit position projected by the line-structured light during the rotating process of the multifaceted prism, carrying out exposure on an area-array CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) camera during the process that the line-structured light scans the whole area, and establishing a measurement model, wherein the 3D coordinate (xp, yp, zp) of the surface feature point of the measured object is obtained according to a formula by using an image coordinate (u[theta]p, v[theta]p) formed by the area-array CCD camera and [theta]p. The high-speed scanning and overall imaging 3D measurement method is mainly applied to the fast and high-accurate surface 3D topography online measurement.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Ground three-dimensional laser scanning point cloud and image fusion and registration method
InactiveCN105931234AImprove noise immunityEnsuring rotation invarianceImage enhancementImage analysisLaser scanningImage fusion
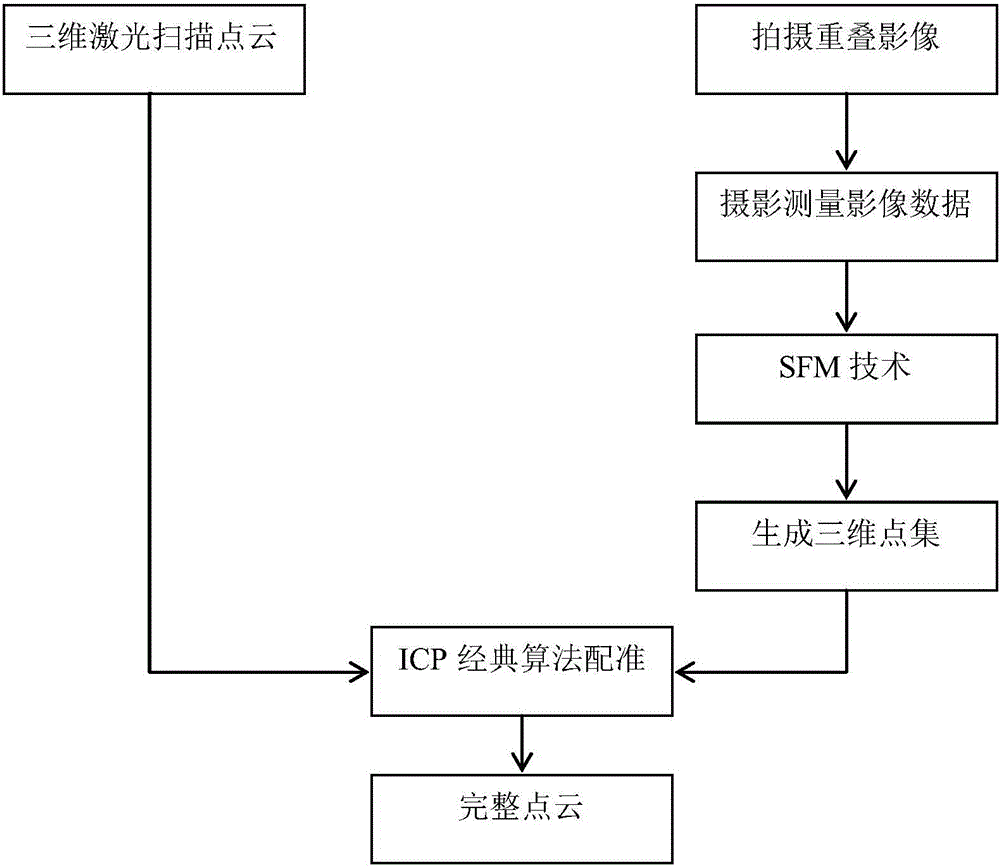
The present invention provides a ground three-dimensional laser scanning point cloud and image fusion and registration method, and the limitation of the scanning of the ground three-dimensional laser scanning technology is overcome. The point cloud data obtained by ground three-dimensional laser scanning often comprises various areas which can not be measured, point cloud holes are generated, and thus local area information of a scanned object is lost. The holes cause that a model can not realize visualization correctly, and model subsequent processing is influenced too. For the above problems, the invention aims to solve the problems through the following technical scheme that an SIFT image is used to carry out mosaic processing of collected image photos by means of an algorithm to obtain a panoramic image, the intensive reconstruction is carried out through the panoramic image to obtain the 3D point cloud data generated by the image photo, and an iterative closest point algorithm (ICP) is used to realize the registration working of laser scanning point cloud and image data generation point cloud.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
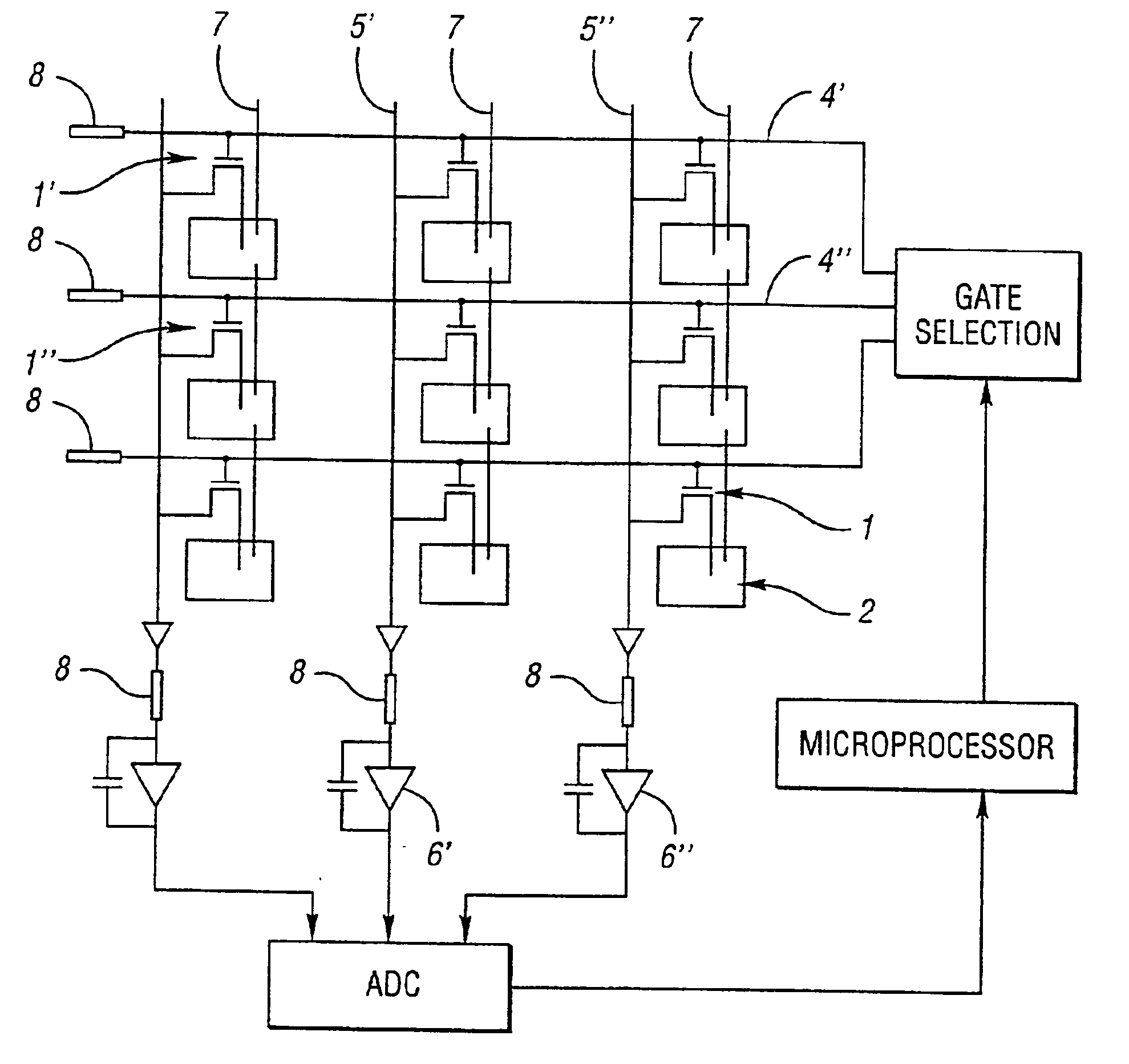
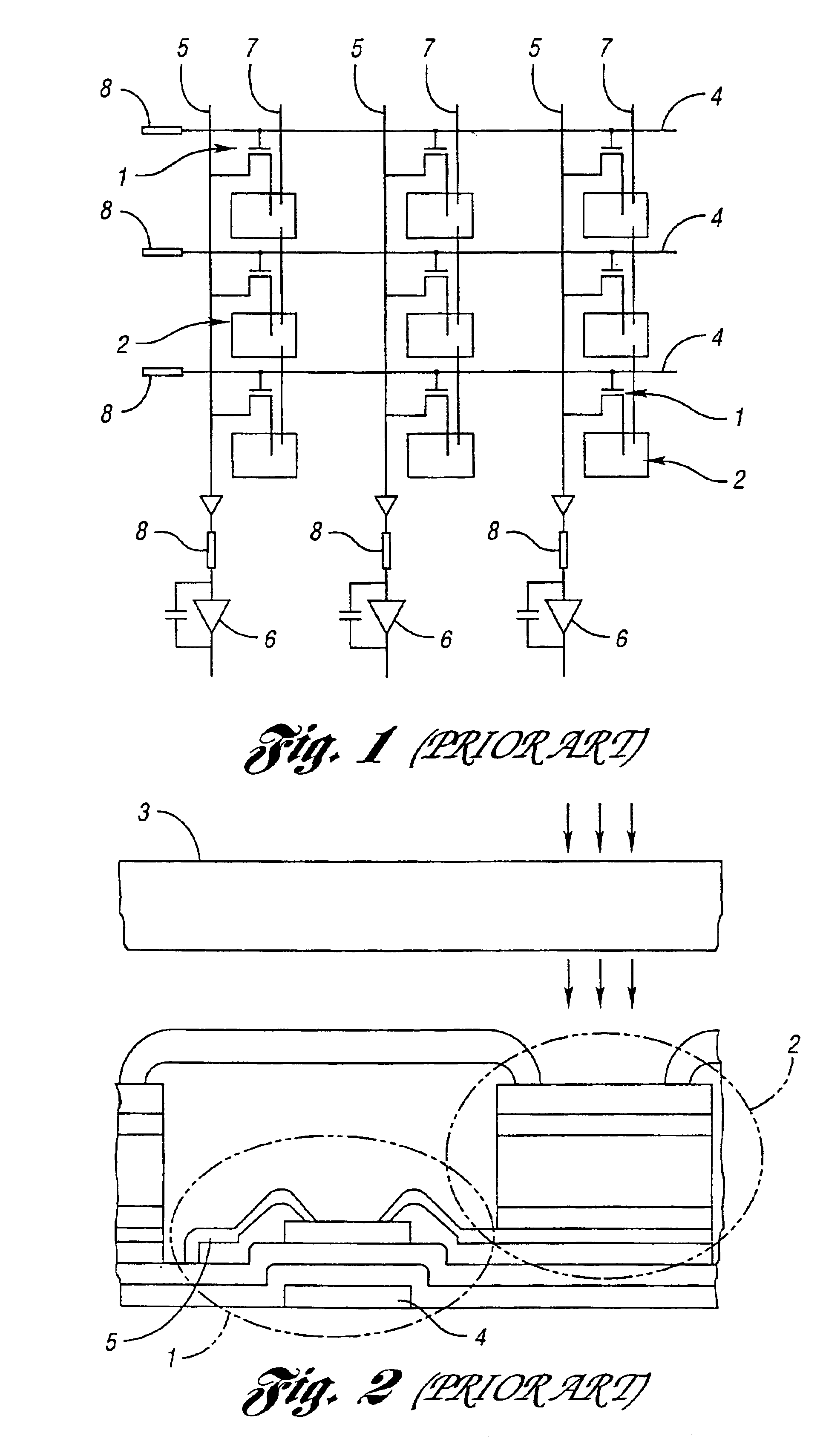
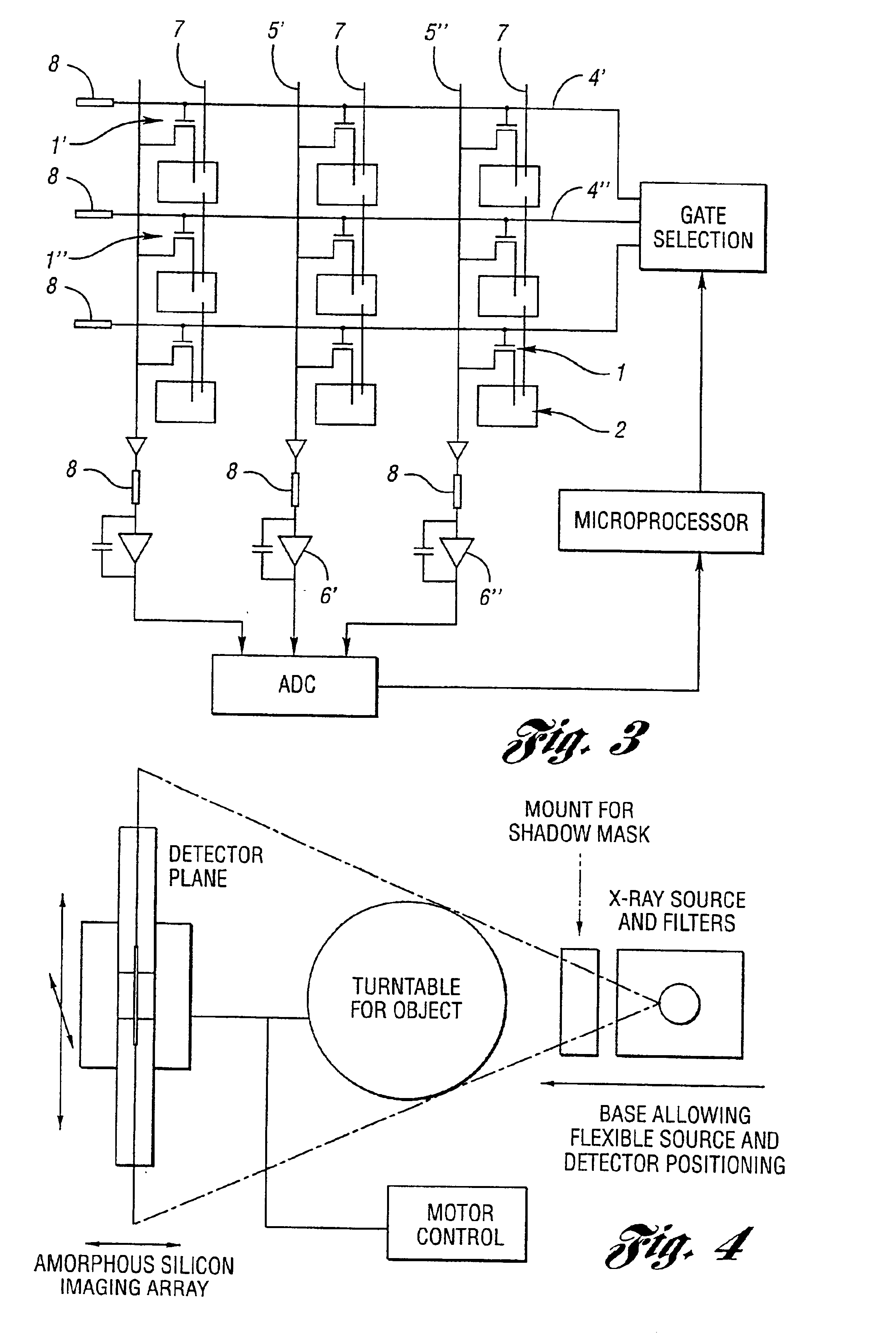
Method, processor and computed tomography (CT) machine for generating images utilizing high and low sensitivity data collected from a flat panel detector having an extended dynamic range
InactiveUS6868138B2Television system detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayFlat panel detector
A method, processor and computed tomography (CT) machine for generating images utilizing high and low sensitivity data collected from a flat panel detector having an extended dynamic range. Hardware modifications for extending the dynamic range include grouping pixel rows and pixel columns into clusters of two. The sensitivity of the rows / columns is modified by positioning optical masks that have different transparencies for different rows / columns. Software modifications for extending the dynamic range include taking two correlated exposure scan measurements at each angle and combining the two data sets into one scan prior to image reconstruction. This method uses a spatially varying pixel exposure method where several adjacent pixels are clustered and each cluster has a different sensitivity. The signals of these clusters are combined to form one image effectively producing an increased dynamic range. The flat panel imager may be an a-Si:H based flat panel detector for use in X-ray imaging, including cone beam computer tomography (CBCT).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
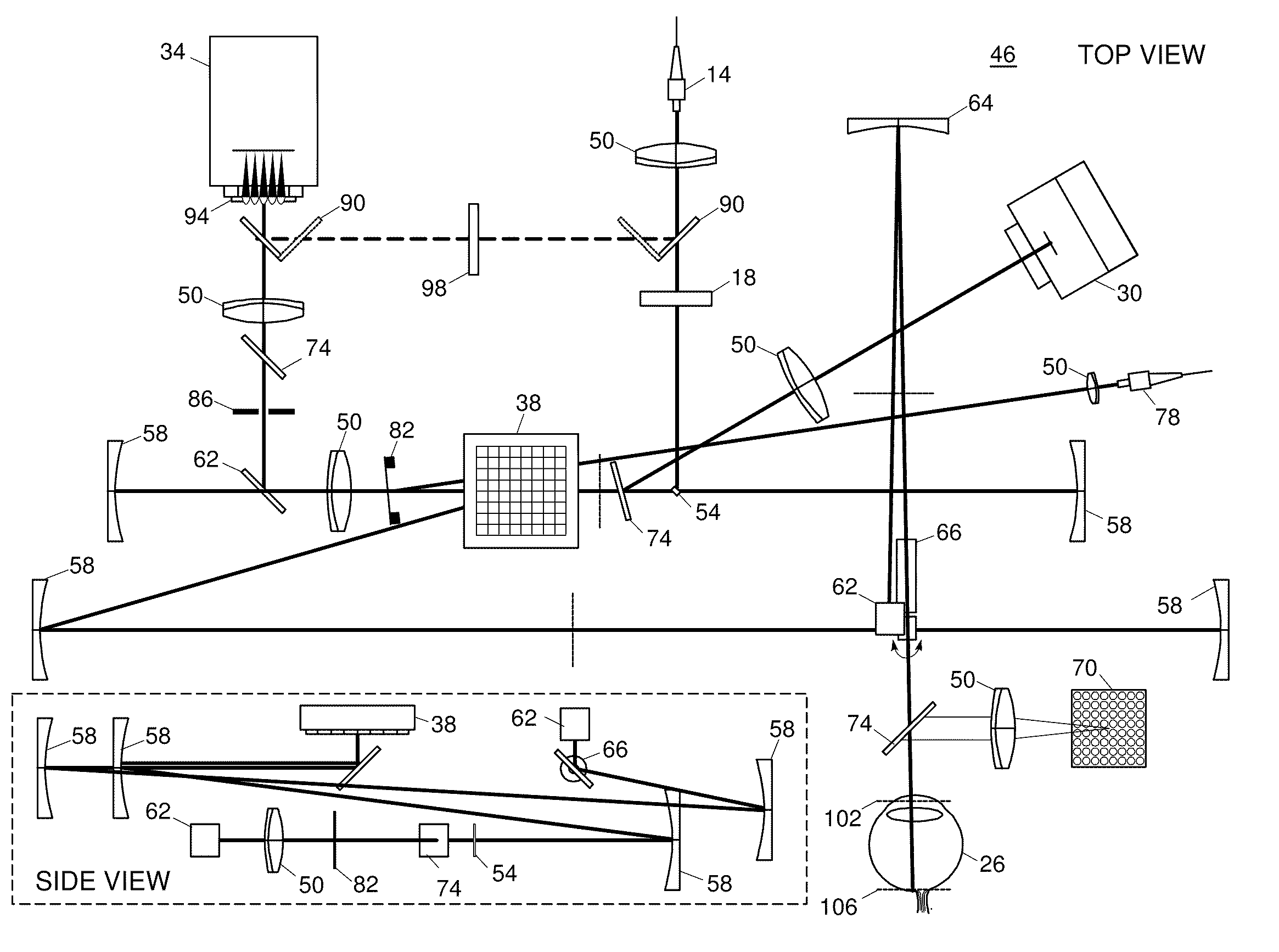
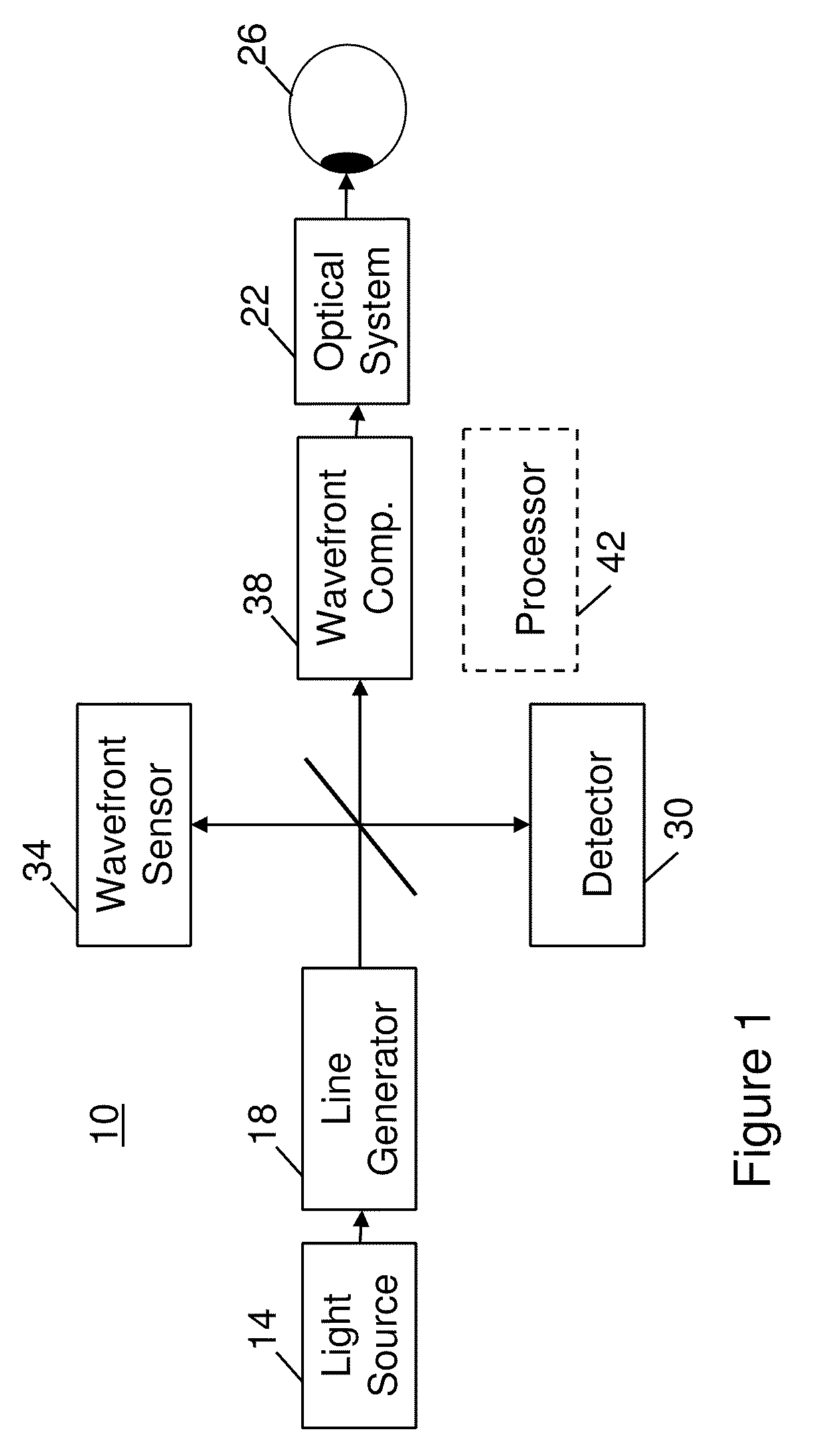
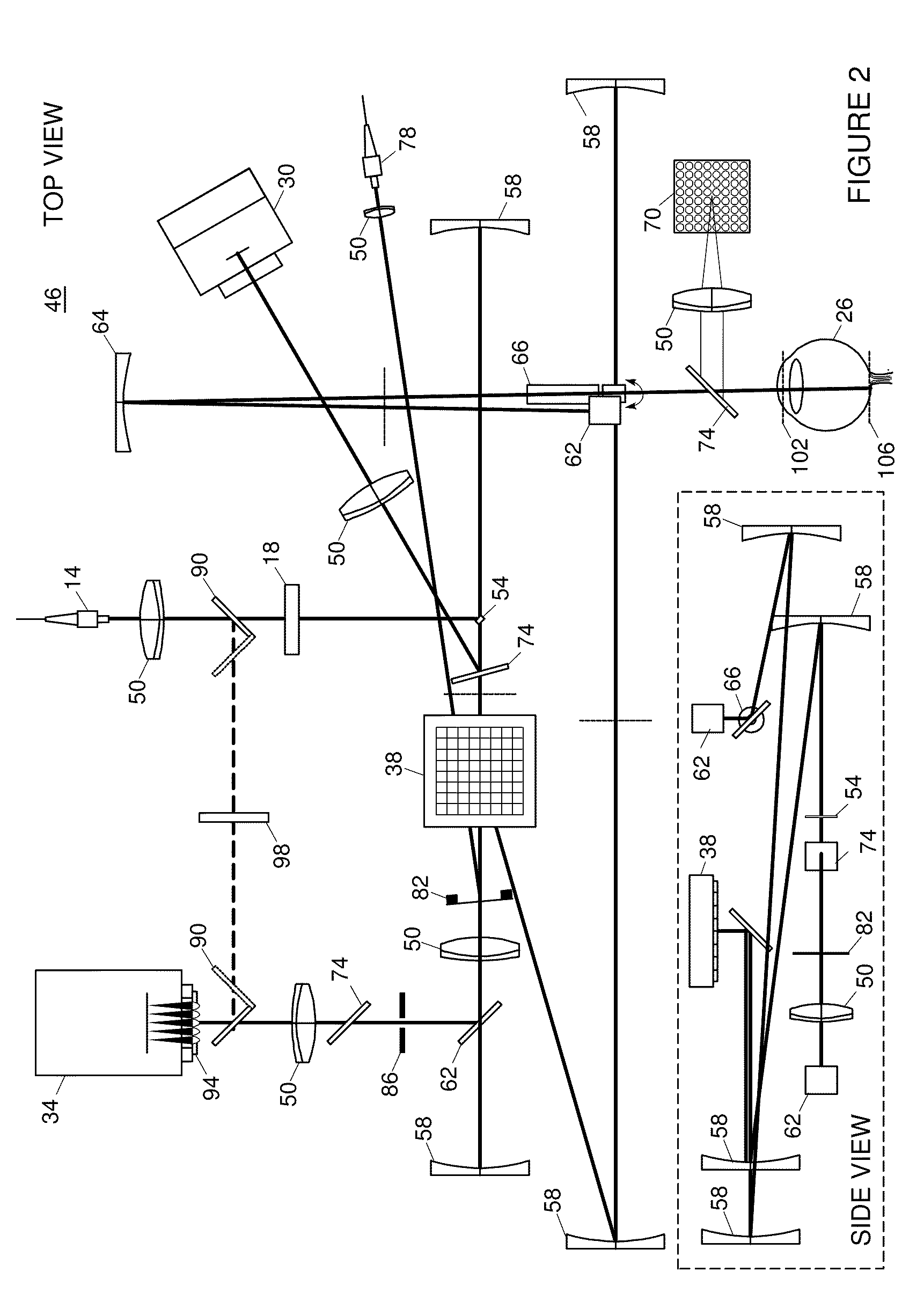
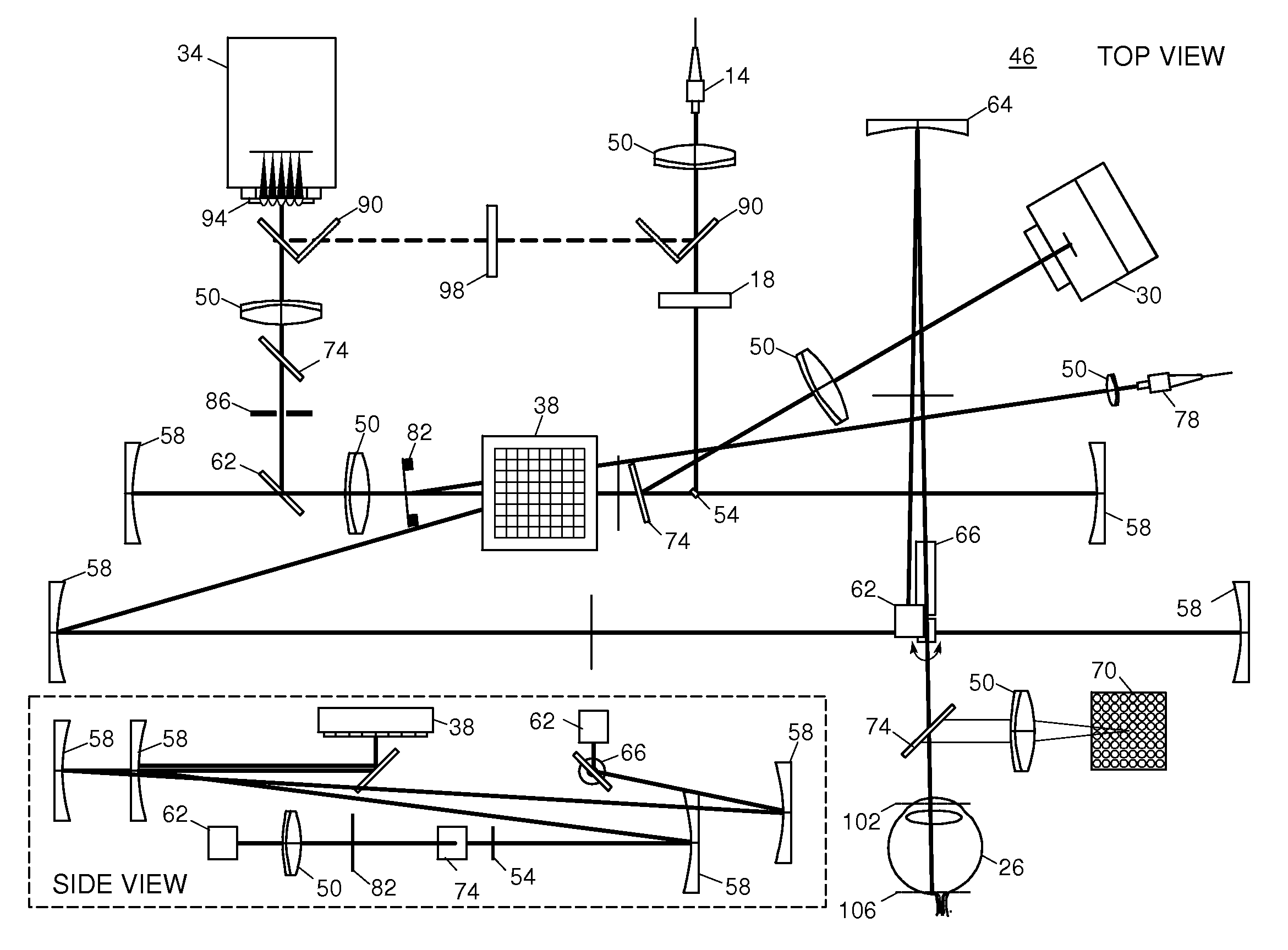
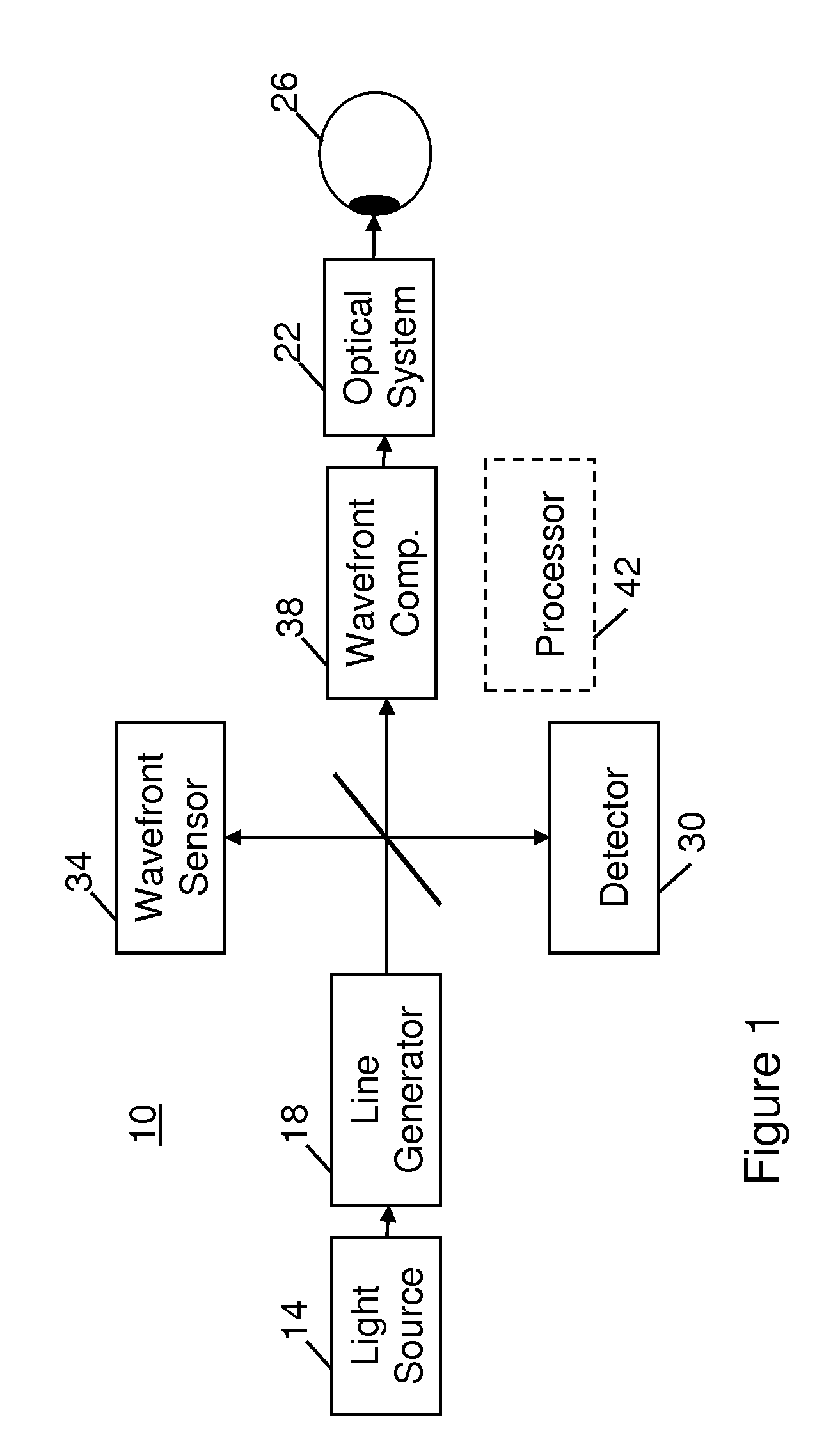
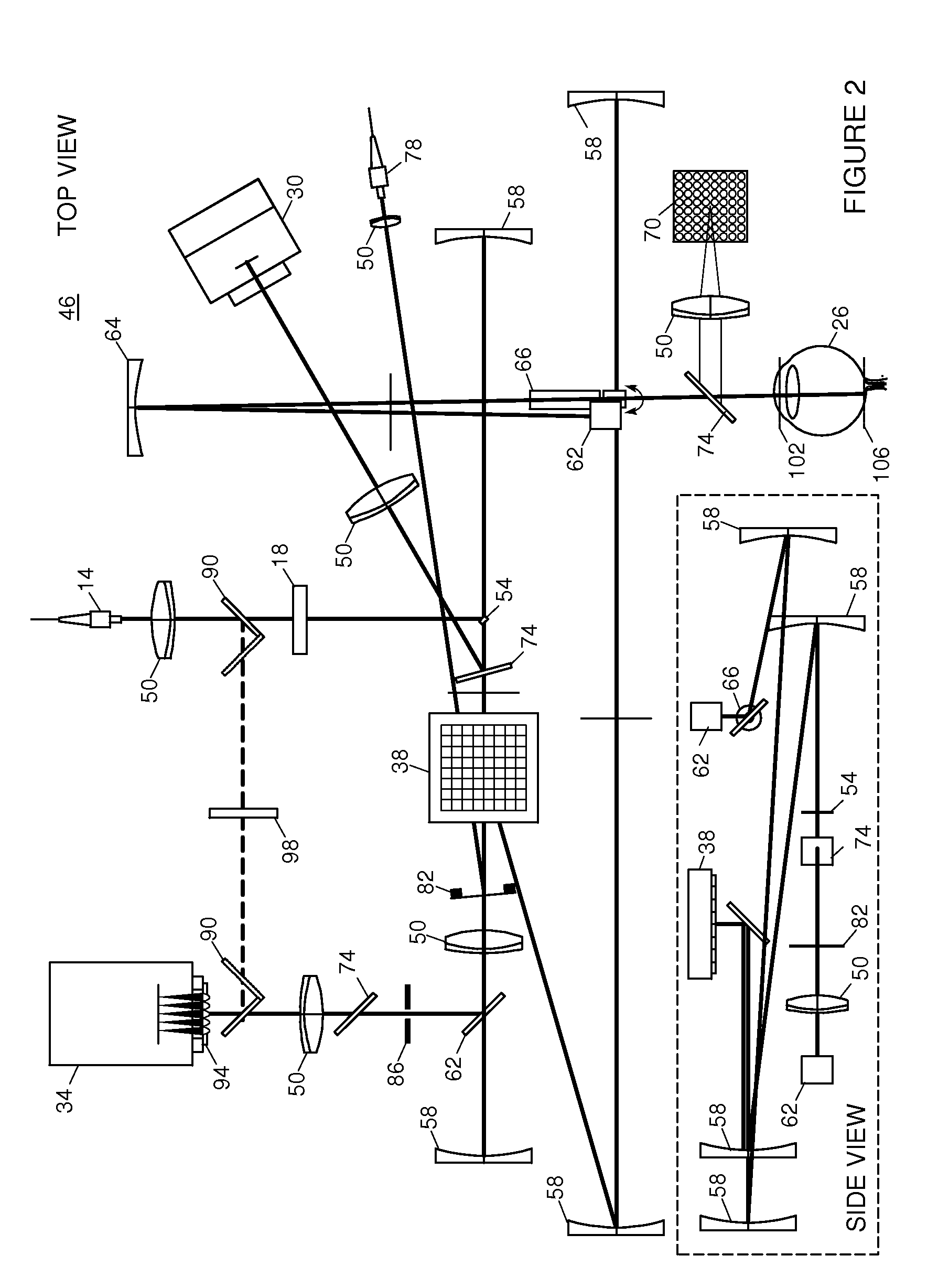
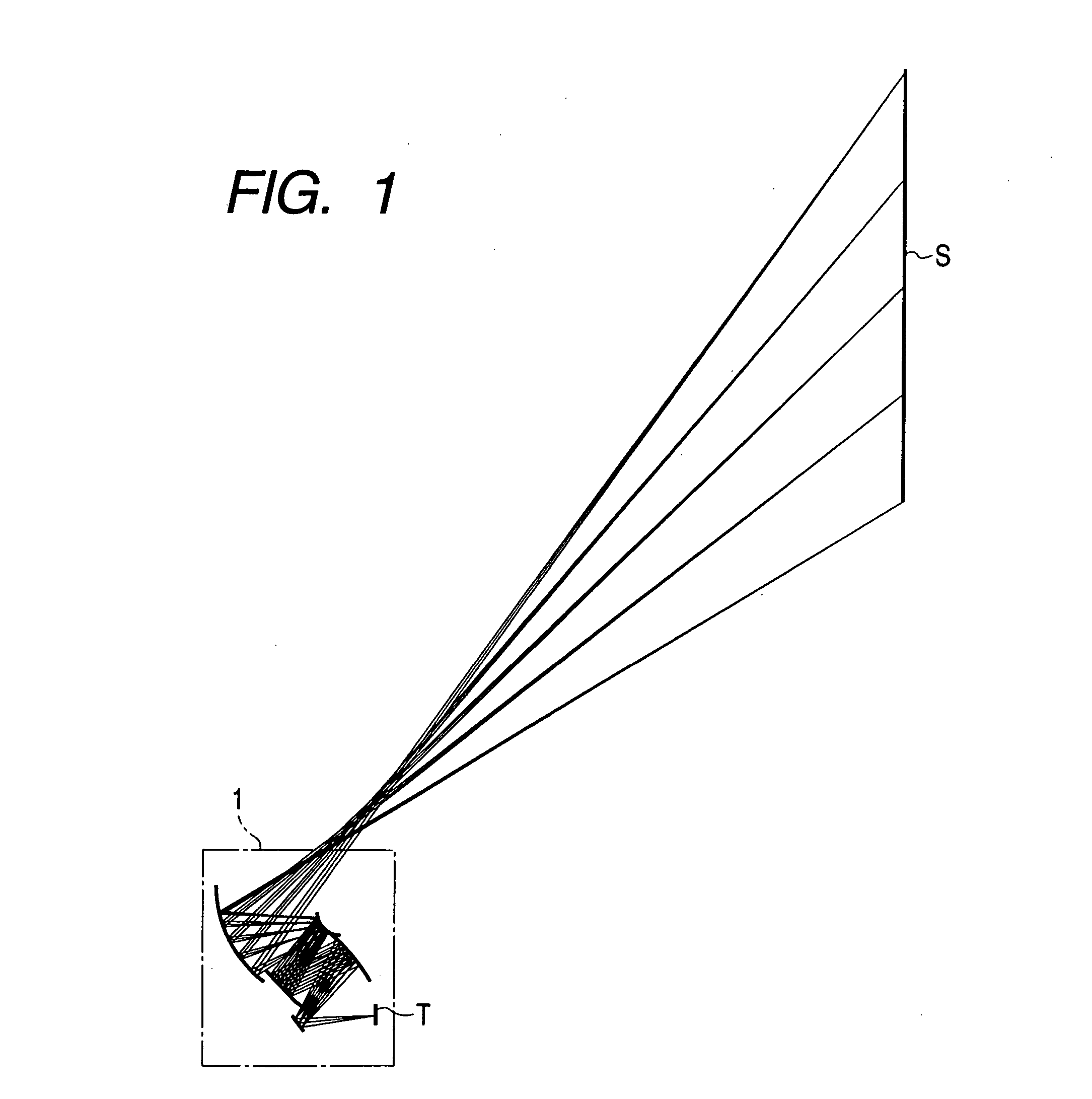
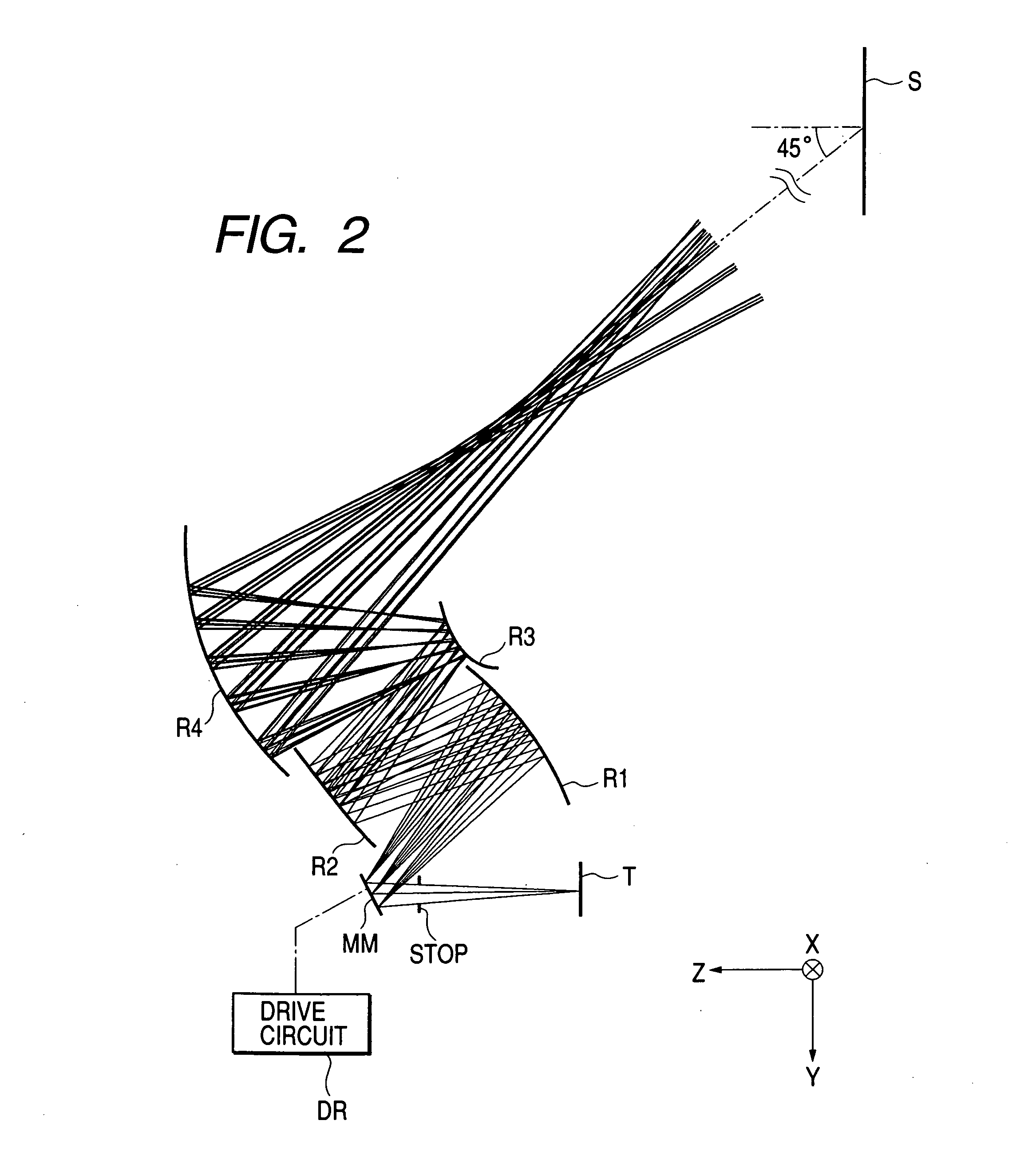
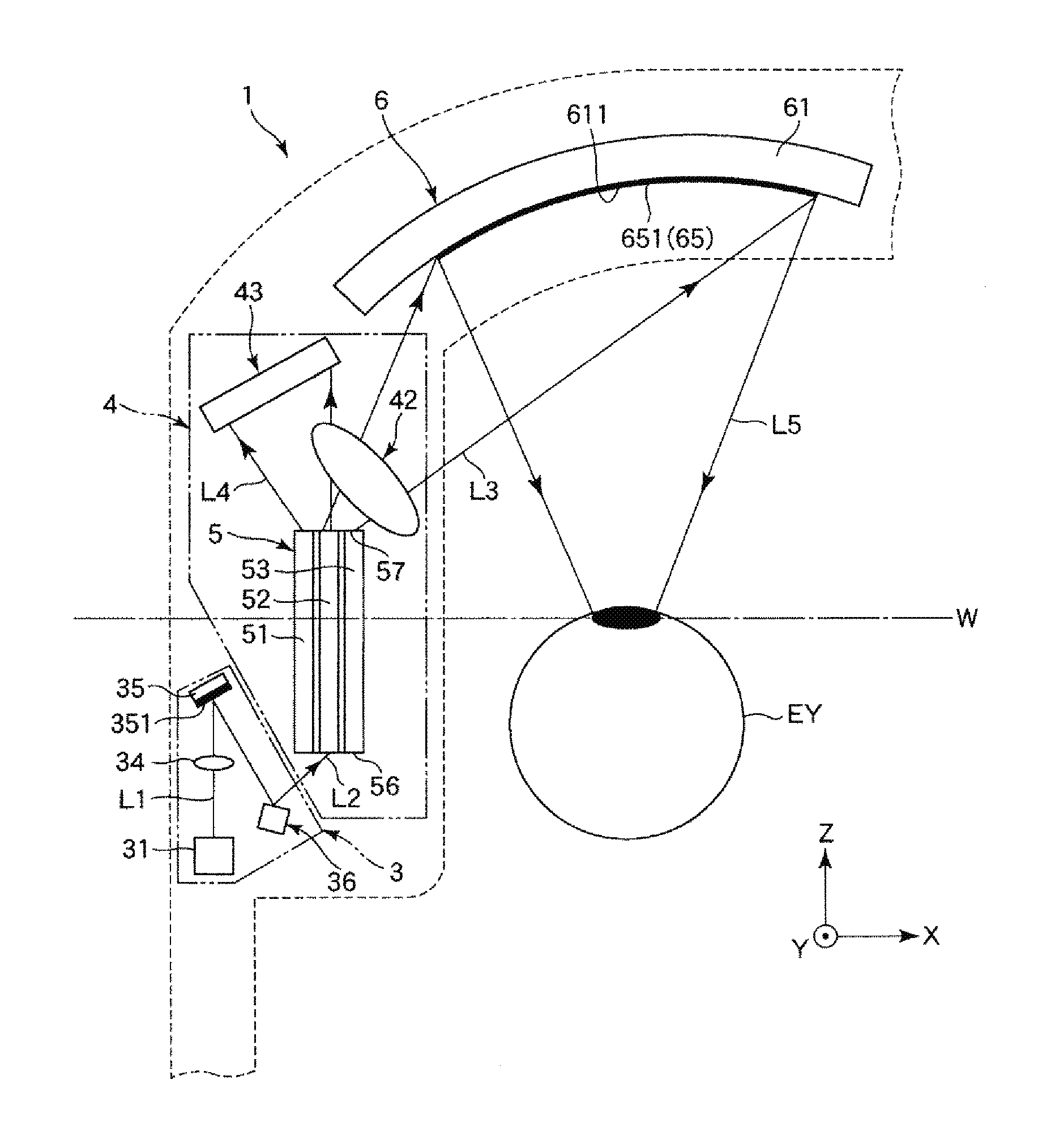
Adaptive optics line scanning ophthalmoscope
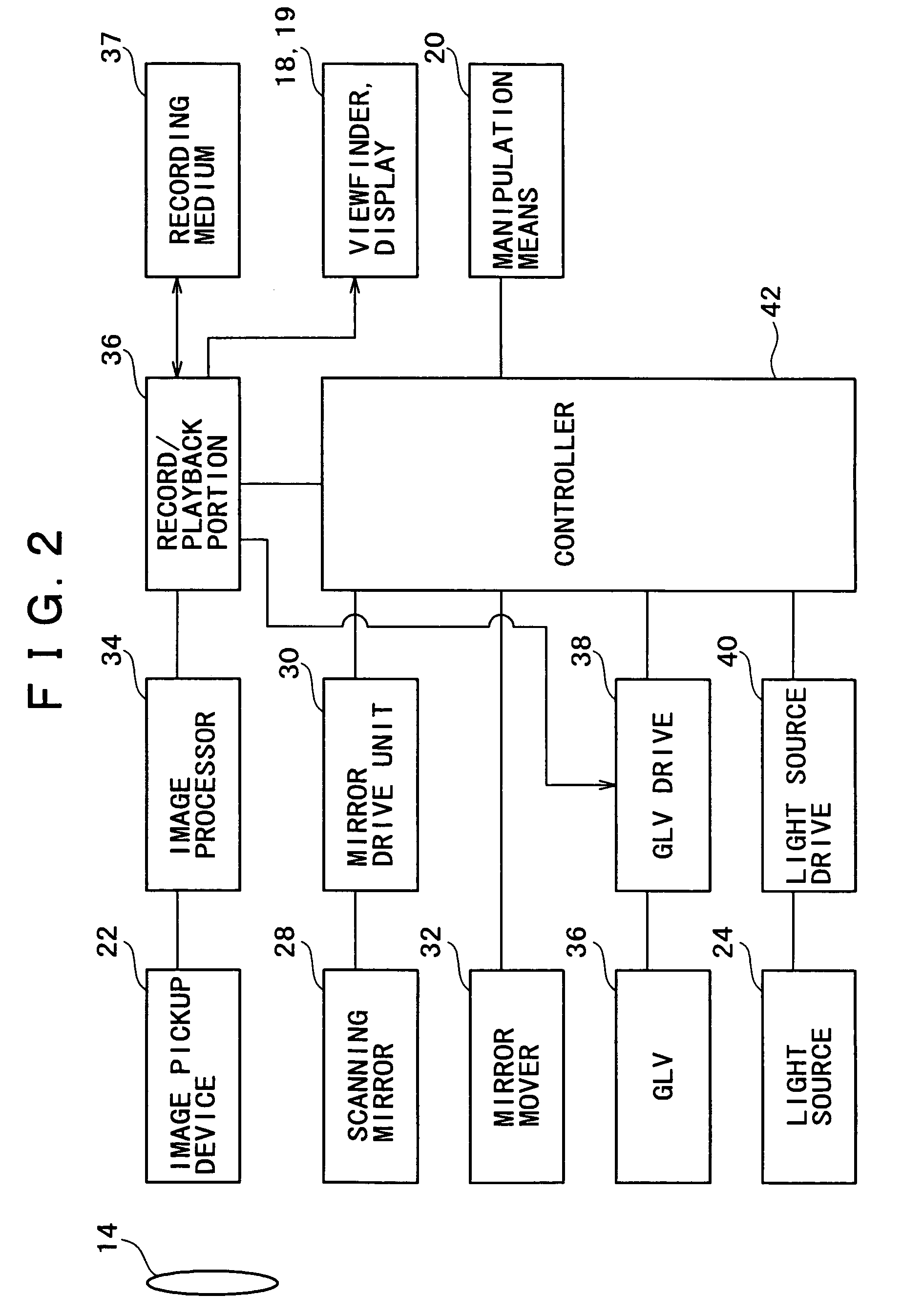
ActiveUS8201943B2Improve understandingSimplied optics, high-speed scanning componentsEye diagnosticsOptical ModuleOphthalmoscopes
A first optical module scans a portion of an eye with a line of light, descans reflected light from the scanned portion of the eye and confocally provides output light in a line focus configuration. A detection device detects the output light and images the portion of the eye. A second optical module detects an optical distortion and corrects the optical distortion in the line of light scanned on the portion of the eye.
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
Adaptive Optics Line Scanning Ophthalmoscope
ActiveUS20100195048A1Advance understanding of visionCompact and simplifiedEye diagnosticsOptical ModuleOphthalmology
A first optical module scans a portion of an eye with a line of light, descans reflected light from the scanned portion of the eye and confocally provides output light in a line focus configuration. A detection device detects the output light and images the portion of the eye. A second optical module detects an optical distortion and corrects the optical distortion in the line of light scanned on the portion of the eye.
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
Confocal scanning endoscope system and image display area adjustment method thereof
There is provided a confocal scanning endoscope system, which is provided with a light source that emits light, a scanning unit that deflects the light emitted by the light source so that the light scans on a subject in two dimensions, an objective optical system that directs the light deflected by the scanning unit to the subject, an extraction unit that extracts only part of the light returning from a convergence point at which the light is converged by the objective optical system on an object side, an image formation unit configured to form an image based on the part of the light extracted by the extraction unit, and a display area adjustment unit configured to measure Encircled Energy of the part of the light extracted by the extraction unit and to adjust a display area of the image based on the measured Encircled Energy.
Owner:HOYA CORP
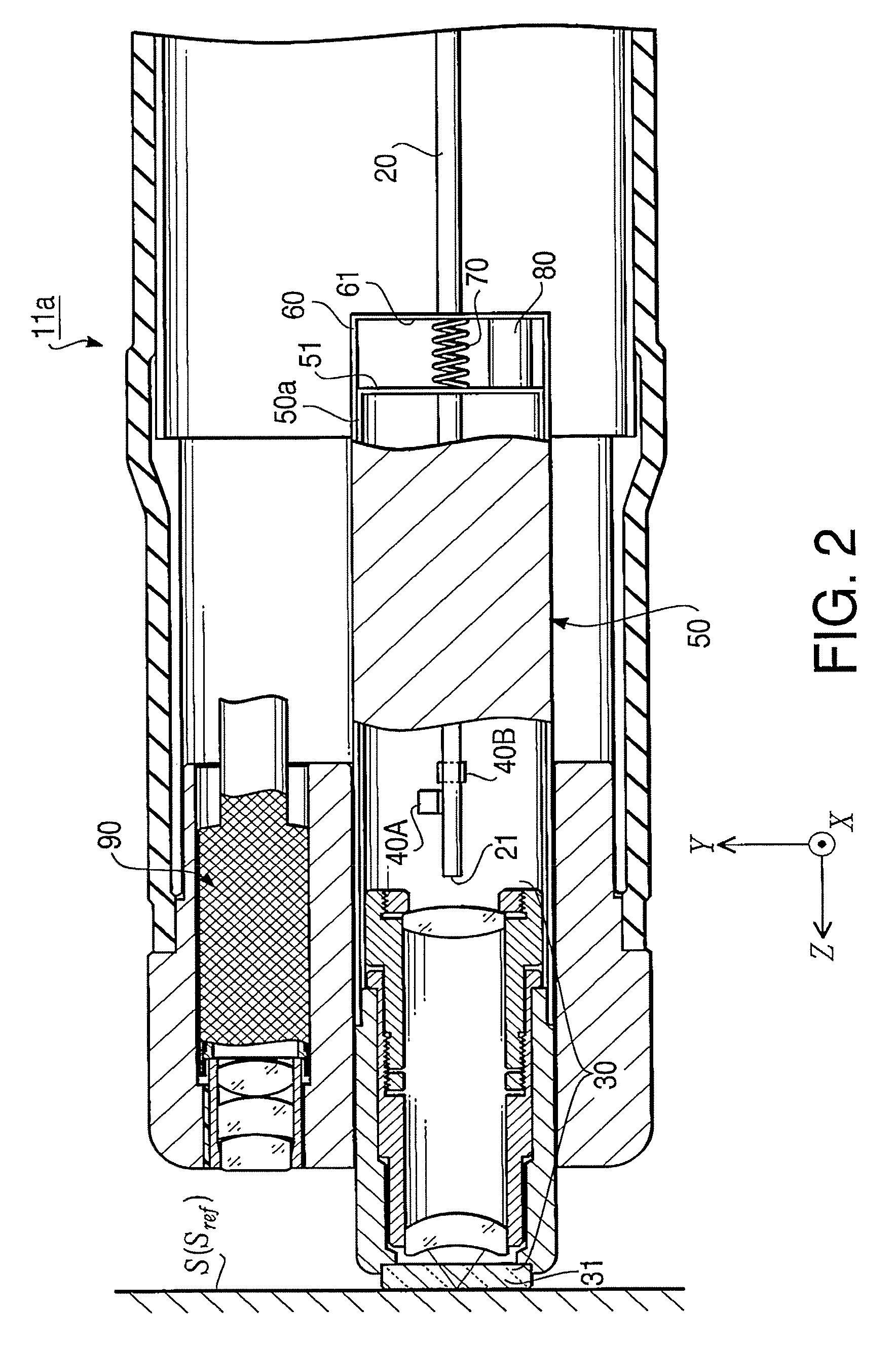
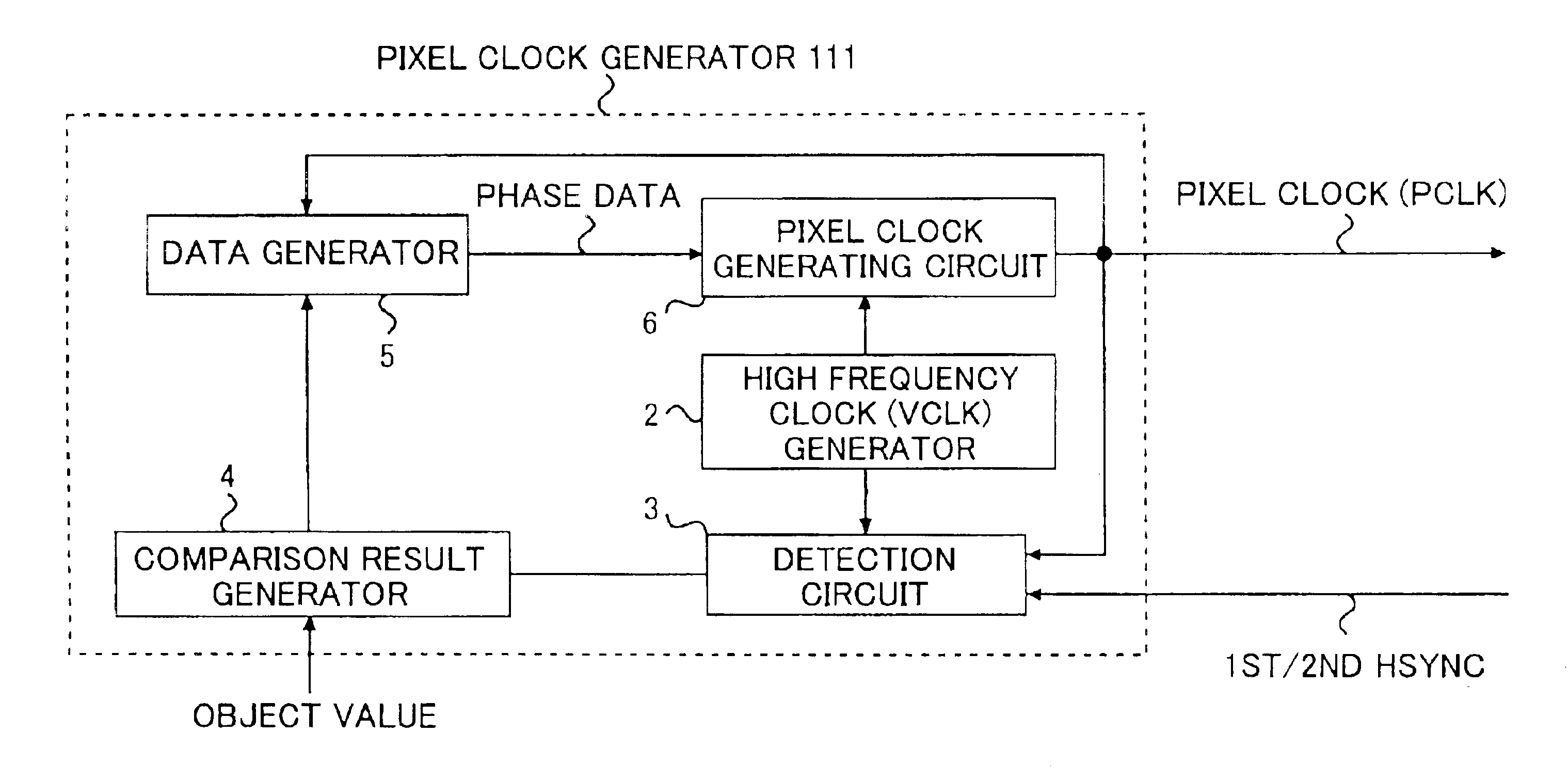
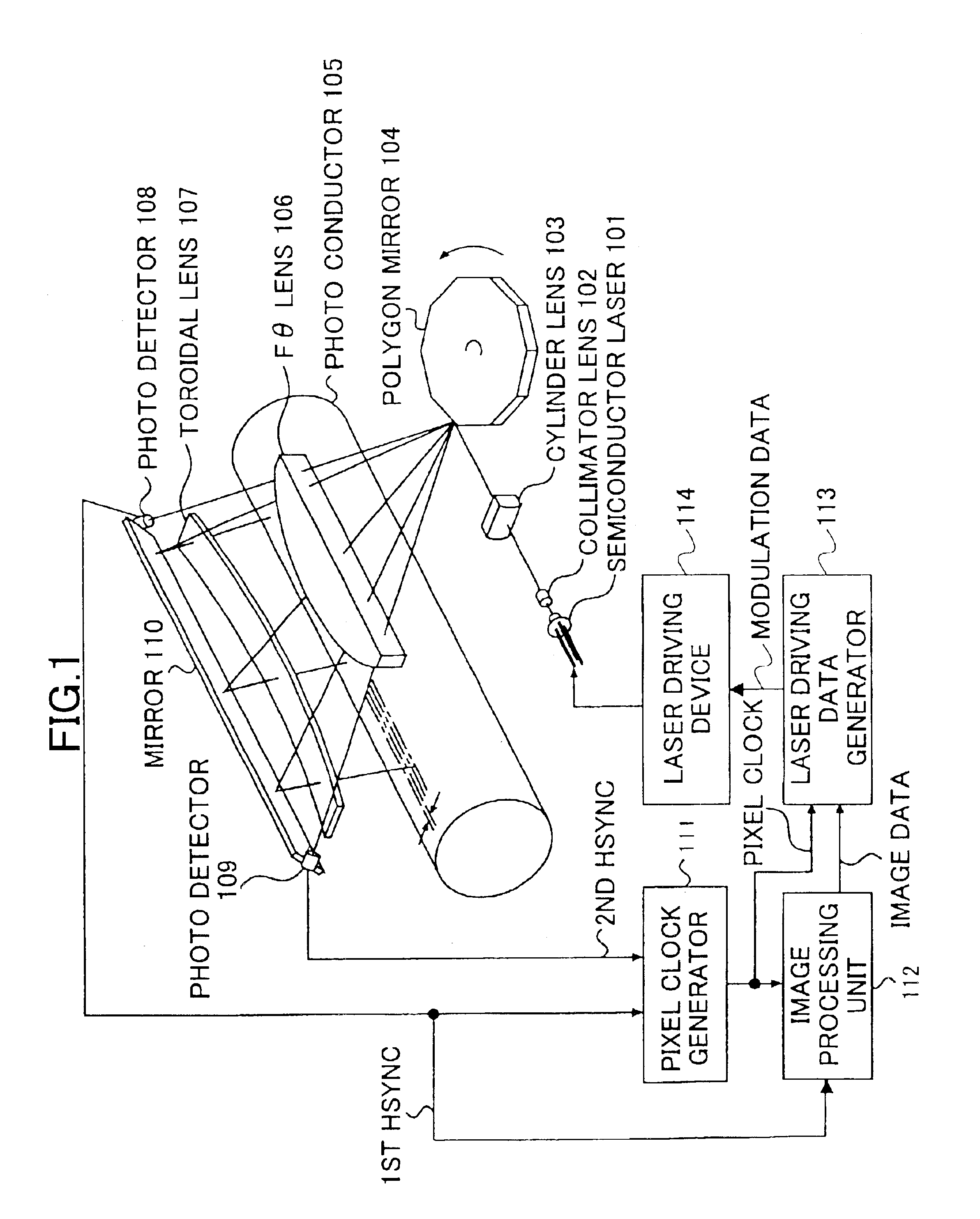
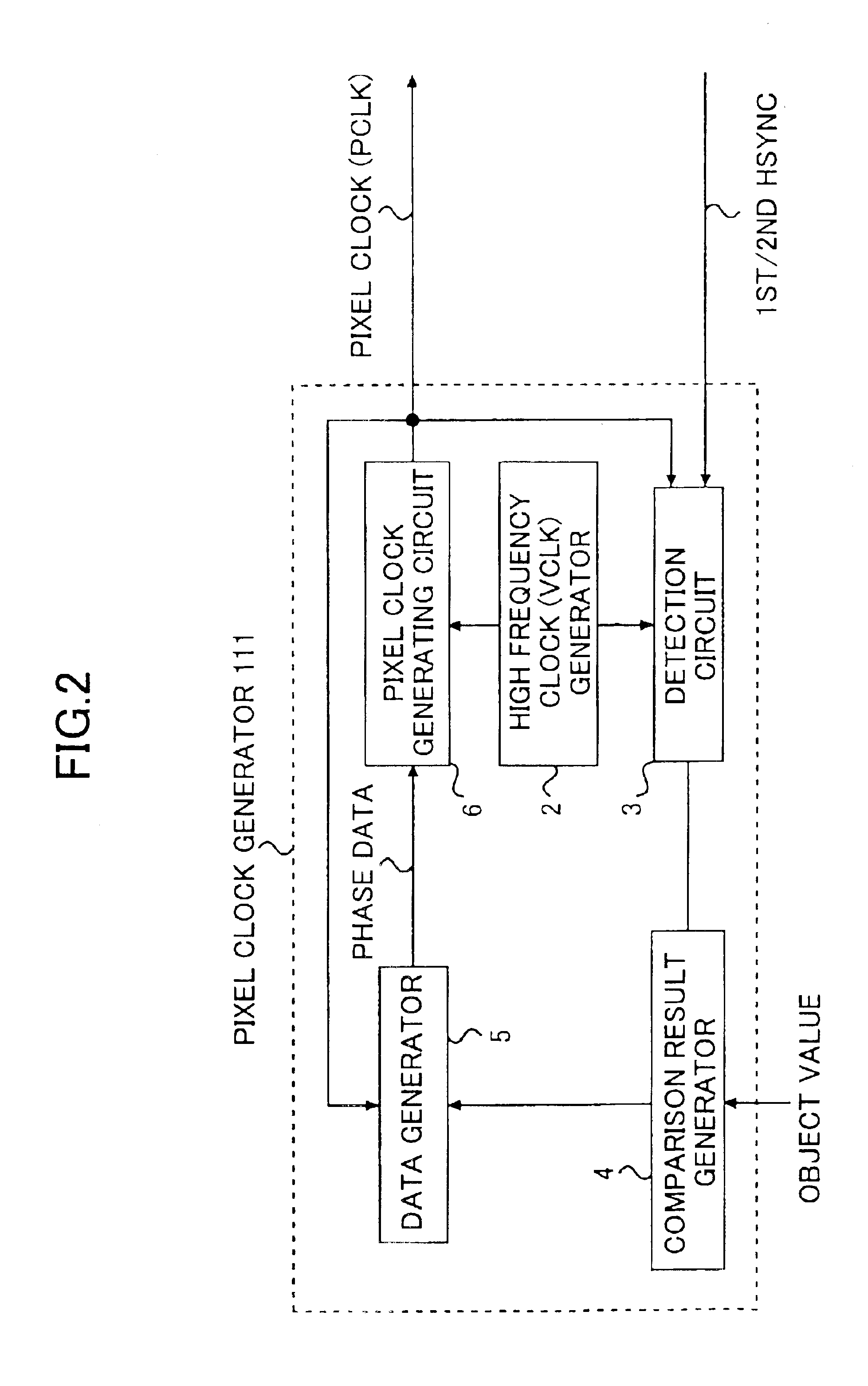
Pixel clock generating device, laser scanning device, and image forming device
InactiveUS6927789B2Simple configurationCorrect fluctuationElectrographic process apparatusPrintingComputer hardwareImage formation
A pixel clock generating device includes a measurement unit that measures a scanning time required for scanning a length and outputs a measured value, a pixel clock generating unit that generates a pixel clock, and a reference clock generating unit that generates a reference clock having a frequency higher than the pixel clock. A phase of the pixel clock is controlled based on (i) the reference clock and (ii) a comparison result between the measured scanning time and a preset scanning time.
Owner:RICOH KK
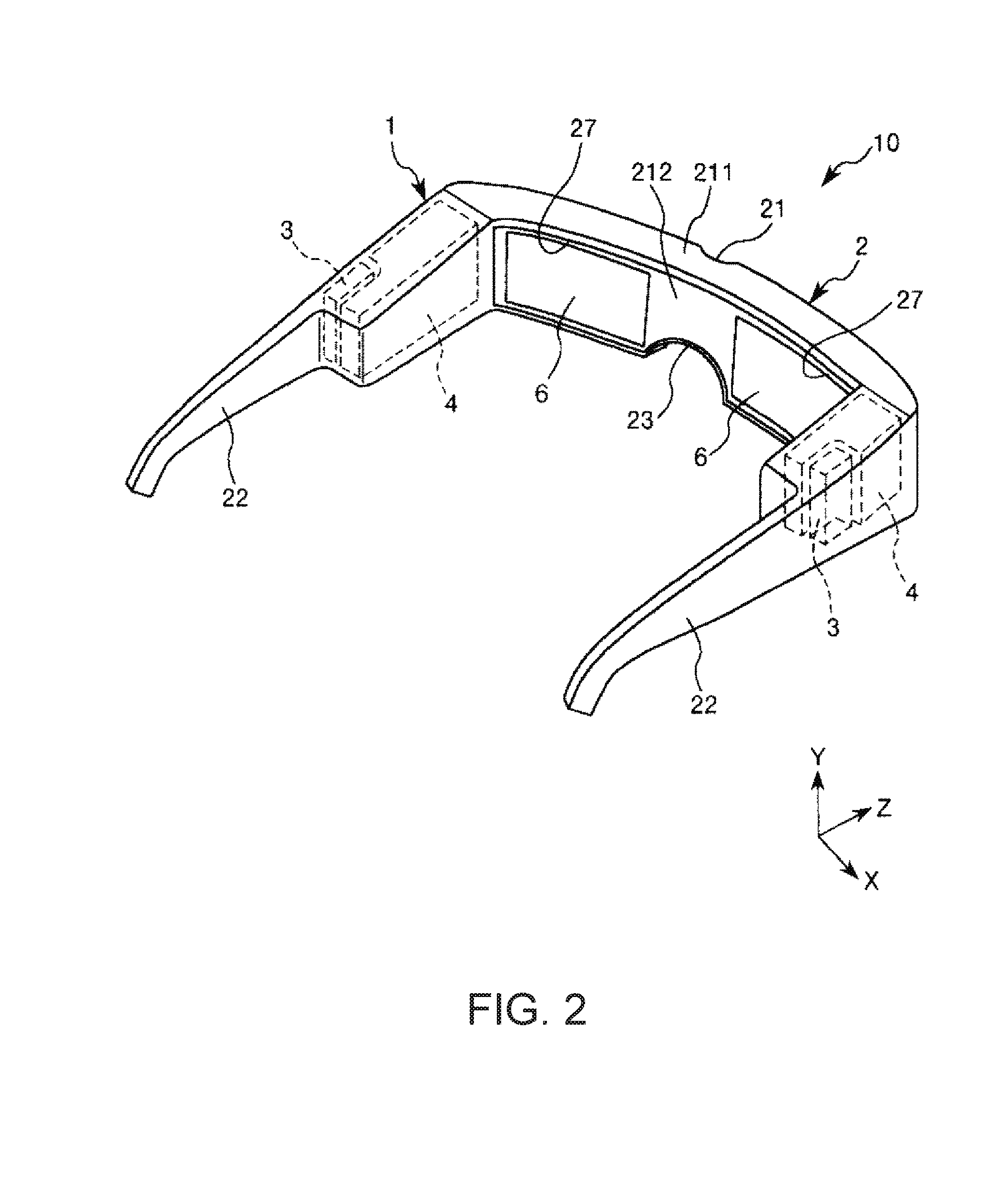
Imaging apparatus
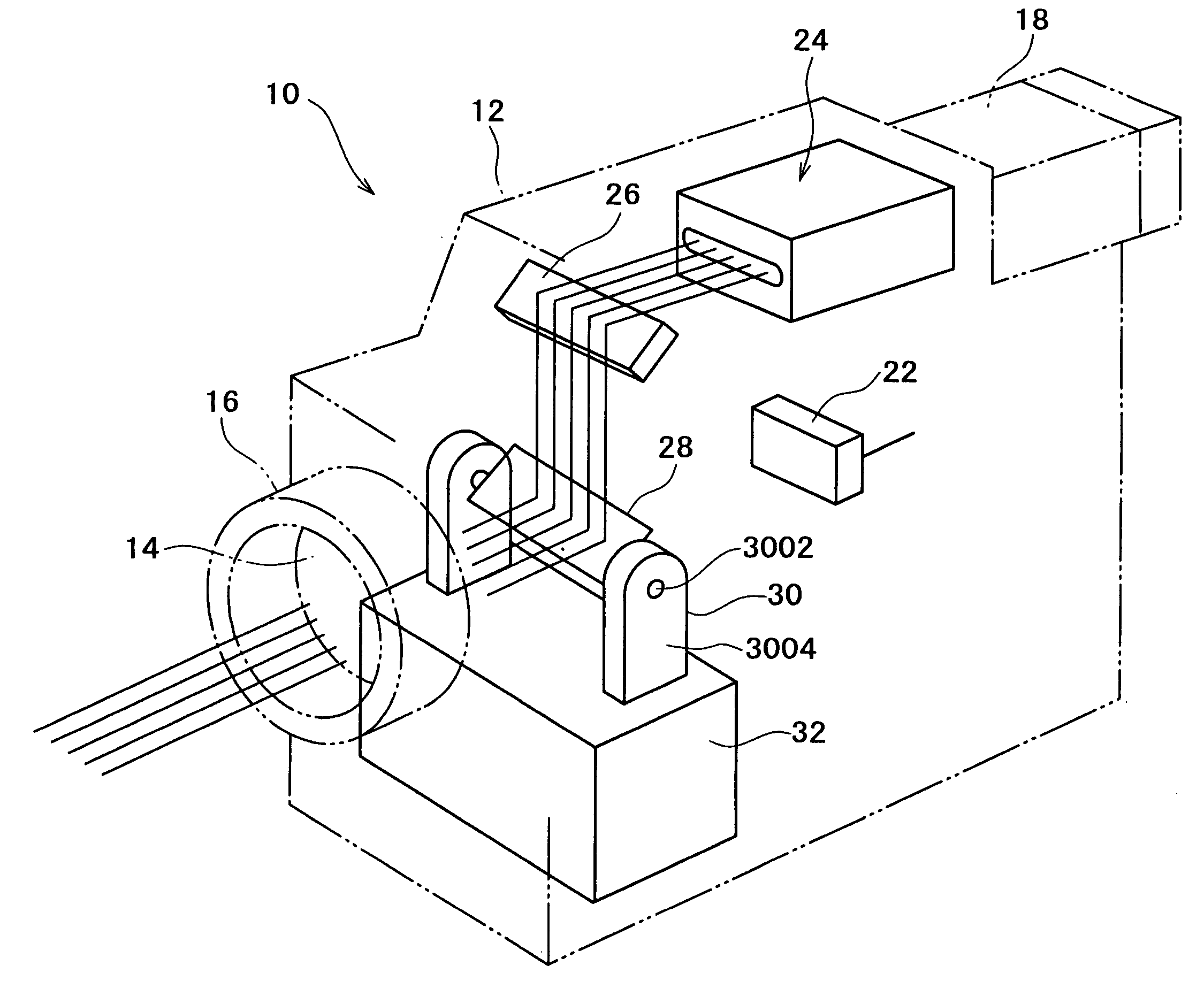
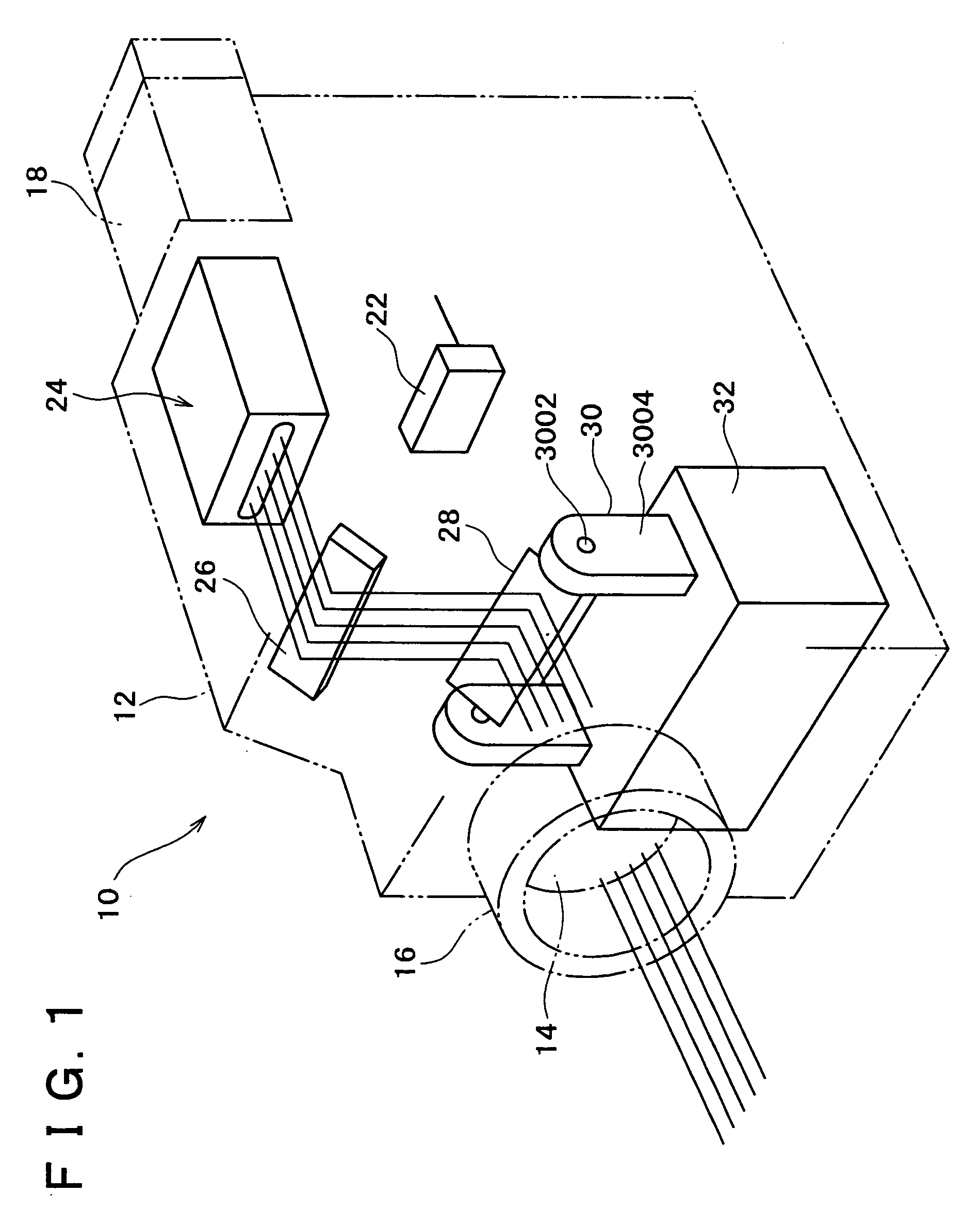
InactiveUS20050099664A1Reduce image sizeSmall sizeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsProjection imageScanning mirror
An imaging apparatus having a projector function which is advantageous in reducing size is provided. A light source of the imaging apparatus is constituted by three semiconductor lasers which respectively frontward emit lights of red, green and blue, each slit-shaped. To a GLV (Grating Light Valve) is applied a drive voltage as modulated by a projection image signal, so that the GLV diffracts the three lights emitted from the light source, with varying the amount or intensity of each light in accordance with the drive voltage or projection image signal. A scanning mirror is disposed between a taking lens and an image pickup device, so as to reflect the lights diffracted by the GLV toward the taking lens, with having each diffracted slit-shaped light scan in a direction.
Owner:SONY CORP
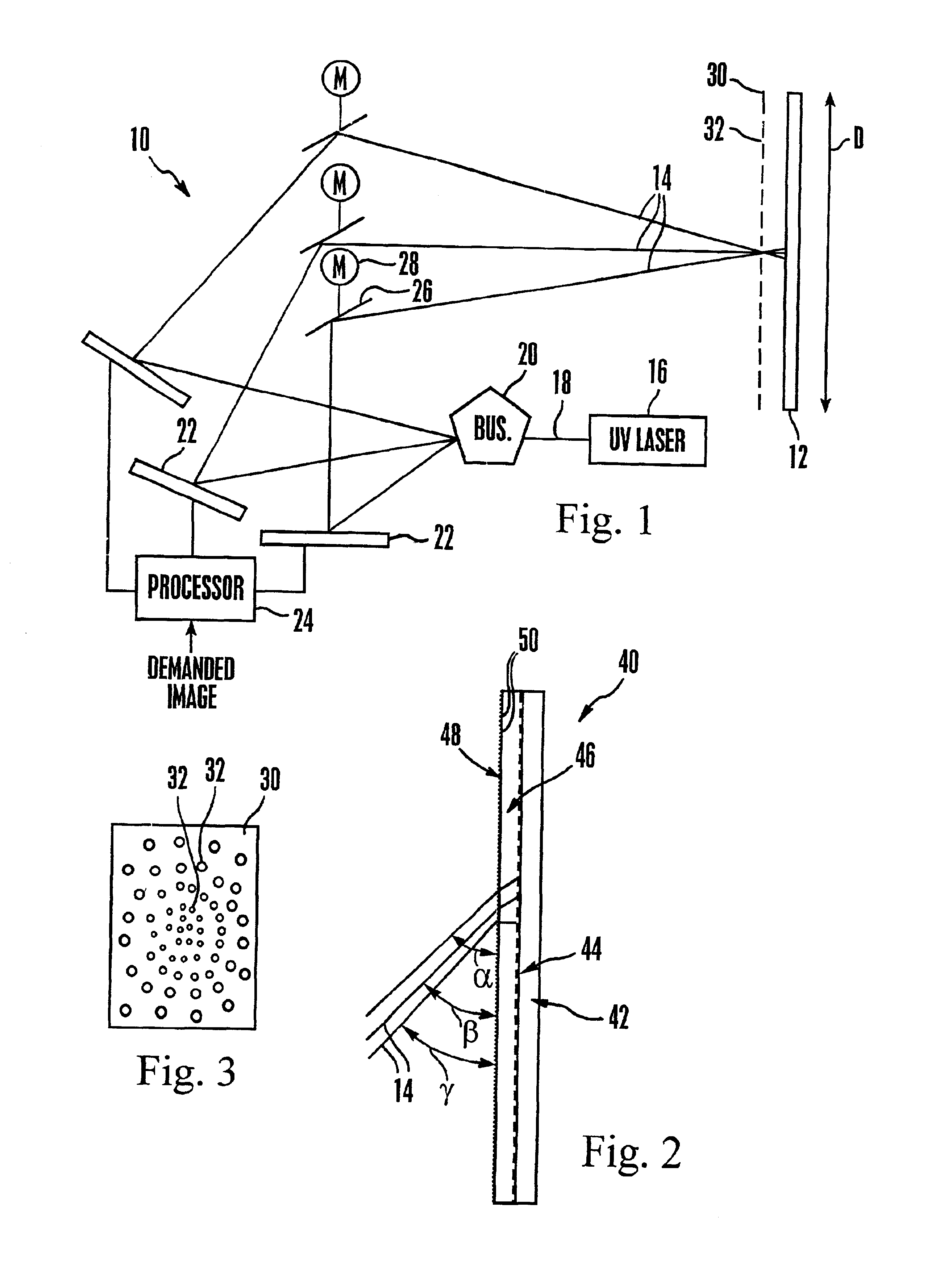
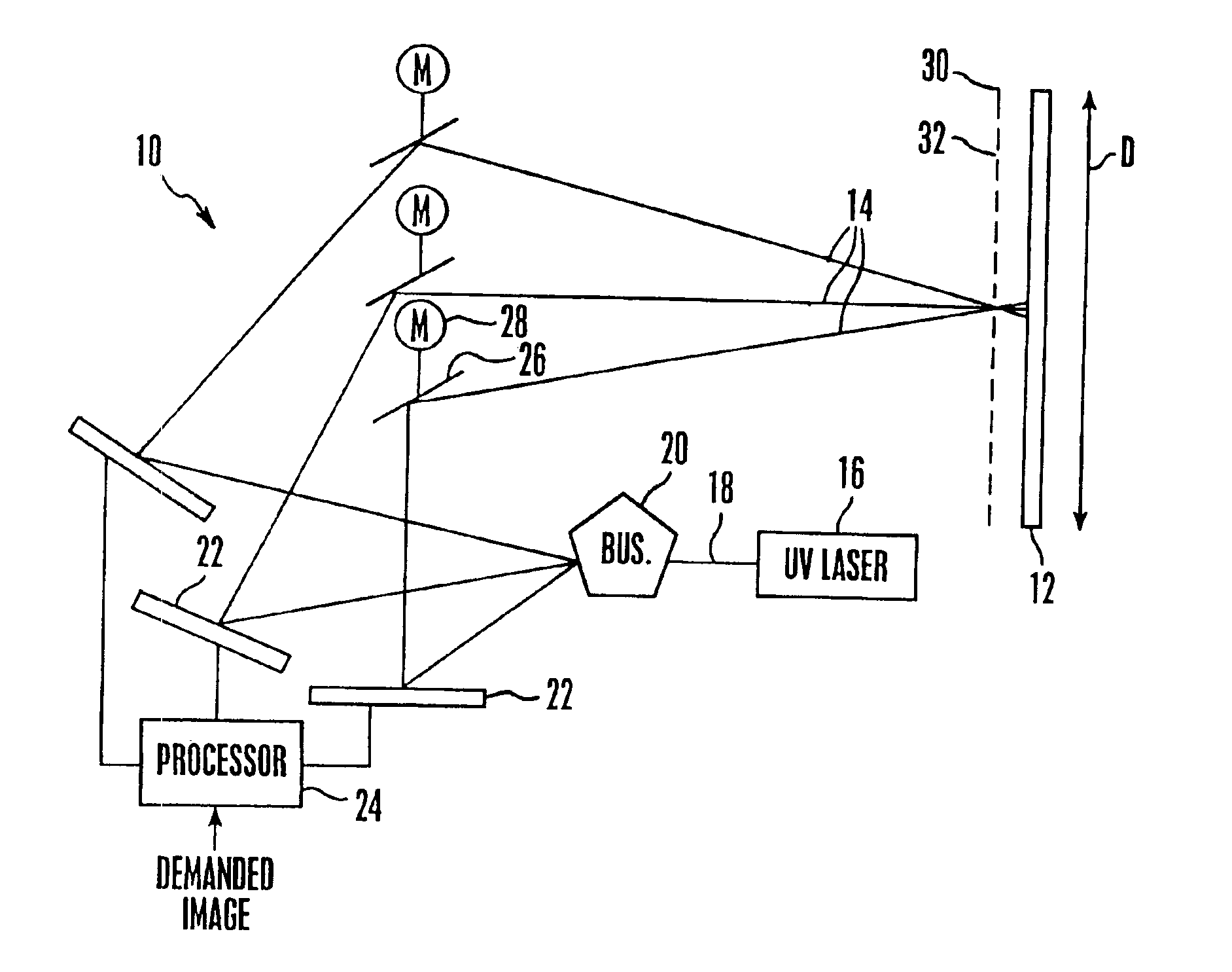
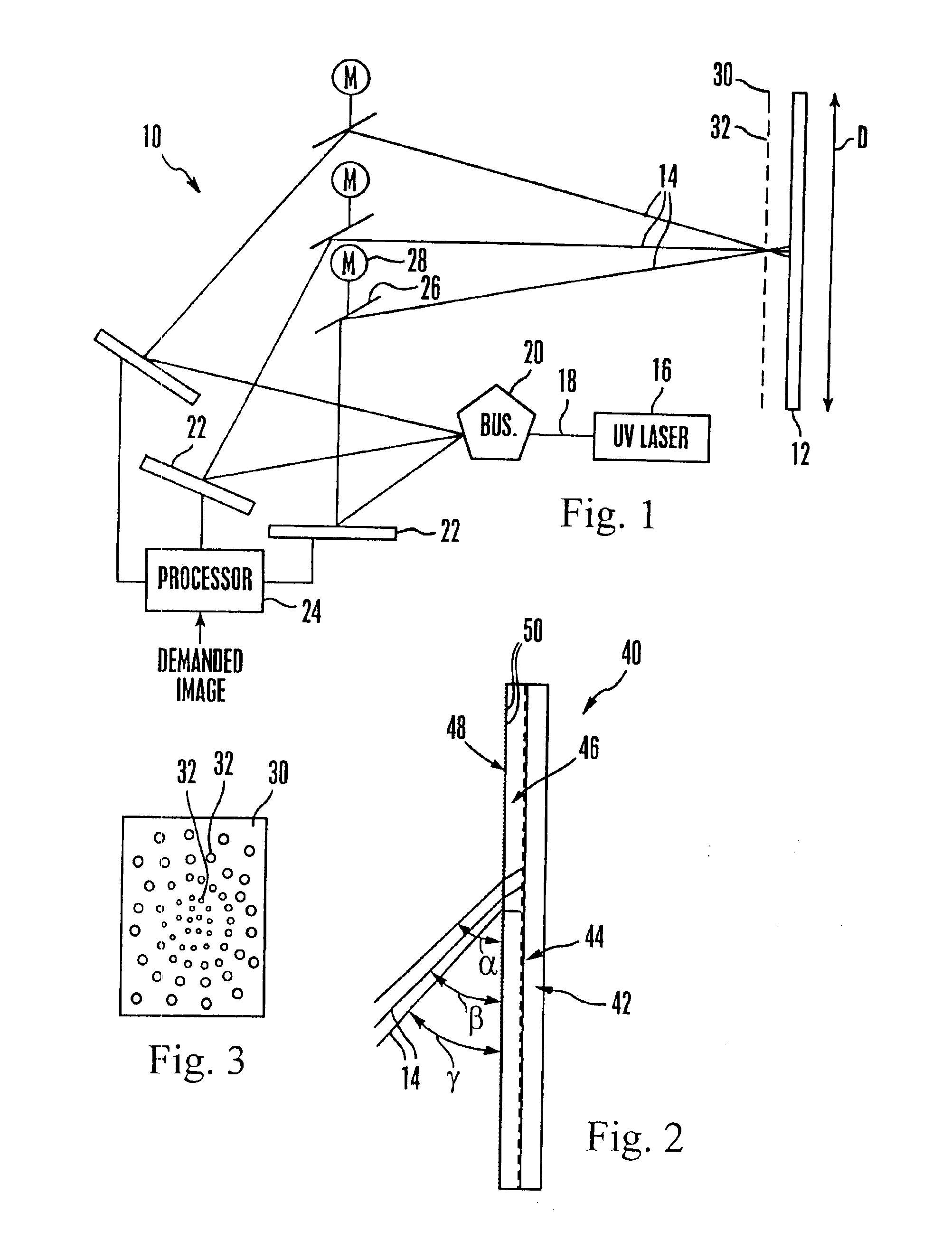
Emissive image display apparatus
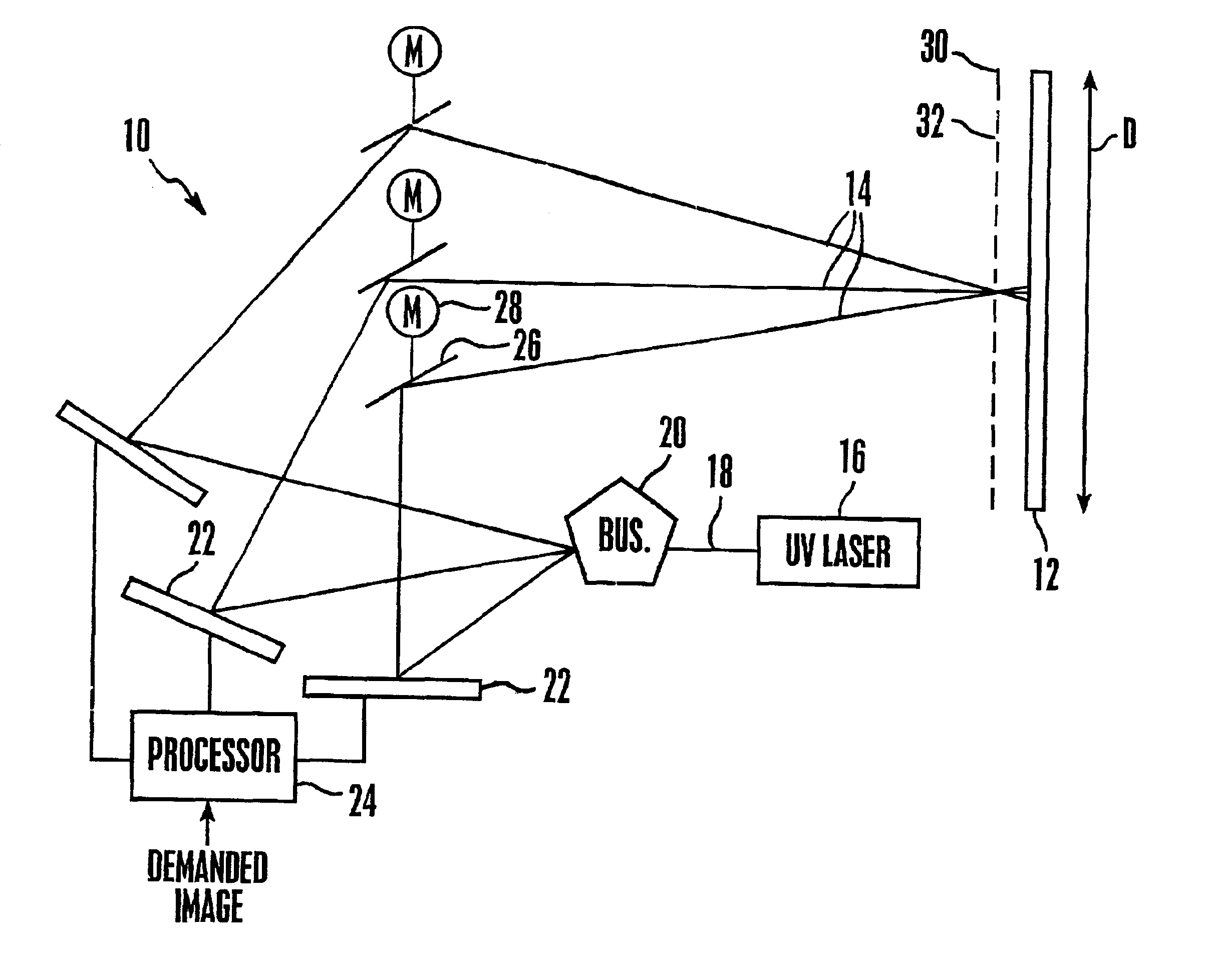
A large screen emissive display operating at atmospheric pressure includes pixels, the red, green, and blue subpixels of which are excited by UV laser light scanned onto the subpixels by a pixel activation mechanism. The pixel activation mechanism includes three grating light valves (GLVs) that are controlled by a processor in response to a demanded image to modulate the UV light as appropriate to produce the demanded image.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Emissive image display apparatus
A large screen emissive display operating at atmospheric pressure includes pixels, the red, green, and blue subpixels of which are excited by UV laser light scanned onto the subpixels by a pixel activation mechanism. The pixel activation mechanism includes three grating light valves (GLVs) that are controlled by a processor in response to a demanded image to modulate the UV light as appropriate to produce the demanded image.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Display device
InactiveUS20100231868A1Improve efficiencyProjectorsColor television detailsBeam splitterDisplay device
A display device is revealed. The display device includes a laser source for emitting a laser beam, a pre-optics for processing the laser beam, a light scan member such as a MEMS mirror for converting the processed laser beam into a scanning light beam, and / or a corresponding post-optics. A switch-control beam splitter is disposed on the light path of the laser beam, after the light scan member so as to divide the scanning light beam into a reflected light beam and a transmitted light beam. They are two different light paths and generate a virtual image as well as a real image respectively.
Owner:ALVIS TECH
Scanning Spectrometer With Multiple Photodetectors
ActiveUS20090046288A1Increased complexityLow costRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A scanning optical spectrometer with a detector array is disclosed, in which position of focused spot of light at the input of a dispersive element such as arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) with a slab input, is scanned using a micro-electro-mechanical (MEMS) tiltable micromirror so as to make the dispersed spectrum of light scan over the detector array coupled to the AWG. Sub-spectra recorded using individual detectors are concatenated by a processor unit to obtain the spectrum of input light.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Two-dimensional micro optical scanner
InactiveUS20080130077A1Reduce scan angleLight would become directionalPictoral communicationOptical elementsOptical scannersLight scan
A two-dimensional micro optical scanner is provided. The two-dimensional micro optical scanner includes a first scanner with a first mirror pivoted in a first direction; a second scanner with a second mirror pivoted in a second direction; and an optical path changing member with a curved mirror. The optical path changing member directs light scanned by the first scanner to the second scanner.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
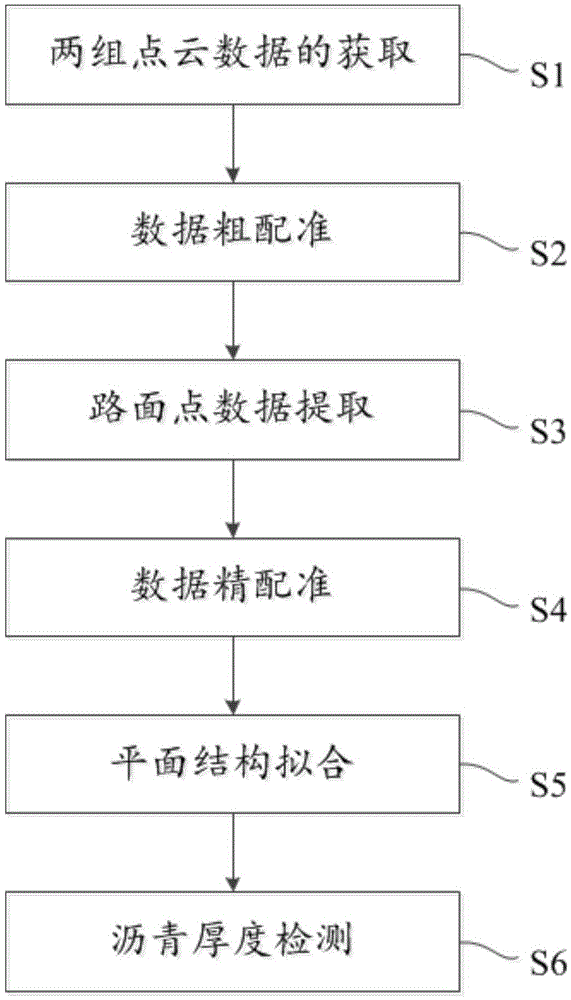
Pavement asphalt thickness detection method based on vehicle-mounted laser scanning spot cloud
InactiveCN105627938AImprove inspection time and costGuaranteed quality and safetyImage analysisUsing optical meansLaser scanningAsphalt
The invention discloses a pavement asphalt thickness detection method based on vehicle-mounted laser scanning spot cloud, comprising steps of obtaining spot cloud data, performing data rough registration through choosing a fixed object, using a pavement extraction algorithm based on the road shoulder to respectively detect two sets of the pavement points of the point cloud data, using the road shoulder point to perform precise registration on the data in the block, performing plane structure fitting on the pavement inside the grid, and detecting the asphalt thickness. The invention can fast and accurately detect and modify the thickness of the road asphalt, greatly reduces the processing time and the labor cost, effectively guarantees the road reconstruction quality and provides important data support to the civil traffic safety.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Coherent Brillouin optical time-domain analysis sensing system based on phase modulation probe light
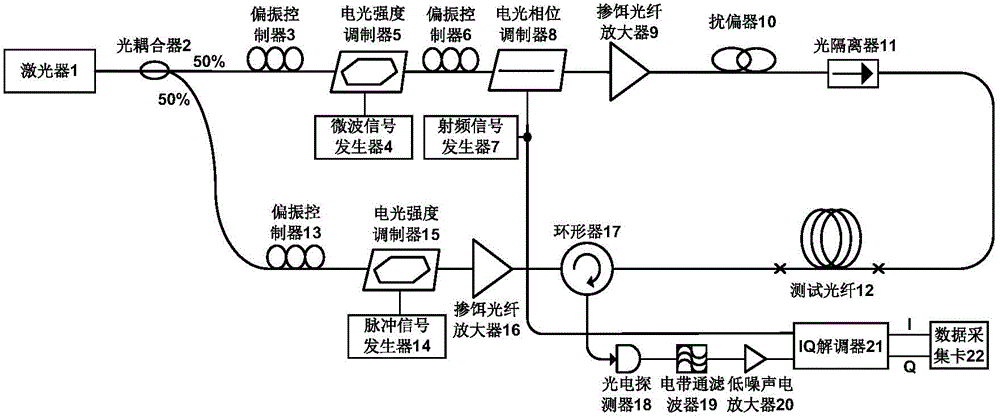
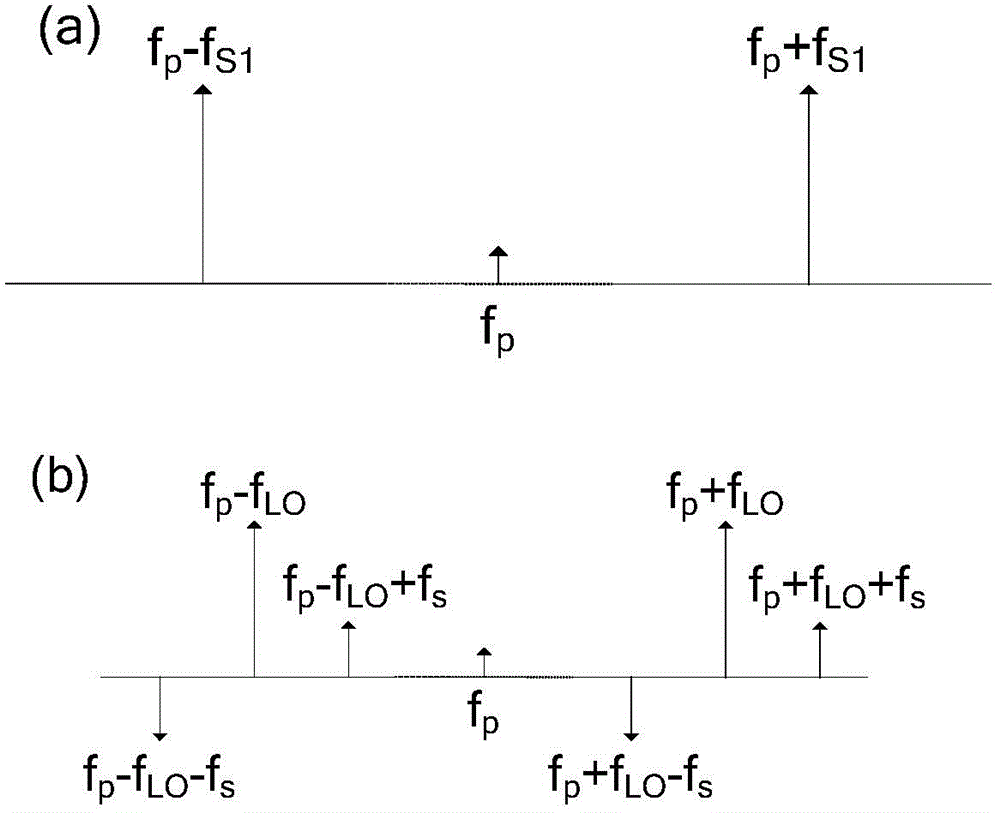
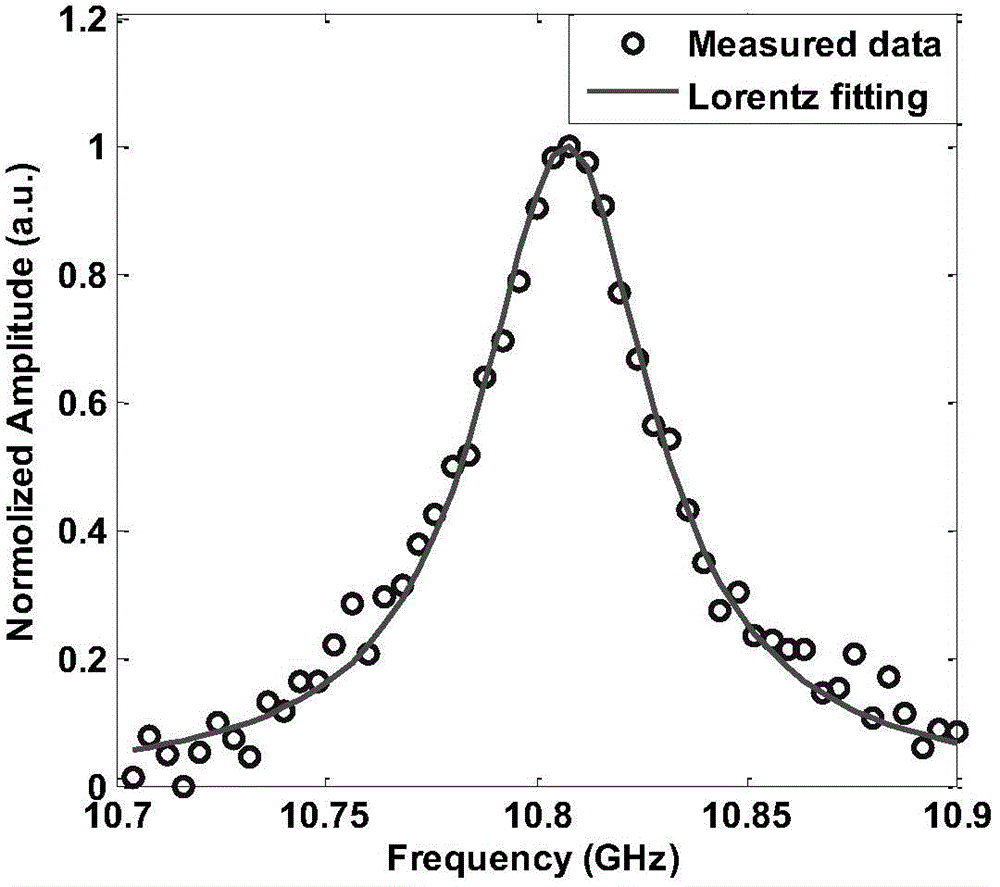
ActiveCN104567960AImprove signal-to-noise ratioAvoid noise damageConverting sensor output opticallyCarrier signalElectrical impulse
The invention discloses a coherent Brillouin optical time-domain analysis sensing system based on phase modulation probe light. In the system, an electro-optic intensity modulator is driven by an electric pulse signal to externally modulate light carrier waves to generate pump light, the electro-optic intensity modulator working at a carrier wave inhibition point is driven by a microwave signal to externally modulate light carrier waves to generate local light, the local light is externally modulated through an electro-optic phase modulator to generate symmetric side bands as the probe light, and the electro-optic phase modulator is driven by a frequency-adjustable radio-frequency signal. Two components of the probe light scan a Brillouin gain area and a loss area of the pump light respectively at the same time, and losses of the pump light can be dynamically compensated so that non-local effects can be reduced while amplitude modulation is carried out on the pump light by a Brillouin gain spectrum. Frequency beating is carried out on the probe light and the local light through a photoelectric detector, information of the Brillouin gain spectrum is loaded to GHz high-frequency carrier waves to avoid base band noise damage, and meanwhile the signal-to-noise ration of the whole system is improved through coherent detection.
Owner:安捷光通科技成都有限公司
Confocal scanning endoscope system and image display area adjustment method thereof
InactiveUS20070035797A1High resolutionQuality improvementPrintersSurgeryImage formationEncircled energy
There is provided a confocal scanning endoscope system, which is provided with a light source that emits light, a scanning unit that deflects the light emitted by the light source so that the light scans on a subject in two dimensions, an objective optical system that directs the light deflected by the scanning unit to the subject, an extraction unit that extracts only part of the light returning from a convergence point at which the light is converged by the objective optical system on an object side, an image formation unit configured to form an image based on the part of the light extracted by the extraction unit, and a display area adjustment unit configured to measure Encircled Energy of the part of the light extracted by the extraction unit and to adjust a display area of the image based on the measured Encircled Energy.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Projection optical system and optical system
InactiveUS20050041220A1Small sizeSmall distortionTelevision system detailsProjectorsProjection opticsProjection image
A projection optical system includes an optical modulation unit which outputs modulated light for displaying an image, an optical scanning unit on which the modulated light output from the optical modulation unit is incident, the optical scanning unit scanning the light from the optical modulation unit to obtain a two-dimensional image, and a plurality of curved reflecting surfaces on which the light scanned by the optical scanning means is sequentially incident, the plurality of curved reflecting surfaces sequentially reflecting the light scanned by the optical scanning means and projecting the light on a projected surface, wherein when an optical path of a ray connecting a center of a pupil of the projection optical system and a center of a projected image is set as a reference axis, the reference axis is inclined with respect to a normal to the projected surface.
Owner:CANON KK
Image display apparatus
ActiveUS20160161755A1Increase awarenessReduce resolutionInput/output for user-computer interactionMechanical apparatusOptical scannersComputer science
An image display apparatus includes an image light generator that generates video light modulated based on a video signal, a light diffracting section (first diffractive optical element) that diffracts the video light outputted from the image light generator, a light sweeper (optical scanner) that spatially scans the video light, and a reflector including a light diffracting section (second diffractive optical element) that diffracts the video light scanned by the light sweeper, and the light diffracting section (first diffractive optical element) is provided on an optical path between the image light generator and the light sweeper. The light diffracting section (first diffractive optical element) preferably has a fixed interval between interference fringes, and the light diffracting section (second diffractive optical element) preferably has portions where intervals between interference fringes differ from each other.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
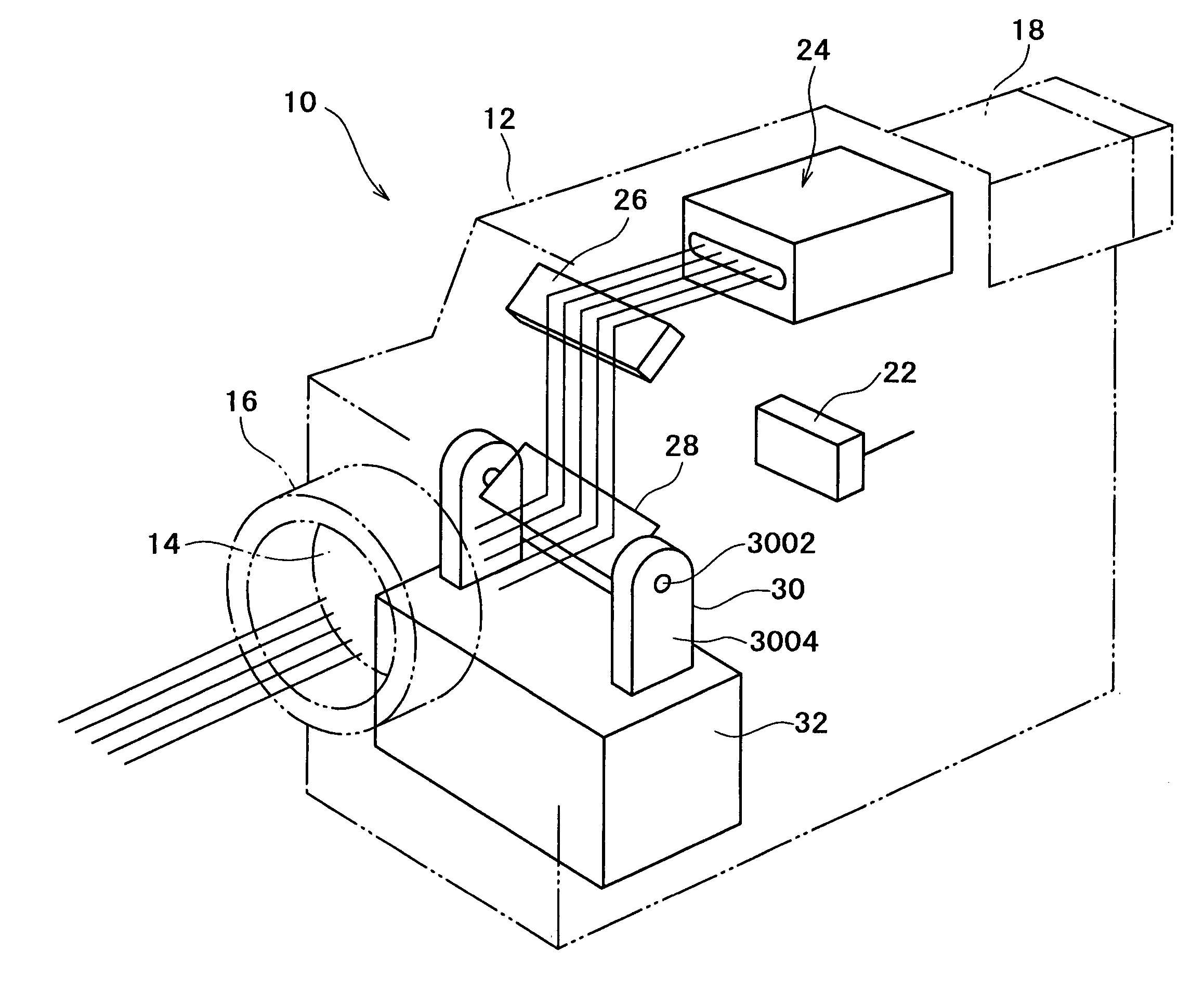
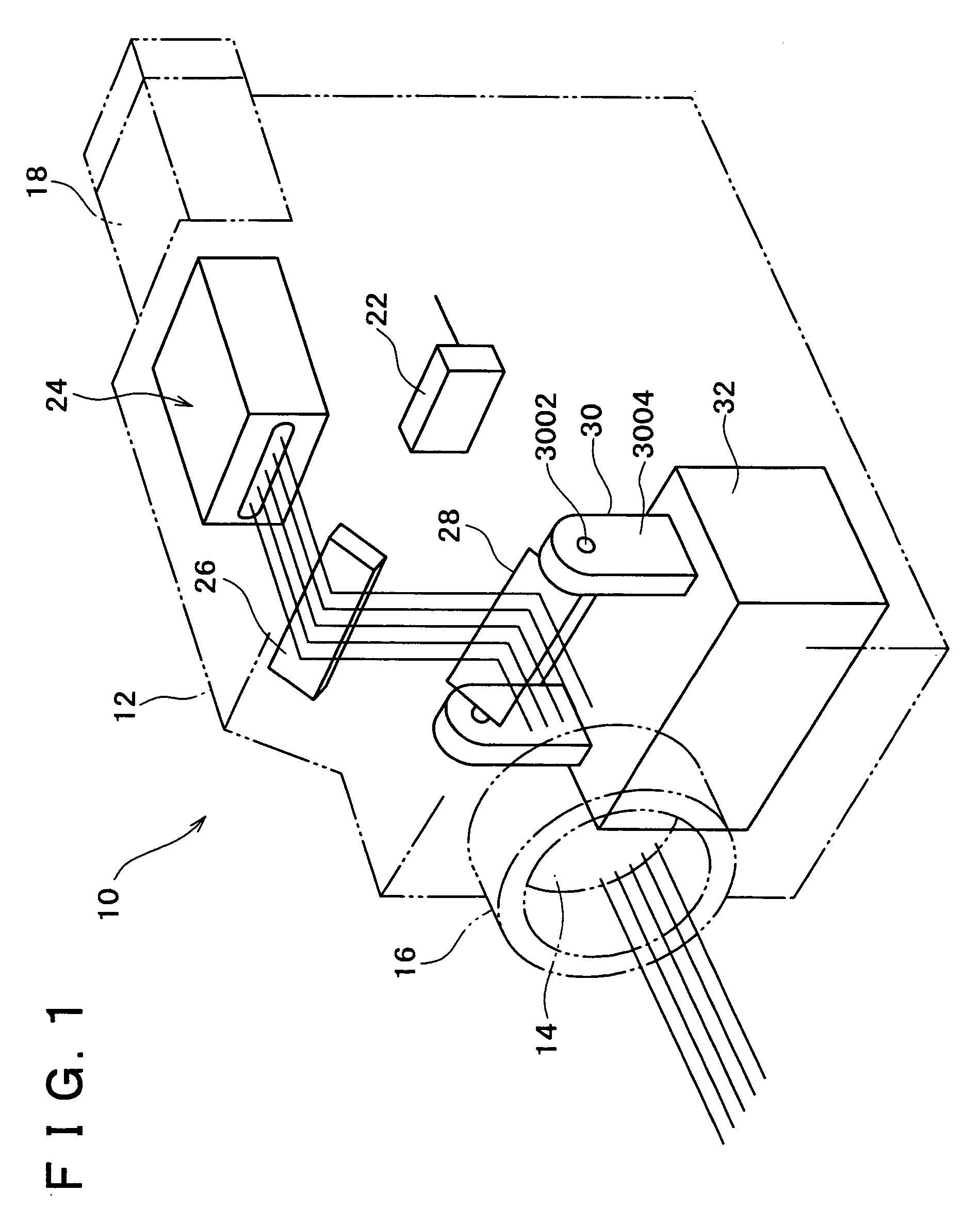
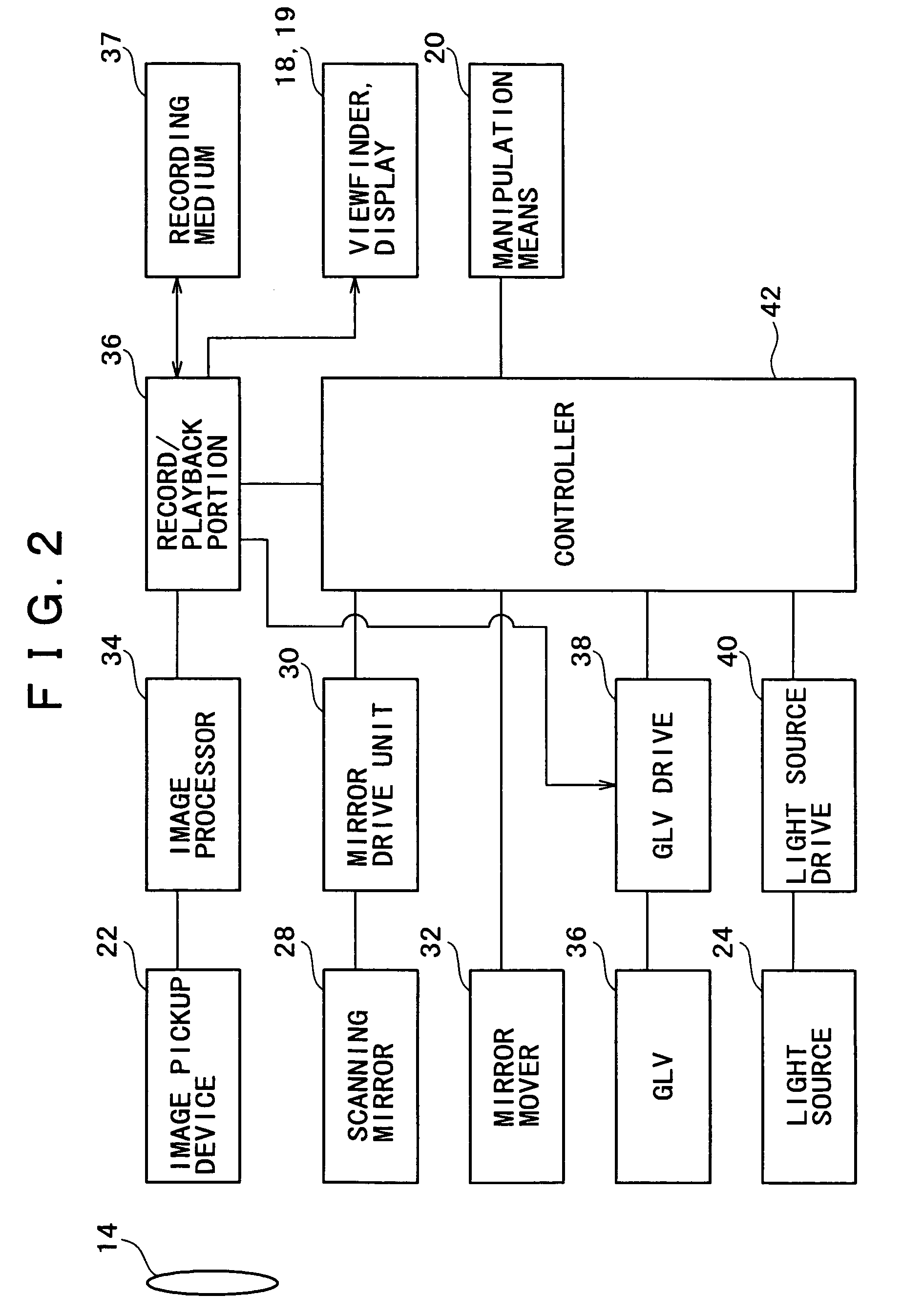
Imaging apparatus
InactiveUS7116455B2Reduce image sizeSmall sizeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMedicineProjection image
An imaging apparatus having a projector function which is advantageous in reducing size is provided. A light source of the imaging apparatus is constituted by three semiconductor lasers which respectively frontward emit lights of red, green and blue, each slit-shaped. To a GLV (Grating Light Valve) is applied a drive voltage as modulated by a projection image signal, so that the GLV diffracts the three lights emitted from the light source, with varying the amount or intensity of each light in accordance with the drive voltage or projection image signal. A scanning mirror is disposed between a taking lens and an image pickup device, so as to reflect the lights diffracted by the GLV toward the taking lens, with having each diffracted slit-shaped light scan in a direction.
Owner:SONY CORP
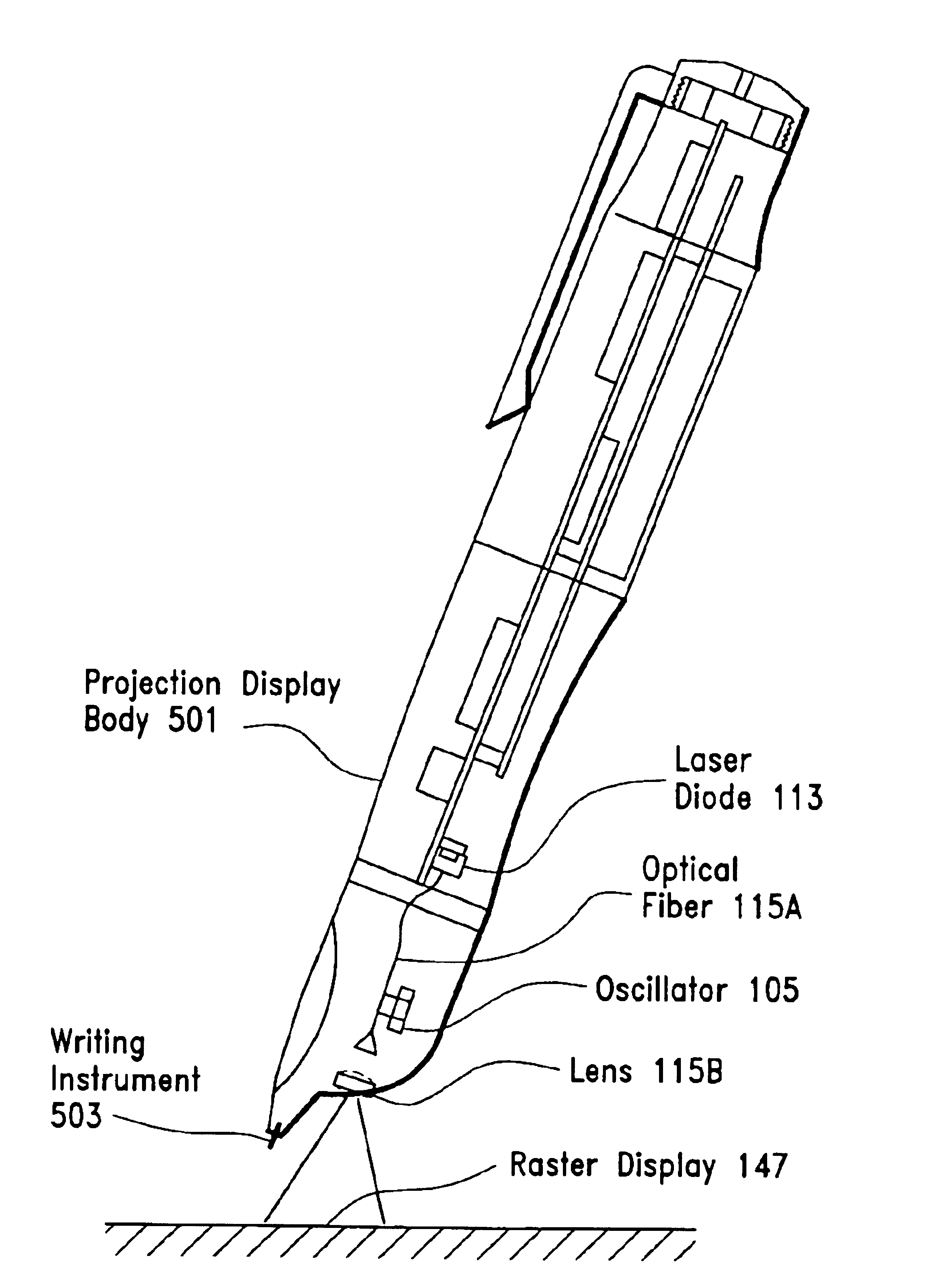
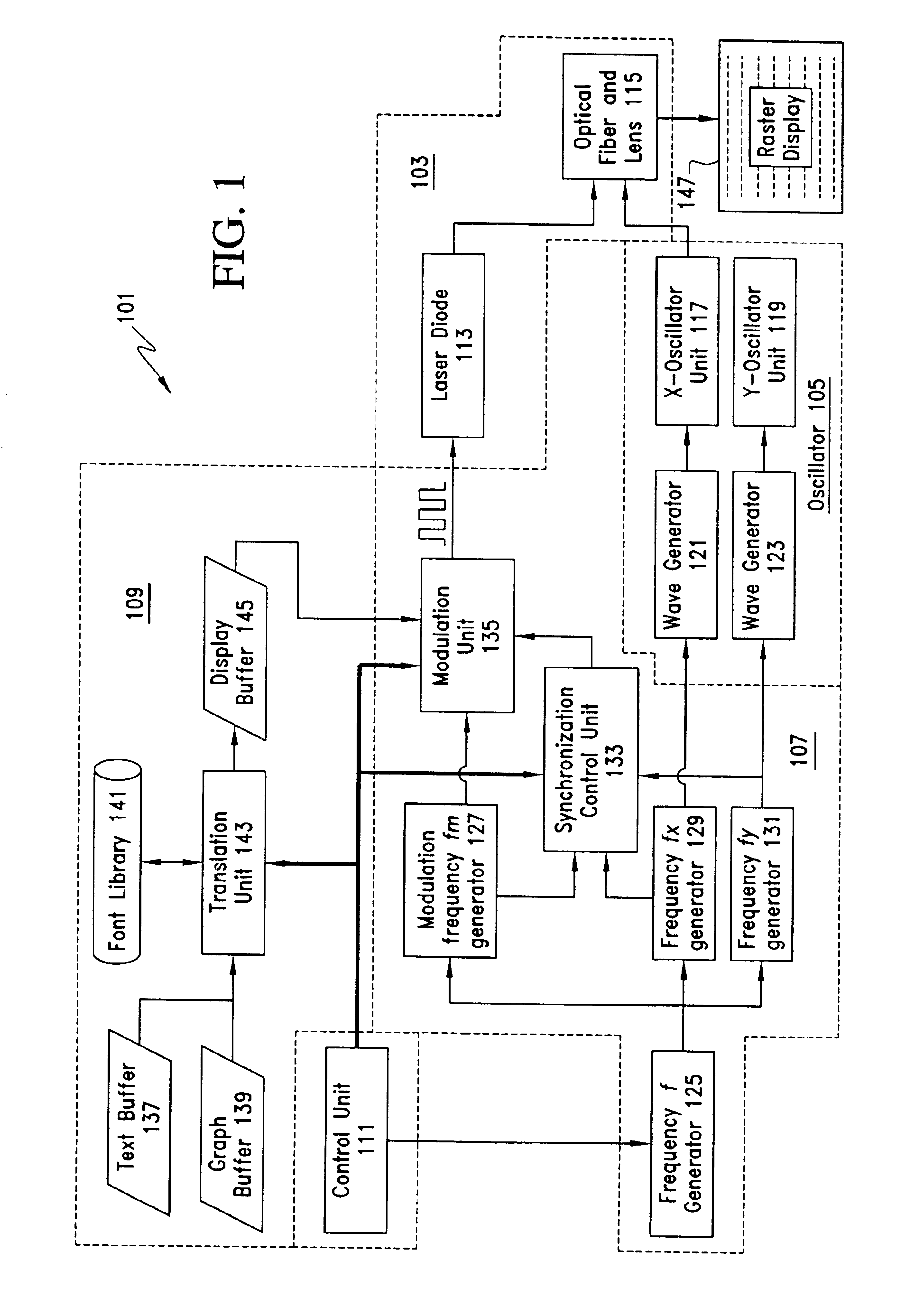
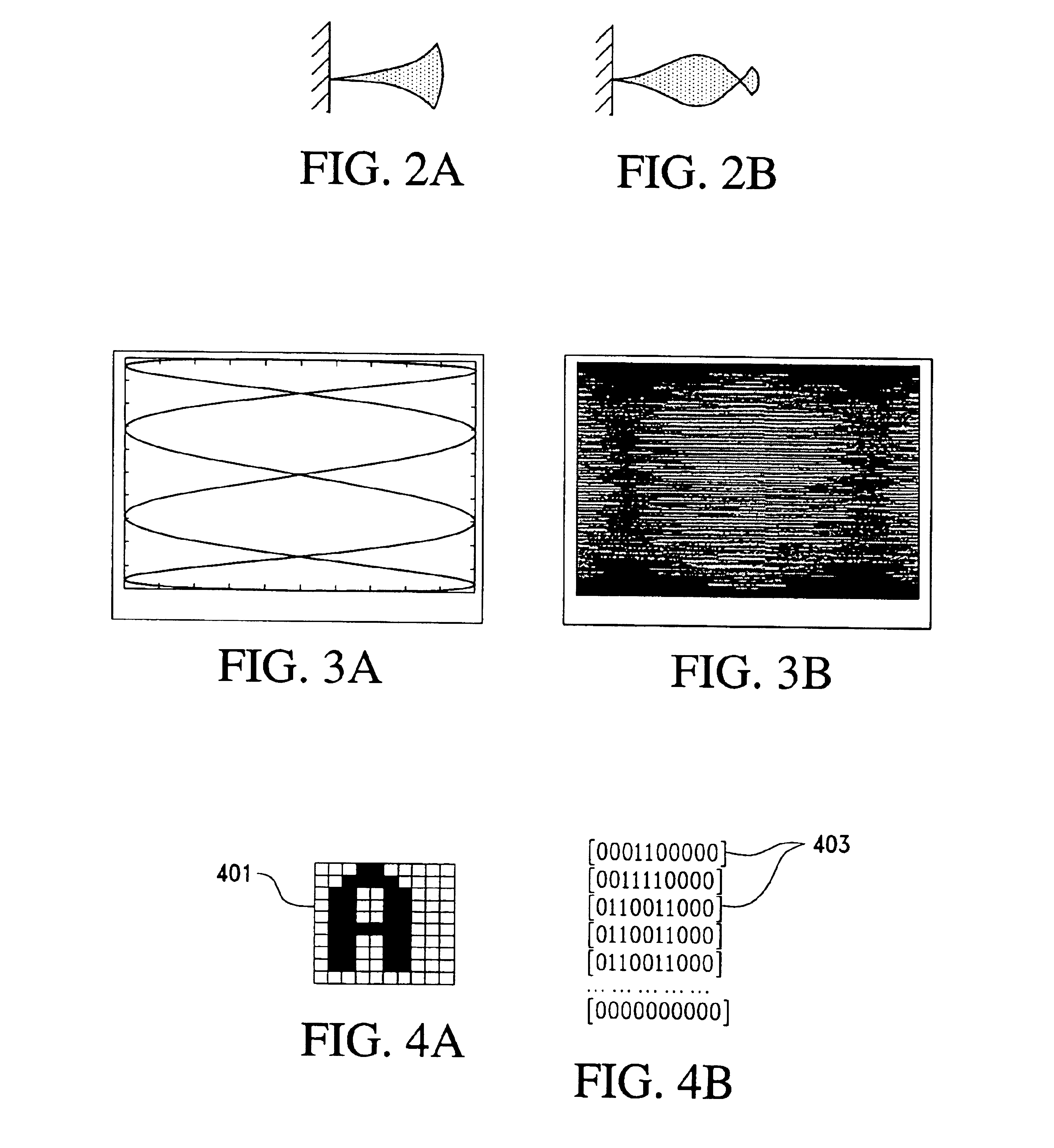
Pen projection display
InactiveUS6964483B2Input/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system scanning detailsGratingDisplay device
The projection display includes a light projector unit for generating and projecting light, an oscillator unit for oscillating light projected from the light projector unit, and a frequency generation and modulation unit. The frequency generation and modulation unit drives the oscillator unit and modulates the light projected by the light projector unit. In turn, the oscillator unit oscillates the light projected by the light projector unit in two dimensions, so that the projected light scans an incident surface in a raster pattern. At the same time, the frequency generation and modulation unit modulates the light produced by the light projector unit in synchronization with the scanning process and image data supplied so that the projected light produces images corresponding to the image data over a scanned area.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
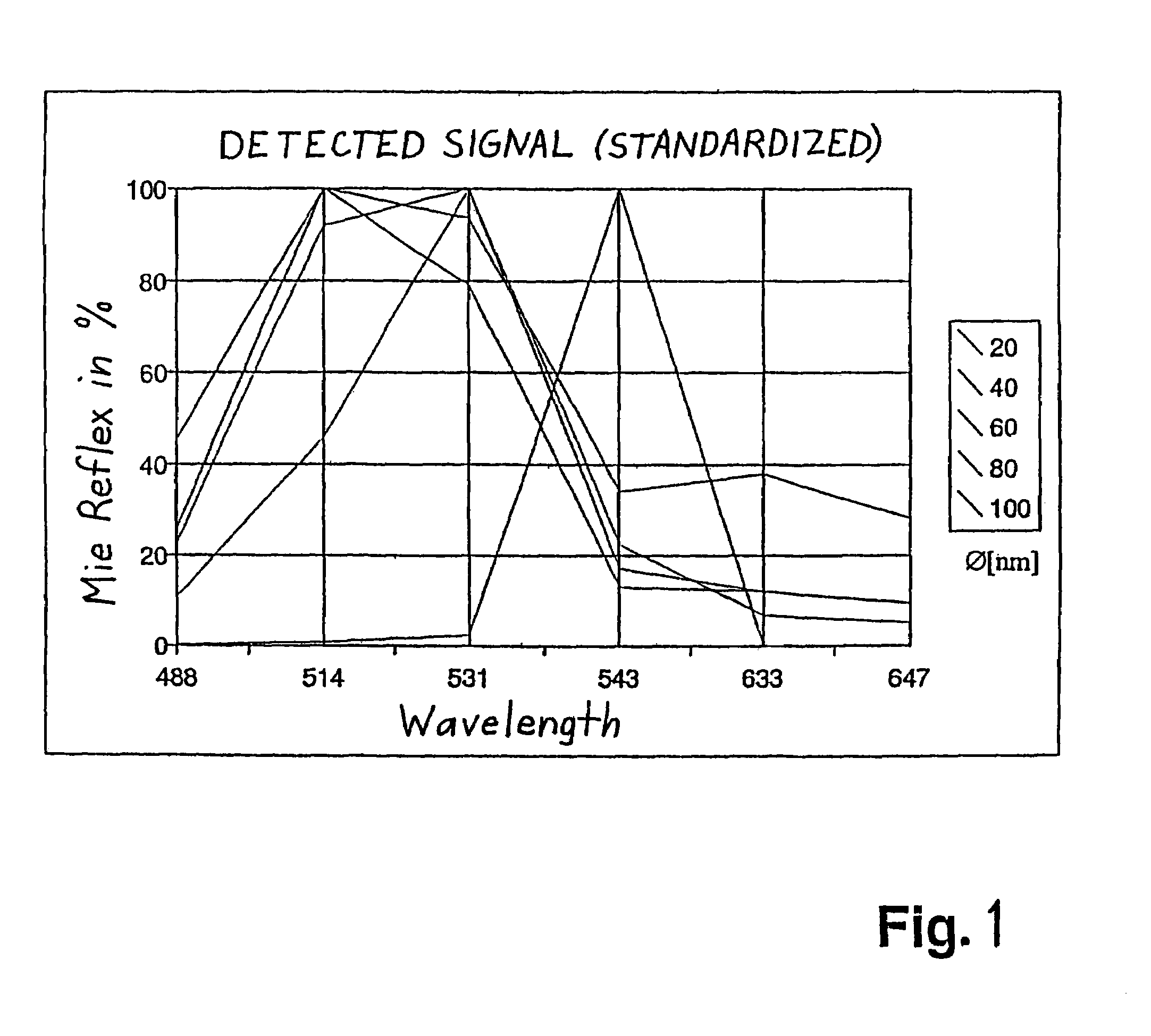
Method for differentiated investigation of diverse structures in preferably biological preparations
The invention relates to a method for examining different structures in preferably biological preparations in a differential manner, especially by means of confocal laser scanning microscopy. The method is characterized in that particles having a specific diameter and specific characteristics are assigned to the structures and in that said structures are detected by detecting the particles which have specifically bonded in or to the preparations. The detection process is carried out in an advantageous manner by marking the structures with metal particles with diameters of 10 nm to 1,500 nm and detecting Mie scattering or a plasmon signal.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Image display device and light conversion panel used in same
ActiveUS20150286120A1Wide wavelength rangeSpeckle reductionStatic indicating devicesProjectorsPhosphorFluorescence
An image display device which reduces speckles in an image display device using a laser source includes: a laser source which emits excitation light; a collecting lens which collects the excitation light; a deflecting element which scans the excitation light collected by the collecting lens; and a light conversion panel which converts a wavelength of the excitation light scanned by the deflecting element and emits fluorescence, wherein the light conversion panel includes a plurality of phosphor layers which are planarly disposed, absorb the excitation light, and emit the fluorescence.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Laser scan range finding device
PendingCN106814366AHomogenization of Angle VariationsReduce manufacturing costUsing optical meansElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser transmitterMagnetic poles
The invention provides a laser scan range finding device comprising a reflector mount, a reflector, a laser emission lens, a laser sleeve, a laser emitter, a top cover, an optical filter, a core frame, a base plate, a motor stator, a motor rotor magnetic pole, a core back plate, a laser receiver array, a receiver lens, and a receiver lens mount. The laser emission lens is used for converting the first light beam emitter by the laser emitter into a parallel light beam; the parallel light beam is reflected on the reflector surface so as to form a second light beam; when the second light beam arrives a tested target object, a third light beam is formed by the surface of the object; the third light beam is focused by the receiver lens so as to form a fourth light beam entering the laser receiver array. Compared with the prior art, the single laser emitter is combined with reflector periodical vibrations so as to realize multi-line laser emission. In addition, the angle between multi-line lasers can be controlled and adjusted through software in a microprocessor, and the angle change can be easily uniformed.
Owner:SHANGHAI SLAMTEC
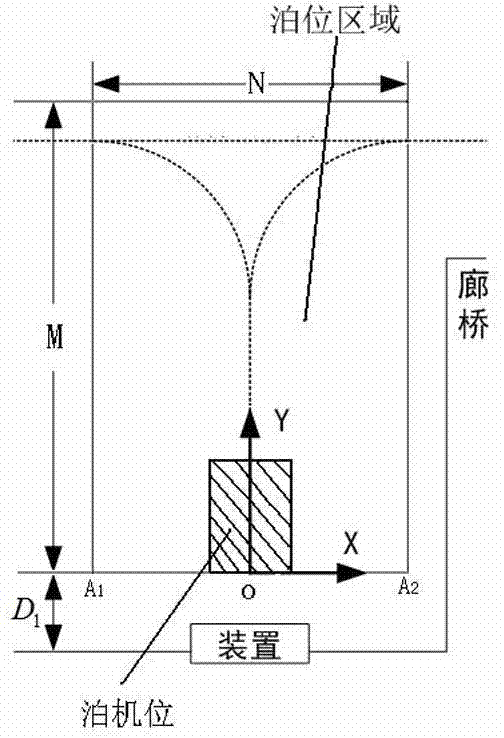
Aircraft berthing automatic guide method and device based on laser ranging technology
ActiveCN103786893AGet rid of dependenceIndependent and accurate parking operationAircraft landing aidsDriver/operatorAirplane
The invention relates to an aircraft automatic berthing technology, in particular to an aircraft berthing automatic guide method and device based on a laser ranging technology. Postures are measured and guided in the aircraft berthing process. The aircraft berthing automatic guide method and device based on the laser ranging technology aim to solve the problems in the prior art. The device comprises a fan-shaped laser scanner, a pitching rotating motor, a processor and a display screen, and the device is arranged at the height position of an aircraft body at the end of the berth of an aircraft. Through the device and an algorithm, the posture of the aircraft is detected in real time when the aircraft is 100 m away from an aircraft stand, guidance (distance, offset and speed) and aircraft type matching information are provided, the information is provided on the display screen in real time, and an aircraft driver is guided to berth the aircraft. When the device is used, no ground manual assistance is needed, and the aircraft driver completes the aircraft berthing operation independently and accurately by relying on prompt information. The device is based on the laser technology, high accuracy is achieved, real-time performance is good, and the device is strong in adaptive capacity under the poor-visibility weather environment, such as haze, snow and rain.
Owner:THE SECOND RES INST OF CIVIL AVIATION ADMINISTRATION OF CHINA
Phase-shift white light interferometry method based on 3*3 optical fiber coupler
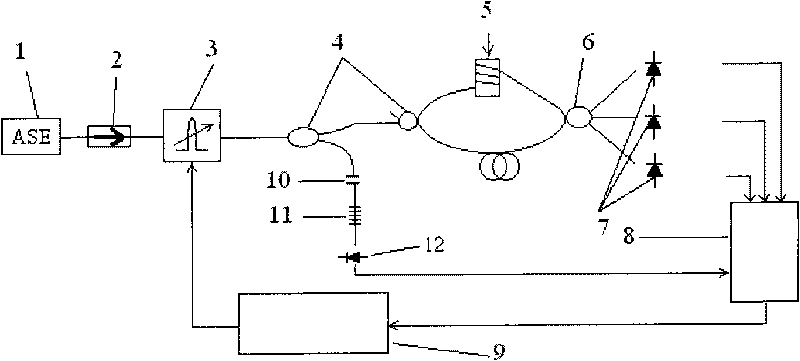
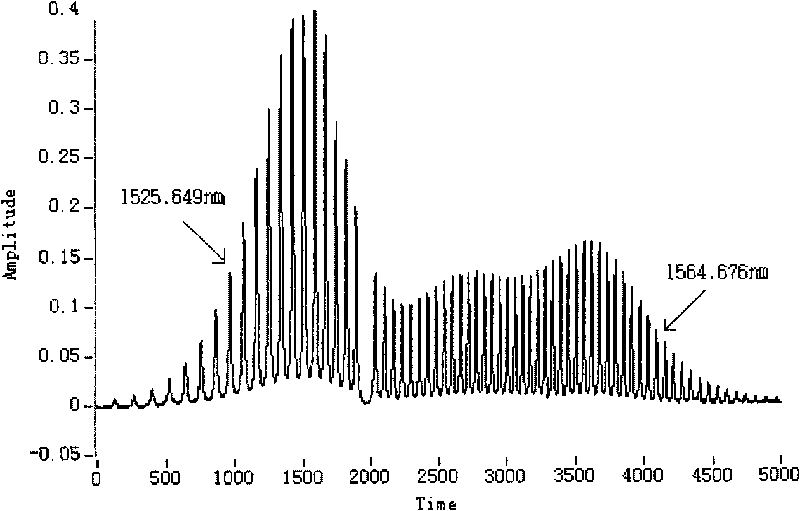
InactiveCN101718563AHigh sensitivityHigh precisionOptical measurementsConverting sensor output opticallyWhite light interferometrySignal on
The invention relates to an optical fiber white light interferometry method, in particular to a phase-shift white light interferometry method based on a 3*3 optical fiber coupler, belonging to the technical field of optical fiber sensing. A 2*2 optical fiber coupler and a 3*3 optical fiber coupler form an optical fiber M-Z interferometer, and a wavelength scanning light is injected into the optical fiber M-Z interferometer. Magnitudes of three paths of output white light interference spectrum signals are equal, and an angle of 120 degrees is formed between every two paths of output white light interference spectrum signals on the phase. When the wavelength scanning light scans from Lambda 1 to Lambda 2, three paths of output signals I1, I2 and I3 are obtained, and Delta is demodulated through computing or constructing two paths of orthorhombic signals and utilizing a derivation cross multiplying method. The Delta is subjected to the unwrapping operation to demodulate linear phase information after computed. The absolute optical path difference of the interferometer can be computed by using the linear phase information. The invention can absolutely measure the optical path difference of the optical fiber interferometer with high precision and high speed.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
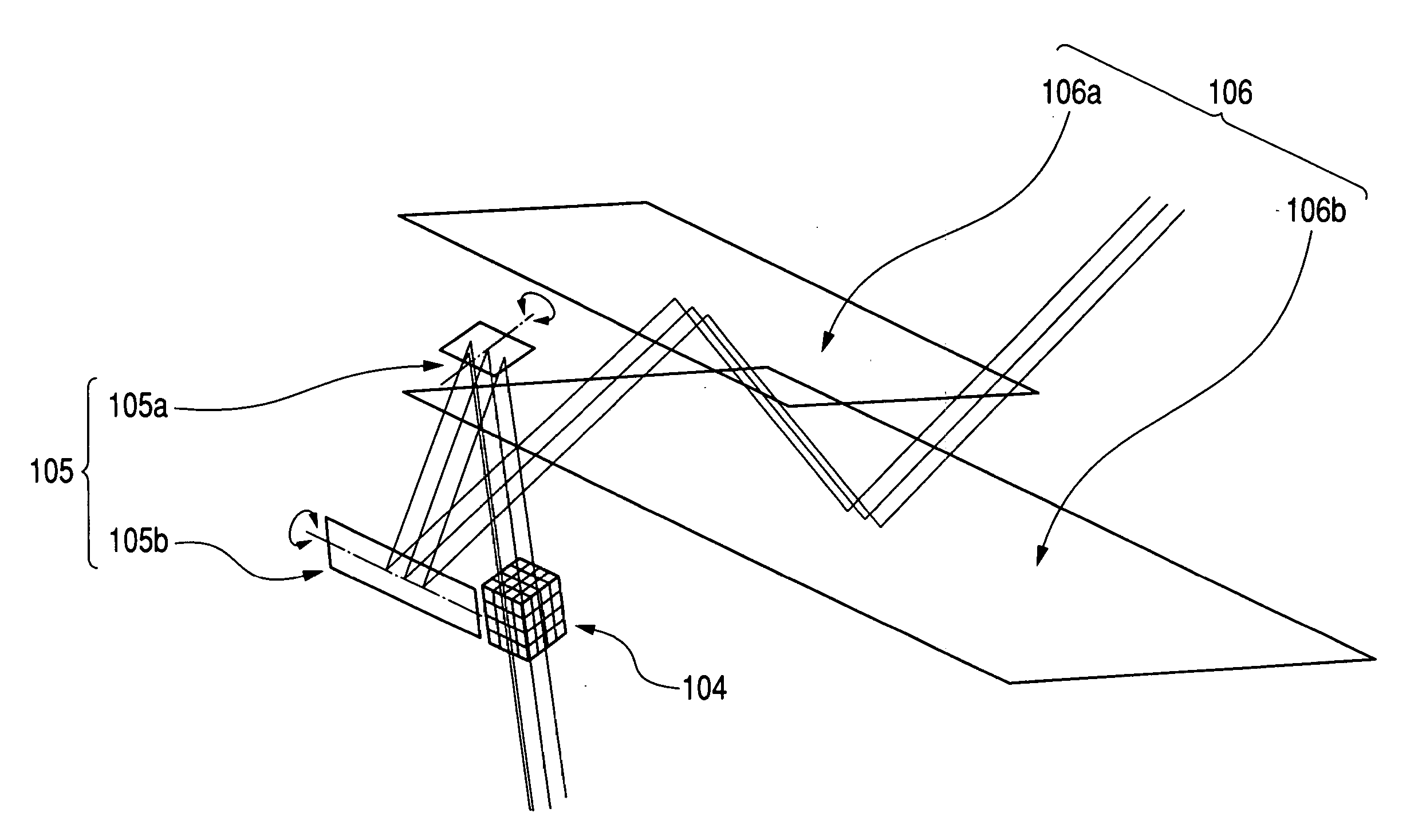
Two-dimensional scanning apparatus and scanning type image displaying apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20050190419A1Correct distortionPicture reproducers using projection devicesOptical elementsLight beamAngle of view
The optical scanning apparatus of the present invention is an optical scanning apparatus for scanning a surface to be scanned with light from a light source, provided with a deflecting optical system for deflecting a beam from a light source optical system in a first scanning direction and a second scanning direction orthogonal to the first scanning direction, and a scanning optical system including at least one reflecting surface of a non-rotation symmetrical shape, and for directing the deflected beam deflected by the deflecting optical system onto the surface to be scanned by the use of the aforementioned at least one reflecting surface of a non-rotation symmetrical shape, wherein the principal ray of the beam incident on the center of the angle of view of the surface to be scanned is incident while being inclined with respect to the surface to be scanned in at least the first scanning direction of the first and second scanning directions.
Owner:CANON KK
Display apparatus using laser and method of using the same
InactiveUS20070296645A1Reduce speckle noiseClear imagingTelevision system detailsLaser detailsOptoelectronicsLaser light
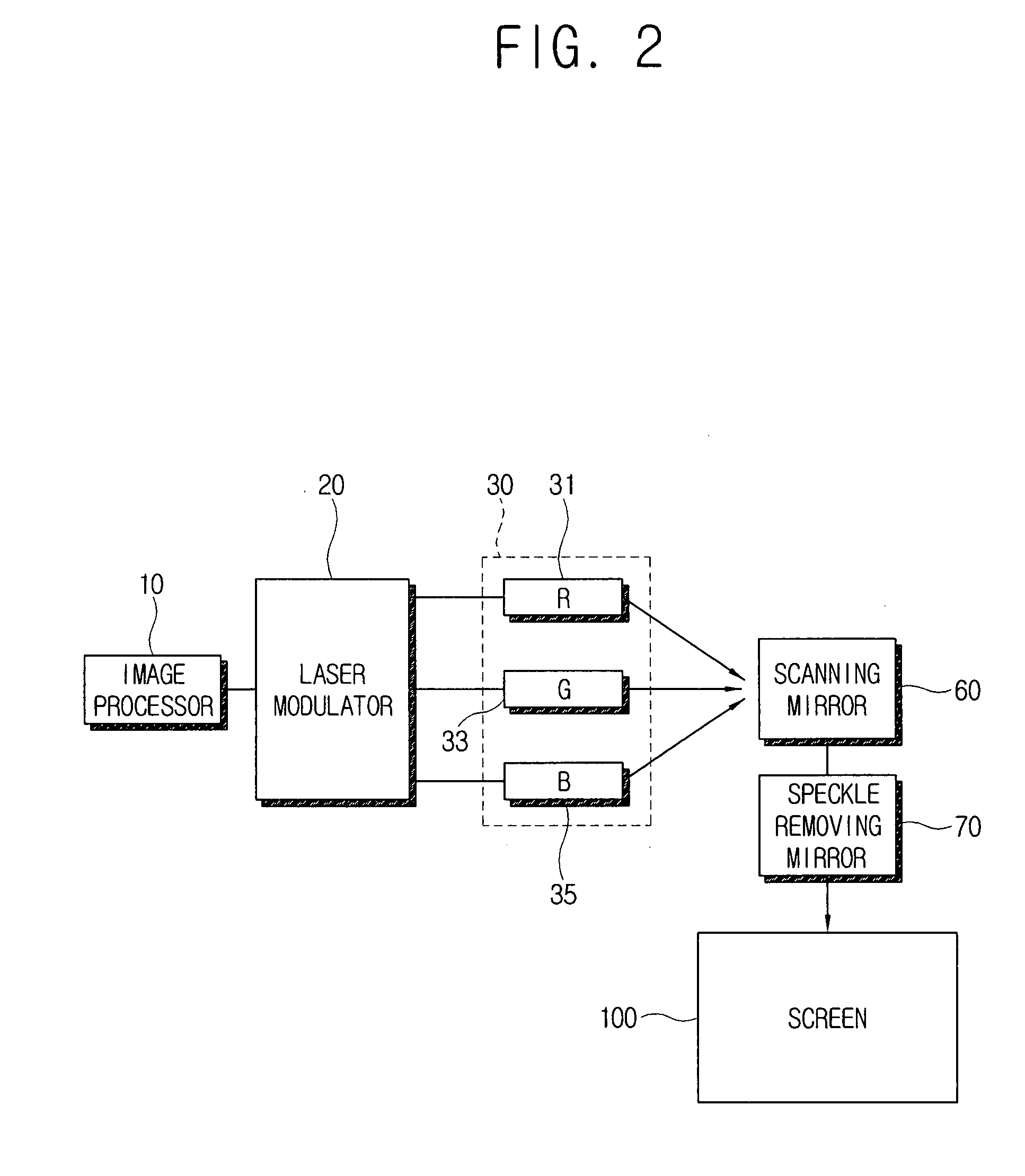
A display apparatus which uses a laser to realize a clear image by reducing speckle noise is provided. The display apparatus comprises a laser light source which emits light a scanning mirror which scans light emitted by the laser light source, a speckle removing mirror which periodically reciprocates within a predetermined rotating angle, and projects the light scanned by the scanning mirror, to a screen, and an image processor which processes image data to shift an image by frame corresponding to the rotation of the speckle removing mirror.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Mining subsidence similar test model device
InactiveCN103823041ABottom-pull structure design for convenient economic empty areaSolve the problem of mining planEarth material testingLaser rangingLaser scanning
The invention relates to a mining subsidence similar test model device including a cubic container with adjustable volume, a model bracket base, a bottom plate, bar-shaped longitudinal beams, a movable plate assembly, a slipping-type laser distance measurement scanner, a laser scanning simple device and the like. A similar material analogic to underground rock soil is utilized for testing, and according to different excavation schemes, an excavation process is simulated through pulling open movable plates of the container bottom plate, so as to induce collapse of a rock-soil body to be simulated in a model bracket. After the collapse stops, an underground goaf top plate form and a simulated earth surface are scanned by the bottom laser scanning simple device and the top slipping-type laser distance measurement scanner which are matched, and three-dimensional coordinate data are obtained. Under conditions with no contact and no disturbance of a structure / engineering entity, the same-kind test device performs one-time test to complete simulation mining of different bottom-pulling modes and different forms of ore-rocks, the goaf top plate three-dimensional form and the overlying strata earth surface subsidence process under induction mining are all-dimensionally disclosed, and requirements of flexible design, convenient operation and controllable data acquisition are satisfied.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Illumination device, projection type image display device, and optical device
ActiveUS20140118702A1Uniform lightEffectively suppressing the speckleProjectorsColor television detailsImage formationStigmatism
To provide an illumination device and a projection type image display device that illuminate an area to be illuminated (image formation area) under conditions where speckle noise is less noticeable.An illumination device according to the present invention includes: a light source 11 that emits coherent light; an optical scanning section 15 that scans the coherent light emitted from the light source 11; a lens array 22 including a plurality of element lenses and configured to diverge the light scanned by the optical scanning section; an optical path conversion system 23 configured to control a diverging angle of the diverging light to be emitted from respective points of the lens array 22 and to allow the diverging light whose diverging angle has been controlled to illuminate an area to be illuminated sequentially in an overlapping manner.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Device and method for displaying an image
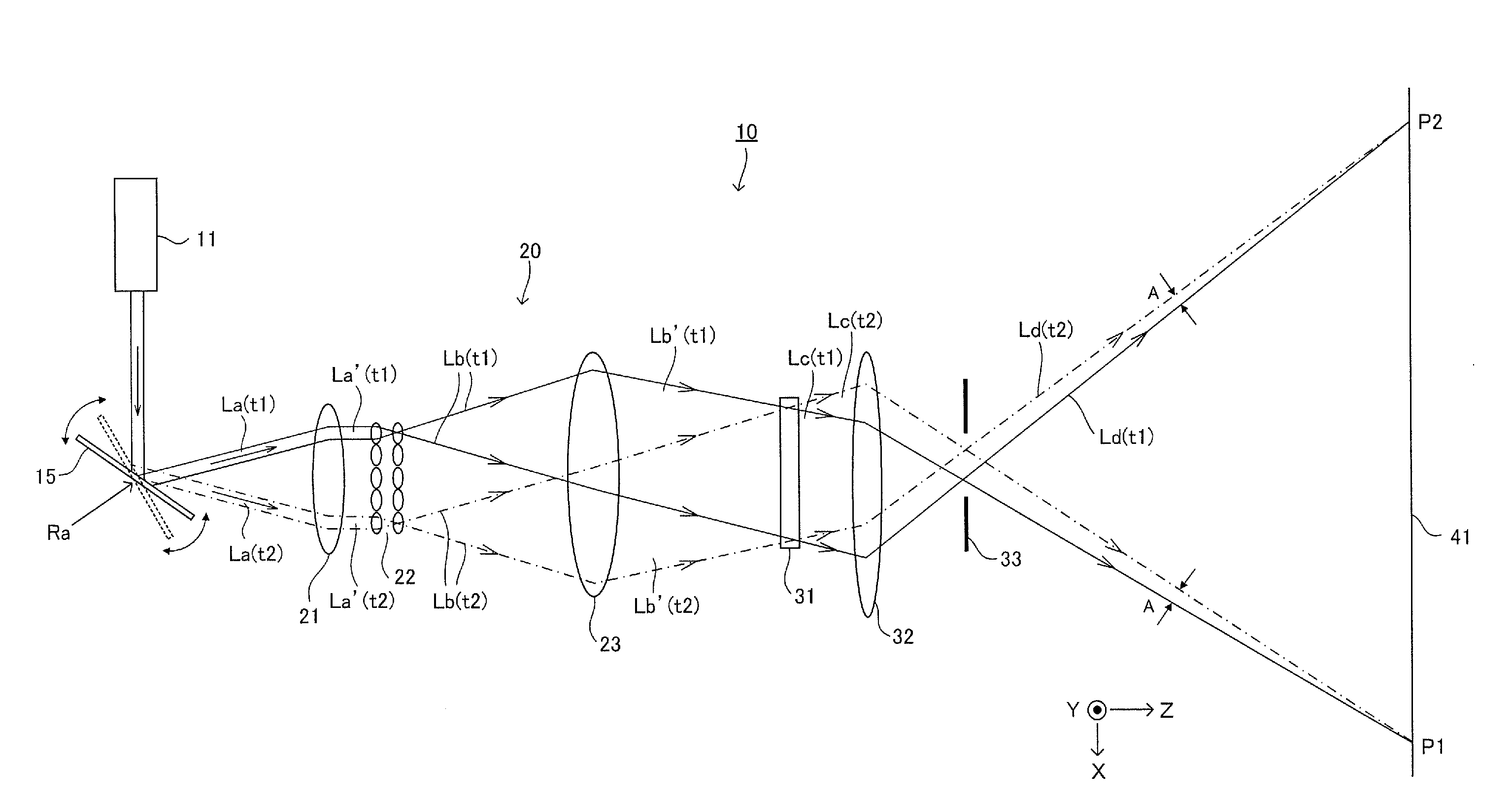
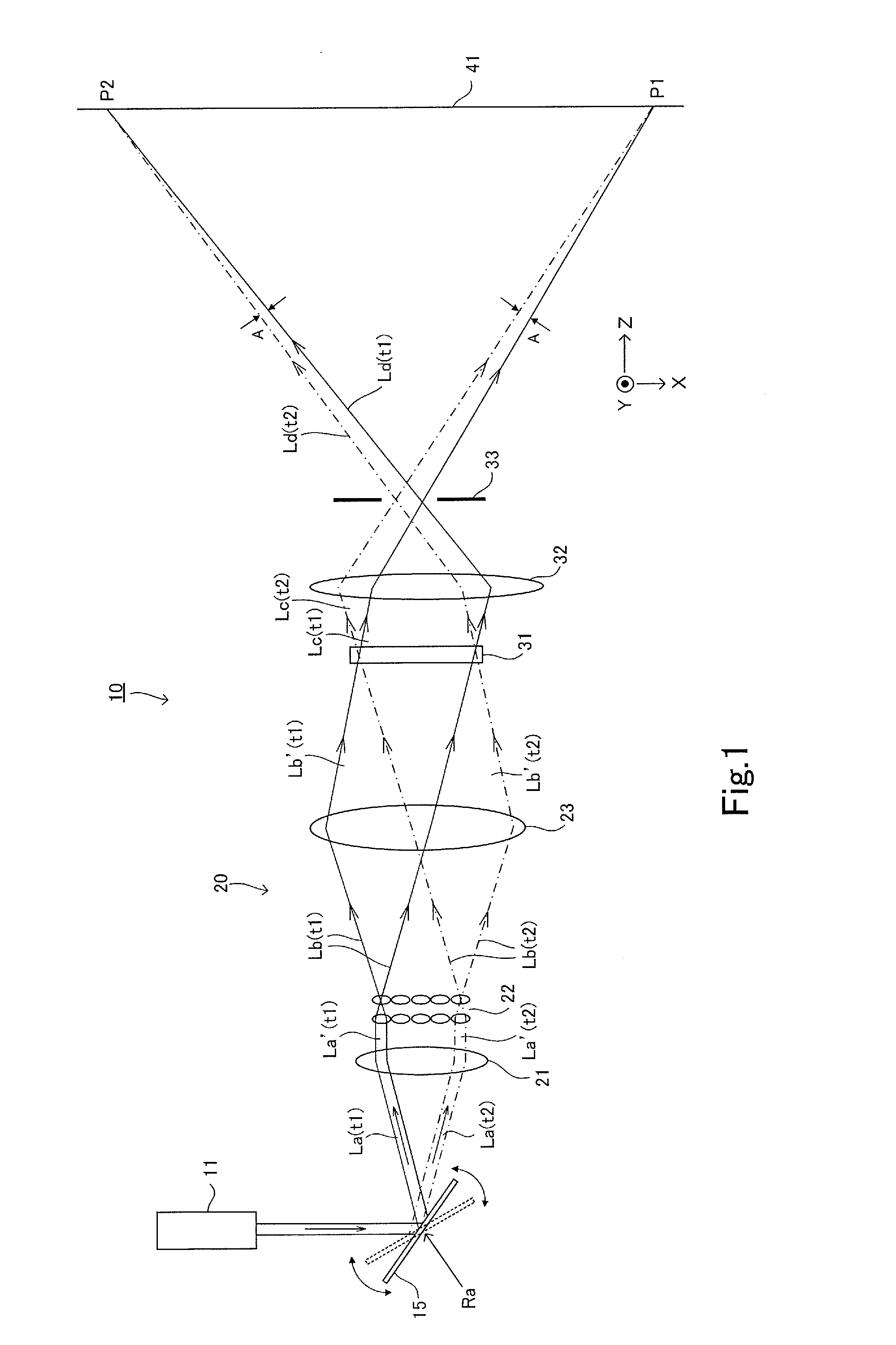
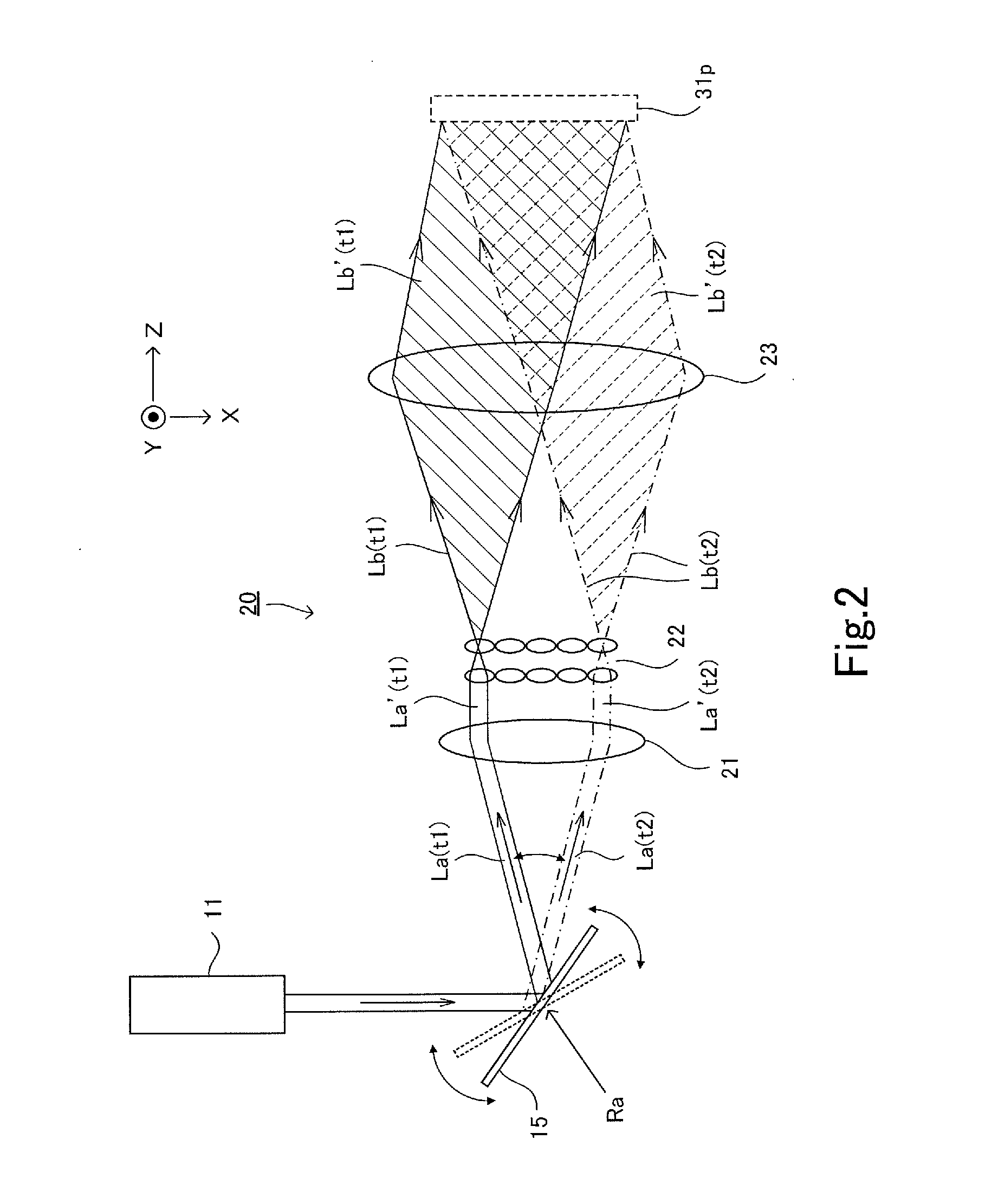
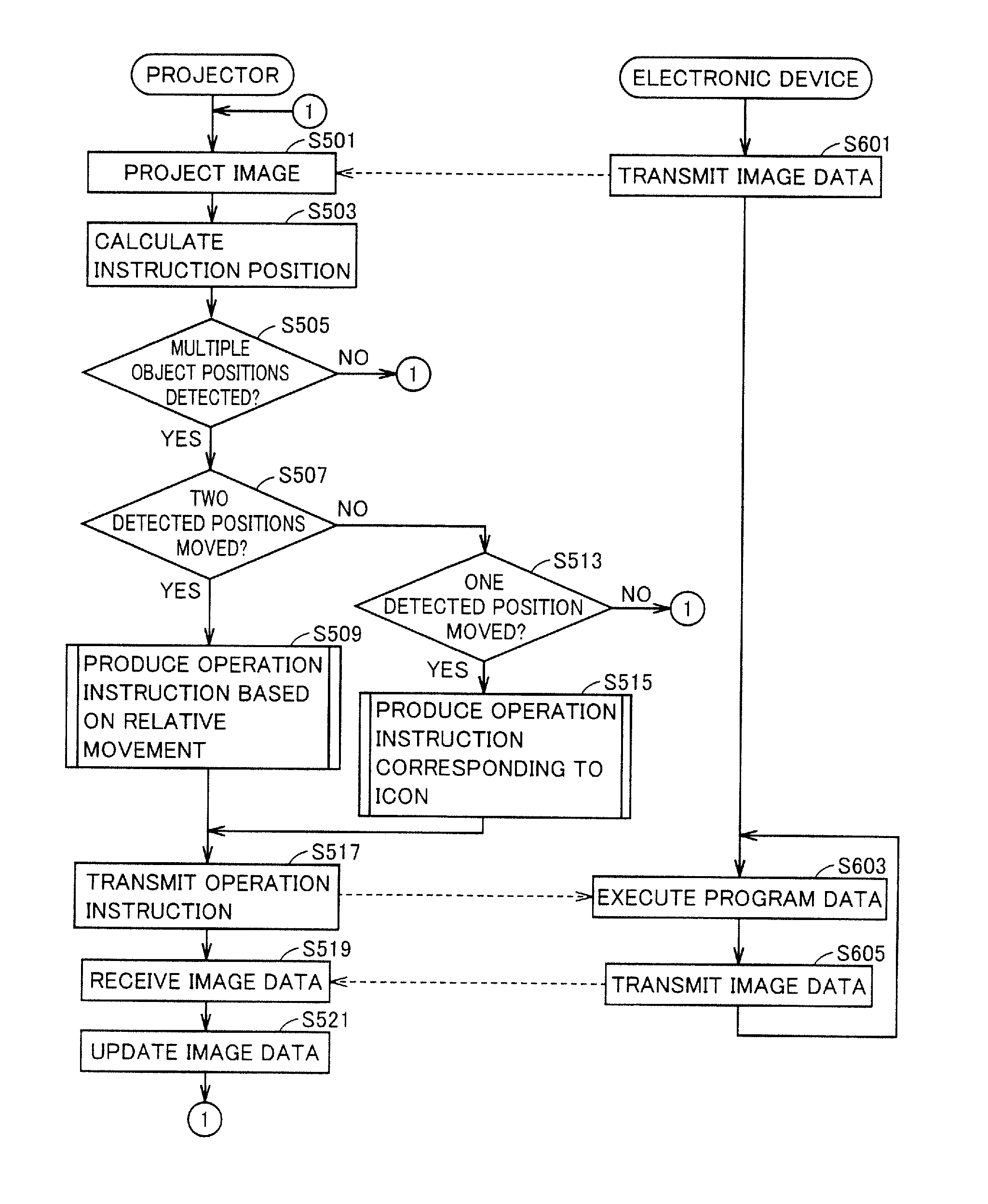
InactiveUS20100253618A1Easy to operateCathode-ray tube indicatorsColor television detailsLight sensingObject based
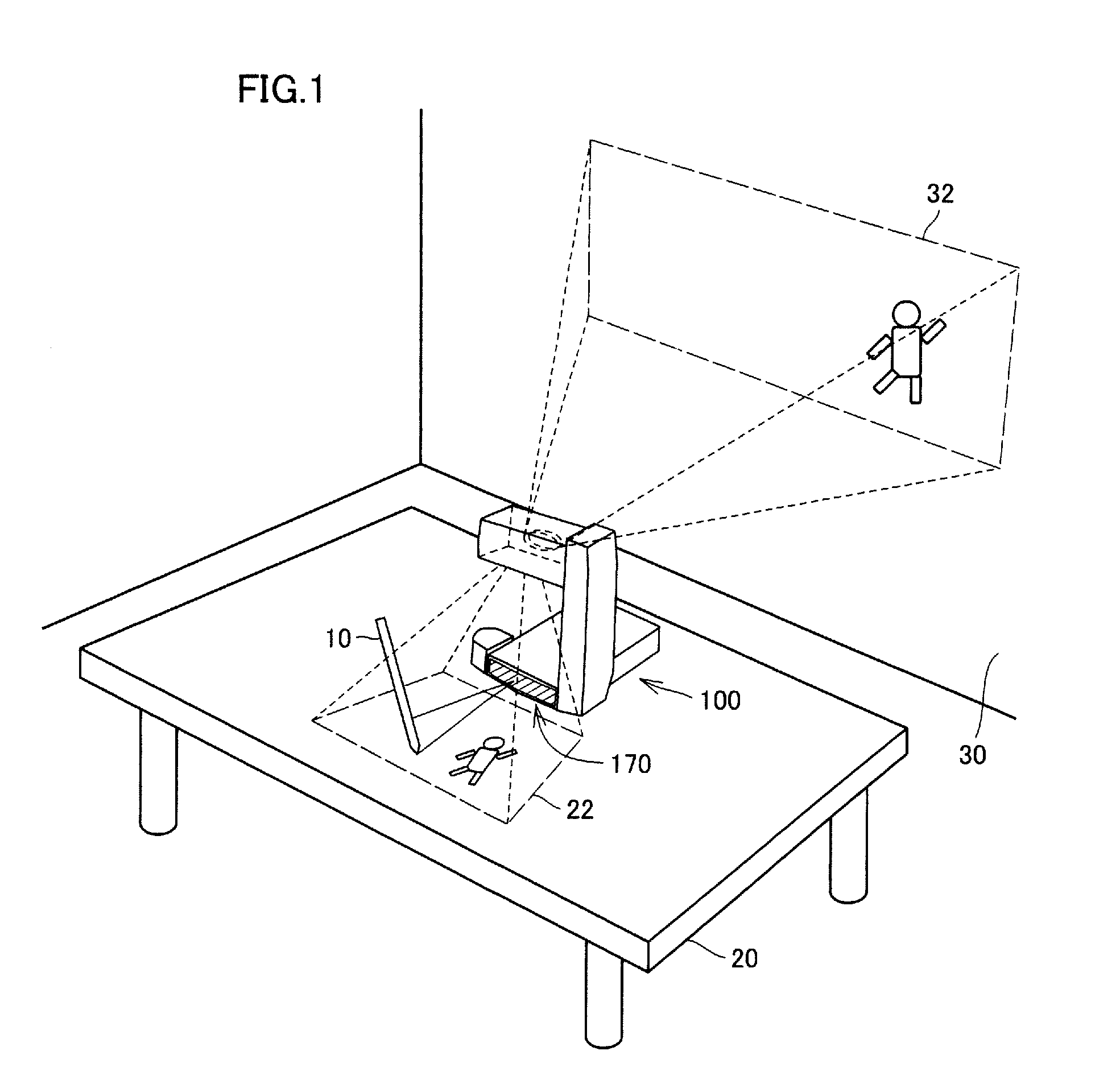
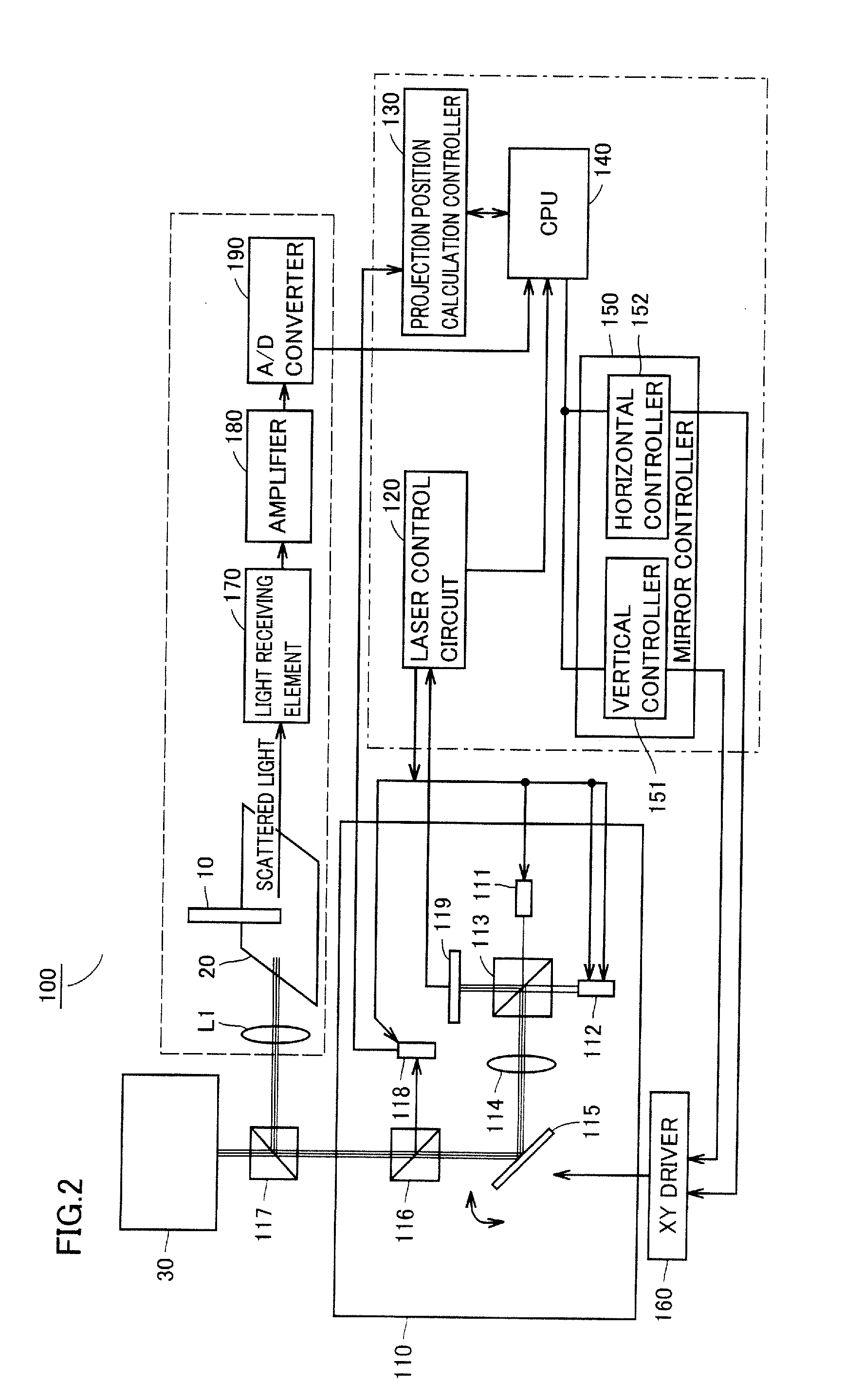
A projector producing an imaginary input plane with high operability is provided. A projector according to an embodiment projects a VUI screen picture onto a desk, and projects a main projection screen picture to a wall. The projector includes a light receiving element. The light receiving element is arranged in a position where light emitted toward the desk (VUI screen picture) and reflected (or scattered) by an object near the desk enters. The projector calculates a position of the object based on light sensing timing by the light receiving element and light scan positions at various points in time. The projector changes a projected screen picture when it determines that object is simultaneously in contact with a plurality of portions of the VUI screen picture and at least one of contact positions moves.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com