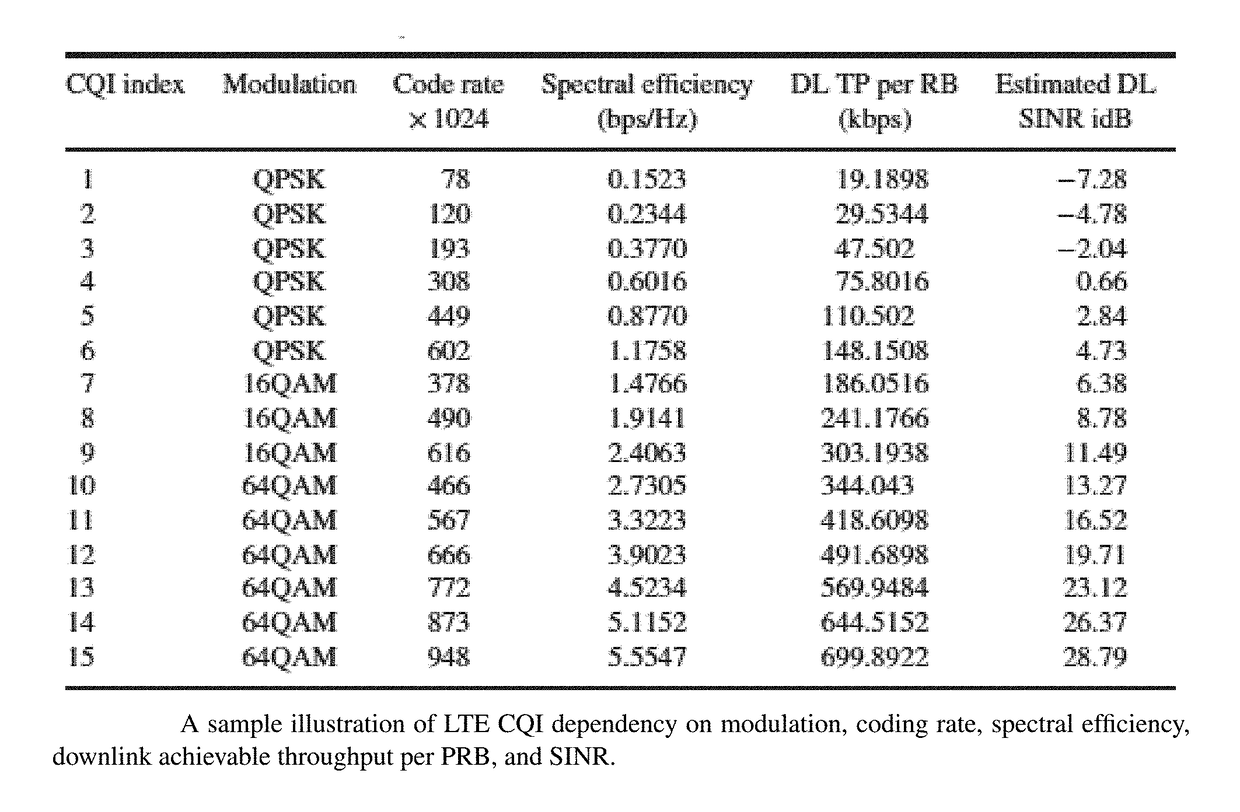
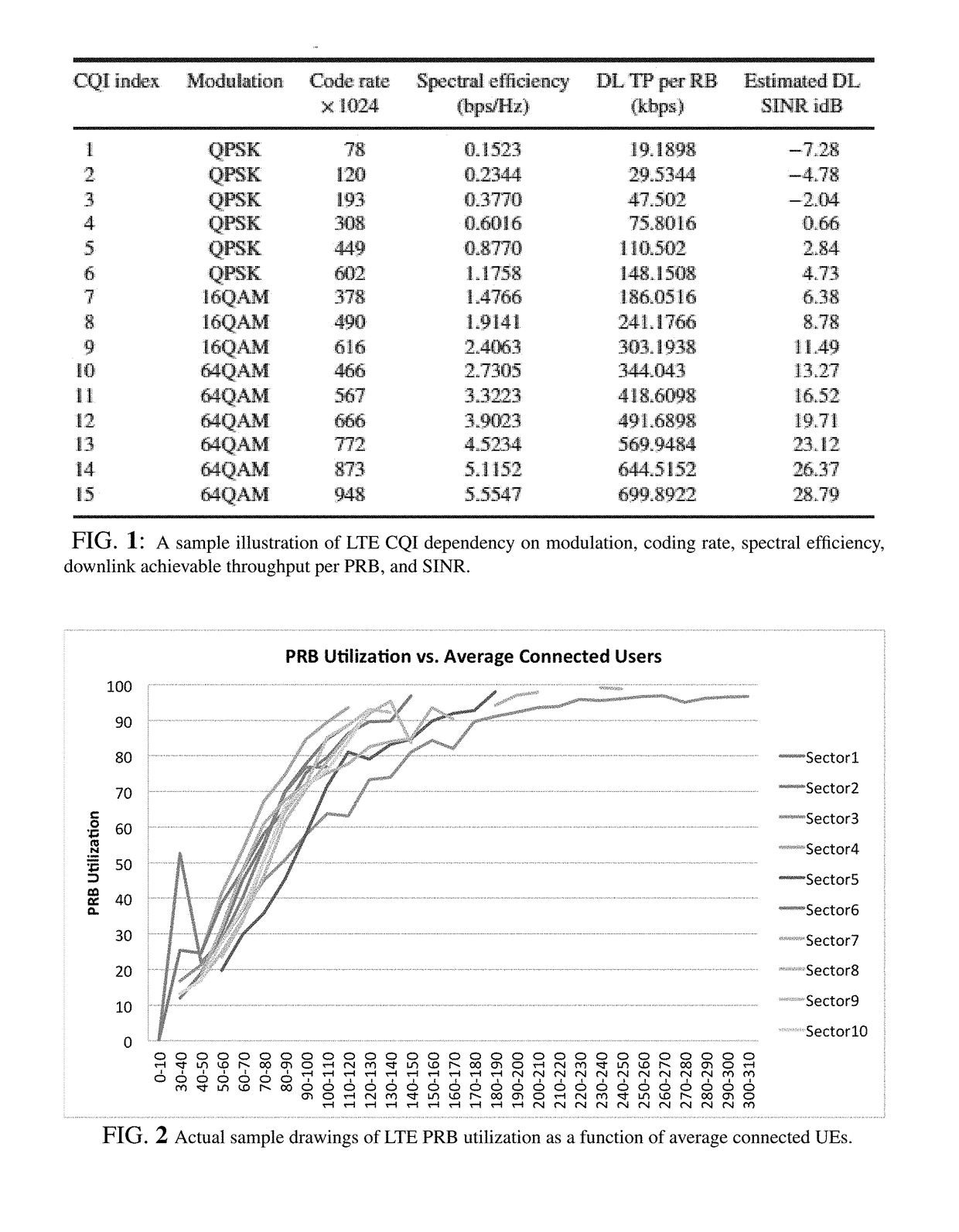
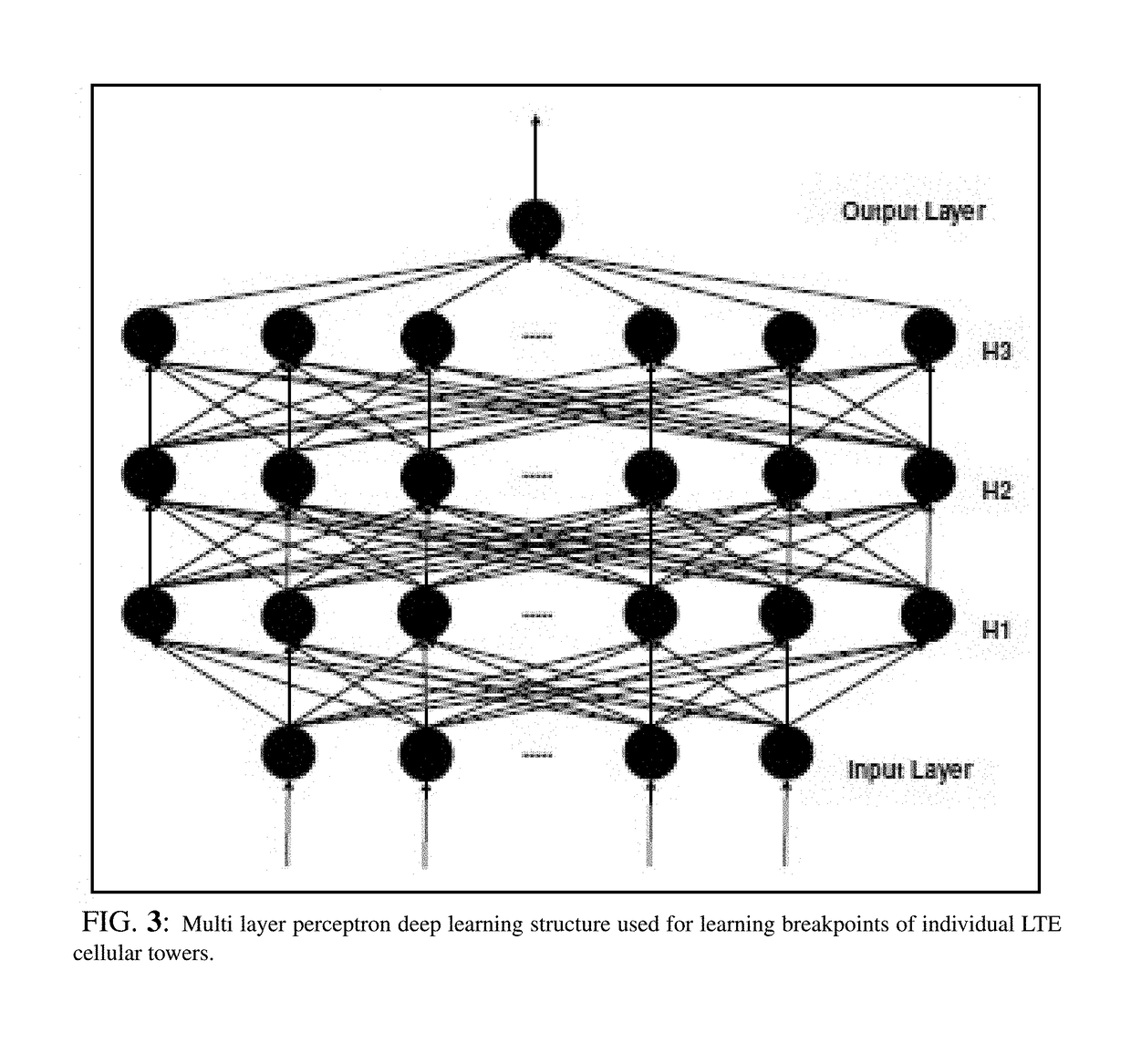
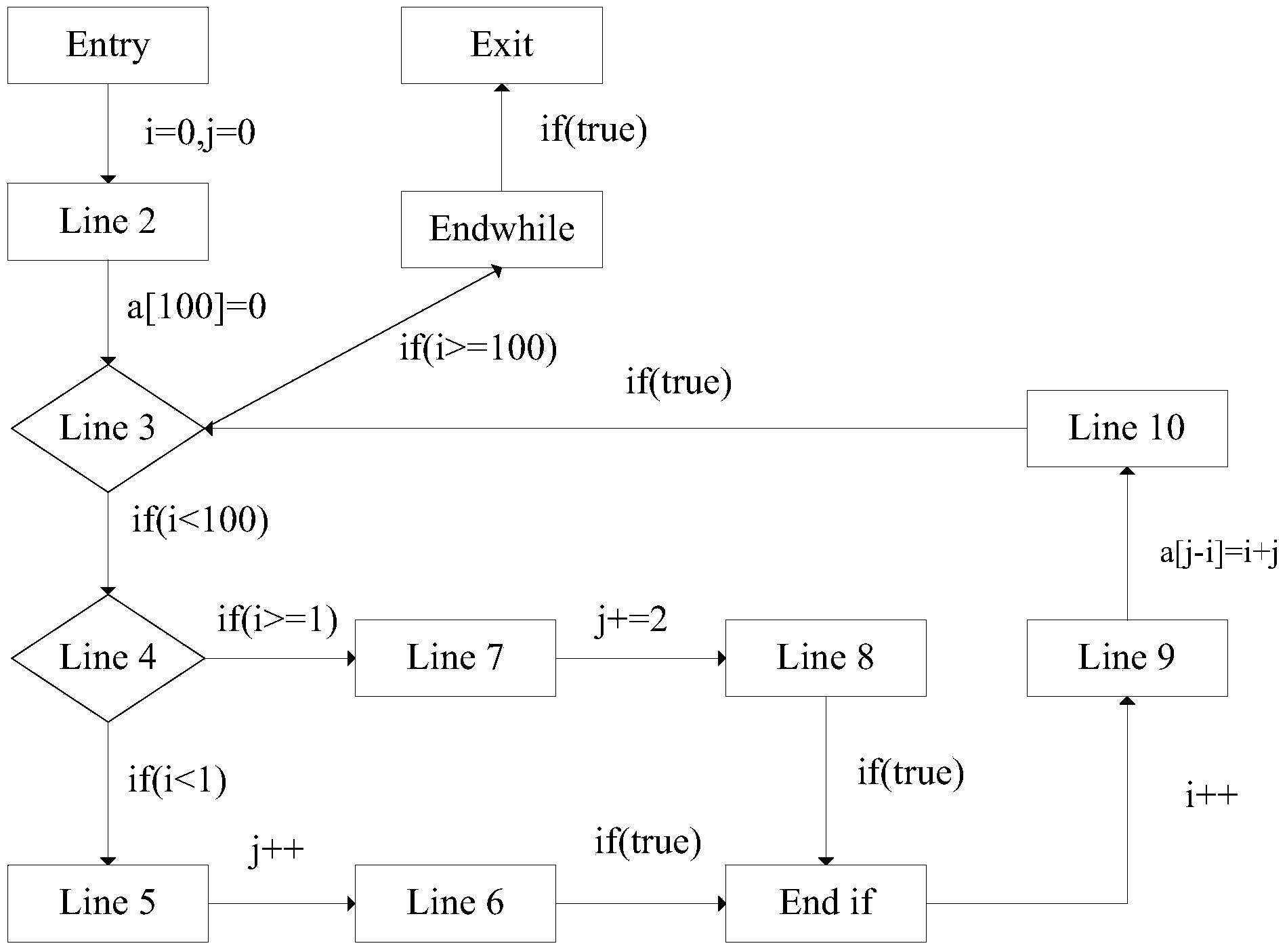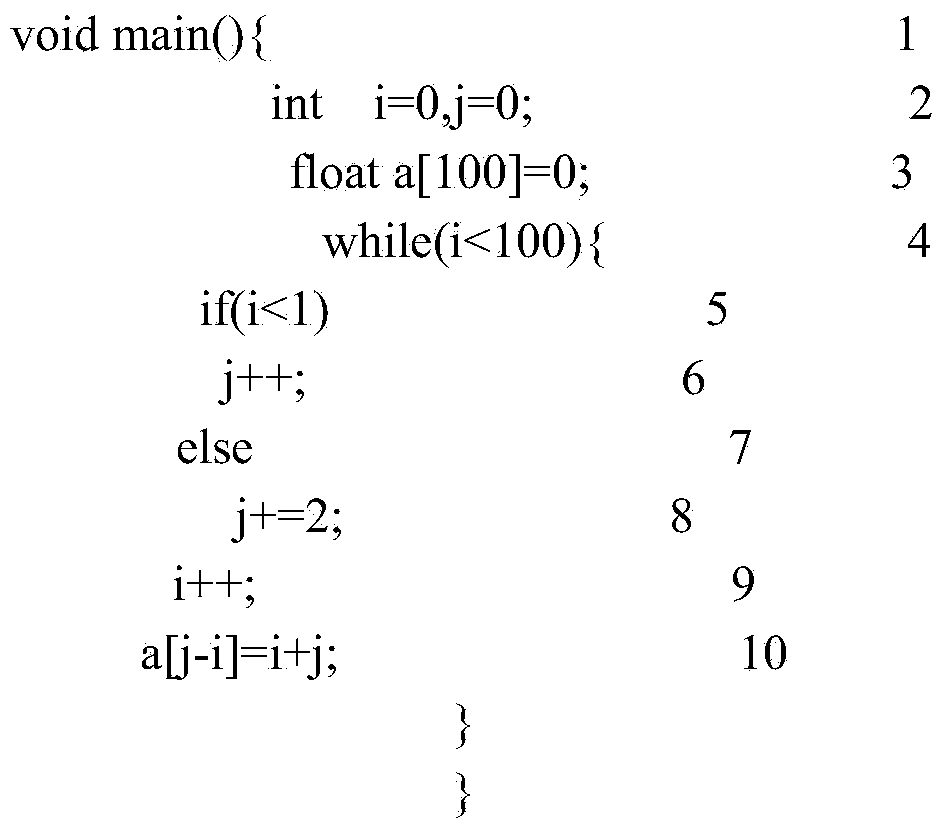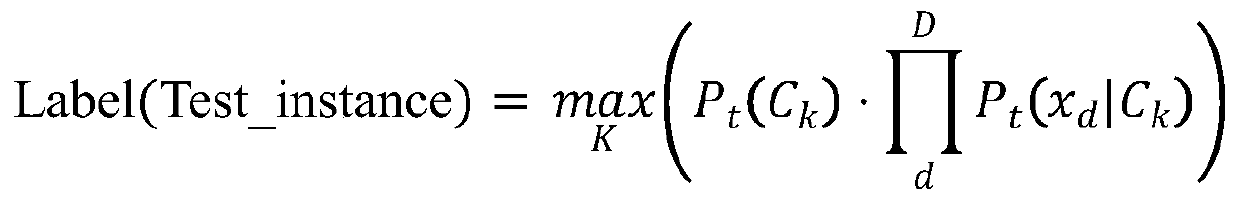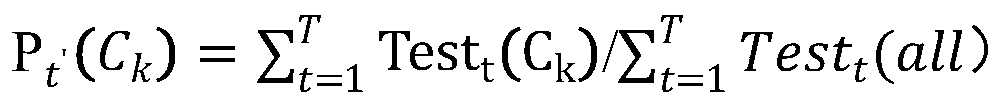Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
63 results about "Iterative methodology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Iterative testing. Definition: A methodology in which a product is tested and changed repeatedly at different stages of design/development to eliminate usability issues before the product is launched.
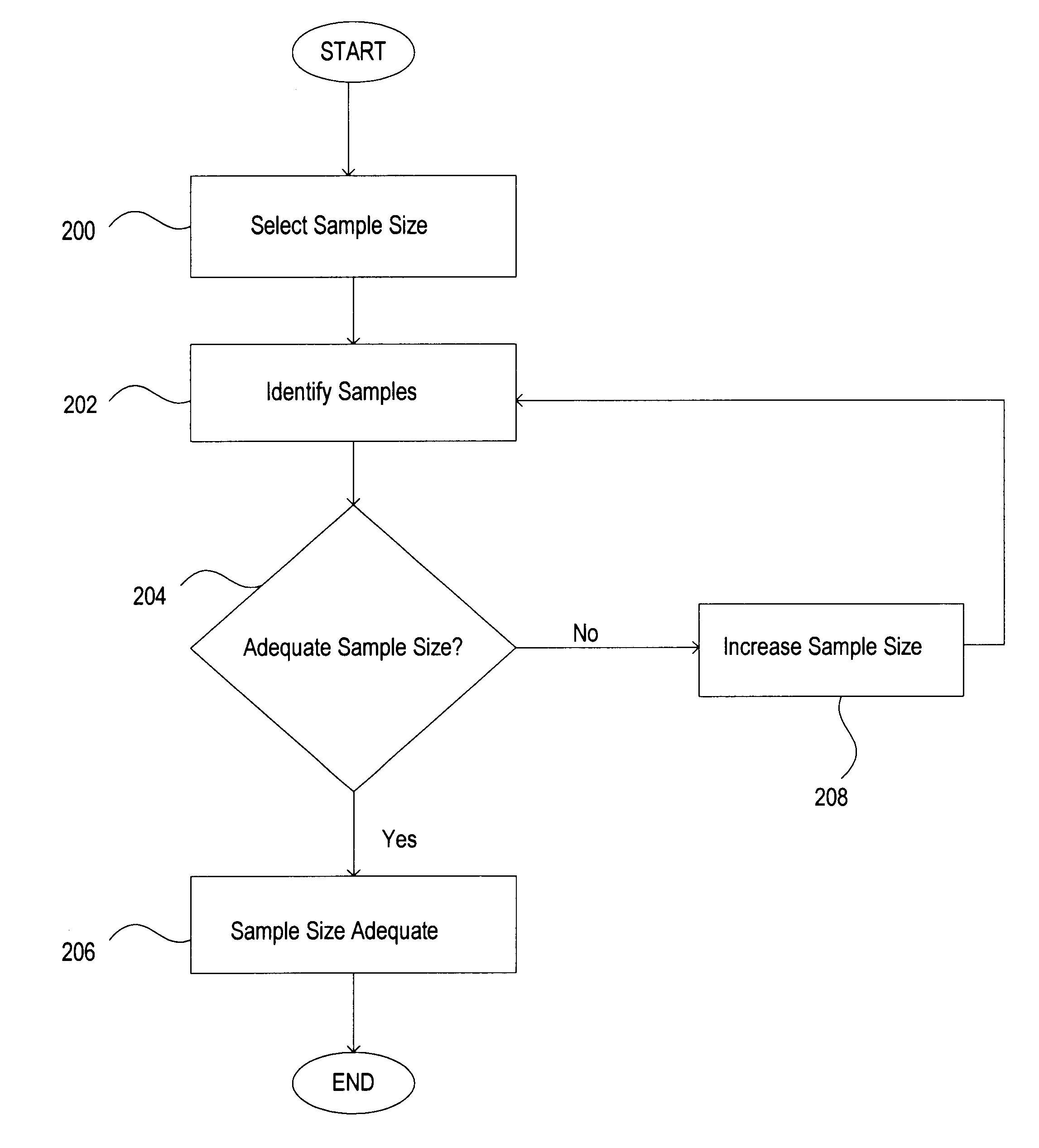
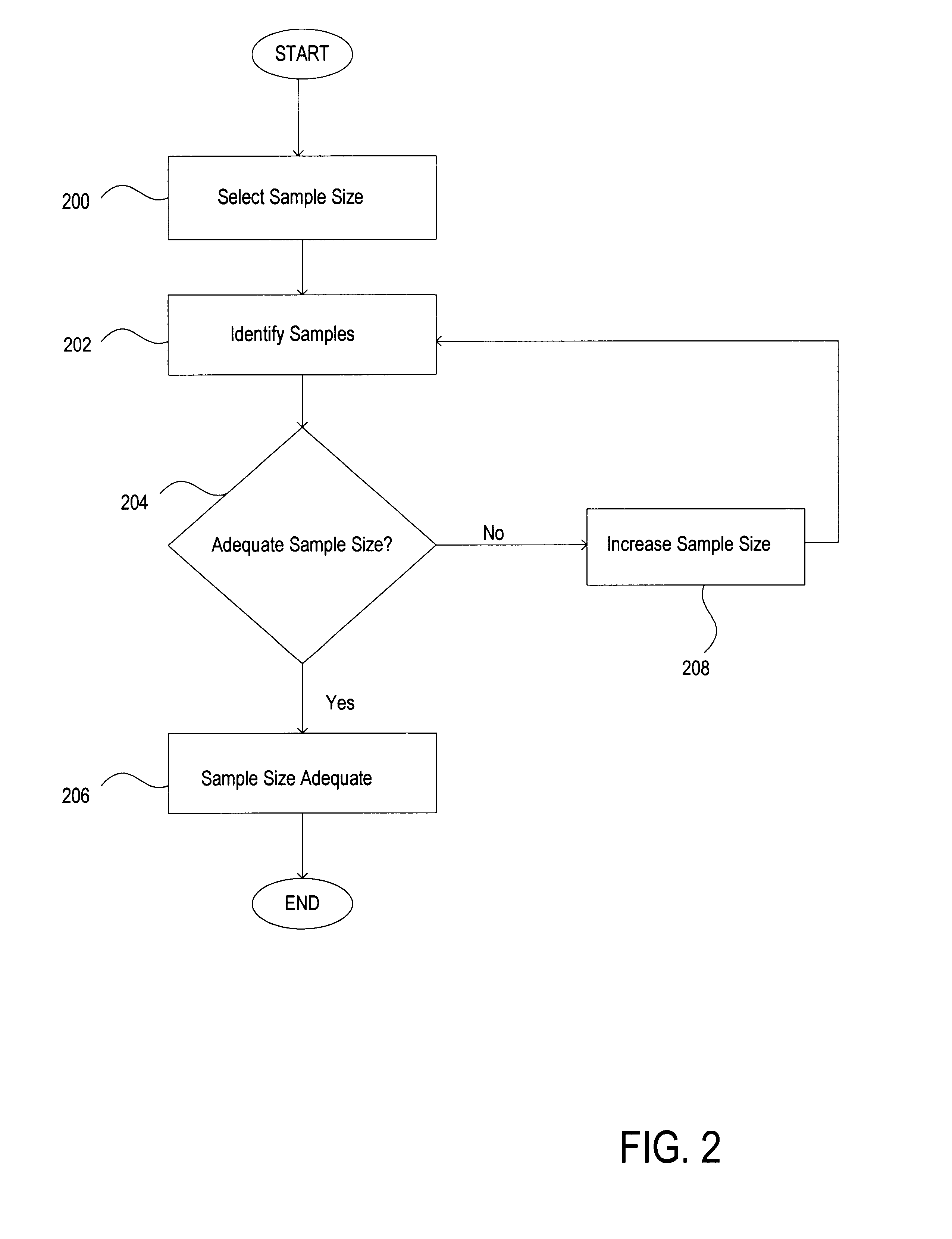
Method and system for sample size determination for database optimizers
InactiveUS6732085B1Quickly and efficiently executedEfficient executionData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalSmall sampleIterative methodology
A system and method for determining an adequate sample size for statistics collection is disclosed. A mechanism for automatically determining an adequate sample size for both statistics and histograms is provided. The sample size determination is accomplished via an iterative approach where the process starts with a small sample, and for each attribute which may need more data, the sample size is increased while restricting the information collected to only those attributes that require the larger sample.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
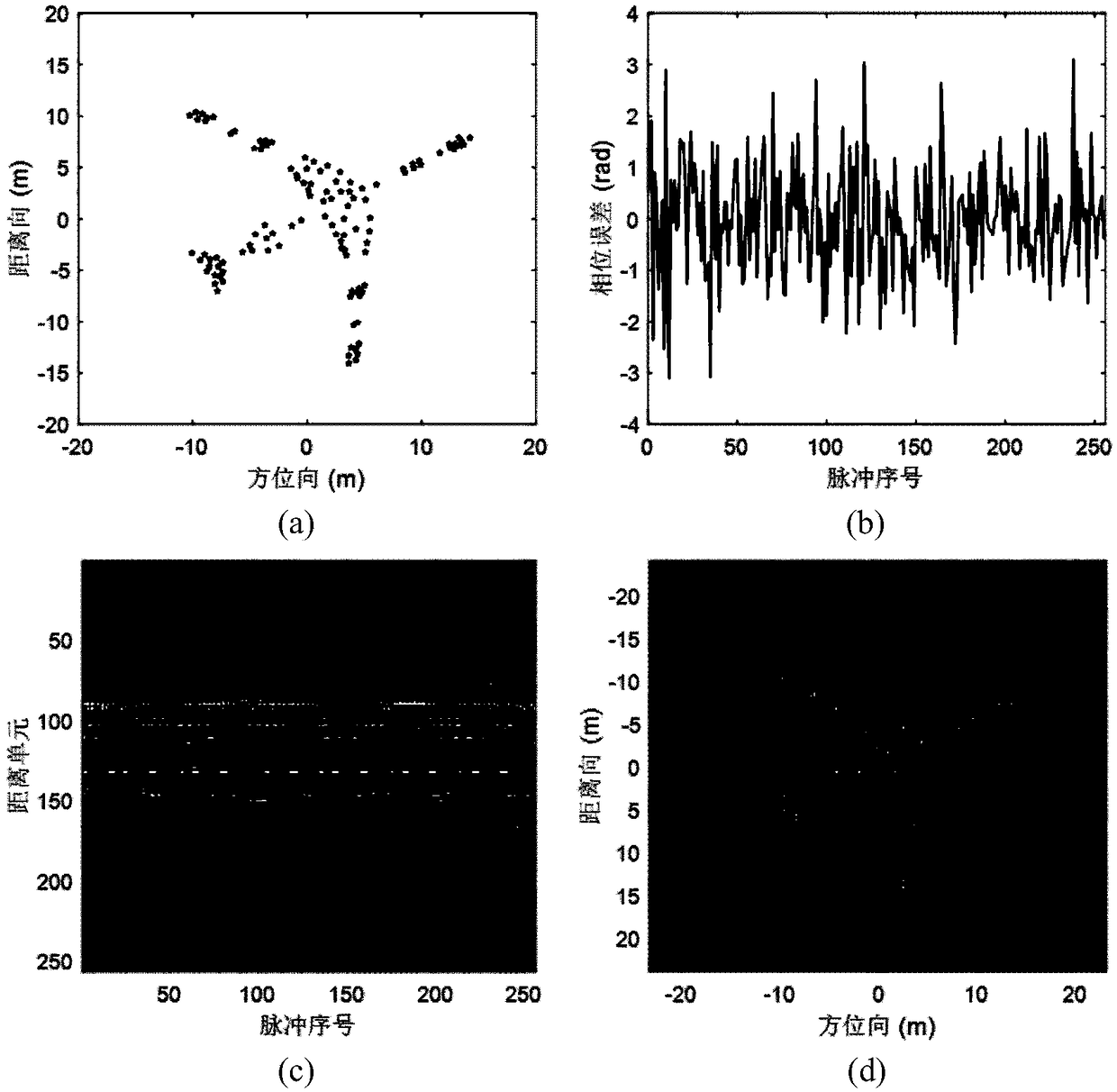
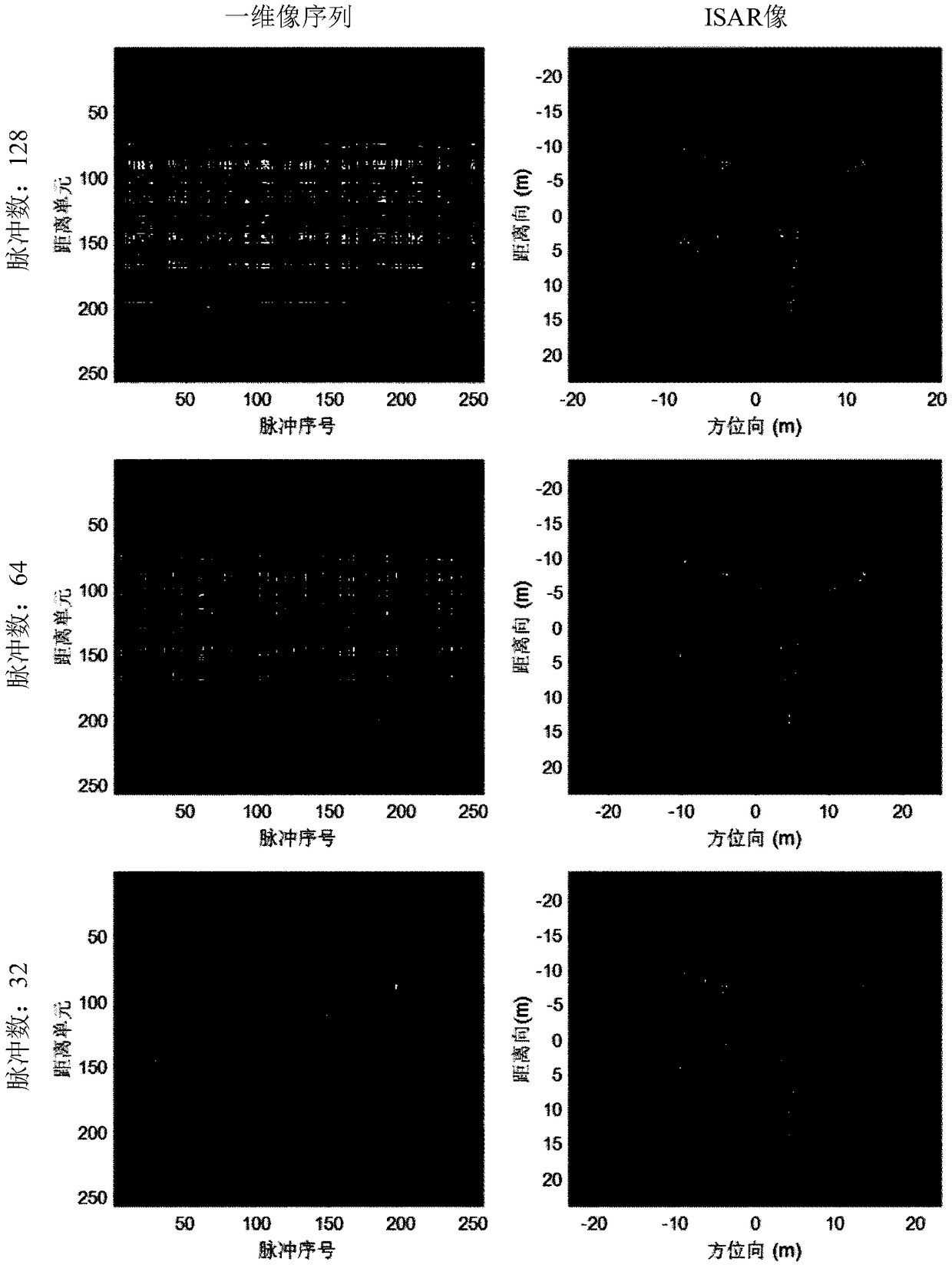
Sparse aperture ISAR self-focusing and lateral scaling method based on Bayesian learning
ActiveCN109100718AFocusHigh resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPattern recognitionIterative methodology
The invention belongs to the field of radar signal processing, and particularly relates to a sparse aperture ISAR self-focusing and lateral scaling method based on Bayesian learning. The method comprises the following steps: firstly performing sparse prior modeling on an ISAR image by using a Laplace layered model, and performing sparse reconstruction on the ISAR image by using a variational Bayesian method, wherein during the reconstruction of the ISAR image, a modified Newton iterative method is used to simultaneously estimate a phase error and a target rotational speed to achieve self-focusing and lateral scaling of the ISAR under the sparse aperture condition. The invention obtains the beneficial effects that: due to the sparse aperture ISAR self-focusing and lateral scaling method based on Bayesian learning, the self-focusing and lateral scaling of the ISAR under the sparse aperture condition can be realized, and the ISAR image with good focusing effect, high resolution and exactlateral scaling can still be obtained under the condition of sparse radar echo data aperture caused by the factors such as low SNR, strong interference and insufficient effective aperture, which has important engineering application value and can provide theoretical support for the design of a compressed sensing radar.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
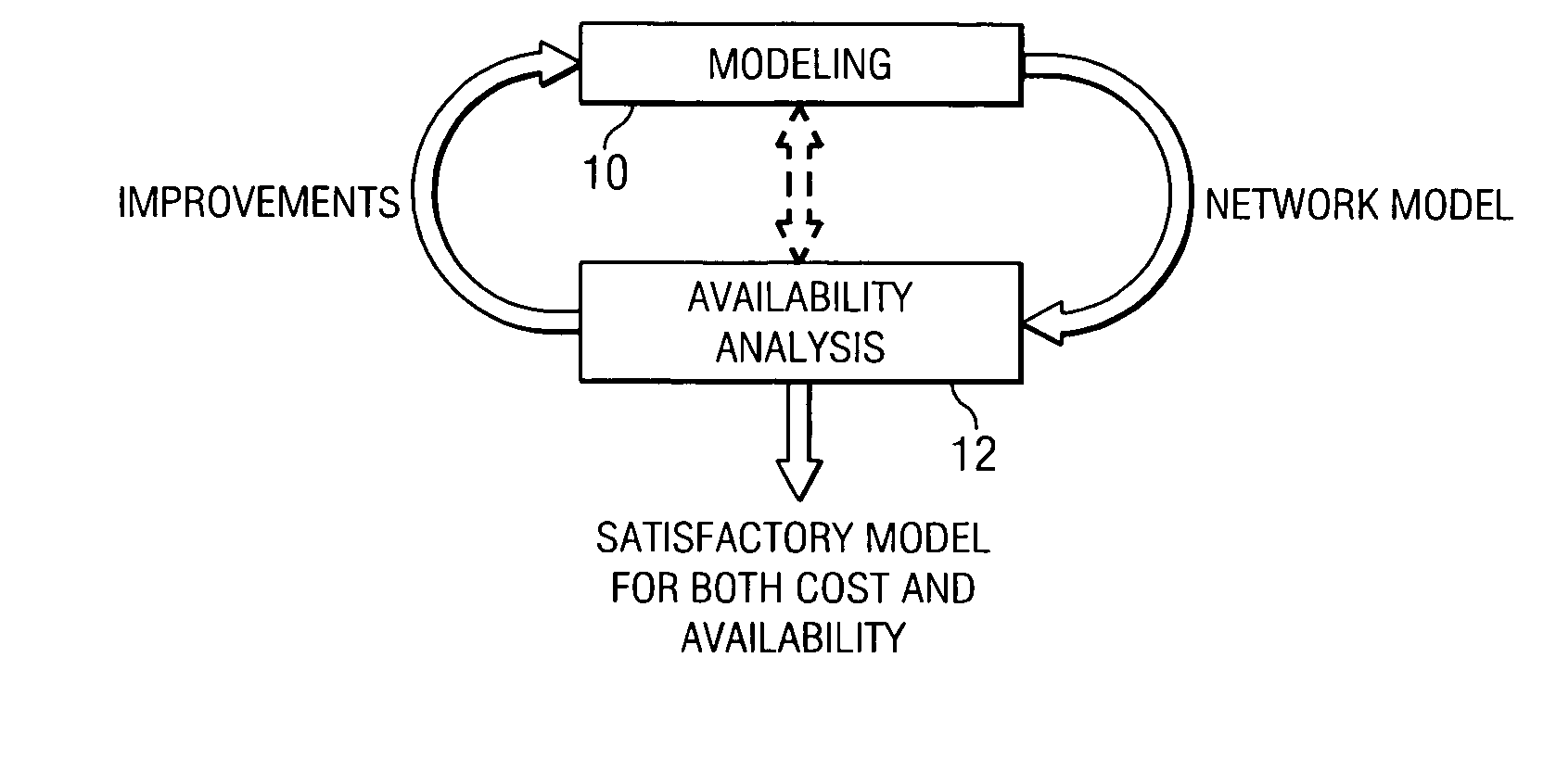
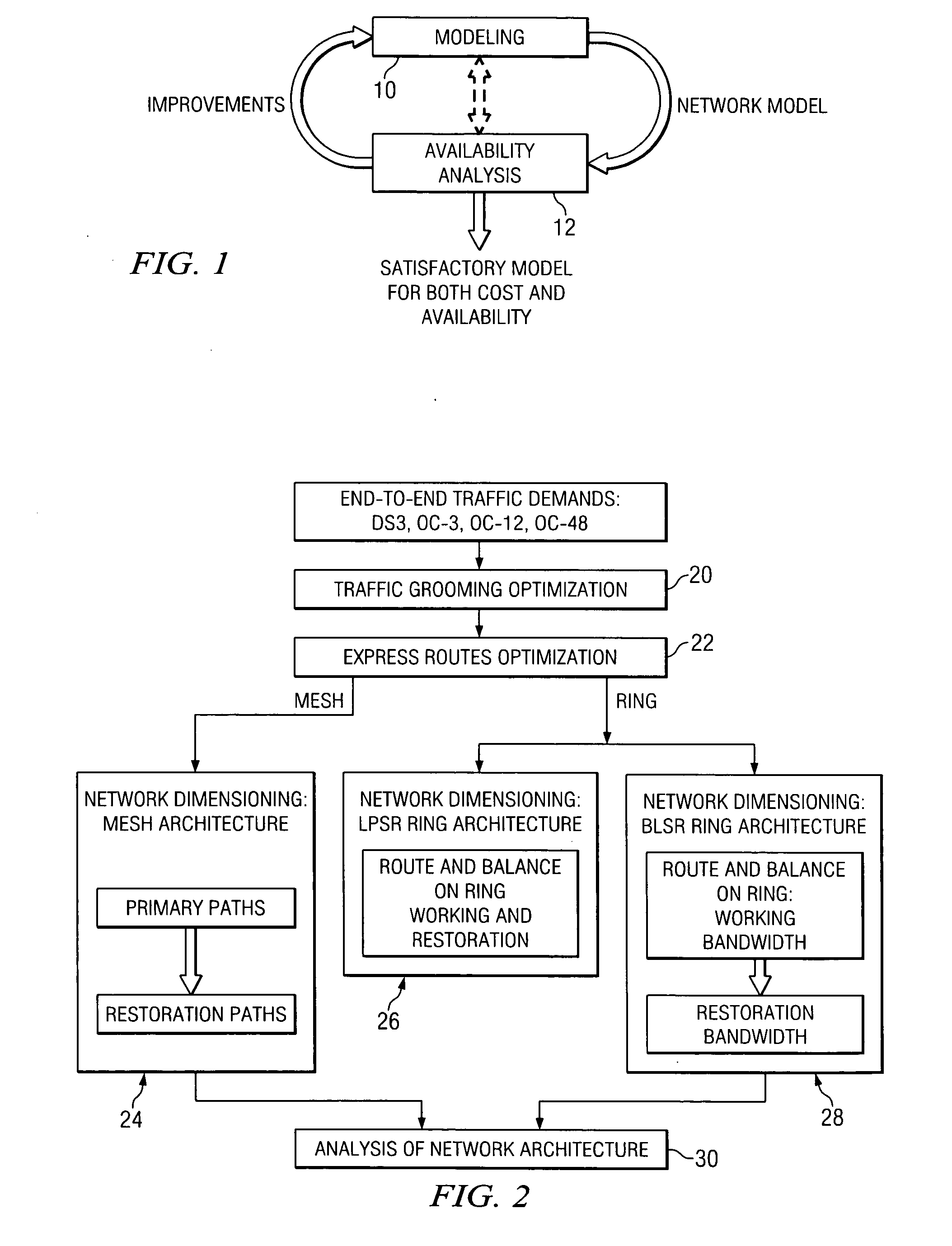
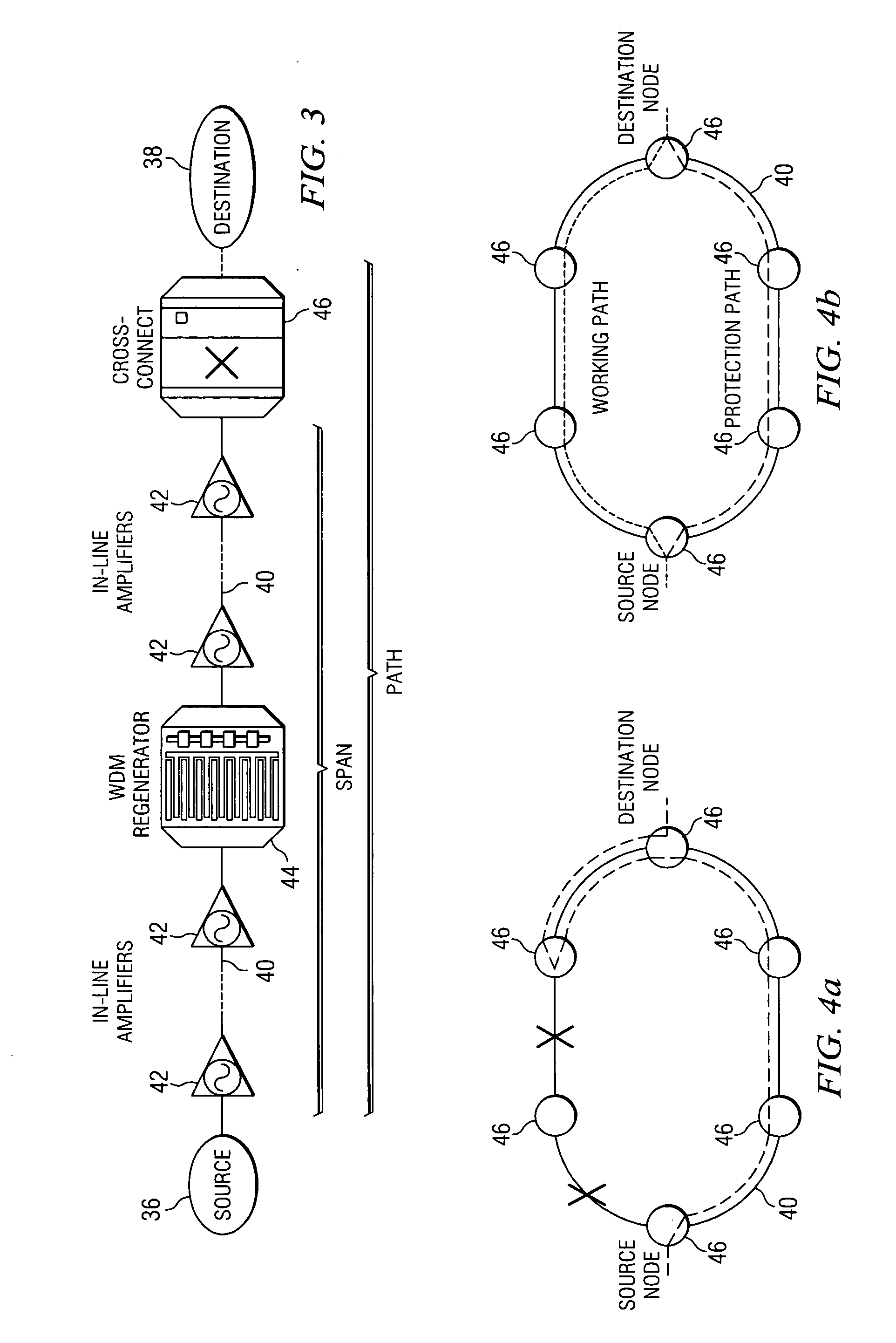
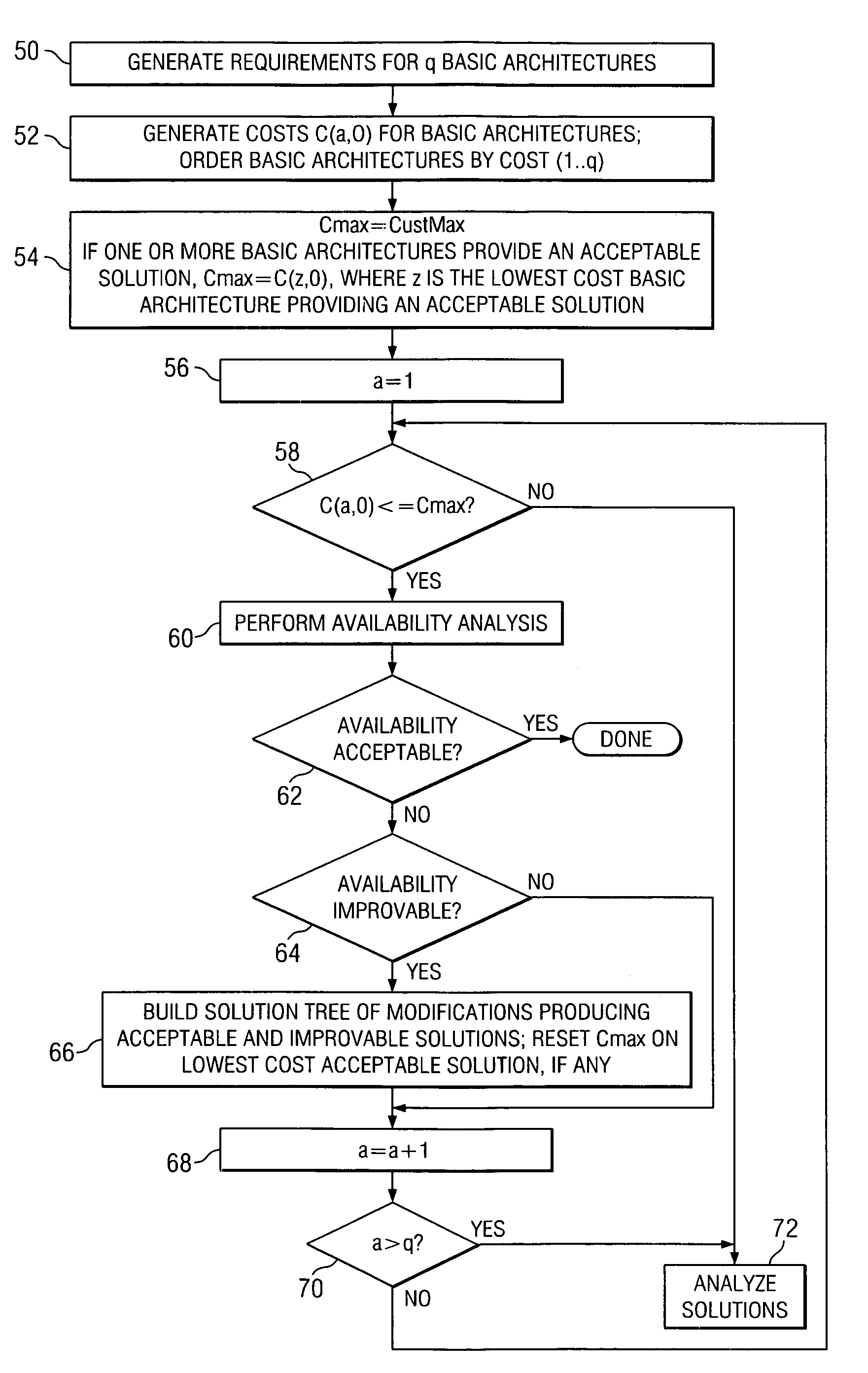
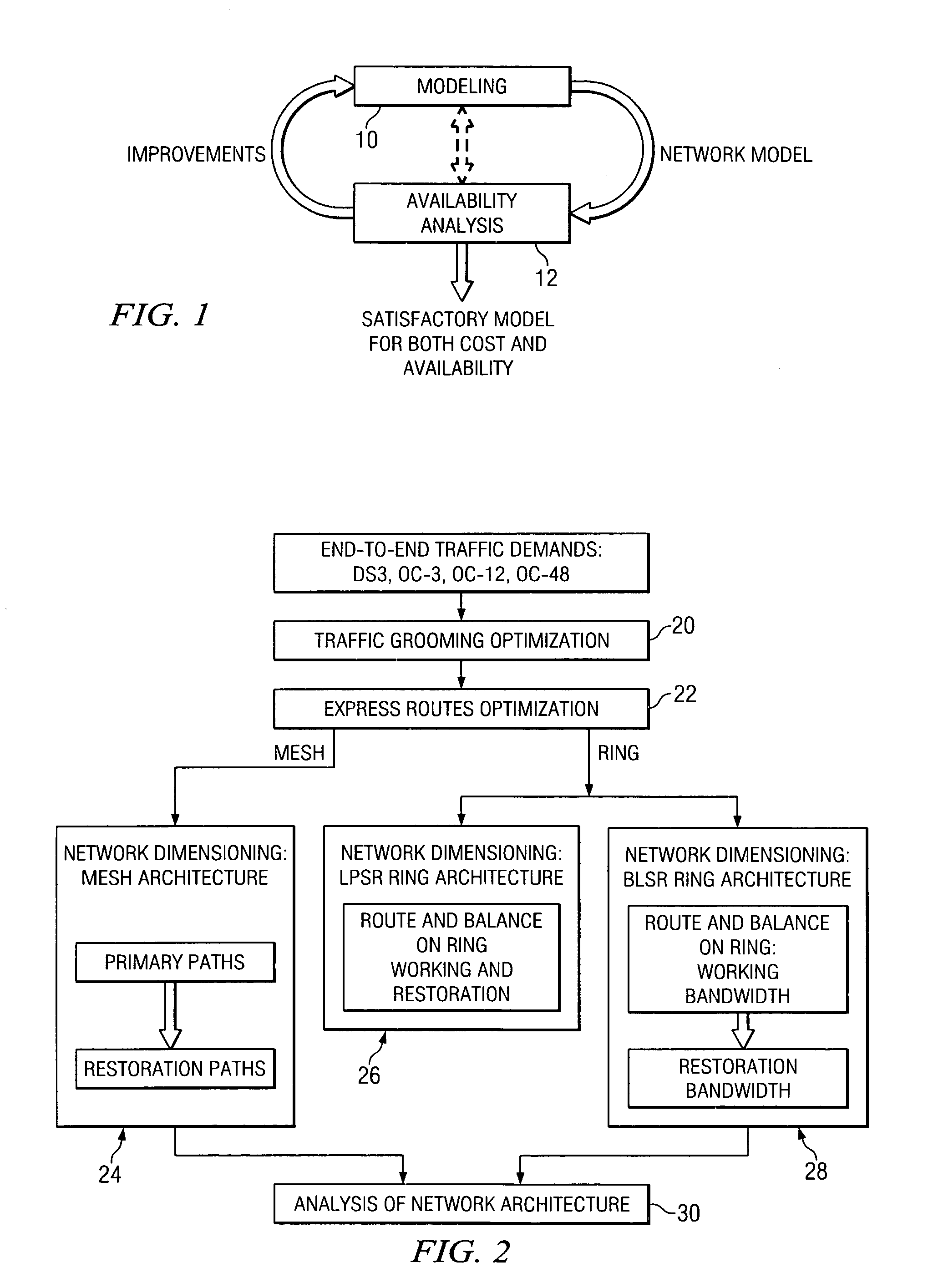
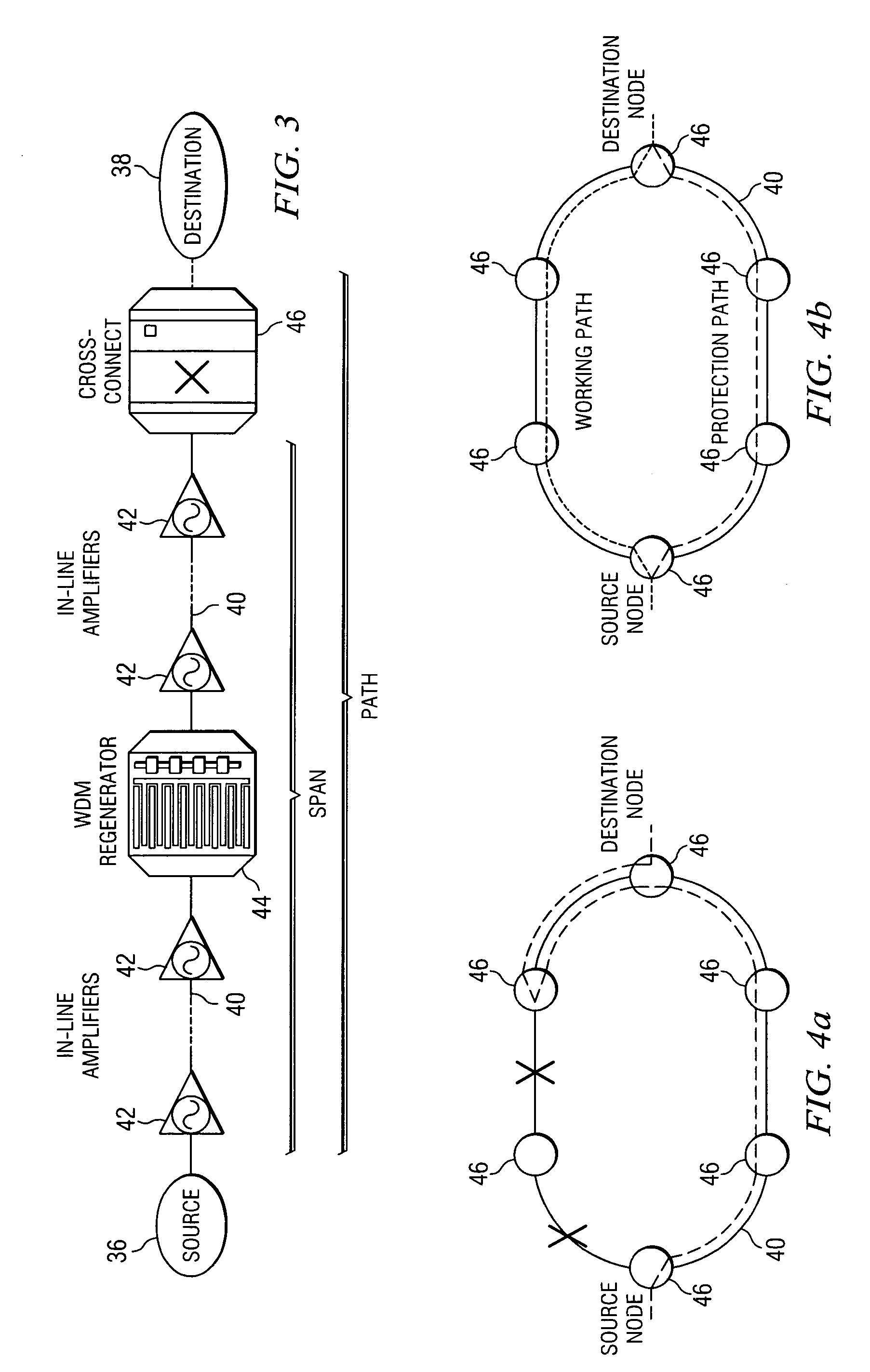
Availability aware cost modeling for optical core networks
InactiveUS20050113098A1Improving network architecture responsiveImprove responseWavelength-division multiplex systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsIterative methodologyNetwork architecture
A sequential iterative methodology is used to generate a solution space with different cost / availability values for multiple network architectures from which an optimal or near-optimal solution can be determined. A modeling module (10) provides a cost value for a network architecture under consideration and, once cost modeling is done, an availability analysis is performed for the architecture under analysis. If a relatively few connections prevent a model from acceptability, the availability analysis module (12) reveals the causing factors of the unsatisfactory availability for those few connections and suggests that the modeling perform further optimisations on those causing factors. This iterative process is repeated until an optimum or near-optimum acceptable solution is found; if no acceptable solution is found, the solutions generated in the availability analysis module are reviewed to find the best available solution.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Learning-constrained optimal enhancement of cellular networks capacity
ActiveUS20170359754A1EffectivelyIncrease network capacityNetwork traffic/resource managementMachine learningIterative methodologyThird generation
Optimal enhancement of 3G cellular network capacity utilizes two components of learning and optimization. First, a pair of learning approaches are used to model cellular network capacity measured in terms of total number of users carried and predict breakpoints of cellular towers as a function of network traffic loading. Then, an optimization problem is formulated to maximize network capacity subject to constraints of user quality and predicted breakpoints. Among a number of alternatives, a variant of simulated annealing referred to as Block Coordinated Descent Simulated Annealing (BCDSA) is presented to solve the problem. Performance measurements show that BCDSA algorithm offers dramatically improved algorithmic success rate and the best characteristics in utility, runtime, and confidence range measures compared to other solution alternatives. Accordingly, integrated iterative method, program, and system are described aiming at maximizing the capacity of 3G cellular networks by redistributing traffic from congested cellular towers to non-congested cellular towers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
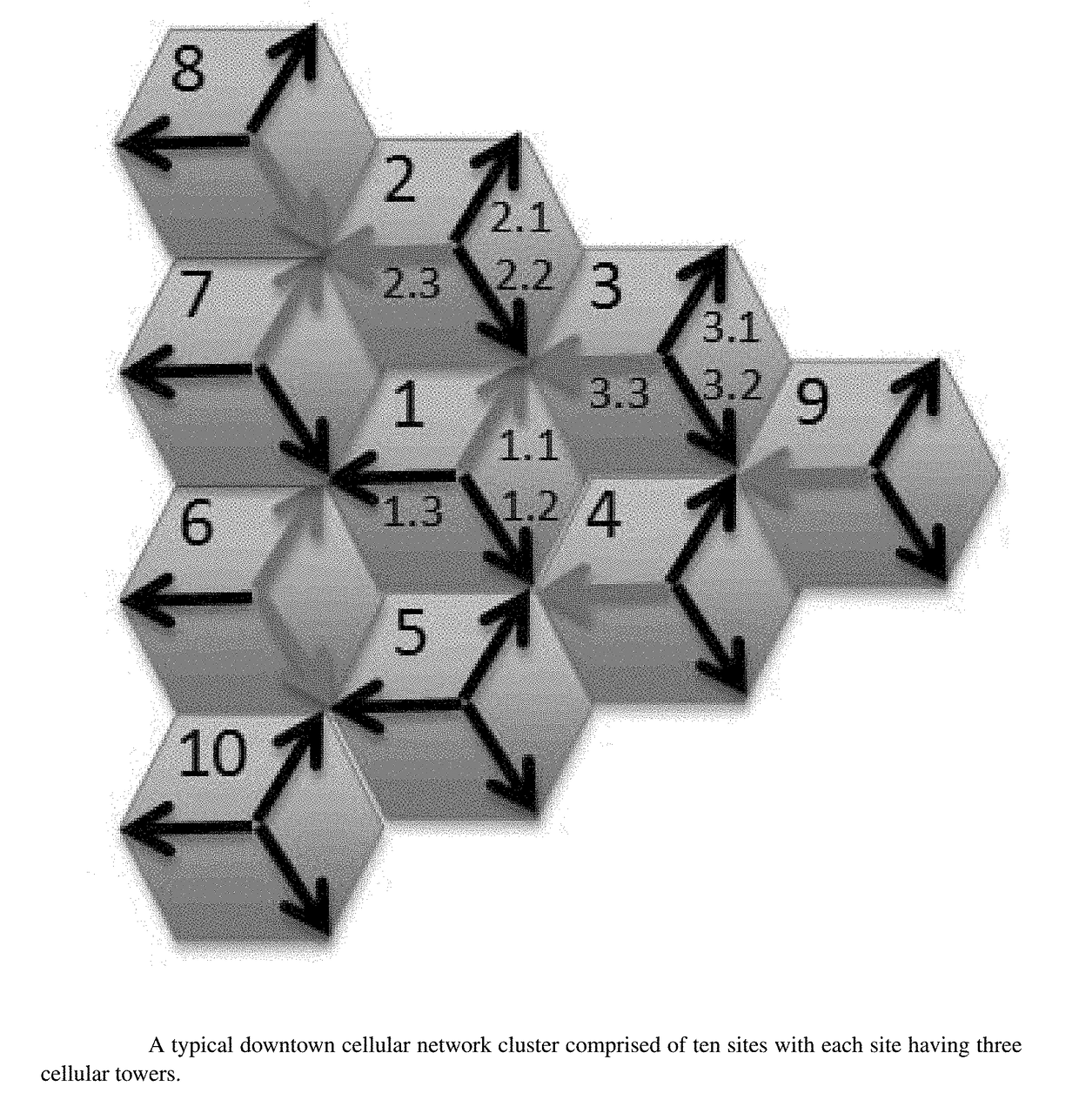
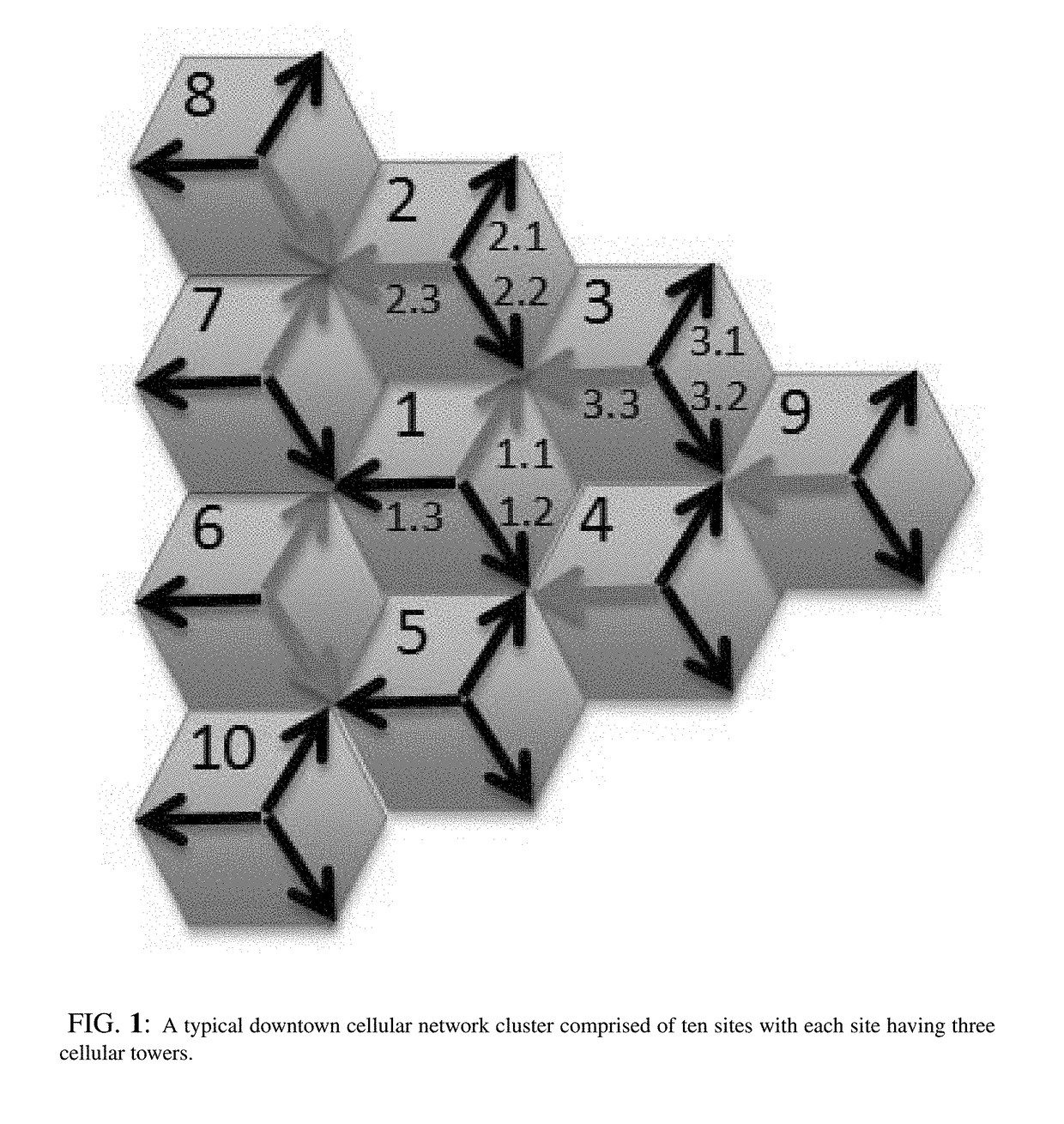
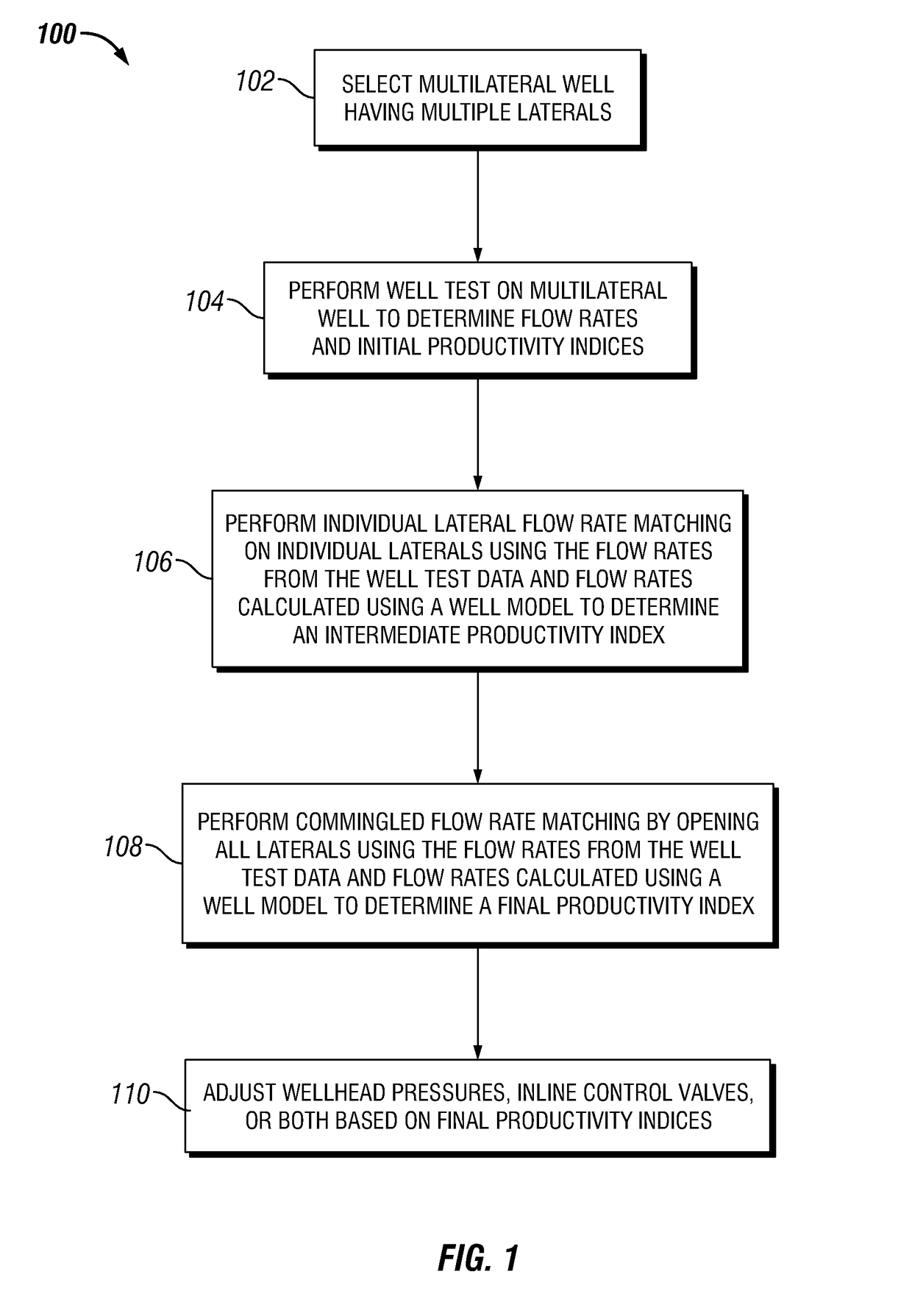
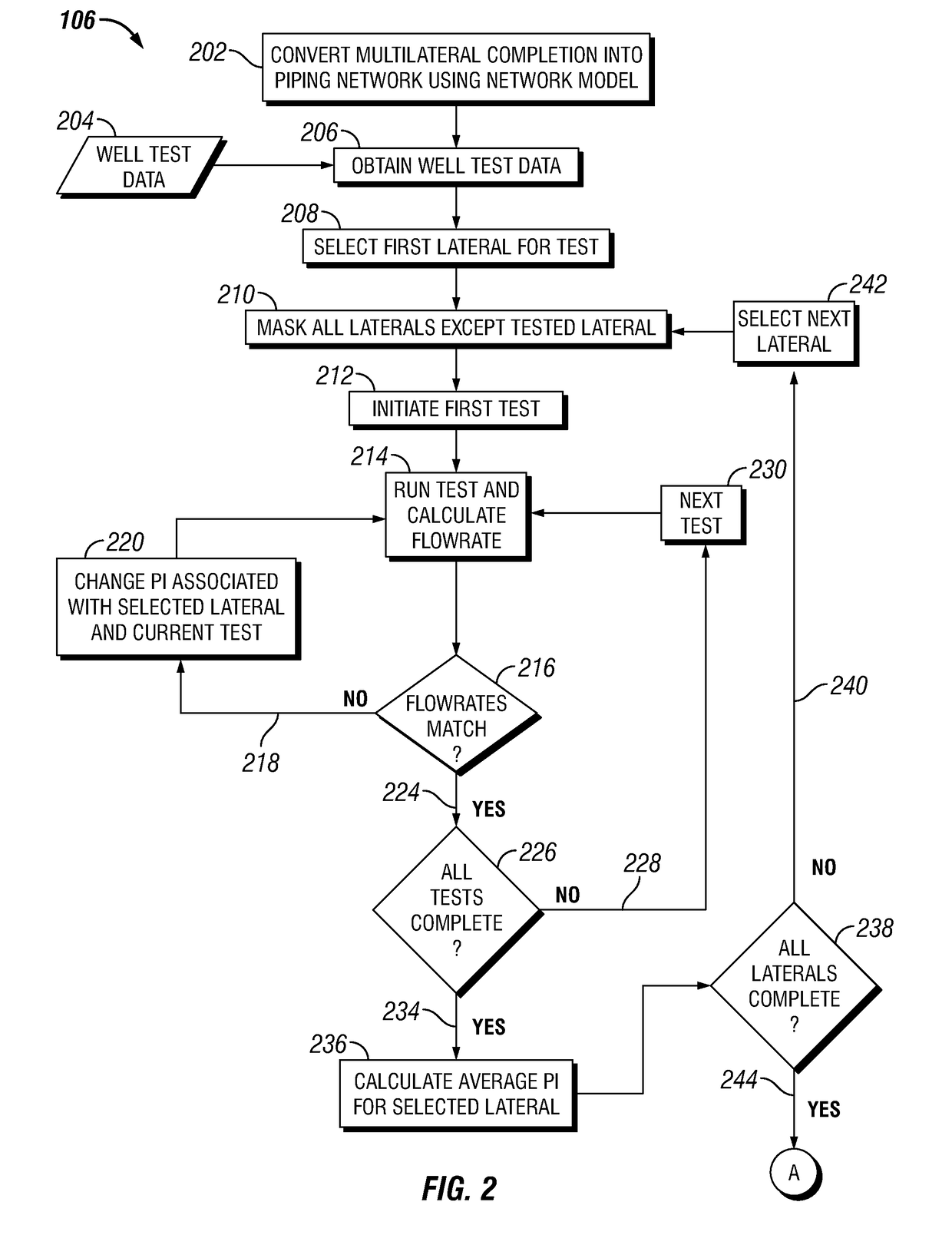
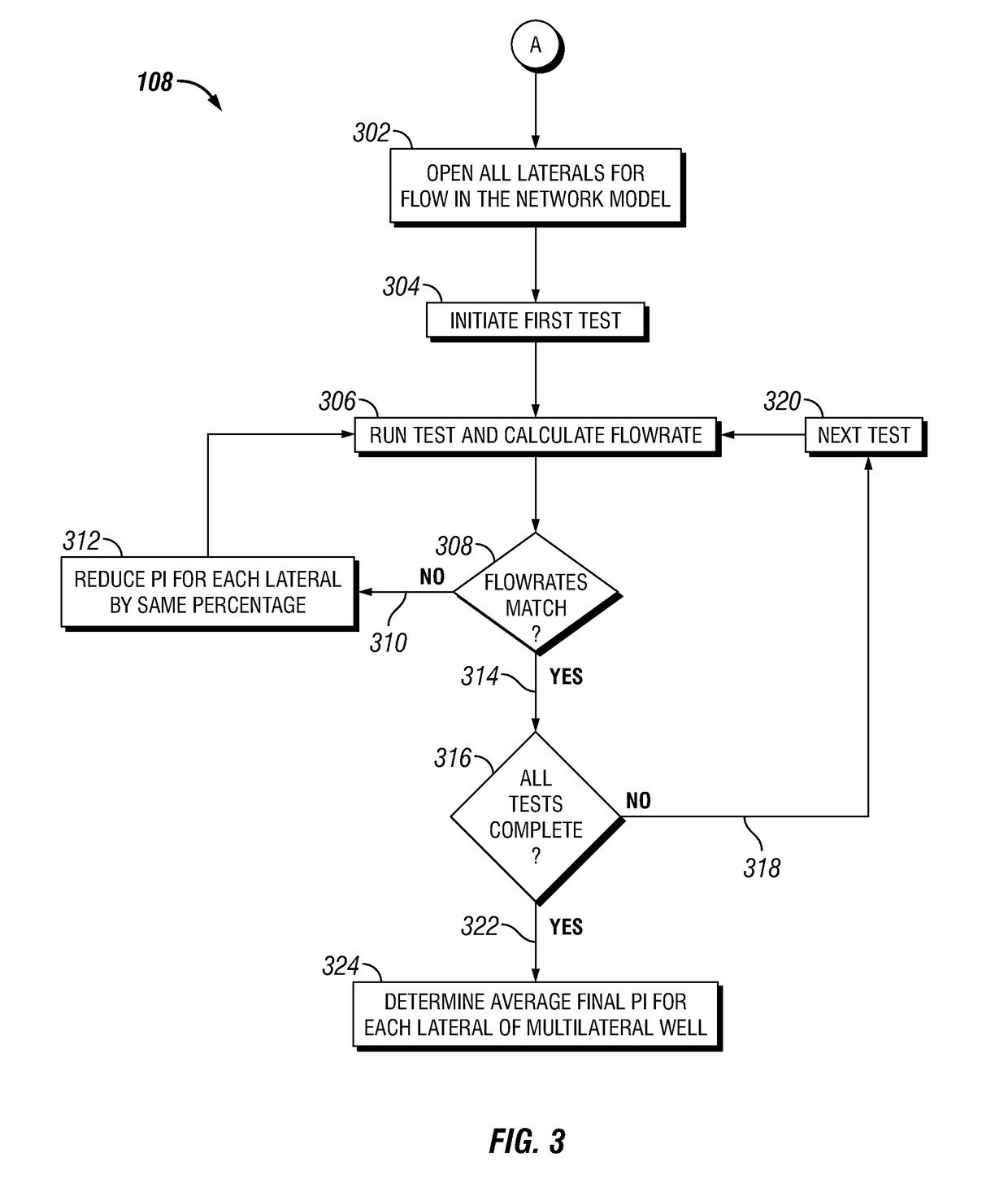
Iterative method for estimating productivity index (PI) values in maximum reservoir contact (MRC) multilateral completions
ActiveUS20180347326A1Rapid assessmentFluid removalAutomatic control for drillingEngineeringControl valves
A process for determining the productivity index of a multilateral completion using data from individual laterals and data from commingled well tests is disclosed. The process includes 1) determining the productivity index for each single lateral by iteratively altering the productivity index until the individual lateral flowrate based on a known reservoir pressure is matched and 2) further determining the productivity index by iteratively altering the productivity index until the commingled flowrate is matched. The productivity index may be used to set wellhead pressures and inline control valve (ICV) settings for production.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
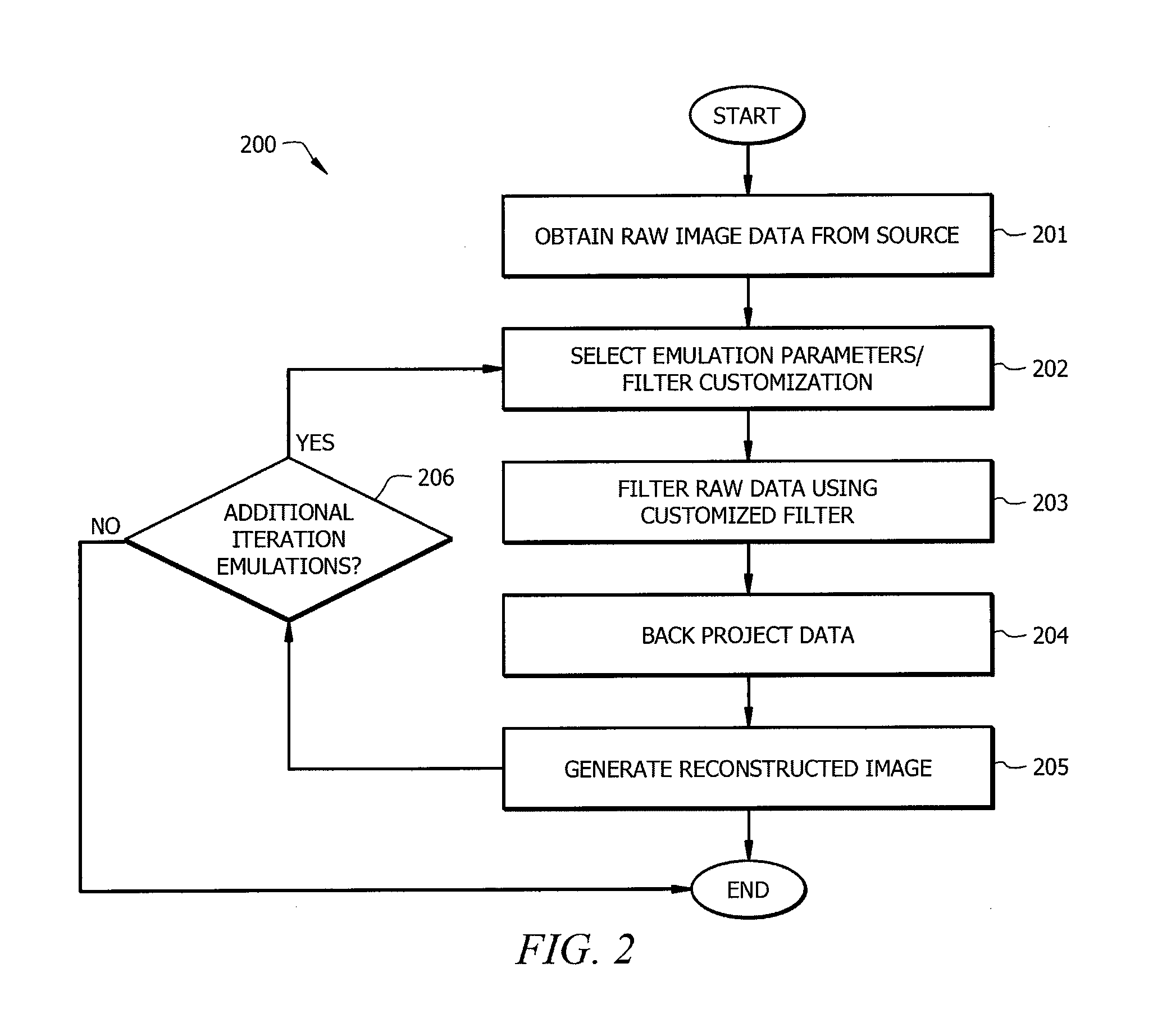
Filtered Backprojection Image Reconstruction with Characteristics of an Iterative Map Algorithm
InactiveUS20130101194A1Fast and efficientMinimal calculation stepReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionIterative methodologyImage resolution
Systems and methods are provided which utilize a fast, efficient filtered backprojection algorithm that can provide noise suppression advantages of an iterative MAP reconstruction algorithm. In some embodiments novel filtered backprojection systems are able to provide an image which emulates an image from an iterative algorithm corresponding to a selected iteration by utilizing control parameters which shape the filter accordingly during the reconstruction process. For example, if a user desires an image which would correspond to the one-hundredth iteration of an iterative algorithm, embodiments can provide a similar quality image using minimal calculation steps. Further, embodiments may provide the resolution quality of such an iteration while also allowing for better shift-invariant performance than an iterative method.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
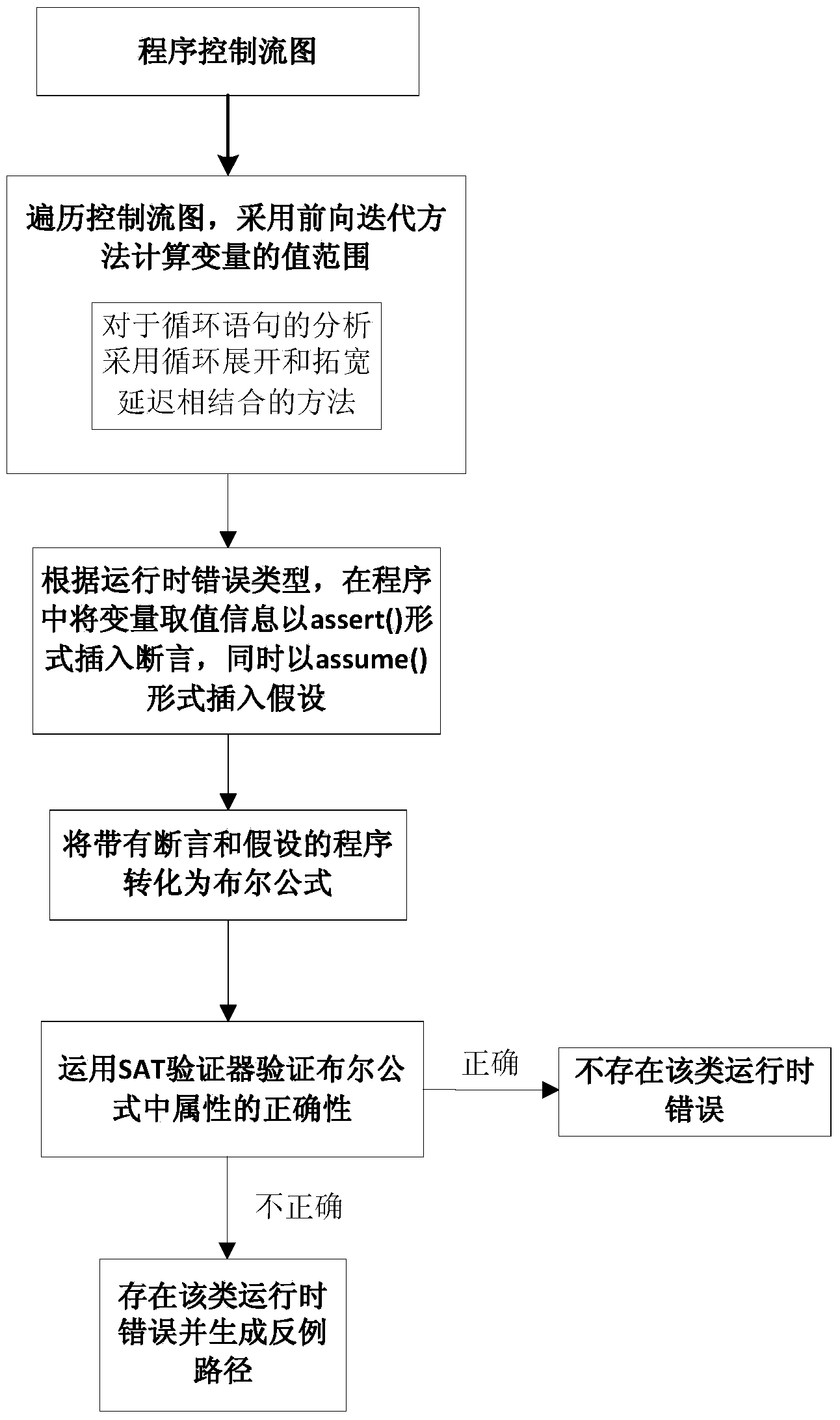
Runtime error analytical method based on abstract interpretation and model verification
ActiveCN103617115AShrink state spaceImprove inspection efficiencySoftware testing/debuggingHypothesisIterative methodology
The invention discloses a runtime error analytical method based on abstract interpretation and model verification. The method includes the following steps that on the basis of the abstract interpretation theory, the program numerical variable value range is analyzed by the adoption of a forward iteration method, the variable value range information is obtained when program points are stable, and the iterative computations of loop nodes are achieved by the way that loop unrolling and delay widening are combined; the variable value range information at the relevant program points needing to be detected is converted to be in an assertion or hypothesis mode to be plugged into a program according to a runtime error type to be analyzed; the assertion or hypothesis programs are converted into a Boolean formula, wherein the Boolean formula comprises limiting conditions and attributes; the correctness of the attributes in the Boolean formula is judged through an SAT verifier, if correct, it shows that relevant runtime errors do not exist, if not correct, it shows that the relevant runtime errors exist, and relevant counter example paths are output. By means of the method, an equilibrium point is acquired between runtime error analysis precision and efficiency.
Owner:中国航天系统科学与工程研究院
Method for remodeling medium objects by electromagnetic inverse scattering
InactiveCN105677937AMesh quality requirements are lowImprove solution efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsIterative methodologyMaxwell's equations
The invention relates to a method for remodeling medium objects by electromagnetic inverse scattering. The method comprises following steps: utilizing Maxwell's equations and constitutive equations to deduce forward and reverse integral equations for electromagnetic scattering; guessing the shape of an object to be detected and discretizing integral equations with a method in order to obtain matrix equations; utilizing a Gauss-Newton minimization method to regularize ill-conditioned equations during the reverse scattering process following discretization, wherein used regularized parameters are obtained by a multiplicative regularization method; and adopting a born iterative method to carry out iteration and obtaining wave number of detected mediums at the needed precision in order to achieve the objective of remodeling mediums.The method helps to avoid the problem in the conventional method that parameters are obtained by a lot of experiment data so that solving efficiency is increased.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Iterative method, system, and user interface for analysis, pattern detection, predictive modeling, and continuous improvement of quality, health, safety, and environmental (QHSE) operations
Disclosed is an iterative method, system, and user interface for analysis, pattern detection, and predictive modeling of quality, health, safety, and environmental (QHSE) from multiple, disparate sources. This iterative method, system, and user interface makes use of user generated qualitative and quantitative data from multiple quality, health, safety, and environmental sources. Sources include; monitoring systems, witness accounts, benchmarks, and other measurement apparatuses from single or multiple geographic locations. Data is acquired, categorized, aggregated, formatted, and isolated through pre-analysis algorithms. The isolated data of significance is then analyzed through an iterative methodology of user selected algorithms. The results go through a series of post-analysis testing to determine the effectiveness of the analysis. Once the post-analysis testing is completed, it is entered into a continuous improvement matrix to determine methodologies and solutions to improve upon existing QHSE processes. These results are processed through integrated or stand-alone computer modules and output to a user interface. The user interface provides the user options for selecting, isolating, and formatting combinations of algorithms and data analysis techniques to detect underlying patterns and predictive models in current QHSE processes and to provide innovative, dynamic, and predictive continuous improvement models for improving QHSE processes.
Owner:CAMERON NATHAN R
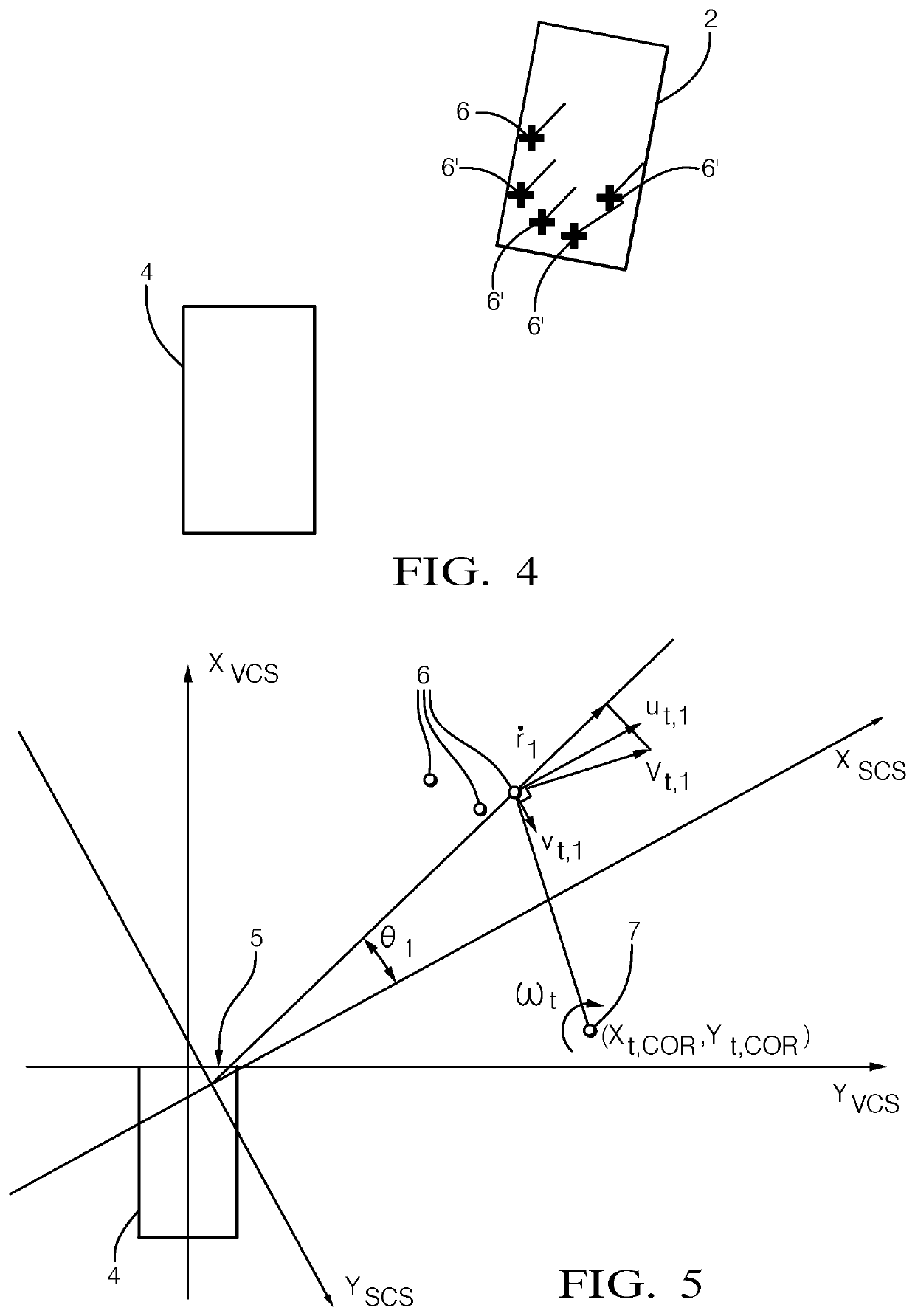
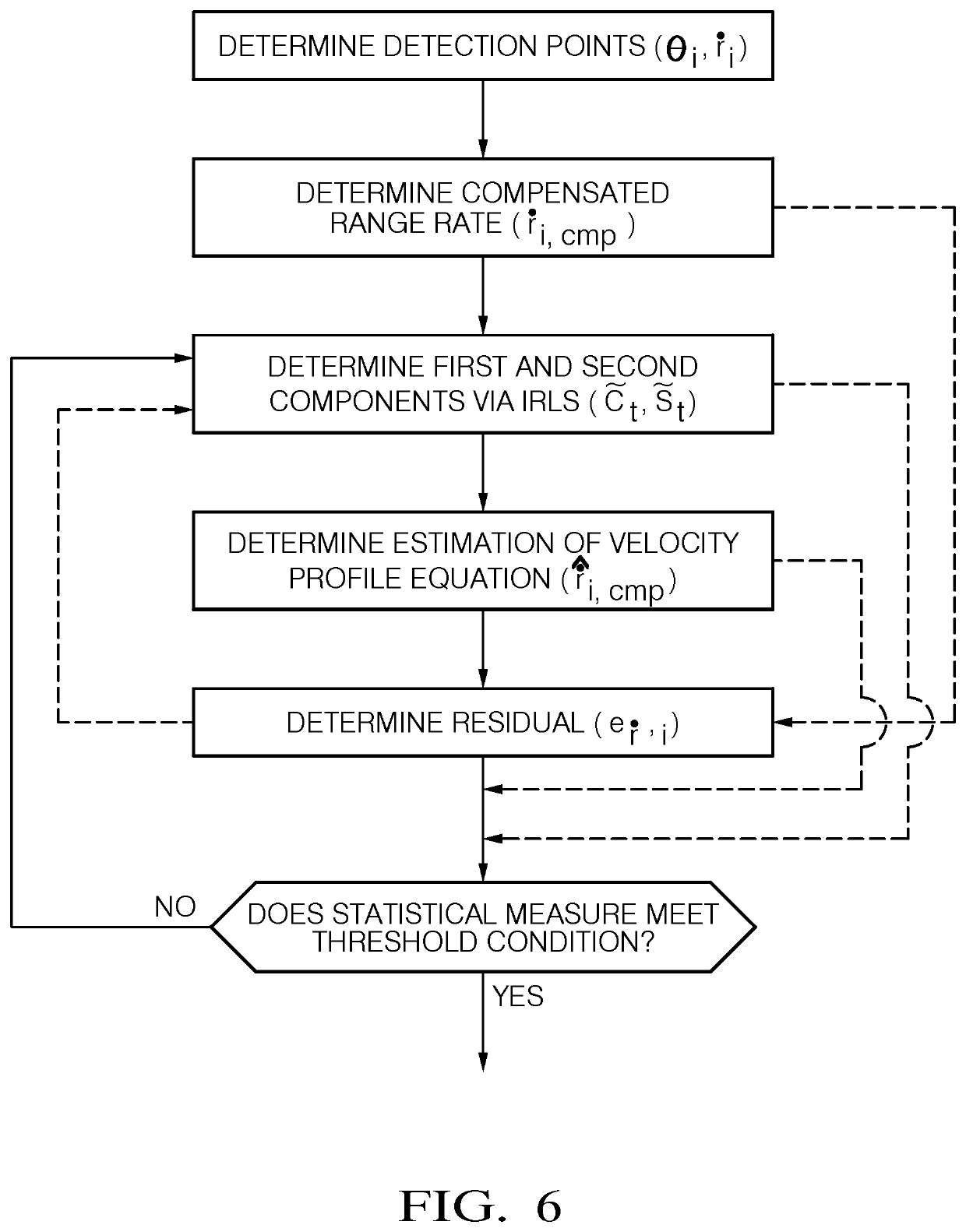
Method for robust estimation of the velosity of a target using a host vehicle
ActiveUS20190369228A1Easy to explainEfficiency tuningRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsIterative methodology
A method for estimating a velocity of a target using a host vehicle equipped with a radar system includes determining a plurality of radar detection points, determining a compensated range rate, and determining an estimation of a first component of a velocity profile equation of the target and an estimation of a second component of the velocity profile equation of the target by using an iterative methodology comprising at least one iteration. The estimations and of the first and second components and of the velocity profile equation are not determined from a further iteration if at least one statistical measure representing the deviation of an estimated dispersion of the estimations and of the first and second components, and of a current iteration from a previous iteration and / or the deviation of an estimated dispersion of the residual from a predefined dispersion of the range rate meets a threshold condition.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
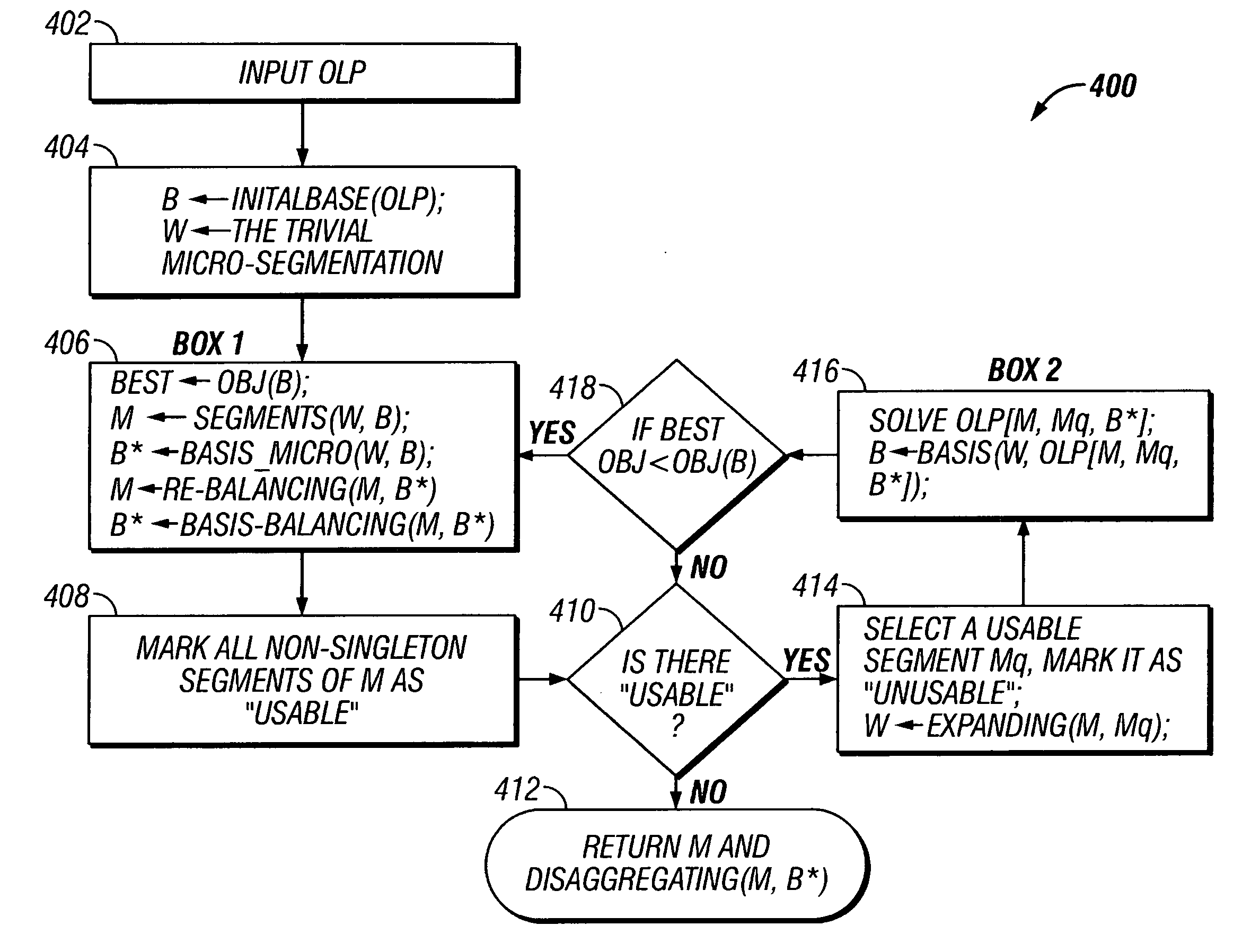
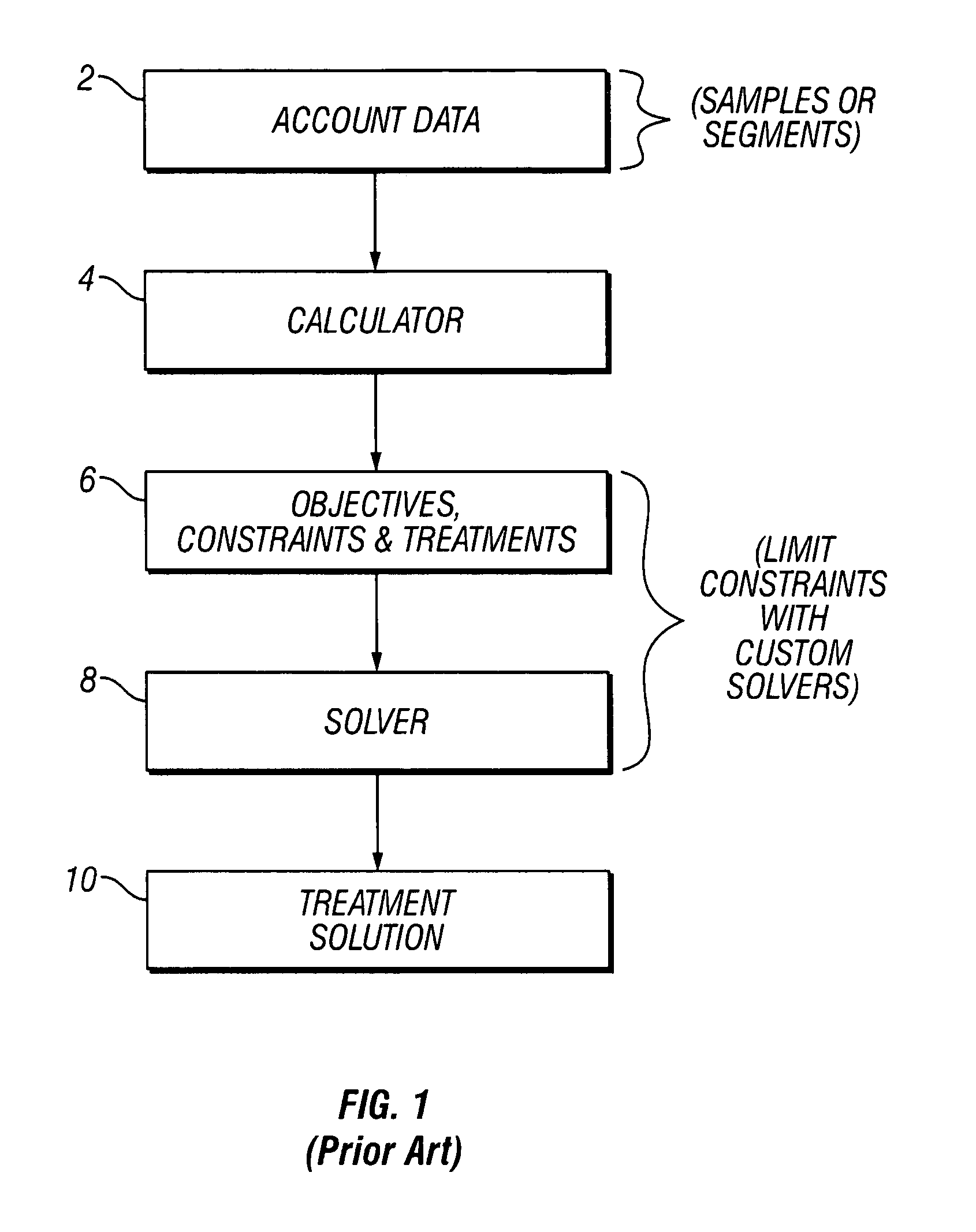
Method and apparatus for a scalable algorithm for decision optimization
ActiveUS7689528B2Eliminate dependenciesImprove approximationDigital computer detailsForecastingIterative methodologyTheoretical computer science
An iterative approach to solving the optimization problem is provided. The invention provides an iteration of four basic operations; determining the segments, balancing the segments, expanding a segment, and solving the segment optimization. The method and apparatus can use any off-the-shelf linear programming (LP) solver, such as Dash Optimization Xpress, by Dash Optimization, during the solve operation. The size of the problem fed into the LP solver remains bounded and relatively small compared to the entire problem size. Thus, the algorithm can solve problems of several orders of magnitude larger. In one embodiment of the invention, the sampling and segmentation techniques are removed to where the problem is solved at the account-level. In the above cases, the solution is produced in a more cost-effective manner and the best possible return is achieved because the doubt of achieving a true global solution is removed.
Owner:FAIR ISAAC & CO INC
Steady waveform optimizing method for MIMO radar in clutter background
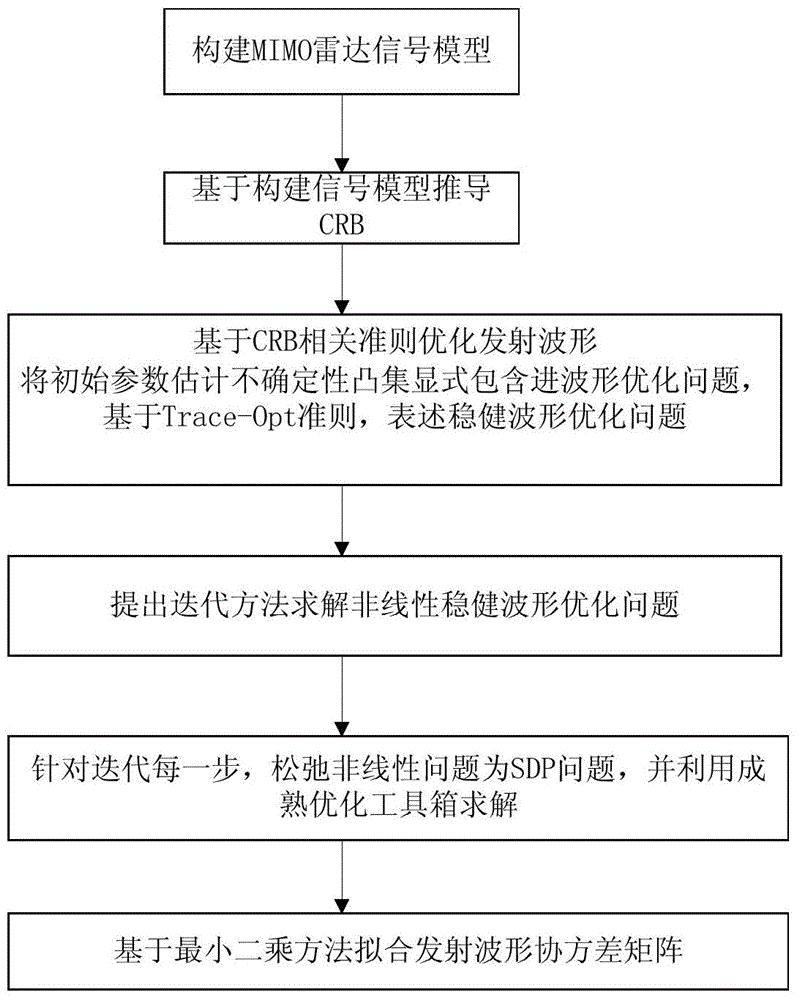
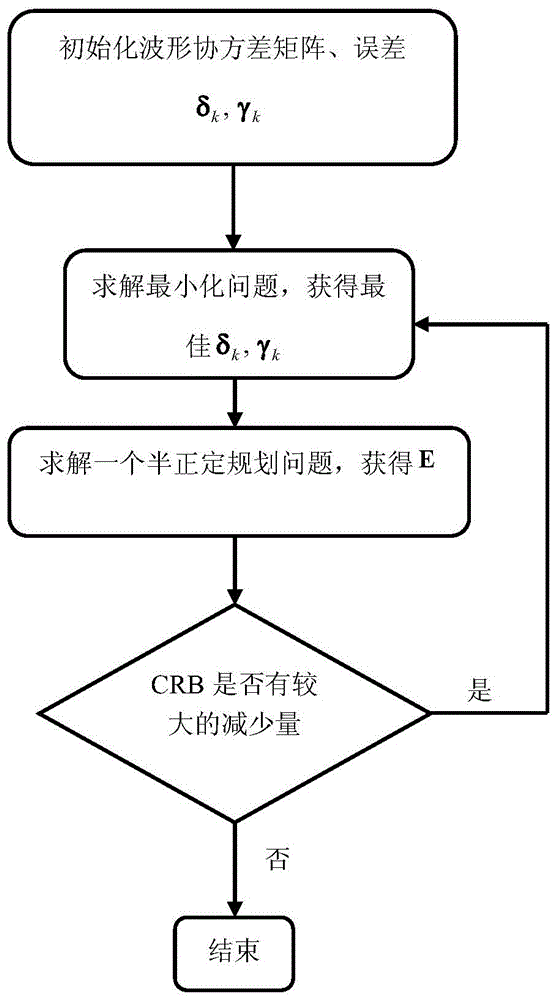
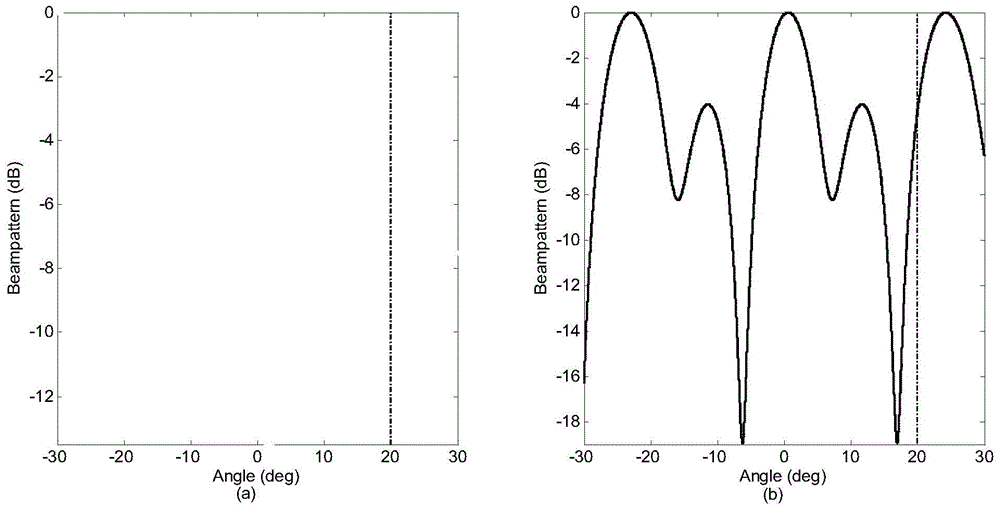
ActiveCN104808180AReduce estimation errorImprove estimation performanceWave based measurement systemsIterative methodologyCovariance matrix
The invention provides a steady waveform optimizing method for an MIMO radar in a clutter background, and relates to the field of signal handling. The method comprises the steps of building an MIMO radar receiving signal model under the clutter background; deducing CRB with parameters to be estimated based on the model; estimating non-determination convex set explicit included waveform optimizing problem according to the initial parameters, and building a steady waveform optimizing model, wherein the minimum and maximum problems are the complex nonlinear problems related to optimization variable. According to the method, the iterating method is carried out to solve the problem; each step of iterating is converted into SDP problem, so that the problem can be efficiently solved; the proposed iterating algorithm is utilized to optimize a waveform covariance matrix; therefore, the parameter estimation performance under the worst condition in the clutter background can be improved; compared with the non-related waveform and non-steady methods, the method is high in steady performance and is close to the engineering application.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Congestion reduction of LTE networks
ActiveUS20170359752A1Reduce congestionNetwork traffic/resource managementIterative methodologyIterative method
Optimal reduction of 4G LTE cellular network congestion utilizes two components of learning and optimization. First, an MLPDL learning approach is used to model cellular network congestion measured in terms of PRB utilization and predict 80% utilization as breakpoint thresholds of cellular towers as a function of average connected user equipments. Then, an optimization problem is formulated to minimize LTE network congestion subject to constraints of user quality and load preservation. Two alternative solutions, namely Block Coordinated Descent Simulated Annealing (BCDSA) and Genetic Algorithms (GA) are presented to solve the problem. Performance measurements demonstrate that GA offers higher success rates in finding the optimal solution while BCDSA has much improved runtimes with reasonable success rates. Accordingly, integrated iterative methods, programs, and systems are described aiming at minimizing the congestion of 4G LTE cellular networks by redistributing traffic from congested cellular towers to non-congested cellular towers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
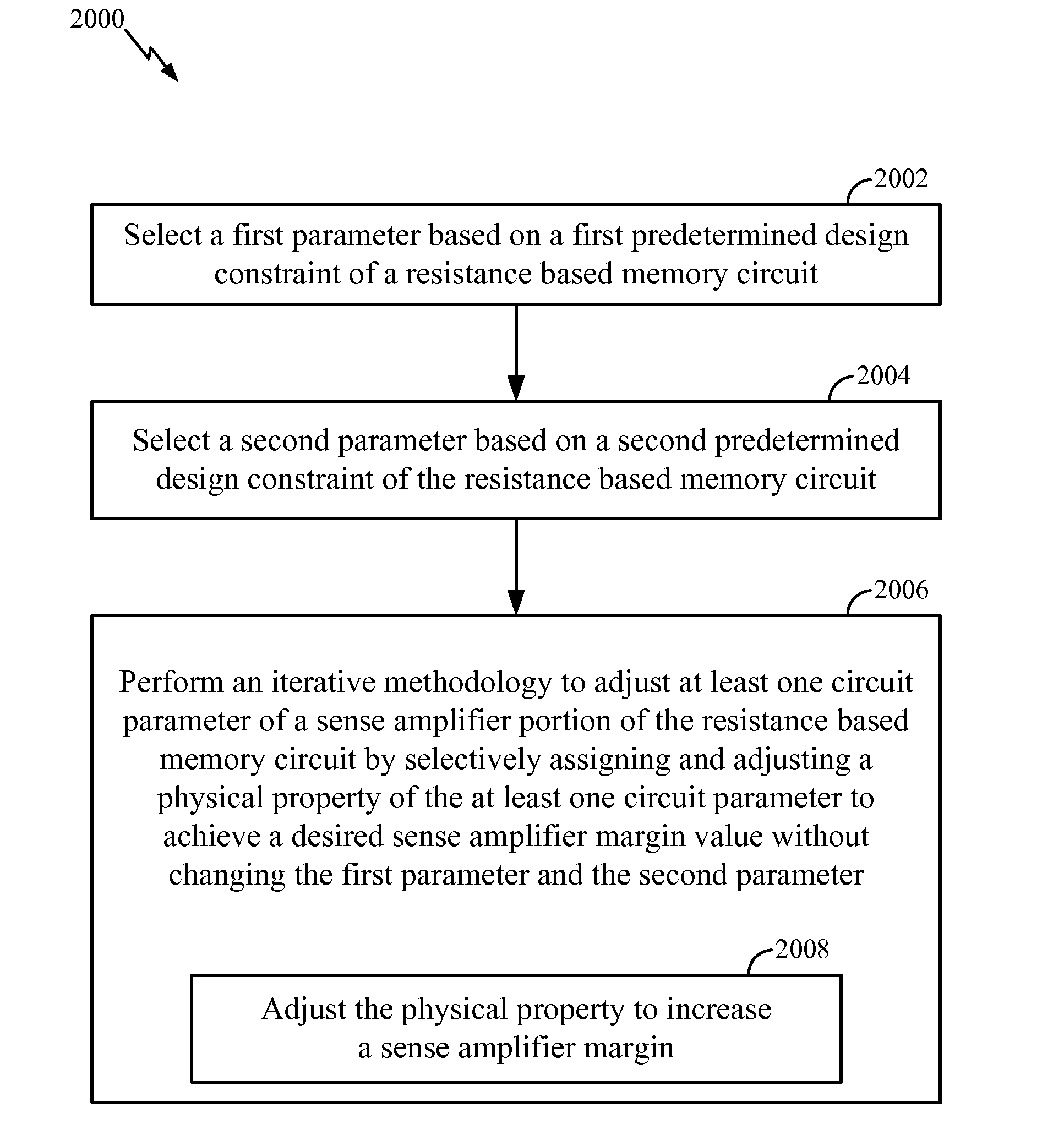
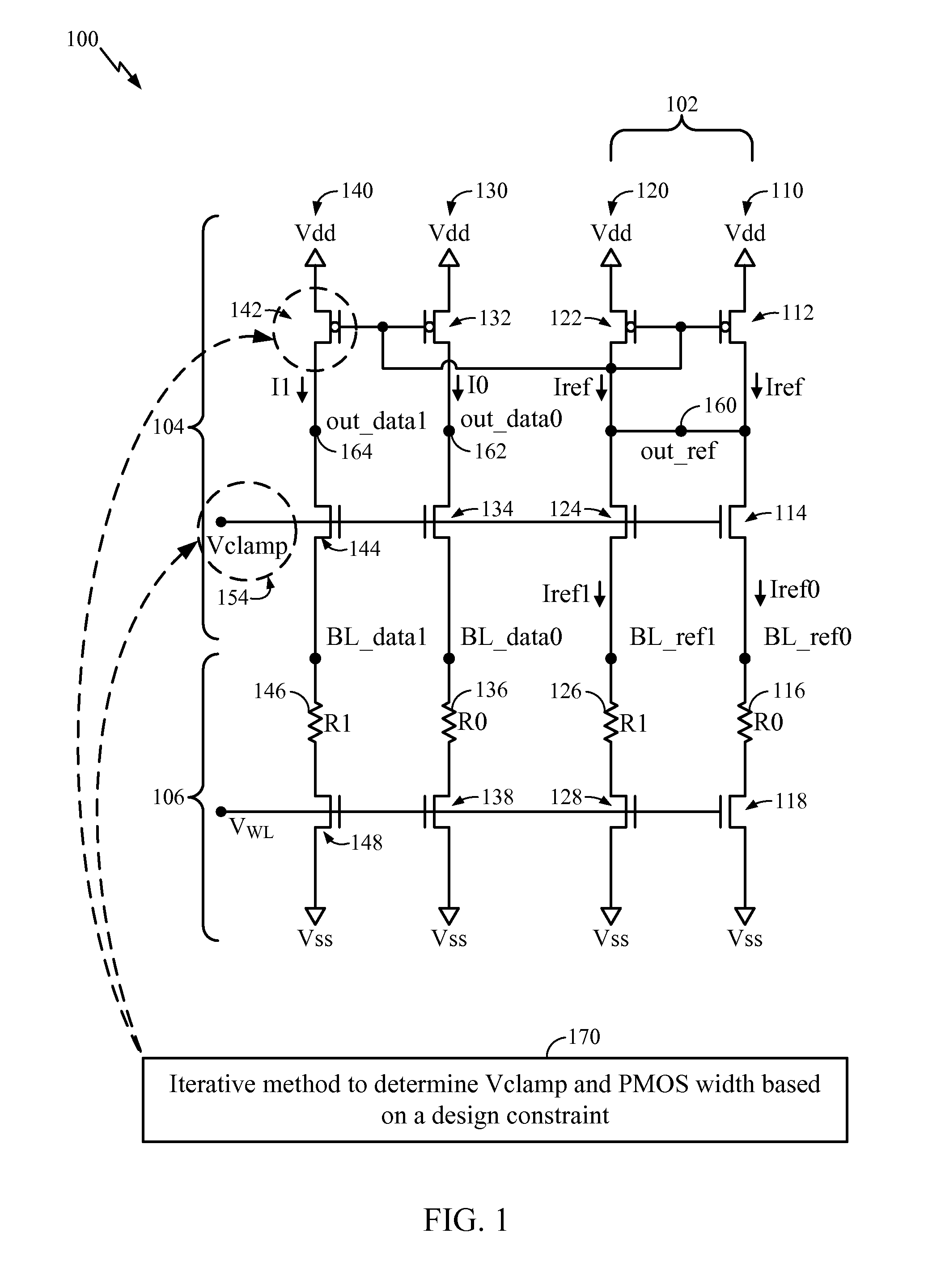
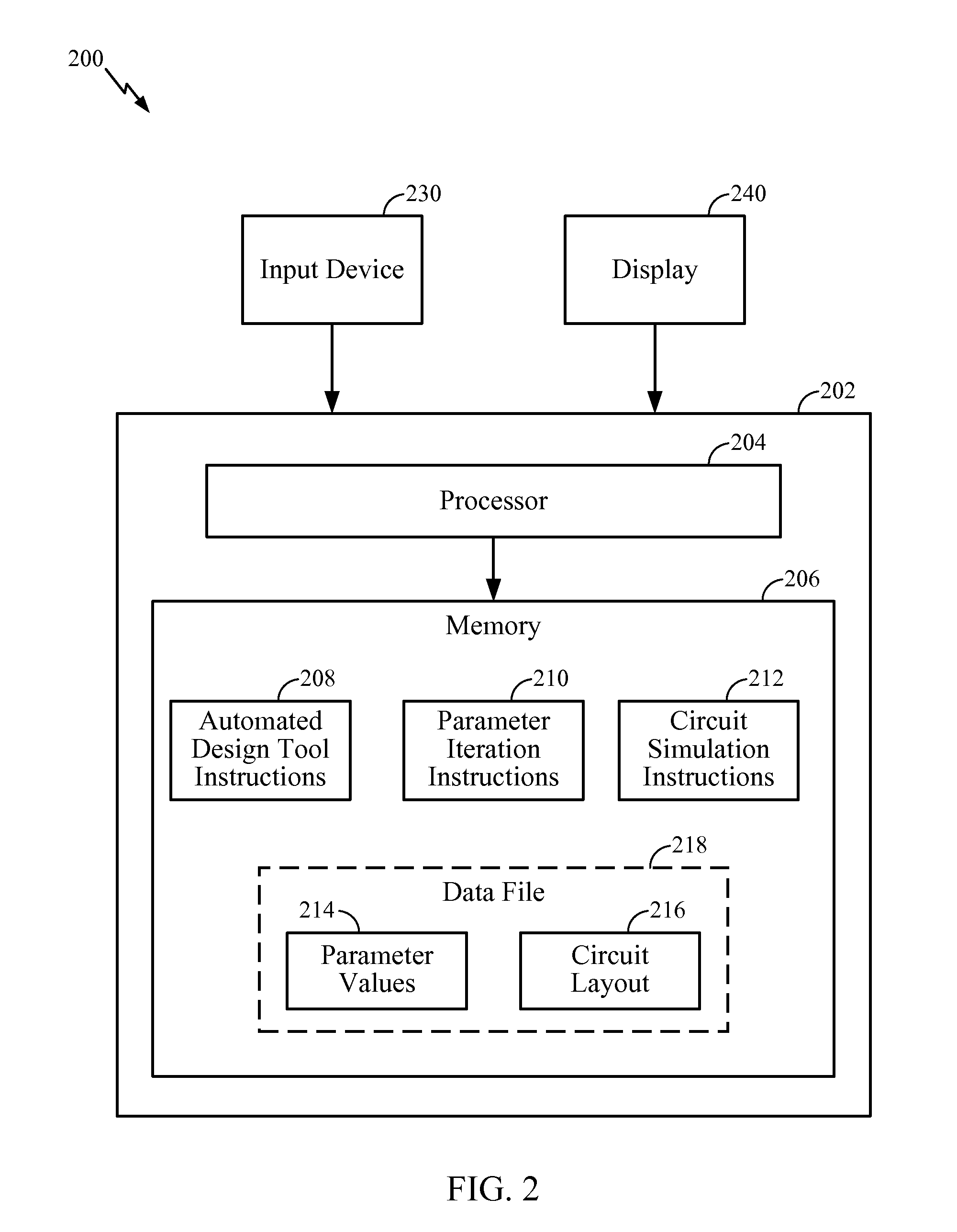
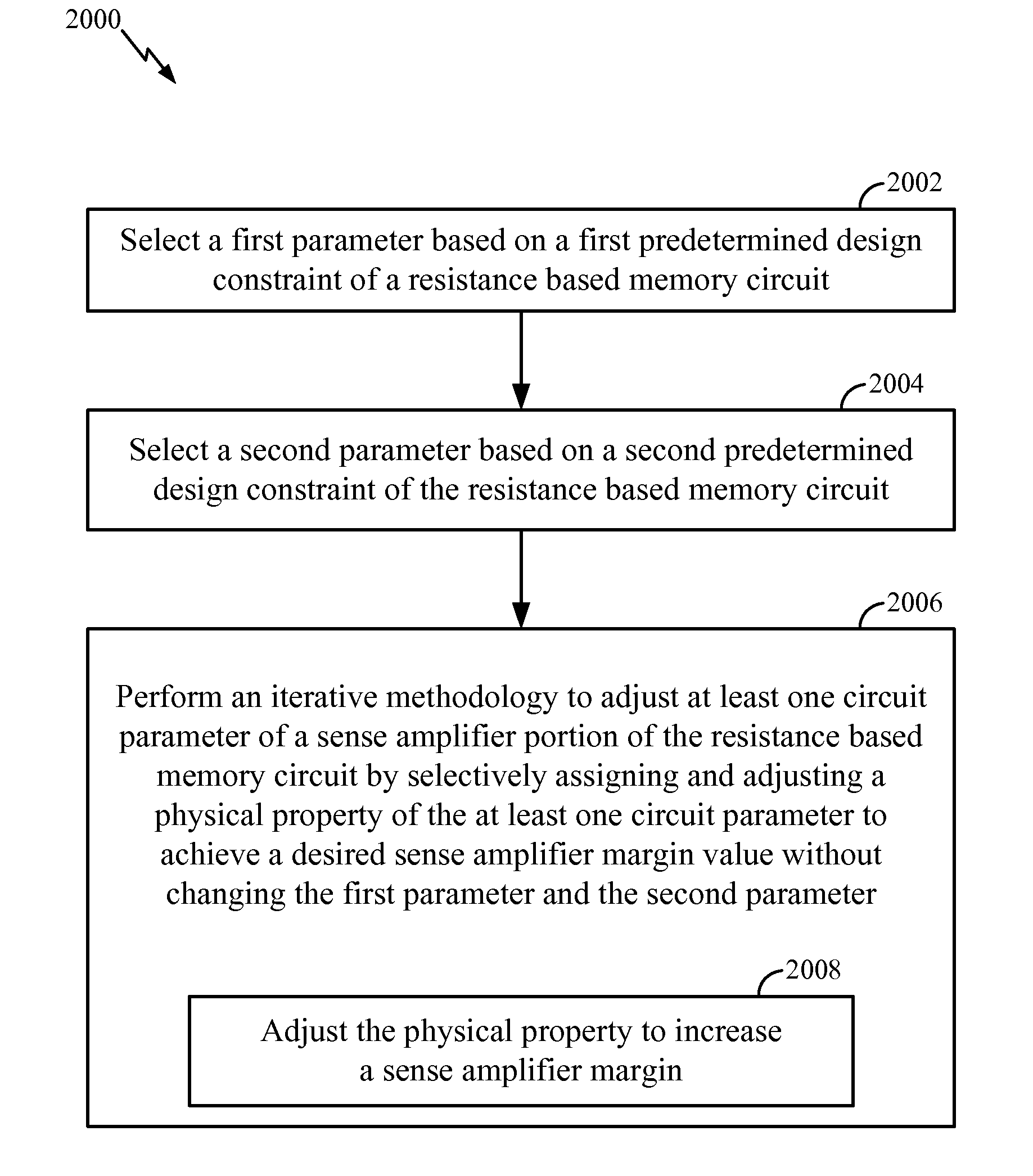
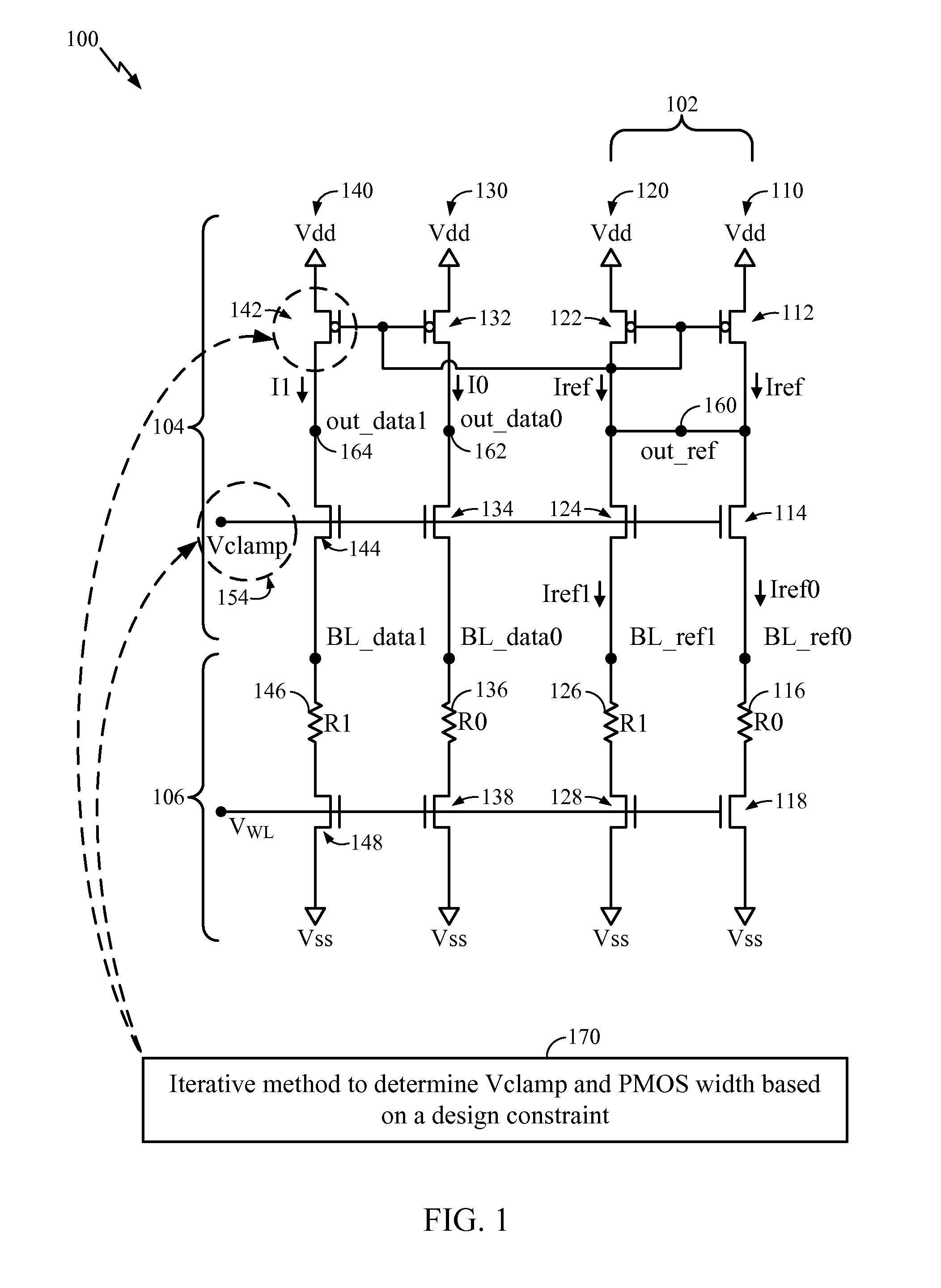
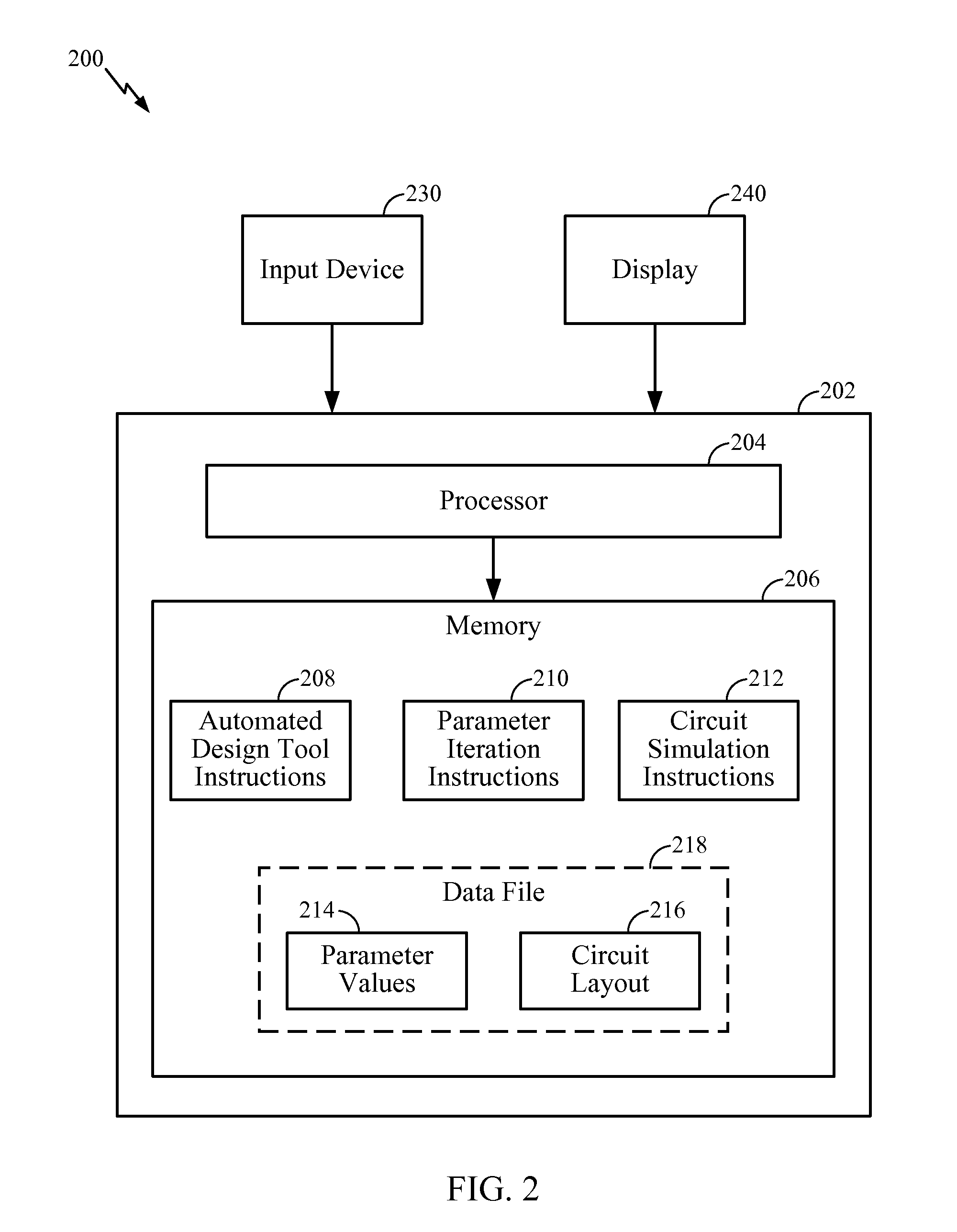
System and Method of Resistance Based Memory Circuit Parameter Adjustment
ActiveUS20090265678A1Efficiently improve sense amplifier marginsDigital storageCAD circuit designElectrical resistance and conductanceAudio power amplifier
Systems and methods of resistance based memory circuit parameter adjustment are disclosed. In a particular embodiment, a method of determining a set of parameters of a resistance based memory circuit includes selecting a first parameter based on a first predetermined design constraint of the resistance based memory circuit and selecting a second parameter based on a second predetermined design constraint of the resistance based memory circuit. The method further includes performing an iterative methodology to adjust at least one circuit parameter of a sense amplifier portion of the resistance based memory circuit by selectively assigning and adjusting a physical property of the at least one circuit parameter to achieve a desired sense amplifier margin value without changing the first parameter or the second parameter.
Owner:YONSEI UNIVERSITY +1
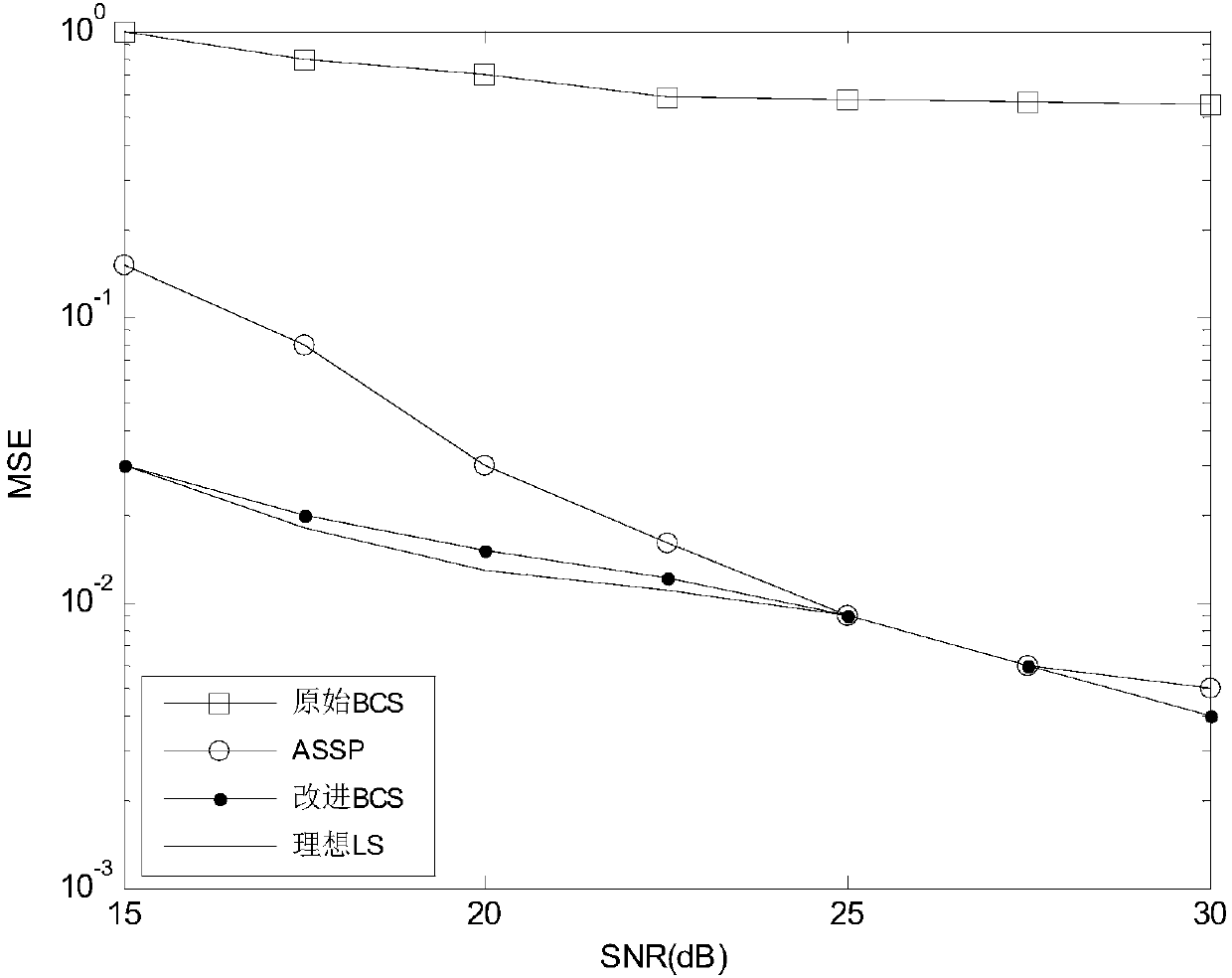
Bayesian compressed sensing channel estimation method based on FDD large-scale MIMO
ActiveCN108365874AAccurate Channel State InformationBaseband system detailsRadio transmissionIterative methodologyEuclidean vector
The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless communication, and provides a Bayesian compressed sensing channel estimation method based on an FDD large-scale MIMO for obtaining accurate channel state information. The invention designs a mode-coupled Gaussian prior model to describe the common sparsity between different antennas, wherein the coefficients in a channel vector are divided into groups of equal lengths, each group has a common hyperparameter, such that the coefficients of each group have the same sparsity; further, Bayesian inference is performed based on the iterative method by expecting the maximization step, wherein the channel coefficient is used as a hidden variable and the hyperparameter is used as an unknown parameter; and finally, the obtained posterior mean of the channel vector is s used as an estimate of the channel. The simulation shows that the BCS method proposed by the invention is much better than the similar method, and can achieve the performanceboundary of the ideal least squares algorithm as the baseline.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
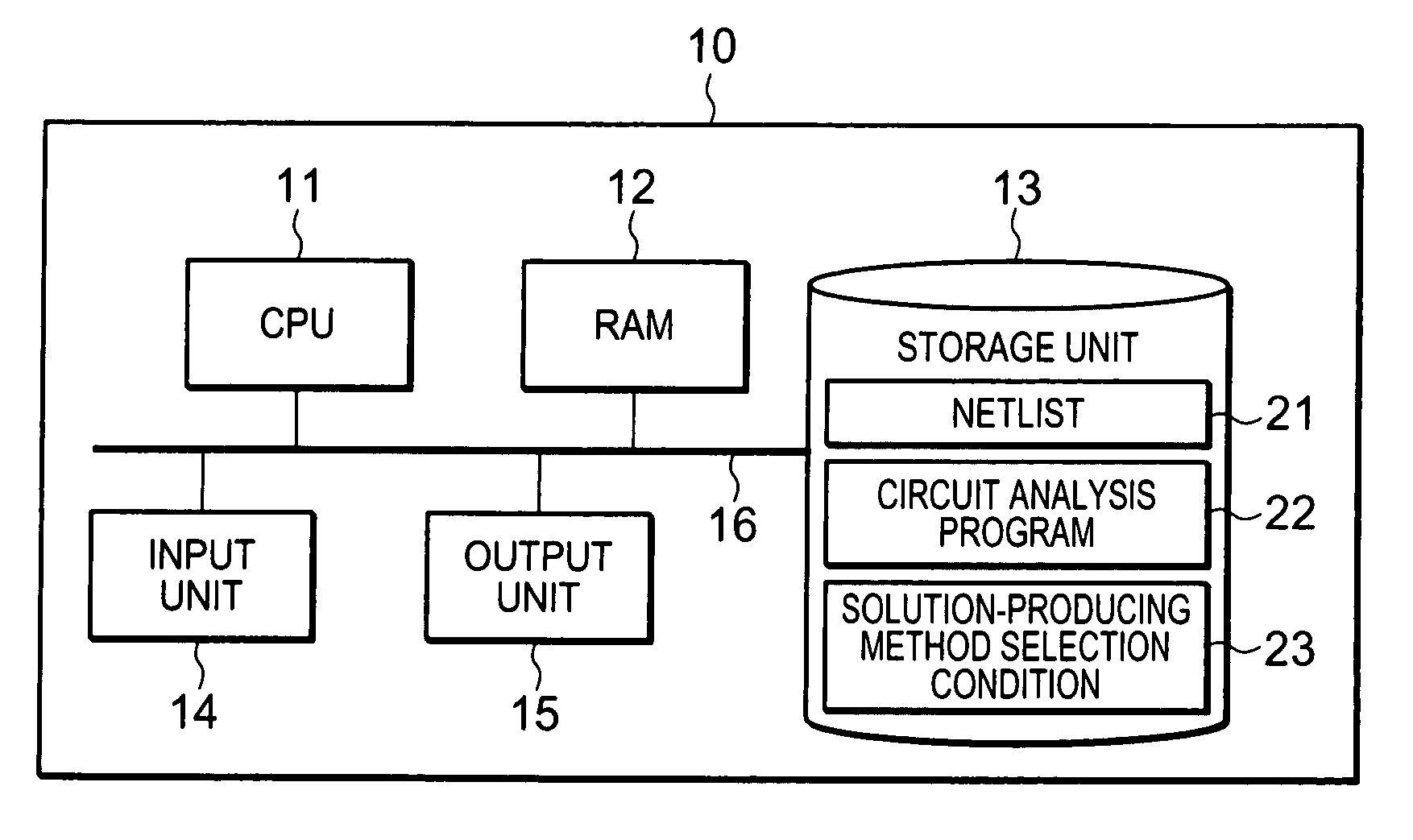
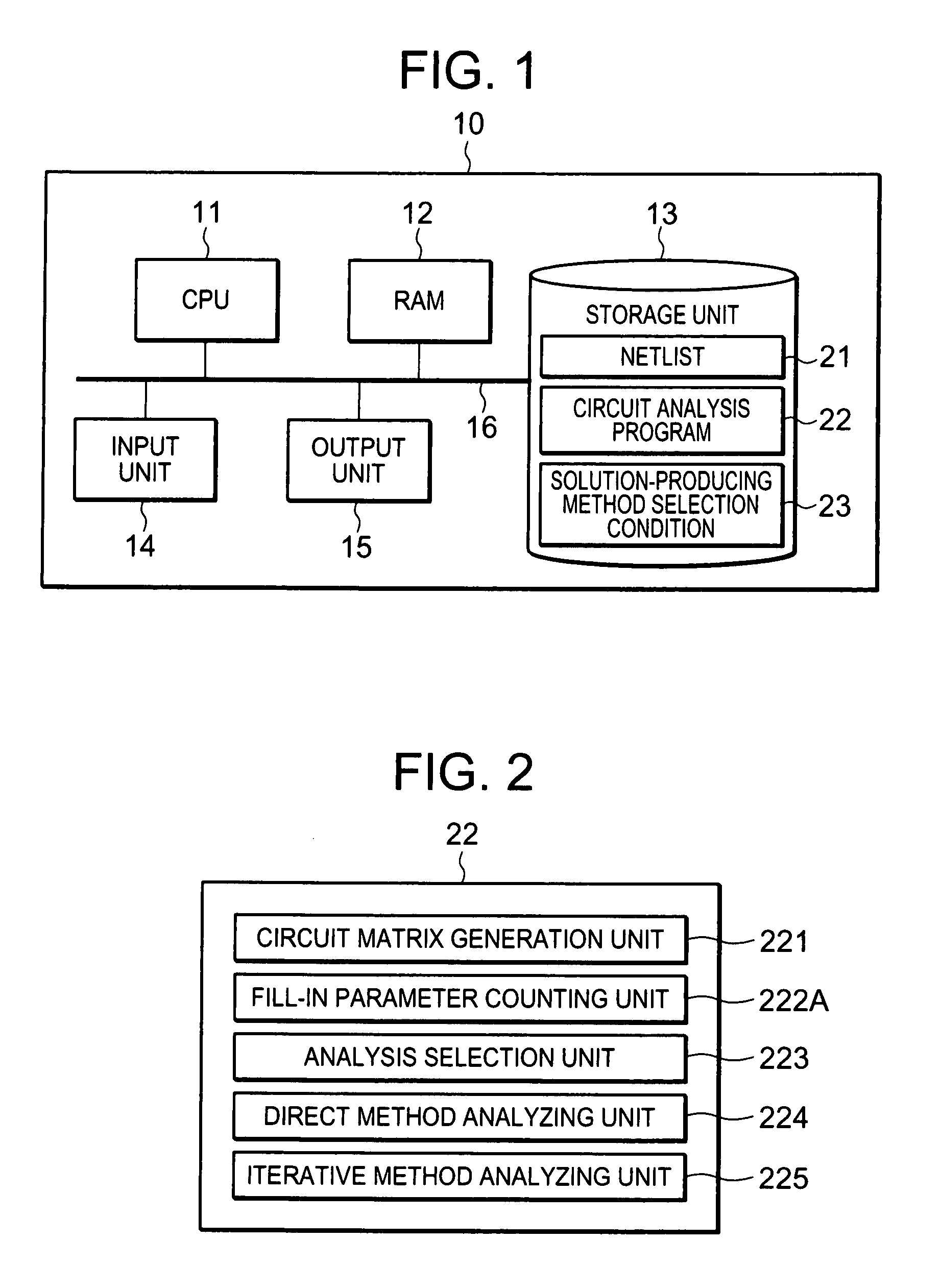
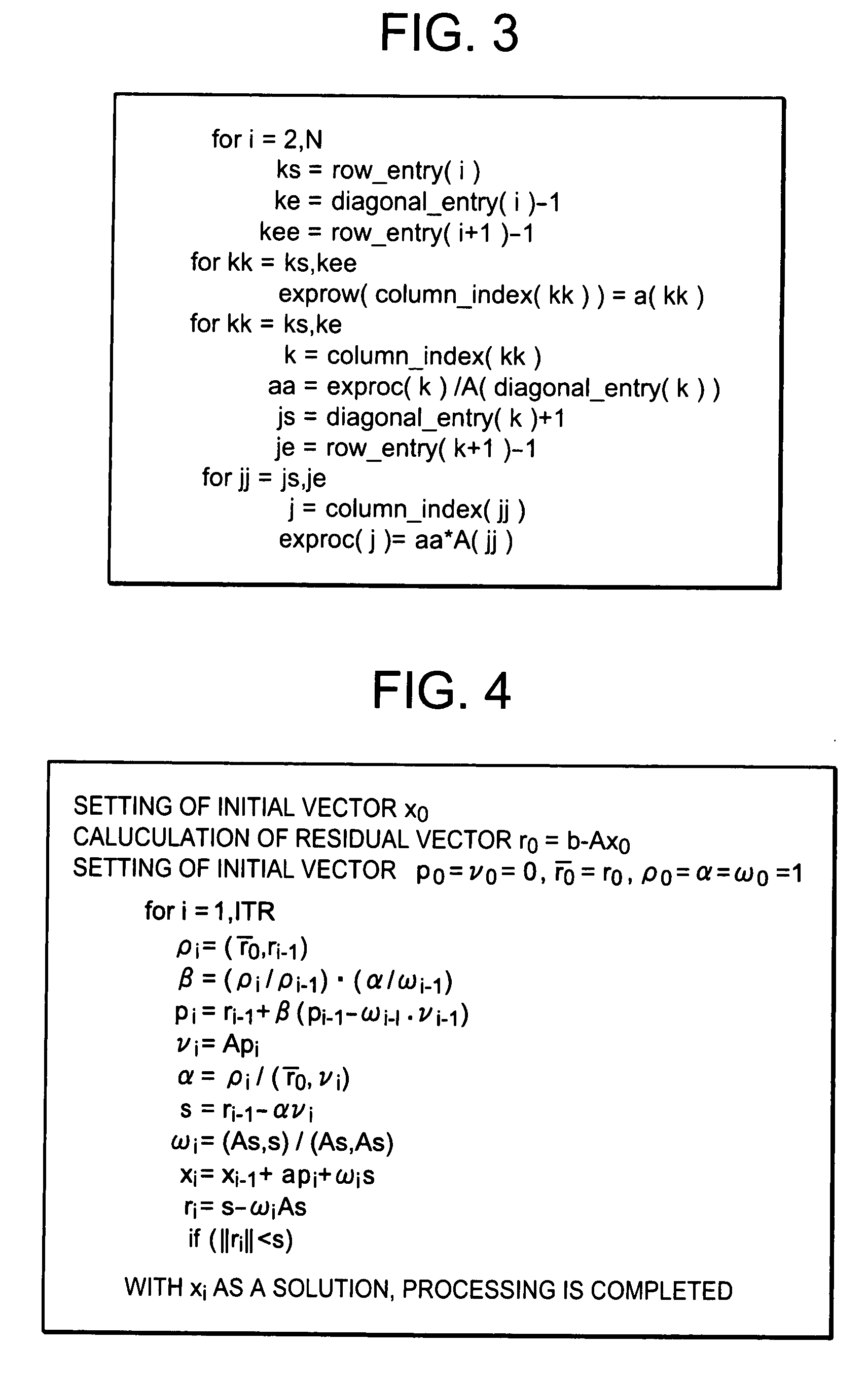
Method and computer program product for circuit analysis and circuit simulation device
InactiveUS20080010329A1Reduce analysis timeShorten analysis timeDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsCoefficient matrixComputer program
A method and a computer program product for a circuit analysis and a circuit simulation device, capable of increasing an analysis speed for circuit analysis, the circuit simulation device includes a circuit matrix generation unit for generating a coefficient matrix based on netlist information corresponding to a circuit to be analyzed, a fill-in parameter counting unit for acquiring a fill-in parameter for the coefficient matrix, an analysis selection unit for selecting either of the direct method or the iterative method as a solution-producing method for the coefficient matrix based on the fill-in parameter, a matrix size of the coefficient matrix and number of non-zero elements of the coefficient matrix and analyzing units for producing a solution of the coefficient matrix as an analysis result of the circuit by a selected one of the direct method and the iterative method.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
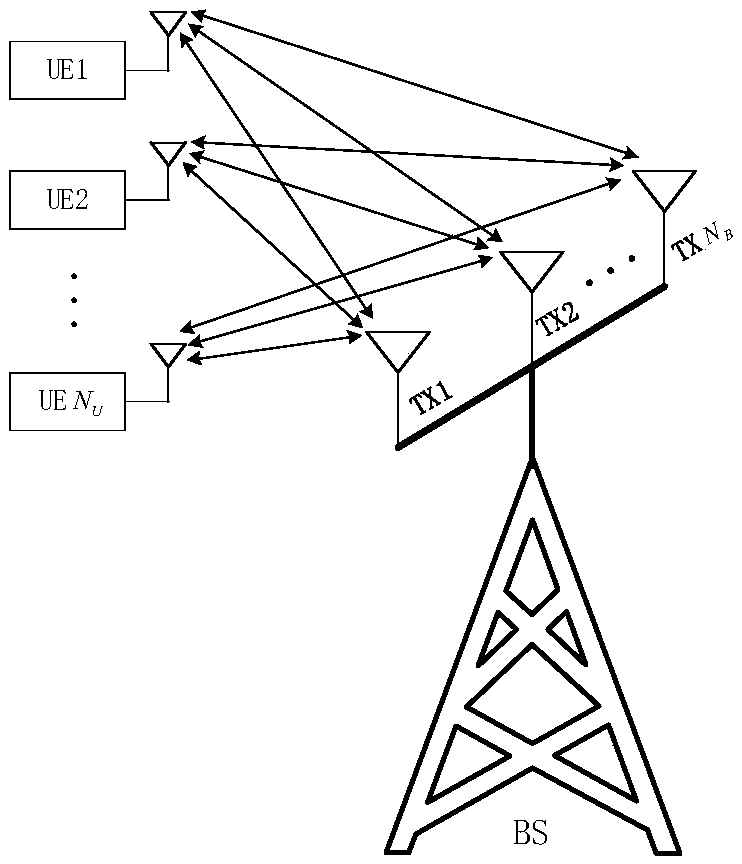
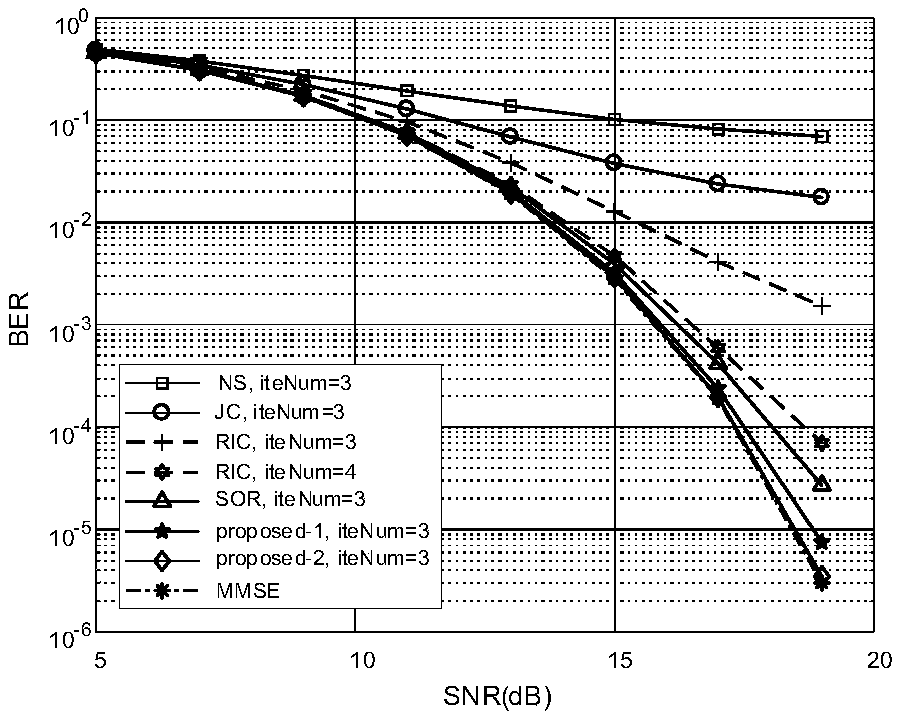
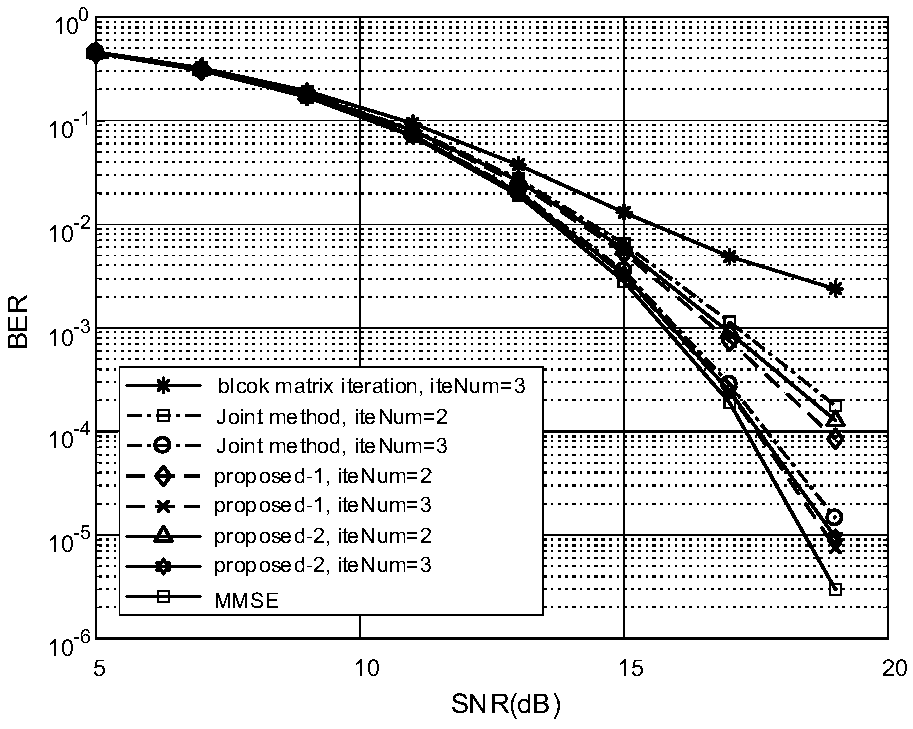
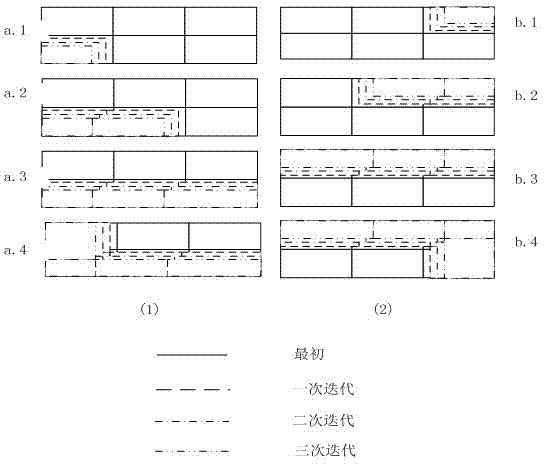
Joint detection method for signals of massive MIMO uplink system
InactiveCN108809383AImprove convergence rateReduce processing complexityError preventionRadio transmissionSteep descentComputation complexity
The invention belongs to the technical field of communication, and relates to a joint detection method for signals of a massive MIMO uplink system. According to the scheme of the invention, the methodincludes the following steps that: firstly, an iterative matrix is constructed, and a low-complexity iterative scheme is proposed based on the constructed matrix; and then, a steepest descent methodand the proposed iterative method are mixed to accelerate the proposed iterative method; in addition, the computational complexity is reduced by skillfully utilizing the properties of inversion of partitioned matrices and a matrix-vector multiplication; and then, the detailed convergence proof and complexity analysis are performed; and finally, simulations prove that the BER performance of the proposed algorithm is better than that of most existing iterative algorithms and the near-optimal performance of an MMSE algorithm can be reached in a small number of iterations.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Adaptive rendering method based on weight local regression
InactiveCN105513120AReduce noiseGood diffuse light3D-image renderingFeature vectorSingular value decomposition
The invention discloses an adaptive rendering method based on weight local regression. The method comprises the following specific steps: filtering and reconstructing an image by use of local regression; constructing a simplified feature space by use of truncated singular value decomposition (TSVD) so as to eliminate noise carried by a feature vector; respectively predicating an optimal feature bandwidth bj and a shared bandwidth h by use of a two-step bandwidth selection algorithm; and distributing available light samples to areas with high errors by use of an iteration method based on a local simplified feature subspace k. The method provided by the invention is a novel adaptive rendering technology and can be applied to processing rendering effects of multiple types in an efficient and robust manner. Compared to prior similar arts, the method has the following advantages: the time for generating results with the same quality is obviously reduced, and the result image effect generated based on equal calculation time and calculation cost is far better than that of the similar arts.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF MEDIA AND COMMUNICATIONS
Finite difference stencil parallelizing method based on iteration space sticks
InactiveCN102200962AAchieve parallelizationImprove data localitySpecial data processing applicationsIterative methodologyIteration space
The invention relates to a finite difference stencil parallelizing method based on iteration space sticks. In the traditional parallel iterative method, synchronous operation for maintaining the data dependence relation is needed both in iteration and among the iterations. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: dividing an iteration space into grid sticks in a time-axis direction to realize multiple recursion-type iteration-step updates on the same grid block, thereby improving the data locality in the sticks at the same time of not changing the property of a serial stencil iterative method; and then reordering the grid sticks to realize the parallelization of staggered sticks in the finite difference stencil method. Compared with the traditional domain decomposition method and a red-black ordering parallel method, the method provided by the invention has better data locality, parallelization efficiency and extensibility.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
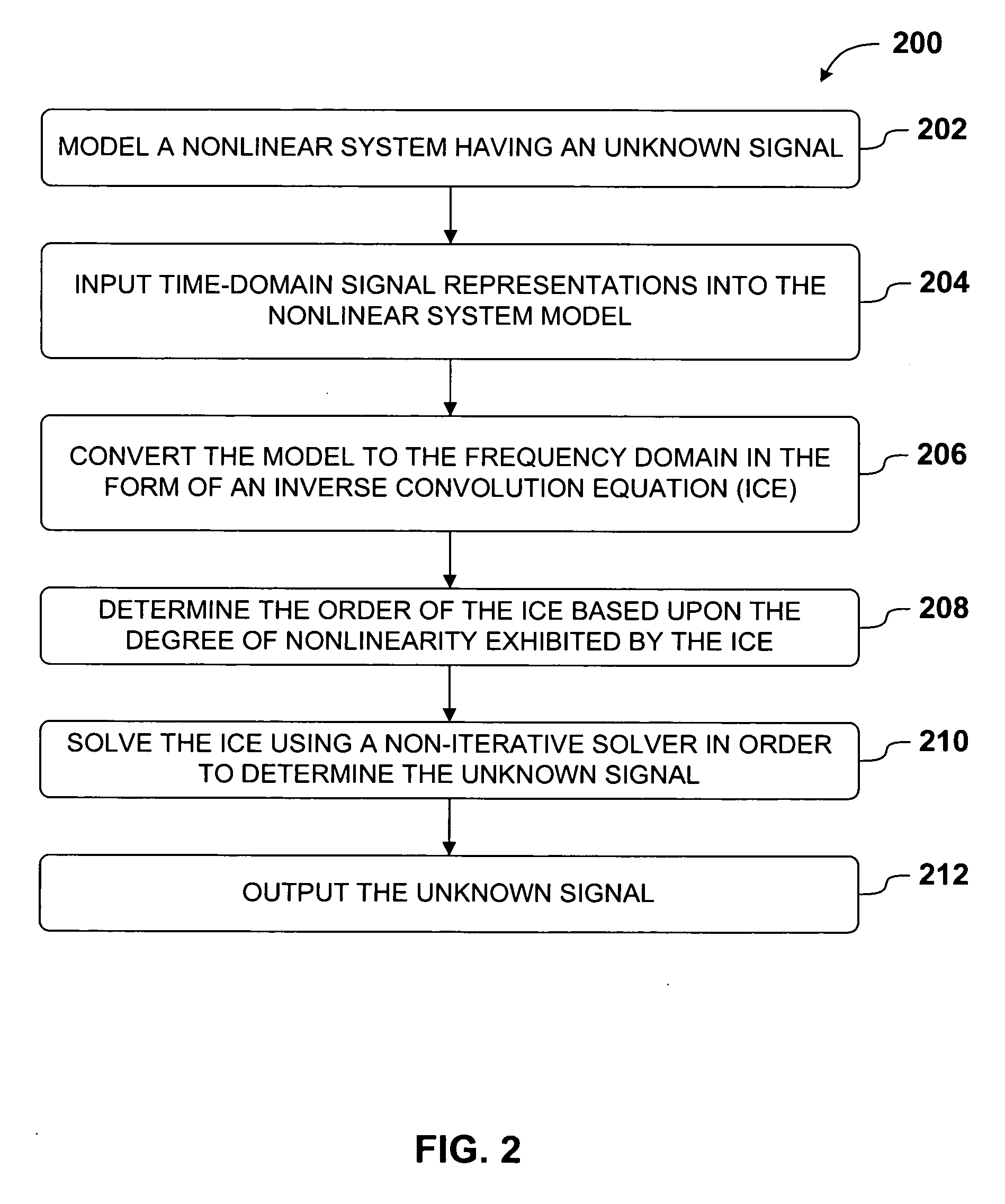
Efficient non-iterative frequency domain method and system for nonlinear analysis
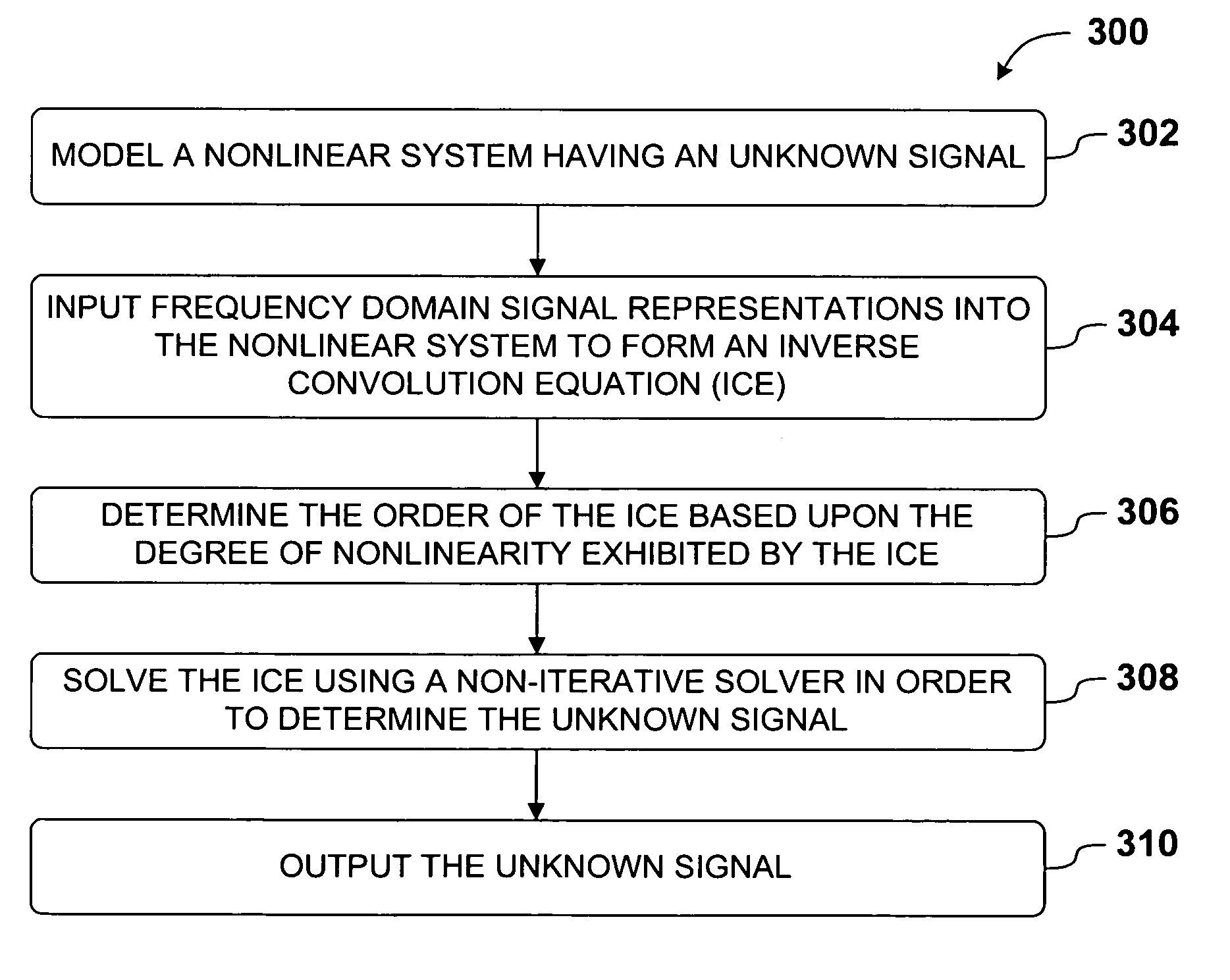
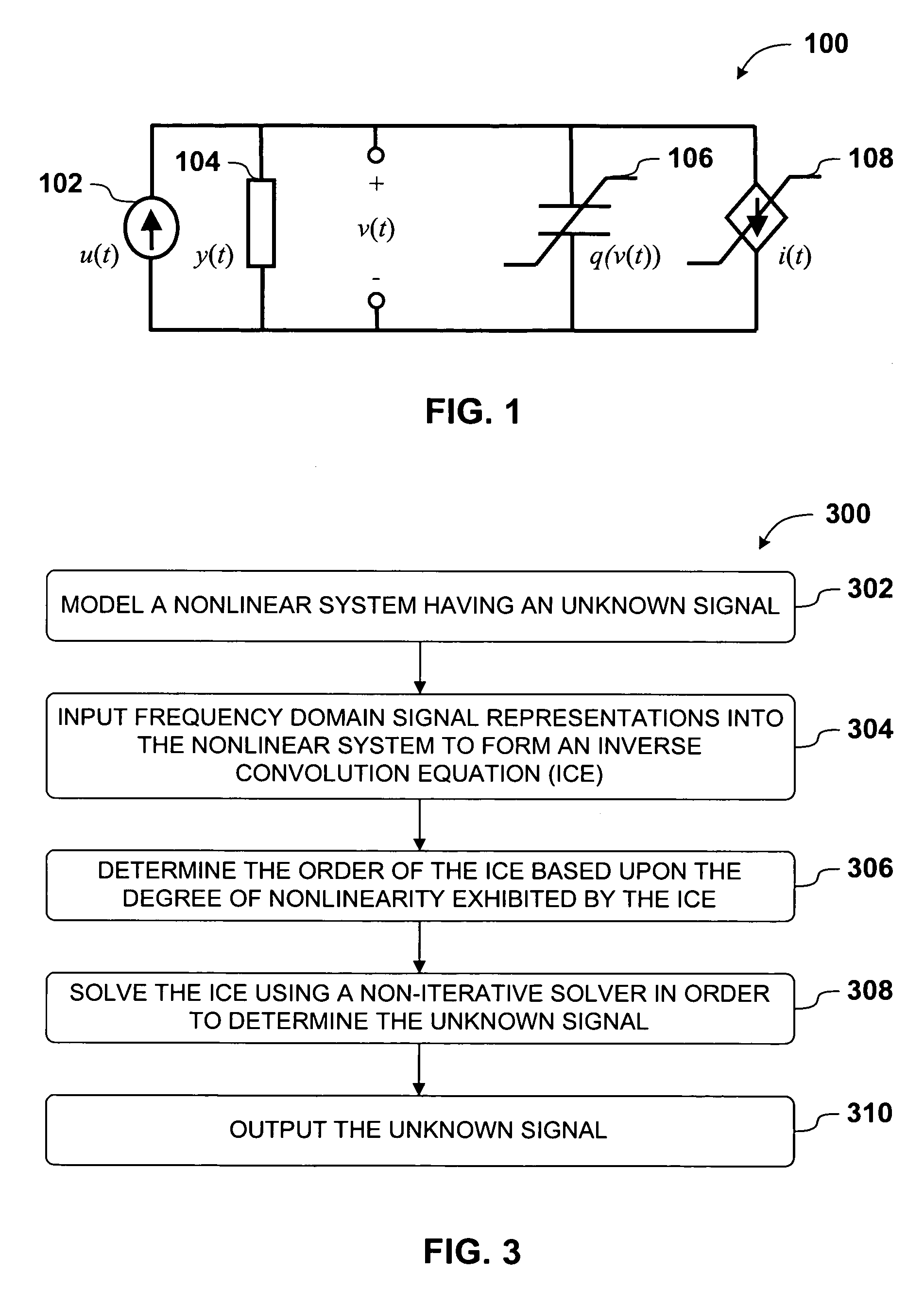
InactiveUS20070033000A1Accurate and Efficient SimulationConvergence issueSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsIterative methodologyEngineering
A non-iterative frequency domain method for the accurate and efficient simulation of nonlinear systems is presented. In one aspect of the present invention, simulating a nonlinear system is accomplished by first modeling the system and generating parameters that describe the nonlinear system. The system is represented in the frequency domain as an inverse convolution equation (ICE), comprising cascaded convolutions and frequency representations of known and unknown signals. Next, the order of the ICE is determined based upon the degree of nonlinearity in the system. Finally, a general ICE solver algorithm is adapted to the ICE order of the frequency model, and the specific ICE solver algorithm is applied to in order to solve for an unknown signal. In another aspect of the invention, the non-iterative method for simulating nonlinear systems is combined with cross-referenced coordinate (CRC) techniques in order to increase the computational efficiency of the simulation.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Hyperbolic fitting method for compressible fluid turbulence measurement test data
ActiveCN111707439AImprove solution accuracyImprove robustnessAerodynamic testingDesign optimisation/simulationMeasurement testIterative methodology
The invention discloses a hyperbolic fitting method for compressible fluid turbulence measurement test data. The method comprises the following steps: (1), carrying out data acquisition preparation; (2), opening a to-be-measured wind tunnel, and carrying out measuring by using a hot-wire anemometer under an incoming Mach number M to obtain a to-be-fitted two-dimensional scatter sequence; (3), performing hyperbolic fitting on the to-be-fitted two-dimensional scatter sequence by using an iterative method based on a Lagrange multiplier neural network, and carrying out solving to obtain a fittingresult; and (4), solving a turbulence degree result. According to the method, hyperbolic fitting is carried out on compressible fluid turbulence measurement test data by using the iterative method based on the Lagrange multiplier neural network and the turbulence is calculated by using the fitting result; compared with a traditional method represented by an SOE method, the method has the advantages that the turbulence solving accuracy is high, the robustness is high, and a feasible method is provided for hyperbolic fitting of compressible fluid turbulence measurement test data.
Owner:INST OF HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS OF CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
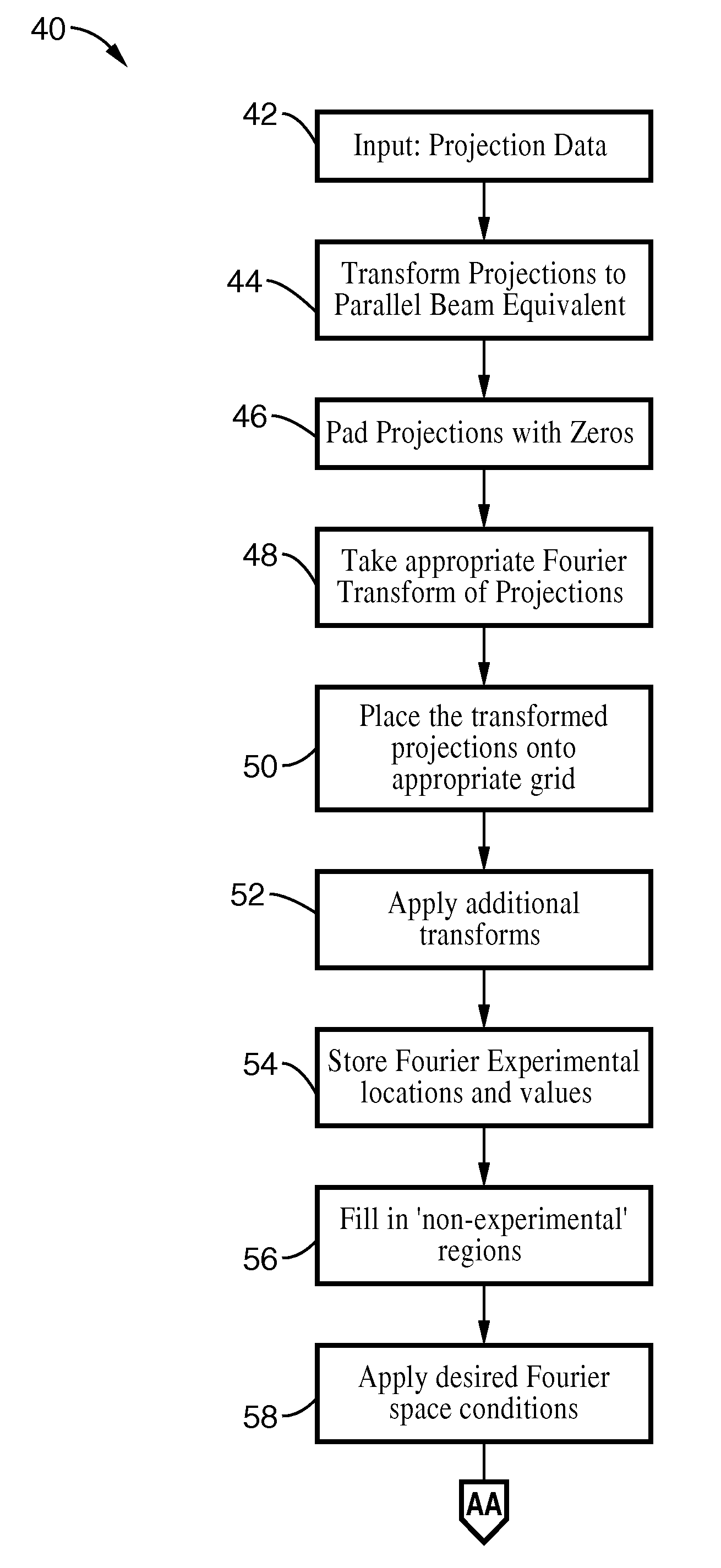
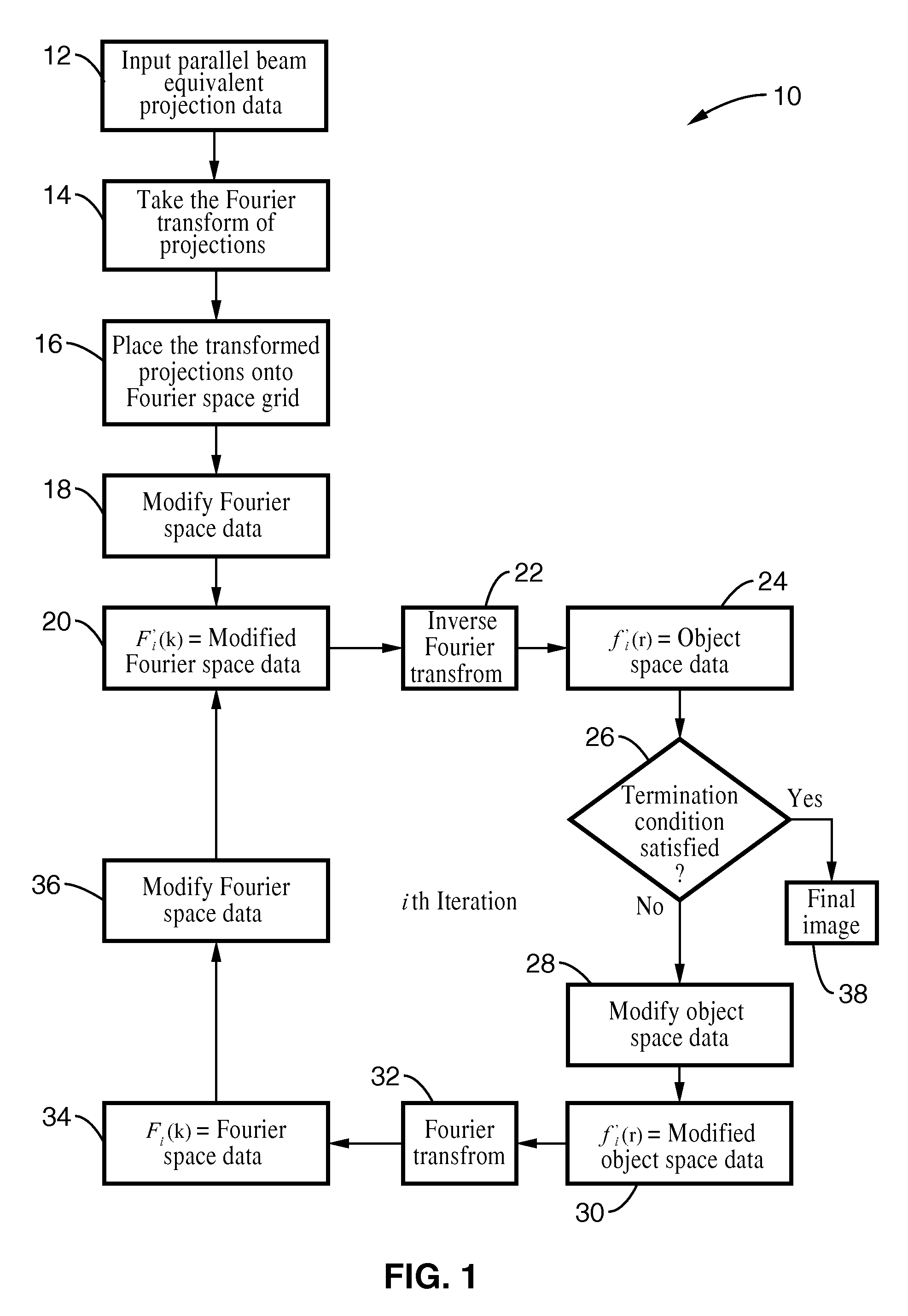
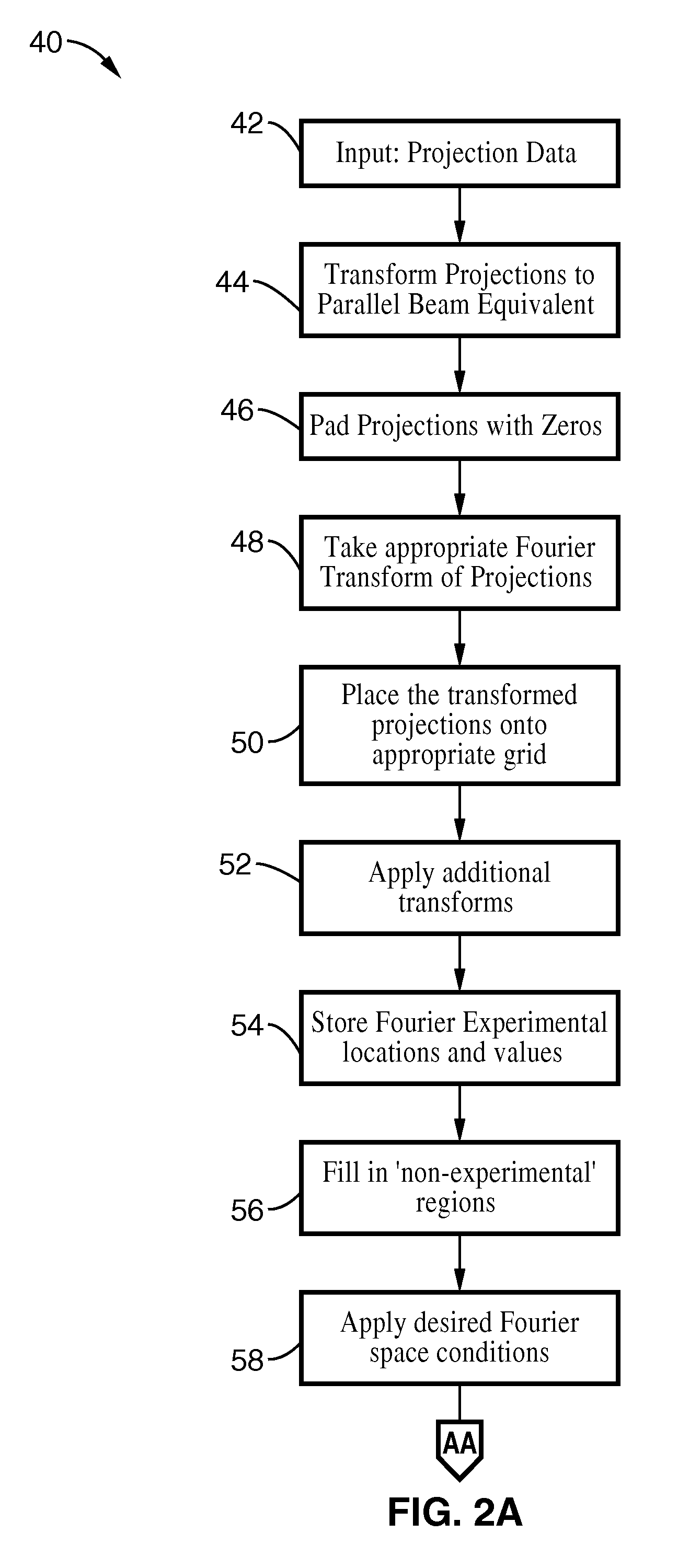
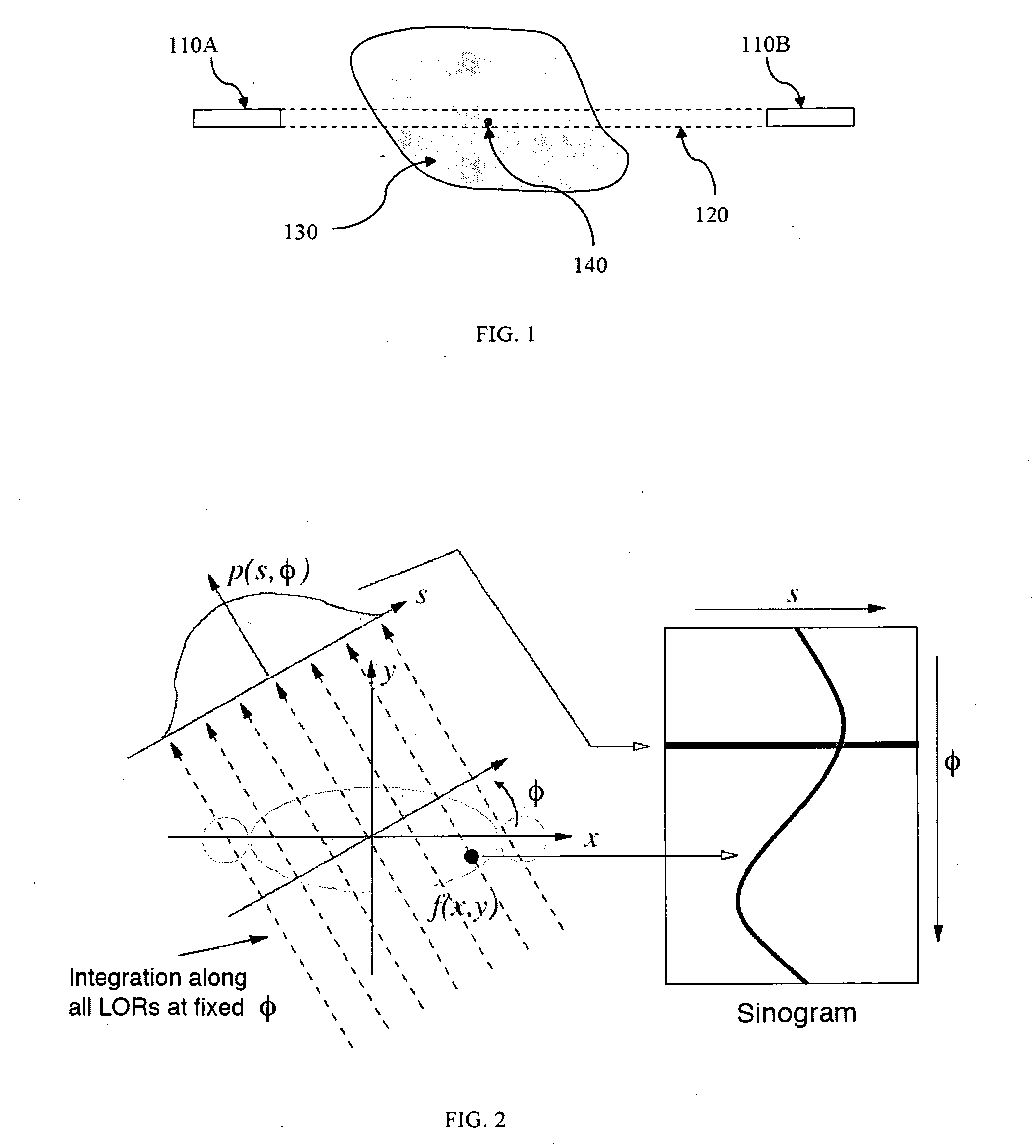
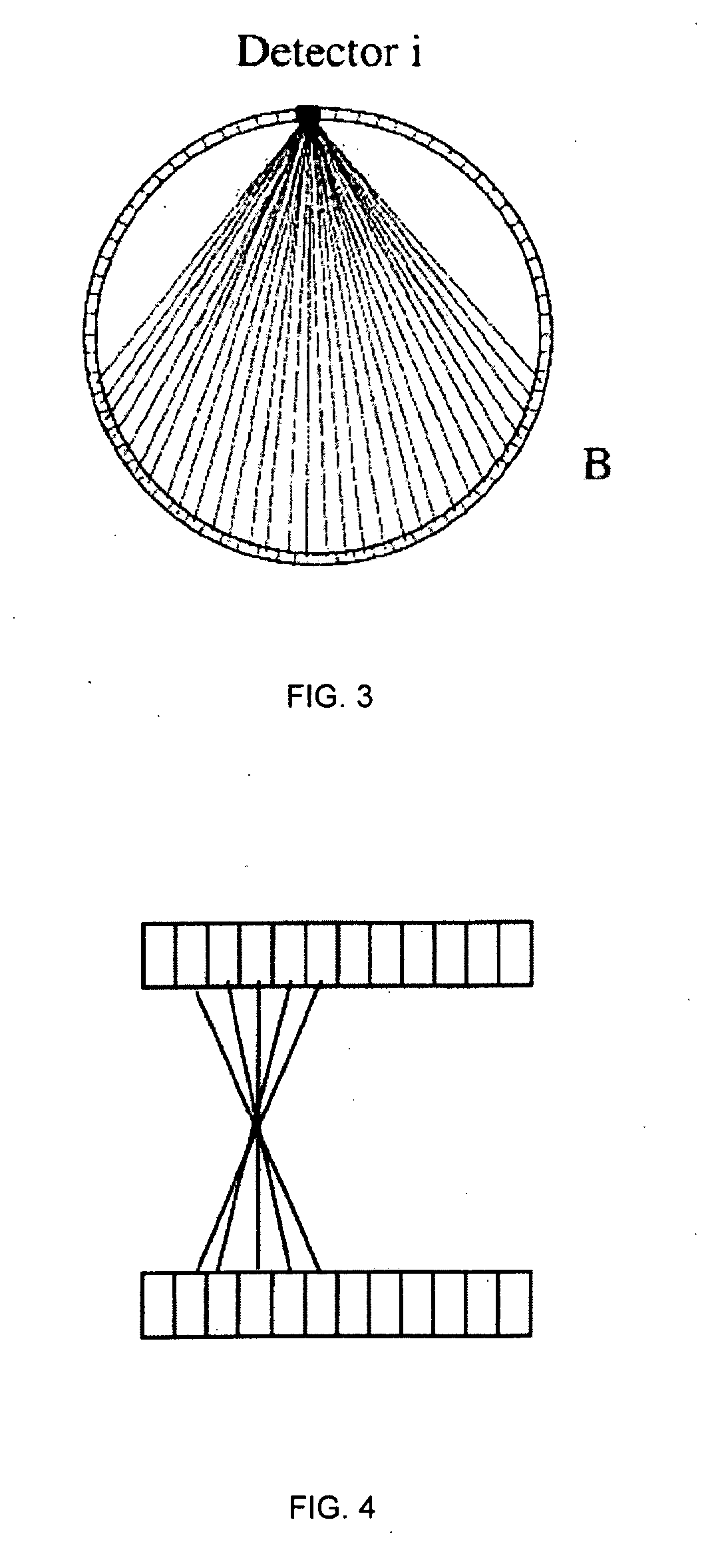
Iterative methods for dose reduction and image enhancement in tomography
InactiveUS8270760B2Eliminate interpolationReduce resolutionImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionIterative methodologyImage resolution
A system and method for creating a three dimensional cross sectional image of an object by the reconstruction of its projections that have been iteratively refined through modification in object space and Fourier space is disclosed. The invention provides systems and methods for use with any tomographic imaging system that reconstructs an object from its projections. In one embodiment, the invention presents a method to eliminate interpolations present in conventional tomography. The method has been experimentally shown to provide higher resolution and improved image quality parameters over existing approaches. A primary benefit of the method is radiation dose reduction since the invention can produce an image of a desired quality with a fewer number projections than seen with conventional methods.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System and method of resistance based memory circuit parameter adjustment
ActiveUS8161430B2Efficiently improve sense amplifier marginsDigital storageCAD circuit designElectrical resistance and conductanceAudio power amplifier
Systems and methods of resistance based memory circuit parameter adjustment are disclosed. In a particular embodiment, a method of determining a set of parameters of a resistance based memory circuit includes selecting a first parameter based on a first predetermined design constraint of the resistance based memory circuit and selecting a second parameter based on a second predetermined design constraint of the resistance based memory circuit. The method further includes performing an iterative methodology to adjust at least one circuit parameter of a sense amplifier portion of the resistance based memory circuit by selectively assigning and adjusting a physical property of the at least one circuit parameter to achieve a desired sense amplifier margin value without changing the first parameter or the second parameter.
Owner:YONSEI UNIVERSITY +1
Estimation of Crystal Efficiency With Axially Compressed Sinogram
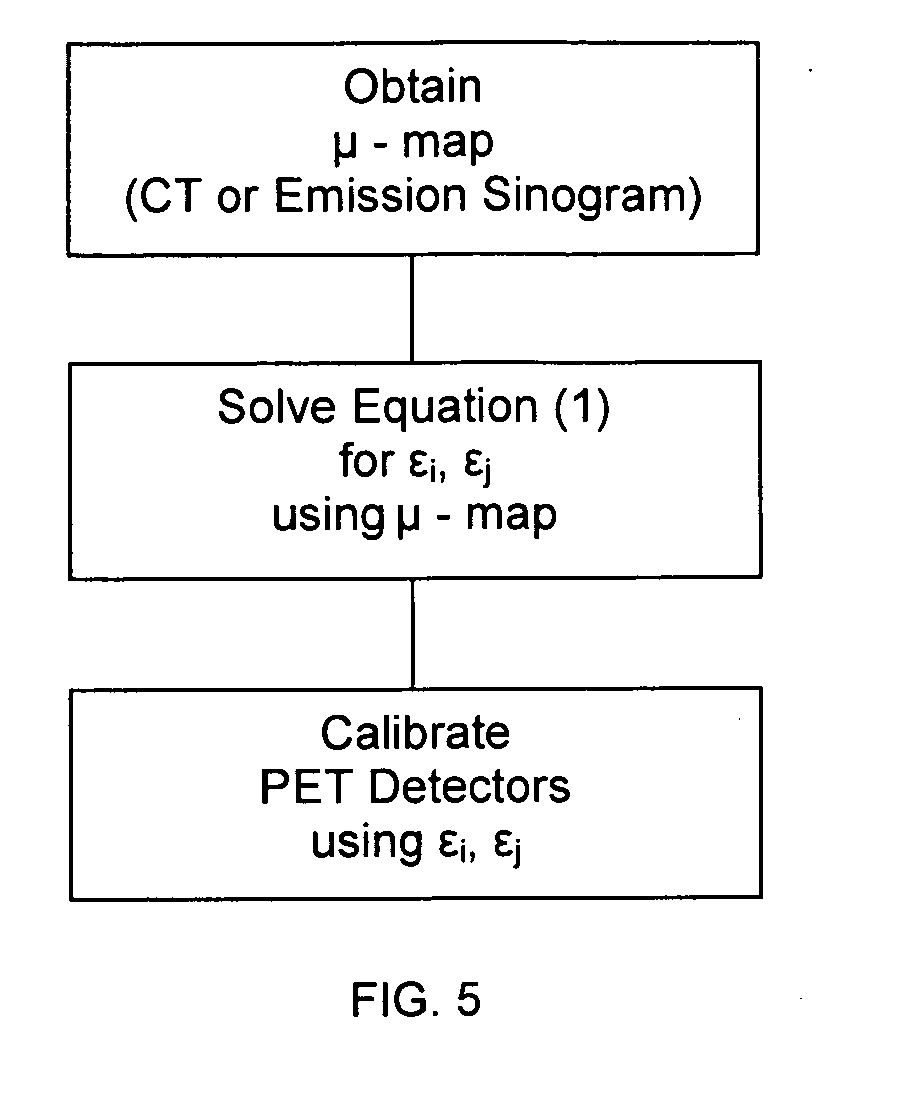
ActiveUS20090072131A1Testing/calibration apparatusCalibration apparatusIterative methodologyGeometric factor
The present invention provides a method for estimating crystal efficiency in a PET detector that takes axial compression into account. It does so via an iterative methodology in which a μ-map is first generated and then is used to obtain a solution for the equationL(ɛi)=∑n∈Nynlog∑i,j∈spangijɛiɛjxij-∑i,j∈spangijɛiɛjxij,wherein gij is a geometric factor for LOR(i,j), εi and εj are the efficiencies for crystal i and crystal j, and xij is the line integral of the source distribution along LOR(i,j). Once efficiencies are determined, they are used to calibrate the PET detector.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
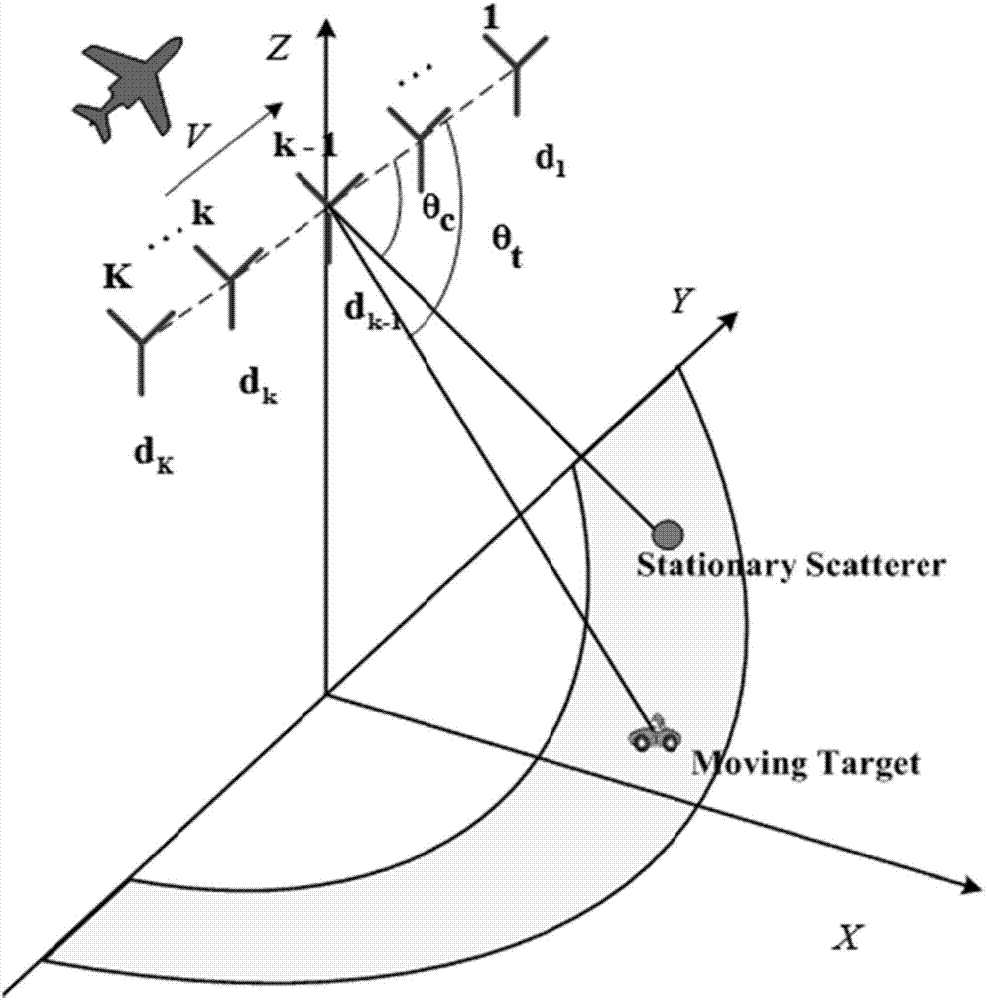
Clutter suppression and parameter estimation method based on Relax algorithm in WAS-GMTI mode
InactiveCN106896350AAccurate estimateGood clutter suppressionWave based measurement systemsWide areaIterative methodology
The invention discloses a clutter suppression and parameter estimation method based on a Relax algorithm in a WAS-GMTI mode, and belongs to the technical field of radar target detection. The invention designs an iterative method of clutter suppression according to the characteristic of wide area monitoring mode echo composition and combined with the Relax algorithm. Then on the basis of clutter suppression, iteration continues to be performed on distance-Doppler units where moving targets exist, and thus precise estimation of parameters of the moving target can be realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Inertial measurement unit calibration method suitable for shaking base environment
ActiveCN111238532AEliminate attitude errorsMeasurement devicesIterative methodologyClassical mechanics
The invention discloses an inertial measurement unit calibration method suitable for a shaking base environment, and relates to the technical field of inertial measurement combination test in aerospace strapdown inertial navigation technology. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a simultaneous equation by using a relationship between a first-order intermediate parameter and a first-order error parameter, and solving to obtain the first-order error parameter based on the established simultaneous equation; calculating to obtain a second-order intermediate parameter of the ithposition by utilizing the first-order error parameter, establishing an equation according to a relationship between the second-order intermediate parameter and a second-order error parameter, and solving to obtain the second-order error parameter which is gyro zero offset; and judging whether the residual error of the first-order error parameter and the second-order error parameter is smaller thana set threshold value or not, and if yes, ending. According to the method, the attitude error introduced by the shaking base environment in the initial alignment process is gradually eliminated by adopting an iterative method so that the method is better suitable for calibration in the shaking base environment.
Owner:THE GENERAL DESIGNING INST OF HUBEI SPACE TECH ACAD
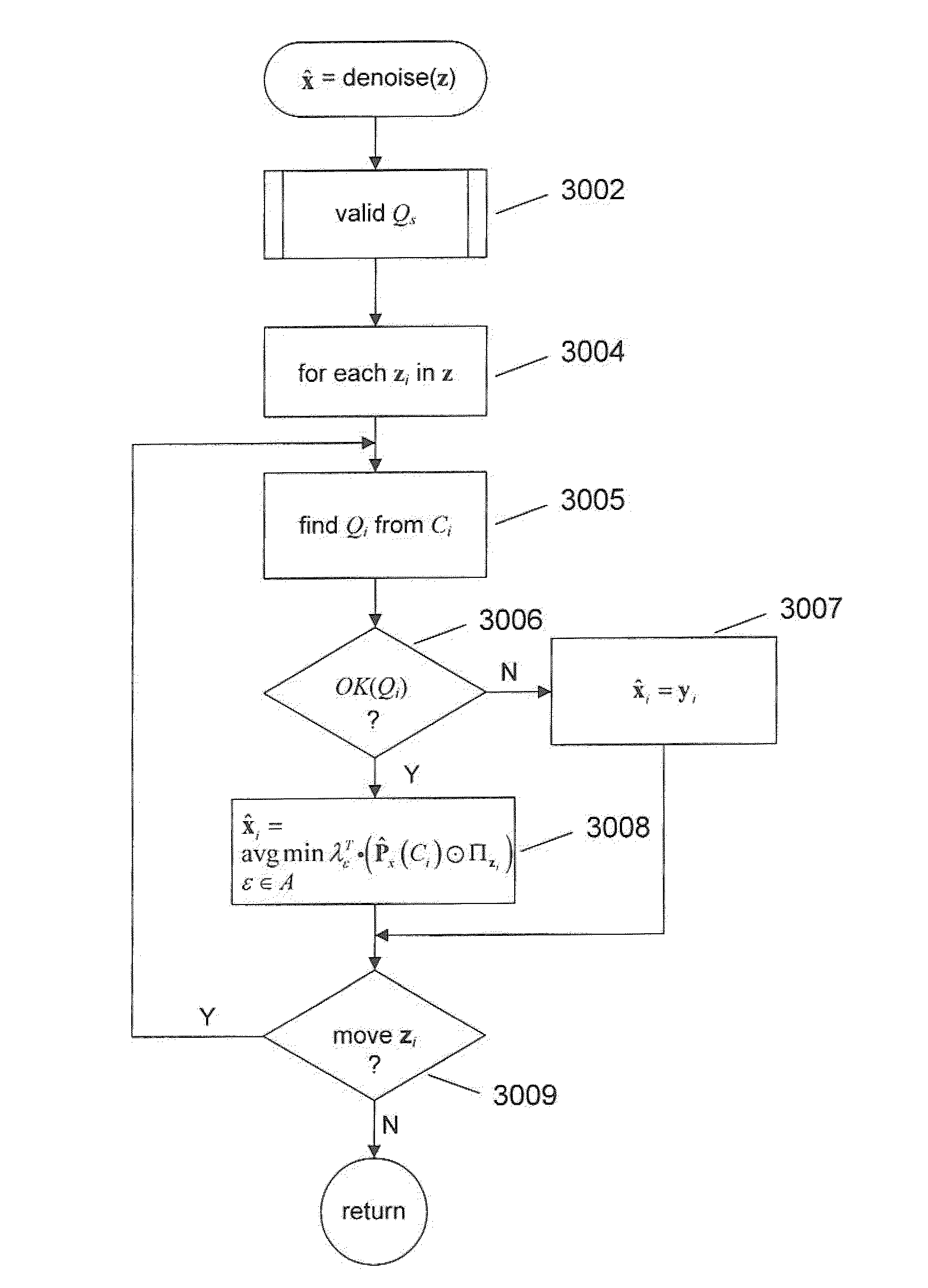
Context-cluster-level control of filtering iterations in an iterative discrete universal denoiser
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to various enhanced discrete-universal denoisers that have been developed to denoise images and other one-dimensional, two-dimensional or higher-dimensional data sets in which the frequency of occurrence of individual contexts may be too low to gather efficient statistical data or context-based symbol prediction. In these denoisers, image quality, signal-to-noise ratios, or other measures of the effectiveness of denoising that would be expected to increase monotonically over a series of iterations may decrease, due to assumptions underlying the discrete-universal-denoising method losing validity. Embodiments of the present invention apply context-class-based statistics and statistical analysis to determine, on a per-context-class basis, when to at least temporarily terminate denoising iterations on each conditioning class. Each iteration of the iterative methods applies context-based denoising only for those conditioning classes that statistical analysis indicates remain valid for denoising purposes.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
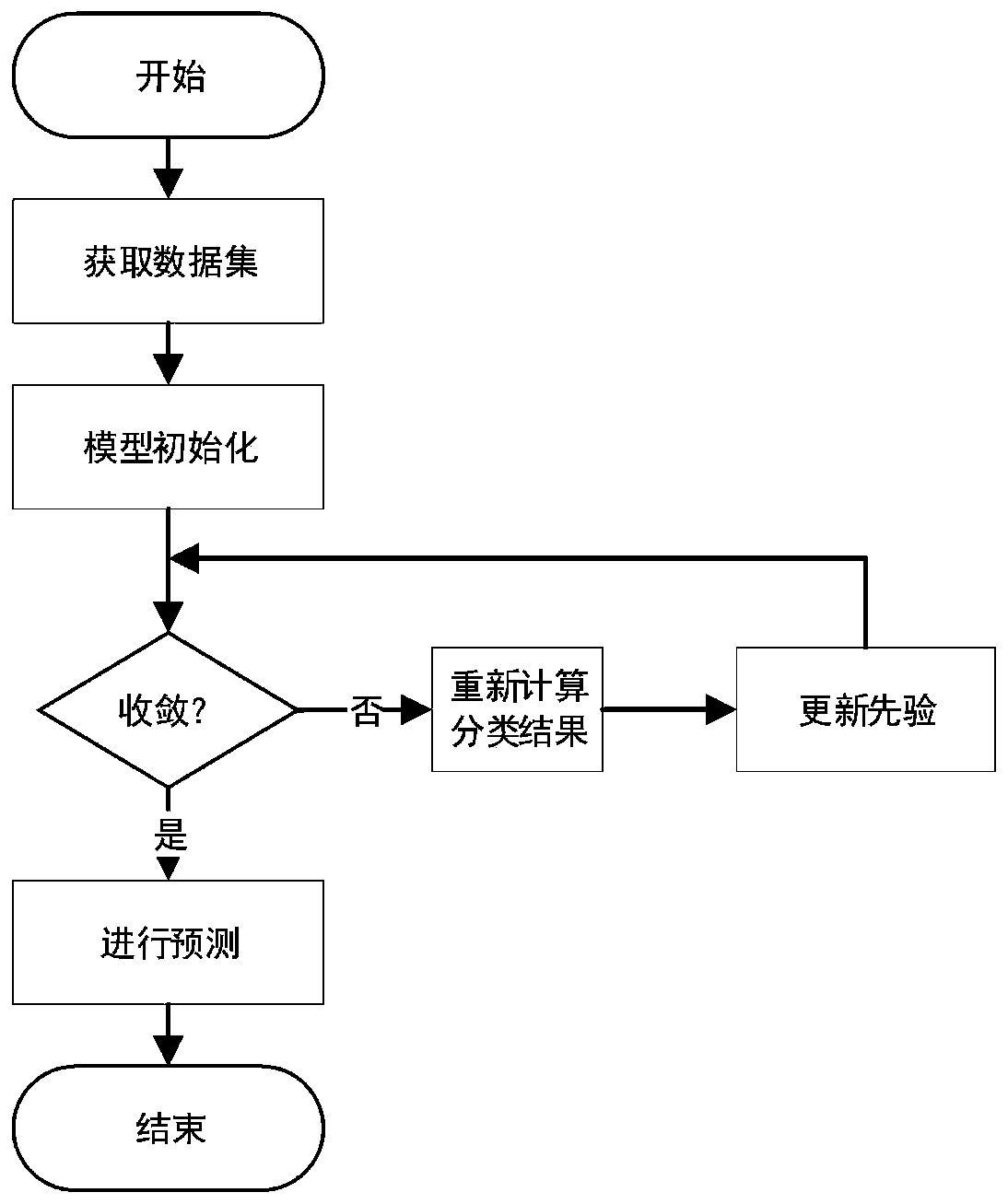
Mean iteration-based multi-task learning model training and prediction method
ActiveCN110738270ATake advantage ofImprove learning efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionData setIterative methodology
A mean iteration-based multi-task learning model training and prediction method comprises the steps of firstly obtaining sample data sets of a plurality of tasks, and dividing the sample data sets ofthe tasks into a training set and a test set; for each task, utilizing the corresponding training set to obtain the prior probability of each class label on each task and the conditional probability of each characteristic variable in each task on each class label, and calculating the class label of each instance in the test set corresponding to each task; updating the prior probability of each type of label on each task based on a mean iteration method; and performing loop iteration continuously until the sum delta of absolute values of prior probability errors of class labels on different tasks is smaller than a set threshold, and performing convergence to obtain a trained multi-task learning model. According to the mean iteration-based multi-task learning model training and prediction method, the multi-task learning efficiency can be significantly improved. Meanwhile, shared information between tasks and priori knowledge of data can be more fully utilized, and a better classificationeffect can be achieved by using fewer computing resources.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Availability aware cost modeling for optical core networks
InactiveUS7646730B2Improve responseWavelength-division multiplex systemsData switching by path configurationIterative methodologyNetwork architecture
A sequential iterative methodology is used to generate a solution space with different cost / availability values for multiple network architectures from which an optimal or near-optimal solution can be determined. A modeling module (10) provides a cost value for a network architecture under consideration and, once cost modeling is done, an availability analysis is performed for the architecture under analysis. If a relatively few connections prevent a model from acceptability, the availability analysis module (12) reveals the causing factors of the unsatisfactory availability for those few connections and suggests that the modeling perform further optimisations on those causing factors. This iterative process is repeated until an optimum or near-optimum acceptable solution is found; if no acceptable solution is found, the solutions generated in the availability analysis module are reviewed to find the best available solution.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Recommendation system strategy iteration method and device, storage medium and server
PendingCN110769034AImprove fluencyImprove experienceTransmissionEnergy efficient computingIterative methodologyDatabase
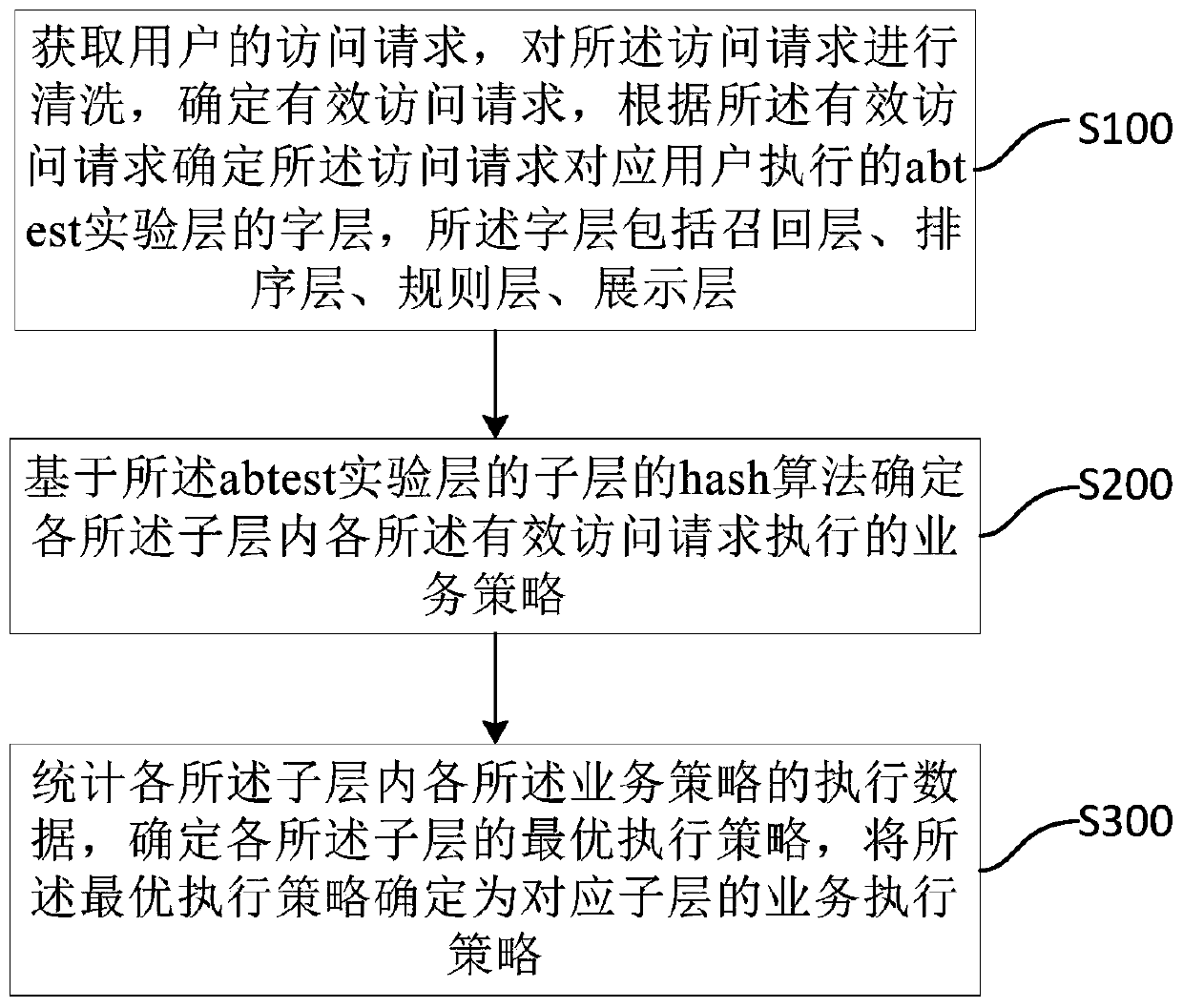
The invention relates to the technical field of data analysis, relational network analysis and intelligent recommendation, and provides a recommendation system strategy iteration method, which comprises the steps of obtaining an access request of a user, cleaning the access request, determining an effective access request, and determining an abtest experiment layer executed by the user corresponding to the access request; determining a service strategy executed by each effective access request in each experiment layer based on the Hash algorithm of each experiment layer; and counting the execution data of each business strategy, determining the optimal execution strategy of each experiment layer, and determining the optimal execution strategy as the business execution strategy of the corresponding experiment layer. According to the method, the execution threshold for cleaning the user request flow and testing the abtest user request is dynamically adjusted; when the abtest testing speed is guaranteed, the data result is more accurate, the operation strategy of the recommended system is iteratively updated quickly, the operation process of the system is optimized, and the fluency and experience in the user access process are improved.
Owner:CHINA PING AN LIFE INSURANCE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com