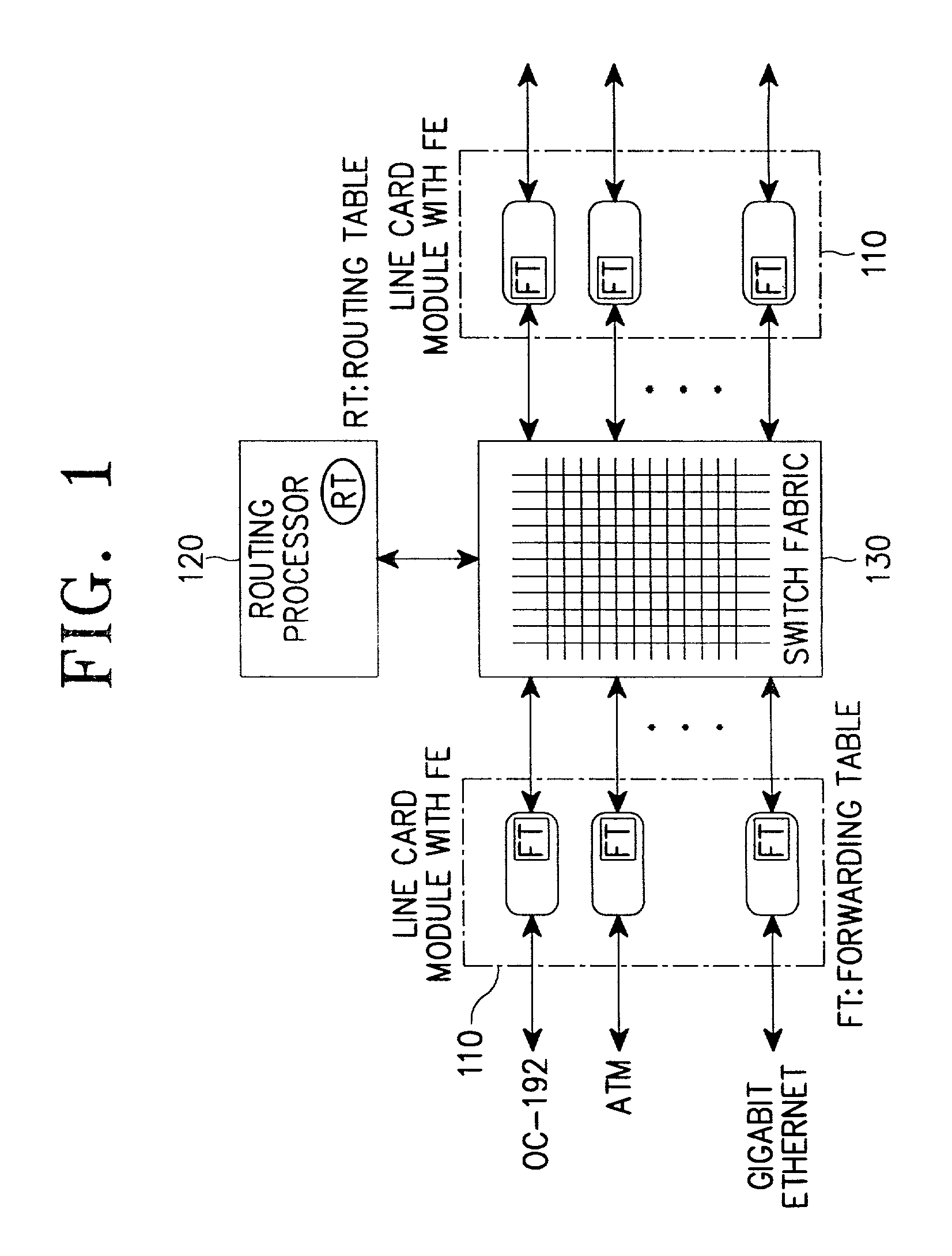
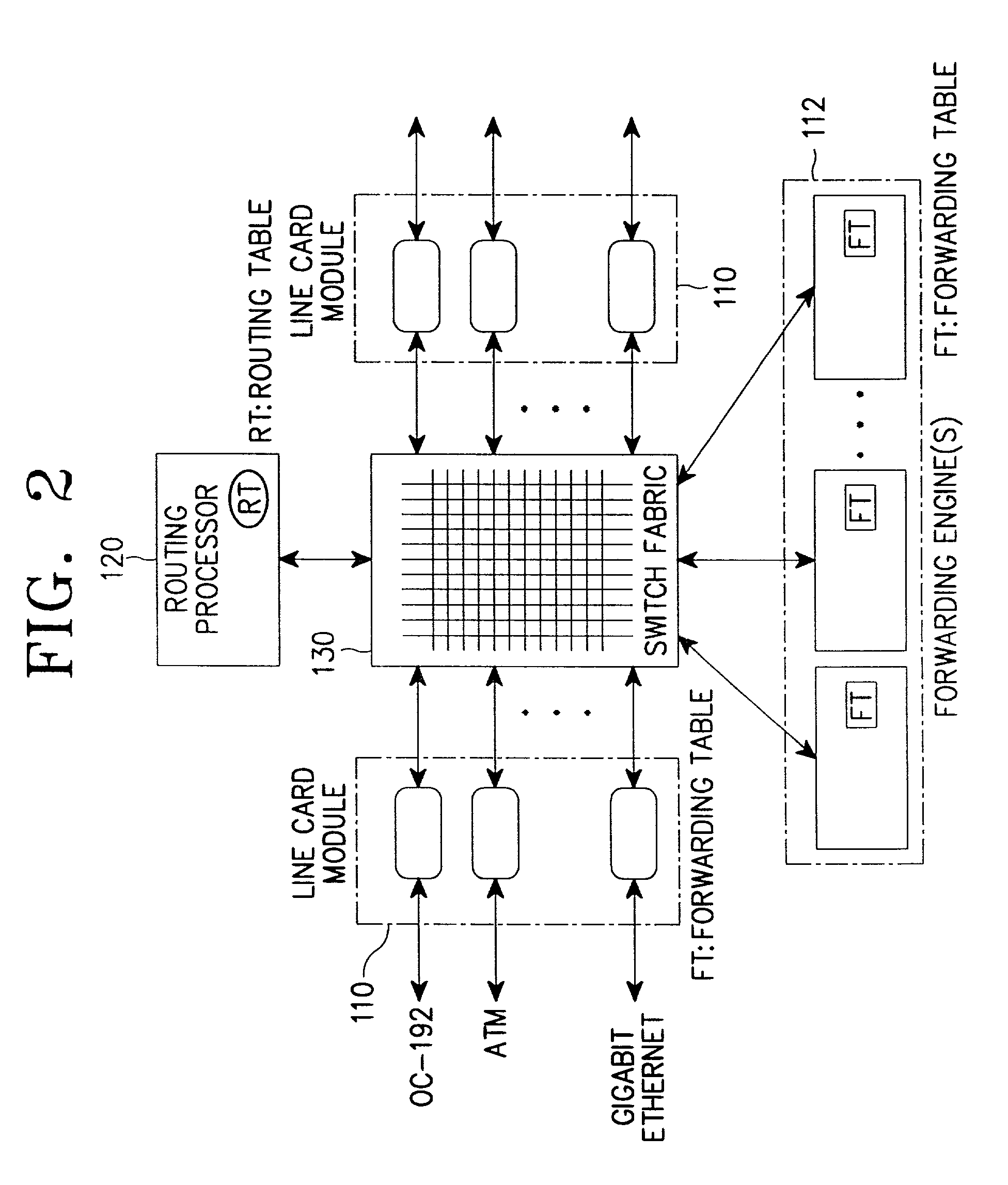
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
273 results about "IP forwarding algorithm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
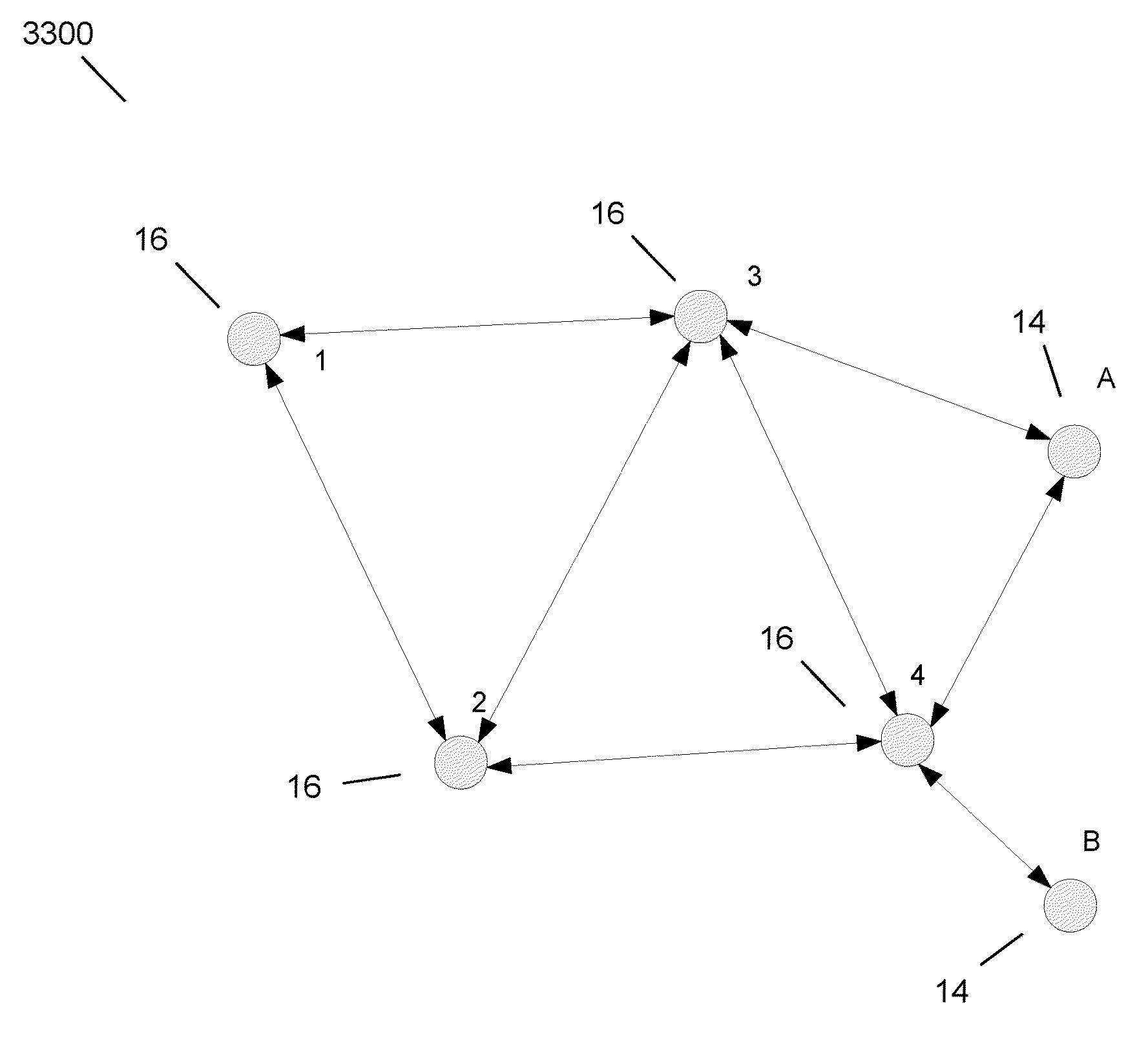
IP routing is the field of routing methodologies of Internet Protocol (IP) packets within and across IP networks. This involves not only protocols and technologies, but includes the policies of the worldwide organization and configuration of Internet infrastructure. In each IP network node, IP routing involves the determination of a suitable path for a network packet from a source to its destination in an IP network. The process uses static configuration rules or dynamically obtained status information to select specific packet forwarding methods to direct traffic to the next available intermediate network node one hop closer to the desired final destination, a total path potentially spanning multiple computer networks.
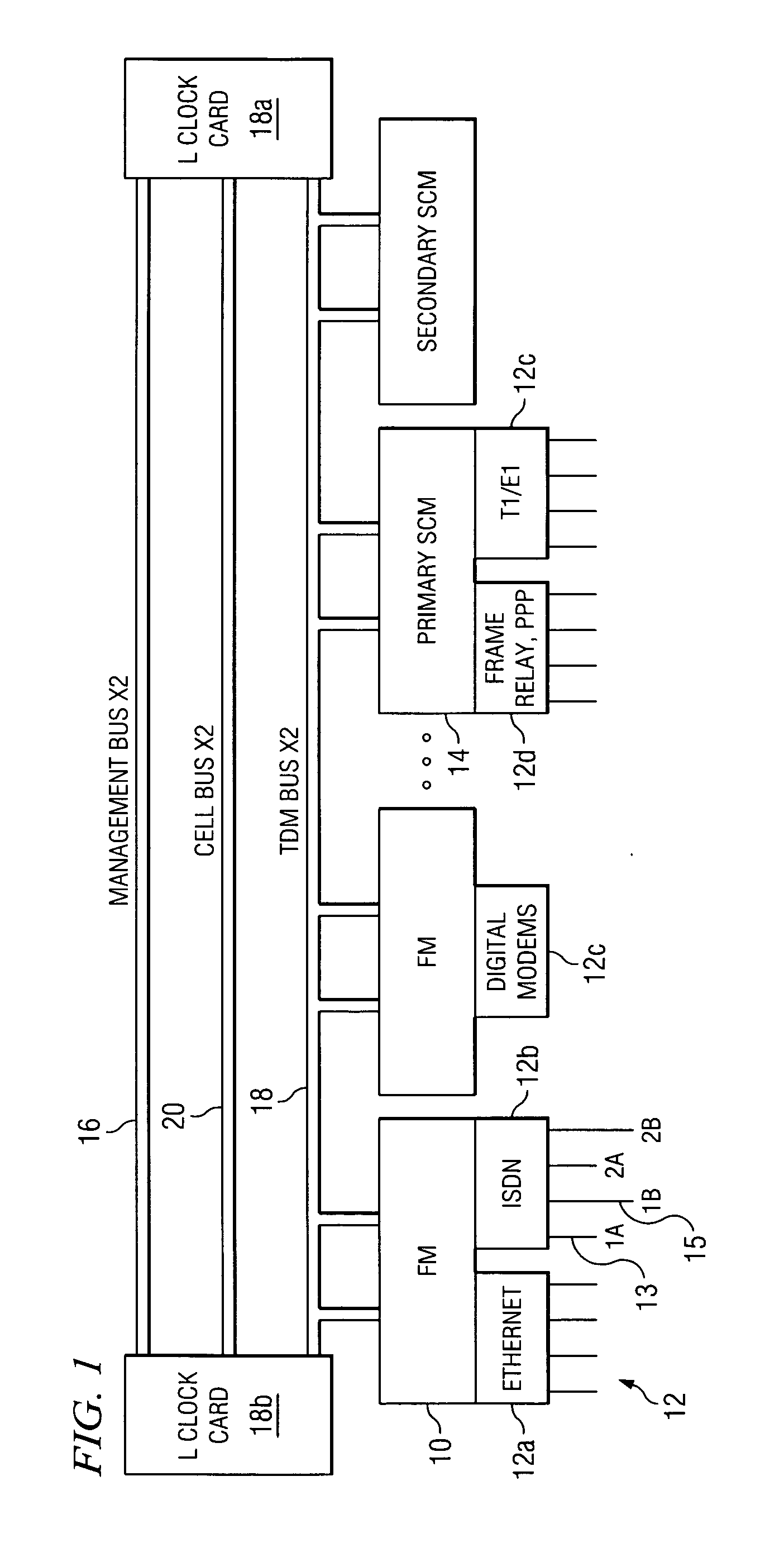
Methods and systems for a mobile, broadband, routable internet
ActiveUS8060017B2Low costFast capacity expansionNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexCellular telephonePeer-to-peer
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for a mobile broadband routable internet (MBRI) providing for carrier-grade, networked, broadband, IP-routable communication among a plurality of mobile devices, where the mobile devices may represent a plurality of nodes that are linked together through a mobile ad-hoc network (MANET). Mobile devices may operate as peers in a peer-to-peer network, with full IP routing capabilities enabled within each mobile device, thereby allowing routing of IP-based traffic, including deployment of applications, to the mobile device without need for infrastructure conventionally required for mobile ad hoc networks, such as cellular telephony infrastructure. Full IP-routing to mobile devices may allow seamless integration to the fixed Internet, such as through fixed or mobile access points, such as for backhaul purposes. Thus, the MBRI may function as a standalone mobile Internet, without connection to the fixed Internet, or as an IP-routable extension of another network, whether it be the Internet, a local area network, a wide area network, a cellular network, a personal area network, or some other type of network that is capable of integration with an IP-based network.
Owner:POWERWAVE COGNITION INC
Mobile internet access
InactiveUS6804720B1Accounting/billing servicesMultiple digital computer combinationsCable Internet accessIp address
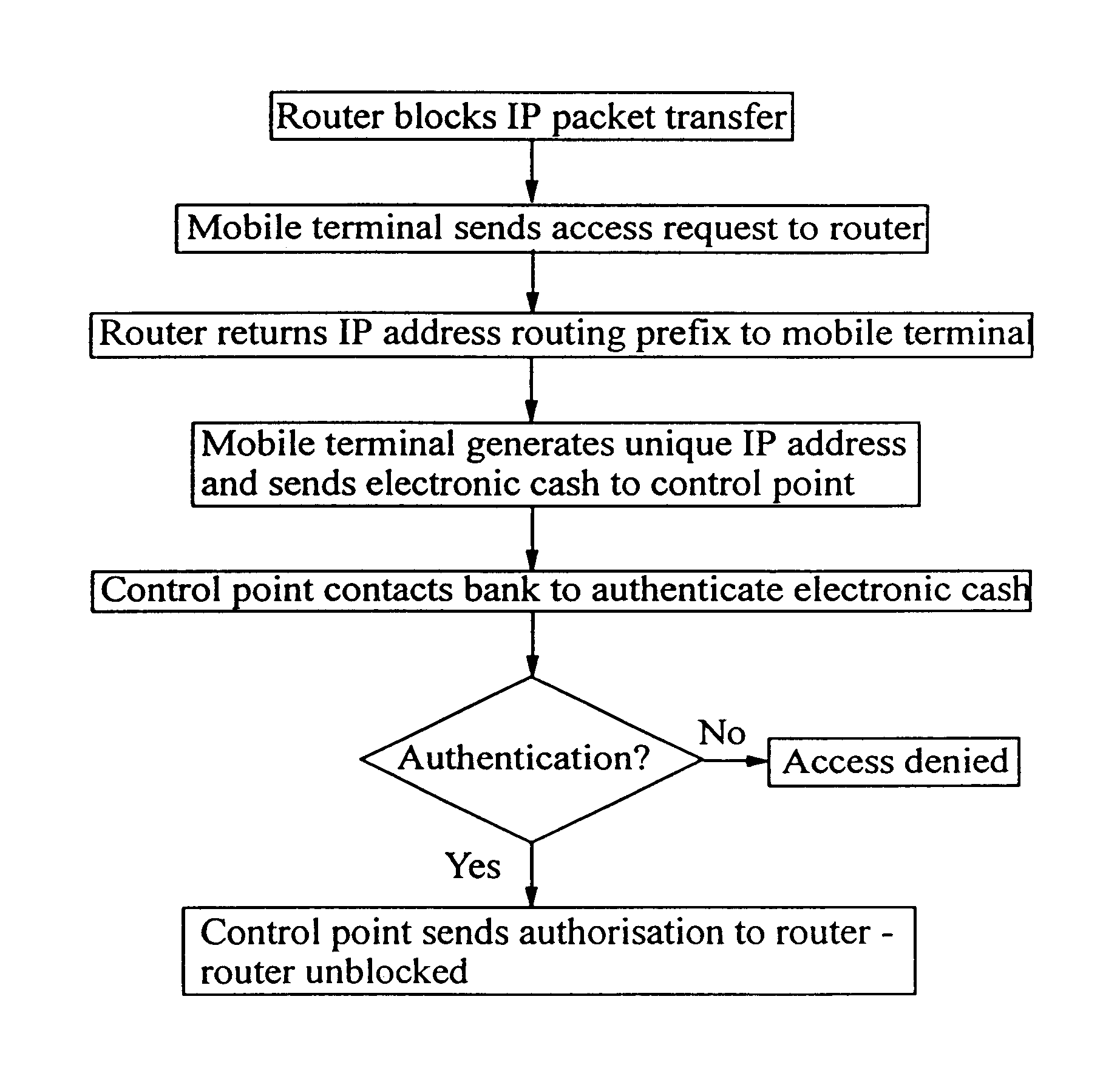
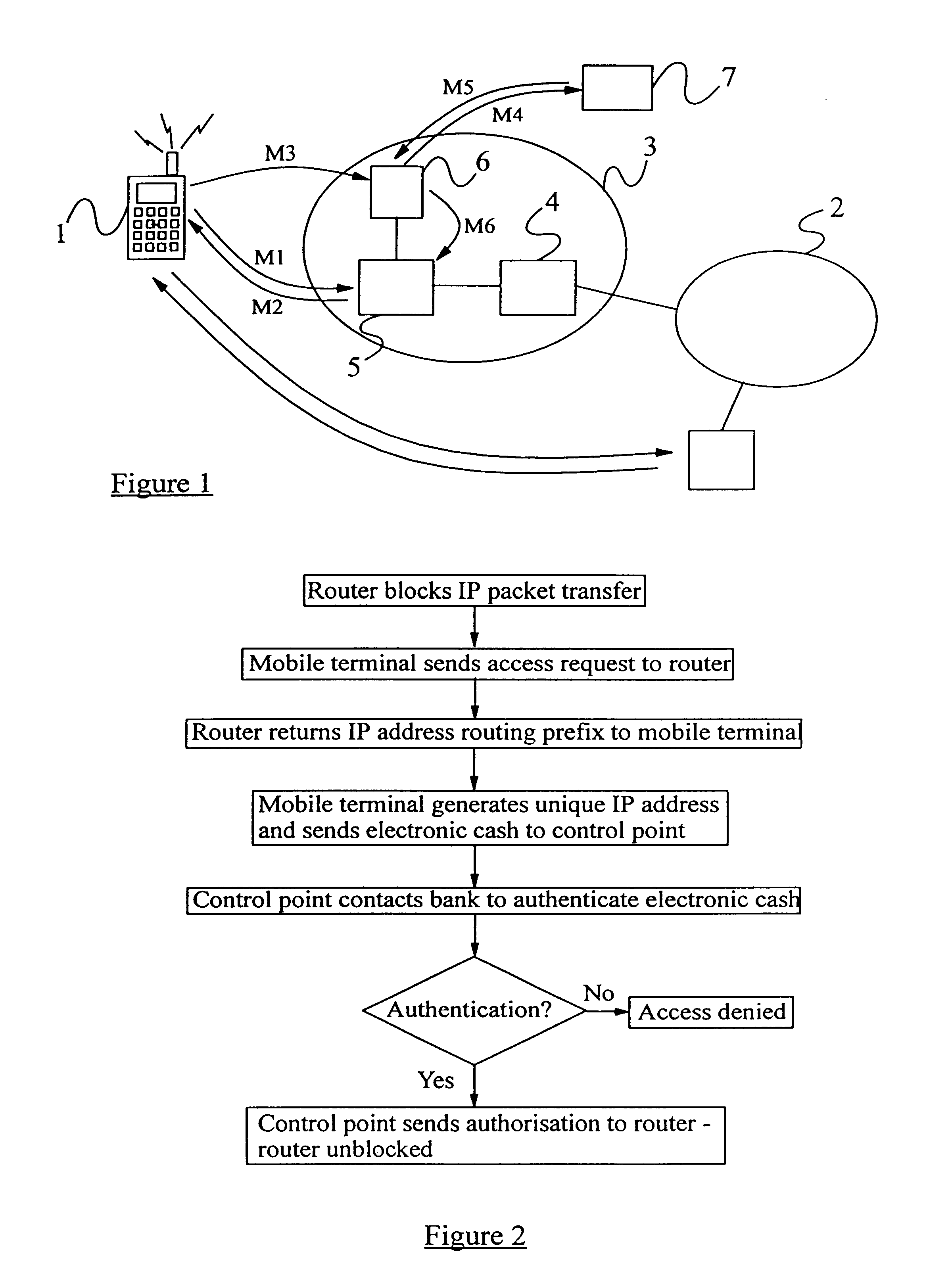
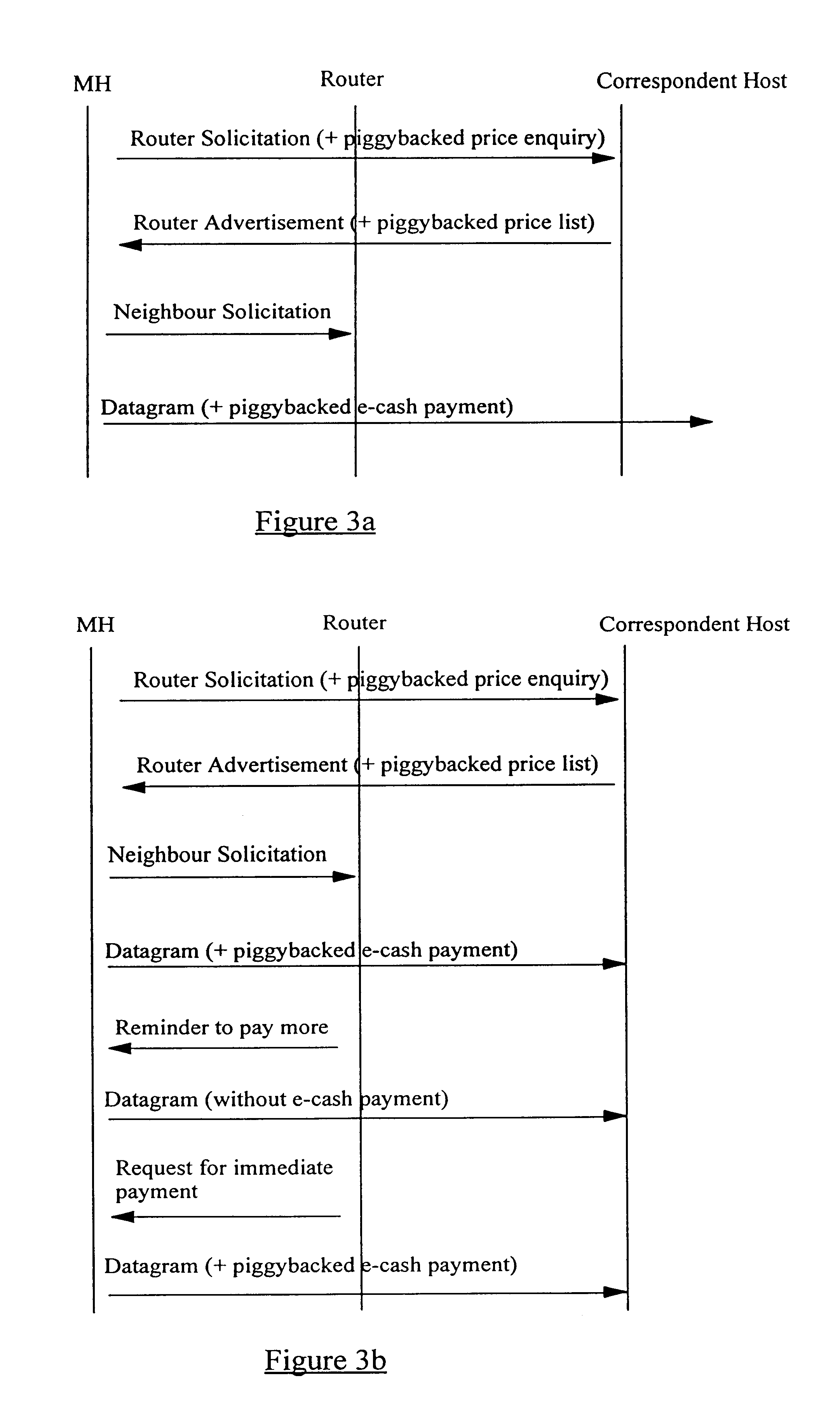
A method of authorizing an Internet Protocol (IP) enabled mobile host 1 to access the Internet 2 via an wireless LAN, GSM, UMTS access network 3 comprises initially sending an IP access request from the mobile host 1 to an IP router 5 within the access network 3. In response to receipt of said access request at the IP router 5, an IP address routing prefix is sent from the IP router 5 to the mobile host 1. Electronic cash is then forwarded from the mobile host 1 to a control point 6 within the access network 3. The control point 6 confirms the authenticity and / or sufficiency of the electronic cash and, providing that confirmation is made, sends an authorization message to the IP router 5. The IP router 5 blocks the transmission of IP packets between the mobile host 1 and the Internet 2 prior to receipt of the authorization message and permits the passage of IP packets only after an authorization message has been received.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
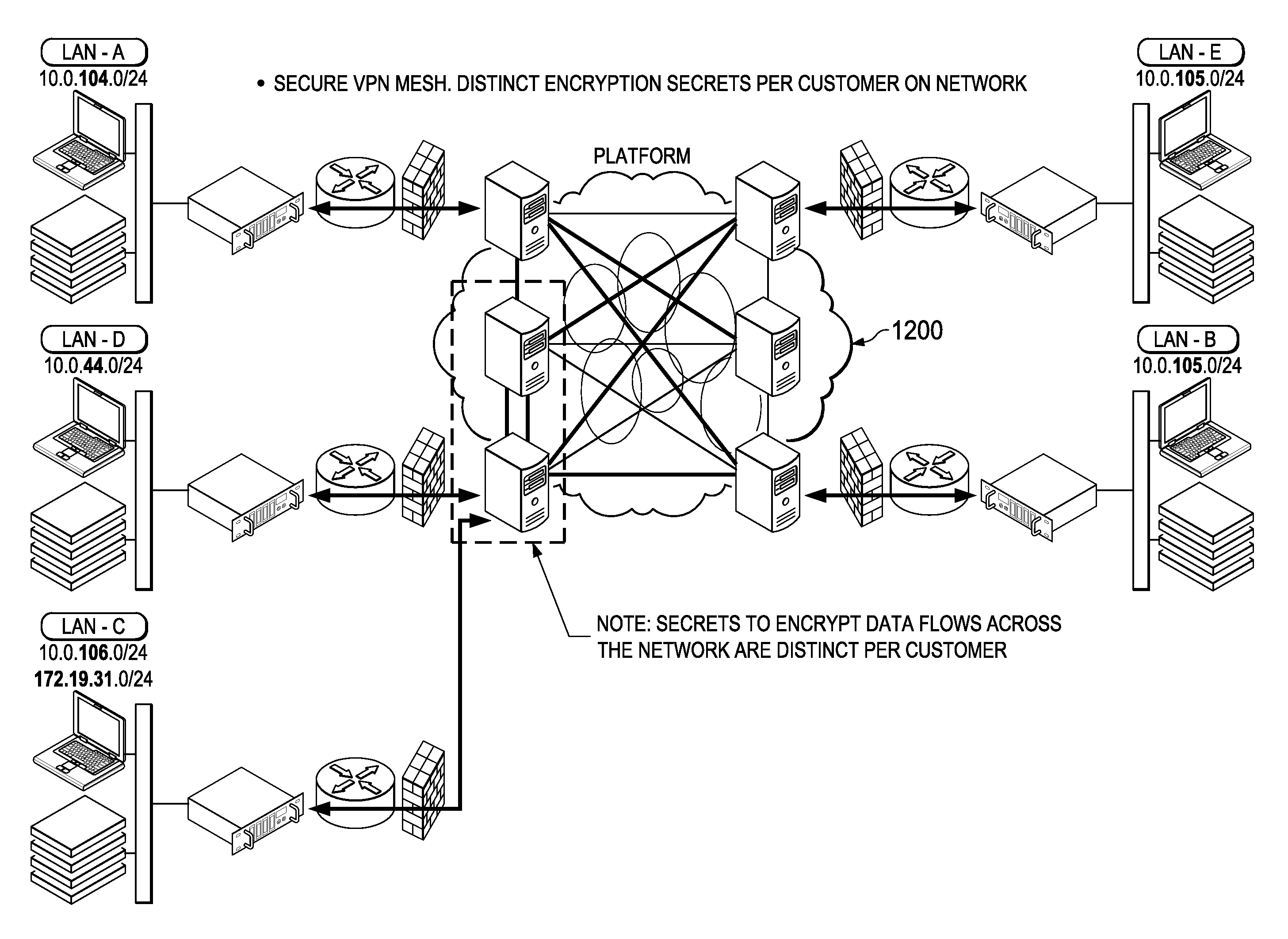
Virtual private network (VPN)-as-a-service with load-balanced tunnel endpoints
ActiveUS20150188823A1Facilitate (VPN)-as-a-serviceEfficient use ofError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPlaintextData stream
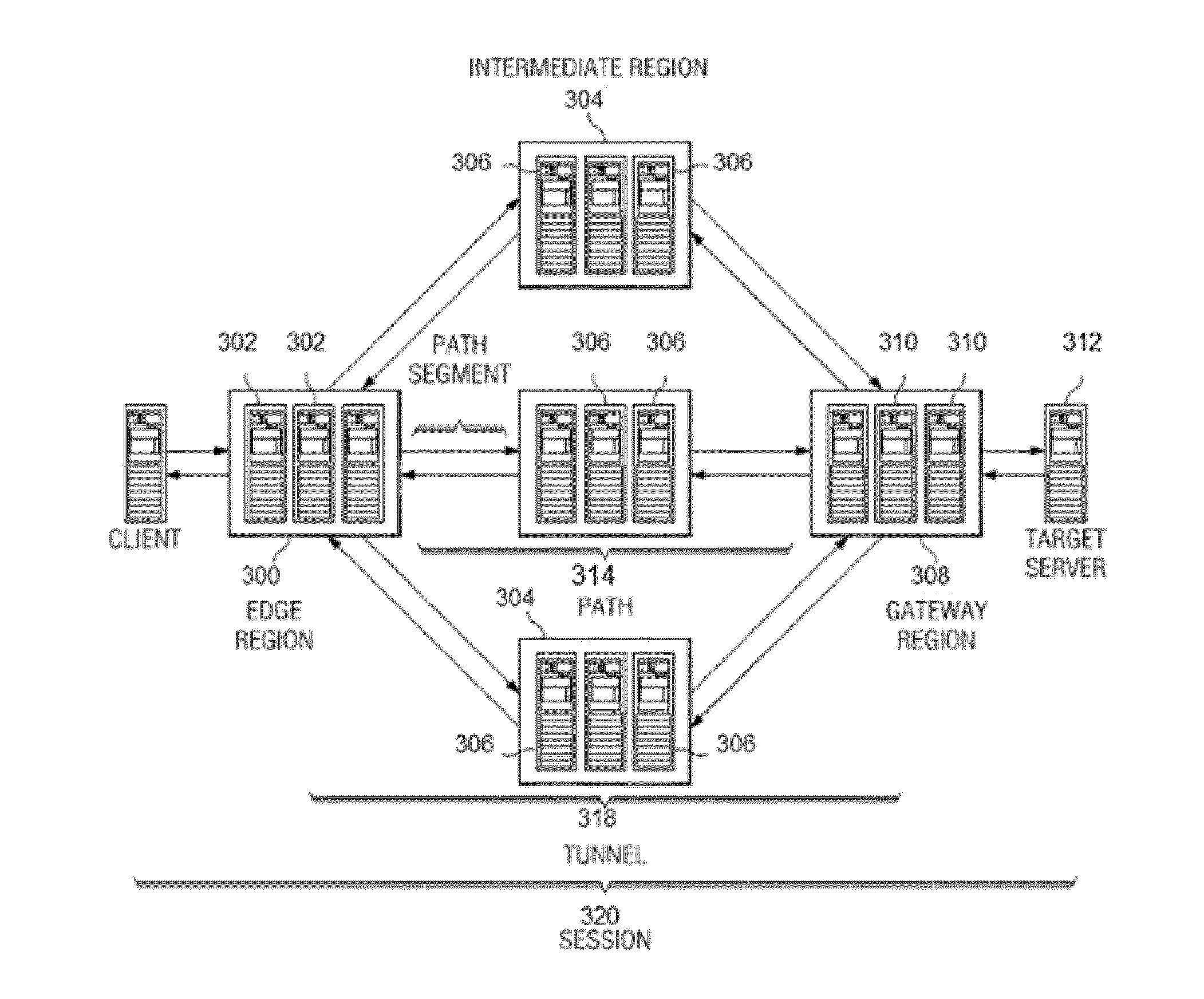
A mechanism to facilitate a private network (VPN)-as-a-service, preferably within the context of an overlay IP routing mechanism implemented within an overlay network. The overlay provides delivery of packets end-to-end between overlay network appliances positioned at the endpoints. During such delivery, the appliances are configured such that the data portion of each packet has a distinct encryption context from the encryption context of the TCP / IP portion of the packet. By establishing and maintaining these distinct encryption contexts, the overlay network can decrypt and access the TCP / IP flow. This enables the overlay network provider to apply one or more TCP optimizations. At the same time, the separate encryption contexts ensure the data portion of each packet is never available in the clear at any point during transport. According to another feature, data flows within the overlay directed to a particular edge region may be load-balanced while still preserving IPsec replay protection.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
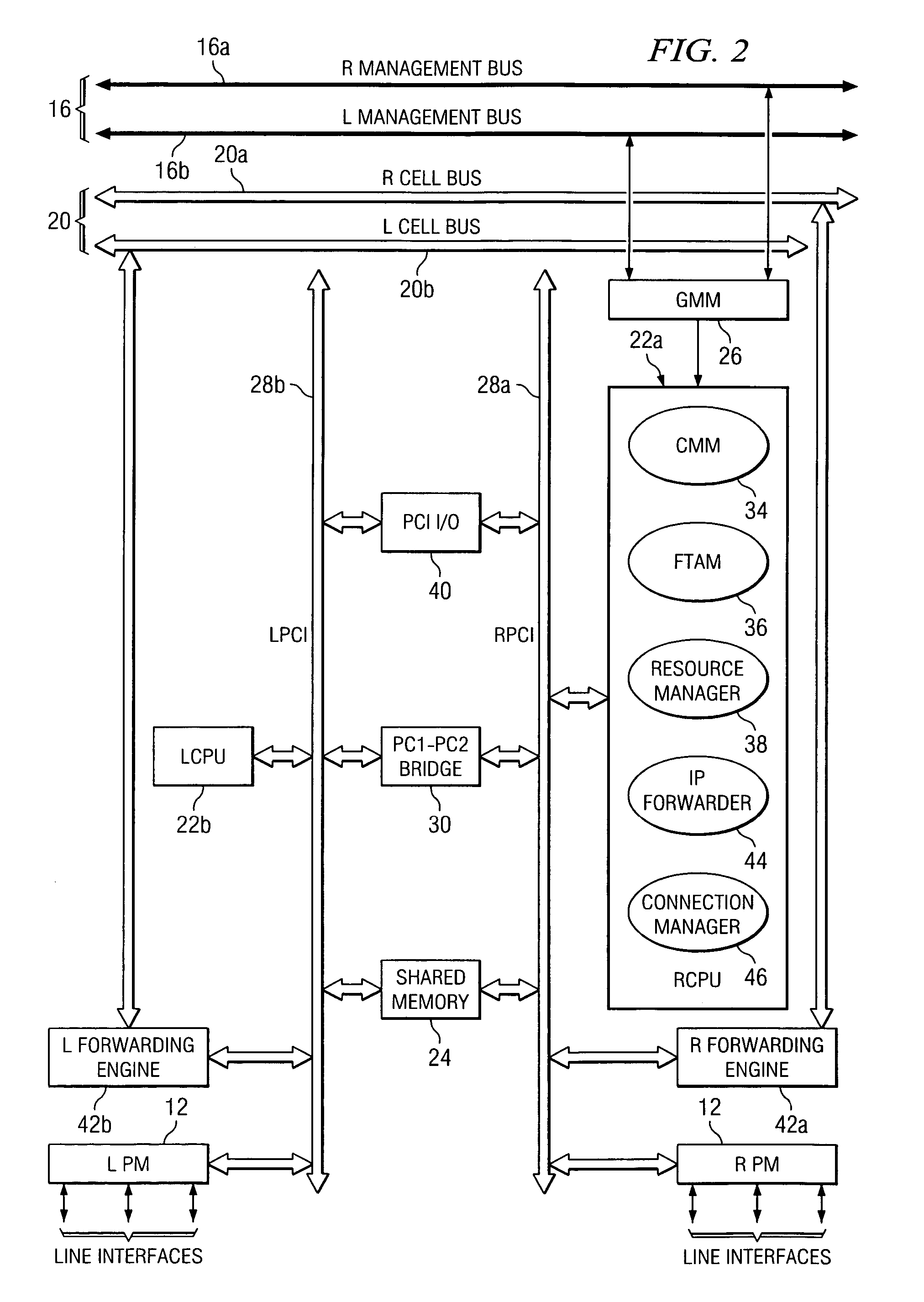
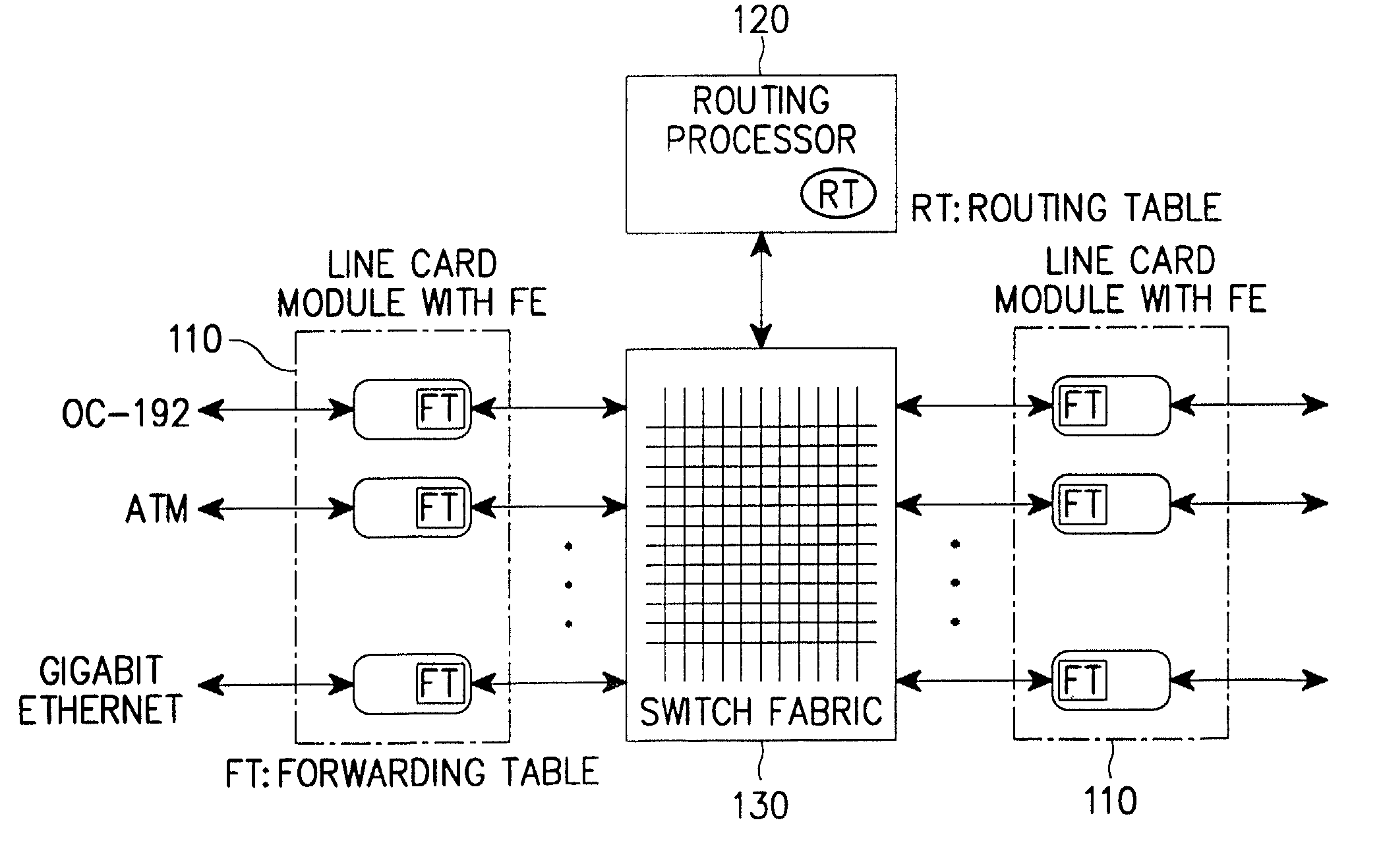
Multi-service network switch
InactiveUS6850531B1Raise priorityReduce dependenceData switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsDomain nameModem device
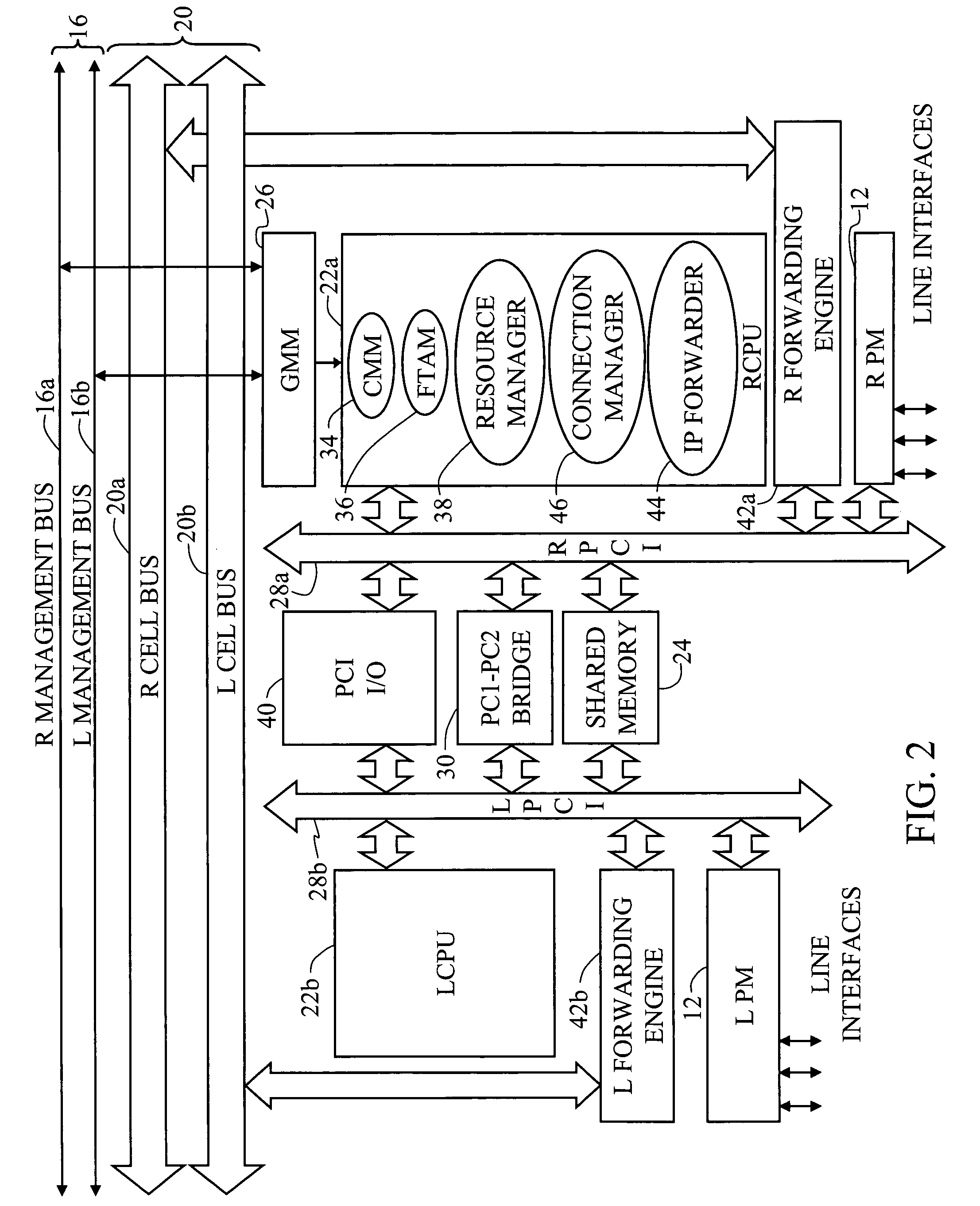
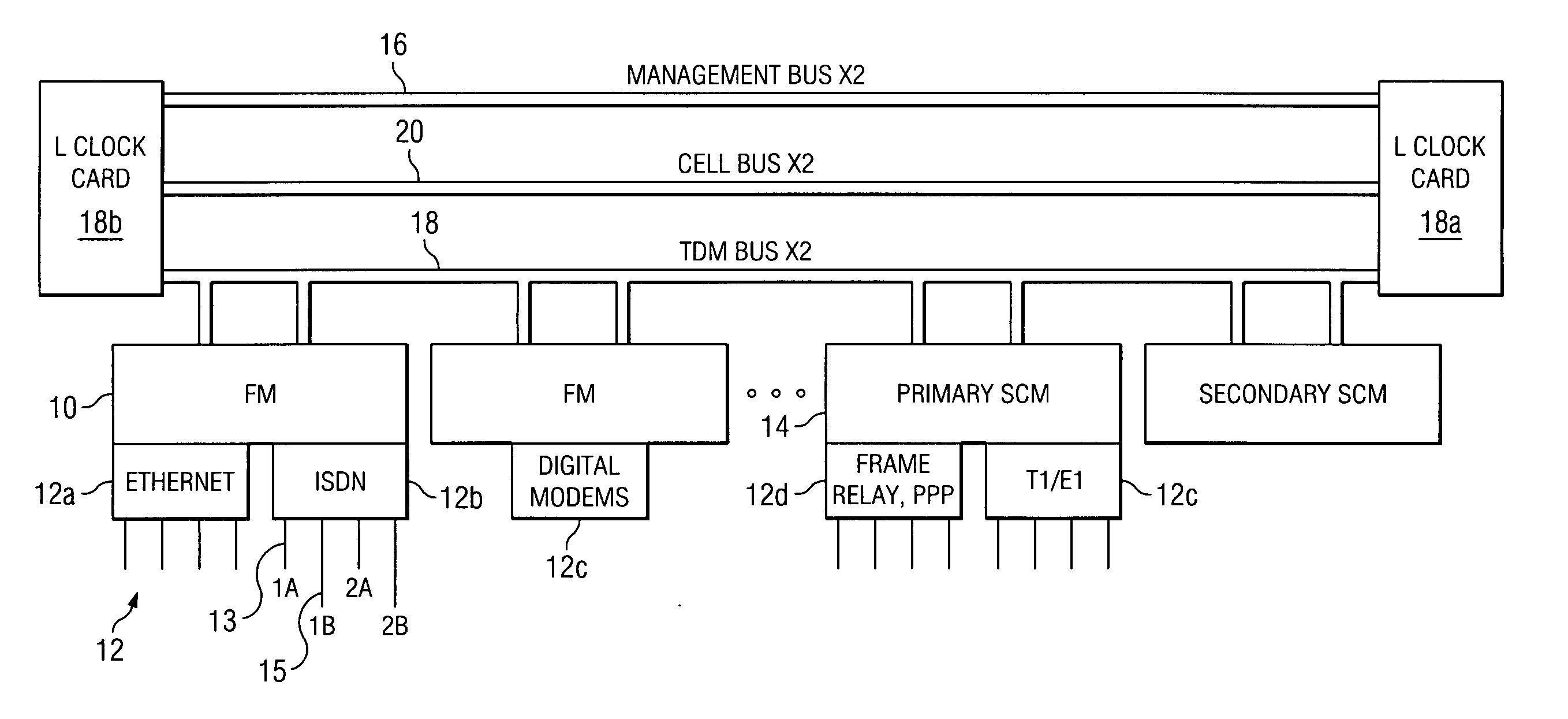
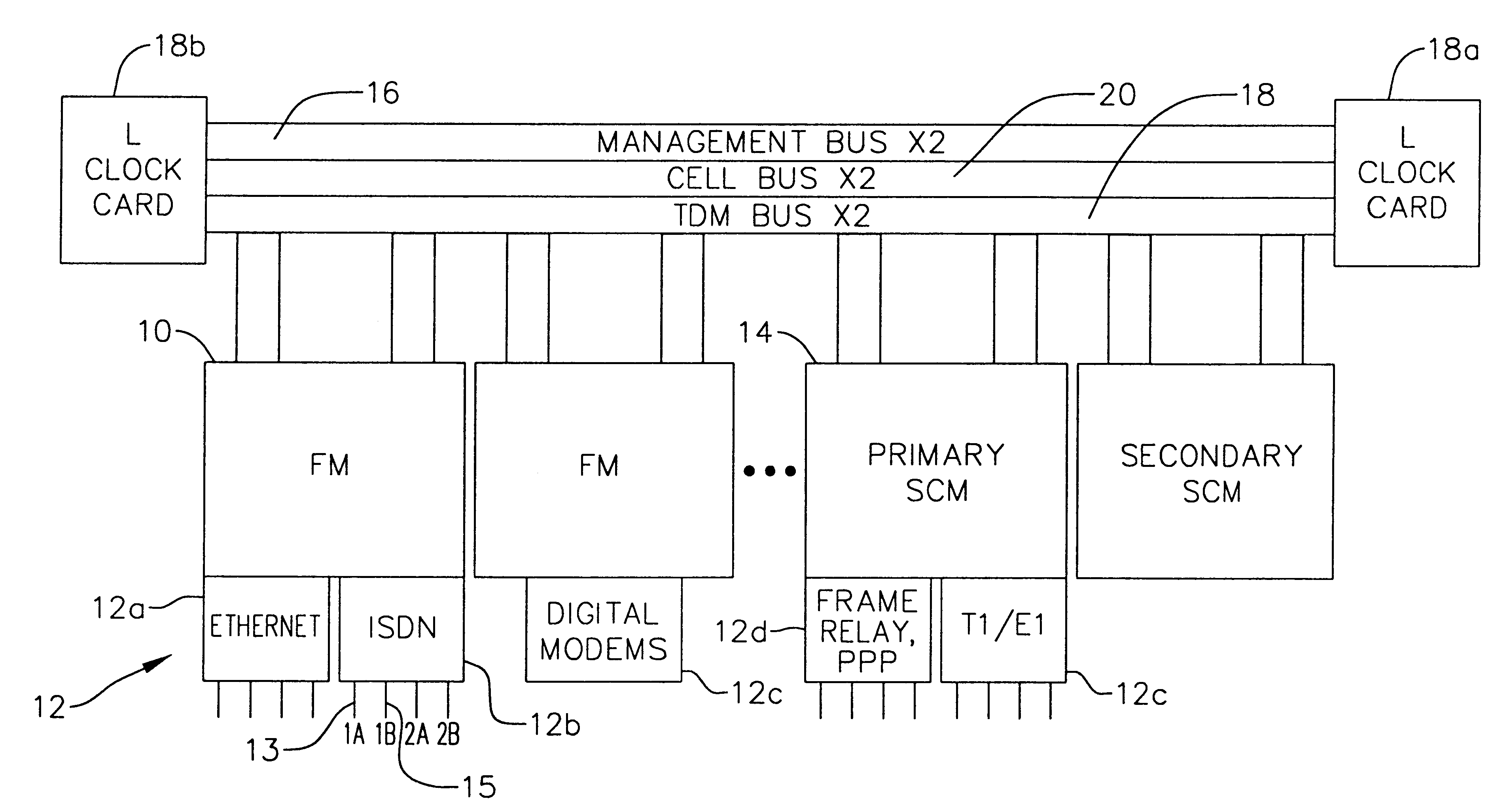
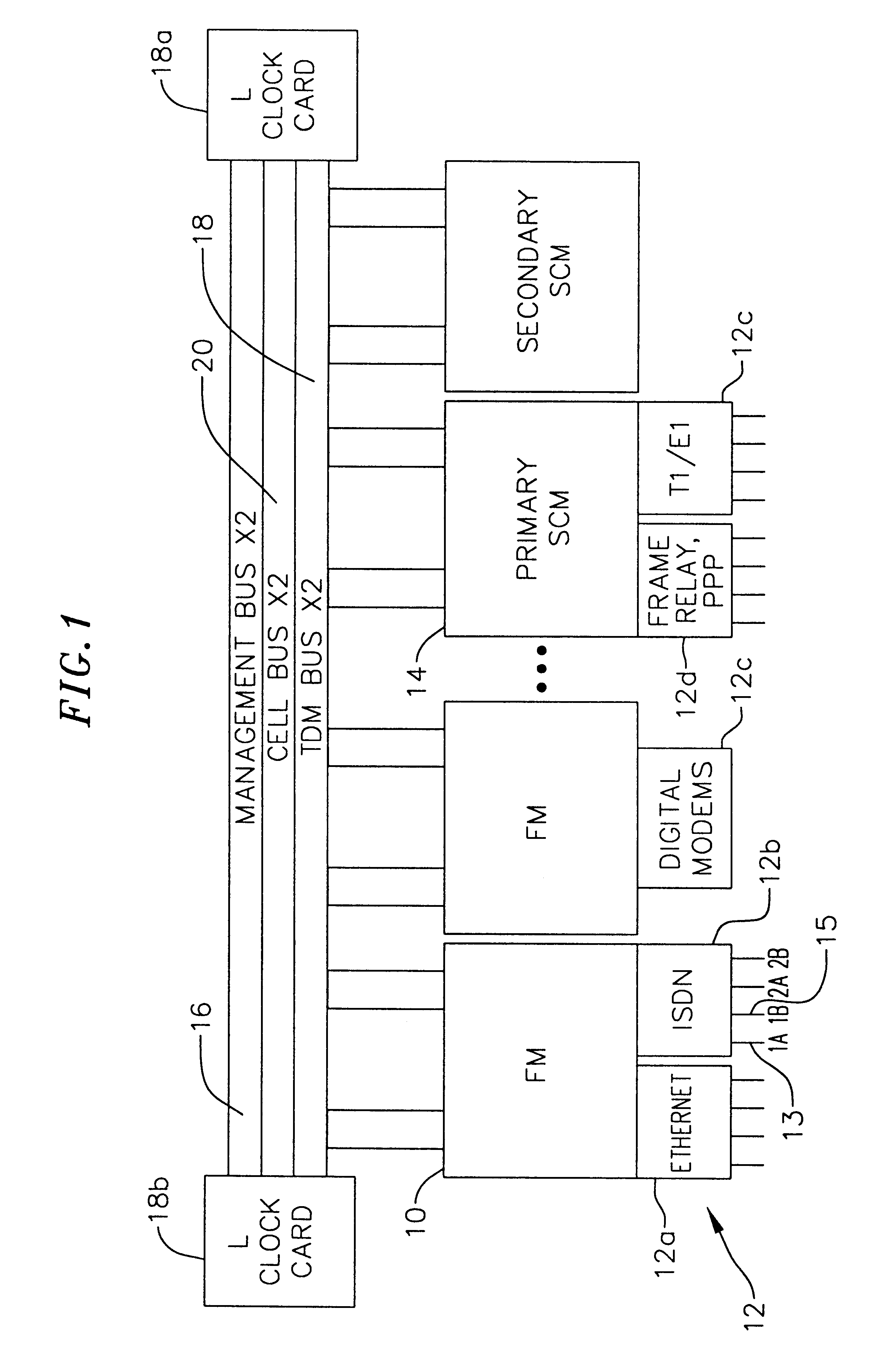
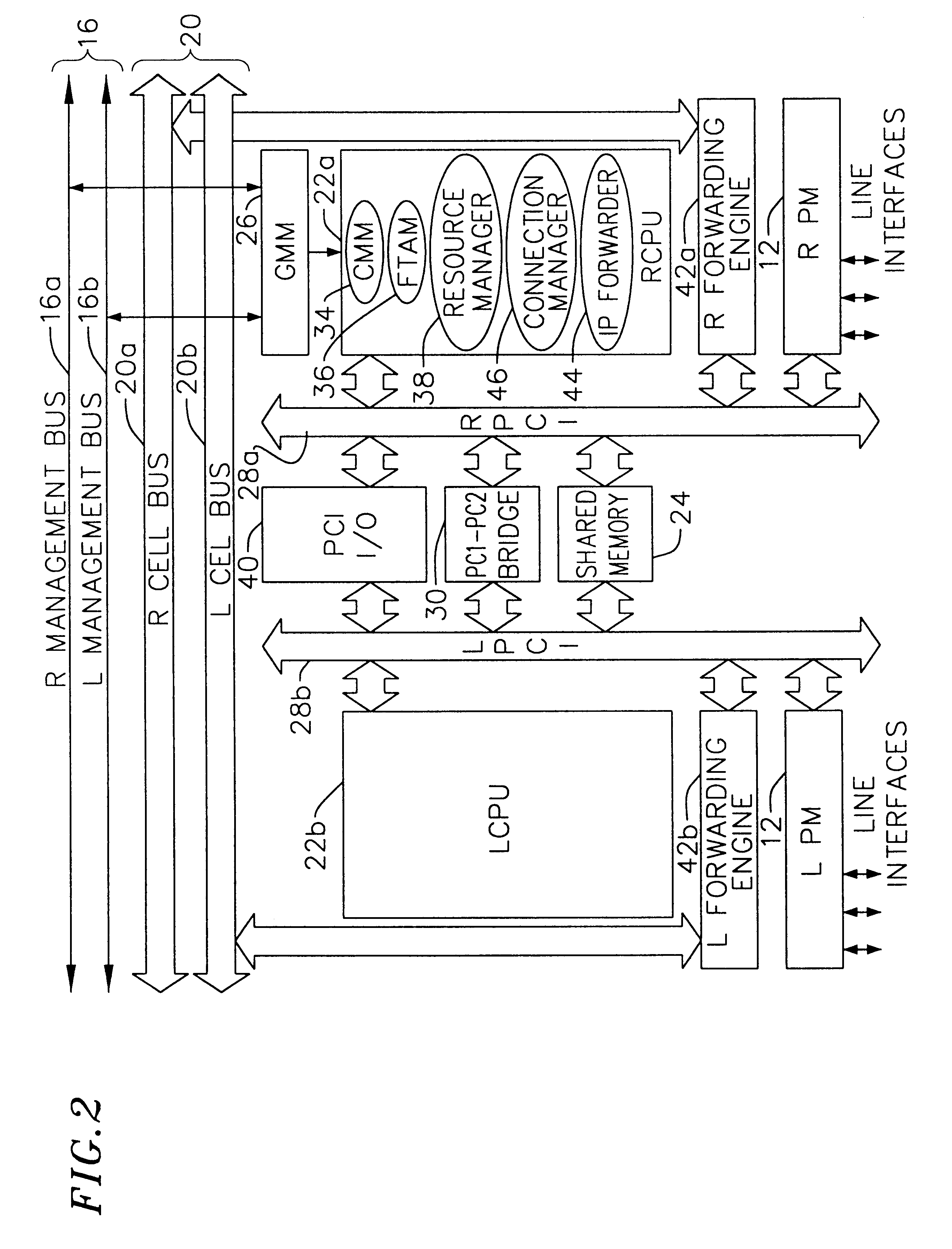
A multi-service network switch capable of providing multiple network services from a single platform. The switch incorporates a distributed packet forwarding architecture where each of the various cards is capable of making independent forwarding decisions. The switch further allows for dynamic resource management for dynamically assigning modem and ISDN resources to an incoming call. The switch may also include fault management features to guard against single points of failure within the switch. The switch further allows the partitioning of the switch into multiple virtual routers where each virtual router has its own set of resources and a routing table. Each virtual router is further partitioned into virtual private networks for further controlling access to the network. The switch supports policy based routing where specific routing paths are selected based on a domain name, a telephone number, and the like. The switch also provides tiered access of the Internet by defining quality of access levels to each incoming connection request. The switch may further support an IP routing protocol and architecture in which the layer two protocols are independent of the physical interface they run on. Furthermore, the switch includes a generic forwarding interface software for hiding the details of transmitting and receiving packets over different interface types.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Routing method for mobile wireless nodes having overlapping internet protocol home addresses
InactiveUS6684256B1Multiple digital computer combinationsWireless network protocolsIp addressWireless data
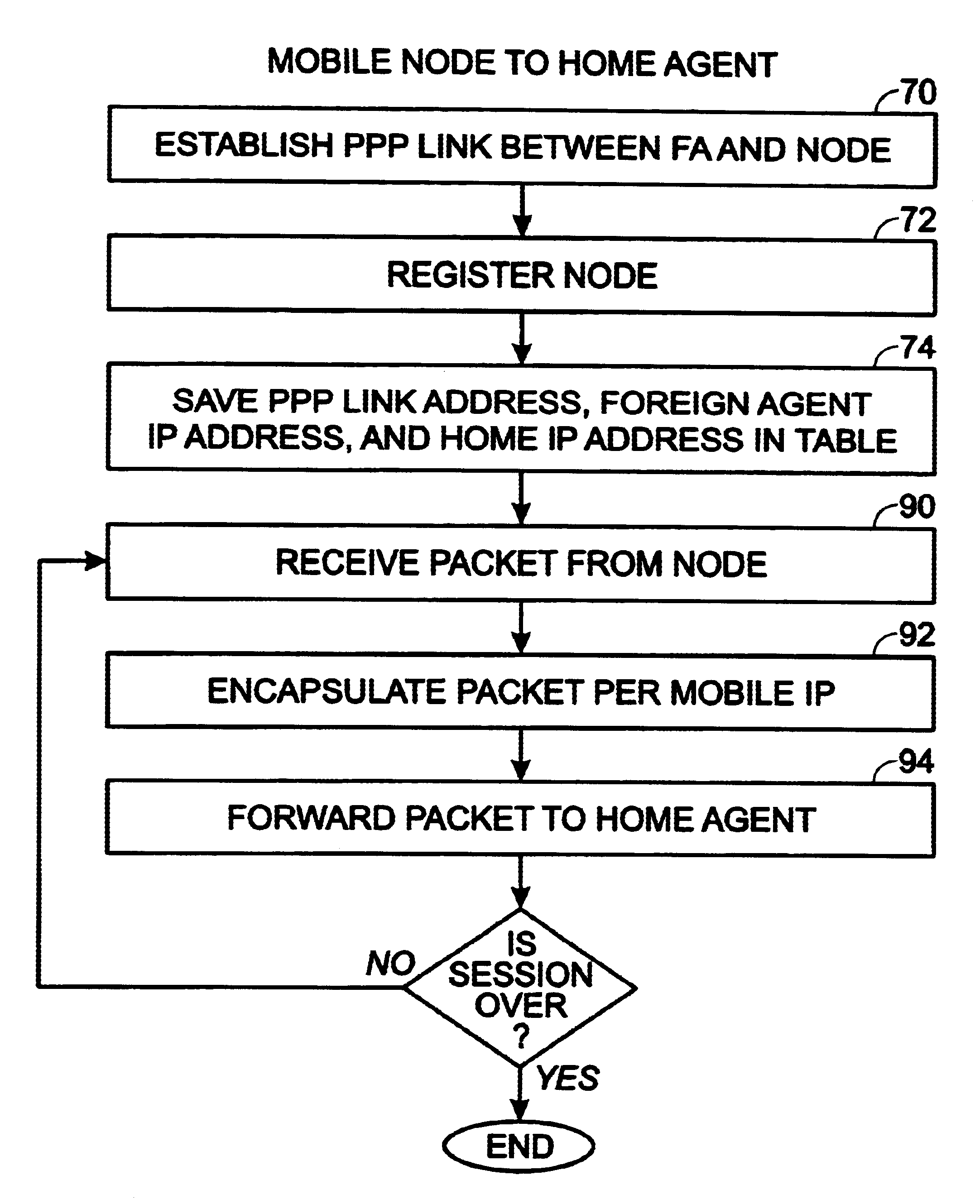
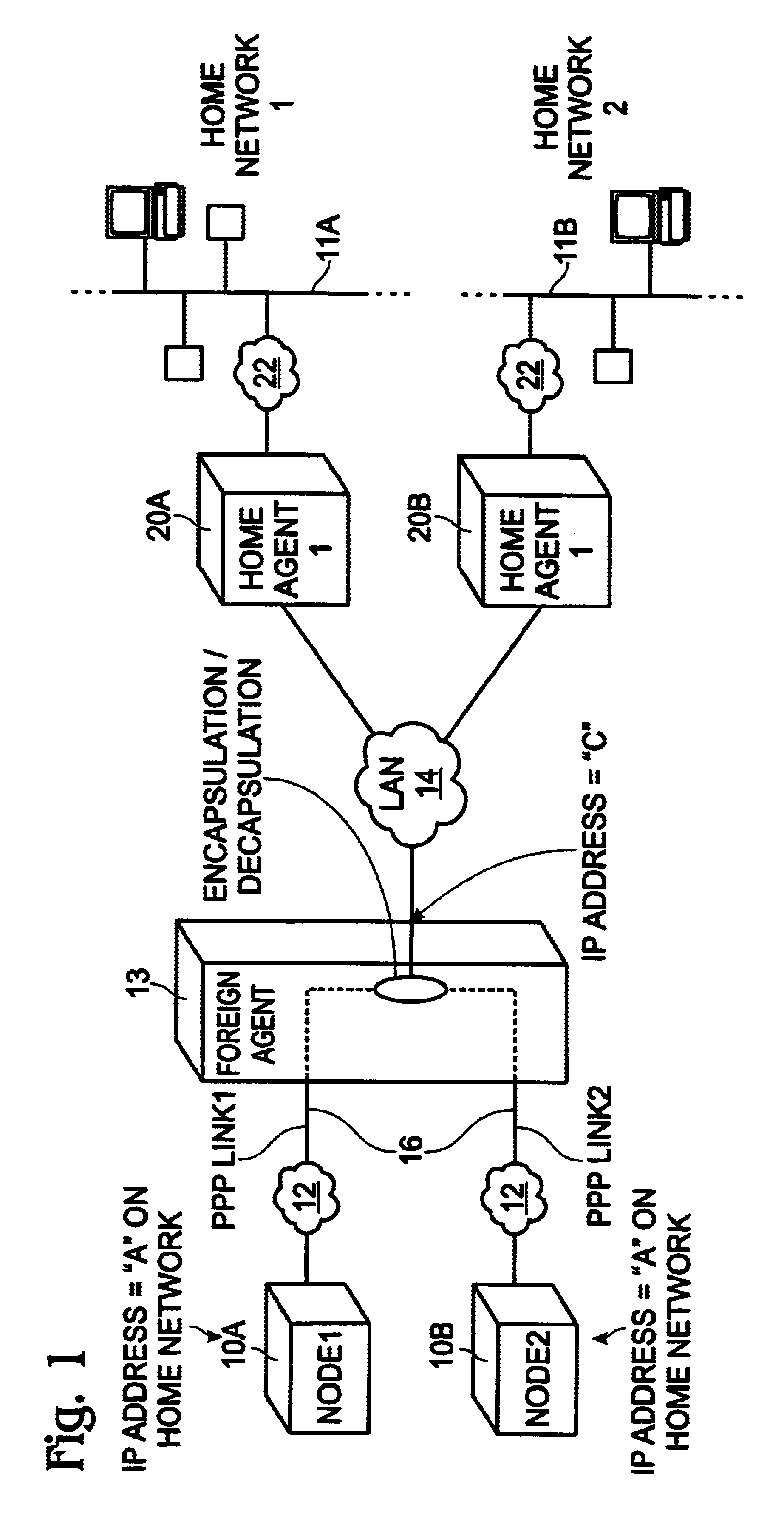
In mobile IP wireless data networking, methods are described for correctly routing packets through a foreign agent to or from wireless nodes where the wireless nodes have the same home network IP address. Instead of using normal IP routing, the foreign agent uniquely identifies the wireless node's home network IP address and home agent IP address with a PPP link address associated with a PPP link between the foreign agent and the wireless node. This association between PPP link addresses, home agent IP addresses, and home network IP addresses, is preferably implemented in software as a table stored in the foreign agent. The routing of packets through the foreign agent to the mobile nodes is performed by reference to the table. The table allows the foreign agent to correctly and efficiently route packets in the situation where multiple wireless nodes are registered with the foreign agent, but more than one of the wireless nodes have the same home network IP address.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
Multi-service network switch with a generic forwarding interface
InactiveUS7116679B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationDomain nameModem device
A multi-service network switch capable of providing multiple network services from a single platform. The switch incorporates a distributed packet forwarding architecture where each of the various cards is capable of making independent forwarding decisions. The switch further allows for dynamic resource management for dynamically assigning modem and ISDN resources to an incoming call. The switch may also include fault management features to guard against single points of failure within the switch. The switch further allows the partitioning of the switch into multiple virtual routers where each virtual router has its own set of resources and a routing table. Each virtual router is further partitioned into virtual private networks for further controlling access to the network. The switch's supports policy based routing where specific routing paths are selected based a domain name, a telephone number, and the like. The switch also provides tiered access of the Internet by defining quality of access levels to each incoming connection request. The switch may further support an IP routing protocol and architecture in which the layer two protocols are independent of the physical interface they run on. Furthermore, the switch includes a generic forwarding interface software for hiding the details of transmitting and receiving packets over different interface types.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Name-based routing system and method
Owner:128 TECH
Multi-service network switch with independent protocol stack architecture
InactiveUS20050180429A1Reduce bottlenecksImprove throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexDomain nameRouting table
A multi-service network switch capable of providing multiple network services from a single platform. The switch incorporates a distributed packet forwarding architecture where each of the various cards is capable of making independent forwarding decisions. The switch further allows for dynamic resource management for dynamically assigning modem and ISDN resources to an incoming call. The switch may also include fault management features to guard against single points of failure within the switch. The switch further allows the partitioning of the switch into multiple virtual routers where each virtual router has its own wet of resources and a routing table. Each virtual router is further partitioned into virtual private networks for further controlling access to the network. The switch's supports policy based routing where specific routing paths are selected based a domain name, a telephone number, and the like. The switch also provides tiered access of the Internet by defining quality of access levels to each incoming connection request. The switch may further support an IP routing protocol and architecture in which the layer two protocols are independent of the physical interface they run on. Furthermore, the switch includes a generic forwarding interface software for hiding the details of transmitting and receiving packets over different interface types.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
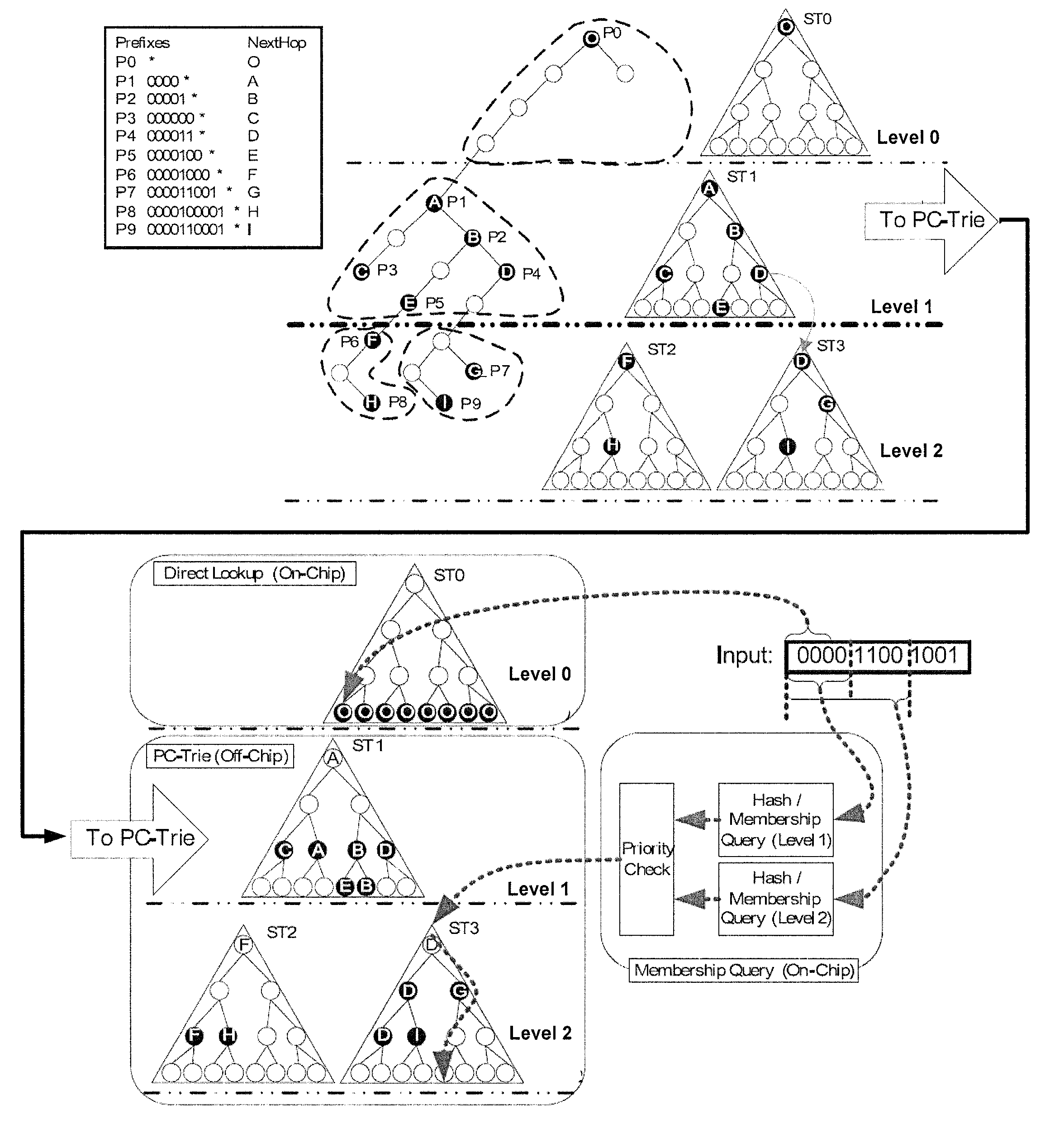
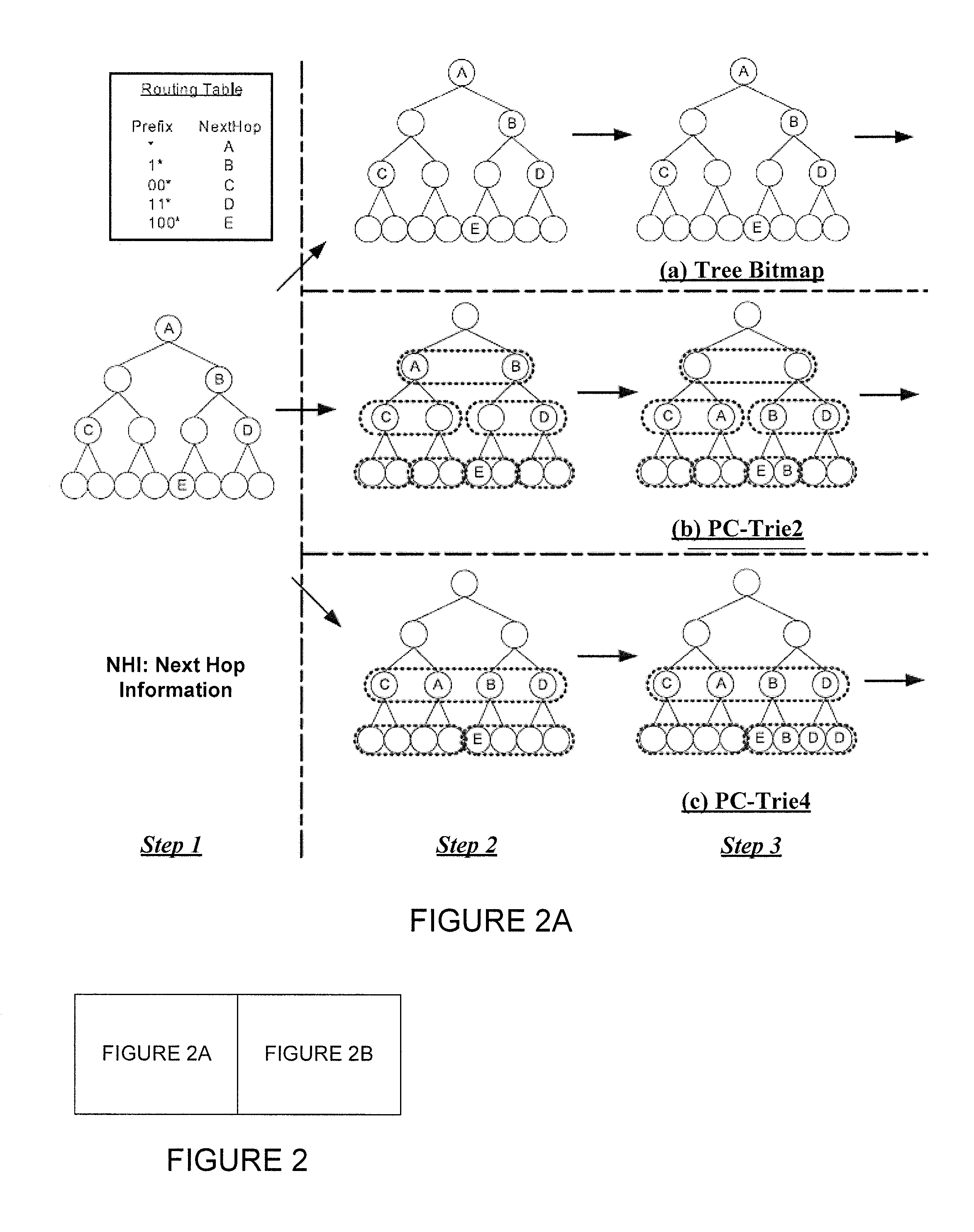
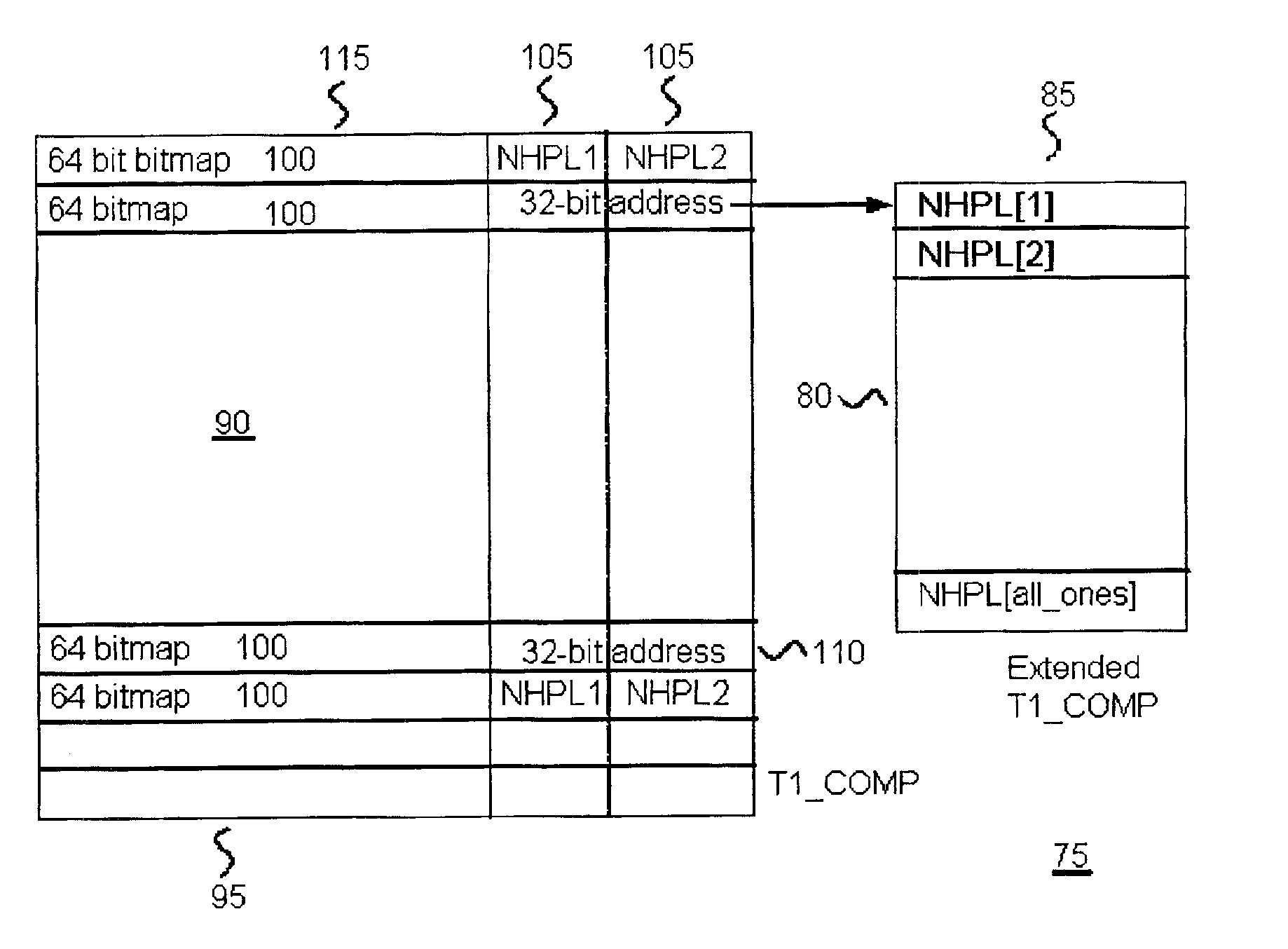
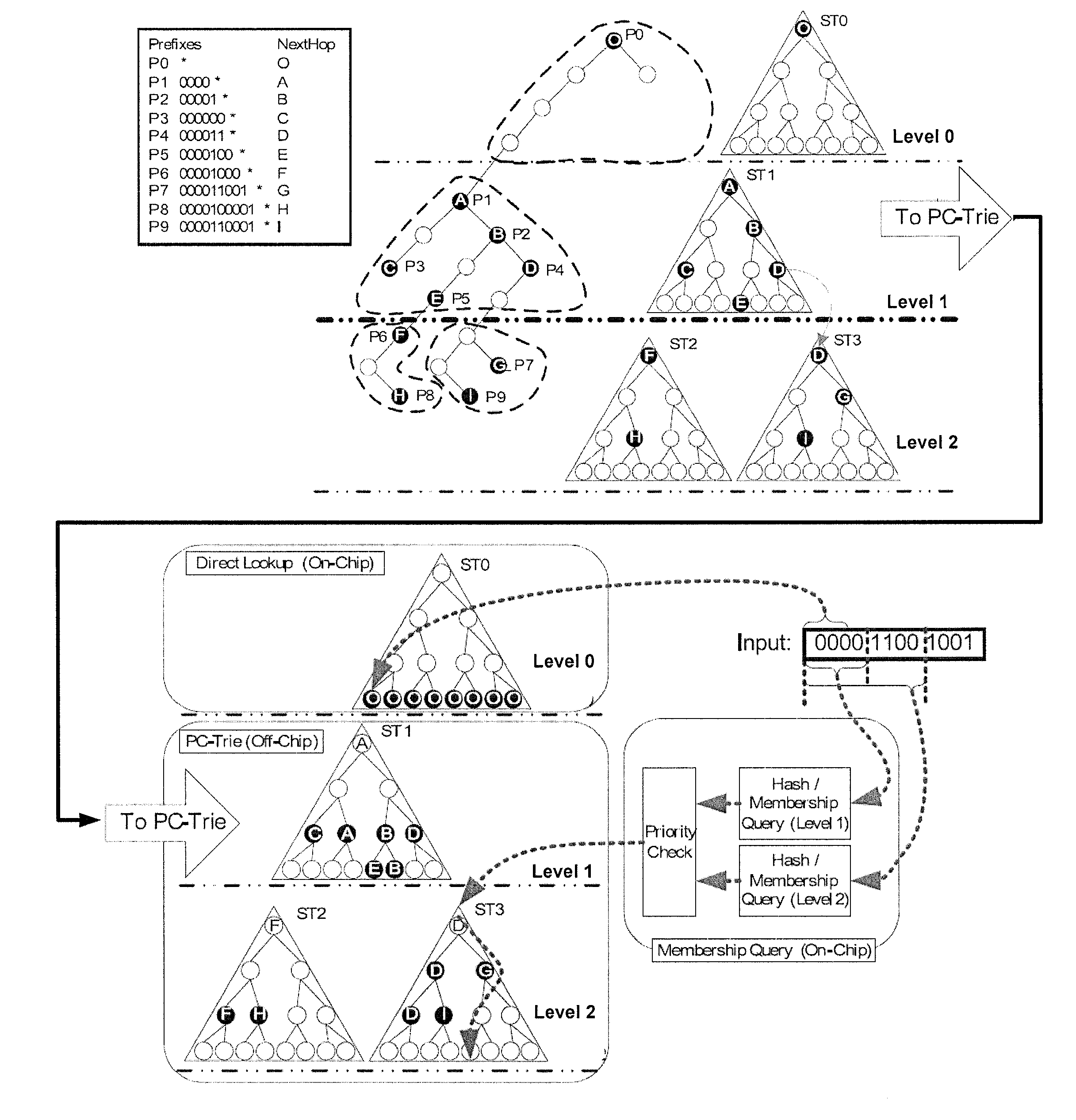
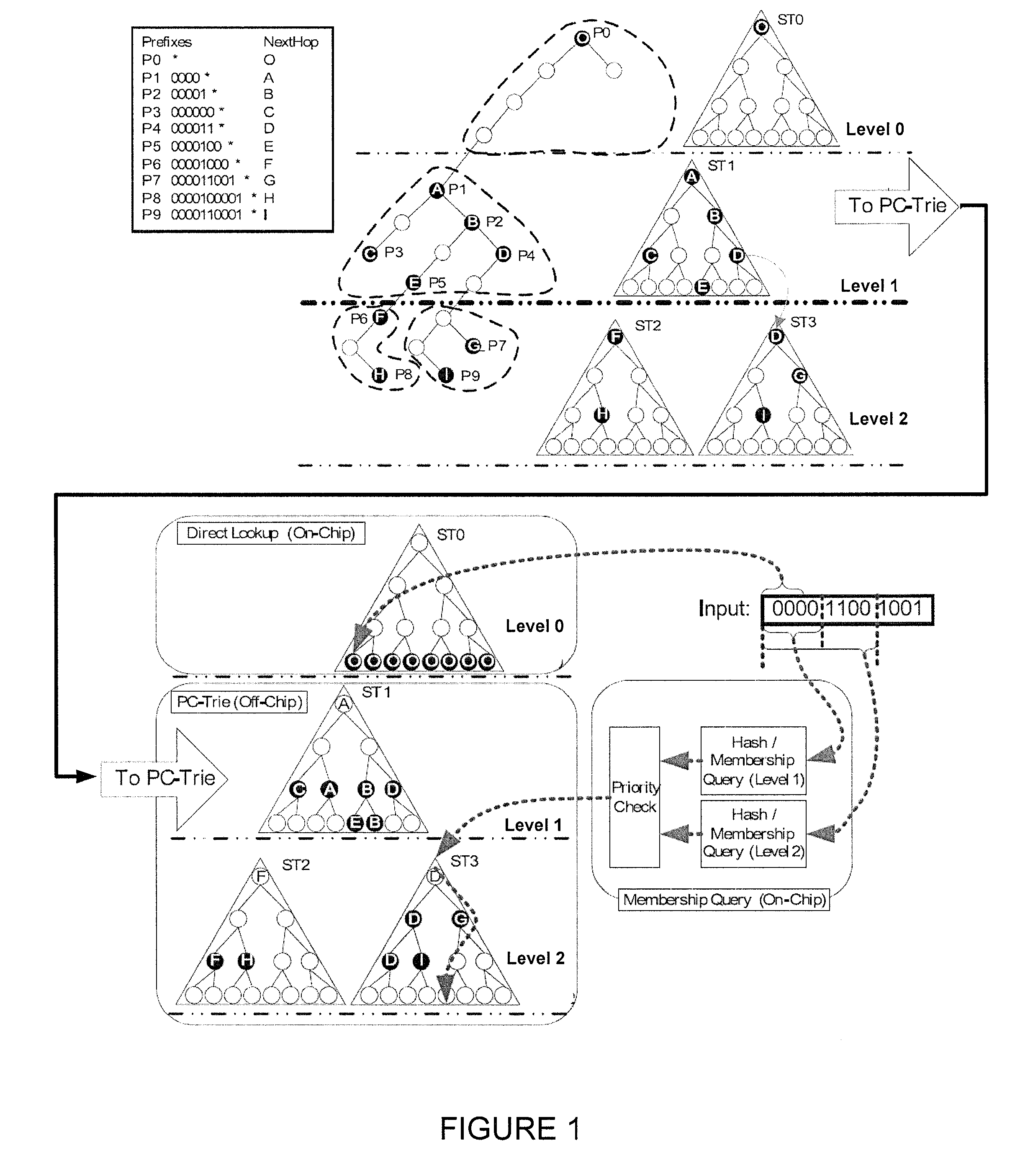
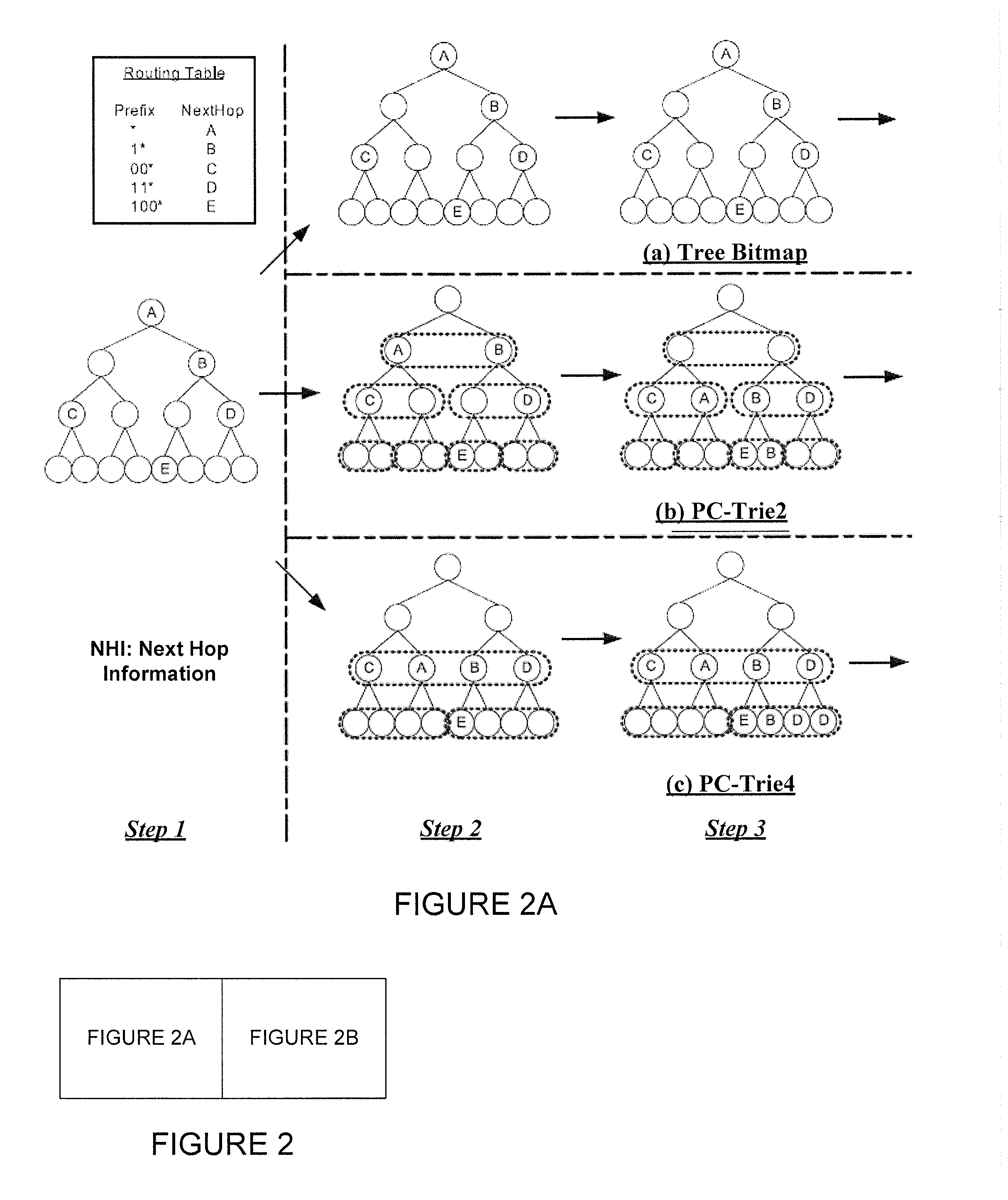
Hash-based prefix-compressed trie for IP route lookup
InactiveUS20110128959A1Data switching by path configurationDistributed computingIP forwarding algorithm
A method and apparatus for performing an Internet Protocol (IP) network lookup in a forwarding device including an internal processor memory storing a first next hop information table and membership query information, and an external processor memory storing a plurality of prefix-compressed trees and a second next hop information table is described. In another embodiment consistent with present invention, a method (and apparatus) for creating stored data structures representing network forwarding information used for network route lookup is described.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
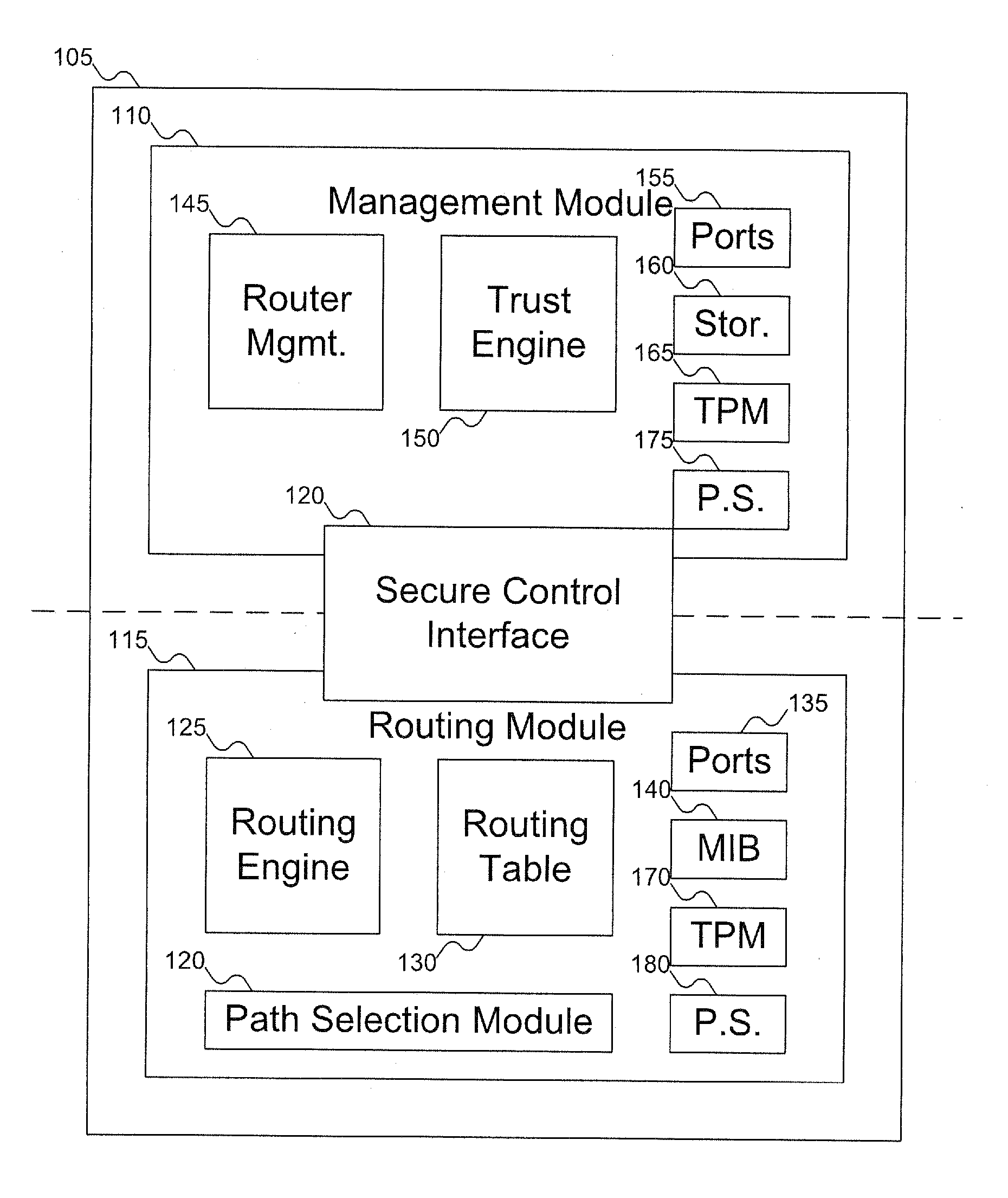
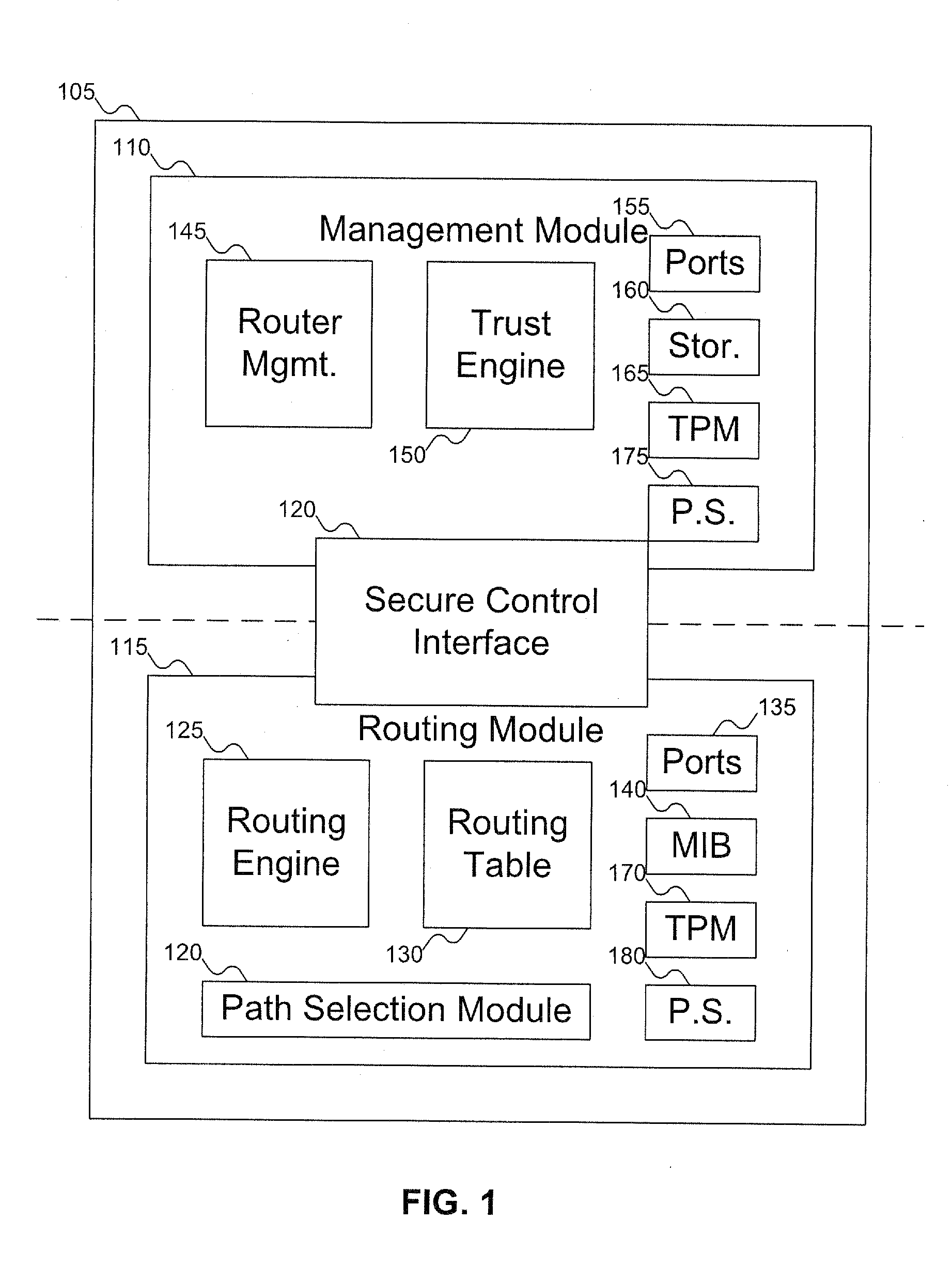
Method and apparatus to establish routes based on the trust scores of routers within an IP routing domain
InactiveUS20070180495A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareTrust score
A router includes a management module and a routing module. The routing module can be used to route data around a network. The management module can be used to manage the operation of the routing module, including generating an integrity report for the router, which can be used to generate a trust report for the router. The trust report can include an integrity / trust score for the router. The management module can control the routing module via a secure control interface.
Owner:KIP SIGN P1 +1
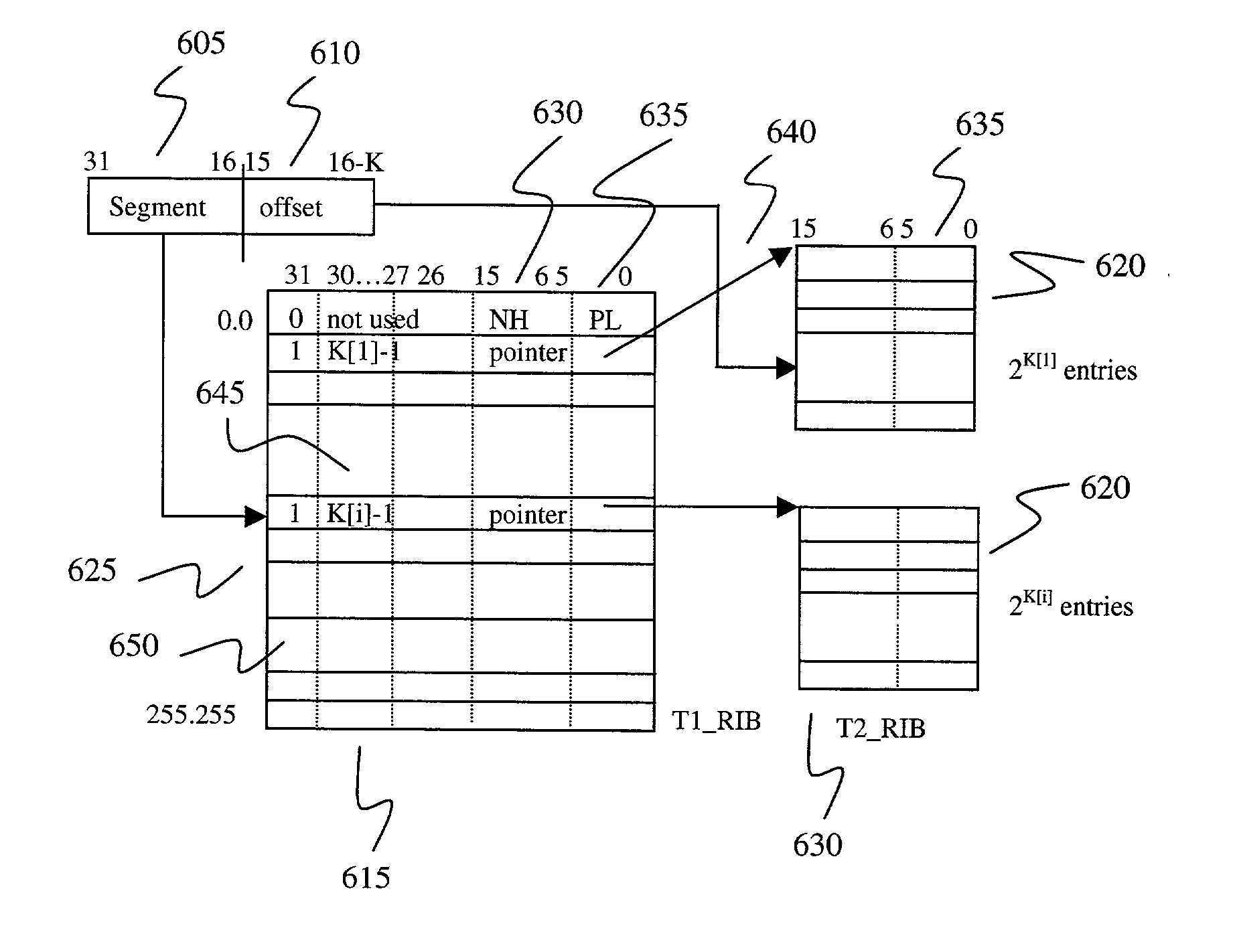
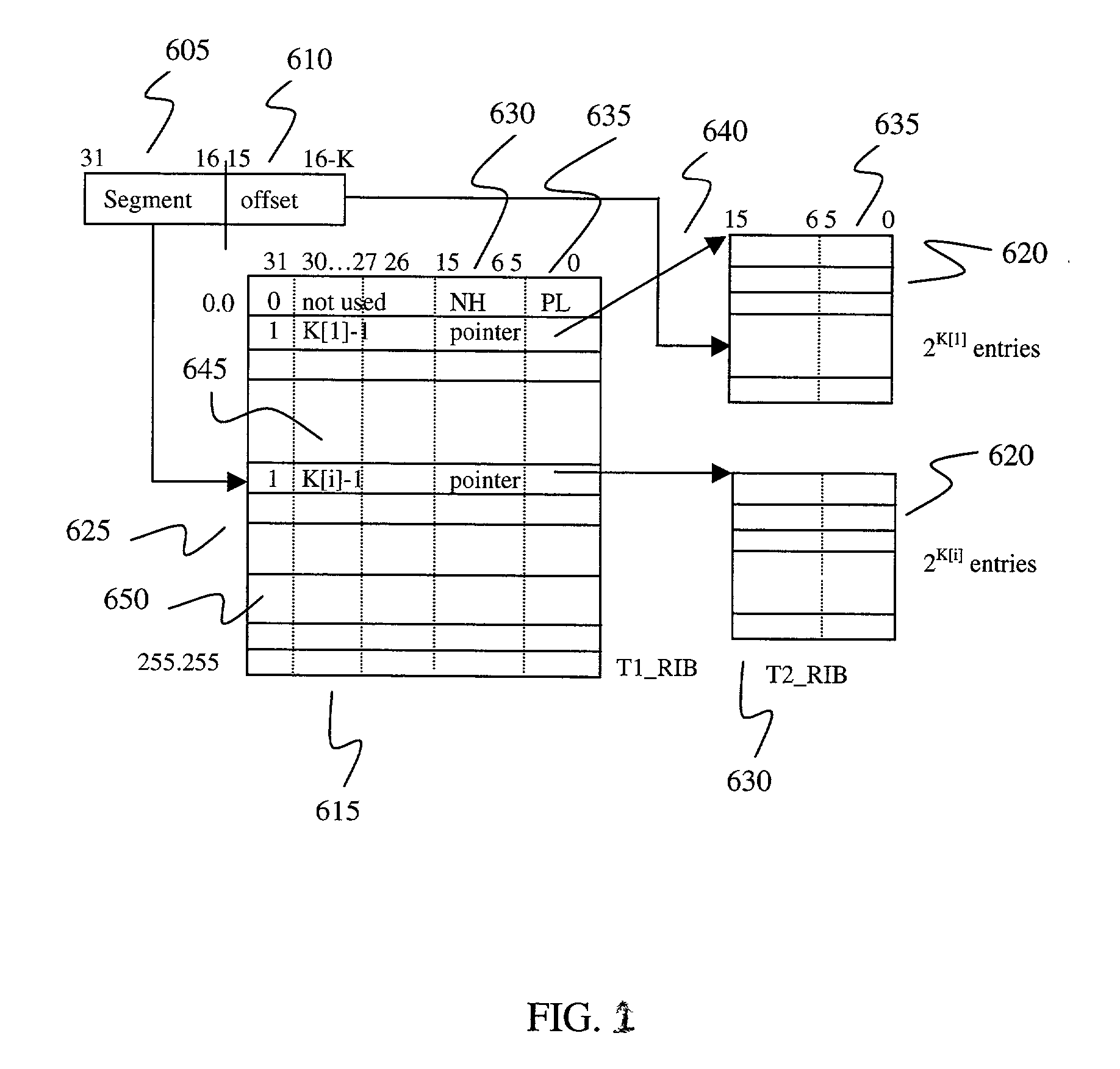
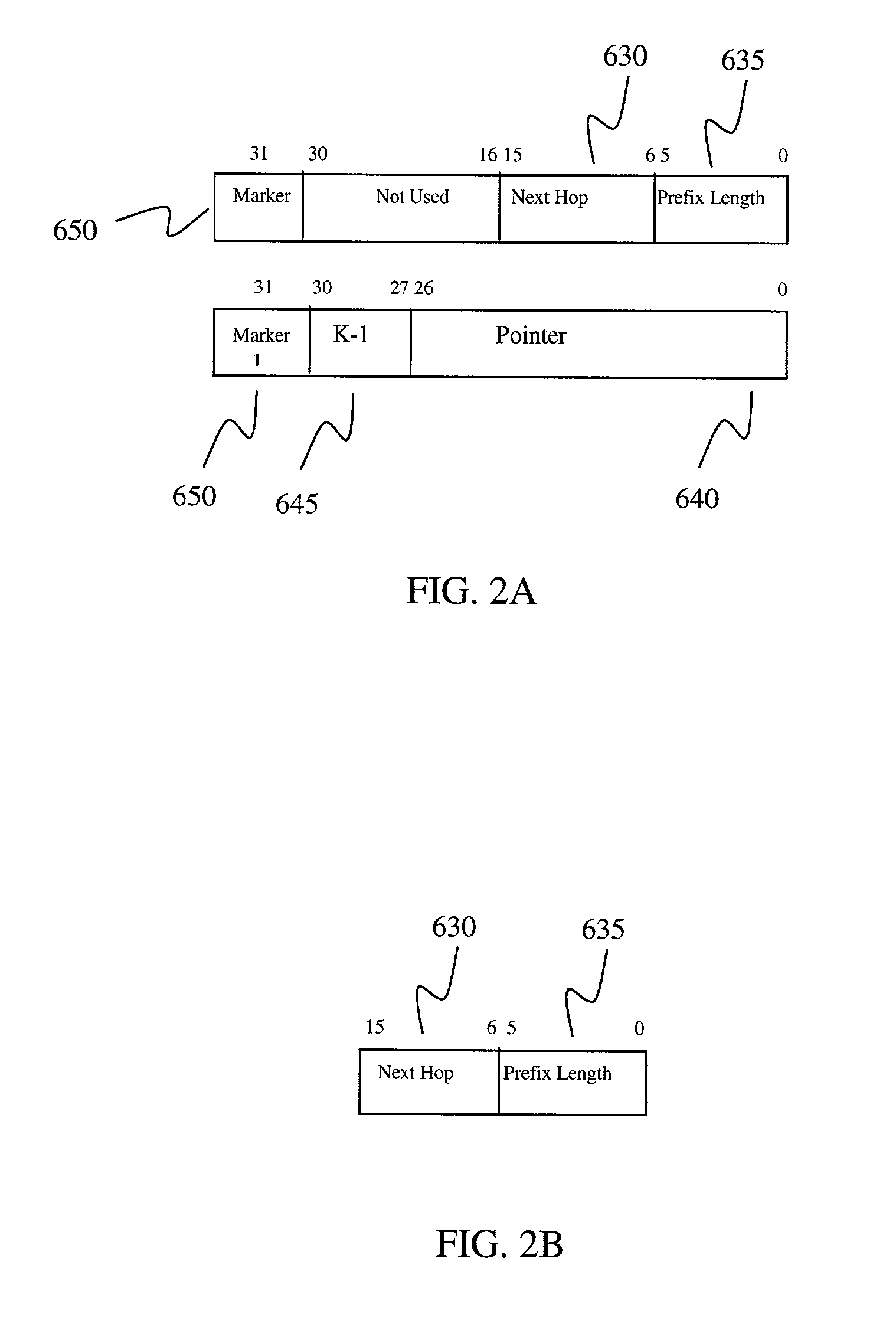
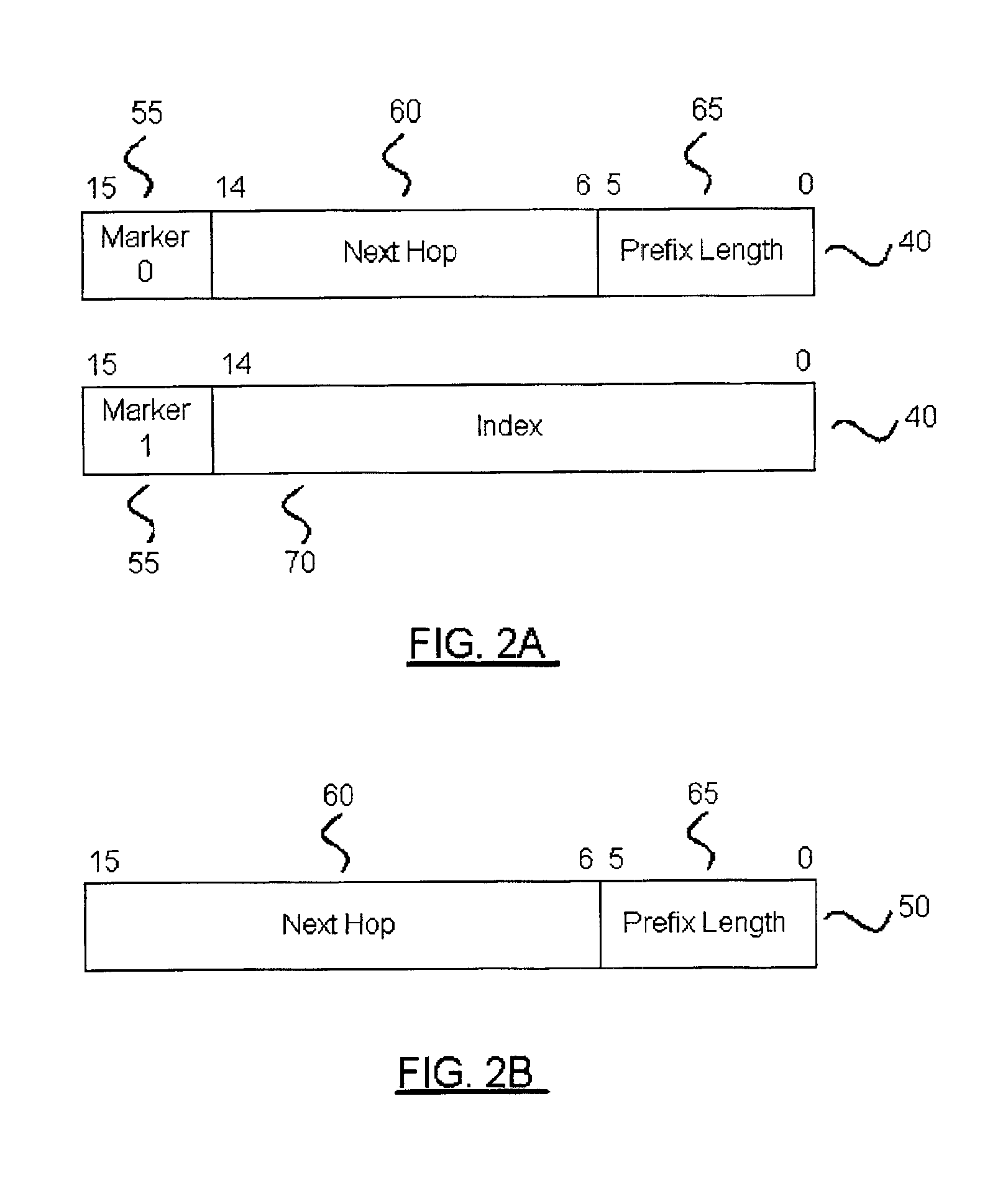
Fast IP route lookup with 16/K and 16/Kc compressed data structures
InactiveUS20020172203A1Data switching by path configurationOther databases indexingPresent dayArray data structure
An advanced data structure allows lookup based upon the most significant 16 bits and the following variable number of K bits of the IP destination address. This 16 / K scheme requires less than 2 MB memory to store the whole routing tables of present day backbone routers. A 16 / Kc version utilizes bitmaps to compress the table to less than 0.5 MB. For the 16 / K data structure each route lookup requires at most 2 memory accesses while the 16 / Kc requires at most 3 memory accesses. By configuring the processor properly and developing a few customized instructions to accelerate route lookup, one can achieve 85 million lookups per second (MLPS) in the typical case with the processor running at 200 MHz. Further, the lookup method can be implemented using pipelining techniques to perform three lookups for three incoming packets simultaneously. Using such techniques, 100 MLPS performance can be achieved.
Owner:TESILICA
Apparatus and method for performing high-speed IP route lookup and managing routing/forwarding tables
InactiveUS7031320B2Minimizing memory access timeUtilization of memoryData switching by path configurationSkip listMaximum level
A method for constructing routing / forwarding tables for an IP address lookup using a skip list. The method comprises dividing a prefix length range of an IP address in a preset method; creating a header node having a maximum level based on a number of clusters divided into the prefix length range, the header node pointing every node in the skip list; and creating subnodes by the number of the divided clusters, the subnodes each having the divided prefix length range as a key.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for realizing equal cost multipath of IP route and device
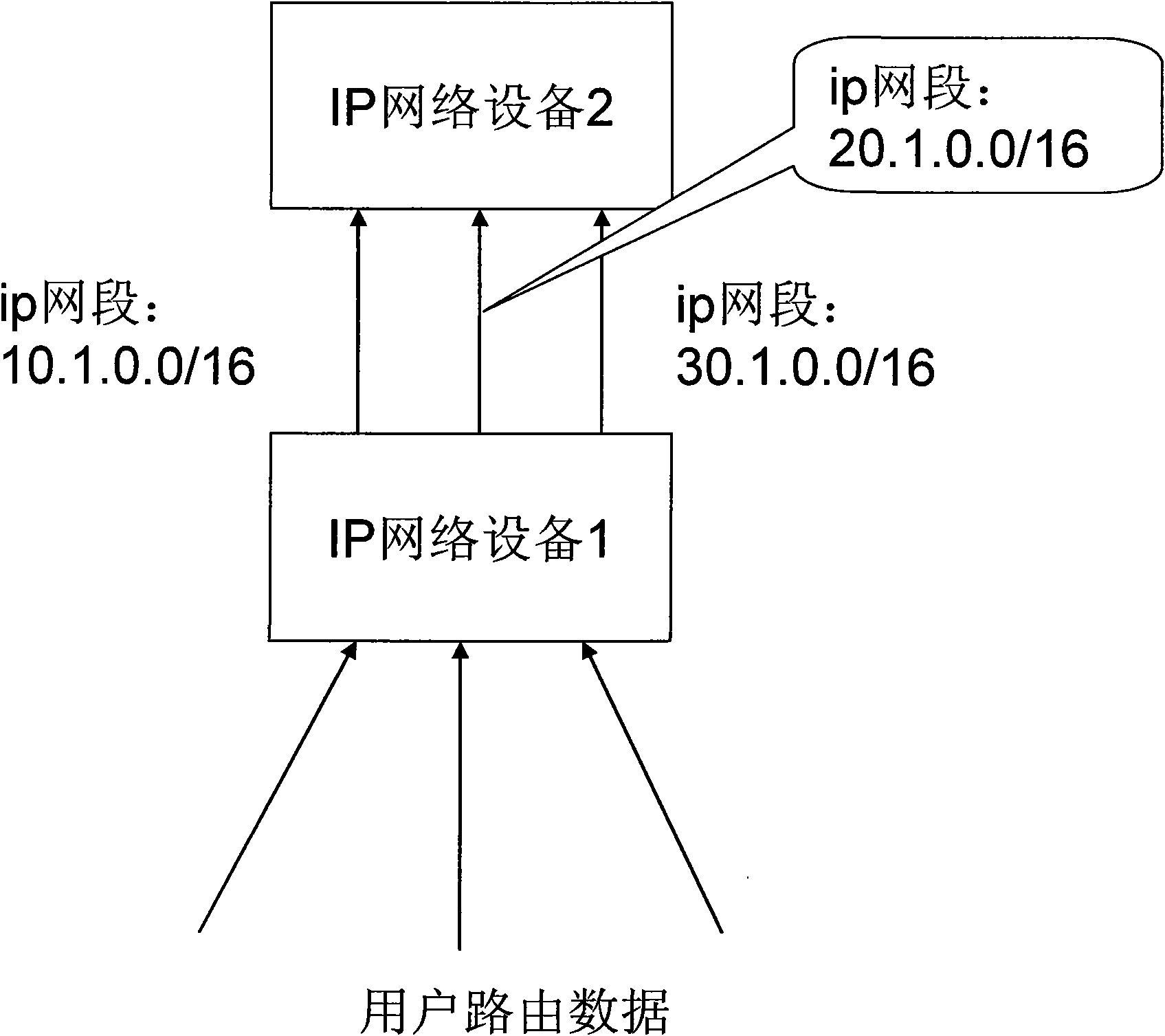
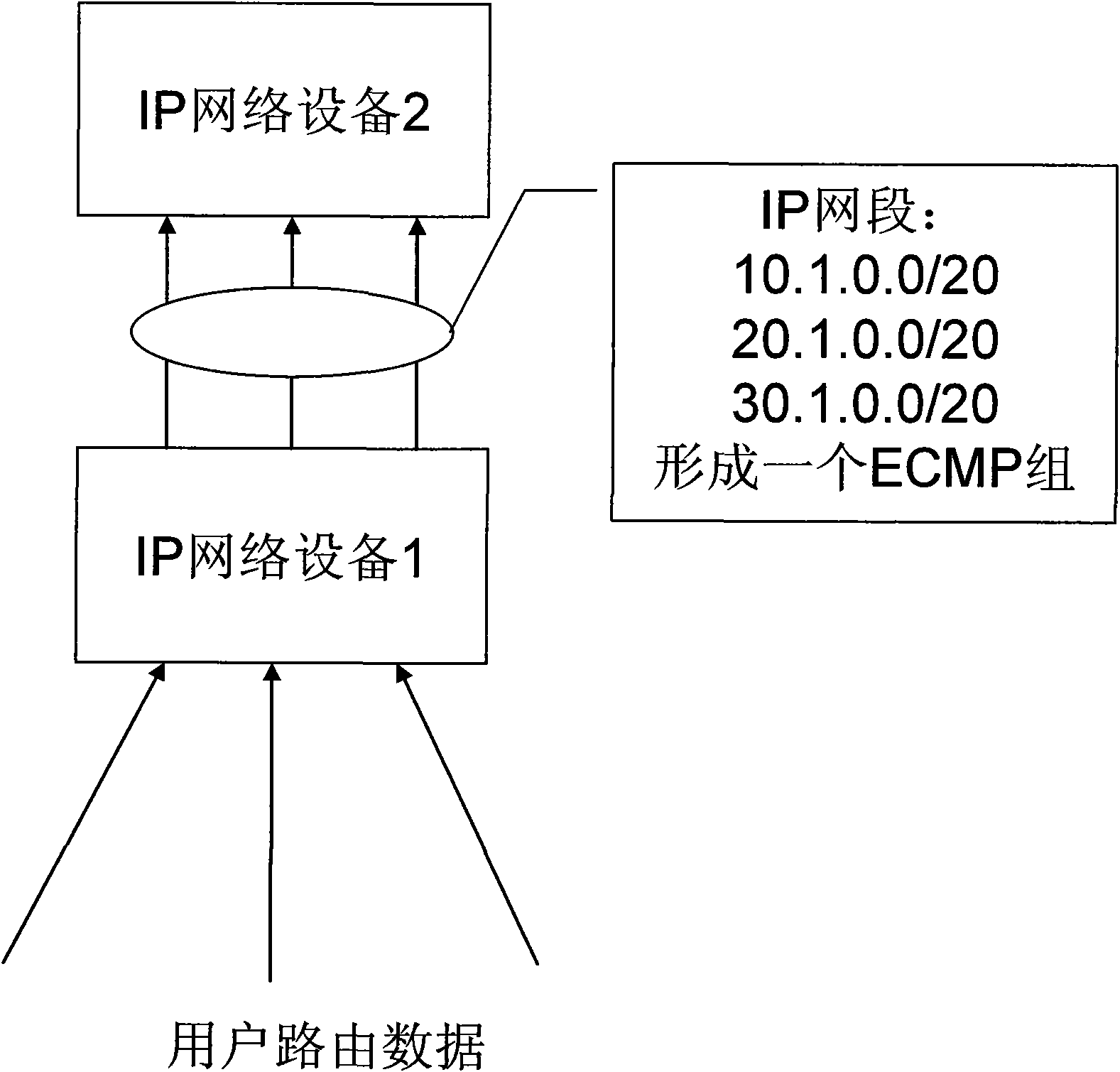
ActiveCN101572667ASolve the problem of routing load sharingEasy to routeData switching networksIp addressTerminal equipment
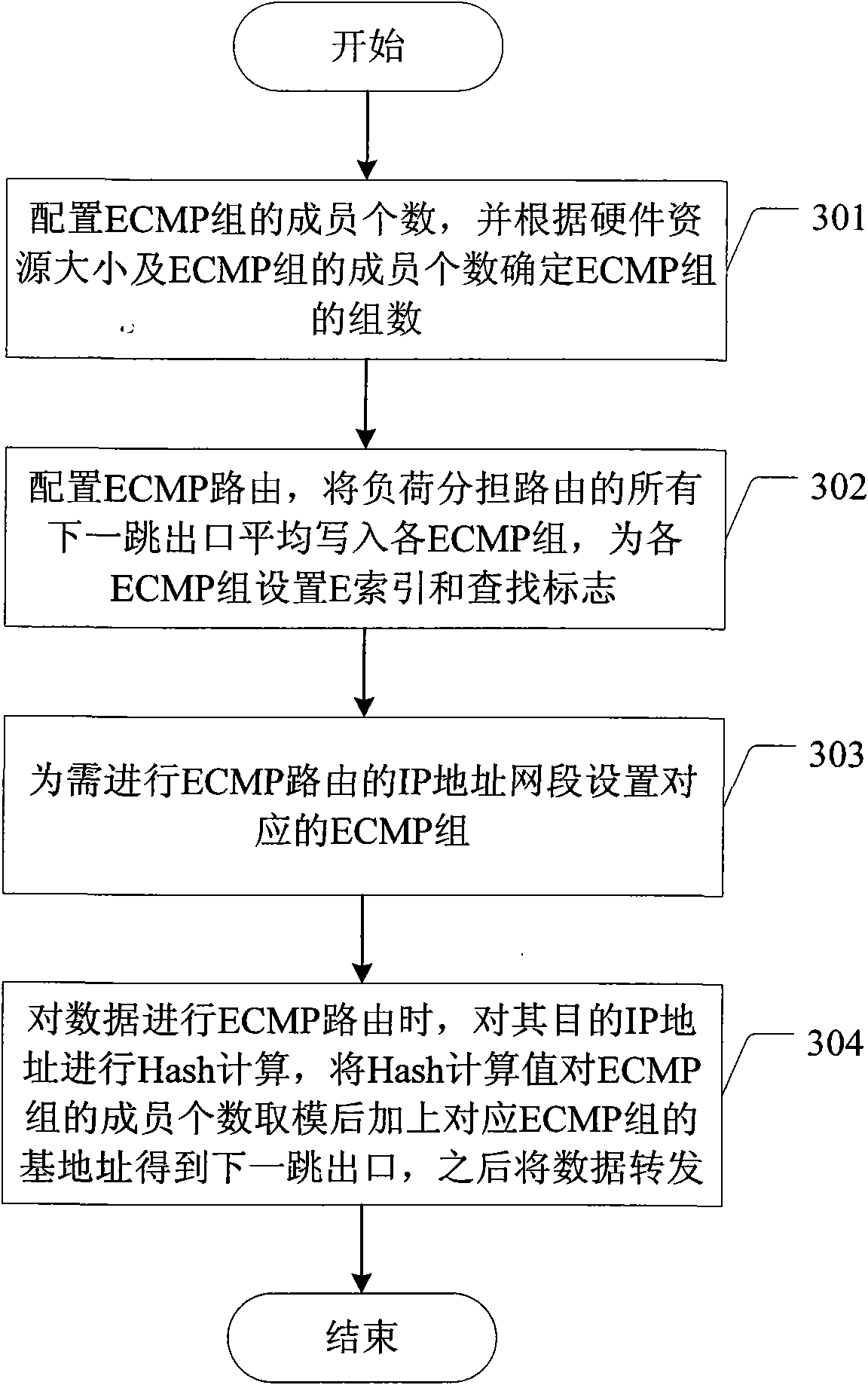
The invention discloses a method for realizing equal cost multipath of IP route and a device; wherein the device comprises an ECMP group generation module, a route ECMP configuration module, a route ECMP searching module; the corresponding method has the following steps: the ECMP group generation module configures the number of members of the ECMP group and determines the number of groups of the ECMP group; the route ECMP configuration module averagely writes all next hop outlets of a load sharing module into the ECMP groups and sets corresponding ECMP groups for IP address network segments which need ECMP routing; when ECMP routing is carried out on data, the route ECMP searching module carries out Hash calculation on target IP addresses of the data, and then uses the Hash calculation values to carry out modulo on the number of members of the ECMP groups and adds base addresses of the ECMP groups corresponding to the data to obtain the next hop outlet, and finally transfers the data from the next hop outlet. With the method and the device of the invention adopted, data can be conveniently, flexibly and uniformly routed to opposite terminal equipment.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Multi-service network switch with modem pool management
A multi-service network switch capable of providing multiple network services from a single platform. The switch incorporates a distributed packet forwarding architecture where each of the various cards is capable of making independent forwarding decisions. The switch further allows for dynamic resource management for dynamically assigning modem and ISDN resources to an incoming call. The switch may also include fault management features to guard against single points of failure within the switch. The switch further allows the partitioning of the switch into multiple virtual routers where each virtual router has its own wet of resources and a routing table. Each virtual router is further partitioned into virtual private networks for further controlling access to the network. The switch supports policy based routing where specific routing paths are selected based on a domain name, a telephone number, and the like. The switch also provides tiered access of the Internet by defining quality of access levels to each incoming connection request. The switch may further support an IP routing protocol and architecture in which the layer two protocols are independent of the physical interface they run on. Furthermore, the switch includes a generic forwarding interface software for hiding the details of transmitting and receiving packets over different interface types.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
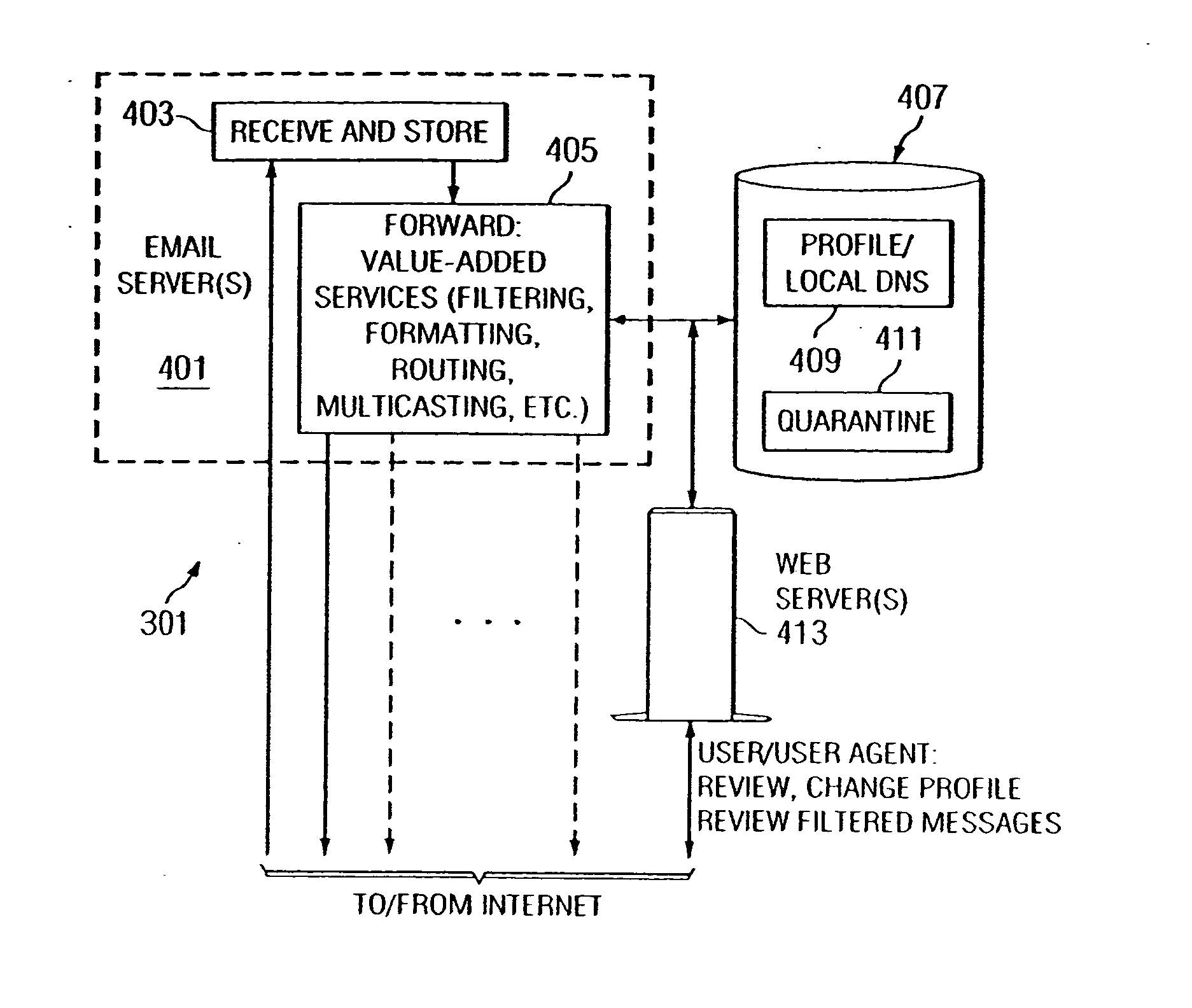
E-mail filtering services and e-mail service enrollment techniques
Disclosed are methods of managing the delivery, including in certain cases the blocking, of electronic messages based at least in part on an electronic message's IP routing information. Also disclosed are methods of managing electronic messages with an intermediate service and the quarantining and user management of quarantined electronic messages and user profiles for the electronic messaging delivery parameters.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
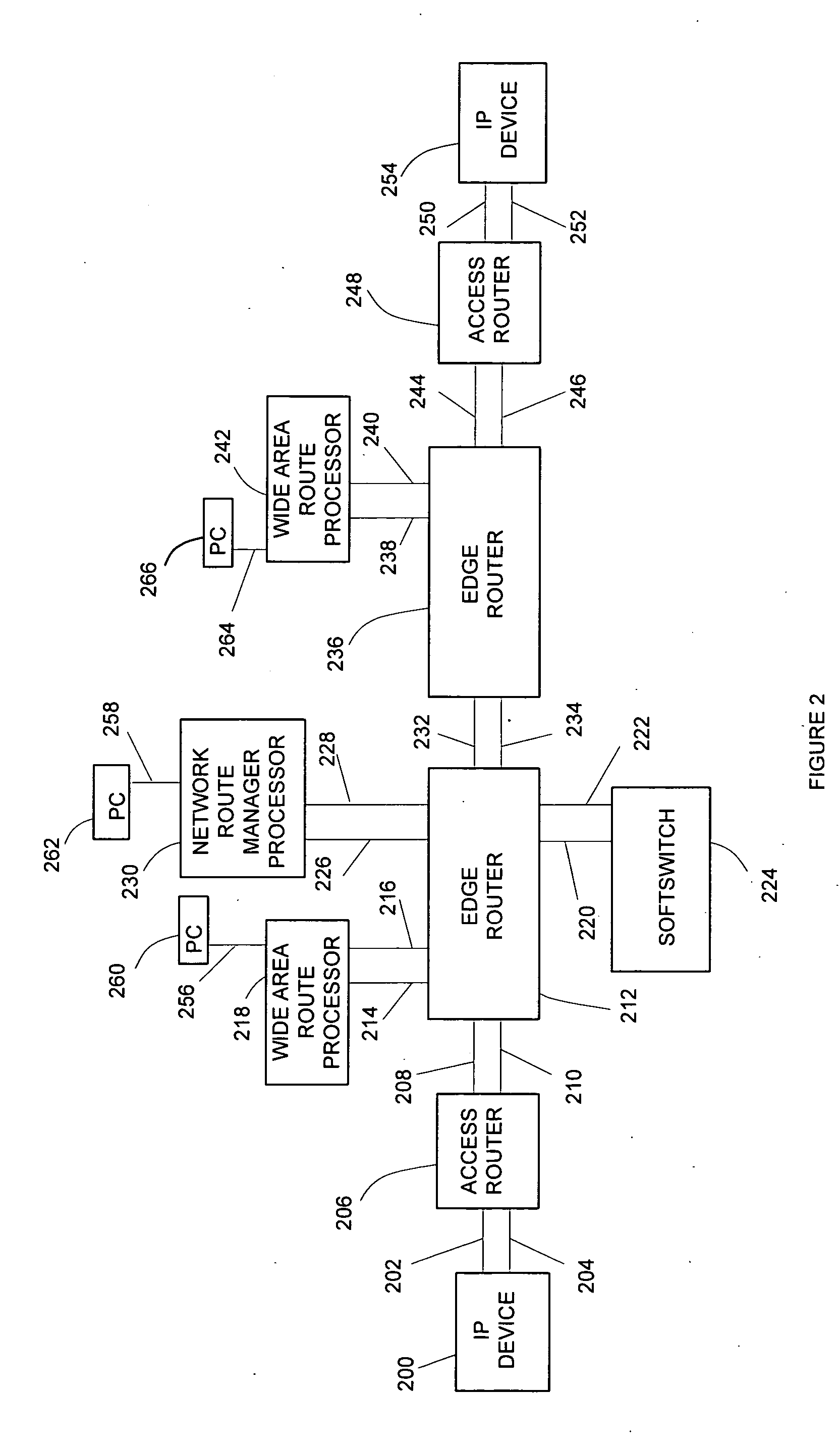
Internet protocol network system for real-time data applications
InactiveUS20060010243A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksQuality of serviceReal-time data
IP routes are established between route processors. The route processors change message addresses, so that signaling and data messages between users or between users and a soft switch are routed through the route processors. The route processors transfer data messages over the IP routes and monitor performance of the IP routes. The performance data is provided to a route manager that manages the IP routes to avoid undesirable service quality.
Owner:DUREE ALBERT D
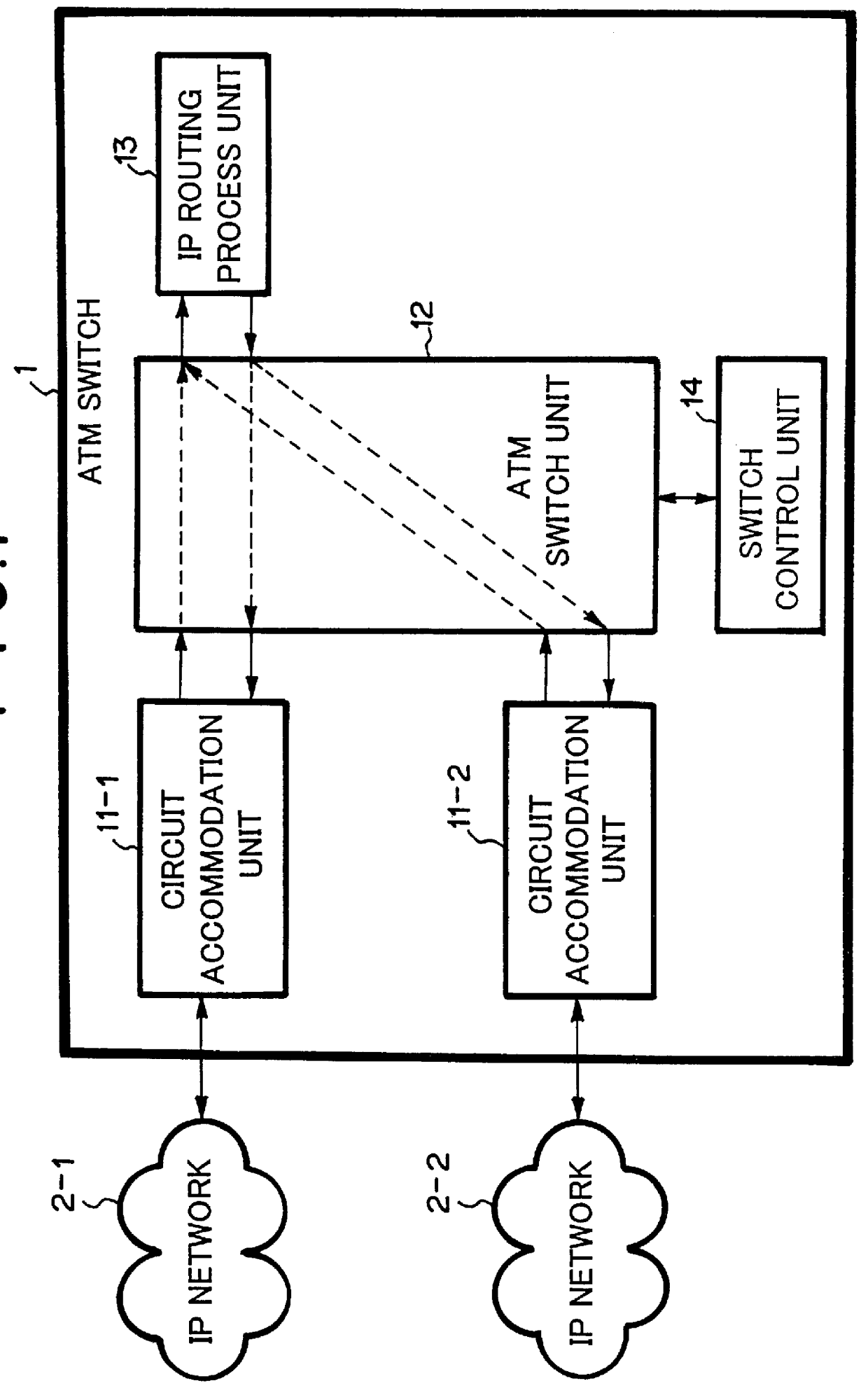
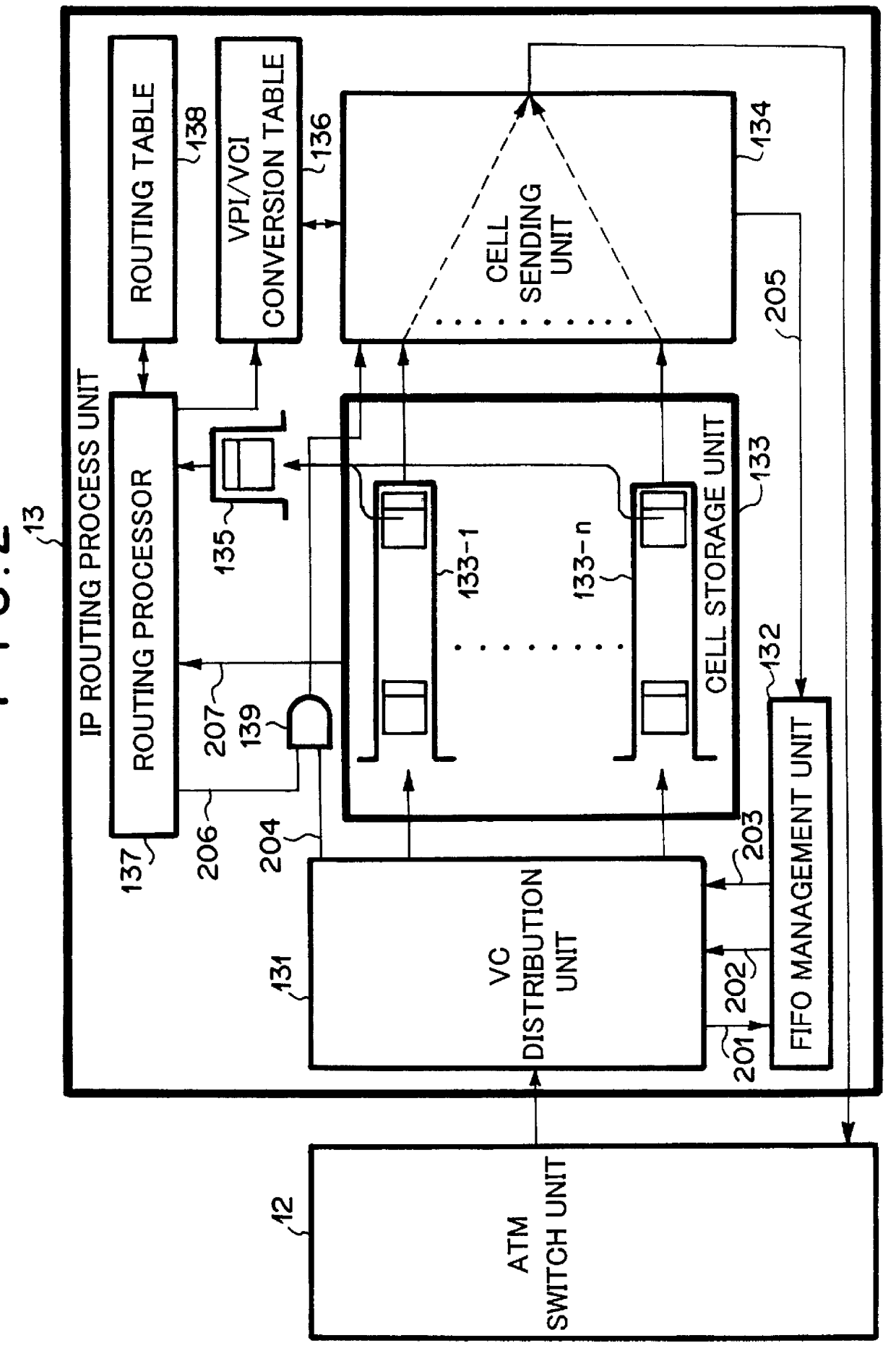
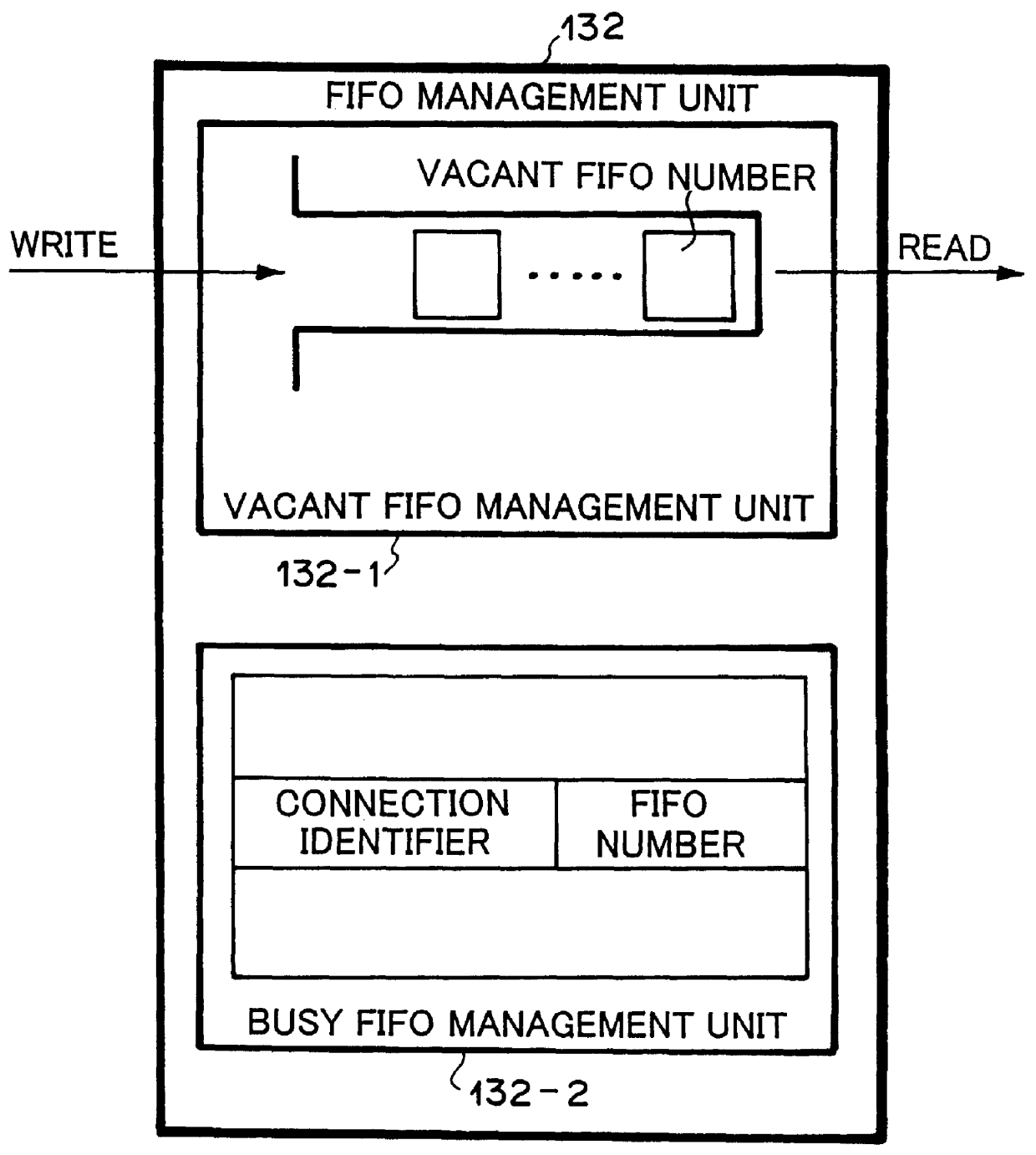
ATM switch capable of routing IP packet
InactiveUS6147999ATelephonic communicationData switching by path configurationIP forwarding algorithmControl unit
Disclosed is an ATM switch which comprises: an ATM switch unit; a switch control unit for controlling the ATM switch unit; one or more circuit accommodation units for connecting the switch with one or more external ATM networks, respectively, and an IP routing process unit for routing IP packets in a form of ATM cells. In the ATM switch, the IP routing process unit may comprise: a cell storage unit having a plurality of memories; a distributing means for distributing the ATM cells received from the ATM switch unit to the plurality of memories while grouping the ATM cells into each of the plurality of memories in accordance with an IP packet to which each of the ATM cells belongs; sending means for sending all the ATM cells belonging to an identical IP packet when the all the ATM cells belonging to the identical IP packet have been stored in respective one of the plurality of memories; and means for converting VPI / VCI (Virtual Path Identifier / Virtual Channel Identifier) of the all the ATM cells belonging to the identical IP packet.
Owner:NEC CORP
Fast IP route lookup with configurable processor and compressed routing table
InactiveUS6888838B1Reduce memory requirementsEqual costData switching by path configurationExtensibilityRouting table
A novel compression method uses bitmaps to reduce the memory storage requirement of routing table information to about 3 MB. The data structure can be used for both route lookup and update. It does not require a separate data structure to be used for route update. A fast route lookup method is also disclosed. An efficient update method supports incremental route update. Through configuring a processor properly and developing a few customized instructions specifically for route lookup, the system can achieve more than 10 million lookups per second (MLPS) at 200 MHz. Using a configurable processor for route lookup / update provides more flexibility and extensibility which supports different data structures and lookup / update methods to meet application specific needs. The data structure and lookup method can be implemented in pure hardware in a pipelined fashion to achieve approximately 100 MLPS.
Owner:TENSILICA
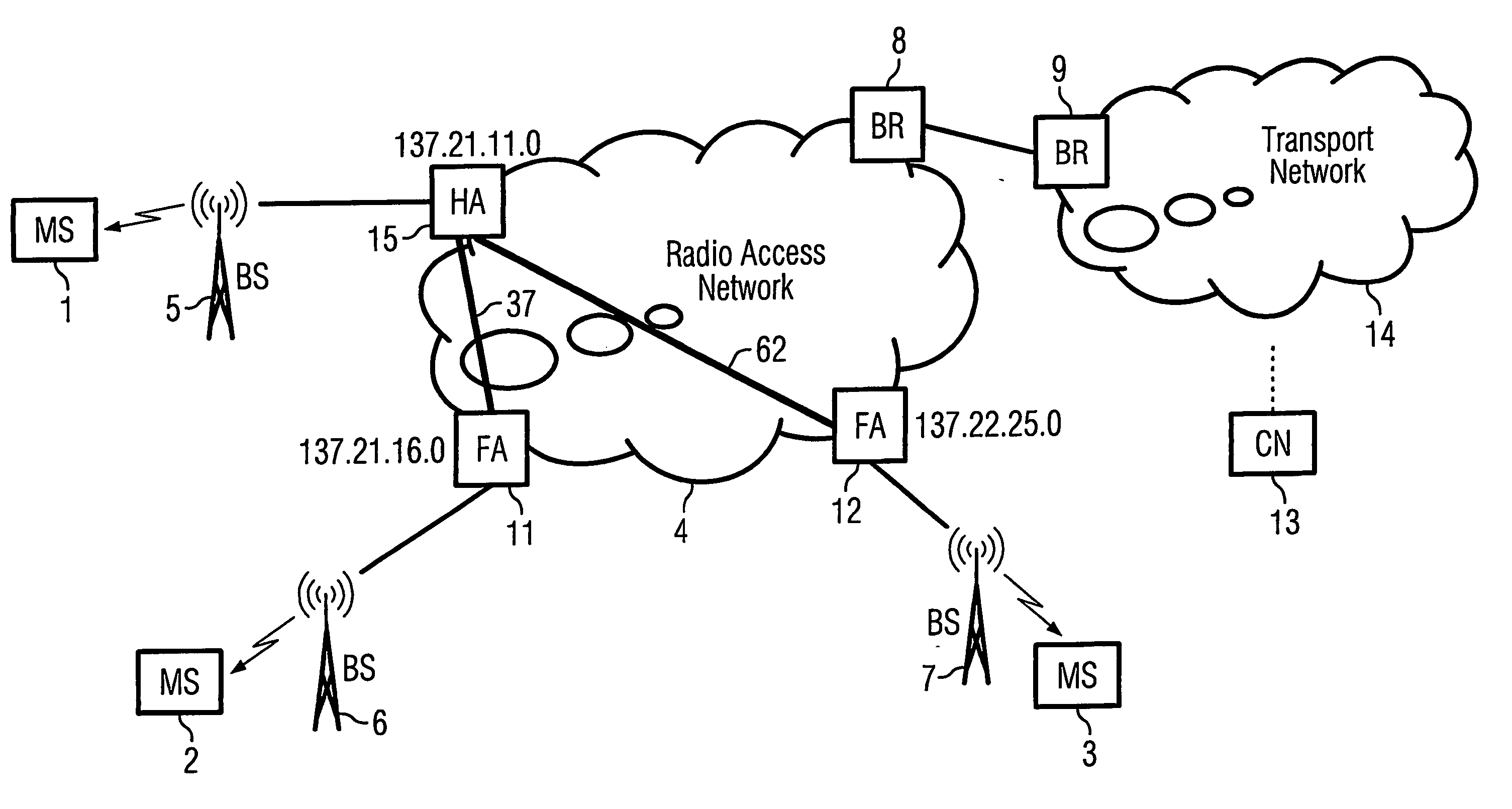
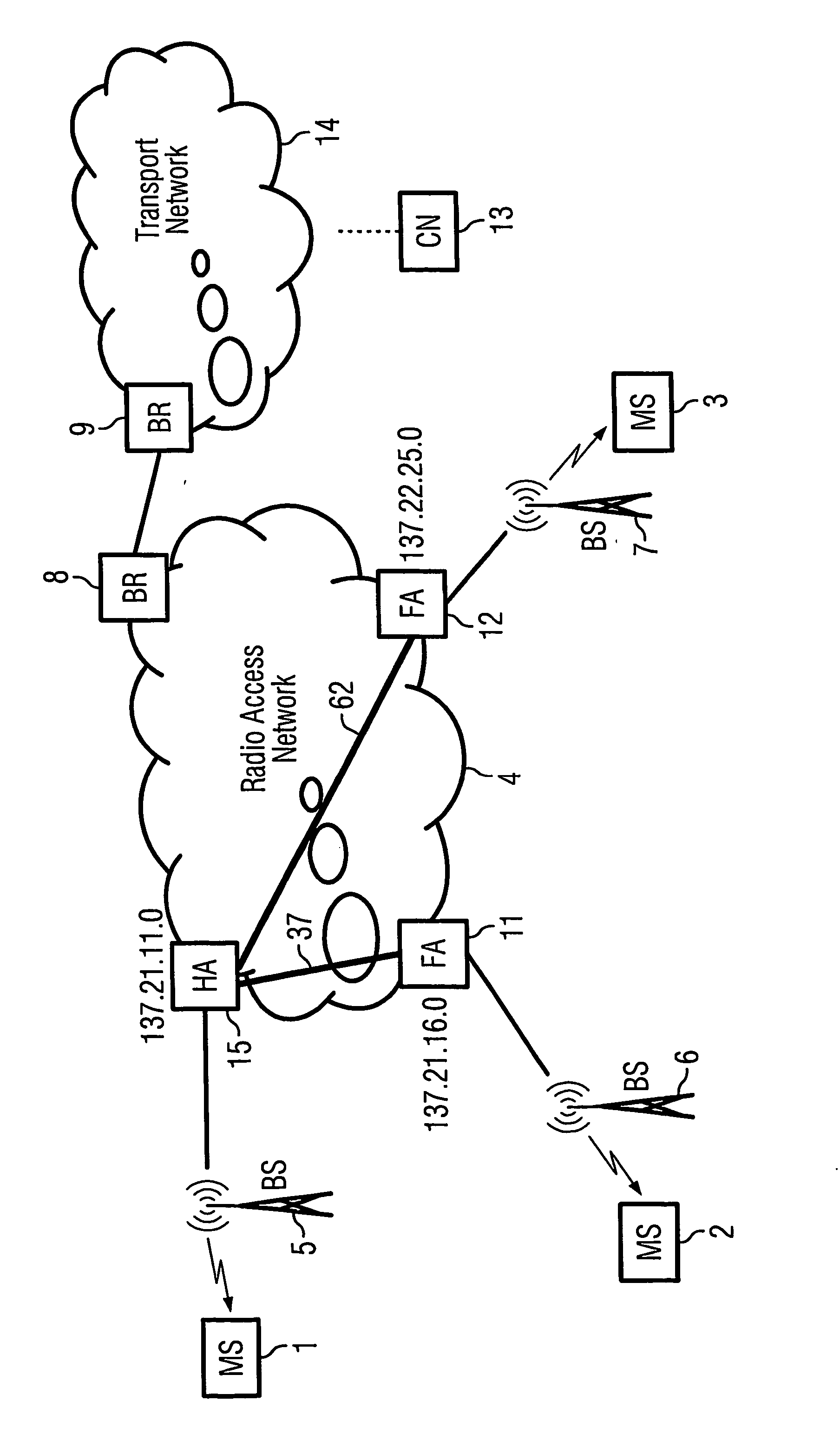
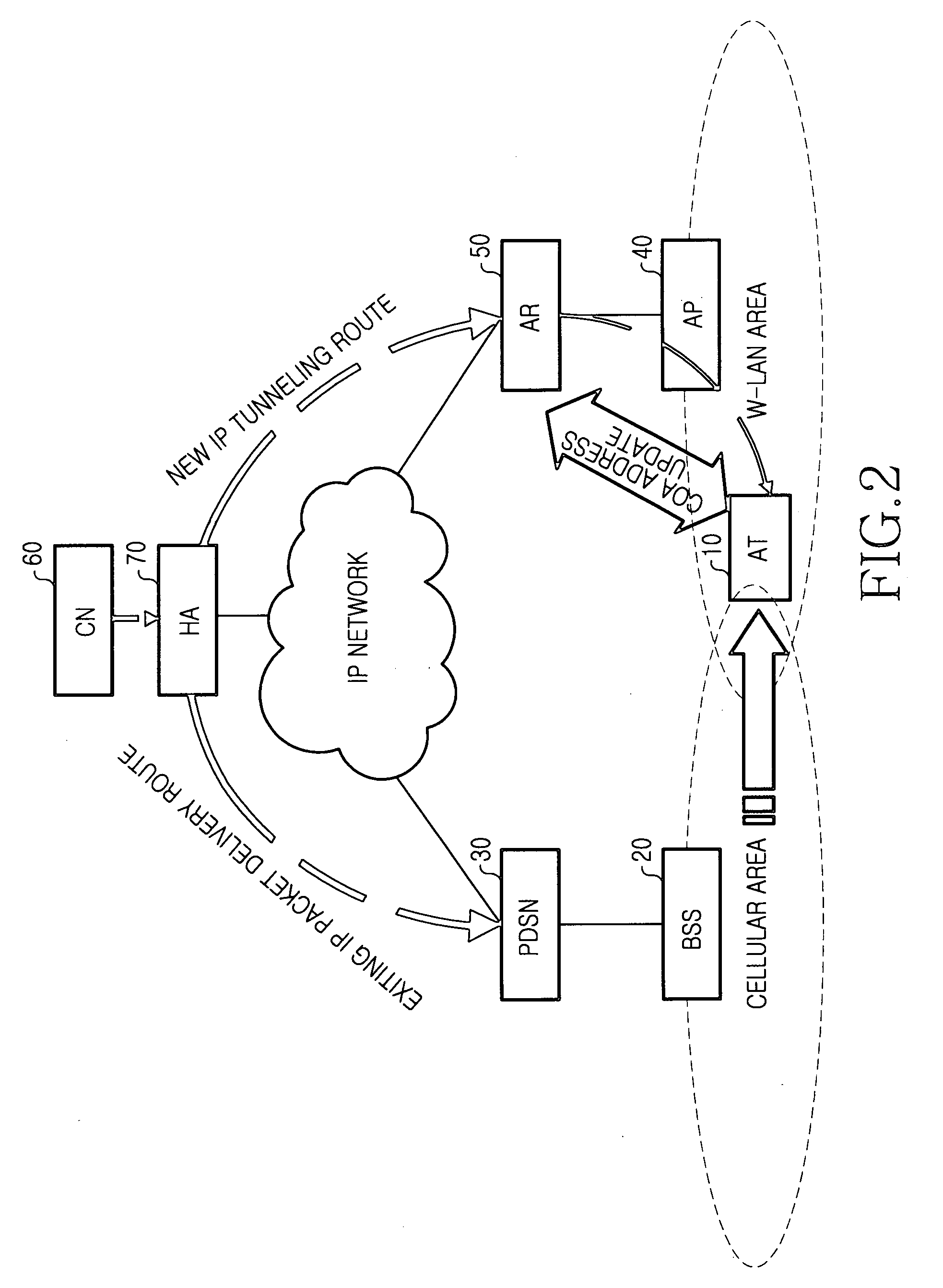
Home agent optimization for handling mobile ip and static mpls (multiprotocol label switching)
InactiveUS20060010250A1Efficient transportTightly coupledData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsRadio access networkForeign agent
For optimized IP-routing the invention discloses a home agent and method for transfer of an IP packet over a path from a sender (CN) over a radio access network (RAN, HA, FA 11) to a mobile host (MS2), wherein, when a home agent (HA) receives an incoming data packet determined for a mobile host (MS2) with a destination address (MS2-address 137.21.16.5), the home agent (HA) examines if there is a match between the destination address (MS2-address: 137.21.16.5) of the packet and a subnetwork address (FA 11-address: 137.21.16.0) of a foreign agent (FA 11) stored in a list of subnetwork addresses (137.21.16.0; 137.22.25.0) stored in a list at the home agent (HA), wherein, if there is a match between the destination address (MS2-address: 137.21.16.5) and a subnetwork address (FA 11-address: 137.21.16.0) of a foreign agent, the home agent examines whether a preconfigured path from the home agent (HA) to this foreign agent exists and wherein the home agent (HA) sends the packet to this foreign agent (FA 11) on this preconfigured label switched path (37) if a label switched path (37) to this foreign agent exists.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
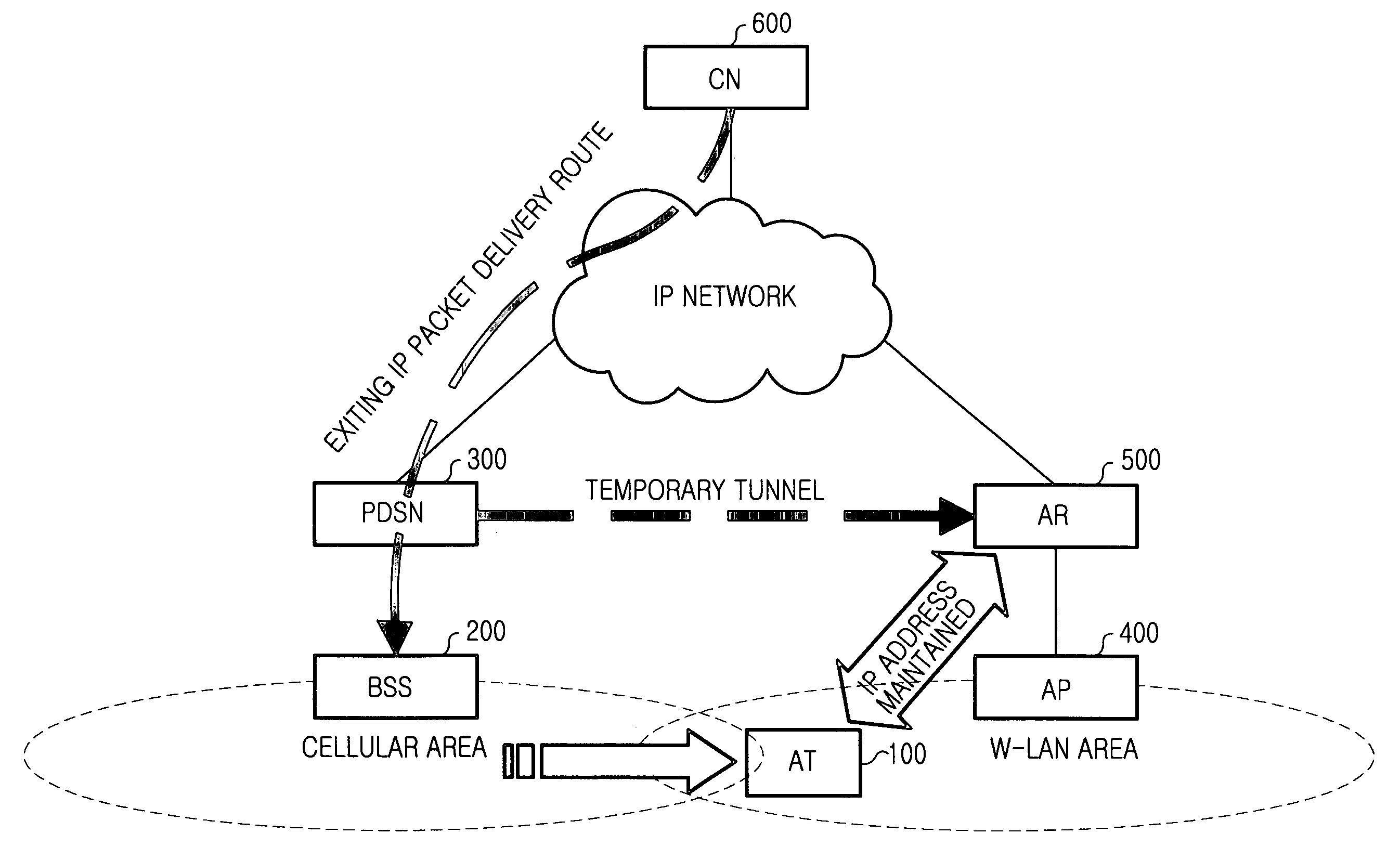
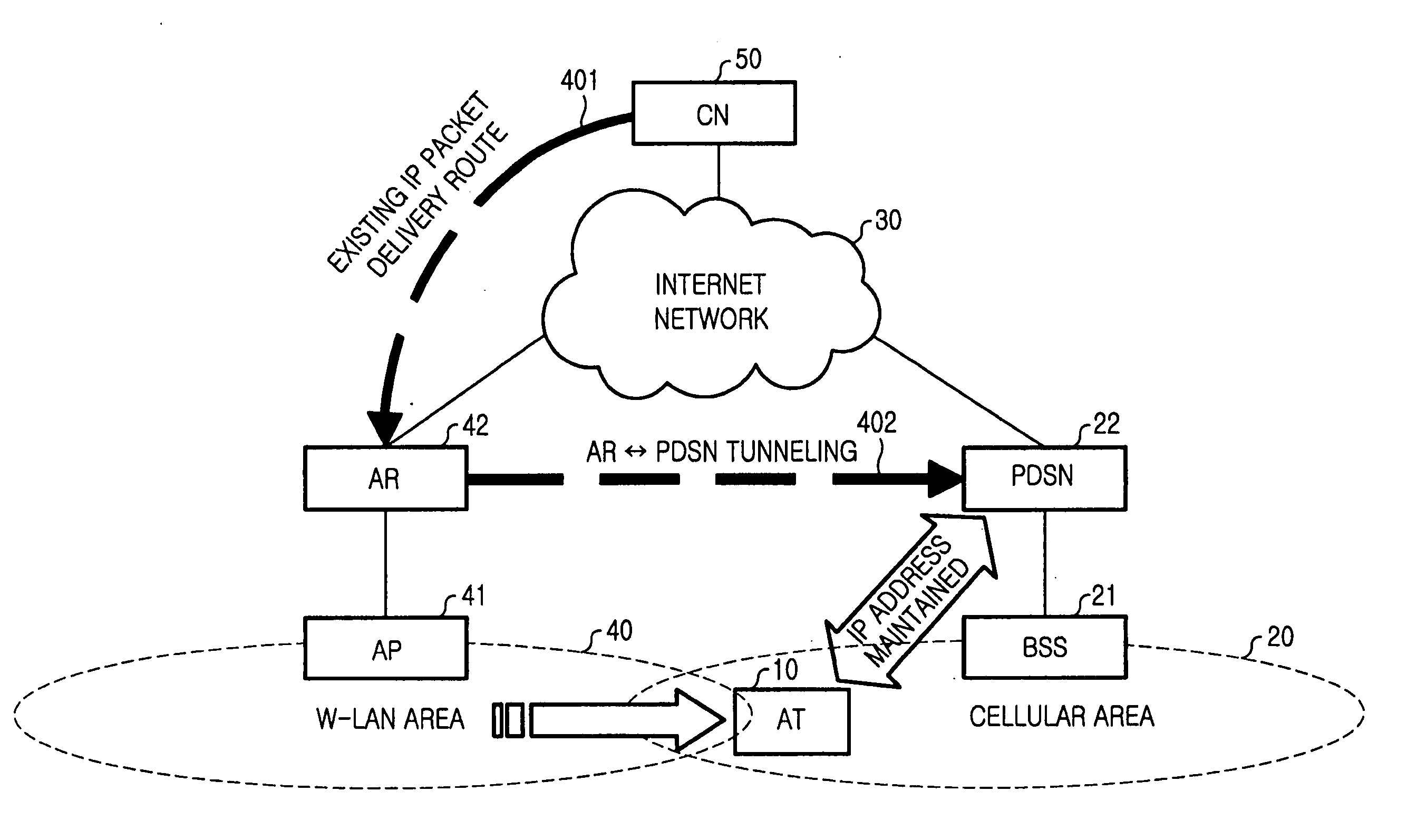
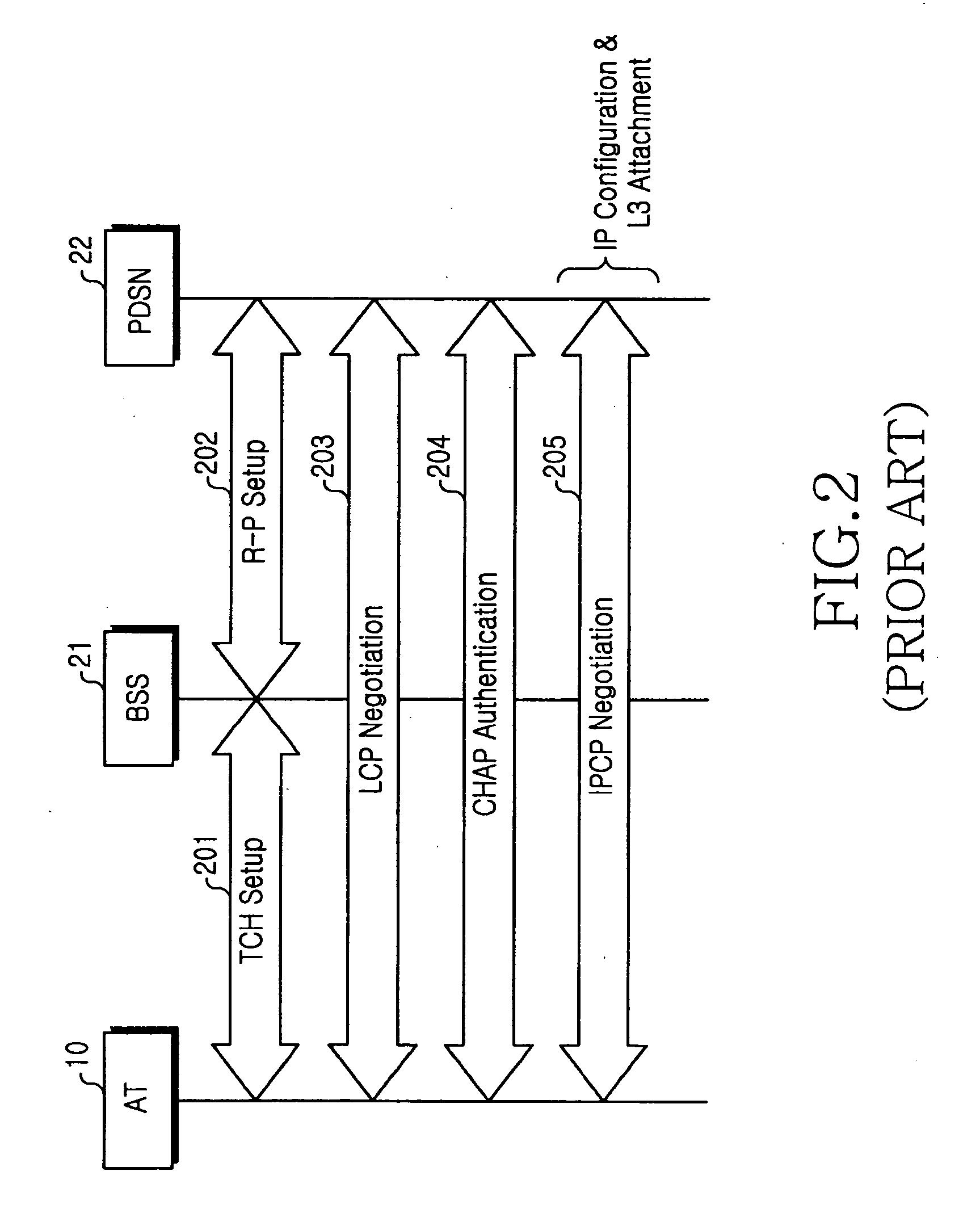
Handoff system and method between mobile communication network and wireless LAN
InactiveUS20060023683A1Avoid lostReduce processing timeNetwork topologiesWireless network protocolsPacket data serving nodeWireless lan
A handoff system and method is provided for performing handoff from a mobile communication network, including a packet data service node (PDSN) connected to a base station system (BSS) for supporting an Internet protocol (IP) routing function, to a wireless local area network (LAN) including an access router (AR) supporting the IP routing function. An access terminal (AT) detects its movement to the wireless LAN and exchanges information with the AR for tunneling between the PDSN and the AR. The AR sets up a tunnel for packet delivery between the AR and the PDSN, and delivers packets delivered from a correspondent node (CN) to the AT via the set tunnel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
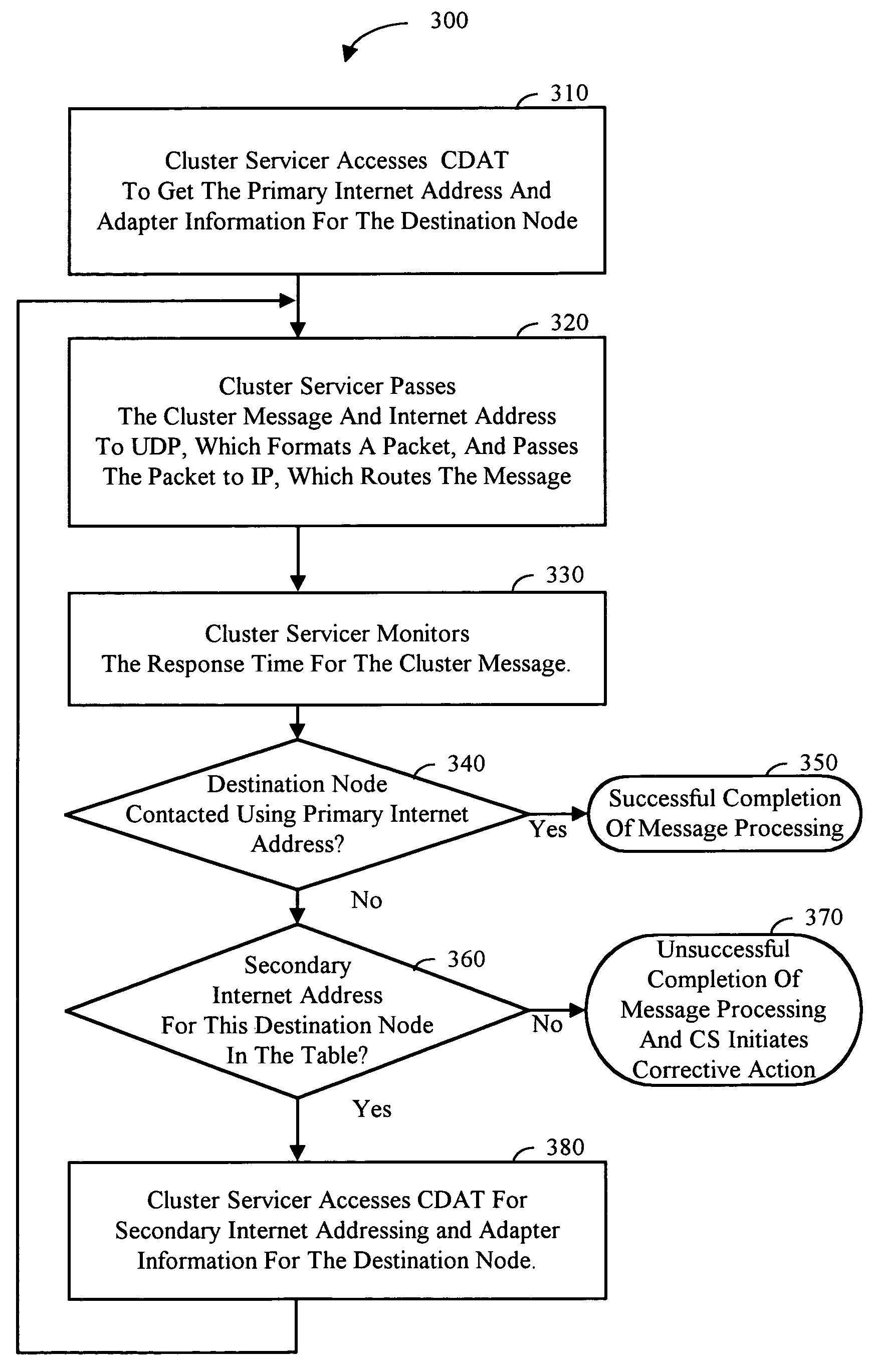
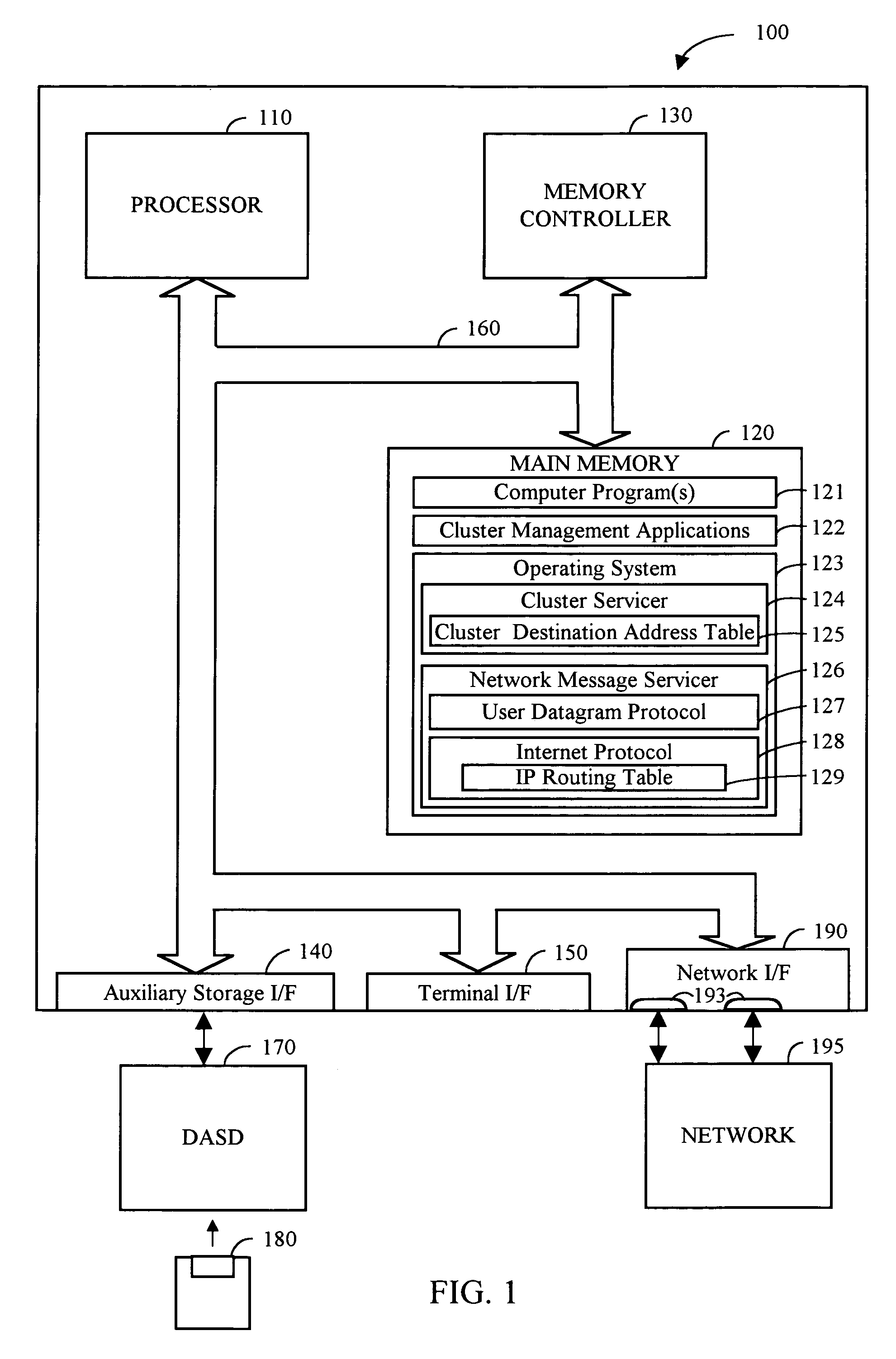
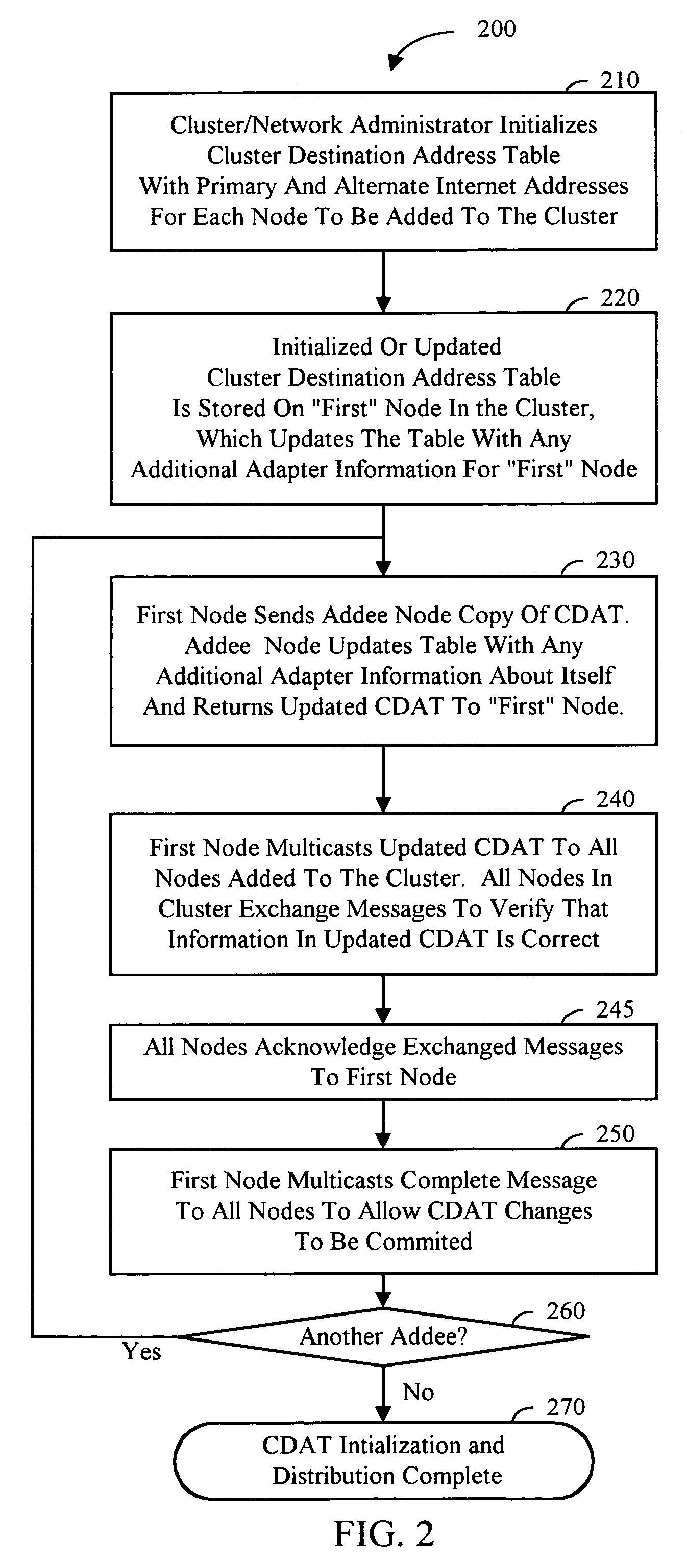
Cluster destination address table-IP routing for clusters
InactiveUS6993034B1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsInternet protocol suiteNetwork Communication Protocols
According to the present invention, a communications protocol supporting cluster configurations more complex than a single LAN is disclosed. A cluster destination address table (CDAT) is used in conjunction with a network message servicer to communicate between computer systems in a cluster. Each computer system preferably contains a cluster servicer, a CDAT, and a network message servicer. The CDAT contains network addresses, status and adapter information for each computer system in a cluster. Although computer systems may have alternate network addresses when they have multiple adapters, the CDAT indexes primary and alternate address information under a single named system. Thus, redundant connections amongst computer systems are identified, while still using the numeric addresses upon which the network message servicer is based. To send a message using the methods of the present invention, the cluster servicer retrieves a network address for a computer system from a CDAT. A message to be sent and the retrieved address are passed to the network message servicer, preferably an Internet Protocol suite. The network message servicer formats the information into a packet and routes the packet.
Owner:IBM CORP
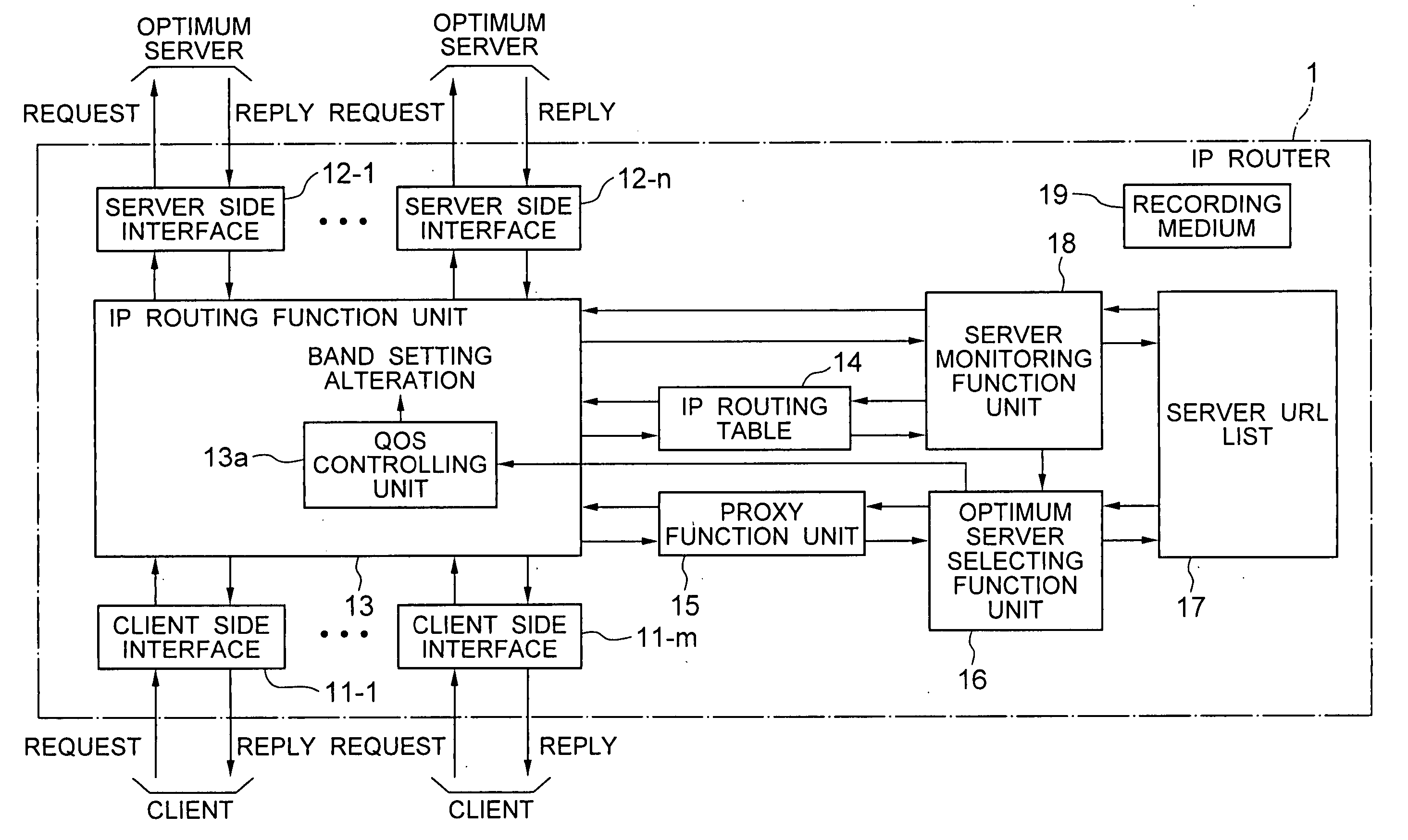
IP router, communication system and band setting method used therein and its program
ActiveUS20040172470A1Digital computer detailsNetworks interconnectionTraffic capacityCommunications system
A server monitoring function unit recognizes a running / stopping state of each server, throughput and the like by performing a health check based on obtained positioning information of an original server and mirror servers, informs an optimum server selecting function unit of the information, and updates a server URL list based on the positioning information. When the server monitoring function unit detects a change in the network topology from a change in an IP routing table, the optimum server selecting function unit alters the selection criteria of the optimum server and informs a QoS controlling unit of a traffic change. The QoS controlling unit alters a band setting for each service class according to the traffic change informed.
Owner:NEC PLATFORMS LTD
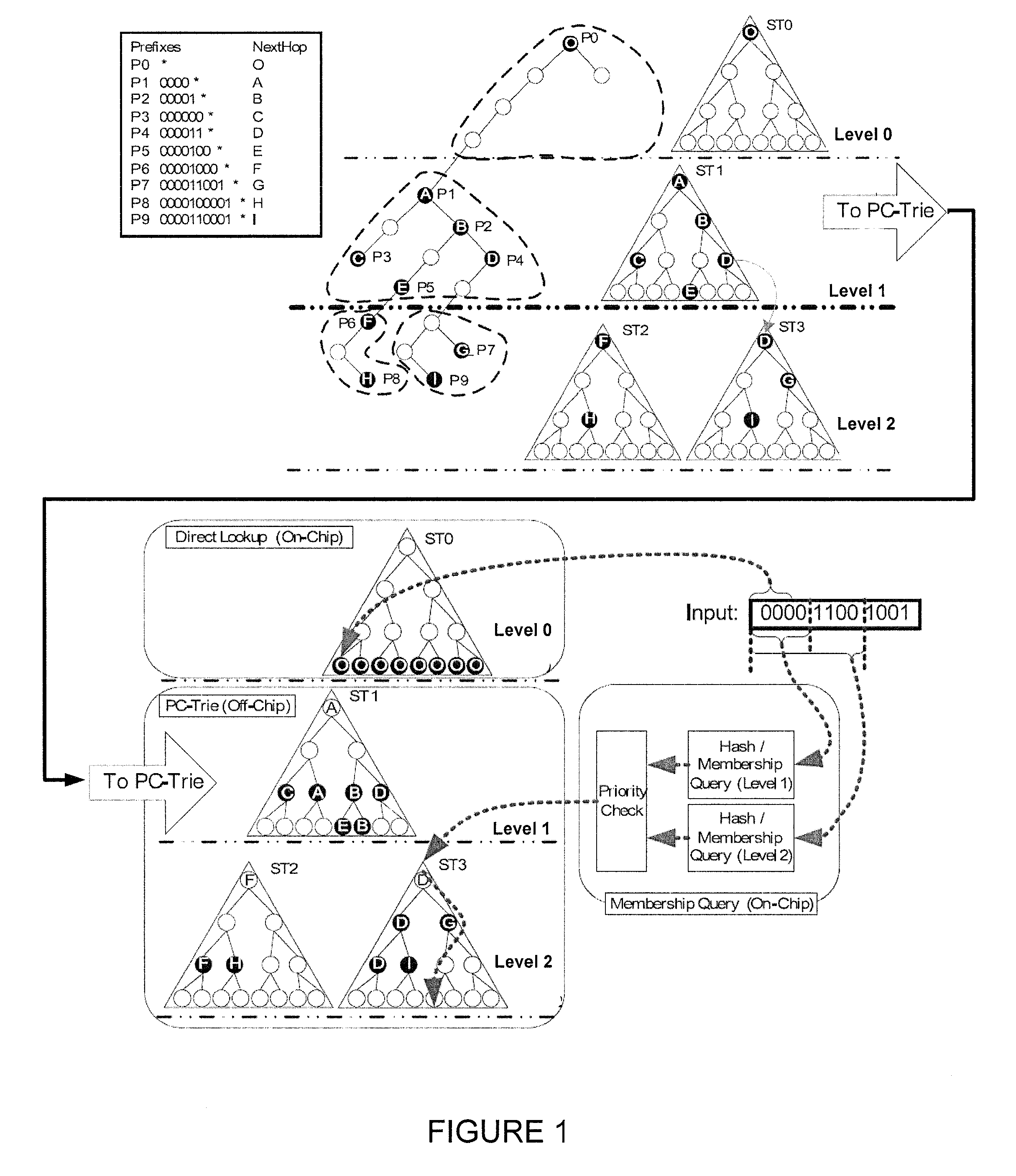
Hash-based prefix-compressed trie for IP route lookup
A method and apparatus for updating stored data structures representing network forwarding information used for network route lookup is described. By making sure there is only one level of dependency between data structures storing forwarding information, these data structures may be updated quickly and with minimal overhead
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
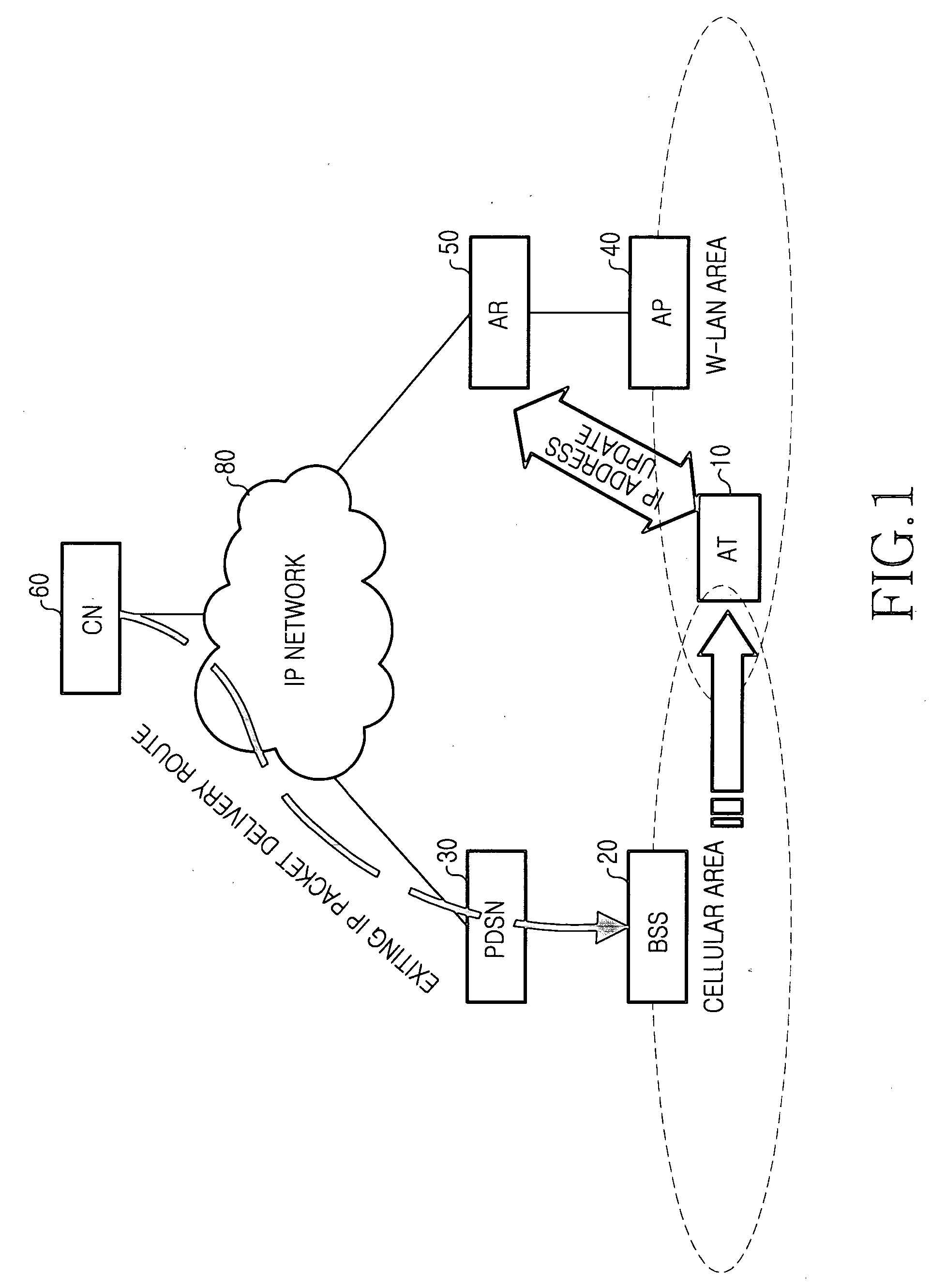
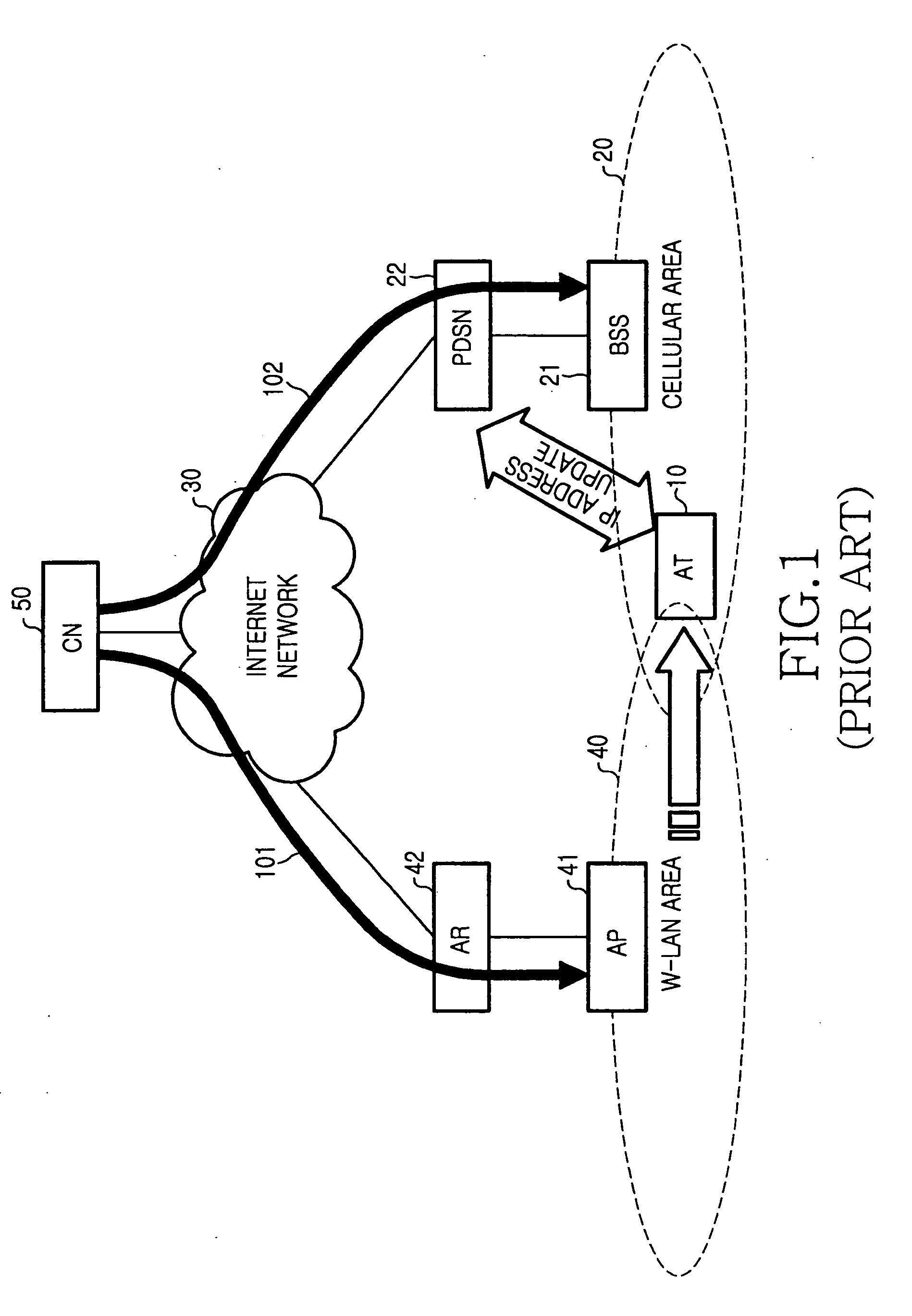
Handoff system and method between a wireless LAN and mobile communication network
InactiveUS20060045049A1Reduce lossesTime-division multiplexConnection managementPacket data serving nodeWireless lan
A method for performing a handoff between a wireless local area network (LAN) including an access router (AR) supporting an Internet protocol (IP) routing function and a mobile communication network including a packet data service node (PDSN) connected to a base station system (BSS), for supporting the IP routing function. An access terminal (AT) detects its movement from the wireless LAN to the mobile communication network, and exchanges information for tunneling between the AR and the PDSN, with the PDSN. The PDSN sets up a tunnel for packet delivery between the PDSN and the AR, and delivers packets to the AT through the set tunnel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
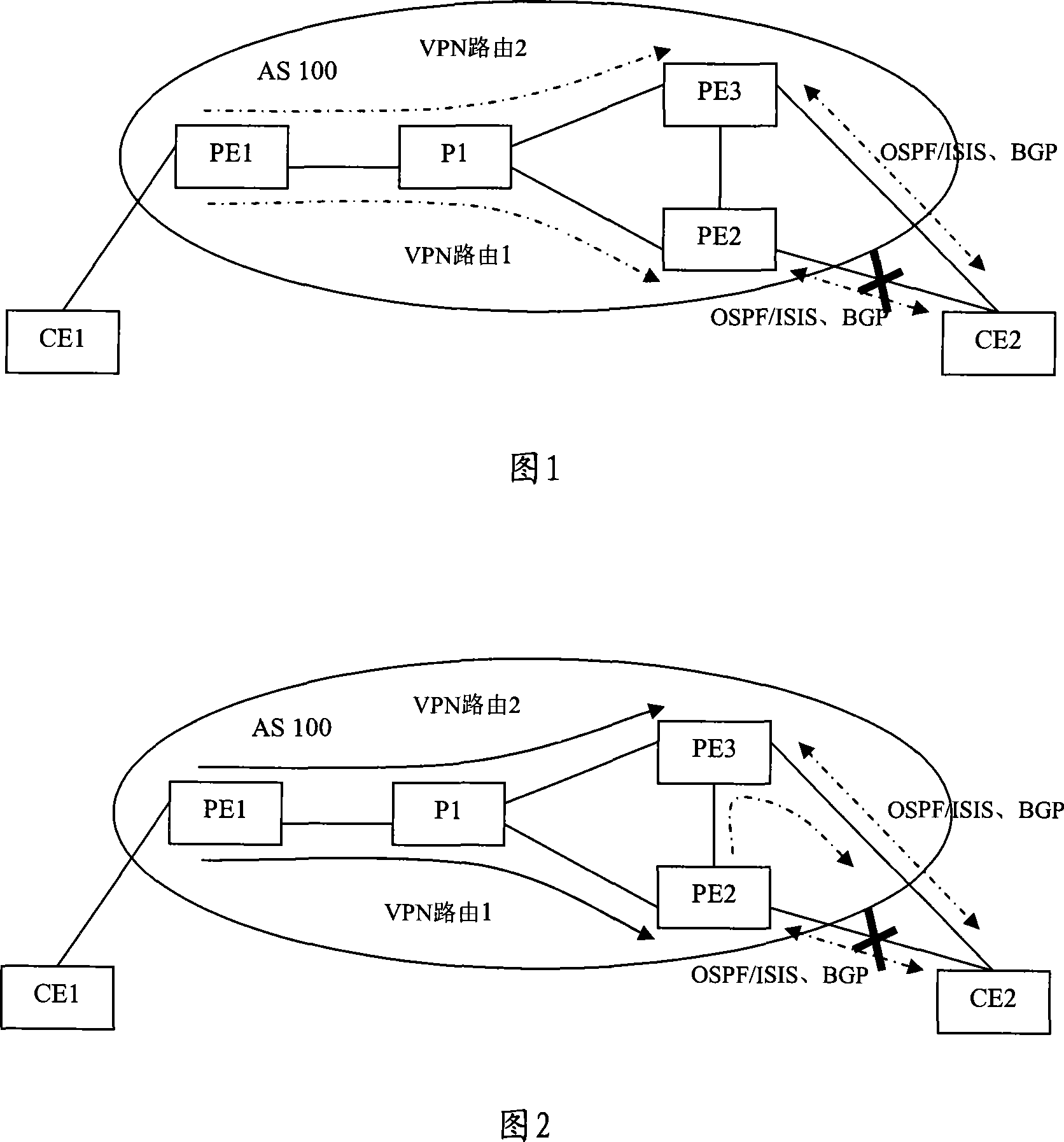
A method to realize fast reroute and router
InactiveCN101217457AFast convergenceMeet real-time business needsNetworks interconnectionPrivate networkIp router
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a router for realizing fast reroute. The method of the invention example comprises that: the main network IP router and the spare virtual private network VPN router is down sent into the route forwarding table of network provider boundary routing equipment PE; the local PE and CE adopt bidirectional forwarding detection to check the link failure; when the link failure is detected, the flow are all switched to the spare VPN router to be forwarded. By adopting the method of the embodiment of the invention, the local PE-CE link failure can be rapidly detected and the main network IP router and the spare virtual private network VPN router can be down sent to the route forwarding table of network provider boundary routing equipment PE. The rapid detection of failure in the local PE-CE link is helpful to realize rapid convergence of VPN business and satisfies the real-time business requirement of the users.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Virtual private network (VPN)-as-a-service with delivery optimizations while maintaining end-to-end data security
ActiveUS20150188943A1Facilitate (VPN)-as-a-serviceEfficient use ofData switching networksPlaintextTransfer procedure
A mechanism to facilitate a private network (VPN)-as-a-service, preferably within the context of an overlay IP routing mechanism implemented within an overlay network. A network-as-a-service customer operates endpoints that are desired to be connected to one another securely and privately using the overlay IP (OIP) routing mechanism. The overlay provides delivery of packets end-to-end between overlay network appliances positioned at the endpoints. During such delivery, the appliances are configured such that the data portion of each packet has a distinct encryption context from the encryption context of the TCP / IP portion of the packet. By establishing and maintaining these distinct encryption contexts, the overlay network can decrypt and access the TCP / IP flow. This enables the overlay network provider to apply one or more TCP optimizations. At the same time, the separate encryption contexts ensure the data portion of each packet is never available in the clear at any point during transport.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Method and apparatus for providing IP mobility and IP routing in ad hoc wireless networks
ActiveUS20080192677A1Network topologiesTime-division multiplexMobility managementIP forwarding algorithm
The invention includes methods and apparatuses for supporting mobility management and packet routing in ad hoc wireless networks. A method for mobility management includes detecting, at a first base station, a request by a wireless device to establish an association with the first base station where the first base station comprises a mobile base station, updating an association table of the first base station to include an association of the wireless device to the first base station, and propagating, toward a second base station, a message adapted to update an association table of the second base station, wherein the second base station is a mobile base station, wherein the message is propagated toward the second base station wirelessly. The packet routing functions of the present invention may be used independent of, or in conjunction with, the mobility management functions of the present invention.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Techniques for integrated routing of call circuit signaling and the internet protocol
InactiveUS20070248103A1Data switching by path configurationSelection arrangementsTTEthernetNetwork link
Techniques for processing an IP packet at a router that supports SS7 signaling include receiving IP routing data that associates a network link and a destination IP address for a node in a signaling network that includes a plurality of signaling nodes. When an ingress IP data packet is received, it is determined whether conditions are satisfied for locally processing an SS7 payload within the ingress IP data packet. If it is determined that conditions are satisfied for locally processing the SS7 payload, then the SS7 payload is processed locally, i.e., without sending the SS7 payload over a network link to a different node in the signaling network. If it is determined that conditions are not satisfied for locally processing the SS7 payload, then the ingress IP data packet is routed normally. These techniques allow reduced numbers of expensive STP devices and expanded routing options in a signaling network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
QoS capable mobile ad-hoc network device
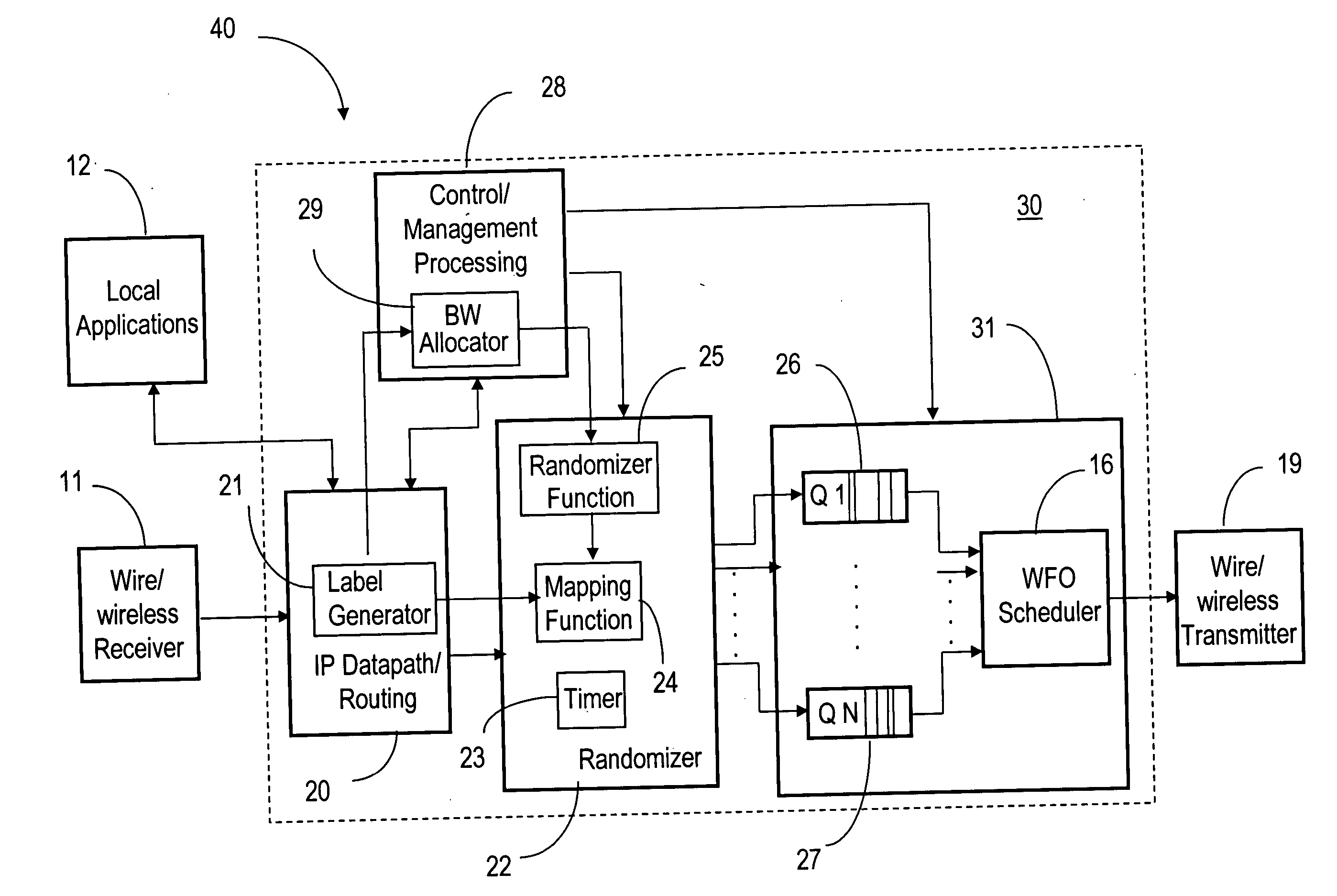
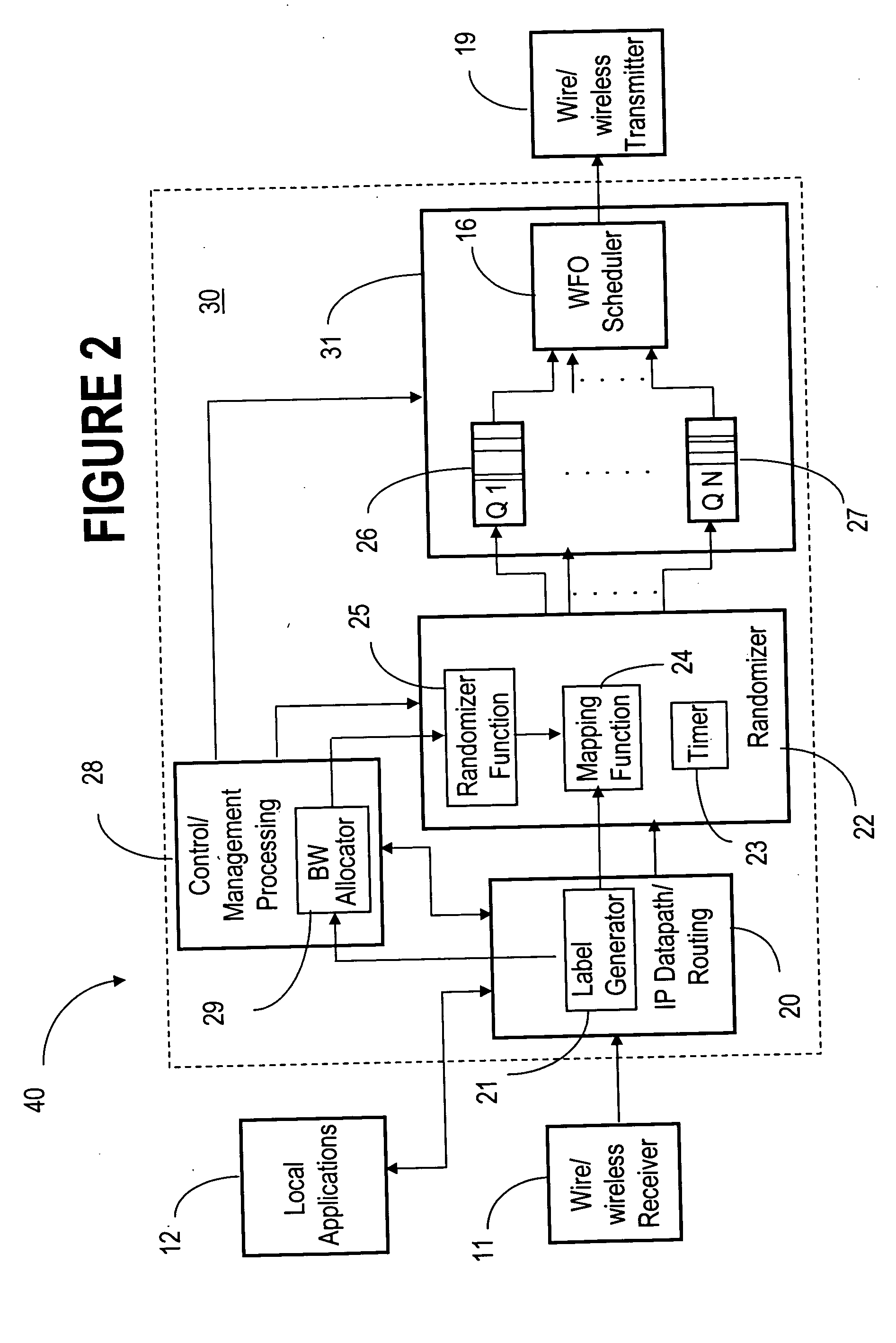
ActiveUS20060056353A1Low costFair distribution of network bandwidthError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceRandom mapping
The ad-hoc router enables a decentralized IP routing network (mobile of fixed) amongst a set of network devices, and can offer quality of services for voice, video and data applications. The ad-hoc router is divided into a receiving, control / management processing, IP datapath / routing, randomizer, scheduler and transmission blocks. The IP datapath / routing block provides, in addition to the standard datapath routing functionality, per packet labels that uniquely identify the source device of the packet in the network. The scheduler maintains a plurality of QoS queues, which are then dequeued with a WFQ scheduler, which can be based on standard technology or a simplified low-cost implementation. The randomizer uses the labels to route the packets to a queue such that all packets from the source device, indicated by the label, enter the same queue. For greater security, the randomizer uses a random mapping function that is re-computed periodically.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Data transmission method and system based on mobile terminal and mobile terminal
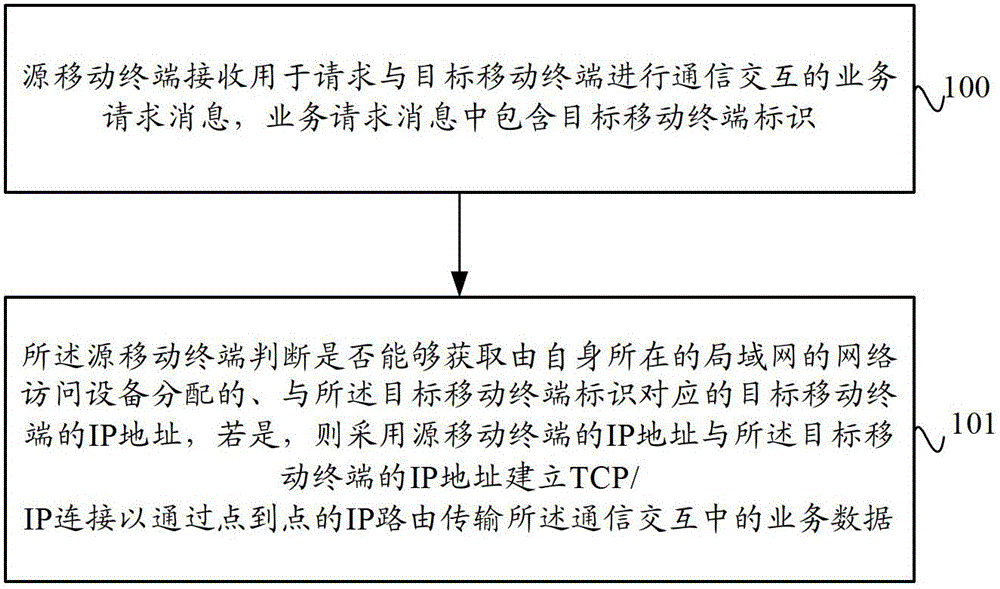
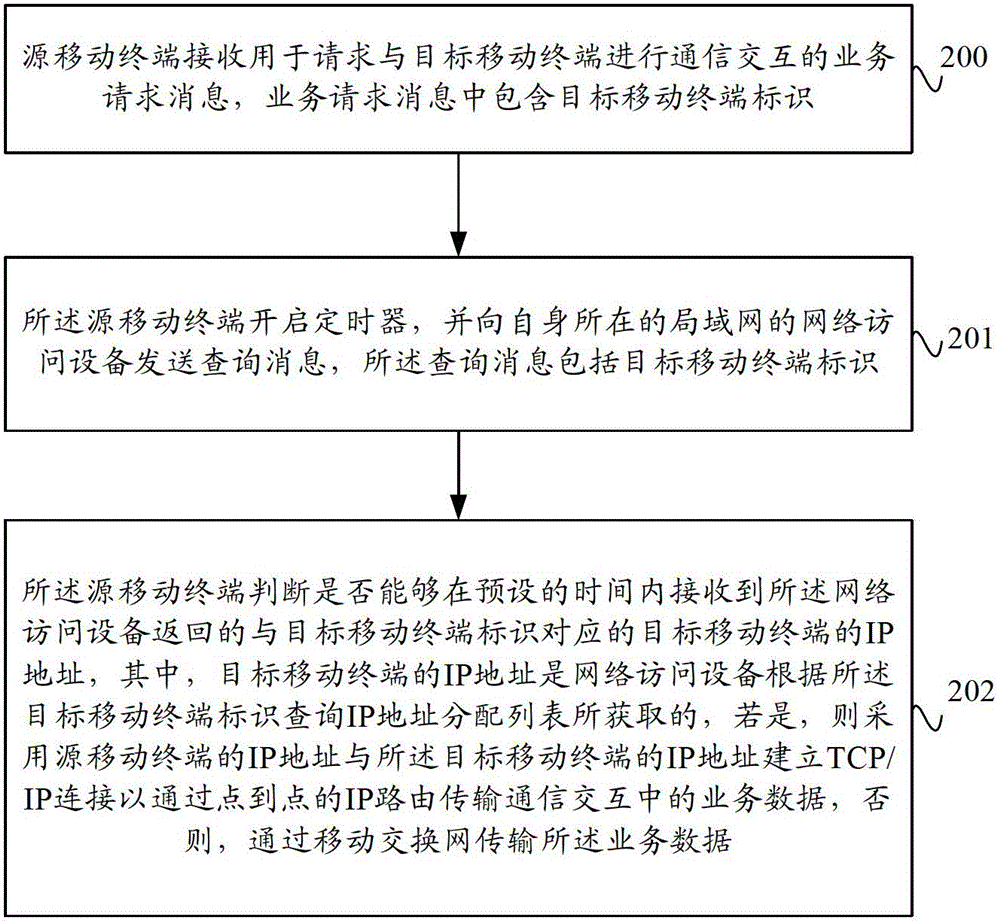
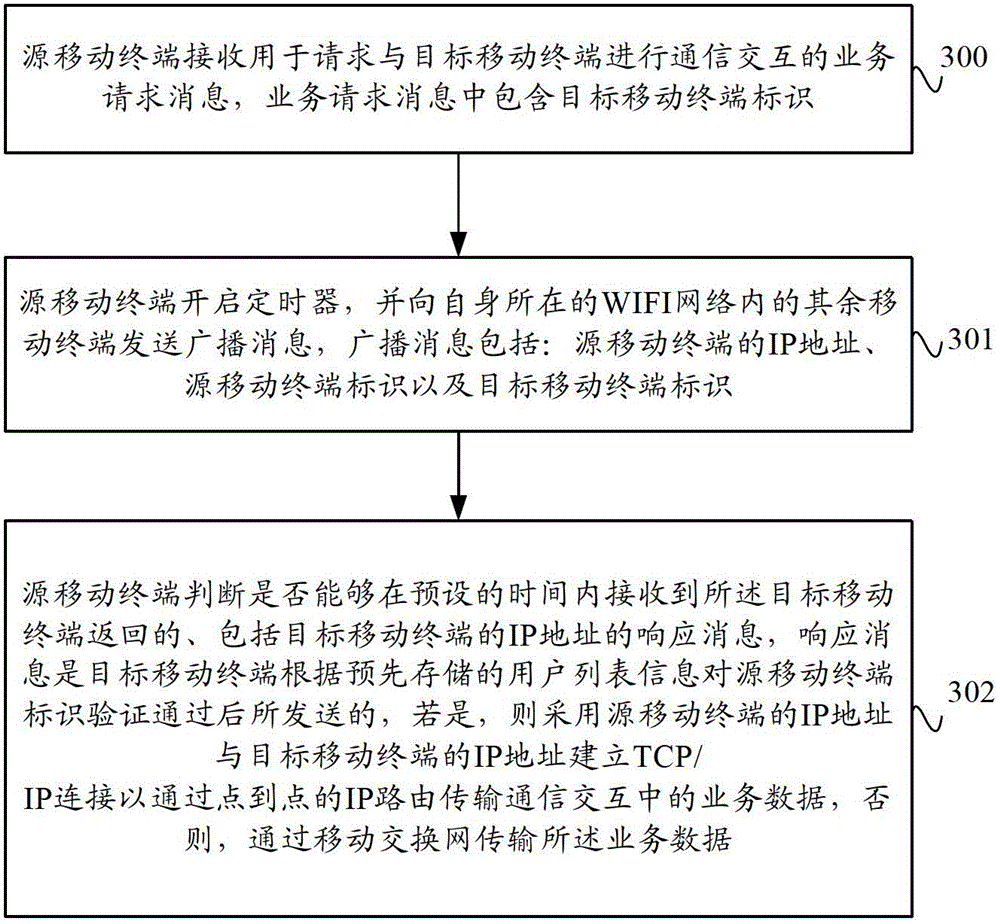
ActiveCN102752748AIncrease distanceReduce power consumptionNetwork data managementIp addressBusiness data
The invention provides a data transmission method and system based on a mobile terminal and the mobile terminal. The method comprises the following steps of receiving a business request message by a source mobile terminal, wherein the business request message comprises target mobile terminal identification, and judging whether an IP (Internet protocol) address of the target mobile terminal corresponding to the target mobile terminal identification and distributed by a network access device of a local area network of the source mobile terminal can be obtained or not, if so, establishing TCP / IP (transmission control protocol / Internet protocol) connection by adopting the IP address of the source mobile terminal and the IP address of the target mobile terminal, so as to transmit business data in communication interaction through a point-to-point IP route. With the adoption of the data transmission method and system based on the mobile terminal and the mobile terminal provided by the invention, the communication interaction between the source mobile terminal and the target mobile terminal is finished through the point-to-point IP route, thus, the distance of data transmission between mobile terminals is increased, the power consumption of the mobile terminal is reduced and the large quantities of data transmission is favored.
Owner:CHINA UNITED NETWORK COMM GRP CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com