Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
186 results about "Fast reroute" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
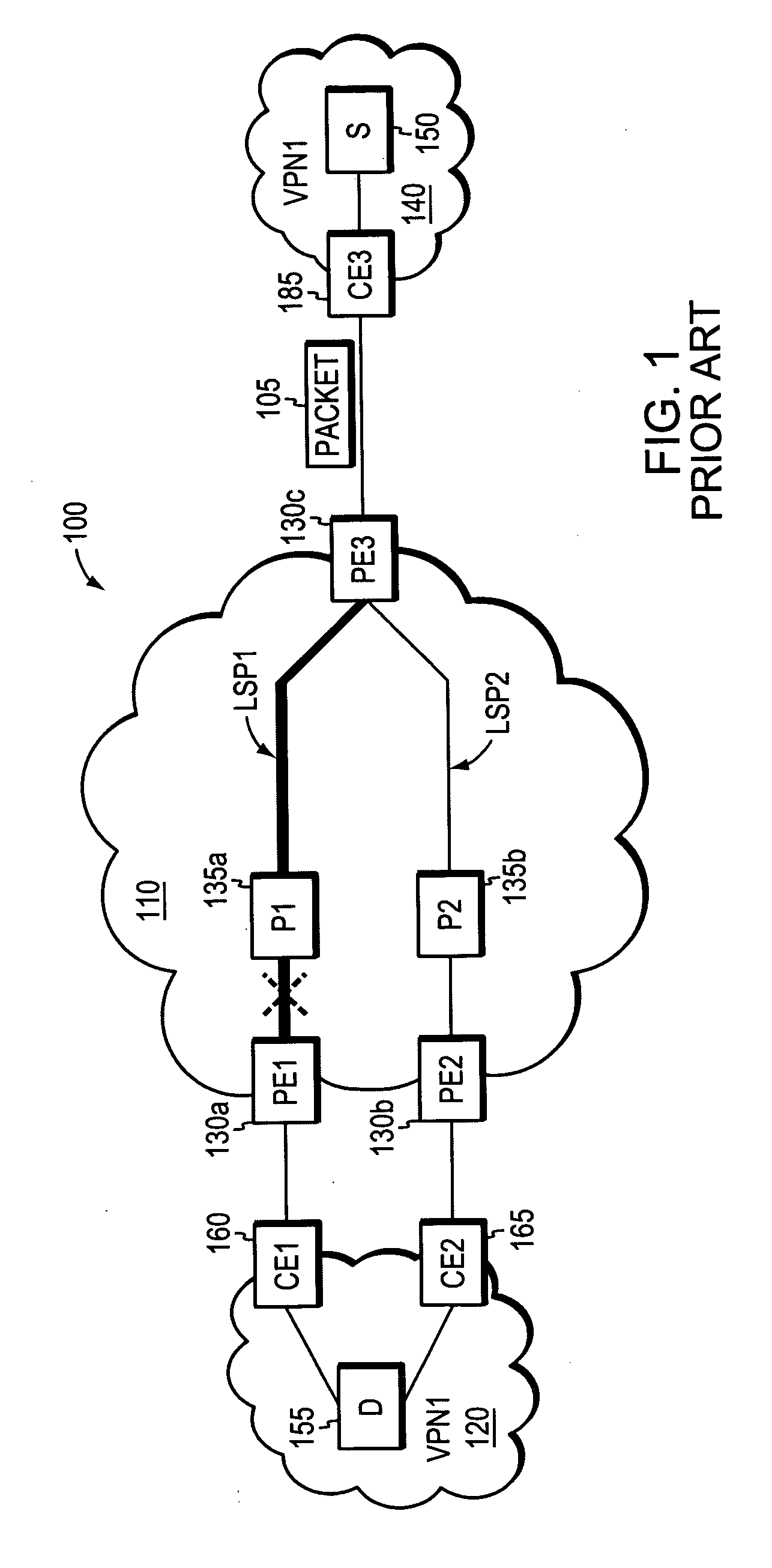
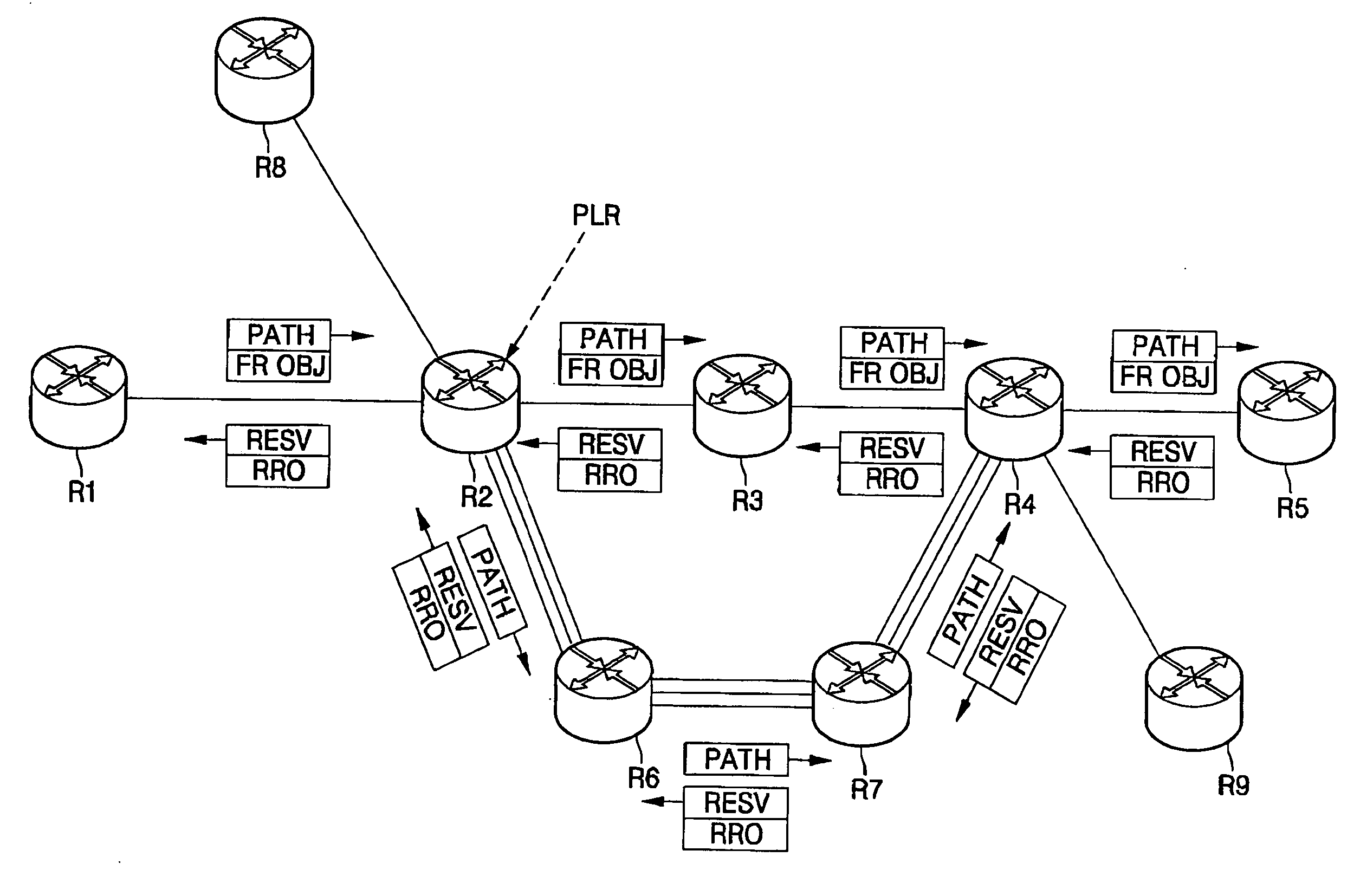
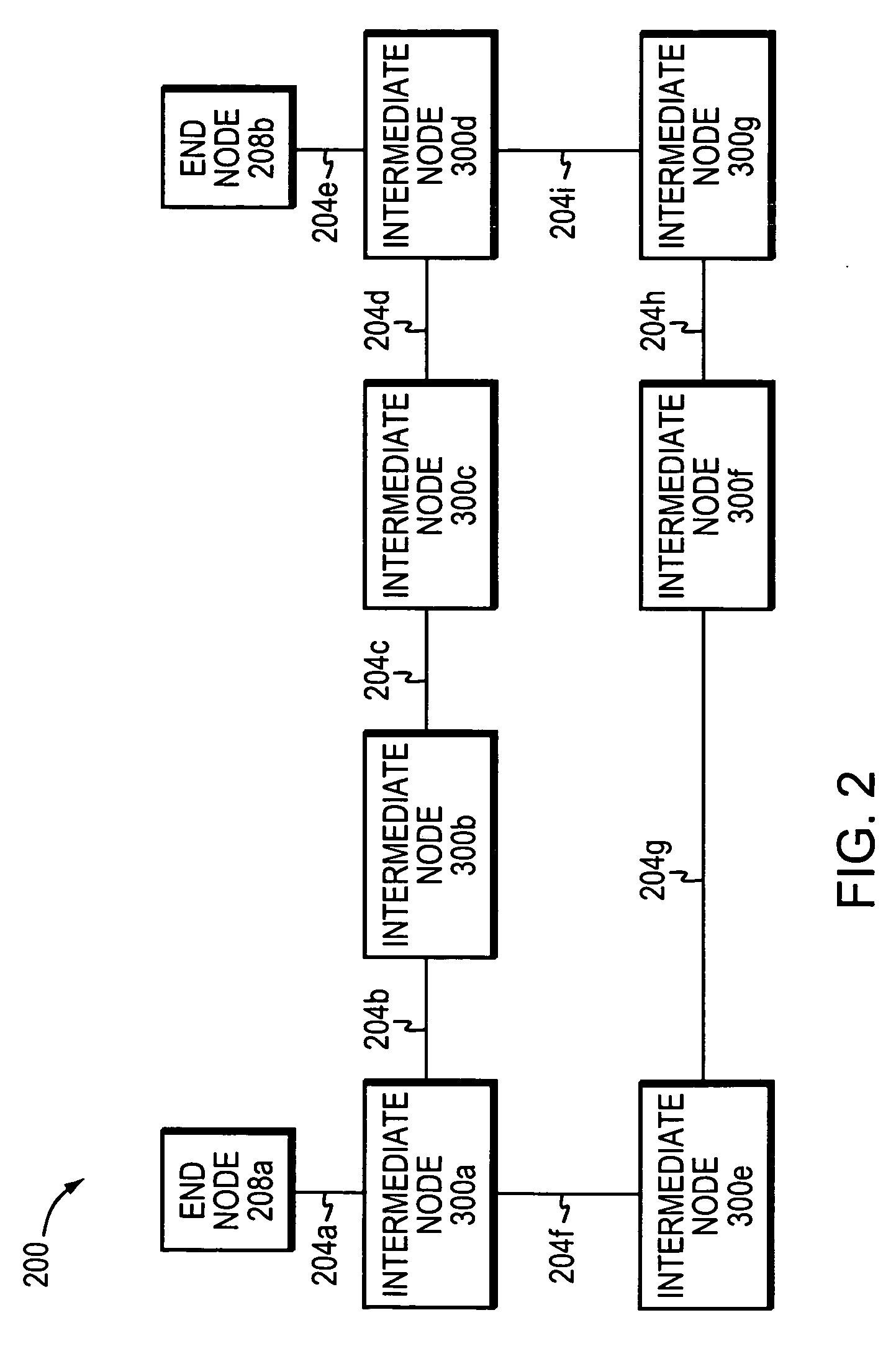
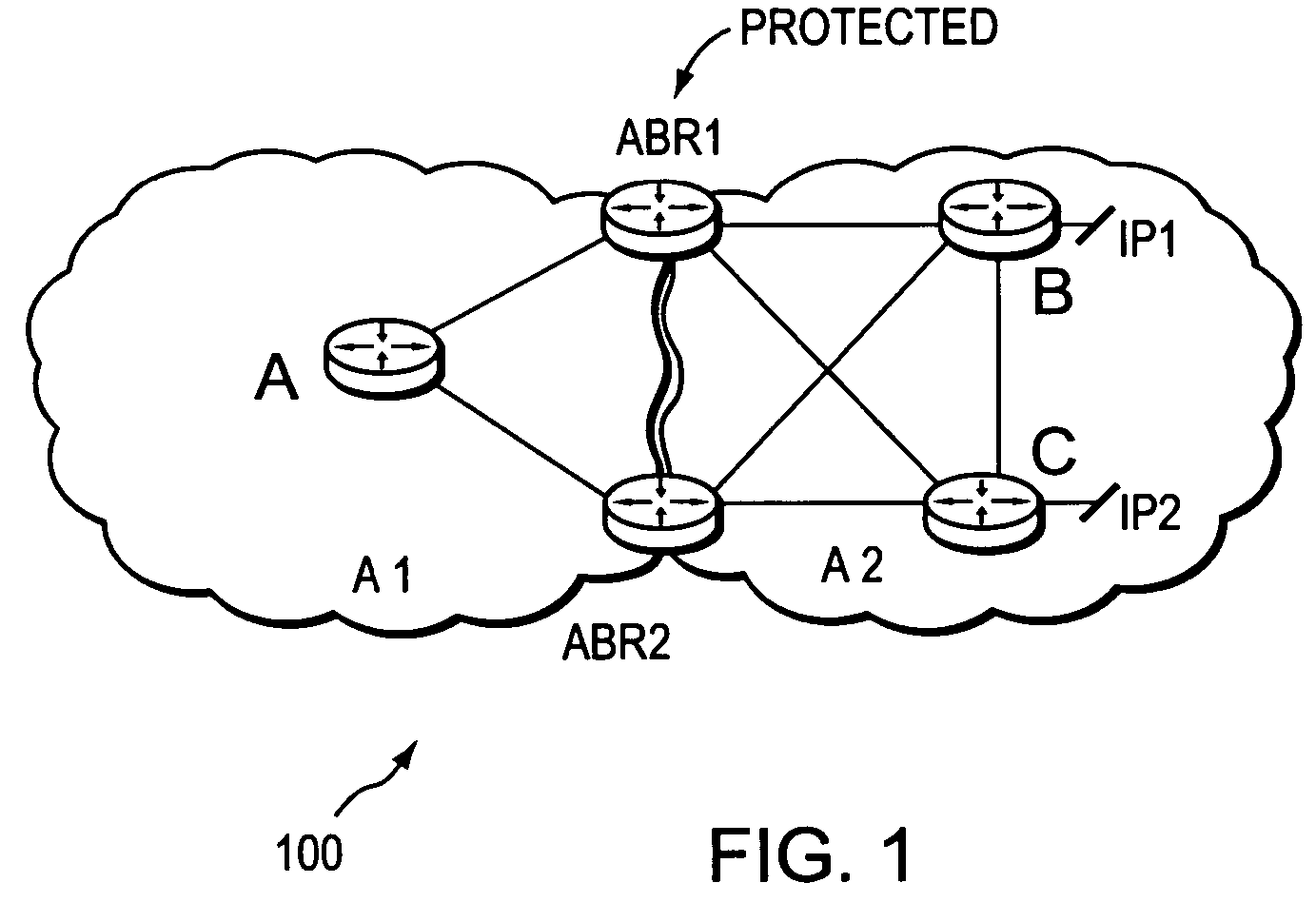
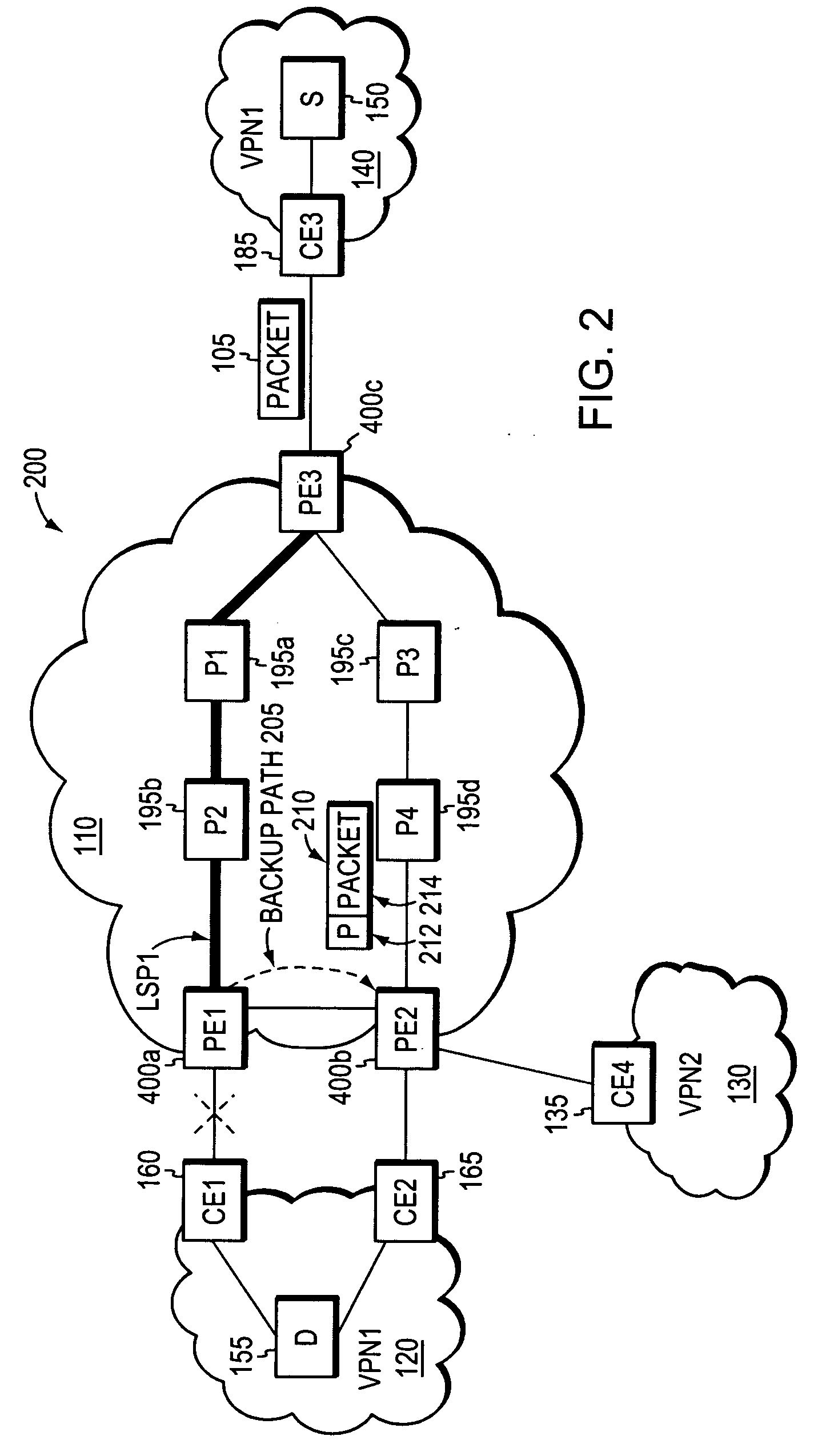
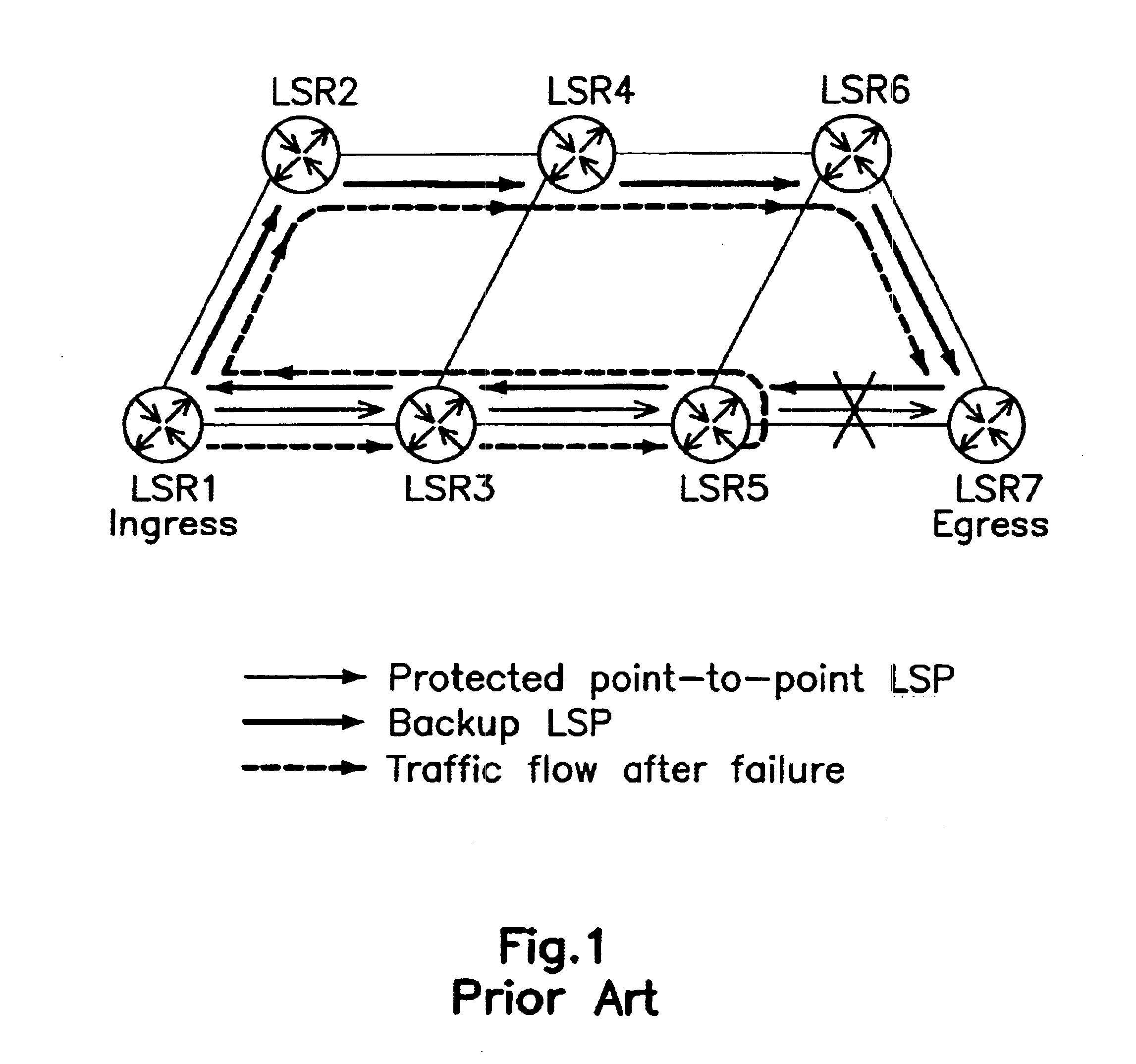
Fast Reroute is a MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) and IP resiliency technology to provide fast traffic recovery upon link or router failures for mission critical services. Upon any single link or node failures, it could be able to recover impacted traffic flows in the level of 50 ms. Industrial implementations can be seen in vendors such as Cisco, Juniper, Brocade, Alcatel-Lucent etc.
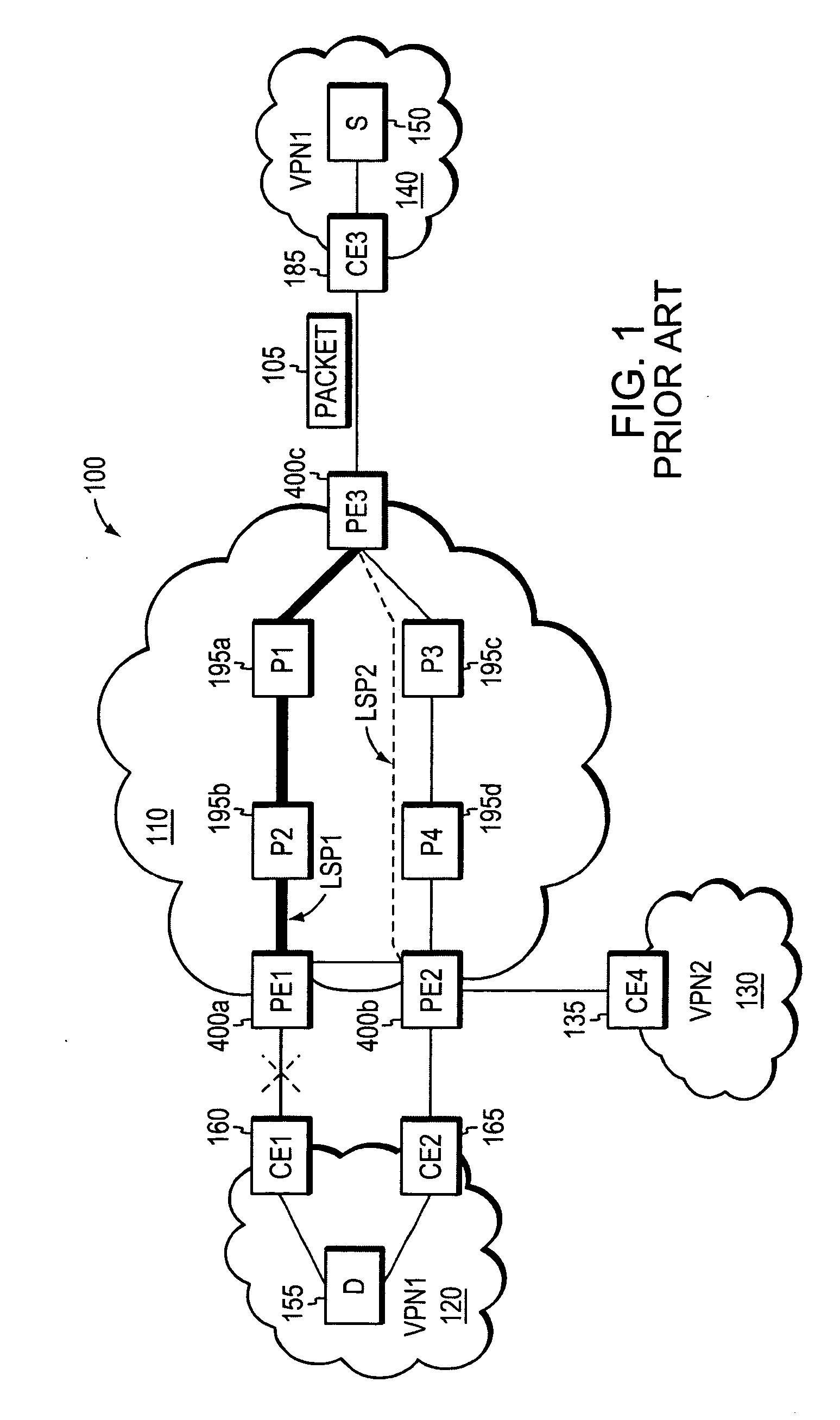
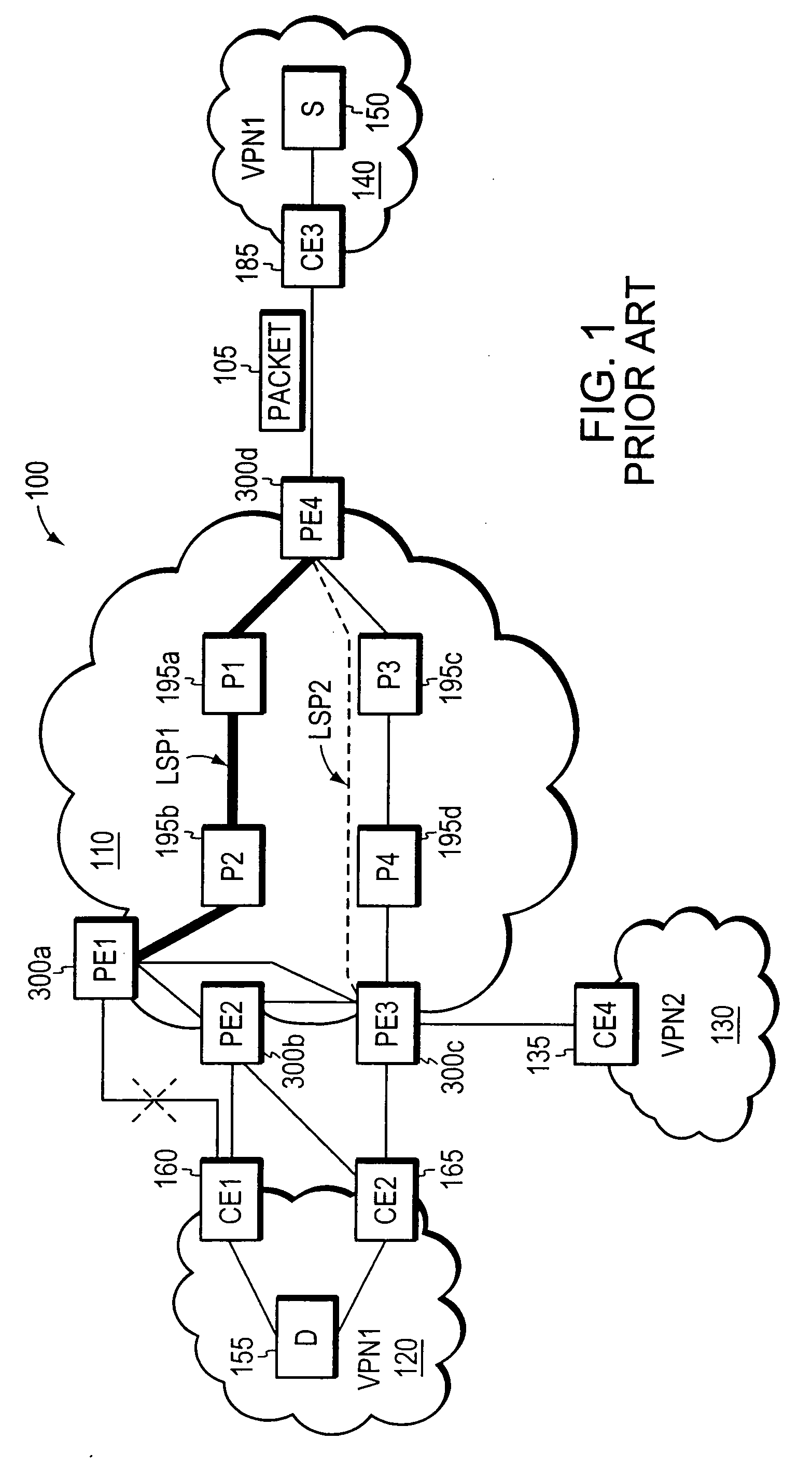
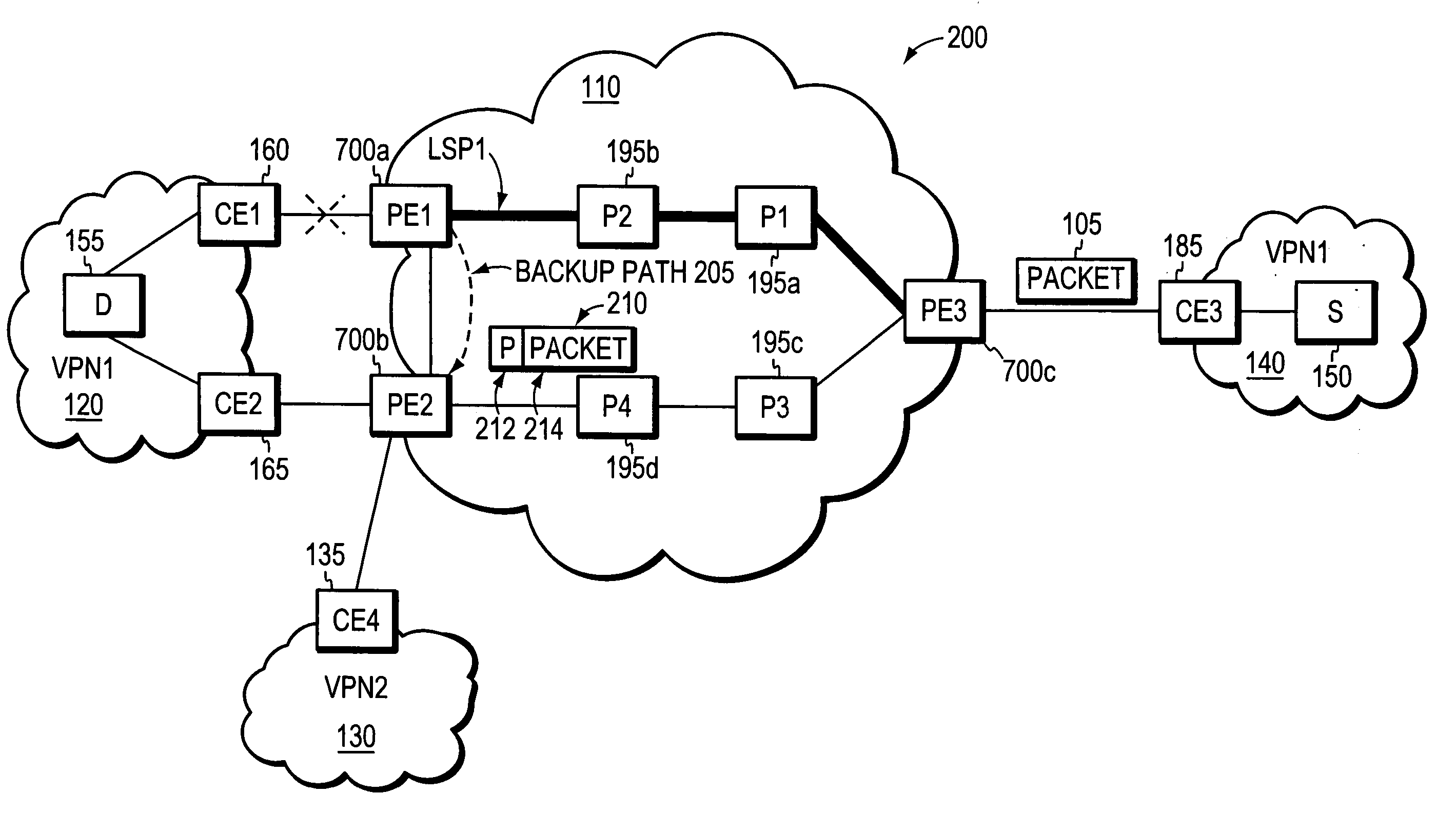
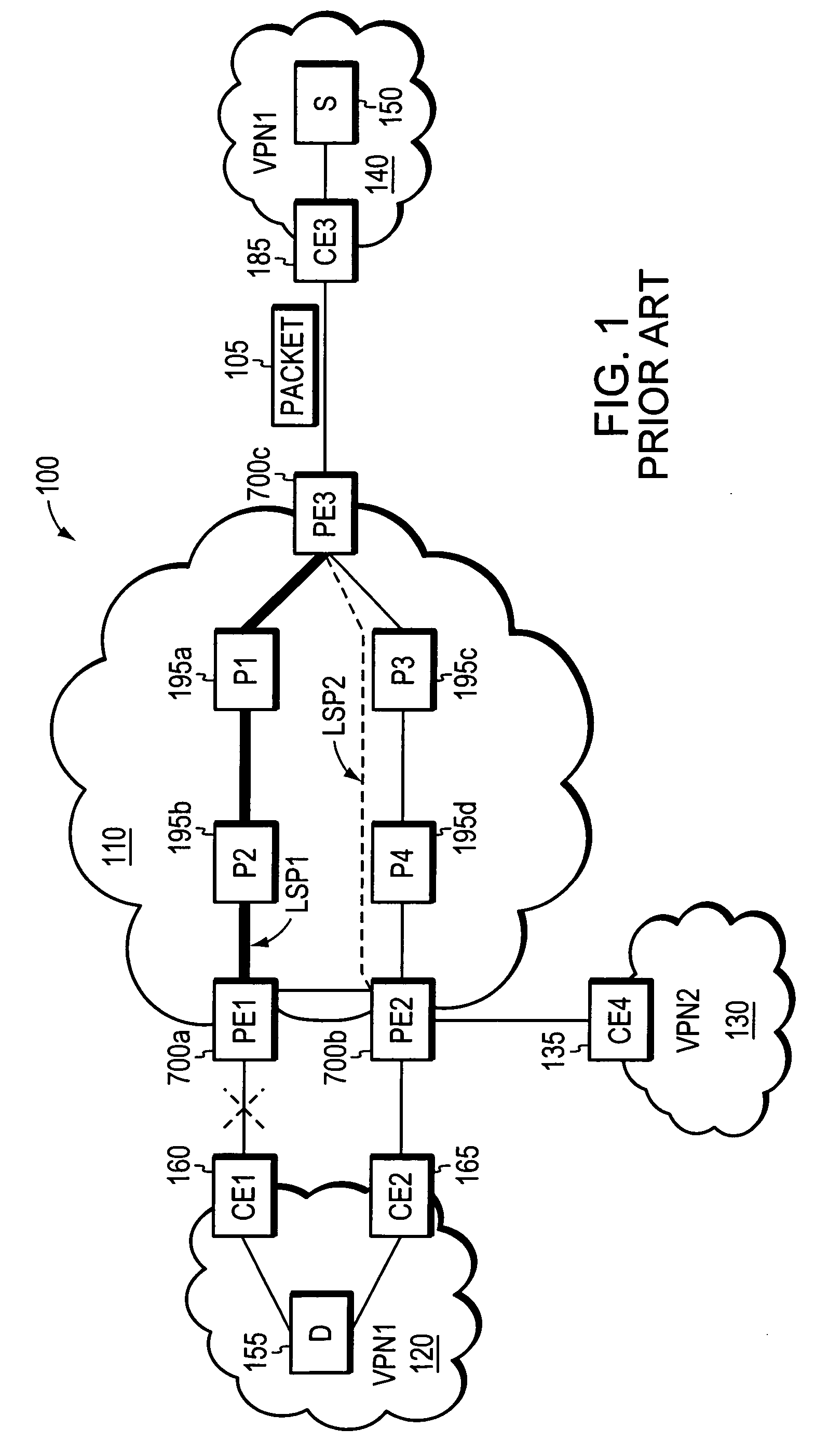
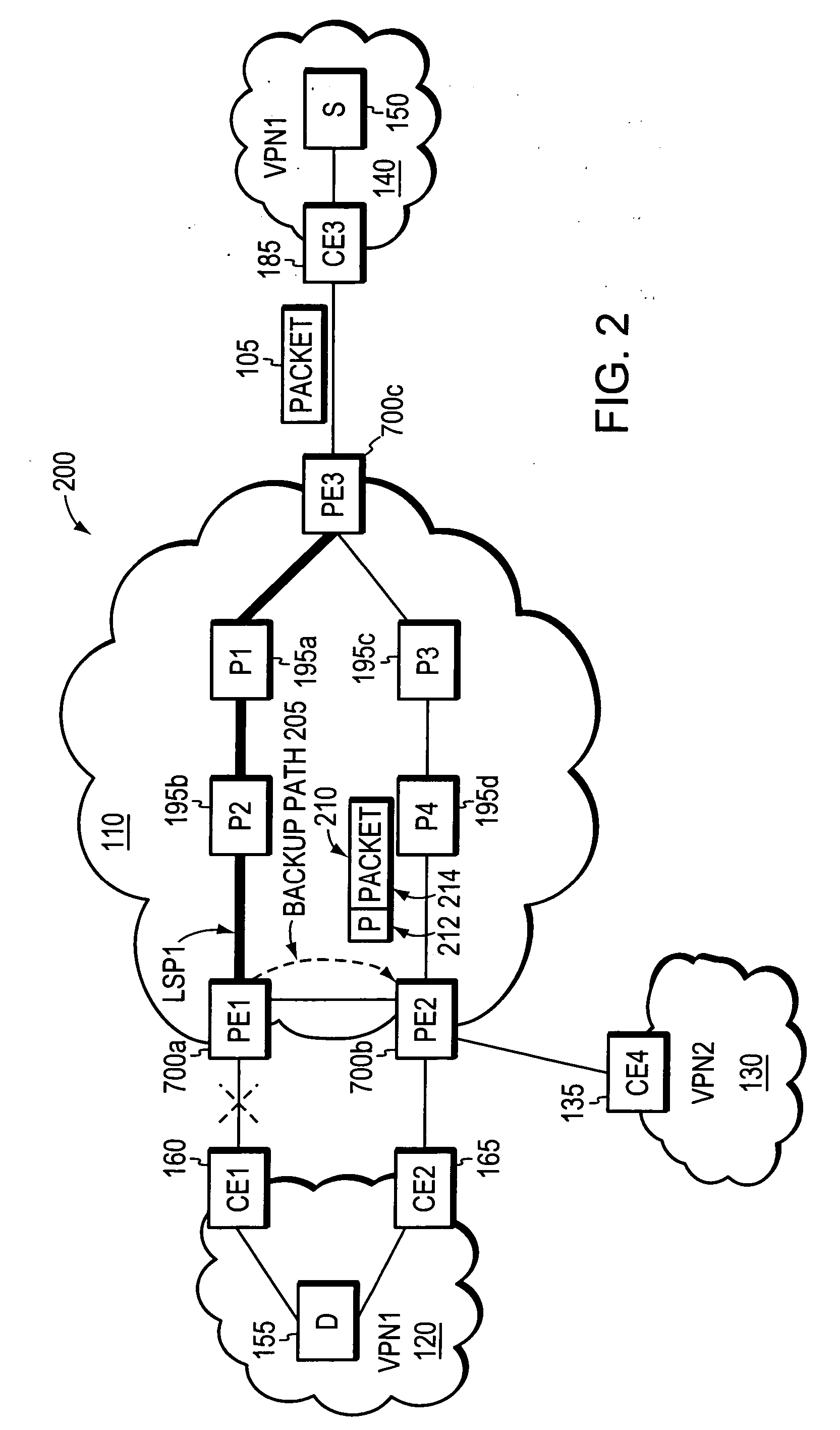
Agile digital communication network with rapid rerouting
ActiveUS7362709B1Low reliabilityImprove reliabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsUser deviceBackup path
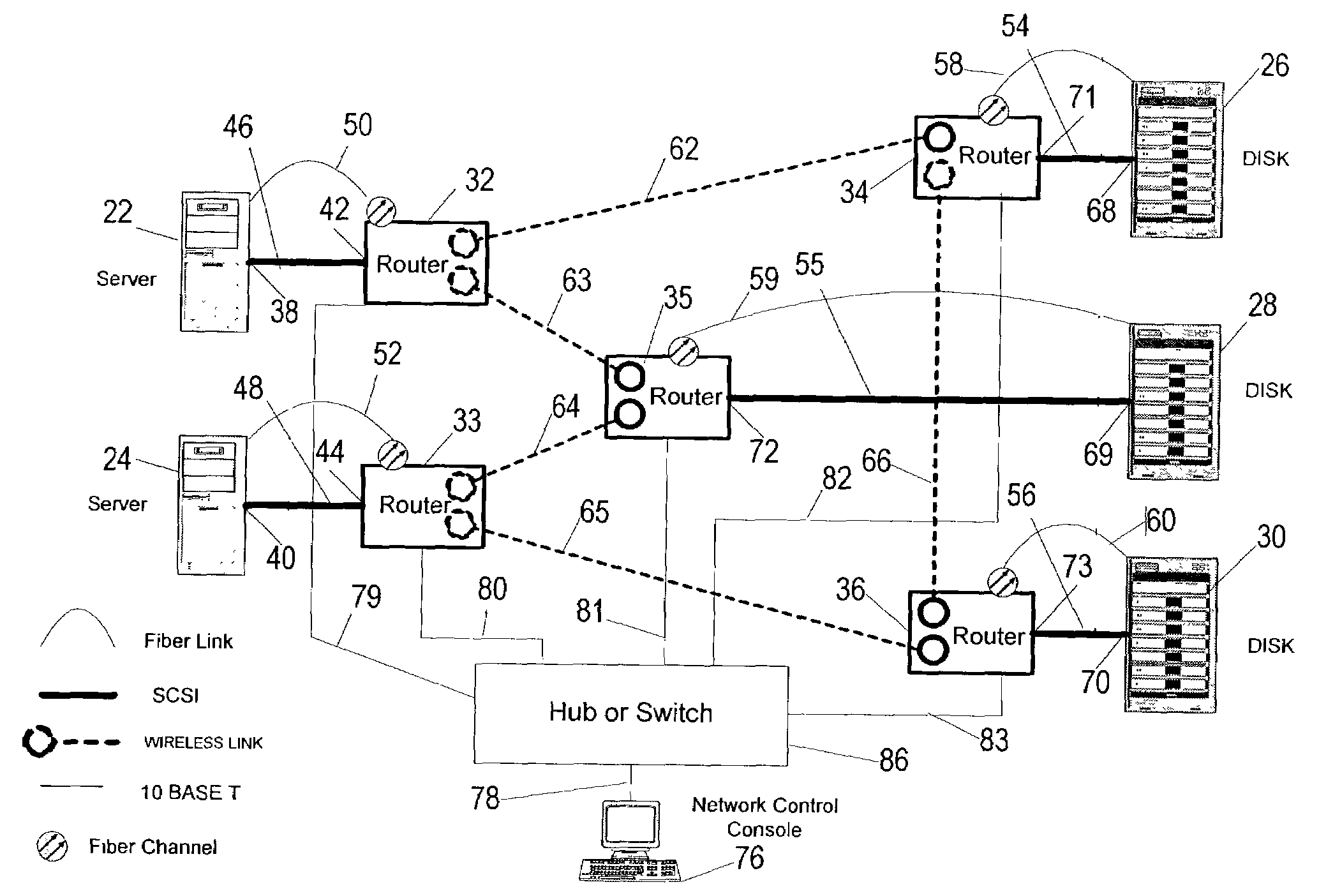
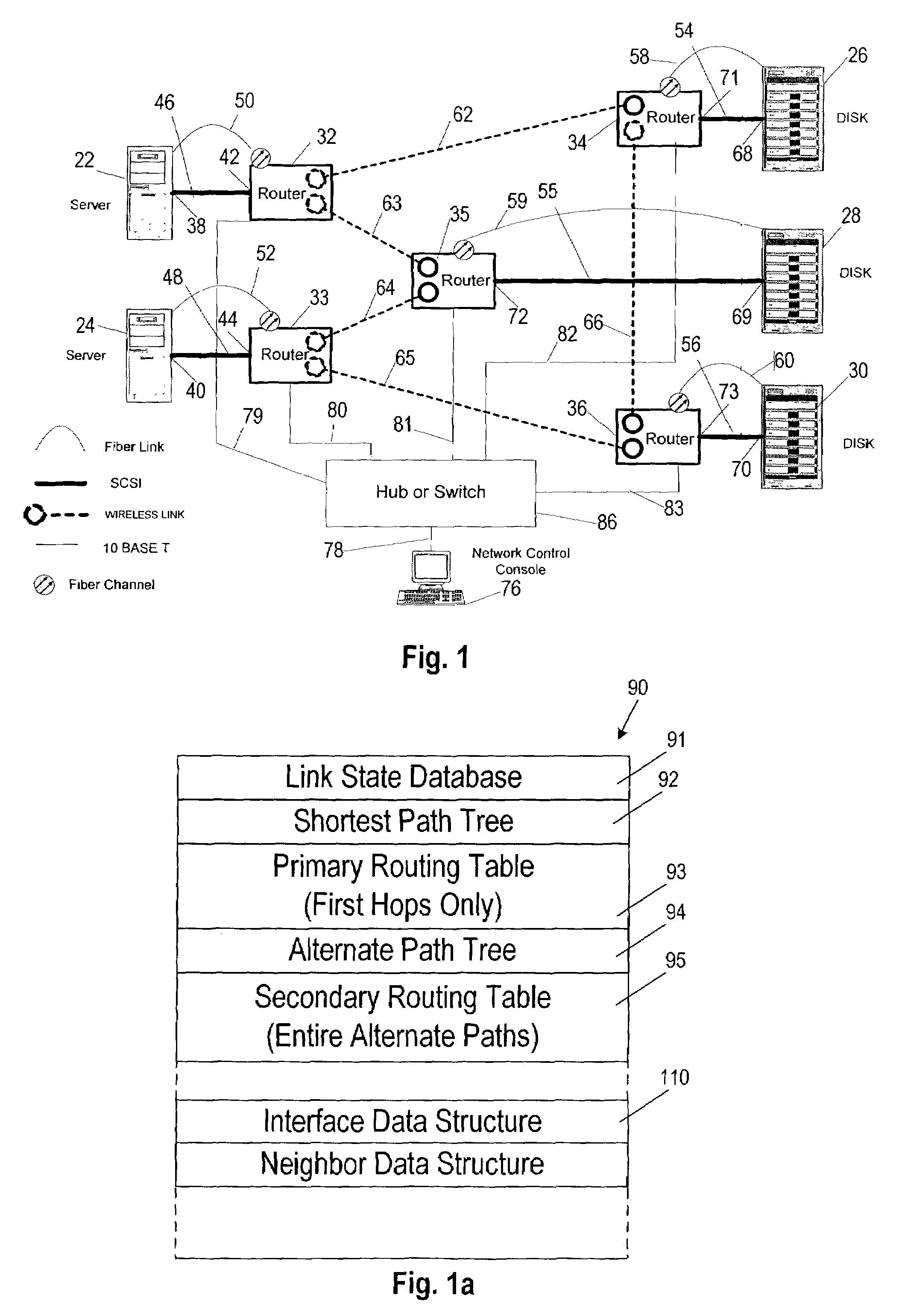
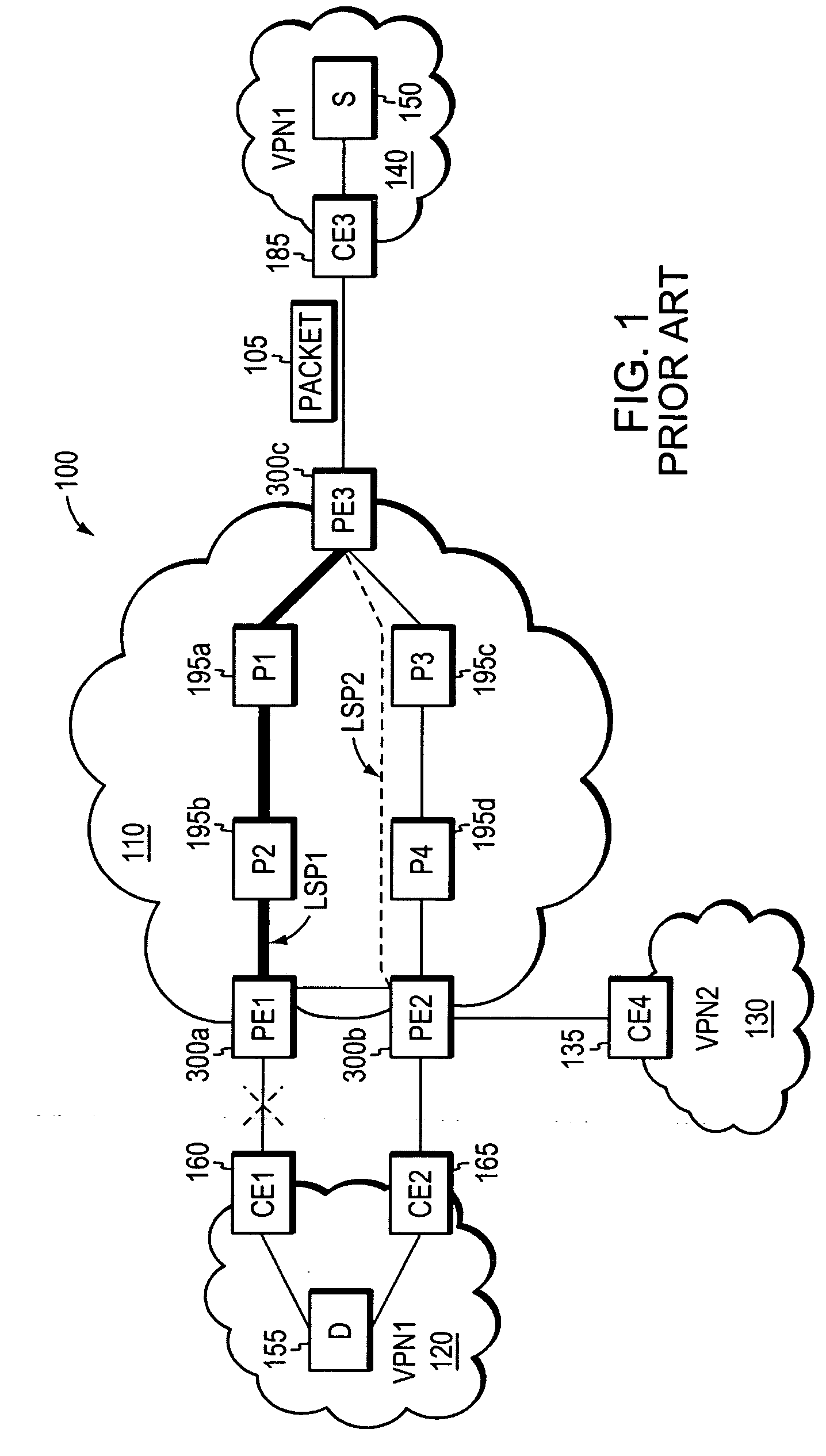
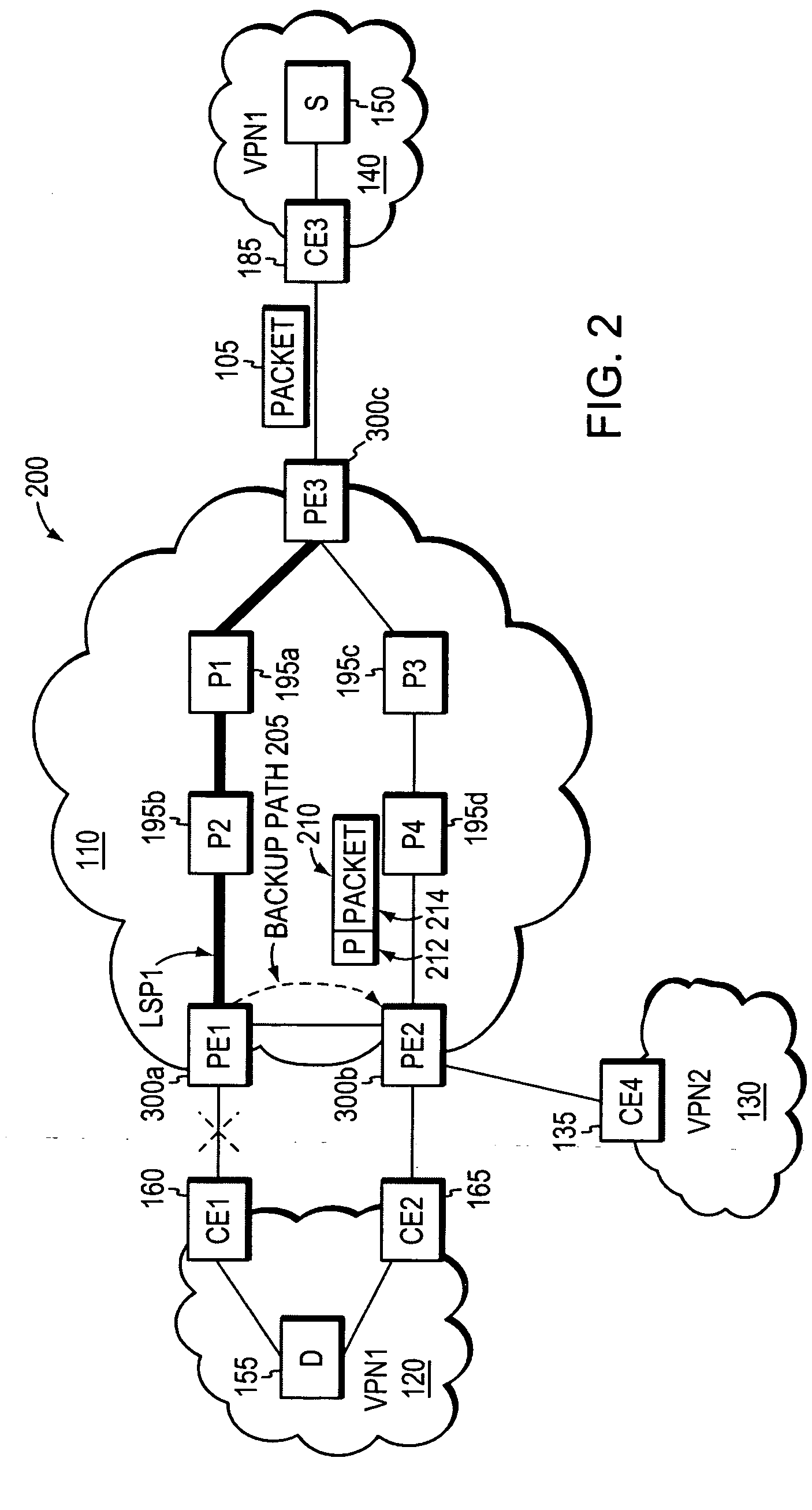
An agile digital communications network has a number of routers that serve as nodes in a mesh network communicating between a user device (e.g., computer, server, etc.) and a target device (e.g., disc storage cabinets, tape, jukebox, etc.). The routers operate on an open shortest path first protocol, each router having two or more interfaces or links to other routers. When a link connected to a router is down and is in the shortest path to another router identified in a communication packet, the packet is forwarded to the identified router on a precalculated alternate route that does not use the unavailable link. IP tunneling assures that routing loops do not occur and send the packet back to the router with the unavailable link because it would have been in the shortest path of an intermediate router. A tunneling technique is provided that maximizes the levels of encapsulation needed at two, regardless of the size or configuration of the network. An unavailable link is not broadcast immediately throughout the network, giving the link an opportunity to be restored before all of the routers are called on to recalculate the shortest paths and alternate paths. During a short interval following the discovery of an unavailable link, then, a router connected to that link is in a state identified as the Use Alternate Path state, and the link is repeatedly checked for availability. Each router calculates and stores the alternative paths to each other router after first calculating the shortest path to each other router. The alternate paths are pulled up and used when an unavailable link is detected. Dijkstra's algorithm is used to calculate the shortest paths. A new algorithm called the iterative dynamic Dijkstra's algorithm is used to calculate the alternative routes.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
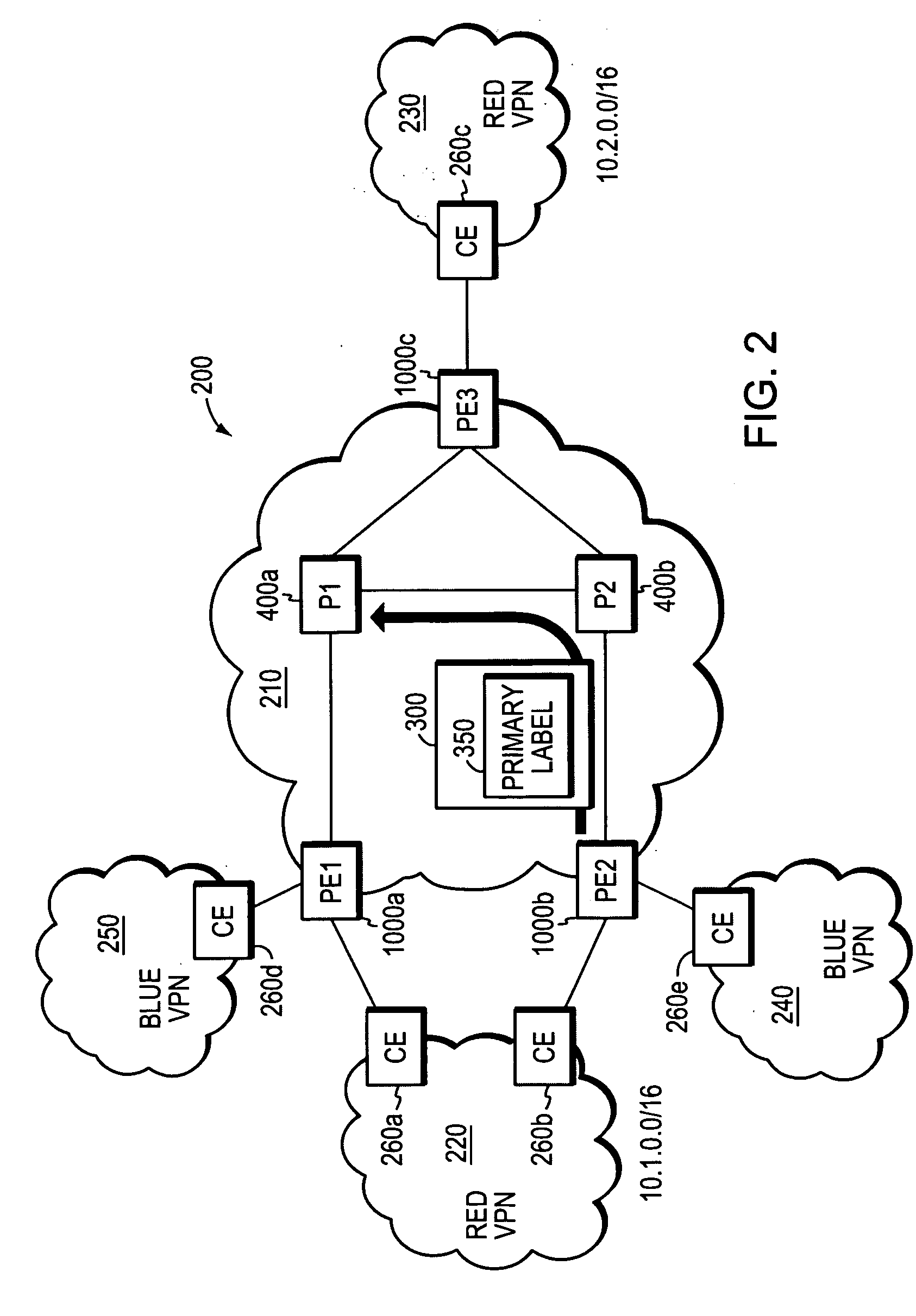
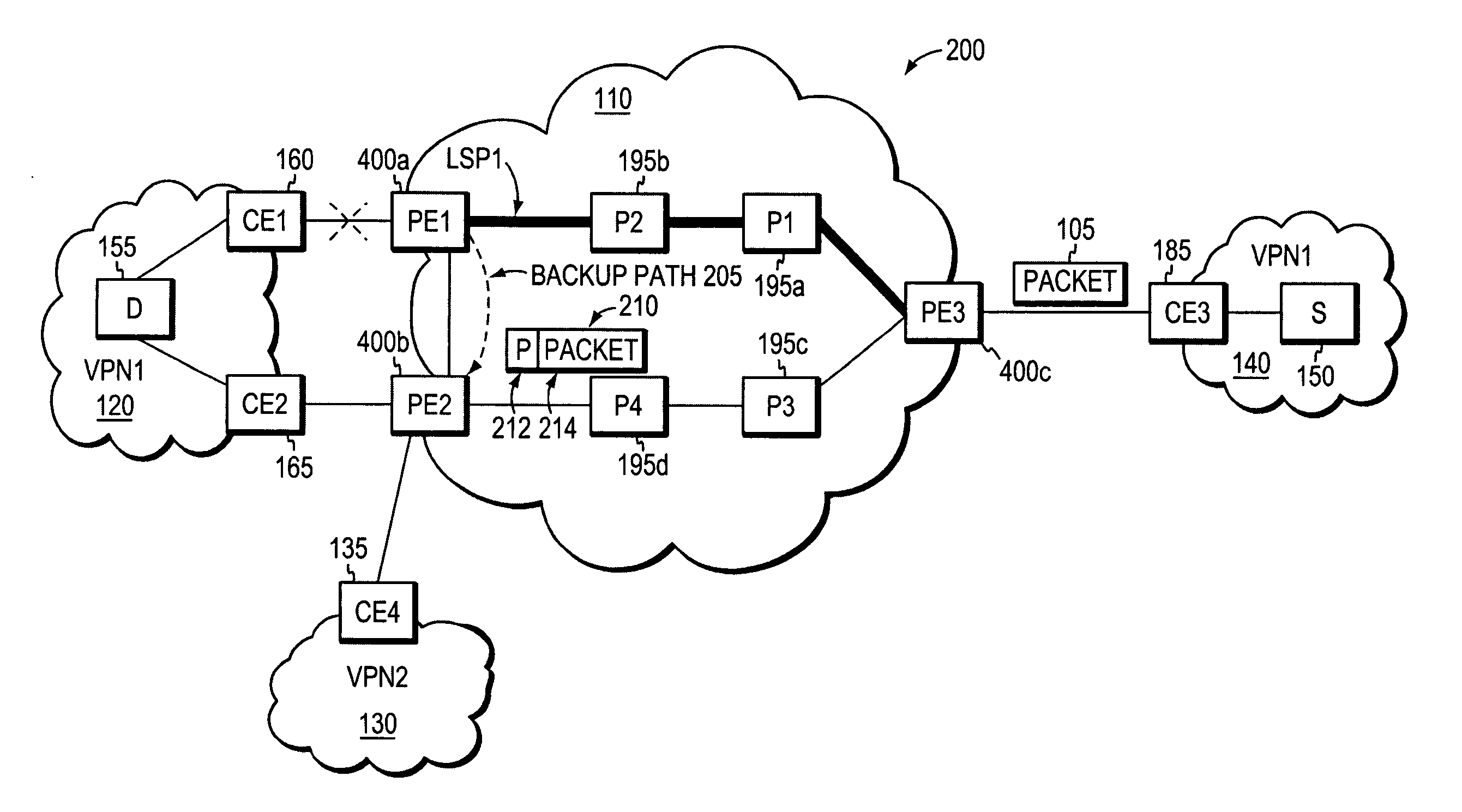
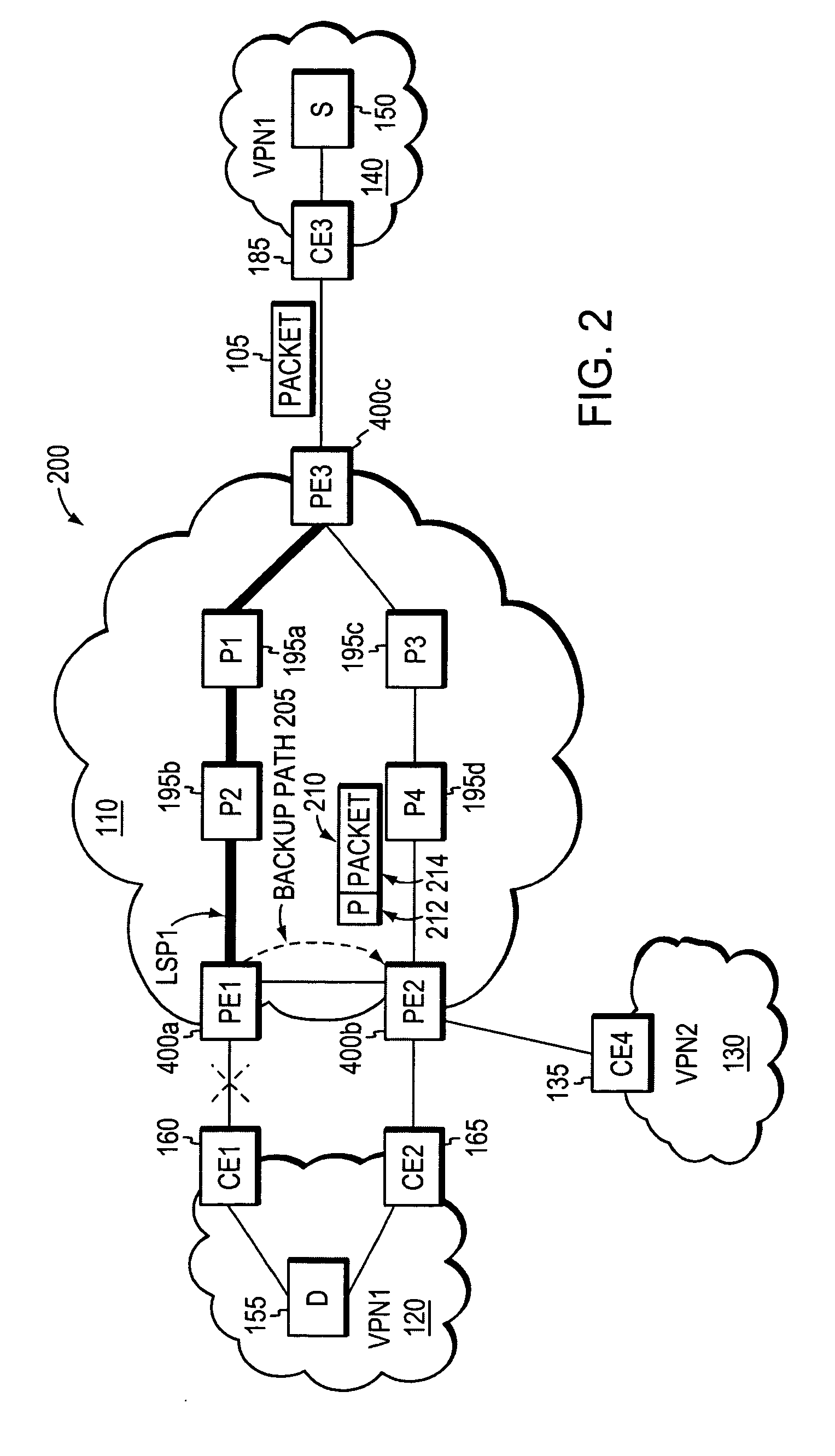
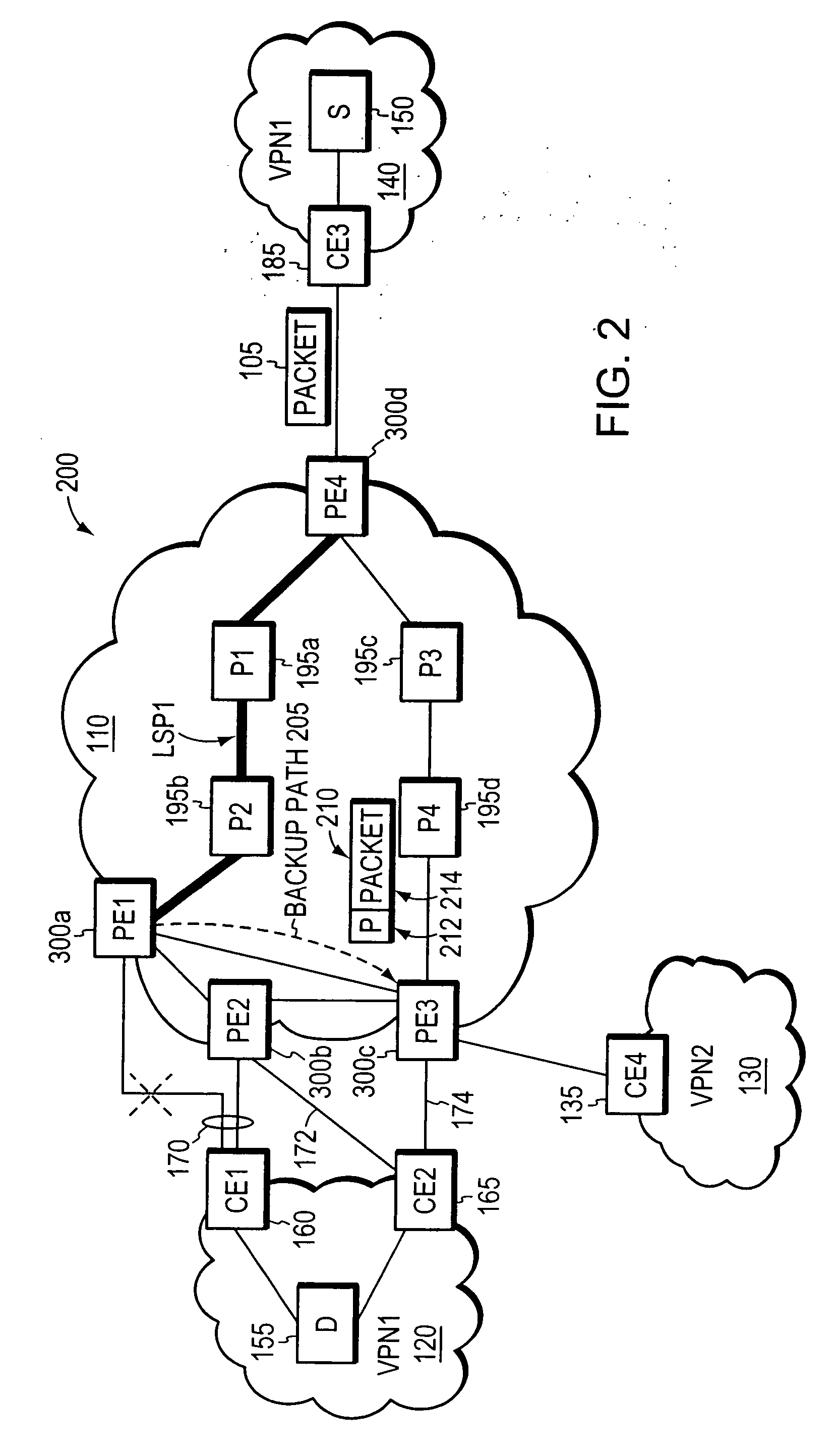
System and method for PE-node protection
ActiveUS20070121486A1Fast reroute (FRR)Quickly and efficiently reroutingError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork ConvergenceNetwork packet
A novel fast reroute (FRR) technique is provided for quickly and efficiently rerouting selected types of network traffic in response to a node or link failure at the edge of a computer network. According to the technique, the network includes first and second edge devices that function as “FRR mates,” such that network traffic originally destined for one FRR mate may be quickly rerouted to the other without having to wait for conventional network convergence. When an edge device receives rerouted packets originally destined for its FRR mate, the device responds by forwarding only those rerouted packets matching the selected traffic types; rerouted packets that do not match the selected traffic types are dropped or otherwise discarded. The first and second edge devices may be statically configured as FRR mates, e.g., by a network administrator, or they may be configured to automatically detect their compatibility as FRR mates.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
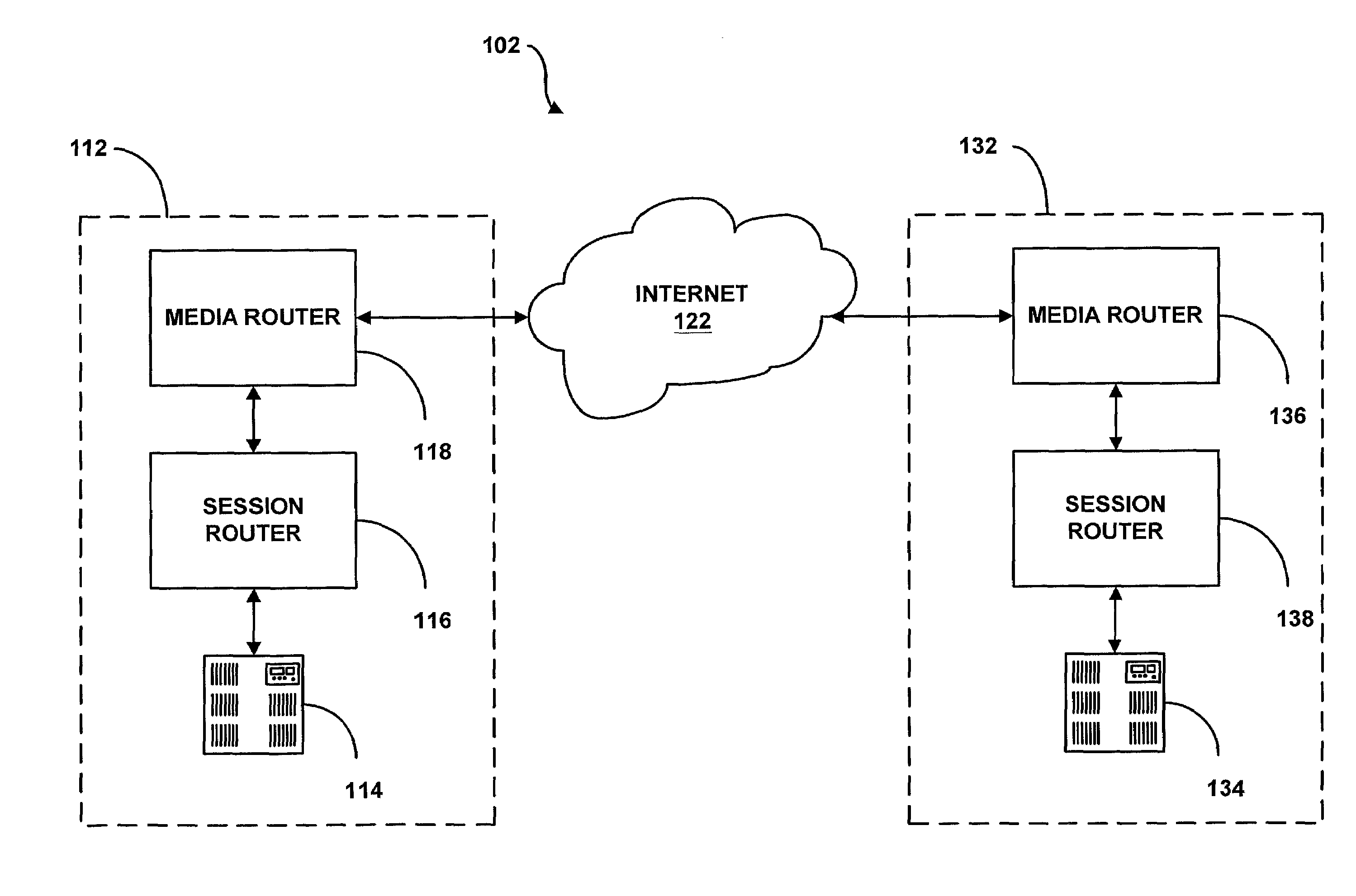
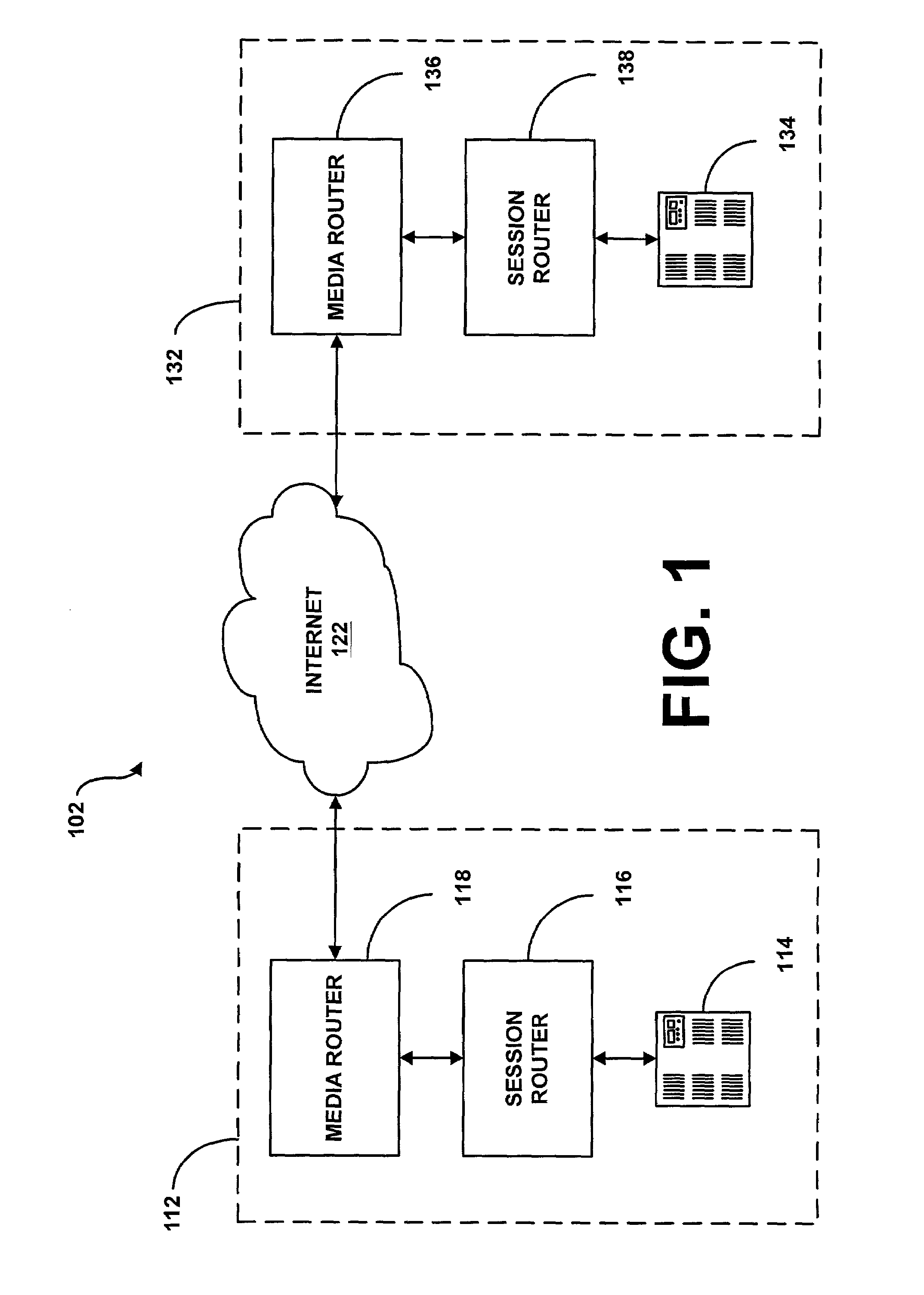
System and method for providing rapid rerouting of real-time multi-media flows
A system and method for providing rapid rerouting of real-time transport protocol (RTP) multi-media flows is disclosed. Generally, a first endpoint is connected to a second endpoint, wherein the first endpoint comprises a transceiver, software stored within the first endpoint defining functions to be performed by the first endpoint, and a processor configured by the software. The processor is configured to perform the steps of, performing flow processing on a data packet received at a first endpoint, from a second endpoint, removing a multi-protocol label switching (MPLS) tag from the data packet, translating a source address and destination address of the data packet, and determining a forwarding destination if more than one destination address of the data packet is provided.
Owner:PRIMARY NETWORKS +1
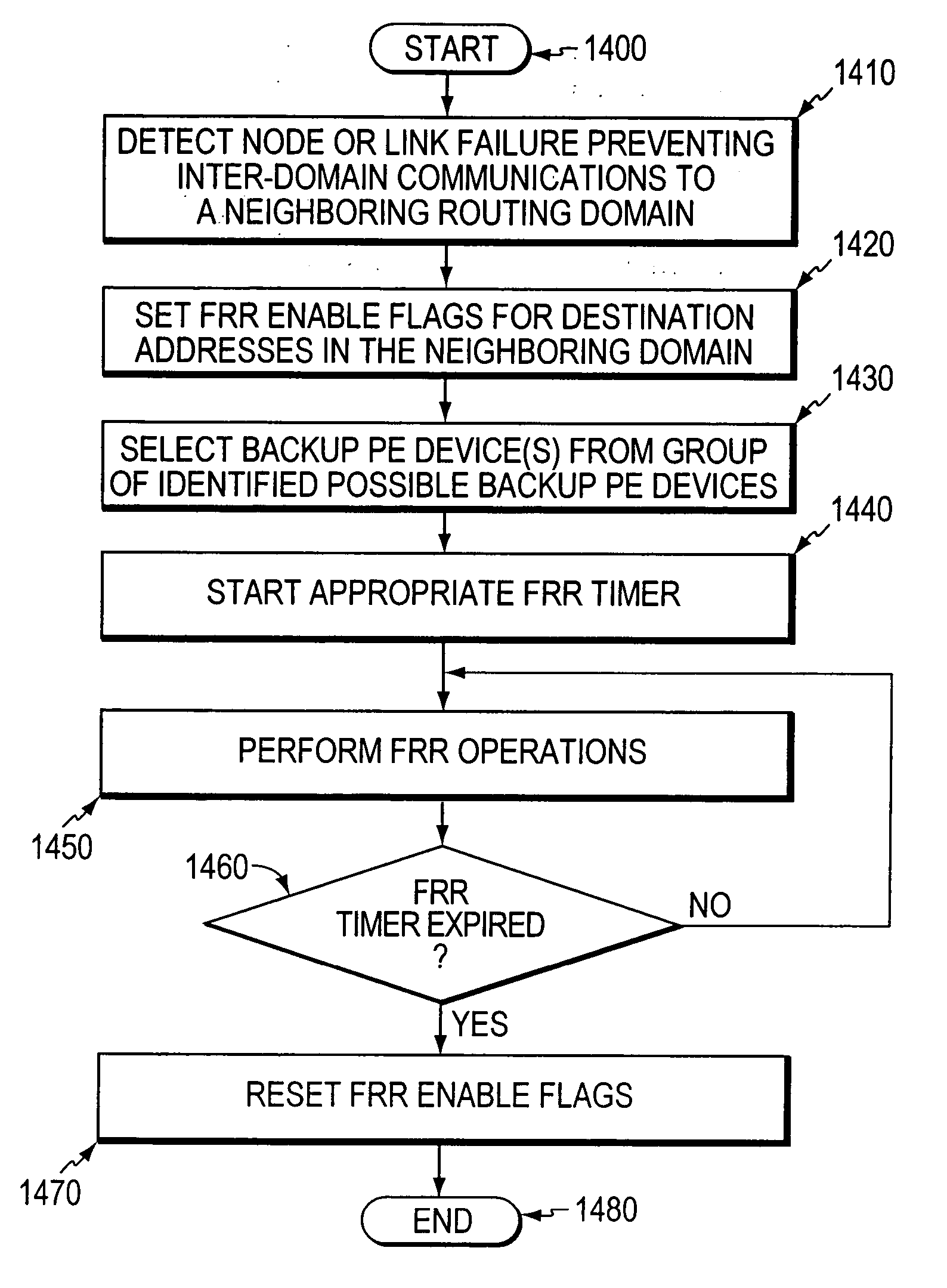
Fast reroute (FRR) protection at the edge of a RFC 2547 network
InactiveUS20060126496A1Quickly and efficiently forwardedFast reroute (FRR)Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRouting domainInter-domain
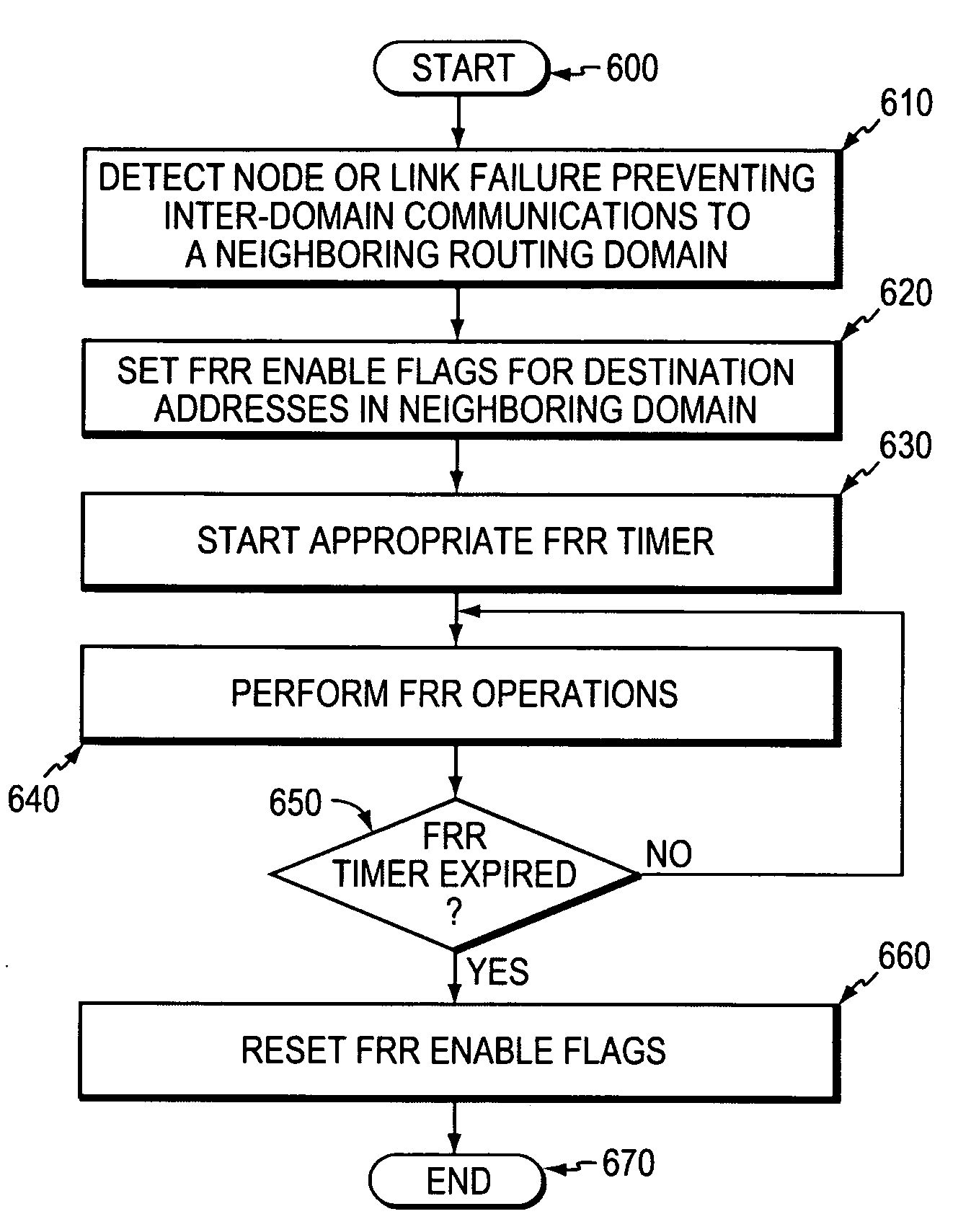
A fast reroute (FRR) technique that may be deployed at the edge of a network having first and second edge devices coupled to a neighboring routing domain. If the first edge device detects a node or link failure that prevents it from communicating with the neighboring domain, the first edge device reroutes at least some data packets addressed to the neighboring domain to the second edge device. The second edge device receives the rerouted packets and then forwards the packets to the neighboring domain. Notably, the second edge device is not permitted to reroute the received packets a second time, e.g., upon identifying another inter-domain node or link failure. As such, loops are avoided at the edge of the network and packets are rerouted to the neighboring routing domain faster and more efficiently than in prior implementations.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
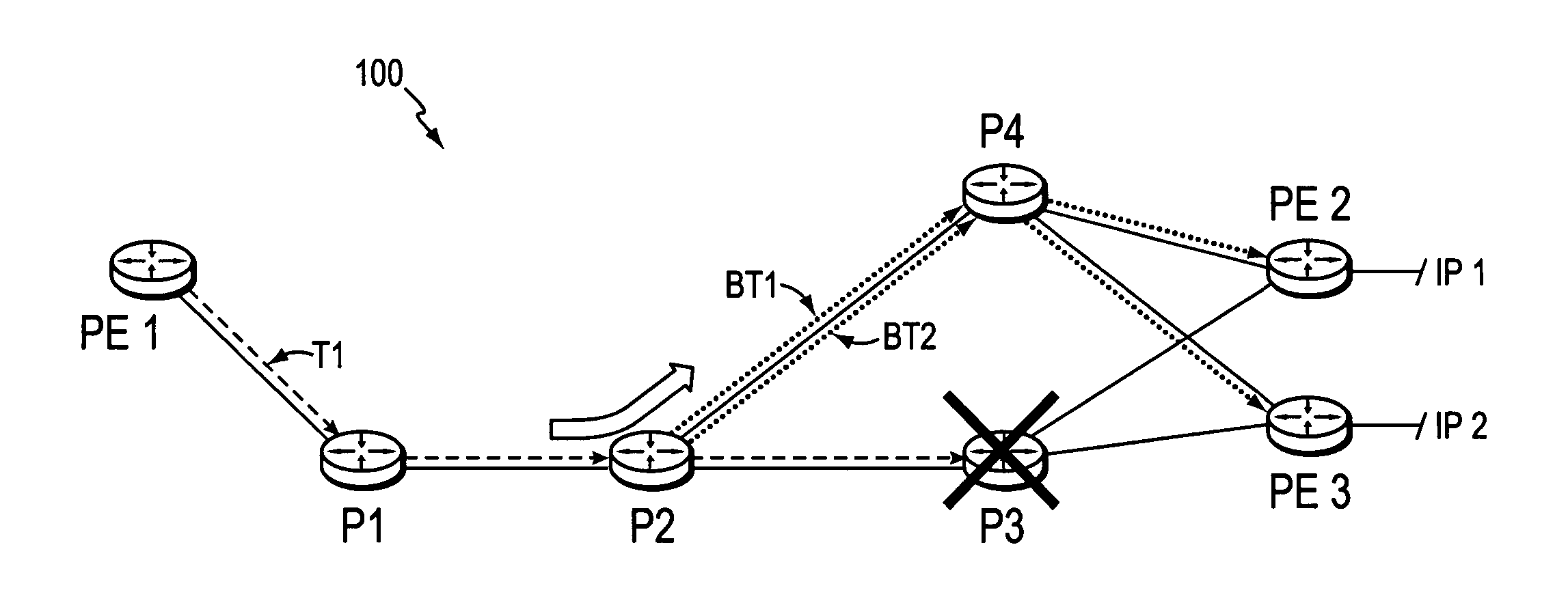
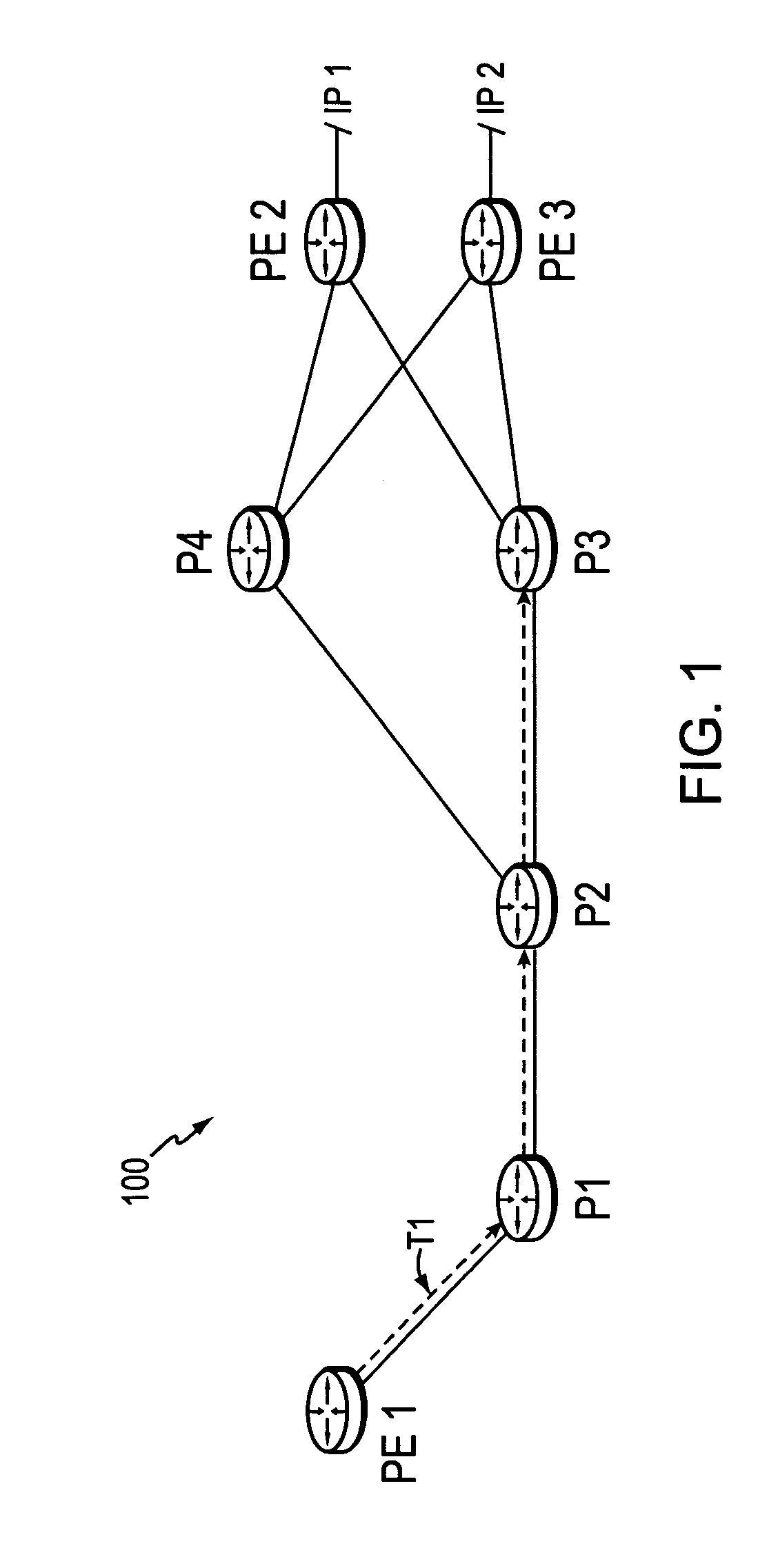
Border router protection with backup tunnel stitching in a computer network
InactiveUS20060153067A1Quick protectionMinimal configurationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic volumeComputer security
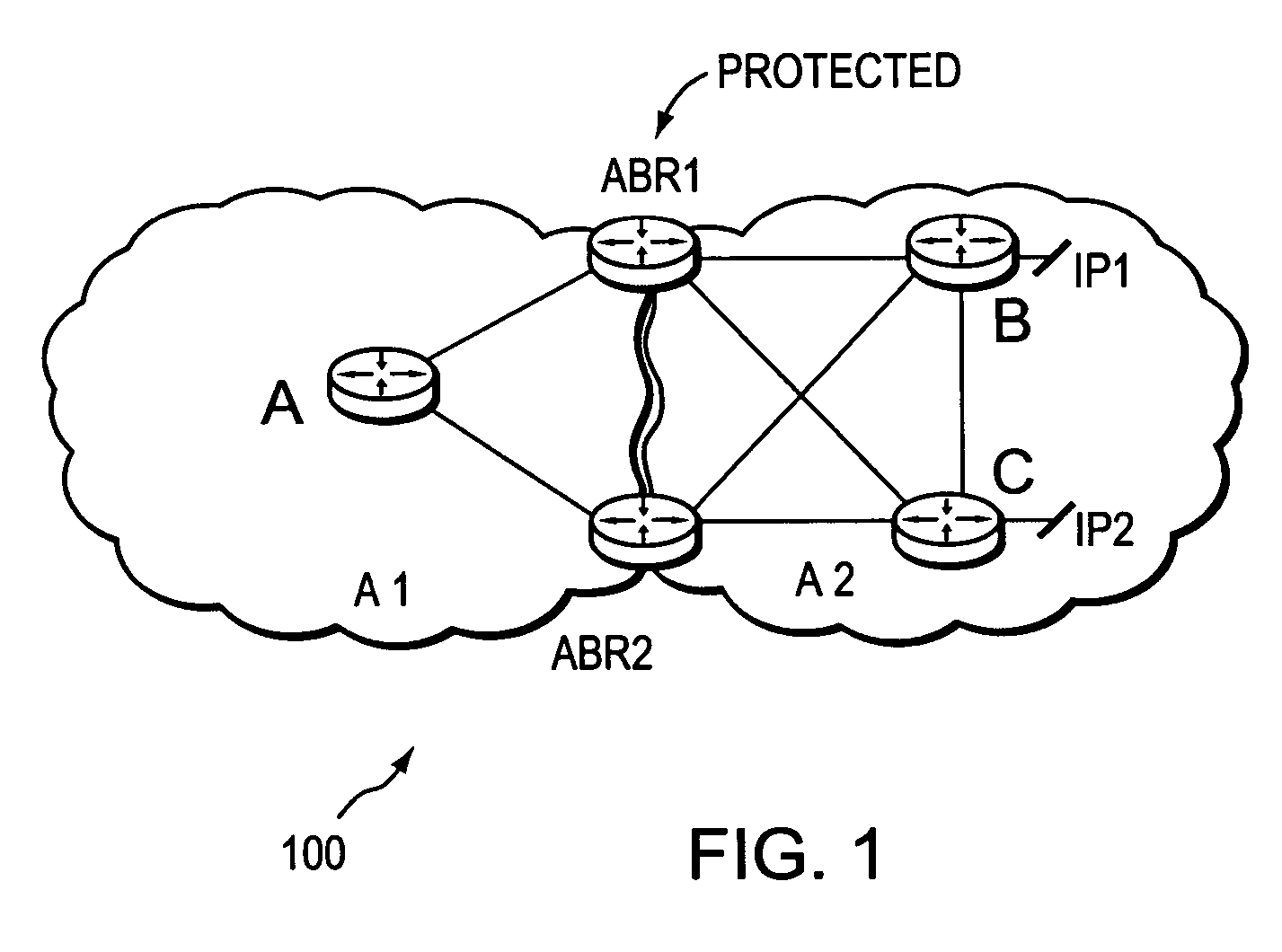
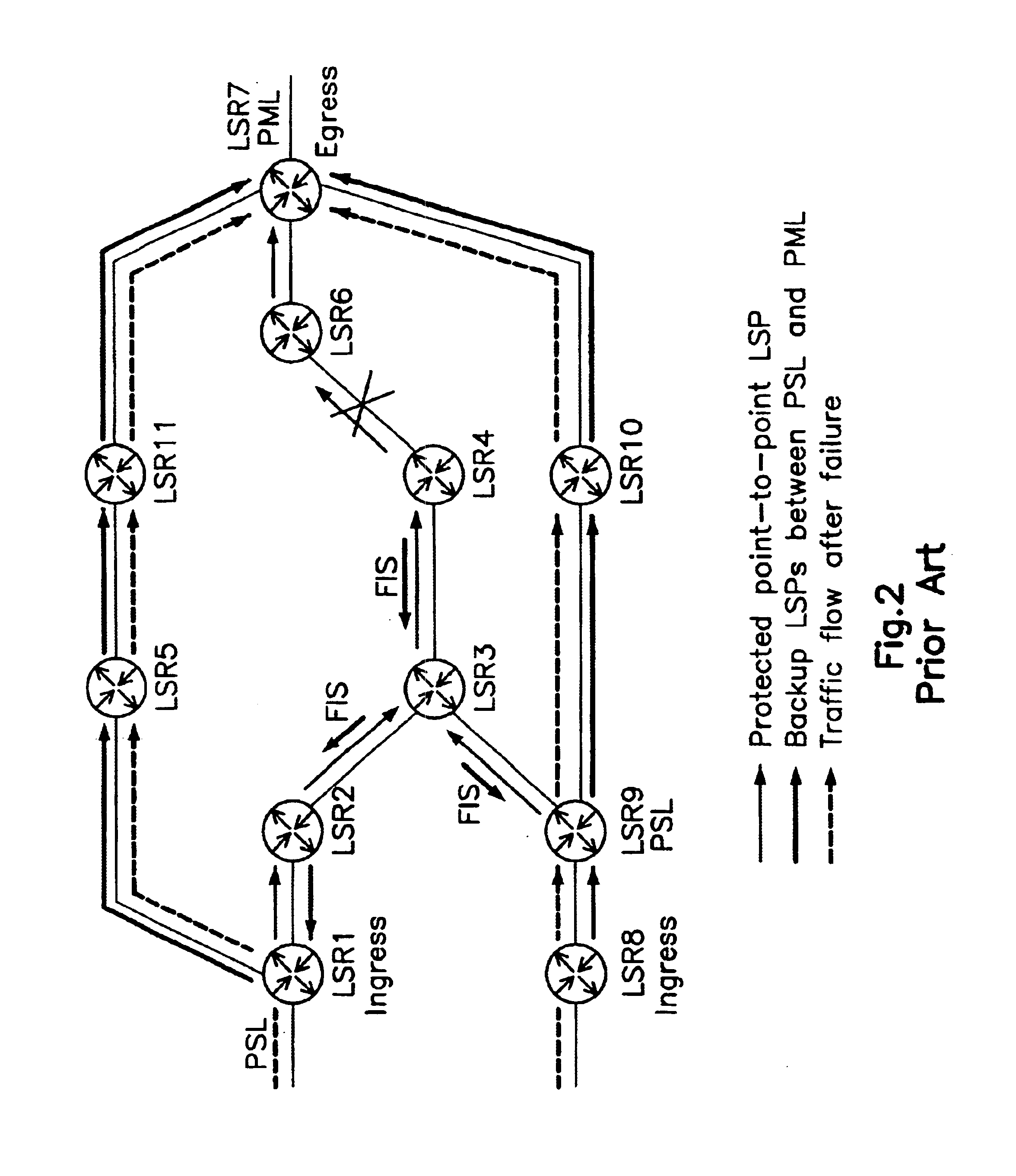
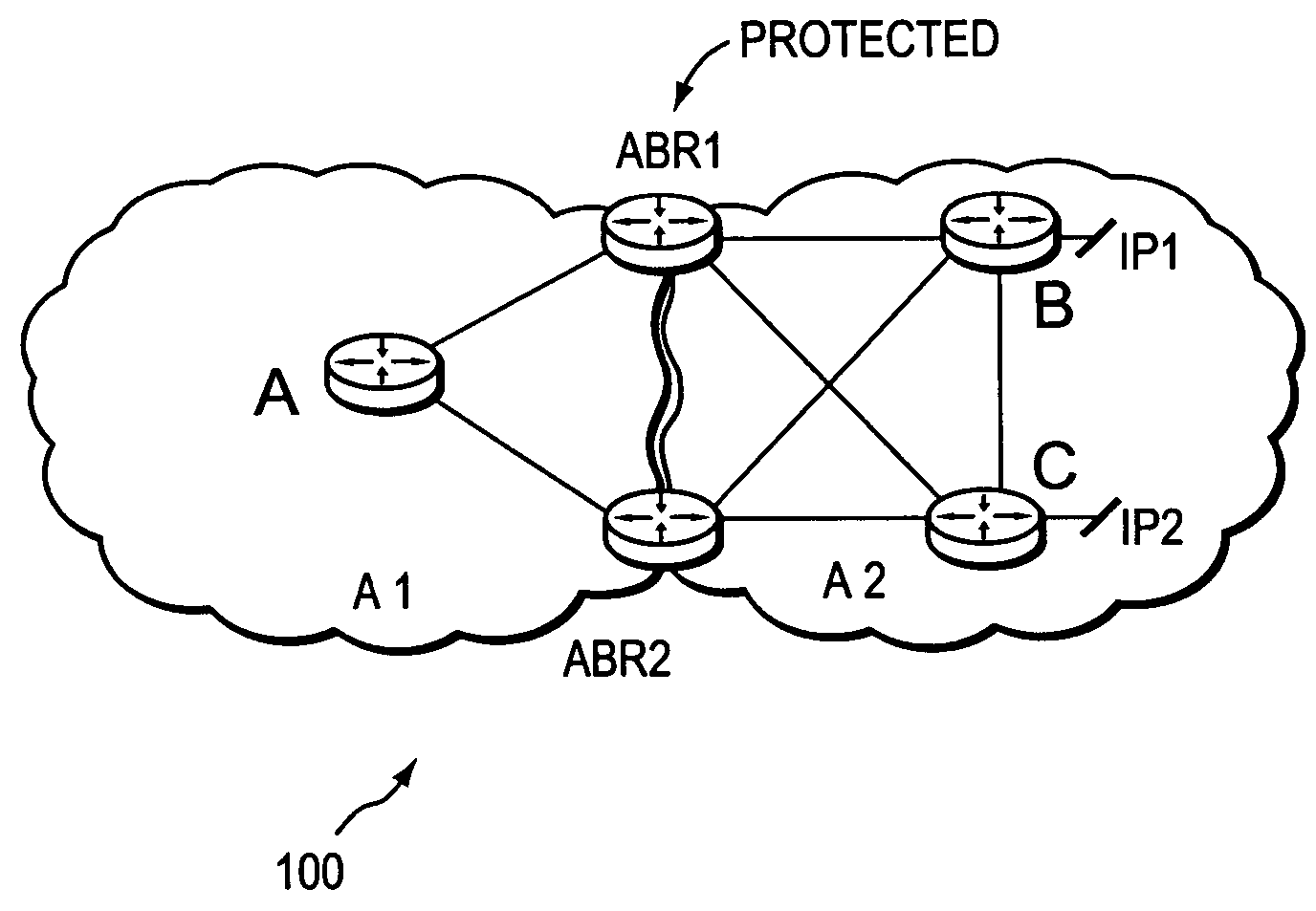
A technique protects against the failure of a border router between two domains in a computer network using Fast Reroute and backup tunnels. According to the technique, the protected border router advertises a list of all its adjacent next-hop routers (i.e., its “neighbors”). A neighbor in the first domain that is immediately upstream to the protected border router and that is configured to protect the border router (i.e., the “protecting router”) selects a neighbor in a second domain (i.e., a “next-next-hop,” NNHOP) to act as a “merge point” of all the NNHOPs of that domain. The protecting router calculates a backup tunnel to the merge point that excludes the protected border router and associates the backup tunnel with all “protected prefixes.” The merge point then “stitches” additional backup tunnels onto the backup tunnel to provide a stitched tunnel to each remaining NNHOP. When the protected border router fails, Fast Reroute is triggered, and all protected prefix traffic is rerouted onto the backup tunnel to the merge point, which either forwards the traffic to its reachable prefixes or to a corresponding stitched tunnel.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Fast rerouting apparatus and method for MPLS multicast
InactiveUS20060159009A1Fast reroutingSpecial service provision for substationError preventionMulticast packetsReal-time computing
Disclosed is a fast rerouting apparatus and method for multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) multicast. The fast rerouting apparatus and method is to rapidly cope with a failure occurring on an MPLS network. The fast rerouting method of redirecting a packet to be transmitted at the nearest location from a location where the failure occurs is applied to the MPLS multicast, so that it is possible to rapidly cope with the failure generated when an MPLS multicast packet is transmitted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
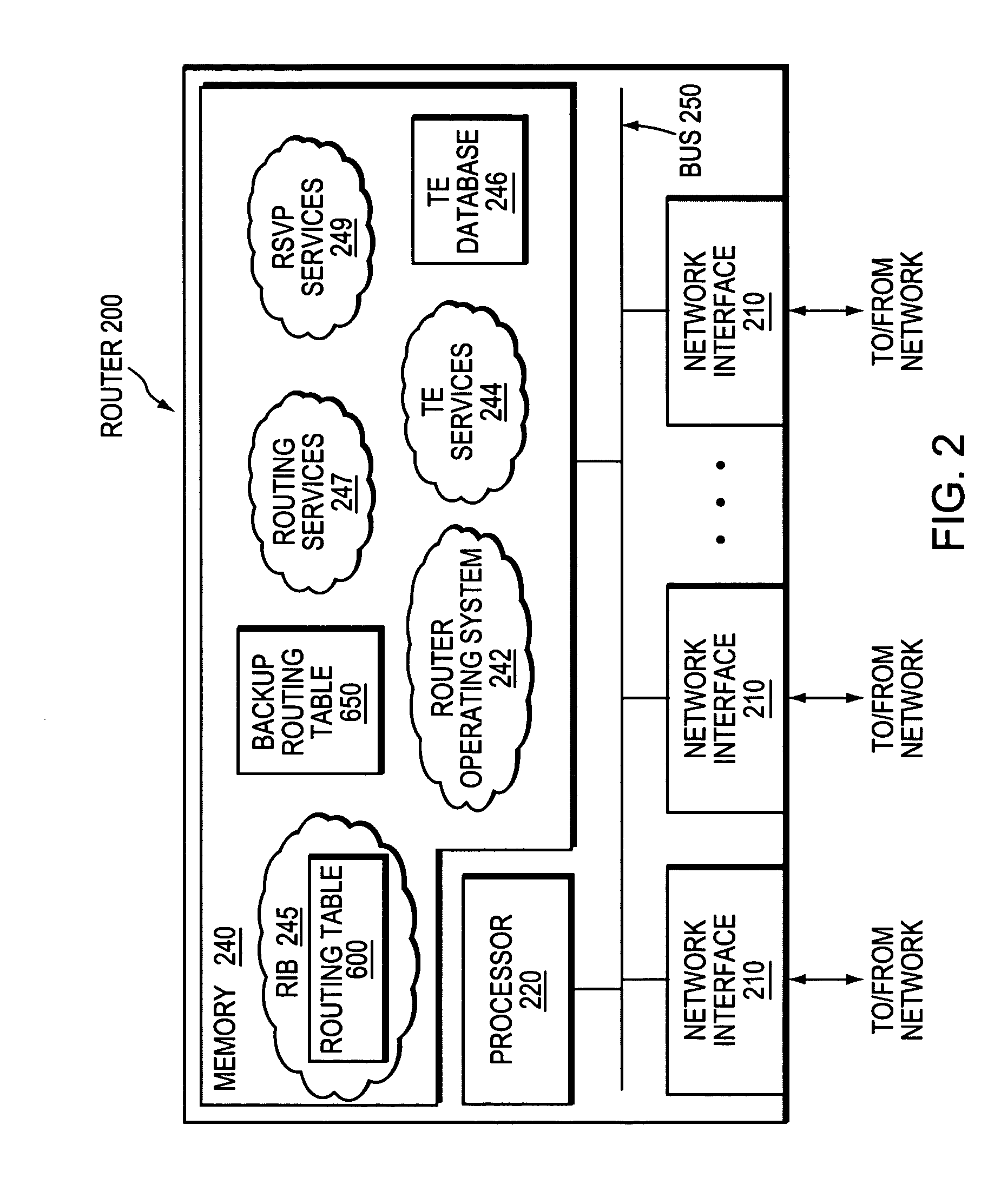
Enhanced switchover for MPLS fast reroute
ActiveUS20050097219A1Digital computer detailsData switching networksForwarding equivalence classDistributed computing
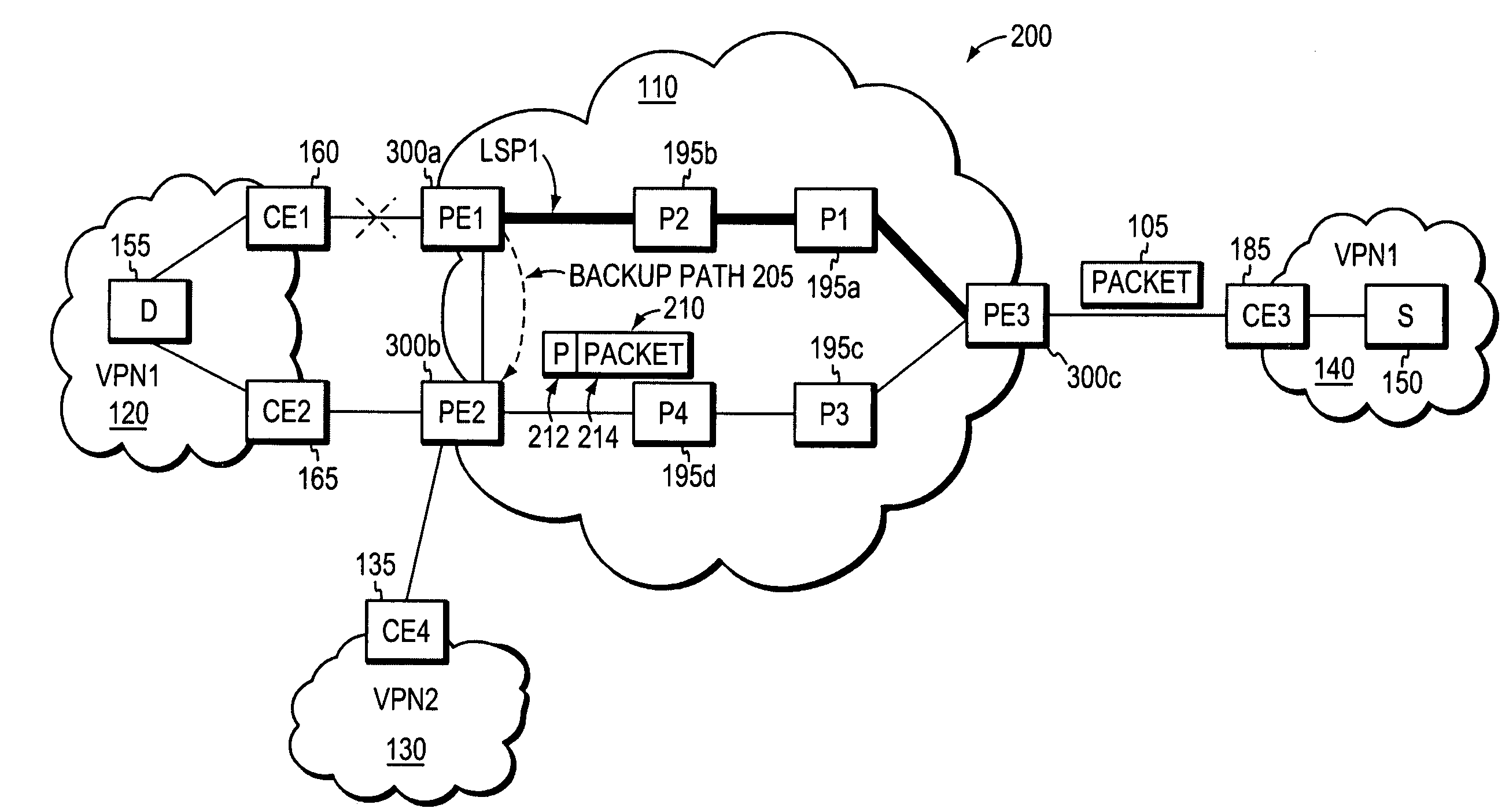
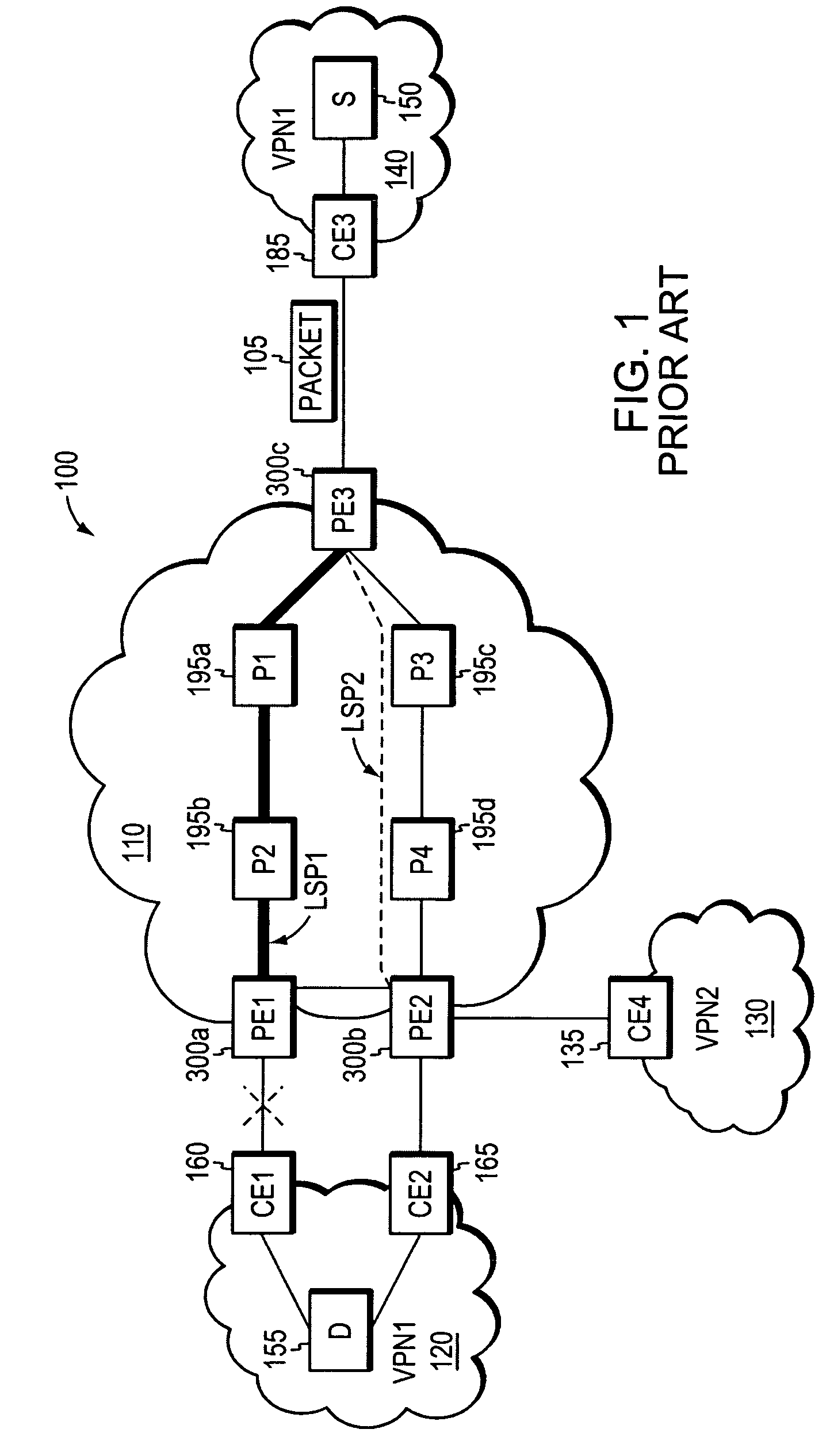
A Fast Reroute implementation where switchover time to backup tunnels upon failure of a protected network element is independent of a number of entries corresponding to forwarding equivalence classes forwarding over LSPs using that element. During normal operation of a packet forwarding device, adjacency information for a received packet is retrieved from a forwarding table based on a look-up of the packet's forwarding equivalence class. Upon failure of a link or node, the appropriate entries in this forwarding table are rewritten to implement the switchover to preconfigured backup tunnels. The switchover is effective even before the rewrite process has completed. Upon detection of the failure, forwarding processing shifts to a fix-up mode. During the fix-up mode, the look-up to the previously mentioned forwarding table is followed by a look-up to a backup tunnel adjacency table based on a pointer retrieved from the forwarding table. Operations relating to use of this backup tunnel adjacency table increase forwarding time somewhat but only during the special fix-up mode.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method for protecting against failure of a TE-LSP tail-end node
InactiveUS20060268682A1Quick protectionMinimal configurationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityLabel switching
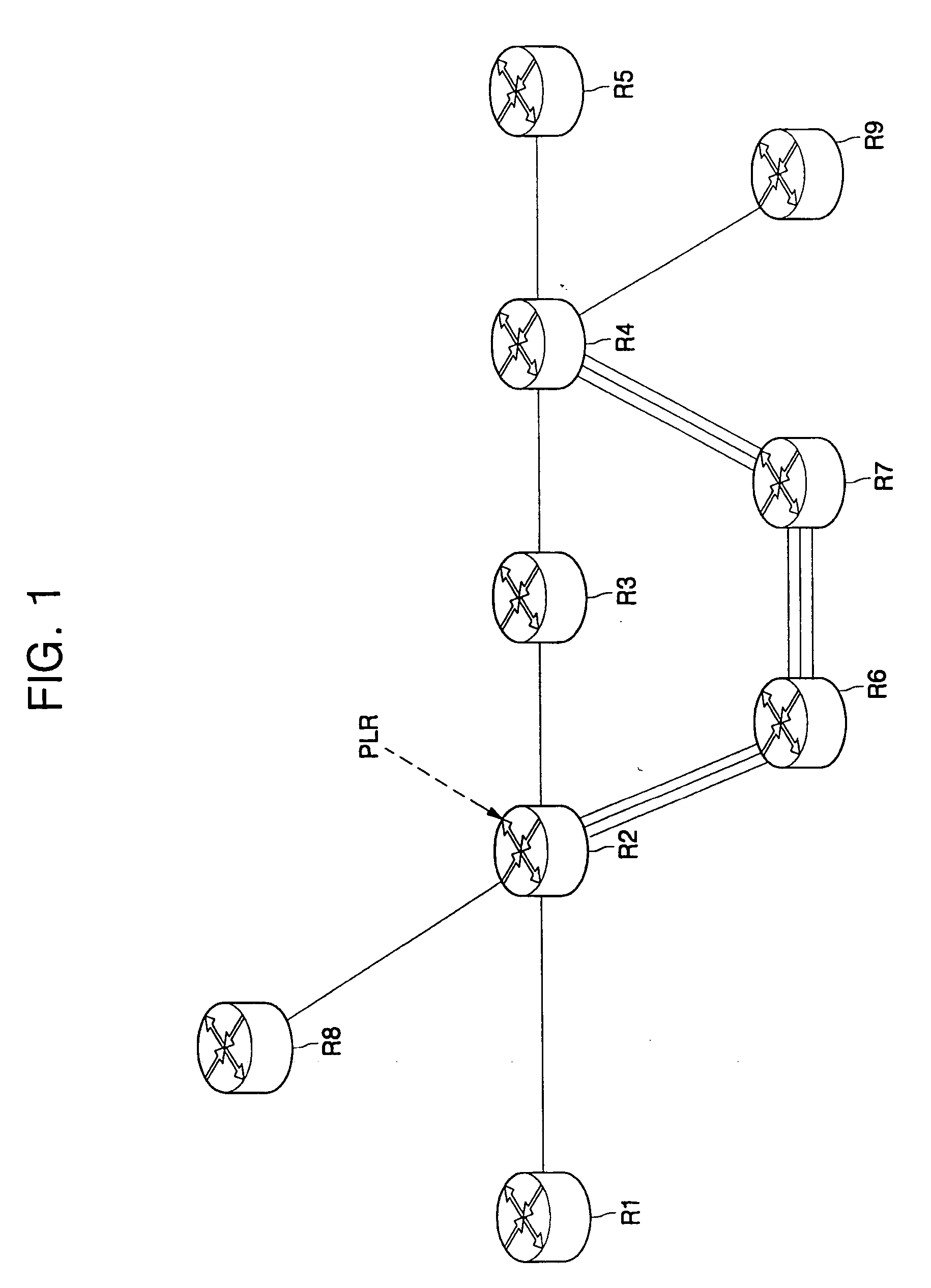
A technique protects against failure of a tail-end node of a Traffic Engineering (TE) Label Switched Path (LSP) in a computer network. According to the protection technique, a node along the TE-LSP that is immediately upstream to the protected tail-end node and that is configured to protect the tail-end node (i.e., the “point of local repair” or PLR) learns reachable address prefixes (i.e., “protected prefixes”) of next-hop routers from the tail-end node (i.e., “next-next-hops,” NNHOPs to the protected prefixes from the PLR). The PLR creates a backup tunnel to each NNHOP that excludes the tail-end node, and associates each backup tunnel with one or more protected prefixes accordingly. When the tail-end node fails, Fast Reroute is triggered, and the protected prefix traffic (from the TE-LSP) is rerouted by the PLR onto an appropriate backup tunnel to a corresponding NNHOP. Notably, the PLR performs a penultimate hop popping (PHP) operation prior to forwarding the traffic along the backup tunnel(s).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
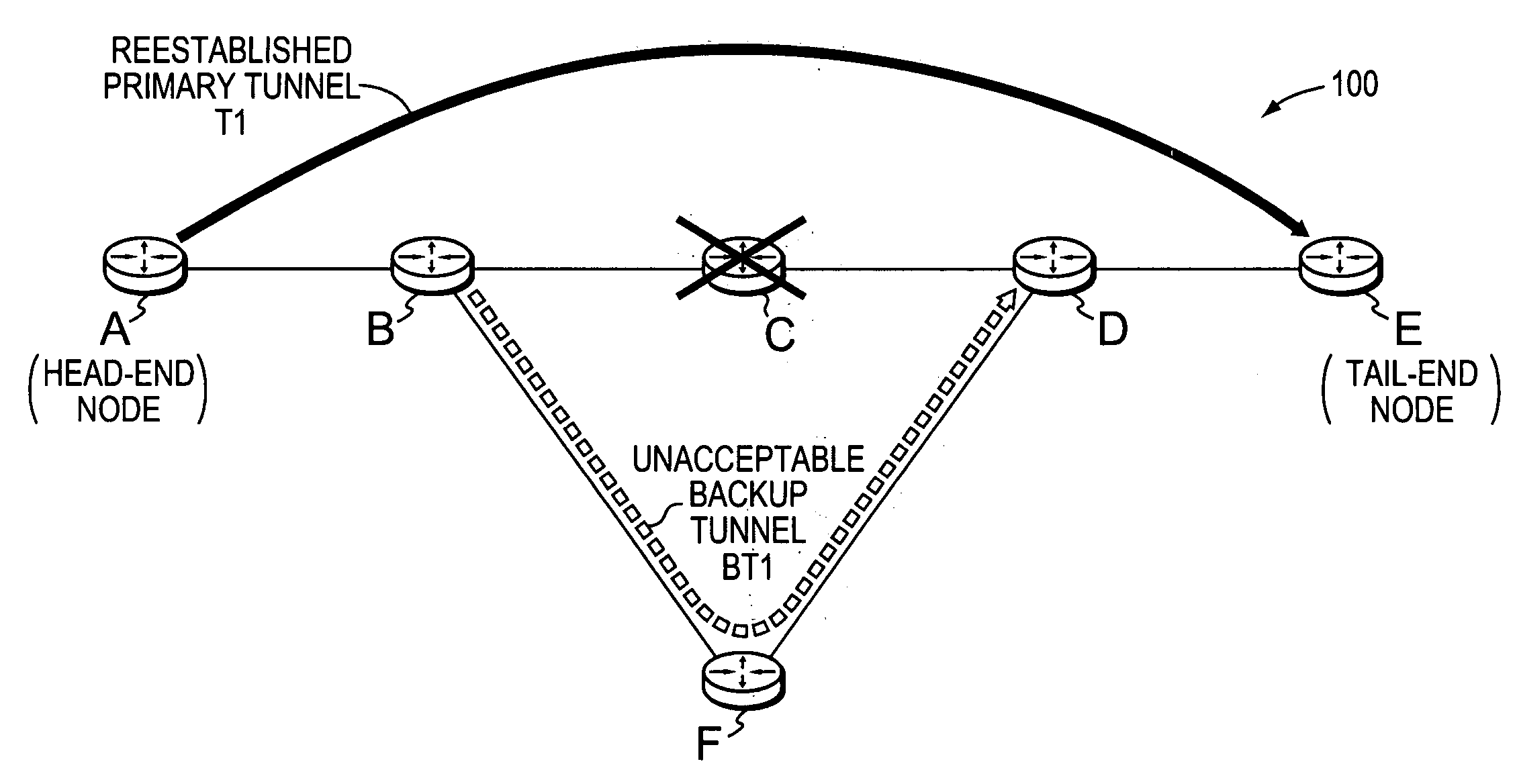
Technique for determining whether to reestablish fast rerouted primary tunnels based on backup tunnel path quality feedback
ActiveUS20070183317A1Promote recoveryReduce needError preventionTransmission systemsNodal analysisDistributed computing
A technique dynamically determines whether to reestablish a Fast Rerouted primary tunnel based on path quality feedback of a utilized backup tunnel in a computer network. According to the novel technique, a head-end node establishes a primary tunnel to a destination, and a point of local repair (PLR) node along the primary tunnel establishes a backup tunnel around one or more protected network elements of the primary tunnel, e.g., for Fast Reroute protection. Once one of the protected network elements fail, the PLR node “Fast Reroutes,” i.e., diverts, the traffic received on the primary tunnel onto the backup tunnel, and sends notification of backup tunnel path quality (e.g., with one or more metrics) to the head-end node. The head-end node then analyzes the path quality metrics of the backup tunnel to determine whether to utilize the backup tunnel or reestablish a new primary tunnel.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
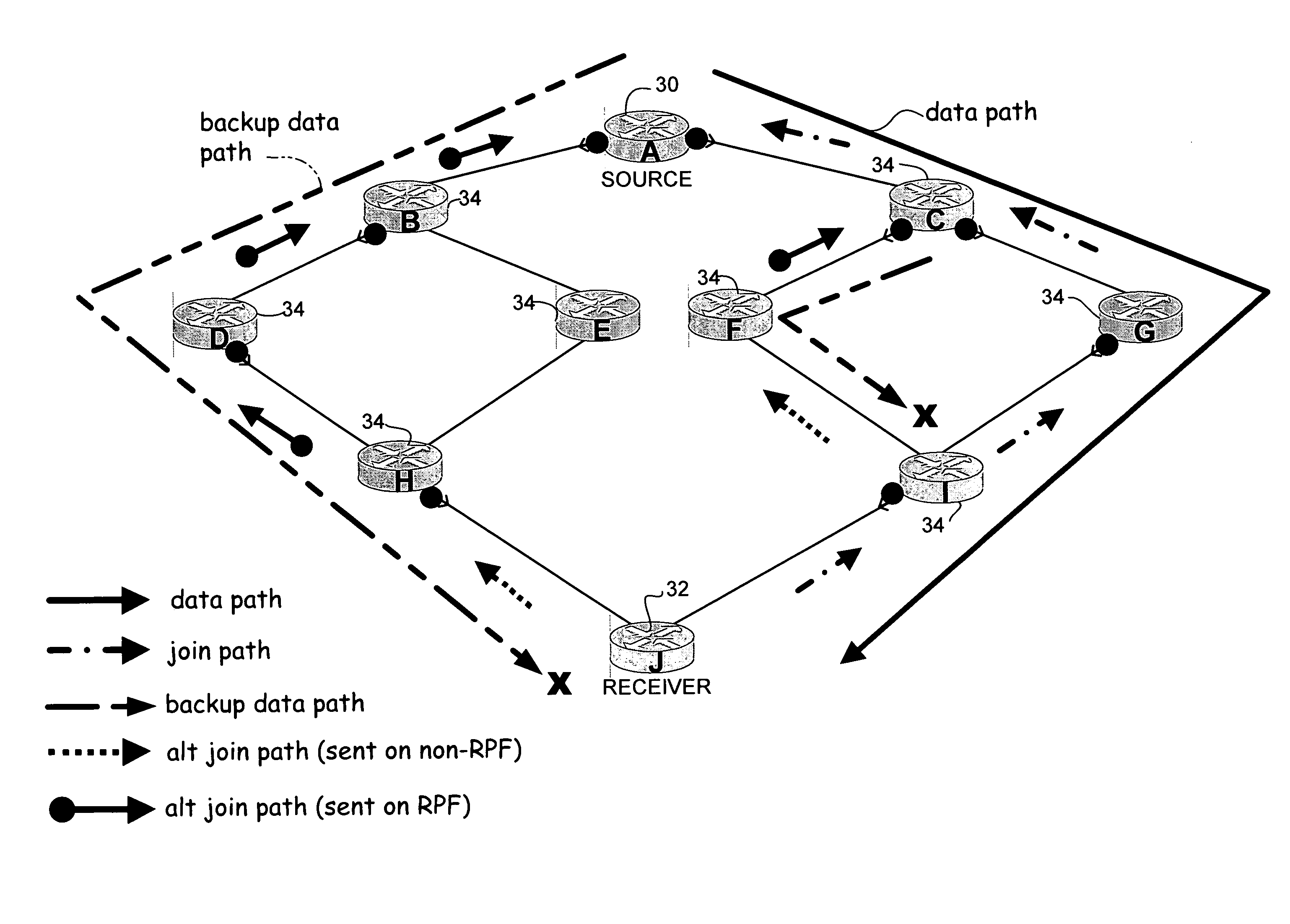
Multicast fast reroute for network topologies
ActiveUS20090201803A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer hardwareNetwork topology
In one embodiment, a method includes receiving a multicast join message at a node having a plurality of interfaces, identifying the interface at which the join message was received, and selecting one or more of the interfaces to transmit the join message based on whether the join message was received on a ring interface. If the join message was received on one of the ring interfaces, the join message is transmitted on another of the interfaces. If the join message was not received on one of the ring interfaces, the join message is transmitted on both of the ring interfaces. The method further includes receiving multicast data and transmitting the multicast data on the interface at which the join message was received.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
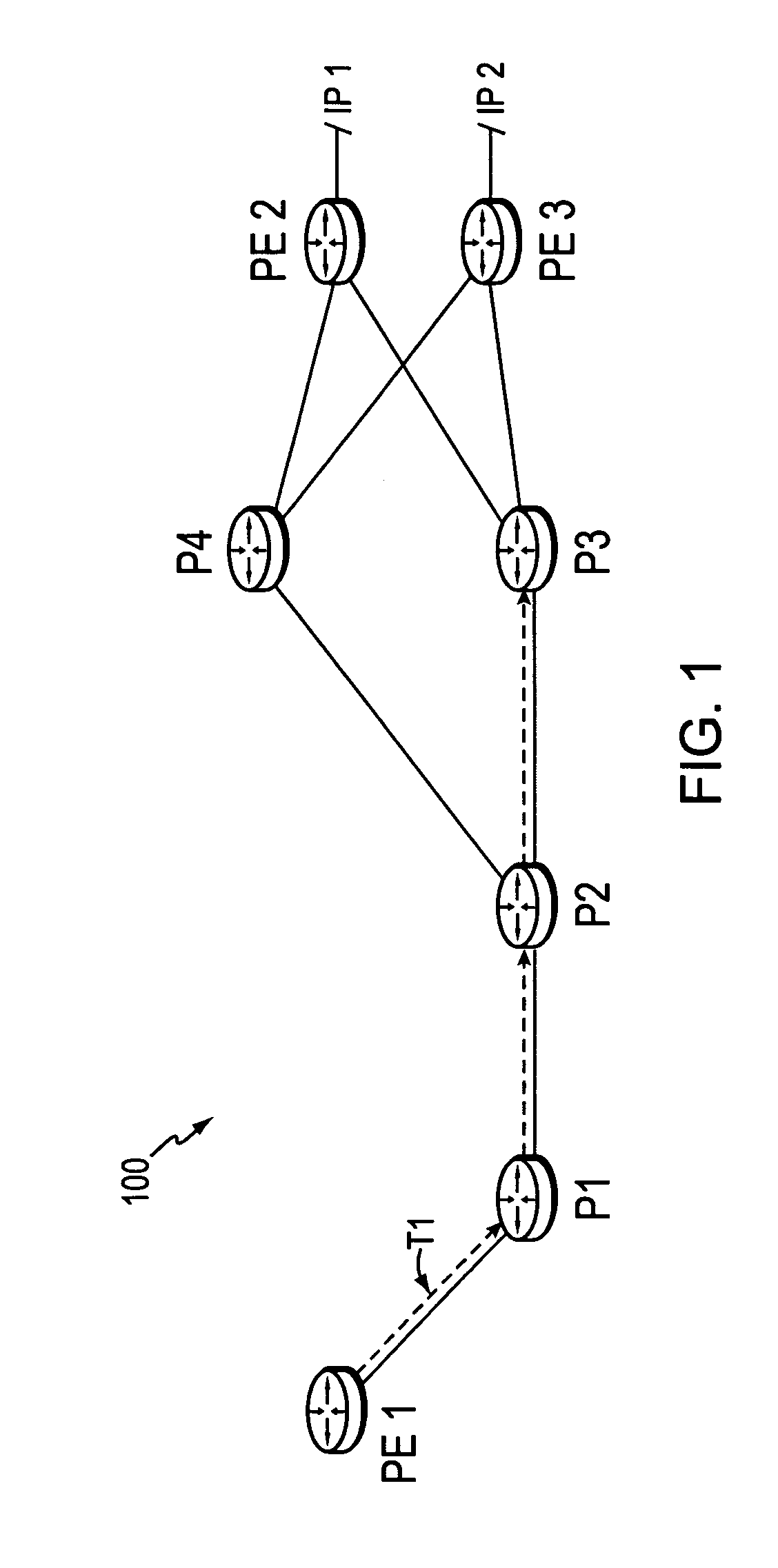
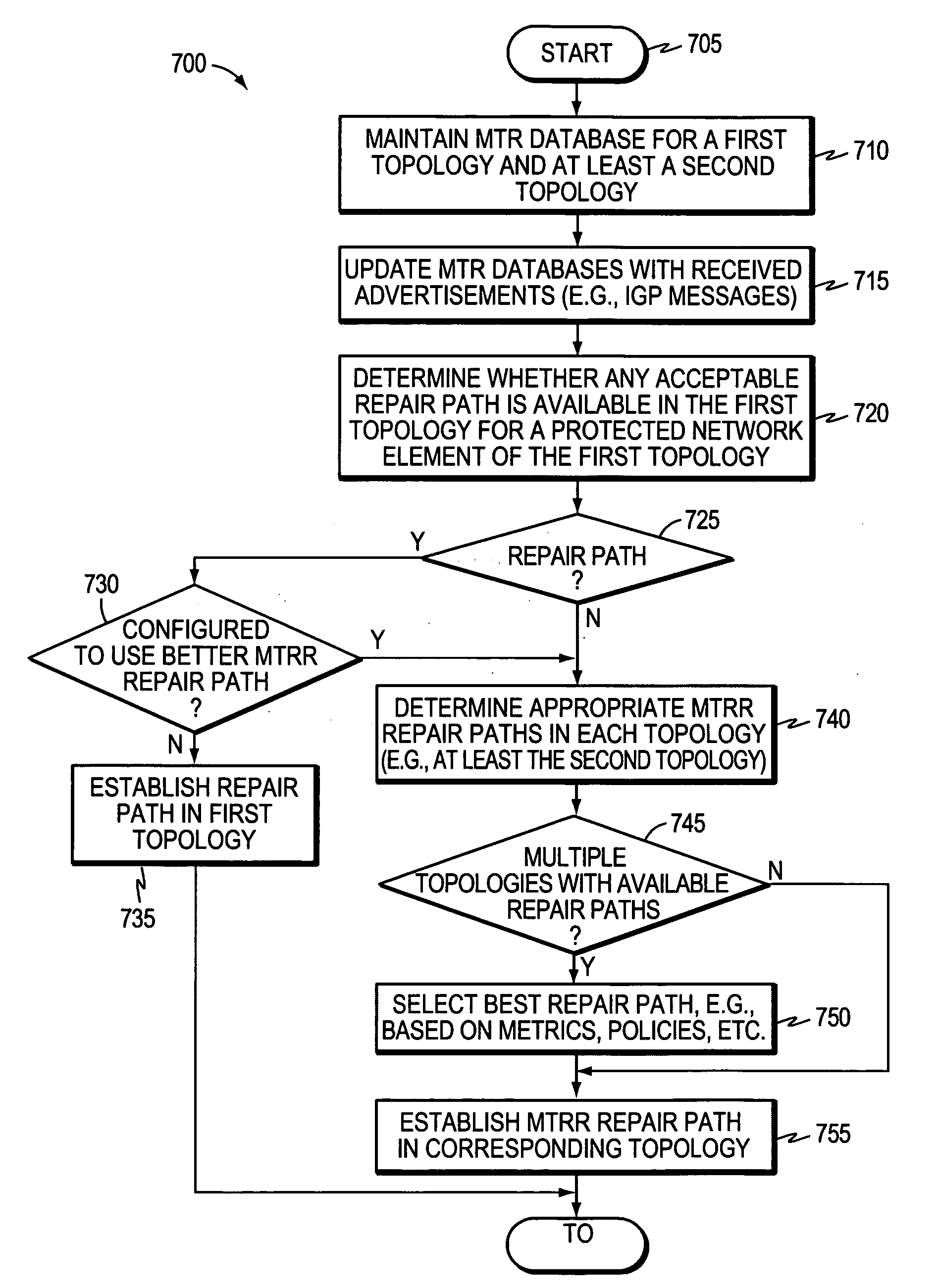
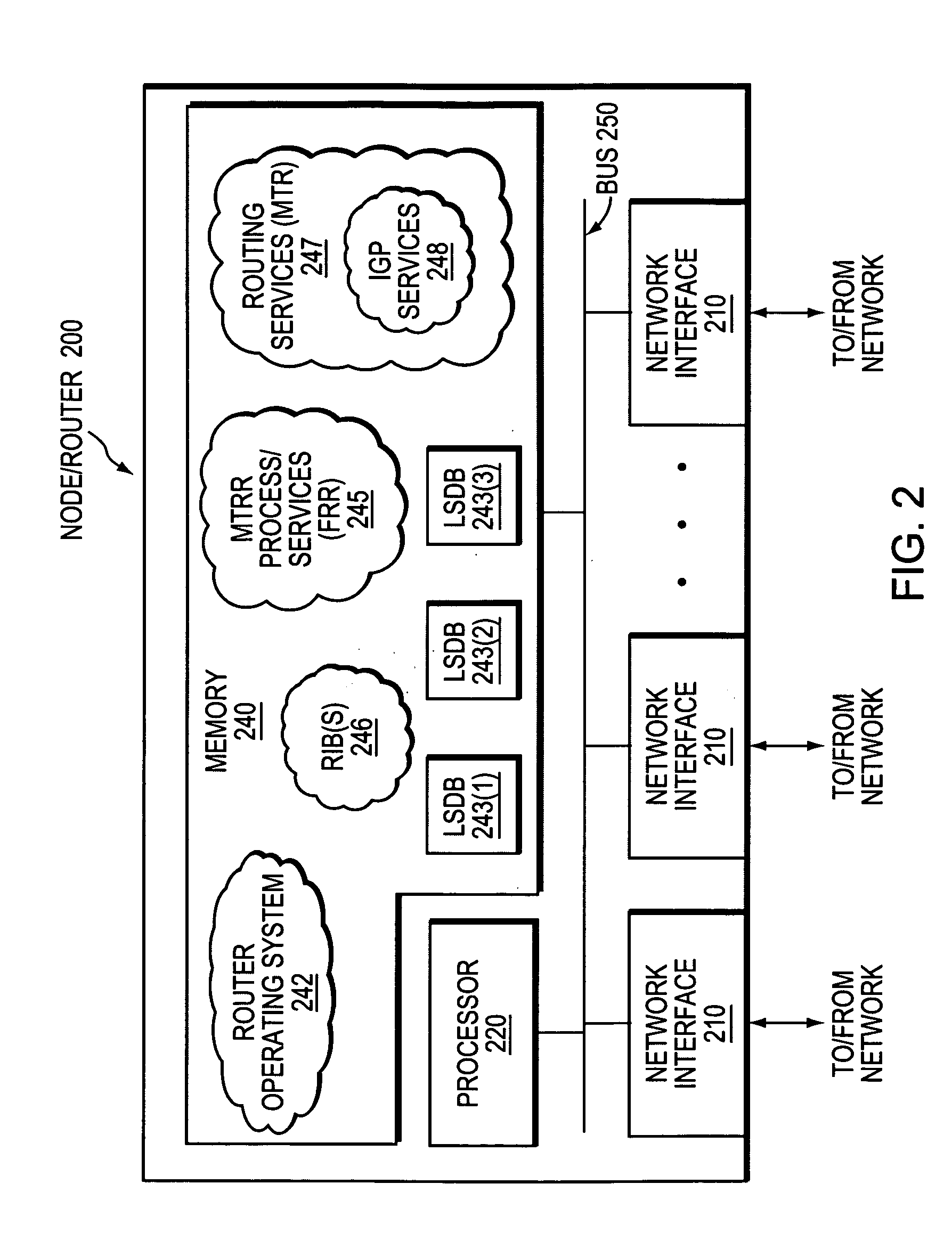
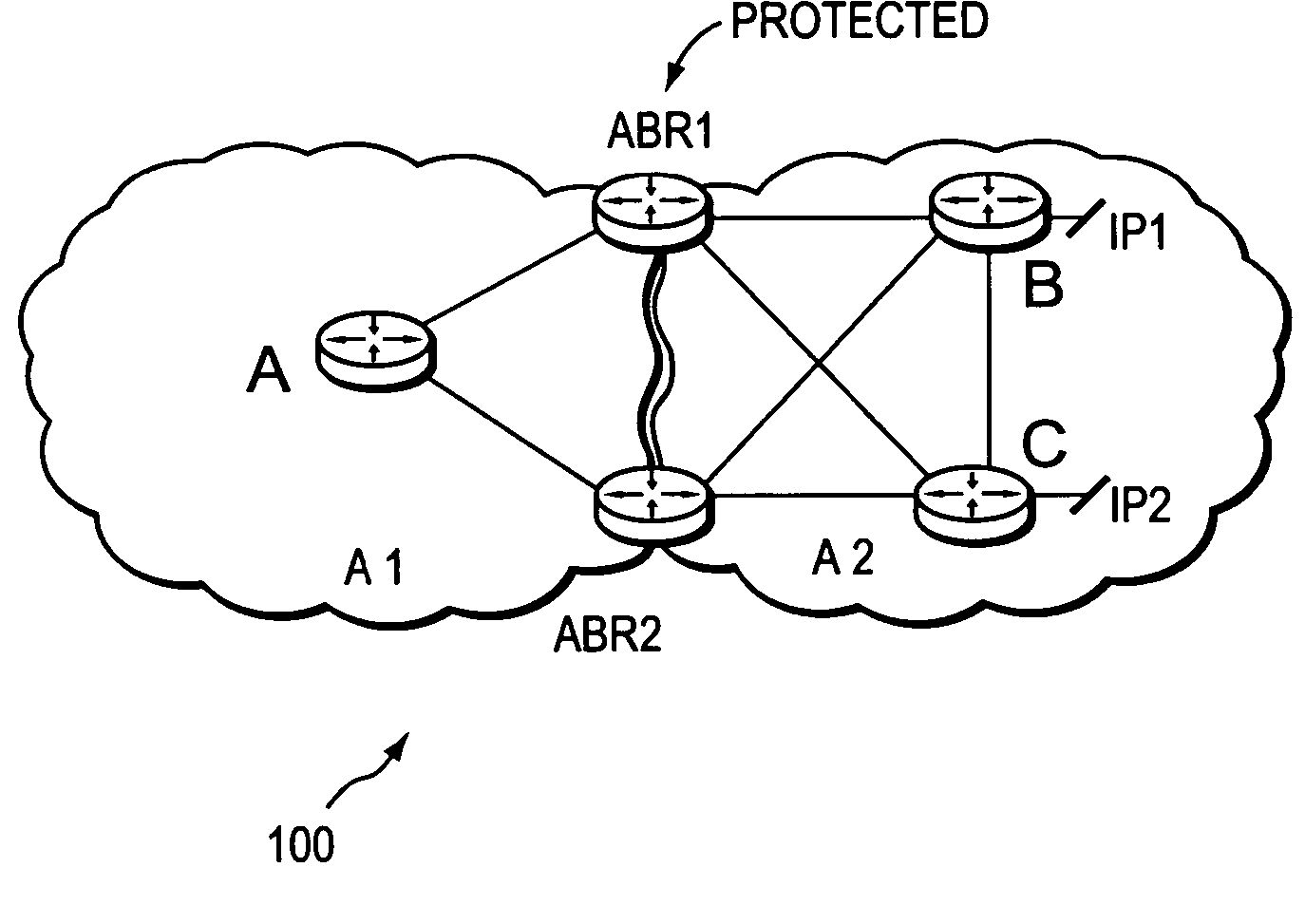
Technique for protecting against failure of a network element using Multi-Topology Repair Routing (MTRR)
ActiveUS20080049622A1Prevent extensionReduce needError preventionTransmission systemsTopological routingDistributed computing
A technique protects against failure of a network element using Multi-Topology Repair Routing (MTRR) in a computer network. According to the novel technique, a protecting node (e.g., a router) maintains Multi-Topology Routing (MTR) databases for a first topology and at least a second topology. The protecting node determines whether any acceptable repair paths are available in the first topology for a protected network element (e.g., node, link, etc.) of the first topology. If not, the protecting node may establish a repair path (e.g., for Fast ReRoute, FRR) in the second topology for the protected network element.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Loop prevention technique for MPLS using two labels
InactiveUS20060164975A1Fast and efficientProtect dataError preventionTransmission systemsInternet trafficRouting domain
A fast reroute (FRR) technique is implemented at the edge of a network. In accordance with the technique, if an edge device detects a node or link failure that prevents it from communicating with a neighboring routing domain, the edge device reroutes at least some data packets addressed to that domain to a backup edge device which, in turn, forwards the packets to the neighboring domain. The rerouted packets are designated as being “protected” (i.e., rerouted) data packets before they are forwarded to the backup edge device. To differentiate which data packets are protected and which are not, the backup edge device employs different sets of VPN label values for protected and non-protected network traffic. That is, the backup edge device may allocate two different VPN label values for at least some destination address prefixes that are reachable through the neighboring domain: a first VPN label value for FRR protected traffic and a second VPN label value for non-protected traffic. Upon receiving a data packet containing a protected VPN label value, the backup edge device is not permitted to reroute the packet a second time, e.g., in response to another inter-domain node or link failure, thereby preventing loops from developing at the edge of the network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
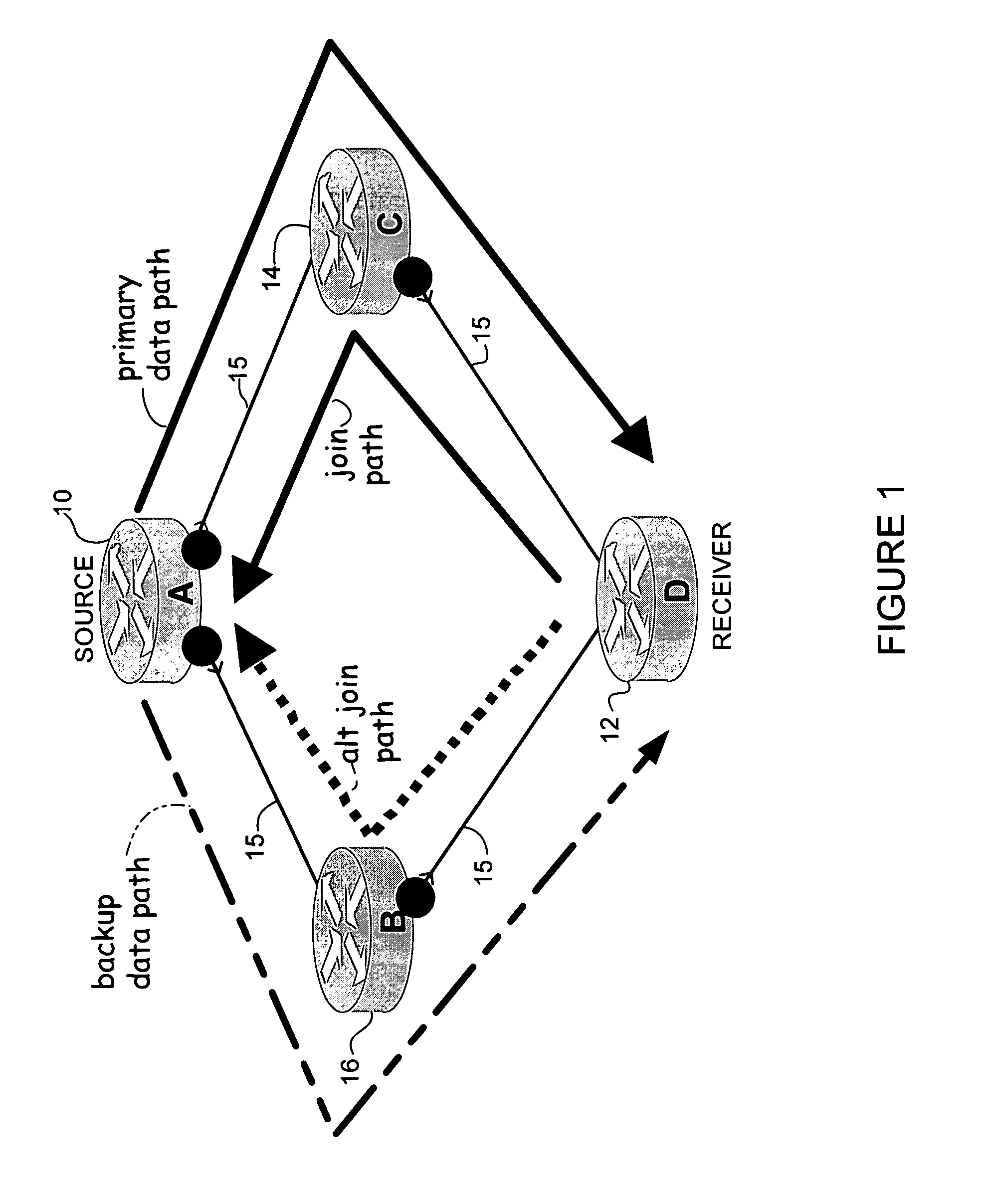
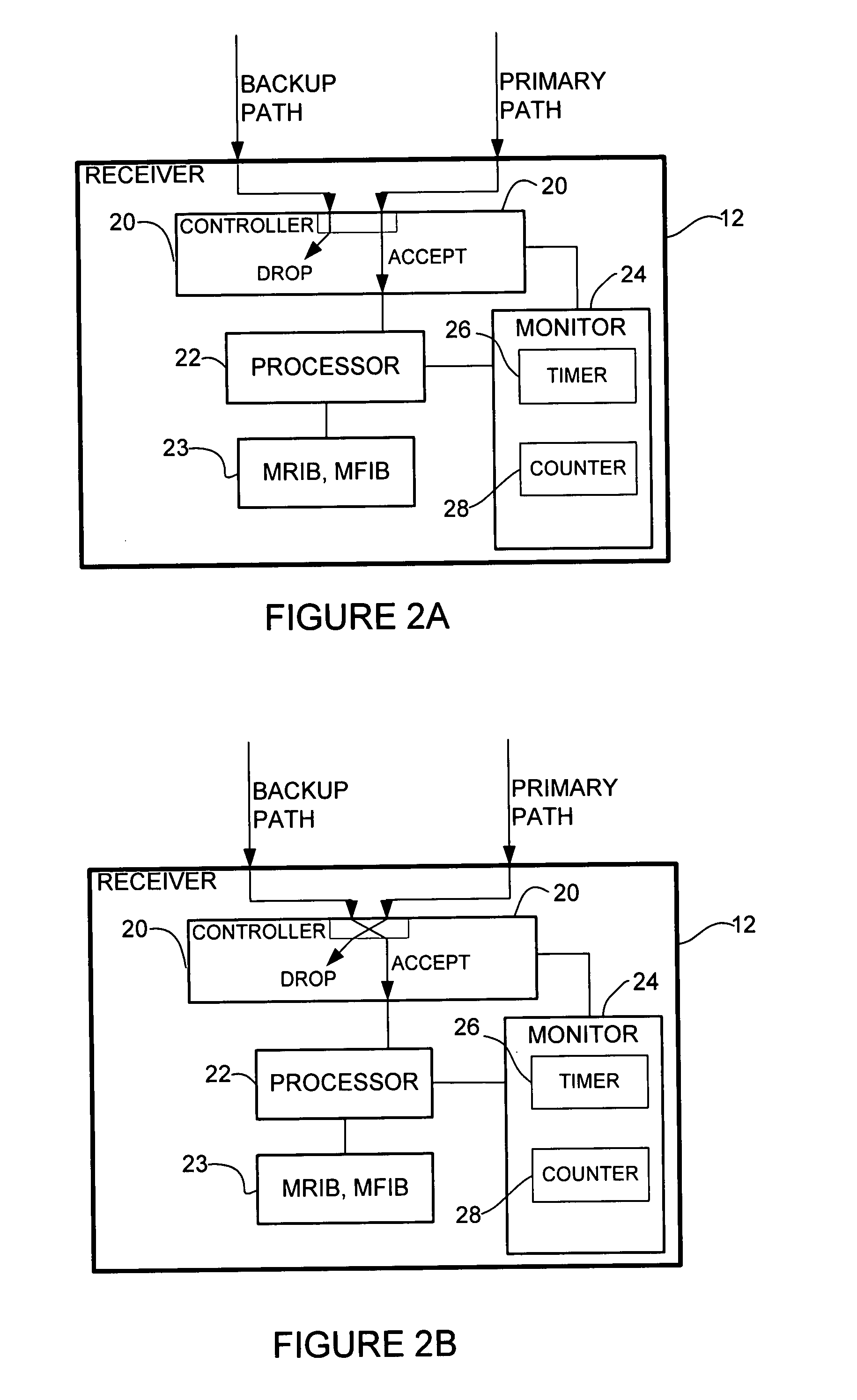
Multicast fast reroute
A method and apparatus for fast reroute of multicast data are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method includes transmitting a multicast join message from a receiver towards a source on a primary path and transmitting an alternate multicast join message from the receiver towards the source on a backup path. Data packets are then received from the primary and backup paths. The method further includes operating in a first mode wherein the data packets received from the primary path are accepted and the data packets received from the backup path are dropped, and switching to a second mode wherein the data packets received from the backup path are accepted, upon detecting a failure in the primary path.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Algorithm for backup PE selection
InactiveUS20060209682A1Reduce settingsError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRouting domainMetric selection
A fast reroute (FRR) technique is implemented at the edge of a computer network. If an edge device detects a node or link failure that prevents it from communicating with a neighboring routing domain, the edge device reroutes at least some data packets addressed to that domain to a backup edge device which, in turn, forwards the packets to the neighboring domain. The backup edge device is not permitted to reroute the packets a second time. According to the inventive technique, the edge device first identifies a group one or more possible backup edge devices and then selects at least one preferred backup edge device from the group. The edge device makes its selection based on the values of one or more metrics associated with the possible backup edge devices. The metrics are input to a novel selection algorithm that selects the preferred backup edge device(s) using a hierarchical selection process or a weighted-metric selection process, or some combination thereof.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Avoiding micro-loop upon failure of fast reroute protected links
ActiveUS20050276216A1NetworkingSpeed andError preventionTransmission systemsBackup pathReal-time computing
A technique incorporates an efficient means for avoiding micro-loops on a backup path associated with a failed protected link. An intermediate node delays updating a forwarding database (FDB) contained in the intermediate node based on the intermediate node's distance from the failed link. Specifically, intermediate nodes near the failed protected link delay updating their FDBs for a longer period of time than nodes farther away from the failed link. By updating FDBs in this manner, micro-loops may be avoided on the failed link's backup path as nodes on the backup path that are close to the failed link do not update their FDBs ahead of nodes farther away on the backup path.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Fast reroute for segment routing traffic
An apparatus and method are disclosed for fast reroute (FRR) for native segment routing (SR) traffic. In one embodiment, a node receives a packet that includes a segment routing (SR) segment identifier (ID) stack. The node determines what type of segment is designated as the active segment in the segment ID stack. Based, at least in part on the type of active segment, the node selects an update routine out of several possible update routines and performs the selected update routine. The update routine modifies the segment ID stack.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method for protecting against failure of a TE-LSP tail-end node
InactiveUS7586841B2Quick protectionAvoid deploymentError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPathPingEngineering
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Loop prevention techniques using encapsulation manipulation of IP/MPLS field
ActiveUS20060221813A1Avoid developmentFast reroute (FRR)Error preventionTransmission systemsRouting domainEdge device
A fast reroute (FRR) technique is implemented at the edge of a computer network. In accordance with the technique, if an edge device detects a node or link failure that prevents it from communicating with a neighboring routing domain, the edge device reroutes at least some data packets addressed to that domain to a backup edge device which, in turn, forwards the packets to the neighboring domain. The rerouted packets are designated as being “protected” (i.e., rerouted) data packets before they are forwarded to the backup edge device. To that end, the edge device incorporates an identifier into the rerouted data packets to indicate that the packets are being FRR rerouted. The identifier may be a predetermined value stored at a known location in the rerouted packets'encapsulation headers, such as in their MPLS or IP headers. Upon receiving a data packet containing the identifier, the backup edge device is not permitted to reroute the packet a second time.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Efficient mechanism for fast recovery in case of border router node failure in a computer network
InactiveUS20060126502A1Quick protectionMinimal configurationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer networkFast recovery
A technique protects traffic (IP) against the failure of a border router between two domains in a computer network using Fast Reroute and backup tunnels. The border router (i.e., the “protected border router”) announces / advertises a list of all its adjacent next-hop routers (i.e., its “neighbors”) residing in first and second domains interconnected by the protected border router. A neighbor in the first domain that is immediately upstream to the protected border router and that is configured to protect the border router (i.e., the “protecting router”) learns address prefixes (i.e., “protected prefixes”) reachable from the next-hop router in the second domain (i.e., “next-next-hops,” NNHOPs to the protected prefixes from the protecting router). The protecting router calculates a backup tunnel to each NNHOP that excludes the protected border router, and associates each backup tunnel with protected prefixes accordingly. When the protected border router fails, Fast Reroute is triggered, and the protected prefixes are rerouted by the protecting router onto an appropriate backup tunnel to a corresponding NNHOP.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Loop prevention technique for MPLS using service labels
ActiveUS20060193248A1Avoid developmentOvercome disadvantagesError preventionTransmission systemsRouting domainInter-domain
A local fast reroute (FRR) technique is implemented at the edge of a computer network. In accordance with the technique, if an edge device detects a node or link failure that prevents it from communicating with a neighboring routing domain, the edge device reroutes at least some data packets addressed to that domain to a backup edge device which, in turn, forwards the packets to the neighboring domain. The rerouted packets are designated as being “protected” (i.e., rerouted) data packets before they are forwarded to the backup edge device. The backup edge device identifies protected data packets as those which contain a predetermined “service” label in their MPLS label stacks. In other words, the service label is used as an identifier for packets that have been FRR rerouted. Upon receiving a data packet containing a service label, the backup edge device is not permitted to reroute the packet a second time, e.g., in response to another inter-domain node or link failure, thereby preventing loops from developing at the edge of the network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
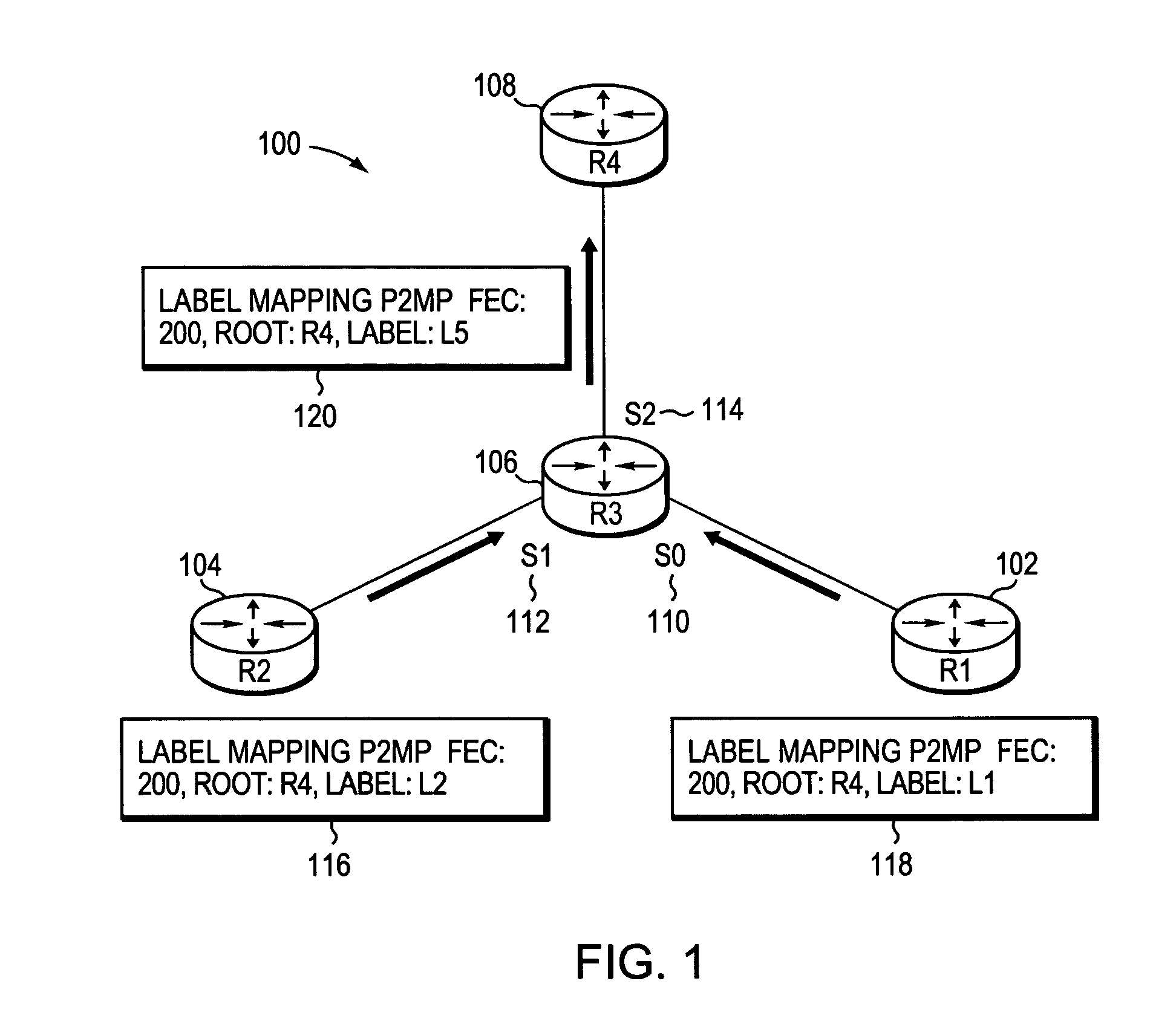
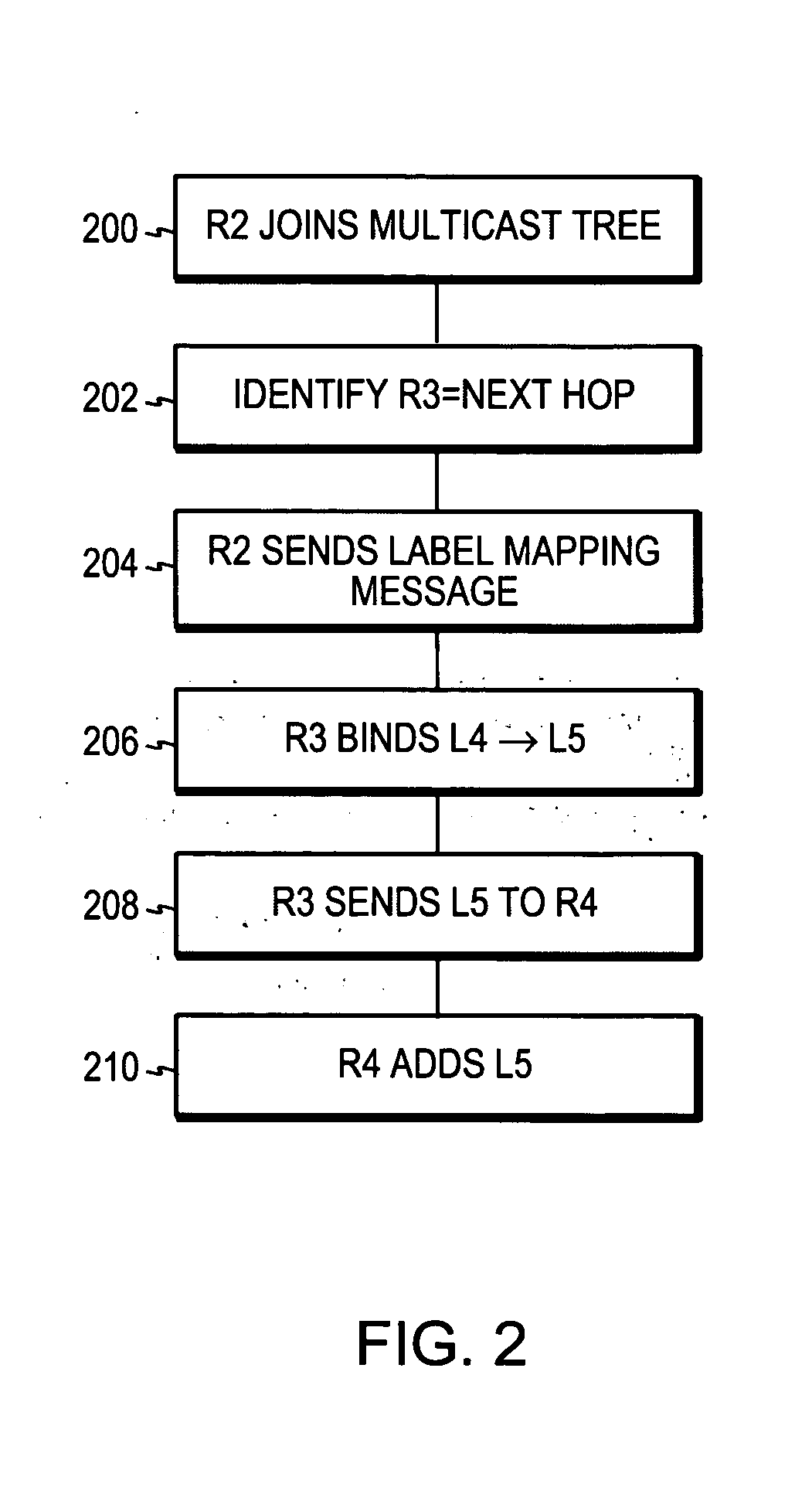
Method and apparatus for forwarding label distribution protocol multicast traffic during fast reroute
A computer apparatus comprising a processor and a forwarding engine arranged to forward LDP multicast traffic along a multicast tree having a primary and a backup path in a converged network topology, the processor being configured to cause the forwarding engine to forward traffic via the backup path upon a topology change and send a changed topology label and path vector to at least one neighbor node in the changed topology.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for high speed rerouting in multi protocol label switching network
InactiveUS6904018B2Minimize packet lossFast trafficMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionTraffic capacityPacket loss
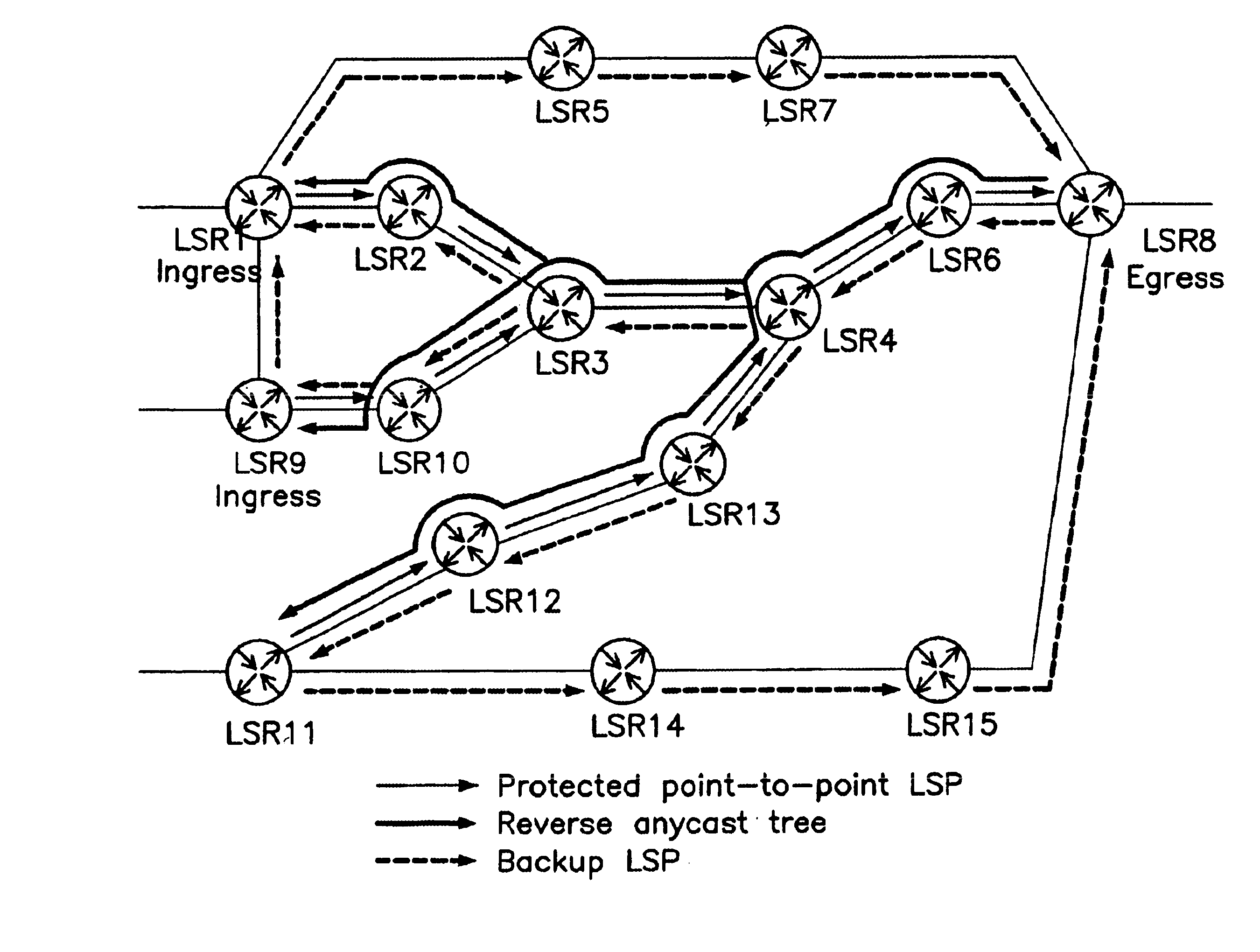
Disclosed is a method for high speed rerouting in a multi protocol label switching (MPLS) network which can minimize a packet loss and enable a fast rerouting of traffic so as to protect and recover a multi point to point LSP occupying most LSPs in the MPLS network. The method for high speed rerouting in a multi protocol label switching (MPLS) network, the method comprising the steps of controlling a traffic stream to flow in a reverse direction in a point where a node or link failure occurs by using a backup Label Switched Path (LSP) comprising an Explicitly Routed (ER) LSP having a reverse tree of a protected multi point to point LSP and an ingress LSR through an egress LSR.
Owner:KOREA TELECOMM AUTHORITY
Algorithm for backup PE selection
InactiveUS7535828B2Reduce settingsError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork packetRouting domain
A fast reroute (FRR) technique is implemented at the edge of a computer network. If an edge device detects a node or link failure that prevents it from communicating with a neighboring routing domain, the edge device reroutes at least some data packets addressed to that domain to a backup edge device which, in turn, forwards the packets to the neighboring domain. The backup edge device is not permitted to reroute the packets a second time. According to the inventive technique, the edge device first identifies a group one or more possible backup edge devices and then selects at least one preferred backup edge device from the group. The edge device makes its selection based on the values of one or more metrics associated with the possible backup edge devices. The metrics are input to a novel selection algorithm that selects the preferred backup edge device(s) using a hierarchical selection process or a weighted-metric selection process, or some combination thereof.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
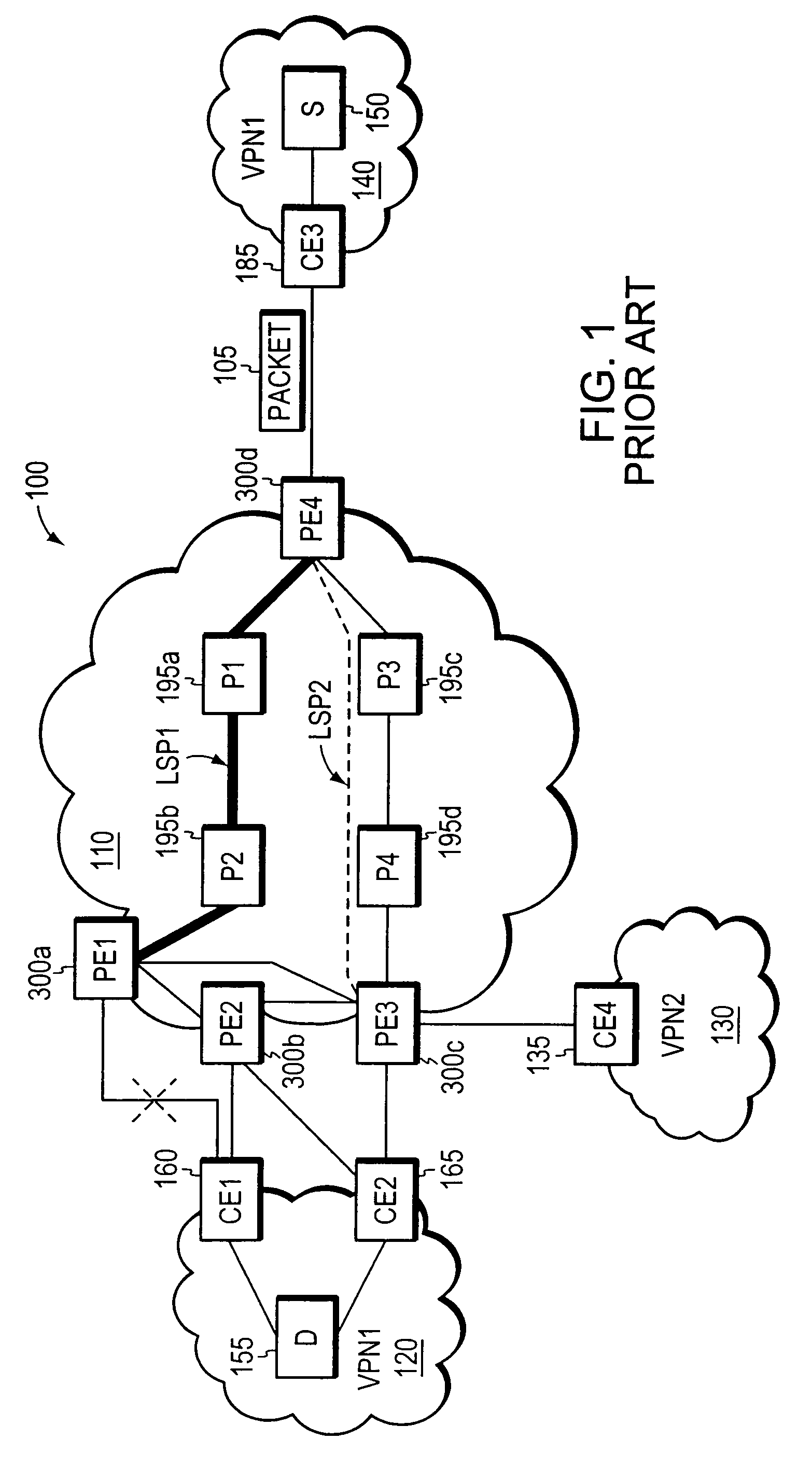
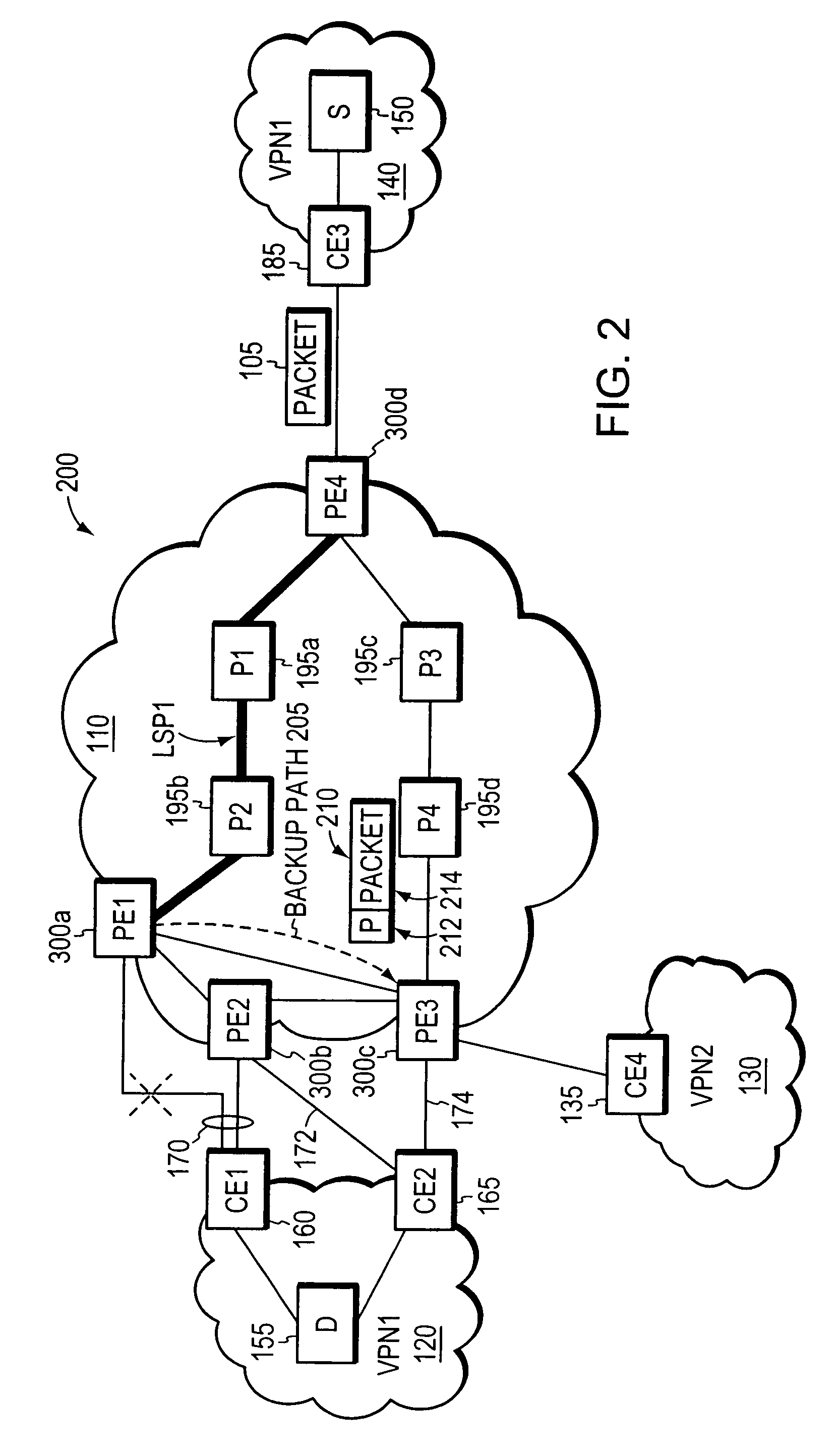
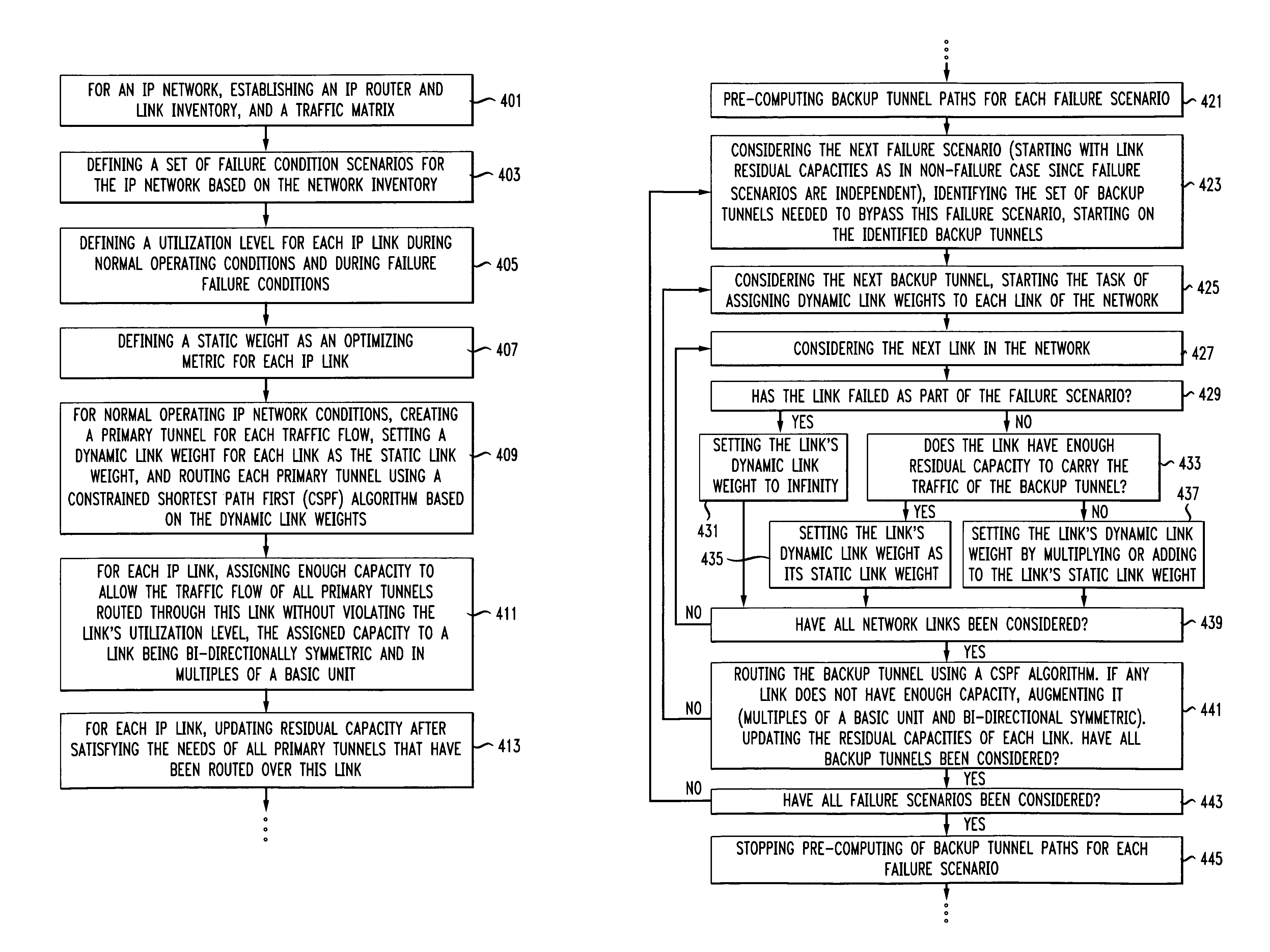
Two-phase fast reroute with optimized traffic engineering
ActiveUS7859993B1Maximize sharingMinimizing capacityLaser detailsError preventionTraffic capacityCost Measures
Systems and methods are described for restoring IP traffic flows routed in an IP network in less than 100 ms after the IP network sustains a network failure. The systems and methods are a two-phase fast reroute that uses distributed optimized traffic engineering during backup tunnel restoration and end-to-end tunnel restoration that maximizes sharing among all independent failure scenarios and minimizes the total capacity, total cost, or a linear combination of the two. For defined failure condition scenarios, restoration traffic is routed using pre-computed backup tunnels using a constrained shortest path first method where link weights along the path are chosen dynamically and depend on available and total capacity of the link, latency, and other cost measures such as IP port costs. During the capacity allocation phase, the method reuses capacity already allocated for other independent failure scenarios as much as possible but also adds capacity, if necessary. When an actual IP network failure occurs, the backup tunnels are used to immediately restore service to affected IP network traffic flows. In parallel, end-to-end tunnels corresponding to each affected traffic flow are rerouted and once the rerouting process is complete, traffic is switched over from the old end-to-end tunnel routes (using backup tunnels) to new end-to-end tunnel routes without using backup tunnels.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Method for implementing fast reroute
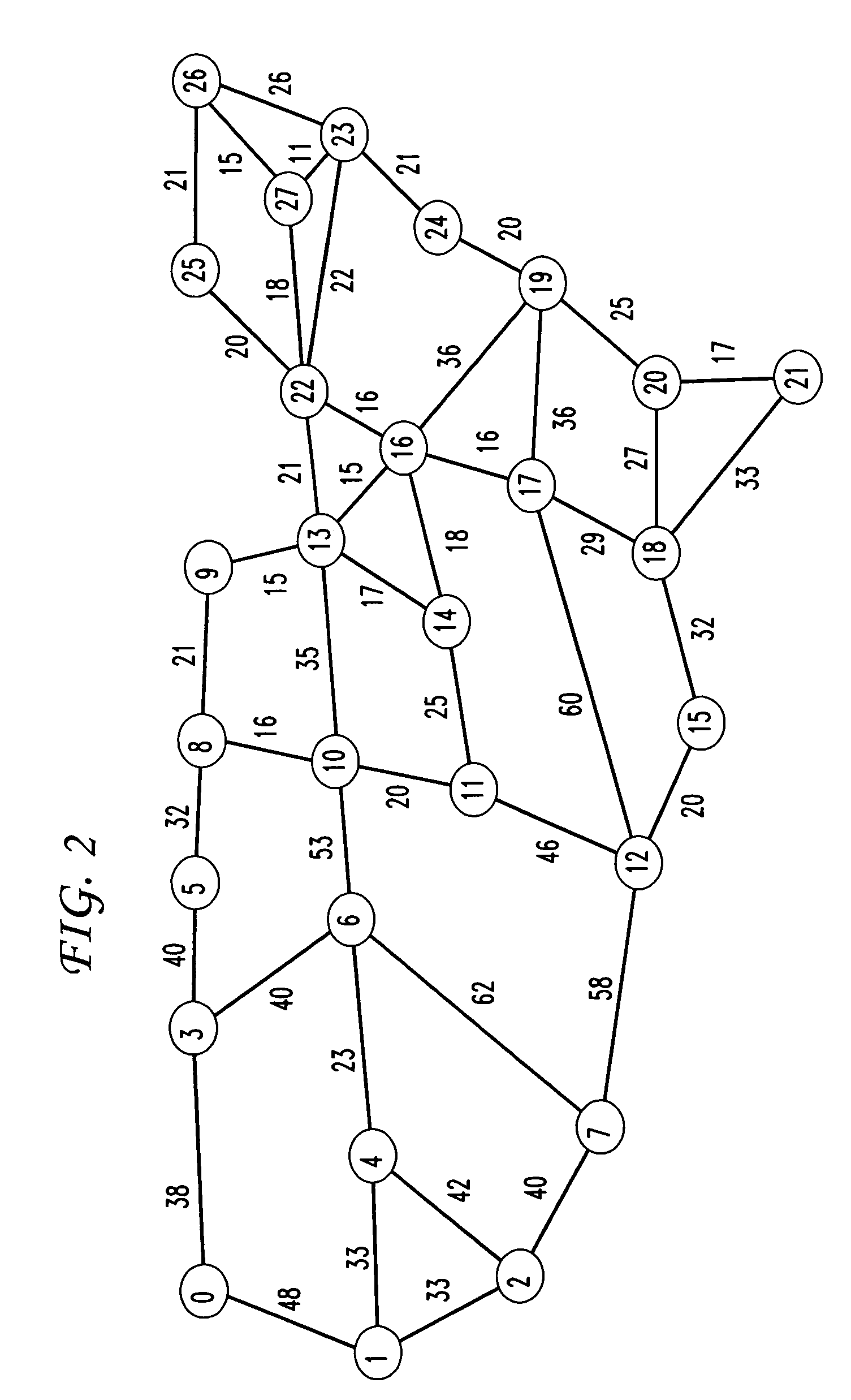
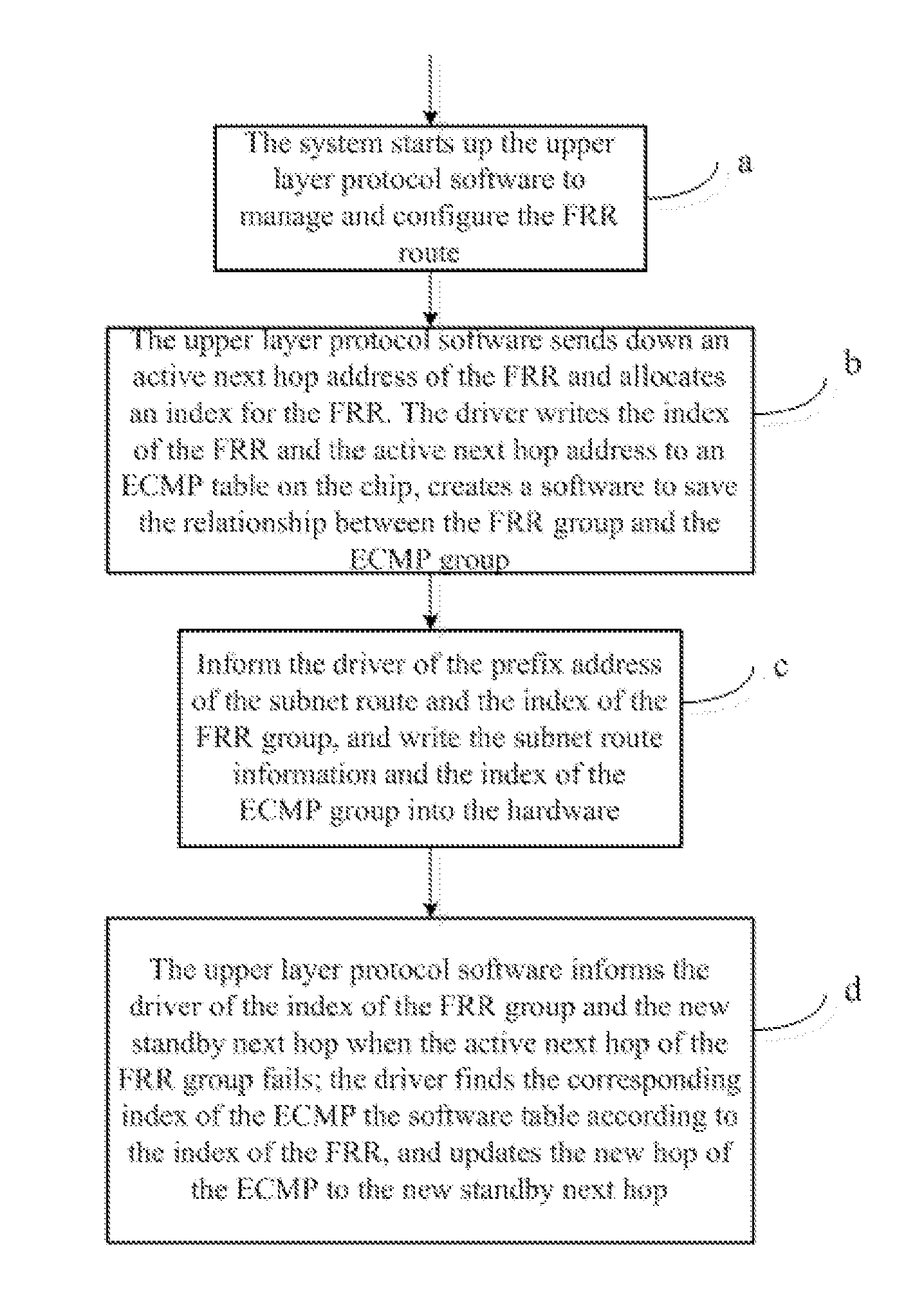
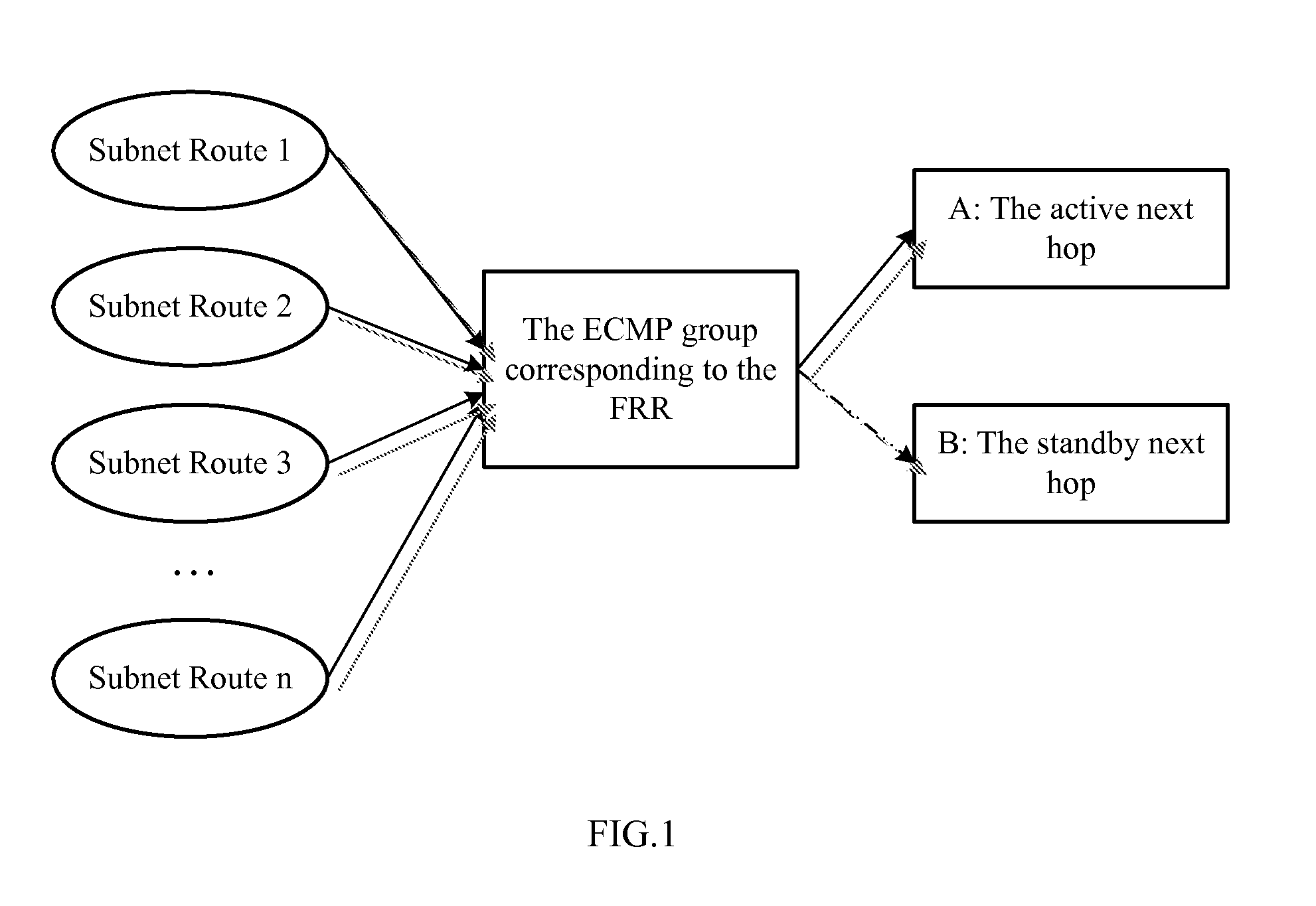
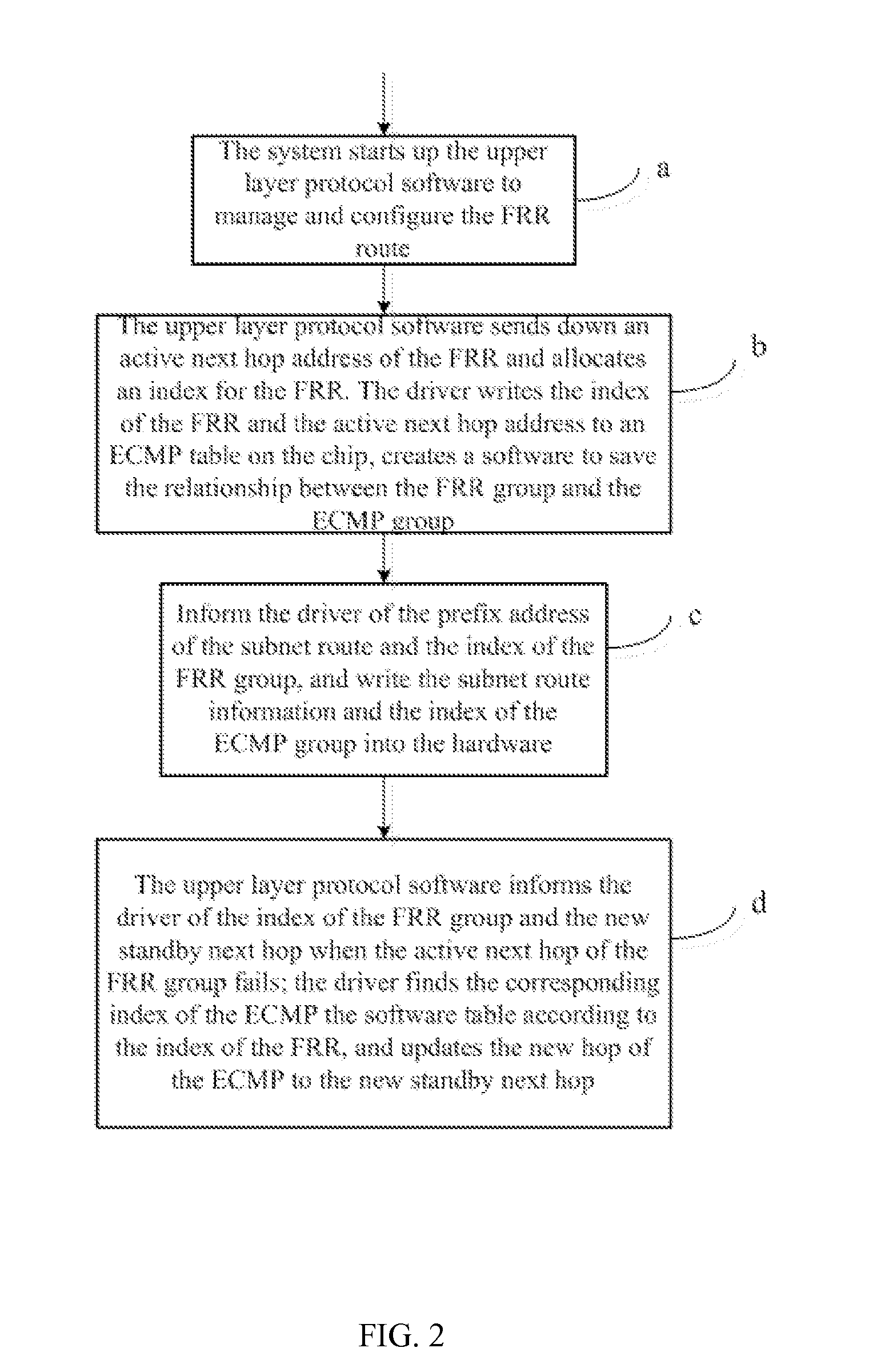
InactiveUS20110249679A1Shorten speedImprove system speedData switching by path configurationIp addressSoftware
A method for implementing FRR comprising_starting up an upper layer protocol software to manage and configure a FRR route; an upper layer protocol software sending down a active next hop of the FRR; a driver writing an IP address of the FRR into an ECMP table and creating a software table to record correspondence between a FRR group and ECMP group; informing the driver of a prefix address of a subnet route and the index of the FRR group, and the driver finding the index of the ECMP group, and writing information of the subnet route and the index of the ECMP group into hardware; an upper layer protocol software informing the driver of the index of the FRR and an IP address of a new standby next hop; the driver looking up for the index of the ECMP group, and updating the next hop address of the ECMP group.
Owner:ZTE CORP
A method to realize fast reroute and router
InactiveCN101217457AFast convergenceMeet real-time business needsNetworks interconnectionPrivate networkIp router
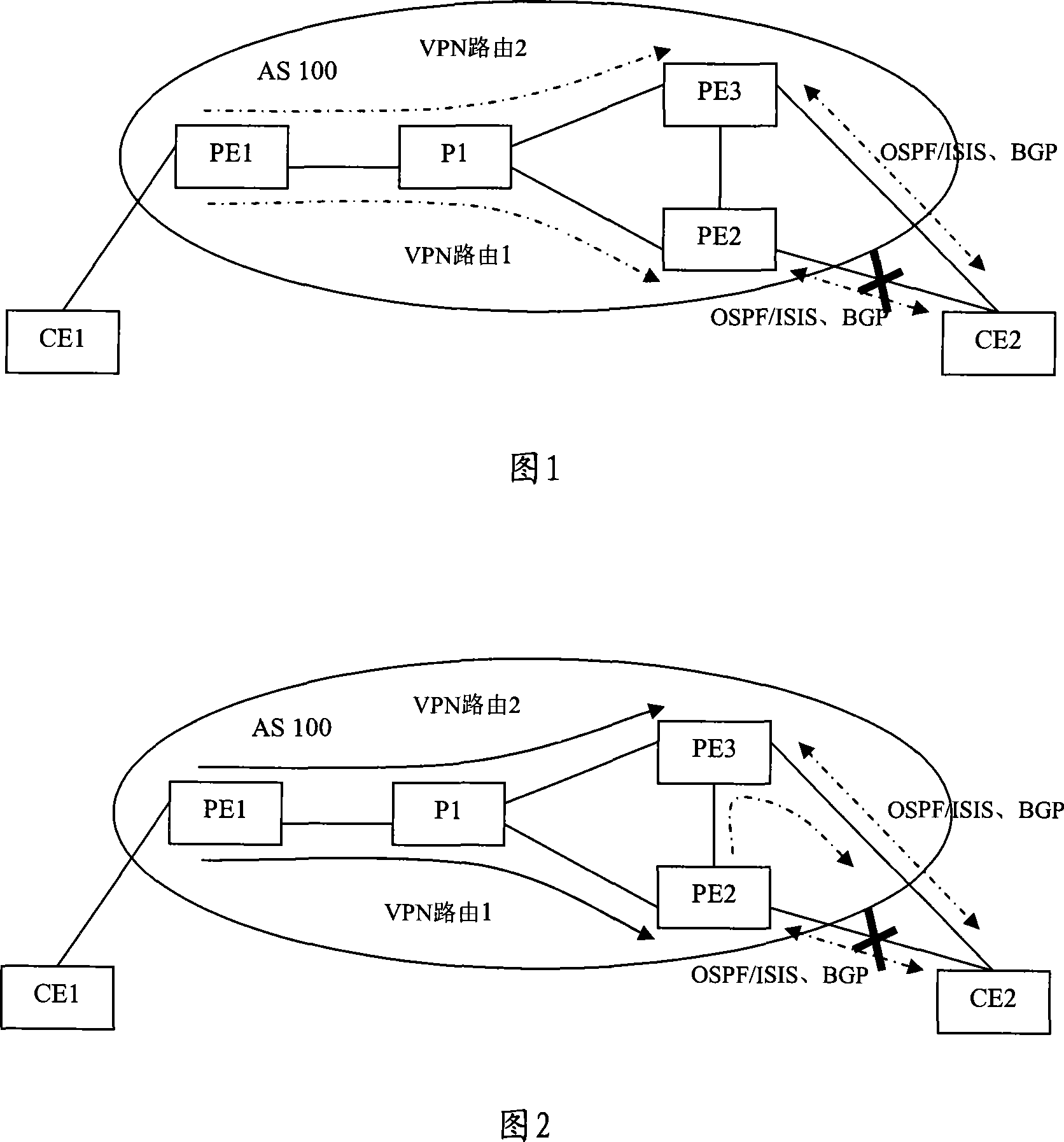
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a router for realizing fast reroute. The method of the invention example comprises that: the main network IP router and the spare virtual private network VPN router is down sent into the route forwarding table of network provider boundary routing equipment PE; the local PE and CE adopt bidirectional forwarding detection to check the link failure; when the link failure is detected, the flow are all switched to the spare VPN router to be forwarded. By adopting the method of the embodiment of the invention, the local PE-CE link failure can be rapidly detected and the main network IP router and the spare virtual private network VPN router can be down sent to the route forwarding table of network provider boundary routing equipment PE. The rapid detection of failure in the local PE-CE link is helpful to realize rapid convergence of VPN business and satisfies the real-time business requirement of the users.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Border router protection with backup tunnel stitching in a computer network
InactiveUS7512063B2Fast Reroute protectionAvoid deploymentError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic volumeComputer security
A technique protects against the failure of a border router between two domains in a computer network using Fast Reroute and backup tunnels. According to the technique, the protected border router advertises a list of all its adjacent next-hop routers (i.e., its “neighbors”). A neighbor in the first domain that is immediately upstream to the protected border router and that is configured to protect the border router (i.e., the “protecting router”) selects a neighbor in a second domain (i.e., a “next-next-hop,” NNHOP) to act as a “merge point” of all the NNHOPs of that domain. The protecting router calculates a backup tunnel to the merge point that excludes the protected border router and associates the backup tunnel with all “protected prefixes.” The merge point then “stitches” additional backup tunnels onto the backup tunnel to provide a stitched tunnel to each remaining NNHOP. When the protected border router fails, Fast Reroute is triggered, and all protected prefix traffic is rerouted onto the backup tunnel to the merge point, which either forwards the traffic to its reachable prefixes or to a corresponding stitched tunnel.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Fast reroute (FRR) protection at the edge of a RFC 2547 network
InactiveUS7551551B2Fast reroute (FRR)Faster and more efficientlyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRouting domainInter-domain
A fast reroute (FRR) technique that may be deployed at the edge of a network having first and second edge devices coupled to a neighboring routing domain. If the first edge device detects a node or link failure that prevents it from communicating with the neighboring domain, the first edge device reroutes at least some data packets addressed to the neighboring domain to the second edge device. The second edge device receives the rerouted packets and then forwards the packets to the neighboring domain. Notably, the second edge device is not permitted to reroute the received packets a second time, e.g., upon identifying another inter-domain node or link failure. As such, loops are avoided at the edge of the network and packets are rerouted to the neighboring routing domain faster and more efficiently than in prior implementations.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method for providing rapid rerouting of real-time multi-media flows
InactiveUS20060187927A1Data switching by path configurationAutomatic exchangesTransceiverMulti protocol
A system and method for providing rapid rerouting of real-time transport protocol (RTP) multi-media flows is disclosed. Generally, a first endpoint is connected to a second endpoint, wherein the first endpoint comprises a transceiver, software stored within the first endpoint defining functions to be performed by the first endpoint, and a processor configured by the software. The processor is configured to perform the steps of, performing flow processing on a data packet received at a first endpoint, from a second endpoint, removing a multi-protocol label switching (MPLS) tag from the data packet, translating a source address and destination address of the data packet, and determining a forwarding destination if more than one destination address of the data packet is provided.
Owner:ACME PACKET
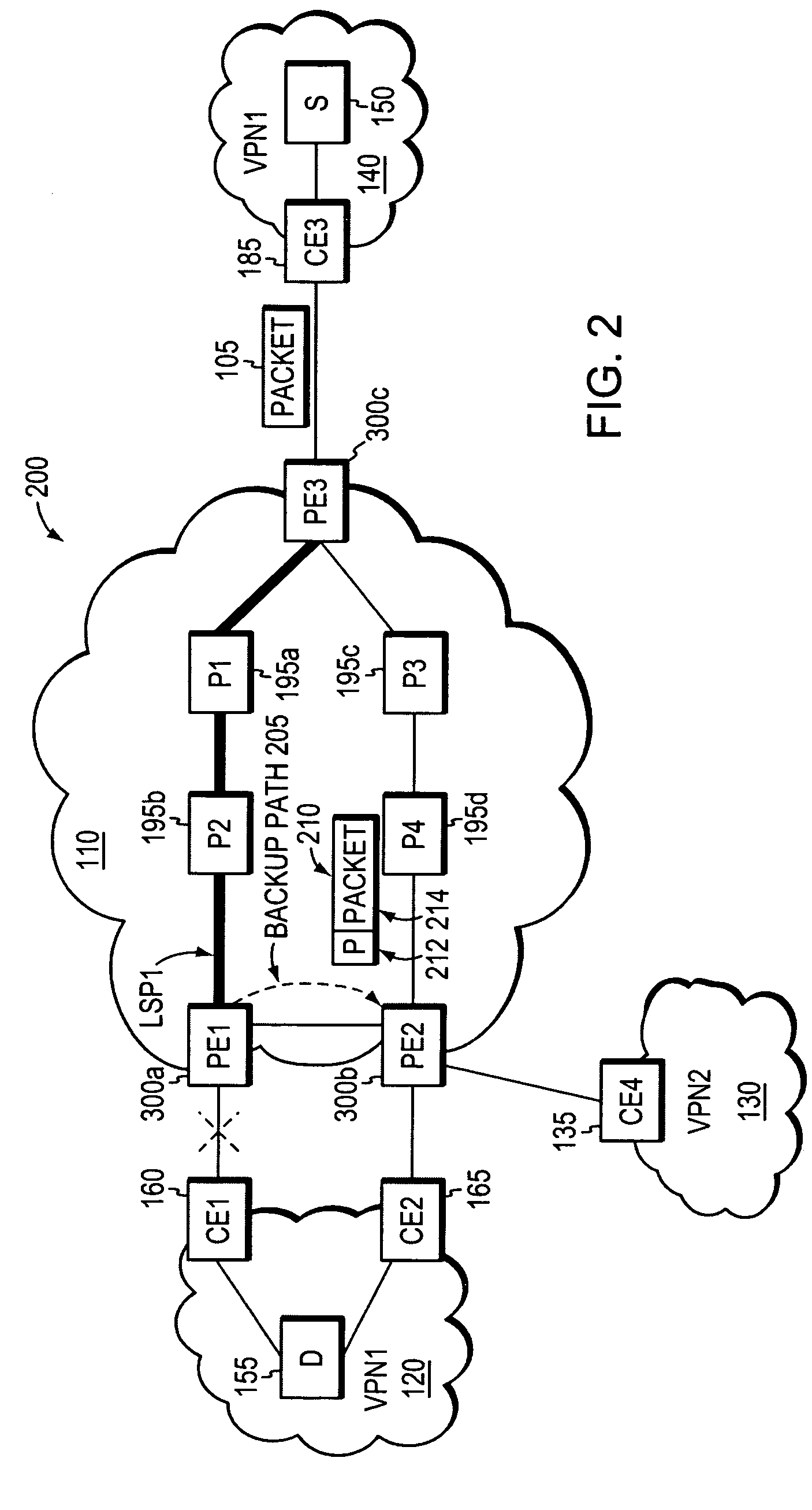
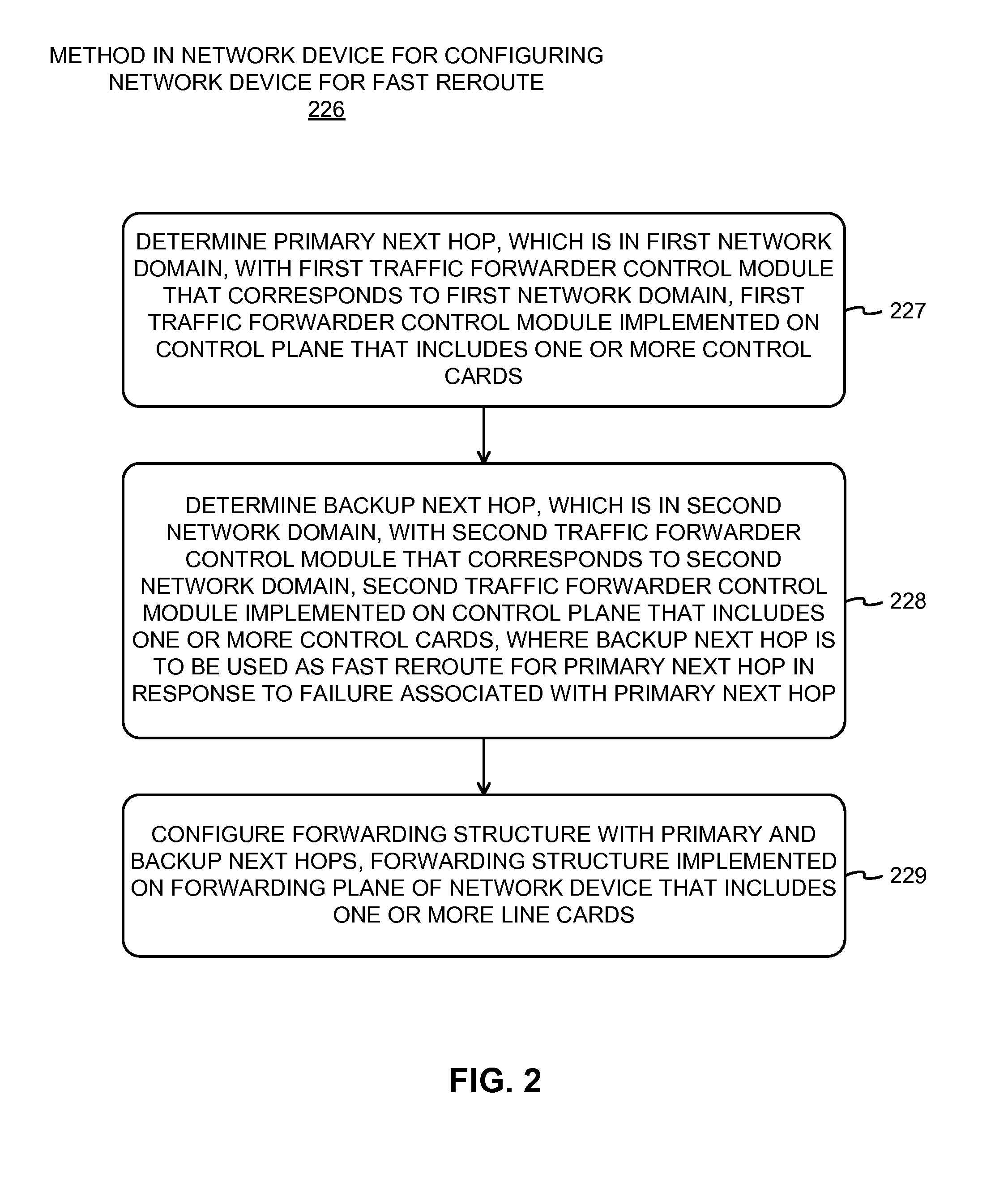
Inter-domain fast reroute methods and network devices
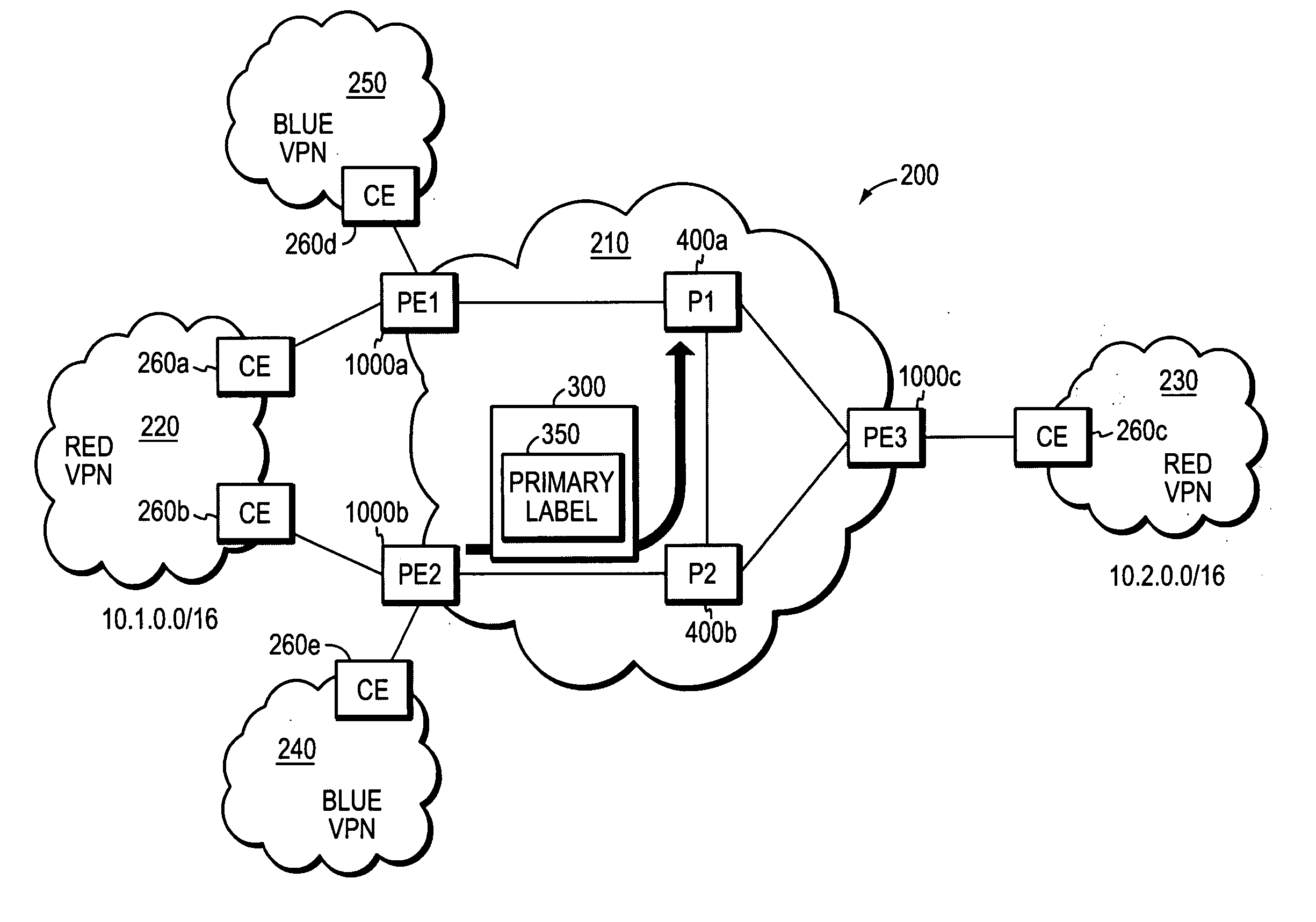
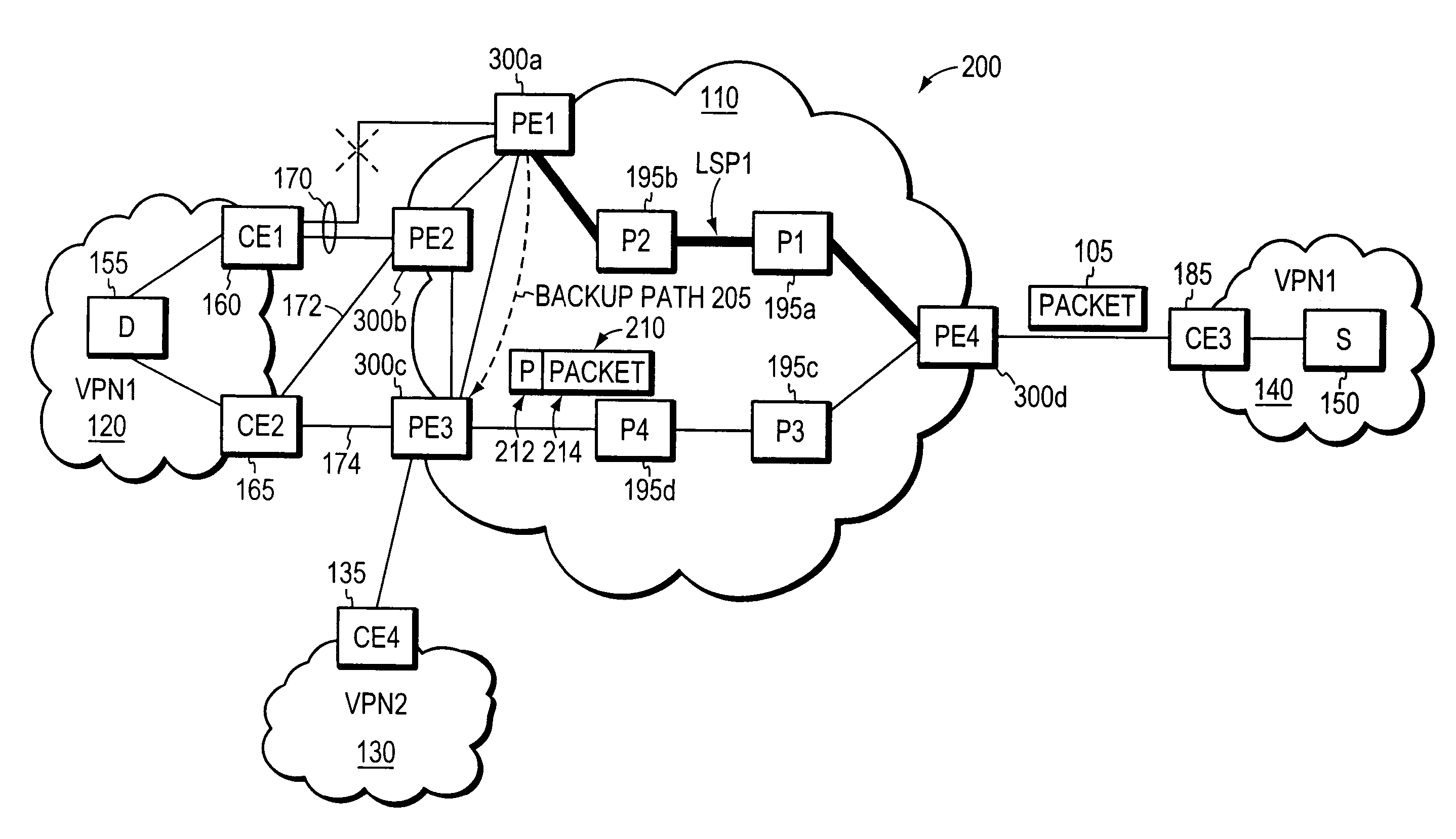
A network device, is to be deployed in a network between a first network domain and a second network domain, and is to be configured for fast reroute. The network device includes a first traffic forwarder control module, corresponding to the first network domain, which is to determine a primary next hop in the first network domain. The control plane includes a second traffic forwarder control module, corresponding to the second network domain, which is to determine a backup next hop in the second network domain. The backup next hop is to be used as a fast reroute for the primary next hop in response to a failure associated with the primary next hop. The control plane includes a controller module, in communication with the first and second traffic forwarder control modules, which is to configure a forwarding structure of the forwarding plane with the primary and backup next hops.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com