Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
429 results about "IEEE 1394" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
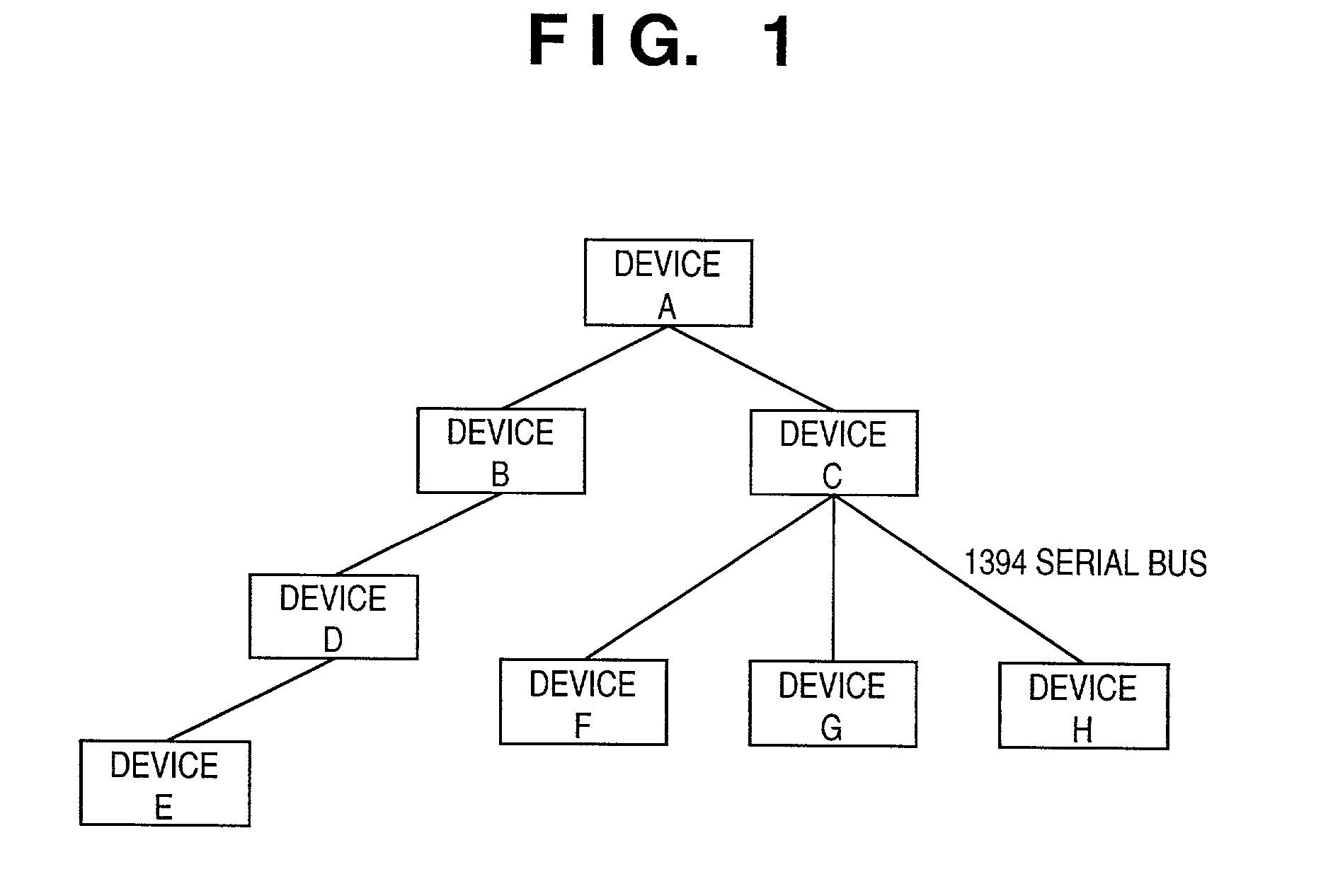
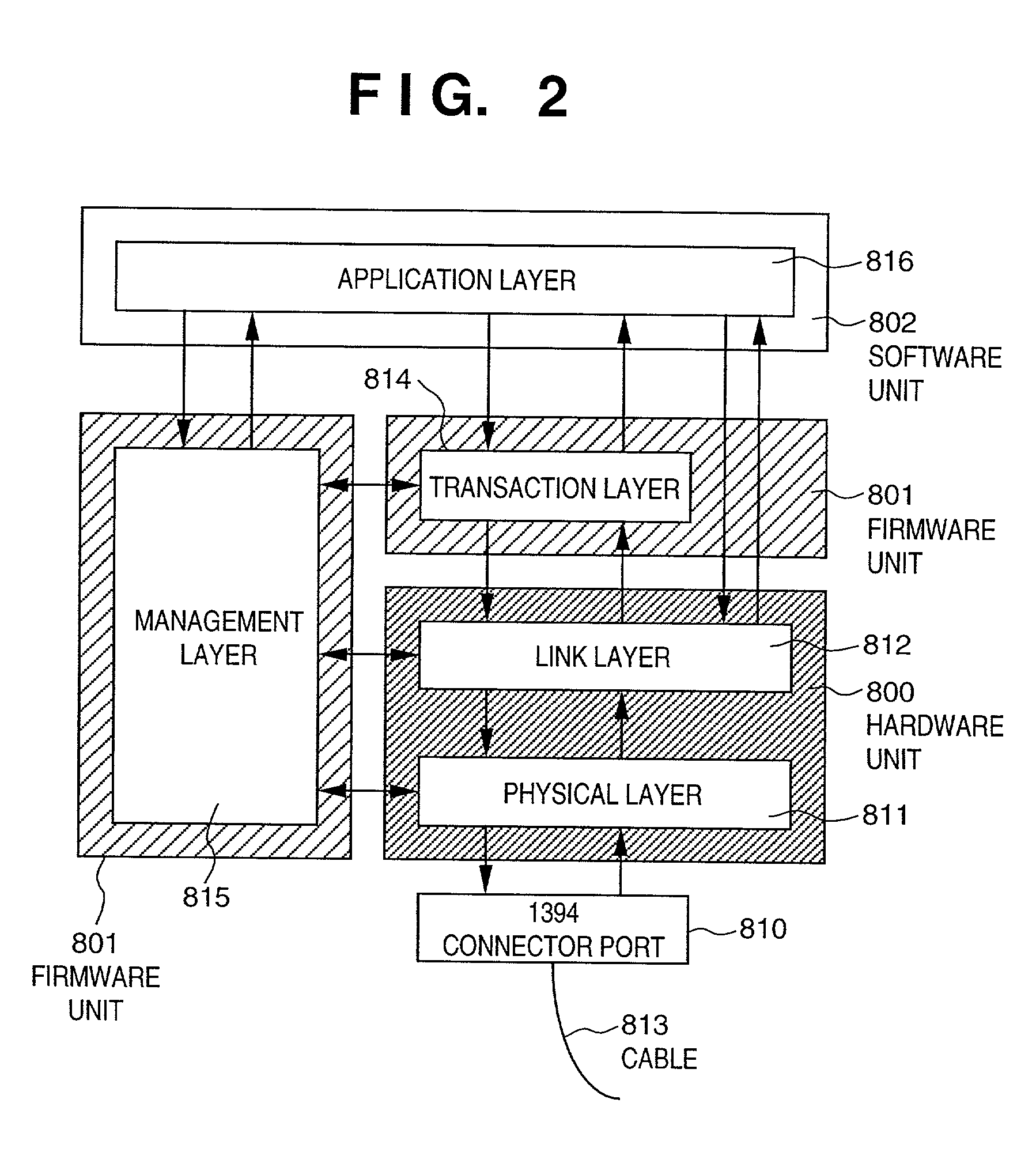
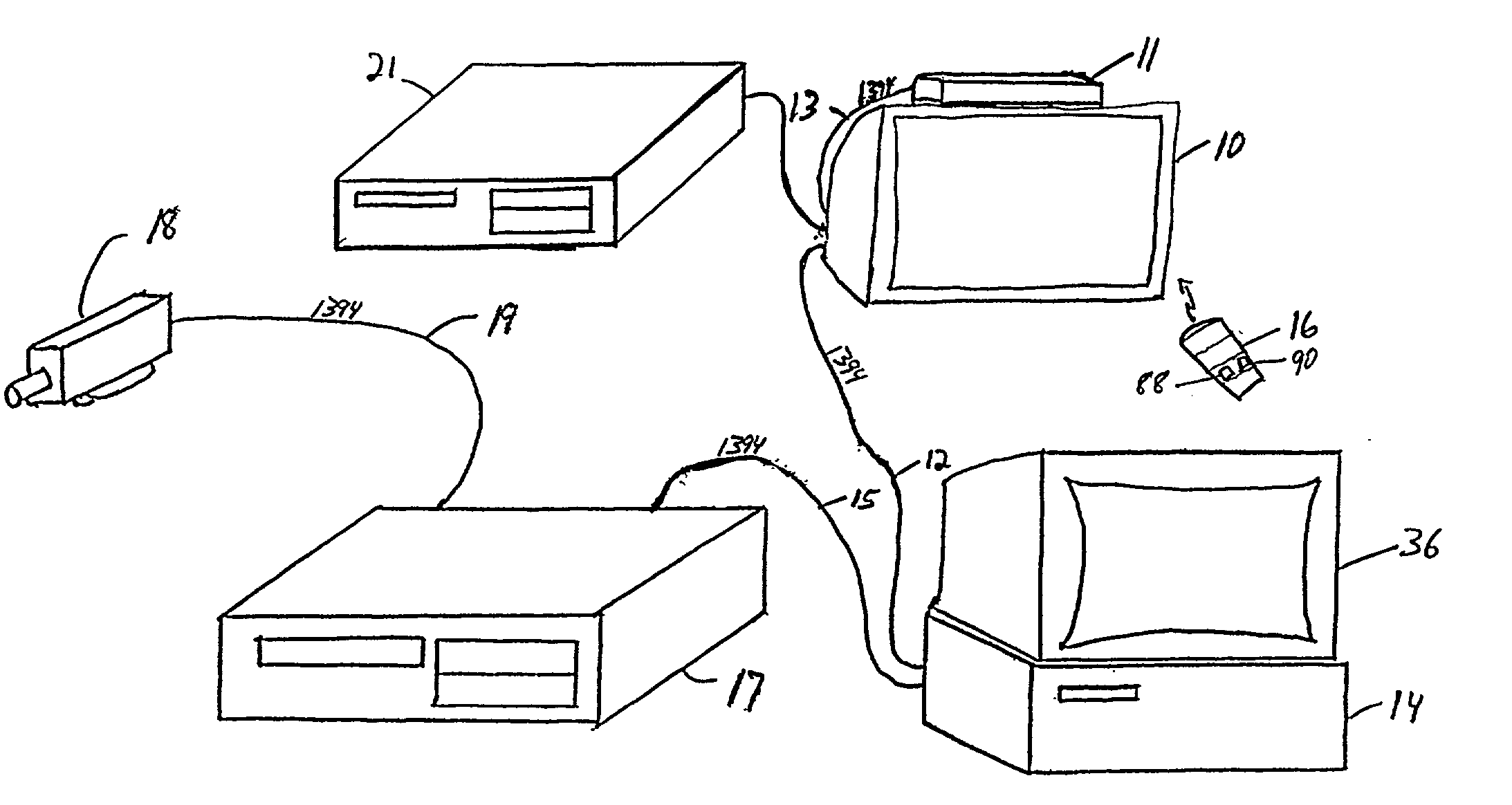
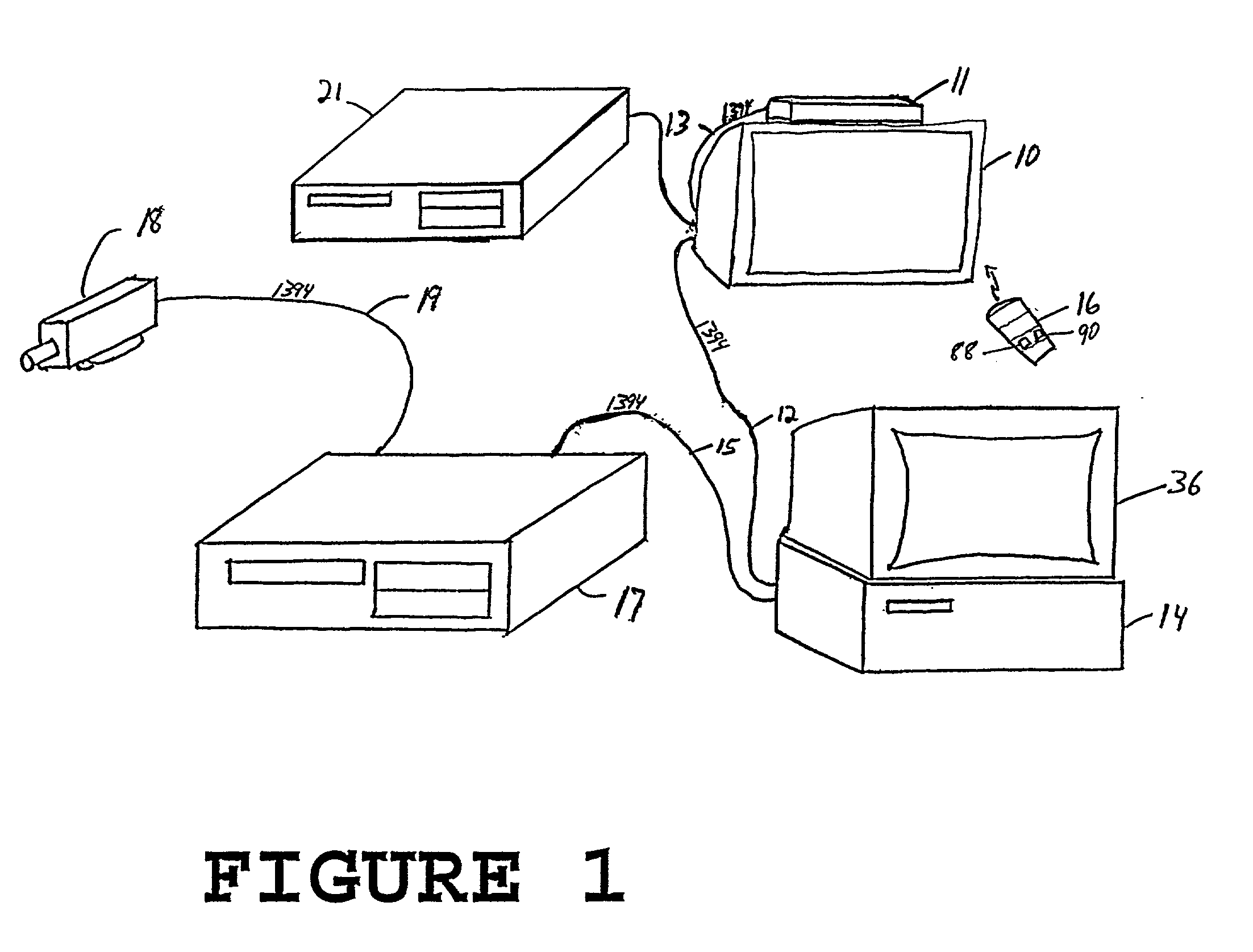
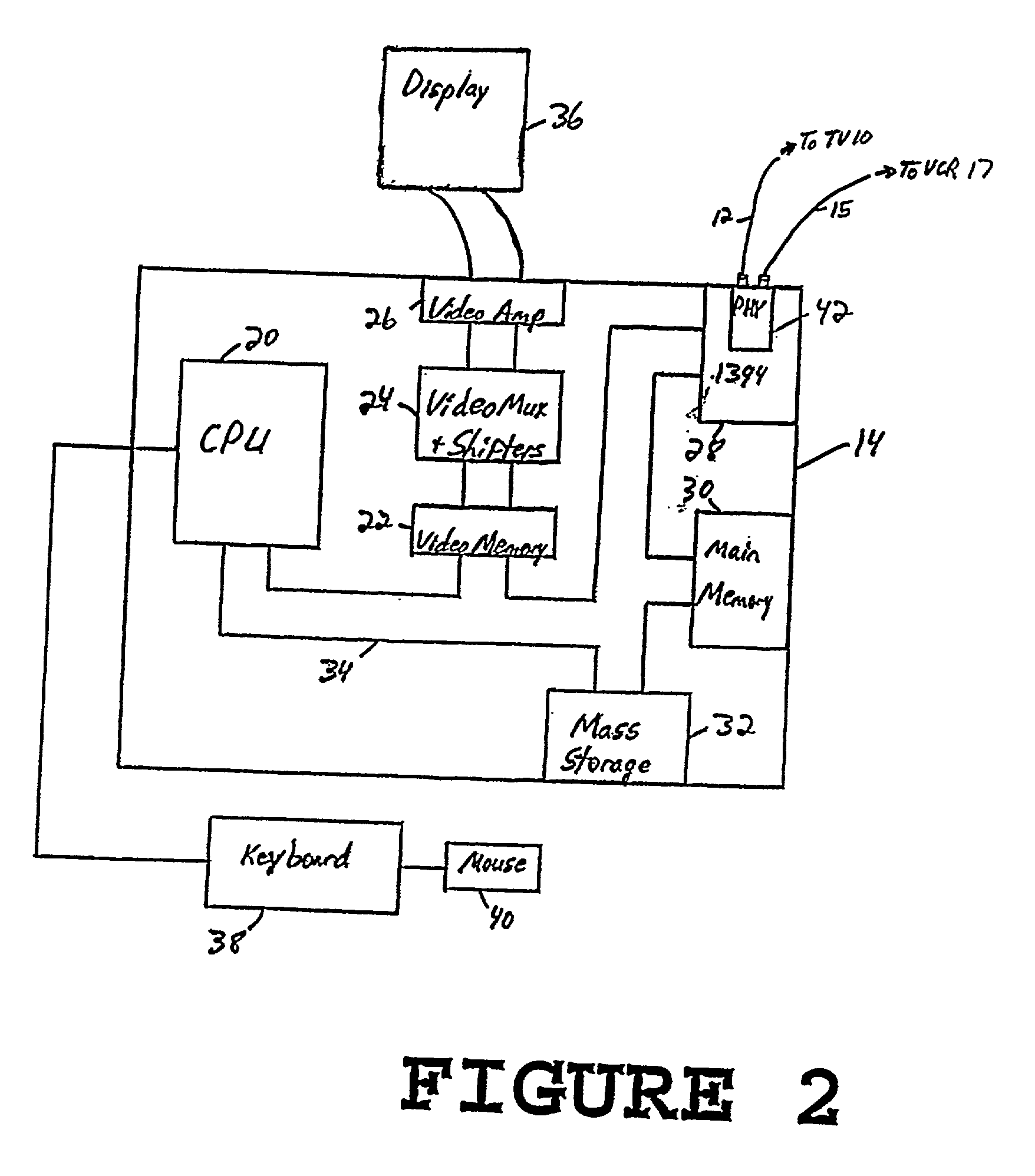
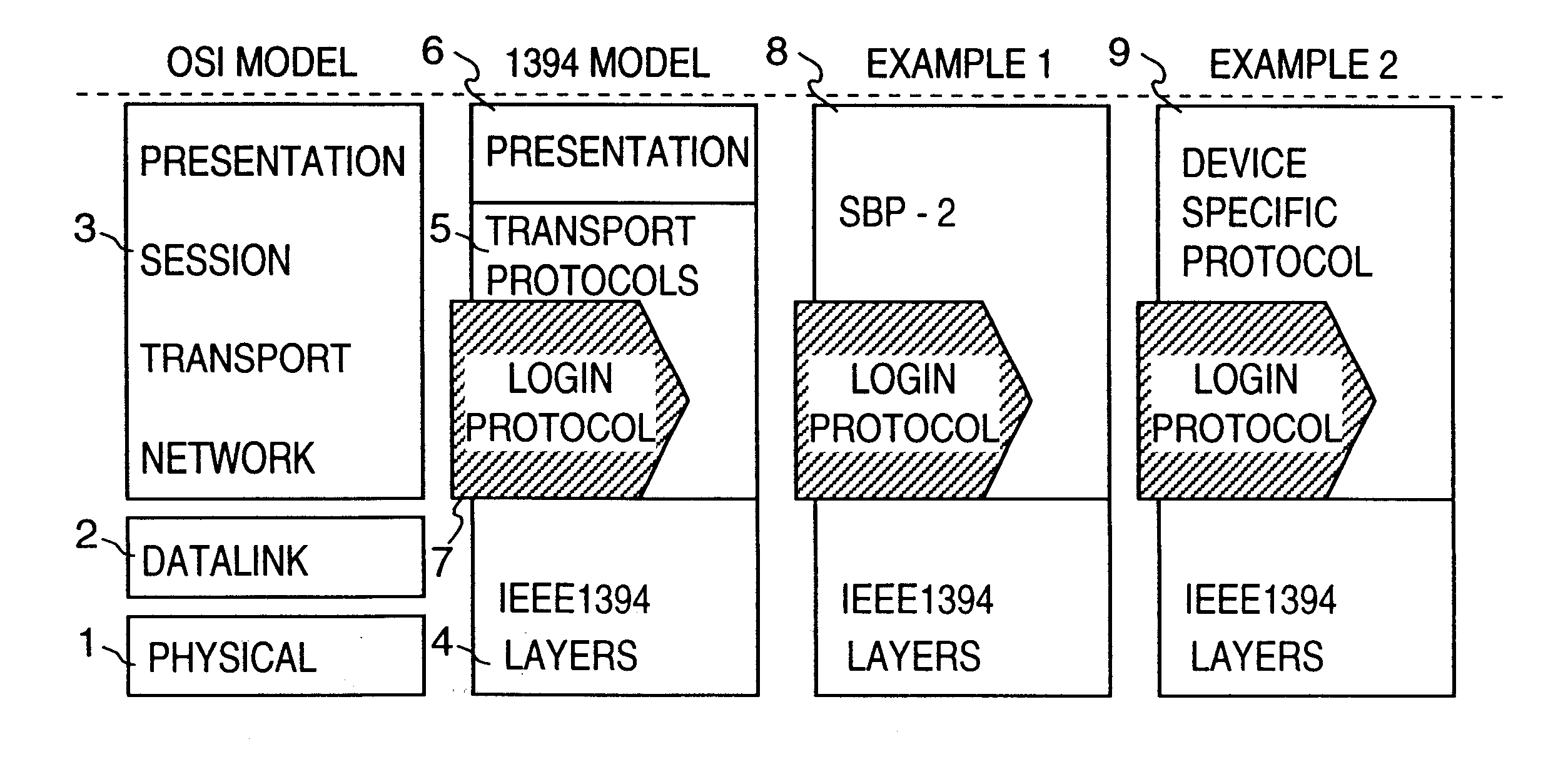
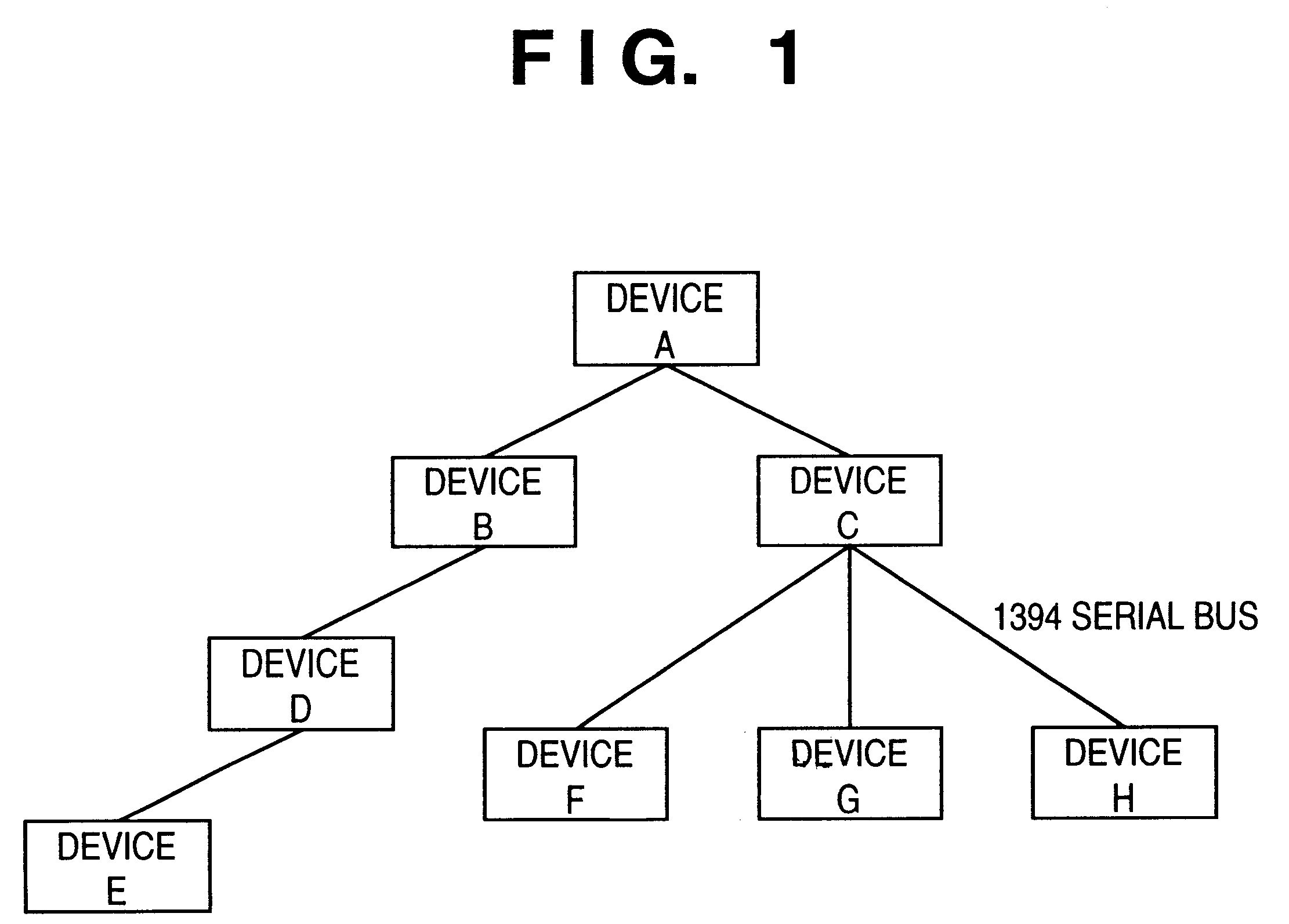
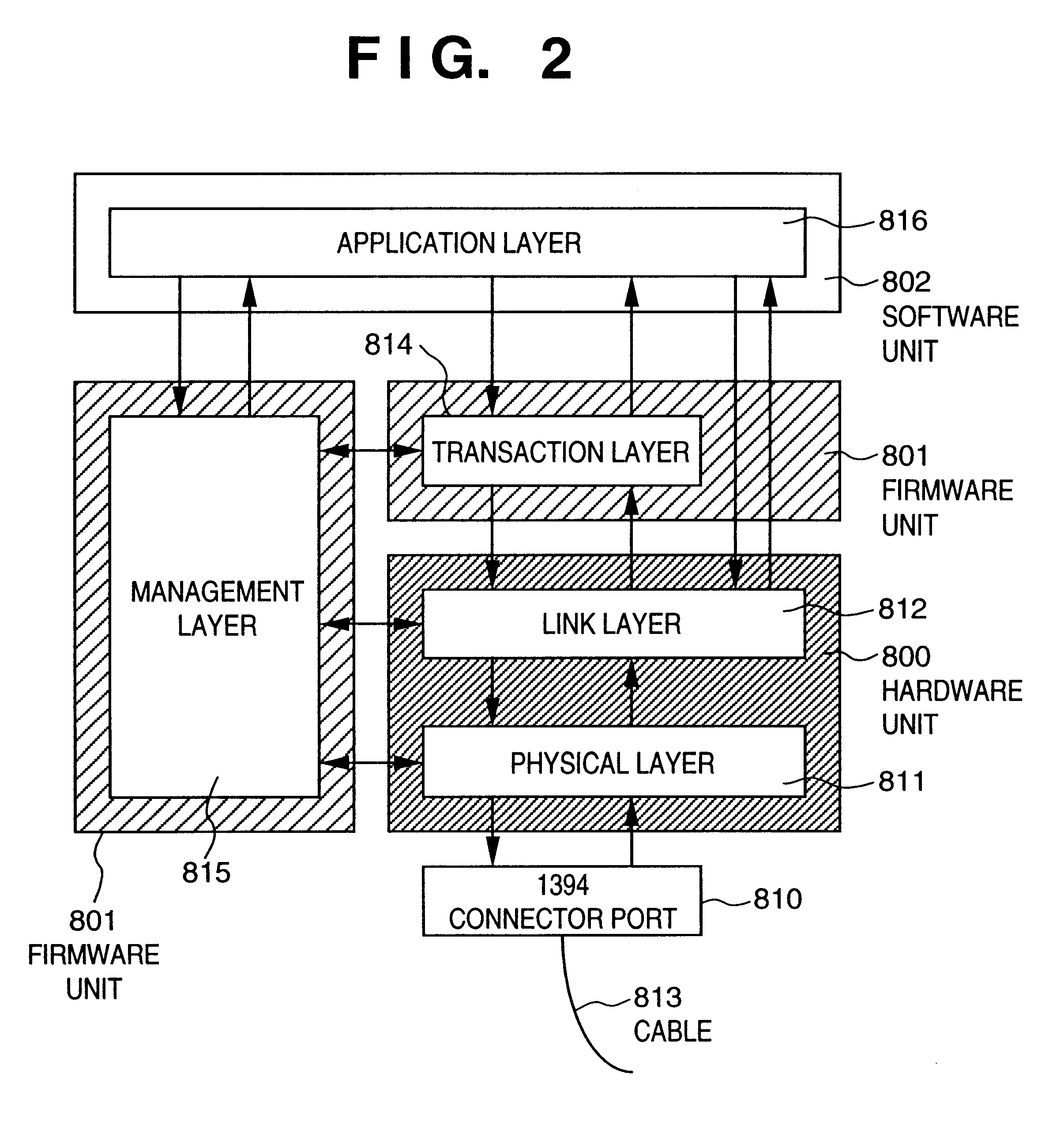
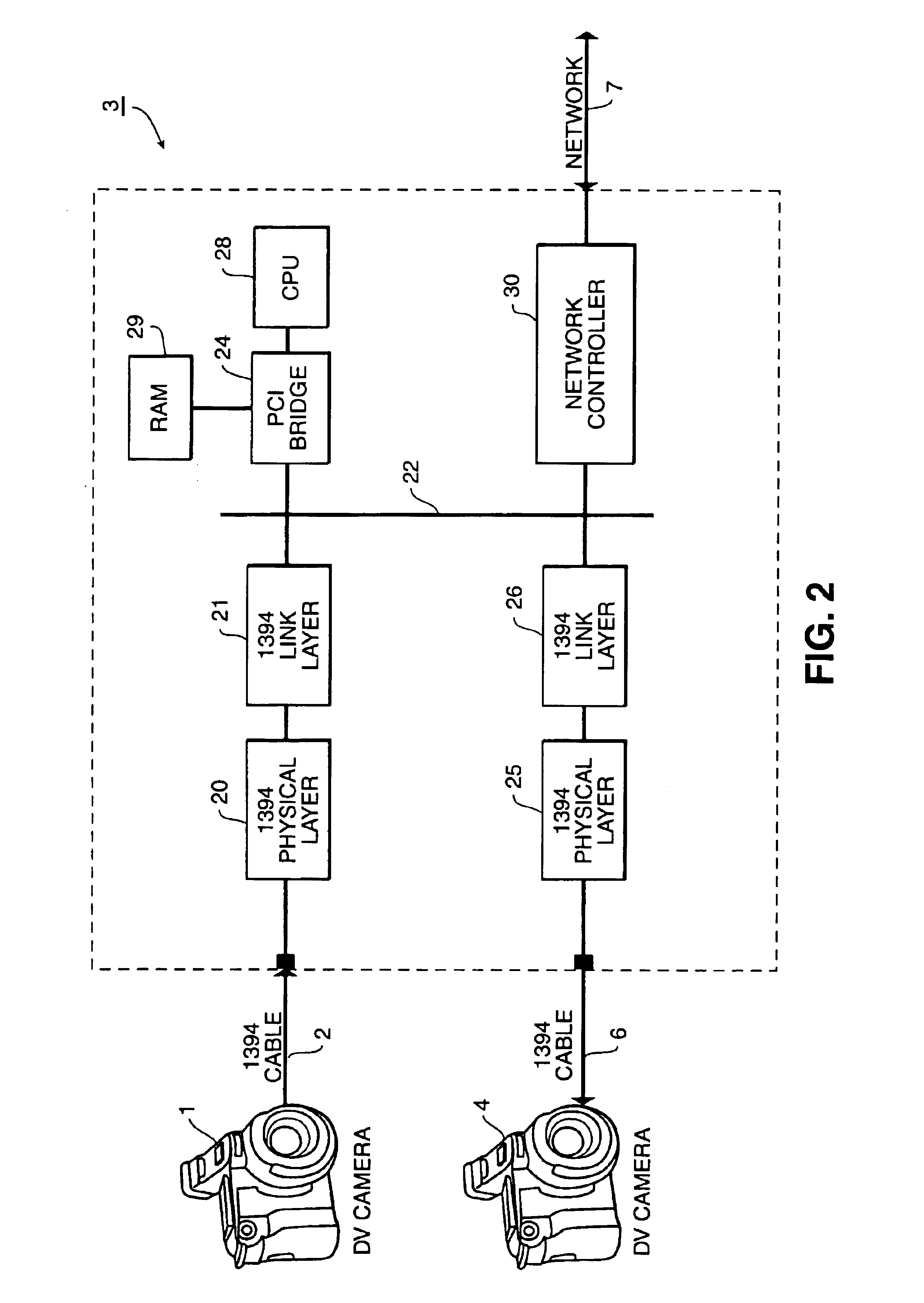
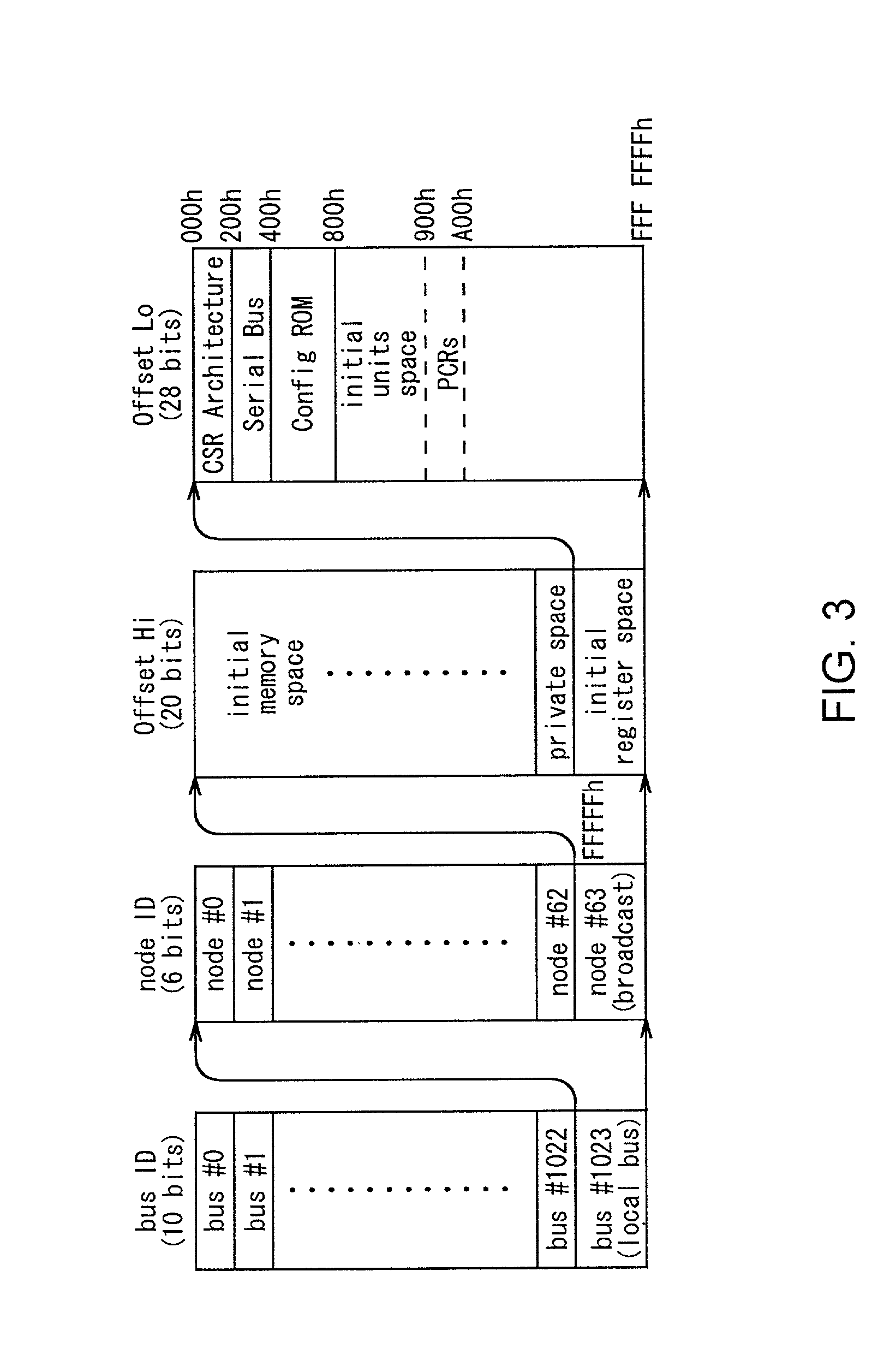
IEEE 1394 is an interface standard for a serial bus for high-speed communications and isochronous real-time data transfer. It was developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s by Apple, which called it FireWire, in cooperation with a number of companies, primarily Sony and Panasonic. The 1394 interface is also known by the brands i.LINK (Sony), and Lynx (Texas Instruments).
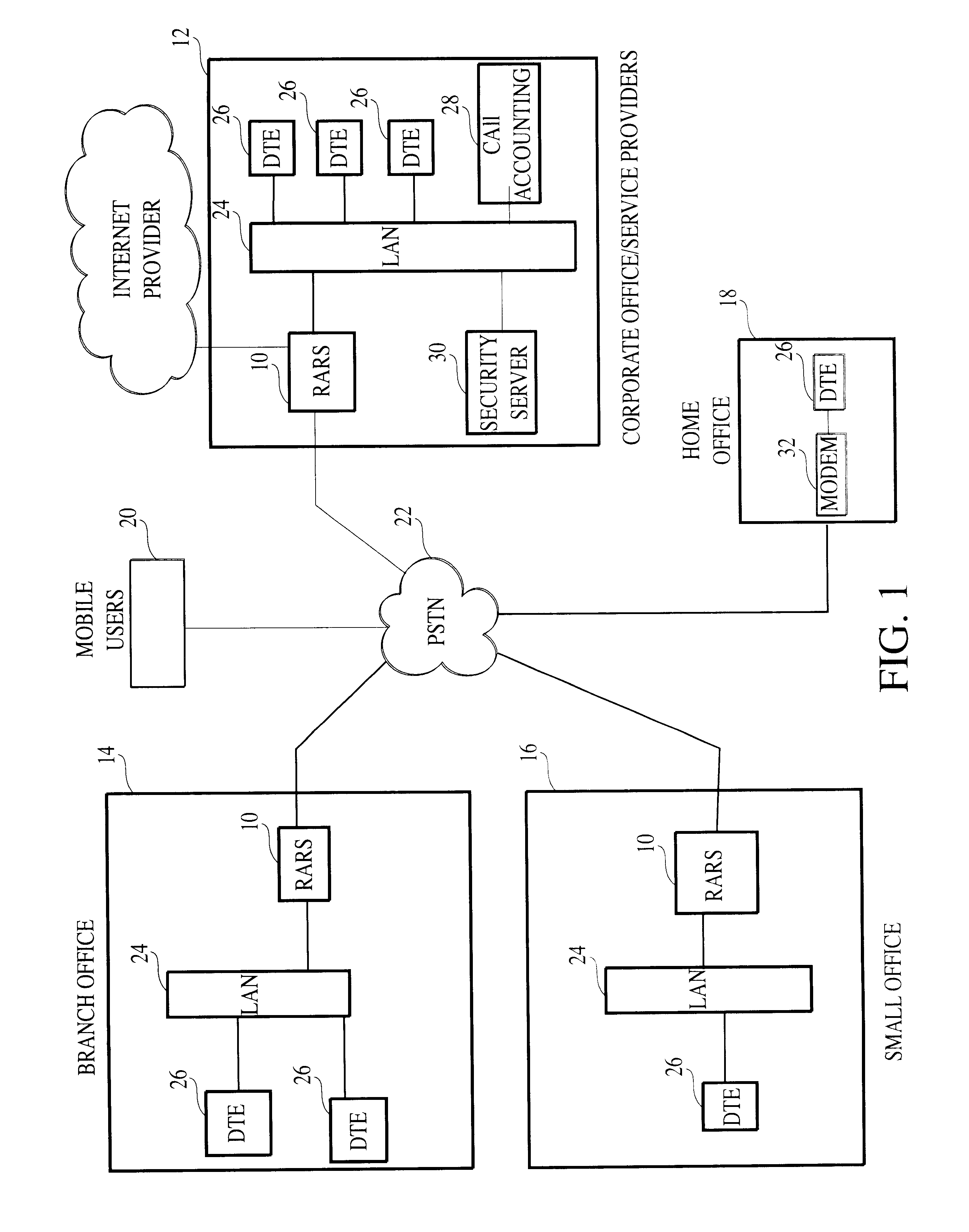
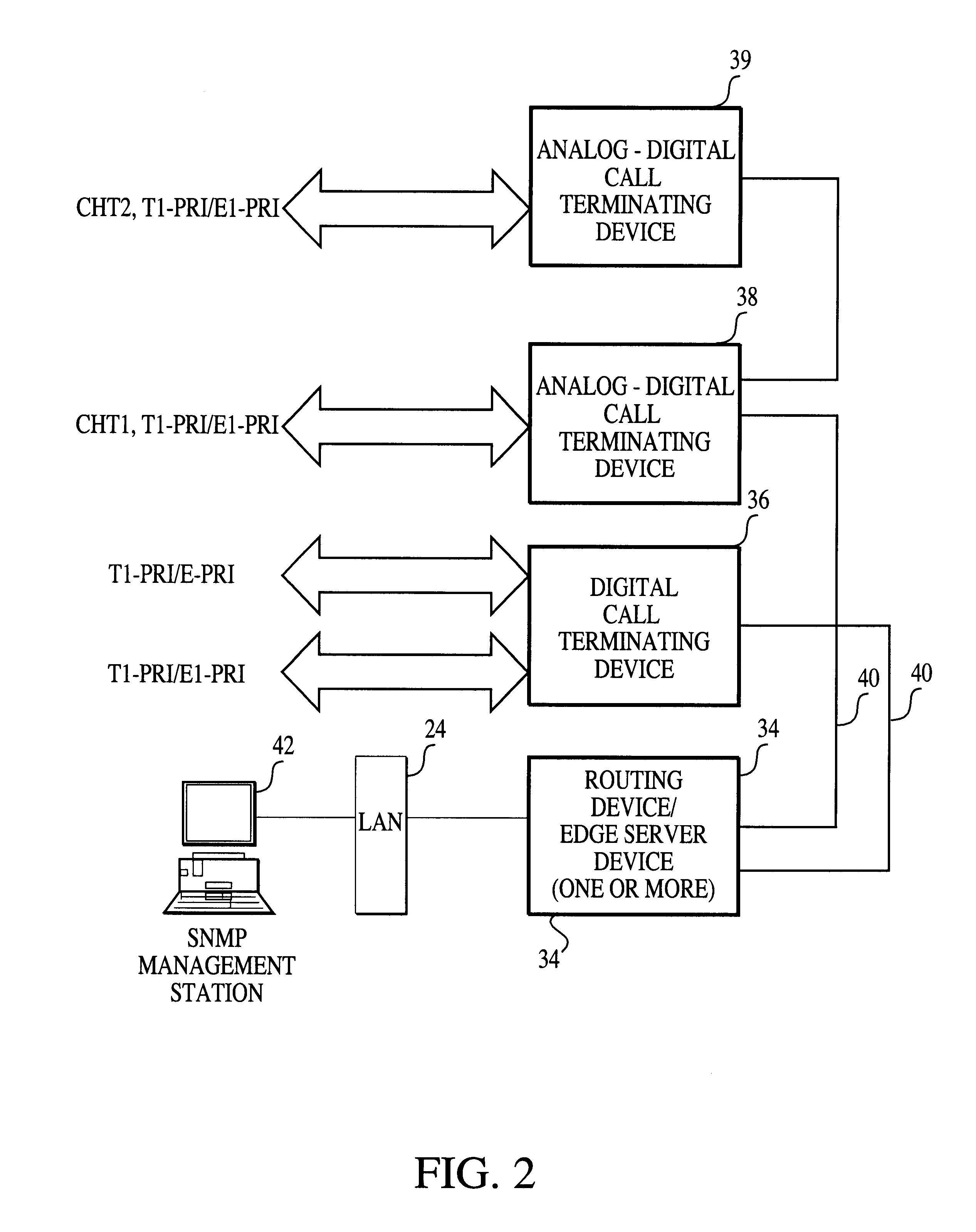
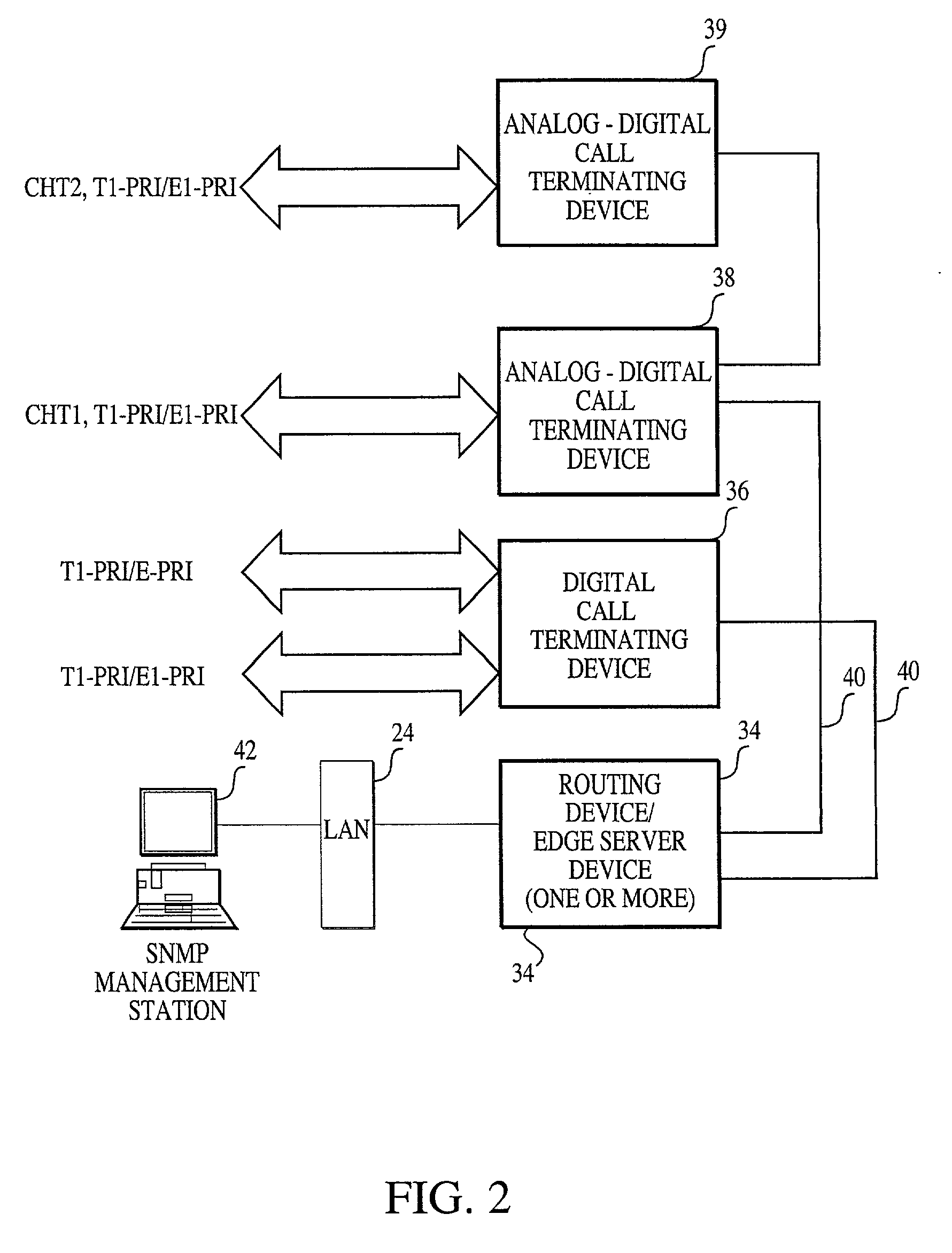
Internet appliance system and method
InactiveUS20060200253A1Minimize timeTelevision system detailsAdvertisementsPhysical securityThe Internet
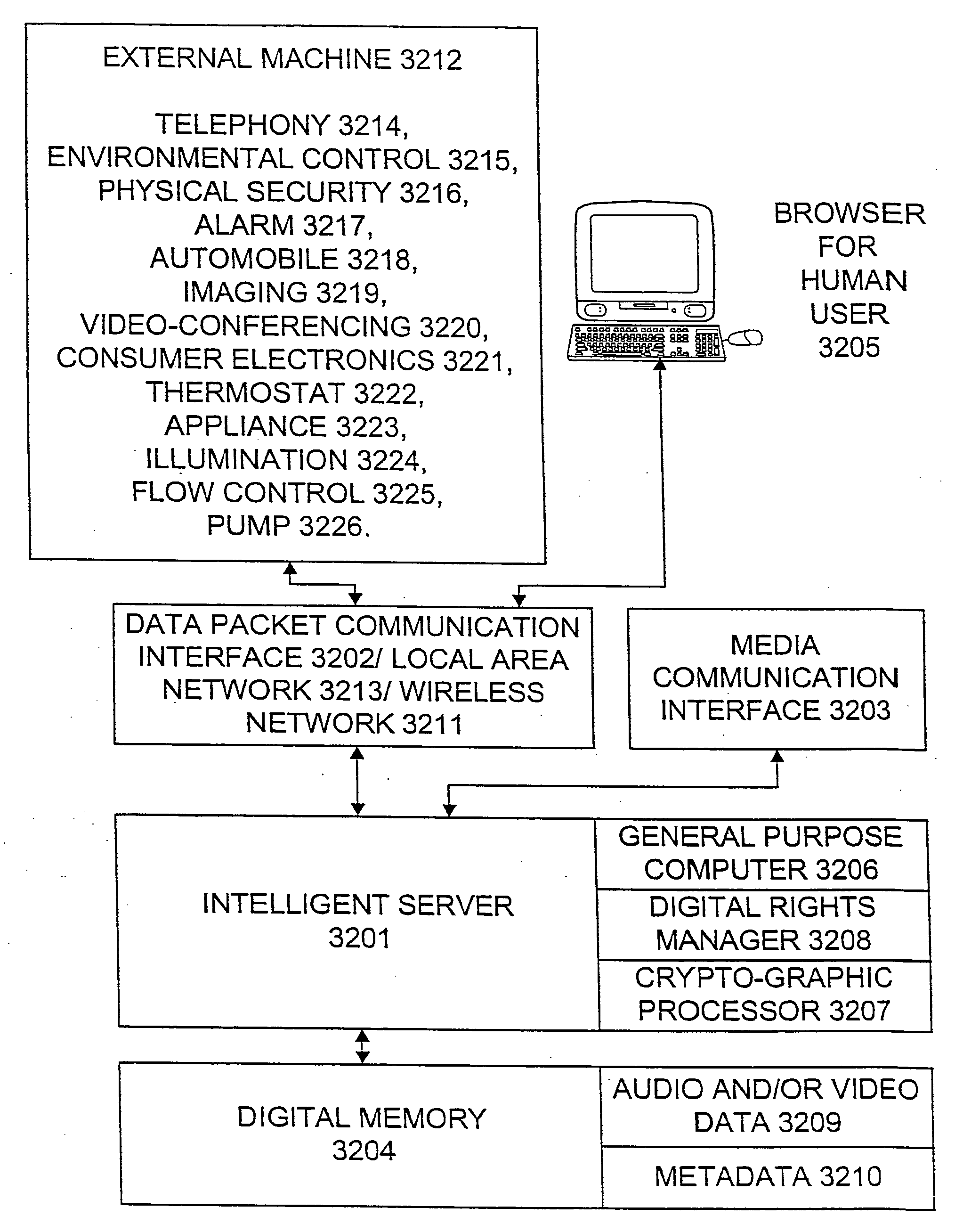
An Internet appliance, comprising, within a single housing, packet data network interfaces, adapted for communicating with the Internet and a local area network, at least one data interface selected from the group consisting of a universal serial bus, an IEEE-1394 interface, a voice telephony interface, an audio program interface, a video program interface, an audiovisual program interface, a camera interface, a physical security system interface, a wireless networking interface; a device control interface, smart home interface, an environmental sensing interface, and an environmental control interface, and a processor, for controlling a data transfer between the local area network and the Internet, and defining a markup language interface communicated through a packet data network interface, to control a data transfer or control a remote device.
Owner:BLANDING HOVENWEEP
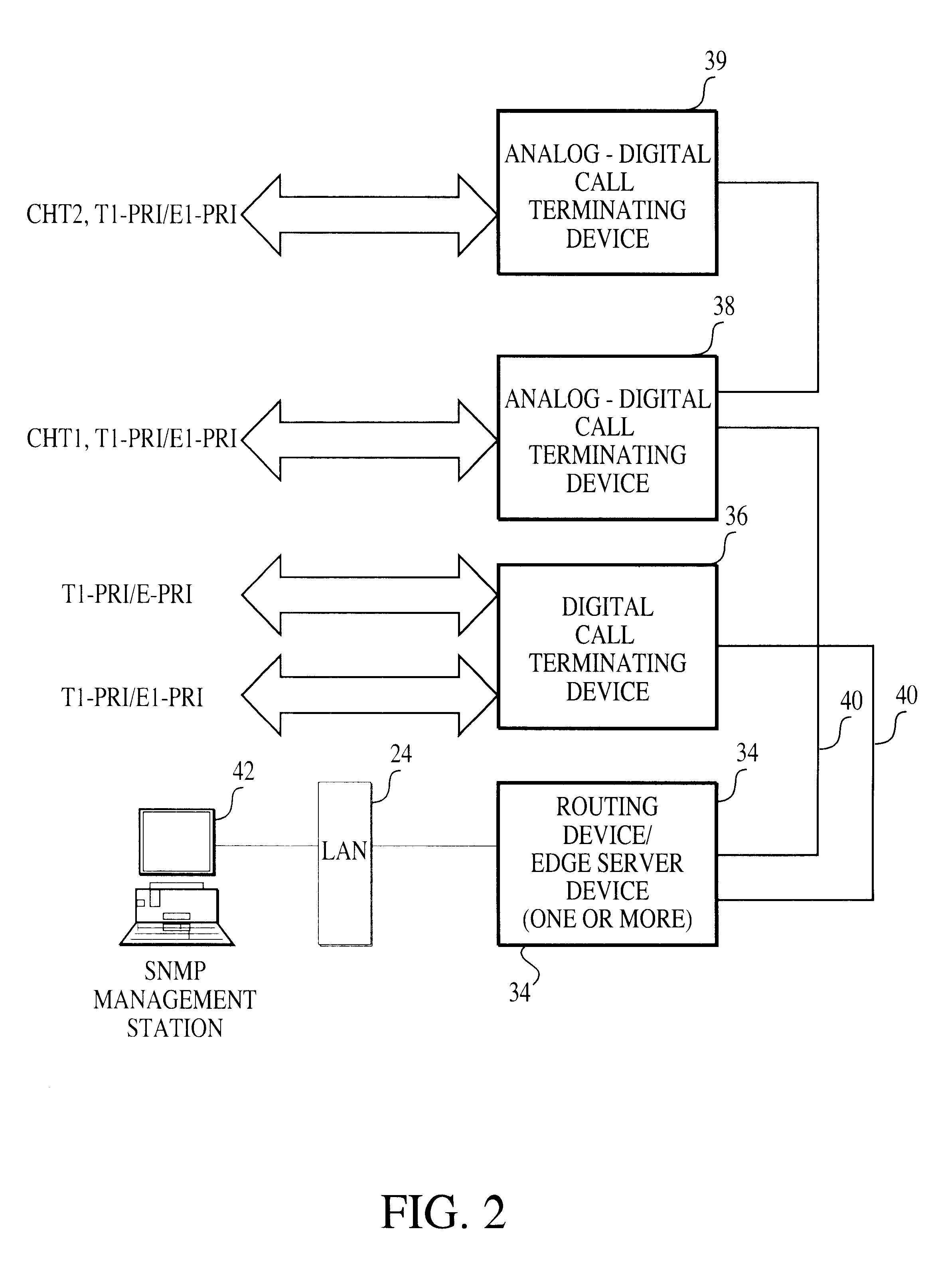
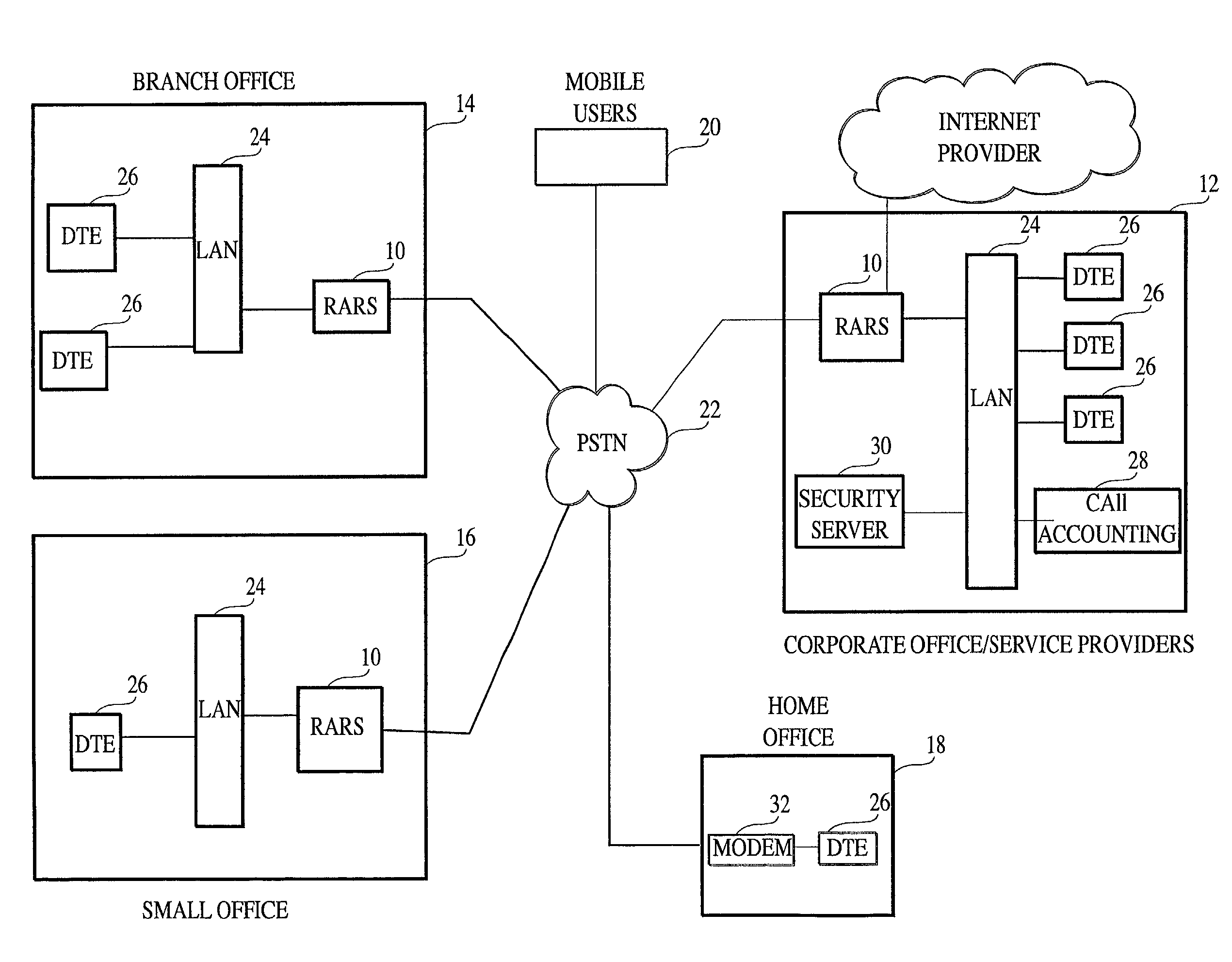
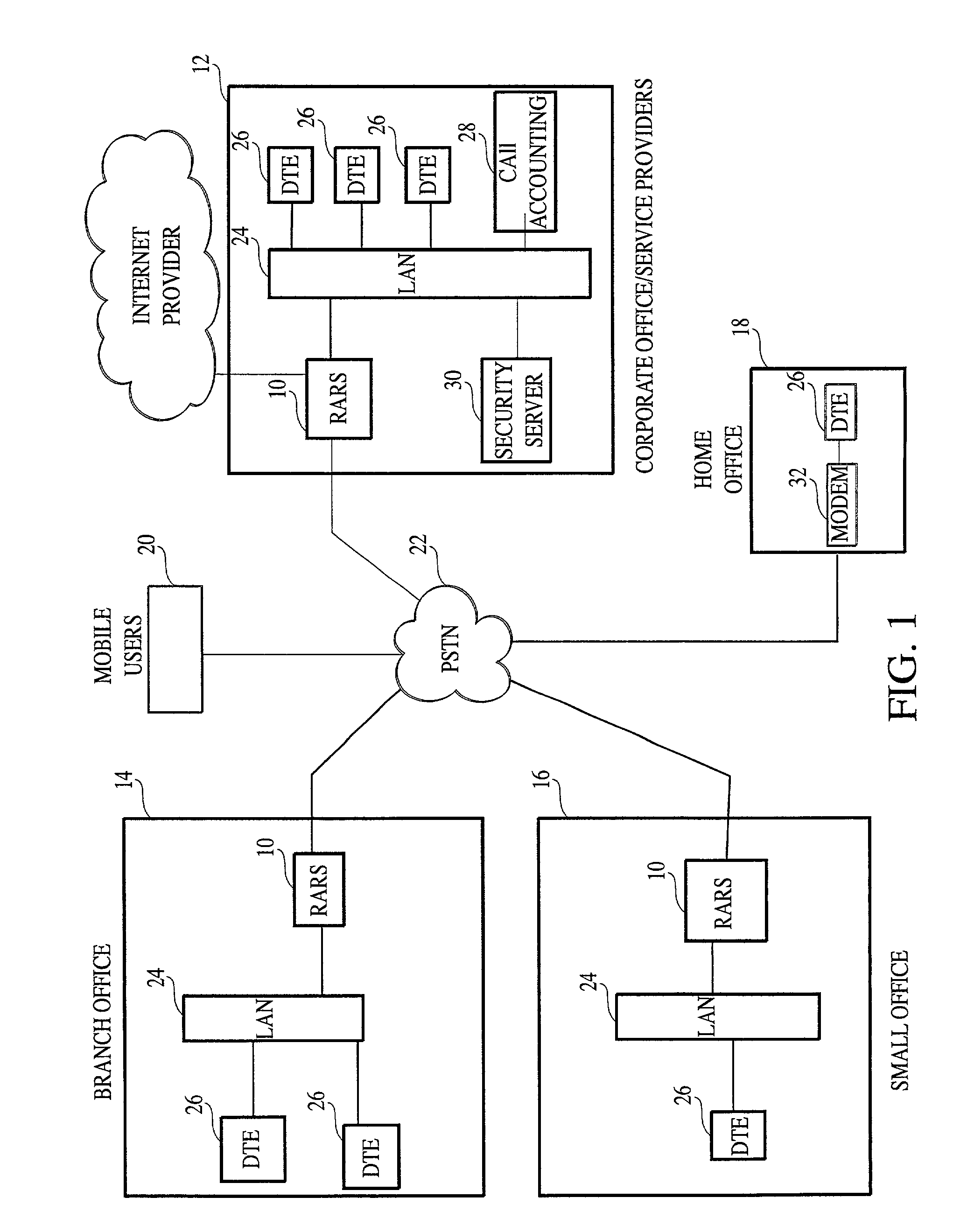
Method and apparatus for operating the internet protocol over a high-speed serial bus
InactiveUS6219697B1Efficiently and correctly determineDigital computer detailsTransmissionInternet protocol suiteTransport layer
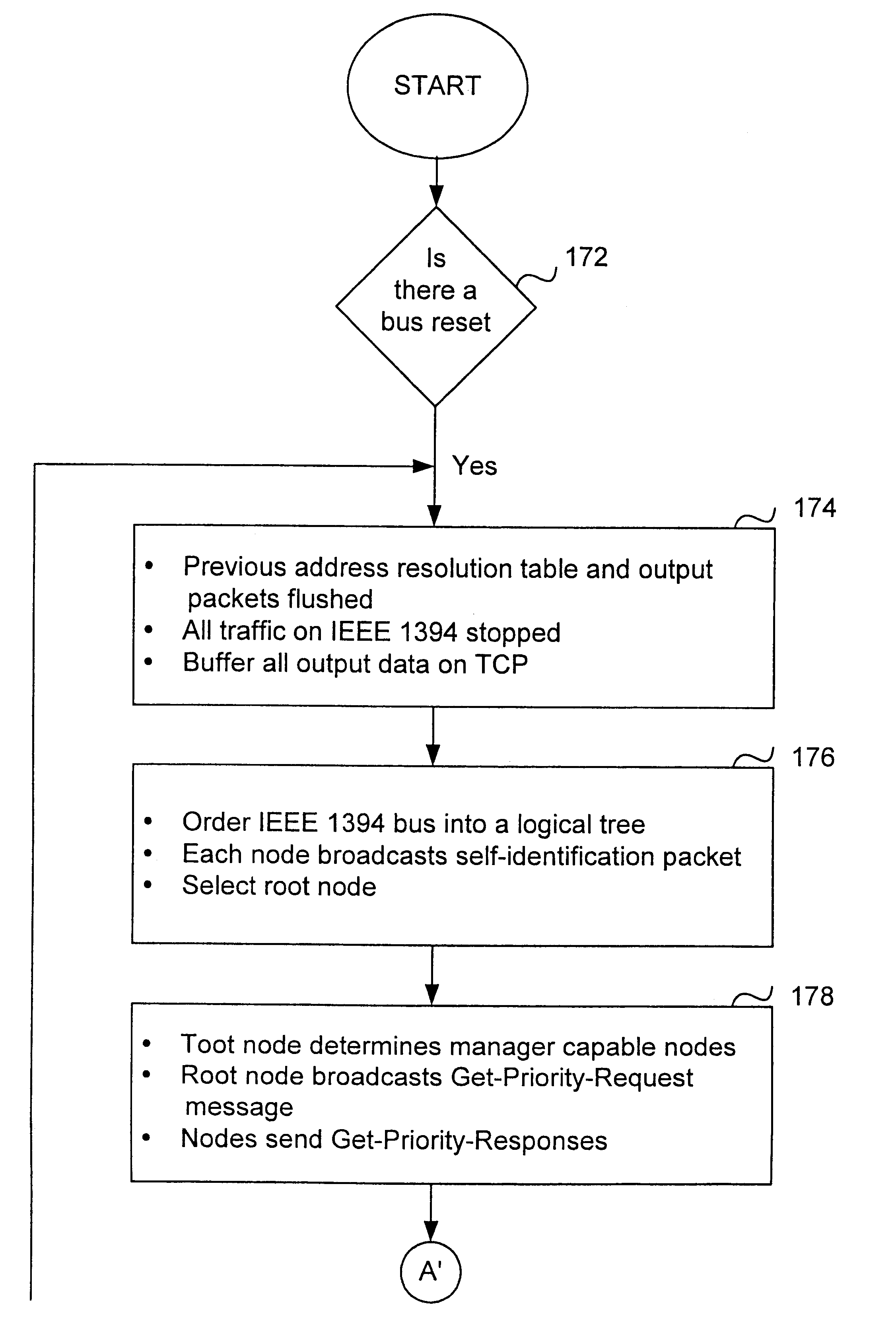
A method and apparatus of integrating the IEEE 1394 protocol with the IP protocol in which the IEEE 1394 high speed serial bus operates as the physical and link layer medium and the IP operates as the transport layer. There are differences in the protocols which require special consideration when integrating the two protocols. The IEEE 1394 configures packets with memory information and the IP operates under channel based I / O thereby necessitating a modification of the data transfer scheme to accomplish IP transfers over the IEEE 1394. Further, due to differences in packet headers, the IEEE 1394 packet header is modified to encapsulate IP packets. Moreover, in order to determine network packets quickly and efficiently, an identifier is inserted in each network packet header indicating that the packet should be processed by the network. Finally, in order to support the ability to insert or remove nodes on the network without a loss of data, the IP interface must not be disturbed. This is accomplished by maintaining constant IP addresses across bus resets which are caused by insertion or removal of nodes from the network.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
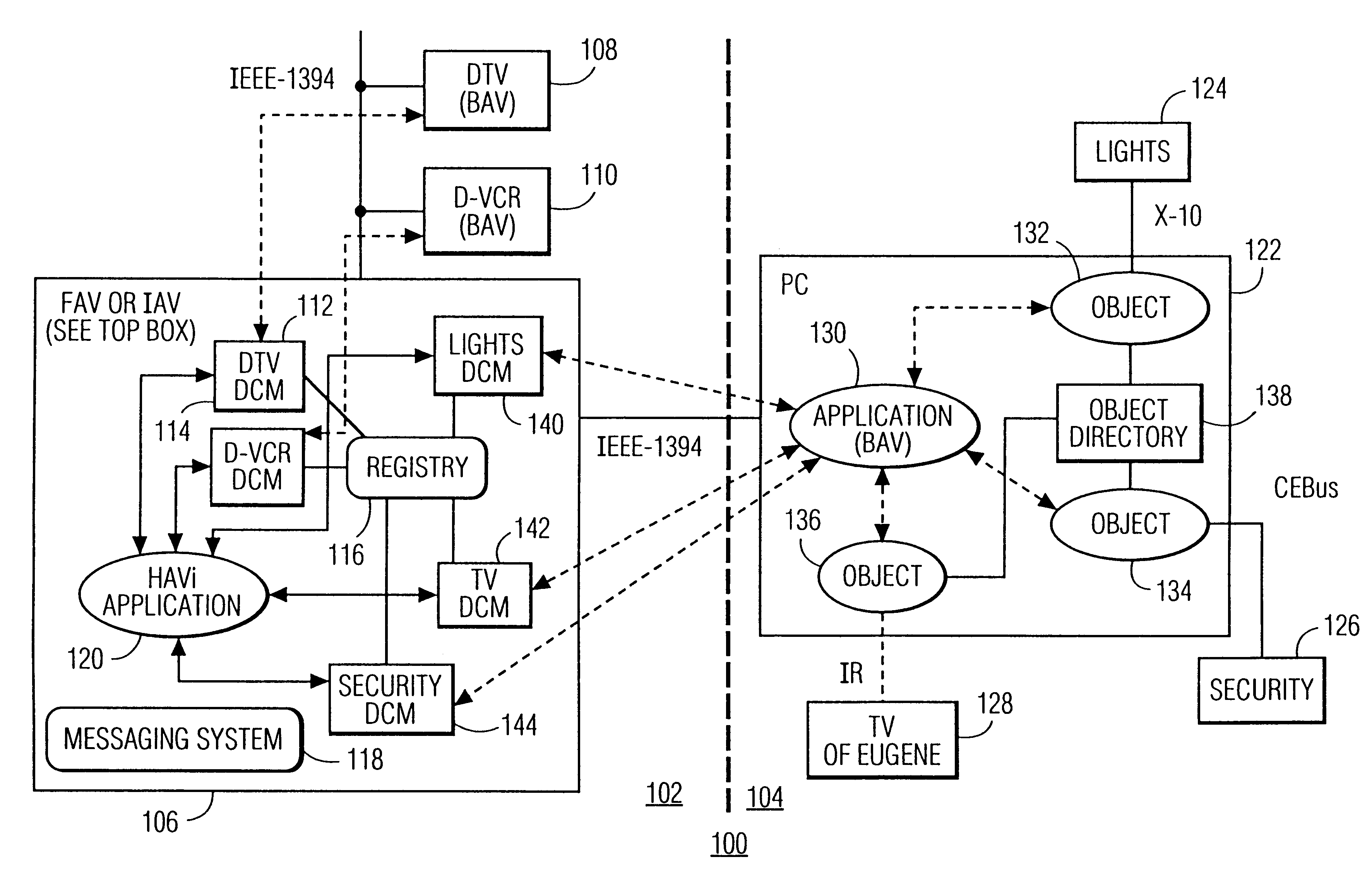
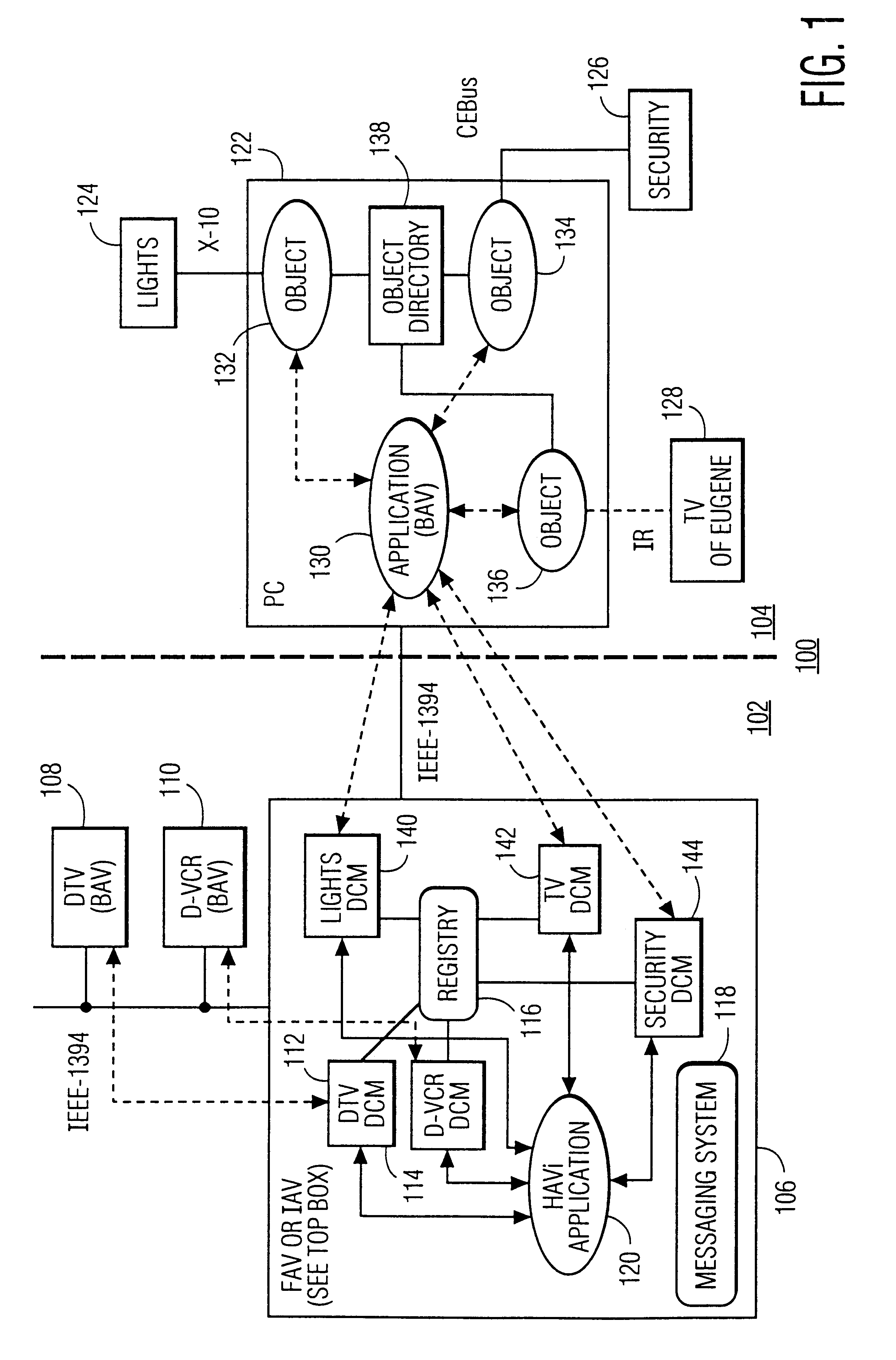
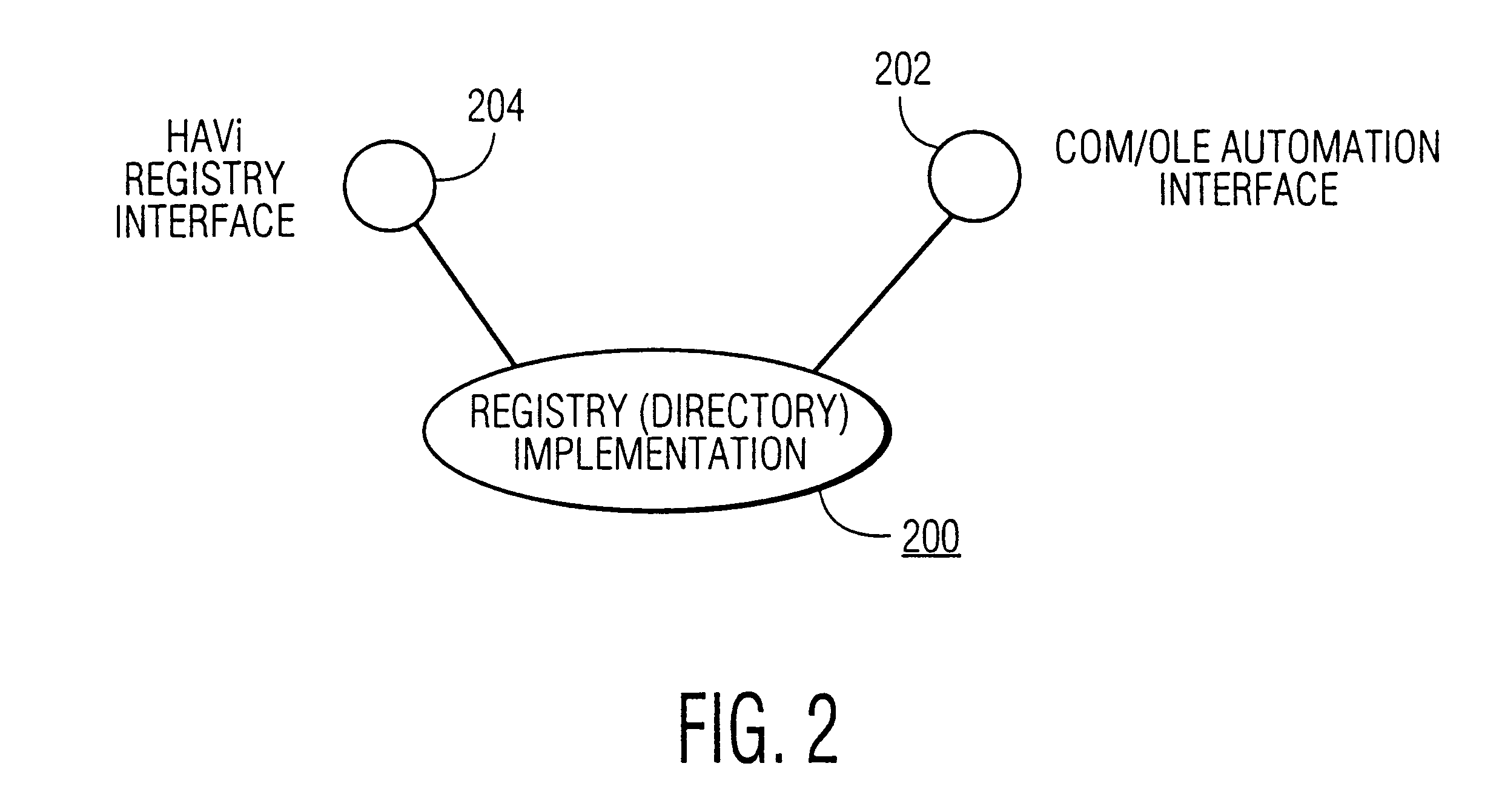
Method and apparatus for a low data-rate network to be represented on and controllable by high data-rate home audio/video interoperability (HAVi) network
InactiveUS6199136B1Function increaseMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationVideo equipmentEmbedded system
A PC-based home automation system uses a low data-rate transport layer and COM-based software components for control of devices in a home automation network. The home automation system is merged with a messaging-based HAVi-network that uses IEEE 1394 as a high data-rate transport layer. The HAVi-network controls audio / video equipment in a home entertainment system. The home automation services and devices are registered as a HAVi-compliant elements with the HAVi network's FAV or IAV device. The home automation resources (devices and services) have both COM OLE Automation Interfaces and HAVI-compliant interfaces to permit control of the home automation system from the HAVi-network.
Owner:U S PHILIPS CORP
Recording/reproducing apparatus, program recorded medium, recorded medium, cache device, and transmitter
InactiveUS6584552B1Improve system reliabilityImprove reliabilityTelevision system detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer hardwareTransmitter
A recording and reproducing apparatus is characterized in that said apparatus has: inputting means for receiving a packet data which is based on IEEE 1394, and in which signal information for indicating copy right information of an AV data (hereinafter, referred to as EMI) is provided in a header of a packet according to IEEE 1394; and recording and reproducing means for recording and reproducing an AV data and the EMI which are held in the packet data received by said inputting means. Four kinds of EMI are used, and, when an AV data indicating allowance "copy one generation" among them is to be recorded, said recording and reproducing means performs recording while rewriting the EMI to EMI indicating "no more copy."
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
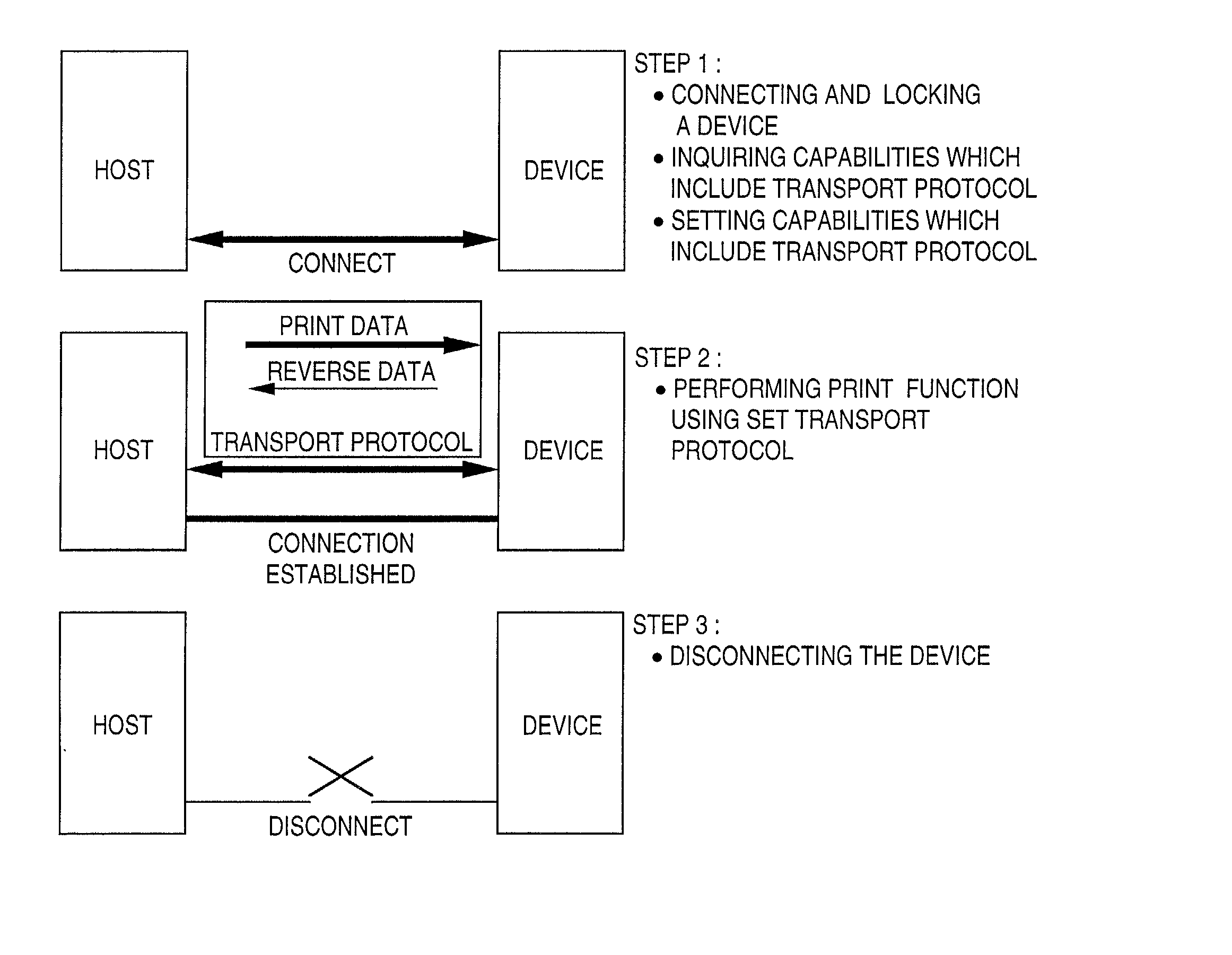
Data communication apparatus and method
InactiveUS20020062407A1Reduce frequencyAvoid inefficiencyPulse modulation television signal transmissionHybrid switching systemsComputer hardwareData shipping
In response to a request from a host device using an initial protocol, capability information including information indicative of a plurality of communication protocols is returned to the host device, and a communication protocol, designated by the host device based on the capability information, is set, and print data is received from the host device by the set communication protocol. In a system using an interface connected to various types of devices, e.g., an IEEE 1394 serial bus, a communication protocol, which is used when a host device transfers print data to a printer, is not limited to that unique to the manufacturer of the device.
Owner:CANON KK
Power subsystem for a communication network containing a power bus
InactiveUS6125448AVolume/mass flow measurementData switching current supplyComponent LoadCurrent limiting
A method and apparatus of powering components on a network by using a load-share technique and by using over-voltage and current-limiting circuitry. The power subsystem for a component in a network is designed in a load-share manner whereby the power subsystem will supply power to the network bus and to the component load. Under normal operation of the power subsystem, the load will be powered directly from the power subsystem. In the event of a failure, the load will immediately pull power from the bus and thereby maintain network operation. The power subsystem and the power supply are protected from disruptions due to voltage or current surges. Further, the power subsystem is in compliance with the IEEE 1394 specifications in terms of recommended current levels and galvanic isolation of the power sources.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
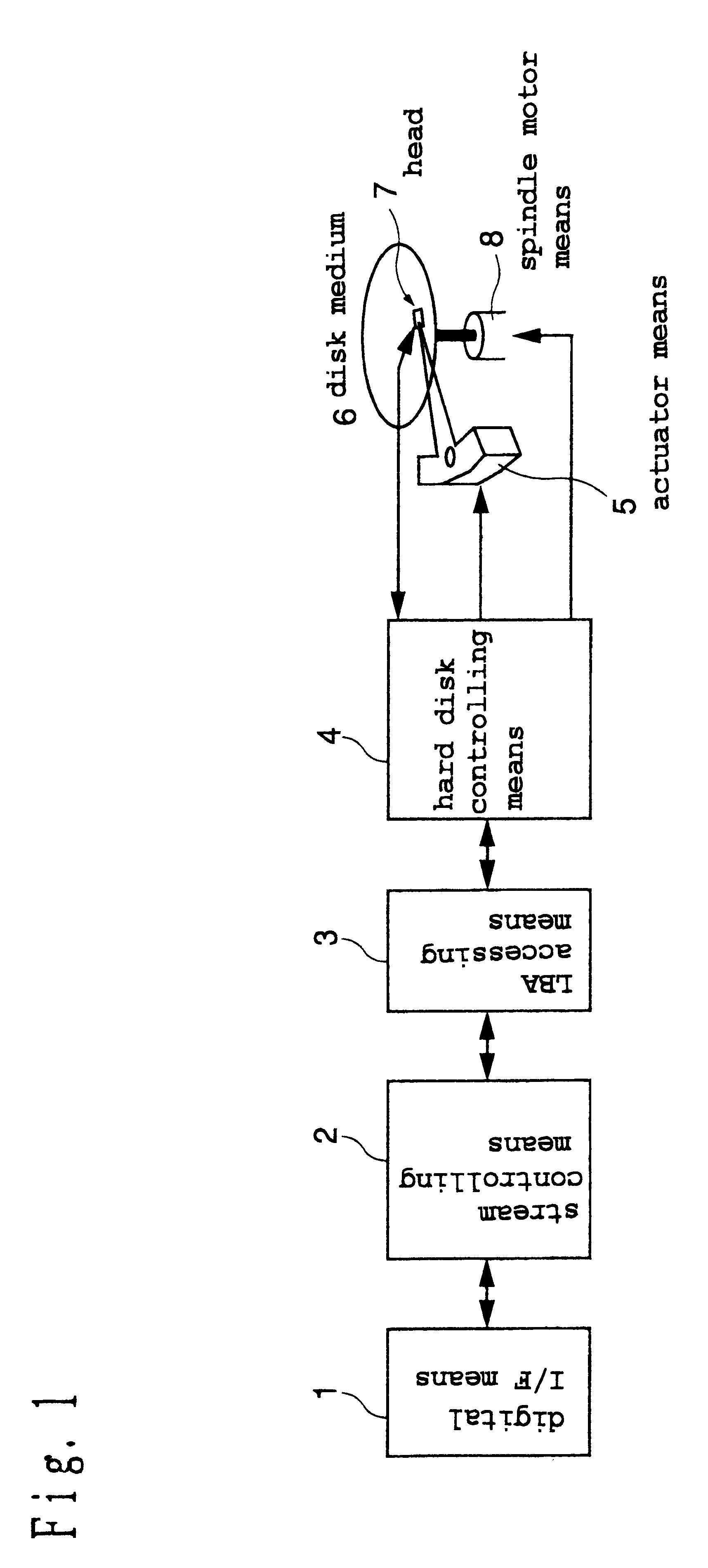
Video recording device including the ability to concurrently record and playback
InactiveUS20020057892A1Television system detailsElectronic editing analogue information signalsMass storageHard disc drive
A video recording device includes the ability to record a video broadcast or video program while concurrently replaying a previously recorded video broadcast. This previously recorded video broadcast can be the same video broadcast that is recording or a different video broadcast. The record and playback operations are preferably triggered and controlled through a television on which the user can watch the playback of the recorded program. The viewer enters the data and commands for recording and playback preferably using a remote control device. Video programs are preferably recorded on a mass storage device. Preferably, the mass storage device is a hard disk drive coupled to the television through an IEEE 1394 serial bus network. Alternatively, any other appropriately configured memory device can be used to store the video programs. The television uses write commands to transmit to and record the program onto the mass storage device and read commands to retrieve previously recorded portions of a program to be replayed from the mass storage device. When playing back a previously recorded program or the recorded portions of a program which is still being recorded, the television will retrieve the packets of data from the mass storage device in sequence, using read commands to read from the appropriate locations where the appropriate packets have been stored. Each packet is then retrieved in sequence from the beginning of the program, even if the end portion of the program is still being recorded.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Data communication on a serial bus using an initial protocol executed in a transaction layer
InactiveUS6425019B1Reduce frequencyAvoid inefficiencyInput/output for user-computer interactionPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer hardwareNetwork Communication Protocols
In response to a request from a host device using an initial protocol, capability information including information indicative of a plurality of communication protocols is returned to the host device, and a communication protocol, designated by the host device based on the capability information, is set, and print data is received from the host device by the set communication protocol. In a system using an interface connected to various types of devices, e.g., an IEEE 1394 serial bus, a communication protocol, which is used when a host device transfers print data to a printer, is not limited to that unique to the manufacturer of the device.
Owner:CANON KK
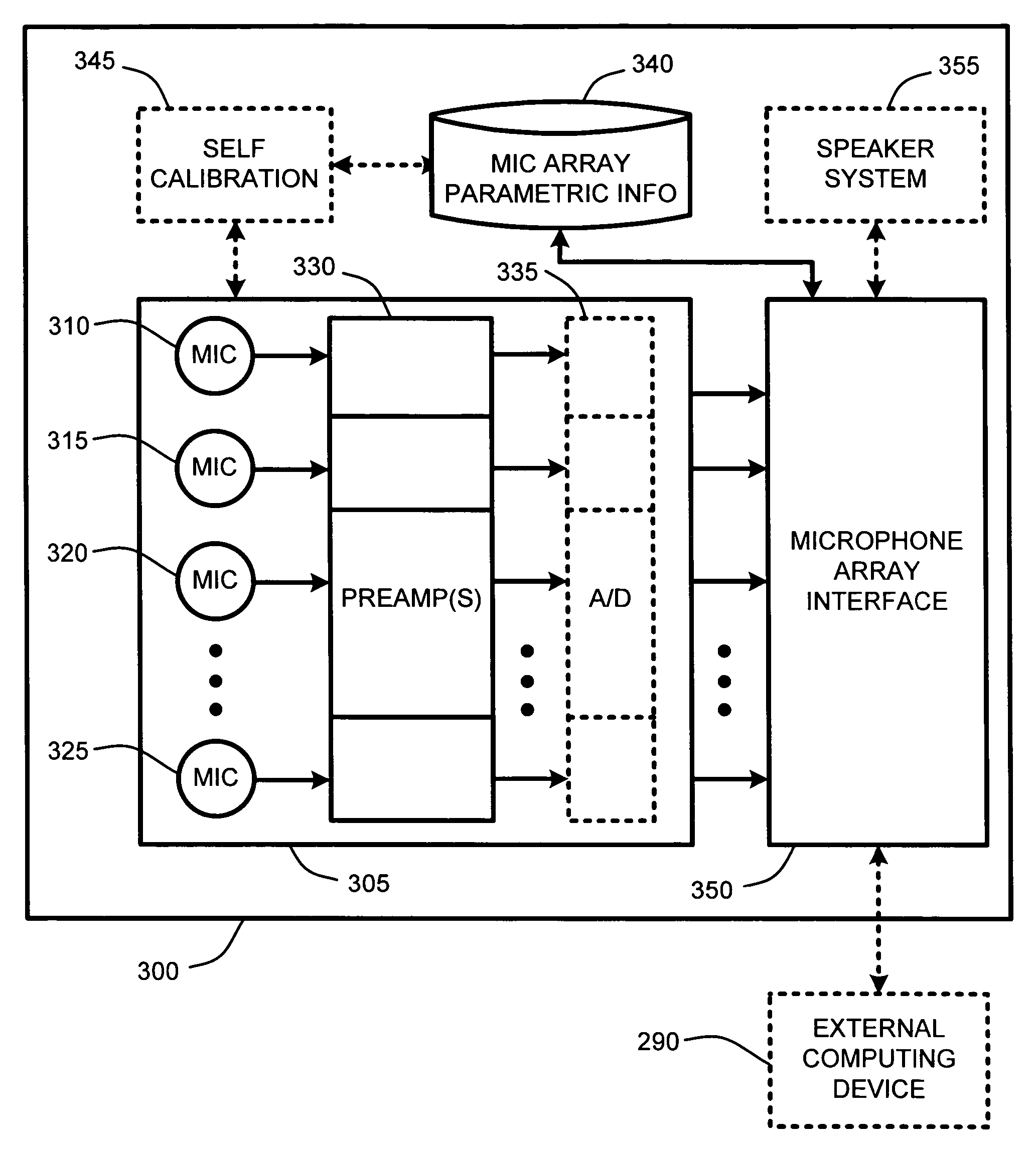
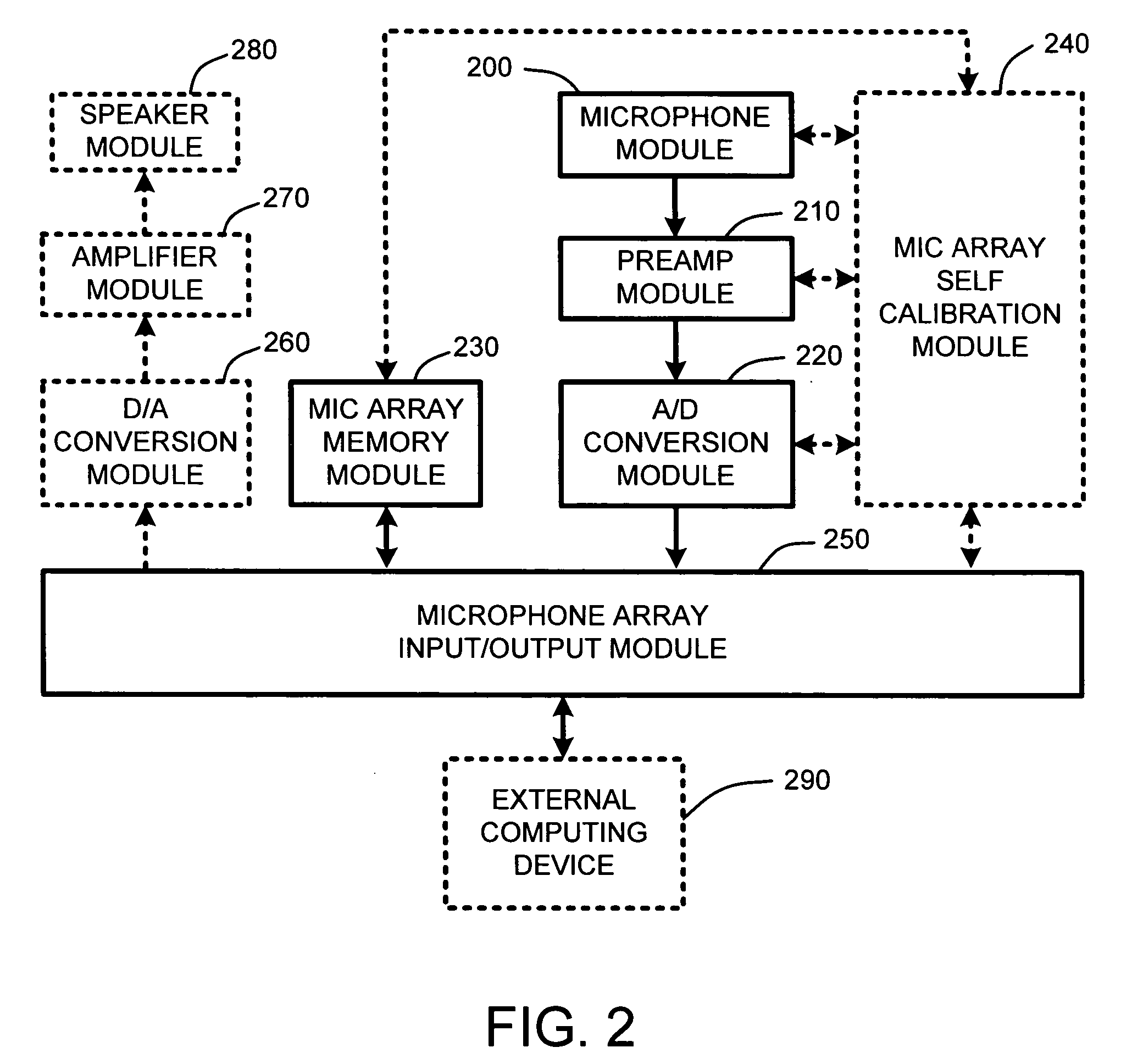
Self-descriptive microphone array
ActiveUS20050175190A1Reduce manufacturing costReducing microphone array costMicrophones signal combinationTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsConventional memoryUSB
A self-descriptive microphone array includes a microphone array memory, such as, for example a ROM, EEPROM, or other conventional memory, which contains a microphone array device description. This device description includes parametric information which defines operational characteristics and configuration of the microphone array. In further embodiments, the microphone array uses any of a variety of conventional wired or wireless computer interfaces, including serial, IEEE 1394, USB, Bluetooth™, etc., to connect to a computing device. Once connected, the microphone array provides its device description to the computing device. Sound processing software residing within the computing device is then automatically configured for optimally interacting with one or more analog or digital audio signals provided by the microphone array. In another embodiment, the microphone array performs integrated self calibration for automatically updating the device description. The self calibration is performed either upon connection to the computing device, or upon regular or user-specified intervals.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
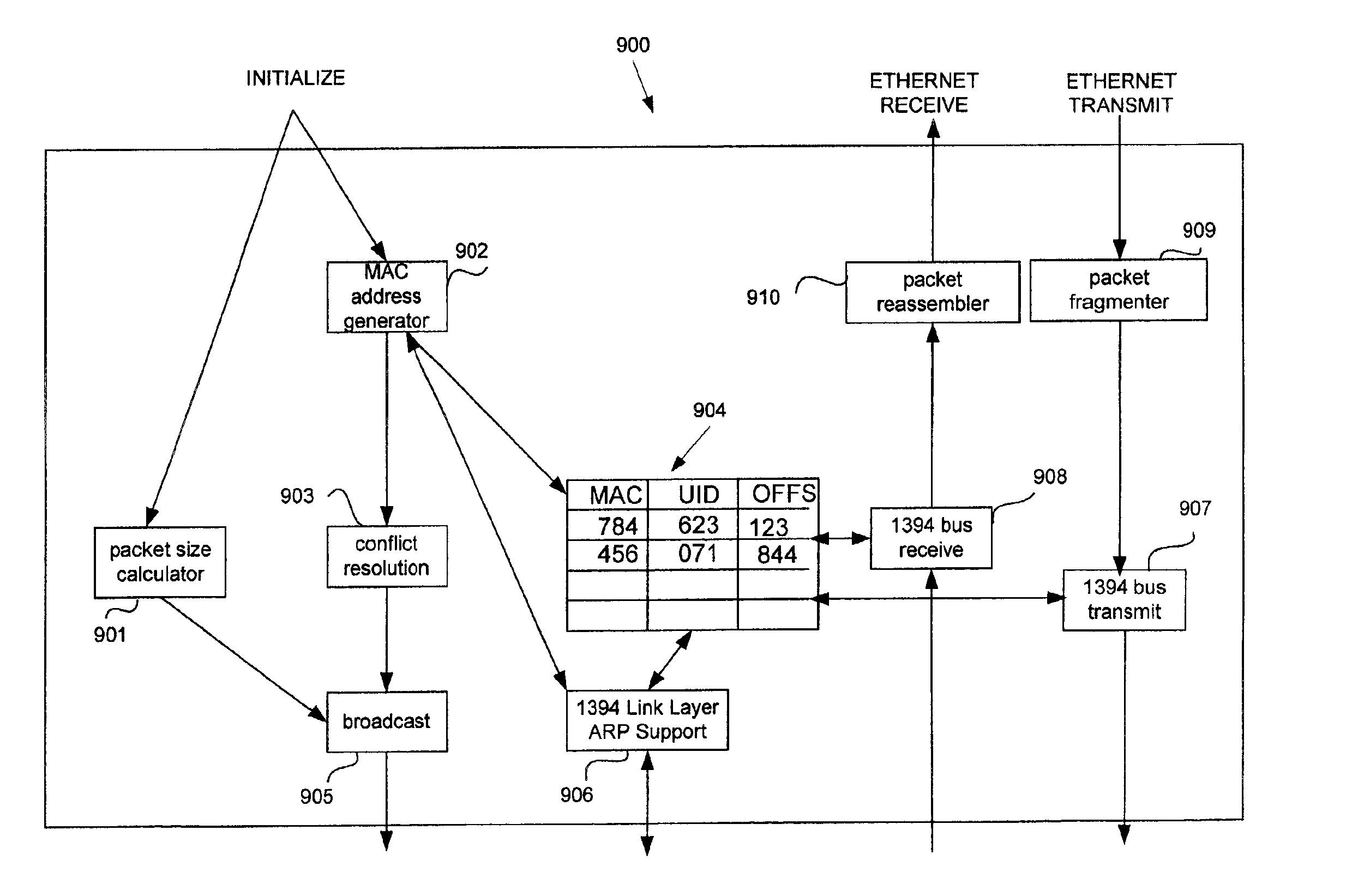
Method and apparatus for emulating ethernet functionality over a serial bus
InactiveUS6977939B2Time-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionNetwork packetDigital Signature Algorithm
The invention allows applications to transparently use a bus, such as the IEEE-1394 serial bus, as if it were an Ethernet (IEEE 802.3). In a conventional Ethernet, each node is assigned a unique 6-byte MAC address in order to receive frames addressed to it over the LAN. According to the invention, IEEE-1394 bus node identifiers are mapped to Ethernet MAC addresses using for example a digital signature algorithm. Ethernet frames are then “wrapped” into 1394 bus packets and addressed to the destination node using the hashed address. The receiver unwraps the 1394 packet and restores the Ethernet frame to its original form. An optimum packet size for transmission of Ethernet packets over the 1394 bus is selected with reference to speed topology maps in the 1394 bus nodes, and this optimum size is transmitted to bus nodes. This packet size is reported to TCP to specify the packet size, and all packets larger than that size are fragmented and reassembled at the receiving node. The protocol works transparently across networks that are linked via bridges.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
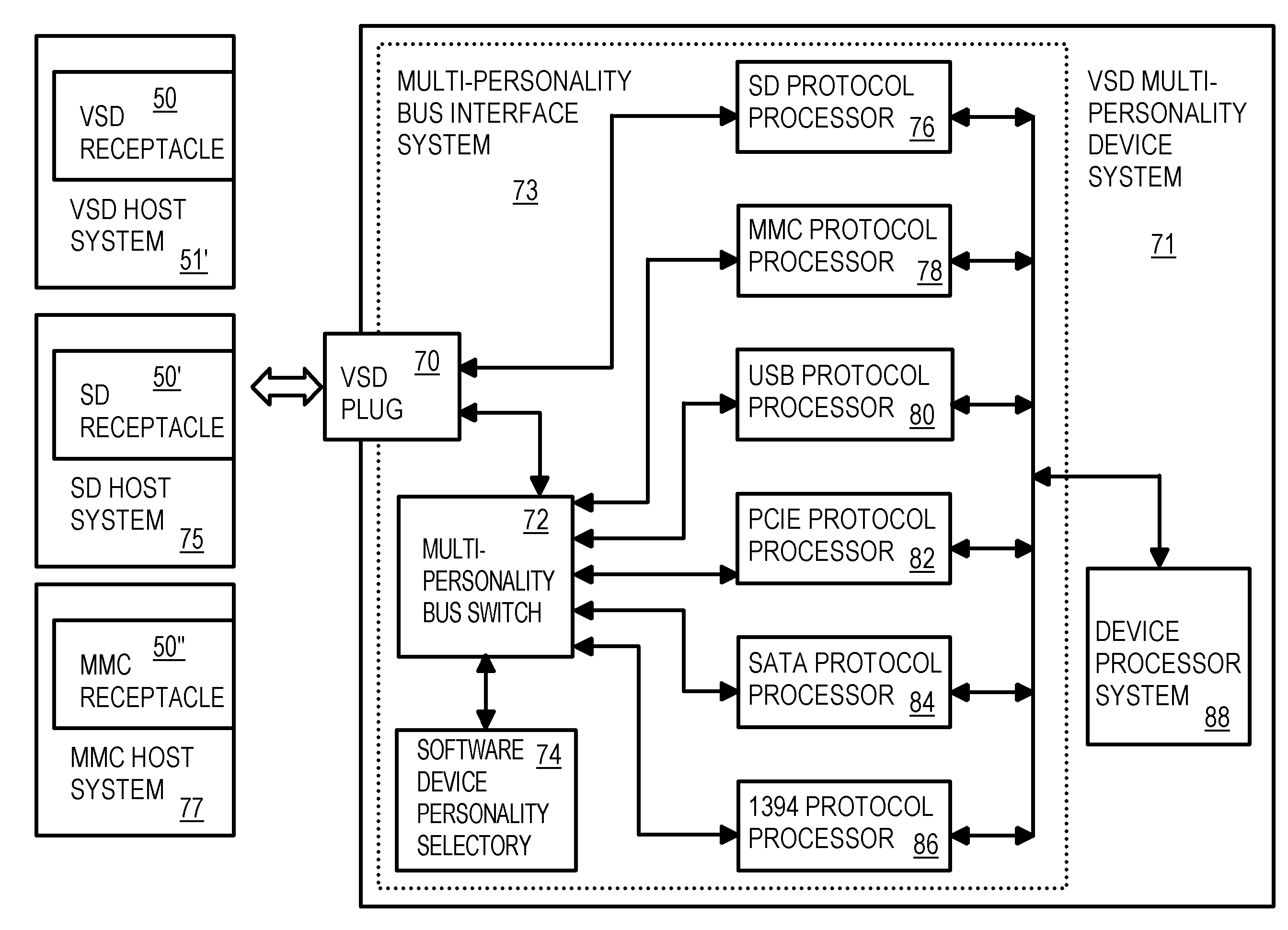
Extended-Secure-Digital interface using a second protocol for faster transfers
An extended Secure-Digital (SD) card has a second interface that uses some of the SD-interface lines. The SD card's mechanical and electrical card-interface is used, but 2 or 4 signals in the SD interface are multiplexed for use by the second interface. The second interface can have a single differential pair of serial-data lines to perform Universal-Serial-Bus (USB) transfers, or two pairs of differential data lines for Serial-Advanced-Technology-Attachment (SATA), Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIE), or IEEE 1394 transfers. A card-detection routine on a host can initially use the SD interface to detect extended capabilities and command the card to switch to using the second interface. The extended SD card can communicate with legacy SD hosts using just the SD interface, and extended SD hosts can read legacy SD cards using just the SD interface, or extended SD cards using the second interface. MultiMediaCard and Memory Stick are alternatives.
Owner:SUPER TALENT ELECTRONICS
Power subsystem for a communication network containing a power bus
InactiveUS6243818B1Volume/mass flow measurementData switching current supplyComponent LoadCurrent limiting
A method and apparatus of powering components on a network by using a load-share technique and by using over-voltage and current-limiting circuitry. The power subsystem for a component in a network is designed in a load-share manner whereby the power subsystem will supply power to the network bus and to the component load. Under normal operation of the power subsystem, the load will be powered directly from the power subsystem. In the event of a failure, the load will immediately pull power from the bus and thereby maintain network operation. The power subsystem and the power supply are protected from disruptions due to voltage or current surges. Further, the power subsystem is in compliance with the IEEE 1394 specifications in terms of recommended current levels and galvanic isolation of the power sources.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method and apparatus for operating the internet protocol over a high-speed serial bus
InactiveUS20020035623A1Efficiently and correctly determineDigital computer detailsTransmissionInternet protocol suiteTransport layer
A method and apparatus of integrating the IEEE 1394 protocol with the IP protocol in which the IEEE 1394 high speed serial bus operates as the physical and link layer medium and the IP operates as the transport layer. There are differences in the protocols which require special consideration when integrating the two protocols. The IEEE 1394 configures packets with memory information and the IP operates under channel based I / O thereby necessitating a modification of the data transfer scheme to accomplish IP transfers over the IEEE 1394. Further, due to differences in packet headers, the IEEE 1394 packet header is modified to encapsulate IP packets. Moreover, in order to determine network packets quickly and efficiently, an identifier is inserted in each network packet header indicating that the packet should be processed by the network. Finally, in order to support the ability to insert or remove nodes on the network without a loss of data, the IP interface must not be disturbed. This is accomplished by maintaining constant IP addresses across bus resets which are caused by insertion or removal of nodes from the network.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
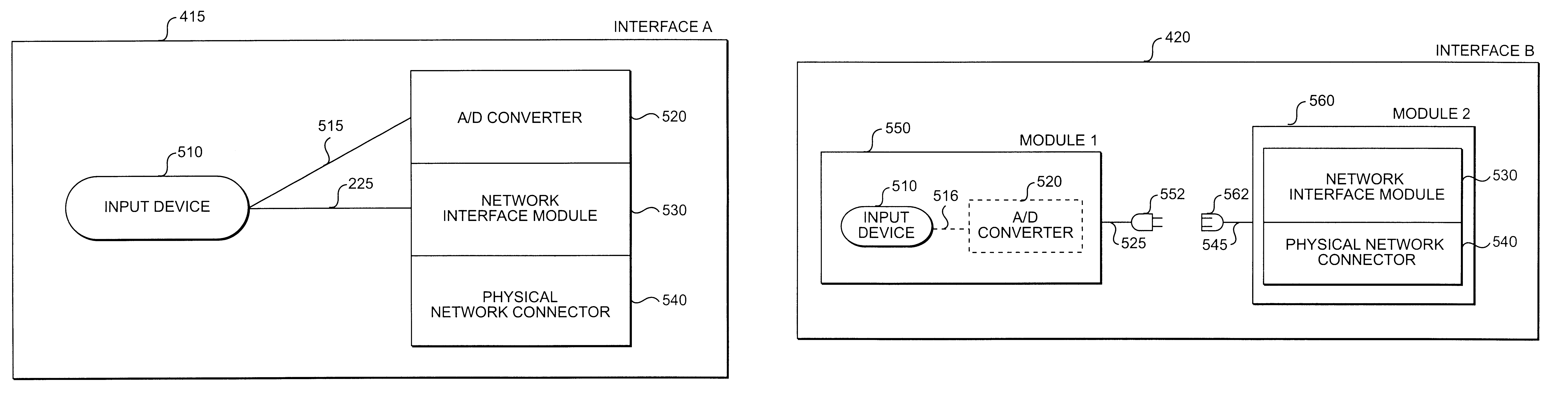
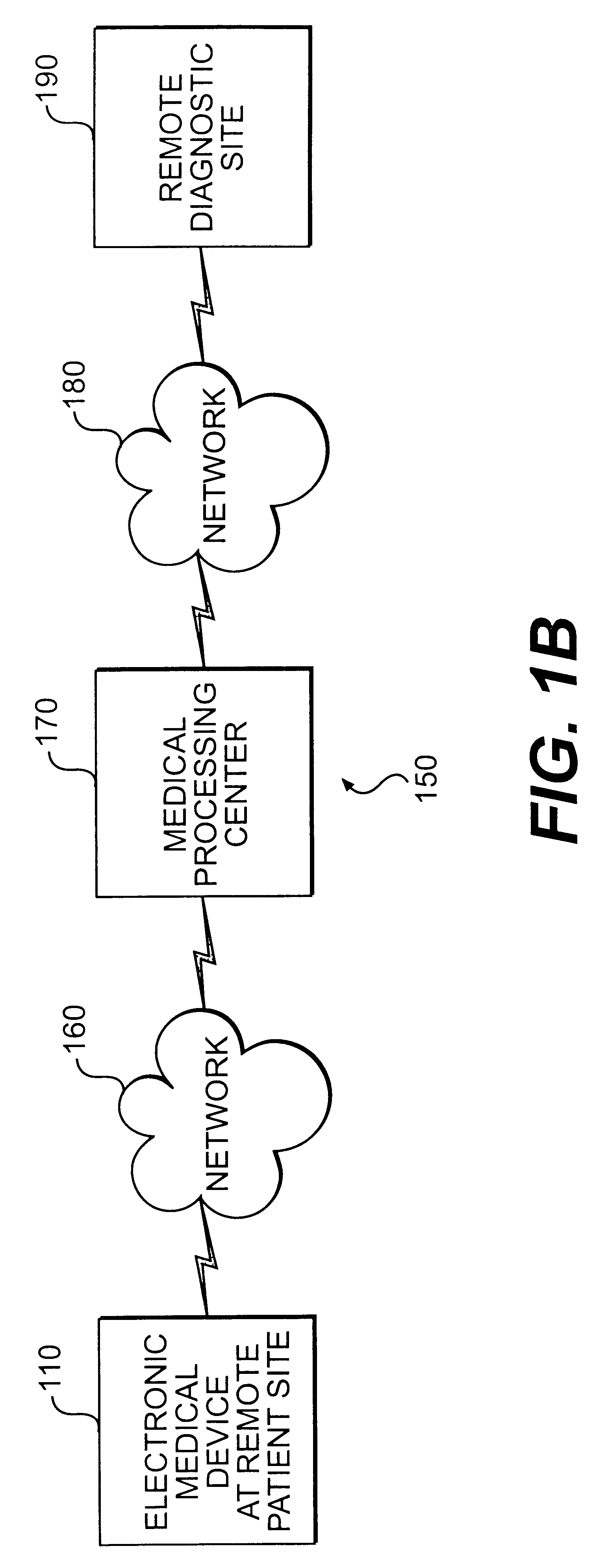
Methods and apparatus for processing, transmitting, and receiving data from a modular electronic medical device
InactiveUS6598084B1Overcomes shortcomingMedical communicationTelemedicineComputer hardwareModularity
This disclosure describes systems and methods for processing medical information from an electronic medical device connected to a patient via a serial bus at one site for transmission and receipt over a network to a remote diagnostic site or medical processing center for a medical diagnosis. The systems and methods encompass any electronic medical device that produces a signal that may be communicated via a serial bus. The systems and methods prepare the signal from the serial bus for transmission over a network and entail the receipt of the signal at a remote diagnostic site or medical processing center. At the remote diagnostic site or medical processing center, the signal is then presented to a physician or other medical technician for analysis and diagnosis. After diagnosis of the signal at the remote diagnostic site or medical processing center the diagnosis may be provided to the patient. Systems and methods consistent with the present invention are compatible with electronic medical devices that communicate a signal via a serial bus, including but not limited to a universal serial bus, a high performance serial bus according to the IEEE 1394-1995 standard, or a high performance serial bus according to the IEEE P1394.1 standard.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
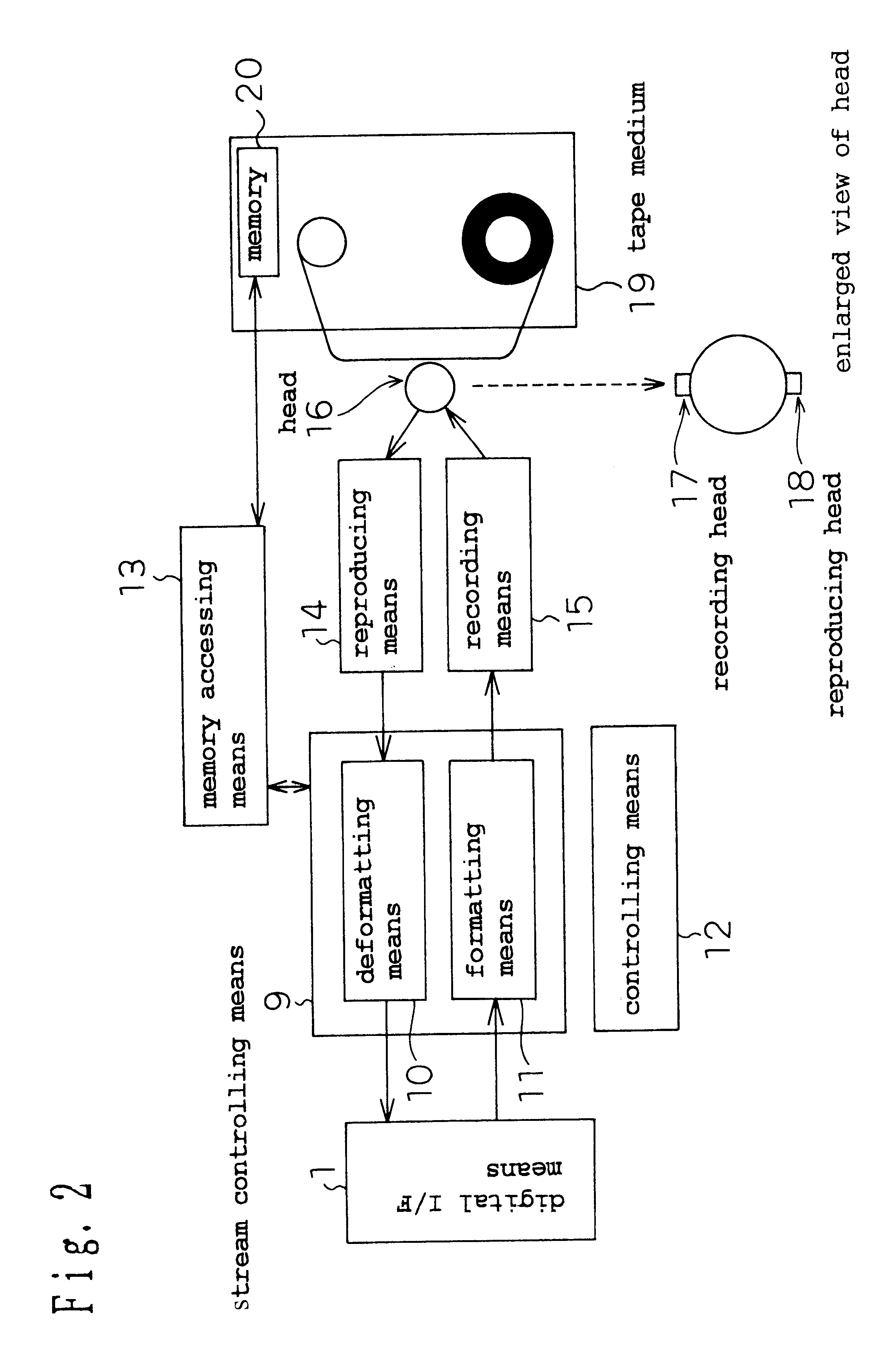
Data transfer method
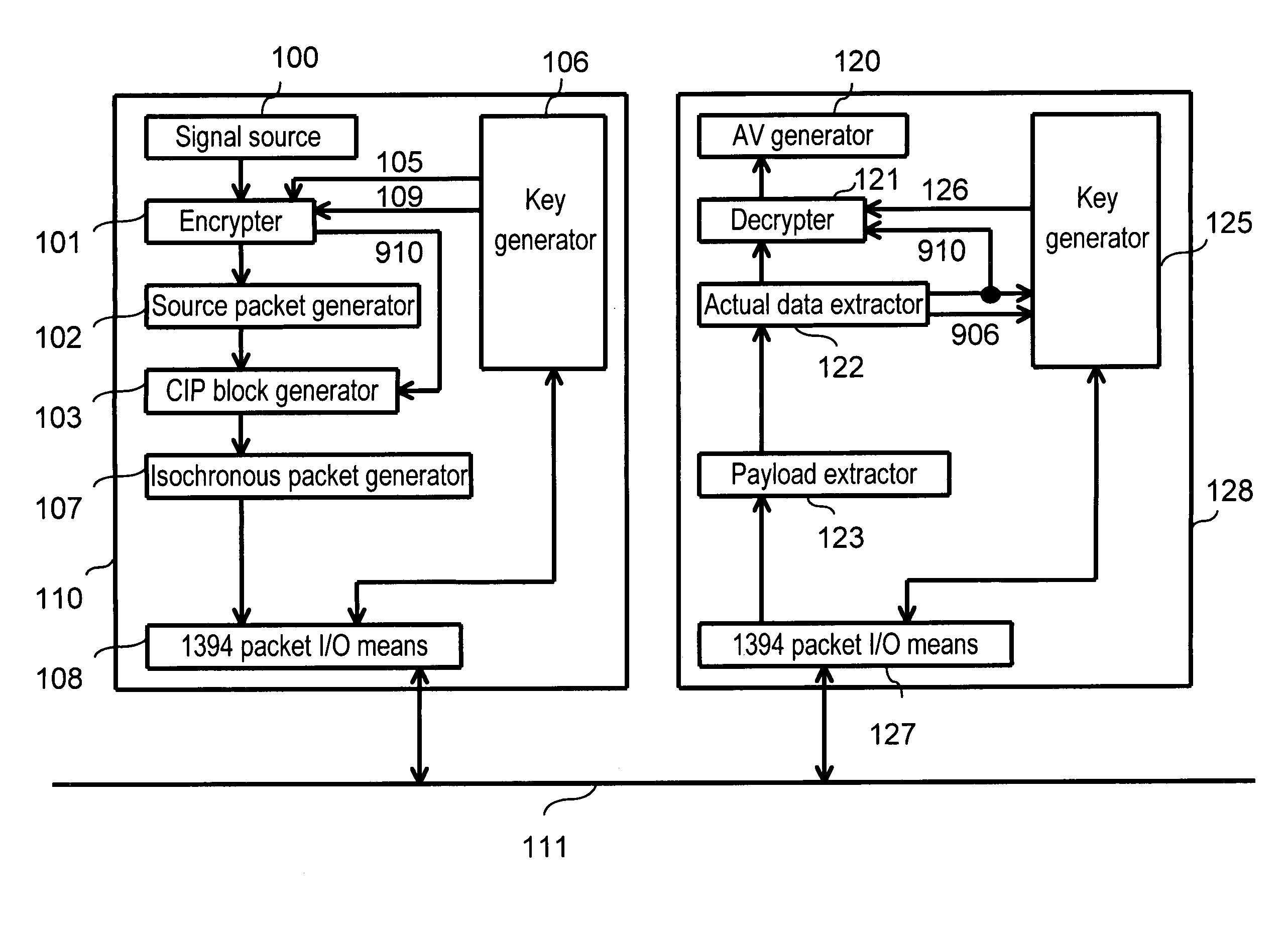
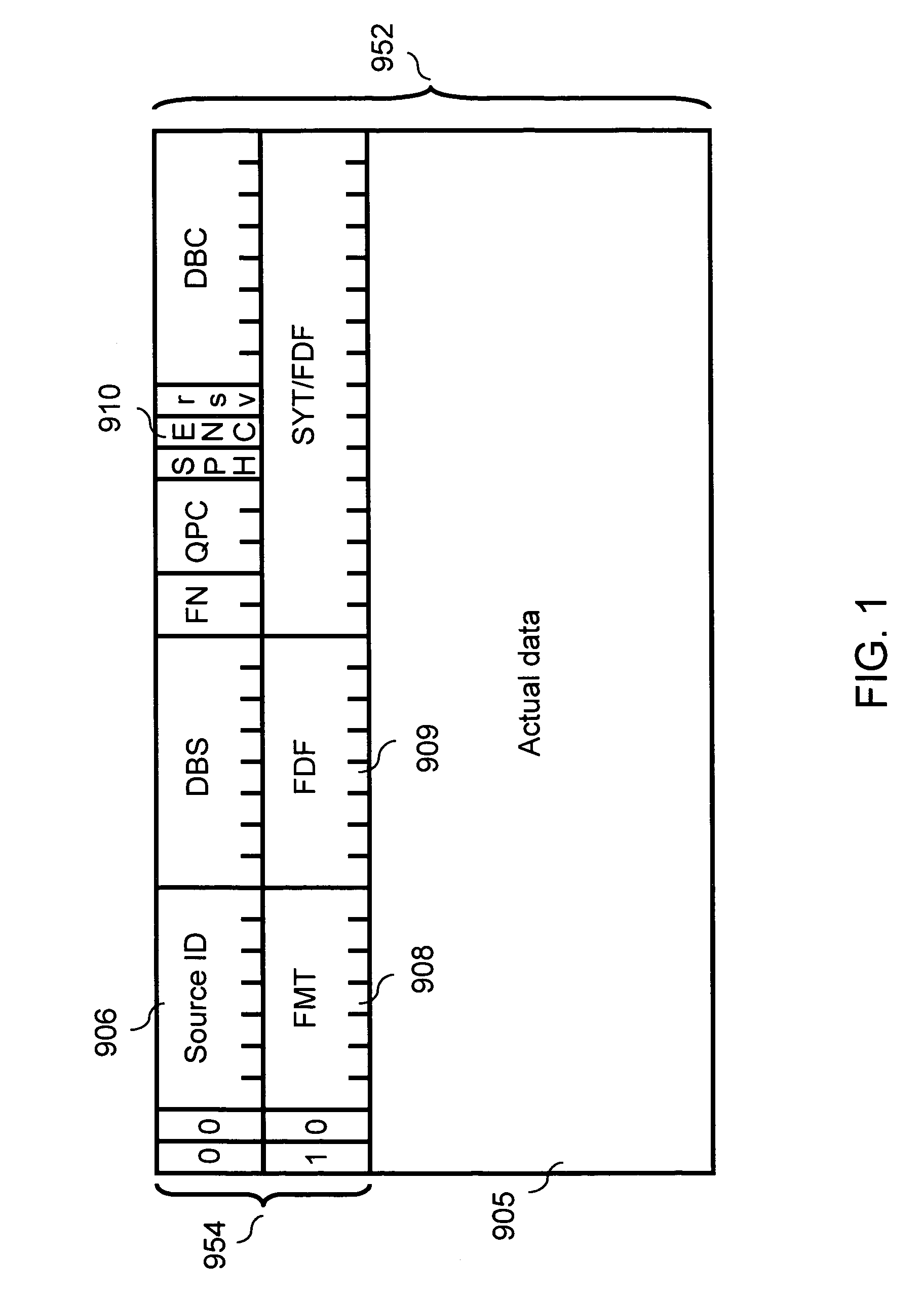
InactiveUS7218736B1Simple procedureAvoid misuseHybrid switching systemsTelevision systemsComputer hardwareData transmission
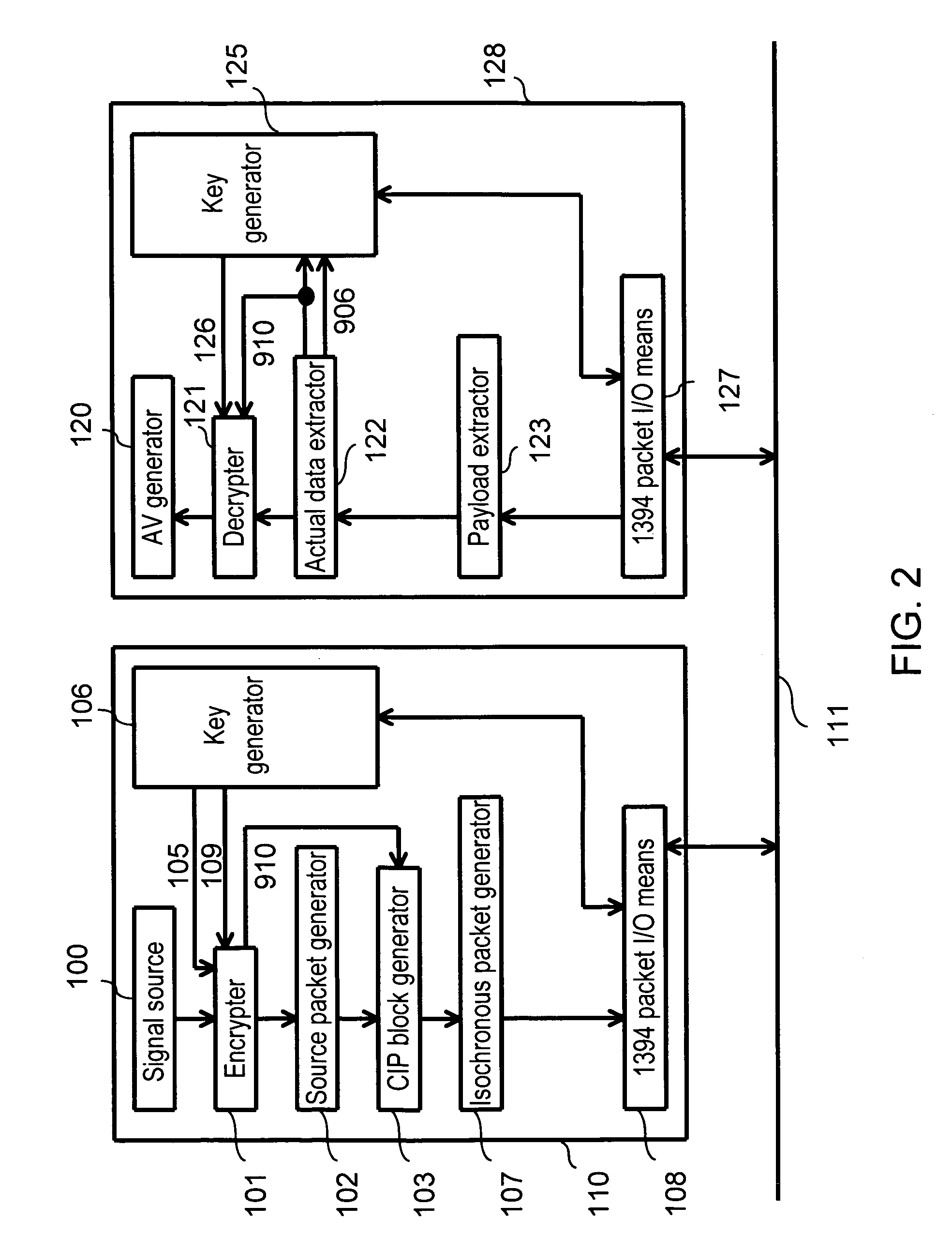
A data transfer method which eliminates erroneous operation of conventional devices not supporting encryption when copy-protected AV information is encrypted and sent on an IEEE 1394 bus. Synchronous data transferred through isochronous communication contains i) encryption identification information for indicating encryption of actual data and ii) actual data. Only the actual data is encrypted. Encryption identification information indicating encryption of actual data in synchronous data is sent together with actual data from the sending device. A receiving device detecting encryption of actual data from this encryption identification information requests decrypting information from the sending device. The receiving device decrypts the actual data using decrypting information received from the sending device according to this request.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
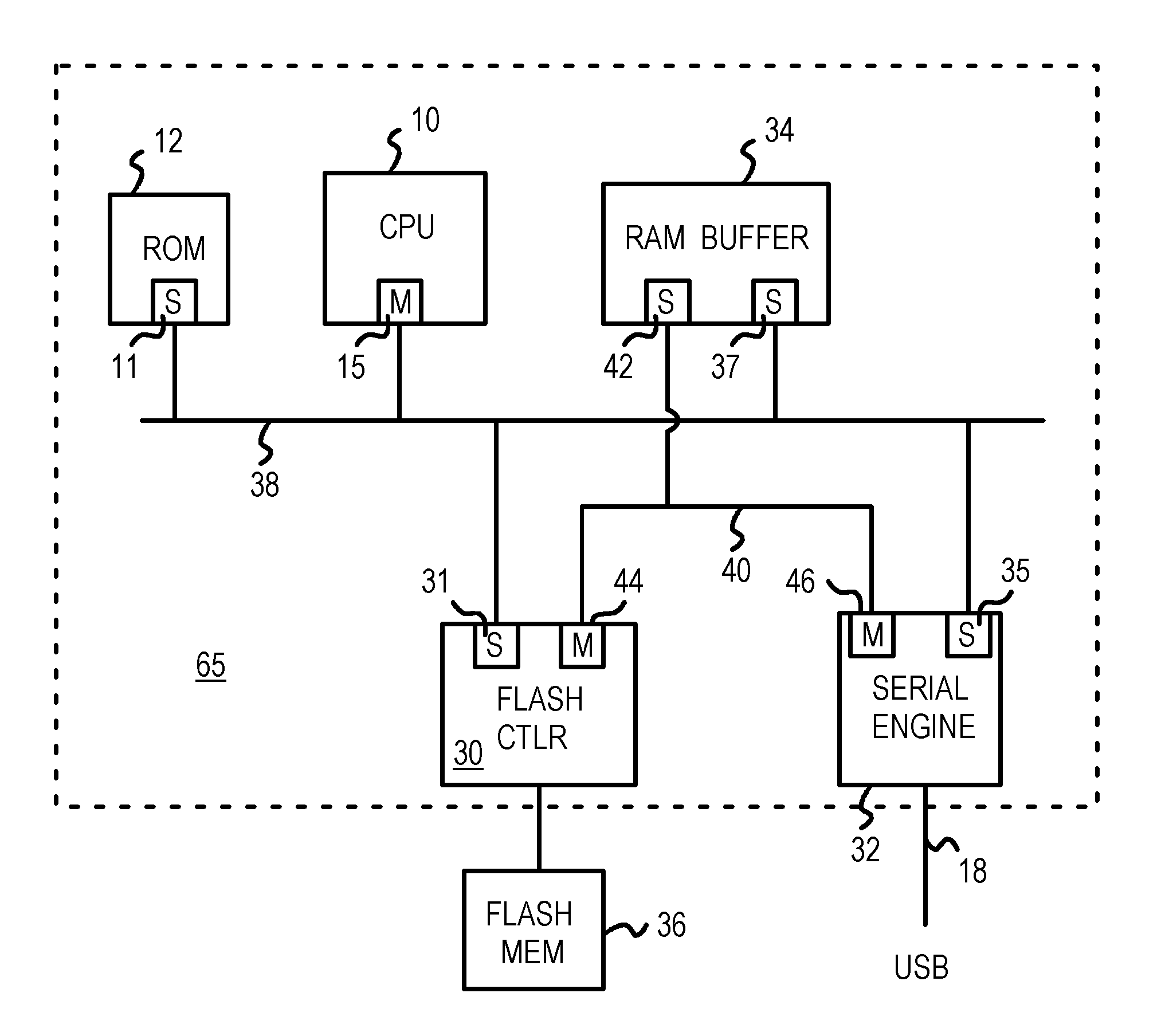
Flash drive/reader with serial-port controller and flash-memory controller mastering a second RAM-buffer bus parallel to a CPU bus
InactiveUS6874044B1Input/output to record carriersRead-only memoriesPersonal computerFlash memory controller
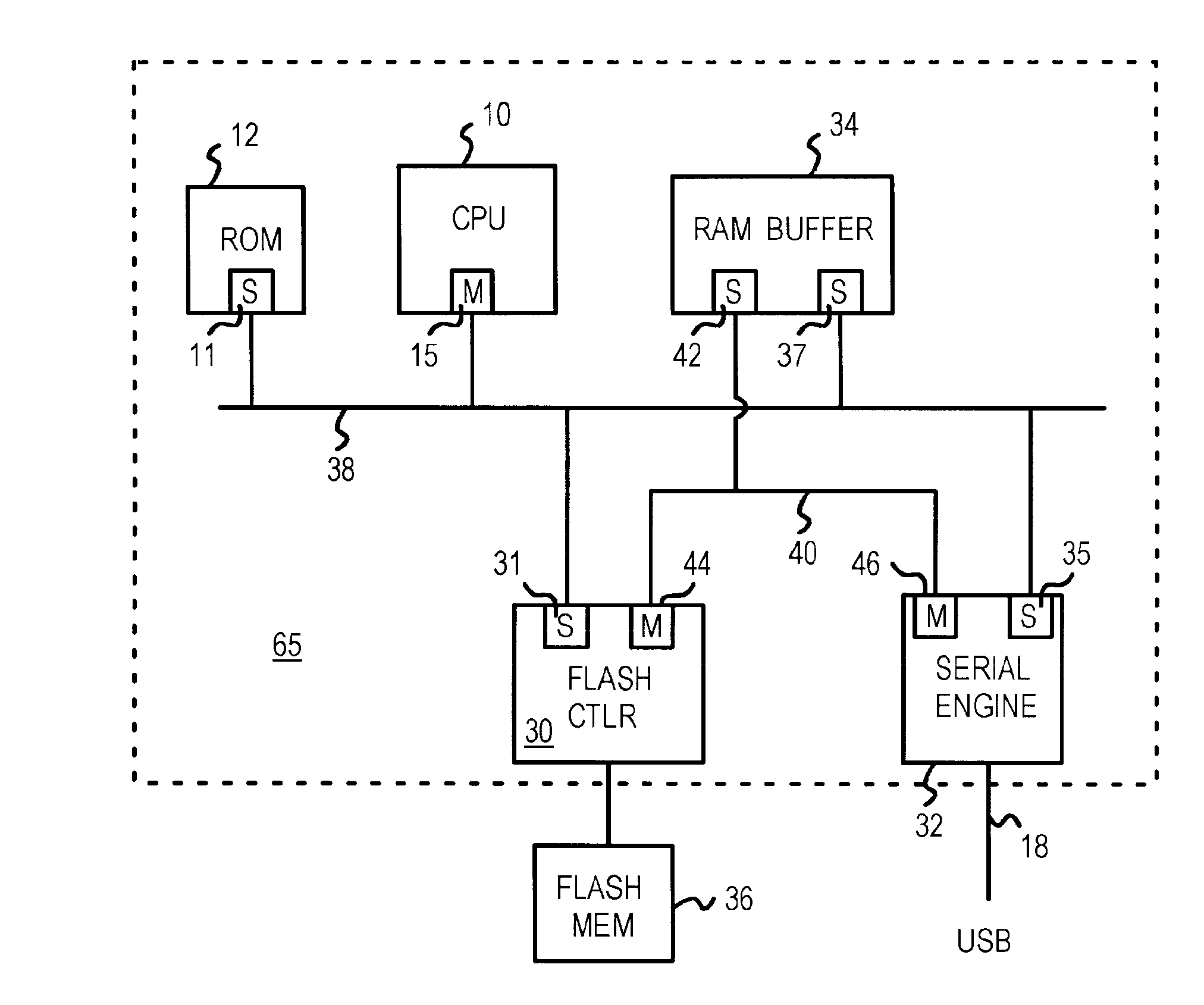
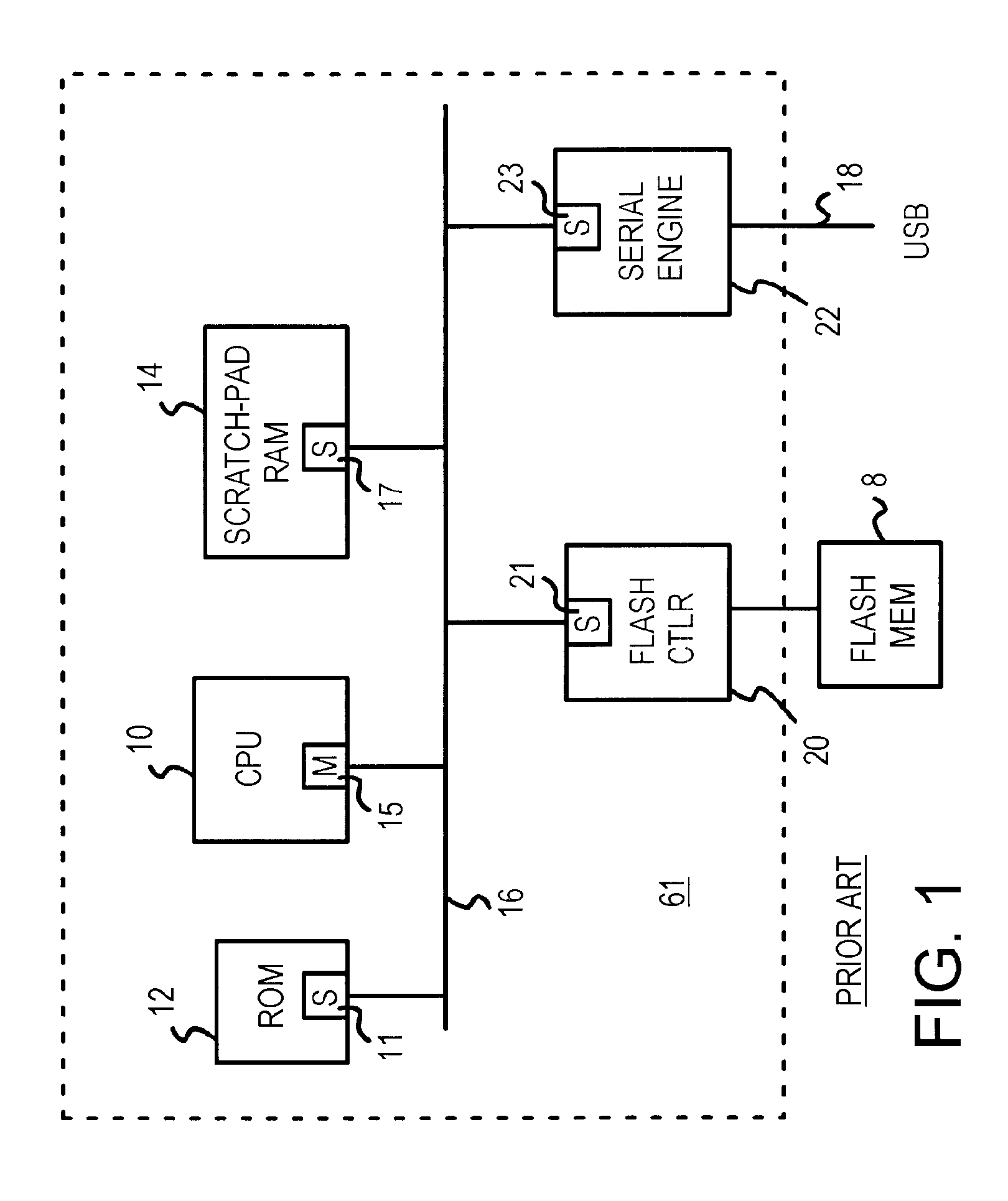
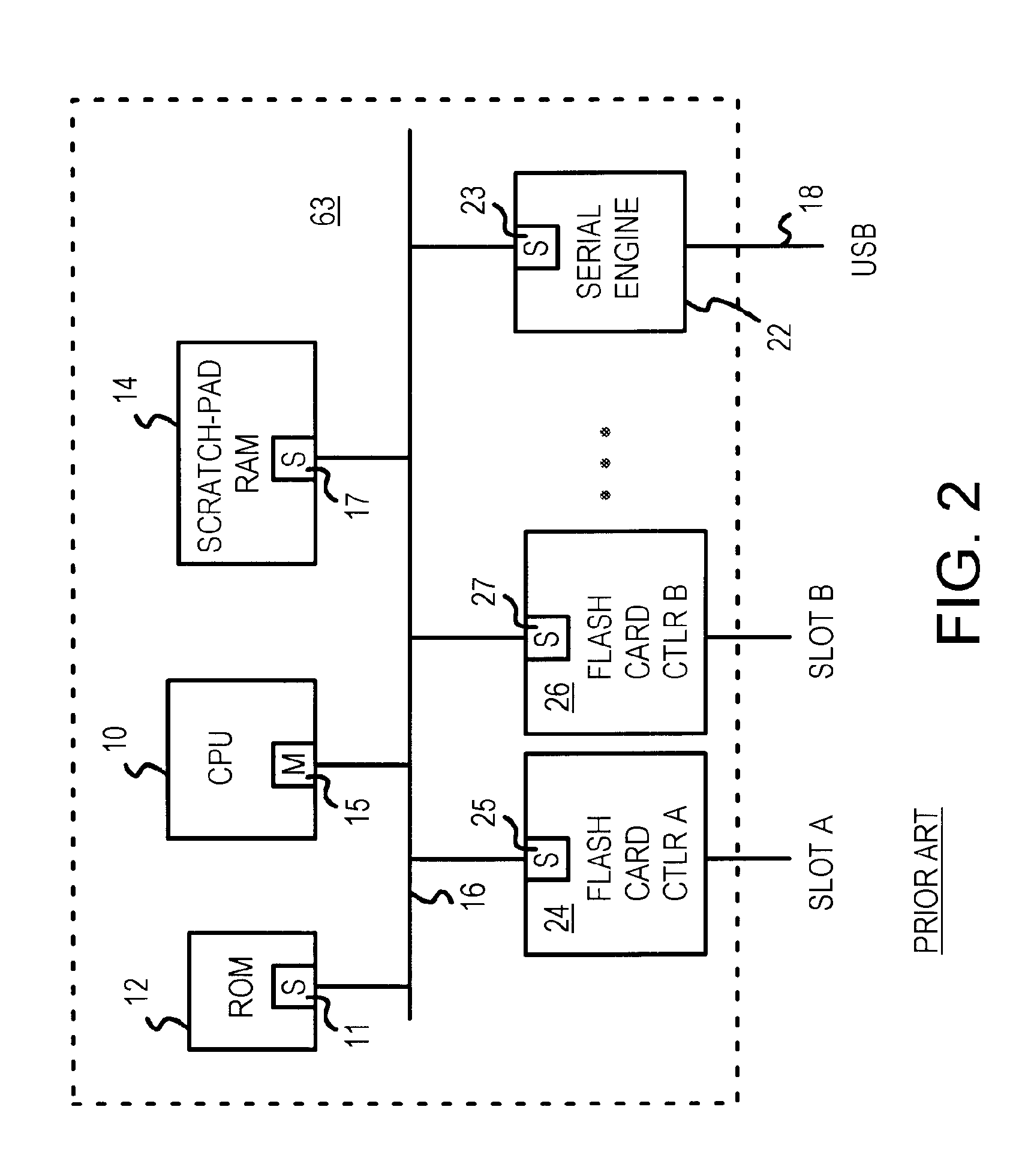
A flash-drive or flash-card reader connects to a personal computer (PC) through a serial link such as a Universal-Serial-Bus (USB), IEEE 1394, SATA, or IDE. A local CPU acts as the bus master of a CPU bus that connects to slave ports on a flash-memory controller, a serial engine, and a RAM buffer. A second bus in parallel to the CPU bus connects a second slave port on the RAM buffer to a master port on the flash-memory controller and to a master port on the serial engine. The flash-memory controller or the serial engine can use their master ports to transfer data to and from the RAM buffer using the second bus, allowing the CPU to retain control of the CPU bus. The second bus is a flash-serial buffer bus that improves data transfer rates. The flash-memory controller can prefetch into the RAM buffer.
Owner:SUPER TALENT ELECTRONICS
Communication node and communication terminal
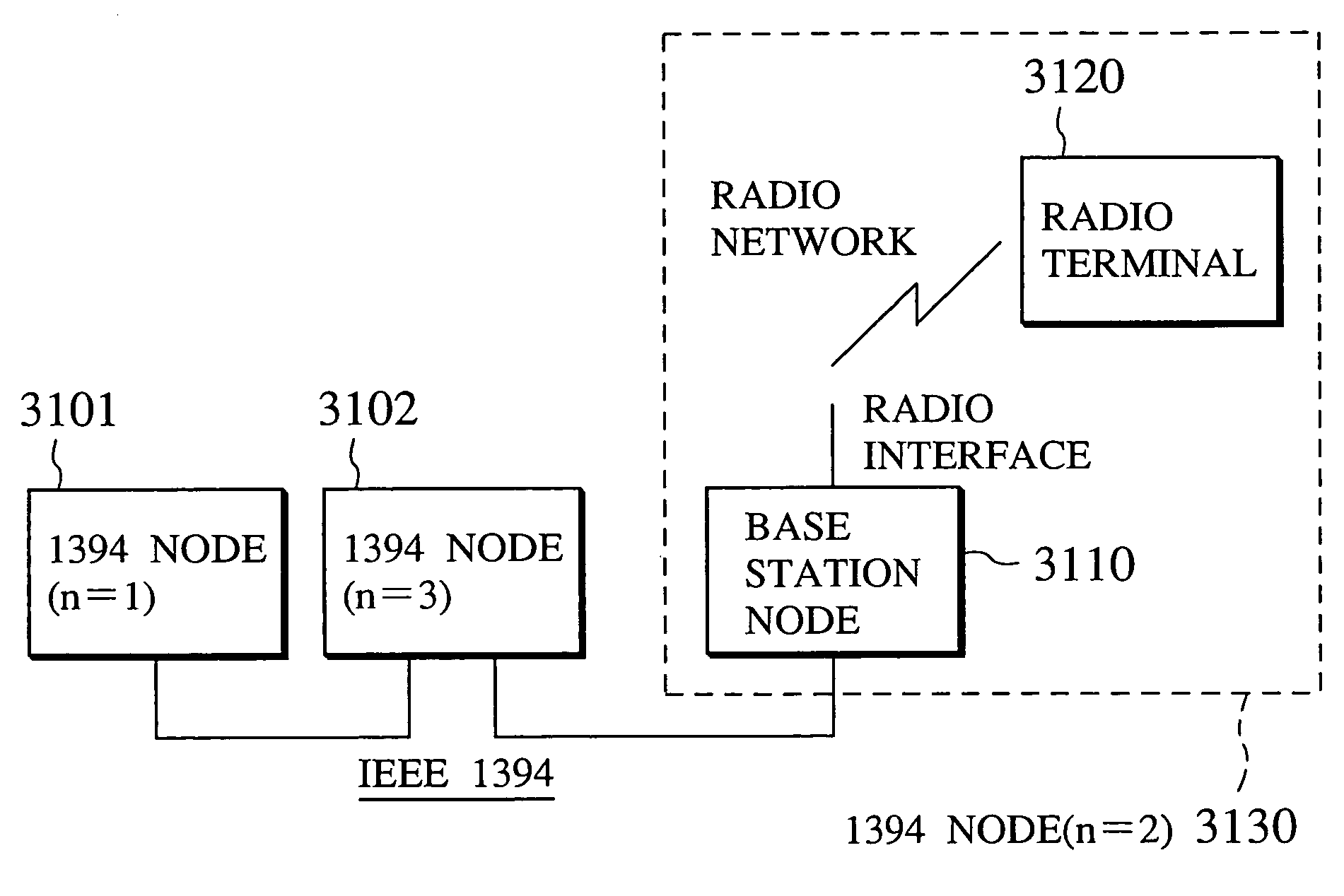
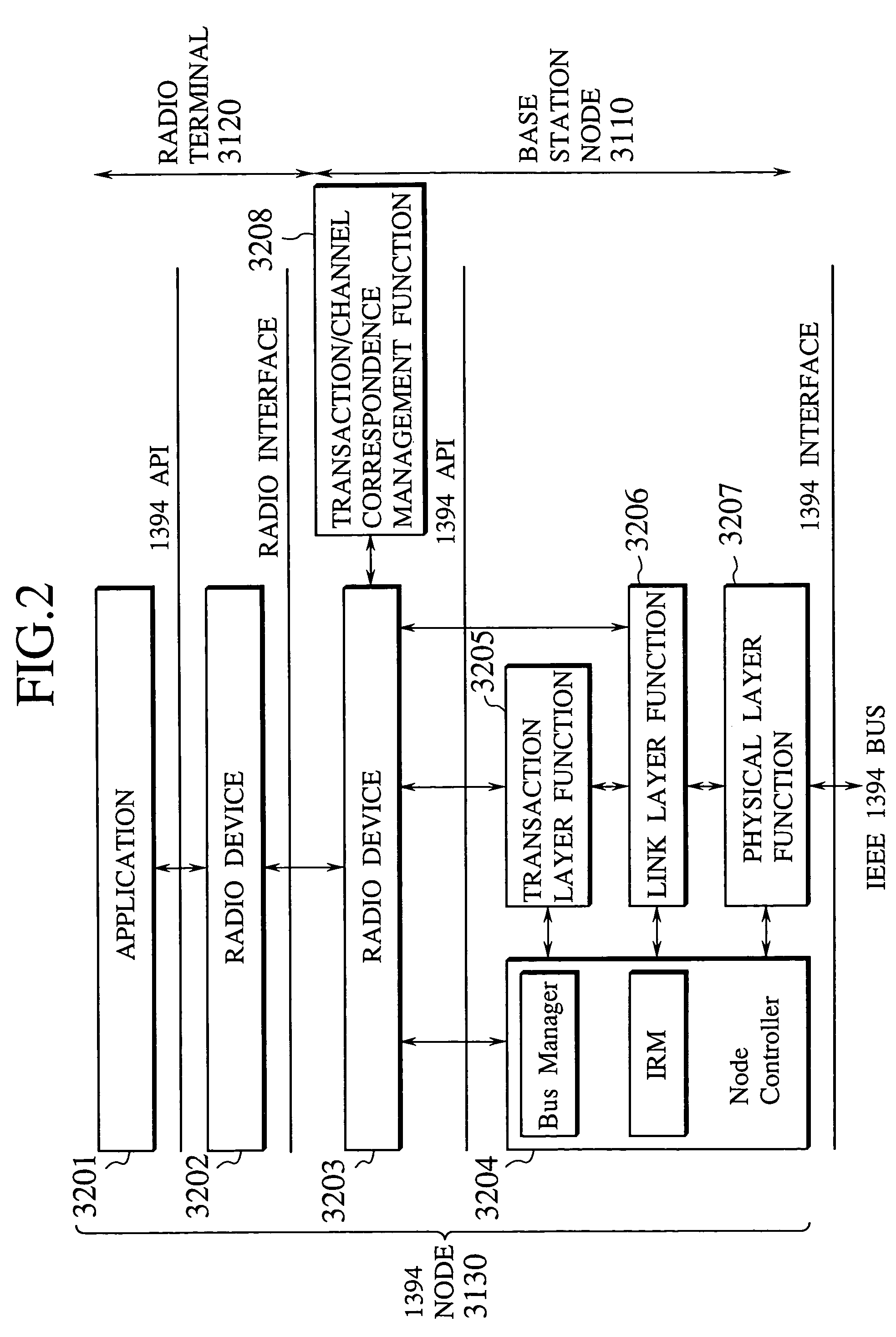
The disclosed communication node has a function for recognizing one communication node on the first network as one of constituent elements in own communication node, and a function for disclosing an own configuration information regarding the constituent elements as recognized above, to another communication node on the second network. Also, the disclosed communication terminal has a function for disclosing functions in the own communication terminal as Sub Units in an AV / C (Audio / Visual Control) protocol executed on an IEEE 1394 bus, and a function for receiving at least a part of information regarding Sub Units existing in the communication node on the second network with which it is communicating. Together, these communication node and communication terminal make it possible to transmit various information transferred on the IEEE 1394 bus, to the radio node that is connected by the radio interface, and it becomes possible to execute the data communications as if the connection to the IEEE 1394 bus is made by the radio interface.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Channel protocol for IEEE 1394 data transmission
InactiveUS7013354B1Data switching by path configurationElectric digital data processingBroadcast channelsPrefix header
A system for transmitting and receiving data formatted in IEEE 1394 standard between devices using a same IEEE 1394 broadcast channel includes a CPU interfaced to a bus, a first 1394 interface connected to the bus via a first physical and link layers, and a second 1394 interface connected to the bus via a second physical and link layer. The CPU is configured for 1) receiving data from the bus, prefixing a header to the received data, and retransmitting the received data with the prefixed header onto the bus; and 2) receiving data prefixed with a header, interpreting the header to identify which of the first or second interfaces should receive the data, and transmitting the data over the bus to the identified 1394 interface.
Owner:CANON KK
Initialization of flash storage via an embedded controller
A digital system including flash memory, coupled to a system-on-a-chip within which a flash memory subsystem controller is embedded, is disclosed. The system-on-a-chip includes support for a standard external interface, such as a Universal Serial Bus (USB) or IEEE 1394 interface, to which a host system such as flash memory test equipment can connect. Initialization of the flash memory is effected by opening a communications channel between the host system and the embedded flash memory subsystem controller. The host system can then effect initialization of the flash memory subsystem, including formatting of the flash memory arrays, loading application programs, and the like, over the communications channel.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Flash drive/reader with serial-port controller and flash-memory controller mastering a second ram-buffer bus parallel to a CPU bus
InactiveUS20050055481A1Input/output to record carriersRead-only memoriesFlash memory controllerPersonal computer
A flash-drive or flash-card reader connects to a personal computer (PC) through a serial link such as a Universal-Serial-Bus (USB), IEEE 1394, SATA, or IDE. A local CPU acts as the bus master of a CPU bus that connects to slave ports on a flash-memory controller, a serial engine, and a RAM buffer. A second bus in parallel to the CPU bus connects a second slave port on the RAM buffer to a master port on the flash-memory controller and to a master port on the serial engine. The flash-memory controller or the serial engine can use their master ports to transfer data to and from the RAM buffer using the second bus, allowing the CPU to retain control of the CPU bus. The second bus is a flash-serial buffer bus that improves data transfer rates. The flash-memory controller can prefetch into the RAM buffer.
Owner:SUPER TALENT ELECTRONICS
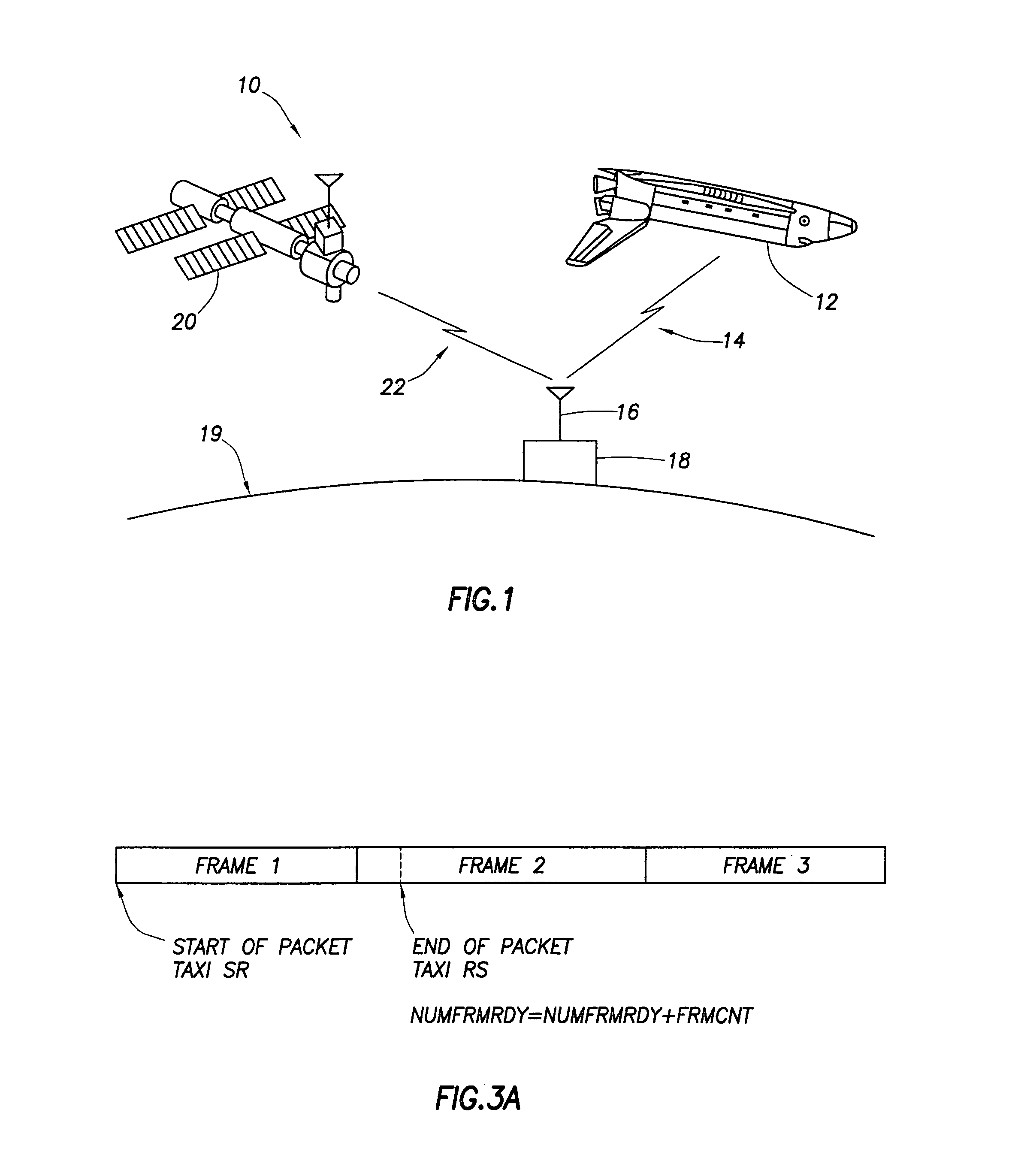
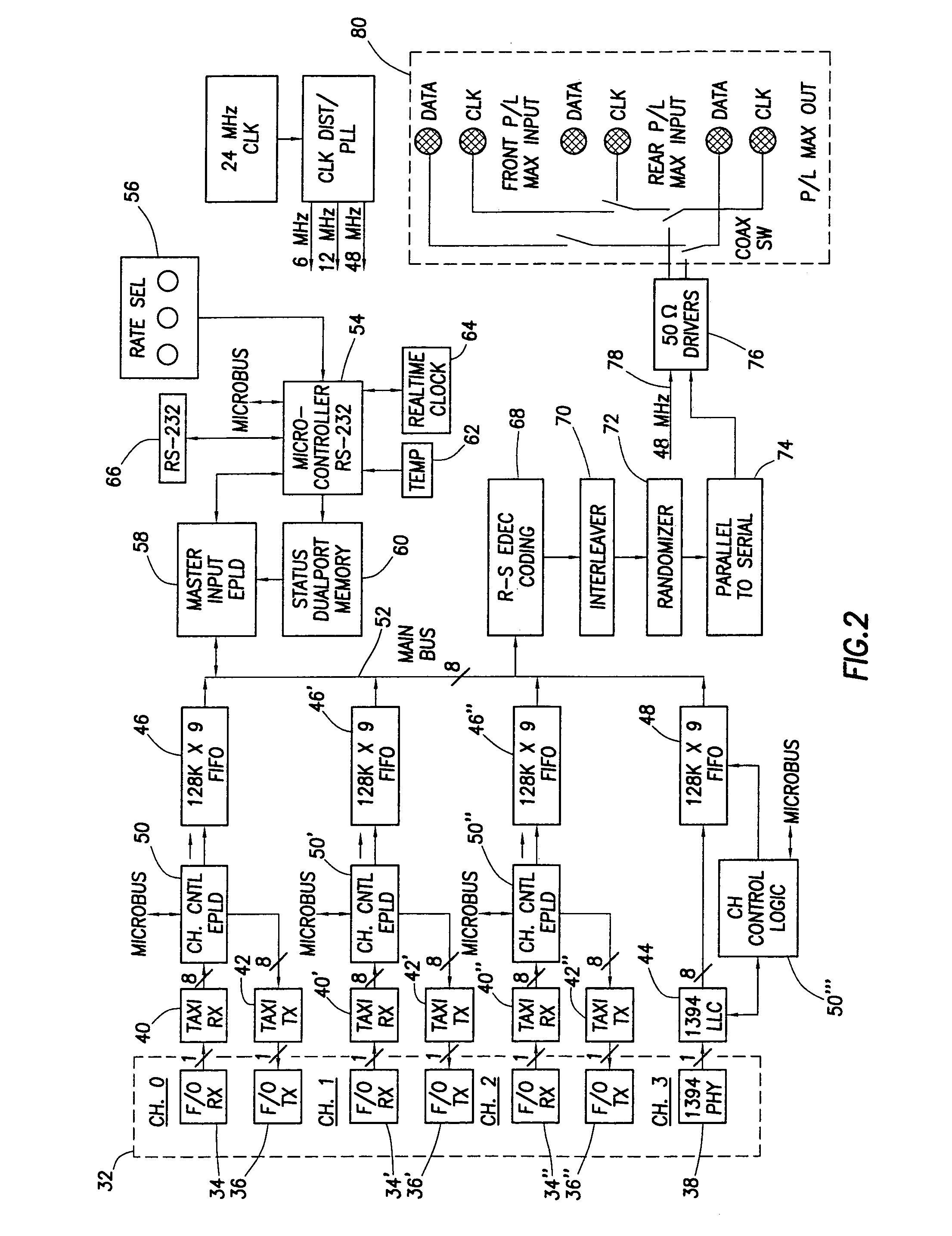
Downlink data multiplexer
A data multiplexer that accommodates both industry standard CCSDS data packets and bits streams and standard IEEE 1394 data is described. The multiplexer provides a statistical allotment of bandwidth to the channels in turn, preferably four, but expandable in increments of four up to sixteen. A microcontroller determines bandwidth requested by the plurality of channels, as well as the bandwidth available, and meters out the available bandwidth on a statistical basis employing flow control to the input channels.
Owner:NASA
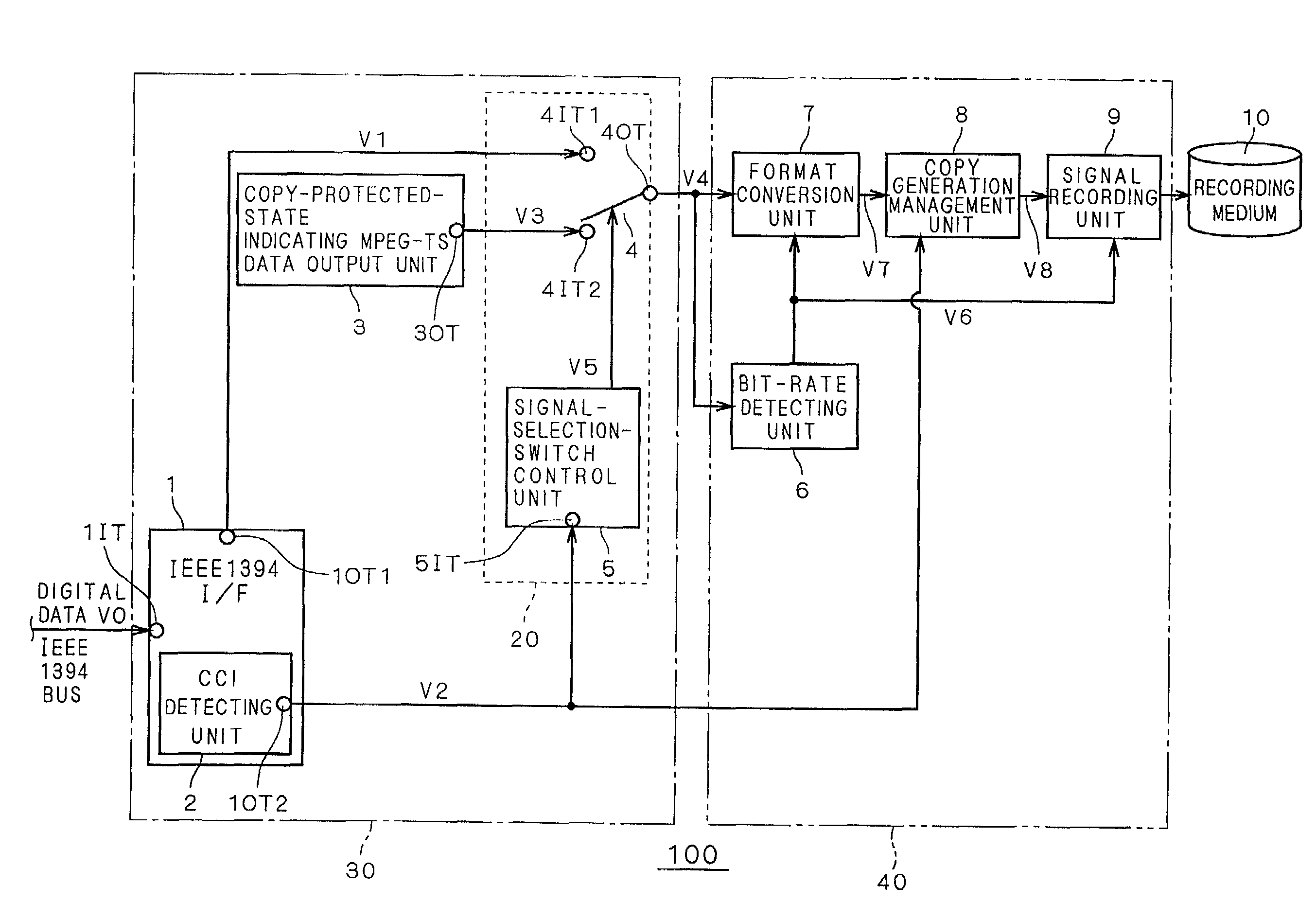
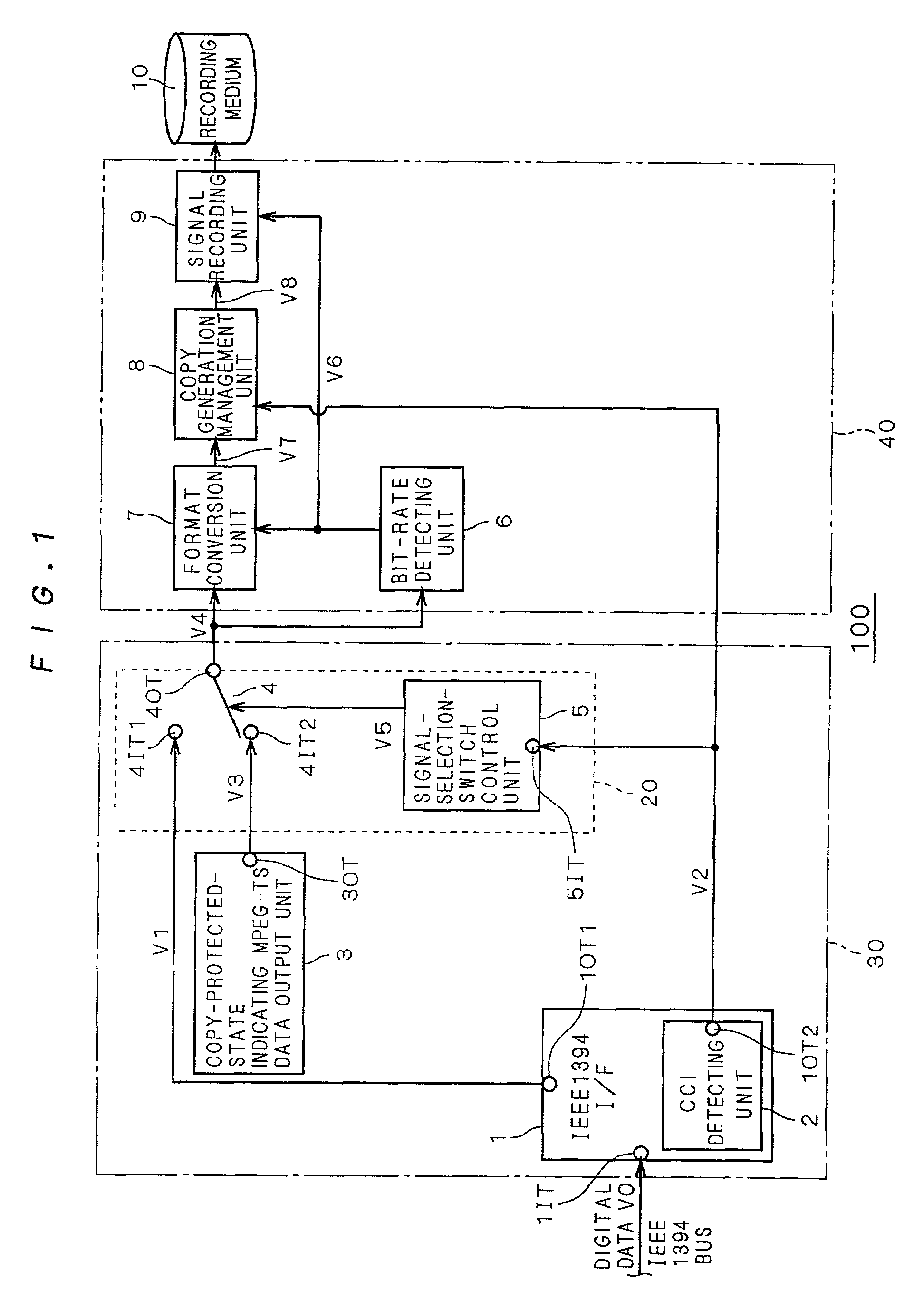
MPEG data recorder having IEEE 1394 interface
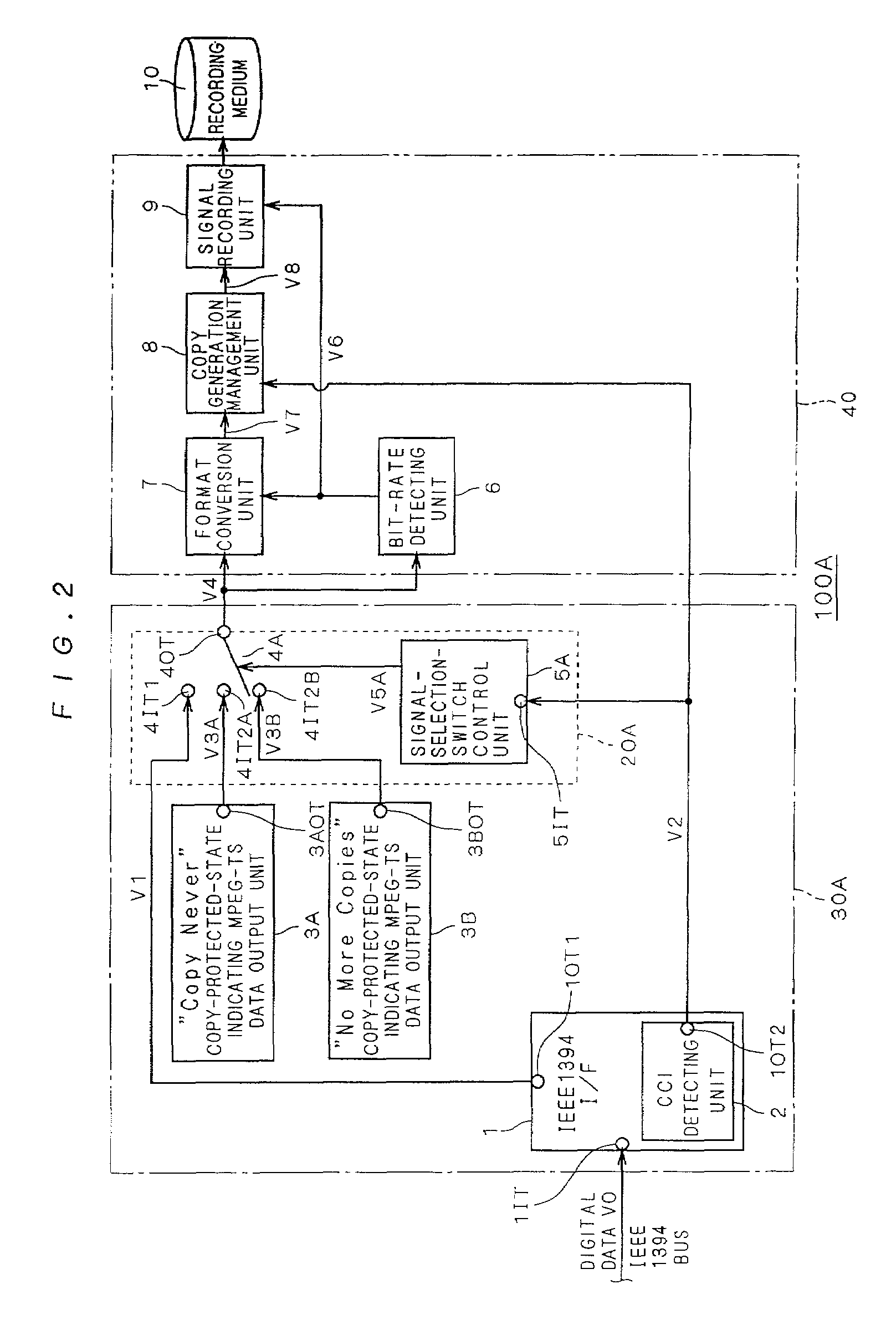
InactiveUS7227953B2Easily find outSimple circuit configurationTelevision system detailsDigital data processing detailsCopy controlIEEE 1394
A copy-protected-state indicating MPEG-TS data output unit (3) holds a bit stream obtained by previously compressing and encoding image and / or audio data representing that recording desired by the user has ended in failure because the contents is copy-protected. When copy control information (V2) outputted from an IEEE 1394 interface (1) indicates a copy-protected state, a selecting unit (20) selects copy-protected-state indicating MPEG-TS data (V3) outputted from the copy-protected-state indicating MPEG-TS data output unit (3) and outputs it as to-be-recorded MPEG-TS data (V4). Thereby, the data (V3) is recorded.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
System and method for achieving interoperability in home network with IEEE 1394 and UPnP devices
InactiveUS20070101024A1Easy transferTime-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer networkInteroperability Problem
Owner:SONY CORP +1
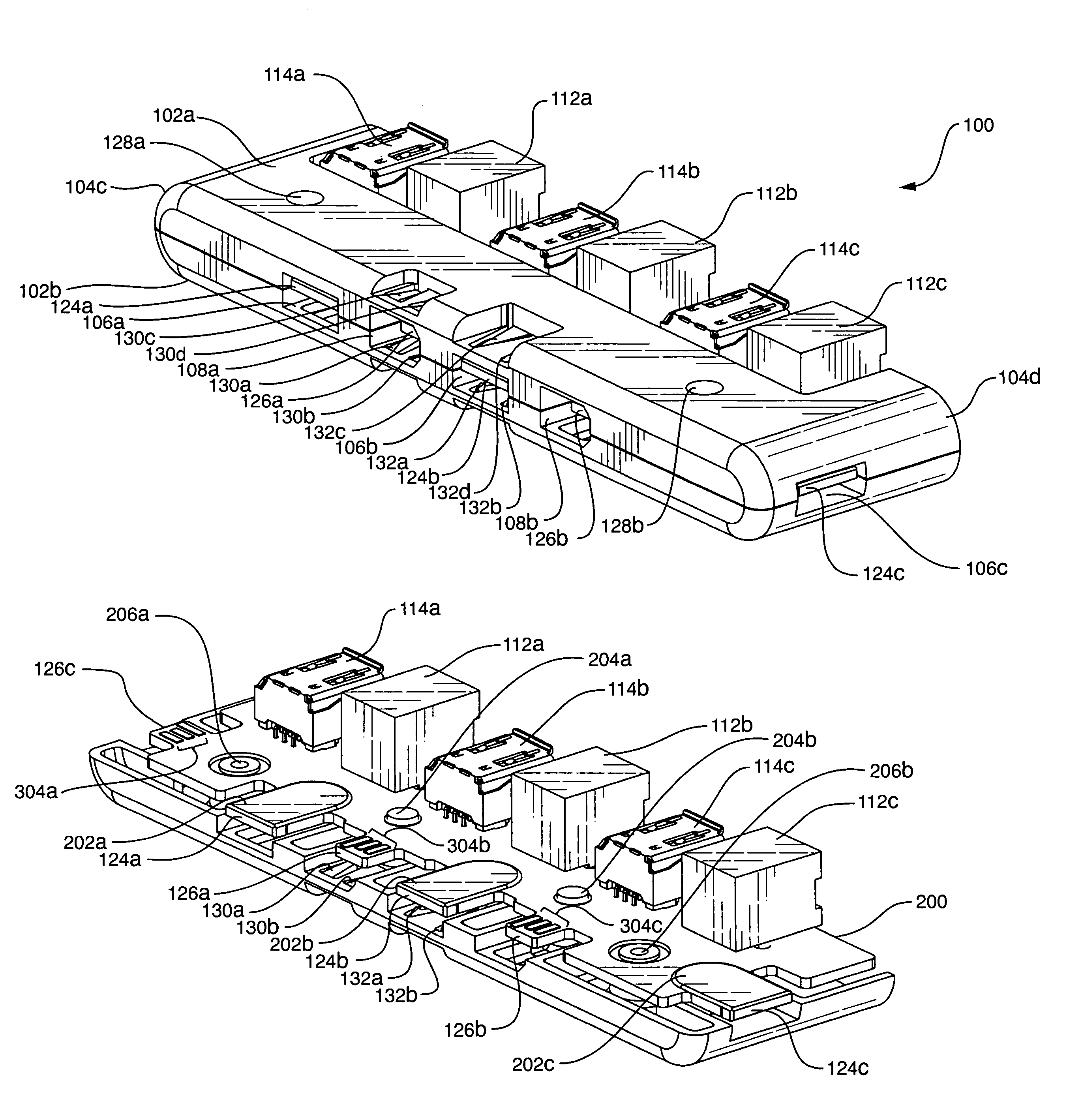
Computer input/output connector assembly
InactiveUS7118414B2Good adhesionDigital data processing detailsCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsPersonal computerEngineering
A computer input / output connector assembly which uses connector port holders that can easily be snapped into a metal retaining bracket. In one preferred embodiment, the bracket of the present invention is mounted on the front of a personal computer tower. Connected to the bracket is a first connector port holder with two USB connector ports, a second connector port holder with an IEEE 1394 high speed communication port, a third connector port holder with three audio ports (e.g., audio in, audio out and microphone) and a fourth connector port holder with two video ports (e.g., RCA composite video and S-video). The connector port holder is preferably made of a durable, heat resistant plastic. This connector port holder includes movable cantilever strips with lock tabs which can firmly snap into holes in the bracket for mounting.
Owner:NORTHSTAR SYST CORP
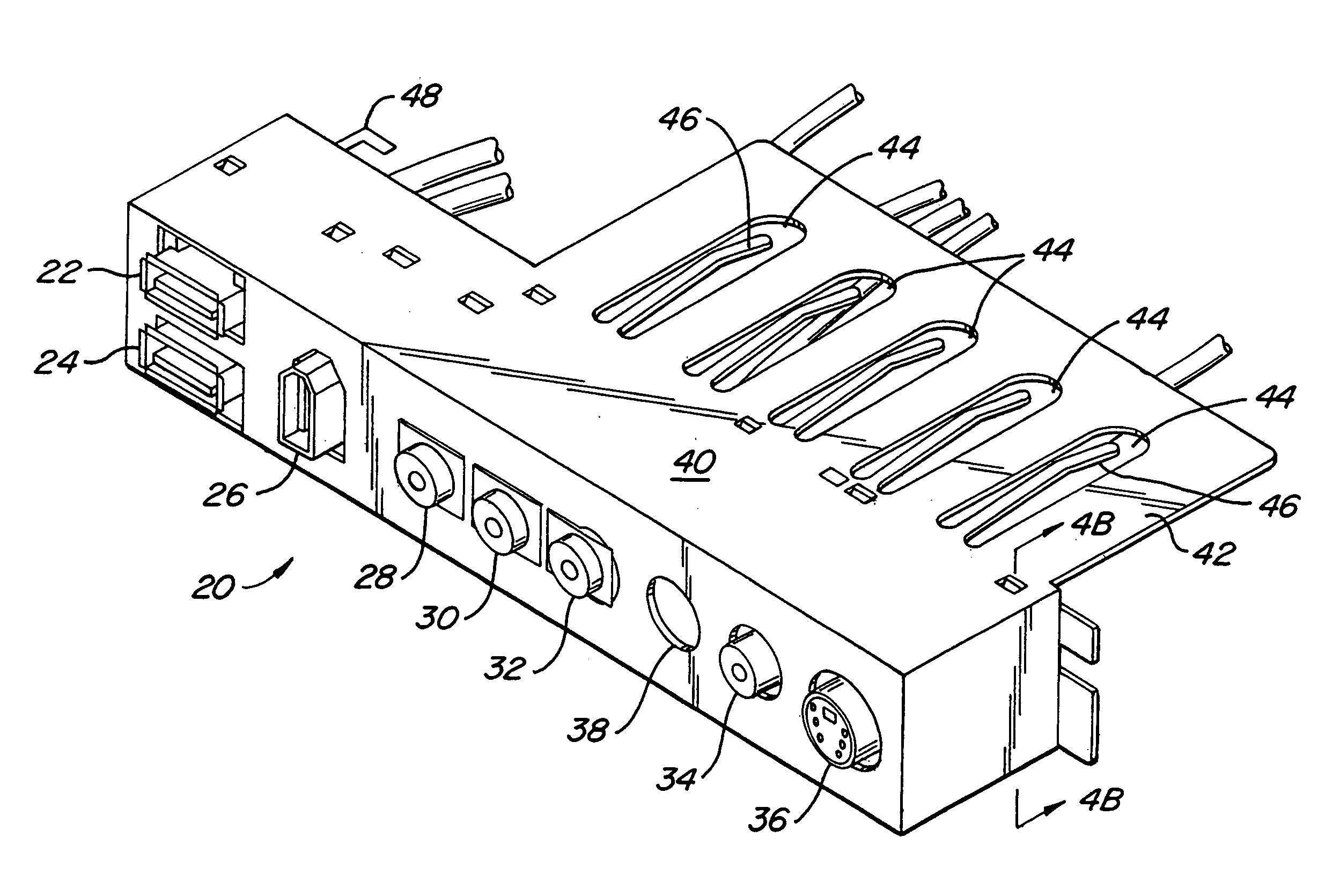
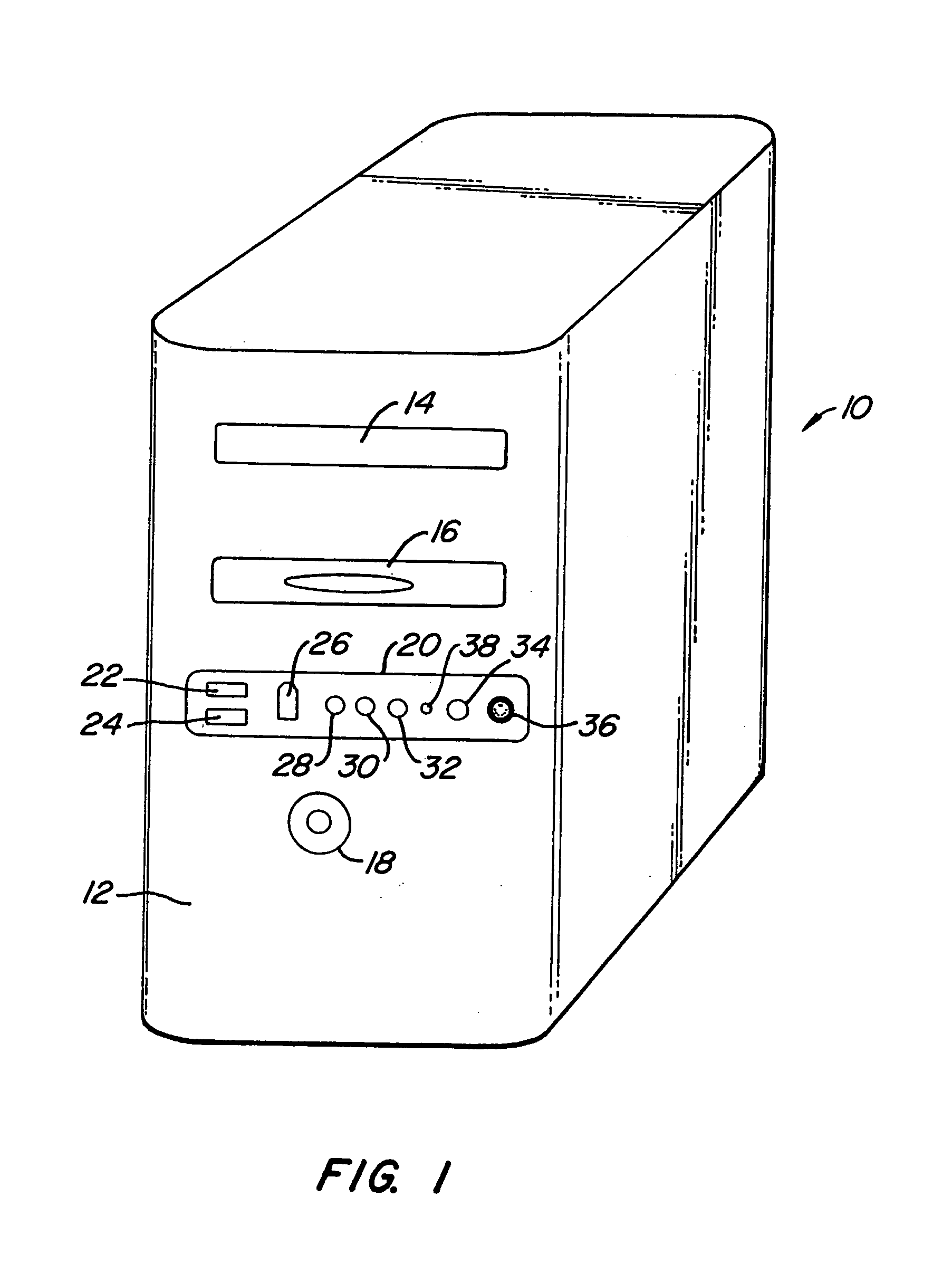
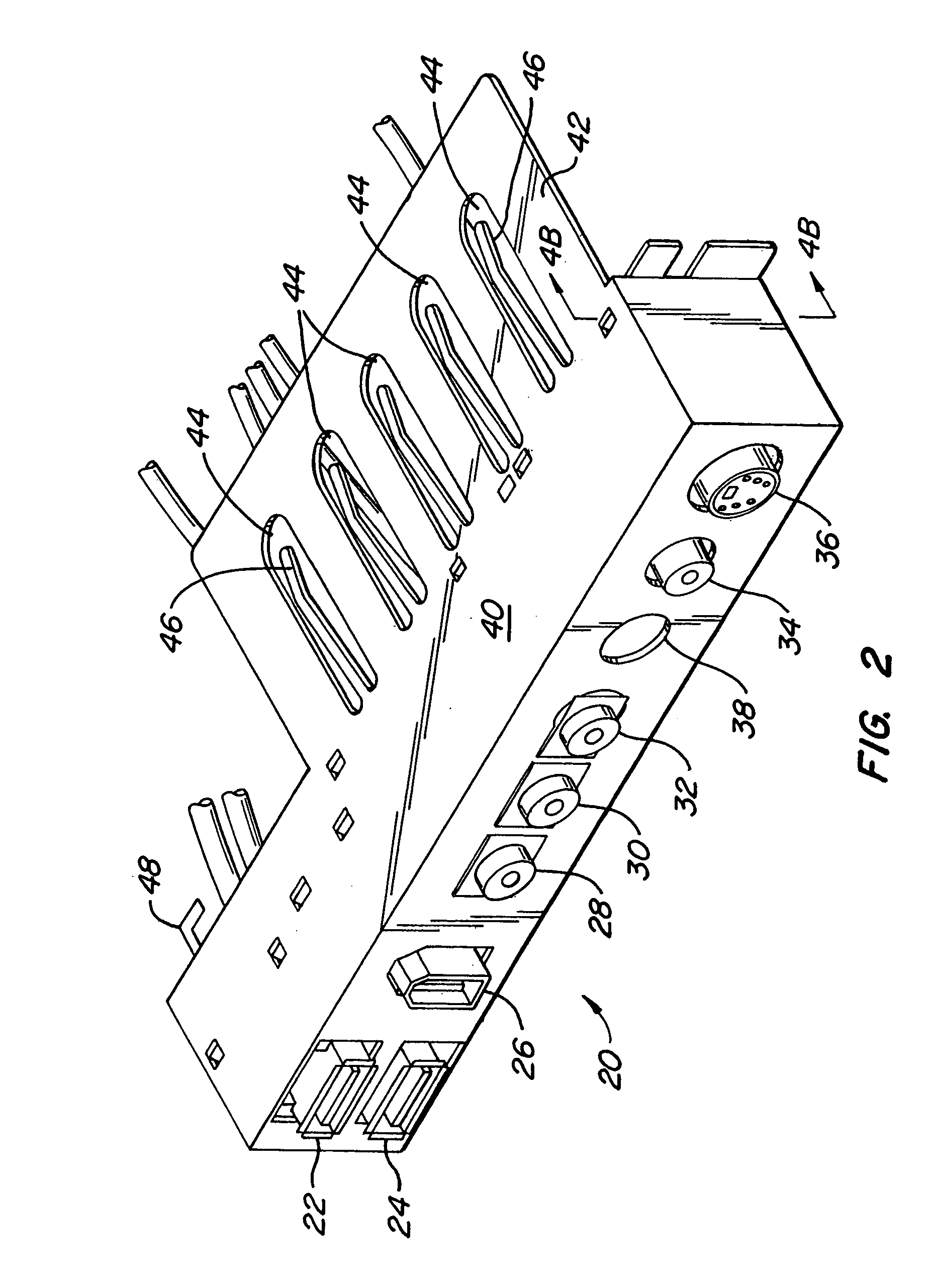
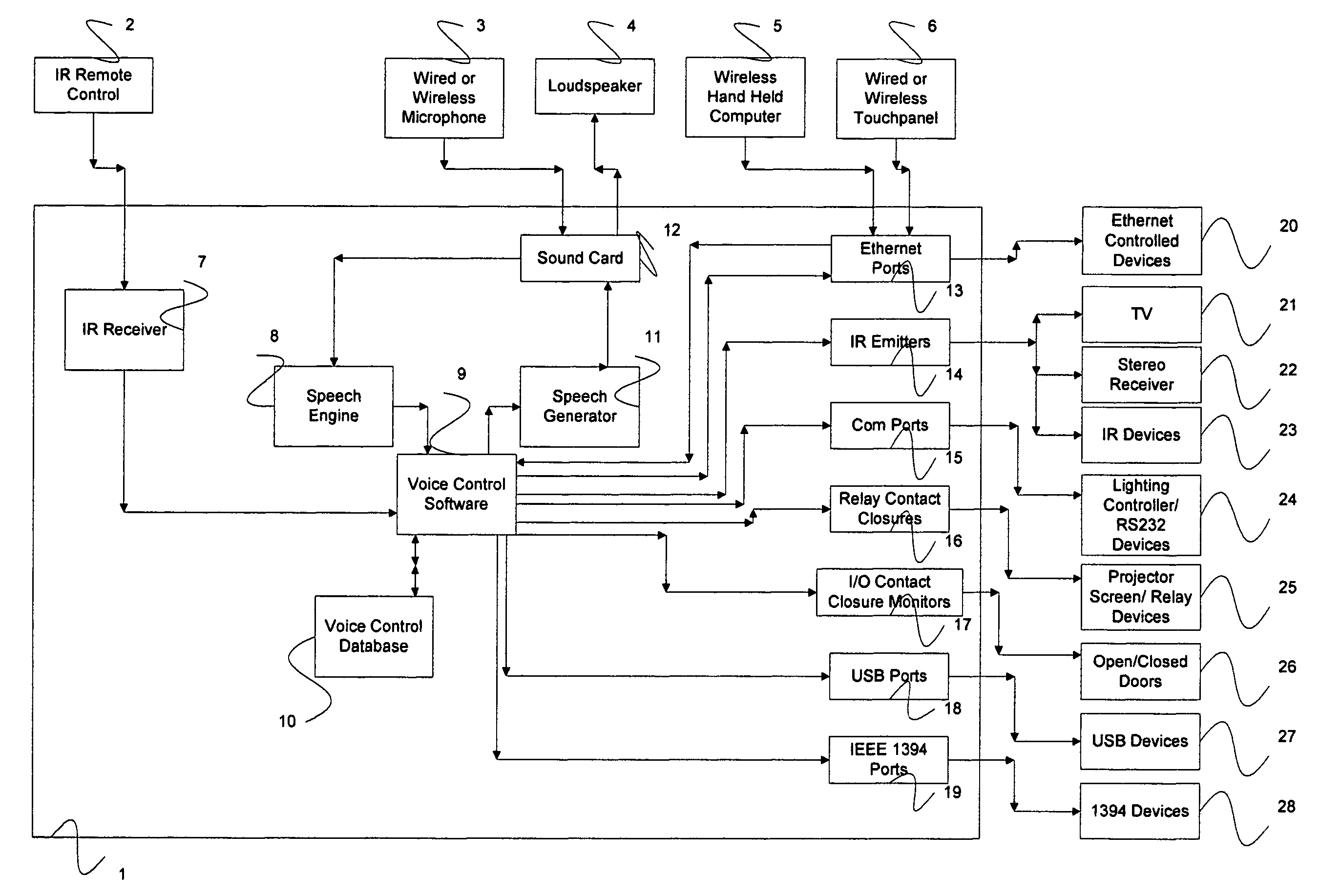
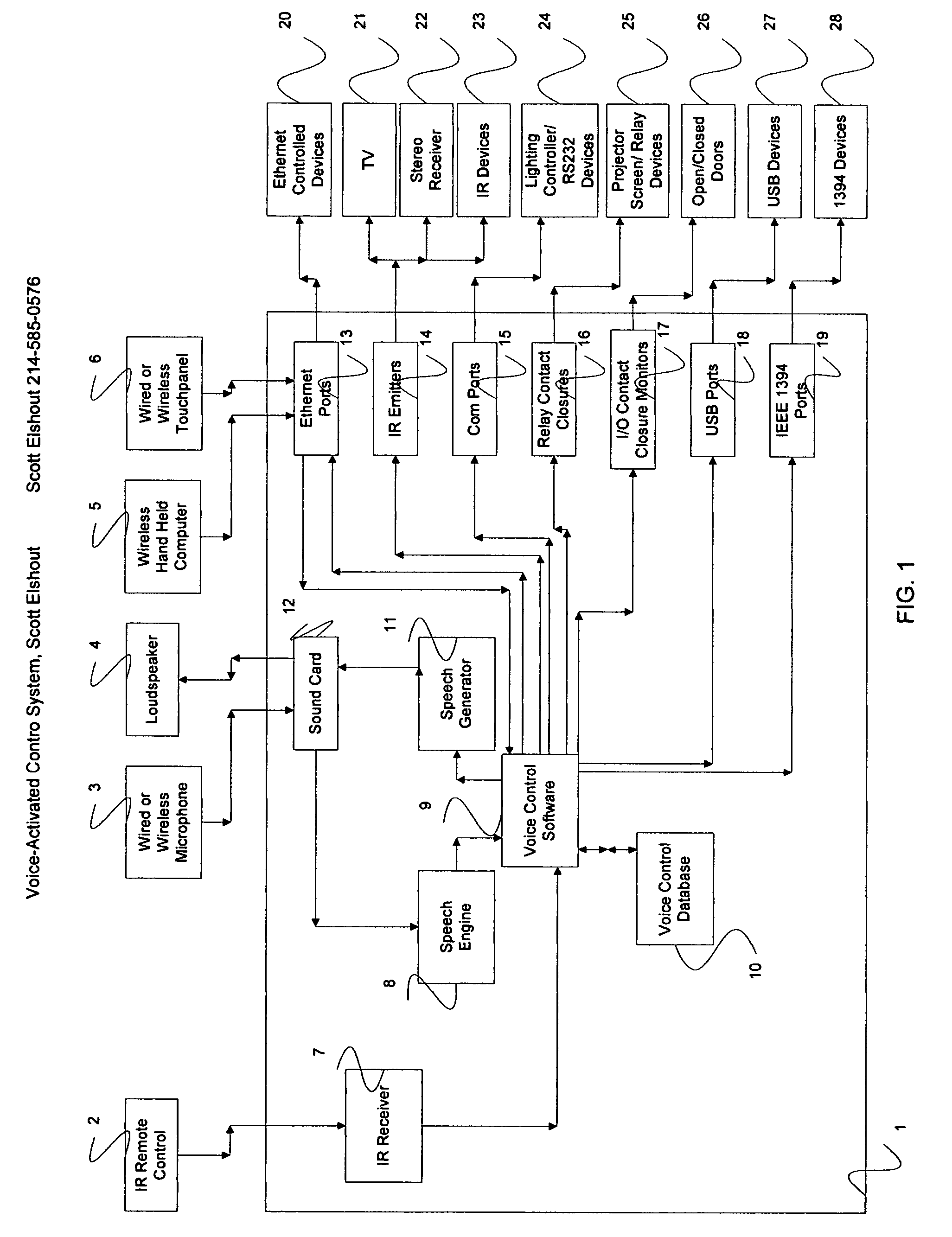
Voice-activated control system
A voice activated control system that uses a microphone to accept verbal commands from the user to control a plurality of electronic and electric devices such as a TV, DVD player, stereo receiver, projector, security system, sprinkler system, computer and the like using their inherent control methods. This is a computer-based system with associated software, which allows input of Infrared (IR) signals, voice commands, and various typed commands or strings and stores these in a database. It then allows for the user to assign one or more commands of any stored type to a virtually unlimited number of unique voice commands for controlling the plurality electronic and electric devices. Said system controls the plurality of electronic and electric devices using their inherent control methods such as IR, Contact Closure, Serial, Ethernet, TCP / IP, USB, IEEE 1394, etc.
Owner:ELSHOUT SCOTT
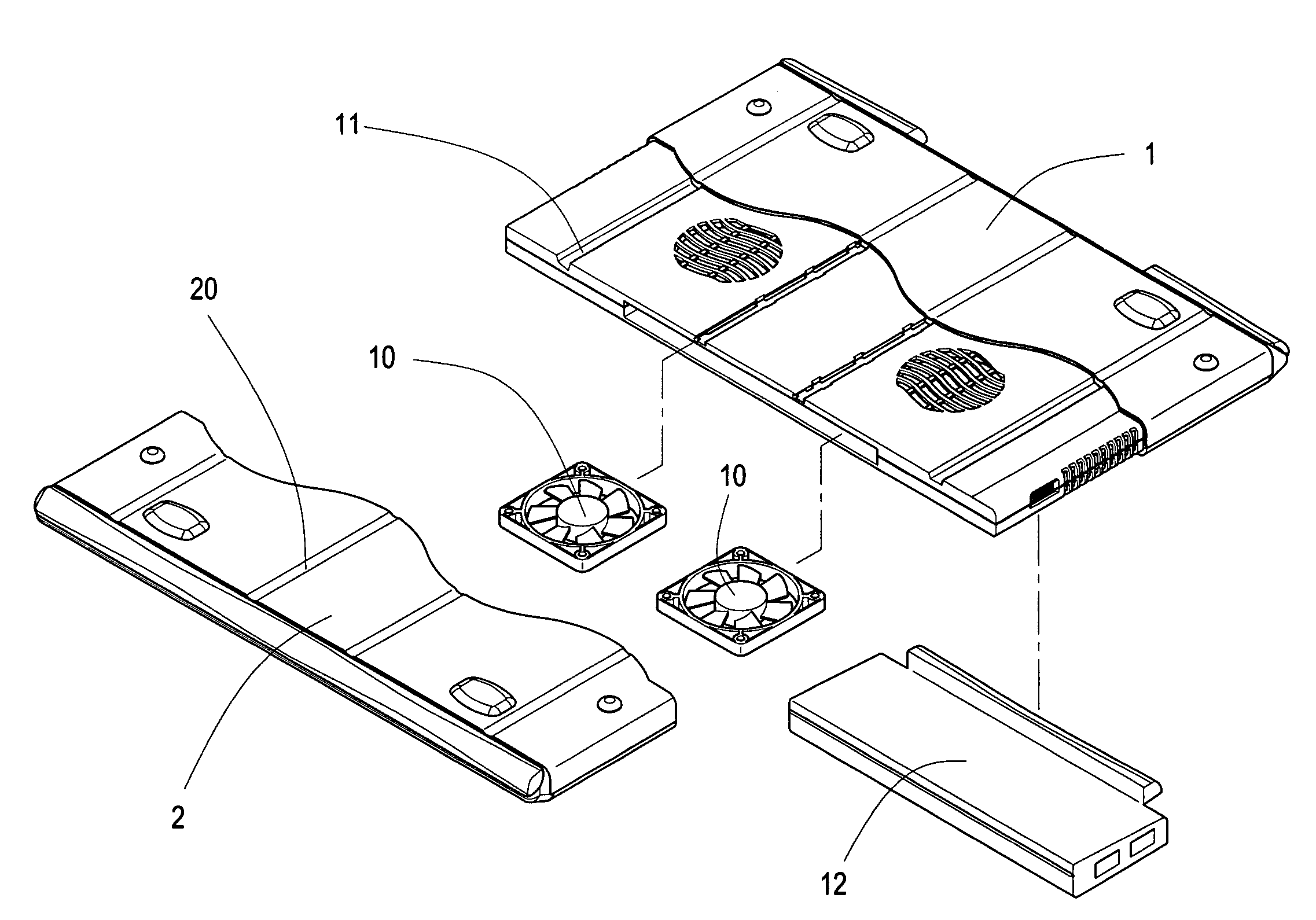
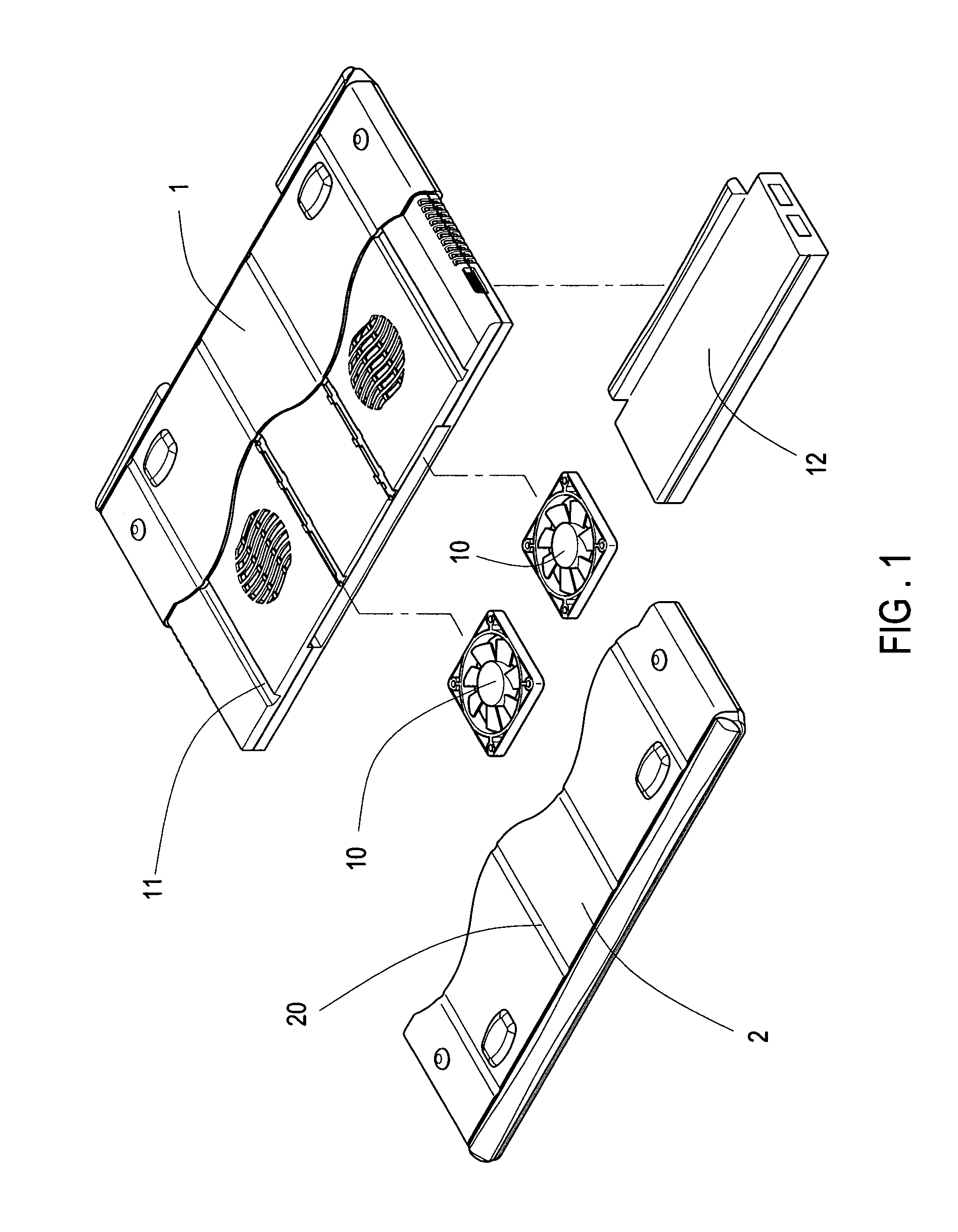
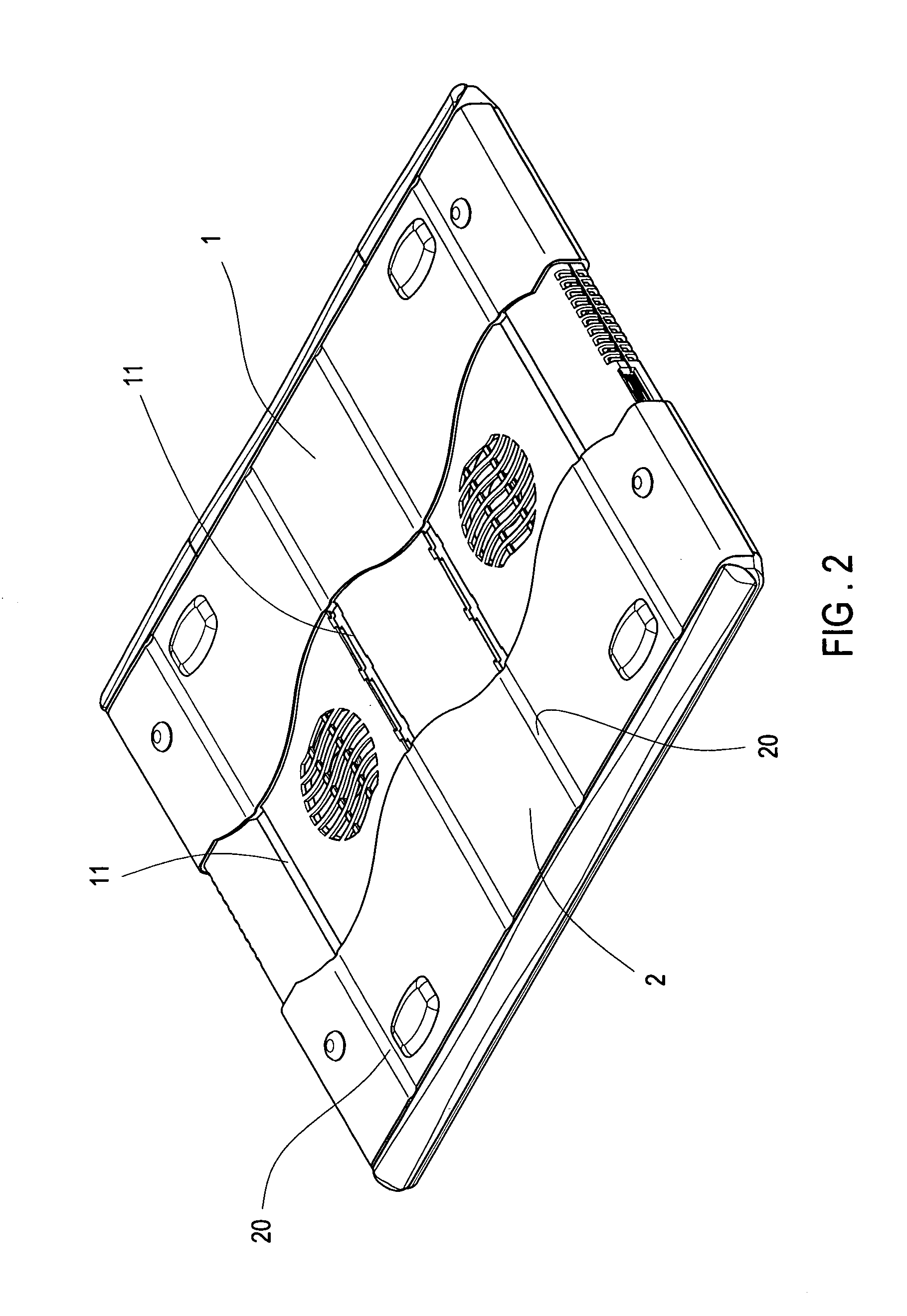
Contractible and extentable laptop computer external cooler pad
InactiveUS7038909B1Small volumeEasy to carryDigital data processing detailsCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsDocking stationUSB hub
A contractible laptop computer cooler comprising a main shell body with at least one cooling fans installed internally, two sliding sleeves each is installed on one side of the main shell body, each of the sliding sleeves wraps one side of the main body shell externally; a plurality of sliding slots are on top and bottom of the main body shell, the top and bottom of the sliding sleeves have a plurality of protruding ribs corresponding to the sliding slots; an expansion port is on the bottom of the main body shell to connect to other peripherals, such as USB Hub, Fireware (IEEE 1394), Network communication, multiple specification card reader and Port Replicater or a various of computer connectors collectively called Docking Station. Based on the structure, the present invention is easy for users to carry and store.
Owner:WIN WIN OPTO ELECTRONICS
FTTH system for broadcast/communication convergence using IEEE 1394
InactiveUS20050169632A1Bathroom accessoriesBroadcast transmission systemsOutside broadcastingOptical network unit
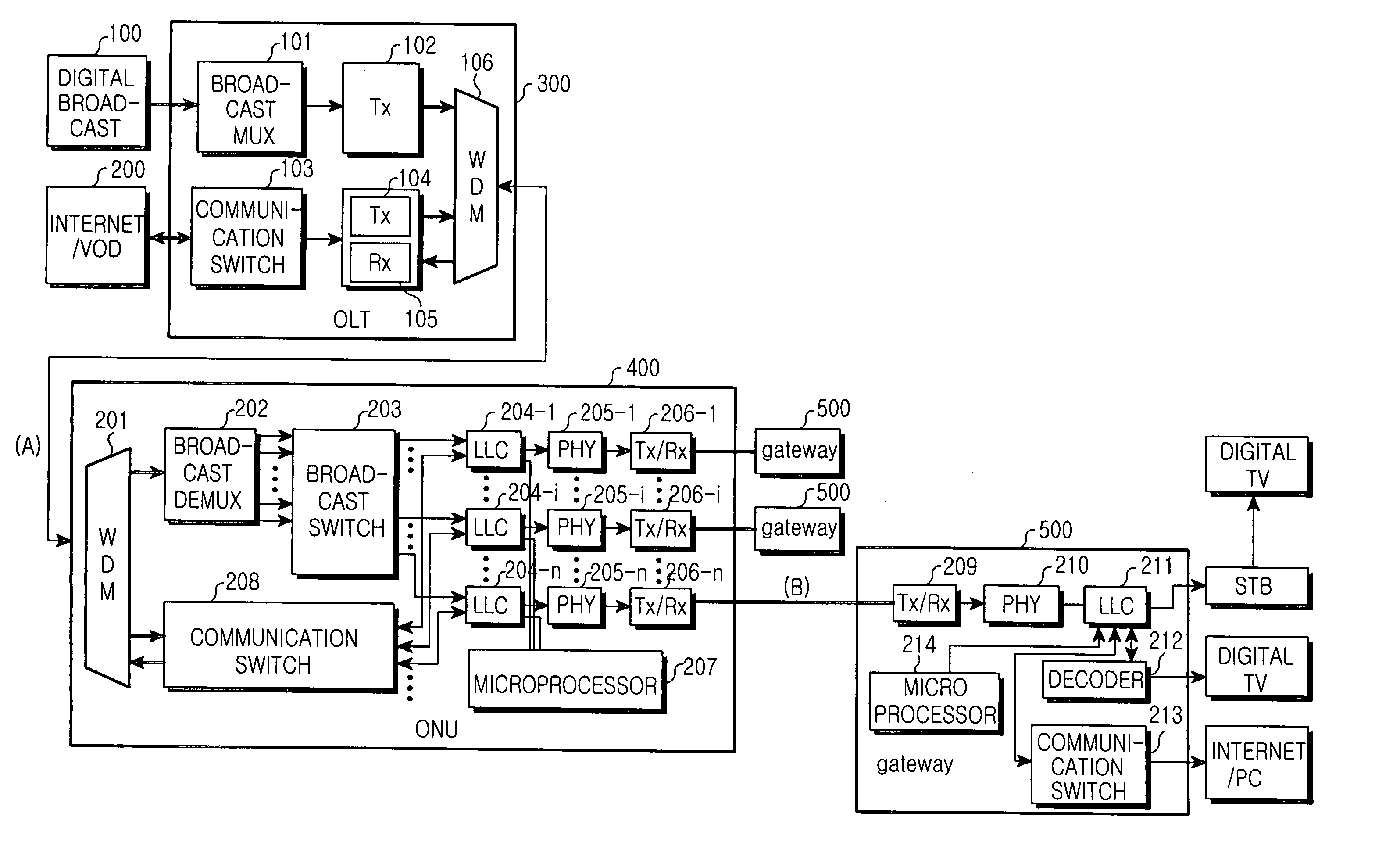
A broadcast / communication convergence system, and an FTTH (Fiber To The Home) system that can accommodate broadcast signals of various channels and variable band signals by converging broadcast and communication signals and transmitting the converged broadcast and communication signals using an IEEE 1394 transmission method serving as a standard interface in the FTTH system for broadcast / communication convergence. An OLT (Optical Line Terminal) transfers a plurality of broadcast signals and a communication signal received from external broadcast and communication providers through a single optical signal (A). An ONU (Optical Network Unit) receives the optical signal (A) from the OLT, separates the received optical signal into the plurality of broadcast signals and the communication signal, opto-electrically converts the plurality of broadcast signals and the communication signal, switches the converted broadcast signals subscriber by subscriber, combines the converted communication signal with the switched converted broadcast signals. The result is transferred to a corresponding subscriber through a single optical signal (B). A gateway at each subscriber is implemented by IEEE 1394 protocol to receive the optical signal (B) from the ONU, separate the received optical signal into the broadcast signals and the communication signal, and transfer the broadcast signals and the communication signal to a corresponding subscriber device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Communication control method and communication control apparatus
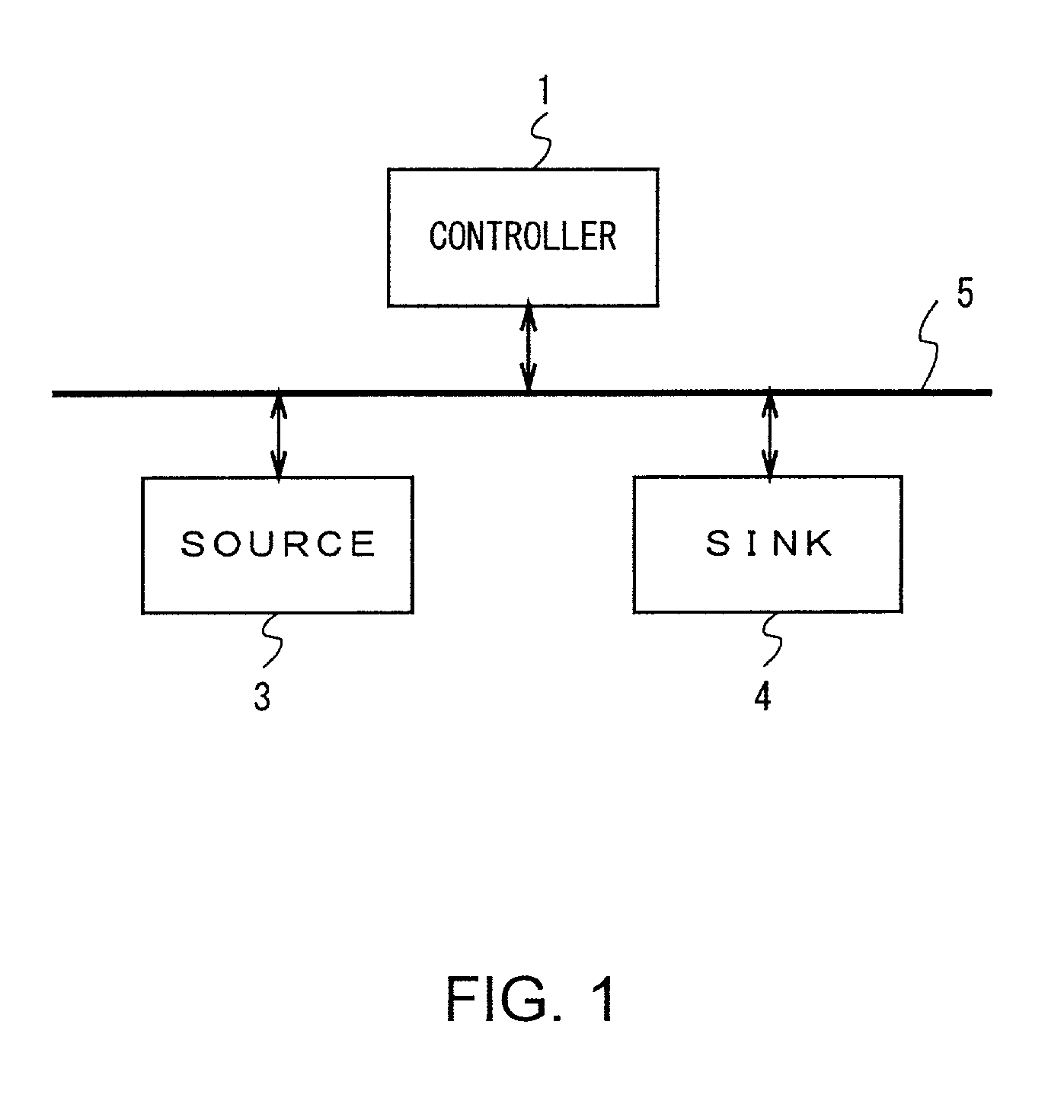
A communication control method and a communication control apparatus are provided for preventing truncation at the beginning upon receipt of data, for example, between devices interconnected through a bus line in conformity to the IEEE 1394 standard. In a communication system 100 which comprises an output device 3 for outputting stream data through a data bus 5, which includes predetermined connecting means, an input device 4 for acquiring the stream data from the output device 3 through the data bus 5, and a communication controller 1 for controlling the output device 3 and the input device 4, all of which are interconnected through the data bus 5, the communication controller 1 requests the output device 3 and the input device 4 to start communicating stream data, forces the input device 4, which has been requested to start the communication, to notify the output device 3 that the input device 4 has completed a preparation for receiving the stream data, and forces the output device 3 to transmit the stream data to the input device 4 through the data bus 5 when the completion of preparation for the reception is notified to the output device 3, thereby making it possible to prevent truncation at the beginning upon receiving the stream data at the input device.
Owner:SONY CORP
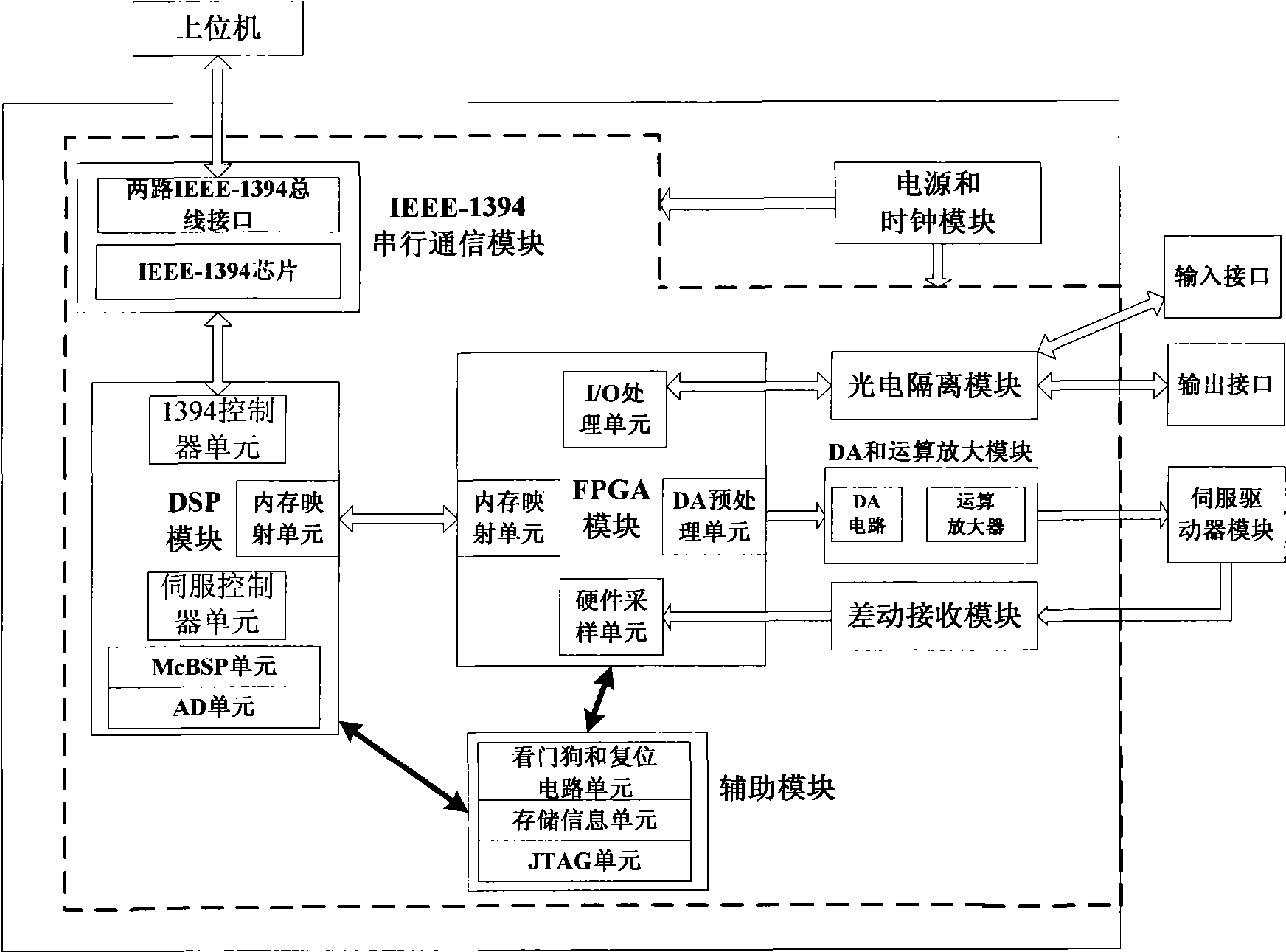
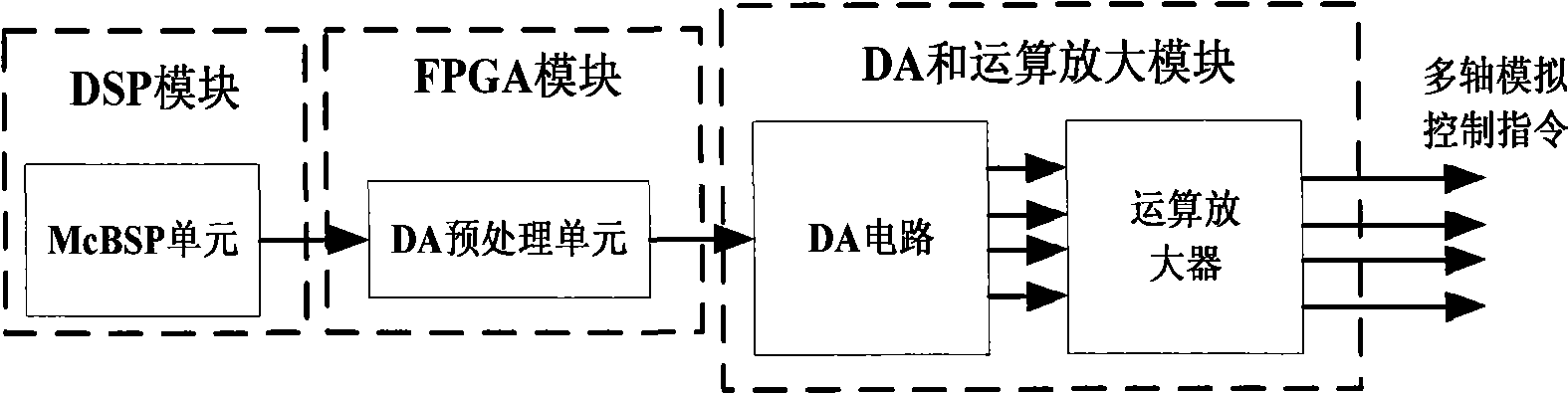
Programmable multi-axis controller based on IEEE-1394 serial bus
ActiveCN101546185AReal-time transmissionReliable transmissionNumerical controlNumerical controlDisk controller
The invention relates to a programmable multi-axis controller based on an IEEE-1394 serial bus in the technical field of numerical control. The programmable multi-axis controller comprises an IEEE-1394 serial communication interface module, a DSP module, an FPGA module, a differential motion reception module, a DA and operation amplification module, a photoelectric isolation module, a power supply and clock module and an auxiliary module, wherein the DSP module receives motion control information transmitted from the IEEE-1394 serial communication interface module and transmits a generated multi-axis motor pulse instruction to the FPGA module; and the FPGA module outputs the multi-axis motor pulse instruction to the DA and operation amplification module after the storage and frequency division treatment of the instruction so as to complete digital-analog conversion and operation amplification treatment and further control the operation of a multi-axis motor. The programmable multi-axis controller reduces the number of controller elements and the volume of an integrated circuit card, improves the flexibility and the expansibility of a system, and meets the requirements of the multi-axis real-time, high-speed and high-accuracy control in the technical field of numerical control.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Electronic device with integral connectors
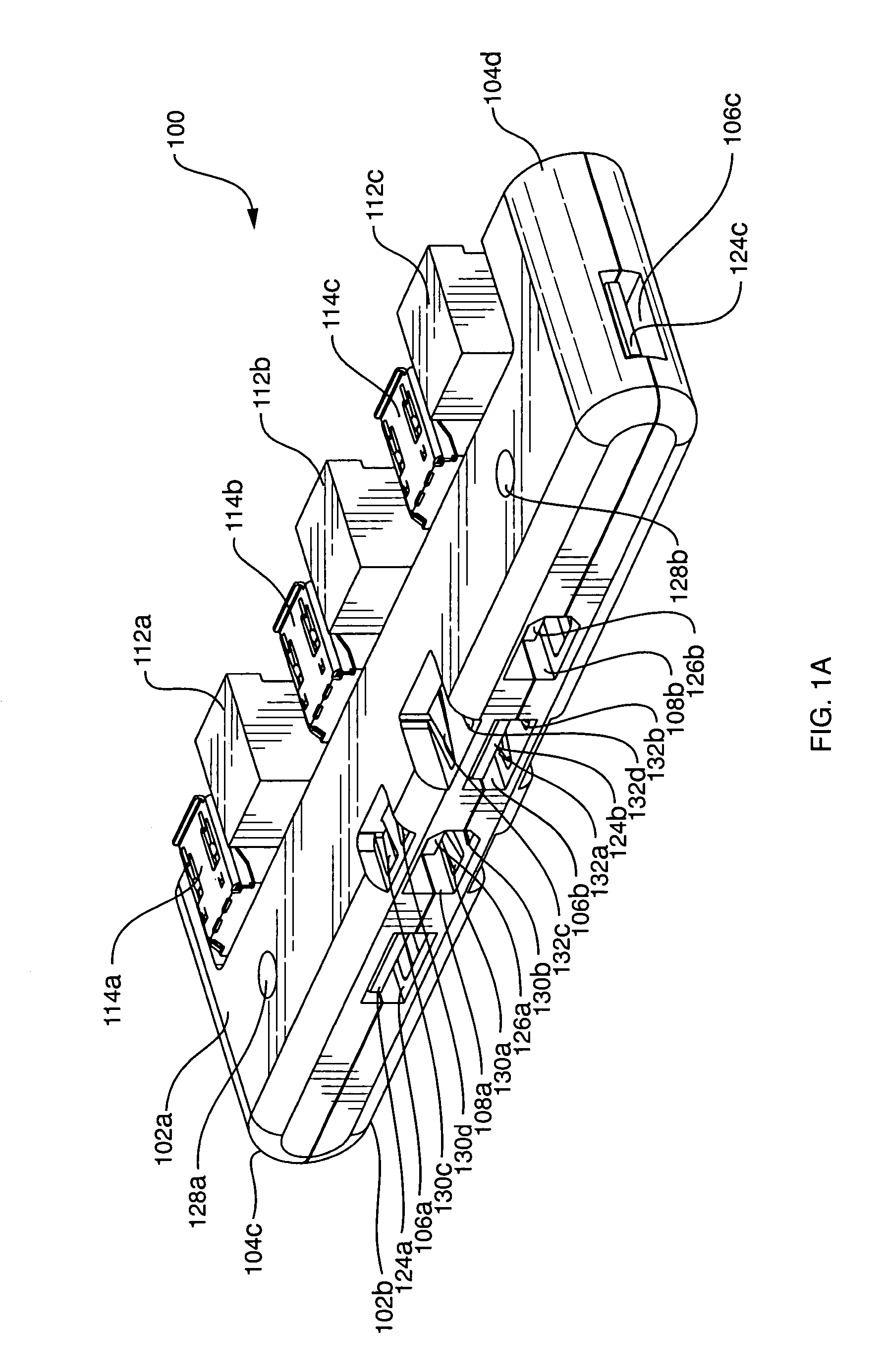
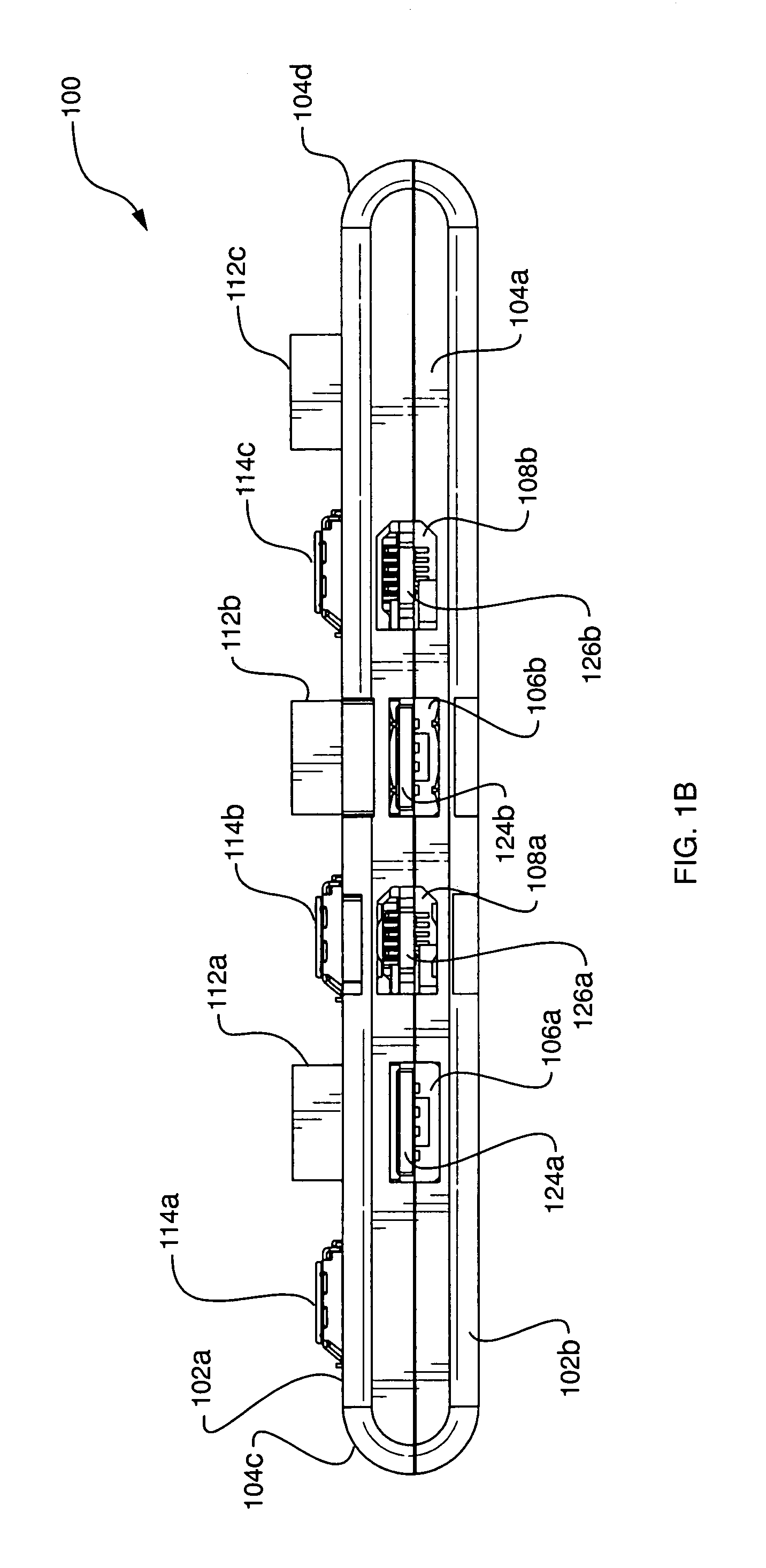
InactiveUS7247032B2Reduce manufacturing costPrinted circuit aspectsTwo-part coupling devicesElectricityMating plug
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com