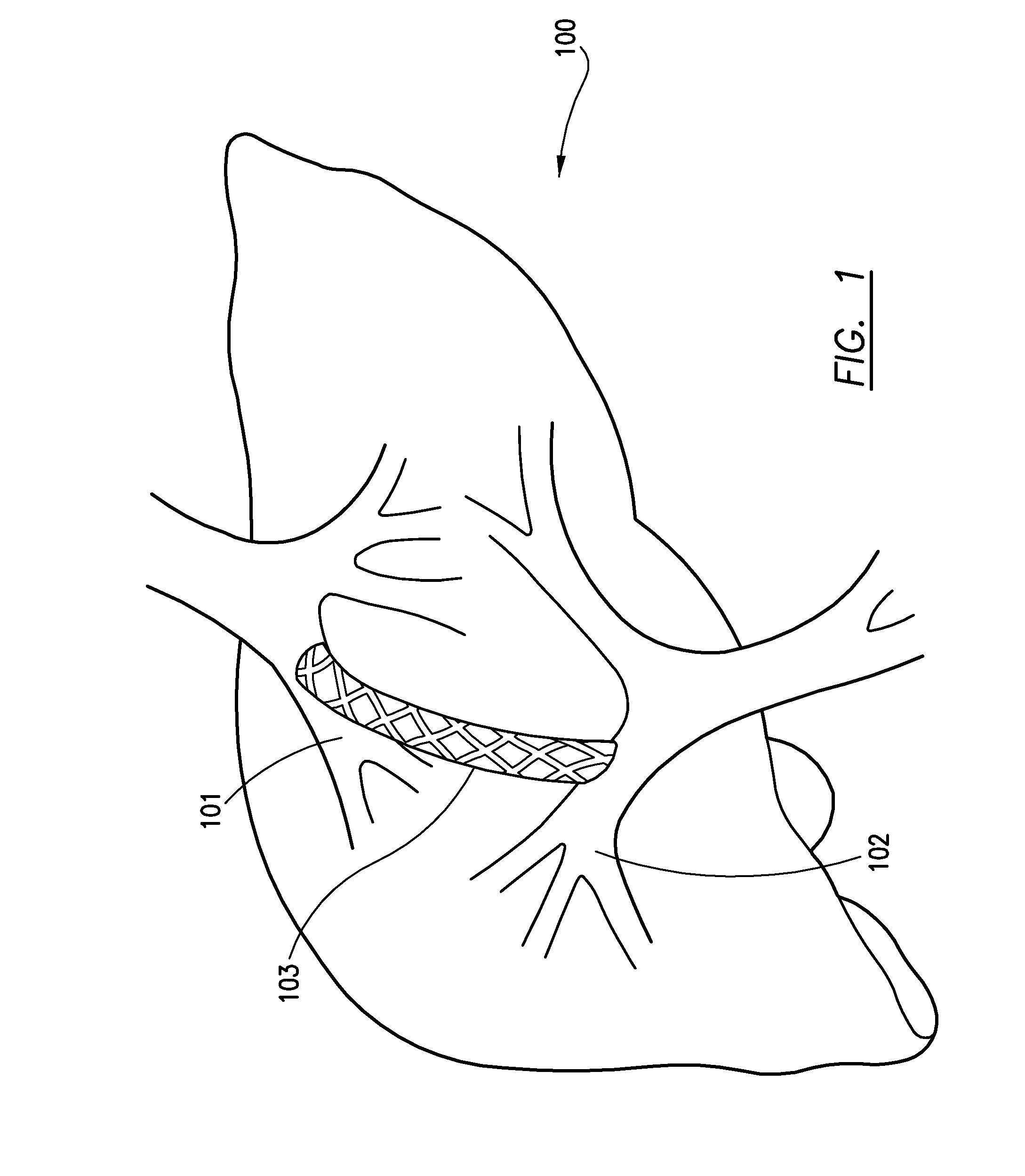
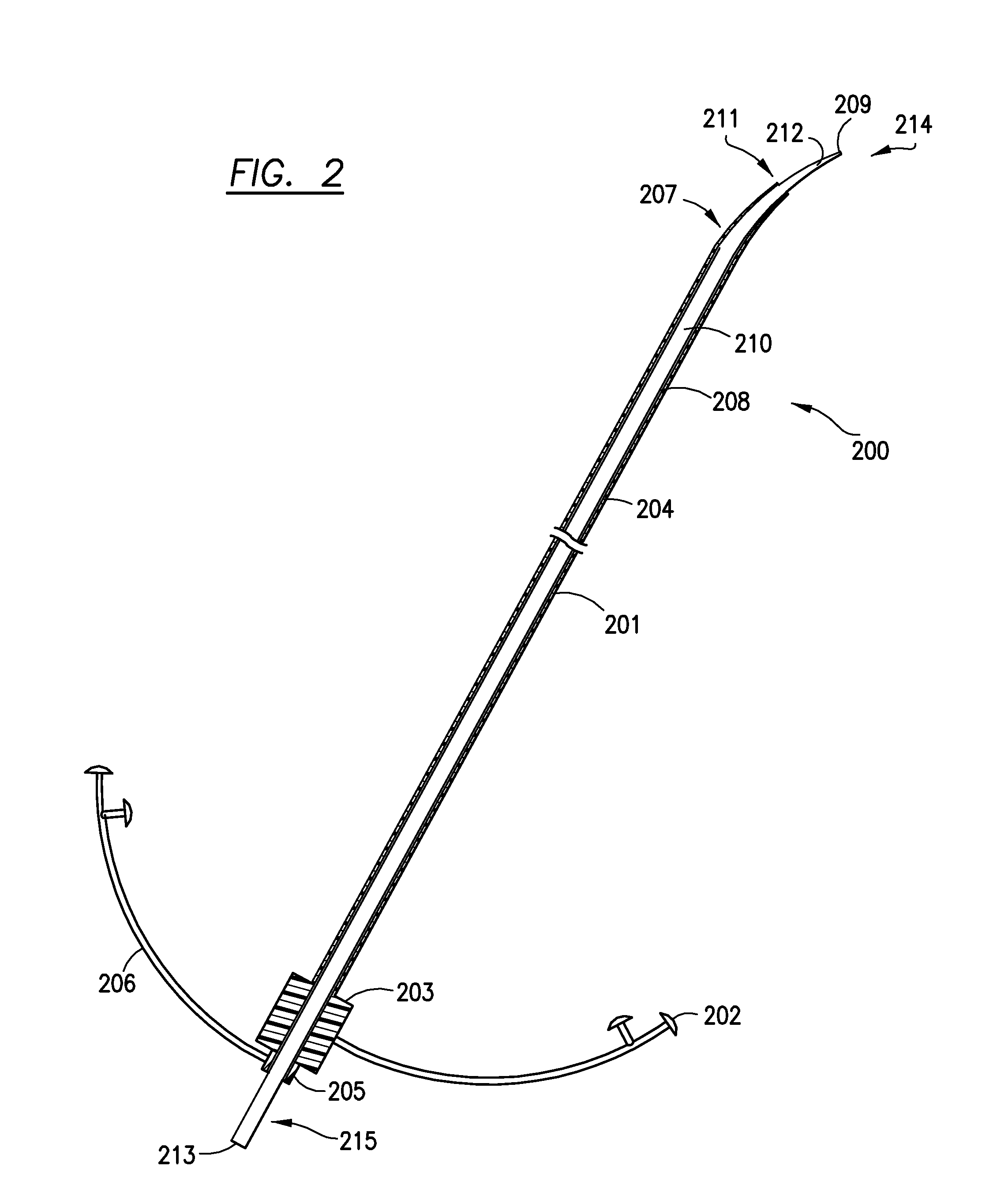
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
66 results about "Hepatic veins" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
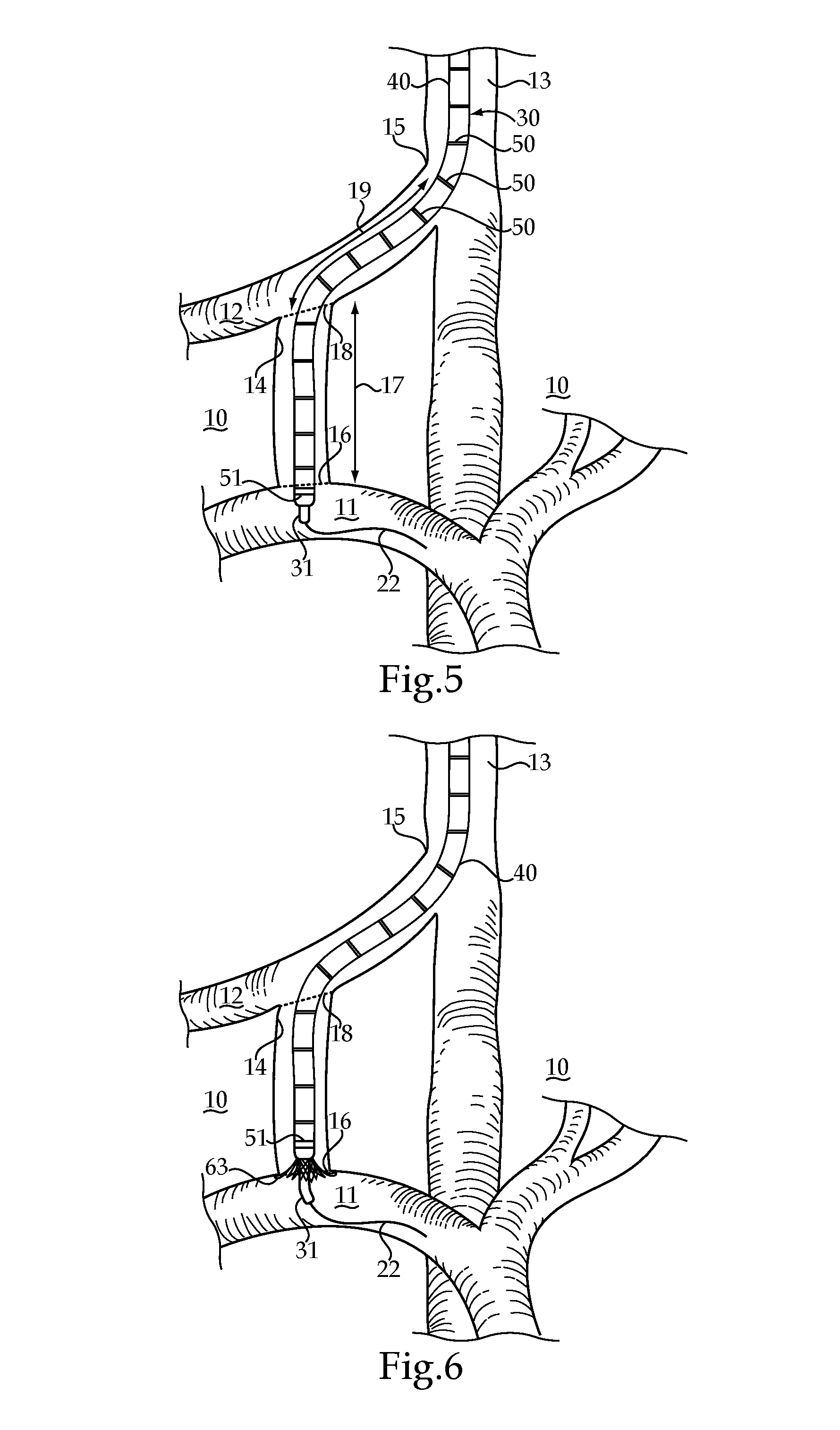
The hepatic veins are the veins that drain de-oxygenated blood from the liver into the inferior vena cava. There are usually three upper hepatic veins draining from the left, middle, and right parts of the liver. These are larger than the group of lower hepatic veins that can number from six to twenty. All of the hepatic veins drain into the inferior vena cava.
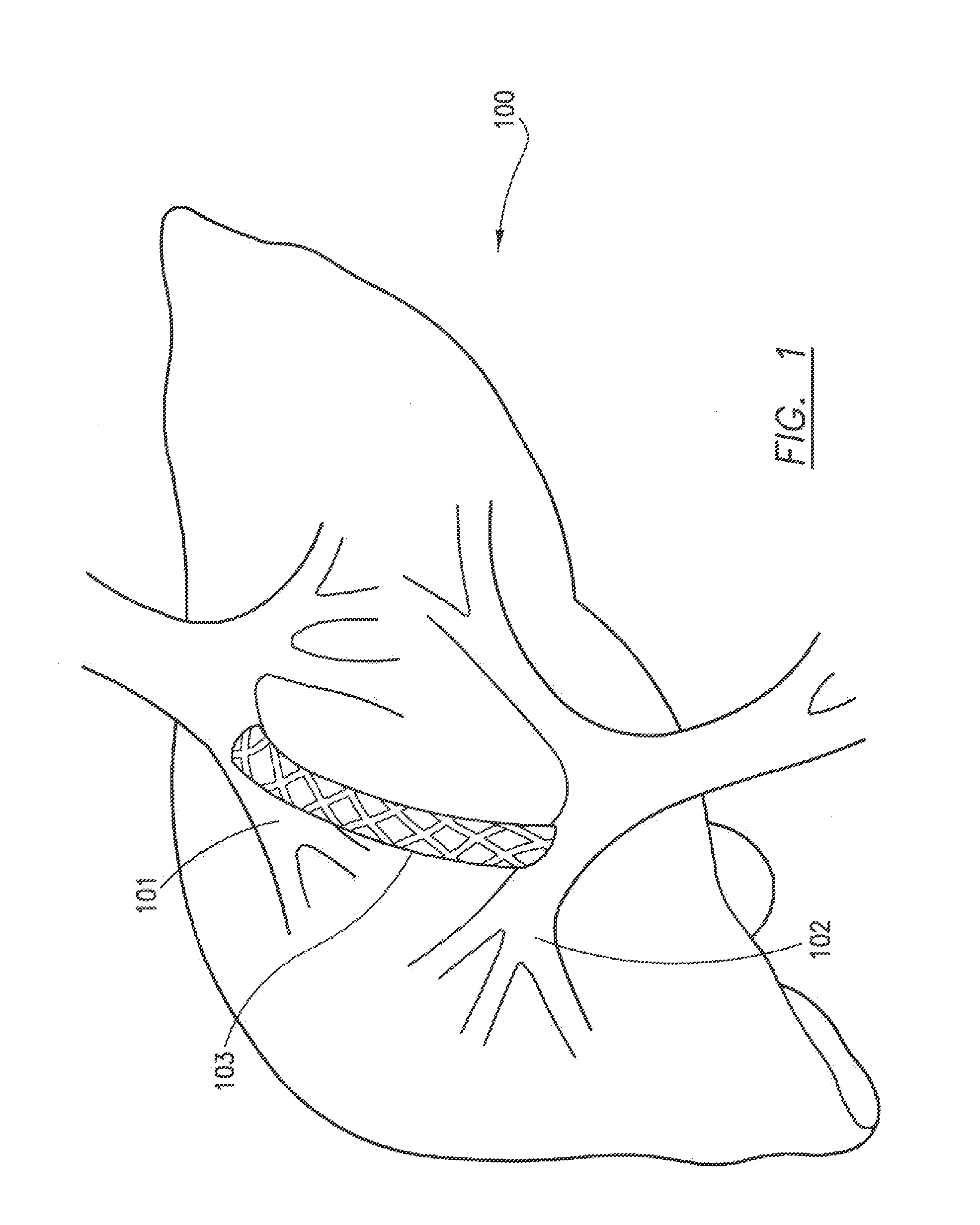
Hepatic portal vein tree modeling method and system thereof
InactiveCN101393644AEnhancement effect is goodEfficient removalImage enhancementImage analysisLiver parenchymaFiltration
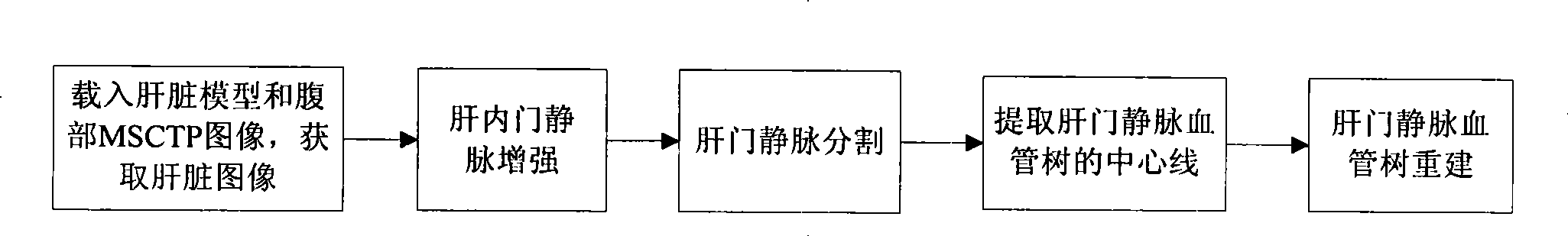
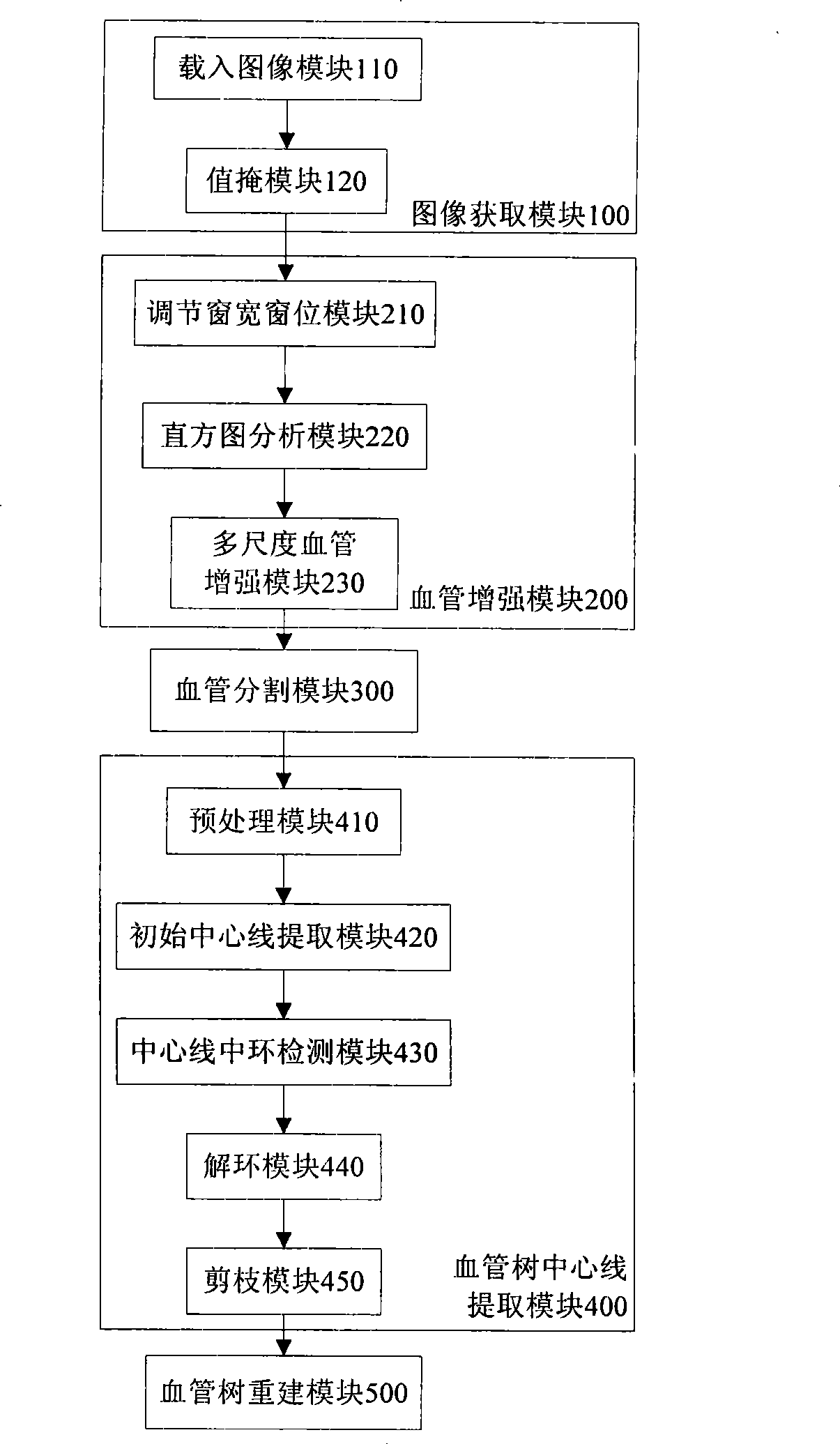
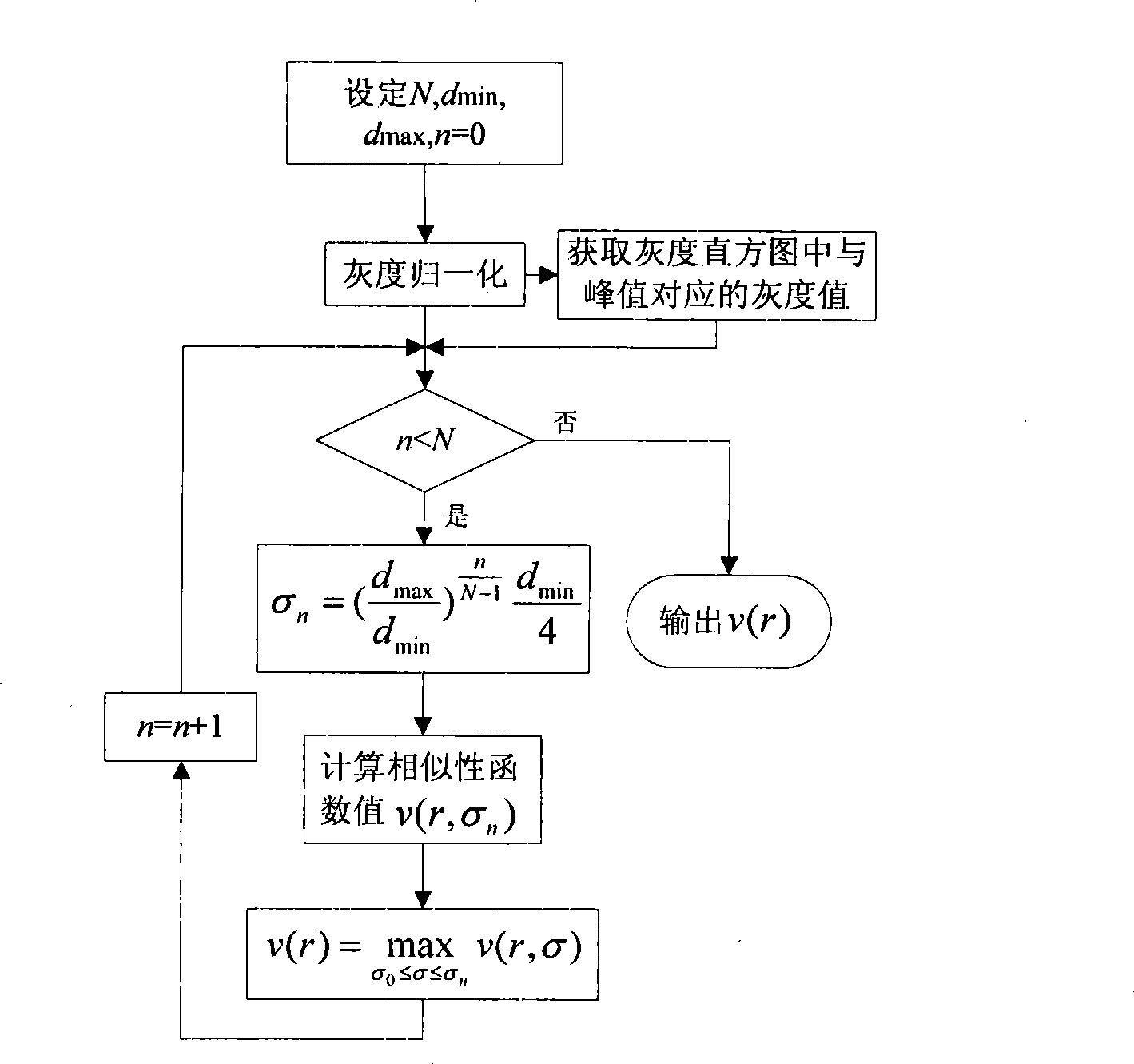
The invention discloses a hepatic vein vascular tree modeling method and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: using a liver model to obtain a liver image, and utilizing the multi-scale filtration method to strengthen a blood vessel; cutting a hepatic vein; extracting a central line of the hepatic vein; detecting and removing a link in the central line; and utilizing OSG / VTK to rebuild the hepatic vein vascular tree after pruning. The system comprises an image acquisition module, a blood vessel strengthening module, a blood vessel cutting module, a vascular tree central line extracting module and a vascular tree rebuilding module. The invention improves similarity functions in the filtering process, analyzes the characteristics of the ring and adopts corresponding unlinking methods for different links; and utilizes the relation of radius of blood vessel and the branch length when pruning. The invention effectively enhances the hepatic vein, improves the contrast between the blood vessel and liver parenchyma, and can extract more than five class branches, effectively unlink and prune the central line of the hepatic vein, rebuild the hepatic vein vascular tree and directly display the branches of the heptatic vein.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
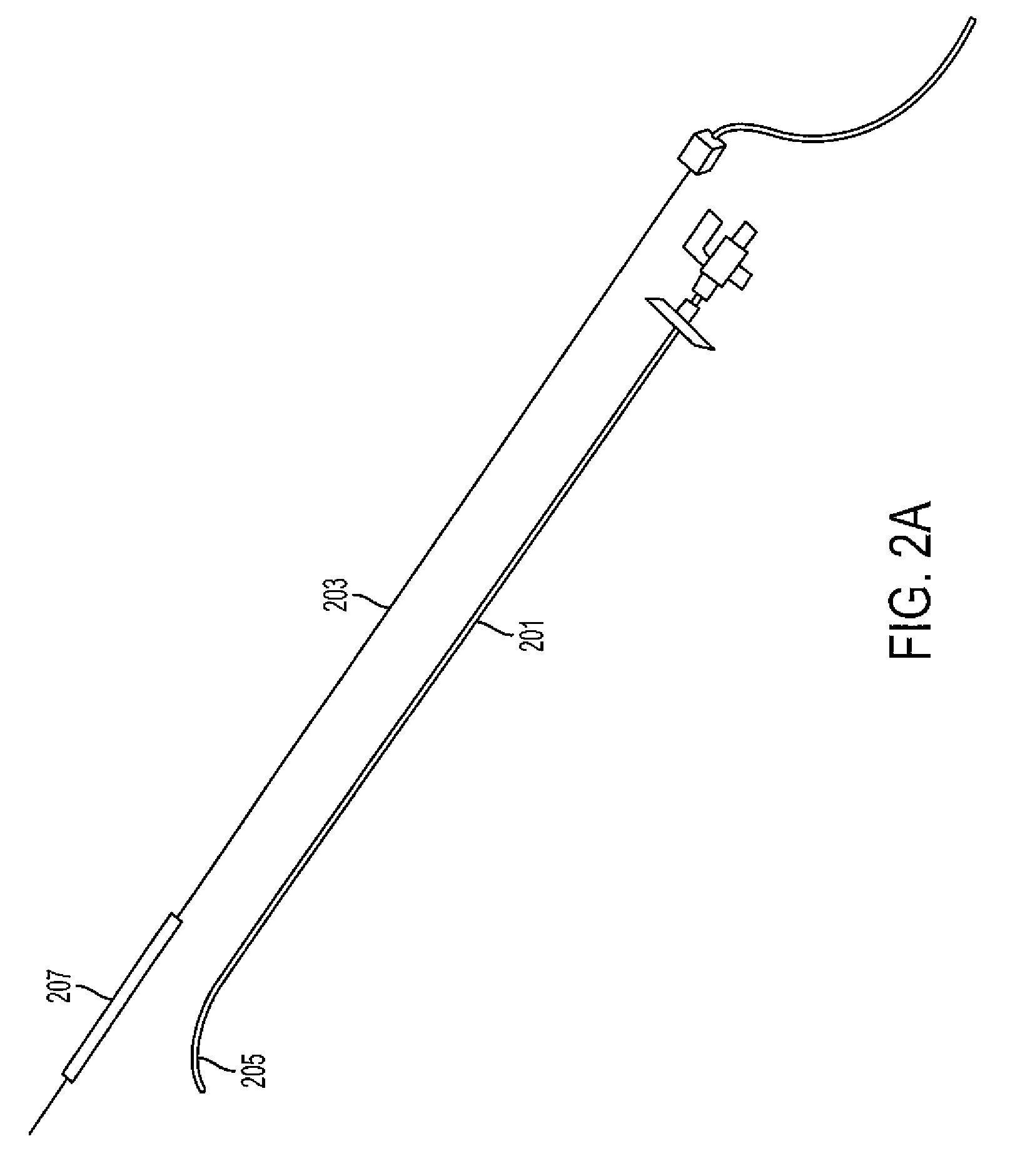
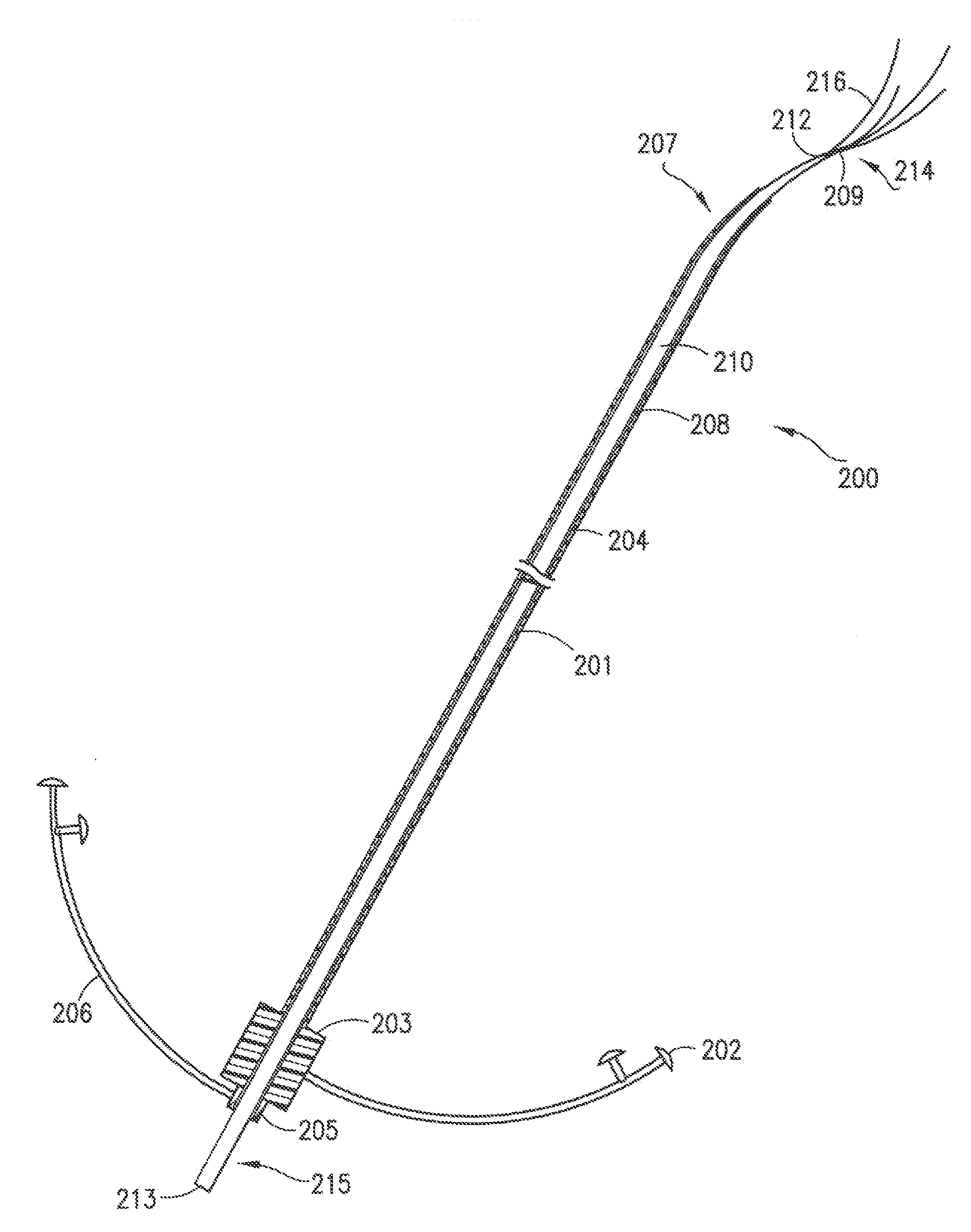
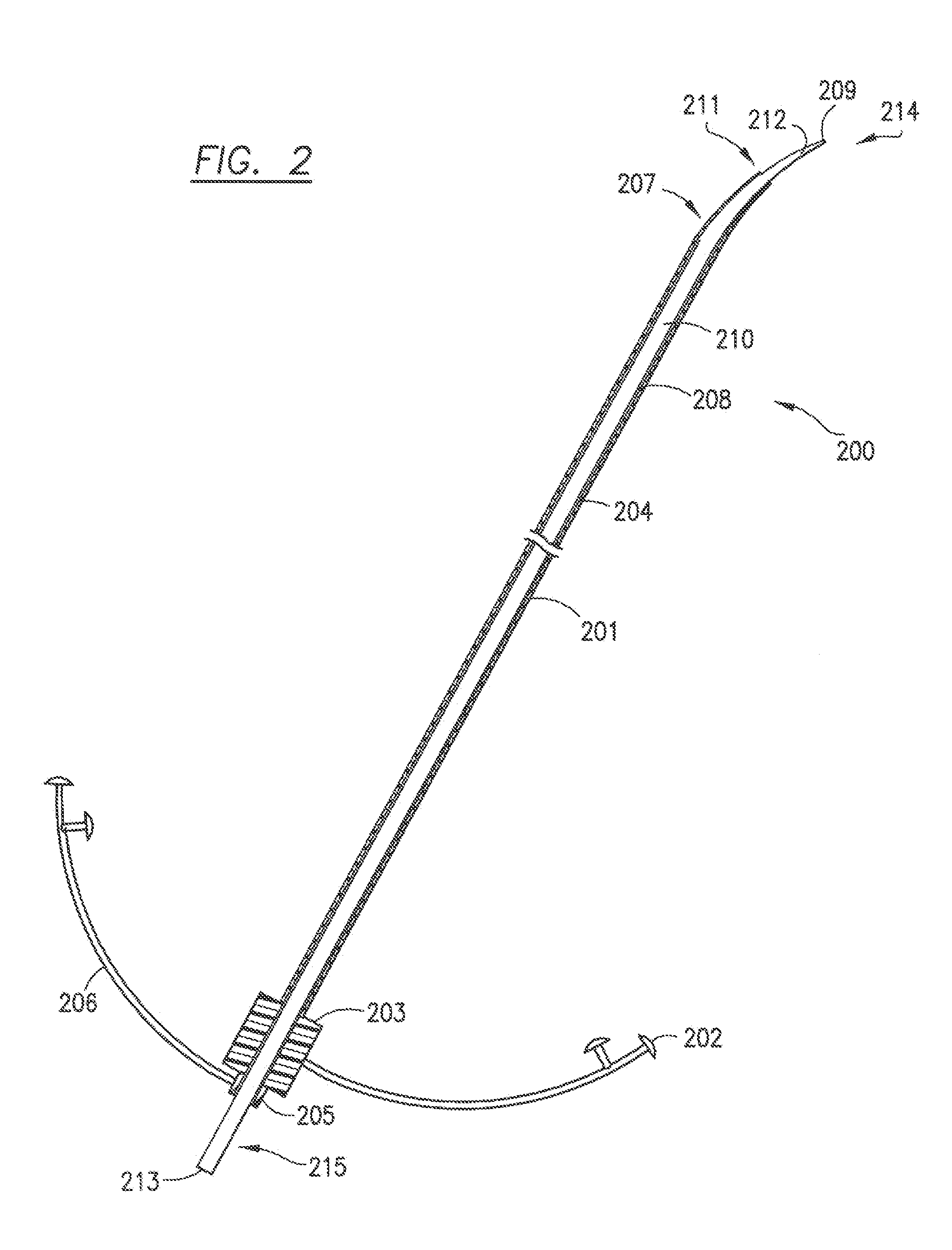
Method, system and devices for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) procedures
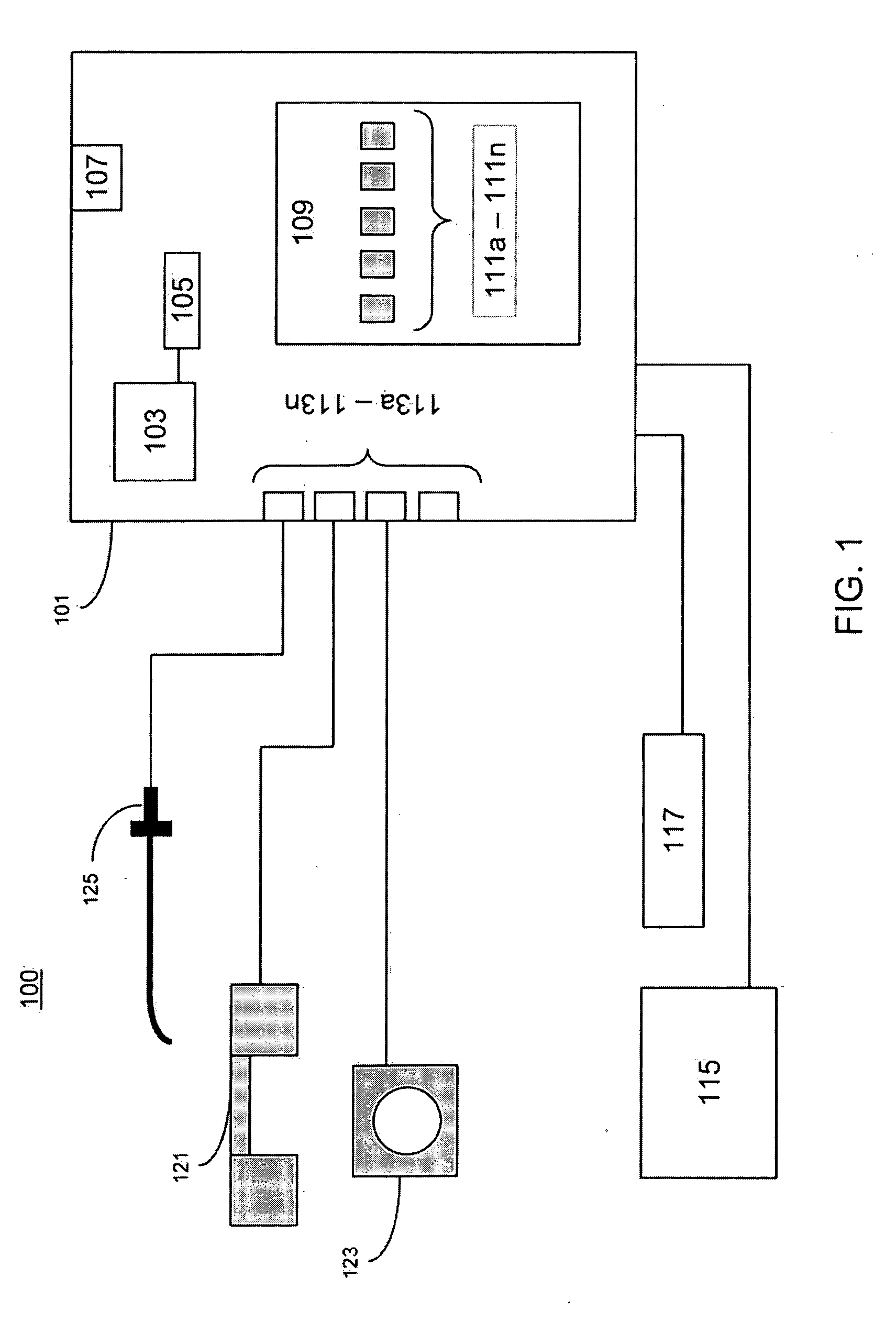
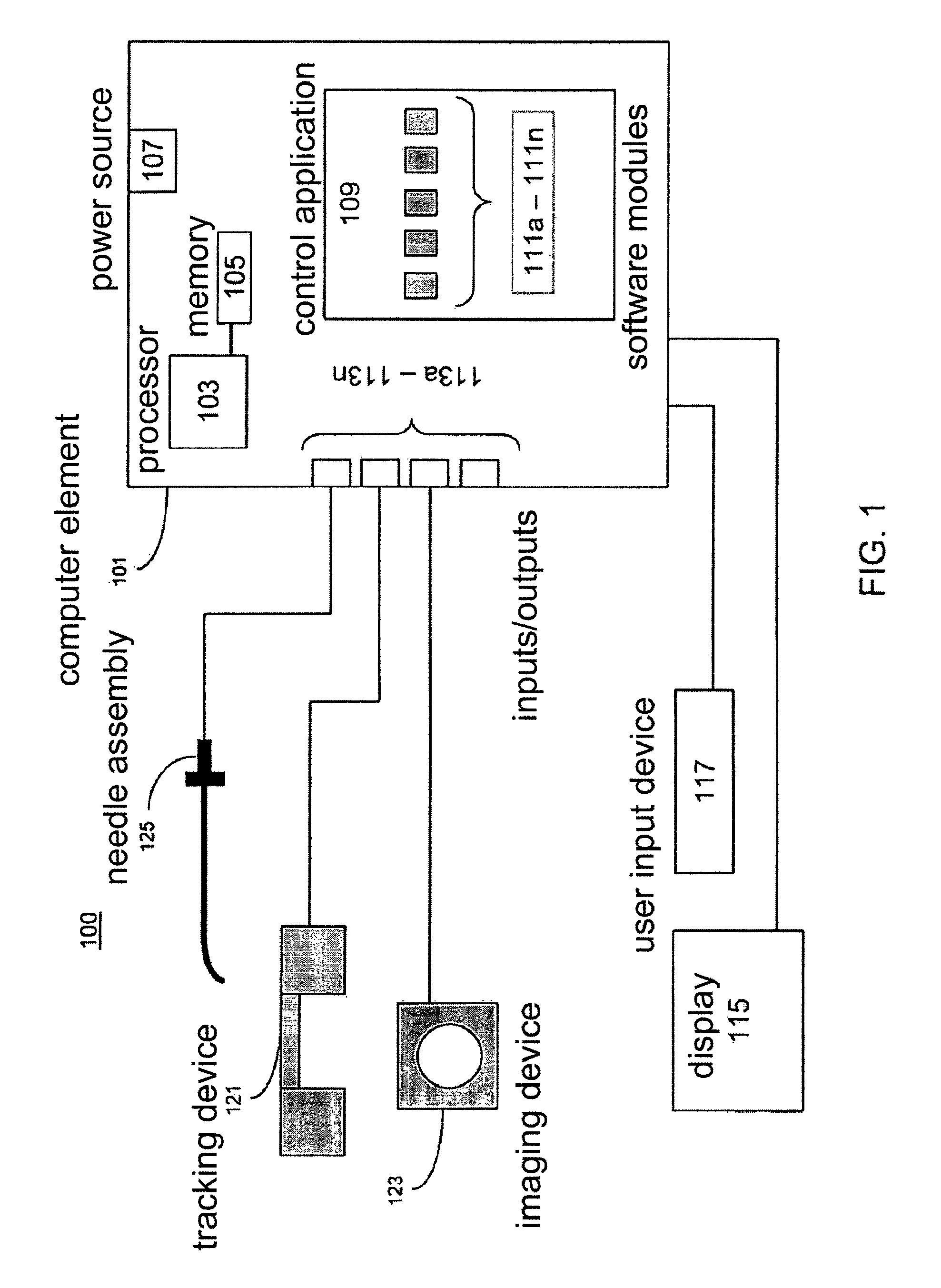
ActiveUS20100217117A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesHepatic veinsFlow diverter
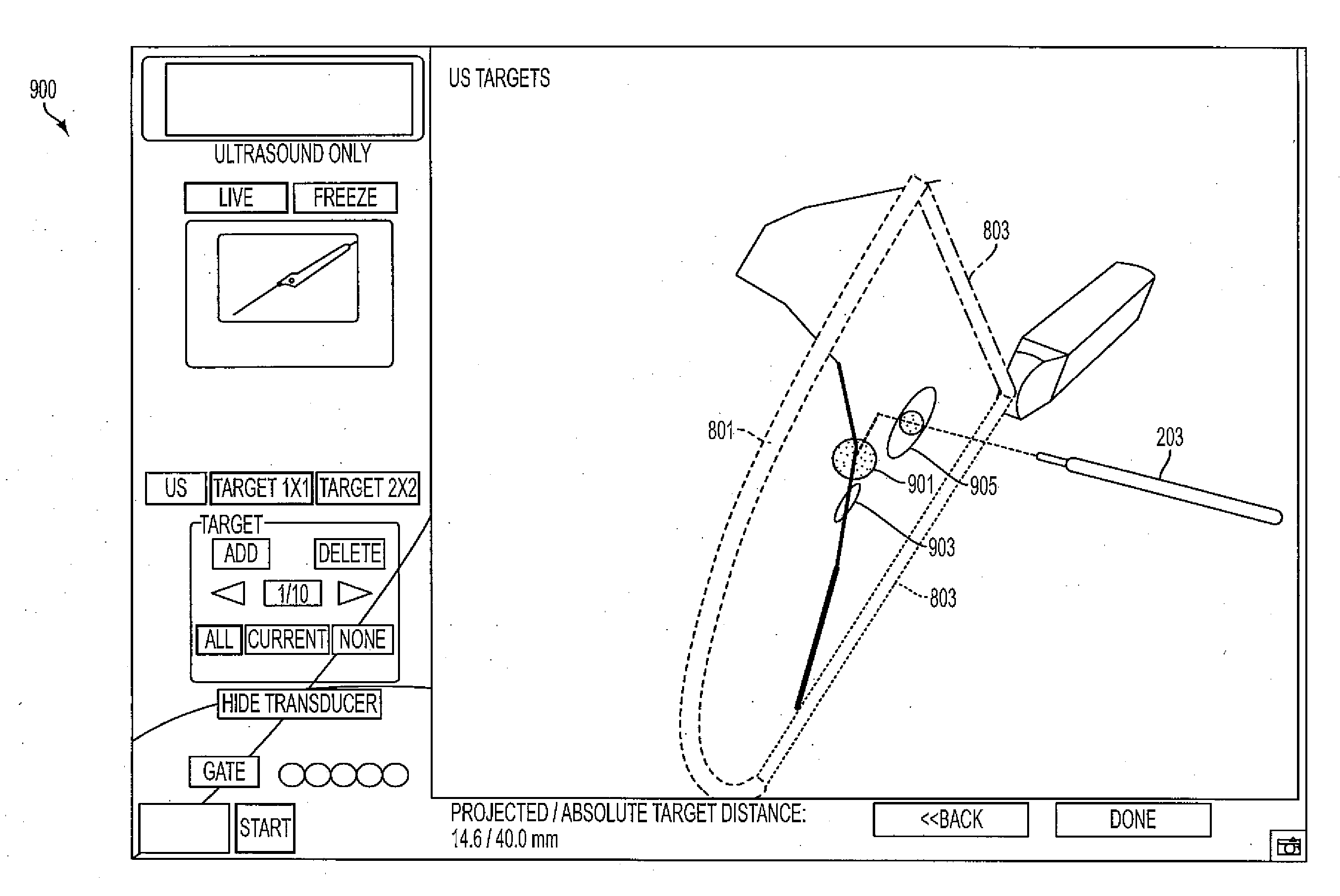
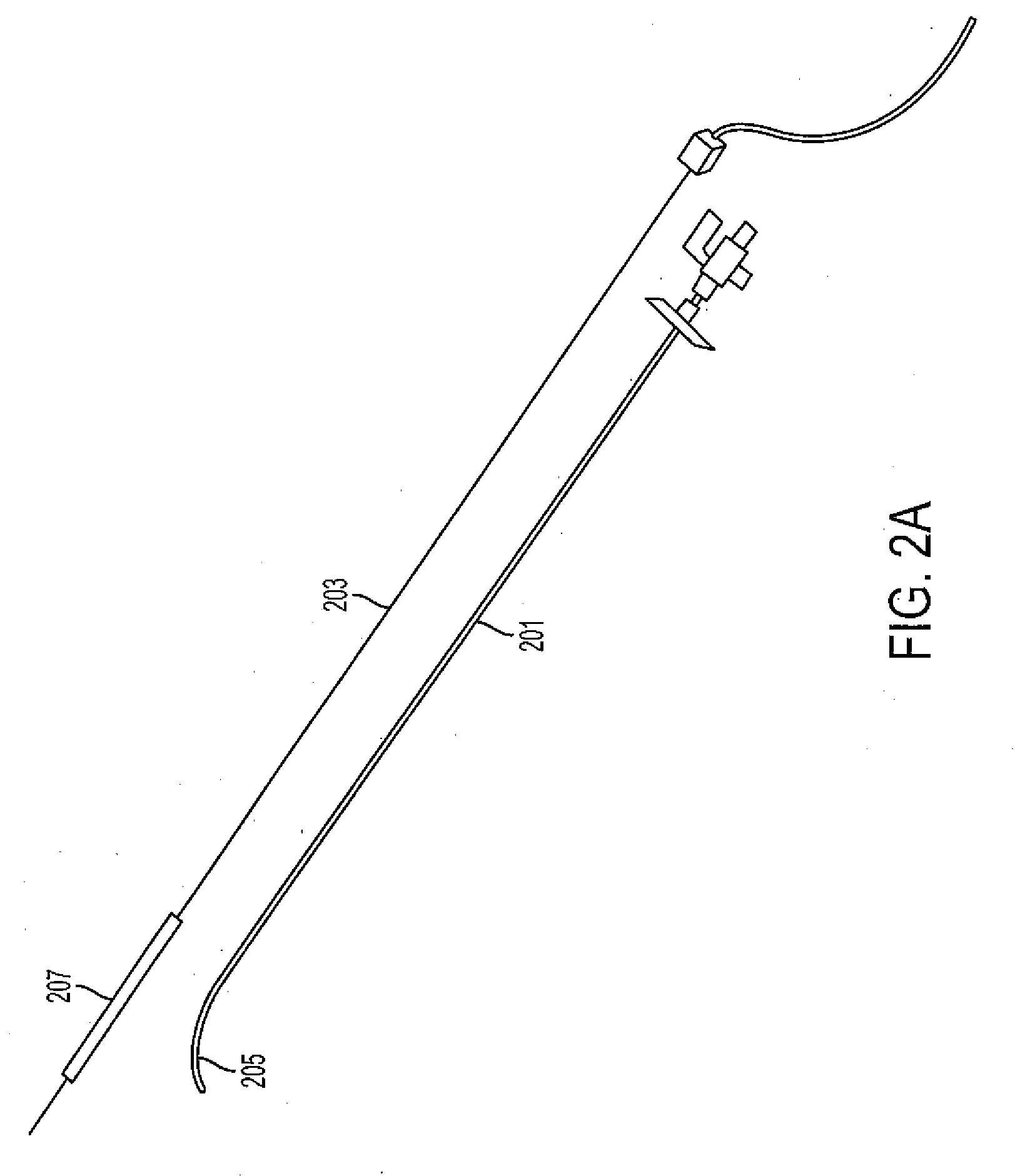
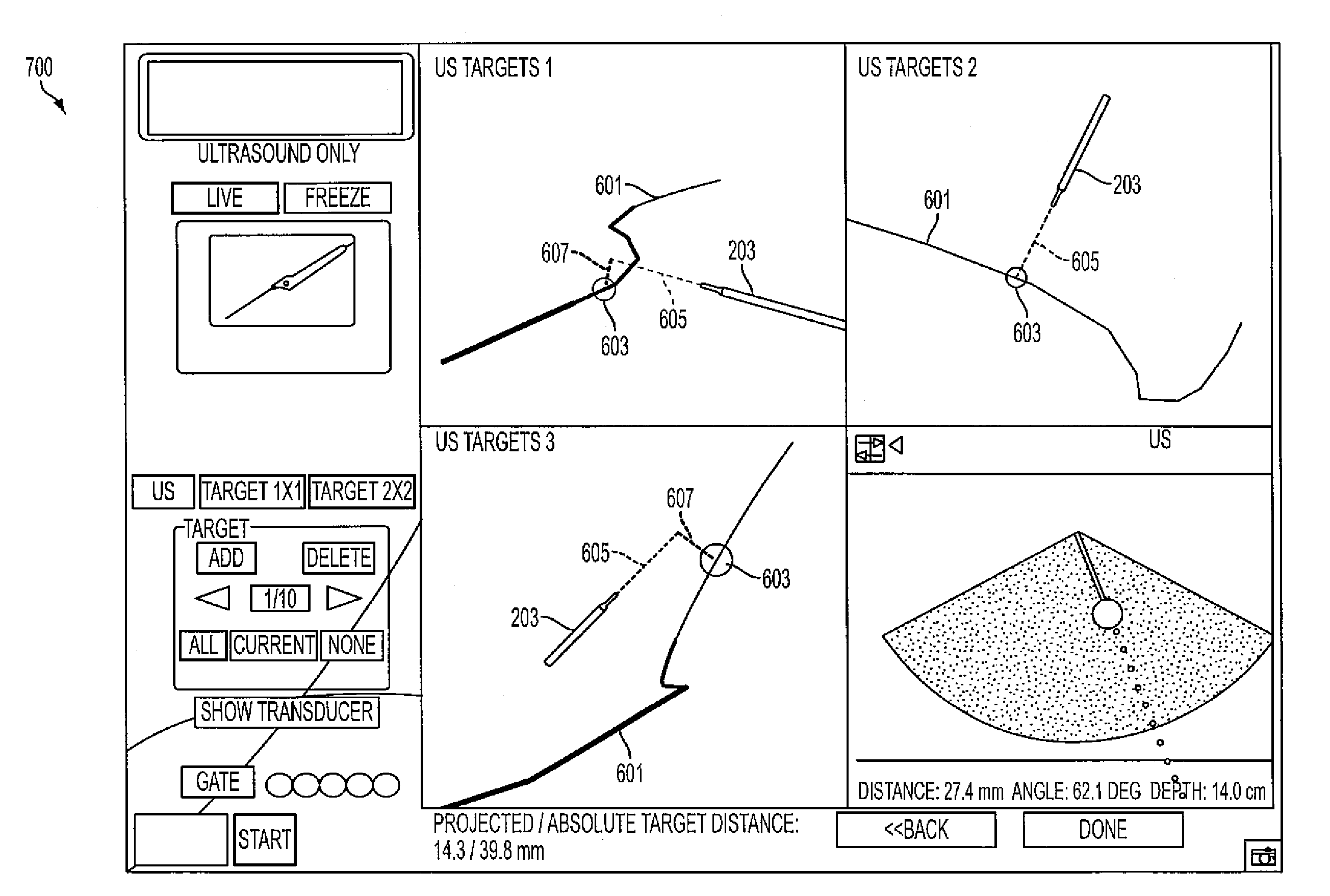
The invention provides systems and methods for assisting / performing image-guided transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) procedures in a portion of an anatomy of a patient, including a guide needle portion comprising a hollow tube having a bend toward its distal tip and a puncture needle portion that includes at least one position indicating element at its tip. The puncture needle is slidably mounted within the hollow tube of the guide needle such that a distal tip of the puncture needle can be extended from an opening in the distal tip of the guide needle and used to place a shunt between the portal and hepatic veins of a patient. The position indicating element of the puncture needle is used to produce a display of the puncture needle relative to a target vessel, including a projected path of the puncture needle that can be adjusted to accurately locate a shunt.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Method, system and devices for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) procedures
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
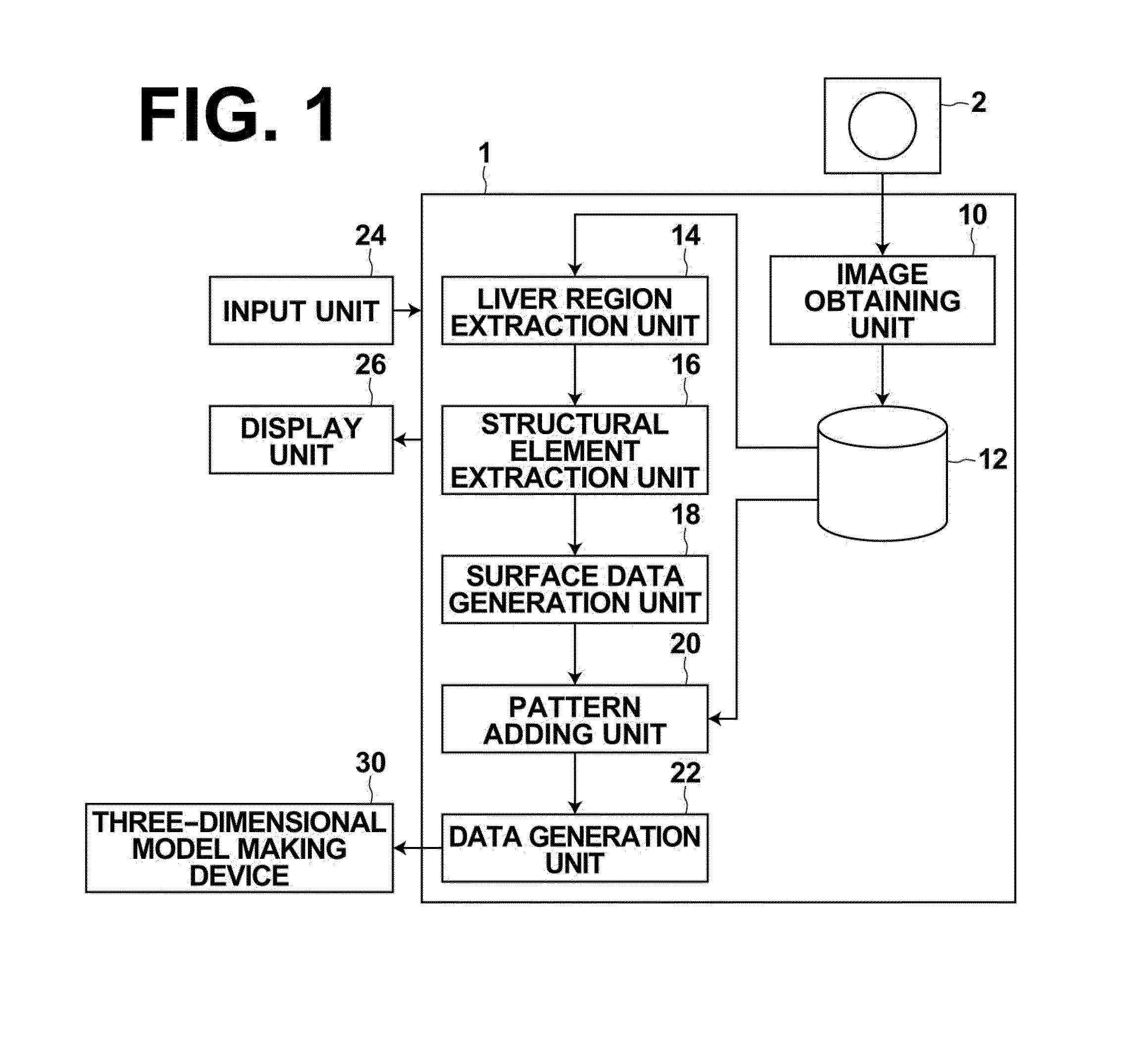
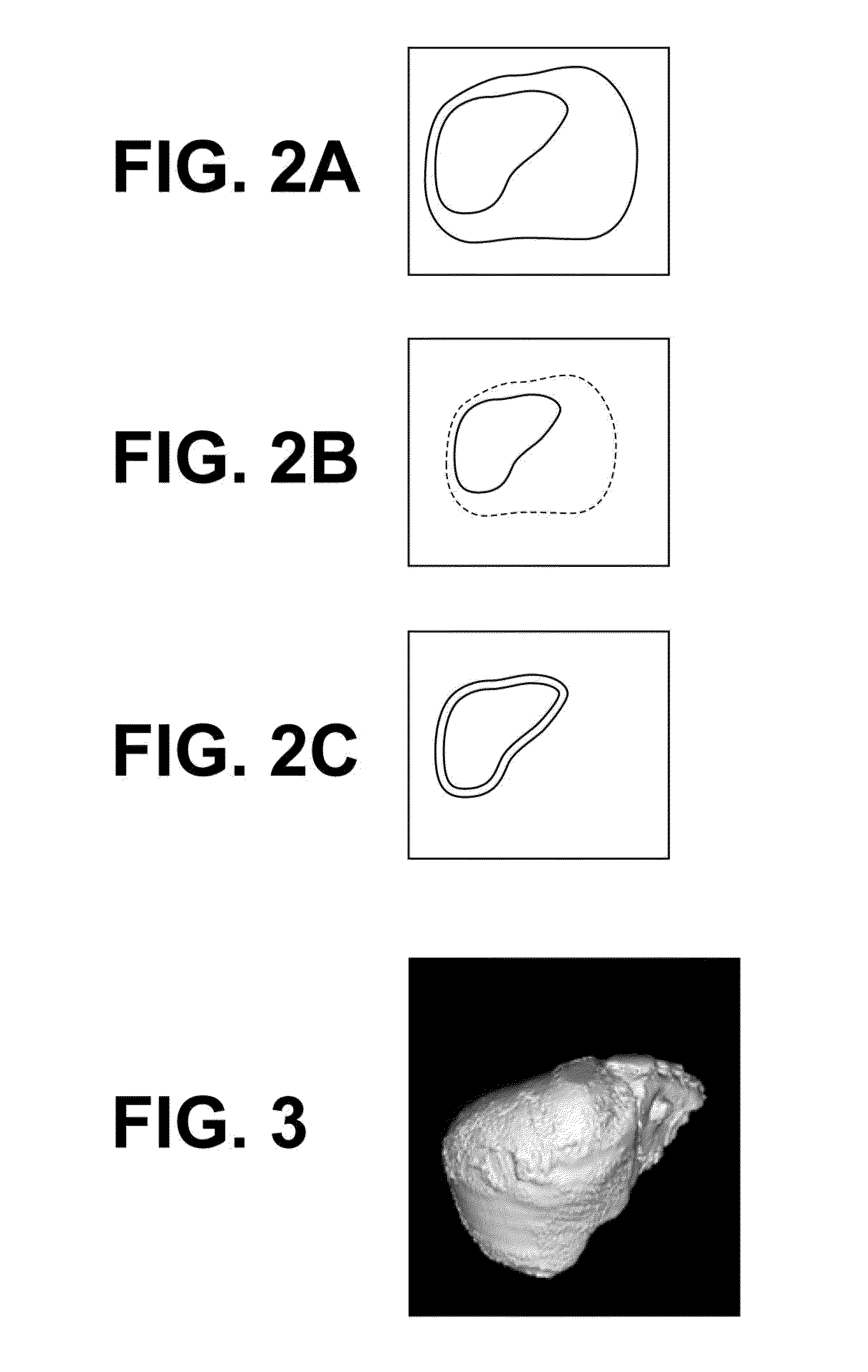
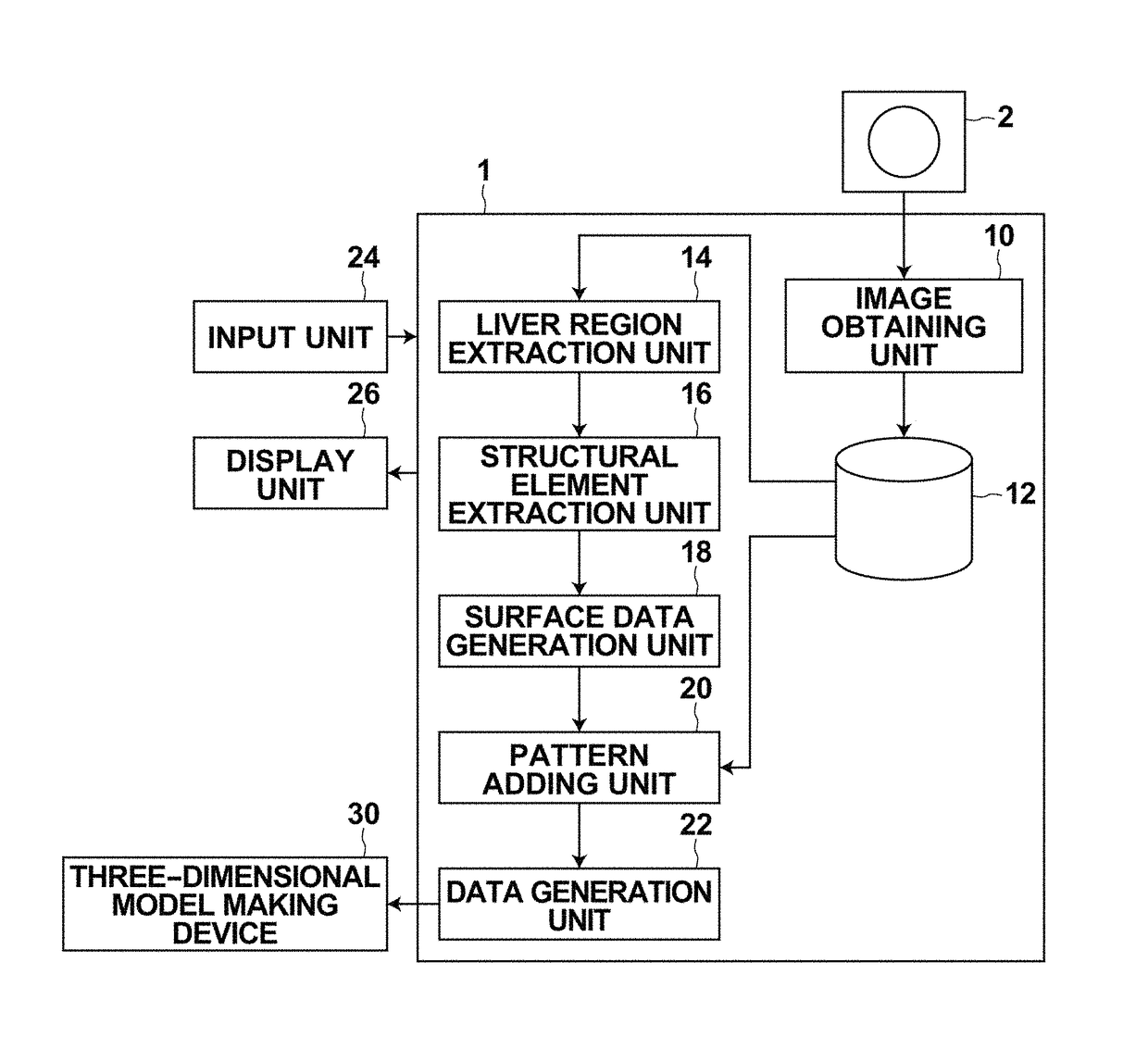
Three-dimensional model data generation device, method and program
ActiveUS20150029184A1Simple and inexpensive mannerSimple and inexpensiveImage enhancementImage analysisHepatic veinsComputer graphics (images)
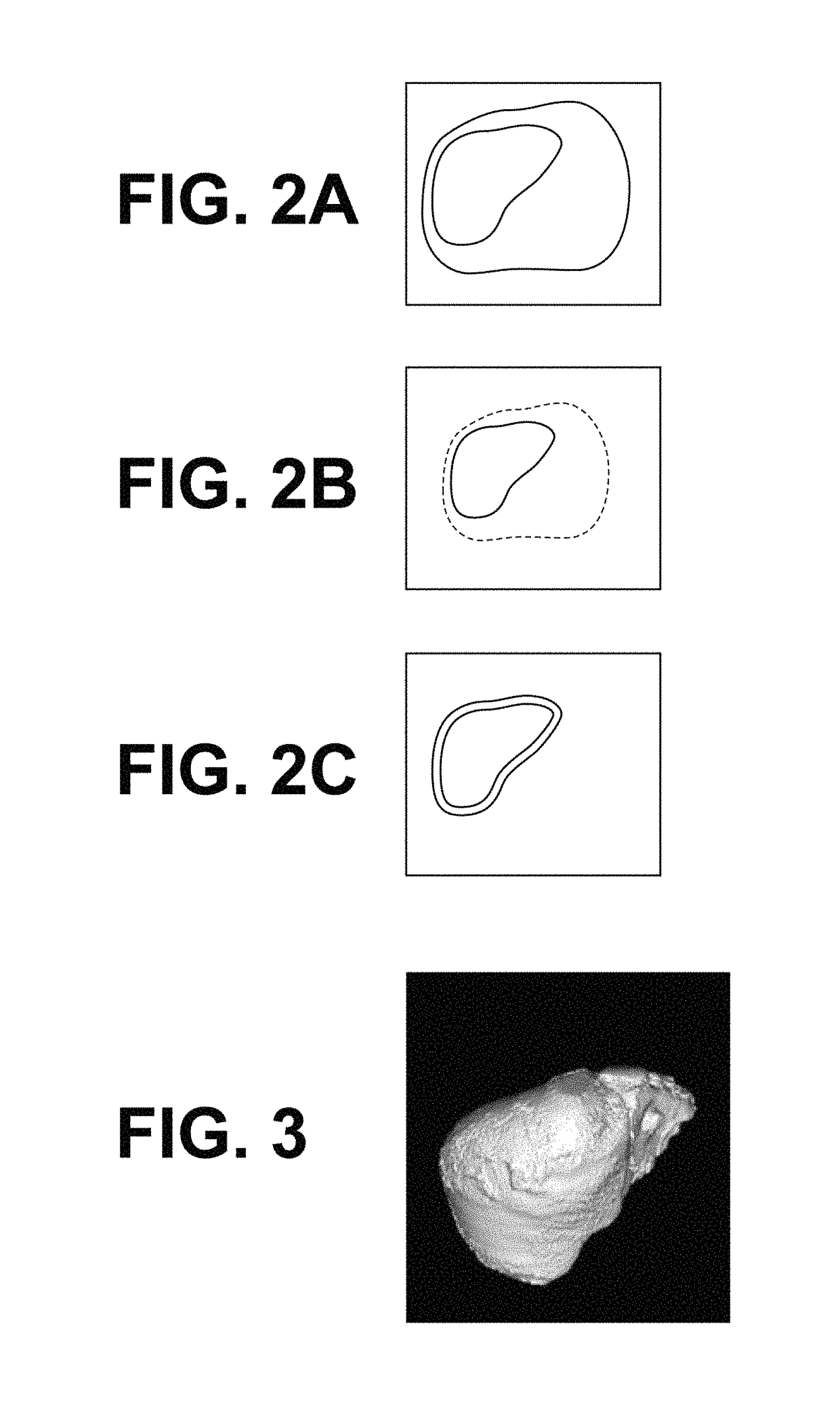
A liver region extraction unit and a structural element extraction unit extracts the liver region and structural elements, such as the hepatic artery and the hepatic vein, from a three-dimensional image, and a surface data generation unit generates surface data of the liver region and surface data of the structural elements. A pattern adding unit adds a textured pattern to at least one of the surfaces of the liver region and the structural elements, and a data generation unit generate three-dimensional model data by combining the surface data of the liver region and the surface data of the structural elements after the addition of the textured pattern. A three-dimensional model making device makes a three-dimensional model of the liver based on the three-dimensional model data.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Measurement method of virtual hepatic vein pressure gradient
The invention belongs to the field of early-stage non-invasive diagnosis and relates to a measurement method of a virtual hepatic vein pressure gradient. The measurement method of the virtual hepatic vein pressure gradient comprises the following steps: carrying out three-dimensional modeling on a hepatic vein-portal vein system; dividing a mathematical model by a finite element mesh; and calculating the virtual hepatic vein pressure gradient (vHVPG) by fluid mechanical emulation. The three-dimensional modeling of the vein-portal vein system, the finite element mesh division and the fluid mechanical emulation calculation are optimized and completed, and a vHVPG detection novel technology with better diagnosis advantages is constructed and identified; and a non-invasive manner which is safe and novel and can accurately measure is provided for the early-stage non-invasive diagnosis of patients with portal hypertension.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
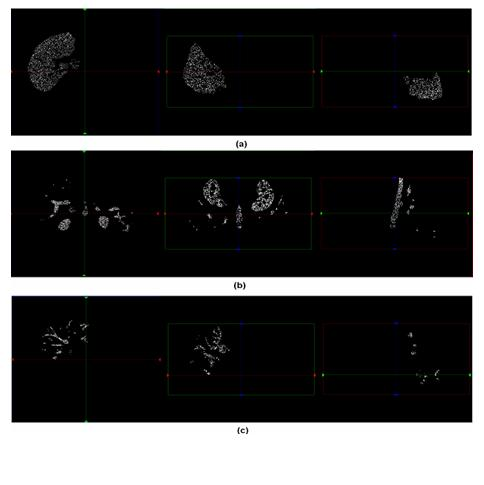
Segmentation method of viscera and internal blood vessels thereof in surgical planning system
ActiveCN102663416AOvercoming the deficiency of error accumulationImprove robustnessImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionThree dimensional ctPattern recognition
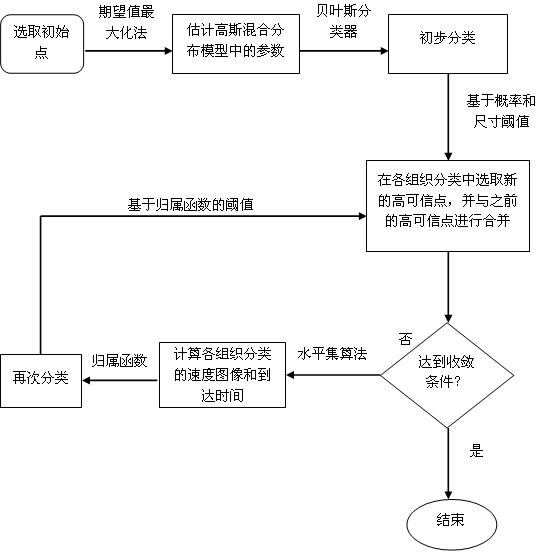
The invention relates to a segmentation method of medical images, and specifically relates to a segmentation method of viscera and internal blood vessels thereof in a surgical planning system. The method designs a segmentation method of images of liver parenchyma, portal veins and hepatic veins based on minimal supervised classification of the three-dimensional CT images of the viscera and internal tubular tissues thereof. The method applies methods of statistics and spatial information, introduces high credible points, and obtains segmentation results based on arrival time of fast march of grey level. The method assumes that spatially adjacent points belong to a same organ, and performs segmentation calculation on the images by using a classification algorithm based on the above assumption, wherein the segmentation calculation comprises the steps of: acquiring estimated values of parameters of a Gaussian mixture distribution model; selecting the high credible points; and calculating the mean value of the grey level of the images and calculating the arrival time by using a fast marching algorithm to obtain arrival time images of three tissue classifications. According to the invention, good robustness and good anti-noise interference capability are obtained, accumulated errors are eliminated effectively, classification accuracy is improved, and great application value in clinical treatment is achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU DIKAIER MEDICAL TECH
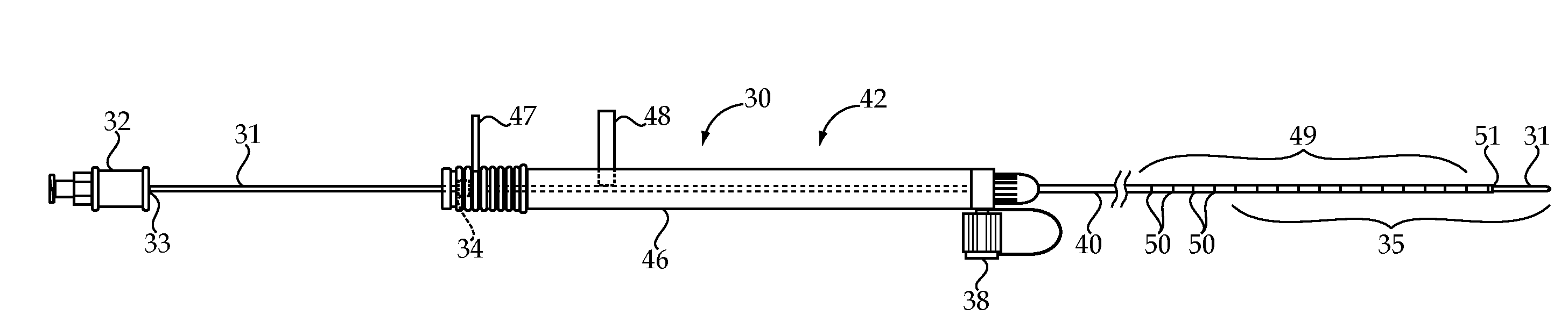
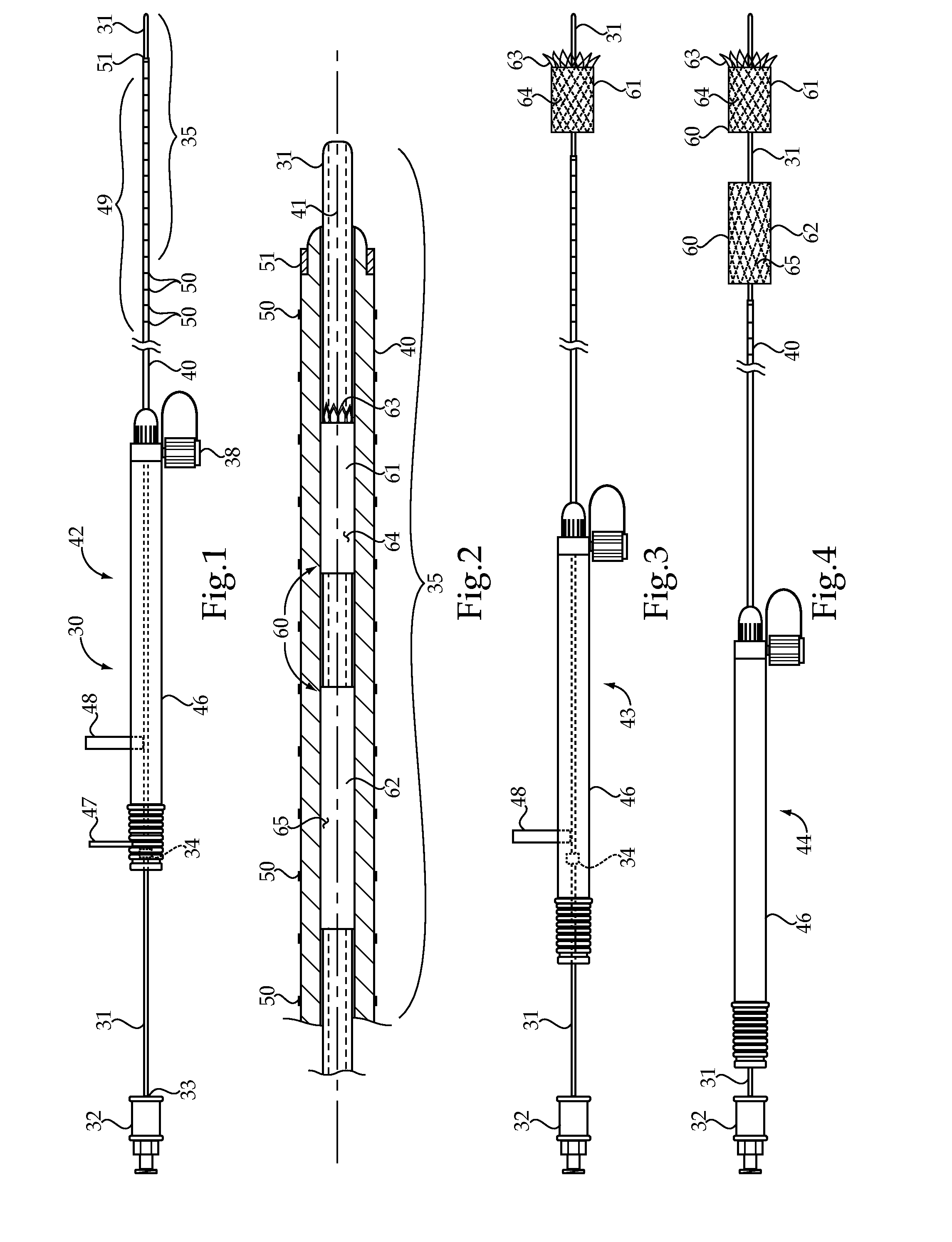
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt device
ActiveUS20130245533A1Improve securityImprove efficacySurgical needlesWound drainsHepatic veinsPortal vein
An apparatus method for establishing a Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt between the portal vein from a hepatic vein. The apparatus comprises an elongated hollow outer guide; an outer handle having an inner lumen and a first luer lock, the outer handle attached at a proximal end of the outer guide, the outer guide in flow communication with the inner lumen and the first luer lock; an elongated hollow inner needle; and a hub having a second luer lock, the hub attached at a proximal end of the inner needle, the inner needle in flow communication with the second luer lock. The inner needle is slidingly received into the outer guide through the inner lumen. The inner needle rotates within the outer guide by manipulation of the hub; and a distal tip of the inner needle is deployed out of and beyond a distal tip of the outer guide.
Owner:HATCH MEDICAL
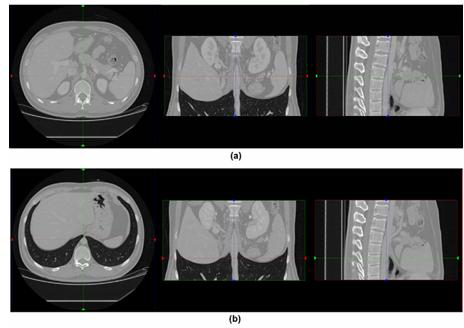
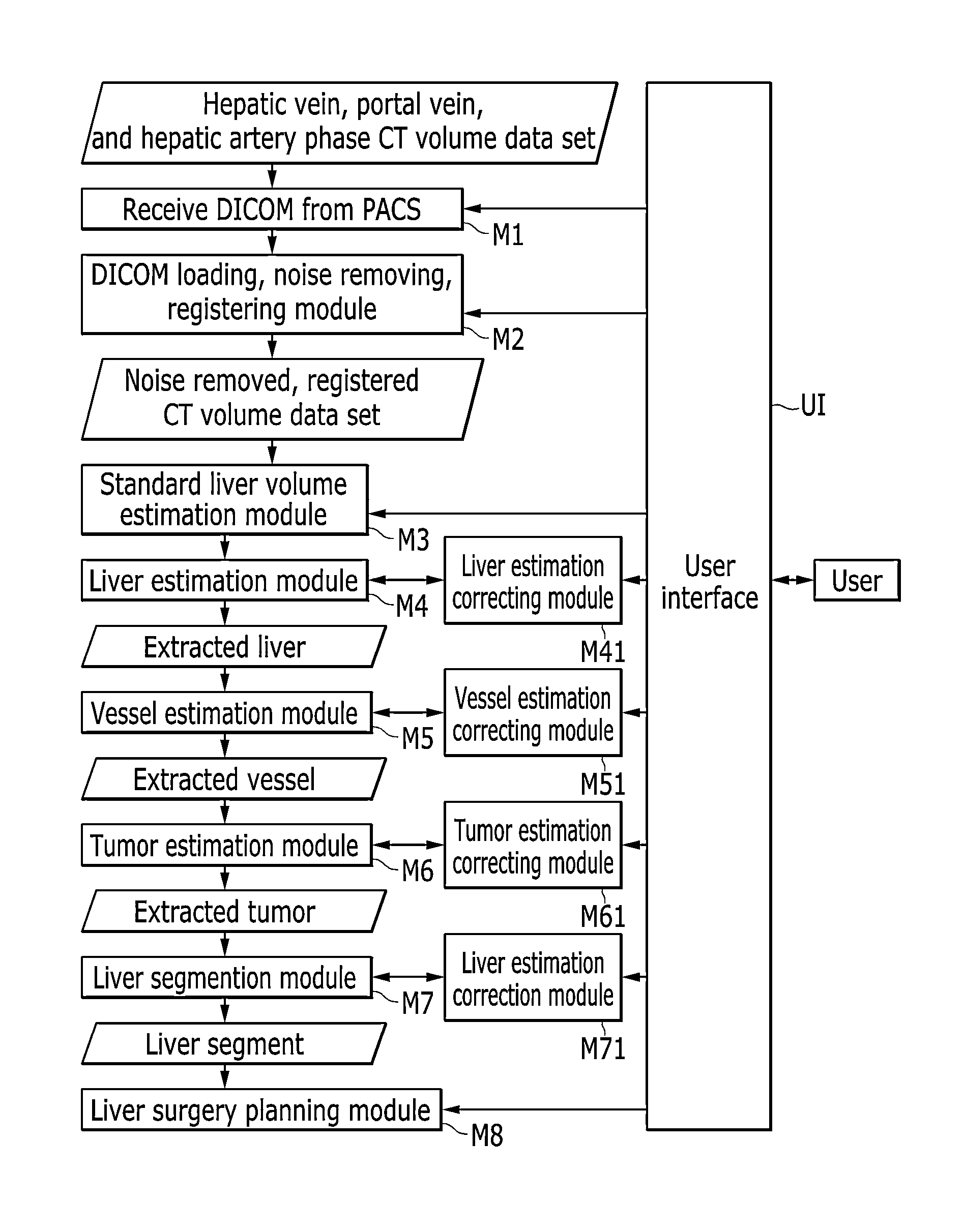
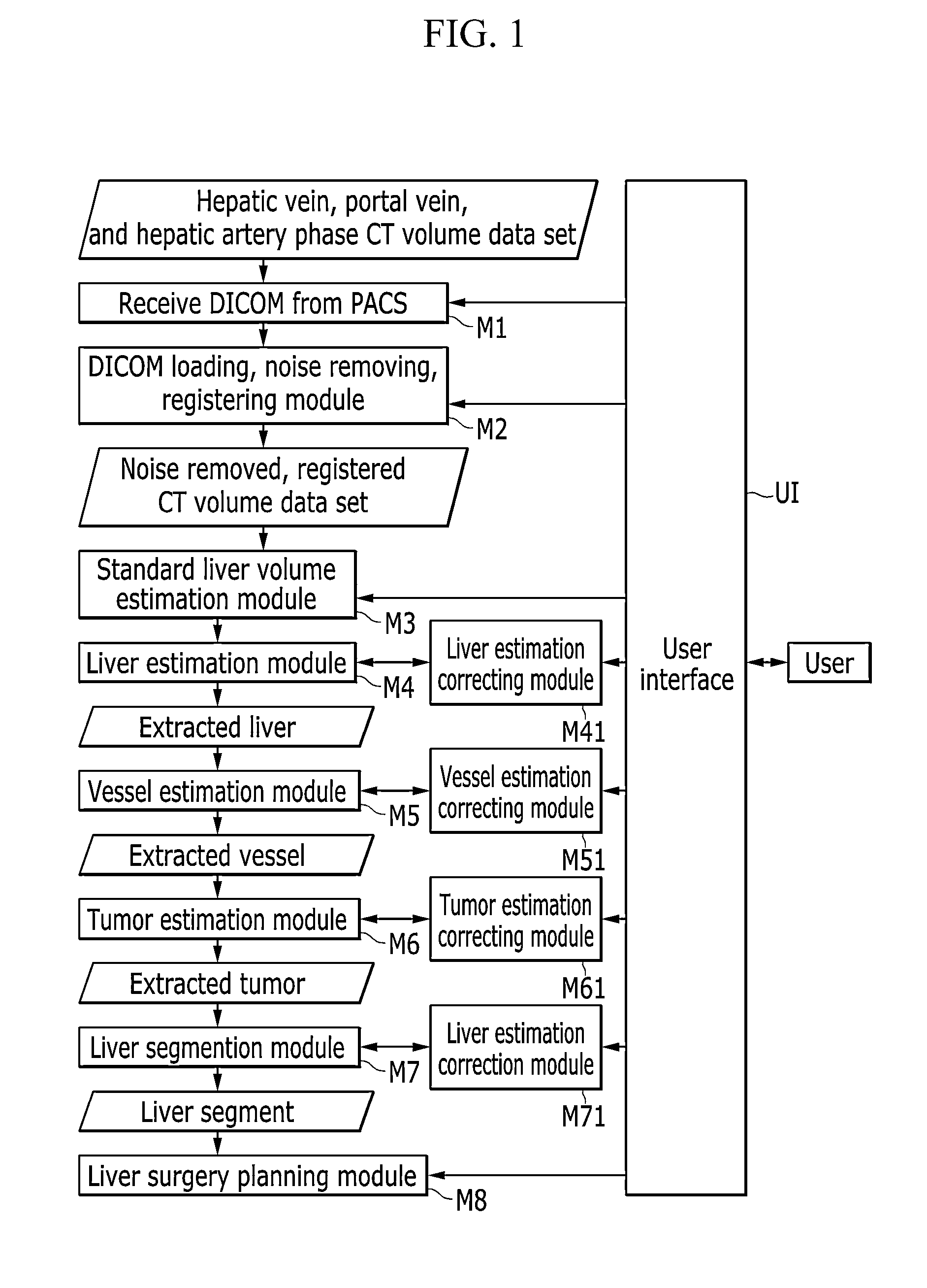
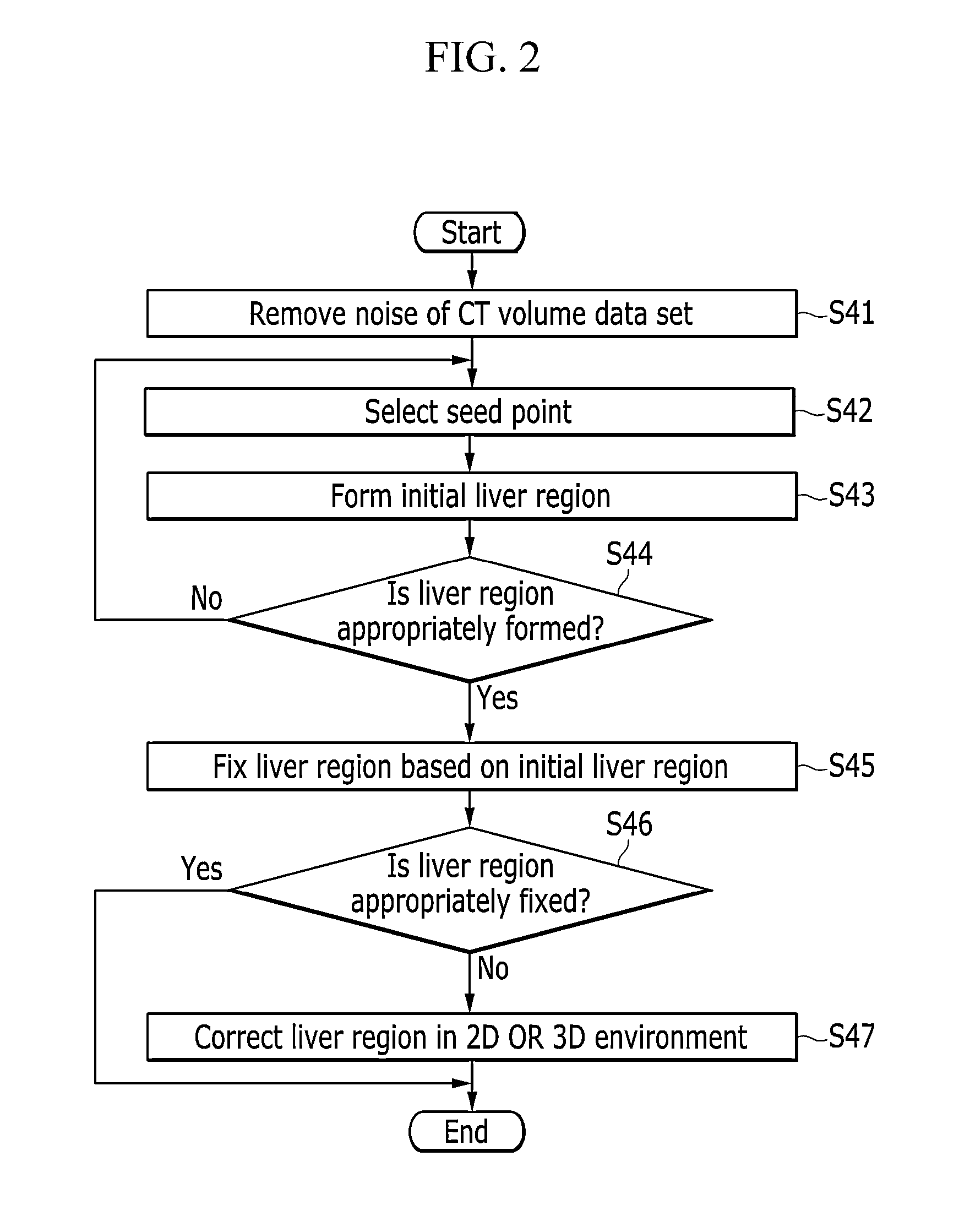
Three-dimensionlal virtual liver surgery planning system
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention provides a three-dimensional virtual liver surgery planning system including: a digital imaging and communications in medicine (DICOM) receiving module which receives an abdomen computer tomography (CT) volume data set from a picture archiving and communication system (PACS) server; a DICOM loading and noise removing module which loads the received abdomen CT volume data set and remove noises; a standard liver volume estimation module which estimates a standard liver volume (SLV) from the denoised abdomen CT volume data set; a liver extraction module which extracts a three-dimensional liver region; a vessel extraction module which extracts a three-dimensional vessel region including a portal vein, a hepatic artery, a hepatic vein, and an inferior vena cava (IVC); a tumor extraction module which extracts a three-dimensional tumor region; a liver segmentation module which divides the extracted three-dimensional liver region into several segments using landmarks which are selected by a user or a segmentation sphere; and a liver surgery planning module which makes a three-dimensional liver surgery plan using a resection surface, a liver segments, or the segmentation sphere.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND +1
Method for segmenting liver
InactiveCN104463860AFacilitate surgeryGood resultsImage enhancementImage analysisHuman bodyHepatic veins
The invention relates to the field of medical image processing and provides a method and system for segmenting the liver. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, an obtained medical human body nuclear magnetic resonance sequence image is segmented, the liver part, the hepatic vein part, the portal vein part and the hepatic artery part are segmented and extracted, wherein the hepatic vein part, the portal vein part and the hepatic artery part are located in the liver part; secondly, all the branch points of a vessel tree are extracted according to the segmented hepatic vein part, the portal vein part and the hepatic artery part; all the main branches of blood vessels are analyzed according to all the branch points of the vessel tree; the main branches of the hepatic vein part, the portal vein part and the hepatic artery part are marked, and the liver is segmented according to the occupied space proportion of all the main branches of the vessel tree in liver body data. The method and system for segmenting the liver provide visual reference and guarantee for clinical operations or medical experiments.
Owner:冯炳和
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt device
ActiveUS9072596B1Improve safety and efficacyFacilitating rapid catheterizationGuide needlesSurgical needlesHepatic veinsPortal vein
Owner:HATCH MEDICAL
Construction method of radiology-based hepatic venous pressure gradient calculation model
ActiveCN107945878AIncrease operational difficultyInvasive riskMedical simulationImage enhancementBurden of diseaseHepatic veins
The invention provides a construction method of a radiology-based hepatic venous pressure gradient (rHVPG) calculation model. An advantageous hepatic vein pressure gradient calculation model can be constructed on this basis, and a new approach is provided to calculate the early noninvasive indexes of patients with portal hypertension. The invention also provides a rHVPG calculation system. The method can overcome many limitations of an existing noninvasive measurement method. The rHVPG calculation system is feasible, and is expected to provide a new idea for the noninvasive measurement of portal pressure, and plays an active role in improving the quality of life of patients with portal hypertension and reducing the burden of disease in families and society.
Owner:祁小龙
Duet stent deployment system and method of performing a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting procedure using same
A duet stent deployment system is used in a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt procedure. The device has a versatility of adjusting to a patient's anatomy in vivo. The system includes exactly two self expanding stents mounted on an inner catheter and covered by an outer sheath that is moved among a pre-deployment configuration, a first deployment configuration and a second deployment configuration to position the stents in an overlapping configuration from the portal vein, through a shunt and into the hepatic vein, and terminating at the junction with the vena cava.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt device
ActiveUS8628491B2Improve safety and efficacyFacilitating rapid catheterizationGuide needlesStentsHepatic veinsPortal vein
Owner:HATCH MEDICAL LLC
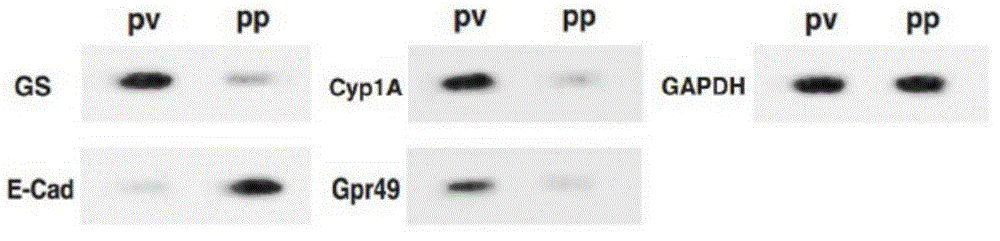
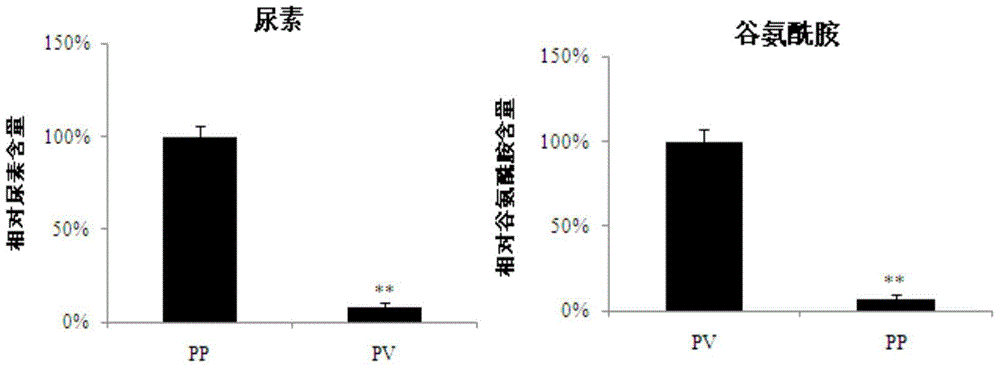
Separation method and application of hepatic cells peripheral to pig portal veins or hepatic cells peripheral to hepatic veins
ActiveCN105219701AEasy to separateIncrease vitalityVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsPig liverHepatic veins
The invention discloses a separation method and application of hepatic cells peripheral to pig portal veins or hepatic cells peripheral to hepatic veins. By means of the method, a great number of hepatic cells peripheral to the portal veins or hepatic cells peripheral to the hepatic veins which are high in activity can be separated out of a pig liver, the obtained cells can maintain good morphological characteristics, hepatocellular functions and cell multiplication activity of primary hepatic cells, and a basis is provided for separation and identification of the hepatic cells peripheral to the portal veins or the hepatic cells peripheral to the hepatic veins, in vitro study on cell metabolism differences of the hepatic cells peripheral to the portal veins or the hepatic cells peripheral toward the hepatic veins and deeper exploration on liver nutrient substance metabolism.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Semi-automatic liver segmenting method
InactiveCN105574862AFacilitate surgeryGood resultsImage enhancementImage analysisHuman bodyMain branch
The invention relates to the field of medical image processing, and provides a semi-automatic liver segmenting method and system. The semi-automatic liver segmenting method comprises the following steps of firstly segmenting an obtained medical human body nuclear magnetic resonance sequence image, and segmenting and extracting a liver part, and a hepatic vein, a portal vein and a hepatic artery in the interior of the liver; analyzing each main branch of blood vessels according to branch points of each blood vessel tree; obtaining segmenting seed points by manually marking each main branch of the hepatic vein, the portal vein and the hepatic artery, and the liver internal segmenting points; and performing segmenting on the liver according to the occupied space ratio of the marked seed points in the liver body data. The invention provides the semi-automatic liver segmenting method and system, so that visualized reference and guarantee are provided for clinical operations or medical experiments.
Owner:林康艺
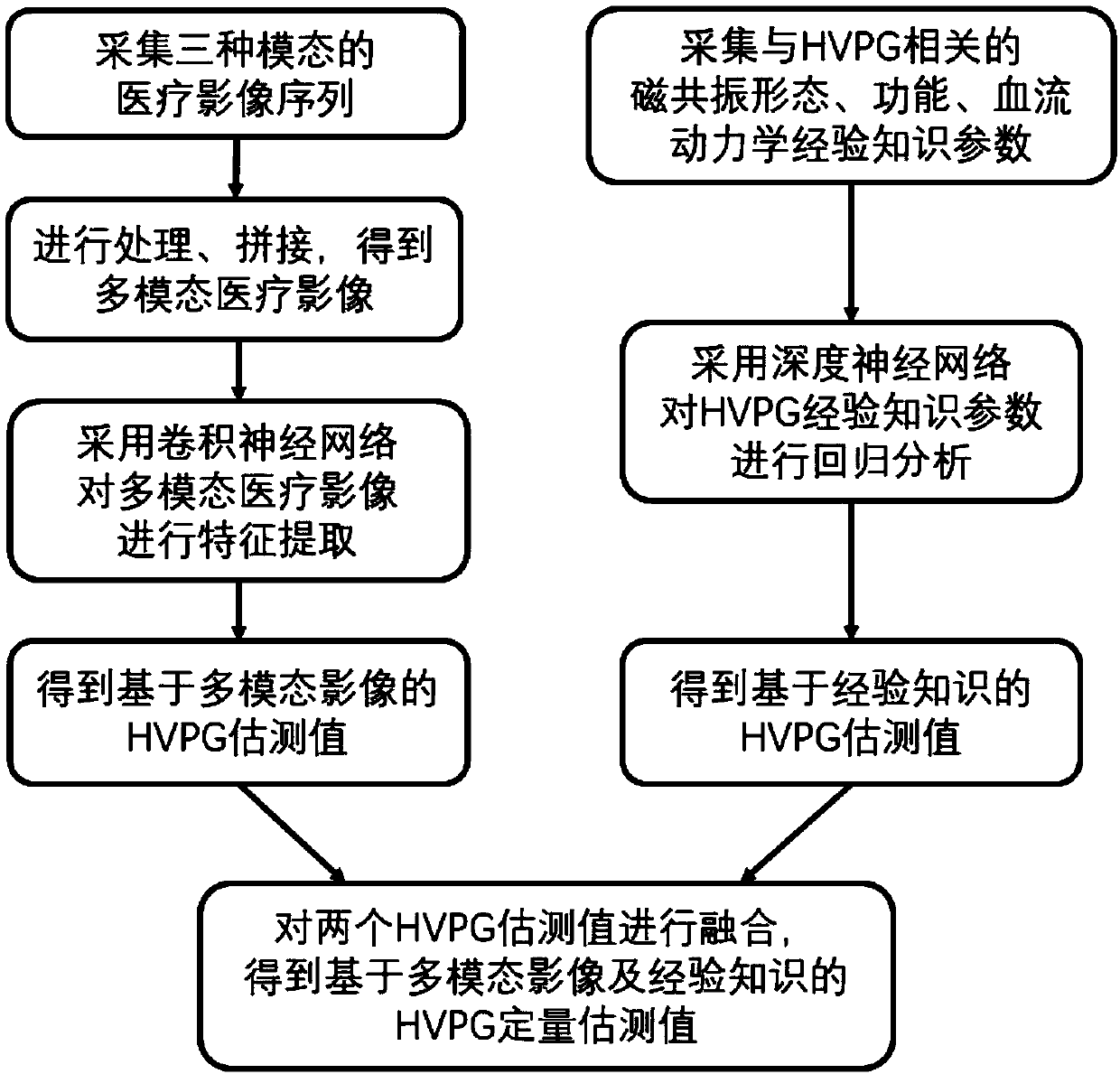
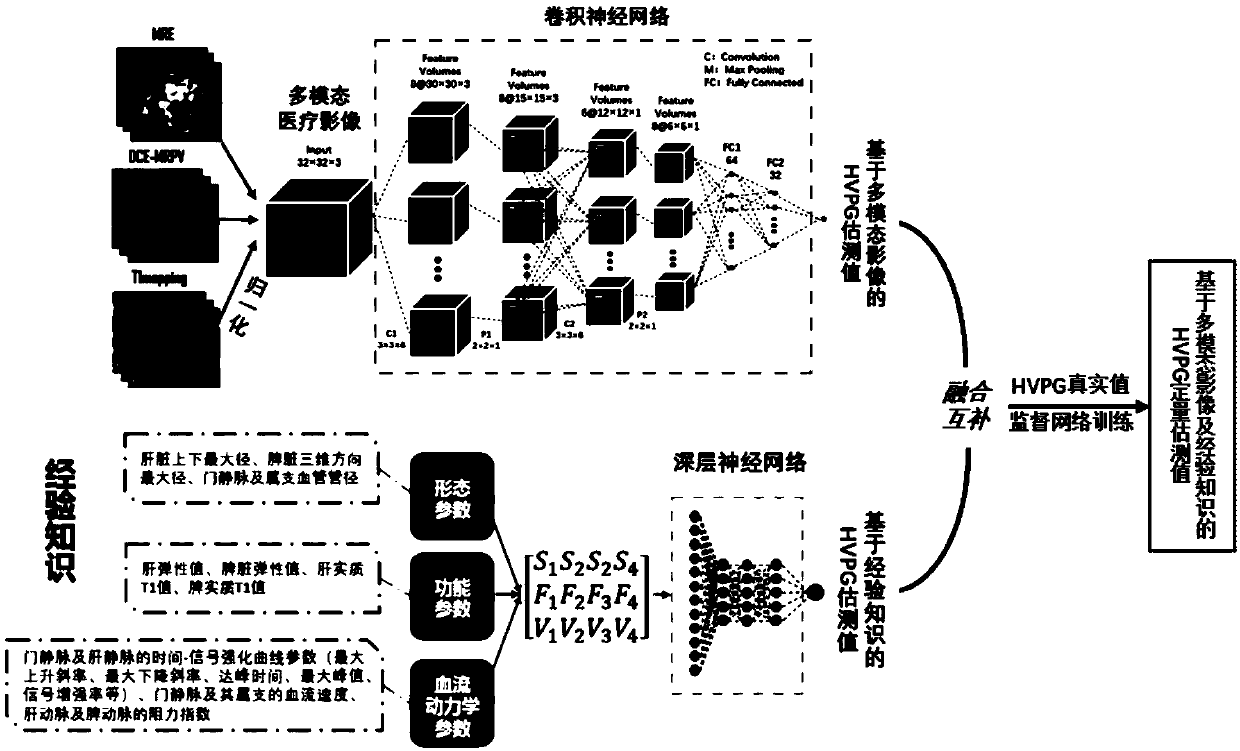
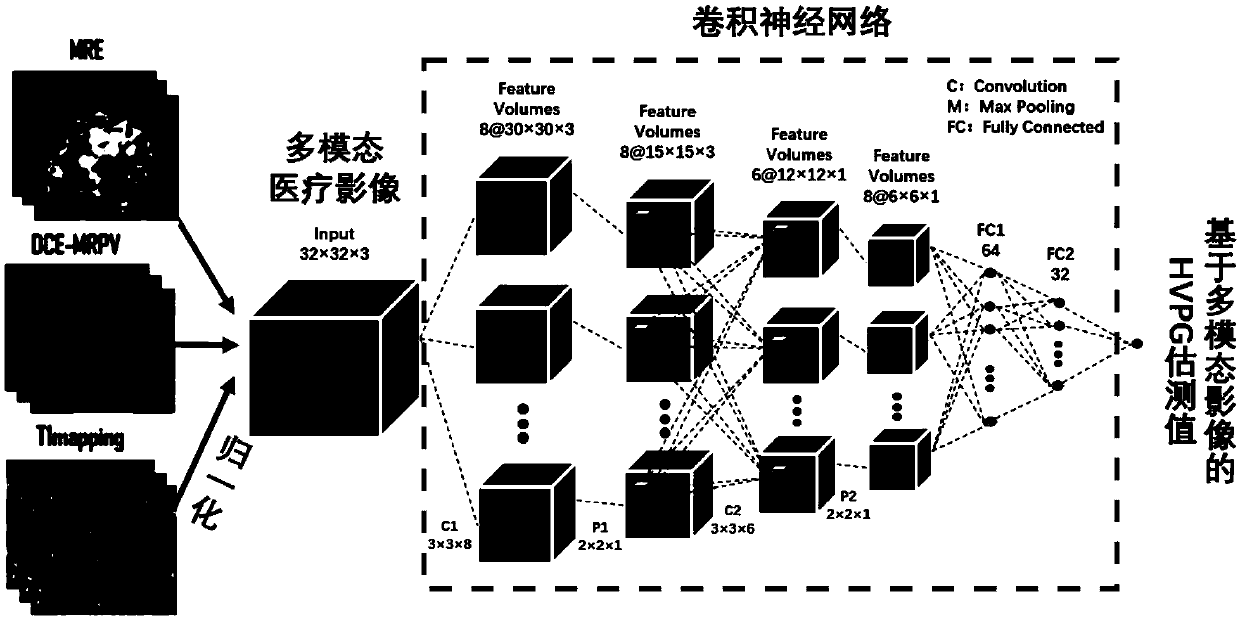
Non-invasive evaluation method of hepatic vein pressure gradient based on multi-modal images and empirical knowledge
ActiveCN109528196AAccurate quantification of non-invasive HVPG estimatesThe result is accurateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsComputerised tomographsHepatic veinsFeature extraction
The invention discloses a non-invasive evaluation method of hepatic vein pressure gradient based on multi-modal images and empirical knowledge. A convolutional neural network is used for feature extraction of multi-modal medical images, and the estimation value of HVPG based on the multi-modal images is obtained. The deep neural network is used for regression analysis of relevant empirical knowledge parameters of the HVPG and the HVPG estimation values based on empirical knowledge are obtained; the HVPG estimation values based on the multi-modal images and empirical knowledge and obtained fromthe steps are fused, and the fused HVPG estimation value is obtained. The convolutional neural network and the deep neural network are trained jointly by an optimization algorithm; after the trainingis completed, the HVPG can be accurately predicted, and the HVPG quantitative estimation value based on the multi-modal images and empirical knowledge is obtained. The complementary information of multi-modal medical images is taken into account, features are supplemented by the corresponding empirical knowledge, and the method is more in line with the medical pertinence.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for measuring hepatic vein pressure gradient based on portal vein characteristics
InactiveCN109758136AAccurate assessmentObjective and Accurate EvaluationEvaluation of blood vesselsAngiographyHepatic veinsPortal vein
The invention relates to the field of non-invasive measurement, discloses method for measuring a hepatic vein pressure gradient based on portal vein characteristics, and solves the problem that a prior invasive method for measuring portal vein pressures has high risk, high cost and large operation difficulty, while the accuracy of a current clinical non-invasive prediction model is still influenced by various interference factors. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a portal vessel three-dimensional model by using a CTA layer sequence of a liver cirrhosis portal hypertension patient, and extracting the characteristics of the portal vein; by means of LASSO regression analysis, screening out the vein characteristics closely related to HVPG, and therefore constructing the model based on portal vein characteristics to predict HVPG. The method is suitable for non-invasive measurement of the hepatic vein pressure gradient.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Biomarker composite test for hepatic vein pressure gradient and cirrhosis treatment
Diagnostic biomarker panel, method, kit, and device for diagnosing the severity and / or prognosis of cirrhosis are provided. More specifically, the invention provides a novel biomarker panel correlating to HVPG and esophageal varices. The invention further provides a biomarker panel and non-invasive test methods that predict non-clinically significant portal hypertension HVPG and non-clinically significant esophageal varices when the expression of the biomarker panel correlates with HVPG of less than 12 mmHg. The invention further provides that the patients with the expression of the biomarker panel correlating to non-clinically significant HVPG and esophageal varices can be excluded from undergoing esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) screening and those correlating to HVPG equal to or greater than 12 mmHg are indicated for EGD.
Three-dimensional model data generation device, method and program
ActiveUS9697639B2Simple and inexpensiveSimple and inexpensive mannerImage enhancementImage analysisHepatic veinsComputer graphics (images)
A liver region extraction unit and a structural element extraction unit extracts the liver region and structural elements, such as the hepatic artery and the hepatic vein, from a three-dimensional image, and a surface data generation unit generates surface data of the liver region and surface data of the structural elements. A pattern adding unit adds a textured pattern to at least one of the surfaces of the liver region and the structural elements, and a data generation unit generate three-dimensional model data by combining the surface data of the liver region and the surface data of the structural elements after the addition of the textured pattern. A three-dimensional model making device makes a three-dimensional model of the liver based on the three-dimensional model data.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
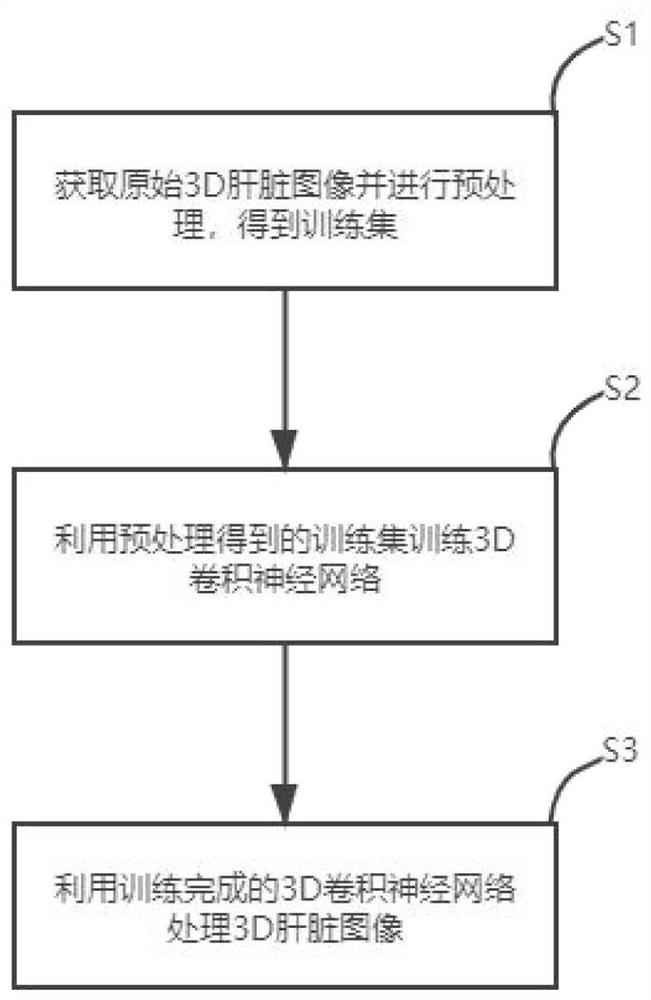
Liver blood vessel segmentation method based on CT image
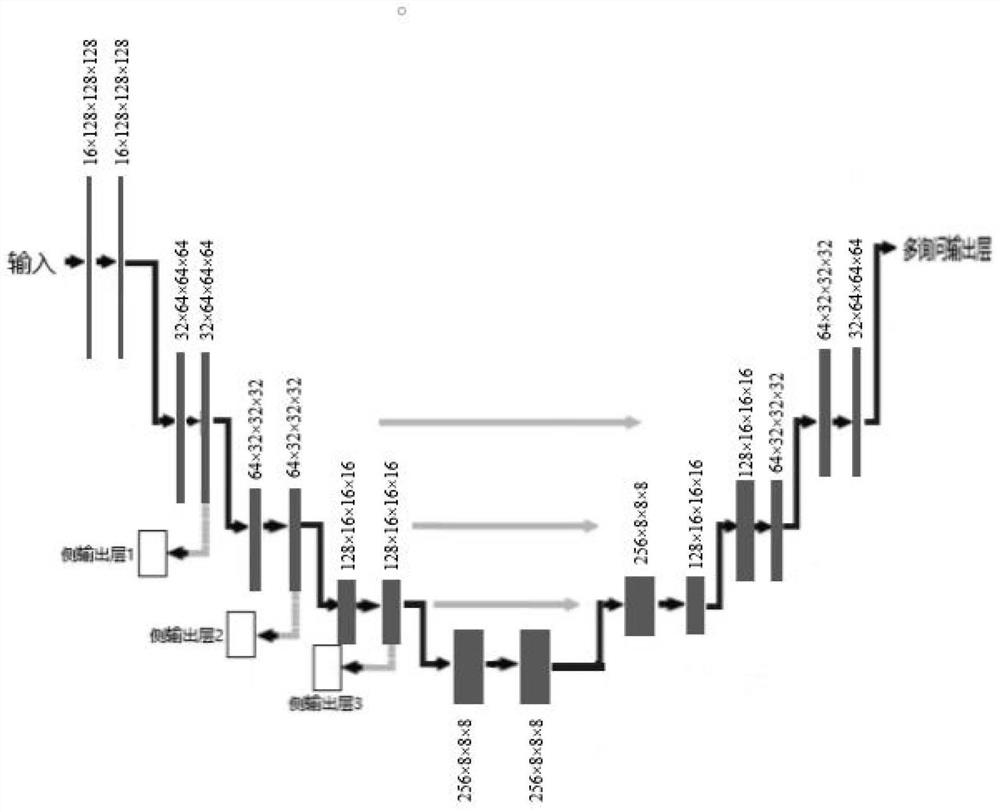
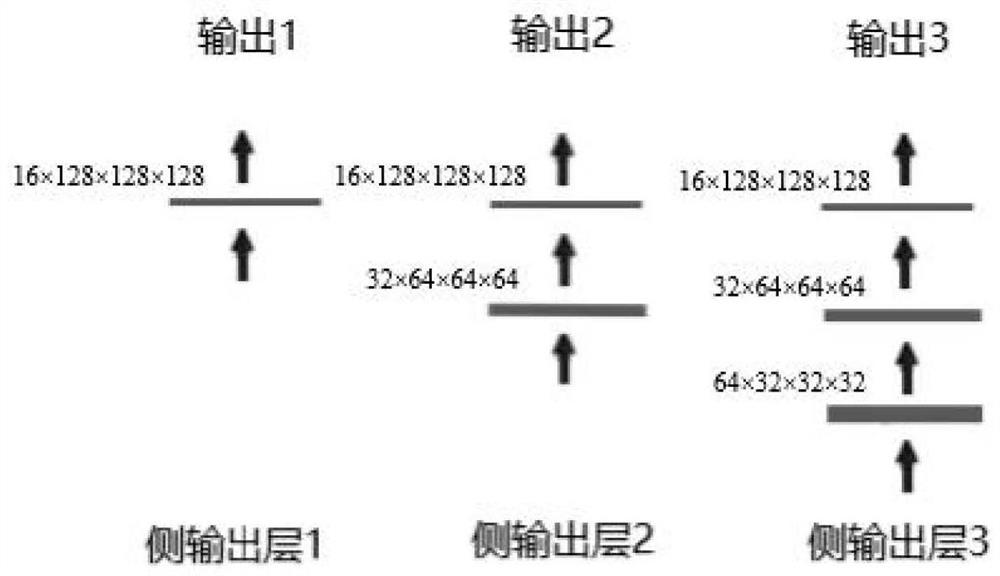
The invention discloses a liver blood vessel segmentation method based on a CT image, and the method comprises the steps of: firstly obtaining an original 3D liver image, and carrying out the preprocessing, and obtaining a training set; then using the training set obtained through preprocessing for training a 3D convolutional neural network, wherein the adopted 3D convolutional neural network adopts a Unet network structure, an encoder is provided with a side output layer for deeply supervising the structure of the convolutional network system, an output end is provided with two parallel branches, the upper branch is used for extracting features, different from the background, of the hepatic vein and the portal vein, and the lower branch is used for extracting features for distinguishing the hepatic vein and the portal vein; and finally processing the 3D liver image by using the trained 3D convolutional neural network to obtain a liver blood vessel segmentation result. According to the method, a side output layer is added from an encoder part to help bottom layer features to extract more semantic information, and meanwhile, two parallel branches are arranged at the output end, so that the segmentation effect of the hepatic vein and the portal vein in the liver image is improved.
Owner:北京精诊医疗科技有限公司
Magnetic device for establishing intrahepatic portacaval shunt under intervention
InactiveCN102835978AAvoid the disadvantages of stenosis and even occlusionWon't staySurgeryCatheterHepatic veinsPortal vein
The invention discloses a magnetic device for establishing intrahepatic portacaval shunt under intervention. The magnetic device comprises a pair of permanent magnet groups, wherein each permanent magnet group consists of a first permanent magnet and a second permanent magnet; the first permanent magnets and the second permanent magnets attract each other end to end; each first permanent magnet is provided with a catheter matched with the first permanent magnet; one end of the catheter passes through the central hole of each first permanent magnet for fixing; and each second permanent magnet is provided with a central hole of which the diameter is larger than the outer diameter of the catheter. Shunt from a portal vein branch to a hepatic vein is completed by using two permanent magnets of corresponding sizes and shapes, so that the defect of gradual narrowing even blockage of an inner support tube for shunting is overcome; moreover, an established sub-channel is smooth on the surface, and can be kept smooth for a long time; and after the formation of a sub-channel between the portal vein branch and the hepatic vein, two magnets can be taken out through the catheter left in the operation, and the retention of foreign matters in vivo is prevented.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
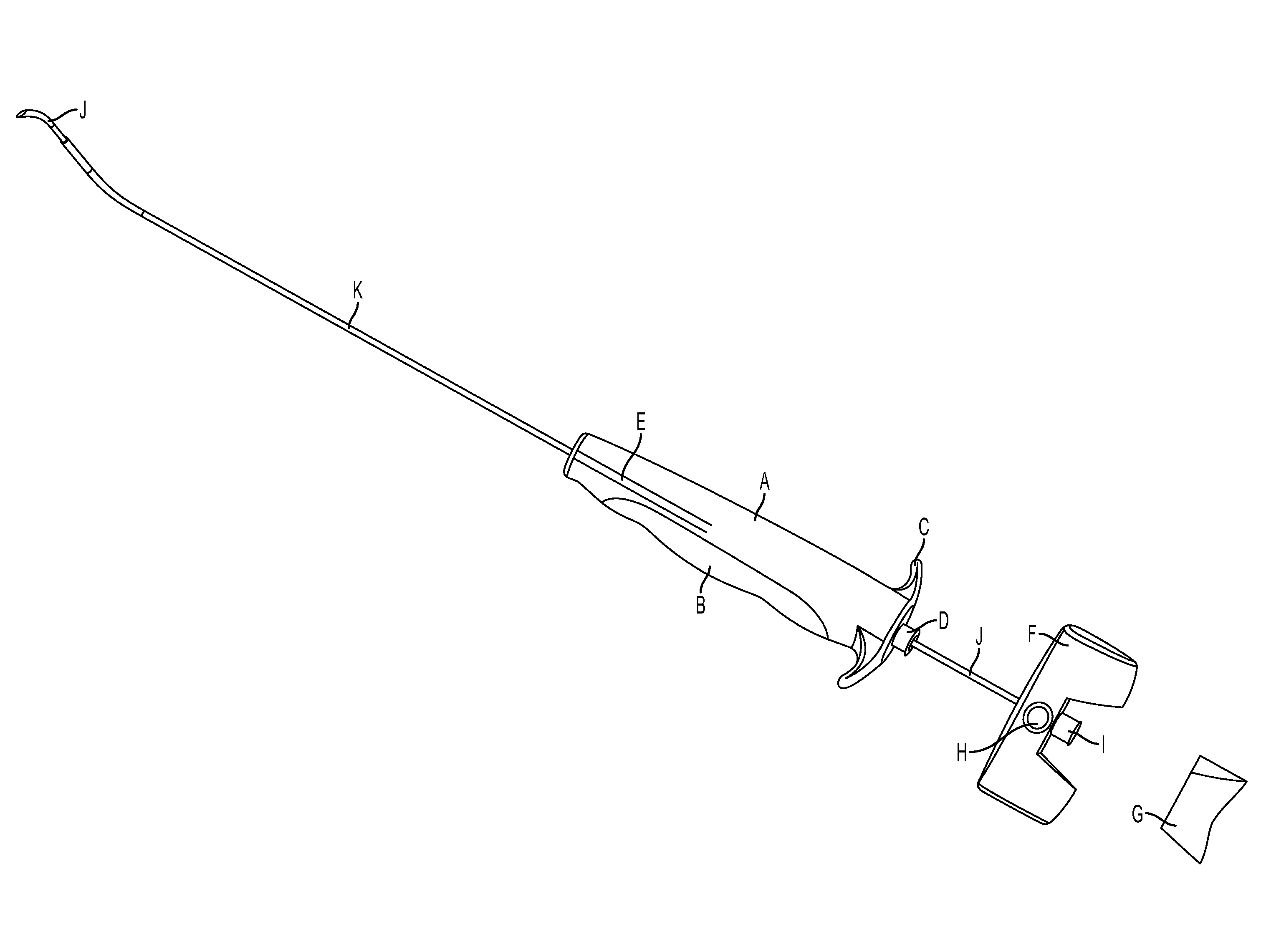
Recoverable transjugular portosystemic shunt thrombolysis catheter
A recoverable transjugular portosystemic shunt thrombolysis catheter is provided. The recoverable transjugular portosystemic shunt thrombolysis catheter comprises a conduit segment and a draw segment;it is characterized in that the conduit segment comprises a portal vein part, a connecting part and a liver vein part; the connecting part connects the portal vein part and the liver vein part; the draw segment is connected with the liver vein part; the draw segment is a solid segment; during usage, the draw segment is fixed after extending out from the portal vein to the jugular vein and then extending to the outside or extending to a subclavian vein or an upper arm vein to be fixed in an infraclavicular region or the upper arm vein; during usage, the portal vein part is arranged in the portal vein; the liver vein part is arranged in the liver vein; besides, the portal vein part and the liver vein part are arranged as mesh structures; the connecting part is a structure does not include meshes. After the conduit is imbedded and thrombus in portal vein is removed, the thrombus can be taken out by the draw segment; the purpose of the setting of the draw segment solid is to ensure that blood flow through the portal vein into the inferior vena cava after passing through the hepatic vein, but not into the liver parenchyma or in vitro through the draw segment.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Multi-needle transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt device
An apparatus method for establishing a Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (“TIPS”) between the portal vein from a hepatic vein. The apparatus comprises a multi-needle TIPS device designed to facilitate safer and more rapid catheterization of the portal vein. The method utilizes the multi-needle TIPS device to access the portal vein from the hepatic vein approach. The multi-needle TIPS device and method provides numerous benefits over previous TIPS devices and procedures and results in shorter and safer procedures. Use of multiple needles increases the probability of finding the portal vein more quickly.
Owner:HATCH MEDICAL
Endovascular stent special for TIPS operations
PendingCN109662804AInhibit hyperplasiaImprove long-term patencyStentsBlood vesselsStent occlusionHepatic veins
The invention relates to an endovascular stent special for TIPS operations. The endovascular stent aims at solving the problem that blood flow of portal veins and hepatic veins is seriously influencedwhen a straight cylindrical covered stent is applied to the TIPS operations, and simultaneously solving the problem that traditional bare stents are likely to cause stent occlusion resulted from tissue proliferation into stent lumens. The endovascular stent comprises a straight cylindrical framework and a tubular covering film. The tubular covering film is fixedly arranged in the middle of the straight cylindrical framework to enable the two ends of the straight cylindrical framework to form exposed anchoring parts. Both ends of the endovascular stent can form anchoring parts with through holes, the positioning effect is excellent, blood flow can pass through the through holes, and the influence on the blood flow in blood vessels at the anchoring parts can be reduced when the endovascularstent is applied.
Owner:李卫校
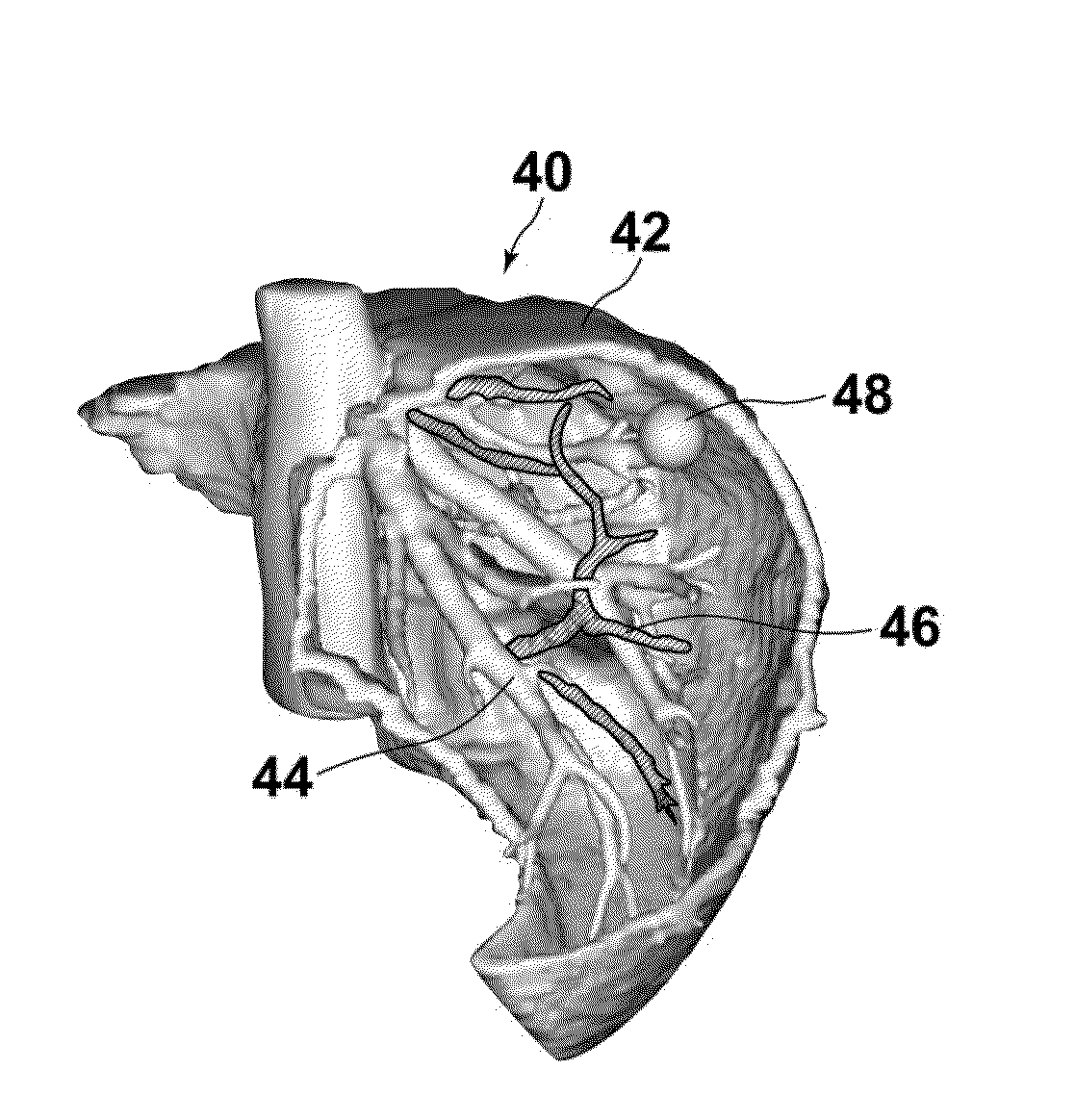
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and image processing program
InactiveUS20140232725A1Accurately specifiedMaximize degree of similarityImage enhancementMedical imagingGraphicsNODAL
A graph estimated to represent hepatic veins is extracted from image data. Shape models representing partial tree structures branched from a point of origin within a tree structure representing a common shape of hepatic veins are obtained. A cost function correlates the graph with the shape models. Whether parts extending from the peaks of correlated graph parts and not correlated with a shape model exist within the extracted graph is judged. Positional data of the peaks are obtained as data representing the position of the point of origin in the case that no such parts exist, or positional data of a node closest to an estimated position of the point of origin, specified by tracing along the nodes of such parts from the peaks to approach the estimated position, is obtained as data representing the position of the point of origin, in the case that such parts exist.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method of Determining Virtual Hepatic Venous Pressure Gradient
The present disclosure relates to the field of early non-invasive diagnosis, and specifically, to a method of determining a virtual hepatic venous pressure gradient. The method includes: constructing a 3-dimensional (3D) hepatic vein-portal vein model; establishing a finite element division mathematical model; and applying fluid dynamics to compute and simulate a virtual hepatic venous pressure gradient (vHVPG). The method optimizes and improves a more complete 3D hepatic vein-portal vein model, finite element division, and fluid dynamic simulation computation, constructing and validating a new vHVPG determination technology providing better diagnosis, providing a safe, non-invasive, accurate, and quantitative method for early non-invasive diagnosis of a portal vein high pressure patient.
Owner:XIAOLONG QI
Laparoscopic liver operation simulation training system
PendingCN109545057AAvoid bleedingAvoid massive bleeding during surgery due to loose ligationEducational modelsLaparoscopySimulation
The invention provides a laparoscope liver operation simulation training system of a laparoscope operation simulation training system, which comprises a workbench, a human organ simulation box, a display and a display panel. A plurality of bulbs are arranged on the display panel. A plurality of operation holes are arranged on the human organ simulation box. The human organ simulation box comprisesa simulated liver, a simulated hepatic vein, a simulated portal vein, a simulated hepatic artery, a simulated bile duct, a hepatic falciform ligament, a sickle ligament, a coronary ligament, a left triangular ligament, and a right triangular ligament. The hepatic round ligament, the falciform ligament, the coronary ligament, the left triangular ligament and right triangular ligament are respectively spliced together with the simulated liver by a number of independent cables, and each of which is connected to the corresponding bulb. The switch device is arranged on the simulated liver vein, the simulated portal vein, the simulated liver artery and the simulated bile duct, and the corresponding bulb is bright during ligation. The laparoscopic liver operation simulation training system can display the ablation process, the ablation effect, the ligation effect and the like. The system is close to the real situation, thereby achieving a good learning effect.
Owner:BEIJING TONGREN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
TIPSS interventional therapy training device
PendingCN113129719AQuality improvementIntensive exercisesCosmonautic condition simulationsEducational modelsVenous vesselVena porta
The invention discloses a TIPSS interventional therapy training device. The TIPSS interventional therapy training device comprises a vein blood vessel system, a cardiovascular system and a human body shell wrapping the vein blood vessel system and the cardiovascular system. Blood vessels of the vein blood vessel system are fixedly connected with a blood vessel fixing device and a circulating power device; the vein blood vessel system comprises a cerebral vein intervention module, a TIPSS intervention module, a heart intervention module and an inferior vena cava intervention module; two inlets are formed in the tail ends of the superior sagittal vein and the left and right iliac veins, and a total liquid outlet is formed in the right atrium to provide liquid for the whole device; two sheath entering tube openings are formed above the left iliac vein and the right iliac vein and are used for the entering of a catheter guide wire; the blood vessel fixing device comprises cerebral vein, heart, hepatic vein, portal vein and inferior vena cava blood vessel fixing bases; an operation display module comprises a movable high-definition camera and a high-definition display screen; the circulating power device comprises a circulating system box body, a controllable pressure adjusting motor and a pipeline. According to the device, the human body vein blood vessel system is highly restored, the device can be disassembled and assembled, blood vessels at the same part can be replaced, the flexibility of interventional operation simulation is improved, various types of operation simulation can be carried out, and the popularization and development of TIPSS interventional operations are promoted.
Owner:曾欢
Devices and methods for intrahepatic shunts
The invention provides methods and devices for treating liver cirrhosis or portal hypertension by creating an intrahepatic shunt, or new passage, from a portal vein of a patient to a hepatic vein using a device with intravascular imaging capabilities and pressure sensing capabilities or positioning mechanisms. The integration of intravascular imaging aids in the precise placement of the shunt and pressure measurement may verify successful shunt creation. An apparatus may include a catheter with an extended body for insertion into a hepatic vein of a patient, an intravascular imaging device and a needle exit port on the distal portion of the extended body, and a needle disposed within a lumen in the catheter and configured to be pushed out of the exit port and extend away from a side of the extended body, in which the needle includes a pressure sensor.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV +1
Novel ascites hepatic-vein bypass anti-thrombus stent device with controllable one-way valve
PendingCN108309521AAvoid formingSolve cannot be placedStentsSurgical needlesAbdominal cavityHepatic veins
The invention discloses an ascites hepatic-vein bypass anti-thrombus stent device with a controllable one-way valve. The device includes a puncture retracting outfit for creating a bypass channel, a main channel stent and a retractable anti-backflow one-way valve stent. According to the device, a hepatic vein is punctured from a jugular vein to an abdominal cavity through the puncture outfit to create the bypass channel, the main channel stent is placed in the bypass channel, the smoothness of the channel is maintained, and the retractable anti-backflow one-way valve stent is placed into the main channel stent to create an anti-flowback one-way channel to facilitate bypass of liquid in the abdominal cavity into the hepatic vein, and meanwhile blood in the hepatic vein does not flow back into the abdominal cavity. Once thrombus is formed in the main channel stent, the anti-backflow one-way valve stent can be taken out again for replacement. The surfaces and inner surfaces of the main channel stent and retractable anti-backflow one-way valve stent are all coated with anti-congealing, antibacterial and hydrophilic membrane coatings to prevent formation of thrombus. Meanwhile, a retractable ring is arranged on the valve stent, once thrombus is formed, the retractable ring can be taken out of the human body for replacement, and the sectional main channel stent can adapt to a crookedbypass channel.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com