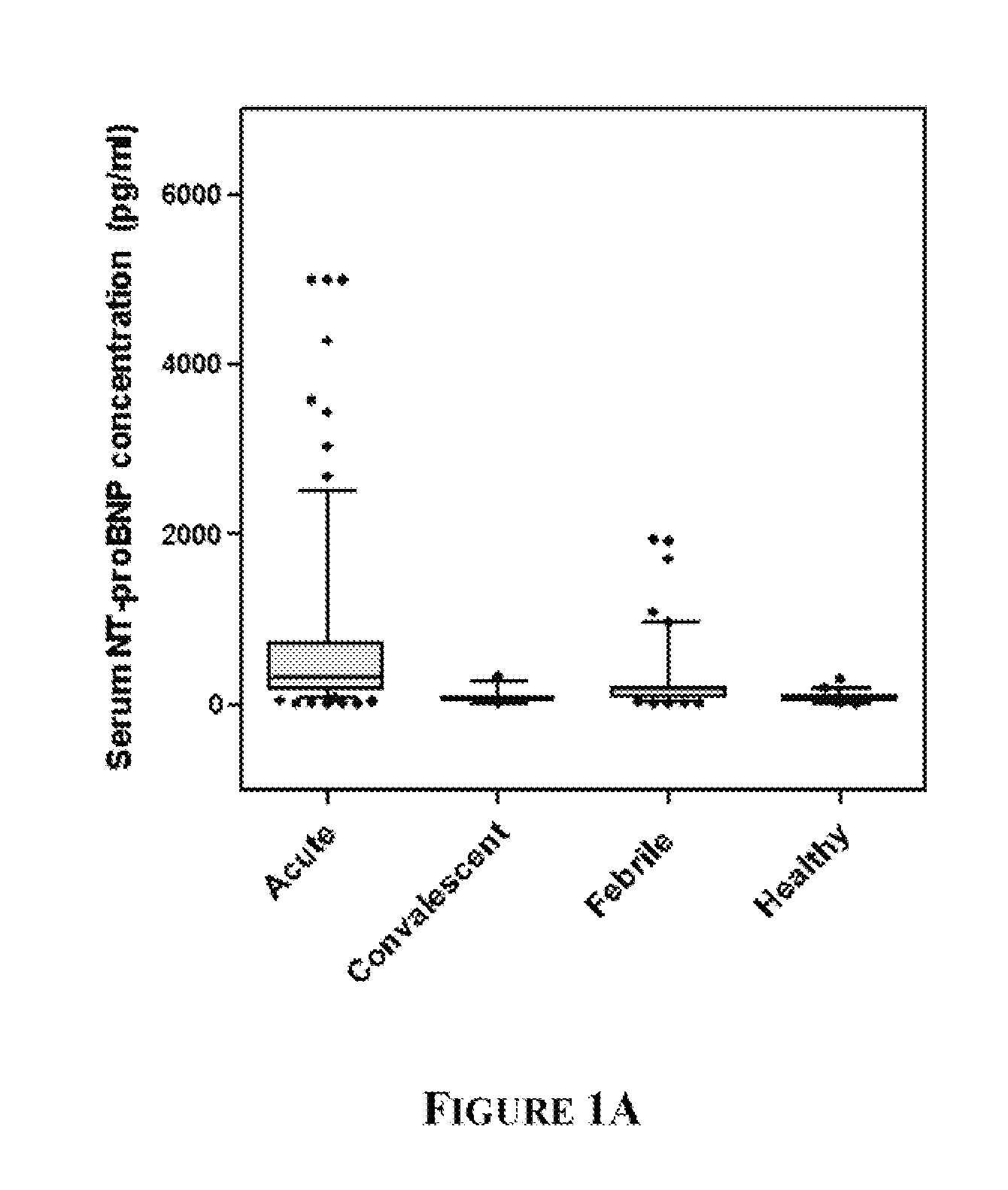
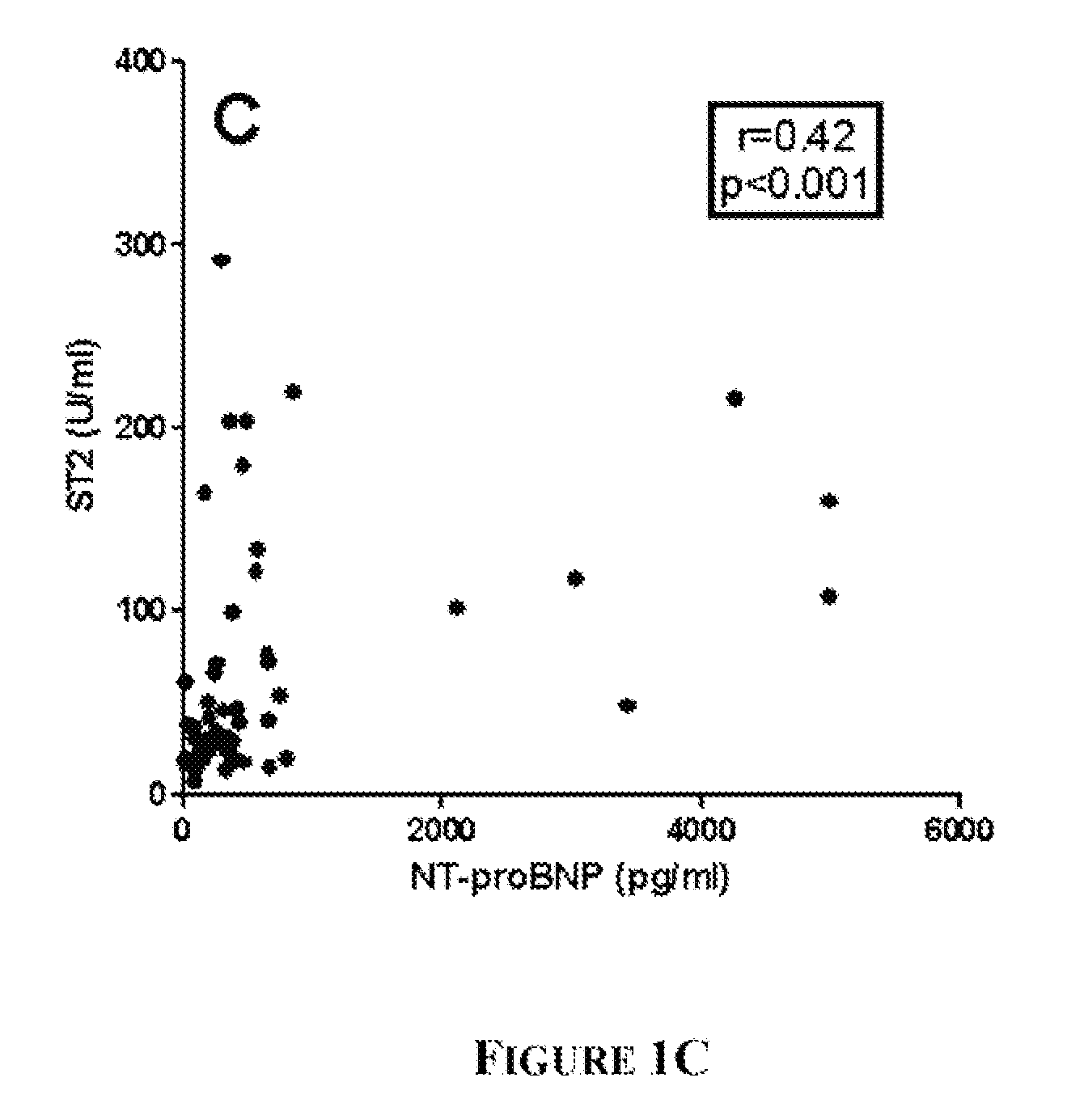
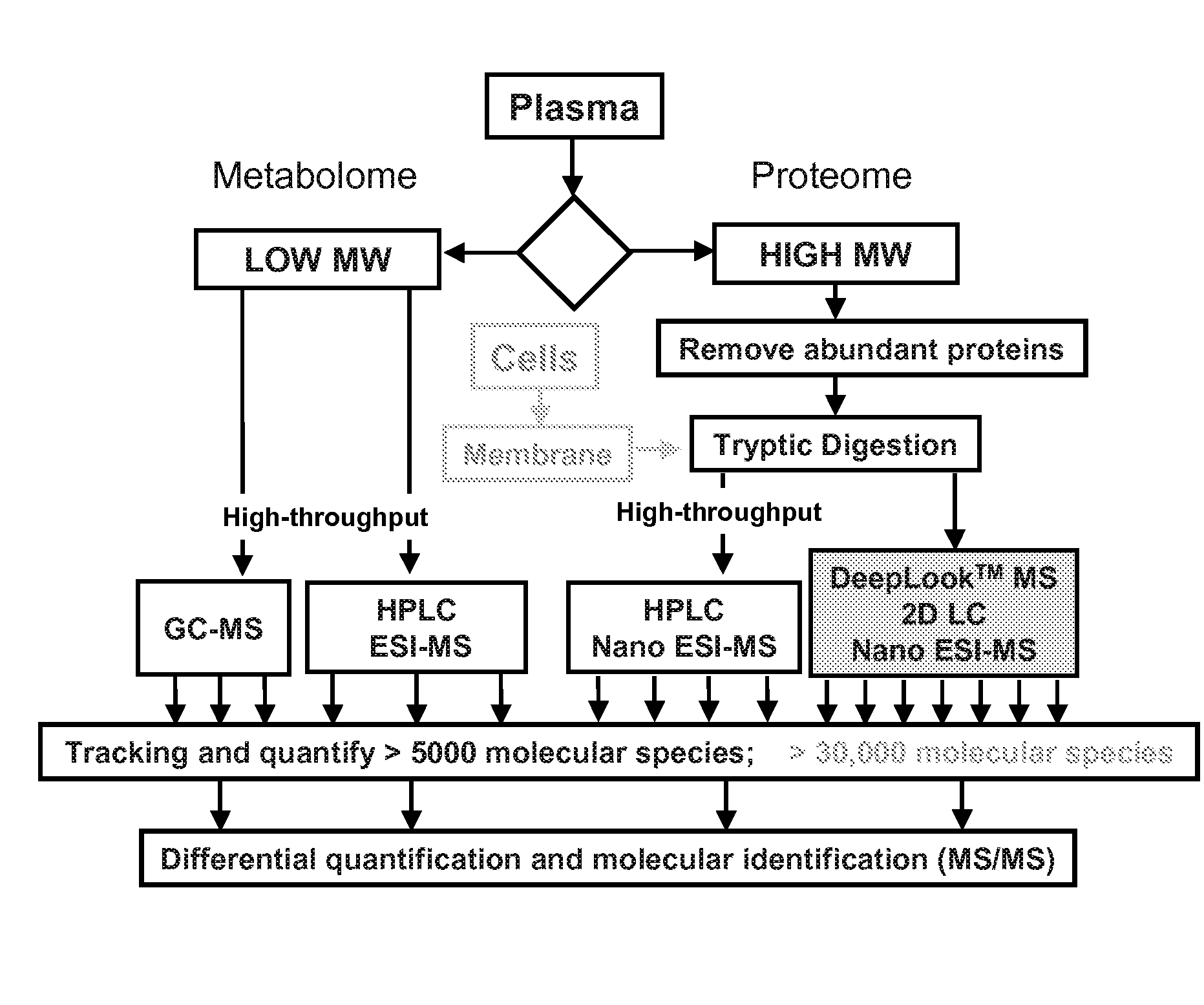
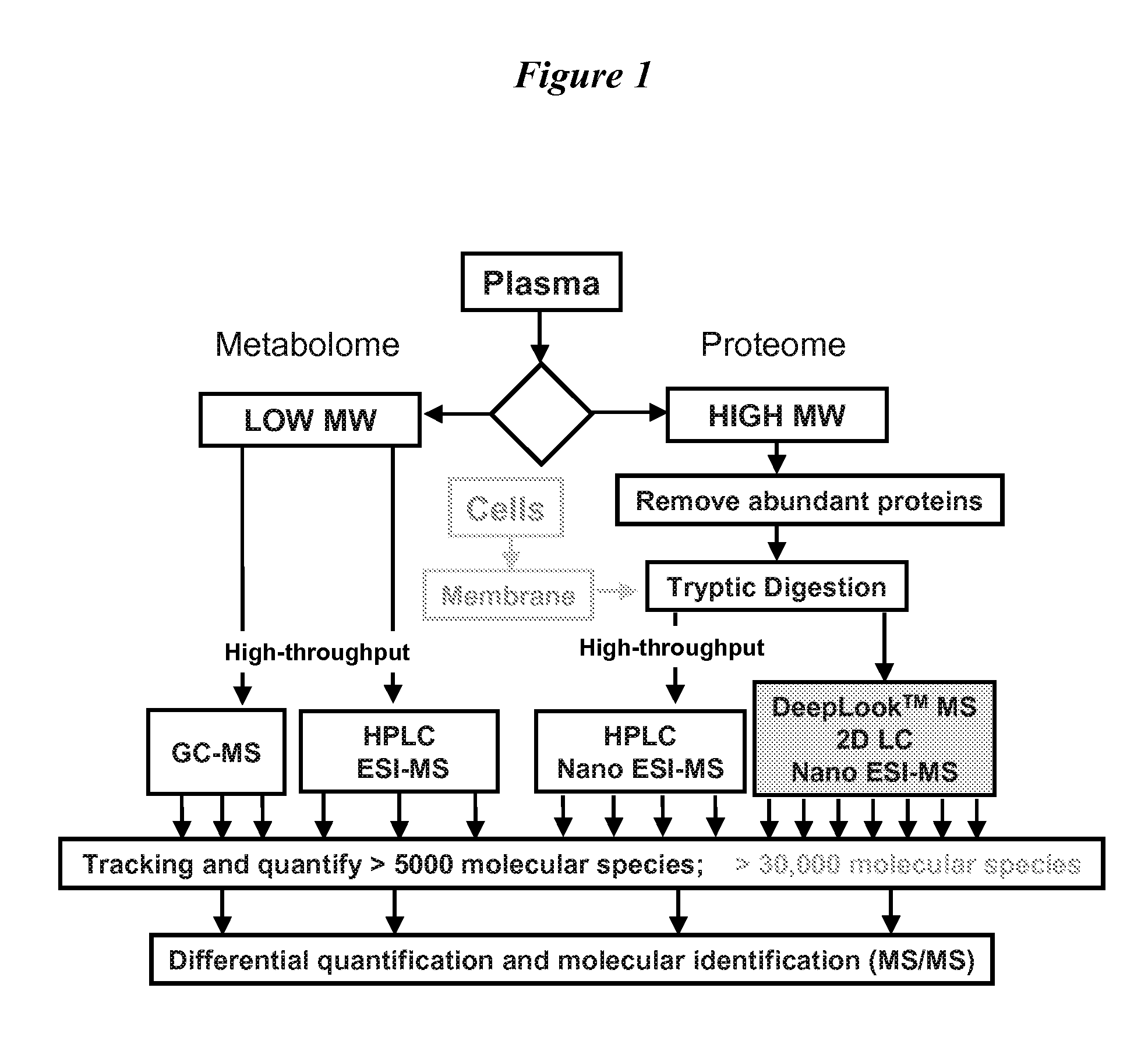
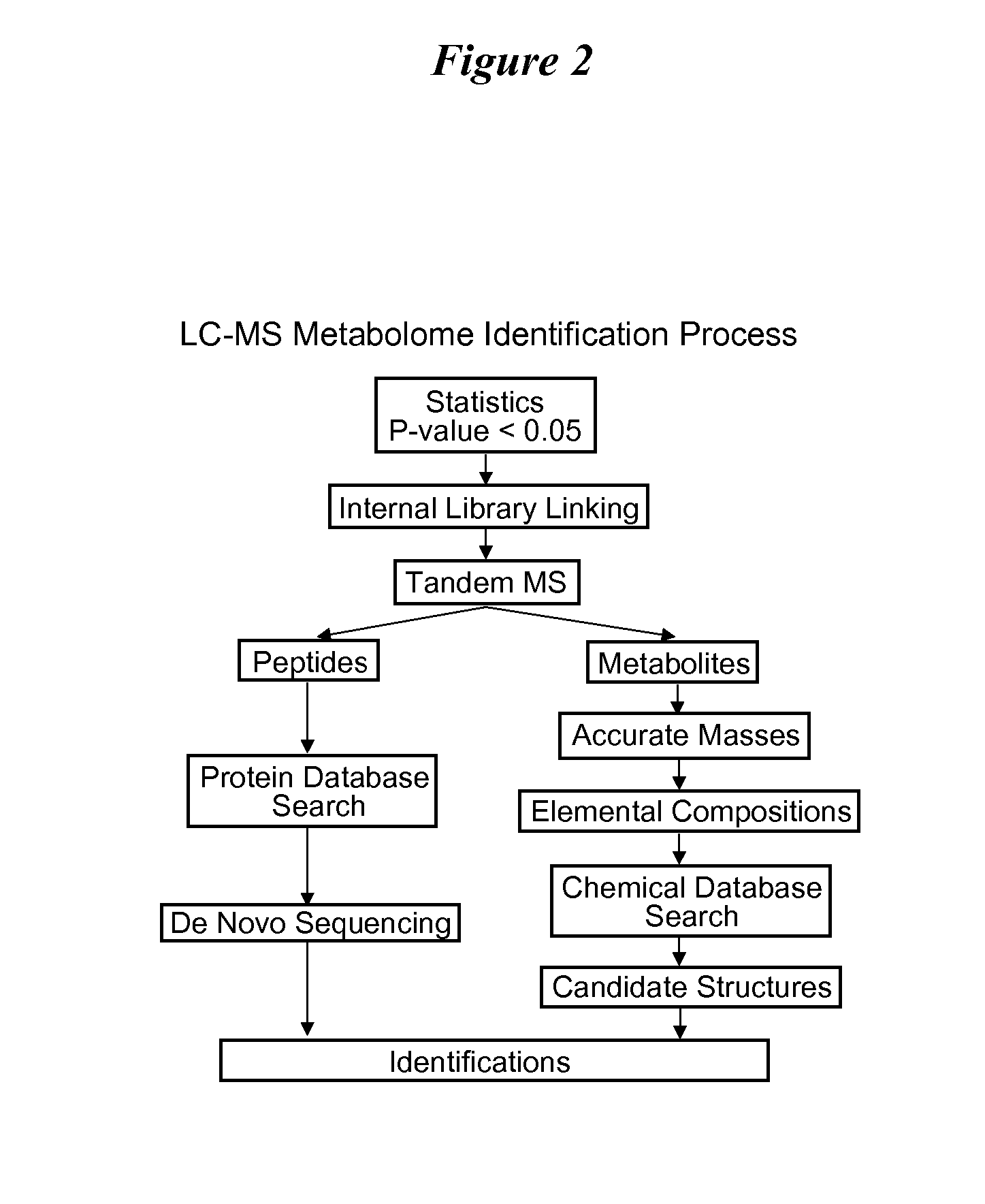
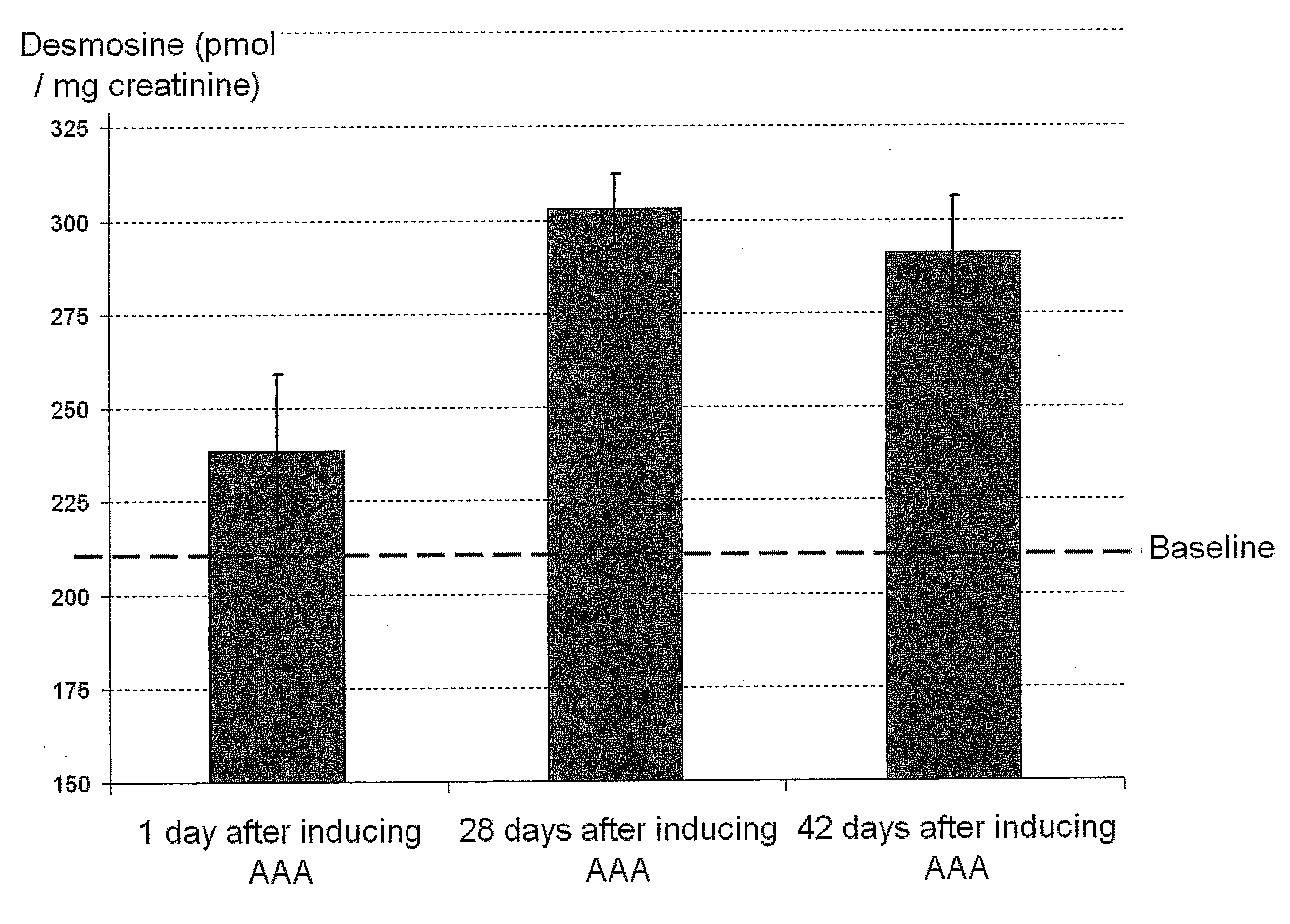
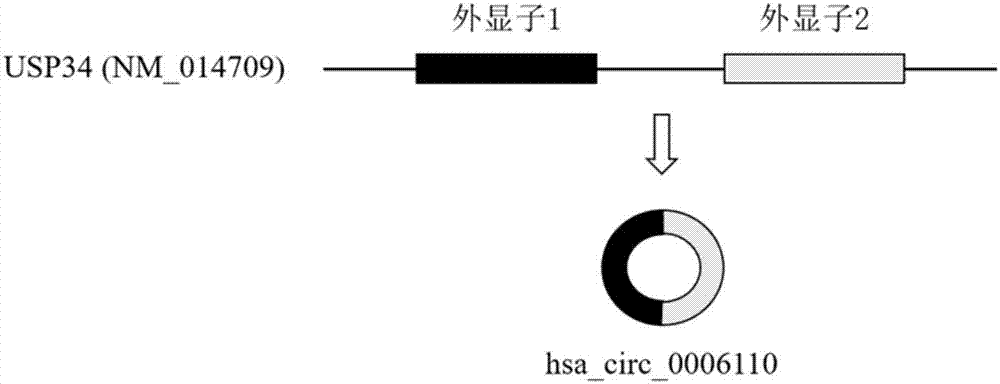
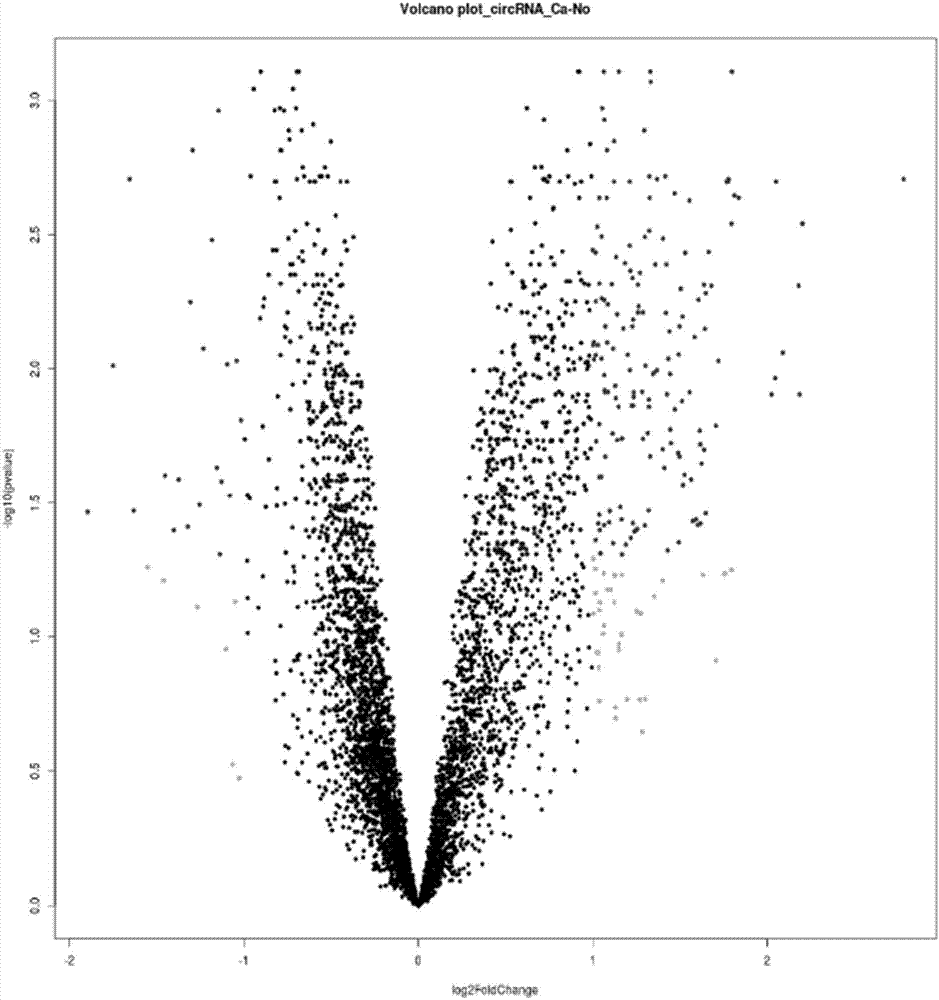
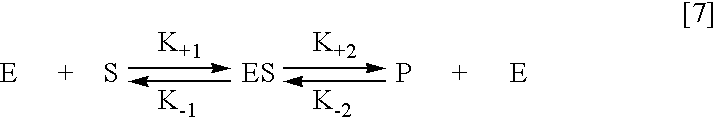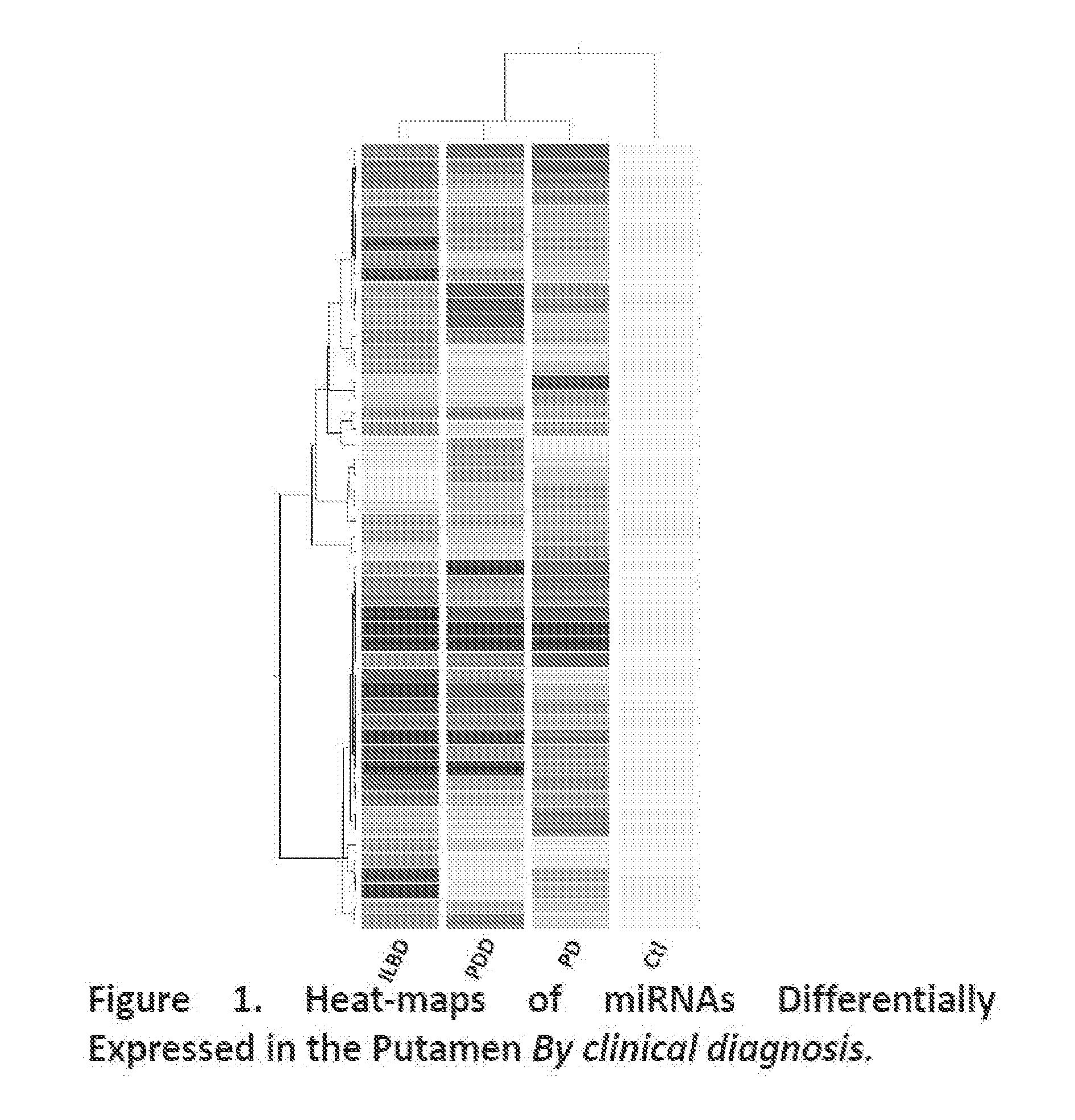Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
152 results about "Diagnostic biomarker" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Overview. Diagnostic biomarkers are used to confirm that a patient has a particular health disorder. For example, the presence of mutations in the CFTR gene indicate that a newborn has cystic fibrosis. A test used to diagnose a disease often measures a type of biomarker called a “surrogate.". Diagnostic biomarkers may facilitate earlier detection...
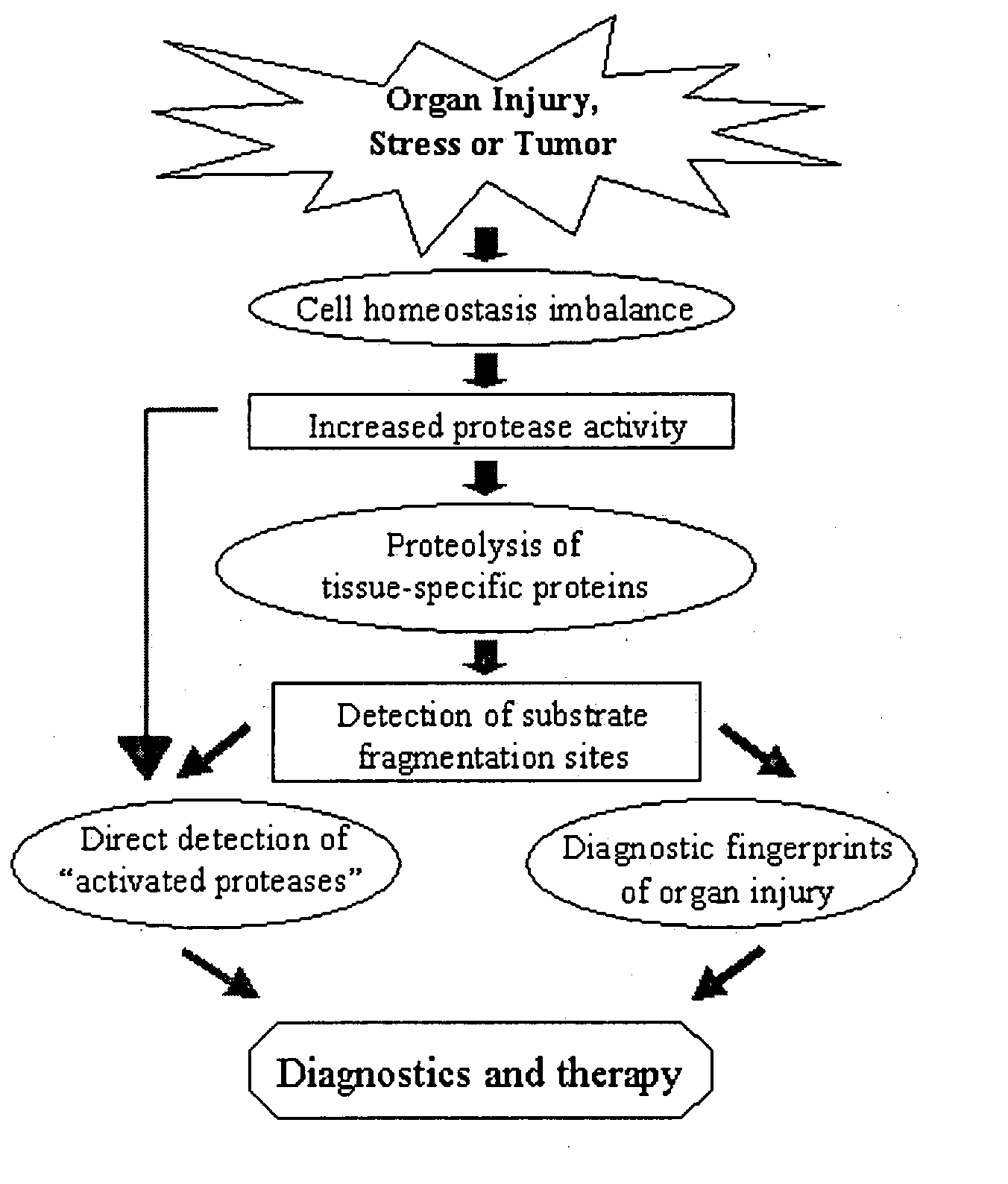
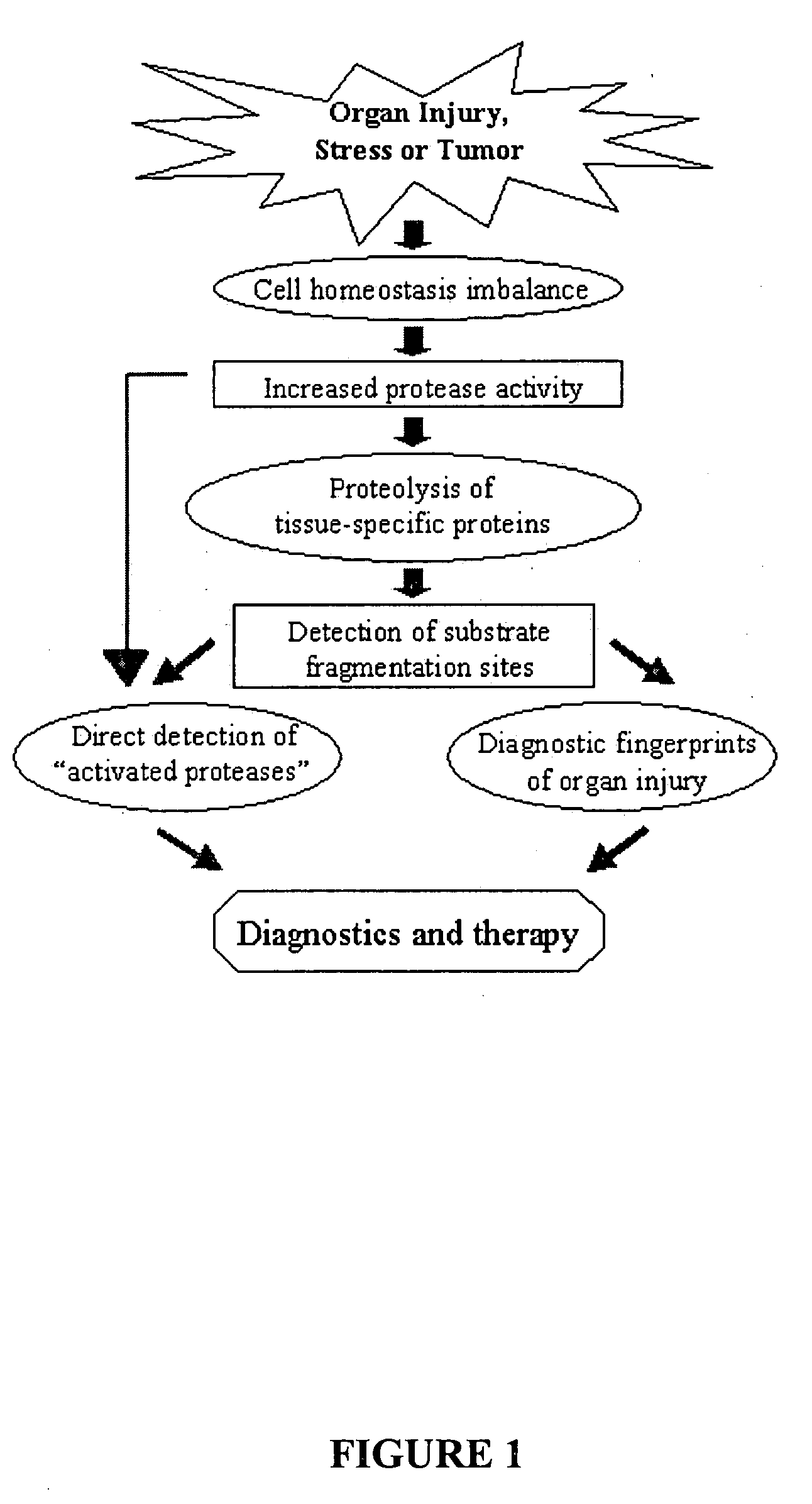
Proteolytic markers as diagnostic biomarkers for cancer, organ injury and muscle rehabilitation/exercise overtraining
ActiveUS20050260697A1Reliable detectionReliable identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingOvertrainingMedicine
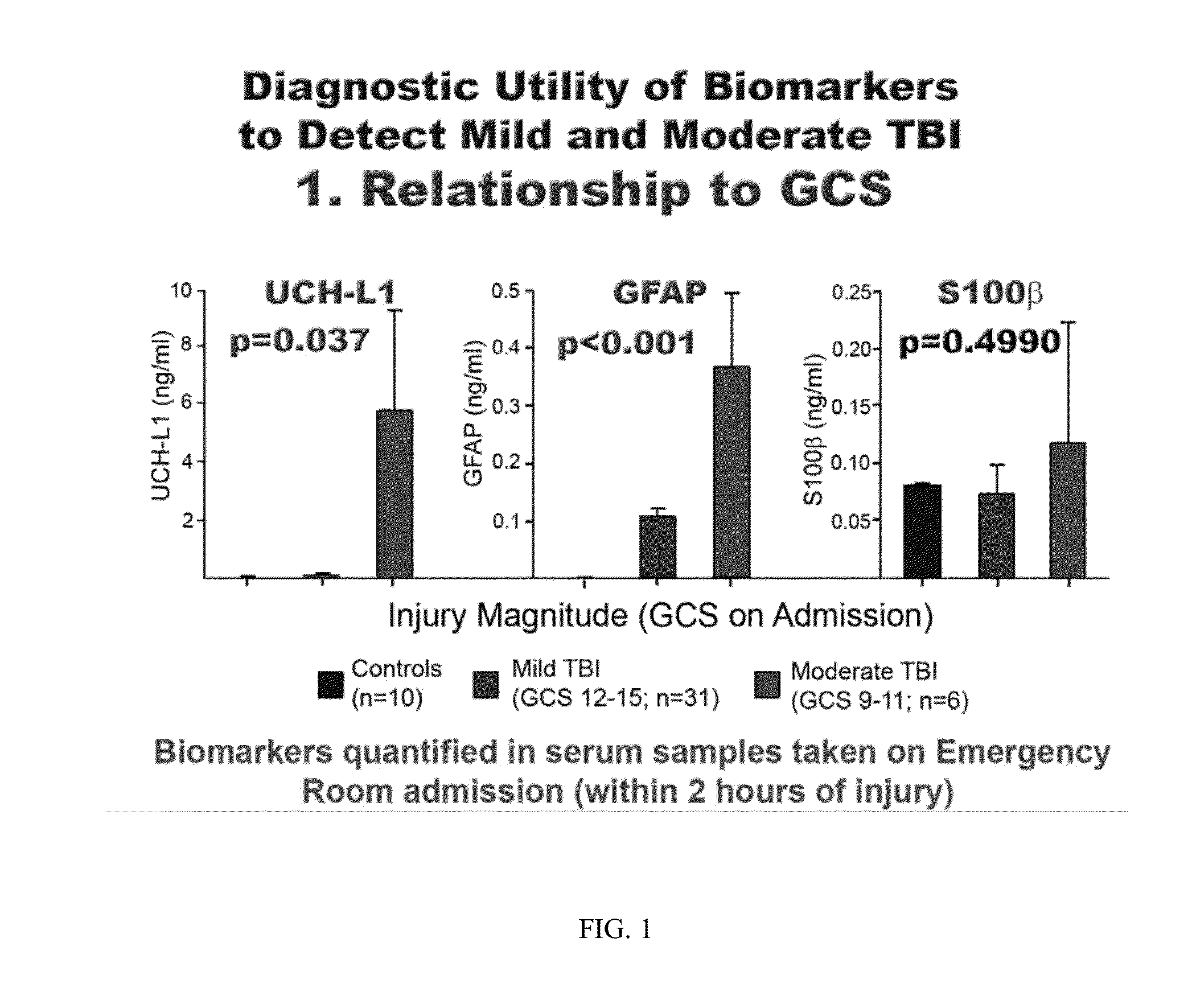
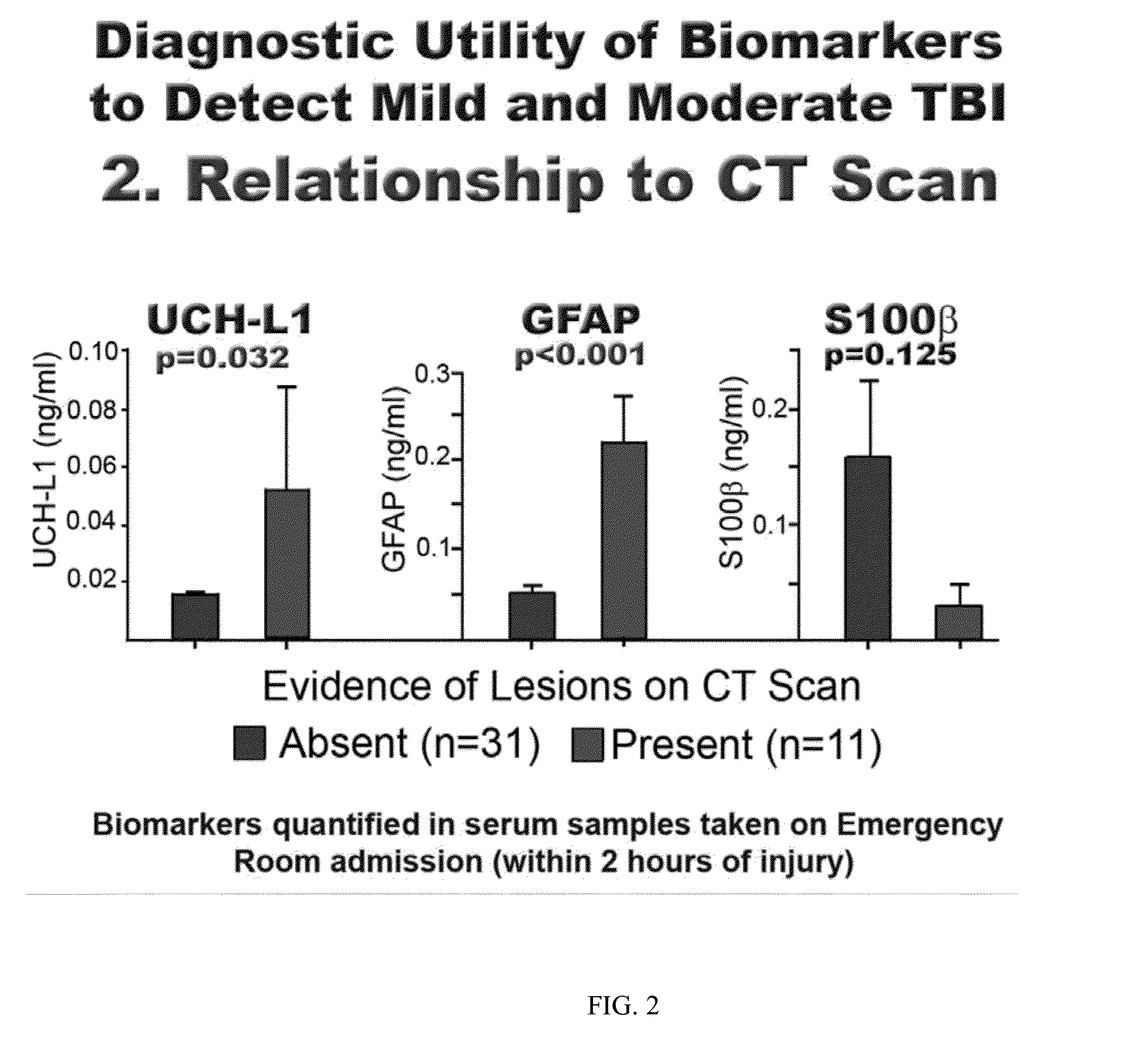
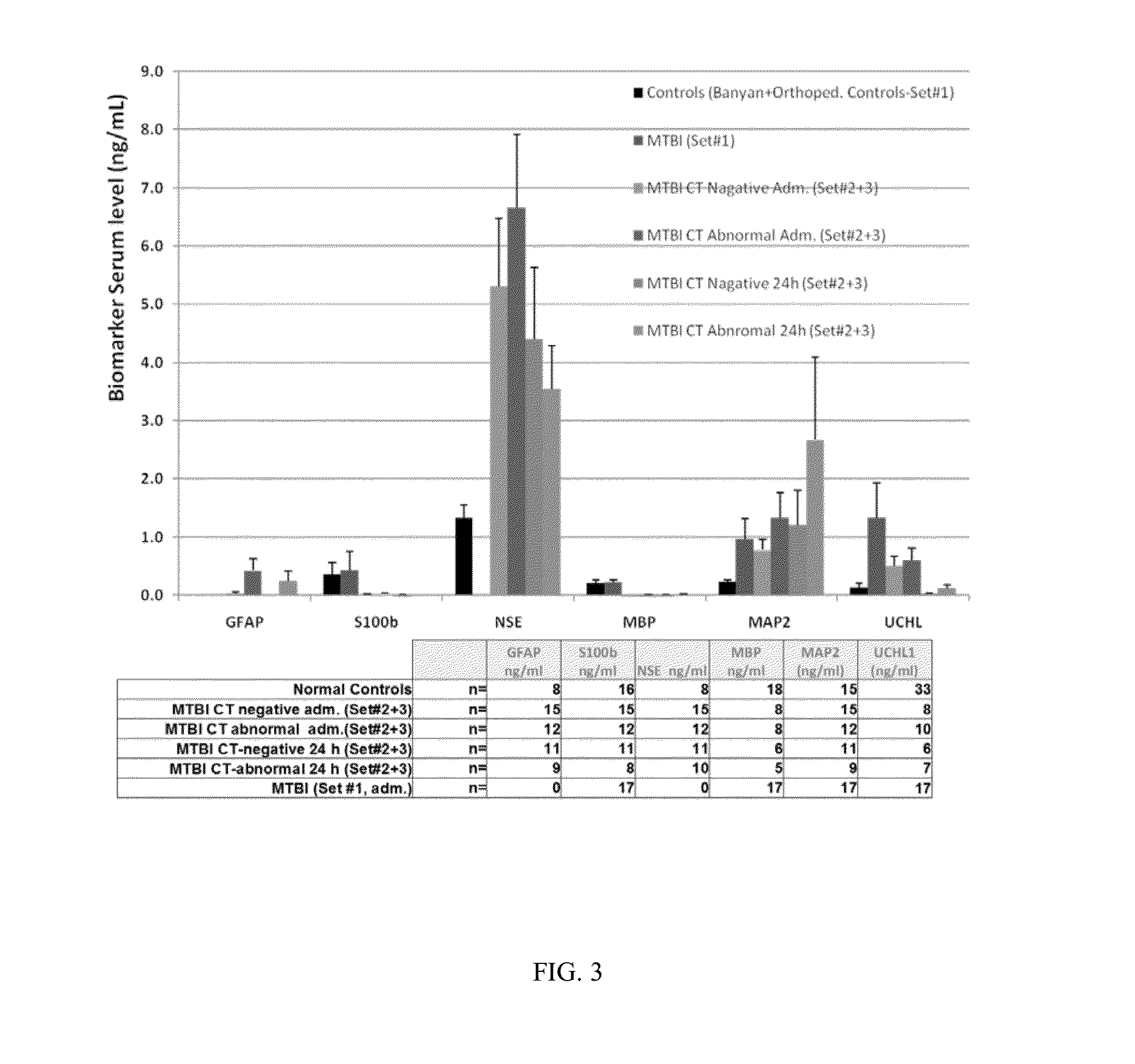
The present invention identifies biomarkers that are diagnostic of nerve cell injury, organ injury, and / or neuronal disorders. Detection of different biomarkers of the invention are also diagnostic of the degree of severity of nerve injury, the cell(s) involved in the injury, and the subcellular localization of the injury.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC +1
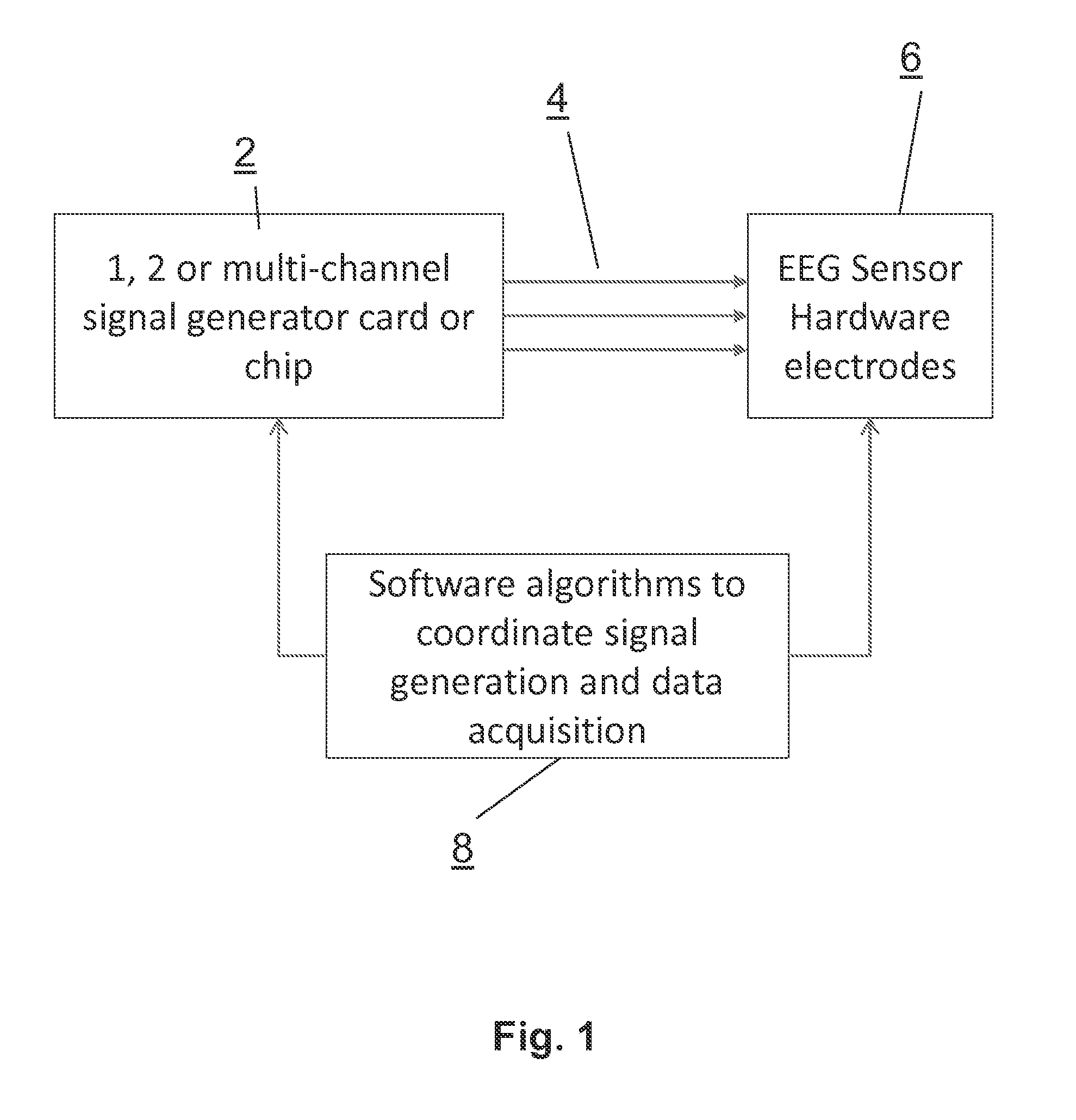
Systems and methods for the physiological assessment of brain health and the remote quality control of eeg systems
InactiveUS20150038869A1Verify performanceElectroencephalographyAutomatic recalibrationPortable EEGData acquisition
A system for calibrating and / or verifying system performance of a remote portable EEG system having at least one EEG sensor. Embodiments of the invention can provide various reference signals to calibrate and quality control the remote performance of the data acquisition EEG system. In addition a calibration cable connects a reference signal source to the EEG sensors to enable remote calibration and quality control assessment. Further, a diagnostic biomarker is included to assess the state or function of a subject's brain and enables the classification, prognosis, diagnosis, monitoring of treatment, or response to therapy applied to the brain by measuring any one of a list of candidate features extracted from a given cognitive or sensory task, and measuring changes in the EEG feature and task combination over time, among multiple states, or compared to a normative database.
Owner:CERORA
Protein Biomarkers and Methods for Diagnosing Kawasaki Disease
InactiveUS20110189698A1Improve diagnostic accuracyComponent separationDisease diagnosisKawasaki diseaseBiology
A method, kit and device for diagnosing Kawasaki Disease are provided. The invention provides detecting an expression level of at least two Kawasaki Disease diagnostic biomarkers in a biological sample from a patient with a capture agent and diagnosing the patient as having Kawasaki Disease when the expression levels of the at least two diagnostic biomarkers in the patient biological sample are higher than the normal expression levels of the same biomarkers in a biological sample from a control subject. The first Kawasaki Disease diagnostic biomarker disclosed in the present invention is a cardiomyocyte biomarker, and the second Kawasaki Disease diagnostic biomarker is an inflammatory biomarker. The invention further provides detecting an expression level of a third biomarker, interferon type-I biomarker, in the patient biological sample with a capture agent and diagnosing the patient as having Kawasaki Disease when the expression level of interferon type-I biomarker is lower than the expression level in a control subject.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Diagnostic biomarkers for neurodevelopmental disorders
ActiveUS20070003922A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisClinical psychologyCytometry
The present invention provides methods of identifying biomarkers indicative of the presence of a neurodevelopmental disorder, including an autism spectrum disorder, in an individual, using cytometry and mass spectrometry. The invention further provides methods of using the identified biomarkers to diagnose the presence of a neurodevelomental disorder, including an autism spectrum disorder.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Diagnostic biomarkers for vascular aneurysm
InactiveUS20090186370A1Increase propensityMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisBiological activationBiomarker (petroleum)
Biomarkers for diagnosis and monitoring of vascular aneurysms are described in the context of the use of assays to measure a plurality of these biomarkers. Tissue degeneration, particularly elastin and / or collagen degradation, can be monitored within patient blood (serum) and / or urine to diagnose the presence, the progression, or the likelihood of rupture of aneurismal disease. Additionally, enzymes responsible for this degradation and other biomarkers responsible for the activation or inhibition of these enzymes can be monitored additionally or alternatively. Prompt diagnosis can provide the opportunity for intervention and potentially increase the health of patients by tempering the development of debilitating and life-threatening vascular aneurysms.
Owner:VATRIX MEDICAL INC
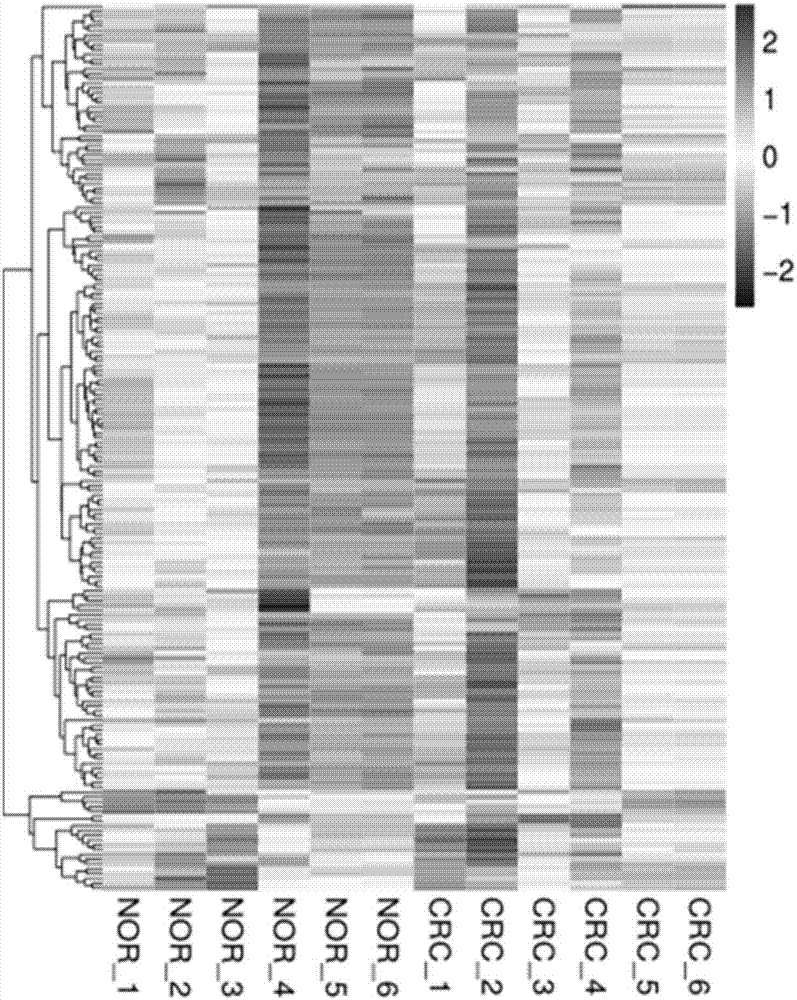
Colorectal cancer diagnostic biomarker and application thereof
ActiveCN107447033AAccurate judgmentQuick judgmentNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurement5 year survival rateMortality rate
The invention relates to a colorectal cancer diagnostic biomarker and application thereof. A nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1. The colorectal cancer diagnostic biomarker provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that hsa_circ_0006110 gene expression is discovered to be closely related to a colorectal cancer for the first time; through detecting the expression of hsa_circ_0006110 in a subject colorectal tissue, whether a subject suffers from the colorectal cancer or the risk of the colorectal cancer exists or not can be more accurately and quickly judged, so that a prevention or treatment scheme is provided for a clinician. A target gene as a drug for treating the colorectal cancer provides a new treatment targets and treatment approach for colorectal cancer treatment; compared with a traditional detection means, the diagnostic biomarker is more timely and more specific to diagnose, so that the five-year survival rate of a colorectal cancer patient is improved, and the death rate is reduced, therefore, the application prospect is wide.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
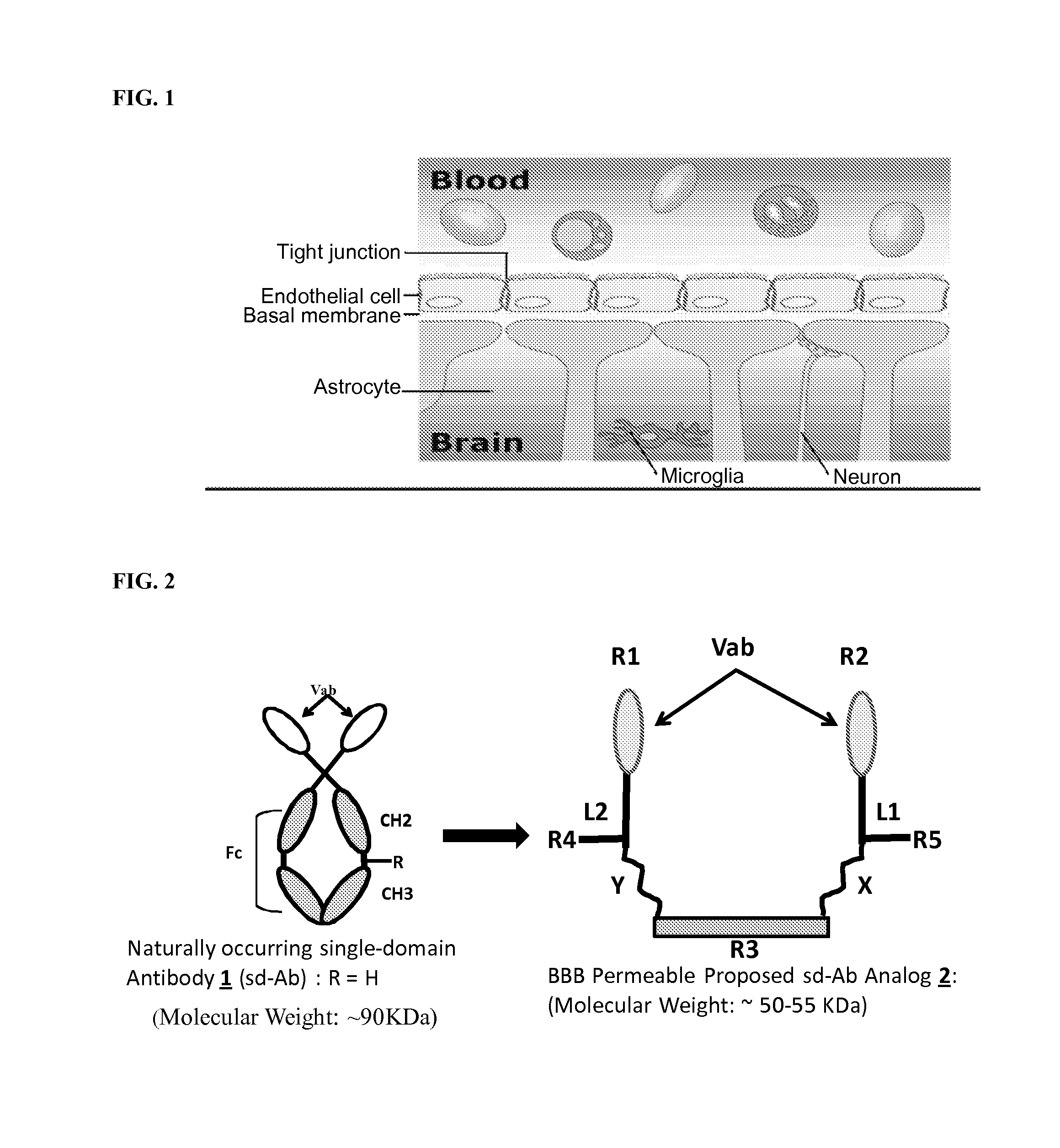
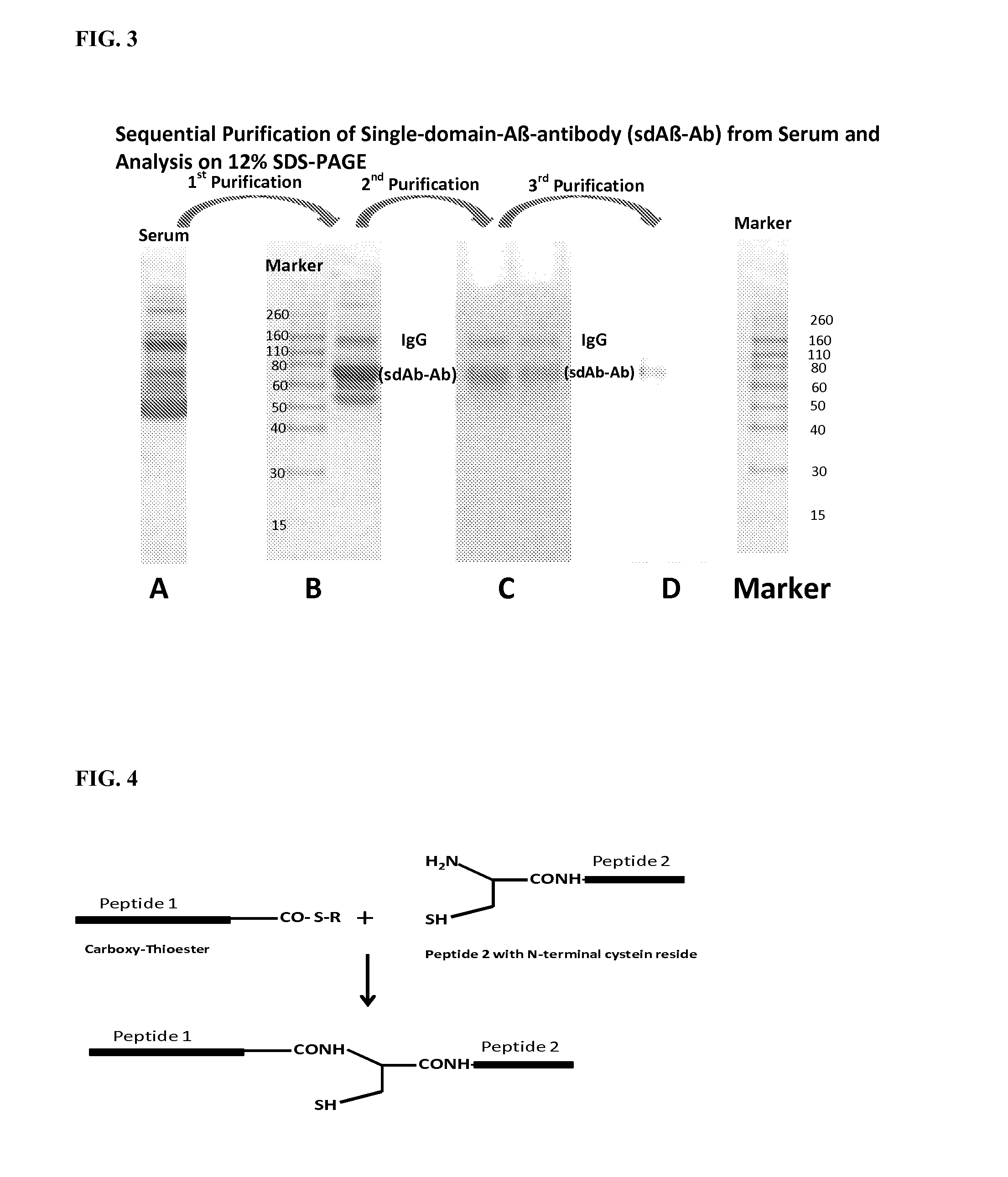
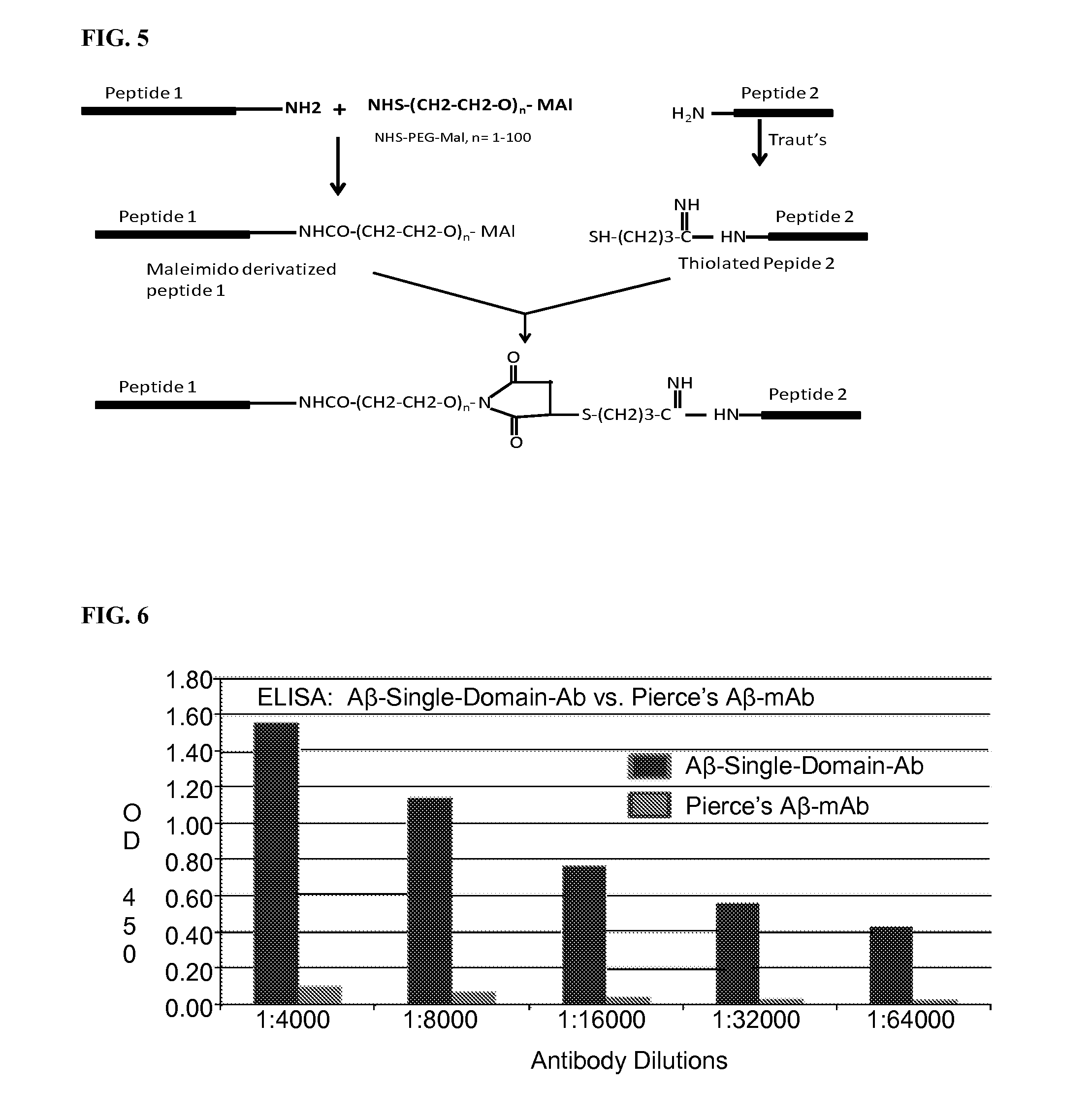
Blood-brain barrier permeable peptide compositions
ActiveUS20130177568A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAmyloid betaCamelid
Blood-brain barrier permeable peptide compositions that contain variable antigen binding domains from camelid and / or shark heavy-chain only single-domain antibodies are described. The variable antigen binding domains of the peptide compositions bind to therapeutic and diagnostic biomarkers in the central nervous system, such as the amyloid-beta peptide biomarker for Alzheimer's disease. The peptide compositions contain constant domains from human IgG, camelid IgG, and / or shark IgNAR. The peptide compositions include heavy-chain only single-domain antibodies and compositions with one or more variable antigen binding domain bound to one or more constant domains.
Owner:ICB INT
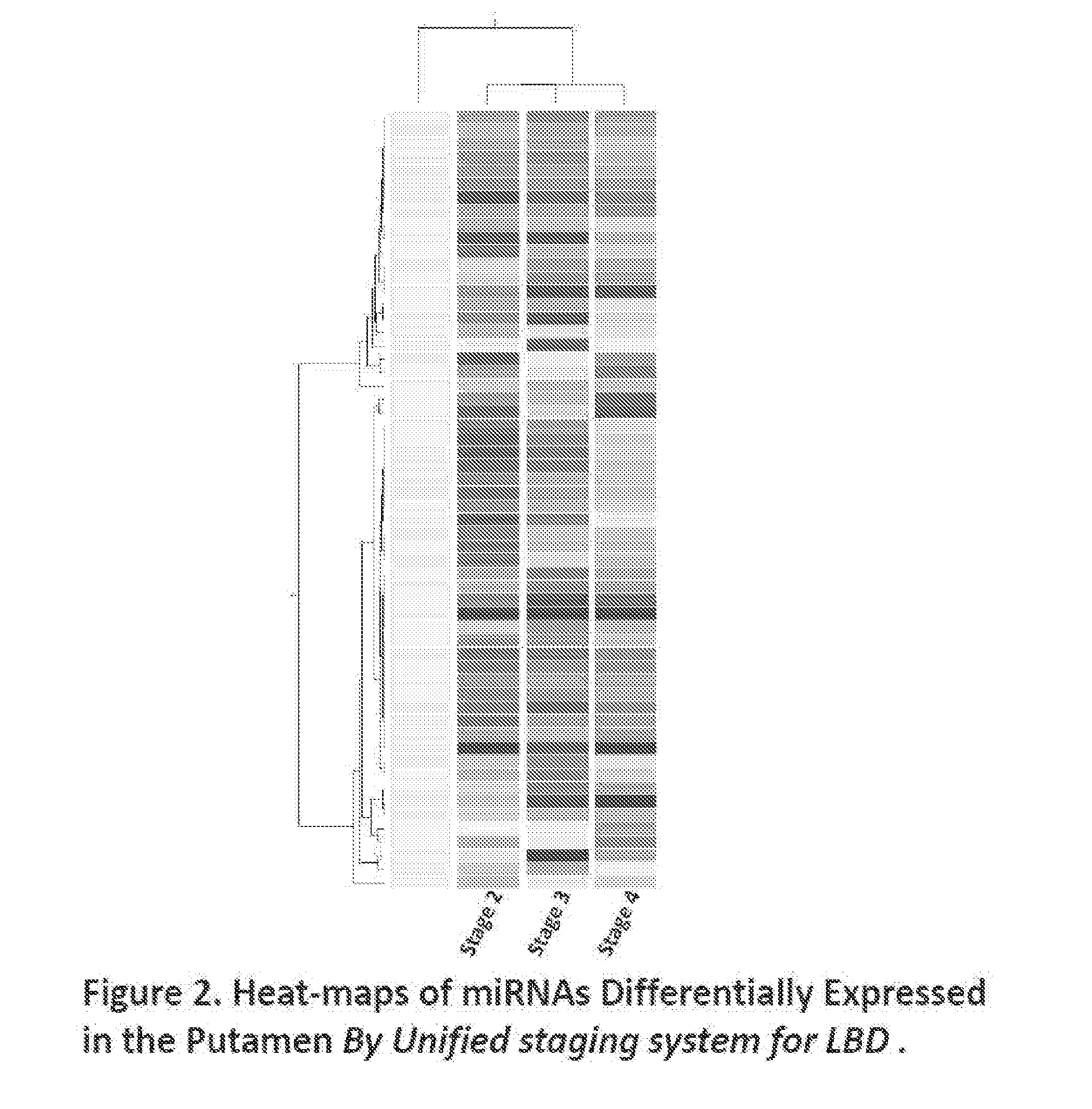
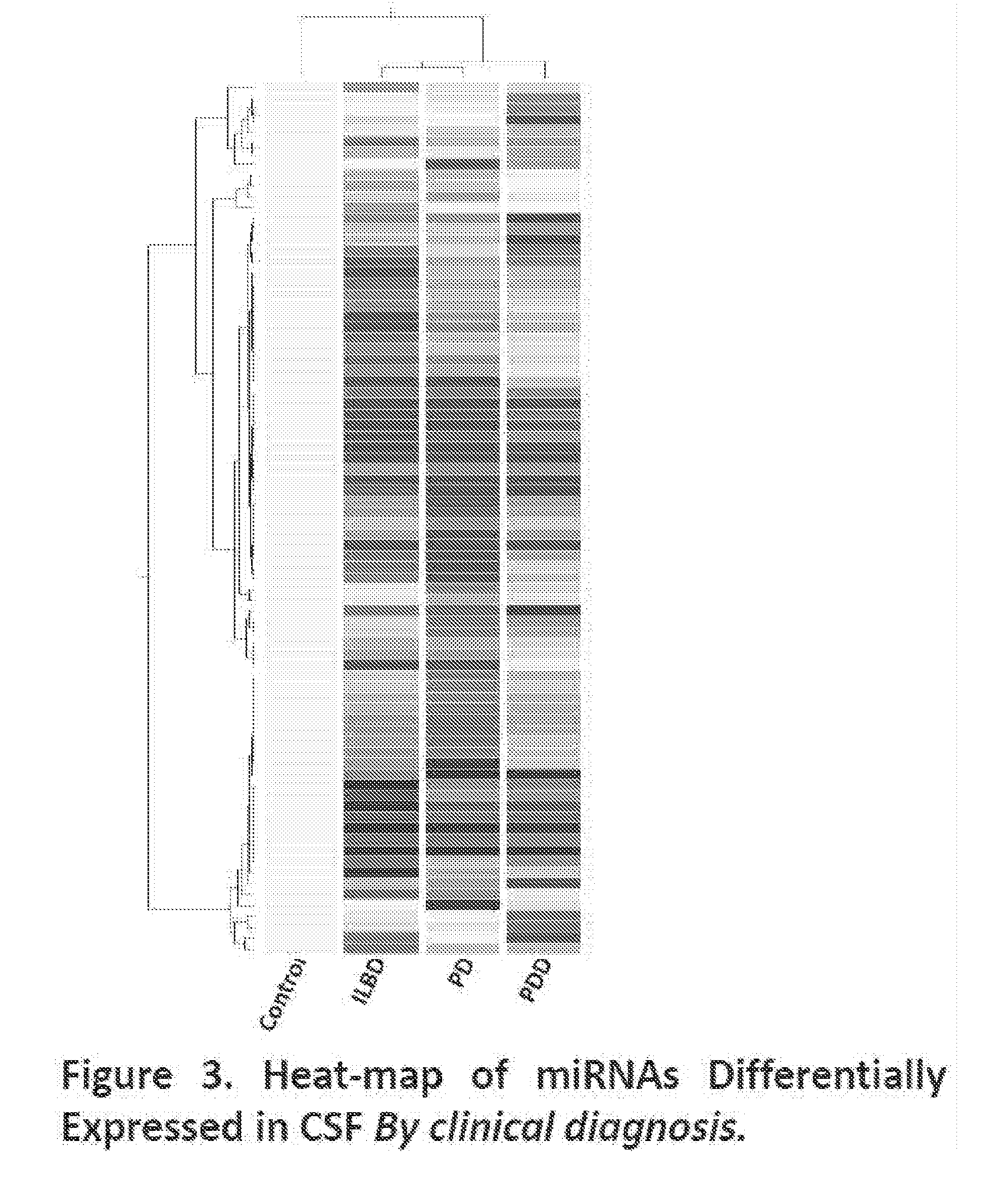
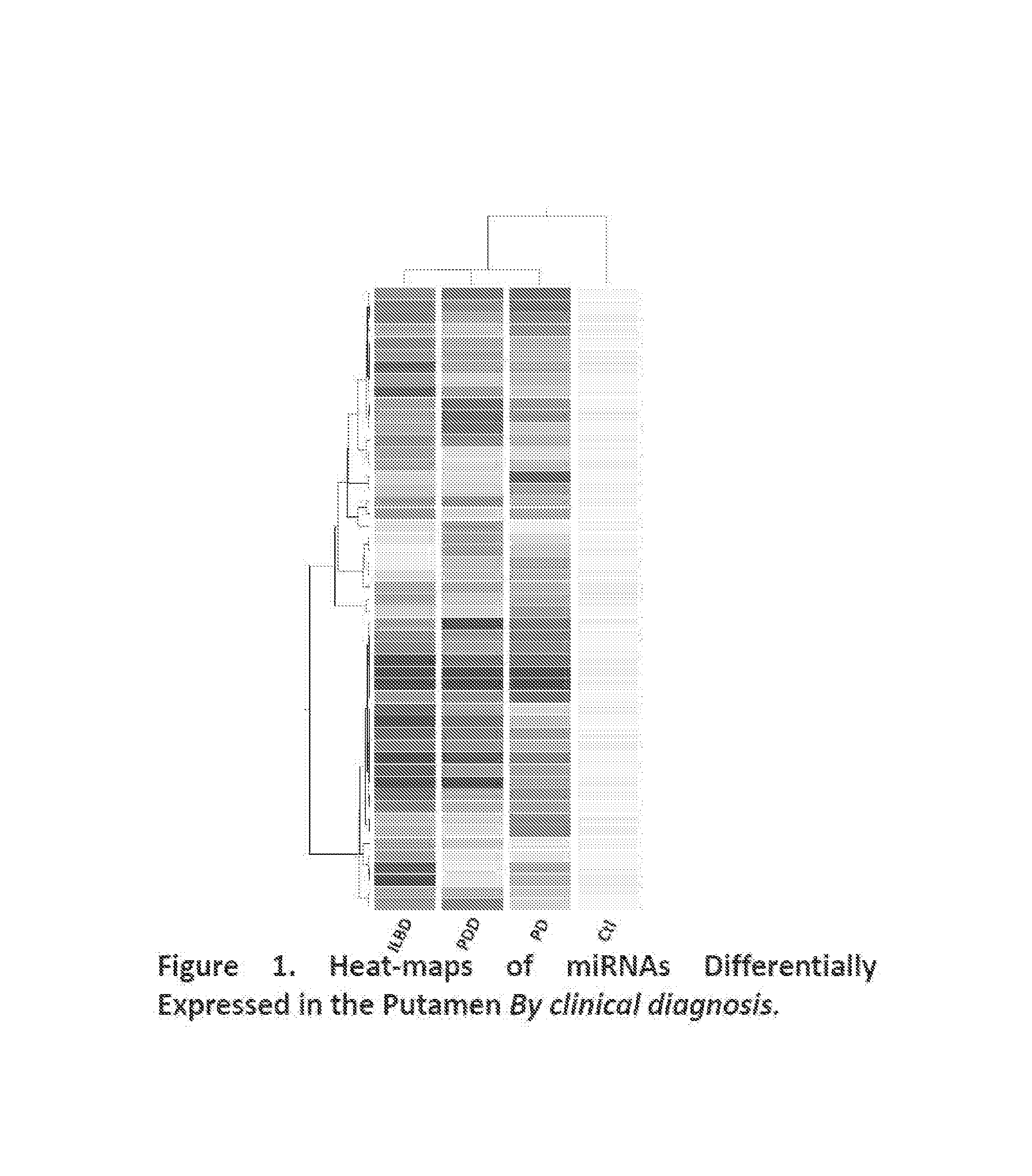
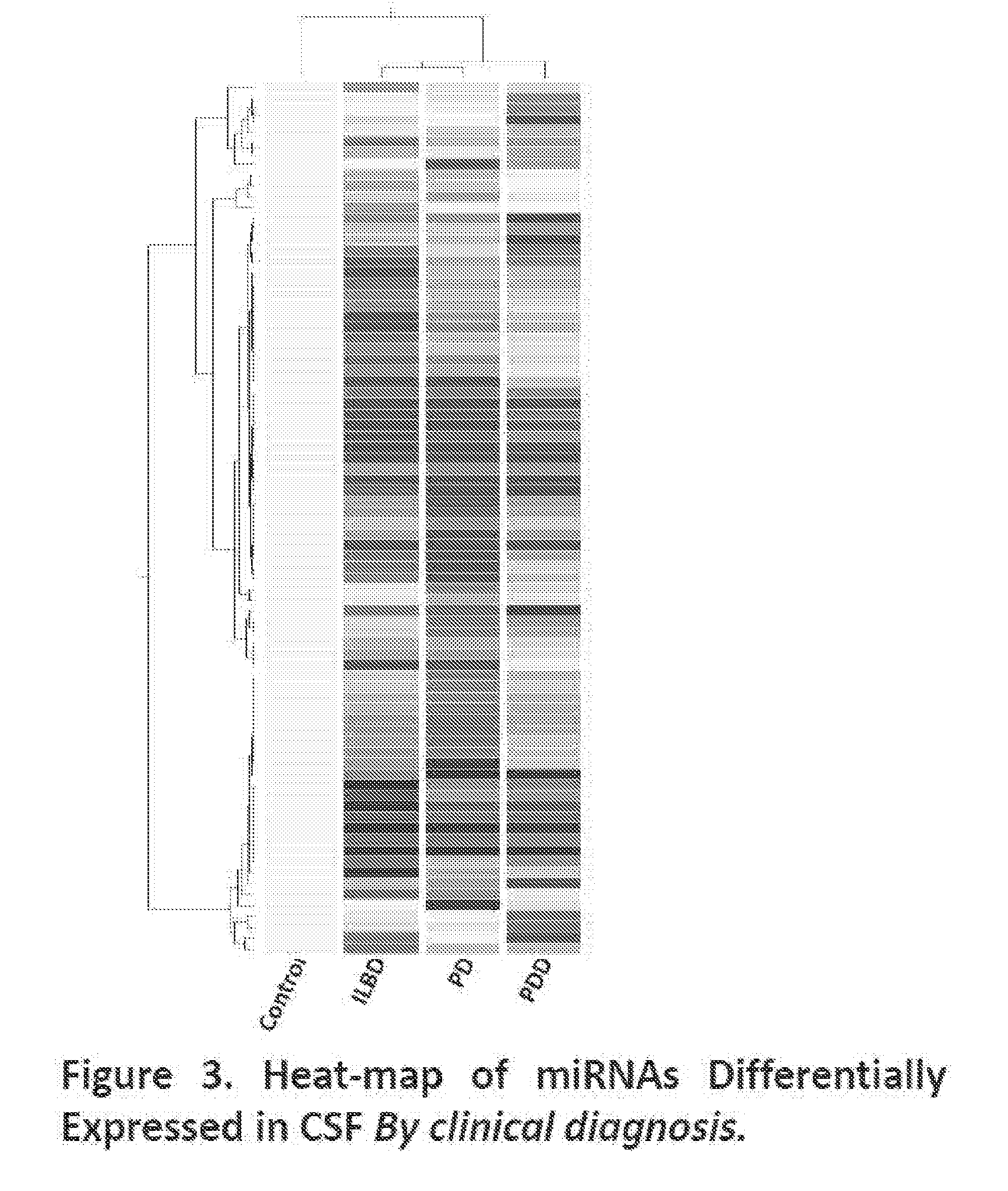
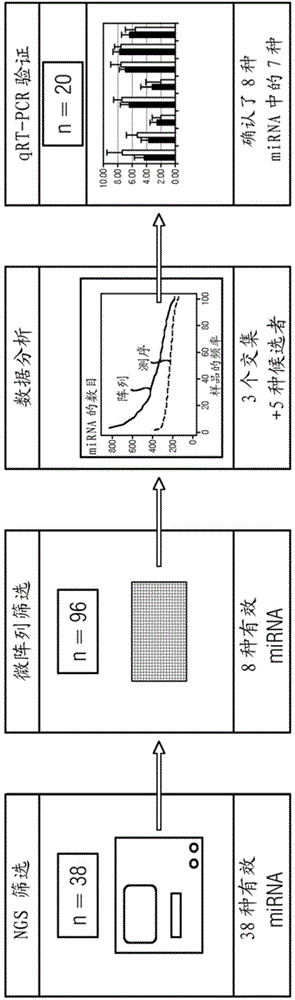
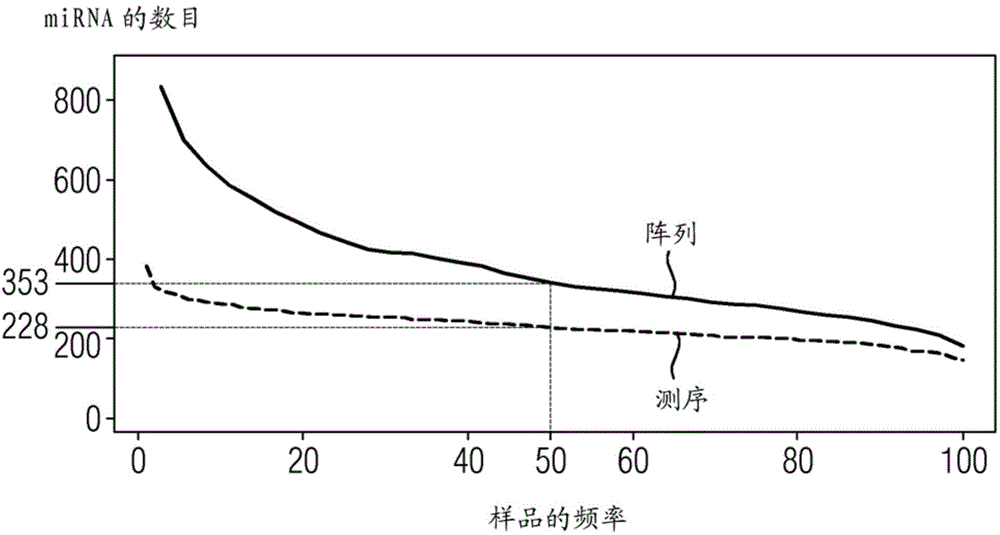
miRNAs as Novel Therapeutic Targets and Diagnostic Biomarkers for Parkinsons Disease
ActiveUS20150275299A1Preventing and reducing risk of PDSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesNucleotideMedicine
The disclosure provides pharmaceutical compositions including an oligonucleotide that down-regulates the over-expression of at least one miRNA of SEQ ID NOs: 1-283. The oligonucleotide may be complementary to the nucleotide sequence of at least one of SEQ ID NOs: 1-283, or hybridizes under stringent conditions to a nucleotide sequence of at least one of SEQ ID NOs: 1 -283. Further provided are methods of diagnosing Parkinson's Disease (PD) in a subject. The methods may include detecting the level of expression of at least one miRNA of SEQ ID NOs: 1-283 in a biological sample from the subject, and comparing the level of expression in the sample to the level of expression in a reference. Further provided are methods for treating, preventing, or reducing the risk of PD. Kits are also provided.
Owner:RUSH UNIV MEDICAL CENT
Neural specific s100b for biomarker assays and devices for detection of a neurological condition
InactiveUS20150141528A1Auxiliary diagnosisBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsDisplay deviceNeuronal disease
An in vitro diagnostic (IVD) device is used to detect the presence of and / or severity of neural injuries or neuronal disorders in a subject. The IVD device relies on an immunoassay which identifies biomarkers that are diagnostic of neural injury and / or neuronal disorders in a biological sample, such as whole blood, plasma, serum, and / or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). An IVD device may measure one or more of several neural specific markers in a biological sample and output the results to a machine readable format, either to a display device or to a storage device internal or external to the IVD.
Owner:BANYAN BIOMARKERS INC
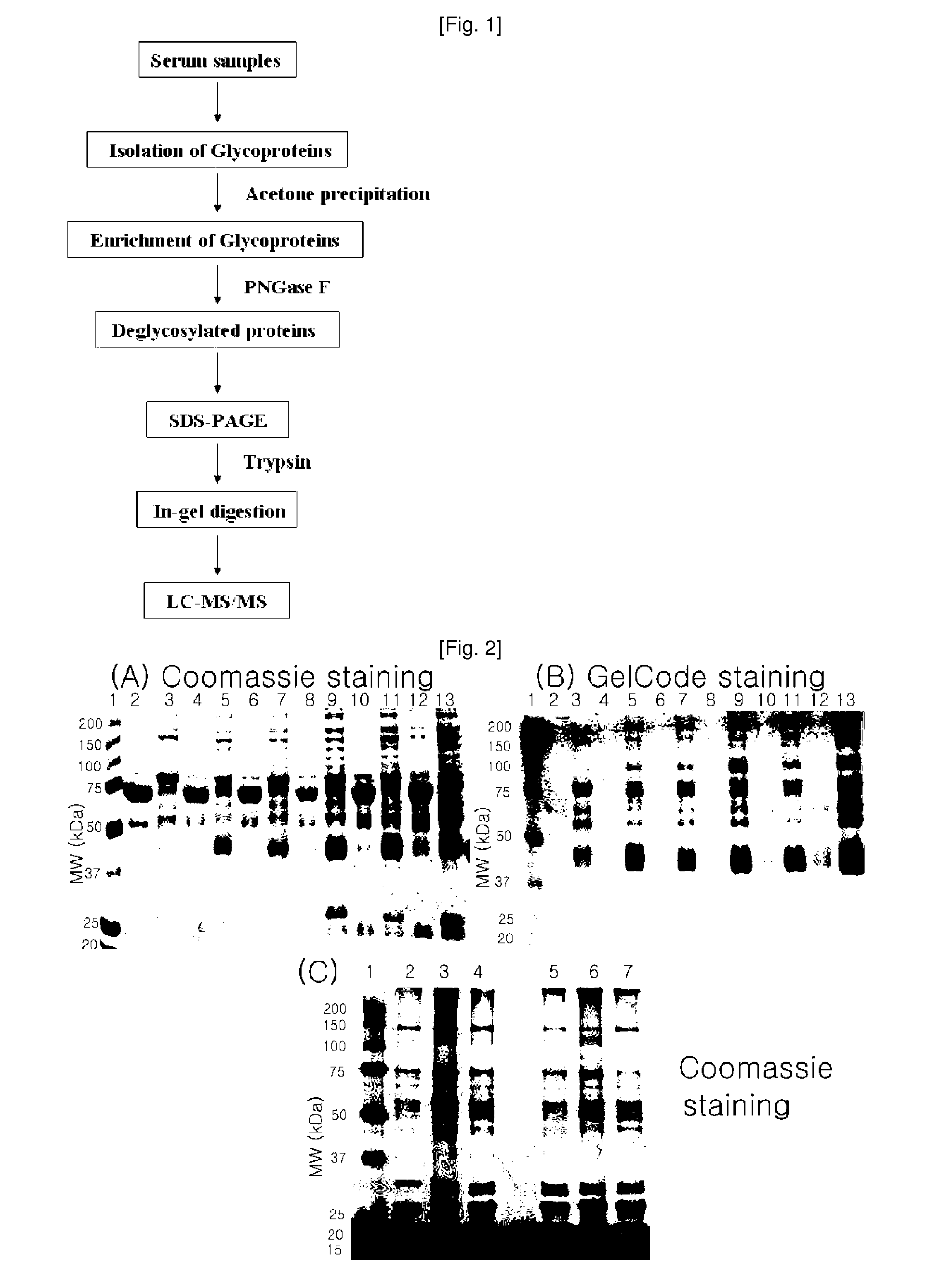
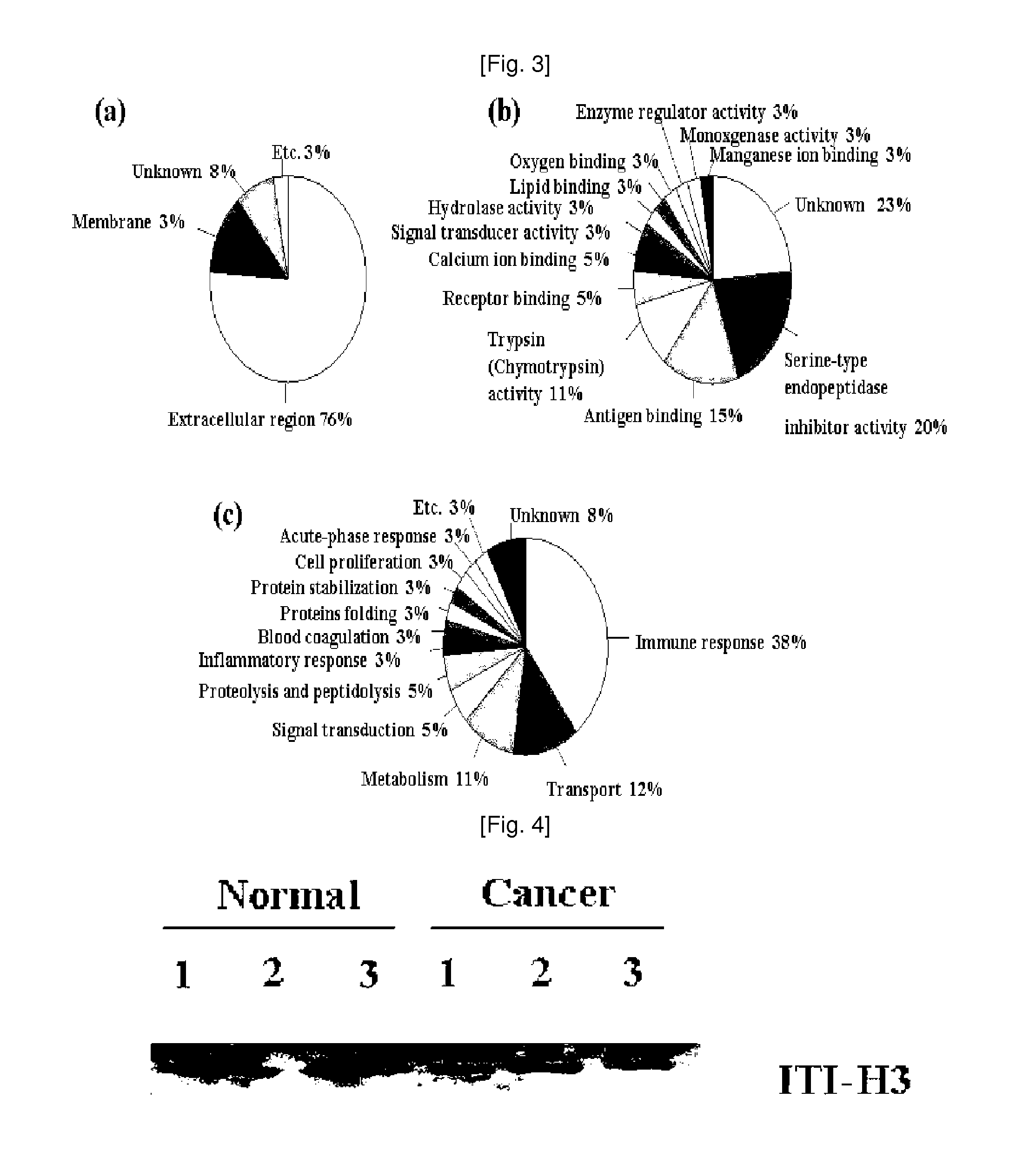
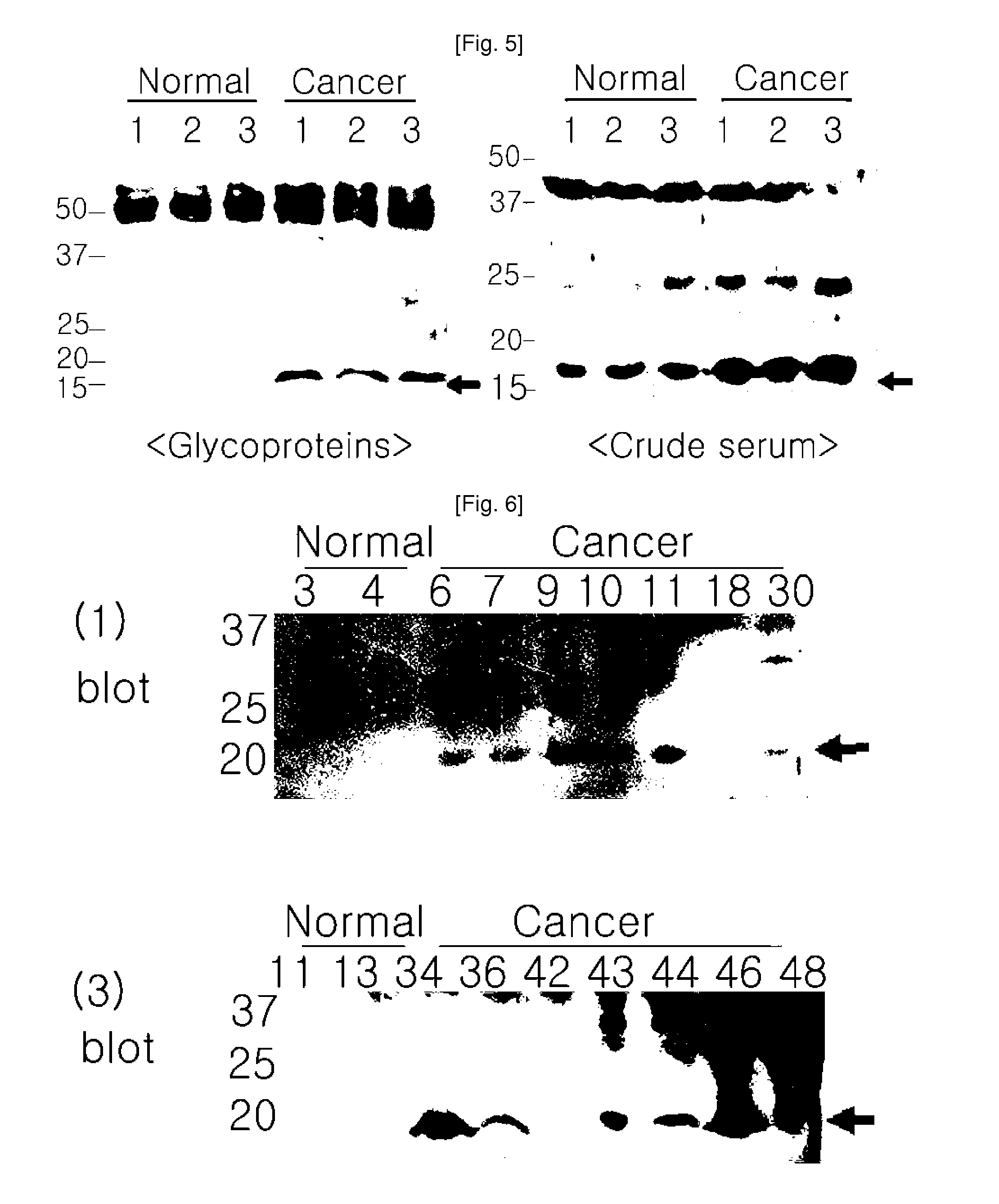
Plasma kallikrein fragments as diagnostic biomarkers for lung cancers
InactiveUS20100285507A1Efficient use ofUseful for diagnosing lung cancer and estimatingSugar derivativesHydrolasesDiagnostic biomarkerPlasma kallikrein inhibitor
Disclosed herein are diagnostic markers for lung cancer, isolated from serum glycoproteins. The disclosed diagnostic markers for lung cancer are specifically expressed only in the sera of lung cancer patients at high levels, and thus will be very useful for diagnosing lung cancer and estimating disease progression and treatment.
Owner:PROTAN BIO INC
Diagnostic transcriptomic biomarkers in inflammatory cardiomyopathies
Molecular signatures that function as very sensitive diagnostic biomarker for myocarditis, heart disease and disorders thereof, are identified.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
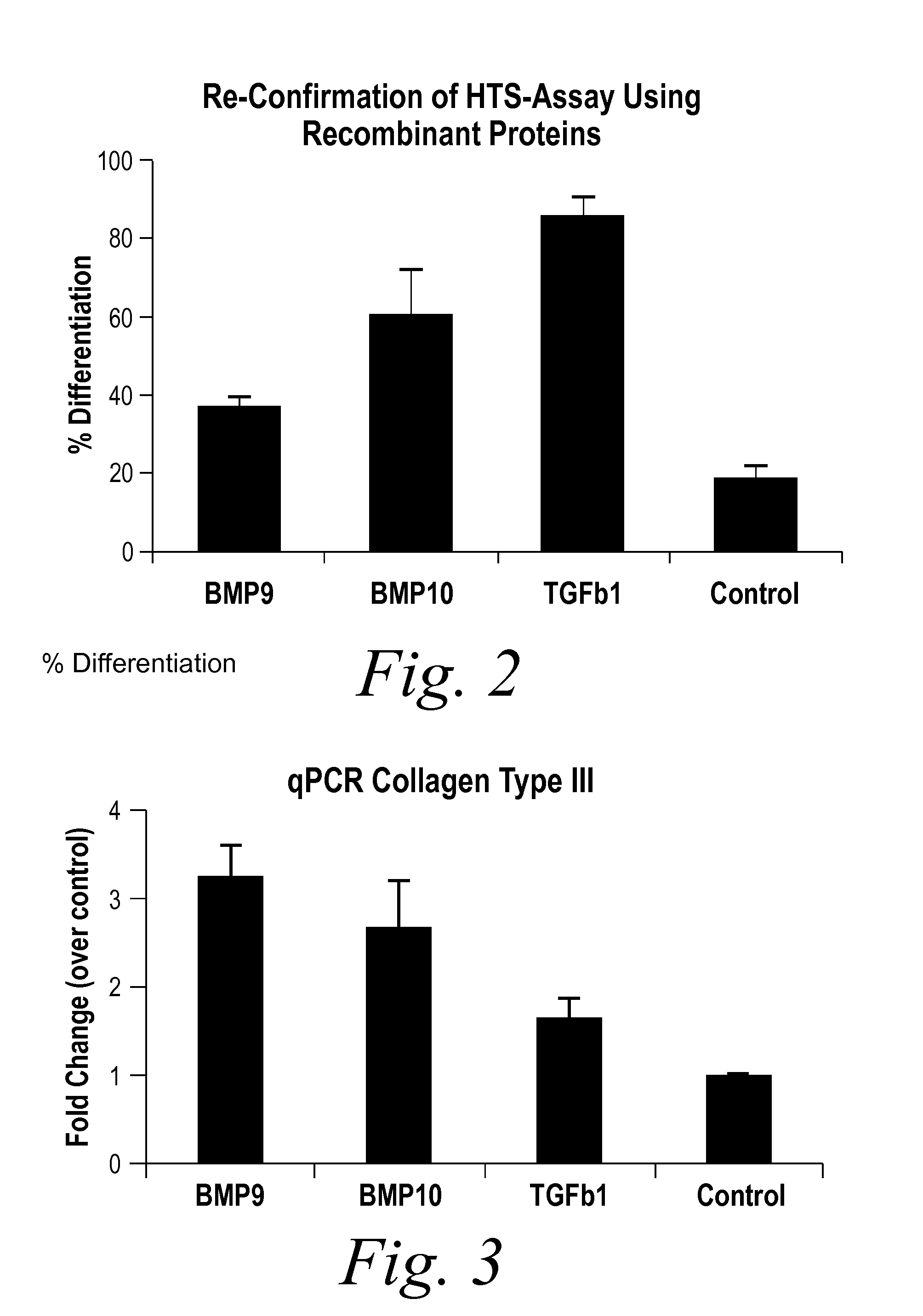
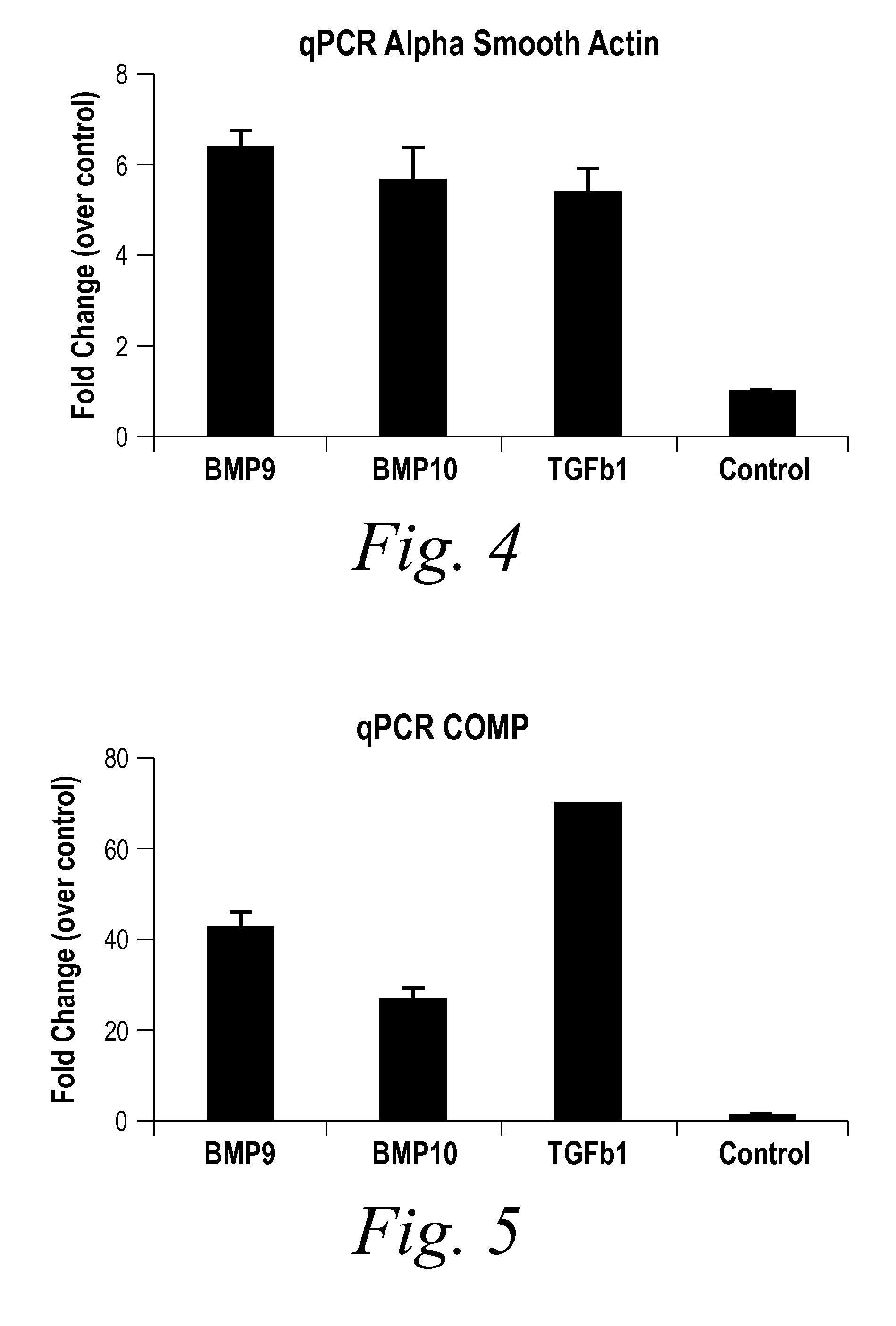
Diagnostic BioMarkers for Fibrotic Disorders
InactiveUS20130209490A1Easy to detectOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsFiberFibrosis
The present invention provides novel methods of inhibiting fibrosis, as well as methods of treating or inhibiting fibrotic disorders, using BMP9 and / or BMP10 antagonists. The present invention also provides methods of assessing whether a subject has or is at risk of developing a fibrotic disorder by detecting levels of BMP9 and / or BMP10. Further provided are methods of assessing the efficacy of a treatment regimen for treating a fibrotic disorder by detecting and comparing pre-treatment levels of BMP9 and BMP10 with post-treatment levels of BMP9 and BMP10.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Processes and kits to detect and monitor for diagnostic biomarkers for post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and to differentiate between suicidal and non-suicidal form of the disorder
InactiveUS20150259740A1Accurate detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPeptide librariesSUICIDAL TENDENCYEmotional and behavioral disorders
Life-threatening traumas such as terrorist attacks, war, disasters, mental or physical assault, severe accidents and violence frequently provoke emotional and behavioral disturbances known as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and suicide related thereto. Accurate diagnosis and treatment planning for PTSD and suicide remain difficult. The discovery of specific markers creates new opportunities for more accurate clinical assessments identifying groups that may experience better outcomes when exposed to an intervention. The present invention provides a process of detection of P-11, UBE3A, STY1, EMAP-II, SIP1, ORC5L, DCX, SCYE protein in a biological sample of a subject suspected of suffering from PTSD and / or having suicidal tendencies, and provides additional PTSD markers which are specific to gender.
Owner:BANYAN BIOMARKERS INC +1
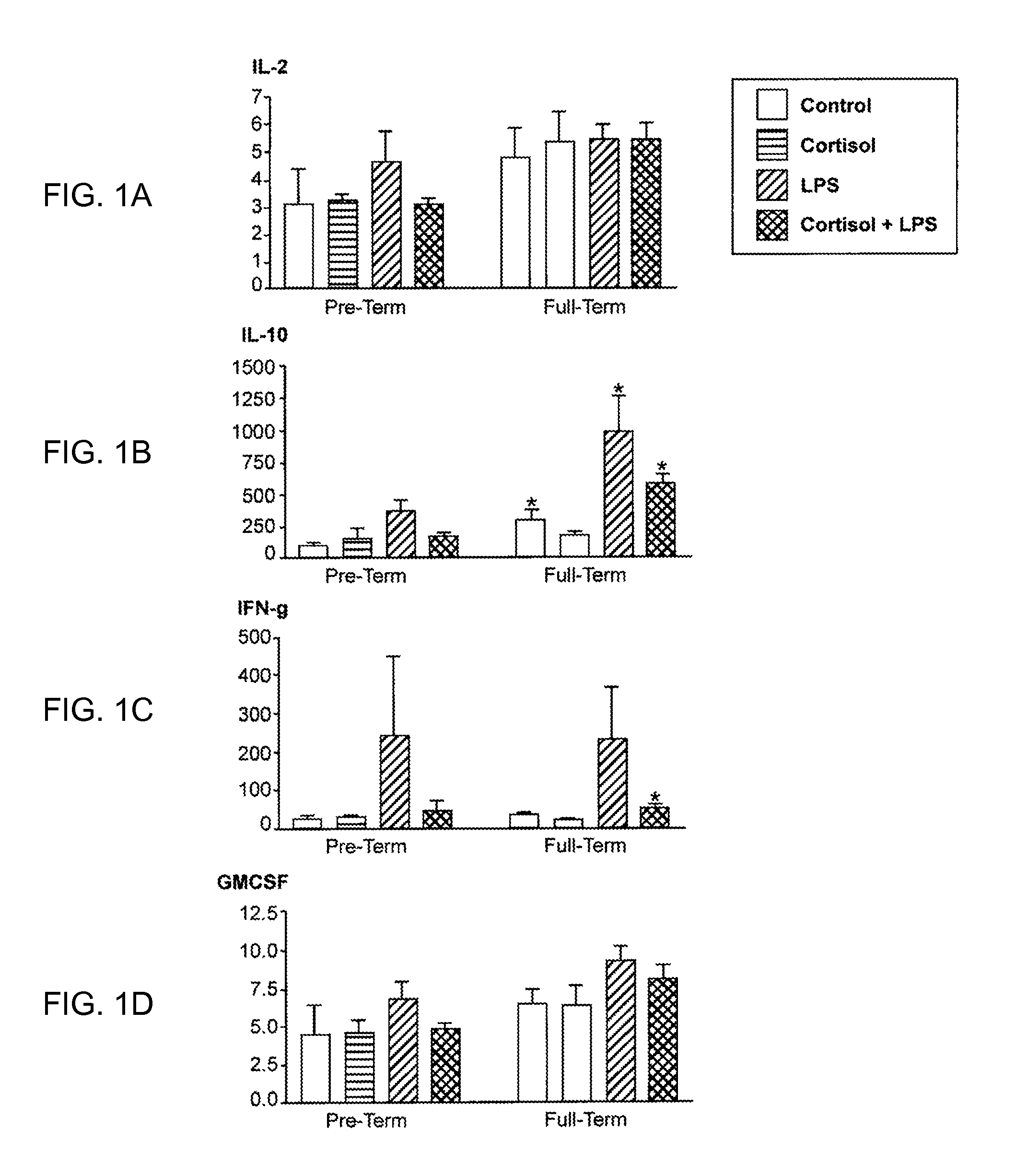
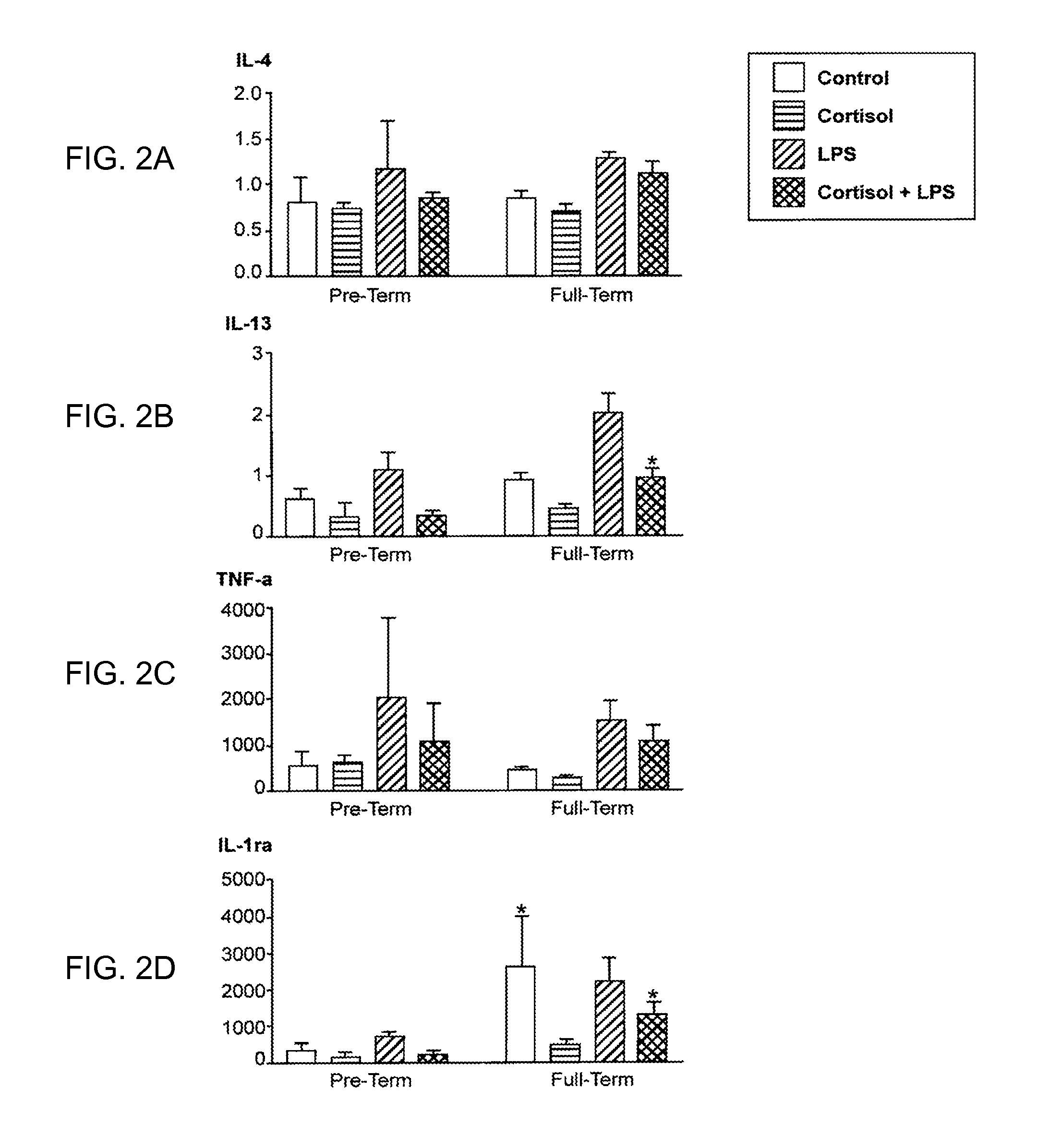
Diagnostic biomarker to identify women at risk for preterm delivery
InactiveUS20120238469A1Peptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementObstetricsDiagnostic biomarker
The invention relates to biomarkers associated with preterm delivery. More specifically, the invention provides methods of measuring biomarkers found in women that are at risk for preterm delivery.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
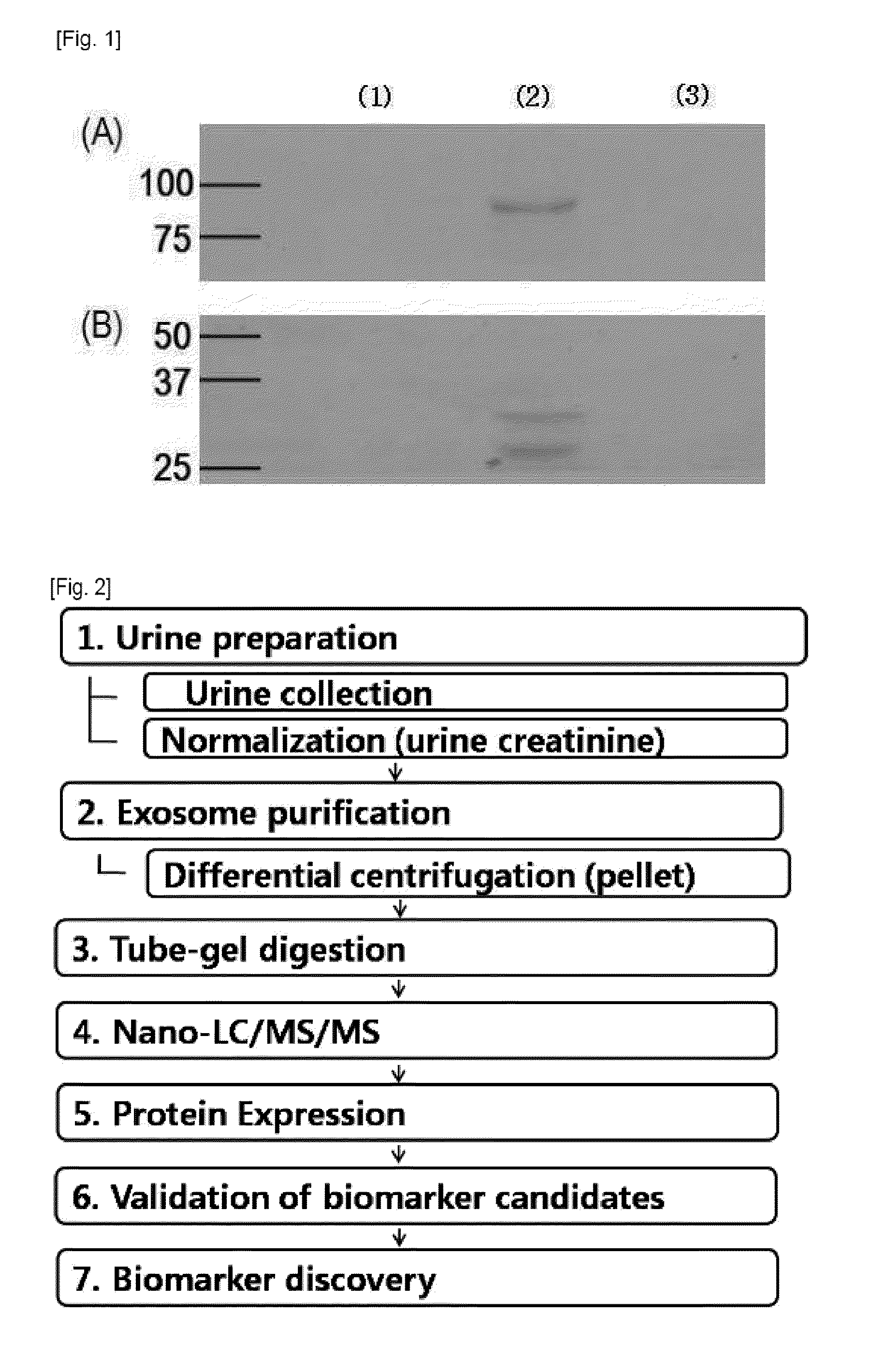
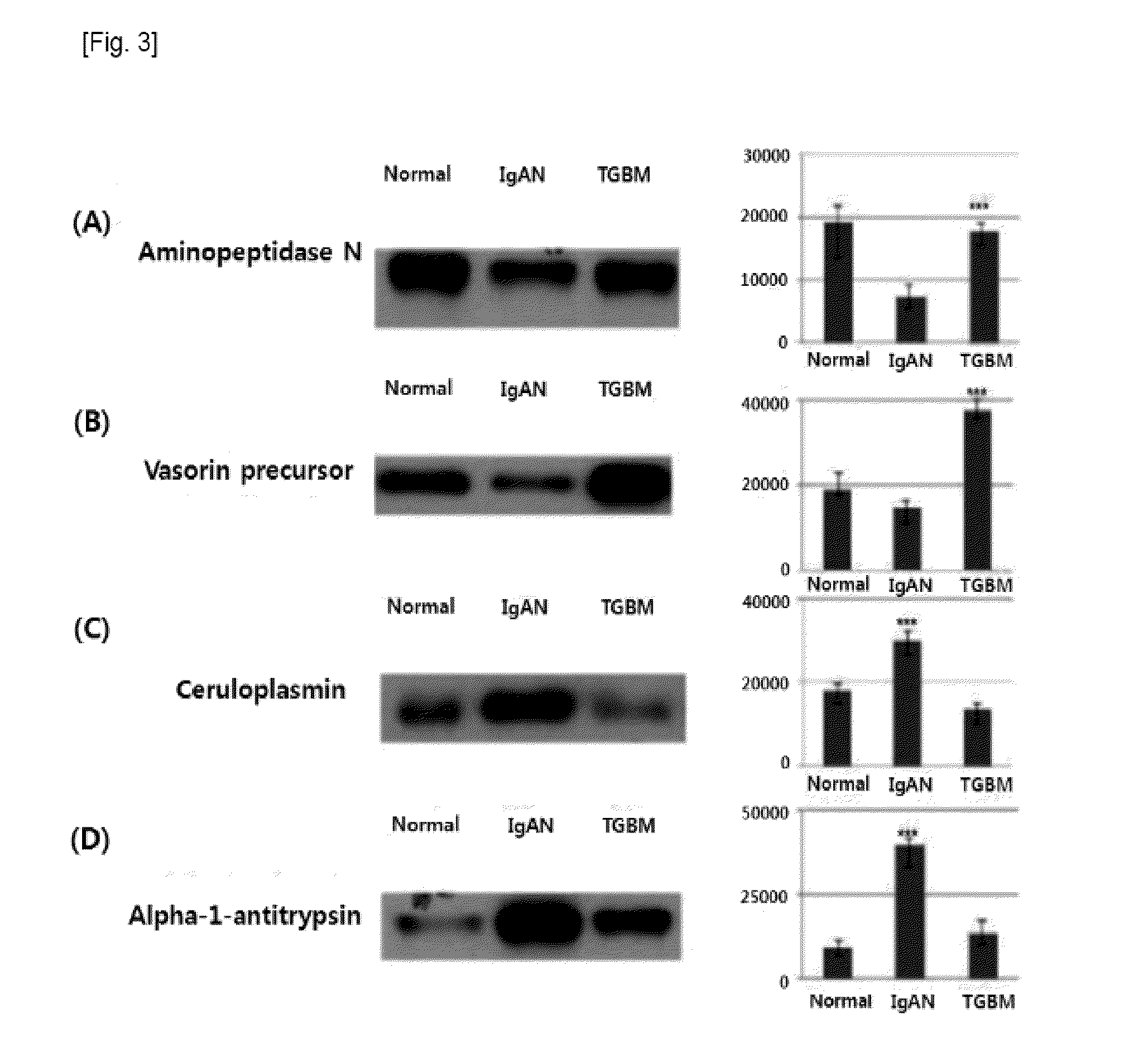
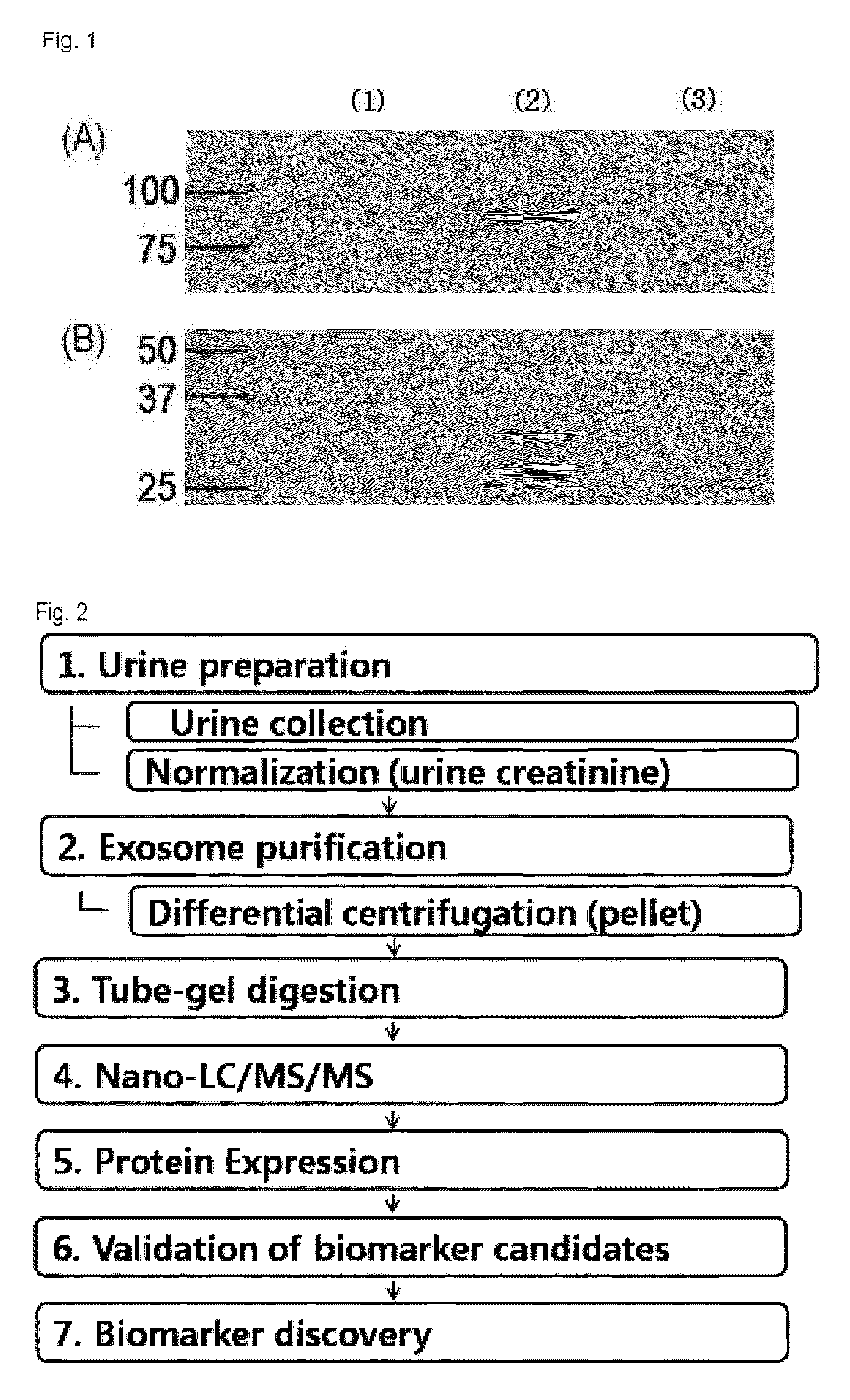
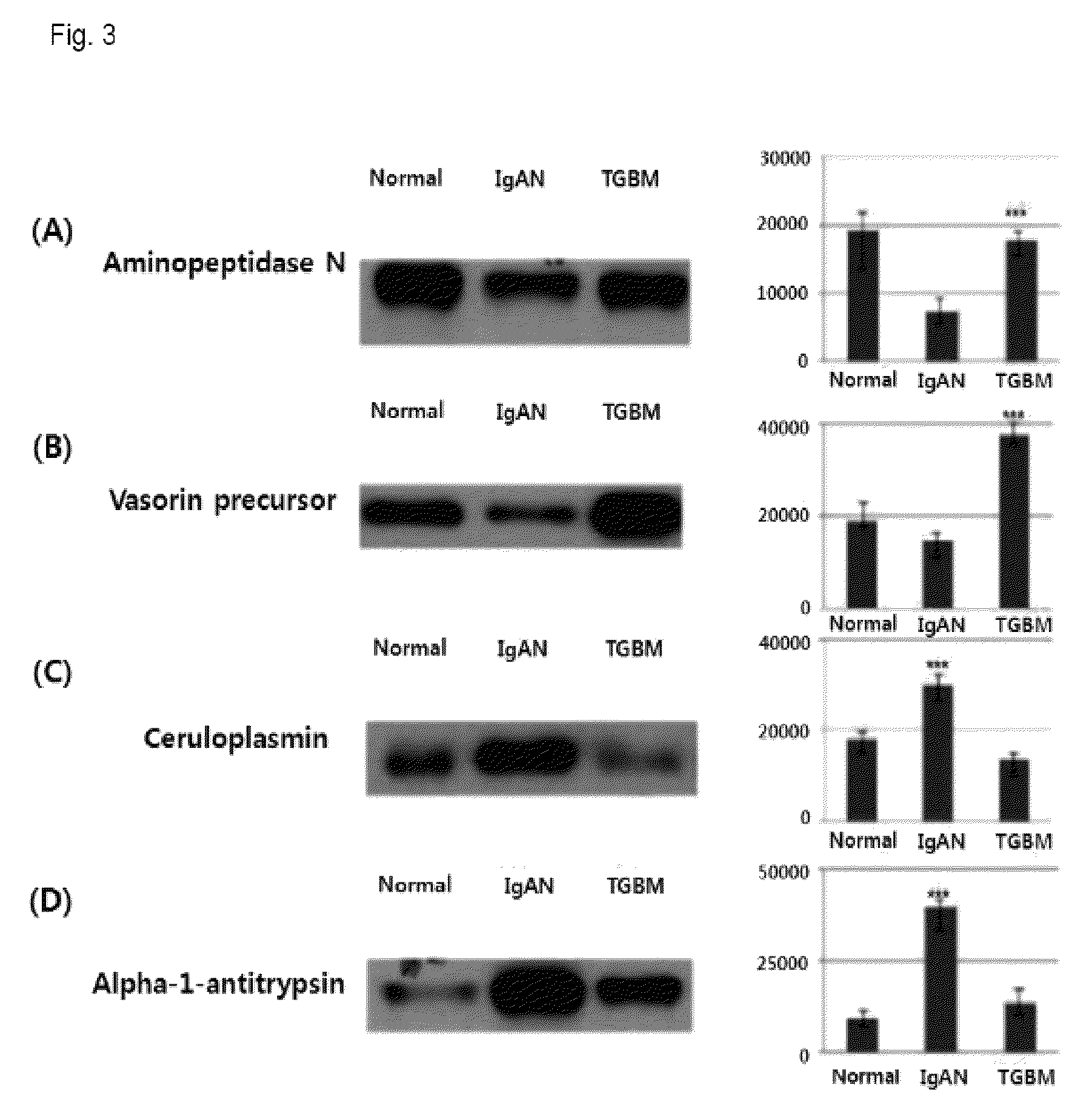
Compostion and kit for diagnosing immunoglobulin a nephropathy and TGBM nephropathy
InactiveUS20110236913A1Easy diagnosisEarly diagnosisSamplingMicrobiological testing/measurementTargeted proteomicsDisease cause
Disclosed is the development of a protein used as a biomarker for diagnosing IgA nephropathy and TGBM (thin-glomerular-basement-membrane) using urine through a target proteomics method. The disclosed development relates to a diagnosis biomarker protein and a kit for diagnosing IgA nephropathy and TGBM and predicting progress of the nephropathy in advance using the protein. The protein level is increased or decreased in urine from a patient with IgA nephropathy or TGBM nephropathy compared to urine from a normal patient. According to the disclosed development, the degree of the disease can be grasped by detecting IgA nephropathy and TGBM, enabling early diagnosis and confirming progress from the patient's urine. In addition, a monoclonal antibody produced based on the diagnosis biomarker protein can be used for an immunoassay kit (ELISA, antibody coated tube test, lateral-flow test, potable biosensor). As well, the monoclonal antibody is used in early diagnosis and progress detection of IgA nephropathy and development of a novel drug for the purpose of treatment.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
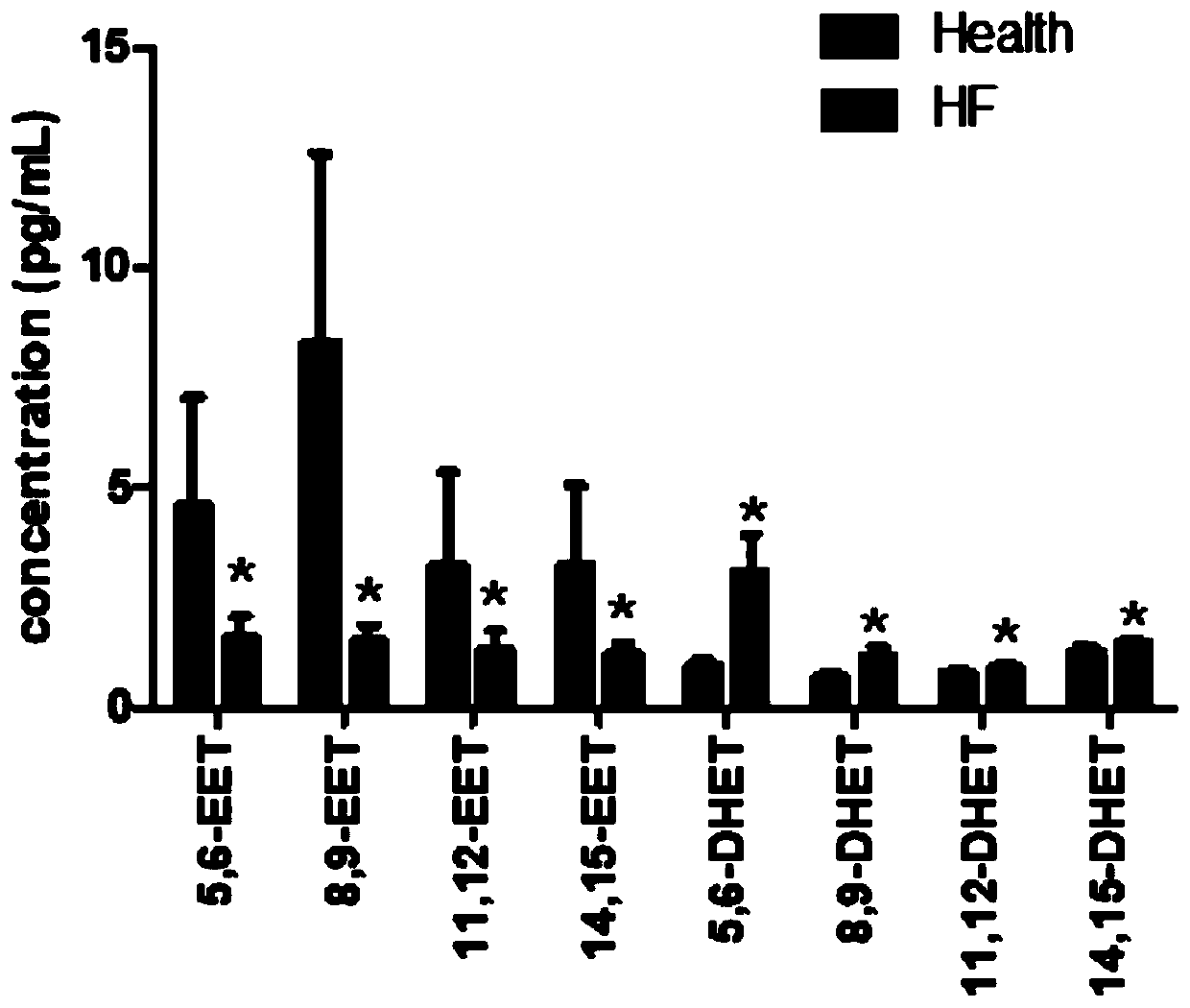
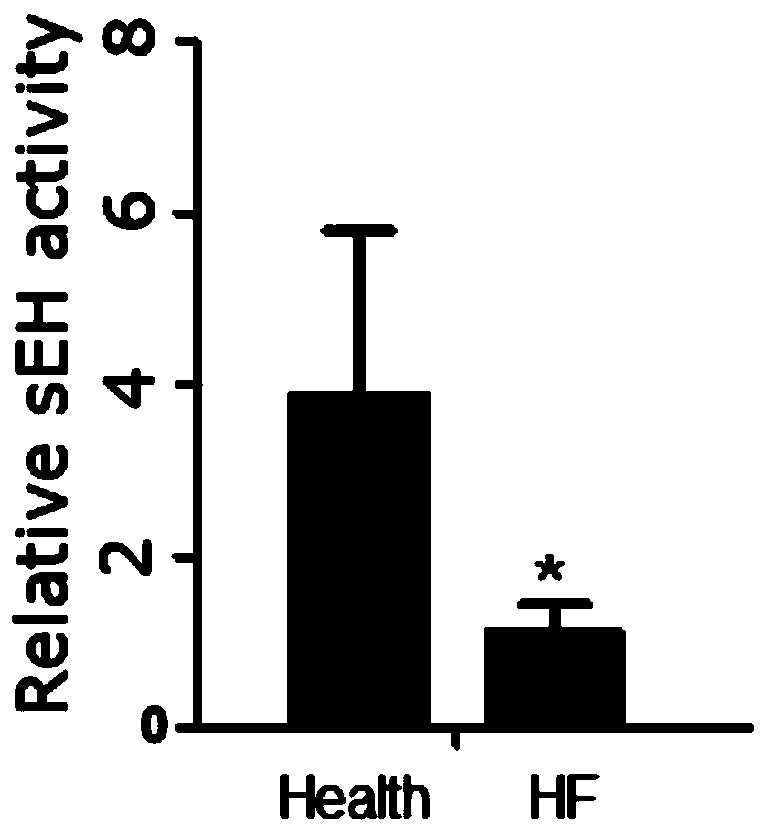
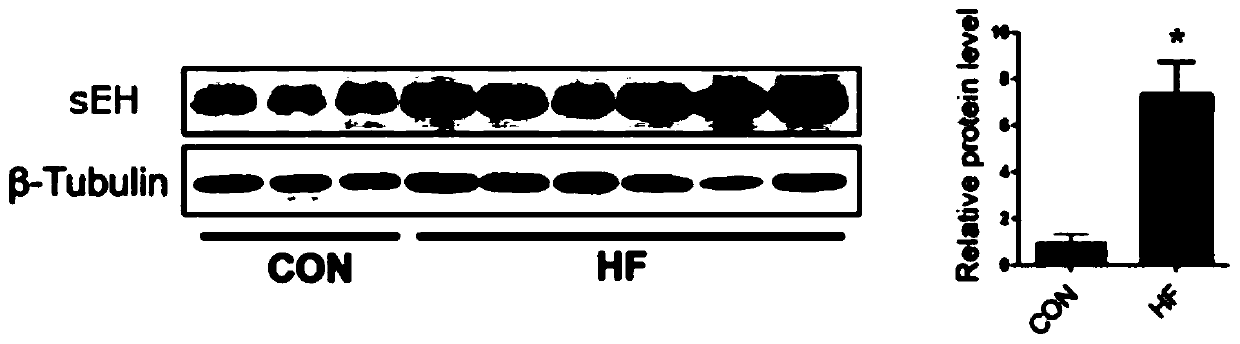
Application of EETs, sEH and sEH inhibitors in chronic heart failure
ActiveCN110161242AEasy diagnosisGood treatment effectComponent separationDisease diagnosisMedicineTreatment field
The invention discloses an application of EETs, sEH and sEH inhibitors in chronic heart failure, and belongs to the field of diagnosis, prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Two novel biomarkers-EETs and sEH are found, the effect of the biomarkers-EETs and sEH in the diagnosis of biomarkers in the chronic heart failure is proved as well as the effect of the biomarkers-EETs and sEH as a drug target in preventing, alleviating and / or improving the chronic heart failure; therefore, by detecting the EETs and sEH levels, the EETs and the sEH can predict and assist in the diagnosis ofthe chronic heart failure or assess the prognosis of the chronic heart failure; and meanwhile, the EETs level is controlled through drugs, diseases can be subjected to more intensive diagnosis and follow-up treatment, thus the EETs and the sEH haves huge application value in clinical practice.
Owner:TONGJI HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI TECH
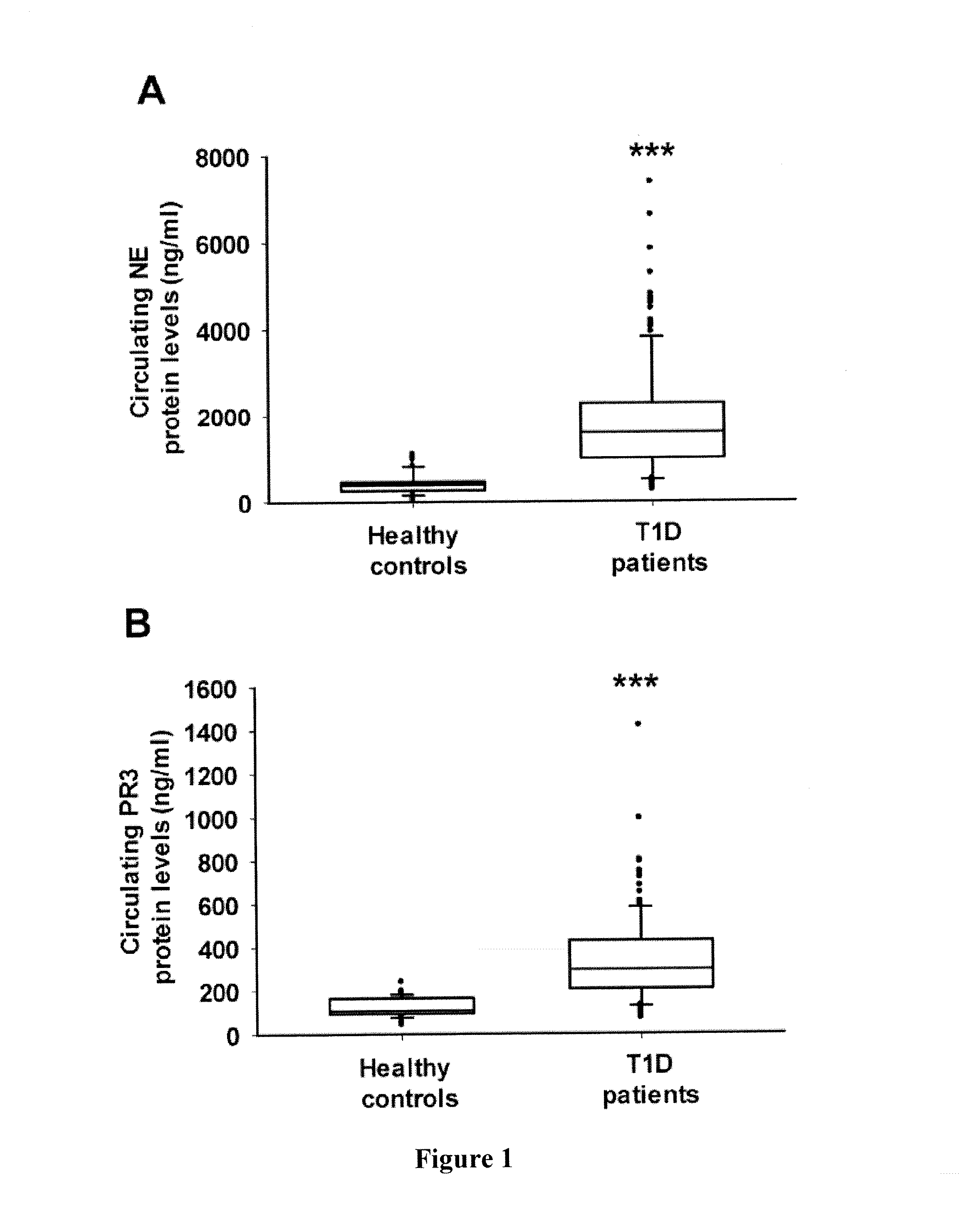
Methods and Compositions for Use of Neutrophil Elastase and Proteinase 3 as Diagnostic Biomarkers
ActiveUS20150346203A1Reduce riskReduce development riskMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningProteinase activityAutoimmune diabetes
Methods and compositions for identifying autoimmune diabetes are provided. One aspect provides a method for the evaluation of risk and progression of autoimmune diabetes in mammalian subjects. The method includes measuring the enzymatic activities and / or protein concentrations of neutrophil elastase and proteinase 3 in a subject and comparing the measured levels of these proteases to respective reference levels.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
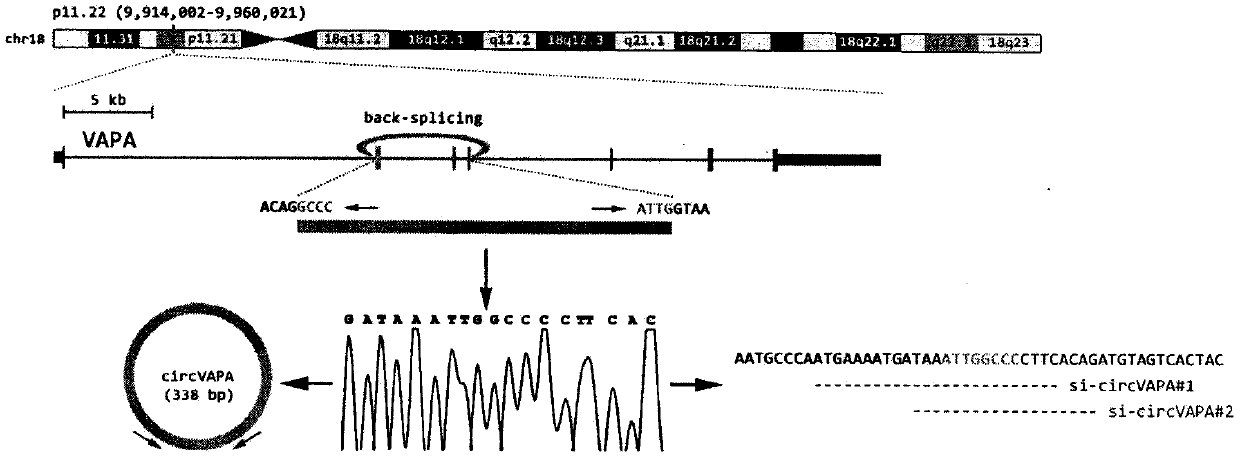
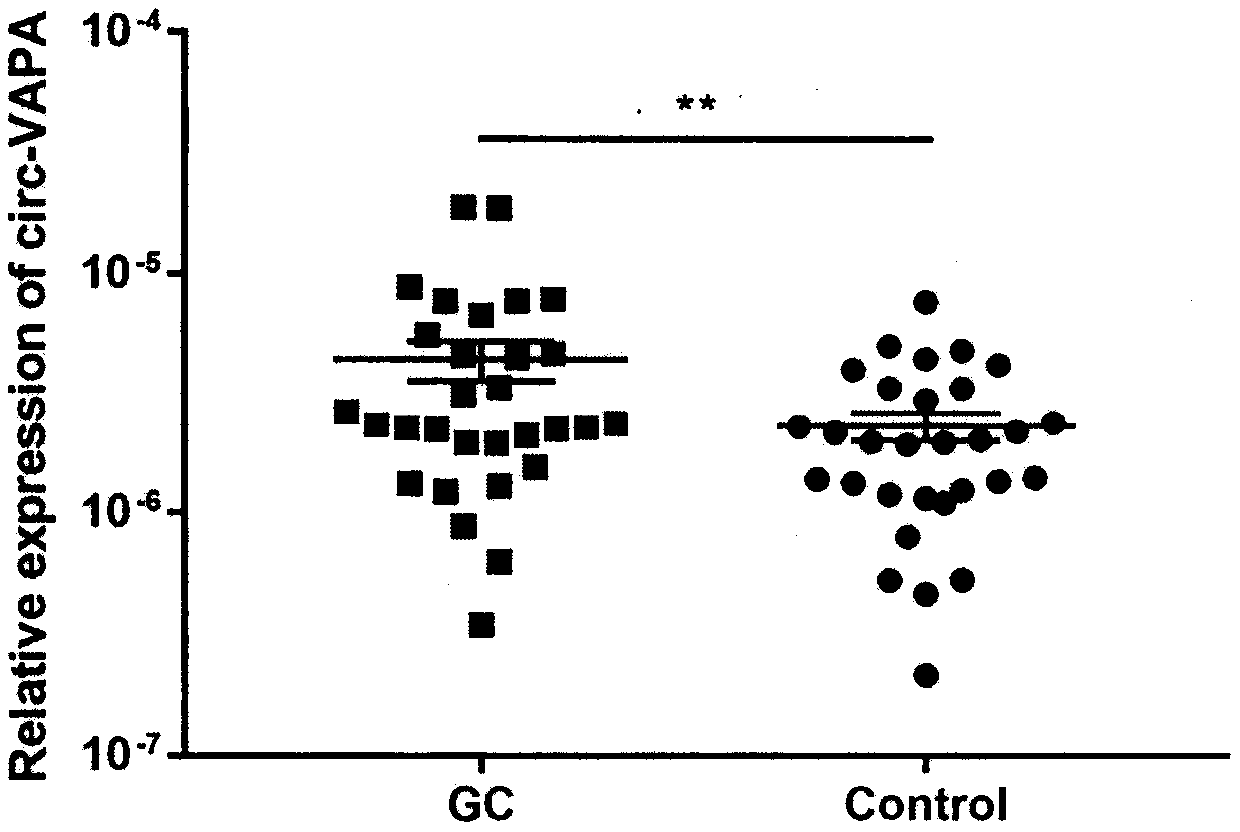
Application of circ-VAPA as gastric cancer and colorectal cancer diagnosis biomarker and treatment target point
InactiveCN109576373APrevent proliferationMicrobiological testing/measurementTreatment targetsNormal tissue
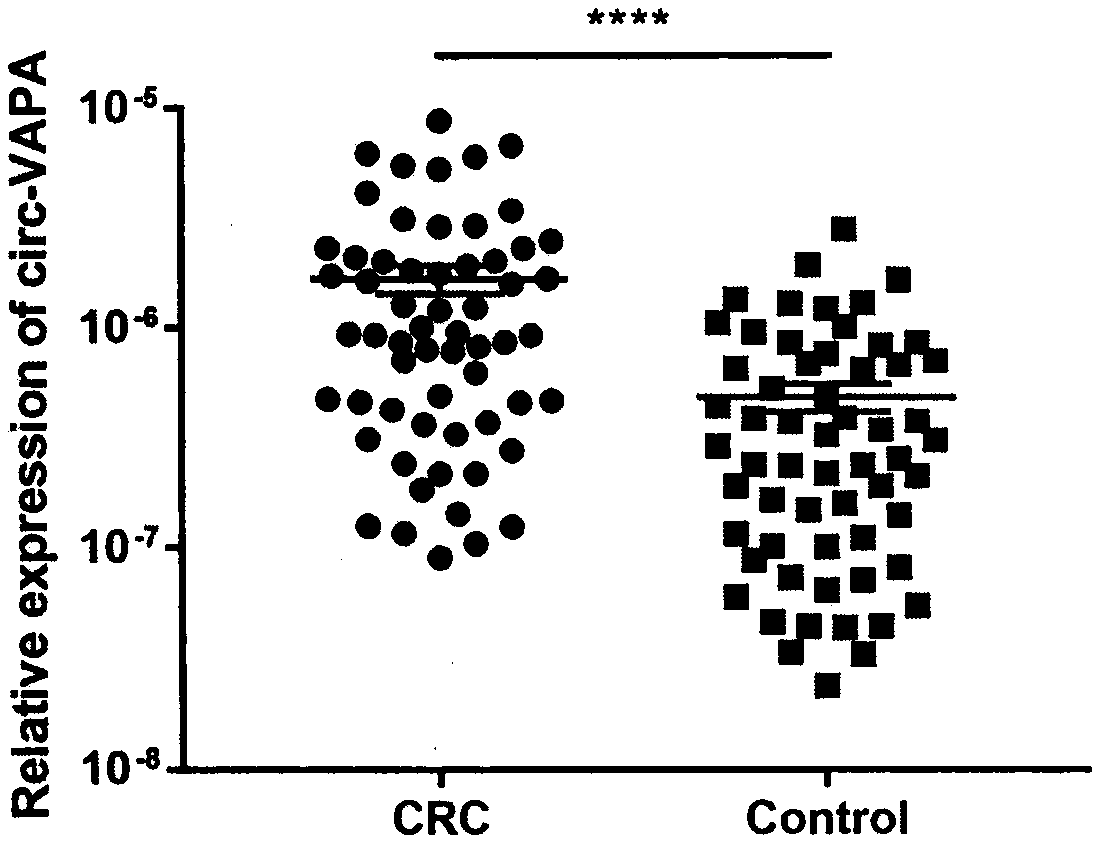
The invention discloses application of annular RNA VAPA (circ-VAPA) as a novel potential gastric cancer and colorectal cancer diagnosis biomarker and treatment target point. The circ-VAPA (hsa_circ_0006990|chr18:9931806-9937063+|VAPA) is formed by 2nd to 4th exons of a VAPA gene through reverse shearing and connection; the cyclization sequence has 338 basic groups. A qRT-PCR primer of the circ-VAPA and small interference RNA (siRNA) of in vitro interference circ-VAPA are prepared. Compared with normal tissues, the expression of the circ-VAPA in tumor tissues of patients with gastric cancer andcolorectal cancer is obviously up-regulated. In vitro experiments show that the circ-VAPA plays the role of the cancer promoting gene in the gastric cancer and colorectal cancer cells. The study results of the invention show that the circ-VAPA is a novel potential gastric cancer and colorectal cancer diagnosis biomarker and treatment target point.
Owner:BEIJING CHAOYANG HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Diagnostic Biomarker Profiles for the Detection and Diagnosis of Parkinsons Disease
The present invention provides methods, compositions and kits for the detection of Parkinson' disease (PD) diagnostic biomarkers, for the diagnosis of PD, for the identification of a subject at risk for developing PD, and for the generation of patient-specific PD diagnostic biomarker profiles.
Owner:ROWAN UNIVERSITY
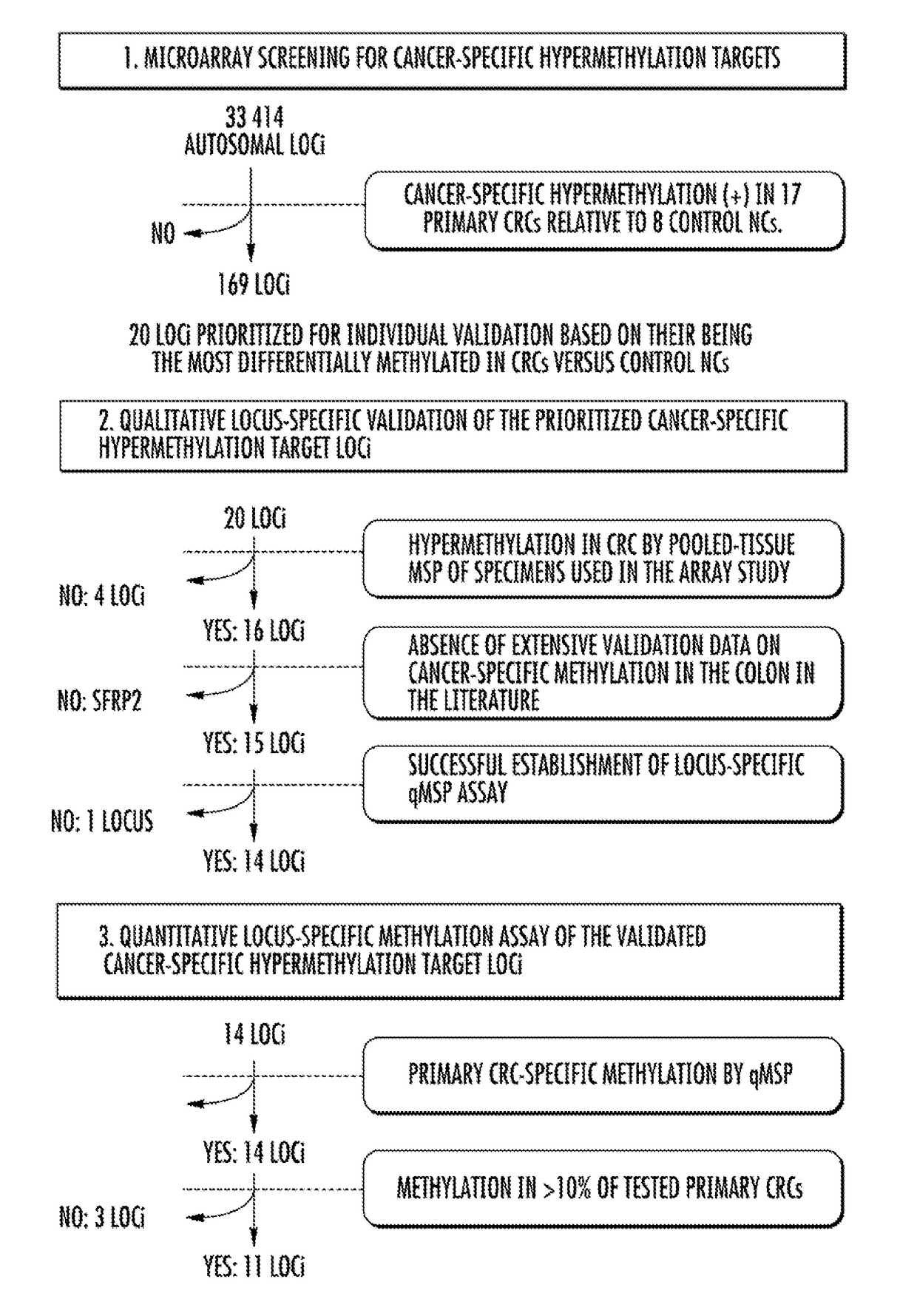
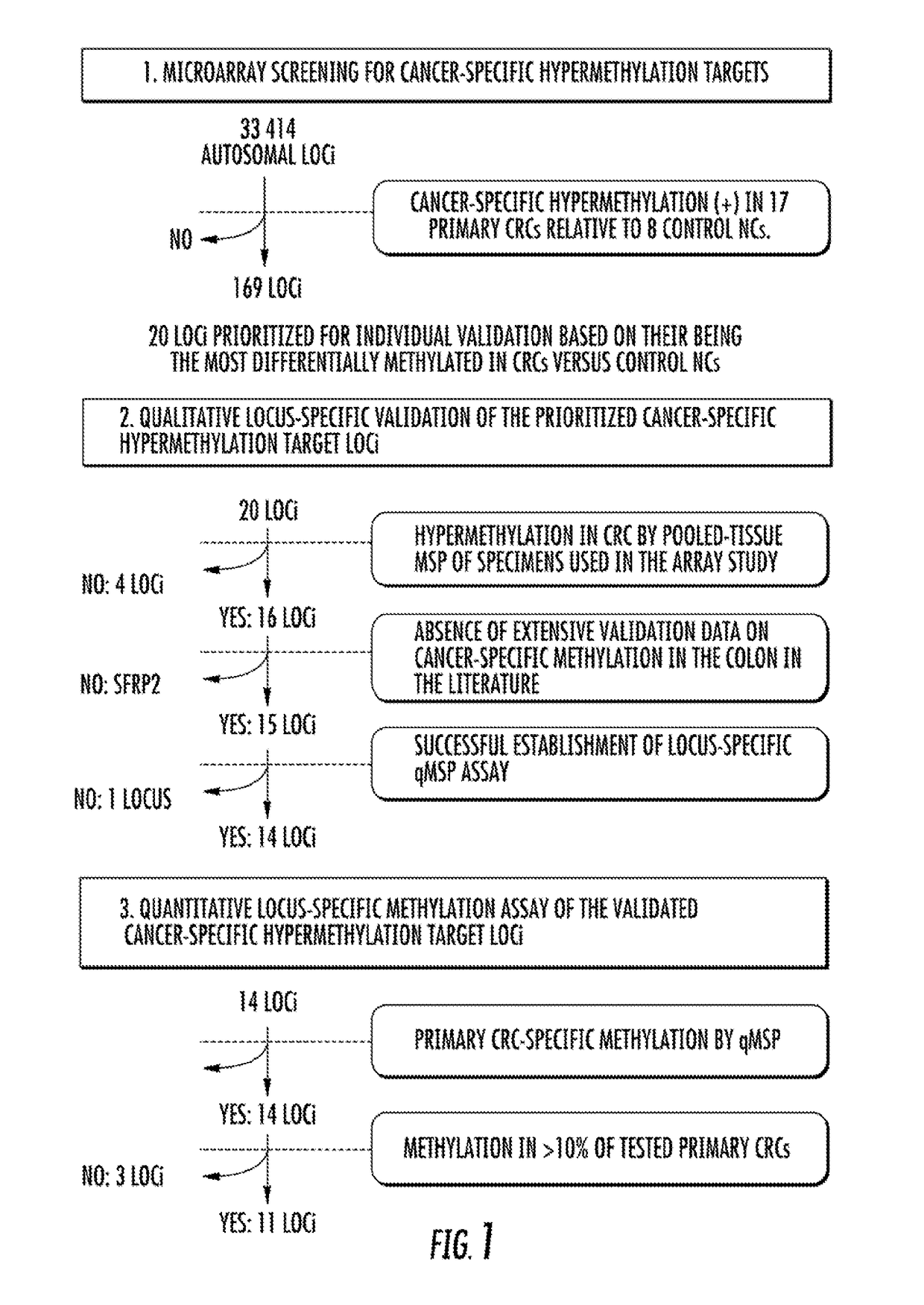
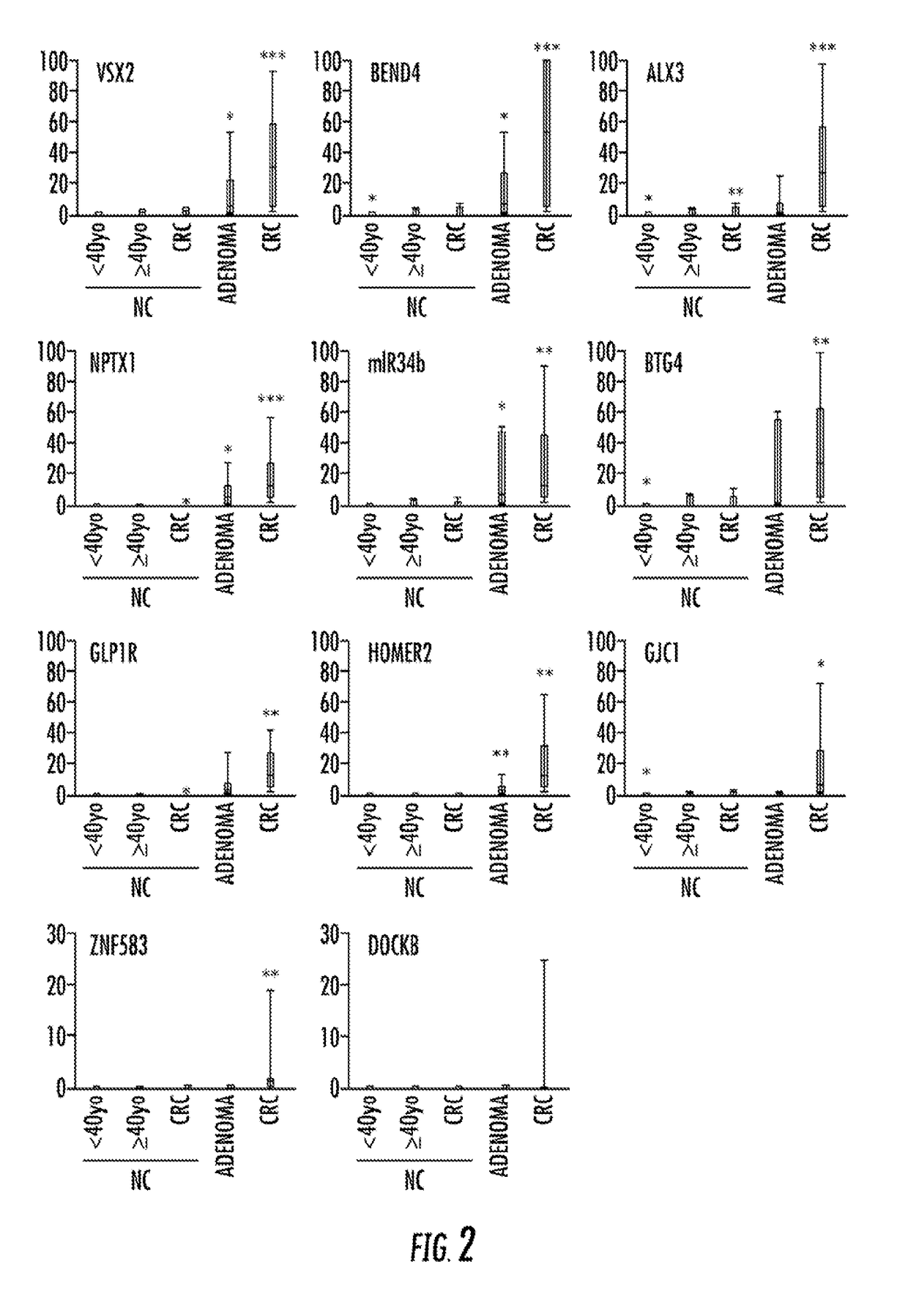
DNA hypermethylation diagnostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer
ActiveUS9957570B2Improve accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDiagnostic biomarkerBiomarker (petroleum)
The present invention relates to the field of cancer. More specifically, the present invention relates to the use of biomarkers to detect colorectal cancer. In one aspect, the present invention provides methods for qualifying colorectal cancer status including, but not limited to, diagnosis, prognosis, and risk stratification, in patients. In one embodiment, a method for diagnosing colorectal cancer (CRC) in a patient comprises the steps of (a) collecting a sample from the patient; (b) measuring the methylation levels of one or more biomarkers in the sample collected from the patient; and (c) comparing the methylation levels of the one or more biomarkers with predefined methylation levels of the same biomarkers that correlate to a patient having CRC and predefined methylation levels of the same biomarkers that correlate to a patient not having CRC, wherein a correlation to one of the predefined methylation levels provides the diagnosis.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Method for diagnosing immunoglobulin A nephropathy and TGBM nephropathy
InactiveUS8927220B2Easy diagnosisDiagnose diabetic nephropathy earlyMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationTargeted proteomicsDisease progression
A protein used as a biomarker for diagnosing IgA nephropathy and TGBM (thin-glomerular-basement-membrane) using urine through a target proteomics method. A diagnosis biomarker protein and a kit for diagnosing IgA nephropathy and TGBM and predicting progress of the nephropathy in advance using the protein are provided. The degree of the progression of the disease can be grasped by detecting IgA nephropathy and TGBM, enabling early diagnosis and confirming progress from the patient's urine. In addition, a monoclonal antibody produced based on the diagnosis biomarker protein can be used for an immunoassay kit (ELISA, antibody coated tube test, lateral-flow test, potable biosensor). The monoclonal antibody is used in early diagnosis and progression detection of IgA nephropathy and development of a novel drug for the purpose of treatment.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
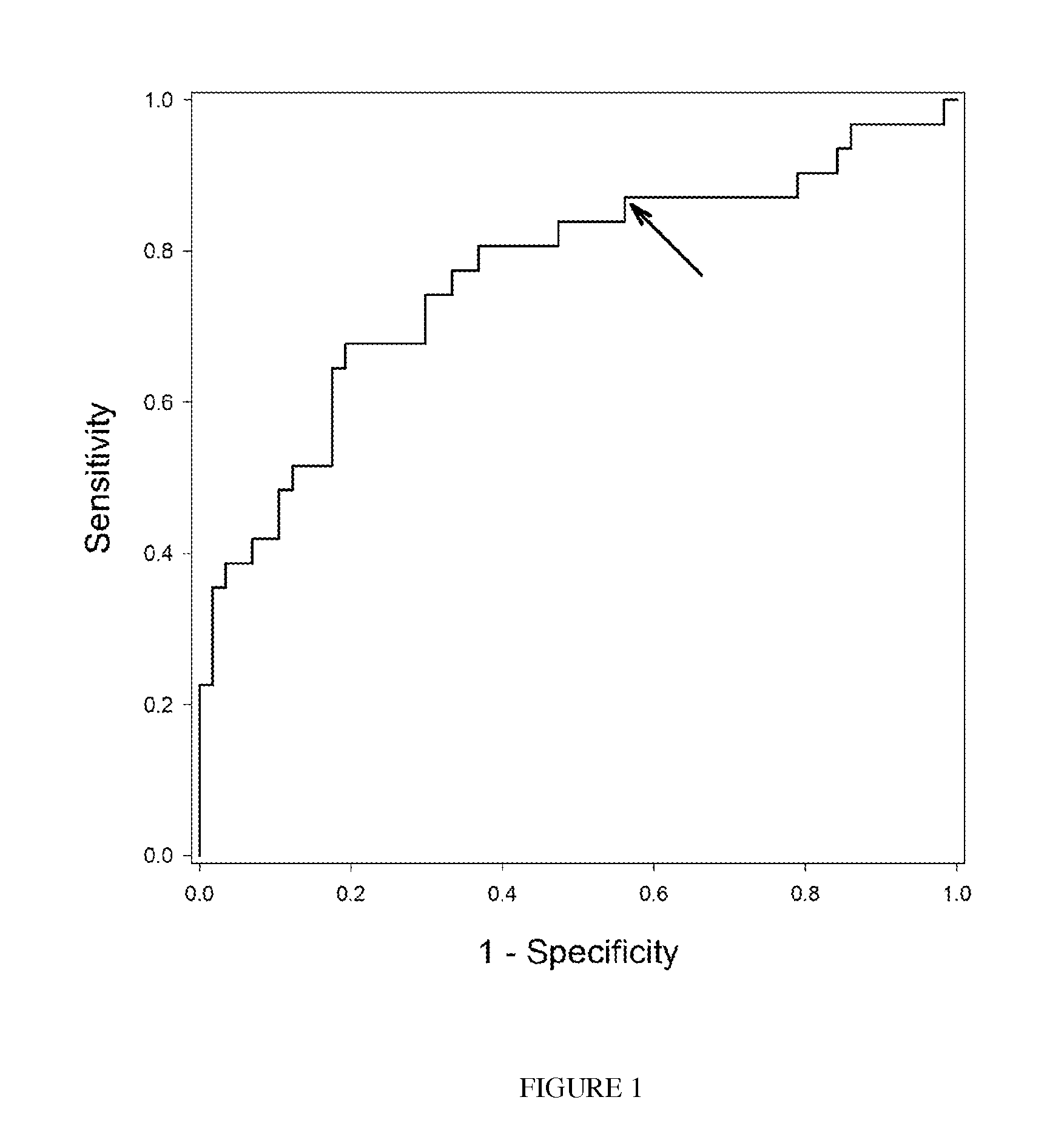
Biomarker composite test for hepatic vein pressure gradient and cirrhosis treatment
Diagnostic biomarker panel, method, kit, and device for diagnosing the severity and / or prognosis of cirrhosis are provided. More specifically, the invention provides a novel biomarker panel correlating to HVPG and esophageal varices. The invention further provides a biomarker panel and non-invasive test methods that predict non-clinically significant portal hypertension HVPG and non-clinically significant esophageal varices when the expression of the biomarker panel correlates with HVPG of less than 12 mmHg. The invention further provides that the patients with the expression of the biomarker panel correlating to non-clinically significant HVPG and esophageal varices can be excluded from undergoing esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) screening and those correlating to HVPG equal to or greater than 12 mmHg are indicated for EGD.
MiRNAs as novel therapeutic targets and diagnostic biomarkers for parkinsons disease
The disclosure provides pharmaceutical compositions including an oligonucleotide that down-regulates the over-expression of at least one miRNA of SEQ ID NOs: 1-283. The oligonucleotide may be complementary to the nucleotide sequence of at least one of SEQ ID NOs: 1-283, or hybridizes under stringent conditions to a nucleotide sequence of at least one of SEQ ID NOs: 1-283. Further provided are methods of diagnosing Parkinson's Disease (PD) in a subject. The methods may include detecting the level of expression of at least one miRNA of SEQ ID NOs: 1-283 in a biological sample from the subject, and comparing the level of expression in the sample to the level of expression in a reference. Further provided are methods for treating, preventing, or reducing the risk of PD. Kits are also provided.
Owner:RUSH UNIV MEDICAL CENT
Exosomes and diagnostic biomarkers
ActiveUS20140113305A1Bacterial antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomics methodsSpectroscopy
The invention provides methods for the detection of M. tuberculosis proteins in or on exosomes derived from infected individuals. The methods can use a proteomic approach including mass spectroscopy, data mining and multiplex reaction monitoring to quickly examine a large amount of M. tuberculosis proteins to determine the best biomarkers for use in diagnostic tests to identify active TB patients.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY +1
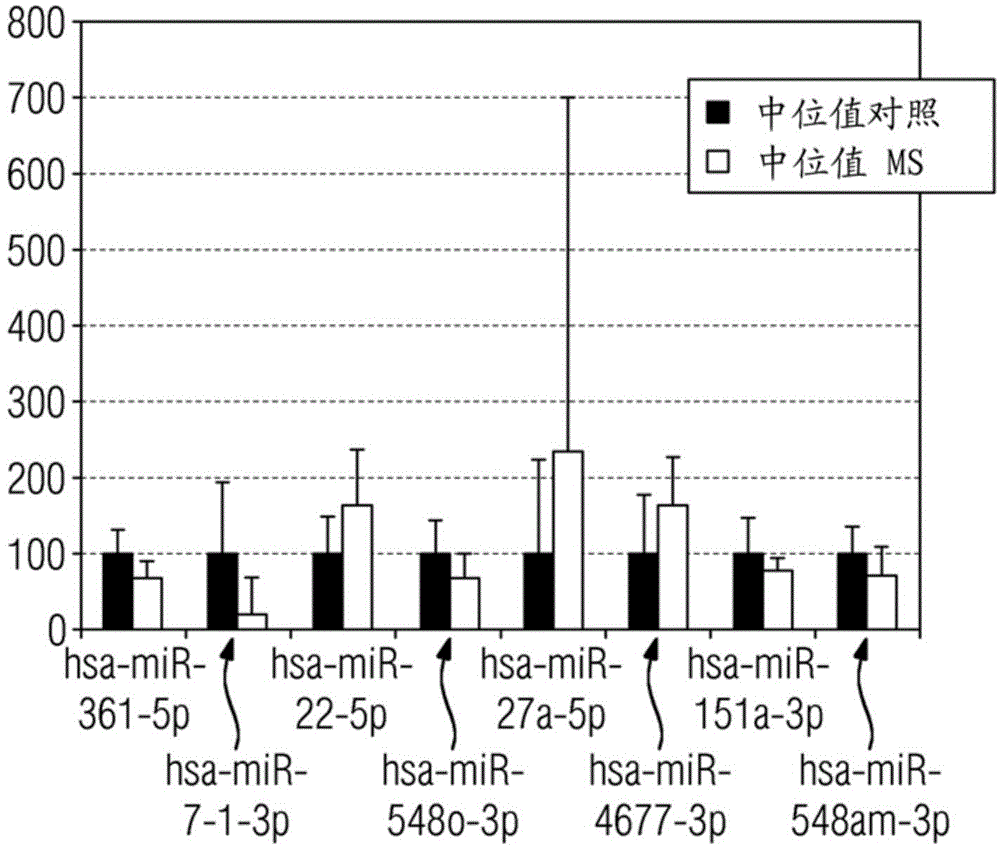
Diagnostic miRNA profiles in multiple sclerosis
The invention relates to methods for diagnosing mulötiple sclerosis with miRNA markers. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis (MS) can be challenging in patients with atypical presentations and during a first neurological deficit possibly related to inflammatory demyelination. Towards the identification of biomarkers for diagnosis of MS, a comprehensive analysis of miRNA expression patterns was obtained. Significantly deregulated miRNAs were identified, which have previously not been related to MS according to the microRNA disease database. These miRNAs could potentially serve as future diagnostic biomarkers for MS and help in diagnosis, monitoring disease activity, and evaluation of treatment responses in patients with MS.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Diagnostic biomarker to identify women at risk for preterm delivery
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
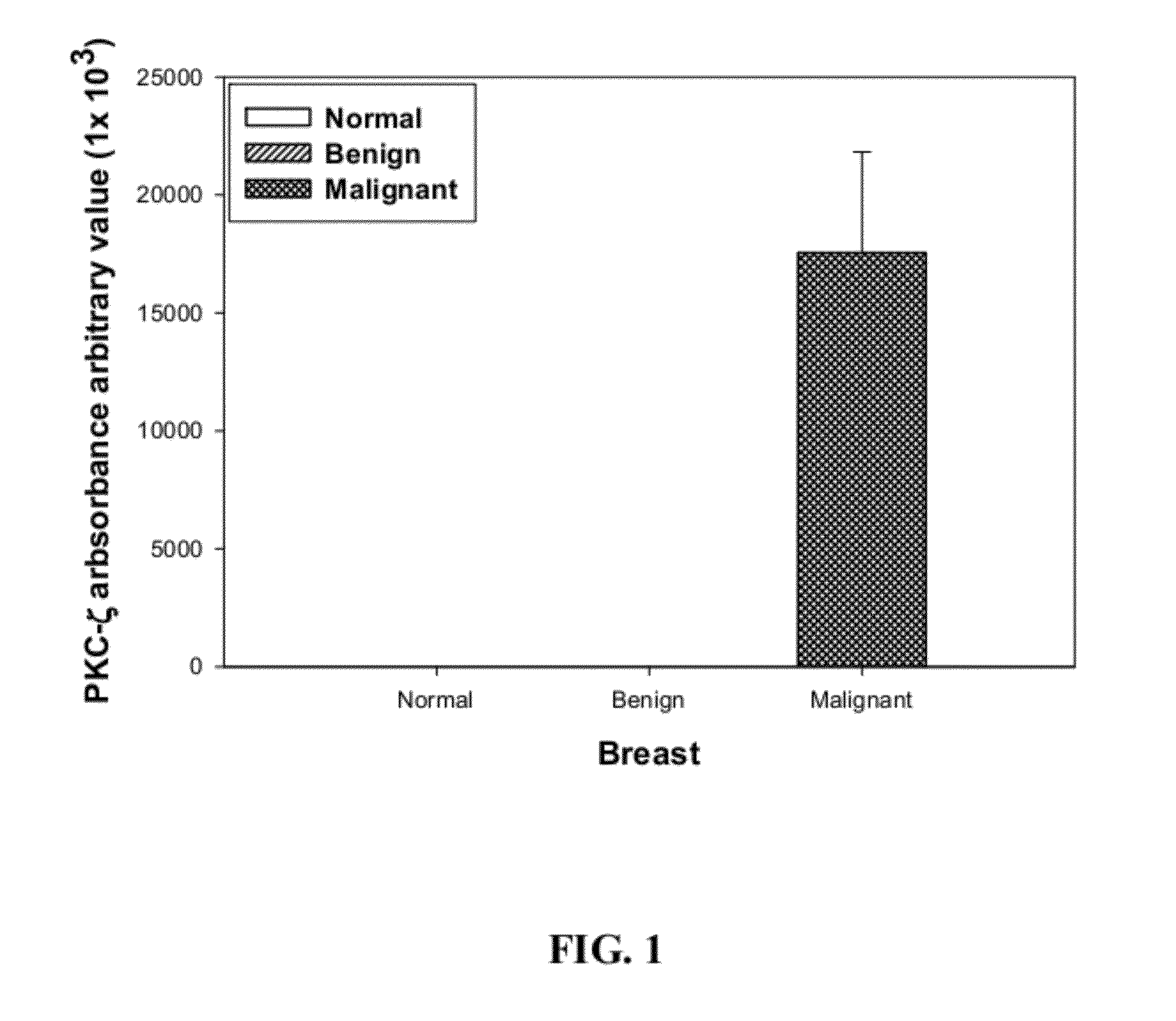
Use of pkc-zeta as a breast cancer tumorigenic biomarker as well as a target for treatment of breast cancer
InactiveUS20120171219A1Organic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiagnostic biomarkerOncology
The present invention provides use of protein kinase C-zeta (PKC-ζ) as a diagnostic biomarker for breast cancer tumorigenesis. Also provided are uses of PKC-zeta inhibitors for inhibiting breast cancer tumorigenesis and for treatment of breast cancer.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +1
Biomarkers for detecting colorectal cancer or adenoma and methods thereof
ActiveCN113711044AMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesComponent separationSerum samplesDiagnostic biomarker
A group of diagnostic biomarkers usable for diagnosis of colorectal cancer or colorectal adenoma. A method for detecting colorectal cancer or colorectal adenoma using the group of diagnostic biomarkers is also provided. For example, the method is a non-invasive approach that may utilize serum samples for detecting colorectal cancer. Moreover, the method for detecting colorectal cancer may detect colorectal cancer of different stages (e.g., pre-cancer stage, early stage, middle stage, late stage).
Owner:中精普康(北京)医药科技有限公司
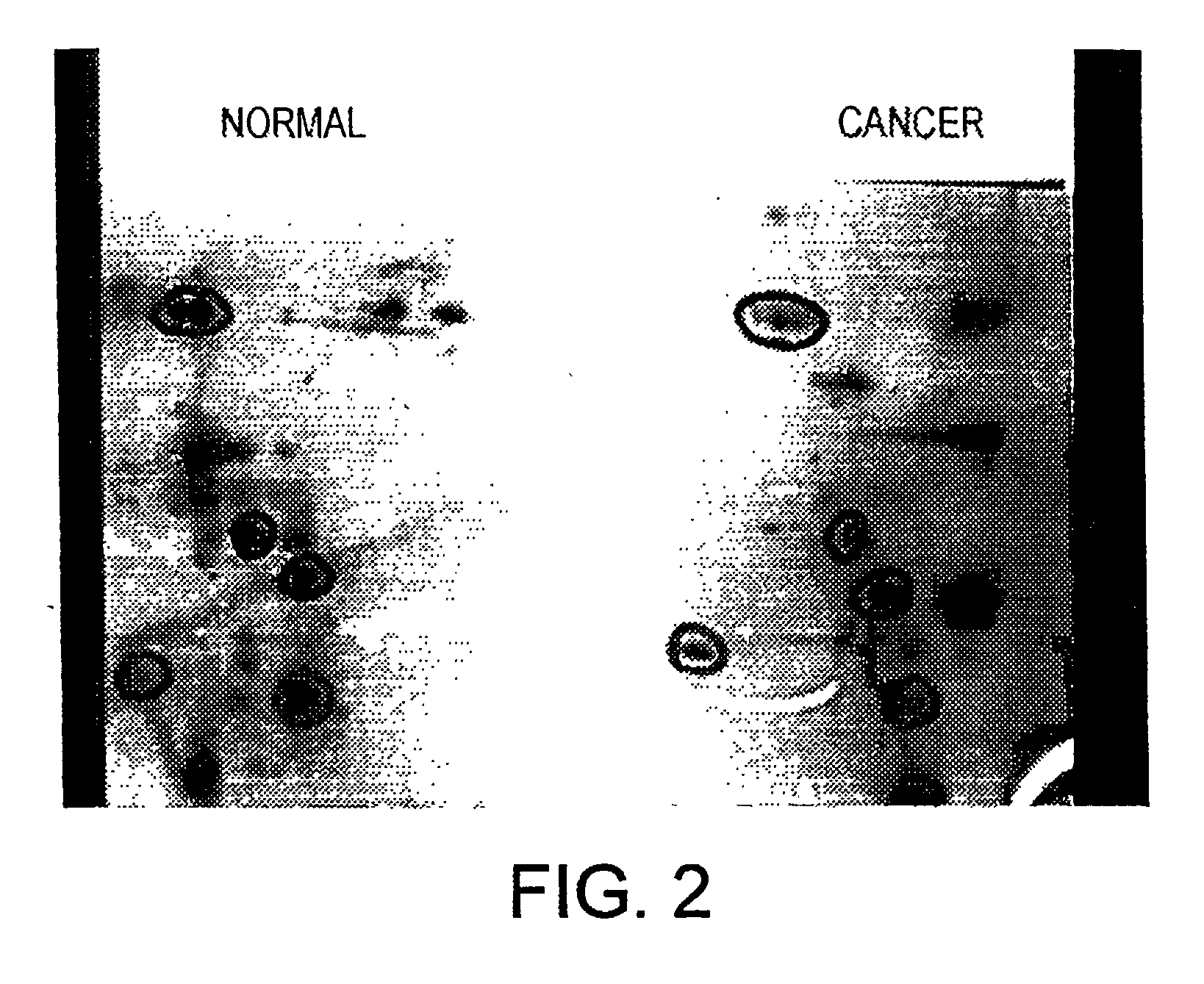
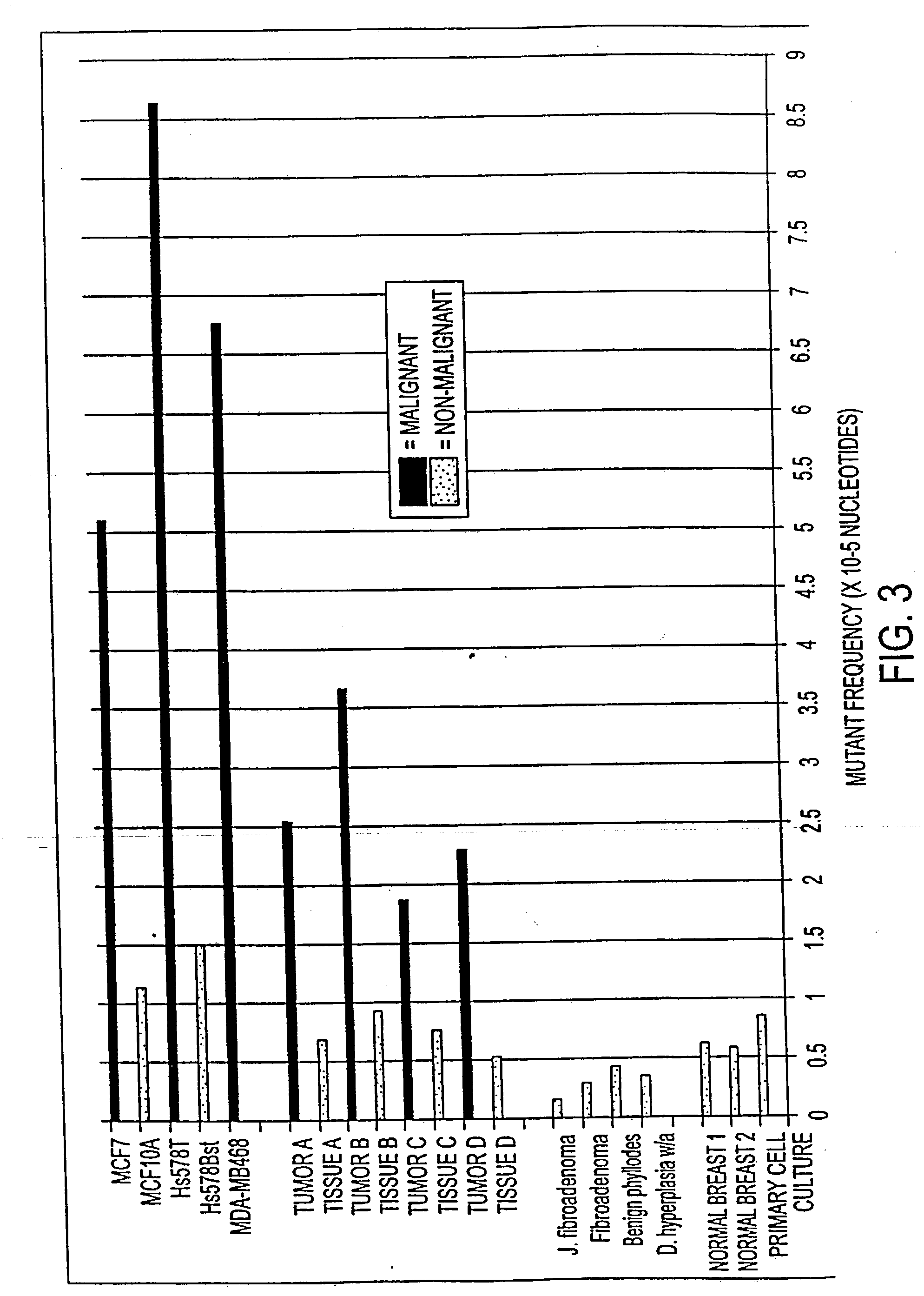
Altered DNA synthesome components as biomarkers for malignancy
InactiveUS20060073477A1Guaranteed functionChange activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMalignant phenotypeNeoplasm
Owner:SCHNAPER LAUREN
Biomarker of granulosa cells used for polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) diagnosis, and screening method and diagnostic kit thereof
PendingCN110747269AGood technical versatilityQuick fixMicrobiological testing/measurementGranular leucocyteGranulosa cell
The invention relates to a biomarker of granulosa cells used for polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) diagnosis as well as a screening method and a diagnostic kit thereof. The novel diagnostic biomarker is discovered by screening PCOS-related biomarkers in the whole genome by adopting combined analysis of RNA-seq, miRNA-seq and MBD-seq. The biomarker comprises miR-429, miR-141-3p and miR-126-3p, and / or XIAP gene, BRD3 gene, MAPK14 gene and SLC7A5 gene. Compared with the prior art, the biomarker of granulosa cells used for PCOS diagnosis has the advantages of being high in detection sensitivity, high in accuracy and so on.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com