Diagnostic transcriptomic biomarkers in inflammatory cardiomyopathies
a transcriptomic and myocardial disease technology, applied in the field of myocarditis biomarkers, can solve the problems of limiting the efficacy of treatment, difficult to achieve consensus among pathologists, and difficult diagnosis of myocarditis,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Diagnostic Transcriptomic Biomarkers in Inflammatory Cardiomyopathies
[0150]Table 13 depicts the baseline clinical variables of patients included in the initial case-control population with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy (IDCM) and Dallas criteria defined lymphocytic myocarditis. By design, there were no differences in gender, age, functional parameters or medication between the two groups.
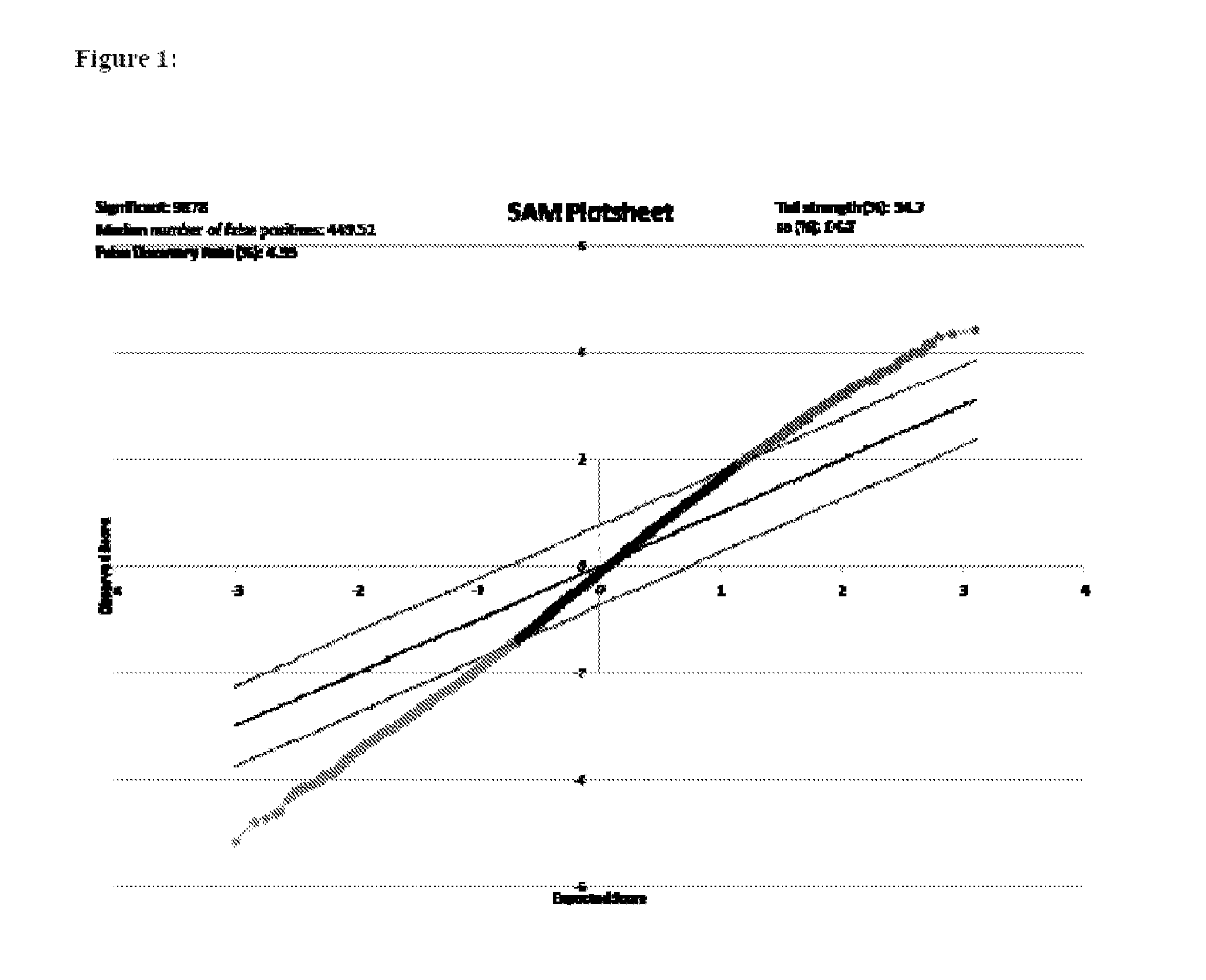
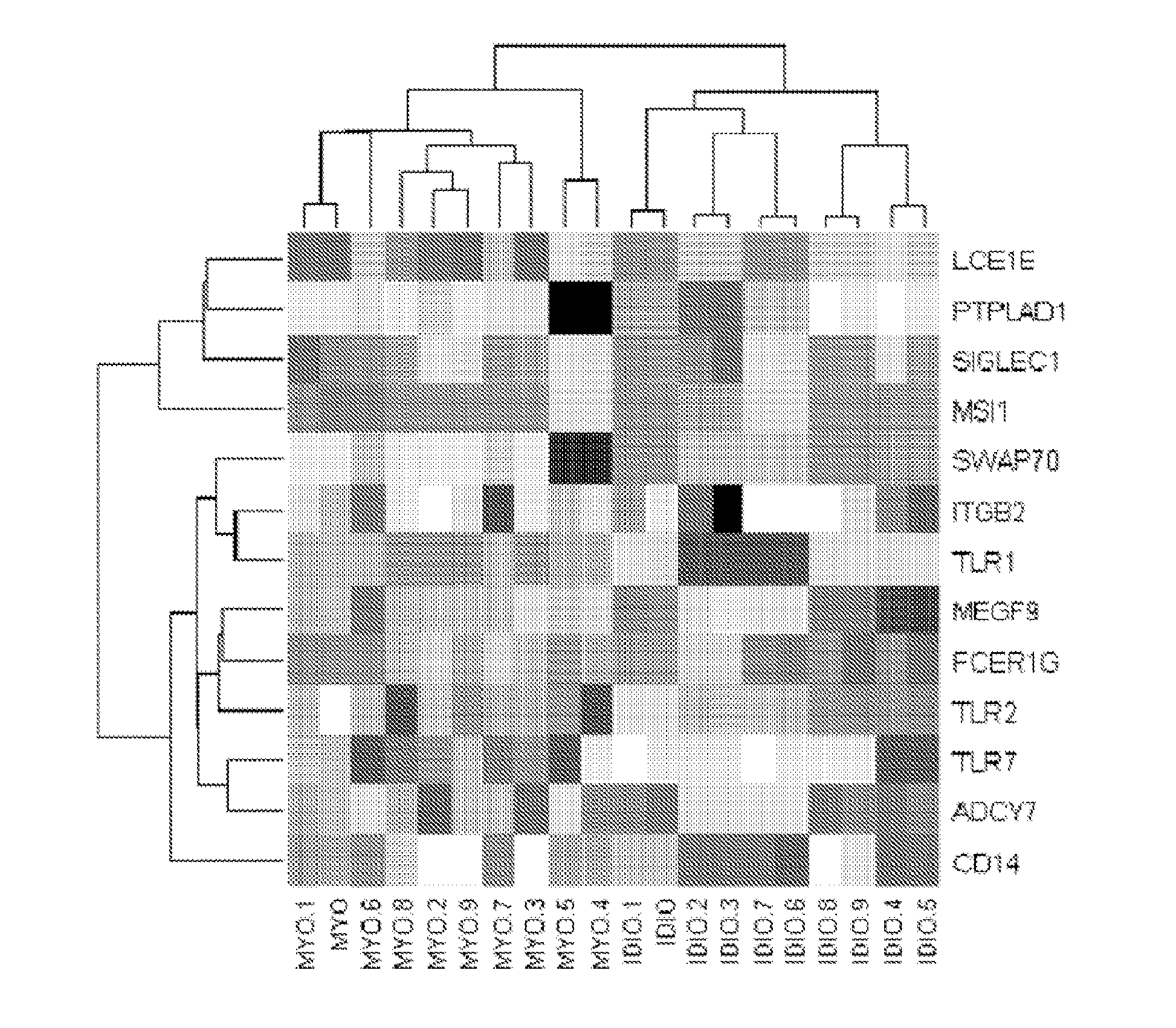
[0151]Discovery of phenotype specific differences in gene expression and involved pathways: To identify differential gene expression between patients with IDCM (n=32) and those with lymphocytic myocarditis (n=1.6), oligonucleotide microarrays were used to analyze RNA obtained from endomyocardial biopsies (EMBs) from affected patients at first presentation with new onset heart failure. 9,878 differentially expressed genes (q1.2) were identified in patients with IDCM compared to myocarditis (FIG. 1). Transcripts with FC>2 (141 over-expressed and 16 down-regulated transcripts) are provided as in Ta...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com