Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Gingival fibroblast" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
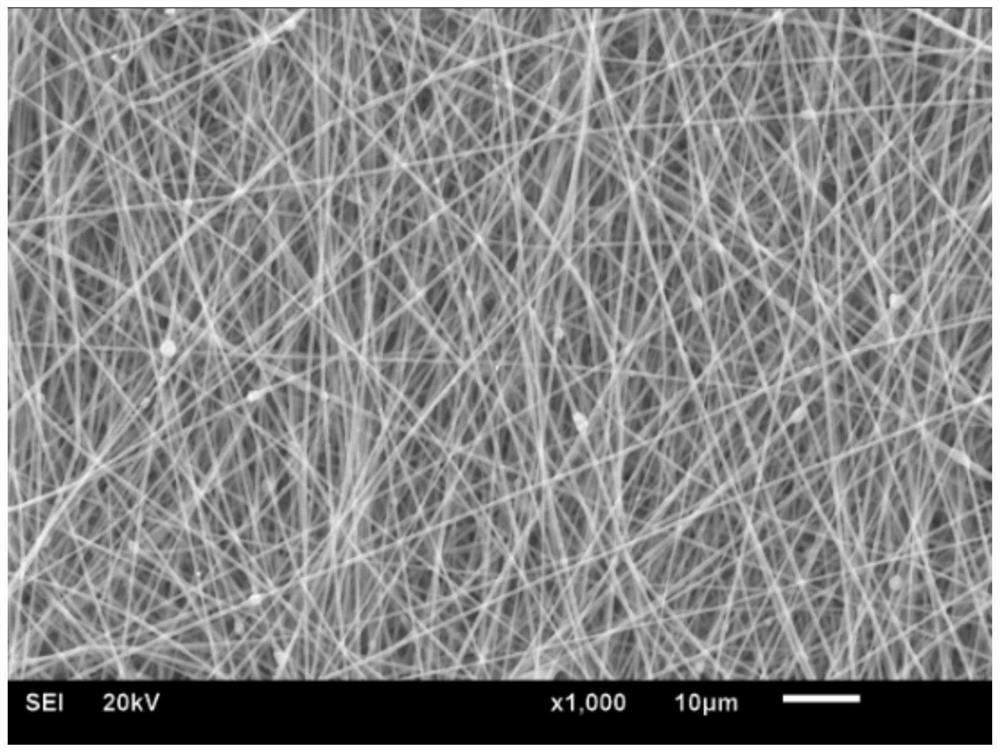
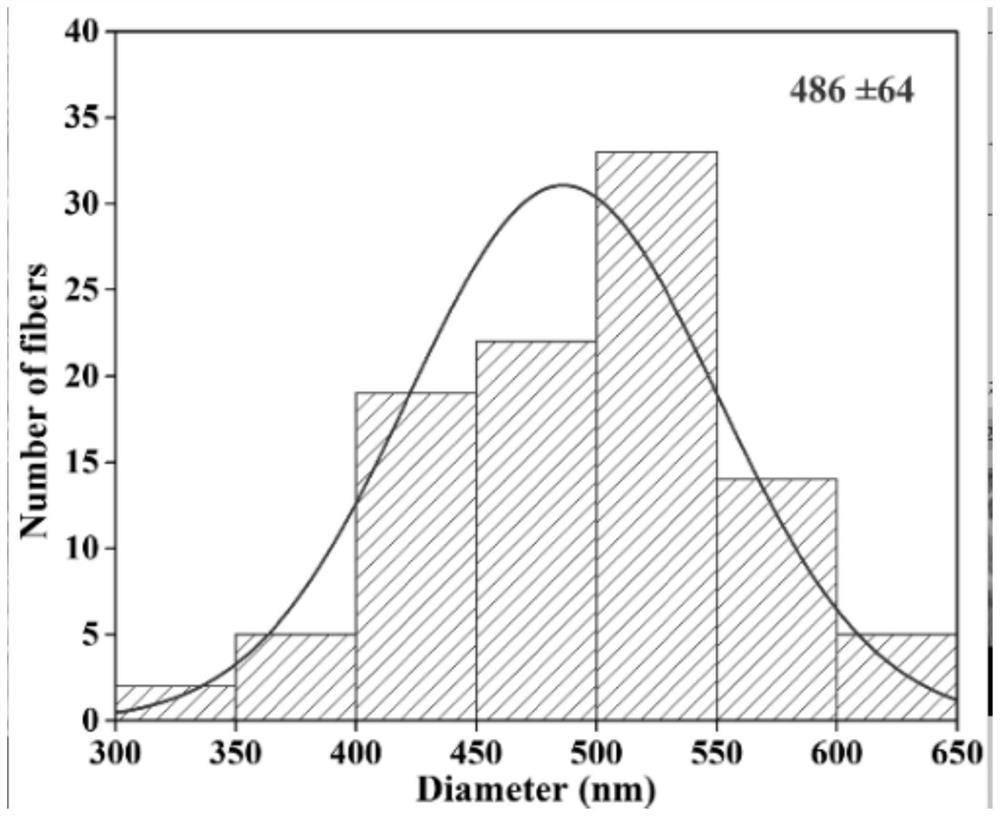
Gradient material for guiding regeneration of periodontal hard and soft tissues and preparation method of gradient material
ActiveCN110141687AAchieving Synchronous RepairAll-in-one repairSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismFiberGradient material
The invention discloses a gradient material for guiding regeneration of periodontal hard and soft tissues, and a preparation method of the gradient material. The gradient material is constructed by combining an electrostatic spinning technology with a biological 3D (three dimensional) technology. A micropore structure of an electrostatic spun fibrous membrane can prevent gingival fibroblasts frommigrating to a root surface to play a mechanical barrier role and facilitate transmission of nutrition and metabolism substances; and individualized repair of alveolar bone can be achieved according to clinical requirements since a structure and a shape of a 3D printing scaffold layer are highly designable. The method is simple and stable in preparation technology, and the gradient material integrates a periodontal guided tissue regeneration membrane and an alveolar bone repair scaffold material and has a potency to achieve clinical customized treatment. The gradient material has a good effectof guiding the repair of the hard and soft tissues in vivo and can be better applied to the synchronous regeneration and repair of the alveolar bone and the periodontal tissues.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Application of L.p (lactobacillus paracasei) R3-10 in preparation of medicines for preventing or treating oral inflammatory diseases
ActiveCN111904985AInhibition of secretionInhibit aggregationCosmetic preparationsAntipyreticInflammatory factorsNeutrophil granulocyte
The invention discloses an application of L.p R3-10 in preparation of medicines for preventing or treating oral inflammatory diseases, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. Inactivatedand non-inactivated fermentation supernatant and bacterial suspension of the L.p R3-10 disclosed by the invention have the effect of inhibiting LPS from stimulating human gingival fibroblasts to secrete cell inflammatory factors IL6, TNF-alpha and PGE2 in vitro; in an in-vivo inflammation model, neutrophils and macrophages can be remarkably inhibited from being gathered to the inflammation position of the tail fin of a zebra fish, and clearing of the neutrophils and the macrophages at the inflammation position of the tail fin of the zebra fish is remarkably promoted; and meanwhile, damage repair of the tail fin of the zebra fish can be remarkably promoted. The L.p R3-10 disclosed by the invention has a huge potential application prospect in the aspect of treating and / or preventing the oral inflammatory diseases.
Owner:广东南芯医疗科技有限公司 +2
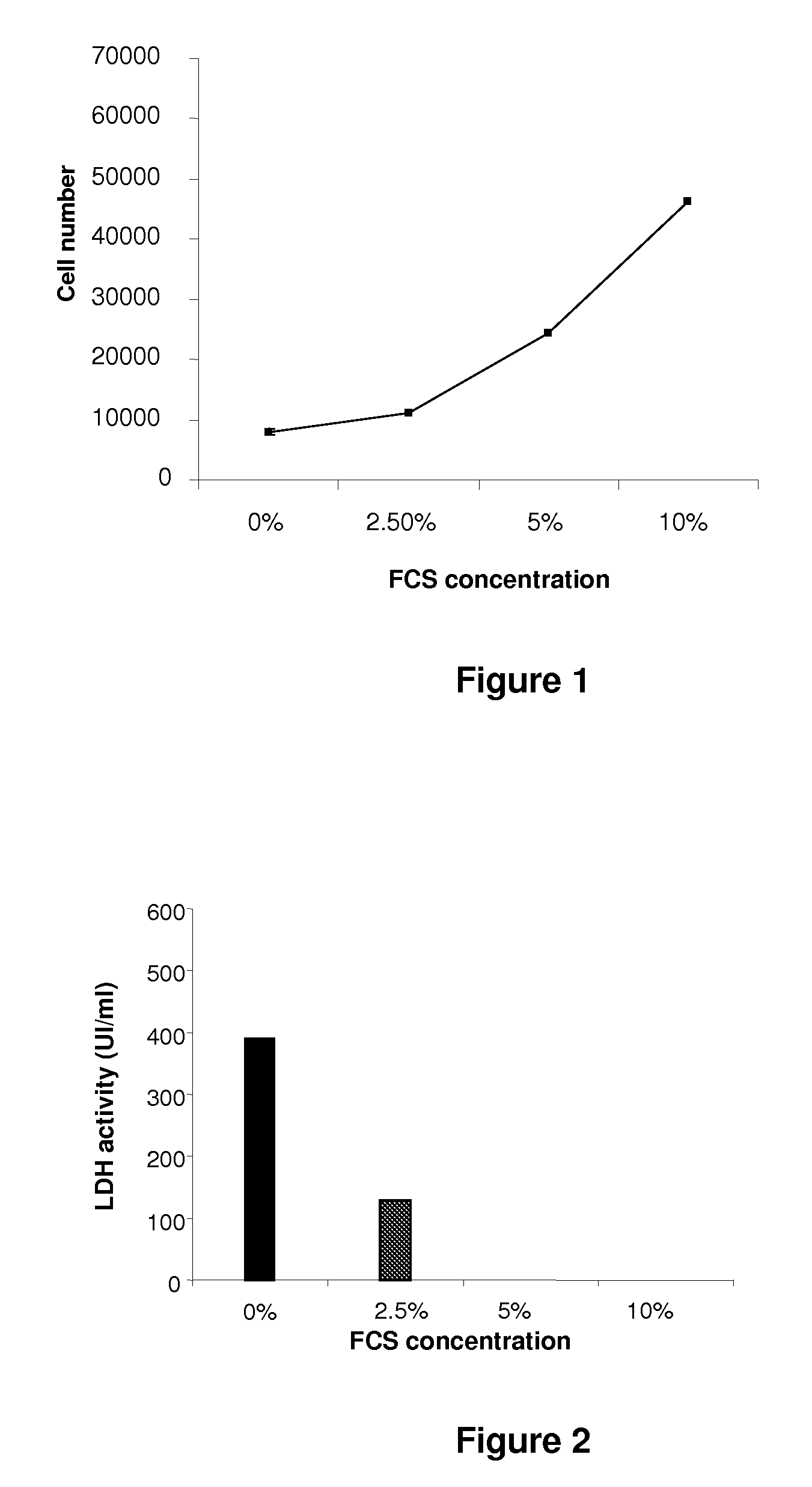
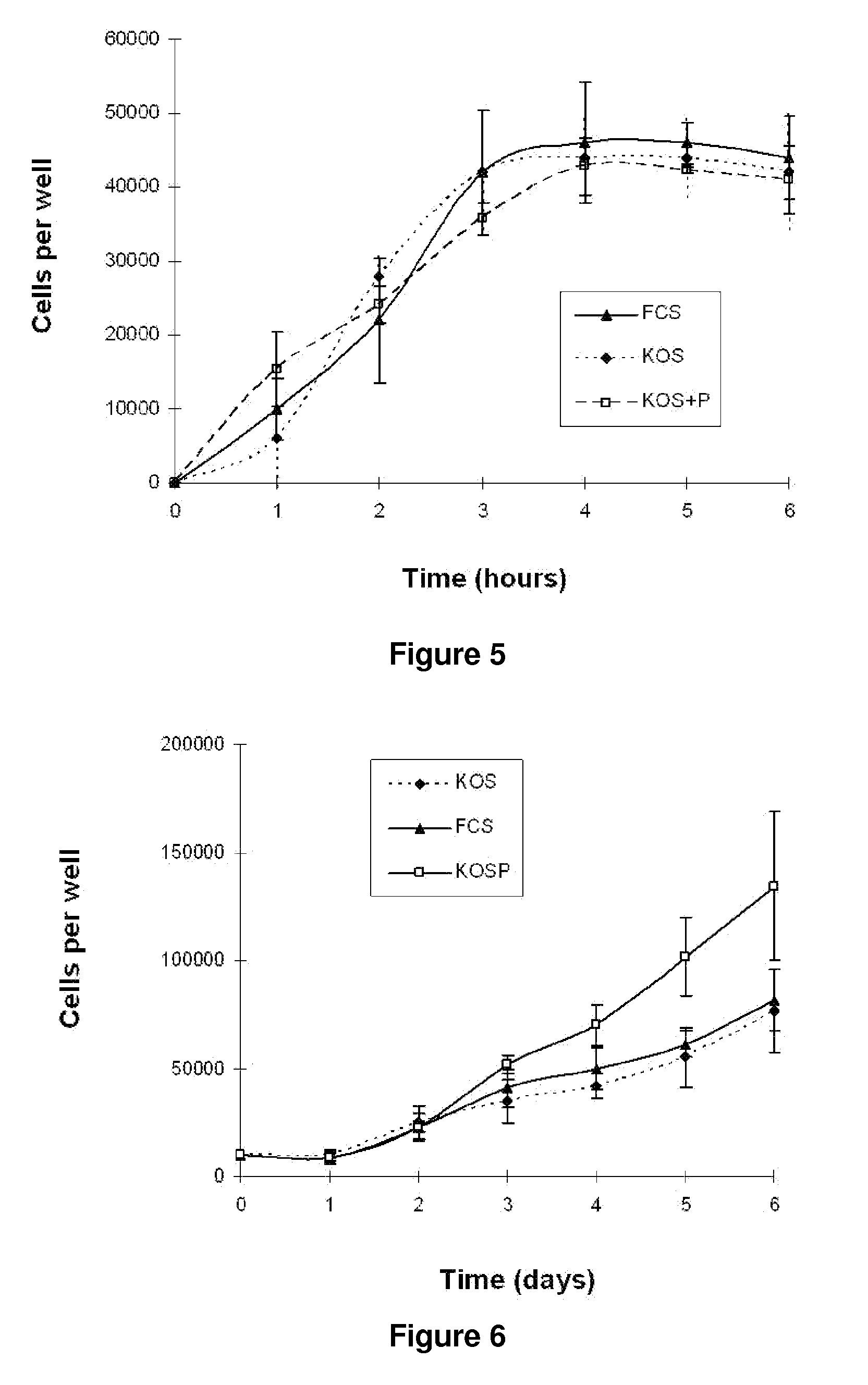
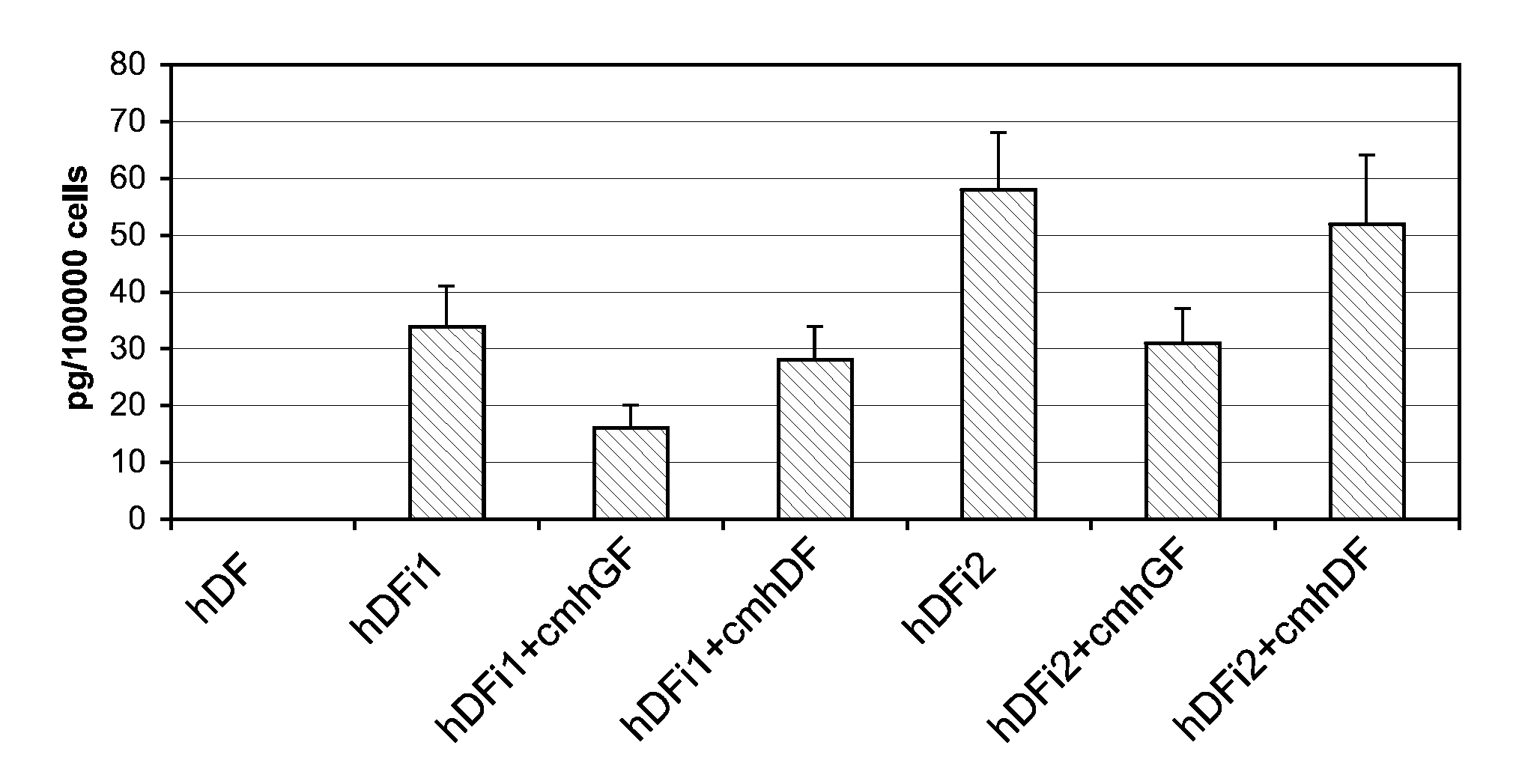
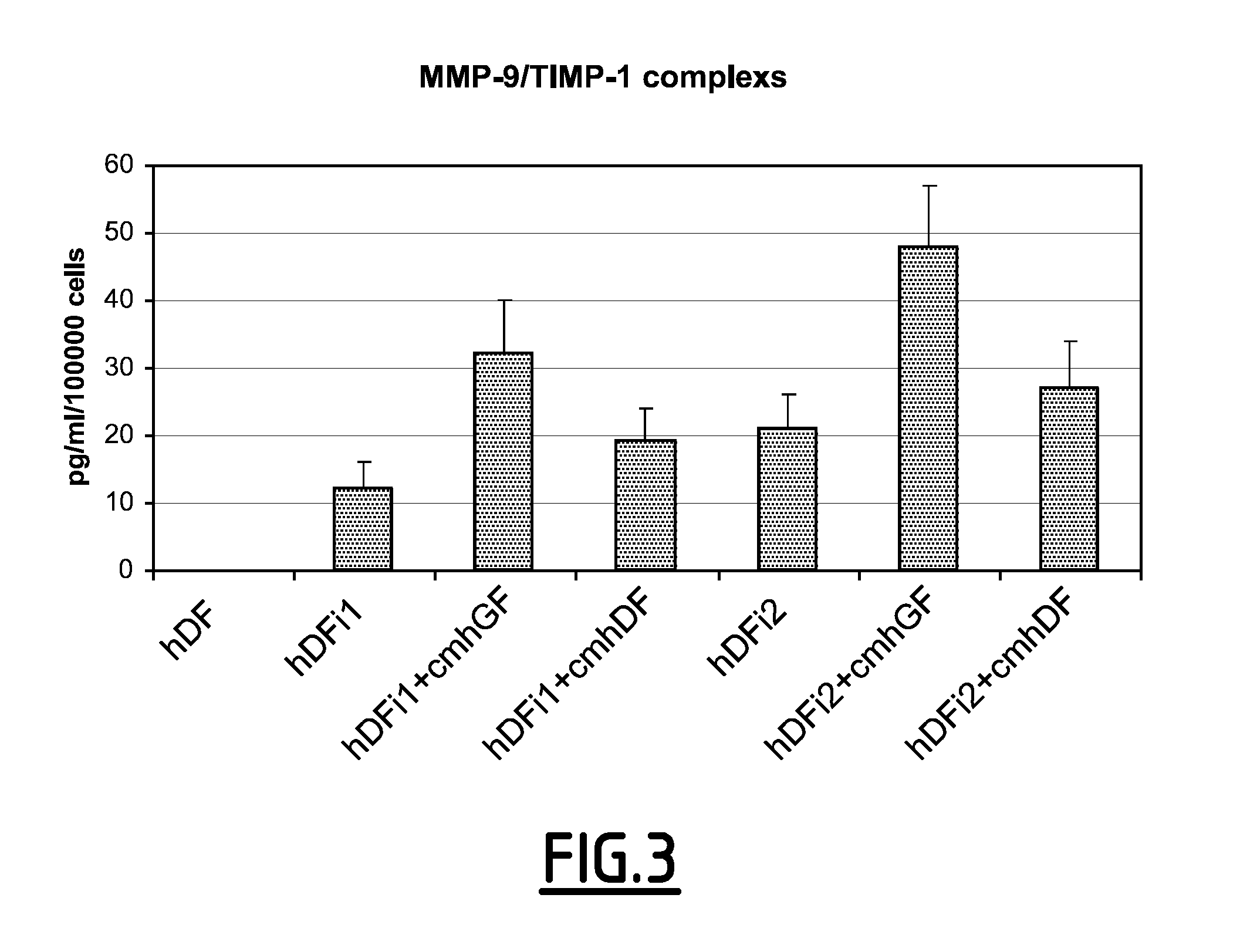
Culture medium for gingival fibroblasts
InactiveUS7951593B2Improve scalabilityCulture processArtificial cell constructsBiotechnologyCell culture media
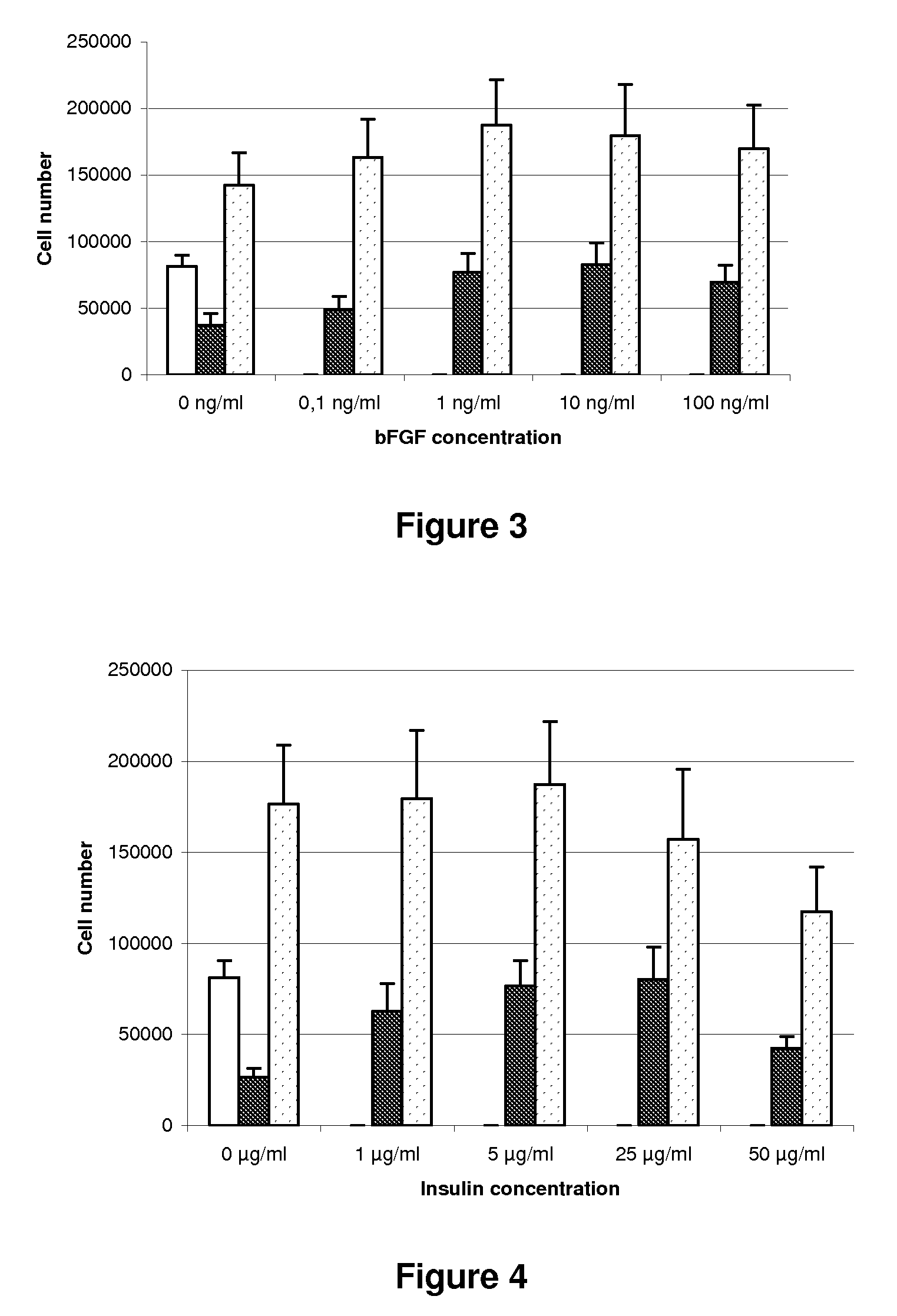
The present invention relates to a gingival fibroblast culture medium free of animal serum, comprising an animal cell culture medium, free of animal serum, to which is added:from 0.1 ng / ml to 100 ng / ml bFGF, and / orfrom 1 μg / ml to 50 μg / ml insulin.
Owner:PARIS DESCARTES UNIV 50 PART INTEREST +2
Pure titanium dental implant and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN110811882APromote growthImprove adsorption capacityDental implantsSoft tissue closureBone tissue
The invention relates to a pure titanium dental implant, which is characterized in that a plurality of micron-sized grooves are formed in the surface of the pure titanium dental implant, and nanotubesperpendicular to the central axis of the dental implant are arranged in the grooves. A width of each groove is 50 [mu] m, a depth of each groove is 10 [mu] m, and the distance between adjacent grooves is 50-53 [mu] m. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, a middle groove in the surface of the dental implant is manufactured; then manufacturing the nanotube is manufactured on the groove so that the surface of the top of the nanotube is an inclined plane, and a contact surface between the inclined plane and a bone tissue interface and between the inclined plane and a soft tissue interface is large; the contact surface between the nanotube and a bone tissue interface and between the nanotube and a soft tissue interface is large, the micron-sized groove can induce bone tissue cells and soft tissue cells to better grow along the grooves, and the nanotube is also beneficial to adsorption of protein, oxygen and nutrients. The size of the groove is just slightly smaller than thatof the bone marrow stromal stem cells and gingival fibroblasts which are not stretched, so that the cells cannot fall into the groove, and the cells can grow along the groove. The proliferation of gingival fibroblasts and the expression of soft tissue closure related genes can be promoted, so that the effects of osteogenesis and soft tissue closure are achieved.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF PUTIAN UNIV (THE SECOND HOSPITAL OF PUTIAN CITY)
Dental implant with nano antibacterial structure ring at gingival penetrating part and processing method of dental implant
ActiveCN113679495AReduce the risk of periodontal infectionImprove adhesionDental implantsLaser beam welding apparatusEngineeringGingival fibroblast
The invention relates to a dental implant with a nano antibacterial structure ring at a gingival penetrating part and a processing method of the dental implant. The gingival penetrating part of the dental implant has a three-level micro-nano composite structure, and the three-level micro-nano composite structure endows the surface of the gingival penetrating part of the implant with functions of promoting adhesion and proliferation of gingival fibroblasts and gingival mesenchymal stem cells and inhibiting adhesion and growth of various oral bacteria. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, injecting bioactive, wear-resistant or corrosion-resistant C, N, Ca and P elements into the gingival penetrating part of the dental implant by a plasma injection method; and then manufacturing the three-level micro-nano composite structure at the part where the elements are injected. According to the invention, the surface with the bioactive components and the three-level micro-nano composite structure is prepared at the gingival penetrating part of the implant, so that the adhesion and proliferation of the gingival fibroblasts and the gingival mesenchymal stem cells can be effectively promoted, the adhesion and growth of various oral bacteria on the implant can be inhibited, the periodontal infection risk after the implant is implanted can be effectively reduced, and the implantation success rate is improved.
Owner:BEIJING VANJEWEL MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
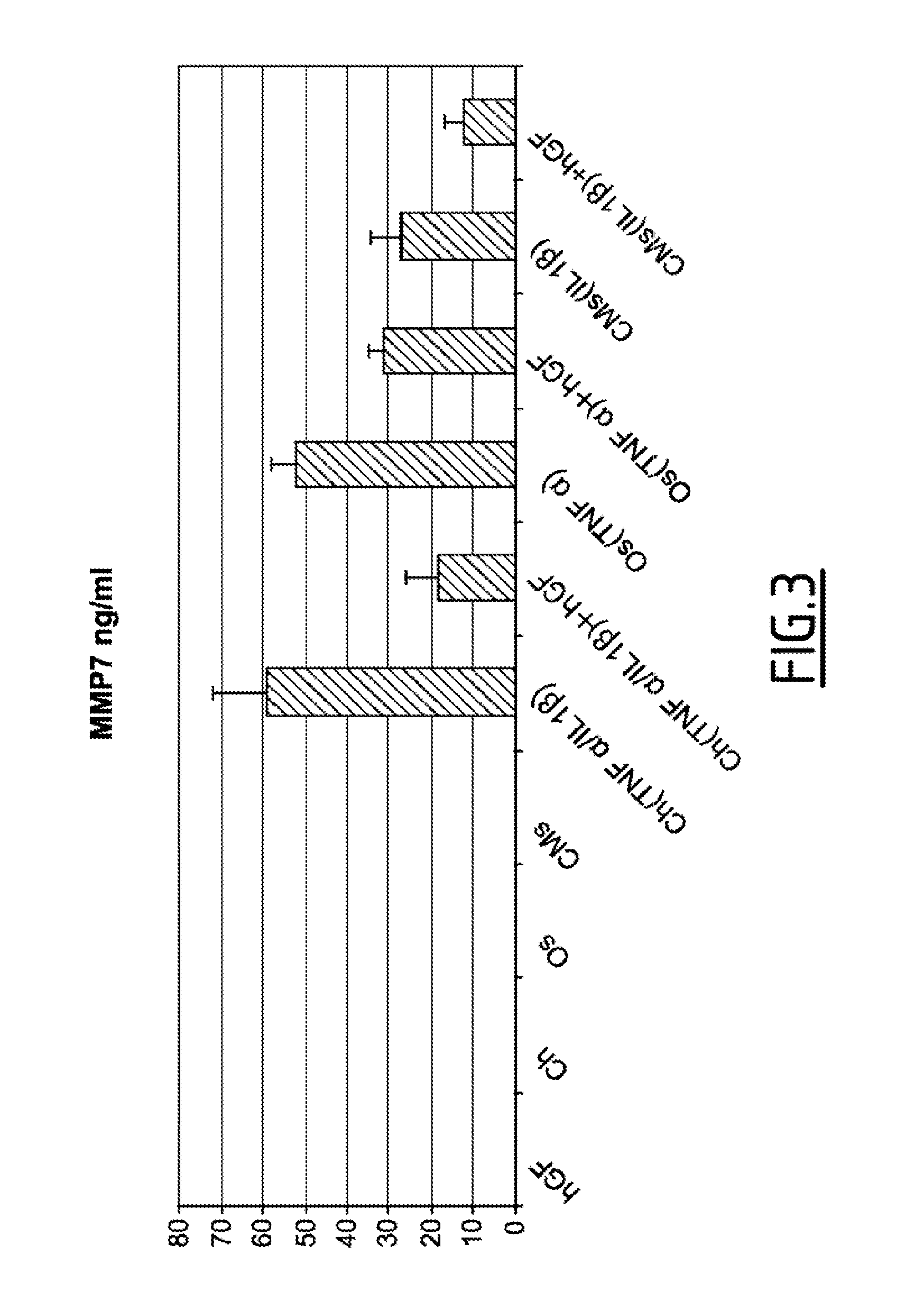
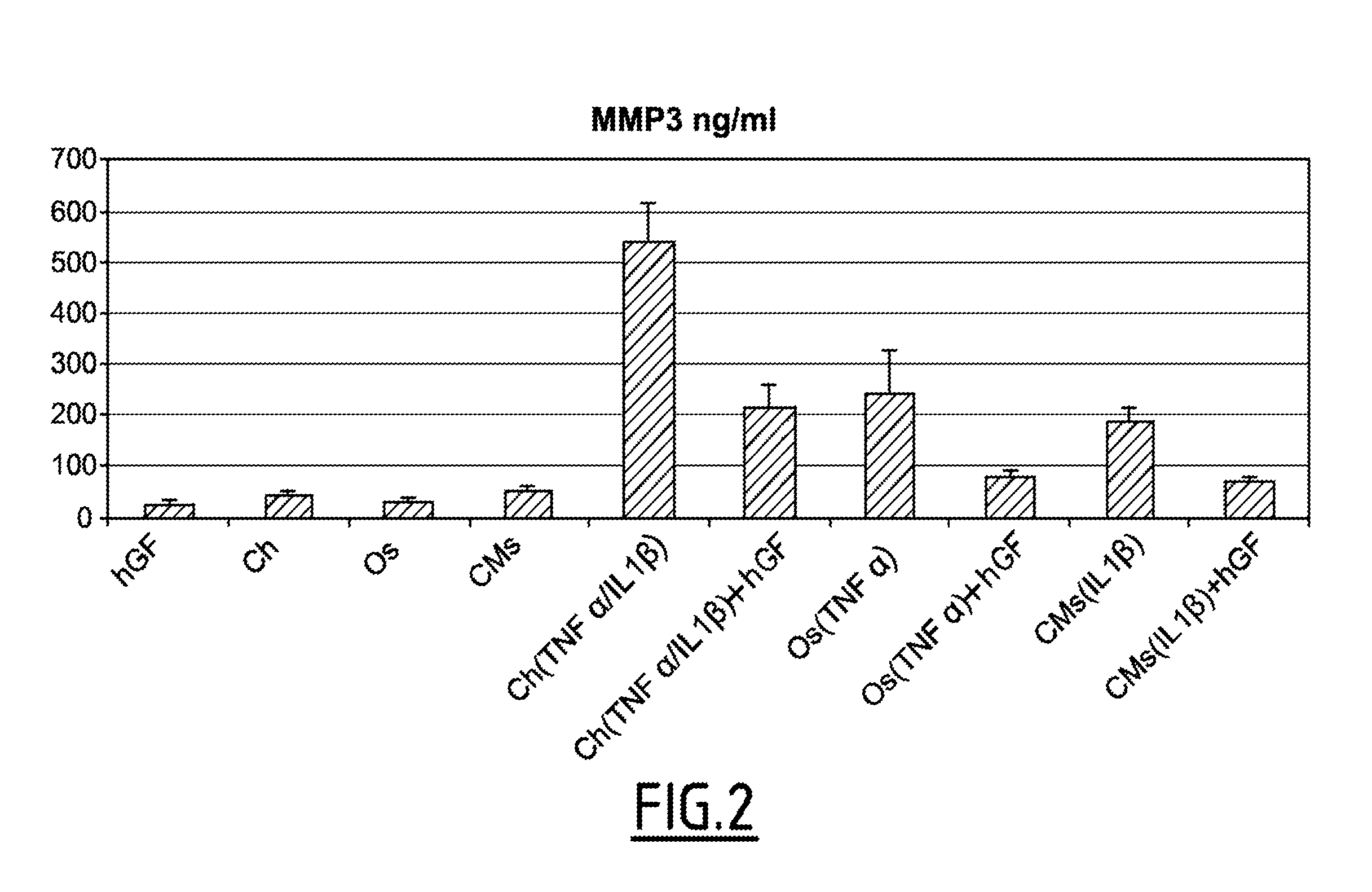
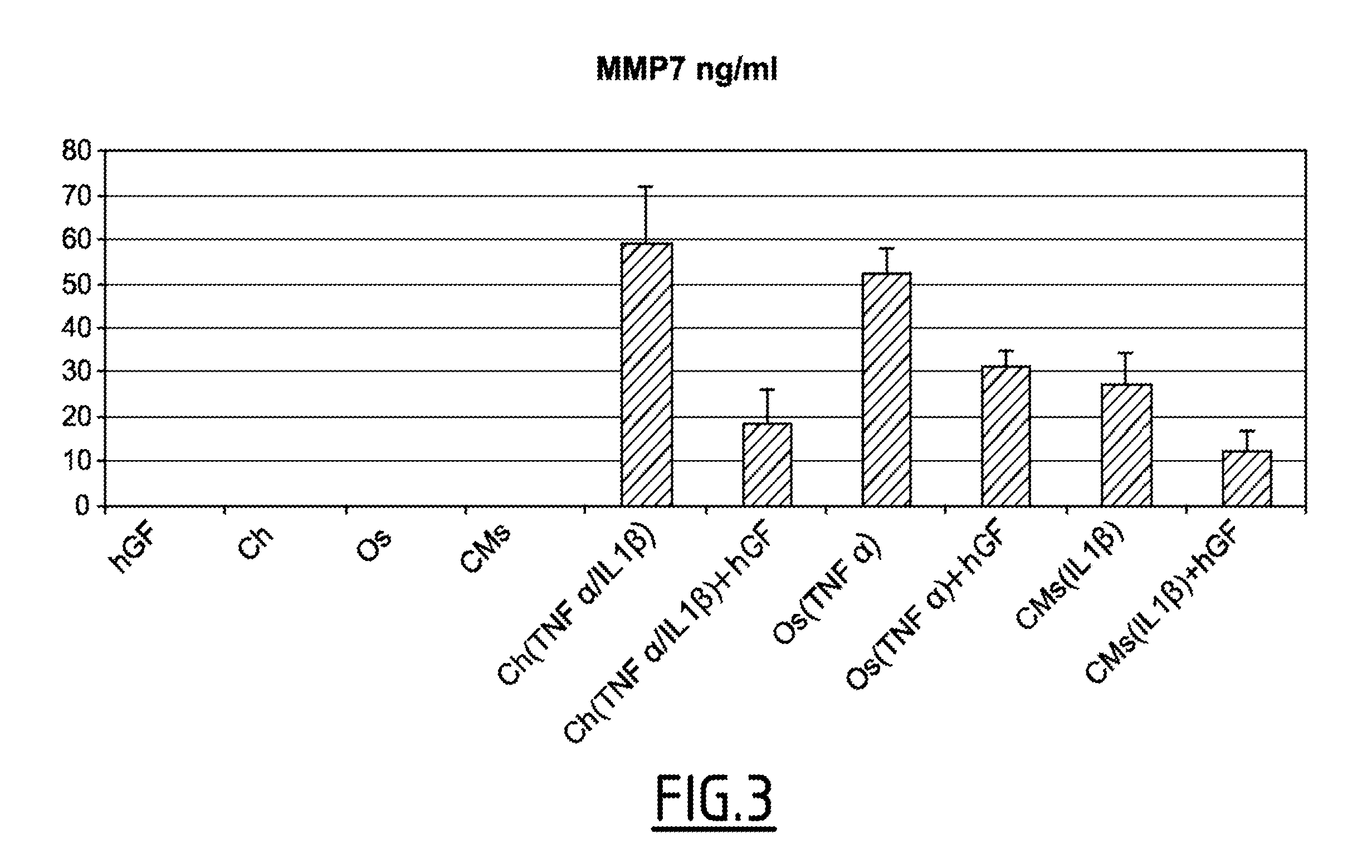
Pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of orthopedic pathologies
InactiveUS20150258146A1Inhibiting MMP activityEasily sampled and culturedSkeletal disorderUnknown materialsPlastic surgeryGingival fibroblast
The present invention relates to a gingival fibroblast-derived product for use in the prevention or treatment of orthopedic pathologies in an individual.
Owner:SCARCELL THERAPEUTICS
Pharmaceutical composition and method for the treatment of orthopedic pathologies
PendingUS20160256496A1Easily sampled and culturedIncrease growth rateSkeletal disorderUnknown materialsPharmaceutical drugSurgery
The present invention relates to a gingival fibroblast-derived product and its use in methods for the prevention or treatment of orthopedic pathologies in an individual.
Owner:SCARCELL THERAPEUTICS
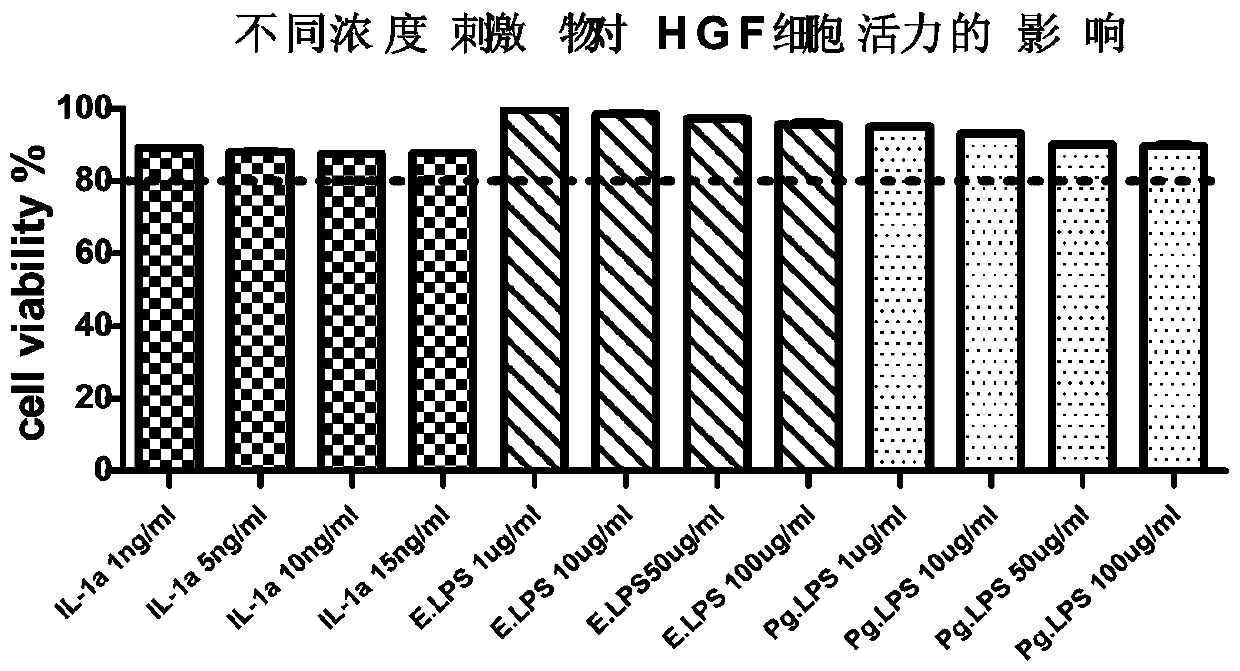
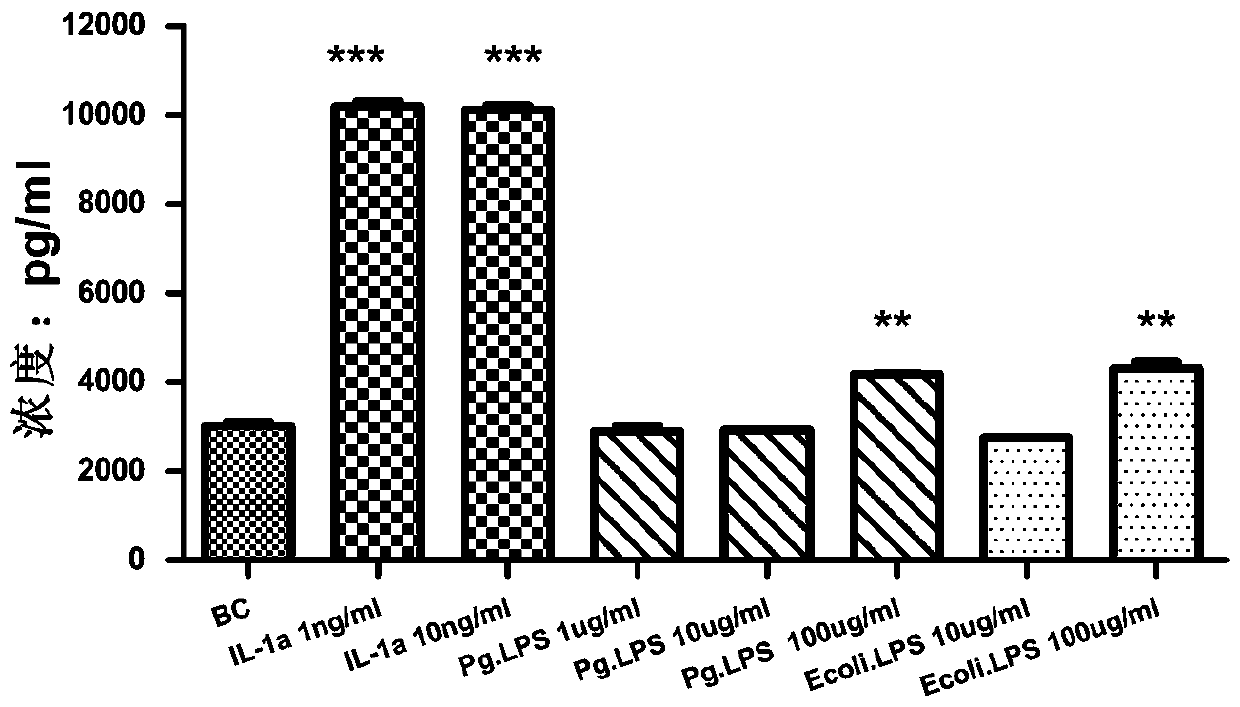
Application and method of IL-1a in establishing human gingival fibroblast oral anti-inflammatory model
PendingCN111139219AReal, comprehensive and accurate evaluation of anti-inflammatory effectCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsMouth careEfficacy
The invention provides an application and a method of IL-1a in establishing a human gingival fibroblast oral anti-inflammatory model and the human gingival fibroblast inflammation model. The human gingival fibroblast oral anti-inflammatory model provided by the invention can more comprehensively reflect efficacy of oral care products, and provides a more objective, scientific and accurate evaluation mode for evaluating efficacy of oral anti-aging products.
Owner:GUANGDONG BOXI BIO TECH CO LTD
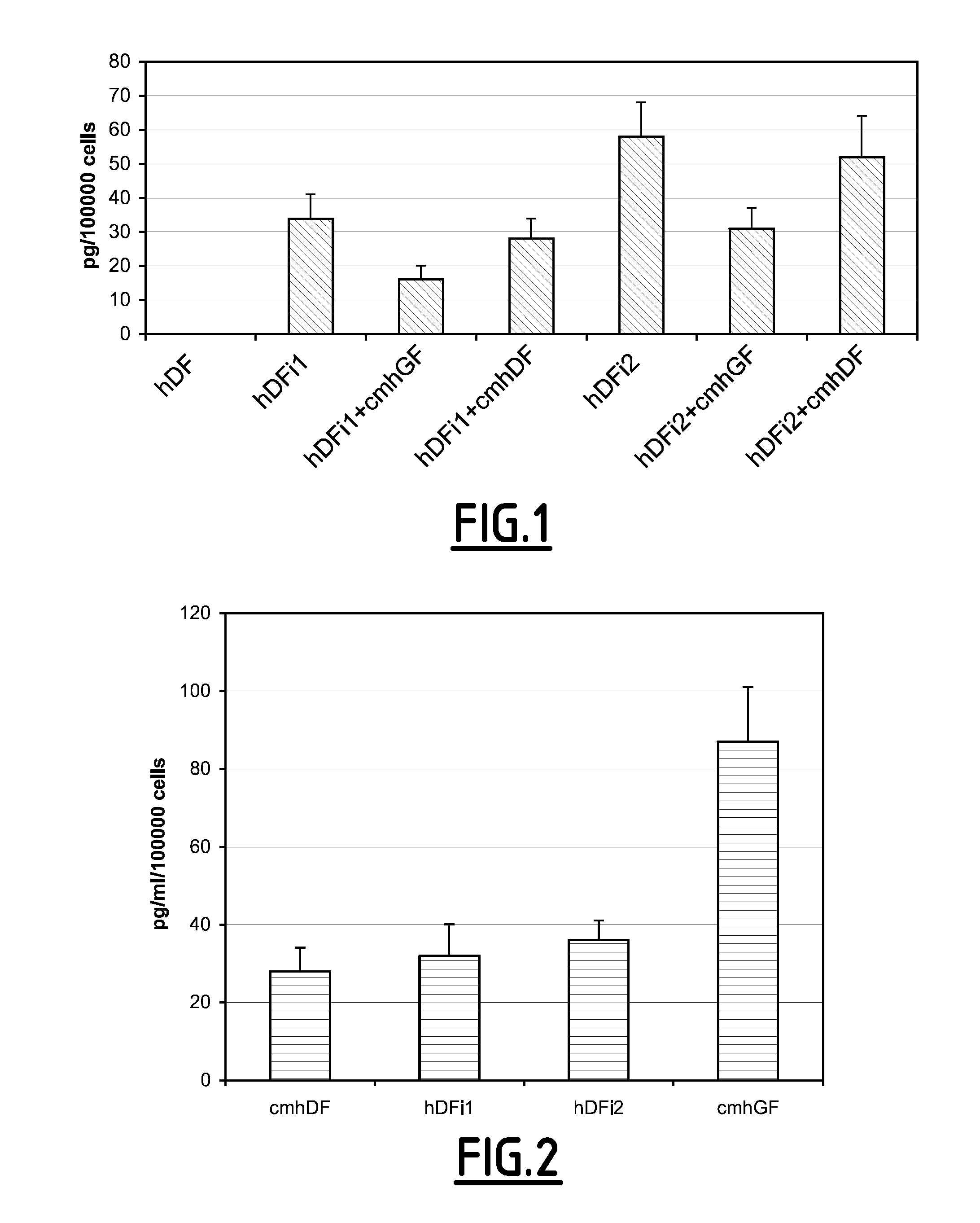
Culture medium for gingival fibroblasts
InactiveUS20090061512A1Improve scalabilityCulture processArtificial cell constructsBiotechnologyCell culture media
The present invention relates to a gingival fibroblast culture medium free of animal serum, comprising an animal cell culture medium, free of animal serum, to which is added:from 0.1 ng / ml to 100 ng / ml bFGF, and / orfrom 1 μg / ml to 50 μg / ml insulin.
Owner:PARIS DESCARTES UNIV 50 PART INTEREST +2
Method for the Cosmetic Treatment of Skin Ageing
The present invention relates to a method for the cosmetic prevention or treatment of skin ageing in an individual, comprising administering to said individual a cosmetically active quantity of a gingival fibroblast-derived product.
Owner:SCARCELL THERAPEUTICS
Compositions useful for the treatment of immune-related diseases
ActiveUS20190269736A1Inhibition of secretionCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseRelated disorder
The present invention relates to a gingival fibroblast-derived product for use in the treatment or prevention of an immune-related disease in an individual.
Owner:SCARCELL THERAPEUTICS
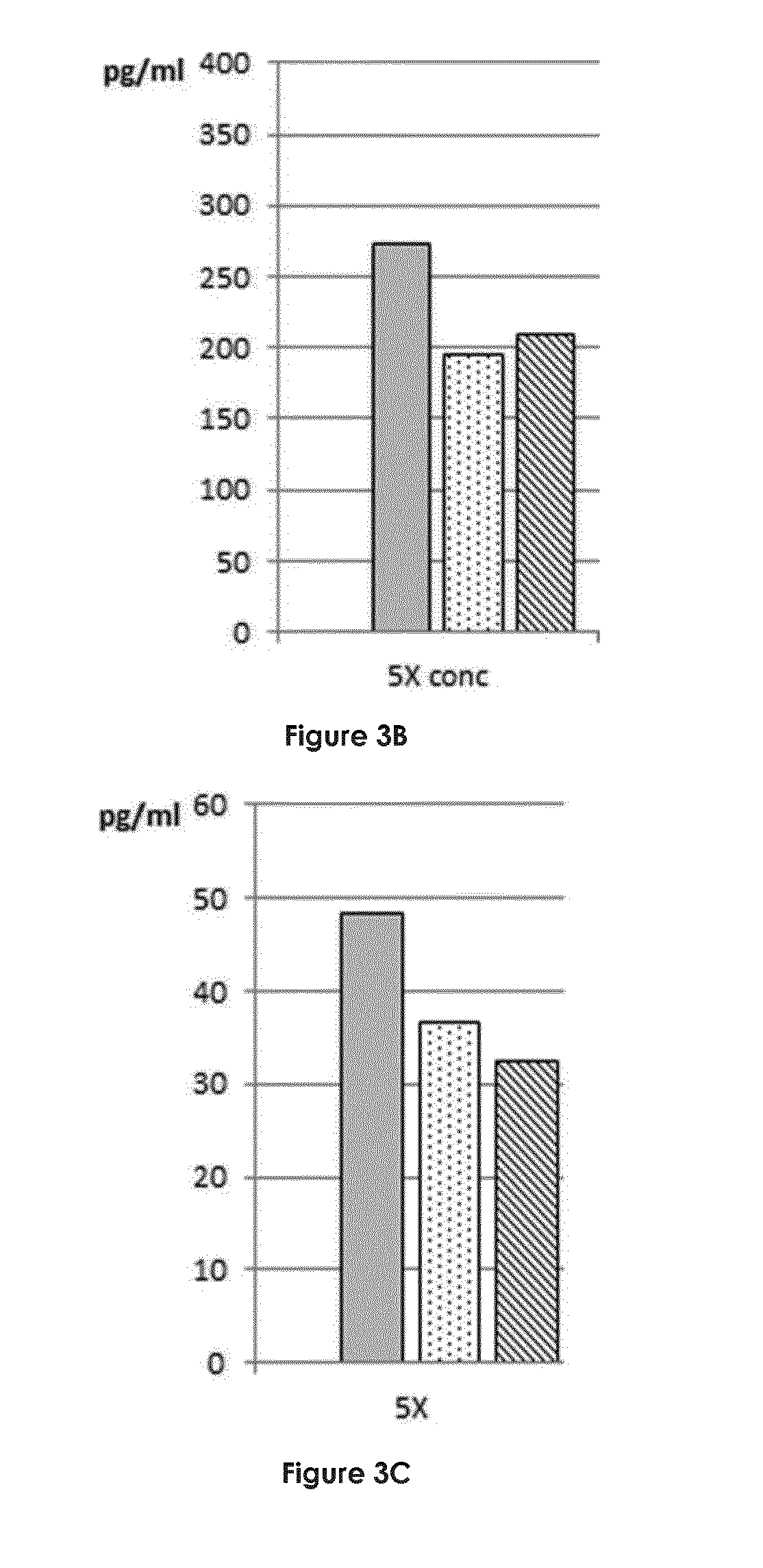
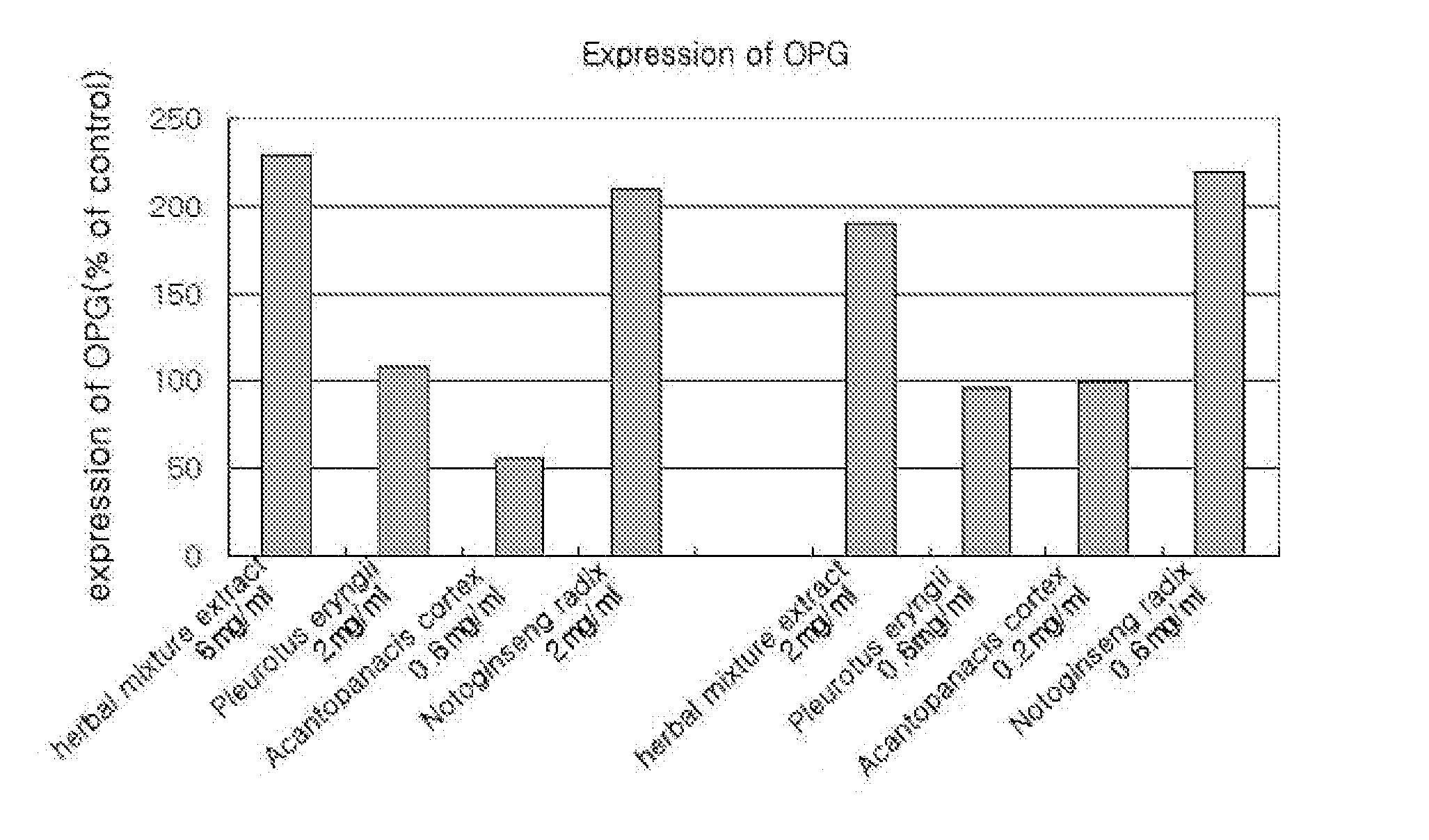
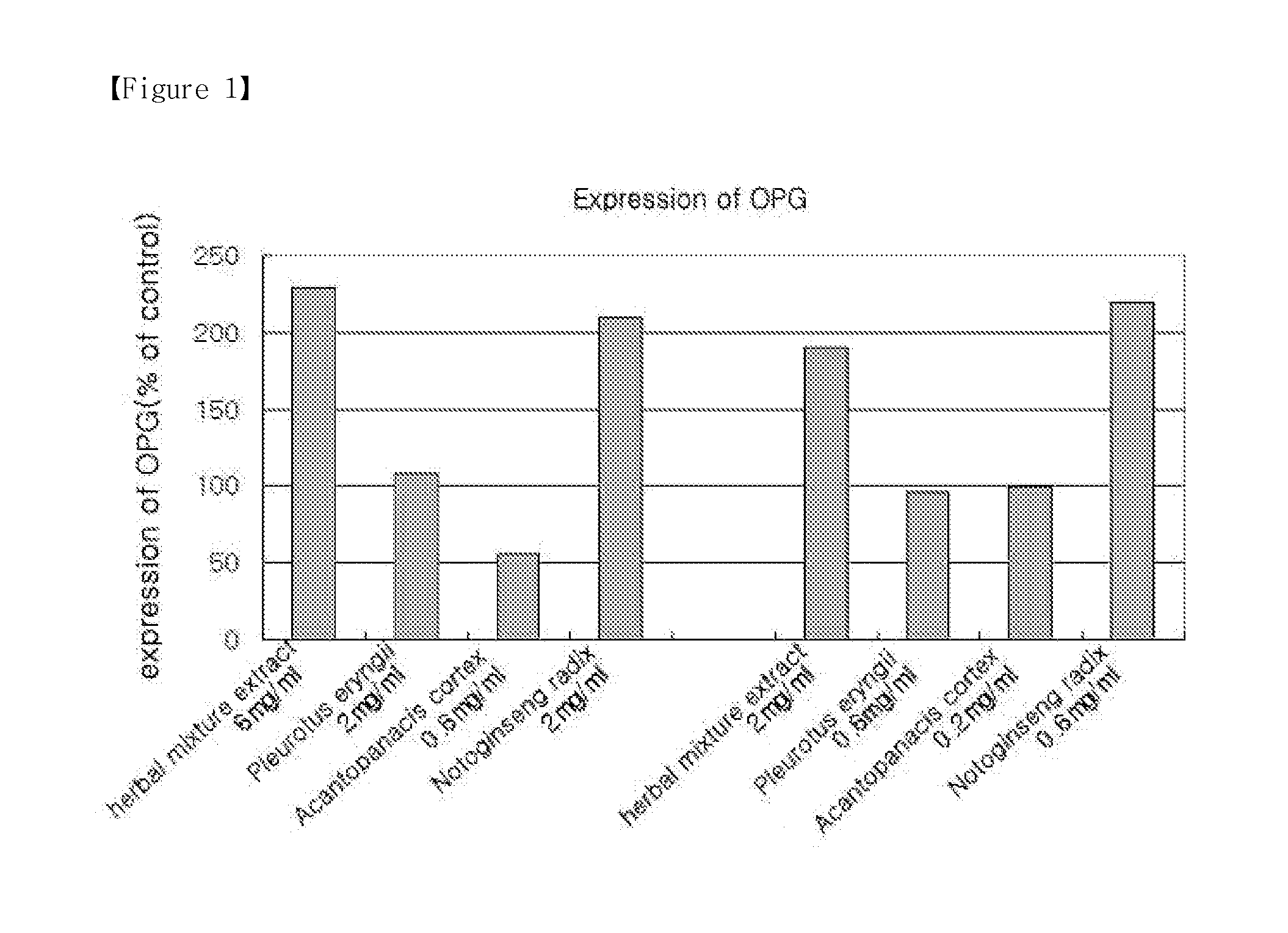
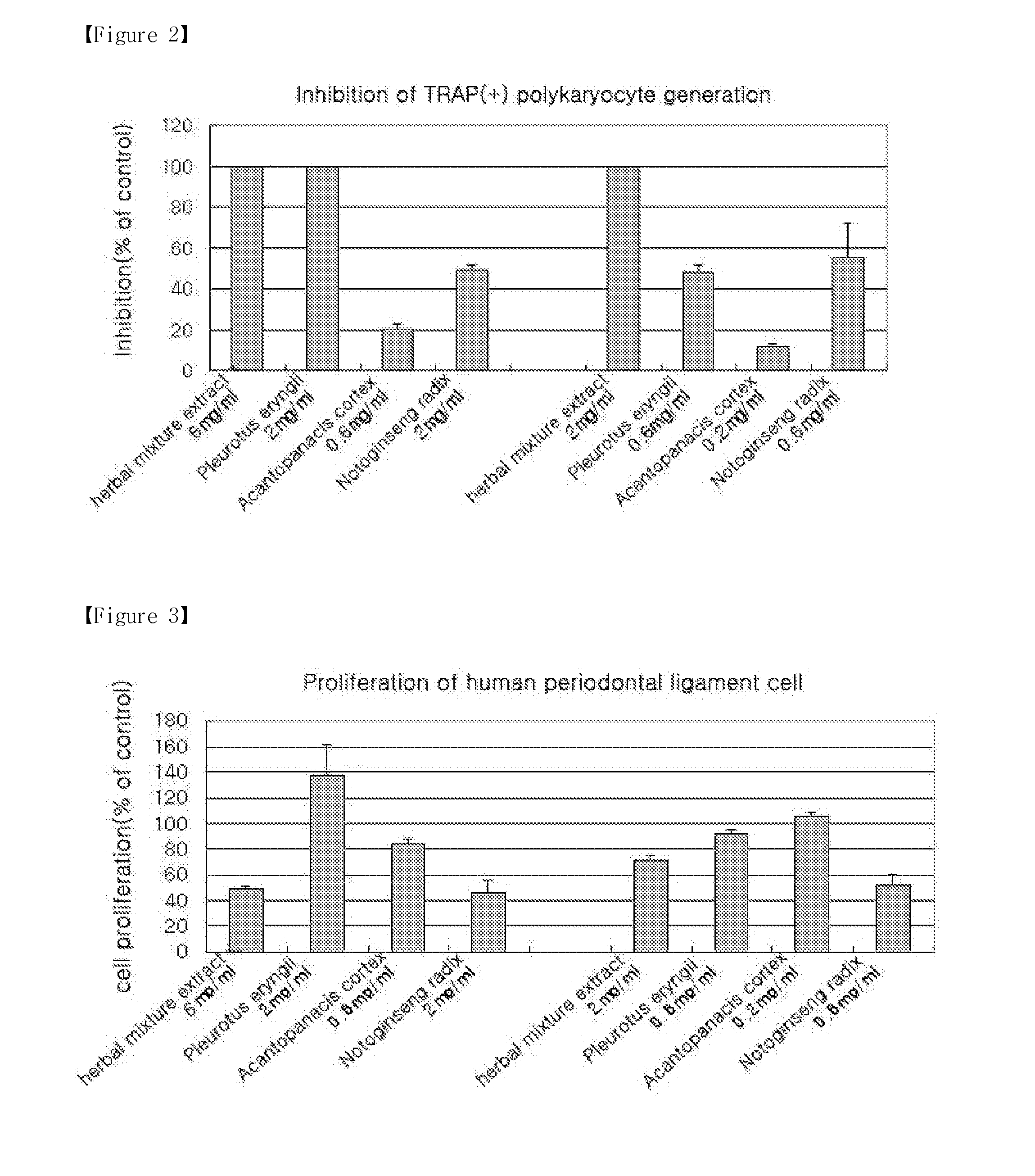
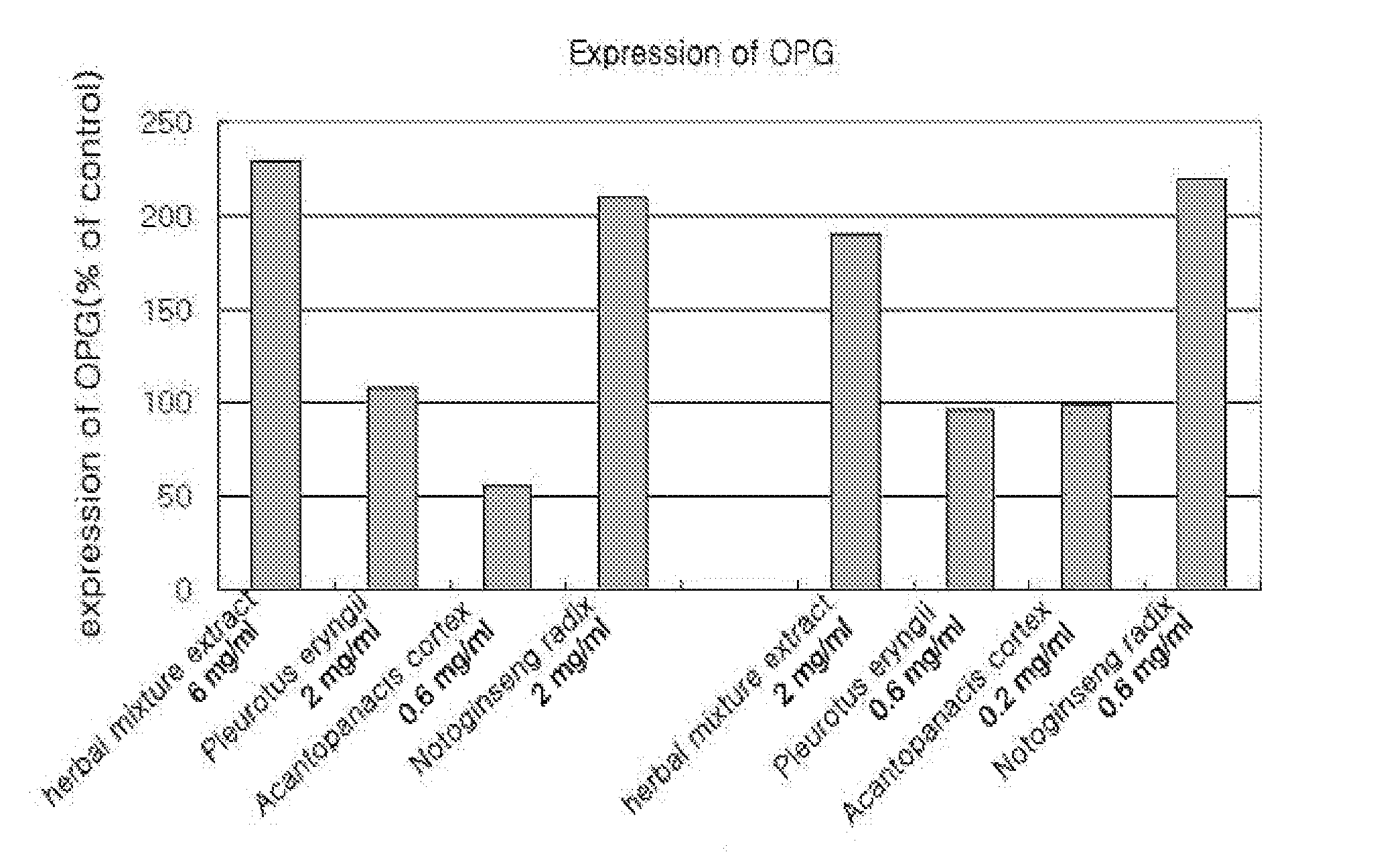
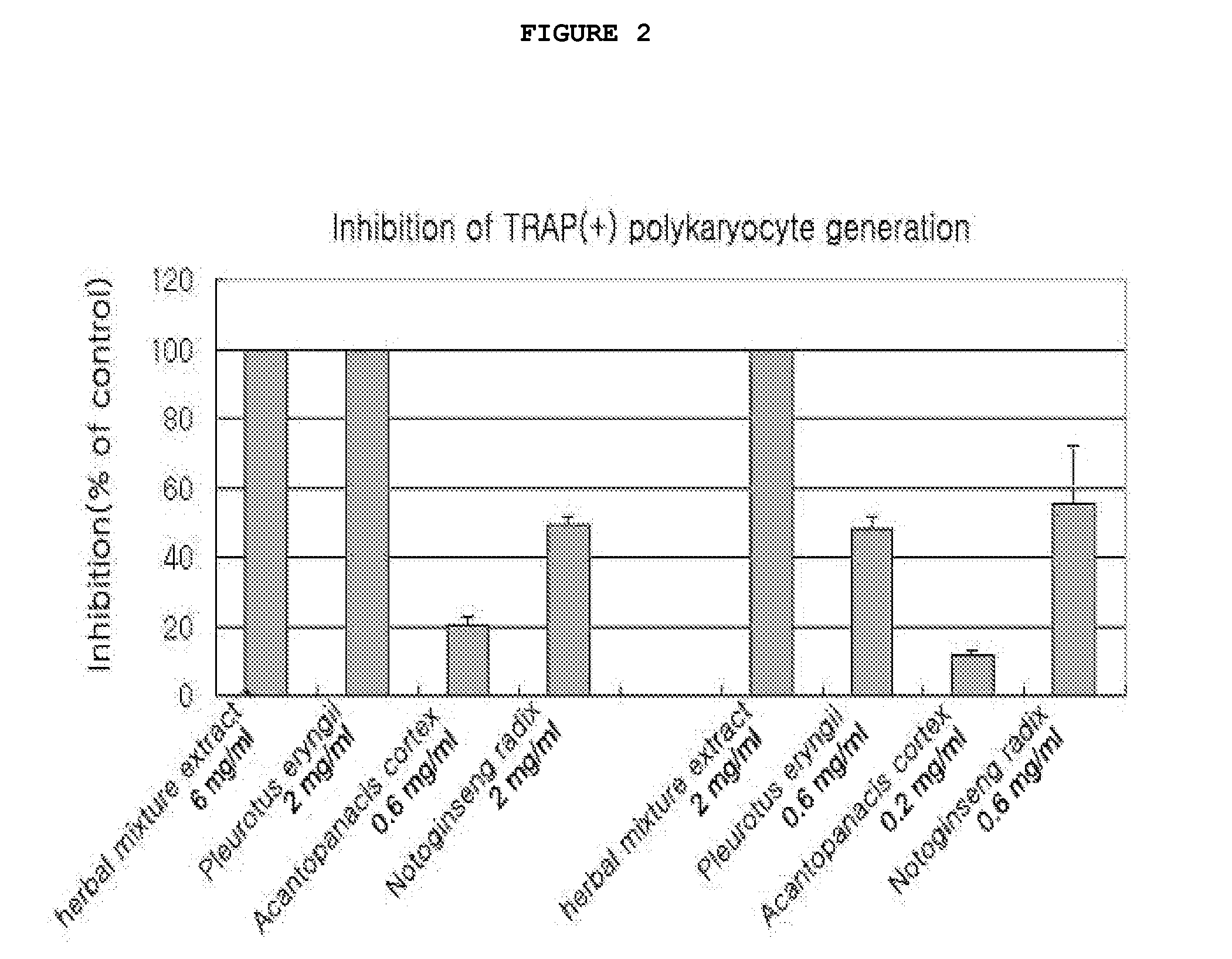
Herbal mixture extract of pleurotus eryngii, acanthopanacis cortex and notoginseng radix and a composition comprising the same for prevention and treatment of periodontitis
The present invention relates to a herbal mixture extract of Pleurotus eryngii, Acanthopanacis Cortex and Notoginseng Radix and a composition for prevention and treatment of periodontal disease containing the herbal mixture extract as an active ingredient, more precisely, a herbal mixture extract having activities of inhibiting the generation and activation of osteoclasts by enhancing the expression of osteoprotegerin (OPG) in osteoblasts, preventing alveolar bone from destruction by inhibiting the proliferation of osteoclasts and maintaining the growth of periodontal ligament cells and gingival fibroblasts, and a composition for prevention and treatment of periodontal disease containing the above mixture as an active ingredient.
Owner:OSCOTEC INC
Use of gingival fibroblasts in the treatment of alopecia
ActiveUS20160151274A1Promote growthHigh densityCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsHair growthHair loss
The present invention relates to the use of gingival fibroblasts-derived products to reduce hair loss and promote hair growth. Specifically, the invention relates to a product derived from gingival fibroblasts to be used in the treatment or prevention of alopecia, as well as in the promotion of natural hair growth and / or in the control of natural hair loss.
Owner:ASSISTANCE PUBLIQUE HOPITAUX DE PARIS +4
Micro-nano double-layer structure antibacterial stent as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN114425101AGood compatibilityImprove antibacterial propertiesAntibacterial agentsDigestive systemMicro nanoBiology
The invention provides a micro-nano double-layer structure antibacterial stent as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of oral medical products. The preparation method of the micro-nano double-layer structure antibacterial stent provided by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) mixing a polyhydroxyalkanoate material with a nano antibacterial drug, and adding an organic solvent for dissolving to obtain a polyhydroxyalkanoate solution; (2) pouring a polyhydroxyalkanoate solution into a mold, immersing the mold filled with the polyhydroxyalkanoate solution into the poor solvent of the polyhydroxyalkanoate material, and carrying out solution replacement to obtain a semisolid stent; and (3) freeze-drying the semi-solid scaffold to obtain the micro-nano double-layer structure antibacterial scaffold. The micro-nano double-layer structure antibacterial scaffold provided by the invention has good cytocompatibility and antibacterial property, and can effectively promote adhesion and proliferation of gingival fibroblasts and reduce bacterial infection of wounds.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SCHOOL OF STOMATOLOGY
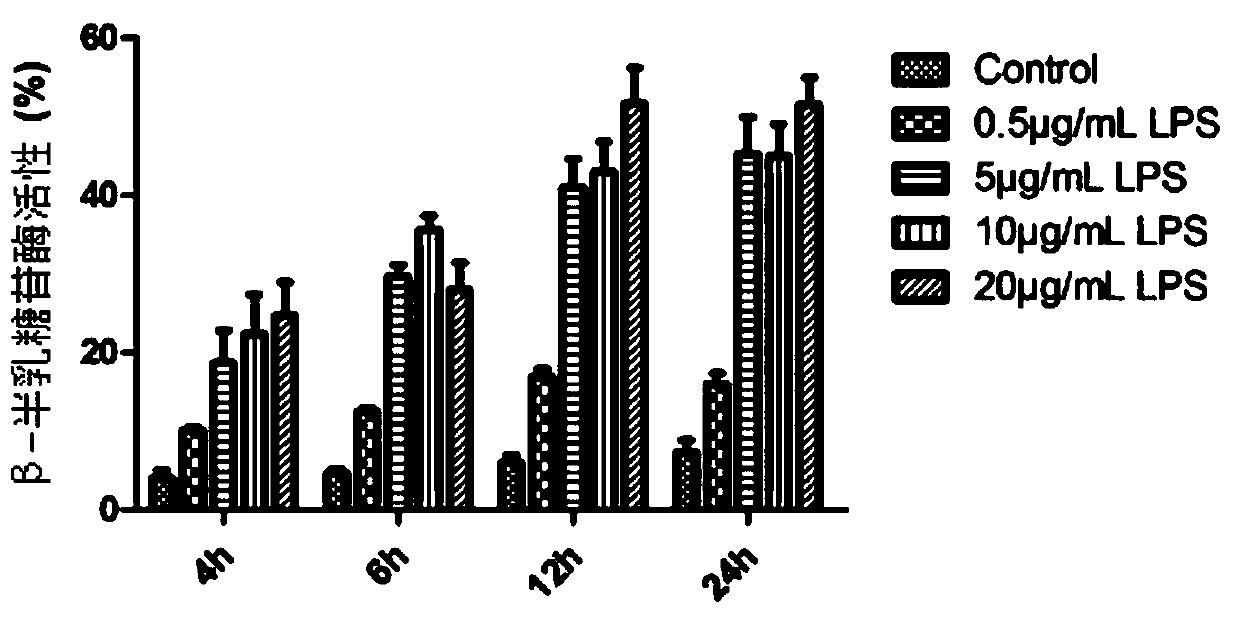
Application of lipopolysaccharide in establishing human gingival fibroblast stress aging model
PendingCN110862957AIncreased inflammatory damageObjective evaluation modelMicrobiological testing/measurementSkeletal/connective tissue cellsFibroblastDentistry
The invention provides an application of lipopolysaccharide in establishment of a human gingival fibroblast stress aging model, a method and the human gingival fibroblast stress aging model. The humangingival fibroblast stress aging model provided by the invention can reflect non-aging stress oral aging more comprehensively, and provides a more objective, scientific and accurate evaluation mode for efficacy evaluation of oral anti-aging products.
Owner:GUANGDONG BOXI BIO TECH CO LTD
Use of gingival fibroblasts for vascular cell therapy
ActiveUS8119122B2BiocideMammal material medical ingredientsAortic dissectionPercent Diameter Stenosis
The invention relates to the use of gingival fibroblasts for obtaining a cellular composition for treating arterial-remodelling pathology, for example an aneurysm, post-cryoplasty stenosis and restenosis, an aortic dissection or atherosclerosis.
Owner:ASSISTANCE PUBLIQUE HOPITAUX DE PARIS
Method for treating cancer
InactiveUS20160158290A1Epidermal cells/skin cellsMammal material medical ingredientsOncologyGingival fibroblast
The present invention relates to a method for preventing or treating cancer in an individual comprising administering the individual with a prophylactically or therapeutically effective quantity of a gingival fibroblast-derived product.
Owner:UNIV RENE DESCARTES PARIS V
A gradient material for guiding periodontal hard and soft tissue regeneration and its preparation method
ActiveCN110141687BAchieving Synchronous RepairAll-in-one repairSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMetaboliteGradient material
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Herbal mixture extract of pleurotus eryngii, acanthopanacis cortex and notoginseng radix and a composition comprising the same for prevention and treatment of periodontitis
The present invention relates to a herbal mixture extract of Pleurotus eryngii, Acanthopanacis Cortex and Notoginseng Radix and a composition for prevention and treatment of periodontal disease containing the herbal mixture extract as an active ingredient, more precisely, a herbal mixture extract having activities of inhibiting the generation and activation of osteoclasts by enhancing the expression of osteoprotegerin (OPG) in osteoblasts, preventing alveolar bone from destruction by inhibiting the proliferation of osteoclasts and maintaining the growth of periodontal ligament cells and gingival fibroblasts, and a composition for prevention and treatment of periodontal disease containing the above mixture as an active ingredient.
Owner:OSCOTEC
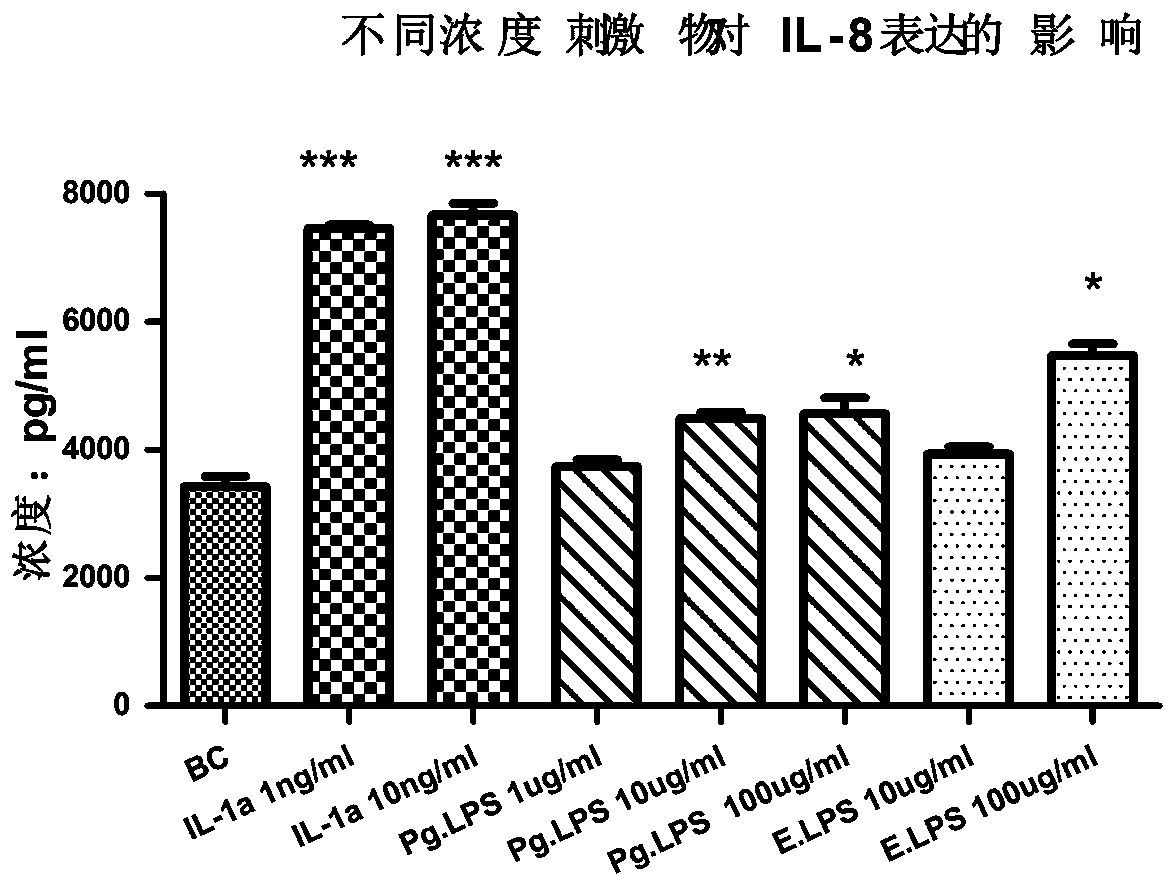
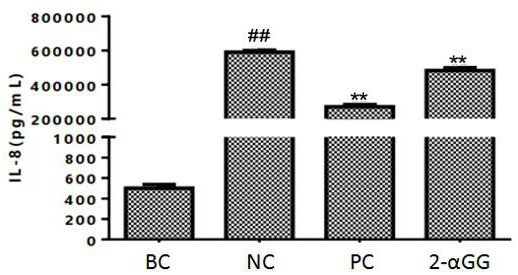
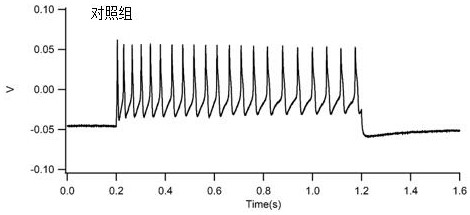
Application of a kind of glycerol glucoside in the preparation of oral care products
ActiveCN113712841BReduce frequencyWeakening rangeCosmetic preparationsAntipyreticInflammatory factorsMouth care
The invention discloses an application of glycerol glucoside in the preparation of oral care products. The stereo configuration of the glycerol glucoside is 2‑αGG. Glycerol glucoside can inhibit the secretion of inflammatory factors such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) and interleukin-8 (IL-8) from gingival fibroblasts; it can significantly reduce the release frequency and amplitude of action potentials in neurons, and has neuronal Sexual antisensitivity effect. Applying the glycerol glucoside to oral care products can treat or relieve periodontitis, relieve dentin sensitivity, and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN SHINESKY BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Compositions useful for the treatment of immune-related diseases
Owner:SCARCELL THERAPEUTICS
Use of gingival fibroblasts for vascular cell therapy
The invention relates to the use of gingival fibroblasts for obtaining a cellular composition for treating arterial-remodelling pathology, for example an aneurysm, post-cryoplasty stenosis and restenosis, an aortic dissection or atherosclerosis.
Owner:UNIVERSITÉ PARIS CITÉ
Use of gingival fibroblasts in the treatment of alopecia
ActiveUS10624838B2Promote growthHigh densityCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsAlopecia treatmentHair growth
The present invention relates to the use of gingival fibroblast-derived products to reduce hair loss and promote hair growth. Specifically, the invention relates to a product derived from gingival fibroblasts to be used in the treatment or prevention of alopecia, as well as in the promotion of natural hair growth and / or in the control of natural hair loss.
Owner:ASSISTANCE PUBLIQUE HOPITAUX DE PARIS +4
Application of Lactobacillus paracasei l.p R3-10 in the preparation of drugs for preventing or treating oral inflammatory diseases
ActiveCN111904985BInhibit aggregationEasy to removeCosmetic preparationsBacteriaInflammatory factorsNeutrophil granulocyte
The invention discloses the application of a strain of Lactobacillus paracasei L.p R3-10 in the preparation of medicines for preventing or treating oral inflammatory diseases, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The inactivated and inactivated fermentation supernatant and bacterial suspension of Lactobacillus paracasei L.p R3-10 disclosed by the present invention have the ability to inhibit LPS from stimulating human gingival fibroblasts to secrete inflammatory factors IL-6 and TNF-α in vitro , the role of PGE2; and in the in vivo inflammation model, it can significantly inhibit the accumulation of neutrophils and macrophages to the zebrafish caudal fin inflammation, and significantly promote the clearance of neutrophils and macrophages at the zebrafish caudal fin inflammation; At the same time, it can also significantly promote the damage repair of zebrafish caudal fin. The Lactobacillus paracasei L.p R3‑10 disclosed by the present invention has great potential application prospects in the treatment and / or prevention of oral inflammatory diseases.
Owner:广东南芯医疗科技有限公司 +2
Use of gingival fibroblasts for vascular cell therapy
ActiveUS8609085B2BiocideMammal material medical ingredientsAortic dissectionPercent Diameter Stenosis
The invention relates to the use of gingival fibroblasts for obtaining a cellular composition for treating arterial-remodelling pathology, for example an aneurysm, post-cryoplasty stenosis and restenosis, an aortic dissection or atherosclerosis.
Owner:UNIV PARIS CITÉ
Application of glycerol glucoside in preparation of oral care product
ActiveCN113712841AReduce frequencyWeakening rangeCosmetic preparationsAntipyreticInflammatory factorsMouth care
The invention discloses an application of glycerol glucoside in preparation of an oral care product. The glycerol glucoside has a stereoscopic configuration of 2-alpha GG. Glycerin glucoside can inhibit gingival fibroblasts from secreting inflammatory factors such as tumor necrosis factors (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-8 (IL-8); can significantly reduce release frequency and amplitude of the action potential of neuron cells, and has a neurological anti-allergy effect. When the glycerol glucoside is applied to an oral care product, periodontitis can be treated or relieved, dentin hypersensitivity can be relieved, and the like.
Owner:深圳杉海创新技术有限公司
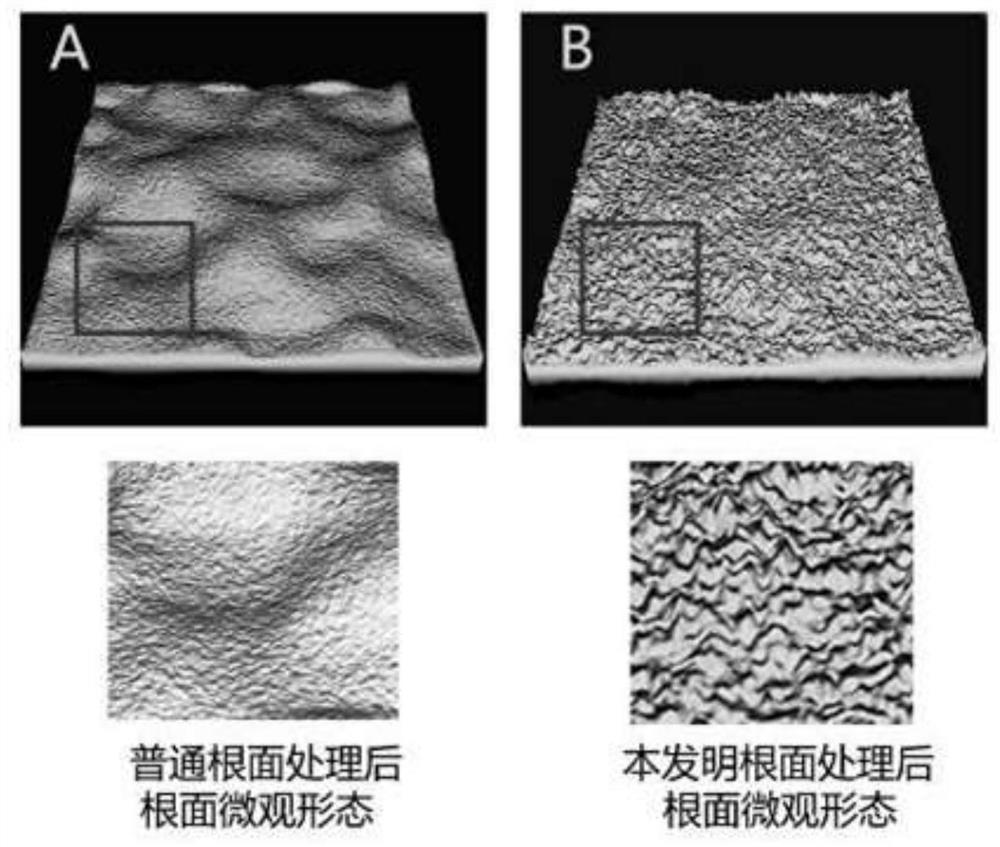
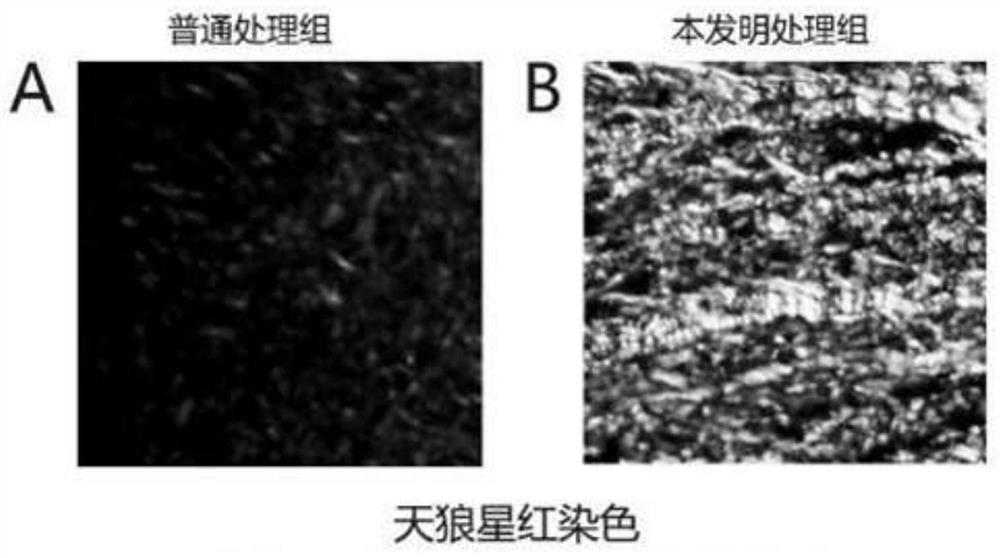
A tooth root surface treatment agent
ActiveCN113208929BReduces risk of gum attackClean thoroughlyImpression capsDentistry preparationsBiotechnologyPolythylene glycol
The invention discloses a tooth root surface treatment agent, which comprises a decontamination composition 1 and a regeneration composition 2; the components in the decontamination composition 1 and their mass percentages are: poloxamer 407 13-17% , Triton X-114 1-3%, propylene glycol 3-7%, glycerin 1-2%, tetrahydropiperine 1-2%, sycamore enol 1-3%, the rest is water; each of the regeneration composition 2 The components and their mass percentages are: 0.5-2% of chlorhexidine gluconate, 15-31% of regeneration agent, 1-3% of minocycline hydrochloride, 0.3-0.5% of polyethylene glycol diacrylate, and the remaining is water; the regeneration agent consists of enamel matrix derivatives, bone morphogenic protein 2, bone morphogenic protein 4, and fibroblast growth factor 2. The invention can realize high-efficiency cleaning of the tooth root surface, can improve the reattachment effect of gingival fibroblasts, and is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for treating cancer
InactiveUS20180028571A1Epidermal cells/skin cellsMammal material medical ingredientsOncologyGingival fibroblast
The present invention relates to a method for preventing or treating cancer in an individual comprising administering the individual with a prophylactically or therapeutically effective quantity of a gingival fibroblast-derived product.
Owner:UNIV RENE DESCARTES PARIS V +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com